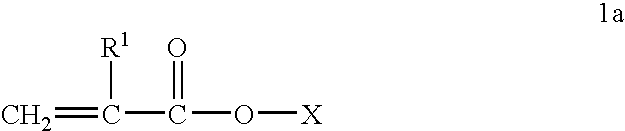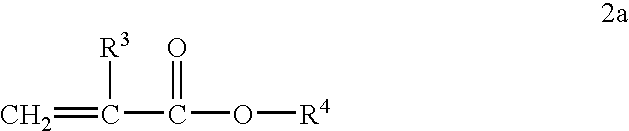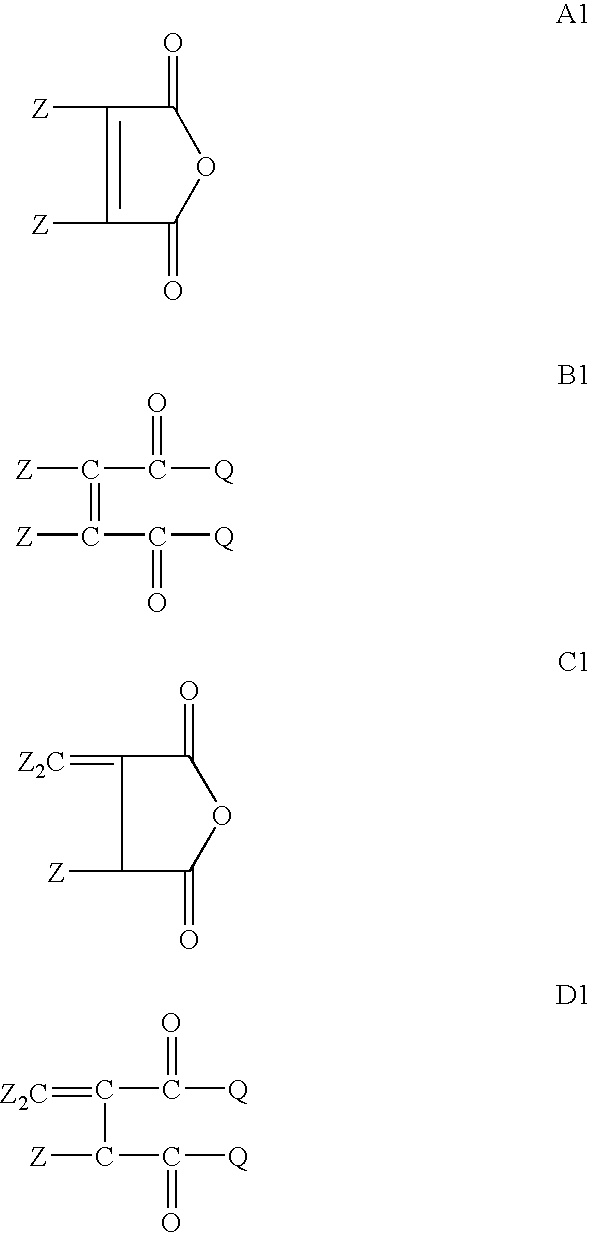Patents
Literature
132results about How to "Extend service hours" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
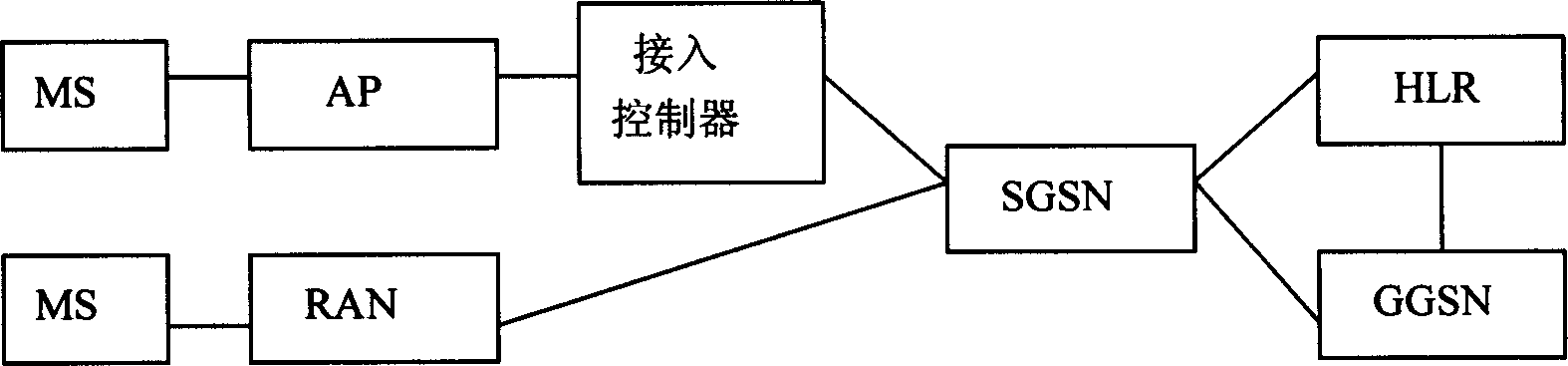
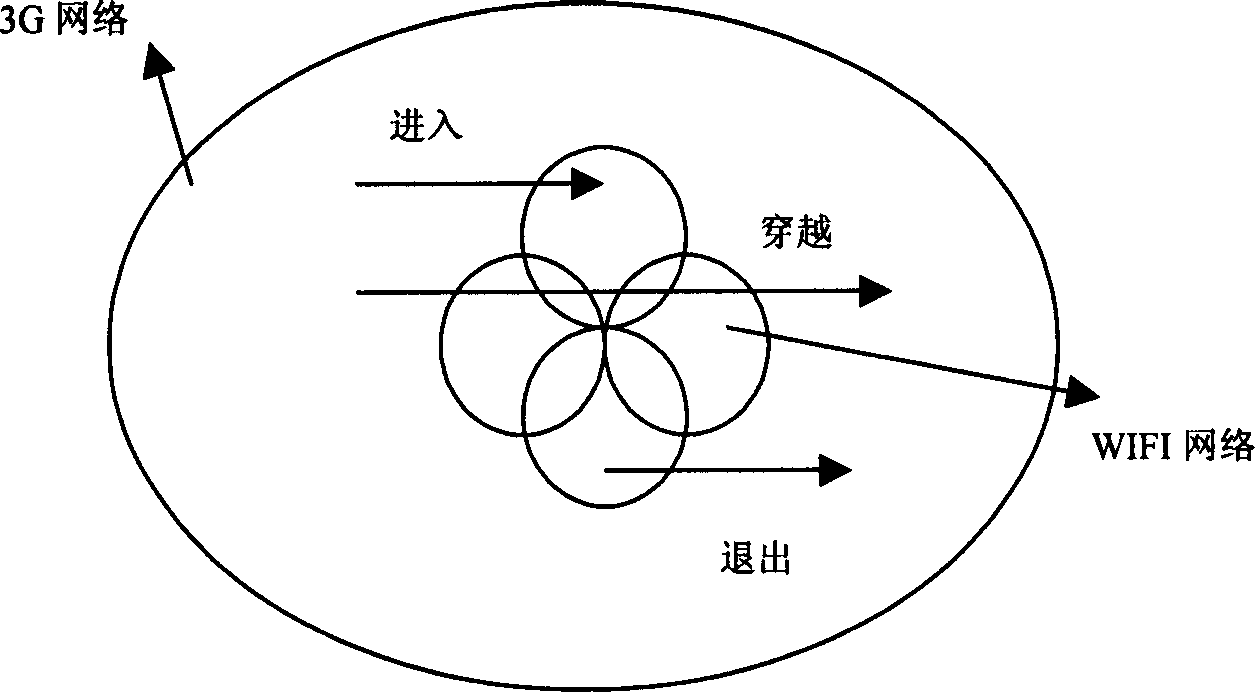
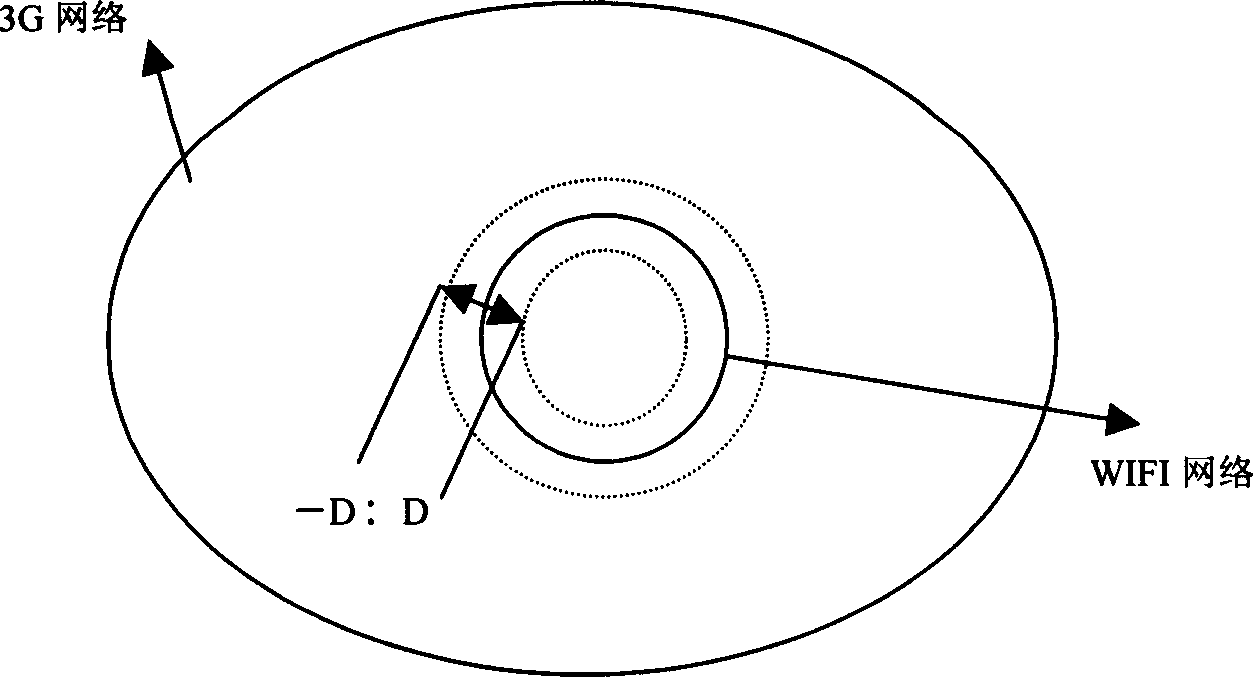
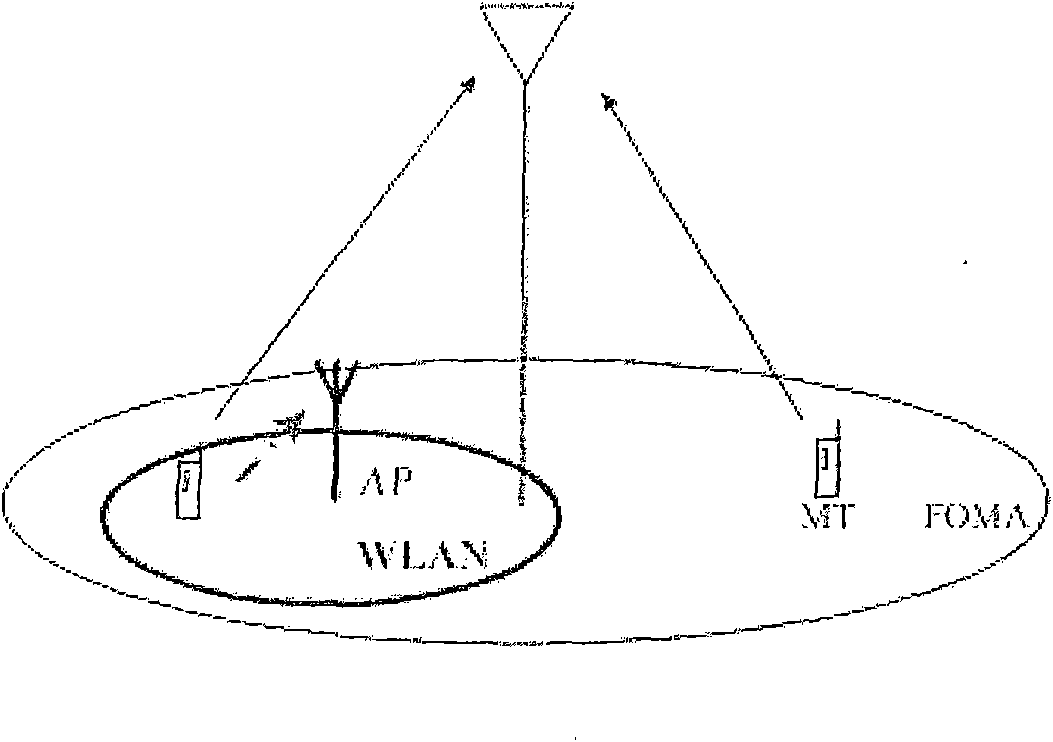
Switchover method between 3G network and WIFI network based on location information
InactiveCN1794681AEasy to compareImprove the success rate of switchingData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWifi networkThird generation
This invention puts forward a switch method between 3G netwqork and WIFI network, which differentiates the switch between a cellular network and the WIFI network into different kinds to switch and judge based on the position information of periodic measurement commonly provided by the network and the terminal and the information of the velocity and directions and angles along with it to increase the switch efficiency among heterogeneous networks and reduce unnecessary switch times.
Owner:上海贝豪通讯电子有限公司
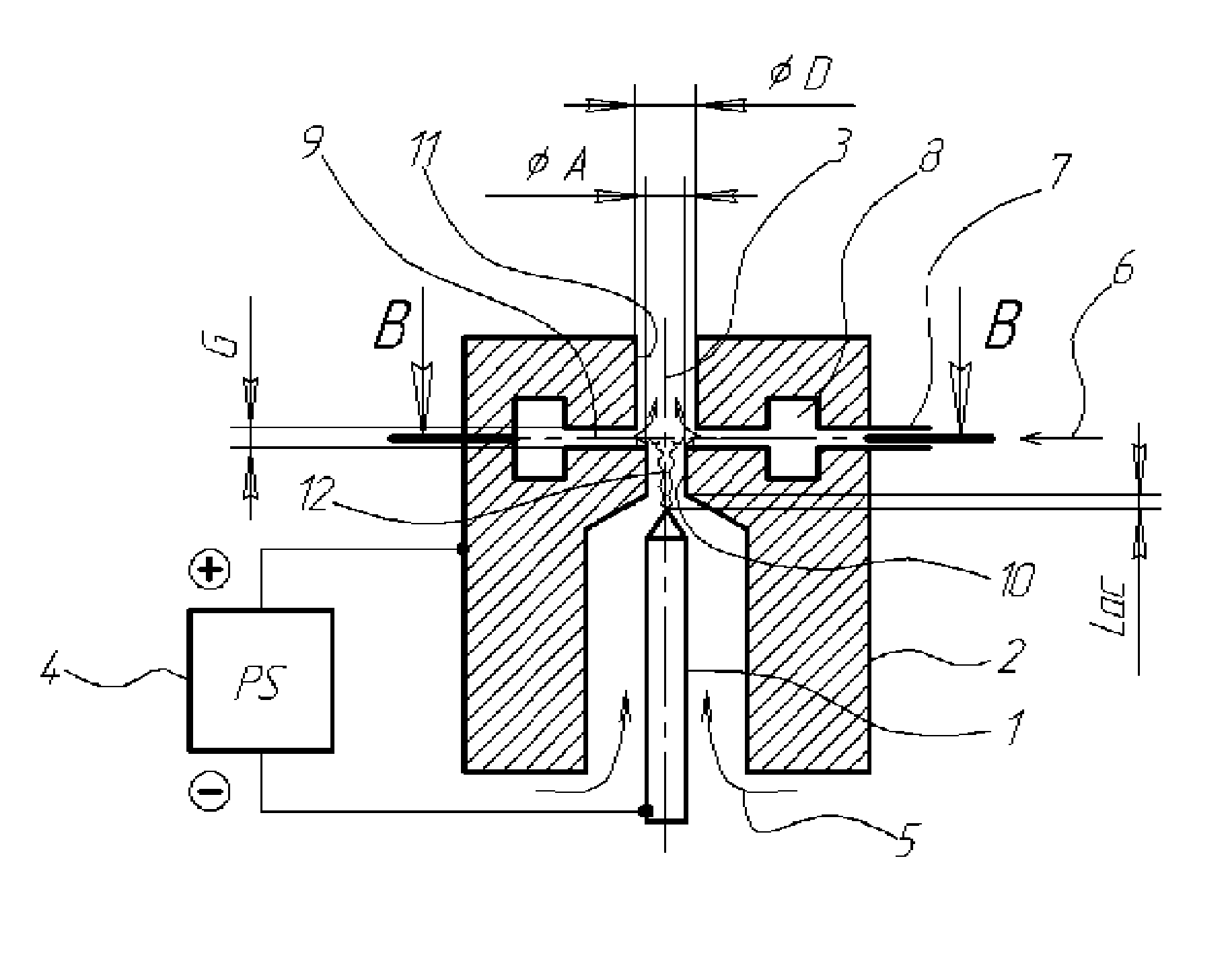
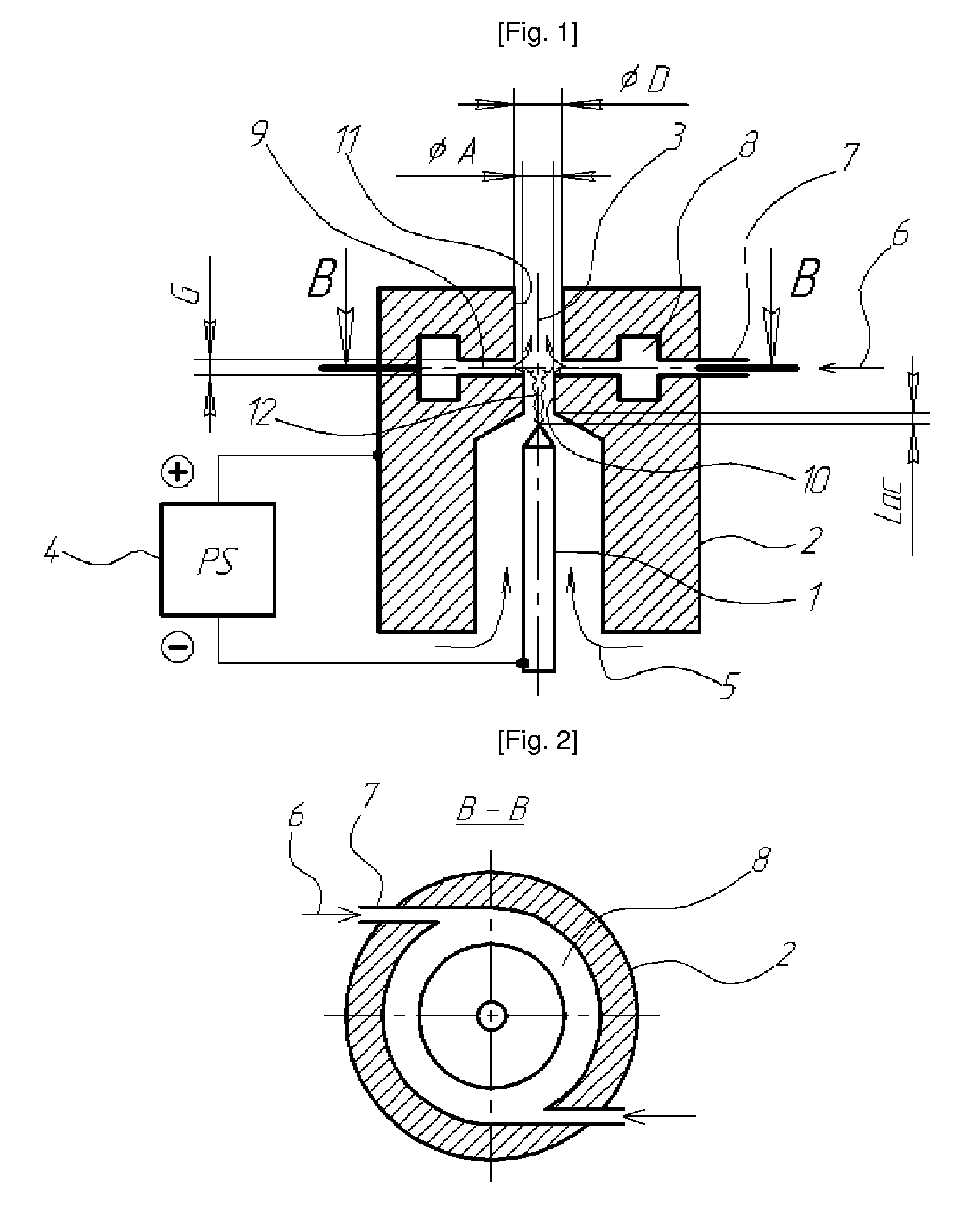
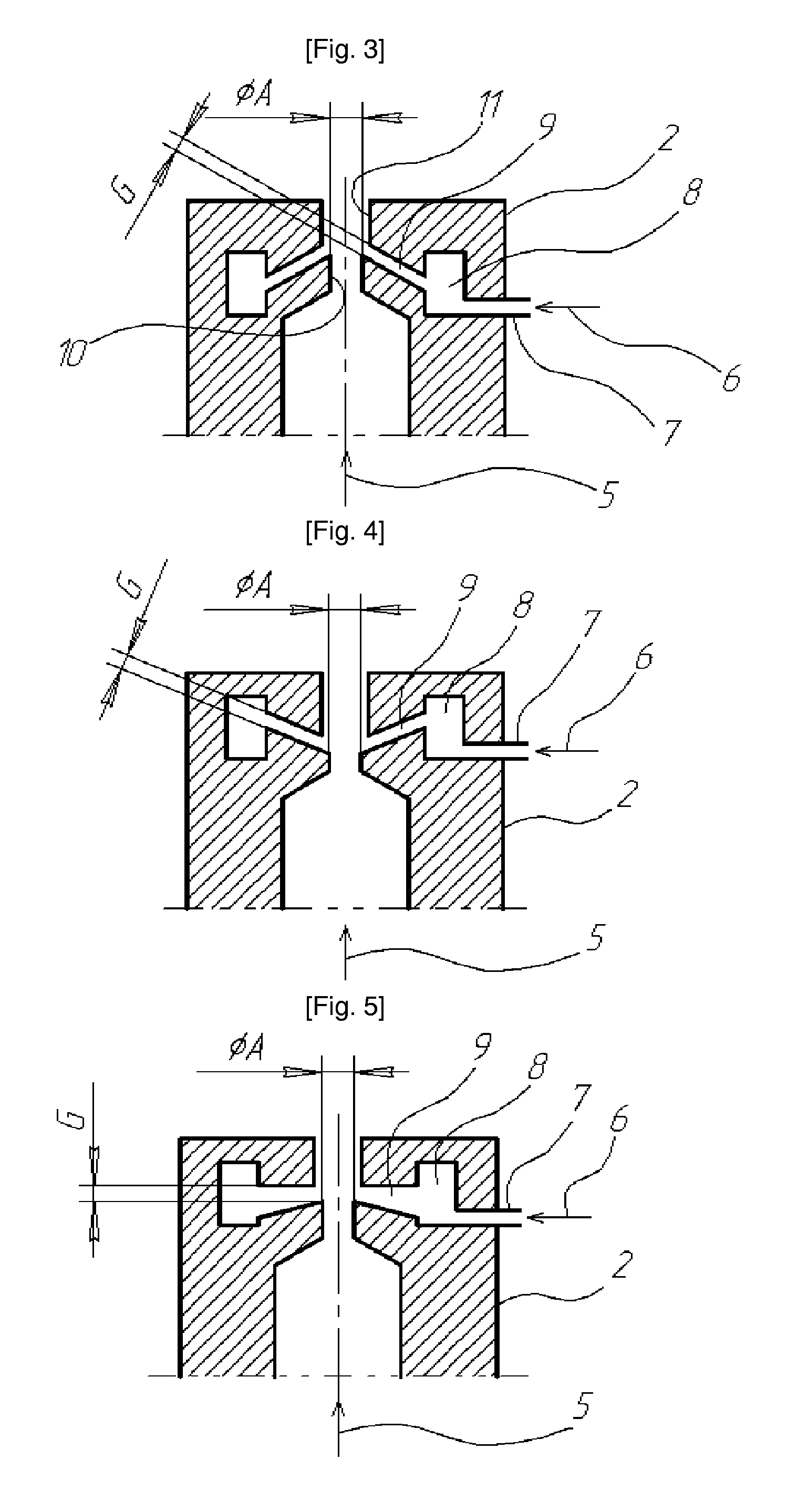
DC arc plasmatron and method of using the same
InactiveUS8129654B2Improve efficiencyHigh strengthPicture framesSpecial ornamental structuresChemical reactionForming gas
The present invention relates to a plasmatron structure for heating working gas in a DC arc discharge at the atmospheric or lowered pressures and can be used for different electronic, engineering, or vehicle-building industries and for medicine. An object of the invention is to provide improved effectiveness of process gas activation and increased completeness of plasma-chemical reactions. These objects are achieved in a DC arc plasmatron comprising a rod cathode, a nozzle anode having a body member and a through axial orifice, a power supply unit connected to both electrodes, and a gas system for feeding plasma-forming gas into inter-electrode space and supplying suitably selected technologic gas or gas mixture into the anode orifice through an internal opening communicating with said orifice and positioned between its inlet and outlet parts. In the plasmatron according to the invention, said opening is configured as a continuous circular axial gap between said parts of said anode orifice, while the size of said gap can be smaller or larger than the diameter of the inlet part of said anode orifice and the diameter of the outlet part of said anode orifice can also be smaller or larger than the inlet part of said anode orifice. In addition the inventive plasmatron can be successfully applied in vacuum conditions to extend lifetime of the activated process gas and to provide the clean treatment procedure.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND JEJU NAT UNIVERSTIY
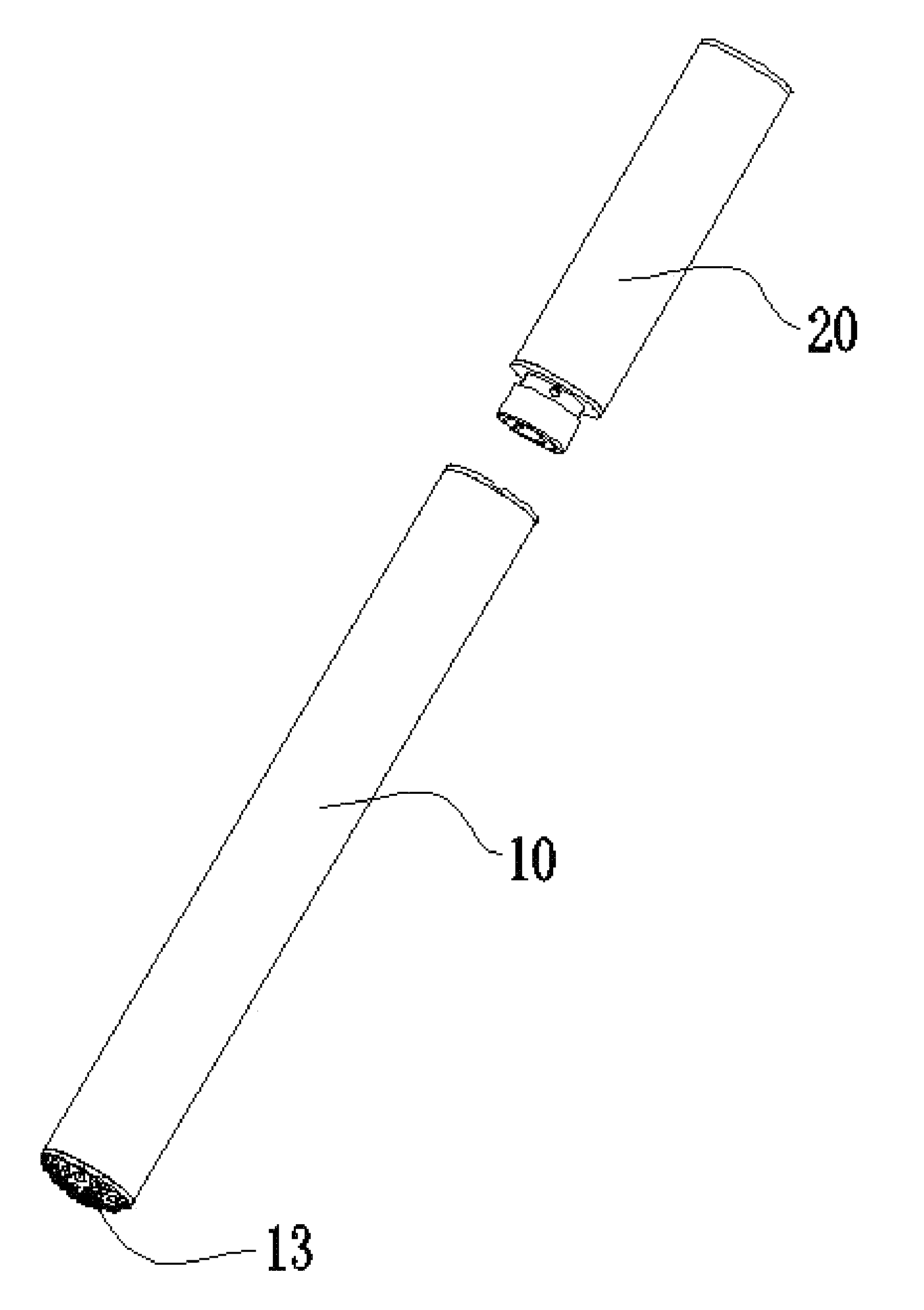
Battery assembly and electronic cigarette having same
ActiveUS20150083145A1Increase volumeExtend service hoursTobacco pipesTobacco devicesElectricityElectrical battery
The present disclosure relates to an exemplary battery assembly for an electronic cigarette. The battery assembly includes a housing, a battery received in the housing, an AAES electrically connected with the battery, an end cover fixed at one end of the housing, and a holder. The end cover defines a receiving space. The holder includes a bottom wall, a side wall, and a plurality of spaced protruding stages. The side wall extends from a first surface of the bottom wall. The protruding stages are formed on an opposite second surface of the bottom wall. The side wall and the bottom wall cooperatively define an accommodating space. The AAES is received in the accommodating space in such a manner that the protruding stages face the battery. The holder is received in the receiving space.
Owner:SHENZHEN FIRST UNION TECH CO LTD
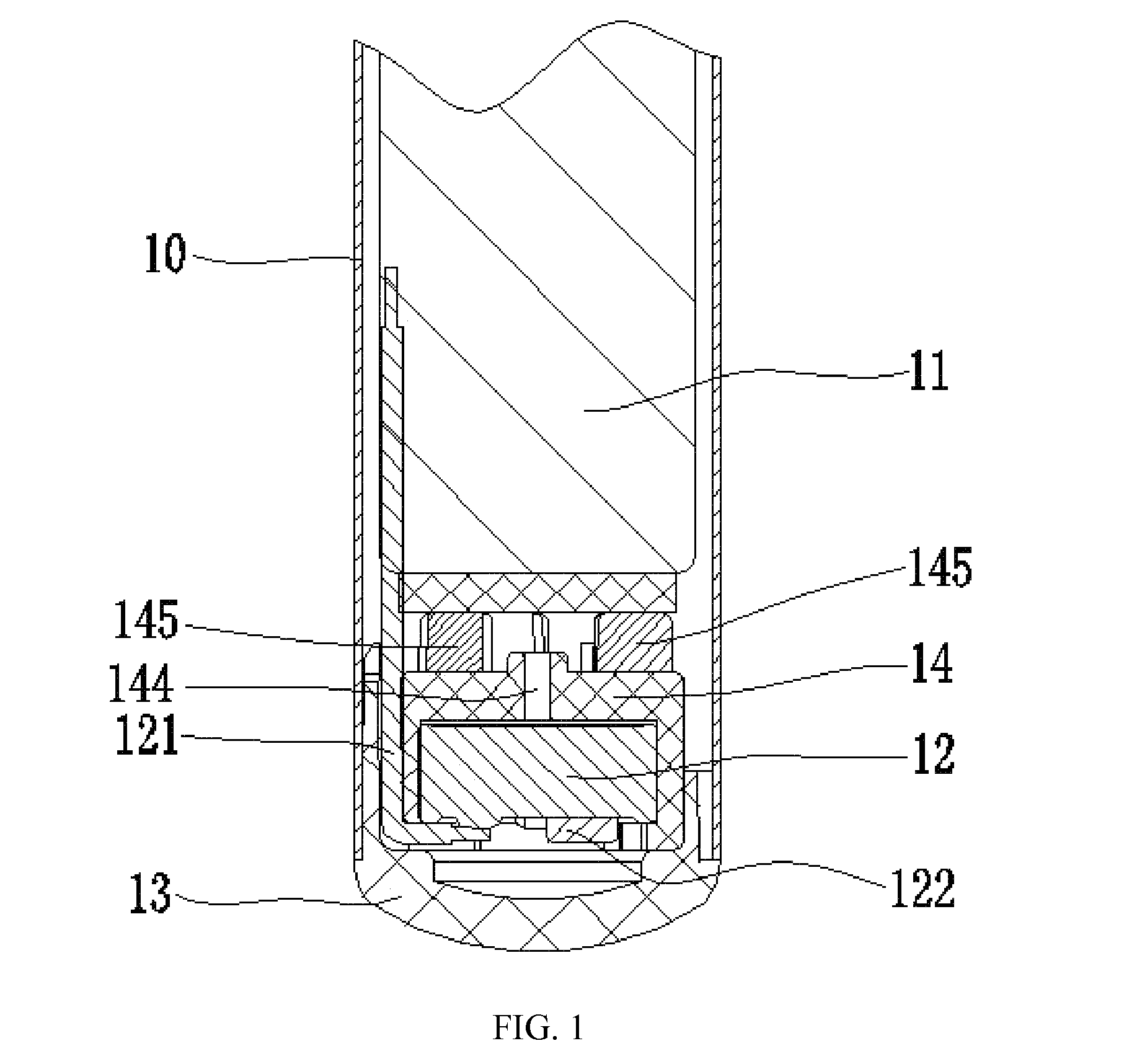
Battery for electronic cigarette
InactiveUS20150280273A1Extend service hoursSimple designFinal product manufactureCylindrical casing cells/batteryElectronic cigaretteEngineering
A battery for an electronic cigarette including a core, a control plate, a positive contact, a negative contact, an insulating ring, a fixing ring, a pad, an insulting piece, and a steel pipe. The positive contact is disposed at the top of the core, and passes through the insulating ring, the fixing ring, and the pad in sequence to connect to a positive electrode of the core. The insulating piece, the control plate, and the negative contact are disposed in sequence close to the rear part of the core, and the negative contact contacts with an outer ring of the core whereby connecting to a negative electrode of the core. The control plate and the positive contact are connected to the core by electric welding wires.
Owner:LIU TUANFANG
Goods management method, device and system
InactiveCN106127564AExtend service hoursEasy to buyAutomatic card filesPayment architecturePaymentIdentity recognition
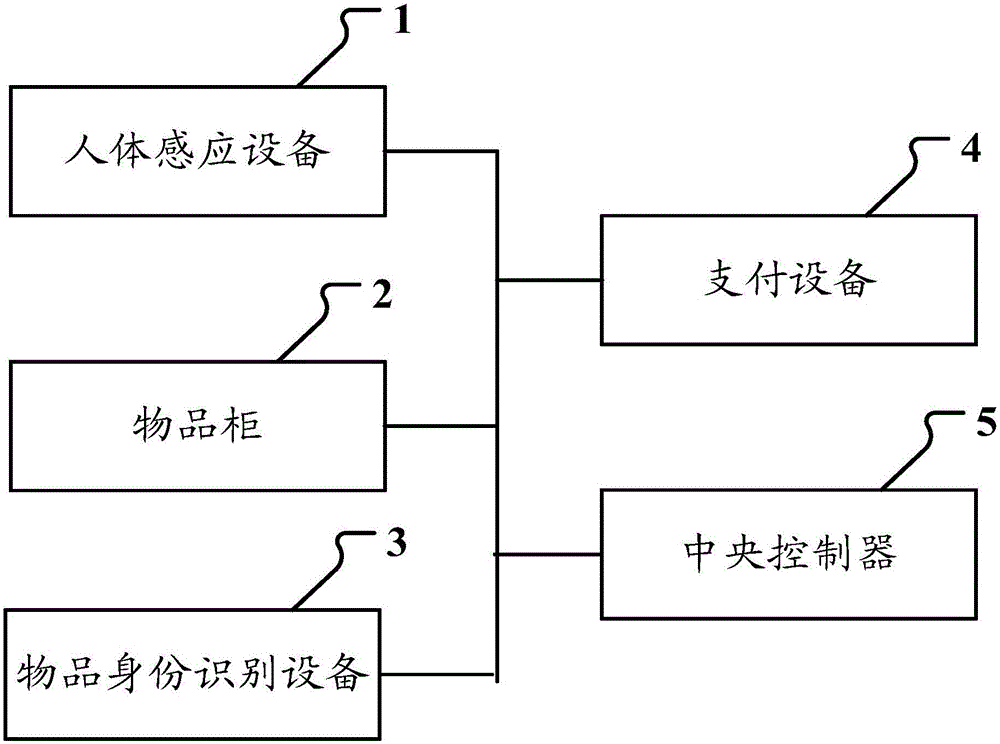
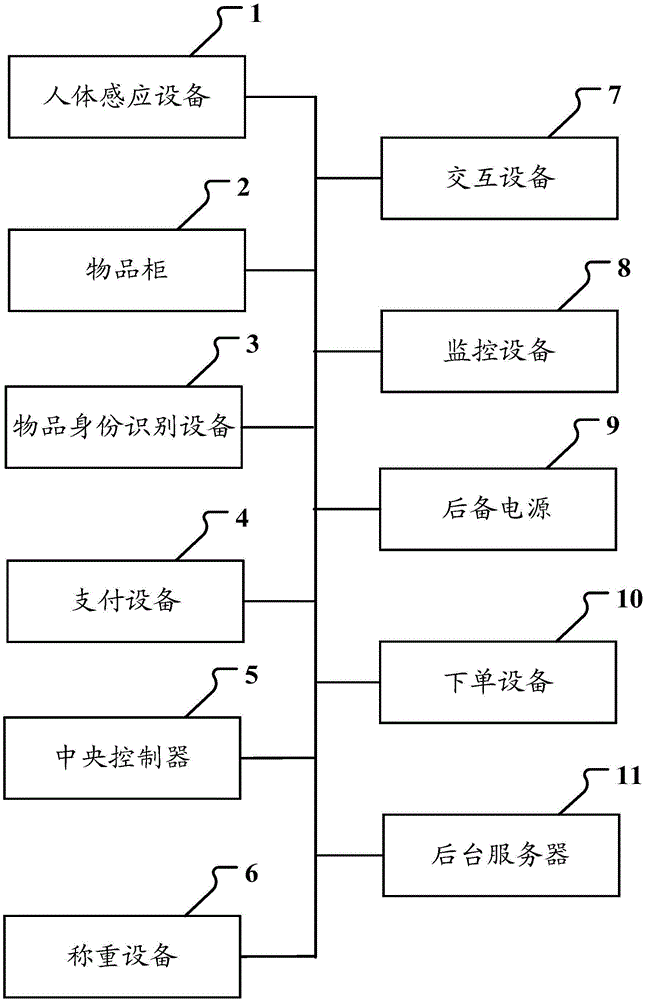
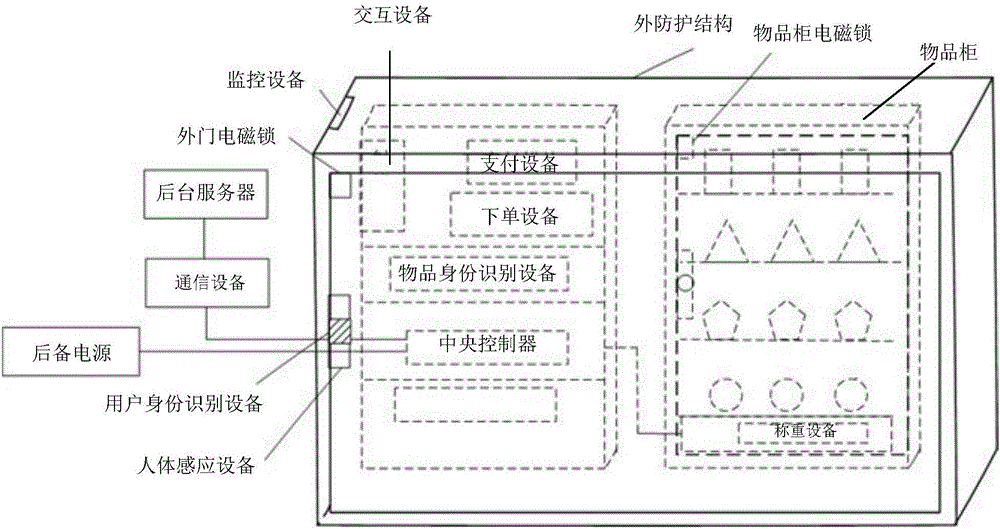
The disclosure relates to a goods management method, device and system. The goods management system comprises a human body induction device, a goods cabinet, a goods identity recognition device, a payment device and a central controller, wherein the human body induction device is arranged in a shopping zone and is used for determining whether any user is in the shopping zone, the goods cabinet is arranged in the shopping zone and is used for displaying and selling goods, the good identity recognition device is used for identifying goods being sold, and the payment device is used for the user to make payments; the central controller is used for managing and controlling the human body induction device, the goods cabinet, the goods identity recognition device and the payment device that are all connected with the central controller. Via use of the goods management method, device and system, convenient unmanned self-help shopping can be realized.
Owner:科识通网络科技(南京)有限公司
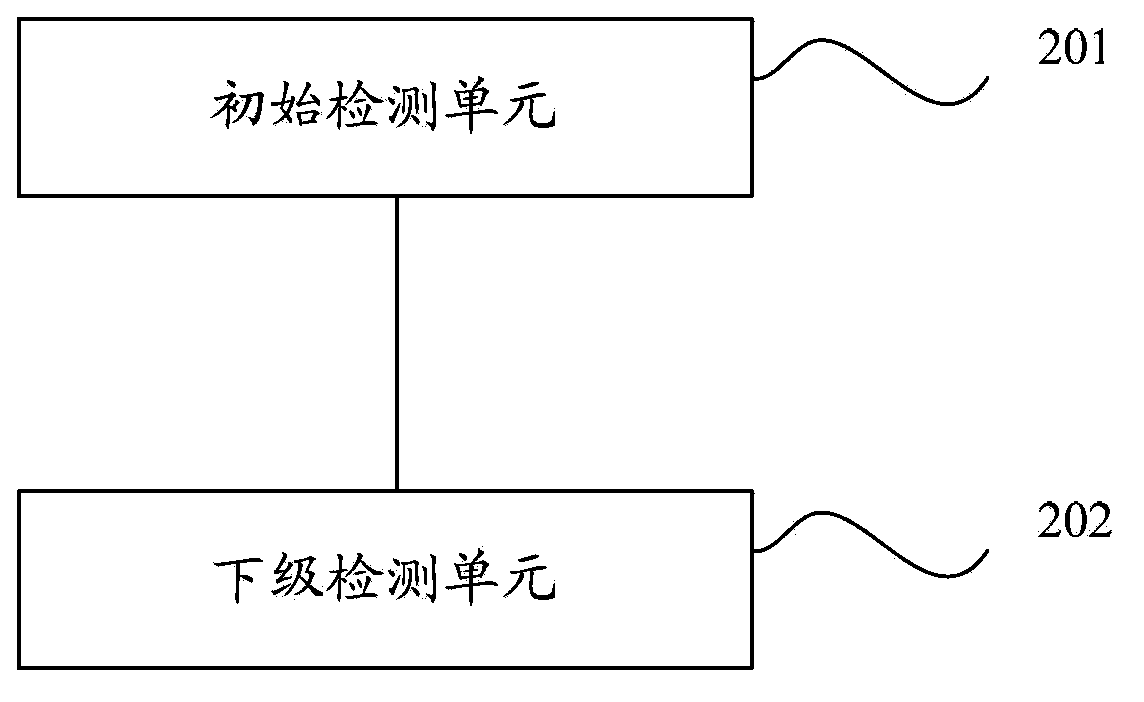
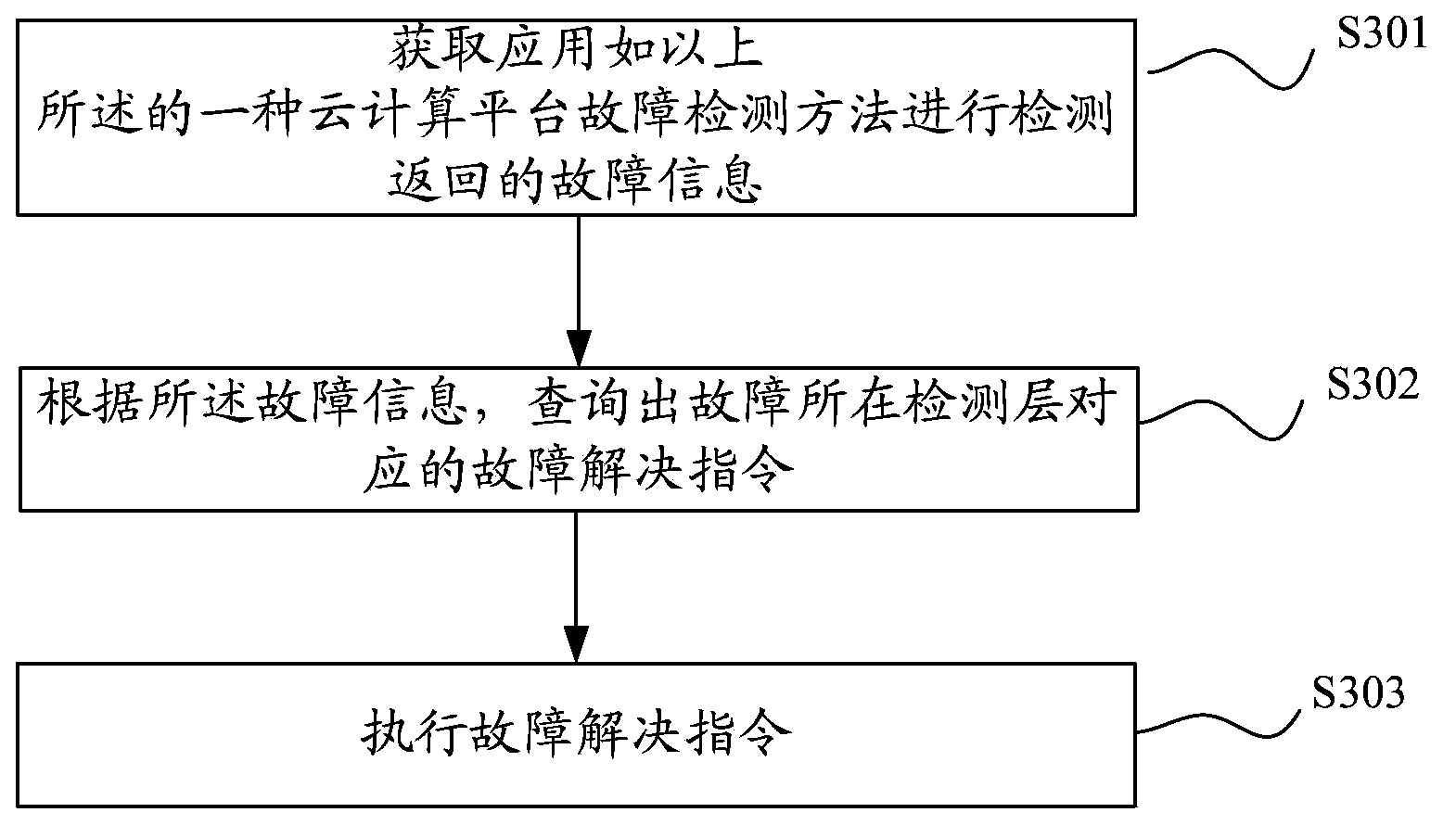
Cloud computing platform fault detection method, cloud computing platform fault detection method, solving method and solving device
ActiveCN103701627AReduce downtimeQuickly restore serviceEnergy efficient ICTData switching networksFast recoveryCloud computing
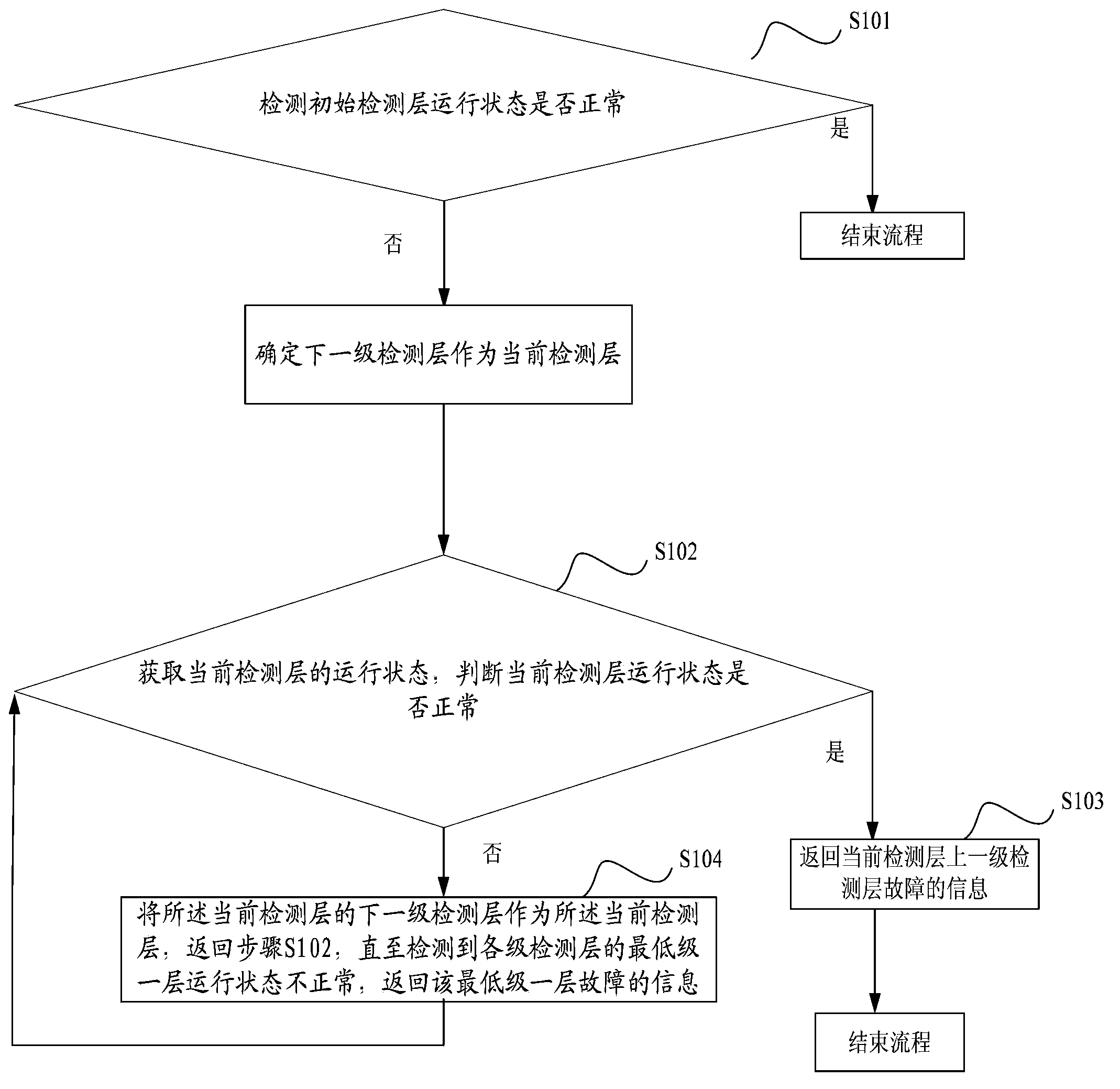
The invention discloses a cloud computing platform fault detection method, a cloud computing platform fault detection method, a solving method and a solving device, and aims to achieve the purpose of automatically discovering and resolving a fault of a cloud computing platform. According to the methods and the devices, the cloud computing platform is divided into various detection layers, whether the operating state of the initial detection layer is normal is detected, the abnormality of an operating state of the initial detection layer is taken as an entrance for each stage of the detection layer, and the operating state of the current detection layer is obtained by detecting the next stage of the detection layer as the current detection layer stage by stage, so that the lowest stage detection layer of which the operating state is abnormal is searched and the detection layer on which the final fault is positioned is determined; therefore, the purpose of automatically discovering the fault is achieved; in addition, on the aspect of resolving the fault, different solving mechanisms are made to solve the problems of each stage of the detection layer to reduce the fault time as possible by judging the detection layer on which the fault is positioned, so that the purpose of recovering service quickly is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING SOHU NEW MEDIA INFORMATION TECH
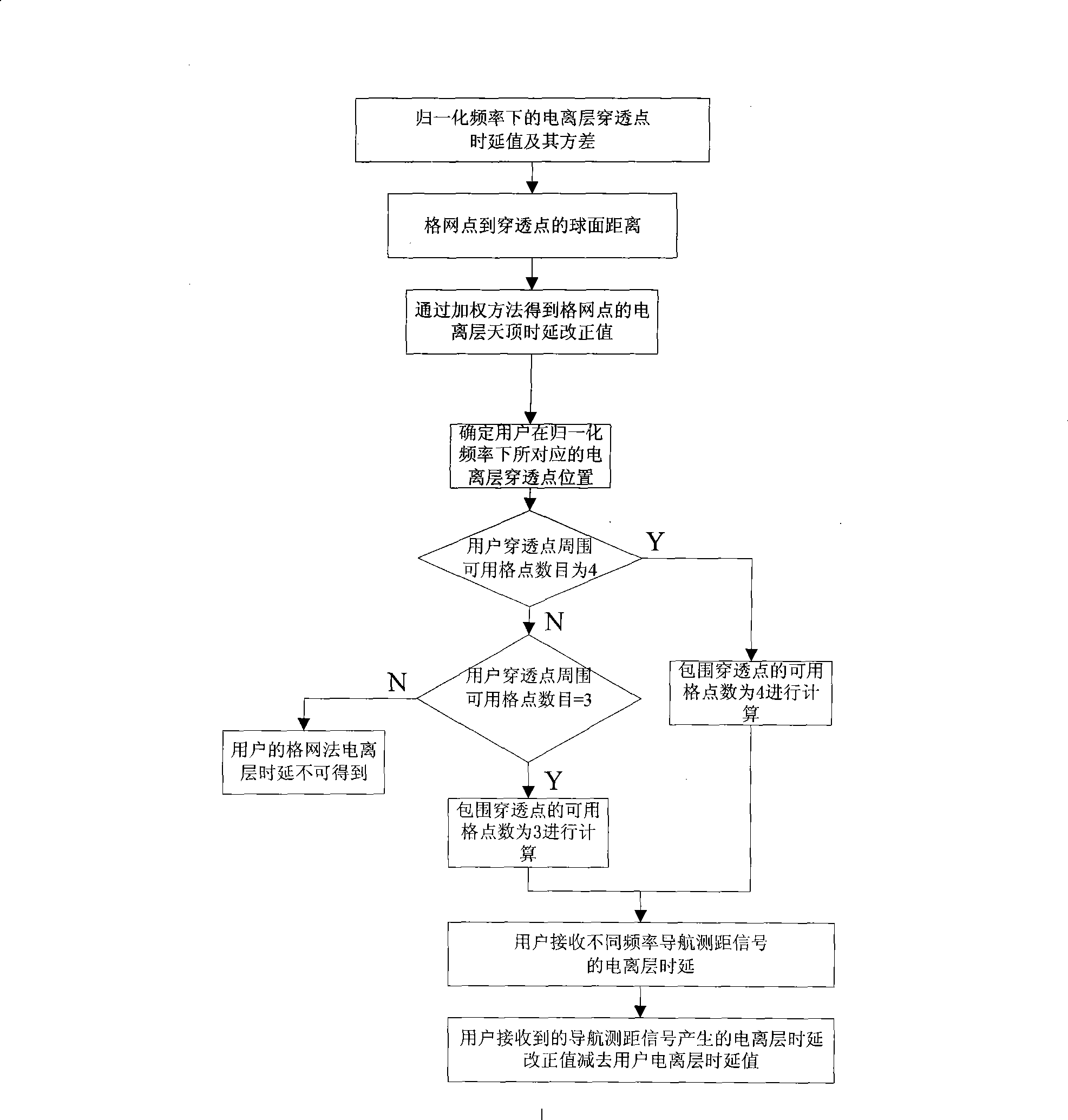
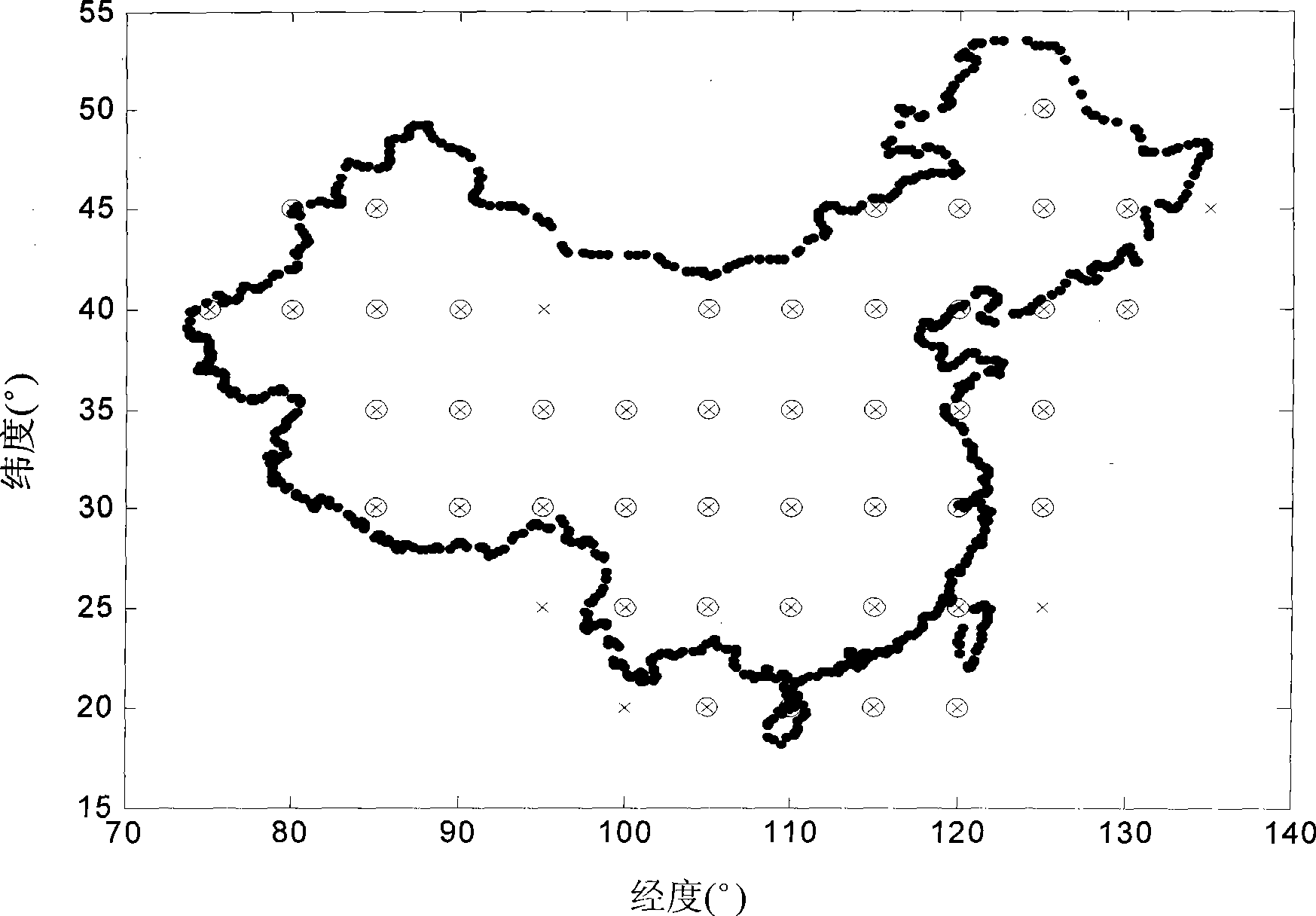
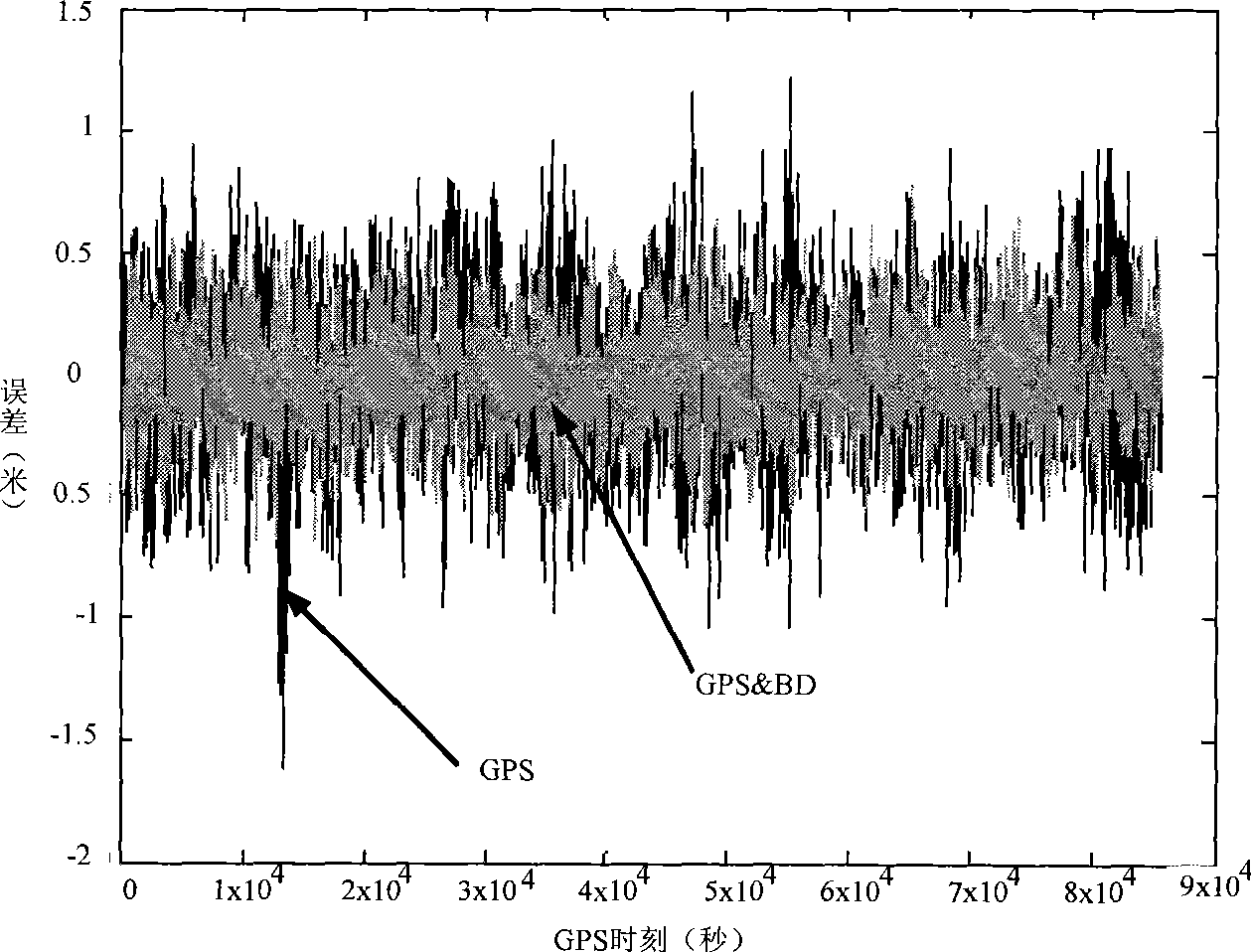
Ionospheric layer grid regulation method suitable for multi-module satellite navigation system
InactiveCN101487883AExtend service hoursReduce delay correction errorBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationIonospheric pierce pointDelayed time
The invention discloses a method for correcting an ionospheric grid which is applied to a multimode satellite navigation system, comprising the following steps: according to data from different satellite navigation systems, normalizing the time delay correction value of the ionosphere and the variance thereof to a specified frequency; according to the normalized time delay value and variance of the breakthrough point of the ionosphere, carrying out weighing calculation respectively to determine the time delay correction value of the ionosphere zenith of the grid point in the specified frequency; utilizing the time delay correction value of the ionosphere zenith of the grid point to carry out interpolation, and determining the time delay correction value of the zenith ionosphere of the satellite ranging signals received by a user in the normalized frequency; finally determining the ionosphere time delay correction value when navigation and ranging signals with different frequencies are received by the user; and deducting user ionosphere time delay value from the ionosphere time delay correction value generated by the navigation and ranging signals received by the user to obtain the user ionosphere delay time value after elimination. By adopting the method, errors of ionosphere time delay correction are reduced, correction precision of the ionospheric grid is improved and location precision of the user can be greatly improved when the pseudo-range value of the user is used for location calculation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
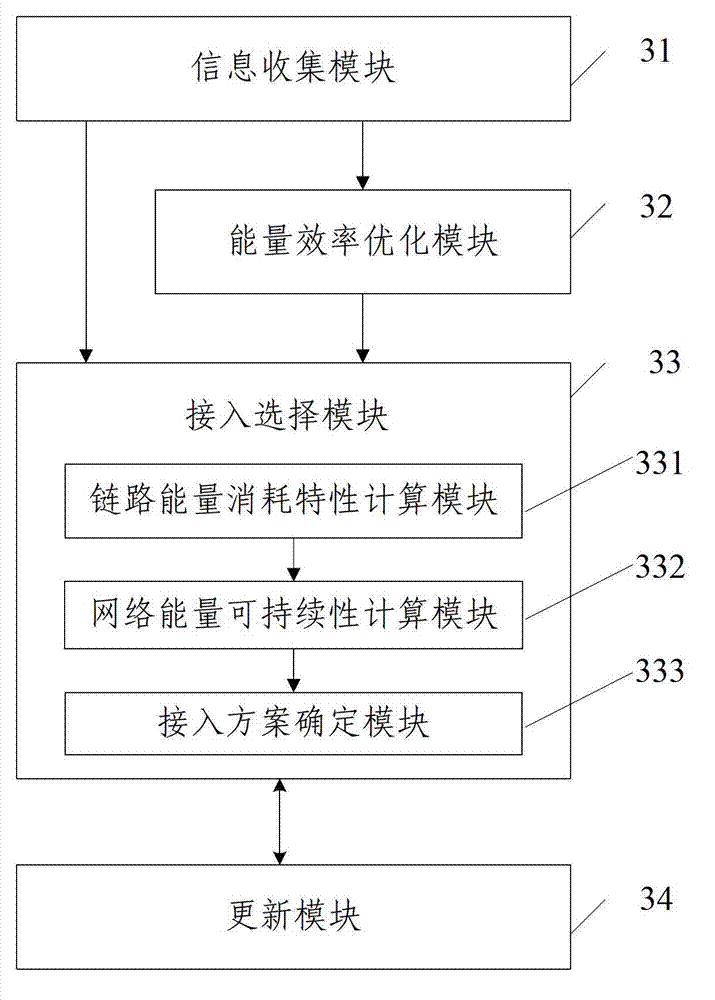
Renewable energy supply base station access selection method and system
ActiveCN103052134AImprove uniformityExtend service hoursPower managementAssess restrictionRenewable energy supplyEnergy sustainability
The invention discloses a renewable energy supply base station access selection method and a renewable energy supply base station access selection system. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring information which affects candidate base station access selection in a renewable energy supply wireless communication network; calculating optimal energy efficiency, which can be reached by a link, and a link energy consumption characteristic when a terminal is accessed to a candidate base station according to the received information which affects the candidate base station access selection; initializing a terminal set accessed to each candidate base station, judging whether a network with energy balance is an initial access terminal or not and sustainably determining an access scheme according to network energy with energy balance; and judging whether a non-accessed terminal is available or not, updating the terminal set accessed to each candidate base station to continuously perform access selection if the non-accessed terminal is available and otherwise finishing selection. According to the method and the system, energy sustainability and balance of all base stations in the entire network are improved, the integral energy consumption of the network is minimized, and the service time of the network is prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
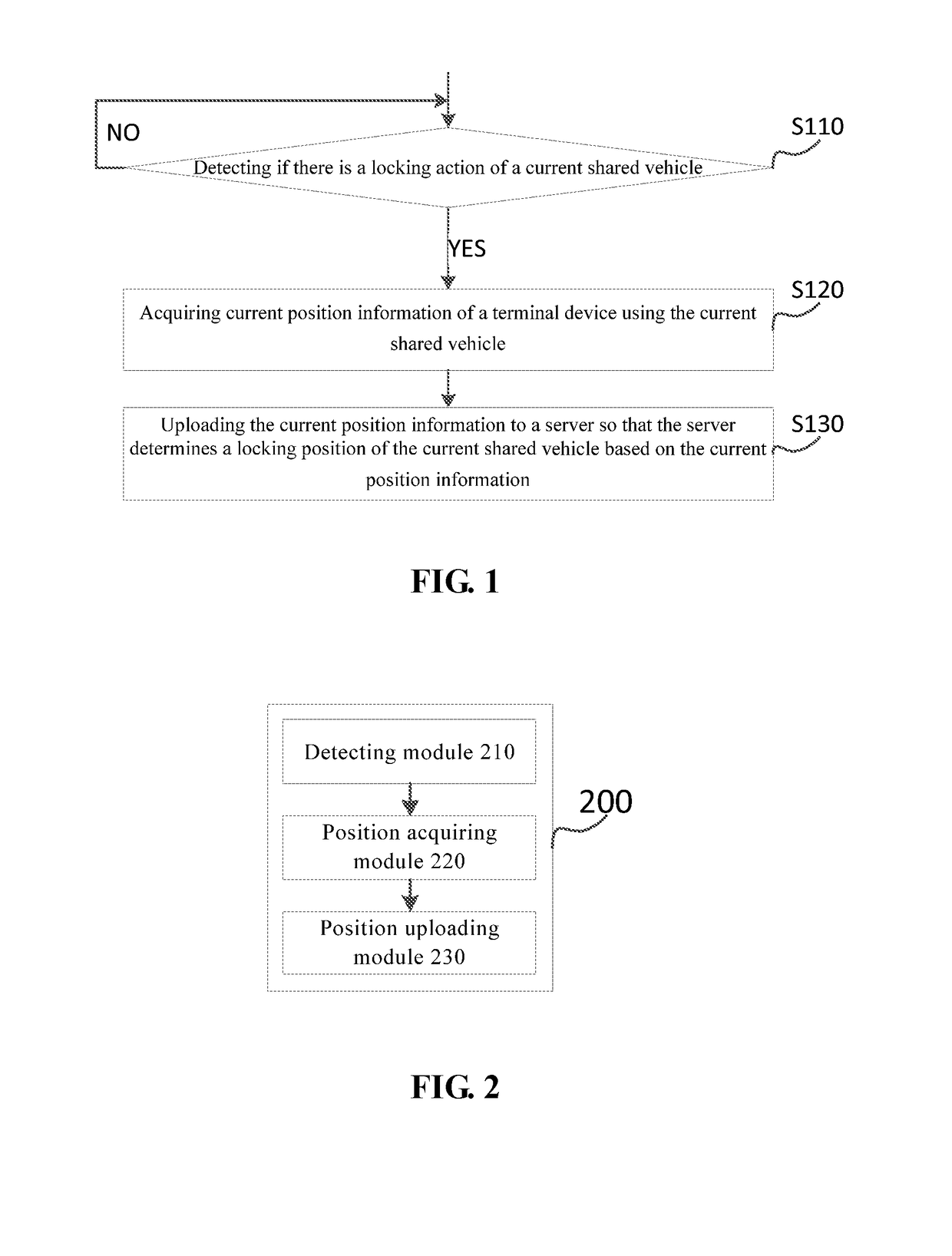
Shared vehicle positioning method and apparatus, and terminal device
InactiveUS20180301037A1Low costReduce power consumptionInstruments for road network navigationRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTerminal equipmentComputer module
Described is a shared vehicle positioning method and apparatus, and a terminal device. The positioning method comprises: detecting if there is a locking action of a current shared vehicle; if yes, acquiring current position information of a terminal device using the current shared vehicle; and uploading the current position information to a server so that the server determines a locking position of the current shared vehicle based on the current position information. Using the positioning method of the present invention, a shared vehicle without a GPS positioning module can be positioned. In this way, the hardware cost and power consumption of the shared vehicle can be reduced, the service time of the battery of the shared vehicle can be extended, and the followed maintenance cost of the shared vehicle can be reduced as well.
Owner:BEIJING MOBIKE TECH CO LTD
Easily adjustable tripod
ActiveUS8636429B2Evenly distributedExtend service hoursStands/trestlesCamera body detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CHEN QINGYUAN
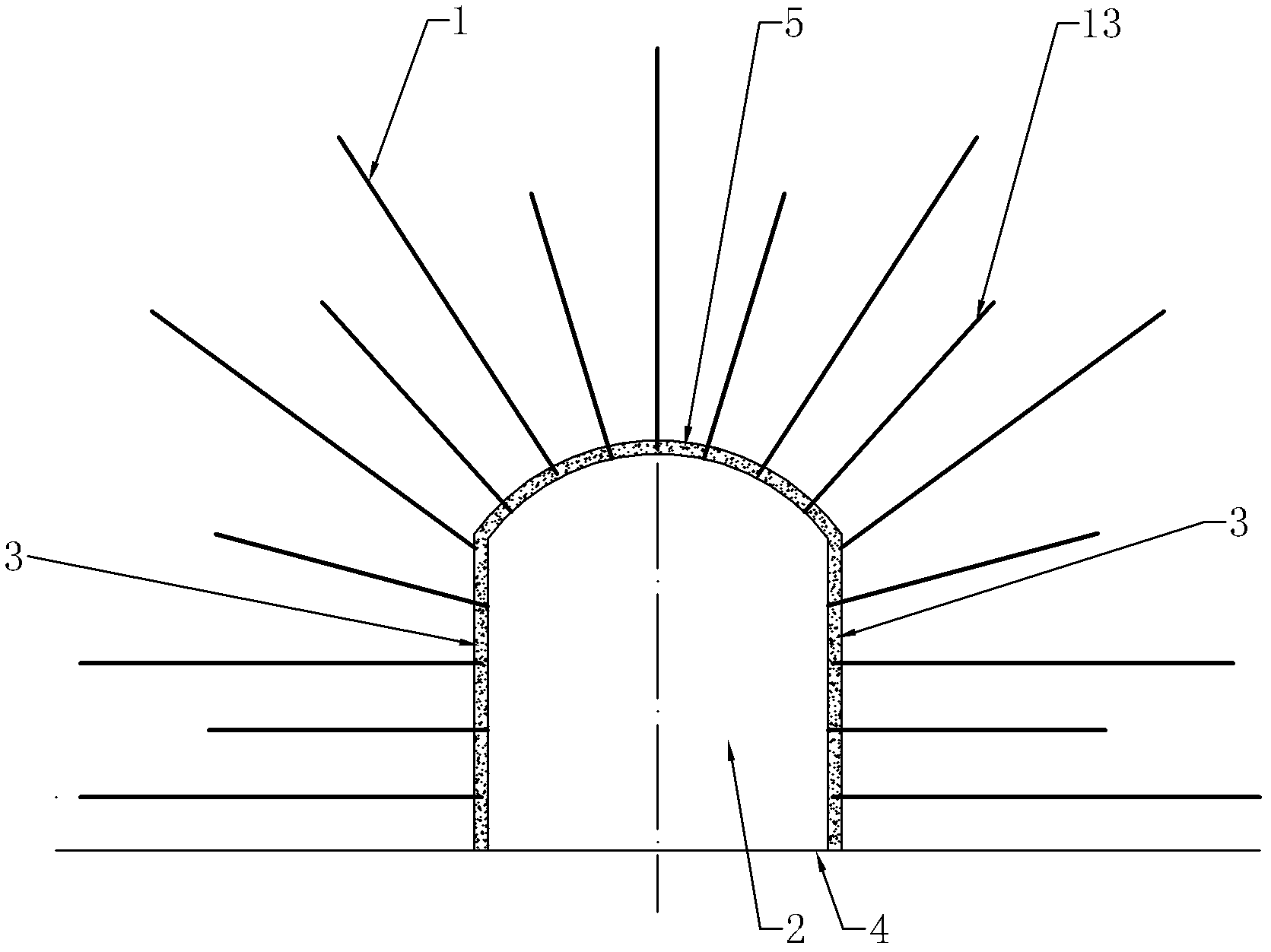
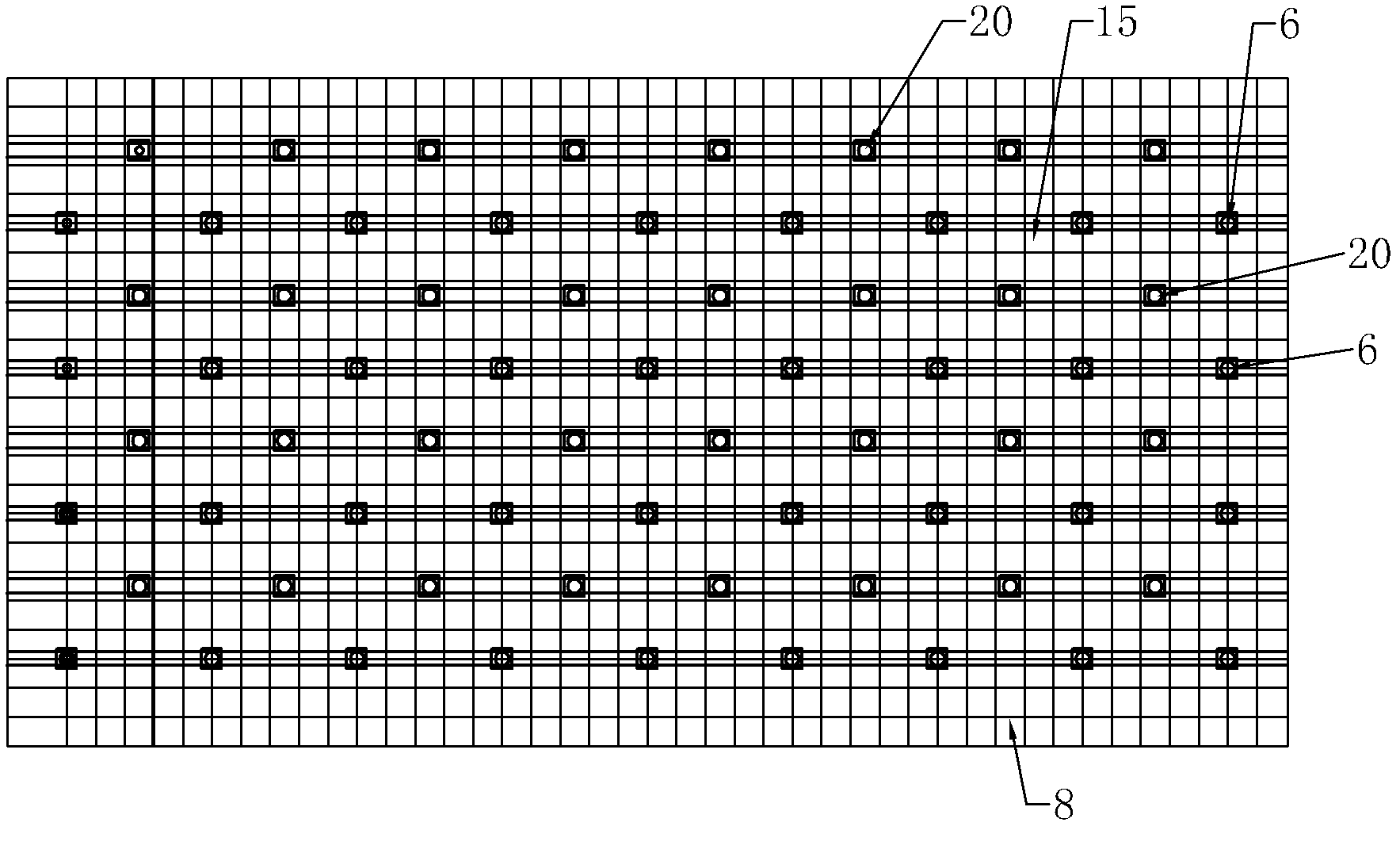
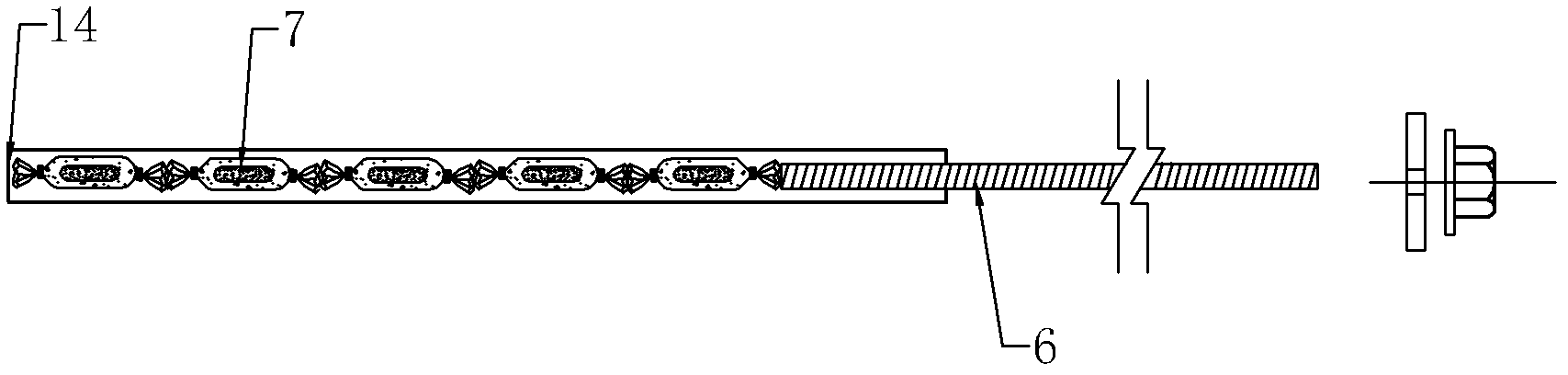
Full-length anchoring supporting method with intensive resin anchor rod and anchor-shotcrete net
InactiveCN102562093AAvoid deformationExtend service hoursUnderground chambersTunnel liningShotcretePre stress
The invention relates to a supporting method by use of resin anchor rod and anchor-shotcrete net for roadway for special growth conditions, such as soft and broken ore rocks, fissuring and cracks. The invention aims to provide a full-length anchoring supporting method with intensive resin anchor rod and anchor-shotcrete net, which can improve the supporting effect, prolong the roadway service time and improve the recovery rate. The supporting method comprises the following steps: A) carrying out loose rock removal after explosion of roadway; B) carrying out primary 50mm simple concrete spraying to the roadway; C) drilling a plurality of rows of main anchor rod hole groups vertical to a roadway rock wall; D) installing the main anchor rods; E) netting by using reinforcing steel bars; F) installing double rib bars on the main anchor rod group; G) endowing prestressing force to the main anchor rod, wherein the prestressing force of each main anchor rod is not less than 78.4kN; H) carrying out secondary 100mm concrete spraying; I) setting a row of reinforced anchor rod hole groups between two adjacent rows of main anchor rod hole groups; J, installing the reinforced anchor rod; K) installing the double rib bars on the reinforced anchor rod groups; and L) endowing prestressing force to the reinforced anchor rod.
Owner:SHANDONG SHENGDA MINING
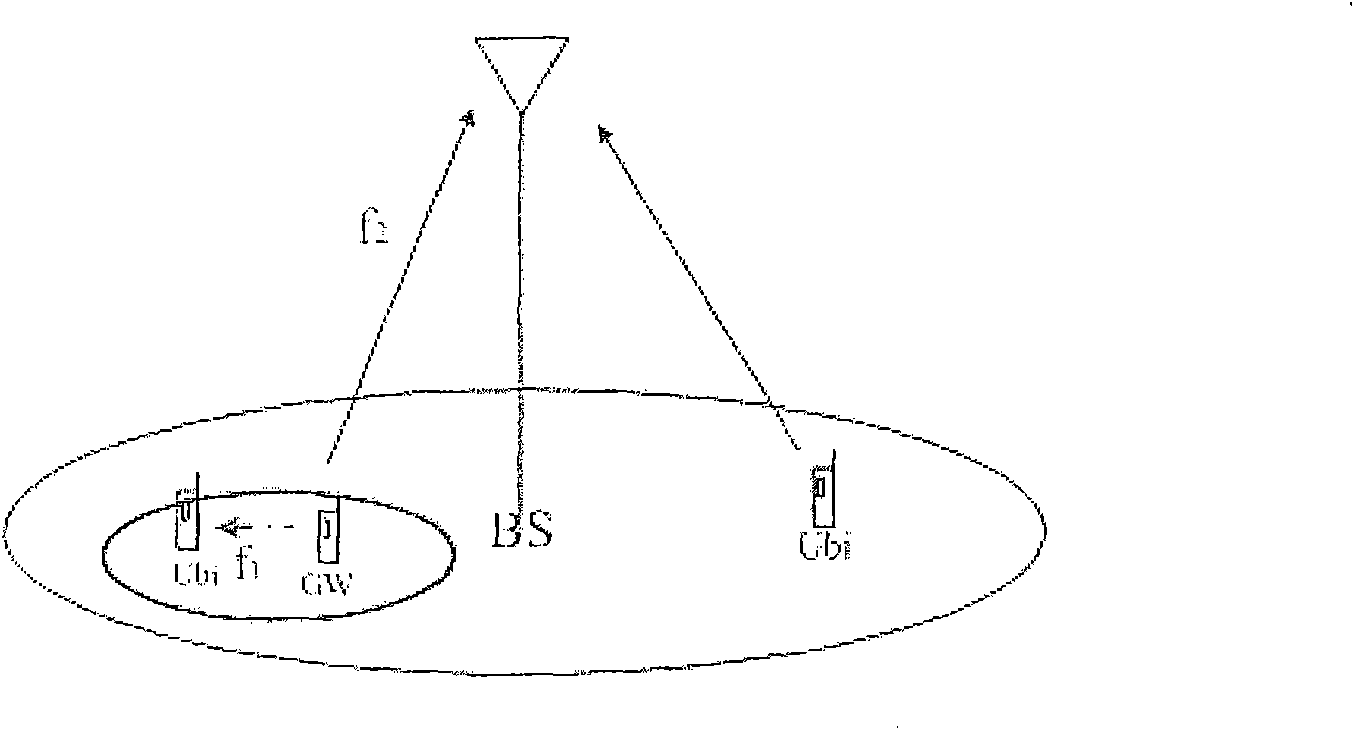
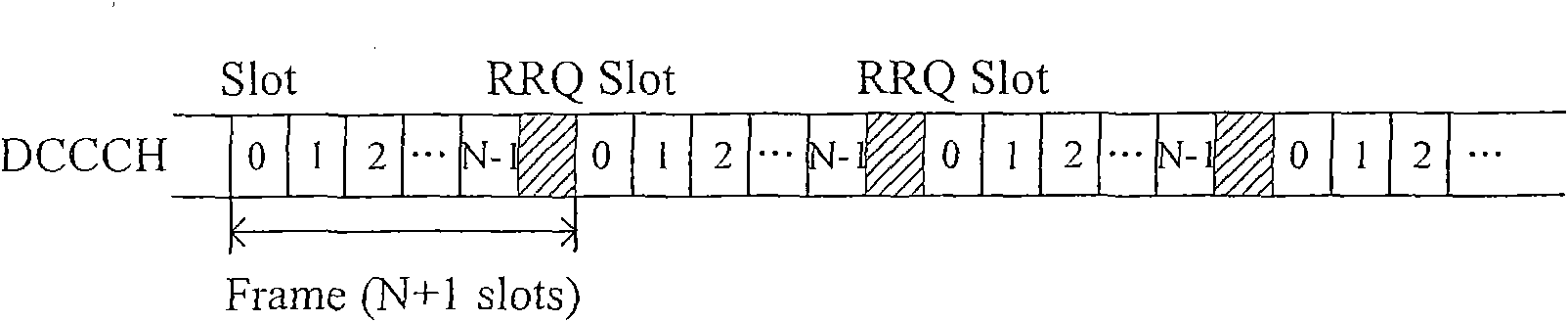
Method for accessing hybrid network and gateway equipment, wireless terminal and communication system thereof
ActiveCN101562903AExtend service hoursReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesCommunications systemSignal on
The invention discloses a method for accessing a hybrid network comprising a wide-area network and a distributed network and gateway equipment, a wireless terminal and a gateway communication system thereof, aiming at reducing the consumption of the wireless terminal accessing a gateway. The method comprises the following steps: the gateway equipment monitors a relay request timeslot on a downlink public control channel of the wide-area network; the wireless terminal sends a relay request message which requests to conduct relay on the data grouping to be sent in the relay request timeslot on the downlink public control channel; and if the gateway equipment monitors the relay request message from the wireless terminal in the relay request timeslot, a connection with the wireless terminal is established under an environment of the distributed network. Therefore, the gateway equipment only accesses the wireless distributed network when the peripheral wireless terminals have data relay demand without monitoring the signals on two networks simultaneously, thus reducing power consumption.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
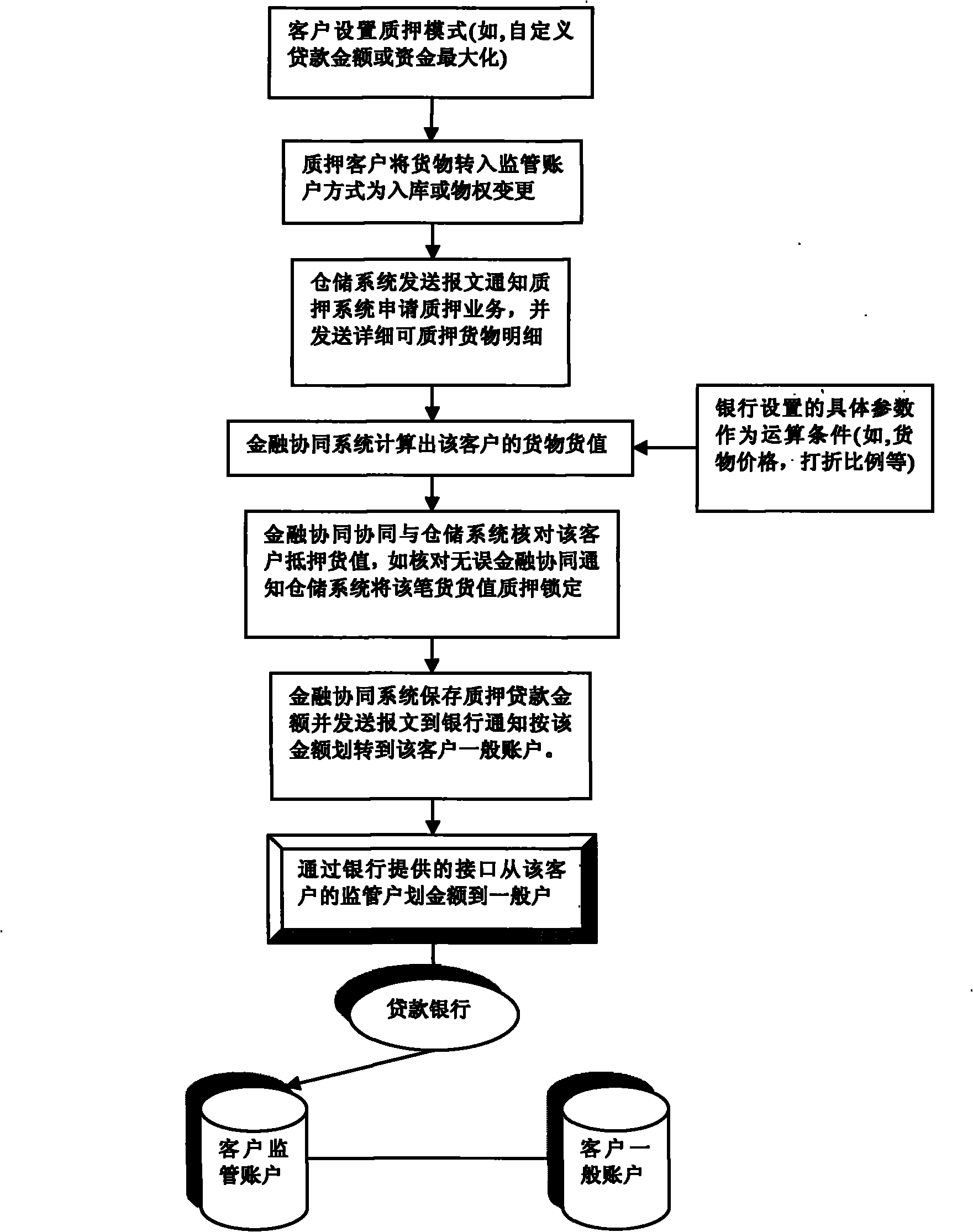
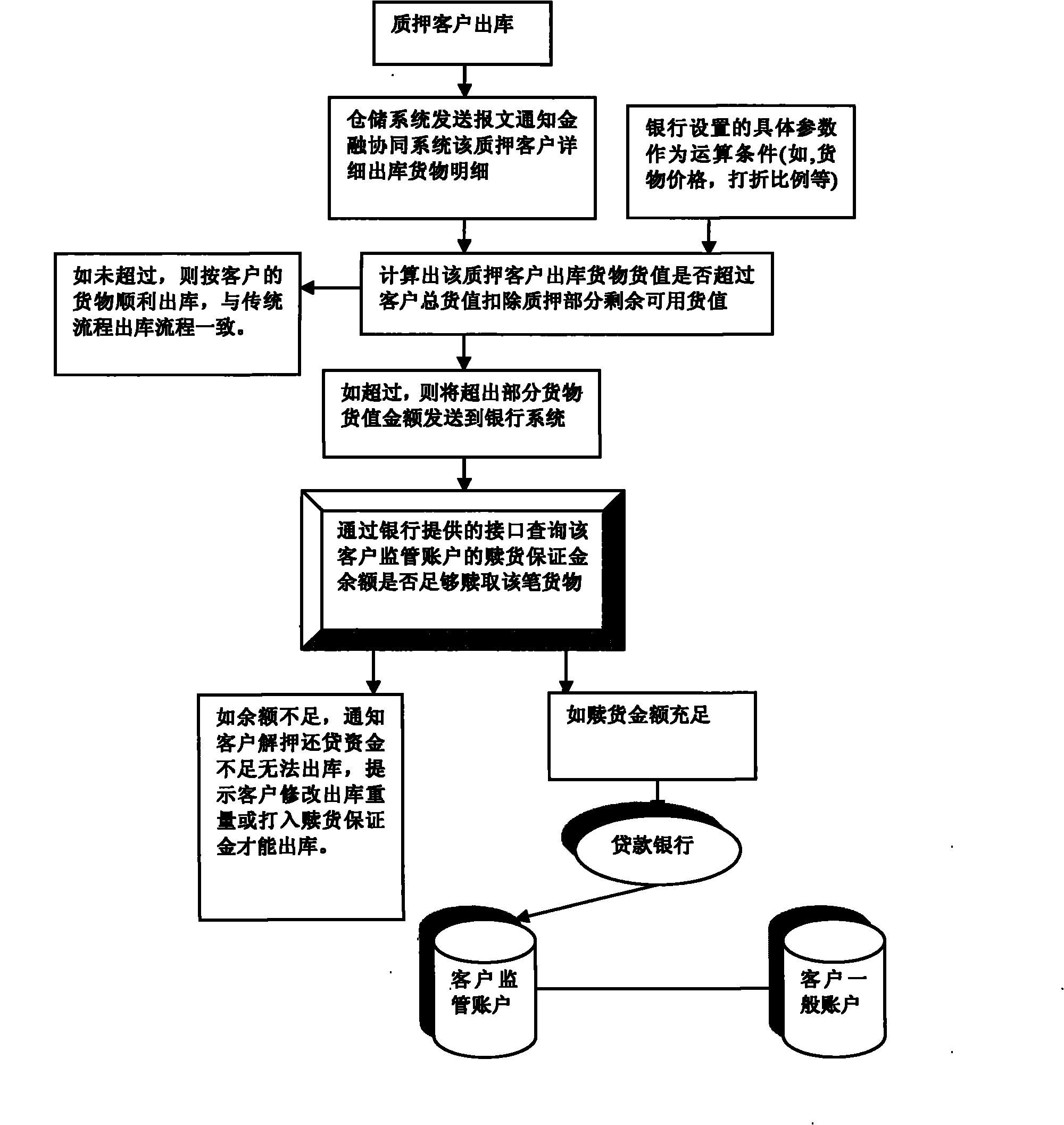
Fourth-party financial synergy service system and service method thereof
The invention discloses a fourth-party financial synergy service system and a service method thereof. The system comprises a pledge customer, a bank, a third-party logistics storage enterprise and a fourth-party bank, and also comprises a financial service information system which connects a digital storage system of the third-party logistics storage enterprise and a business to business (B2B) system of a fourth-party bank in a seamless way. In the method, the digital storage system of the third-party logistics storage enterprise is connected with an independently researched and developed financial service information system and a bank B2B system in a seamless way so as to realize the informatization of a bank pledge business of the storage of logistics products in metal material industry; and bank capital flow and enterprise logistics are integrated organically so as to provide an integrated storage service business system which integrates a plurality of bank services such as financing, account settling and the like for small and medium enterprise costumers.
Owner:重庆文迅科技股份有限公司
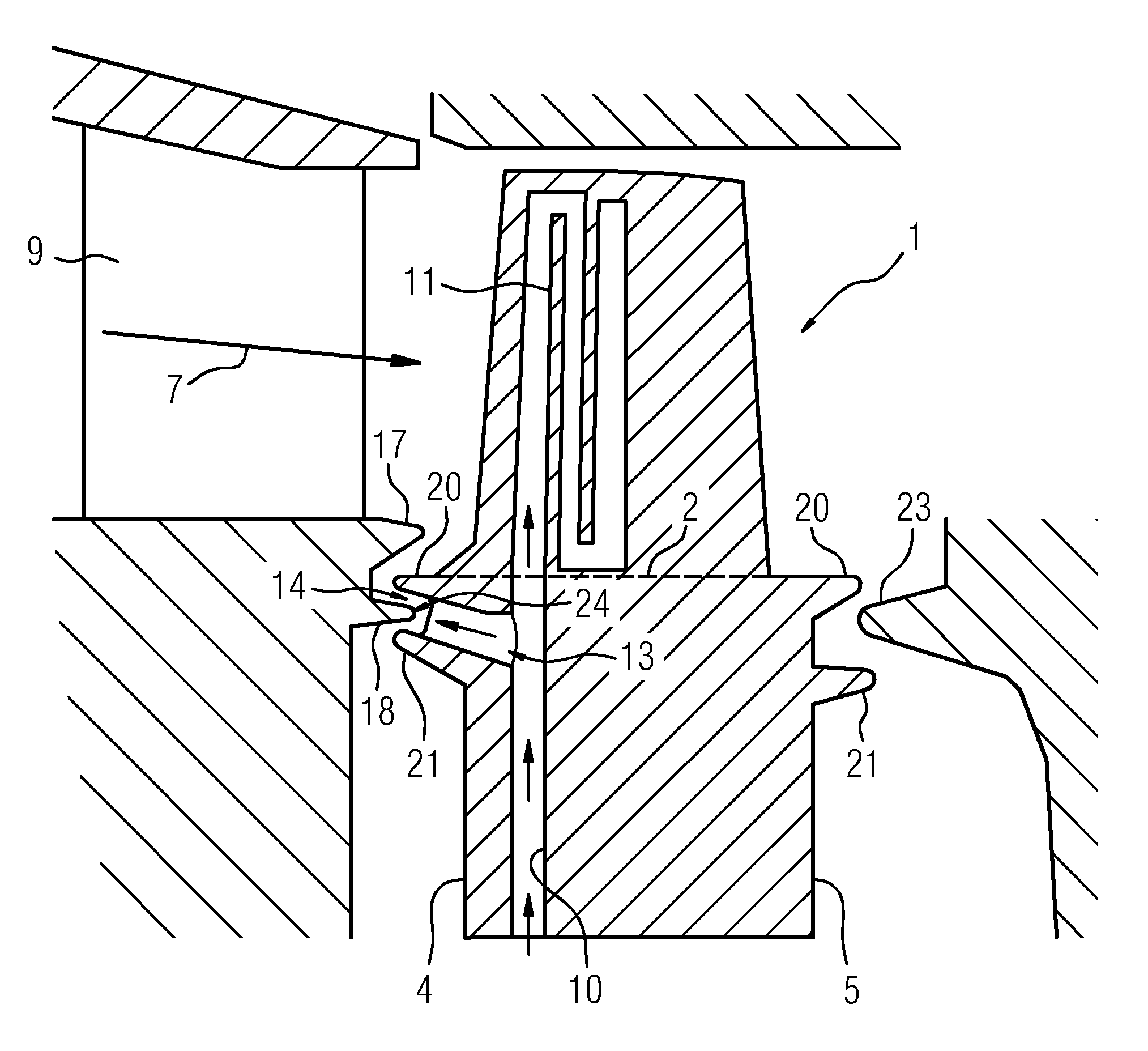
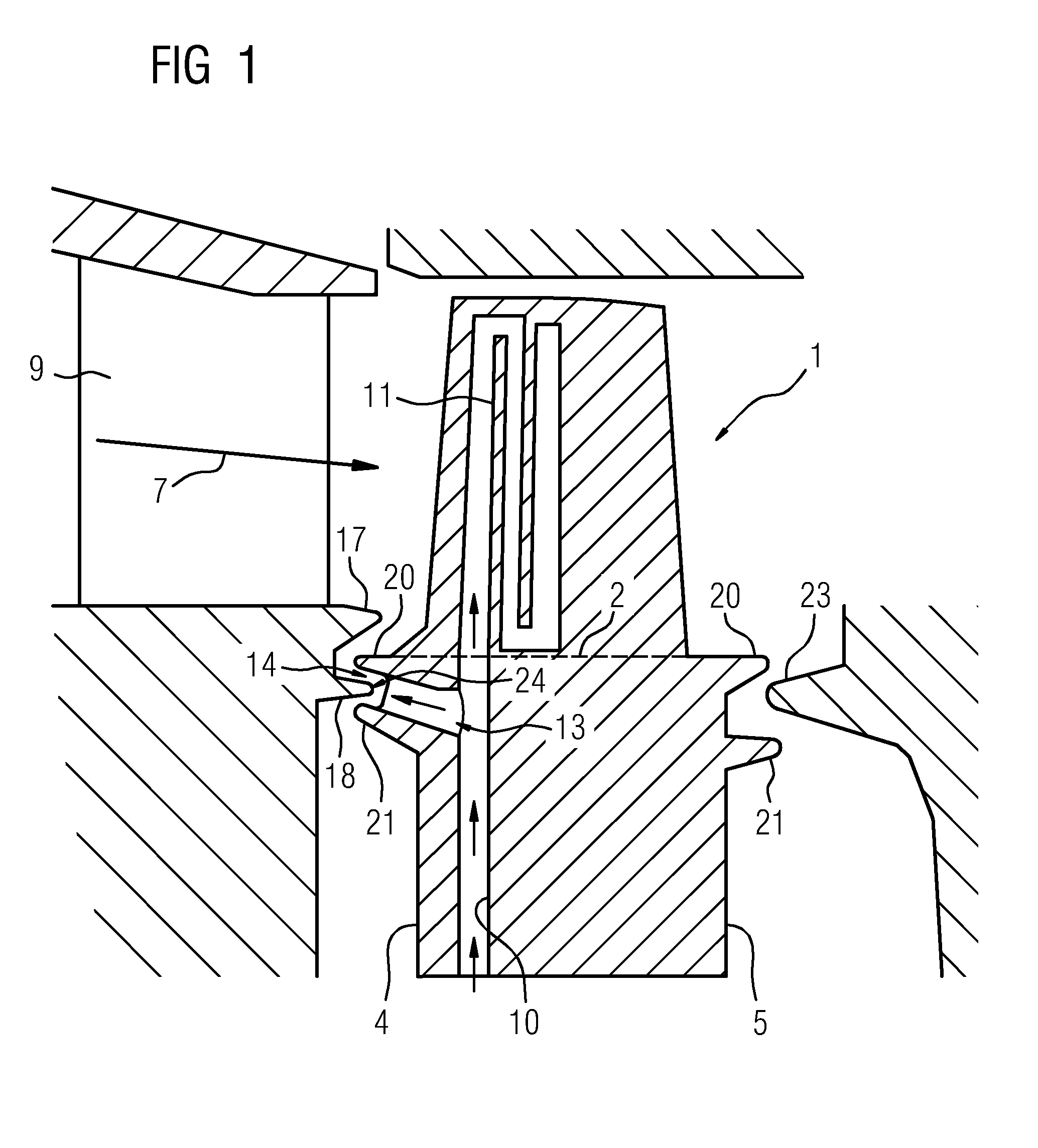
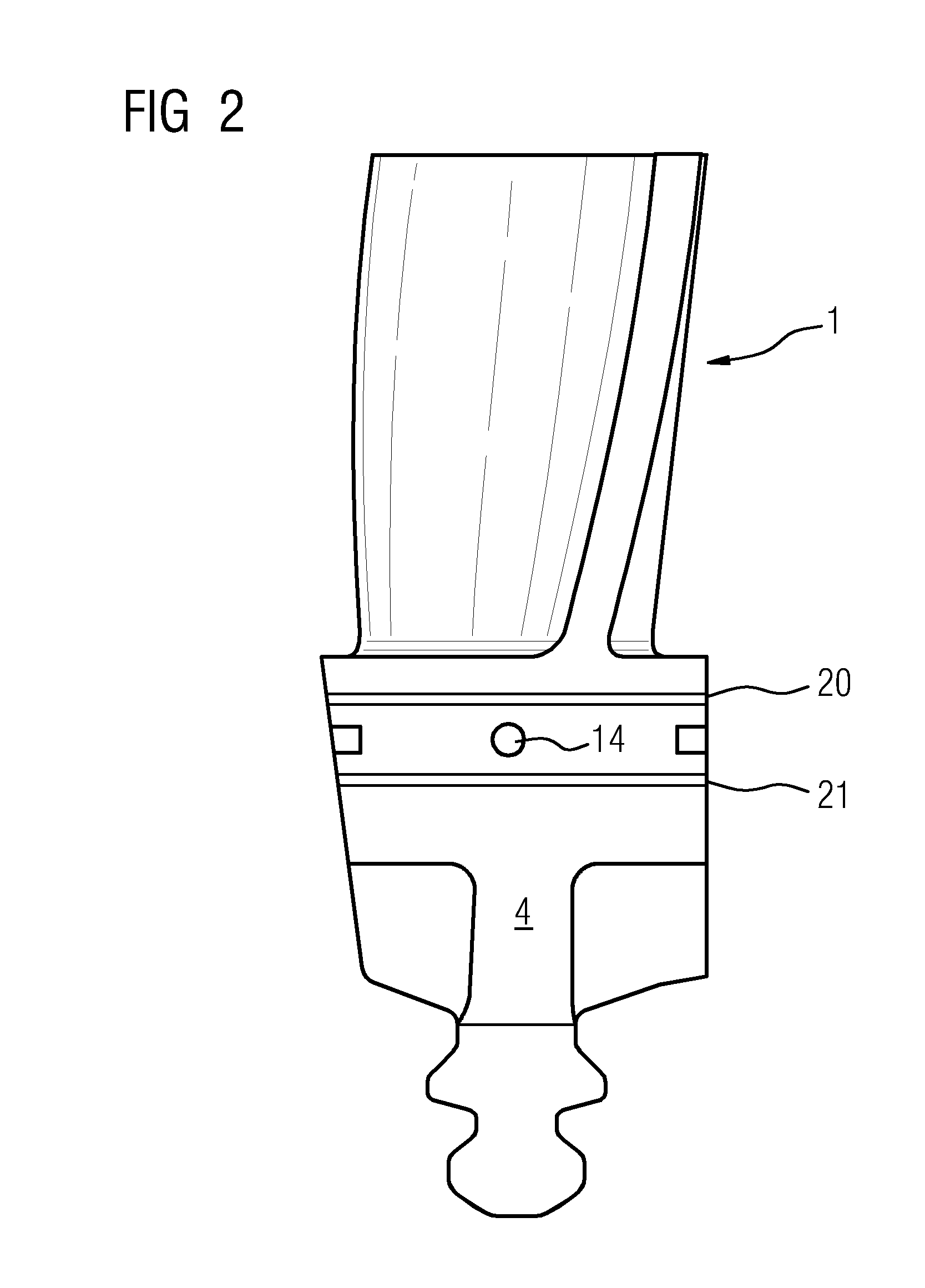
Blade for a turbo machine
InactiveUS20130156598A1Reduce the overall diameterHigh strengthPropellersPump componentsGas turbinesEngineering
A blade for a turbomachine, for example a gas turbine, is provided. The blade is arranged on a turbine rotor of the gas turbine. The blade includes a root portion having two narrow sides and two broad sides, a cooling air supply passage in the root portion, and a cooling air bleed which is arranged in the root portion and is in fluid connection with the cooling air supply passage. The cooling air bleed includes a nozzle on one of the narrow sides of the root portion, wherein the nozzle is formed by a hole and wherein an axial direction of the hole is inclined upward between 92° and 135° with respect to a longitudinal direction of the blade.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
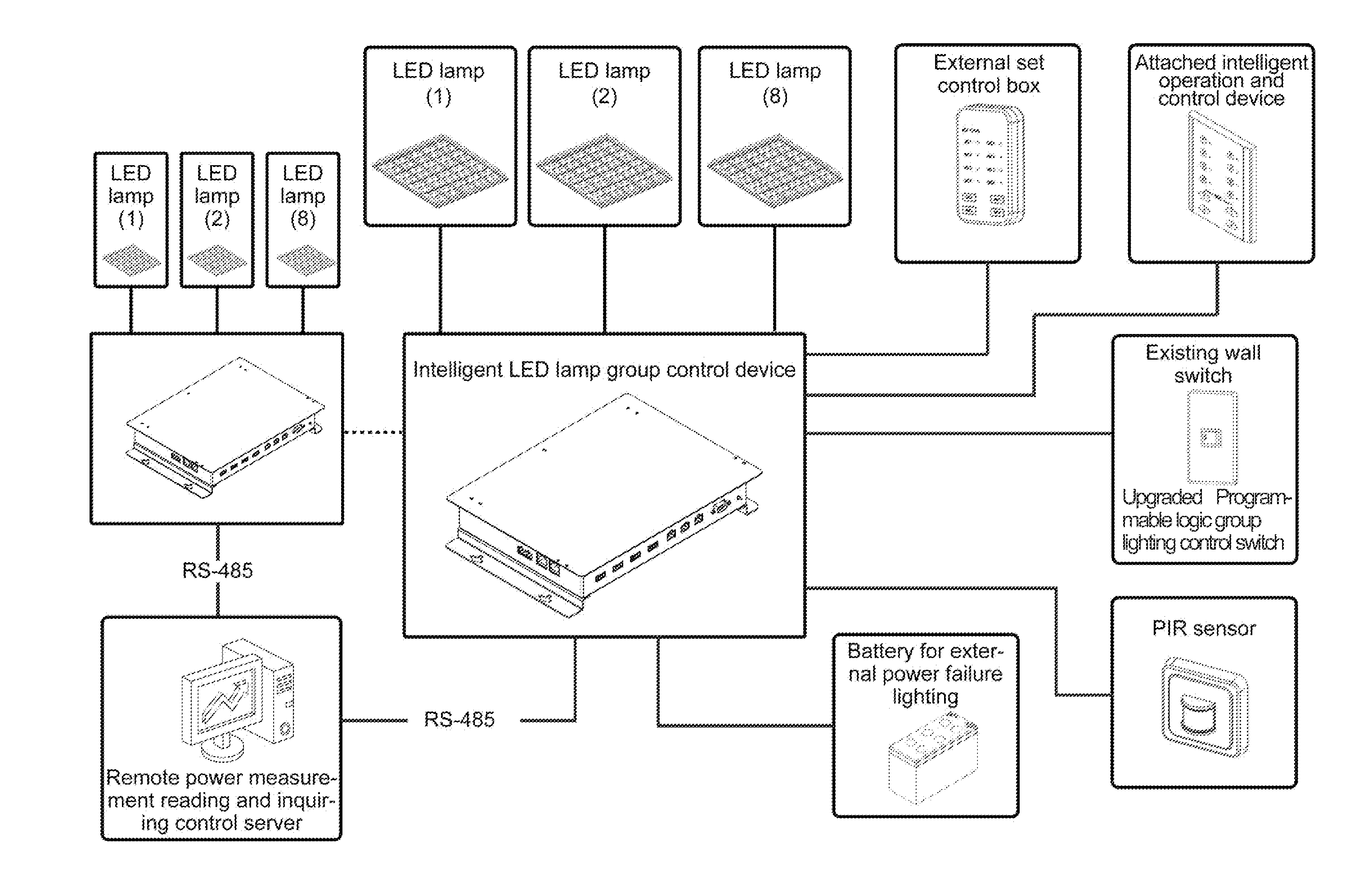
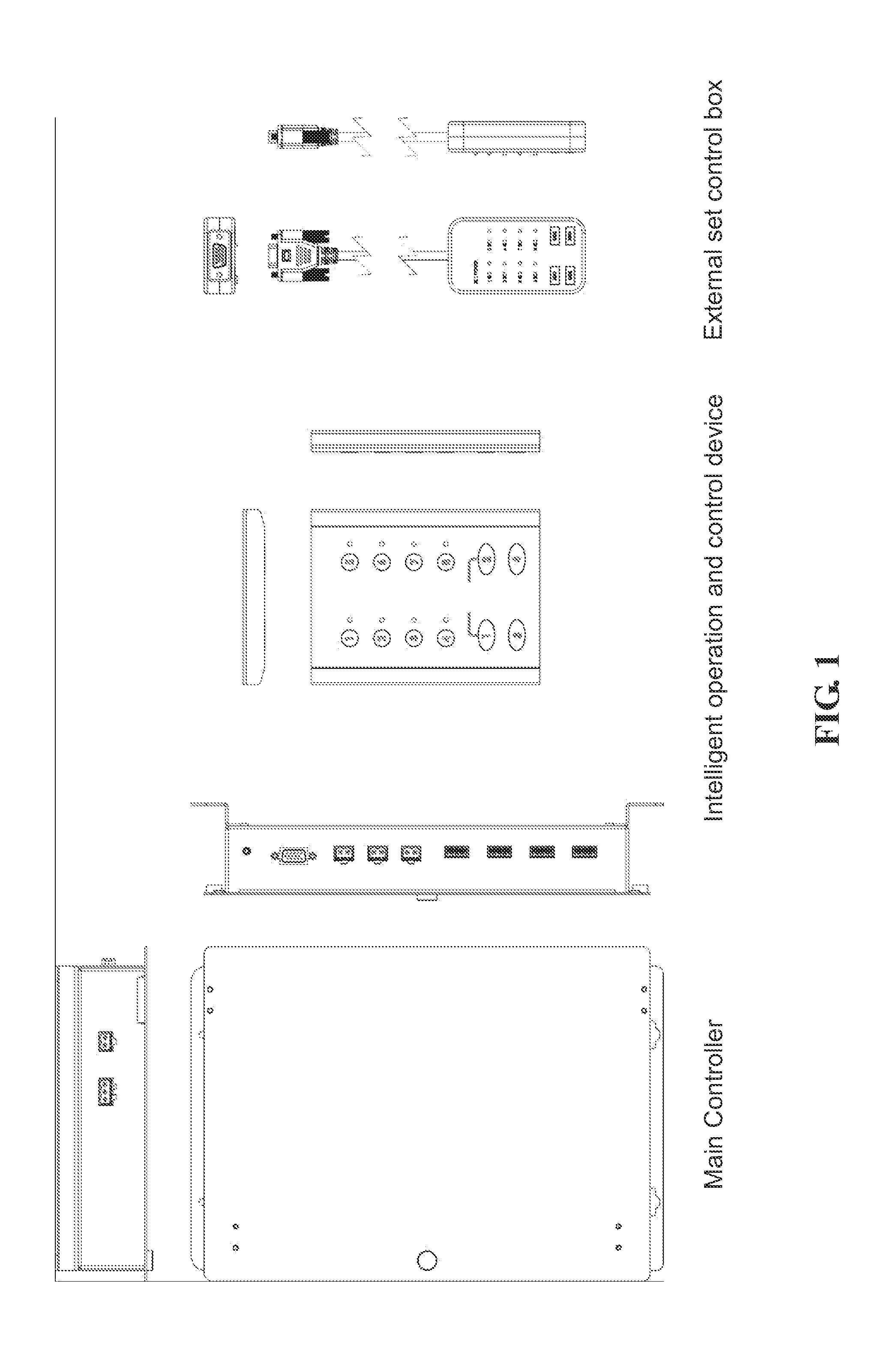
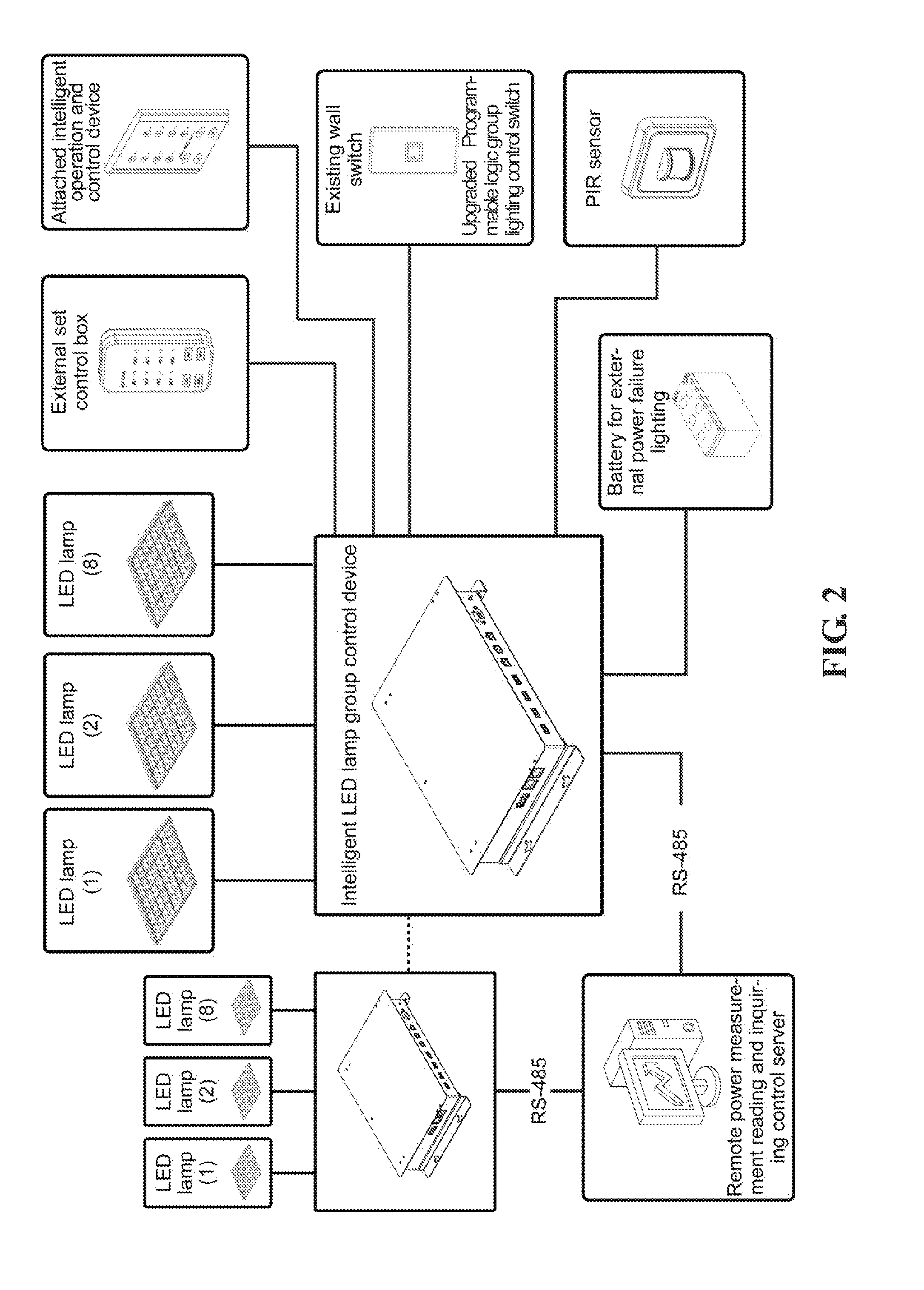
Intelligent LED lamp group control device using existing wall switch
InactiveUS20130093332A1Extend service hoursElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementElectrical batteryEngineering
An intelligent LED lamp group control device using an existing wall switch for controlling a group of LED lamps includes an AC power converter, an interface for intelligent control using an interface circuit for upgrading the existing wall switch for scene group control. The device further includes a night lamp control input port, an emergency operation switch, an external set control box connector, a wall switch input unit, a control configuration set interface, a power failure battery input port and a night lamp and RS-485 serial port. The device enables one single controller to achieve control of and provide power supply to multiple LED lamps, and uses a communication control interface for converting the power supply originally provided to the LED lamps into a logic control signal so that the wiring layout and location of the original lighting control wall switch can be used.
Owner:ENERGY INTELLIGENCE CORP
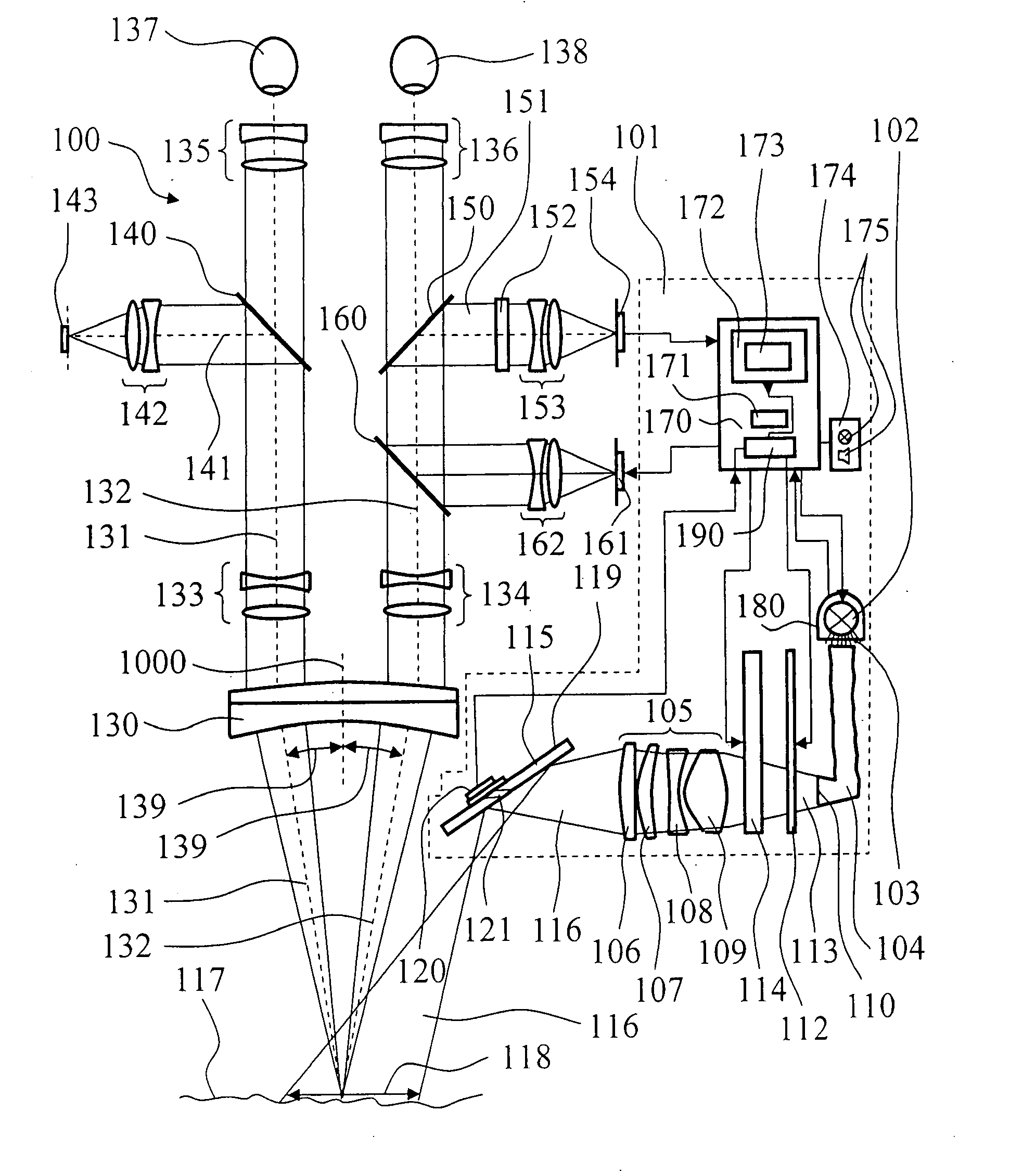
Surgical microscope having an illuminating arrangement
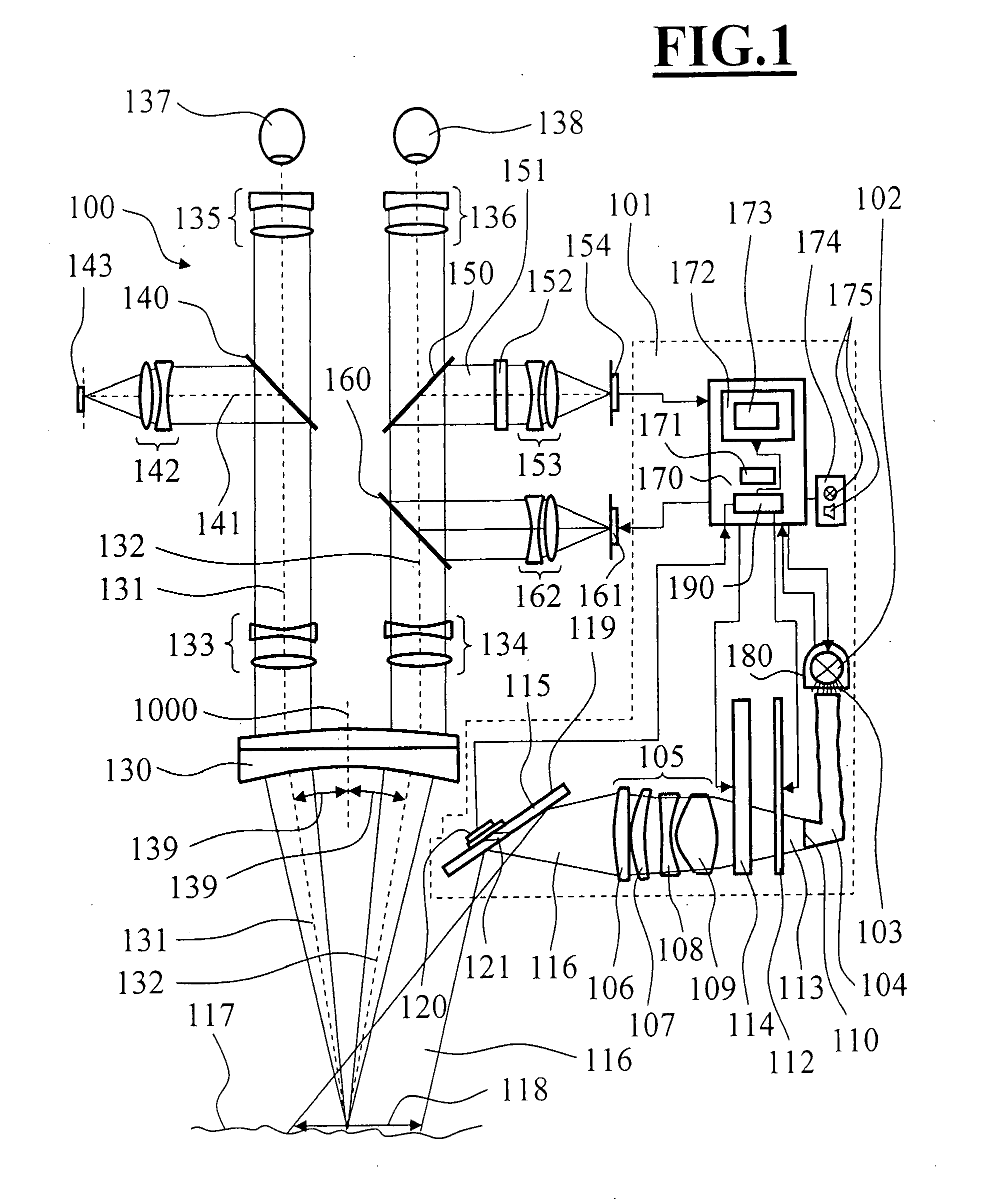
ActiveUS20080049314A1Extend service hoursEasy to undertakeSurgeryMicroscopesSurgical microscopeLimit value
A surgical microscope (100) is especially suited for use in neurosurgery. The surgical microscope has an illuminating arrangement (101) for making available illuminating light in an operating region (117) to be examined with the surgical microscope (100). The illuminating arrangement (101) contains a high-power light source (102) which includes an intensity adjusting device (112). The intensity adjusting device (112) makes possible to adjust the intensity of the illuminating light (116), which is guided to the object region (117), between a maximum value and a minimum value. The surgical microscope (100) has a control unit (170) for the illuminating arrangement (101) which includes an operator-controlled module (172) via which the illuminating arrangement (101) can be activated and controlled. For adjusting the intensity of the illuminating light (116) guided to the operating region (117), the control unit coacts with the adjustable filter unit (112). A signal generator (175) is provided which outputs a warning signal when an intensity of the illuminating light is adjusted via the operator-controlled module (172) which exceeds the safety limit value stored in a memory (171).
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Mobile edge computing unmanned aerial vehicle group auxiliary communication method for explosive flow
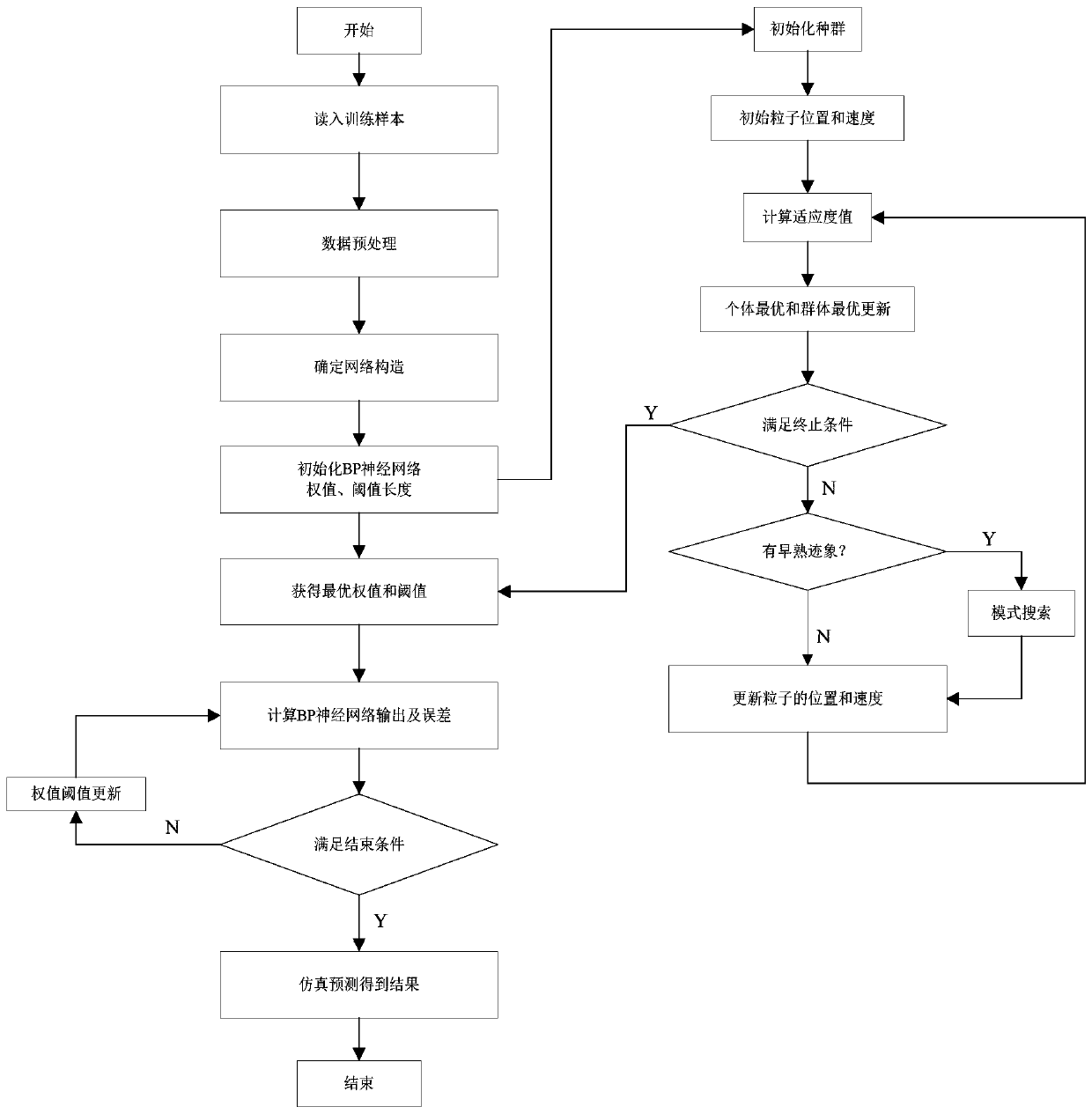
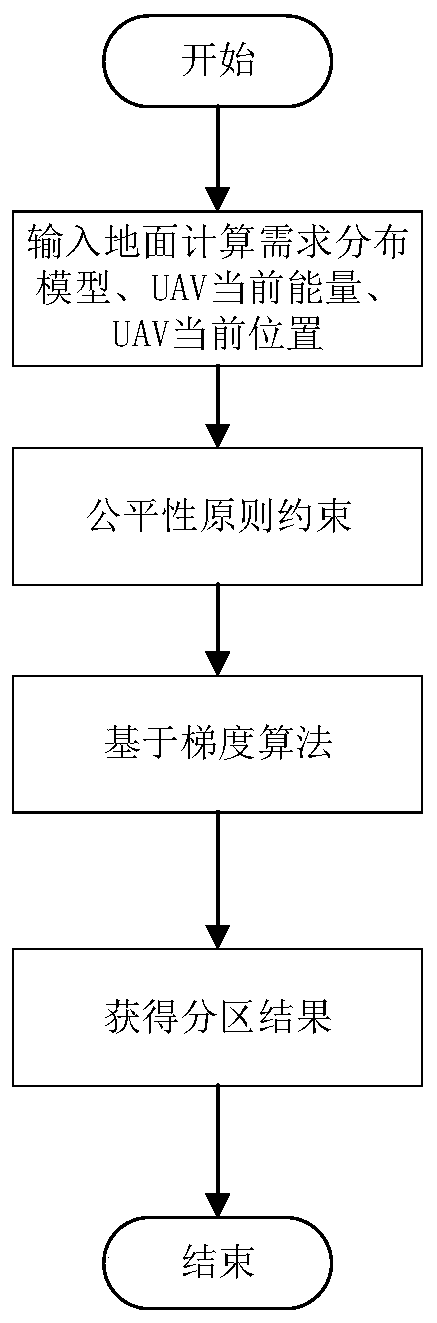
ActiveCN110602633AReduce energy consumptionMinimize energy consumptionParticular environment based servicesForecastingUncrewed vehicleMobile edge computing
The invention discloses a mobile edge computing unmanned aerial vehicle group auxiliary communication method for explosive traffic, which is responsible for providing computing service for users withcomputing requirements on the ground when a network is congested. Firstly, in the prediction part, an improved PSO-BP neural network is used for predicting the calculation demand distribution situation of a target area, and unmanned aerial vehicles supporting mobile edge calculation are deployed as required; secondly, a demand partitioning part is calculated, a target area is partitioned based ona fairness principle, and each unmanned aerial vehicle serves users in a sub-area; and finally, the unmanned aerial vehicle energy optimization part in each sub-region performs joint optimization on the unmanned aerial vehicle calculation frequency and the unmanned aerial vehicle flight path on the premise of meeting the user calculation requirement, so that the energy consumption of the unmannedaerial vehicle in each sub-region is minimum, the energy consumption of the whole unmanned aerial vehicle group is minimum, and the service time of the unmanned aerial vehicle group is prolonged.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Construction technology for soft rock large-deformation tunnel by de-stressing method and matched bracket
The invention discloses construction technology for a soft rock large-deformation tunnel by a de-stressing method and a matched bracket, and belongs to a high-burial depth large-deformation soft rock tunnel method and a support. The technology comprises the following steps: 1, performing tunnel tunneling construction and tunneling; 2, constructing mesh beam and shotcrete supports of the tunnel; 3, excavating a bottom plate de-stressing groove backwards from the tunneled working surface at the tunneled tunnel bottom plate; 4, constructing a tunnel wall de-stressing groove at the wall position of the tunnel; 5, setting up the matched bracket from the rear to the front; and 6, concreting at the bottom plate of the tunnel. The construction technology has the advantages that: 1, the de-stressing groove is excavated at a bottom groove, so that the tunnel is positioned in a low stress region at the initial stage of the excavation and the influence on and damage to the tunnel due to high stress are reduced after the tunnel excavation; 2, an enclosed structure where a full section and the tunnel section are adapted has high deformation resistance; 3, the bracket has a multi-stage variable bearing structure, and can prolong the time in the tunnel; and 4, an intensity-controlled buffer cushion block controls the variation rate of the bracket timely. In addition, the construction technology also has the advantages of simple structure and strong engineering practicability.
Owner:XUZHOU MINING BUSINESS GROUP
Alkyl acrylate copolymer vi modifiers and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080026964A1Extend service timeEnhancing oxidative stability and dispersancyThickenersAdditivesFunctional polymersRadical polymerization
A novel a multi-functional polymer viscosity modifier comprising an additive reaction product obtained by reacting a first monomer comprising an alkylacrylate with a second monomer comprising an olefinic carboxylic acylating agent under conditions effective for free radical polymerization of the first and second monomers to provide a base polymer comprising an acylated alkylacrylate copolymer, and wherein the base polymer optionally may be further reacted with an amine compound to provide a multi-functional polyalkylacrylate copolymer. The base polymer has good thickening efficiency. The multi-functional polyalkylacrylate copolymer dispersant viscosity modifier has good thickening efficiency. The base polymer and the multi-functional polyalkylacrylate copolymer viscosity modifier have good thickening efficiency, low temperature properties, dispersancy, and antioxidancy properties. They also have no precipitation or sedimentation, nor cause or encourage such formations in finished fluids incorporating them.
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL
Well structure of pressure-releasing coal bed gas ground extraction well and arrangement method thereof
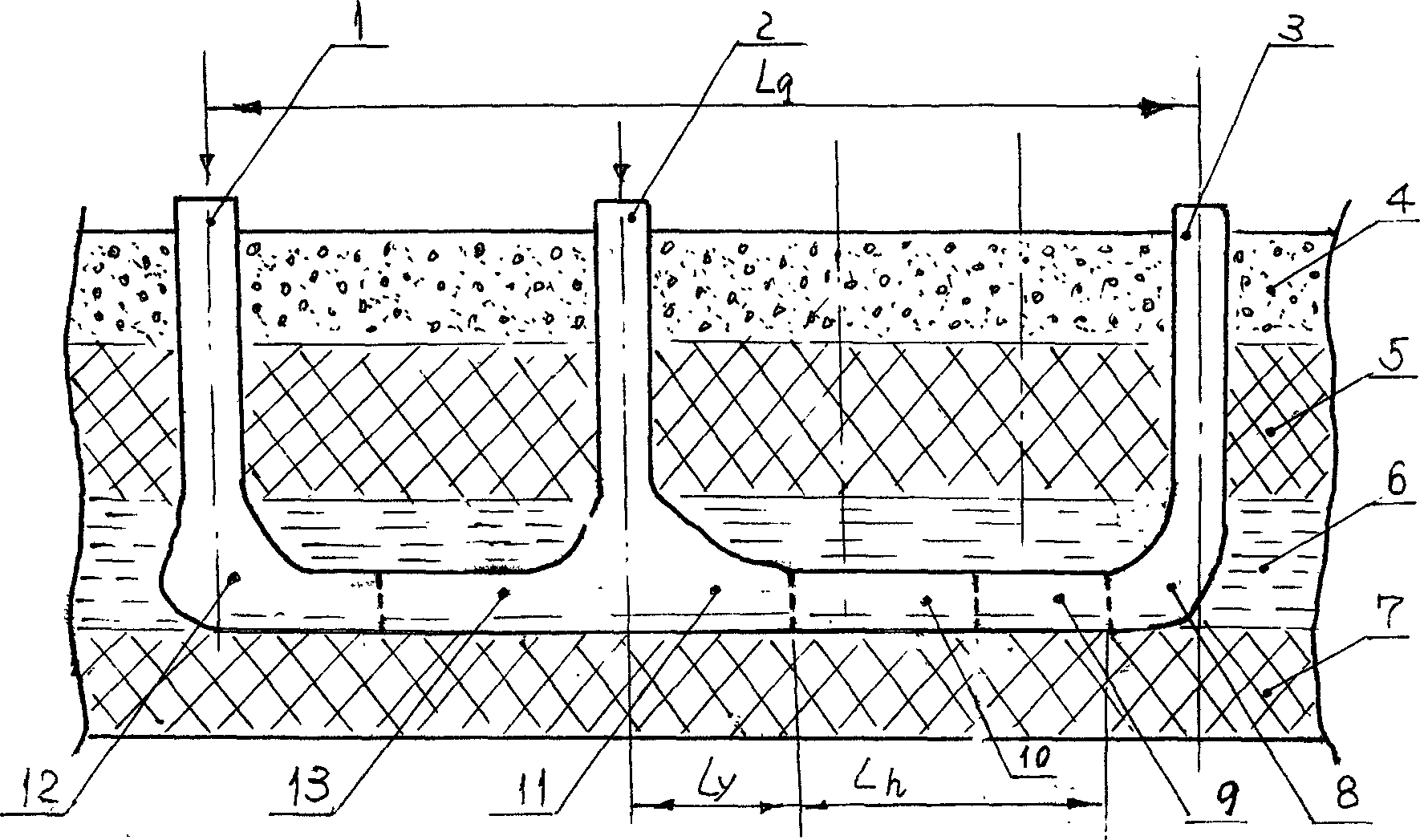
InactiveCN102121364ARock displacement rate is smallHigh borehole stabilityFluid removalDirectional drillingCoalService time
The invention provides a well structure of a pressure-releasing coal bed gas ground extraction well and an arrangement method thereof, wherein the well structure includes a first aperture section, a second aperture section and a third aperture section, wherein the first aperture section is in a first vertical depth of a well deflecting drill, the second aperture section is in a second vertical depth of the well deflecting drill, the second aperture section is in a third vertical depth of a vertical drill, and the third aperture section penetrates deeply in a protected layer. The arrangement method comprises the following steps of: drilling outside an extraction region, directionally deflecting drilling the upper parts of the first aperture section and the second aperture section, adopting a straight well body for the lower part of the second aperture section and the third aperture section, and closing to a boundary final hole in the extraction region so that most of the well structure is arranged out of a mining influence range or the region with little mining influence, the stability of the ground extraction well is greatly increased, the construction danger is reduced, the extraction yielding of the coal bed gas well is improved, the damage to the ground well by movement of cover rocks is effectively reduced, and the service time of the ground extraction well is increased.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Auxiliary mesh type starter
ActiveUS20150097375A1Limit magnitudeLarge slow-turning torquePower operated startersElectric motor startersElectric machineMagnetic switch
An auxiliary mesh type starter, comprising a motor, an electromagnetic switch connected with the motor and relays connected with the electromagnetic switch, wherein the electromagnetic switch comprises a holding coil, an attracting coil, a stop seat arranged at the rear end parts of the holding coil and the attracting coil, a plunger arranged on the inner circumferences of the holding coil and the attracting coil and capable of sliding in an axial direction, a return spring for applying return force to the plunger, and a contact point arranged at the rear end of the plunger; and the relays are connected to a key switch, wherein the relays comprise a first relay and a second relay, with the head end of the attracting coil connects to the key switch via the first relay, and the head end of the holding coil connects to the key switch via the second relay.
Owner:PRESTOLITE ELECTRIC BEIJING
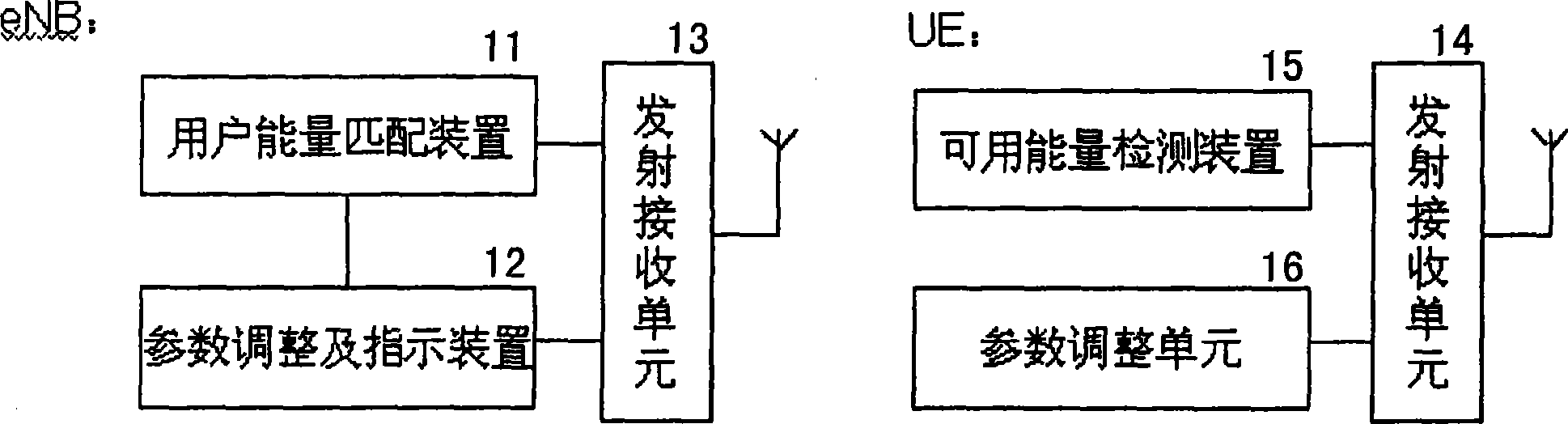
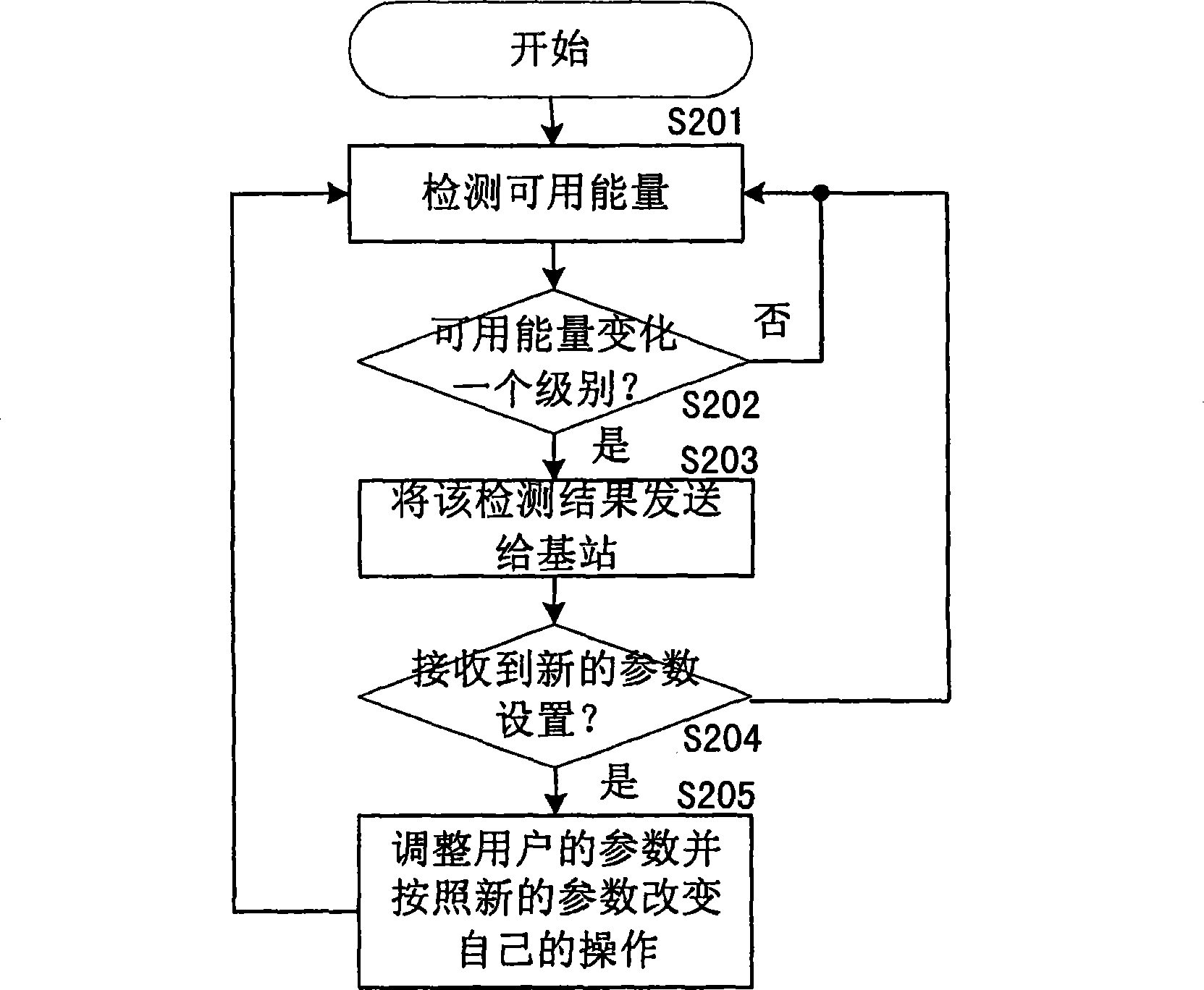
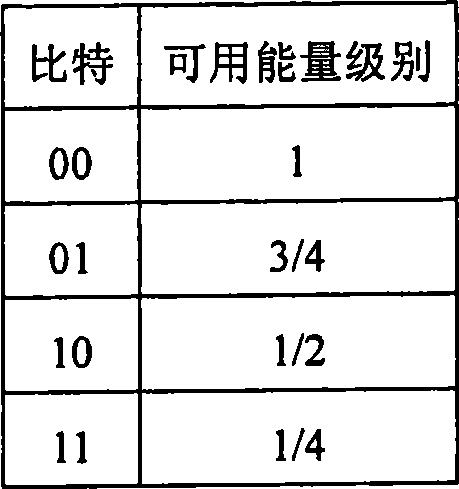
Method and apparatus for setting parameter according to available energy of user equipment
InactiveCN101483858AExtend standby timeExtend service hoursEnergy efficient ICTSubstation equipmentComputer scienceUser equipment
The invention discloses a method for setting working parameters of user equipment according to the available energy of the user equipment, which comprises the following steps: the user equipment detects the current available energy and reports detection result to the base station when the available energy changes a level; the base station receives the detection result of the available energy of the user equipment and matches between the level of the available energy of the user equipment and the working parameter variation factors to determine that the user equipment needs updated working parameters; the base station adjusts the updated working parameters needed by the user equipment to a preset value corresponding to the level of the detected available energy and controls the user equipment to operate according to the adjusted working parameters. The invention further comprises a device for setting the working parameters of the user equipment based on the available energy of the user equipment.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
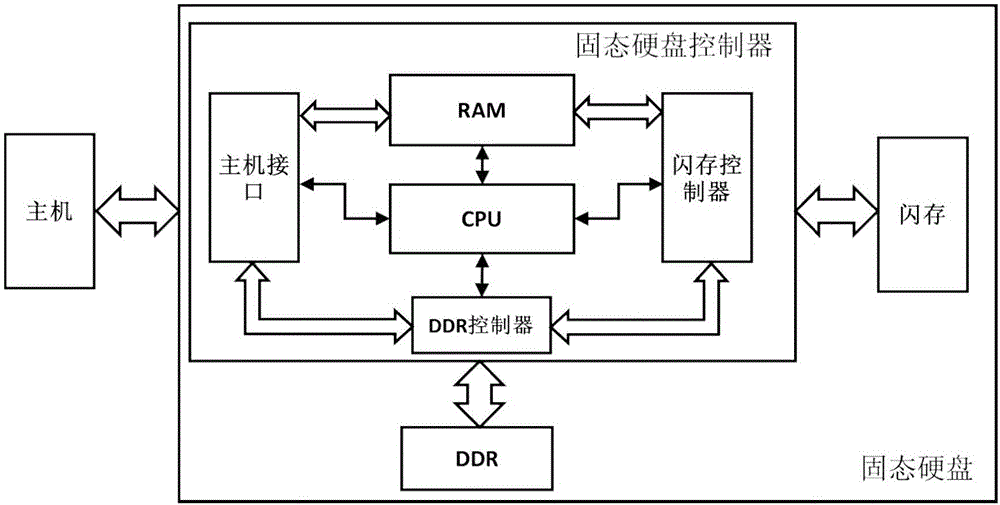
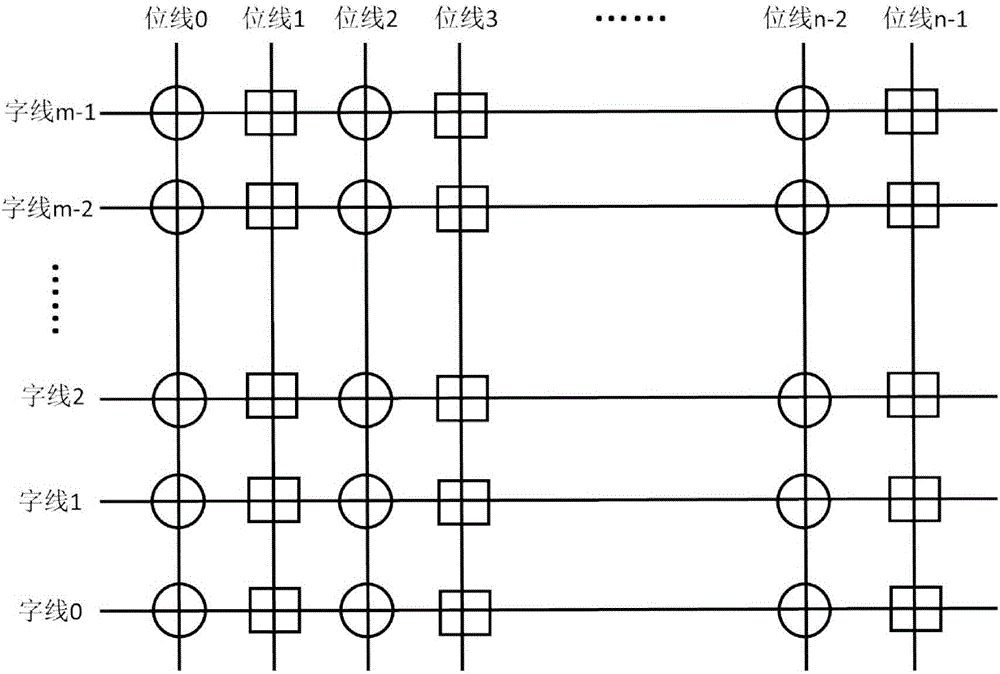
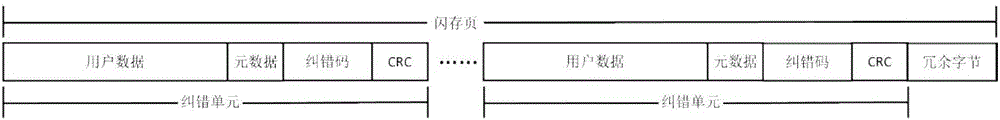
Error management method of flash memory for greatly enhancing service time of solid state disk
The invention provides an error management method of flash memory for greatly enhancing the service time of a solid state disk. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an initial flash memory bad byte table of the solid state disk; querying the flash memory bad byte table when data to be written is written into a flash memory page of the solid state disk, and skipping positions of bad bytes according to the positions of the bad bytes marked by the flash memory bad byte table, so as to write the data to be written; querying the flash memory bad byte table when data to be read is read from the flash memory page of the solid state disk, and skipping positions of bad bytes according to the positions of the bad bytes marked by the flash memory bad byte table, so as to read the data to be read. The method has the benefits that the method can prolong the service time of a page or a block, maintain the available physical capacity and the write-in life of the solid state disk, and further enhance the serviceable time of the solid state disk.
Owner:HUNAN GOKE MICROELECTRONICS
Method for reinforcing drop shaft in underground mine producing area
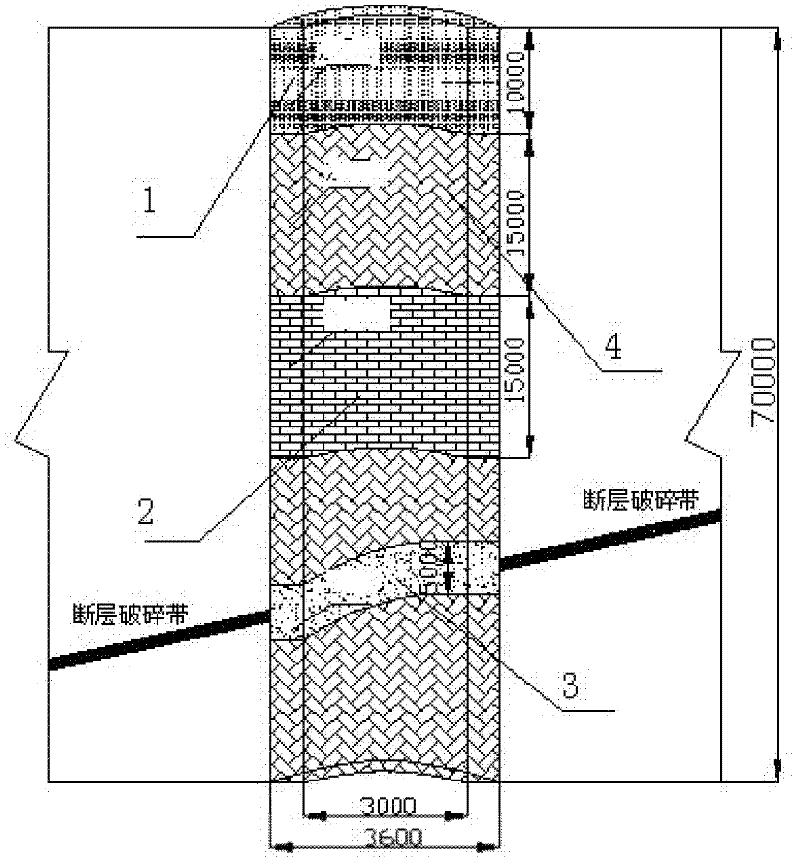
InactiveCN102226397AEasy to deform and shrinkShock absorbing effectAnchoring boltsShaft liningRock engineeringFracture zone
The invention relates to a method for reinforcing a drop shaft in an underground mine producing area and belongs to the field of metal mine and rock engineering reinforcement. The method is characterized in that the movement track of ores in the drop shaft during the ore discharge process is fully considered, model experiments and theoretical analysis method are adopted for determining the property of impact action and an impact failure region to the well wall generated by the ores according to the height of the drop shaft and the diameter of the drop shaft, the drop shaft is hereby divided into four stress regions, namely a first impact failure region, a second impact failure region, a fault fracture zone region and a wear-out failure region, and different forms are further adopted for reinforcement. The method is especially applicable to reinforcement of the drop shafts in the producing areas under soft and broken surrounding rock conditions, can be used for significantly prolonging the service life of the drop shaft and has the advantages of safety in construction, simpleness and low cost.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Arrangement method of semi-continuous process middle bridge in open pit coal mine
ActiveCN108716402AMeet the climbing angle requirementsExtend service hoursOpen-pit miningDeep miningTruck
The invention discloses an arrangement method of a semi-continuous process middle bridge in an open pit coal mine, which is applicable to the open pit coal mine with a deep mining depth and a relatively large inner discharge space. According to the arrangement method, a midpoint of a connecting line between end slopes of two sides of a coal mining step platform is dug down to form a groove; a crushing station is arranged in the groove; a middle bridge is arranged at the pit bottom of the open pit coal mine; the middle bridge comprises an upper layer step and a lower layer step; the upper layerstep is at a same level as the roof of a coal seam; the crushing station is connected with a belt conveyor; a lifting belt conveyor is arranged in an inner dumping site fold line section which is aninner dumping site misplaced position in an open pit mine; one end of the lifting belt conveyor is connected with the belt conveyor at the pit bottom; a contact conveyor is arranged at the ground surface near the inner dumping site fold line section; the other end of the lifting belt conveyor is connected with the contact conveyor; a ground belt conveyor is arranged on the ground surface; and thecontact conveyor is connected with the ground belt conveyor. By adopting the arrangement method, the interaction between a transport truck and a semi-continuous process system is effectively reduced,the mine production stability is improved, and obvious economic benefits are achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Low-Power Face Identification Method Capable of Controlling Power Adaptively
ActiveUS20190244011A1Unnecessary driving powerExtend service hoursThree-dimensional object recognitionPattern recognitionControl power
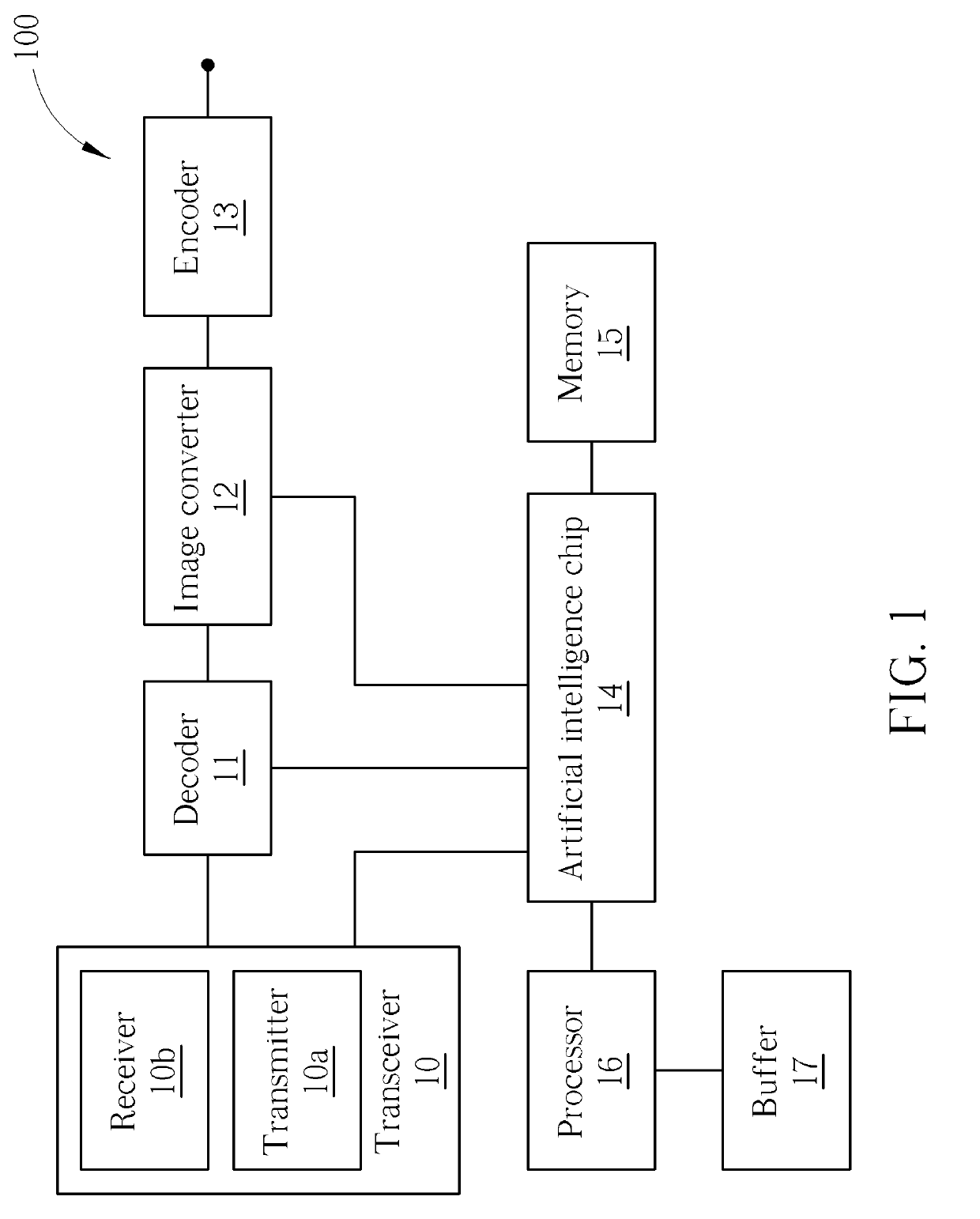
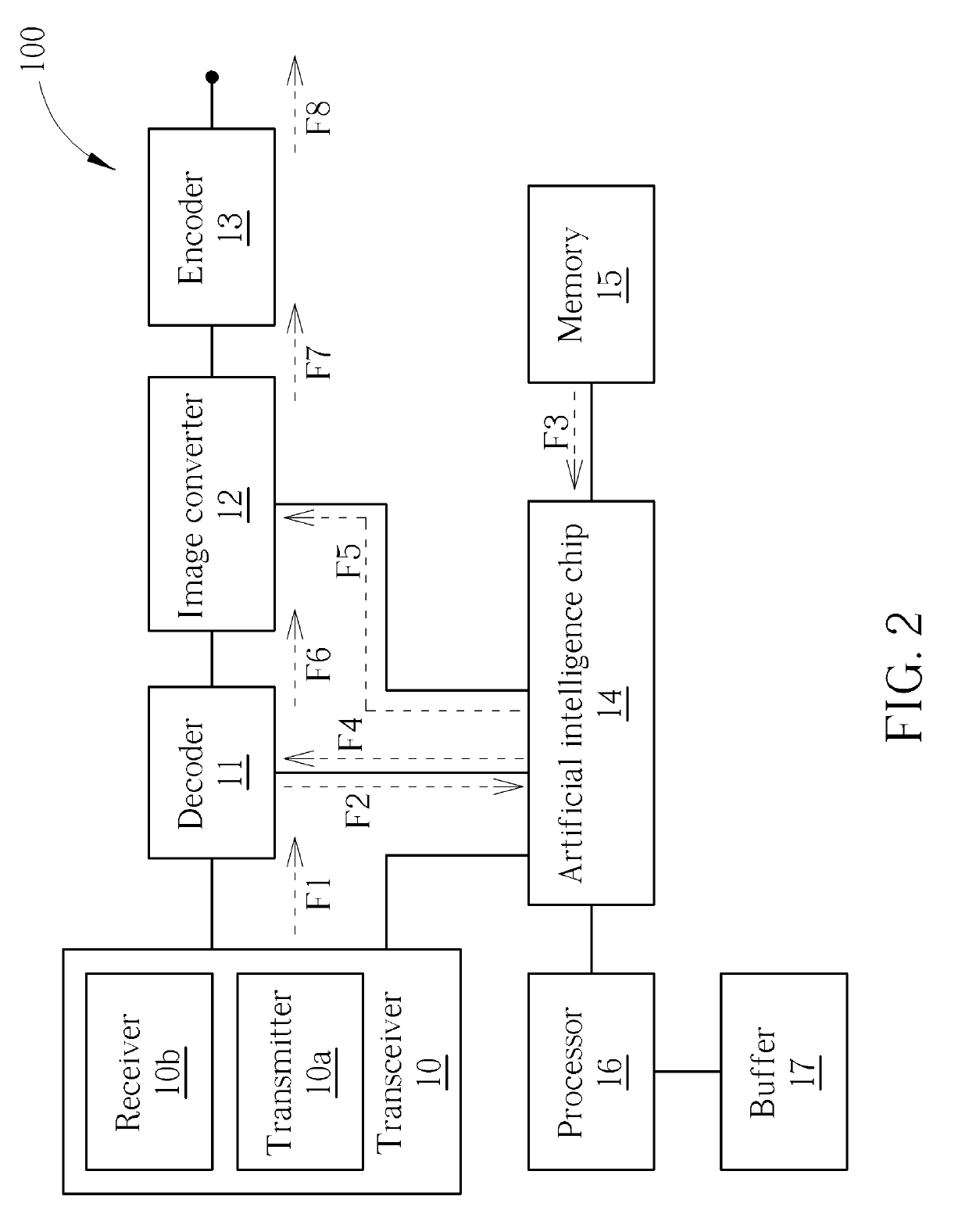
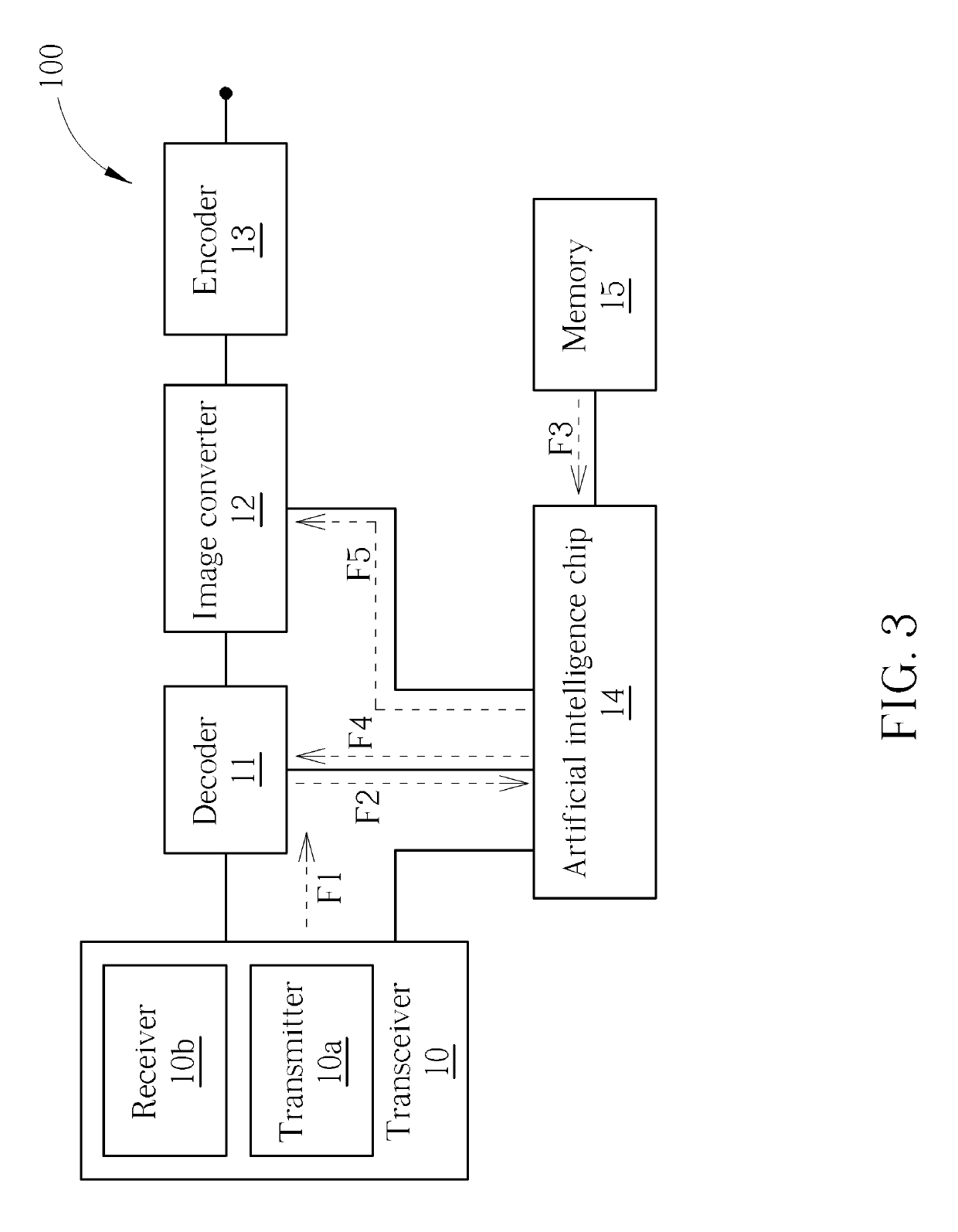
A low-power face identification method includes emitting at least one first light signal to an object, receiving at least one second light signal reflected by the object, decoding the at least one second light signal to generate a decoded light signal, extracting two-dimensional image information from the decoded light signal, performing a two-dimensional face detection function by an artificial intelligence chip according to the two-dimensional image information and two-dimensional face training data, inhibiting a two-dimensional face recognition function when a two-dimensional face is undetected, and disabling an image converter by the artificial intelligence chip in order to inhibit a three-dimensional face recognition function when the two-dimensional face recognition function is inhibited.
Owner:KNERON INC
Truck mounted liquid concrete waste vacuum system
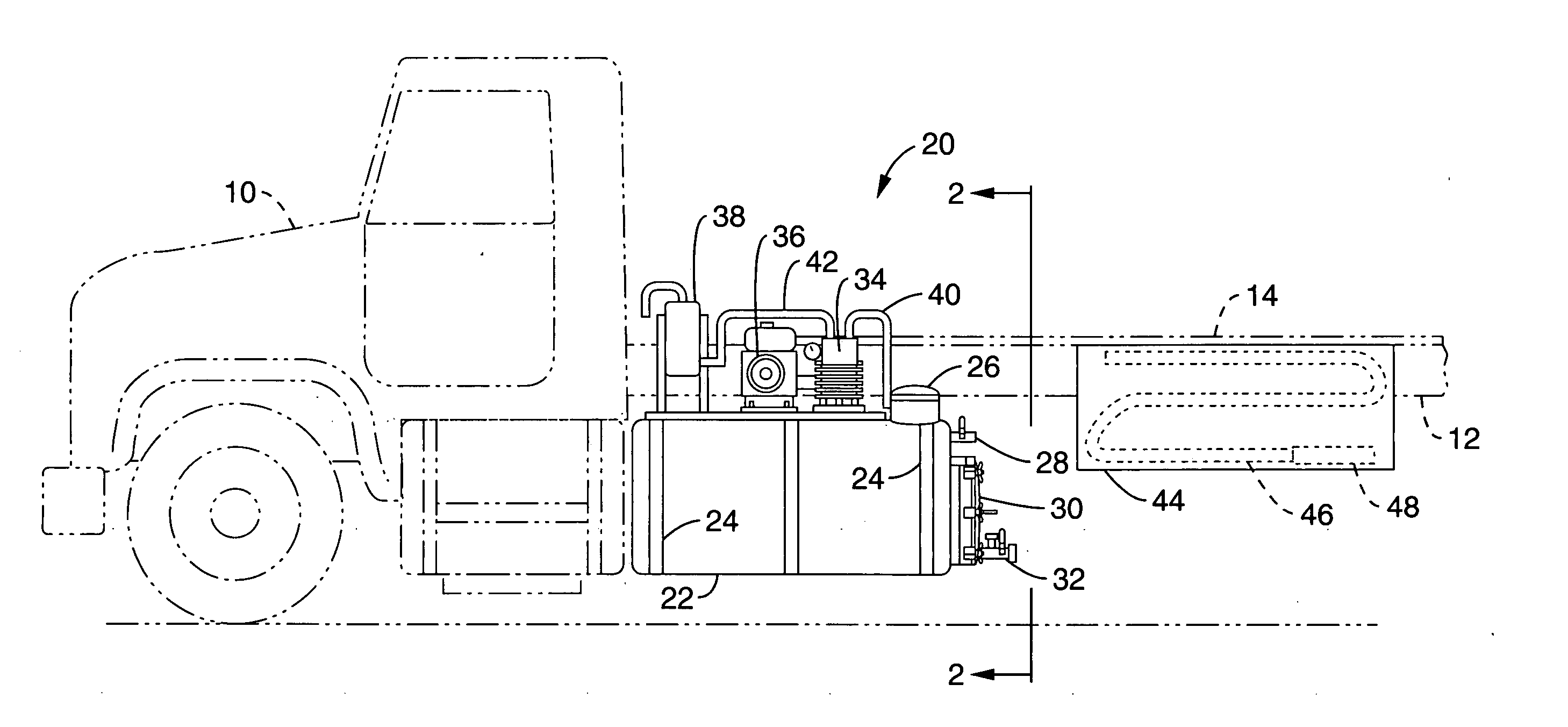
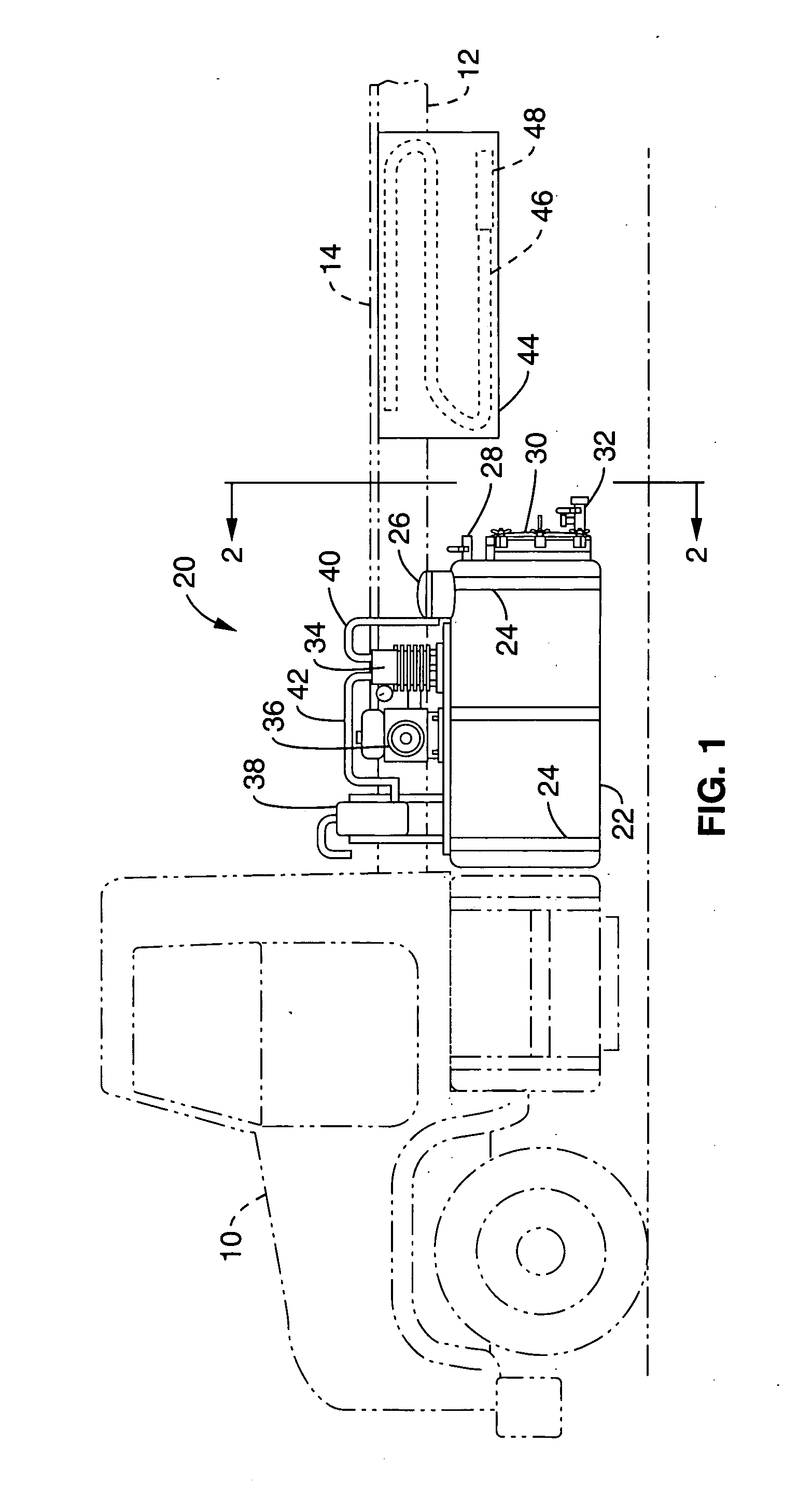
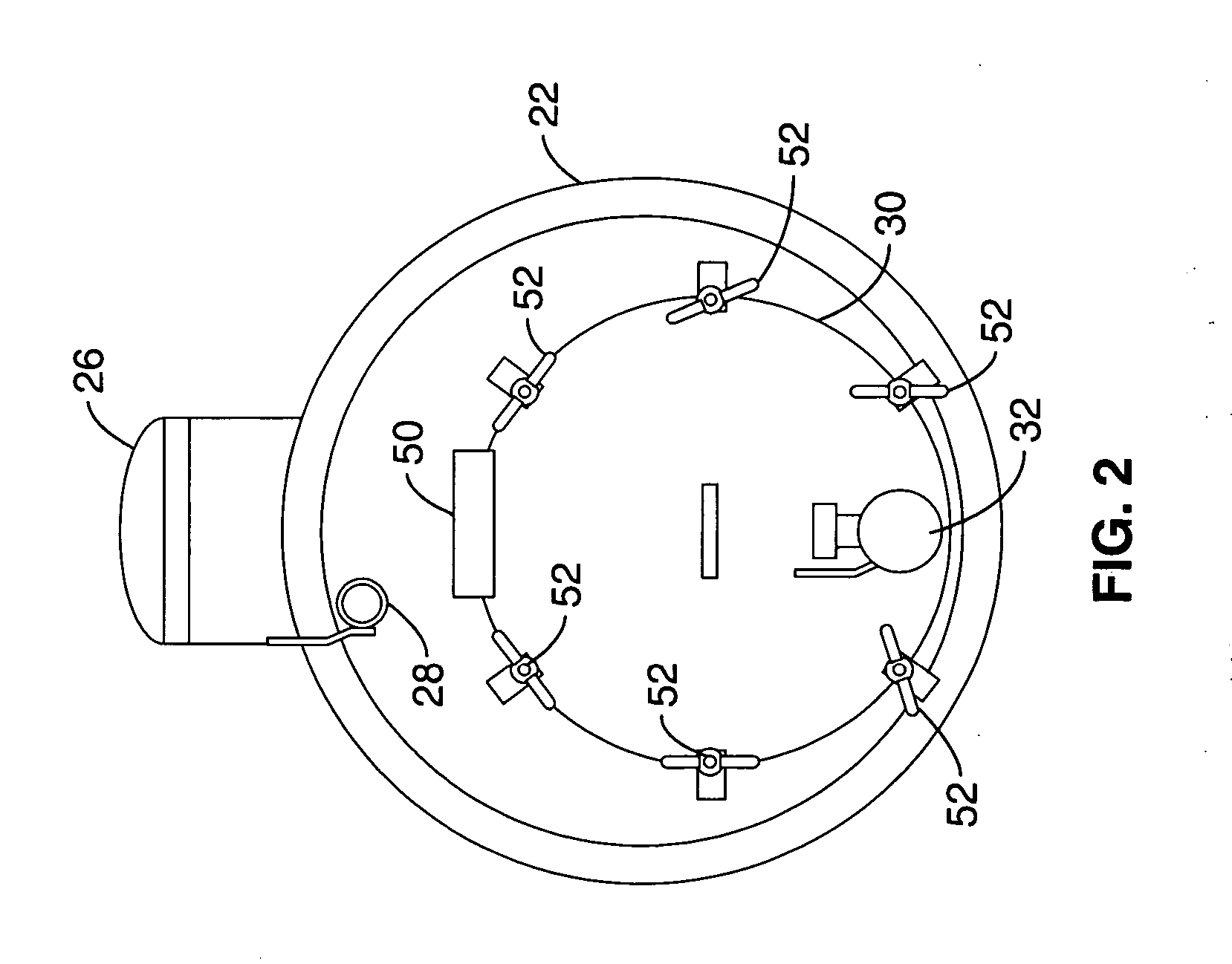
InactiveUS20060059653A1Extend onsite service timeExtend service hoursWaste water treatment from ceramic industriesSuction cleanersLiquid wasteWashout
A truck mounted liquid concrete waste vacuum system with a storage tank adapted to be used in conjunction with a watertight concrete washout bin. The concrete washout bin is configured to roll off a transport vehicle for delivery to a construction site and to contain all solid and liquid concrete washout waste from construction activities. When the concrete washout waste is to be removed from the site, the liquid concrete waste vacuum system attached to the transport vehicle is first used to remove the liquid waste from the washout bin and store it in the tank. The bin containing the remaining solid waste is loaded on the transport vehicle and taken to the treatment facility where both the solid and liquid waste is safely off-loaded.
Owner:CONCRETE WASHOUT SYST
Symbolic gas detecting, regulating and controlling method for underground coal gasification
InactiveCN1667241AHigh calorific valueExtend service hoursSurveyFluid removalProcess engineeringCoal gas
The invention relates to a detecting and controlling method for coal underground gasification indicating gas that belongs to underground coal developing. The invention supplies an enforceable controlling method for coal underground gasification producing. And a new aspect is supplied for the developing of coal industry.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
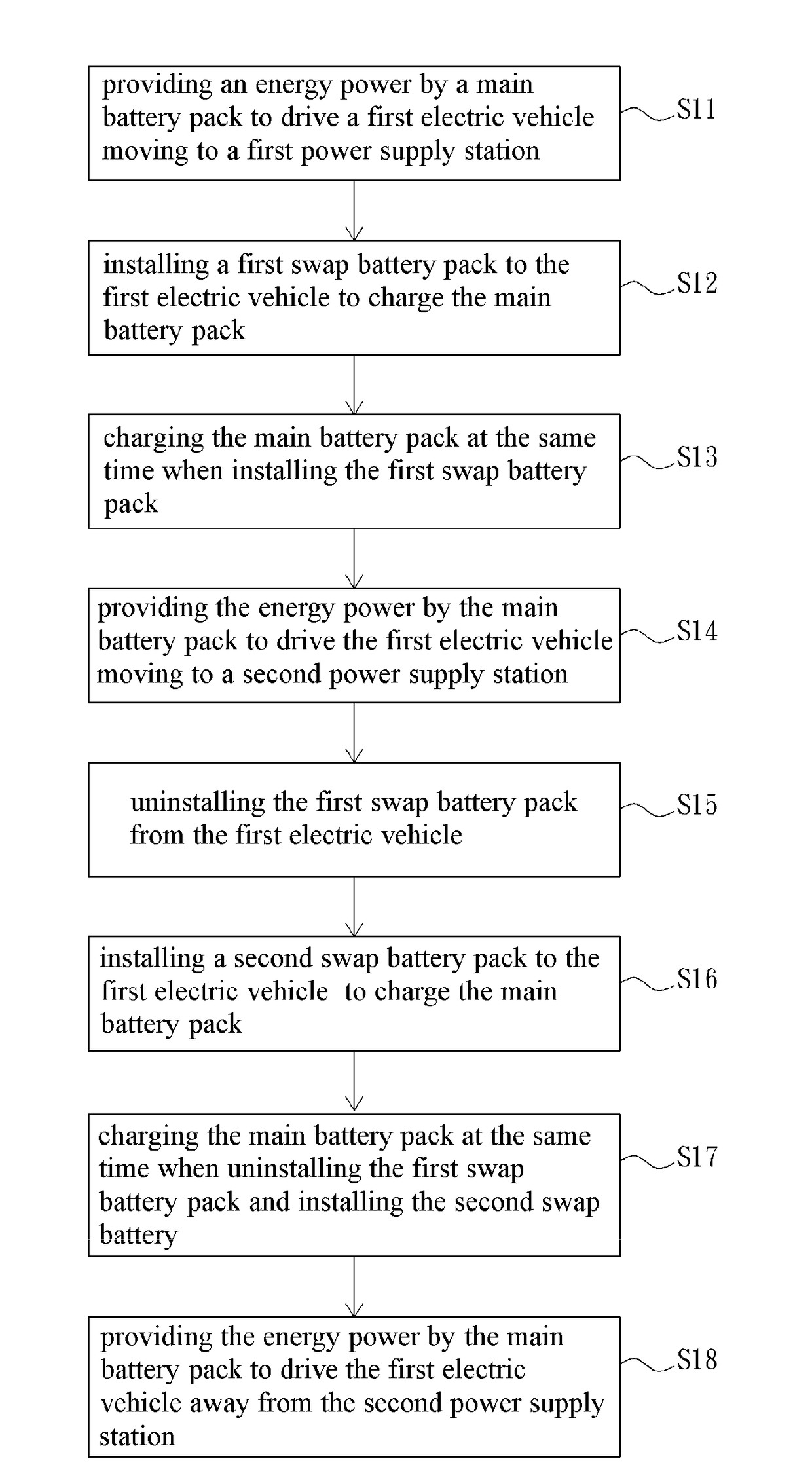
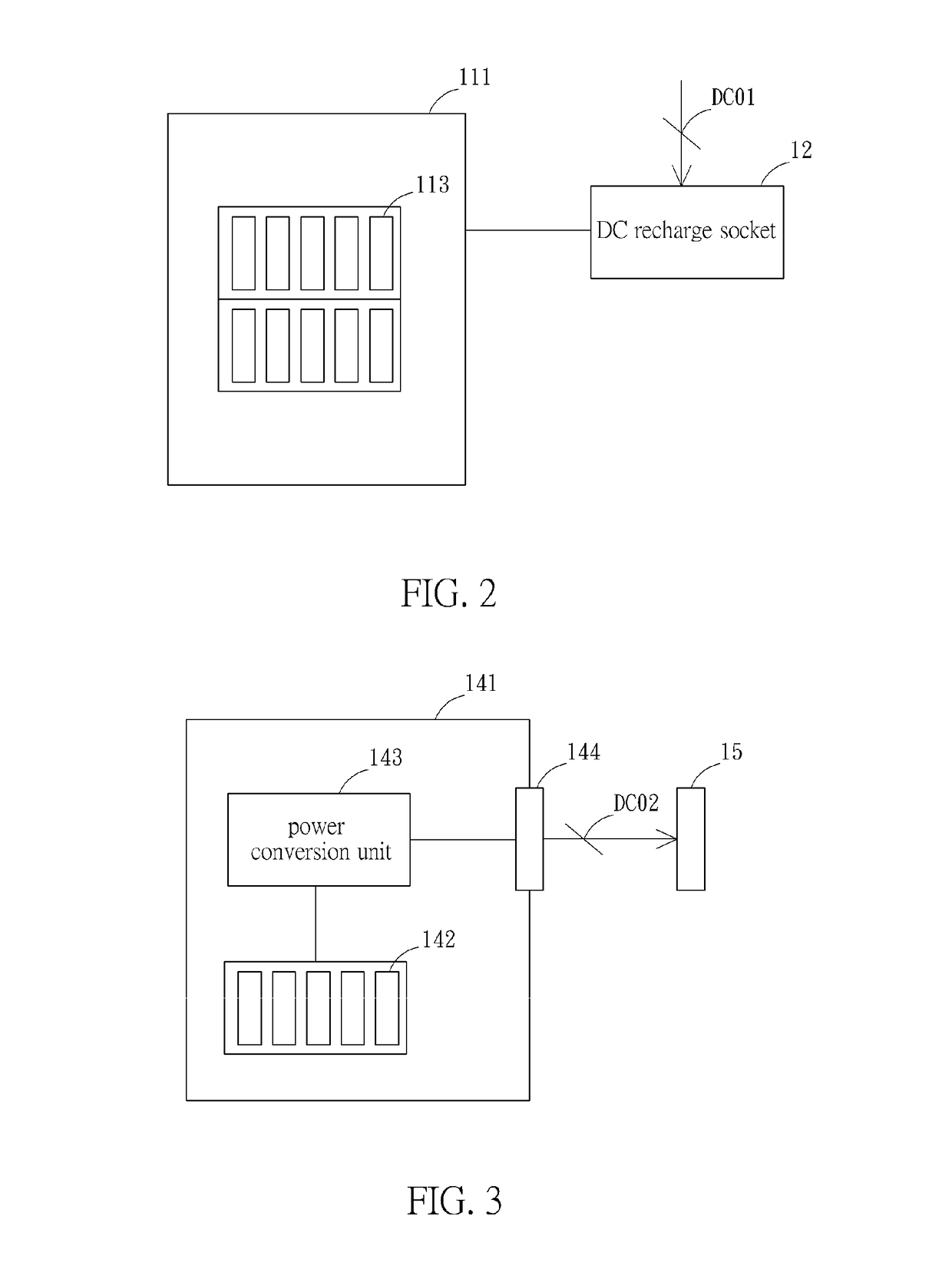
Electric Vehicle, Power Supply Station, and Power Maintaining Method for Electric Vehicle
ActiveUS20170253138A1Easy maintenanceEasy to maintain its power sourceConveyorsCharging stationsElectricityElectrical battery
A power maintaining method of electric vehicle includes the following step. In step 01, an energy power is provided by a main battery pack to drive a first electric vehicle (EV) moving to a first power supply station. In step 02, a first swap battery pack is installed on the first EV at the first power supply station, and the first swap battery pack is electrically connected to the main battery pack of the first EV so that the main battery pack is charged by the first swap battery pack. In step 03, the first EV is driven to a second power supply station from the first power supply station. In step 04, the first swap battery pack is uninstalled from the first EV at the second power supply station. In addition, an electric vehicle and a power supply station is disclosed in the present application.
Owner:GER CHIH CHAN
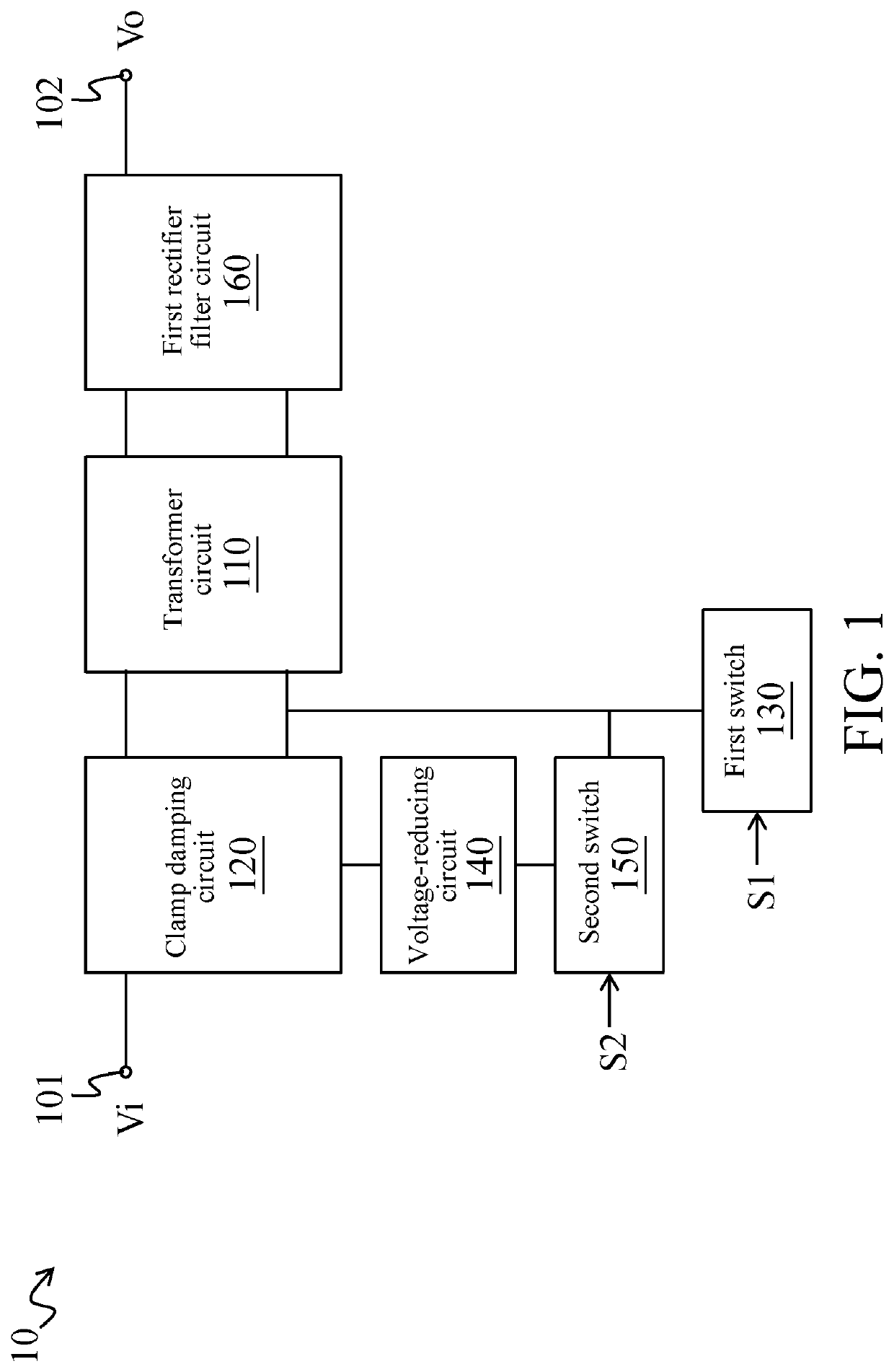
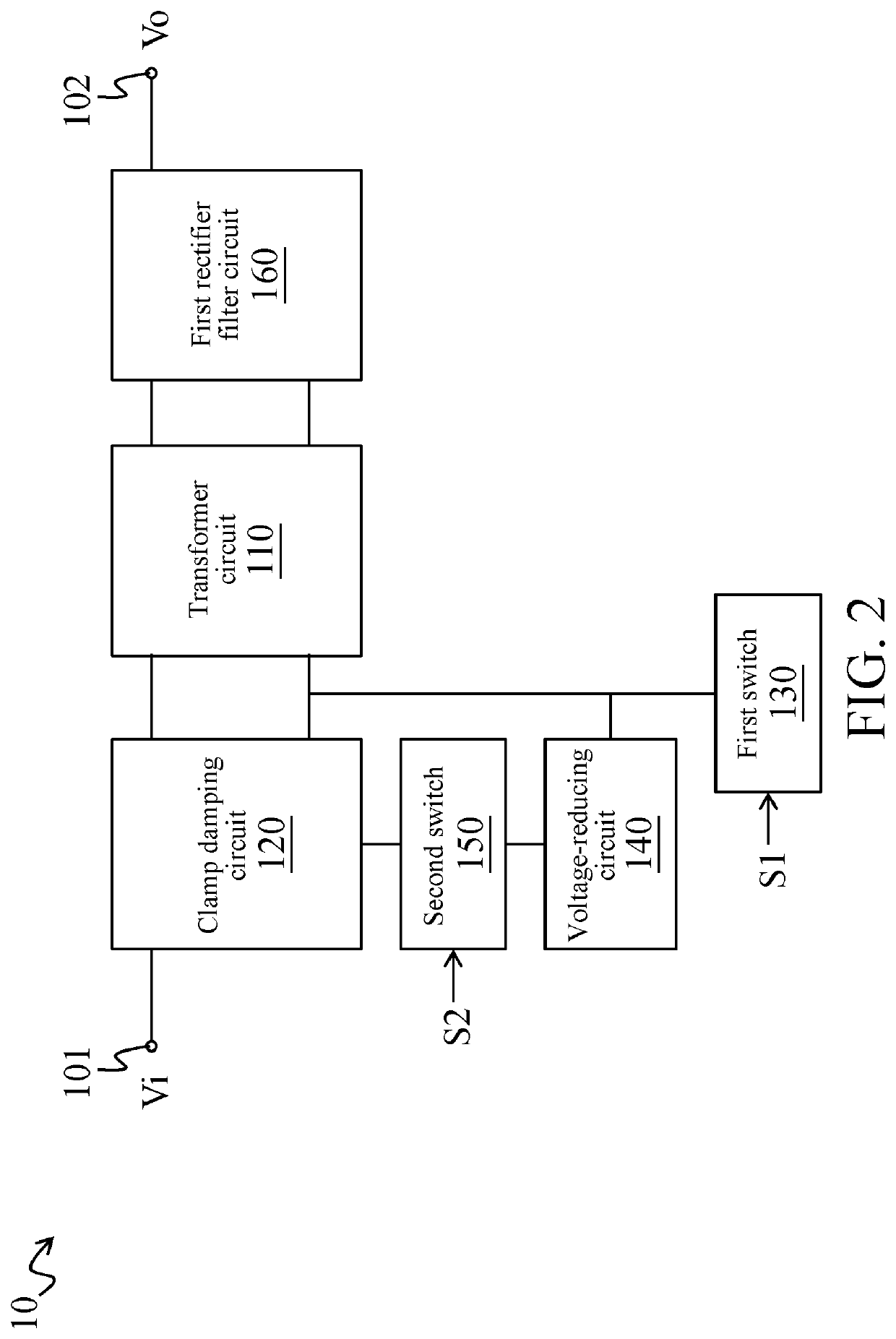
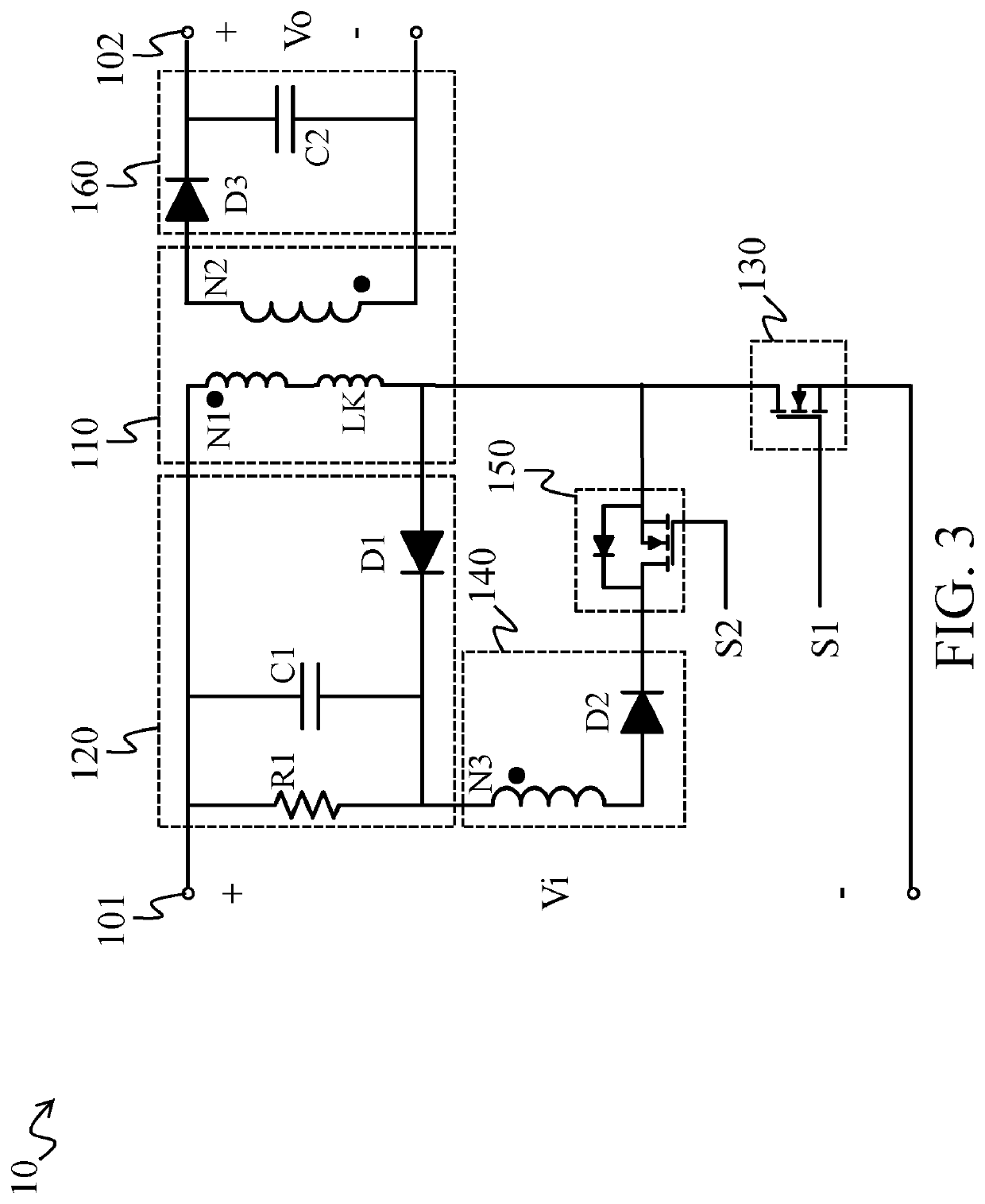
Flyback power-converting device with zero-voltage switching and method for flyback converting power with zero-voltage switching
InactiveUS20200251992A1Reduce the impactExtend product service timeApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationTransformerClassical mechanics
A flyback power-converting device includes a transformer circuit, a clamp damping circuit, a first switch, a voltage-reducing circuit and a second switch. The clamp damping circuit and the first switch are coupled to the transformer circuit. The voltage-reducing circuit and the second switch are coupled in series between the clamp damping circuit and the transformer circuit. Through switching of the first switch, the transformer circuit converts an input power to generate a first converted voltage and to enable the clamp damping circuit to store an inductive energy. In addition, when the second switch is turned on, the clamp damping circuit releases the inductive energy to the transformer circuit via the voltage-reducing circuit, so that the transformer circuit generates a second converted voltage according to the inductive energy.
Owner:CHICONY POWER TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com