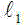Patents
Literature
62 results about "Higher Order Structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
CHROMATIN HIGHER-ORDER STRUCTURE. In the context of chromatin, “higher-order structure” may be defined as any assemblage of nucleosomes that assumes a reproducible conformation in 3D space. The most obvious chromatin higher-order structure is the mitotic/meiotic chromosome in which the DNA is compacted some 10,000- to 20,000-fold.
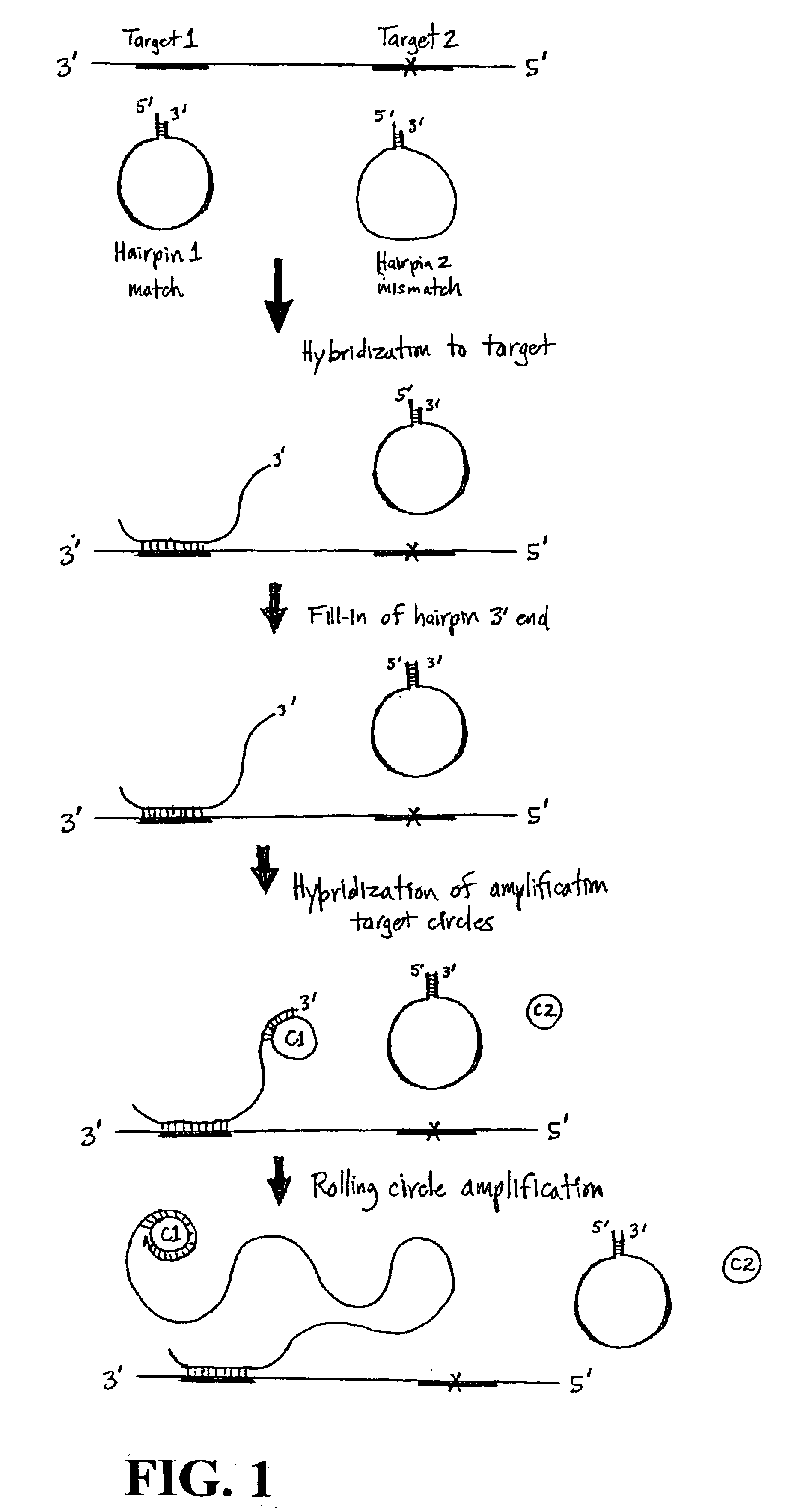
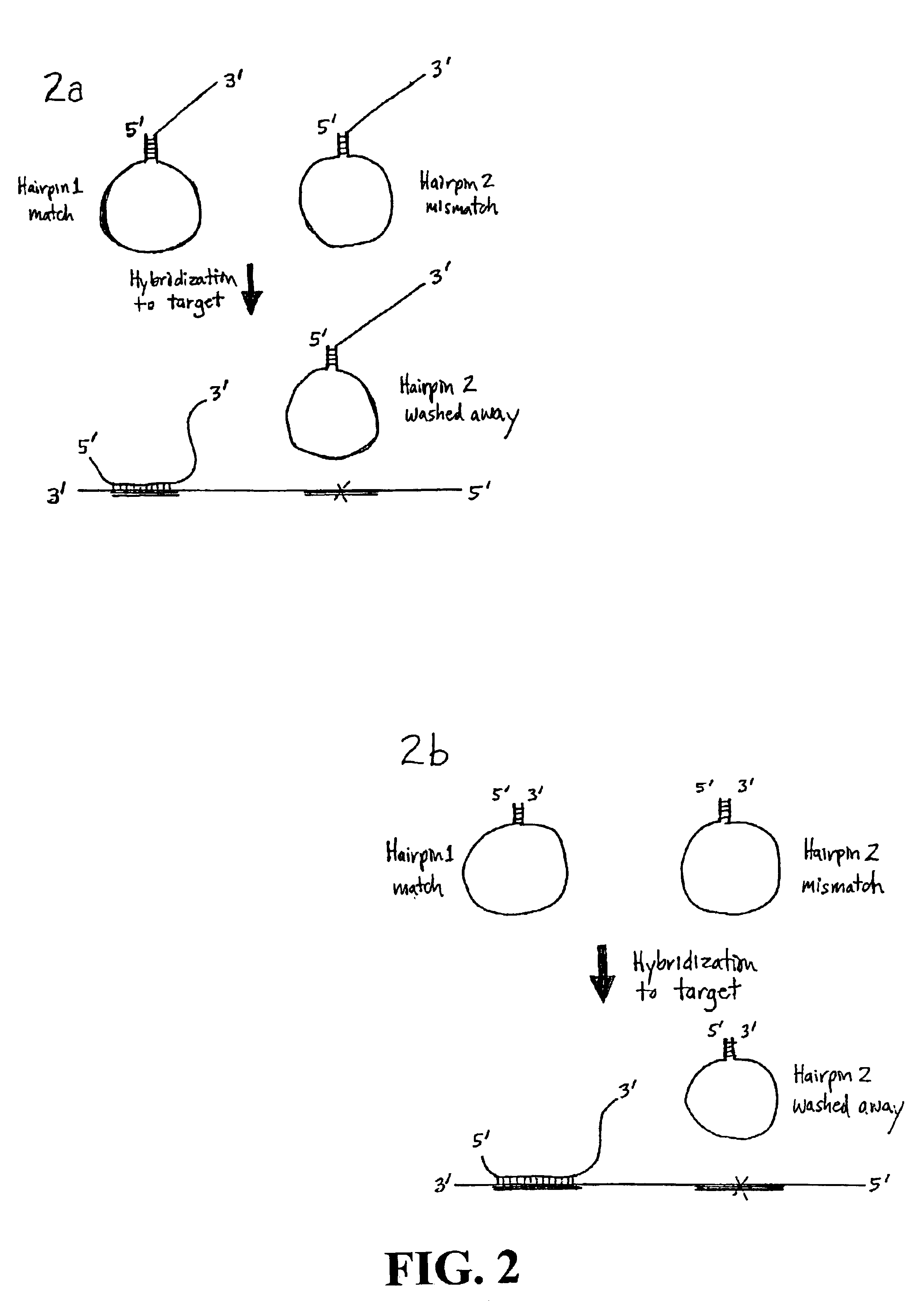
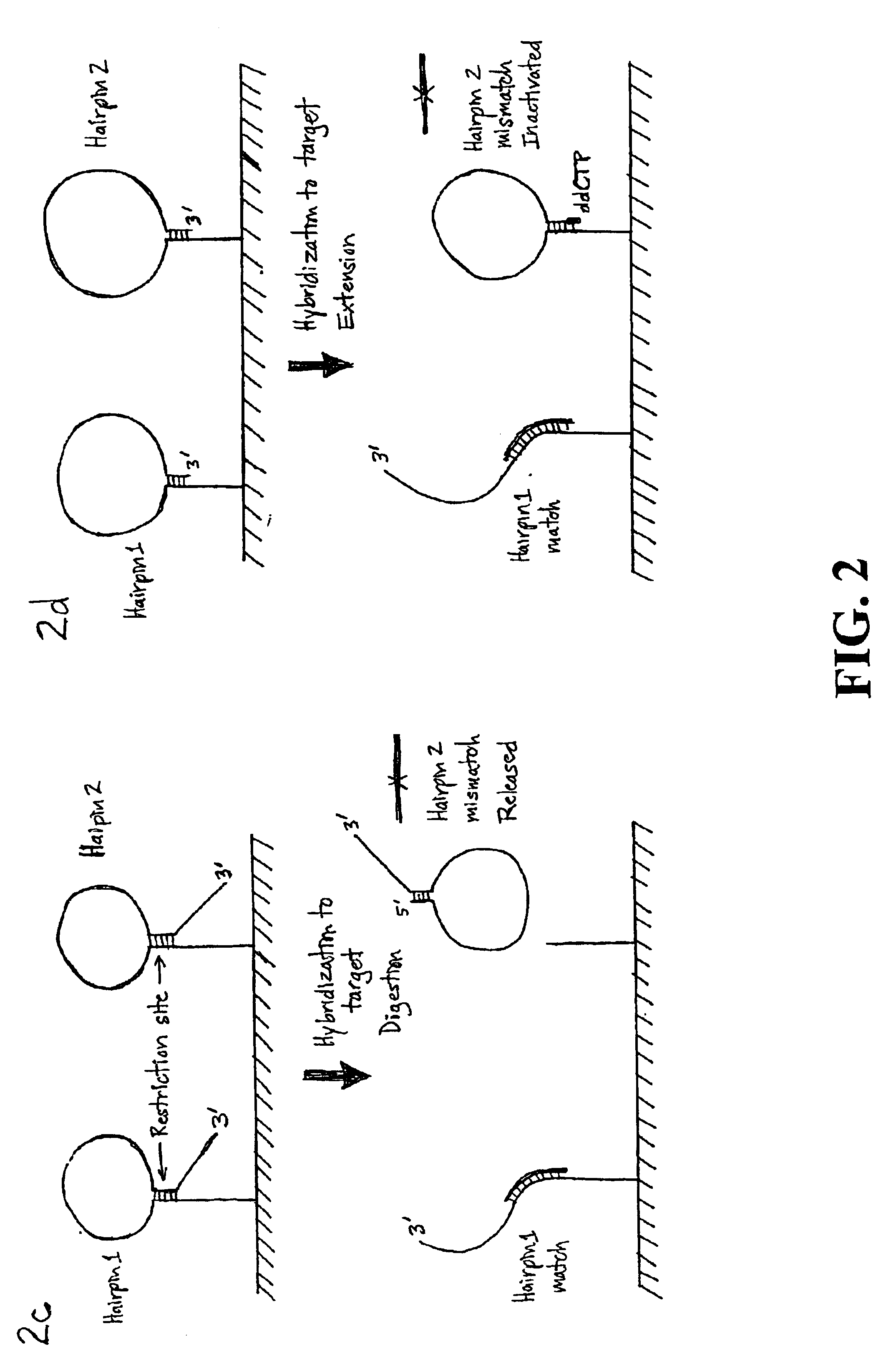
Nucleic acid detection using structured probes
InactiveUS6861222B2Easy to detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed are compositions and a method for detection of nucleic acid sequences. The disclosed method uses a structured probe to distinguish between sequences. Structured probes are bifunctional molecules where one function is as a probe to a target nucleic acid sequence and the other function is as a detection sequence to facilitate detection of the probe. Structured probes include a detection sequence, sequence complementary to a target sequence, and sequences that form duplex regions (higher order structures). The duplex region is stable unless the probe hybridizes to the target sequence. The disclosed method involves hybridizing the structured probe to a target sequence and detecting the detection sequence on the structured probe. The detection sequence is available for detection only if the duplex region of the structured probe is disrupted. This links detection of the structured probe with the hybridization of the structured probe to the target sequence.
Owner:YALE UNIV
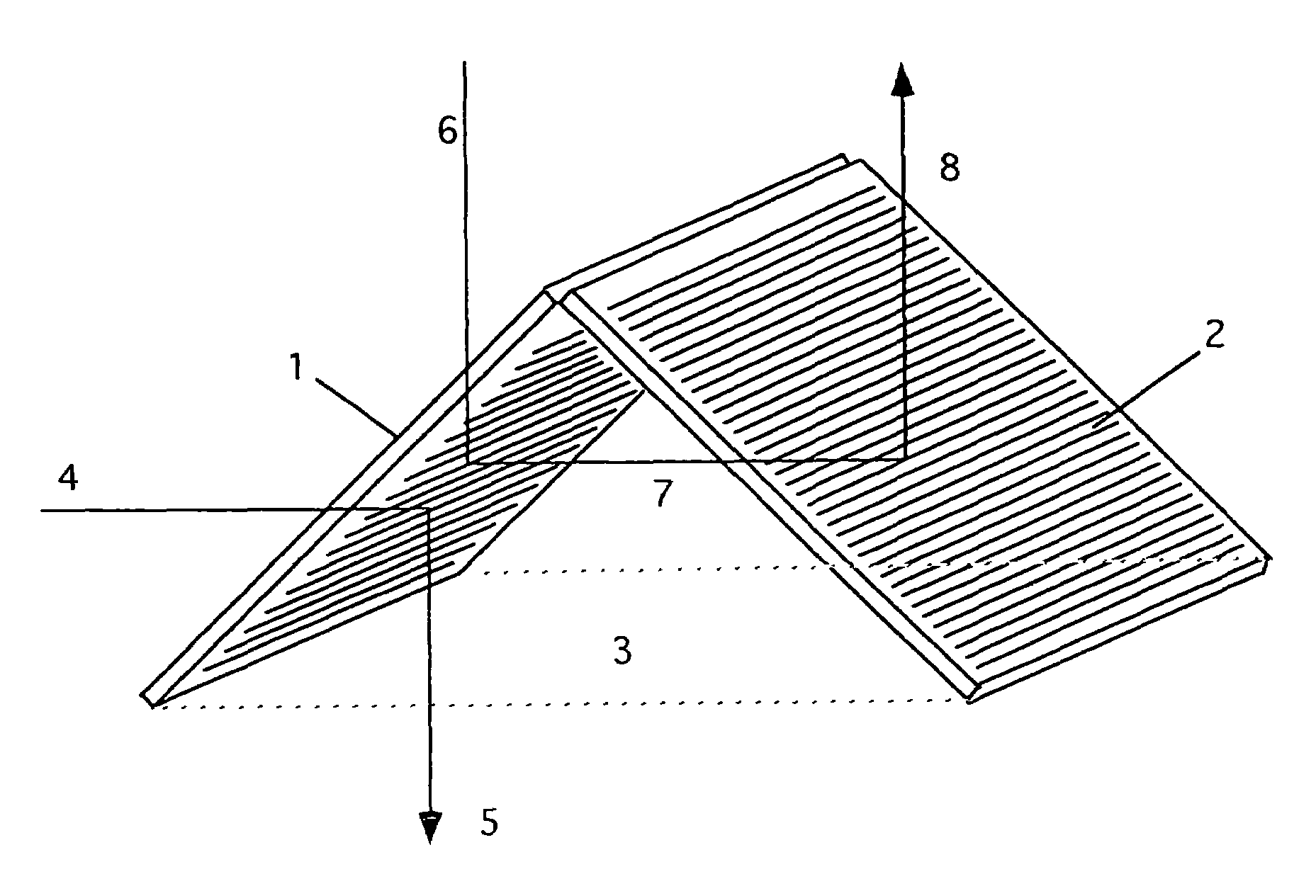
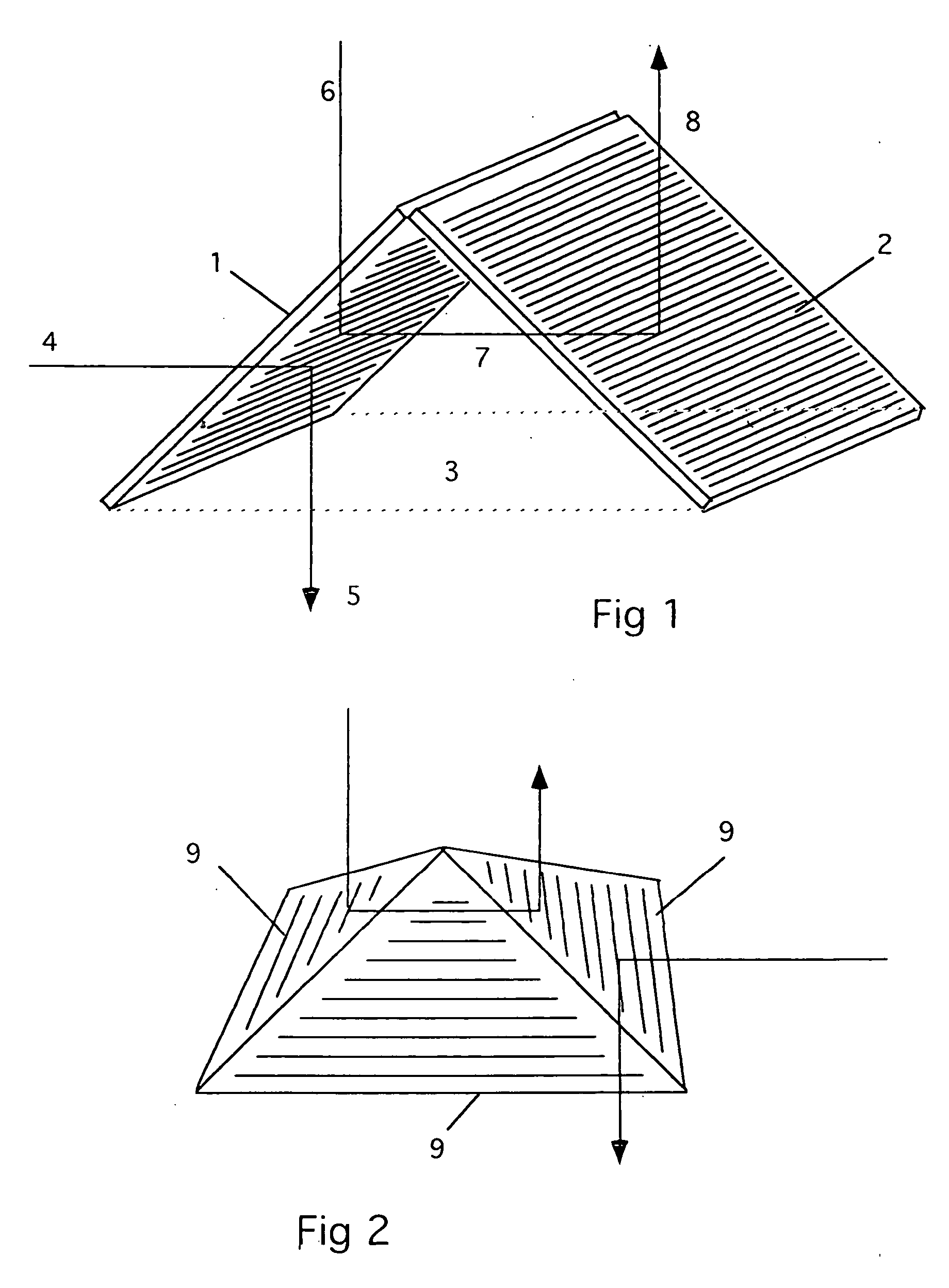
Methods for producing three dimensional, self-supporting, light redirecting roof lighting systems
A self-supporting roof lighting system that accepts low elevation light and rejects high elevation light may be produced by making arrays of parallel laser cuts through, or partly through, a flat sheet of transparent acrylic, cutting the segment containing the arrays from the sheet, positioning the segment over linear heating elements to soften the acrylic along the lines between adjoining laser cut arrays, folding the segment along the softened lines through the angle necessary to form a multi-faceted structure of saddle, pyramid or higher order form and allowing this structure to cool and solidify to produce a self-supporting angle-selective roof lighting system with an array of light redirecting laser cuts on each facet. The sequence of the method may be changed so that a saddle, pyramid or higher order structure is first formed by folding or moulding transparent acrylic and, subsequently, an array of parallel laser cuts is made in each facet of the structure to produce an angle-selective roof lighting system. A conical angle-selective roof lighting system may be produced by making concentric laser cuts through, or partly through, a disc of transparent acrylic with a segment cut out, softening the laser cut disc and moulding the disc into conical form.
Owner:EDMONDS IAN ROBERT
C-class oligonucleotide analogs with enhanced immunostimulatory potency
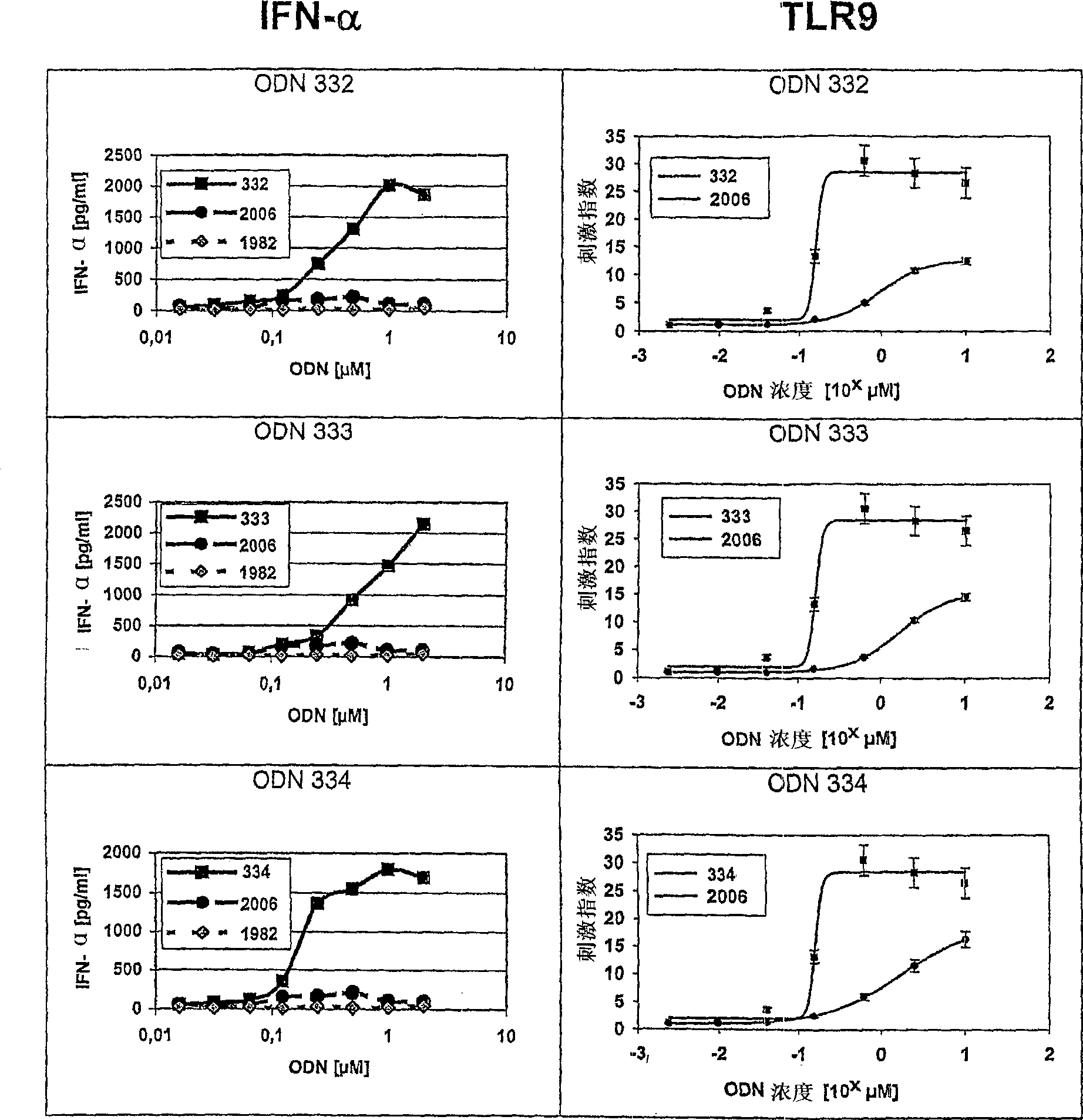
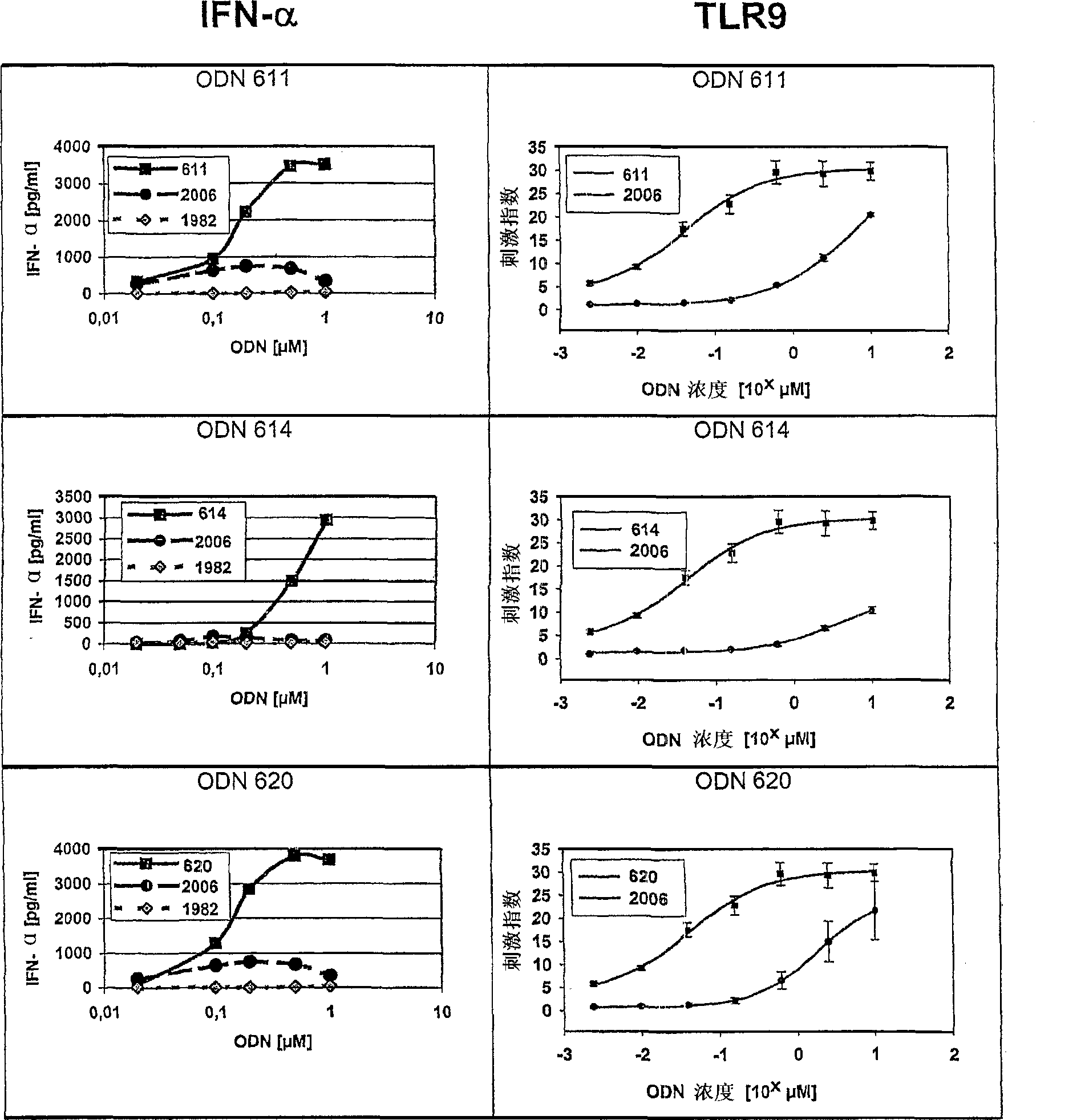
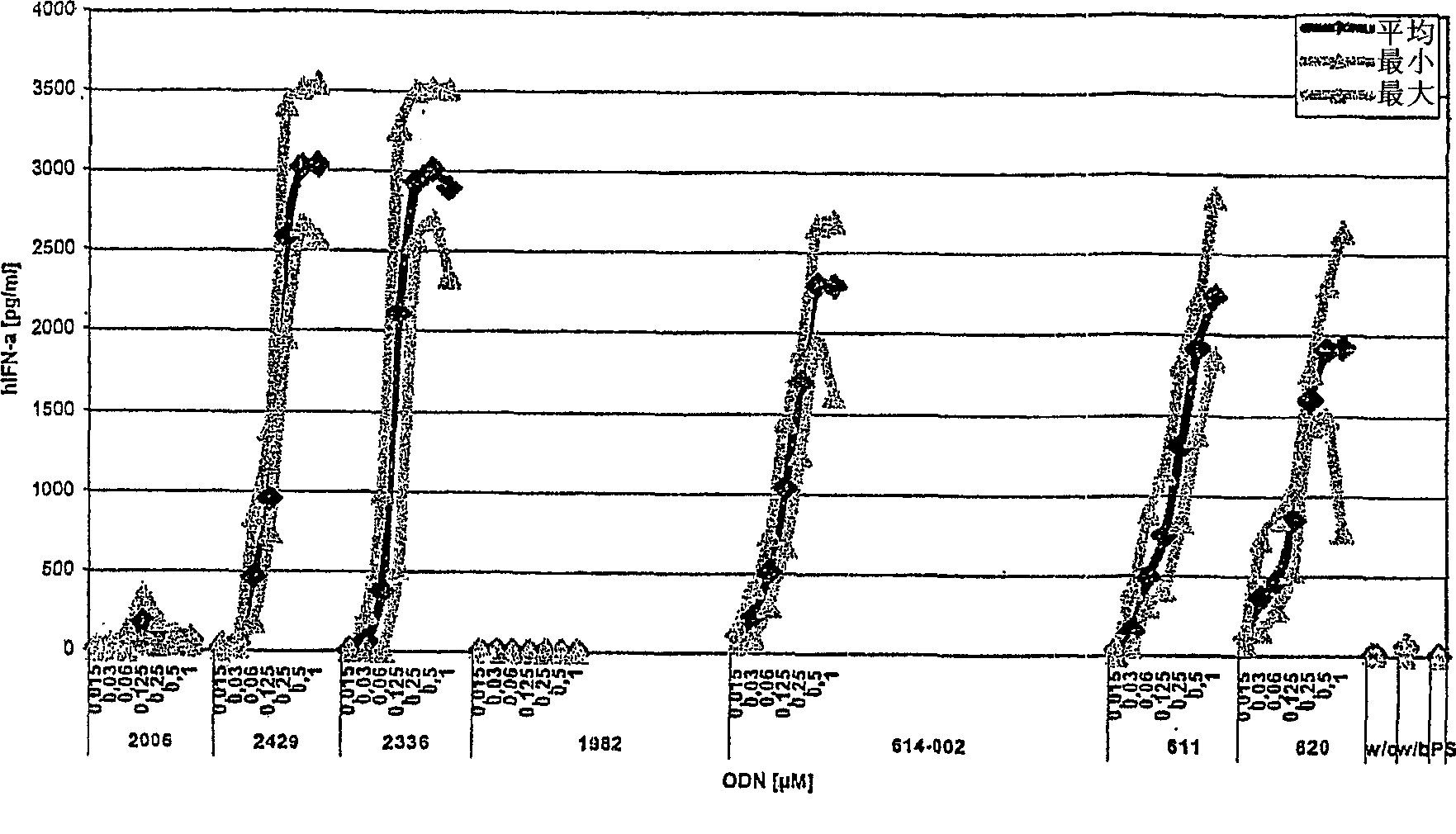
The invention relates to a class of CpG immunostimulatory oligonucleotides containing a CpG immunostimulatory motif and a second motif which is capable of forming secondary structure, including duplex and higher order structures, in vitro and in vivo. The oligonucleotides of the invention are useful as adjuvants in vaccination. The oligonucleotides are also useful for inducing an immune response, inducing expression of a type I interferon (IFN), inducing expression of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), and for treating a variety of conditions, including allergy, asthma, infection, and cancer.
Owner:科勒制药有限公司 +1
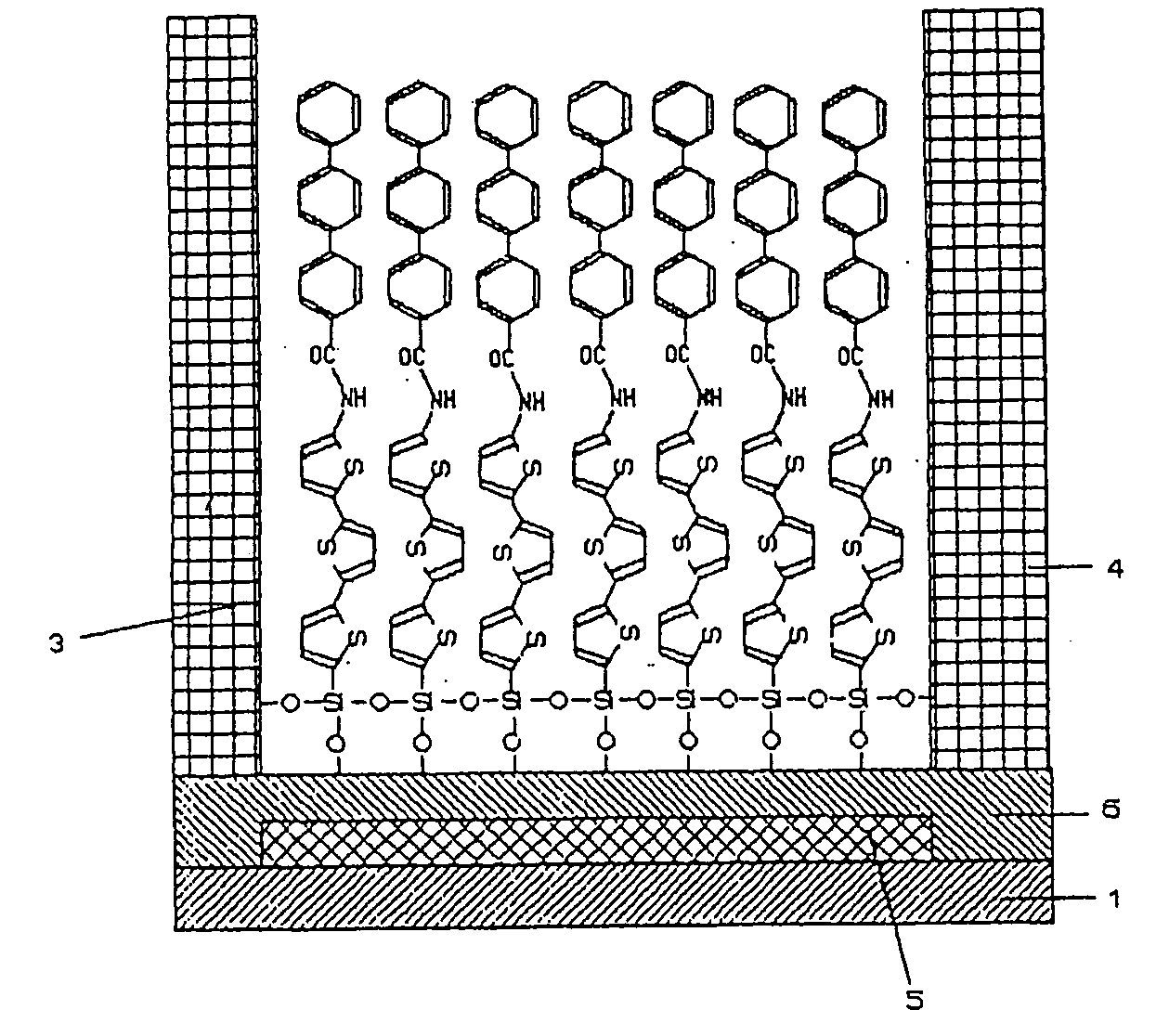
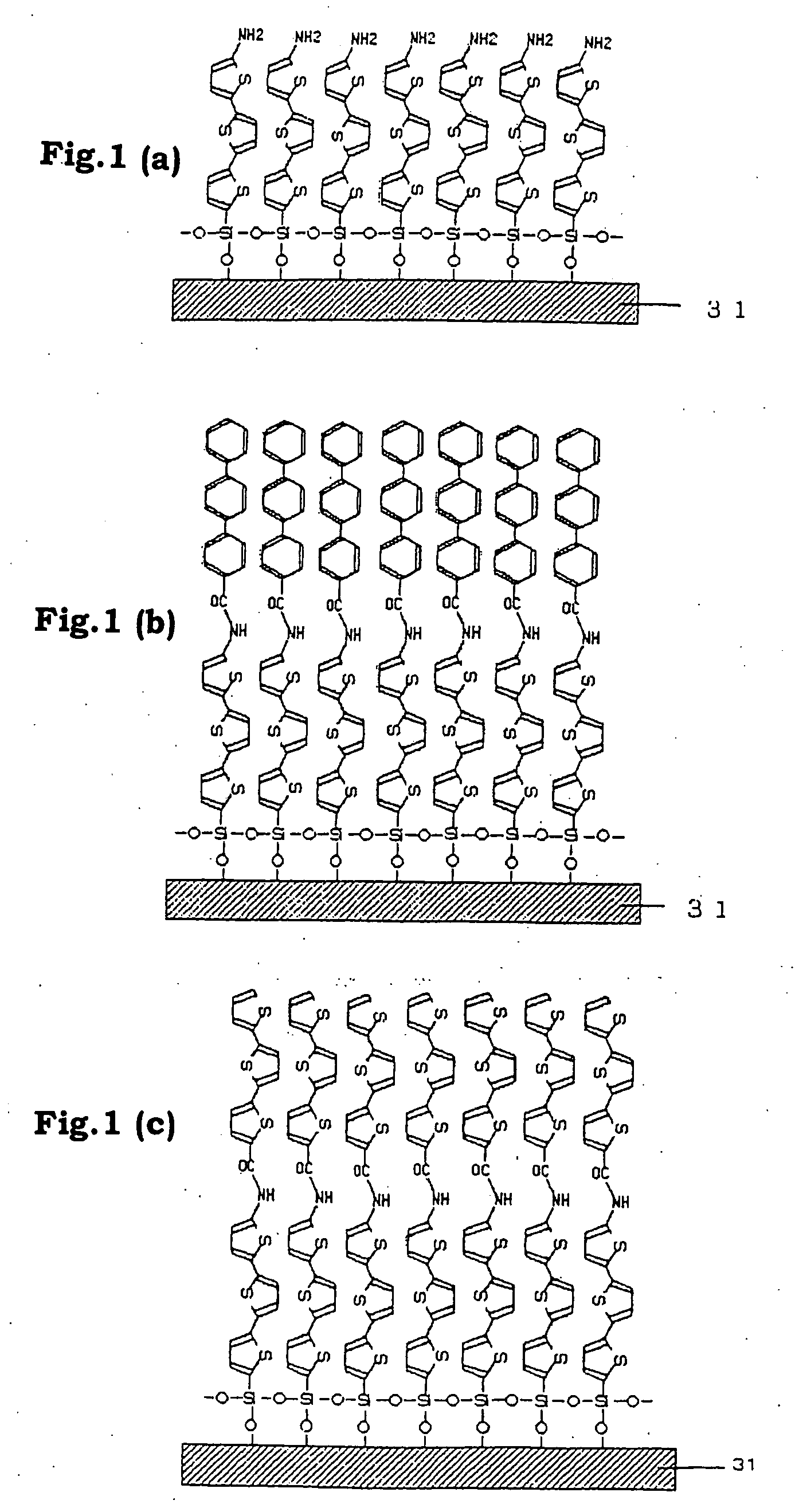
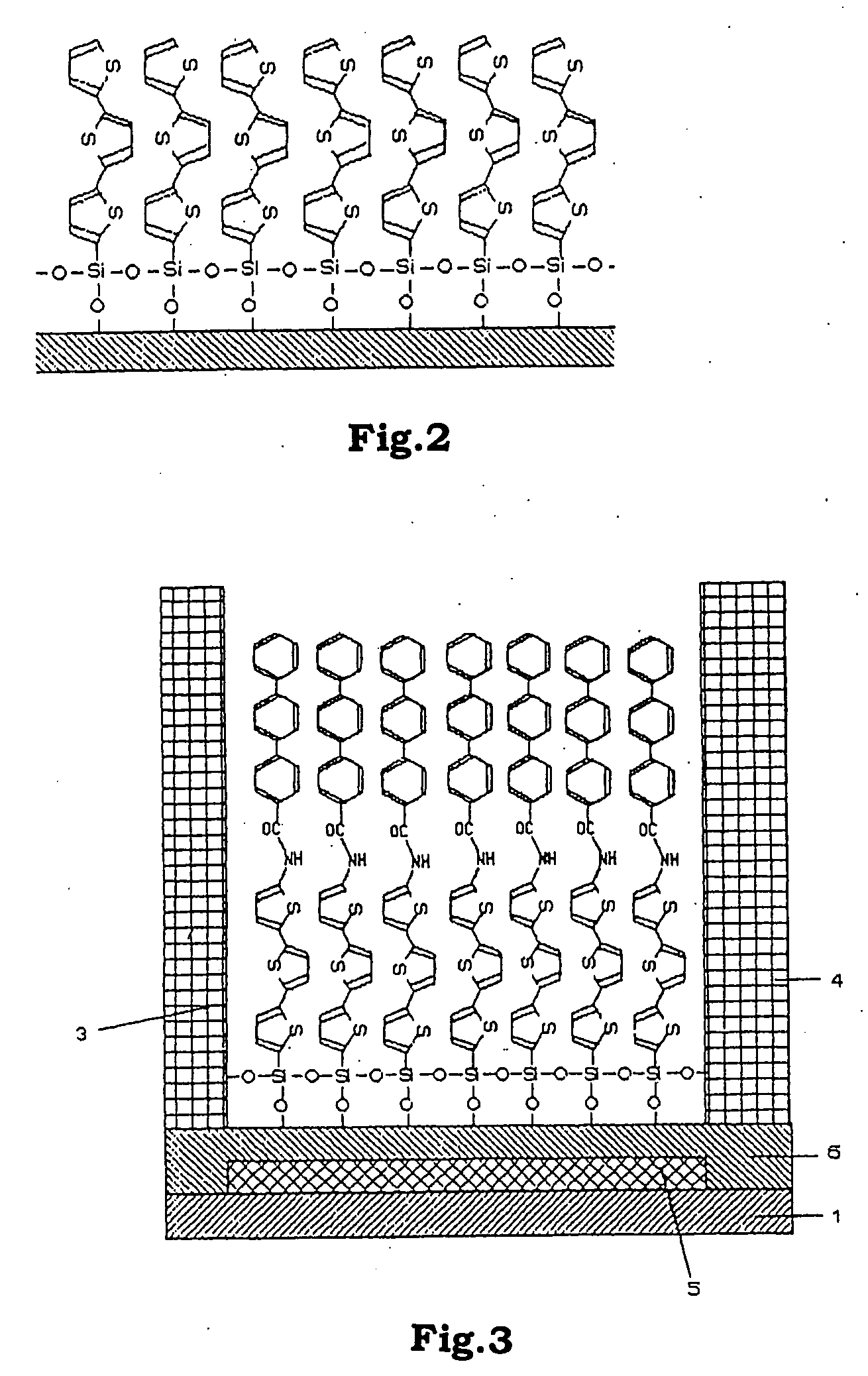
Functional organic thin film, organic thin-film transistor, pi-electron conjugated molecule-containing silicon compound, and methods of forming them
InactiveUS20060231827A1Promote crystallizationPrevent peelingTransistorGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsChemical structureOrganic film
An organic thin film having both a chemical structure of an organic material that is a factor determining a characteristic of the thin film and a high-order structure of the thin film, for example, the crystallinity of molecules, namely, the orientation. A functional organic thin film composed of molecules the main skeleton structure portion of which is arbitrarily given electrical, optical, electrochemical function and a method for simply forming such a functional organic thin film are also disclosed. The functional organic film is formed of a silicon compound expressed by formula R1—SiX1X2X3 (I) where R is an organic residue which may have a terminal replaced by a functional grou p and to which π-electron conjugate units are bonded, and X1, X2 and X3 are the same group or different groups and given a hydroxyl group by hydrolysis.
Owner:SHARP KK
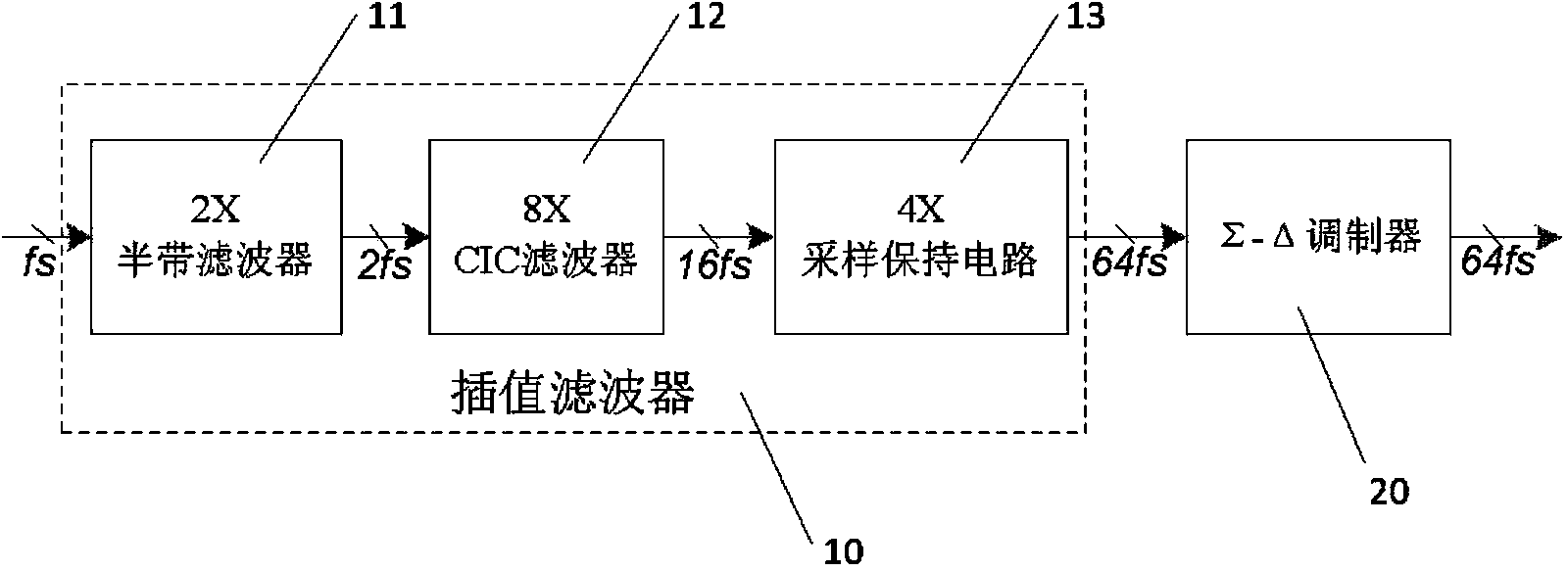
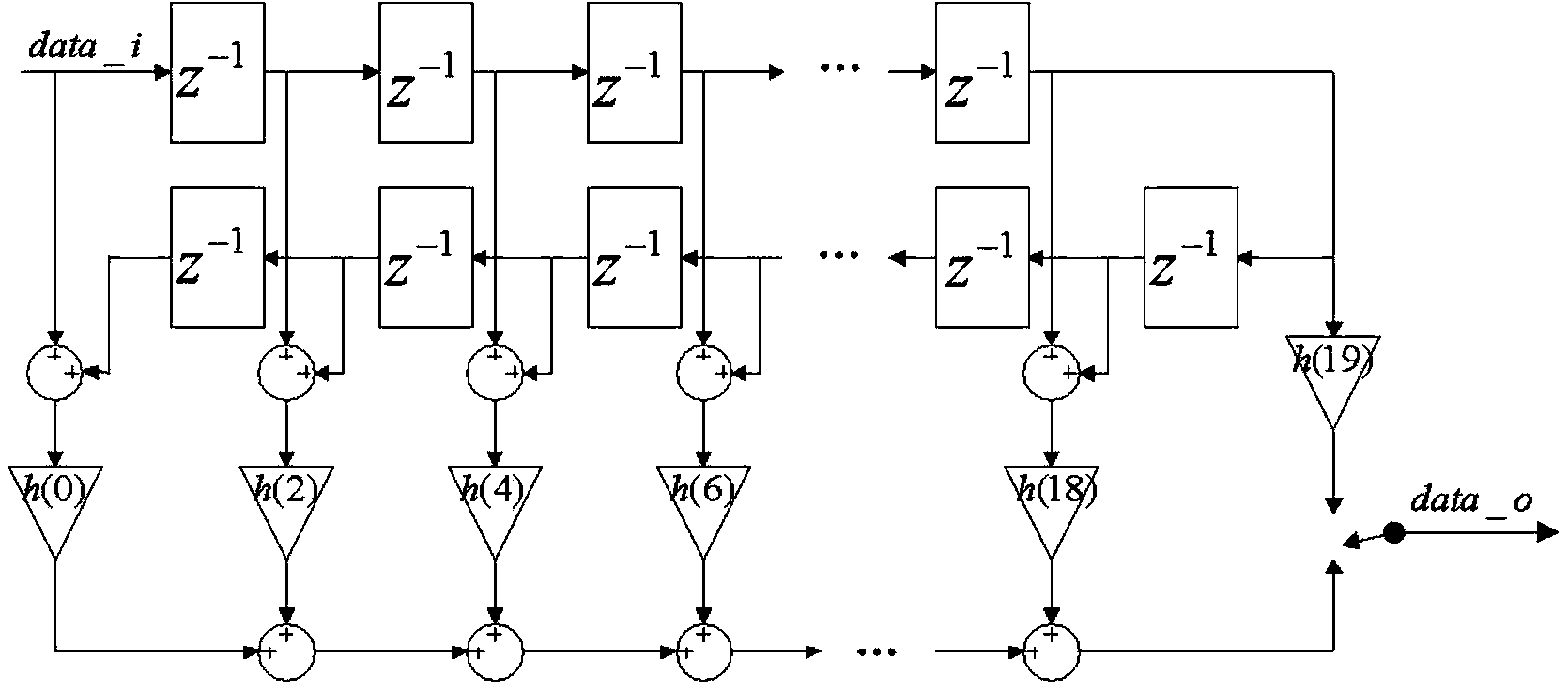
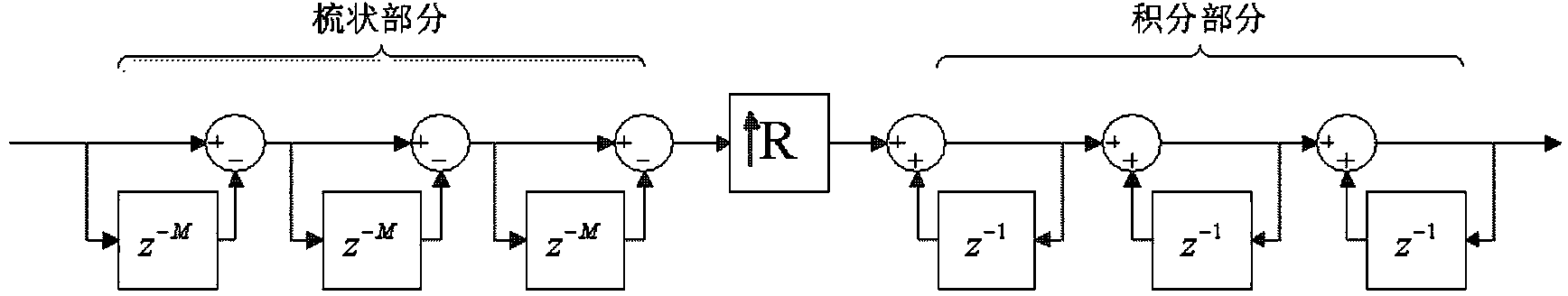
Oversampling 64-time sigma-delta modulation circuit with effective bit being 18
InactiveCN103944575ASimple structureReduce the occupied areaAnalogue conversionReconstruction filterSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides an oversampling 64-time sigma-delta modulation circuit with an effective bit being 18. The circuit comprises an interpolation filter and a sigma-delta modulator. The interpolation filter is used for conducting oversampling interpolation and filtering on digital input signals. The input end of the sigma-delta modulator is connected with the output end of the interpolation filter, the sigma-delta modulator is used for modulating oversampled digital signals, shaping quantized noise introduced by a quantizer, moving noise in the signal bandwidth out of the bandwidth, and meanwhile guaranteeing that transmission of the signals is not affected, and output 1-bit 0 / 1 code streams need to be restored through a backward-stage analog reconstruction filter so as to acquire analog signals. An improved structure is adopted in a half-band filter in the interpolation filter so that the area of the half-band filter can be greatly reduced; for the sigma-delta modulator, a monocycle high-order structure easier to achieve is adopted, the stability problem is analyzed, the high signal to noise ratio is achieved, and meanwhile stability of the modulator is guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
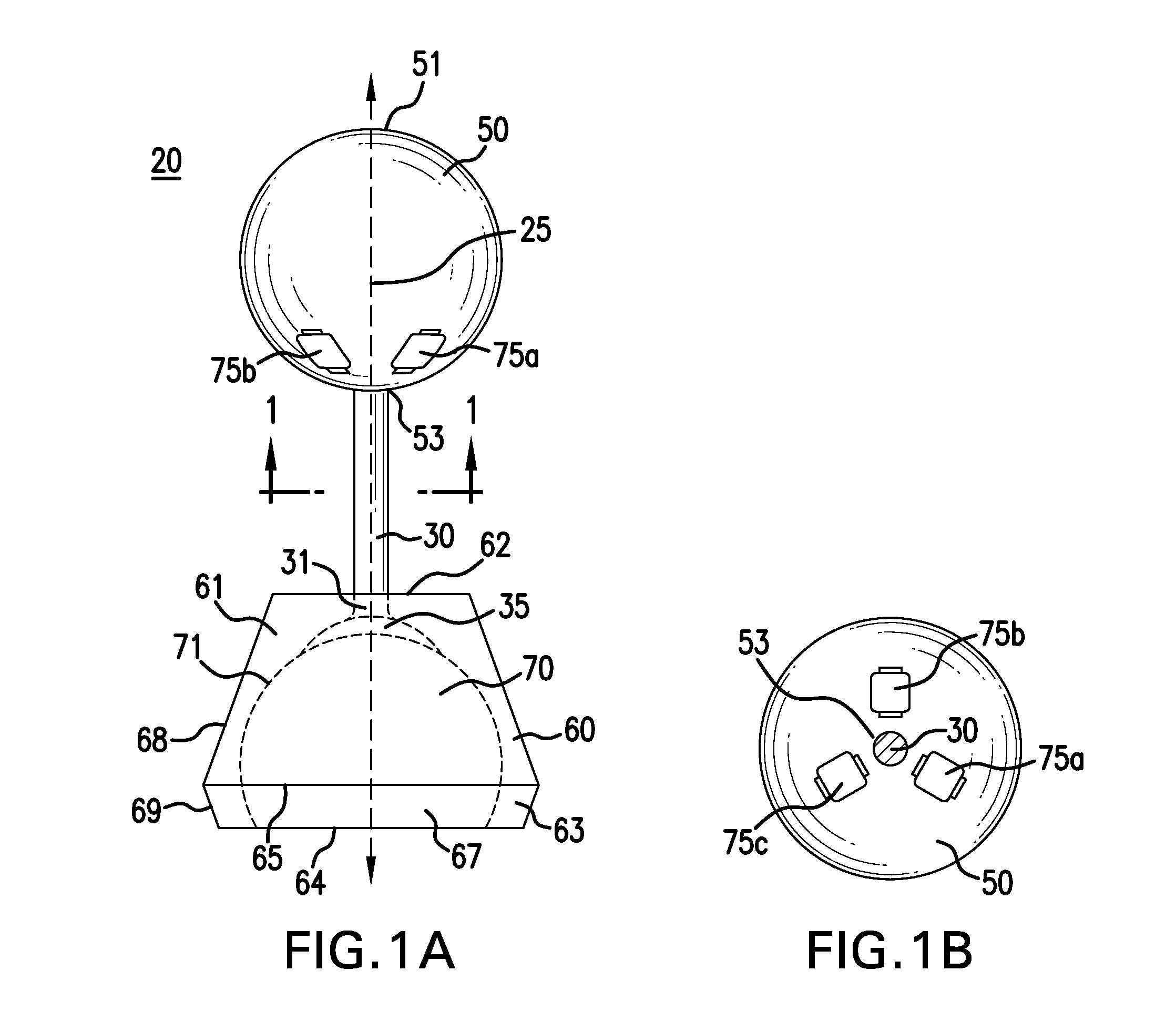
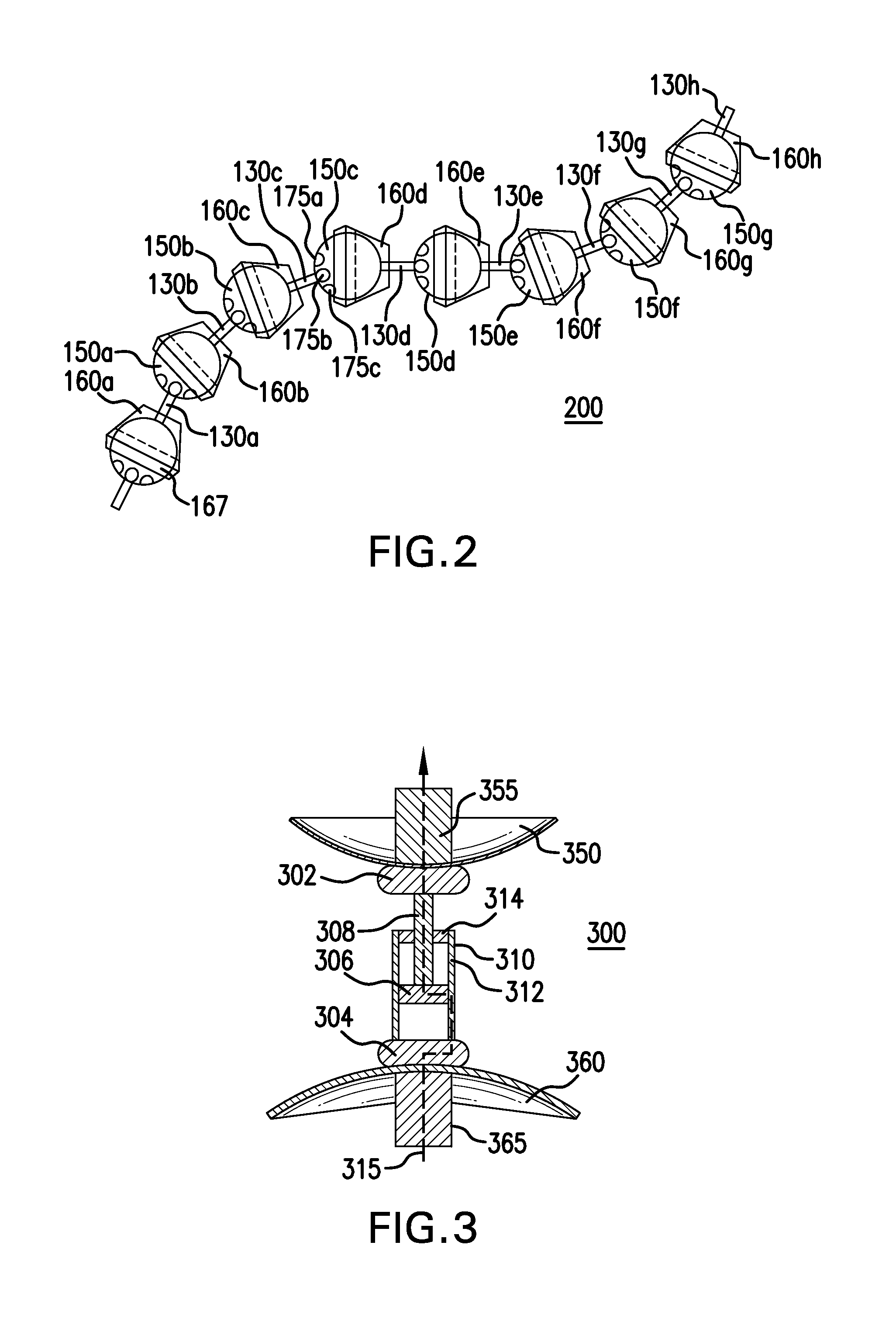
Mobile fibers and elongated structures and units thereof
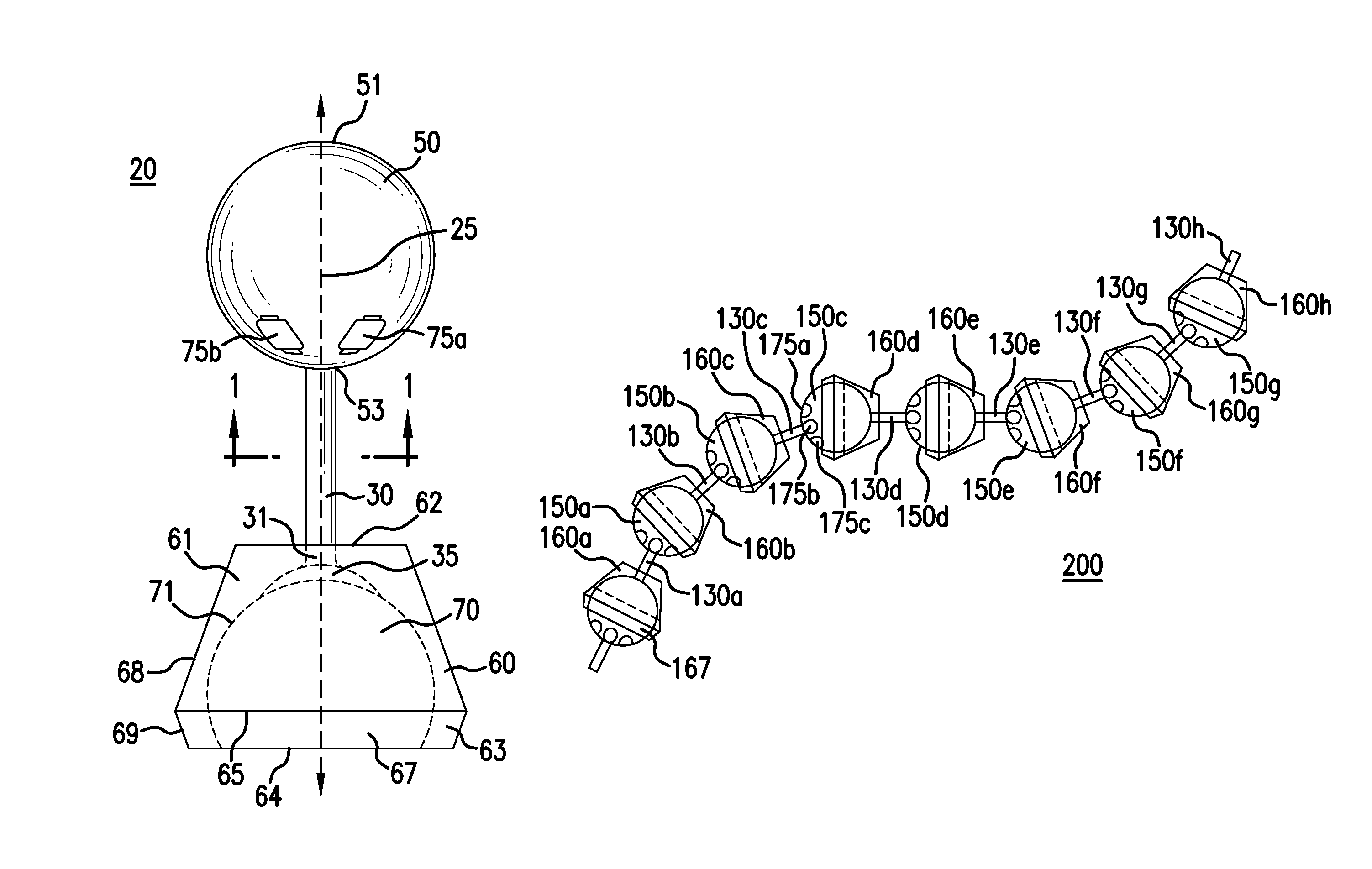
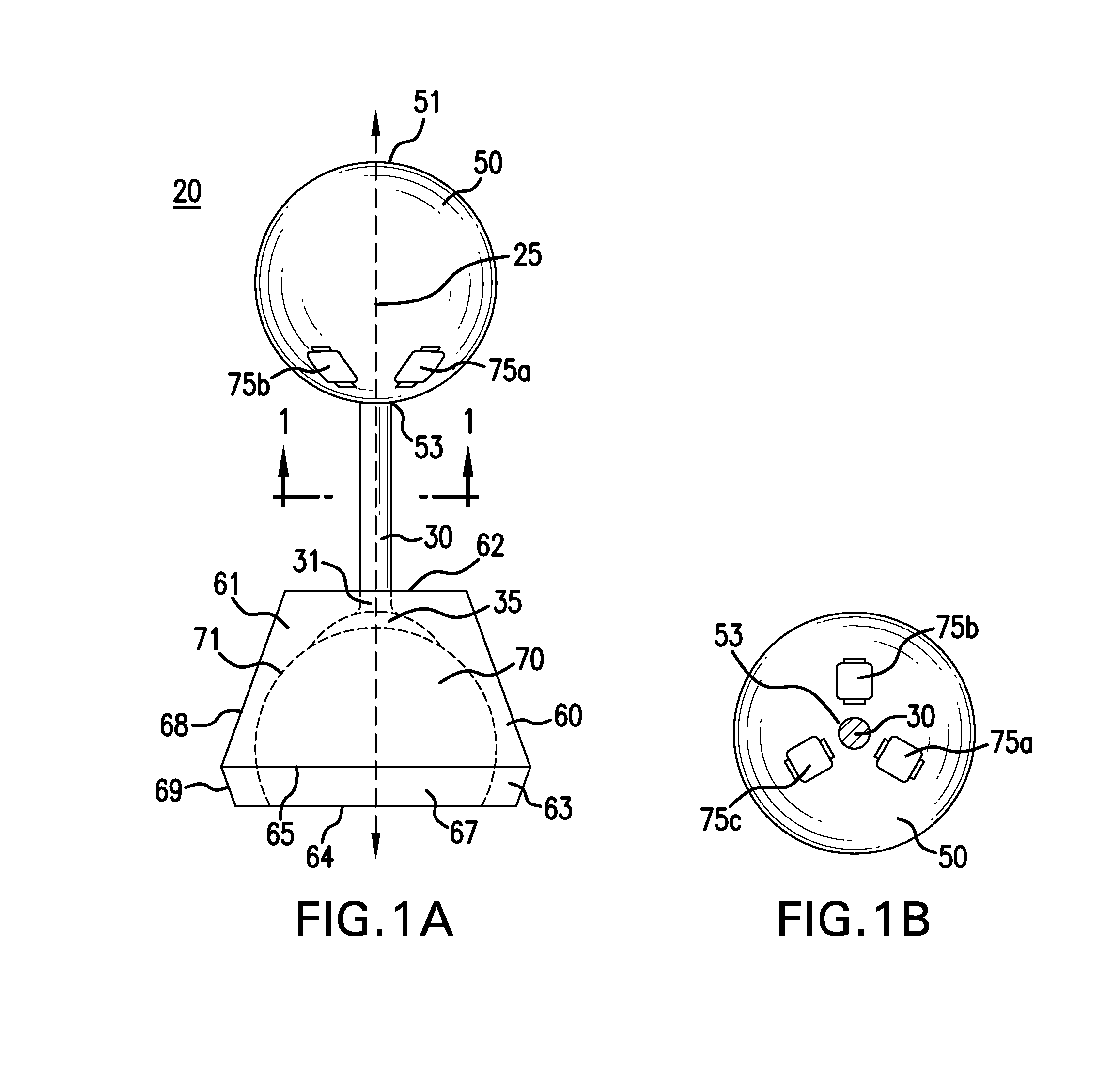
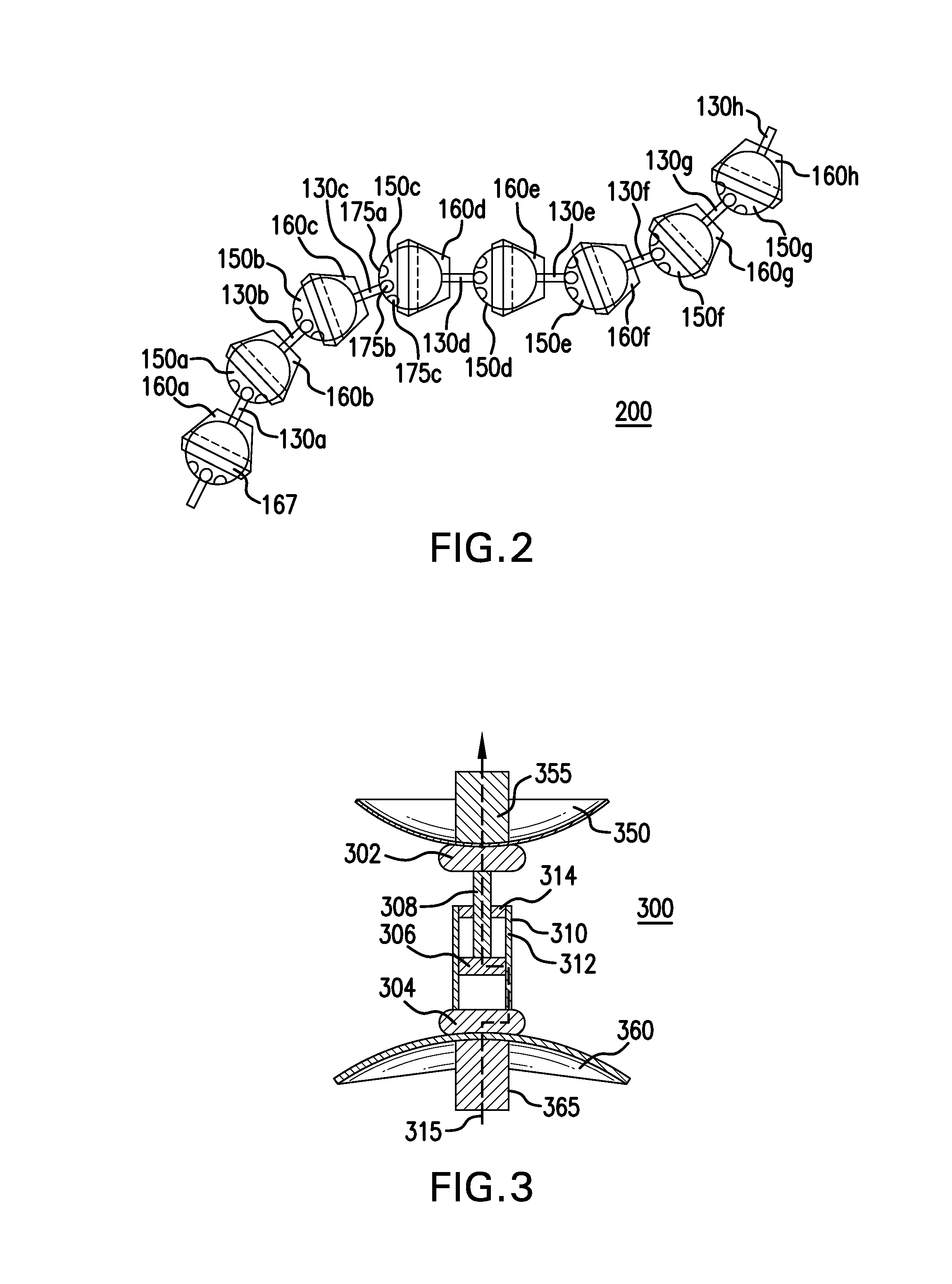
The present invention provides a unit or segment having a ball, a socket and a connector with the connector physically linking the ball and socket together such that a main opening of the socket continuous with the socket cavity faces away from the connected ball. Alternatively, a unit / segment may instead include a ball and a socket coupled directly together. Elongated structures comprising a plurality of units joined together in series, such as through ball joints and other connections, are further provided that may vary greatly in length and size. The ball and socket may have corresponding electromagnets and magnetic materials, respectively, that may attract or repel each other to cause controlled rotational movement of the individual ball joint(s) by controlling the operation of the electromagnets. Higher order structures including one or more elongated structures are further provided. Methods for constructing and / or operating units and / or elongated structures are further provided.
Owner:STERN THOMAS
Polypropylene molded article, sheet-like polypropylene molded article, and method for production of polypropylene thermally molded article
InactiveUS20110014408A1Rigid enoughIncrease awarenessLayered productsBottlesAmorphous phasePolypropylene
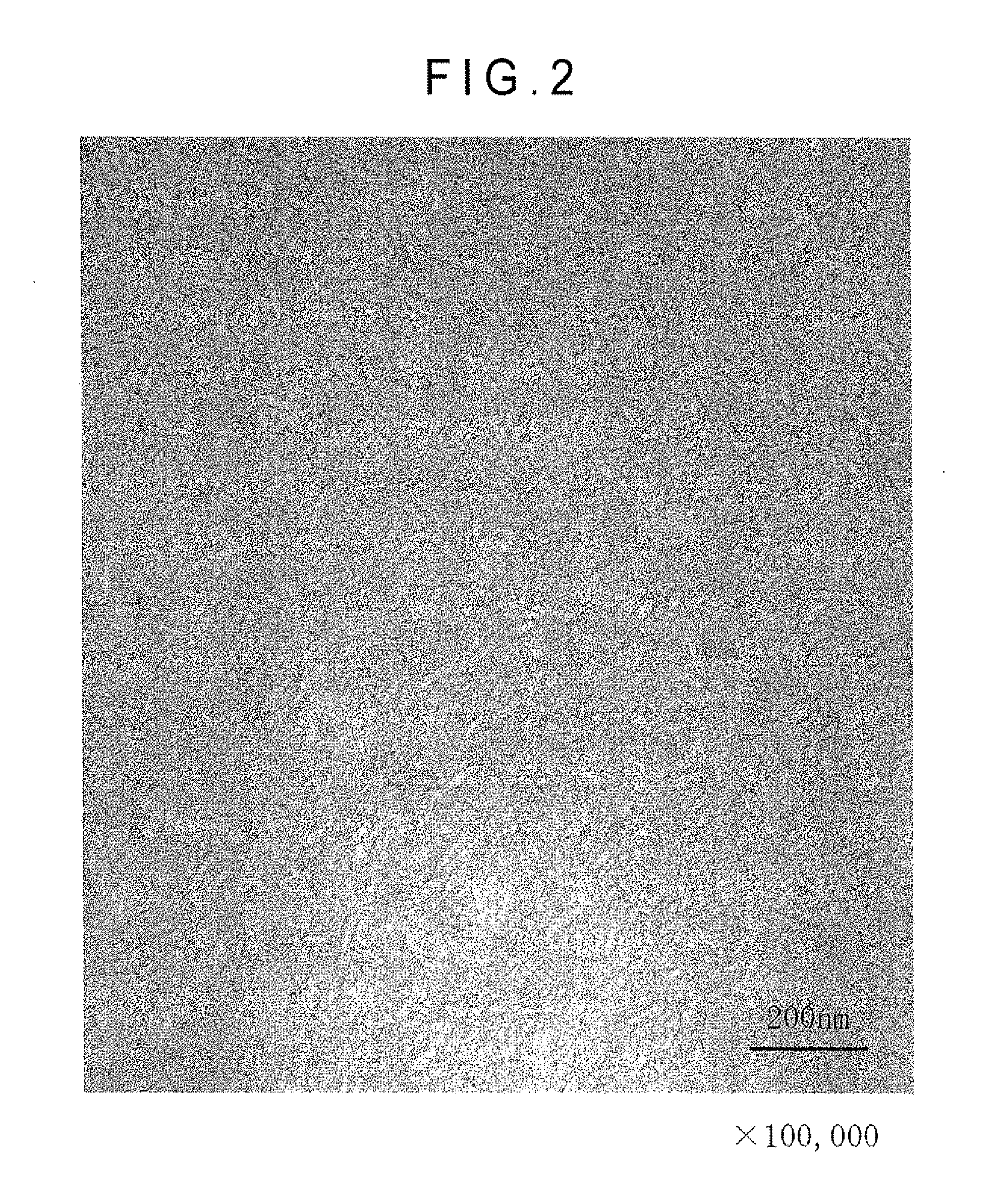
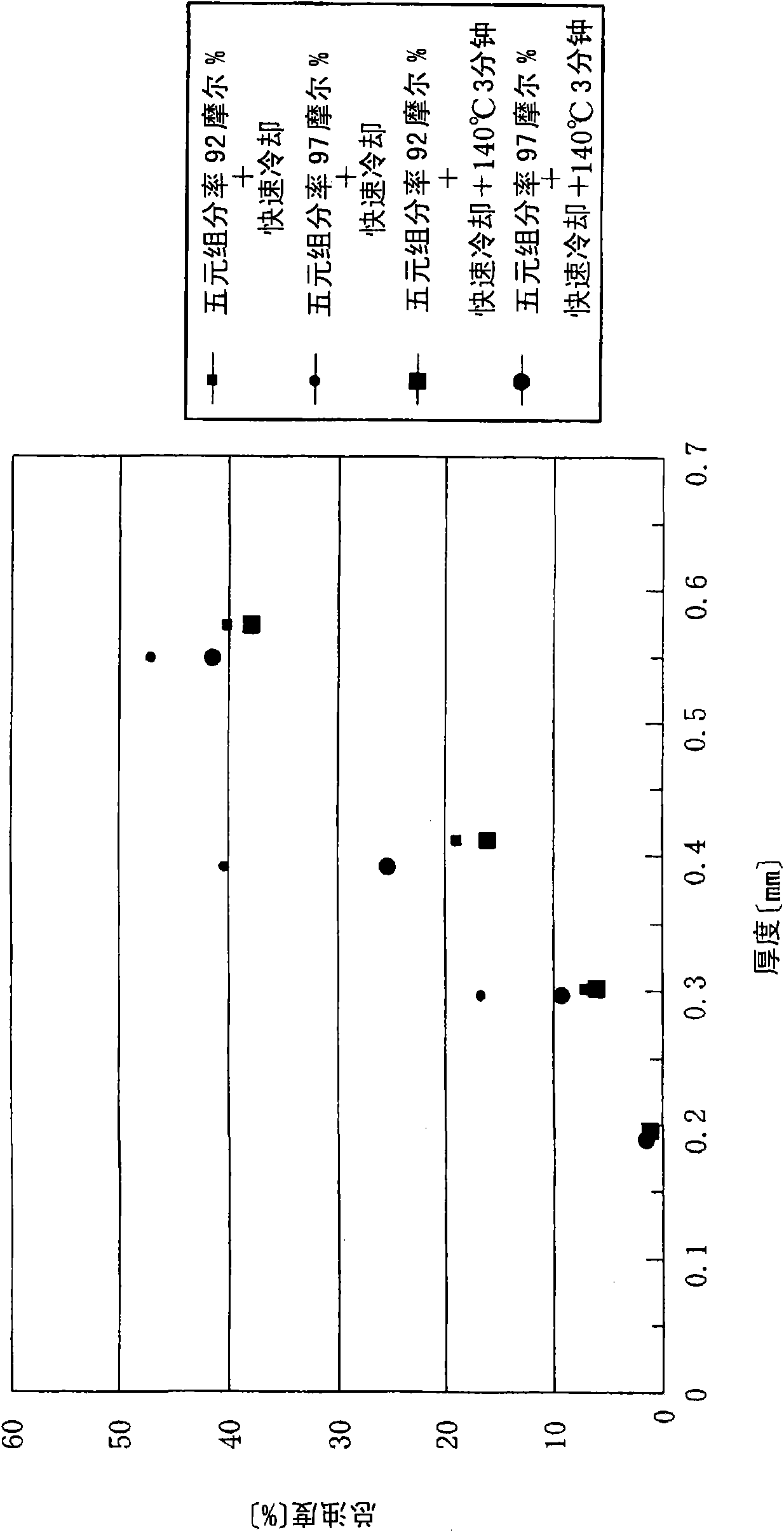
A molten polypropylene having tacticity expressed in terms of an isotactic pentad fraction of 95 mol % or more is flowed. The molten-polypropylene is cooled to a temperature range of −200 degrees C. to 50 degrees C. and maintained at the above temperature for 0.1 second to 100 seconds, thereby providing a rapidly-cooled polypropylene higher order structure of which main constituents are a mesophase or monoclinic crystal domain having a size of 100 nm or less and an amorphous phase. The rapidly-cooled polypropylene higher order structure is heated to a temperature range in which endothermic transition occurs and that is equal to or lower than a melting temperature of polypropylene to be heat-treated.
Owner:IDEMITSU UNITECH CO LTD
Mobile fibers and elongated structures and units thereof
The present invention provides a unit or segment having a ball, a socket and a connector with the connector physically linking the ball and socket together such that a main opening of the socket continuous with the socket cavity faces away from the connected ball. Alternatively, a unit / segment may instead include a ball and a socket coupled directly together. Elongated structures comprising a plurality of units joined together in series, such as through ball joints and other connections, are further provided that may vary greatly in length and size. The ball and socket may have corresponding electromagnets and magnetic materials, respectively, that may attract or repel each other to cause controlled rotational movement of the individual ball joint(s) by controlling the operation of the electromagnets. Higher order structures including one or more elongated structures are further provided. Methods for constructing and / or operating units and / or elongated structures are further provided.
Owner:STERN THOMAS
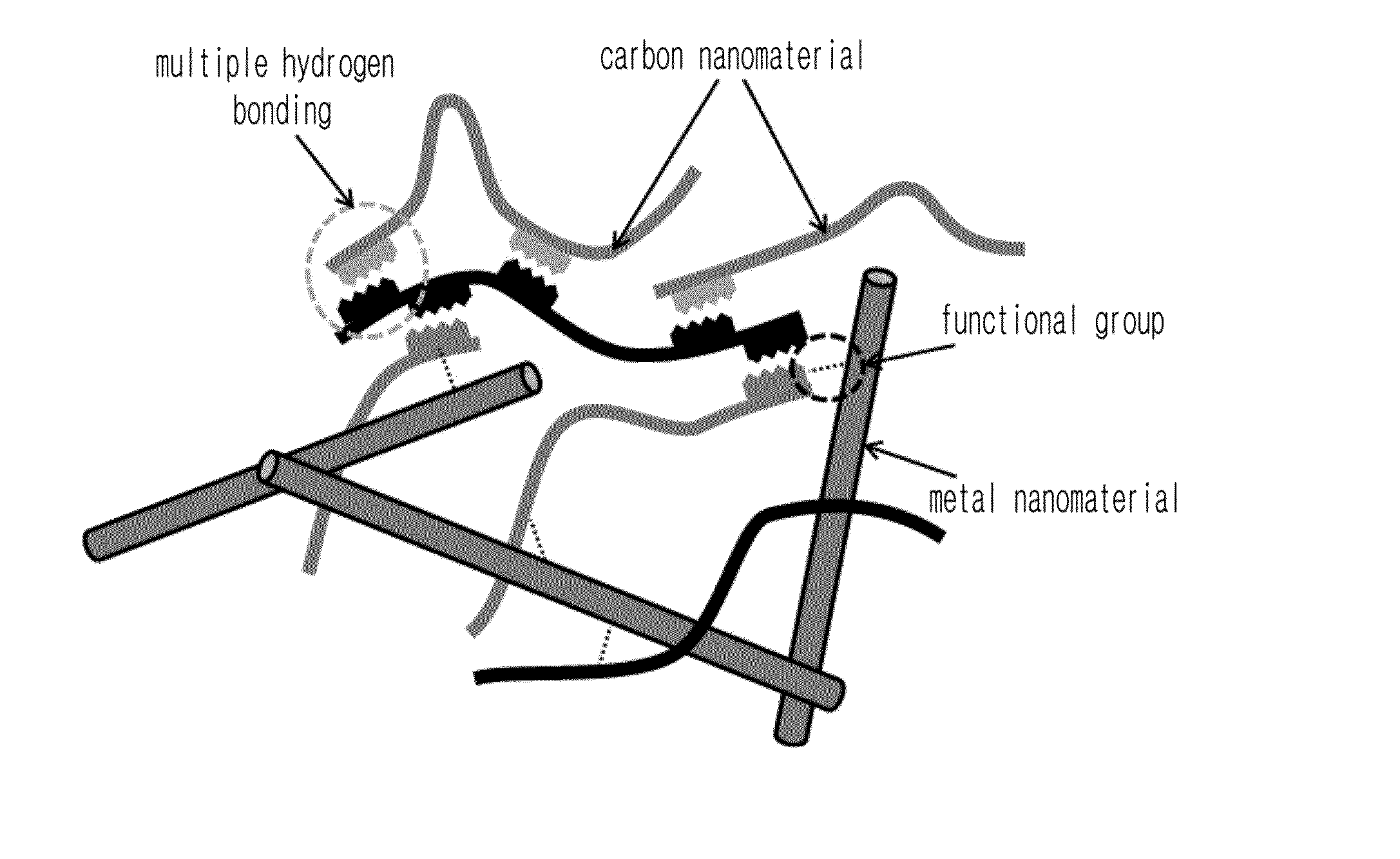
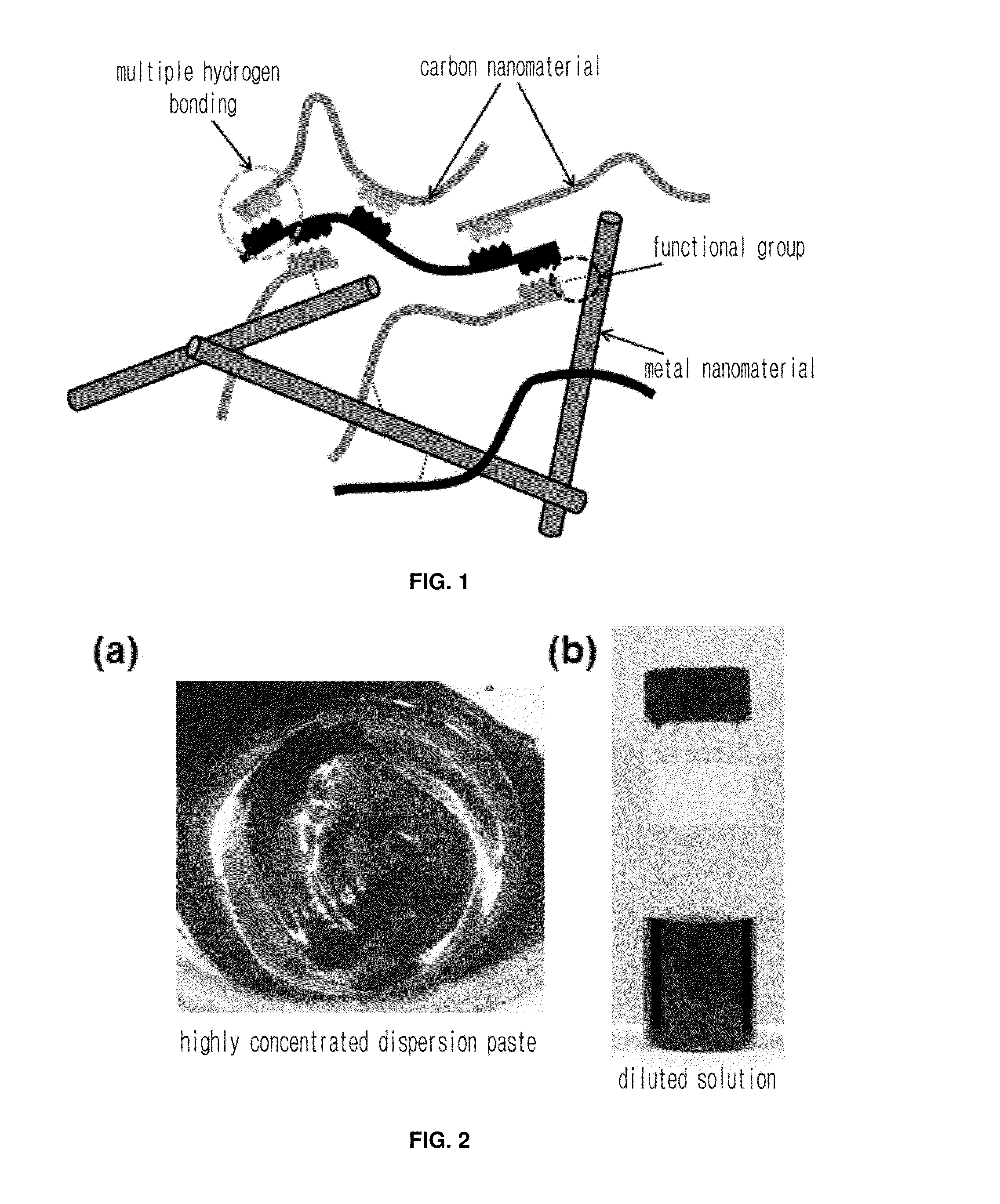
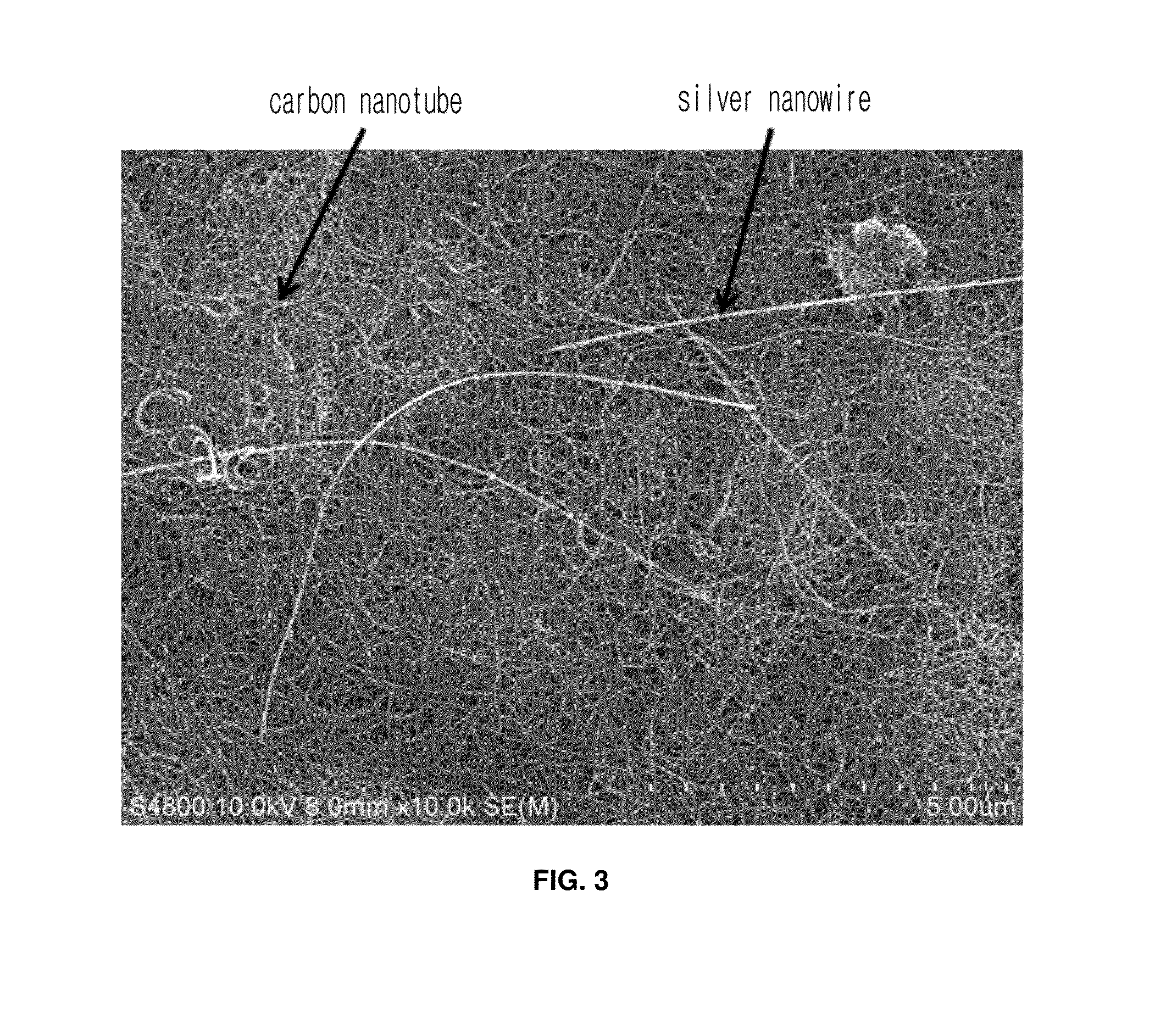
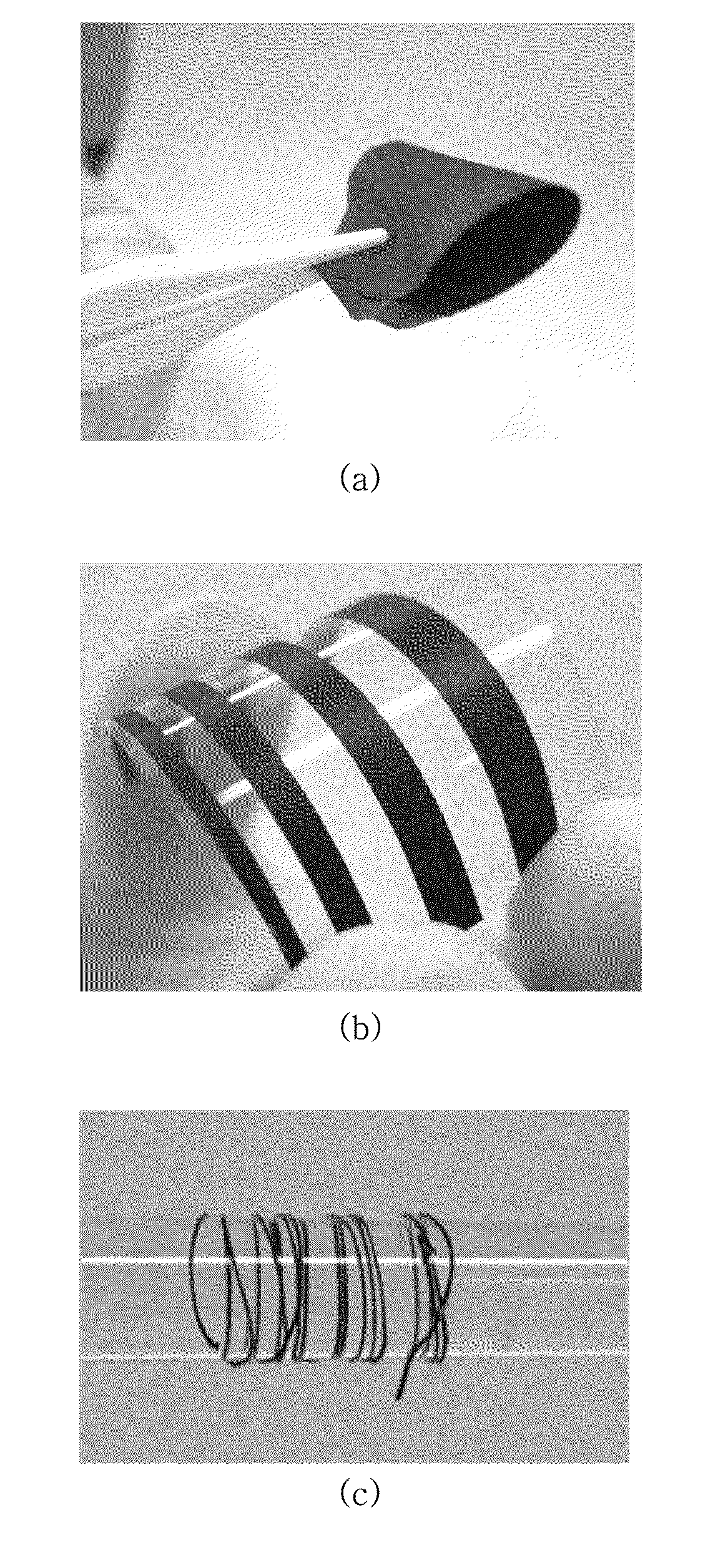
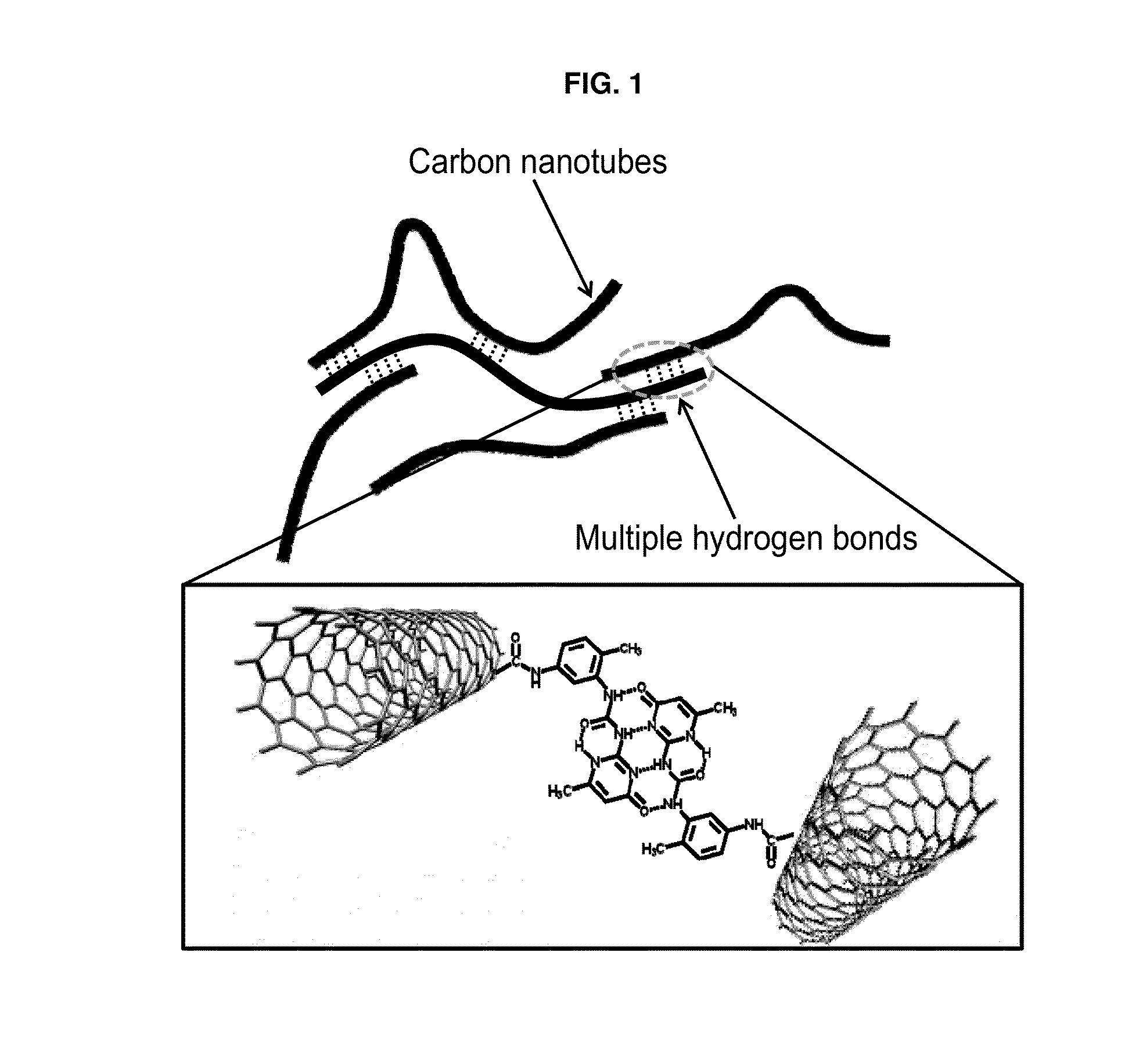
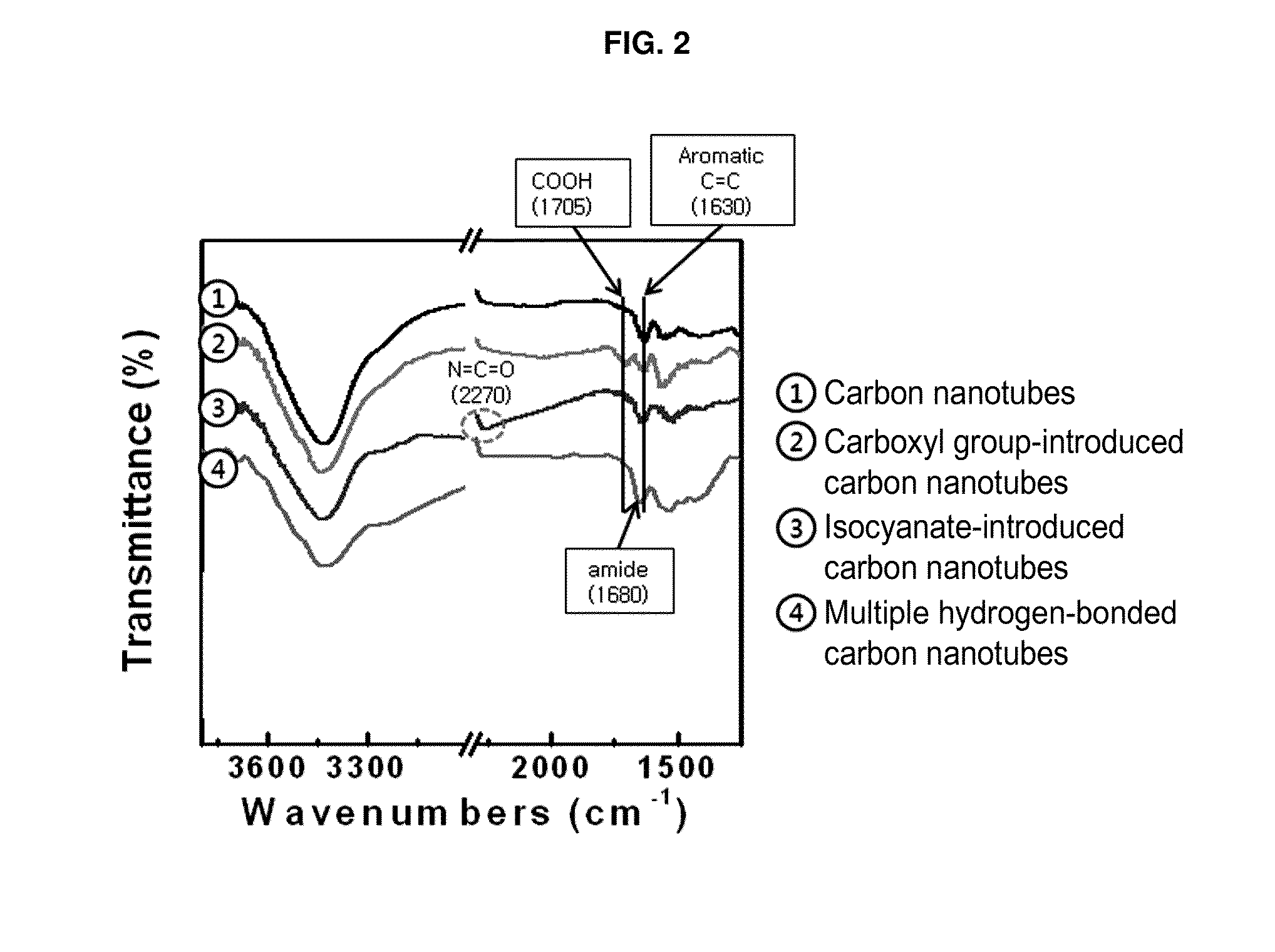
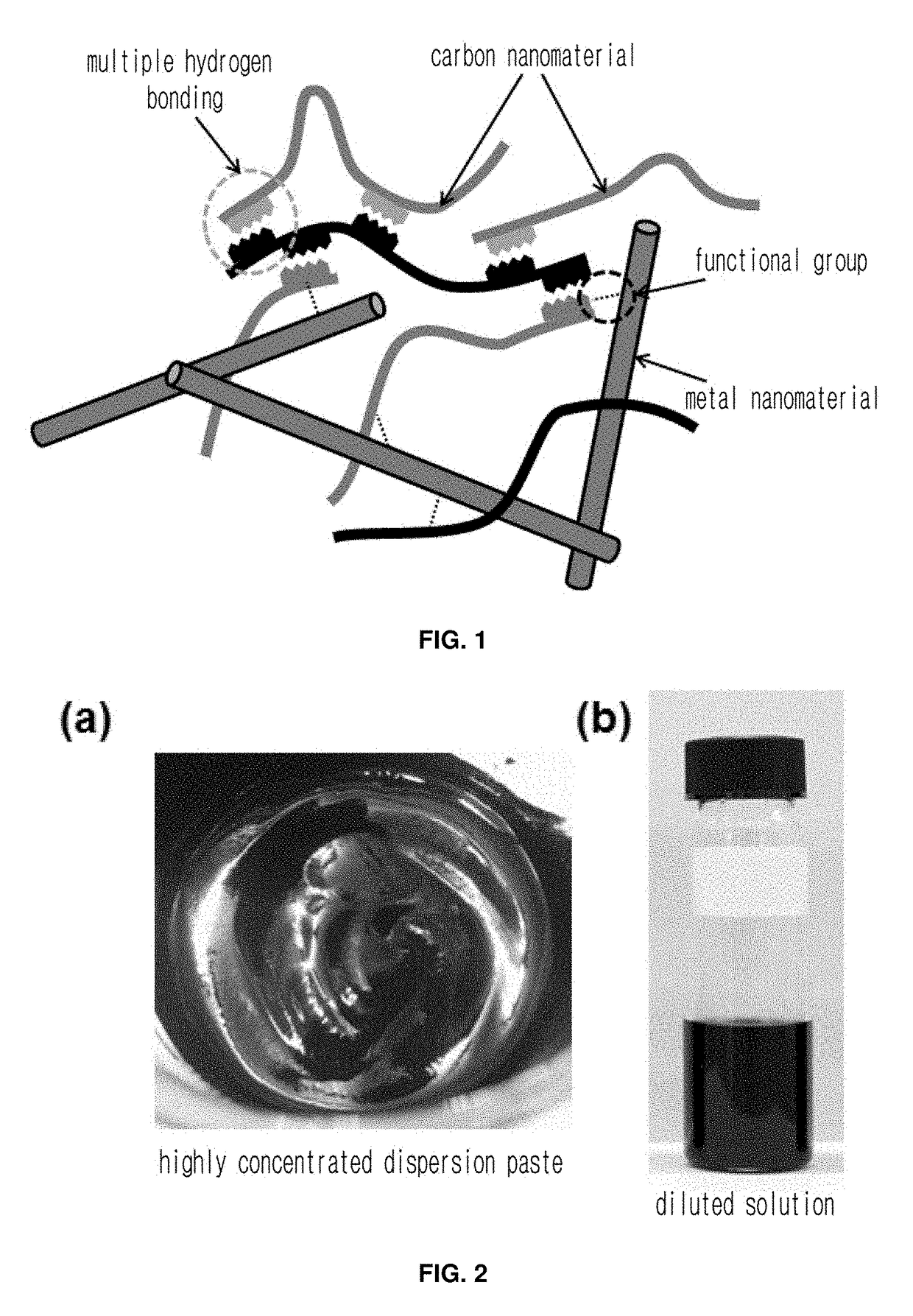
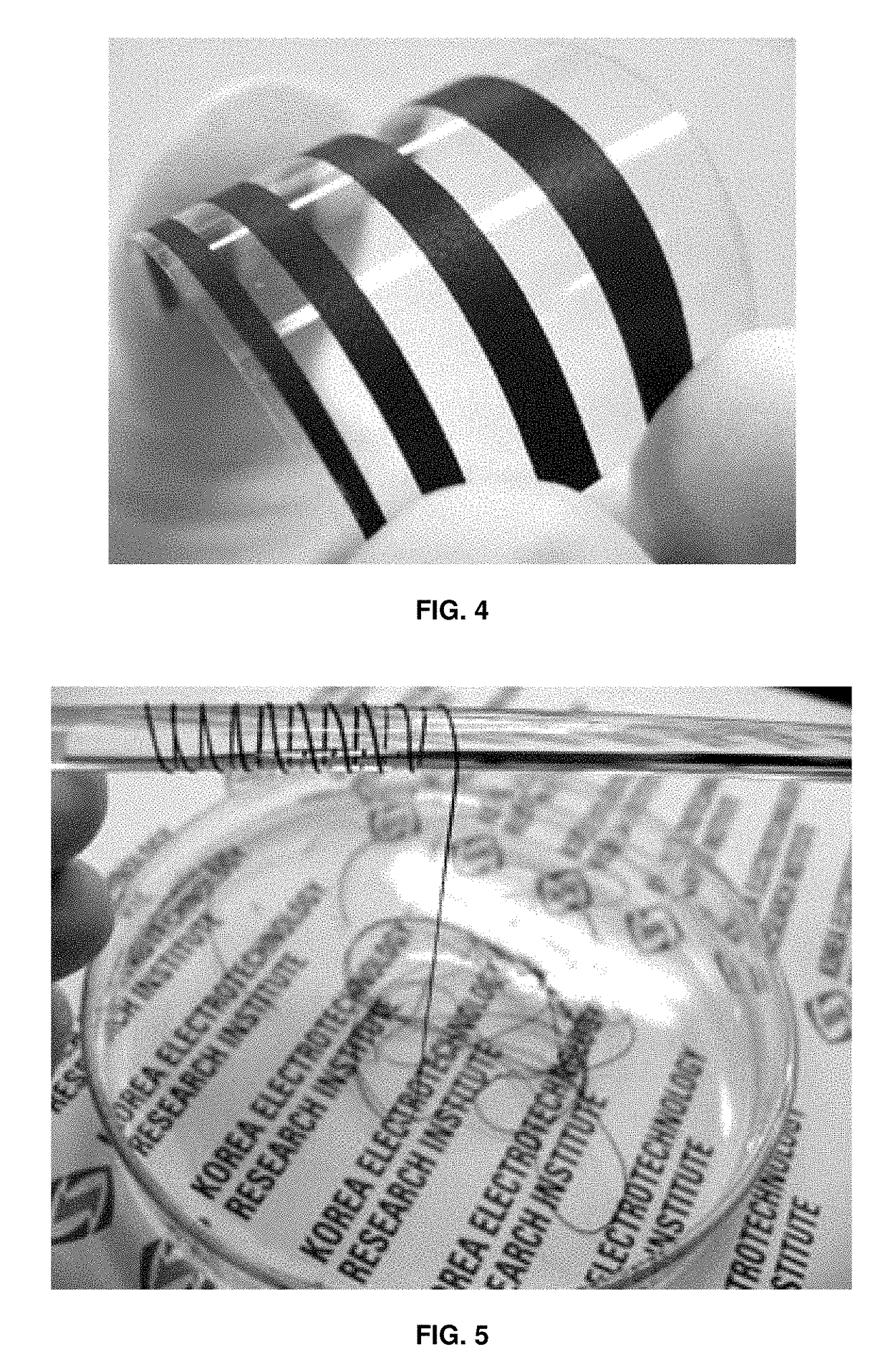
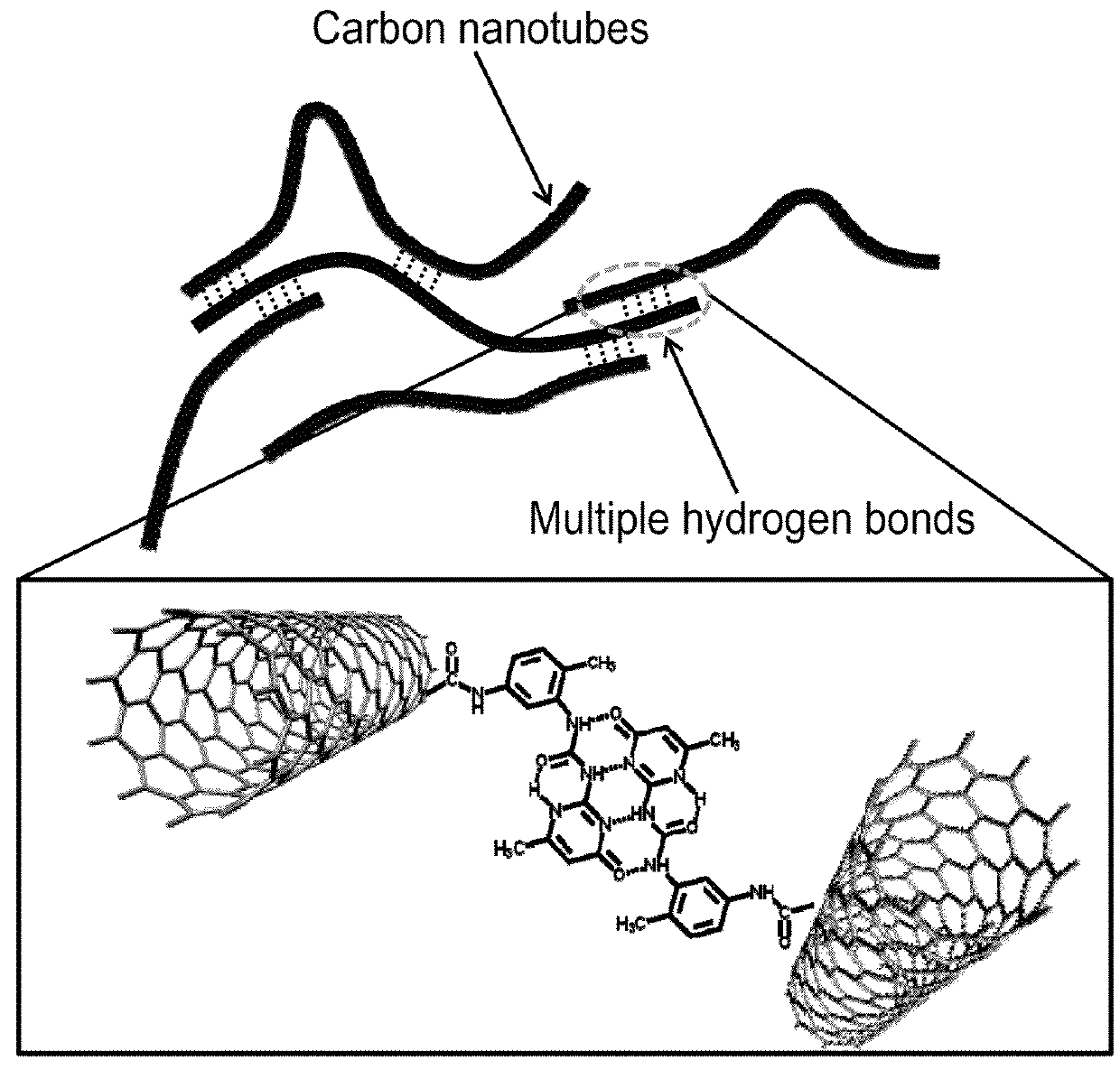
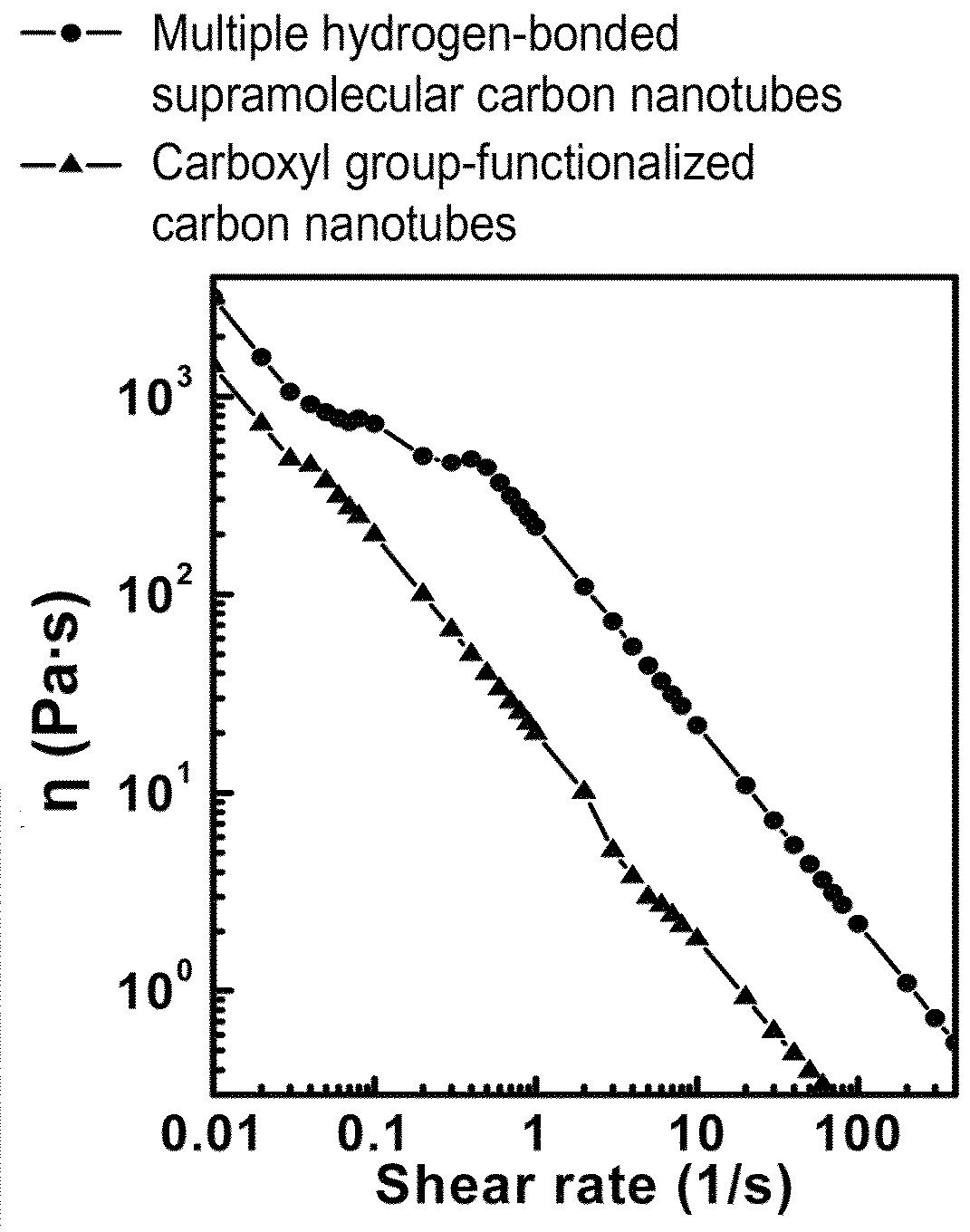
Highly conductive material formed by hybridization of metal nanomaterial and carbon nanomaterial having higher-order structure due to multiple hydrogen bonding, and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20160009934A1Simple structureMaterial nanotechnologyShielding materialsHydrogenConductive materials
The present invention relates to a highly conductive material formed by hybridization of a metal nanomaterial and a carbon nanomaterial having a higher-order structure due to multiple hydrogen bonding, and to a manufacturing method therefor. The technical essence of the present invention is a highly conductive material formed by hybridization of a metal nanomaterial and a carbon nanomaterial having a higher-order structure due to multiple hydrogen bonding the invention involving: forming a carbon nanomaterial having a higher-order structure due to multiple hydrogen bonding between conductive carbon nanomaterials by introducing a functional group capable of multiple hydrogen bonding to the carbon nanomaterials; forming a composite material by mixing the carbon nanomaterial having a higher-order structure and a metal nanomaterial.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
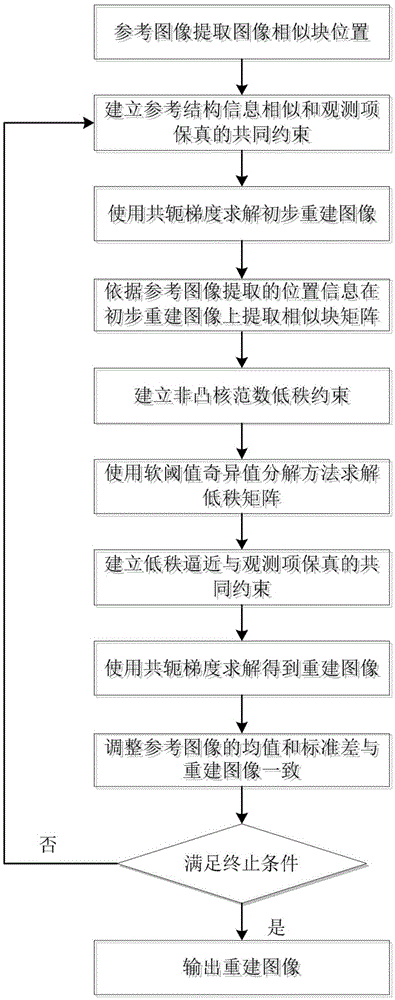
Remote sensing image reconstruction method based on reference image structure constraint and non-convex low rank constraint
ActiveCN105551000AImprove reconstruction accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorReconstruction method
The invention discloses a remote sensing image reconstruction method based on a reference image structure constraint and a non-convex low rank constraint. The method comprises the following steps: structural similarity constraints for a target image and a reference image after high-order filter are firstly built; then, the non-convex low rank constraint is used for replacing a compressed sensing L1norm for constraining a target image sparse coefficient, and a remote sensing image sparse optimization reconstruction model is built and solved. The method of the invention has the beneficial effects that the high-order structure feature vector of the reference image serves as a prior constraint, a generalized non-convex low rank kernel norm serves as a target image sparse coefficient constraint, the complementary advantages of the two are used for constructing an image reconstruction model, and the reconstruction precision of the target image is improved.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Pharmaceutical composition containing an active agent in an amino acid copolymer structure
InactiveUS7018654B2Promote formationContributes bonding capacityPowder deliveryBiocideActive agentCell culture media
A method of protecting a chemical compound from degradation comprising combining the chemical compound with an amino acid polymer. Disclosed are methods of combining chemical compounds with synthetic amino acid polymers for protection from degradation of the chemical compounds and to provide for controlled release of the compounds. A method is described for the selective release of drug substances from a synthetic amino acid polymer in the stomach or small intestine, utilizing pH-dependent changes in a higher order structure. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a drug substance that has been combined with an amino acid polymer and a pharmaceutically acceptable combination of excipients is disclosed. A cell culture media comprising a polypeptide containing glutamine that has been co-polymerized with an amino acid is described.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Polypropylene molded article, sheet-like polypropylene molded article, and method for production of polypropylene thermally molded article
ActiveCN101688005AImprove visual effectsFully rigidFlat articlesThin material handlingAmorphous phasePolypropylene
A molten polypropylene having such a stereoregularity that the isotactic pentad fraction is 95% by mole or more is allowed to flow. The molten polypropylene is cooled to a temperature of -200 to 50 DEG C (inclusive), and is maintained at that temperature for 0.1 to 100 seconds (inclusive), thereby producing a rapidly cooled polypropylene high-order structure mainly composed of a mesophase or monoclinic domain having a size of 100 nm or smaller and an amorphous phase. The rapidly cooled polypropylene high-order structure is heated to a temperature that falls within a temperature range in which endothermic transfer occurs and that is equal to orlower than the melting temperature of the polypropylene.
Owner:IDEMITSU UNITECH CO LTD
Cellular immunity inducing vaccine
ActiveUS20160166665A1Large capacityHigh immune-inducing capacityTumor rejection antigen precursorsTumor specific antigensMHC class IHigh cell
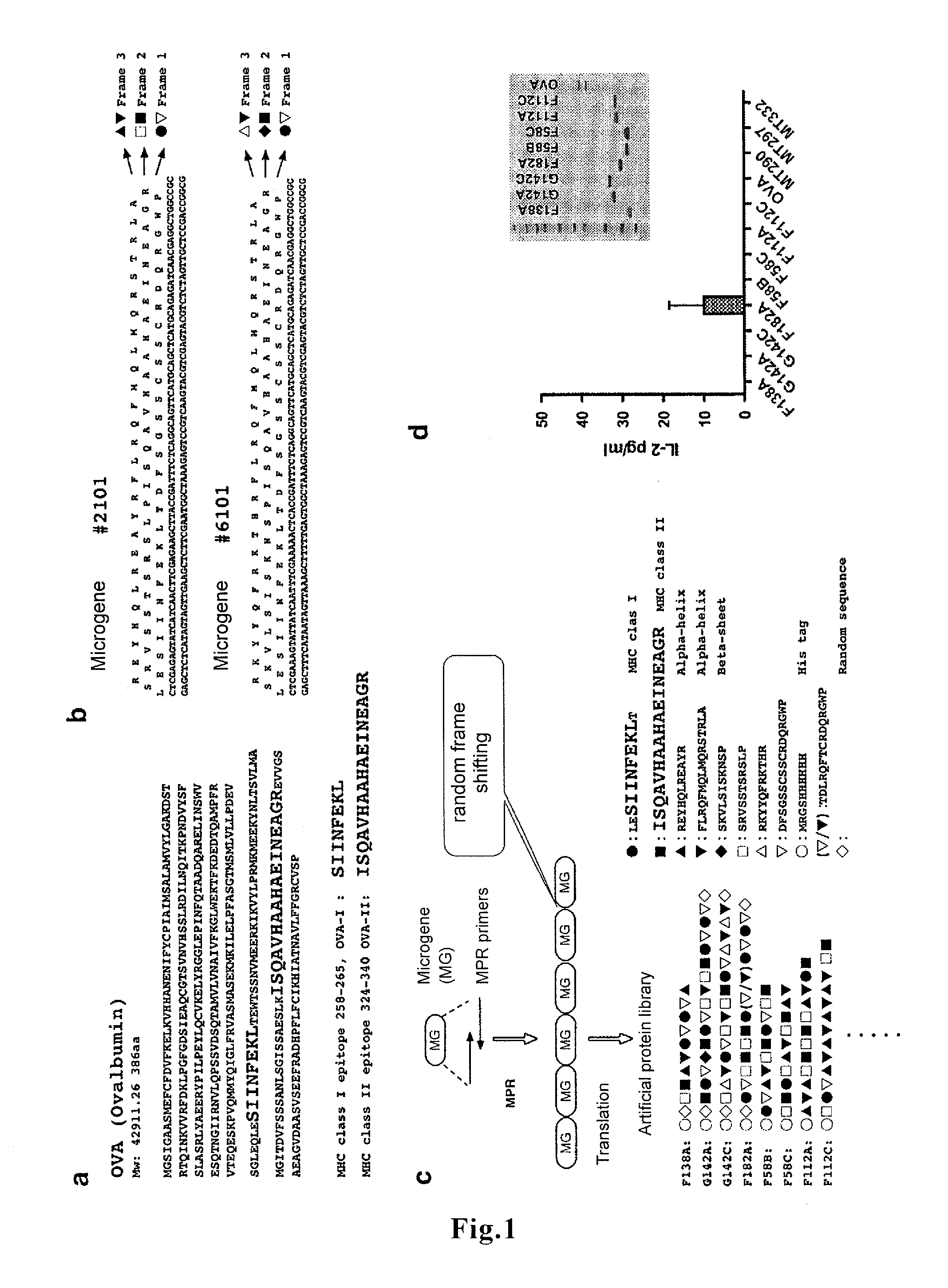
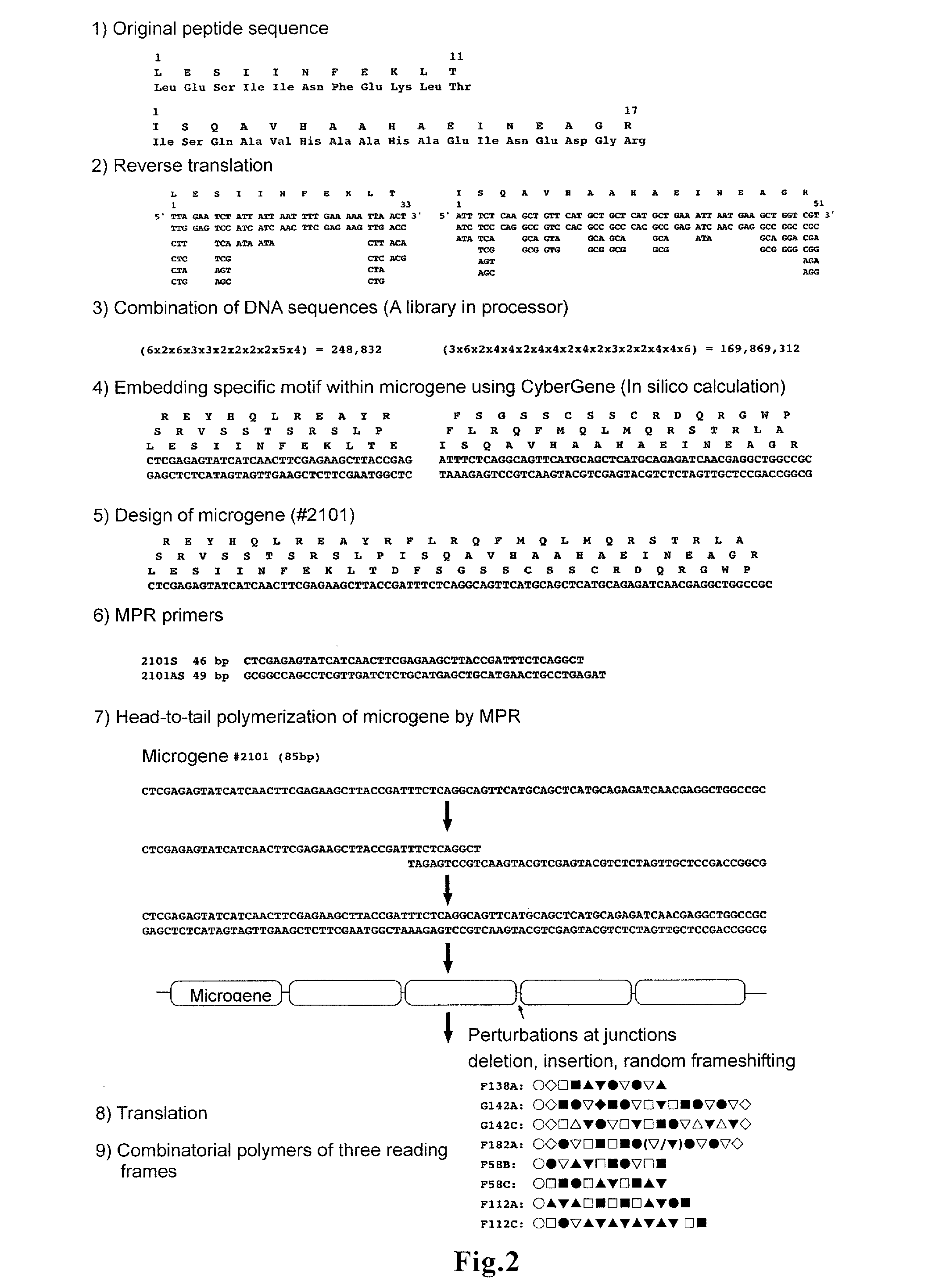
A novel vaccine that can induce sufficiently high cell-mediated immunity is disclosed. The vaccine of the present invention contains, as an effective component, a polypeptide comprising a tandem repeat structure in which an MHC class I epitope region derived from an antigen protein and a spacer sequence are linked to each other alternately and repeatedly at least three times, or a recombinant vector which comprises a polynucleotide encoding said polypeptide and is capable of expressing said polypeptide in vivo. The spacer sequence is, for example, a sequence generated as an amino acid sequence inevitably encoded by a single base sequence which is designed such that the MHC class I epitope region derived from the antigen protein, an MHC class II epitope region derived from the antigen protein, and at least one higher-order-structure-stabilizing region are encoded by different reading frames in said single base sequence.
Owner:JAPANESE FOUND FOR CANCER RES +1
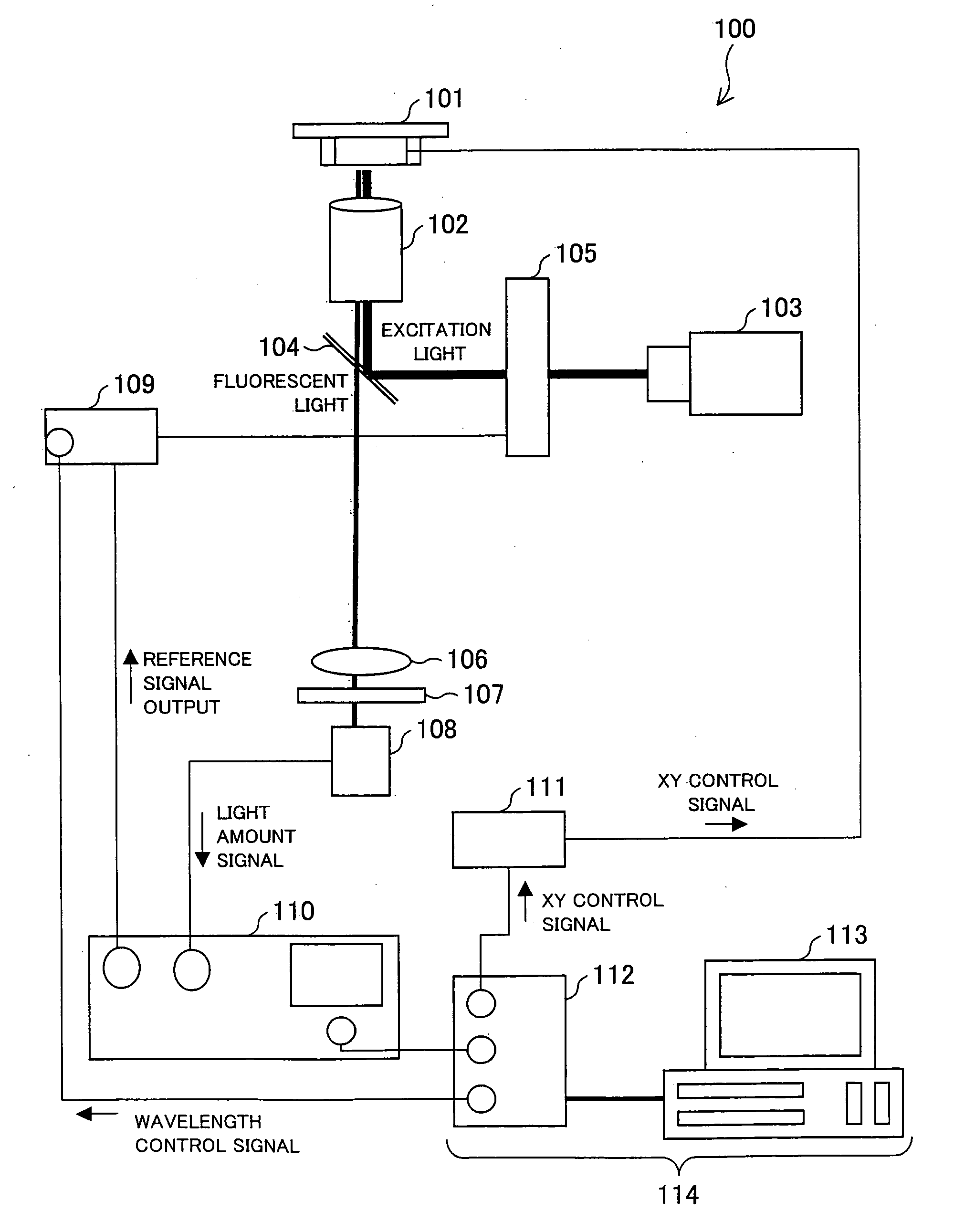
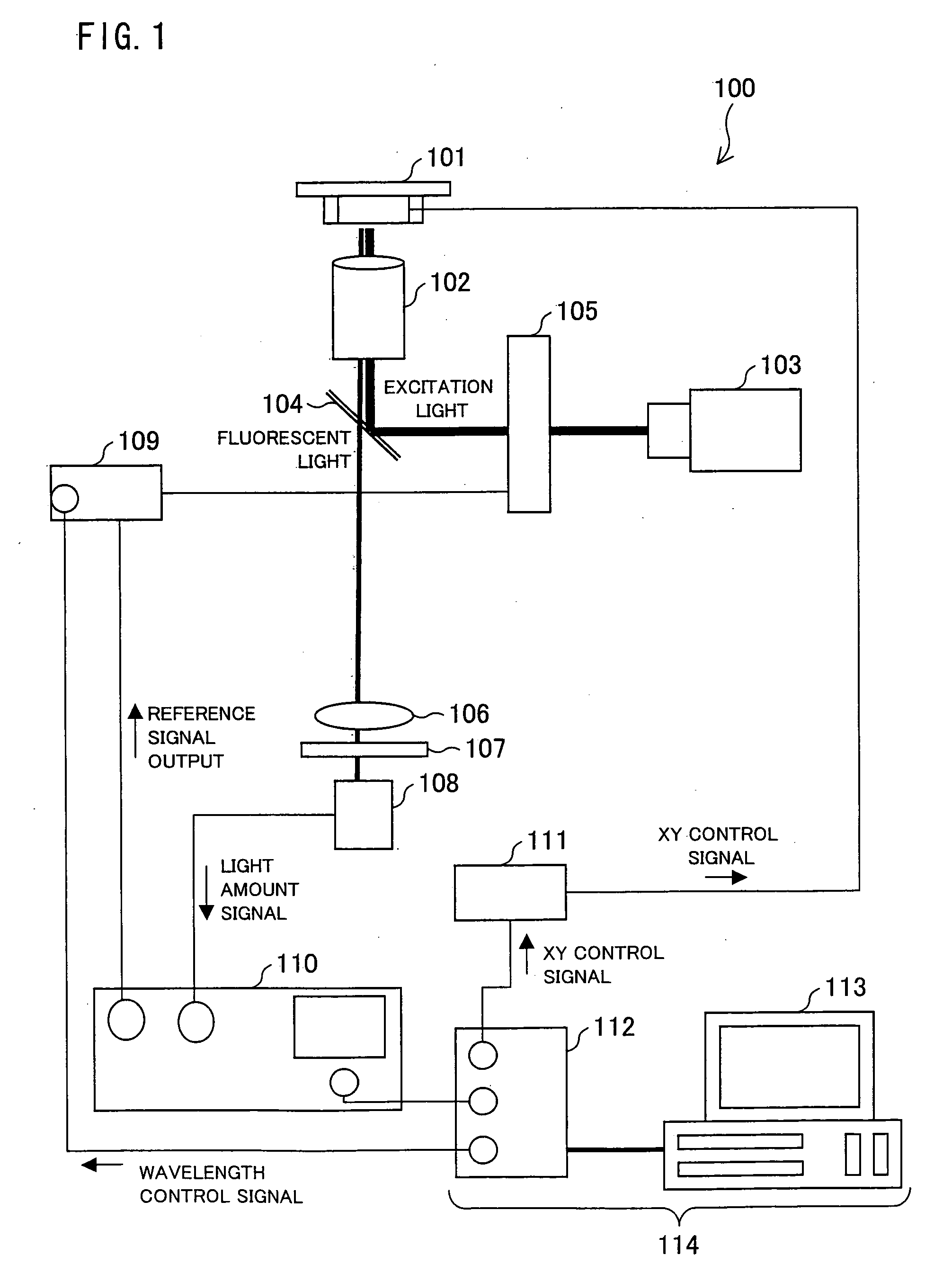
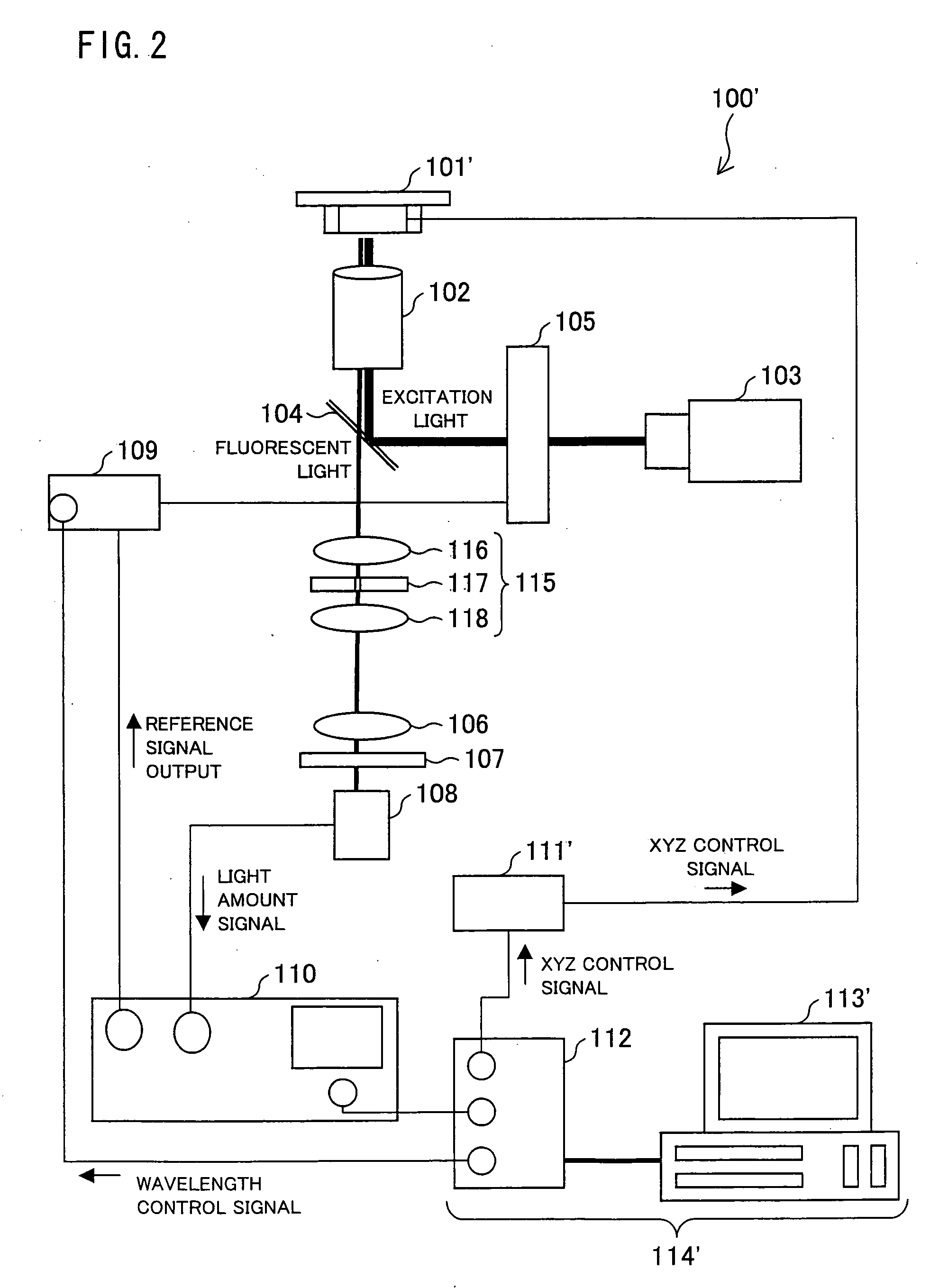
Circular Dichroism Fluorescent Microscope
According to a circular dichroism fluorescent microscope 100, in one embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to analyze, by using a small amount of a sample and directly in a living organism, a high-order structure of the sample such as a biomolecule, for example, protein and the like. The circular dichroism fluorescent microscope includes a confocal section. In the circular dichroism fluorescent microscope, a circularly polarizing / modulating section converts, into right and left circularly polarized lights, a light beam emitted from a light source. Thus obtained right and left circularly polarized light is focused on the sample so that the sample is irradiated with the right and left circularly polarized lights. Then, an optical lens focuses fluorescence emitted from the sample. Further, a wavelength selecting section transmits only fluorescence having a predetermined wavelength. Subsequently, the fluorescence having passed through the wavelength selecting section is detected. Based on fluorescent intensity signals of the fluorescence thus detected, a difference between an intensity of the fluorescence emitted from the sample at the time of irradiation with the use of the right circularly polarized light and an intensity of the fluorescence emitted from the sample at the time of irradiation with the use of the left circularly polarized light is calculated.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
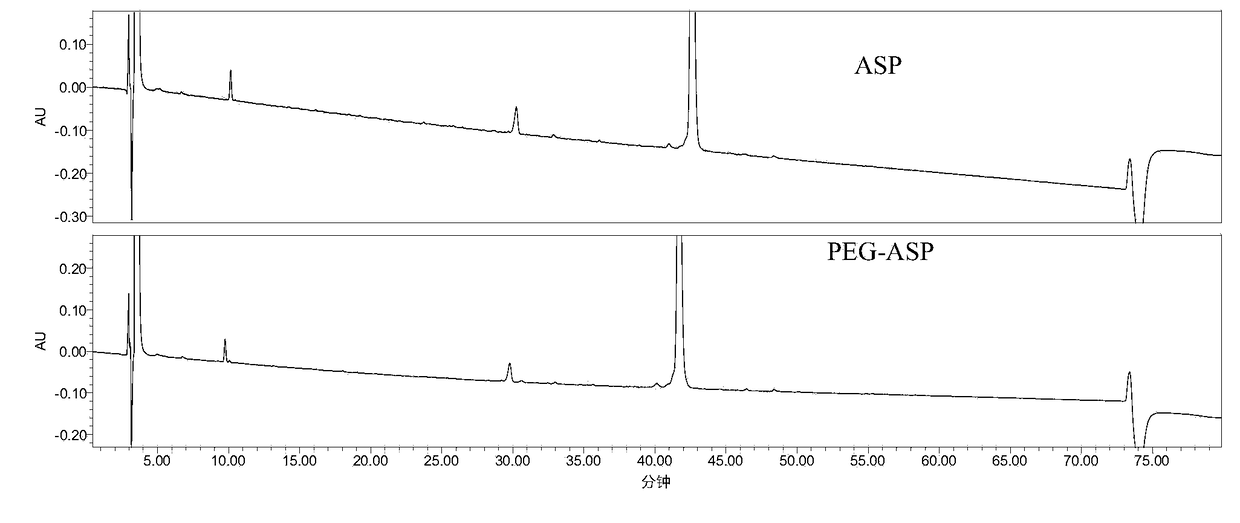
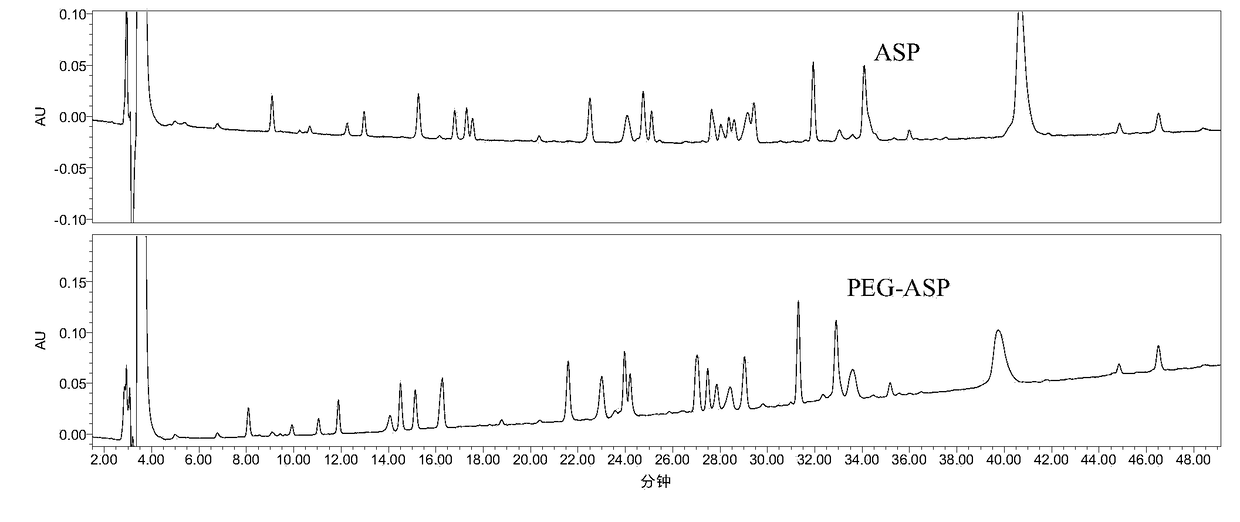
Enzymatic hydrolysis peptide map analysis method for polyethylene glycol modified protein medicine
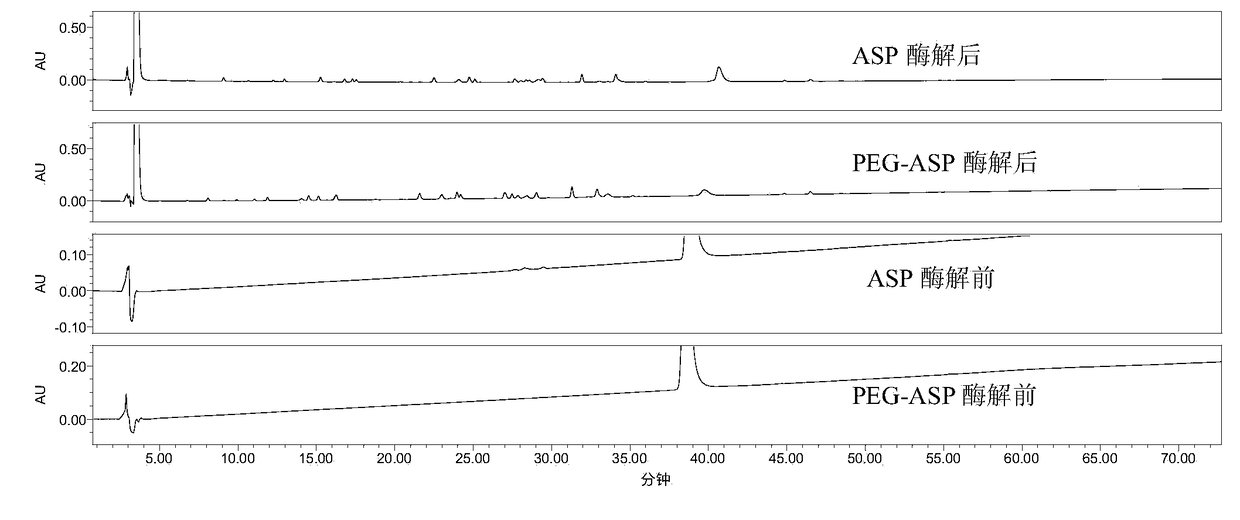
InactiveCN108267534AEfficient detectionComplete enzymatic hydrolysisComponent separationProtein insertionPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a peptide map analysis method for polyethylene glycol modified protein. According to the method, firstly, a high-order structure of the protein needs to be destroyed to fullyexpose restriction enzyme cutting site, and then proteolysis is carried out; secondly, by selecting an appropriate chromatographic packing aperture, the peptide map analysis method with ideal analysisperformance for PEG-modified proteins is obtained. Through effective use of the method, a PEG-modified peptide segment in a peptide map can be effectively detected, and the technical problem that modified protein and unmodified protein cannot be distinguished by conventional methods is solved.
Owner:ZONHON BIOPHARMA INST
Proces for producing protein powder
InactiveUS6723347B1Good release effectObtained cheaper and more simply and convenientlyPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsHigher Order StructureProtein formation
A process for conveniently producing a stable protein powder retaining the higher-order structure at a high level which comprises freezing a protein-containing solution at a cooling rate of about -300 to -10° C. / min. and then drying.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Diagnosis and treatment of friedreich's ataxia
ActiveUS20140128455A1Increased target affinityImproved strand displacementOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to oligonucleotides based on peptide nucleic acid oligonucleotide or an equivalent oligonucleotide analogue, such as morpholino or a locked nucleic acid sequences and the use of such oligonucleotides for the dissociation of higher order structures, including triplex-helix DNA structures, in repeated sequences of DNA in Friedreich's ataxia. The dissociation of such structures may be used in the diagnosis and / or treatment of Friedreich's ataxia. Consequently, the present invention is also directed to a method for diagnosing Friedreich's ataxia and the use of peptide nucleic acid oligonucleotide or an equivalent oligonucleotide analogue, such as morpholino or a locked nucleic acid sequences in the treatment of Friedreich's ataxia. Preferably, the oligonucleotides comprise a sequence selected from the group consisting of (GAA)n, (CTT)n, (JTT)n or a mixed (JTT / CTT)n sequence.
Owner:ZAIN LUQMAN RULA
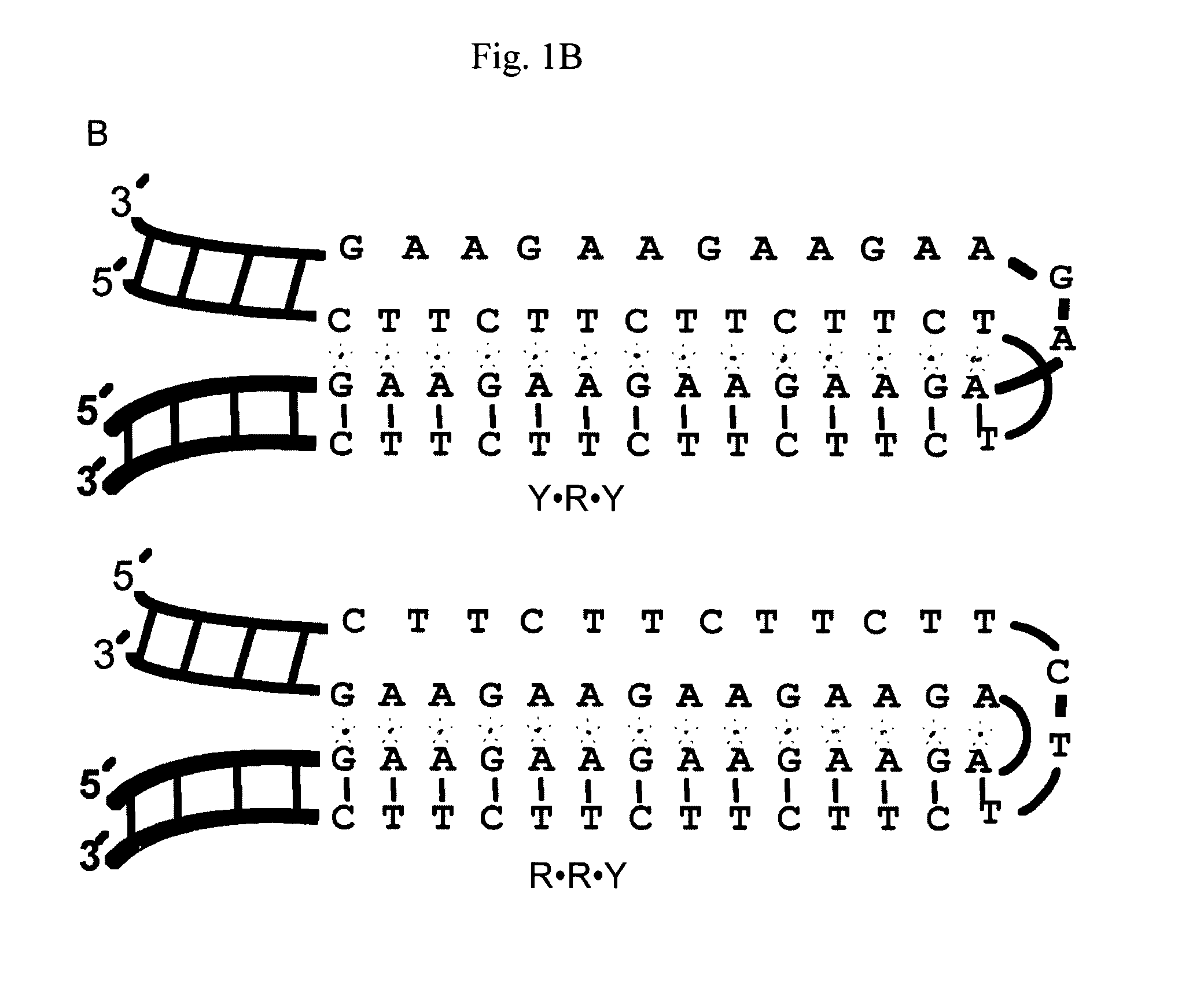
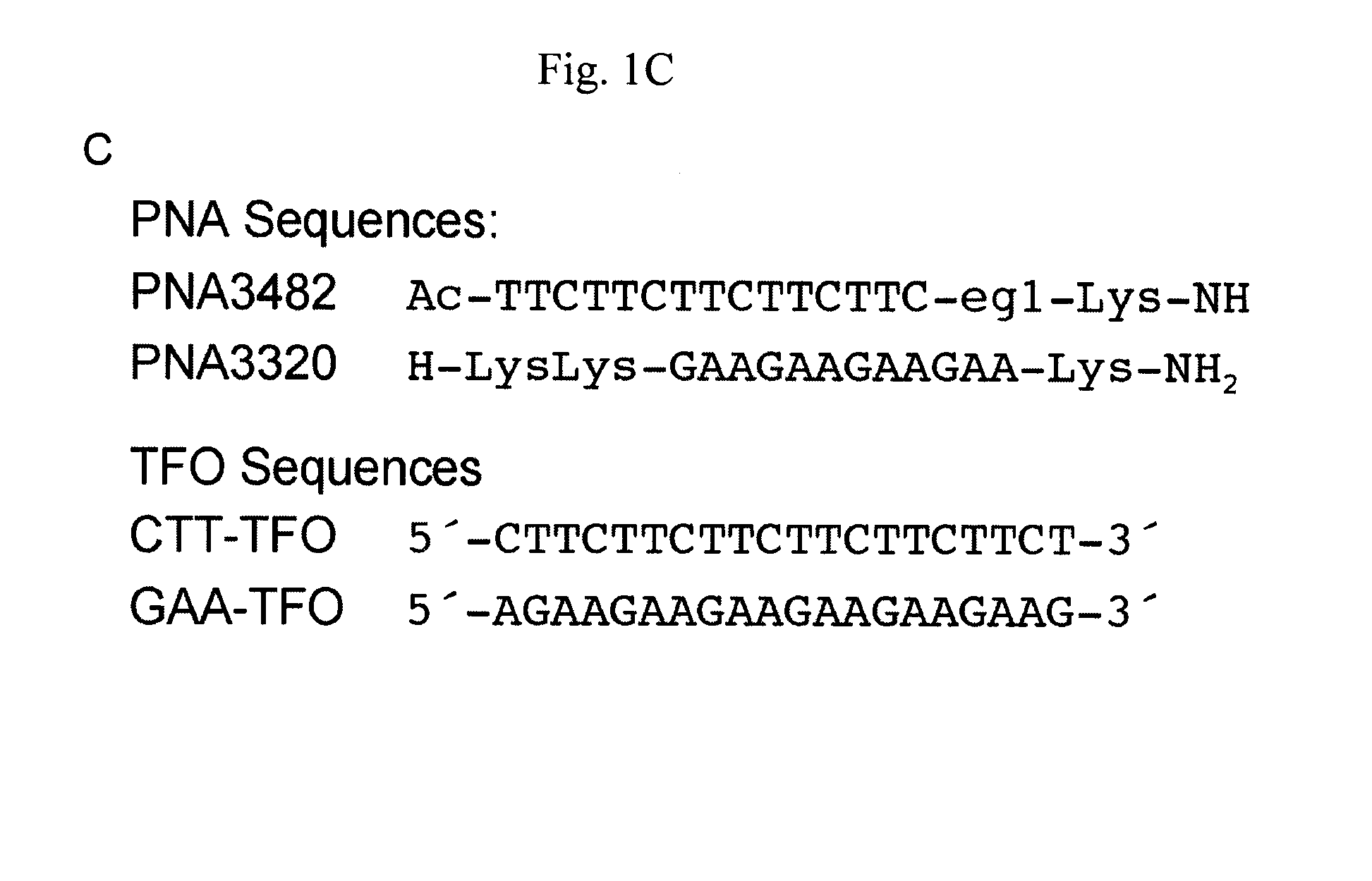
Higher order structure and binding of peptide nucleic acids
InactiveUS6770738B1Easy to identifyStable strand displacementBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTranscription initiationProtein activity
Peptide nucleic acids and analogues of peptide nucleic acids are used to form duplex, triplex, and other structures with nucleic acids and to modify nucleic acids. The peptide nucleic acids and analogues thereof also are used to modulate protein activity through, for example, transcription arrest, transcription initiation, and site specific cleavage of nucleic acids.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC +1
Protein refolding method
ActiveUS20110077384A1Easily and effectively refoldAvoid associationImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDepsipeptidesCrystallographyArginine
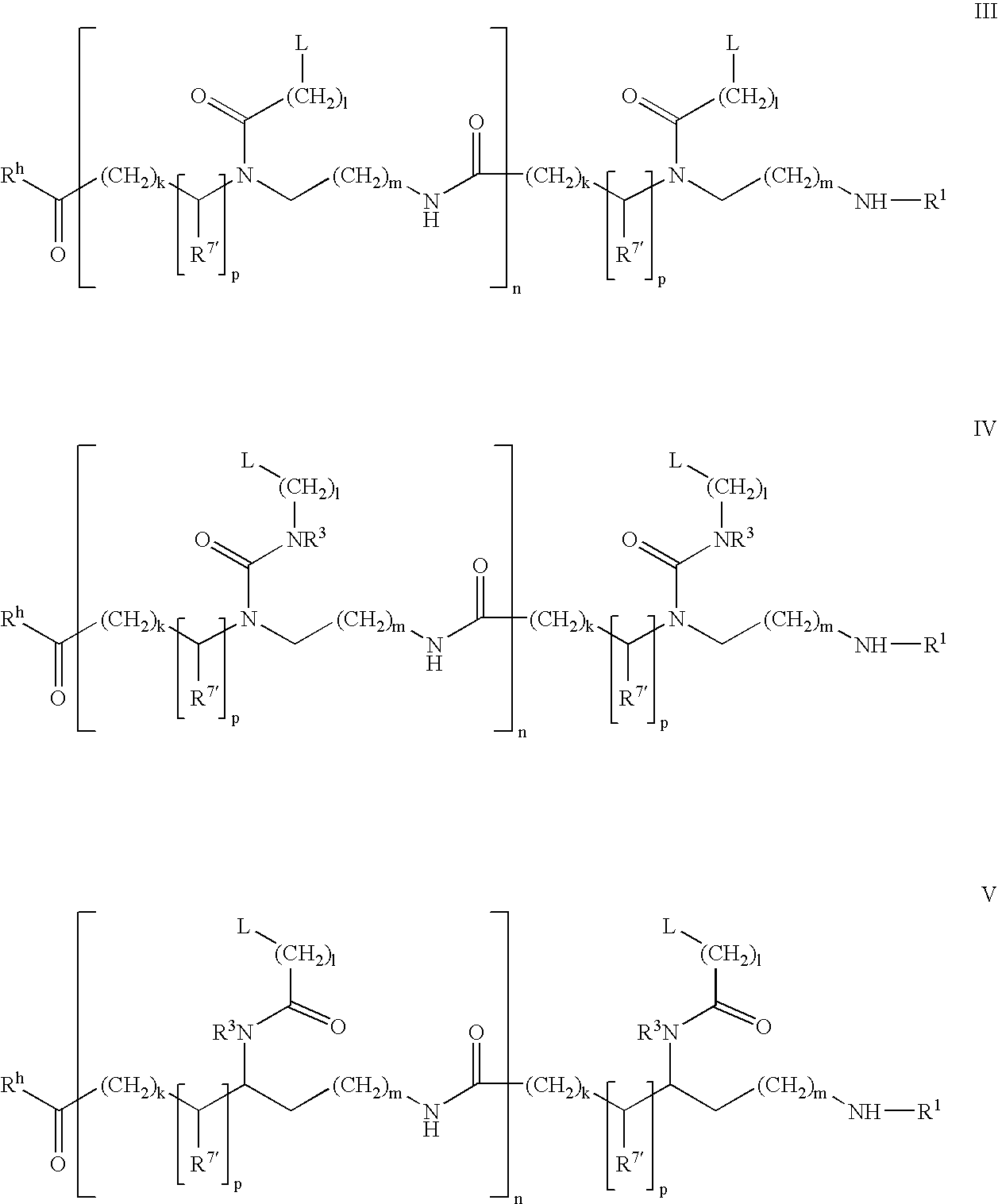
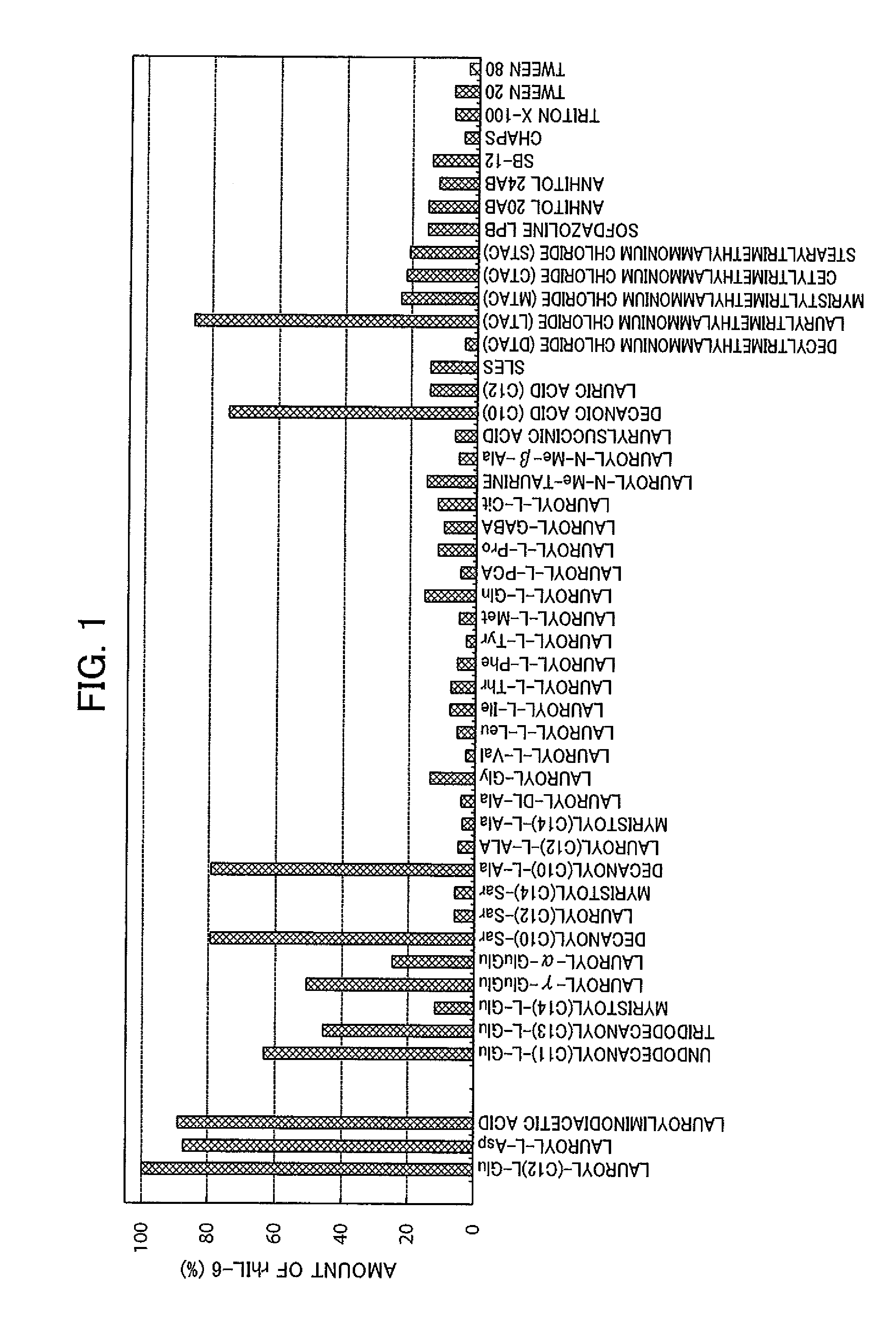
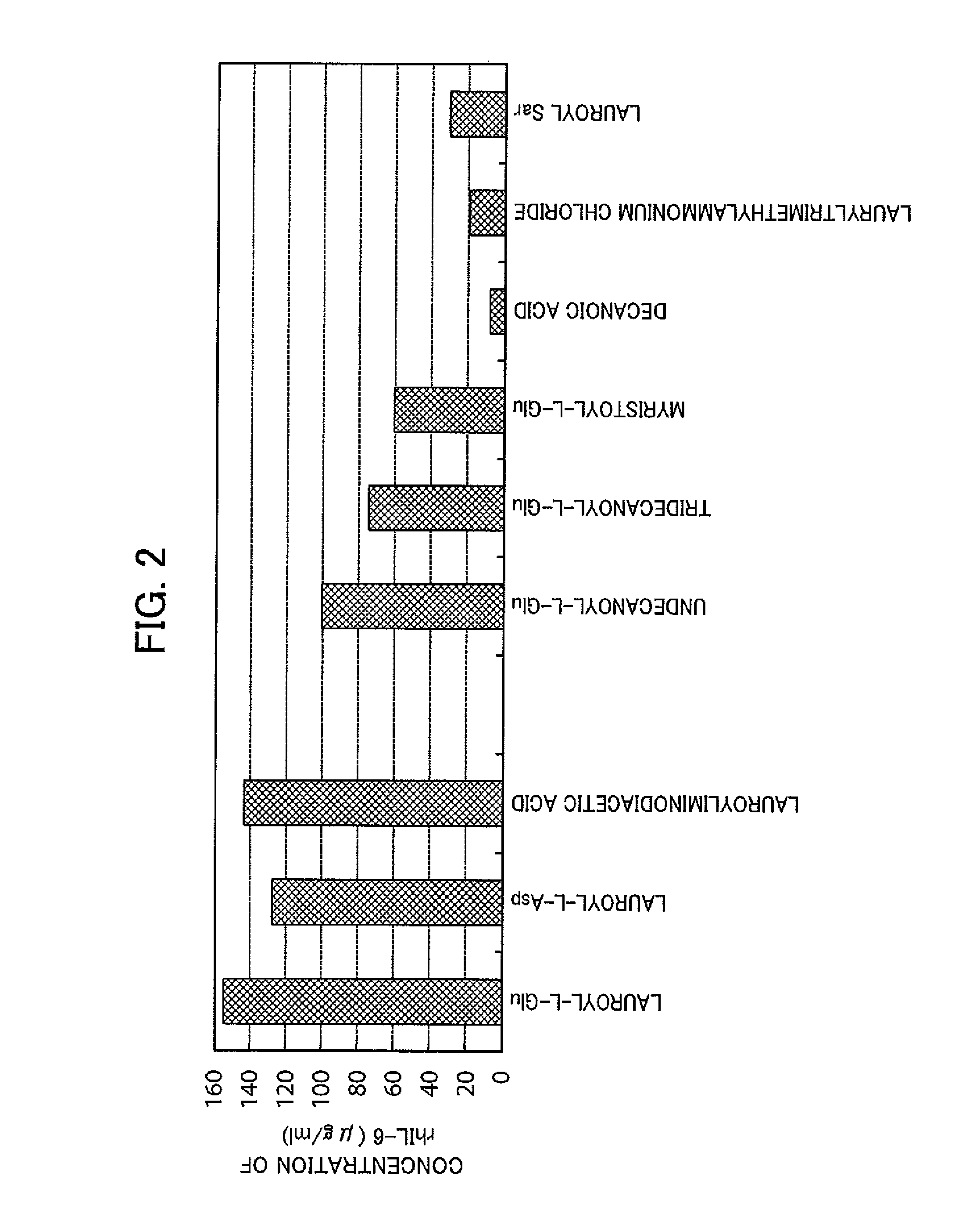
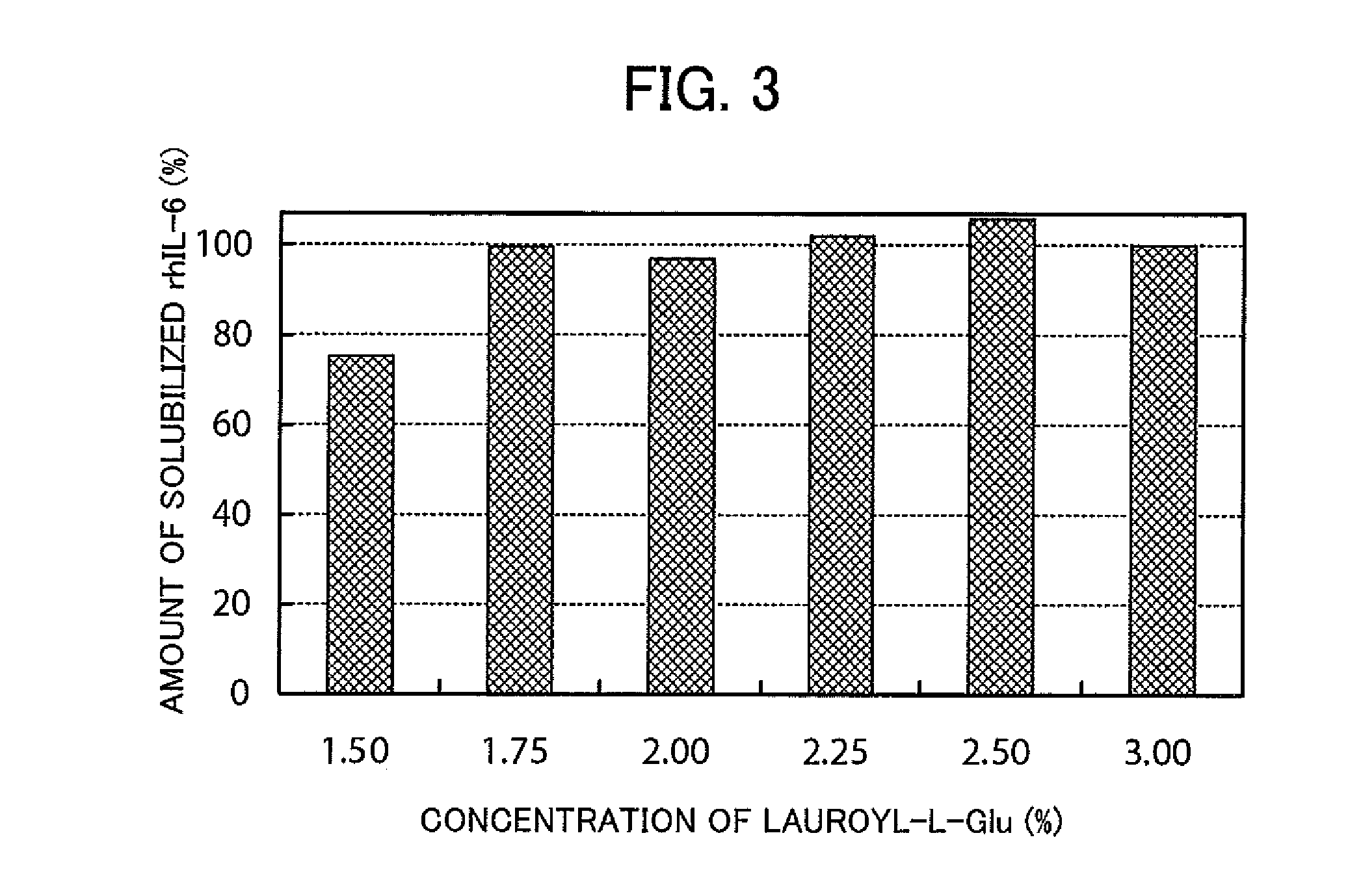
The present invention provides a method for producing a protein which has a restored native higher-order structure by bringing a protein which has lost its native higher-order structure into contact at pH 6.5 to 9.0 with a 1 to 3% aqueous solution of a specific surfactant, such as lauroylglutamic acid to obtain a solubilized solution of the protein; and then adding the solubilized solution to a buffer with pH 6.5 to 9.0 containing arginine or an arginine derivative at a concentration of 0.1 to 1.2 M to lower the concentration of the specific surfactant, such as lauroylglutamic acid, in the obtained mixture solution down to 0.02 to 0.275%. According to the present invention, it is possible to easily restore the native higher-order structure of a protein while smoothly removing the surfactant from the protein.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
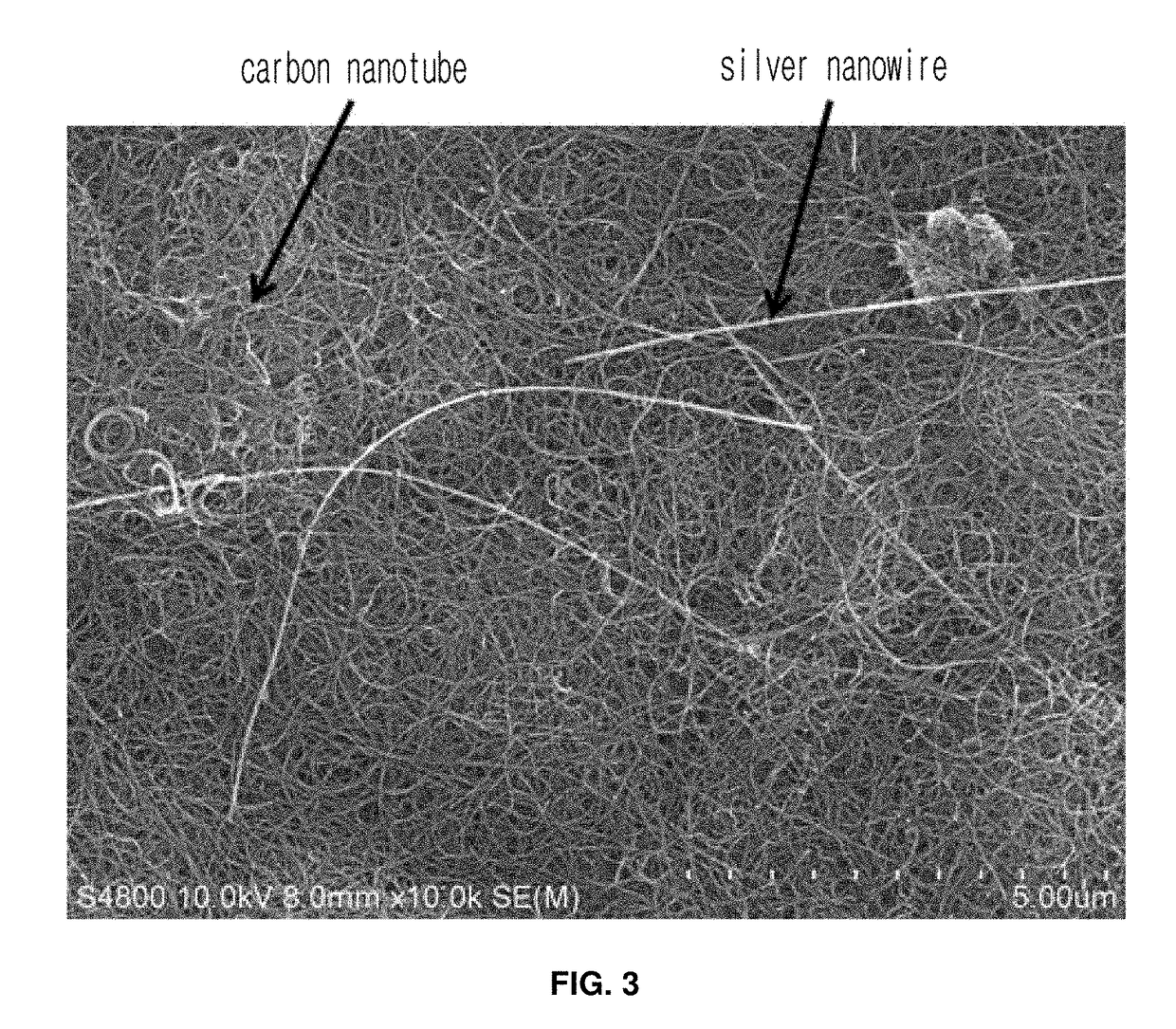
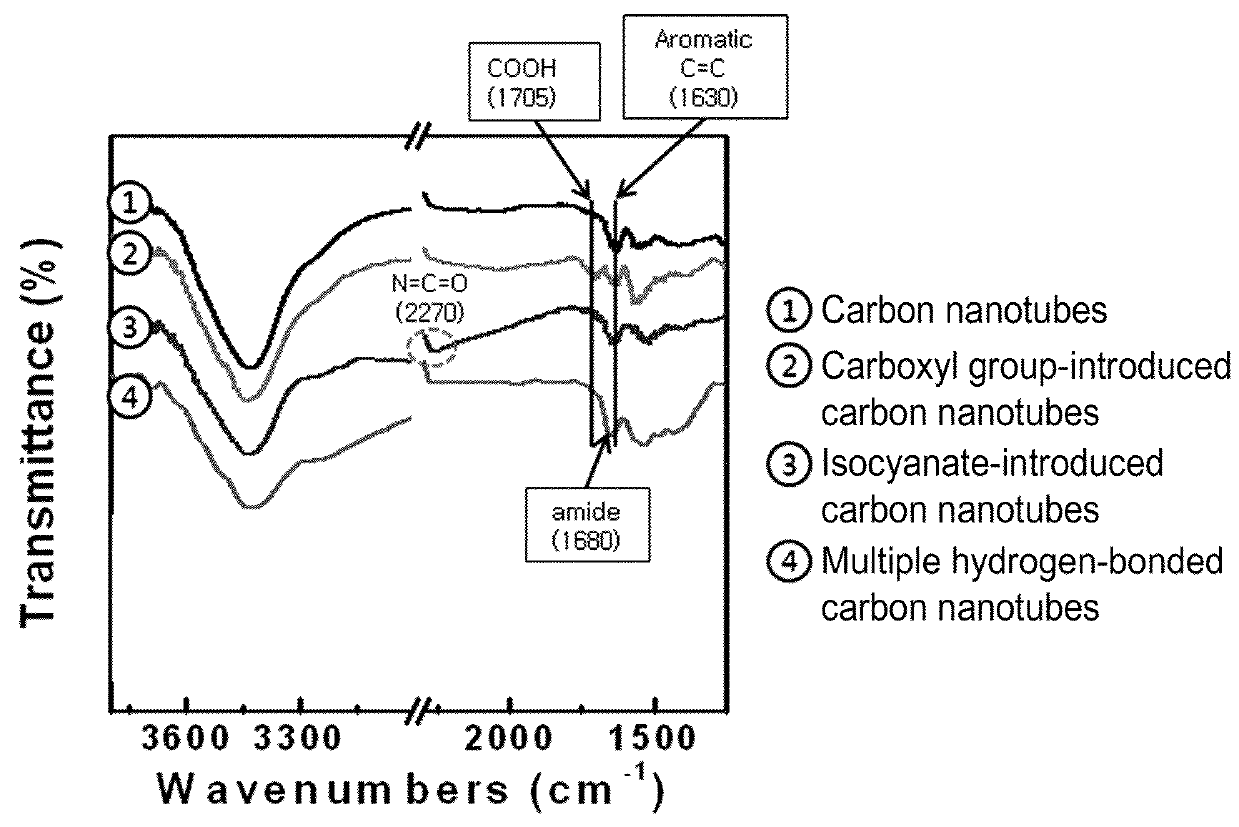
Carbon nanomaterial having higher order structure by means of multiple hydrogen bonds and method for preparing same
ActiveUS20150218108A1Efficient preparationEnable formationMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistryFiberCarbon fibers
The present invention relates to a carbon nanomaterial having a higher order structure by means of multiple hydrogen bonds and to a method for preparing same. One of the key technical features of the present invention is a carbon nanomaterial having a higher order structure, in which a functional group capable of multiple hydrogen bonds reacts with a conductive carbon nanomaterial, into which said functional group is introduced by a surface modification to be functionalized, thus enabling multiple hydrogen bonds between carbon nanomaterials. In addition, another of the key technical features of the present invention is a method for preparing a carbon nanomaterial having a higher order structure by means of multiple hydrogen bonds, comprising: a first step of modifying the surface of a carbon nanomaterial to introduce a functional group for multiple hydrogen bonds into a conductive carbon nanomaterial; a second step of introducing a functional group capable of multiple hydrogen bonds by the reaction with the carbon nanomaterial functionalized in the first step; and a third step of preparing a paste using the carbon nanomaterial of the second step into which the multiple hydrogen bonds are introduced. As described above, a functional group capable of three or more multiple hydrogen bonds is introduced into a conductive carbon nanomaterial such as a carbon nanotube, graphene, carbon fiber or carbon black, thus inducing the formation of a supramolecular structure between materials and thus enabling the carbon nanomaterial of the present invention to be used for printed electronics. Furthermore, the carbon nanomaterial of the present invention can be utilized as an electrode for an energy storage element such as a secondary battery or a super capacitor when formed into a sheet-type conductive membrane, and can be applied for manufacturing conductive fibers.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Methods for producing three dimensional, self-supporting, light redirecting roof lighting systems
A self-supporting roof lighting system that accepts low elevation light and rejects high elevation light may be produced by making arrays of parallel laser cuts through, or partly through, a flat sheet of transparent acrylic, cutting the segment containing the arrays from the sheet, positioning the segment over linear heating elements to soften the acrylic along the lines between adjoining laser cut arrays, folding the segment along the softened lines through the angle necessary to form a multi-faceted structure of saddle, pyramid or higher order form and allowing this structure to cool and solidify to produce a self-supporting angle-selective roof lighting system with an array of light redirecting laser cuts on each facet. The sequence of the method may be changed so that a saddle, pyramid or higher order structure is first formed by folding or moulding transparent acrylic and, subsequently, an array of parallel laser cuts is made in each facet of the structure to produce an angle-selective roof lighting system. A conical angle-selective roof lighting system may be produced by making concentric laser cuts through, or partly through, a disc of transparent acrylic with a segment cut out, softening the laser cut disc and moulding the disc into conical form.
Owner:EDMONDS IAN ROBERT
Method f amplifying dna chip signals
InactiveUS20050130139A1Easy to detectEnhanced signalMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNADouble strand
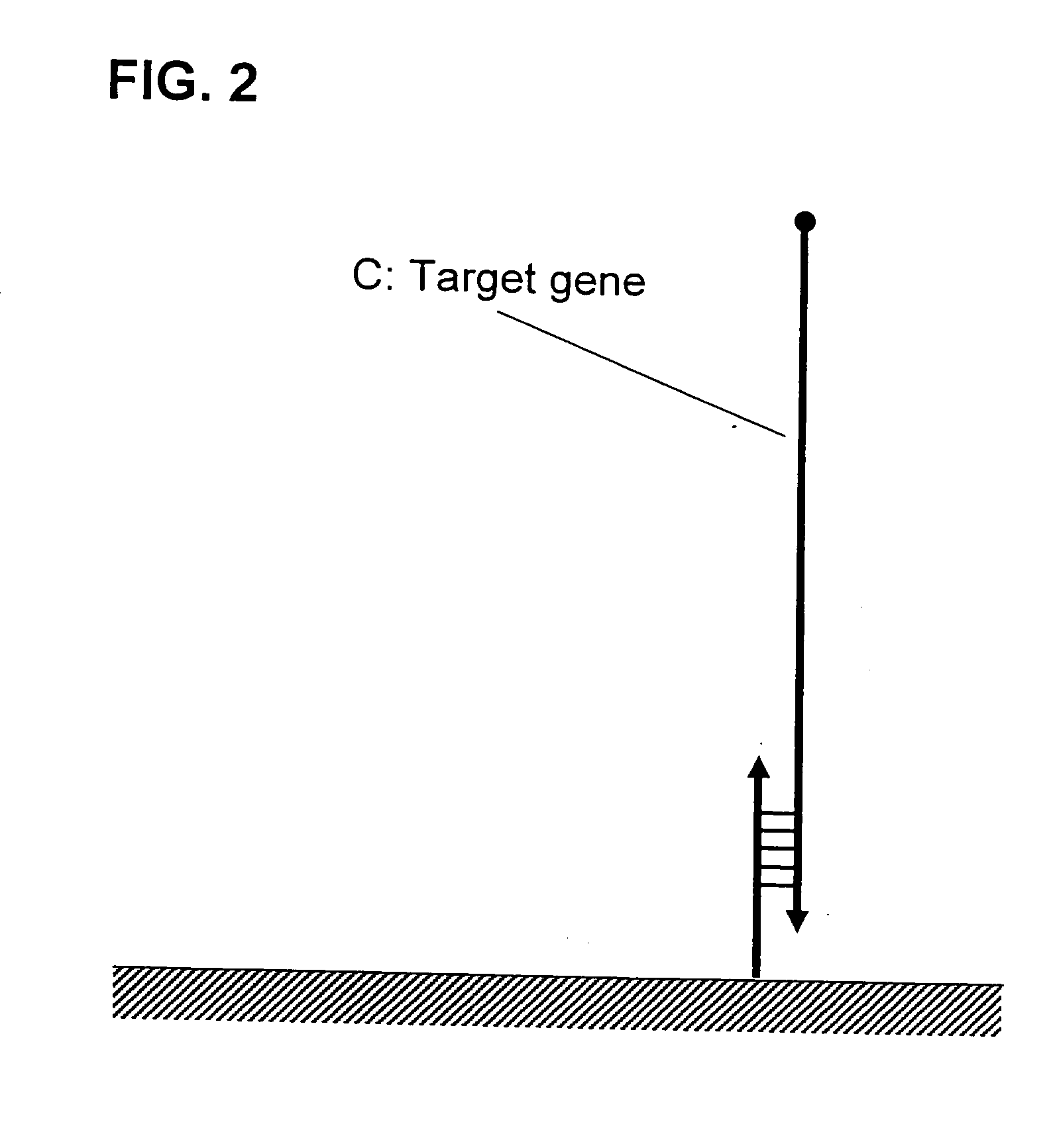
There is provided a signal amplification method for a DNA chip which can establish efficient signal amplification for a target gene captured on the DNA chip by the PALSAR method and can establish a simple detection by contriving design of a pair of HCPs to be used in the PALSAR method. Sensitivity for detection of the target gene on the DNA chip is improved by making use of a self-assembly reaction which forms a double-stranded self-assembly substance having a regular higher-order structure of oligonucleotides.
Owner:SANKO JUNYAKU CO LTD
Bidirectional multi-frequency rectangular lattice type tuned liquid damper
The invention provides a bidirectional multi-frequency rectangular lattice type tuned liquid damper and relates to a building structure shock controlling device. The bidirectional multi-frequency rectangular lattice type tuned liquid damper is formed by a rectangular-section container, a lattice plate, in-built solution and a fixed part. The damper is simple, practical, convenient to maintain, low in cost, suitable for use in a short term and in a long term, good in self-activation, small in required space, simple to install and convenient to use. The transverse and longitudinal earthquake reactions are controlled by adjusting transverse and longitudinal dimensions, the earthquake reactions under the effects of different formations can be controlled by adjusting the transverse dimension of a lattice, and the fact that a tuned liquid damper designed according to natural vibration frequency of a high-order structure is tall and narrow is avoid. The amount of the dampers is increased correspondingly according to increase of formation orders so as to improve sensitivity of controlling of high-order formation wind vibration and earthquake reactions. When meeting with an earthquake or strong wind, the bidirectional multi-frequency rectangular lattice type tuned liquid damper can reduce power reaction of a building structure and has good protecting effect on the building structure.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Highly conductive material formed by hybridization of metal nanomaterial and carbon nanomaterial having higher-order structure due to multiple hydrogen bonding, and manufacturing method therefor
The present invention relates to a highly conductive material formed by hybridization of a metal nanomaterial and a carbon nanomaterial having a higher-order structure due to multiple hydrogen bonding, and to a manufacturing method therefor. The technical essence of the present invention is a highly conductive material formed by hybridization of a metal nanomaterial and a carbon nanomaterial having a higher-order structure due to multiple hydrogen bonding the invention involving: forming a carbon nanomaterial having a higher-order structure due to multiple hydrogen bonding between conductive carbon nanomaterials by introducing a functional group capable of multiple hydrogen bonding to the carbon nanomaterials; forming a composite material by mixing the carbon nanomaterial having a higher-order structure and a metal nanomaterial.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Glycoprotein production method and screening method
InactiveUS20110262945A1Simple structureUniform structureMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesHalf-lifeChain structure
A method for producing a glycoprotein, which is uniform in terms of functions derived from a sugar chain (e.g., a blood half-life) and physiological activities, i.e., a glycoprotein, which is uniform in terms of the amino acid sequence, the sugar chain structure and the higher-order structure; specifically, a method for producing a glycoprotein, which is uniform in terms of the amino acid sequence, the sugar chain structure, and the higher-order structure, includes the following steps (a) to (c): (a) folding a glycoprotein, which is uniform in terms of the amino acid sequence and the sugar chain structure; (b) fractionating the folded glycoprotein by column chromatography; and (c) collecting a fraction having a specified activity.
Owner:GLYTECH
Carbon nanomaterial having higher order structure by means of multiple hydrogen bonds and method for preparing same
ActiveUS9227941B2High order structureSimple structureMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistryFiberCarbon fibers
The present invention relates to a carbon nanomaterial having a higher order structure by means of multiple hydrogen bonds and to a method for preparing same. One of the key technical features of the present invention is a carbon nanomaterial having a higher order structure, in which a functional group capable of multiple hydrogen bonds reacts with a conductive carbon nanomaterial, into which said functional group is introduced by a surface modification to be functionalized, thus enabling multiple hydrogen bonds between carbon nanomaterials. In addition, another of the key technical features of the present invention is a method for preparing a carbon nanomaterial having a higher order structure by means of multiple hydrogen bonds, comprising: a first step of modifying the surface of a carbon nanomaterial to introduce a functional group for multiple hydrogen bonds into a conductive carbon nanomaterial; a second step of introducing a functional group capable of multiple hydrogen bonds by the reaction with the carbon nanomaterial functionalized in the first step; and a third step of preparing a paste using the carbon nanomaterial of the second step into which the multiple hydrogen bonds are introduced. As described above, a functional group capable of three or more multiple hydrogen bonds is introduced into a conductive carbon nanomaterial such as a carbon nanotube, graphene, carbon fiber or carbon black, thus inducing the formation of a supramolecular structure between materials and thus enabling the carbon nanomaterial of the present invention to be used for printed electronics. Furthermore, the carbon nanomaterial of the present invention can be utilized as an electrode for an energy storage element such as a secondary battery or a super capacitor when formed into a sheet-type conductive membrane, and can be applied for manufacturing conductive fibers.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Higher order structure and binding of peptide nucleic acids
InactiveUS20050048552A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove bindingSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsTranscription initiationProtein activity
Peptide nucleic acids and analogues of peptide nucleic acids are used to form duplex, triplex, and other structures with nucleic acids and to modify nucleic acids. The peptide nucleic acids and analogues thereof also are used to modulate protein activity through, for example, transcription arrest, transcription initiation, and site specific cleavage of nucleic acids.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Signal amplification method for detecting mutated gene
InactiveUS20060210983A1High detection sensitivityEfficient signal amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNADouble strand
There is provided a signal amplification method for detecting a mutated gene, which can increase the detection sensitivity of mutated genes on a DNA chip according to the PALSAR method, can establish efficient signal amplification and can establish simple detection by contriving design of oligonucleotide probes for use in the PALSAR method. The signal amplification method comprises a ligation reaction with a DNA ligase and a self-assembly reaction which forms a double-stranded self-assembly substance having a regular higher-order structure of oligonucleotides, wherein the detection sensitivity of the mutated gene on a DNA chip is improved.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Signal amplification method for detecting mutated gene
InactiveUS7632639B2High detection sensitivityEfficient signal amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNADouble strand
There is provided a signal amplification method for detecting a mutated gene, which can increase the detection sensitivity of mutated genes on a DNA chip according to the PALSAR method, can establish efficient signal amplification and can establish simple detection by contriving design of oligonucleotide probes for use in the PALSAR method. The signal amplification method comprises a ligation reaction with a DNA ligase and a self-assembly reaction which forms a double-stranded self-assembly substance having a regular higher-order structure of oligonucleotides, wherein the detection sensitivity of the mutated gene on a DNA chip is improved.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
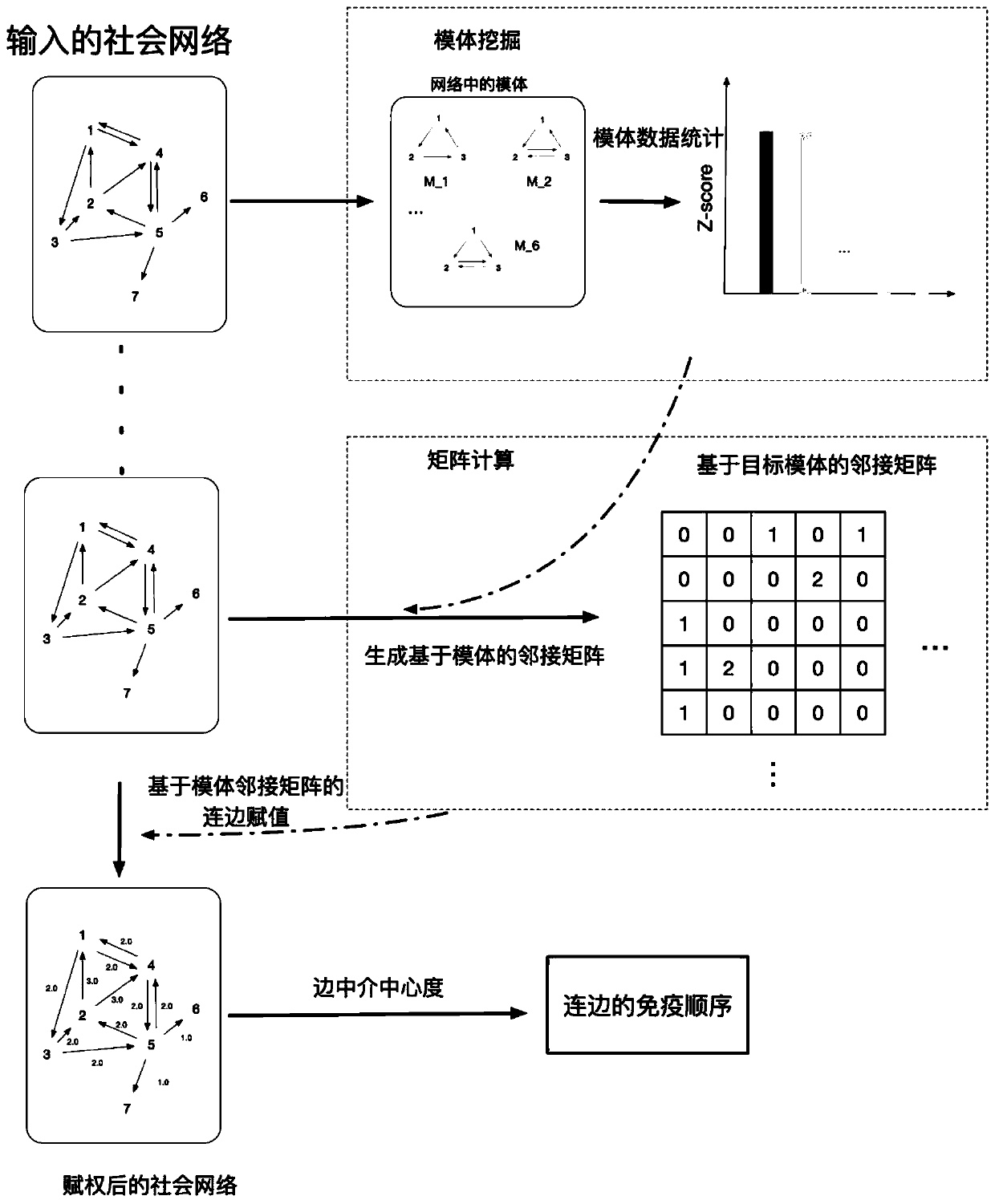
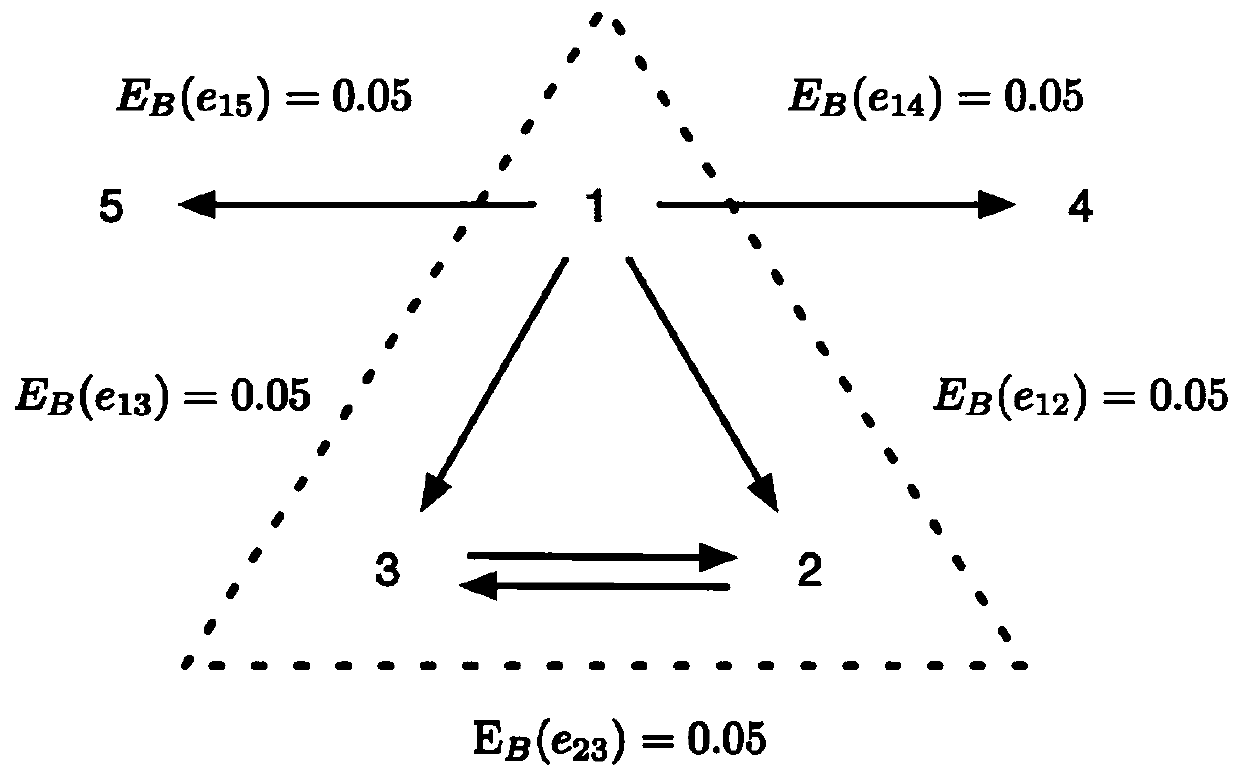
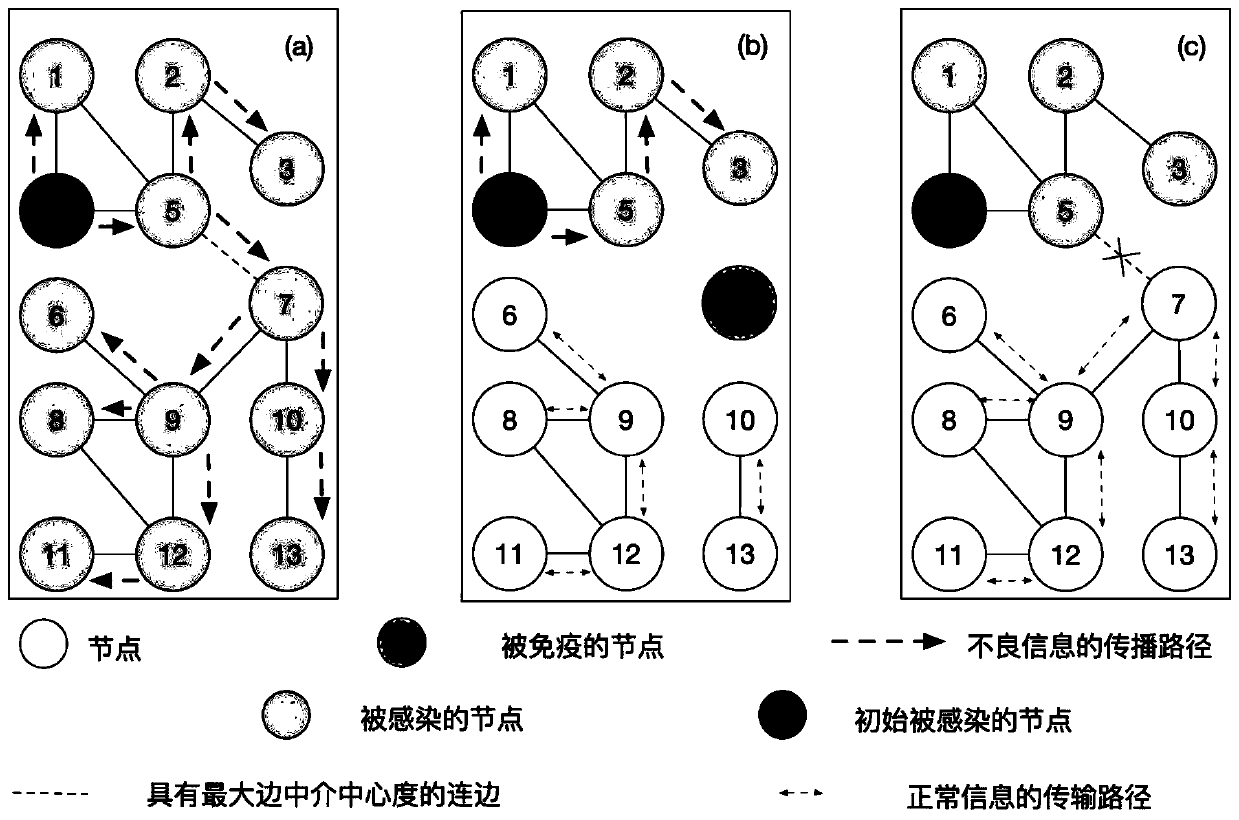
Social network immune algorithm based on network high-order structure
InactiveCN110278110AStructural damage is smallImprove integrityWebsite content managementData switching networksEdge basedSocial network
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer science, and discloses a social network immune algorithm based on a network high-order structure. The algorithm comprises the following steps: excavating a motif in an original network; reconstructing a topological structure of the network, and manufacturing a plurality of random networks; obtaining a Z-score value of each die body through a random network; selecting the motif with the maximum Z-score value as a target motif, and generating an adjacent matrix based on the target motif; setting the weight of the connecting edge according to the value of the connecting edge in the adjacent matrix based on the target die body, and re-weighting the original network to obtain a weighted network; obtaining the intermediary centrality of the connection edges based on the weighted network; sorting the values of the intermediate centralities of the connecting edges from large to small, and selecting the first k connecting edges to deploy immune resources, so as to realize immune operation. According to the algorithm, the problem that the network immune algorithm neglects the high-order connectivity of the network and damages the integrity and functionality of the network in the prior art is solved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com