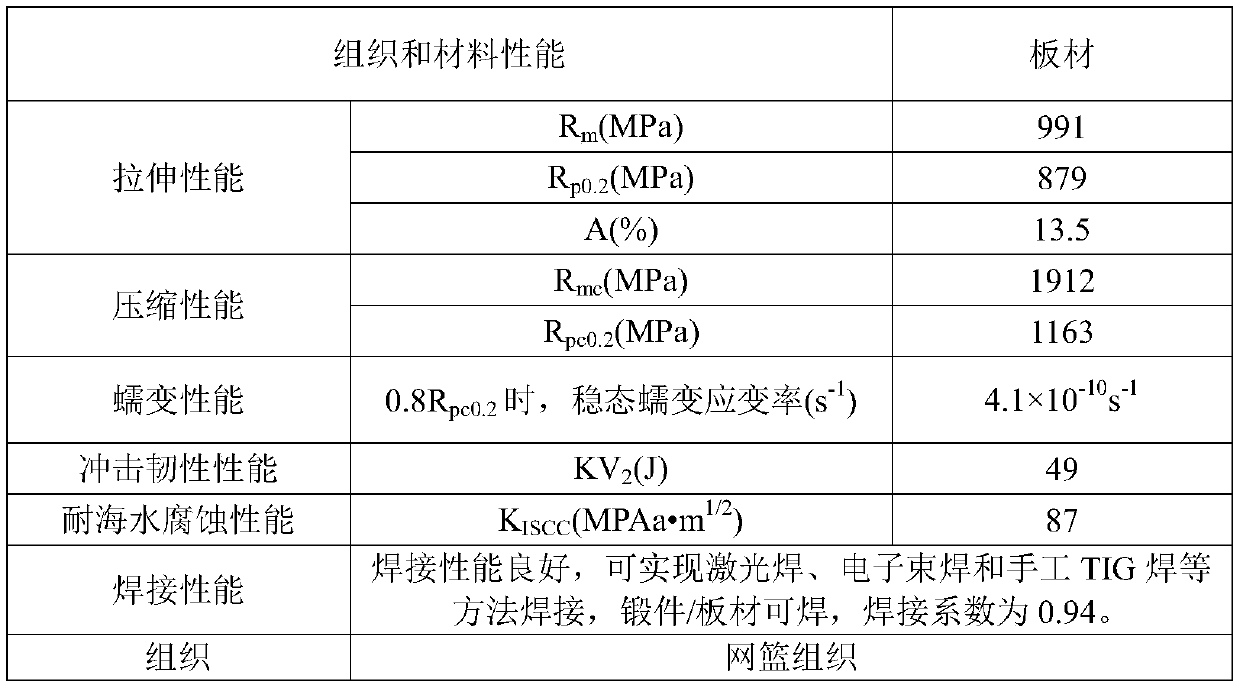
Patents
Literature
72results about How to "Good cold and hot processing performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for manufacturing high-strength 7055 aluminum alloy forge piece formed by spraying
The invention belongs to a manufacturing technology of aluminum alloy and relates to a method for manufacturing a high-strength 7055 aluminum alloy forge piece formed by spraying. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: (a) melting components of 7055 alloy in an intermediate frequency furnace; (b) degassing, deslagging, refining and filtering an aluminum alloy fusant; (c) forming the filtered fusant by spraying to obtain a columnar aluminum alloy ingot blank; (e) carrying out hot extrusion on the aluminum alloy ingot blank formed by spraying; (f) constantly cutting the extrusion ingot as required and then carrying out free forging; (g) carrying out blocker-type forging and / or stamp forging on the blank after the free forging to obtain a stamp forging piece; and (h) carrying out T6 heat treatment on the stamp forging piece. A large-specification and high-property 7055 product can be obtained by using the method which is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU HAORAN SPRAY FORMING ALLOY
LPG boat storage tank steel plate and production method thereof
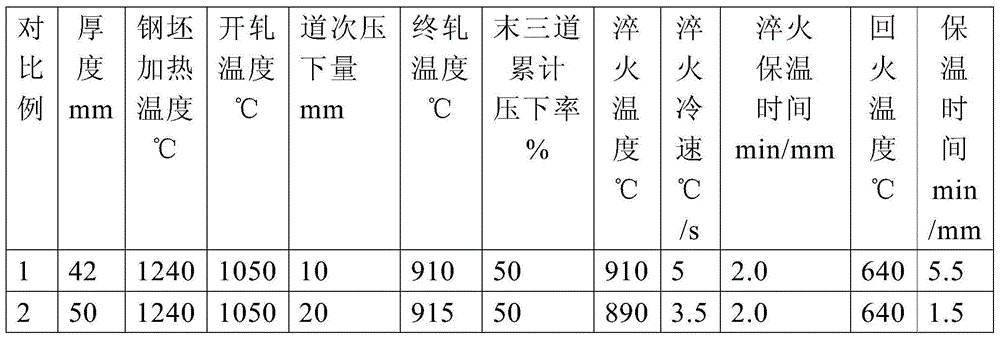
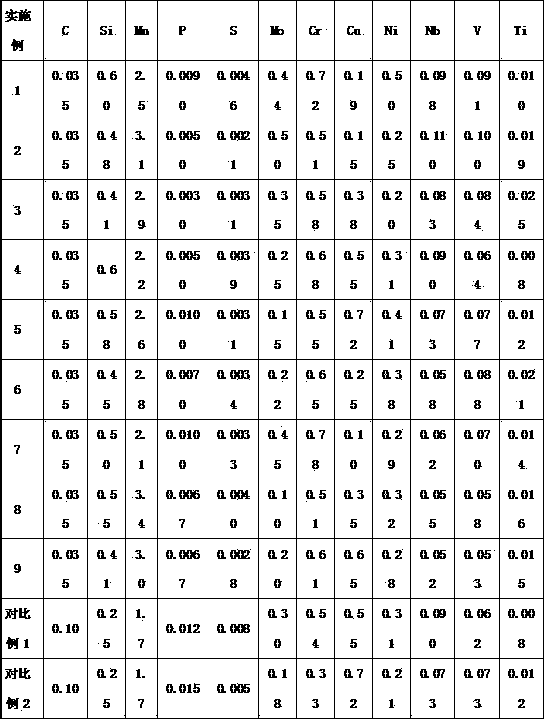
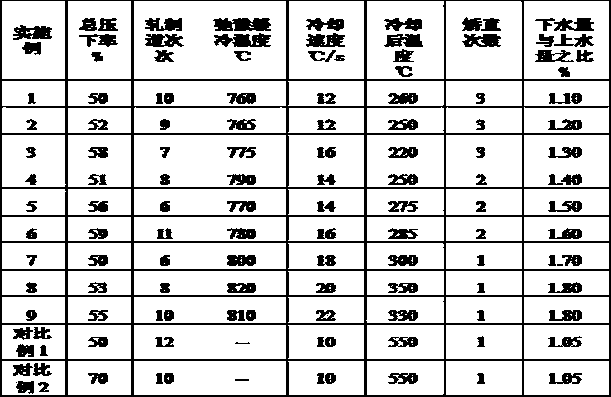
ActiveCN104131235AGood comprehensive mechanical propertiesGood cold and hot processing performanceQuenchingSteel plates
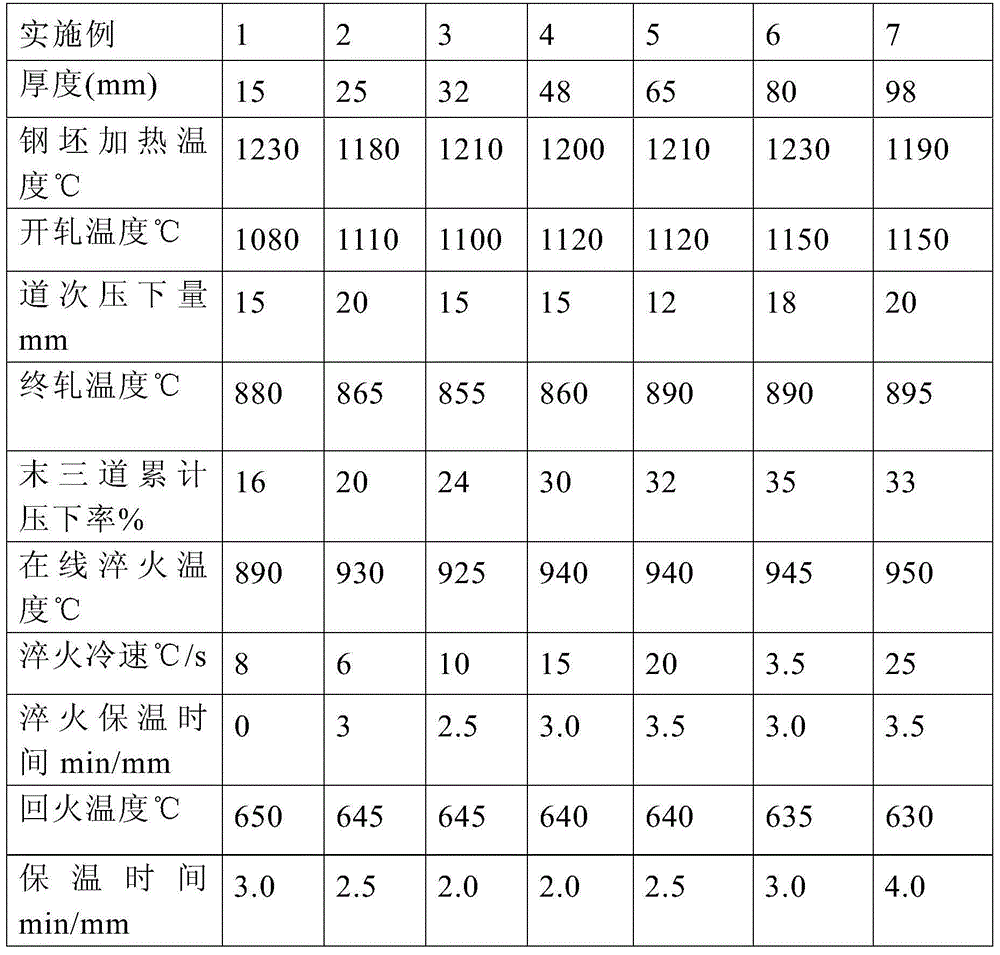
The invention discloses an LPG boat storage tank steel plate and a production method thereof. The steel plate comprises 0.05-0.12wt% of C, 0.30wt% or less of Si, 0.50-1.30wt% of Mn, 0.015wt% or less of P, 0.008wt% or less of S, 0.020-0.060wt% of Al, 0.15-1.20wt% of Cu, 0.20-1.50wt% of Ni, 0.35-1.00wt% of Cr, 0.20-0.60wt% of Mo, 0.008-0.020wt% of Ti, one or more of 0.0020-0.10wt% of Nb, 0.030-0.060wt% of V and 0.0005-0.0020wt% of B, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The method comprises the steps of molten iron advanced desulphurization, converter top and bottom blowing, vacuum treatment, continuous casting, casting blank heating, rolling and heat treatment, the heating temperature of a casting blank is 1170-1250DEG C, and the heating rate of the casting blank is not less than 8min / cm; the blooming temperature is 1050-1150DEG C, the finishing temperature is 850-940DEG C, and the accumulated reduction rate of last three passes is not less than 16%; and heat treatment adopts online quenching and tempering treatment, or adopts offline quenching and tempering treatment. The steel plate obtained in the invention has the advantages of excellent mechanical properties, good hot and cold processing performance, excellent weldability and low sensitivity of weld cracks.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
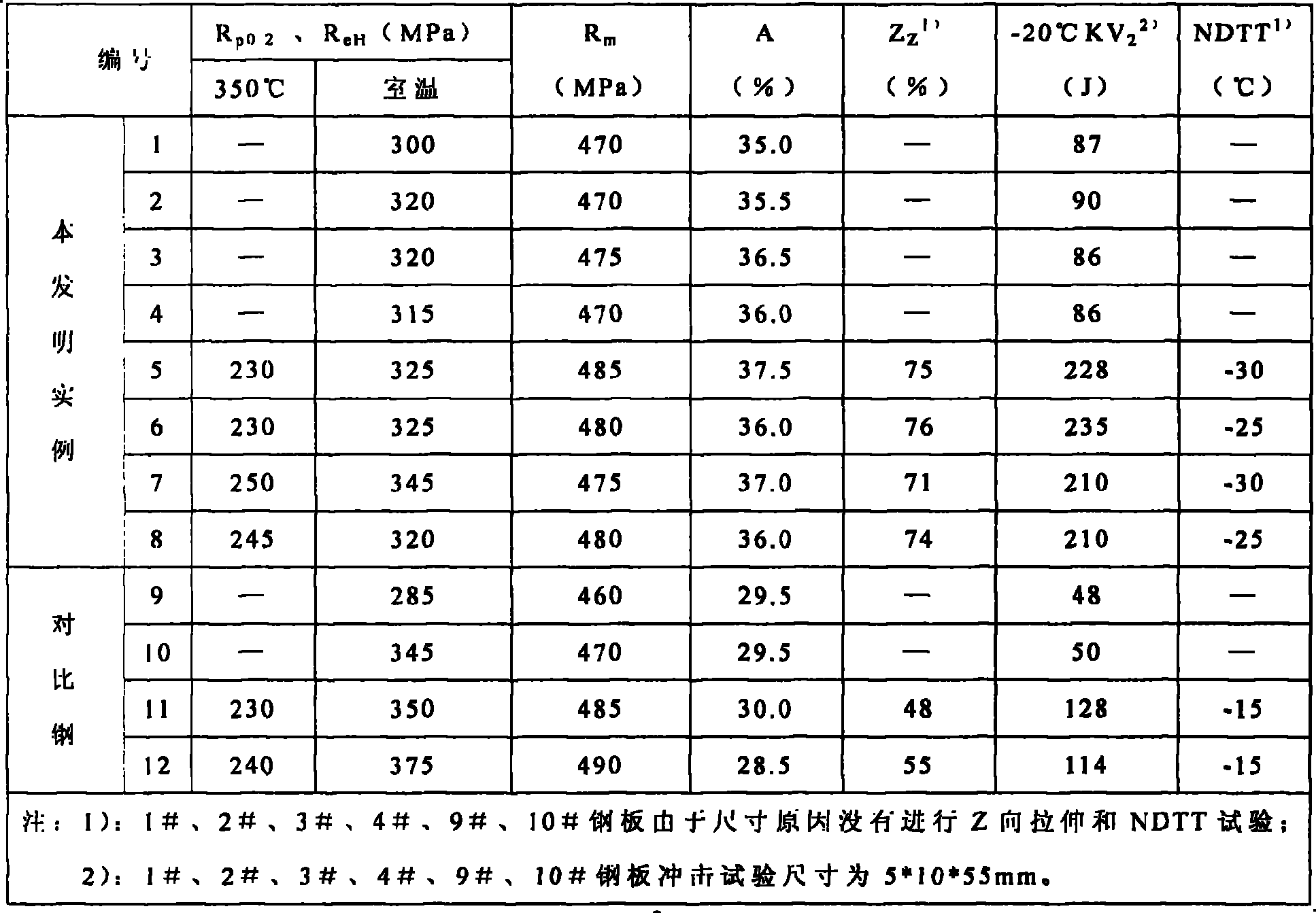
Steel for low-yield-ratio structure with yield strength larger than or equal to 690MPa and production method of steel
Steel for a low-yield-ratio structure with the yield strength larger than or equal to 690MPa comprises, by weight, 0.01-0.05% of C, 0.41-0.60% of Si, 2.10-3.50% of Mn, less than 0.010% of P, less than 0.005% of S, 0.10-0.50% of Mo, 0.51-0.80% of Cr, 0.10-0.80% of Cu, 0.05-0.50% of Ni, 0.052-0.11% of Nb, 0.053-0.10% of V, 0.008-0.025% of Ti, 0.015-0.060% of Als, 0.0010-0.0080% of Ca, 0.0005-0.0050% of Mg, 0.0010-0.0030% of N and 0.0005-0.0025% of O. A production method includes the steps of steel making, continuous casting for billet formation, heating of cast billets, temperature preservation, rough rolling, fine rolling, relaxing and slow cooling of a steel plate, and straightening. The mechanical properties of the steel include RP0.2 is larger than or equal to 690MPa, Rm is larger than or equal to 800MPa, the ductility A is larger than or equal to 22%, KV2 at the temperature of -20 DEG C is larger than or equal to 180J, and RP0.2 / Rm is smaller than or equal to 0.83. The steel after welding is not preheated or the preheating temperature is not higher than 50 DEG C, heating processing is not carried out after welding, welding efficiency is greatly improved, and the steel has good cold and hot machining performance and high deformation resistance.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Corrosion-resistance weldable titanium alloy with high strength and high impact toughness and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a corrosion-resistance weldable titanium alloy with high strength and high impact toughness, and relates to the technical field of titanium alloys. The corrosion-resistance weldable titanium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 4.0-8.0 wt.% of Al, 0.3-6.0 wt.% of Mo, 0.3-6.0 wt.% of V, 0.3-5.0 wt.% of Nb, 0.3-6.0 wt.% of Cr, 0.3-5.0 wt.% of Zr, aluminum equivalent [Al] not less than 6, molybdenum equivalent [Mo] not more than 8.0, and the balance of Ti, interstitial elements and inevitable impurity elements; the interstitial elements are C, H, O and N; and the mass percentage sum of all the elements in the titanium alloy is 100%. The titanium alloy material has comprehensive performances of high strength, high impact toughness, corrosion resistance and weldability, is excellent in cold and hot processing performance, and can be molded as forgings, thick plates and the like.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Low-yield-ratio structural steel with yield ratio equal to or larger than 550MPa and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses low-yield-ratio structural steel with a yield ratio equal to or larger than 550MPa. The low-yield-ratio structural steel with the yield ratio equal to or larger than 550MPa comprises, by weight, 0.03-0.10% of C, 0.30-0.60% of Si, 1.40-2.00% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.010% of P, less than or equal to 0.005% of S, 0.10-0.50% of Mo, 0.10-0.40% of Cr, 0.040-0.10% of Nb, 0.008-0.025% of Ti, 0.015-0.055% of Als, 0.0010-0.0080% of Ca, 0.0005-0.0050% of Mg, 10-30*10<-4>% of N, and 5-25*10<-4>% of O. A manufacturing method of the low-yield-ratio structural steel with the yield ratio equal to or larger than 550MPa comprises the steps of carrying out smelting and continuous casting to form a blank, heating the casting blank and carrying out heat insulation on the casting blank, rough rolling, finish rolling, and carrying out relaxation slow cooling on a steel plate. The mechanical properties of the low-yield-ratio structural steel are that RP0.2>=550Mpa, Rm>=700MPa, ductility A>=25%, -20 DEG C KV2>=200J, and RP0.2 / Rm <= 0.80. According to the low-yield-ratio structural steel with the yield ratio equal to or larger than 550MPa and the manufacturing method thereof, preheating is not needed after welding or the preheating temperature is not larger than 50DEG C, heat treatment is not needed after welding, and therefore welding efficiency is greatly improved; the cold and hot machining performance is good, and resistance to large deformation is achieved; cost is low, and the manufacturing processes are simplified.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Steel for nuclear power pressure equipment with high toughness, high ductility and low irradiation embrittlement and making method thereof
InactiveCN101892442AImprove toughnessImprove ductilityTemperature control deviceChemical compositionNuclear power
The invention discloses a steel for nuclear power pressure equipment with high toughness, high ductility and low irradiation embrittlement and a making method thereof. The steel comprises the following chemical compositions in percentage by weight: 0.08-0.15 percent of C, 0.20-0.35 percent of Si, 0.80-1.60 percent of Mn, P no more than 0.012 percent, S no more than 0.005, 0.01-0.05 percent of Alt, 0.08-0.015 percent of Ti, N no more than 0.010 and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. The chemical compositions of the steel also satisfy that Ni+Cr+Mo+Cu is no more than 0.70, Alt / N is no less than 2.0, Cu+6Sn is no more than 0.30 and Sn+Sb+As+Pb no more than 0.020. In the invention, the making method in a controlled rolling state and a normalized state is designed according to the requirements of different delivery states of steel products and different steel thicknesses, has the advantages of simple rolling technology and high product qualified rate of steel plates and can towel meet the requirements of mass production. The steel can be widely used for making second generation nuclear power pressure equipment, second generation improved nuclear power pressure equipment and third generation nuclear power pressure equipment.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
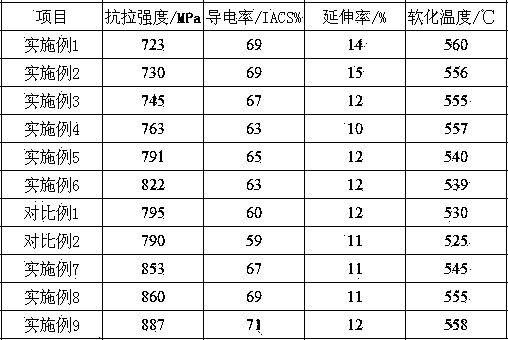
High-strength Cu-Ni-Si alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-strength Cu-Ni-Si alloy and preparation method thereof. The alloy comprises 2.0-6.0% of Ni, 0.5-1.5% Si, 0.5-1.0% of Ti, 0.5-1.0% of Mn, 0.5-1.0% of Ag and the balance of copper and unavoidable impurity elements. The preparation method sequentially comprises the following steps of smelting; casting; homogenization treatment; hot rolling and solution treatment; pre-cold rolling and aging treatment; and cold-rolling deformation. A Ni2Si non-oxide reinforcing phase is generated in the alloy disclosed by the invention; after the rolling is carried out repeatedly, the nucleation positions of precipitated phases can be increased, the more the broken grains, the more grain boundaries, the more nucleation positions of the precipitated phases and the more the precipitated phases; and under the condition that aging treatment is carried out repeatedly, the more precipitated phases are precipitated and thus the comprehensive performance of the alloy is dramatically increased, the strength, the elongation property at a high temperature and the electric conductivity are improved and the bending workability of the alloy is also improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
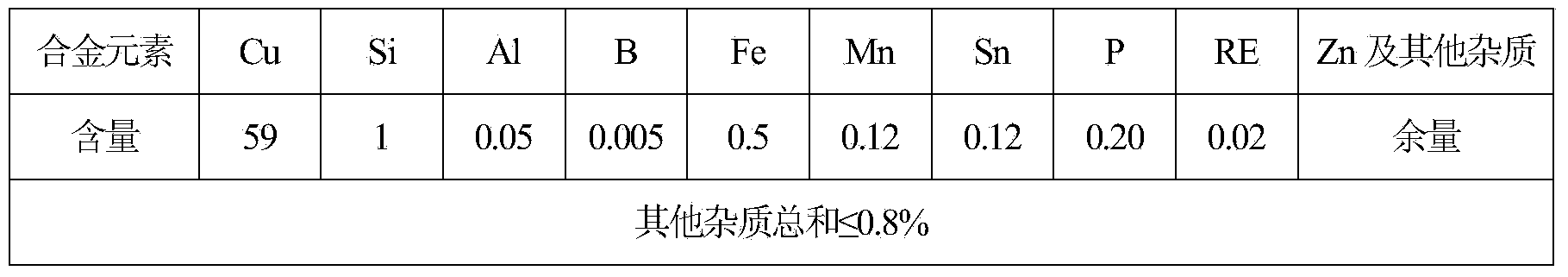
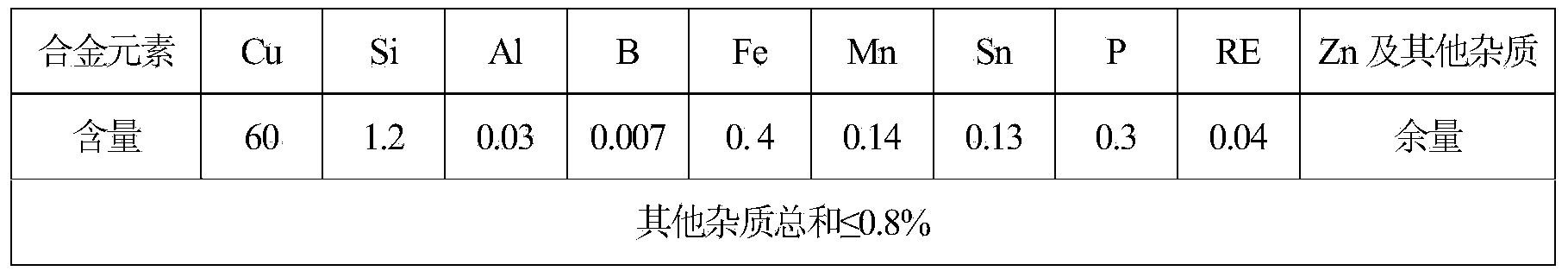
Lead-free silicon brass alloy and preparation method
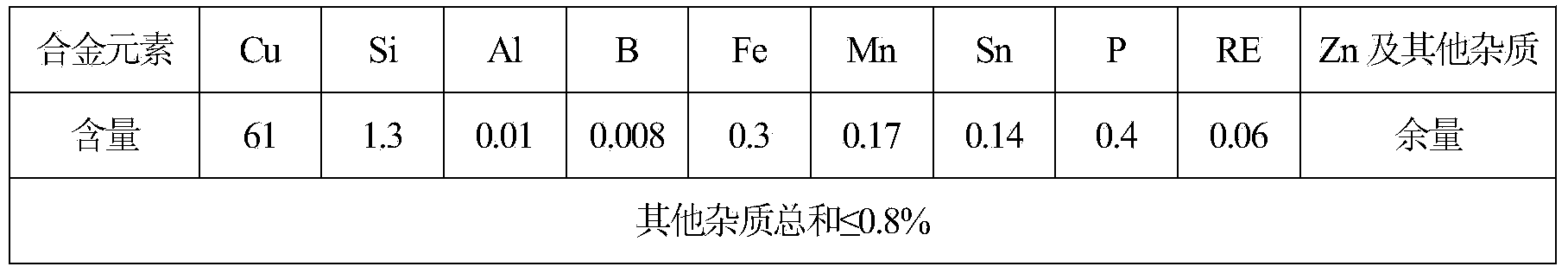
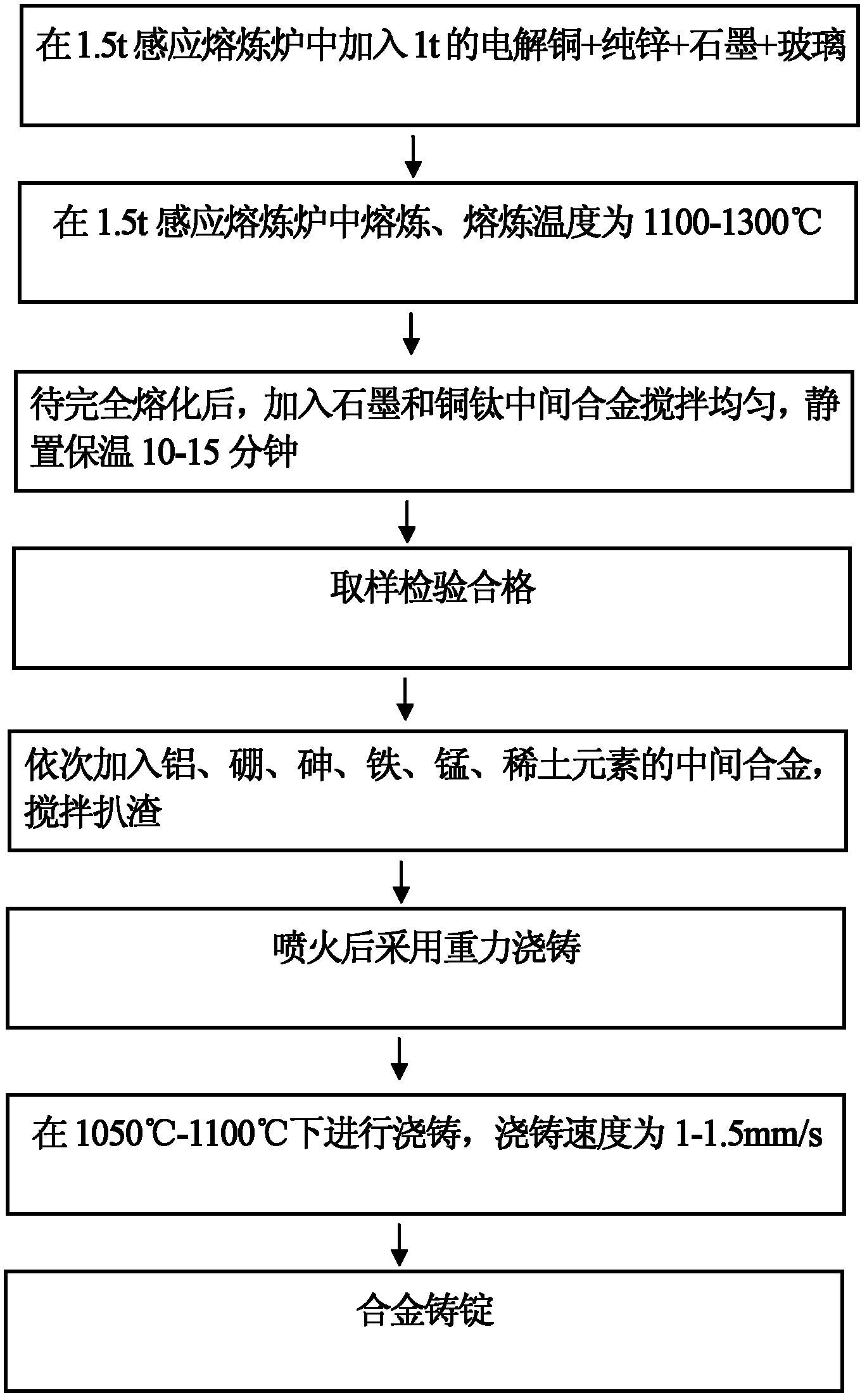
The invention belongs to the technical field of lead-free silicon brass alloy, especially relates to a free-cutting and corrosion-resistant lead-free silicon brass alloy and a preparation method thereof. The alloy is suitable for replacing the lead brass alloy for machining and is a good environment-friendly green metal material. The lead-free silicon brass alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 59-63% of copper, 1-1.5% of silicon, 0.001-0.05% of aluminum, 0.001-0.01% of boron, 0.1-0.5% of iron, 0.1-0.2% of manganese, 0.1-0.15% of tin, 0.05-0.5% of phosphorus, 0.01-0.07% of rare earth element RE, and the balance of zinc and inevitable impurity. During the preparation, the copper-silicon-zinc alloy is firstly melted, the intermediate alloy of iron and aluminum is added into the completely melted copper-silicon-zinc alloy and the mixture alloy is uniformly stirred, the intermediate alloys of the manganese, the boron, the tin, the phosphorus and the rare earth element are sequentially added into the mixture alloy, the mixture alloy is stirred and slagged off, and finally the alloy ingot is formed after the flaming and gravity casting steps. The silicon is added into the lead-free silicon brass alloy to replace the lead, so that on the premise of not reducing the production cost, the lead-free silicon brass alloy has good cutting performance and excellent cold workability and hot workability.
Owner:沈阳亚欧星海铜业有限公司
Anticorrosion white Cu-Mn alloy and method for making its wire material
An anticorrosion white Cu-Mn alloy contains Mn (9-15 wt.%), Zn (4-15 wt.%), Al (0.5-1.5 wt.%), Sn (0-1.5 wt.%) rare-earth element (less than 0.2 wt.%), and Cu (the rest). Said alloy can be used to make wire material through non-vacuum smelting, horizontal conticasting and cold drawing or cold rolling. Its advantages are high machinability and anticorrosion nature and stable lustre. It can replace Ni-contained white Zn-Cu alloy.
Owner:中铜(上海)铜业有限公司 +1
High-zinc leadless brass alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of leadless brass alloy and especially to an easily-cuttable corrosion-resistant high-zinc leadless brass alloy and a preparation method thereof. The alloy can be used to substitute machined lead brass alloy and is an excellent environment-friendly green metal material. The alloy comprises 57 to 63% of copper, 1 to 1 .5% of graphite, 0.05 to 2% of titanium, 0.001 to 0 .05% of aluminum, 0.001 to 0 .05% of boron, 0.02 to 0.06% of arsenic, 0.2 to 0.5% of iron, 0.1 to 0 .2% manganese and 0.001 to 0.07% of a rare earth element RE, with the balance being zinc. During melting, copper zinc alloy is melted at first, graphite and copper titanium intermediate alloy are added after copper zinc alloy is completely molten and are uniformly mixed with molten copper zinc alloy under stirring, then intermediate alloy of aluminum, boron, arsenic, iron, manganese and the rare earth element are sequentially added, stirring and slag removal are carried out, and gravity casting is carried out on an obtained mixture after flaming so as to prepare alloy cast ingots. According to the invention, graphite is added into the high-zinc leadless brass alloy to substitute lead,which enables the high-zinc leadless brass alloy to cost less compared to bismuth brass, the disadvantages of cracks, inclusion and the like of castings to be reduced, brass crystal grains to be refined and the high-zinc leadless brass alloy to have excellent hot and cold processing performances.
Owner:江西九星铜业有限公司
Beta titanium alloy material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a beta titanium alloy material, consisting of the following components in percentage by mass: 83.0 to 88.0 percent of Ti, 8.0 to 13.0 percent of Cr, 0.5 to 1.5 percent of Fe, 2.0 to 4.0 percent of Al, and other trace impurities. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the raw materials according to the mass percentage required by the beta titanium alloy material; smelting the mixture in a vacuum induction furnace with the vacuum degree of between 0 and 5Pa and the smelting power of 200KW after uniform mixing; cutting and removing the sink hole part of an ingot after smelting; and forging the ingot at the temperature which is higher than beta-phase change temperature and lower than 1,000 DEG C. The titanium alloy has the advantages of lower cost, higher strength, higher elongation rate and higher impact toughness; after solid solution treatment, the whole the alloy is a metastable beta-phase tissue, the alloy has excellent cold and heat processing performance, and the cold working rate achieves 87.2 percent.
Owner:LUOYANG SUNRUI TI PRECISION CASTING
Low-lead free-cutting anti-corrosion tin-brass alloy material
The invention discloses a low-lead free-cutting anti-corrosion tin-brass alloy material. The material includes the following components: 60.0 to 65.0 percent of Cu (copper), 0.5 to 1.5 percent of Sn (tin), 0.1 to 0.7 percent of Si (silicon), 0.02 to 0.12 percent of As (arsenic), 0.002 to 0.015 percent of B (boron), 0.01 to 0.25 percent of Pb (plumbum), 0.03 to 0.3 percent of Bi (bismuth), Sb (antimony) and P (phosphorus), as well as zinc and no more than 0.25 percent of impurities, wherein the Bi content is less than 0.10 percent, the Sb content is less than 0.10 percent, the P content ranges from 0.01 percent to 0.1 percent, the Fe (ferrum) content is less than 0.1 percent, the Ni (nickel) content is less than 0.1 percent, the Al (aluminum) content is less than 0.1 percent, the weight ratio of Si and Sn is 0.1-0.5 to 1, and the weight ratio of As and B is 5-60 to 1. The low-lead free-cutting anti-corrosion tin-brass alloy material has the advantages of high machinability, good cold / hot working property, mechanical property and welding property, as well as high dezincification resistance and stress corrosion resistance.
Owner:HENGJI GRP
High-silicon nitrogen-contained austenitic stainless steel and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN106756628AExcellent resistance to high temperature concentrated sulfuric acid corrosionImprove corrosion resistanceRare-earth elementChemical composition
The invention provides high-silicon nitrogen-contained austenitic stainless steel. The high-silicon nitrogen-contained austenitic stainless steel is characterized by comprising chemical compositions including, by mass percent, 15%-20% of Cr, 15%-20% of Ni, 2%-5% of Mn, 4.5%-6.0% of Si, 1%-3% of Mo, 0.5%-1.5% of Cu, 0.1%-0.3% of N, not larger than 1.0% of Al, 0.05%-0.5% of RE, not larger than 0.03% of C, not larger than 0.010% of S, not larger than 0.02% of P and the balance Fe. The invention further provides a preparing method of the above high-silicon nitrogen-contained austenitic stainless steel. The high-silicon nitrogen-contained austenitic stainless steel is mainly used for in the field of chemical engineering, in particular to the sulfuric acid industry; the high-silicon nitrogen-contained austenitic stainless steel can be further used in the fields of food catering instruments, ornaments, environmental protection and the like; and according to the high-silicon nitrogen-contained austenitic stainless steel, by optimizing the silicon content and adding the nitrogen, the copper, the aluminum and the rare earth elements, the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel is improved, and the stainless steel has the excellent cold and heat machining performance and corrosion resistance.
Owner:JIANGSU XIHU SPECIAL STEEL
Medium-strength corrosion-resistant weldable crack-arrest titanium alloy and preparation method thereof
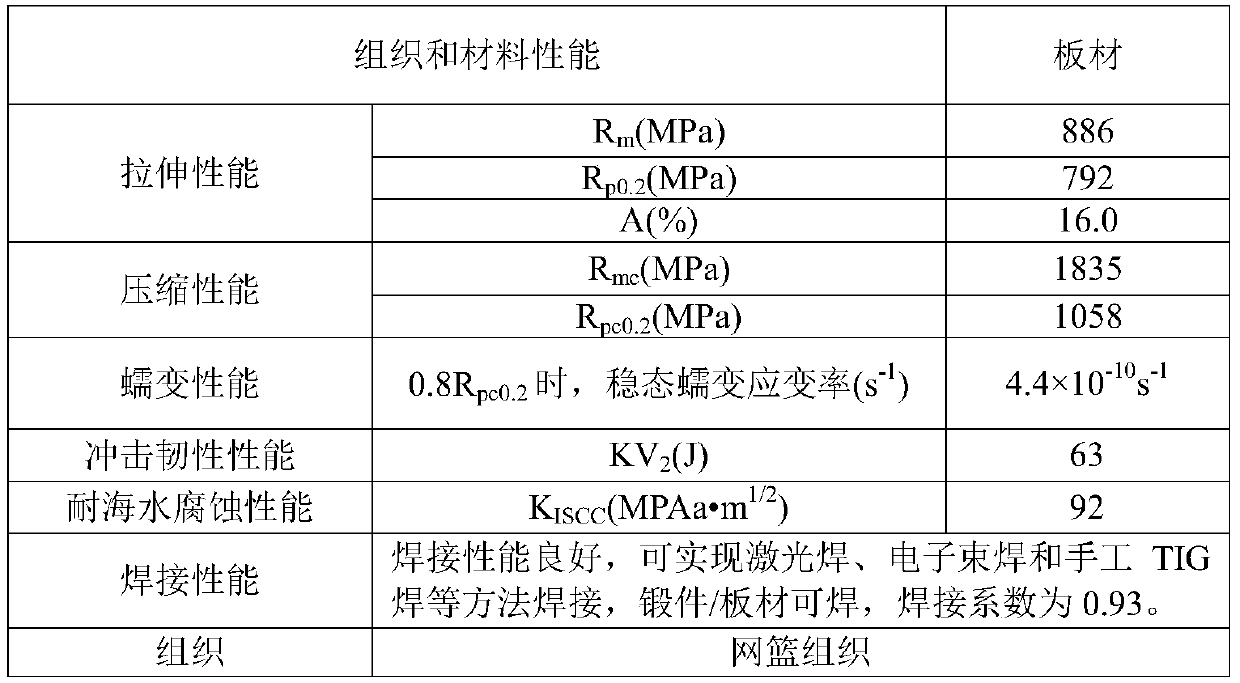
The invention discloses a medium-strength corrosion-resistant weldable crack-arrest titanium alloy. The titanium alloy is composed of, by mass percentage, 3.0-7.0% of an alpha stabilizing element Al, 1.5-4.5% of beta stabilizing elements of Mo, V, Nb and Ni, 0.5-3.0% of neutral elements of Zr and Sn, 0.01-0.3% of a Si element and the balance Ti and inevitable impurities, wherein, by mass percentage, 0-1% of Mo, 0-3% of V, 0-1% of Nb, 0.5% of Ni, 0-2% of Zr and 0-3% of Sn are included. The titanium alloy has the good strength, plasticity and toughness matching, the yield strength Rp0.2 is larger than or equal to 640 MPa, the tensile strength Rm is larger than or equal to 740 MPa, the elongation A is larger than or equal to 15%, the fracture toughness KIC is larger than or equal to 140 MPa.m<1 / 2>, and the impact toughness KV2 is larger than or equal to 80J; the alloy has the good crack arrest performance, and the dynamic tearing energy DTE is larger than or equal to 800 J; and meanwhile the good welding performance and resistance to seawater corrosion are achieved, the welding coefficient is larger than or equal to 0.95, the KISCC is larger than or equal to 95 MPa.m<1 / 2>, and the medium-strength corrosion-resistant weldable crack-arrest titanium alloy has the good technical application and market prospects in the fields of ship and marine engineering.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
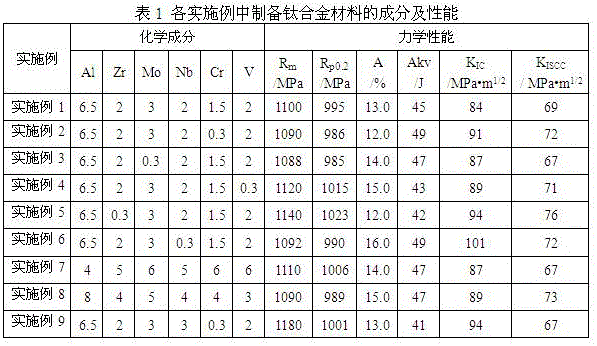
High-intensity, high-toughness and corrosion-resistant titanium alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109161726AGood cold and hot processing performanceGood technical applicationHigh intensityStable element
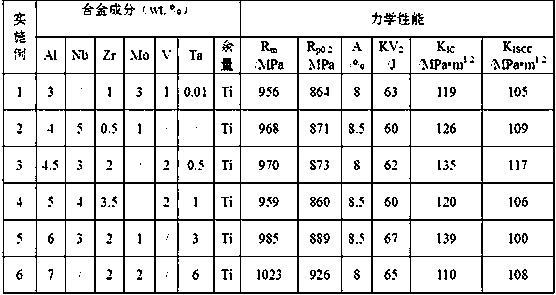
The invention relates to a high-intensity, high-toughness and corrosion-resistant titanium alloy and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of alloys. The titanium alloy is prepared from the following element components (in percentage by mass): 3.0 to 7.0 percent of Al; 2.0 to 6.0 percent of a beta-stable element (Mo+Nb+V), 0.01 to 6.0 percent of Ta, 0.5 to 3.5 percent of Zr and the balance of Ti and unavoidable impurities. The performance of the alloy is as follows: Rp0.2 is greater than or equal to 840 MPa, Rm is greater than or equal to 940 MPa, A is greater than or equal to8 percent, KIC is greater than or equal to 110 MPa.m<1 / 2>, KISCC is greater than or equal to 100 MPa.m<1 / 2>, and KV2 is greater than or equal to 60J. The alloy has good technology application and market prospects in the field of ship, marine engineering and the like.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Ultrahigh-conductivity leadless free-cutting copper alloy material, and preparation method and application thereof
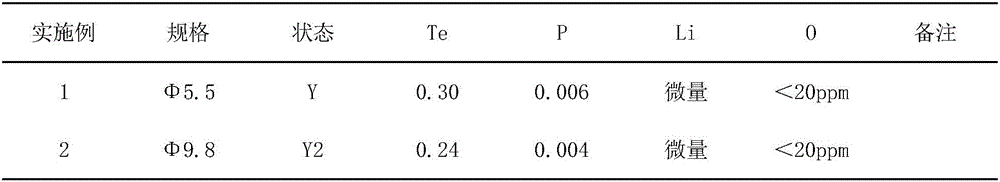
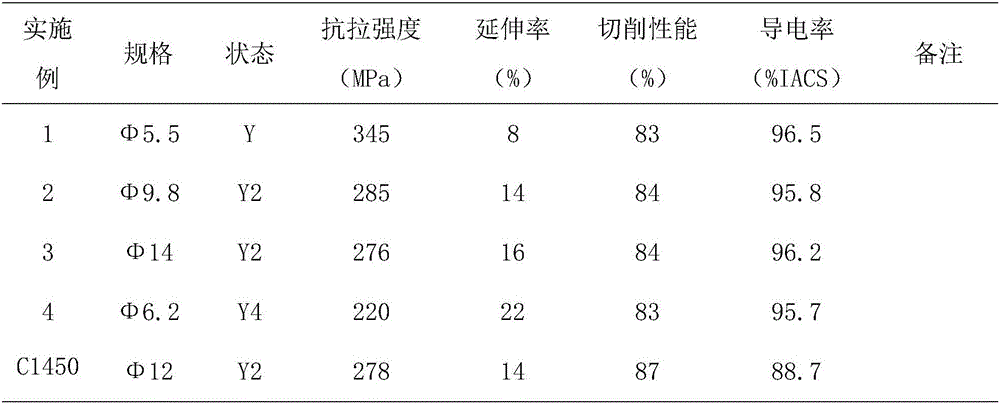
The invention discloses an ultrahigh-conductivity leadless free-cutting copper alloy material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The material is characterized by comprising the following chemical components by weight: 0.10 to 0.30% of Te, 0.003 to 0.009% of P and 99.70 to 99.90% of Cu, wherein the total amount of impurities is less than 0.1%. The preparation method adopts melting, extruding and drawing technology and cooperatively uses a phosphorus-lithium composite deep deoxidation method; and the prepared has oxygen content of less than 20 ppm, reaching the level of oxygen-free copper TU1, and has electrical conductivity of greater than 95% IACS, obviously higher than C14500 conductivity standard (greater than 85% IACS). The material has excellent machinability, electrical conductivity and heat conductivity and resistance to corrosion and electrical ablation, and can be extensively applied to electronic and electrical connection devices, integrated circuit lead frames, welding high-grade gun nozzles, electromotors, switch components and the like with ultrahigh requirements on electrical conductivity.
Owner:CECEP INDAL ENERGY CONSERVATION +1
Fire resistant and weather resistant steel with yield strength larger than or equal 690 MPa and used for welding structure and production method thereof
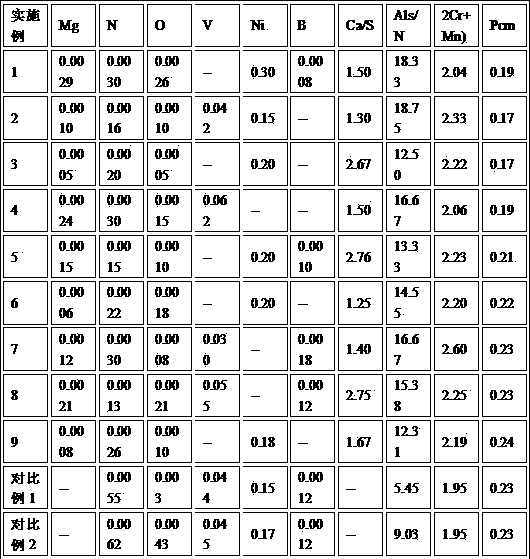
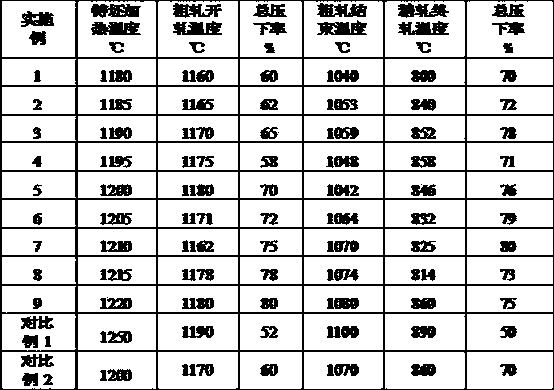
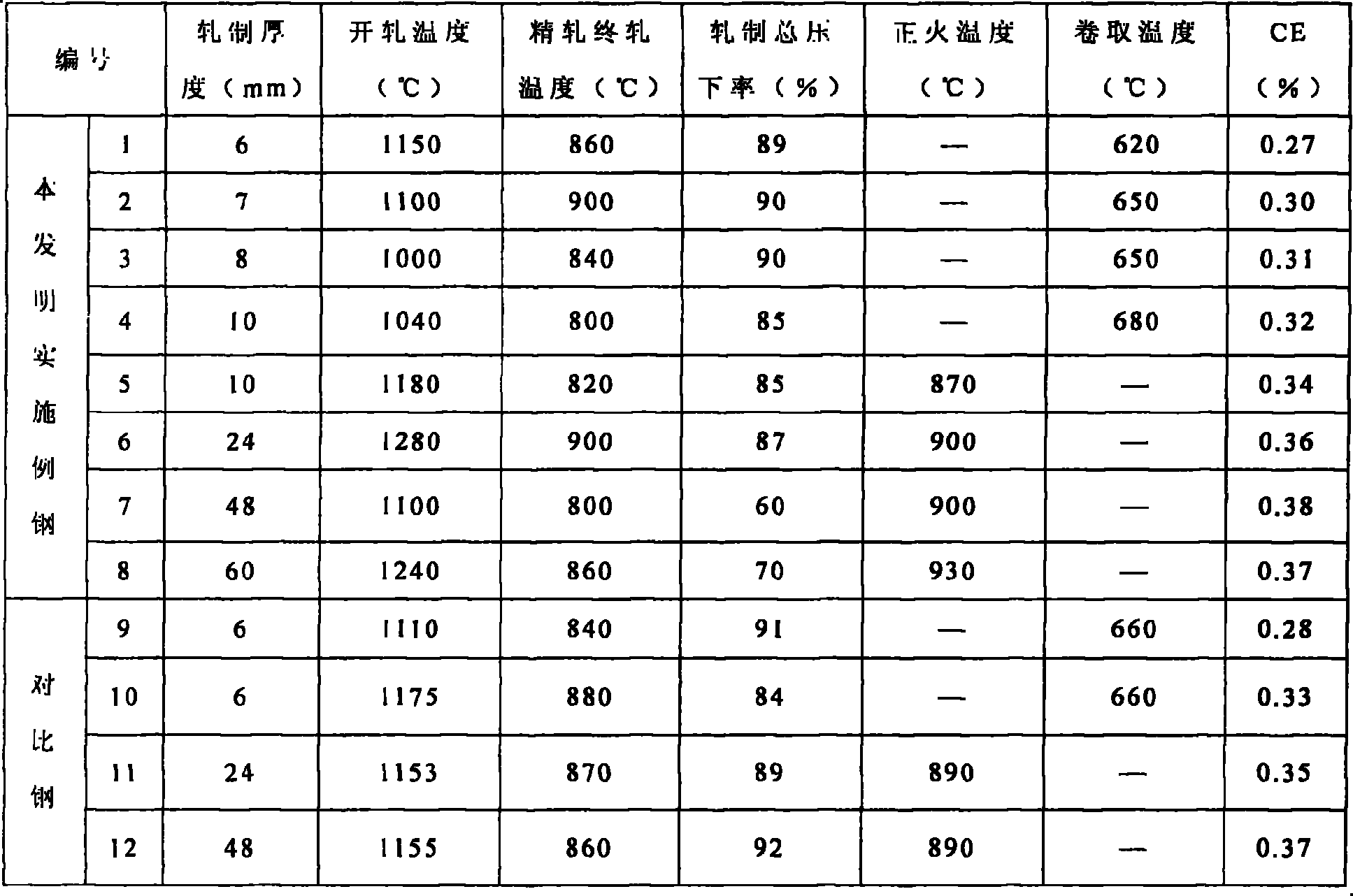
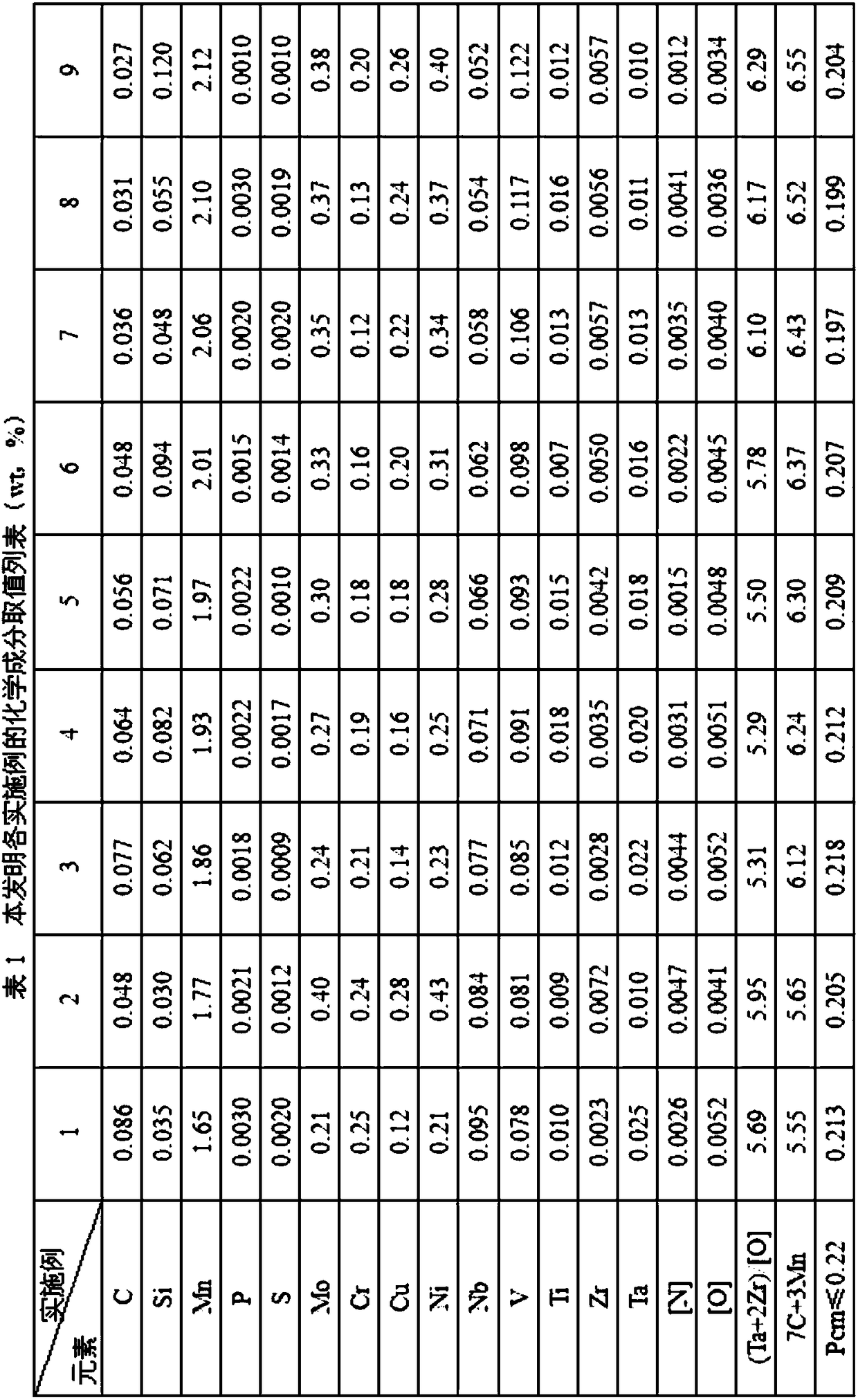
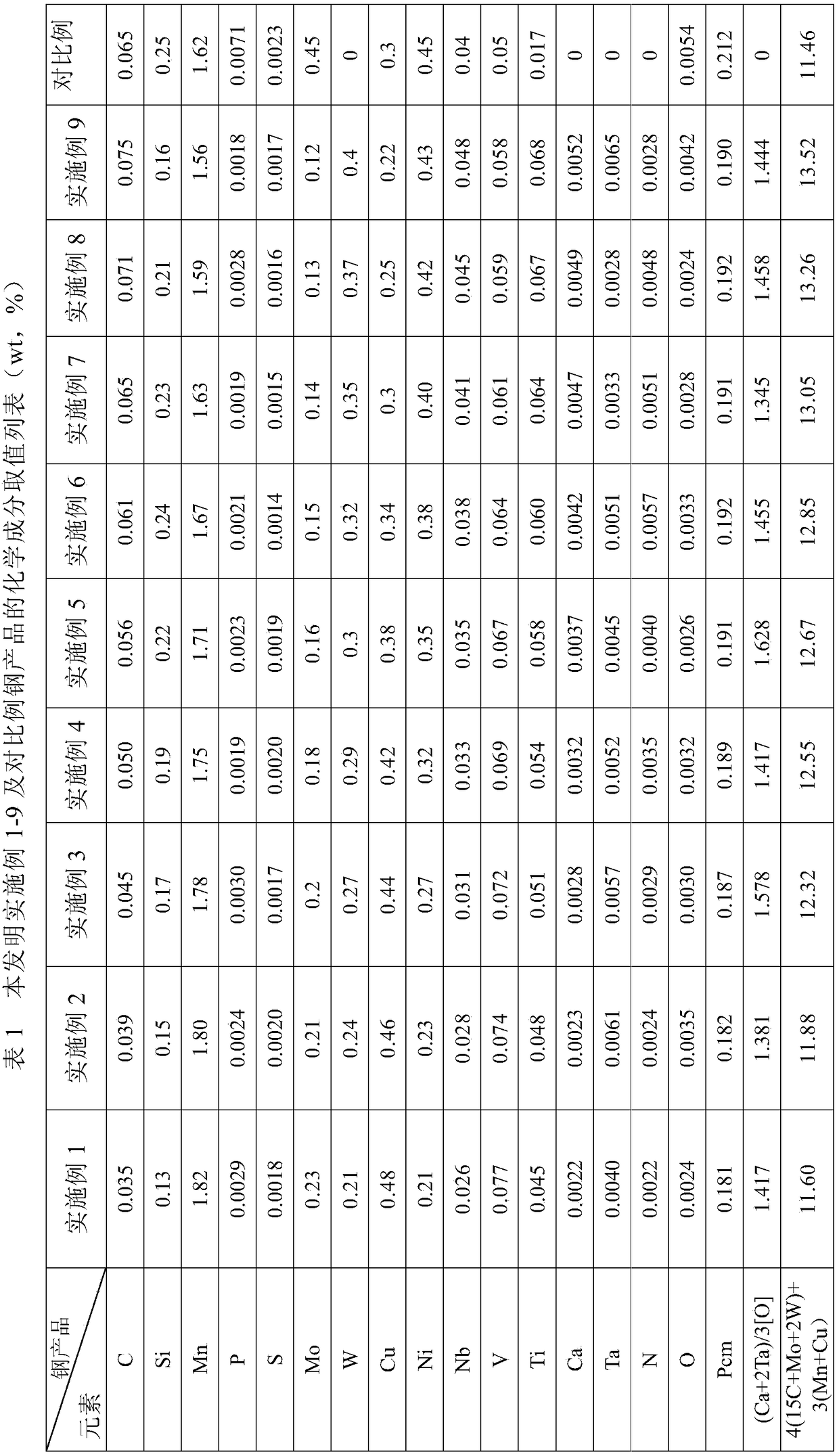
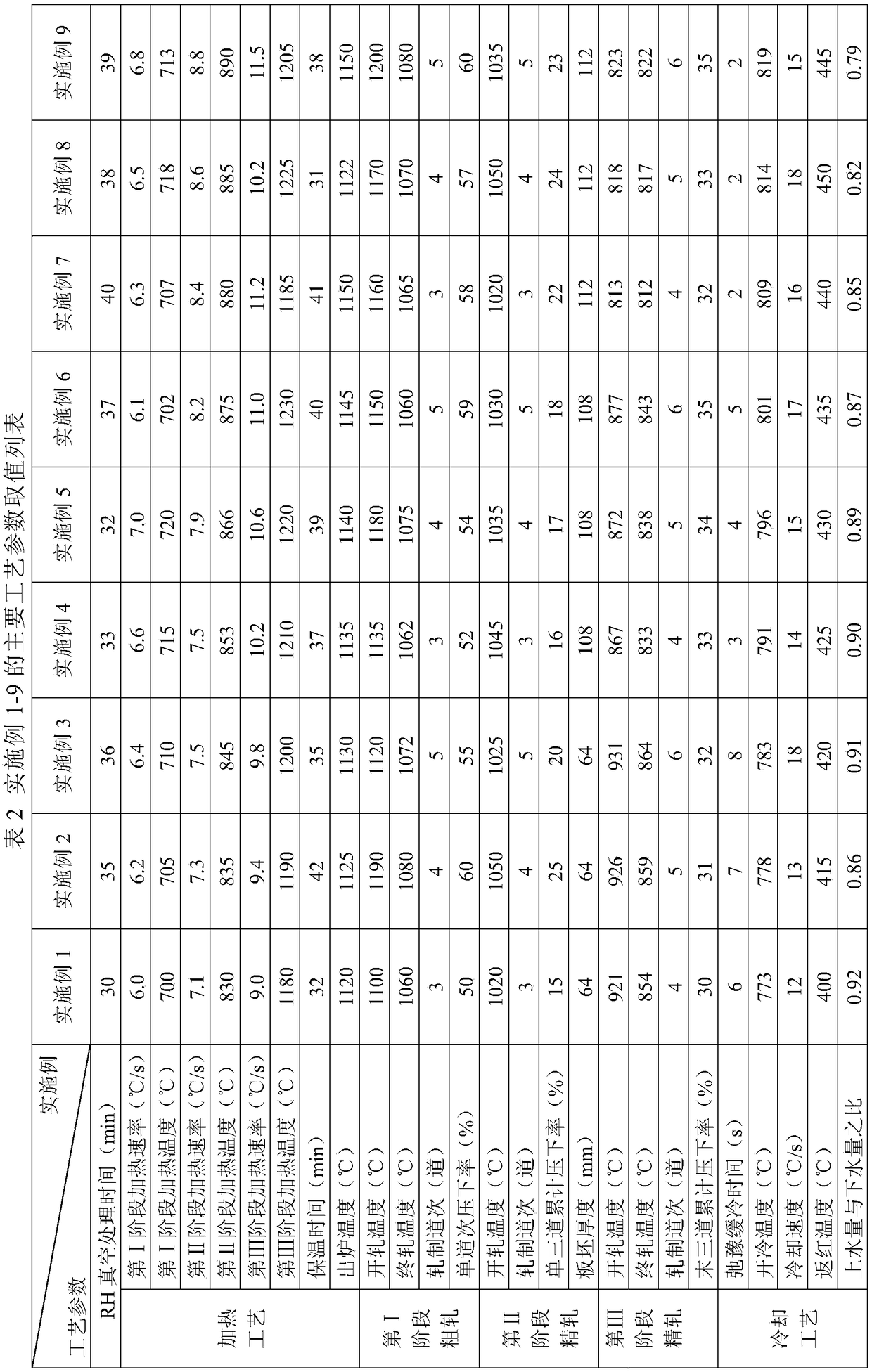
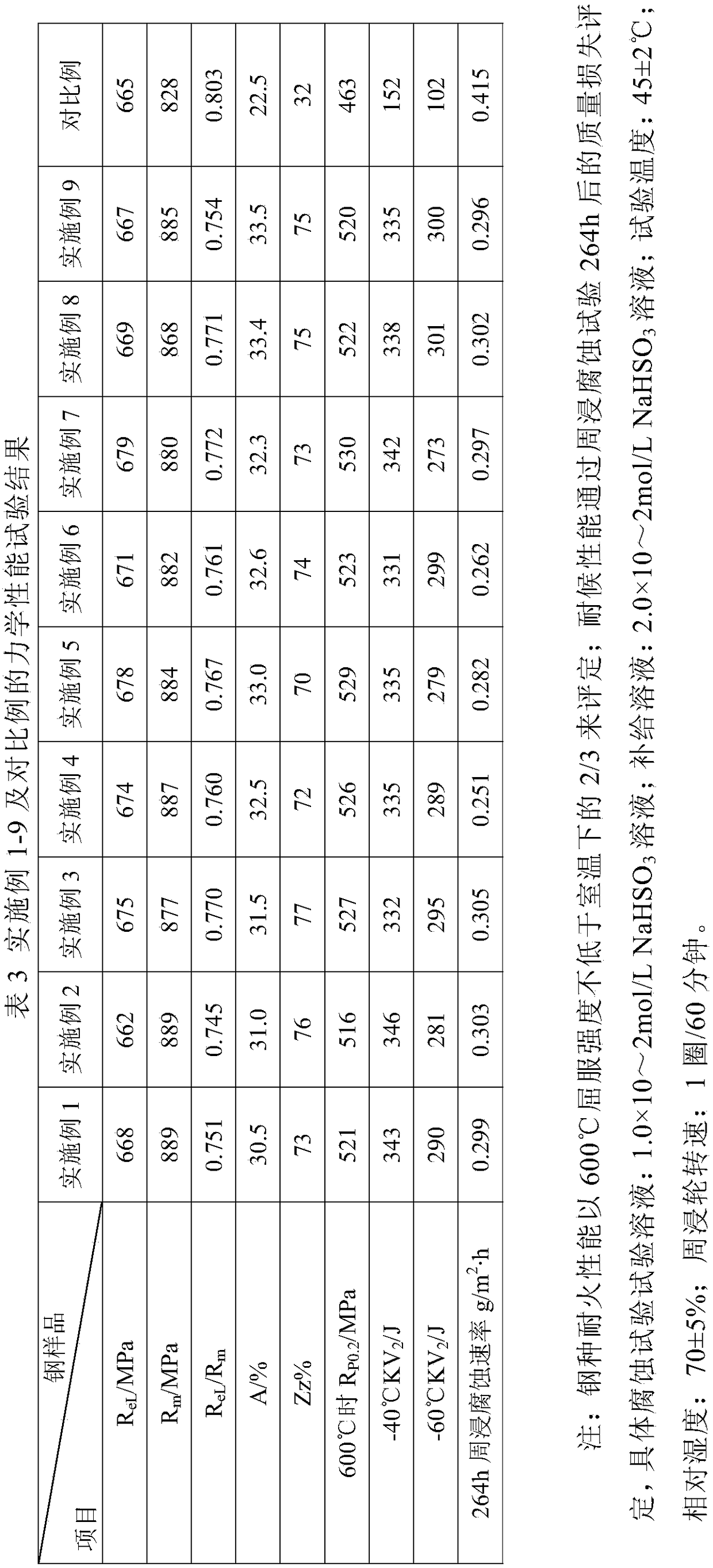
The invention belongs to the field of low alloy steel manufacturing, and particularly provides fire resistant and weather resistant steel with yield strength larger than or equal 690 MPa and used fora welding structure and a production method thereof. The steel comprises, by weight percent, 0.027 to 0.086% of C, 0.03 to 0.12% of Si, 1.65 to 2.12% of Mn, not larger than 0.003% of P, not larger than 0.002% of S, 0.21 to 0.40% of Mo, 0.12 to 0.25% of Cr, 0.12 to 0.28% of Cu, 0.21 to 0.43% of Ni, 0.052 to 0.095% of Nb, 0.078 to 0.122% of V, 0.007 to 0.018% of Ti, 0.0023 to 0.0072% of Zr, 0.010 to0.025% of Ta, 0.0012 to 0.0047% of N, 0.0034 to 0.0052% of O, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. Meanwhile, (2Zr+Ta) / O is equal to 5.28 to 6.31, 7C+3Mn is equal to 5.32 to 6.67%, Pcm is equal to C+Si / 30+(Mn+Cr+Cu) / 20+Ni / 60+Mo / 15+V / 10+5B smaller than or equal to 0.22%, and a product produced through the production method has the high strength toughness, excellent fire resistance and weather resistance(obviously superior to CortenB steel) and lamellar tearing resistance.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Maraging steel based on SLM (Selective Laser Melting) molded part and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110280764ASpread evenlyHigh strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMaraging steelThermal treatment
The invention discloses maraging steel based on an SLM (Selective Laser Melting) molded part and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out SLM molding on the powder of maraging steel used as a raw material to obtain the SLM molded part; then, carrying out surface treatment on the SLM molded part to obtain the compact SLM molded part; and finally carrying out solid solution treatment, aging treatment or direct aging treatment on the compact SLM molded part to obtain the maraging steel based on the SLM molded part. The SLM molded part is subjected to heat treatment by adopting the solid solution treatment, aging treatment or direct aging treatment, so that the mechanical strength and toughness of the SLM molded part are effectively improved; the range of application of the SLM molded part is expanded; the industrial design and manufacturing requirements are satisfied better; and the maraging steel based on the SLM molded part has the microhardness of 400-430HV and the tensile strength of 900-1000Mpa.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Titanium alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of alloy materials, and relates to a titanium alloy and a preparation method thereof, wherein the titanium alloy mainly contains titanium, and further contains, by weight, 4-7.5% of aluminum, 0.2-2% of iron, 0.1-2% of chromium, 0.5-2.5% of molybdenum, and trace unavoidable impurities. The titanium alloy of the present invention has excellent comprehensive performances such as mechanical property.
Owner:BEIJING JINYU SHUNDA TECH CO LTD
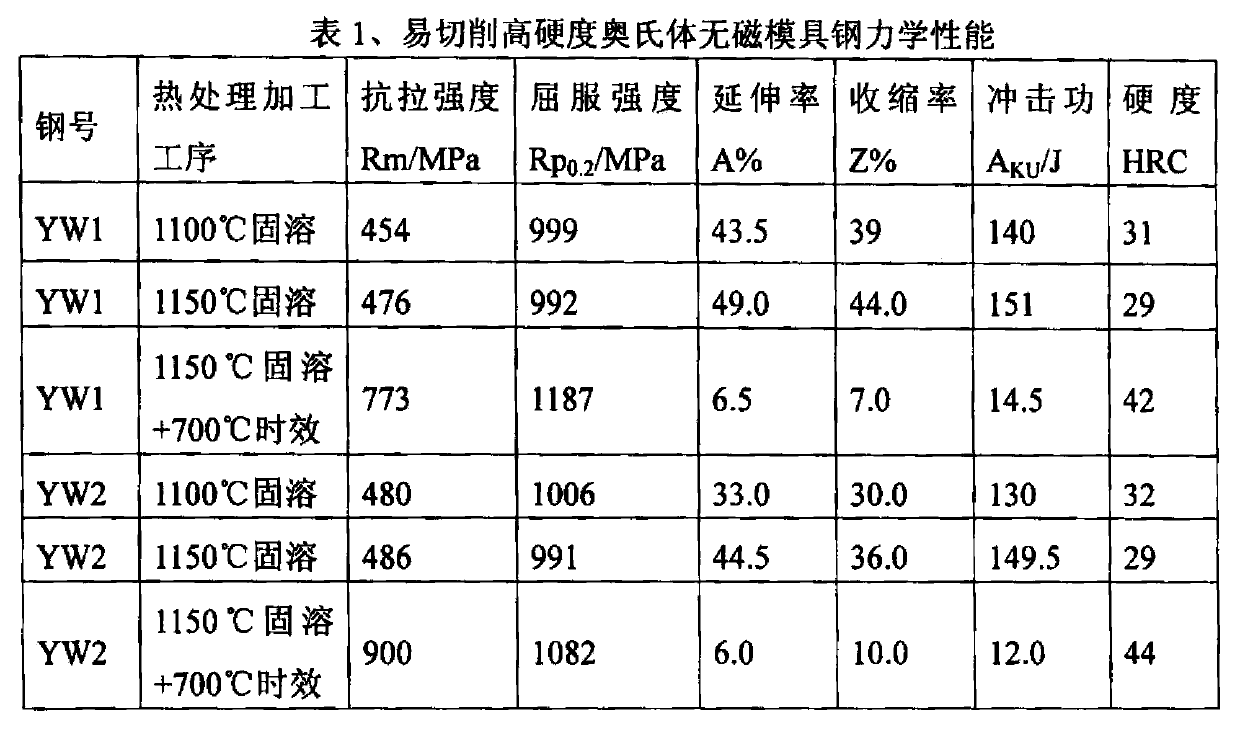
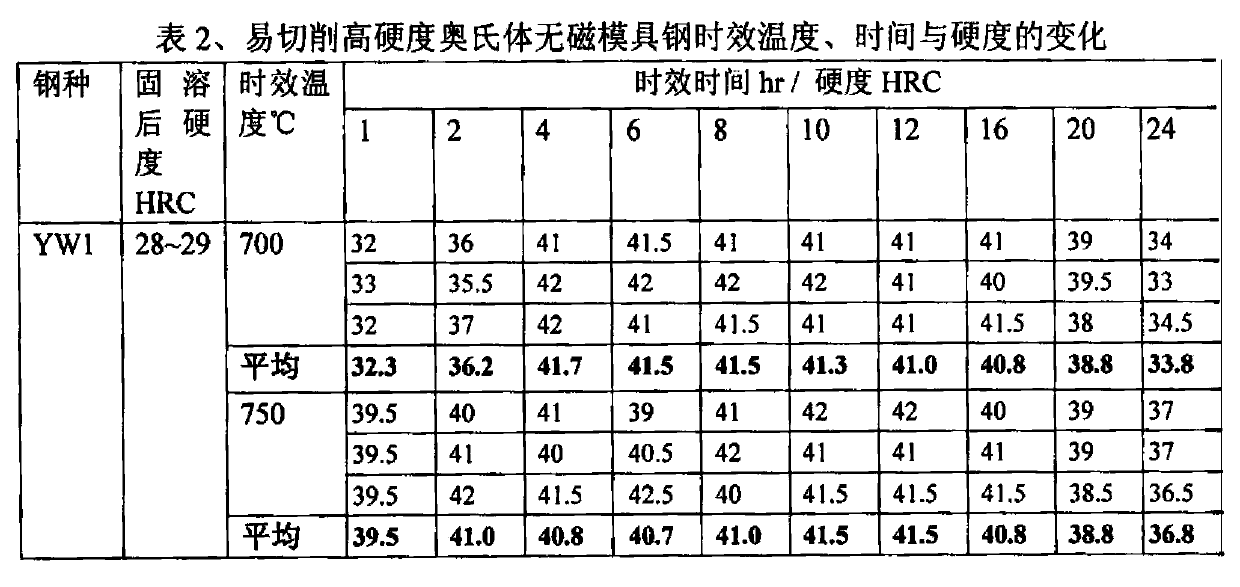
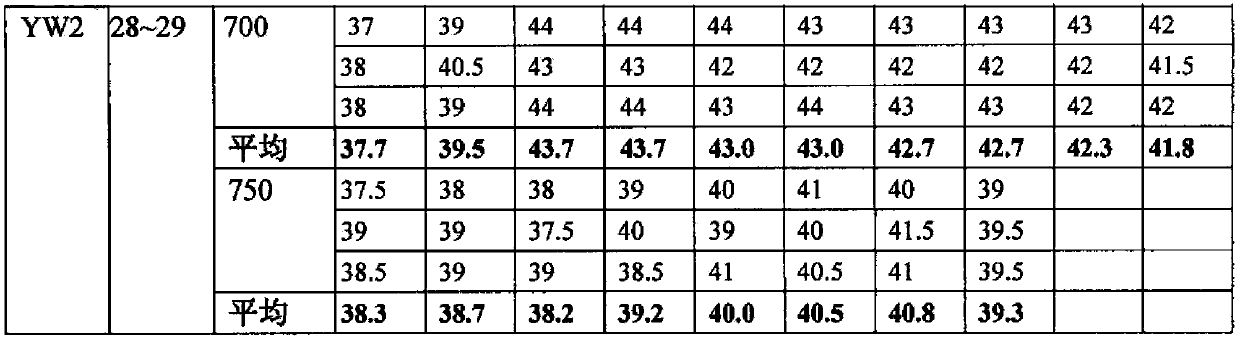
Free-cutting high-hardness austenite nonmagnetic die steel and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103361563AImprove mechanical propertiesGood cold and hot processing performanceMicro structureHardness
The invention relates to free-cutting high-hardness austenite nonmagnetic die steel and a manufacturing method thereof. The free-cutting high-hardness austenite nonmagnetic die steel comprises, by weight, 0.45-0.60% of C, 0.30-0.60% of Si, 12.50-16.00% of Mn, 4.00-6.00% of Cr, 1.50-2.50% of V, 0.30-0.55% of free-cutting elements, and the balance Fe. The free-cutting elements comprise Se, Sn and Cu. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of melting furnace burden in a non-vacuum induction furnace, carrying out remelting refining of electroslag, carrying out hot processing molding, and carrying out heat treatment on the molded steel to obtain the free-cutting high-hardness austenite nonmagnetic die steel. Compared with the prior art, the free-cutting high-hardness austenite nonmagnetic die steel does not produce phase change and always keeps austenite micro-structure in heating and cooling. After solid solution and ageing heat treatment reinforcement, the free-cutting high-hardness austenite nonmagnetic die steel has good integrated mechanical properties, good hot and cold processing performances and excellent free-cutting performances, is convenient for processing, and reduces a processing period. The free-cutting high-hardness austenite nonmagnetic die steel is widely used for dies in electronic product, automobile instrument and motor magnet ring industries.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF MATERIALS CO LTD
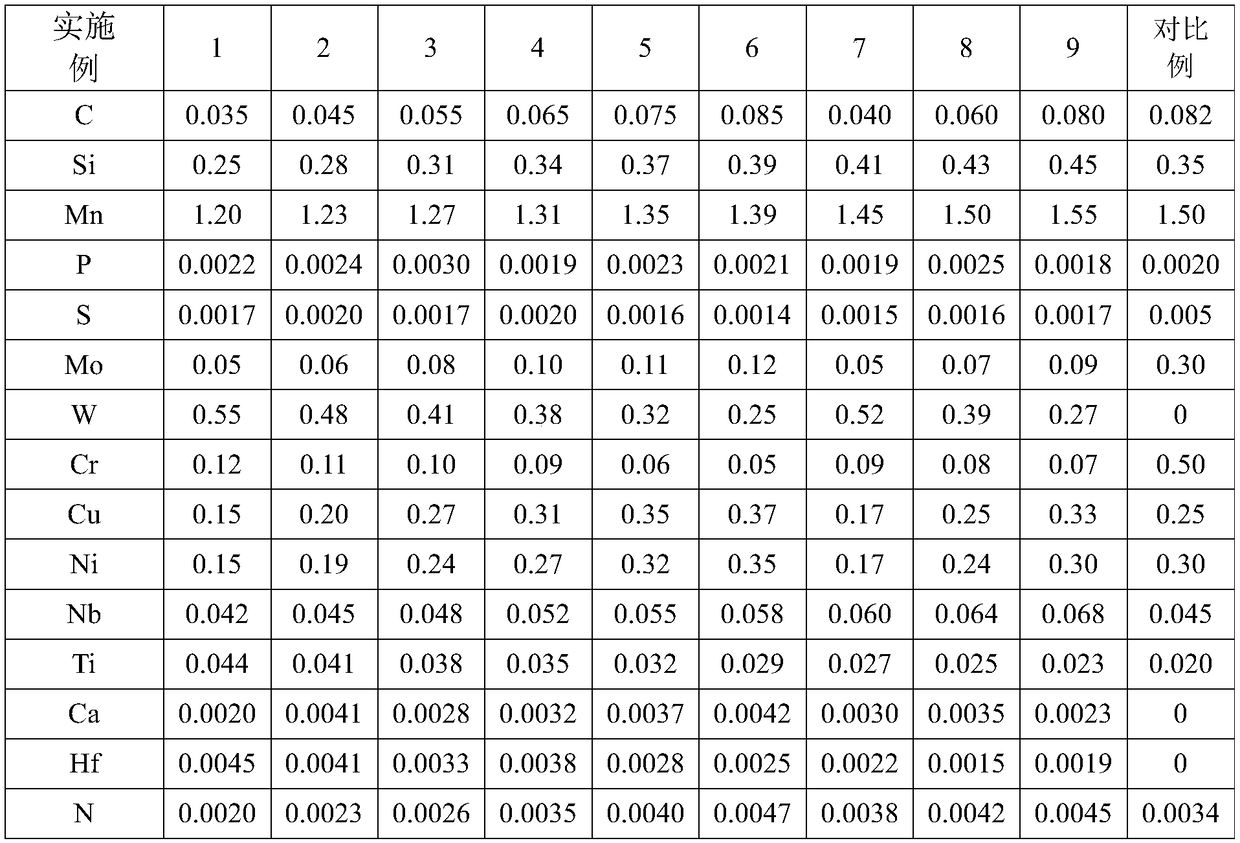
Welding structure fire-resistant and weather-resistant steel with yield strength being 550 MPa or above and production method
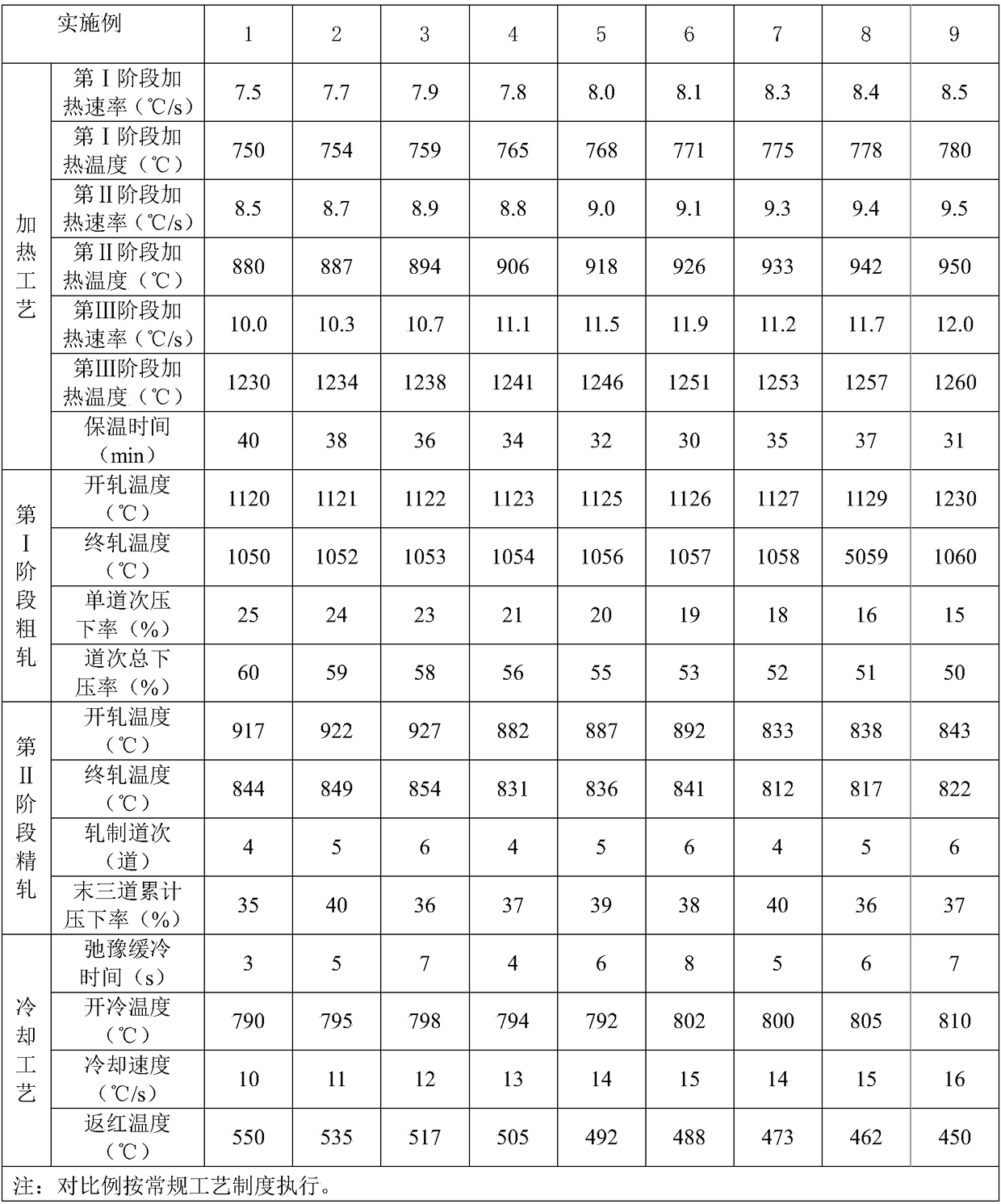
Welding structure fire-resistant and weather-resistant steel with the yield strength being 550 MPa or above comprises components, by weight percent, 0.035 wt%-0.085 wt% of C, 0.25 wt%-0.45 wt% of Si,1.20 wt%-1.55 wt% of Mn, 0.003 wt% or below of P, 0.002 wt% or below of S, 0.05 wt%-0.12 wt% of Mo, 0.25 wt%-0.55 wt% of W, 0.05 wt%-0.12 wt% of Cr, 0.15 wt%-0.37 wt% of Cu, 0.15 wt%-0.35 wt% of Ni, 0.042 wt%-0.068 wt% of Nb, 0.023 wt%-0.044 wt% of Ti, 0.0020 wt%-0.0042 wt% of Ca, 0.0015 wt%-0.0045 wt% of Hf, 0.0020 wt%-0.0047 wt% of N and 0.0025 wt%-0.0045 wt% of O. A production method comprisesthe steps that a casting blank is heated section by section, rough rolling, finish rolling and cooling are sequentially carried out, and air cooling is carried out until the room temperature is reached. According to the welding structure fire-resistant and weather-resistant steel with the yield strength being 550 MPa or above, ReL is 550 MPa or above, Rm is 750 MPa or above, ReL / Rm is 0.78 or below, the ductility A is 30 % or above, the Z-directional performance is 65 % or above, -60 DEG C KV2 is 300 J or above, excellent fire resistance, weather resistance, lamellar tearing resistance, the welding performance, the cold and hot processing performance and the large-deformation resistance are achieved, preheating is not needed before welding, and heat treatment is not needed after welding.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Light ultrahigh-strength and corrosion-resistant weldable titanium alloy wire rope for crane and preparation method of titanium alloy wire rope
ActiveCN113249993AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove antifouling performanceTextile cablesTitanium alloyUltimate tensile strength
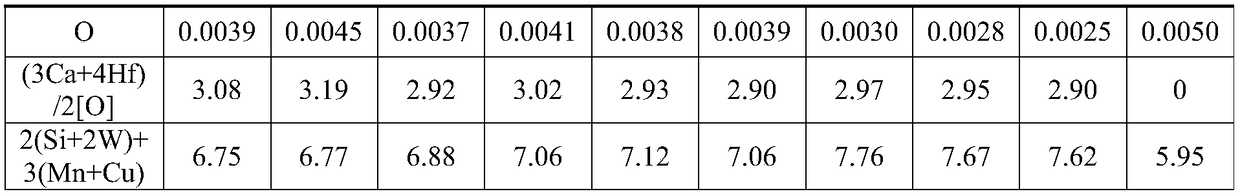
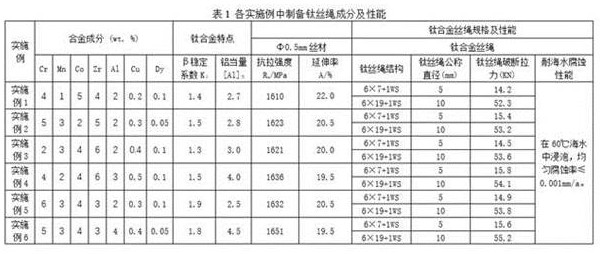
The invention discloses a light ultrahigh-strength and corrosion-resistant weldable titanium alloy wire rope for a crane. Alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight of 2.0 to 6.0 percent of Cr, 1.0 to 3.0 percent of Mn, 2.0 to 5.0 percent of Co, 2.0 to 6.0 percent of Zr, 2.0 to 4.0 percent of Al, 0.2 to 0.5 percent of Cu, 0.05 to 0.10 percent of Dy, less than 0.3 percent of total content of impurity elements C, H, O and N, and the balance of Ti. The titanium alloy wire rope disclosed by the invention has high specific strength, good plasticity and toughness and excellent corrosion resistance and antifouling property, and the weight is reduced by 40% or above; and the titanium alloy wire rope has good technical application and market prospects in the fields of hoisting equipment under the environmental conditions of ports, coasts, ocean platforms and coastal areas.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
Welded structure refractory and weathering steel with yield strength being no less than 620 MPa and production method thereof
The invention relates to a welded structure refractory and weathering steel with yield strength being no less than 620 MPa and production method thereof, and the welded structure refractory and weathering steel with the yield strength being no less than 620 MPa comprises, by mass, 0.035-0.075% of C, 0.13-0.24% of Si, 1.56-1.82% of Mn, no more than 0.003% of P, no more than 0.002% of S, 0.12-0.23%of Mo, 0.21-0.40% of W, 0.22-0.48% of Cu, 0.21-0.43% of Ni, 0.026-0.048% of Nb, 0.058-0.077% of V, 0.045-0.068% of Ti, 0.0022-0.0052% of Ca, 0.0028-0.0065% of Ta. The welded structure refractory and weathering steel with the yield strength being no less than 620 MPa has good mechanical properties, excellent fire resistance, weather resistance and resistance to laminar tearing, as well as the excellent welding property.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Lead-free, easily-cut and high-conductivity calcium-copper material
The invention discloses a lead-free, easily-cut and high-conductivity calcium-copper material. The material is characterized by consisting of the following components in percentage by weight: 0.1 to 1.0 percent of Ca, 0.01 to 0.1 percent of lanthanum-cerium alloy, less than 0.01 percent of Pb and the balance of copper and impurities, wherein the total amount of the impurities is not more than 0.06 percent; the sum of Cu and Ca is more than 99.90 percent; and the sum of Cu, Ca and the lanthanum-cerium alloy is more than 99.94 percent. The calcium-copper material has the advantages of high conductivity and cutting processing property, capability of being subjected to annealing treatment, and high weldability.
Owner:NINGBO XINGAODA ADVANCED METALLIC MATERIALS
Weldable titanium alloy with creep resistance, high impact toughness and corrosion resistance and preparation method
The invention belongs to the field of titanium alloy materials for deep-sea engineering equipment, and discloses a weldable titanium alloy with creep resistance, high impact toughness and corrosion resistance. The weldable titanium alloy is prepared from the components: 4.0-8.0% of Al, 0.3-4.0% of Mo, 0.5-4.0% of Ta, 0.5-4.0% of Zr, 0.03-0.12% of O and the balance of Ti. A preparation method includes the steps that batching is carried out according to the composition of the titanium alloy, raw materials are melted and subjected to ingot casting, cast ingots are broken down, forged, rolled andheat treated, and titanium alloy plates are obtained. The weldable titanium alloy with the creep resistance, high impact toughness and corrosion resistance has excellent compressive creep performance,plastic toughness, mechanical properties and seawater corrosion resistance, can meet the special service conditions for long-time service under deep-sea high-pressure, can be used for preparing the deep-sea engineering equipment of a deep-sea submersible, a deep-sea mobile work station and a large diving depth submarine and the like, and has a good application prospect and economic benefits in the field of the deep-sea engineering equipment and the like.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
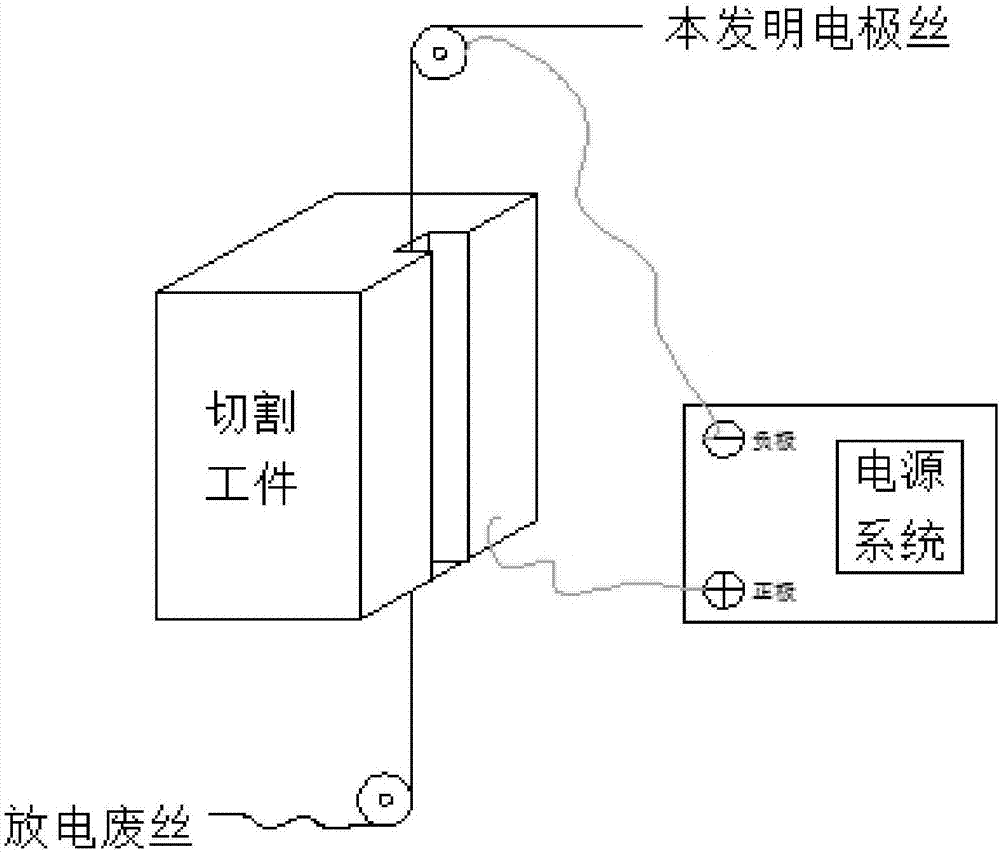
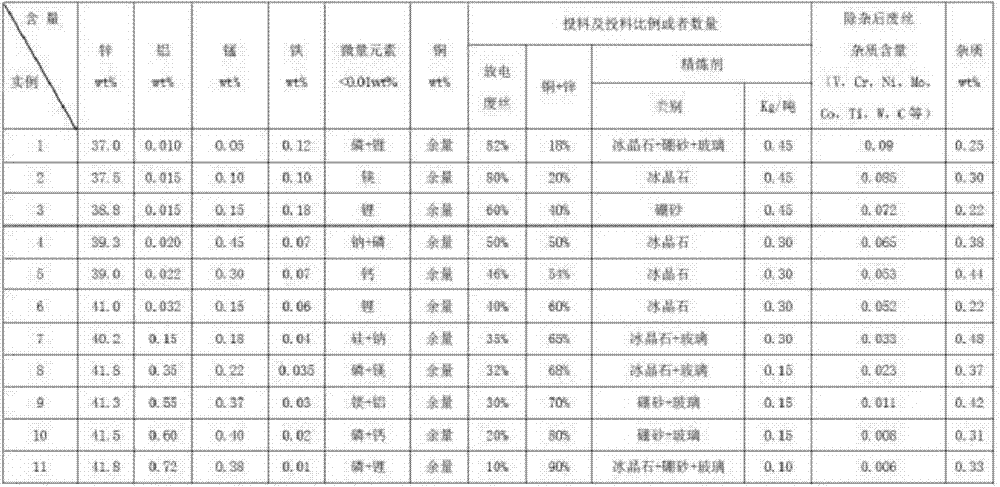
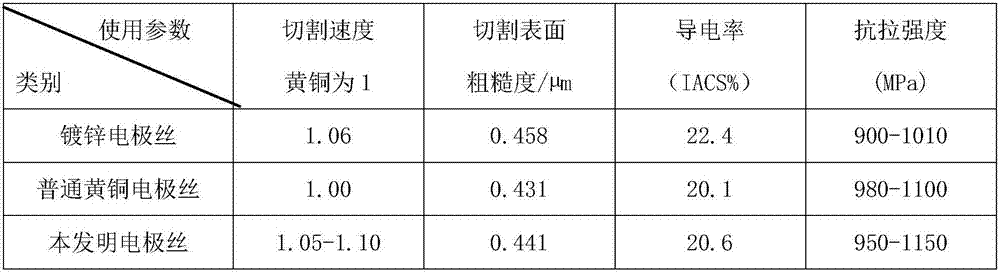
High-zinc-aluminum-manganese-iron-copper alloy for manufacturing of wire electrode for one-way wire winding
The invention provides a high-zinc-aluminum-manganese-iron-copper alloy for manufacturing of a wire electrode for one-way wire winding. The high-zinc-aluminum-manganese-iron-copper alloy is characterized by comprising, by weight, 37.0-42.0% of zinc, 0.0005-0.85% of aluminum, 0.005-0.5% of manganese, 0.01-0.30% of iron, 0.0005-0.01% of microelements, impurities composed of one or several of V, Cr, Ni, Mo, Co, Ti, W and C, less than 0.5% of other inevitable impurity elements, and the balance copper, wherein the microelements include one or more of magnesium, silicon, sodium, lithium, potassium, calcium and phosphorus; the content of all the elements in the impurities is less than 0.005%; the iron and part of copper and zinc are obtained after discharged waste wires are subjected to cleaning and impurity removal. Compared with the prior art, the wire electrode manufactured through the method is stable in gasification performance, higher in mechanical performance, low in processing cost and wide in application and has broad market prospects.
Owner:NINGBO BODE HIGHTECH CO LTD +1
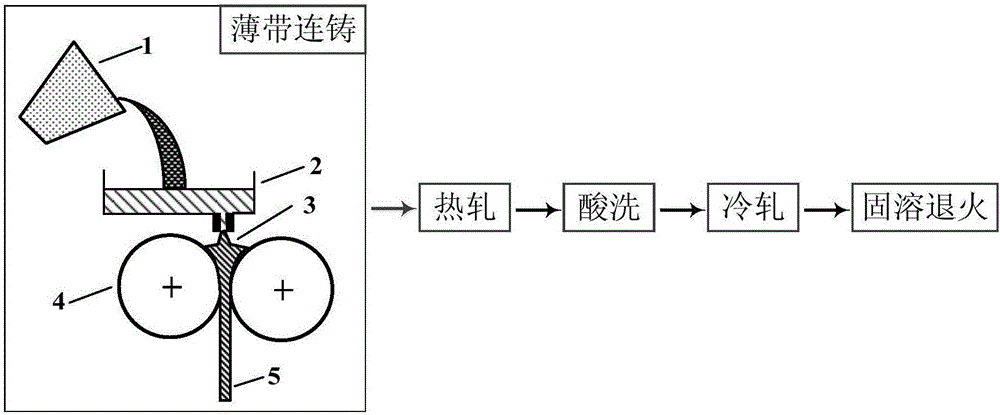
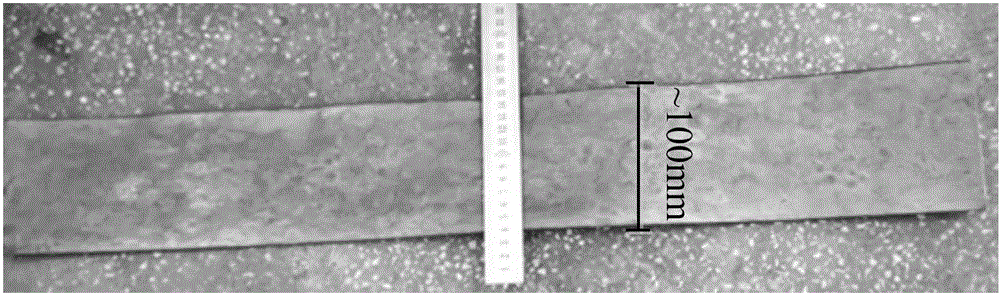
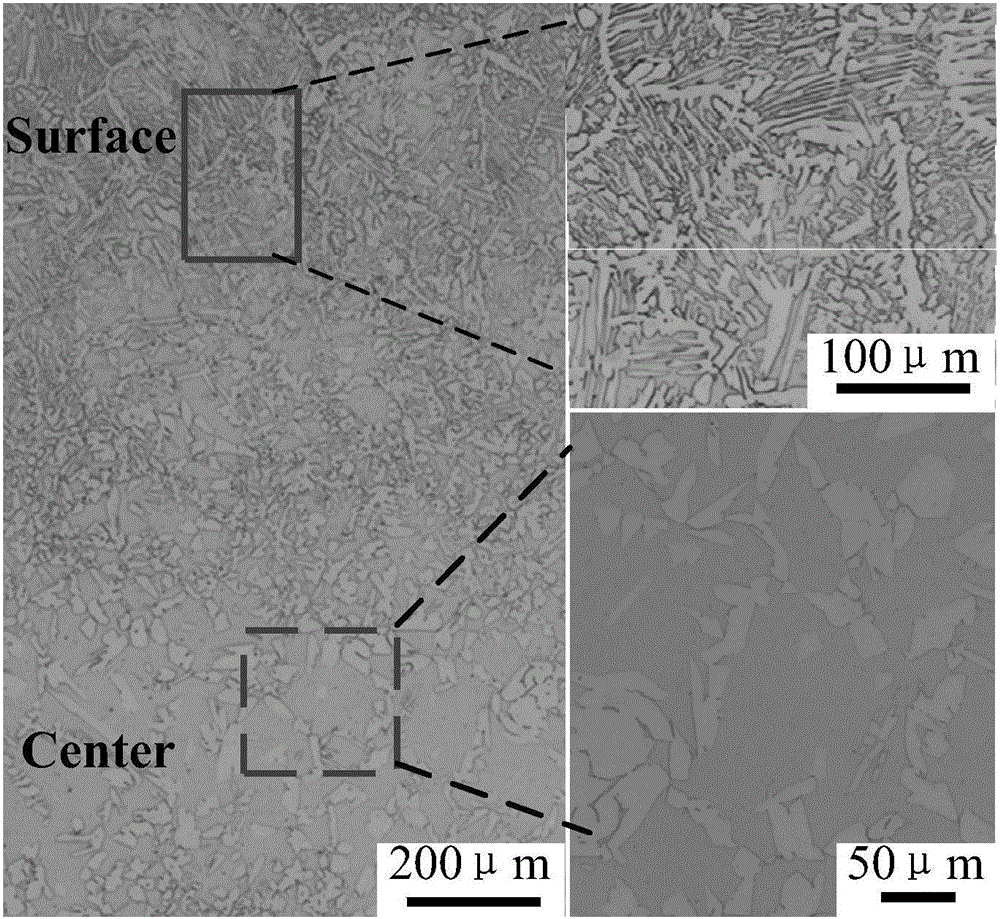
A duplex stainless steel thin strip and its near-net forming preparation method
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
A low-temperature high-strength two-phase titanium alloy
The invention provides a low-temperature-resistant and high-strength two-phase titanium alloy. The low-temperature-resistant and high-strength two-phase titanium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 1.5-3.5% of Al, 4.5-6.5% of Nb, 1.2-3% of Mo and the balance of titanium and unavoidable impurities. At a low temperature of 20K, the low-temperature-resistant and high-strength two-phase titanium alloy has mechanical properties as follows: Rm is greater than or equal to 1400MPa, Rp0.2 is greater than or equal to 1100MPa, and A is greater than or equal to 20%; compared with the conventional low-temperature-resistant titanium alloy, the low-temperature-resistant and high-strength two-phase titanium alloy has more excellent strength-plasticity matching, and can meet relevant requirements on low-temperature-resistant components of high-performance rocket, spacecrafts and spaceships.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
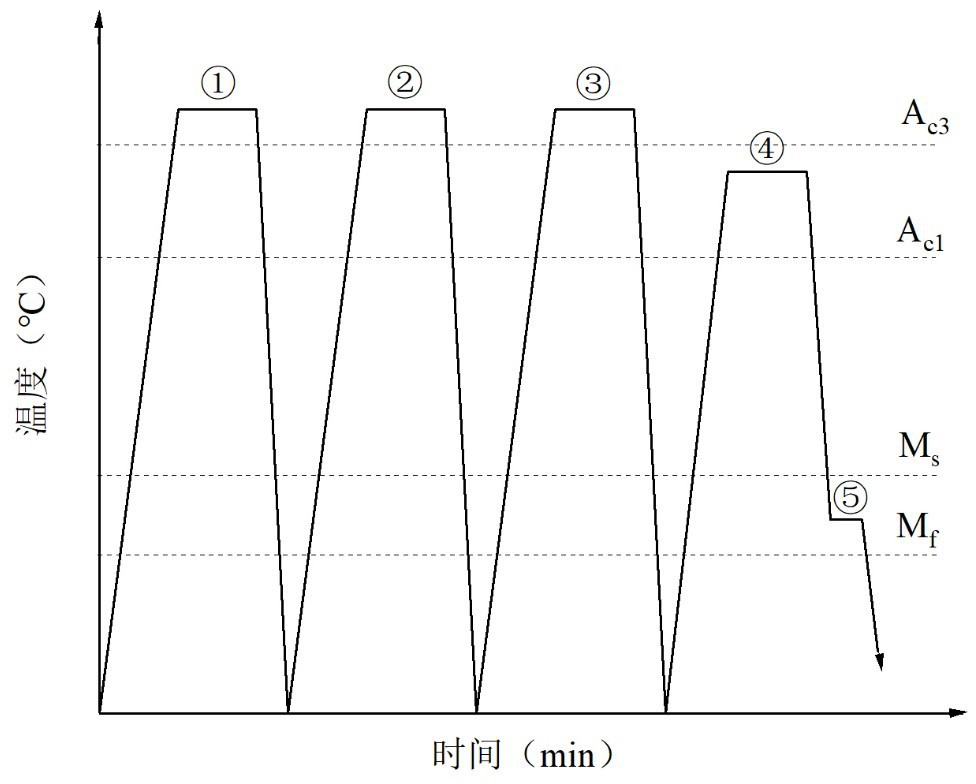
Method for producing medium manganese steel through cyclic quenching and I-Q&P treatment and application of method
The invention relates to the technical field of advanced high-strength steel preparation, in particular to a method for producing medium manganese steel through cyclic quenching and I-Q&P treatment and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a cyclic quenching process is conducted, specifically, steel is heated to be higher than an AC3-1 temperature, the temperature is kept, water quenching is conducted to room temperature, and the steel is treated twice or more according to the process to obtain cyclic quenched steel; (2) critical zone treatment is conducted, specifically, the cyclic quenched steel is heated to be between the AC1-2 temperature and the AC3-2 temperature of the cyclic quenched steel, and then the temperature is kept; and (3) quenching-partitioning treatment is conducted, specifically, the steel obtained in the step (2) is quenched to be between the Ms-2 temperature and the Mf-2 temperature, the temperature is kept, finally, waterquenching is conducted to the room temperature, and the steel is obtained. The mechanical property of the steel obtained through the process is remarkably higher than that of a hot rolled plate, thesteel has good cold and hot machining properties, and compared with a direct critical annealing treatment process, the process time is short, and the properties of the steel are remarkably improved.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
High-strength nickel silver alloy
ActiveCN100523237CSuitable for commercial productionHigh tensile strengthChemical compositionCupronickel
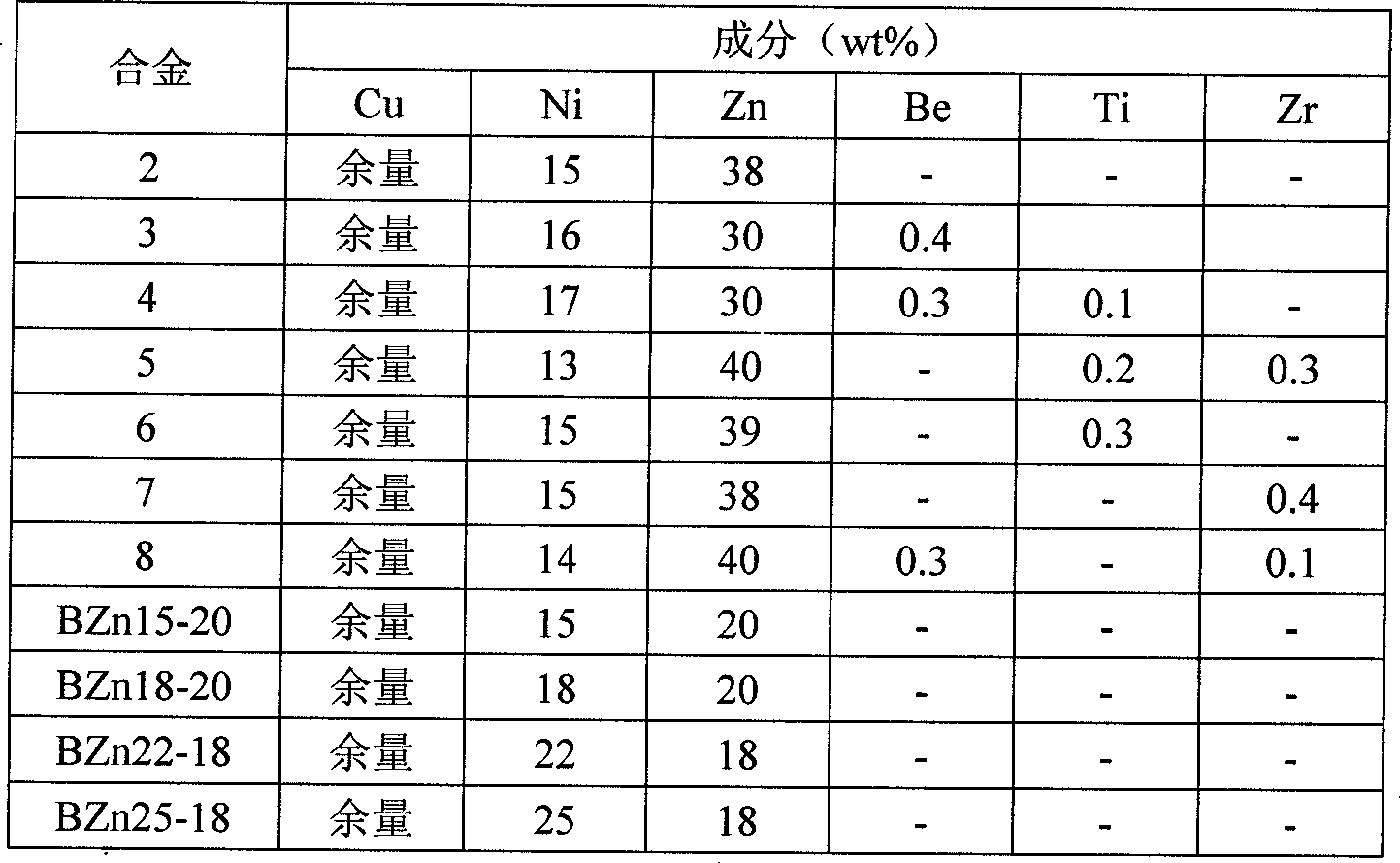
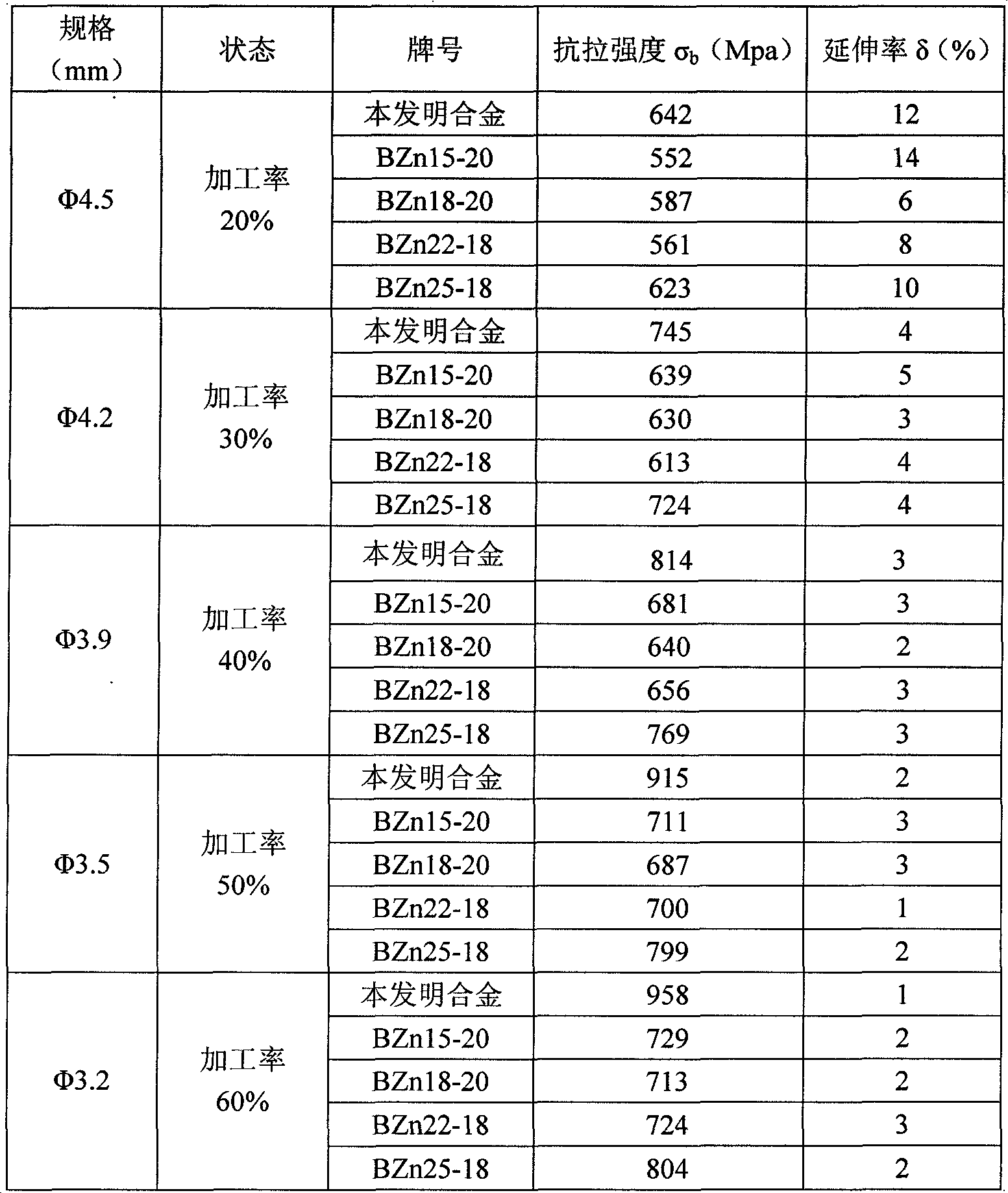
The invention relates to a high-strength zinc-nickel-nickel alloy. The chemical composition of the alloy contains: Zn 38%-45%, Ni 13%-17%, and the balance Cu, wherein the alloy composition includes Cu+Zn+ Ni content ≥ 99.5%. Its chemical composition can also contain: one or two of the three elements Be, Ti, and Zr, and the contents of the three elements of Be, Ti, and Zr are respectively: Be 0%~0.5%, Ti 0%~ 0.5%, Zr 0% ~ 0.4%. The alloy can maintain the corrosion resistance, weldability and color of the original various zinc white copper, and has higher tensile strength; because high zinc and other elements are used to replace part of copper and nickel, the cost of the invented alloy is lower than that of commercial zinc Cupronickel can replace the existing zinc-nickel-nickel copper to make various components; the alloy has good cold and hot processing performance, and can be used to produce pressure-processed products and cast products, which is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NINGBO POWERWAY ALLOY MATERIAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com