Patents
Literature
42results about How to "Low detection efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
LED (Light Emitting Diode) ageing detection screening equipment and method
ActiveCN102172580AExtend detection timeImprove detection efficiencySortingIndividual semiconductor device testingPower flowControl system
The invention discloses LED (Light Emitting Diode) ageing detection screening equipment and method. In the equipment, a push rod is driven by a power device to make each splint press towards a corresponding LED row and a corresponding LED cathode pin is in contact with a corresponding cathode contact, so that electrification of LEDs is realized; meanwhile, detection screening of the LEDs is realized by using a PC (Personal Computer) machine. In the entire ageing process, rated voltage output by a circuit control system is kept at 24V, the rated current output is 50mA, current and voltage input to the LEDs are adjustable, and the rated current and rated voltage are supplied to the ageing of the LEDs for 20-60 minutes; through ageing, LEDs with electrical and process hidden troubles can be eliminated; and after ageing, the power device stops acting on the push rod and each splint returns to an initial position under the action of the acting force of a return spring, so that detection ofLEDs is realized and defective LEDs are eliminated.
Owner:JIANGMEN JIANGHAI DISTRICT KAIHUI PHOTOELECTRIC EQUIP CO LTD
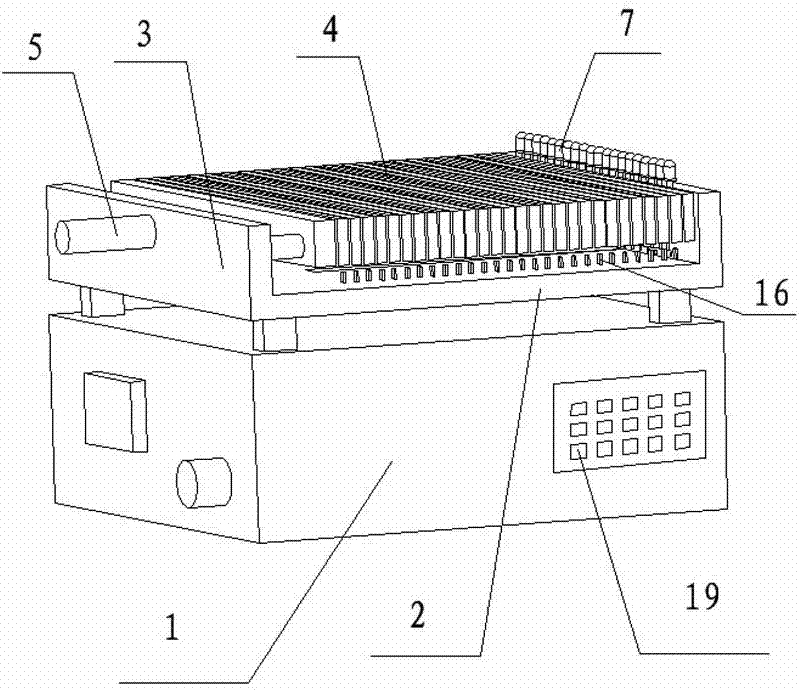
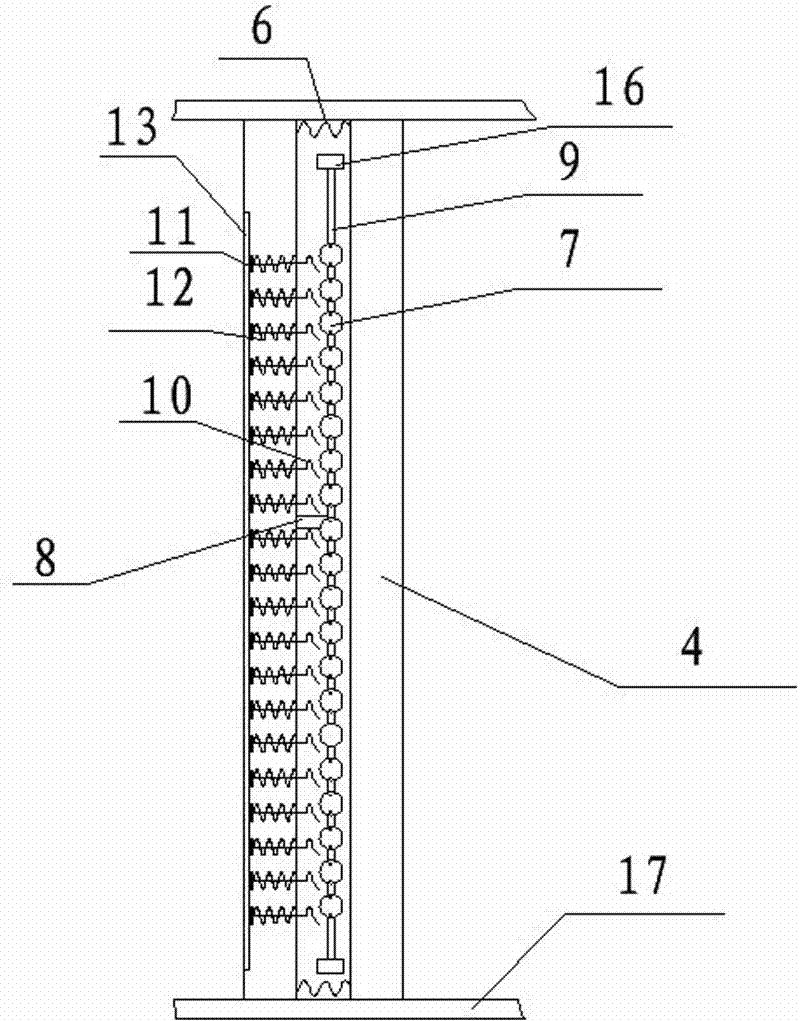
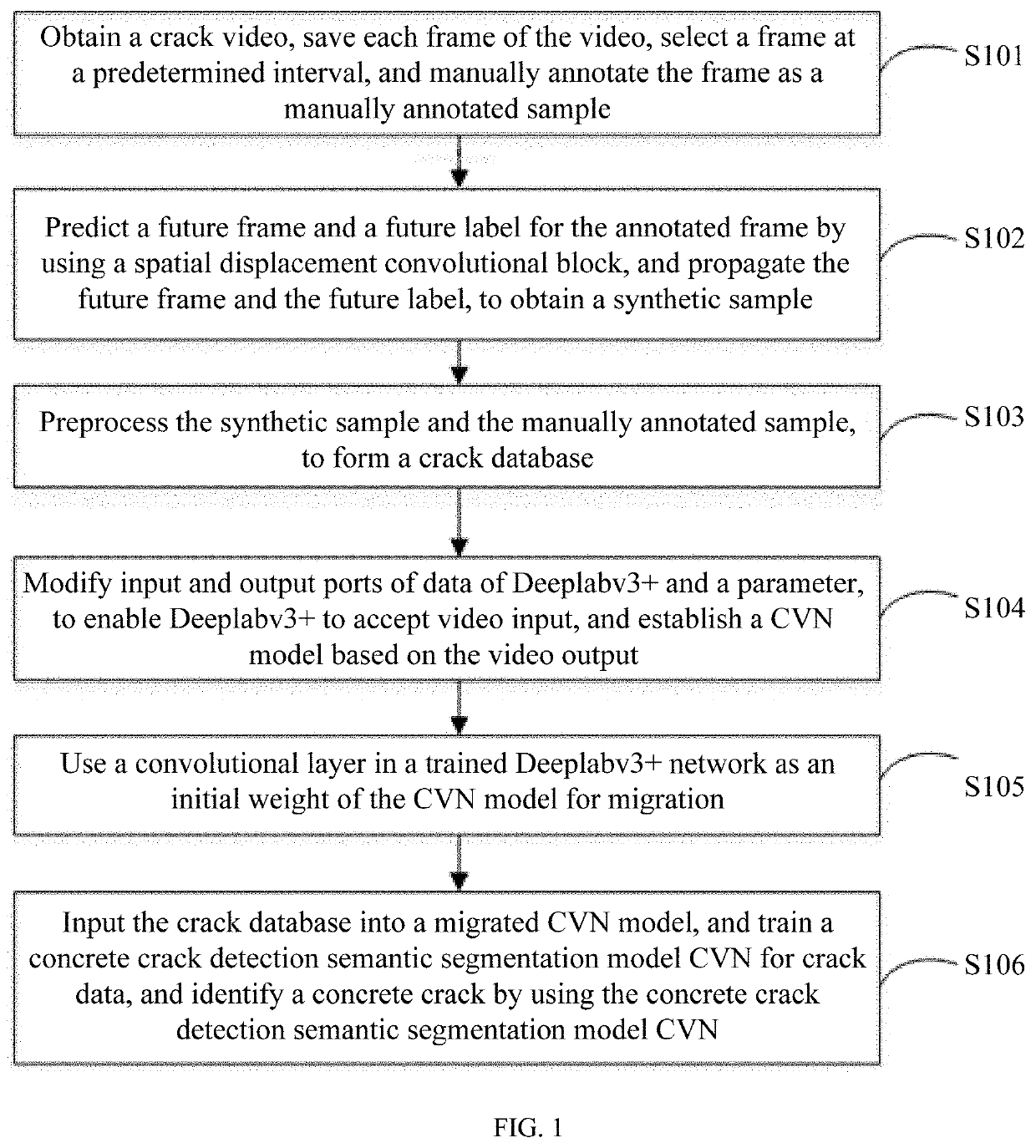
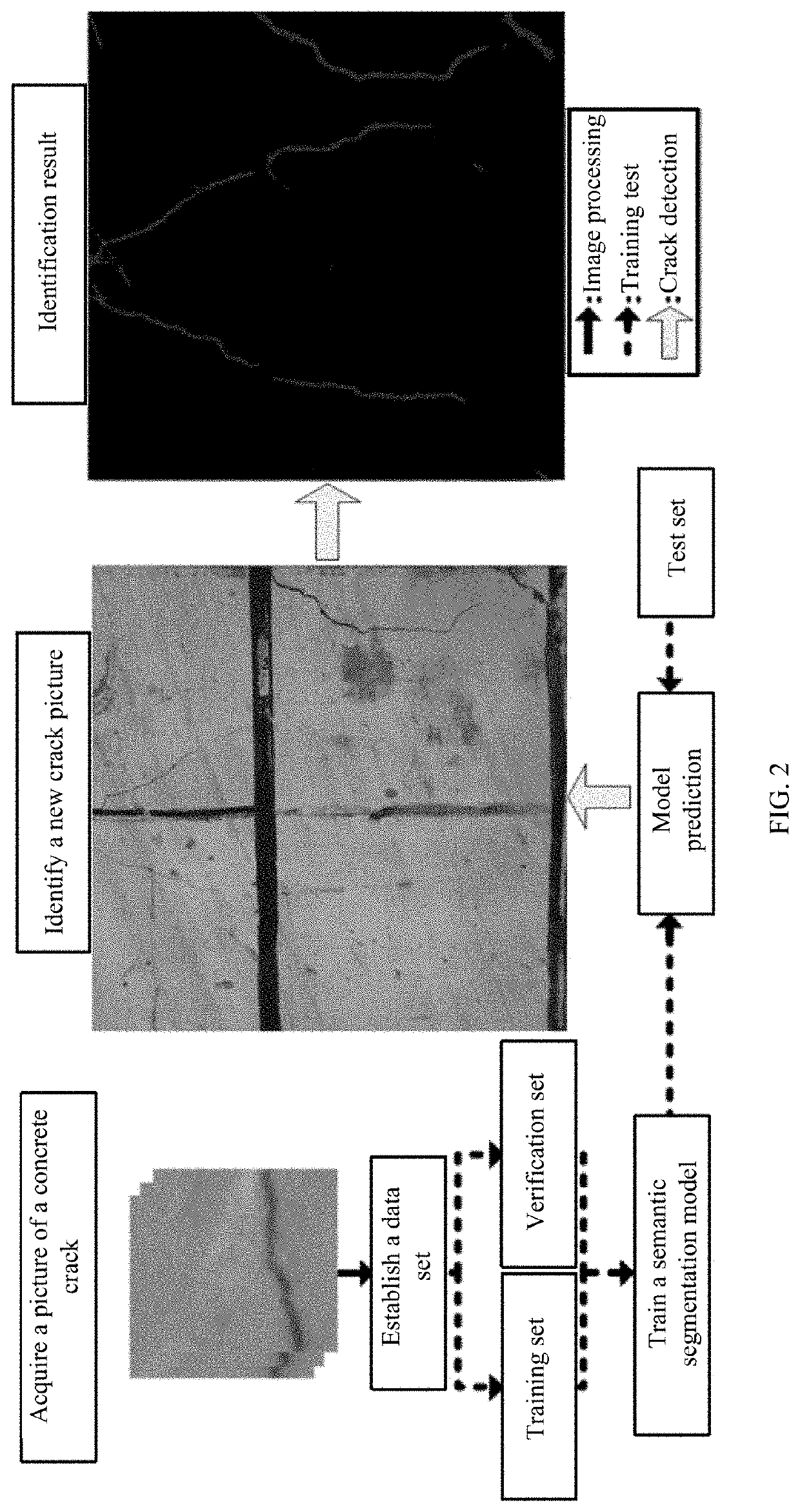
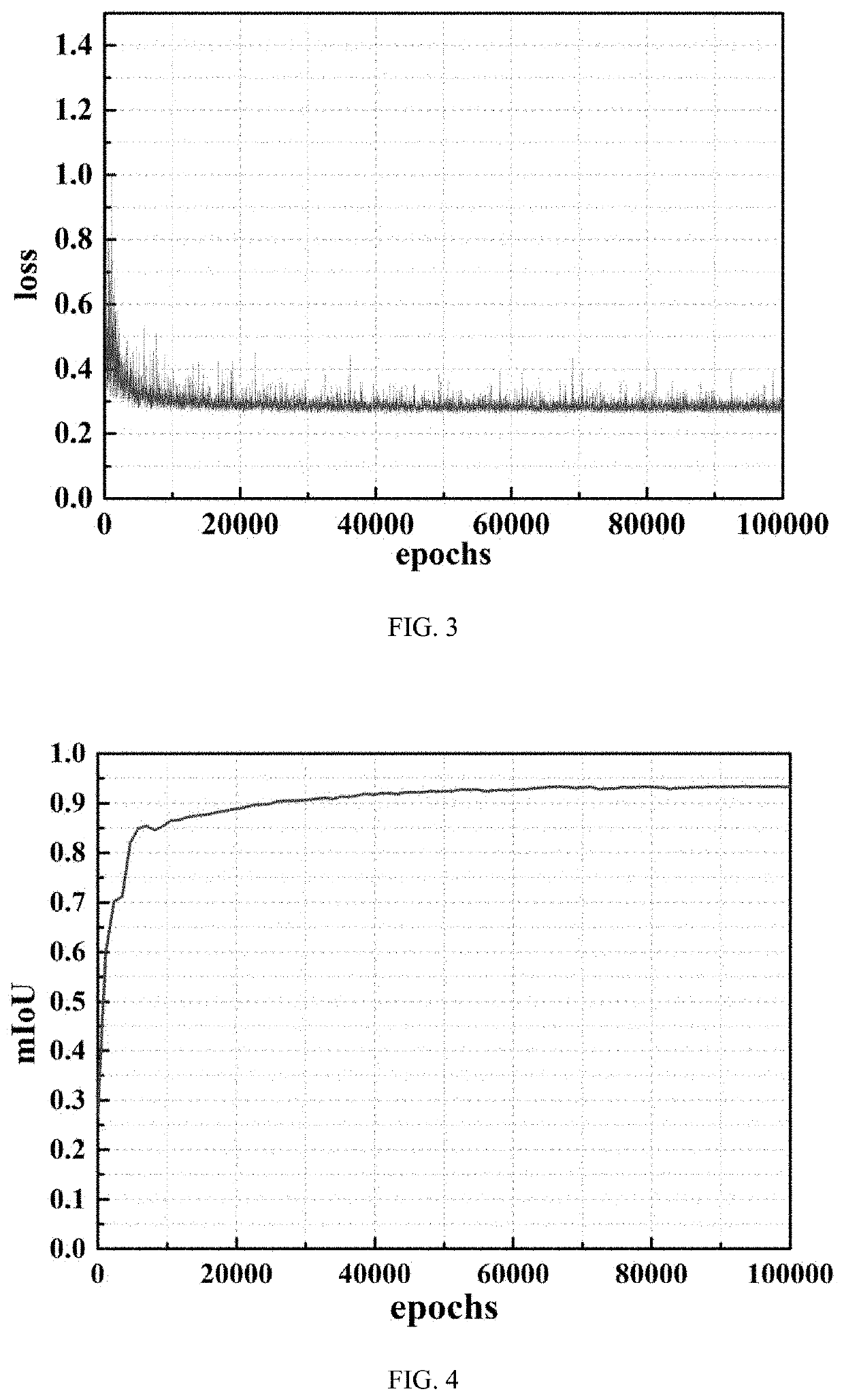
Method and apparatus for identifying concrete crack based on video semantic segmentation technology
ActiveUS20210319547A1High mIoU valueStrong robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionEngineering
A method and apparatus for identifying a concrete crack includes: obtaining a crack video, and manually annotating a video image frame by using a label; predicting a future frame and label for the annotated frame by using a spatial displacement convolutional block, propagating the future frame and label, to obtain a synthetic sample, and preprocessing the synthetic sample, to form a crack database; modifying input and output ports of data of a deep learning model for video semantic image segmentation and a parameter, to enable the deep learning model to accept video input, and establishing a concrete crack detection model based on the video output; using a convolutional layer in a trained deep learning model as an initial weight of the concrete crack detection model for migration; inputting the crack database into a migrated concrete crack detection model, and training the concrete crack detection model for crack data.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
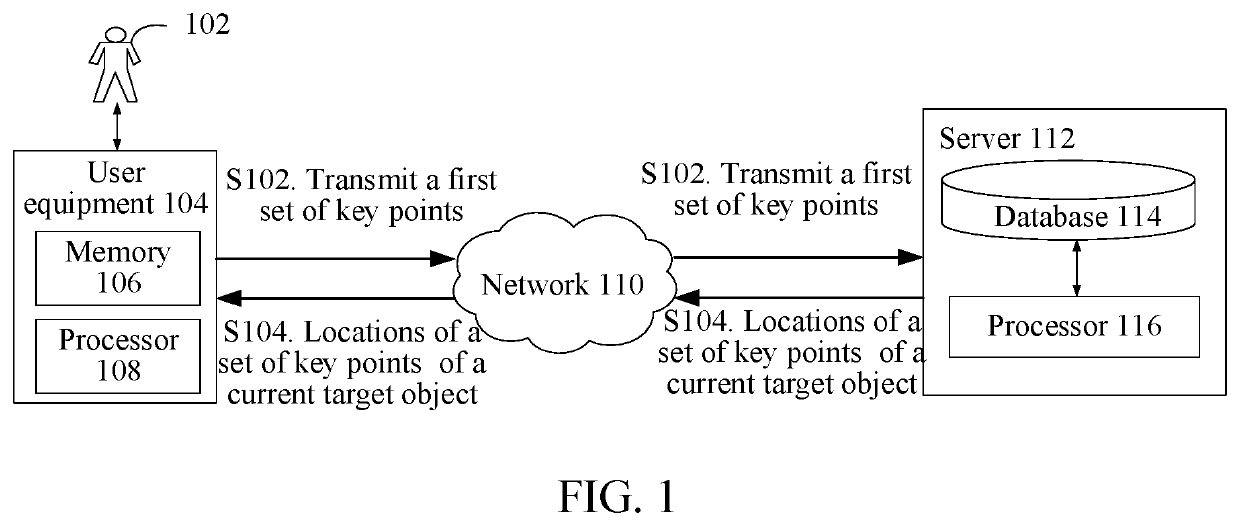
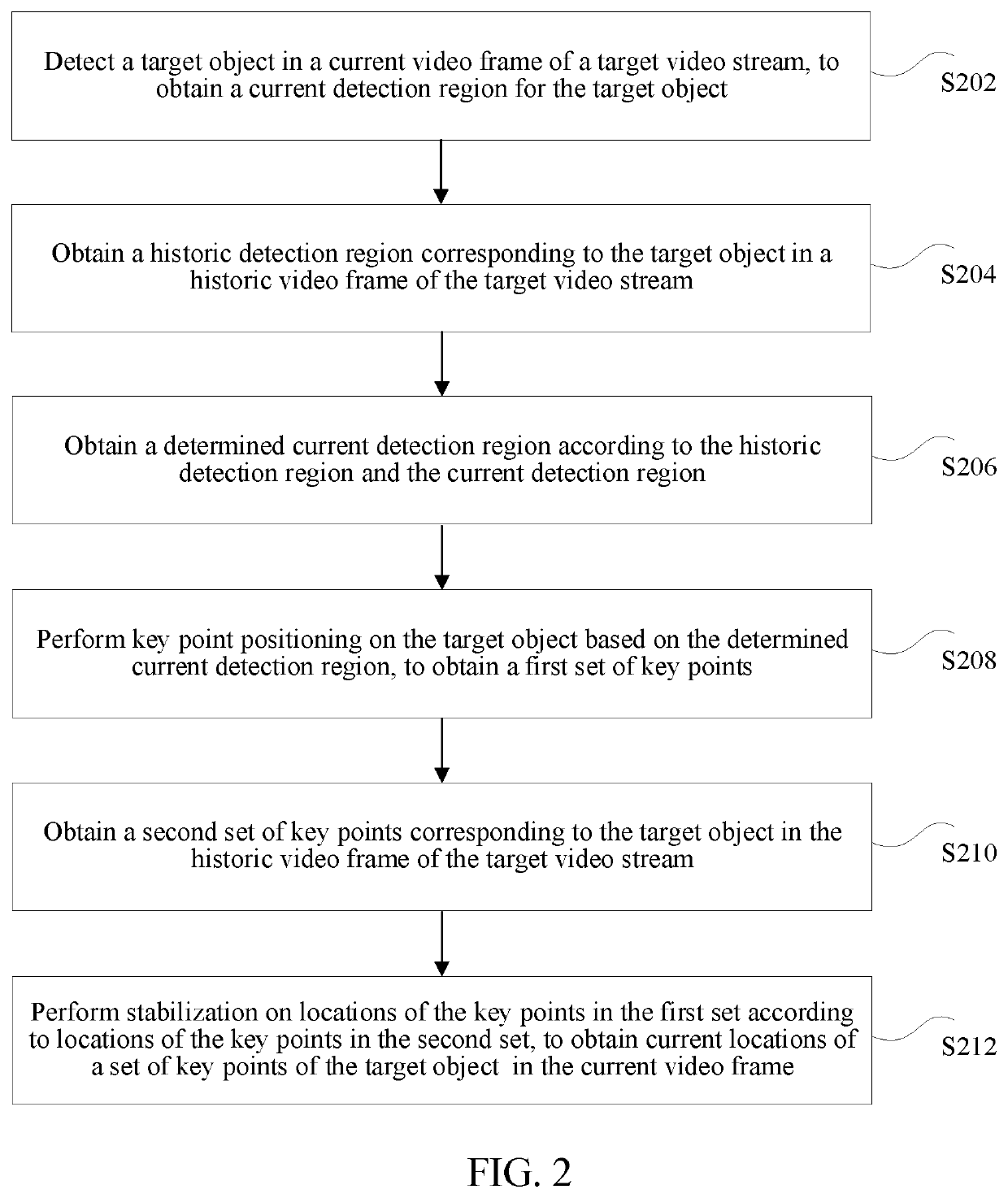
Image processing method and apparatus, and storage medium
ActiveUS20210049395A1High positioning accuracyLow accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
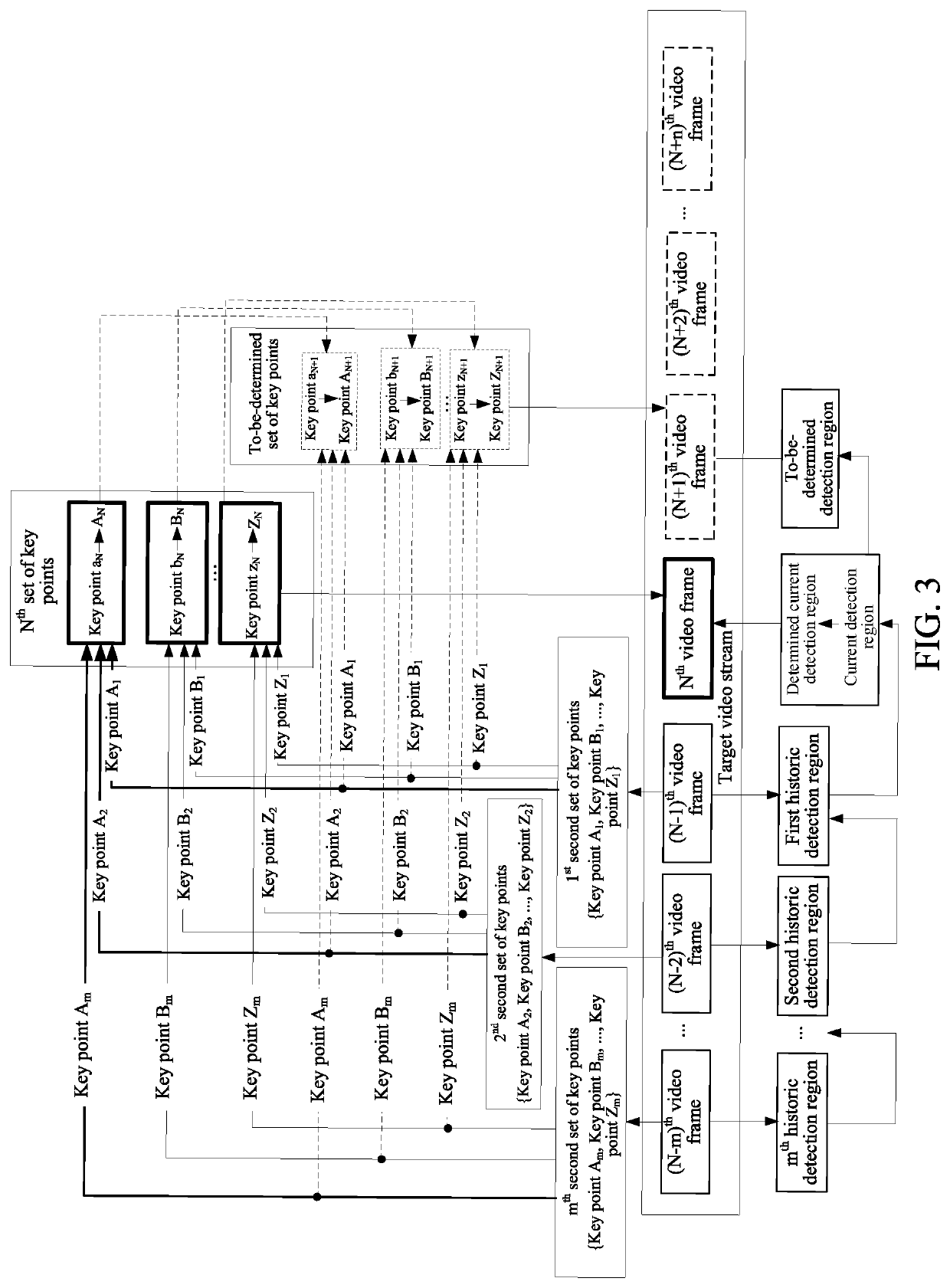
An image processing method and apparatus, and a storage medium are provided. The method includes: detecting a target object in a current video frame of a target video stream, to obtain a current detection region for the target object; adjusting the current detection region according to a historic detection region corresponding to the target object in a historic video frame of the target video stream, to obtain a determined current detection region; performing key point positioning on the target object based on the determined current detection region, to obtain a first set of key points; and performing stabilization on locations of the key points in the first set according to locations of key points in a second set corresponding to the target object in the historic video frame, to obtain current locations of a set of key points of the target object in the current video frame.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Novel dual-energy X-ray imaging detector
ActiveCN103149225AImprove spatial resolutionImprove detection efficiencyMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationFlickering lightEffect light
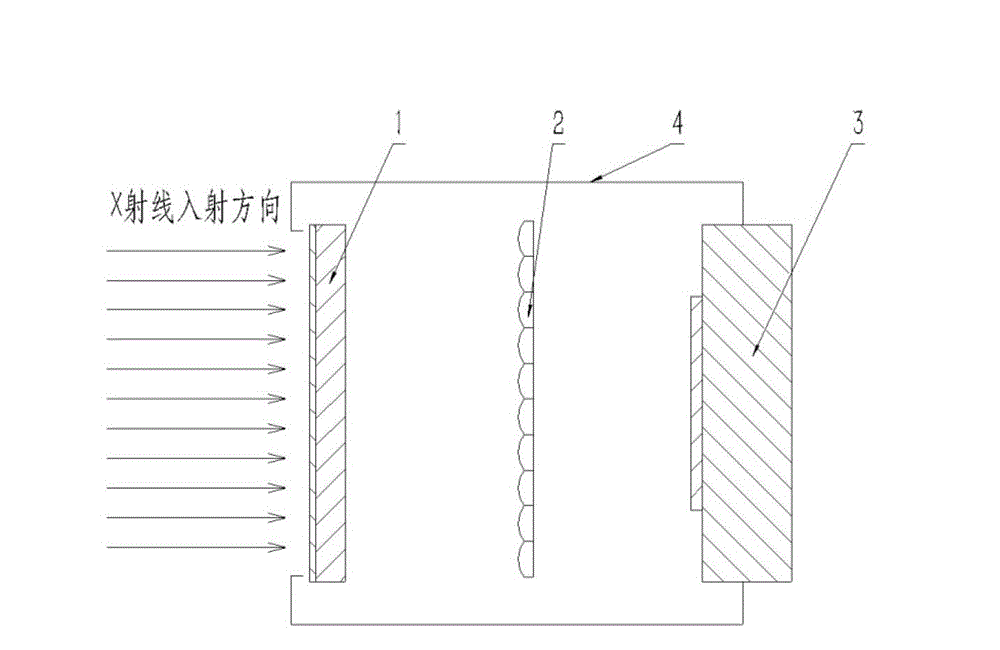
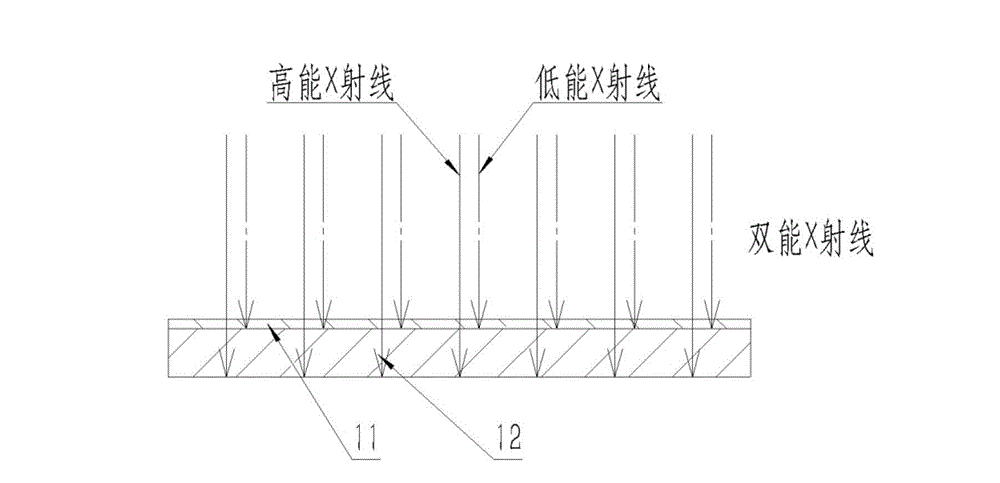
The invention discloses a novel dual-energy X-ray imaging detector. The novel dual-energy X-ray imaging detector comprises a composite flicker body, wherein the composite flicker body is composed of two different sheet flicker bodies. One kind of flicker body is used for absorbing high-energy X-rays in a dual-energy X-ray and producing flickering light. The other kind of flicker body is used for absorbing low-energy X-rays in the dual-energy X-ray and producing flickering light. An optical module is located between the composite flicker body and an imaging sensor. The flicker light produced by the composite flicker body is enabled to form an image on the imaging sensor. The imaging sensor is used for detecting optical field distribution of the image formed on the light-sensitive surface of the imaging sensor and converting the image into a digital image. Three-dimensional spatial distribution information of flicker lighting points is obtained after arithmetic processing is carried out on the digital image. According to the novel dual-energy X-ray imaging detector, image formation of flicker light produced in a flicker body of a continuous structure is available, and the problems that high system complexity and low detection efficiency and the like caused by an independent flicker body array structure are solved.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
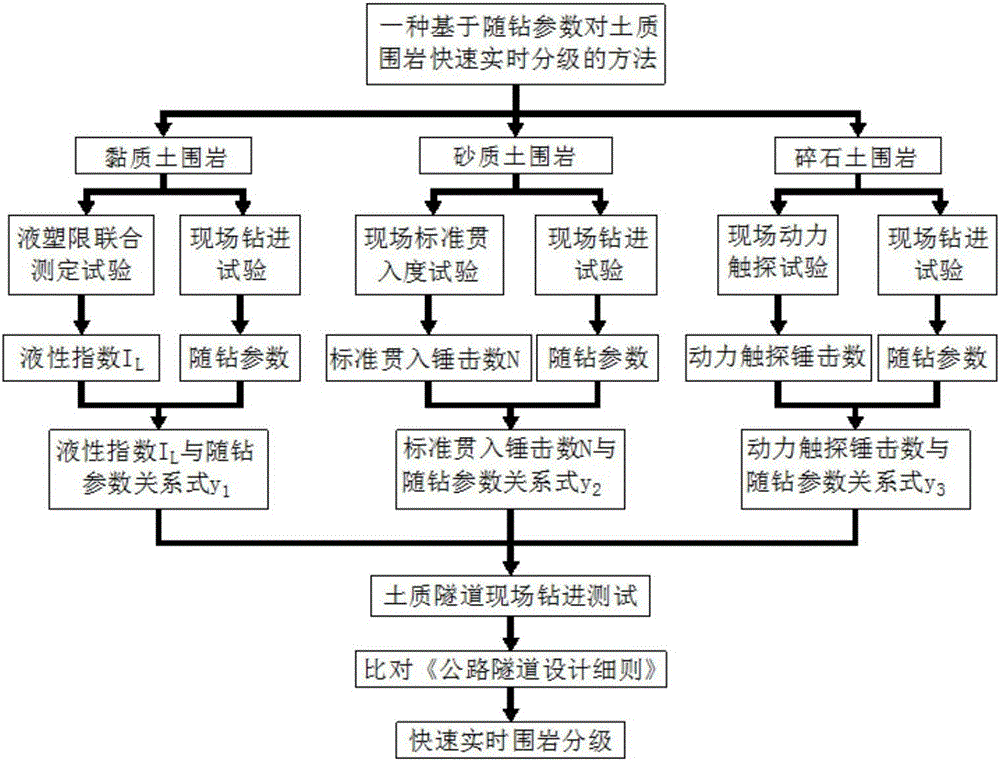
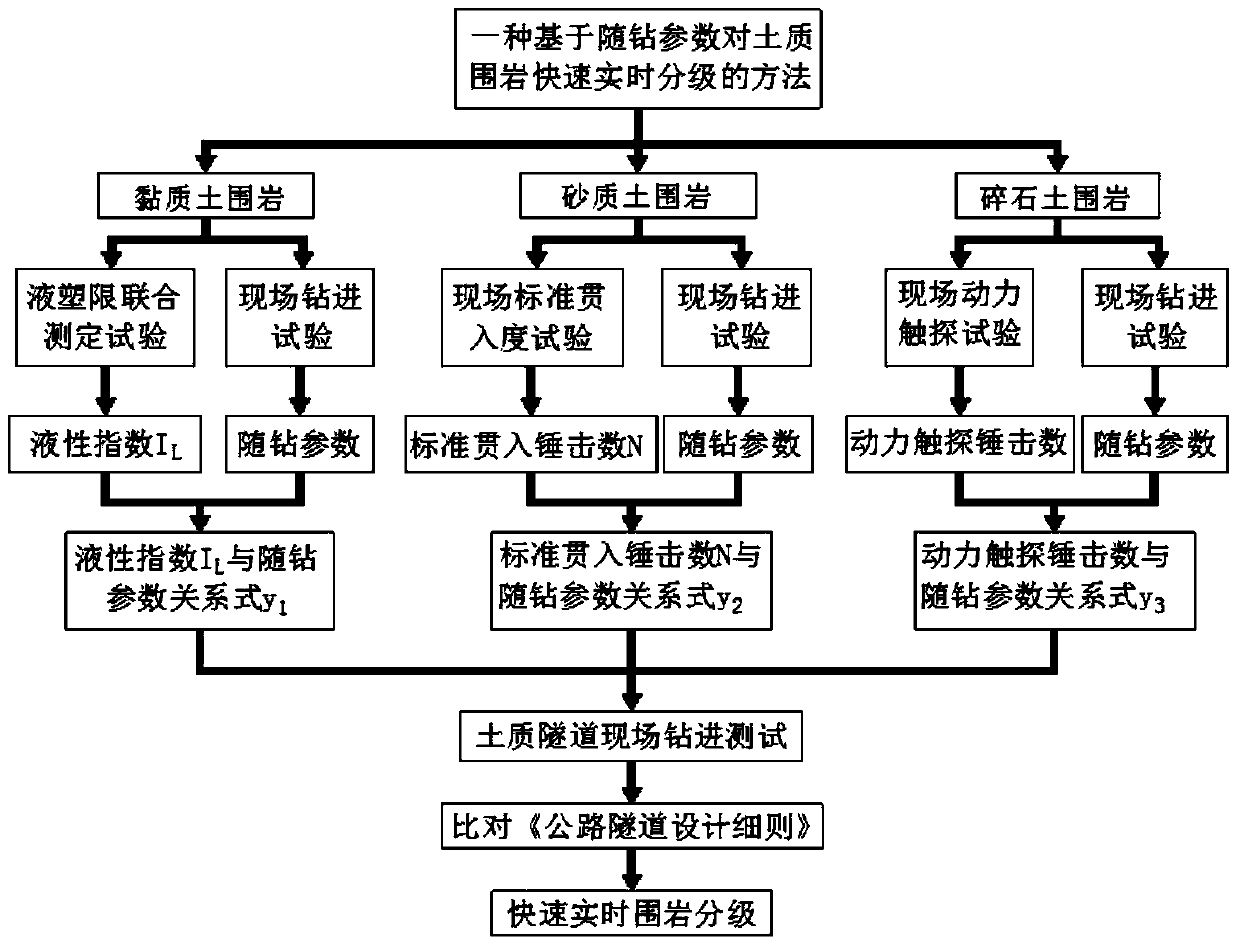
Method for quickly grading terrene surrounding rock in real time on basis of while-drilling parameters
ActiveCN106157181ASolve problems that cannot be used in one wayAvoid disturbanceData processing applicationsGuidelineSoil science
The invention discloses a method for quickly grading terrene surrounding rock in real time on the basis of while-drilling parameters. The relational expression between a clay soil liquidity index and the while-drilling parameters, the relational expression between the sandy soil standard penetration hammering number and the while-drilling parameters and the relational expression between the gravel soil dynamic sounding hammering number and while-drilling parameters can be established, in actual underground engineering, the soil variety of a terrene tunnel is firstly judged, drilling detection is conducted, the obtained while-drilling parameters are substituted into the relational expressions to obtain the liquidity index I<L> of clay soil surrounding rock, the standard penetration hammering number N of sandy soil surrounding rock and the dynamic sounding hammering number N<63.5> of gravel soil surrounding rock, and then quick and real-time grading is conducted on the surrounding rock in front of a tunnel face according to the Guidelines for Design of Highway Tunnel. According to the method for quickly grading the terrene surrounding rock in real time on the basis of the while-drilling parameters, only drilling testing needs to be conducted on the surrounding rock through a drilling machine at an engineering site, other tedious indoor tests or site tests are not needed, quick and real-time grading is conducted on the terrene surrounding rock, the grading efficiency is high, and operation is easy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
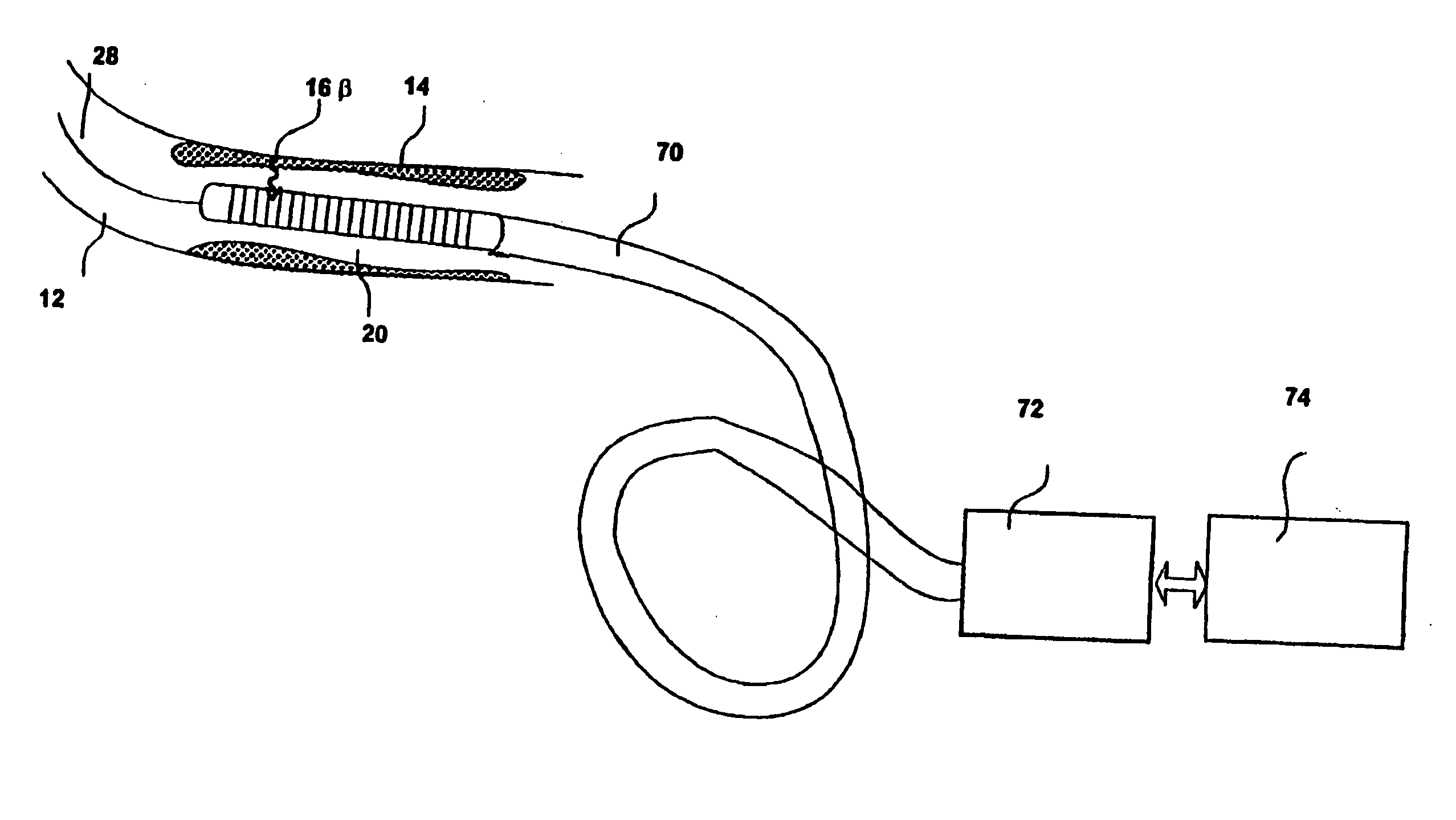
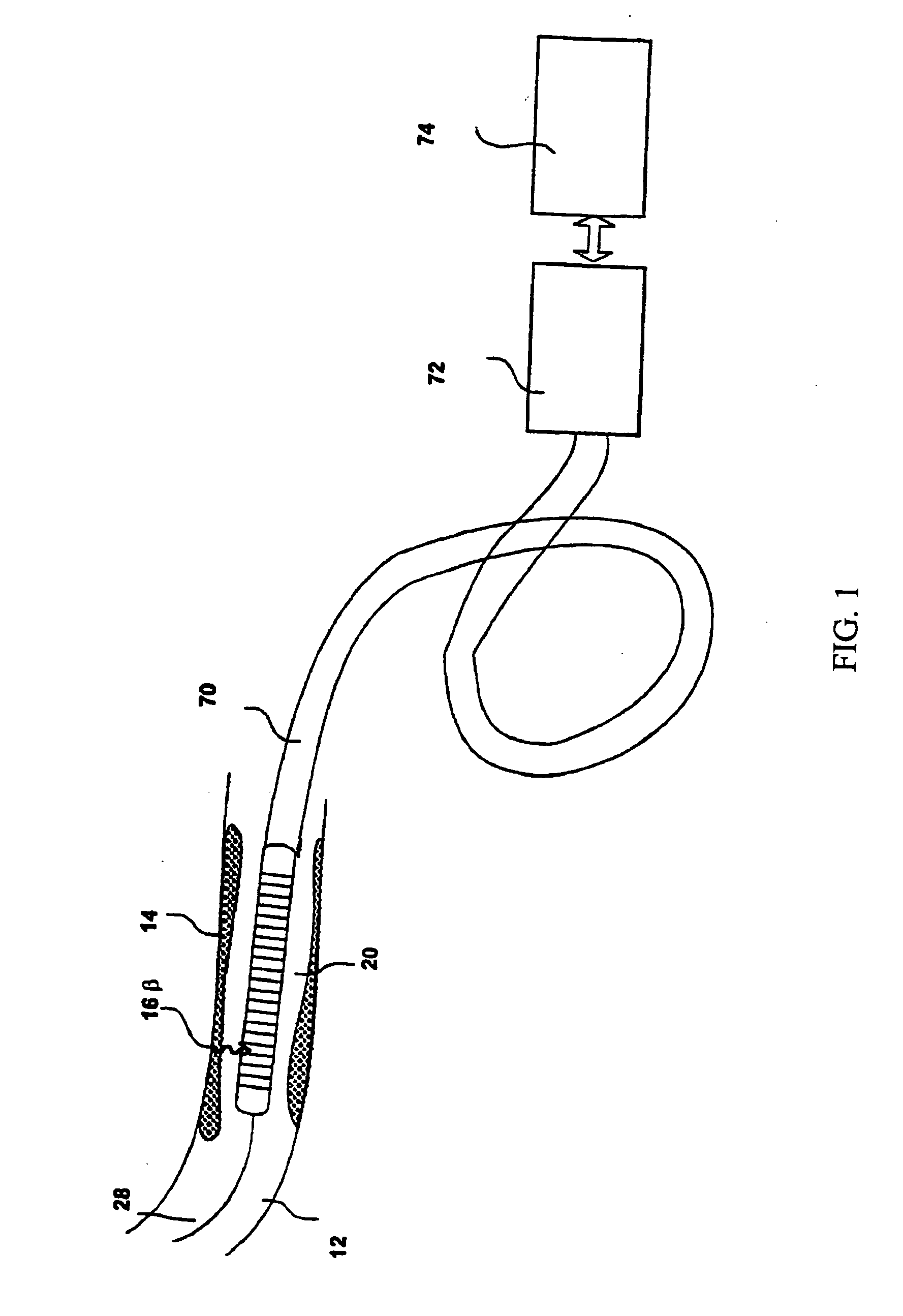
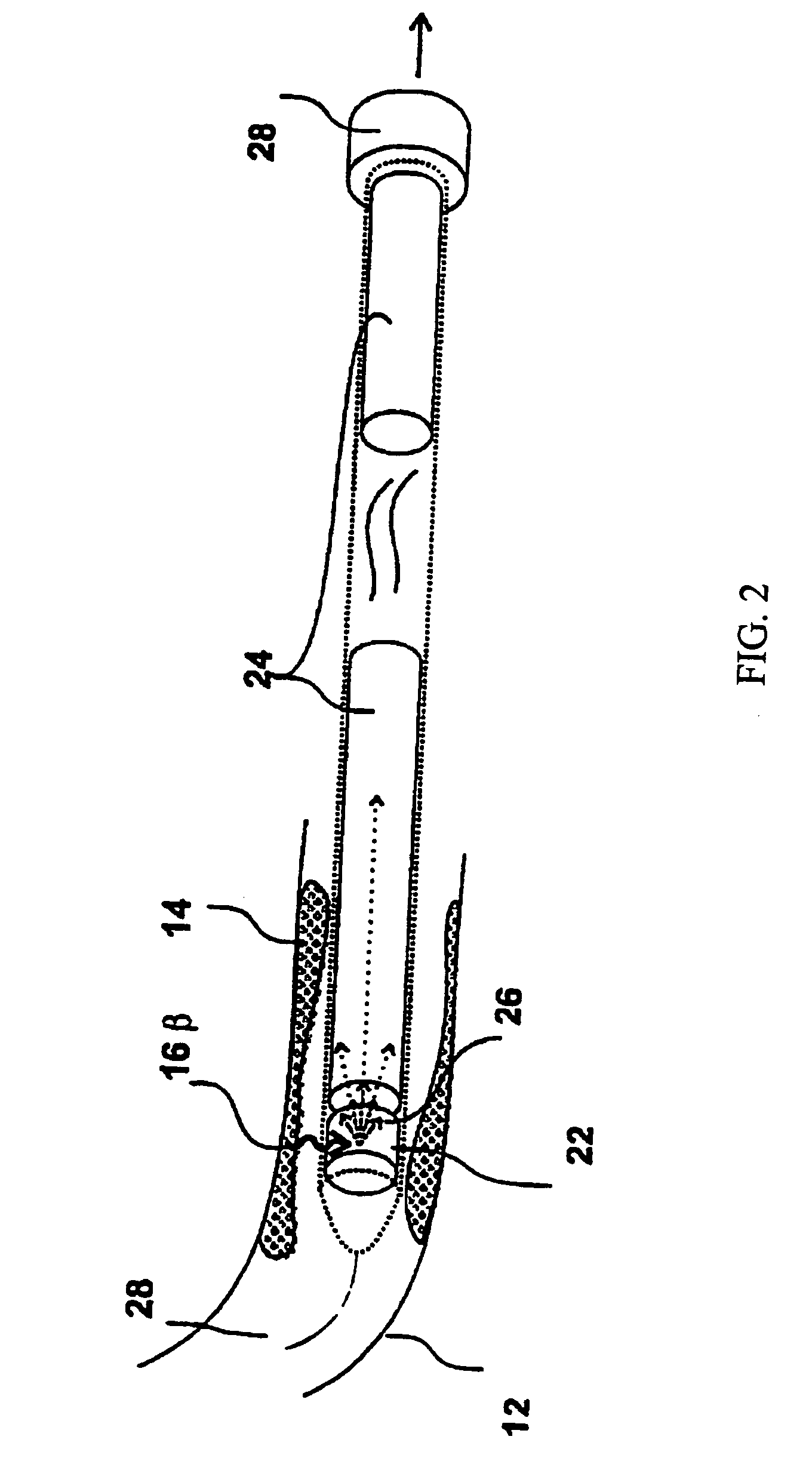
Intravascular imaging detector
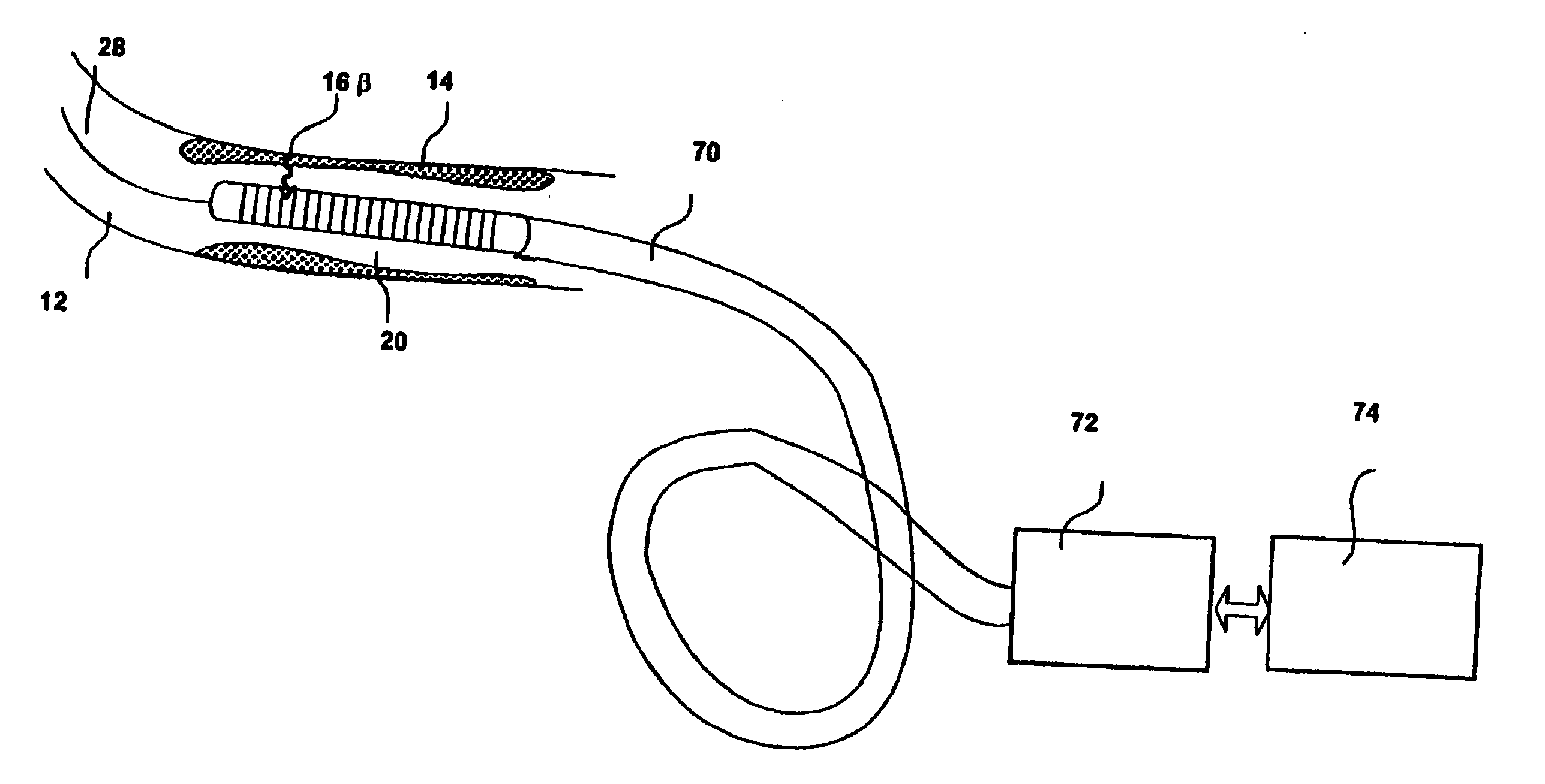
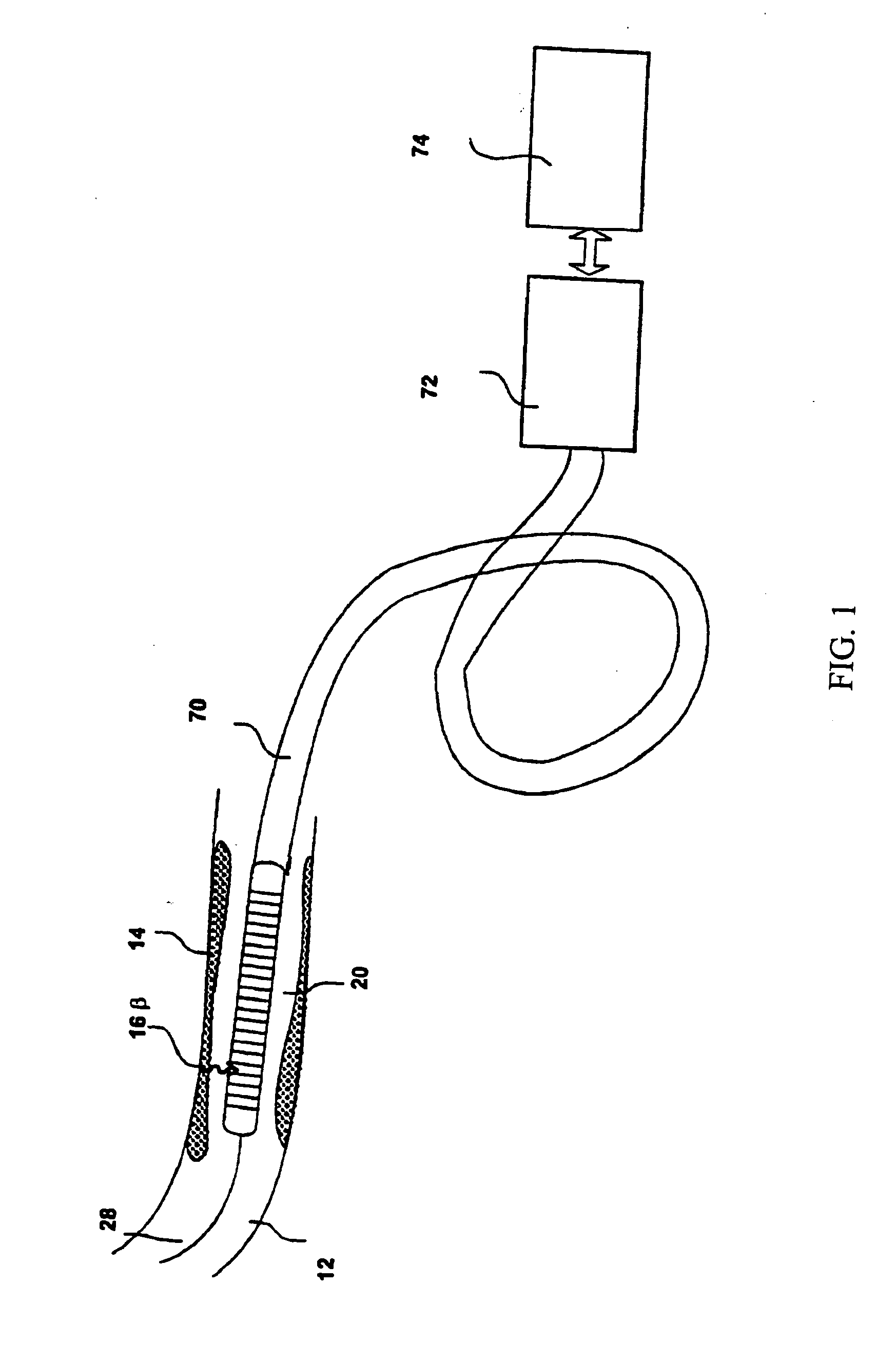
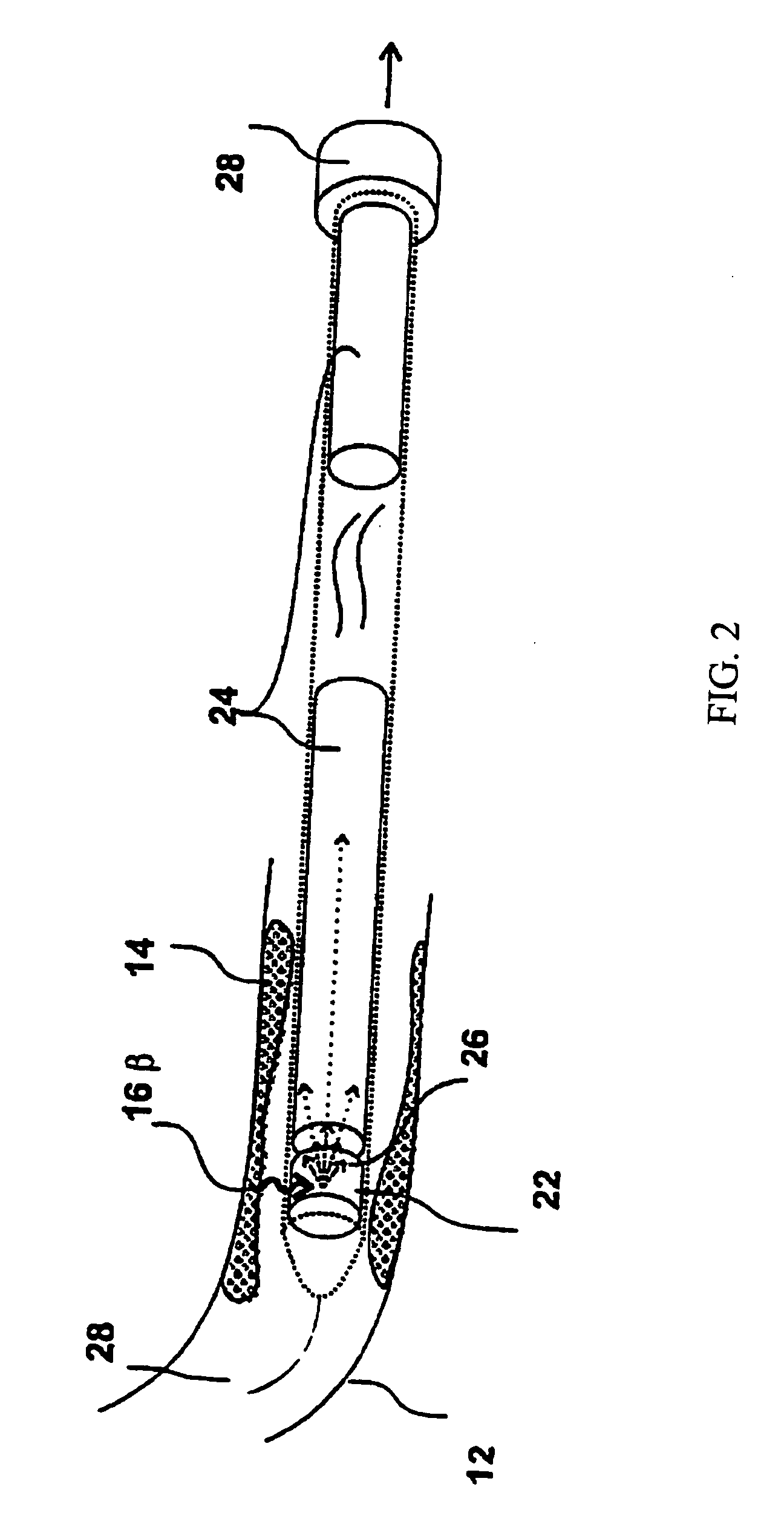
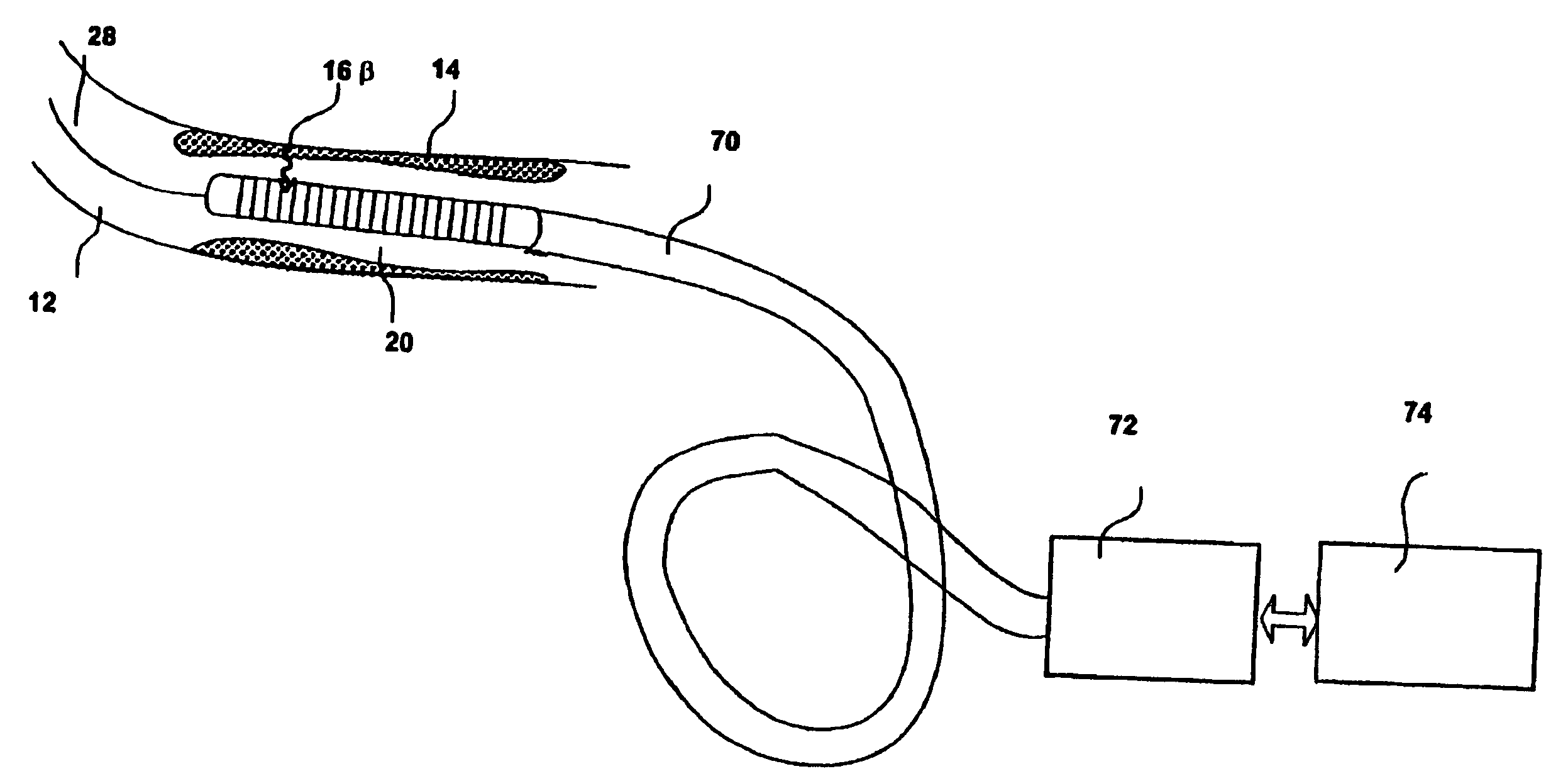
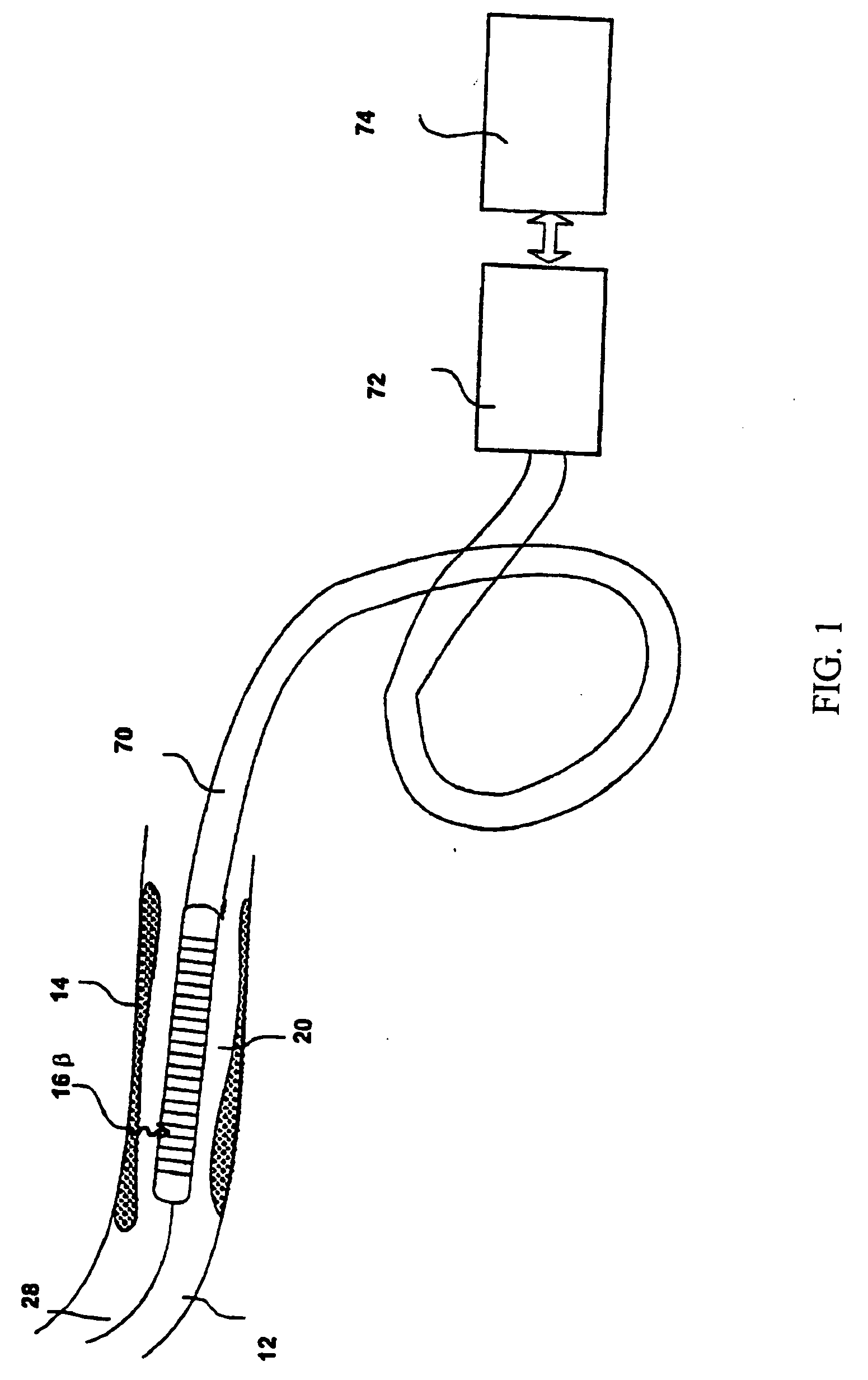
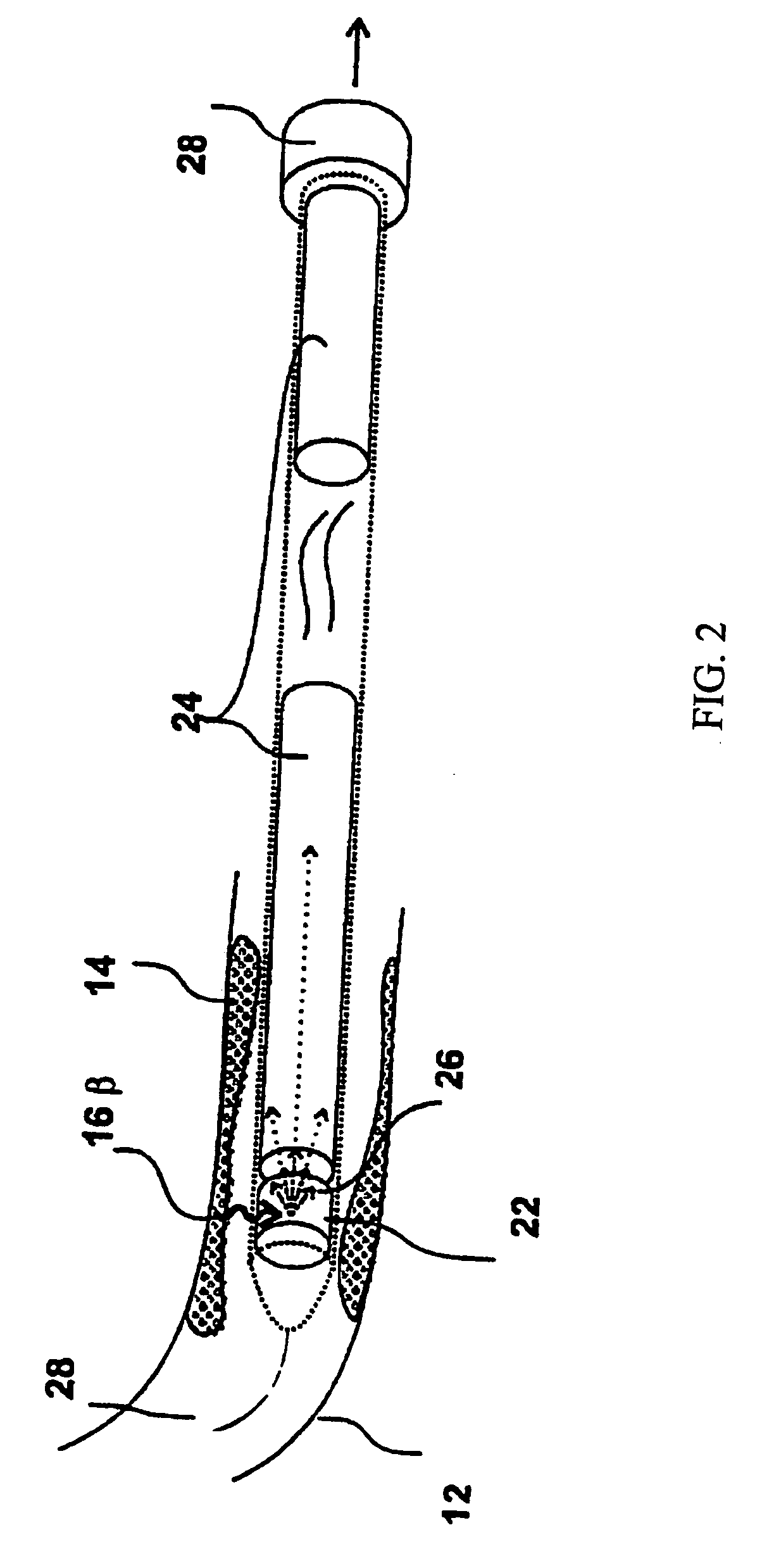
InactiveUS20060178577A1Addressing Insufficient SensitivitySolve the low detection efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood vesselIntravascular imaging
An apparatus for intravascular imaging to detect and characterize early stage, unstable coronary arty plaques. The detector works by identifying and localizing plaque-binding beta-emitting radiopharmaceuticals.
Owner:CMR NAVISCAN CORP +1
Intravascular imaging detector
InactiveUS20060195032A1Solve the low detection efficiencyAddressing Insufficient SensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood vesselIntravascular imaging
An apparatus for intravascular imaging to detect and characterize early stage, unstable coronary arty plaques. The detector works by identifying and localizing plaque-binding beta-emitting radiopharmaceuticals.
Owner:GAMMA MEDICA +1
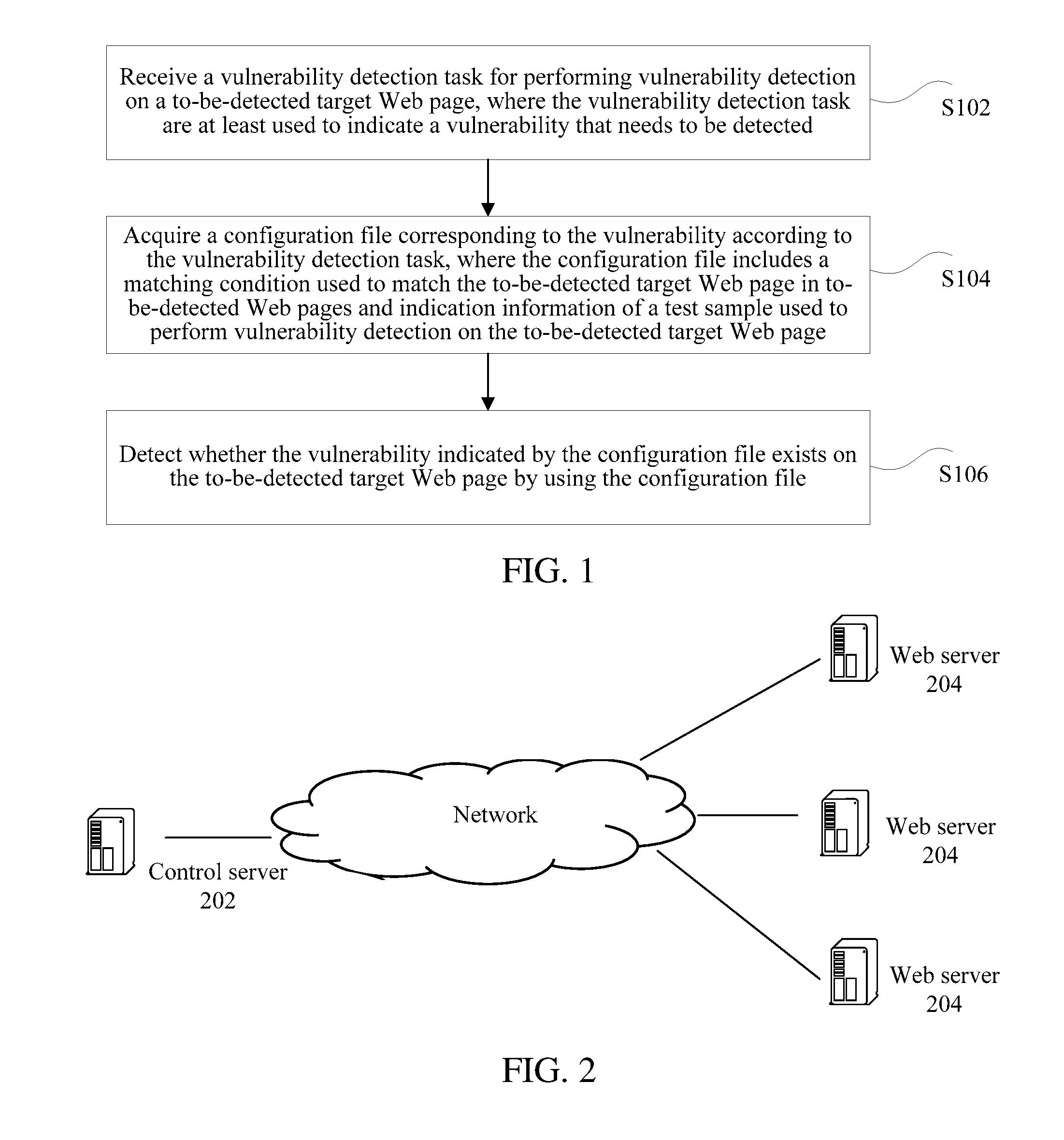
Web page vulnerability detection method and apparatus
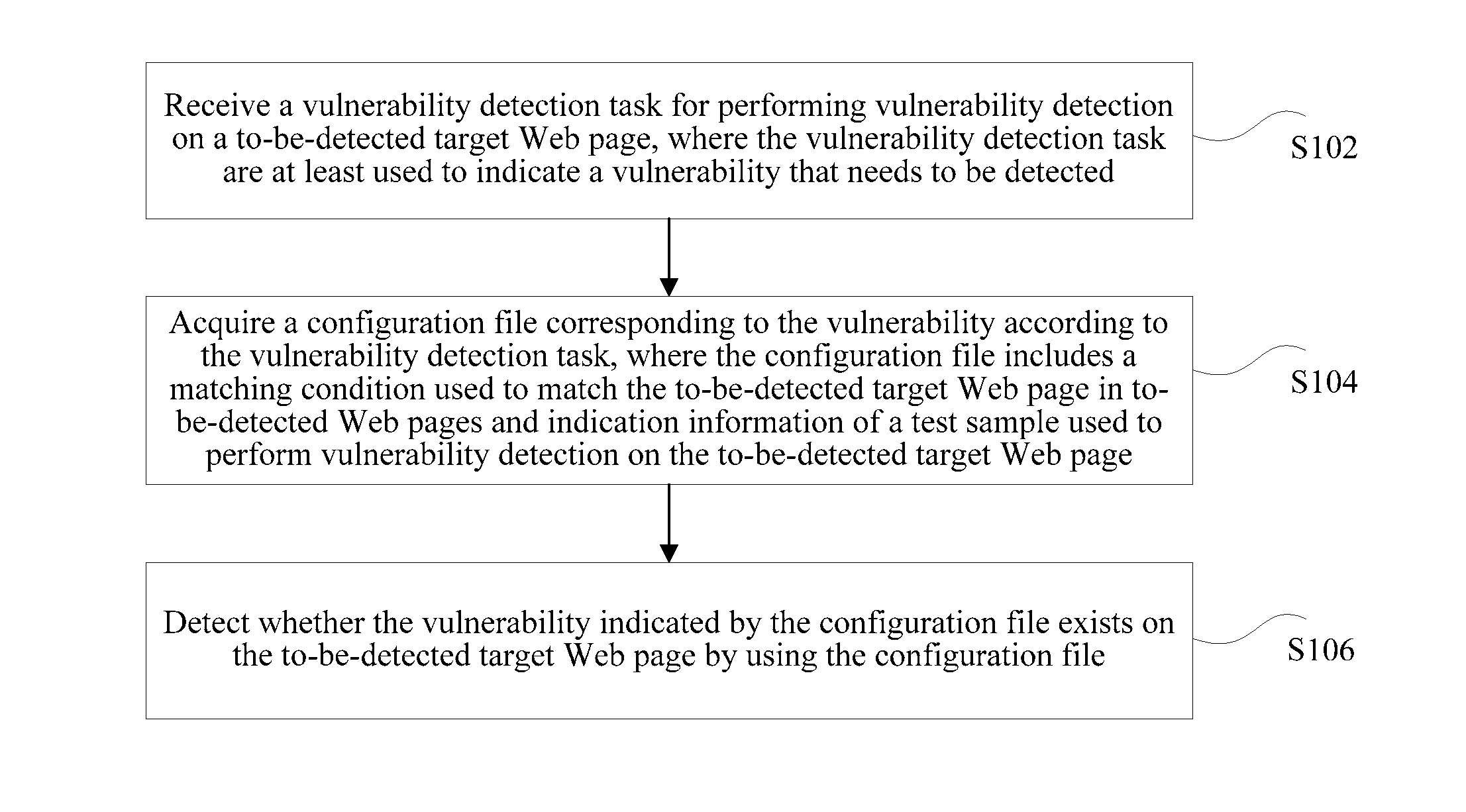
ActiveUS20160337392A1Improve efficiencySave time and costPlatform integrity maintainanceWebsite content managementTest sampleWeb page
A Web page vulnerability detection method and apparatus are described, where the method can receive a vulnerability detection task for performing vulnerability detection on a to-be-detected target Web page; acquiring a configuration file corresponding to the vulnerability according to the vulnerability detection task. The vulnerability detection task being is at least used to indicate a vulnerability that needs to be detected, and the configuration file includes a matching condition used to match the to-be-detected target Web page in to-be-detected Web pages and indication information of a test sample used to perform vulnerability detection on the to-be-detected target Web page. The method also detects whether the vulnerability indicated by the configuration file exists on the to-be-detected target Web page by using the configuration file.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
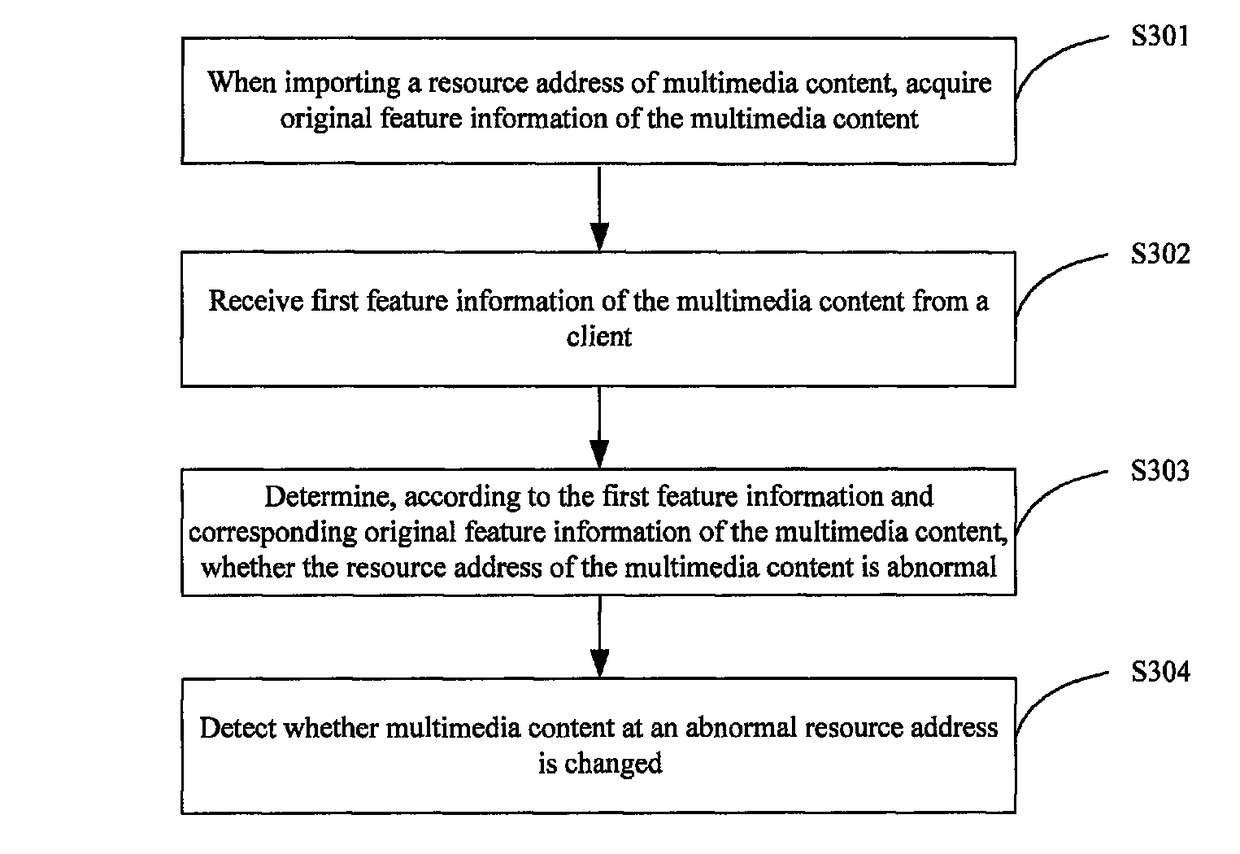
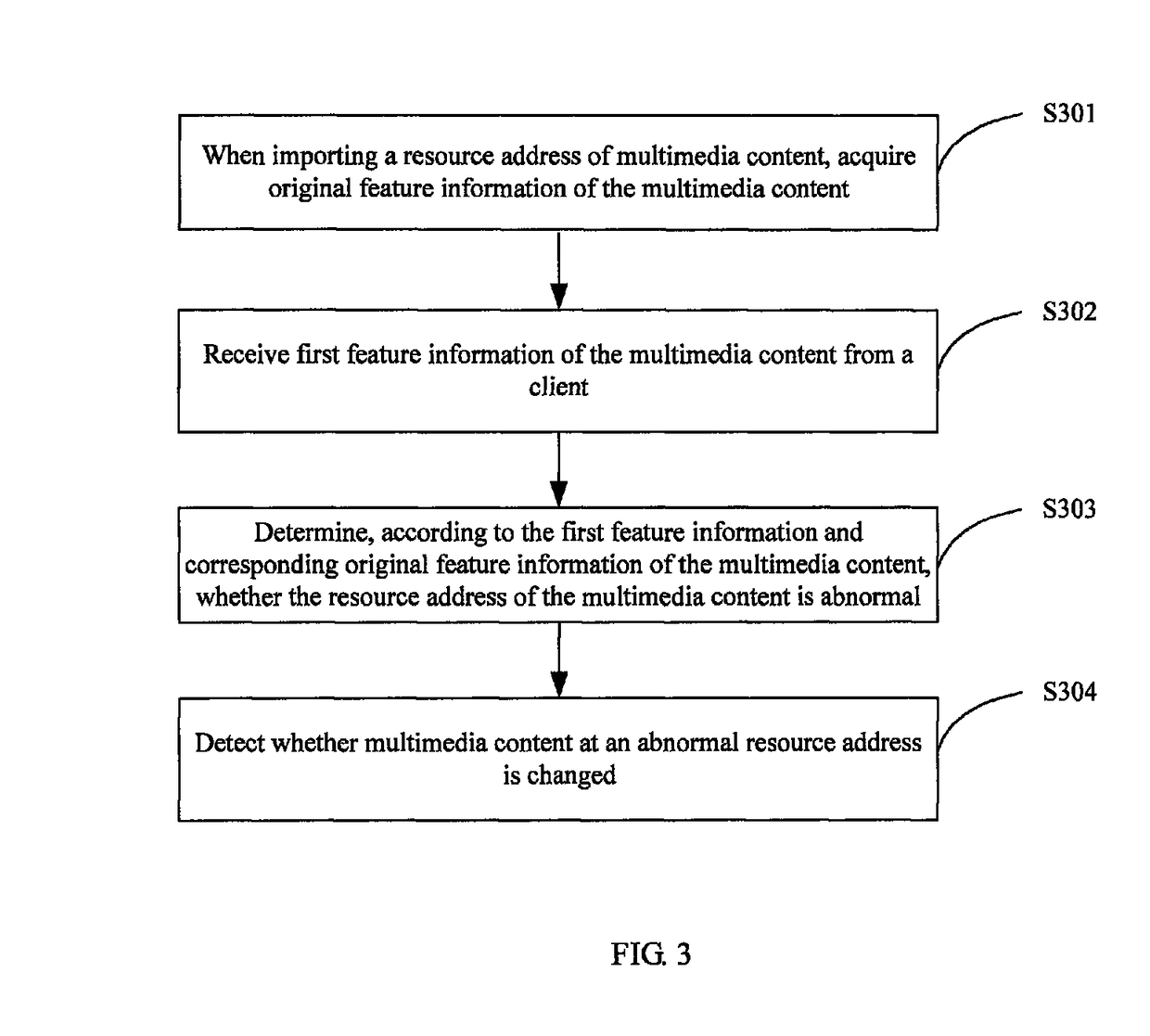
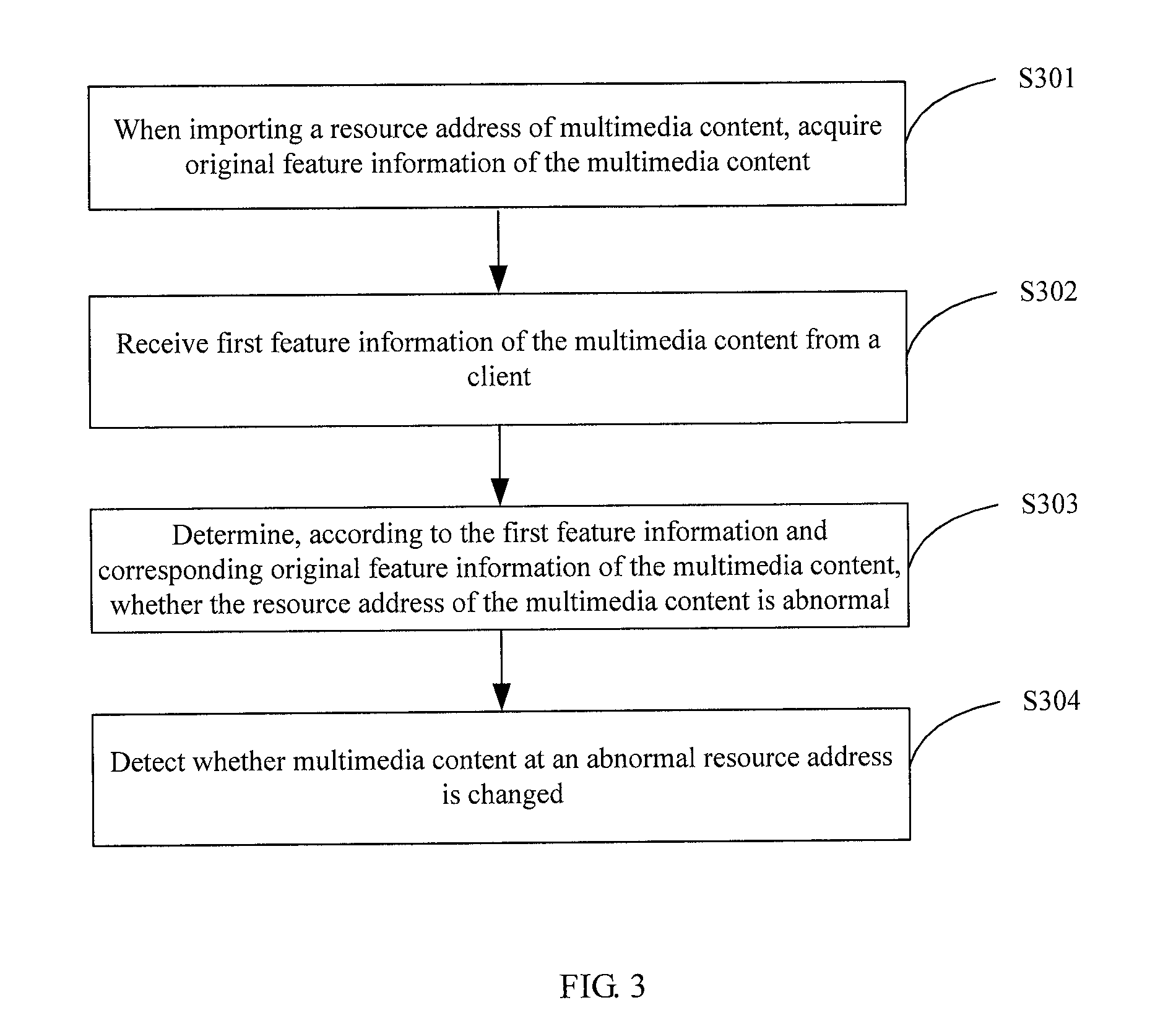
Method and apparatus for detecting multimedia content change, and resource propagation system
A method and apparatus for detecting a multimedia content change, and a resource propagation system. The method comprises: when importing a resource address of multimedia content, acquiring original feature information of the multimedia content; receiving first feature information of the multimedia content from a client; determining, according to the first feature information and corresponding original feature information of the multimedia content, whether the resource address of the multimedia content is abnormal; and detecting whether multimedia content at an abnormal resource address is changed. It is firstly determined whether a resource address corresponding to multimedia content is abnormal, and if the resource address is abnormal, then it is determined whether the multimedia content corresponding to the resource address is changed, thereby preventing repeated checking of a large number of normal resource addresses, improving the detection efficiency, and reducing the detection cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN DEV PROMOTION CENT FOR ENTERPRISES
Neutron energy spectrum measuring device and Bonner sphere spectrometer system
ActiveCN109799527AImprove counting effectAccurate countNeutron radiation measurementNeutron converterBonner sphere
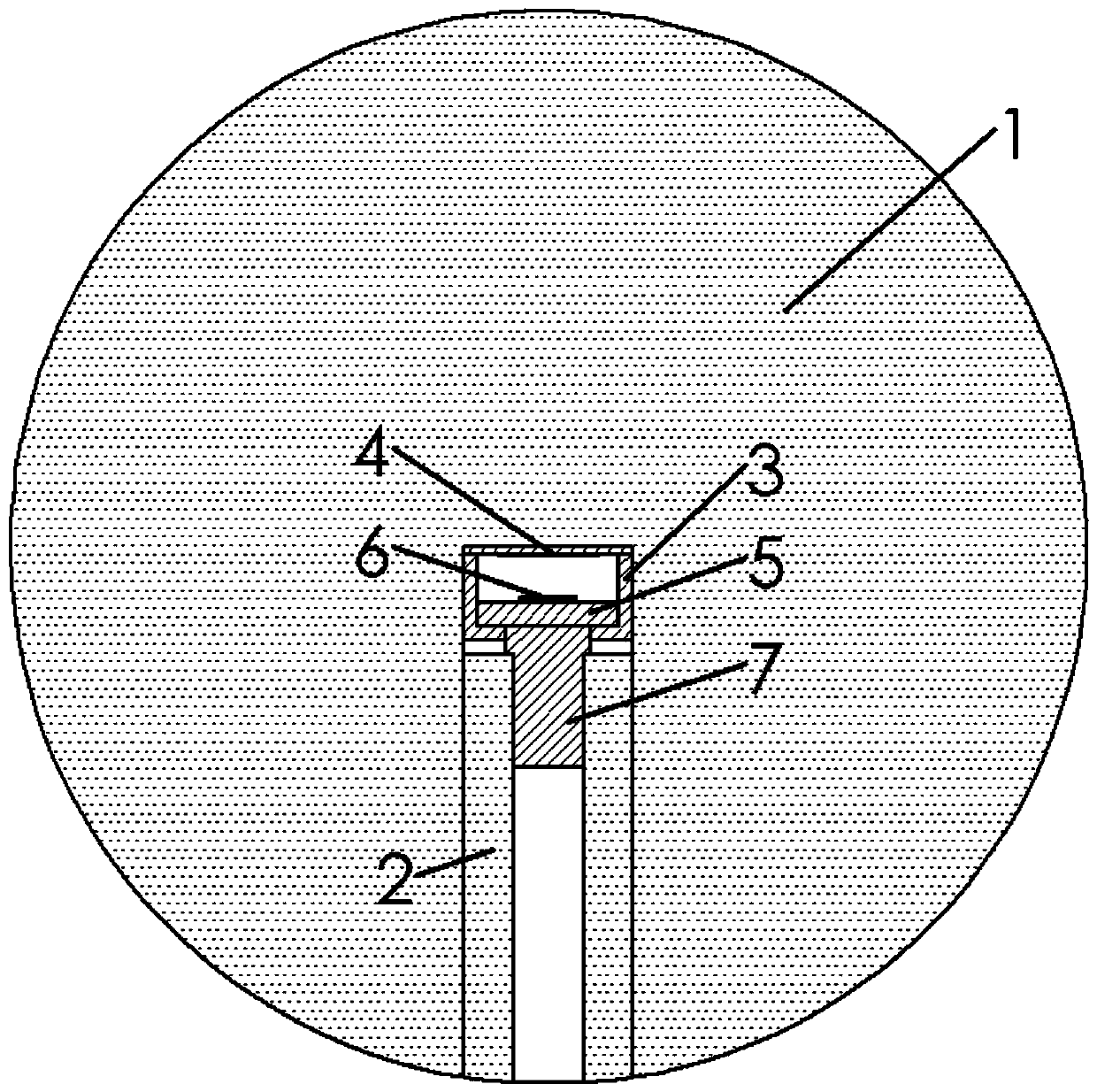
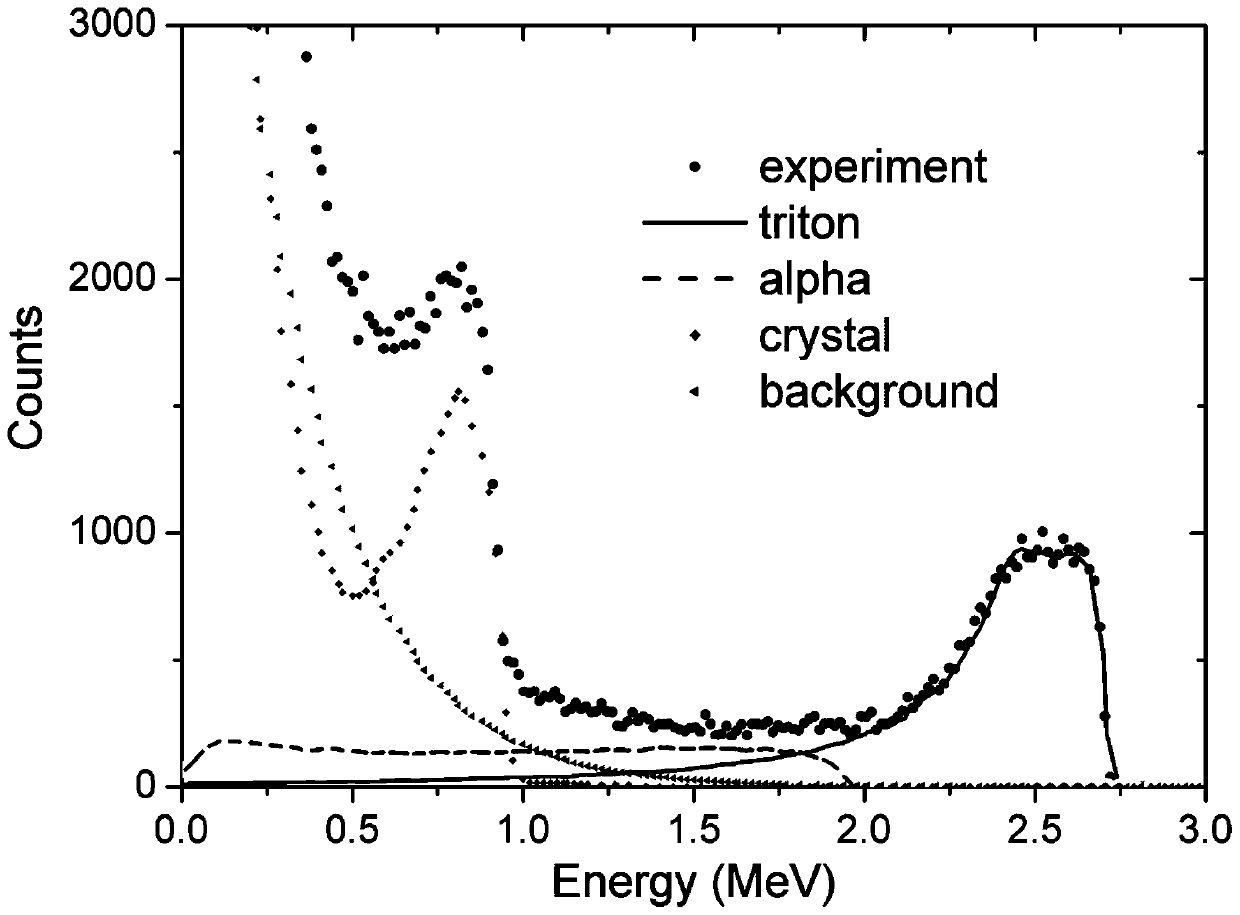
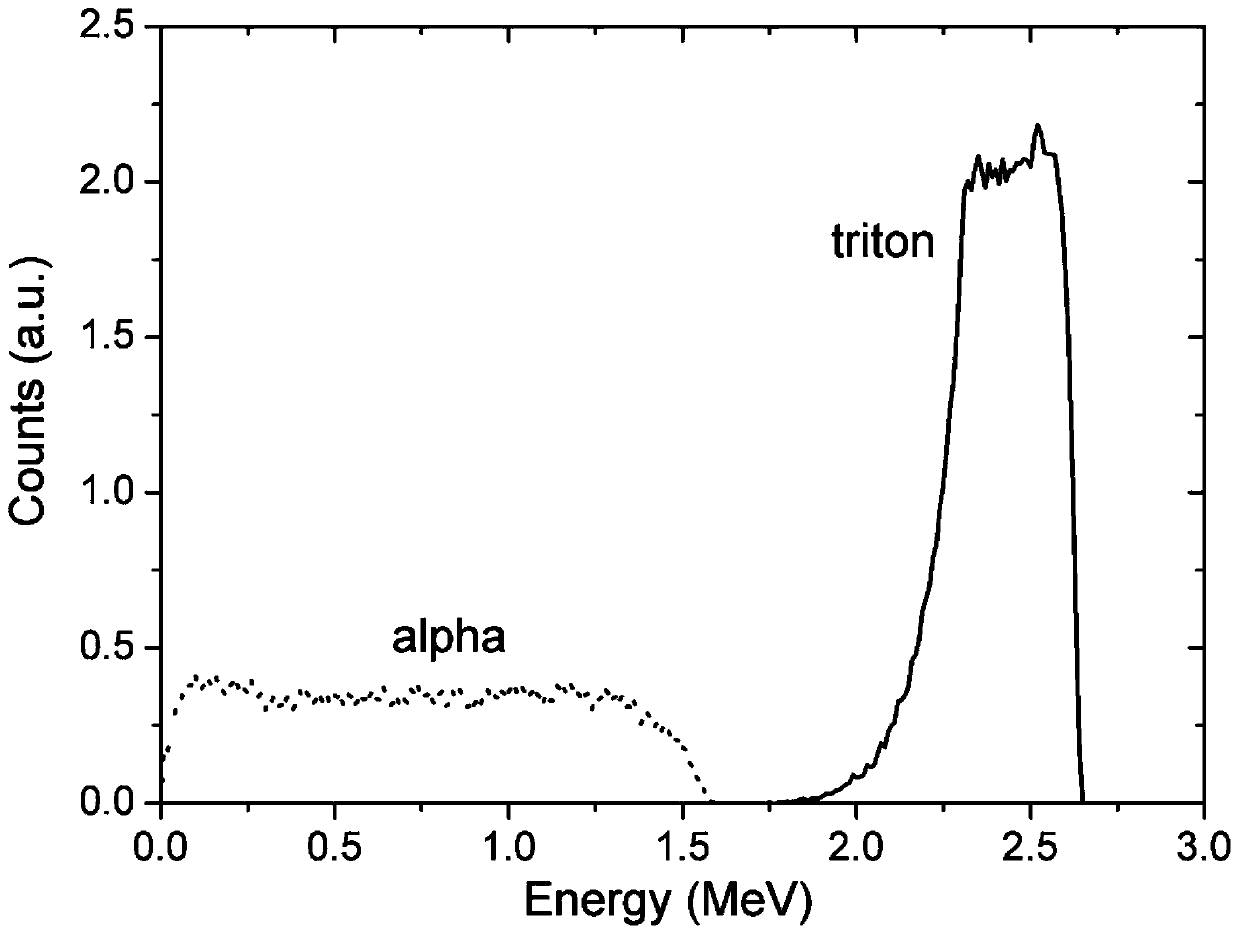
The invention provides a neutron energy spectrum measuring device and a Bonner sphere spectrometer system. A diamond detector is adopted as a thermal neutron counter, the advantage that the diamond detector is low in thermal neutron detection efficiency and quick in response is utilized, data real-time recording can be realized, the problem of detector counting saturation in a strong neutron fieldis avoided, and the device has the advantages of a real-time data recording function that existing active Bonner sphere spectrometers have and an anti-saturation function in a high-throughput neutronfield. A gap is formed between a diamond sensitive unit and a 6LiF neutron converter, so that alpha and tritium particles obtained by thermal neutrons and 6Li reaction can be separated, and tritium particle counting is more accurate. In addition, only one diamond detector is arranged in each spherical moderator, so that electronics and a data collection system are enabled to become simple and bemore convenient for operation, and subsequent data processing is made simple and convenient.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Airplane black box locating and searching sonar equipment
The invention belongs to the field of locating and searching sonar equipment, and in particular relates to an airplane black box locating and searching sonar equipment comprising a combined search sonar array, a real-time information processing sub-system and a search sonar main control system. The combined search sonar array, the real-time information processing sub-system and the search sonar main control system are installed on a search platform, so that monitoring, direction-finding and accurate locating of a black box acoustic beacon signal can be sequentially achieved in real time, and meanwhile navigation information can be provided for the search platform, so that a black box can be quickly and effectively searched. The airplane black box locating and searching sonar equipment provided by the invention is applicable to quickly searching the airplane black box at an initial phase after an airplane is crashed in the water, can be installed on an underwater vehicle for use in a deep sea water area, also can be installed on a surface ship in a shallow water area for searching, and is strong specificity, rich in function and strong in platform adaptation; meanwhile, the detecting work, locating work and searching work of the sonar equipment are completed by using a set of equipment, the collaborative search capacity is stronger, and the search success rate is higher.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method and apparatus for detecting multimedia content change, and resource propagation system
InactiveUS20150304188A1Improve detection efficiencyReduce testing costsWeb data indexingDigital computer detailsClient-sideChange detection
A method and apparatus for detecting a multimedia content change, and a resource propagation system. The method comprises: when importing a resource address of multimedia content, acquiring original feature information of the multimedia content; receiving first feature information of the multimedia content from a client; determining, according to the first feature information and corresponding original feature information of the multimedia content, whether the resource address of the multimedia content is abnormal; and detecting whether multimedia content at an abnormal resource address is changed. It is firstly determined whether a resource address corresponding to multimedia content is abnormal, and if the resource address is abnormal, then it is determined whether the multimedia content corresponding to the resource address is changed, thereby preventing repeated checking of a large number of normal resource addresses, improving the detection efficiency, and reducing the detection cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN DEV PROMOTION CENT FOR ENTERPRISES
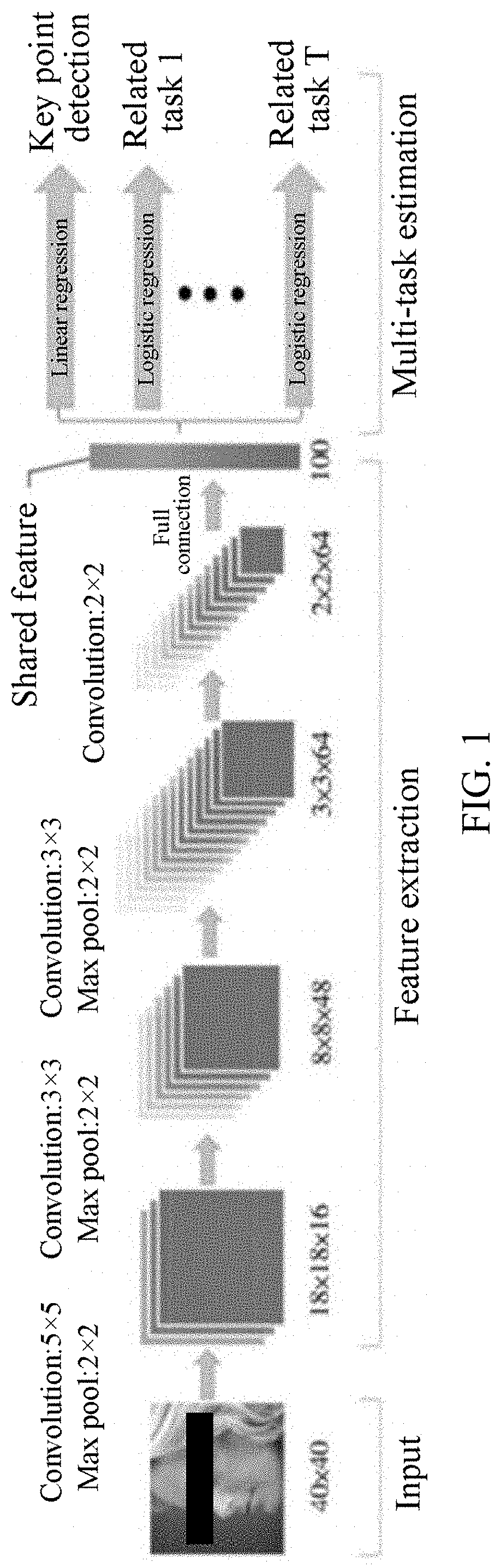
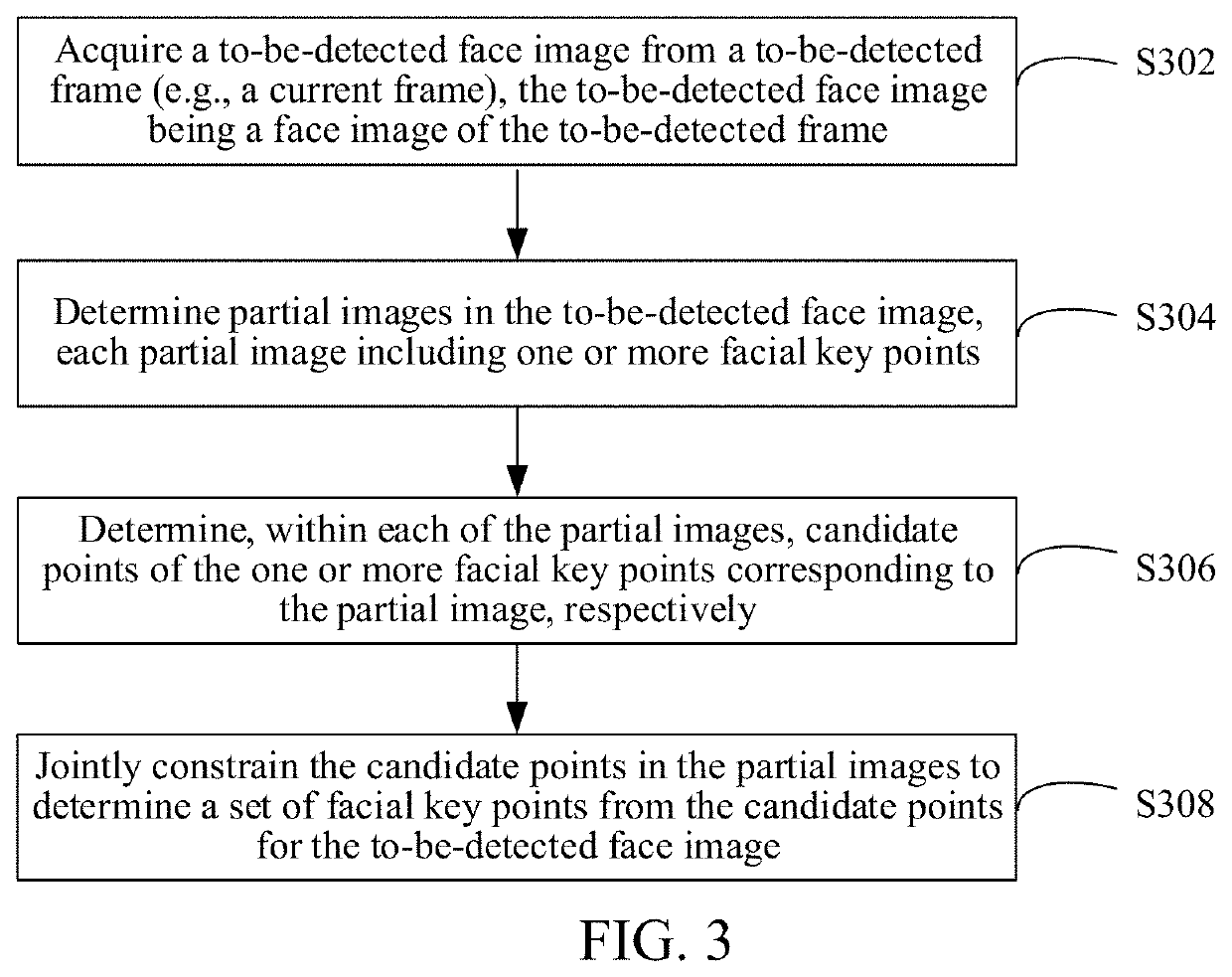
Method and apparatus for detecting facial key points, computer device, and storage medium
PendingUS20210182537A1Reduce amount of calculationEfficiently determineCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsNuclear medicineComputer device
This application relates to a method and an apparatus for detecting facial key points, a computer device, and a storage medium including: acquiring a to-be-detected face image from a current frame; determining partial images in the to-be-detected face image, each partial image including one or more facial key points; determining, within each of the partial images, candidate points of the one or more facial key points corresponding to the partial image, respectively; and jointly constraining the candidate points in the partial images to determine a set of facial key points from the candidate points for the to-be-detected face image. For the partial images in the entire to-be-detected face image, the candidate points of the facial key points corresponding to the partial images are respectively determined. Therefore, a calculation amount may be reduced, and the efficiency of determining the candidate points of the facial key points is improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
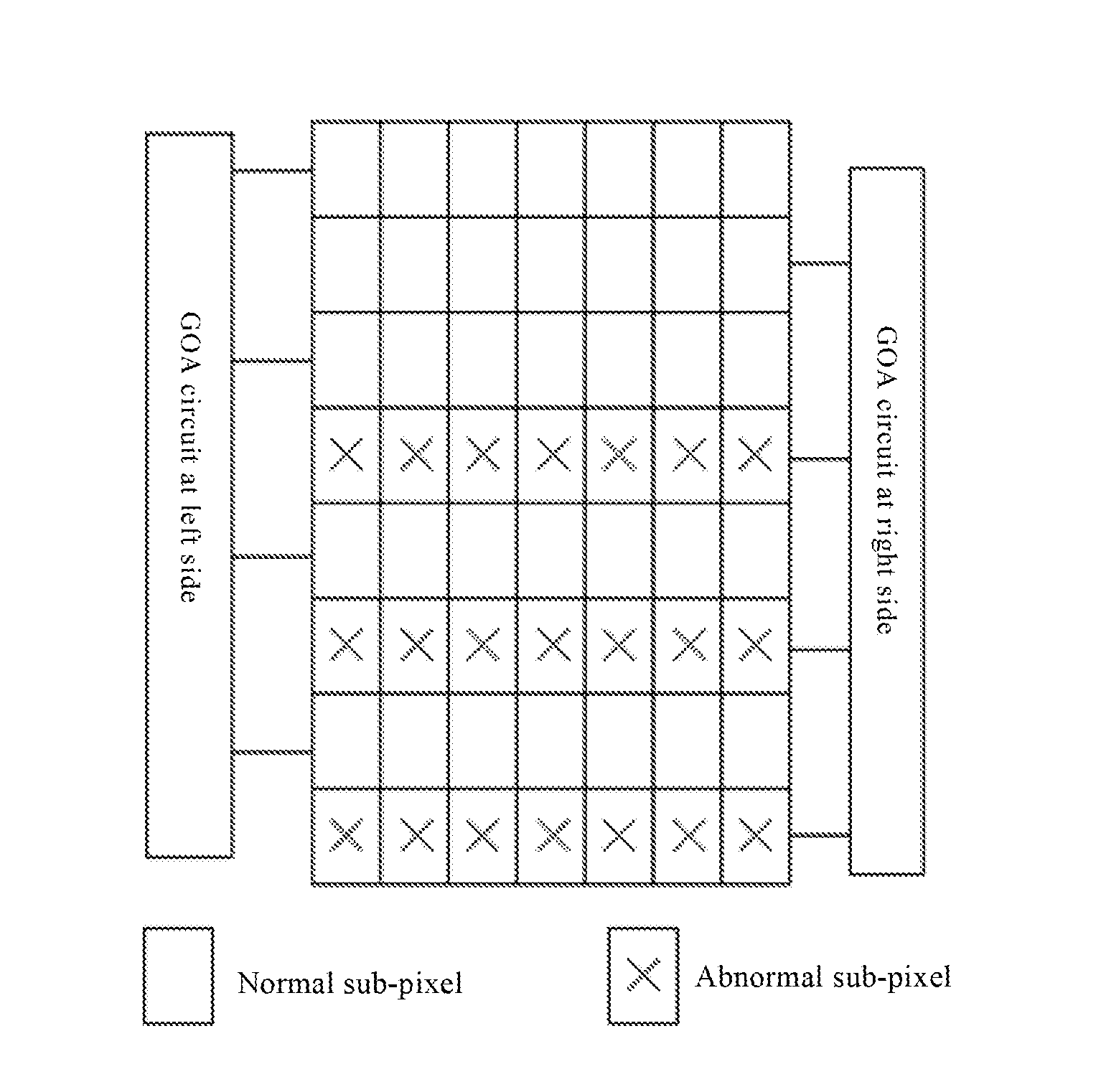
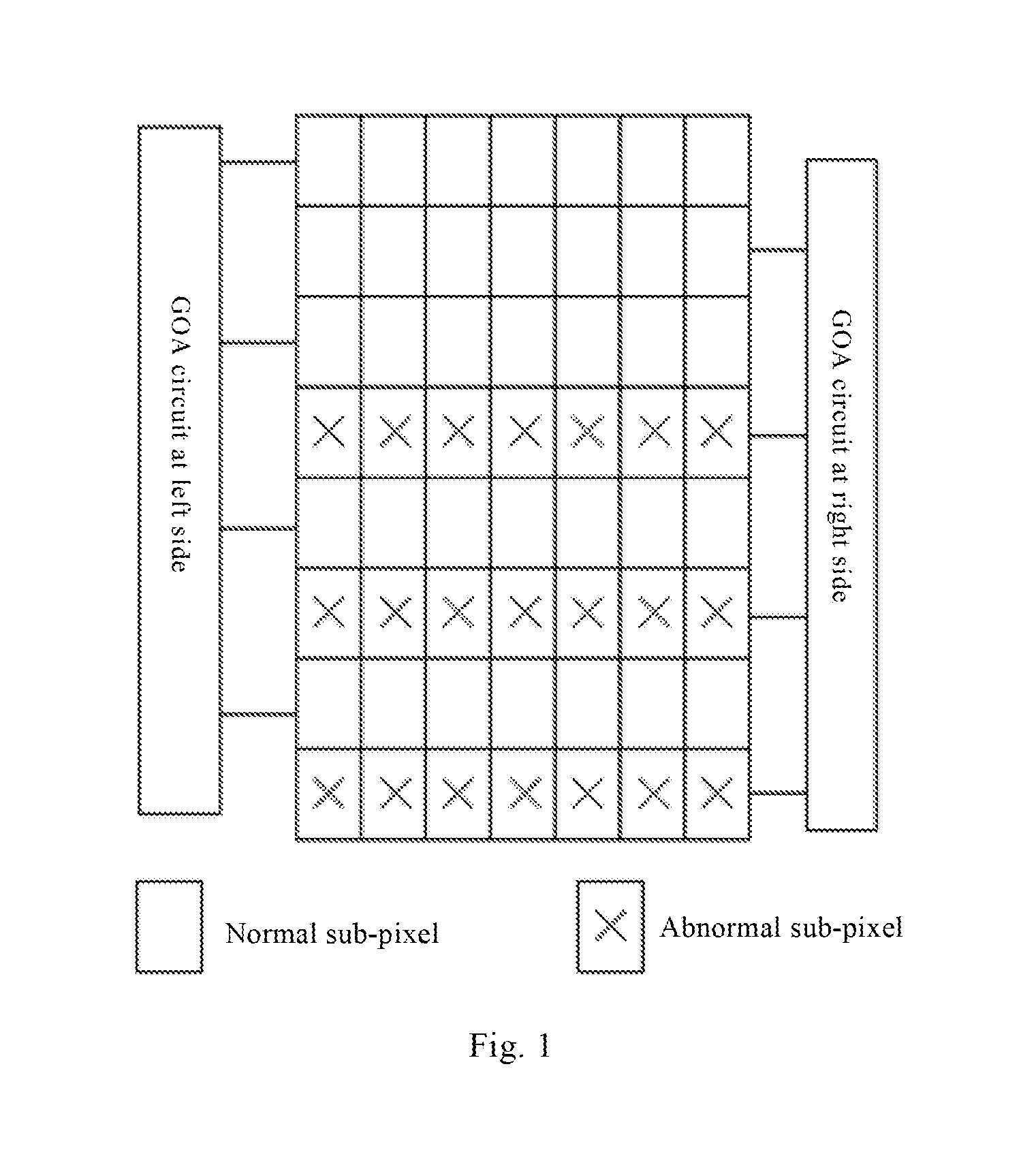
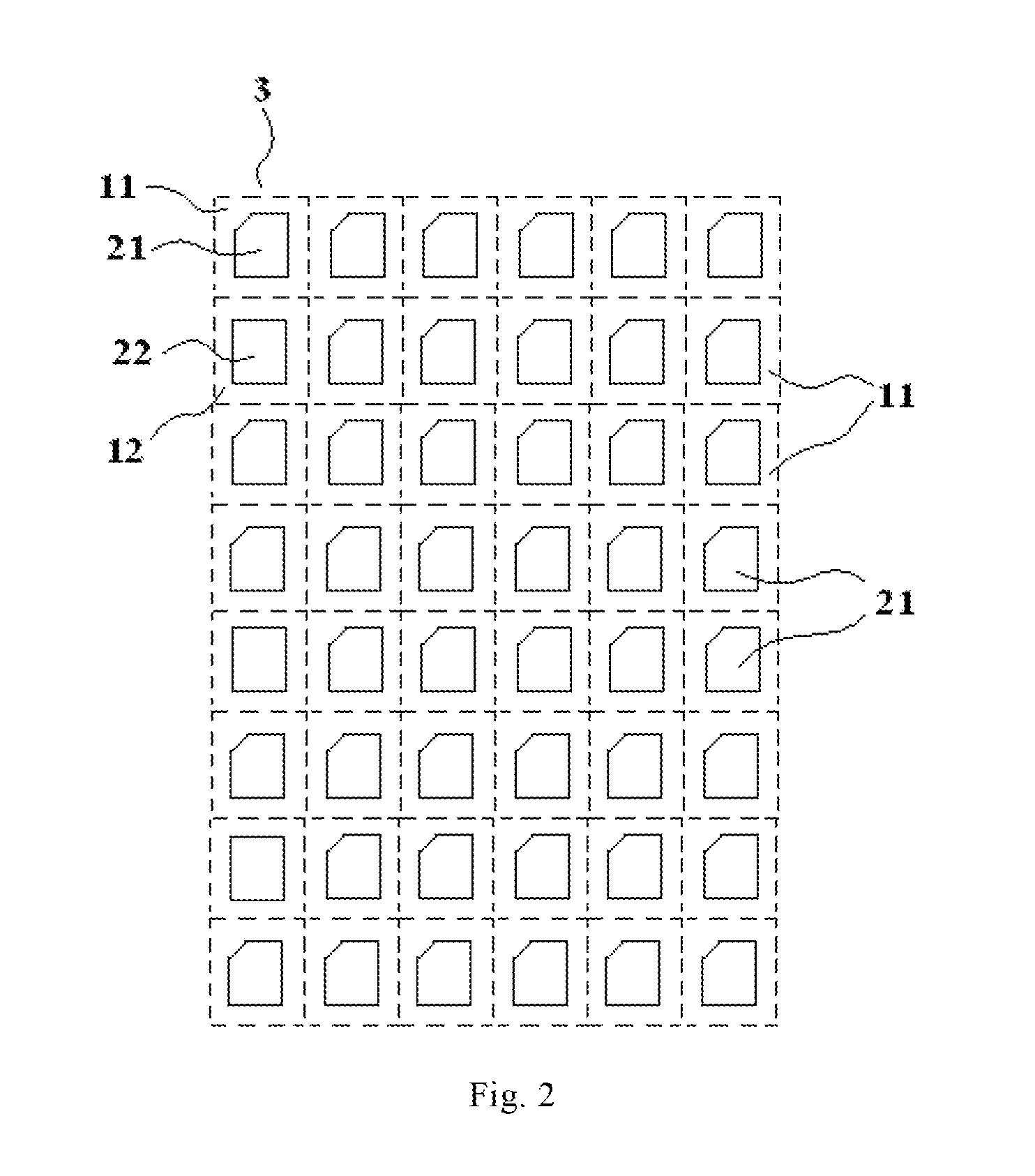
Color filter substrate, display device and detecting method therefor
ActiveUS20160329354A1Solve the detection efficiency is not highRapid positioningStatic indicating devicesOptical filtersColor gelDisplay device
The present invention provides a color filter substrate, a display device and a detection method thereof, aims to solve the problems of difficulty in failure positioning and low detection efficiency in existing display panels. The color filter substrate comprises a plurality of sub-pixels arranged in an array, each of the sub-pixels is provided with a color filter, and at least a part of columns of sub-pixels are marked column of sub-pixels. The shapes of the color filters of a part of sub-pixels of the marked column of sub-pixels are different from those of the remaining sub-pixels. The display device comprises the above-mentioned color filter substrate. The color filter substrate can be used in the display device, particularly suitable for the display device which adopts double side GOA circuits.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Radiation Residue Scanning Device and System
ActiveUS20180228453A1Reduce widthIncrease the number ofRadiation diagnostic device controlComputer moduleCzt detector
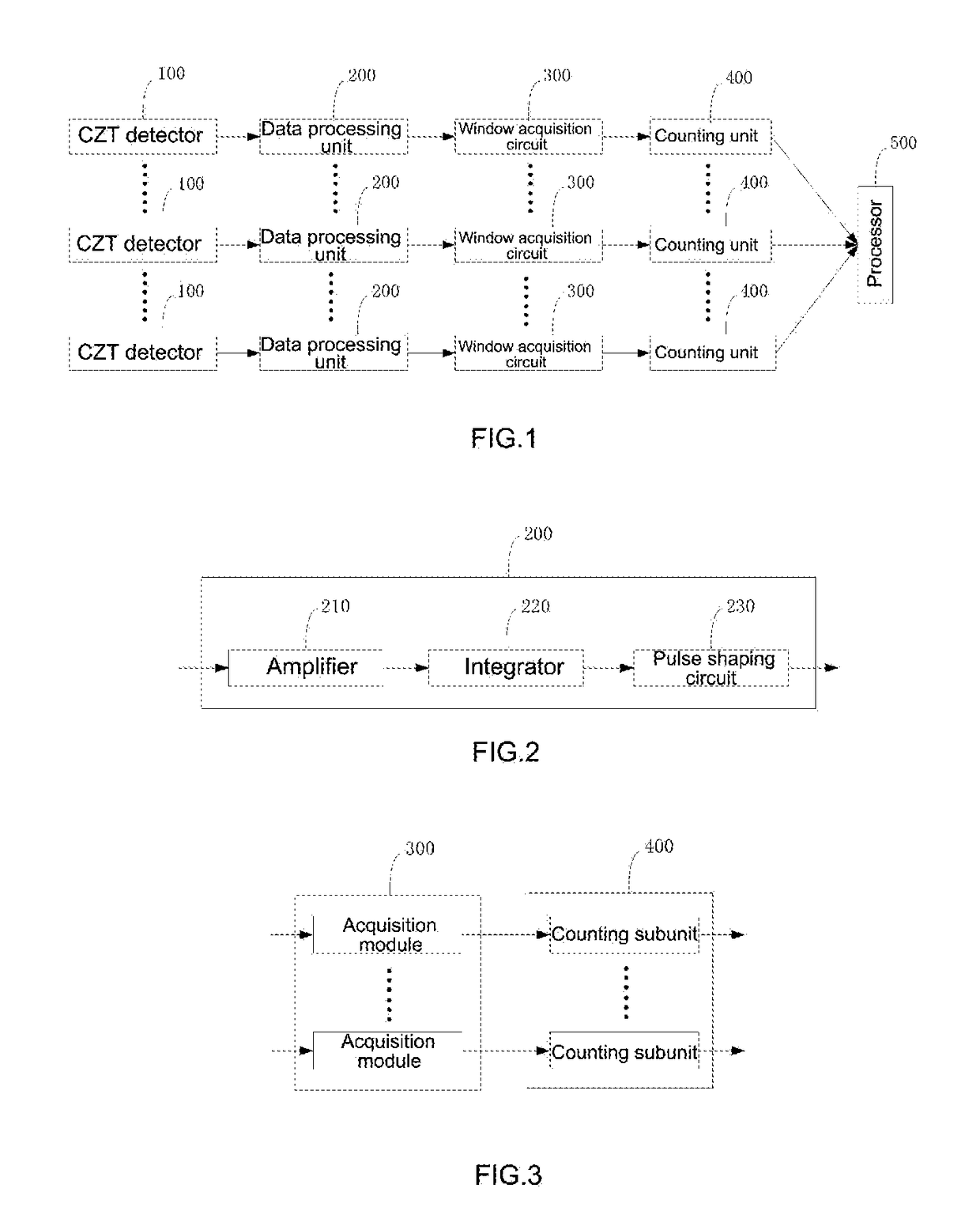
A radiation residue scanning device includes a plurality of CZT detectors, a plurality of data processing units, a plurality of window acquisition circuits, a plurality of counting units, and a processor; the plurality of CZT detectors connected in one-to-one correspondence to the plurality of data processing units; the plurality of data processing units are connected in one-to-one correspondence to the plurality of window acquisition circuits; and the plurality of window acquisition circuits are connected in one-to-one correspondence to the counting units The window acquisition circuit includes a plurality of acquisition modules, and the respective acquisition modules are connected in parallel; the counting unit includes a plurality of counting subunits, the counting subunits are connected in one-to-one correspondence to the acquisition window modules, and the processor is connected to the plurality of counting units.
Owner:BEIJING EXPLORE TIMESTECH CO LTD
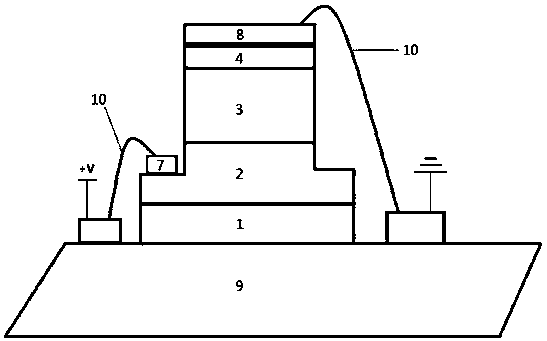
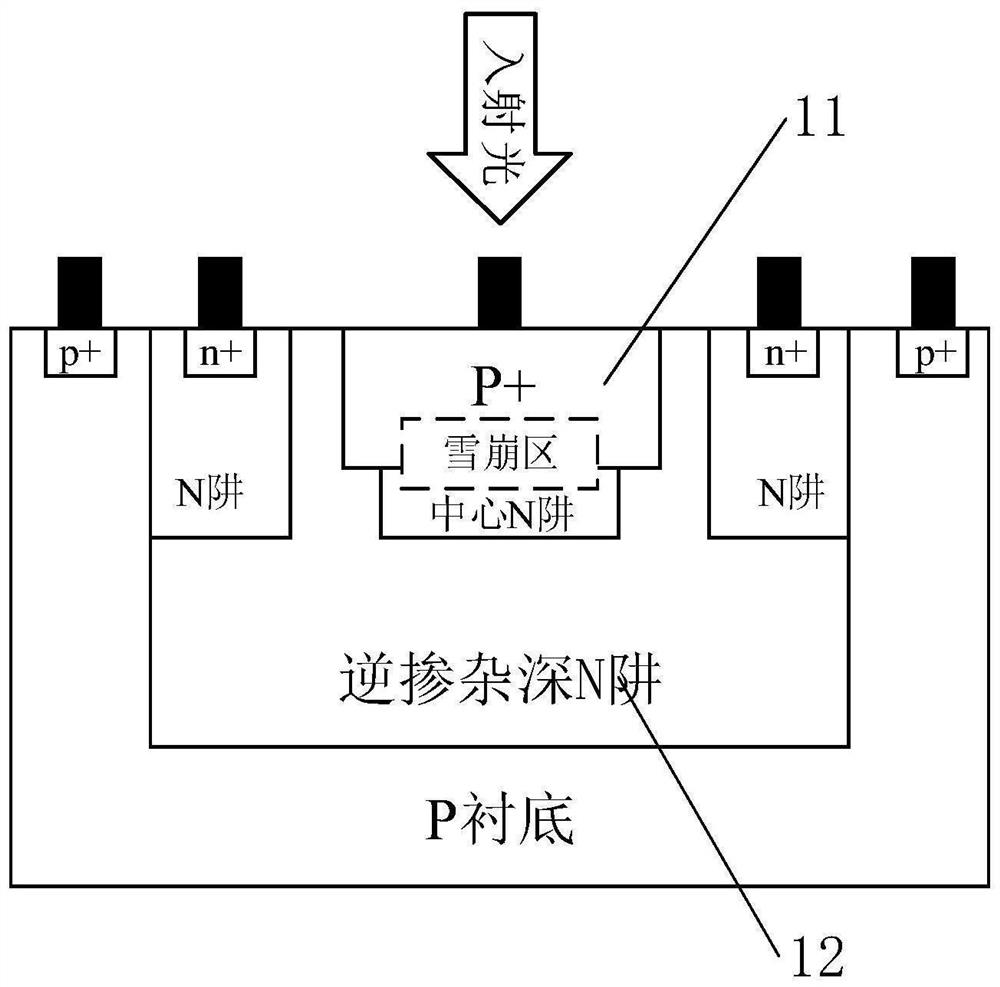
CMOS SPAD (Single Photon Avalanche Diode) photoelectric device with deep N well adopting inverse doping distribution
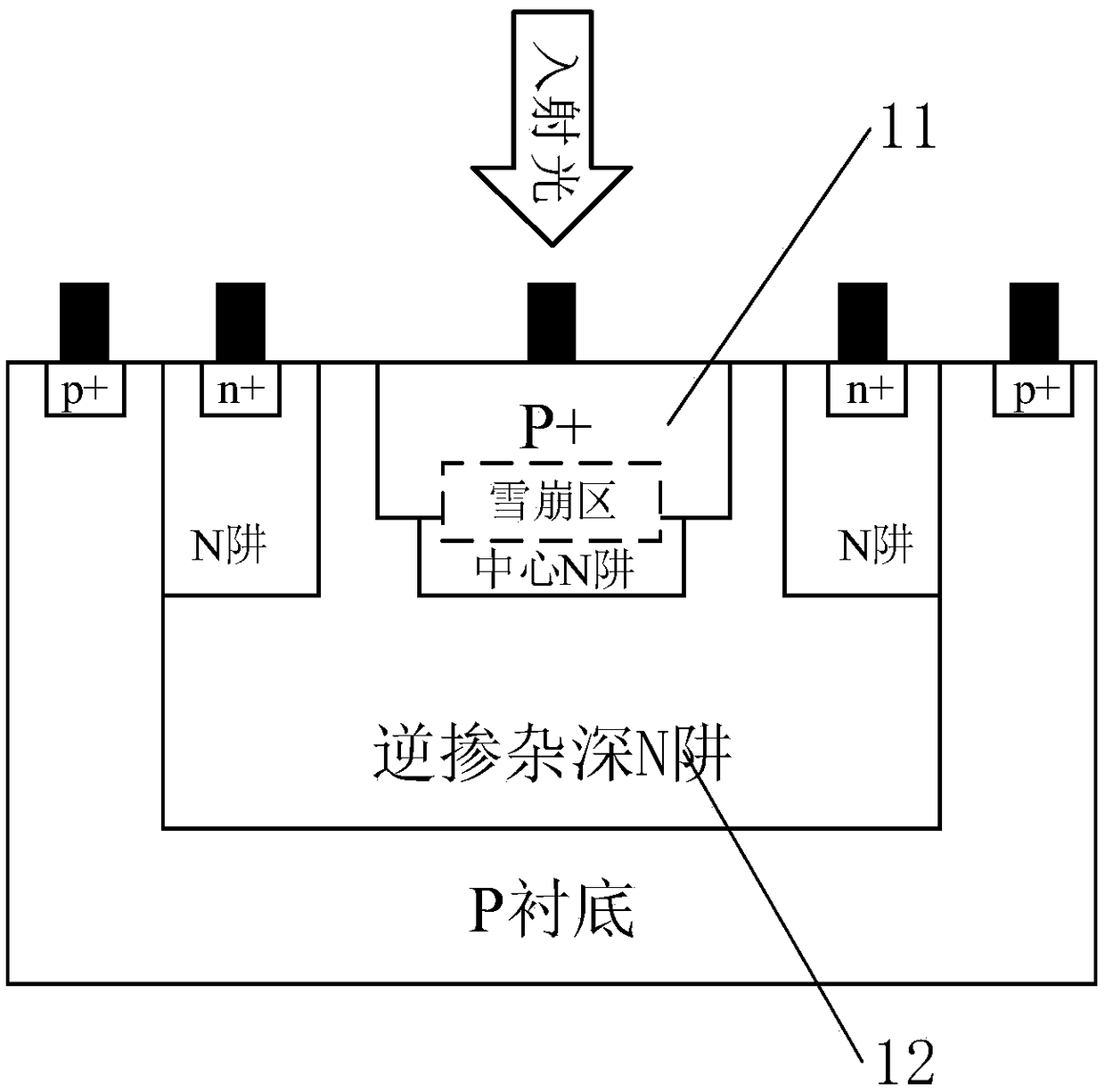
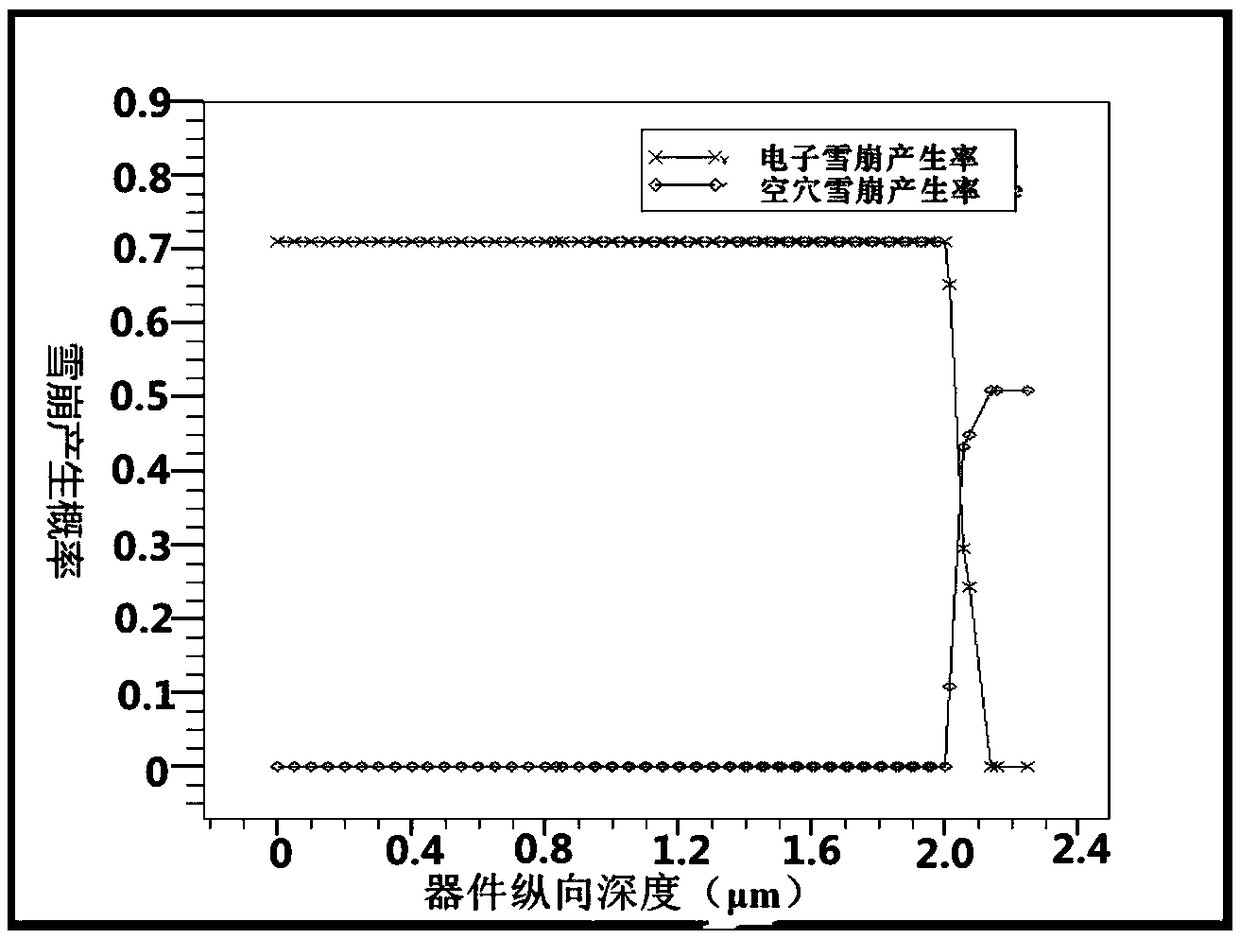
InactiveCN109285901AImprove detection efficiencyReduce utilizationSemiconductor devicesCMOSQuantum efficiency
The invention relates to a CMOS SPAD (Single Photon Avalanche Diode) photoelectric device with a deep N well adopting inverse doping distribution, which comprises a P substrate, wherein the P substrate is provided with a deep N well, a central N well and a P+ layer, two sides of the deep N well are provided with N wells, the deep N well adopts an inverse doping distribution structure, that is, thedeep N well close to the device surface is low in concentration and the concentration of the deep N well increases along the increase in vertical depth away from the device surface, the transverse diffusion exists between the two lateral N wells and the central N well in the deep N well, an n- virtual protection ring is formed at the edge of a PN junction, incident photons are mainly absorbed bythe deep N well when shooting to the internal part of the device, most of the photons can be utilized by the P+ layer / central N well junction to form photon-generated carriers, and only a few of the photons penetrate through the deep N well and form photon-generated carriers on the P substrate. The photon detection efficiency of the device is improved by mainly increasing the thickness of an absorption region of the device and optimizing the quantum efficiency of the device.
Owner:重庆亚川电器有限公司
Method and apparatus for word detection in application program
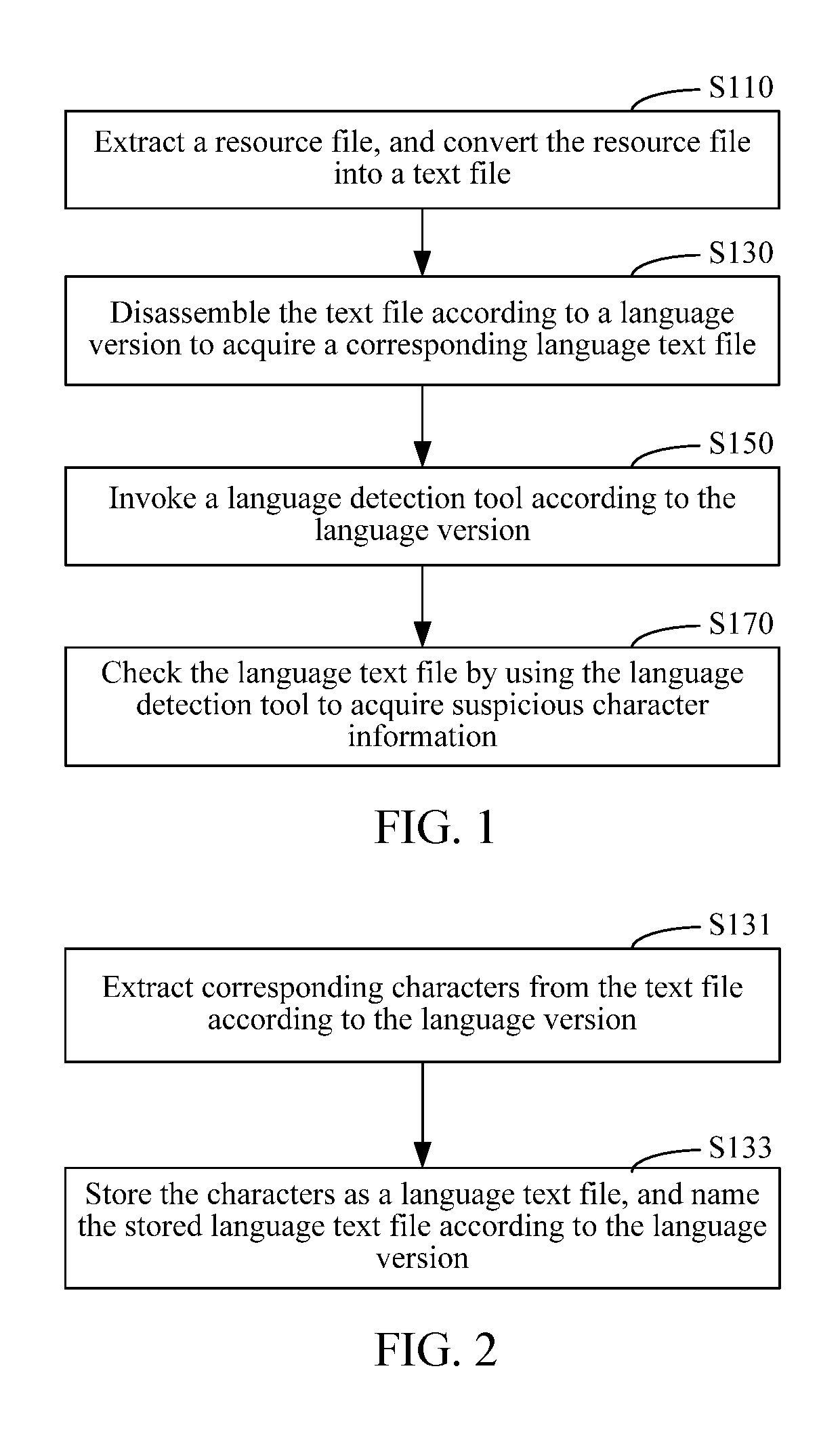
ActiveUS20170364501A1Low detection efficiencyImprove system efficiencyNatural language translationExecution for user interfacesNatural language processingText detection
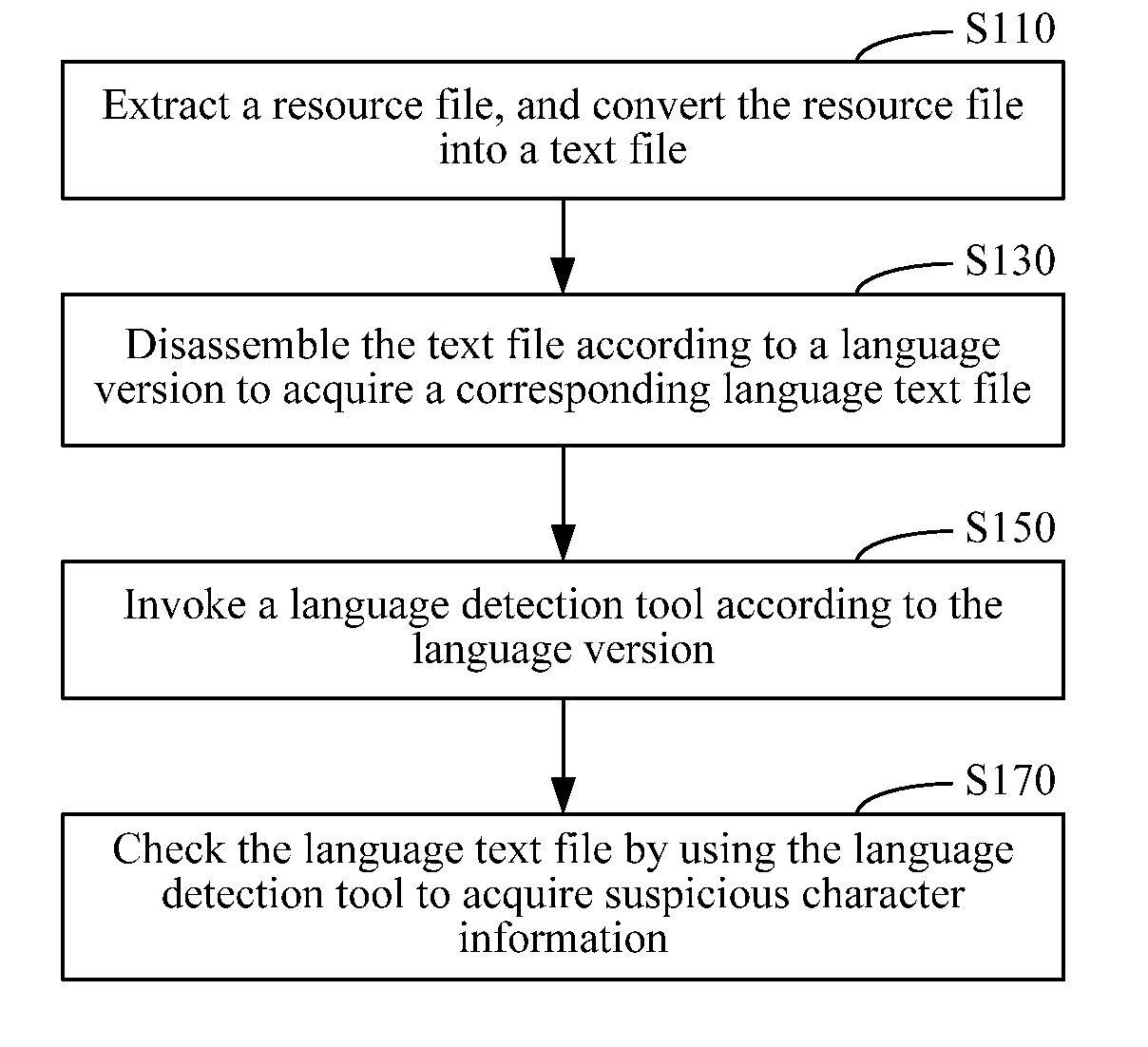
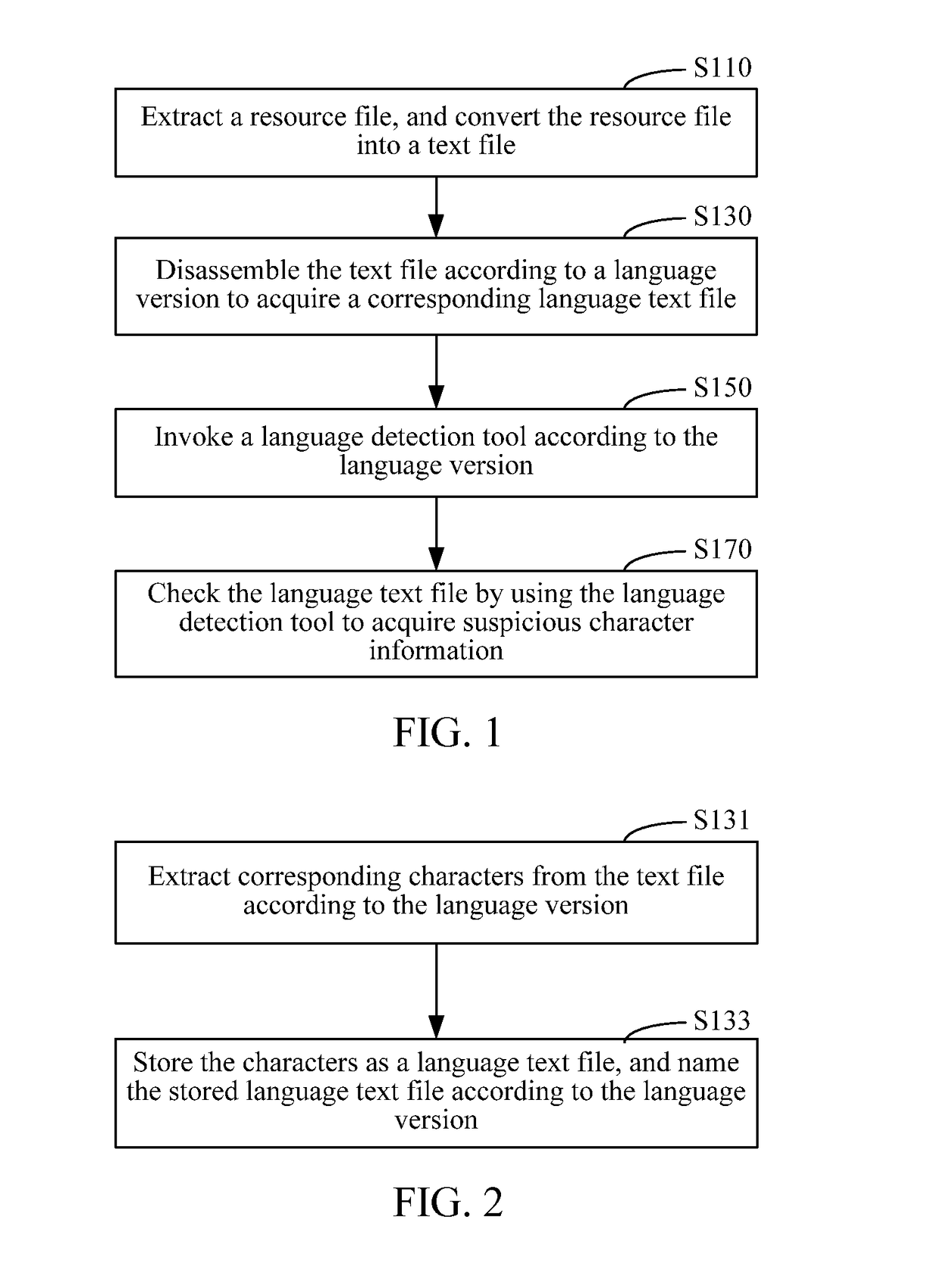
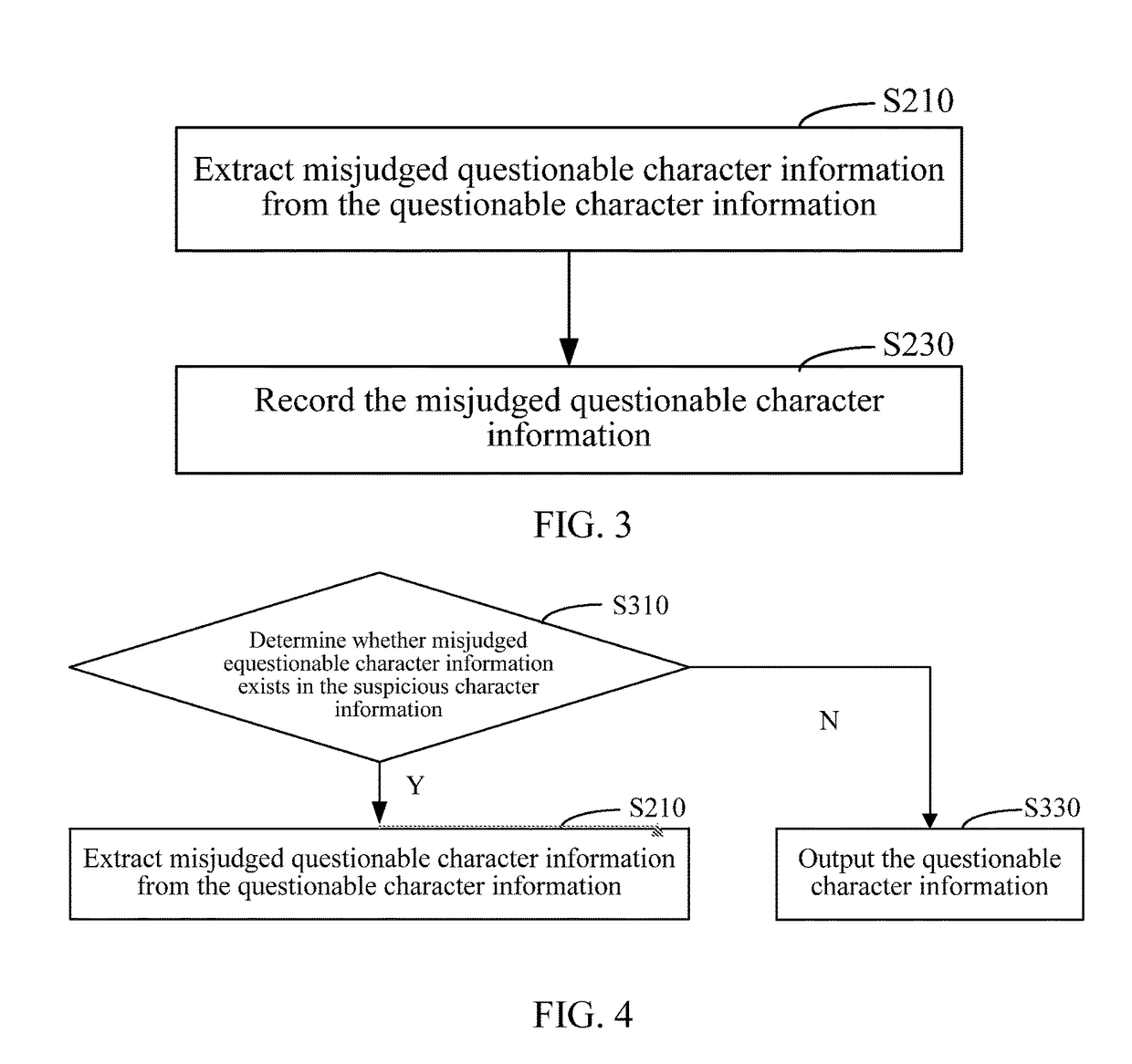
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and an apparatus for word detection in an application program. The method includes extracting a resource file from a multilingual application program installation package and converting the resource file into a text file. The method further includes disassembling the text file according to a language version to acquire a corresponding language text file; invoking a language detection tool according to the language version; and checking the language text file by using the language detection tool to identify questionable character information. The apparatus for word detection includes a file processing module, configured to extract a resource file from a multilingual application program installation package, and convert the resource file into a text file; and a disassembling module, configured to disassemble the text file according to a language version to acquire a corresponding language text file. The apparatus further includes a tool invoking module, configured to invoke a language detection tool according to the language version; and a text detection module, configured to check the language text file by using the language detection tool to identify questionable character information. Word detection efficiency in an application program can be improved by adopting the present disclosure.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
A p-gan/i-gan/n-bn neutron detector
ActiveCN106684177BImplement detectionResolve conflicting requirements that can only run in one directionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEvaporation (deposition)Etching
The invention discloses a p-GaN / i-GaN / n-BN neutron detector. The neutron detector is composed of an Al2O3 substrate layer, an n-BN layer, an i-GaN layer and a p-GaN layer. The preparation method is as follows: on an Al2O3 substrate with a certain thickness, firstly grow n-BN by using metal organic chemical vapor deposition technology, then grow undoped i-GaN, and finally grow p-GaN, and then use inductively coupled plasma etching. The n-BN is etched out, and finally ohmic contact metal electrodes are evaporated on the n-BN and p-GaN layers by electron beam evaporation to complete the fabrication of the neutron detector. The invention has simple preparation process, does not need to prepare a neutron conversion layer separately, has high energy resolution, high detection efficiency and simple structure, and has important application value in aerospace exploration, nuclear energy utilization and development, generation and application of radioisotopes and some special fields .
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
CMOS SPAD photoelectric device with deep N well in reverse doping distribution
InactiveCN113659030AImprove detection efficiencyReduce utilizationSemiconductor devicesCMOSQuantum efficiency
The invention relates to a CMOS SPAD photoelectric device with a deep N well in reverse doping distribution. The CMOS SPAD photoelectric device comprises a P substrate, the deep N well, a central N well and a P + layer are arranged on the P substrate, N wells are arranged at the two sides of the deep N well, the deep N well is of a reverse doping distribution structure, namely, the concentration of the deep N well close to the surface of the device is low, and the concentration of the deep N well is higher with the longitudinal depth away from the surface of the device is increased, transverse diffusion exists between the N wells at the two sides in the deep N well and the central N well, an n-virtual protection ring is formed at the edge of the PN junction, when incident photons are emitted into the device and are mainly absorbed by the deep N well, most photons can be utilized by the P + layer / central N well junction to form photon-generated carriers, and only a small number of photons penetrate through the deep N well to form a photon-generated carrier on the P substrate. The photon detection efficiency of the device is improved mainly from two aspects of increasing the thickness of the absorption region of the device and optimizing the quantum efficiency of the device.
Owner:重庆亚川电器有限公司
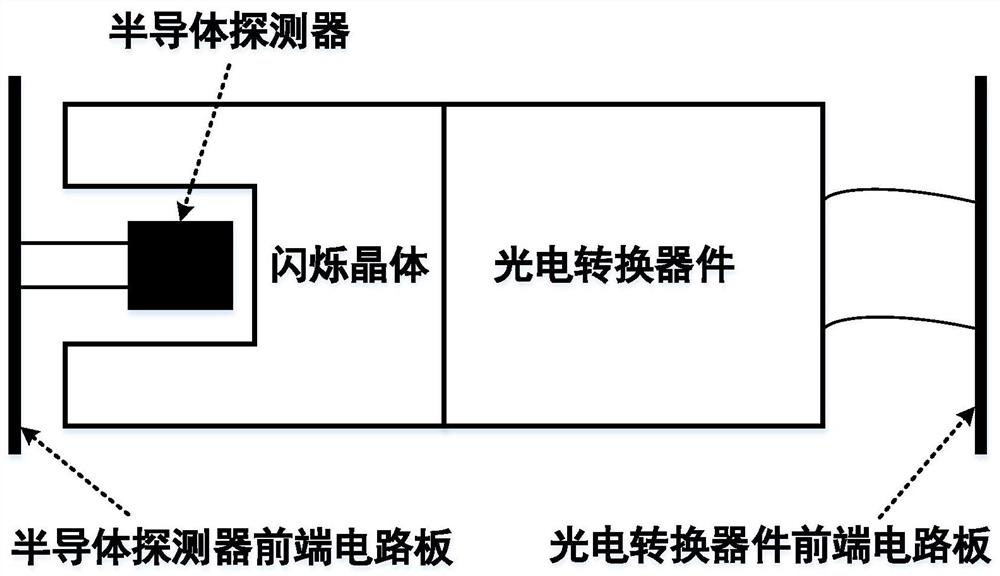
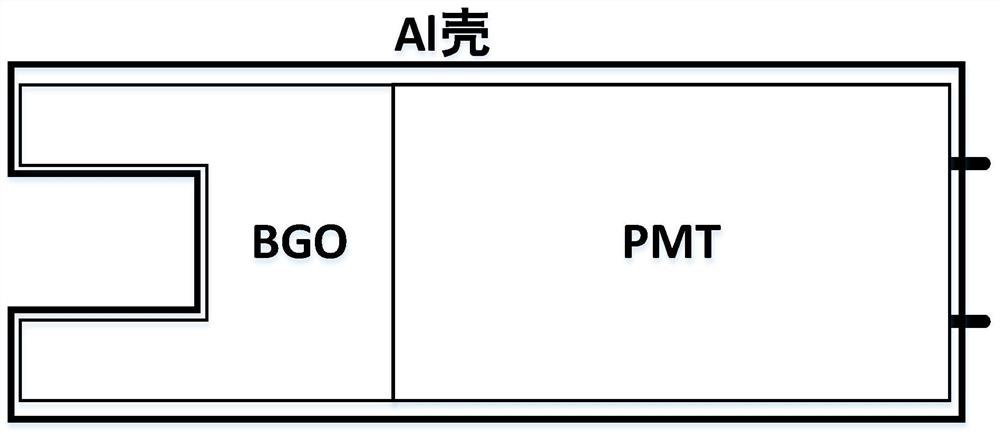
Miniaturized composite gamma spectrometer
ActiveCN112764086ALow detection efficiencyReduce volumeX-ray spectral distribution measurementNuclear energy generationDoses rateNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a miniaturized composite gamma spectrometer. The spectrometer specifically comprises a semiconductor detection unit, a scintillation crystal, a photoelectric conversion device and a reading circuit. The innovation point is that a high-energy-resolution room-temperature semiconductor gamma detector is compactly arranged in a small-size cavity of a cup-shaped inorganic scintillation crystal, and the advantages of high detection efficiency of the inorganic scintillation crystal and high energy resolution of a semiconductor detector are integrated, so the spectrometer has the functions of low background gamma counting and high-resolution anti-Compton gamma-ray energy spectrum measurement, and can better meet the use requirements under different conditions. According to the technical scheme, gamma radiation detection in a wide dose rate range can be realized, refrigeration is not needed, a miniaturized and lightweight portable probe is easy to design, and a traditional high-purity germanium detector with an anti-Compton function can be replaced in part of application fields; and the spectrometer has a wide application prospect in the aspects of environmental radiation monitoring, radionuclide identification and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
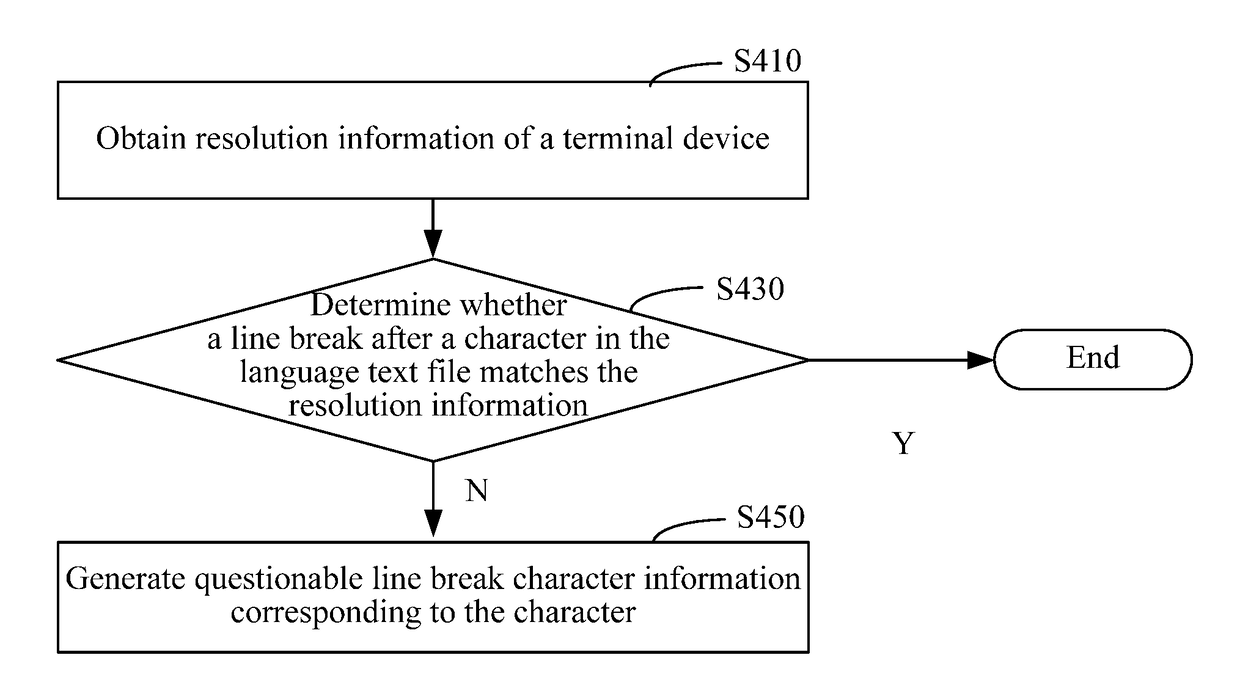
Correcting questionable line breaks after an OCR
ActiveUS9767090B2Low detection efficiencyImprove system efficiencyNatural language translationExecution for user interfacesProgramming languageText detection
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and an apparatus for word detection in an application program. The method includes extracting a resource file from a multilingual application program installation package and converting the resource file into a text file. The method further includes disassembling the text file according to a language version to acquire a corresponding language text file; invoking a language detection tool according to the language version; and checking the language text file by using the language detection tool to identify questionable character information. The apparatus for word detection includes a file processing module, configured to extract a resource file from a multilingual application program installation package, and convert the resource file into a text file; and a disassembling module, configured to disassemble the text file according to a language version to acquire a corresponding language text file. The apparatus further includes a tool invoking module, configured to invoke a language detection tool according to the language version; and a text detection module, configured to check the language text file by using the language detection tool to identify questionable character information. Word detection efficiency in an application program can be improved by adopting the present disclosure.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Intravascular imaging detector
InactiveUS20060195031A1Addressing Insufficient SensitivitySolve the low detection efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood vesselIntravascular imaging
An apparatus for intravascular imaging to detect and characterize early stage, unstable coronary arty plaques. The detector works by identifying and localizing plaque-binding beta-emitting radiopharmaceuticals.
Owner:GAMMA MEDICA IDEAS
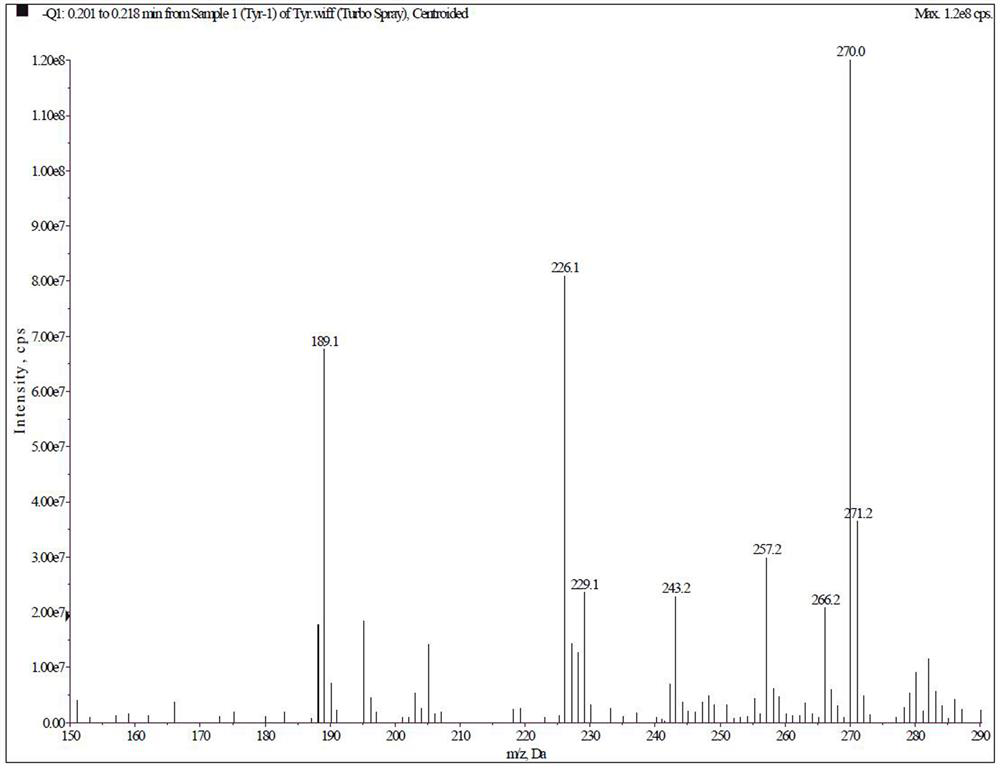
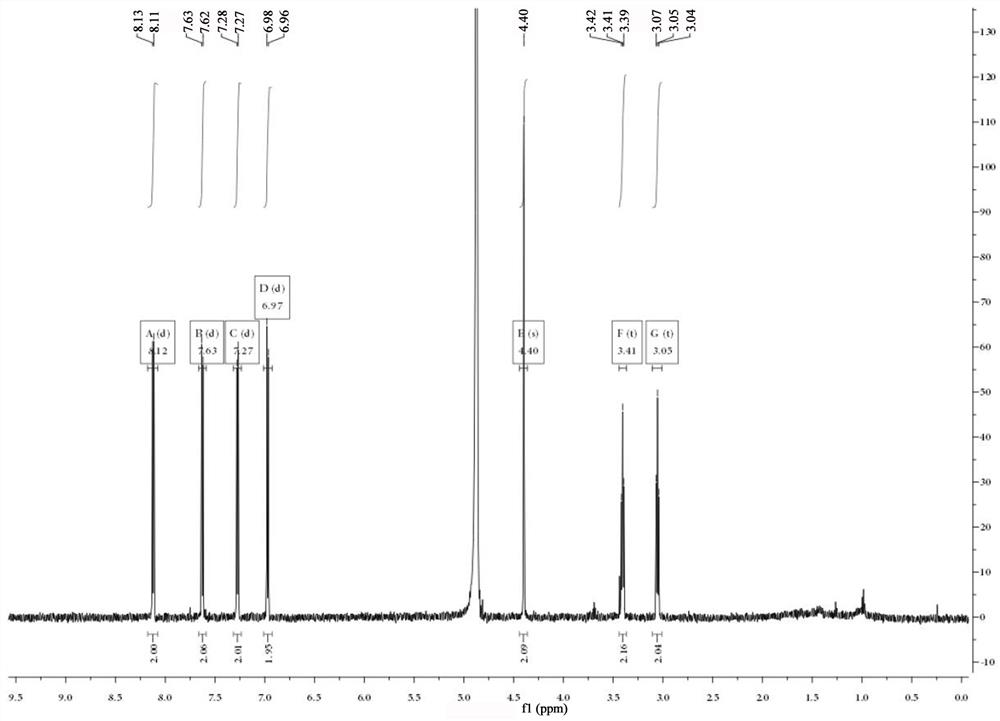
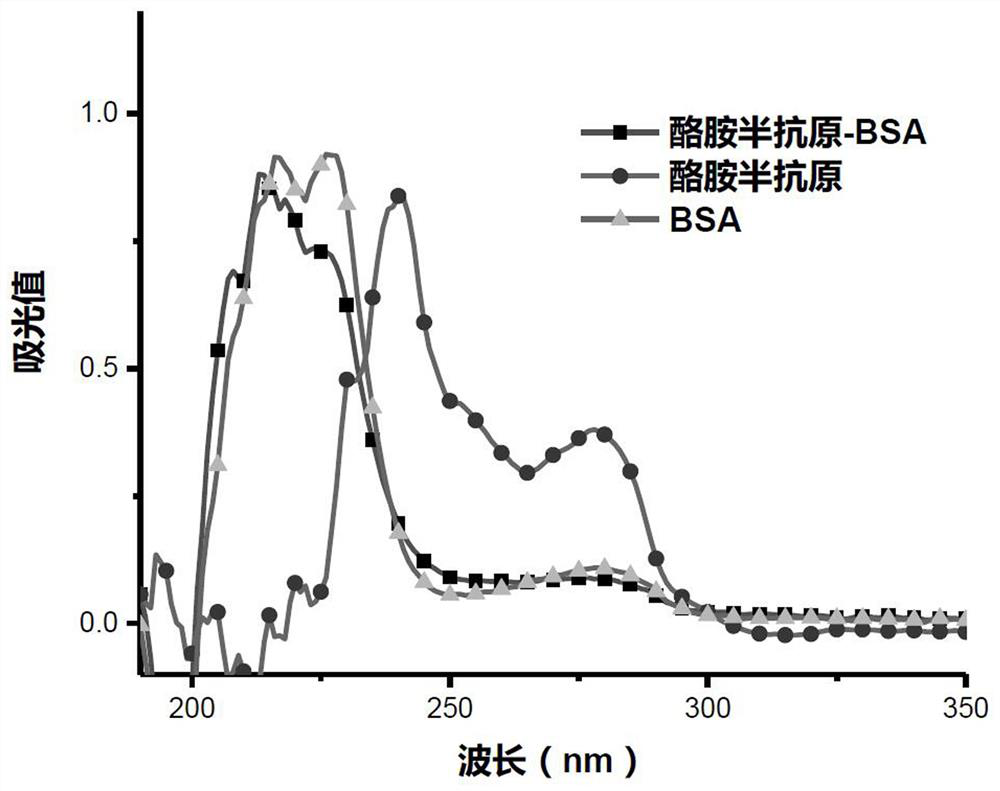
A kind of tyramide hapten, antigen and antibody and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112028786BStrong specificityImprove accuracyOrganic compound preparationOvalbuminTiterAntiserum
The invention provides a tyramide hapten, artificial antigen, antibody and preparation and application thereof. The tyramide hapten has the molecular structure shown in formula I (formula I), and the tyramide artificial antigen has the molecular structure shown in formula II (formula II). The invention solves the defects of unreasonable and poor repeatability in the tyramide artificial antigen and antibody preparation scheme in the prior art. The titer of the antiserum obtained by immunizing animals with the artificial antigen prepared by the hapten of the present invention can reach 1:1000, the minimum detection limit is 26.8 ng / mL, and the half-inhibitory concentration is as low as 391.0 ng / mL, and the antibody has specificity High, good sensitivity, high accuracy, wide linear range and other significant advantages.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
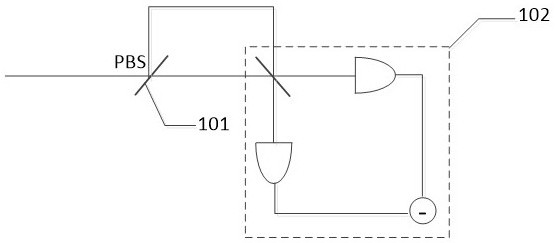
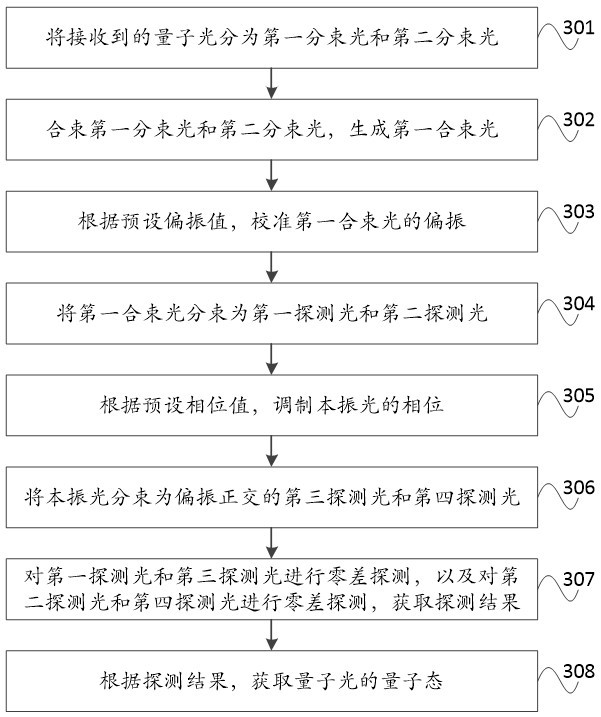
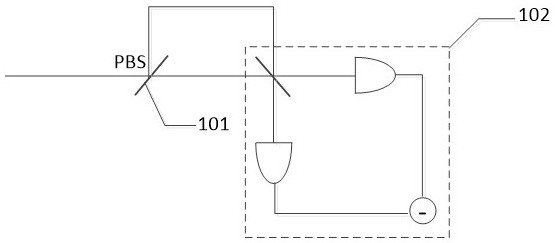
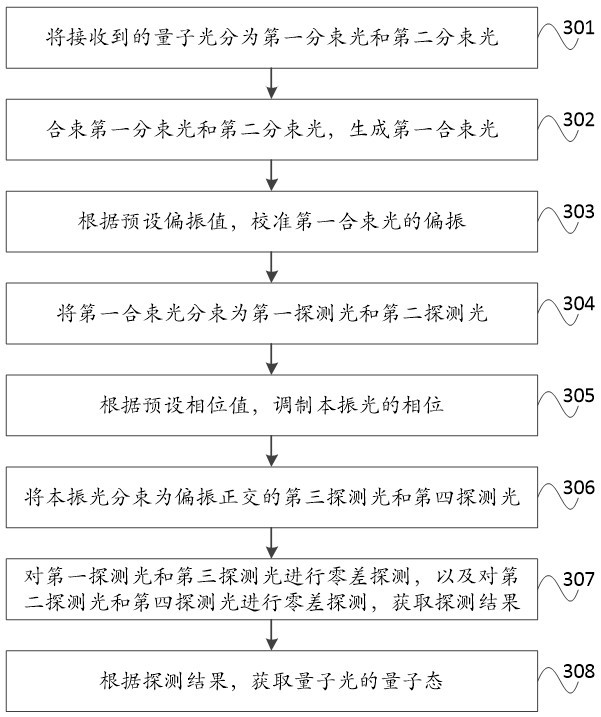
Signal detection method and device for continuous variable quantum key distribution system
ActiveCN112929170ALow detection efficiencyImprove bit rateKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationEngineeringHomodyne detection
The invention discloses a signal detection method and device for a continuous variable quantum key distribution system. The method comprises the following steps: splitting received quantum light into first split light and second split light; combining the first split light and the second split light to generate first combined light; calibrating the polarization of the first combined beam according to a preset polarization value; splitting the first combined beam into first detection light and second detection light; modulating the phase of the local oscillation light according to a preset phase value; splitting the local oscillation light into third detection light and fourth detection light which are polarized and orthogonal; carrying out the homodyne detection on the first detection light and the third detection light, carrying out the homodyne detection on the second detection light and the fourth detection light, and obtaining a detection result; and obtaining the quantum state of the quantum light according to the detection result. According to the invention, because the strong light of the local local oscillation light is introduced, even if the transmission process is too long and the reference light is attenuated, the local local oscillation light can also complement the reference light, so that the detection efficiency of a receiver is prevented from being reduced, and the code rate of the system is further improved.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGCHUANGWEI NANJING QUANTUM COMM TECH CO LTD
A method for rapid real-time classification of soil surrounding rock based on parameters while drilling
ActiveCN106157181BSolve problems that cannot be used in one wayAvoid disturbanceData processing applicationsSoil scienceGuideline
The invention discloses a method for quickly grading terrene surrounding rock in real time on the basis of while-drilling parameters. The relational expression between a clay soil liquidity index and the while-drilling parameters, the relational expression between the sandy soil standard penetration hammering number and the while-drilling parameters and the relational expression between the gravel soil dynamic sounding hammering number and while-drilling parameters can be established, in actual underground engineering, the soil variety of a terrene tunnel is firstly judged, drilling detection is conducted, the obtained while-drilling parameters are substituted into the relational expressions to obtain the liquidity index I<L> of clay soil surrounding rock, the standard penetration hammering number N of sandy soil surrounding rock and the dynamic sounding hammering number N<63.5> of gravel soil surrounding rock, and then quick and real-time grading is conducted on the surrounding rock in front of a tunnel face according to the Guidelines for Design of Highway Tunnel. According to the method for quickly grading the terrene surrounding rock in real time on the basis of the while-drilling parameters, only drilling testing needs to be conducted on the surrounding rock through a drilling machine at an engineering site, other tedious indoor tests or site tests are not needed, quick and real-time grading is conducted on the terrene surrounding rock, the grading efficiency is high, and operation is easy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
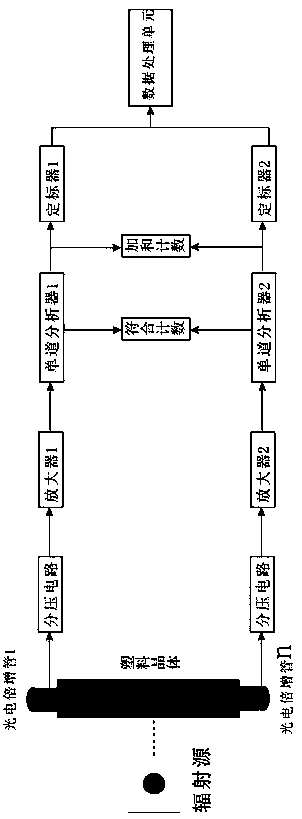
Access control detection system and detection method using energy spectrum recognition algorithm
PendingCN111060954AImprove detection efficiencyLow detection efficiencyX-ray spectral distribution measurementAlgorithmPhotomultiplier
The invention discloses an access control detection system and a detection method using an energy spectrum recognition algorithm. According to the detection method, when a plastic scintillator is long, an optical path of photons generated by incident ions far away from a light collection point to the collection point is long, the attenuation of light signals is severe, the light collection efficiency is reduced, and the detection efficiency is reduced. The access control detection system is composed of a plastic scintillator, wherein two ends of the plastic scintillator are connected with photomultipliers respectively; the two ends of the plastic scintillator are electrically connected with a signal acquisition system for signal acquisition; two paths of single-channel analyzers of the signal acquisition system are connected by means of a coincidence counter and are used for measuring two paths of coincidence counts; and output ends of the single-channel analyzers of the signal acquisition system are connected by means of a summing counter and used for summing the two paths of signals. The detection method is used for detecting iodine-125 particles in access control.
Owner:TECHN PHYSICS INST HEILONGJIANG ACADOF SCI
Time domain stacking surface wave detection method based on pseudo random signals
ActiveCN109541025AImprove detection efficiencyBig advantageAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionTime domainFourier transform on finite groups
The invention discloses a time domain stacking surface wave detection method based on pseudo random signals. The method comprises the steps of: the step 1, obtaining pseudo random signals, wherein theobtained pseudo random signals must have the directionality and are in full spectrum band distribution or in a spectrum band range of 1Hz-1000Hz, and the mode of obtaining the pseudo random signals is that vehicle vibration noise, vibration noise of a river with a flow speed larger than 2m / s or vibration noise loaded by manual operation; the step 2, performing t-p transform of the obtained pseudorandom signals to obtain time-speed domain signals; and the step 3, performing overlapping of the obtained time-speed domain signals in the time-speed domain, namely performing Fourier transform onceat the time domain to transform the time domain to a frequency domain to obtain frequency-speed domain signals. The time domain stacking surface wave detection method has the advantages of high detection precision and good consistency, at the same point, the speeds obtained by testing at different times have an error of less than 10%, the precision is very high, and therefore the time domain stacking surface wave detection method can be used as an effective testing method for testing.
Owner:YELLOW RIVER ENG CONSULTING
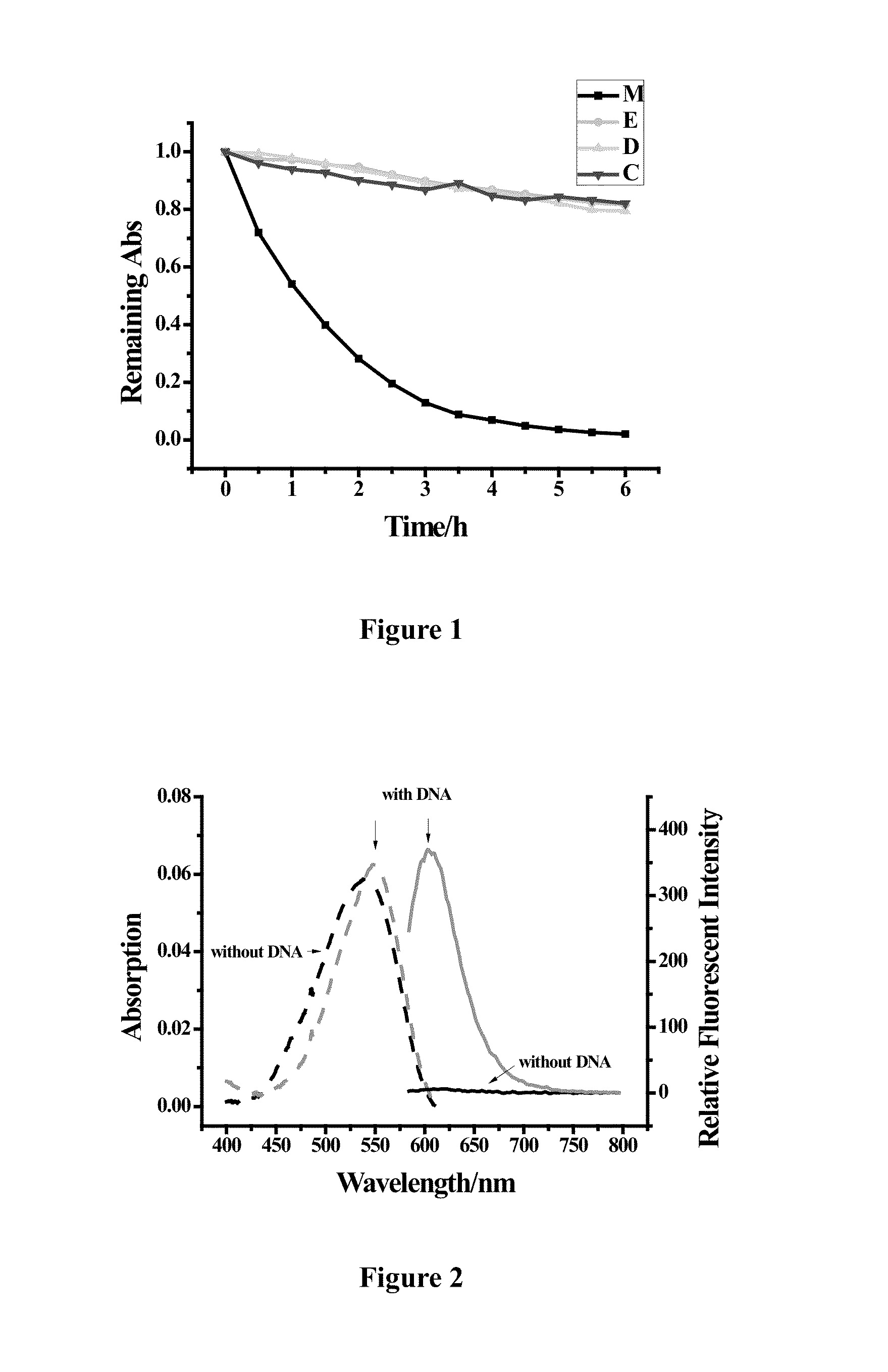
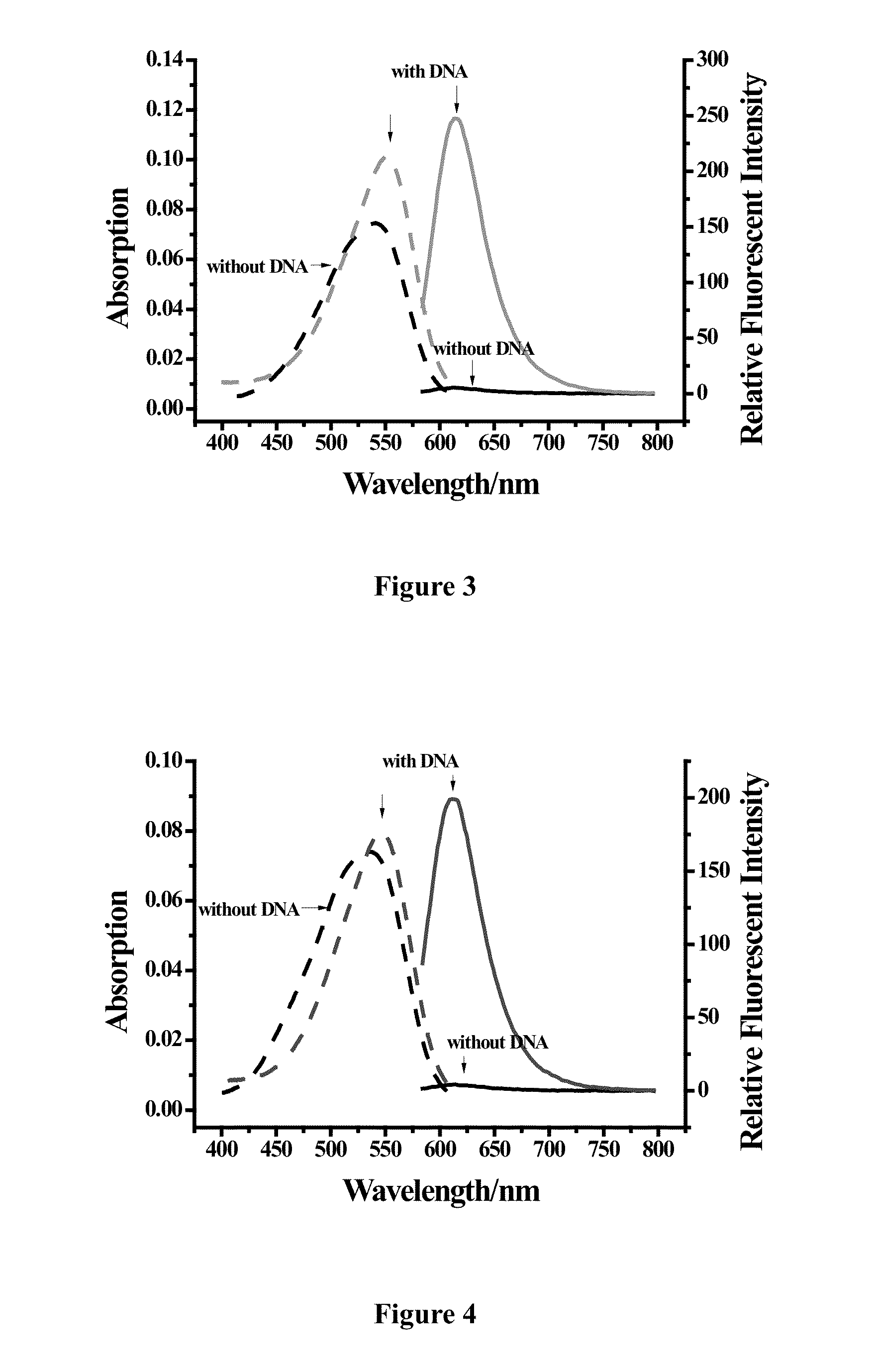
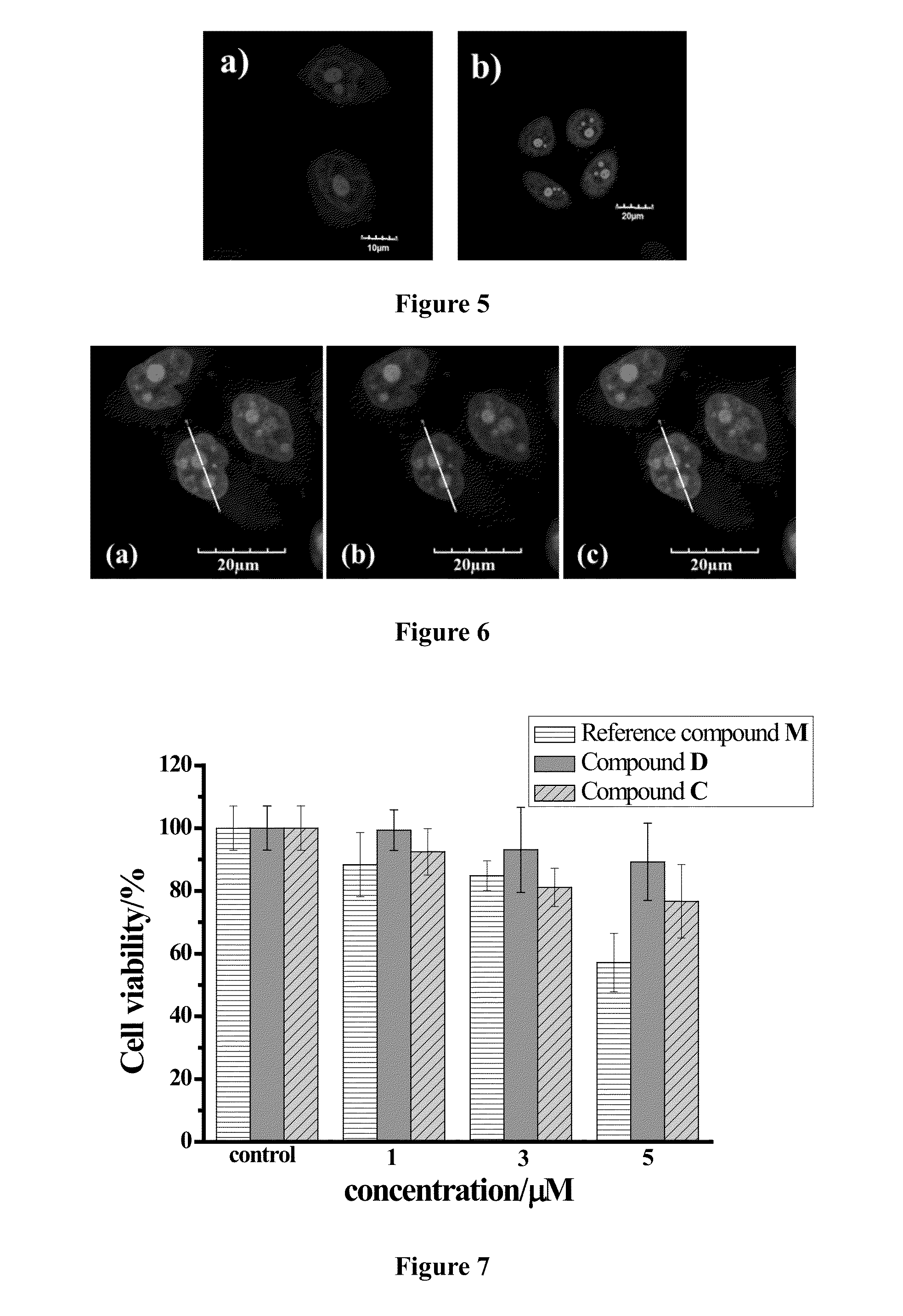
Class of cyano-substituted asymmetric cyanine dyes, synthesizing method and application thereof
ActiveUS20150118703A1Simple structureHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantum yieldCyanine
The present invention provides a category of cyano-substituted asymmetric cyanine dyes having the following general structural Formula I and its synthesizing method. The cyano-substituted asymmetric cyanine dyes in present invention are easily synthesized and have long emission wavelength, high molar extinction coefficient, high sensitivity, good light stability, high fluorescence quantum yield after binding with nucleic acid, and low cell toxicity, which is beneficial for application as fluorescent dyes and could also be used in the field of identifying nucleic acid molecules, clinical diagnostics, and immunoassay testing etc.
Owner:SICHUAN ANKERUI NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Signal detection method and device for continuous variable quantum key distribution system
ActiveCN112929170BLow detection efficiencyImprove bit rateKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationLocal oscillatorParticle physics
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGCHUANGWEI NANJING QUANTUM COMM TECH CO LTD
Incident light redistribution to compensate for radial gradient in detector
ActiveUS20060285204A1Increase volumeIncrease intensityMirrorsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFluorescenceUltimate tensile strength
Nonuniformities in the efficiency of detection of individual fluorescing reaction mixtures in a well plate with a two-dimensional array well array are corrected. The nonuniformities arise both from the stimulation pattern and the detection pattern, and are corrected by adding additional segments to a pair of segmented mirrors. The additional segments are oriented to direct light to the outermost reaches (i.e., the four corners) of the array and thereby produce a stimulation pattern that has a greater intensity in the outermost regions. This compensates for a radial decline in the efficiency of the detector in detecting the emissions from the well plate, the radial decline being an artifact of systems that utilize CCDs or similar components as detectors.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com