Patents
Literature
236results about How to "Reduce hardware requirements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
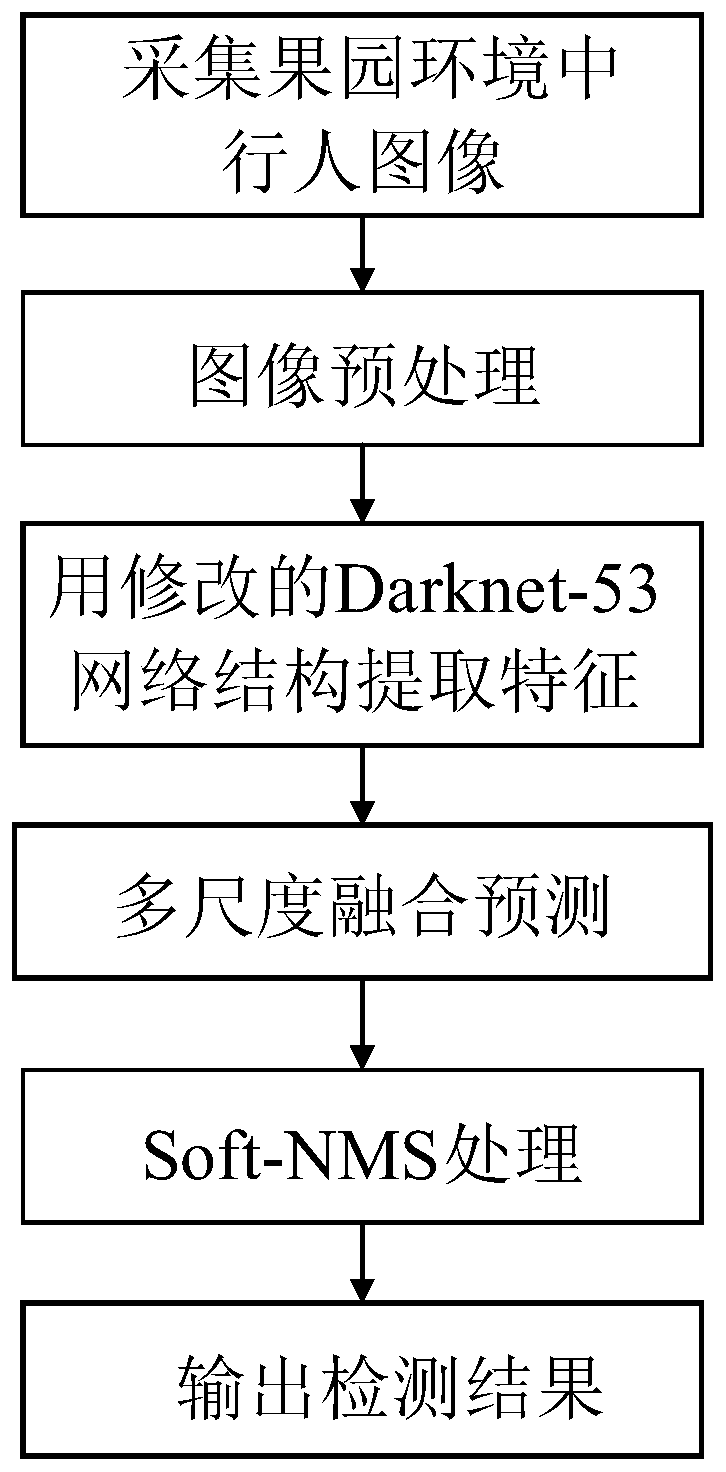
An orchard pedestrian detection method based on a YOLOv3 algorithm
PendingCN109934121AImprove robustness and generalizationReduce hardware requirementsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesMachine learningOrchard
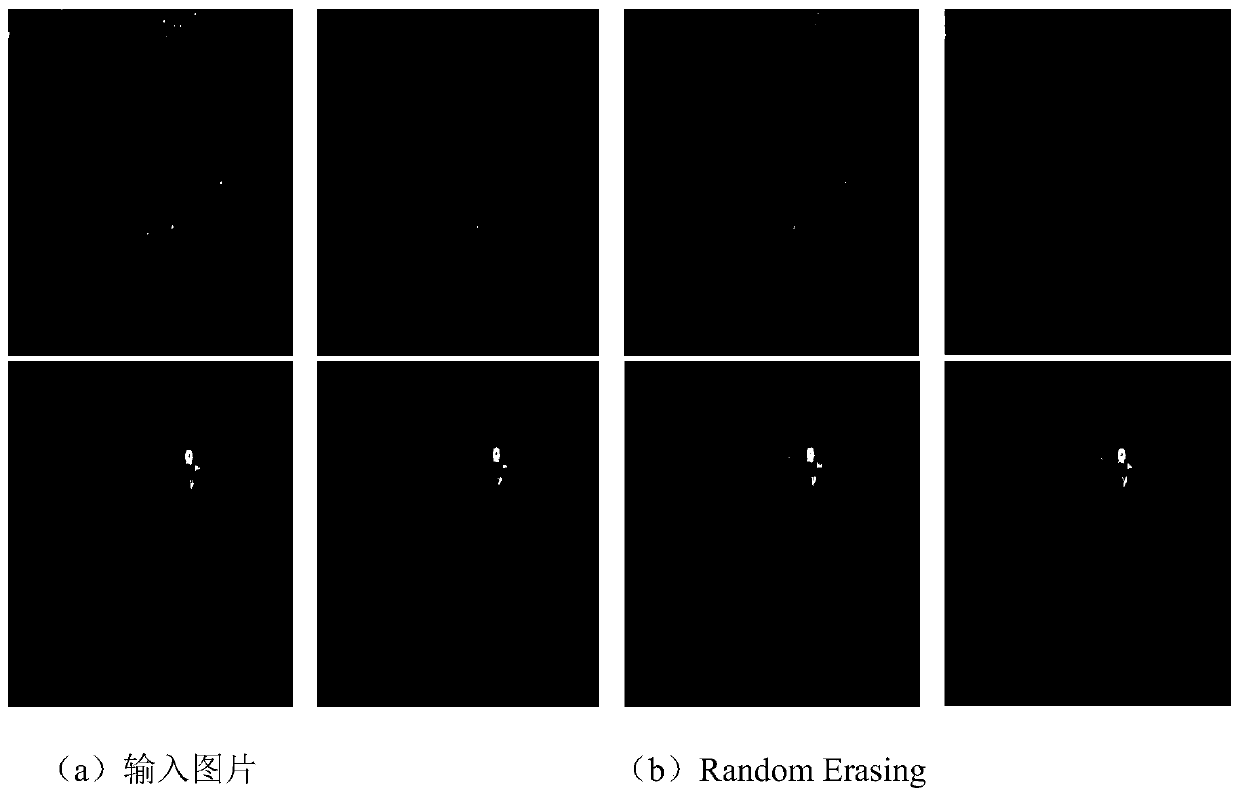
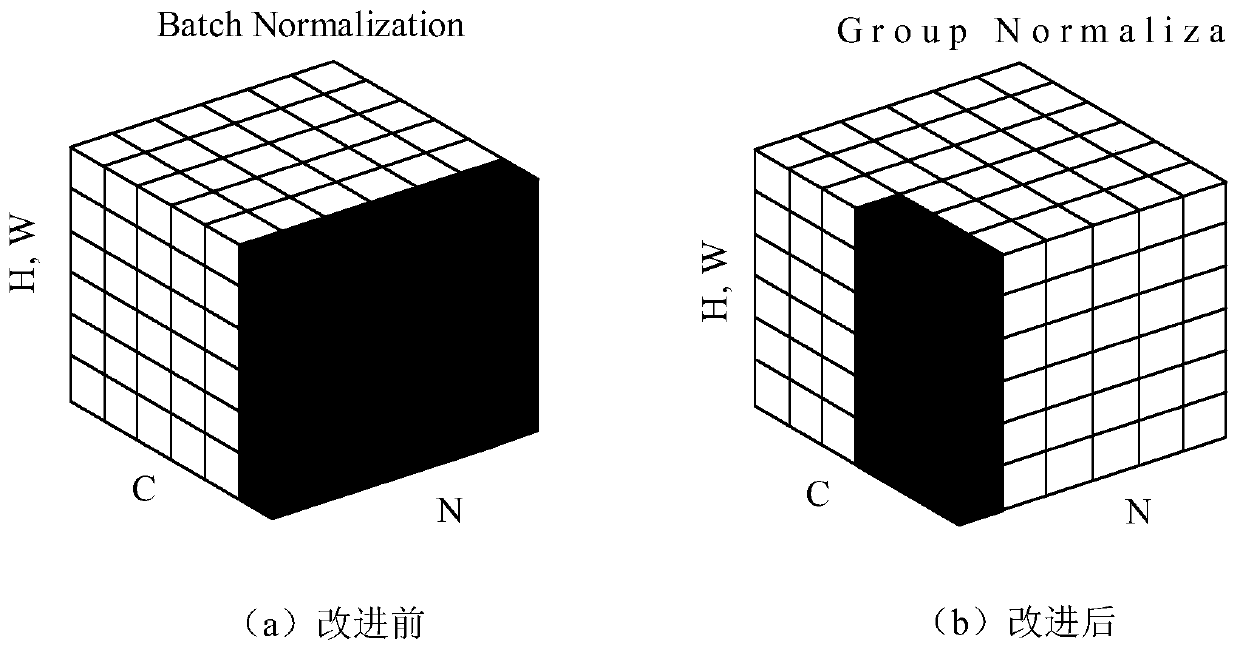
The invention discloses an orchard pedestrian detection method based on a YOLOv3 algorithm. The method specifically comprises the steps of collecting pedestrian images in an orchard; Preprocessing thecollected images, and constructing a standard pedestrian detection data set; Placing a training set into the modified Darknet-53 network structure to extract pedestrian features; Generating a predicted pedestrian boundary frame by using a K-means clustering method, performing category prediction by using a binary cross entropy loss function, and performing multi-scale fusion prediction by using asimilar FPN network; Finally, removing redundant prediction boundary frames through the Soft-NMS, and outputting final prediction boundaries and categories. The pedestrian detection accuracy is high,the real-time performance is good, the robustness of a training model to a complex background is enhanced by aiming at data augmentation methods such as Random Eraging proposed in an orchard environment, and through the adopted Soft-NMS algorithm, the recall rate of detection can be increased, and the introduced group normalization Group Normalizations can reduce the requirements of a trained model on hardware.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method and device for optimizing driver assistance systems
ActiveCN105579320AReduce hardware requirementsVehicle sub-unit featuresControl devicesSubjective perceptionEngineering
The invention relates to a method for optimizing a driver assistance system A, which method comprises the steps of specifying at least one driver assistance system A to be optimized, determining at least one vehicle parameter function that characterizes an operating state of a vehicle and at least one environment parameter function that characterizes the environment of the vehicle, calculating at least one driving situation characteristic value function that characterizes a driving situation of the vehicle, at least on the basis of the at least one vehicle parameter function and / or the at least one environment parameter function, calculating at least one control intervention characteristic value function that characterizes the activity of driver assistance system A, and calculating a correction function that depends on the at least one driving situation characteristic value function and characterizes a subjective perception of the driving situation by at least one vehicle occupant, at least on the basis of the of the at least one control intervention characteristic value function and on the basis of the at least one vehicle parameter function and / or the at least one environment parameter function.
Owner:AVL LIST GMBH
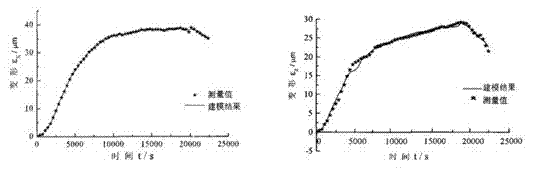
BP neutral network heavy machine tool thermal error modeling method optimized through genetic algorithm
InactiveCN104597842AImprove convergence speedImprove accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlRobustness testingOptimal weight
The invention discloses a BP neutral network heavy machine tool thermal error modeling method optimized through a genetic algorithm. Through the establishment of the structure of a BP neutral network, global optimization is conducted on the initial weight and threshold of each layer of the BP neutral network through a training sample. After the error objective is set, global optimization is conducted on the initial weight and threshold of the BP neutral network structure through the genetic algorithm, and the optimal weight and threshold found by the genetic algorithm is substituted into the BP neutral network to be conducted with sample training. Based on the decline principle of the error gradient, quick search is conducted near the extreme point until the training is end and thermal error prediction model is obtained. Finally, robustness testing is conducted on the obtained thermal error prediction model. The global optimization is conducted on the initial weight and threshold of the BP neutral network structure through the utilization of the genetic algorithm, the self-characteristics of the BP neutral network is overcome, and the quickness, the accuracy and the robustness of convergence when the optimal weight and threshold is trained can be improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
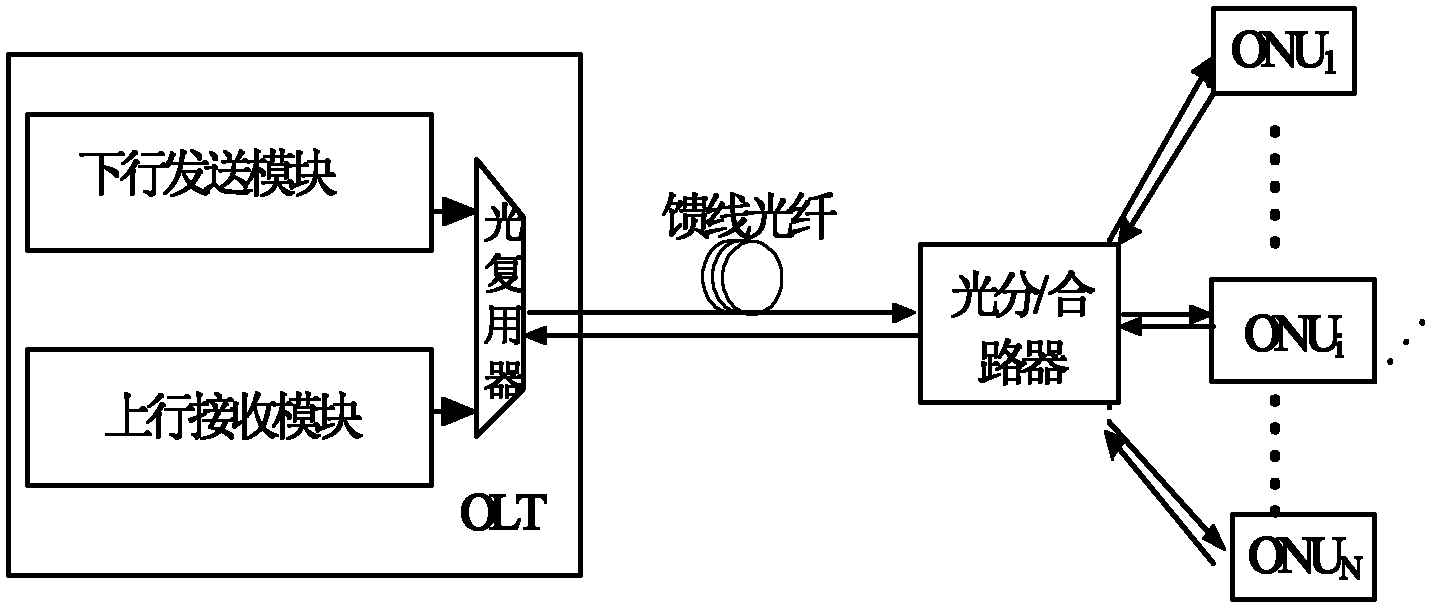
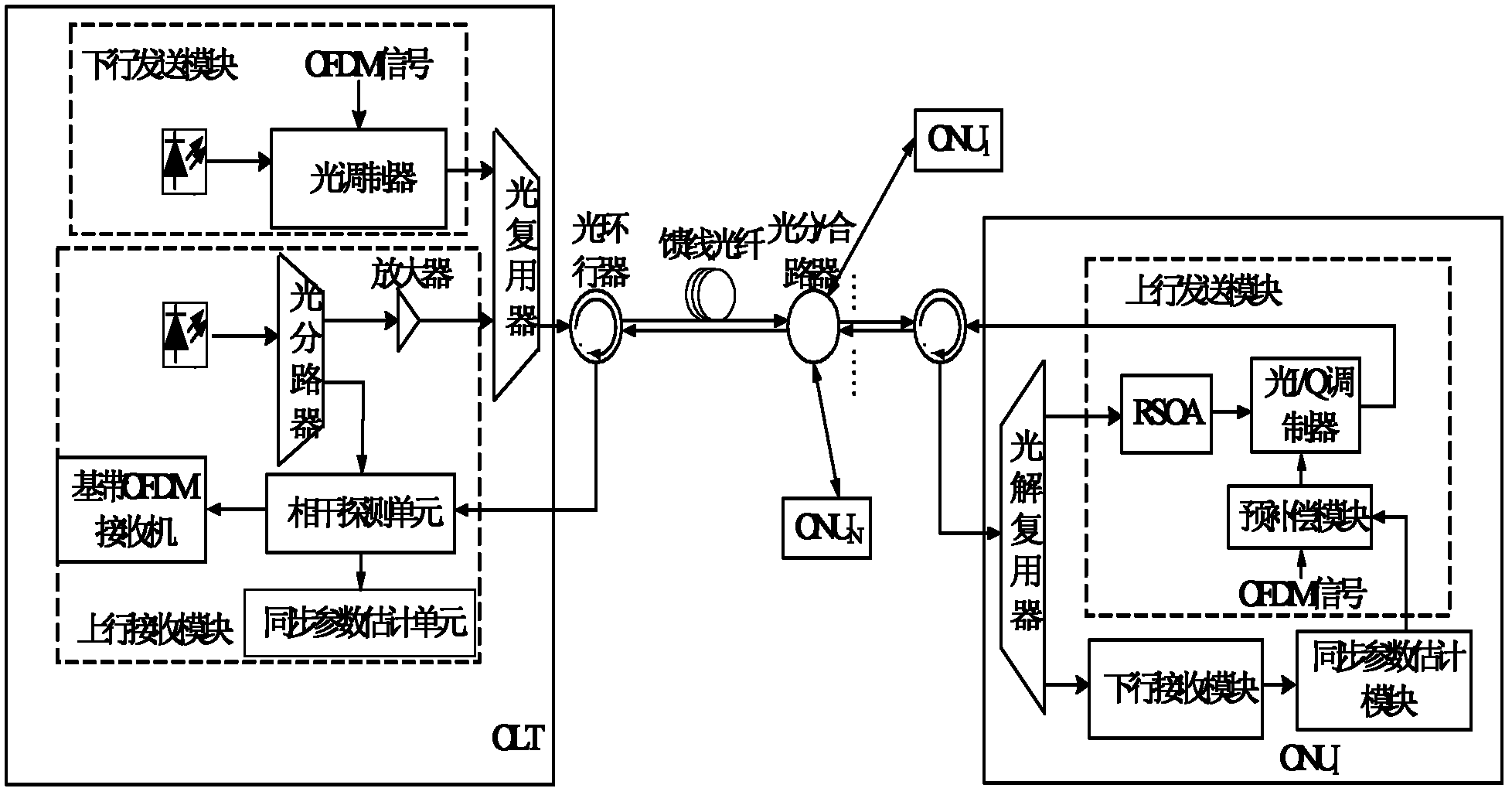
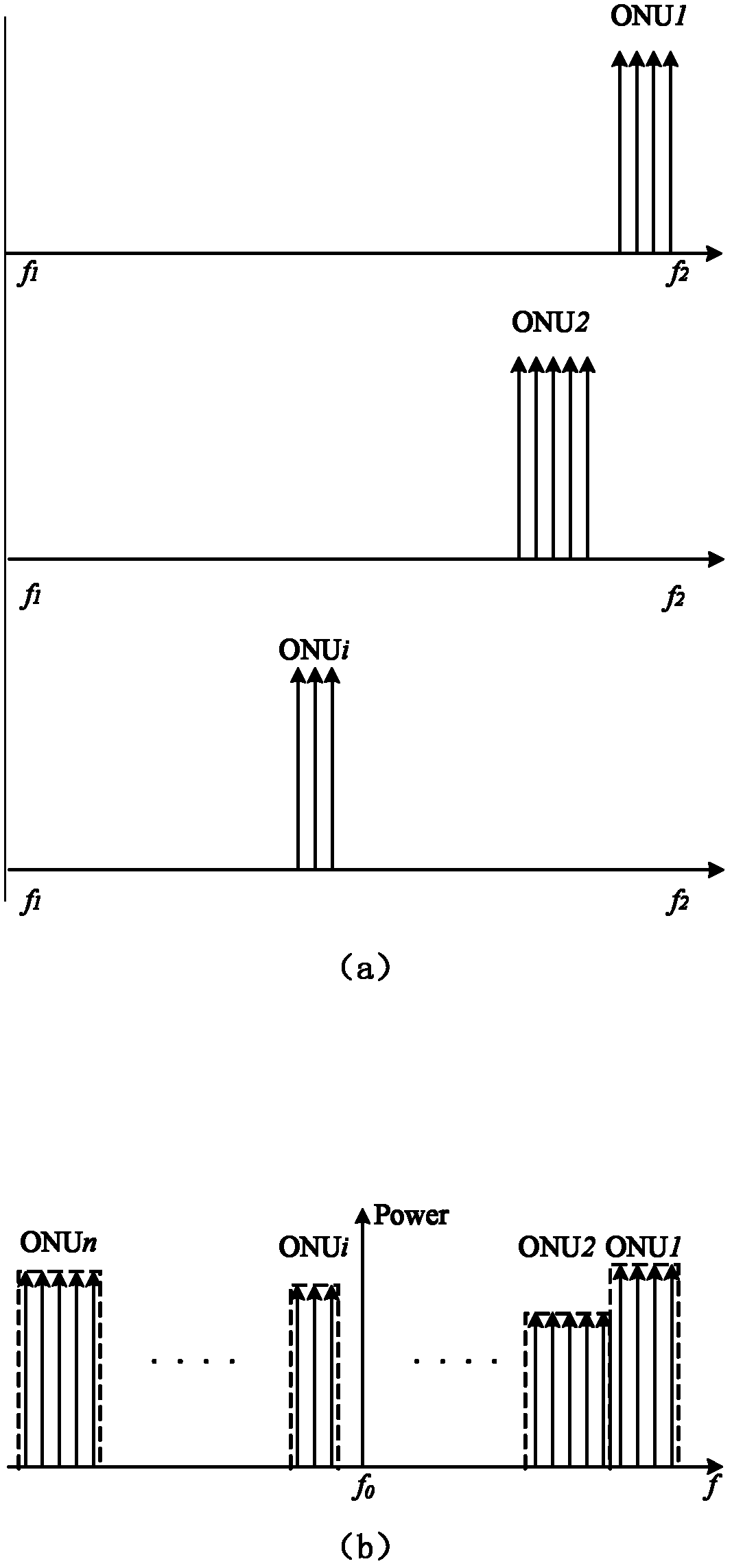
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing passive optical network system
InactiveCN102202248AAllocation mechanism is flexibleImprove spectrum utilizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsMulti-frequency code systemsData streamFrequency spectrum
The invention provides an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing passive optical network system, which modulates an uplink data stream by using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) on the basis of not increasing hardware cost and media access control (MAC) complexity. The system adopts OFDM modulation for both uplink transmission and downlink transmission. In the OFDM modulation of uplink data, the positions and bandwidths of frequency bands allocated to each optical network unit and used for bearing valid uplink data in the whole converged OFDM frequency band are variable. Different frequency bands are allocated to uplink channels of different optical nodes, so that the frequency bands allocated to all the ONUs in the system and used for bearing the valid uplink data are positioned at different positions of the whole OFDM frequency spectrum, and are not overlapped with one another. An uplink transmission module can perform adaptive source configuration, dynamically allocate the number of sub-carriers according to the traffic of a user and regulate the bandwidths of the frequency bands used for bearing the valid uplink data.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
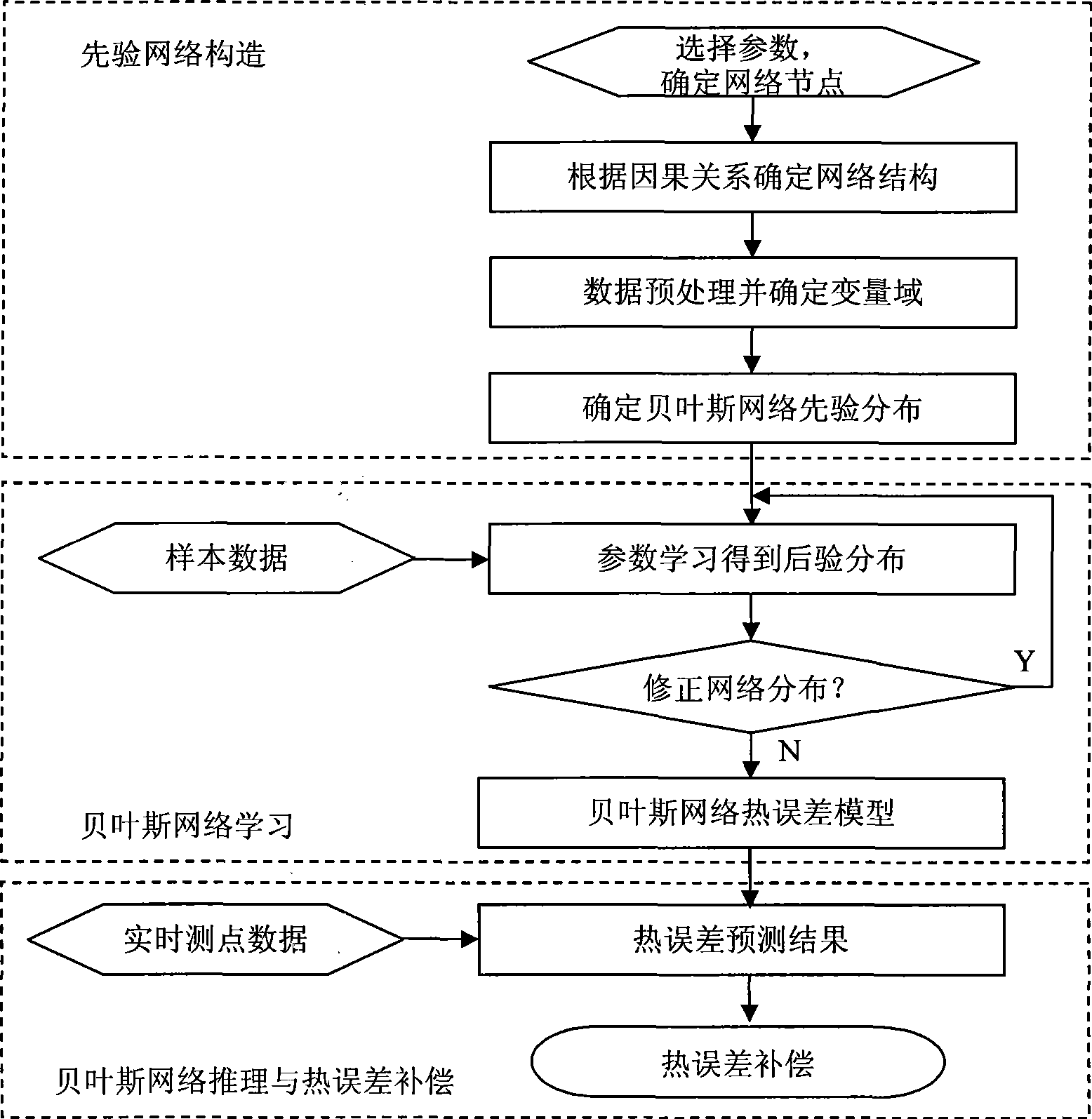
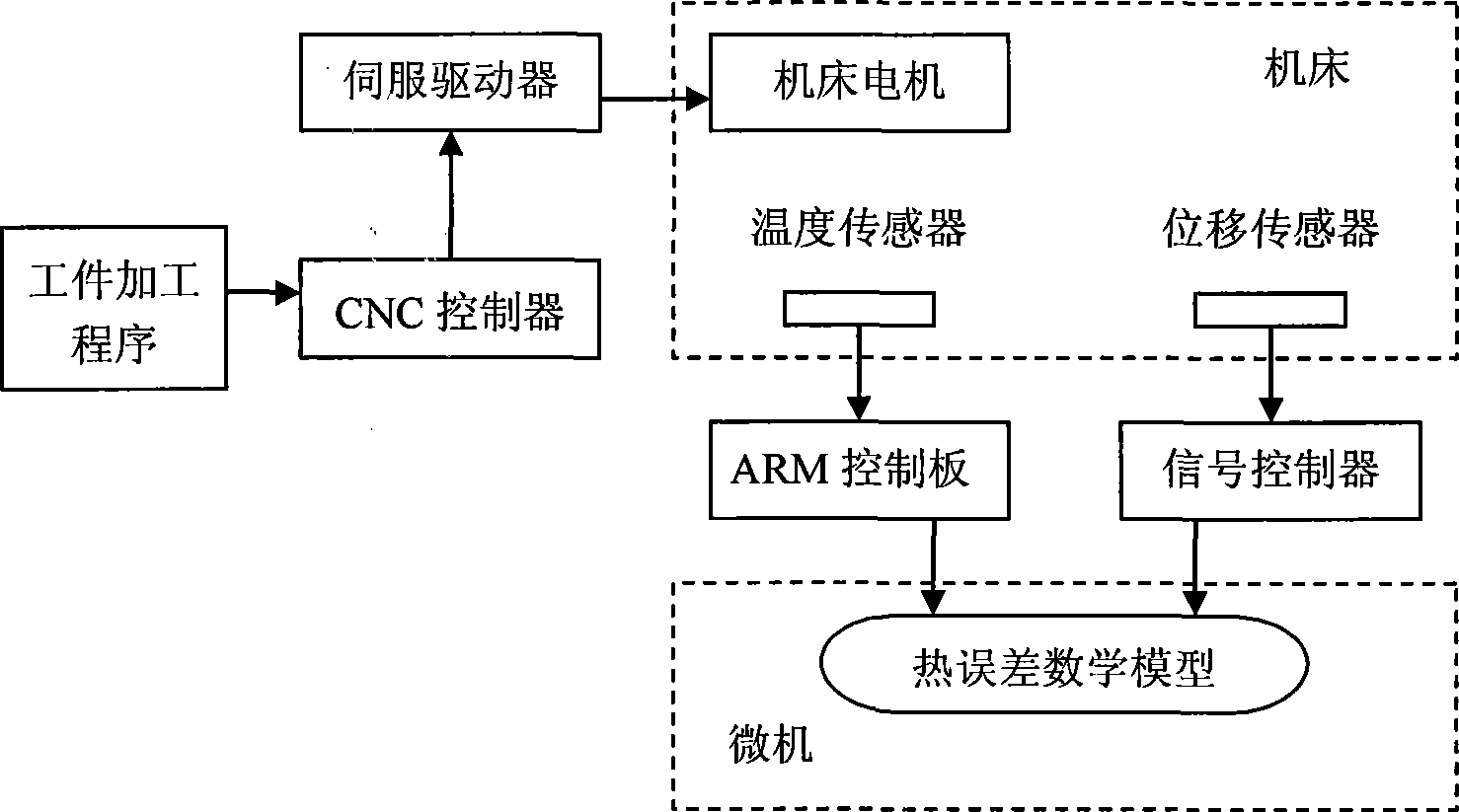
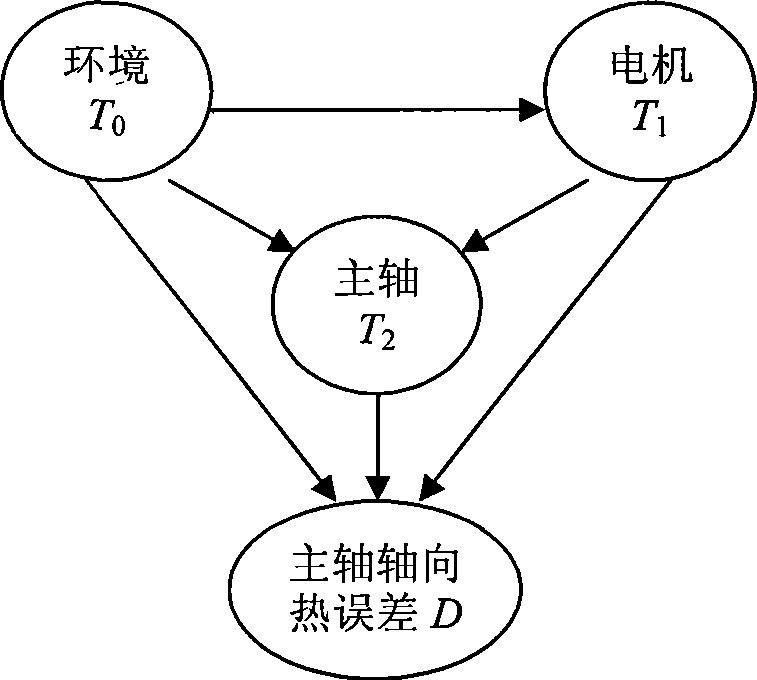
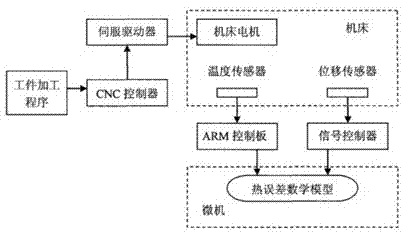
Numerical control machining tool heat error Bayes network compensation method
InactiveCN101436057AIntuitiveReduce computational complexityProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlGaussian network model
The invention discloses a Bayesian network compensation method for thermal error of a numerical control machine tool, which comprises the following steps: (1) a Bayesian network thermal error prediction model is constructed according to measured sample data; and (2) the real-time compensation of the thermal error of the machine tool is realized according to the prediction result of the Bayesian network model. The compensation system of the invention has a simple structure and reliable application; and the adopted Bayesian network modeling method, on one hand, uses the language of a graph theory to intuitively express the causal dependency relation among various factors which produce the thermal error, on the other hand, analyzes and utilizes the inherent correlation among the factors according to the principle of probability theory to reduce the calculation complexity of inferential prediction, and has the characteristics of intuitive expression, high modeling accuracy and self-adaptation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
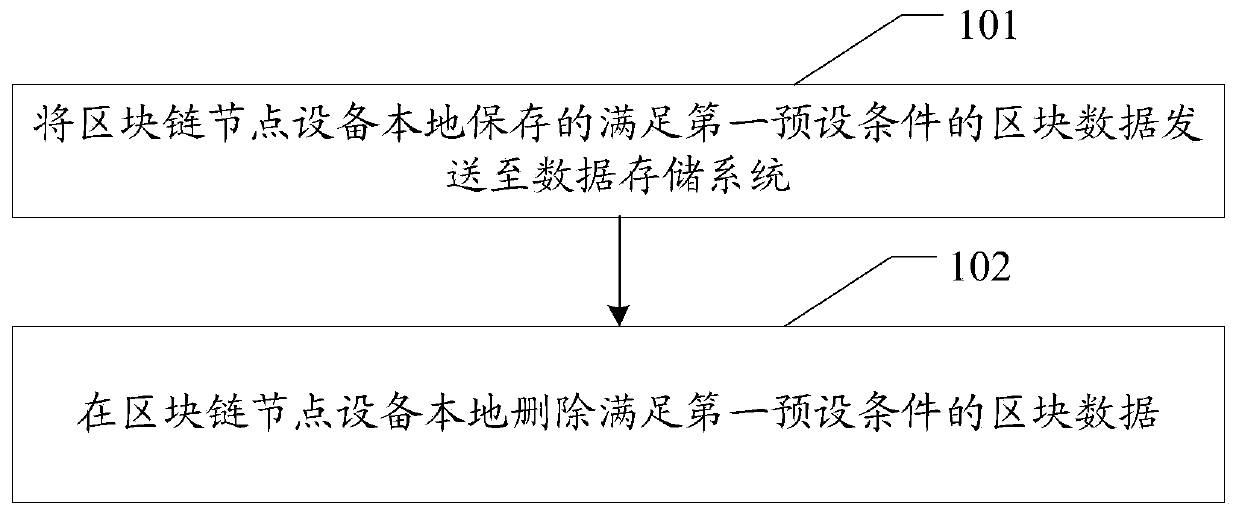
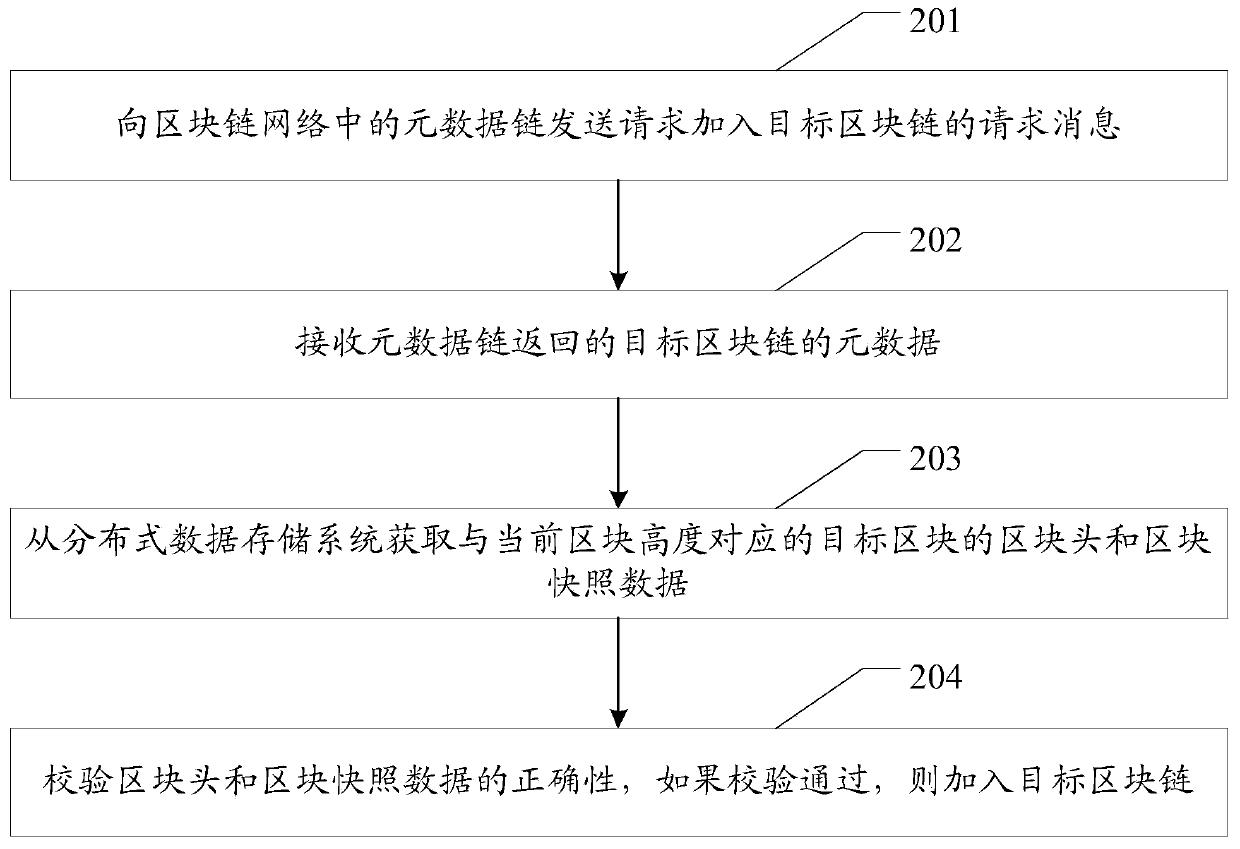
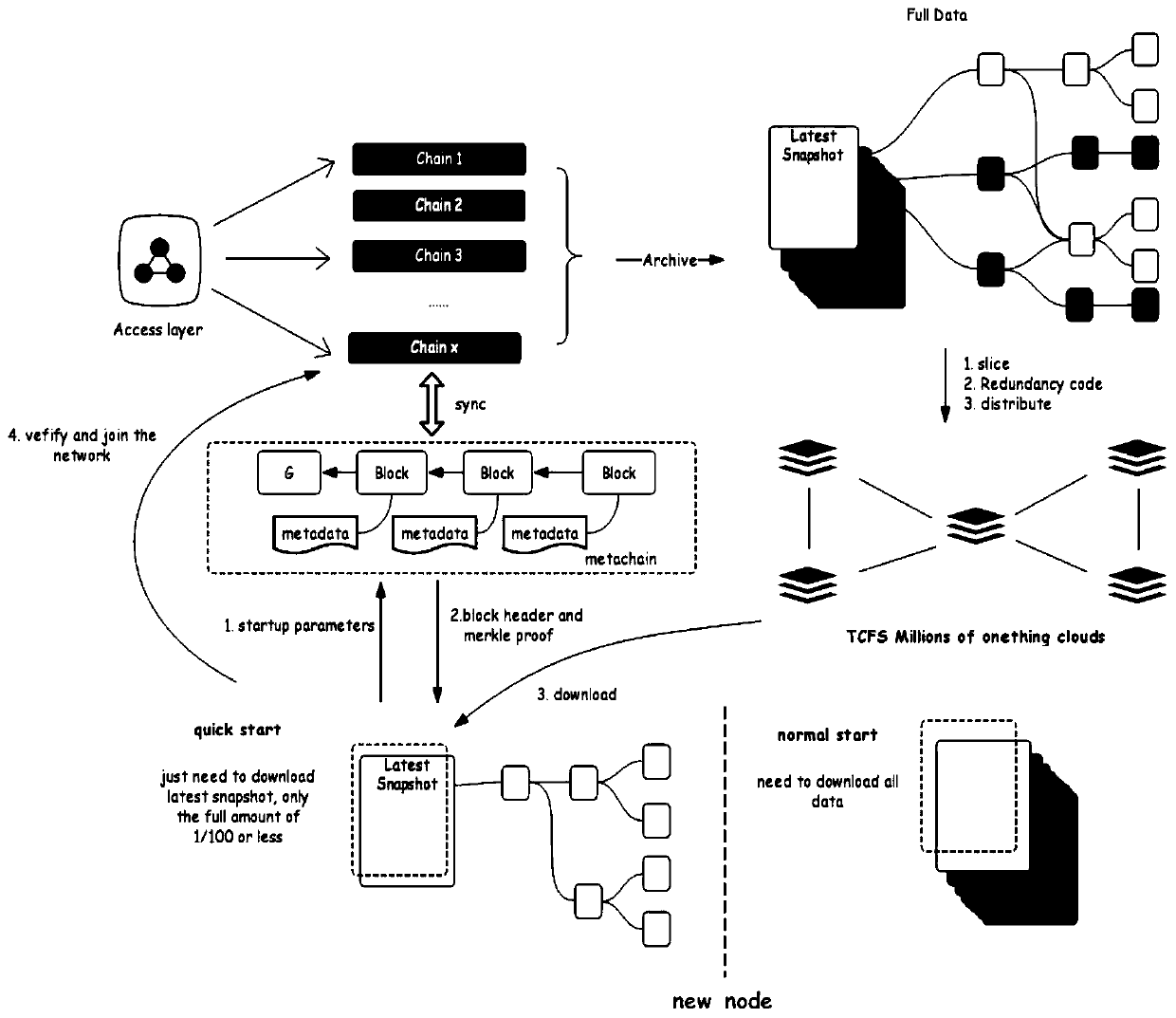
Block chain-based data processing method and system, and related equipment
ActiveCN110011788AQuick joinReduce hardware requirementsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationChain networkMetadata
The invention discloses a block chain-based data processing method and system and related equipment, which are used for reducing block chain data required to be stored by block chain node equipment and reducing hardware requirements of the node equipment for joining a block chain network. The method provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises the following steps: sending a request message for requesting to join in a target block chain to a metadata chain in a block chain network; wherein the metadata of each block in the block chain is stored in the metadata chain, and the metadata comprises the id of the block chain, the block height, the block hash value and the block validity certificate; receiving metadata of the target block chain returned by the metadata chain; obtaining ablock head and block snapshot data of a target block corresponding to the current block height from a distributed data storage system; and verifying the correctness of the block head and the block snapshot data, and if the verification is passed, adding the block head and the block snapshot data into the target block chain.
Owner:SHENZHEN THUNDER NETWORK TECH
Methods and systems for a database
InactiveUS20190361916A1Improve operationIncrease usageInterprogram communicationRelational databasesData setDynamic data
A database system for data storage and retrieval generally includes a transactional database having a distributed data architecture providing real-time access to a dynamic data set configured to accept a query expression to the transactional database is abstracted from at least one underlying data structure of the transactional database. The database system includes a user interface configured for users to query the transactional database via queries using the query expression. The transactional database delivers a response to a query that reflects a current state of data in the dynamic data set.
Owner:FAUNA INC
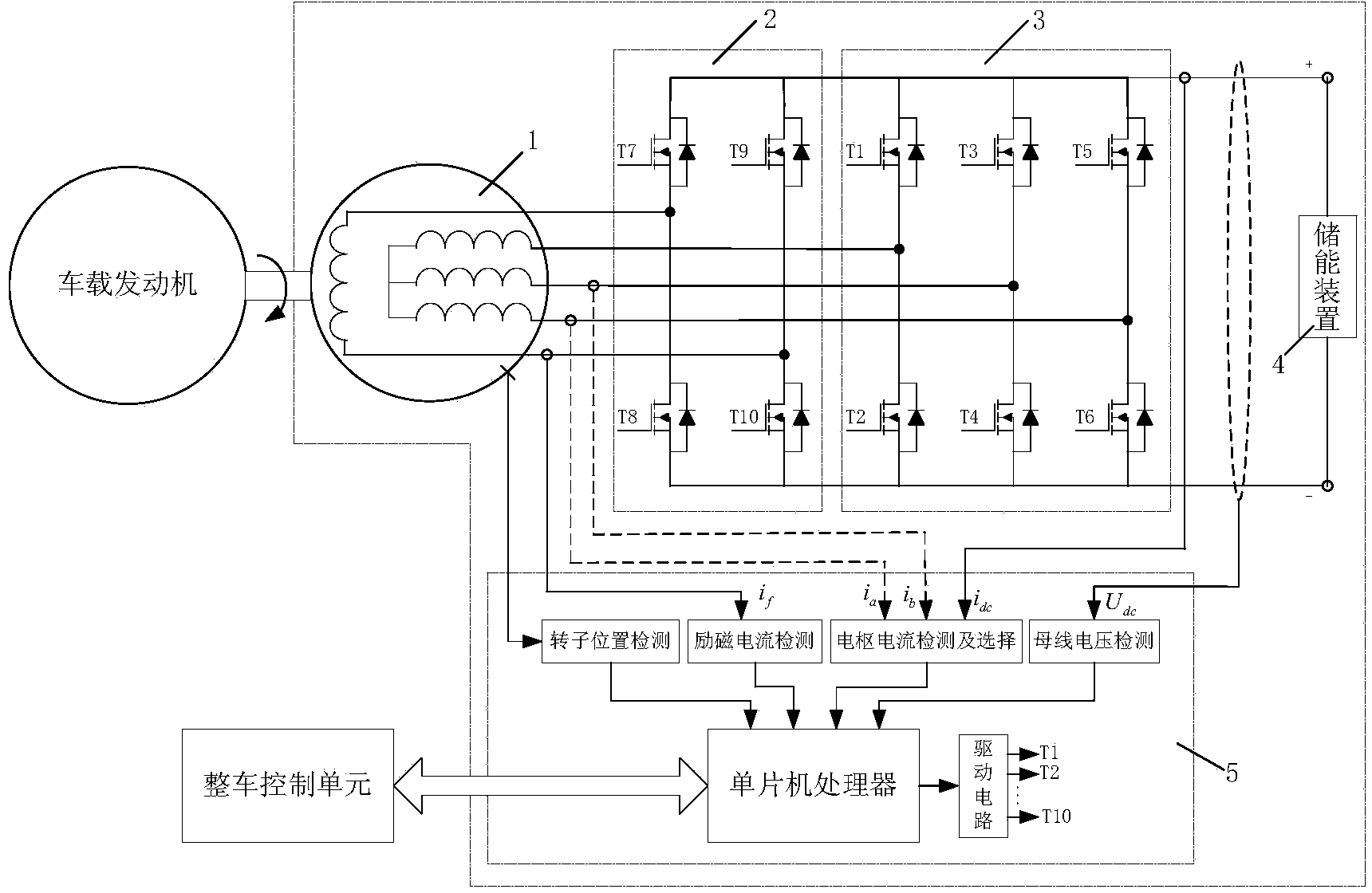
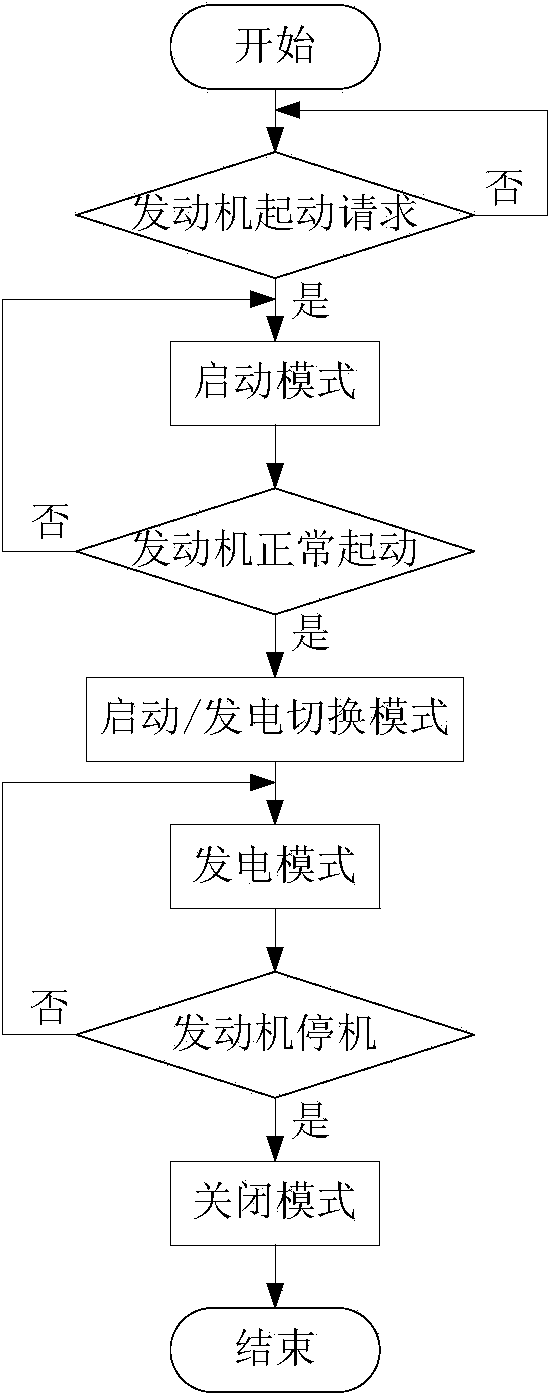
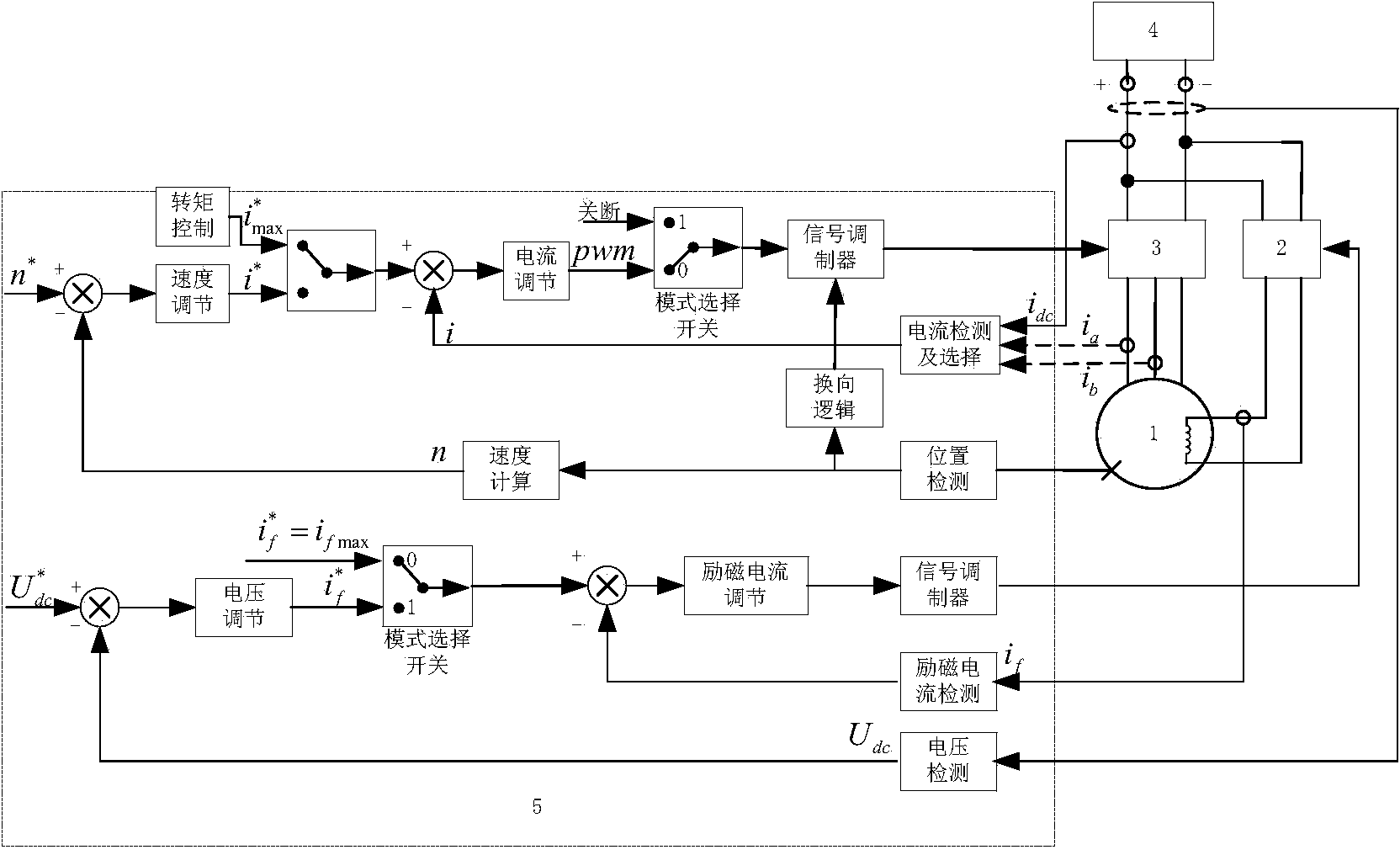
Square wave combining excitation starter/ electric generator control method
InactiveCN103872971AEasy to controlReduce hardware requirementsAC motor controlElectric motor startersElectric generatorAutomotive engine
The invention relates to a starter / electric generator control method, in particular to a square wave combining excitation starter / electric generator control method, and belongs to the field of automobile engine starting / electric generating. A square wave combining excitation motor system comprises a square wave combining excitation motor (1), an excitation regulating unit (2), an inverter (3), an energy storing device (4) and a single-chip microcomputer control unit (5). When an engine sends a starting request, the square wave combining excitation motor (1) enters the starting mode, a speed controlling or torque controlling method is adopted in the starting mode, and the engine is started quickly. When a vehicle is driven normally, the square wave combining excitation motor (1) enters an electricity generating mode, the inverter (3) serves as an uncontrollable rectifier bridge, a voltage outer ring and exciting current inner ring control method is adopted, the air gas field is adjusted by regulating an exciting current, and the output voltage is stabilized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
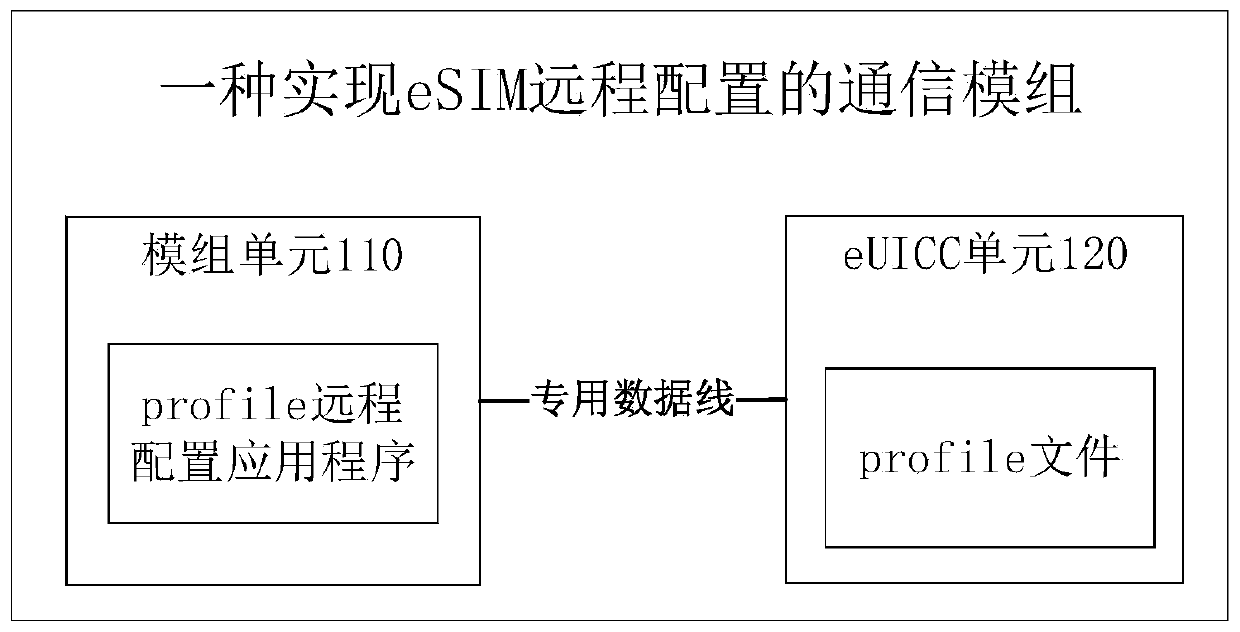
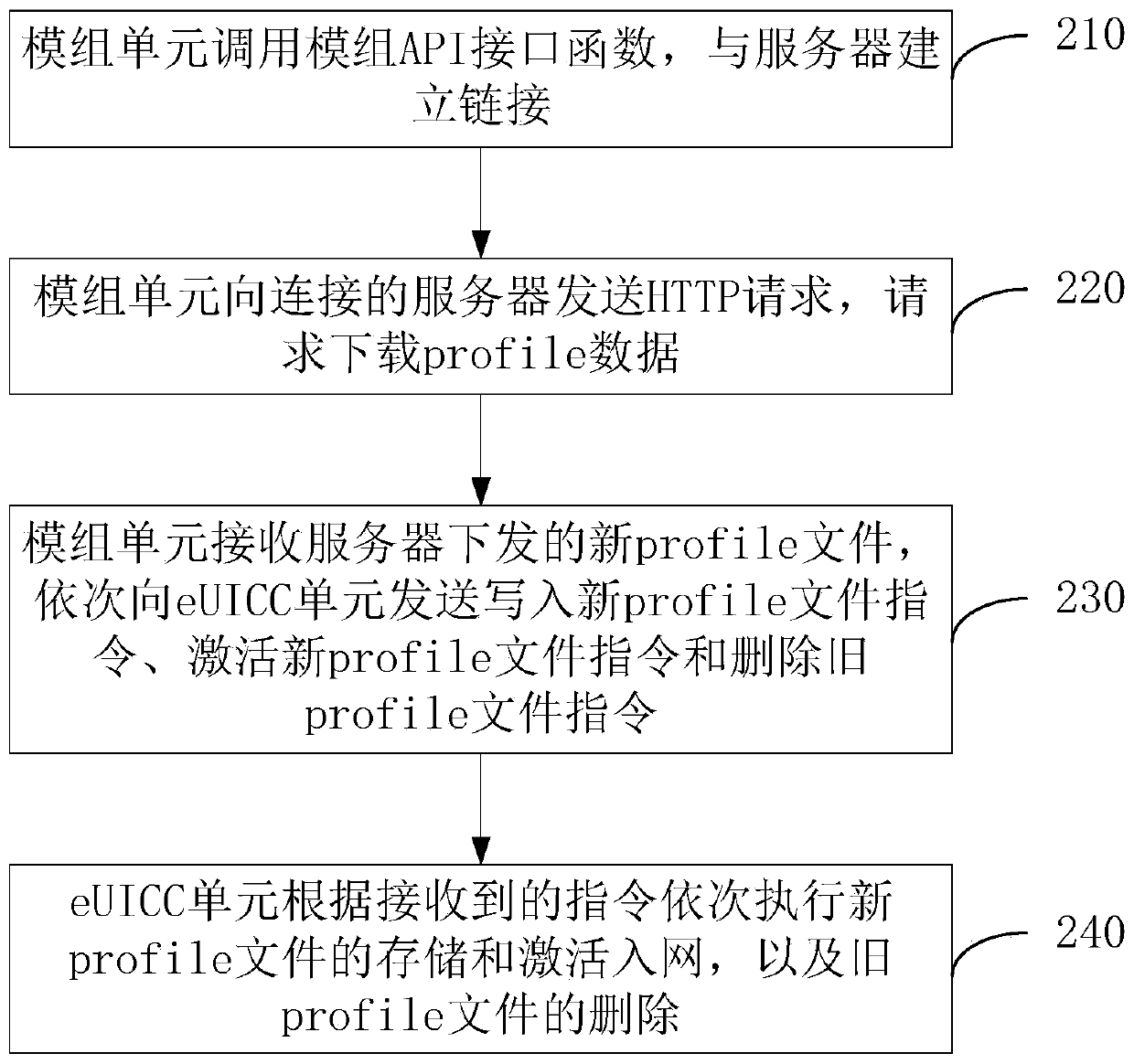
Communication module, communication method and system for realizing eSIM remote configuration
ActiveCN110446201AReduce developmentReduce hardware requirementsNetwork data managementComputer hardwareCommunications system
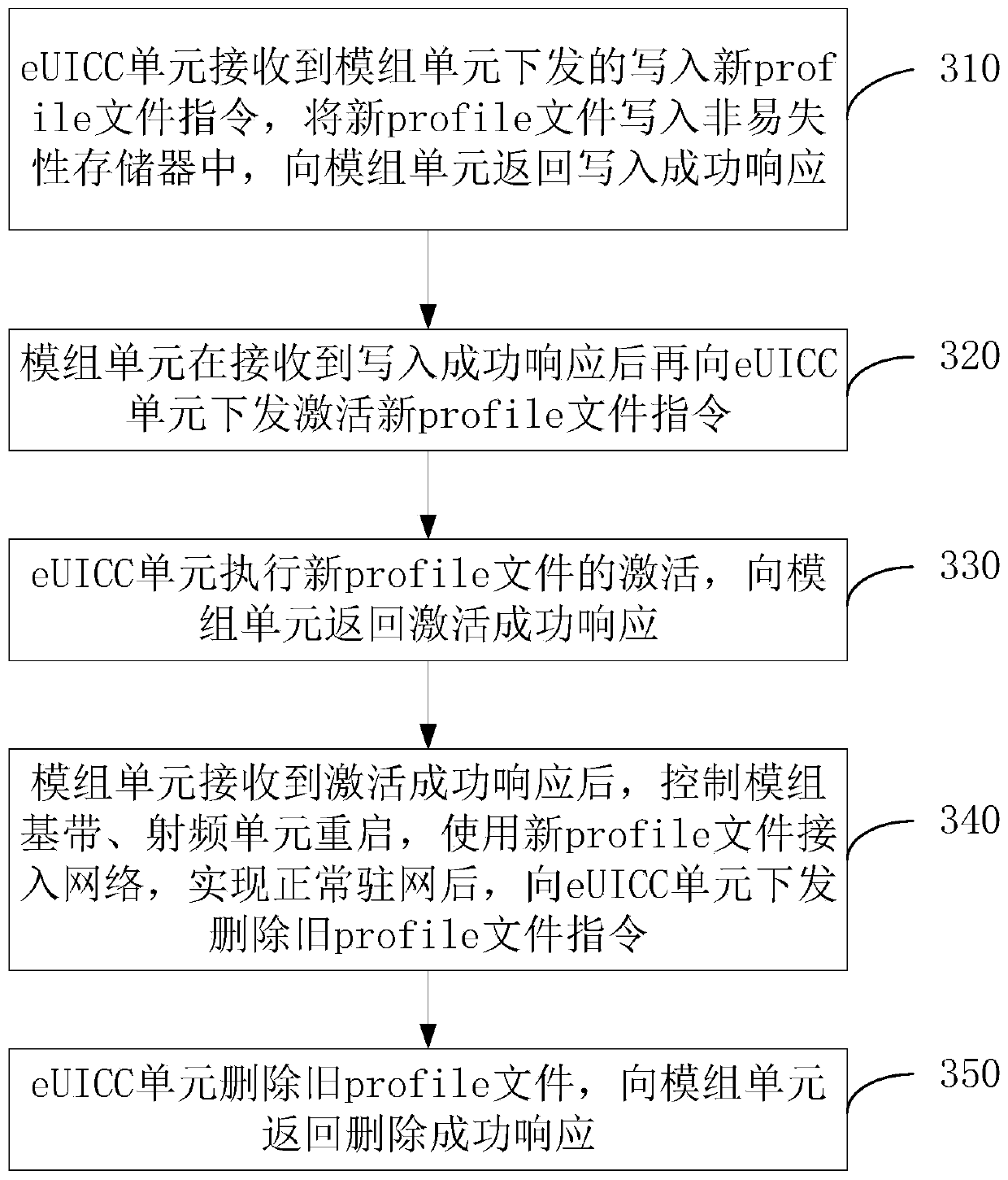
The invention discloses a communication module, a communication method and a communication system for realizing eSIM remote configuration. The communication module is integrated in the terminal equipment and comprises a module unit and an eUICC unit. The module unit comprises a profile remote configuration application program and is used for communicating with a server to download a new profile file and controlling the eUICC unit to realize communication network access of the eUICC unit through an instruction; and the eUICC unit is an integrated circuit card in which user identity informationand card authentication information are stored, and is used for storing and installing a new profile file, and activating and accessing the new profile file according to an instruction of the module unit. By adopting the communication module provided by the invention, profile remote configuration can be directly carried out with a server, and hardware requirements on a terminal and development ofterminal software are reduced.
Owner:HENGBAO
Data transmission method, input device, cloud server and cloud game system
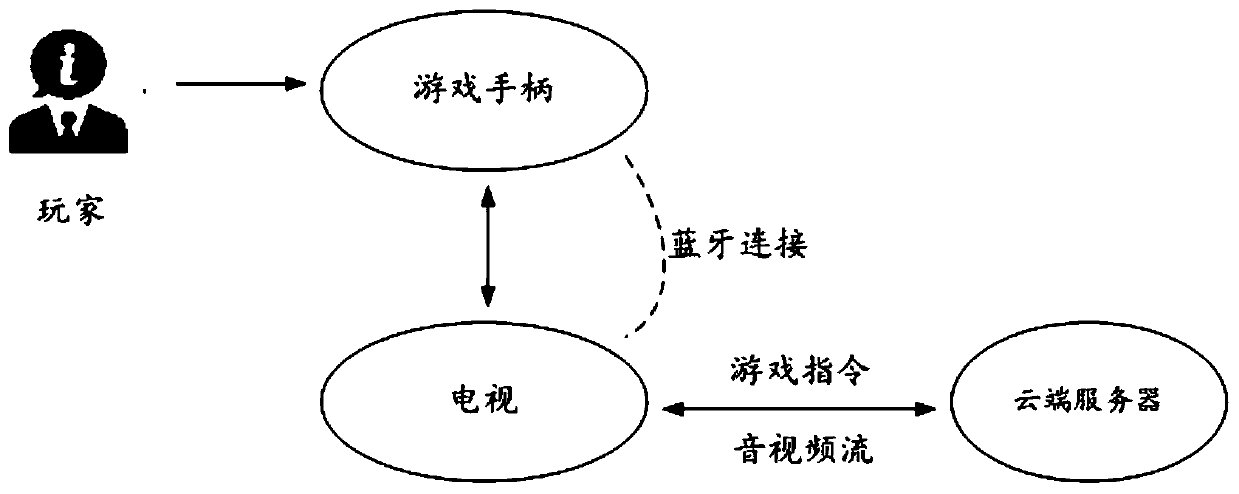
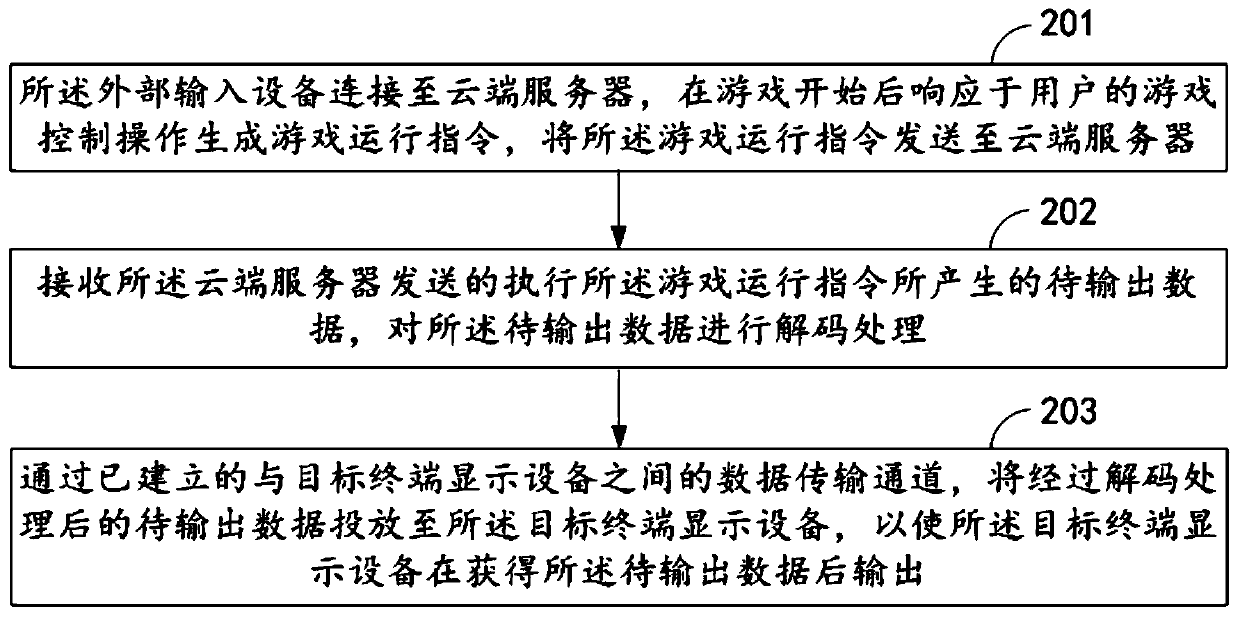
ActiveCN110572469AReduce hardware requirementsImprove convenienceVideo gamesTransmissionDisplay deviceComputer terminal
The invention provides a data transmission method, input equipment, a cloud server and a cloud game system. The method comprises the steps that an external input device is connected to a cloud server,responds to game control operation of a user to generate a game running instruction after a game is started, and sends the game running instruction to the cloud server; to-be-output data generated byexecuting the game operation instruction and sent by a cloud server is received, and the to-be-output data is decoded; and the decoded to-be-output data is released to the target terminal display device through the established data release channel with the target terminal display device, so that the target terminal display device outputs the to-be-output data after obtaining the to-be-output data. In this way, the hardware requirement for the terminal display device can be further reduced.
Owner:BEIJING CYBER CLOUD TECH
Redundant Network Implementation Method
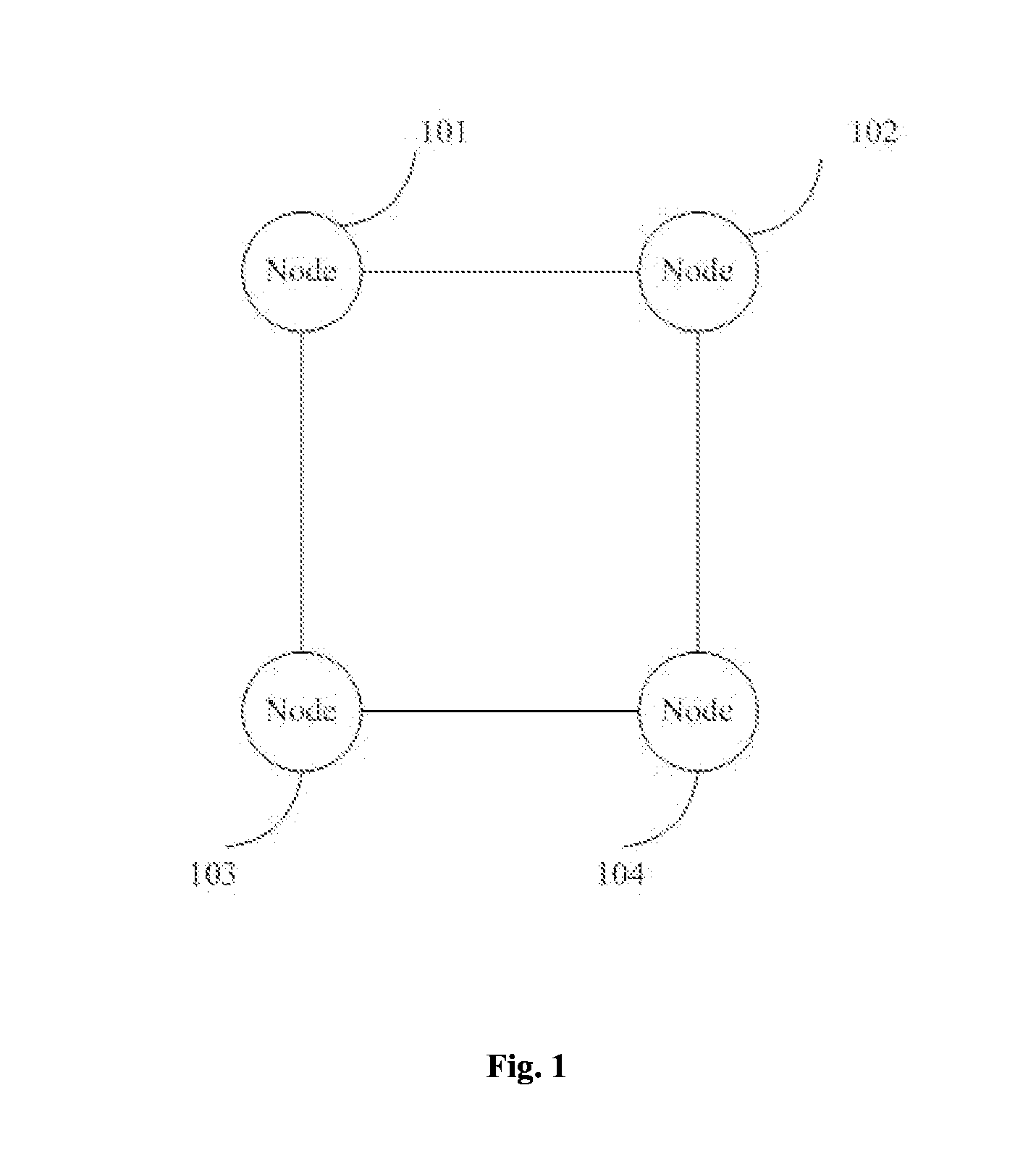
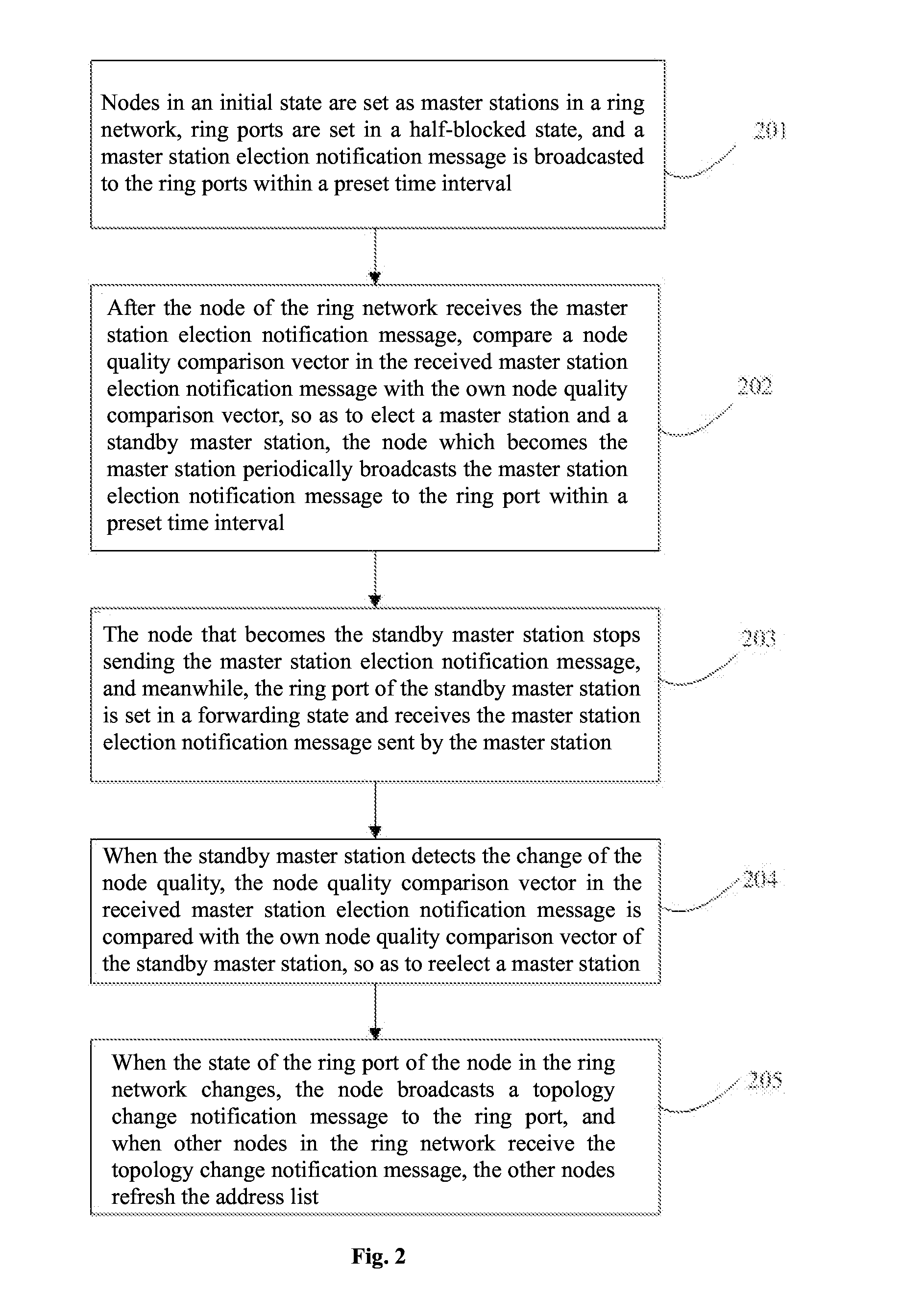
ActiveUS20150138950A1Reduce loop operation complexityReduce hardware requirementsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMaster stationRing network
Disclosed is a method of implementing a redundant network. Ring network nodes in an initial state are set as master stations, ring ports are set in a half-blocked state, a master station election notification message is broadcast to the ring ports within a preset time interval, the nodes receive the master station election notification message, a node quality comparison vector is compared with node quality comparison vectors of the nodes to elect a master and standby stations, one of the ring ports is in the half-blocked state, the other ring ports are in a forwarding state, the master station broadcasts the master station election notification message to the ring ports, the standby master station stops sending the master station election notification message, the ring ports are in the forwarding state, and the message sent by the master station is received.
Owner:KYLAND TECH CO LTD
Nailing robot system and nailing control method thereof
ActiveCN111297479AReduce training timeQuick releaseComputer-aided planning/modellingSurgical manipulatorsRobotic systemsPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
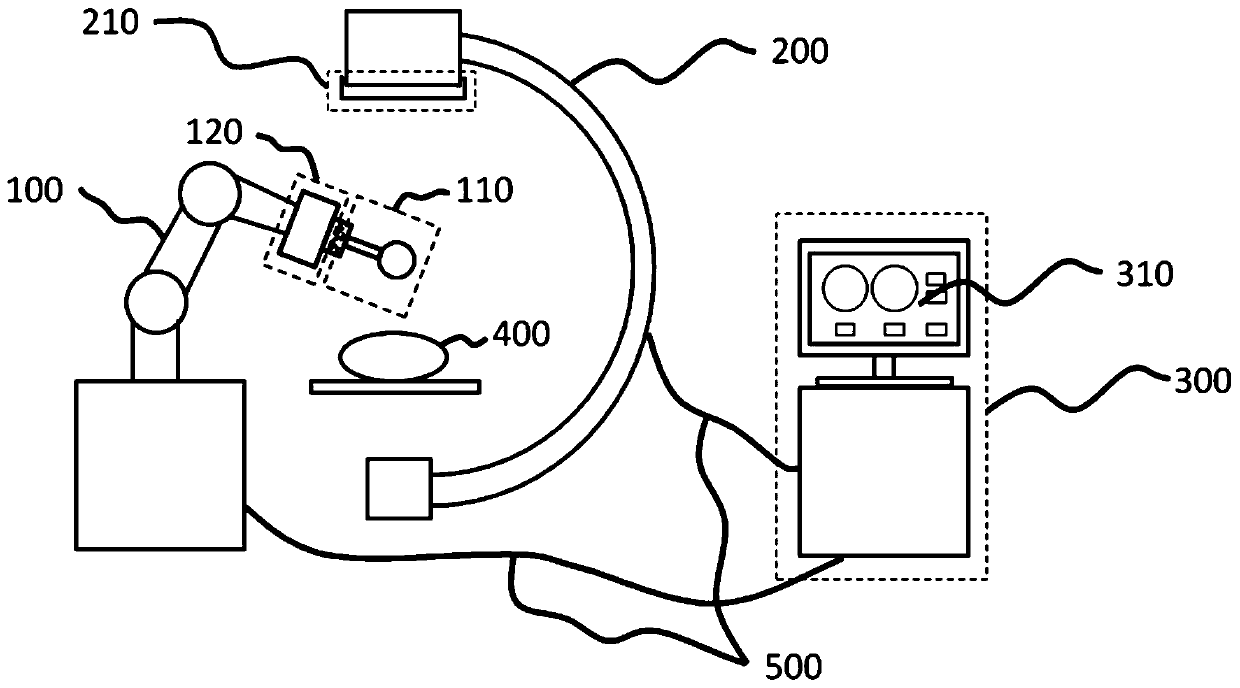
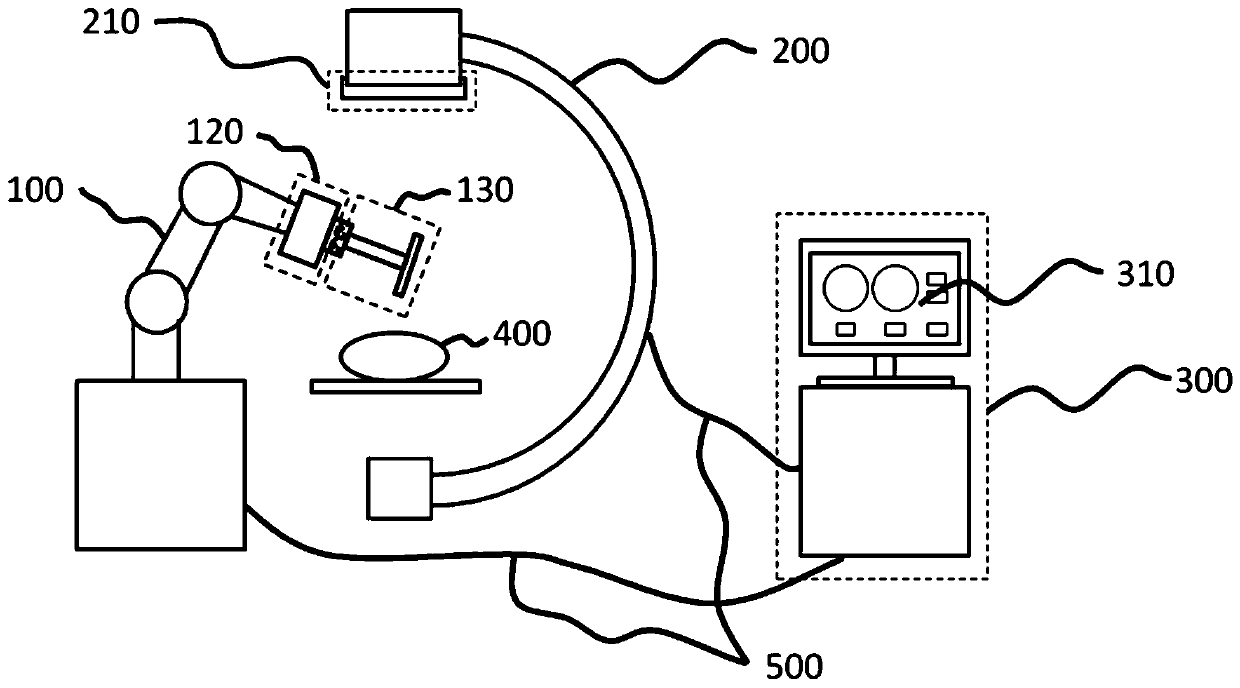
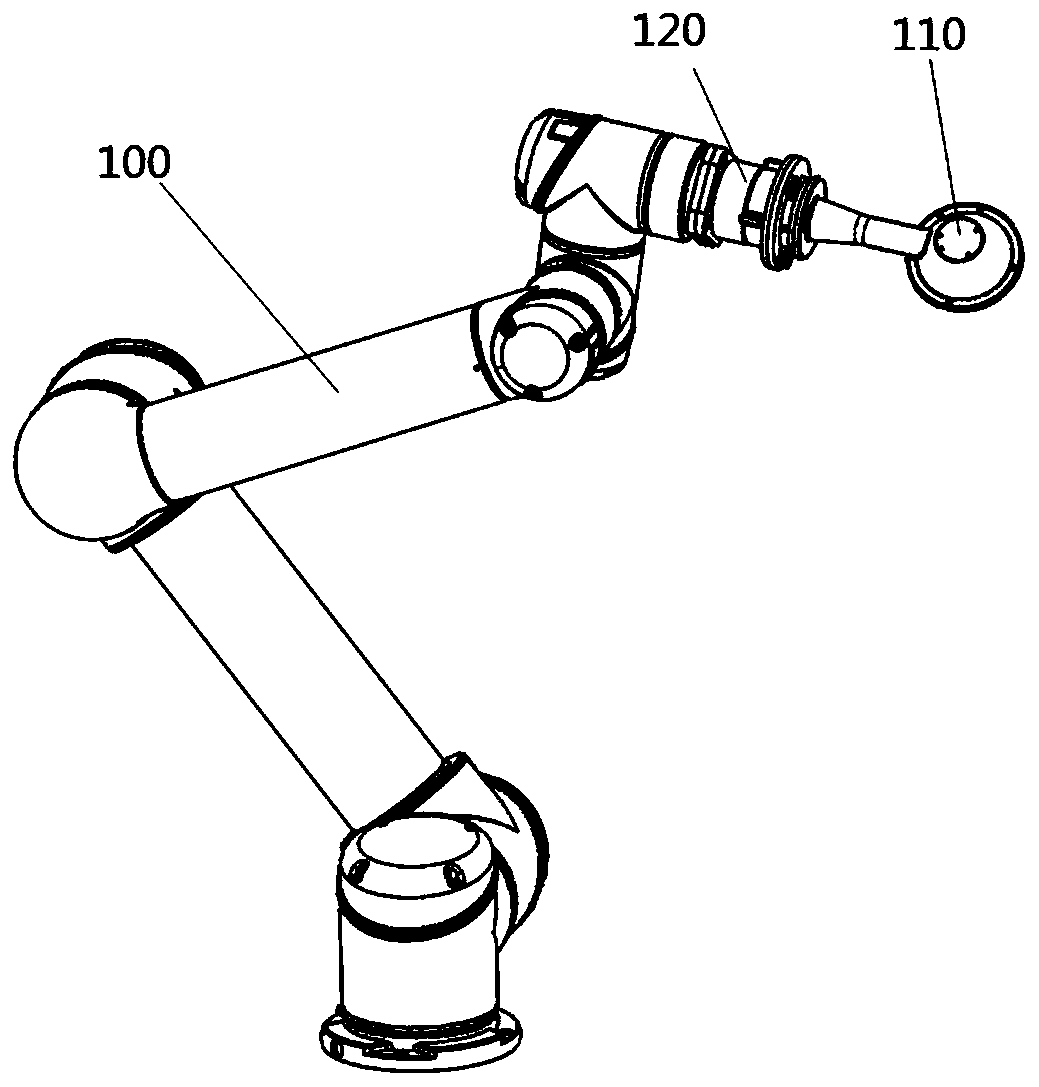
The invention discloses a nailing robot system and a nailing control method thereof. The nailing robot system comprises a mechanical arm, wherein a force sensor, a registration device and a surgical instrument are mounted at the front end of the mechanical arm; the force sensor is mounted between the mechanical arm and the surgical instrument and used for detecting the change of force in a drilling and nailing process; the registration device is installed in a mechanical interface position of the front end of the mechanical arm and used for registration between the mechanical arm and an imageacquisition device; an image distortion correcting device is connected with the image acquisition device and used for distortion correction of the image acquisition deice; the image acquisition deviceis used for acquiring surgical images; a remote workstation is connected with the mechanical arm and the image acquisition device through data lines, and is used for processing the surgical images acquired by the image acquisition device, planning a nailing path and controlling the mechanical arm to move. The system has a low hardware equipment requirement, and can reduce the surgical cost, makeadjustment according to image information fed back in a surgery in real time and improve the nailing accuracy.
Owner:拓博特医疗科技(武汉)有限公司
Neural network system and method suitable for portable power inspection
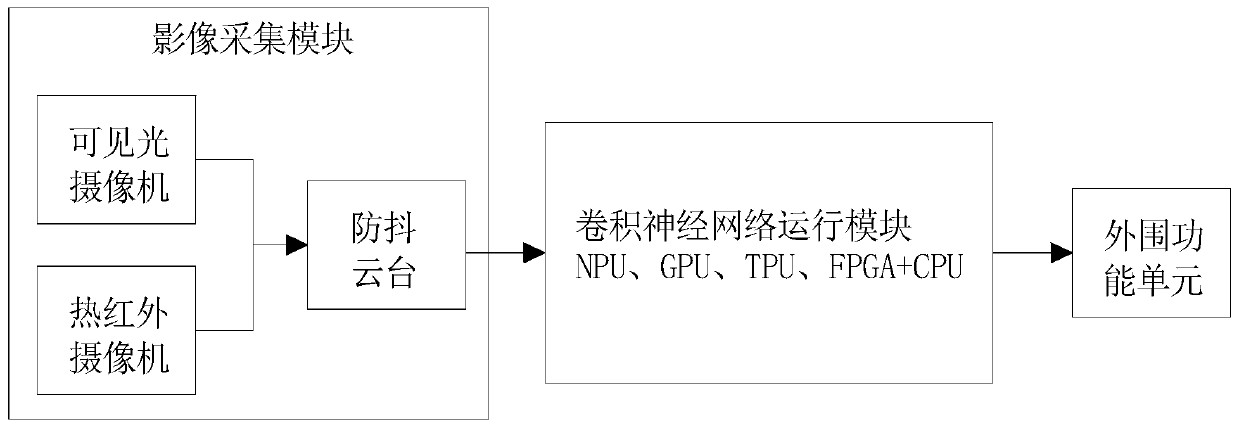
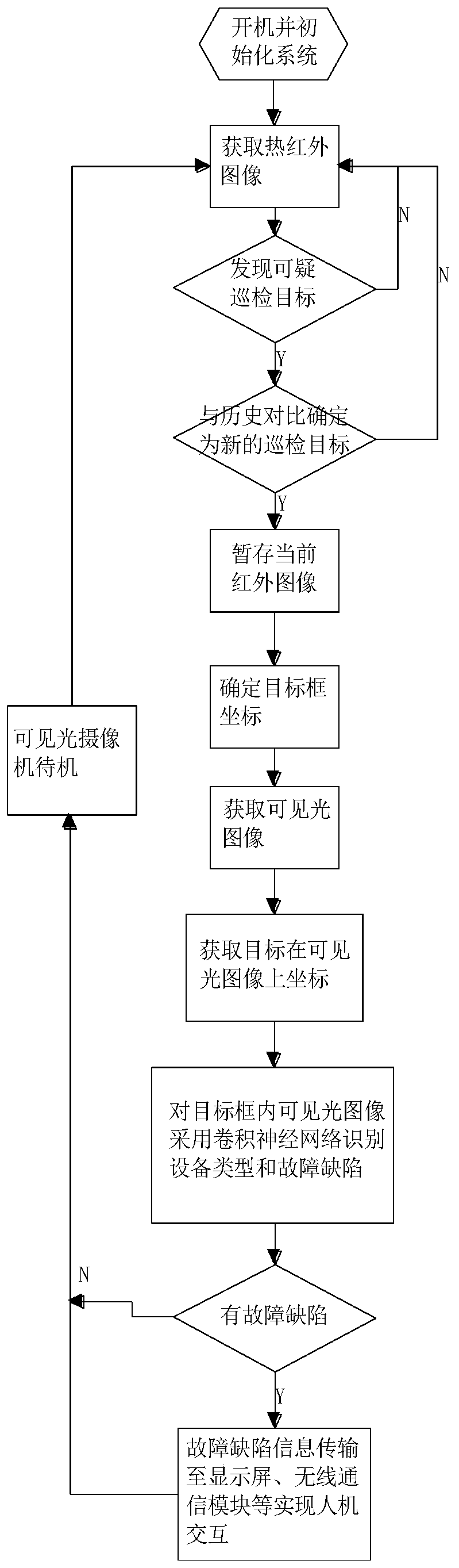
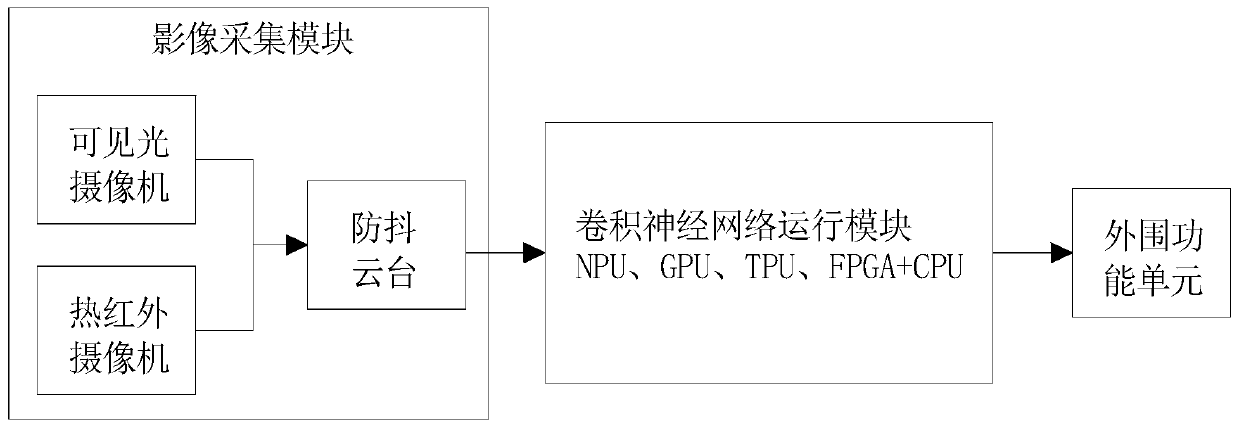
InactiveCN110009530AThe infrared features of the inspection target are obviousReduce the impact of target identificationData processing applicationsImage analysisNeural network systemImaging processing
The invention discloses a neural network system and method suitable for portable power inspection. The system comprises an image acquisition module, a convolutional neural network operation module anda peripheral function unit. The image acquisition module comprises a thermal infrared camera, a visible light camera and an anti-shake holder. The convolutional neural network operation module is mainly used for the operation of a convolutional neural network for processing image information. The convolutional neural network operation module is mainly composed of a CPU and hardware of a GPU, an NPU, a TPU and an FPGA or a system-on-chip composed of the hardware. The invention discloses a neural network system and method suitable for portable power inspection. A thermal infrared camera is adopted to determine the position of the power equipment; the visible light camera is used for studying and judging the state of the power equipment at the position, the influence of a complex backgroundon target recognition is effectively reduced, the infrared image information is less than visible light image information, the image processing speed is higher when the convolutional neural network isused for processing the image, and therefore the requirements for model precision and hardware are reduced.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST STATE GRID SHANXI ELECTRIC POWER +1
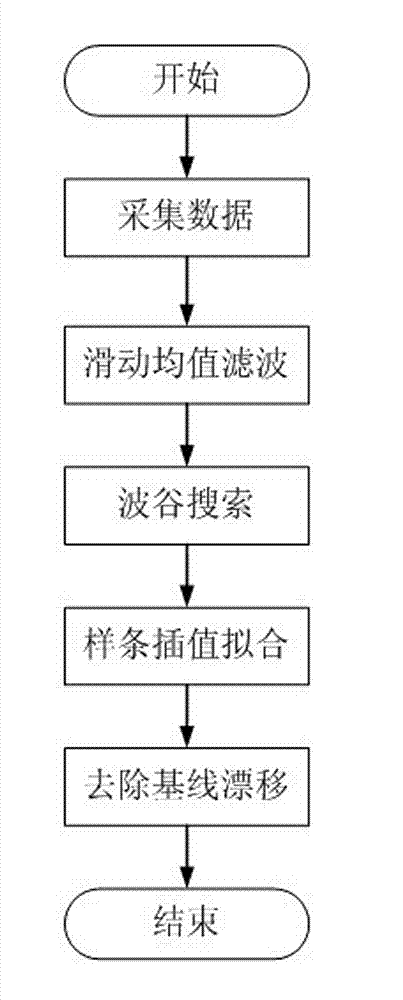
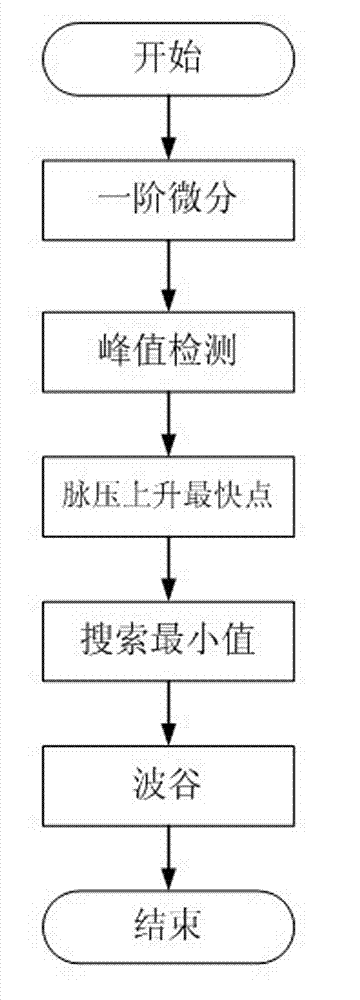
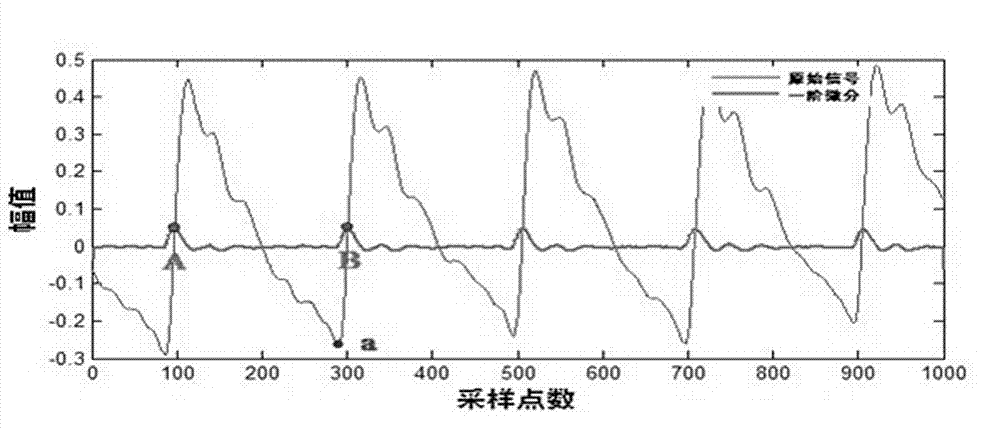
Method for removing baseline drift from pulse wave signal
InactiveCN102885616ASmall amount of calculationReduce hardware requirementsCatheterAnti jammingPulse wave
The invention discloses a method for removing baseline drift from a pulse wave. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a pulse wave signal; pre-treating the acquired pulse wave signal to obtain an alternating current component in the pulse wave signal; performing sliding mean filtering on a section of obtained alternating current signal, and inhibiting the power frequency interference to obtain an original signal of the pulse wave; finally, searching wave troughs of the original signal to recognize the positions of all wave troughs of the pulse wave signal; performing spline interpolation between two adjacent wave troughs to fit a drifting baseline; and substracting the drifting baseline from the original signal to obtain a pulse wave signal in which the baseline drift is removed. According to the method, the power frequency interference in the signal is inhibited through sliding mean filtering, and the baseline drift in the signal is found by a spline interpolation fitting method; compared with the traditional method, the invention has the advantages that the method is accurate, stable, anti-jamming, simple, easy, and updated in real time; and the method has good practical application value.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Method and device for providing information to be displayed
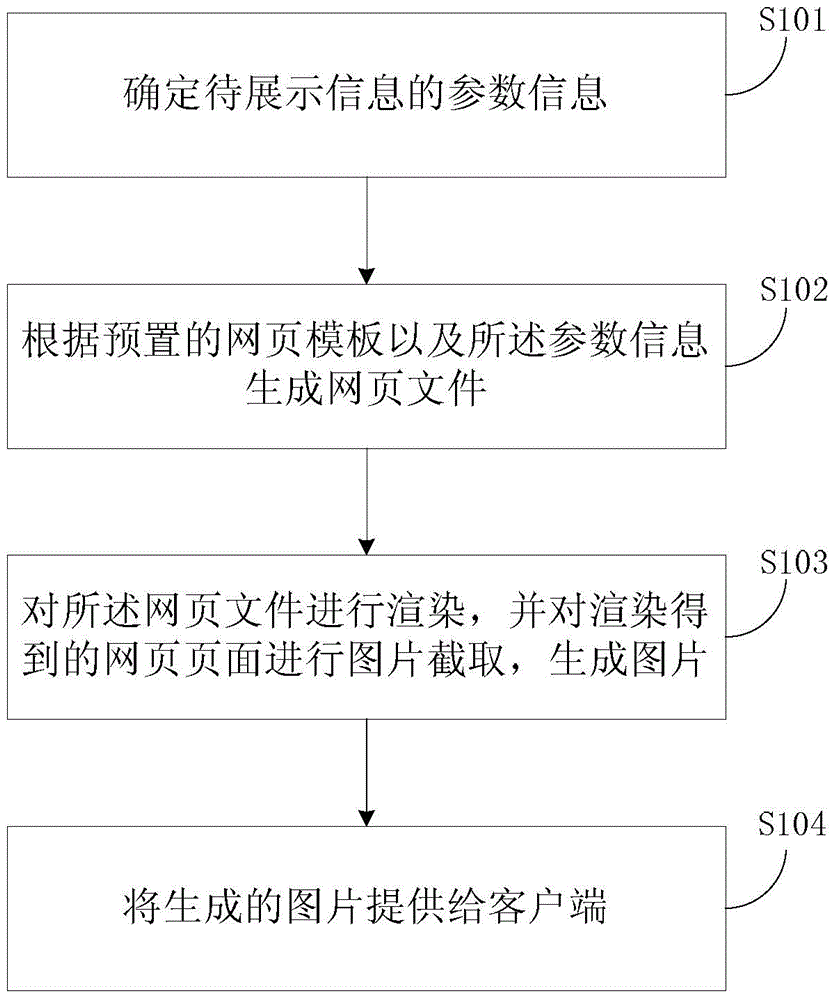
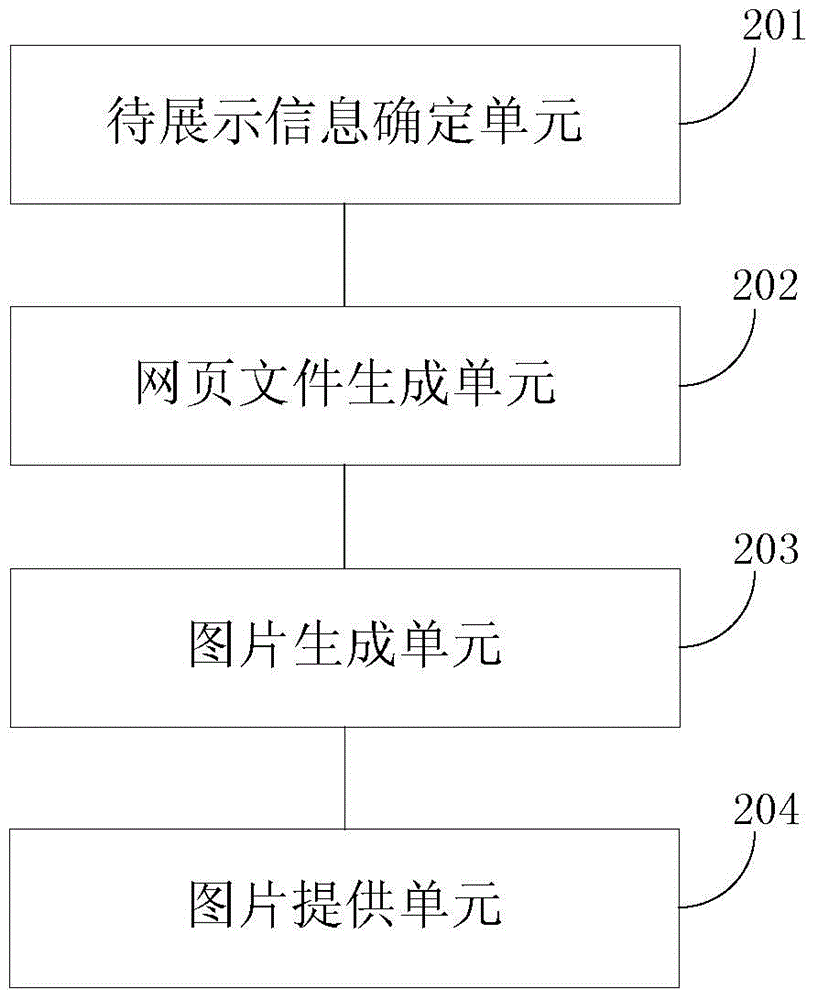
ActiveCN104615776AReduce hardware requirementsSimple and convenient displaySpecial data processing applicationsWeb data browsing optimisationClient-sideImage capture
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for providing information to be displayed. The method comprises the following steps of: determining parameter information of the information to be displayed; according to a preset webpage template and the parameter information, generating a webpage file; rendering the webpage file and carrying out image capturing on a webpage obtained after rendering so as to generate an image; providing the generated image to a client, so that the client provides the image to a user. By the method and the device for providing the information to be displayed, display on expanded information can be more simply and conveniently realized.
Owner:BEIJING QIYI CENTURY SCI & TECH CO LTD
Image multi-scale fusion method, device, storage medium and terminal
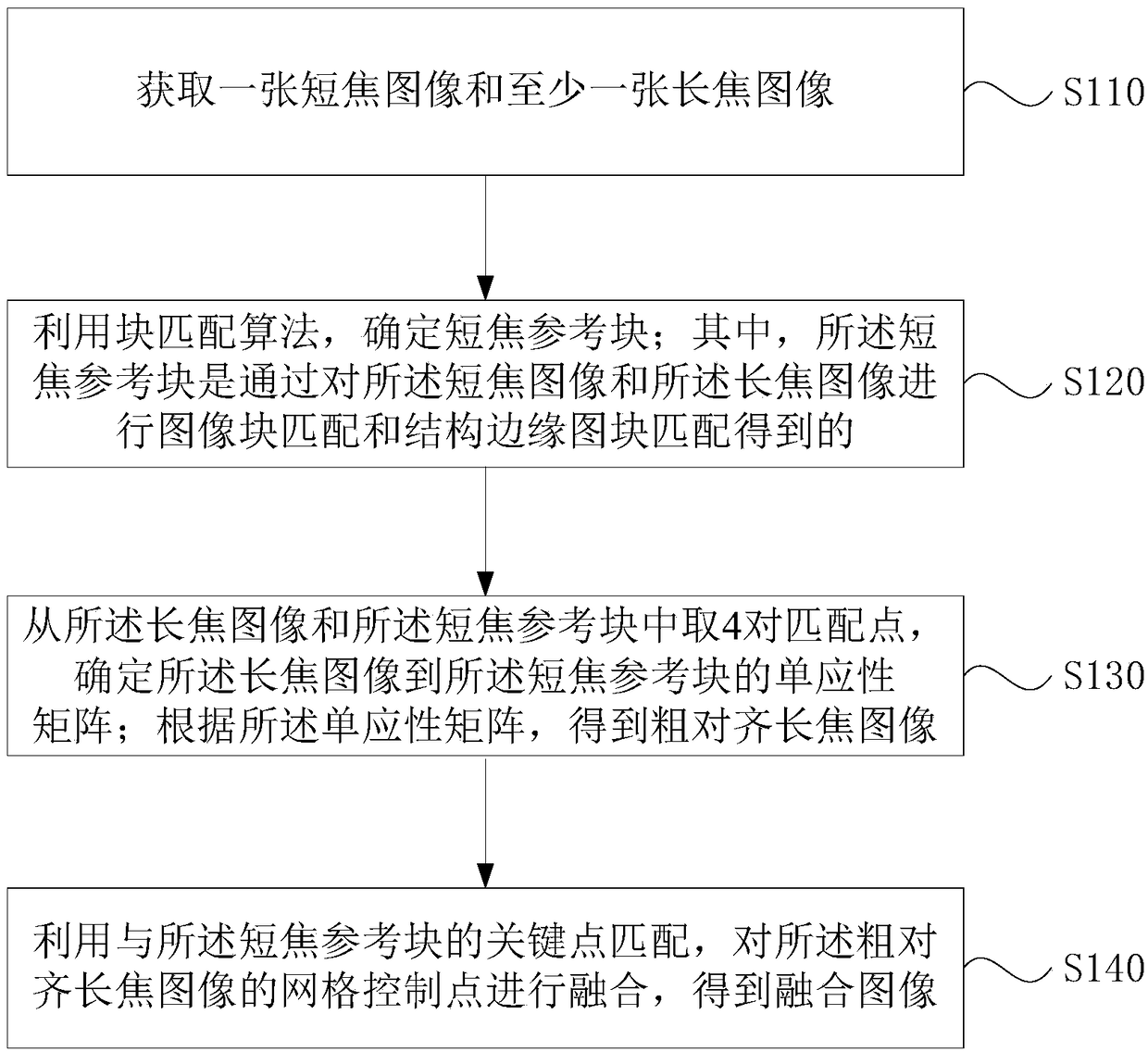
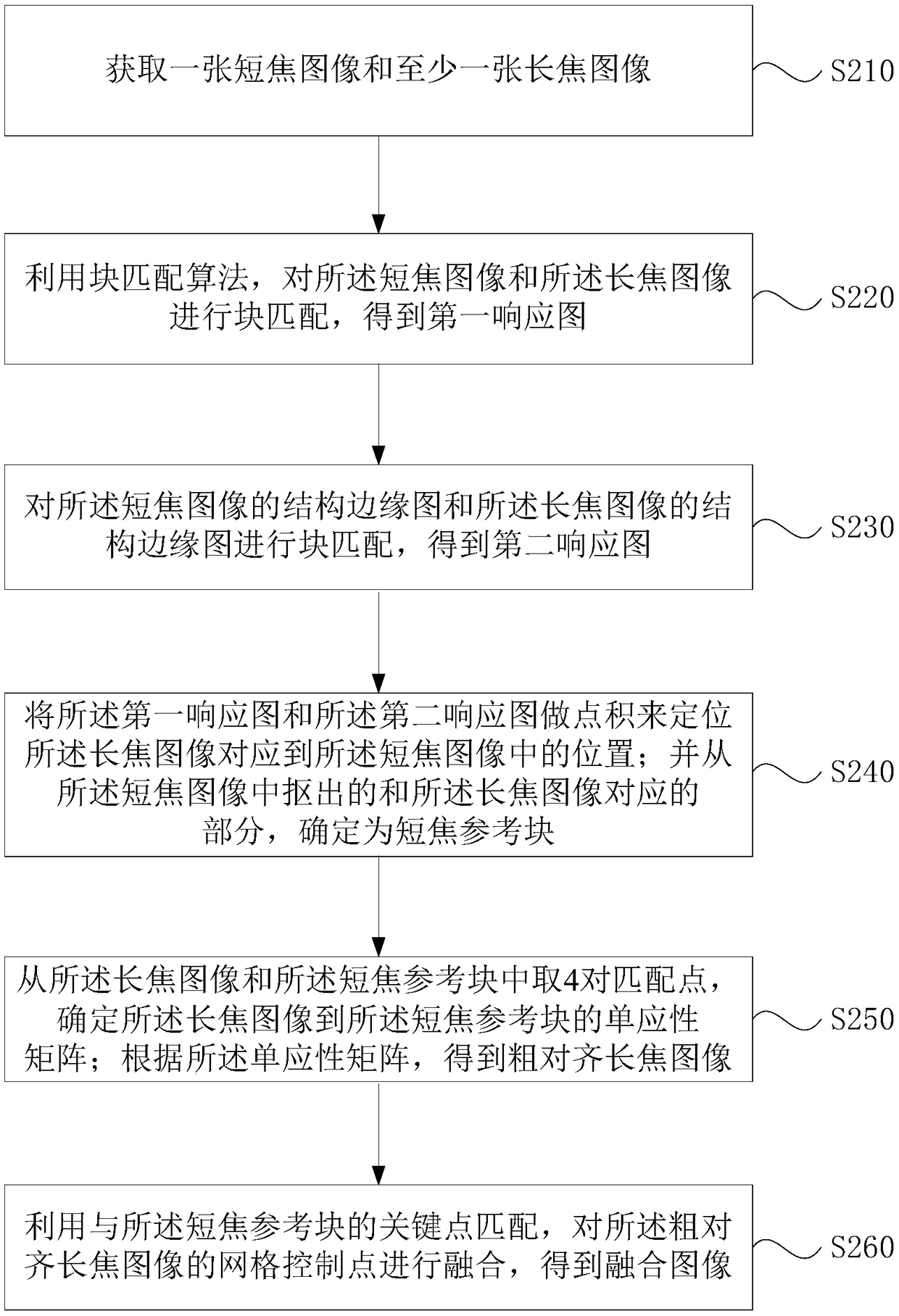
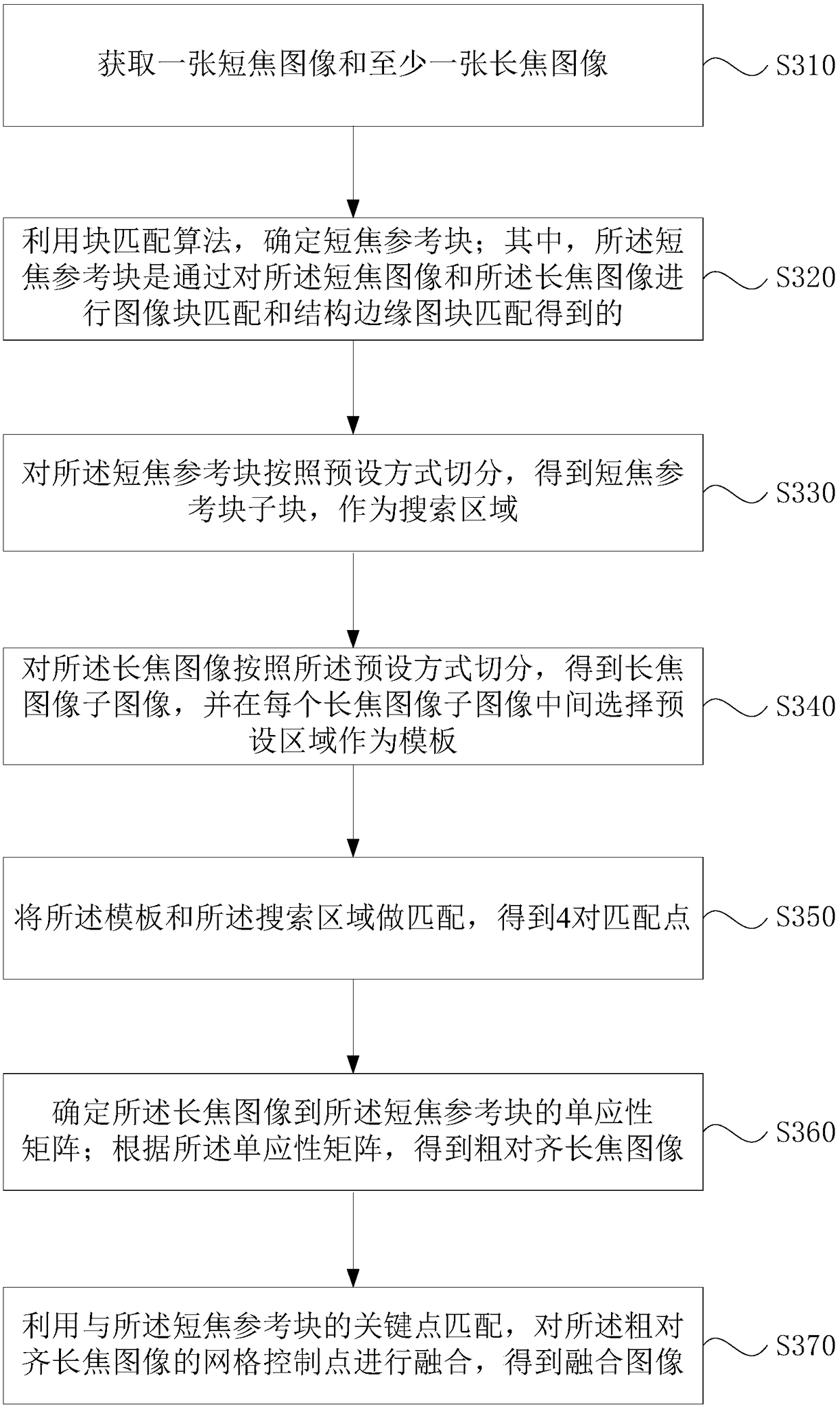
ActiveCN109285136AReduce hardware requirementsHigh speedImage enhancementImage analysisReference blockCamera array
Embodiments of the present application disclose a multi-scale image fusion method, apparatus, storage medium, and terminal. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a short focus image and at least one long focus image; a short-focus reference block is obtained by matching the short-focus image and the long-focus image with image block matching and structural edge block matching; selecting 4 pairs of matching points from the long-focus image and the short-focus reference block to determine a homography matrix of the long-focus image to the short-focus reference block; obtaining acoarsely aligned long focal image according to the homography matrix; the mesh control points of the coarsely aligned long focus image are fused by matching with the key points of the short focus reference block to obtain a fused image. By adopting the technical proposal provided by the application, the method can be integrated into an unstructured camera array for realizing the effects of reducing hardware requirements and improving image fusion speed and robustness.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
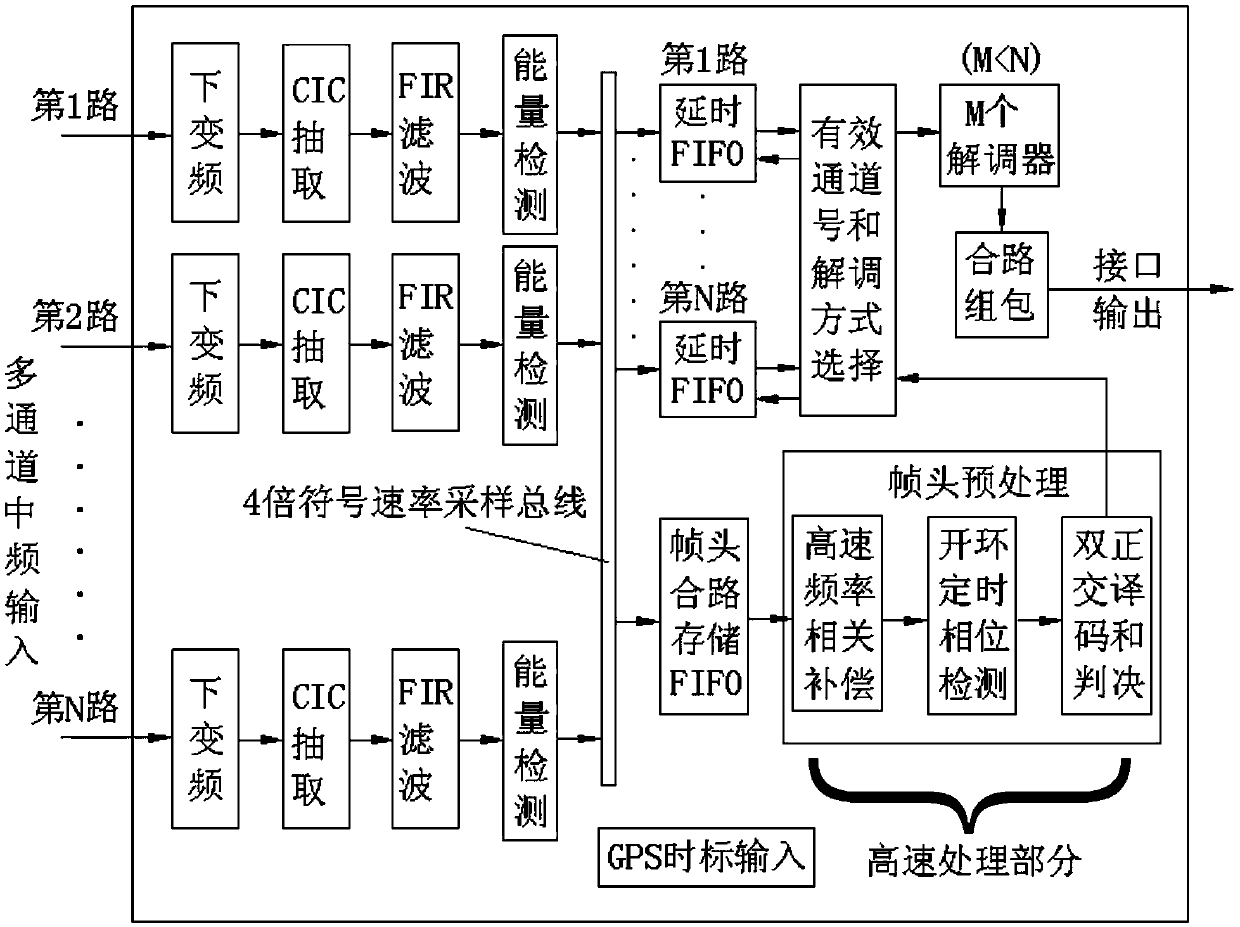
VDE-based processing system of multi-path channel detection
ActiveCN109547091AReduce time slot occupancyReduce processing delaysCarrier regulationRadio transmissionVIT signalsTarget signal
The invention provides a VDE-based processing system of multi-path channel detection. The system includes a burst energy detection module, a frame head combined-way storage module, a high-speed frequency correlation compensation module, an open-loop timing and phase detection module, a bi-orthogonal decoding and decision module, a valid-channel selection module, a demodulator group module and a combined-way group package output module. Through the multi-path VDE channel detection processing system based on a VDE communication protocol mechanism of the invention, the number of receiving demodulators is greatly reduced, and hardware pressure of a receiving system is alleviated. The processing system has very important significance and very broad application prospects for multi-path receivingof VDE sea-air target signals.
Owner:SHANGHAI SPACEFLIGHT ELECTRONICS & COMM EQUIP RES INST
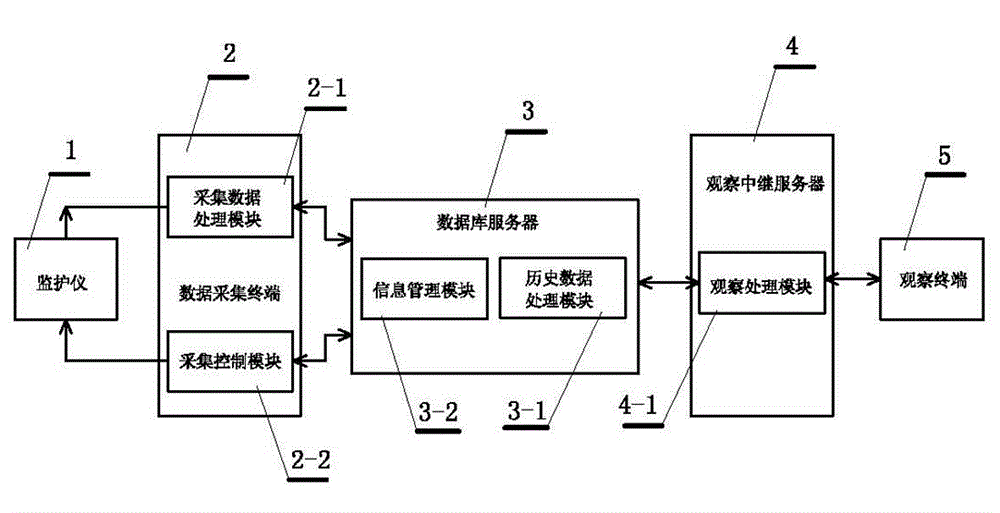
Real-time monitoring system and method suitable for mobile health care
ActiveCN104055500ASave disk spaceReduce hardware requirementsSensorsBlood characterising devicesMonitoring dataLocal area network
The invention discloses a real-time monitoring system and method suitable for mobile health care. The system comprises a monitor, a data acquisition terminal, a database server, an observing relay server and an observing terminal. The method is an asynchronous real-time monitoring method, and comprises a step of requesting real-time monitoring through the observing terminal and a step of requesting to check history data. The monitor, the data acquisition terminal, the observing relay server, the observing terminal and the database server are connected to the Internet or a local area network, and share one database server with a plurality of hospitals, a plurality of areas and even the whole country, so that share of patient monitoring data is realized, the observing terminal only requests current real-time data while requesting real-time monitoring data without requesting history real-time data, real-time data are only requested when a real-time data duration is greater than a buffering duration, the transmission data size of real-time data is reduced, and the stable transmission of real-time data is ensured; history data are transmitted after being compressed, so that the network transmission data size is reduced, and the network pressure is lowered.
Owner:CONTEC MEDICAL SYST
Random playing method and device
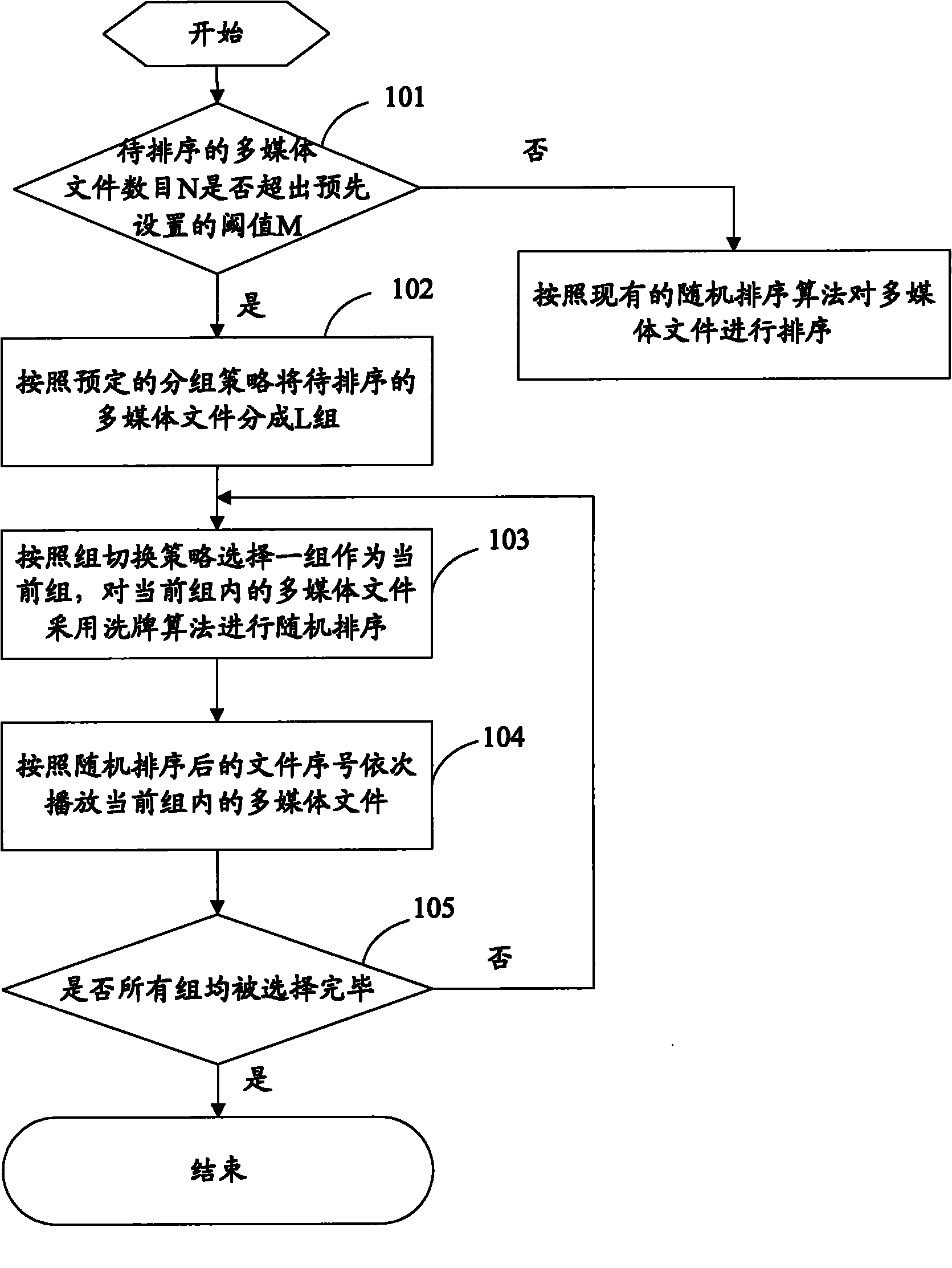
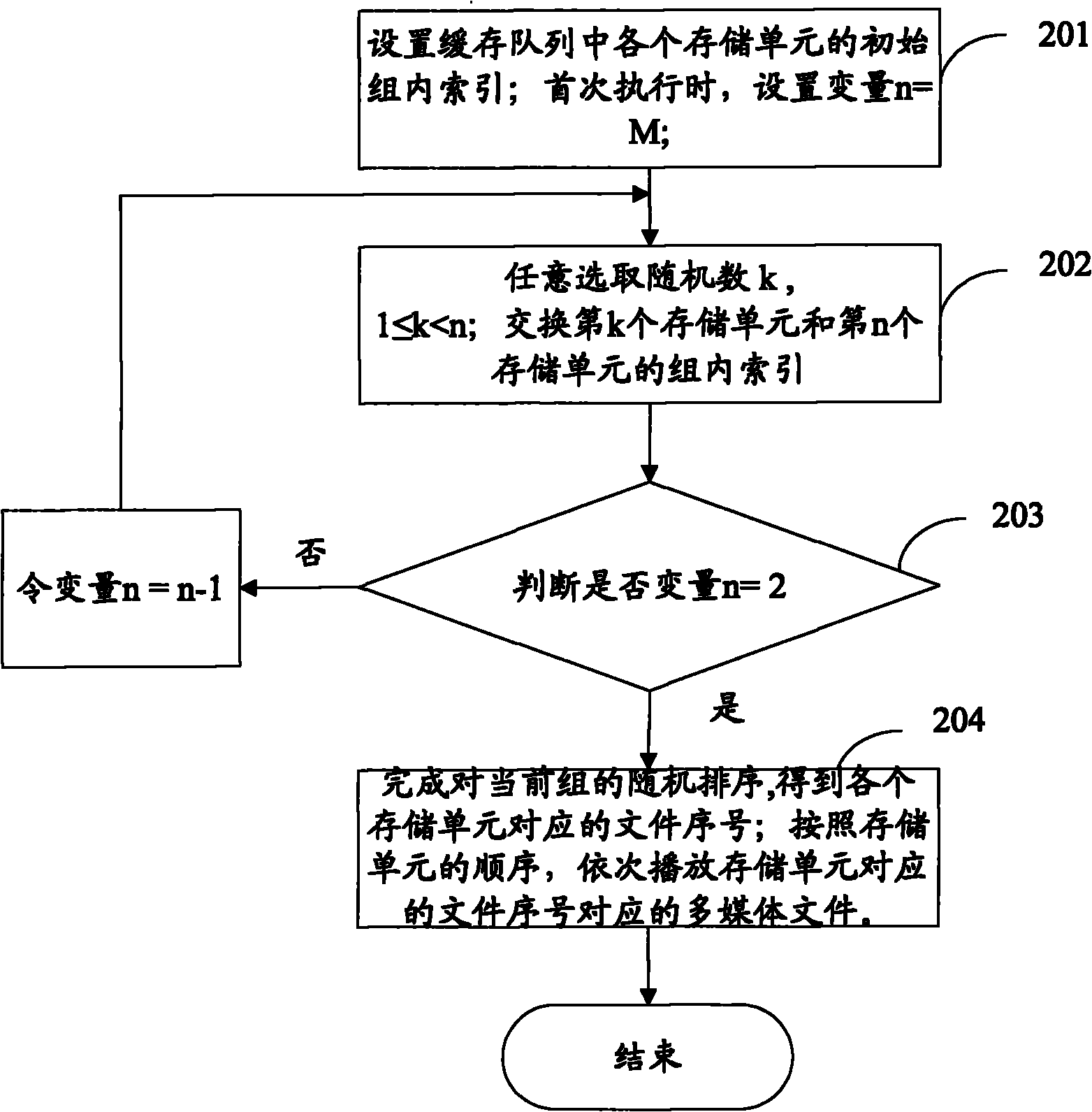
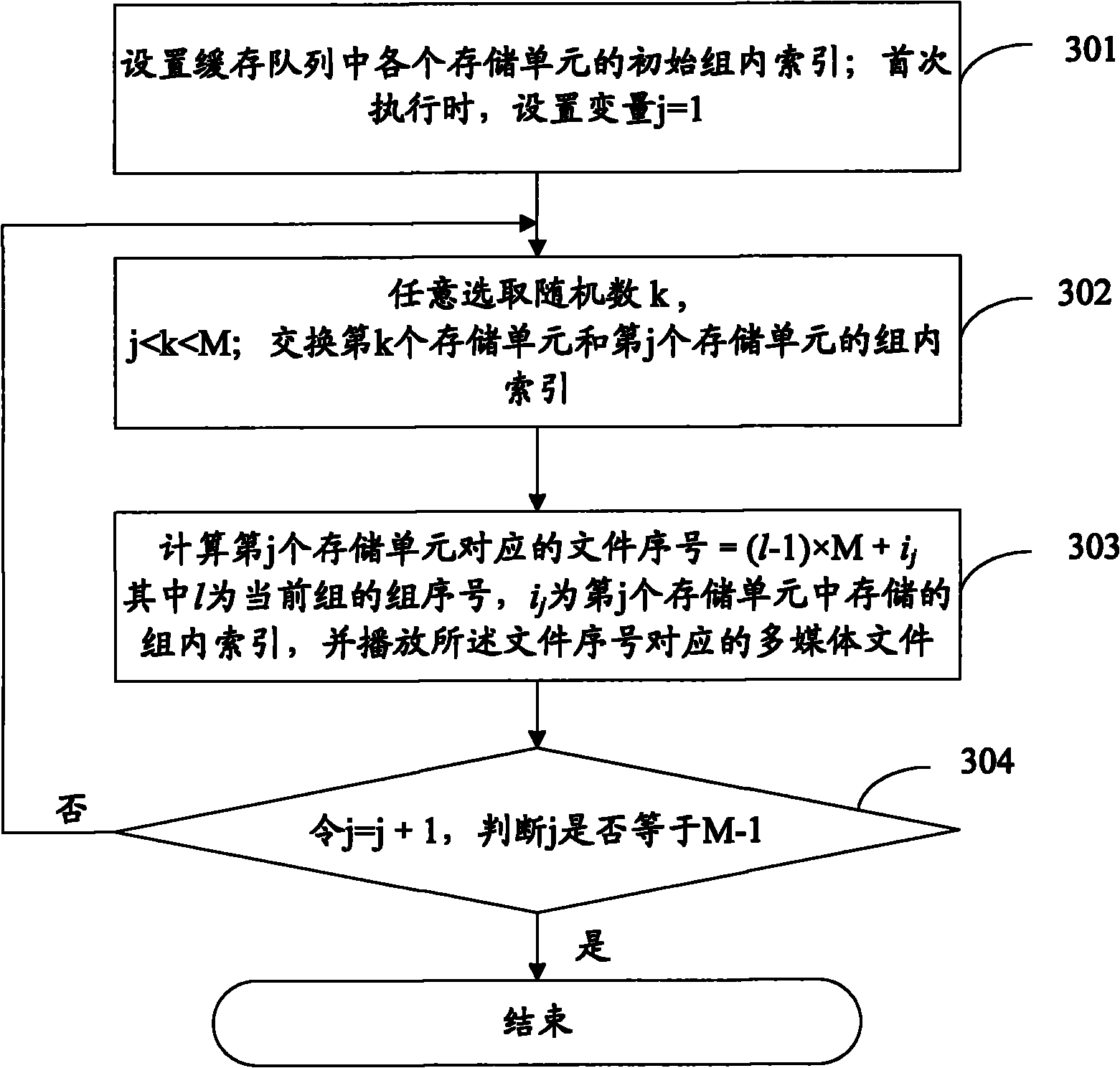
InactiveCN102054509AReduce hardware requirementsSmall amount of calculationElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsCarrier indexing/addressing/timing/synchronisingNumerical precisionGroup strategy
The invention discloses a random playing method which comprises the following steps: grouping multimedia documents to be played according to a predetermined grouping strategy; and playing each group of multimedia documents in a random sequencing mode according to a shuffle algorithm. The invention also discloses a multimedia playing device. By utilizing the scheme of the invention, the calculated amount required for sequencing can be reduced greatly, the hardware requirements for the multimedia playing device can be lowered, and simultaneously the numerical precision of the hardware of the media playing device can satisfy the requirement of random sequencing.
Owner:ACTIONS SEMICONDUCTOR
CNN convolution kernel hardware design method based on cascade form
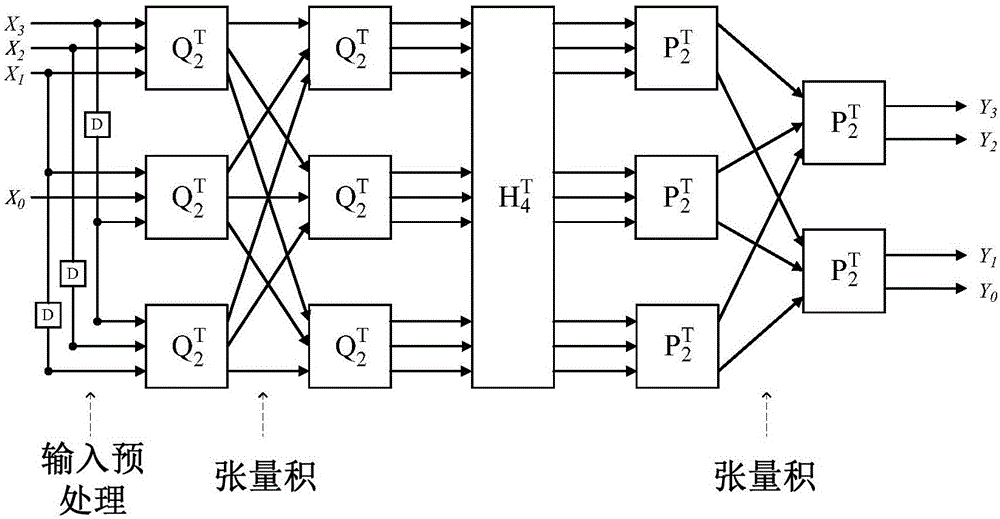
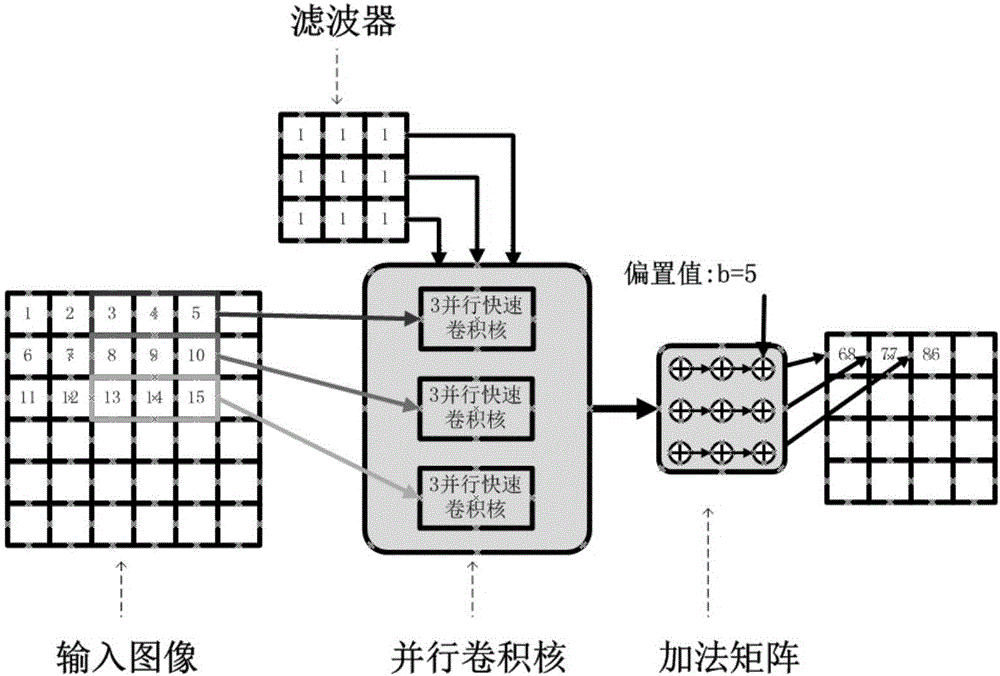
InactiveCN106845635AReduce complexityStay flexible and configurableNeural architecturesPhysical realisationHardware architectureAlgorithm
The invention discloses a CNN convolution kernel hardware design method based on a cascade form. The method comprises the first step of defining a convolution fundamental matrix, and adopting hardware implementation to obtain a convolution fundamental module; the second step of presenting linear convolution using a fast convolution algorithm in a form of matrix multiplication, and conducting cascading on the convolution fundamental module according to the presenting mode to form a cascade convolution module; the third step of adding an addition matrix which is achieved by a summator into the cascade convolution module to achieve parallel processing, addition operation of an offset value and two-dimensional convolution sum so that the final fast convolution kernel can be obtained. According to the CNN convolution kernel hardware design method based on the cascade form, compared with a traditional two-dimensional convolution kernel, the hardware demand is lowered, and the system velocity is increased at the same time; secondly, the shortcoming that when fast convolution kernels are different in size, a hardware architecture needs to be redesigned is avoided.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A fermentation process fault monitoring method based on DLAE
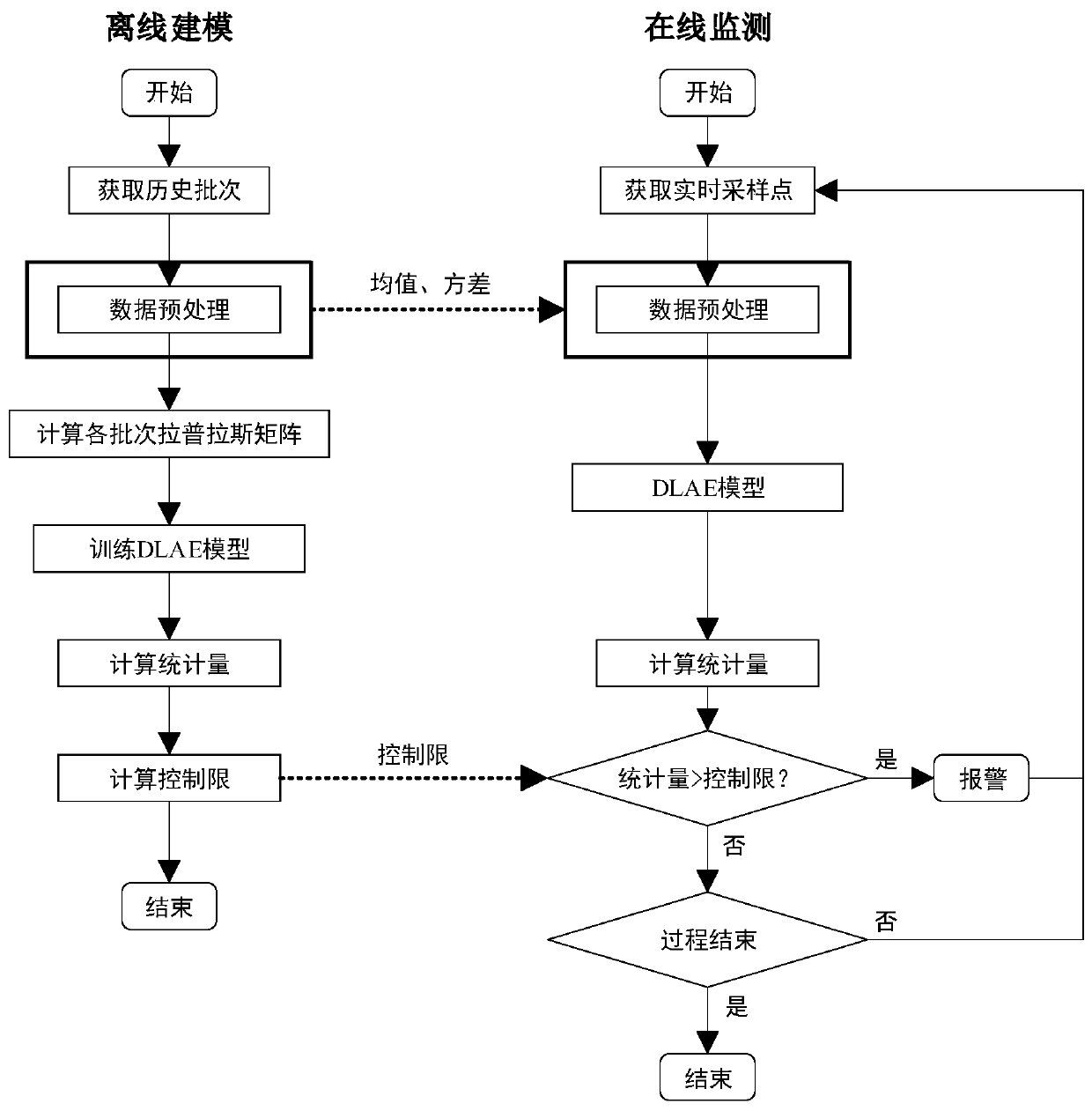
ActiveCN109740687ACost reduction needsReduce hardware requirementsRegistering/indicating working of machinesCharacter and pattern recognitionThree dimensional dataPenicillin fermentation
The invention discloses a novel method for carrying out real-time fault monitoring on a penicillin fermentation process. The method comprises two stages of off-line modeling and on-line monitoring. The off-line modeling comprises the following steps: firstly, processing three-dimensional data of a fermentation process; then respectively calculating a Laplacian matrix of the data of each fermentation batch to represent local structure information of the data in each batch; and finally, carrying out modeling by using a noise reduction Laplace automatic encoder (DLAE) to construct monitoring statistics, and determining a control limit by using a kernel density estimation method. The on-line monitoring comprises the following steps: processing newly collected data according to a model, calculating the statistical magnitude of the data, comparing the statistical magnitude with a control limit, and judging whether the fermentation process runs normally or not. According to the method, the local structure of data in batches can be effectively utilized, and meanwhile, the training cost and the hardware requirement of the Laplace automatic encoder are reduced. Meanwhile, the robustness of the model is enhanced by adopting a noise reduction training mode, and the fault monitoring accuracy is relatively high.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Integration of a robotic system with one or more mobile computing devices
ActiveCN104662578AReduce hardware requirementsRich user interfaceData processing applicationsComputerized toysRobotic systemsPhysical space
A robotic system is integrated with one or more mobile computing devices. Physical configurations of individual components of the system in physical space, or agents, under control of a user or users, are duplicated in a representation in virtual space. Some degree of real-time parity is maintained between the physical and virtual spaces, so as to implement a virtual environment that mirrors the physical one. Events occurring within one environment can directly influence and bear consequence on the course of events occurring within the other environment. Elements of virtual space thereby become truly interdependent and unified on a peer footing with elements in physical space. In at least one embodiment, the system of the present invention is implemented as an application in entertainment, such as the manifestation of a video game in physical space.
Owner:ANKI INC
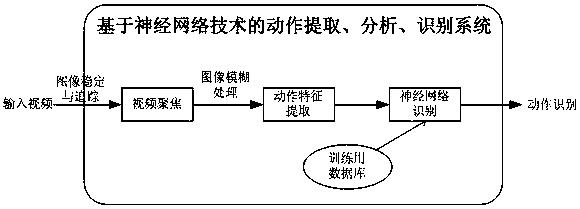
Deep learning-based quick dynamic human body action extraction and identification method
InactiveCN106096518AQuick extractionAvoid slow recognitionImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyShortest distance
The invention relates to a deep learning-based quick dynamic human body action extraction and identification method. At present, existing human body identification technology and application have the following deficiencies in multiple aspects: a human skeleton is a complicated structure body, and different human action habits correspond to different human action modes, so that human body identification is difficult generally. The method comprises the following steps of firstly describing whole information of size, color, edge, contour, shape and depth of a human body target; providing useful clues for action identification; extracting effective motion features from a video sequence; performing trace analysis by utilizing a motion trace of the target under the long-distance condition; and performing two-dimensional or three-dimensional modeling on four limbs and trunk of the target by utilizing information extracted from an image sequence under the short-distance condition. The method is used for extracting and identifying quick dynamic human body actions based on deep learning.
Owner:HARBIN MAX TELEGENT SCI & TECH DEV CO LTD
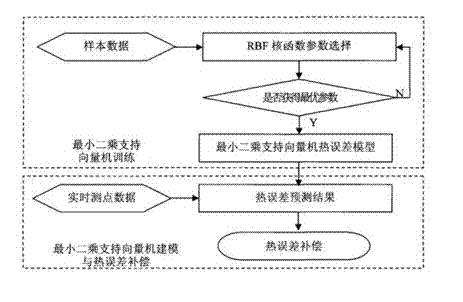
Novel least square support vector machine modeling method for thermal error of numerical control machine
InactiveCN102479261AImprove self-learning abilityAdaptableSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical controlAlgorithm
The invention discloses a novel least square support vector machine modeling method for a thermal error of a numerical control machine. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting a kernel function and determining parameters; and (2) according to a principle of the least square support vector machine, establishing a machine thermal error model. A compensating system in the invention is simple in structure and reliable in application; and by means of the least square support vector machine modeling method, the model precision and the generalization capability are improved, and the defects of low precision, low generalization capability and the like of the conventional predicting method are overcome.
Owner:DALIAN CHUANGDA TECH TRADE MARKET
Fault-tolerant modulation method for co-busbar double-end cascade type five-level inverters
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Method for video synchronization rendering in environment of cloud desktop
ActiveCN105025335AReduce hardware requirementsImprove experienceTransmissionExecution for user interfacesData synchronizationComputer graphics (images)
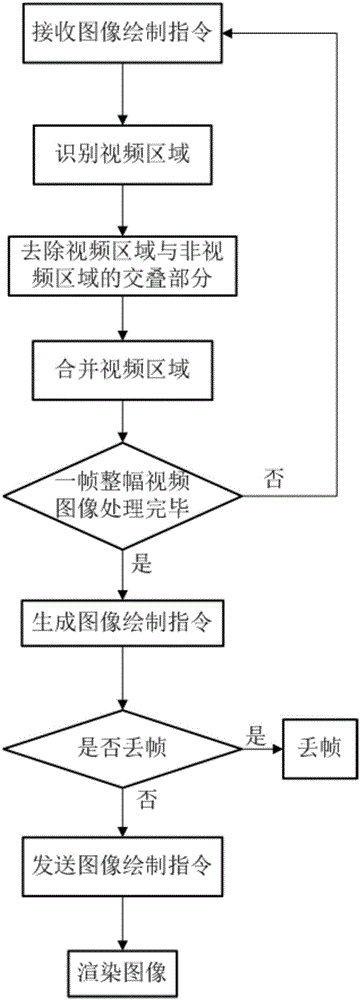
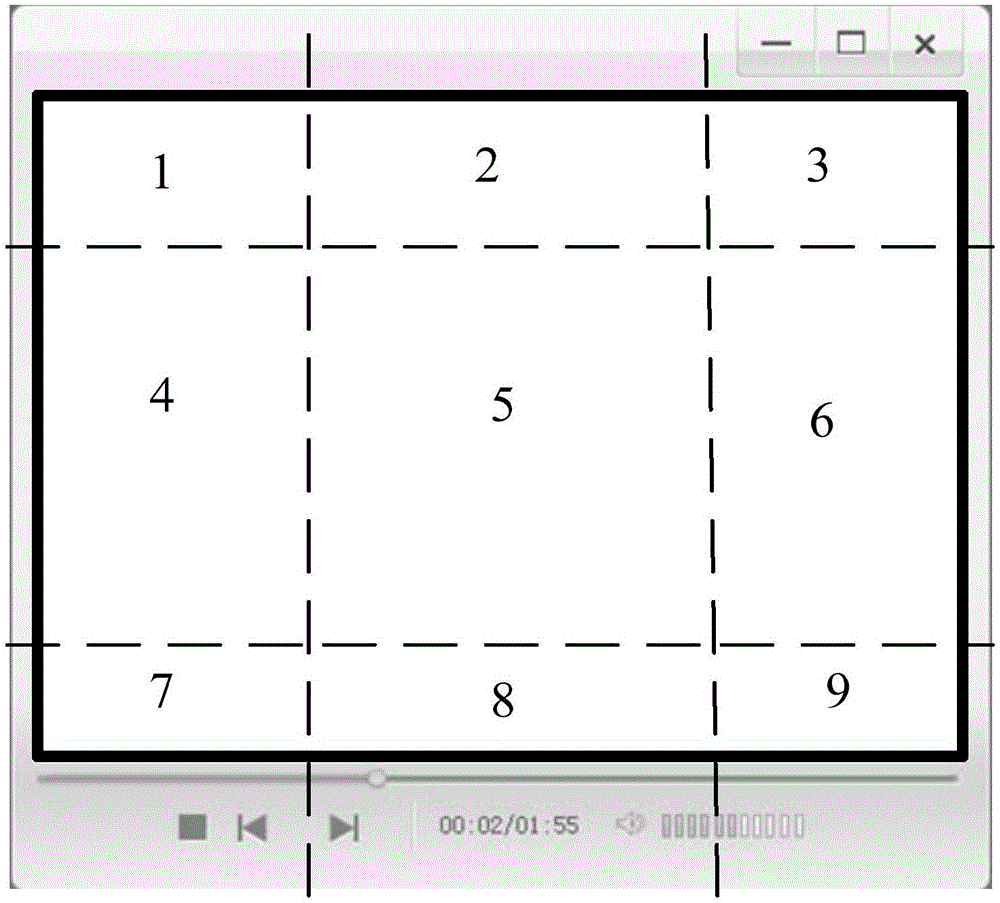
The present invention provides a method for video synchronization rendering in an environment of cloud desktop. The method comprises the following steps: an image draw command is divided into a draw command at a video and image area and an image draw command at a non-video area according to updated frequency; a portion overlapping with the video area in the non-video area is eliminated; a video and image draw command is generated through merging adjacent or overlapped video areas and is sent to a client; and rendering display of the image is immediately carried out after the client receives the video draw command, such that the synchronization rendering at the non-video area and at the video area is completed. The method provided by the invention is capable of maintaining synchronization rendering of videos when the present image draw command is detected as a video stream by a server, thereby user experience is improved.
Owner:安徽中科云信创信息技术有限公司
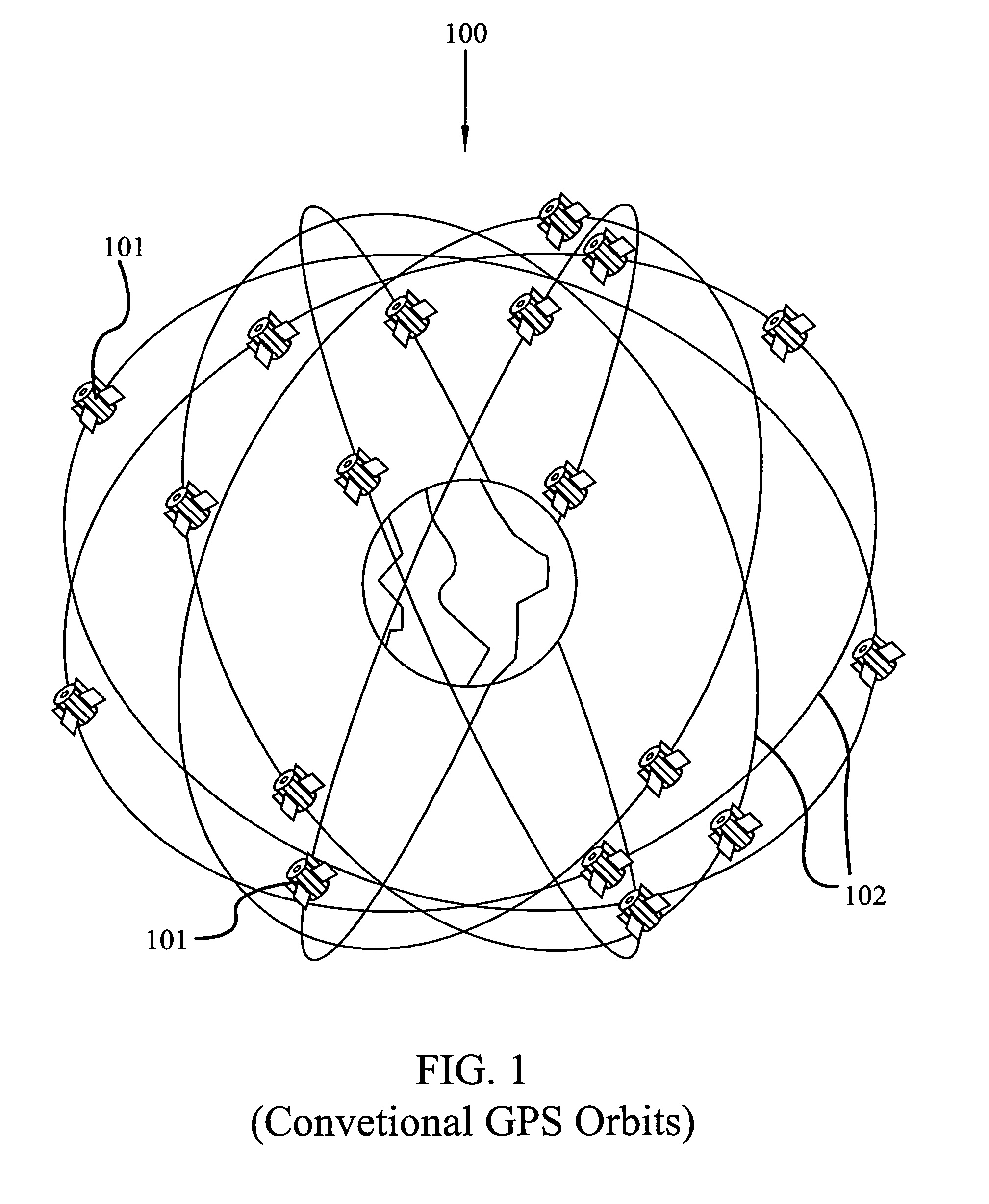
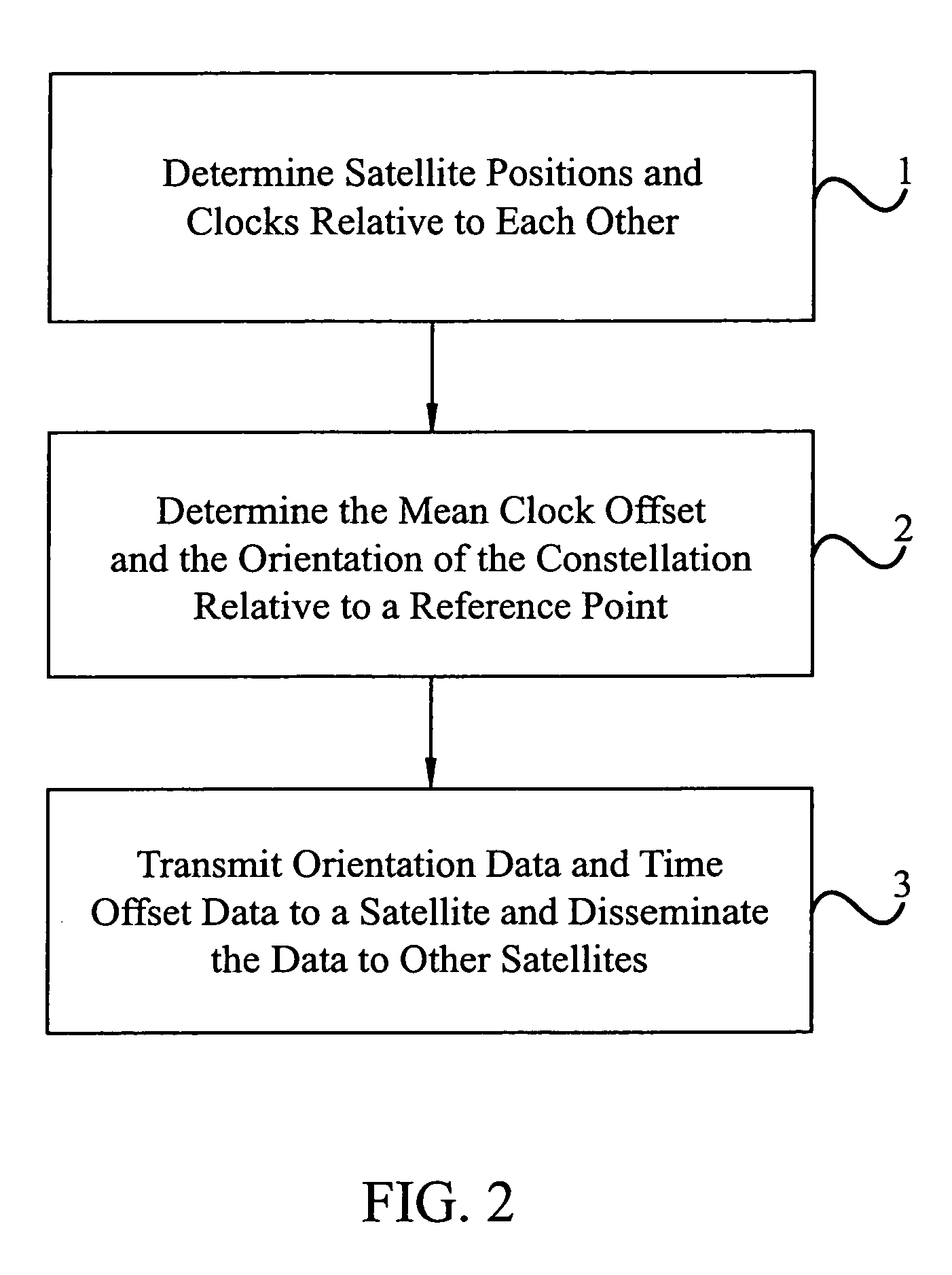
Satellite positioning system
InactiveUS6950060B1Reduce processReduce hardware requirementsInstruments for comonautical navigationArtificial satellitesSignal monitoringSatellite positioning
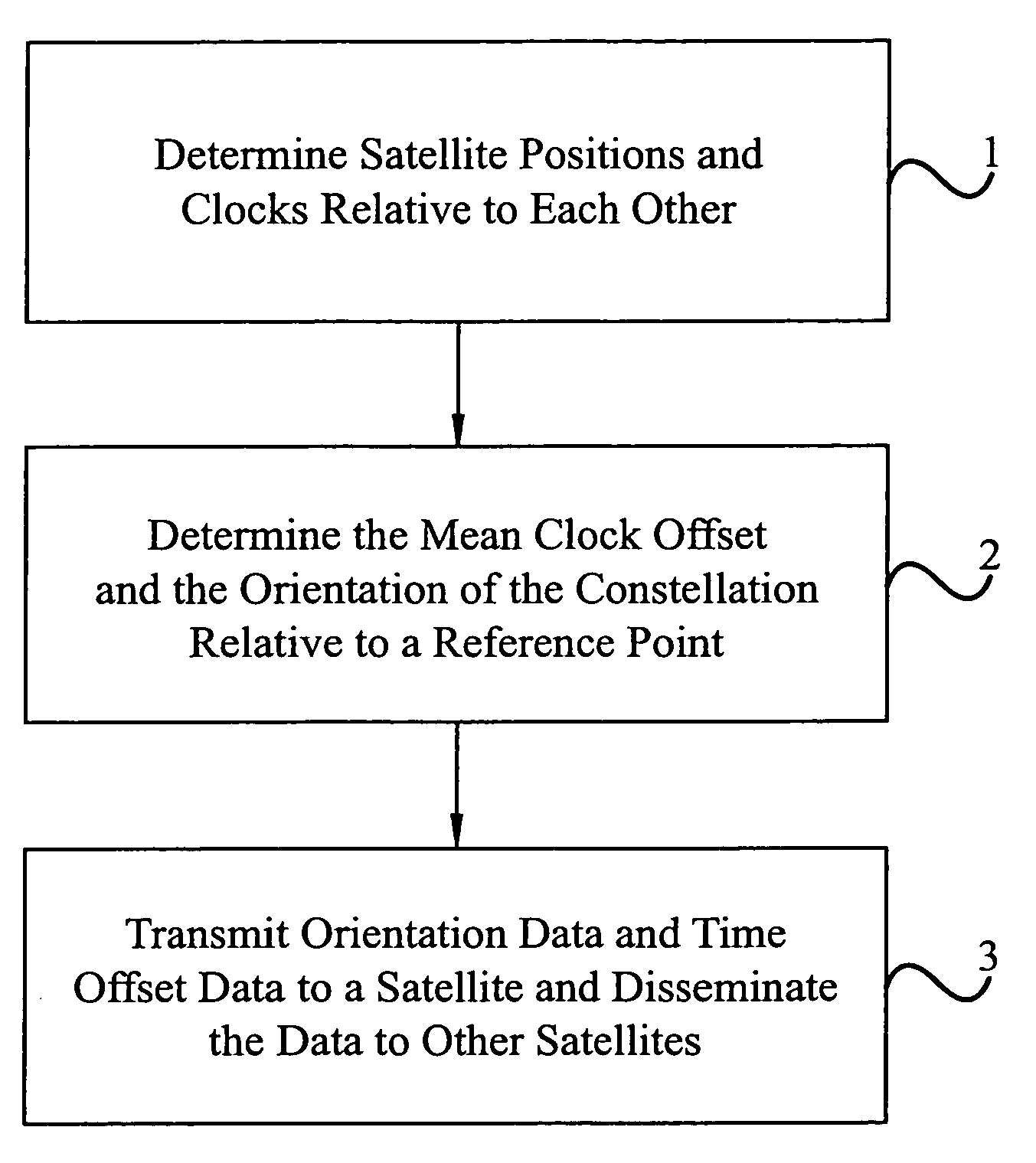
A satellite positioning system and method of maintaining the positioning and clock data of a satellite using as few as one or two monitoring stations is disclosed. Each satellite of the positioning system determines its own positioning and clock data relative to other satellites in a constellation. One or more satellite signal monitoring stations receive relative clock and positioning data from a plurality of satellites in the constellation. A constellation solution which is applicable to all of the satellites in the constellation is calculated by treating the constellation as a rigid body at a fixed point in time. The constellation solution is transmitted to a satellite of the constellation which disseminates the solution through a crosslink network within the constellation for use by each satellite to update its individual positioning and clock data as needed. Due to the stability of the position and clock measurements using the method of the present invention, satellite uploads need only occur for one satellite in a constellation once each two or more days rather than every day for every satellite as is conventionally done. The use of mobile monitoring stations and the capacity of the positioning system to assist in updating the position and clock data of satellites passing the constellation are disclosed. In particular embodiments of the invention, the satellite positioning system is configured as a global positioning system (GPS).
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS C4 SYSTEMS
Method for measuring laser linewidth of ultra-narrow linewidth laser
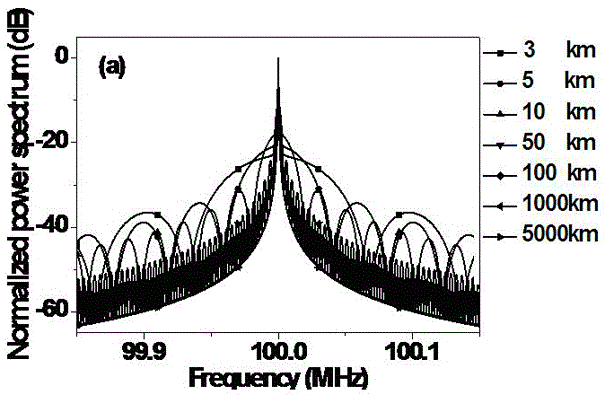
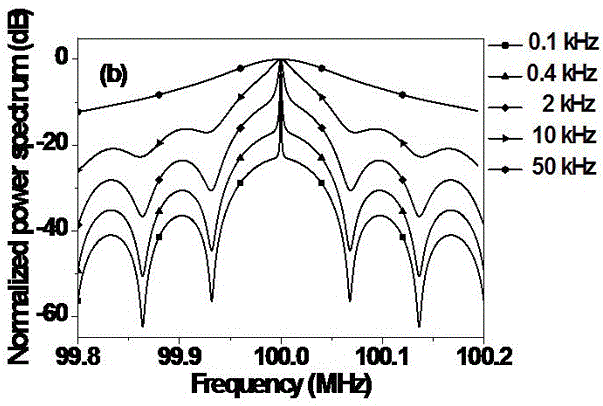
ActiveCN105571830ARealize measurementSolve the noise problemTesting optical propertiesFiberLine width
The invention discloses a method for measuring laser linewidth of an ultra-narrow linewidth laser. The method is creatively characterized in that by use of an automatic heterodyne detection system, a power spectrum of the ultra-narrow linewidth laser under an automatic heterodyne conduction is obtained; and a peak and a valley which are adjacent to each other in terms of positions are selected from an area beyond high-peak pulses on the power spectrum, a difference delta S between the contrast of the peak and the valley on the power spectrum are respectively calculated, and the laser linewidth delta f is calculated according to the delta S. The method for measuring the laser linewidth of the ultra-narrow linewidth laser, brought forward by the invention, has the following technical advantages that the method can realize measurement of ultra-narrow linewidth under the condition of quite short delay fibers, greatly reduces hardware demands, can effectively prevent the problem of noise brought by large-length delay fibers and is quite good in measurement precision.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Edge strengthening method and device of Bel image and color image pick-up system
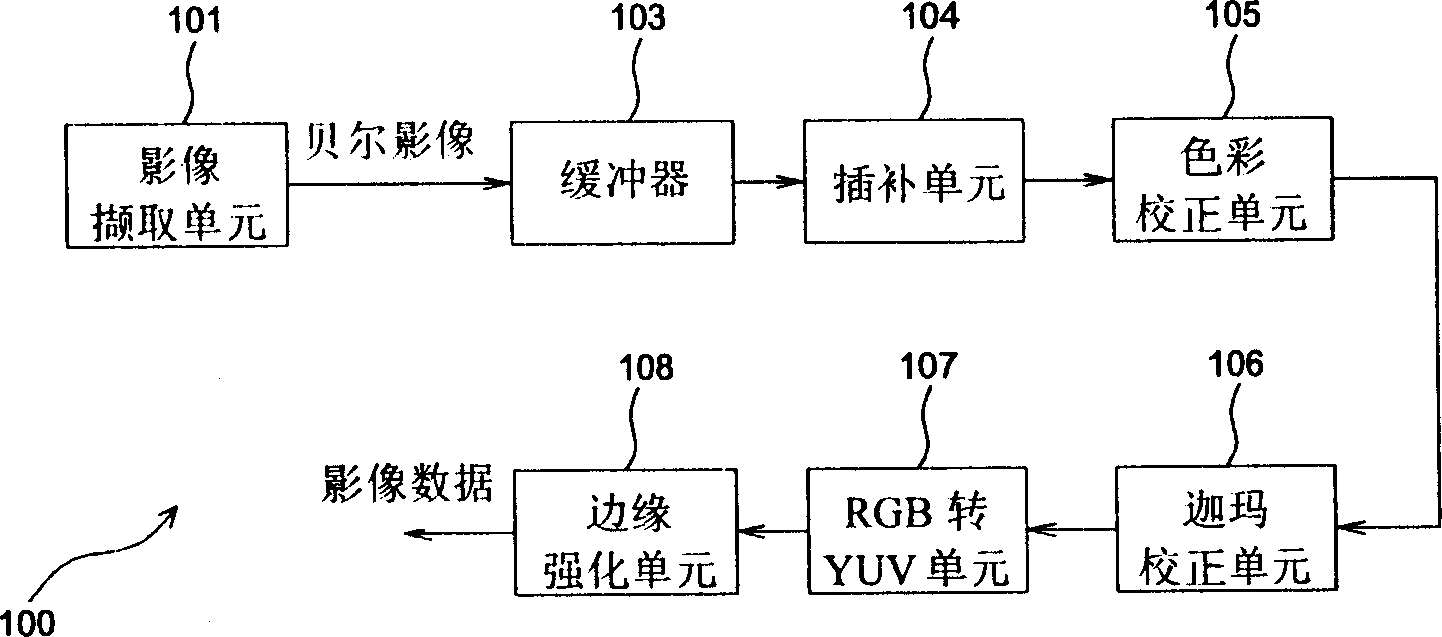
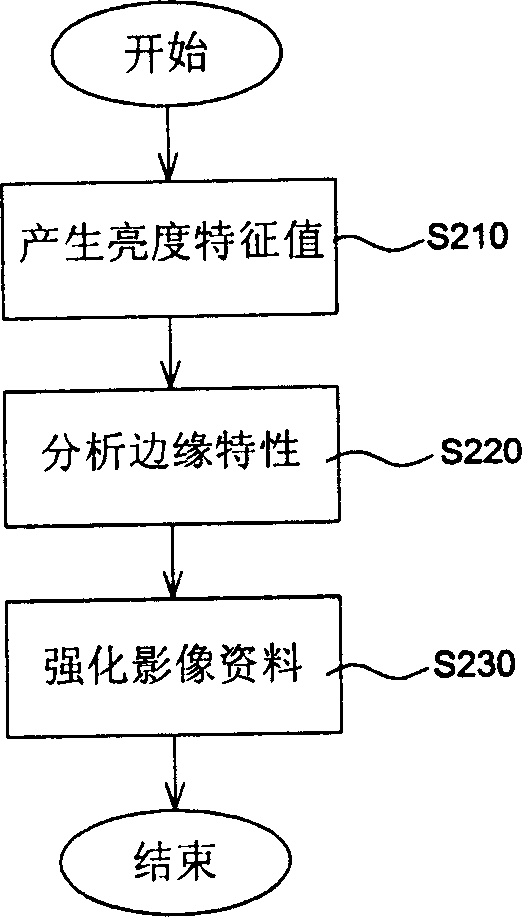
ActiveCN1870048ASimplify complexityImprove bindingImage enhancementColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionColor image
An edge intensification device of Bel image is prepared as storing original Bell image data into buffer storage and carrying out brightness character value calculation and edge character analysis by directly fetching out original Bell image data from buffer storage, outputting edge character data and intensifying edge of original Bell image data according to analyzed edge character data.
Owner:ICATCH TECH INC
Target tracking method based on YOLOv3 and DSST algorithm
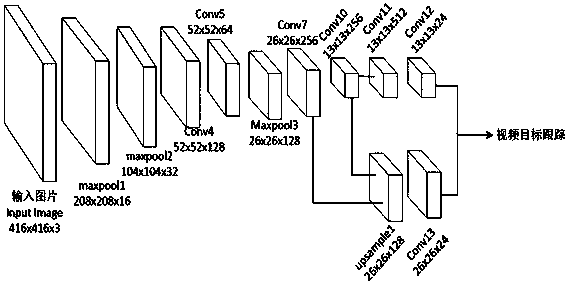
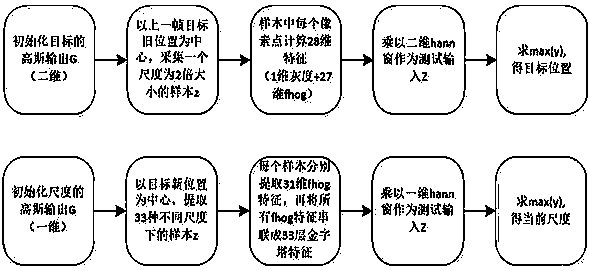
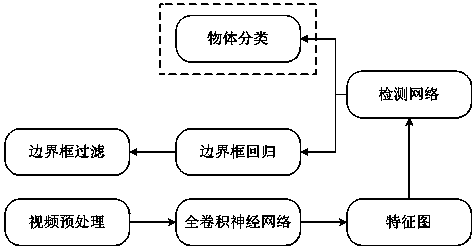
PendingCN110490905AImprove anti-interferenceImprove success rate and real-time performanceImage enhancementImage analysisScale modelNoise immunity
The invention discloses a target tracking method based on a YOLOv3 algorithm and a DSST algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: training a target detection model, inputting an image, evaluating a position, detecting a target, taking a position model, a scale model, a target position and a target scale as inputs in the step 3) when a next frame of image comes, and repeating the steps 3) to 4) to complete a video target tracking function. The method is beneficial to fully verifying and objectively evaluating the composition factor influence of the overall effect of the method in twostages of the implementation process, and is also convenient to clarify the improvement and reinforcement targets of the target tracking method. The operation amount of a detection algorithm is effectively reduced, so that the operation speed is increased and the hardware requirement is reduced. The anti-interference performance of the tracking algorithm can be improved, and the success rate andreal-time performance of the tracking algorithm are further improved.
Owner:JIANGXI LIANCHUANG PRECISION ELECTROMECHANICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com