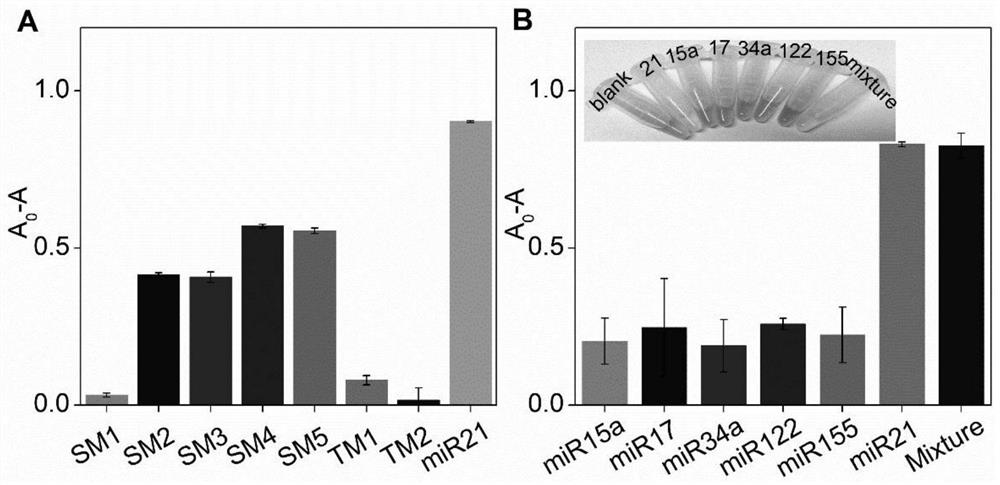
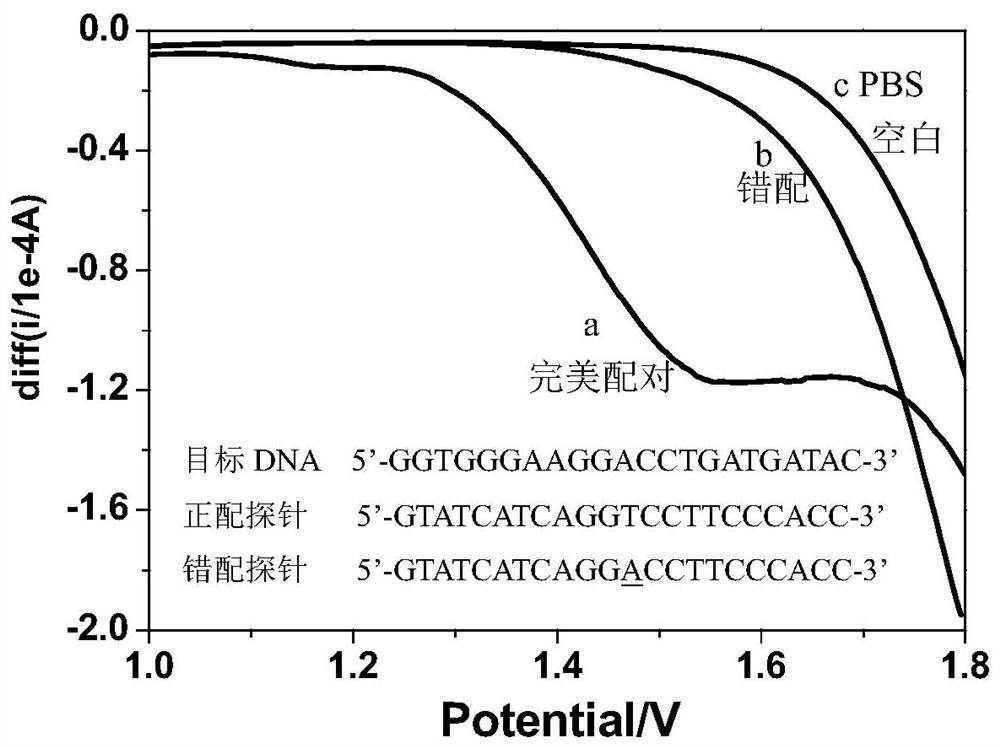
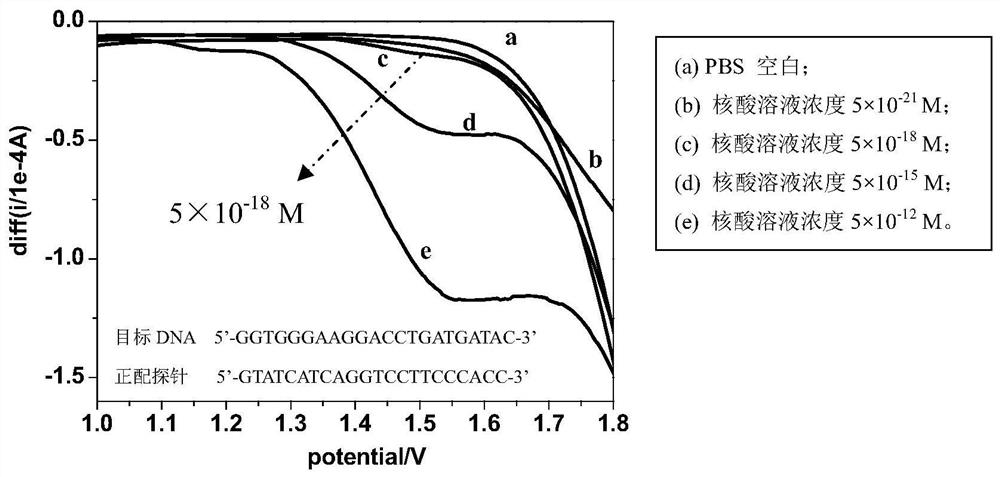
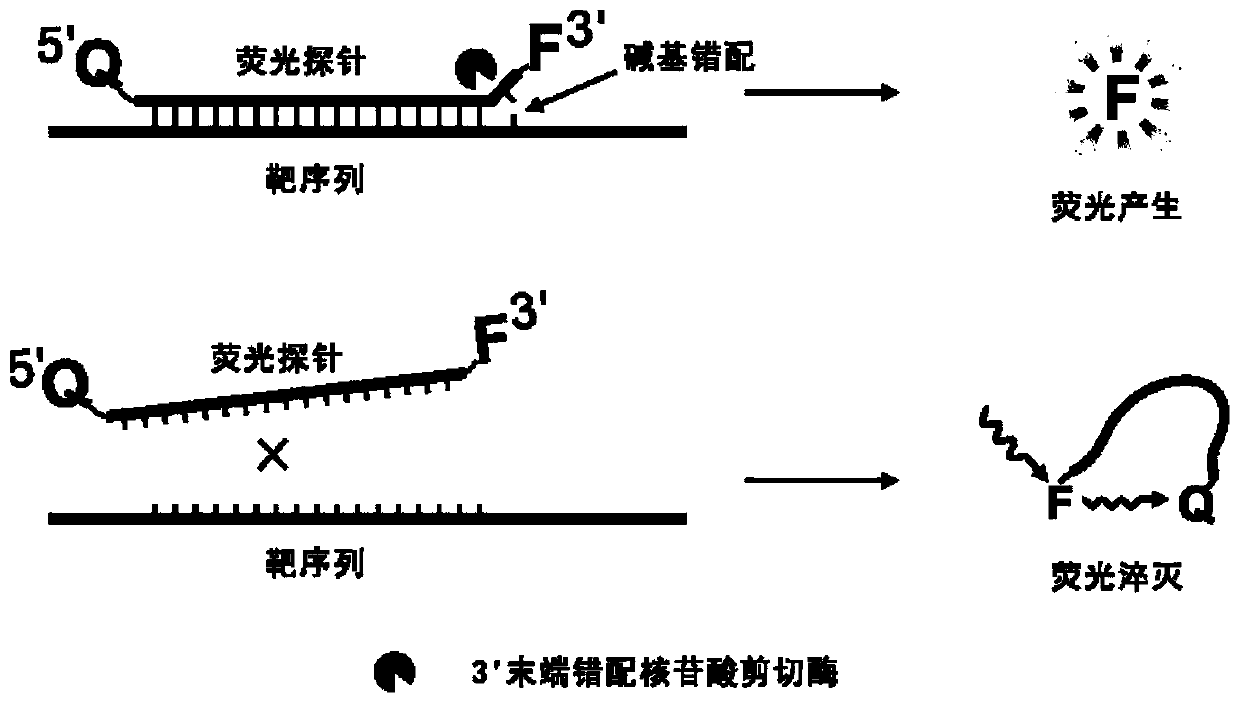
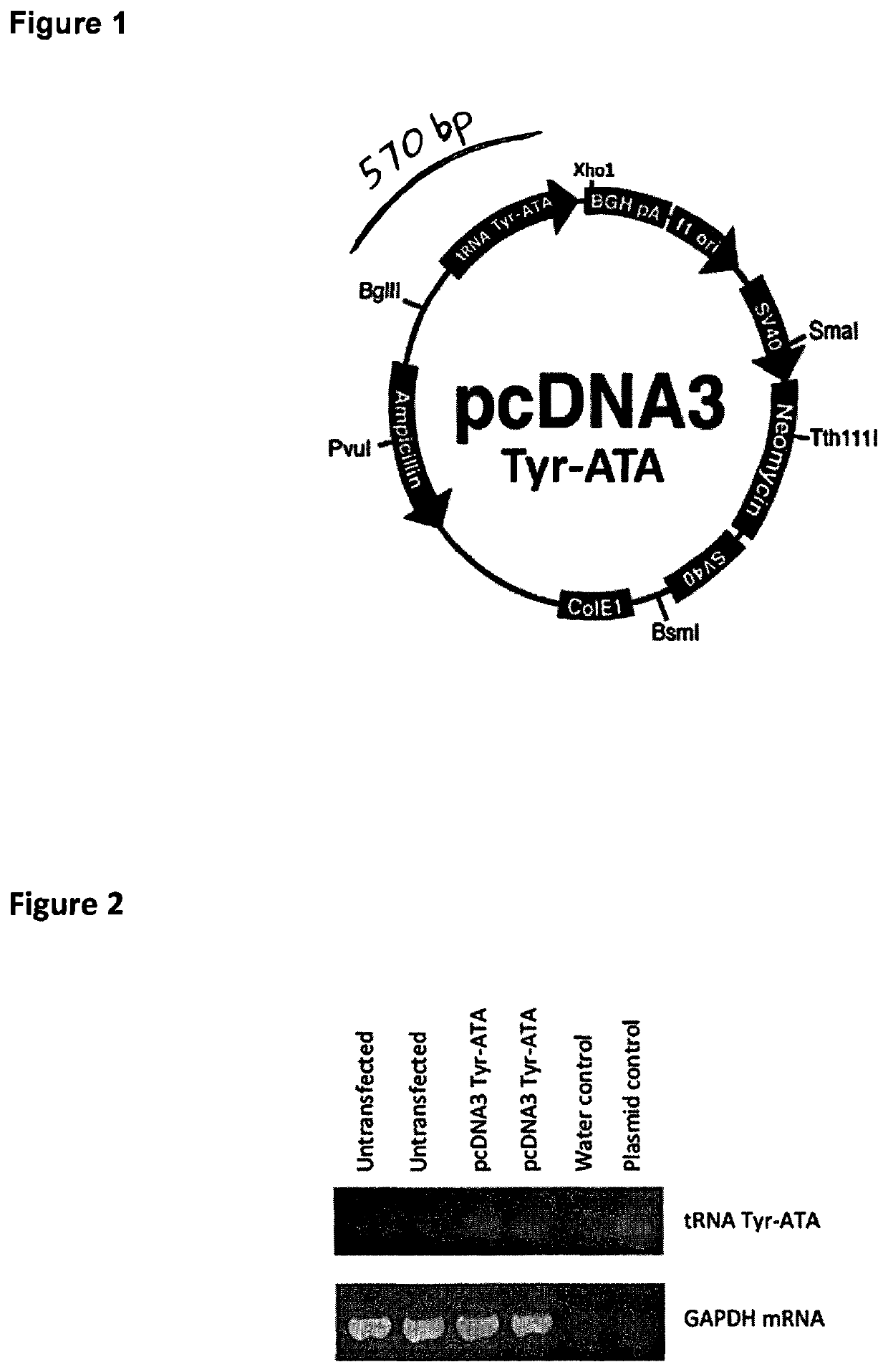
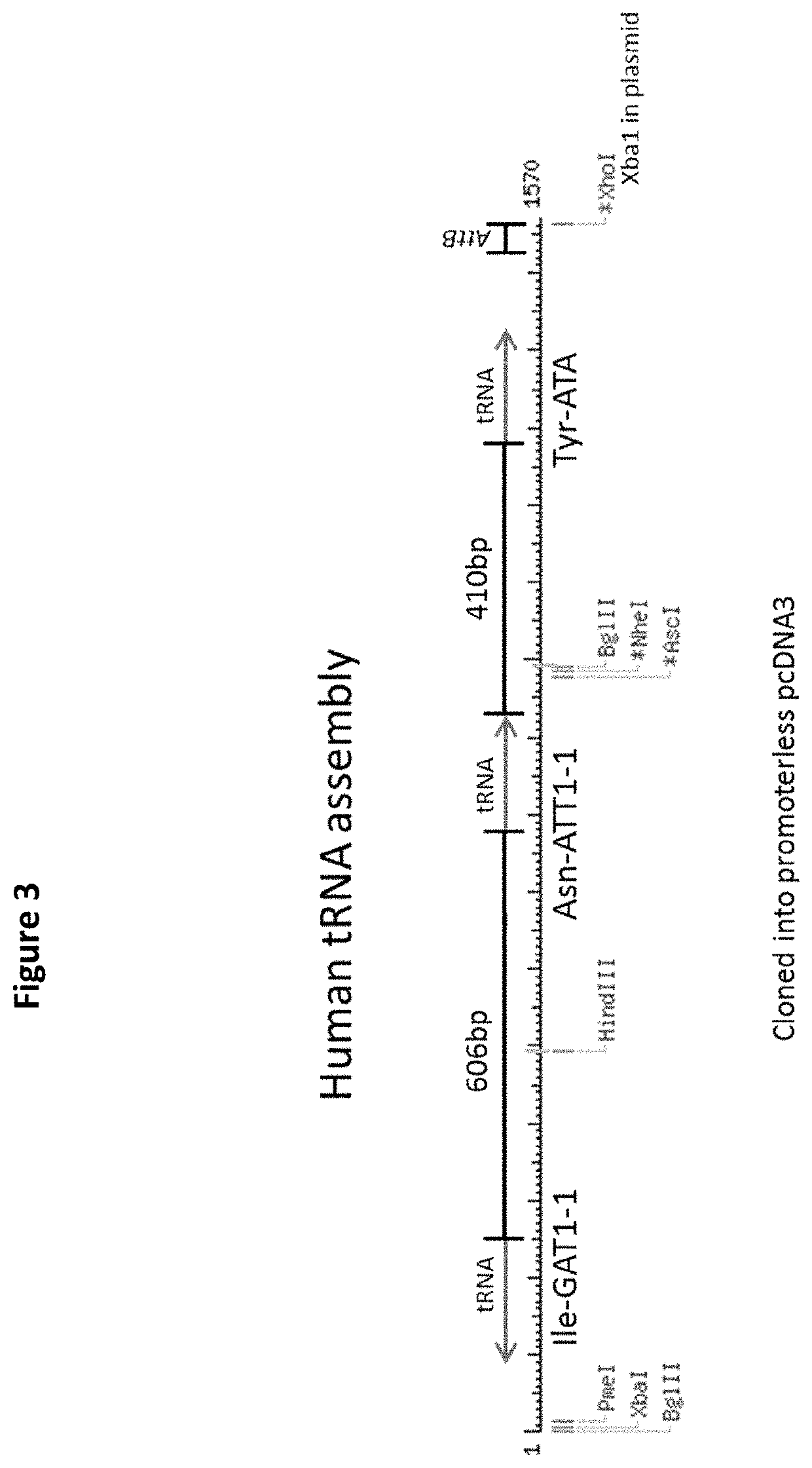
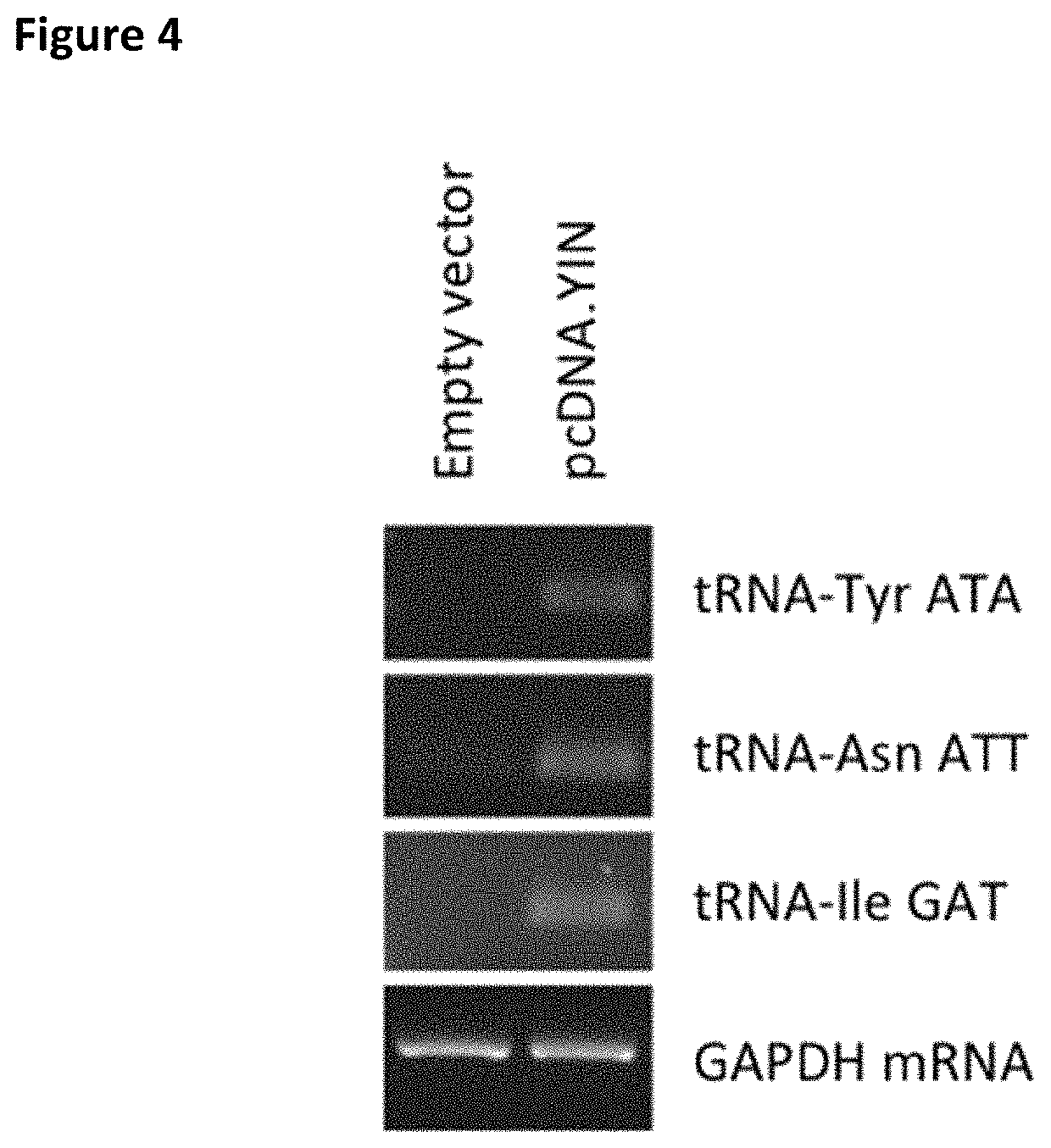
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Base-Base Mismatch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
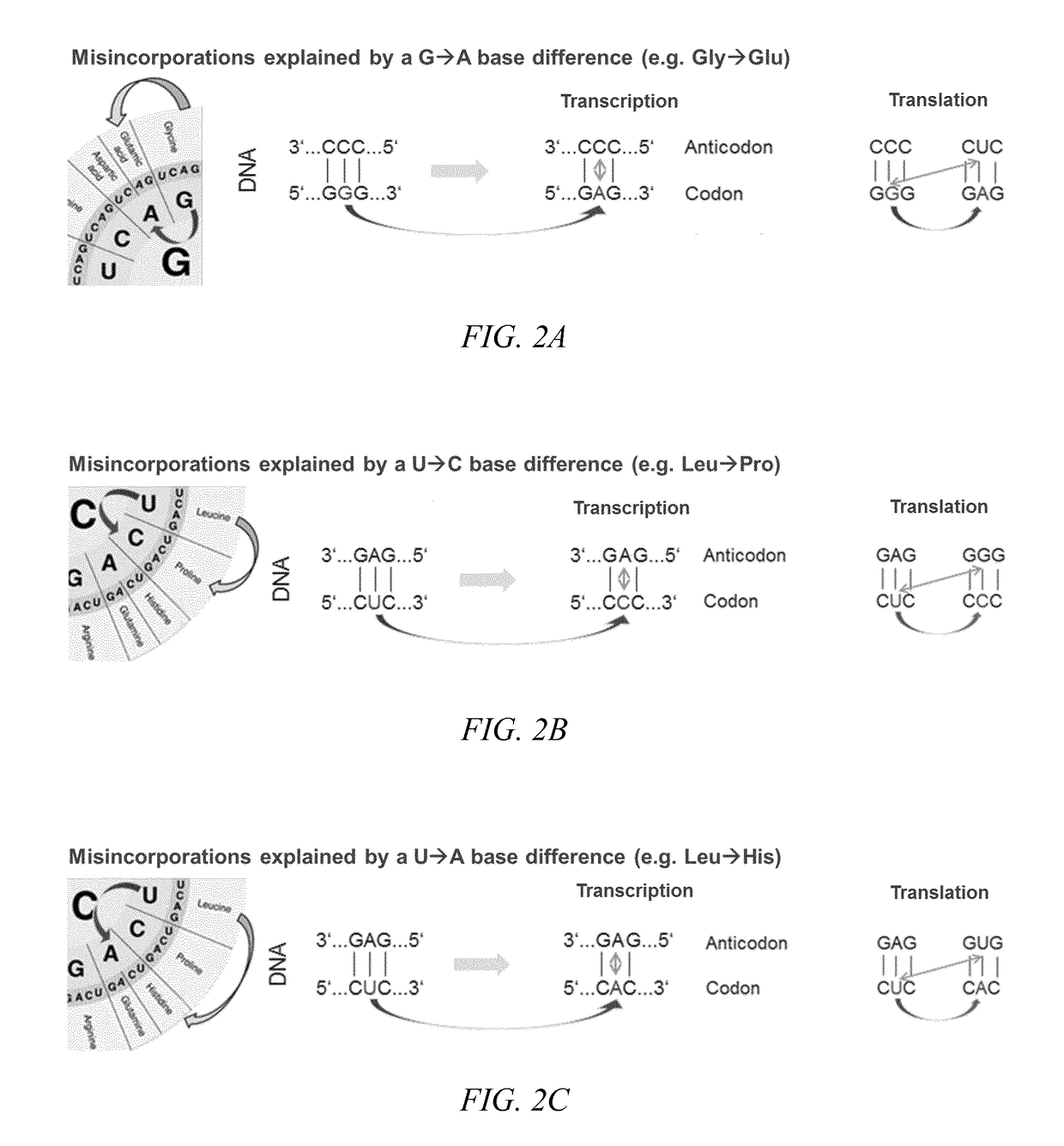
Base-Base Mismatch results from mutagenic factors that induce chemical modification of DNA bases so that pairing between specific bases on complementary DNA strands is eliminated causing mispairing.
Detection of nucleic acid differences using endonuclease cleavage/ligase resealing reactions and capillary electrophoresis or microarrays
InactiveUS20090123913A1Reduce noiseObstruction is producedMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHeteroduplexA-DNA
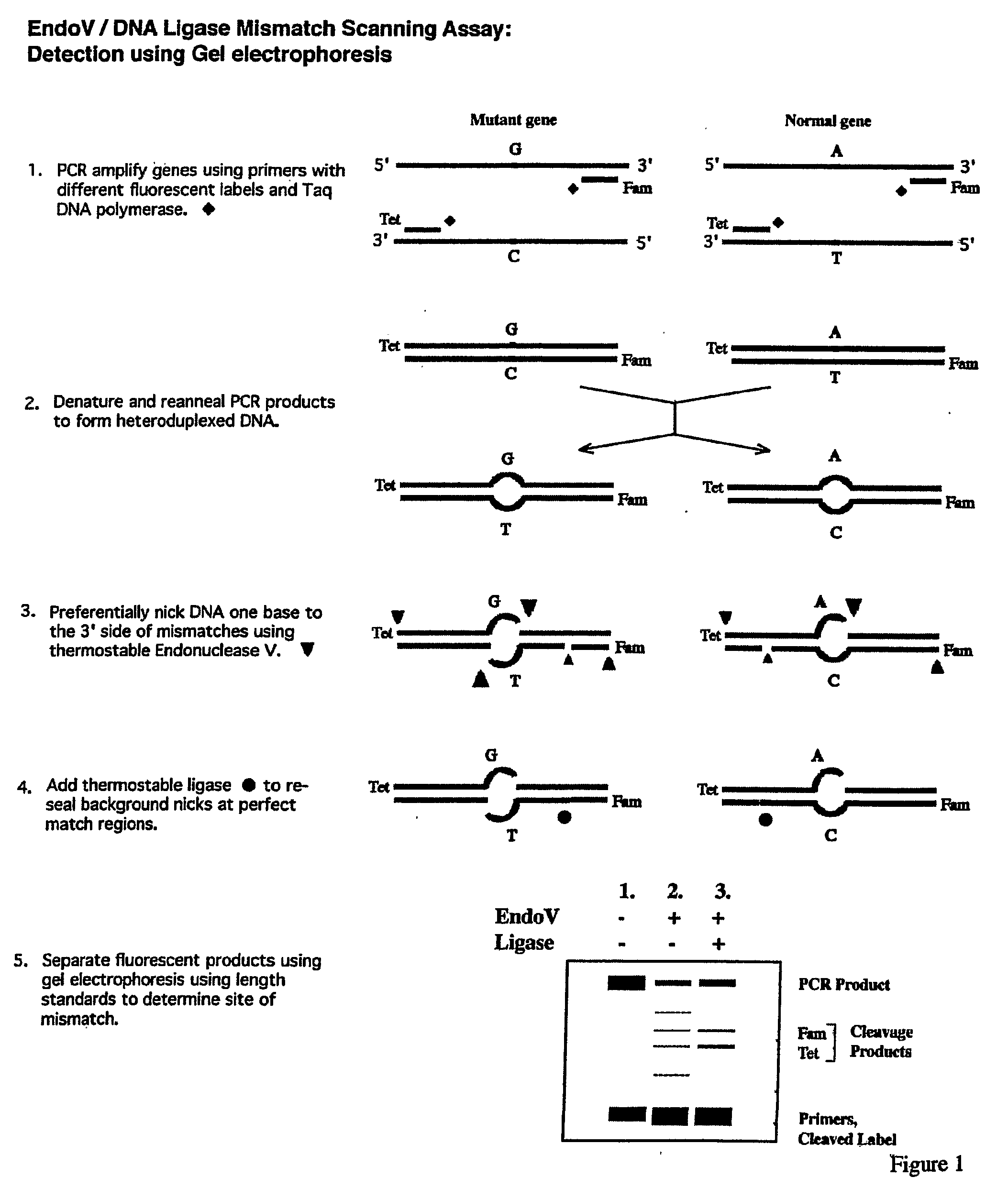
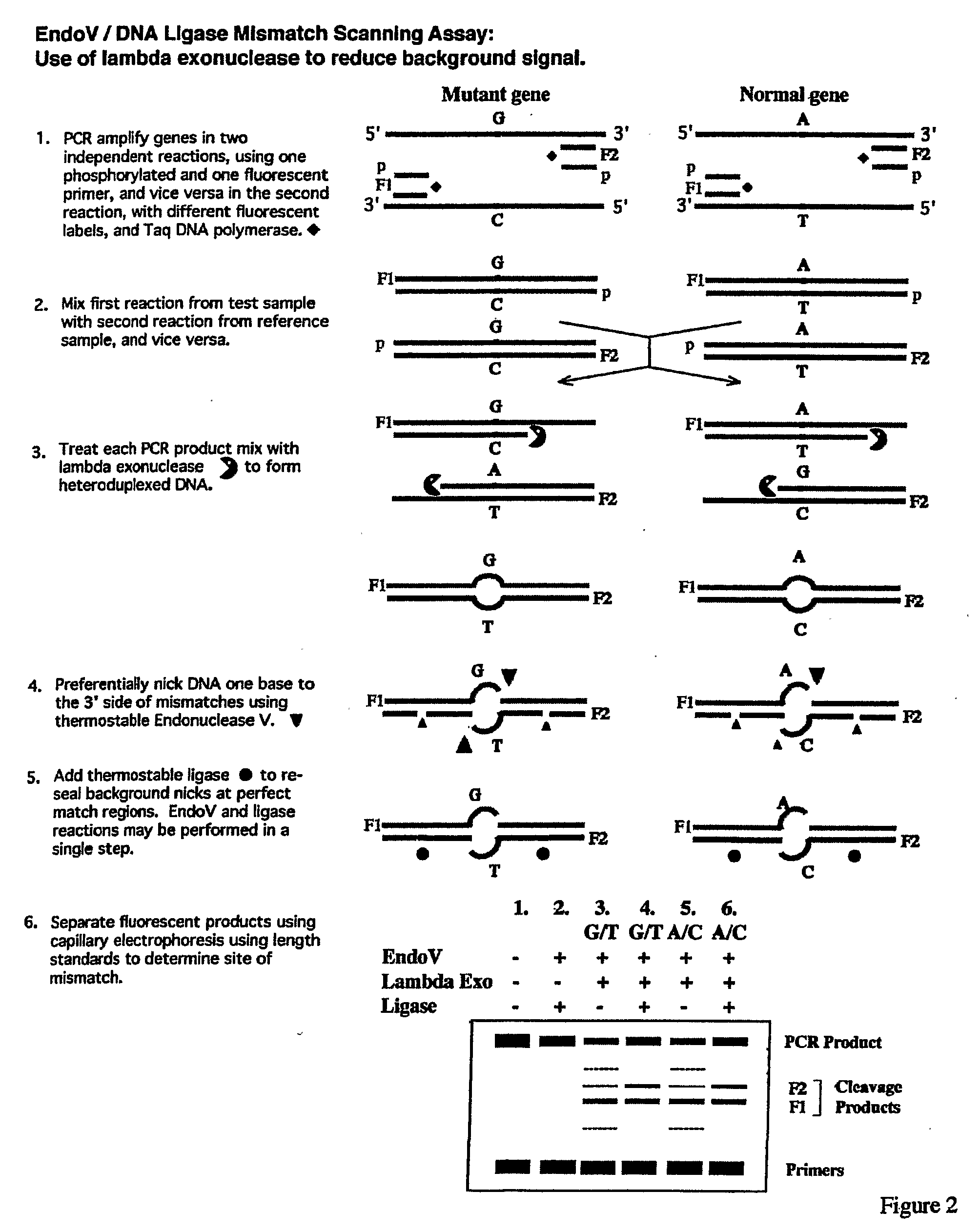
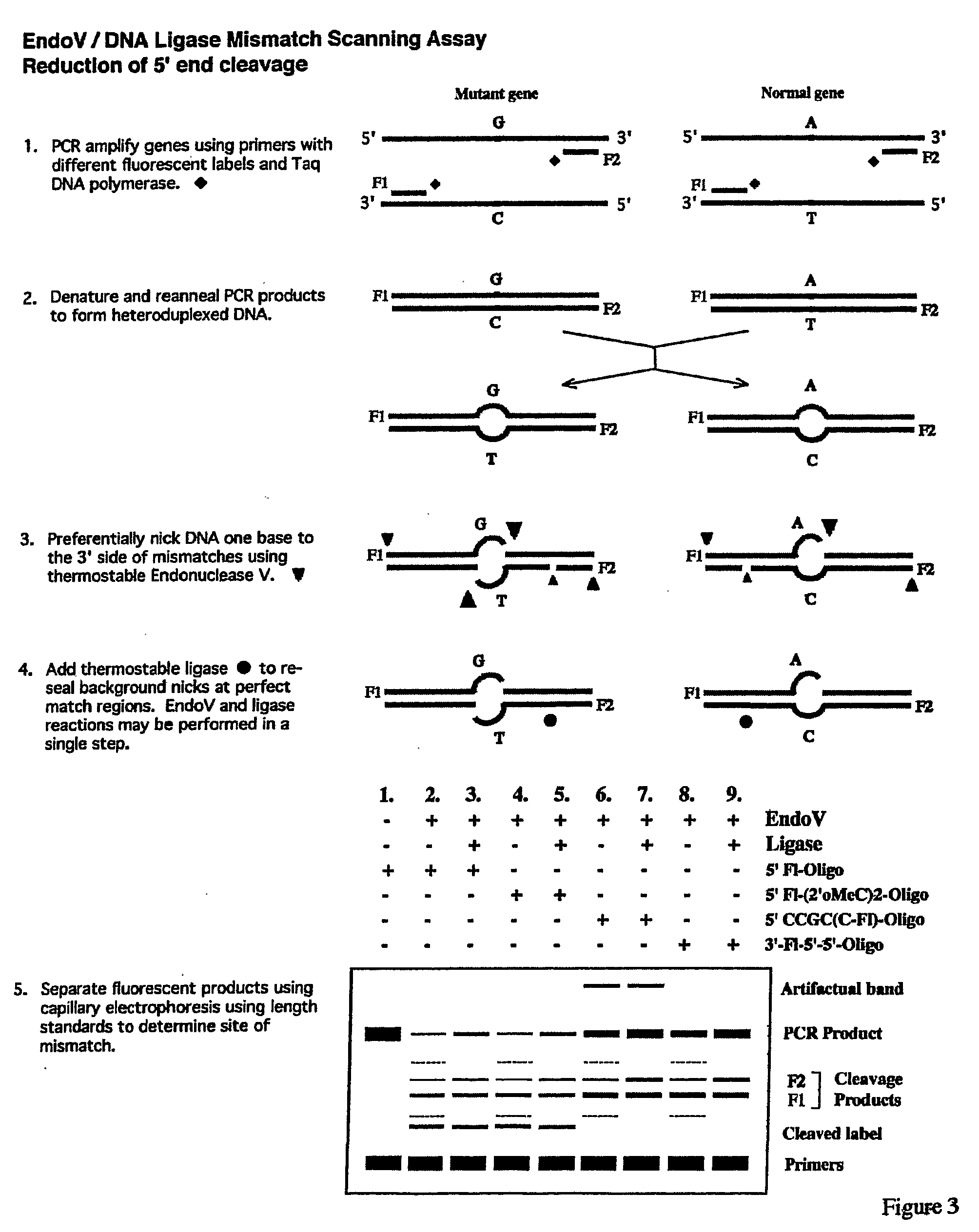
The present invention is directed to various methods for detecting DNA sequence differences, including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and, to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
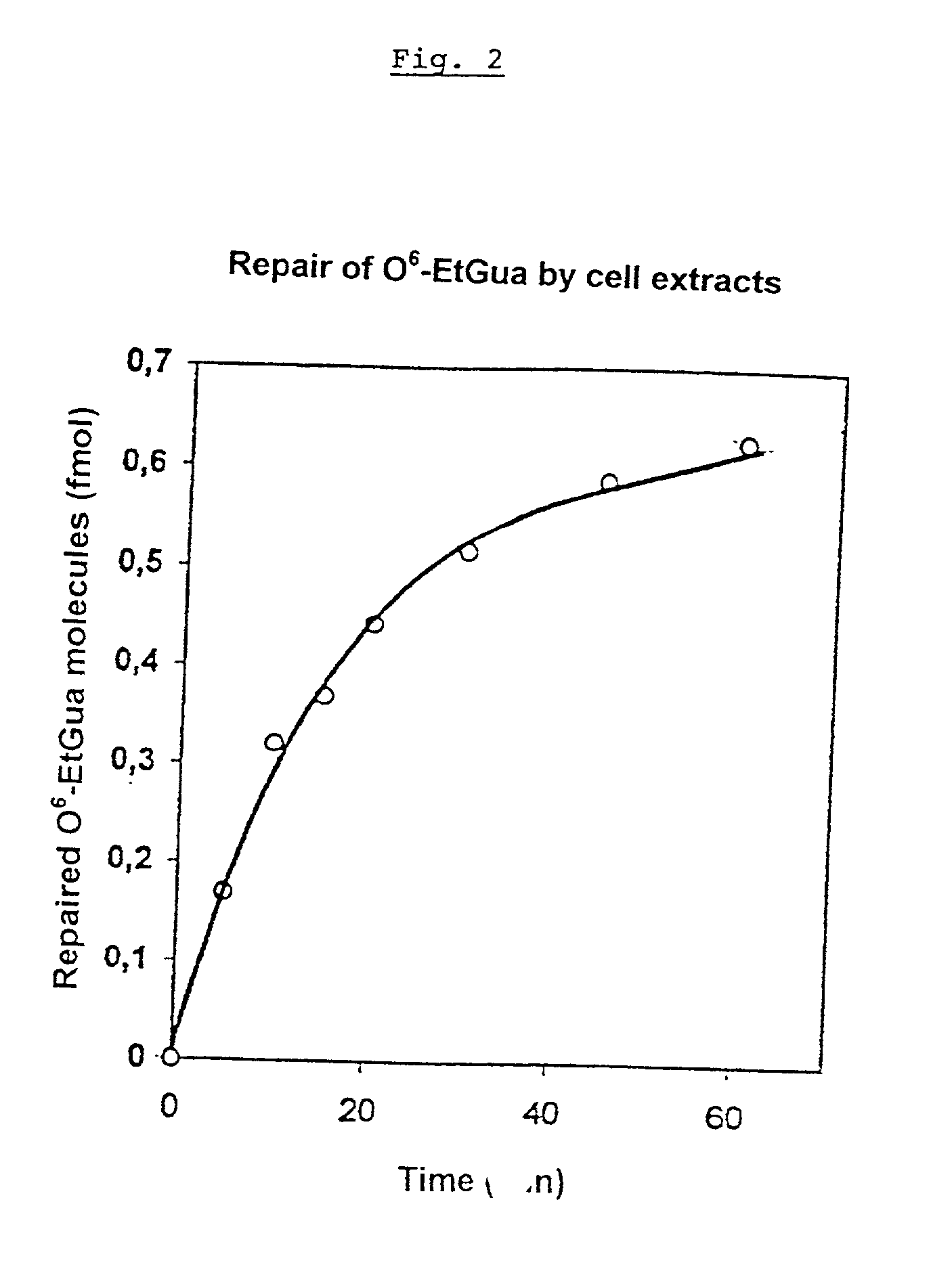
Method and test kit for analyzing DNA repair
InactiveUS20020022228A1Solution presentedQuick fixSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JPurine
A method for analyzing the repair of DNA modifications and base mispairings as well as apurinic and apyrimidinic sites by DNA repair enzymes, comprising the following steps: contacting (a) single- or double-stranded DNA molecules which were covalently coupled to a solid-phase matrix carrying primary or secondary amino groups by reaction with a reactive squaric acid derivative, and which have modifications and / or base mispairings and / or apurinic or apyrimidinic sites, with (b) a composition containing DNA repair enzymes; and determining the elimination of the DNA modifications and / or base mispairings and / or apurinic or apyrimidinic sites. The DNA molecules are covalently coupled to the solid state matrix via a primary or secondary amino group incorporated in the DNA molecule at the 5'-end or at the 3'-end of the DNA or in the 2'-position of at least one deoxyribosyl residue.
Owner:RUBYCON CORPORATION
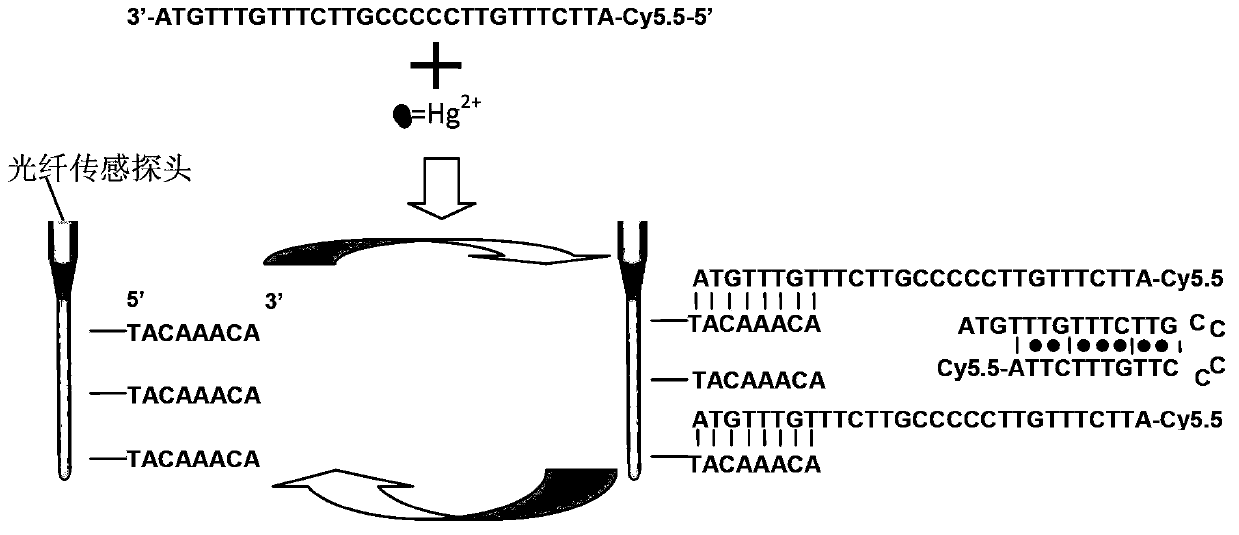
Detecting method for divalent mercury ions
The invention discloses a detecting method for divalent mercury ions. The principle for detecting mercury ions by using the method is as follows: a single-chain DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) molecule B modified by fluorescein contains a sequence which is complementary with a sequence of a DNA catching needle (a single-chain DNA molecule A) fixed on the surface of a probe, and also contains a T-T base pair mismatch structure which can be combined with the divalent mercury ions. During detection, the single-chain DNA molecule B modified by the fluorescein and the mercury ions are simultaneously input to the surface of an optical fiber sensor probe for evanescent waves, and the divalent mercury ions are combined with the single-chain DNA molecule B modified by the fluorescein by the DNA catching needle in a competition way. The more the concentration of the divalent mercury ions is, the fewer the single-chain DNA molecule B modified by the fluorescein and combined with the DNA catching needle on the optical fiber sensor probe for evanescent waves is, so that a fluorescence intensity signal detected by an optical detecting platform for evanescent waves is weaker. An effective means is provided for the rapid on-site and real-time detection of heavy metal mercury ions in the fields of foods, medicines and environments.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION +1
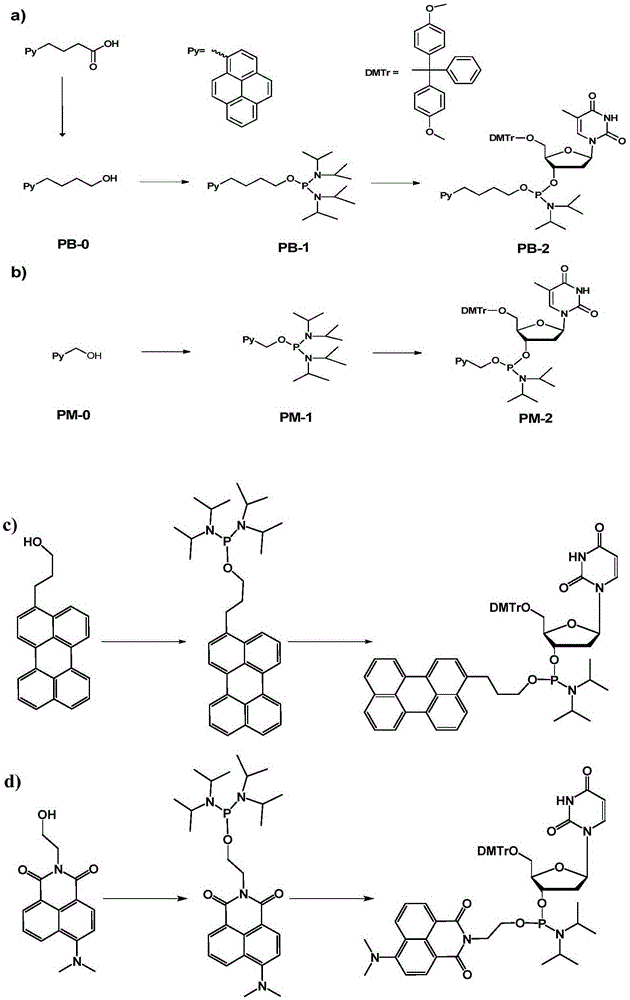
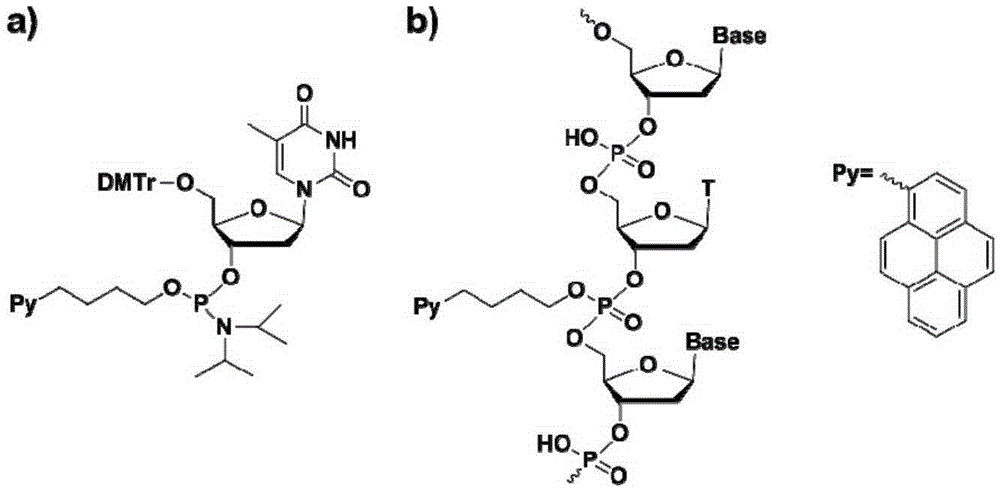
Chromophore-modified deoxynucleoside phosphoramidite monomer compound, preparation method therefor and application thereof
InactiveCN105348343AStability is not affectedDoes not affect the structureSugar derivativesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsFluorescenceDouble strand
The invention discloses a chromophore-modified deoxynucleoside phosphoramidite monomer compound, a preparation method therefor and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: connecting chromophores such as pyrene, perylene or naphthalene carboxamide with bis(diisopropylamino) chlorophosphine to obtain a phosphorous intermediate; and reacting the phosphorous intermediate with DMT-protected deoxynucleoside to obtain a chromophore-modified deoxynucleoside phosphoramidite monomer compound. By virtue of solid-phase synthesis of DNA, the compound is inserted into oligonucleotide at a fixed point to obtain a chromophore-modified fluorescent oligonucleotide probe with a stable double-chain structure. The fluorescent oligonucleotide probe is free of fluorescence-emission, and only being combined with a perfectly matching target chain, the fluorescence can be enhanced by 23.5 times, and the response speed is fast. Mismatched bases are obviously identified with nearly no fluorescence-emission, so that single base mismatch can be obviously identified. The compound can be applied to single base mutation analysis of a gene and detection of a PCR reaction process and the like, and is wide in application prospect in aspects of single base polymorphism detection and nucleic acid detection in a biochemical sample and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Positive feedback amplification electrochemical sensor based on exonuclease (Exo) III
ActiveCN109738503AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesExonuclease IC-DNA
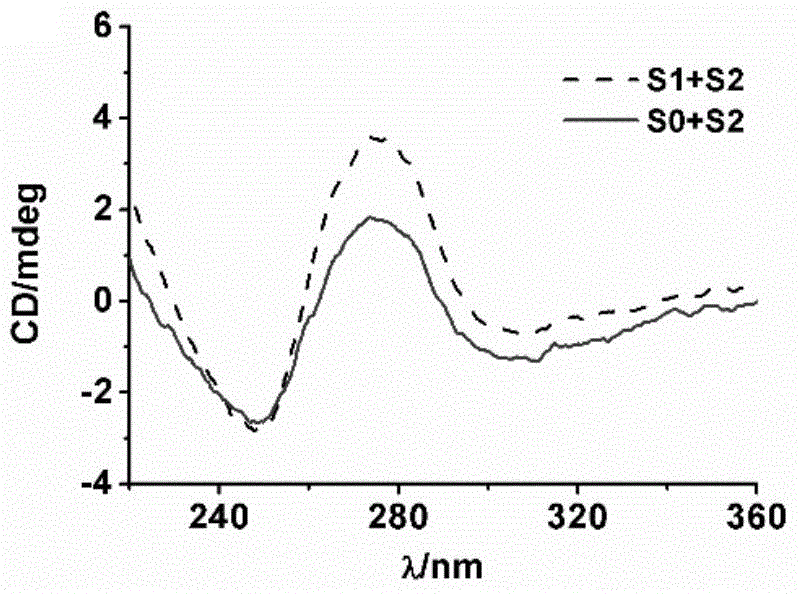
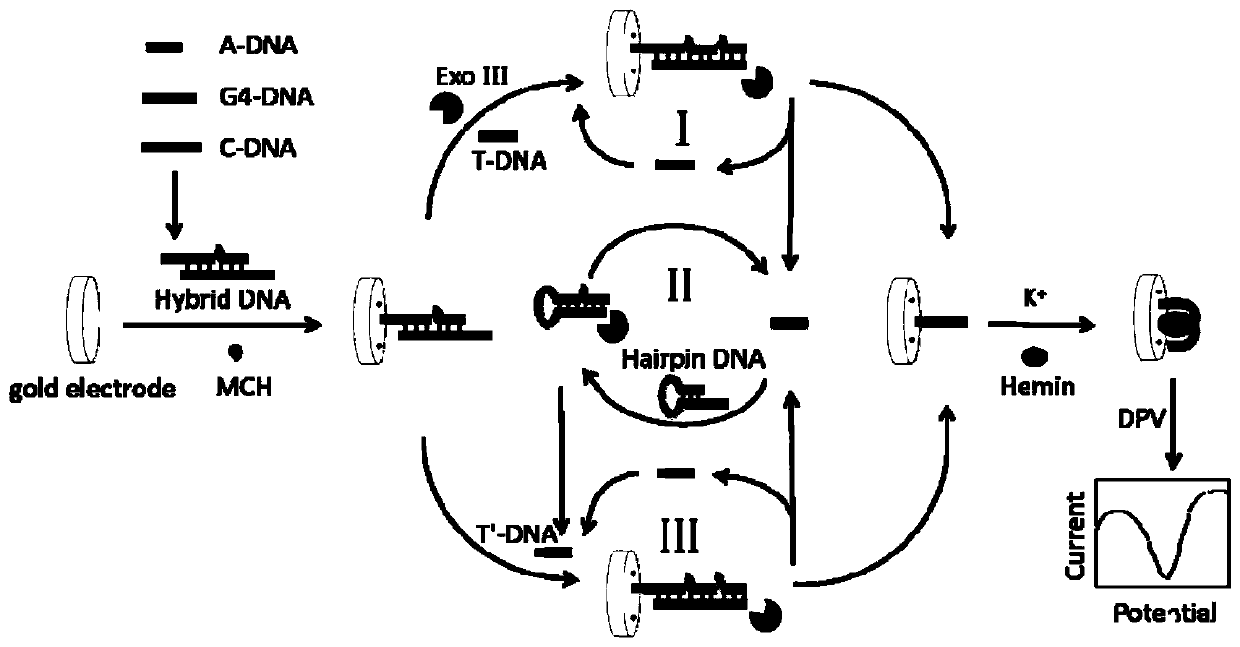
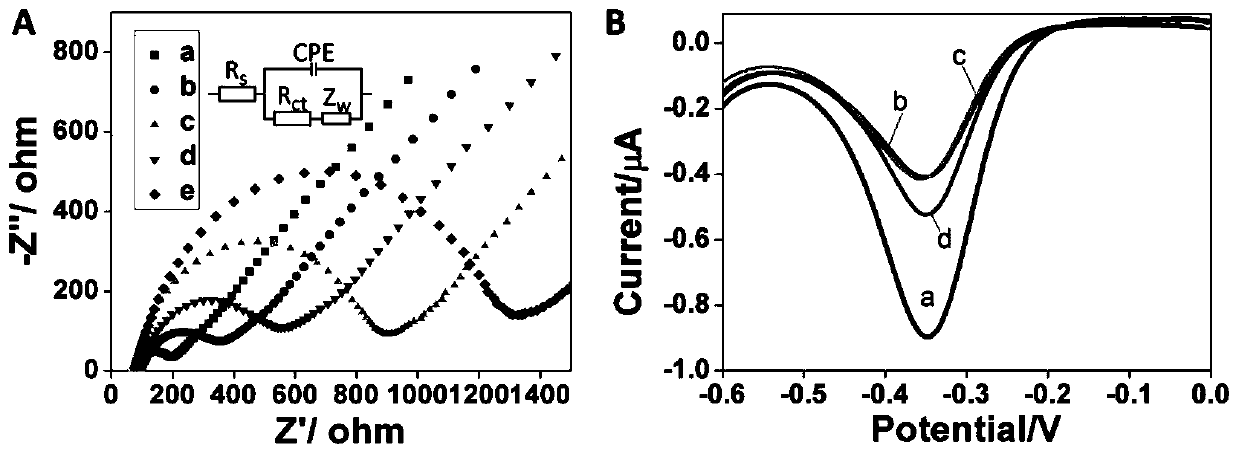
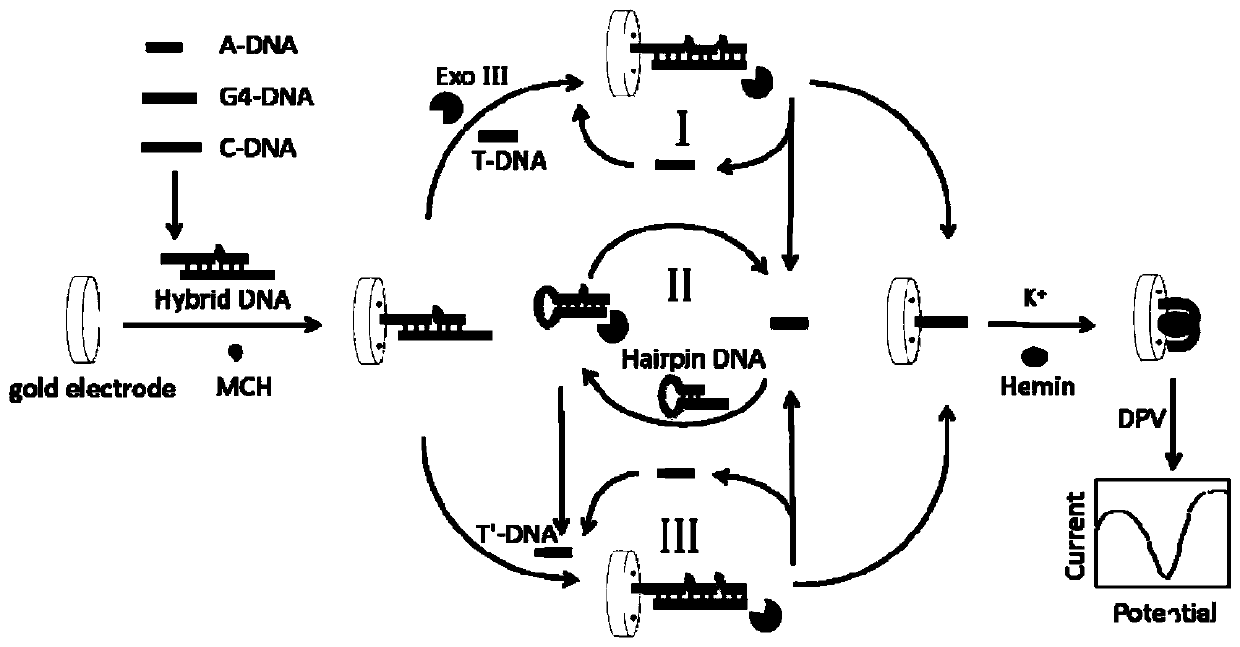
The invention discloses a positive feedback amplification electrochemical sensor based on exonuclease (Exo) III. The positive feedback amplification electrochemical sensor comprises a gold electrode and Hybrid DNA fixed to the gold electrode; the Hybrid DNA sequentially comprises a sulfur-hydrogen bond, a double-stranded DNA structure and a single-stranded DNA structure from the 5' end to the 3' end; the double-stranded DNA structure is prepared from C-DNA and A-DNA as well as G4-DNA which are hybridized; the basic group sequence of the single-stranded DNA structure is complementary with the basic group sequence of T-DNA; and the Hybrid DNA is fixed to the gold electrode through an S-Au key. Through Hairpin DNA and the Hybrid DNA which are ingeniously designed, and target object circular amplification based on the Exo III, a positive feedback amplification strategy combining a homogeneous phase reaction with a heterogeneous phase reaction is achieved; and the strategy shows ultra-highsensitivity, the detection limit is as low as 0.12 aM T-DNA, and high selectivity for the T-DNA and other base group mismatch DNA is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
DNA molecular machine and single-base mutation detection method based on DNA molecular machine as well as application of method
InactiveCN103571831ARich varietyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationNanoparticleMutation detection
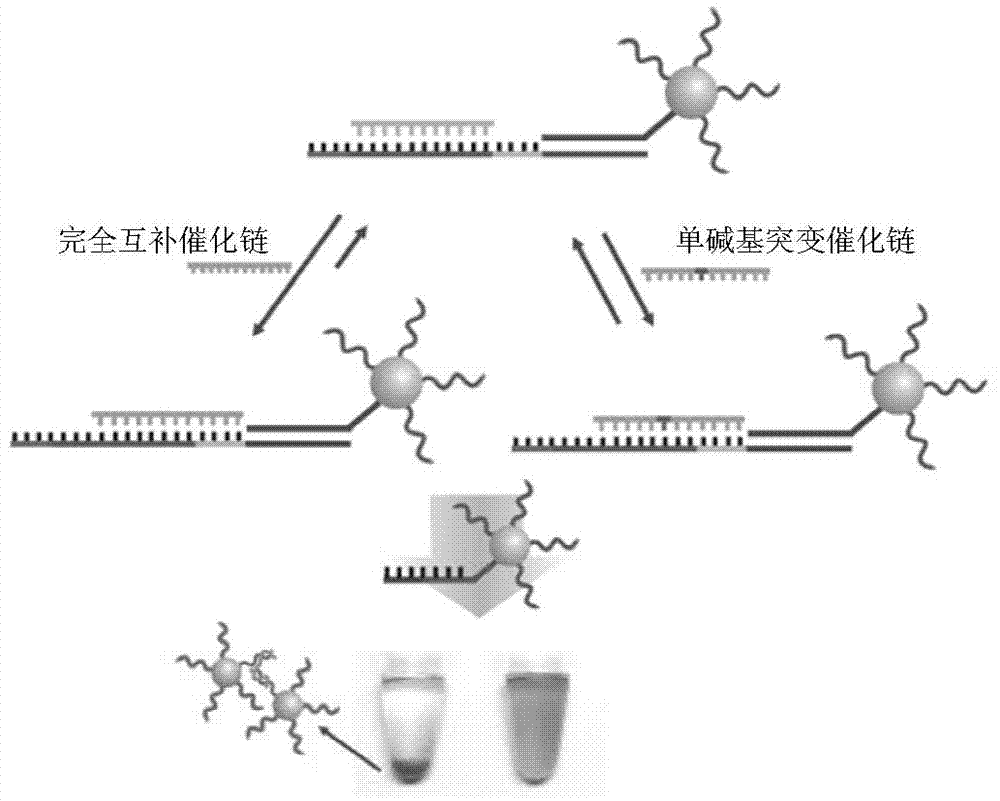
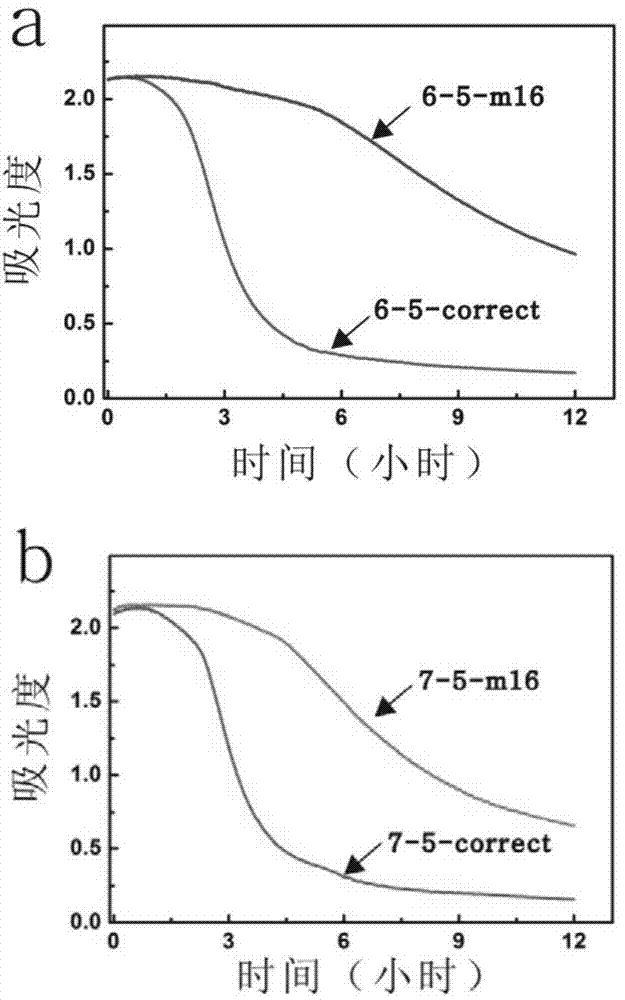
The invention provides a DNA molecular machine and also provides a single-base mutation detection method based on the DNA molecular machine. The method comprises the following steps: initiating different running capabilities of the DNA molecular machine by utilizing different catalytic chains, combining assembly of gold nanoparticles, observing the reaction difference of a catalytic chain system in which completely complementary catalytic chains are added and the catalytic chain system with single-base mutation through a contrast experiment, and finally realizing the single-base mutation detection based on the DNA molecular machine. Strict operating conditions are not needed in the detection means, and the operation is simple. The detection means of the signal is simple and can be identified through colors and ultraviolet spectrums in actual application. The difficulty that complex operation exists or a precise instrument needs to be used for observation in a conventional detection technology is solved. The detected base mutation type is comprehensive and comprises all base mutation forms, namely base mismatch, base deletion and base insertion, and a mutation position of the detected DNA chain is random.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
DNA or RNA detection system, detection method and application thereof
InactiveCN110672569ALow detection limitDiscriminate mismatchesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceWild typeA-DNA
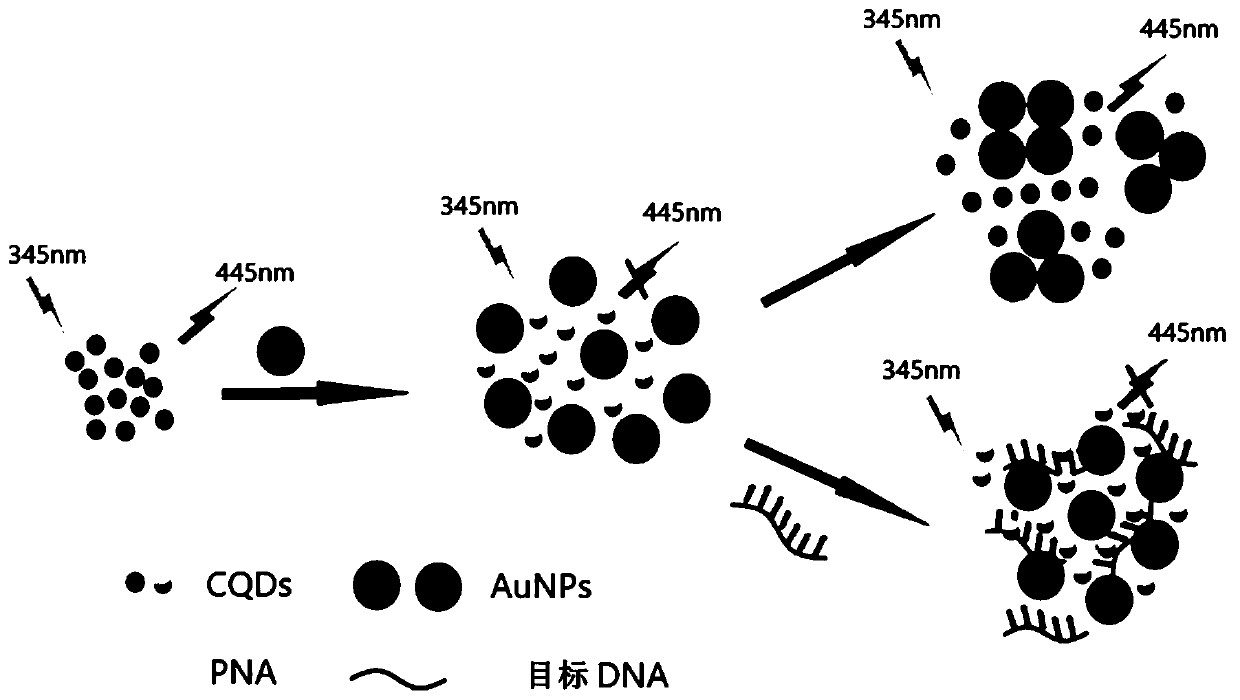
This application discloses a DNA or RNA detection system. The DNA or RNA detection system is a saline solution system, and comprises peptide nucleic acid, gold nanoparticles and carbon quantum dots. The peptide nucleic acid can be hybridized with target DNA or RNA to form double strands. This application further discloses a DNA or RNA detection method, a DNA or RNA detection system, and application of the detection method. The method has characteristics of being fast, economic, simple, and convenient. Neither large-scale instrument and equipment is required, nor precise temperature control anda strict washing step are required. According to the method, a detection limit on wild-type target DNA is relatively low, the method can be applied to detection of DNA in a cell lysis solution, and single-base mismatch can be distinguished.
Owner:CIXI INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
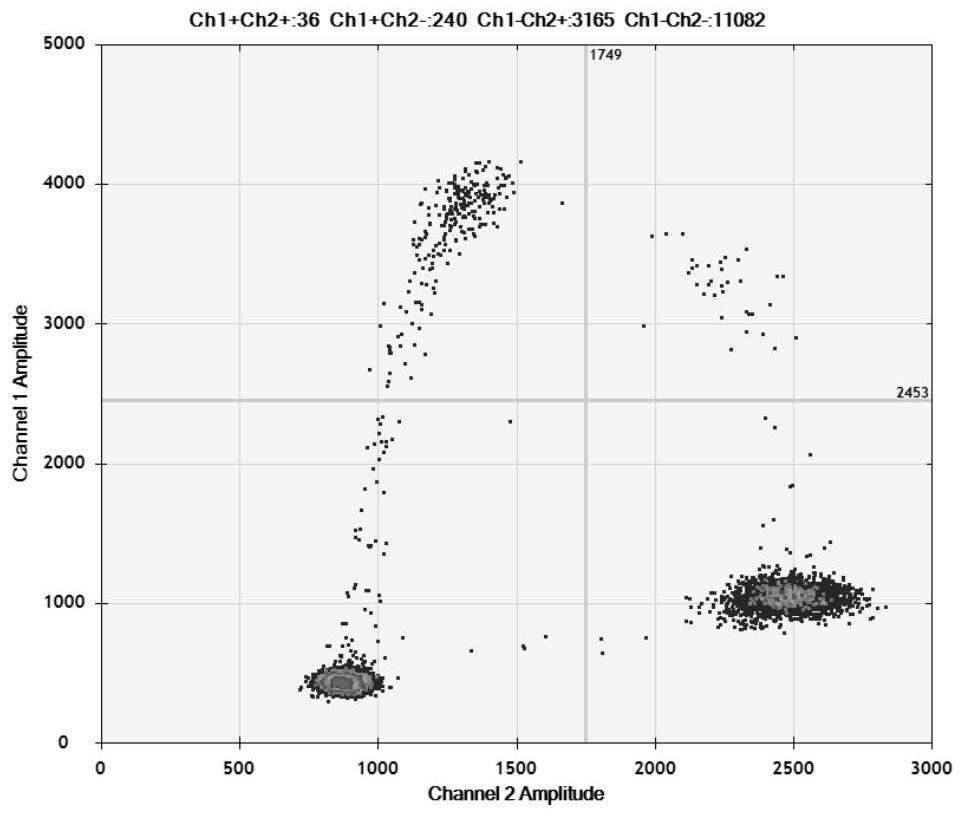
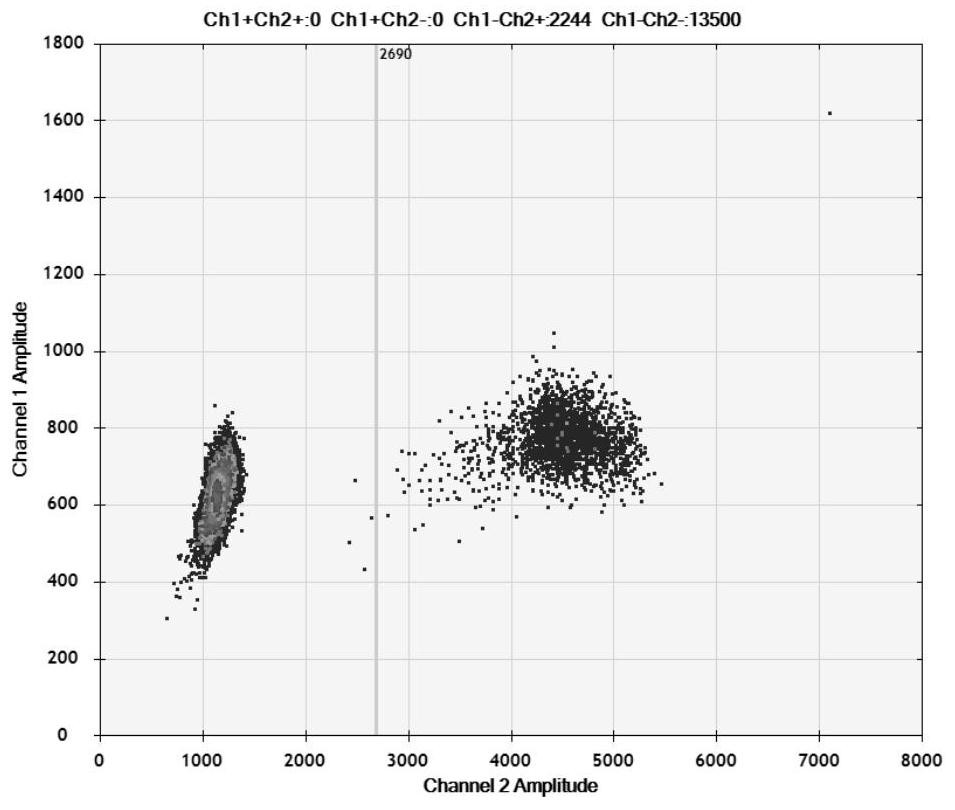
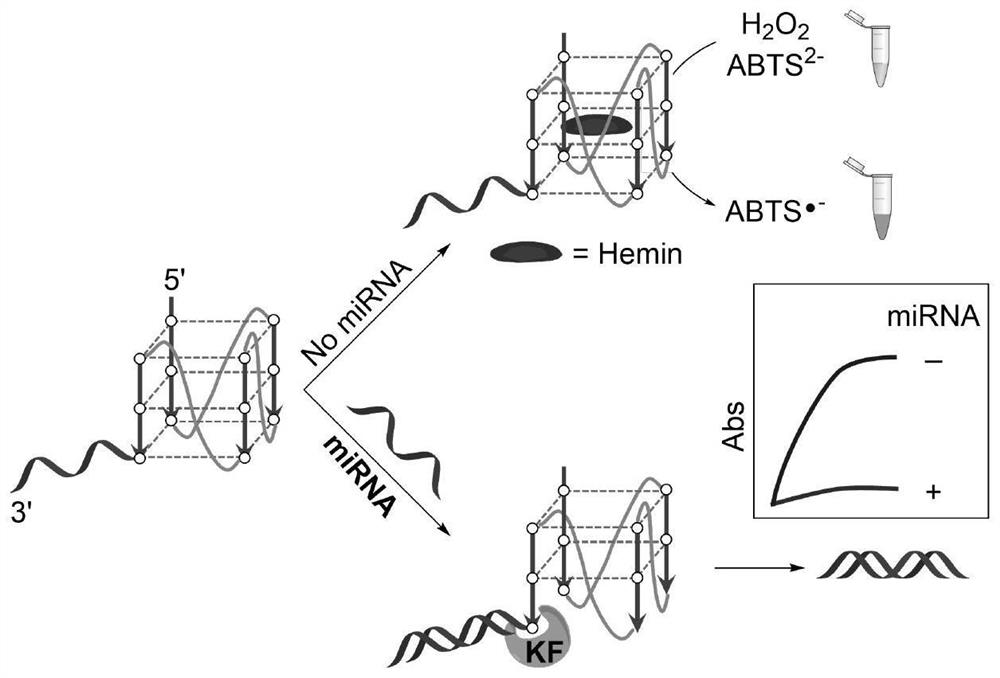
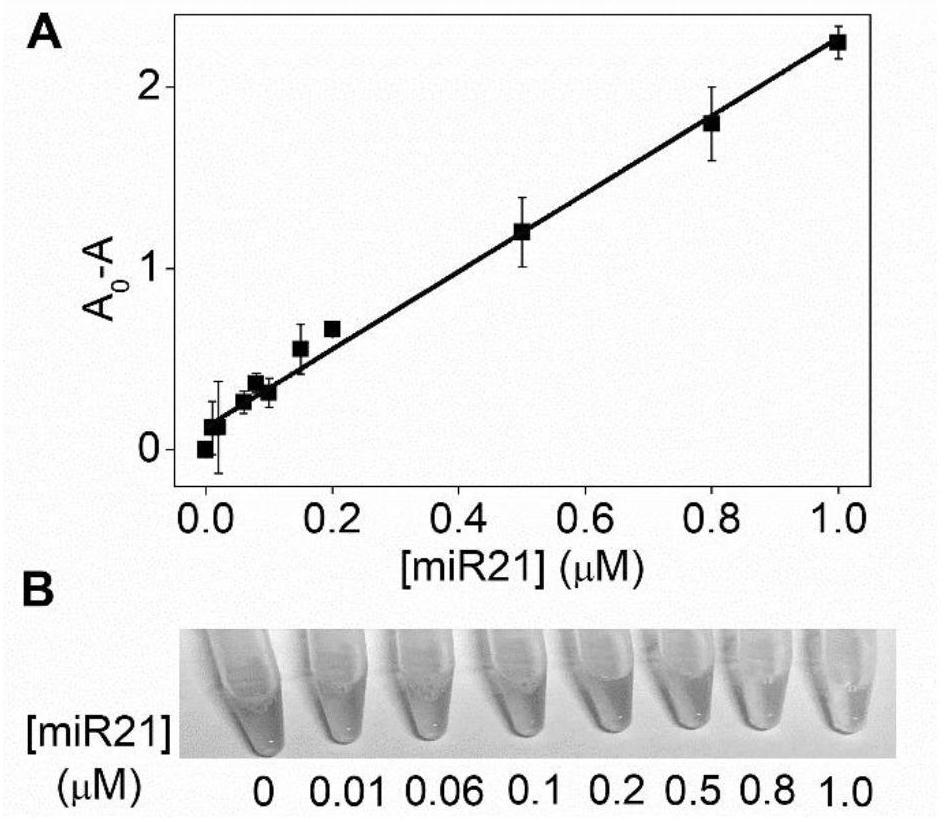
Detection method for visual recognition of microRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) on the basis of G-quadruplex probe structure unwinding
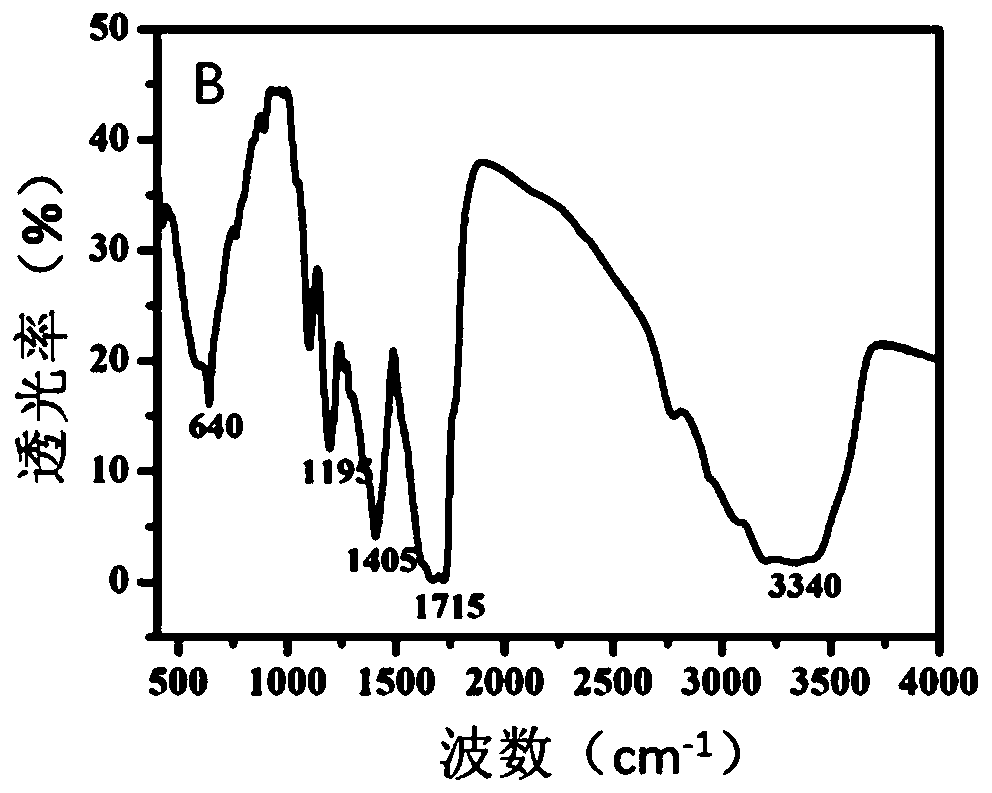
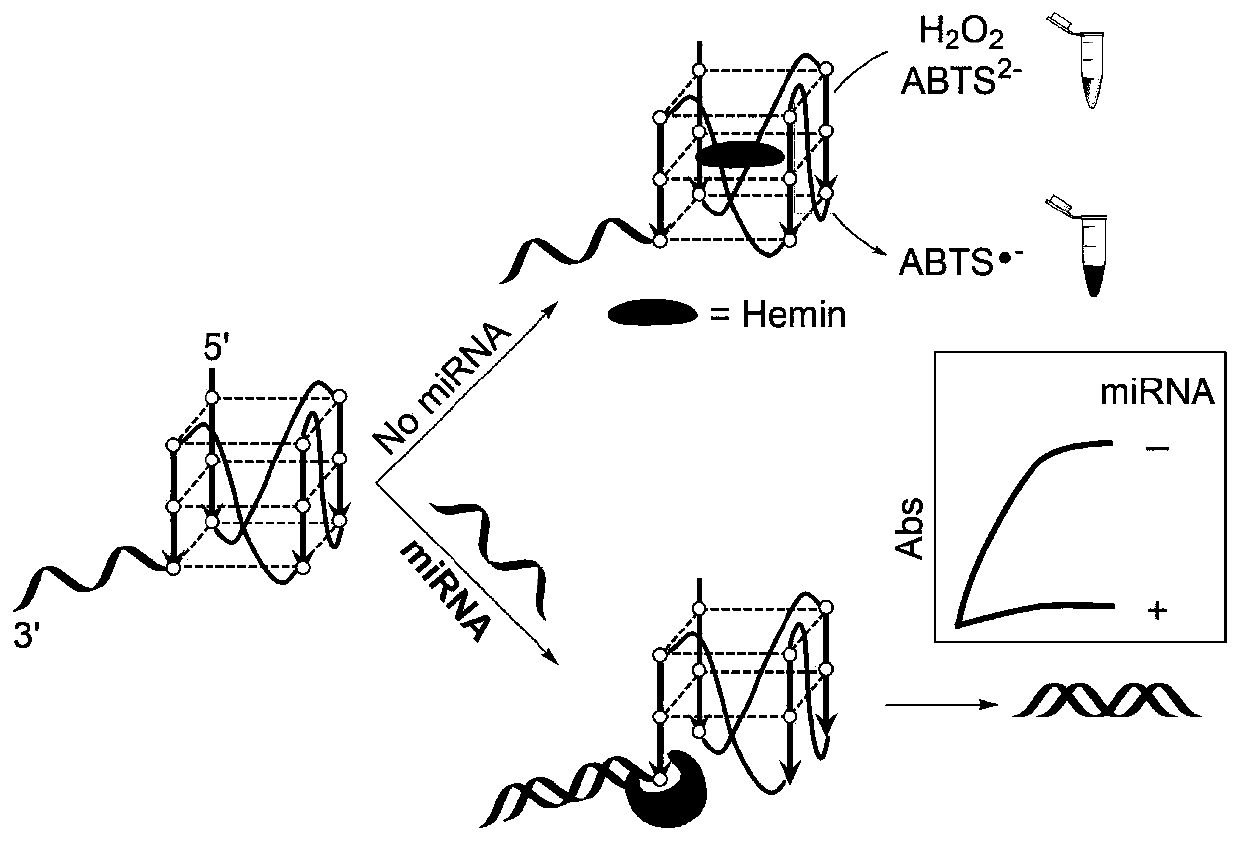
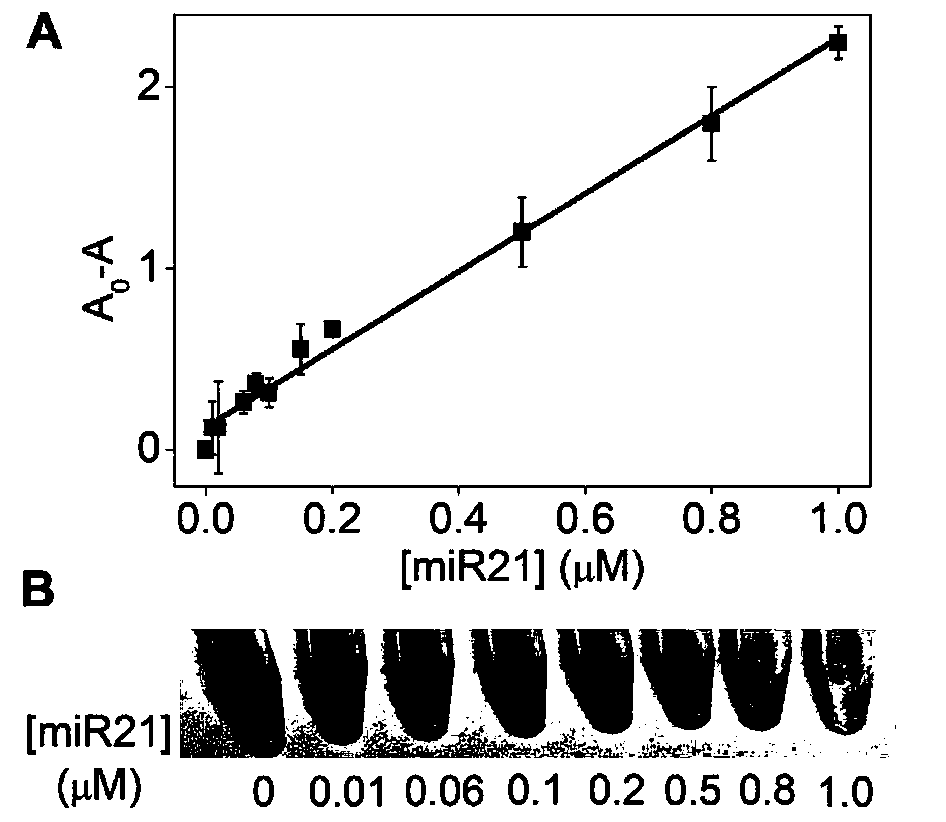
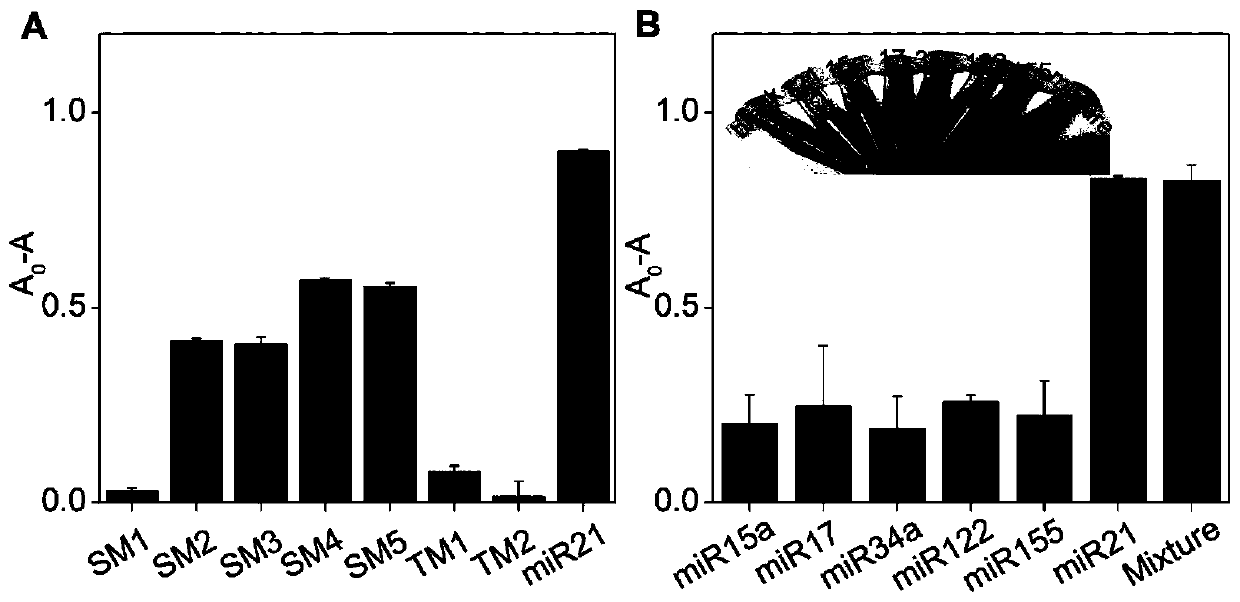
InactiveCN110229872ASimple designDoes not involve complicated reaction processMicrobiological testing/measurementUltrasound attenuationHeme
The invention discloses a detection method for the visual recognition of microRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) on the basis of G-quadruplex probe structure unwinding. A signal attenuation method constructed bycombining catalytic characteristic of a G-quadruplex combined with heme with the structure change of the G-quadruplex can distinguish miRNAs of single-base mismatch and multibase mismatch, and also can distinguish different miRNA family members. On the basis of signal attenuation, sensitivity still can be 4.5nmol / L. The probe used by the invention is simple in design, and does not relate to a complex reaction process. The detection method has an important meaning for the detection of miRNA.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-fidelity Pfu DNA polymerase mutant, coding DNA of high-fidelity Pfu DNA polymerase mutant and application of high-fidelity Pfu DNA polymerase mutant in NGS
ActiveCN113388596AImprove fidelityThe results obtained by the analysis and identification are true and reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBase JWild type
The invention provides a high-fidelity Pfu DNA polymerase mutant. The high-fidelity Pfu DNA polymerase mutant is characterized in that on the basis of a wild type Pfu DNA polymerase, mutation of one, three or six amino acid sites is carried out, and the mutation sites are selected from the following sites: Y403A, P411H, V438K, A741S, R757Q and S768K. The invention also discloses coding DNA of the high-fidelity Pfu DNA polymerase mutant and application of the high-fidelity Pfu DNA polymerase mutant in NGS. The high-fidelity Pfu DNA polymerase mutant has ultrahigh fidelity and high amplification efficiency, can be stably and efficiently applied to the library enrichment process in next-generation sequencing, effectively improves the library sequencing quality, reduces the base mismatch rate, and can be used for precise analysis and interpretation of genetic information.
Owner:YEASEN BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Primers for detecting mutation of human B-raf gene V600E, primer probe composition and kit
PendingCN111647650ANo mismatchHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerMutation detection
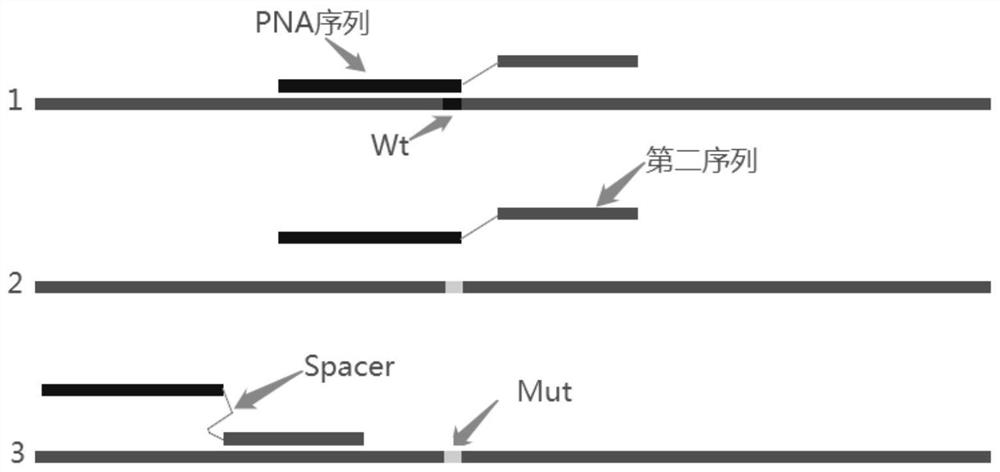
The invention discloses primers for detecting mutation of human B-raf gene V600E, primer probe composition and a kit. The kit comprises a B-raf gene V600E mutation detection primer pair and detectionprobe, an internal quality control primer pair and a quality control probe. A forward primer of the detection primer pair comprises three parts arranged in the following order from the 5' end to the 3' end: 1) a first sequence: the first sequence is used for identifying mutation hot spots, is a peptide nucleic acid PNA sequence hybridizing with a wild type template, is completely matched with thesequence of the wild type template and has a base mismatched with the sequence of a mutant template; 2) Spacer: the Spacer is connected with the 3' end of the first sequence and the 5' end of a secondsequence; 3) the second sequence: the second sequence is bound with a sequence upstream of a mutation site, 3-6bp of the sequence of the 3' end of the second sequence overlaps with the 5' end of thefirst sequence, Tm value of the first sequence is 6.3-11.3 DEG C higher than that of the second sequence. The kit is simple and quick, has sensitivity up to 1 permillage, and has high specificity, and the false positive rate is greatly reduced.
Owner:河南赛诺特生物技术有限公司
Sequence Variants
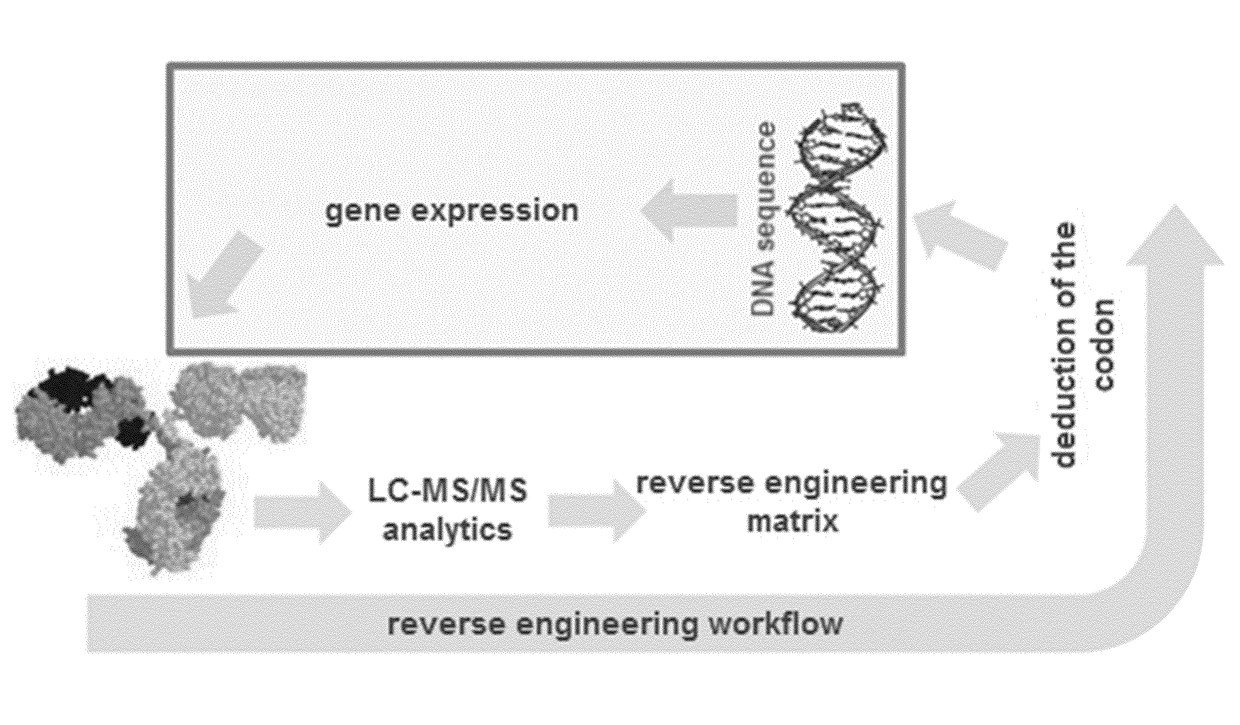
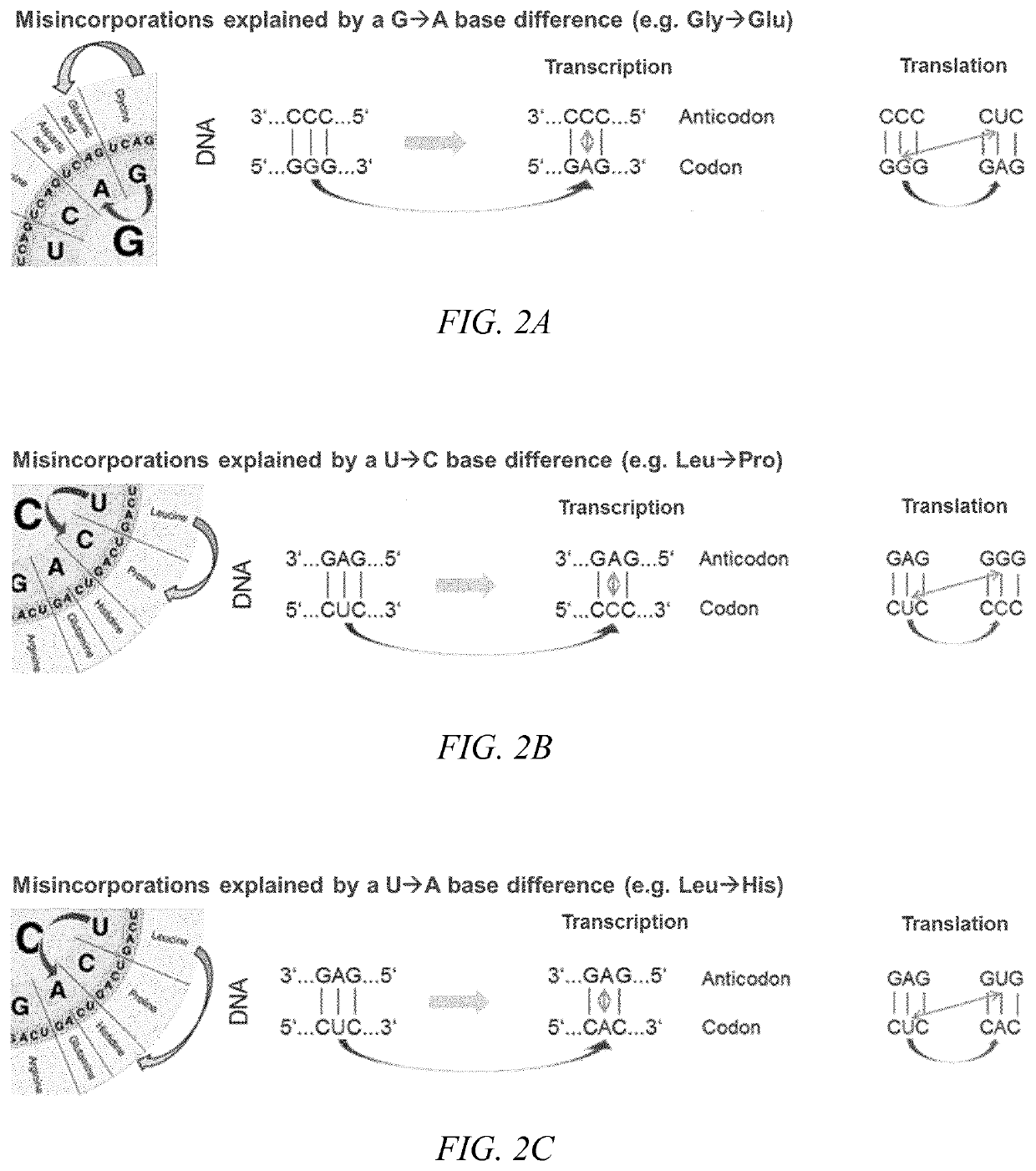
Amino acid residue misincorporations are necessarily found in sequence variants at low concentrations in admixture with expressed polypeptides, resulting from one or more base mismatches within codons susceptible to amino acid residue misincorporation during transcription and / or translation. The invention provides a method of optimizing the coding sequences of a polynucleotide that encodes a polypeptide, wherein at least one codon is susceptible to amino acid residue misincorporation. The method of the invention can be used to reverse-engineer an unknown coding sequence, which encodes the same polypeptide, but differs in said at least one codon from the known coding sequence. The method can further be used to alter the immunogenic potential of an expressed polypeptide. Thus, the invention is useful in engineering optimized polynucleotides encoding polypeptides.
Owner:SANDOZ AG
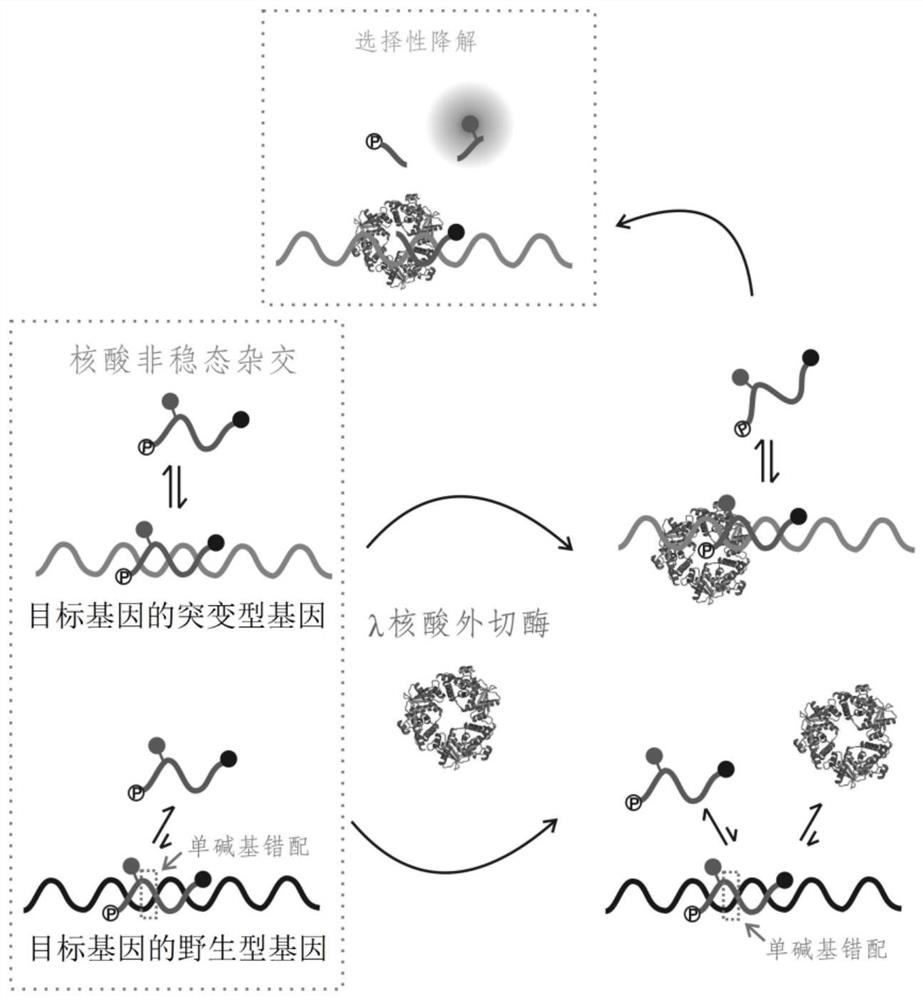
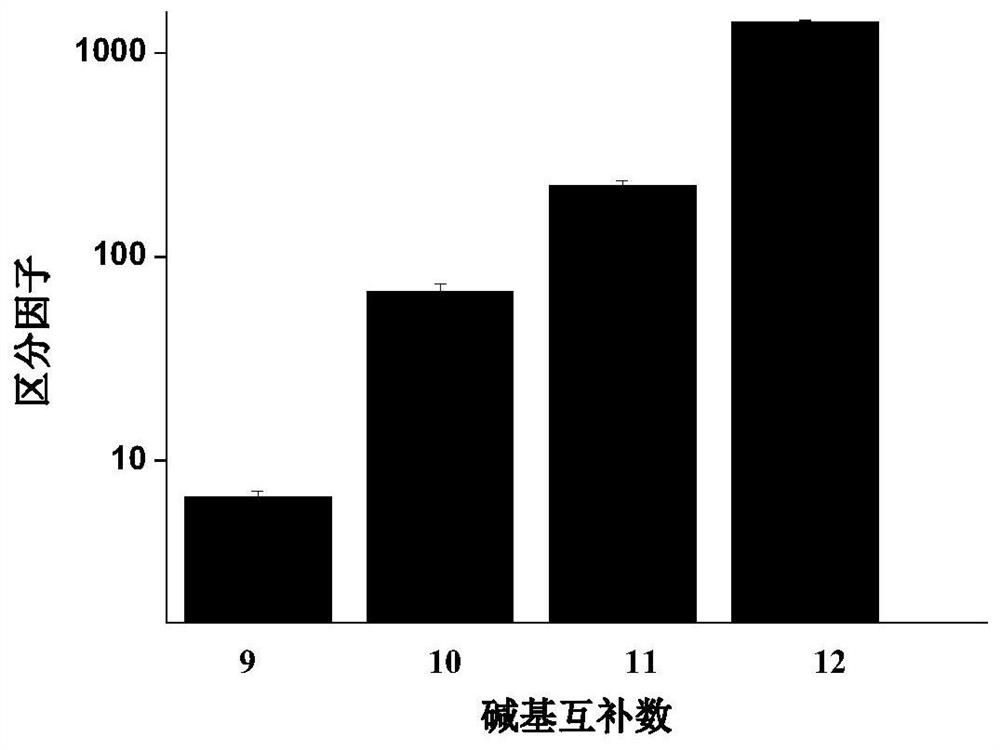
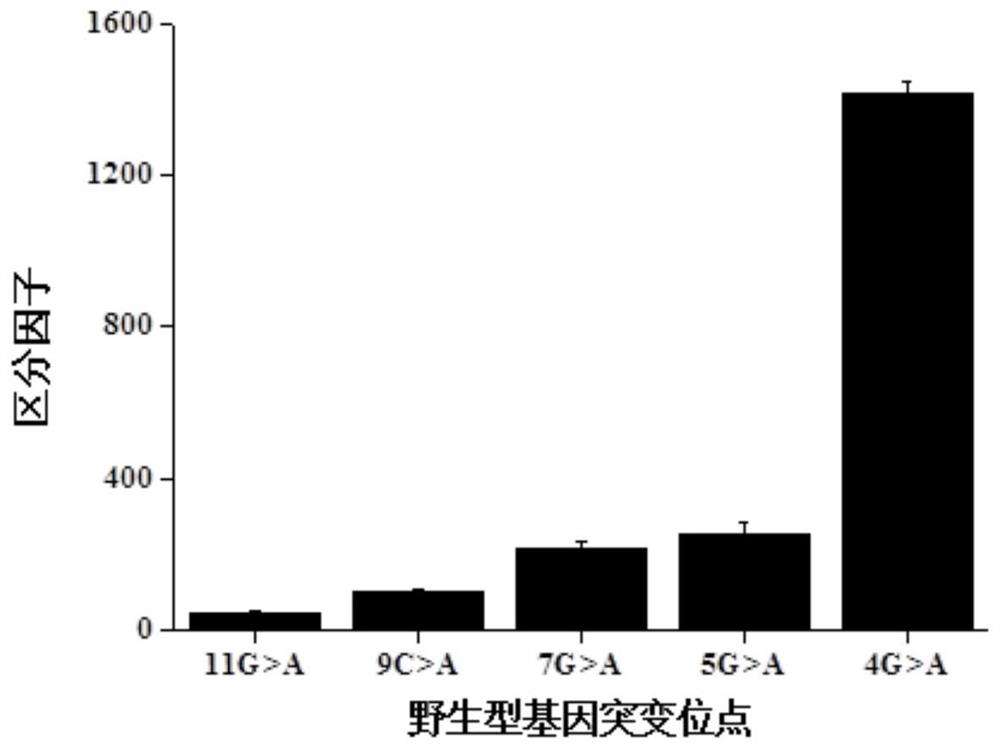
A method for detecting single base mutation
ActiveCN107723341BAccurate detectionGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation detectionWild type
The invention relates to a method for detecting single base mutation in the field of gene mutation detection. The method comprises the following steps: S1, designing a fluorescent signal probe according to the target gene; the fluorescent signal probe is completely complementary to the mutant gene of the target gene, and forms a single base mismatch with the wild-type gene of the target gene; S2, Add the sample to be tested of the target gene and λ exonuclease to the solution containing the fluorescent signal probe to form a reaction system; S3, obtain the real-time fluorescence curve of the reaction system during the reaction, and judge whether the sample to be tested of the target gene is There is a single base mutation. The method of the invention can quickly and accurately detect the single-base mutation gene sequence, has high selectivity for the single-base mutation gene sequence, and can be used for low-abundance mutation detection. In addition, the detection cost of the method is low, easy to prepare, easy to operate, high in repeatability, and easy to be extended to non-professionals for operation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
A Positive Feedback Amplified Electrochemical Sensor Based on Exonuclease Ⅲ
ActiveCN109738503BHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesBase JSingle strand
The invention discloses a positive feedback amplification electrochemical sensor based on exonuclease (Exo) III. The positive feedback amplification electrochemical sensor comprises a gold electrode and Hybrid DNA fixed to the gold electrode; the Hybrid DNA sequentially comprises a sulfur-hydrogen bond, a double-stranded DNA structure and a single-stranded DNA structure from the 5' end to the 3' end; the double-stranded DNA structure is prepared from C-DNA and A-DNA as well as G4-DNA which are hybridized; the basic group sequence of the single-stranded DNA structure is complementary with the basic group sequence of T-DNA; and the Hybrid DNA is fixed to the gold electrode through an S-Au key. Through Hairpin DNA and the Hybrid DNA which are ingeniously designed, and target object circular amplification based on the Exo III, a positive feedback amplification strategy combining a homogeneous phase reaction with a heterogeneous phase reaction is achieved; and the strategy shows ultra-highsensitivity, the detection limit is as low as 0.12 aM T-DNA, and high selectivity for the T-DNA and other base group mismatch DNA is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
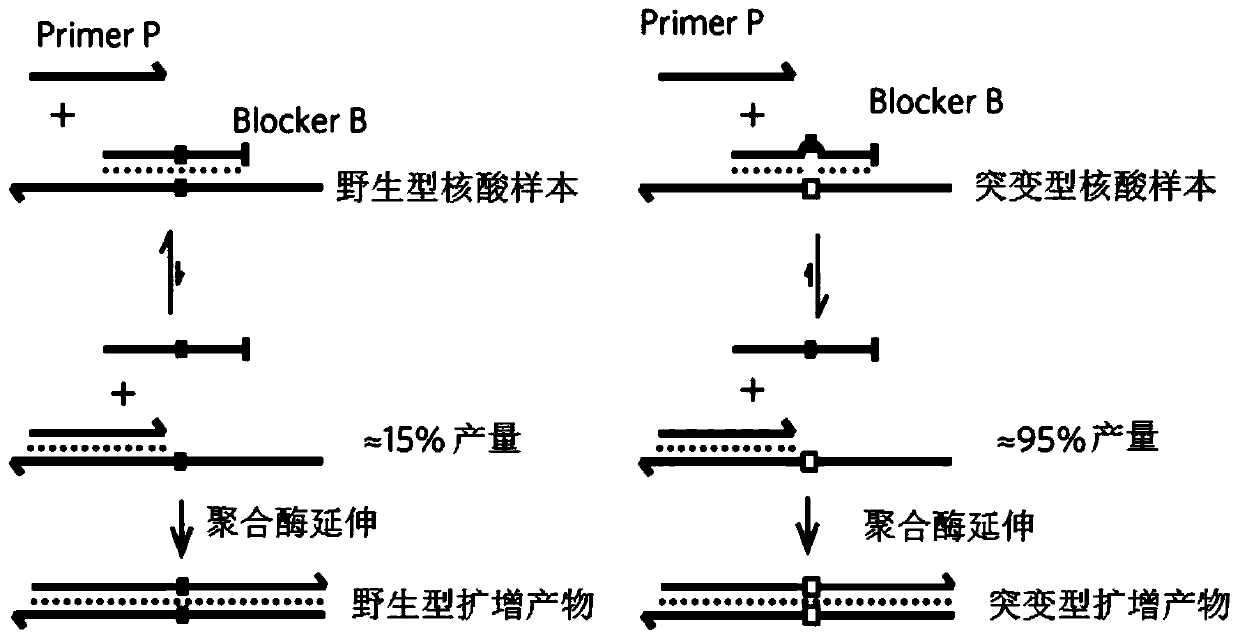
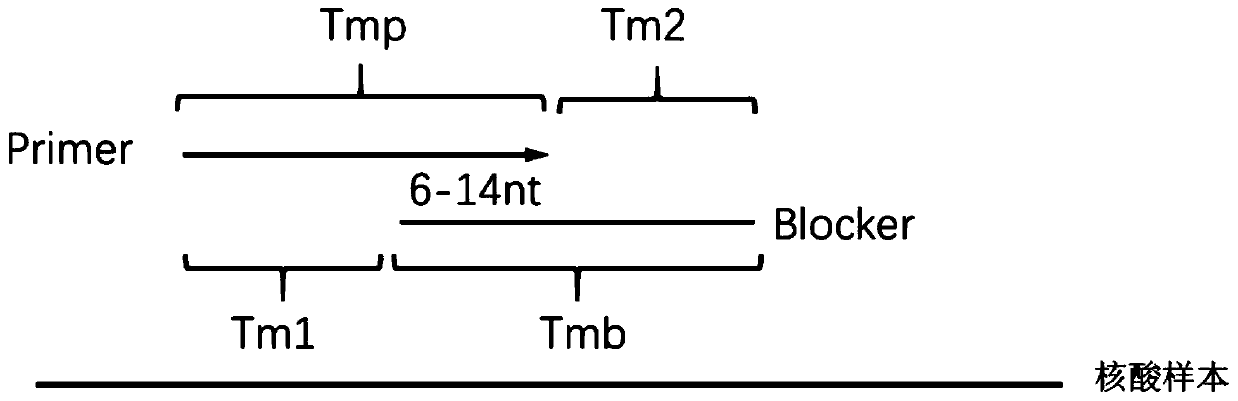
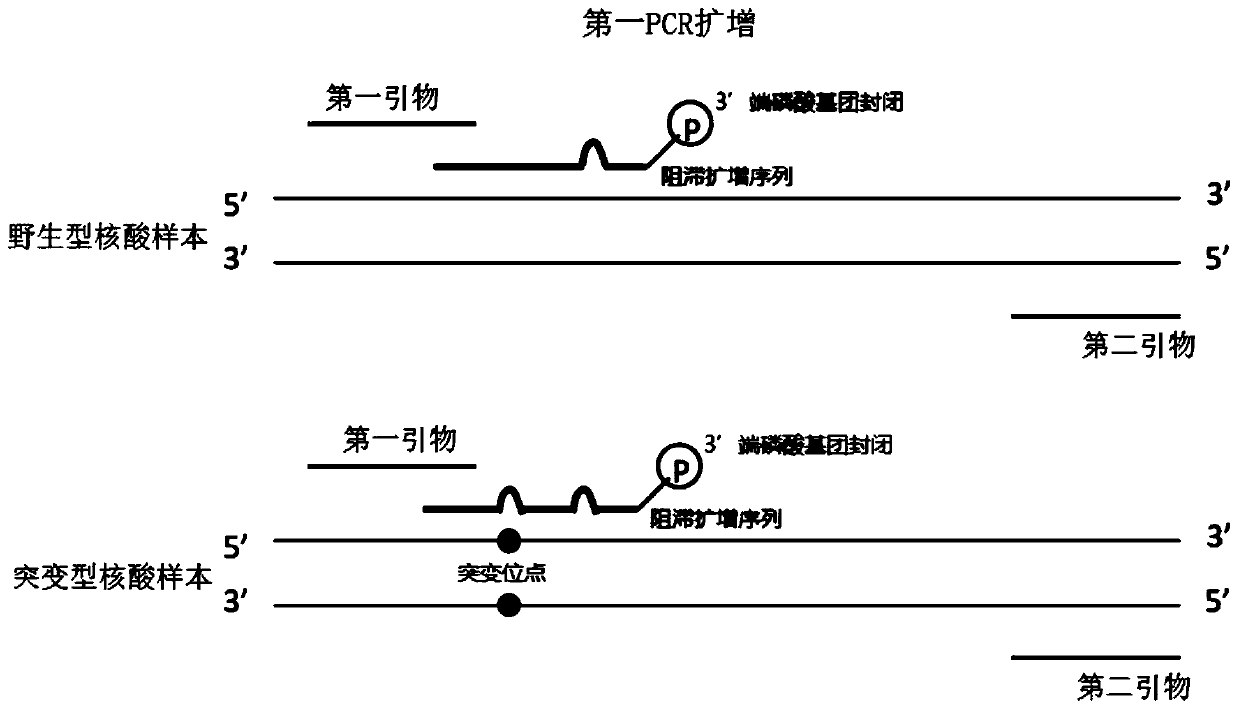
Method for carrying out blocking, substitution, amplification, enrichment and detection on target mutation based on blocker introducing extra base mismatch
The invention relates to a method for enriching and detecting gene mutation of a target area. The method for enriching and detecting the gene mutation of the target area comprises the following steps:mixing a nucleic acid sample containing a to-be-detected target area with a first primer, a second primer and a blocking and amplification sequence, and carrying out first PCR amplification to obtaina first amplification product; and carrying out second PCR amplification by utilizing the first primer and the second primer based on the first amplification product to obtain a second amplificationproduct, wherein the 3' tail end of the blocking and amplification sequence contains a blocking group, the blocking and amplification sequence and the first primer contain a partial overlapping sequence, the to-be-detected target area is located in a matching area of the blocking and amplification sequence and the nucleic acid sample, the 3' tail end of the first primer is located at the upstreamof the to-be-detected target area, at least one base mismatching site exists between the blocking and amplification sequence and the nucleic acid sample, and the at least one base mismatching site isdifferent from a site of the to-be-detected target area. Therefore, high-precision detection for low-frequency gene mutation can be realized.
Owner:杭州瑞普基因科技有限公司
Sequence variants
Amino acid residue misincorporations are necessarily found in sequence variants at low concentrations in admixture with expressed polypeptides, resulting from one or more base mismatches within codons susceptible to amino acid residue misincorporation during transcription and / or translation. The invention provides a method of optimizing the coding sequences of a polynucleotide that encodes a polypeptide, wherein at least one codon is susceptible to amino acid residue misincorporation. The method of the invention can be used to reverse-engineer an unknown coding sequence, which encodes the same polypeptide, but differs in said at least one codon from the known coding sequence. The method can further be used to alter the immunogenic potential of an expressed polypeptide. Thus, the invention is useful in engineering optimized polynucleotides encoding polypeptides.
Owner:SANDOZ AG
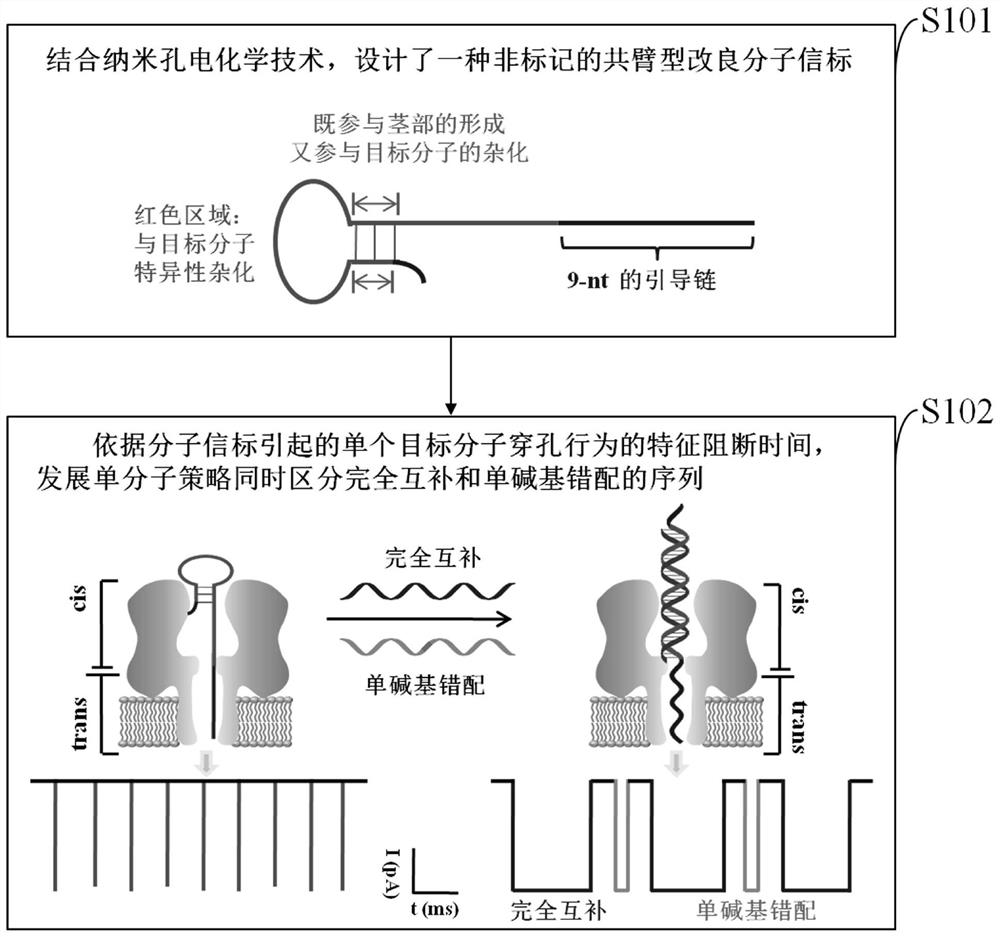
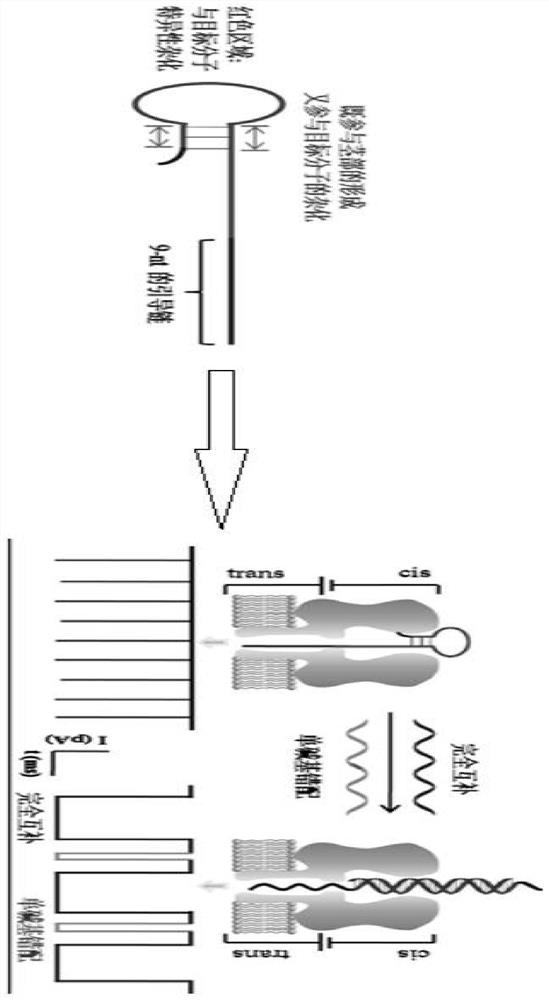
A method for simultaneously distinguishing single-base mismatches at the single-molecule level
ActiveCN108593728BImprove letter-to-background ratioHigh thermodynamic stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesNanoporeClinical diagnosis
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
HBV BCP region 1762/1764 mutation digital PCR detection kit and use method thereof
PendingCN114262752AImprove accuracySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBase JMutation detection
The invention provides a digital PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for 1762 / 1764 mutation in an HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) BCP (Bovine Colored Protein) region and a use method of the digital PCR detection kit. The kit comprises a primer and a probe for detecting two mutation sites A1762T and G1764A, an HBV wild type primer and a probe, an internal reference primer and a probe, a PCR reaction mixed solution, a positive control and a negative control. Locked nucleic acid is added from the 15th basic group and the 20th basic group at the 5'end of the primer for detecting the two mutation sites A1762T and G1764A for modification. The upstream primer for detecting the A1762T mutation site is provided with a base mismatch from the 21st site of the 5'end; and a downstream primer for detecting the G1764A mutation site is respectively provided with a base mismatch from the 20th site and the 22th site at the 5'end. Through an ARMS-PCR primer design technology and a locked nucleic acid technology, the accuracy of mutation detection is improved, and the kit has high sensitivity and specificity and is simpler and more convenient to operate compared with a sequencing method.
Owner:WUHAN BIOTECH GENE ENG +1
A detection method for visual identification of microRNAs based on structural unwinding of G-quadruplex probes
InactiveCN110229872BSimple designDoes not involve complicated reaction processMicrobiological testing/measurementHeme bindingMicroRNA
The invention discloses a detection method for the visual recognition of microRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) on the basis of G-quadruplex probe structure unwinding. A signal attenuation method constructed bycombining catalytic characteristic of a G-quadruplex combined with heme with the structure change of the G-quadruplex can distinguish miRNAs of single-base mismatch and multibase mismatch, and also can distinguish different miRNA family members. On the basis of signal attenuation, sensitivity still can be 4.5nmol / L. The probe used by the invention is simple in design, and does not relate to a complex reaction process. The detection method has an important meaning for the detection of miRNA.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and application of rapid detection of nucleic acid based on electrochemical potential pretreatment technology
ActiveCN107988318BEnable mismatch detectionHigh selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrolytic agentHigh selectivity
The invention discloses a method and application for rapidly detecting nucleic acid based on electrochemical potential pretreatment technology. In the method, the PBS buffer is used as the electrolyte, the probe and the target nucleic acid fragment are added into the PBS buffer, and a nucleic acid hybridization solution is formed according to the principle of complementary base pairing. The sensing electrode is subjected to electrochemical pretreatment in a potential range greater than 1.8V, and then SWV is used to selectively detect target nucleic acids. The nucleic acid detection method of the electrochemical pretreatment technology is applied in the fields of disease characteristic miRNA-related electrochemical biosensing detection, medical diagnosis, and pathogen detection in food and environment. When this detection method is applied to nucleic acid, it has the following characteristics: high selectivity, which can detect single base mismatches for nucleic acid molecules; high sensitivity, with a detection sensitivity of 5×10 ‑18 M; the test results can be completely repeated; the operation process is economical and simple, there is no chain reaction, no amplification, no fluorescent indicator.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Fluorescent probe
PendingCN110724729ASensitive detectionEasy to manufactureMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleic acid detectionNucleotide
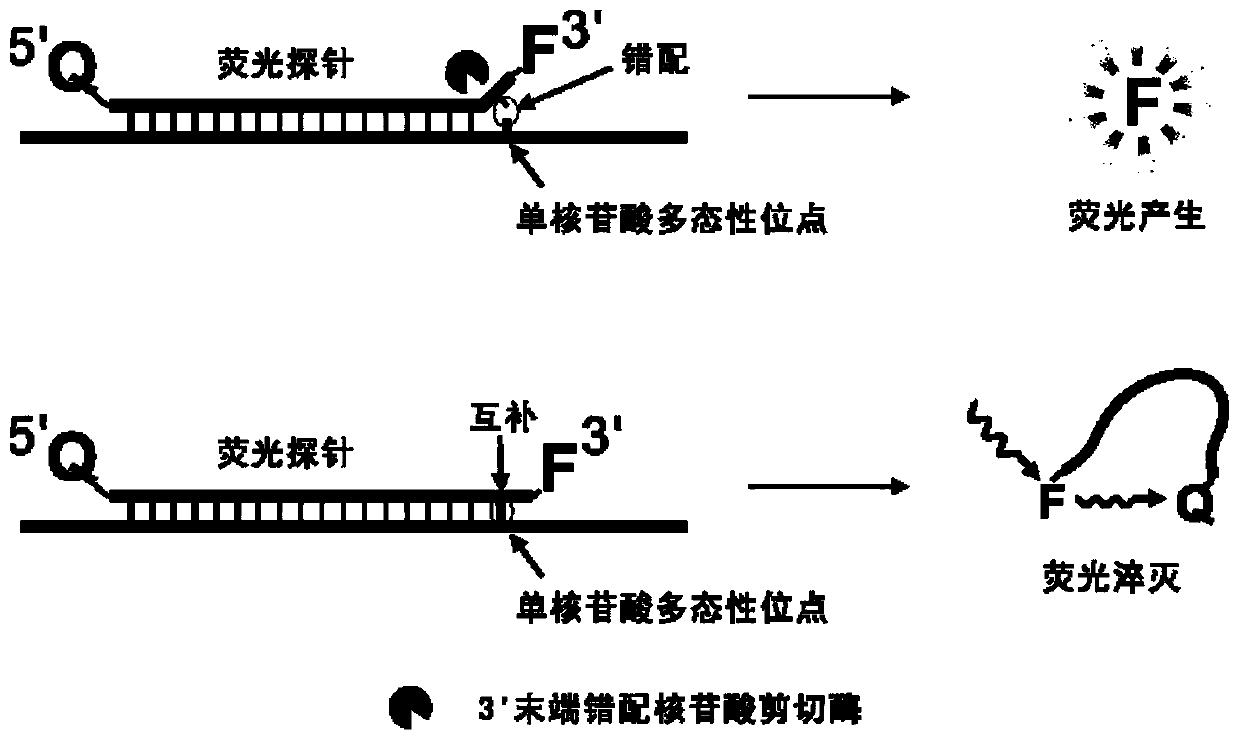
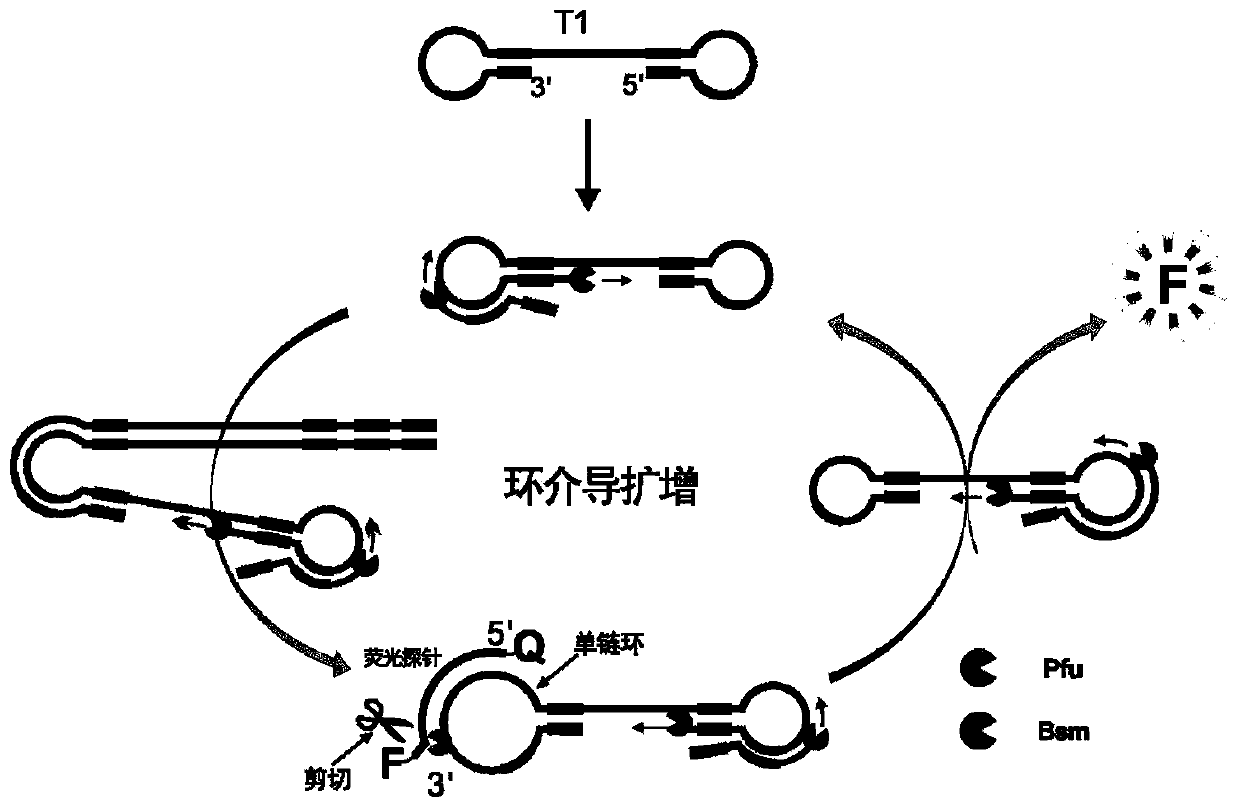
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and provides a specific nucleic acid probe capable of achieving target molecule qualitative and real-time fluorescent quantitative detection. A 5' terminal and a 3' terminal of the probe are marked with a quenching group and a fluorescent group respectively, after the probe and a target sequence are subjected to complementation, atleast one base pair mismatch is formed at the 3' terminal, and under the effect of a 3' terminal mismatch nucleotide cleavage enzyme, the probe is cleaved, and then a fluorescent signal is released.A last base of the 3' terminal of the probe is designed at a single-nucleotide polymorphic site, and thus single-nucleotide polymorphism detection can be achieved. The probe can be further combined with a nucleic acid amplification strategy to detect target nucleic acids more sensitively. The specific nucleic acid probe is simple in design, and can be widely applied to all nucleic acid detection systems into which the 3' terminal mismatch nucleotide cleavage enzyme can be introduced.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
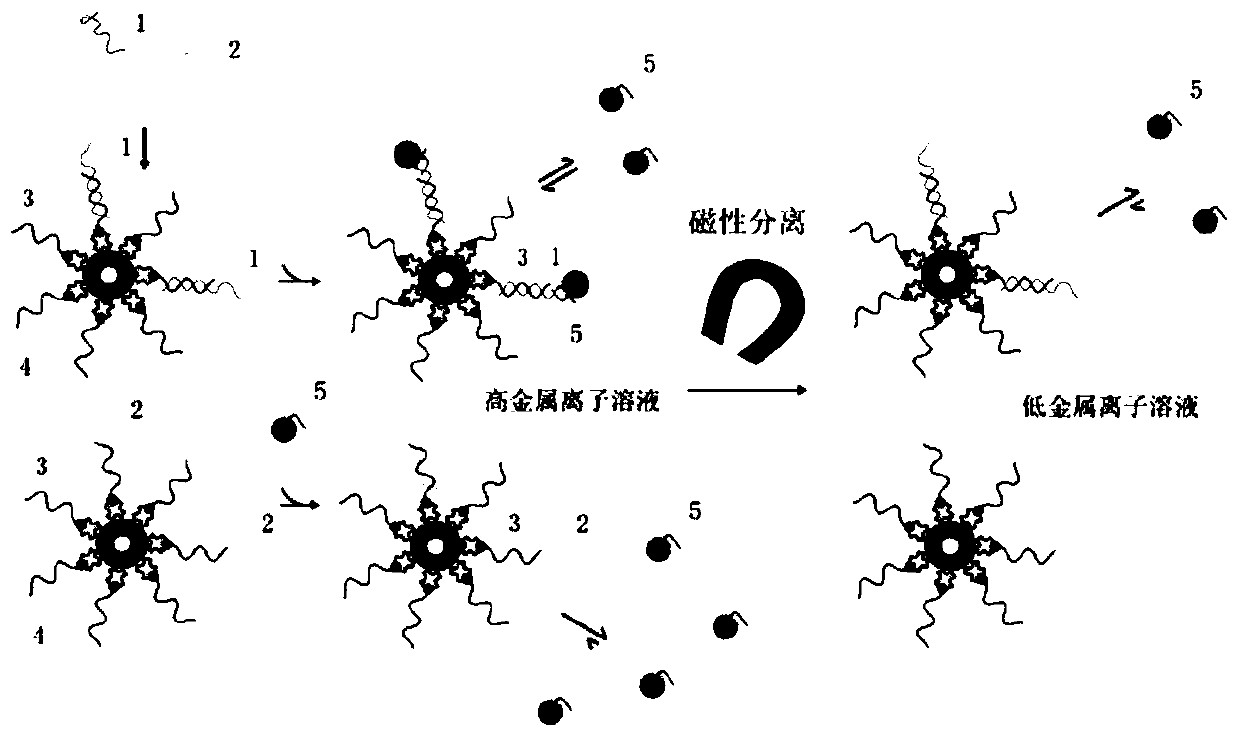
A single base mutation detection method
ActiveCN106755460BAccurate detectionGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation detectionWild type
The invention relates to a single base mutation detection method combining nucleic acid temporary hybridizing and magnetic separating. The method comprises the following steps: A, designing a capturing probe and a signal probe according to a target gene; B, preparing a magnetic sphere solution from a magnetic sphere coupled with the capturing probe, adding the signal probe to conduct nucleic acid hybridization with a to-be-detected sample; C, conducting magnetic separation after finishing the nucleic acid hybridization, and then re-suspending the magnetic sphere in a low-metal ion solution; D, conducting magnetic separation again, detecting an obtained liquid supernatant, judging whether single base mutation exists in the to-be-detected sample, wherein the capturing probe is completely complementary with a non-mutation part of the target gene; the signal probe is completely complementary with a mutant type gene of the target gene, and forms a single base mismatch with a wild type gene of the target gene. The detection method is fast, and can be used in low-abundance mutation detection.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
A new method for simple and convenient detection of SNPs
ActiveCN108315396BLower requirementGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideGenetics
The invention discloses a new method for simple and convenient detection of SNP. The primer set provided by the present invention; primer set I includes two upstream primers and one downstream primer; the difference between the FX1 primer and the FY1 primer: the first nucleotide at the 3' end, the FX1 primer corresponds to the X polymorphism of the specific SNP, FY1 The primers correspond to the Y polymorphism; FX1 primers and FY1 primers are both base mismatch primers; primer set II includes two upstream primers and one downstream primer; the difference between FX2 primers and FY2 primers: the first nucleotide at the 3' end is different, The FX2 primer corresponds to the X polymorphism of the specific SNP, and the FY2 primer corresponds to the Y polymorphism; 10-20 random nucleotides are added to the 5' end of the FY2 primer; both the FX2 primer and the FY2 primer are base mismatch primers. The primer set provided by the invention can be widely used in the detection of various target SNP sites, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:山东玄康种业科技有限公司
Recombinant protein production
ActiveUS11268101B2Reduce dependenceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGene conversionGenetic code
Owner:THE UNIV OF YORK
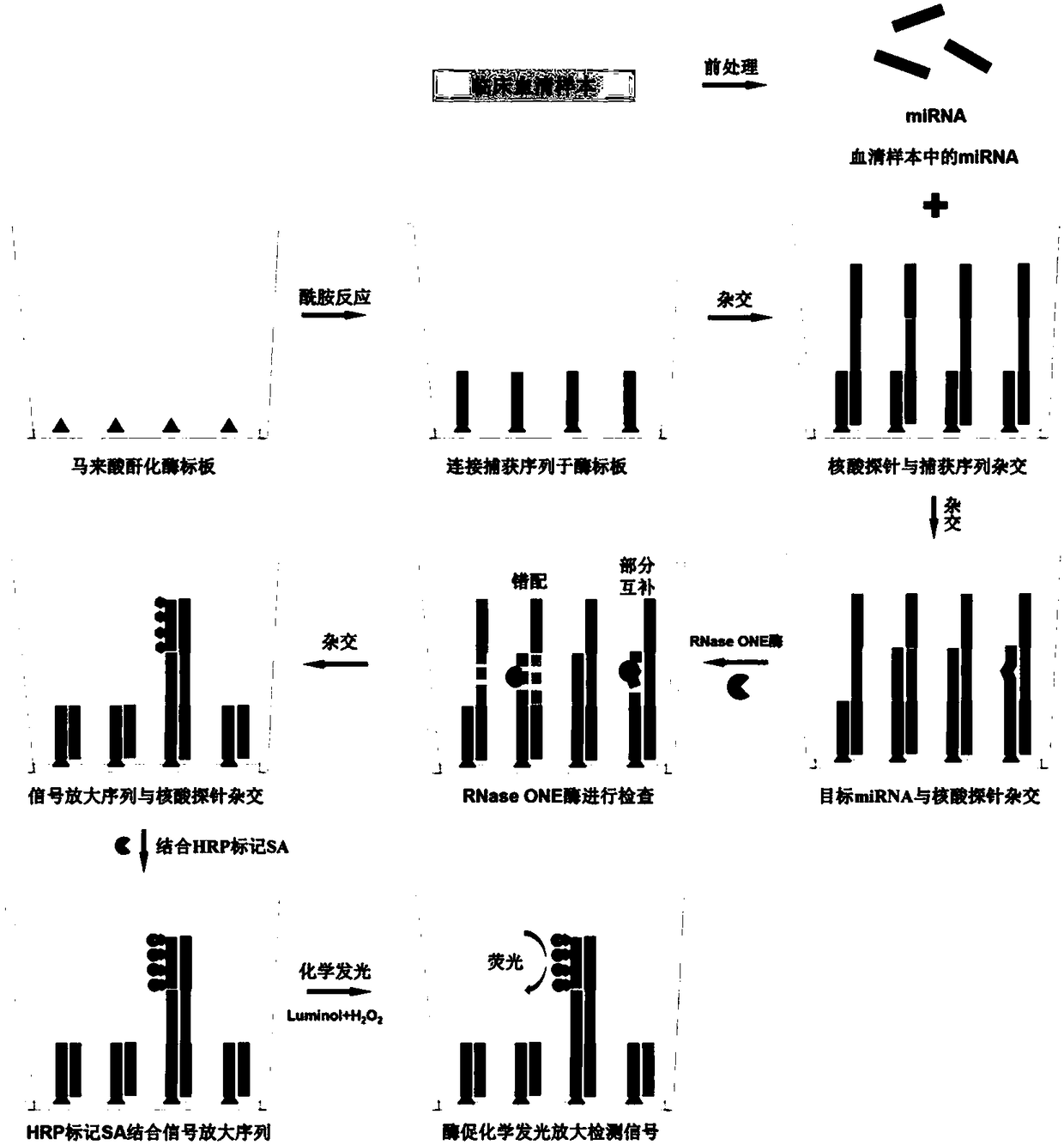
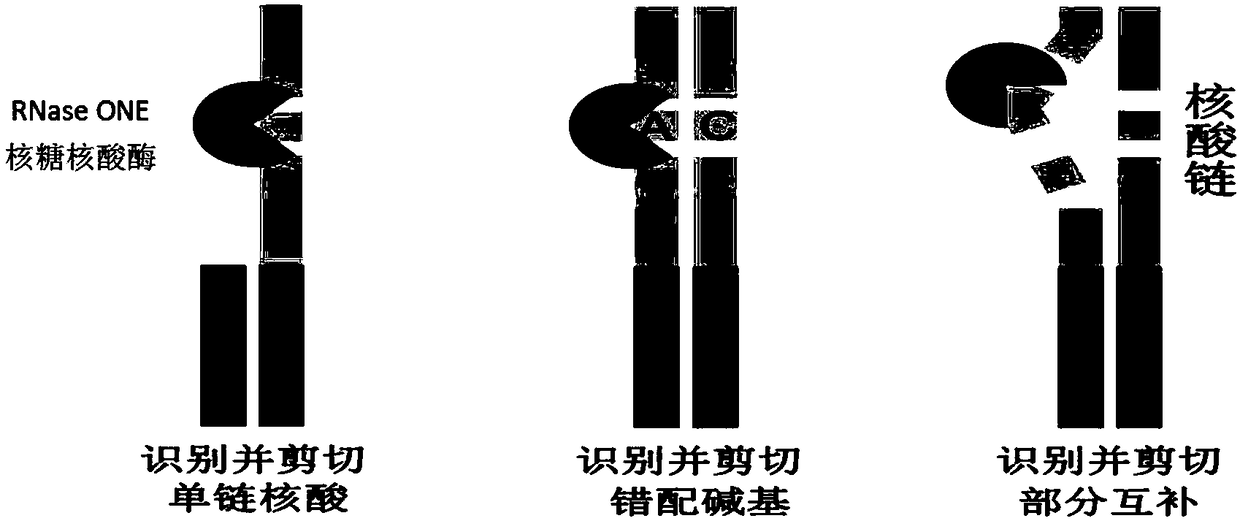
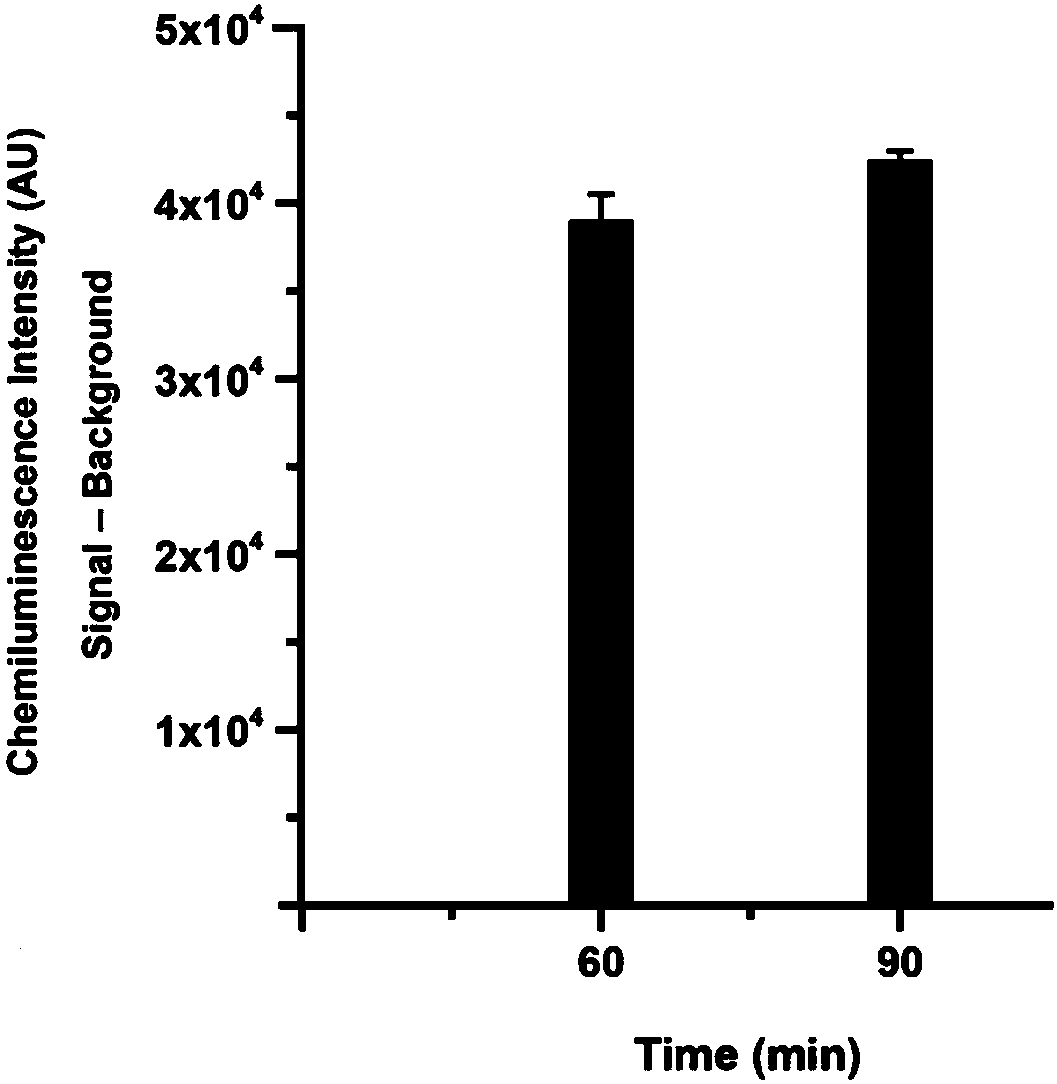
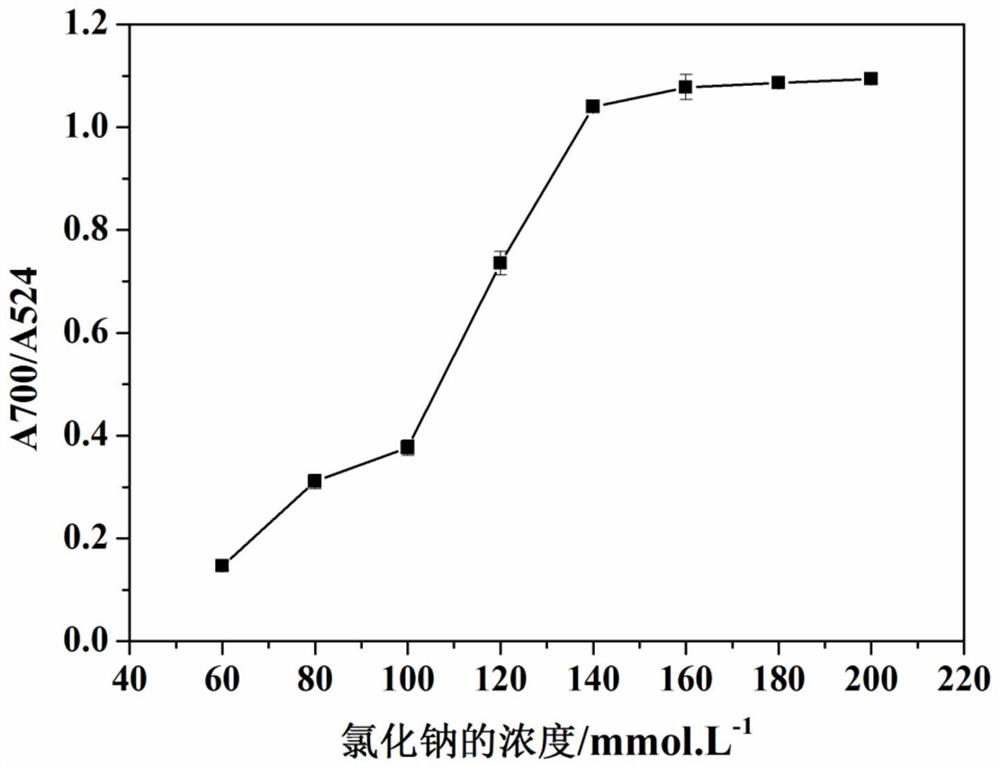
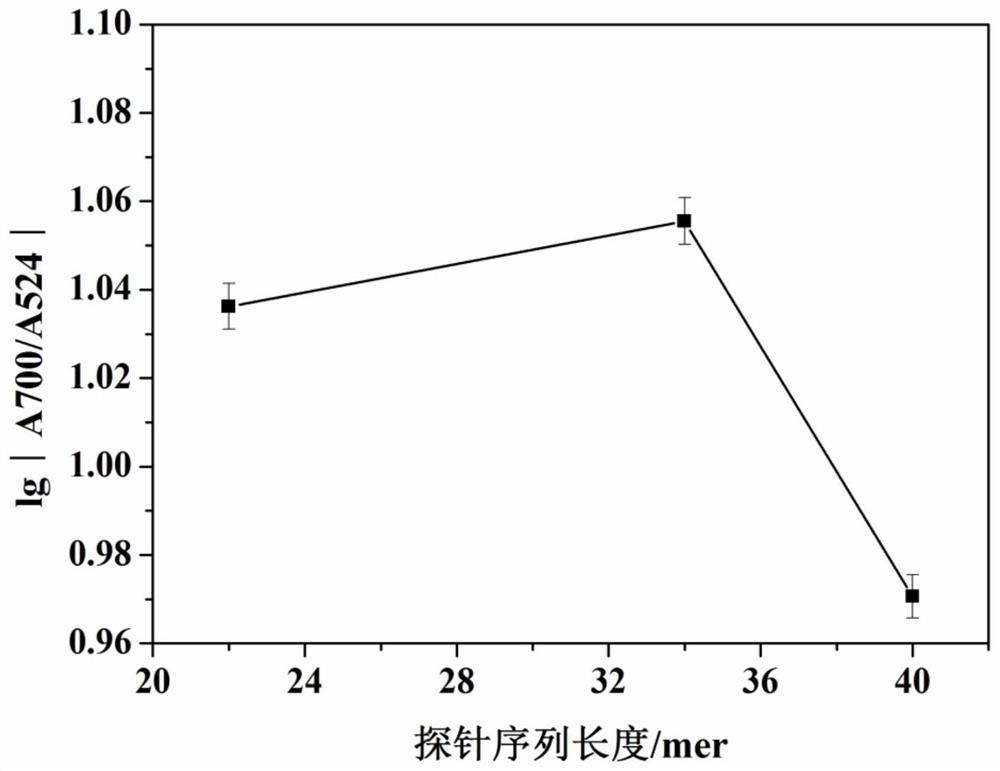
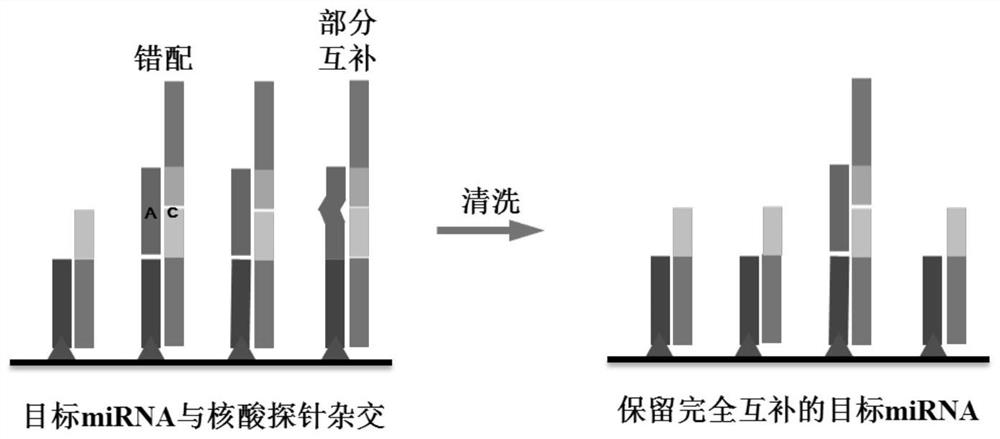
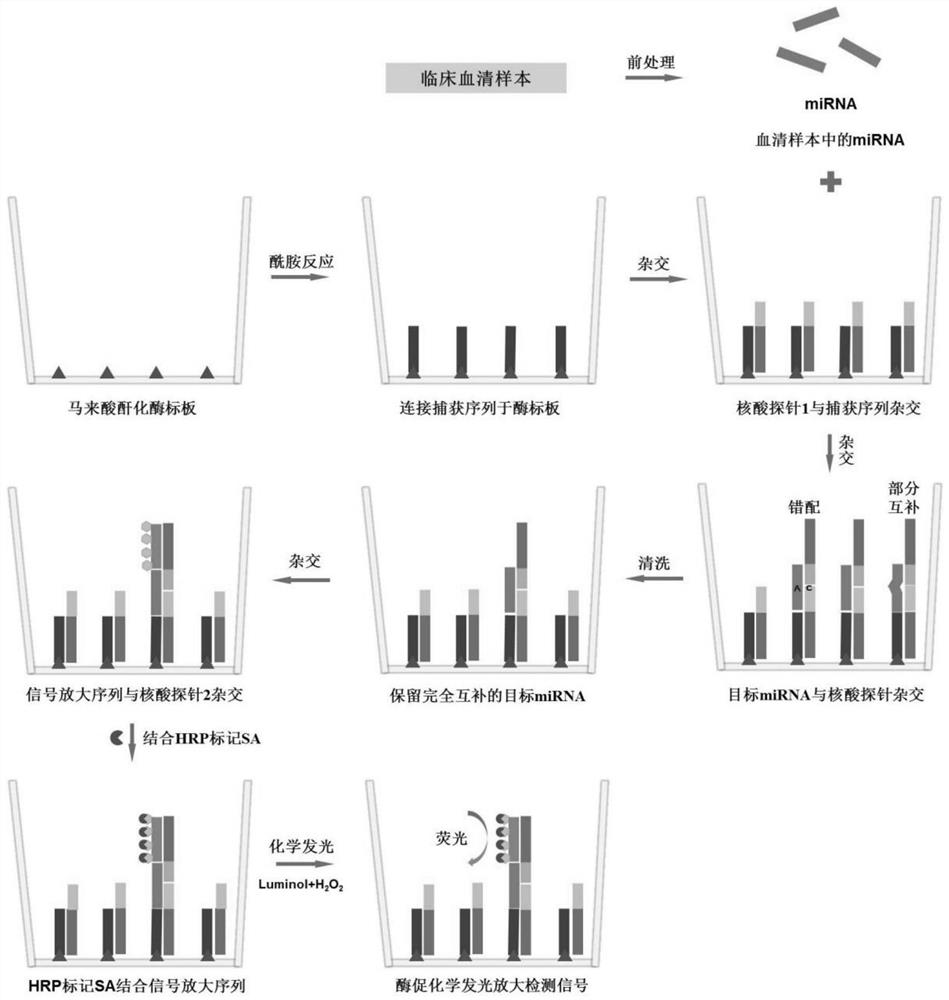
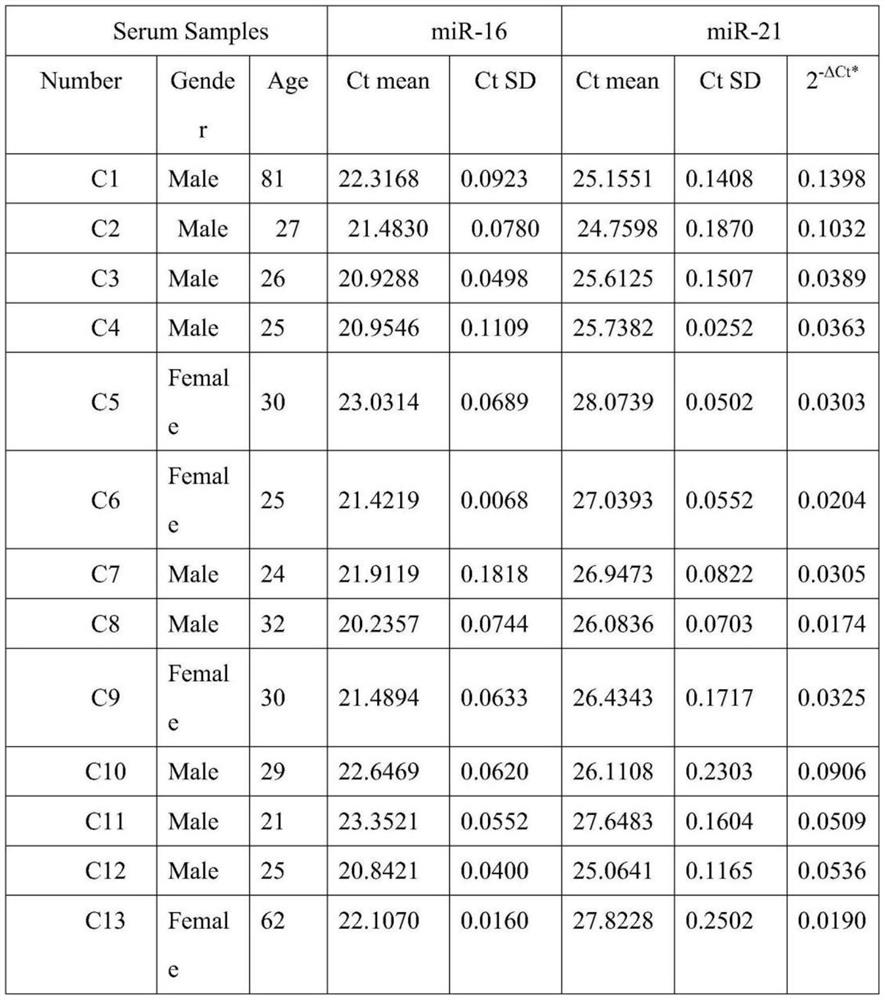
Method for quantitatively assaying serum miRNA by utilizing RNase ONE nuclease and chemiluminescence technology
InactiveCN108152274AAmplify the signal valueHigh detection specificityChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePreparing sample for investigationHeterologousHeteroduplex
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively assaying a serum miRNA (microRNA) marker by utilizing RNase ONE ribonuclease and the chemiluminescence technology. According to the method, a serumsample is first pretreated, a captured sequence is fixed on an ELISA (enzyme-linked immune-sorbent assay) plate, a DNA-RNA hybrid probe and target miRNA in the serum are then hybridized in sequence,RNase ONE ribonuclease is then utilized to identify and cut base mismatch caused by heteroduplex hybridization or point mutation and partial complementation caused by unpaired base insertion / deletion,and finally, a signal amplification sequence and the chemiluminescence technology are utilized to assay the content of target miRNA in the serum. The method provided by the invention has high sensitivity and high specificity, and can meet the requirement of clinical assay.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE +3
Application of dideoxynucleoside phosphoramidite monomer containing succinimide structure in recognition of mismatched bases
ActiveCN111269967AGood effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideRNA - Ribonucleic acid
The invention discloses an application of a dideoxynucleoside phosphoramidite monomer containing a succinimide structure in recognition of mismatched bases, and belongs to the technical field of application of non-natural oligonucleotides. The preparation method comprises the following steps: constructing the dideoxynucleoside phosphoramidite monomer containing the succinimide structure into artificial deoxyribonucleic acid; replacing part of phosphodiester bonds in natural nucleic acid with butanediamide bonds, the butanediamide bonds being used as a probe sequence to detect the base mismatchcondition in a complementary sequence. A melting point determination experiment is used for detecting a mismatch unit containing T-C, a good effect is achieved, and a new research thought is providedfor designing a novel detection unit.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
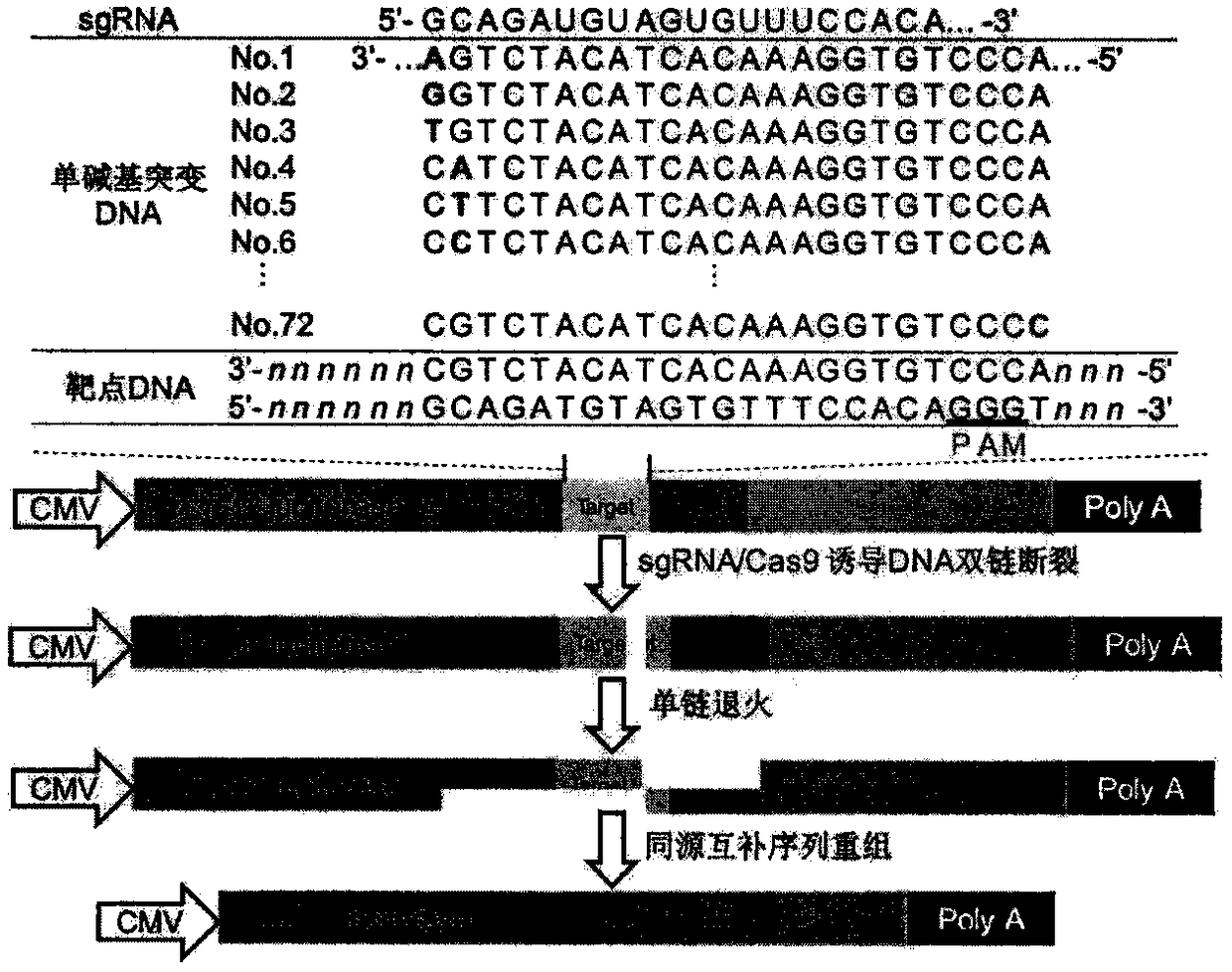
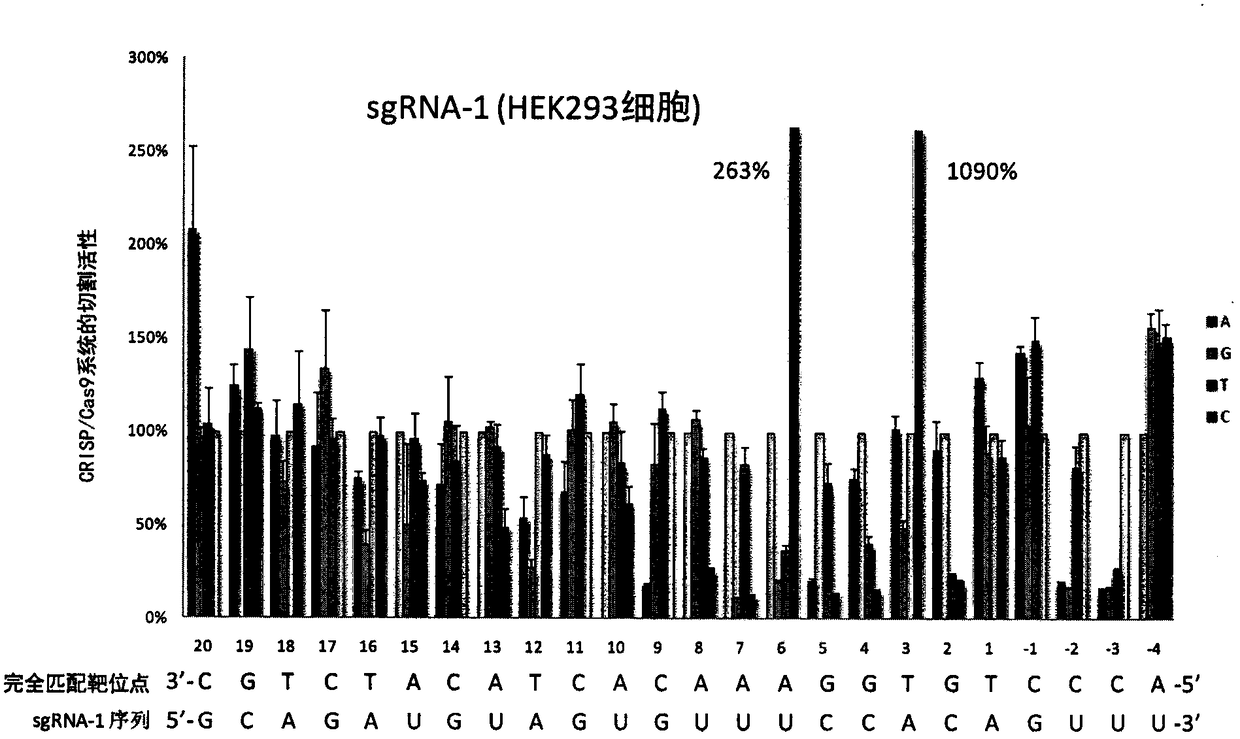
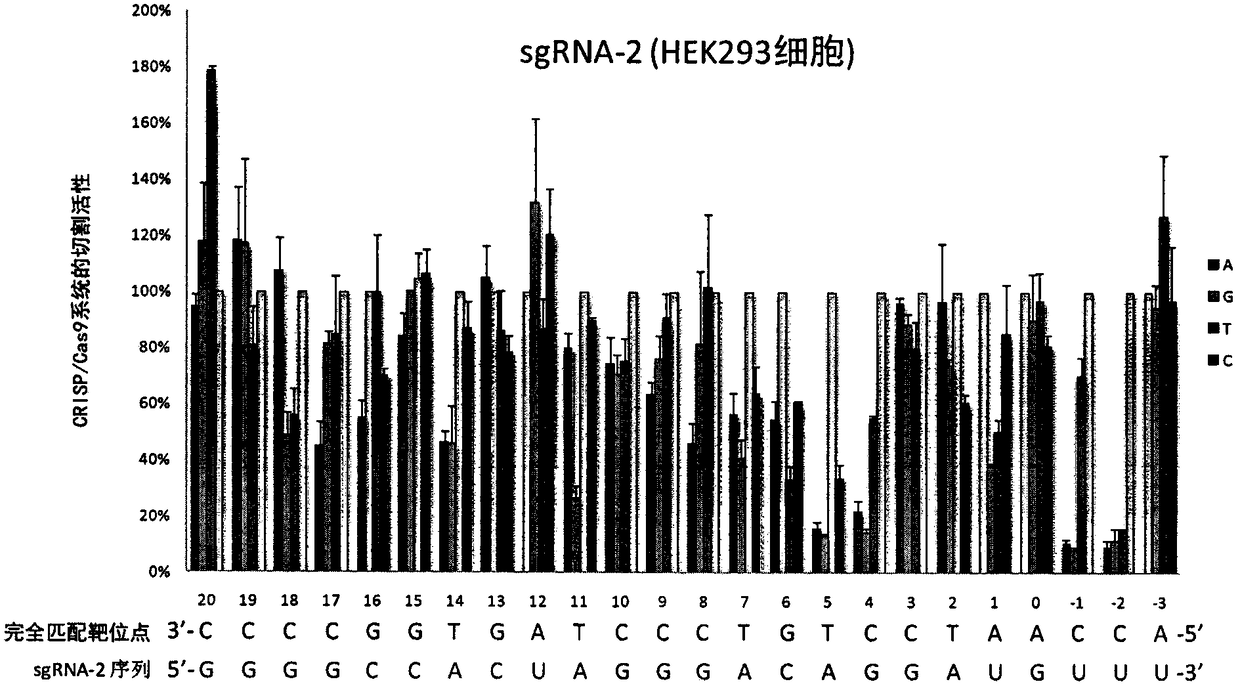
A sgRNA base mismatch target site library and its application
ActiveCN105316322BOff-target effects are precise and comprehensiveAccurate evaluationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JDNA
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Dna probe for enriching low-frequency dna mutation and its application
ActiveCN109161543BImplement mutation detectionRealize dynamic monitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBase JWild type
Owner:杭州瑞普基因科技有限公司
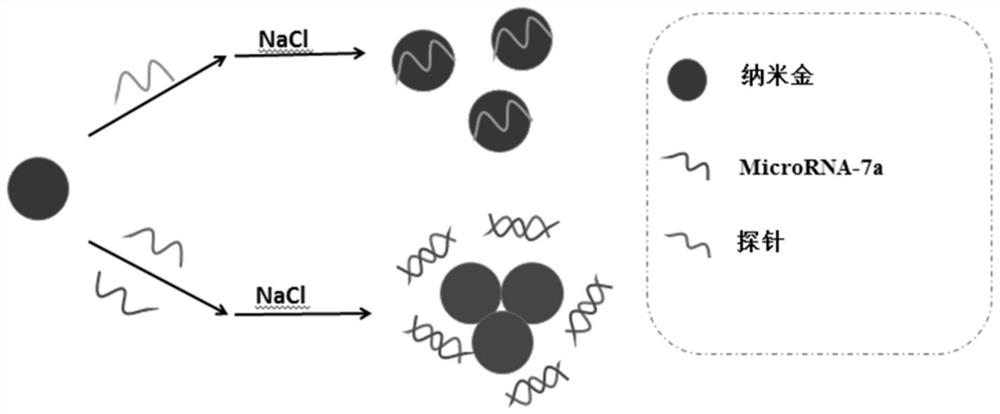
A rapid detection method for microRNA-7a based on nano-gold colorimetry
ActiveCN109342338BThe detection method is simpleThe process is simple and convenientMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JSingle strand
The invention discloses a rapid detection method for microRNA-7a based on nano-gold colorimetry. Using the electrostatic difference between single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA, the different interactions (color changes) with gold nanometers under high salt concentration are used for colorimetric detection of the target, and the target is indirectly detected by combining the absorbance value of the UV-visible spectrometer. concentration. The detection concentration lower limit of the present invention reaches 5.3nmol / L, and the linear regression equation is A=0.002C+0.238, r=0.990. This method can not only perform specific analysis on unlabeled microRNA-7a, but also distinguish single-base mismatch sequences well, with strong specificity, simple method, fast analysis speed, and the lower limit of detection of the concentration of the target visible to the naked eye. It can be widely used in practical detection.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A method for detecting serum miRNAs in cancer patients based on short nucleotide chain ligation
ActiveCN107099612BImprove throughputReliable test resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleic Acid Probes
The invention discloses a method used for detecting serum miRNA of patients with cancer based on short nucleotide chain connection. According to the method, specific recognition and cutting of unpaired single strand nucleic acids and double-stranded nucleic acids with mismatched bases are carried out, mismatching and partial complementation of hybridization of a nucleic acid probe with target miRNA are detected, fluorescence is generated via enzymatic reaction of horse radish peroxidase combined on the nucleic acid probe with a chemiluminescent substrate, rapid amplification of detection signals is realized, and the target miRNA content is determined based on fluorescence intensity. The detection results are accurate; operation is simple and convenient; cost is low; detection throughput is high; and nucleic acid extraction or amplification is not needed.
Owner:深圳市展行生物有限公司
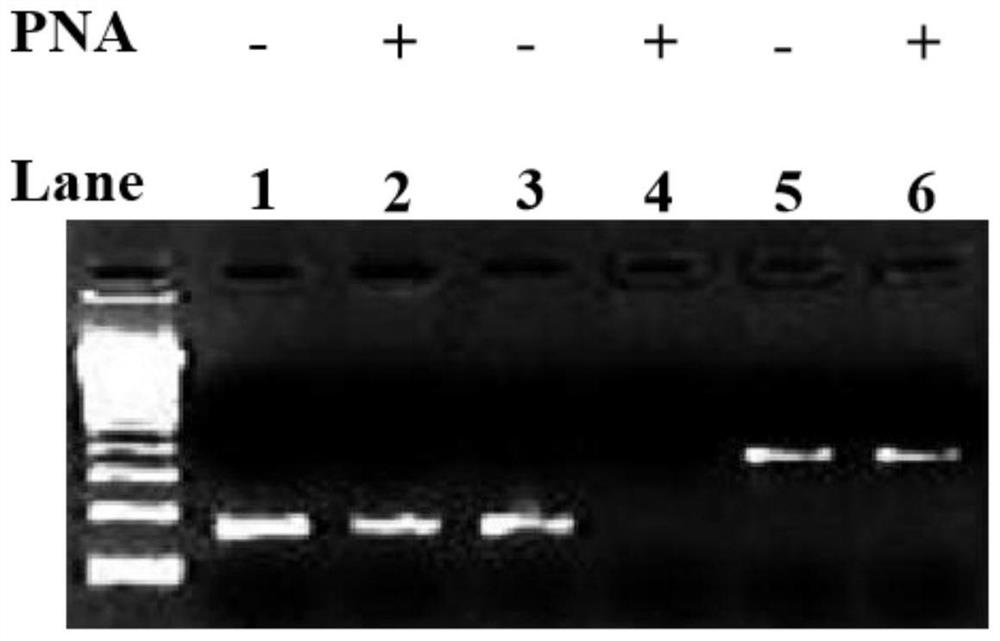
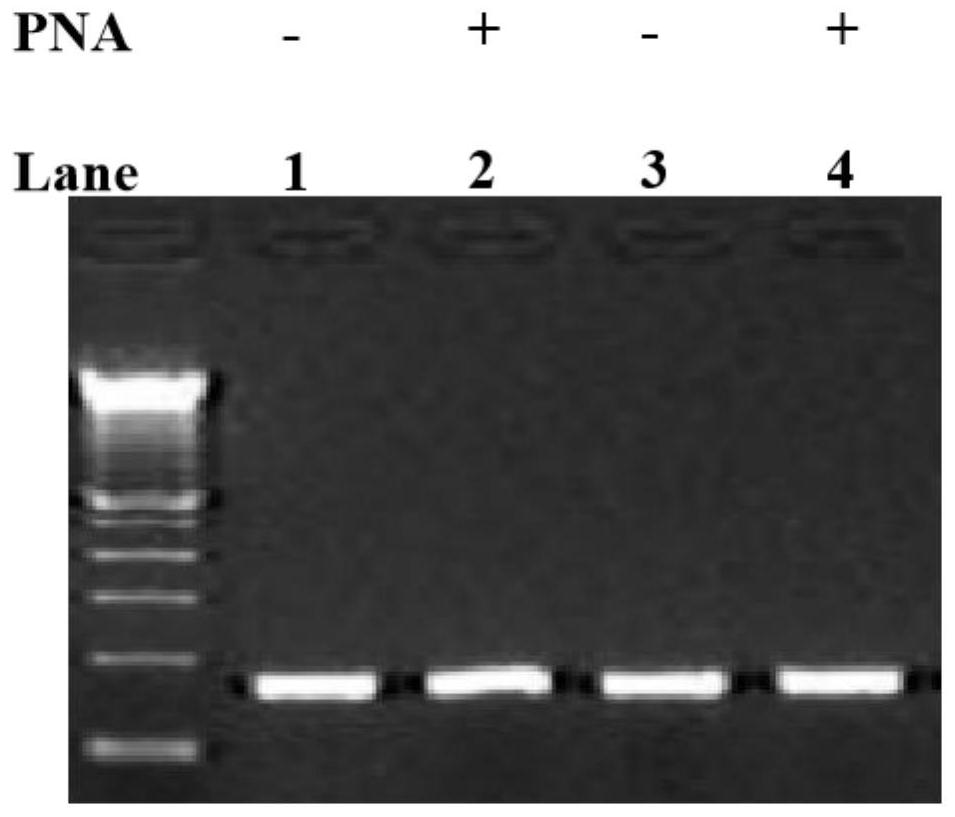
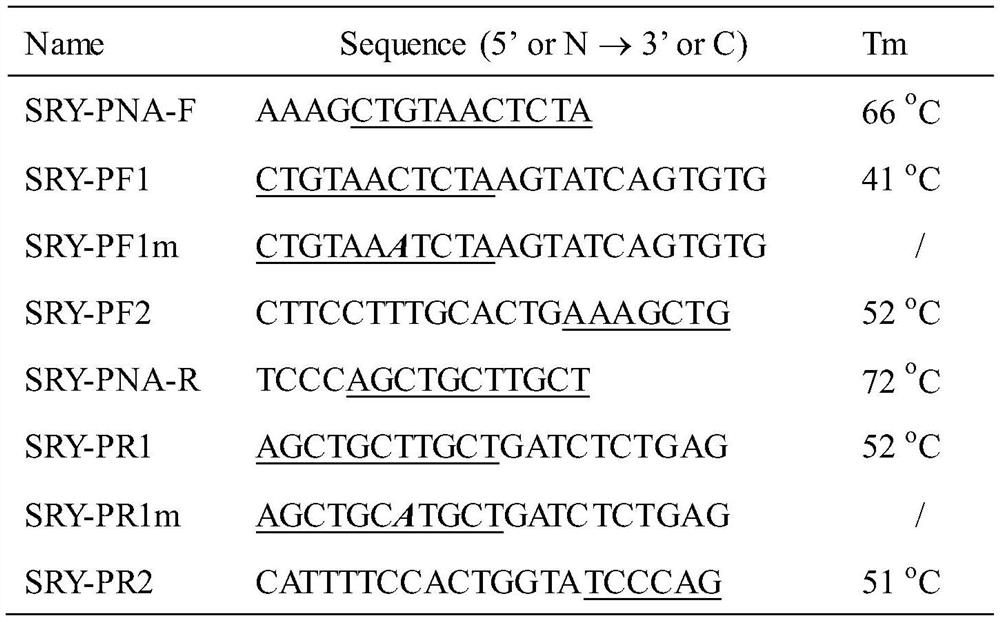
Method for improving PNA-based PCR inhibition efficiency, and application
PendingCN112176039AHigh suppression efficiencyEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JCirculating tumor DNA
The invention discloses a method for improving PNA-based PCR inhibition efficiency. The method is characterized in that a nucleic acid amplification primer adopts a single-base mismatch primer, and amismatch site is positioned in the middle of an overlapping sequence of a PNA probe and the amplification primer. According to the method, the single-base mismatch primer is used, so that the PNA-based PCR inhibition efficiency can be greatly improved. According to the method, a short DNA fragment is selectively amplified, and the PCR amplification of large background DNA is inhibited by combiningwith the single-base mismatch primer, so that the PNA can effectively detect a specific DNA fragment, such as can be applied to monitor circulating tumor DNA and circulating fetal DNA.
Owner:浙江原创医疗科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com