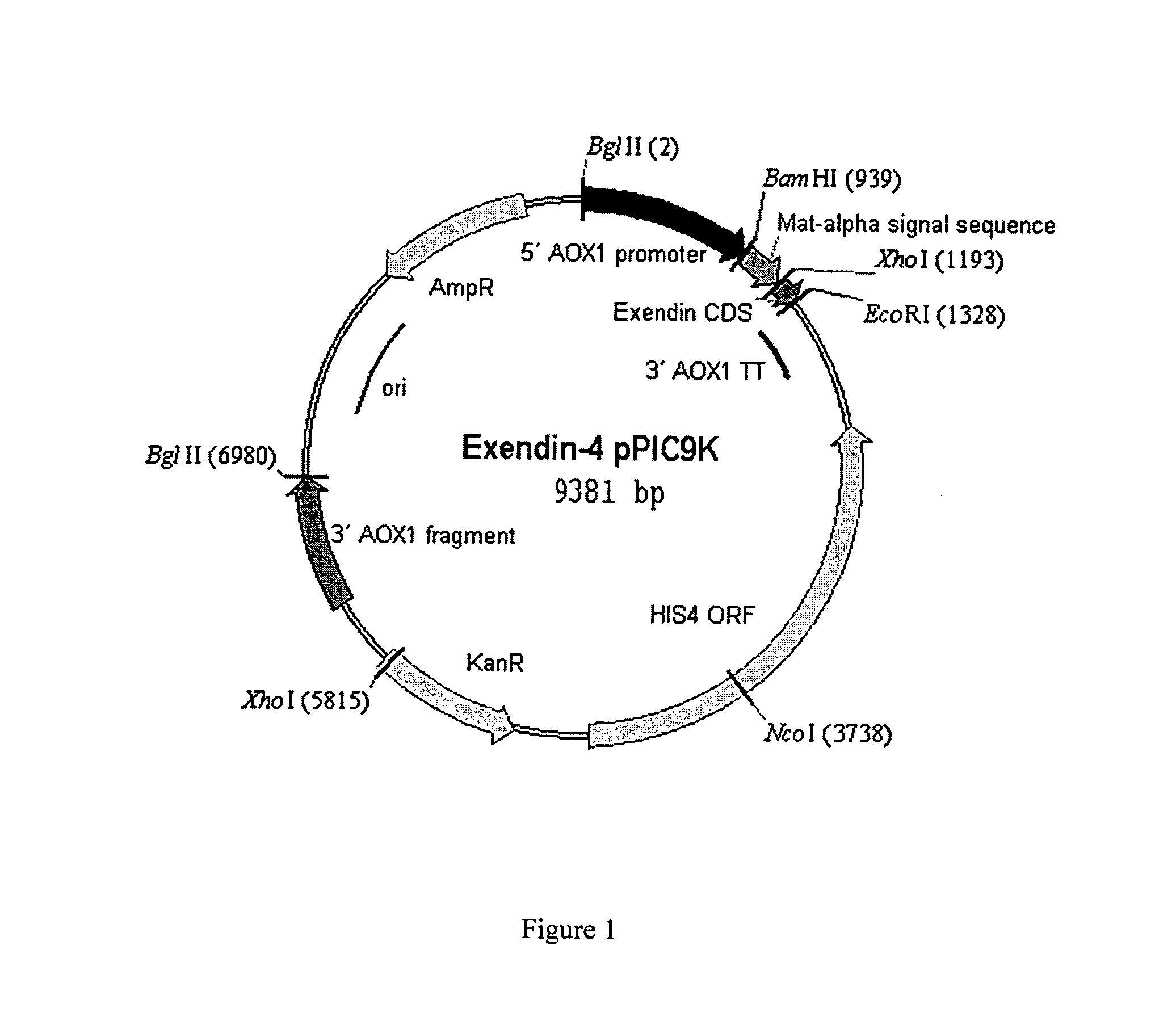
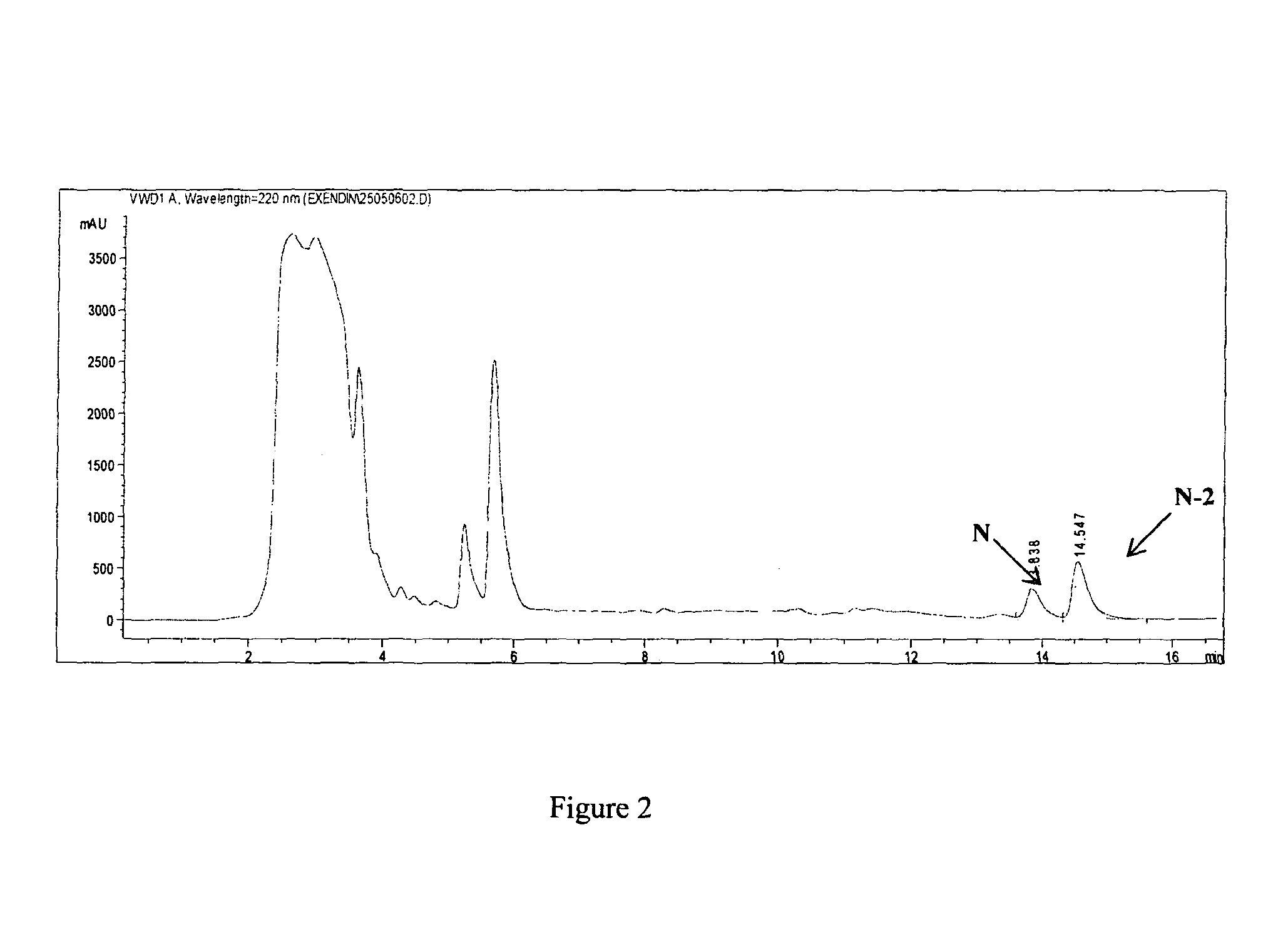
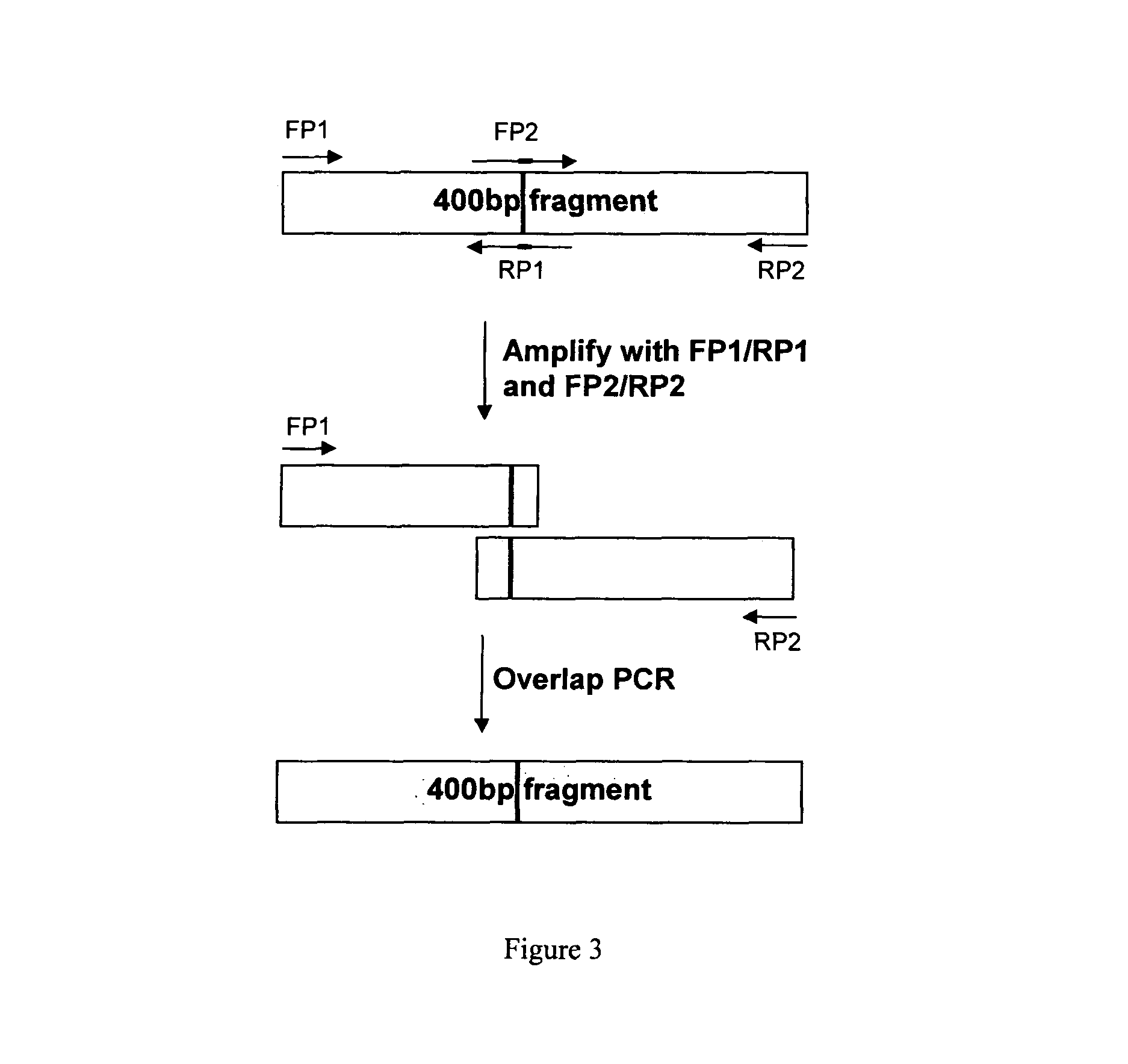
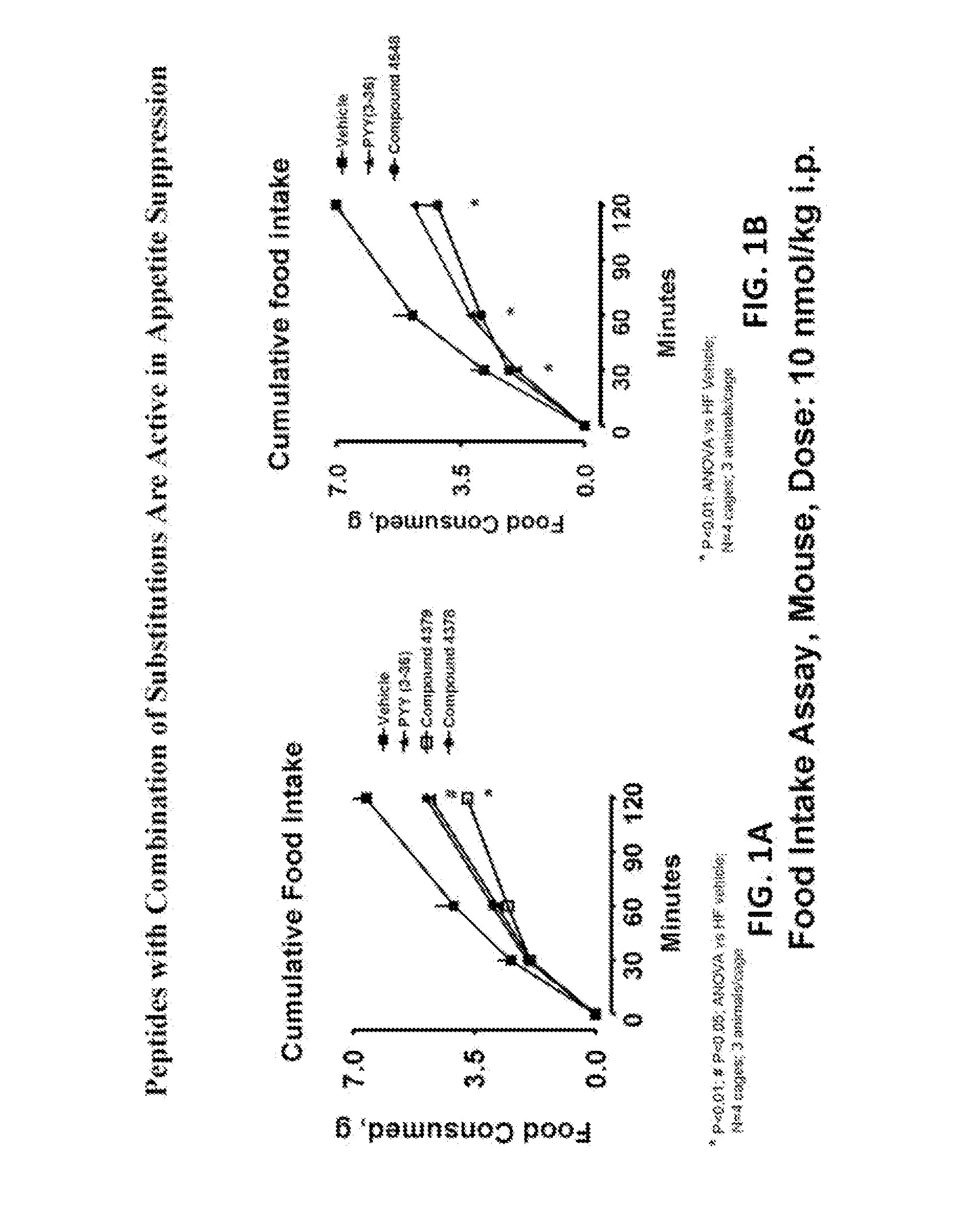
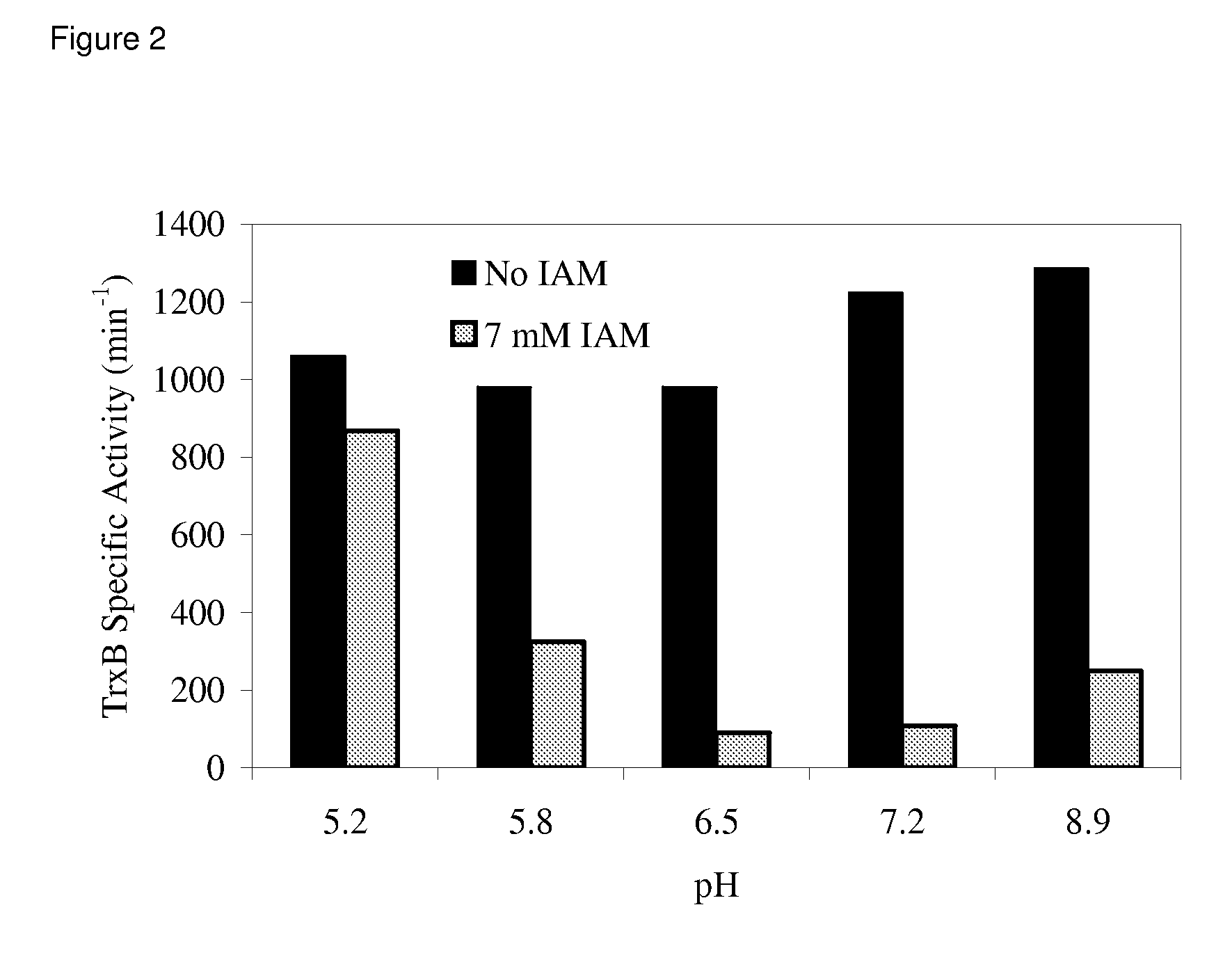
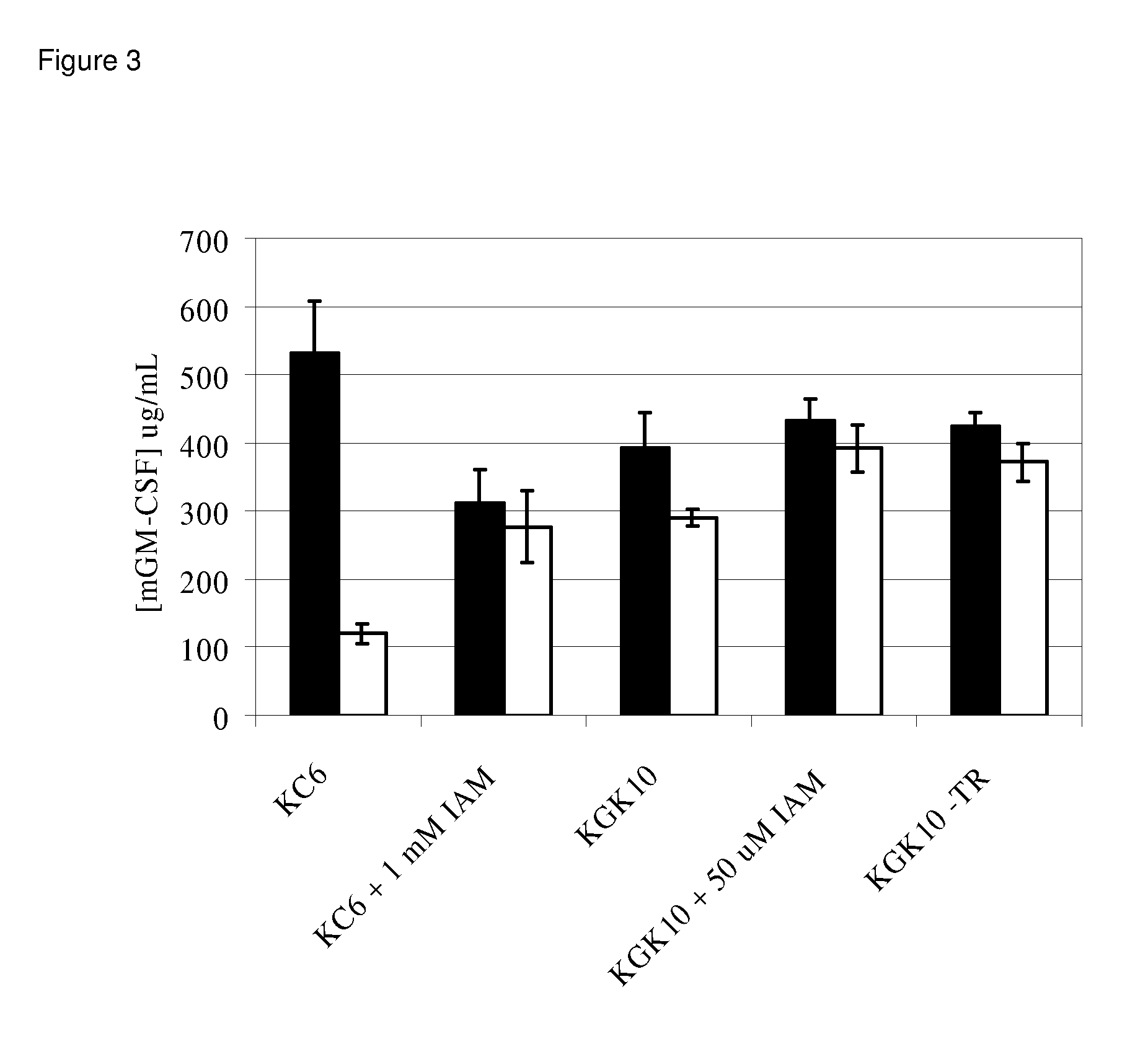
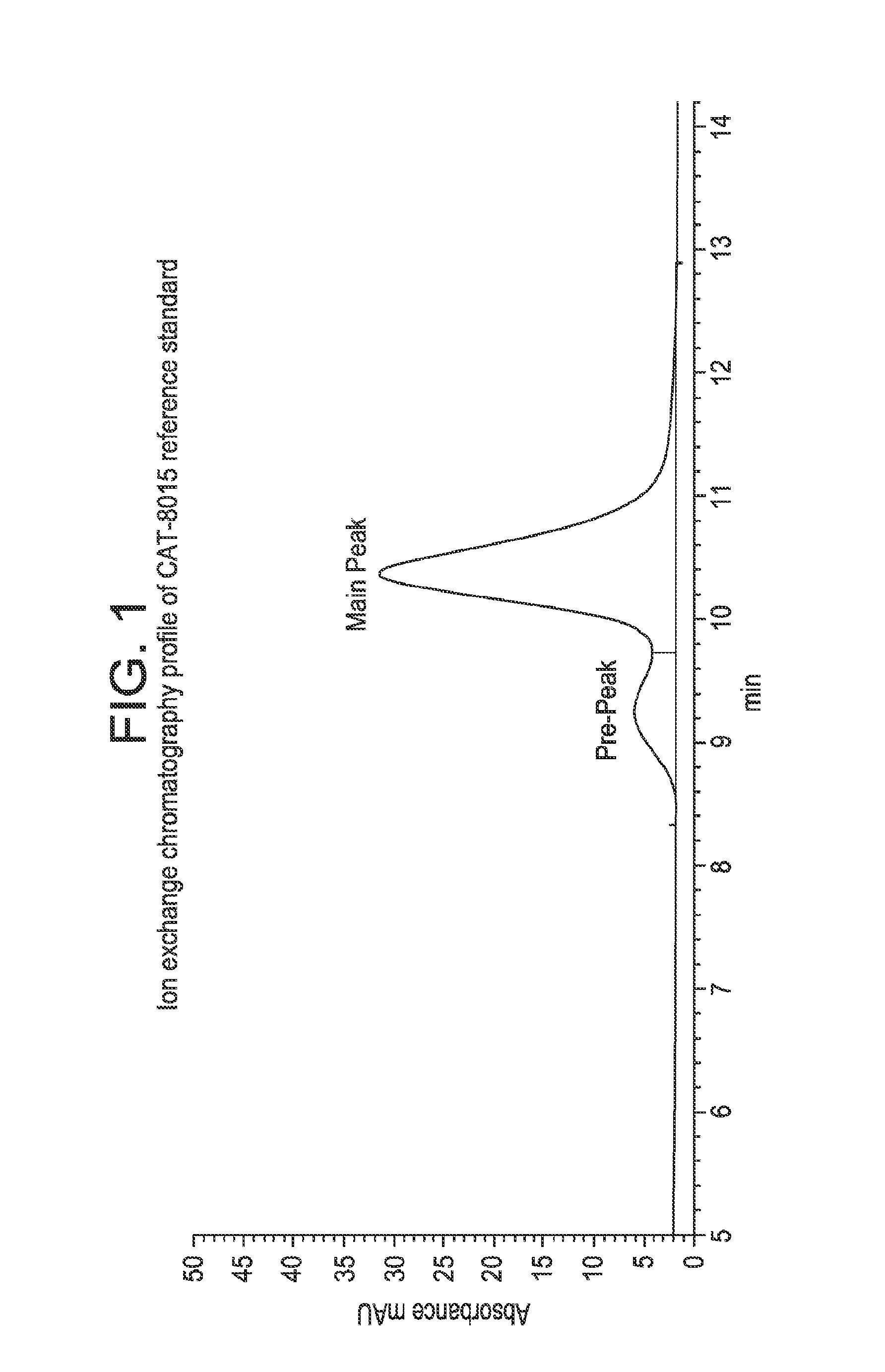
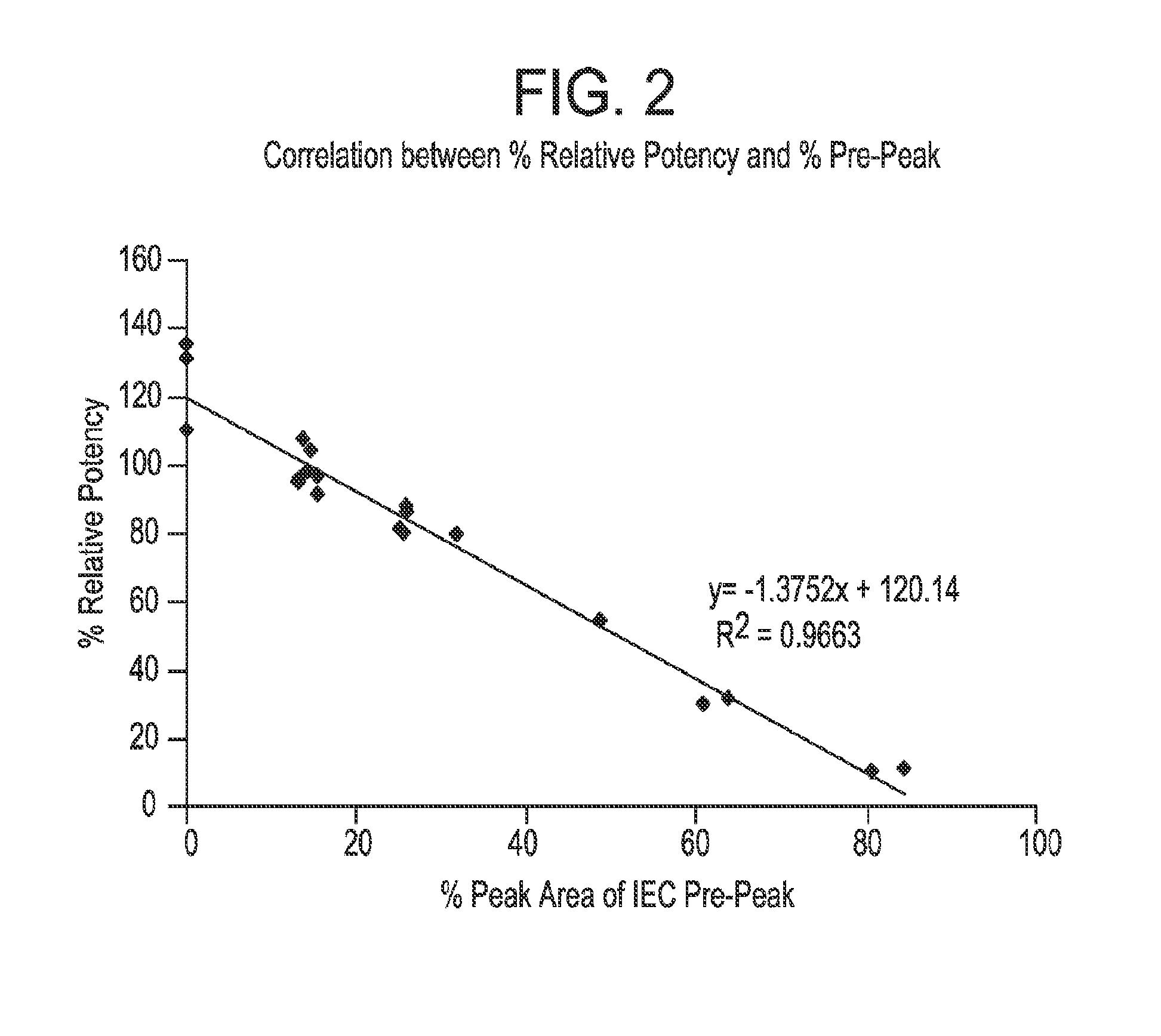
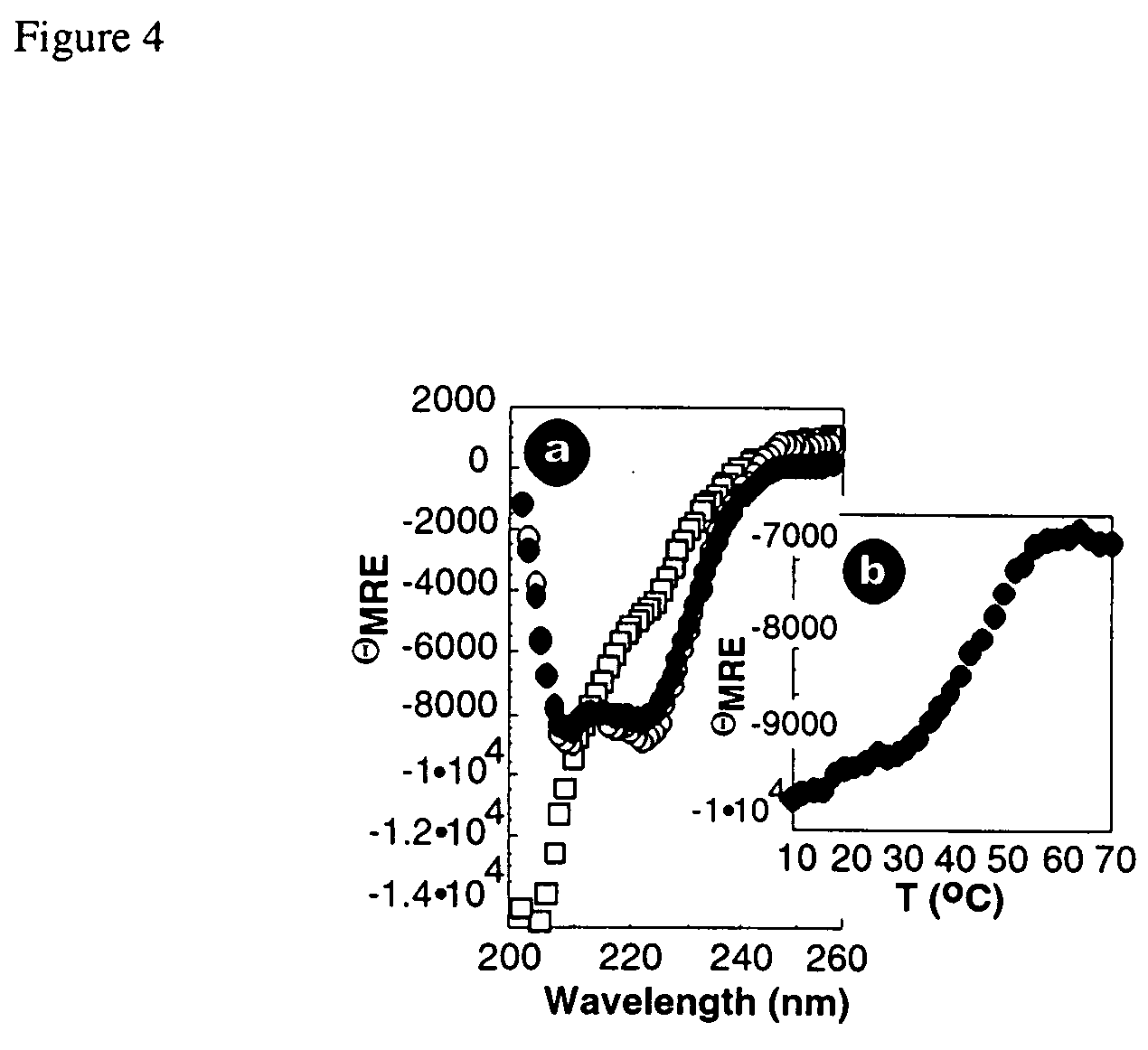
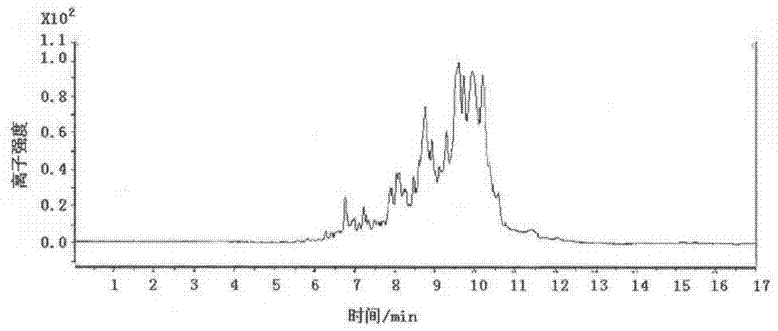
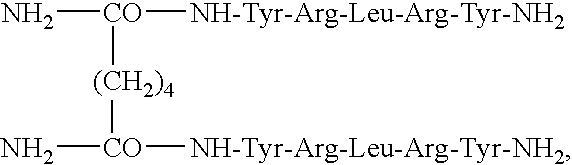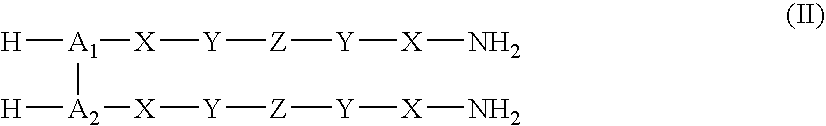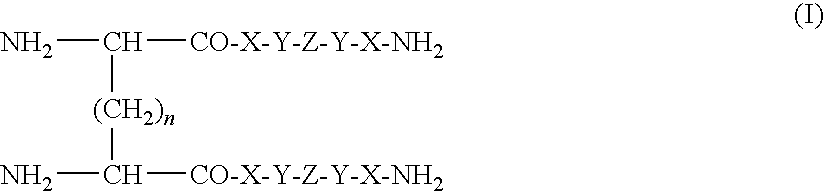Patents
Literature
58 results about "Pancreatic polypeptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
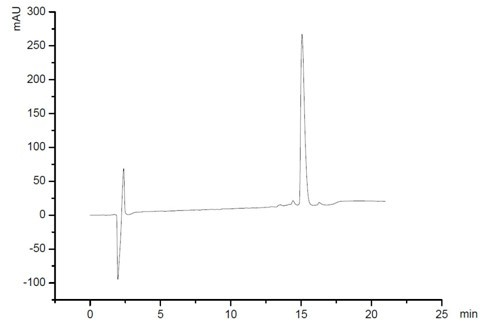
Pancreatic polypeptide (PP) is a polypeptide secreted by PP cells in the endocrine pancreas predominantly in the head of the pancreas. It consists of 36 amino acids and has molecular weight about 4200 Da.
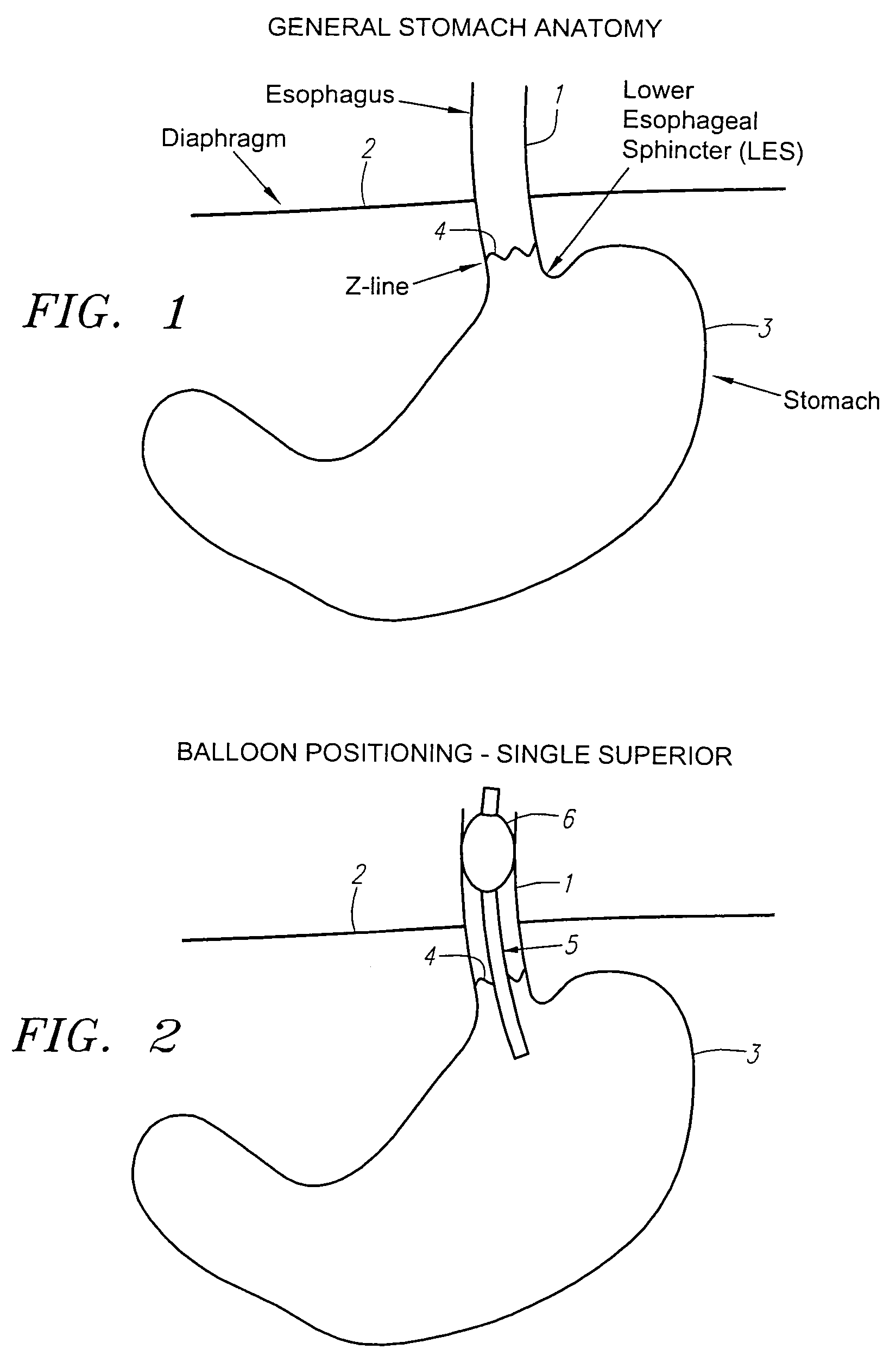
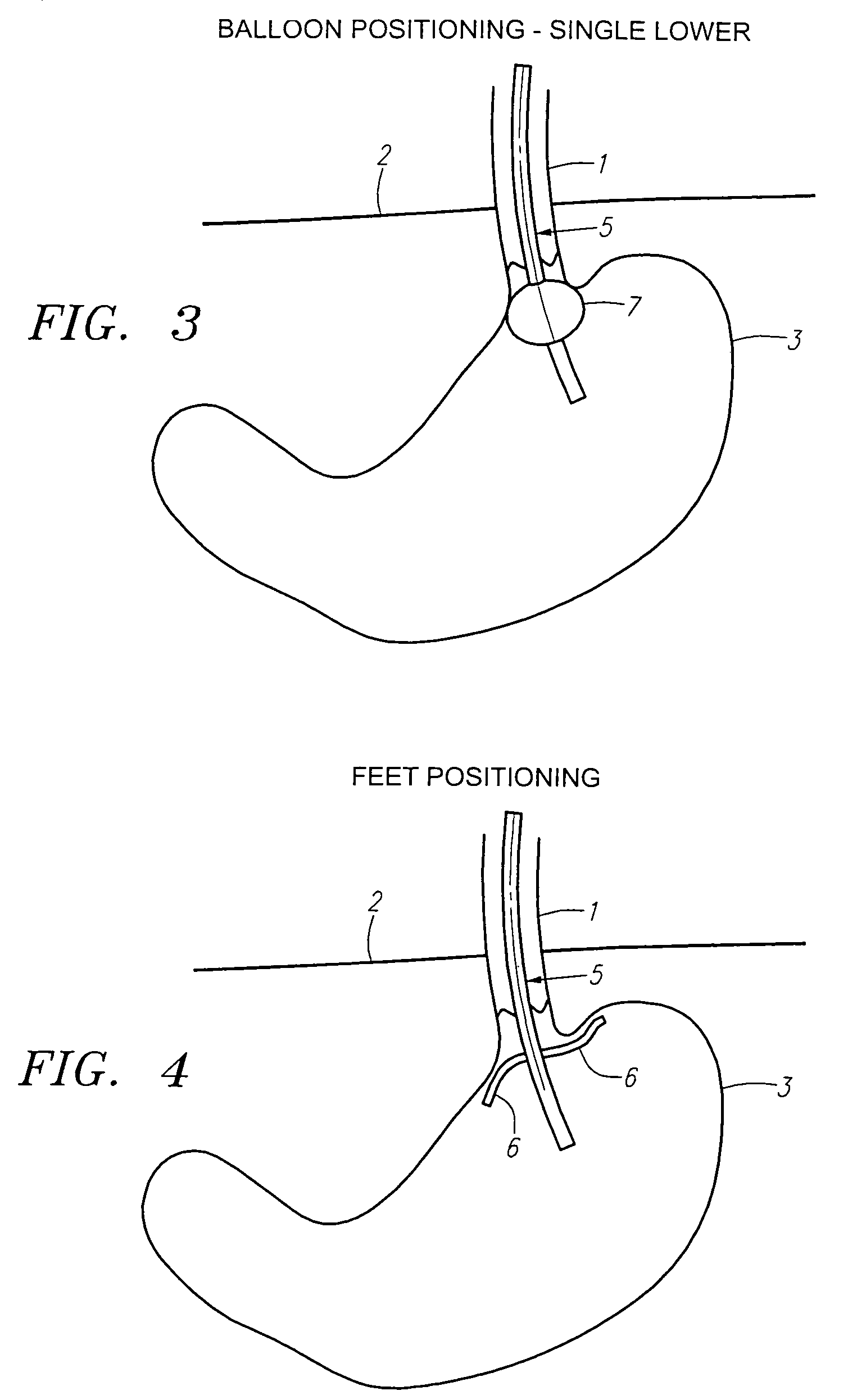
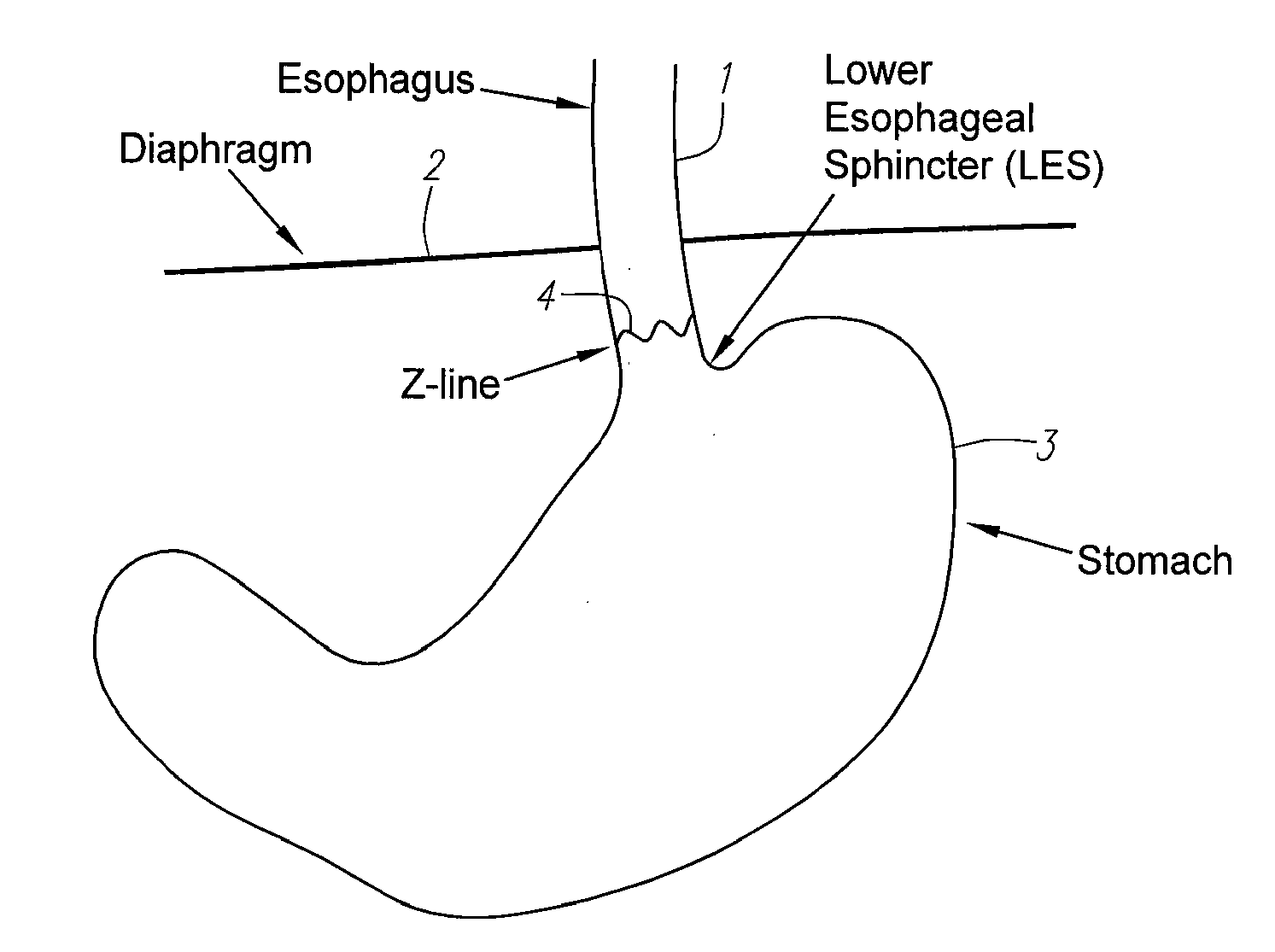
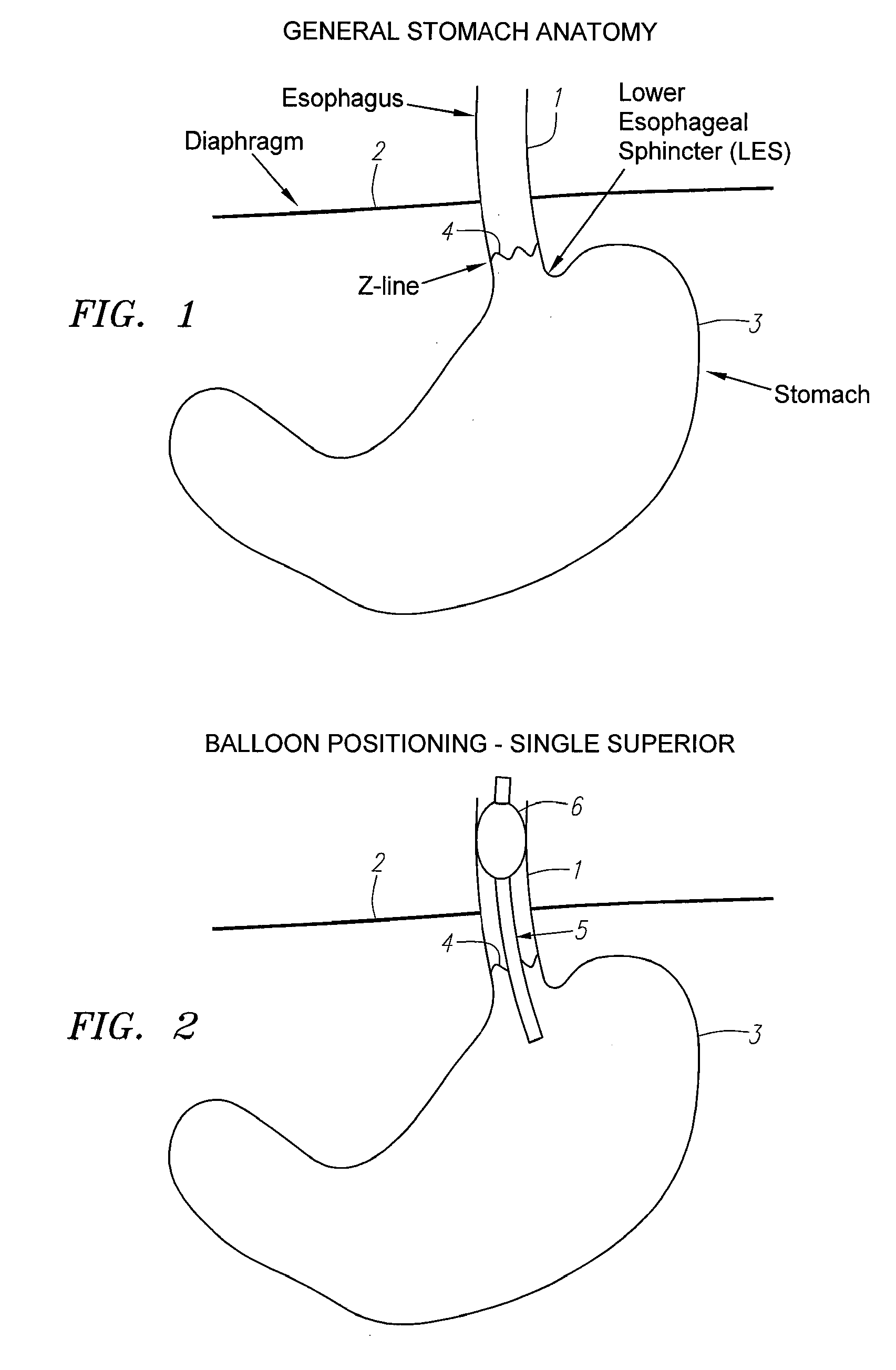
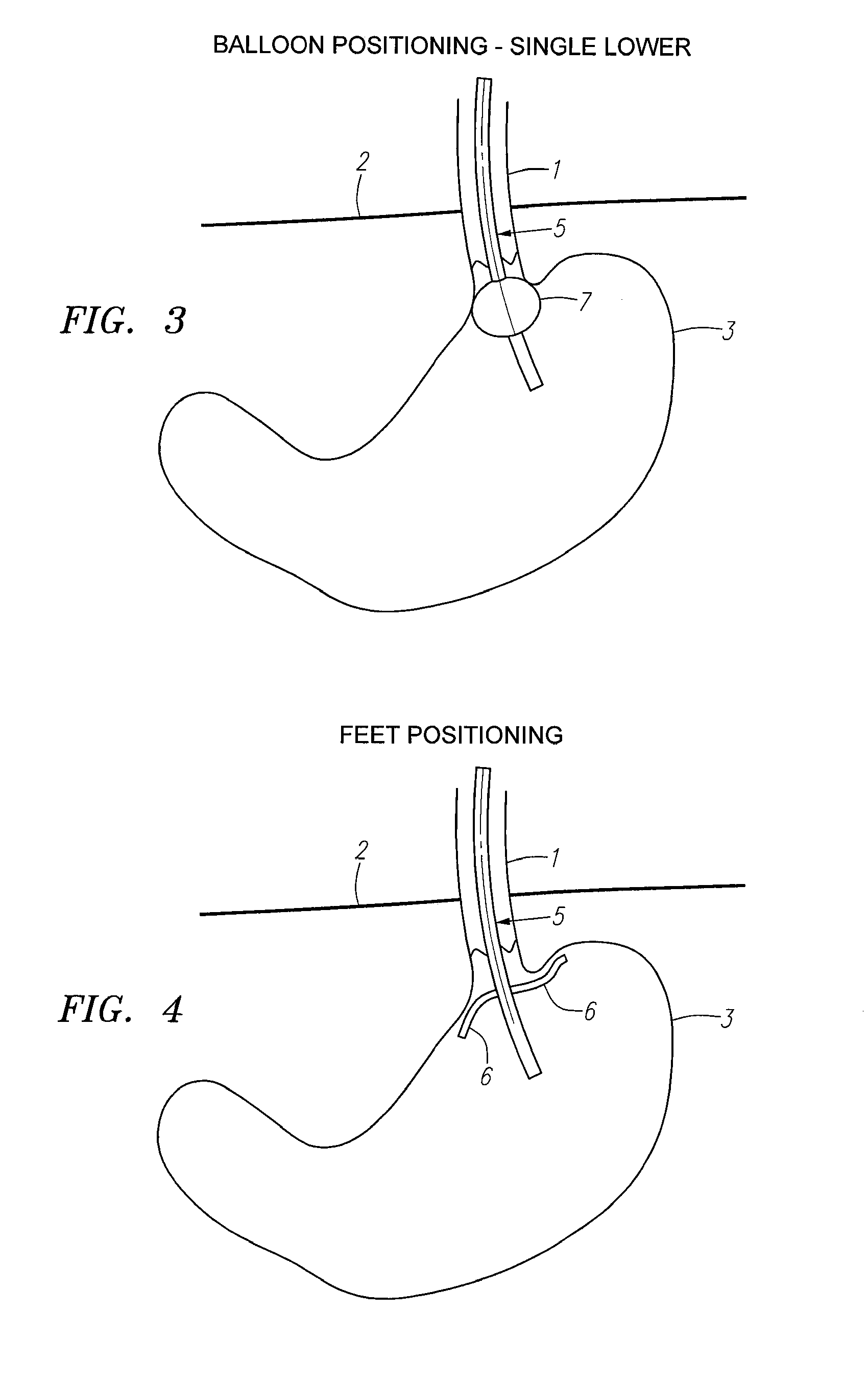
Methods and apparatus for testing disruption of a vagal nerve
InactiveUS20050240231A1Increase energy levelLower energy levelUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyOesophageal tubeHigh energy
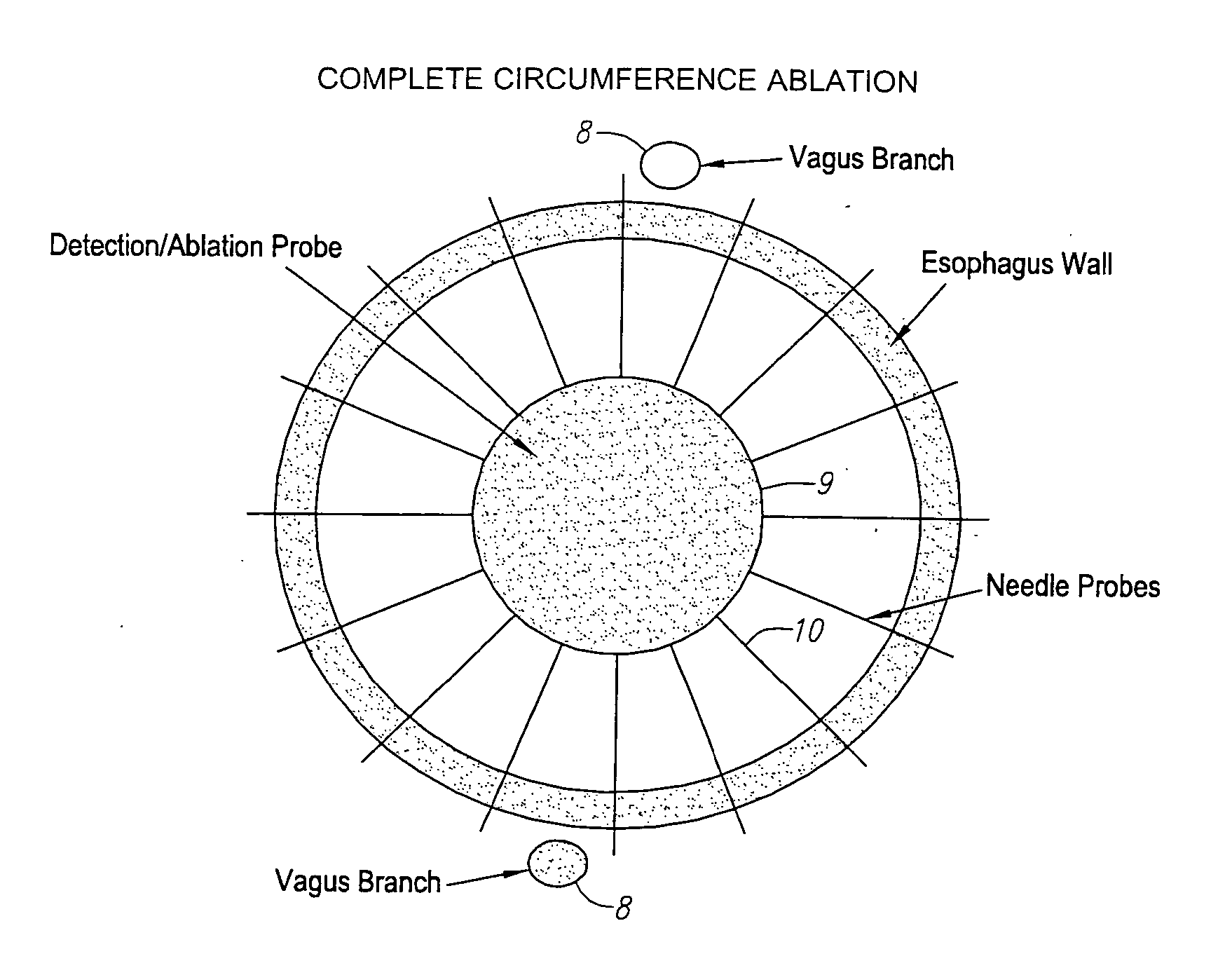
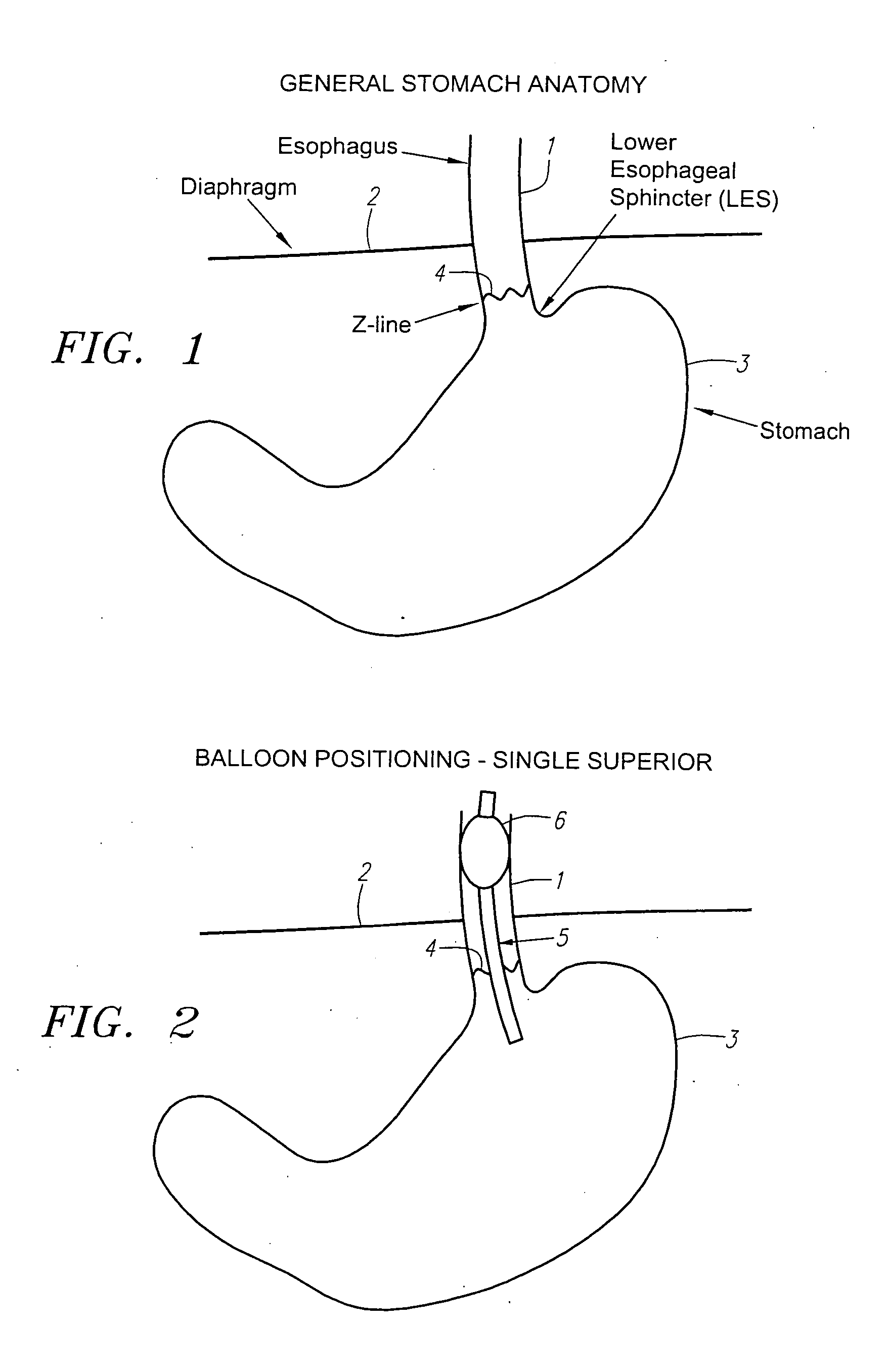
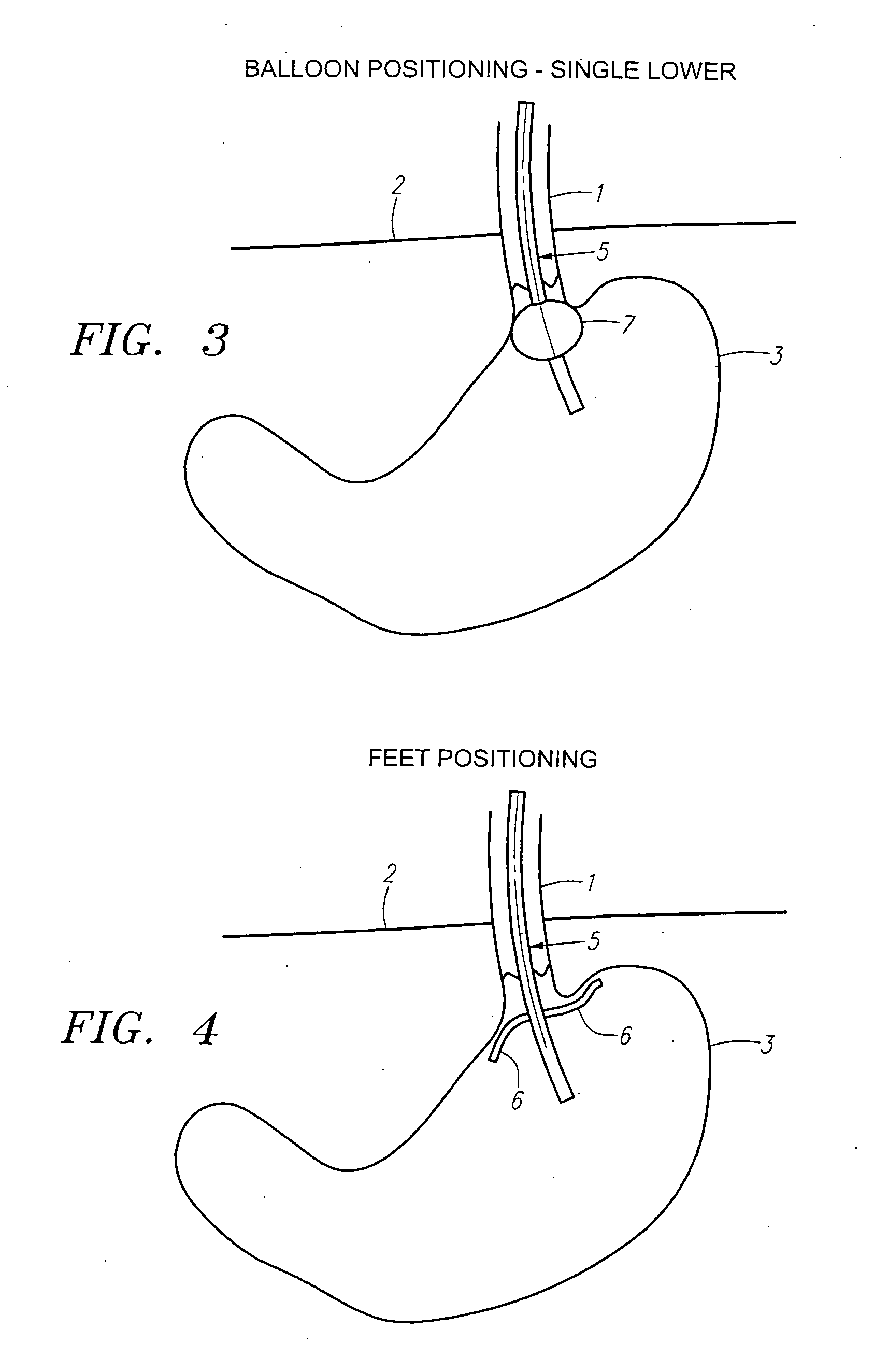
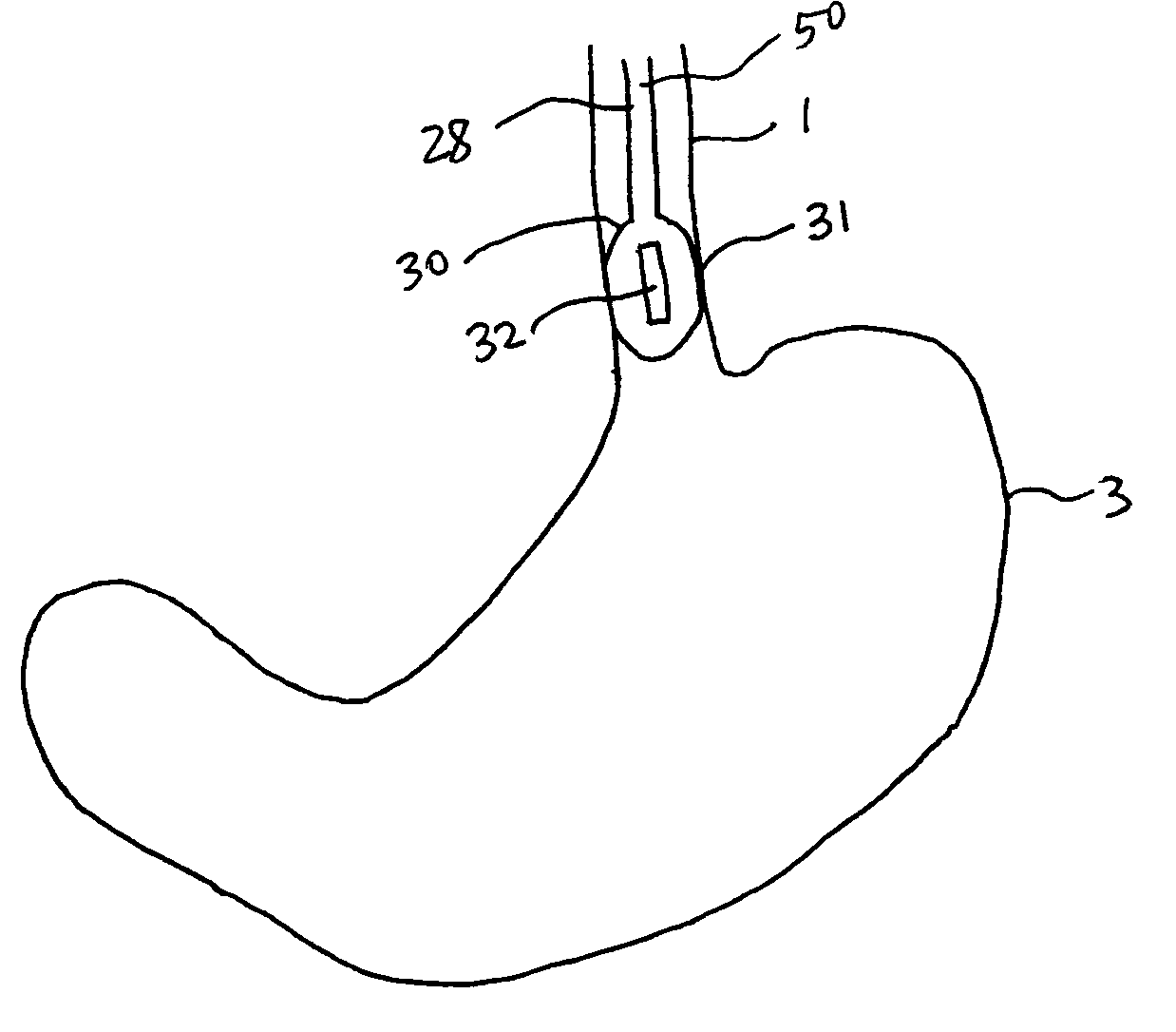
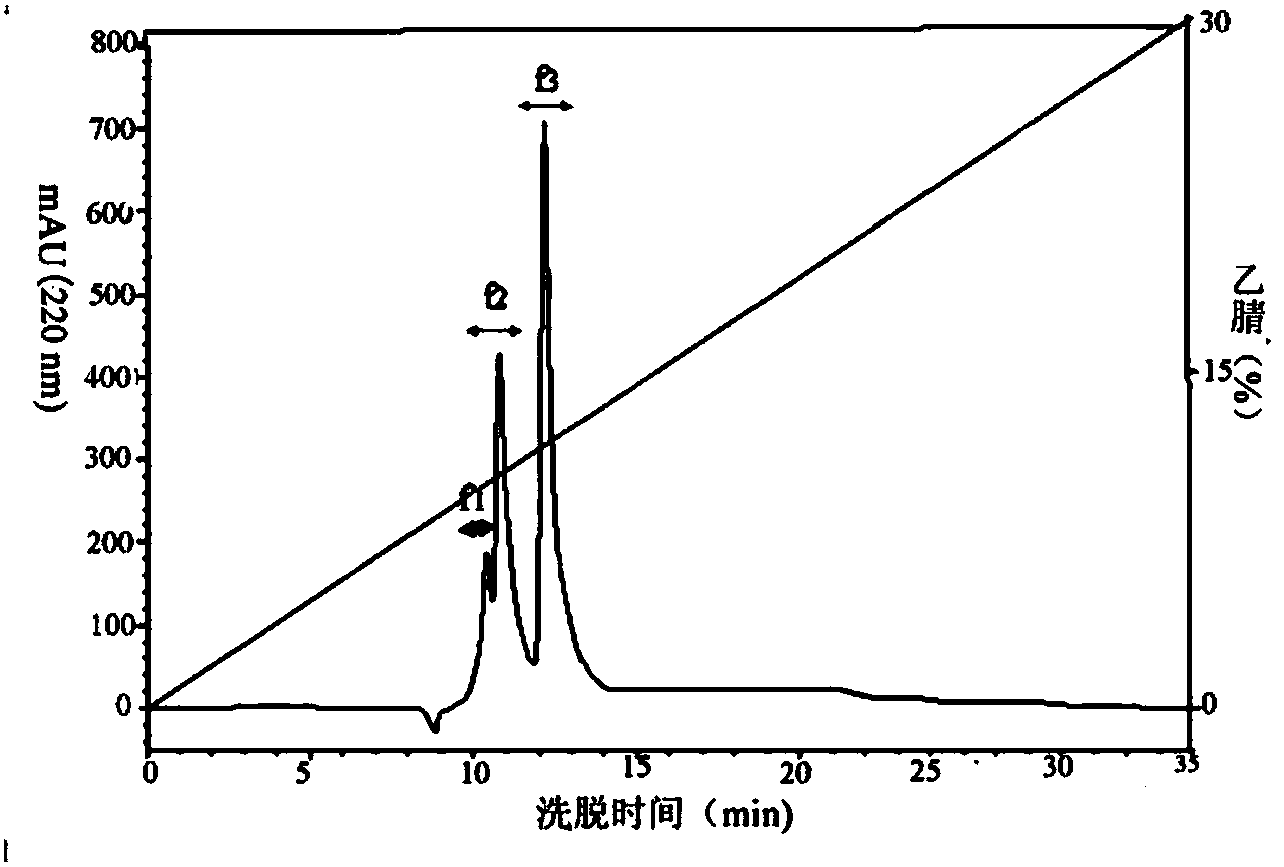
Method and apparatus for disrupting a gastric vagal nerve in the gastroesophageal region and testing the function and disruption of the vagal nerve. In one example embodiment, a treatment device applies ultrasound at a high energy level, such as high intensity focused ultrasound, to a vagal nerve to disrupt it and then ultrasound at a lower energy level to another portion of the vagal nerve, preferably further from the stomach, so as to stimulate the vagal nerve. Alternative ways to test the function or disruption of the vagal nerve involve using PCP-GABA, a pancreatic polypeptide, pressure changes inside the stomach, the gastric mucusol pH, a dye agent in the stomach, and other tests.
Owner:ENDOVX
Methods and apparatus for testing disruption of a vagal nerve
Method and apparatus for disrupting a gastric vagal nerve in the gastroesophageal region and testing the function and disruption of the vagal nerve. In one example embodiment, a treatment device applies ultrasound at a high energy level, such as high intensity focused ultrasound, to a vagal nerve to disrupt it and then ultrasound at a lower energy level to another portion of the vagal nerve, preferably further from the stomach, so as to stimulate the vagal nerve. Alternative ways to test the function or disruption of the vagal nerve involve using PCP-GABA, a pancreatic polypeptide, pressure changes inside the stomach, the gastric mucusol pH, a dye agent in the stomach, and other tests.
Owner:ENDOVX
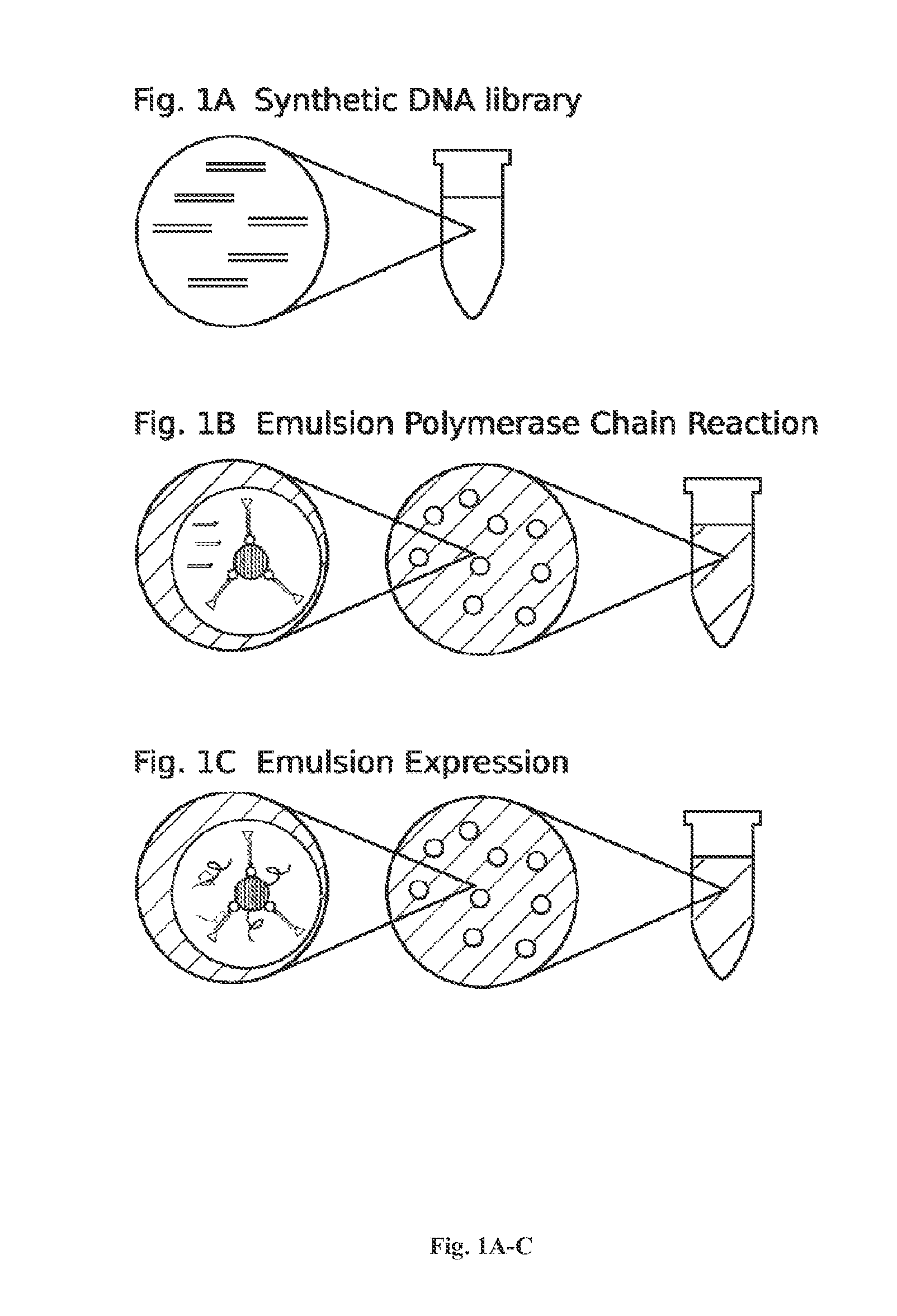
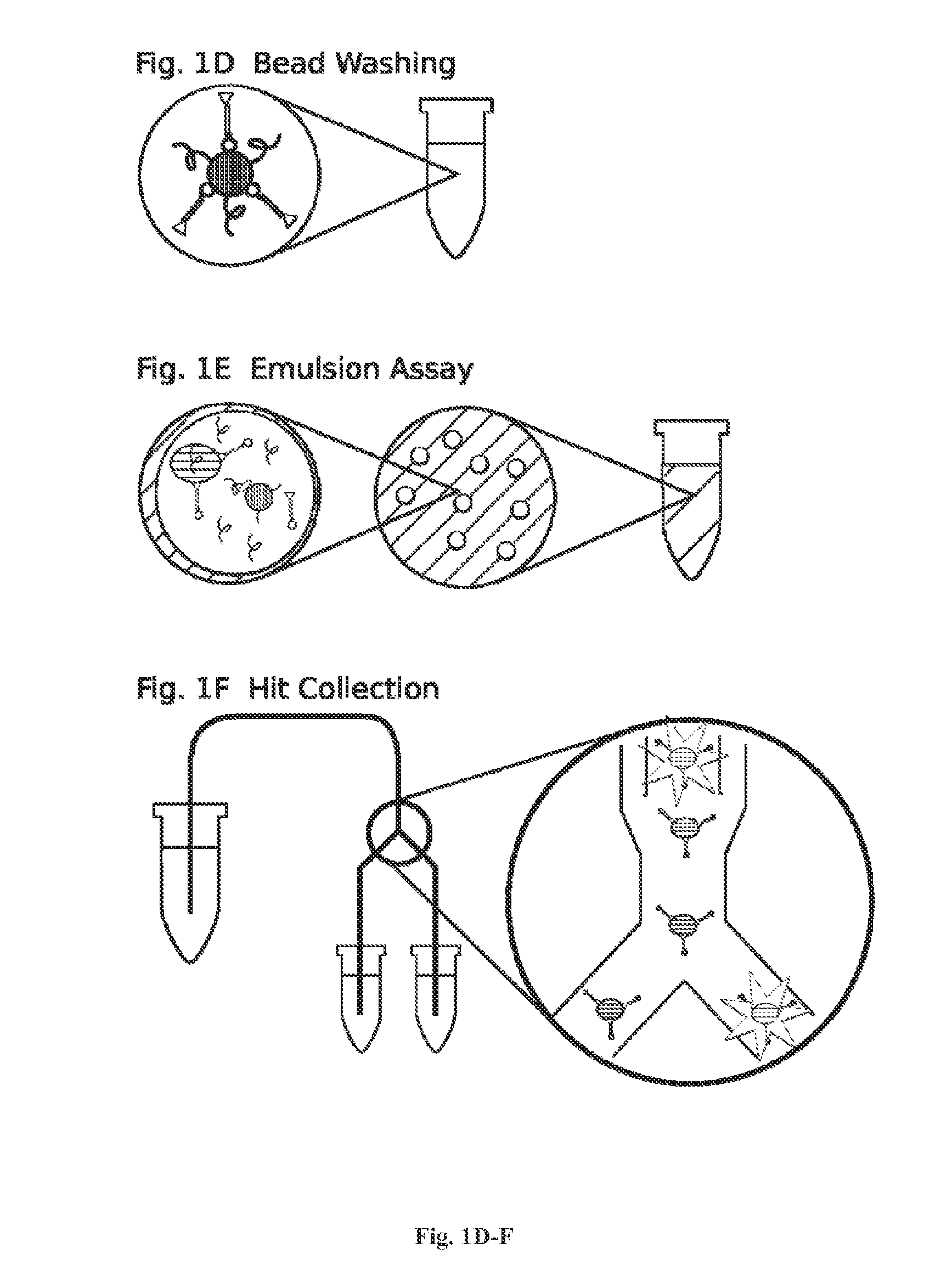
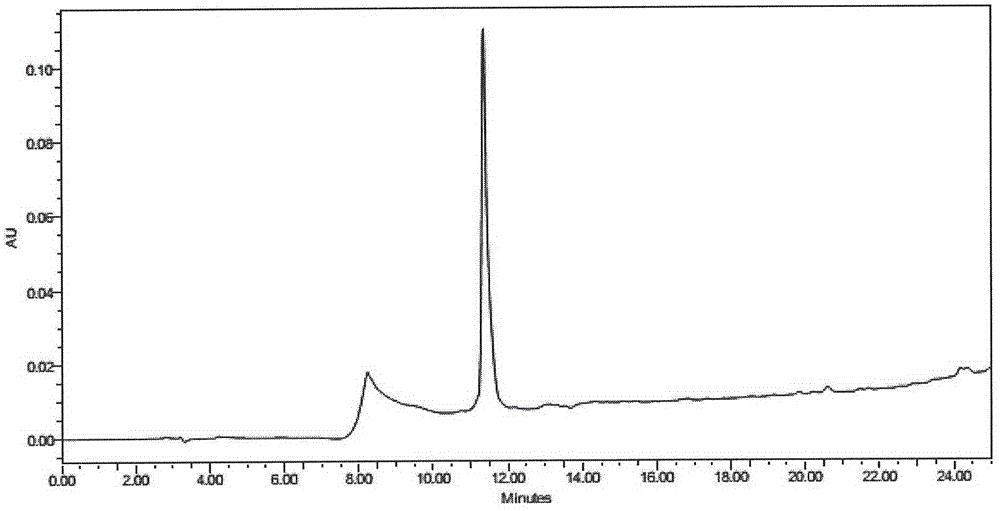
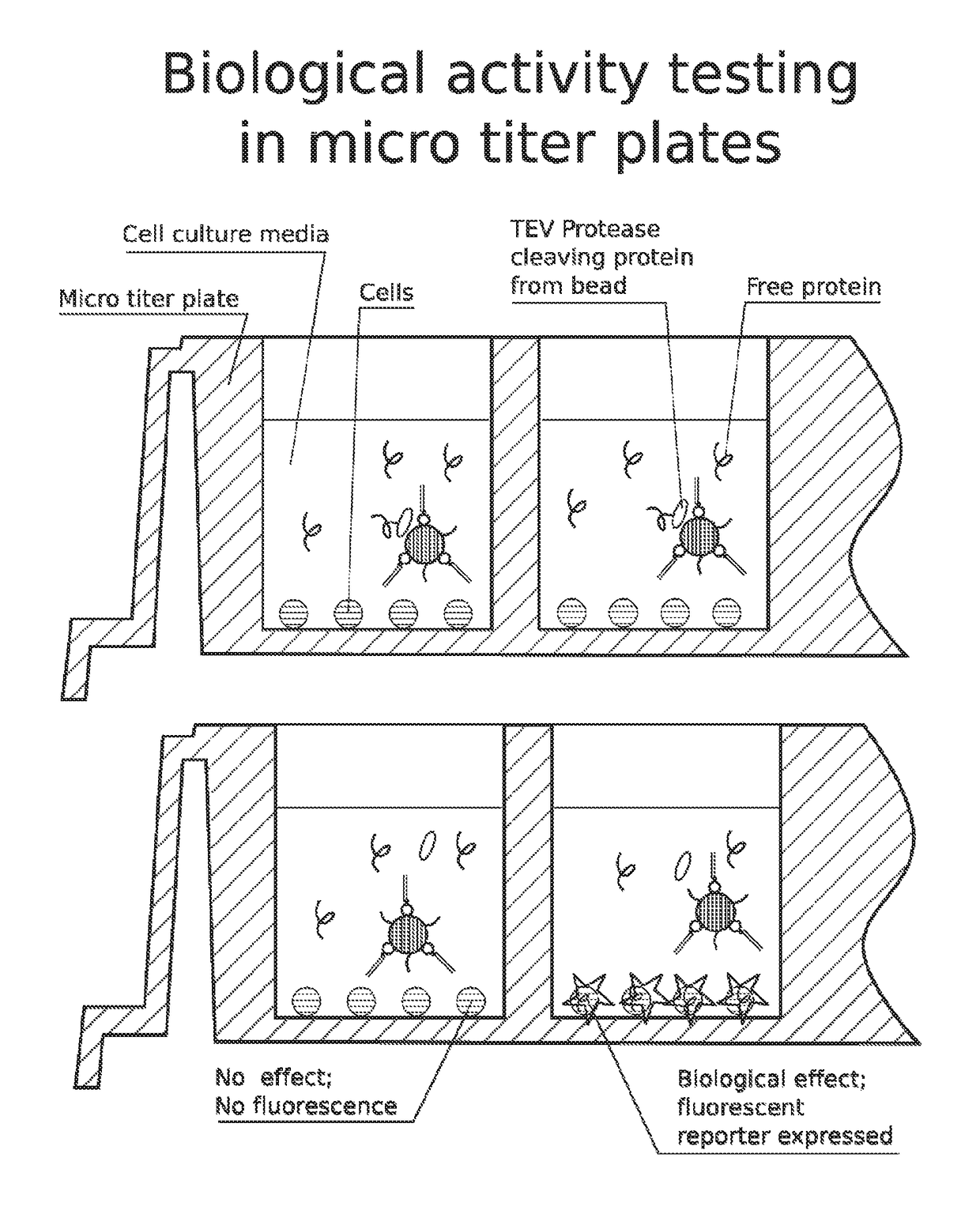
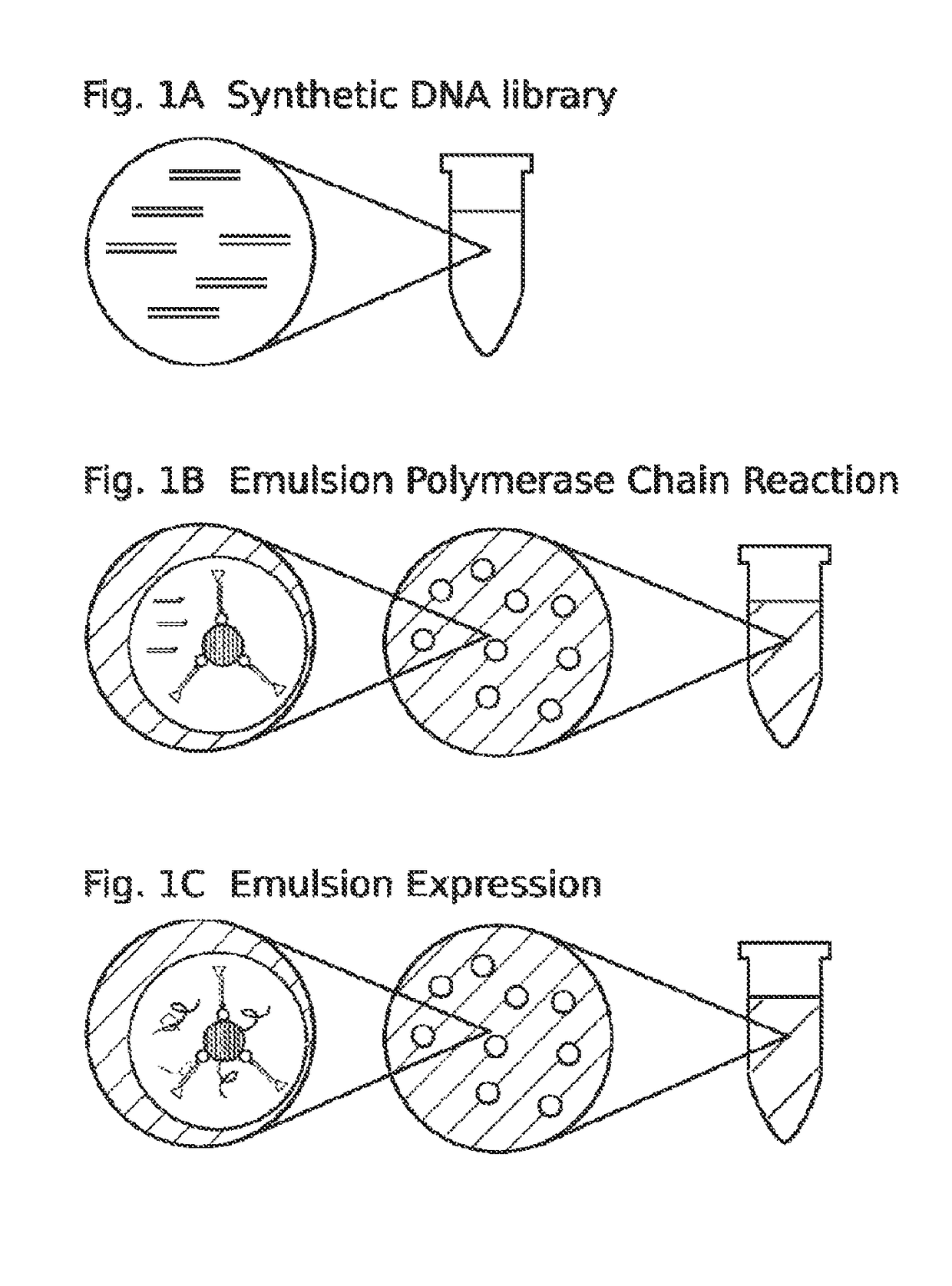
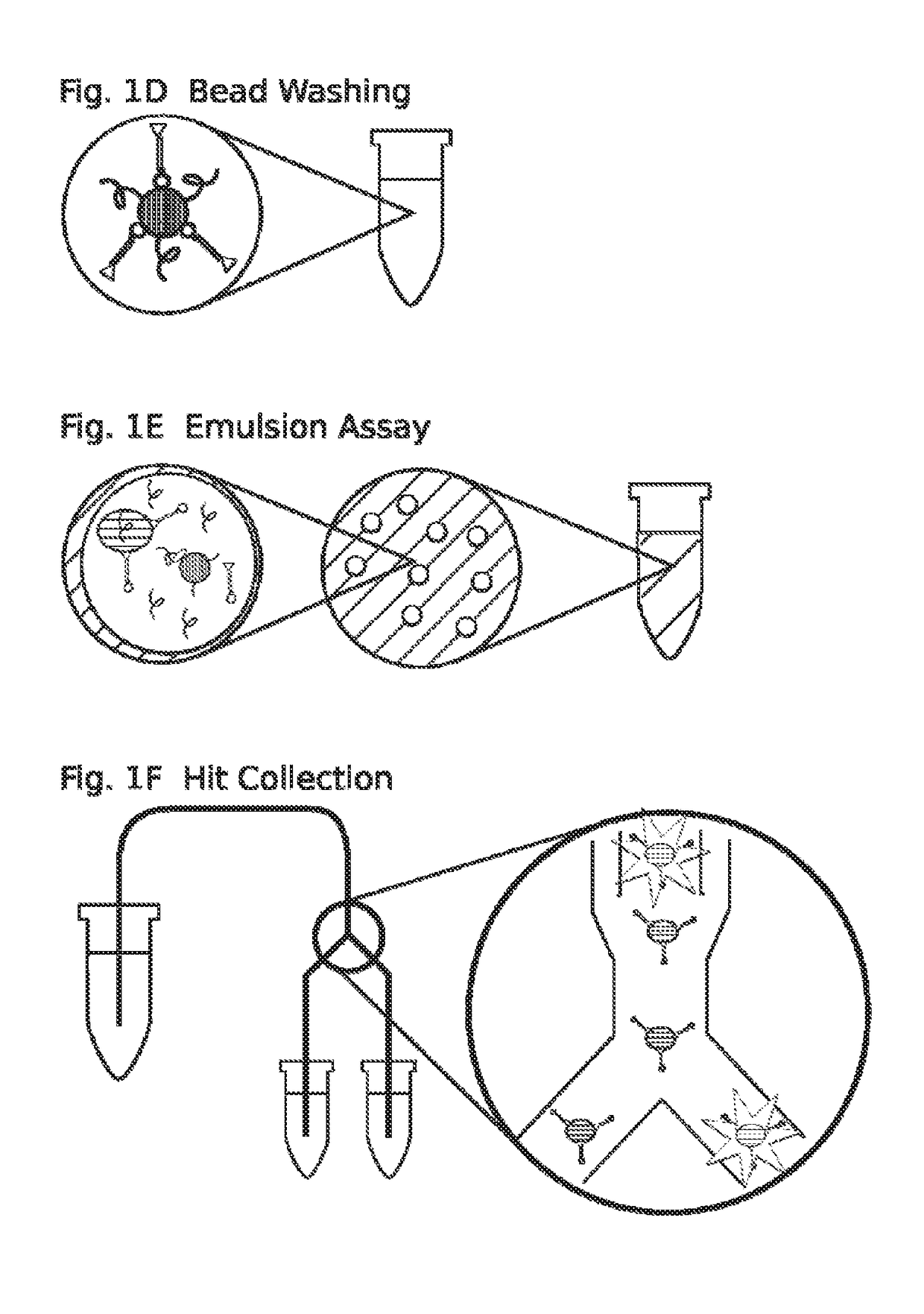
High throughput screen for biologically active polypeptides
InactiveUS20150018236A1Improve efficiencyEfficient separationPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementEmulsionOn cells
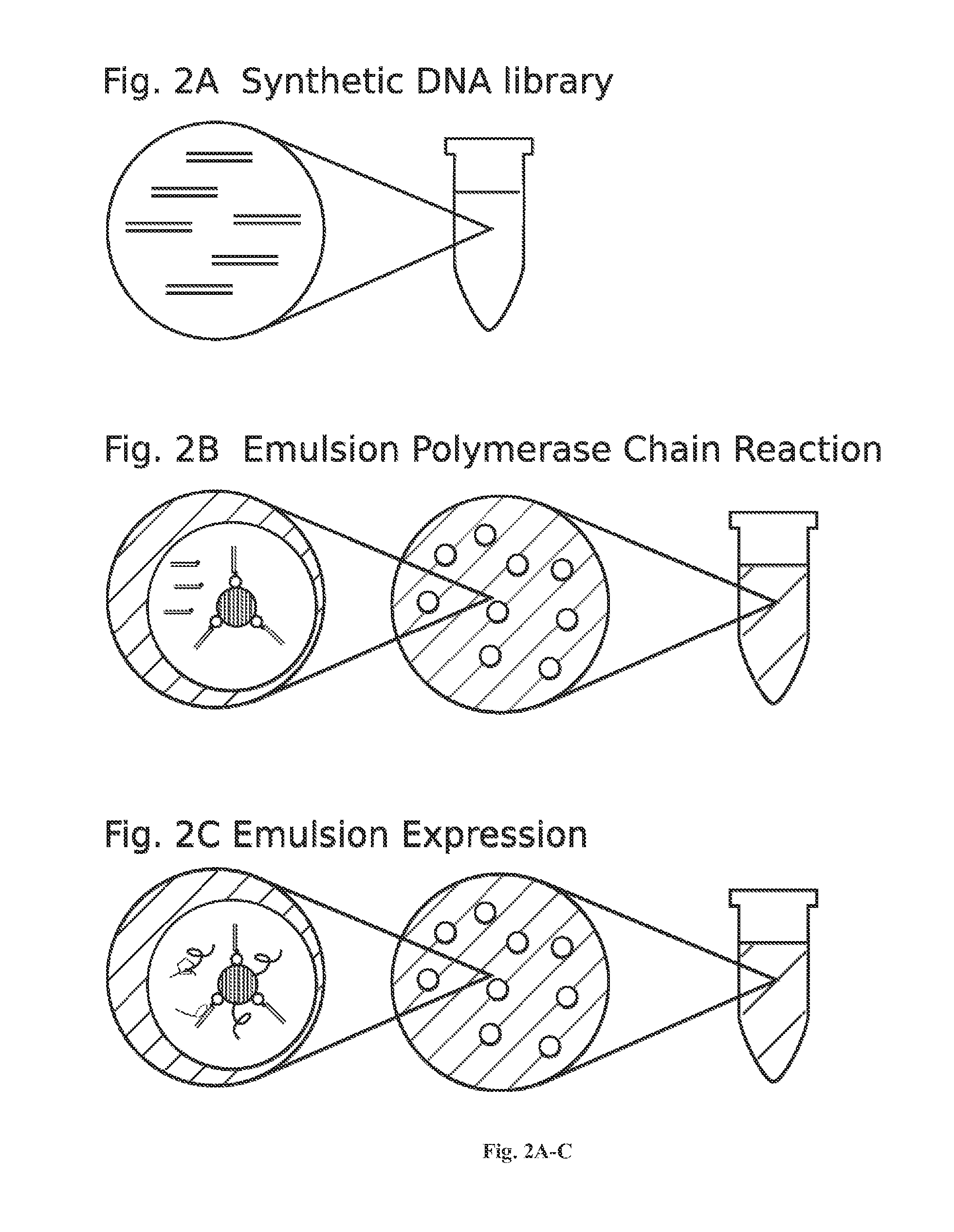
Methods for screening libraries of polypeptides for biologically activity on cells. For example, polypeptides can be synthesized and encapsulated along with their coding sequences in microcapsules of an emulsion. Emulsion microcapsules can then be fused with microcapsules comprising test cells and biological activity on the cells is assessed to identify biologically active polypeptides and nucleic acid molecules encoding the same.
Owner:INVENRA INC
Fusion polypeptides, vaccines and compositions of FKBP chaperones and target polypeptides
The present invention relates to the cloning and expression of foreign protein or polypeptides in bacteria, such as Escherichia coli. In particular, this invention relates to expression tools comprising a FKBP-type peptidyl prolyl isomerase selected from the group consisting of FkpA, SlyD, and trigger factor; methods of recombinant protein expression, the recombinant polypeptides thus obtained, as well as to the use of such polypeptides.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Methods and Apparatus for Testing Disruption of a Vagal Nerve
InactiveUS20080194956A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyOesophageal tubeHigh energy
Method and apparatus for disrupting a gastric vagal nerve in the gastroesophageal region and testing the function and disruption of the vagal nerve. In one example embodiment, a treatment device applies ultrasound at a high energy level, such as high intensity focused ultrasound, to a vagal nerve to disrupt it and then ultrasound at a lower energy level to another portion of the vagal nerve, preferably further from the stomach, so as to stimulate the vagal nerve. Alternative ways to test the function or disruption of the vagal nerve involve using PCP-GABA, a pancreatic polypeptide, pressure changes inside the stomach, the gastric mucusol pH, a dye agent in the stomach, and other tests.
Owner:ENDOVX
Compounds for control of appetite
This invention relates generally to neuropeptide Y (“NPY”) Y4 receptor agonists including pancreatic polypeptide (PP), analogs thereof, and peptide fragments of PP, e.g. PP(32-36), and analogs thereof, to pharmaceutical compositions containing such Y4 receptor agonists, and to methods for treatment of mammals using the same. The NPY Y4 receptor agonists may be administered to mammals either alone or in combination with NPY Y2 receptor agonists including peptide YY (PYY) (3-36), analogs thereof, and to peptide fragments of PYY(3-36), e.g. PYY(22-36) and PYY(25-36), and analogs thereof, such as to control food intake in mammals, blood pressure, cardiovascular response, libido, circadian rhythm, hyperlipidimia, chronic pancreatitis, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease including nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Owner:CINCINNATI UNIV OF
Active polypeptide separated from anchovy
ActiveCN103937864AAvoid damageImprove antioxidant capacityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsArginineThreonine
The invention aims to provide an active polypeptide separated from an anchovy fermentation liquid. The molecular weight of the nerve cell injury resistant polypeptide obtained by the invention is 2,181Da; and the polypeptide is composed of 11 amino acids such as aspartic acid, threonine, glutamic acid, glycine, alanine, isoleucine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, histidine, lysine, arginine and the like, and is a novel active polypeptide with activity. According to the polypeptide obtained by the invention, in a glutamine nerve cell injury model, the addition of the active polypeptide provided by the invention can obviously increase the survival rate of PC12 nerve cells; and when the final concentration is 50 mug / mL, the cell survival rate is increased by 26.4% in comparison with an injury group, thereby effectively relieving glutamine-induced nerve cell injury. Besides, the cell mechanism study on the nerve cell protective action of the polypeptide discovers that the addition of the active polypeptide obviously increases the intracellular total oxidation resistance and has a certain promoting action on increase of SOD (superoxide dismutase) activity.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Intestinal brake inducing intraluminal therapeutic substance eluting devices and methods
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Method of producing biologically active polypeptide having insulinotropic activity
The present invention relates to a method of producing a biologically active polypeptide having insulinotropic activity, the method comprising steps of: (a) transforming a genetically modified host cell that has protease gene knockout, with a polynucleotide vector encoding the polypeptide; and (b) growing the transformed host cell to produce the biologically active polypeptide; and a method of producing a biologically active polypeptide having an N-terminal recognition site His-Gly with insulinotropic activity, the method comprising steps of: (a) transforming a genetically modified Pichia pastoris that has protease gene STE13 knockout, with a polynucleotide vector encoding the polypeptide; and (b) growing the transformed Pichia pastoris to produce the biologically active polypeptide.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
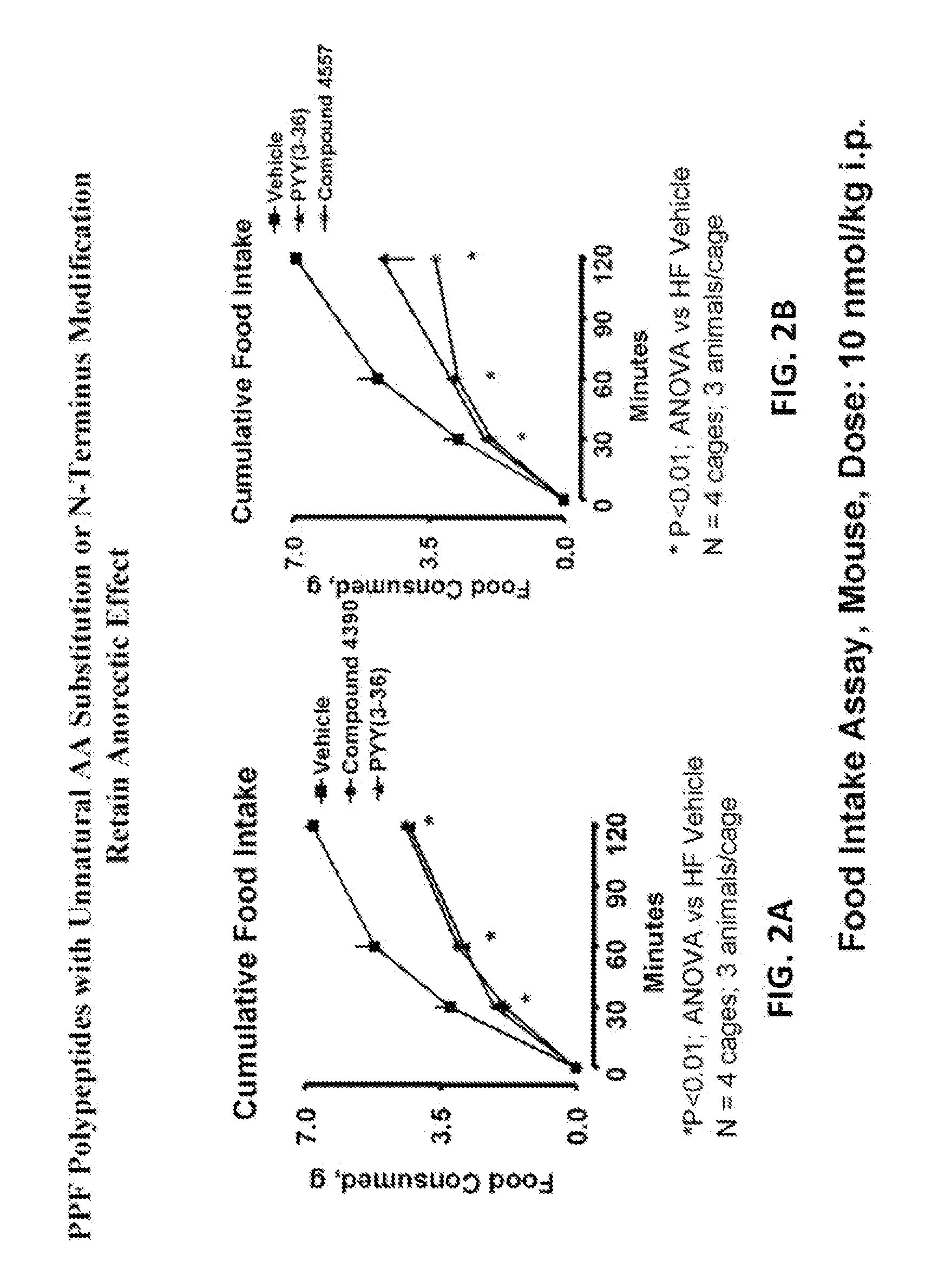
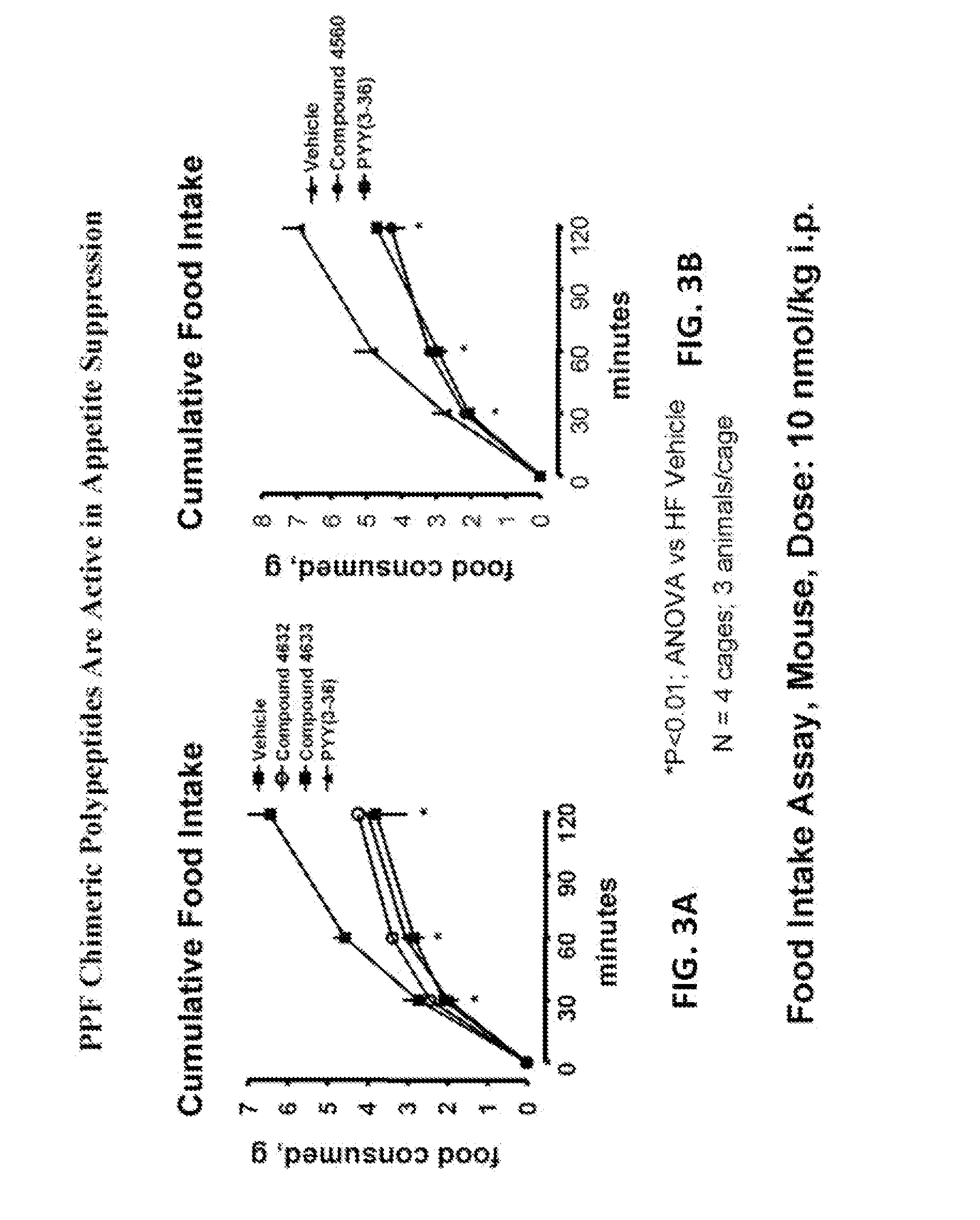
Pancreatic polypeptide family motifs, polypeptides and methods comprising the same
InactiveUS20130303442A1Hormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsCell biologyPancreatic polypeptide
The present invention provides novel Pancreatic Polypeptide Family (“PPF”) polypeptides and methods for their use.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
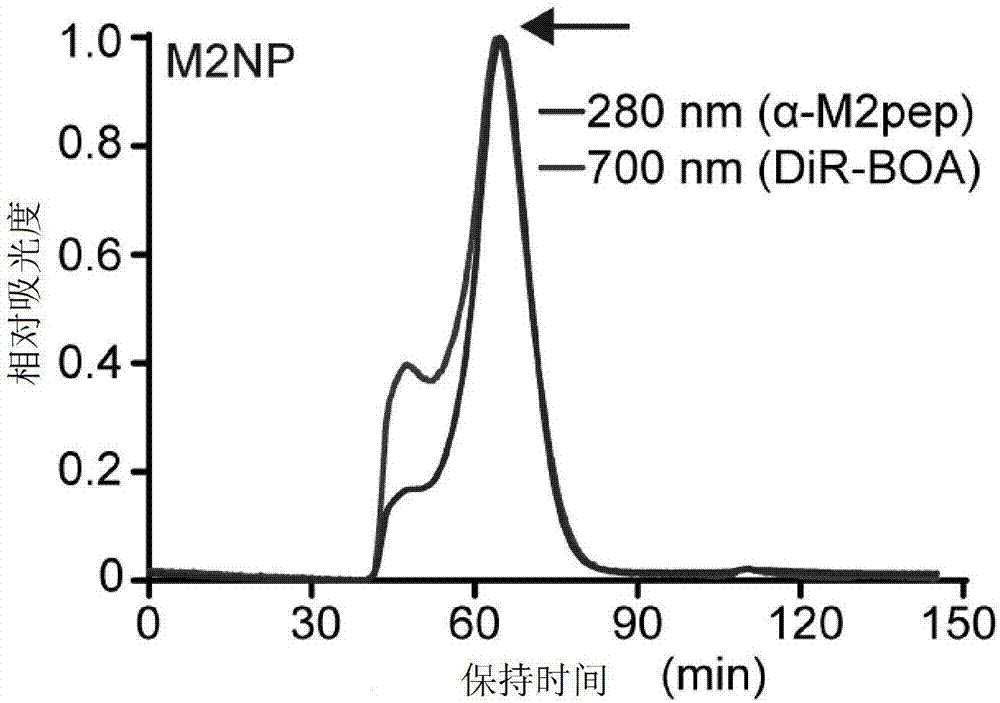
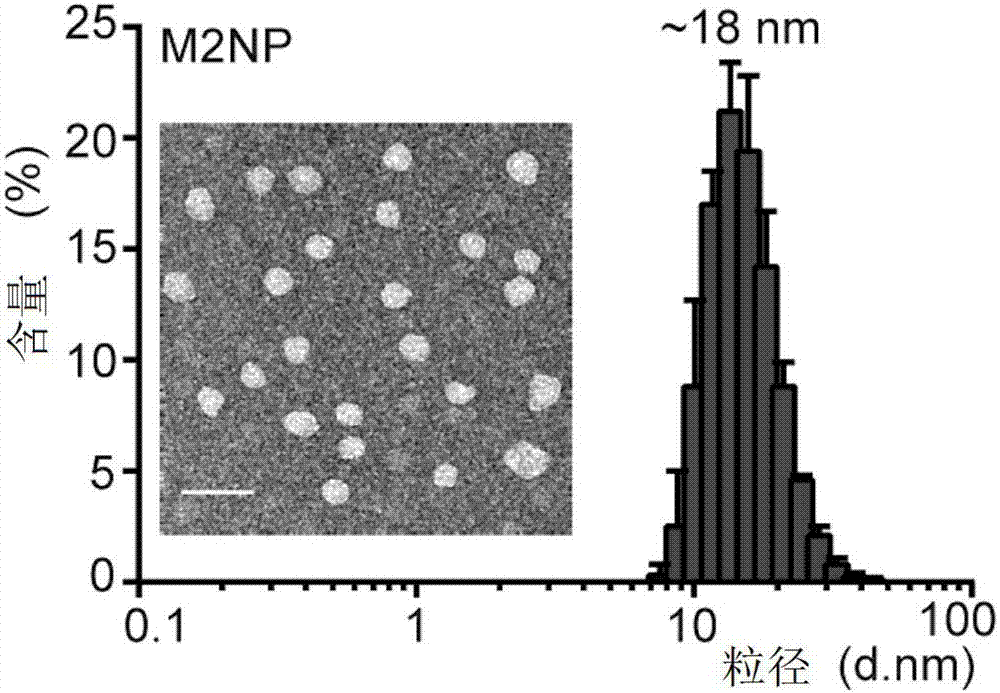
Double-target polypeptide of tumor-associated macrophage, nano particle, preparation and application
ActiveCN107573418AGrowth inhibitionGood physical and chemical propertiesMacromolecular non-active ingredientsHybrid peptidesSide effectAlpha helix
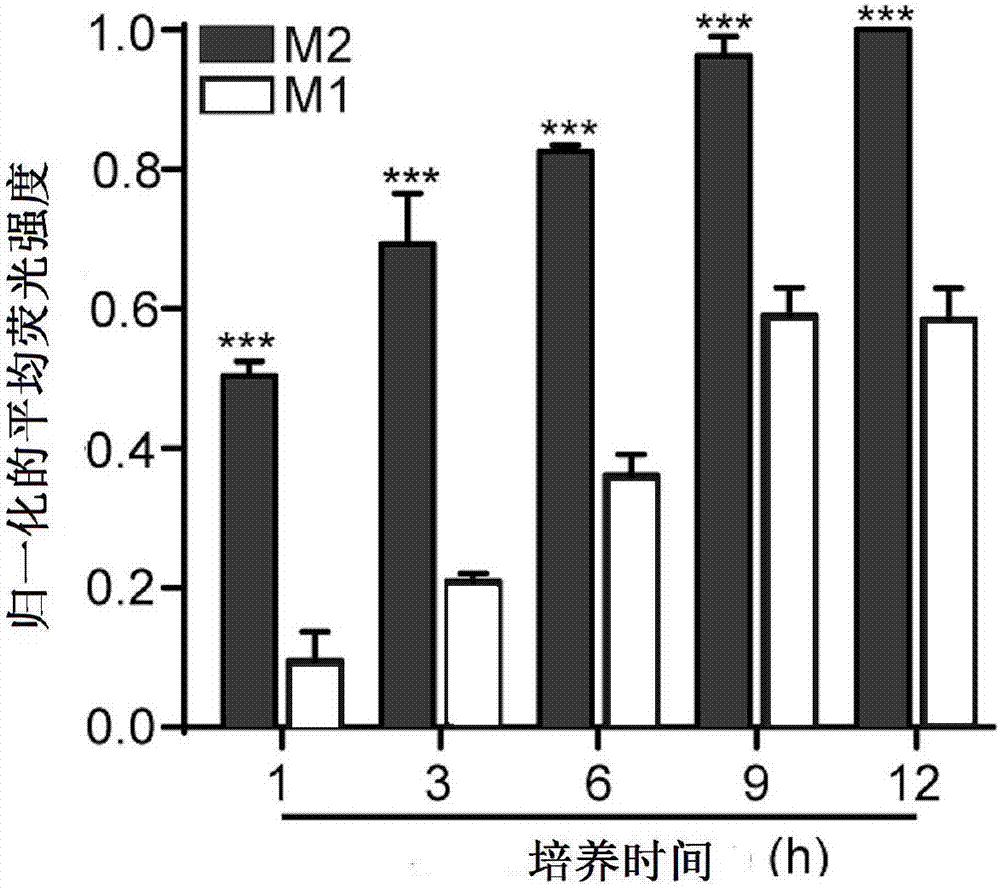
The invention discloses double-target polypeptide of a tumor-associated macrophage, a nano particle, preparation and an application and relates to the technical field of bioscience and drug carriers.The double-target polypeptide is prepared by series connection of alpha helix polypeptide, a catenation sequence and M2 macrophage target peptide in a covalent bond form. The nano particle prepared bythe double-target polypeptide can perform efficient targeted transportation of drugs to the tumor-associated macrophage, so that the tumor-associated macrophage is specifically eliminated and tumor growth is inhibited; a preparation technology of the nano particle targeting to the tumor-associated macrophage is simple; large-scale production is facilitated; most raw materials for preparing the nano particle are used clinically or used in clinical experiments; and a detection result shows that no toxic or side effects are caused on physiologic and biochemical indexes of a mouse.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method of inducing an immune response
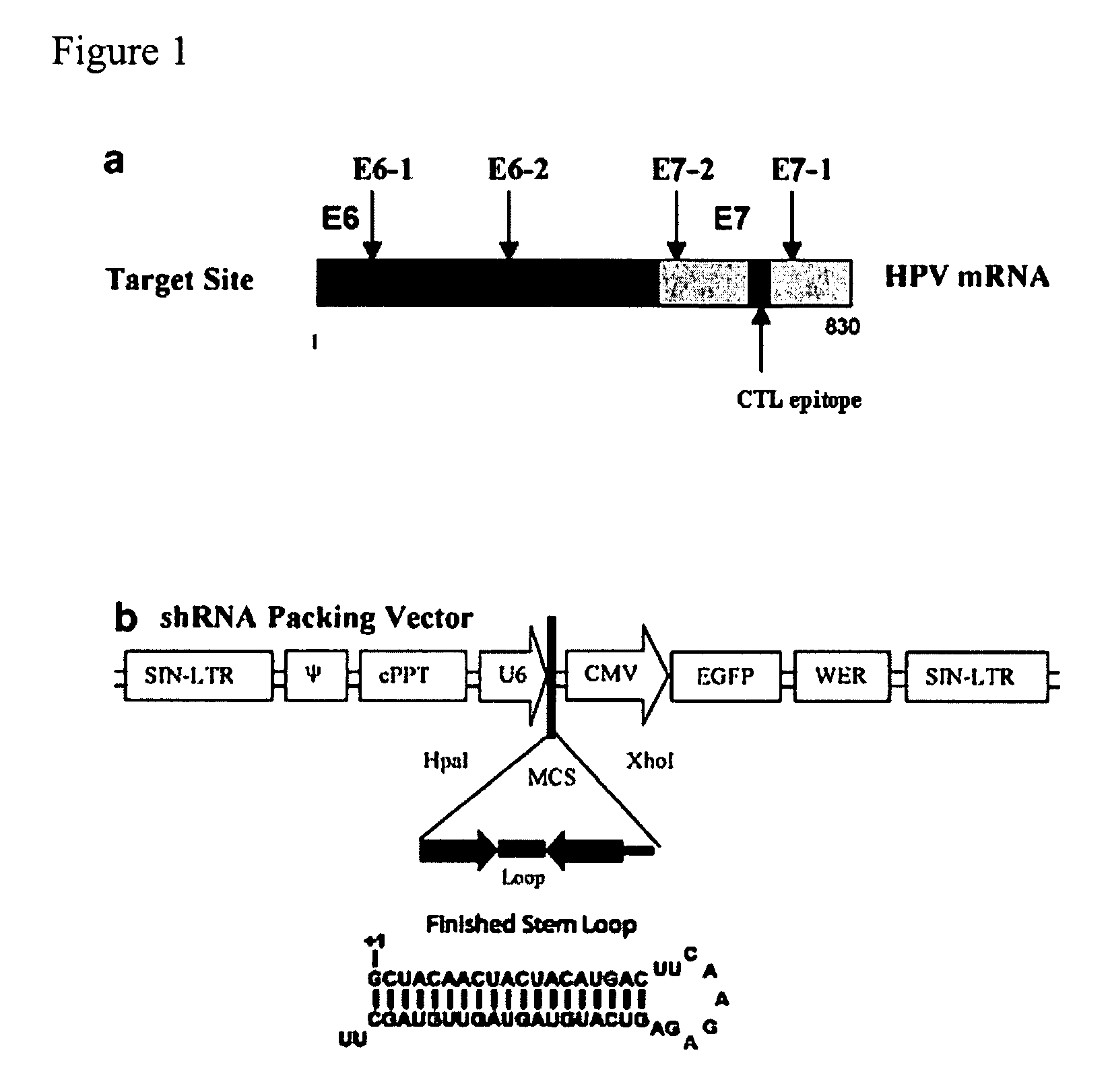
A method is provided for inducing or enhancing an immune response in a mammal to a target polypeptide expressed in a plurality of cells of the mammal, which method comprises administering to the mammal an inhibitory nucleic acid which targets a region of a ribonucleic acid (RNA) which encodes said polypeptide. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition comprising an inhibitory nucleic acid which targets a region of an RNA which encodes a target polypeptide expressed in a plurality of cells of a mammal, such that translation of an aberrant form of the target polypeptide occurs in said cells, said truncated form of the target polypeptide comprising one or more T cell epitopes; together with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIV OF THE
Active polypeptide capable of promoting osteogenesis and inhibiting osteoclast and application of active polypeptide
ActiveCN108276487AReduce osteoclastsReduce osteoporosisPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderViewpointsCalcium phosphate coating
The invention discloses an active polypeptide capable of promoting osteogenesis and inhibiting osteoclast and application of the active polypeptide. N-terminal serine is phosphorylated on the basis ofPTH1-34, and three repeated sequences of glutamic acid or aspartic acid are introduced at a C terminal; the sequence of the polypeptide is shown in SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:2, and the polypeptide hasosteoinductive activity similar to BMP2 and an osteoclast inhibiting effect similar to parathyroid hormones (PTH). Random coils of the polypeptide can be avoided by bonding the C-terminal repeated sequences of the polypeptide to the surface of a calcium phosphate material or a material with a calcium phosphate coating, no addition of organic reagents is needed, and therefore the activity of the polypeptide is protected effectively; furthermore, slow controlled release can be achieved through cleavage of peptide bonds, and long-term intermittent injection of the PTH1-34 can be avoided, so thatthe injection pain of patients is reduced, and effects of osteoblast promotion and osteoporosis inhibition are achieved; a conventional viewpoint that the PTH1-34 cannot be administered locally is changed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
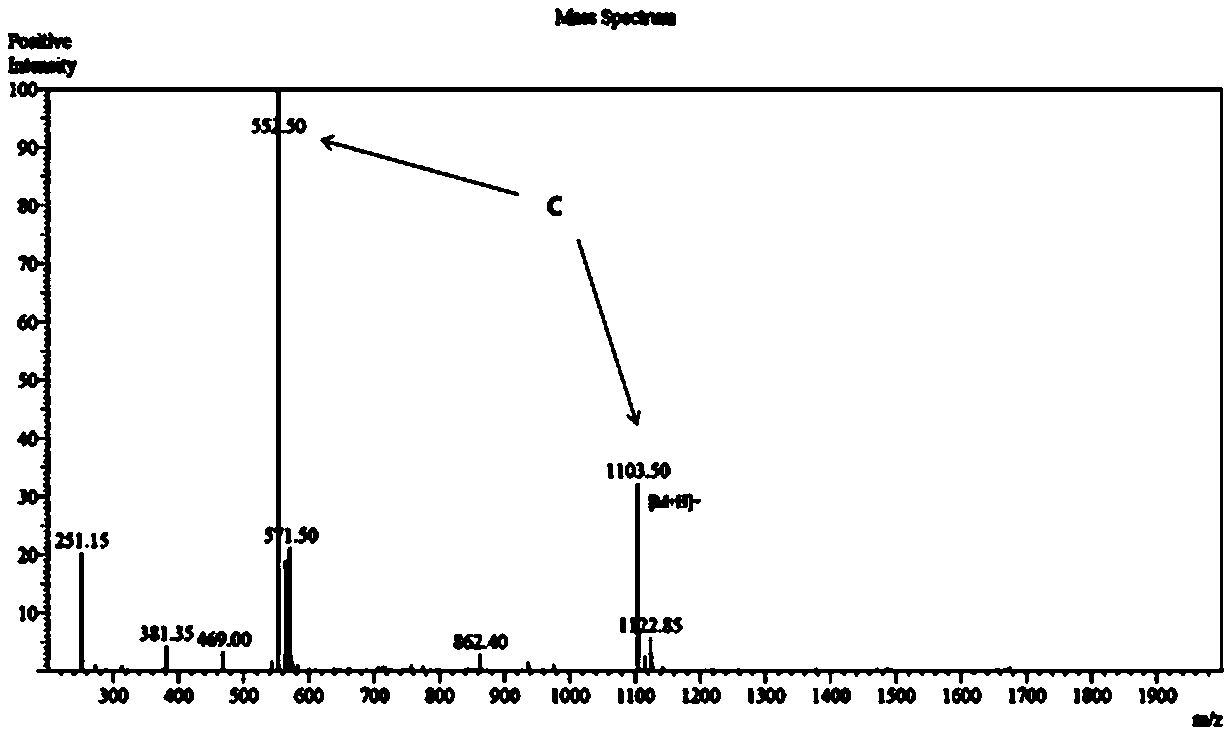
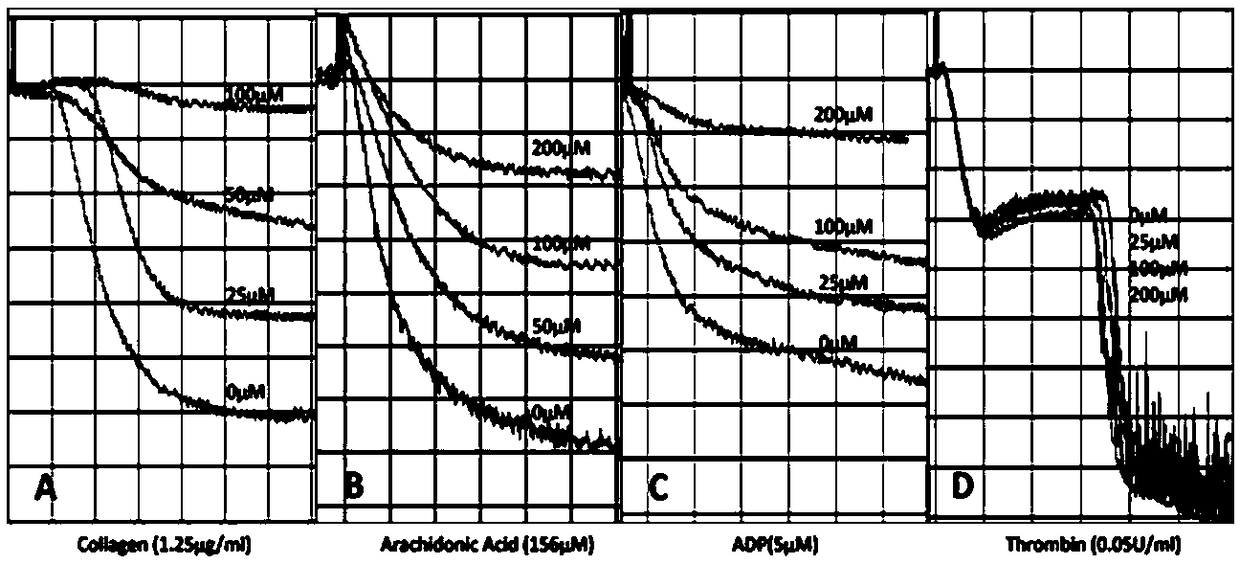
Anti-platelet-aggregation polypeptide
ActiveCN108503689AInhibit aggregationEnhanced inhibitory effectPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesAnti plateletInduced platelet aggregation
The invention discloses an anti-platelet-aggregation polypeptide, belongs to the field of medical biotechnology, and in particular relates to a novel polypeptide having the function of inhibiting platelet aggregation. The polypeptide is a polypeptide KM6 consisting of 10 amino acids, having a sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, and having a molecular weight of 1103. 19 Da, and the sequence of the polypeptide KM6 is Gln-Leu-Ser-Asn-Gly-Asn-Arg-Thr-Leu-Thr. The polypeptide has obvious inhibitory effects on collagen, ADP, arachidonic acid and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation, can be used for exploringthe influence of the polypeptide KM6 and other platelet activators (such as epinephrine and ristomycin) on the effect and related functions of platelets, and can also be used to monitor existing antiplatelet therapies.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF KUNMING MEDICAL UNIV
Method of inducing an immune response
InactiveUS20080214485A1Extended half-lifeImprove permeabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalDiluent
A method is provided for inducing or enhancing an immune response in a mammal to a target polypeptide expressed in a plurality of cells of the mammal, which method comprises administering to the mammal an inhibitory nucleic acid which targets a region of a ribonucleic acid (RNA) which encodes said polypeptide. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition comprising an inhibitory nucleic acid which targets a region of an RNA which encodes a target polypeptide expressed in a plurality of cells of a mammal, such that translation of an aberrant form of the target polypeptide occurs in said cells, said truncated form of the target polypeptide comprising one or more T cell epitopes; together with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIV OF THE
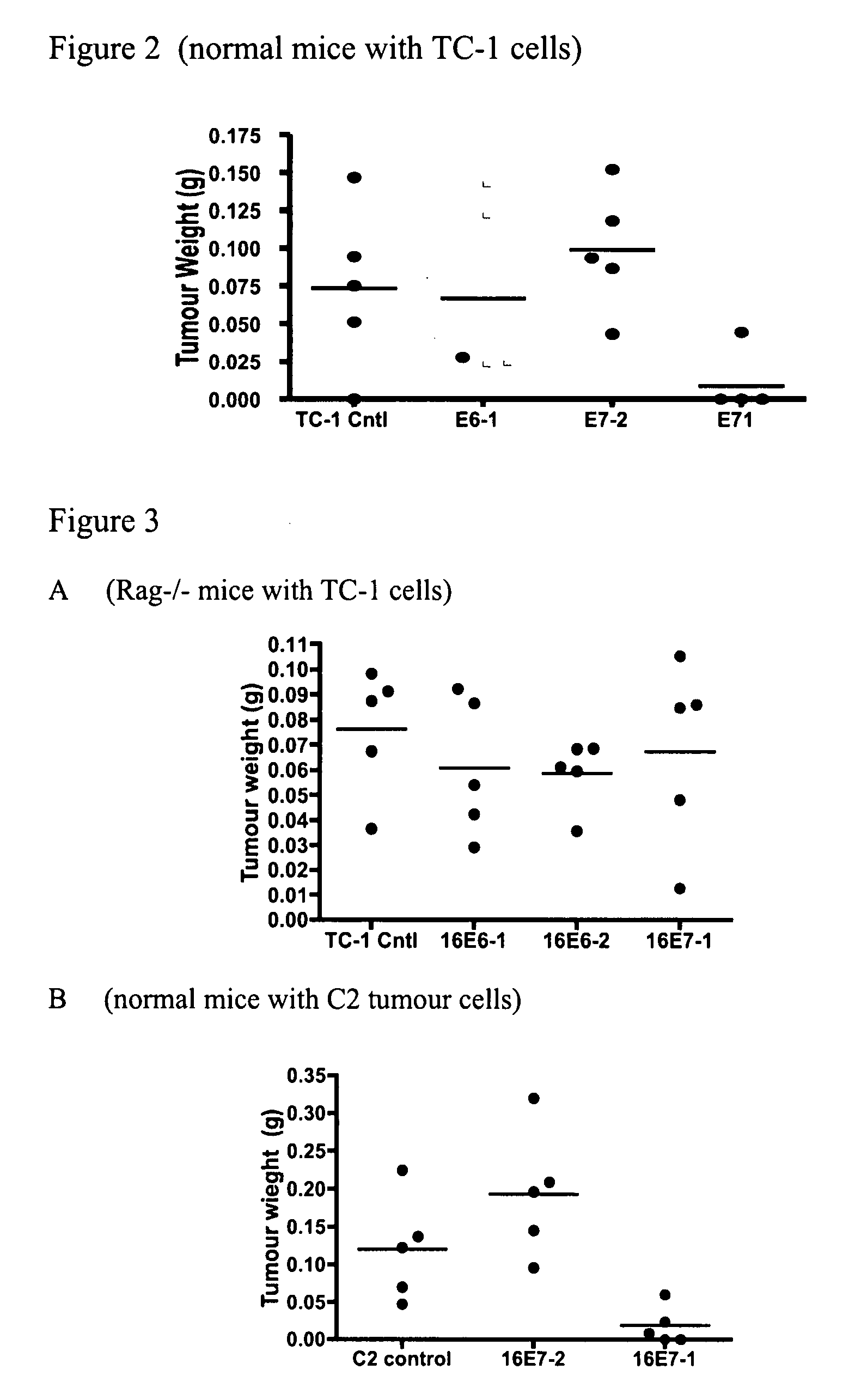
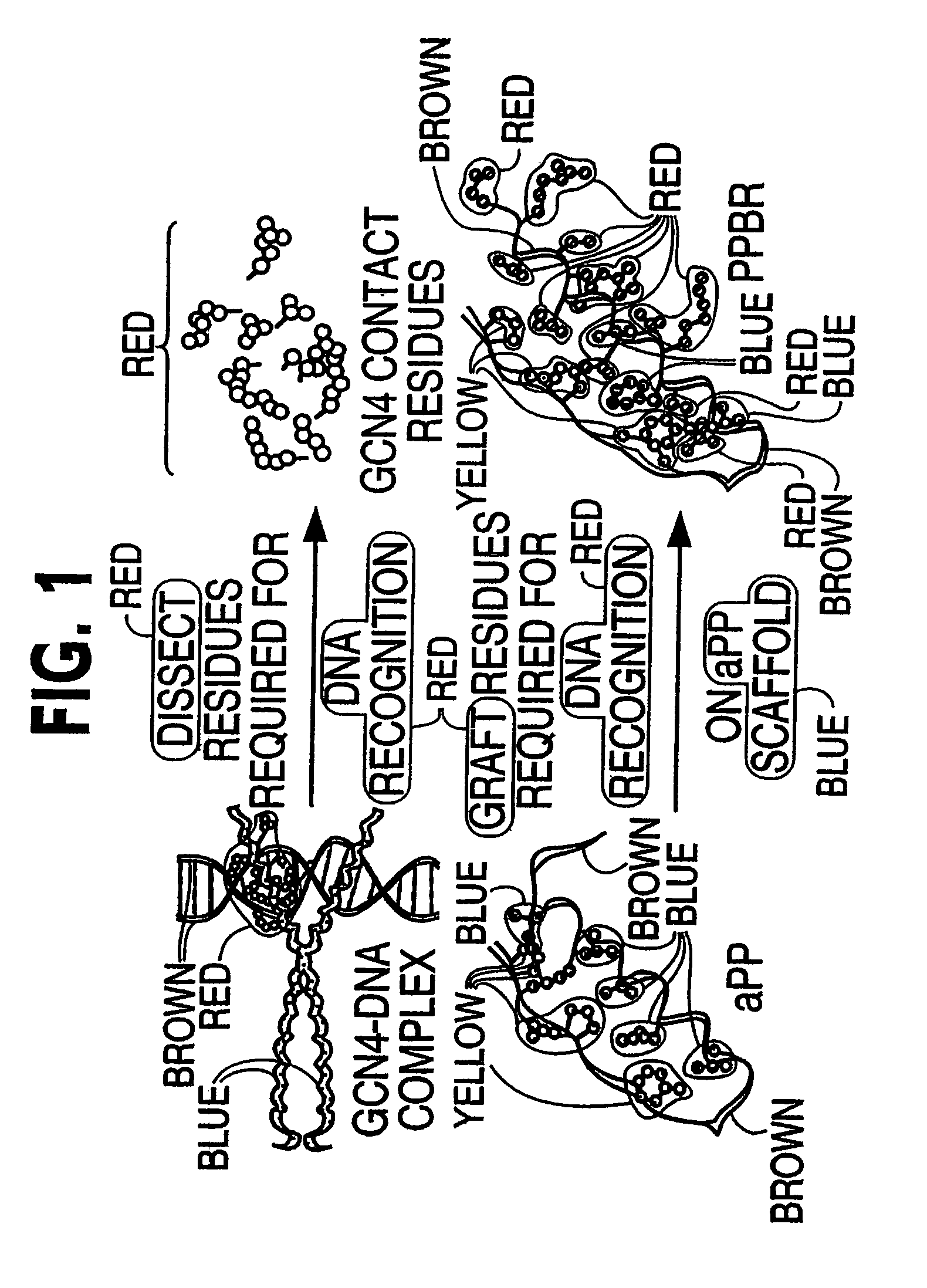
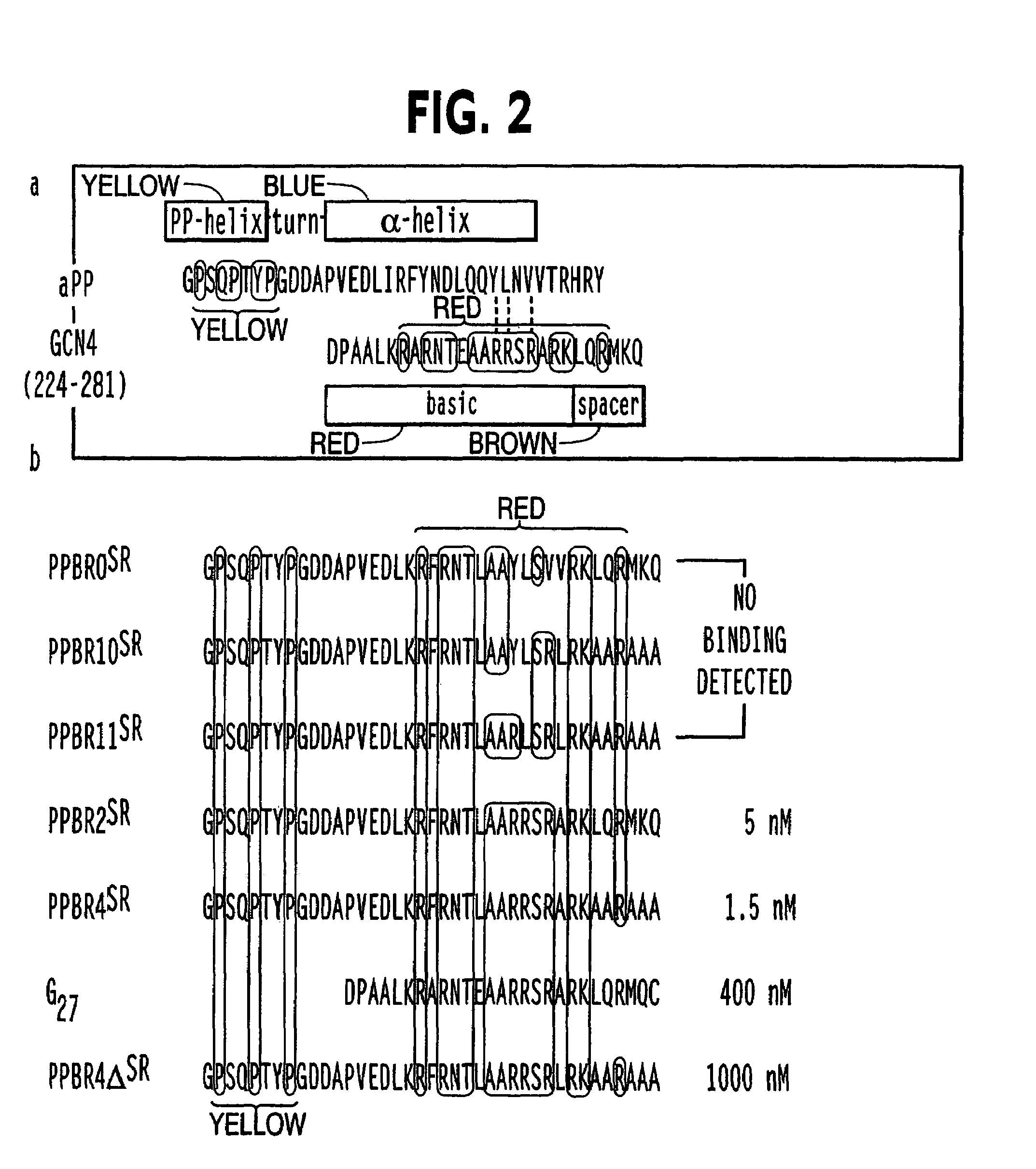
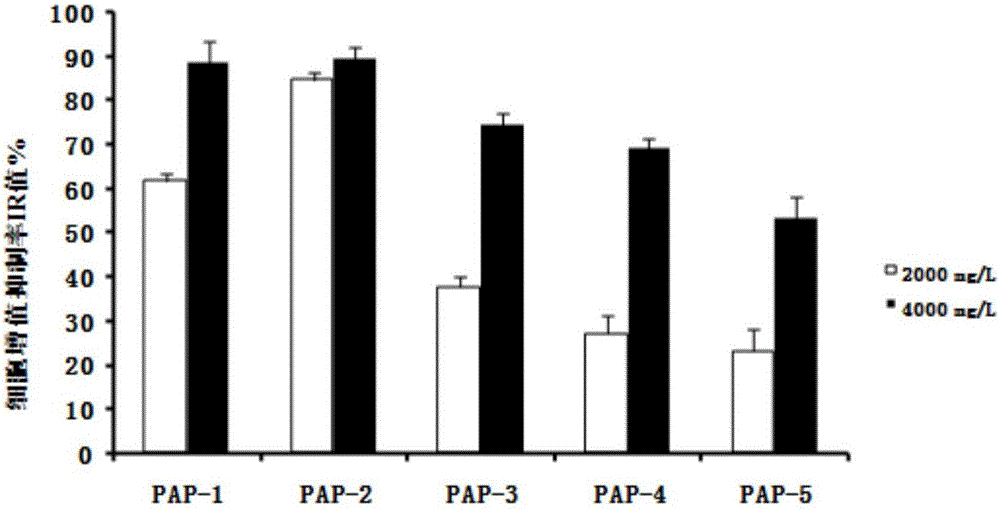
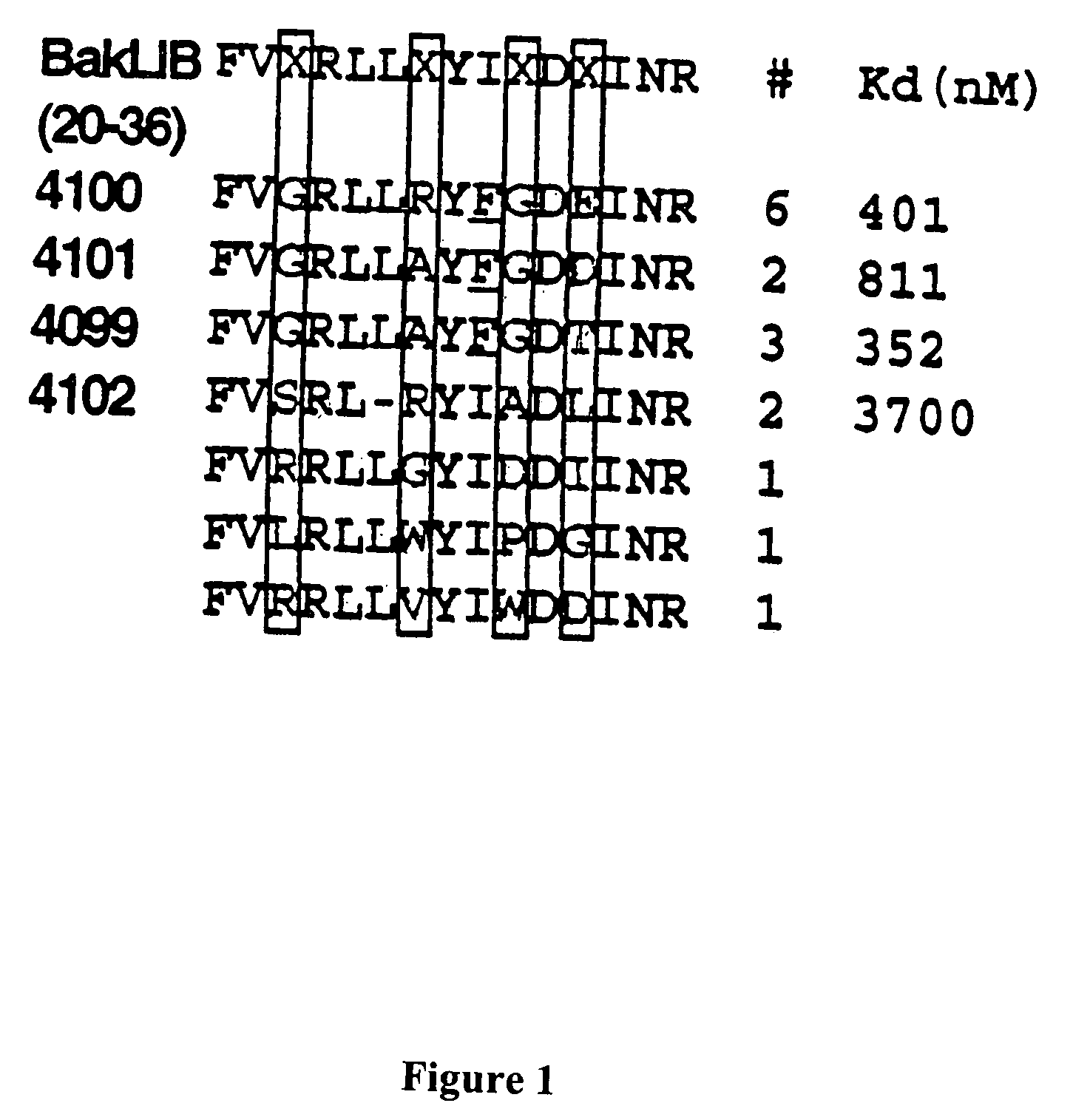
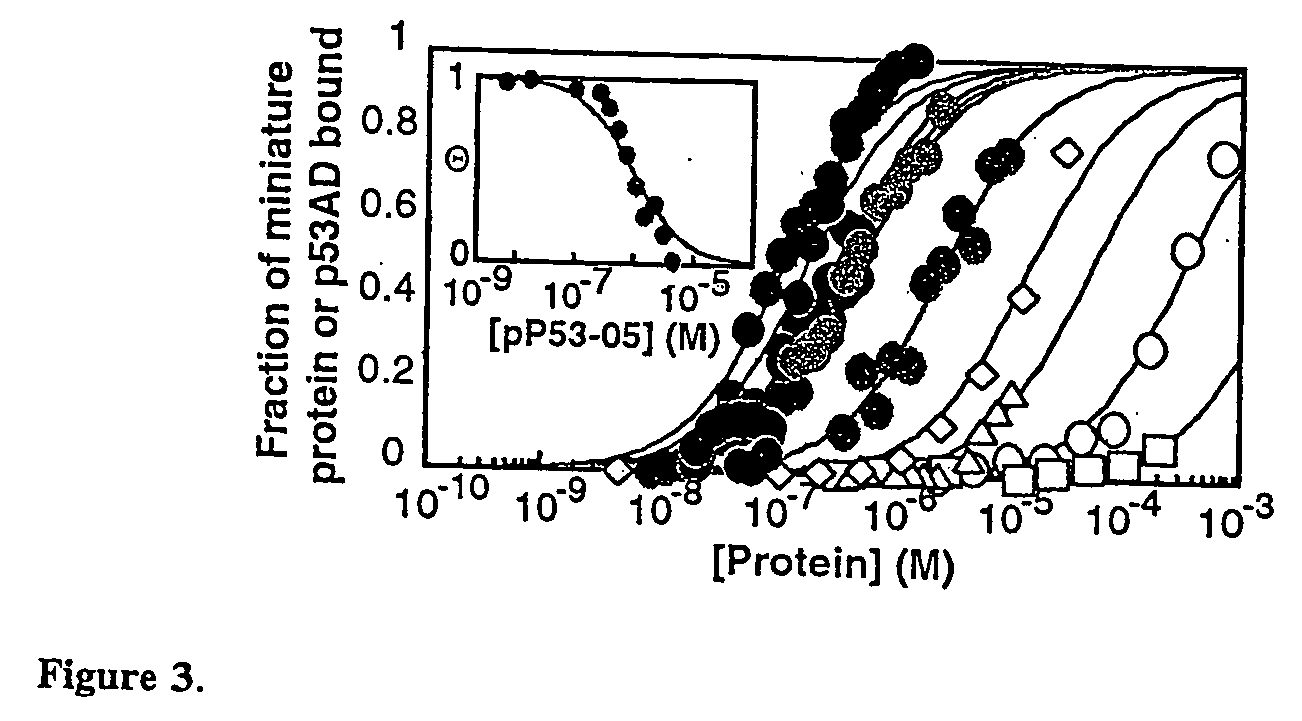
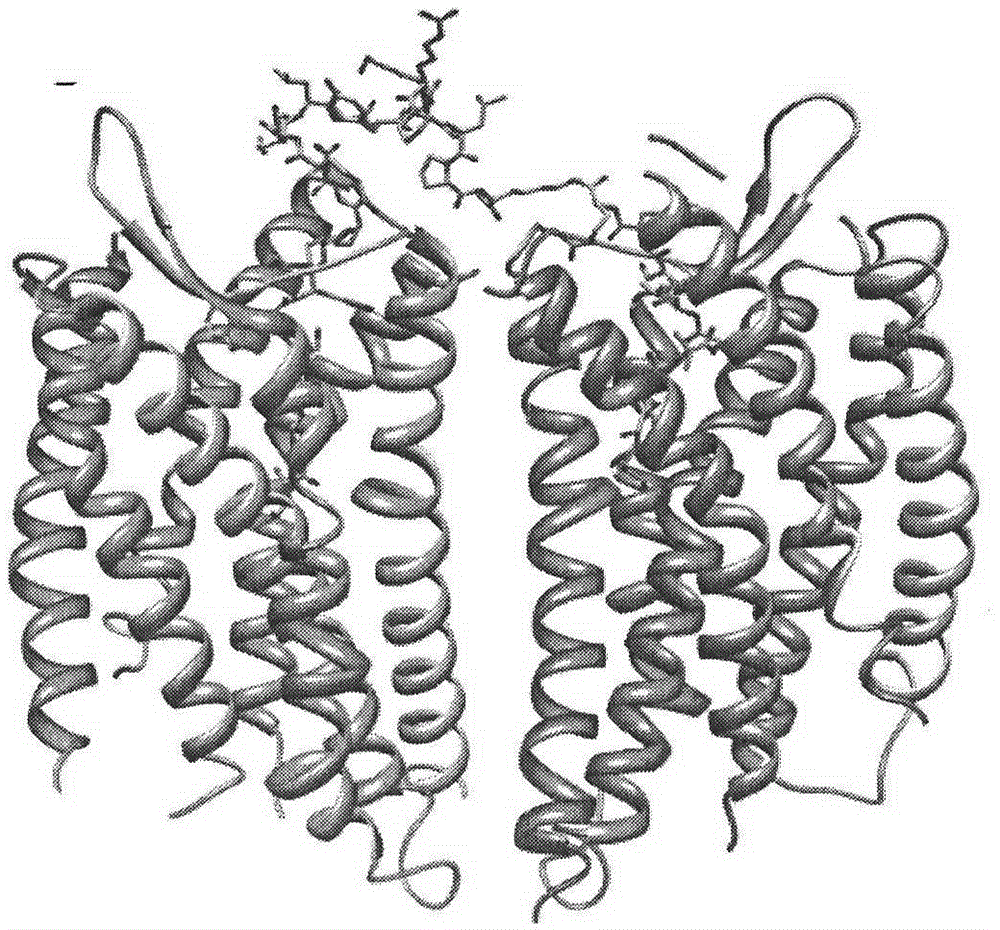
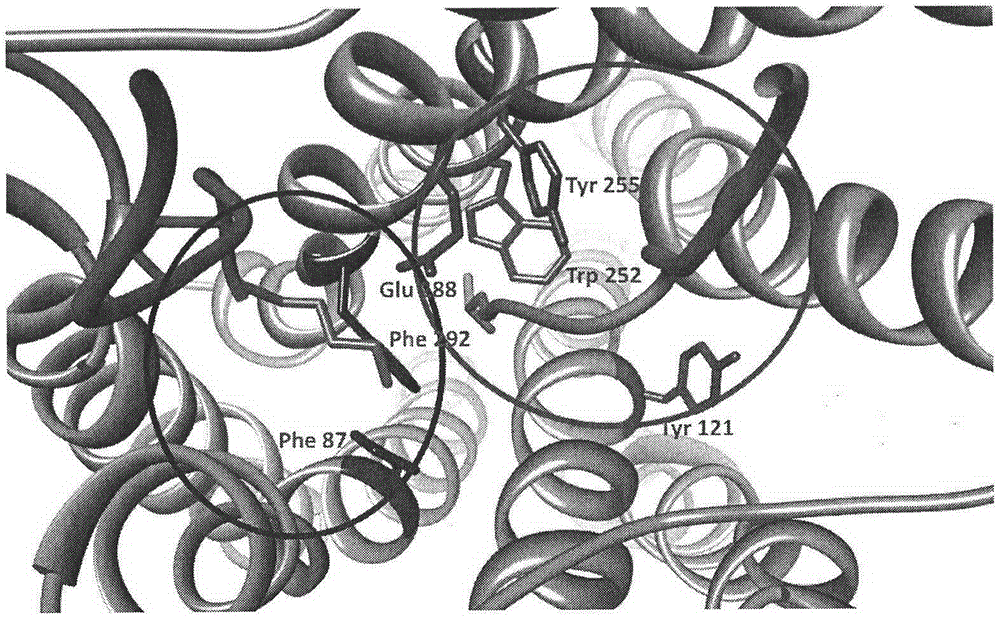
Modified avian pancreatic polypeptide miniature binding proteins
The present invention provides a protein scaffold, such as an avian pancreatic polypeptide, that can be modified by substitution of two or more amino acid residues that are exposed on the alpha helix domain of the polypeptide when the polypeptide is in a tertiary form.
Owner:YALE UNIV
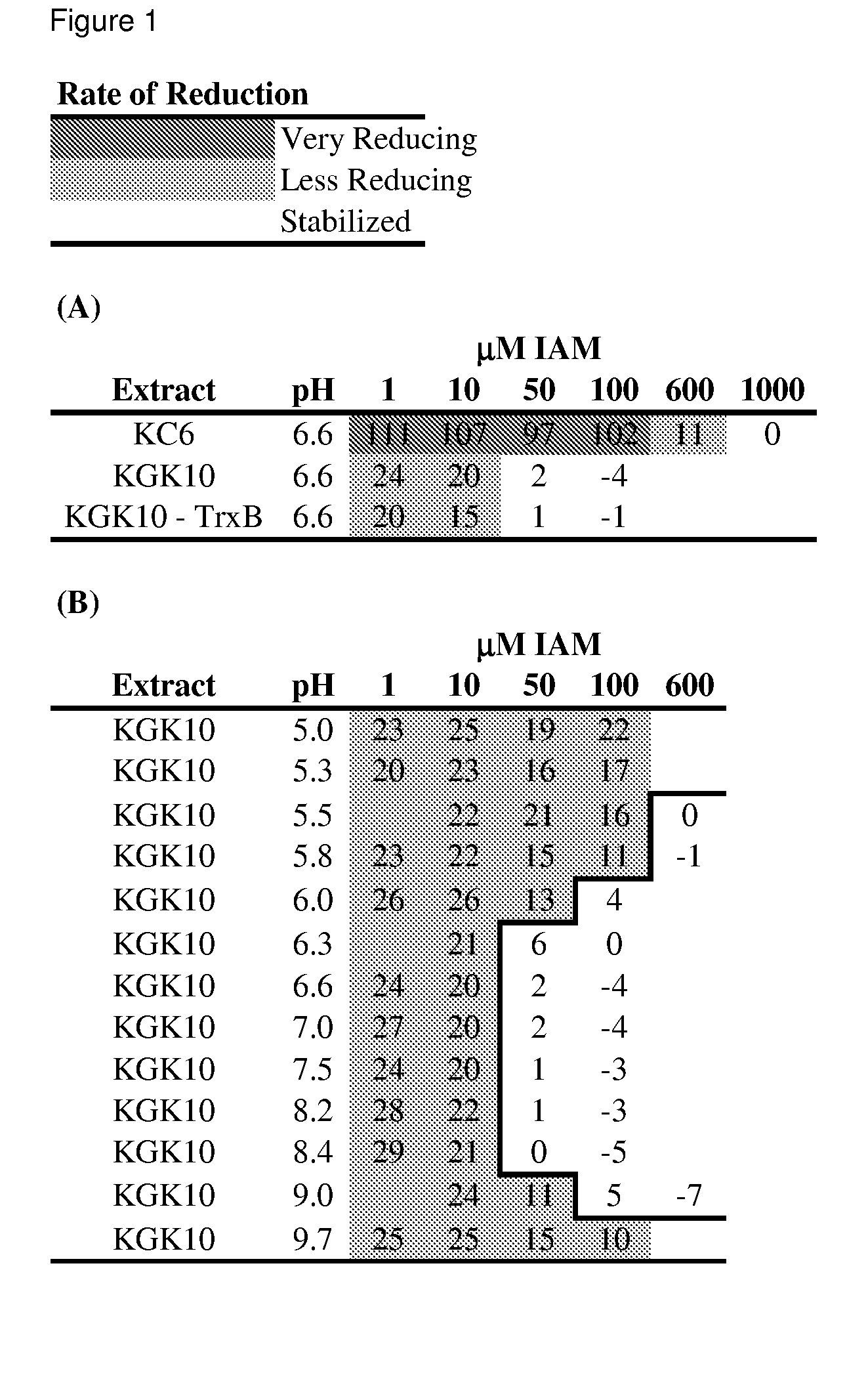
Enhanced cell-free synthesis of active proteins containing disulfide bonds
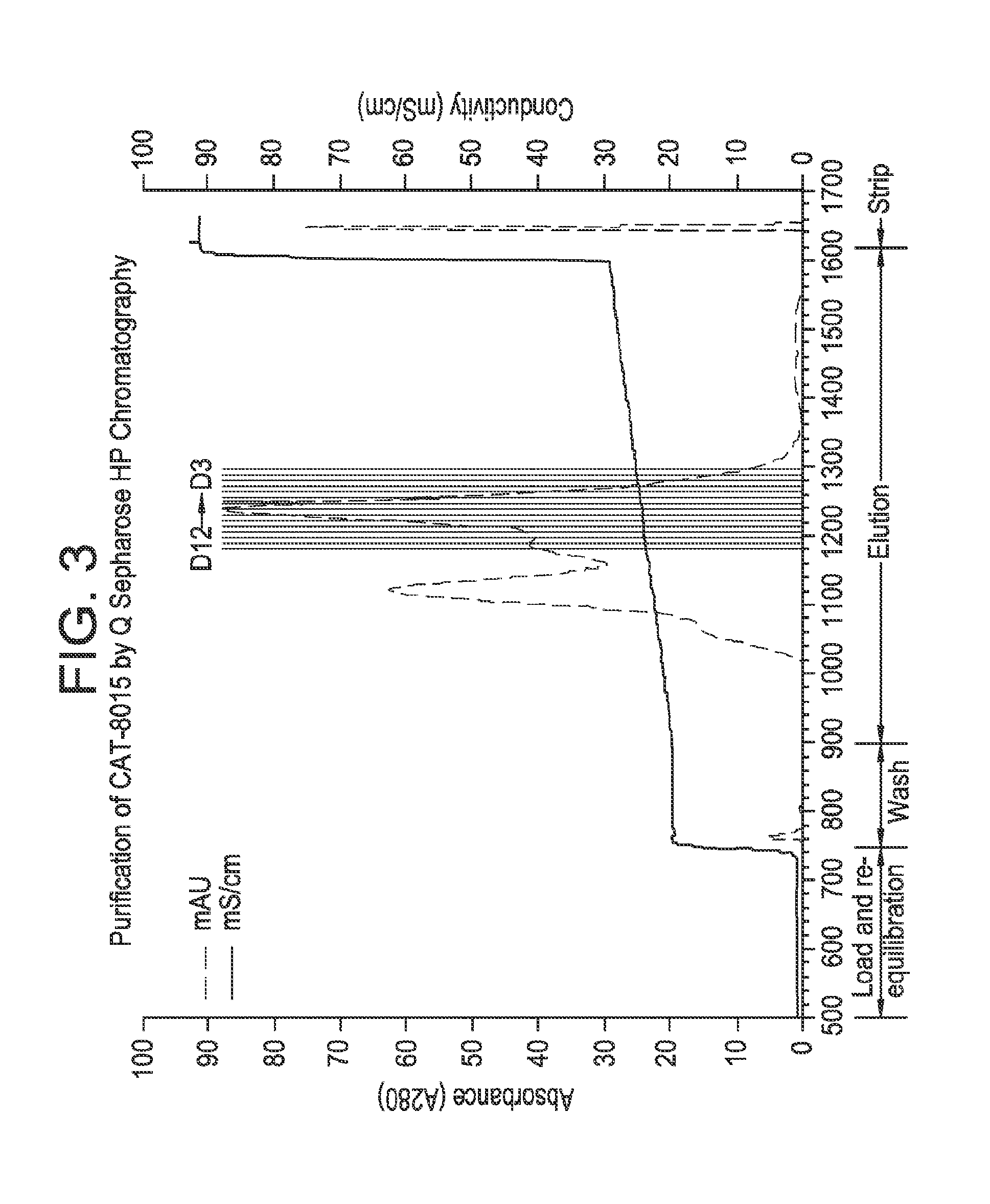
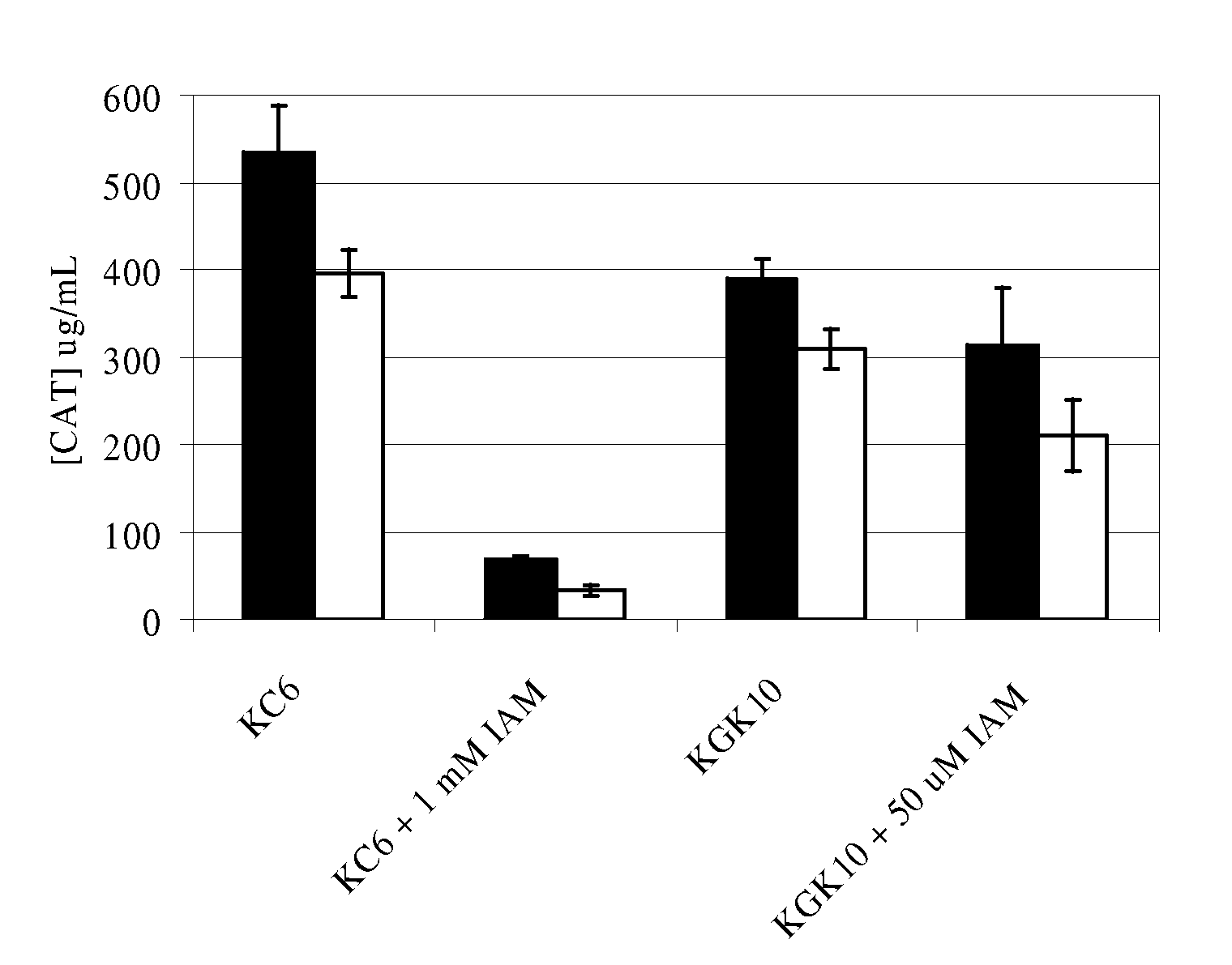
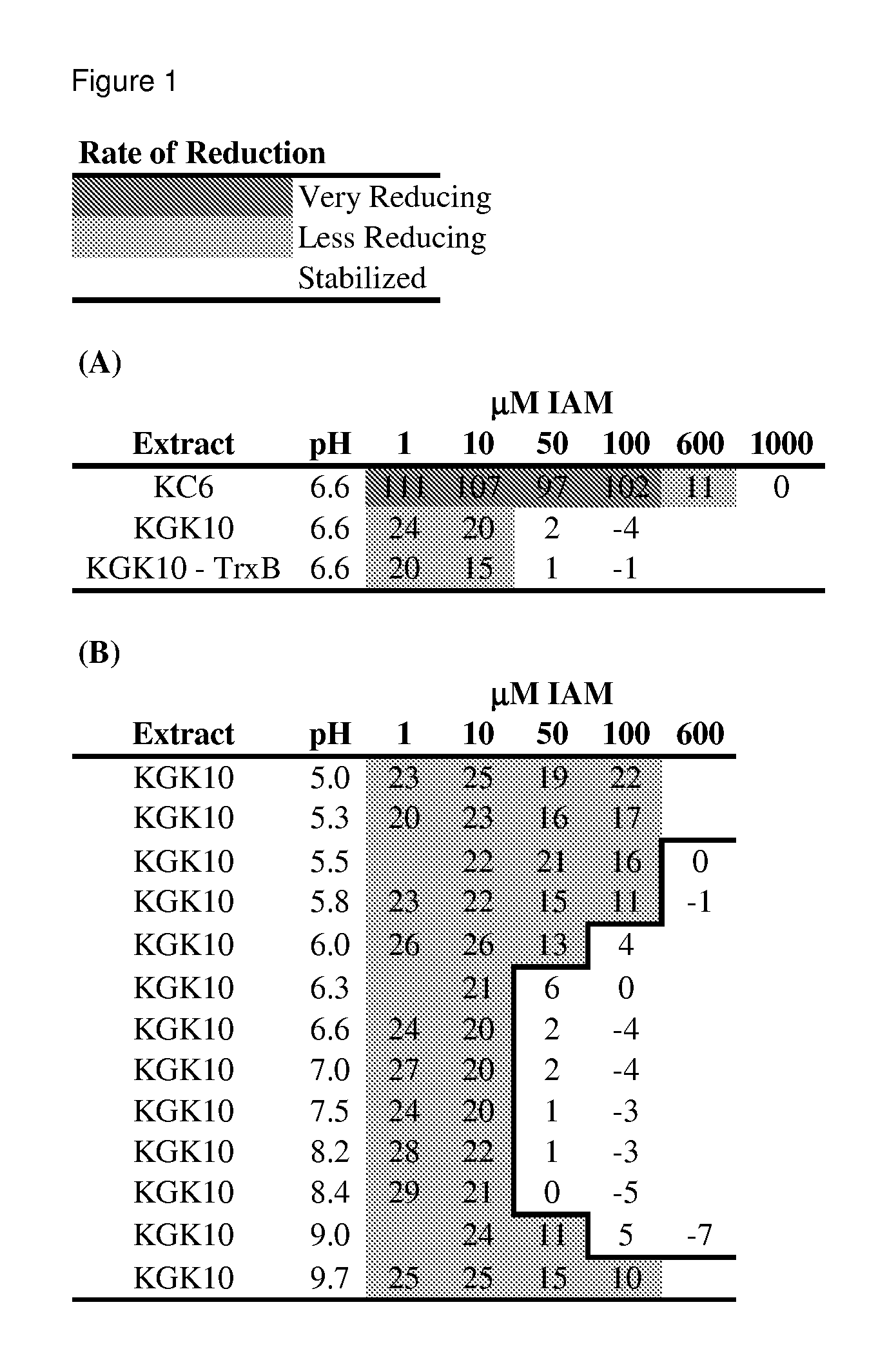
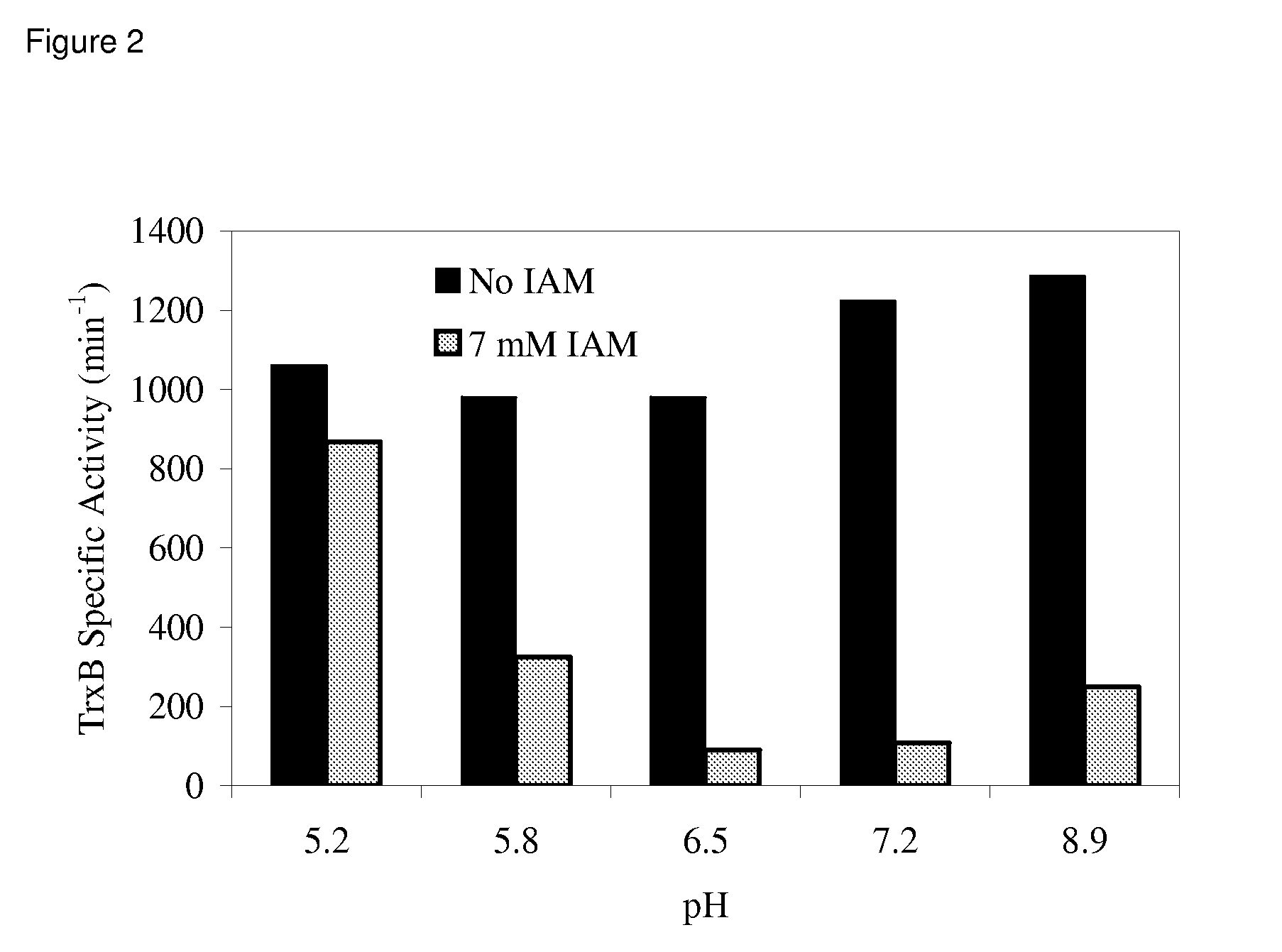
ActiveUS7871794B2Improve bindingLow costDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsCell freeActive protein
Compositions and methods are provided for the enhanced in vitro synthesis of active polypeptides containing disulfide bonds. In certain embodiments of the invention, the reaction mix includes a biological extract derived from a bacterial cell in which the glutathione reductase gene has been inactivated, which is pre-treated with a low concentration of a sulfhydryl inactivating agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for purifying active polypeptides or immunoconjugates
ActiveUS20130202626A1Chromatographic anion exchangersInorganic non-active ingredientsAnion-exchange chromatographyAnion Exchange Proteins
The present invention provides methods for isolating an active polypeptide or immunoconjugate by purification of a solution containing both the active polypeptide or immunoconjugate and an acidic variant thereof, such as a deamidated variant, using anion exchange chromatography.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
Enhanced cell-free synthesis of active proteins containing disulfide bonds
ActiveUS20080248521A1Stabilizing redox potentialAccelerate rate-limiting covalent stepPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesCell freeActive protein
Compositions and methods are provided for the enhanced in vitro synthesis of active polypeptides containing disulfide bonds. In certain embodiments of the invention, the reaction mix includes a biological extract derived from a bacterial cell in which the glutathione reductase gene has been inactivated, which is pre-treated with a low concentration of a sulfhydryl inactivating agent.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
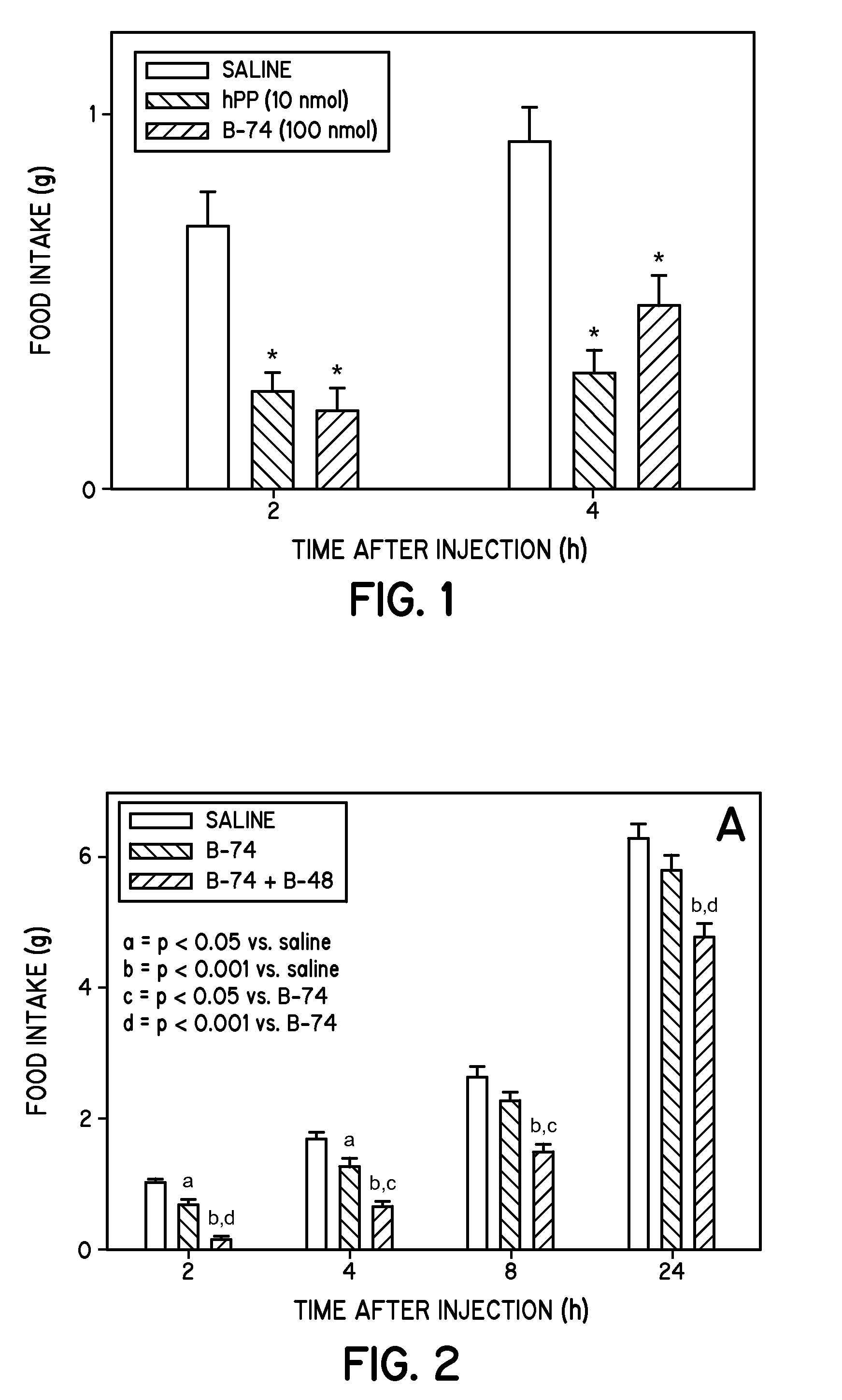
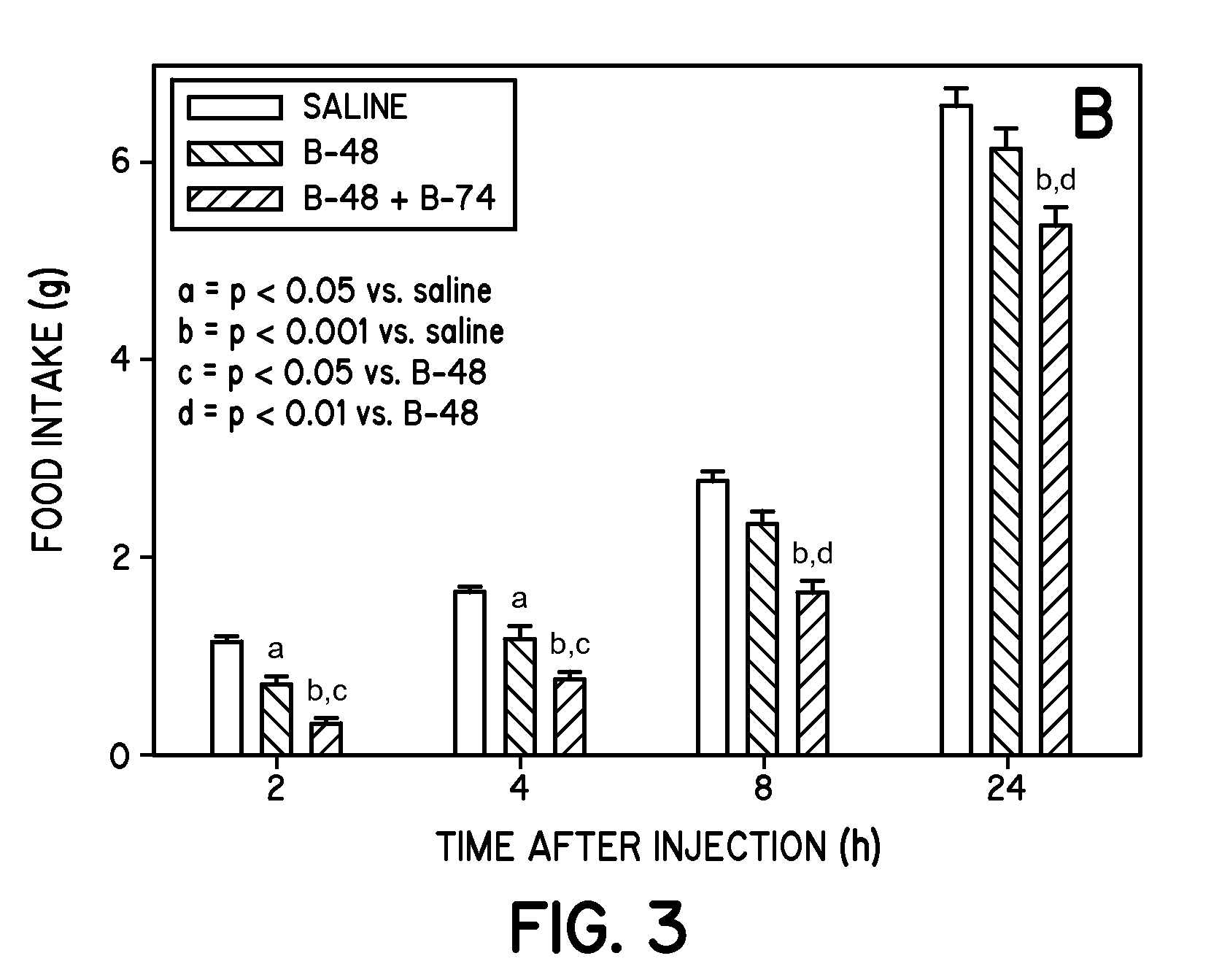
Compounds for control of appetite
ActiveUS20090227519A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPancreatic polypeptidomaPancreatic stent
This invention relates generally to neuropeptide Y (“NPY”) Y4 receptor agonists including pancreatic polypeptide (PP), analogs thereof, and peptide fragments of PP, e.g. PP(32-36), and analogs thereof to pharmaceutical compositions containing such Y4 receptor agonists, and to methods for treatment of mammals using the same. The NPY Y4 receptor agonists may be administered to mammals either alone or in combination with NPY Y2 receptor agonists including peptide (PYY) (3-36), analogs thereof and to peptide fragments of PYY(3-36), e.g. PYY(22-36) and PYY(25-36), and analogs thereof such as to control food intake in mammals, blood pressure, cardiovascular response, libido, circadian rhythm, hyperlipidimia, chronic pancreatitis, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease including nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Preparation method of Nereis succinea anti-lung-cancer polypeptides
ActiveCN106755230AStrong growth inhibitory effectGood medical application valuePeptide preparation methodsFermentationUltrafiltrationAnion-exchange chromatography
The invention discloses a preparation method of Nereis succinea anti-lung-cancer polypeptides. The method comprises the following steps: (1) sample pretreatment; (2) enzymolysis; (3) ultrafiltration; (4) anion exchange chromatography; (5) SephadexG25 gel chromatography; and (6) high performance liquid chromatography separation purification, thereby finally obtaining the Nereis succinea anti-lung-cancer polypeptides. The method has the advantages of high safety, mild reaction conditions and controllable process. The Nereis succinea anti-lung-cancer polypeptides have high purity, have obvious proliferation inhibiting actions on lung cancer cells A549 and H1299, and have favorable medical application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Protein binding miniature proteins
InactiveUS20050287542A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPancreatic polypeptidomaAlpha helix
The present invention provides a protein scaffold, such as an avian pancreatic polypeptide, that can be modified by substitution of two or more amino acid residues that are exposed on the alpha helix domain of the polypeptide when the polypeptide is in a tertiary form.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Preparation method of half pea polypeptide of chickpea and application thereof
ActiveCN107988301ARetain biological activityImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsFood additiveNeutral protease
The invention relates to a preparation method of half pea polypeptide of chickpea and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of fully degreasing the grease componentin the pea half of the chickpea, extracting by a phosphate buffer solution, hydrolyzing by neutral protease, alkaline protease, trypsin or papain, and adopting an ultrafiltration membrane technique to prepare the polypeptide with molecular weight of 6 to 10kDa, 3.5 to 6kDa and 1 to 3.5kDa; spray-drying, or freeze-drying, so as to obtain the half pea polypeptide. The polypeptide powder has the advantages that the bacteria and fungi-resistant activity is realized, the broad microorganism-resistant activity is realized, the function of enhancing the immunity of body liquid and whole body is realized, and the polypeptide and protein from pure natural plants which can be easily digested and absorbed by a human body are contained. The protein has the characteristics that the original biologicalactivity of the chickpea is reserved, the waste is changed into the valuable, and the resources can be fully utilized; the protein is used as a natural antibacterial agent, a food additive or a medicine, and can be applied to food and medicine industries.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Interest protein preparation method and purpose thereof
ActiveCN103131713AHigh expressionEasy to purifyNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideHydroxylamine Hydrochloride
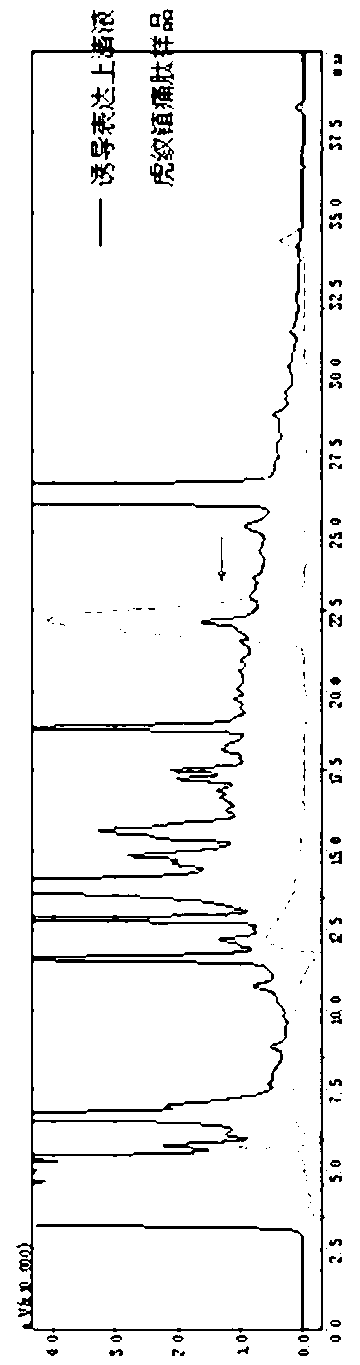
The invention relates to an interest protein preparation method and a purpose of the interest protein preparation method. The interest protein preparation method comprises the steps of obtaining interest protein nucleotide sequence fragments, constructing interest protein recombinant expression vectors, expressing interest protein in an inducible mode, purifying the interest protein and cutting purified products. The fronts of the interest protein nucleotide sequence fragments are inserted into monomer cutting recognition sites. Preferably, the upper streams of the interest protein nucleotide sequence fragments are introduced into kex2 enzyme cutting sites, and the down streams of the interest protein nucleotide sequence fragments are introduced into hydroxylamine hydrochloride enzyme cutting sites. The interest protein is obtained through sequence of event (SOE) technology, and is introduced into monomer cutting recognition sites through primers. The interest protein can be human nerve growth factors such as thymosin, tiger stripe pancreatic polypeptide and tiger stripe analgesic peptide. By adopting the interest protein preparation method, obtained interest protein is high in expression quality and easy to purify. Genetic expression products are interest protein monomer, no extra amino acid residue is carried, and thus not only is the good biology activity of interest protein products ensured, but also multicopy cutting cost is saved, the purification is simple and the mass production is facilitated.
Owner:SINOBIOWAY BIOMEDICINE
Anti-herpes simplex virus (HSV) active polypeptide of Tibetan Pi scorpion and application thereof
InactiveCN102382839AEffective treatmentThe effect is obviousPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismChemical synthesisMedicine
The invention discloses an anti-HSV active polypeptide of Tibetan Pi scorpion and application thereof. According to the invention, through the methods of molecular biology and chemical synthesis, the anti-HSV active polypeptide of Tibetan Pi scorpion, AHSVP1, is obtained; the antiviral activity of AHSVP1 to HSV is determined by using the method of plaque array. The invention also discloses externally used anti-HSV gel which is prepared from 0.5 wt % of the medicine AHSVP1 and 1.5 wt % of a carboxymethylcellulose matrix. The gel provided in the invention is used for anti-HSV infection; the products of the gel are stable and are suitable for storing and transporting. A production process for the gel has the advantages of simple and reasonable design, low production cost and suitability for mass industrial production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Clean preparation method for plant polypeptide/protein
ActiveCN105907826AImprove qualityEffective controlPeptide preparation methodsFermentationSolubilityNeutral protease
The invention discloses a clean preparation method for plant polypeptide / protein with a controllable molecular weight interval. The method comprises the following steps of 1, pretreatment of raw materials; 2, pulp mixing; 3, extraction and separation; 4, purification to obtain protein liquid; 5, enzymolysis, wherein the protein liquid is heated for denaturation, Na2SO3 is added, then protease is added, and protease is selected from Alcalase, neutral protease AS1398, pepsin and papain; 6, debittering of polypeptide; 7, separation through a nanofiltration membrane to obtain a polypeptide solution; 8, drying and dewatering to obtain the polypeptide product. The product prepared through the method has the controllable molecular weight interval and the advantages of high solubility, low viscosity, acid soluble stability, low bitterness and the like. The product can be widely applied to food, sport food, curative healthcare food, protein drinks, diet food and novel fermented food.
Owner:SHANDONG BOAOKE BIOTECH
Active polypeptide with function of antagonizing chemokine receptor CXCR4 as well as design preparation and biomedical application of active polypeptide
ActiveCN104892744AImprove binding efficiencyRole of the strong anti-chemokine receptor CXCR4Peptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsDiseaseMyeloid leukemia
The invention discloses an active polypeptide designed to have a natural chemotactic factor N-end region. The active polypeptide inhibits HIV-1 from invading and infecting cells by antagonizing the activity of the chemokine receptor. The invention further discloses a design method for the active polypeptide. According to molecular dynamic simulation, an appropriate connecting bridge is designed for connecting two polypeptide fragments, so that the polypeptide synthesis sequence is determined, the polypeptide is synthesized in a solid-phase mode, and finally the biologic activity of the active polypeptide is tested. The active polypeptide disclosed by the invention can be used as a CXCR4 receptor antagonist, a precursor medicine for treating AIDS and a stem cell mobilizer, and is used for treating acute myeloid leukemia and various CXCR4-associated diseases.
Owner:徐岩 +1
High throughput screen for biologically active polypeptides
InactiveUS9701959B2Deficiency in polypeptide screening systemsImprove efficiencyDNA preparationEmulsionDrug biological activity
Methods for screening libraries of polypeptides for biologically activity on cells. For example, polypeptides can be synthesized and encapsulated along with their coding sequences in microcapsules of an emulsion. Emulsion microcapsules can then be fused with microcapsules comprising test cells and biological activity on the cells is assessed to identify biologically active polypeptides and nucleic acid molecules encoding the same.
Owner:INVENRA INC
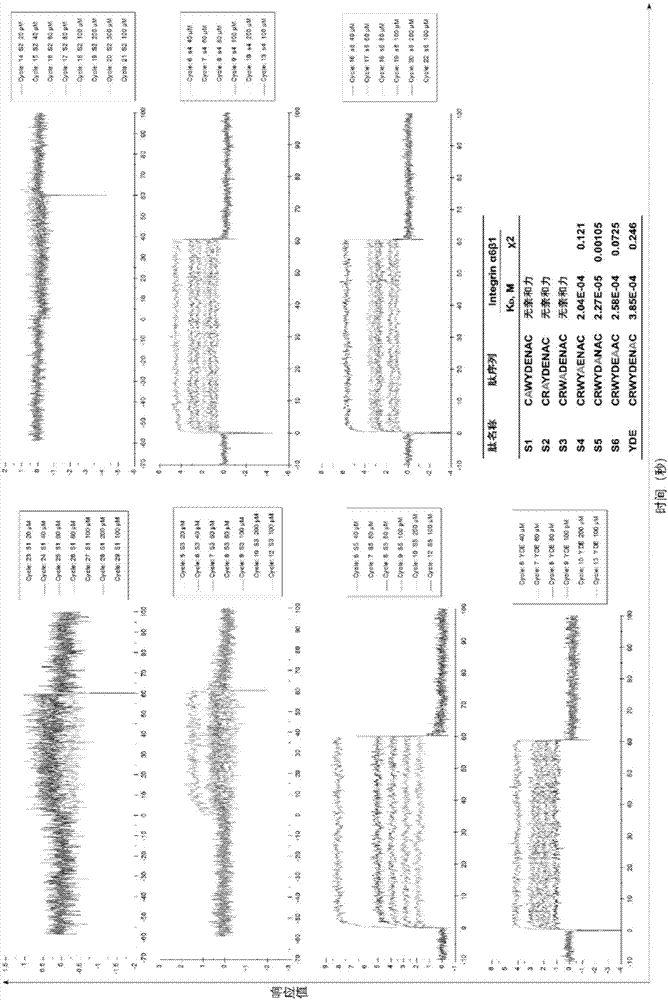
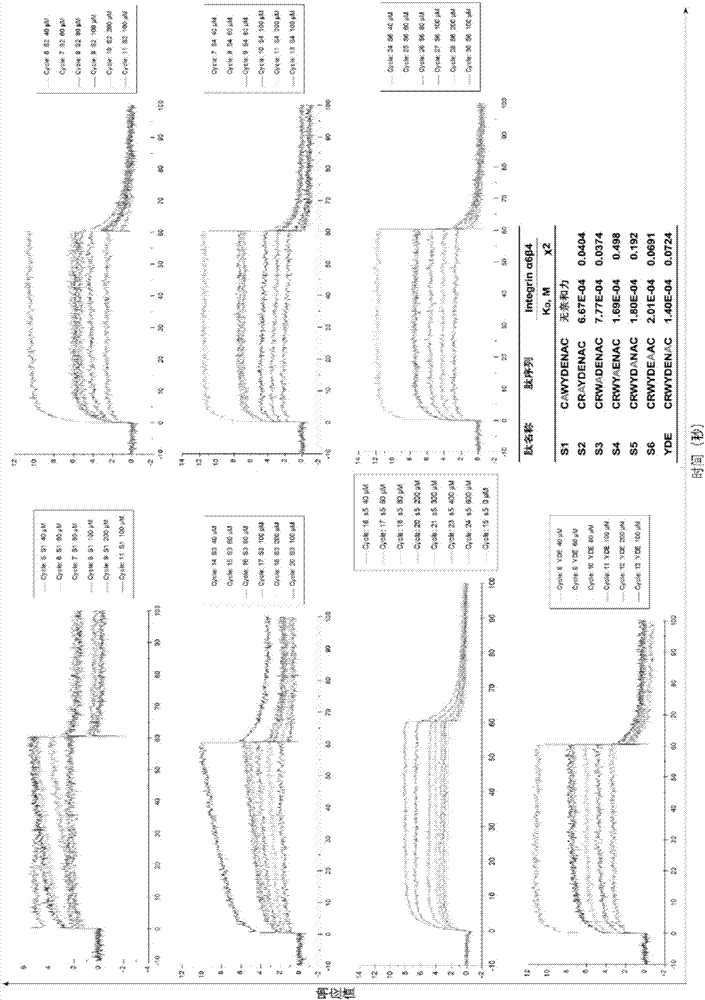
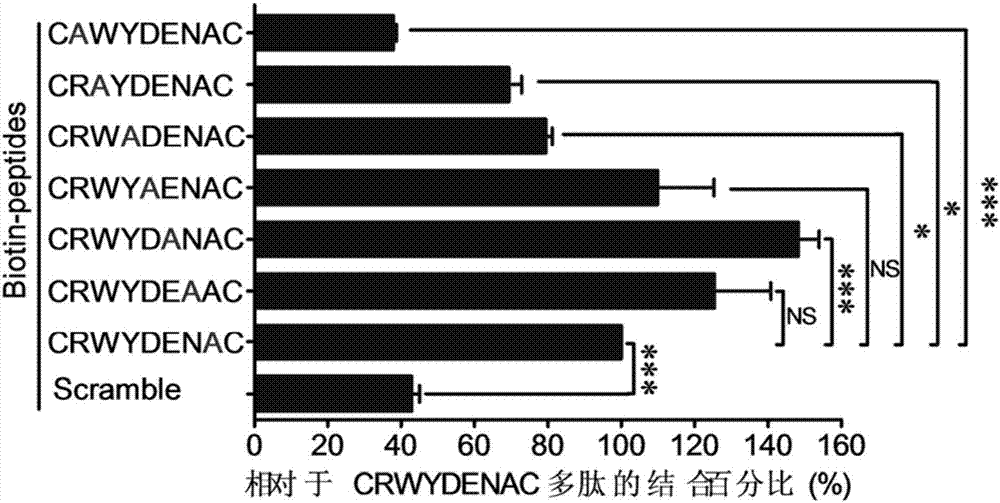
Integrin alpha 6 target polypeptide and application
ActiveCN107987127AHigh affinityMolecular Imaging RealizedRadioactive preparation carriersPeptidesMolecular imagingDisintegrin
The invention discloses integrin alpha 6 target polypeptide and application, and the sequence motif of the polypeptide is RWYXXXA. The integrin alpha 6 target polypeptide has very good affinity with integrin alpha 6, is relatively stable in vivo, and can serve as a target carrier. The integrin alpha 6 target polypeptide can be applied to molecular imaging of multiple kinds of integrin alpha 6 overexpression tumors, and has an important value in the molecular imaging of tumors. By coupling the polypeptide with a molecular imaging probe, the molecular imaging can be carried out on the multiple kinds of integrin alpha 6 overexpression tumors, and can be applied to diagnosis and screening of tumors very well.
Owner:广州珺柏诺医疗科技有限公司
Elastic polypeptide capable of improving fish intestine elasticity, fish intestines and preparation method thereof
PendingCN109912698APrevent oxidationIncrease elasticityDepsipeptidesSausage casingsIntestinal structureFishery
The invention discloses elastic polypeptide capable of improving fish intestine elasticity, fish intestines and a preparation method thereof. An amino acid sequence of the elastic polypeptide is VGVAPGAVALGILLGCASLAT, and the elastic polypeptide can remarkably improve elasticity of the fish intestines. The fish intestines comprise meat stuffing and casings, the meat stuffing comprises, by weight,65-70 parts of fish cream, 3-5 parts of chicken meat, 3-5 parts of lean fat, 3-5 parts of shrimp meat, 0.5-1 part of soybean isolate protein and 10-15 parts of elastic polypeptide, and the casings comprise 50-60 parts of algae vulcanized polysaccharide, 30-35 parts of tylorrhynchus extract, 10-25 parts of fish skin collagen and 30-35 parts of elastic polypeptide. The fish intestines prepared by the method are high in fish meat proportion and elasticity, nutritional and healthy. The casings are prepared by combining the tylorrhynchus extract and the elastic polypeptide with the collagen, thereby being high in elasticity, nutritional and healthy, so that the fish intestines are of higher popularization significance, and the preparation method is simple.
Owner:福建御冠食品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com