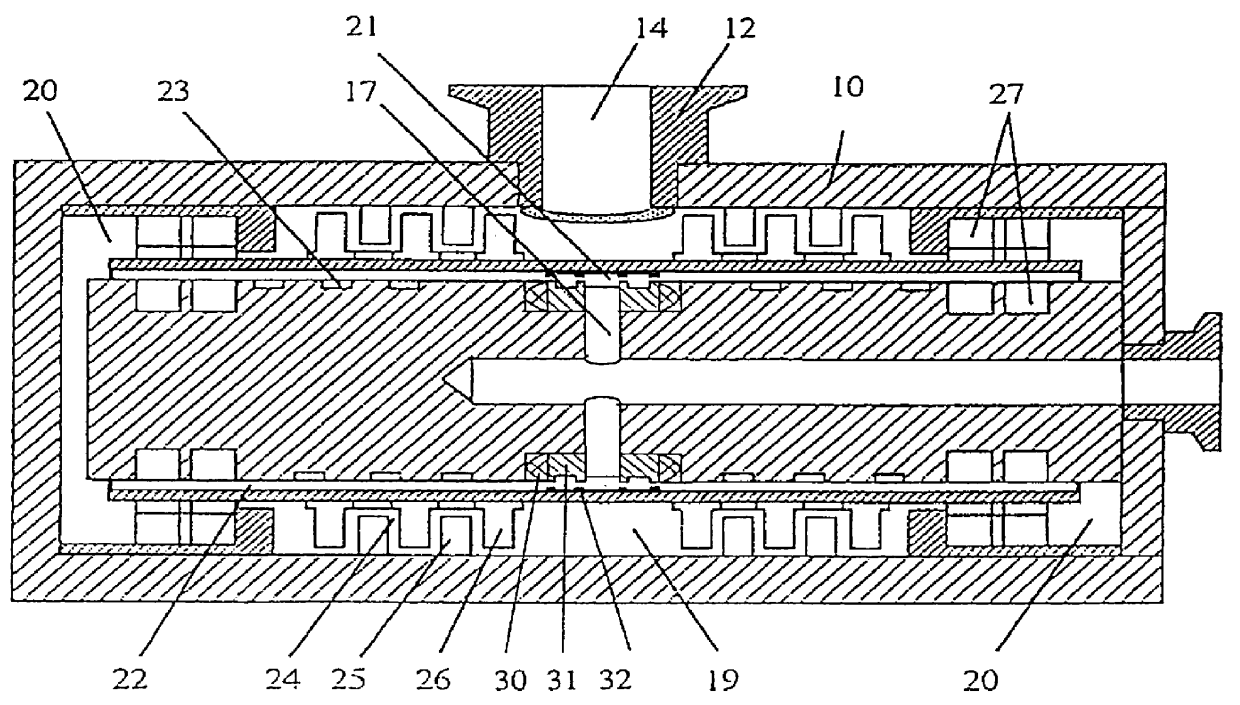
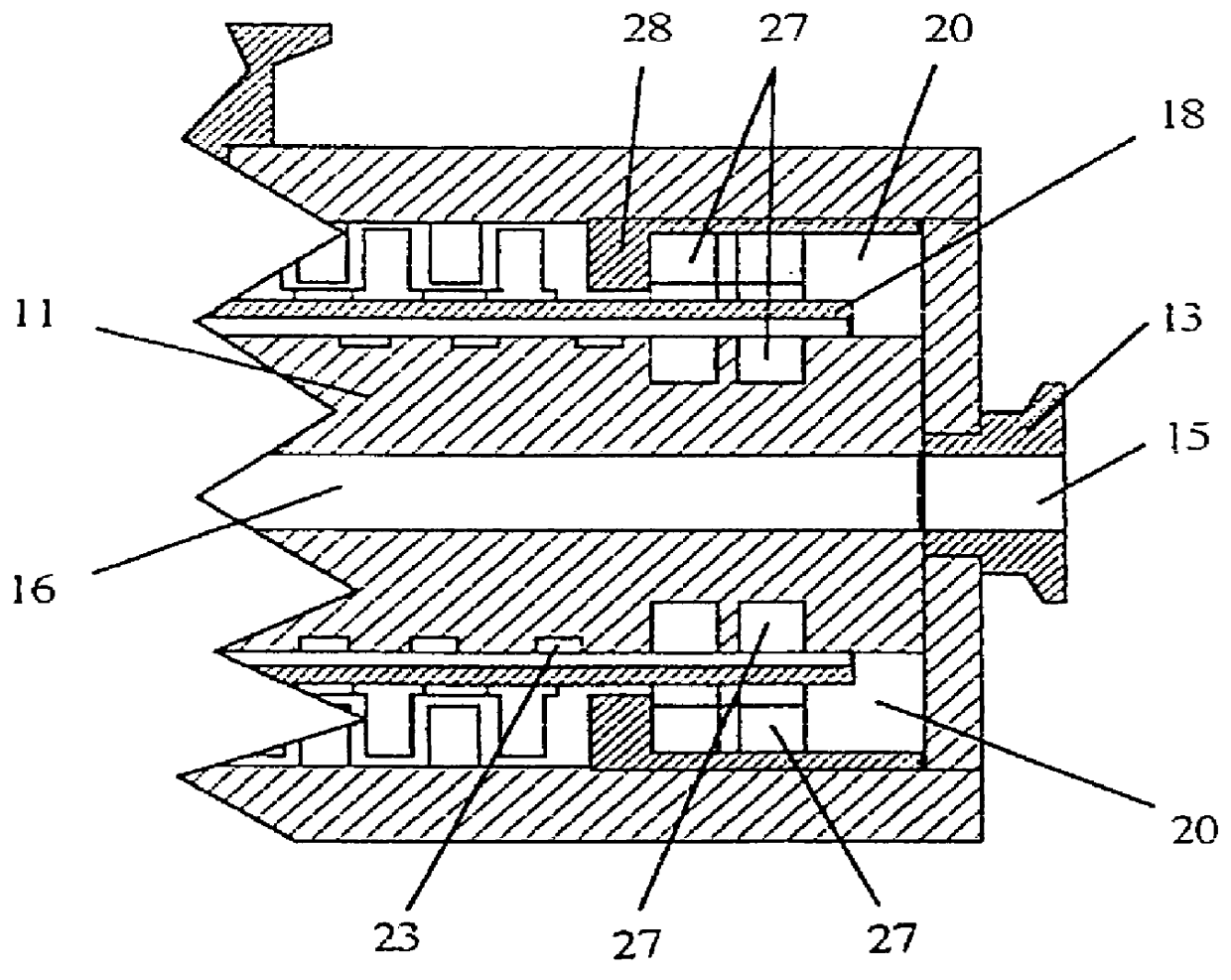
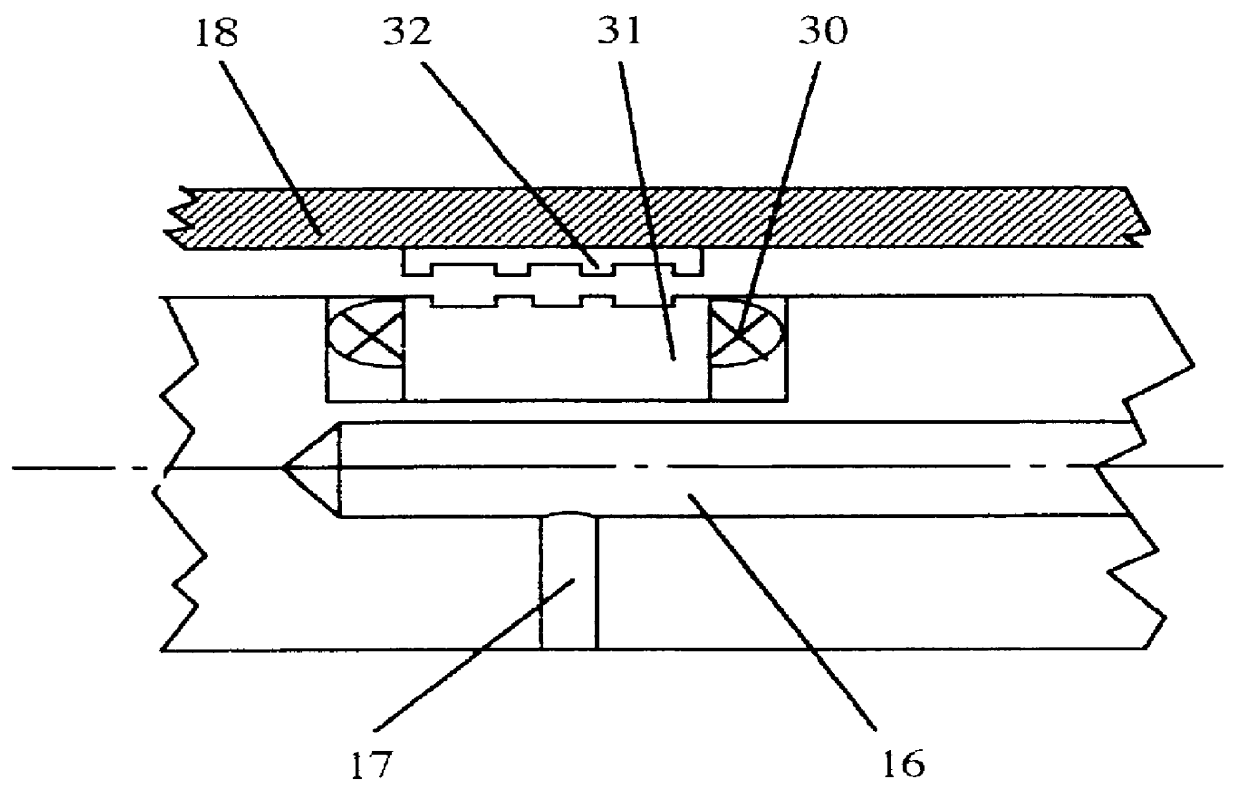
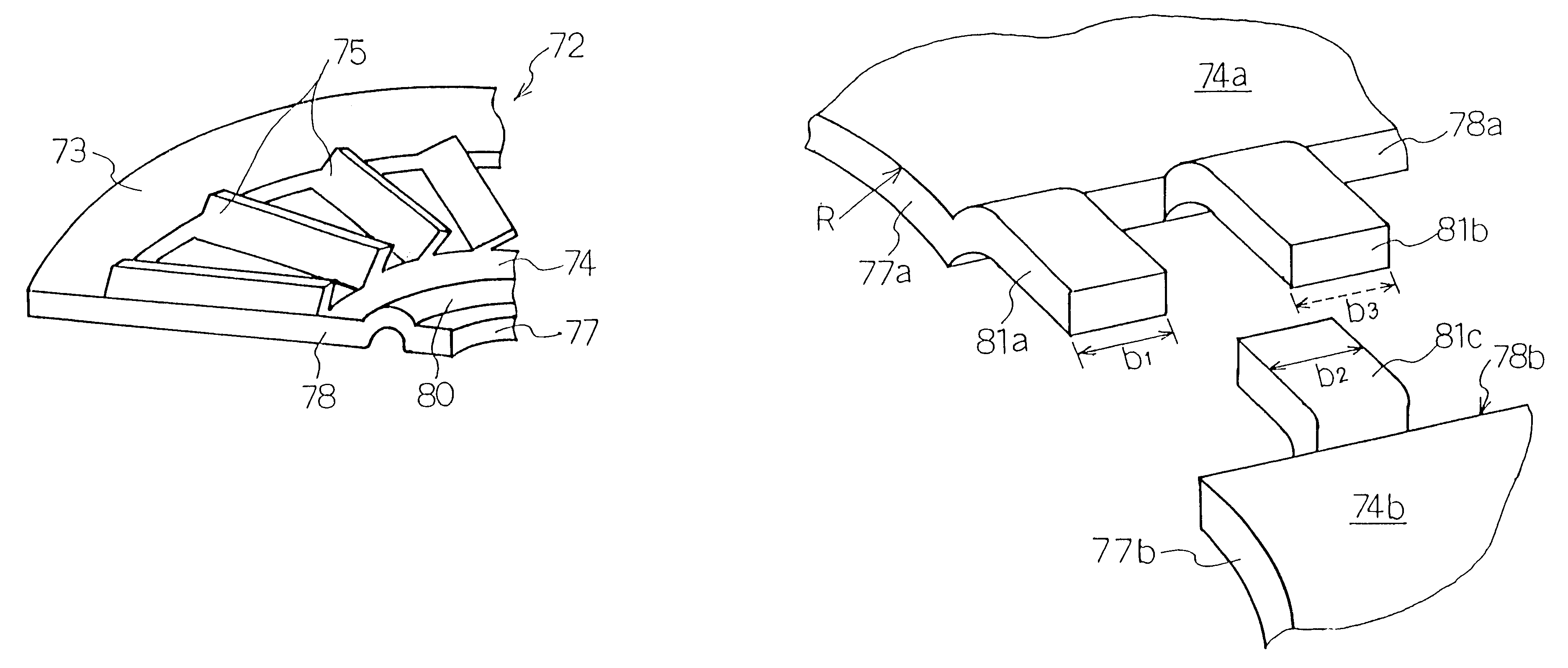
Patents
Literature
376 results about "Turbomolecular pump" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
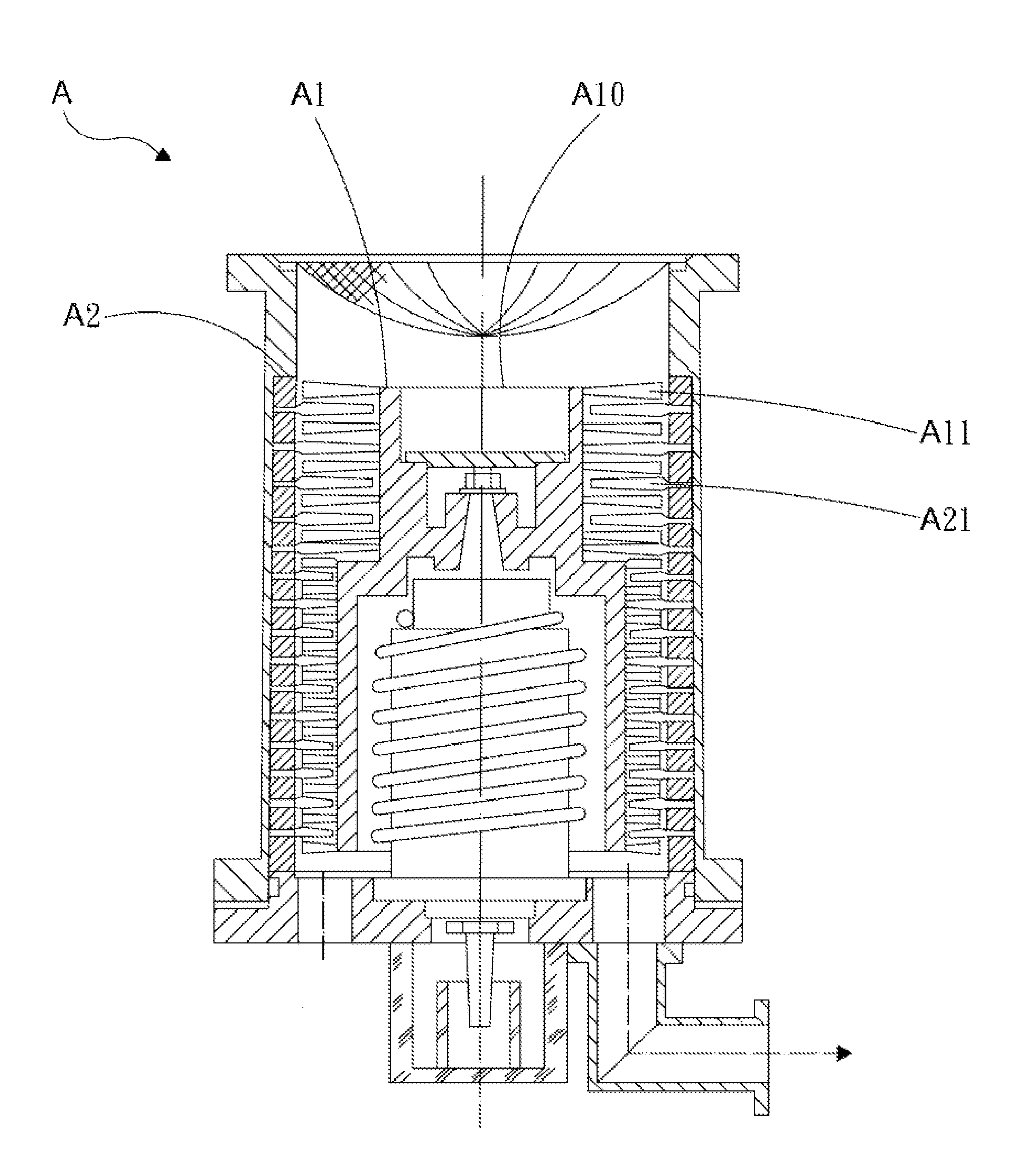
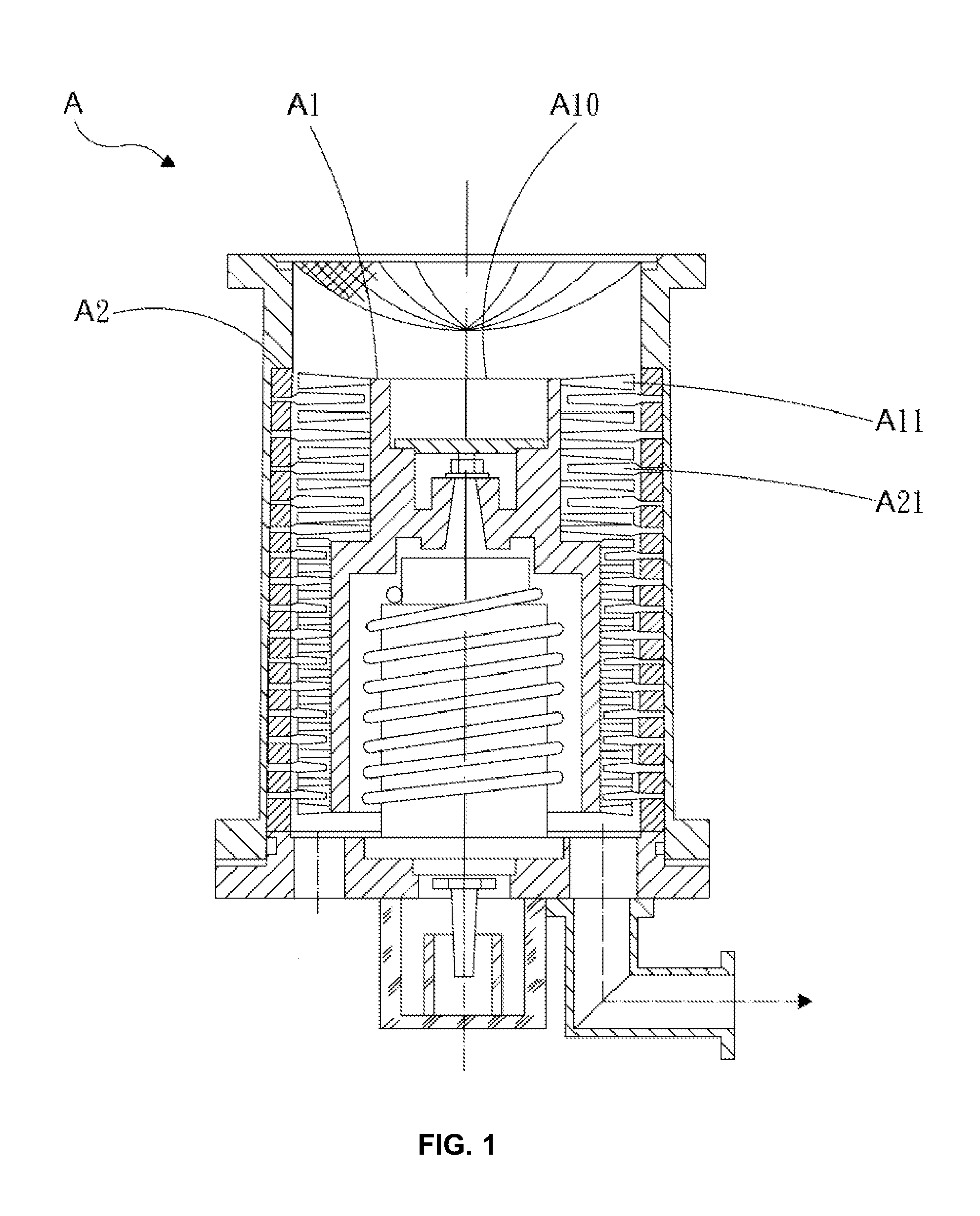
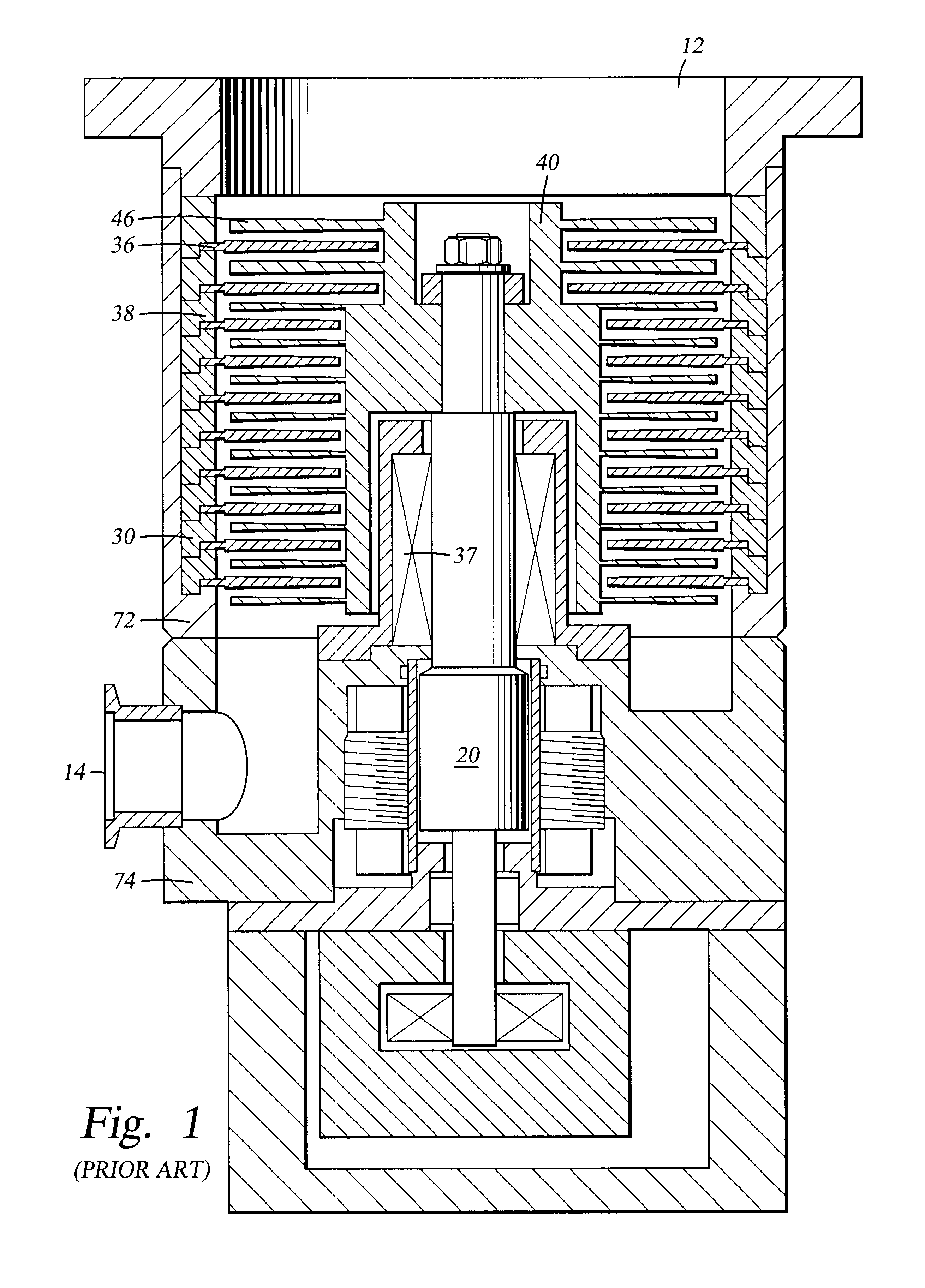
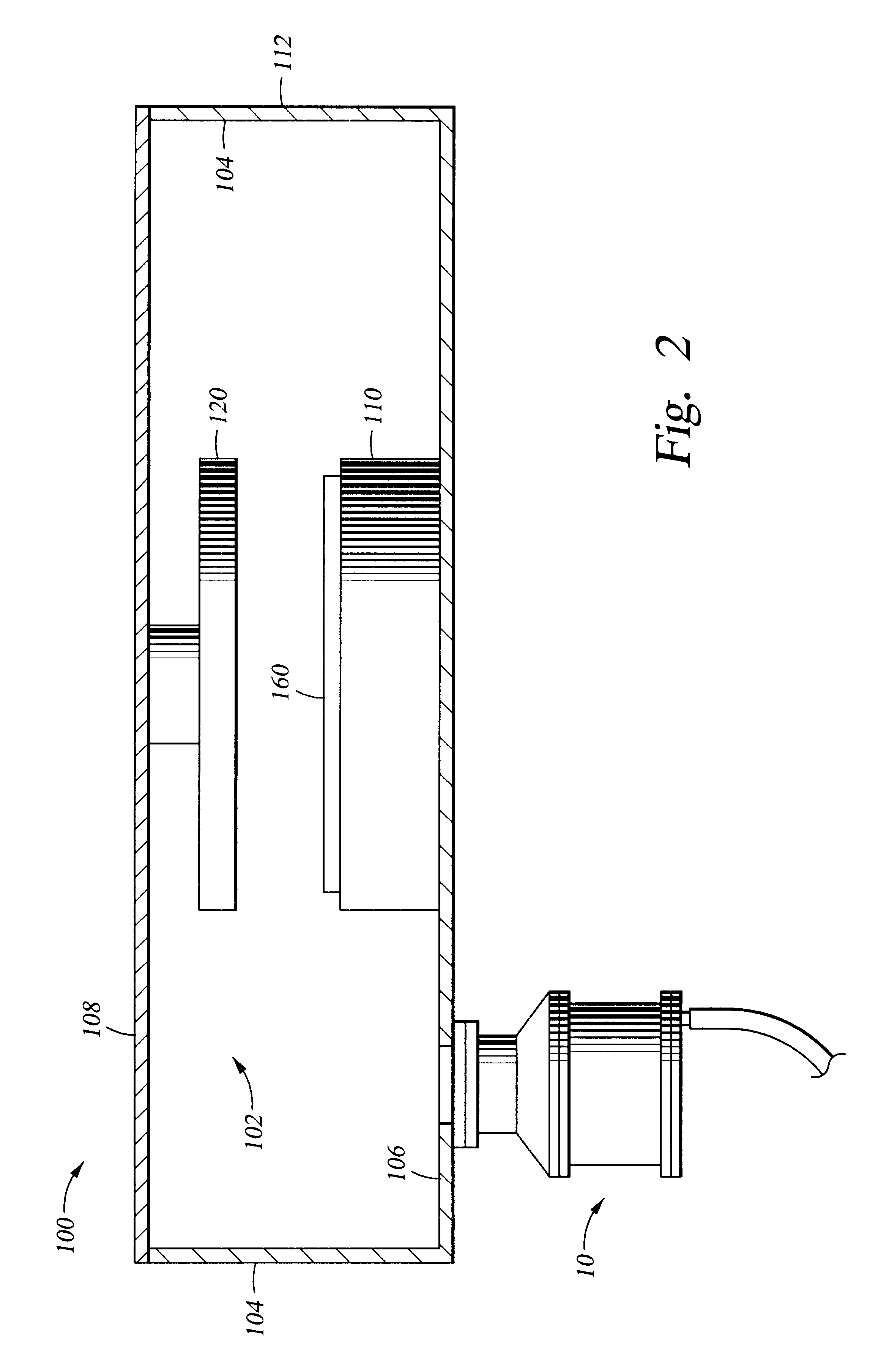
A turbomolecular pump is a type of vacuum pump, superficially similar to a turbopump, used to obtain and maintain high vacuum. These pumps work on the principle that gas molecules can be given momentum in a desired direction by repeated collision with a moving solid surface. In a turbomolecular pump, a rapidly spinning fan rotor 'hits' gas molecules from the inlet of the pump towards the exhaust in order to create or maintain a vacuum.
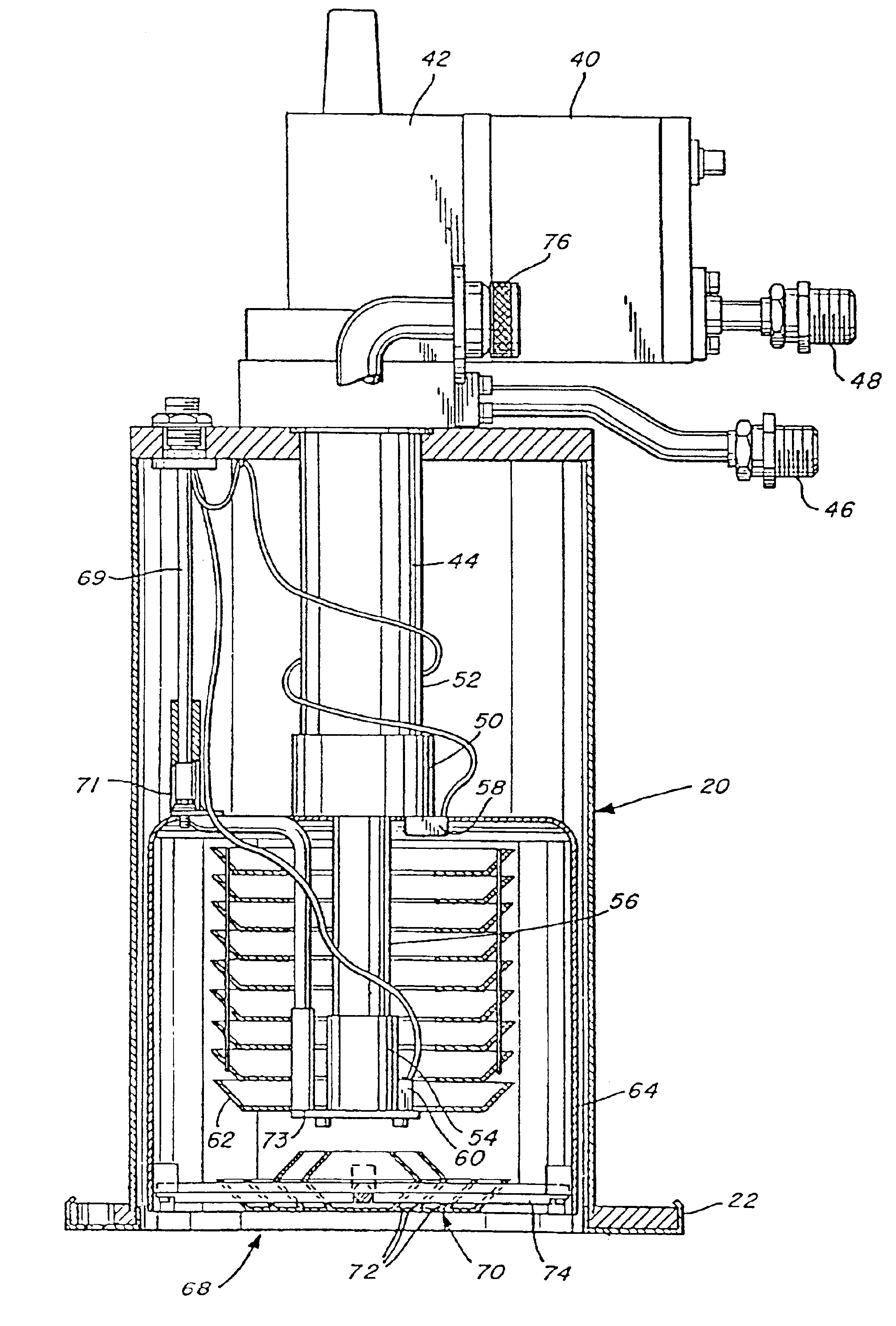
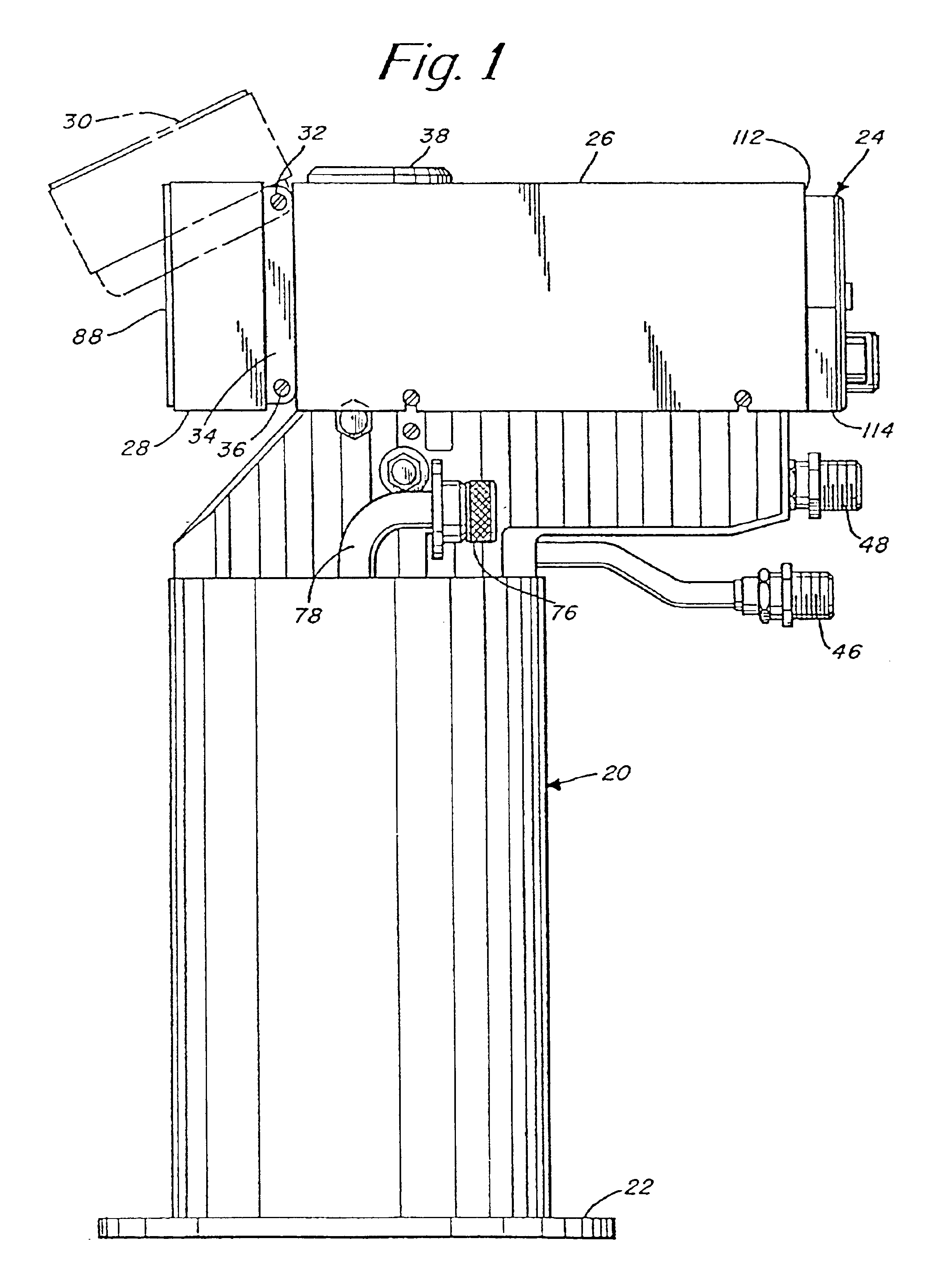
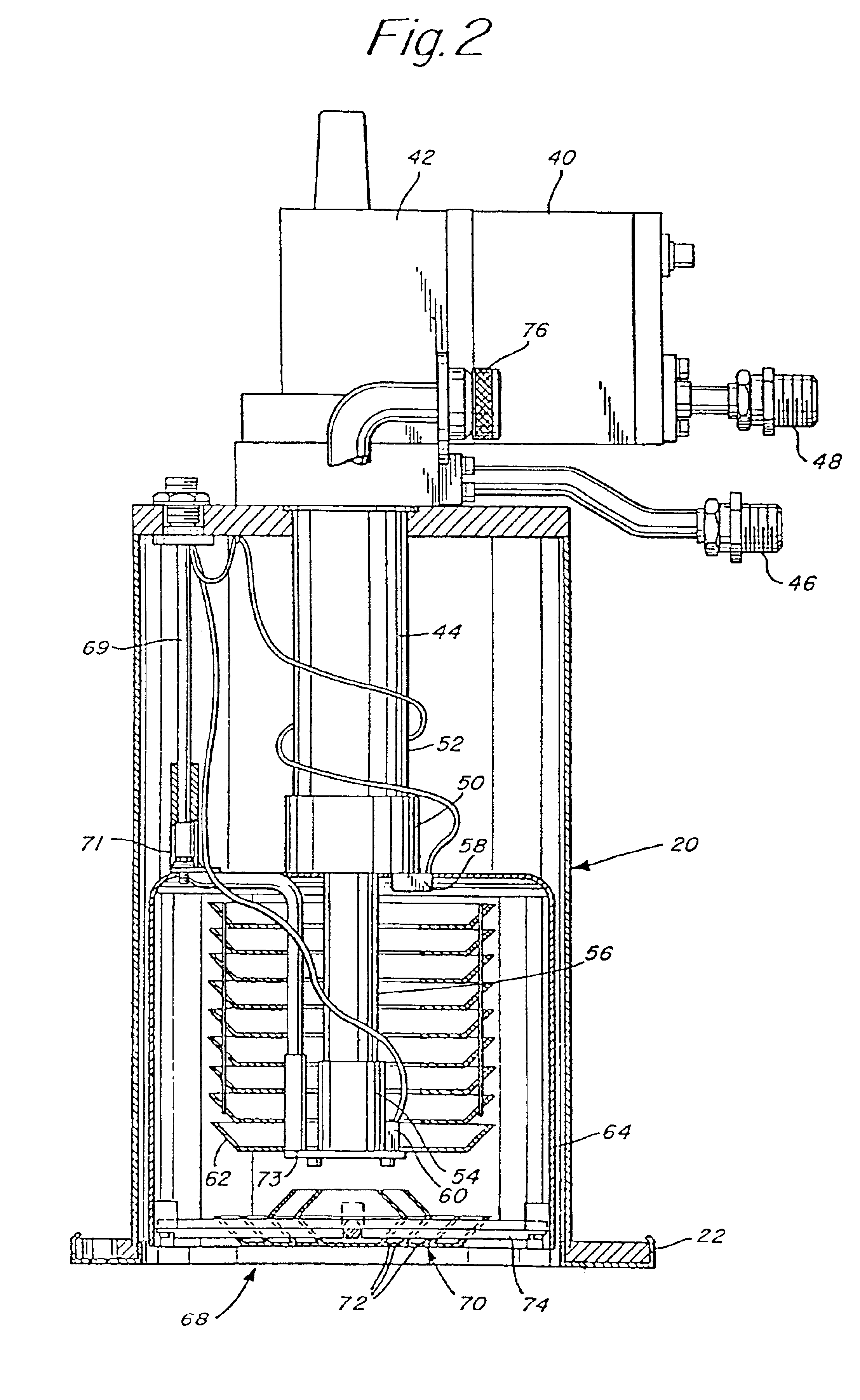
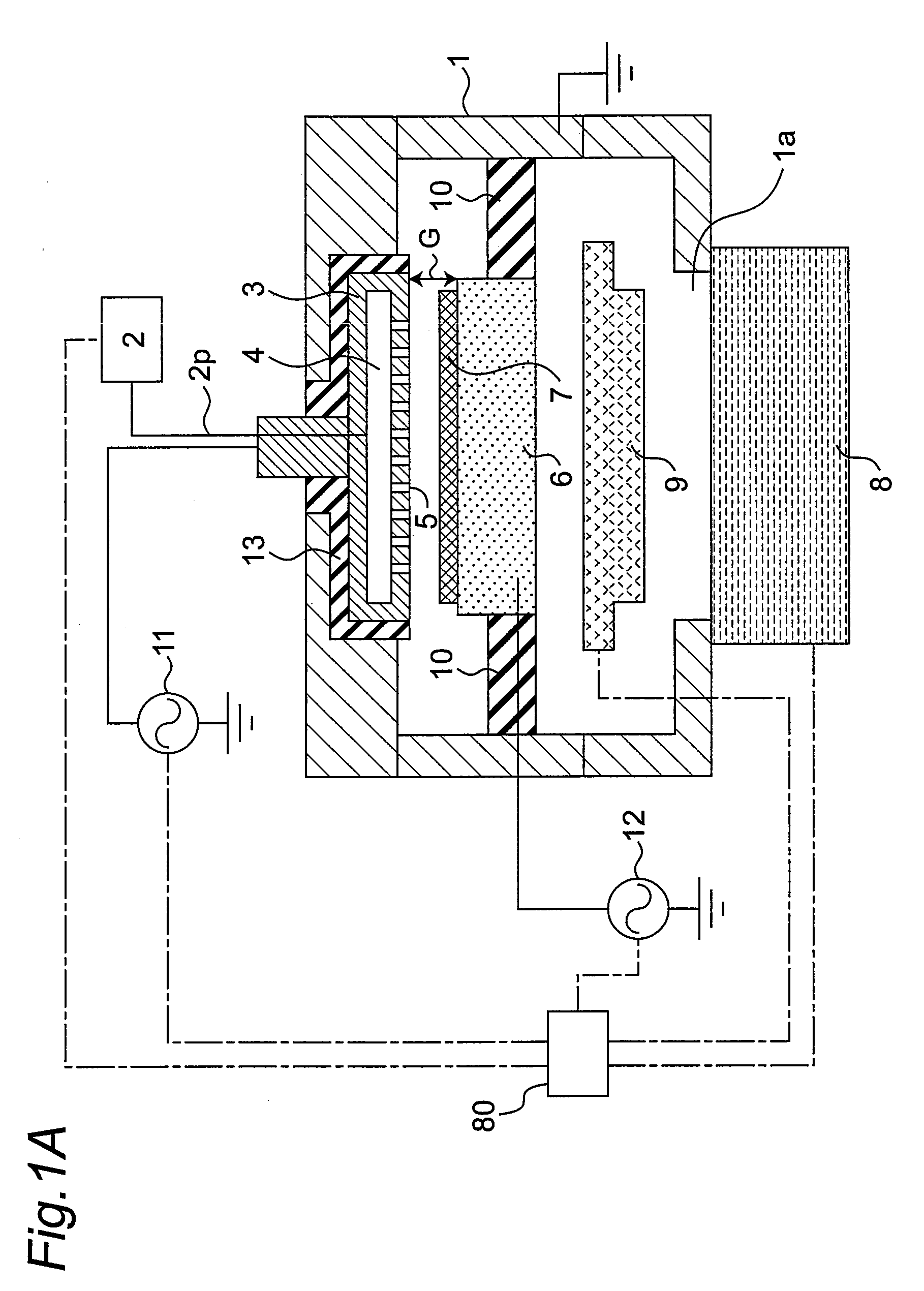
Electronically controlled vacuum pump
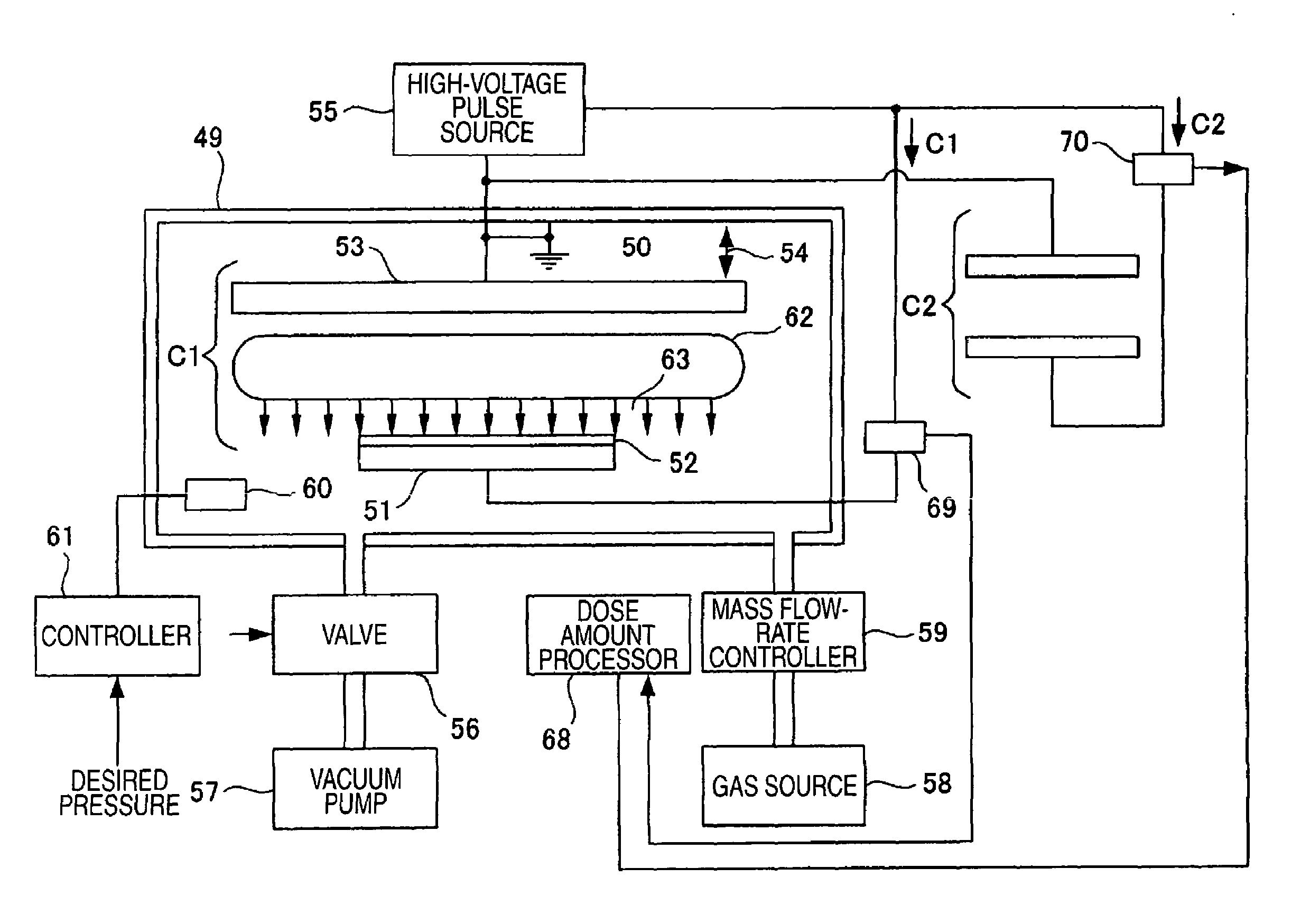
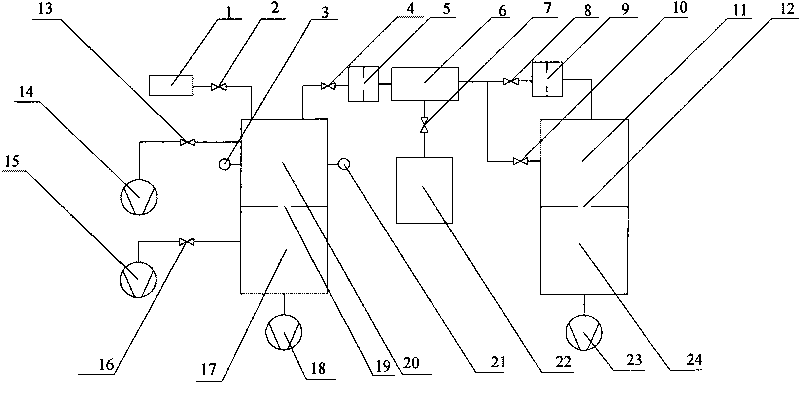
A vacuum system comprises, as an integral assembly, a vacuum pump with drive motor, a purge valve, a roughing valve and an electronic control module. A cryogenic vacuum pump and a turbomolecular vacuum pump are disclosed. The control module has a programmed processor for controlling the motor and valves and is user programmable for establishing specific control sequences. The integral electronic control module is removable from the assembly and is connected to the other devices through a common connector assembly. In the turbomolecular pump system proper introduction of a purge gas through the purge valve is detected by detecting the current load on the pump drive or by detecting foreline pressure. To test the purge gas status, the purge valve may be closed and then opened as drive current or pressure is monitored. After power failure, the controller will continue normal drive of the turbomolecular pump so long as the speed of the pump has remained above a threshold value. Otherwise the vent valve will have been opened, and a start-up sequence must be initiated. During shutdown, power to the pump drive motor is discontinued and the vent valve is opened before the roughing valve is closed.
Owner:BROOKS AUTOMATION INC
Turbo-Molecular pump with metal matrix composite rotor and stator
The invention provides a vacuum processing system comprising a vacuum processing chamber and a turbo-molecular pump having a rotor and / or stator comprised of metal matrix composites. Another aspect of the invention provides a turbo-molecular pump having a rotor and / or a stator comprised of metal matrix composites. Because metal matrix composites are able to withstand higher operating temperatures than the aluminum alloys currently used in rotors and stators, the rotor vanes and the stator vanes that are made of metal matrix composites can provide a higher exhaust capacity with faster rotor rotations.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
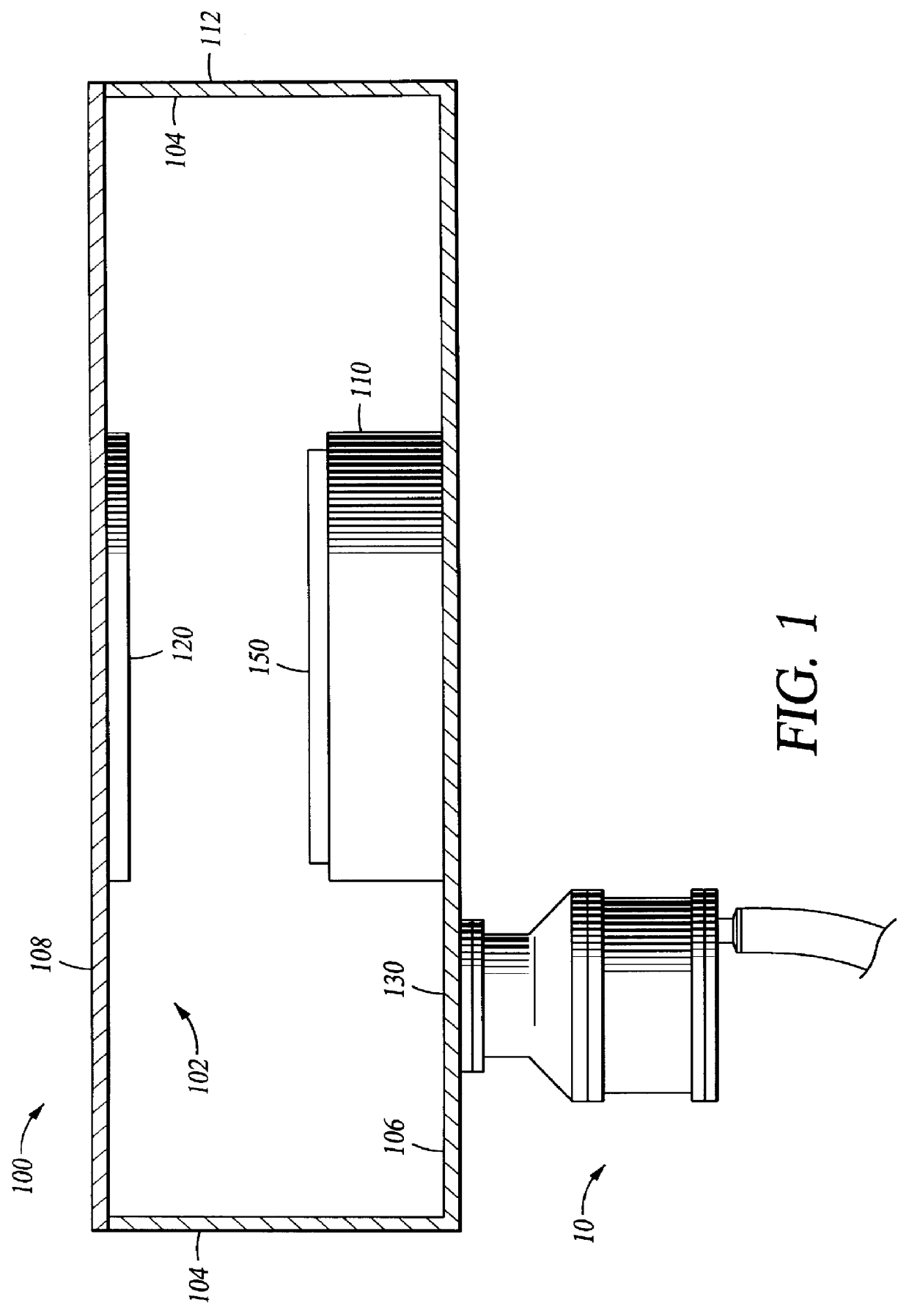
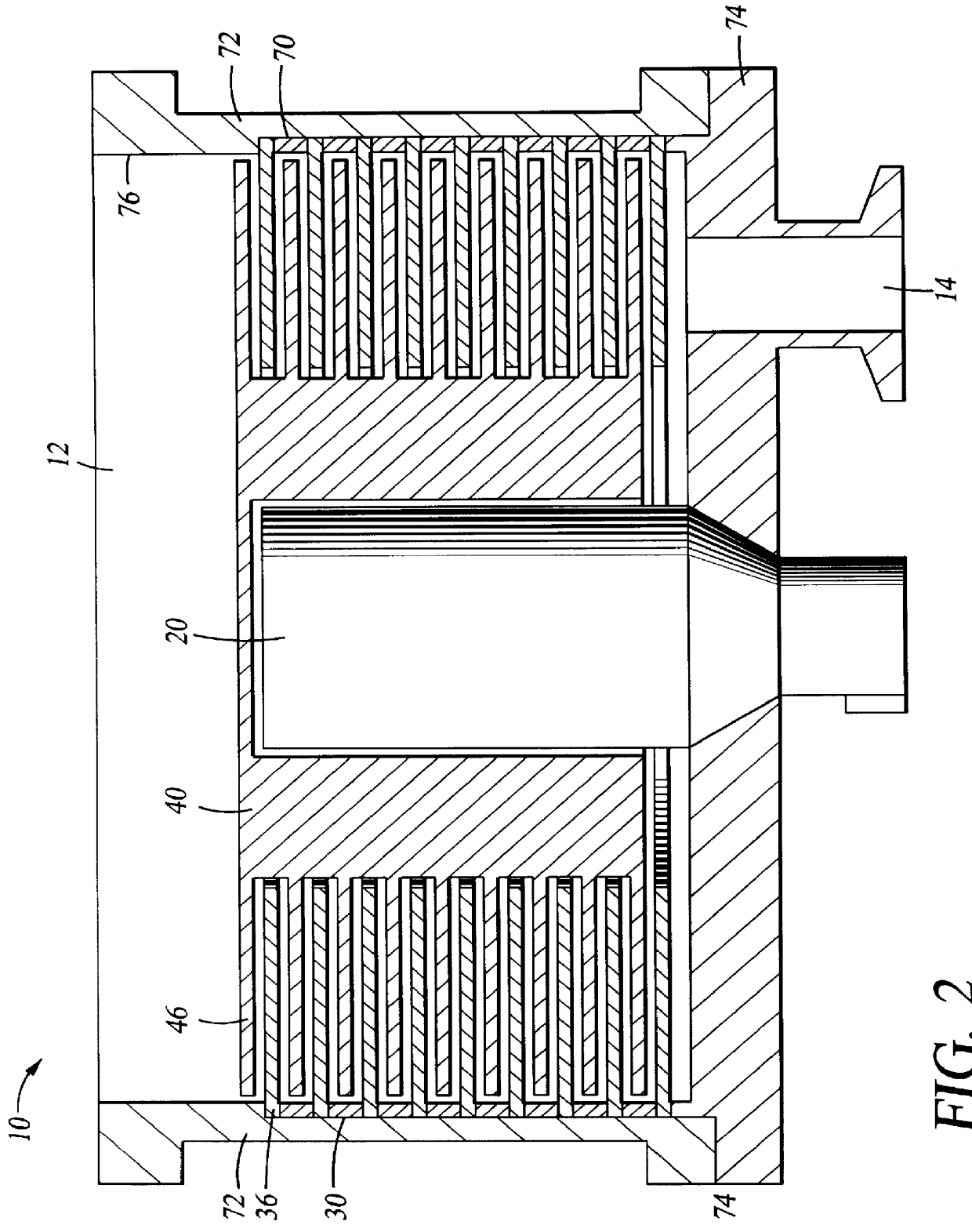
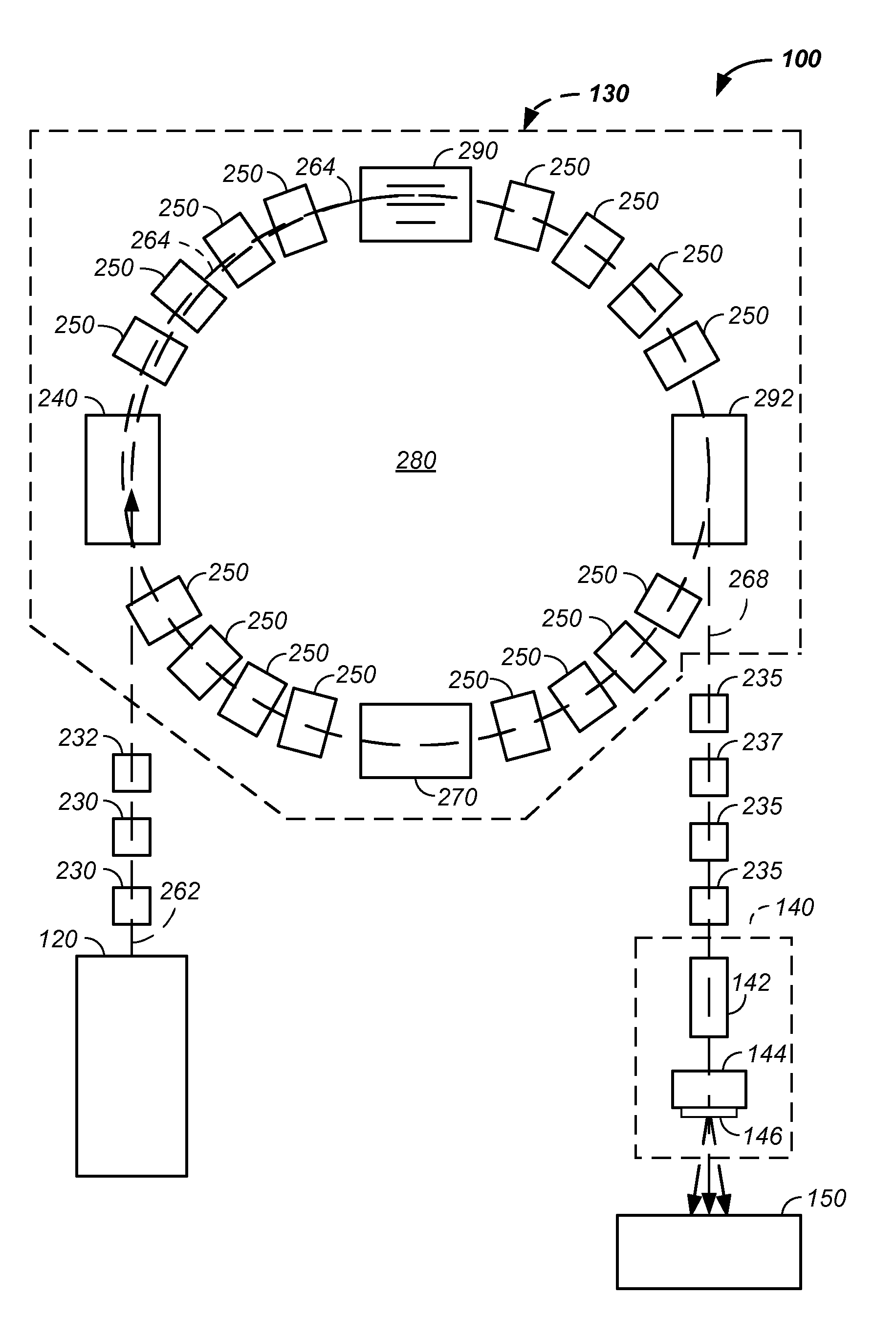
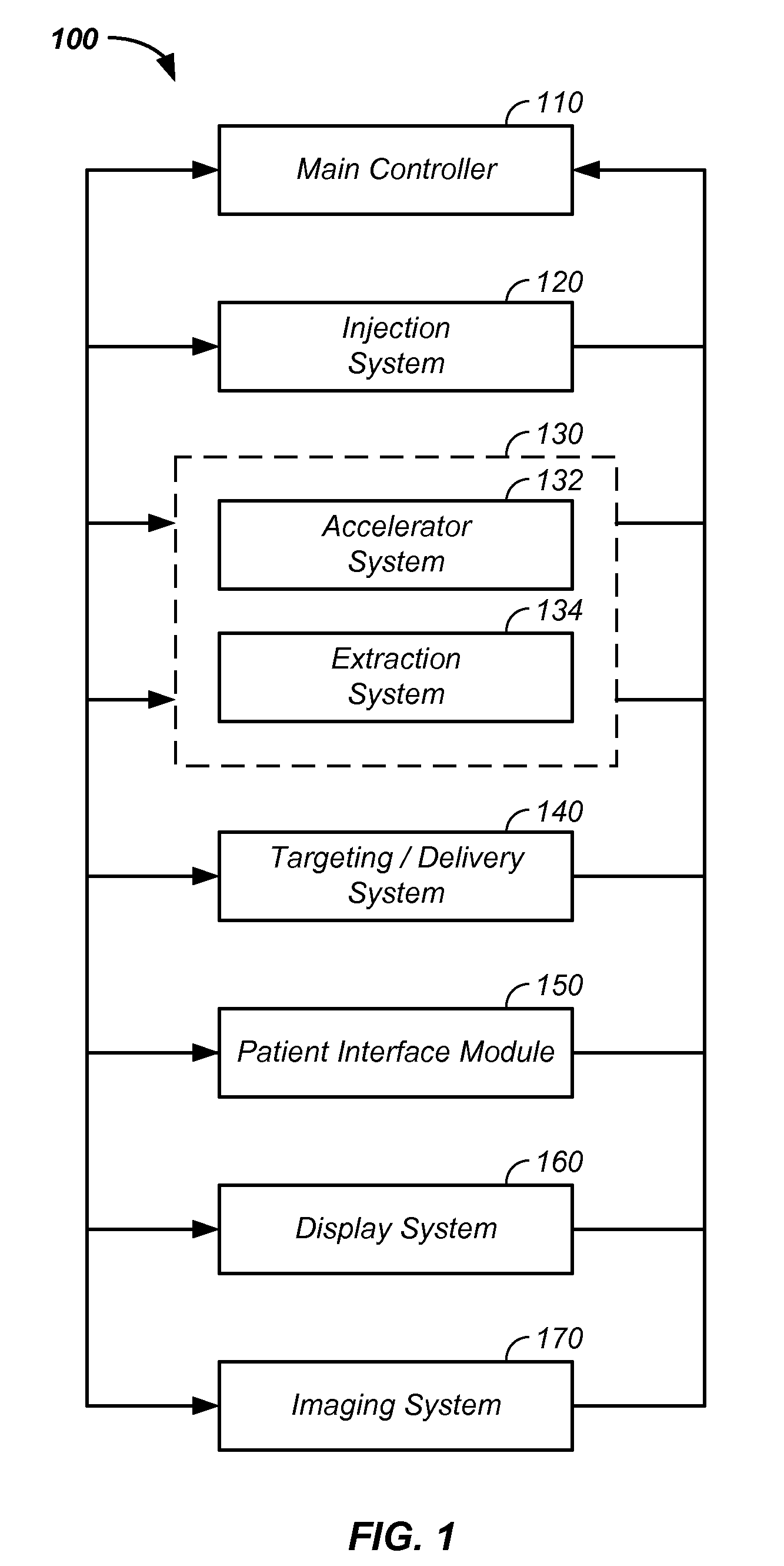
Negative ion beam source vacuum method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
ActiveUS8129694B2Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsIon beamCombined use
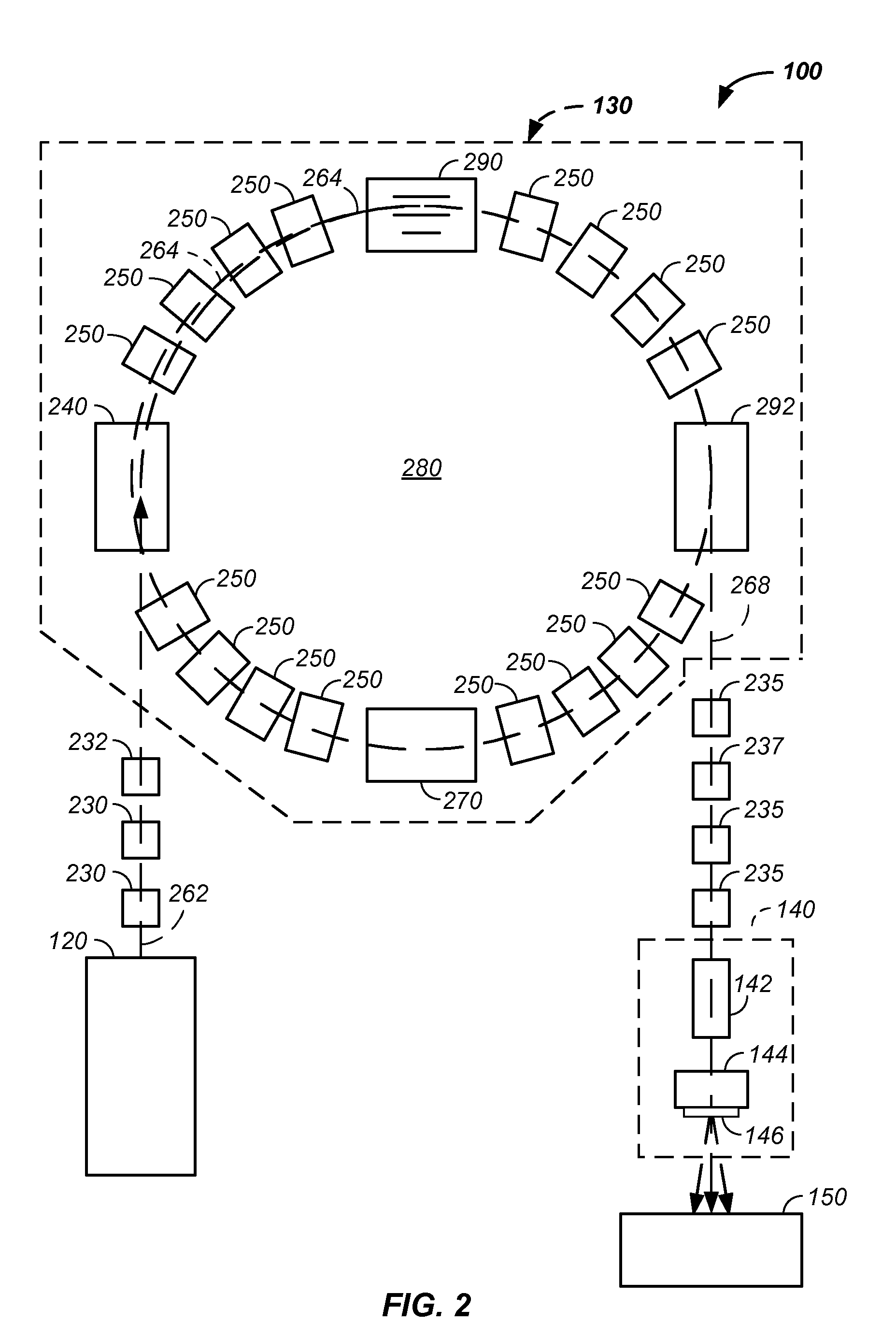
The invention comprises a negative ion beam source vacuum method and apparatus used as part of an ion beam injection system, which is used in conjunction with multi-axis charged particle or proton beam radiation therapy of cancerous tumors. The negative ion beam source contains a vacuum chamber isolated by a vacuum barrier from the vacuum tube of the synchrotron. The negative ion beam source vacuum system preferably includes: a first pump turbo molecular pump, a large holding volume, and a semi-continuously operating pump. By only pumping ion beam source vacuum chamber and by only semi-continuously operating the ion beam source vacuum based on sensor readings about the holding volume, the lifetime of the semi-continuously operating pump is extended.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
Permanent-magnetic biased axial radial magnetic bearing
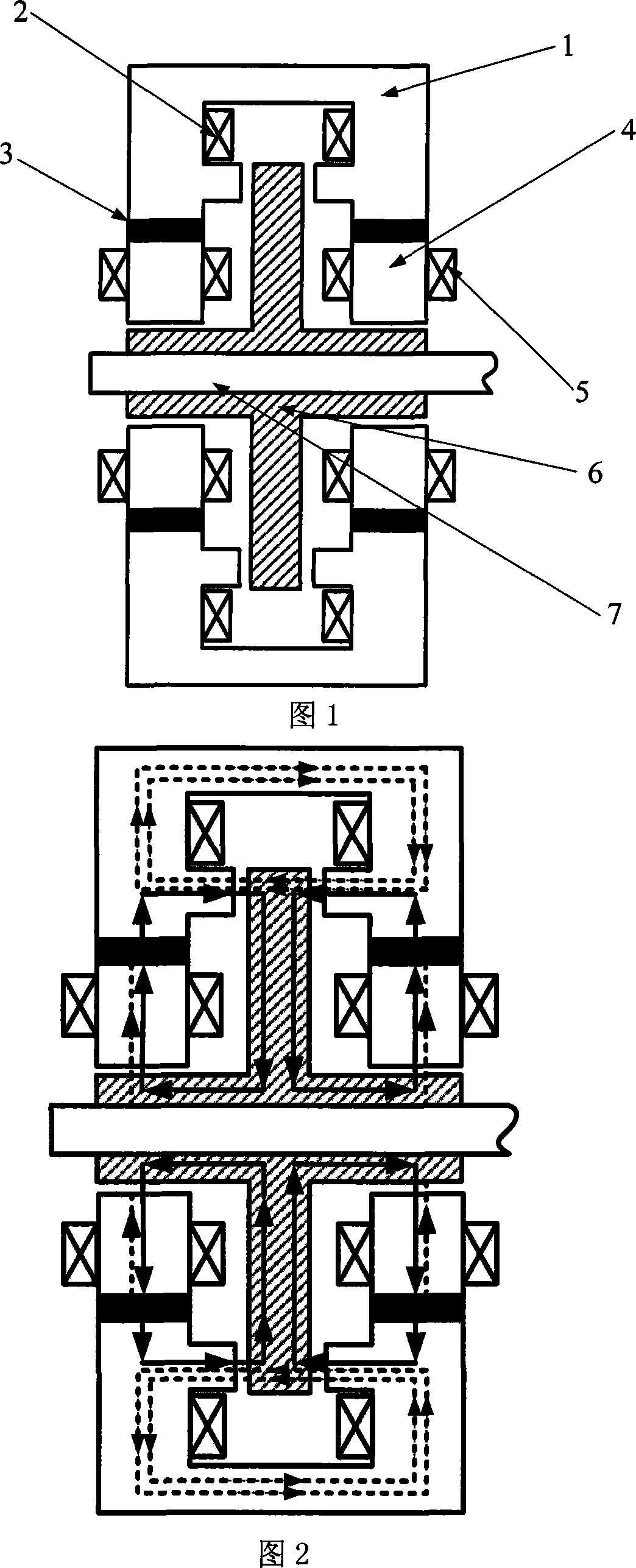
The permanently magnetic biased axial and radial magnetic bearing as one mixed magnetic bearing includes one axial stator, one axial control winding, two radial magnetized ring permanent magnets, two radial stator with three poles, one radial control winding, and one rotor with jacketed iron core. The permanently magnetic biased axial and radial magnetic bearing has one static bias magnetic field established with two radial magnetized ring permanent magnets, one closed magnetic path formed with one external axial magnetic pole iron core, one rotor iron core and one radial stator, one axial suspension controlled by the axial superposed magnetic flux, and one two freedom suspension controlled by the radial superposed magnetic flux. The present invention has simple structure, high critical rotation speed, low power consumption, and broad application foreground in energy storing flywheel, air conditioner compressor and other high speed application fields.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Electronically controlled vacuum pump
InactiveUS20050196284A1Potential damage to the bearings with the prompt pressure change is avoidedImprove scalabilitySolidificationLiquefactionDriving currentCurrent load
A vacuum system comprises, as an integral assembly, a vacuum pump with drive motor, a purge valve, a roughing valve and an electronic control module. A cryogenic vacuum pump and a turbomolecular vacuum pump are disclosed. The control module has a programmed processor for controlling the motor and valves and is user programmable for establishing specific control sequences. The integral electronic control module is removable from the assembly and is connected to the other devices through a common connector assembly. In the turbomolecular pump system proper introduction of a purge gas through the purge valve is detected by detecting the current load on the pump drive or by detecting foreline pressure. To test the purge gas status, the purge valve may be closed and then opened as drive current or pressure is monitored. After power failure, the controller will continue normal drive of the turbomolecular pump so long as the speed of the pump has remained above a threshold value. Otherwise the vent valve will have been opened, and a start-up sequence must be initiated. During shutdown, power to the pump drive motor is discontinued and the vent valve is opened before the roughing valve is closed.
Owner:BROOKS AUTOMATION INC
Pump bearing arrangement
InactiveCN101809292AImprove cooling effectRolling contact bearingsPump componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
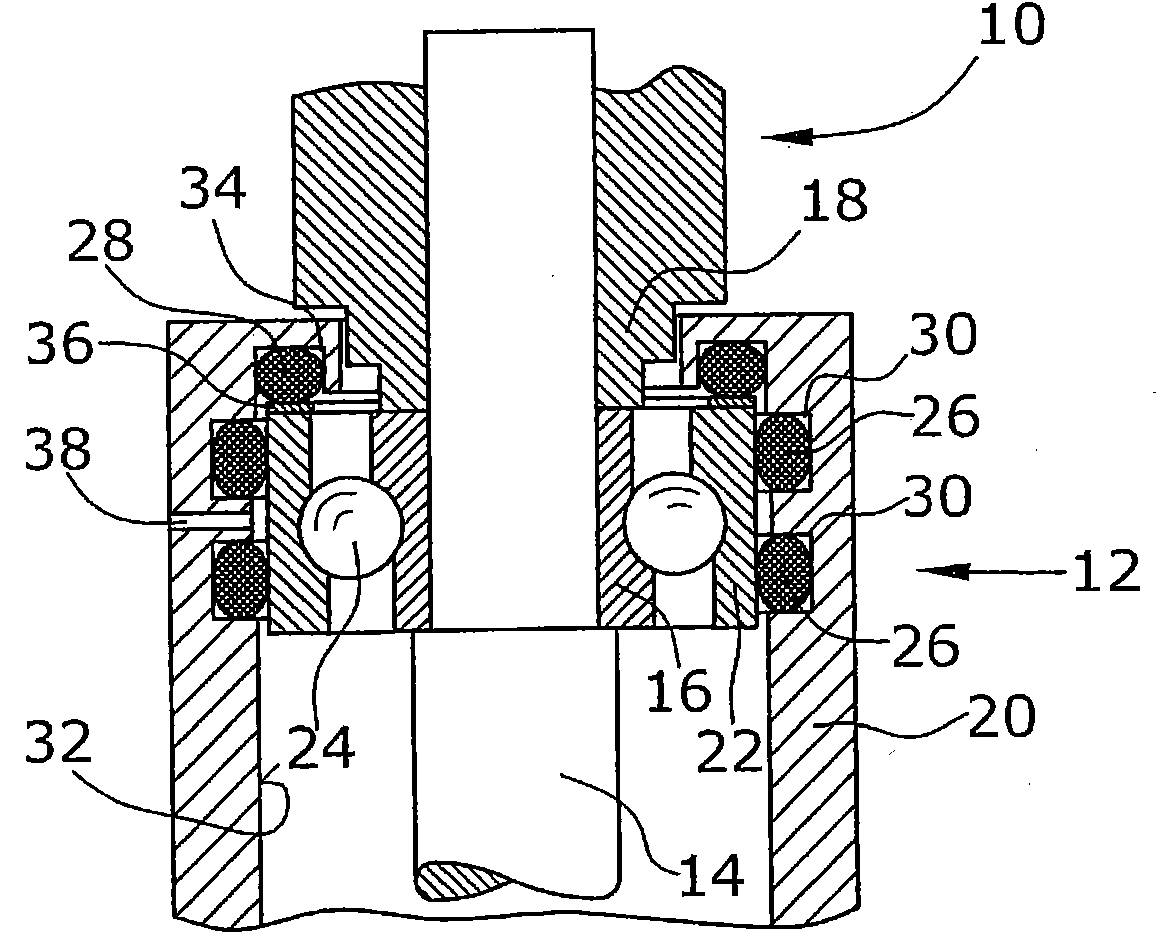
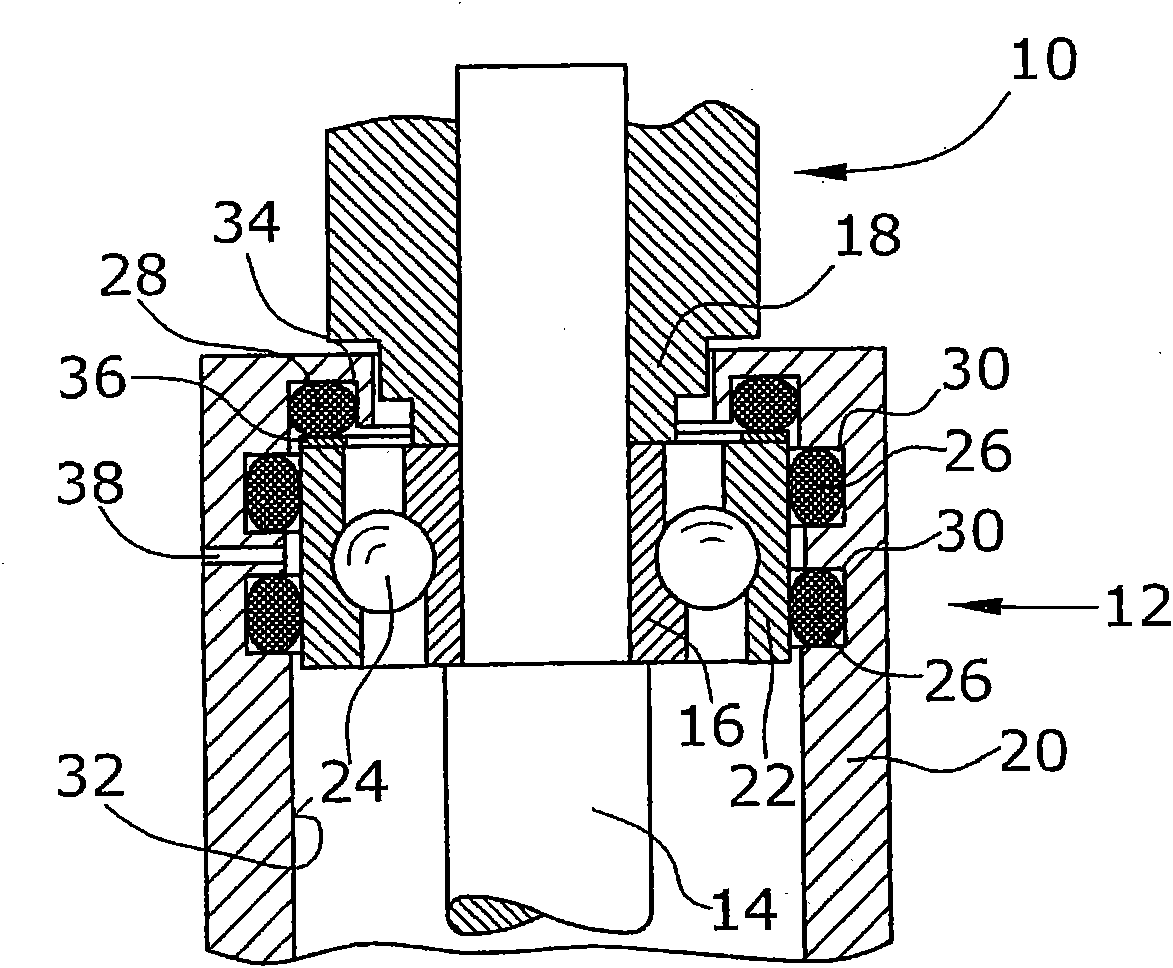
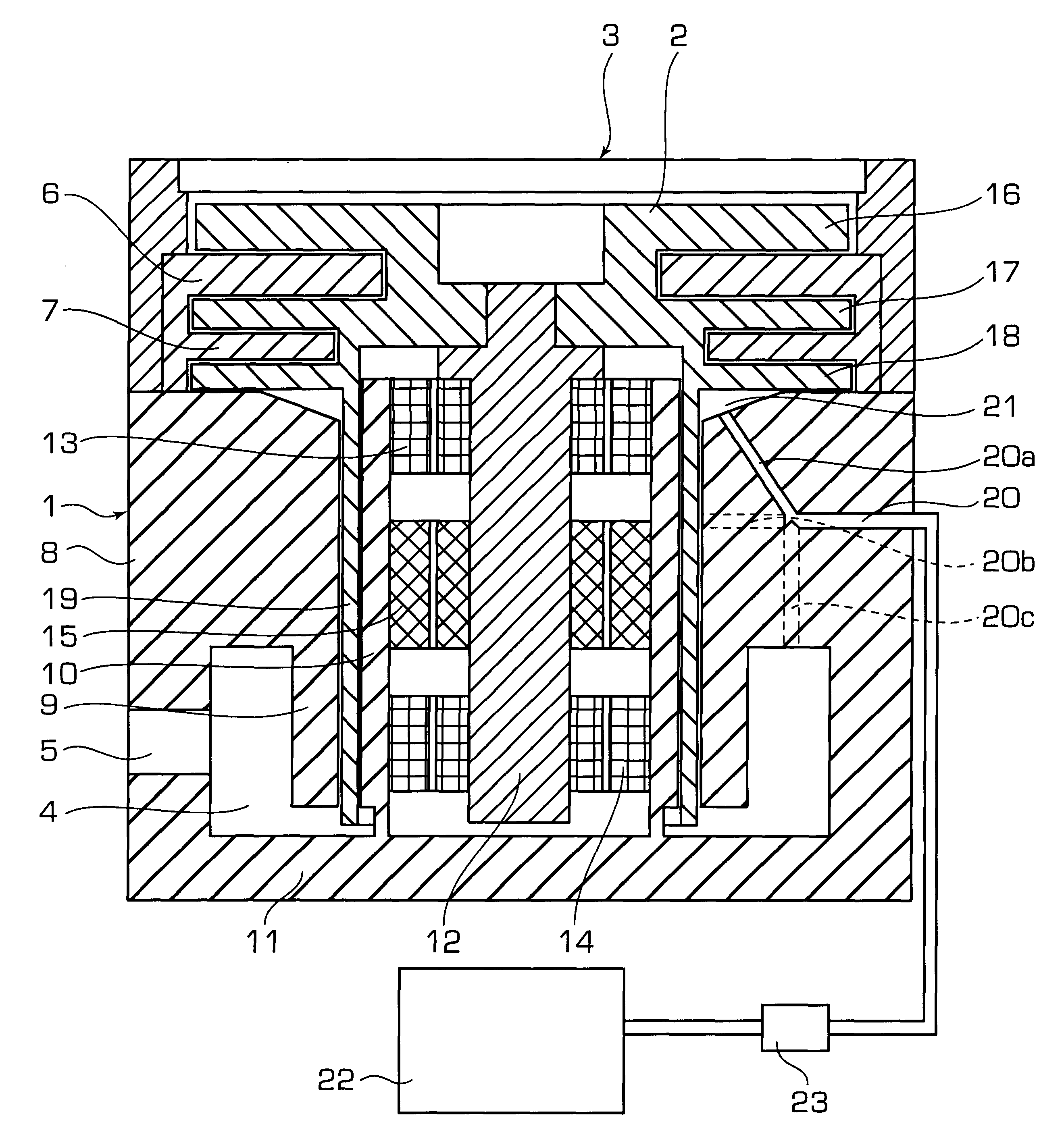
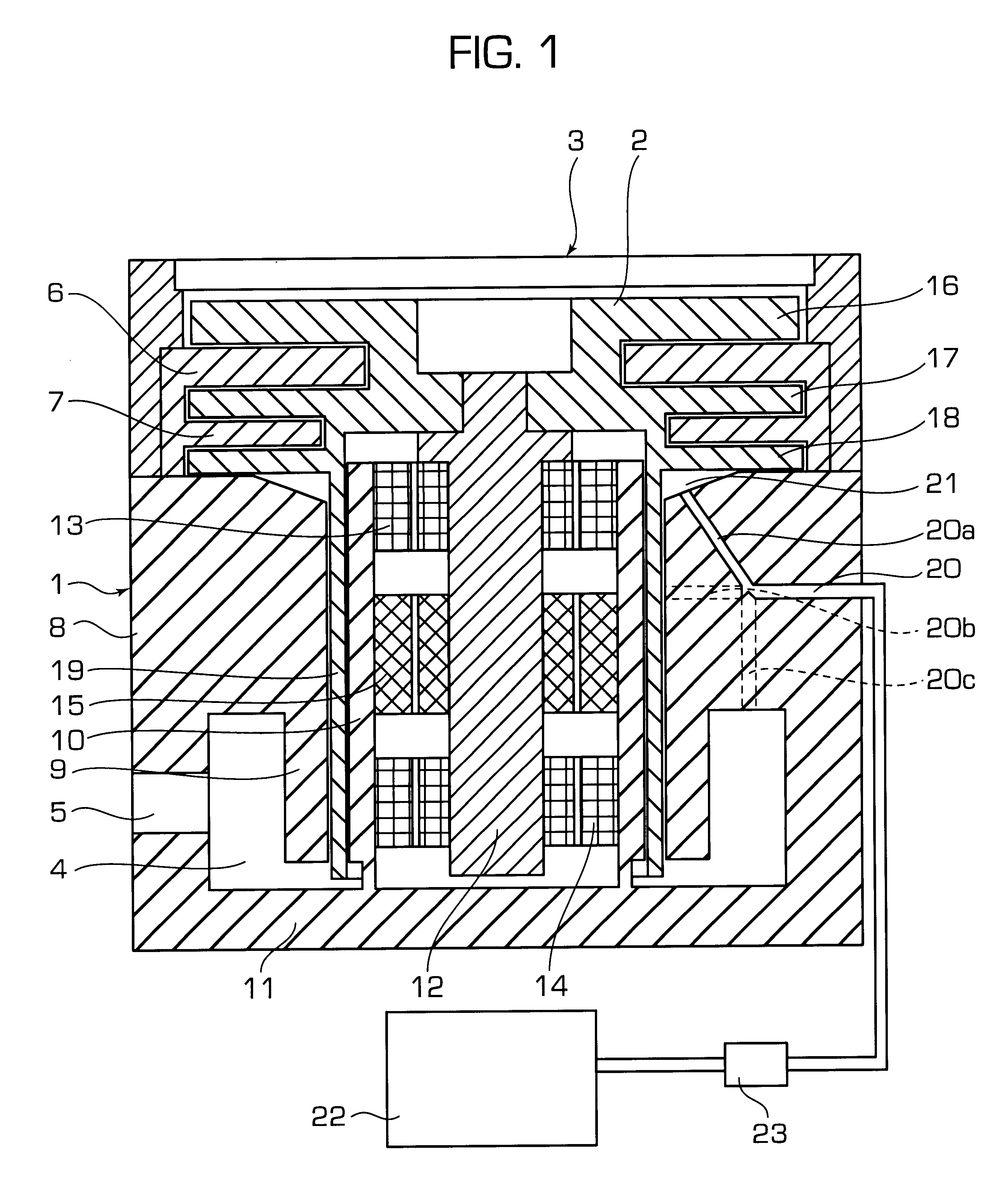
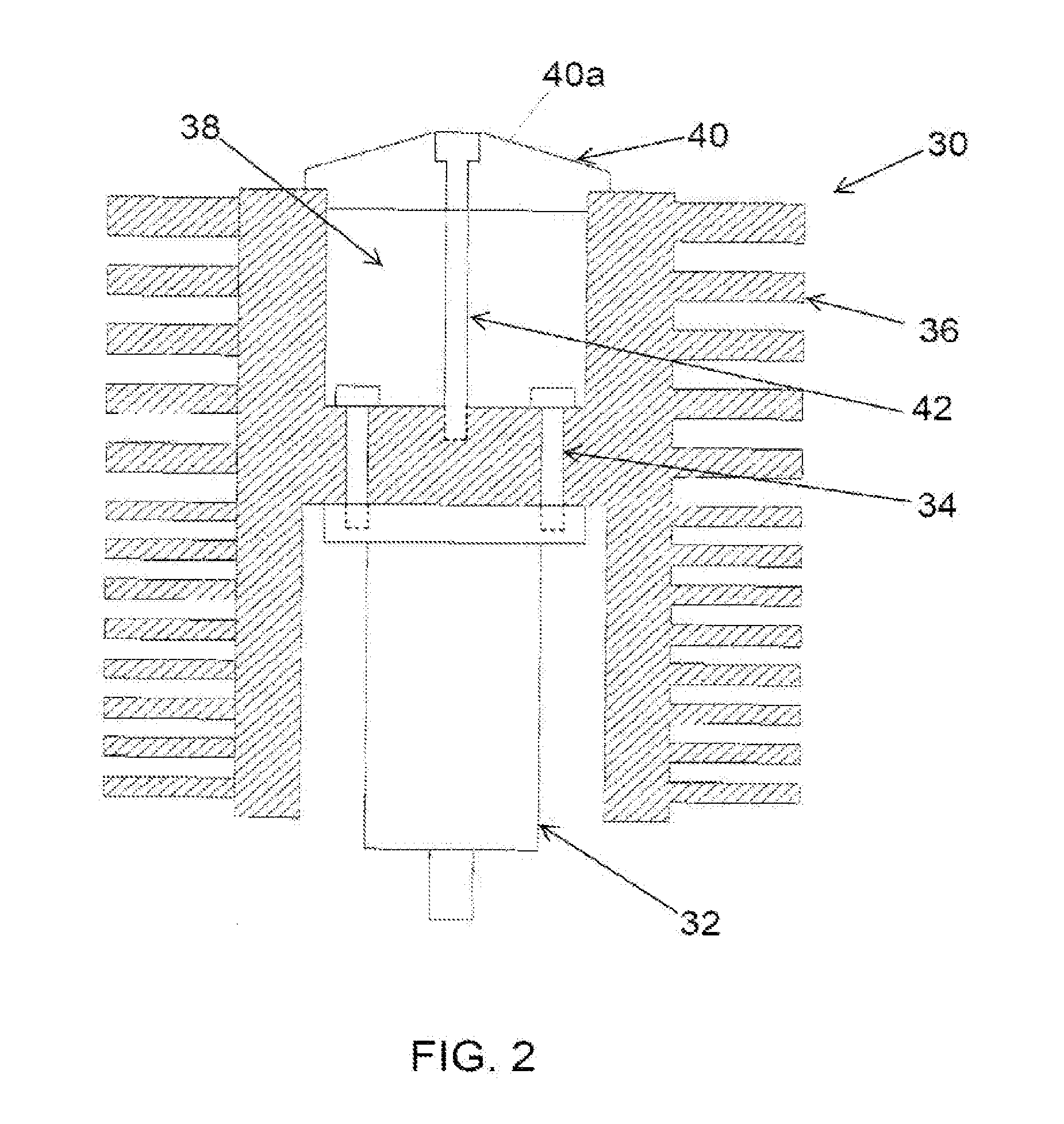
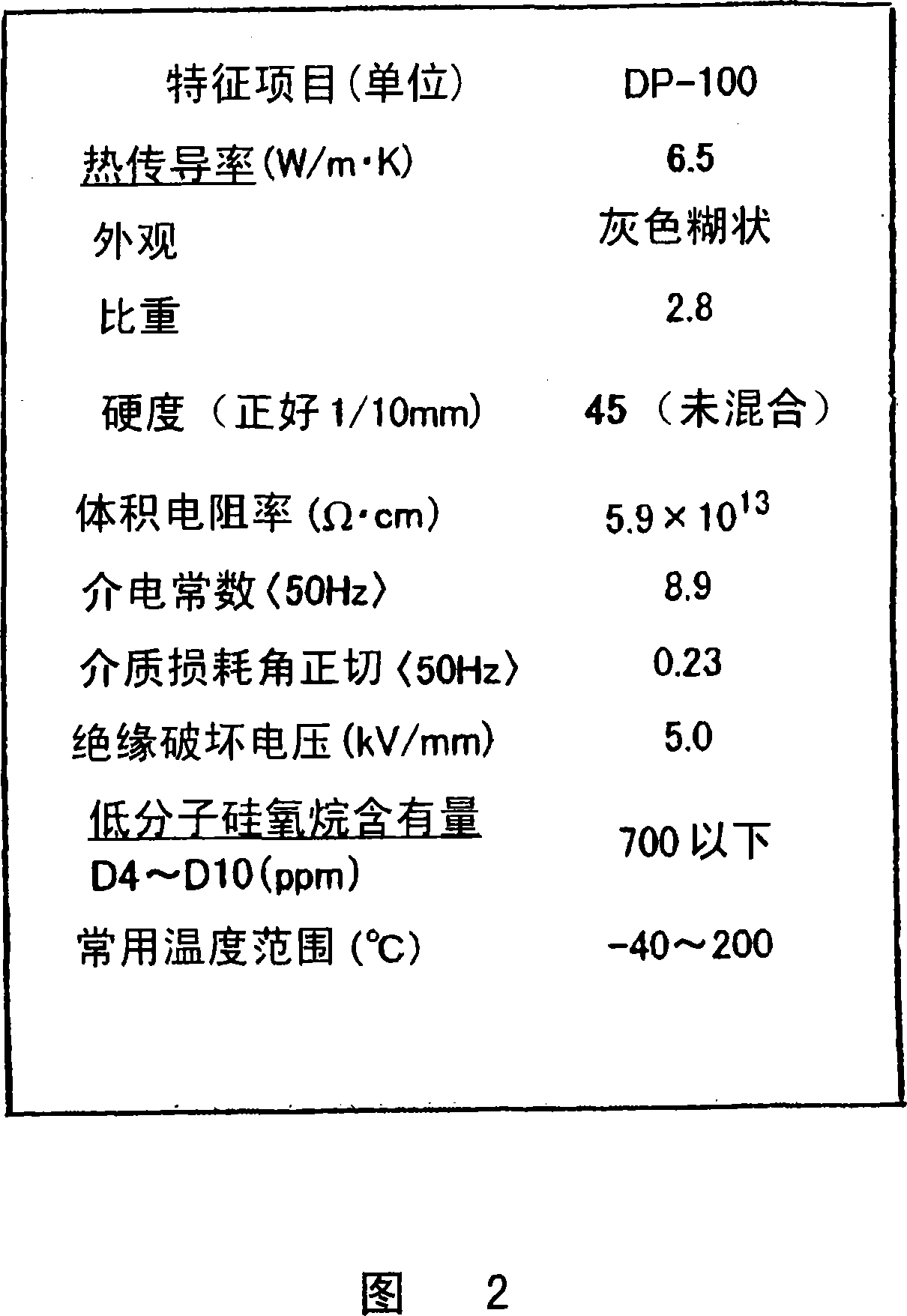
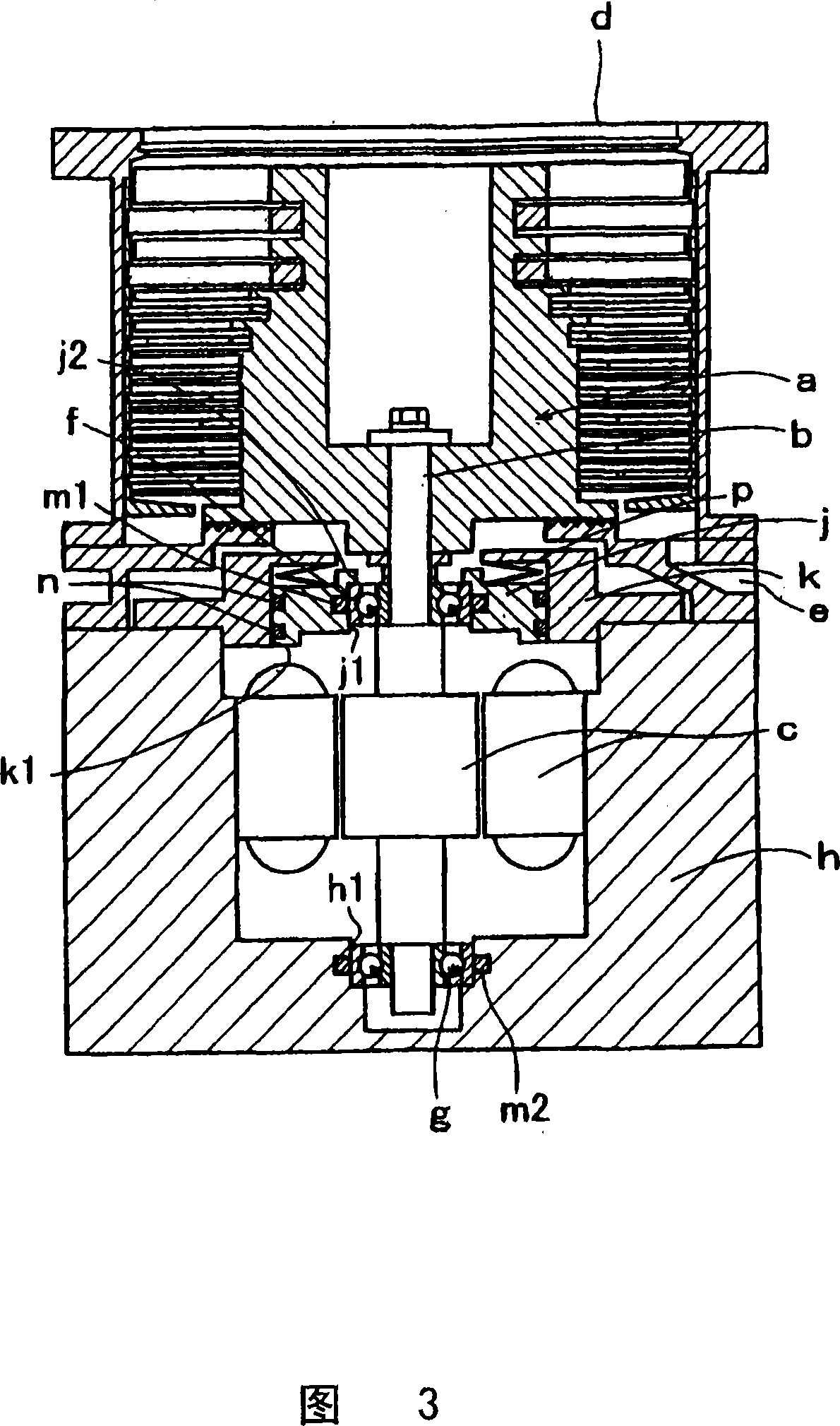
The invention relates to a pump bearing arrangement suitable particularly for rapidly rotating pumps, such as turbomolecular pumps, having a pump rotor (10) connected to a rotor shaft. The rotor shaft (14) is supported in a shaft housing (20) by two bearing devices (12). Each bearing device (12) has an inner bearing ring (16) connected to the rotor shaft (14) and an outer bearing ring (22) connected to the shaft housing (20). Bearing supports (24) are disposed between the two bearing rings. According to the invention, at least one vibration element (26) is provided between the outer bearing ring (22) and the shaft housing (20), serving for damping and further having a thermal conductivity of at least 0.3 W / mK for dissipating heat.
Owner:OERLIKON LEYBOLD VACUUM
Motor control system and vacuum pump equipped with the motor control system
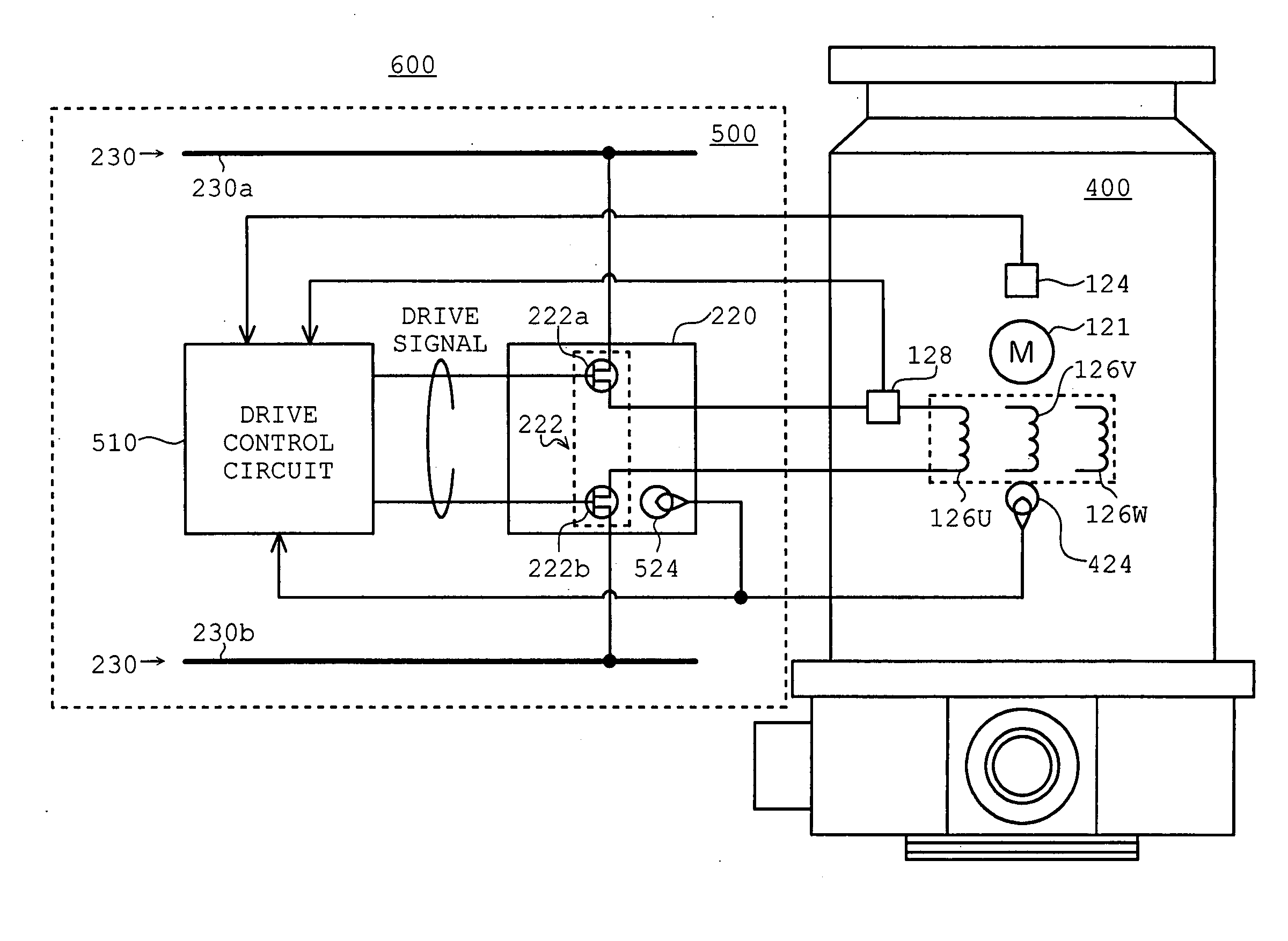
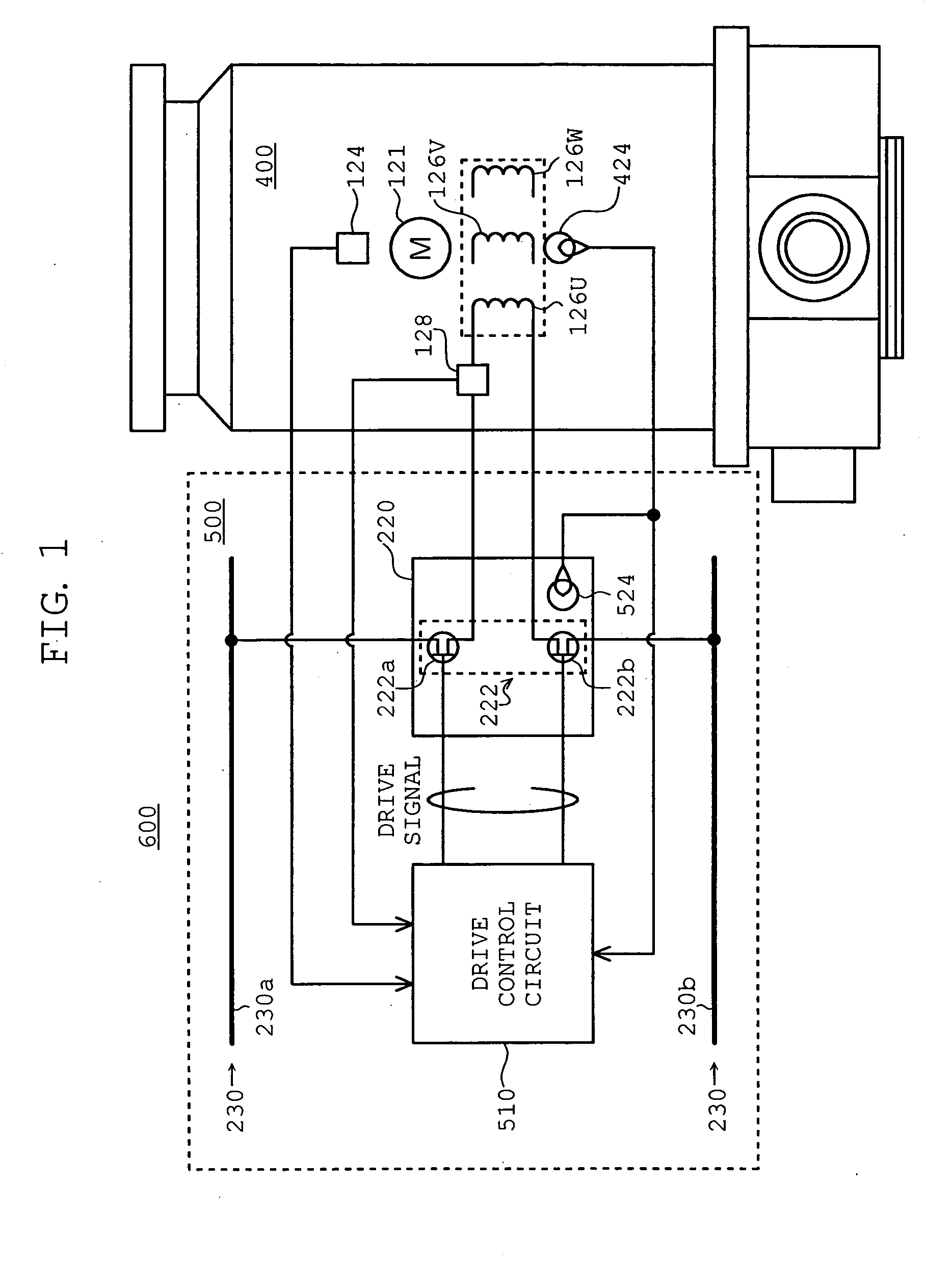
InactiveUS20050052146A1Shorten the production cycleExtended service lifeAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlStart timeControl system
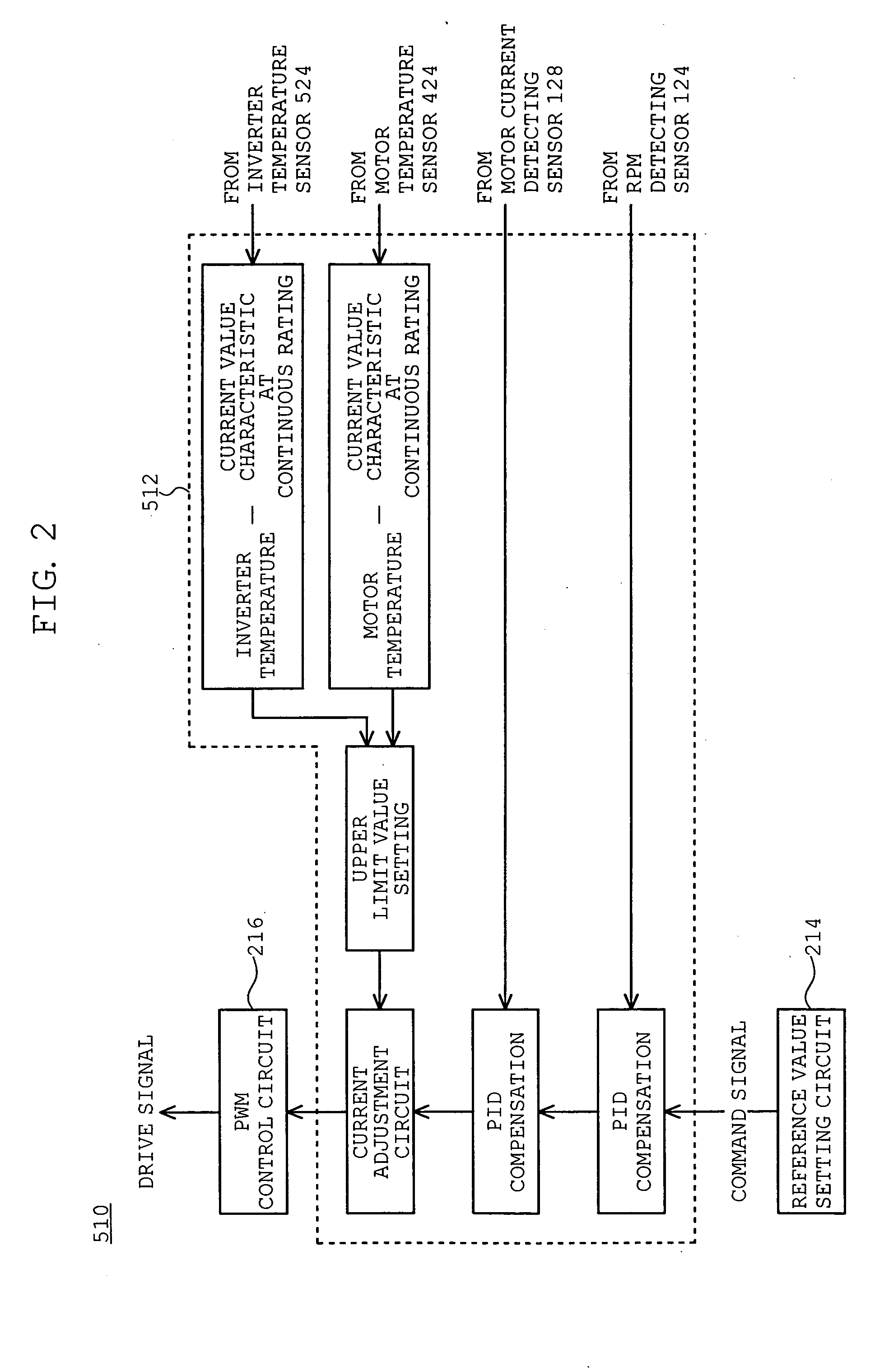
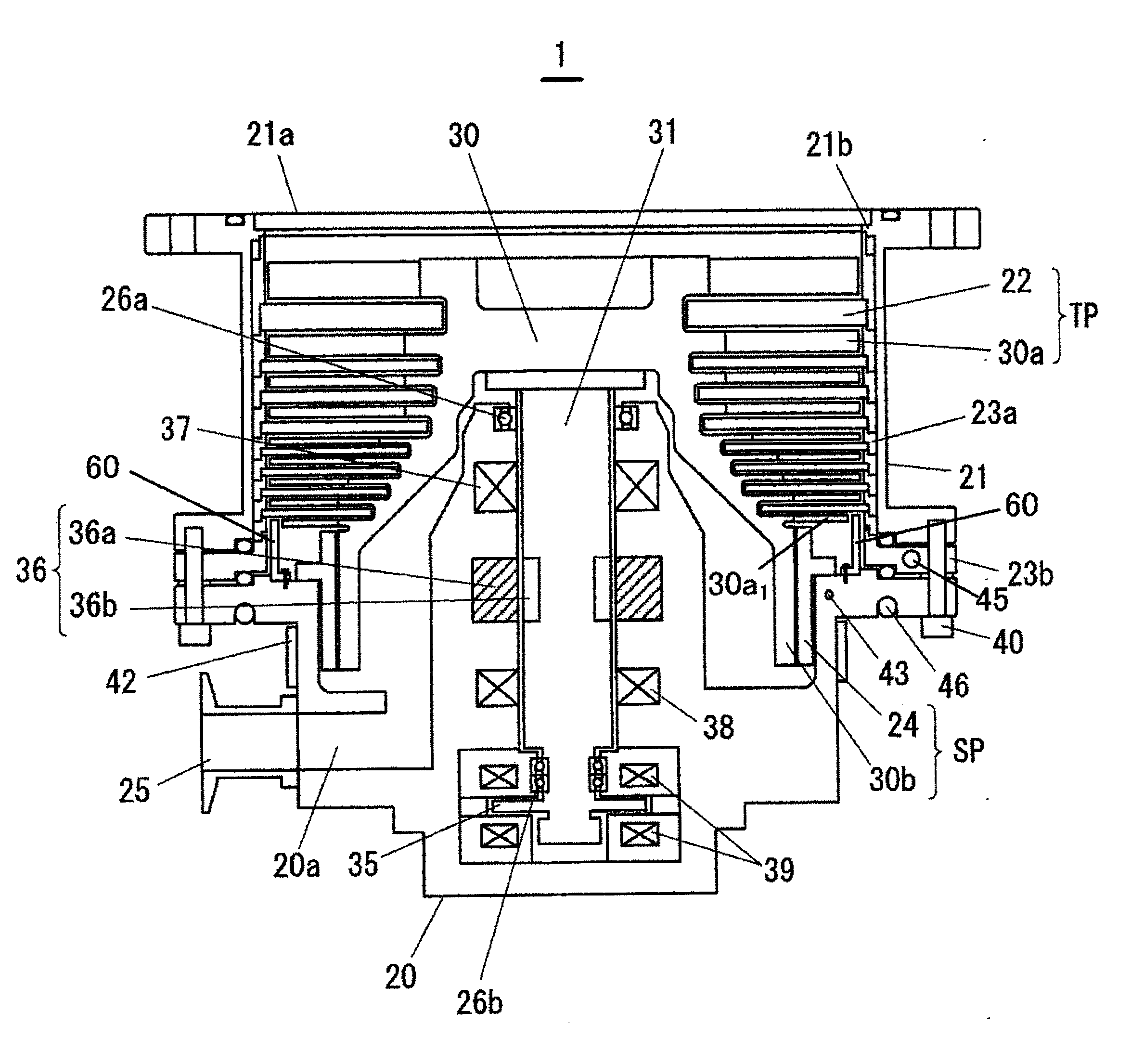
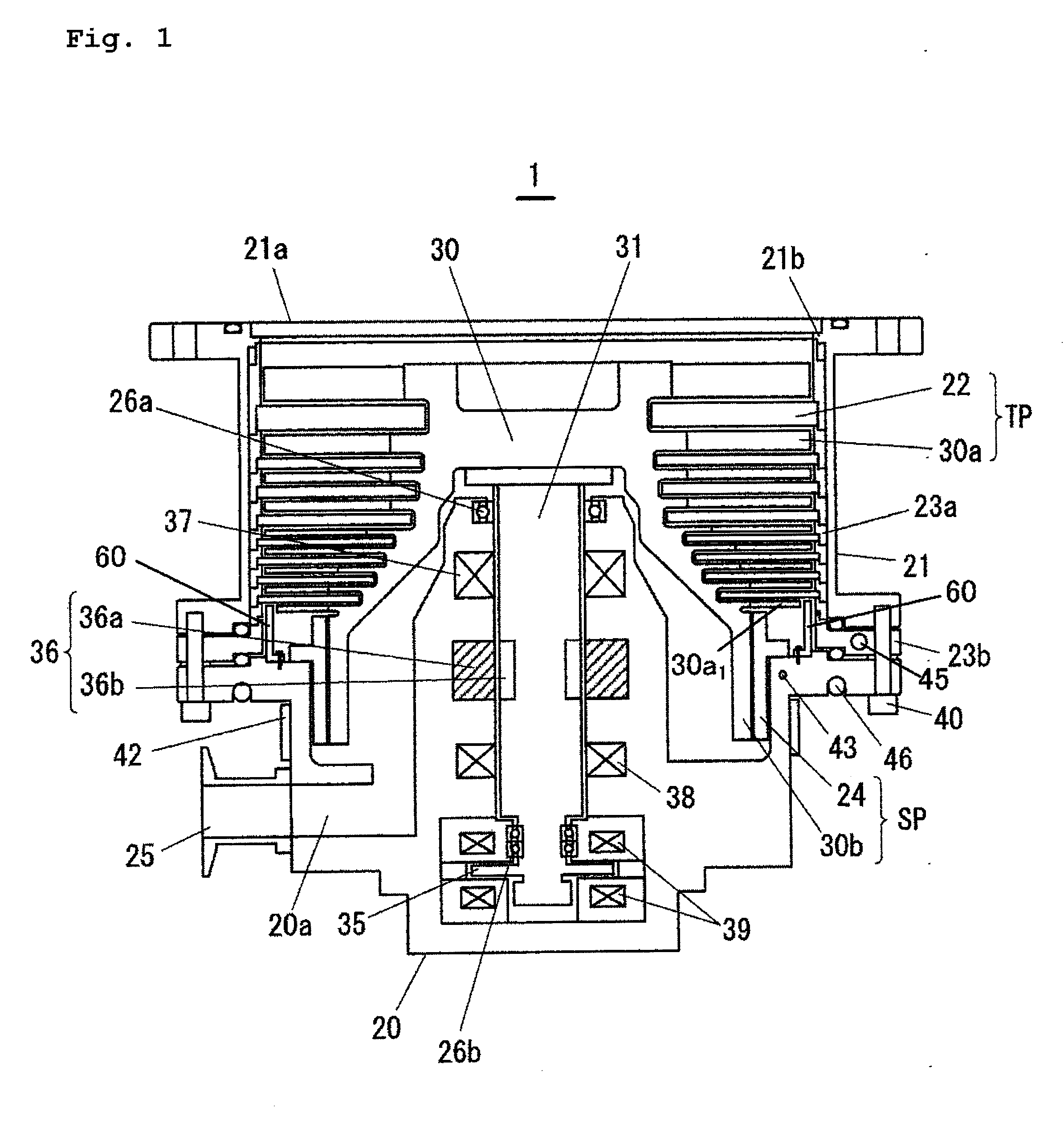
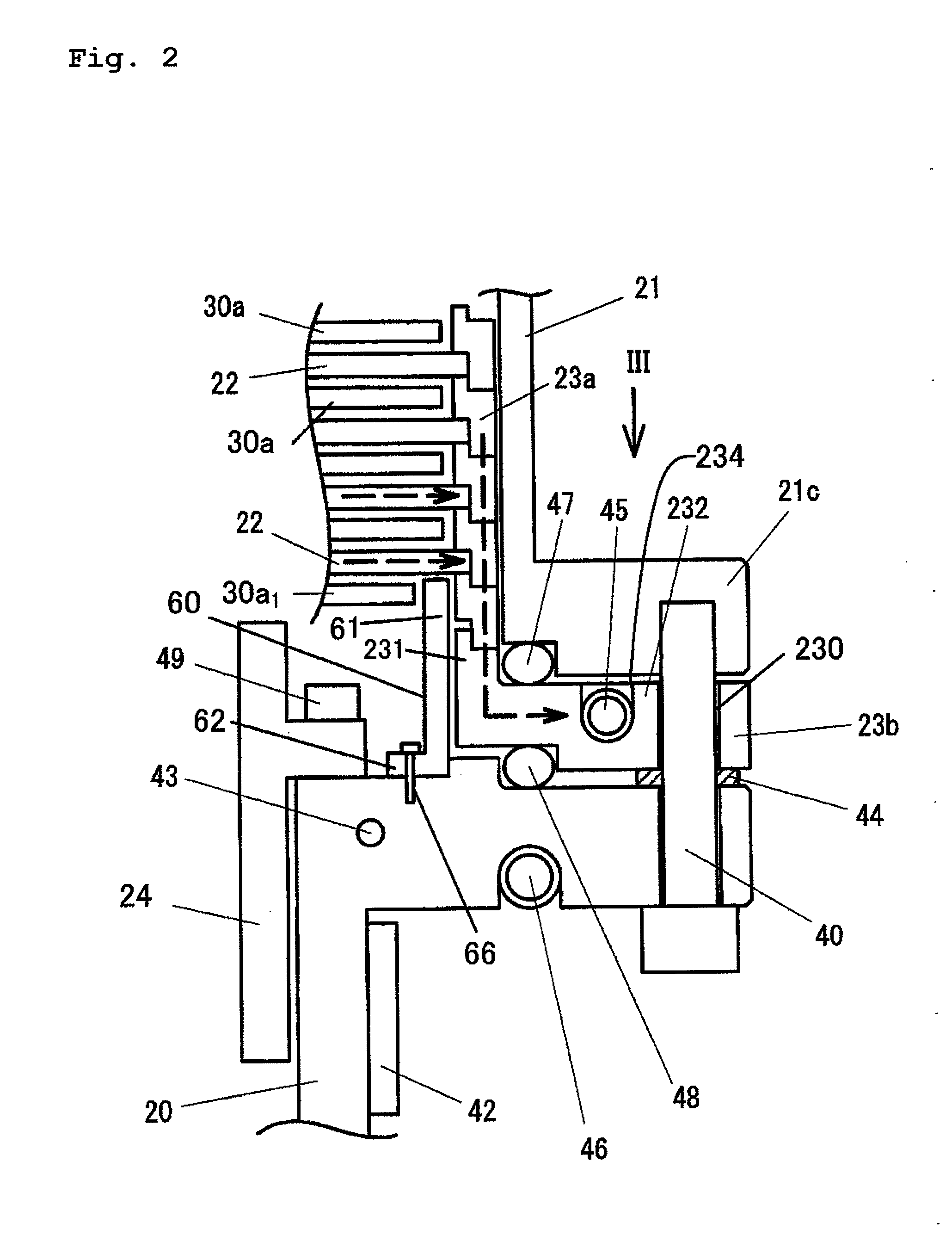
Disclosed are a motor control system capable of shortening the starting time of a turbo molecular pump and a vacuum pump equipped with the motor control system. A motor control system (600) is equipped with a motor temperature sensor (424) and an inverter temperature sensor (524). Detection signals from the motor temperature sensor (424) and the inverter temperature sensor (524) are input to a comparator (512) of a drive control circuit (510). In accordance with a characteristic curve and based on the temperatures detected by the motor temperature sensor (424) and the inverter temperature sensor (524), the comparator (512) sets, in a current adjustment circuit, a current value at continuous rating satisfying both motor windings (126U, 126V, and 126W) and inverter circuits (222) as the upper limit value of a motor current Im.
Owner:EDWARDS JAPAN
Method and apparatus for preventing deposits from forming in a turbomolecular pump having magnetic or gas bearings
InactiveUS6224326B1Inhibition formationIncrease temperaturePump componentsEngine fuctionsAtmosphereElectrical and Electronics engineering
In the invention, deposits that disturb electrical discharges between the rotor and the stator inside a turbomolecular pump with a plurality of stages on magnetic or gas bearings are prevented from forming by injecting an active gas at at least one suitable location inside the pump via at least one gas intake pipe, which active gas reacts with the deposit-generating molecules and forms gaseous compounds that are removed by the pump. Such deposits are thus prevented from forming without disturbing the conductance of the pump or adversely affecting the atmosphere present in the enclosure to which the pump is connected.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Turbo-molecular pump
InactiveUS6926493B1Simple structureReduce frictionPump componentsCombination enginesElectrical and Electronics engineeringTurbomolecular pump
A turbo-molecular pump of high safety and reliability was presented, so that if an abnormal condition should develop on the rotor side, it will not lead to any damage to the stationary portions such as the stator or pump casing to cause loss of vacuum in a vacuum processing system. The turbo-molecular pump includes a rotor; a stator assembly surrounding the rotor; and a casing portion surrounding the stator assembly, wherein at least a partial clearance is formed between the stator assembly and the casing portion, so that, when an abnormal torque is applied from the rotor to the stator assembly, direct impact transmission is prevented from the stator assembly to the casing portion.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Turbomolecular pump device and controlling device thereof
ActiveUS20100247350A1Increasing device space efficiencyMiniaturization of the controlling device casePump componentsPiston pumpsThermal energyElectrical resistance and conductance
A turbomolecular pump having a pump main unit having, at least, a rotary vein provided on a rotor, a static vein for working in cooperation with the rotary vein to perform a vacuum exhaust, and a motor for driving the rotor, comprising: a controlling device that includes a motor driving circuit for converting into thermal energy, in a regenerative braking resistance, the regenerative electric current that is produced at the time of regeneratively driving the motor; and a cooling device for cooling the controlling device. A rod-shape heating resistive element is used as the regenerative braking resistance, where this resistive heating element is routed along the inner peripheral surface of an end portion 14a of the controlling device case that contacts the cooling device.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Vacuum pump
ActiveUS20110103934A1Good precisionReduce the impactPump componentsEngine fuctionsEngineeringDigital filter
Provided is a vacuum pump which can detect precisely physical contact between a rotor portion and a stator portion, and contact between the rotor portion and the stator portion that occurs as the amount of deposited solid product reaches the clearance between the rotor portion and the stator portion.A vibration sensor is provided, taking advantage of a clearance, at the outer peripheral of a thread groove spacer. Contact between the rotor portion and the stator portion is decided, when a particular vibration during contact between the rotor portion and the stator portion exceeds a predetermined threshold value. The vibration sensor is mounted on the outer peripheral of the thread groove spacer at the end of the side of an exhaust port. The thread groove spacer is fixed on a casing via an elastic member (an O-ring) that have a vibration absorption (vibration damping) function of a cutoff frequency (fc1). A vibration signal outputted from the vibration sensor is converted into a digital vibration signal, and is inputted to a digital filter having a passing band of fc1 to fc2 [Hz]. If the vibration level of the vibration signal having passed through the digital filter exceeds a predetermined threshold value, it is detected that contact between the rotor portion and the stator portion has occurred in a turbo-molecular pump.
Owner:EDWARDS JAPAN
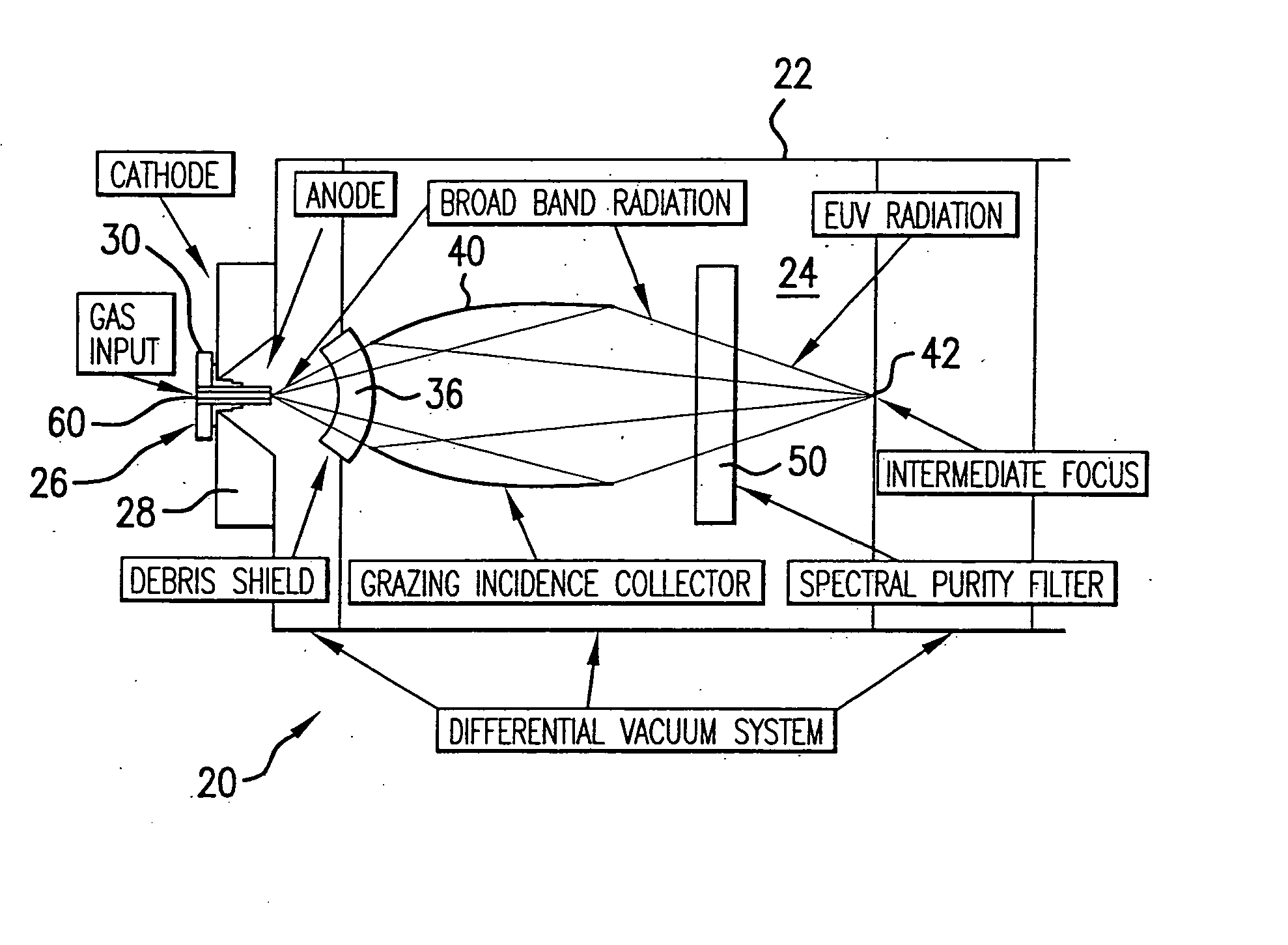
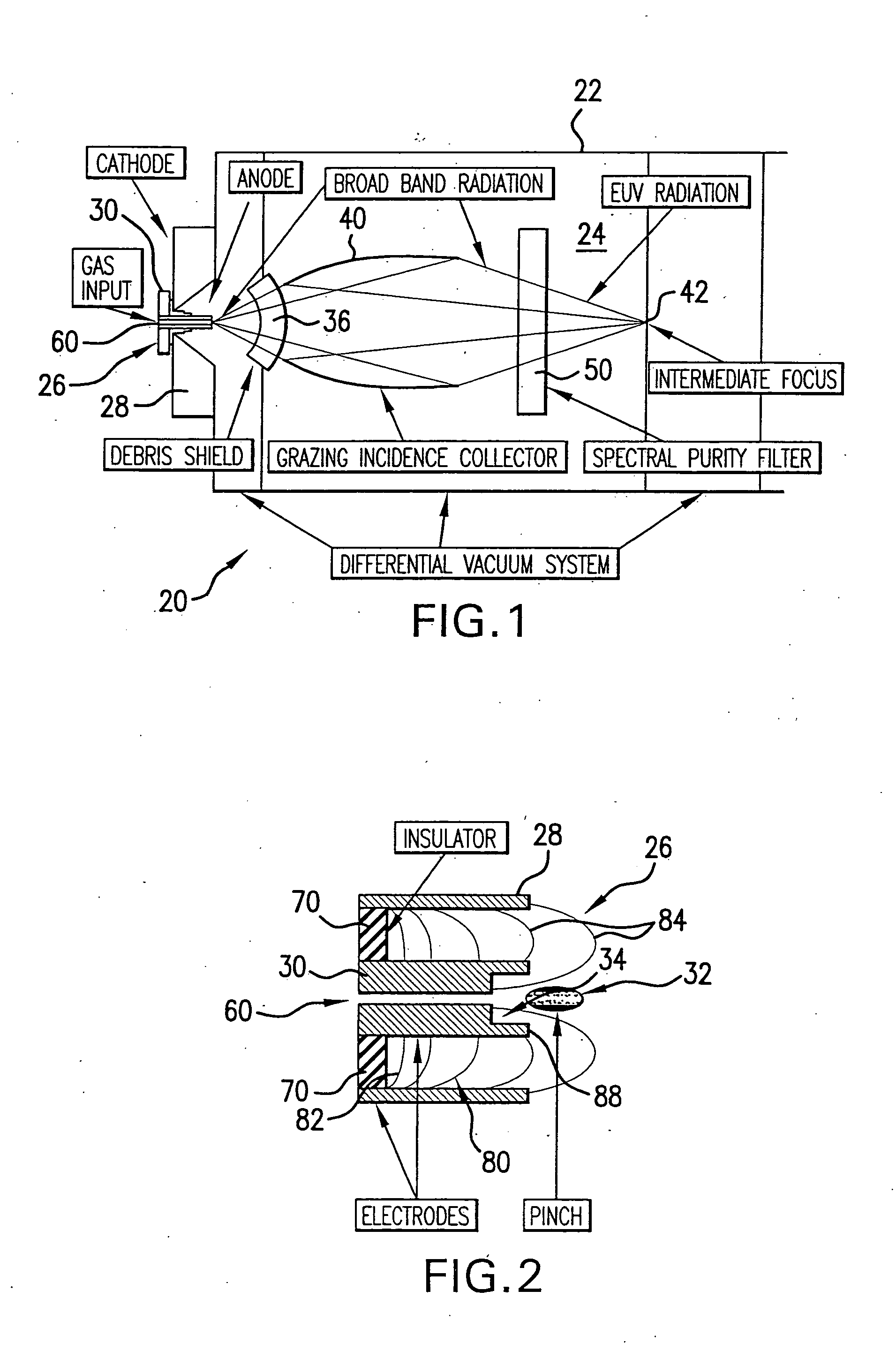
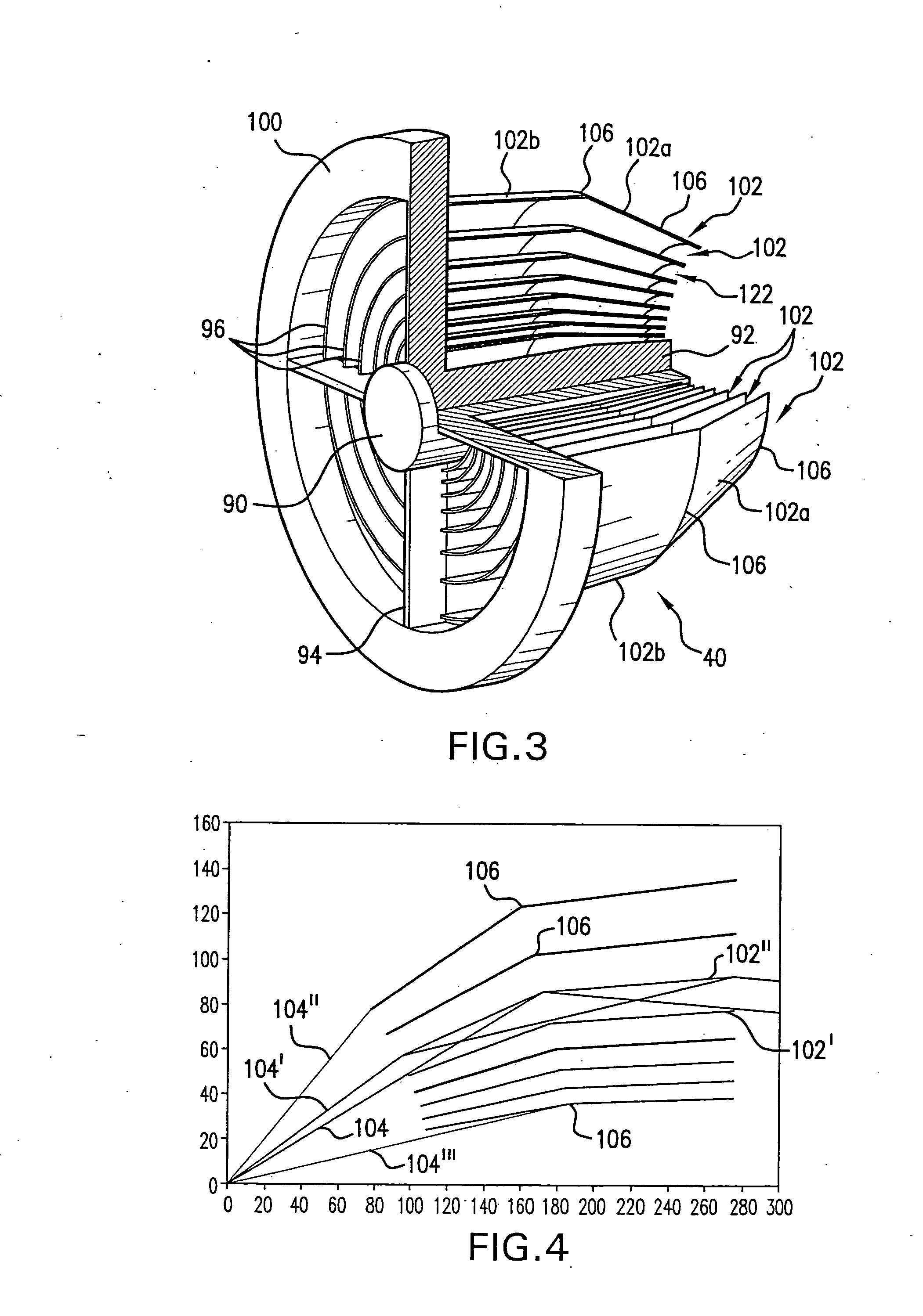
Discharge produced plasma EUV light source
InactiveUS20070023711A1Uniform separationNanoinformaticsElectrode and associated part arrangementsAngle of incidencePeak value
An DPP EUV source is disclosed which may comprise a debris mitigation apparatus employing a metal halogen gas producing a metal halide from debris exiting the plasma. The EUV source may have a debris shield that may comprise a plurality of curvilinear shield members having inner and outer surfaces connected by light passages aligned to a focal point, which shield members may be alternated with open spaces between them and may have surfaces that form a circle in one axis of rotation and an ellipse in another. The electrodes may be supplied with a discharge pulse shaped to produce a modest current during the axial run out phase of the discharge and a peak occurring during the radial compression phase of the discharge. The light source may comprise a turbomolecular pump having an inlet connected to the generation chamber and operable to preferentially pump more of the source gas than the buffer gas from the chamber. The source may comprise a tuned electrically conductive electrode comprising: a differentially doped ceramic material doped in a first region to at least select electrical conductivity and in a second region at least to select thermal conductivity. The first region may be at or near the outer surface of the electrode structure and the ceramic material may be SiC or alumina and the dopant is BN or a metal oxide, including SiO or TiO2. The source may comprise a moveable electrode assembly mount operative to move the electrode assembly mount from a replacement position to an operating position, with the moveable mount on a bellows. The source may have a temperature control mechanism operatively connected to the collector and operative to regulate the temperature of the respective shell members to maintain a temperature related geometry optimizing the glancing angle of incidence reflections from the respective shell members, or a mechanical positioner to position the shell members. The shells may be biased with a voltage. The debris shield may be fabricated using off focus laser radiation. The anode may be cooled with a hollow interior defining two coolant passages or porous metal defining the passages. The debris shield may be formed of pluralities of large, intermediate and small fins attached either to a mounting ring or hub or to each other with interlocking tabs that provide uniform separation and strengthening and do not block any significant amount of light.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV +1
Low consumption permanent magnetism biased axial radial magnetic bearing
InactiveCN101235848AReduce lossSimple structureShaftsEngine componentsMagnetic bearingFlywheel energy storage
The invention relates to a low loss permanent magnet biased axial radial magnetic bearing, which belongs to a mixed magnetic bearing, which comprises an axial stator (1), an axial control winding (2), a radial magnetizing ring permanent magnet (7), a radial stator (3), a radial control winding (4) and a rotor (5) which is sleeved with an iron core (6). The low loss permanent magnet biased axial radial magnetic bearing uses the radial magnetizing ring permanent magnet to build a static bias magnetic field, a closed magnetic circuit is formed through an external axial pole core, a rotor iron core and a radial stator, and the axial control winding produces a controlling flux and a bias flux which are stacked to control axial suspension. A control winding is surrounded on a radial stator of a four-tooth two-antipode structure which is not retained gaps between magnetic poles, the windings on the two corresponding teeth are connected in series, and the superposition of the controlling flux and the bias flux are produced to achieve radial two freedom suspension. The structure is simple, the critical speed is high, the power consumption is low, and the low loss permanent magnet biased axial radial magnetic bearing has wide application prospect in high speed application fields which are flywheel energy storage, air conditioning compressors and turbomolecular pumps and the like.
Owner:NANJING COLLEGE OF CHEM TECH
Magnetically suspended high velocity vacuum pump
High velocity vacuum pump, such as turbomolecular pump, drag pump, centrifugal pump or the like, comprising a stator (10) and a rotor (18,43,53), which is axially and radially suspended with respect to the stator (10) by magnetic bearings (27). The vacuum pump may comprise two at the same rotor provided, parallelly acting pump portions, each one comprising two pumping steps. The rotor may be cylindrical and rotates around an inner stator shaft and within an outer stator portion. In that way, one pumping step (22) is formed between the inner stator shaft and the rotor and another pumping step (24) between the outer stator portion (10) and the rotor. The magnet bearing comprises at least one rotation symmetric magnet (27) and is disposed to give rise to a rotation symmetric magnetic field which is centered around the rotational axis. When and only when the rotor tends to leave the predetermined path, the magnetic field generates induced eddy currents in the rotor, which give rise to restoring stabilizing forces.
Owner:MAGNETAL
Turbomolecular pump
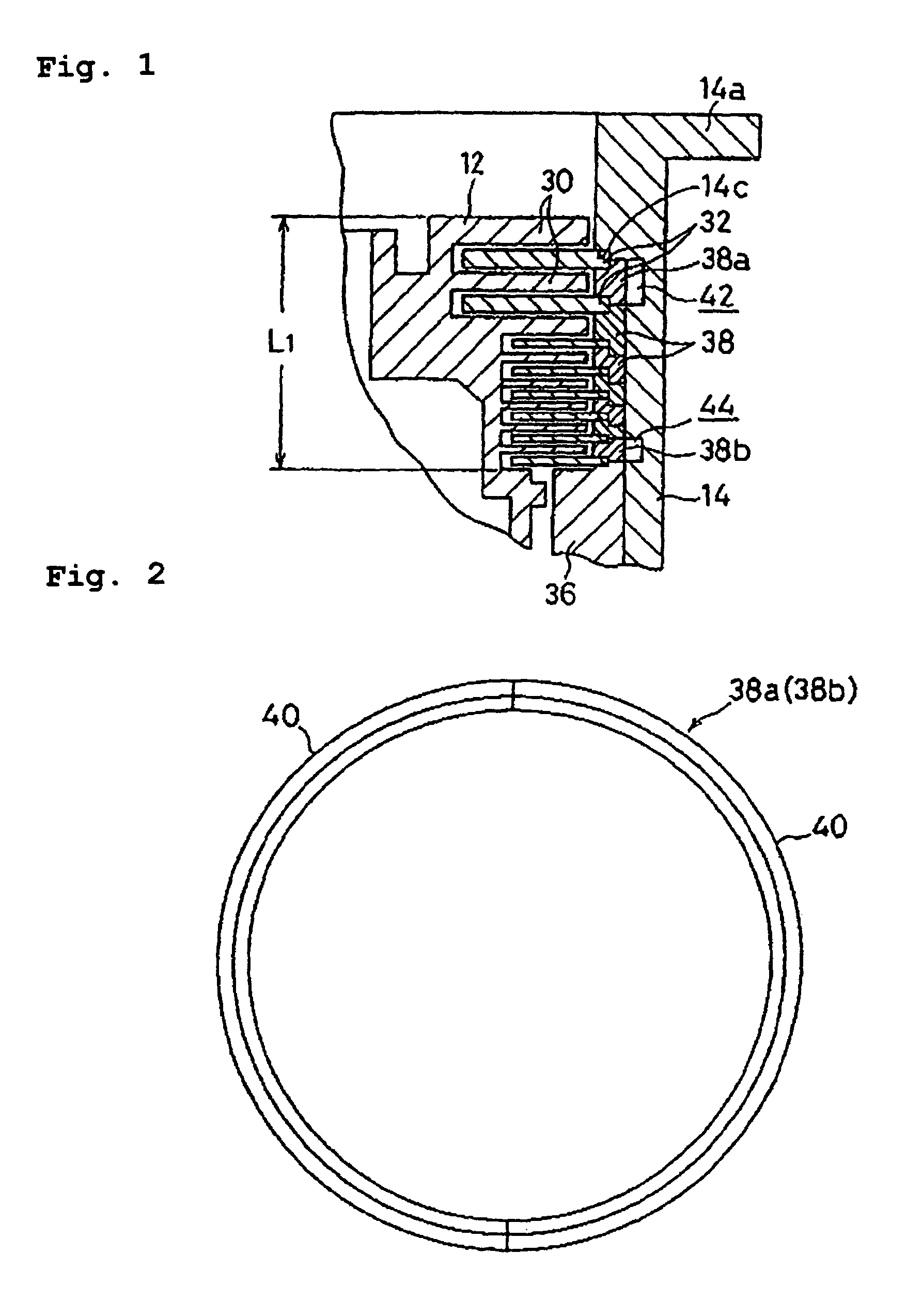
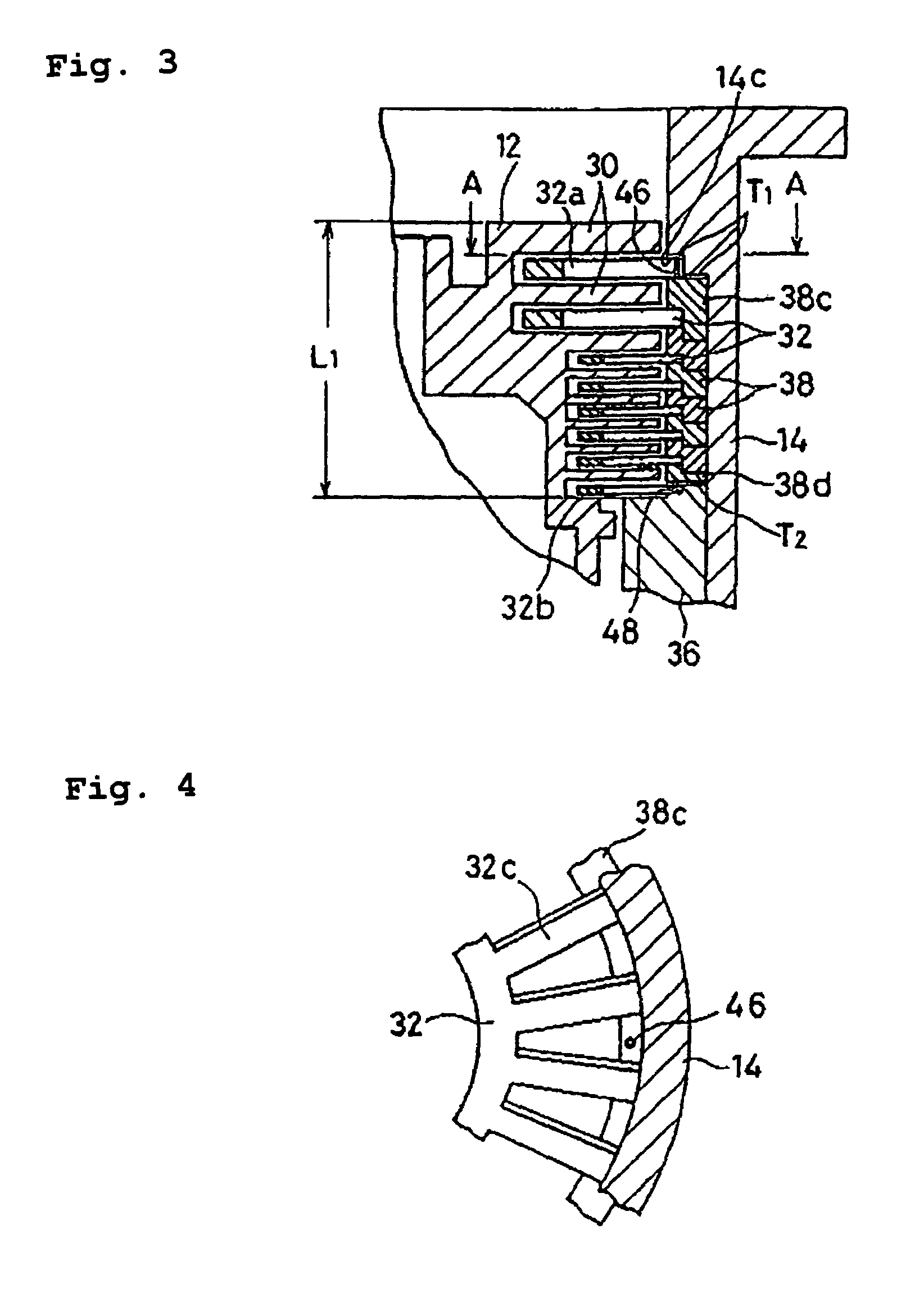
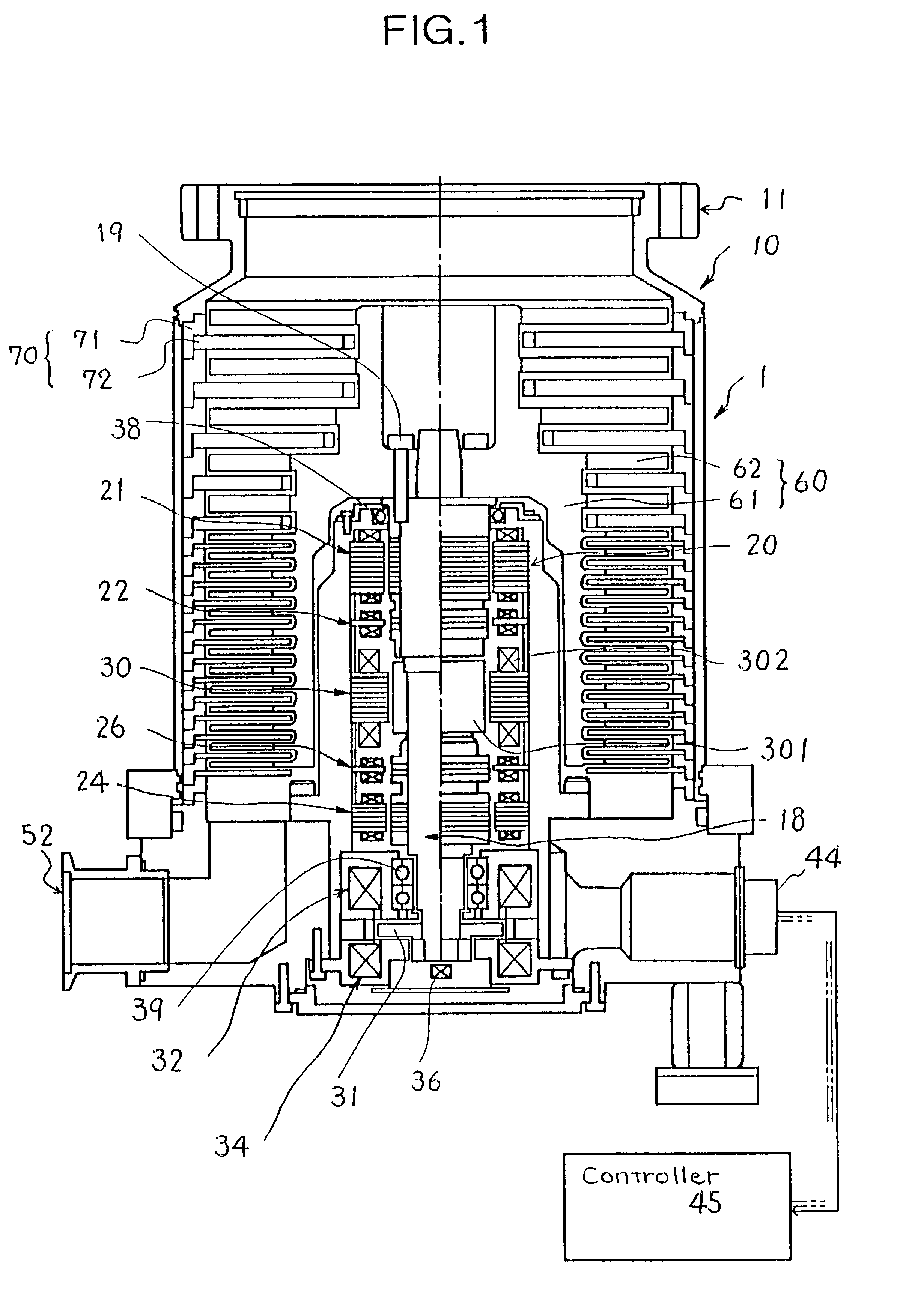
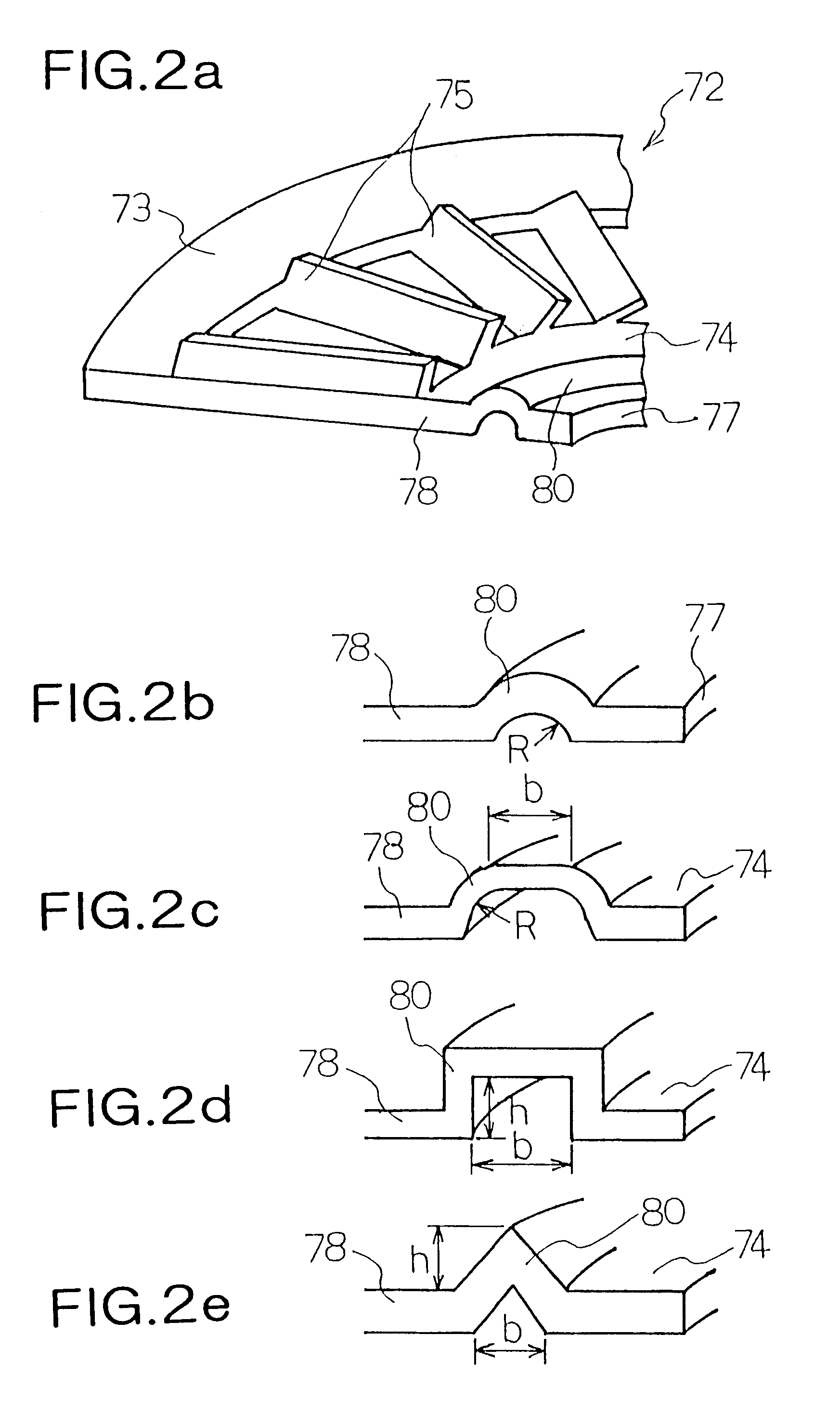
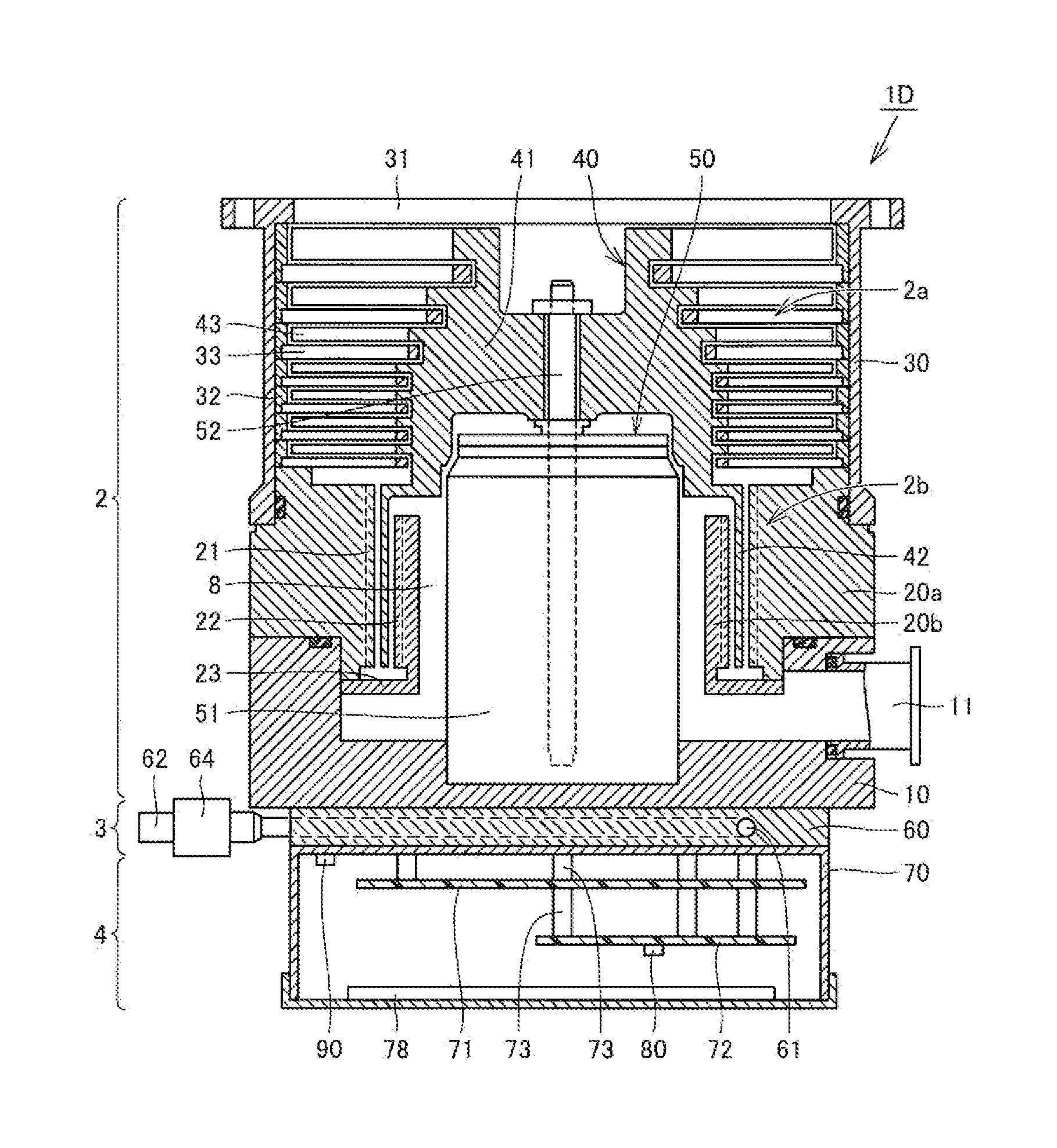
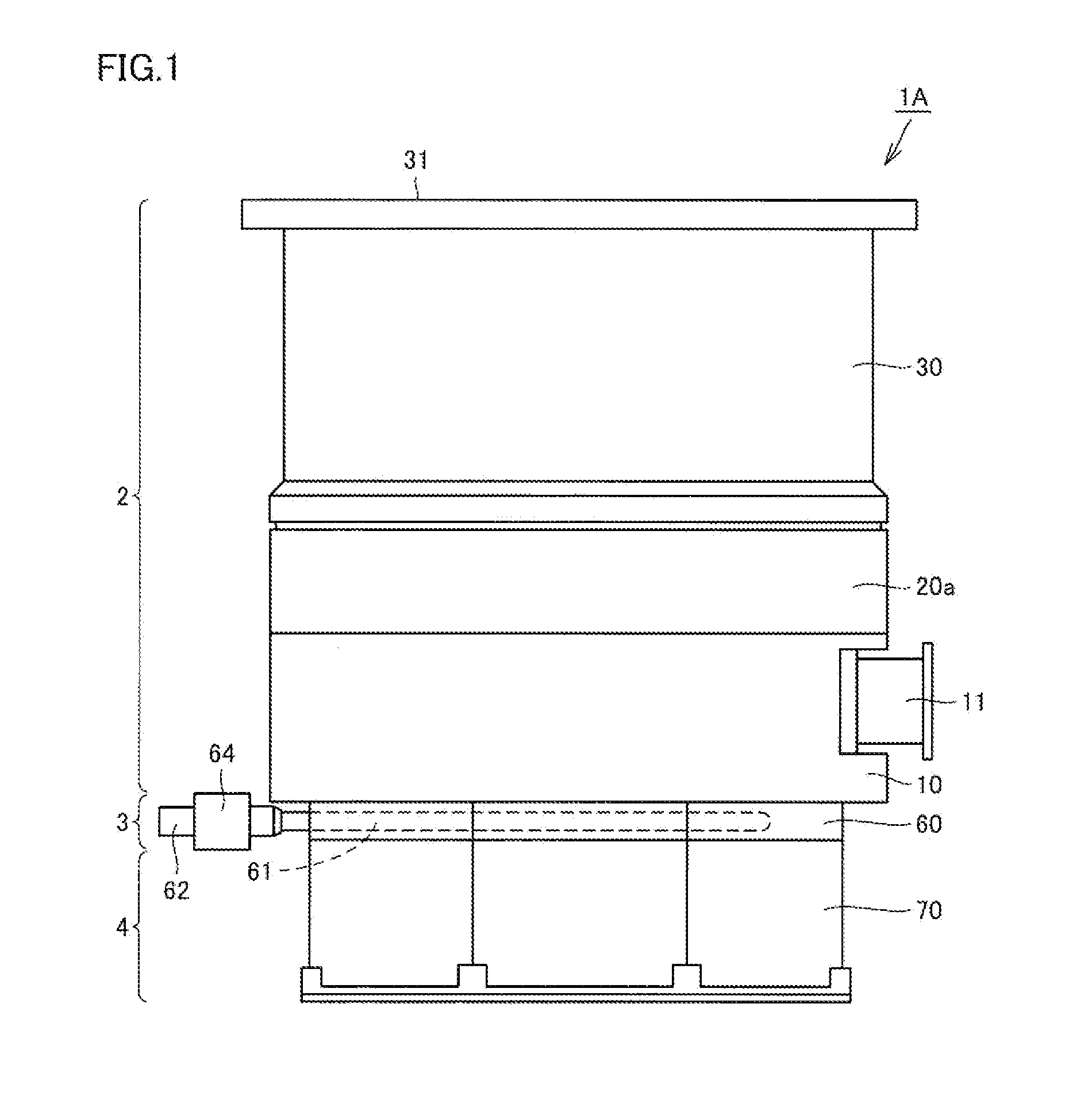
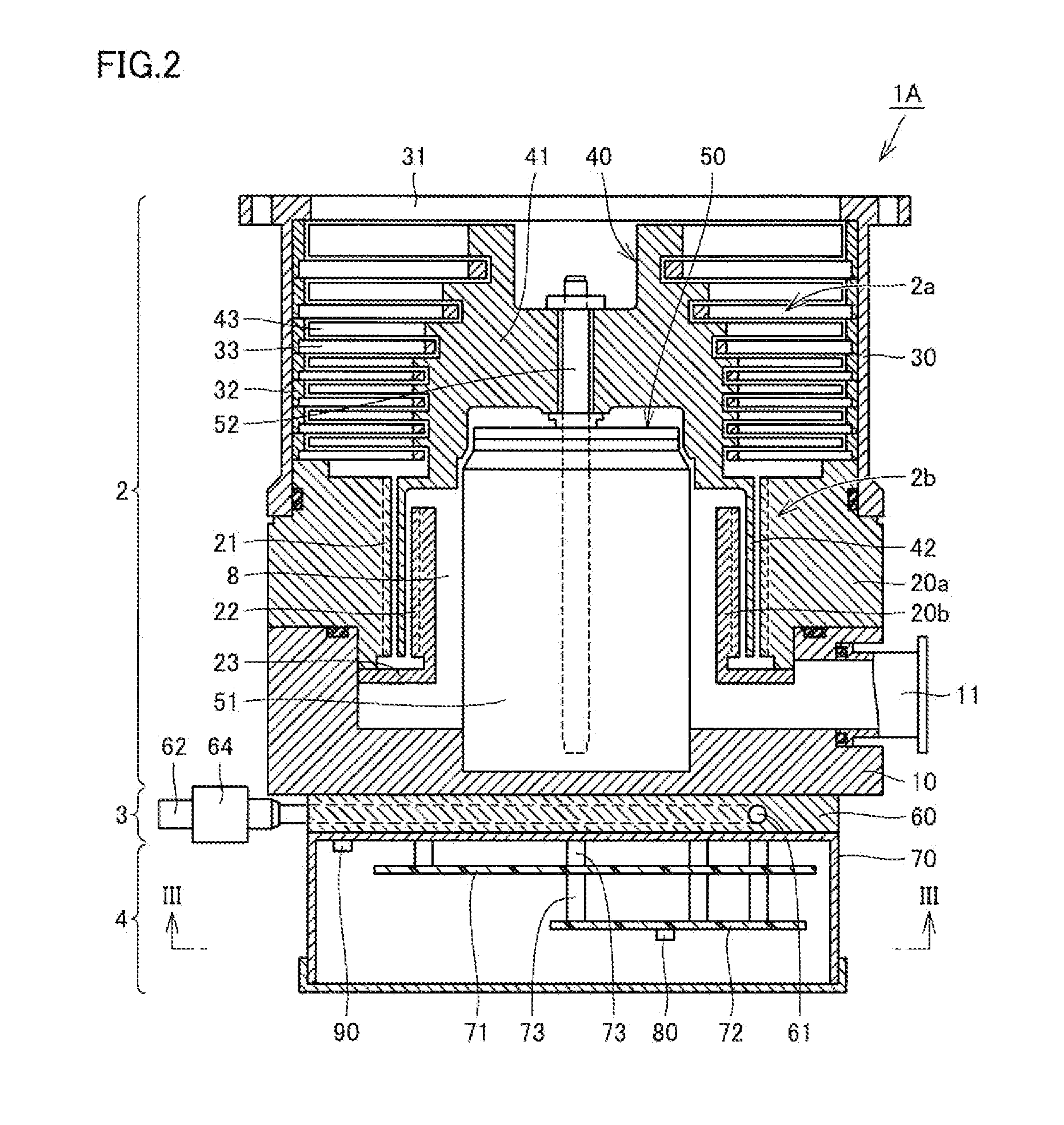
A turbomolecular pump comprises a casing, a rotor having a rotor blades arranged in multiple stages in the casing axially thereof, and a stator having stator blades arranged in multiple stages and alternately located between the rotor blades. Each of the stator blades has an inner ring portion, an outer ring portion spaced-apart from the inner ring portion, and blades connected between the inner and outer ring portions along a circumferential direction thereof. Each of the blades has a first end connected to an outer peripheral edge of the inner ring portion and a second end opposite the first end connected to an inner peripheral edge of the outer ring portion. A reinforcement member is disposed on the inner ring portion of each of the stator blades along the entire circumference of the inner ring portion for reinforcing the stator blade.
Owner:EDWARDS JAPAN
Terminal structure and vacuum pump
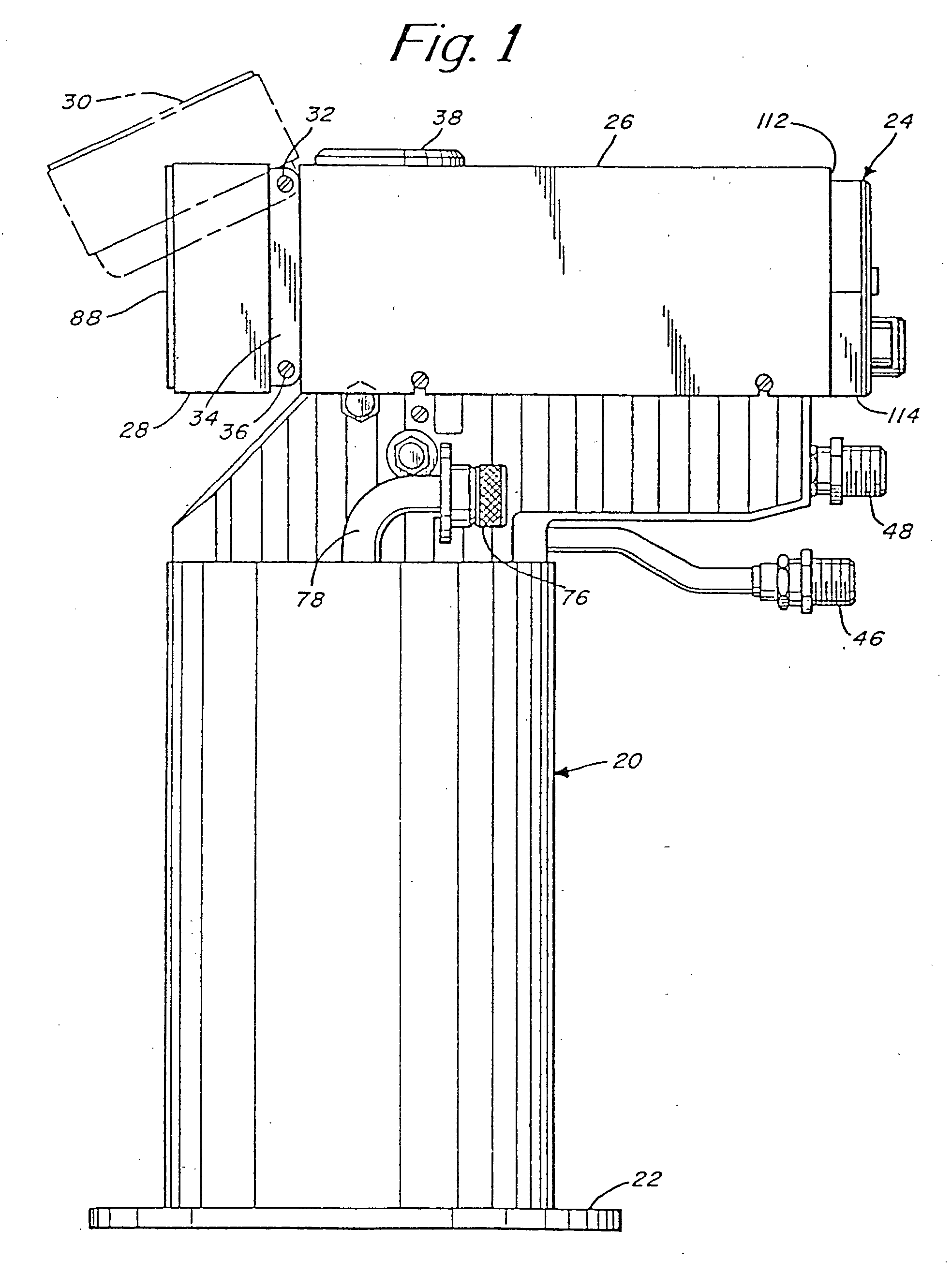
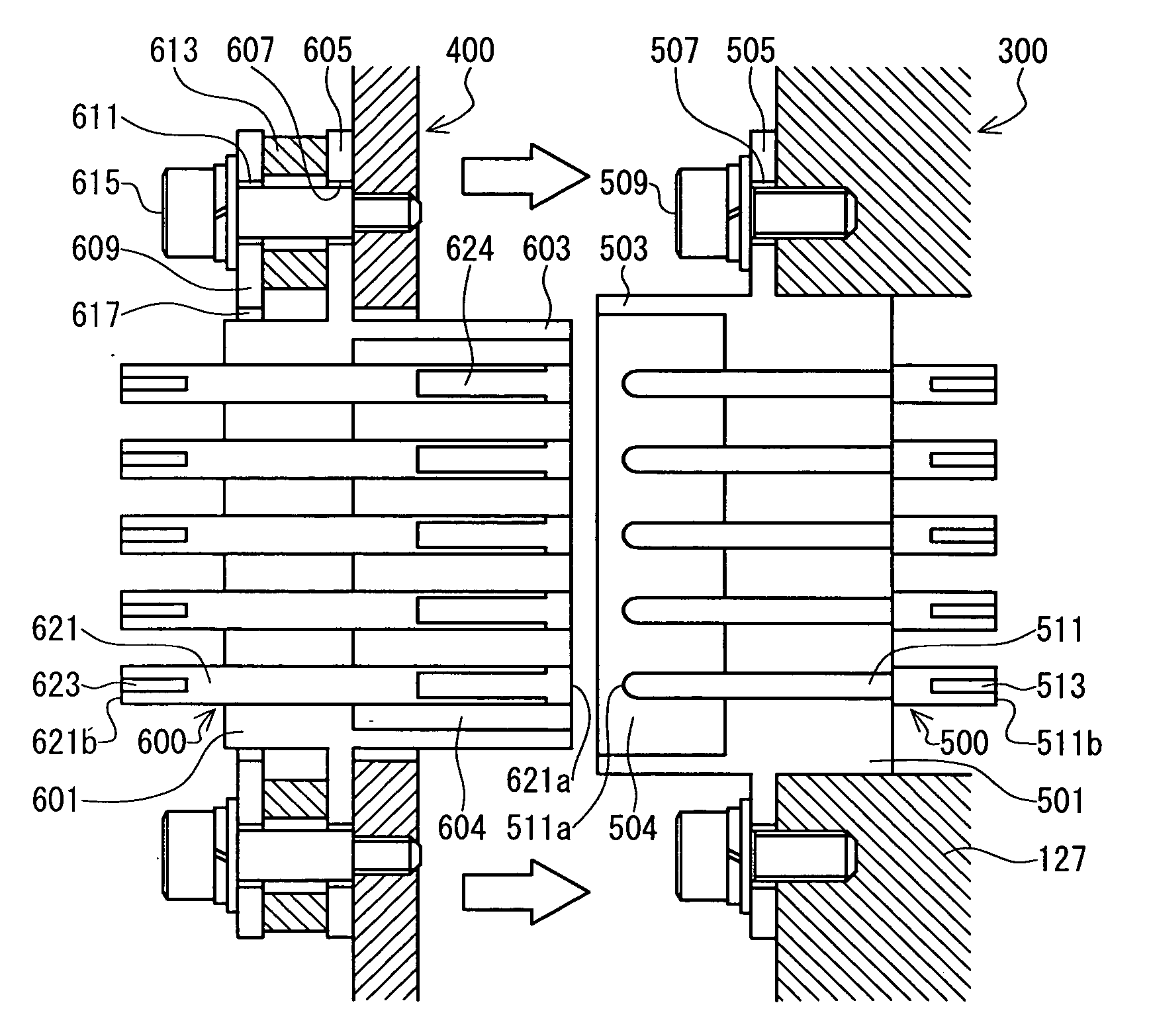
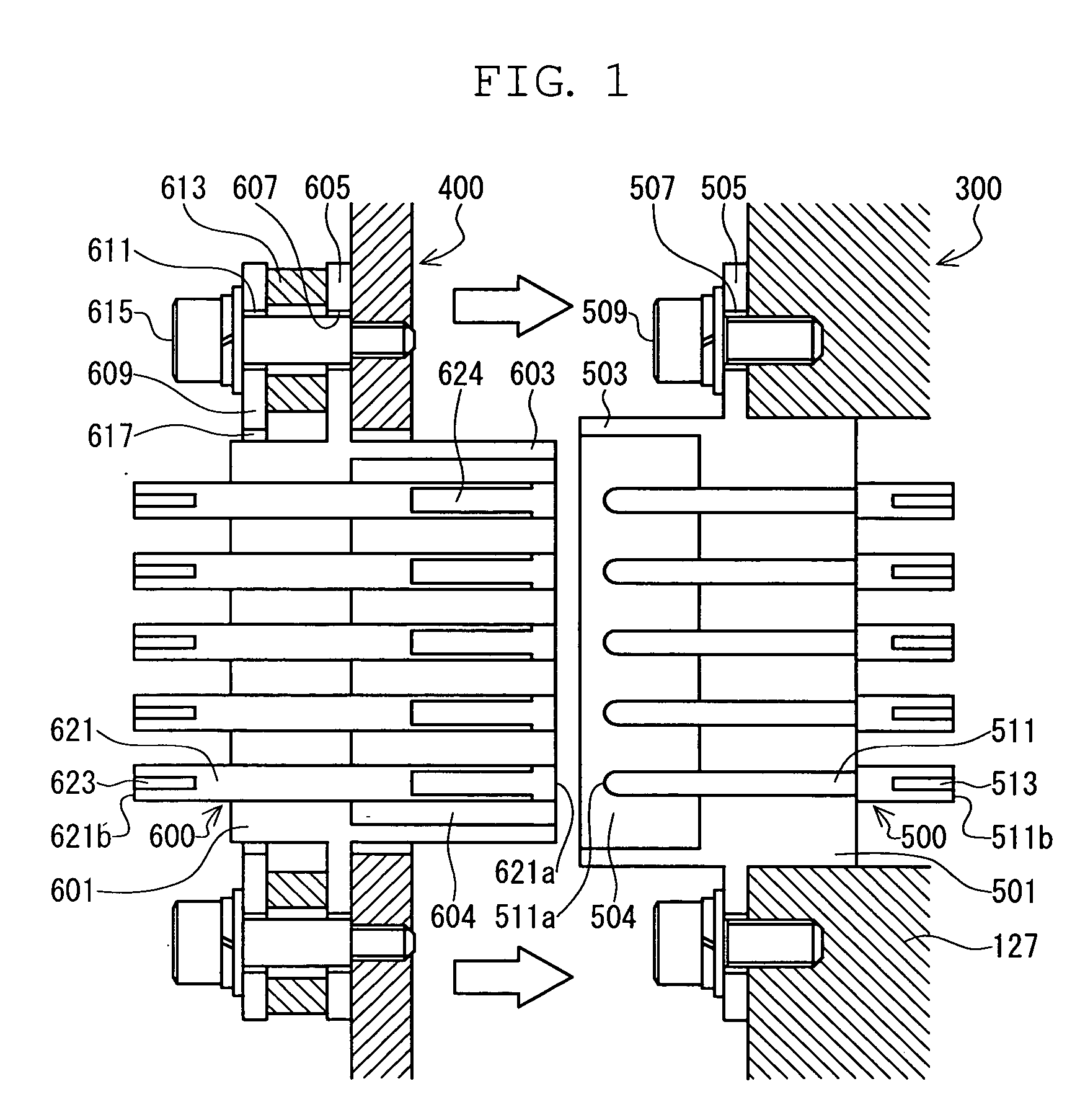
InactiveUS20060281352A1Improve sealingAvoid damageIncorrect coupling preventionPump installationsEngineeringVacuum pump
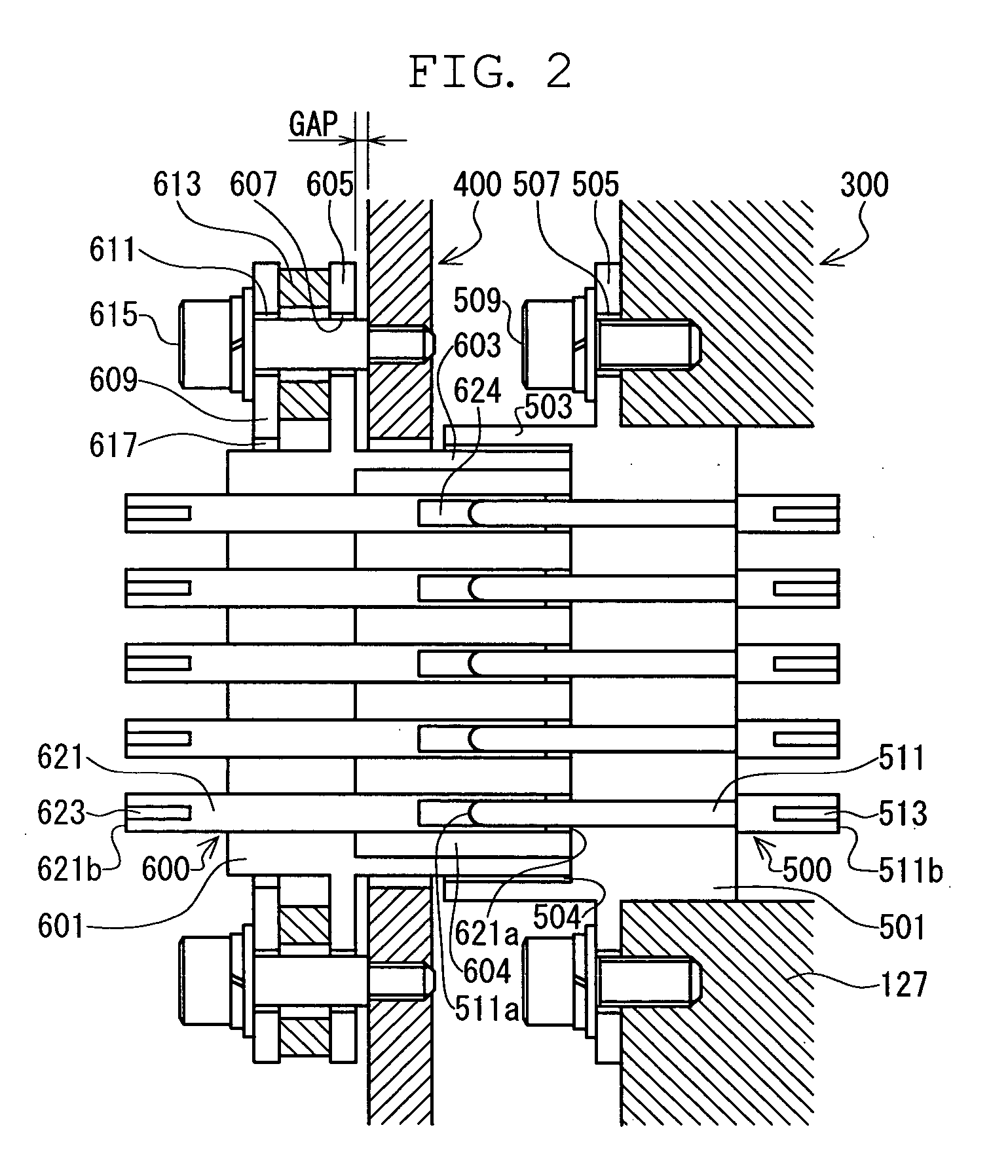
Provided are a terminal structure capable of preventing damage due to an excessive force and having high sealing property, and a vacuum pump to which the terminal structure is applied. When a control device (400) undergoes transition to a turbo molecular pump main body (300), a cylindrical wall (603) of a female connector (600) is fit-engaged with a cavity (504) of a male connector (500). As the connection progresses, head portions (511a) at one ends of male pins (511) are inserted into pin insertion elongated holes (624). When, after that, a forward end of the cylindrical wall (603) of the control device (400) abuts a bottom portion (501) of the female connector (600), the female connector (600) on the control device (400) side, which is of low rigidity, is pushed back against an elastic force of waved washers (613). As a result, even when an excessive force is applied to the female connector (600) and the male connector (500), the force can be mitigated through deformation of the waved washers (613), so there is no fear of the connectors suffering damage.
Owner:EDWARDS JAPAN
Method and apparatus for plasma processing
InactiveUS7601619B2Accurate monitoringImprove controllabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesHigh frequency powerEngineering
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
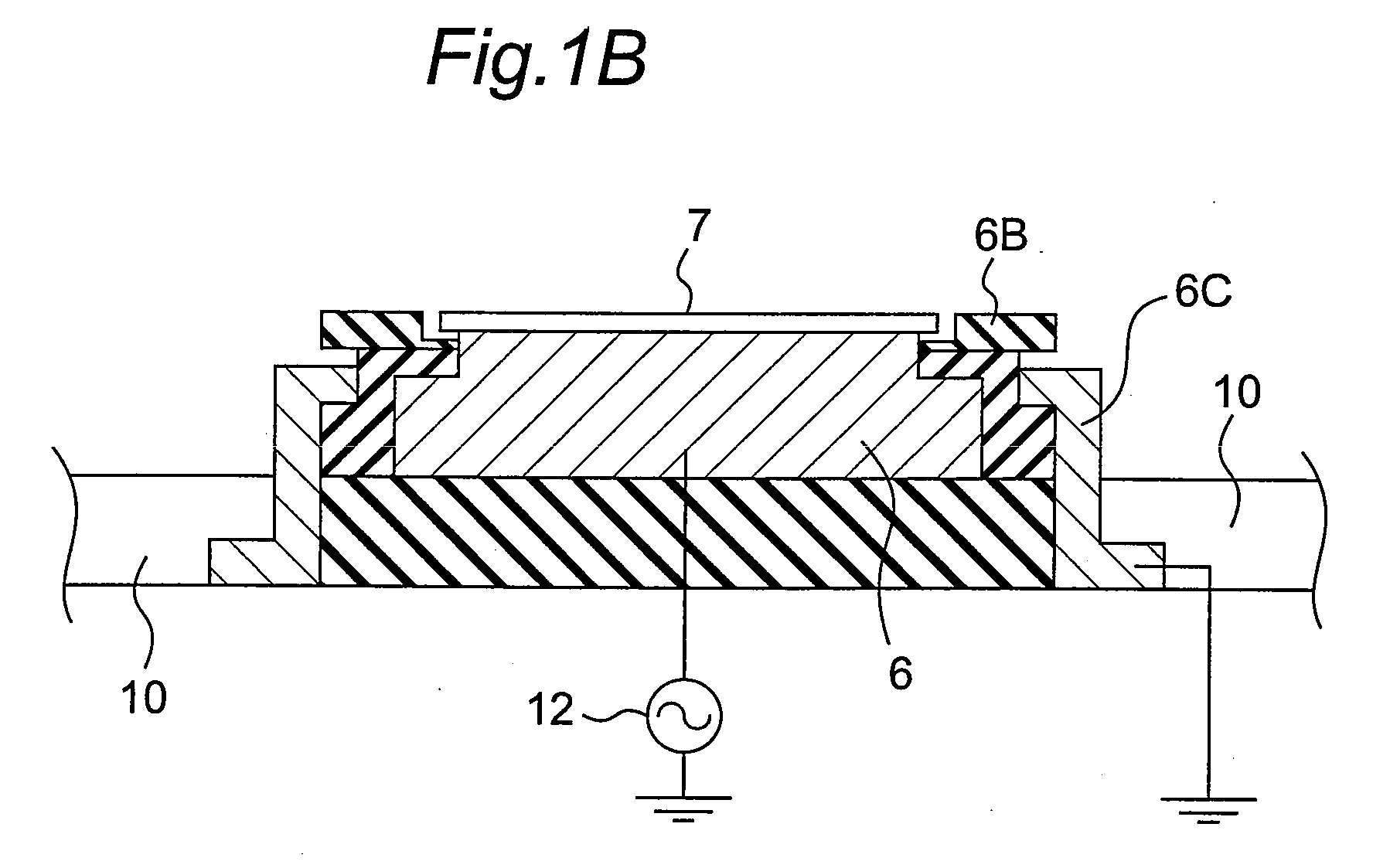
Molecular pump
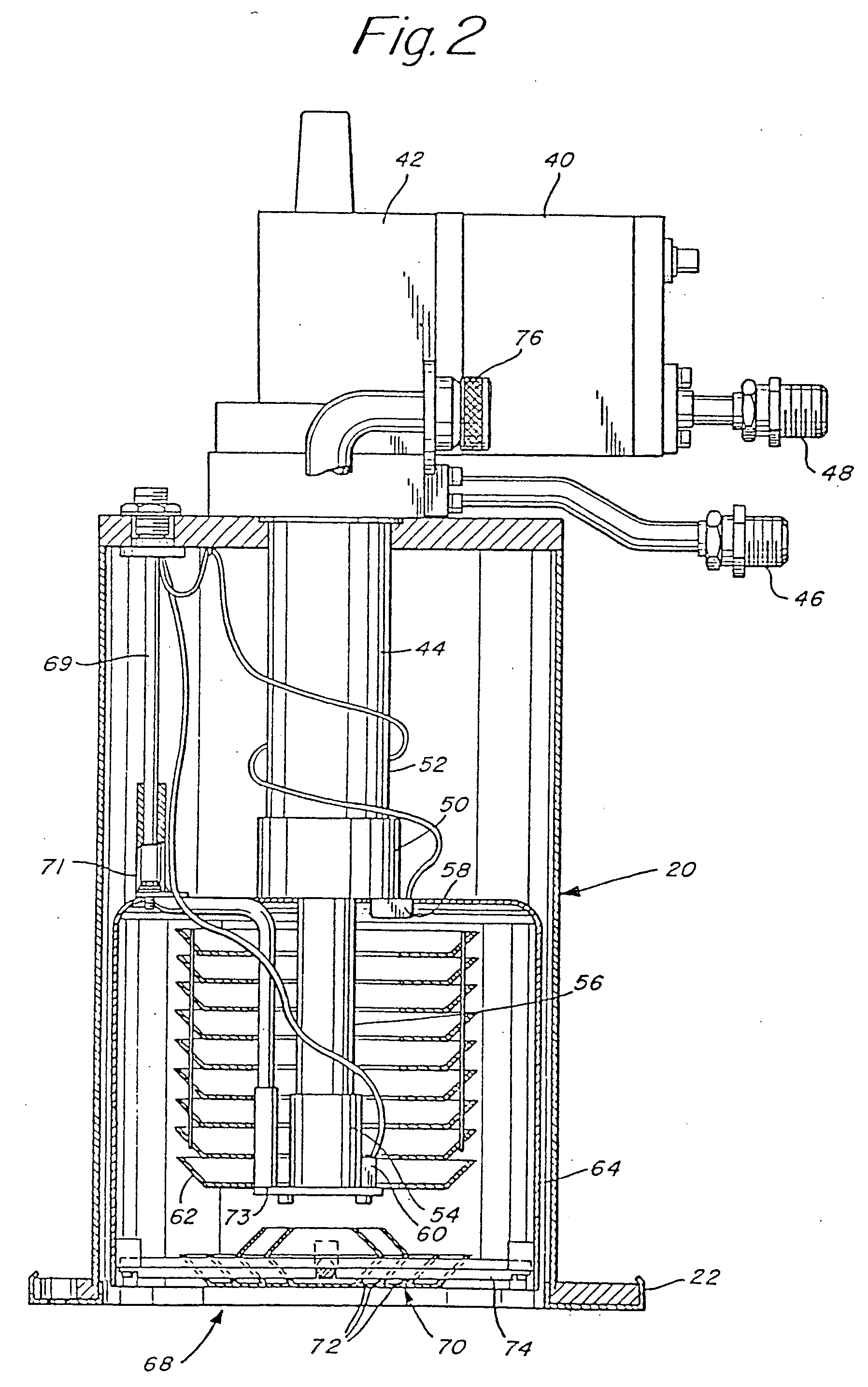
ActiveUS20150184665A1Easy to operateAccurate humidityWind motor controlPump componentsControl cellEngineering
A molecular pump includes a pump body provided with a turbo molecular pump portion, a control unit provided with a control portion and a power supply portion, and a cooling unit for cooling the pump body and the control unit. A first temperature detecting portion is provided in a first position, which is a position inside the control unit and has a low temperature. A second temperature detecting portion also serving as a humidity detecting portion is provided in a second position, which is a position inside the control unit and has a high temperature. The control portion controls the operation of the cooling unit in accordance with a relative humidity in the first position, calculated based on temperature information detected by the first temperature detecting portion and based on temperature information and humidity information detected by the second temperature detecting portion also serving as a humidity detecting portion.
Owner:OSAKA VACUUM
Device and method for calibrating flow-dividing vacuum leaking hole
ActiveCN101713696AWide measurement rangeReduce measurement uncertaintyDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateUltra-high vacuumEngineering
The invention relates to a device and a method for calibrating a flow-dividing vacuum leaking hole, in particular to the device and the method for calibrating the vacuum leaking hole, the leakage value of which is less than 1*10-8 Pa.m3 / s by adopting flow-dividing technology, and belongs to the field of measuring technology. The device consists of the calibrated leaking hole, a valve, an ionization gauge, a small hole, a flow-dividing chamber, a non-evaporable getter pump, an ultrahigh vacuum calibrating chamber, a metering hole, a very high vacuum pumping chamber, an oil-free bi-turbo molecular pump air exhauster set, a quadrupole mass spectrometer, a flow meter, a super-high vacuum calibrating chamber, the metering hole, a super-high vacuum pumping chamber and a common molecular pump air exhauster set. The method adopts a fixed flow method gas micro-flow meter to provide a known gas flow rate, so the measuring range of the flow rate is wide and uncertainty of the measurement is low; and by adopting a flow-dividing method to calibrate the vacuum leaking hole, the method of the invention completely avoids a nonlinear error of the quadrupole mass spectrometer and can precisely calibrate the vacuum leaking hole the leakage value of which is less than 1*10-8 Pa.m3 / s.
Owner:NO 510 INST THE FIFTH RES INST OFCHINA AEROSPAE SCI & TECH
Turbine Cap for Turbo-Molecular Pump
A turbine assembly mounted to a pump rotor via mounting bolts. The turbine includes fins extending therefrom for pumping gasses and suspended particles from a semiconductor processing chamber. The tops of the bolts are recessed from the top surface of the turbine in a bolt cavity having an open end. A cap member is mounted over and seals the open end of the bolt cavity via a center bolt. The cap member has a shaped upper surface (conical, parabolic, squared, rounded) for deflecting particles away from the center of the turbine and toward the turbine's fins. The cap member's upper surface can include particle deflecting features such as fins, channels or asymmetric shapes to enhance particle deflection as the cap member rotates. The cap member can include a compressible o-ring for a friction fit mounting to the turbine.
Owner:TEXAS CAPITOL SEMICON INC
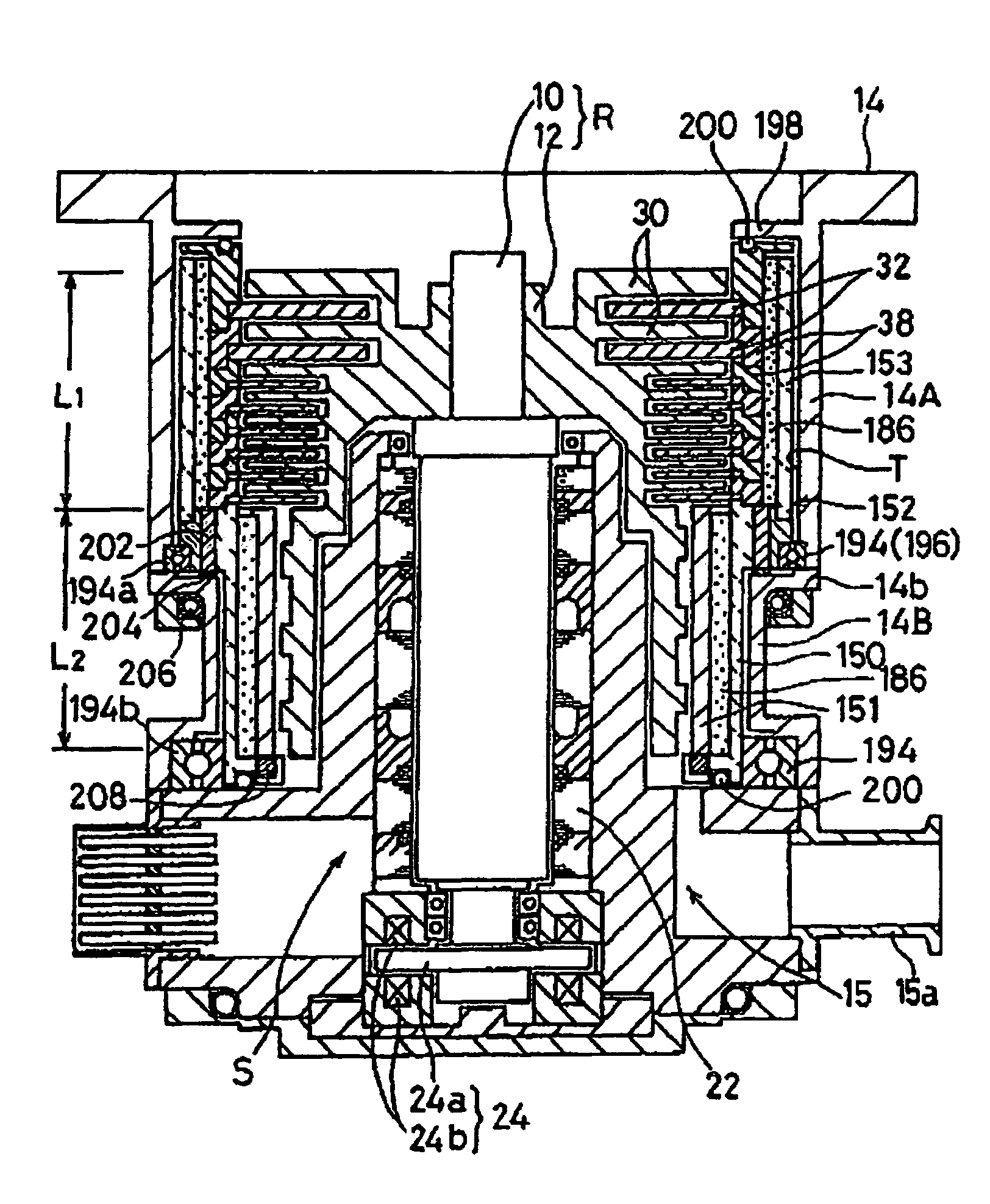
Turbo-molecular pump and touchdown bearing device
InactiveUS20080206079A1Extended service lifeRotation speed is limitedRolling contact bearingsPump componentsMagnetic bearingEngineering
A touchdown bearing device includes an outer ring fixed to a housing, an inner ring radially opposed to the outer ring, an intermediate ring radially interposed between the outer ring and the inner ring, a first ball interposed between the outer ring and the intermediate ring, and a second ball interposed between the intermediate ring and the inner ring. The touchdown bearing device is configured so that when a magnetic bearing normally operate, a rotary shaft and the inner ring are brought into a noncontact state, and that meanwhile, when the magnetic bearing does not normally operate, the rotary shaft is supported by the inner ring so as to support the rotary shaft against the housing.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
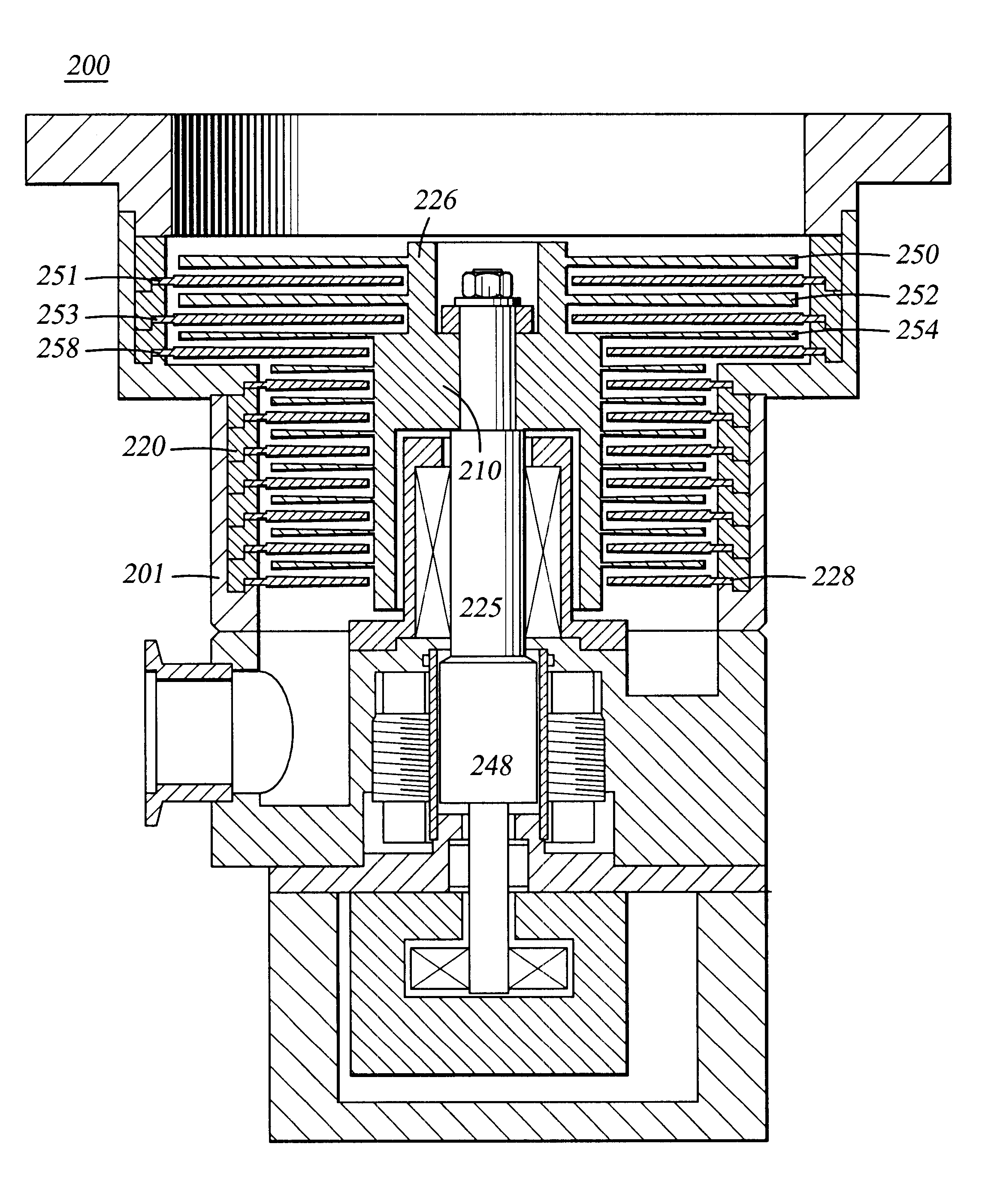
Turbo Molecular Pump with Improved Blade Structures
InactiveUS20120148390A1Improve blade structureElevate pumping speed and stability of pumpPump componentsStatorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention discloses a turbo molecular pump with improved blade structures. The turbo molecular pump comprises a rotor and a stator, wherein the rotor includes five rotor blade assemblies and the stator includes five stator blade assemblies, and wherein the blade number and the blade angle of each rotor blade assembly and stator blade assembly are adjusted to optimization, so as to enhance the pumping speed and the stability of the turbo molecular pump as well as to reduce the difficulty for manufacturing the turbo molecular pump.
Owner:PROSOL
Turbo-molecular pump having enhanced pumping capacity
In one aspect, a vacuum processing system comprising a vacuum processing chamber and a turbo-molecular pump disposed on the vacuum processing chamber is provided. The turbo-molecular pump comprises a casing having an inlet port and an outlet port, a stator disposed on an inner wall of the casing, a rotor disposed in the stator, and a motor extending coaxially with the rotor, wherein at least the first stage of the pump is enlarged with no correspondingly larger pump components other than the corresponding upper portion of the housing.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
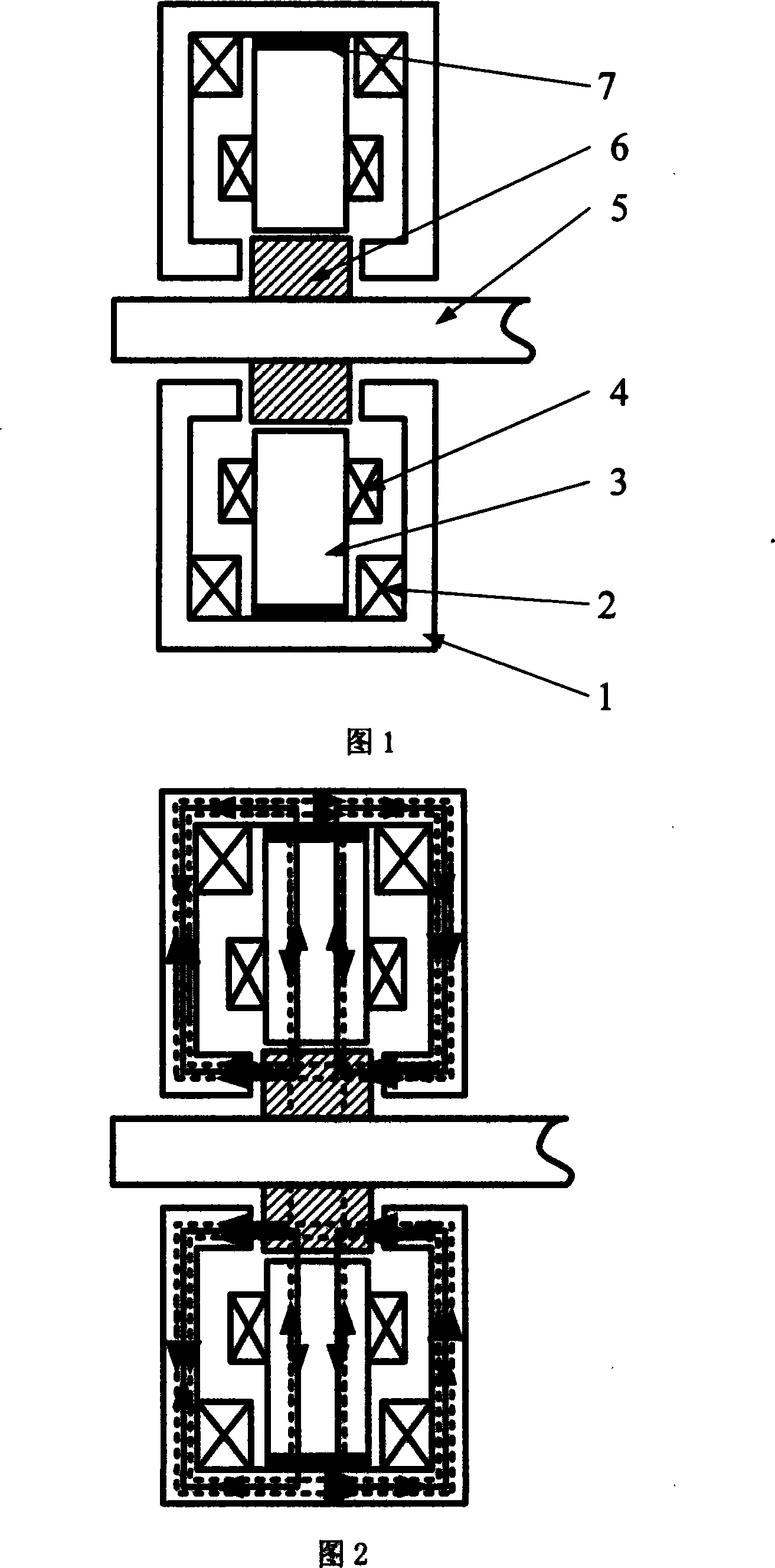
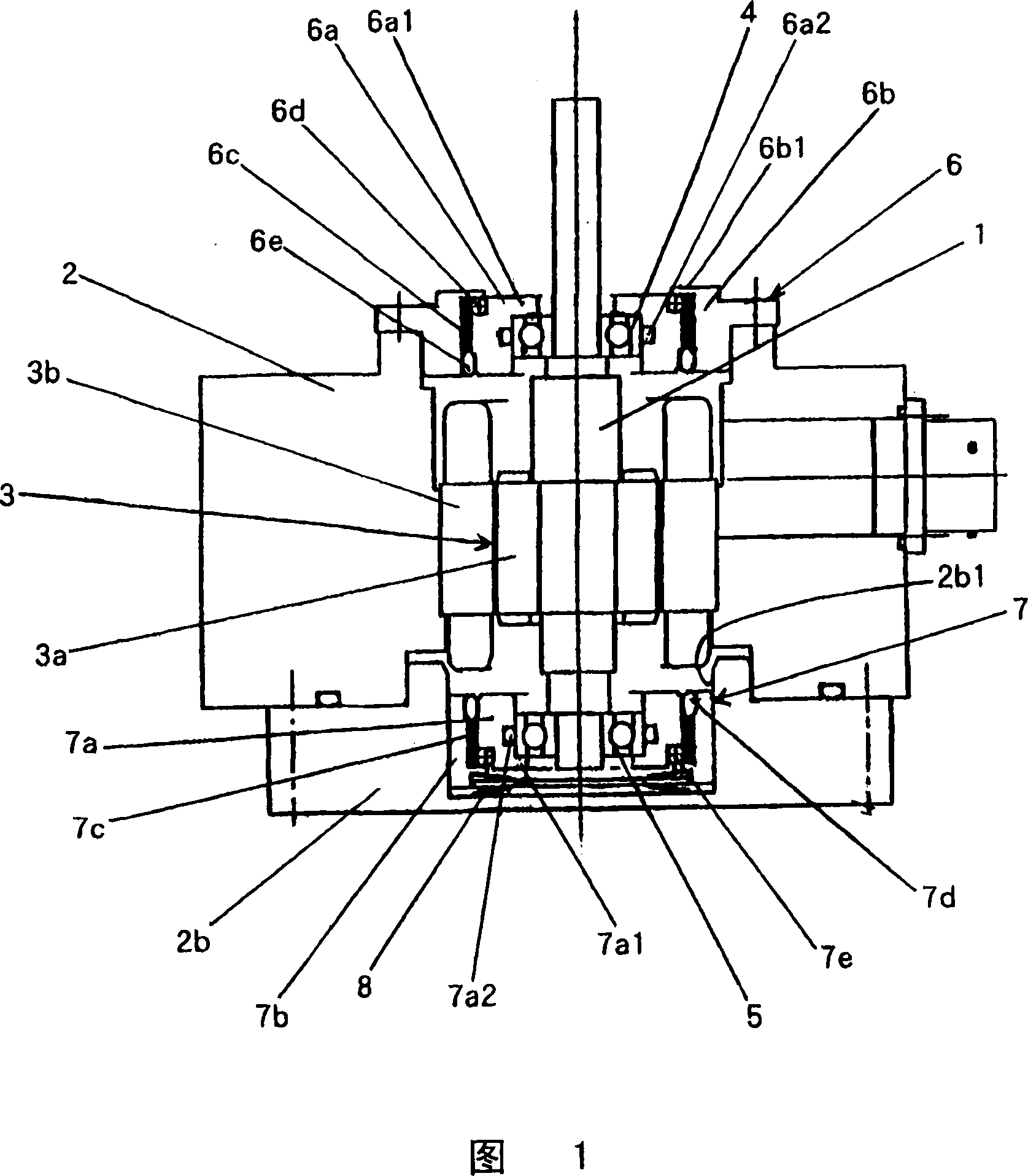
Bearing support structure for turbomolecular pump
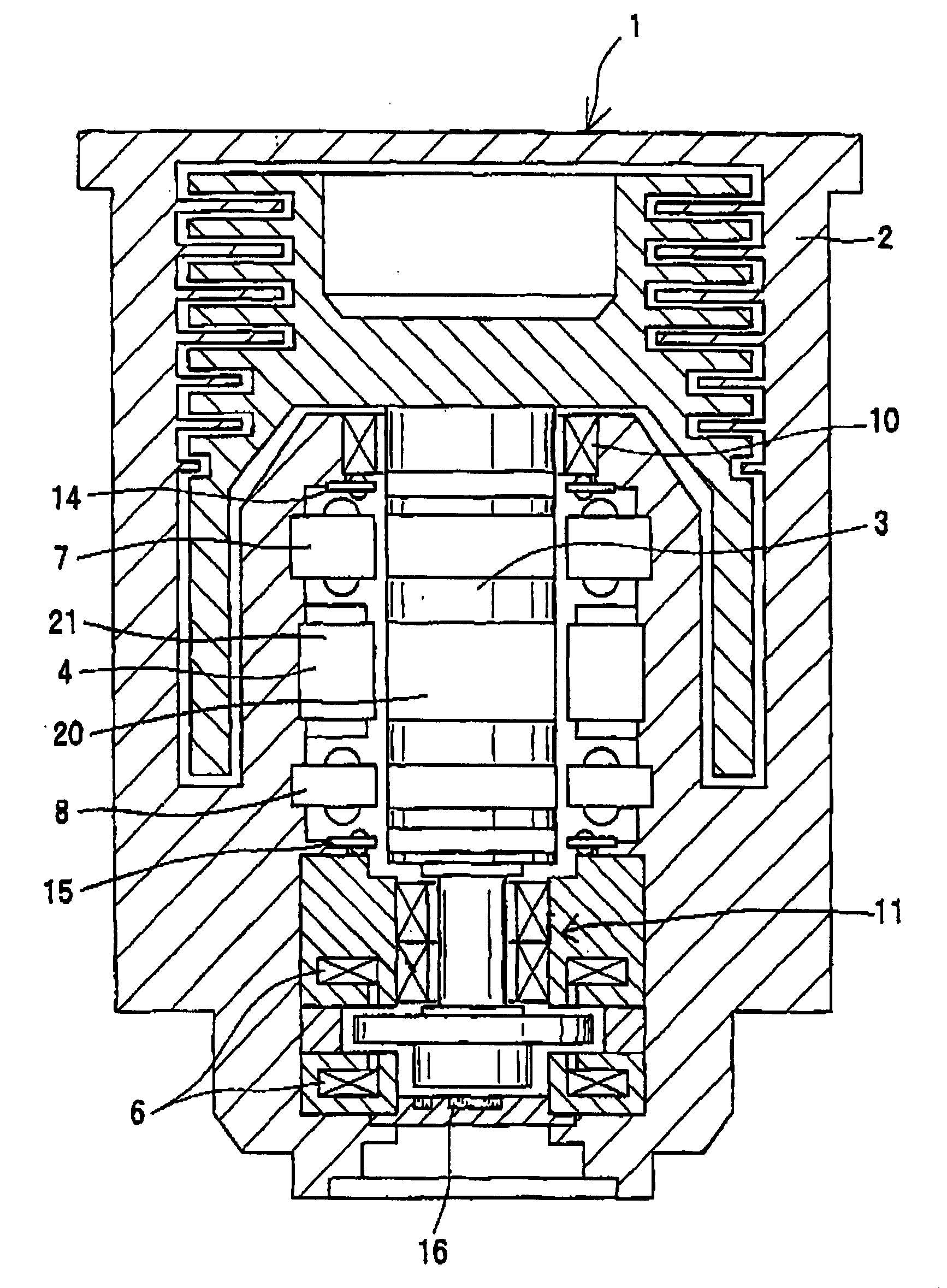
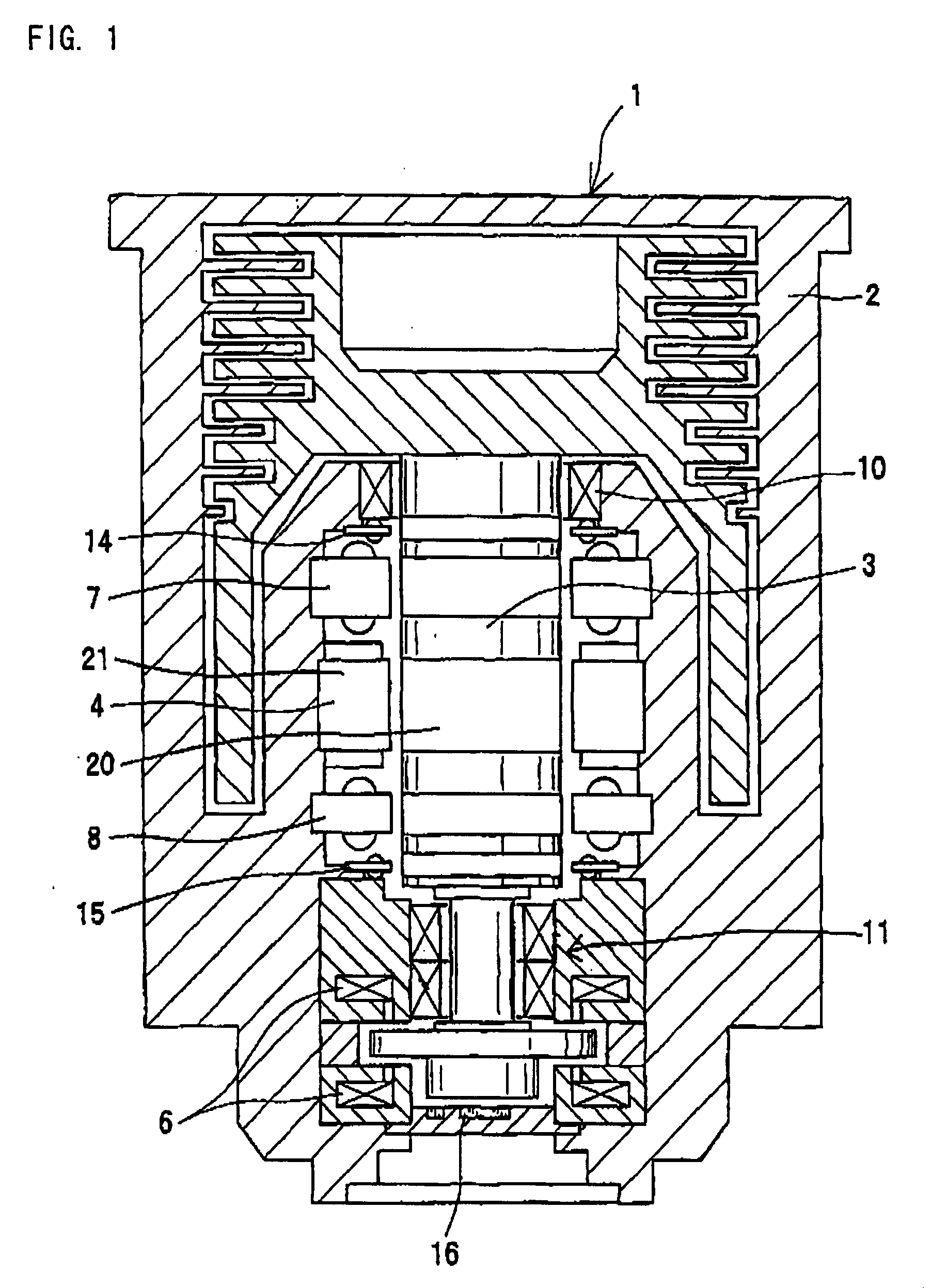
InactiveCN1973134AIncreased durabilitySolution to short lifePump componentsShaftsBall bearingRolling-element bearing
A bearing support structure for a turbomolecular pump, capable of absorbing fine vibration occurring in a bearing section in a turbomolecular pump of a type in which a rotation shaft of a rotor is supported by rolling bearings, capable of cooling heat produced at the bearing section, having long life, and being safe. A bearing support structure for a turbomolecular pump, where ball bearings (4, 5) for supporting a rotation shaft (1) are fitted in position so as to be in contact with an upper first sleeve (6) and a lower second sleeve (7), respectively, at the outer periphery and one end surface of each of the bearings (4, 5). The first sleeve (6) and the second sleeve (7) are each formed in a double structure constructed from an inner sleeve and an outer sleeve, and gel layers (6c, 7c) having predetermined heat conductivity are provided between the inner sleeve and the outer sleeve. In front and rear of the gel layers (6c, 7c), there are provided O-rings (6d, 6e) and O-rings (7d, 7e) to seal up the gel layers (6c, 7c).
Owner:OSAKA VACUUM
Turbo-molecular pump
ActiveUS20150086328A1Increase heat absorptionImprove cooling effectWind motor controlPump componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A turbo-molecular pump comprises: a rotor having a plurality of stages of rotor blades and a cylindrical section; a plurality of stages of stationary blades alternately arranged with respect to the rotor blades; a stator arranged with a gap from the cylindrical section, the stator together with the cylindrical section constituting a screw groove pump section; a plurality of spacers stacked on a base, the spacers including at least one cooling spacer having a cooling section; a heater heating the stator; a temperature regulation section controlling the heater to regulate the temperature of the stator so as to be a reaction product accumulation prevention temperature; and an auxiliary ring for reaction product accumulation prevention at least a part of which is located in a space between the spacer facing a bottom step rotor blade, and the bottom step rotor blade.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
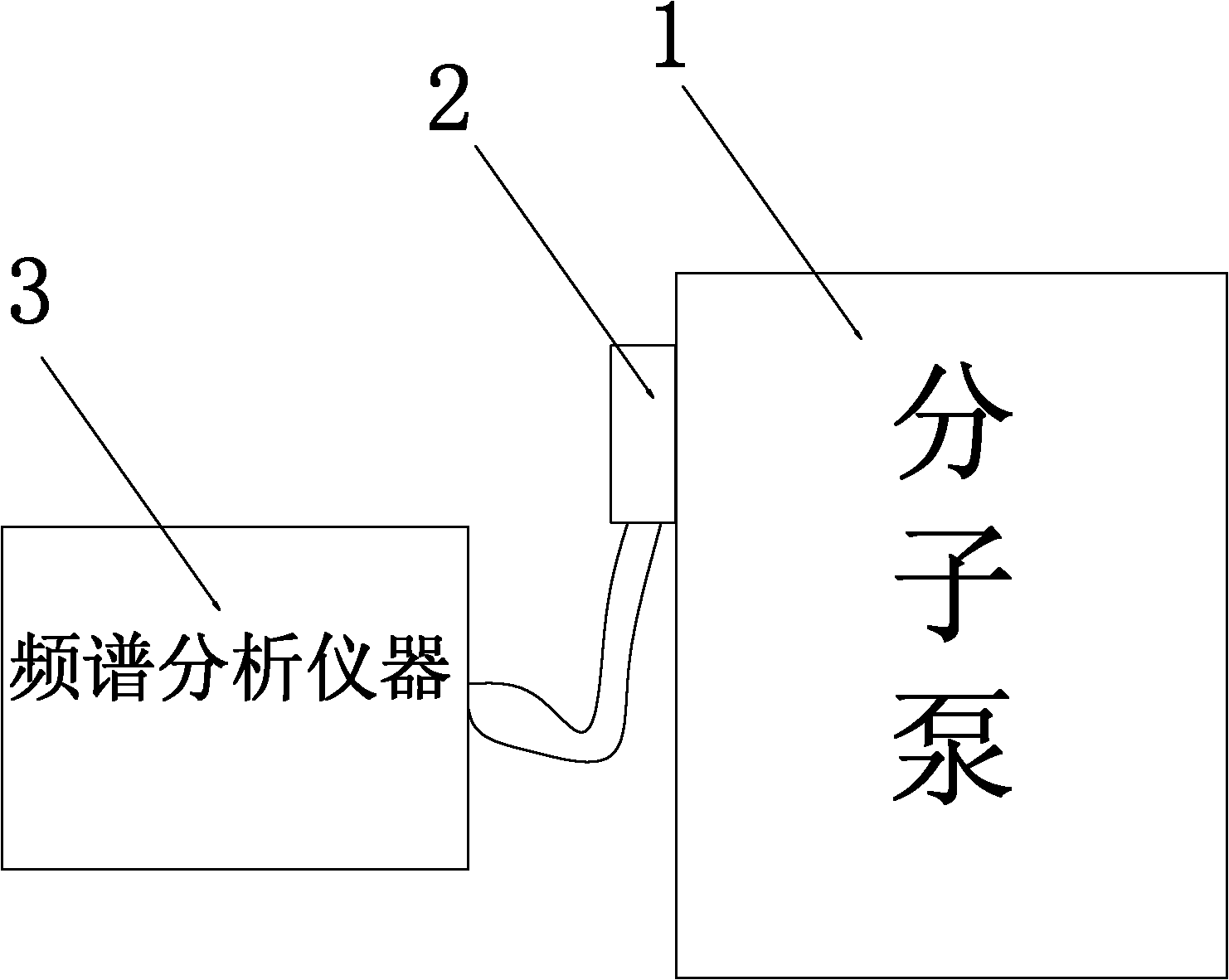
Method for detecting state of high-speed high-vacuum turbomolecular pump
InactiveCN102155425ASimple methodEasy to detectPump controlAxial flow pumpsFrequency spectrumSpectrum analyzer
The invention relates to a method for detecting the state of a high-speed high-vacuum turbomolecular pump. The method comprises the following steps: A) sticking an acceleration sensor on the outer shell of the turbomolecular pump; B) starting up the turbomolecular pump, measuring the shake acceleration value of the turbomolecular pump utilizing the acceleration sensor, and transmitting the value to a spectrum analysis instrument; C) acquiring the data of acceleration value spectrum variation in a certain frequency range utilizing the spectrum analysis instrument; and D) judging the bearing running state of the turbomolecular pump utilizing the data of the acceleration value spectrum variation in a certain frequency range: (D1) when in a high frequency state, the acceleration signal value is less and has no mixed frequency, which means that the turbomolecular pump is in a good running state; (D2) when in a high frequency state, the acceleration signal value is great and has mixed frequency, which means that the turbomolecular pump is in a poor running state; and (D3) when in a high frequency state, the acceleration signal value is great and thick, and has much mixed frequency, which means that the turbomolecular pump is in a very poor running state and needs to be maintained. By the method, the state of the turbomolecular pump is convenient and rapid to grasp for users, the conclusions of normal, risk and danger and the like can be obtained, the possible defects of the core component of the turbomolecular pump can be found out timely, the enlargement of the stoppage of the turbomolecular pump can be avoided, unexpected stopping rate of a machine is reduced, and cost is saved.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN GONGXIANG PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
Vacuum pumping system design for vacuum container
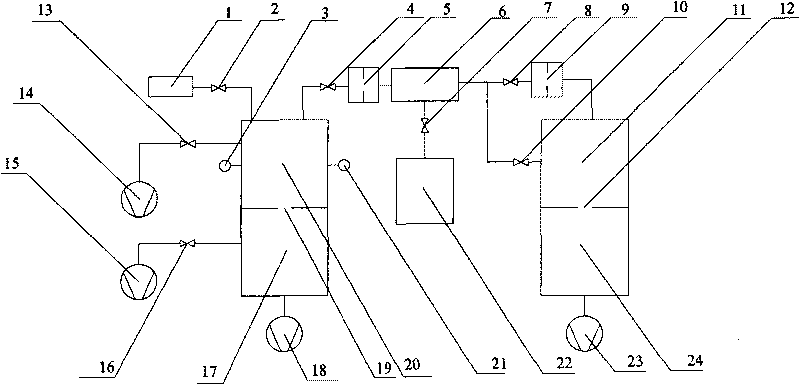
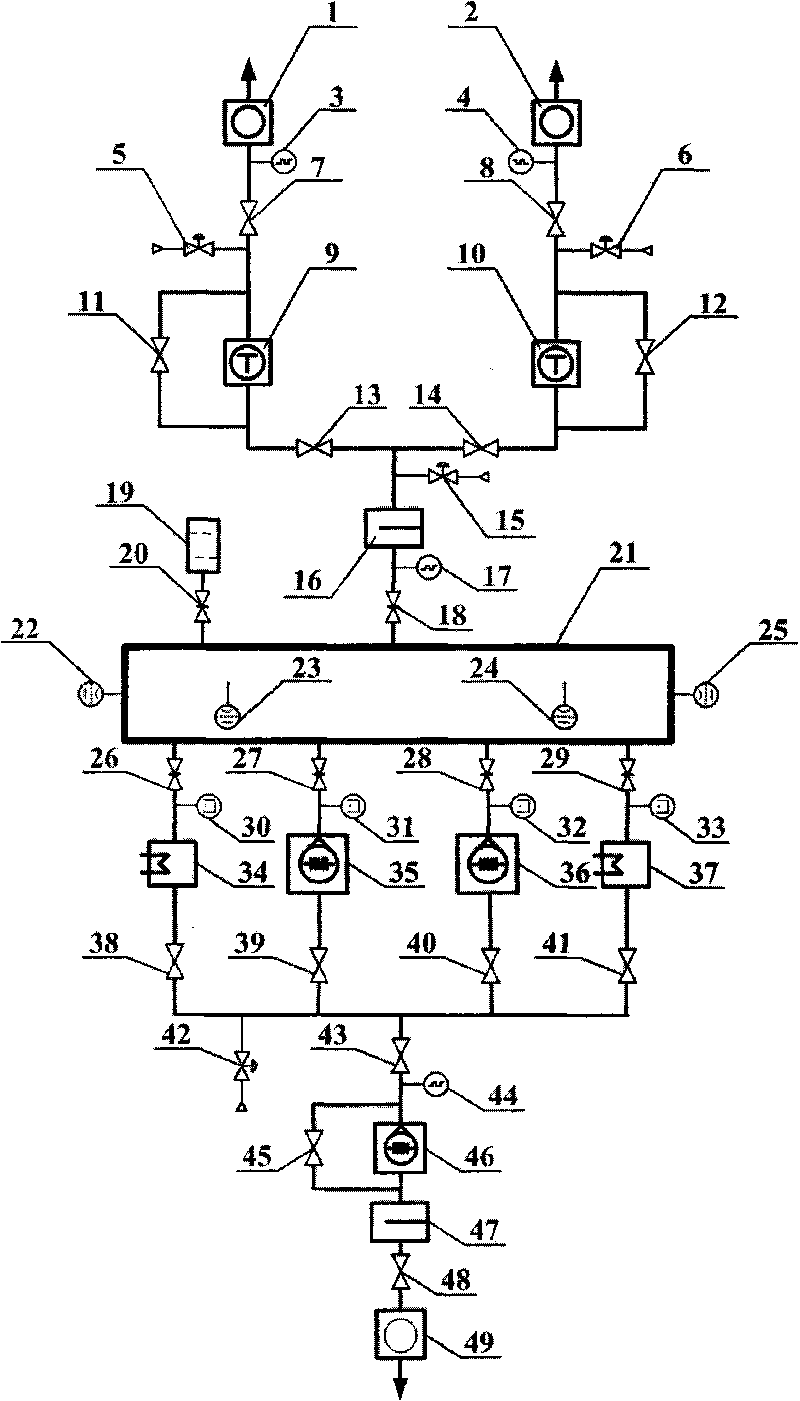
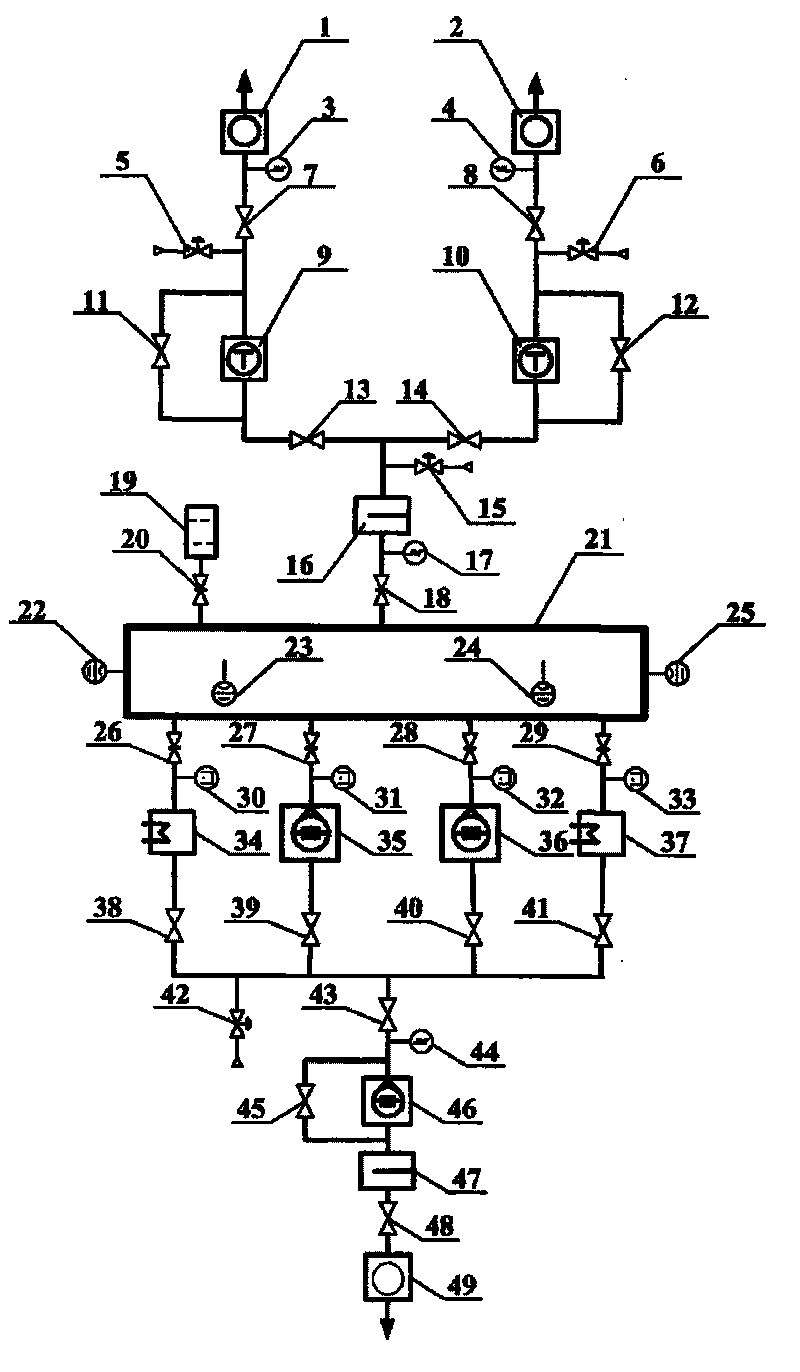
InactiveCN101725502AAvoid pollutionAnti-greasingRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsSolidificationSystems designUltra-high vacuum
The invention relates to a vacuum pumping system for a vacuum container, which comprises a low vacuum pumping system, a high vacuum pumping system, an ultra-high vacuum pumping system, a measuring system of the vacuum container and a repressing system of the vacuum container. A liquid nitrogen cold trap is mounted in a vacuum pumping pipeline, thereby preventing oil return of the system and avoiding polluting the vacuum container; two sets of low vacuum pumping mechanical pumps which can work simultaneously or independently are adopted, thereby improving the running reliability of the system;two sets of turbo-molecular pumps which can work simultaneously or independently are adopted, thereby improving the running reliability of the system; two sets of refrigeration machine low-temperature pumps which can work simultaneously or independently are adopted, thereby improving the running reliability of the system; a low-temperature pump regeneration pumping system is matched, thereby being capable of carrying out precooling before the start-up of the low-temperature pumps; the vacuum pumping system is matched with an air relief valve, thereby preventing the oil return of the system; the whole pumping system is clean; and a variety of vacuum gauges are mounted in the pipeline of the vacuum pumping system and the vacuum container, thereby realizing full-range pressure measurement.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Film forming apparatus
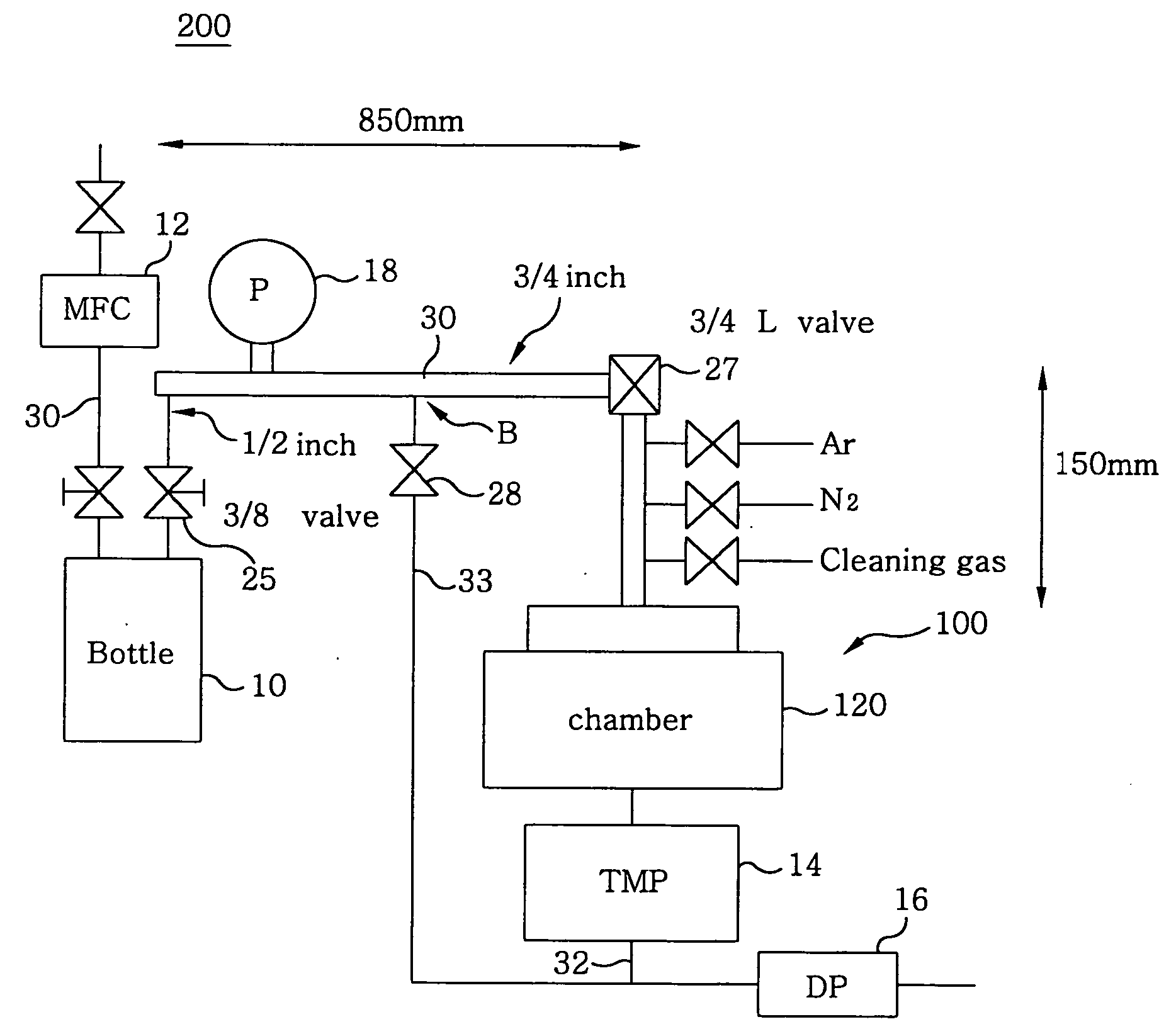
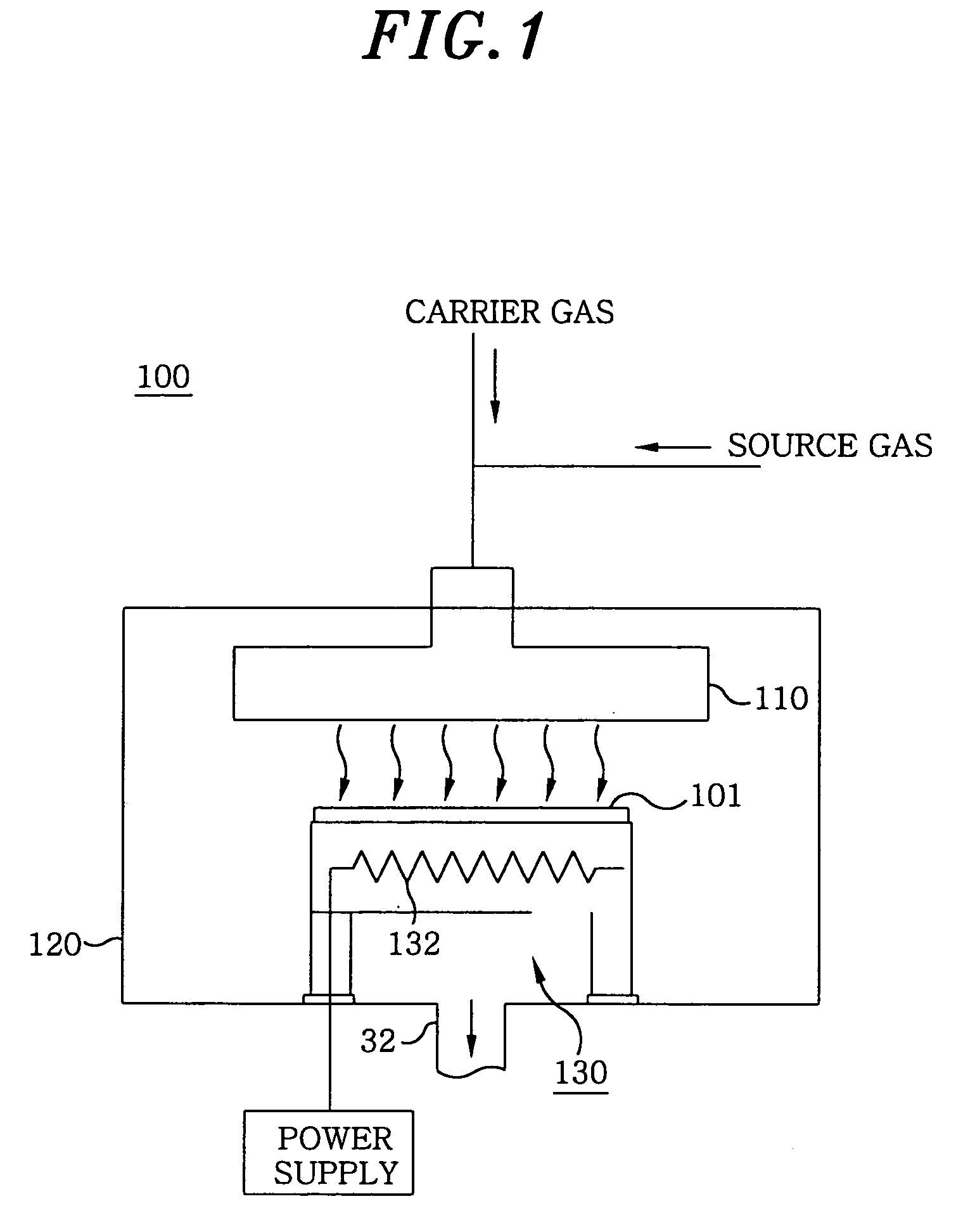
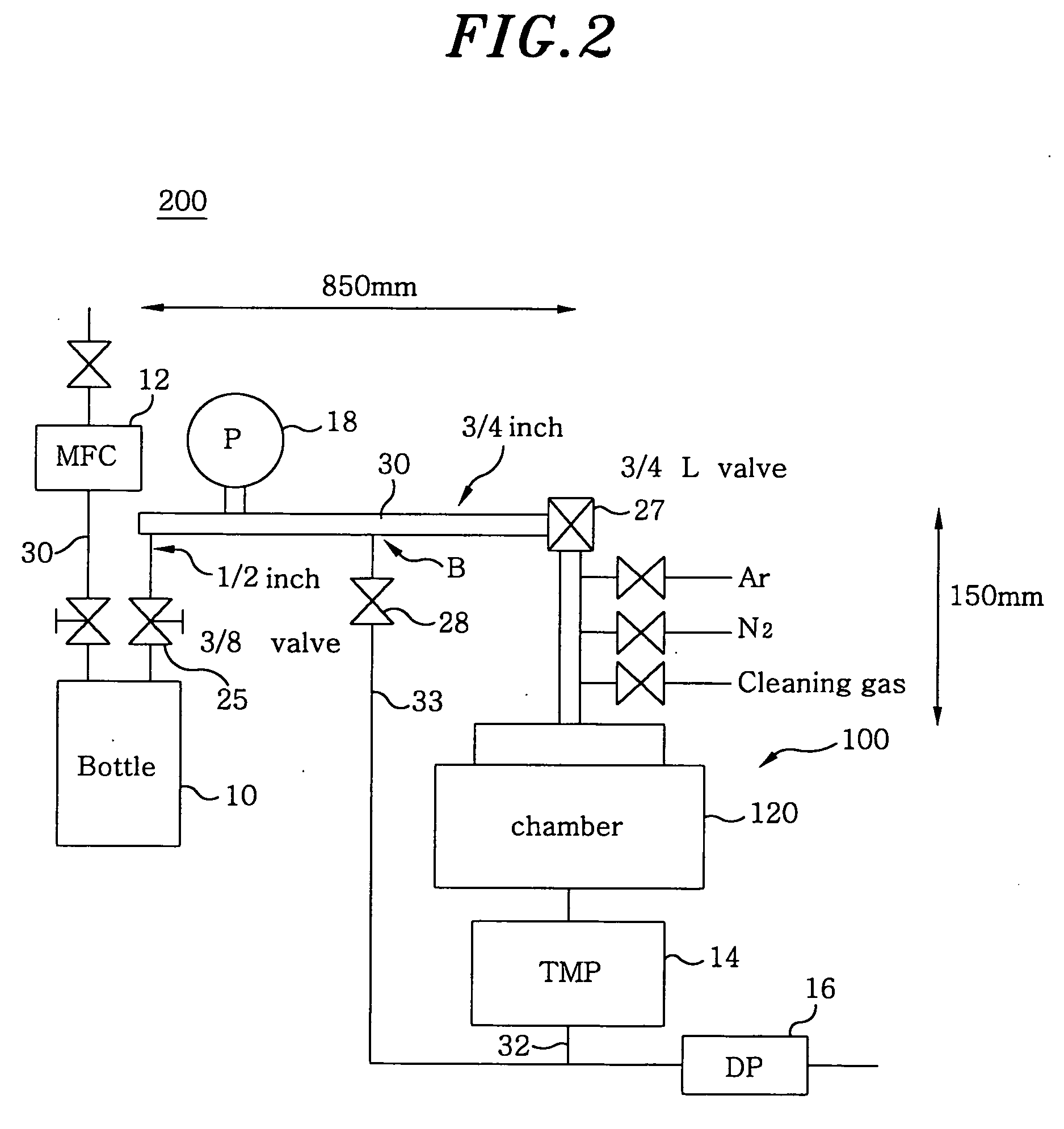
InactiveUS20050120955A1High film forming rateIncrease flow rateChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringSystem structure
A film forming unit includes a source vessel for receiving a raw material from which source gas is produced, a processing vessel for applying a film forming process on a semiconductor substrate, a source supply line for supplying the source gas from the source vessel to the processing vessel, a gas exhaust line for exhausting gas from the processing vessel, having a vacuum pump system structured by a turbo molecular pump and a dry pump, and a pre-flow line branching off from the source supply line while bypassing the processing vessel and the turbo molecular pump, and joining to the gas exhaust line. Moreover, the source supply line includes piping having an inner diameter greater than 6.4 mm, and a turbo molecular pump is provided in the pre-flow line.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
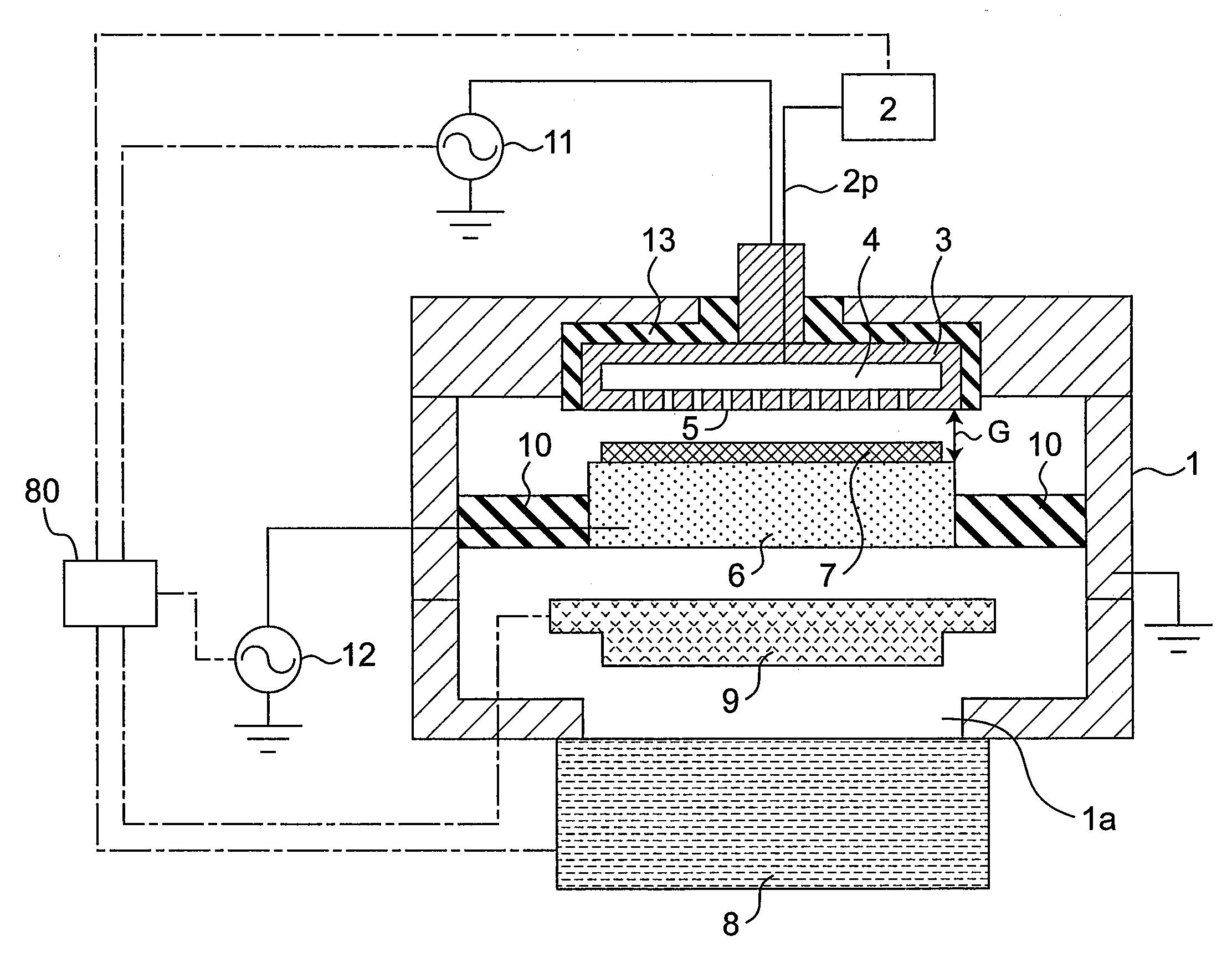
Plasma doping method and apparatus
InactiveUS20080233723A1Prevent implantationGood reproducibilityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceEngineering
There are provided a plasma doping method and an apparatus which have excellent reproducibility of the concentration of impurities implanted into the surfaces of samples. In a vacuum container, in a state where gas is ejected toward a substrate placed on a sample electrode through gas ejection holes provided in a counter electrode, gas is exhausted from the vacuum container through a turbo molecular pump as an exhaust device, and the inside of the vacuum container is maintained at a predetermined pressure through a pressure adjustment valve, the distance between the counter electrode and the sample electrode is set to be sufficiently small with respect to the area of the counter electrode to prevent plasma from being diffused outward, and capacitive-coupled plasma is generated between the counter electrode and the sample electrode to perform plasma doping. The gas used herein is a gas with a low concentration which contains impurities such as diborane or phosphine.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
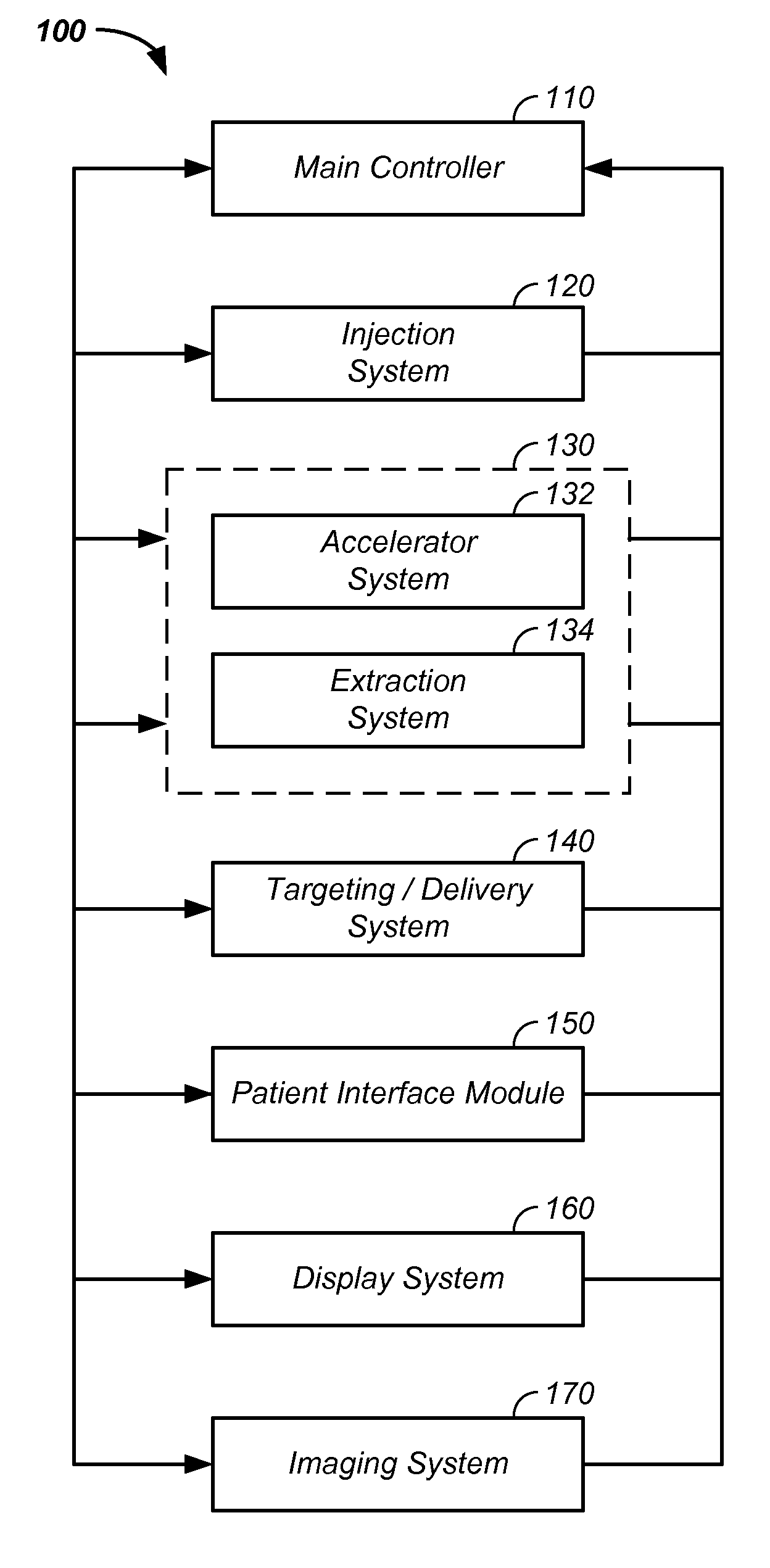
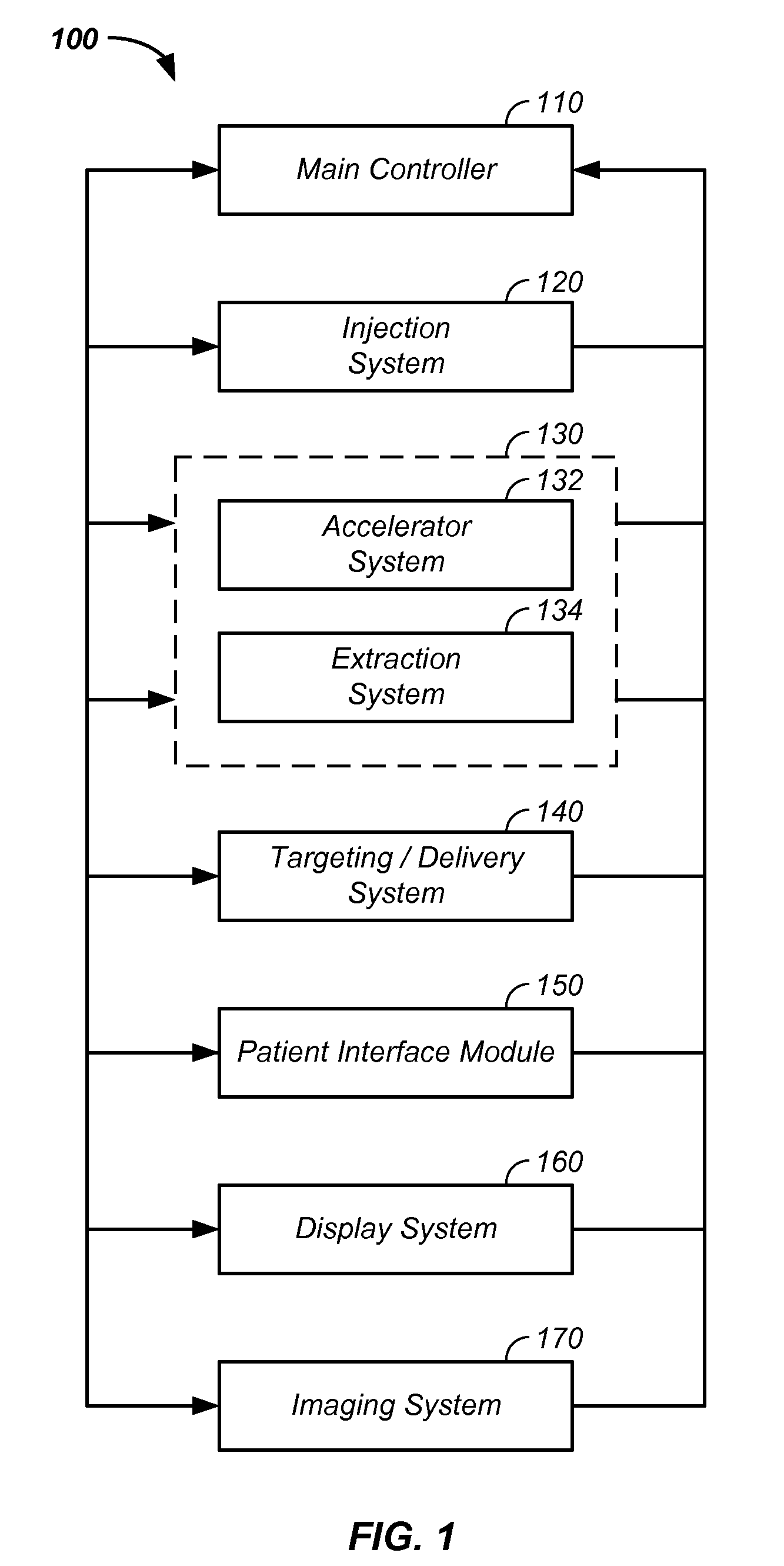
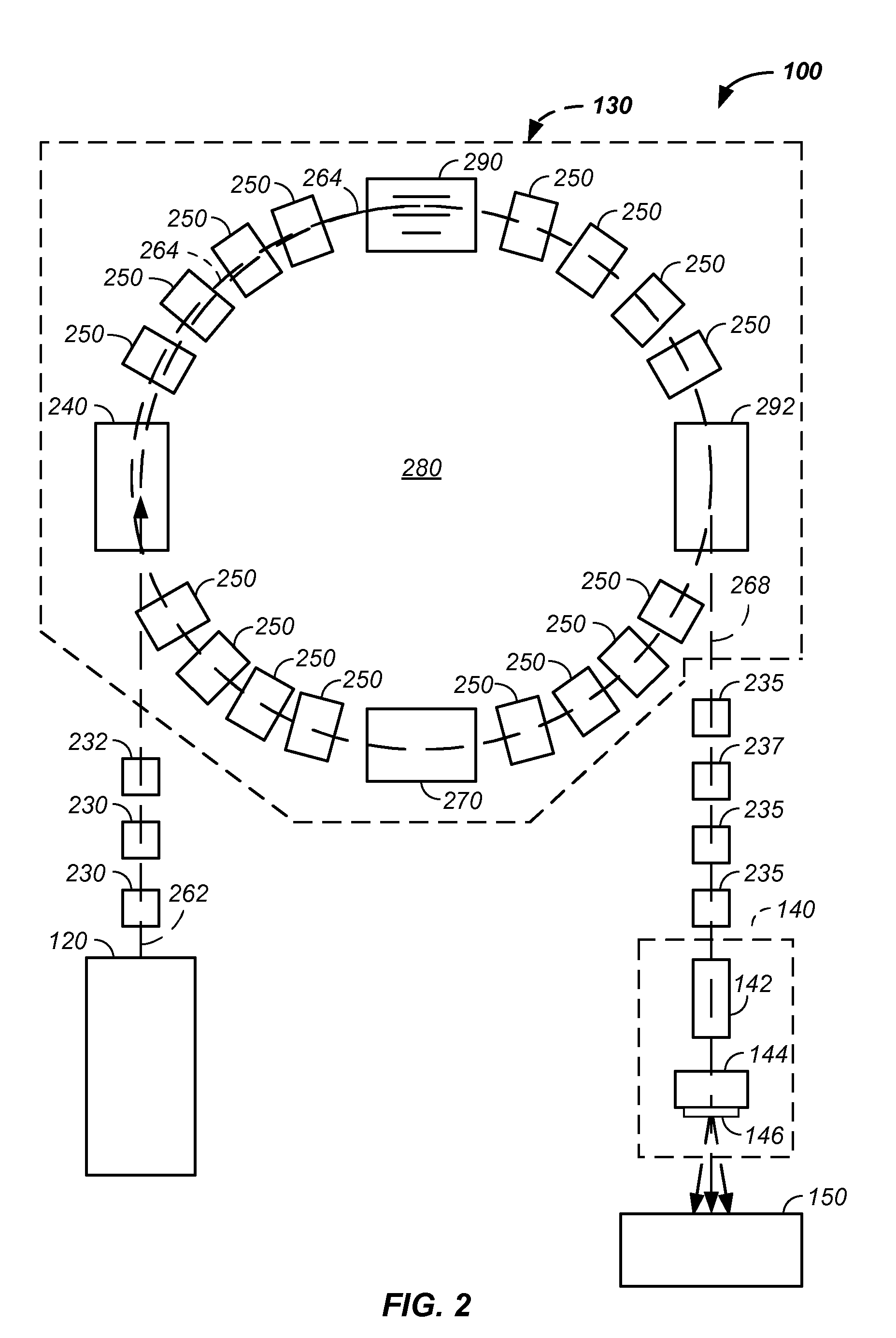
Negative ion beam source vacuum method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
ActiveUS20100014640A1Magnetic resonance acceleratorsMaterial analysis by optical meansAbnormal tissue growthSynchrotron
The invention comprises a negative ion beam source vacuum method and apparatus used as part of an ion beam injection system, which is used in conjunction with multi-axis charged particle or proton beam radiation therapy of cancerous tumors. The negative ion beam source contains a vacuum chamber isolated by a vacuum barrier from the vacuum tube of the synchrotron. The negative ion beam source vacuum system preferably includes: a first pump turbo molecular pump, a large holding volume, and a semi-continuously operating pump. By only pumping ion beam source vacuum chamber and by only semi-continuously operating the ion beam source vacuum based on sensor readings about the holding volume, the lifetime of the semi-continuously operating pump is extended.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com