Patents
Literature
33 results about "Vaccine evaluation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any process by which immunogenicity, immune response, toxicity, metabolism, absorption, preferred route of administration, safe dosage range, etc., for a vaccine or group of vaccines is determined through assessment in humans, animals or cells.
Models for vaccine assessment
ActiveUS20080008653A1Improve accuracyImprove predictabilityCompounds screening/testingCrankshaftsAdjuvantBiological Immunotherapy
The present invention is directed to methods for constructing and using in vivo and in vitro models of aspects of human immunity and, in particular, construction of a human immune system model for the testing of, for example, vaccines, adjuvants, immunotherapy candidates, cosmetics, drugs, biologics and other chemicals. The present invention comprises both in vivo and in vitro models of aspects of human immunity that are useful for assessing the interaction of substances with the immune system, and thus can be used to accelerate and improve the accuracy and predictability of, for example, vaccine, drug, biologic, immunotherapy, cosmetic and chemical development. The invention is also useful for the generation of human monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV +1
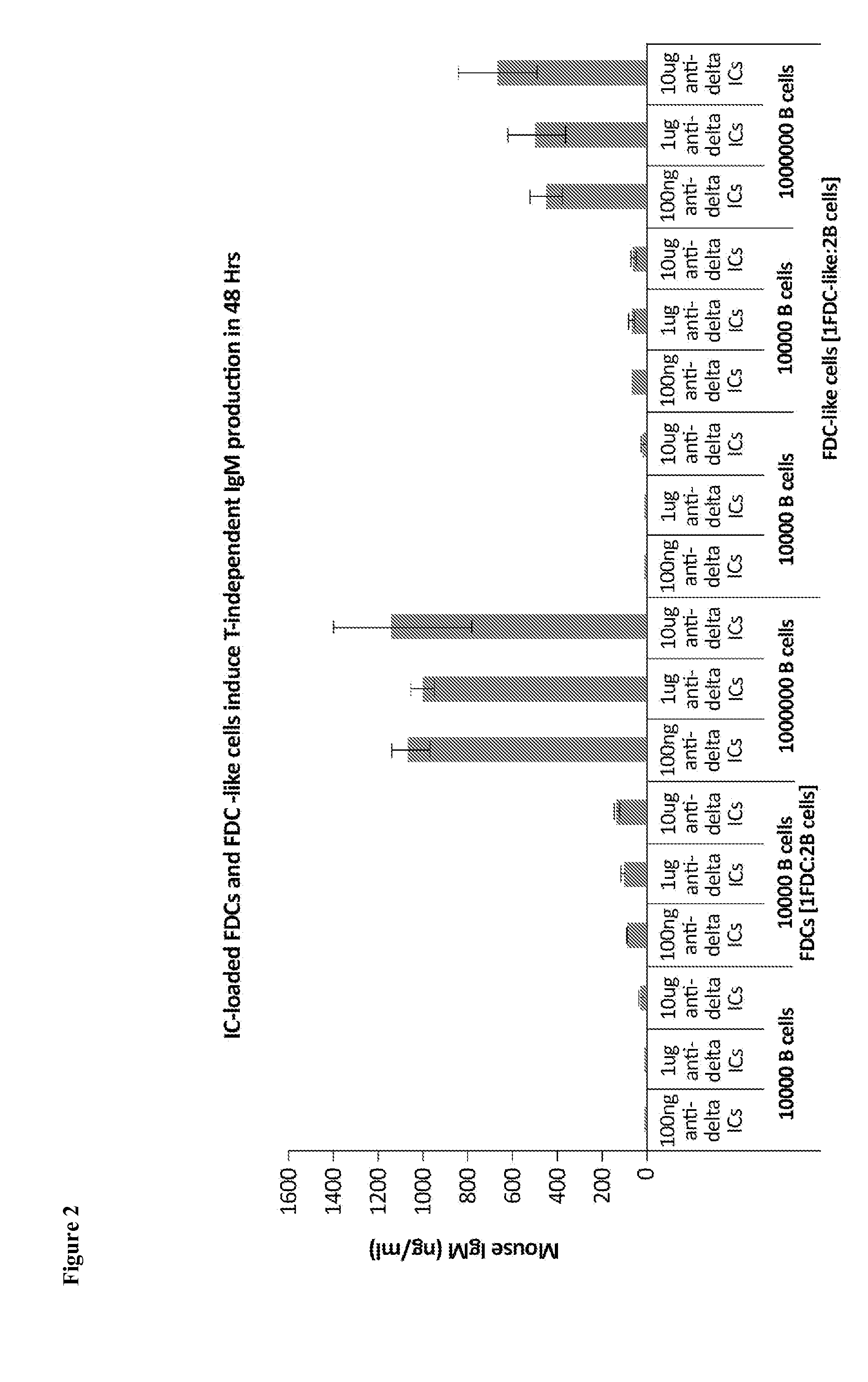
Rapid generation of t cell-independent antibody responses to t cell-dependent antigens
InactiveUS20090104221A1Easy to demonstrateLess immunogenicMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug screeningEndemic diseasesGerminal center
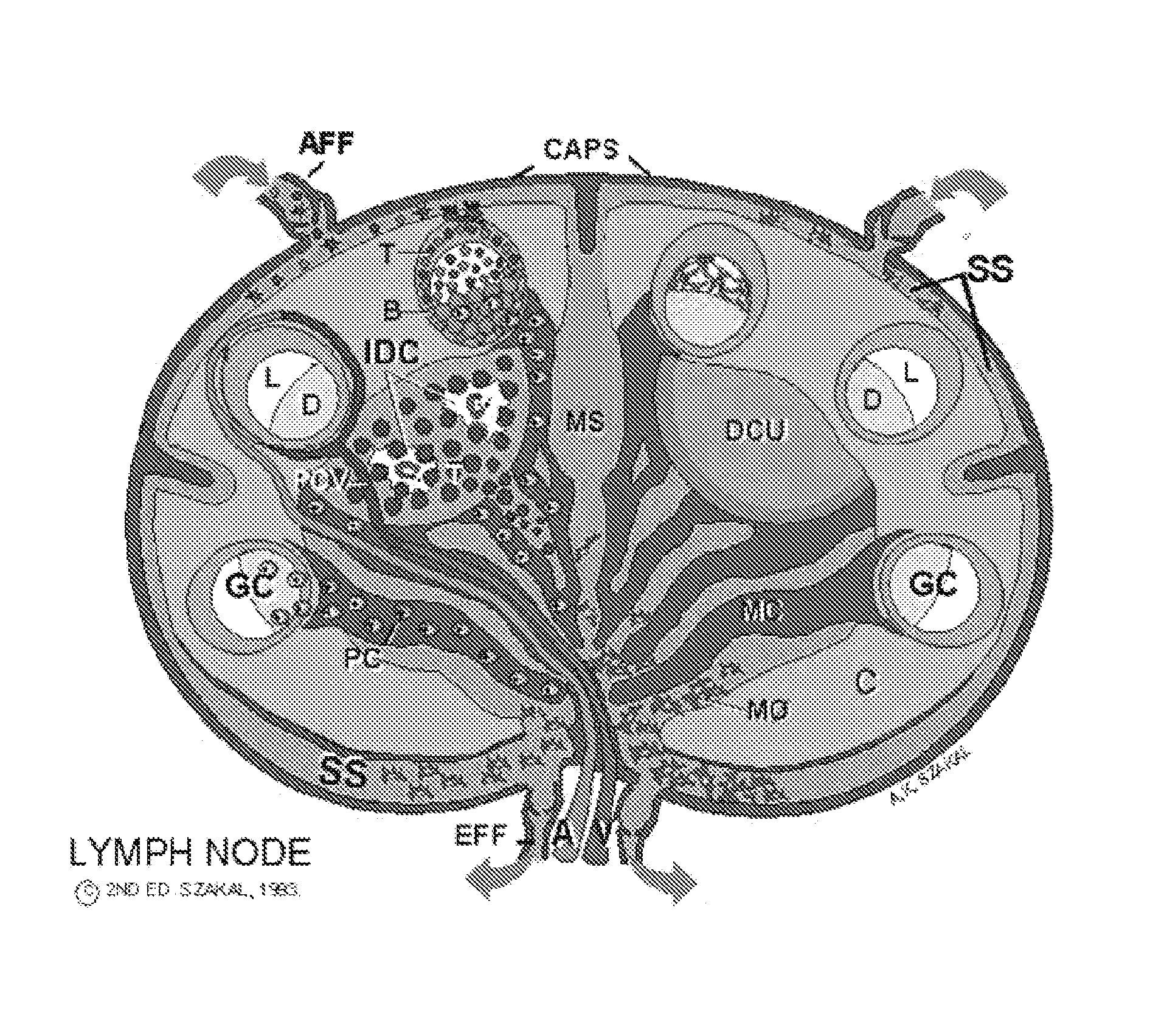
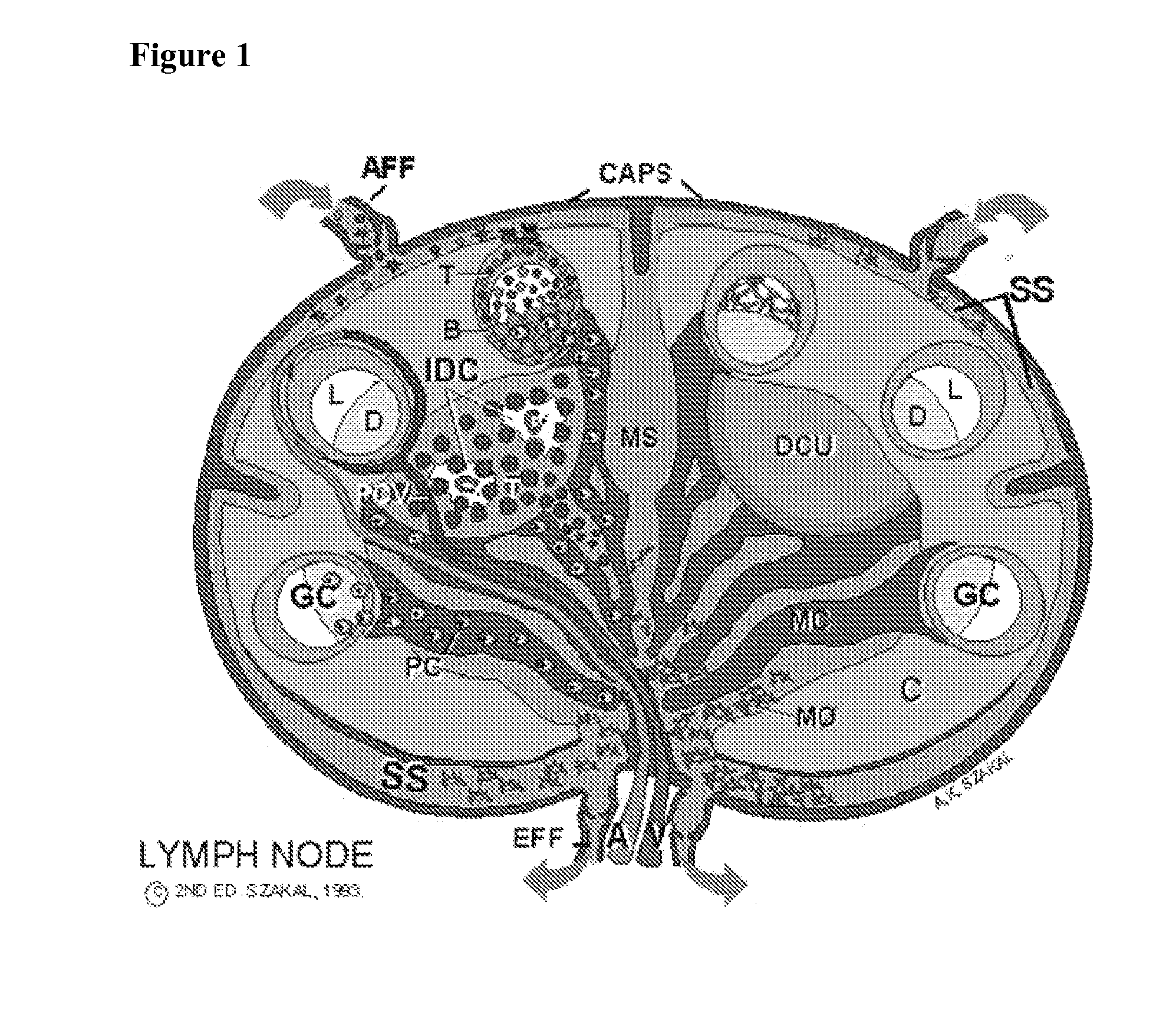
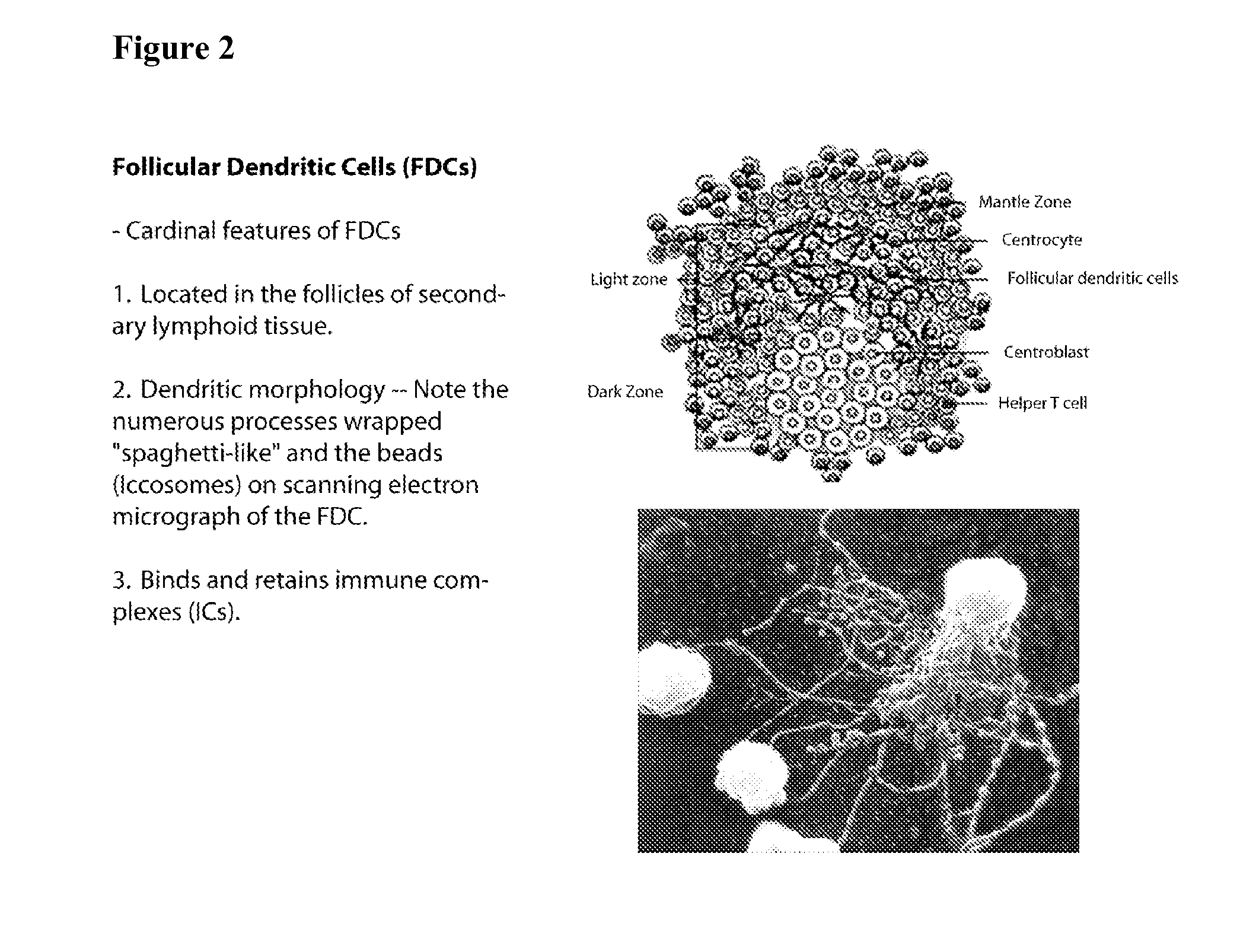
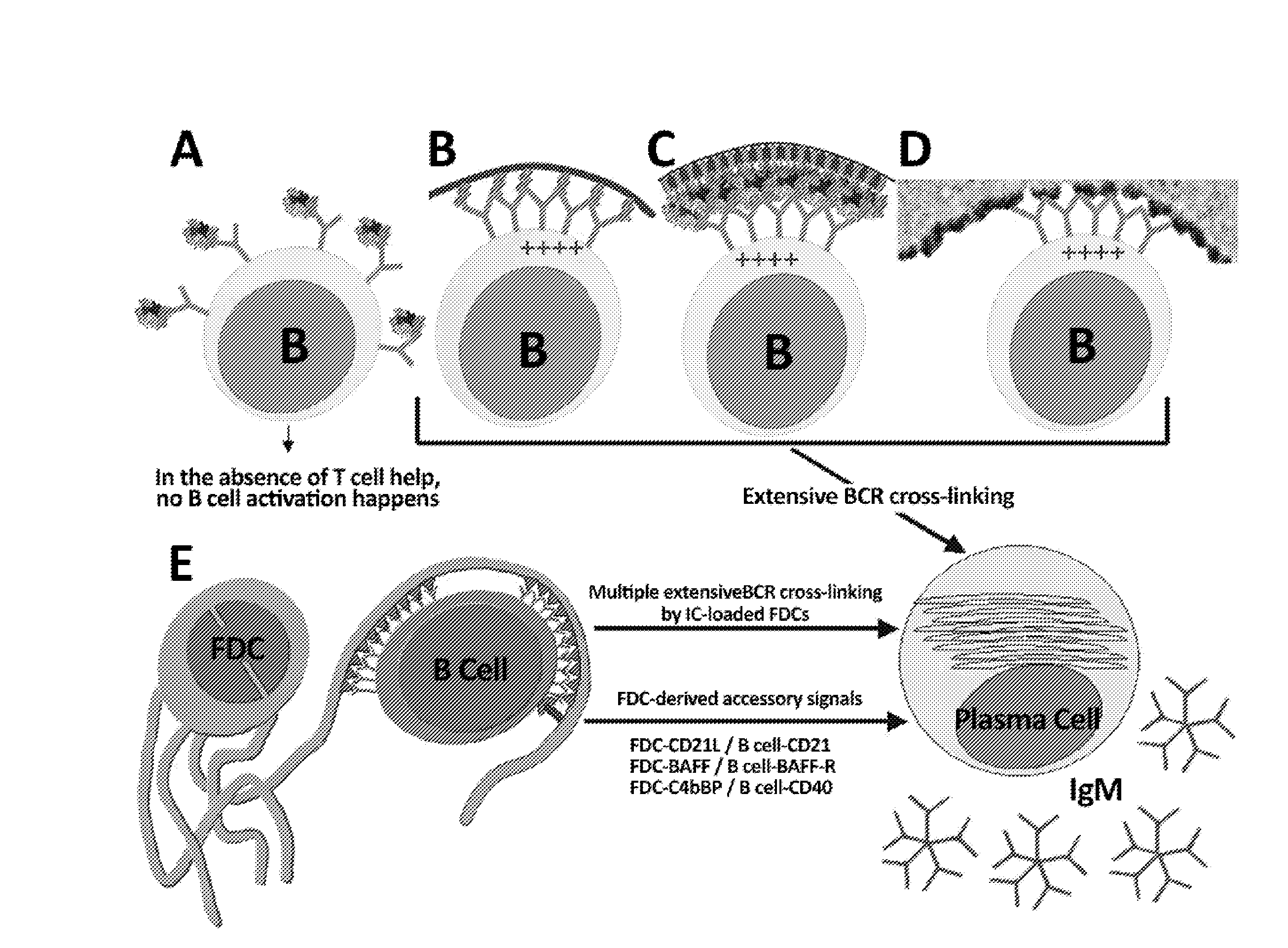
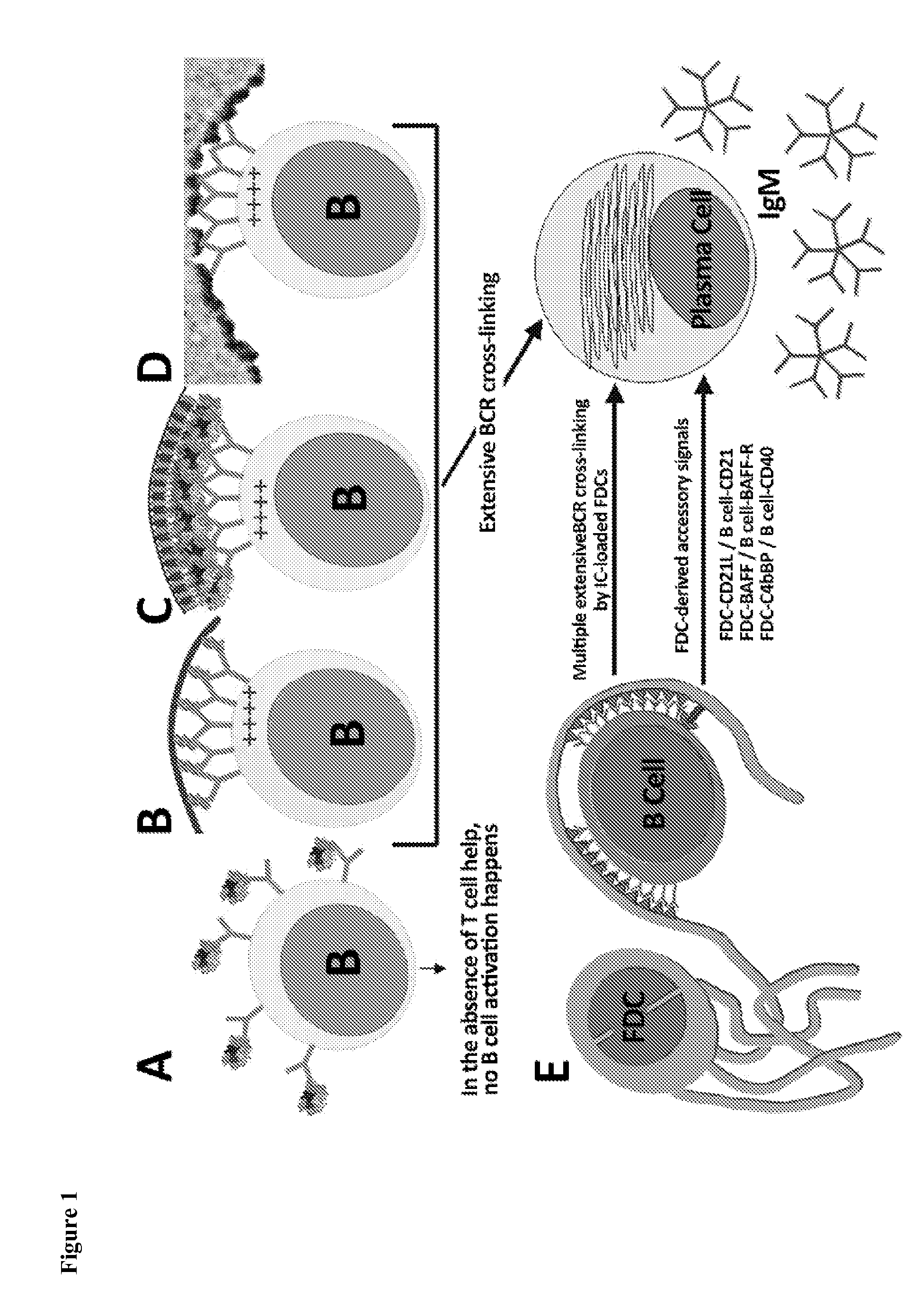
The present invention comprises the use of follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) or FDC-like cells to generate FDC-dependent, but T cell-independent, B cell responses to T cell-dependent antigens, with antigen-specific and polyclonal antibody production in ˜48 h. In another embodiment, a germinal center (GC) lymphoid tissue equivalent (LTE) was used to generate antigen-specific IgM, followed by switching to IgG. The GC LTE model can be used in vaccine assessment. Dual forms of immunogen were used in the GC LTE and in vivo. Dual immunogens resulted in rapid, specific IgM responses and enhanced IgG responses. This vaccine design approach can be used, for example, to provide rapid IgM protection (˜24-48 h) and high-affinity IgG more quickly in people moving to areas with endemic disease, or in people with T cell insufficiencies, who can be immunized to rapidly generate protective IgM.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR VAX DESIGN +1
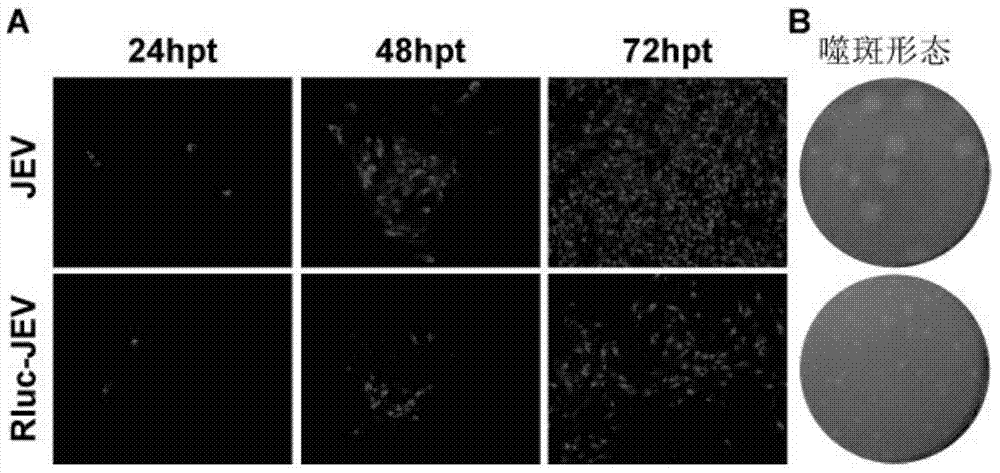
Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infectious clone with luciferase gene and building method and application thereof
InactiveCN103497972ASolve the phenomenon of not copyingFast growing trendMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuciferase GeneVaccine evaluation
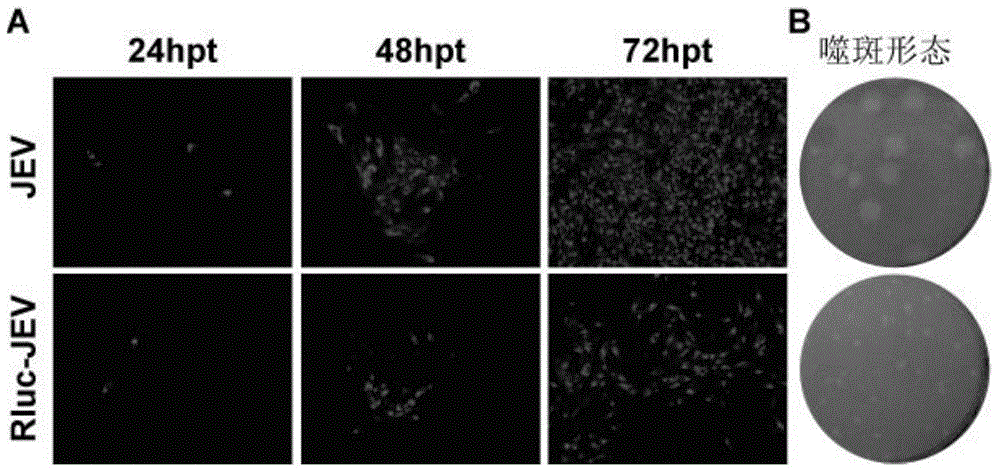
The invention discloses a Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infectious clone with a luciferase gene, and a building method and application thereof. The JEV infectious clone with the luciferase gene is prepared by the following steps: (1) sectional synthesis of a JEV SA14 strain gene sequence; (2) assembling and building of the JEV infectious clone; (3) building of the JEV infectious clone with the luciferase gene. It is proved that a Rluc-JEV report virus with the same growth tendency as the JEV virus can be saved by the JEV infectious clone with the luciferase gene built by the method, and the JEV infectious clone has wide application value in the aspects of an animal model, virus replication and pathogenesis, drug screening and drug action mechanism, live animal imaging and vaccine evaluation and the like through the experiments of immunofluorescence, Rluc activity detection, virus bacteriophage plaque, drug inhibition, live animal imaging, vaccine evaluation and the like.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
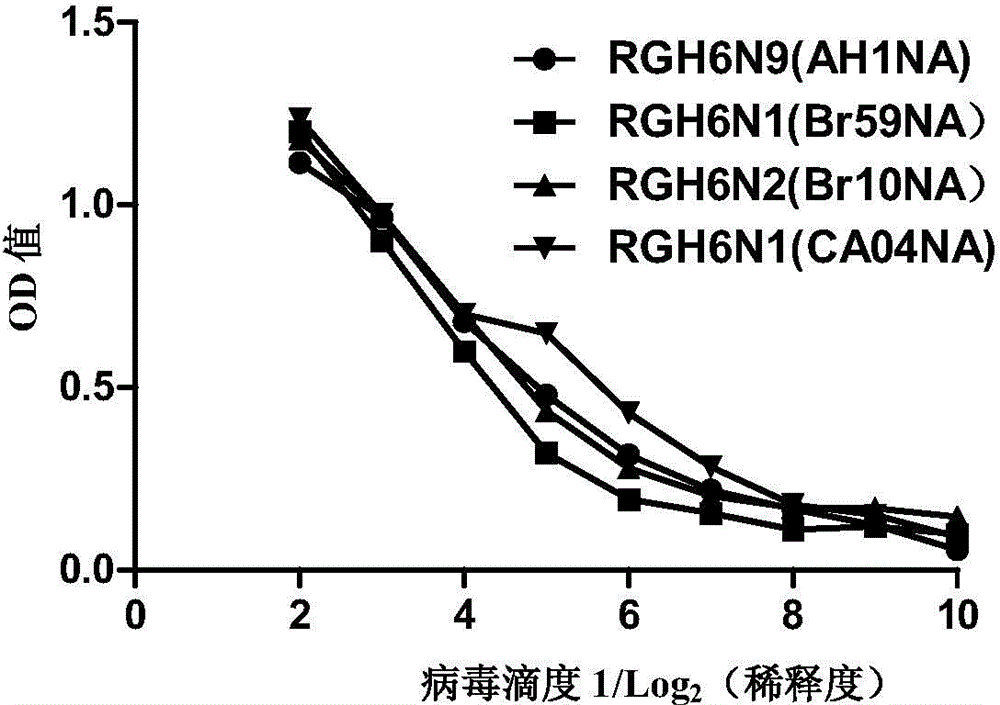
Recombinant influenza virus and application thereof
InactiveCN104312983AAvoid interferenceIncrease productionAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesHemagglutininNeuraminidase
The invention discloses a recombinant influenza virus and application thereof and provides a preparation method of the recombinant virus. The preparation method comprises the following steps: guiding an HA6 subtype influenza virus hemagglutinin encoding gene, an influenza virus neuraminidase (NA) gene and six genes including PB2, PB1, PA, NP, M and NS in an influenza virus into a host cell together, and packing to obtain the recombinant virus. The invention also discloses a detection method for detecting antibodies for inhibiting activities of seasonal influenza N1, N2, 2009H1N1N1 and 2013H7N9N9 enzymes by virtue of the recombinant virus. The detection method comprises the steps of sample treatment and result analysis. According to the invention, the immune response to NA of people can be rapidly and effectively measured, the operation is simple, the application is convenient, and viable technical support is provided for clinical detection and vaccine evaluation.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所
Method and use for constructing AIDS primate model
The present invention discloses a kind of HIV infection model of Chinese macaque as one kind of primate animal. HIV is inoculated to Chinese macaque via intravenous injection to constitute the HIV infection model of Chinese macaque successively. By means of understanding the infecting course, pathological characteristic, pathogenesis and body's resistance of HIV inside the model, are researched the infected target organ, target tissue and target cell, the attack to the immunity system, the reaction of the immunity system cell, etc. The HIV infection model has non-replaceable effect in AIDS research, anti-AIDS medicine screening, vaccine evaluation, etc.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Tissue constructs and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150152385A1Promote colonizationAssess safetyCulture processArtificial cell constructsTissue constructComputational biology
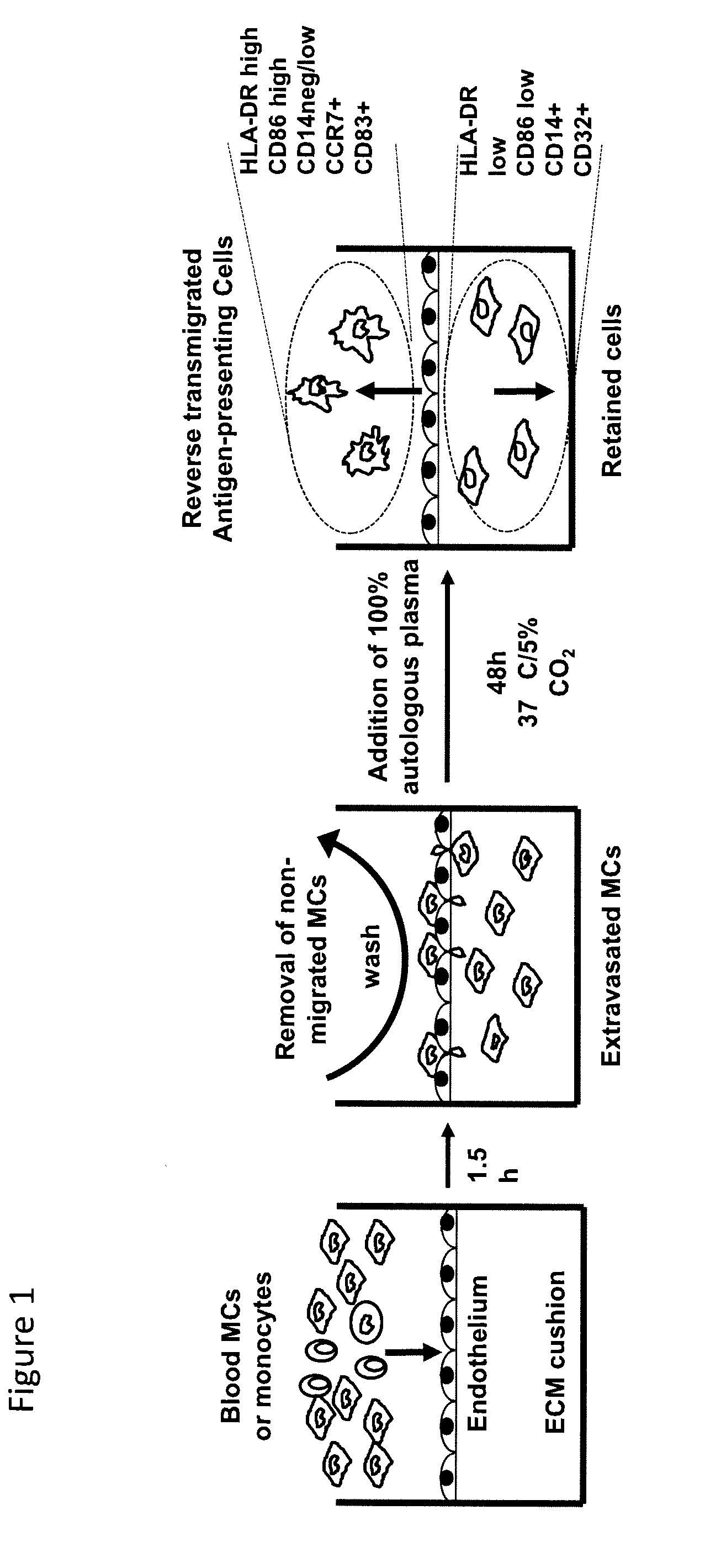
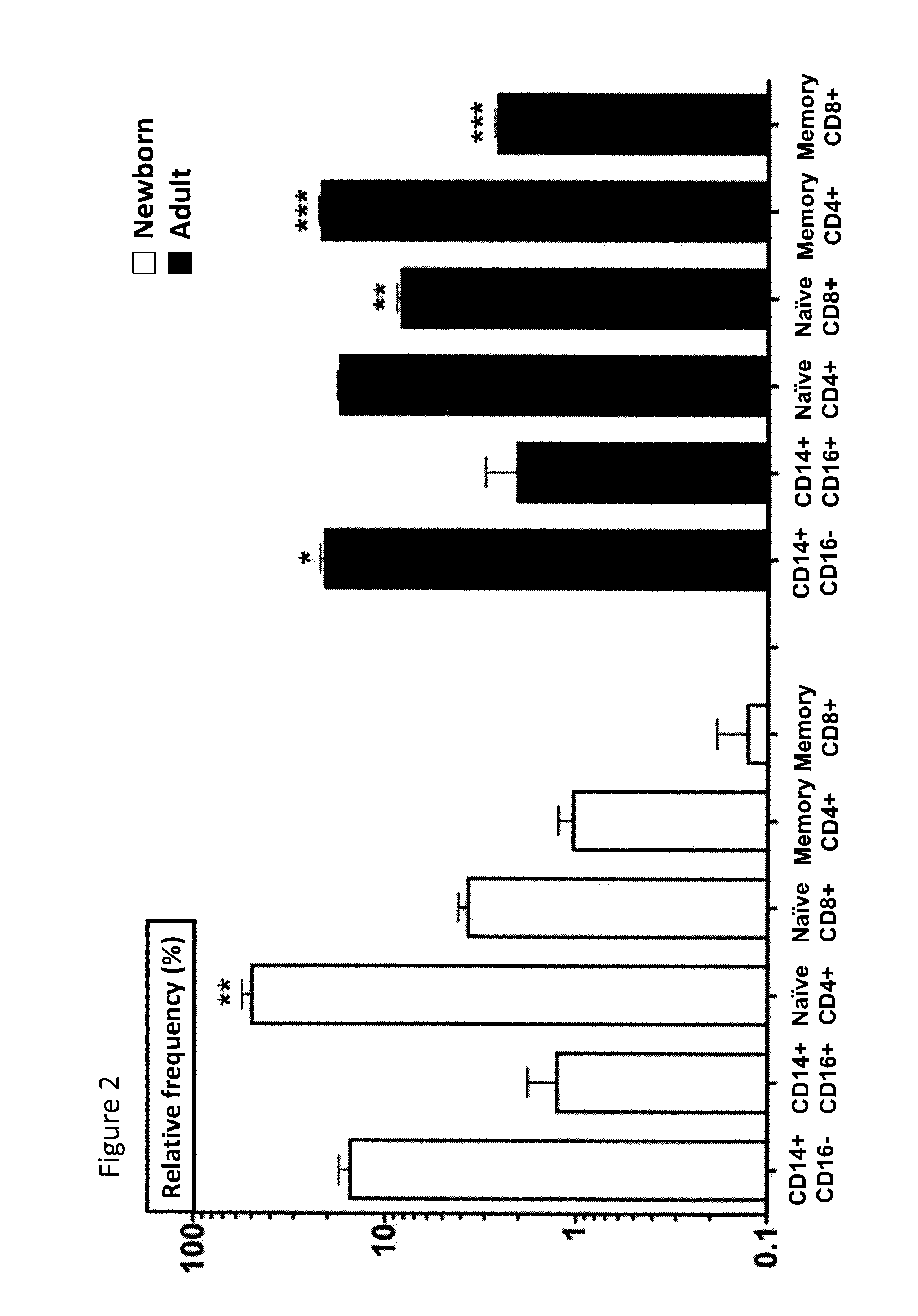
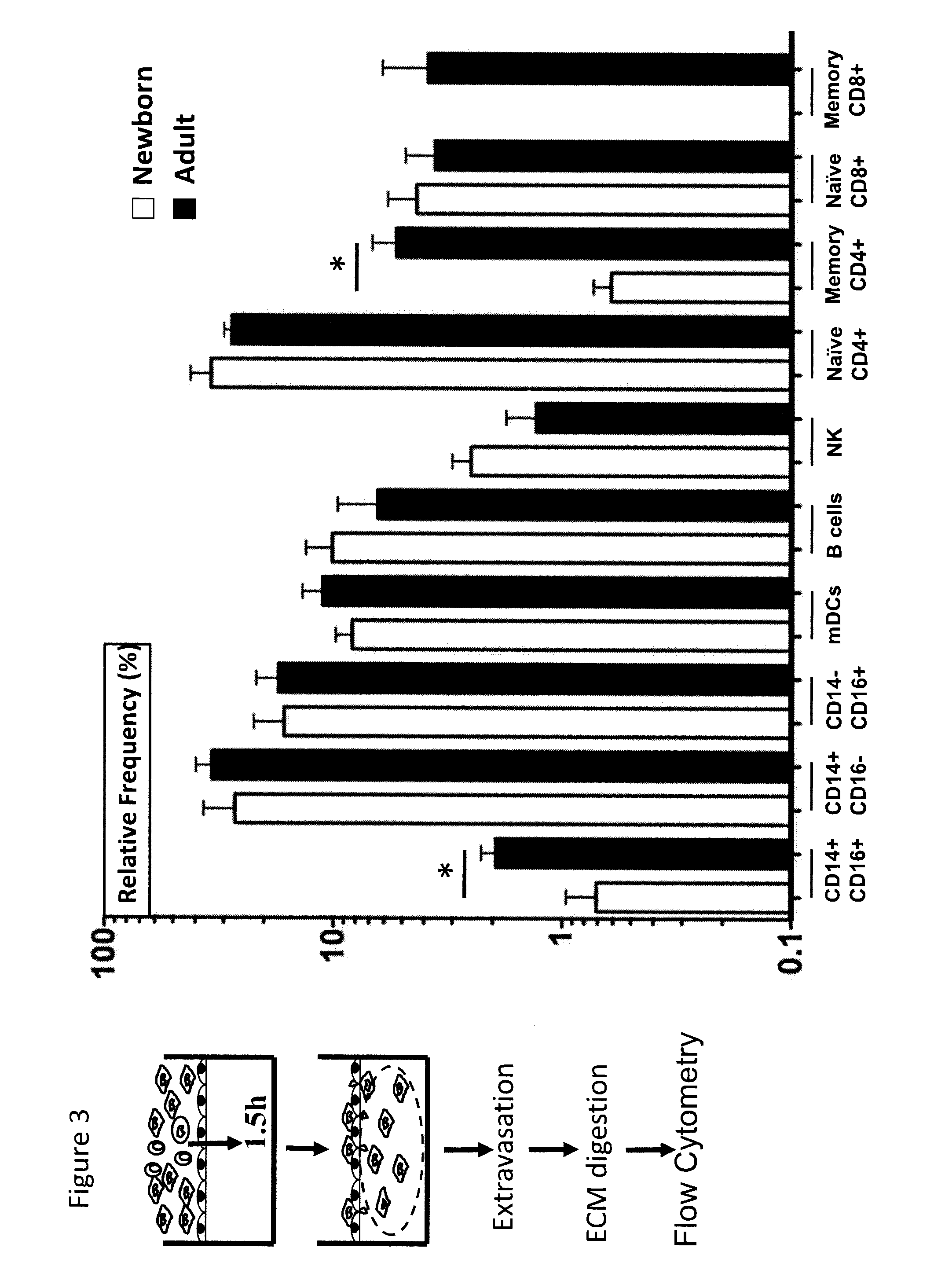
Artificial tissue constructs (TCs), methods of making the TCs, uses thereof, and kits comprising the TCs are provided. TCs are useful for vaccine evaluation for human adult, human non-newborn, and newborns.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
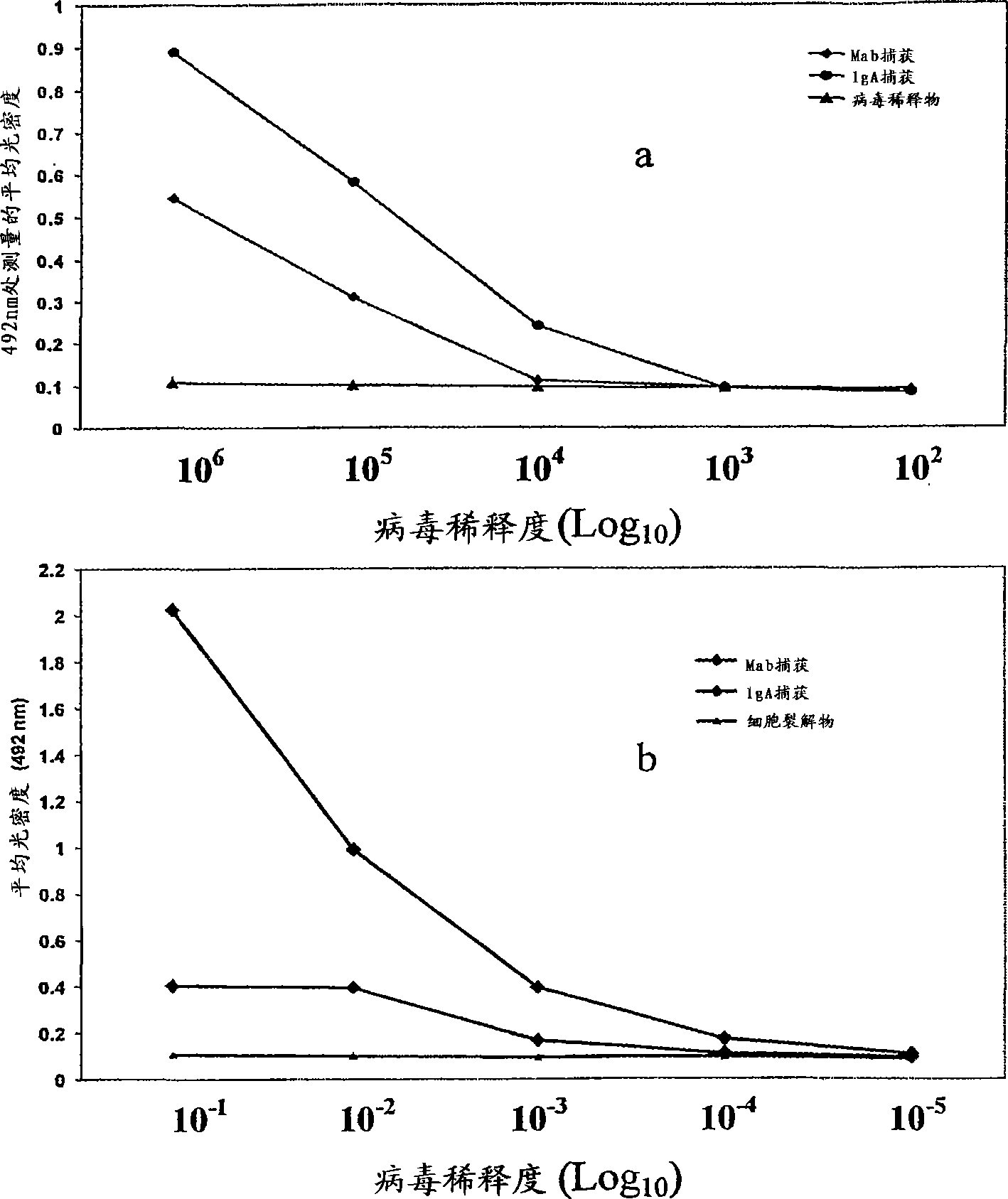
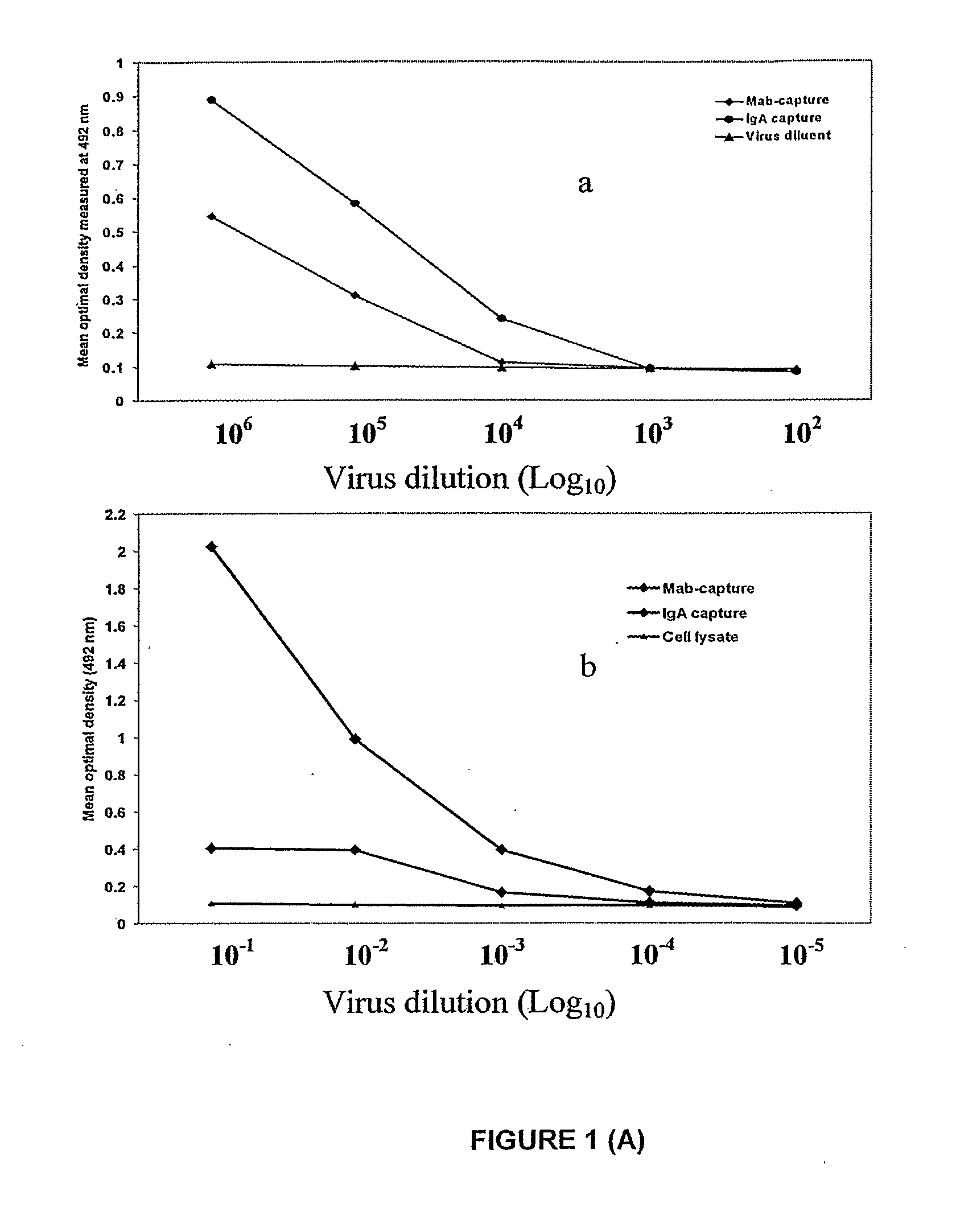
Competitive enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (C-ELISA) for the detection of a flavivirus specific antibody
InactiveCN101449165ASsRNA viruses positive-senseBiological material analysisSpecific immunitySecondary Infections
A competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (C-ELISA), using flavivirus member specific immunological agents was developed to detect antibody specific to members of the flaviviruses indicative of exposure to flavivirus. The test is based on a competition for epitope binding on the envelope protein of the flavivirus antigen captured using anti-flavivirus IgA in the presence of flavivirus positive serum. This test has comparable sensitivity specificity and speed to the virus neutralization assay (VNT). C-ELISA is a versatile technique, which could have various applications. Slight modifications of this protocol could lead to a C-ELISA-based detection method of secondary infection or one that could be used for serotype specific sero-epidemiological studies and / or vaccine evaluation. The protocol developed for C-ELISA was demonstrated using dengue lysate antigen and dengue specific monoclonal antibody. This can be used against other flaviviruses and the results for Japanese encephalitis illustrates this.
Owner:NATIONAL ENVIRONMENT AGENCY
DNA fragment and application thereof in preparation of H5N1-subtype flu Guassia luciferase reporter virus
InactiveCN104513820ASimplify the titration procedureTrue Response Proliferation StatusViruses/bacteriophagesVector-based foreign material introductionSerum igeNucleotide
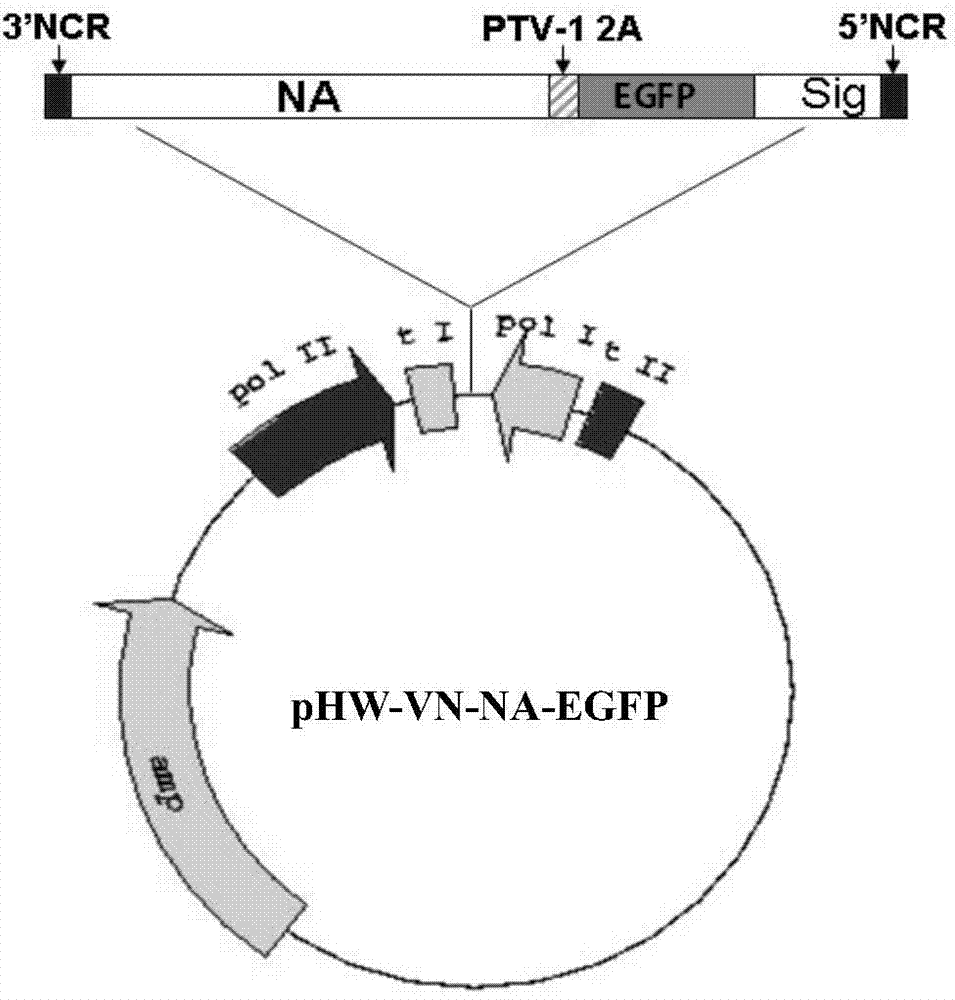
The invention discloses a DNA fragment and an application thereof in preparation of an H5N1-subtype flu Guassia luciferase reporter virus. The nucleotide sequence of the DNA fragment is composed of following sequences in a successive series manner: an H5N1-subtype flu virus NA segment 3'-terminal noncoded region coding gene sequence, an H5N1-subtype flu virus NA gene encoded region coding sequence, a PTV-1 virus 2A peptide encoded gene sequence, a Gaussia luciferase encoded gene sequence, a H5N1-subtype flu virus NA segment 5'-terminal packaged signal encoded gene sequence, and a H5N1-subtype flu virus NA segment 5'-terminal noncoded region coding sequence. By means of the recombined H5N1-subtype flu reporter virus prepared with the DNA fragments, quantitative detection on viruses in a sample can be objectively carried out quickly and accurately through activity of luciferase in cellular supernatant or animal serum. The H5N1-subtype flu Guassia luciferase reporter virus can not only save time but also improve accuracy and reliability of a detection result, thereby providing a new convenient and effective tool for drug screening and vaccine assessment of anti-H5N1-subtype flu virus drugs.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Enhanced green fluorescent protein recombinant H5N1 subtype influenza virus and its application
ActiveCN103555679ASimplified pathogenic mechanismAccelerate the pathogenic mechanismBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceWild type
The invention discloses an enhanced green fluorescent protein recombinant H5N1 subtype influenza virus and its application. The genome of the recombinant H5N1 subtype influenza virus is composed of eight RNA fragments of the following a) and b): a) seven RNA fragments which are same as the genome of wild type H5N1 subtype influenza virus contains RNA fragment 1 encoding PB2 protein, RNA fragment 2 encoding PB1 and PB1-F2 proteins, RNA fragment 3 encoding PA protein, RNA fragment 4 encoding HA protein, RNA fragment 5 encoding NP protein, RNA fragment 7 encoding M1 and M2 proteins, RNA fragment 8 encoding NS1 and NS2 proteins; b) fragment 6' which is obtained by the insertion of RNA fragment containing green fluorescent protein coding RNA to 5'-noncoding region of RNA fragment 6 encoding NA protein in the genome of wild type H5N1 subtype influenza virus. According to the invention, rapid quantitative determination of the recombinant virus can be performed by observation of fluorescence positive cell number and fluorescence intensity, cumbersome procedure of regular titration is saved, and a convenient and effective tool for anti-H5N1 subtype influenza virus drug screening and vaccine evaluation is provided.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Building method of EBV (epstein barr virus) guinea pig animal model
ActiveCN102812924AImprove the level ofMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryTGE VACCINEGuinea pig
The invention provides a building method of an EBV (epstein barr virus) guinea pig animal model. The method comprises the following steps that EBV inoculation is carried out on guinea pigs; the guinea pig peripheral blood lymphocyte separation is carried out; RNA (ribonucleic acid) extraction is carried out; RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) reverse transcription is carried out; Nested-PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is carried out, the targeted DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segments are recovered and purified, then, the DNA is connected onto pGEM-T vectors to be subjected to conversion, plasmid extraction and digestion identification, then, the DNA is conveyed to a sequence testing company to test the sequence, the EBV guinea pig animal model is built so that the etiology, the immunology, the pathogenesis and the like of the EBV can be conveniently studied, and the important effect is realized in the application aspects of relevant medicine screening, vaccine evaluation and the like.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
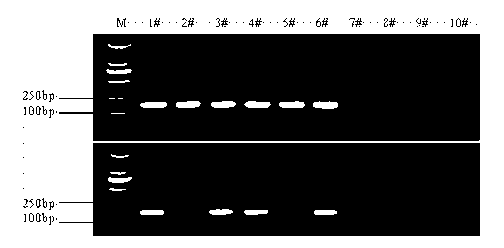
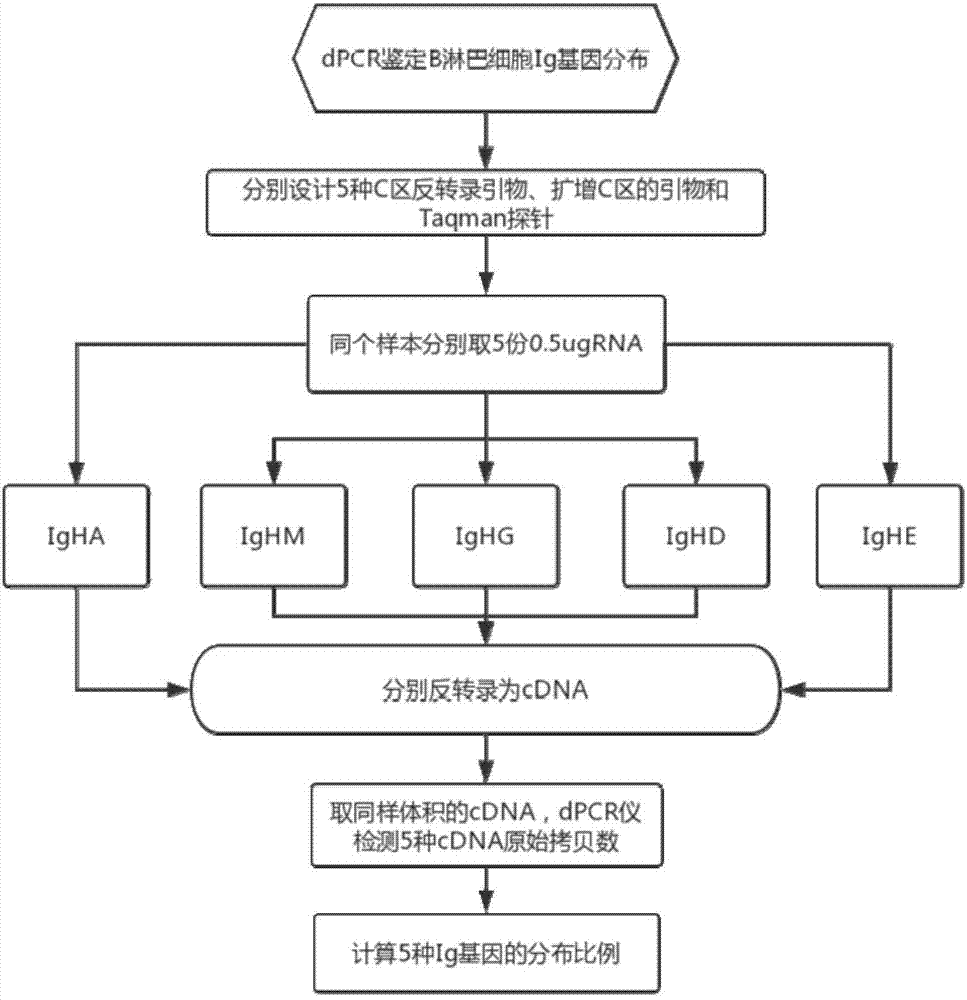
Method for identifying Ig gene distribution of B lymphocytes by digital PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
InactiveCN107312863AVerify accuracyData results are reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for identifying Ig gene distribution of B lymphocytes by digital PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). The method comprises the following steps: 1) designing five sets of primers according to five Ig heavy chain C regions, wherein each set of primers comprises a reverse transcription primer, an amplification primer and / or a taqman probe, and the reverse transcription primer is the same as a reverse primer in the amplification primer; 2) carrying out reverse transcription on 5 identical RNA of the same sample to be tested to generate cDNA, then carrying out digital PCR detection to obtain an original copy number of corresponding Ig genes in the 5 cDNA, and calculating copy number distribution of the 5 Ig genes in the sample to be tested. The method disclosed by the invention can identify the expression of 5 Ig genes and does not have the preference problem, and can reflect the proportion of the 5 Ig in the original sample. The digital PCR technology is used for identifying the Ig gene distribution to verify whether a preference exists in a sequencing result, and the correction of the preference of the primer amplification is facilitated. The accuracy of the Ig ratio is conducive to the research of disease immune response, vaccine evaluation and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
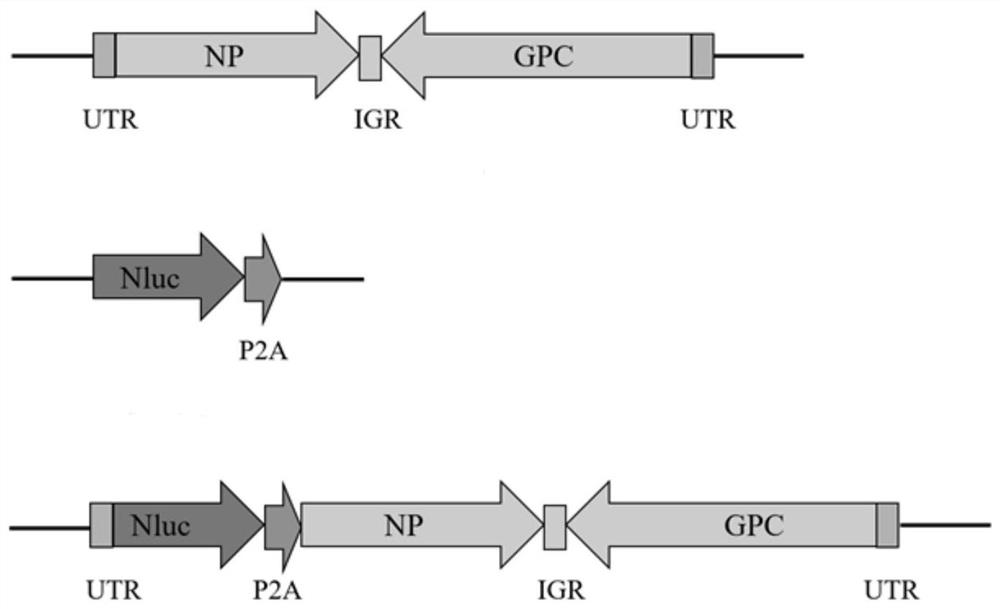
Lymphatic choriomeningitis virus for expressing luciferase gene as well as construction method and application of lymphatic choriomeningitis virus
PendingCN114231562ADoes not affect processing modificationDoes not affect assemblyCompounds screening/testingSsRNA viruses negative-senseEnzyme GeneTranslation (biology)
The invention discloses a lymphatic choriomeningitis virus for expressing a luciferase gene as well as a construction method and application of the lymphatic choriomeningitis virus, and relates to the technical field of biology. The luciferase gene is inserted between the 5 'UTR of the LCMV virus genome and the N end of the NP protein sequence to construct the virus genome marked by the luciferase reporter gene, the result does not affect protein processing modification after virus translation, and the generated luciferase protein does not affect assembly of filial generation virus particles. A sequence containing a recombinant virus genome is inserted into a vector and transfected with a host cell, so that a recombinant virus capable of efficiently and stably expressing luciferase can be saved, and the luciferase recombinant virus strain can be used for establishing a rapid and high-throughput antiviral drug screening technology or platform by virtue of a mouse bioluminescence in-vivo imaging system. Wide application values are provided for living animal imaging, drug screening, drug action mechanism, vaccine evaluation and the like.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
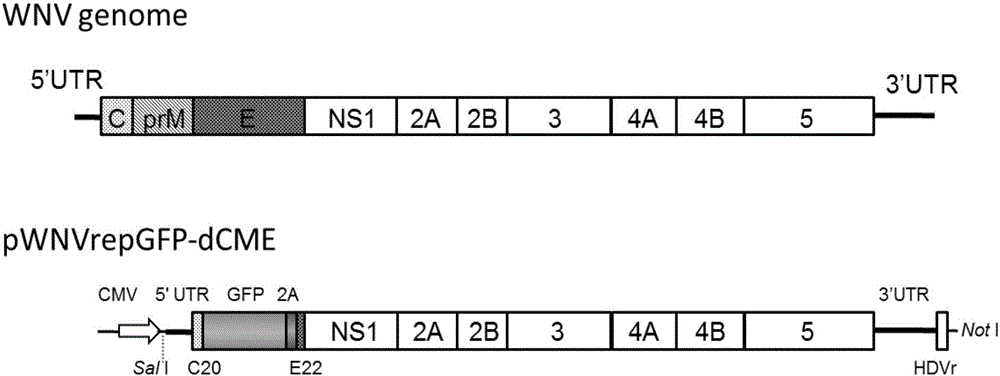
Restrictive replicated west nile virus system for expressing green fluorescent protein and application thereof
ActiveCN106754982AStrong indicatorImprove securityCompound screeningSsRNA viruses positive-senseAnti virusAntiviral drug
The invention discloses a restrictive replicated west nile virus system for expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) and an application thereof. The restrictive replicated west nile virus system for expressing the green fluorescent protein, disclosed by the invention, comprises a west nile virus restrictive replicon plasmid and a recombinant cell line capable of stably expressing west nile virus C-prM-E protein. A restrictive replicated west nile virus (deltaWNV) obtained by the system is obtained, and the virus has properties similar with a WNV whole virus in a BWNV-CME cell line; the GFP can be expressed and the system has a visual effect; more importantly, the virus only can be replicated in the system; when other cells are infected, progeny viruses are not generated, so that the safety is extremely high; and the restrictive replicated west nile virus system can be used for detecting a WNV neutralizing antibody and screening an anti-virus medicine. According to the restrictive replicated west nile virus system, the safety and convenience of WNV related operation are improved, and the system does not depend on BSL-3 high-grade biological safety condition; and a good technical means is provided for WNV vaccine evaluation, anti-virus medicine screening and researches of a virus pathogenic mechanism.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
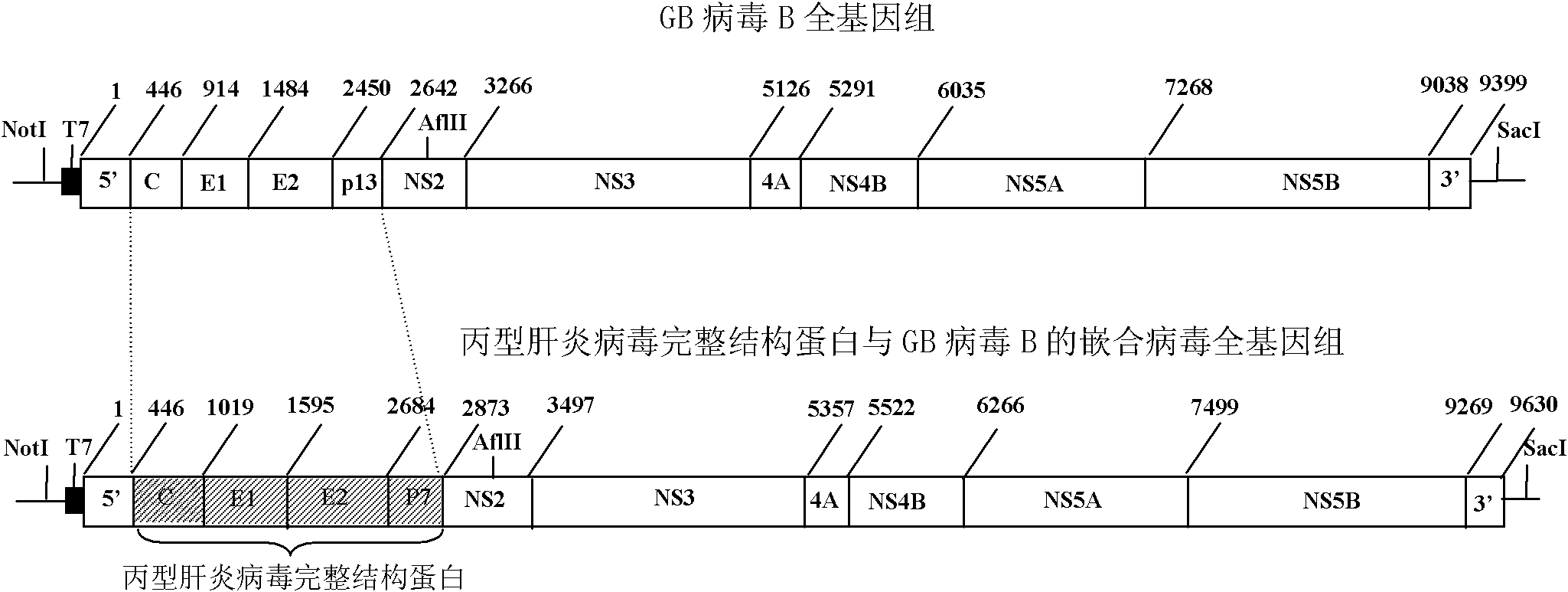
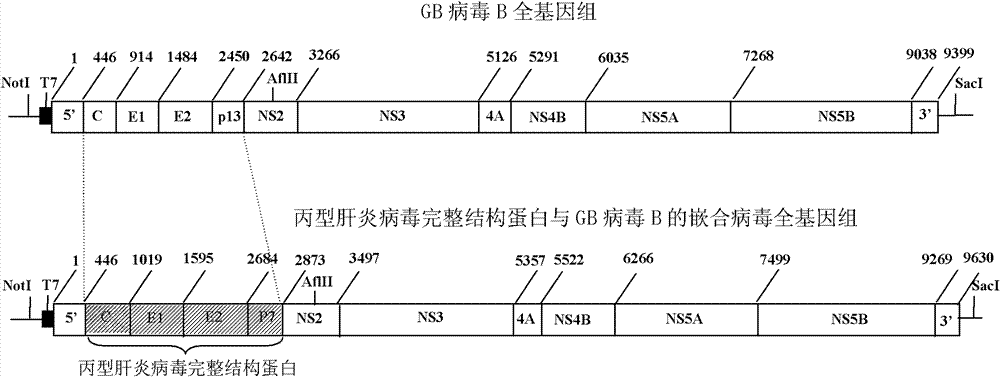
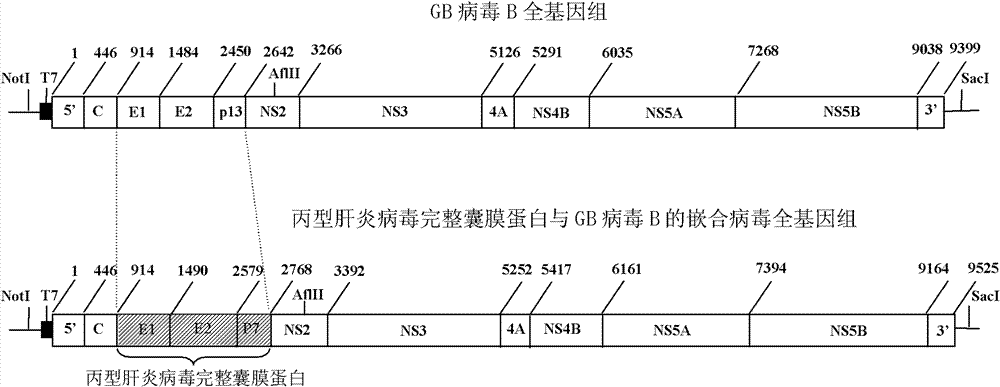
Chimeric virus of complete structural protein of hepatitis C virus and GB virus B
ActiveCN102154227ATrue reflection of the immune responseLearn about preclinical researchViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationPrimateGenotype
The invention relates to a virus, a composition and the field of preparation or purification thereof, in particular to a chimeric virus of the complete structural protein of a hepatitis C virus and a GB virus B. The chimeric virus is formed by connecting the sequence of a non-coding region on the 5' terminal of the GB virus B, the gene sequence of the complete structural protein of the hepatitis C virus, a nonstructural protein of the GB virus B and the sequence of a non-coding region on a 3' terminal in turn, wherein the gene sequence of the complete structural protein of the hepatitis C virus is the gene sequence of the complete structural protein of 1b genotype hepatitis C virus. The chimeric virus can be used to infect marmoset effectively through the intrahepatic or intravenous injection of the chimeric virus-containing serum of a primary marmoset. The chimeric virus simulates the infection and immune state of the hepatitis C virus in bodies of primates, a platform for testing and evaluating the immunity to the complete structural protein of the hepatitis C virus is provided, and the scientific problems such as limitation on the research on immunity, prevention and control ofhepatitis C virus and vaccine evaluation due to lack of small infected models of primates are solved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
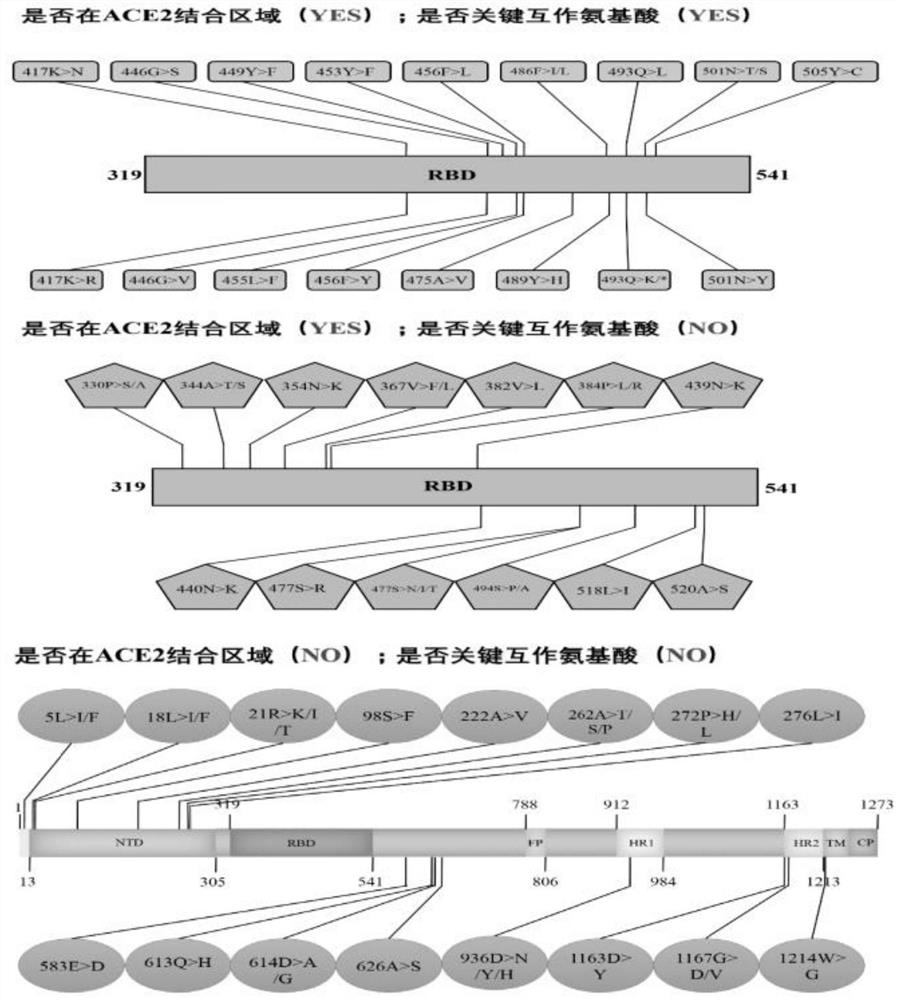
Construction of virus S protein mutant pseudovirus disc, and vaccine evaluation application of virus S protein mutant pseudovirus disc
PendingCN113444745AAvoid mismatchIncrease coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceImmune effectsTGE VACCINE
The invention discloses construction of a virus S protein mutant pseudovirus disc and vaccine evaluation application of the virus S protein mutant pseudovirus disc. The construction comprises the following steps of: step 1, constructing a pseudovirus system; step 2, detecting the activity of the pseudovirus; and step 3, evaluating the immune effect of the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine by using the pseudovirus. In the step 1, according to a SARS-CoV-2 genome sequence number GenBank: MN908947, mutation sites with a large number of variation site strains and a wide propagation range in a database are analyzed and counted, and 40 kinds of mutation sites are selected to be used for constructing the pseudovirus. In the step 2, the activity of the S protein pseudovirus is detected, and a SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus disc is formed after classification and statistics. In the step 3, the pseudovirus disc is applied to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine effect evaluation, the immune effect of the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine can be evaluated more comprehensively, and especially whether the existing SARS-CoV-2 vaccine can effectively prevent infection and prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 mutant strains or not is evaluated.
Owner:ANHUI PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL +2
Building method for mouse model systemically infected with pseudomonas aeruginosa
InactiveCN105766785AReduce dosageInfection conditions are easy to controlCompounds screening/testingBacteria material medical ingredientsAeruginosa pseudomonasInfrared lamp
The invention relates to a building method for a mouse model systemically infected with pseudomonas aeruginosa. The building method comprises the following steps that 1, a mouse is irradiated by an infrared lamp for 3 minutes, and the vein vessels on the two sides of the tail of the mouse are obviously filled and dilated; 2, pseudomonas aeruginosa is intravenously injected into the tail of the mouse. According to the method, the mouse can be effectively infected, and the model systemically infected with the pseudomonas aeruginosa is successfully built. The infected mouse model is stable and can be used for vaccine evaluation and protective mechanism research.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method for PRRSV
PendingCN112379105AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityBiological testingImmunoassaysImmune effectsSerum neutralization test
The invention discloses an IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method for PRRSV, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biological detection. The IPMA neutralizing antibody detection methodfor PRRSV comprises the following steps: inoculating an isopyknic PRRSV virus solution and clinical serum onto Marc145 cells, fixing, adding a primary antibody, adding a secondary antibody and developing. The method provided by the invention provides certain technical support for prevention, vaccine evaluation and immune evaluation of PRRSV infected pigs; and the serum neutralization test can be used for detecting the PRRSV antibody level and evaluating the immune effect of the PRRS vaccine, and is expected to be applied to the production of actual vaccines. According to the method, target cells are infected after interaction of whole viruses and antibodies, and the situation of interaction of viruses and neutralizing antibodies is truly reflected; the method has the characteristics of strong specificity, high sensitivity and simple operation.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
Competitive enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (c-elisa) for the detection of a flavivirus specific antibody
InactiveUS20100041015A1Rapid and low cost and straightforward assayStrong specificitySsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific immunitySerotype
A competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (C-ELISA), using flavivirus member specific immunological agents was developed to detect antibody specific to members of the flaviviruses indicative of exposure to flavivirus. The test is based on a competition for epitope binding on the envelope protein of the flavivirus antigen captured using anti-flavivirus IgA in the presence of flavivirus positive serum. This test has comparable sensitivity specificity and speed to the virus neutralization assay (VNT). C-ELISA is a versatile technique, which could have various applications. Slight modifications of this protocol could lead to a C-ELISA-based detection method of secondary infection or one that could be used for serotype specific sero-epidemiological studies and / or vaccine evaluation. The protocol developed for C-ELISA was demonstrated using dengue lysate antigen and dengue specific monoclonal antibody. This can be used against other flaviviruses and the results for Japanese encephalitis illustrates this.
Owner:NATIONAL ENVIRONMENT AGENCY
IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method of CSFV
PendingCN112611866AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityImmunoassaysImmune effectsSerum neutralization test
The invention discloses an IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method of CSFV and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention discloses an IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method for CSFV. The IPMA neutralizing antibody detection method comprises steps of virus inoculation, plate laying, fixation, primary antibody addition, secondary antibody addition and color development. The method provided by the invention provides certain technical support for prevention, vaccine evaluation and immune evaluation of pigs infected with CSFV; and the serum neutralization test can be used for detecting the level of the CSFV antibody and evaluating the immune effect of the CSF vaccine, and is expected to be applied to the production of actual vaccines. According to the method, target cells are infected after interaction of whole viruses and antibodies, and the situation of interaction of viruses and neutralizing antibodies is truly reflected; the kit has the characteristics of strong specificity, high sensitivity and simple operation.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
Chimeric virus of complete structural protein of hepatitis C virus and GB virus B
ActiveCN102154227BTrue reflection of the immune responseViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationPrimateGenotype
The invention relates to a virus, a composition and the field of preparation or purification thereof, in particular to a chimeric virus of the complete structural protein of a hepatitis C virus and a GB virus B. The chimeric virus is formed by connecting the sequence of a non-coding region on the 5' terminal of the GB virus B, the gene sequence of the complete structural protein of the hepatitis C virus, a nonstructural protein of the GB virus B and the sequence of a non-coding region on a 3' terminal in turn, wherein the gene sequence of the complete structural protein of the hepatitis C virus is the gene sequence of the complete structural protein of 1b genotype hepatitis C virus. The chimeric virus can be used to infect marmoset effectively through the intrahepatic or intravenous injection of the chimeric virus-containing serum of a primary marmoset. The chimeric virus simulates the infection and immune state of the hepatitis C virus in bodies of primates, a platform for testing and evaluating the immunity to the complete structural protein of the hepatitis C virus is provided, and the scientific problems such as limitation on the research on immunity, prevention and control ofhepatitis C virus and vaccine evaluation due to lack of small infected models of primates are solved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of 820 strains of chicken infectious bronchitis virus and its application
InactiveCN104263702BStrong pathogenicityStrong morbidityMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesDiseaseMortality rate
The invention relates to the field of avian infectious bronchitis virulent strain models in veterinarian biological products, in particular to an avian infectious bronchitis 820 strain of which the preservation serial number is CGMCC No.9571 and application of the avian infectious bronchitis 820 strain in the effect test of an avian infectious bronchitis vaccine. The avian infectious bronchitis virus 820 strain has high morbidity rate and high dead rate in inoculated chicken flock, has toxic substance counteracting effect close to clinic morbidity and lethal levels, has the capability of simulating clinic virus morbidity, and can effectively evaluate the protection level of the vaccine, thereby reducing economic losses caused by the disease. The avian infectious bronchitis 820 strain has wide application prospects in vaccine evaluation field.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A kind of recombinant influenza virus and its application
InactiveCN104312983BAvoid interferenceIncrease productionAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesHemagglutininNeuraminidase
The invention discloses a recombinant influenza virus and application thereof and provides a preparation method of the recombinant virus. The preparation method comprises the following steps: guiding an HA6 subtype influenza virus hemagglutinin encoding gene, an influenza virus neuraminidase (NA) gene and six genes including PB2, PB1, PA, NP, M and NS in an influenza virus into a host cell together, and packing to obtain the recombinant virus. The invention also discloses a detection method for detecting antibodies for inhibiting activities of seasonal influenza N1, N2, 2009H1N1N1 and 2013H7N9N9 enzymes by virtue of the recombinant virus. The detection method comprises the steps of sample treatment and result analysis. According to the invention, the immune response to NA of people can be rapidly and effectively measured, the operation is simple, the application is convenient, and viable technical support is provided for clinical detection and vaccine evaluation.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Chimeric virus of complete envelope protein of HCV (hepatitis C virus) and GB virus B
InactiveCN102154226BTrue reflection of the immune responseViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationGenotypeUnstructured Proteins
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
A challenge method for rainbow trout vaccine evaluation
ActiveCN110800660BAdjust storage spacePrevent secondary traumaClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAquatic productSurgery
The invention relates to a virus challenge method for rainbow trout vaccine evaluation, belonging to the technical field of aquatic product challenge methods. In order to solve the problems that the existing rainbow trout vaccine evaluation and challenge method is inconvenient to operate and the parallelism of the challenge effect is poor, the present invention provides a challenge method for rainbow trout vaccine evaluation. The body length and body height were measured on the operation platform of the challenge experiment, the body width was measured after the dorsal fins of the rainbow trout were fixed upward, and the depth of the syringe needle was determined according to the body size of the rainbow trout. After the rainbow trout is awake in the fish body awakening pond, it swims back to the fish body culture pond by itself through the entry conduit. The invention quickly, efficiently, safely and stably completes the operations of fish body anesthesia, challenge and recovery in the rainbow trout challenge experiment platform system, without the need for round-trip transportation, saving time and effort, and not only ensuring the safety of the fish body, but also ensuring the attack experiment. parallelism.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
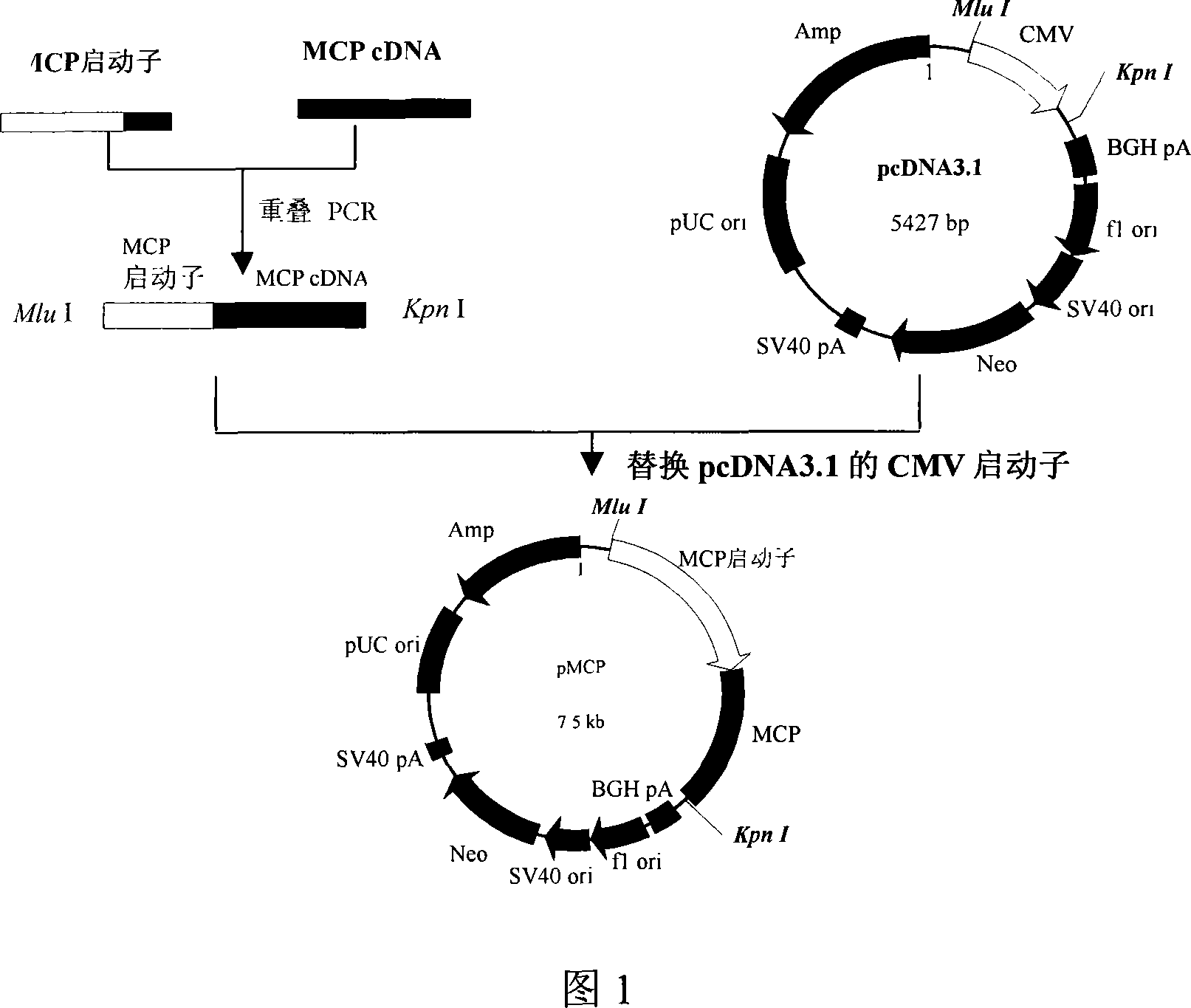
Human membrana cofactor protein mini-gene pmcp constructing method
The invention relates to a construction method for human membrane cofactor protein mini gene, belonging to pathogenic biology field, which is characterized that a human blood cell genome DNA is selected as a template, and a promoter of the human membrane cofactor protein gene is cloned with a PCR method; a human membrane cofactor protein mini gene cDNA is amplified with pSG5-MCP template; then the MCP promoter is spliced with the cDNA with the PCR overlapping method; a CMV promoter of the pcDNA3.1 is replaced by the obtained DNA fragment, and the human membrane cofactor mini gene pMCP is constructed. A transgenic mouse built by the invention can change the situation that the ideal animal model is scarce in prior study of human specific pathogen infectious disease, and break through the limits of infectious pathogenesis of corresponding pathogen, vaccine evaluation, drug evaluation and other aspects.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Microfluidic platform device and method for identifying neutralizing and/or enhancing antibodies through direct functional assays
The microfluidic platform device of the claimed invention makes use of a high throughput lab-on-a-chip format to determine the functional profile of antibodies elicited by infection or vaccination against infection for any pathogen. It can be used to evaluate vaccines, evaluate whether vaccinated individuals show indices of protection, determine whether individuals display resistance or susceptibility to infection, discover new vaccine antigens, discover and test therapeutic interventions, or evaluate mechanisms of disease.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Construction method and application of a novel animal model of hepatitis A virus
ActiveCN105343898BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMarmota himalayanaComplete sequence
The invention relates to the technical field of medical biology, in particular to a building method and application of a novel hepatitis A virus animal model. The preservation number of a hepatitis A virus strain is CGMCC No. 11200, and the complete sequence of the hepatitis A virus strain is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The quantified hepatitis A virus strain is inoculated to an experimental animal to produce the animal model, wherein the experimental animal is a marmot and preferably a woodchuck or a Himalayan marmot. The application of the novel hepatitis A virus animal model includes application of the novel hepatitis A virus animal model to researches on hepatitis A viruses or in-vivo infection process and pathogenesis of human hepatitis A viruses and medicine screening or vaccine evaluation.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所
Toxin-attack method for rainbow trout vaccine evaluation
ActiveCN110800660AAdjustable storage spacePrevent secondary traumaClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAquatic productCatheter
The invention relates to a toxin-attack method for rainbow trout vaccine evaluation, and belongs to the technical field of aquatic product toxin-attack methods. In order to solve the problems of inconvenient operation and poor parallelism of the toxin-attack effect of the existing toxin-attack method for rainbow trout vaccine evaluation, the invention provides the toxin-attack method for rainbow trout vaccine evaluation, which includes, after anaesthetizing a rainbow trout used in the experiment, placing the rainbow trout on a toxin-attack experiment operation platform to measure body length and body height, fixing the back fin of the rainbow trout upwards, measuring the body width, determining the needle insertion depth of a syringe according to the size specification of the rainbow trout, carrying out toxin-attack injection on the part to be injected on the back of the sterilized rainbow trout, placing the rainbow trout into a fish body awakening pool, after awakening, swimming, by the rainbow trout, back to a fish body culture pool by a catheter. The method can quickly, efficiently, safely and stably complete the operations of anesthesia, toxin attack and awakening of the fish body in the rainbow trout toxin-attack experiment platform system, and does not need to carry back and forth, and thus time and labor are saved, not only the safety of the fish body can be guaranteed,but also the parallelism of the toxin-attack experiment can be ensured.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
A kind of jev infectious clone with luciferase gene and its construction method and application
InactiveCN103497972BSolve the phenomenon of not copyingFast growing trendMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuciferase GeneIndividual animal
The invention discloses a Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infectious clone with a luciferase gene, and a building method and application thereof. The JEV infectious clone with the luciferase gene is prepared by the following steps: (1) sectional synthesis of a JEV SA14 strain gene sequence; (2) assembling and building of the JEV infectious clone; (3) building of the JEV infectious clone with the luciferase gene. It is proved that a Rluc-JEV report virus with the same growth tendency as the JEV virus can be saved by the JEV infectious clone with the luciferase gene built by the method, and the JEV infectious clone has wide application value in the aspects of an animal model, virus replication and pathogenesis, drug screening and drug action mechanism, live animal imaging and vaccine evaluation and the like through the experiments of immunofluorescence, Rluc activity detection, virus bacteriophage plaque, drug inhibition, live animal imaging, vaccine evaluation and the like.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Enhanced green fluorescent protein recombinant H5N1 subtype influenza virus and its application
ActiveCN103555679BSimplified pathogenic mechanismAccelerate the pathogenic mechanismBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typePB2 proteins
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com