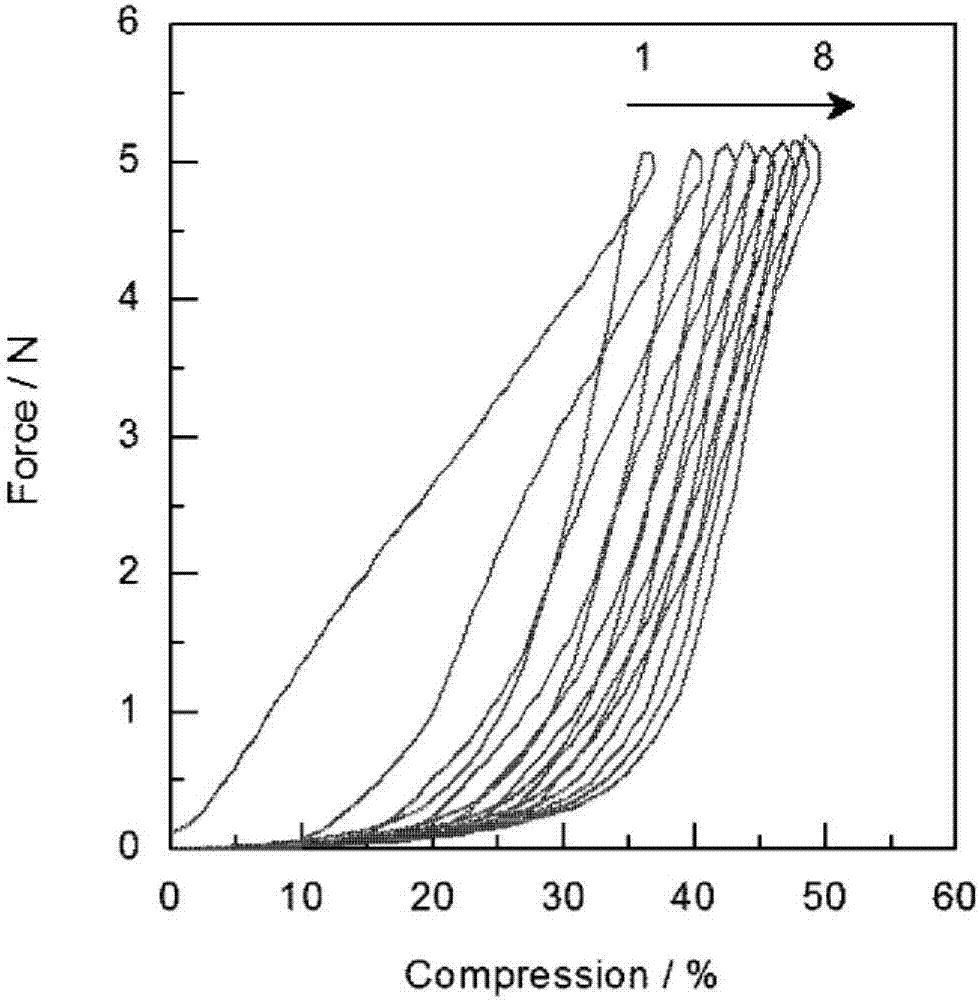
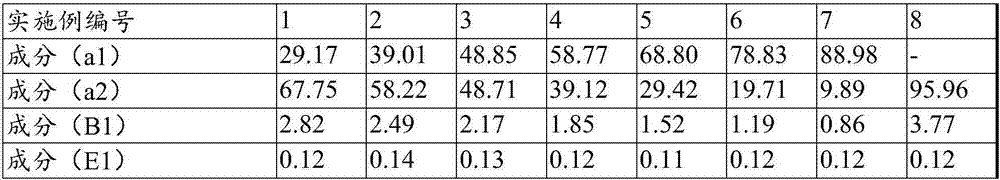
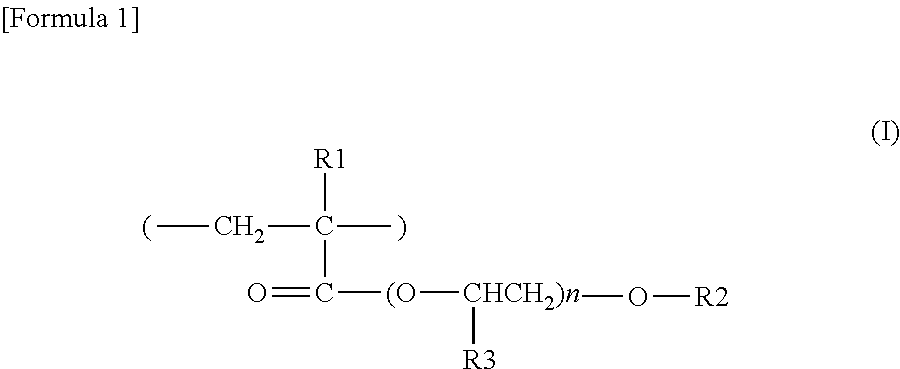
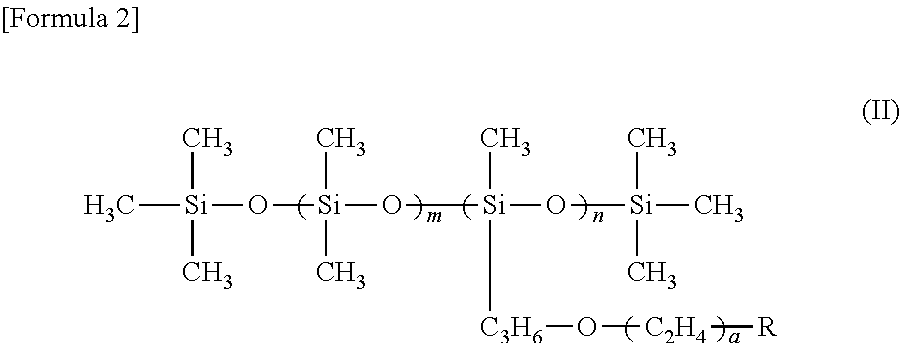
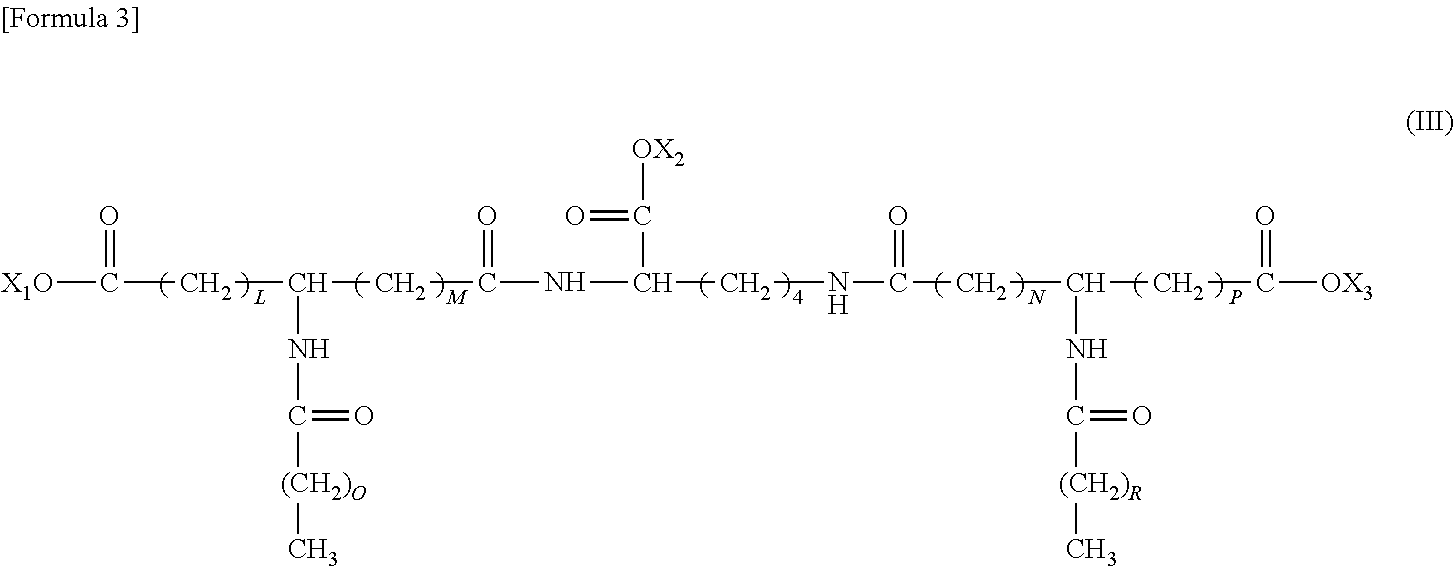Patents
Literature
63results about How to "Improved recovery properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
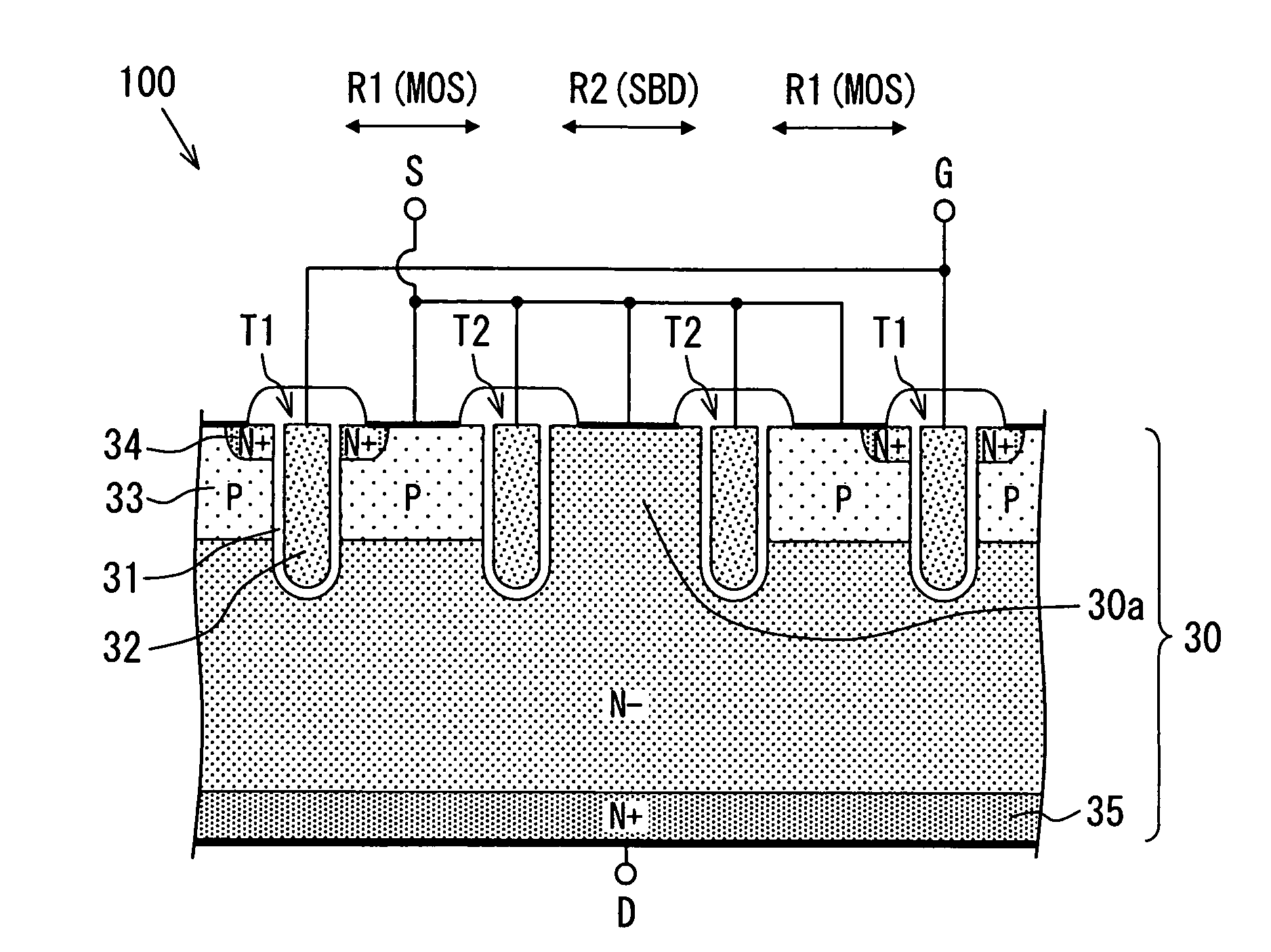
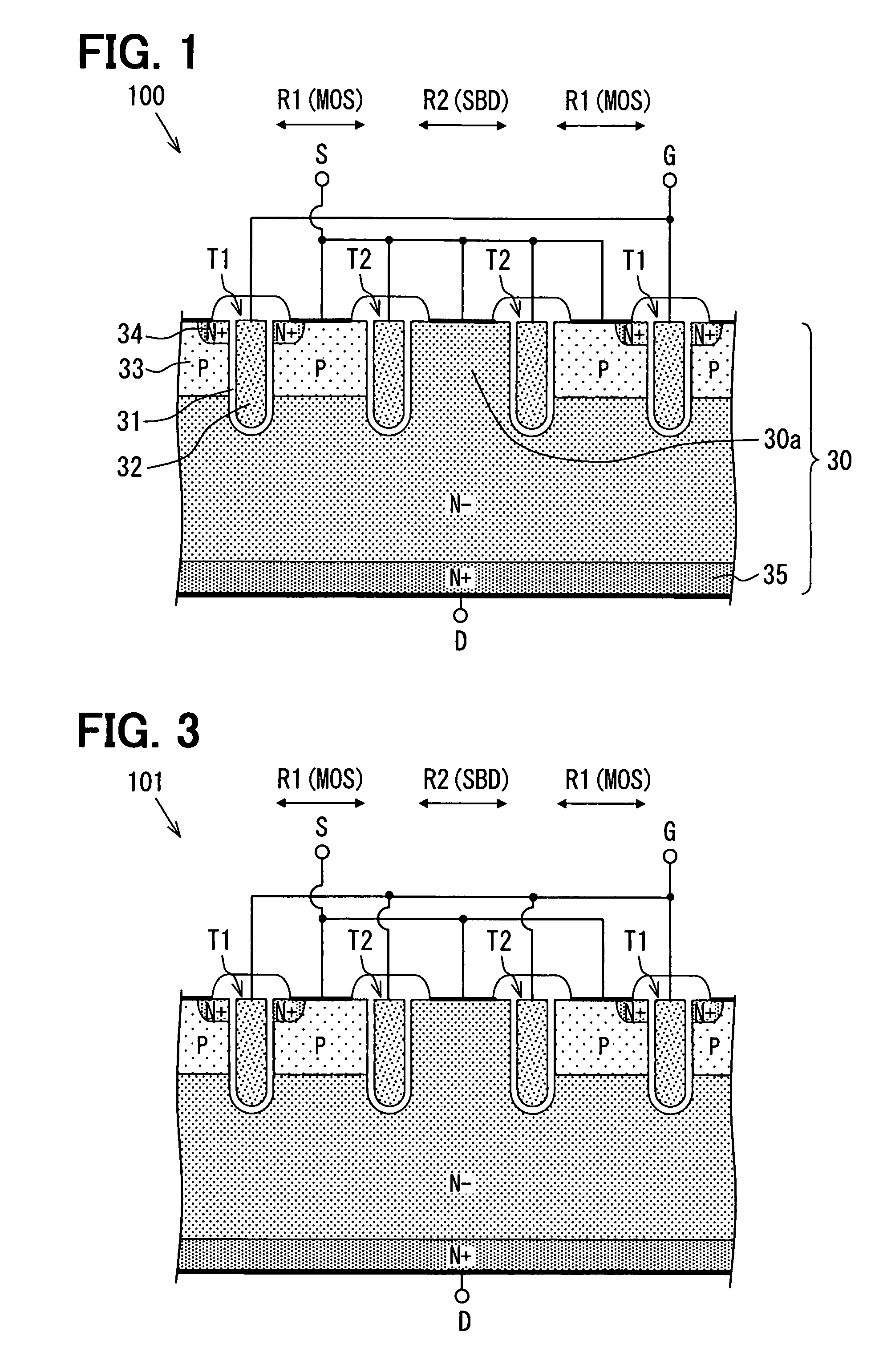
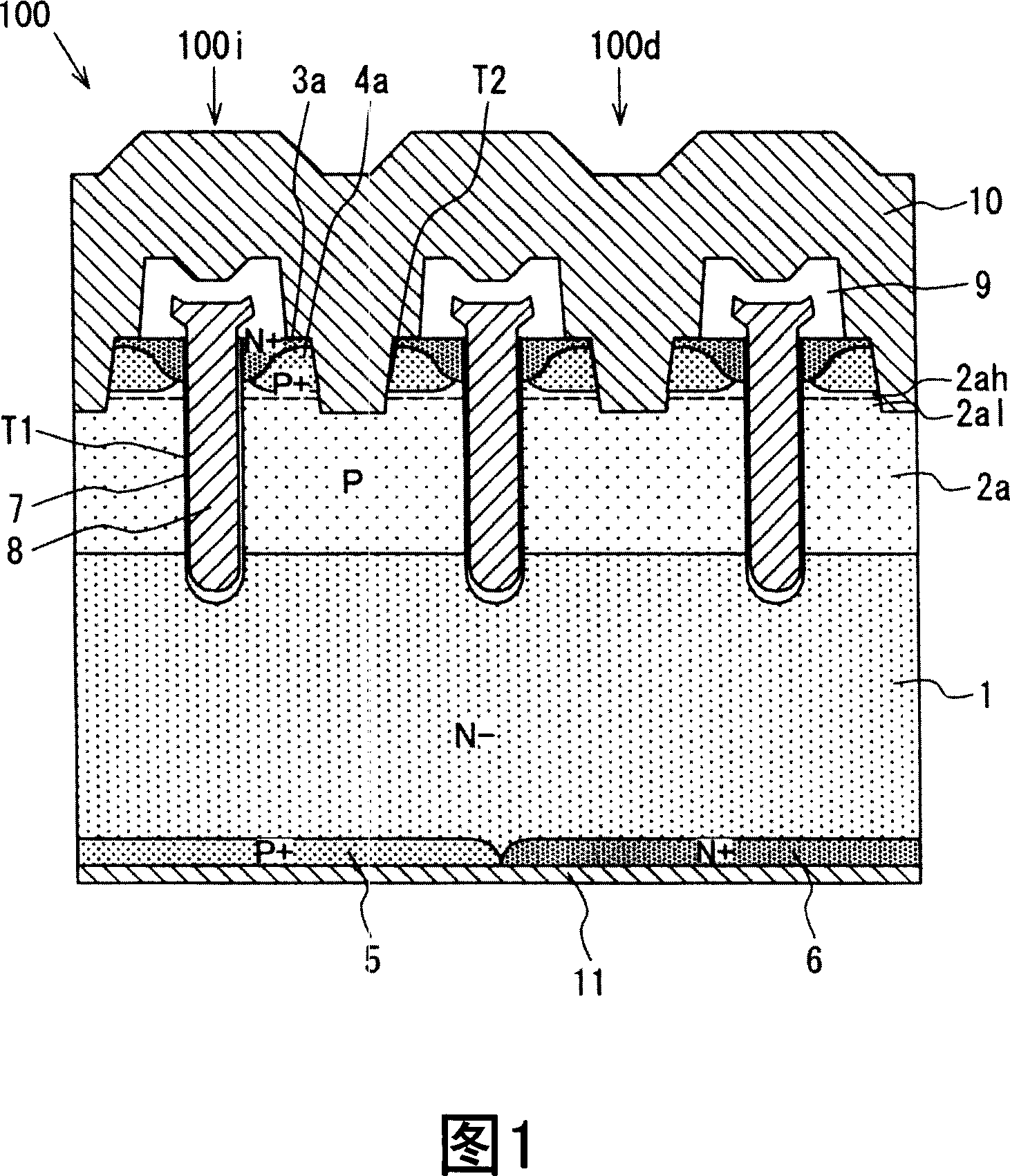
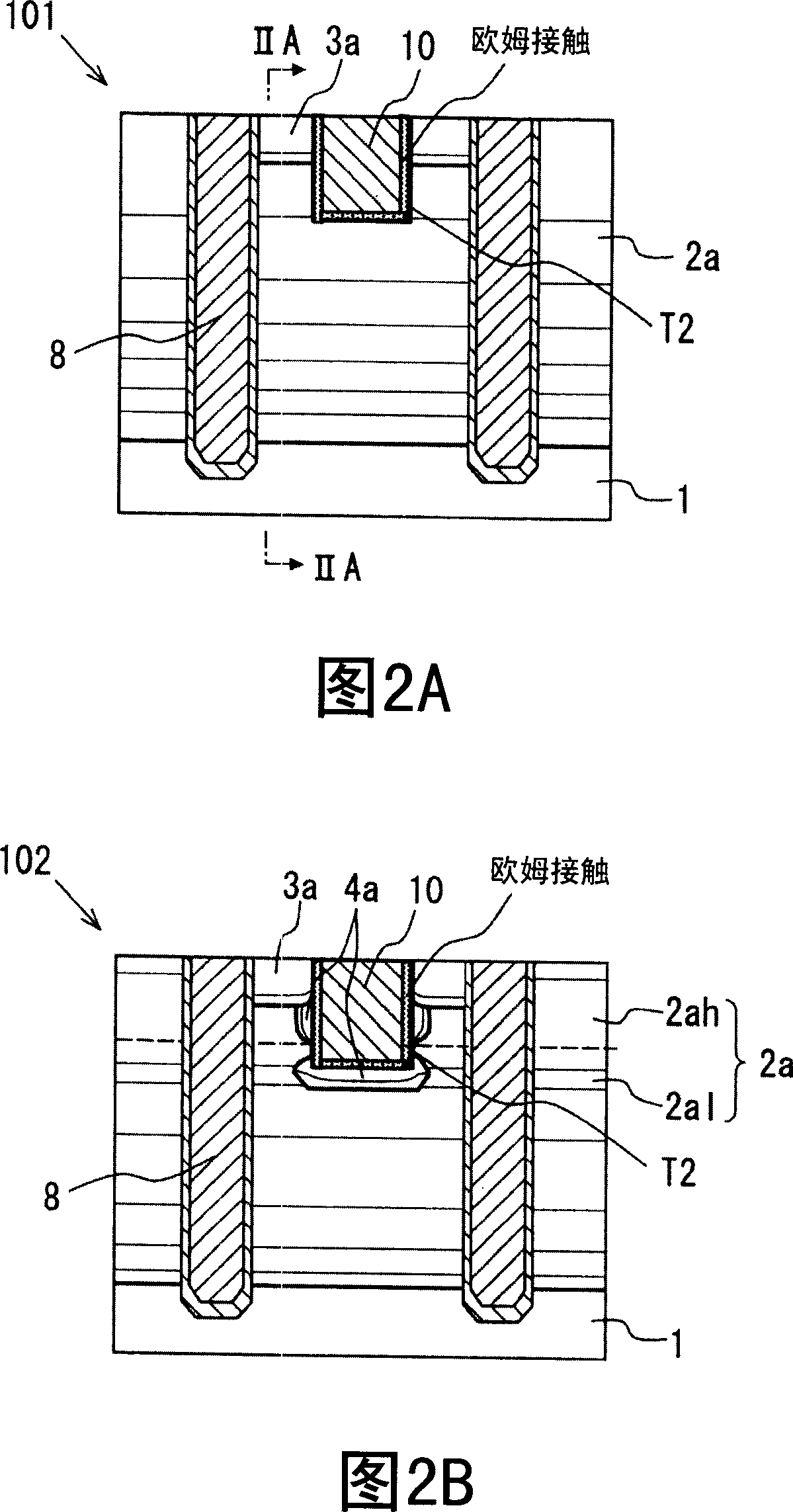
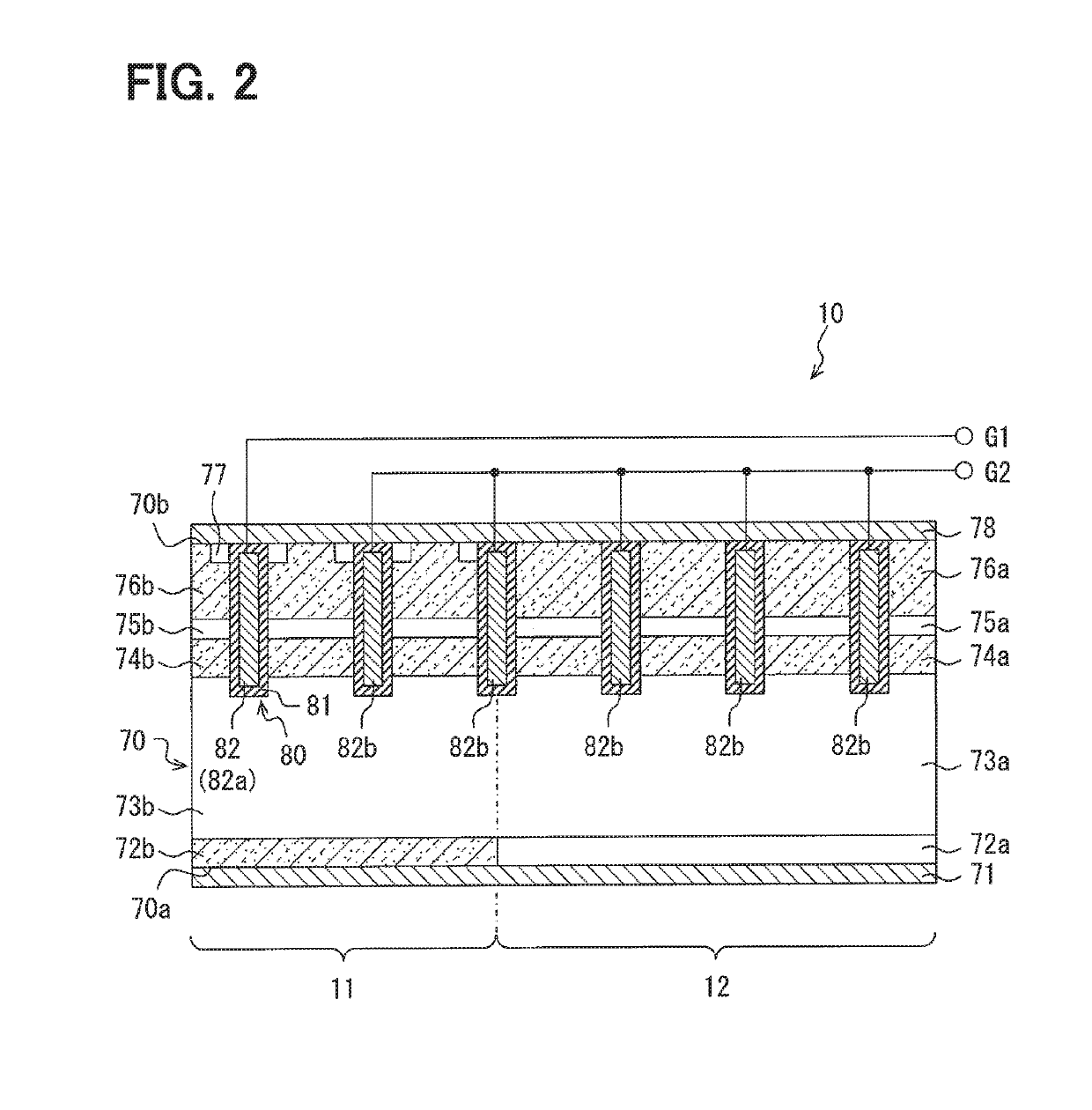
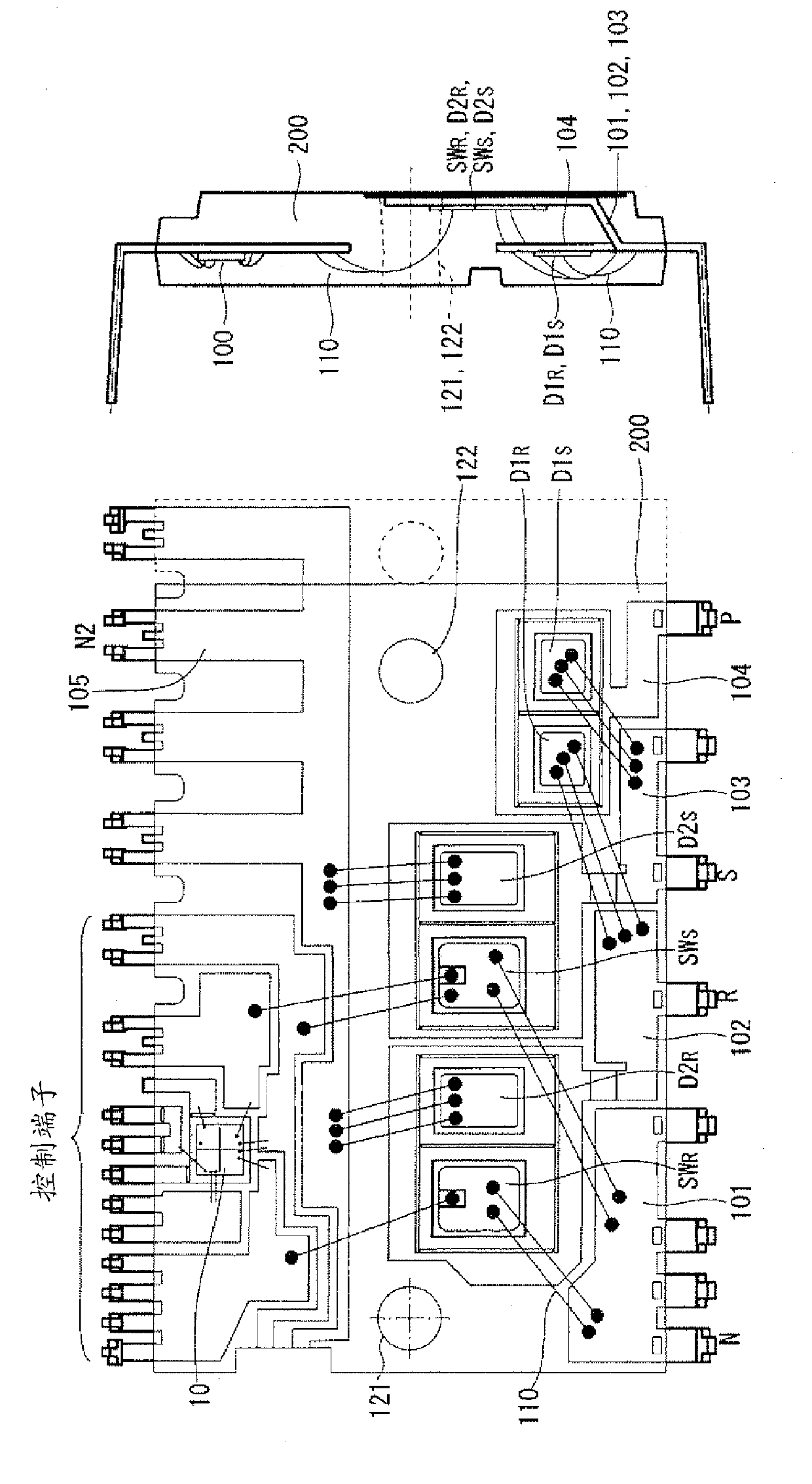
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080012050A1Recovery propertyImprove directionTransistorDiodeSchottky barrierDevice material
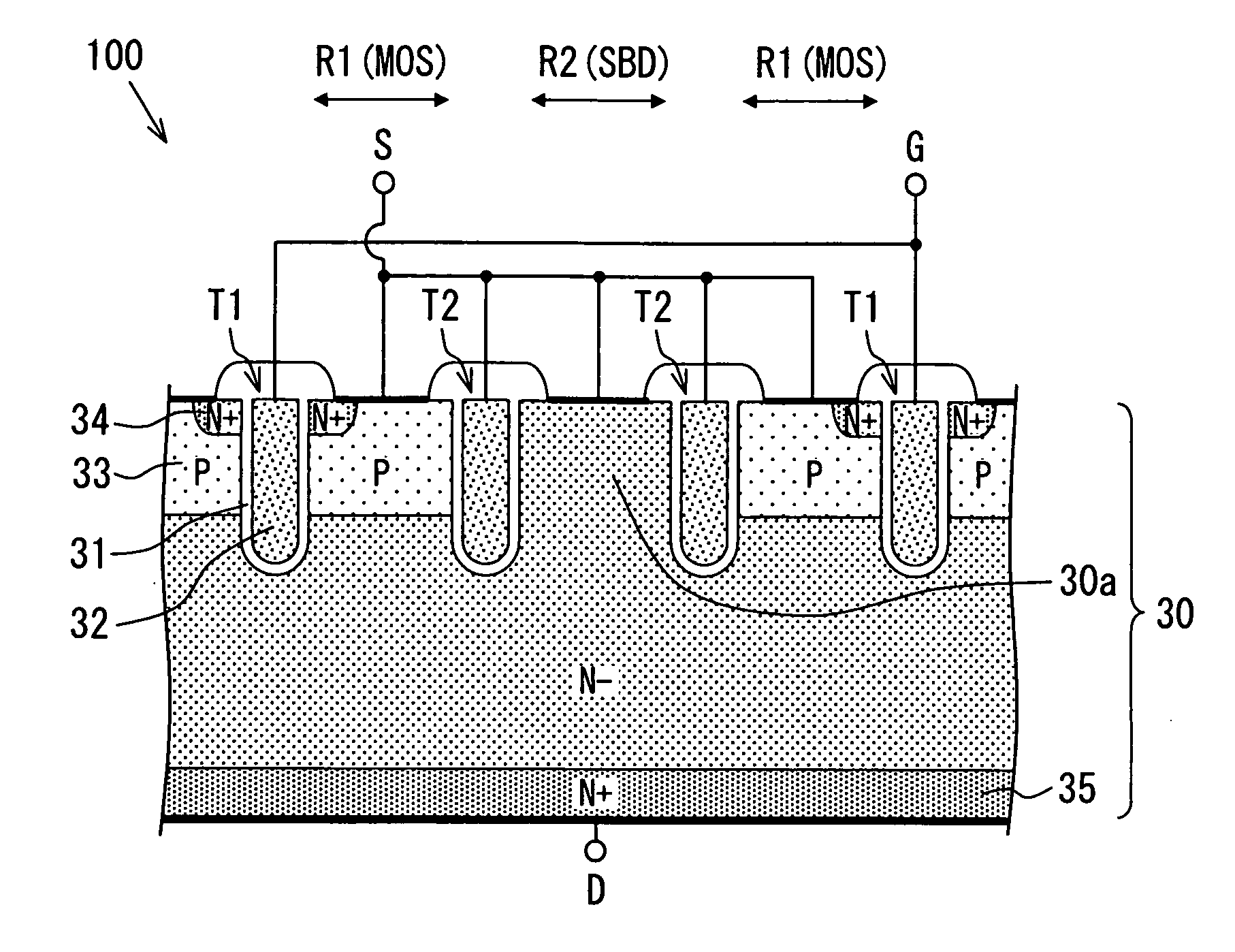
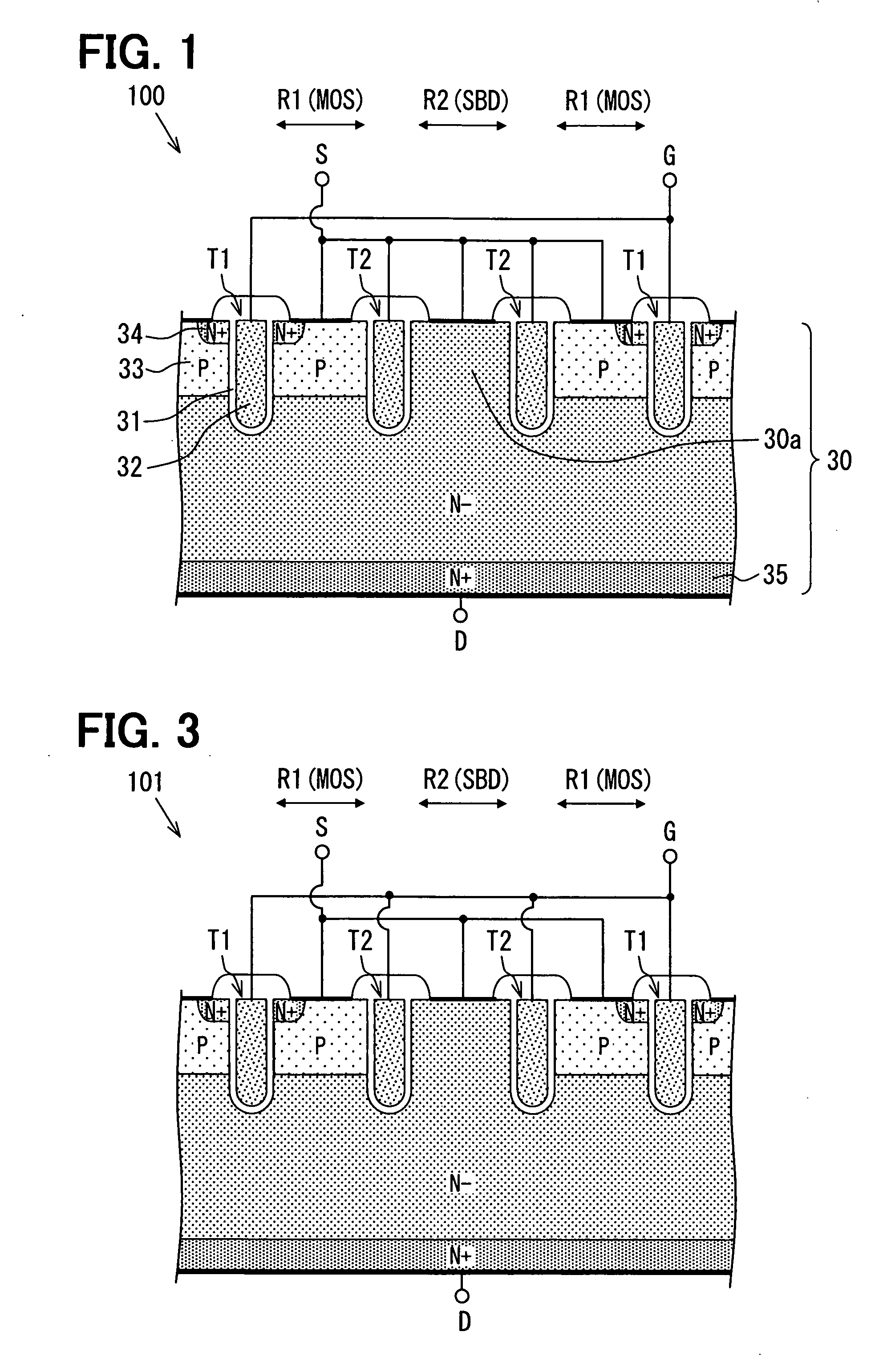
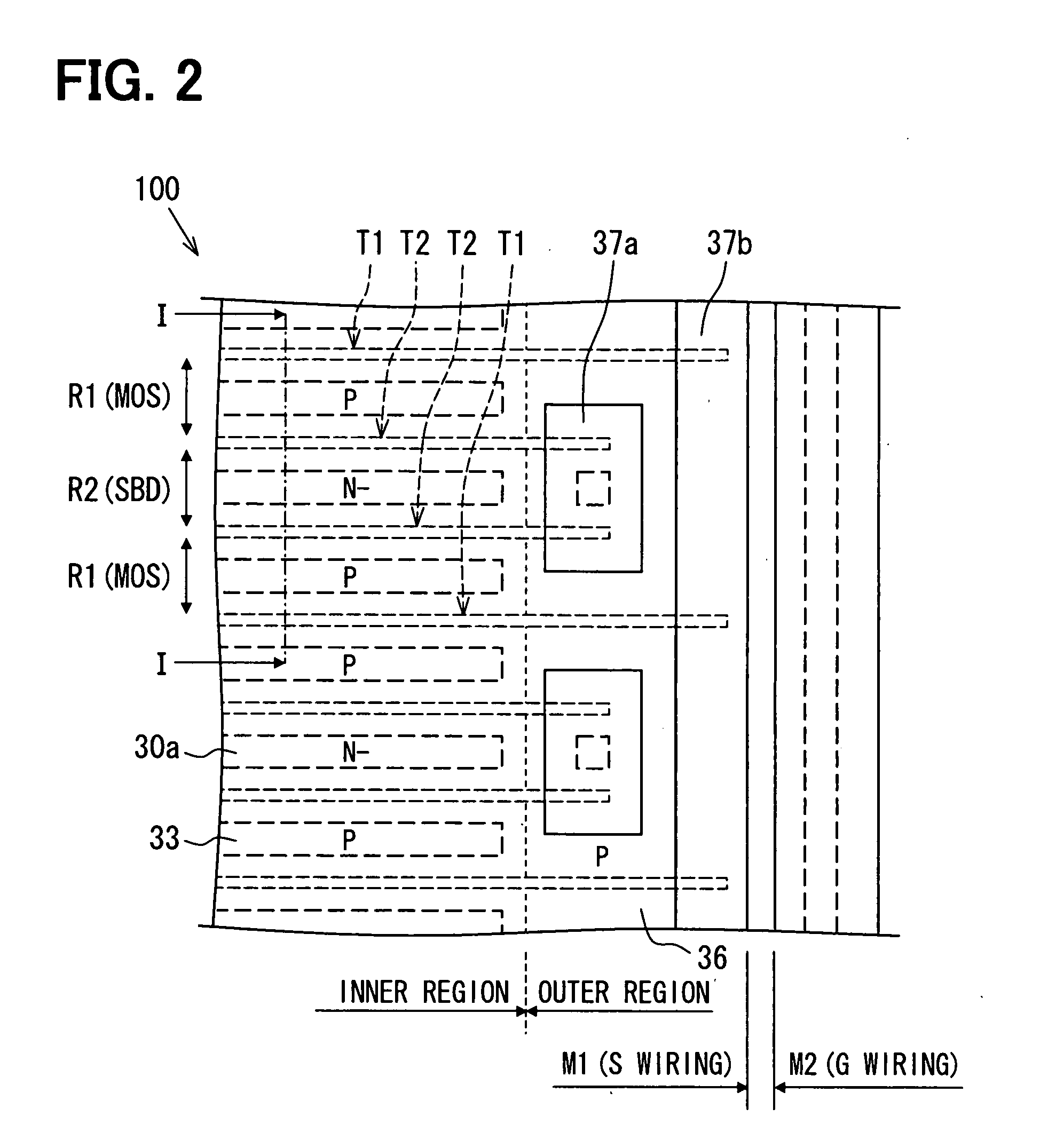
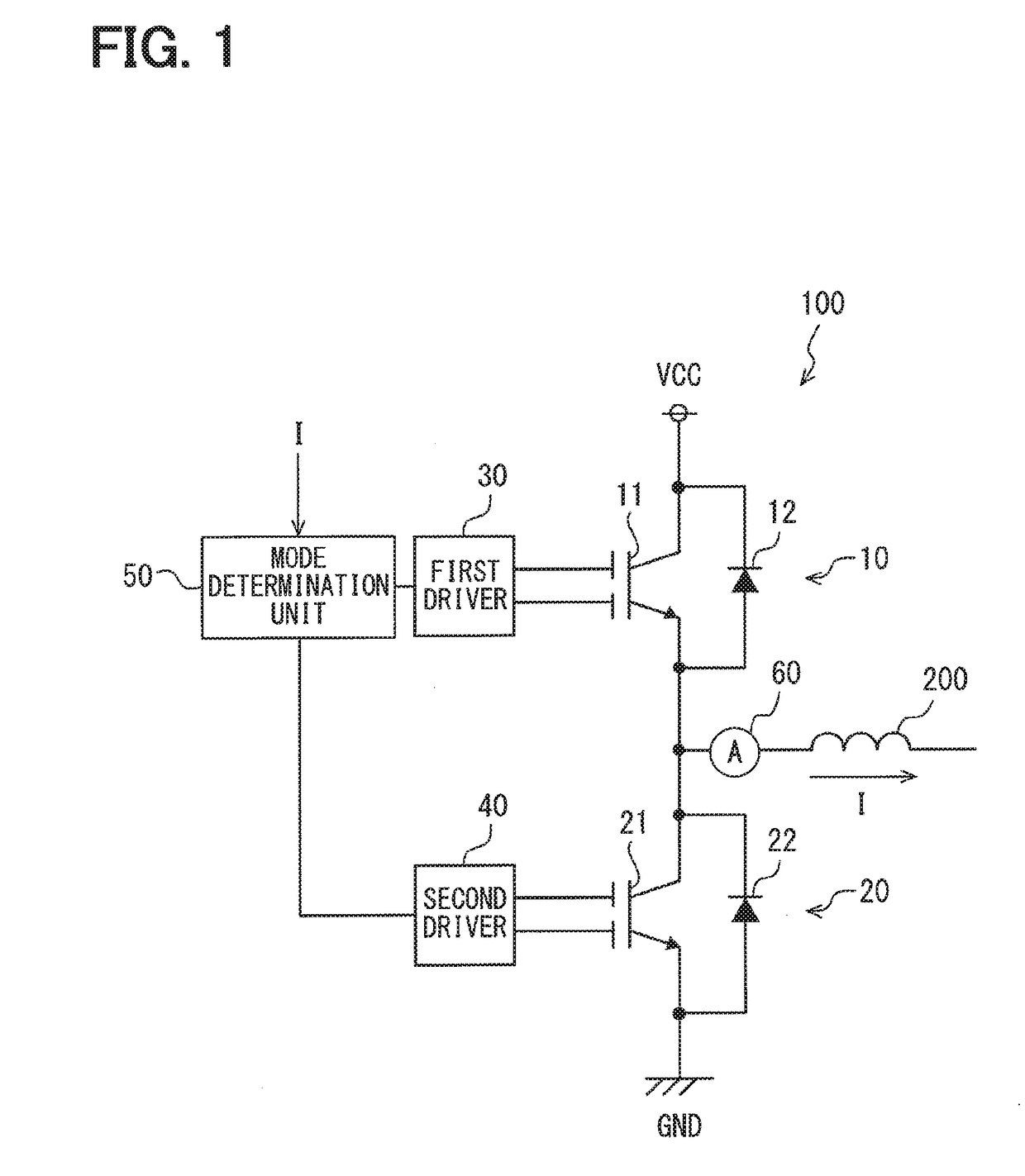
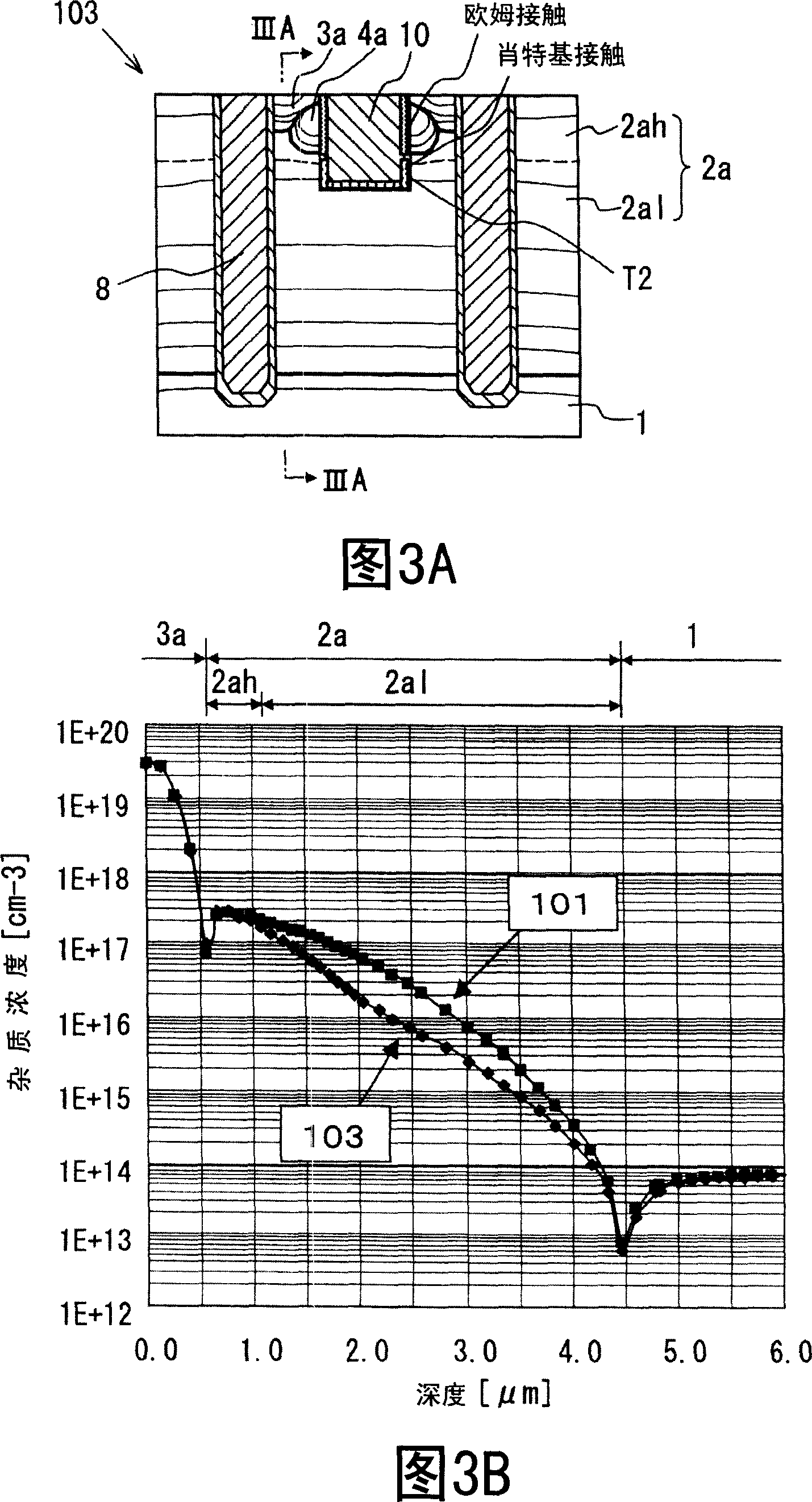
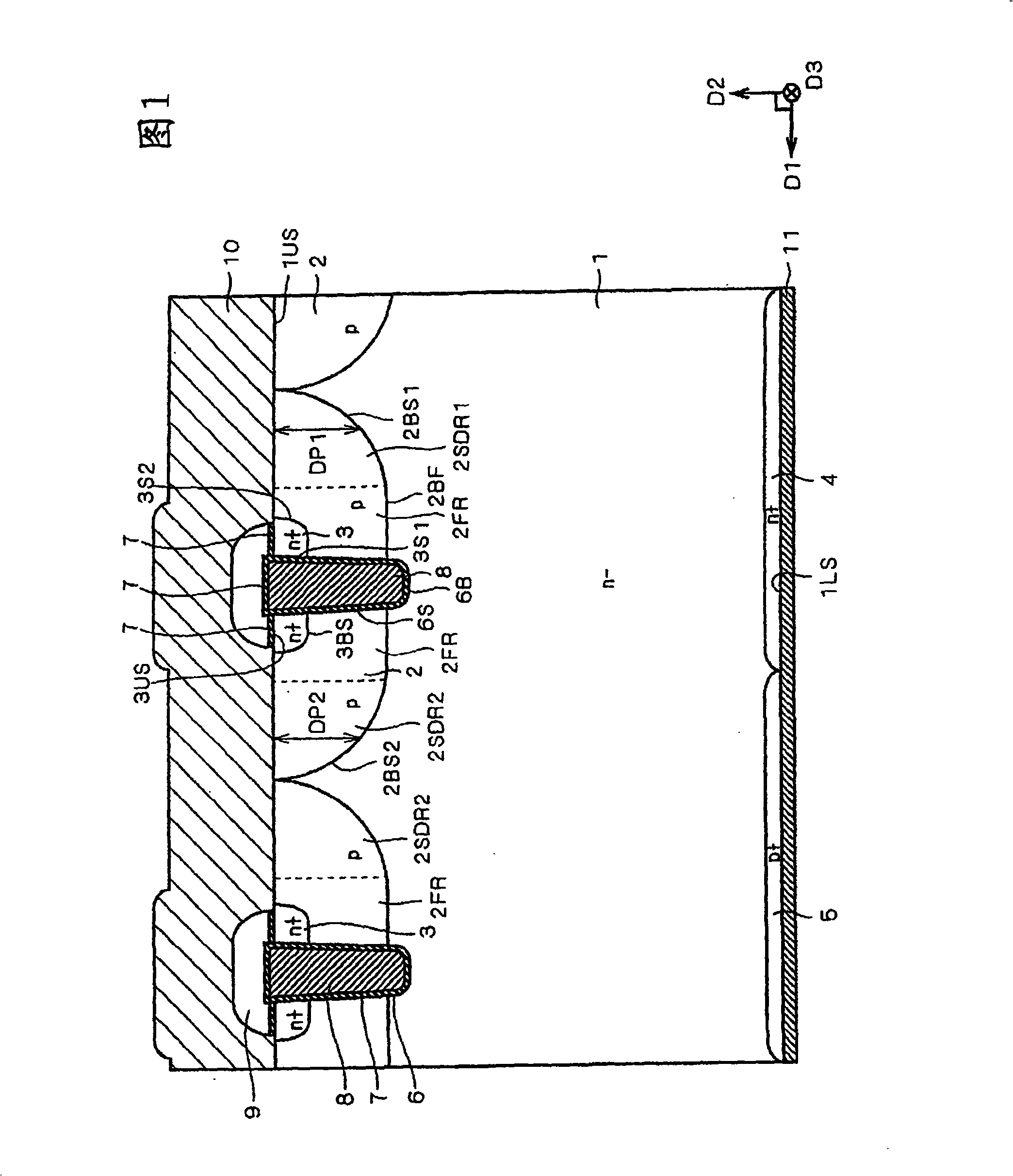
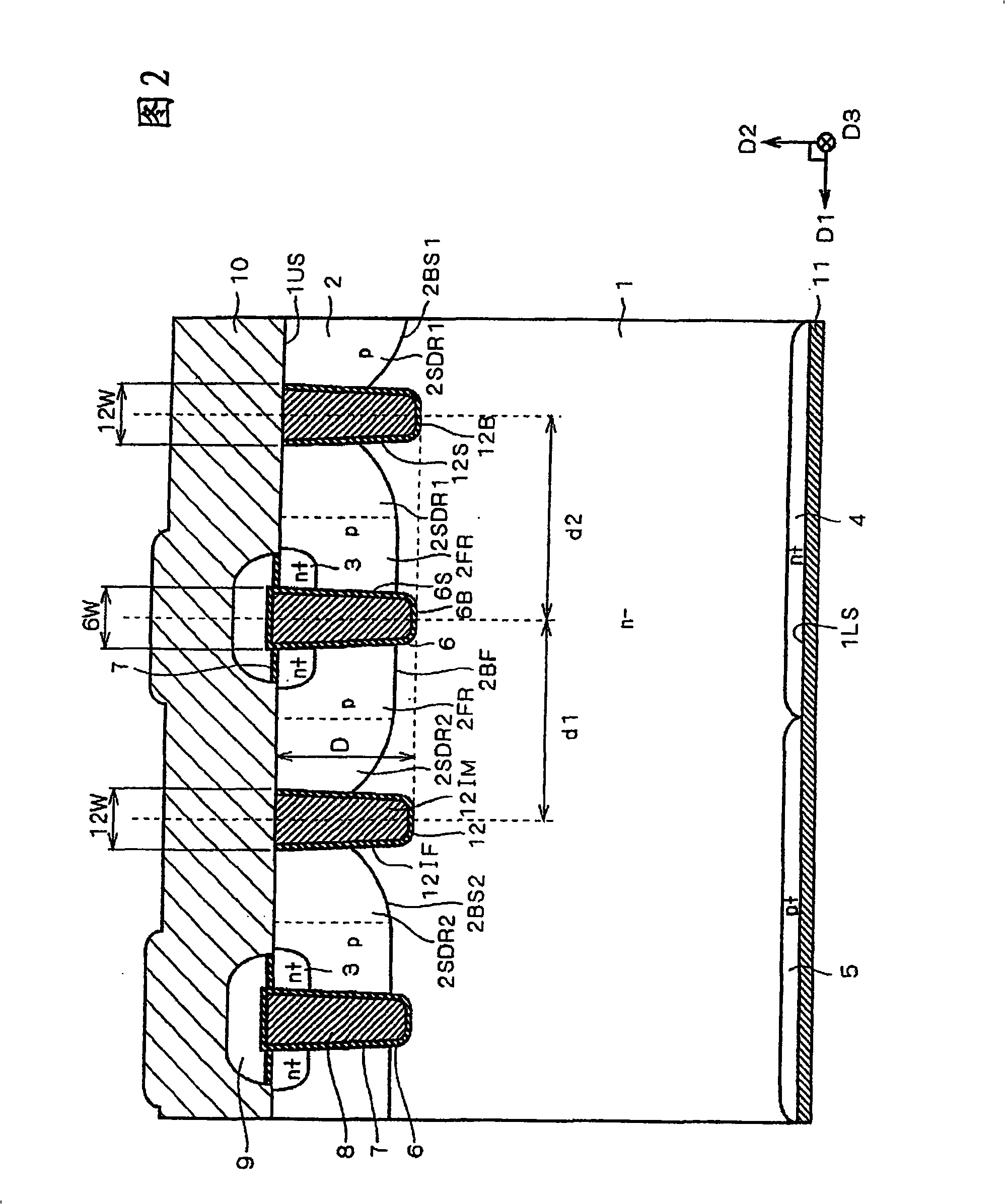
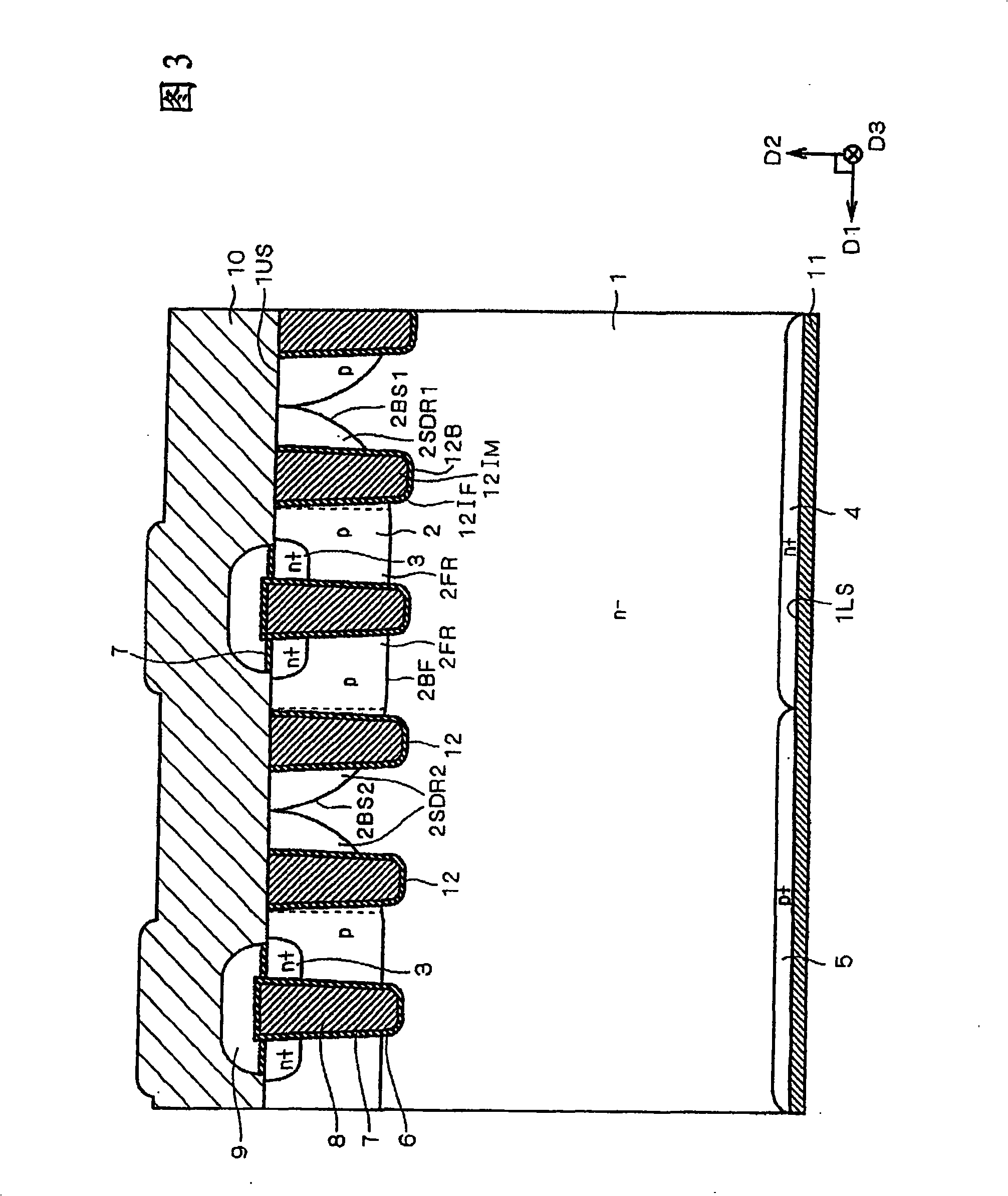
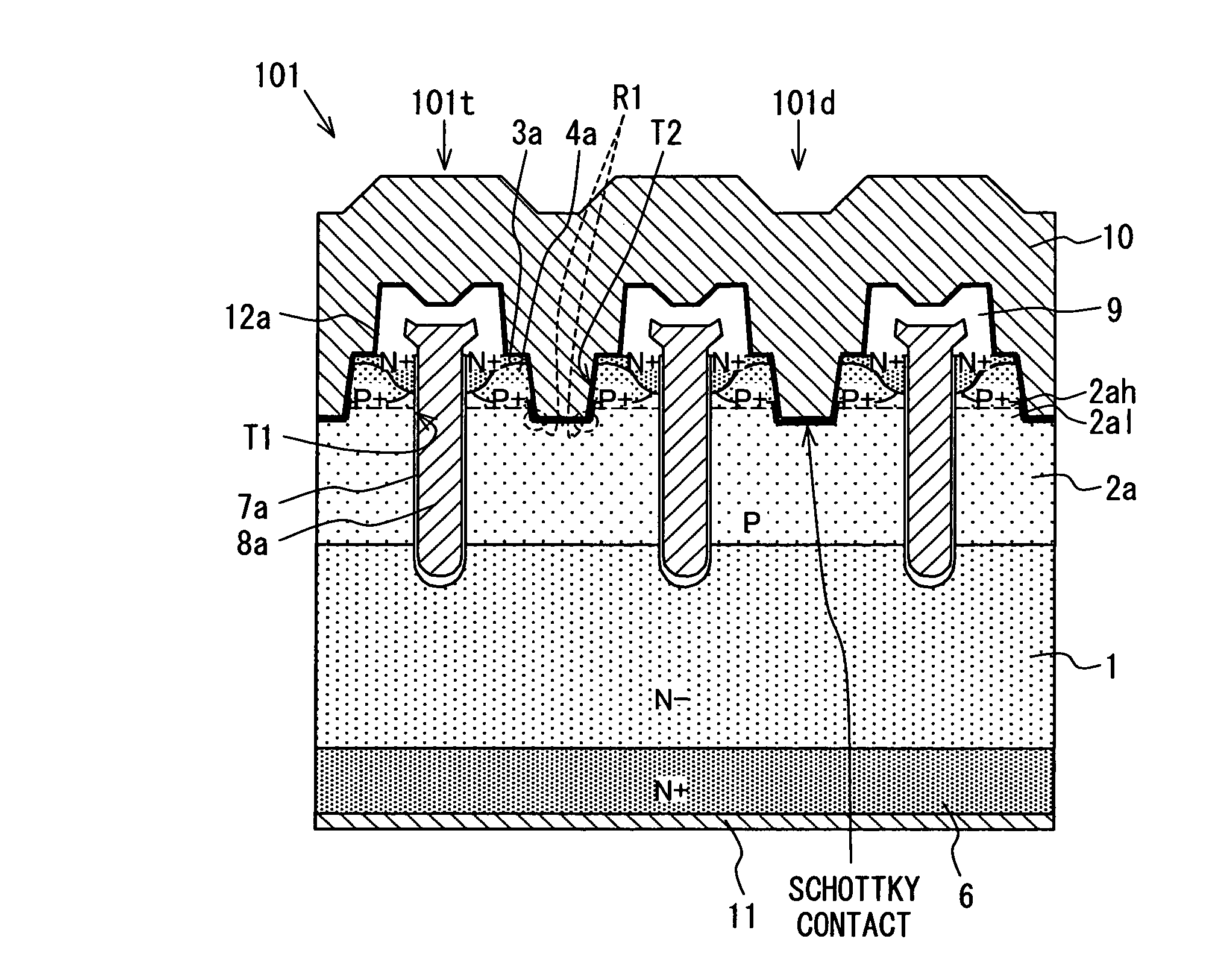
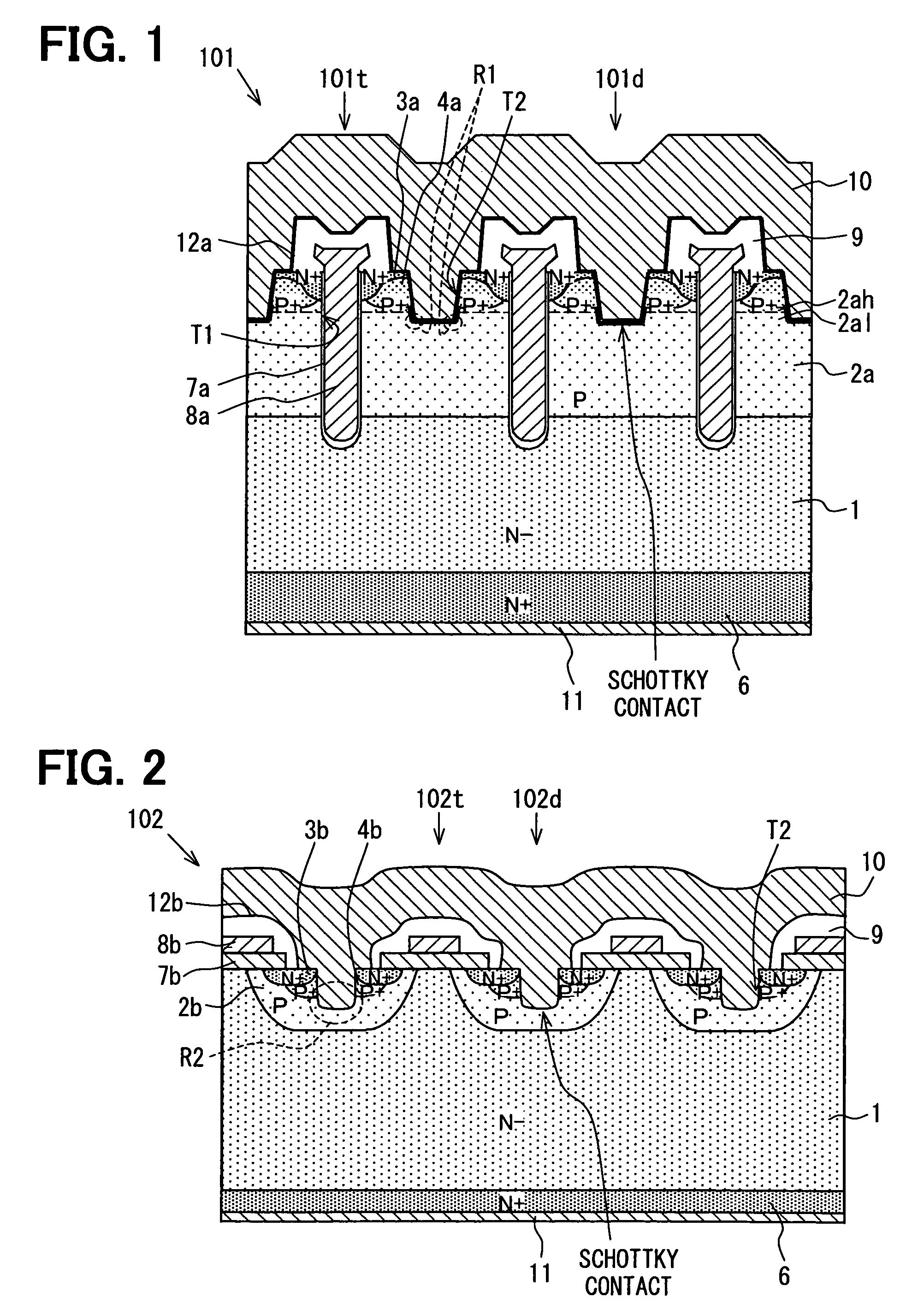
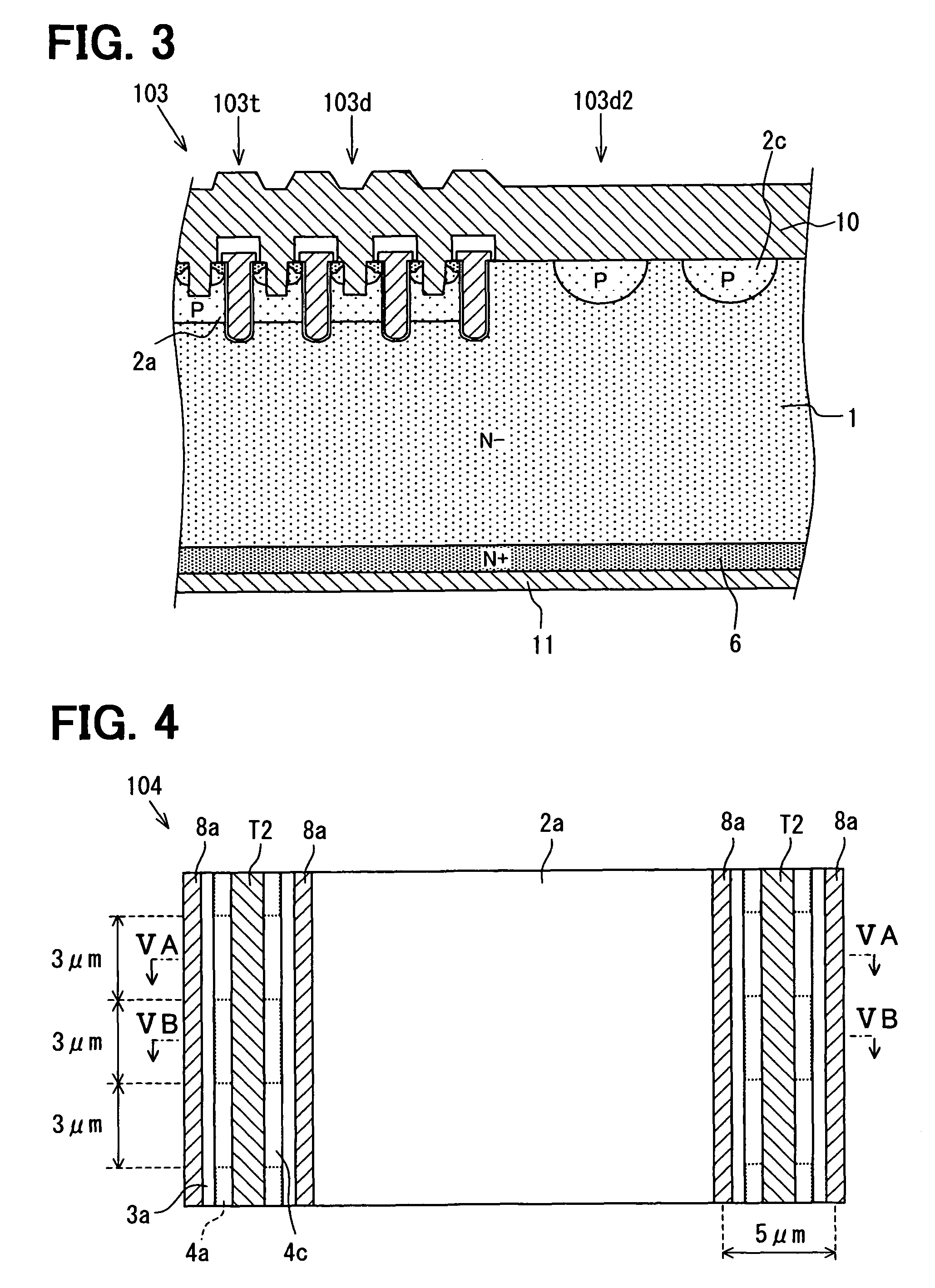
A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor substrate; a vertical type trench gate MOS transistor; a Schottky barrier diode; multiple trenches having a stripe pattern to divide an inner region into first and second separation regions; and a poly silicon film in each trench. The first separation region includes a first conductive type region for providing a source and a second conductive type layer for providing a channel region. The first conductive type region is adjacent to a first trench. The poly silicon film in the first trench is coupled with a gate wiring. A second trench is not adjacent to the first conductive type region. The poly silicon film in the second trench is coupled with a source or gate wiring. The substrate in the second separation region is coupled with the source wiring for providing a Schottky barrier.
Owner:DENSO CORP
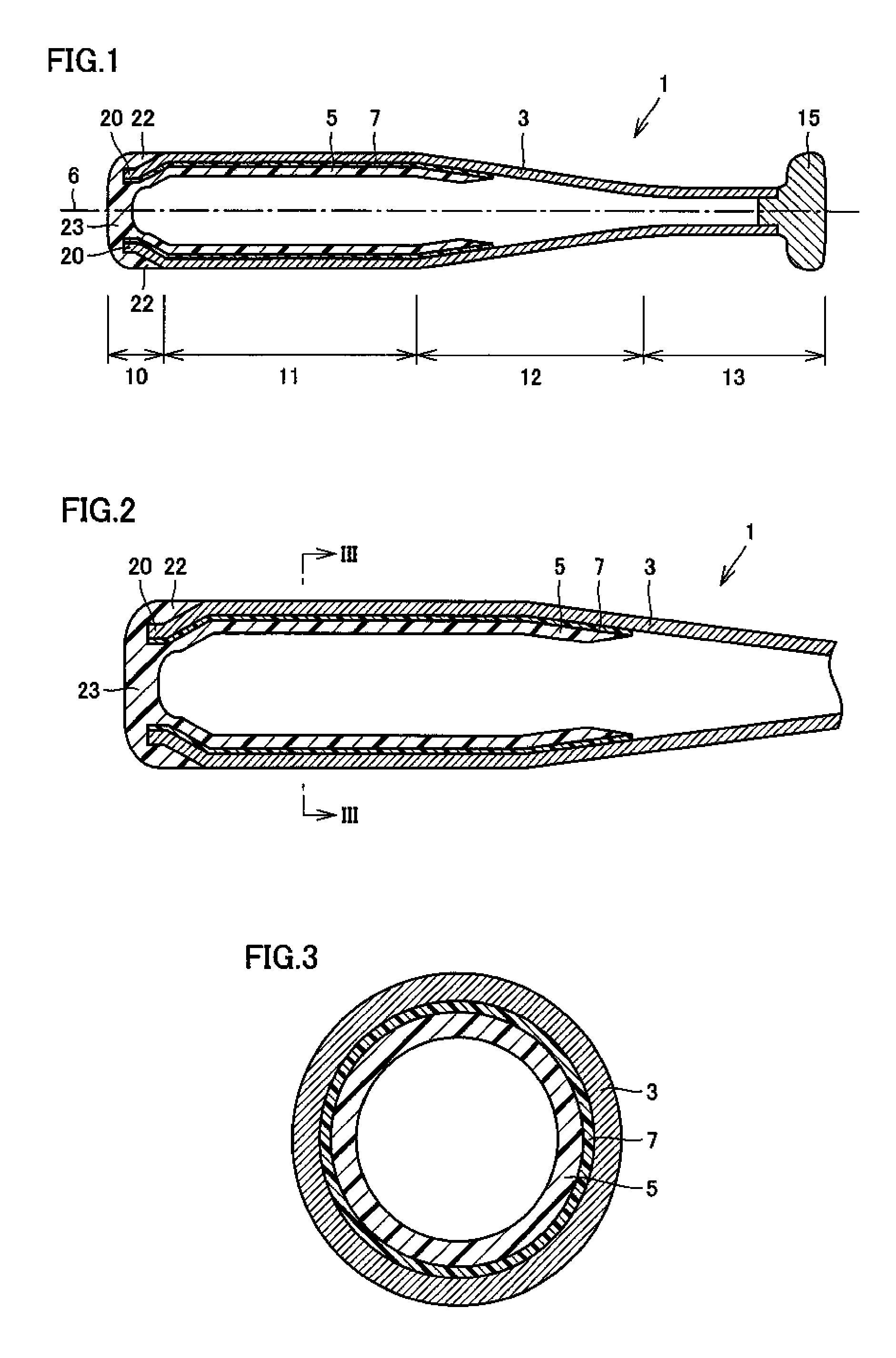
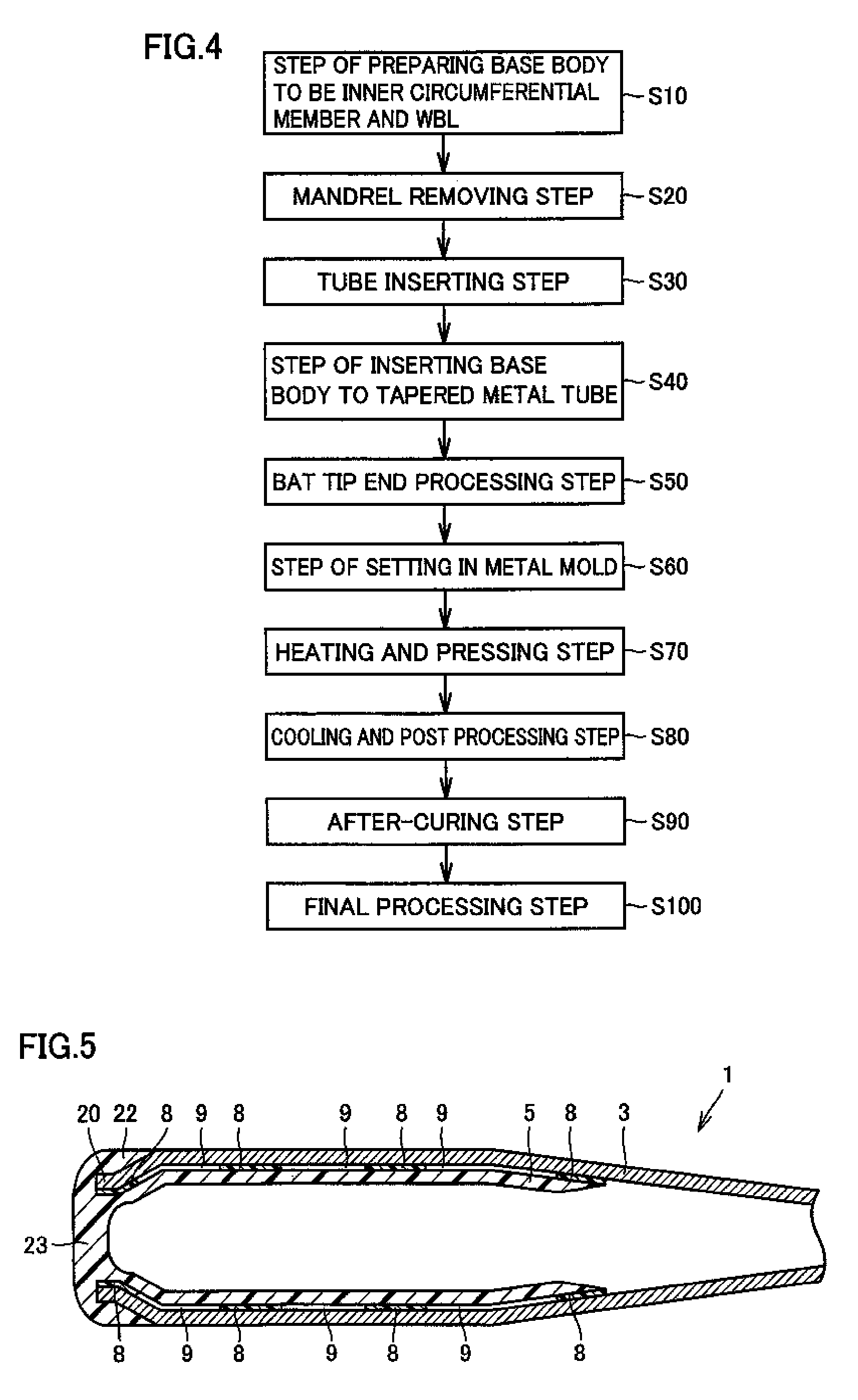
Baseball or softball bat
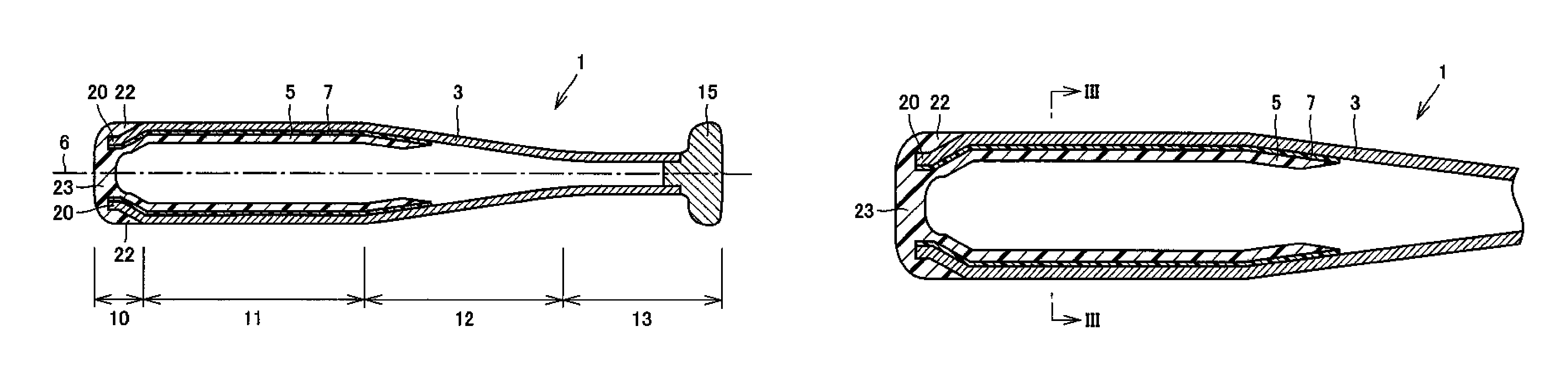
InactiveUS7585235B2Improved recovery propertiesPreventing degraded feel of hittingRacket sportsEngineeringExtremity Part
Owner:MIZUNO CORPORATION
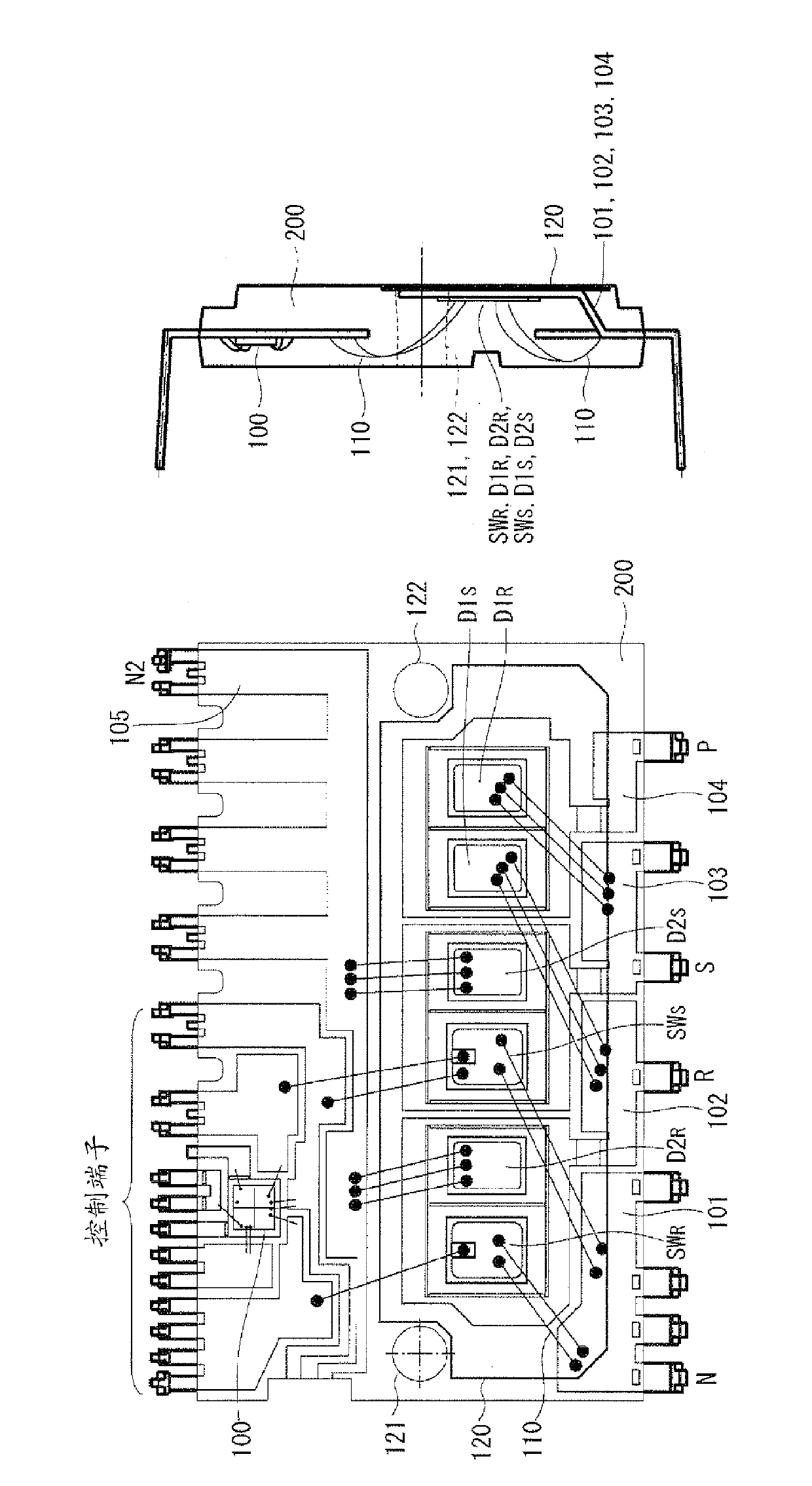
Semiconductor device
Owner:DENSO CORP
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20170077216A1Improve featuresImproved recovery propertiesTransistorConversion constructional detailsSemiconductorSemiconductor device
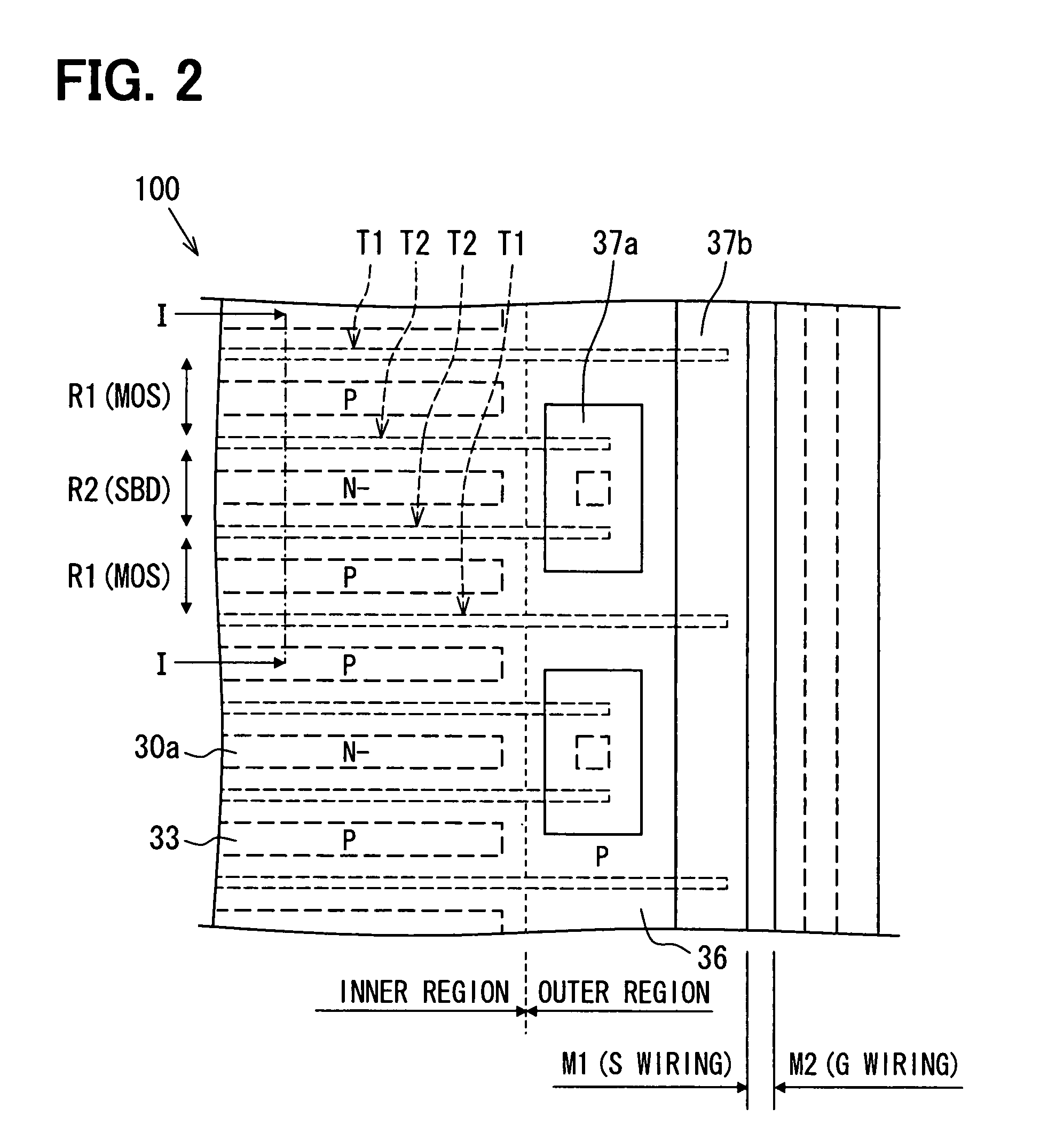
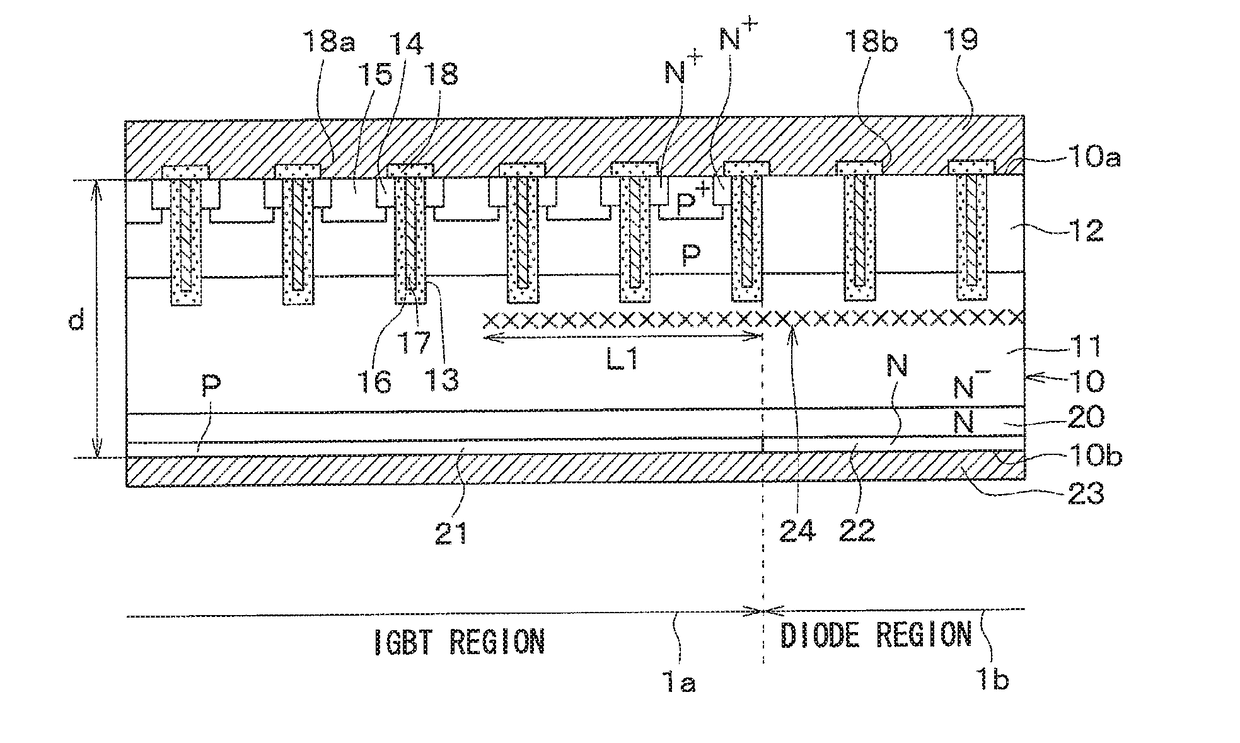
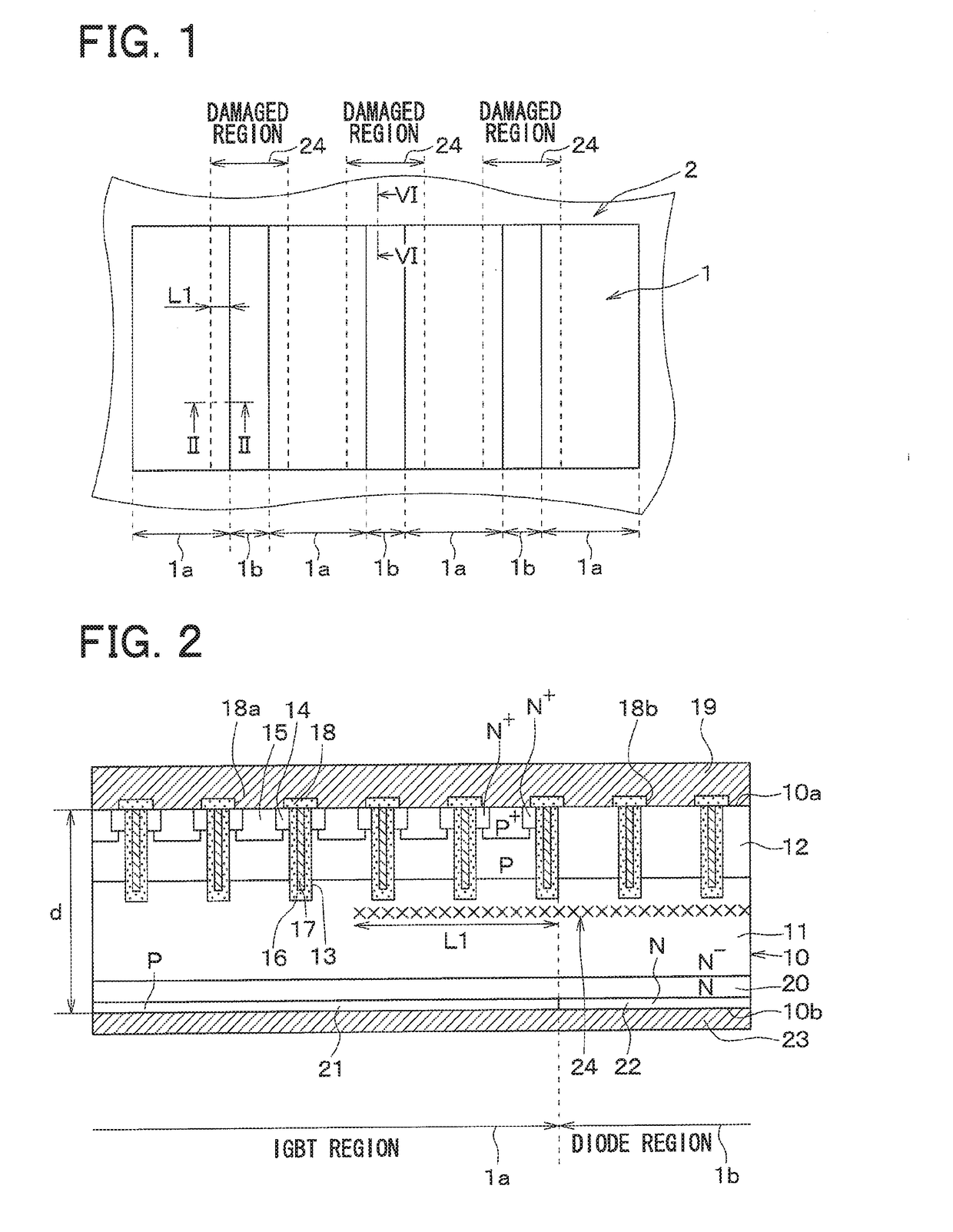
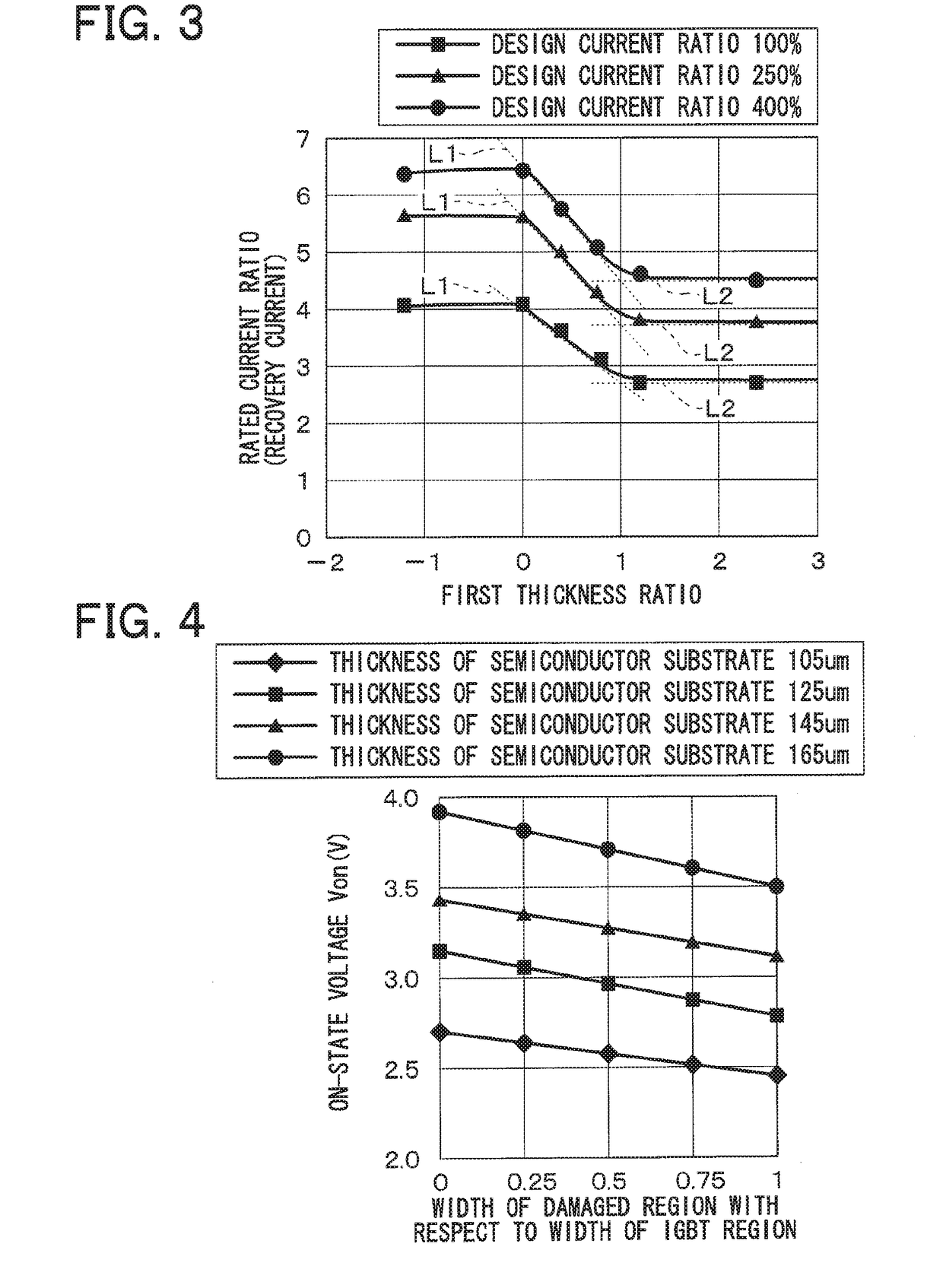
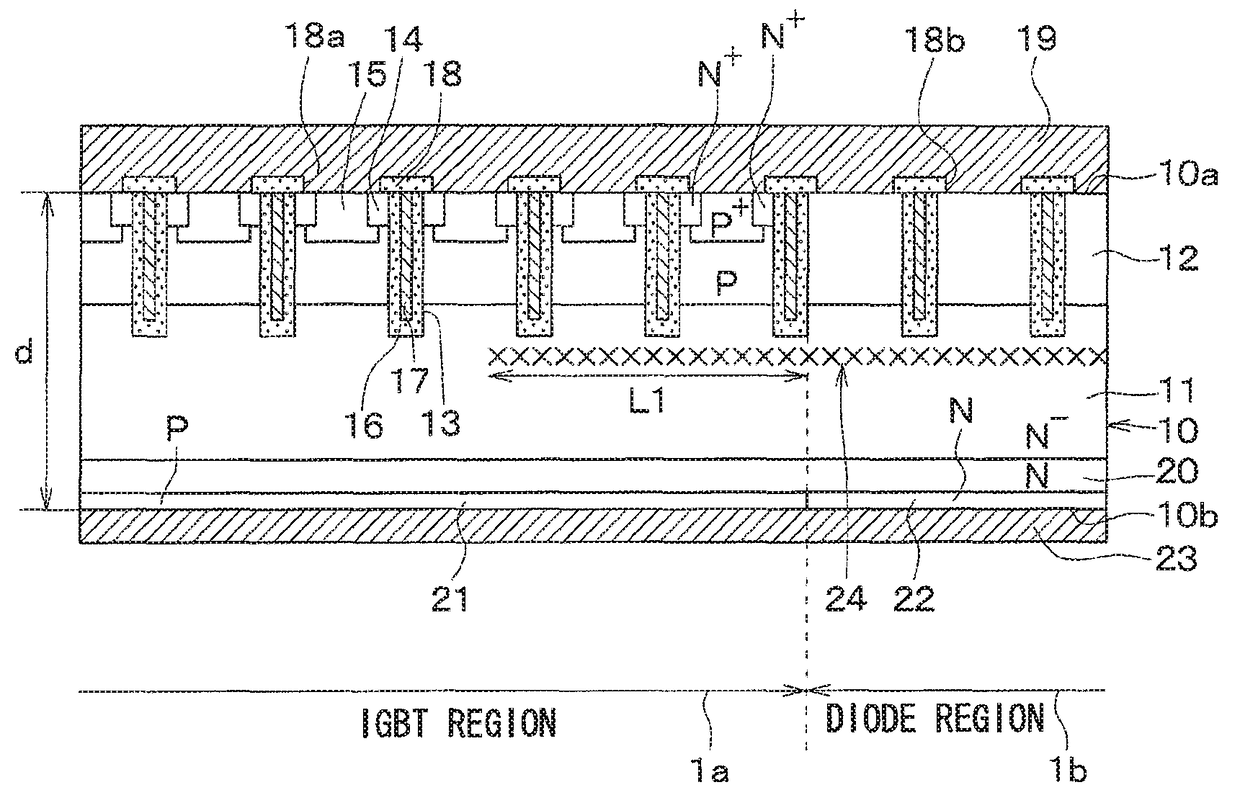
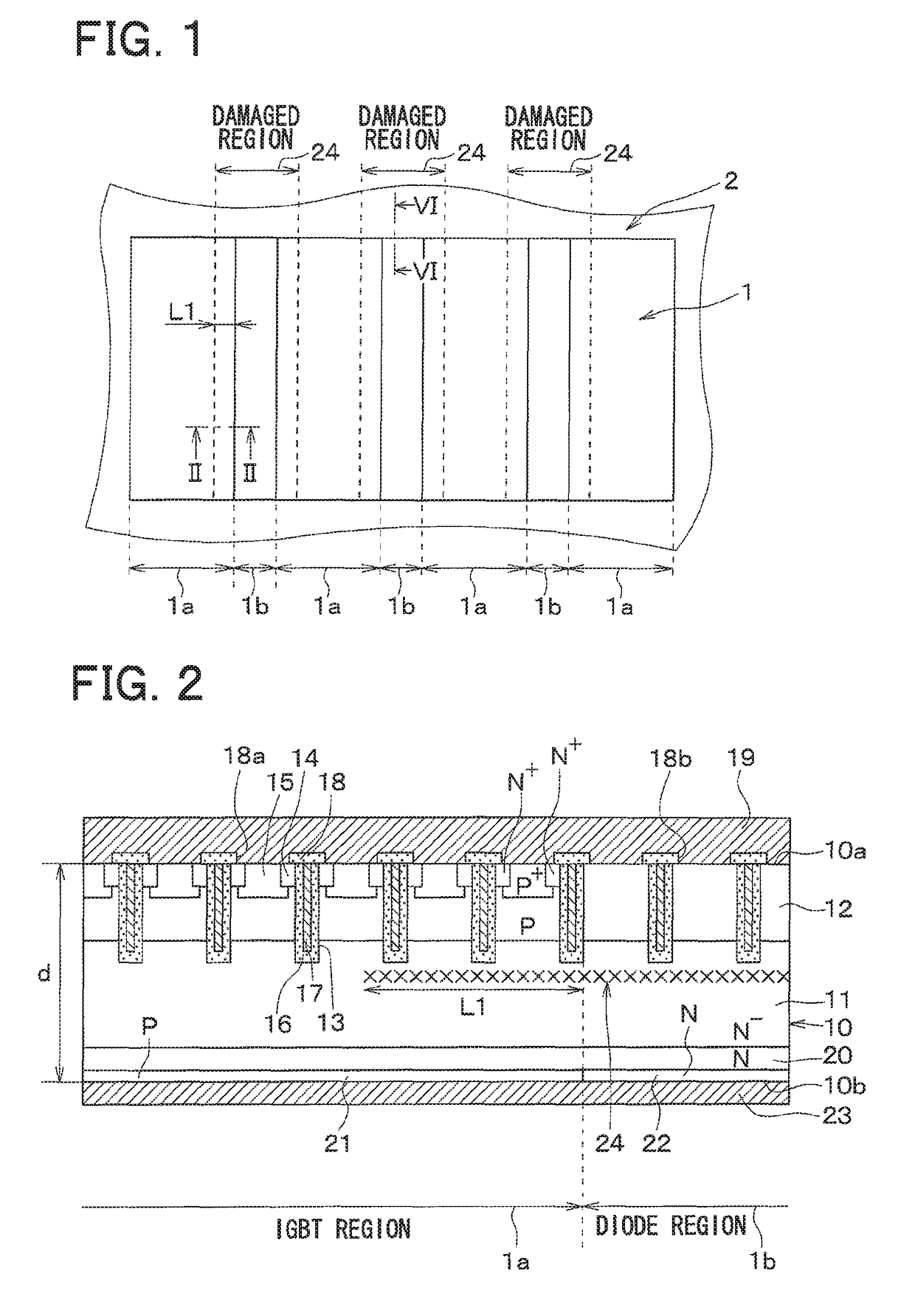
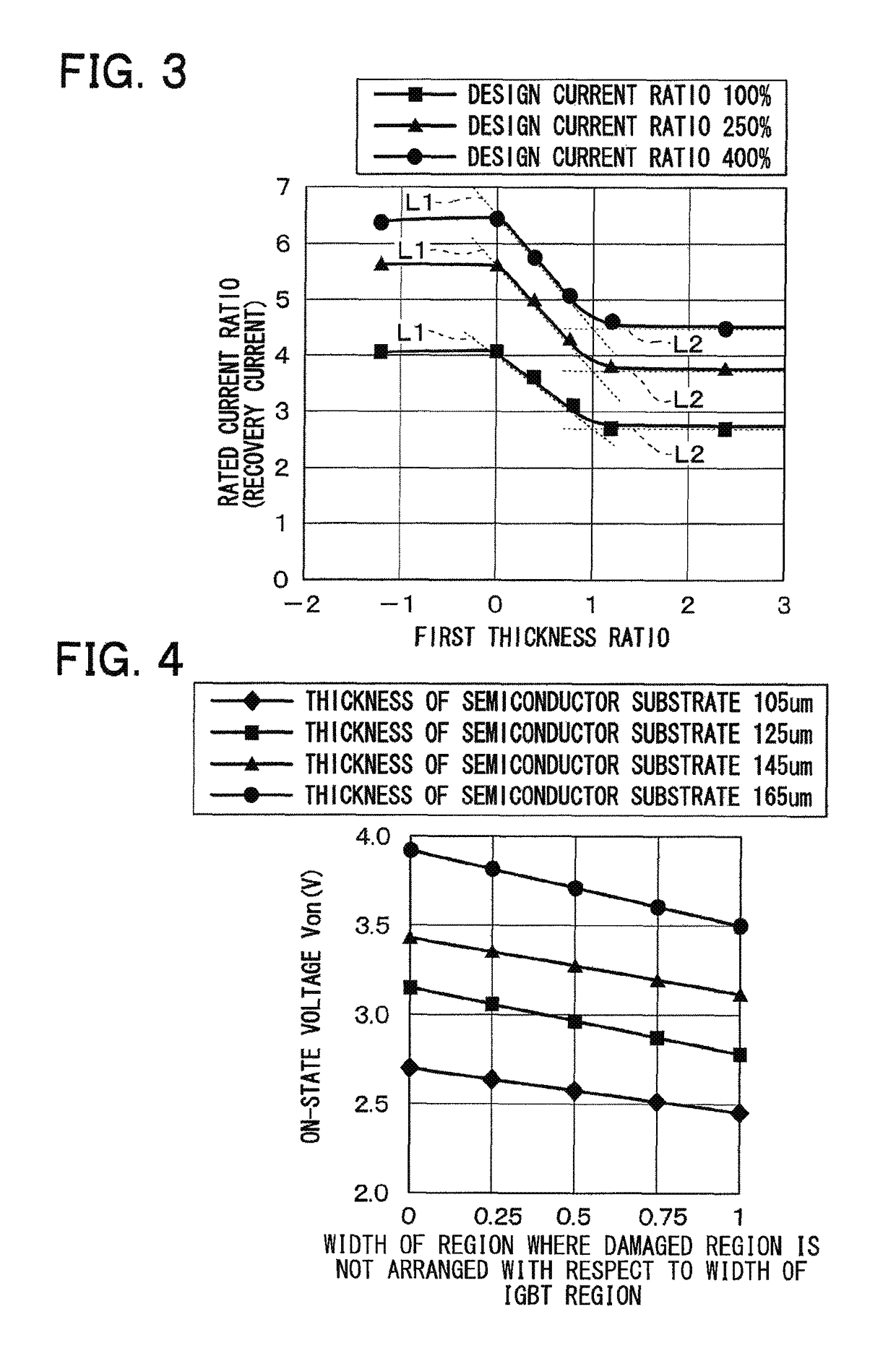
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate with: a drift layer; a base layer; and a collector layer and a cathode layer. In the semiconductor substrate, when a region operating as an IGBT device is an IGBT region and a region operating as a diode device is a diode region, the IGBT and diode regions are arranged alternately in a repetitive manner; a damaged region is arranged on a surface portion of the diode region in the semiconductor substrate. The IGBT and diode regions are demarcated by a boundary between the collector and cathode layers; and a surface portion of the IGBT region includes: a portion having the damaged region at a boundary side with the diode region; and another portion without the damaged region arranged closer to an inner periphery side relative to the boundary side.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20180308757A1Lower forward voltageIncrease in forward voltageTransistorThyristorEngineeringGate voltage
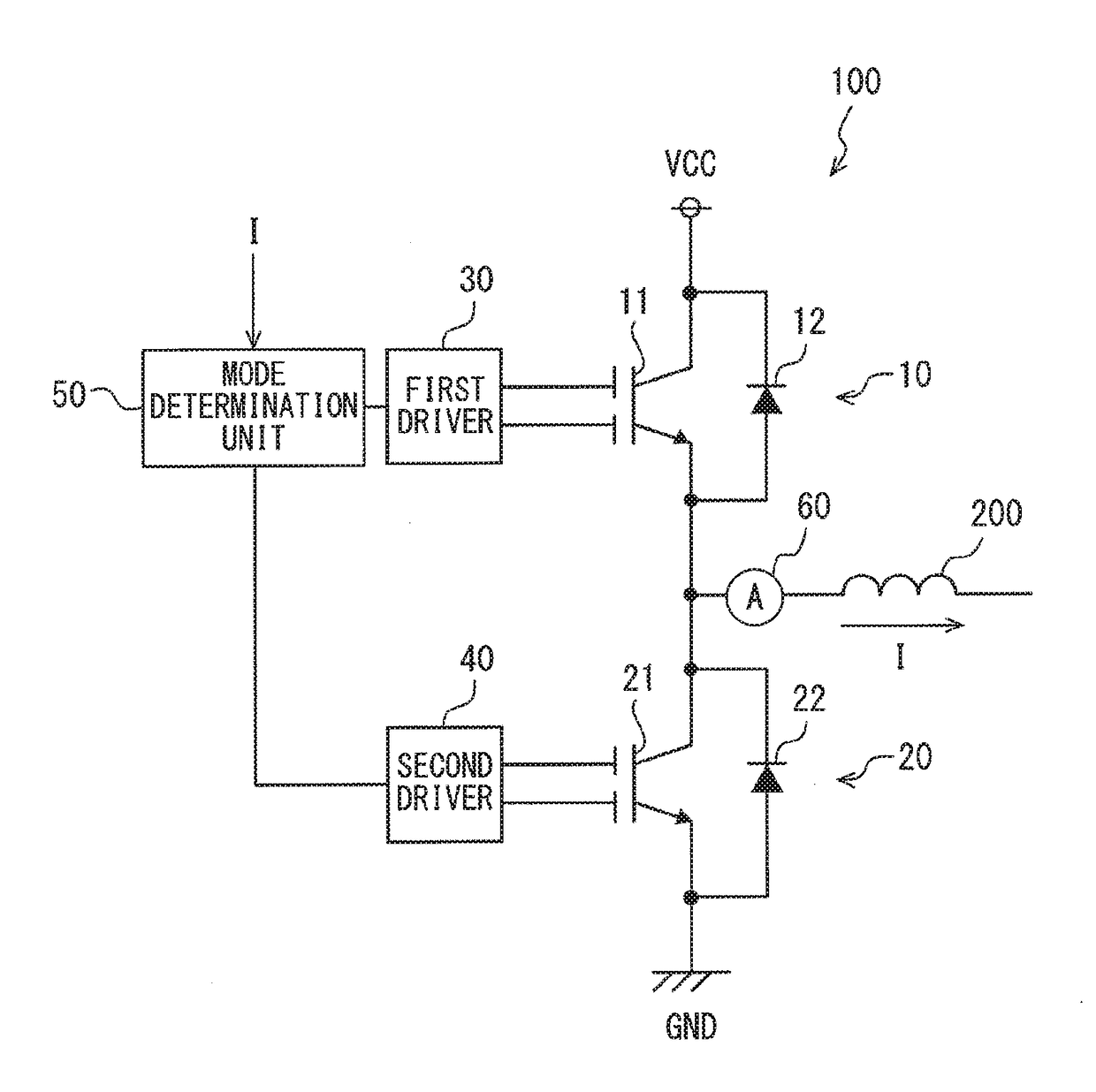
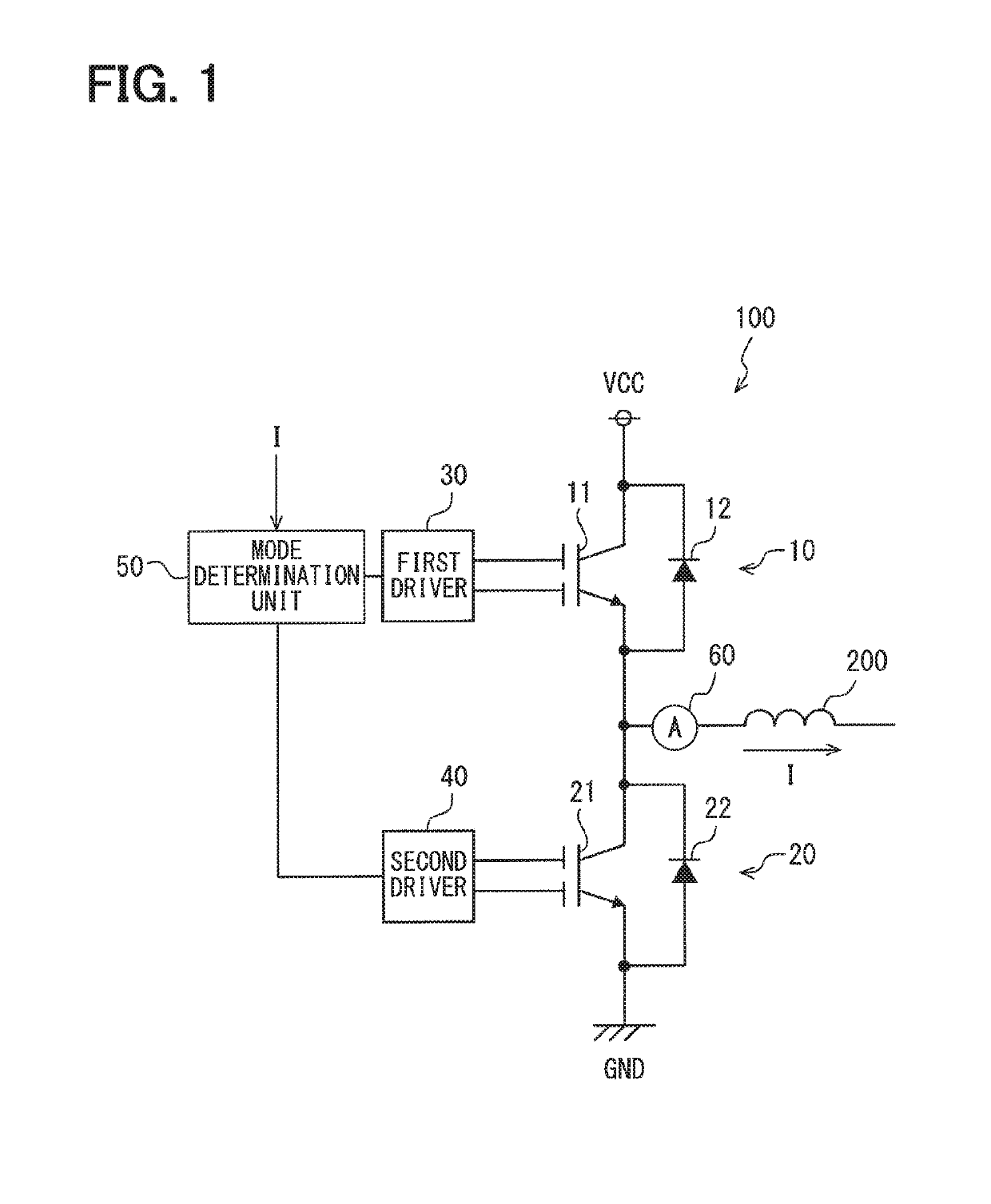
A semiconductor device includes: reverse conducting switching elements-in each of which a diode element and a switching element are arranged in parallel on a single semiconductor substrate; a driver applying a gate voltage to a plurality of gate electrodes in the reverse conducting switching elements; and a mode determination unit determining whether a forward conduction mode in which a current mainly flows through the switching element or a reverse conduction mode in which the current flows through the diode element is being operated.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Pad Comprising an Extruded Mesh and Method of Making Thereof
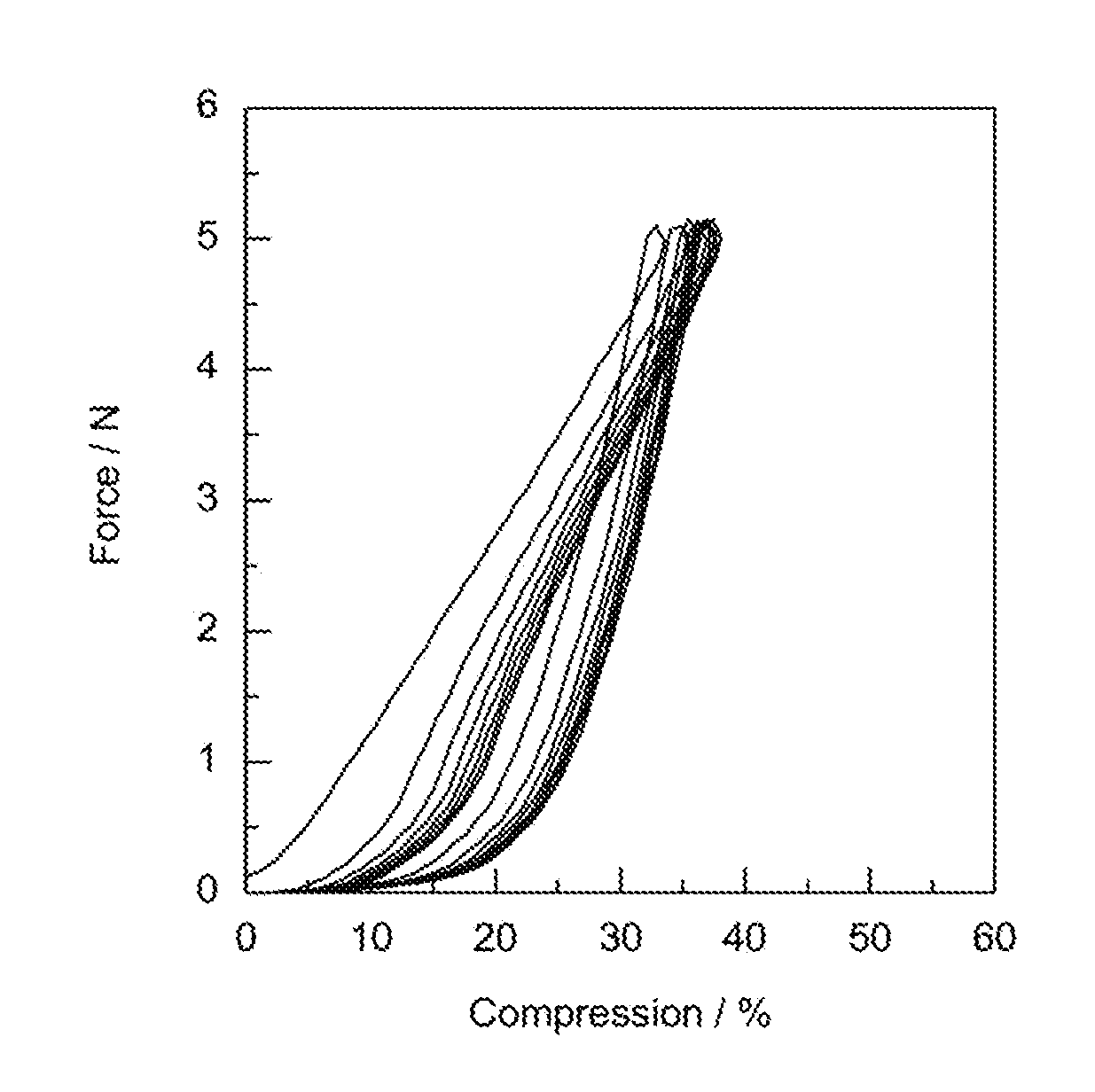
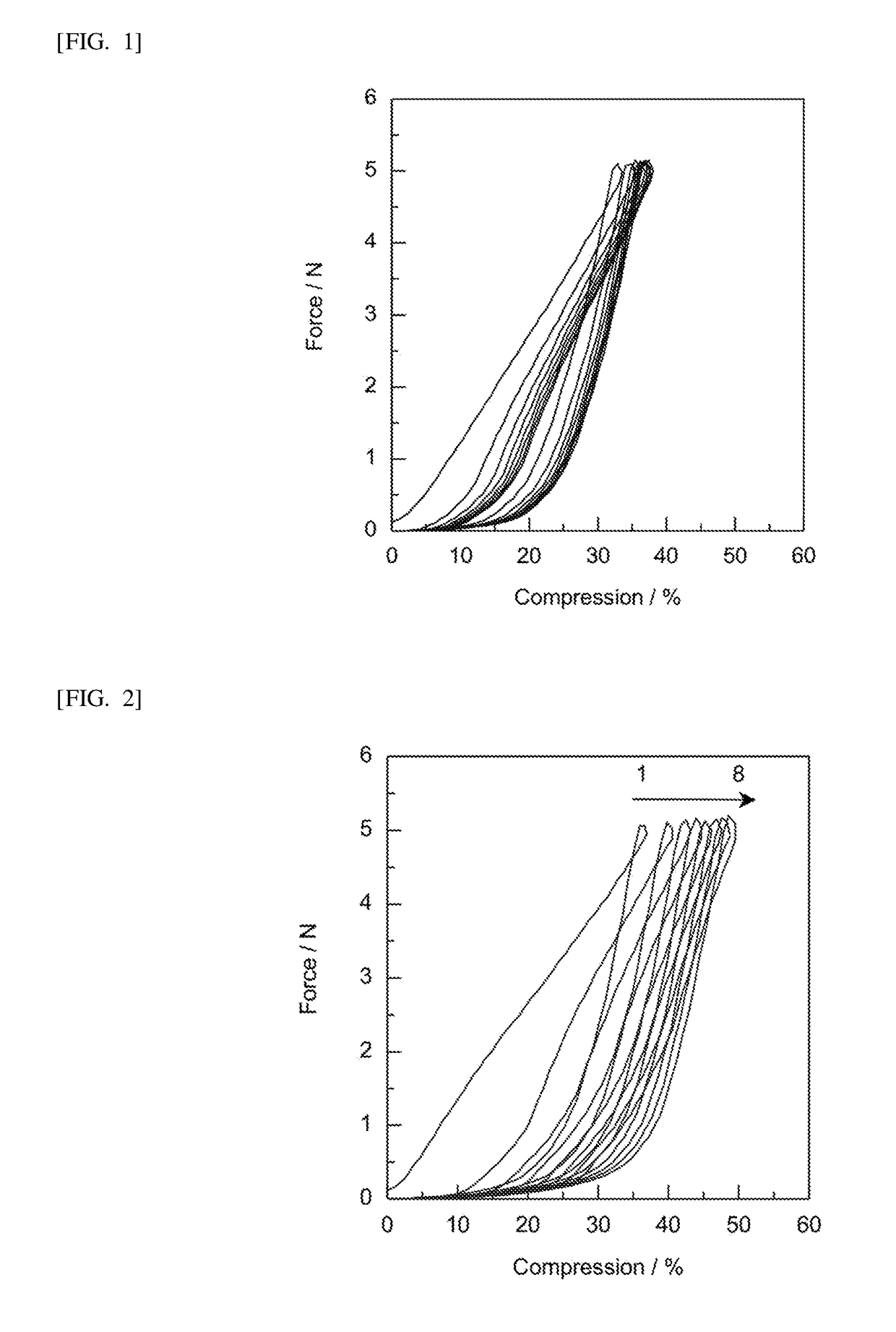
ActiveUS20140272270A1Excellent elastic behaviorHigh through thickness compressibilitySolesInsolesNormal loadCompressibility
A structure for use in a compressible resilient pad. The structure contains both axially elastomeric strands and relatively inelastic strands co-extruded in various patterns. The structure has a high degree of both compressibility under an applied normal load and excellent recovery (resiliency or spring back) upon removal of that load.
Owner:ALBANY INT CORP
Ink composition for ink jet recording
InactiveUS20110192317A1Brown discolorationLow water solubilityDuplicating/marking methodsInksAlcohol sugarsWater soluble
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Pad comprising an extruded mesh and method of making thereof
ActiveUS9545773B2Excellent elastic behaviorGood compressibilitySolesInsolesEngineeringCompressibility
A structure for use in a compressible resilient pad. The structure contains both axially elastomeric strands and relatively inelastic strands co-extruded in various patterns. The structure has a high degree of both compressibility under an applied normal load and excellent recovery (resiliency or spring back) upon removal of that load.
Owner:ALBANY INT CORP
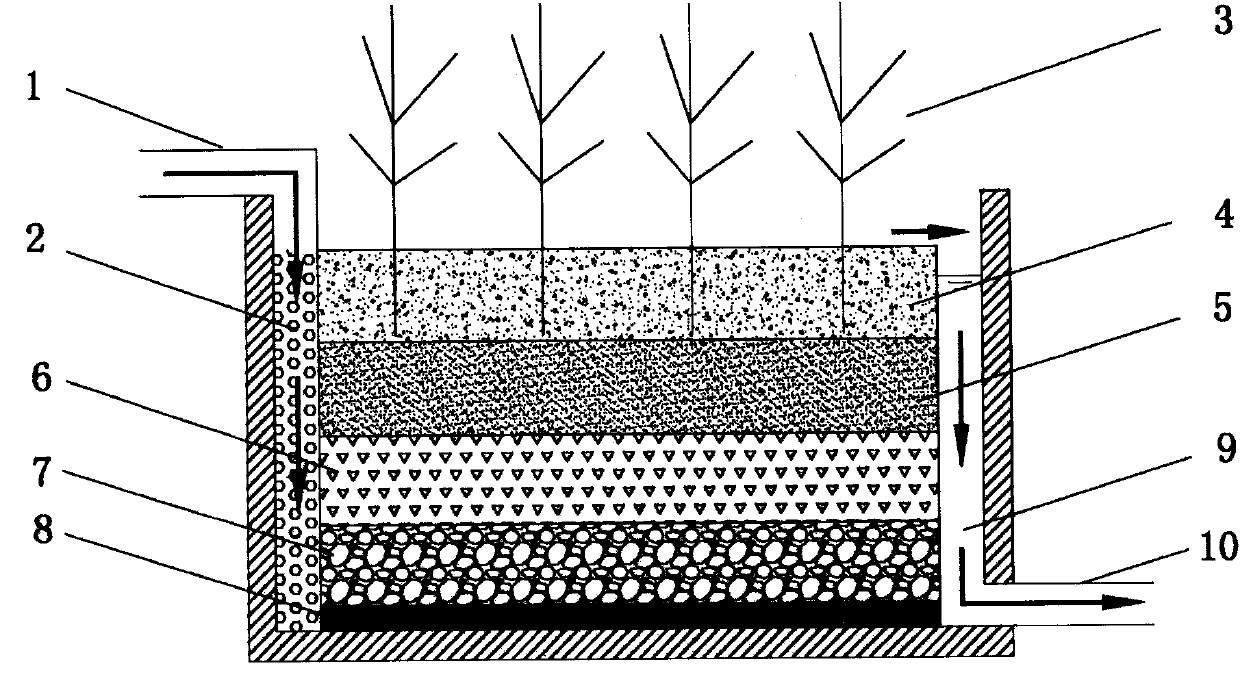
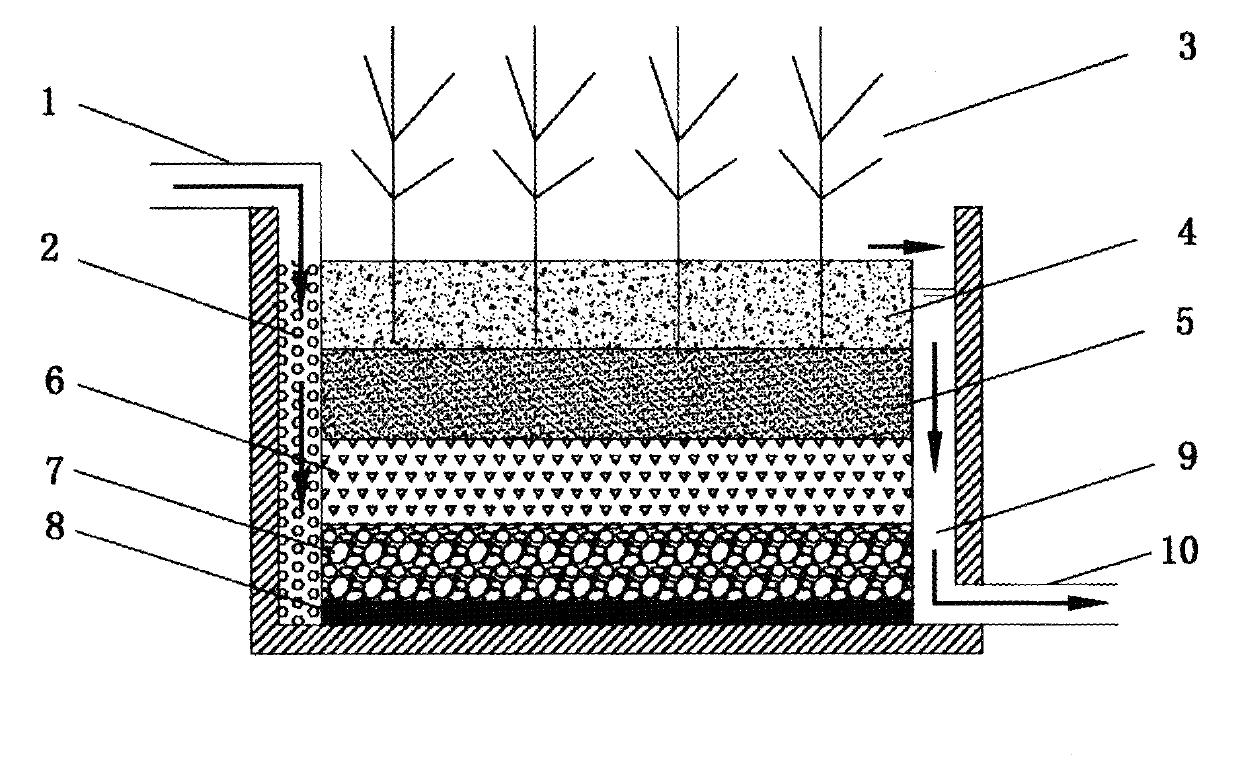
Underflow type constructed wetland system with coke powder-steel slag compound filler
InactiveCN101851023AGood removal effectGuaranteed uptimeTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentConstructed wetlandSlag
The invention provides a sewage treatment system of an underflow type constructed wetland based on disadvantages of the prior art. The sewage treatment system adopts coke powder-steel slag as compound filler, and has the advantages of simple structure, convenient management, no easy blockage and good denitrification and dephosphorization effect, thereby enhancing the treatment effect of sewage of the constructed wetland and improving the quality of the secondary effluent of the urban sewage treatment plant. The system mainly comprises a water inlet pipe, a water distribution area, an underflow type constructed wetland tank body, a coke powder-steel slag compound filler bed, a catchment area, a water outlet pipe and the like, wherein the coke powder-steel slag compound filler bed arranged in the sewage treatment system of the underflow type constructed wetland is provided with a sand soil covering layer, coke powder, steel slag and gravels in sequence from top to bottom, aquatic plants which have high capability of sewage purification and are suitable for local environmental conditions are grown on the sand soil covering layer, and the bottom of the filler bed adopts an impermeable layer made of natural clay as a waterproof structure.
Owner:BEIJING SINORICHEN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
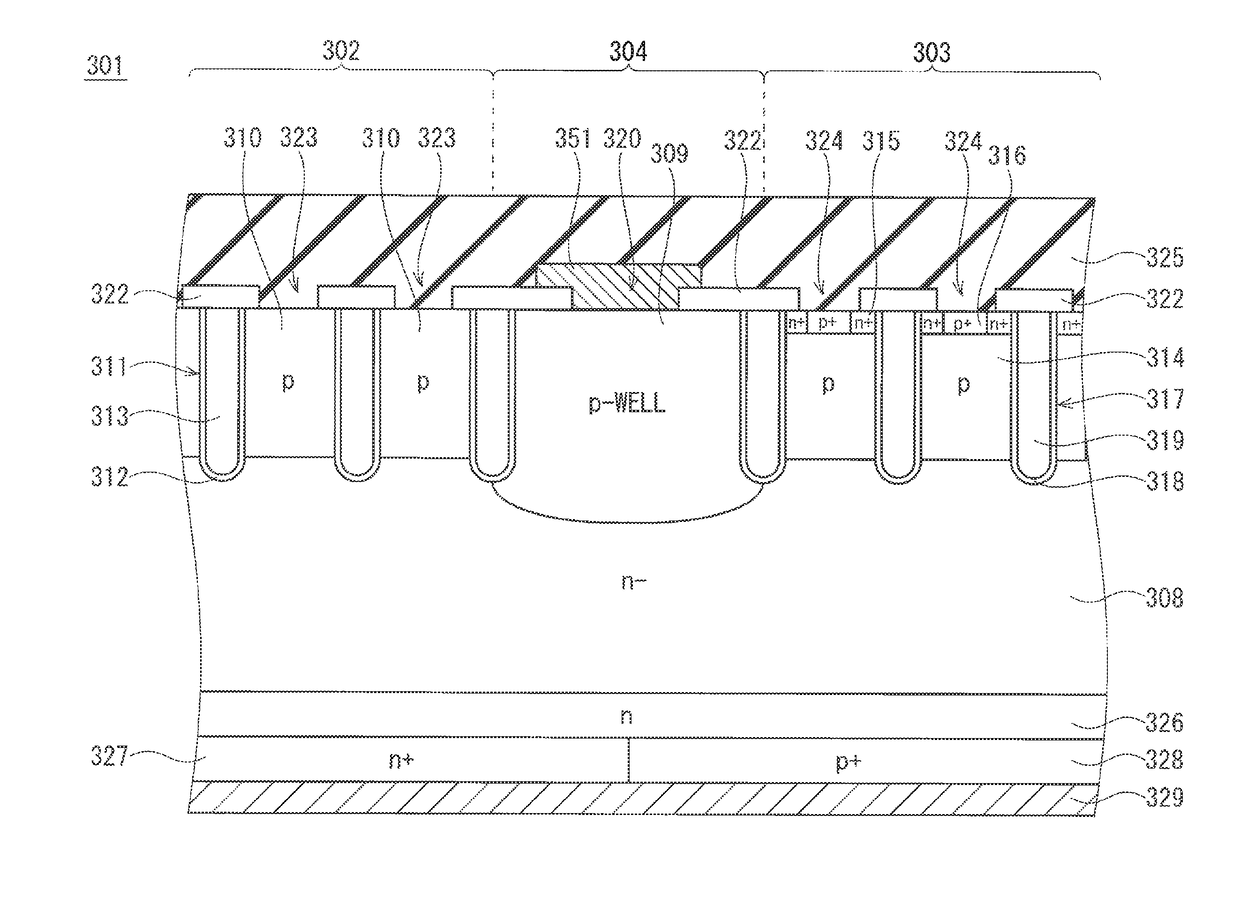
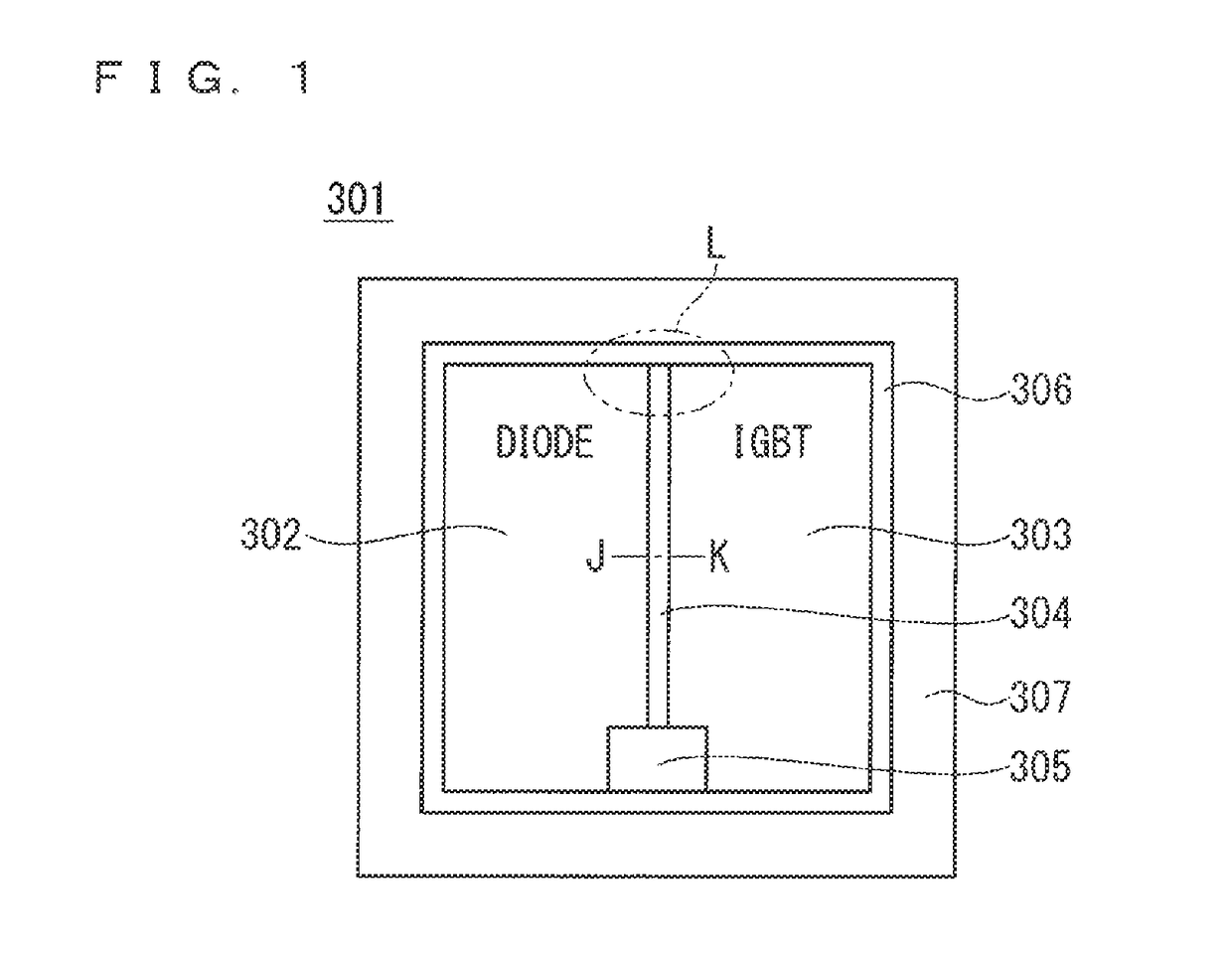
Semiconductor device having IGBT and diode
ActiveCN101000911ASufficient IGBT performanceSufficient surge withstand voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorCathode
A semiconductor device includes: a substrate having a first side and a second side; an IGBT; and a diode. The substrate includes a first layer, a second layer on the first layer, a first side N region on the second layer, second side N and P regions on the second side of the first layer, a first electrode in a first trench for a gate electrode, a second electrode on the first side N region and in a second trench for an emitter electrode and an anode electrode, and a third electrode on the second side N and P regions for a collector electrode and a cathode. The first trench penetrates the first side N region and the second layer, and reaches the first layer. The second trench penetrates the first side N region, and reaches the second layer.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Circuit arrangement having a free-wheel diode
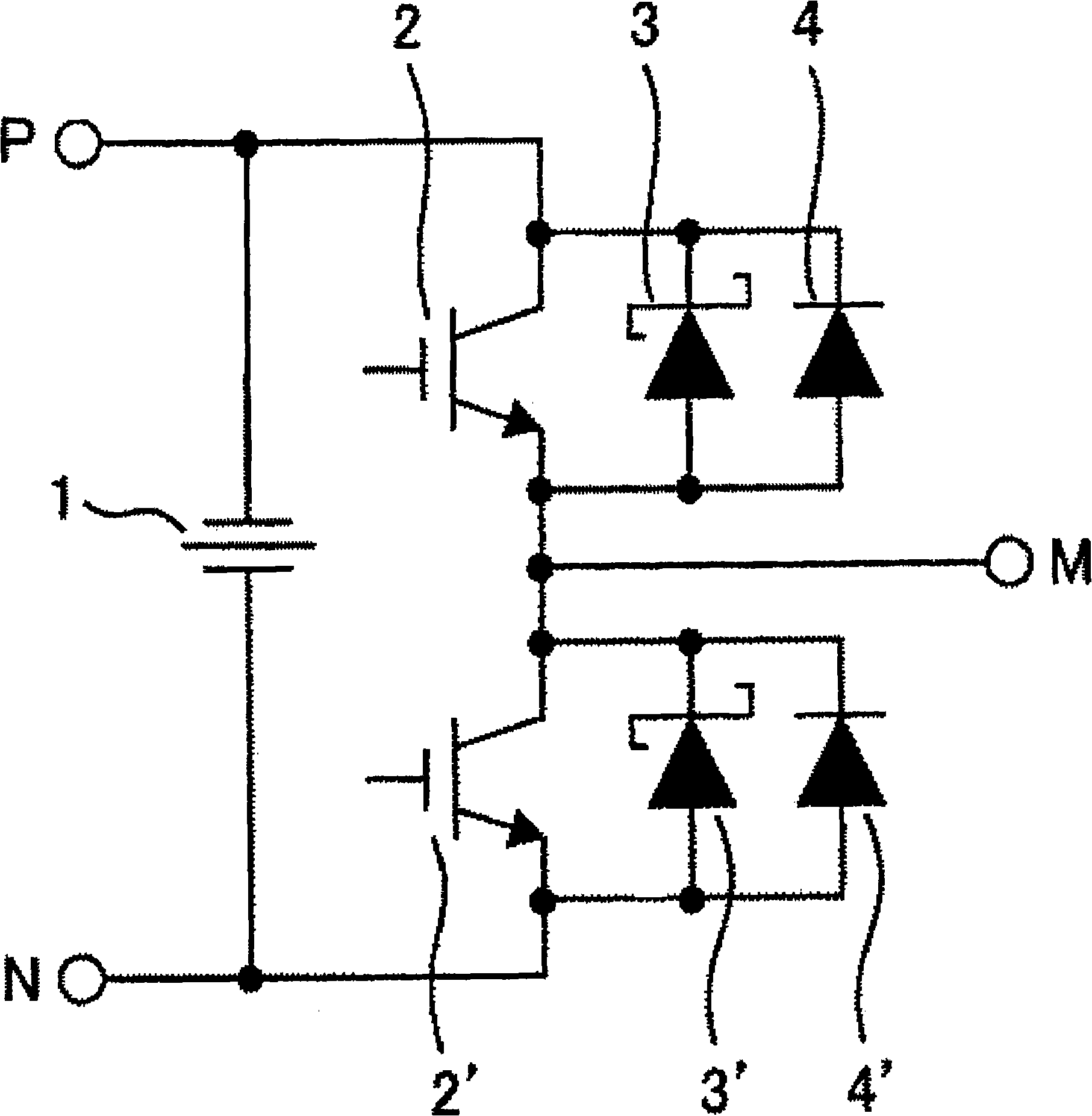
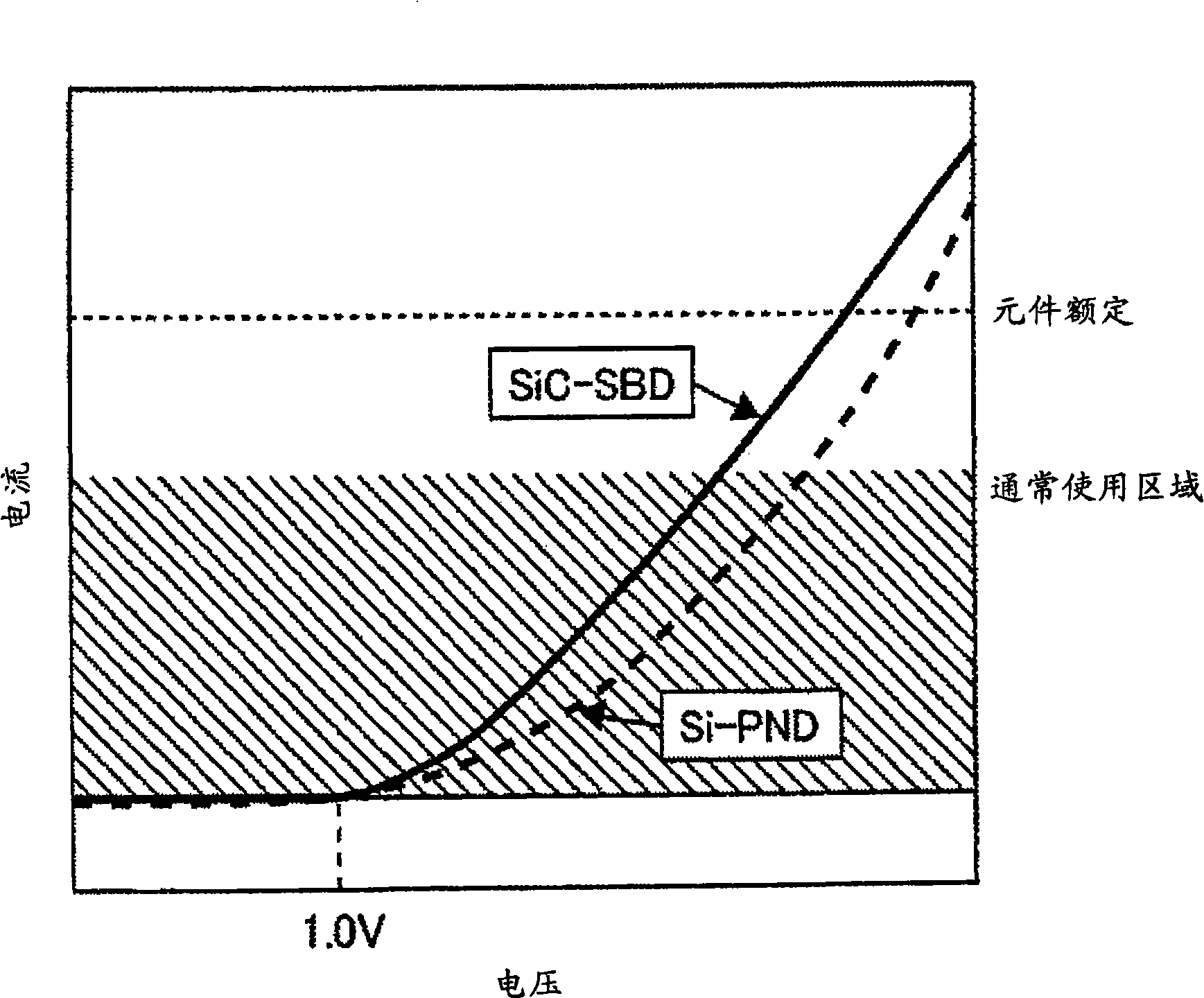
InactiveCN101290927AImproved recovery propertiesReduce noiseConversion constructional detailsSolid-state devicesSchottky barrierSemiconductor materials
The invention provides a circuit device capable of reducing noise in a current converting circuit and reducing conduction consumption of a circuit. A representative embodiment of the invention is as follows: a circuit device is at least provided with more than one switching component and free-wheel diode connected in shunt that is composed of a schottky barrier diode (SBD) with a semiconductor material greater than silicon with a gap as the parent metal, and a silicon PiN diode connected in shunt; theses SBDs and silicon PiN diodes are formed of different chips.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS10056450B2Improved recovery propertiesReduce conduction voltage dropTransistorConversion constructional detailsSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate with: a drift layer; a base layer; and a collector layer and a cathode layer. In the semiconductor substrate, when a region operating as an IGBT device is an IGBT region and a region operating as a diode device is a diode region, the IGBT and diode regions are arranged alternately in a repetitive manner; a damaged region is arranged on a surface portion of the diode region in the semiconductor substrate. The IGBT and diode regions are demarcated by a boundary between the collector and cathode layers; and a surface portion of the IGBT region includes: a portion having the damaged region at a boundary side with the diode region; and another portion without the damaged region arranged closer to an inner periphery side relative to the boundary side.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Fluoroalkyl-containing curable organopolysiloxane composition, cured object obtained therefrom, and electronic component or display device including cured object
ActiveCN107532002AHigh transparencyHigher than the dielectric constantStatic indicating devicesSynthetic resin layered productsHydrogen atomHydrogen
The invention provides a curable composition attaining a high permittivity and satisfactory transparency; a dielectric layer for display devices which is a cured object obtained from the curable composition; and a display device. The invention further provides a fluoroalkyl-containing curable organopolysiloxane composition that comprises (A) a fluoroalkyl-containing organopolysiloxane which has atleast two alkenyl groups in the molecule and an average degree of polymerization less than 150 and in which at least 10 mol% of all the substituents on the silicon atoms are accounted for by a specific fluoroalkyl group, (B) an organohydrogenpolysiloxane having at least two silicon-bonded hydrogen atoms in the molecule, the amount of the component (B) being such that the amount of the silicon-bonded hydrogen atoms in the component (B) is 0.1-1.0 mol per mol of all the alkenyl groups contained in the component (A), (C) an effective amount of a catalyst for hydrosilylation, and (D) any solventas an optional component; a cured object obtained from the fluoroalkyl-containing curable organopolysiloxane composition; and uses of the cured object.
Owner:DOW TORAY CO LTD
Ink composition for ink jet recording
InactiveUS20110265686A1High crystallinityBrown discolorationDuplicating/marking methodsInksAlcohol sugarsWater soluble
An ink composition for ink jet recording is provided. The ink composition includes at least a colorant, water, a poor water-soluble both-end-type alkanediol, a crystalline sugar alcohol that is solid at 20° C., and a poly(alkylene glycol). The poor water-soluble both-end-type alkanediol includes one or two alkyl substituents on its main chain having two hydroxyl groups.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Insulated gate transistor incorporating diode and inverter circuit
The invention provides an insulated gate bipolar transistor and an inverter circuit and improves the recovery characteristic of diode action in a FWD built-in type nsulated gate bipolar transistor. A p-type base layer shaped like a well is formed for each of IGBT cells, and a p<+>-type collector layer (5)and an n<+>-type cathode layer(4) are formed on a surface opposite to a surface on which the p-type base layer is formed so as to be situated just below the p-type base layer. The p-type base layer (2) of each of the IGBT cells includes a flat region including an emitter region and a bottom surface penetrated by a main trench (6), and first and second side diffusion regions between which the flat region is interposed. The first side diffusion region is situated just above the n<+>-type cathode layer (4)and each of the bottom surfaces of the side diffusion regions forms a parabola-shaped smooth curve in longitudinal section. By replacing the p<+>-type collector layer (5) with the n<+>-type cathode layer (4), it is possible to apply features of the above structure to a power MOSFET.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
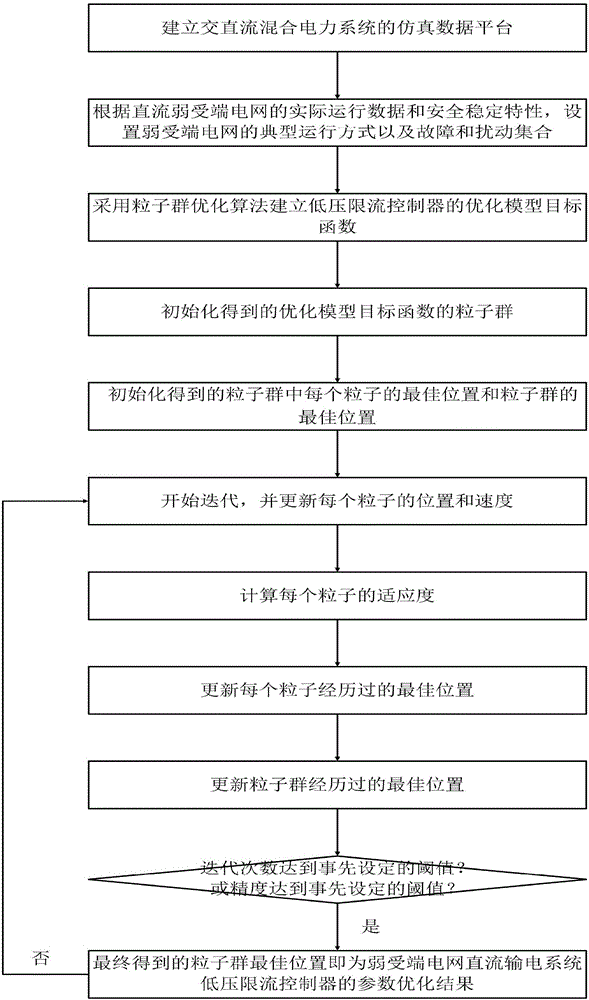
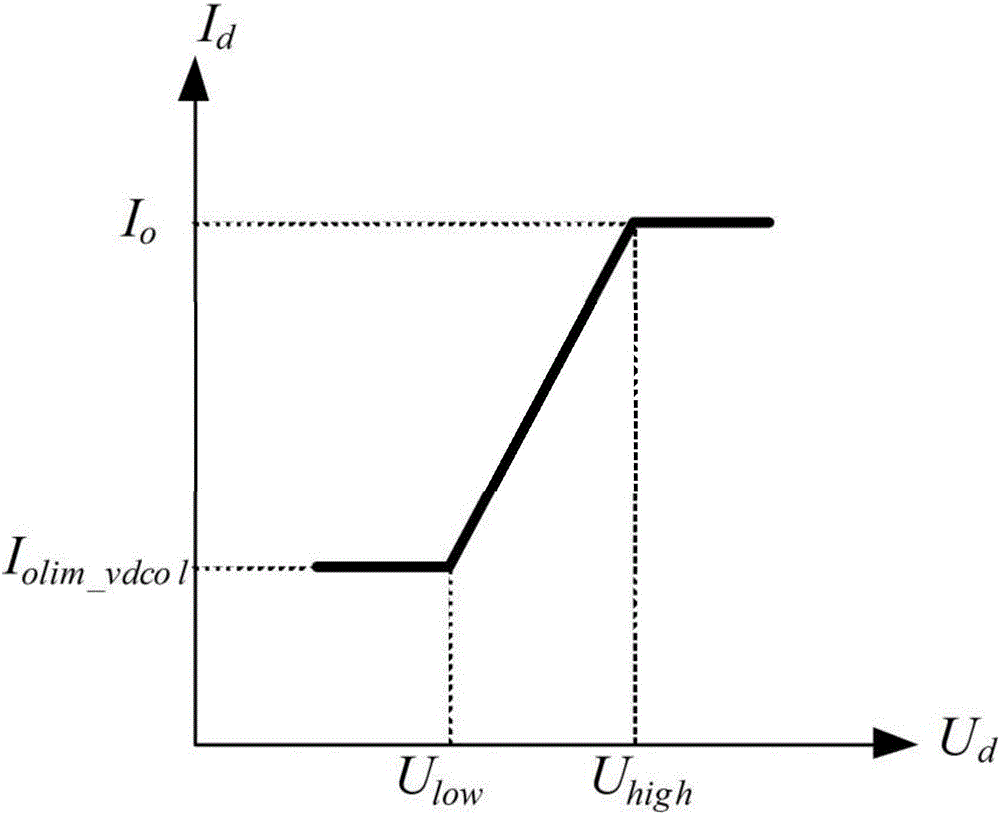
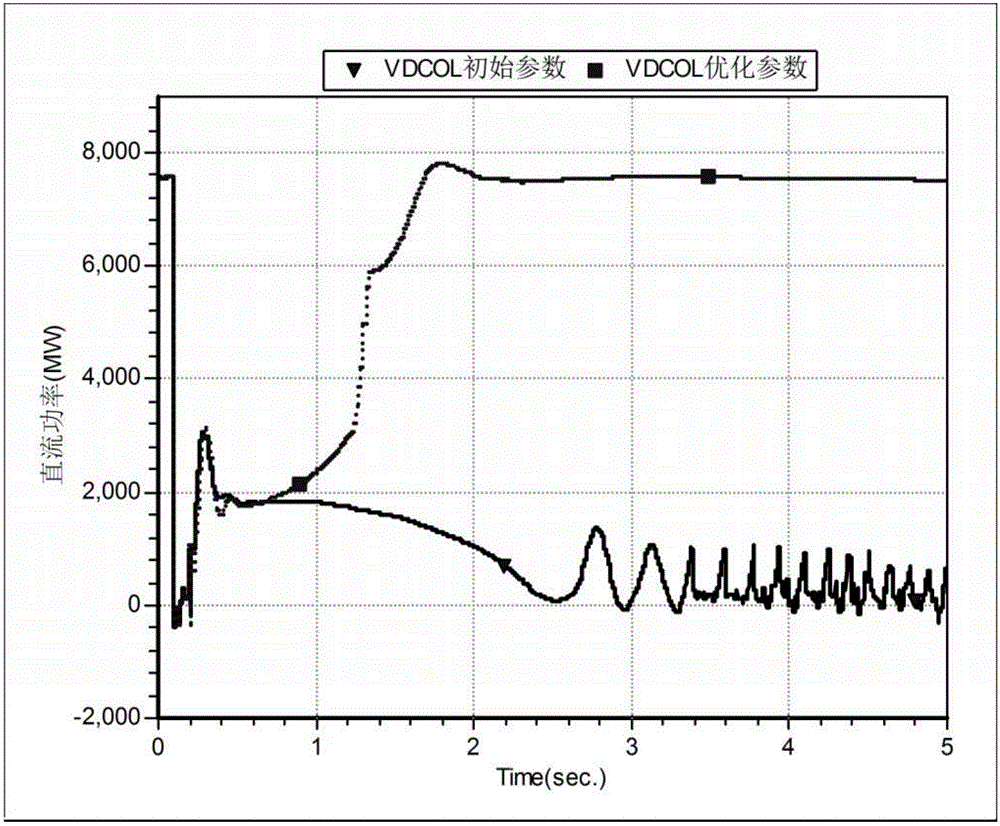
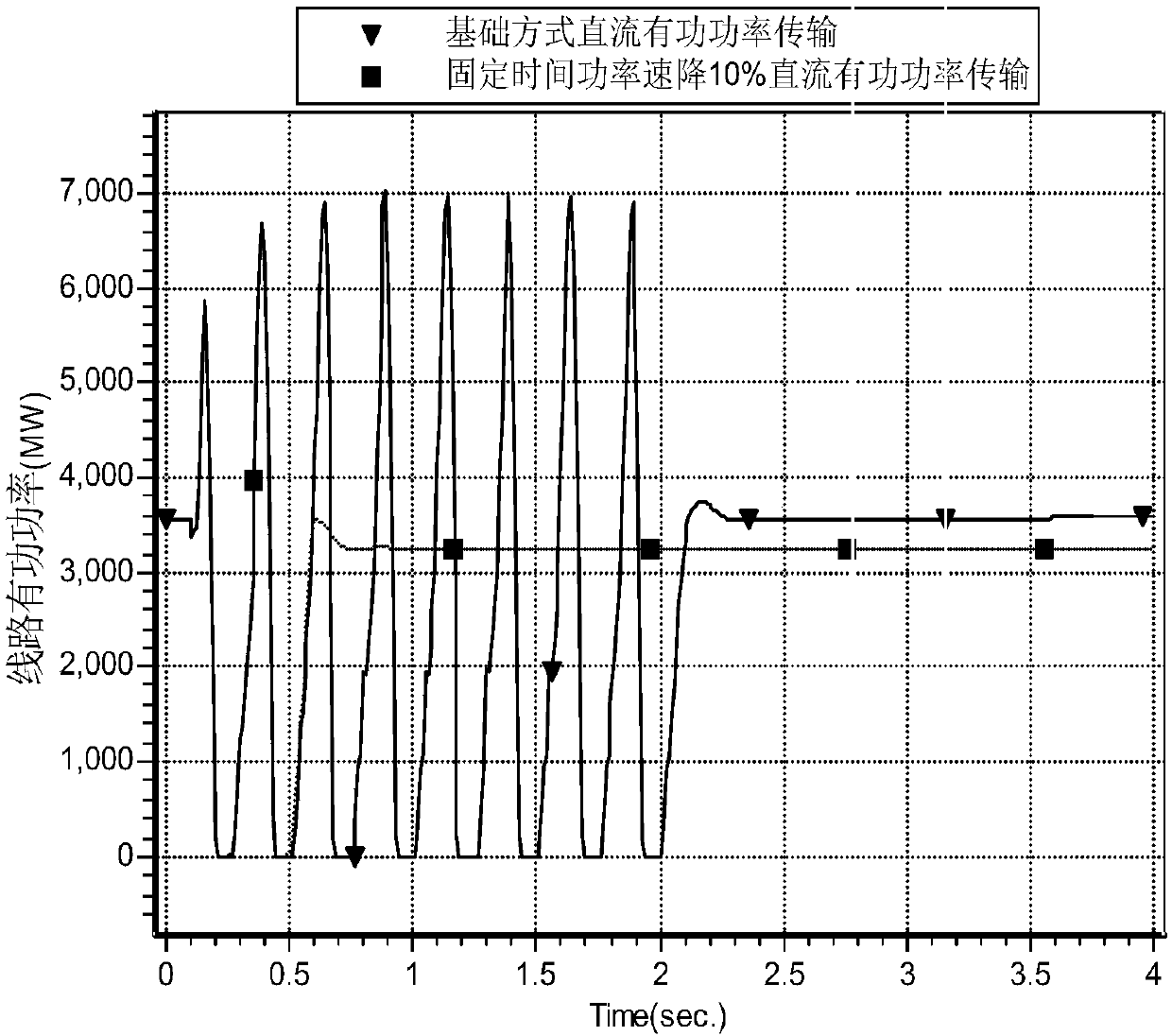
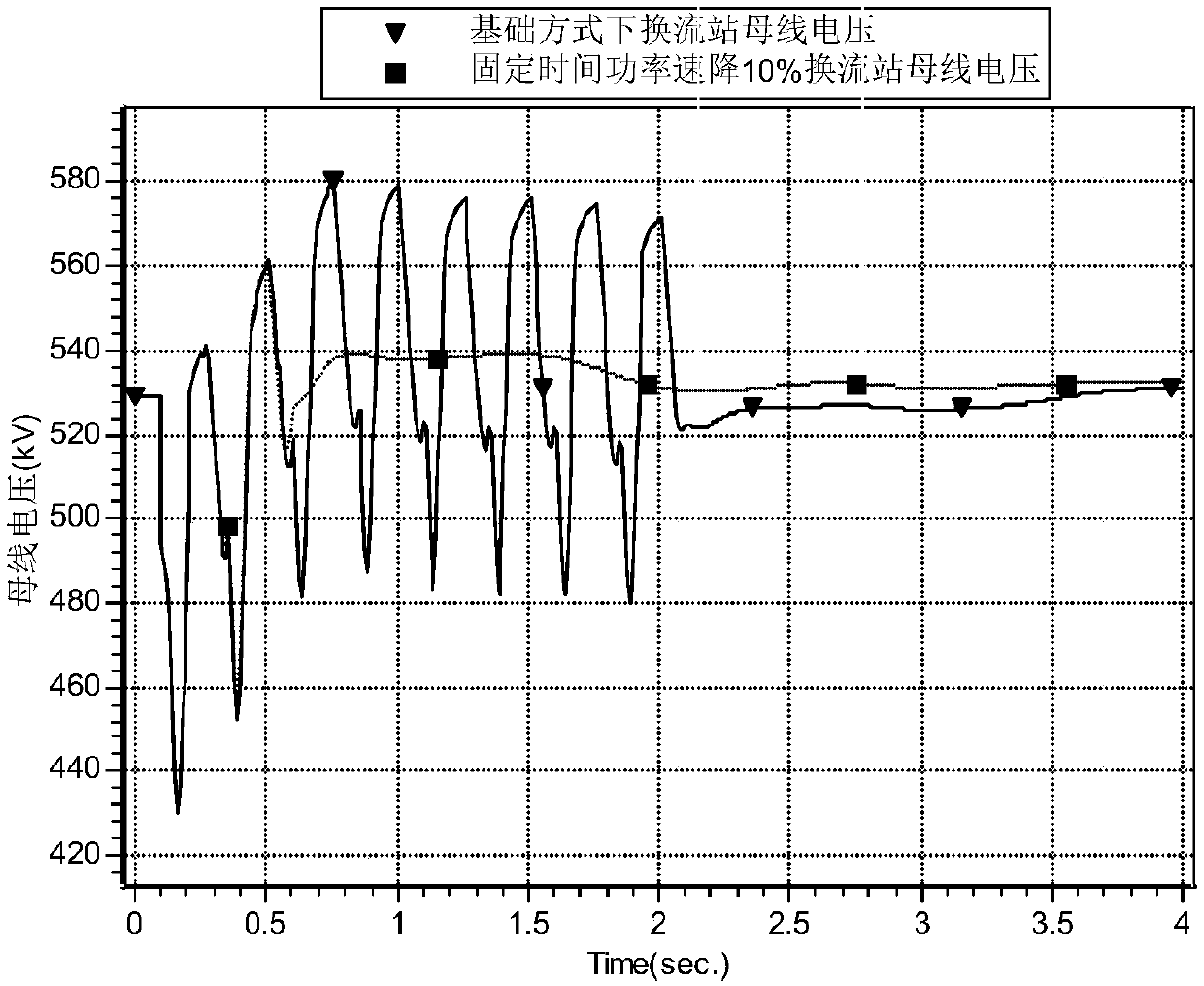
Method for optimizing parameters of low-voltage current-limiting controller of weak receiving terminal power network direct-current transmission system
ActiveCN106356825AImproved recovery propertiesImprove control effectElectric power transfer ac networkEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentLow voltageControl parameters
The invention discloses a method for optimizing parameters of a low-voltage current-limiting controller of a weak receiving terminal power network direct-current transmission system. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a simulated data platform; setting a running mode and a fault disturbance set; establishing an optimized model object function by adopting a particle swarm optimization algorithm; initializing a particle swarm, an optimum position of each particle and an optimum position of the particle swarm; starting iteration and updating the position and speed of each particle; calculating fitness of each particle; updating an optimum position through which each particle passes and an optimum position through which the particle swarm passes; and repeating the steps to obtain a parameter optimization result. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the establishment of the simulated data platform enables the optimized model object function to be able to accurately reflect the influence of VDCOL control parameters on safe and stable characteristics of an AC-DC power network, so that the parameters optimized by the method disclosed by the invention can achieve a better control effect under the condition with different running modes, faults and disturbance of a weak receiving terminal power network, thereby improving restoration characteristics of an AC-DC system, and promoting the safety and reliability levels of the system.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
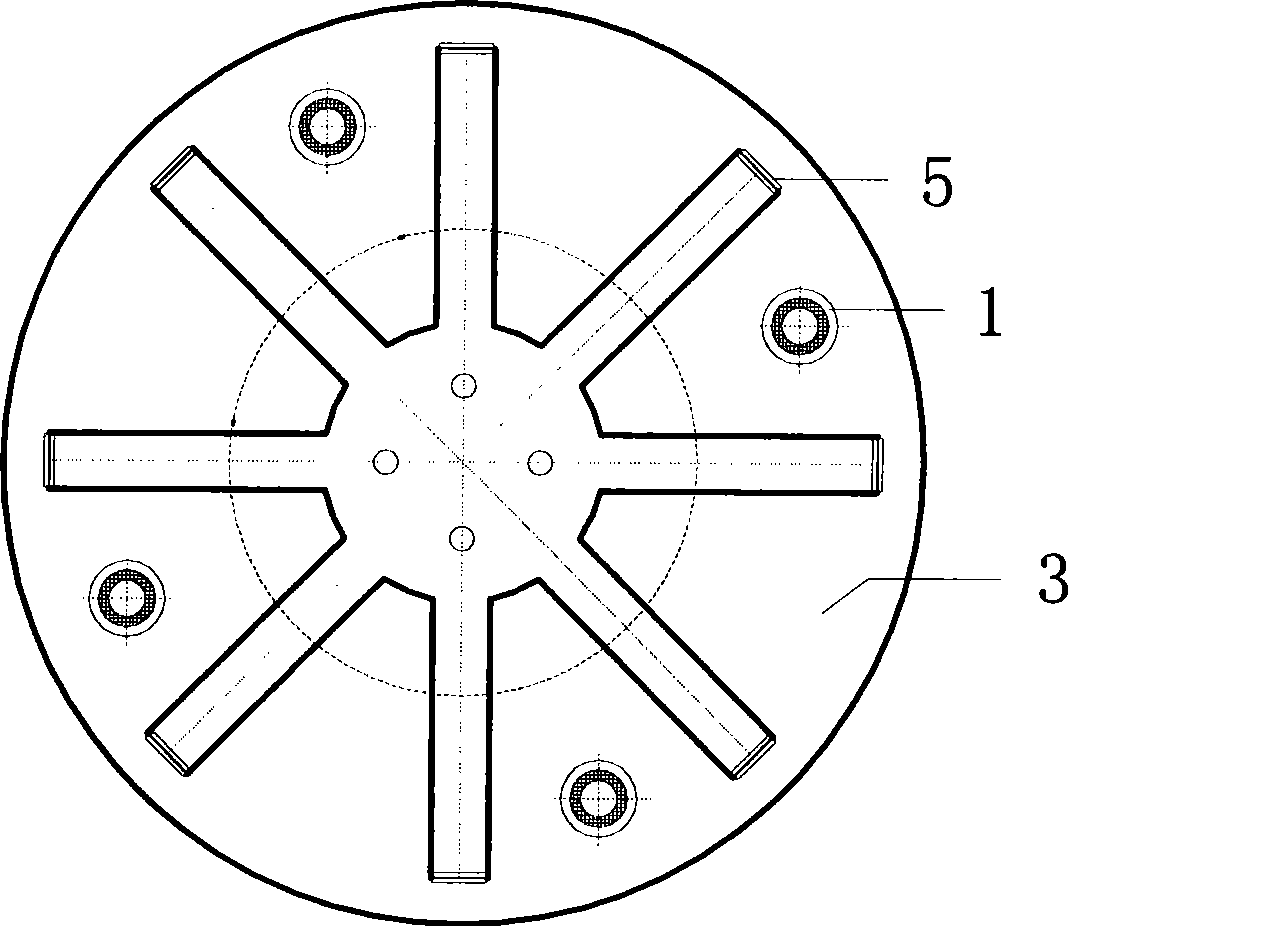
Large-tonnage vertical shock insulation damping device
ActiveCN101413297ASolve the problem of small tonnageImprove vertical bearing capacityProtective foundationShock proofingBall bearingAbsorption capacity
The invention relates to a large-tonnage vertical shock insulation and absorption device, which is the vertical shock insulation and absorption device for resisting vibration (shocking) vertically for civil engineering structures and mechanical engineering. The device comprises lead extrusion dampers (1), a steel plate spring (2), an upper steel plate (3), and a lower steel plate (4). On the overall structure, the steel plate spring (2) is arranged in the centre, while a plurality of lead extrusion dampers (1) are arranged on the periphery symmetrically; the upper part of each damper (1) is connected to the upper steel plate (3) respectively while the lower part of each damper (1) is connected with the lower steel plate (4) respectively, so that all the dampers (2) are connected into a whole; and the upper part of the steel plate spring (2) in the centre is connected with the upper steel plate (3) through a ball bearing (5) while the lower part thereof is connected with a steel block (9) through a bolt (6), and the steel block (9) is connected with the lower steel plate (4). The invention combines the advantages of the lead extrusion dampers (1) and the steel plate spring (2) to form the large-tonnage vertical shock insulation and absorption device. The large-tonnage vertical shock insulation and absorption device has the advantages of good vertical shock insulation and absorption capacity, low price and convenient manufacturing.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7999314B2Improved recovery propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes an n-conductive type semiconductor substrate having a main side and a rear side, a p-conductive type layer arranged over the main side of the substrate, a main side n-conductive type region arranged in the p-conductive type layer, a rear side n-conductive type layer arranged over the rear side of the substrate, a first trench which reaches the substrate and penetrates the main side n-conductive type region and the p-conductive type layer, a second trench which reaches an inside of the p-conductive type layer, a second electrode layer, which is embedded in the second trench and connected to the p-conductive type layer. Hereby, the semiconductor device, in which the recovery property of a diode cell can be improved without damaging the property of a MOS transistor cell or an IGBT cell and the surge withstand property does not deteriorate, can be obtained.
Owner:DENSO CORP
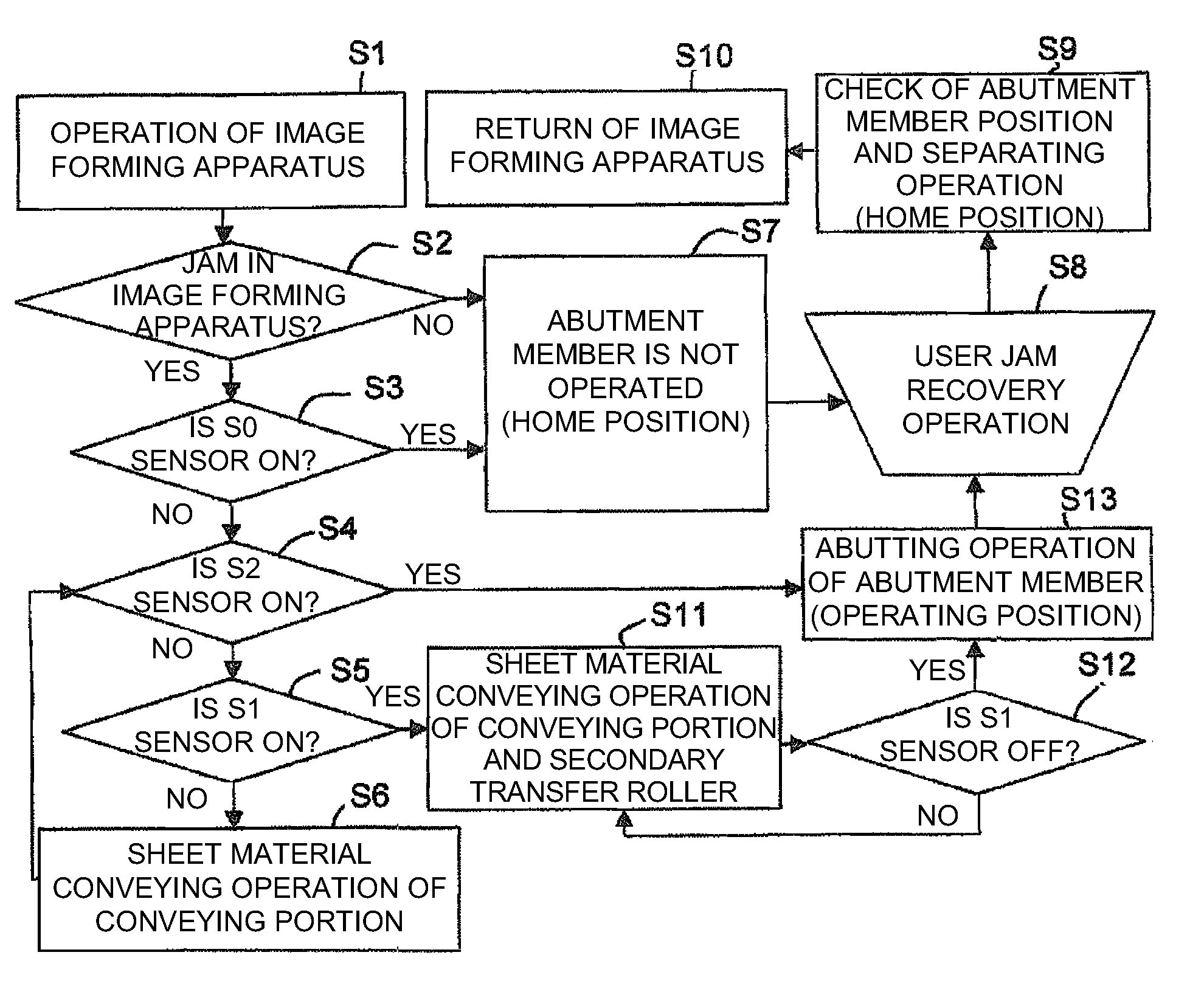
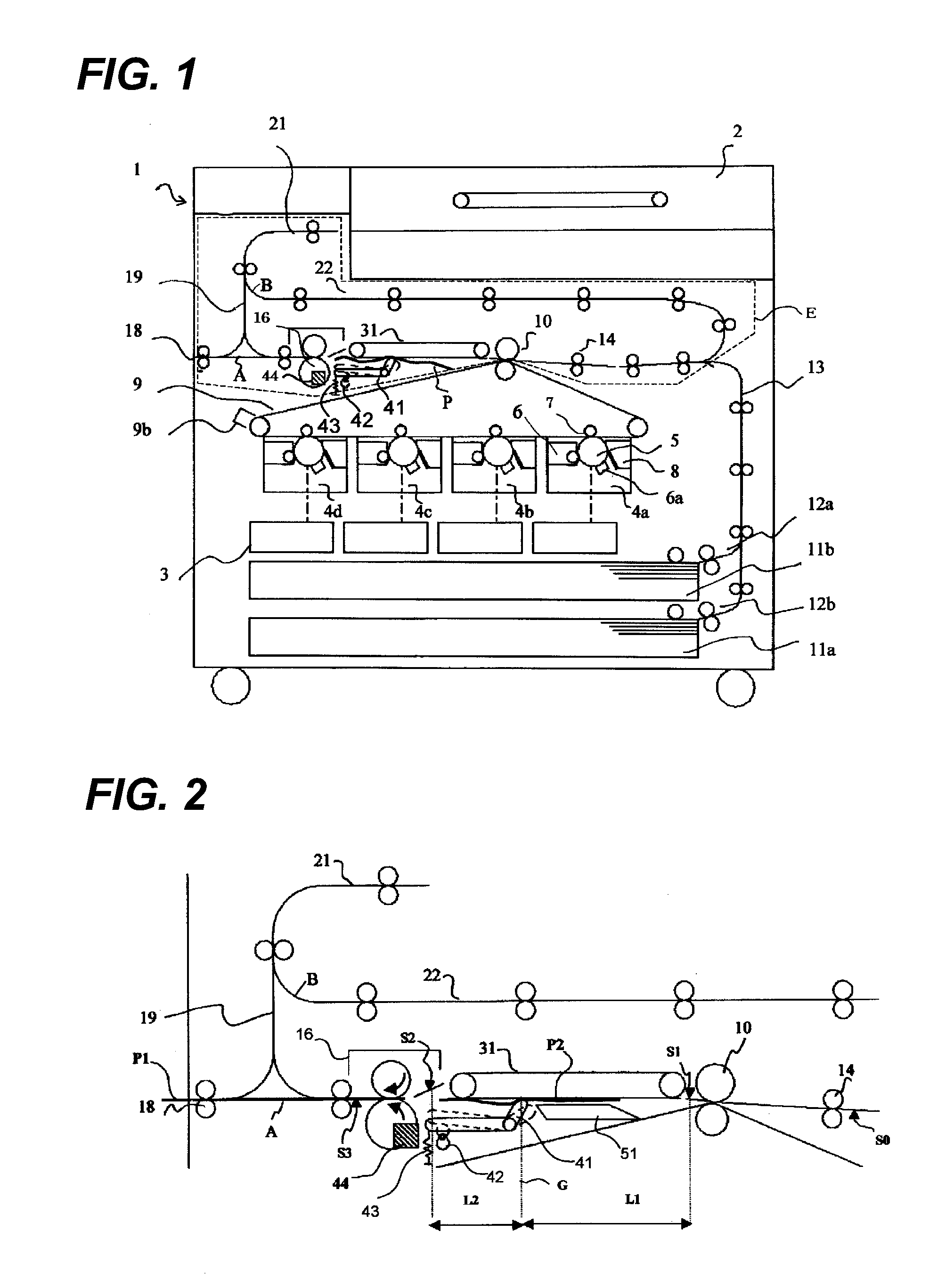
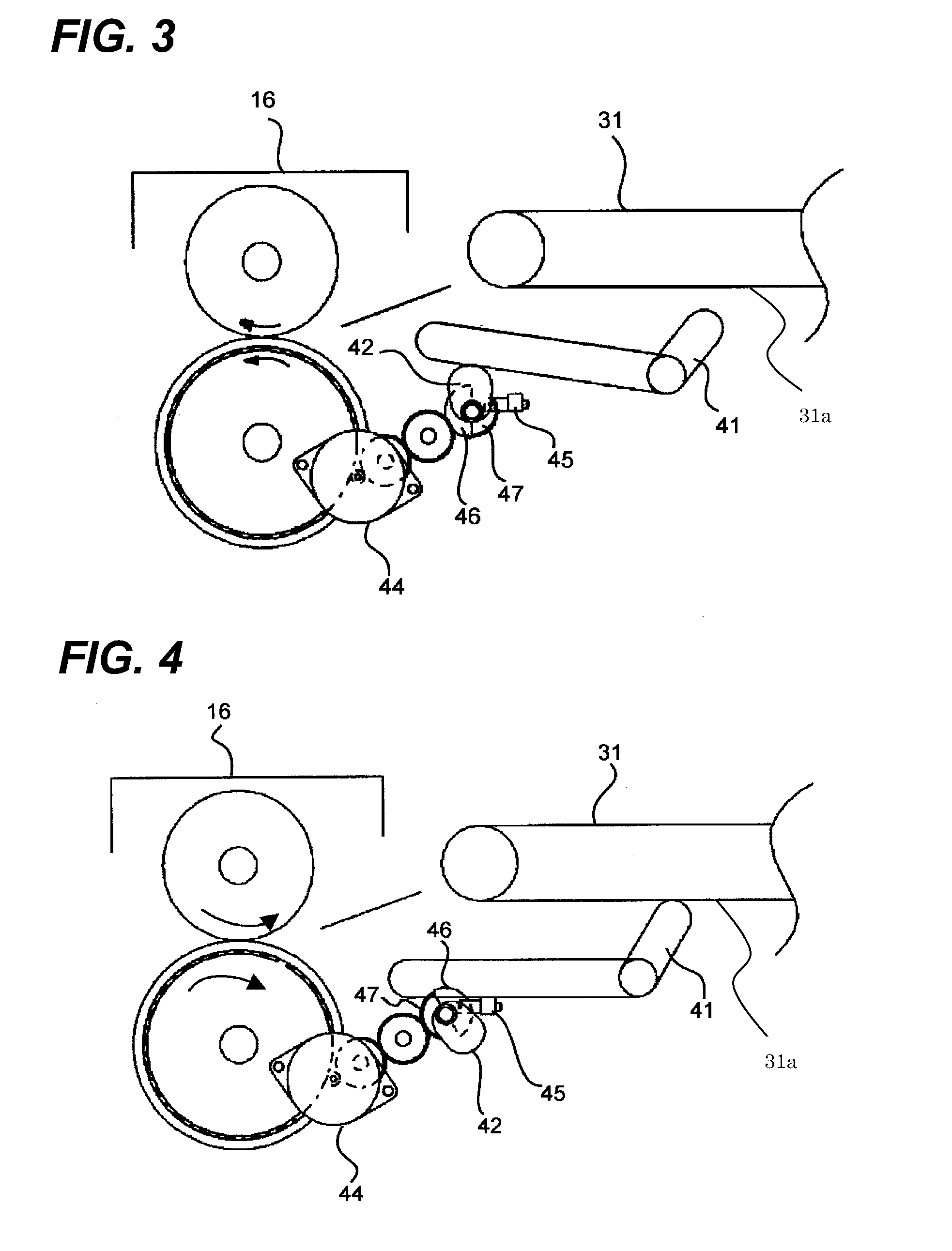
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20090304398A1Improved jam recovery propertyImprove productivityElectrographic process apparatusImage formationAbutment
An image forming apparatus which can draw out a pre-fixing conveying portion and a fixing device from an apparatus body has an abutment member which can abut a conveying surface of the pre-fixing conveying portion and can be separated therefrom, the abutment member being separated from the conveying surface of the pre-fixing conveying portion when the apparatus body is operated and abutting the conveying surface of the pre-fixing conveying portion in the event that a jam is detected by a sheet detection sensor.
Owner:CANON KK
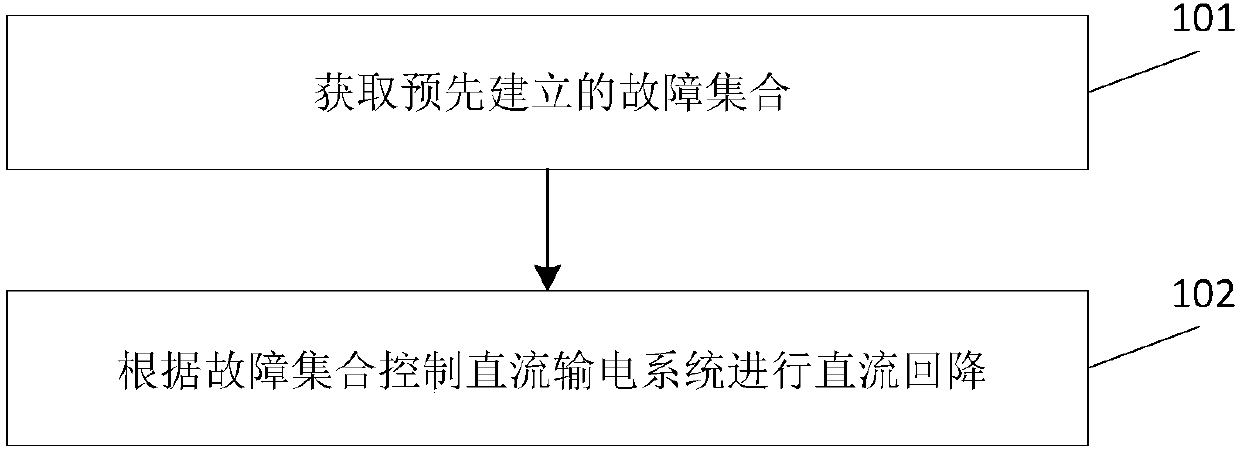
Method and device for preventing from DC blocking
ActiveCN109659964AReduced dropImproved recovery propertiesElectric power transfer ac networkPower modeTransmission system
The invention relates to a method and a device for preventing from DC blocking. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring a pre-established fault set; and controlling a DC power transmission systemto perform a DC fallback according to the fault set, wherein the fault set is established by employing the number of times of commutation failure of all the DC transmission system accessed in an AC grid after faults are generated. Through adoption of a fallback DC power mode, the drop amplitude of the voltage is reduced when faults are generated, the voltage recovery feature is improved, the number of times of DC continuous commutation failure is reduced, and DC blocking caused by DC continuous commutation failure is avoided.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Fluoroalkyl-containing curable organopolysiloxane composition, cured object obtained therefrom, and electronic component or display device including said cured object
ActiveUS20180065347A1High transparencyEasy to processStatic indicating devicesSynthetic resin layered productsHydrogenHydrogen atom
A curable organopolysiloxane composition containing a fluoroalkyl group is disclosed. The composition comprises: (A) an organopolysiloxane containing a fluoroalkyl group, having at least two alkenyl groups in a molecule, where 10 mol % or more of all substitution groups on the silicon atoms is a fluoroalkyl group, and the average degree of polymerization is less than 150; (B) an organohydrogen polysiloxane having at least two silicon-bonded hydrogen atoms in a molecule at an amount where the silicon-bonded hydrogen atoms in the component is 0.1 to 1.0 mol with regard to a total of 1 mol of the alkenyl groups in component (A); (C) an effective amount of a hydrosilylation reaction catalyst; and optionally, (D) a solvent. The composition generally has a high dielectric constant and favorable transparency. A cured product and applications of the composition and the cured product thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:DOW TORAY CO LTD
Silicone hydrogel, medical device, lens for eye and contact lens (as amended)
ActiveUS20170204213A1High uniformity of polymerization rateMaintain good propertiesTissue regenerationProsthesisOptical propertyMeth-
In order to provide a silicone hydrogel which has high uniformity in polymerization rates of polymerization components used for copolymerization, excellent mechanical characteristics, excellent optical characteristics and good shape recoverability and in order to also provide various medical devices and ocular lenses having an excellent balance among elasticity, wettability and transparency, the present invention provides a silicone hydrogel which has a repeating unit derived from a monofunctional linear silicone (meth)acrylate and a repeating unit derived from a hydrophilic (meth)acrylate, and wherein the content of the repeating units derived from (meth)acrylates is more than 80% by mass.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS10438852B2Improved recovery propertiesLower forward voltageTransistorThyristorPower semiconductor devicePower flow
A semiconductor device includes: reverse conducting switching elements-in each of which a diode element and a switching element are arranged in parallel on a single semiconductor substrate; a driver applying a gate voltage to a plurality of gate electrodes in the reverse conducting switching elements; and a mode determination unit determining whether a forward conduction mode in which a current mainly flows through the switching element or a reverse conduction mode in which the current flows through the diode element is being operated.
Owner:DENSO CORP
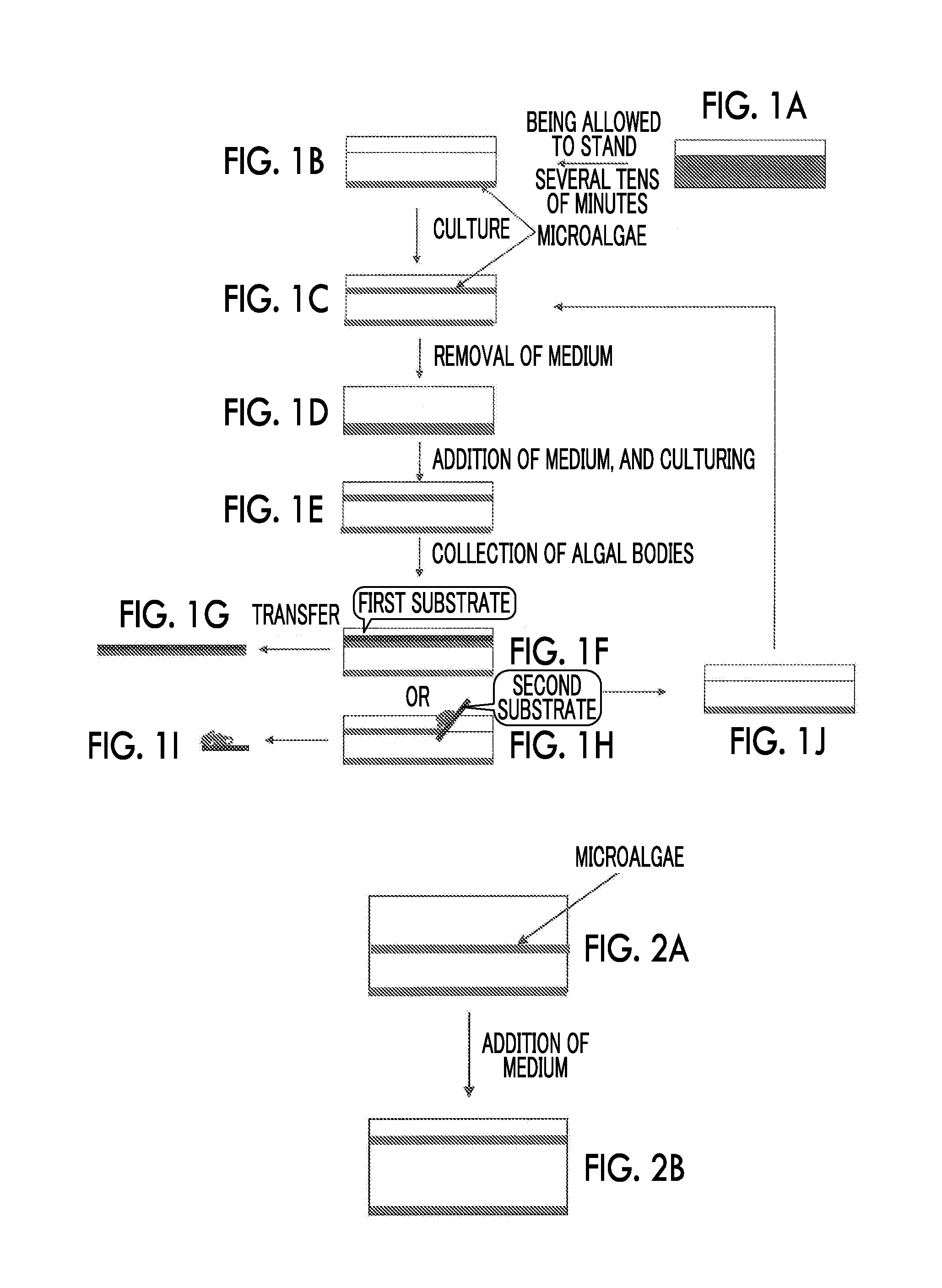
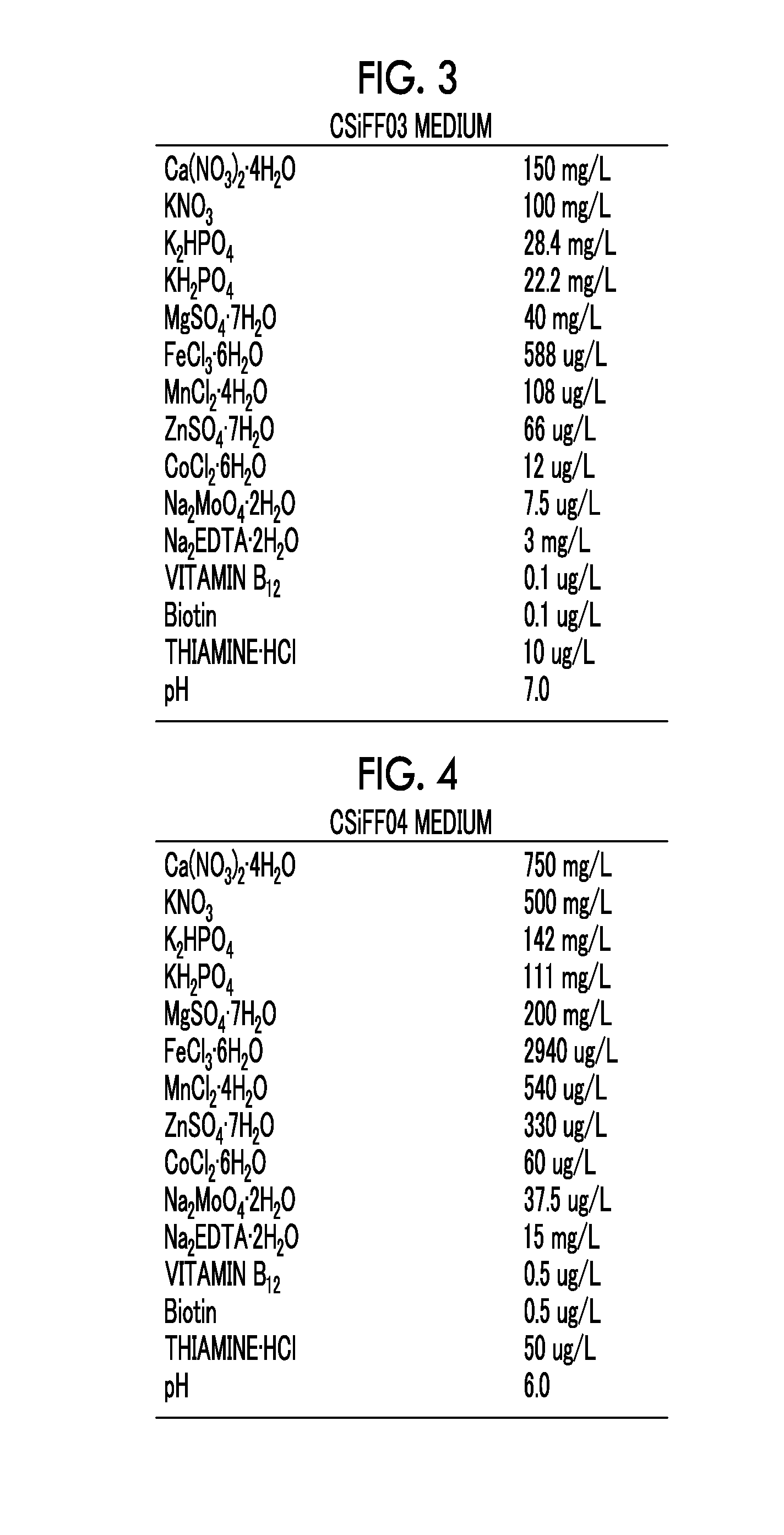
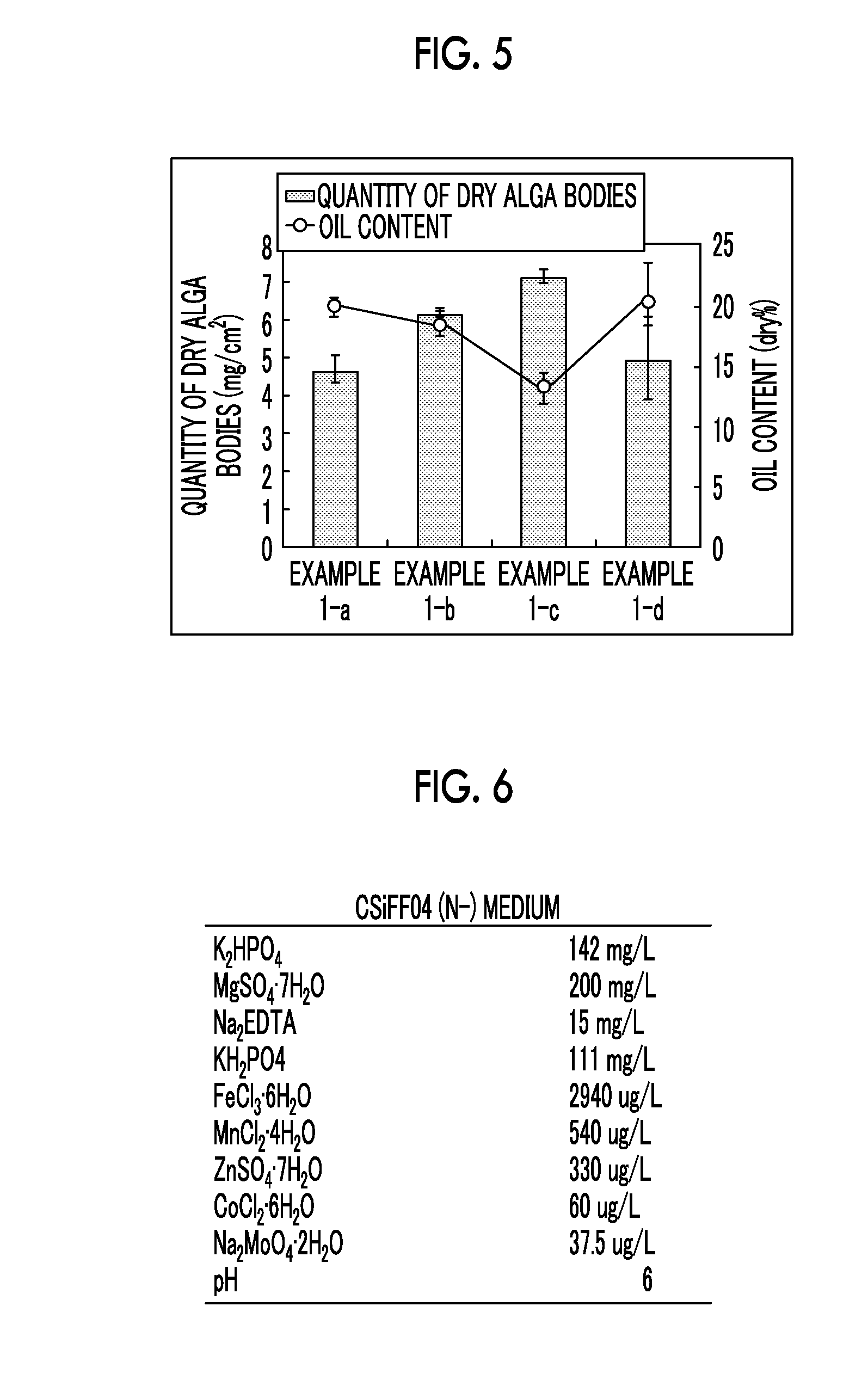
Culture method for microalgae that improves oil content ratio, method for manufacturing algal biomass, and novel microalga
InactiveUS20160194671A1Easy to implementMinimize impactUnicellular algaeChemical recyclingProliferation rateLiquid surfaces
In a liquid surface-floating culture method in which culturing of microalgae is performed on the liquid surface, there is provided a culture method in which the oil content in microalgae is improved. In addition, there is a provided a method for decreasing the probability of recovery of bottom surface algae. Furthermore, an object of the present invention is to provide a culture method in which the proliferation rate of microalgae is improved.Culturing is performed such that a medium is suctioned from a region, in which there is a small quantity of microalgae between the liquid surface and the bottom surface, is discarded, and is replaced with a medium of which the concentration of a nitrogen compound or a phosphorus compound is lower than that of the above-described medium. In addition, a liquid is added thereto immediately before collecting microalgae on the liquid surface, and the water depth in a culture vessel is made to be deep. In addition, the microalgae are subjected to liquid surface-floating culture using a medium containing sugar. In the present invention, microalgae which can form a biofilm on the liquid surface and have at least one characteristic selected from the group consisting of the following (1) to (8) when being cultured in a medium within a culture vessel may be used. (1) The sum of the quantity of algal bodies of microalgae existing on the liquid surface and in a region from 1 cm below the liquid surface to the liquid surface, and the quantity of algal bodies of microalgae on the bottom surface of a culture vessel is greater than or equal to 10 times the quantity of algal bodies existing in the other region within the culture vessel; (2) the specific gravity of microalgae on the liquid surface is smaller than that of microalgae on the bottom surface of the culture vessel; (3) the specific gravity of microalgae on the liquid surface is greater than that of water; (4) the oil content of microalgae on the liquid surface is higher than that of microalgae on the bottom surface; (5) the size of microalgae on the liquid surface is larger than that of microalgae on the bottom surface; (6) a formed biofilm includes a film-like outer layer and an inner layer which has a plurality of bubble-like structures, and the outer layer is thicker than the inner layer; (7) a part of a formed biofilm has a pleat-like structure in a medium; and (8) in a case where microalgae obtained by collecting a biofilm which has been formed and subjecting the collected biofilm to suspension treatment are seeded on the liquid surface of a medium, the microalgae can be deposited in the medium.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Production method for medical pressure-sensitive adhesive tape or sheet
InactiveUS20130022734A1Improved recovery propertiesGood skin adhesionSurgical adhesivesPretreated surfacesPorous substrateIrritation
In the method for producing a medical pressure-sensitive adhesive tape or sheet of the invention, a water dispersion-type copolymer solution having a specific composition is used. Therefore, the problem caused by high thixotropy can be eliminated and a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer can be relatively easily formed on a porous substrate by a direct method. In addition, when the medical pressure-sensitive adhesive tape or sheet obtained by the method of the invention is attached to the skin surface, skin adhesion and tube fixing are excellent and at the same time, irritation to skin is low.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Preparation method of soaping-resistant soft bath towel
InactiveCN107687103AImprove soft feelIncrease elasticityGrip property fibresDyeing processSisal fiberSurface roughness
The invention belongs to the technical field of processing of environment-friendly bath towels, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a soaping-resistant soft bath towel. The preparationmethod comprises preparation, dyeing, color fixation and high temperature setting of blended products. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method of the soaping-resistant soft bath towel disclosed by the invention has the following advantages that a plurality of fibers are reasonably combined to obtain blended fabrics, and modified sisal fibers and pineapple fibers are beneficial for improving wear resistance of the fabrics; sisal fibers are modified before the use, so that the softness of the fabrics can be improved, water absorption performance of the fabrics is also improved, andsurface roughness of the fabrics is reduced; compared with exclusive use of bamboo fibers, combined use of the bamboo fibers and licorice fibers is advantaged in better antibacterial property; becauseof coordination of the licorice fibers and the pineapple fibers, a soft hand feel of the fabrics can be improved, and the obtained fibers are high in elasticity, have better reduction characteristic,are not shrunk after the fibers are wet, and are high in shape retention property; then coordination of variable-speed coloring and low-temperature salt water color fixation is utilized, so that thecolor retention property of the product is improved.
Owner:JIESHOU SHUANGXIN TEXTILE
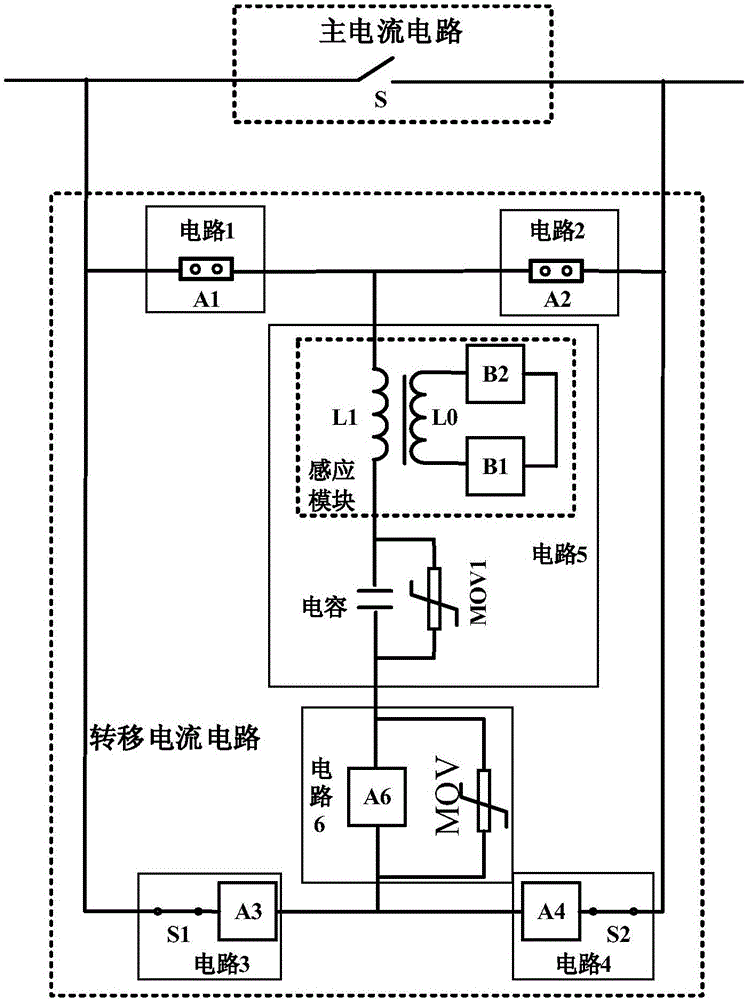
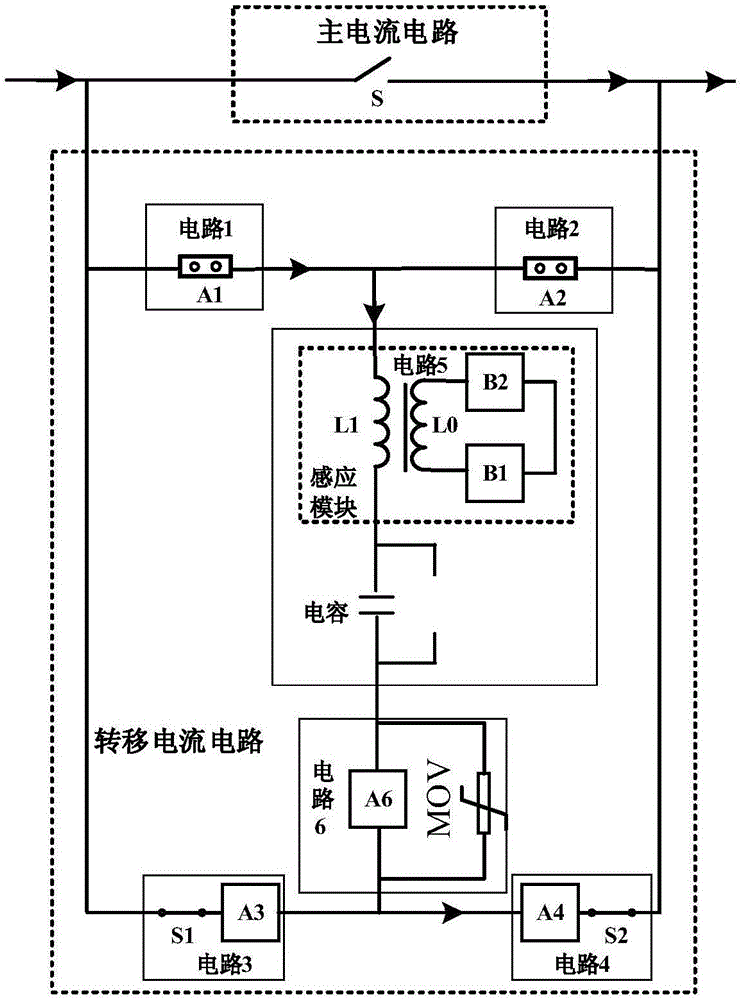
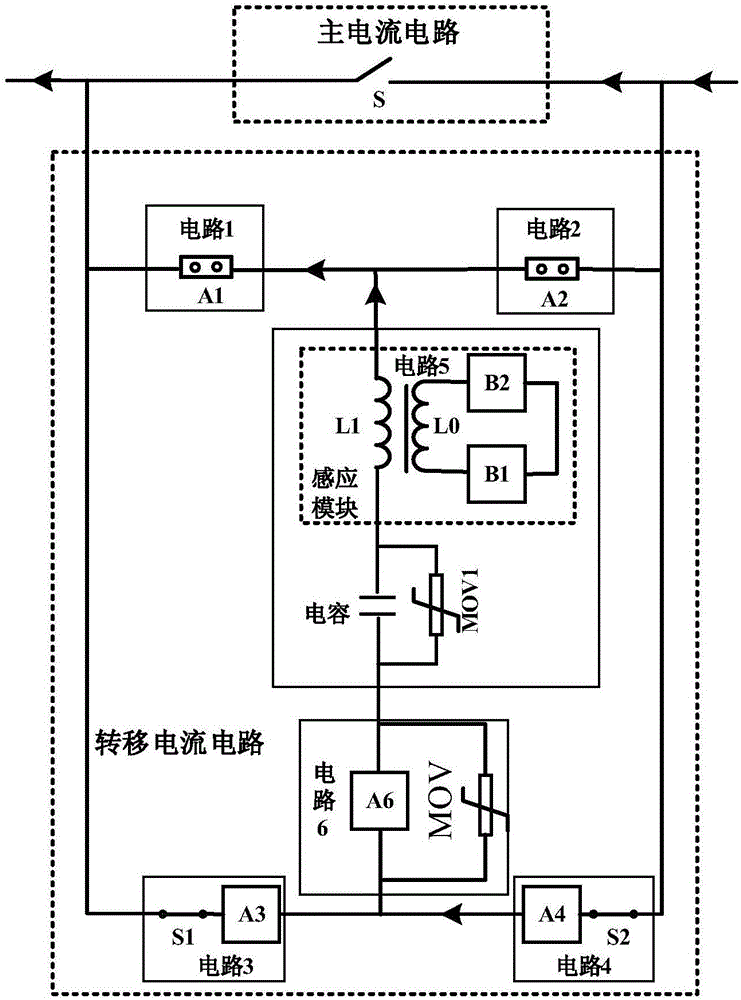
Direct current breaker through combination of magnetic induction transfer and current-limiting protection
InactiveCN106558867AReduce control complexityReduce manufacturing costEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentPower flowCurrent limiting
A direct current breaker through combination of magnetic induction transfer and current-limiting protection comprises a main current circuit and a transfer current circuit. The main current circuit is connected in parallel with the transfer current circuit; the main current circuit is a rapid switch; the transfer current circuit consists of a circuit 1, a circuit 2, a circuit 3, a circuit 4, a circuit 5 and a circuit 6 which form a bridge circuit; the circuit 1 is connected in series with the circuit 2 and is connected in parallel with the main current circuit; and the circuit 1 and the circuit 2 can be vacuum and gas trigger gaps or high-speed mechanical switches or the combination thereof, the transfer current circuit employs the bridge structure and only uses one set of single-direction assembly having the breaking function to realize the dual-direction disconnection of the current, and the usage amount reduces 50% compared to the usage amount of the current structure turn-off device. The transfer circuit is internally provided an auxiliary energy dissipation module circuit 5 and a breaking module circuit 6, the current of the main circuit is transferred to the auxiliary energy dissipation module to further reduce the usage amount of the turn-off assembly in the breaking module, and the total usage amount of the turn-off device can be changed to the 1 / 4 of the current usage amount, and the cost of the breaker is reduced.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
IGBT with built-in diode and manufacturing method therefor
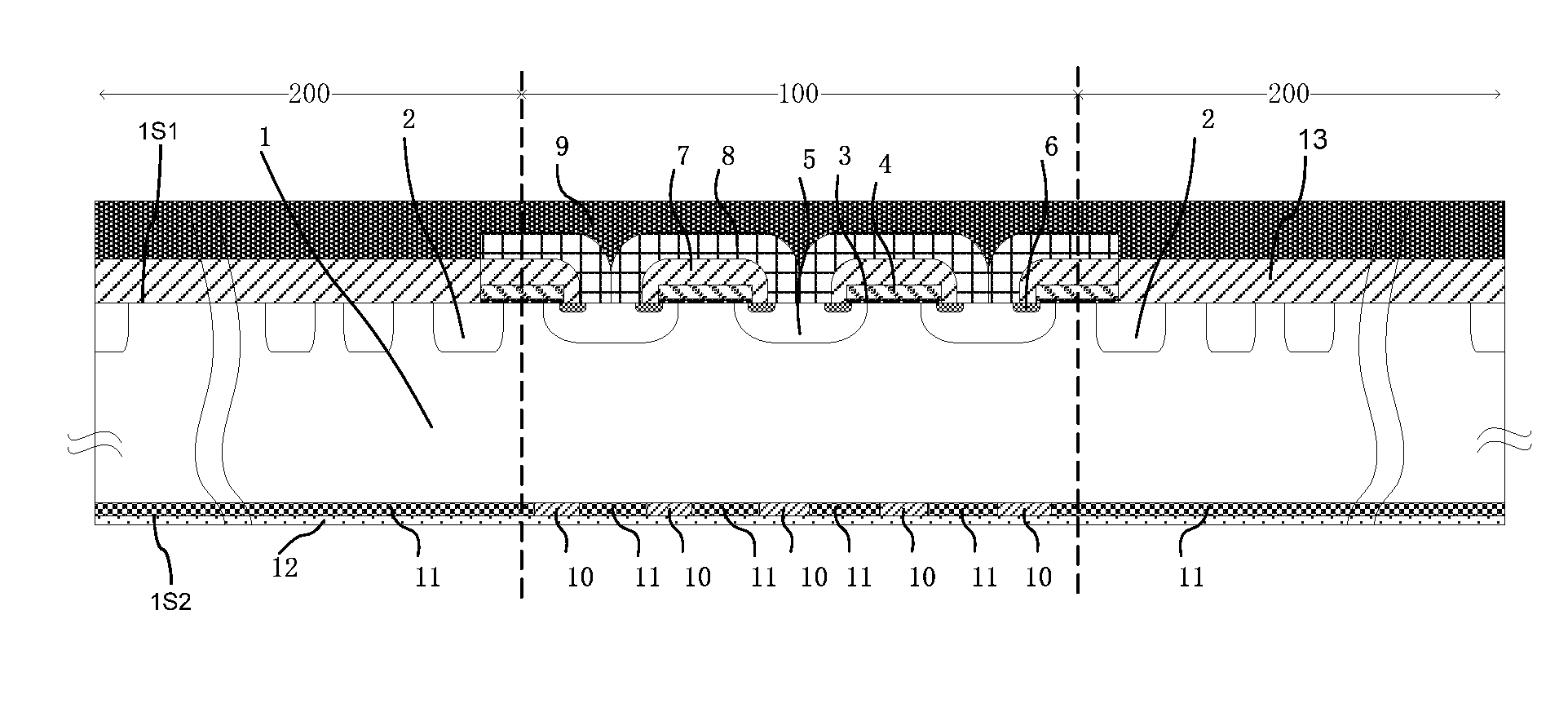
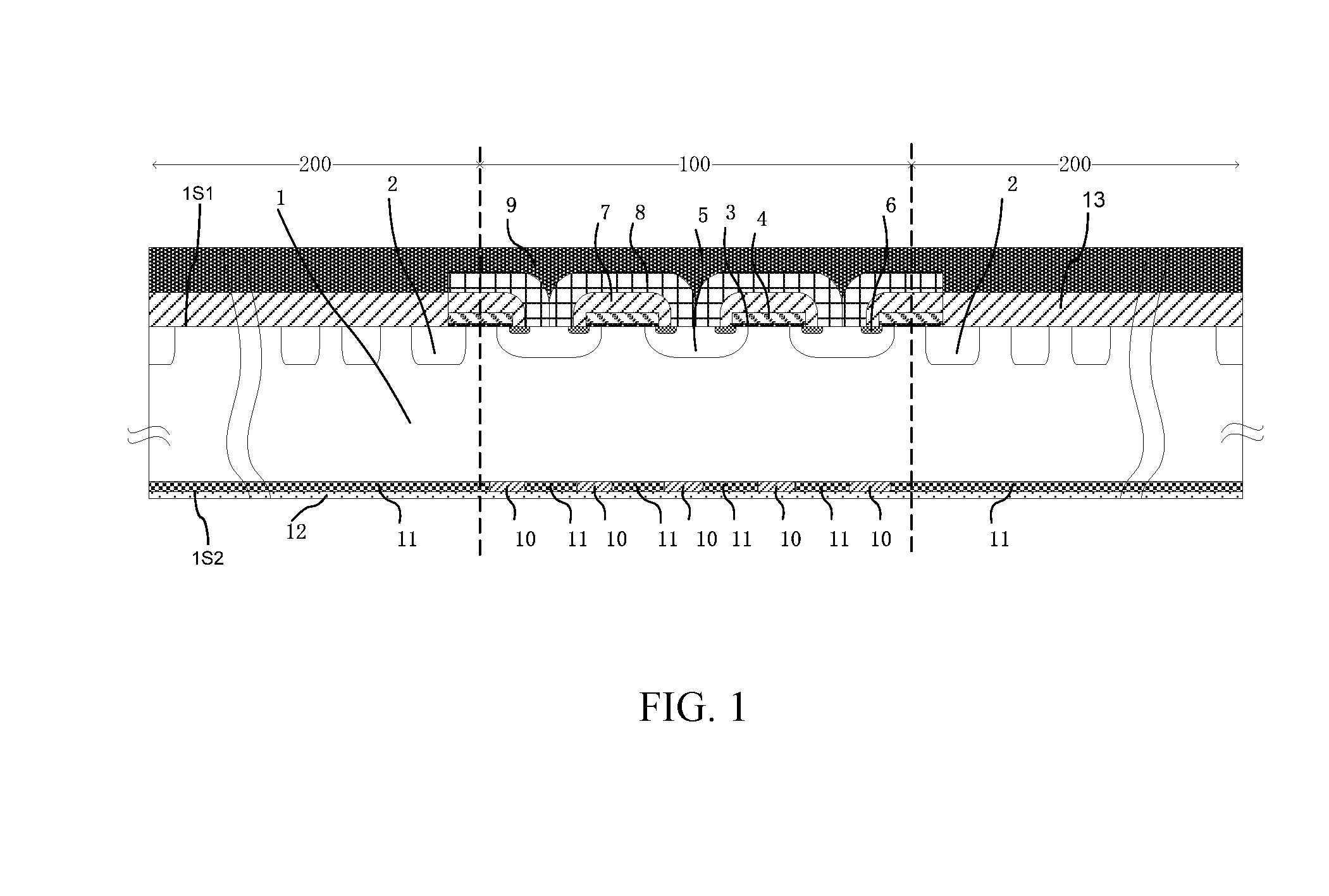
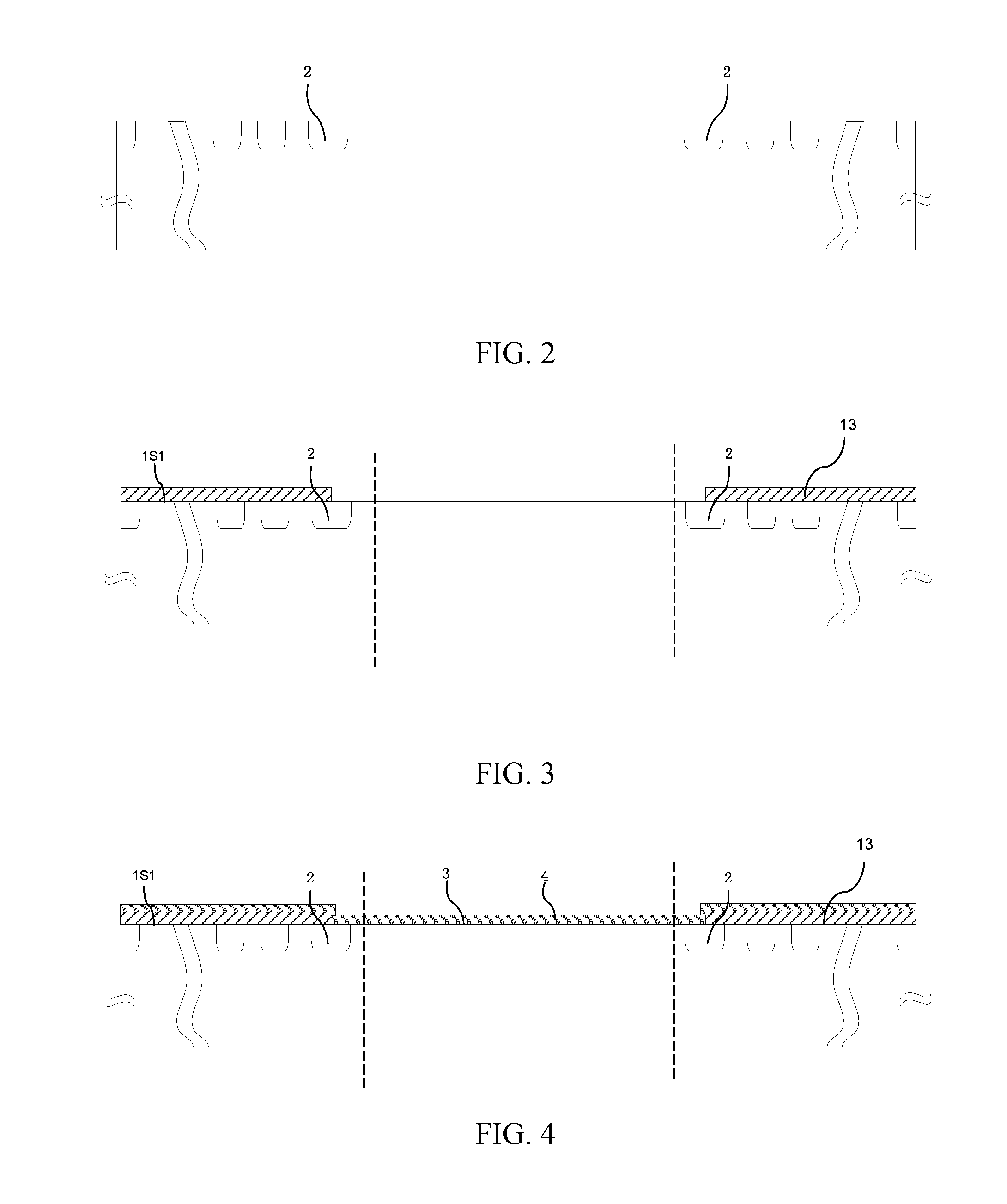
An insulated gate bipolar translator (IGBT) with a built-in diode and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. The IGBT comprises: a semiconductor substrate (1) of the first conduction type which has a first major surface (1S1) and a second major surface (1S2), wherein the semiconductor substrate (1) comprises an active region (100) and a terminal protection area (200) which is located at the outer side of the active region; an insulated gate transistor unit which is formed at the side of the first major surface (1S1) of the active region (100), wherein a channel of the first conduction type is formed thereon during the conduction thereof; and first semiconductor layers (10) of the first conduction type and second semiconductor layers (11) of the second conduction type of the active region, which are formed at the side of the second major surface (1S2) of the semiconductor substrate (1) alternately, wherein the IGBT only comprises the second semiconductor layers (11) in the terminal protection area (200) which is located at the side of the second major surface (1S2) of the semiconductor substrate (1).
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
Semiconductor module
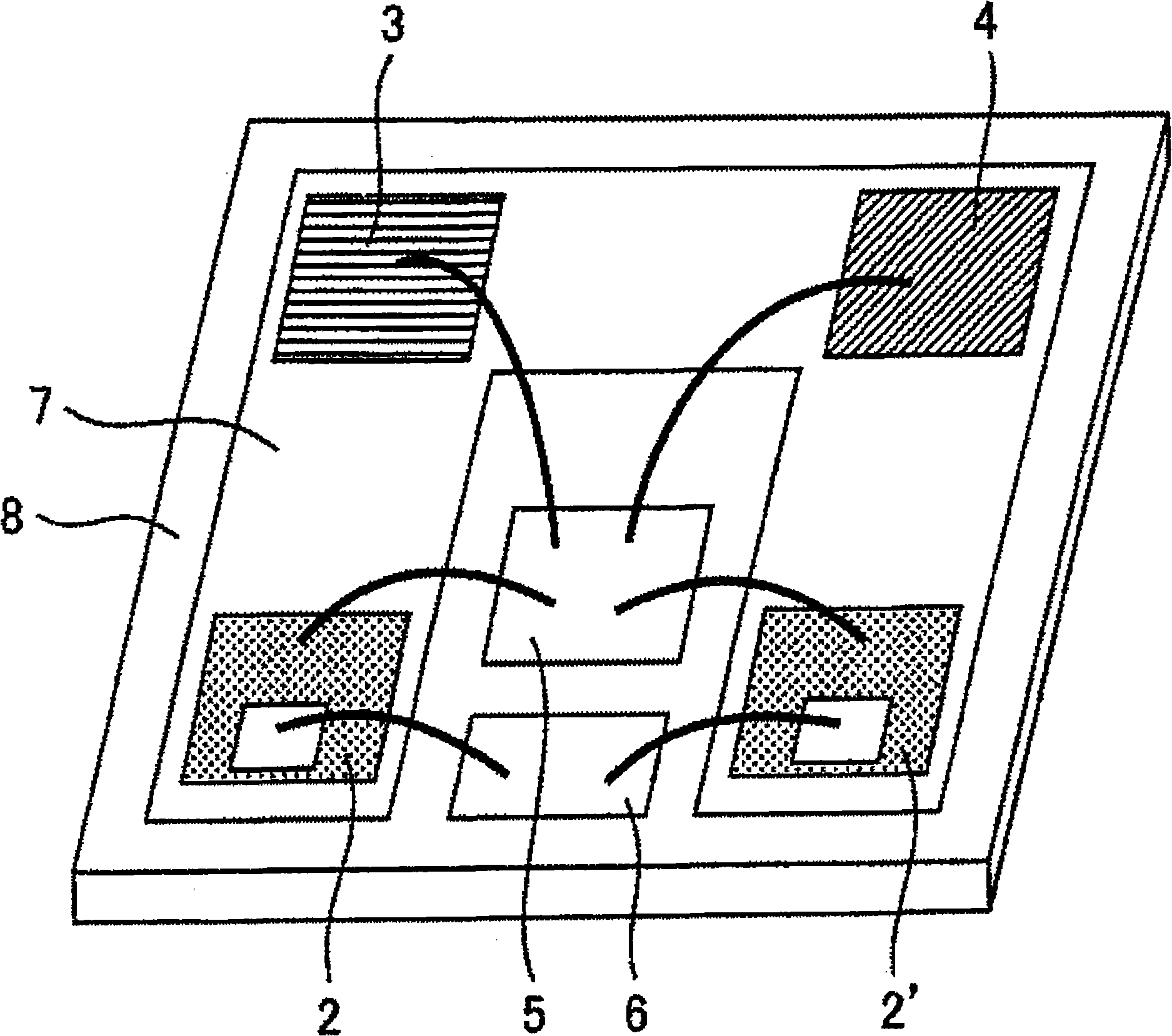
InactiveCN102637679AHelp miniaturizationReduce lossesEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSchottky barrierEngineering physics
A PFC module includes: a diode bridge having first and second diodes in the upper arm, and third and fourth diodes in the lower arm; and first and second switching elements for power factor correction. The first and second diodes are Schottky barrier diodes formed by using a wide bandgap semiconductor. The third and fourth diodes, and the first and second switching elements are Schottky barrier diodes and switching elements respectively formed by using silicon.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS9799648B2Improved recovery propertiesSuppresses injection of holeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesFlyback diodeCathode ray
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com