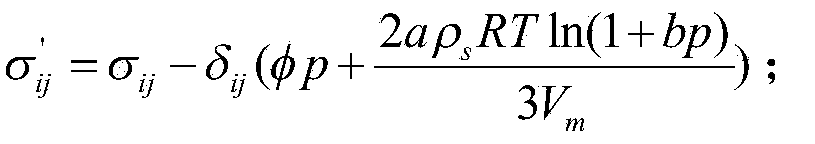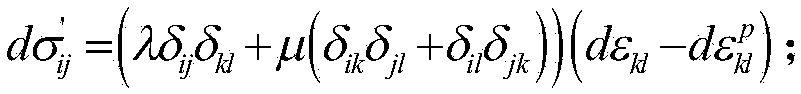Patents
Literature
99 results about "Active volume" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The active volume describes the volume of water in the well where the pumps are actively pumping. This volume is located between two elevations monitored by level sensors. The top level sensor tells the control panel to cycle a pump on while the lower level sensor tells the control panel to cycle the pump off.
Flow fluorometric method
InactiveUS6177277B1Signal to noise conditionLow powerChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceIndividual particle analysisFemtoliterFluorescence
This invention is related to a flow fluorometric device and method employing a two-photon excitation and / or confocal optical set-up. The optical set-up of this invention is optimal for counting small fluorescent biological particles. The active focal volume is diffraction-limited and consequently much smaller than the volume of the flow channel. The excitation and detection concept has been found very efficient for rejection of the background signal. An objective lens with large numerical aperture for focusing the laser and for collecting the fluorescence is used and this restricts the active volume of measurement to a diffraction-limited volume which approximately corresponds to a volume of femtoliter. This volume is significantly smaller than the detection volume of ordinary flow cytometry.
Owner:SOINI ERKKI
Self archiving log structured volume with intrinsic data protection
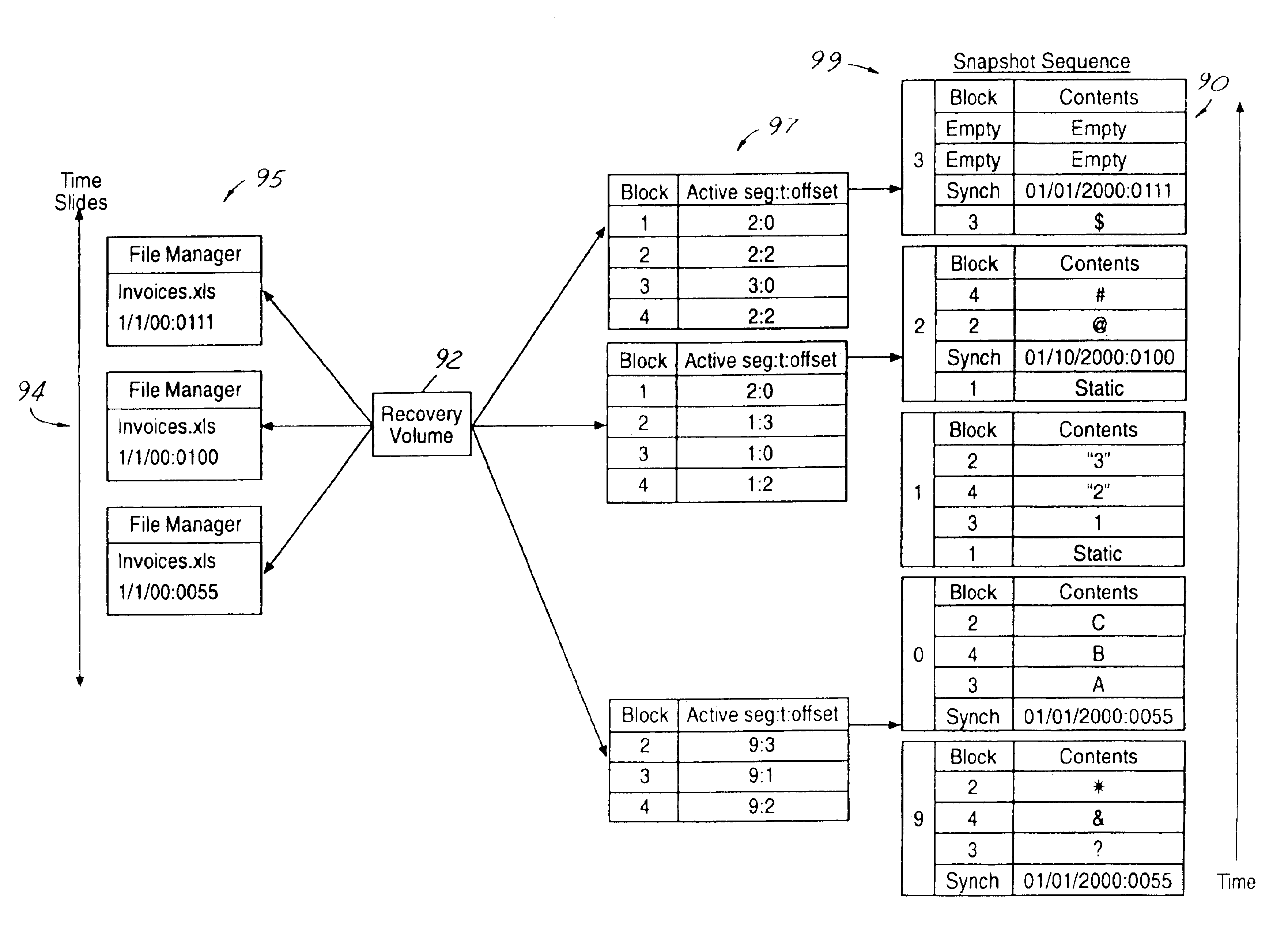
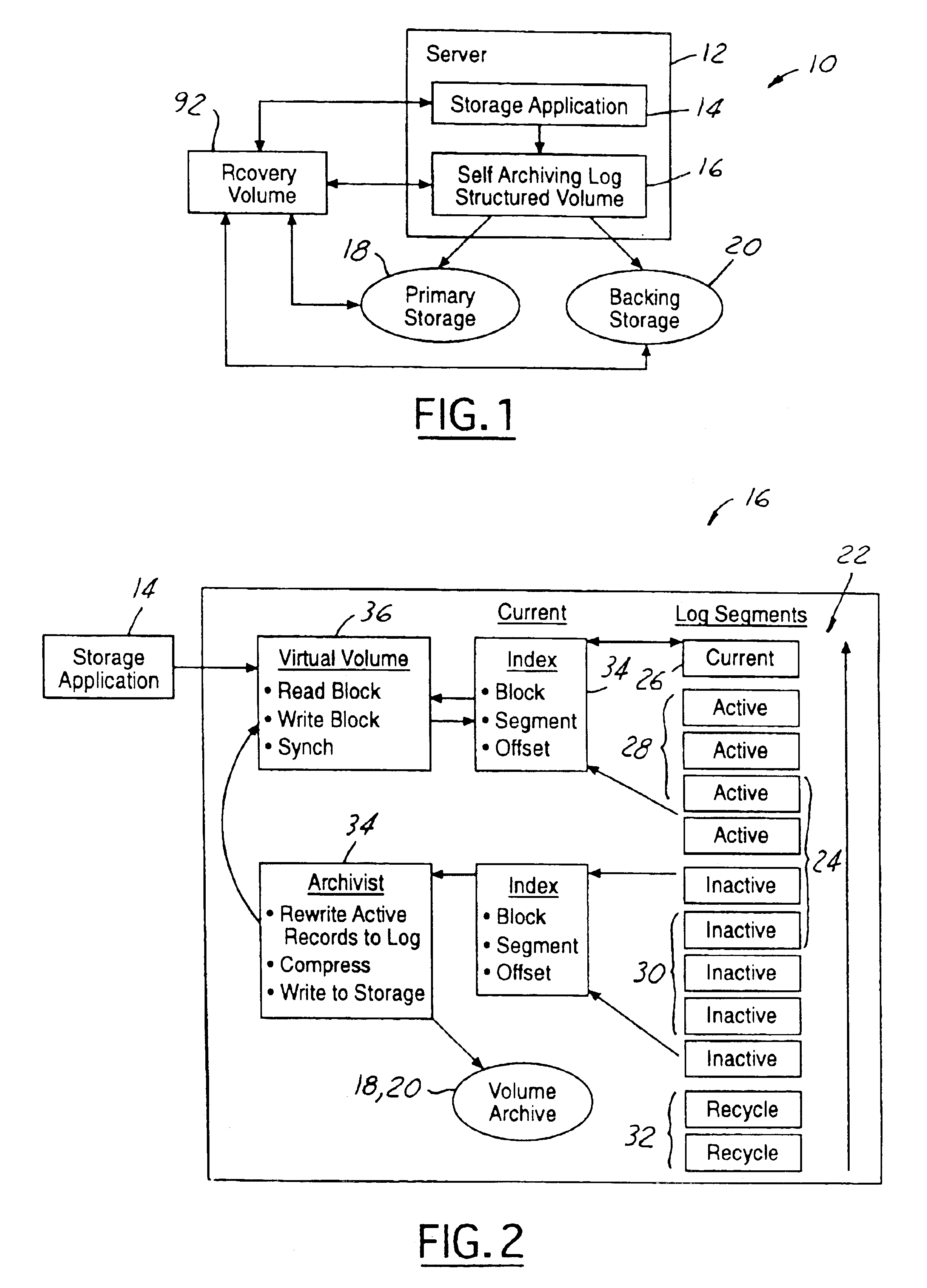
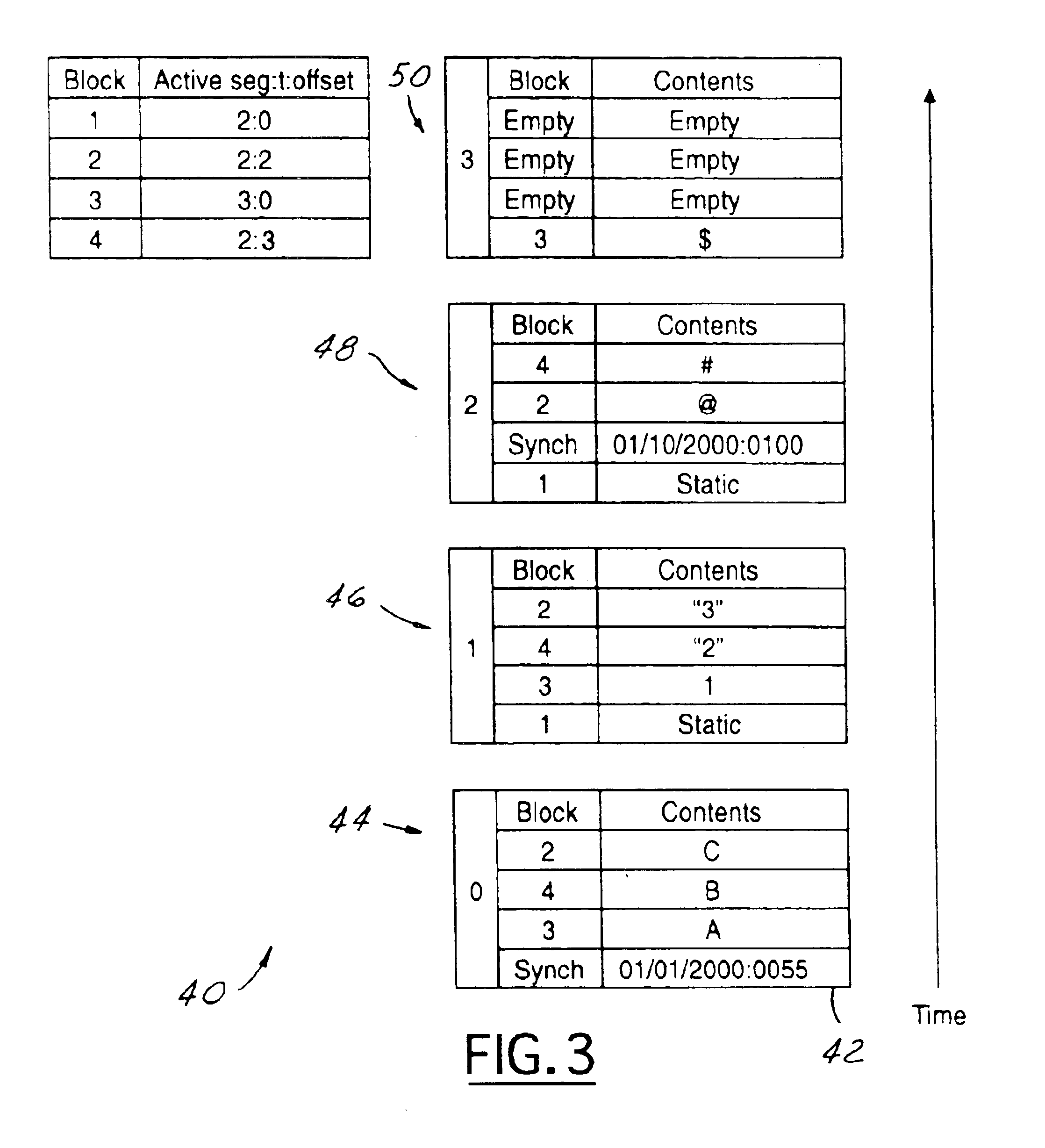
InactiveUS6915315B2Recovery is fast and easy and reliableProtect dataData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsChronological timeApplication software
A data backup system for use with a server running a storage application that writes and reads data blocks. The system includes a self archiving log structured volume for copying blocks from an active volume while the application is running without contending with the application for access to data blocks. The volume records the result of every write event in a new location in primary storage, forming a chronological log of the state changes the volume undergoes. The volume records in the log the points in time (synch events) when the blocks of the volume are in a consistent state with respect to the application. The system further includes backing storage to store the archived blocks and synch events of the volume. The volume migrates inactive segments of its log to the backing storage and ensures that a volume can be reconstructed from a fixed number of log segments.
Owner:STORAGE TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
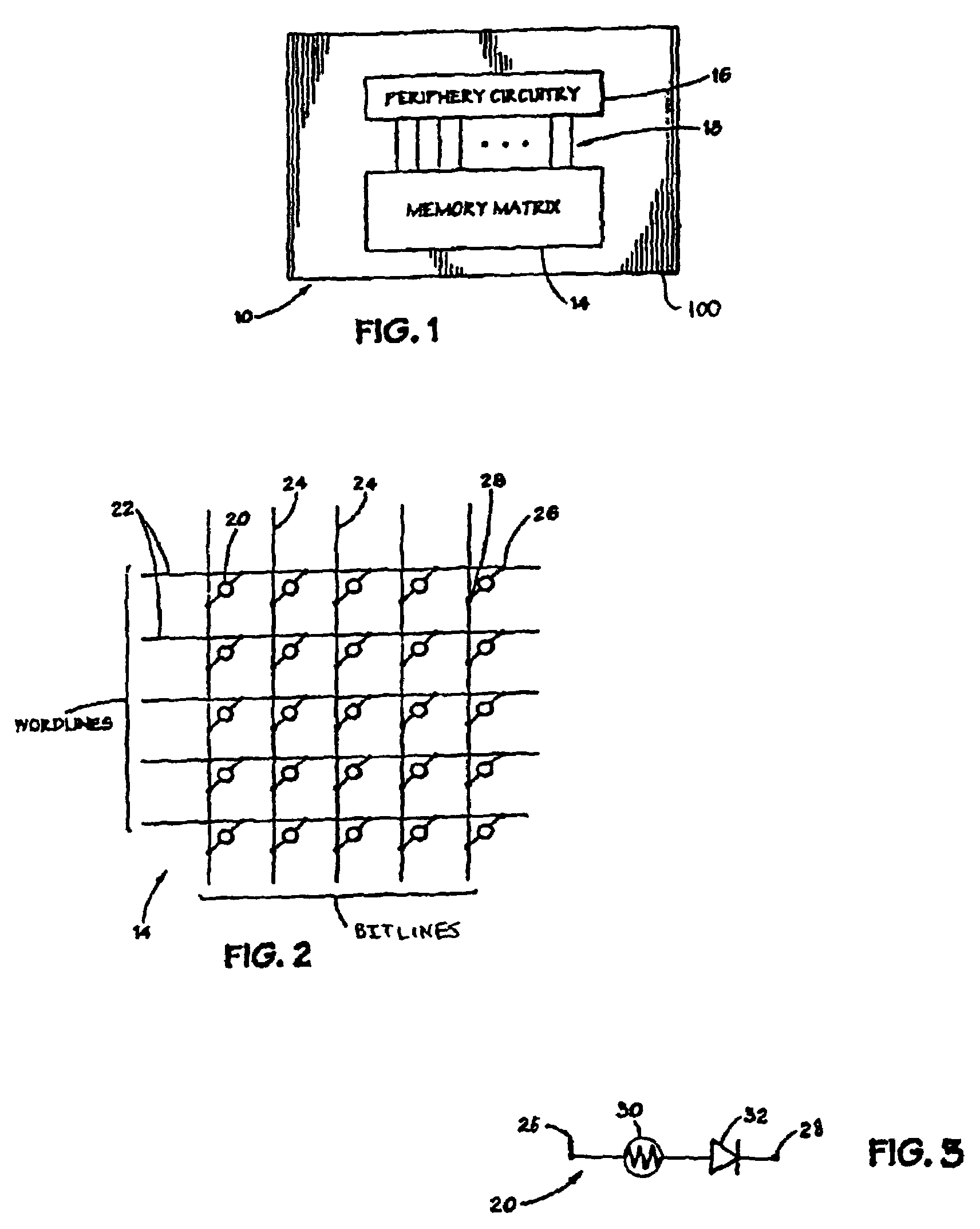
Programmable resistance memory element and method for making same
InactiveUS20080220560A1Lower energy requirementsImprove the immunitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive materialsEngineering
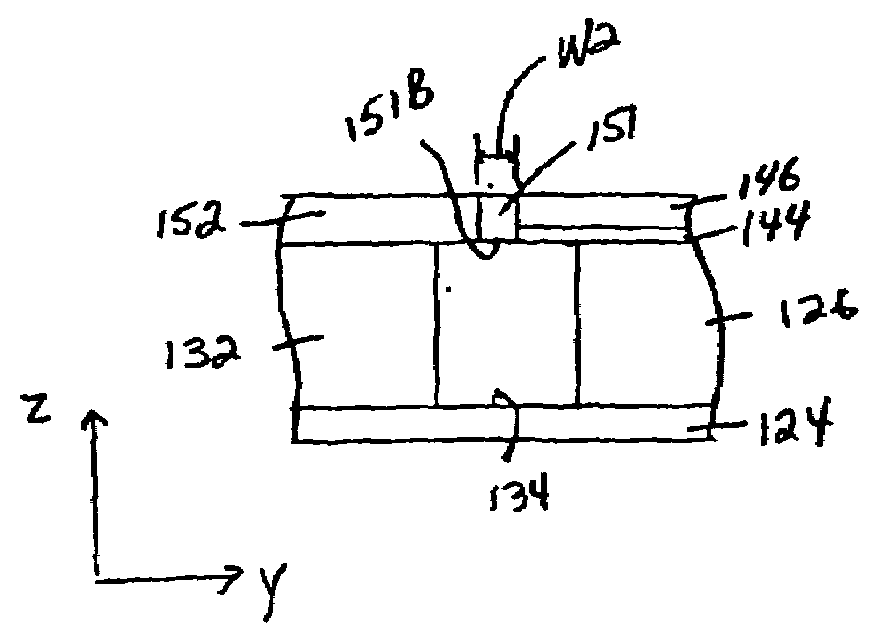
A programmable resistance memory element. The active volume of memory material is made small by the presence of a small area of contact between the conductive material and the memory material. The area of contact is created by forming a region of conductive material and an intersecting sidewall layer of the memory material. The region of conductive material is preferably a sidewall layer of conductive material.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Programmable resistance memory element and method for making same
InactiveUS7833823B2Improve the immunityLower energy requirementsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringConductive materials
A programmable resistance memory element. The active volume of memory material is made small by the presence of a small area of contact between the conductive material and the memory material. The area of contact is created by forming a region of conductive material and an intersecting sidewall layer of the memory material. The region of conductive material is preferably a sidewall layer of conductive material.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
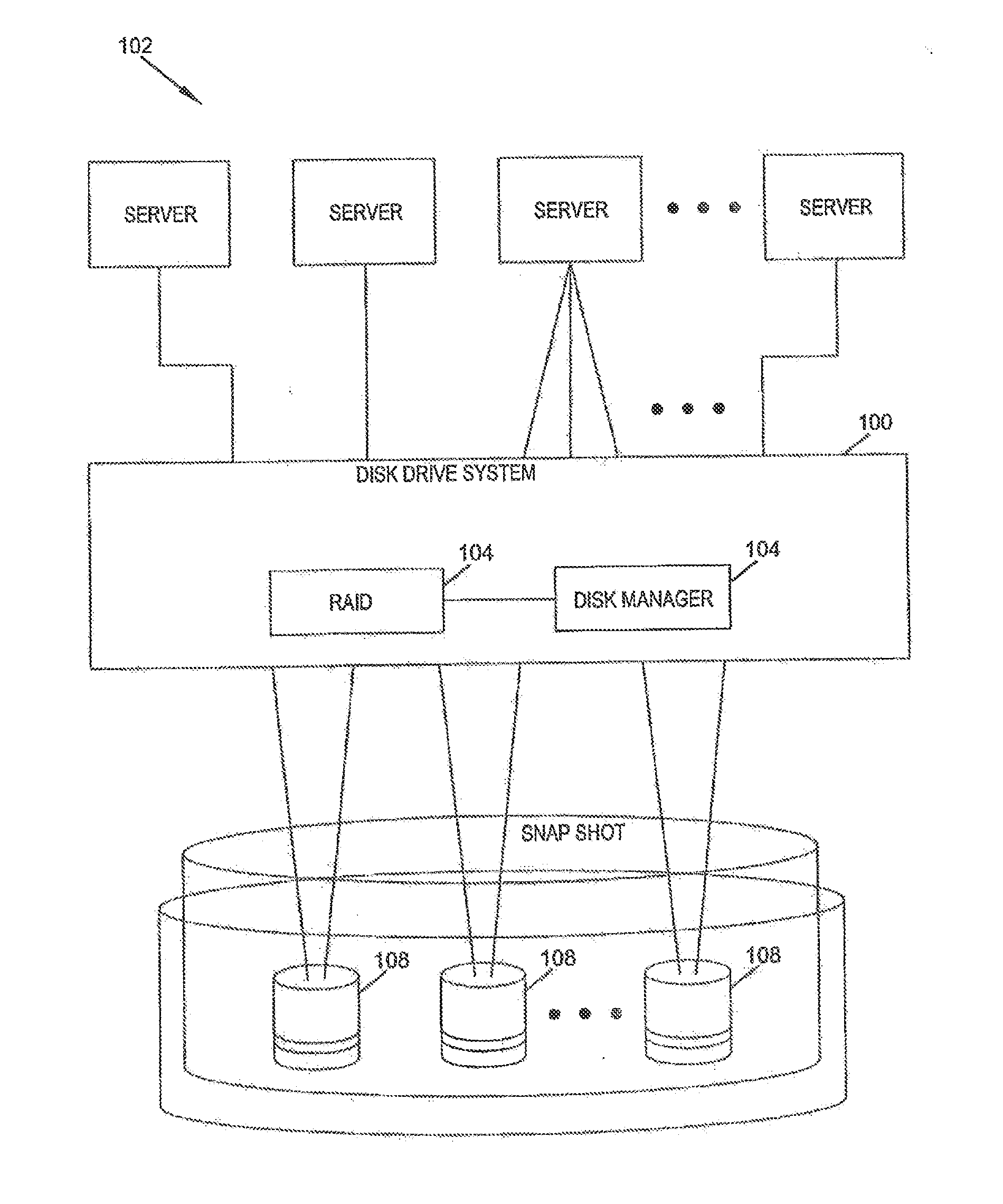
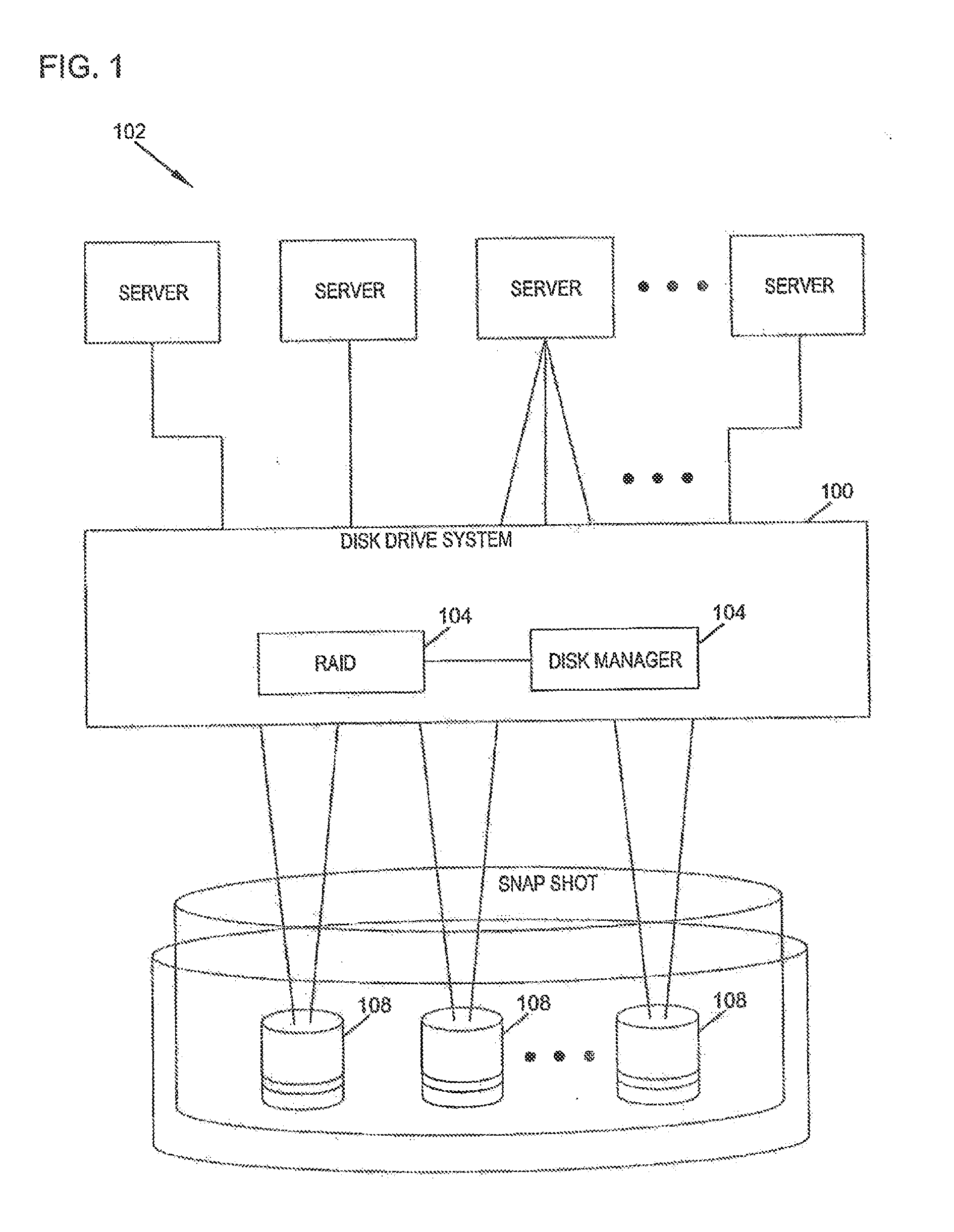
System and method for transferring data between different raid data storage types for current data and replay data
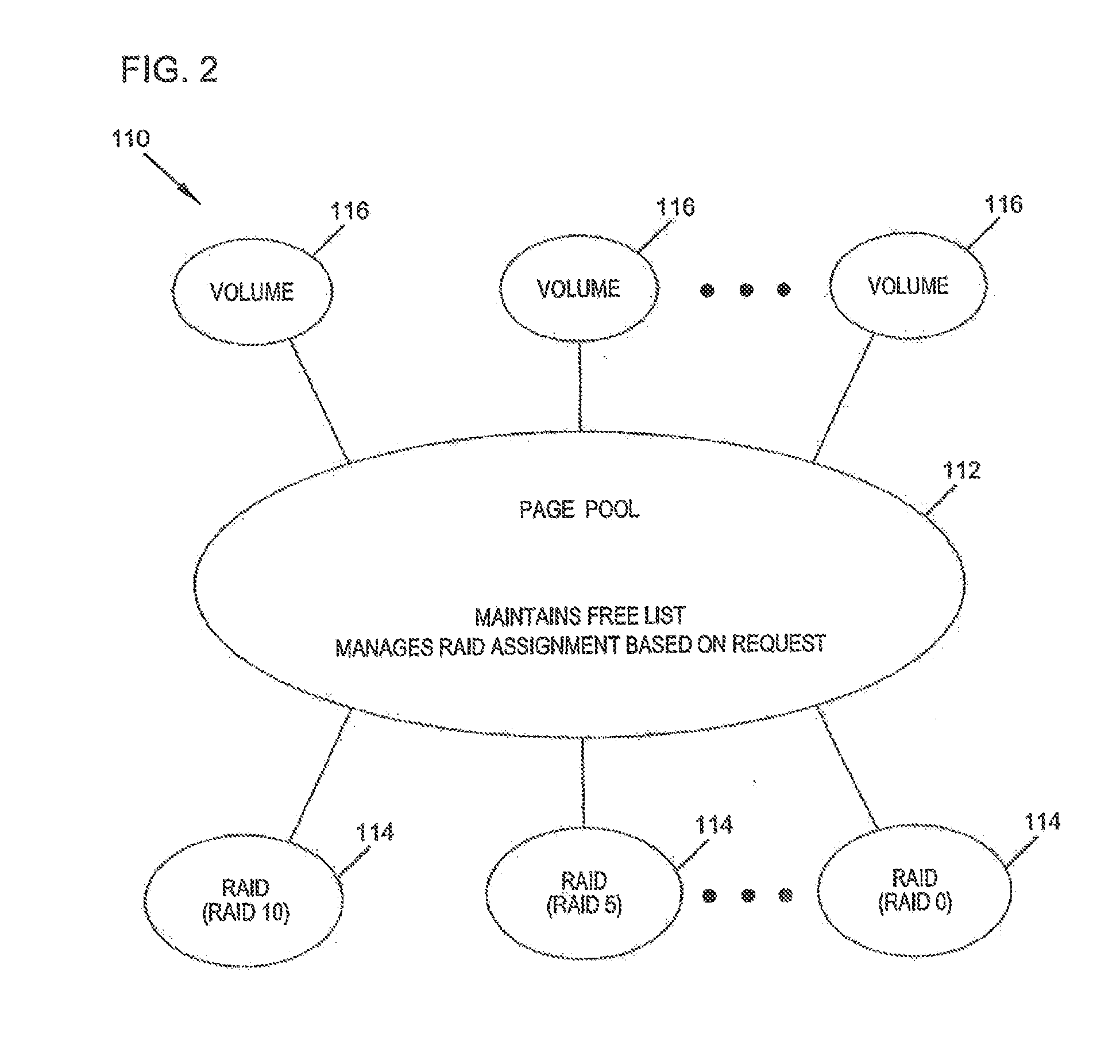
ActiveUS20130124798A1Efficient data storageLow costInput/output to record carriersError detection/correctionRAIDData store
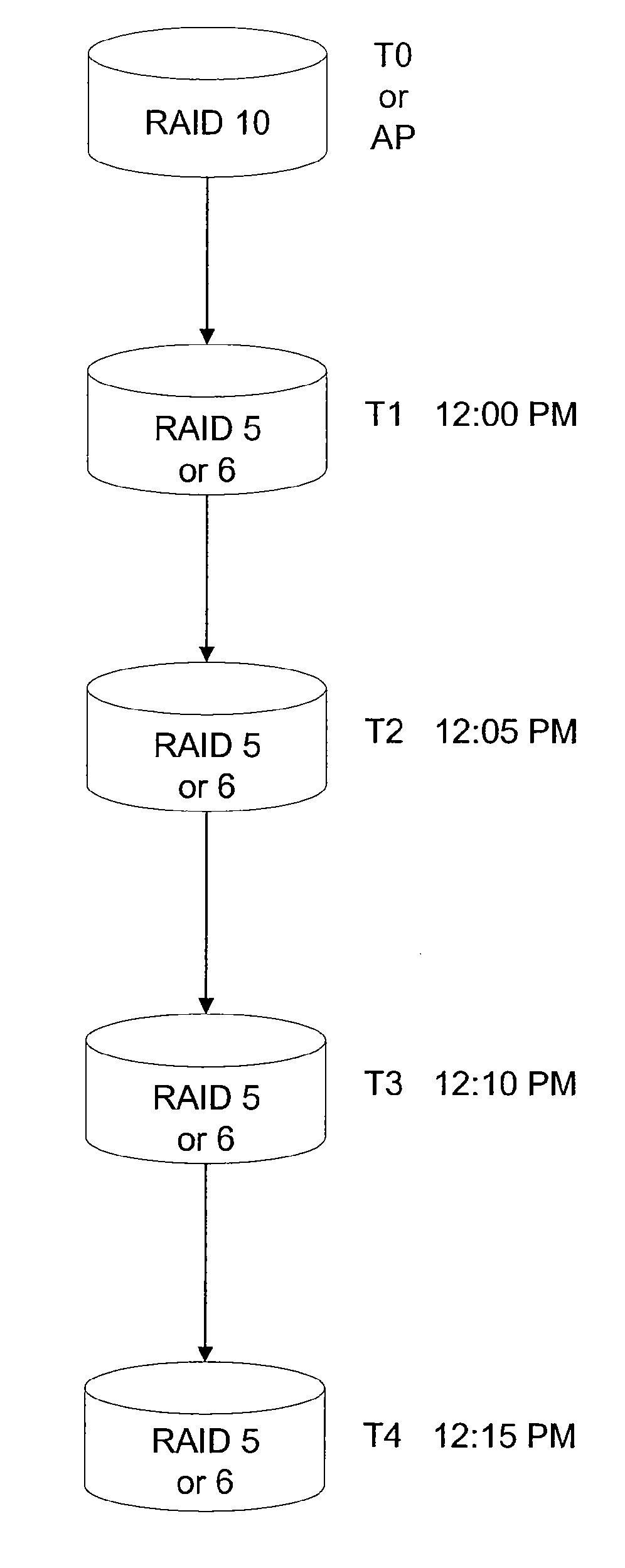
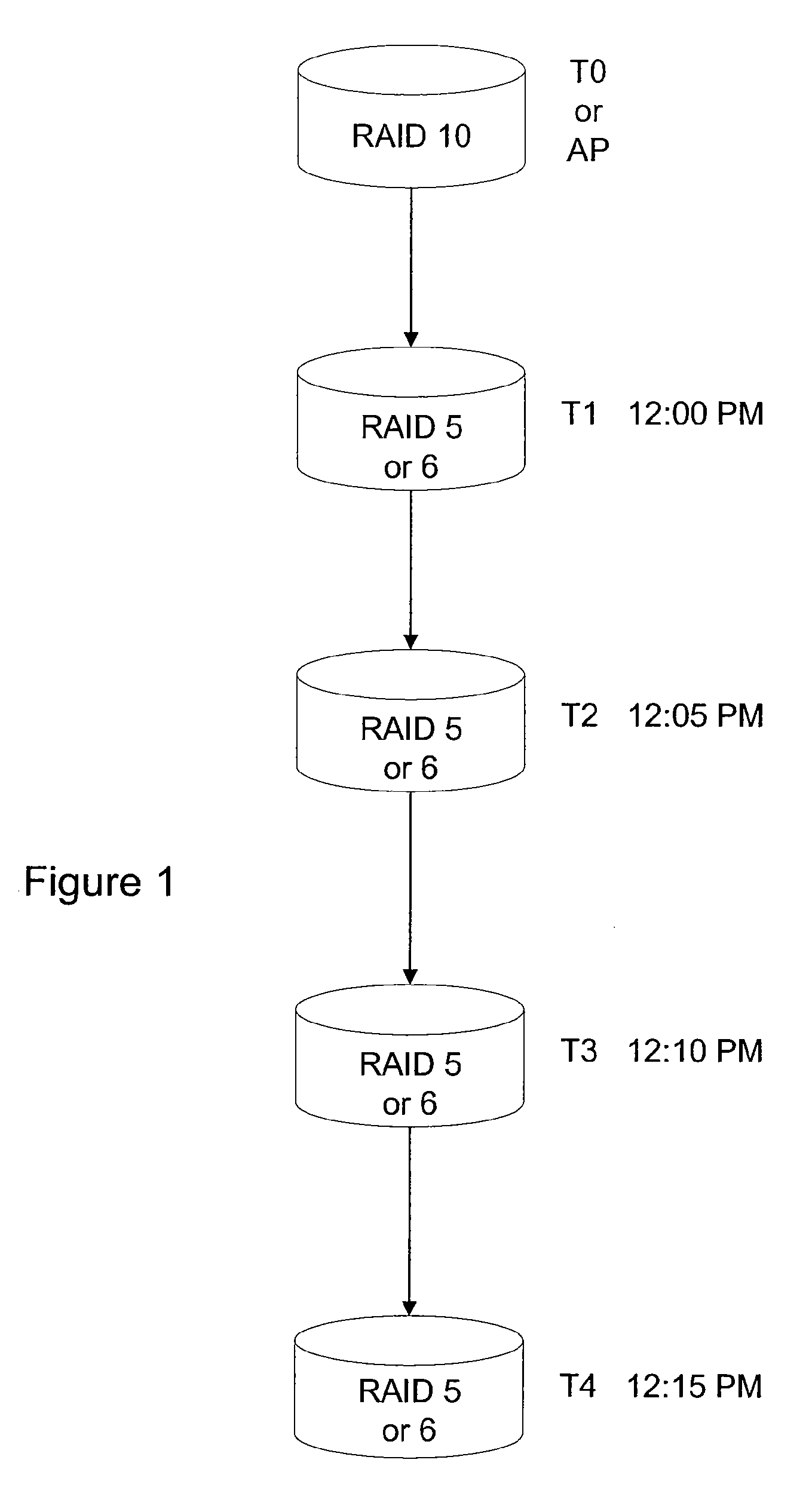
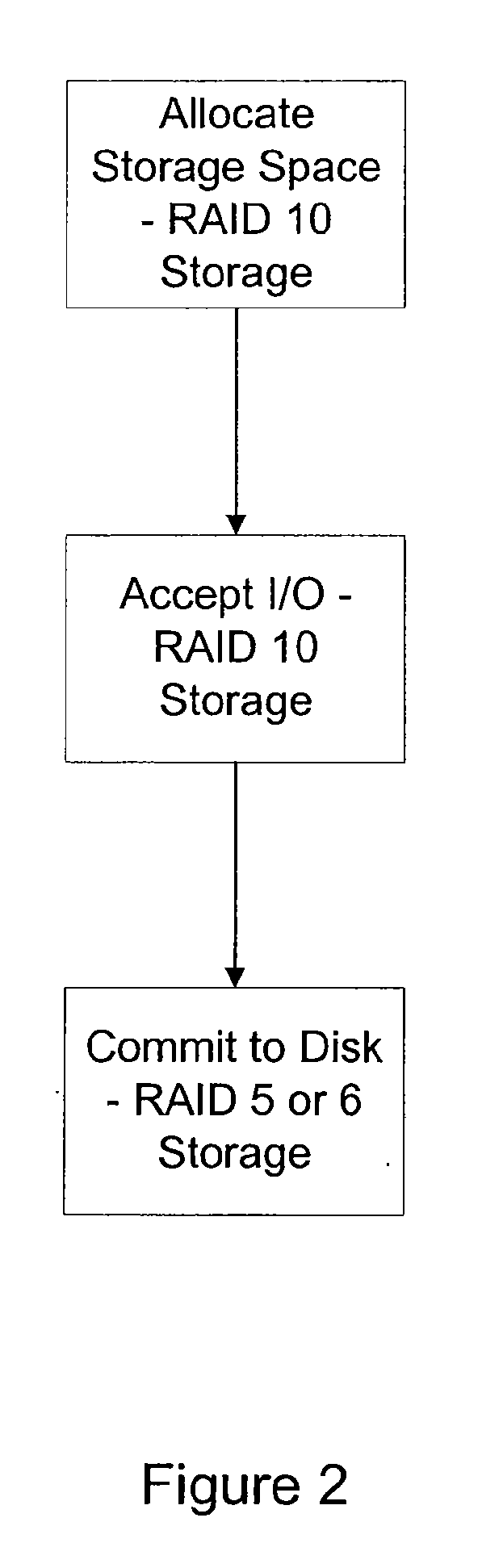
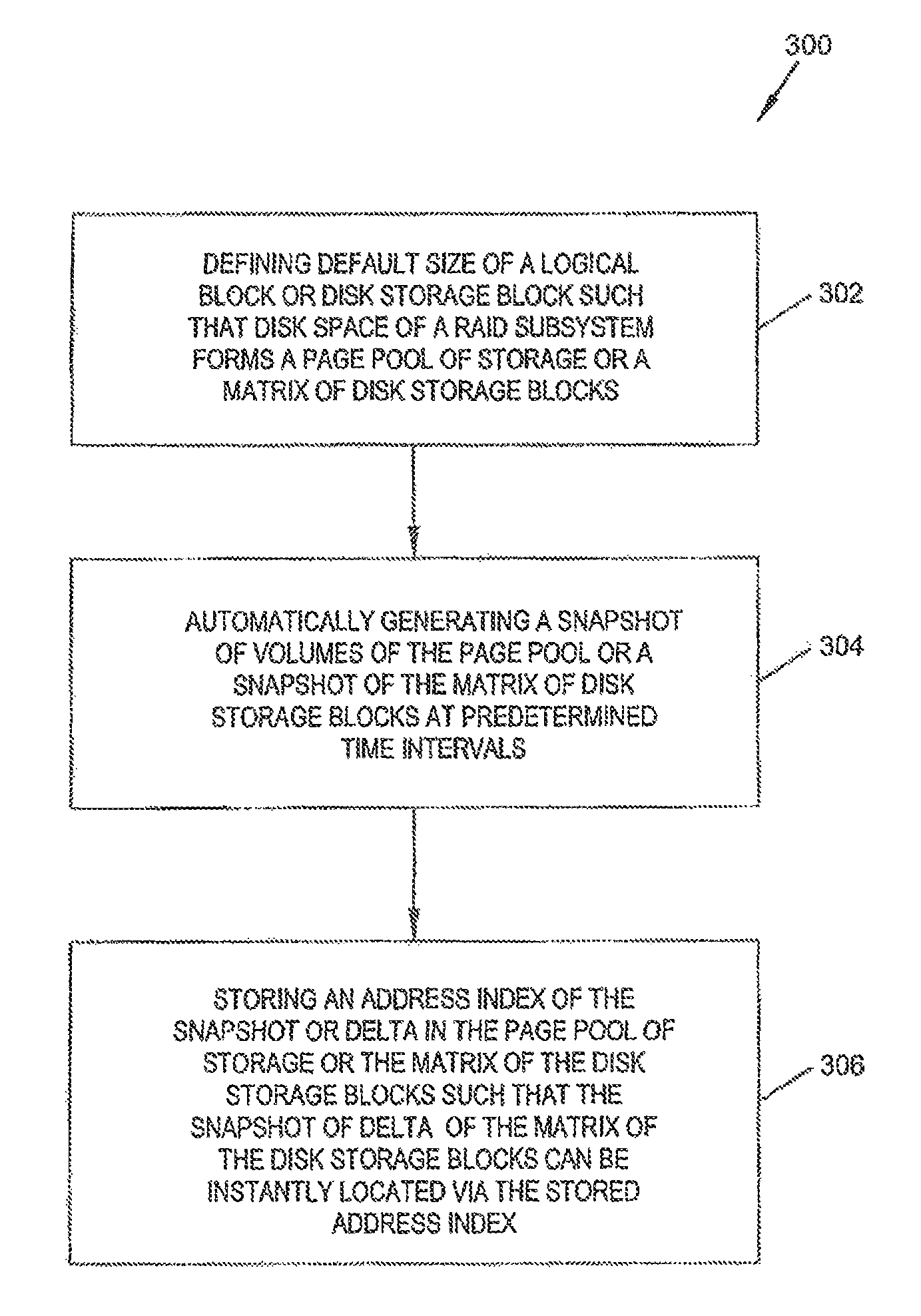
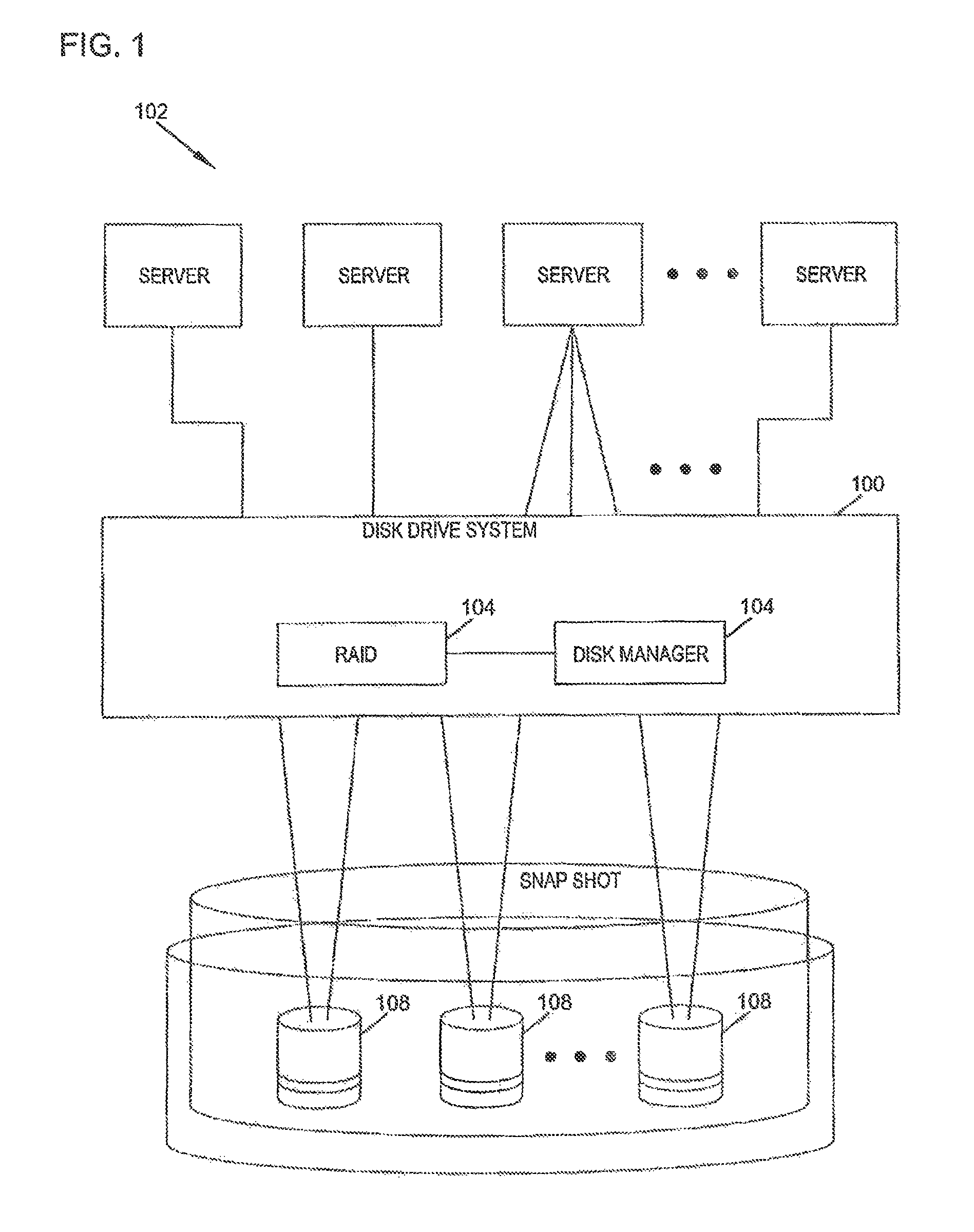
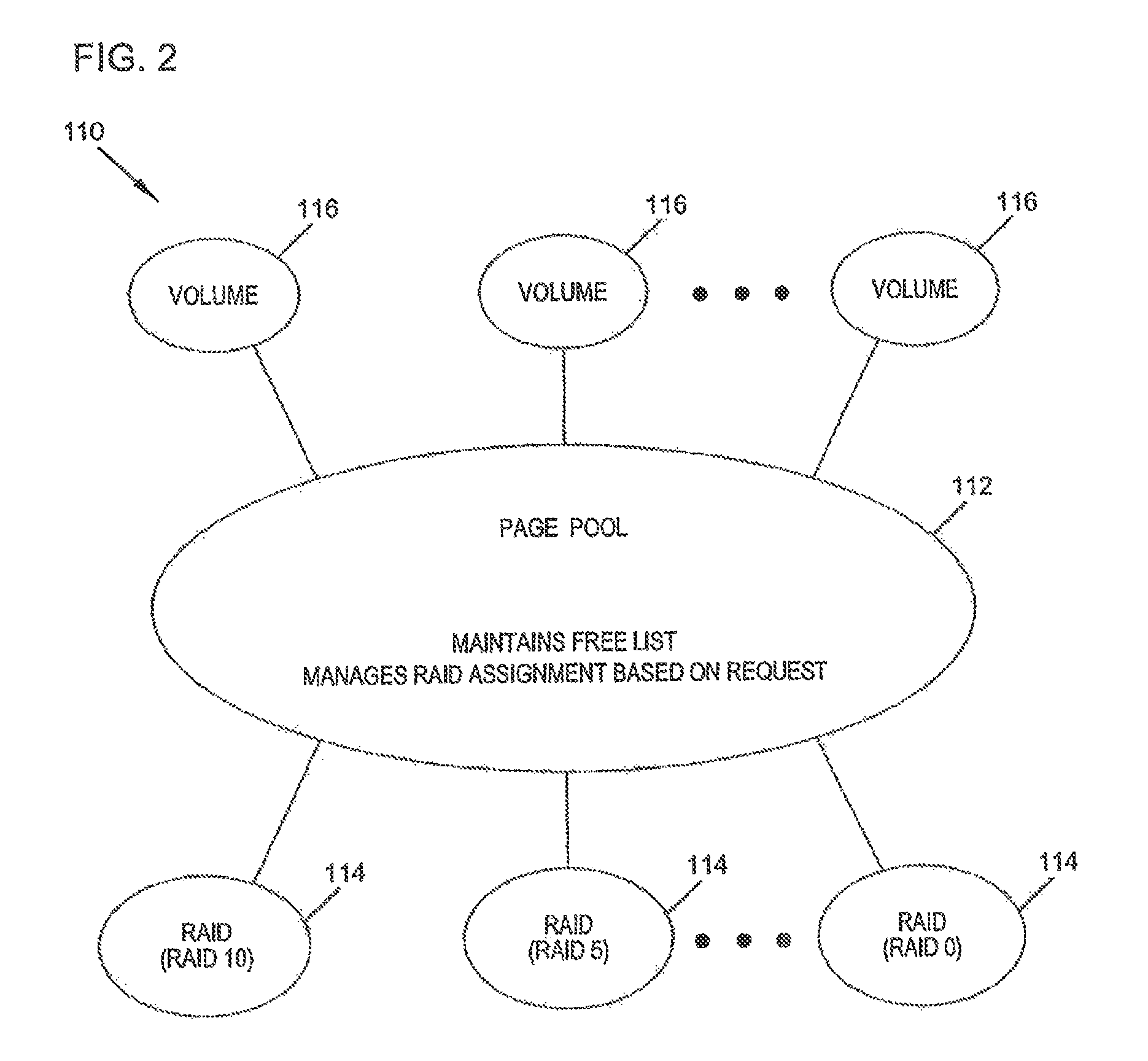
The present disclosure relates to a data storage system including a RAID subsystem having a first and second type of RAID storage. A virtual volume configured to accept I / O is stored on the first type of RAID storage, and snapshots of the virtual volume are stored on the second type of RAID storage. A method of the present disclosure includes providing an active volume that accepts I / O and generating read-only snapshots of the volume. In certain embodiments, the active volume is converted to a snapshot. The active volume includes a first type of RAID storage, and the snapshots include a second type of RAID storage. The first type of RAID storage has a lower write penalty than the second type of RAID storage. In typical embodiments, the first type of RAID storage includes RAID 10 storage and the second type of RAID storage includes RAID 5 and / or RAID 6 storage.
Owner:DELL INT L L C
Method to operate an imaging system, and imaging system
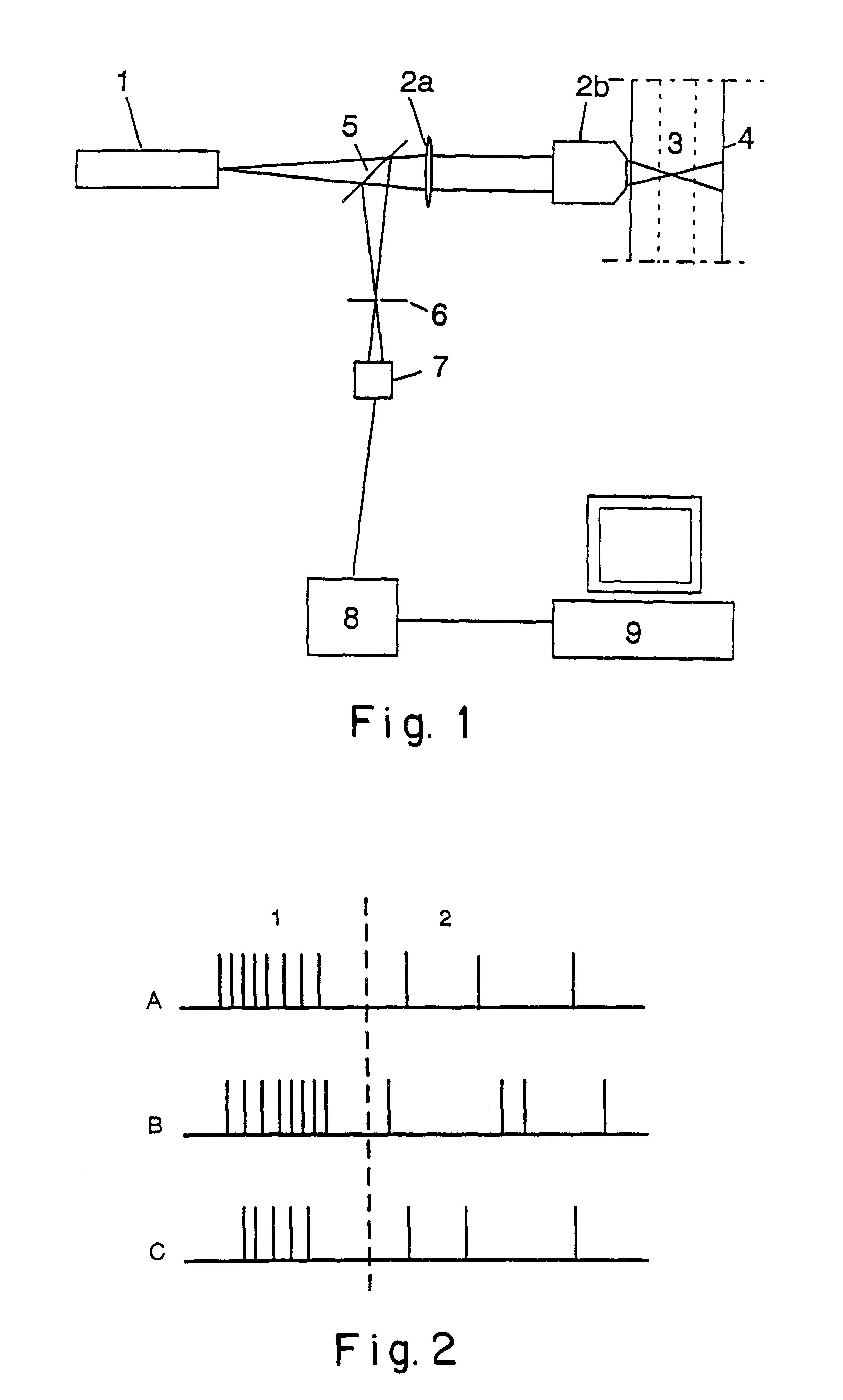
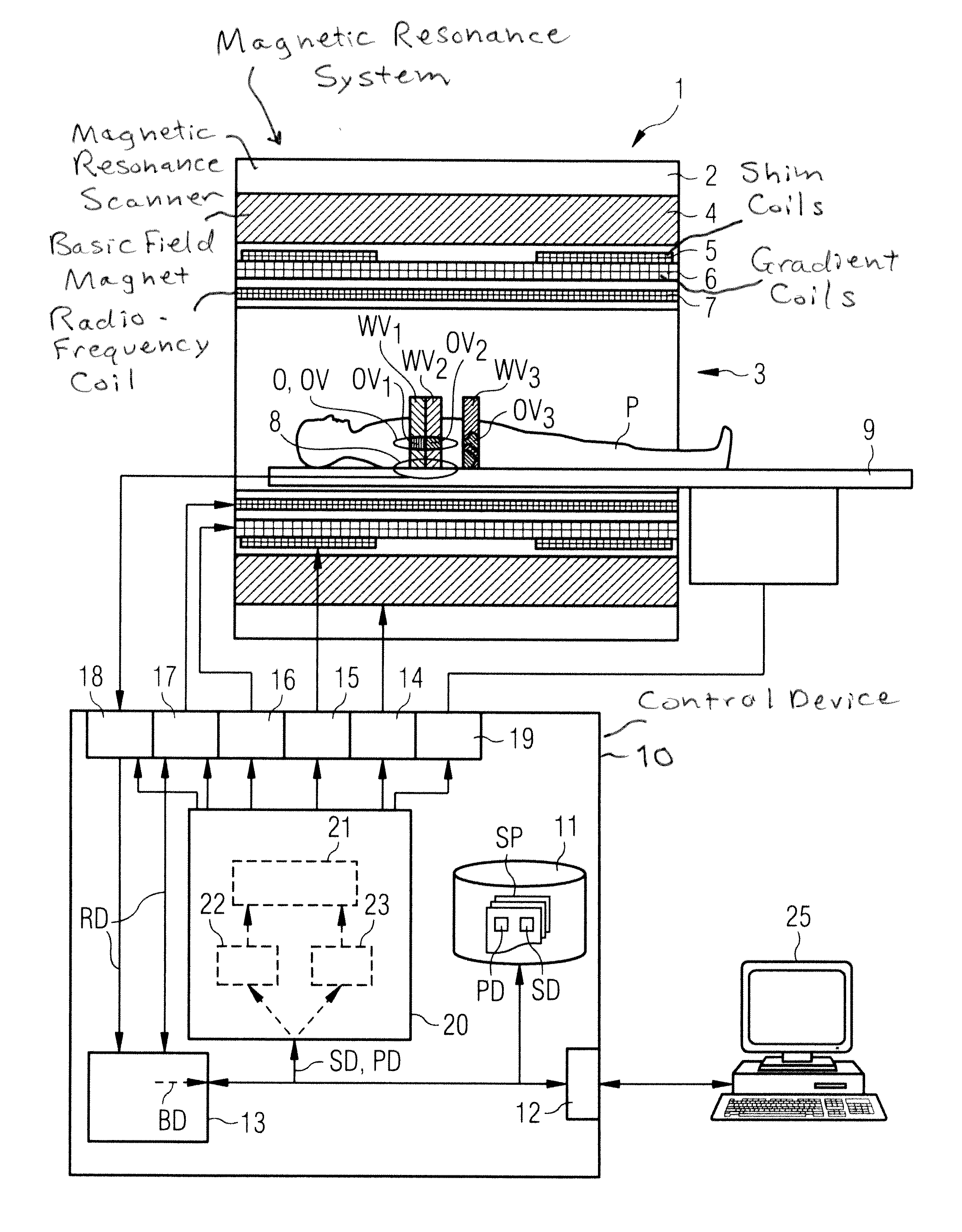
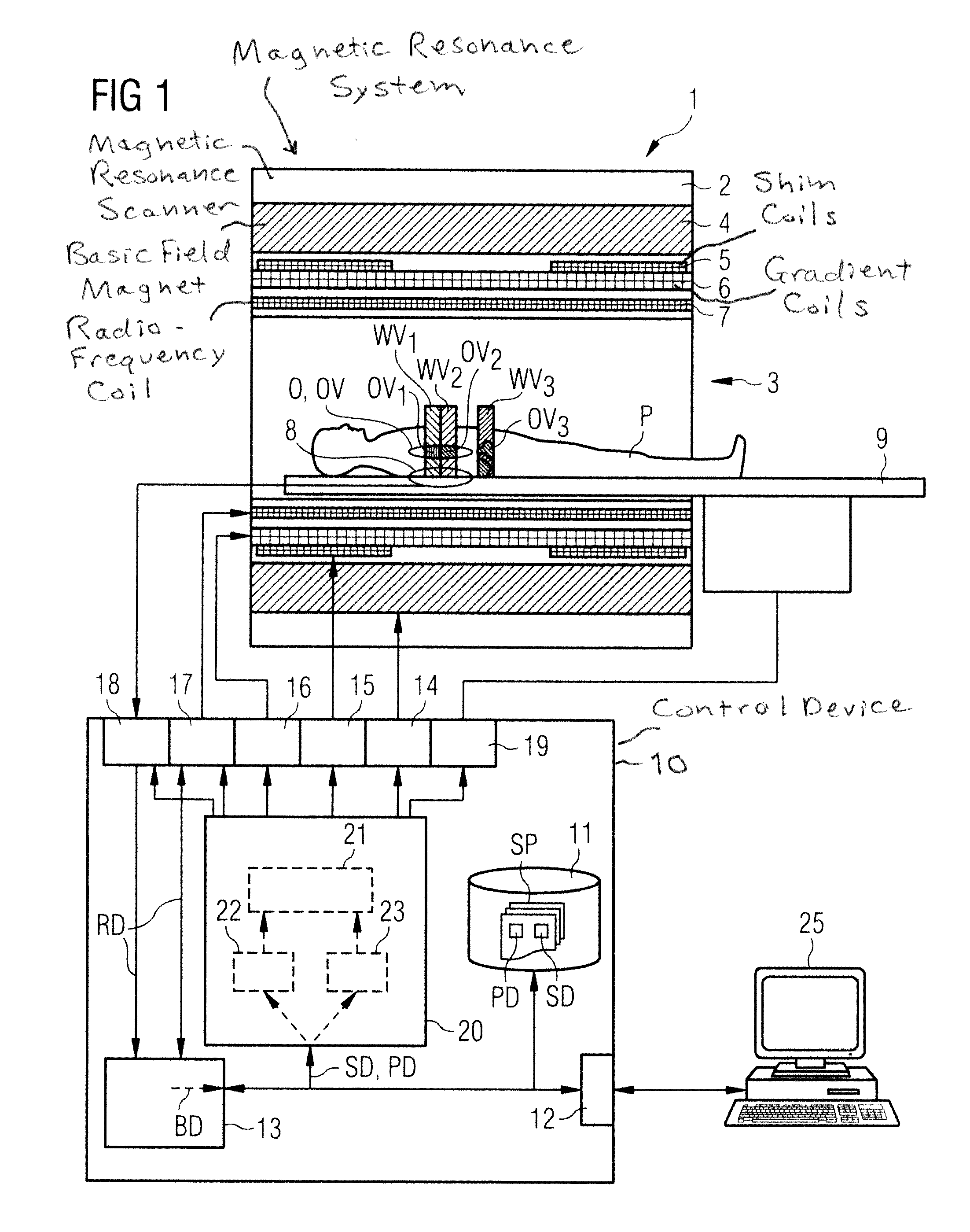
ActiveUS20100286802A1Quality improvementImprovement effortsDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSequence controlControl signal
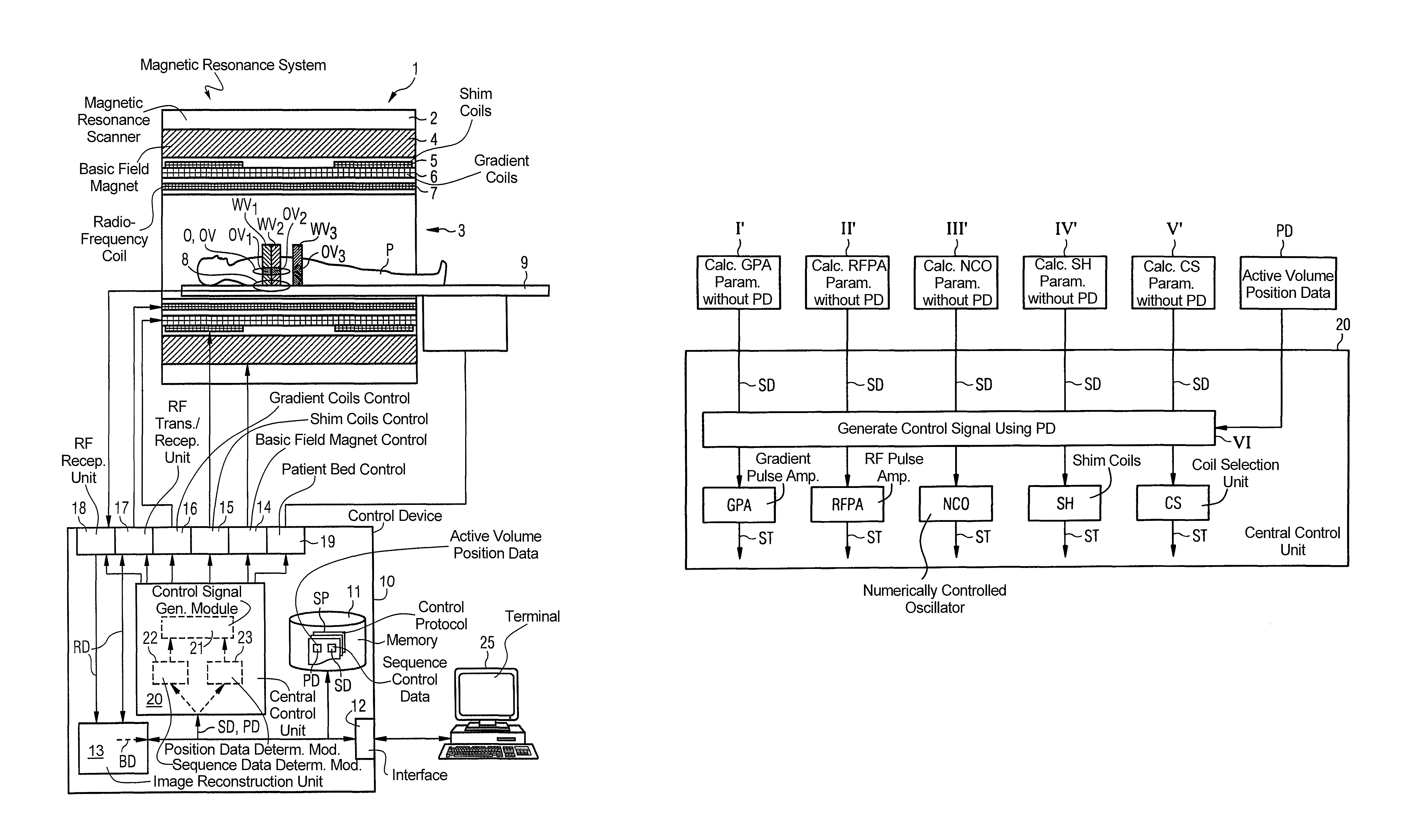
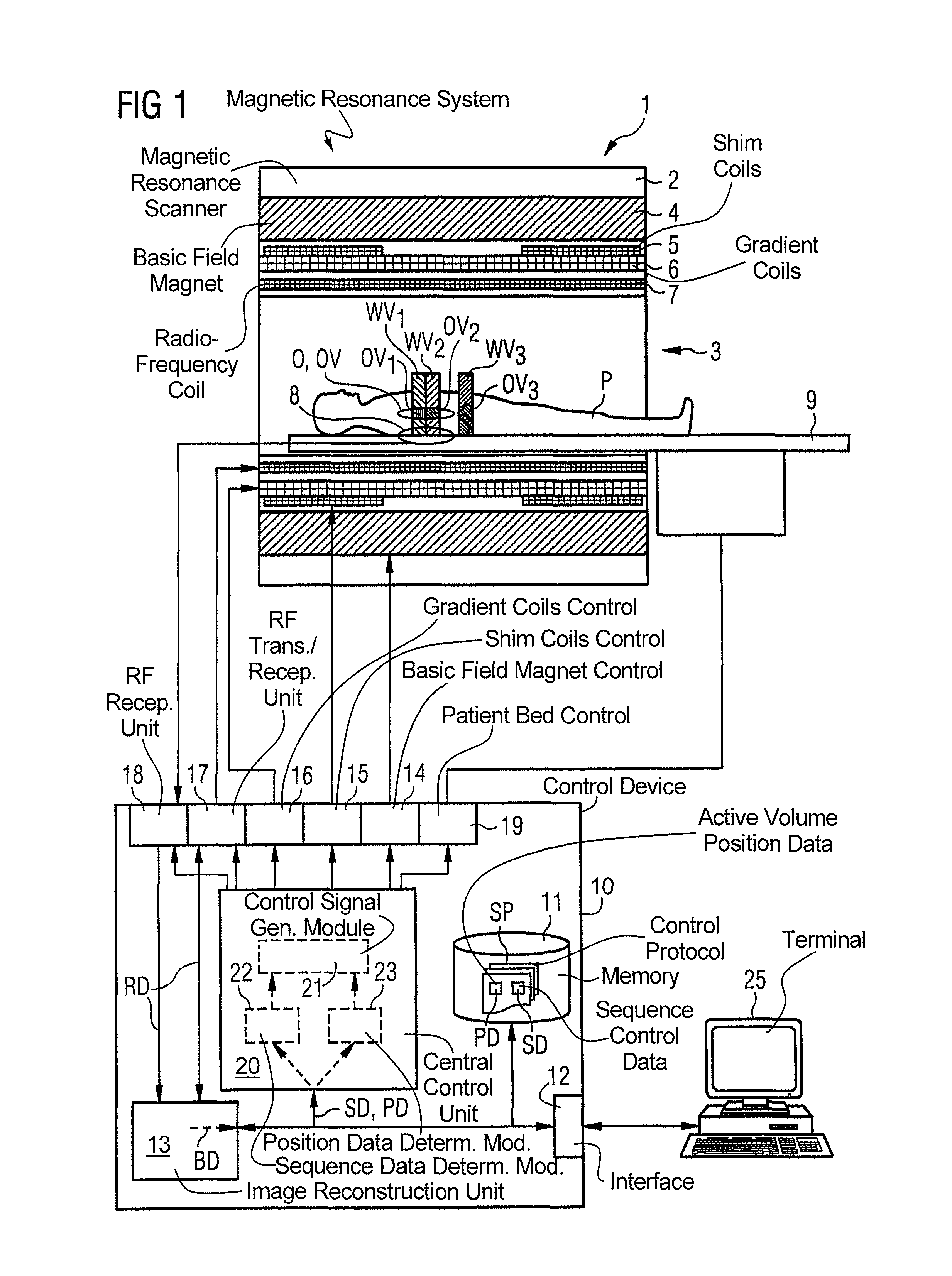
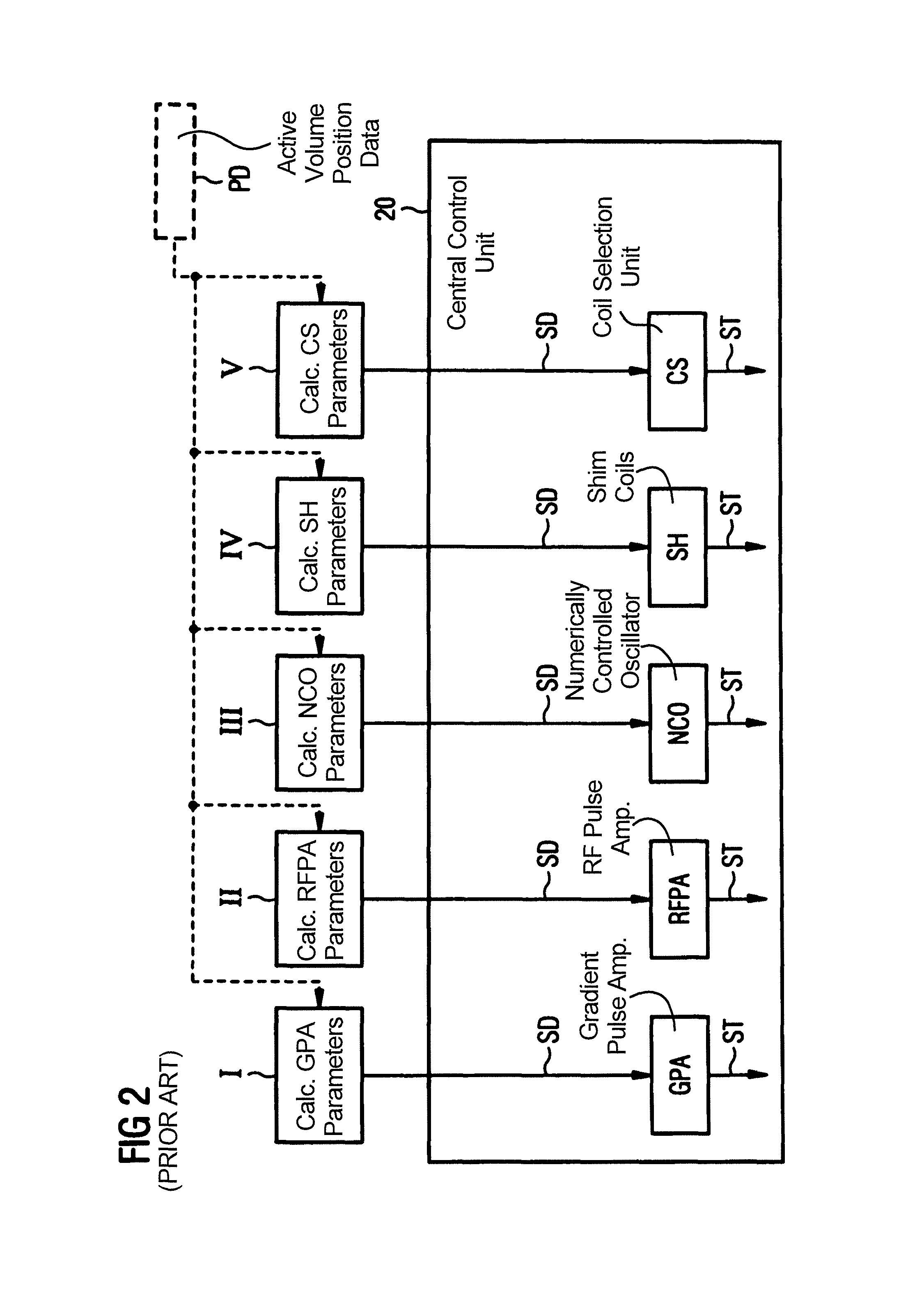
In an imaging system having a number of subsystems and a control device that controls the subsystems in a coordinated manner to implement a measurement sequence and an operating method therefor, sequence control data that define different functional sub-sequences of the measurement sequence are transmitted to the control device. Different active volumes are associated with the functional sub-sequences. In addition to the sequence control data, active volume position data are provided to the control device that define bearing and extent of the active volumes associated with the different functional sub-sequences. Control signals to implement the measurement sequence for the different subsystems are generated automatically by the control device based on the sequence control data and the active volume position data so that the individual functional sub-sequences are locally optimized at least with regard to a sub-region of their associated active volume.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Distillation methods and devices in particular for producing potable water
InactiveUS20060272933A1Improve efficiencyHigh densityGeneral water supply conservationAuxillariesEngineeringSeawater
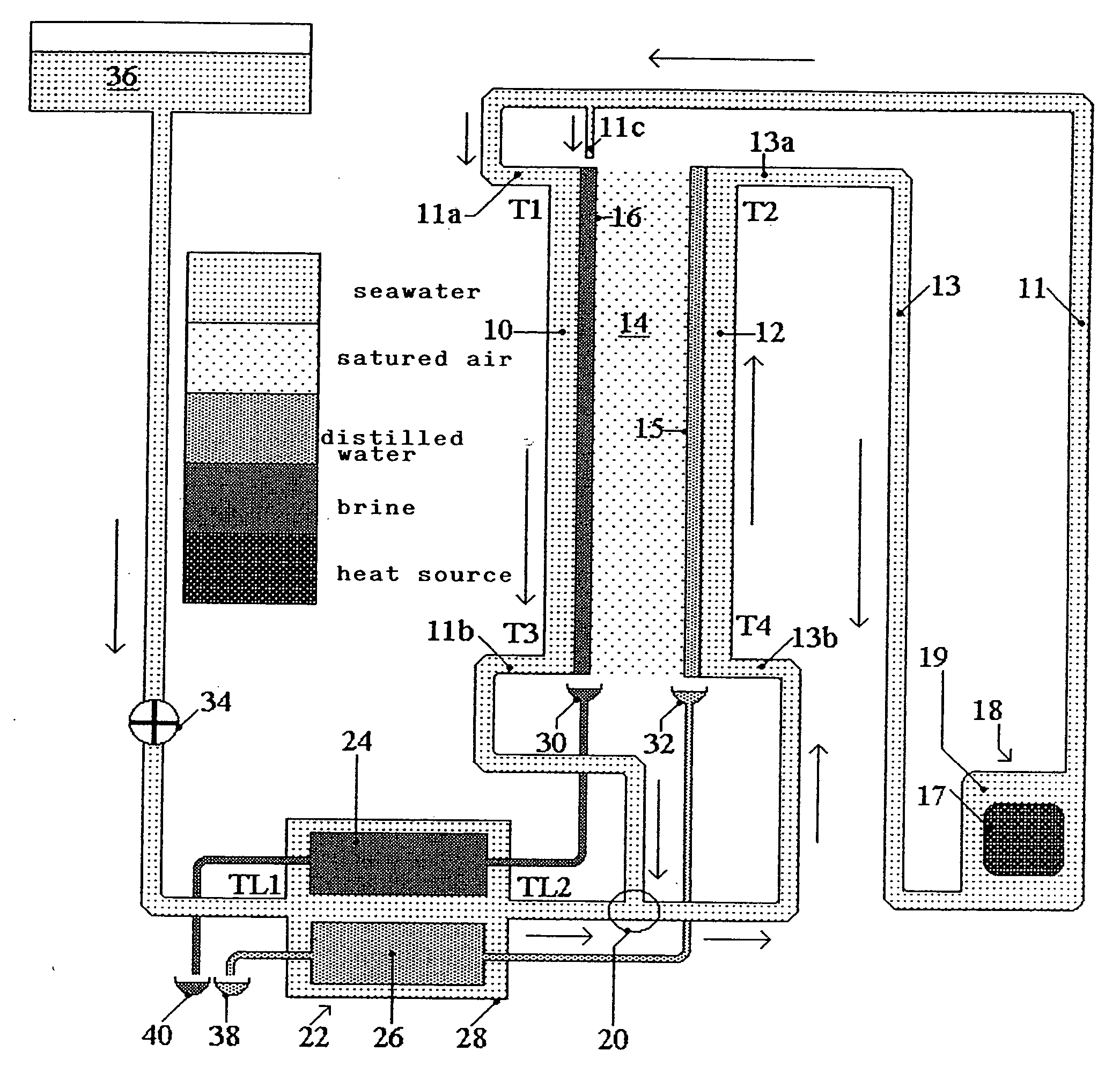
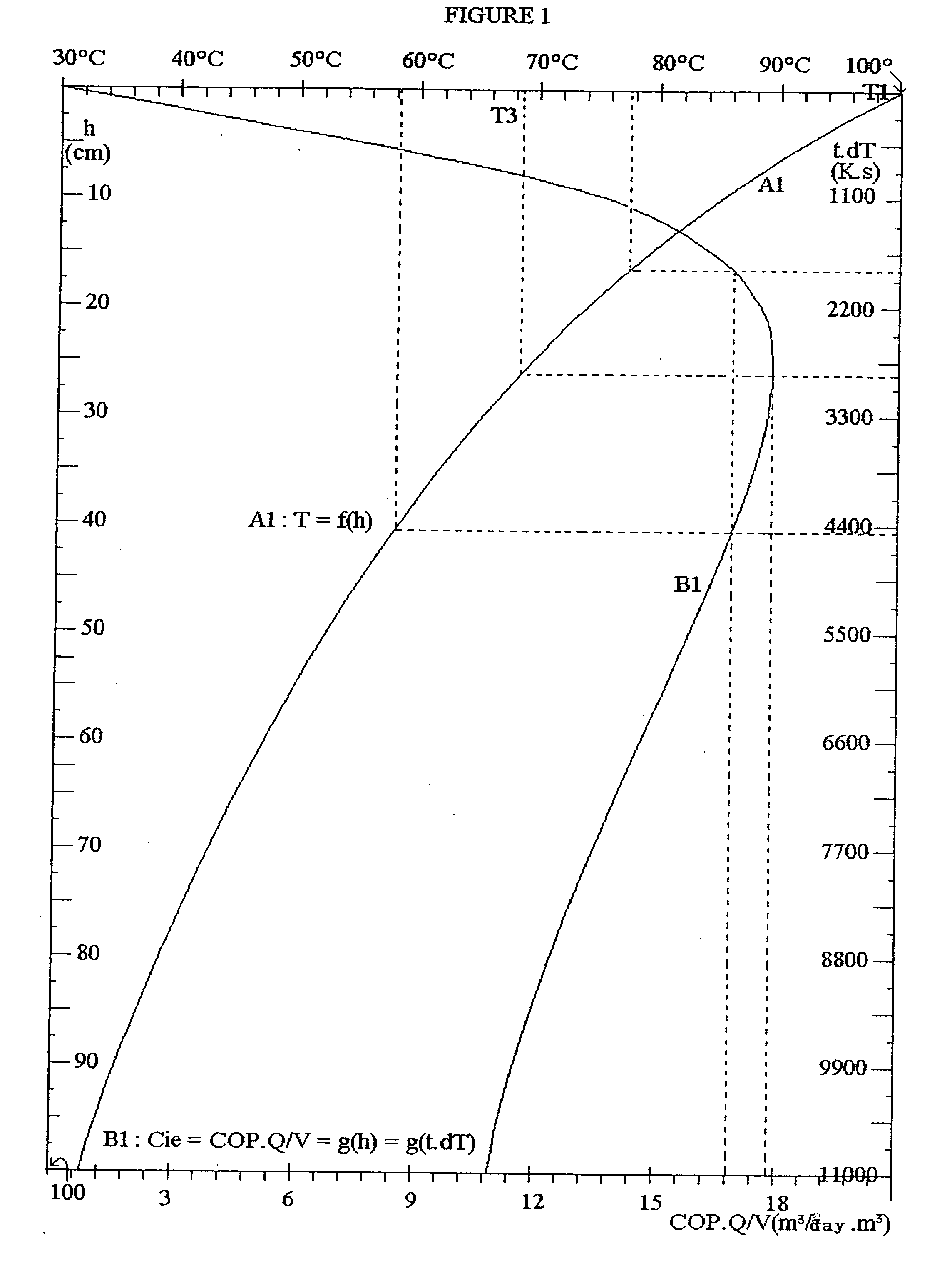
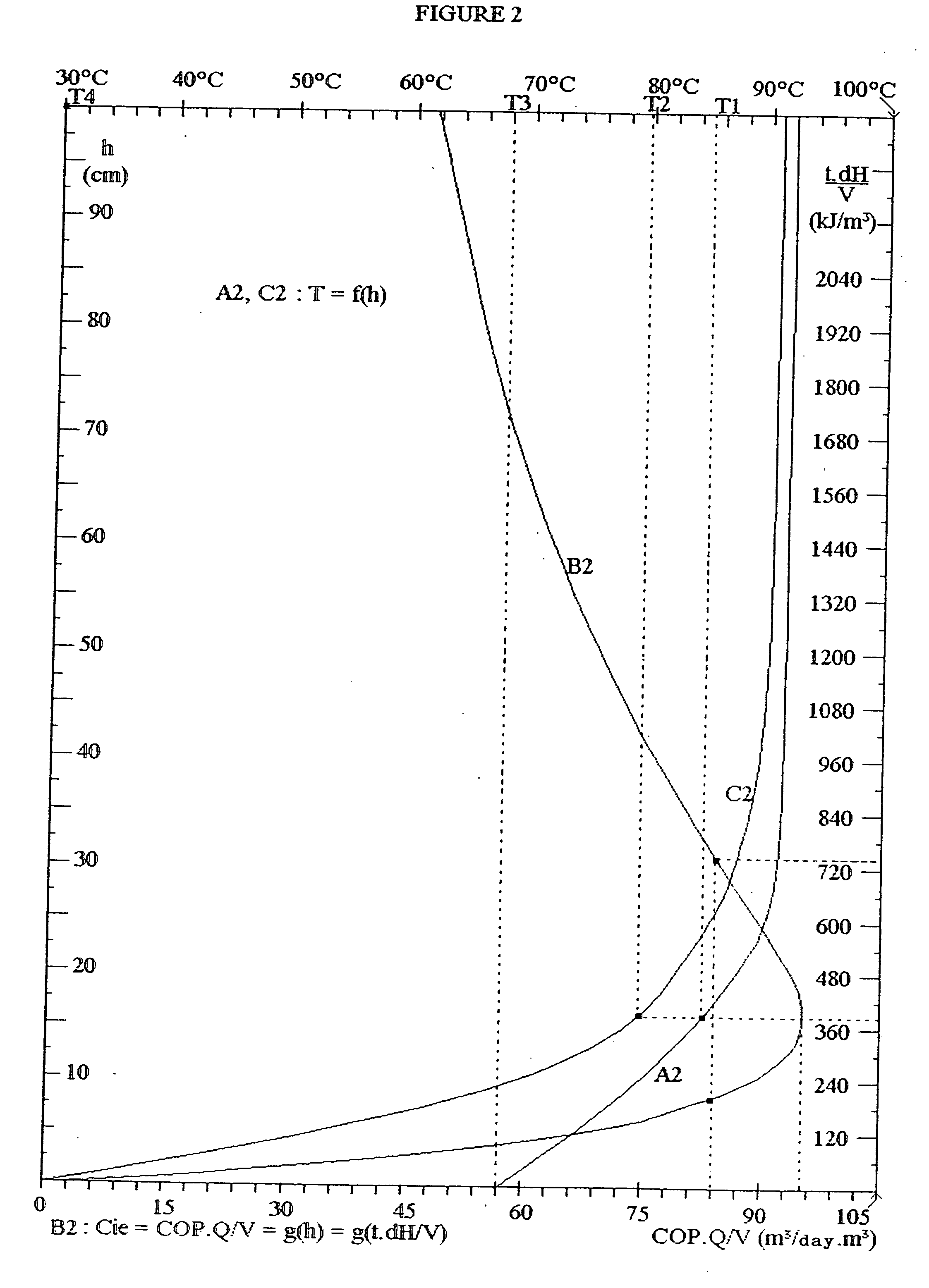
The inventive device is embodied in the form of a chamber-oven for diffusing vapour and saturated hot air which circulate in a closed circuit by natural convection. Said device is embodied in the form of a domestic-use solar energy collecting device provided with a greenhouse whose surface is equal to 1 m2 and produces from 50 to 100 litres / day of distilled water. The device comprises a distillation unit arranged between two furnaces (59′, 79′) in a temperature-controlled container (48′). Said distillation unit comprises 100 flat thin hollow plates having a surface of 20 dm2 by face and an active volume of 200 dm3. The fine and tensioned walls (54) of said plates are provided with a hydrophilic coating (60′) and internal (56′) and inter-plate (58′) spaces. The lower chimney (59′) comprises a greenhouse (118′, 119′) whose bottom is embodied in the form of an impermeable black layer provided with a thin hydrophilic carpet on the rear part thereof. Saturated hot air at a temperature of 80° C. enters inside (56′) hollow plates from bellow and exits from the top at a temperature of 50° C. A high chimney (79′) is provided with a monoblock heat exchanger (84′) which is transversed by a non-potable water to be distilled which, afterwards is spread warm (40° C.) over the hydrophilic coating (60′). During passage through the heat exchanger (84) the air is cooled to 30° C. and moved down by gravity to the inter-plate spaces (58′) and exits therefrom at a temperature of 78° C. The distilled water condensed in the plates and by the heat exchanger is collected and removed. Brine is received in the bottom of the inter-plate space and distributed along the thin hydrophilic carpet of the bottom (122′) of the greenhouse. An air current passes along said hot carpet is heated and saturated and enters the plates. The brine liquor finally flows in an air-preheating tank (63′) which is emptied each morning. The greenhouse can be substituted by a heating tube transversed by a heating fluid or associated with another steam-jet tube. The more powerful chamber-ovens can produce at least 200 m3 / day of distilled water for collective consumption. Said invention can be used for salt removal from seawater, co-generating electricity and potable water and for producing food concentrates.
Owner:THE THIRD MILLENIUM WATER
Active volume energy level large scale sub-sea energy fluids storage methods and apparatus for power generation and integration of renewable energy sources
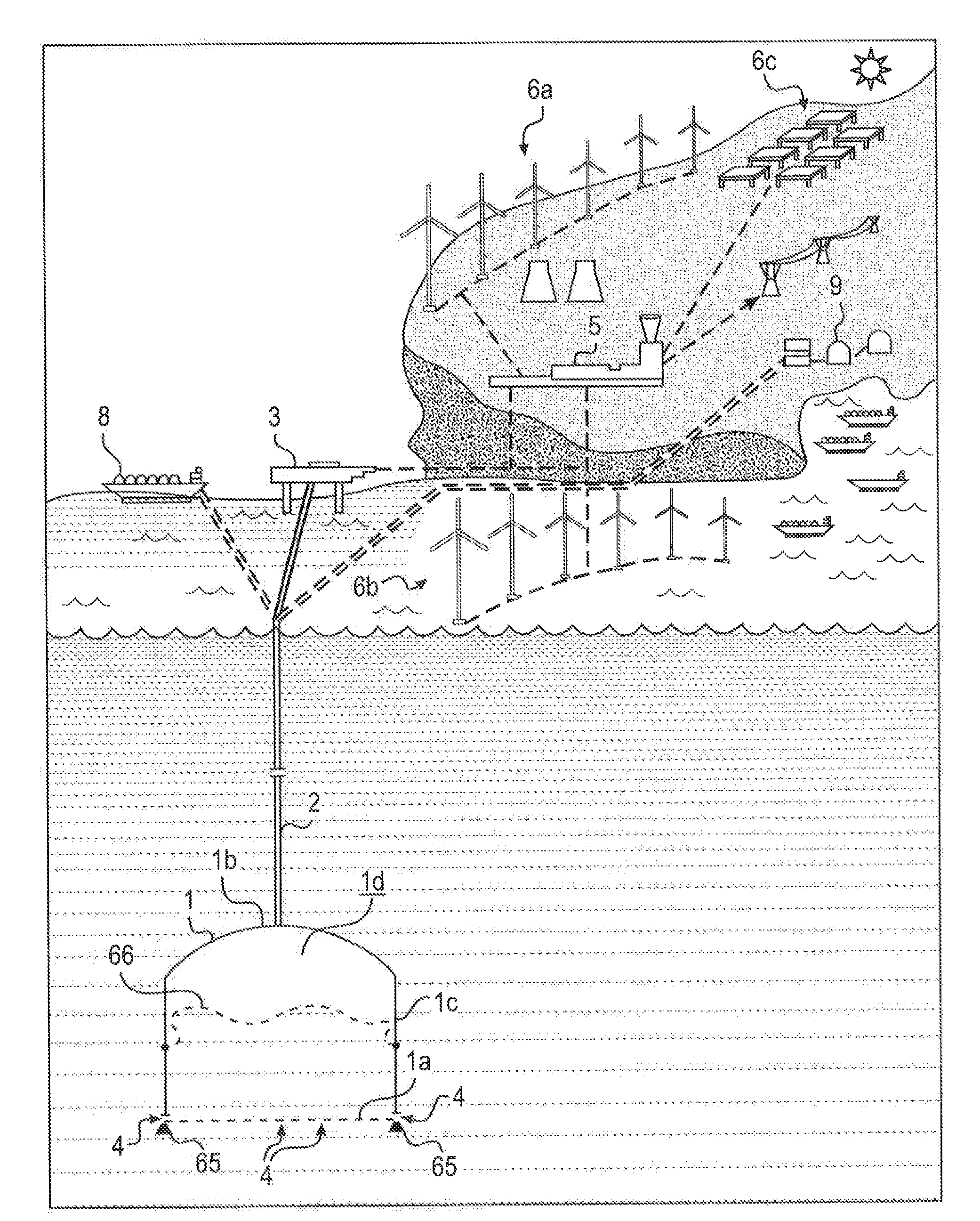
InactiveUS20140261132A1Low costLow-cost materialSeawater treatmentGas handling applicationsEngineeringLiquid gas
Systems and methods for storing energy in gaseous form in submerged thin-walled tanks are secured to the ocean or lake floor but are open to the water at the tank bottoms and are configured to be filled with gas while submerged.A conduit operatively connected to the tanks provides flow from a surface source of an energy-containing gas to the tank interiors. Surface or subsurface pumping apparatus which may include piston-less pressure cylinders or have leveraged pistons provide a preselected flow rate of the energy-containing gas into the containment structure interior against a back pressure essentially equal to the static pressure of the body of water at the location of the tank to displace an equivalent volume of water through the open bottom. The conduit can be configured to allow heat transfer to vaporize liquefied gas prior to storage. Hydrogen gas can be generated and stored within the tank using Aluminum activated with Galinstan.
Owner:KONUKOGLU ZEKERIYE +2
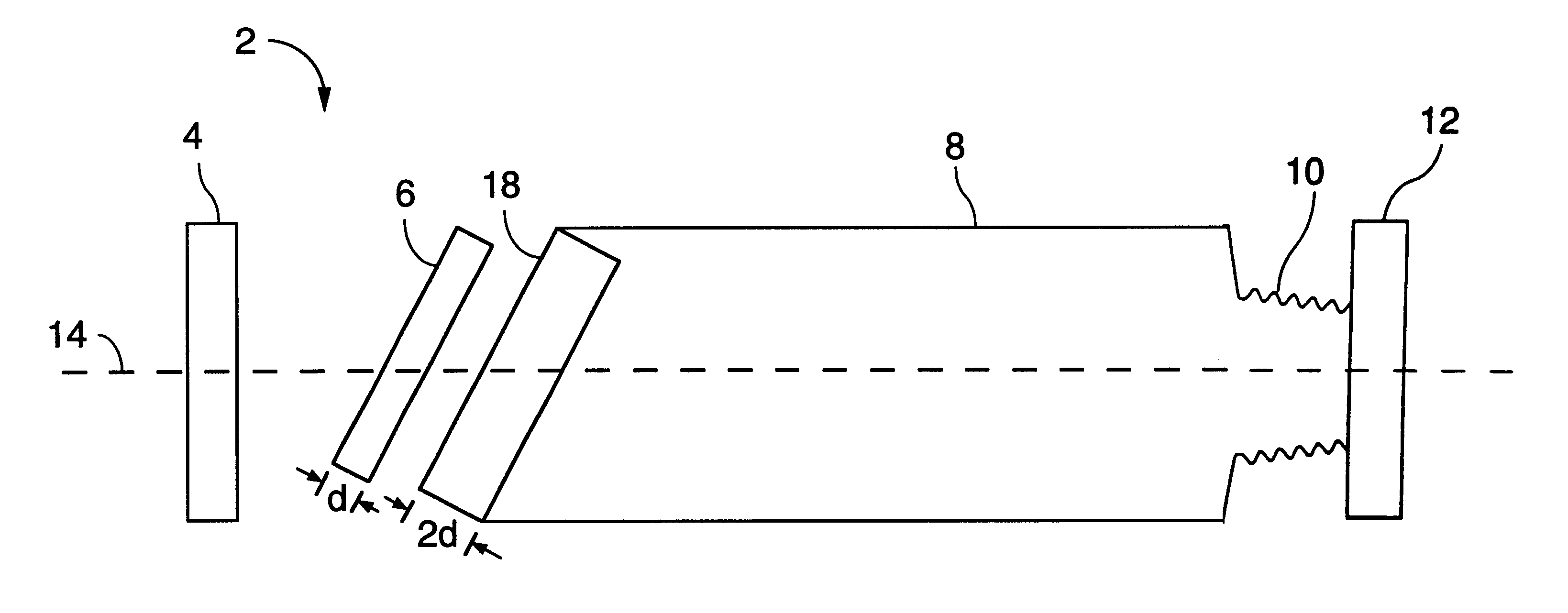
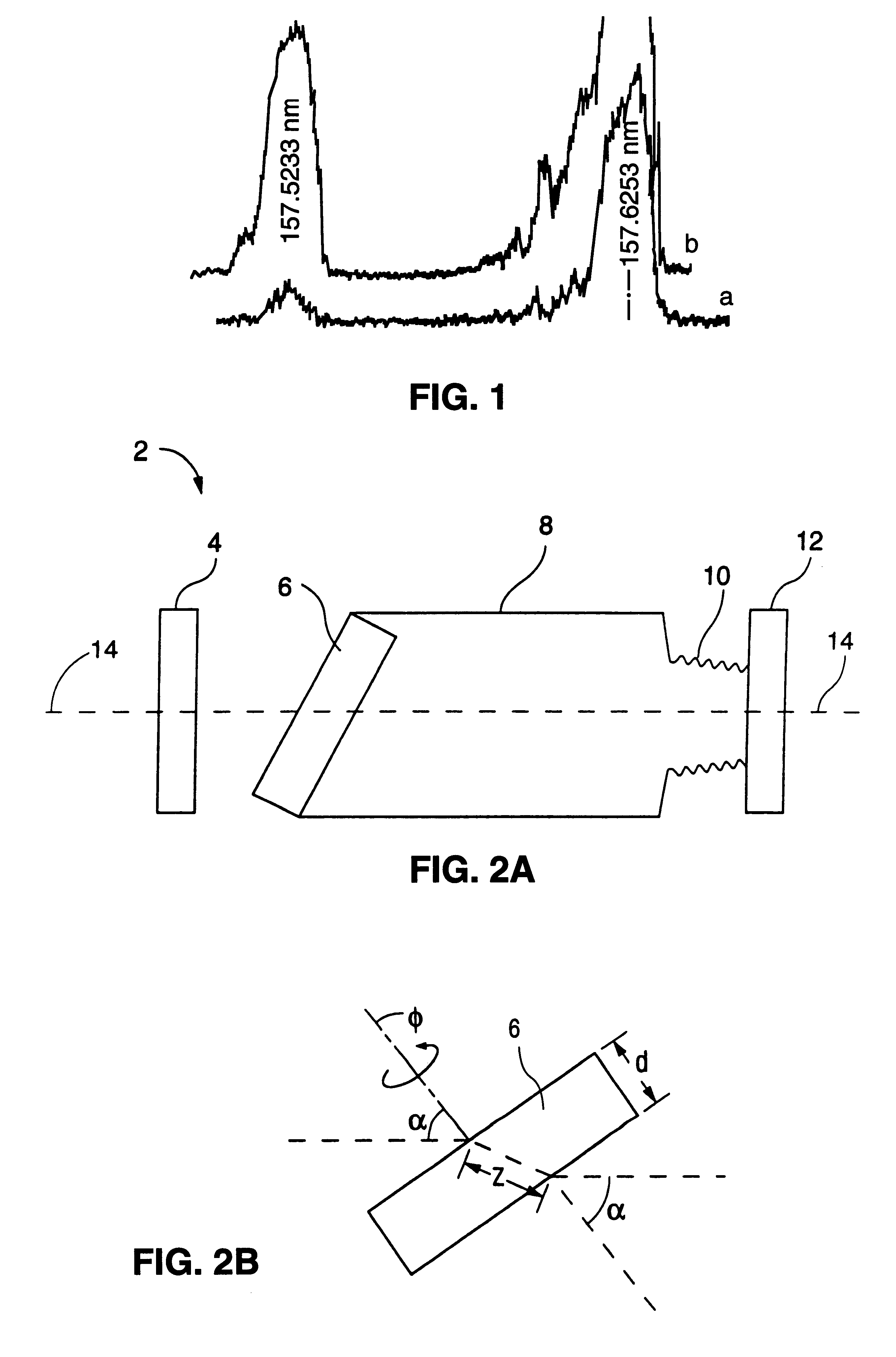
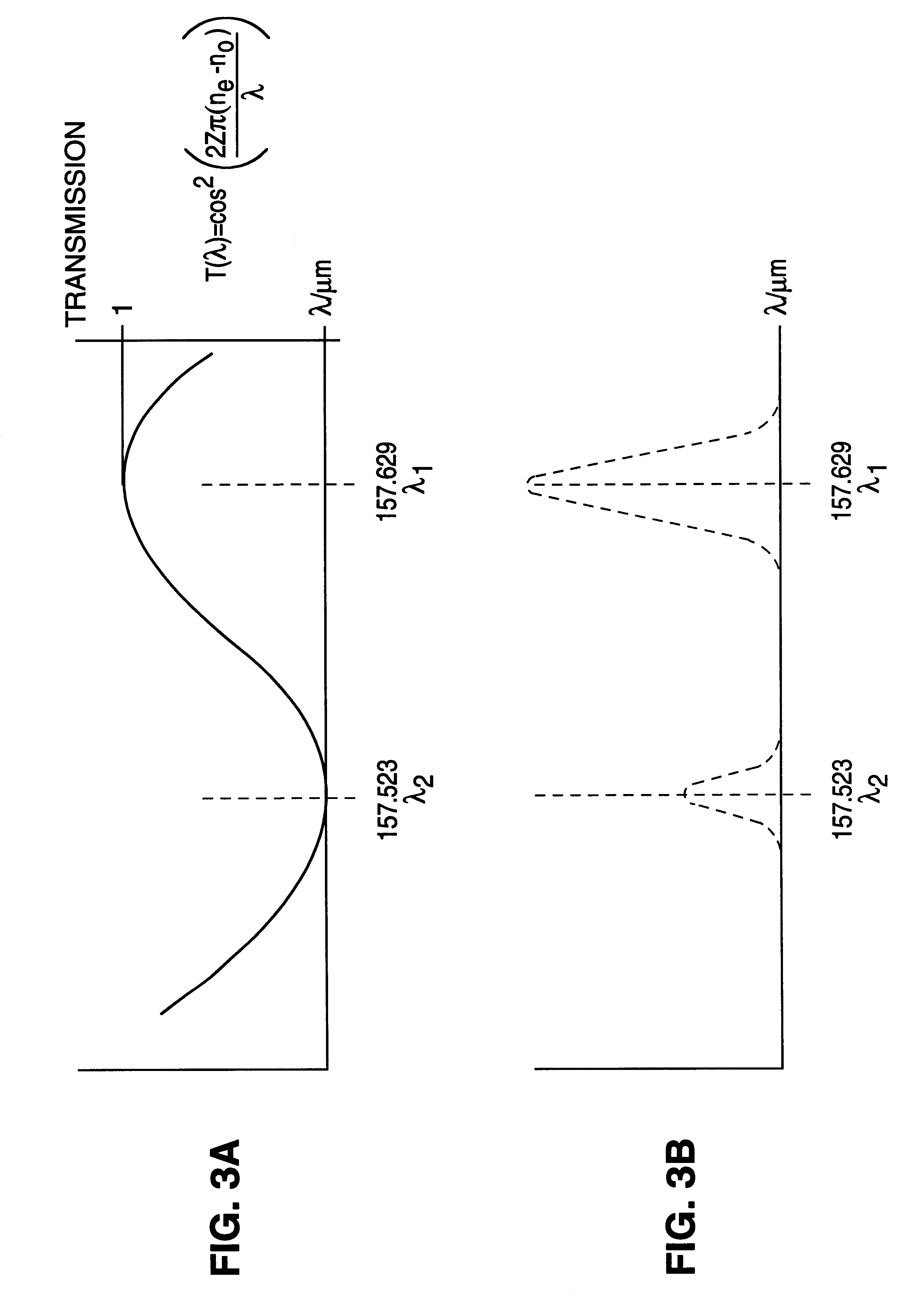
F2-laser with line selection
InactiveUS6345065B1Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialDischarge efficiencyRefractive index
An F2-excimer laser has multiple closely-spaced spectral lines of interest around 157 nm, and one of the lines is selected by wavelength selection optics. The wavelength selection optics of a first preferred embodiment include a birefringent Brewster window enclosing the laser gas volume of the discharge chamber. The window preferably comprises MgF2 and is located at one end of the discharge chamber. One line is selected of the two when the optical thickness of the window is selected in coordination with rotatably adjustable, orthogonal refractive indices of the window. The transmissivity of the window is dependent on the orthogonal refractive indices and the optical thickness of the window. The wavelength selection optics of a second preferred embodiment include are at least partially within the laser active volume. In this way, line selection is performed in a manner which optimizes the combination of optical and discharge efficiency, resonator size and cost. The wavelength selection unit preferably includes a prism having a front surface oriented at Brewster's angle and a back surface oriented to receive and reflect an ordinary refracted ray travelling within the prism at a right angle to the back surface. The back surface also preferably includes a highly reflective coating to serve as the highly reflective surface of the resonator. The wavelength selection unit preferably further comprises an adjustment component for adjusting the orientation of the prism and for enclosing the other end of the housing, opposite the outcoupling end.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
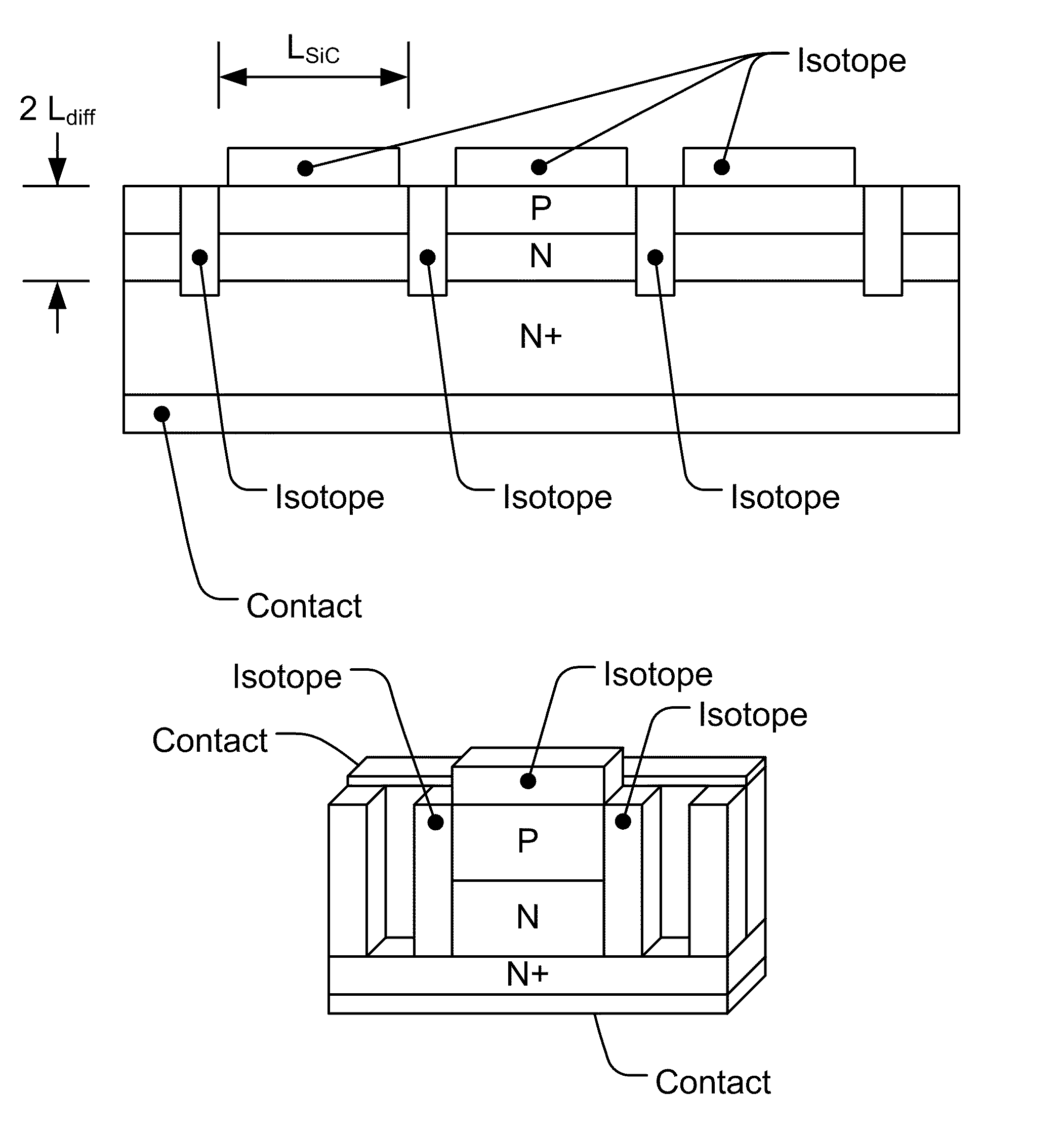
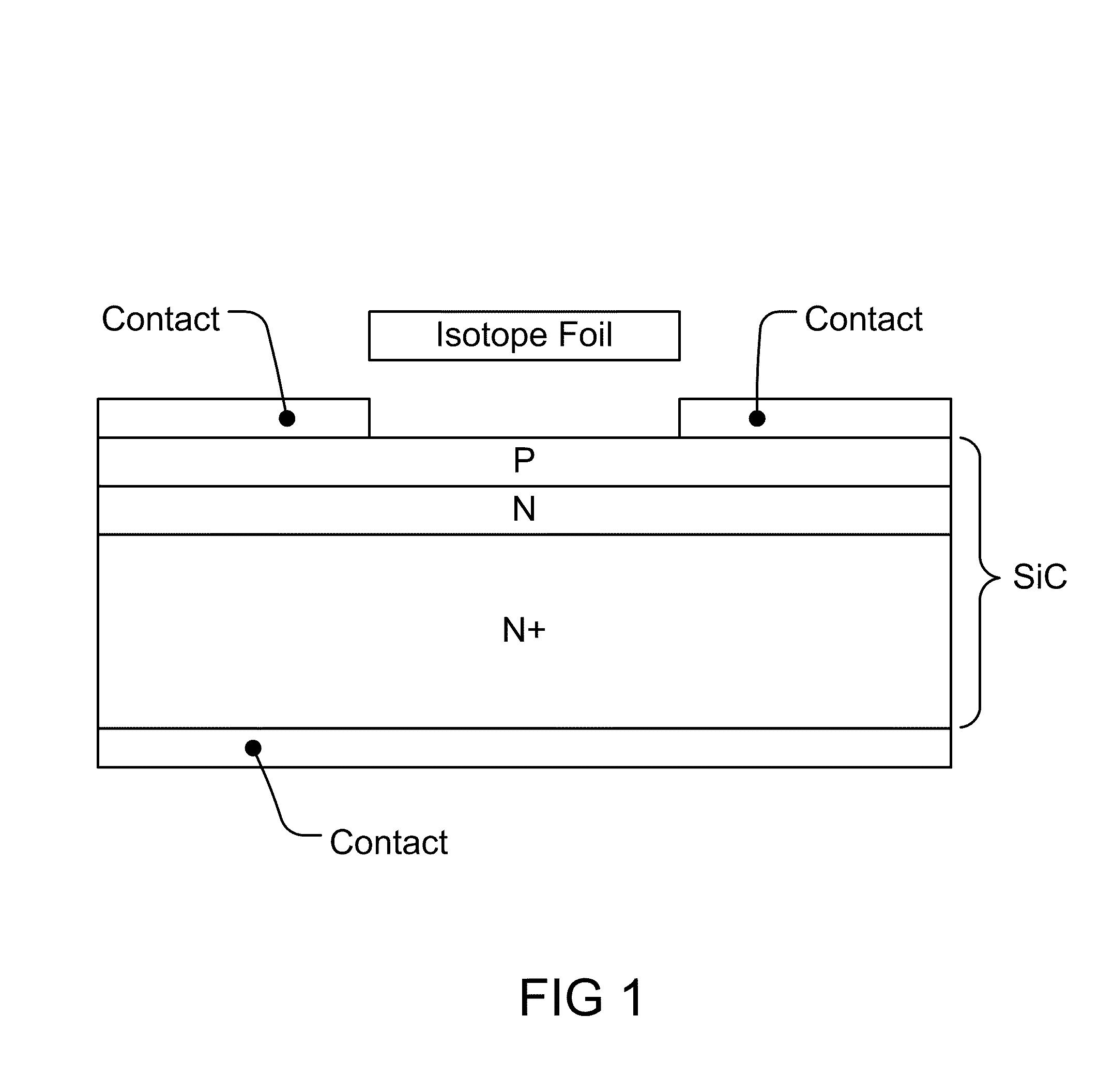
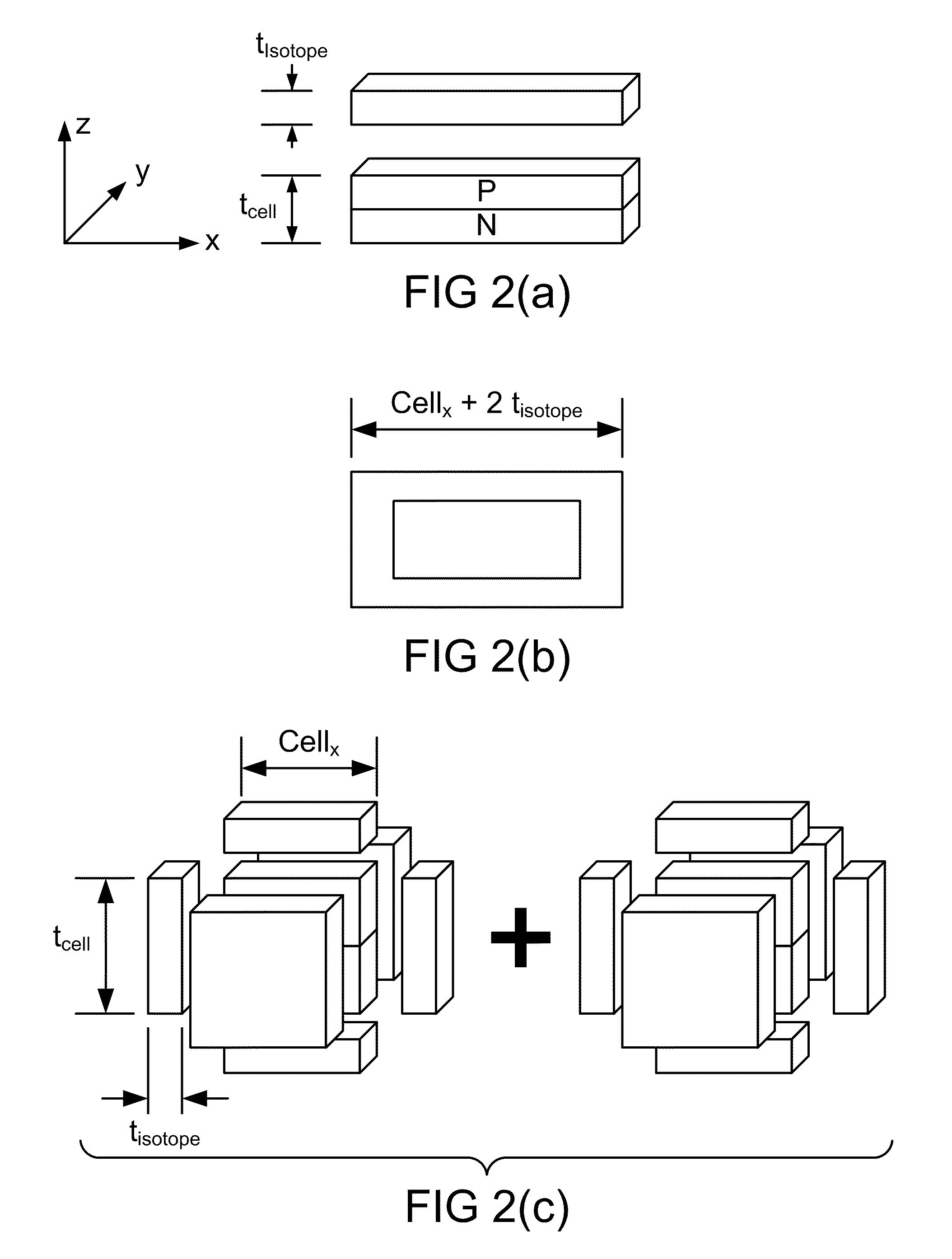
Nuclear batteries
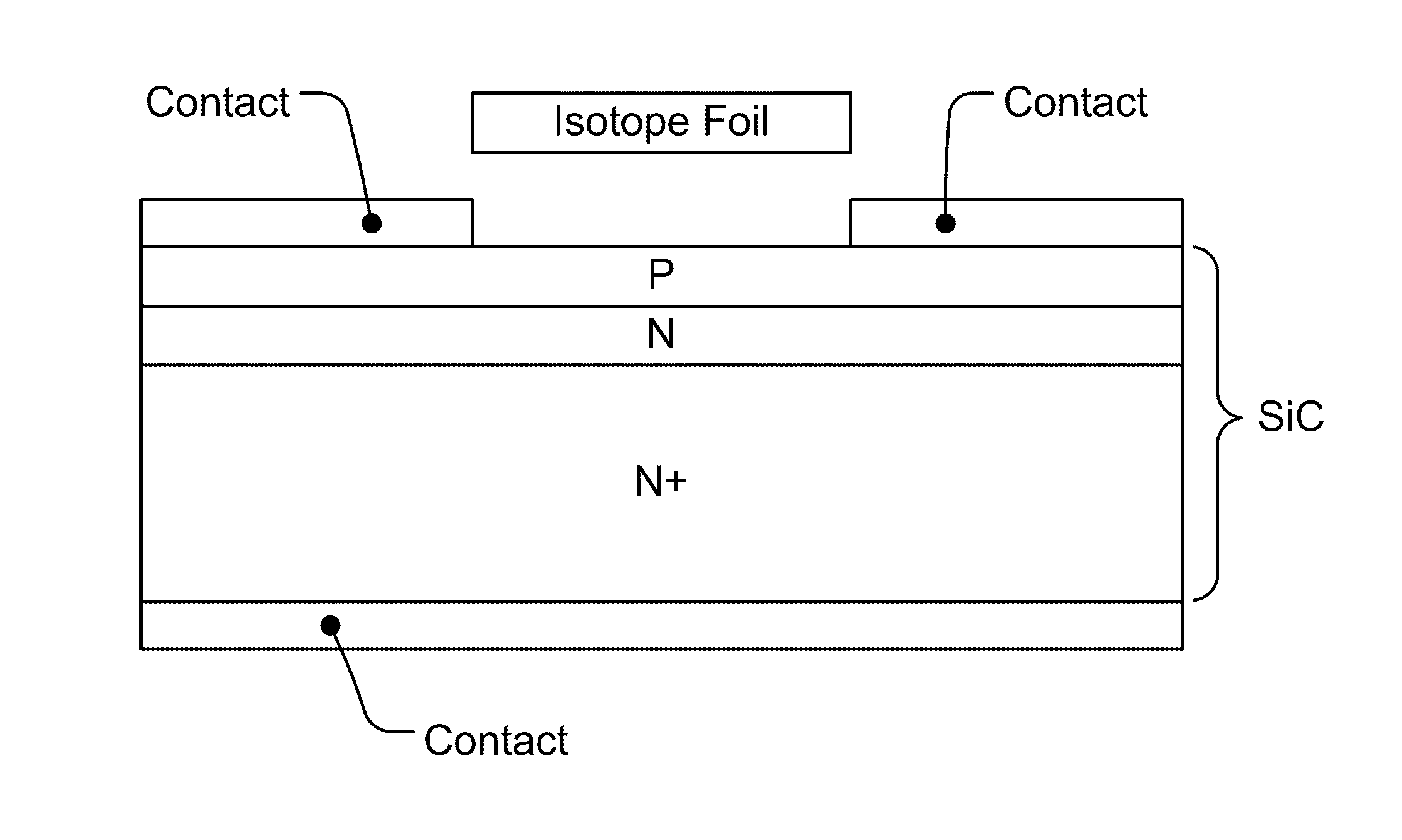
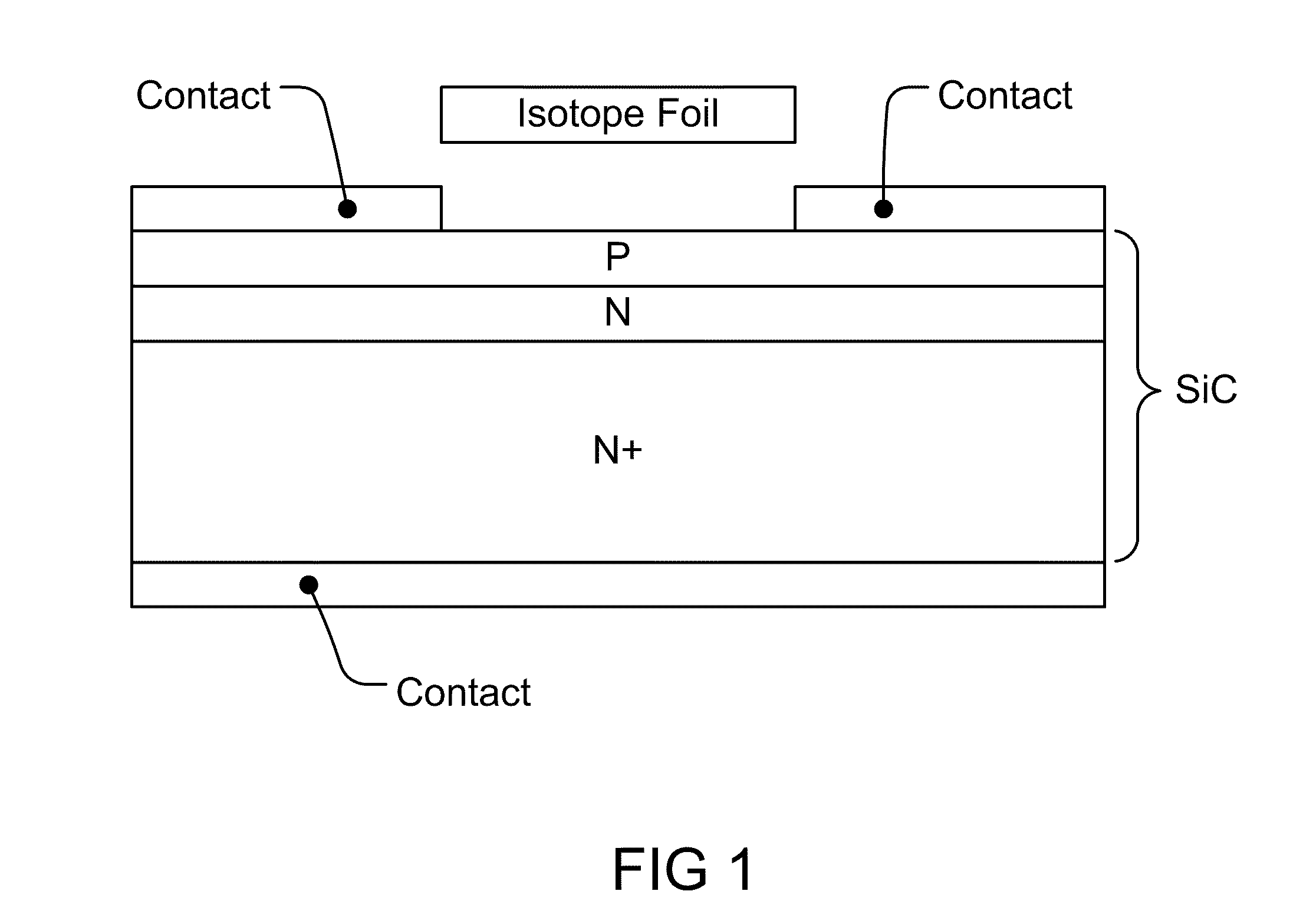
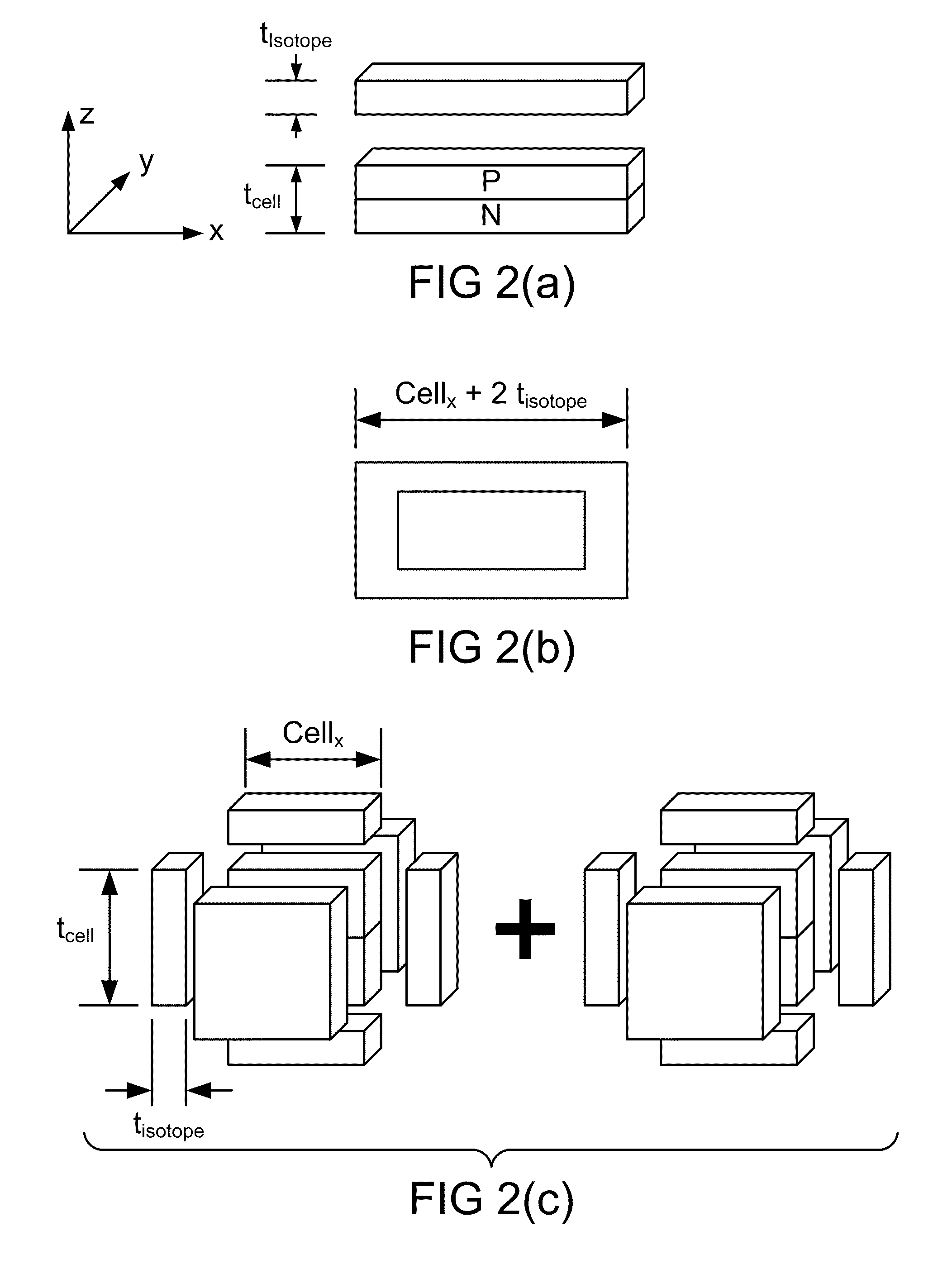
ActiveUS8134216B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIsotopeEngineering
We introduce a new technology for Manufacturable, High Power Density, High Volume Utilization Nuclear Batteries. Betavoltaic batteries are an excellent choice for battery applications which require long life, high power density, or the ability to operate in harsh environments. In order to optimize the performance of betavoltaic batteries for these applications or any other application, it is desirable to maximize the efficiency of beta particle energy conversion into power, while at the same time increasing the power density of an overall device. The small (submicron) thickness of the active volume of both the isotope layer and the semiconductor device is due to the short absorption length of beta electrons. The absorption length determines the self absorption of the beta particles in the radioisotope layer as well as the range, or travel distance, of the betas in the semiconductor converter which is typically a semiconductor device comprising at least one PN junction. Various devices and methods to solve the current industry problems and limitations are presented here.
Owner:WIDETRONIX
Nuclear Batteries
ActiveUS20110241144A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIsotopeP–n junction
We introduce a new technology for Manufactureable, High Power Density, High Volume Utilization Nuclear Batteries. Betavoltaic batteries are an excellent choice for battery applications which require long life, high power density, or the ability to operate in harsh environments. In order to optimize the performance of betavoltaic batteries for these applications or any other application, it is desirable to maximize the efficiency of beta particle energy conversion into power, while at the same time increasing the power density of an overall device. The small (submicron) thickness of the active volume of both the isotope layer and the semiconductor device is due to the short absorption length of beta electrons. The absorption length determines the self absorption of the beta particles in the radioisotope layer as well as the range, or travel distance, of the betas in the semiconductor converter which is typically a semiconductor device comprising at least one PN junction. Various devices and methods to solve the current industry problems and limitations are presented here.
Owner:WIDETRONIX
Hydrogenation reaction system and method
ActiveCN103773490AIncrease the effective volumeReduce in quantityTreatment with hydrotreatment processesChemical/physical processesHydrogenation reactionSolid particle
The invention discloses a hydrogenation reaction system adopting a boiling bed reactor. The hydrogenation reaction system comprises a feeding unit, a boiling bed reactor and a separating unit; the invention also discloses a method for treating direct coal liquefaction effluents by use of the hydrogenation reaction system. The active volume of the reactor is increased, and the operating flexibility and the stability are improved; and besides, a separating device is arranged in a circulating unit of the boiling bed reactor, the content of solid particles in feeding materials of the circulating pump is reduced, the abrasion to the circulating pump is reduced and the service life of the circulating pump is prolonged.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +1
System and method for transferring data between different raid data storage types for current data and replay data
The present disclosure relates to a data storage system including a RAID subsystem having a first and second type of RAID storage. A virtual volume configured to accept I / O is stored on the first type of RAID storage, and snapshots of the virtual volume are stored on the second type of RAID storage. A method of the present disclosure includes providing an active volume that accepts I / O and generating read-only snapshots of the volume. In certain embodiments, the active volume is converted to a snapshot. The active volume includes a first type of RAID storage, and the snapshots include a second type of RAID storage. The first type of RAID storage has a lower write penalty than the second type of RAID storage. In typical embodiments, the first type of RAID storage includes RAID 10 storage and the second type of RAID storage includes RAID 5 and / or RAID 6 storage.
Owner:COMPELLENT TECH
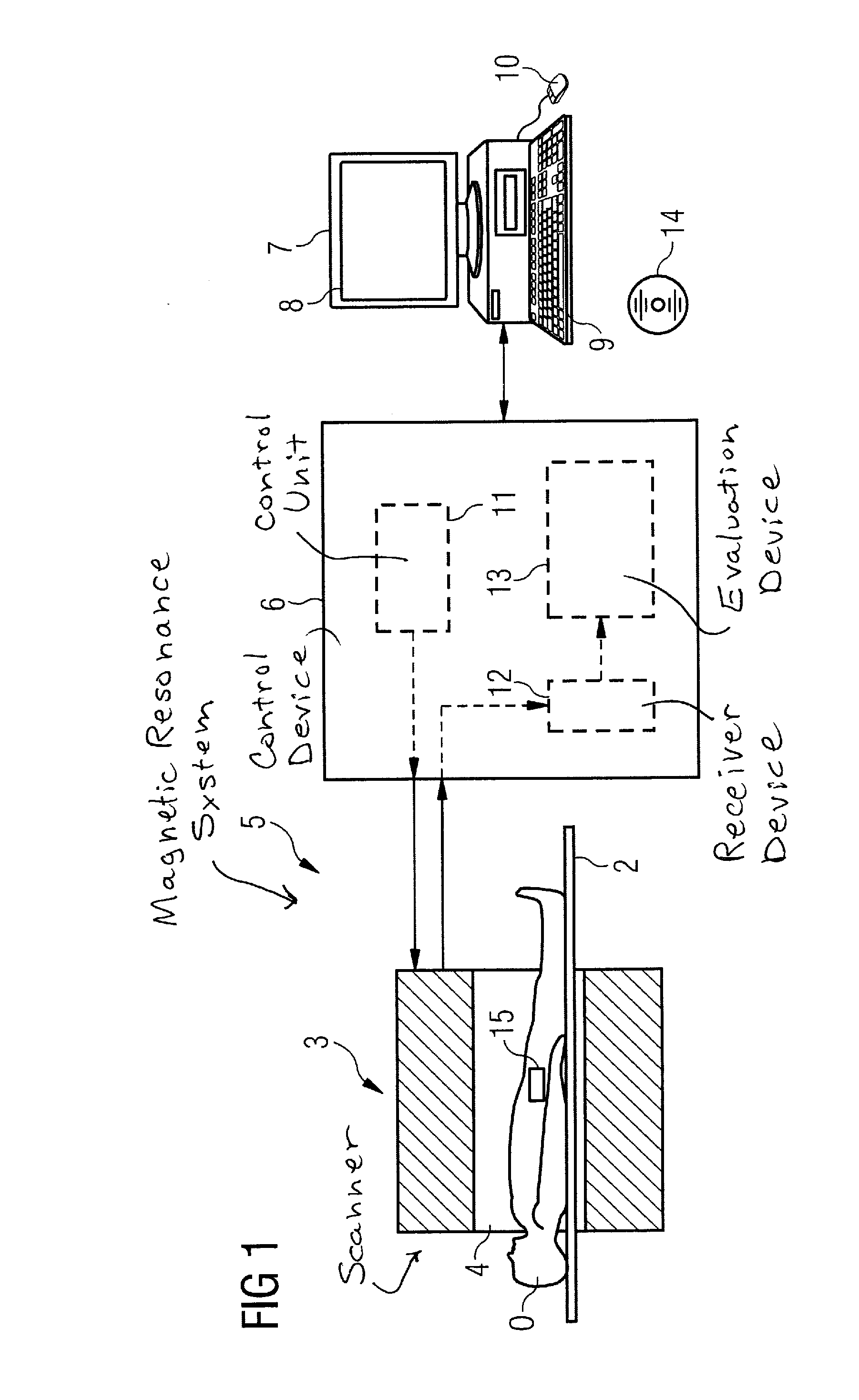
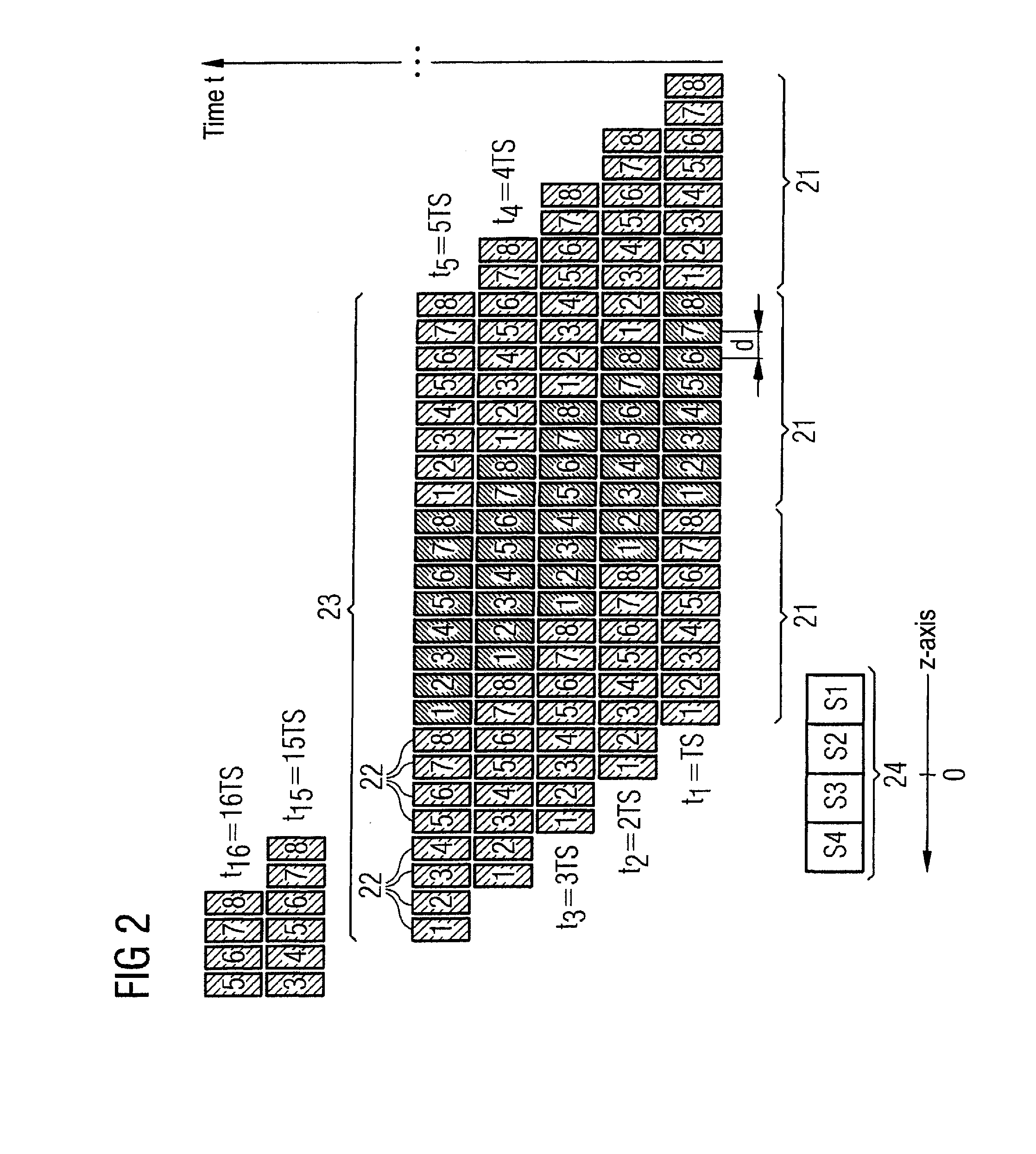
Method and device for controlling acquisition of magnetic resonance data in a magnetic resonance apparatus
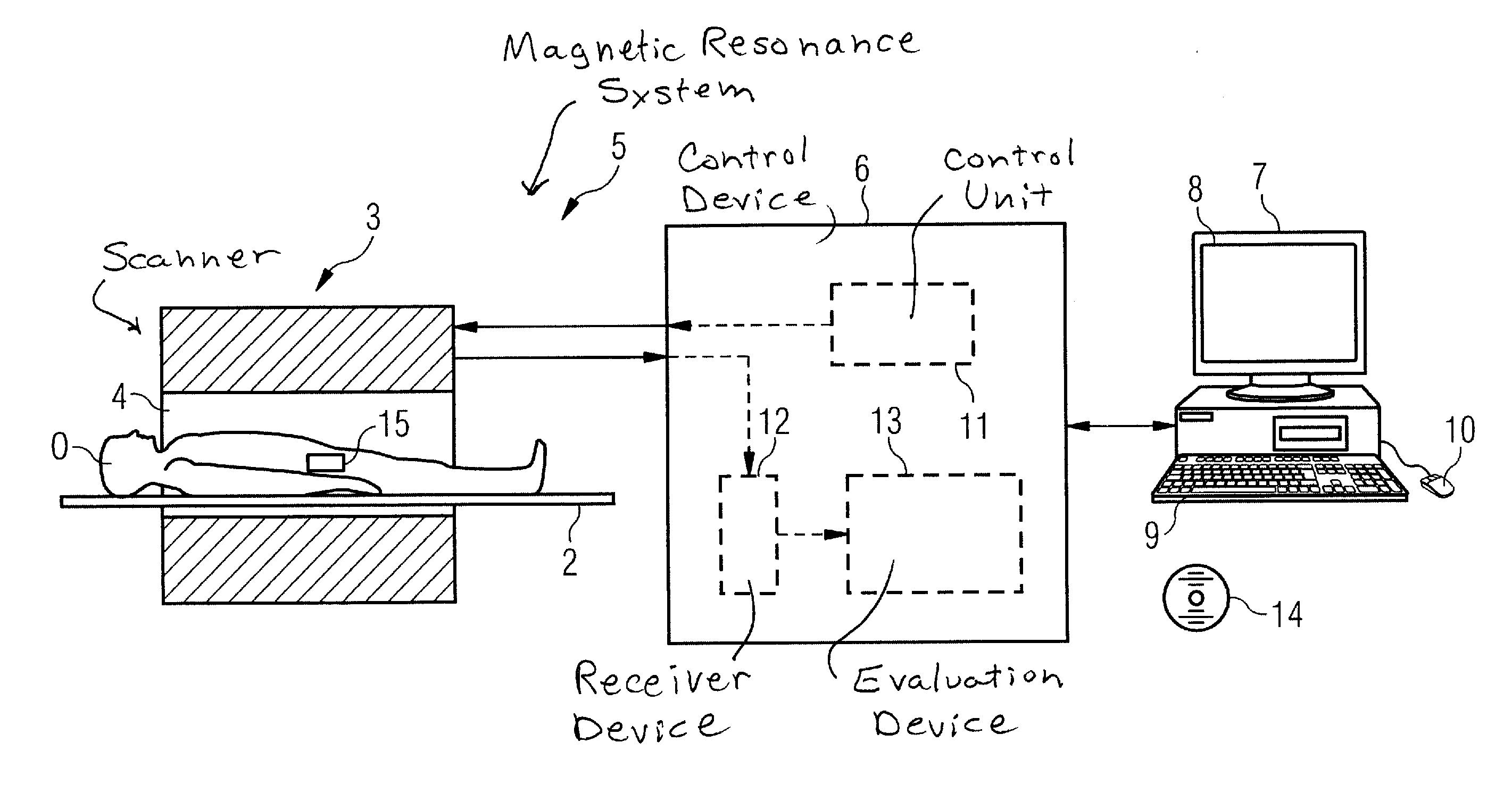
ActiveUS20100237863A1Reduce measurementMeasurement is complicatedCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringImage resolutionResonance
In a method and a device to control the workflow of an MR measurement in a magnetic resonance system, a predetermined volume segment is subdivided into parallel slices with a predetermined slice interval and measured with a continuous table feed. Apart from a start phase and an end phase of the MR measurement, multiple slices of the examination subject are excited and read out in every repetition of the underlying basic sequence, and these multiple slices are located in an active volume inside the magnetic resonance system. The number of slices excited and read out per repetition of the underlying basic sequence is selected automatically depending in particular on the parameters determining an image contrast and an image resolution, and thus cannot be freely set by a user of the magnetic resonance system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
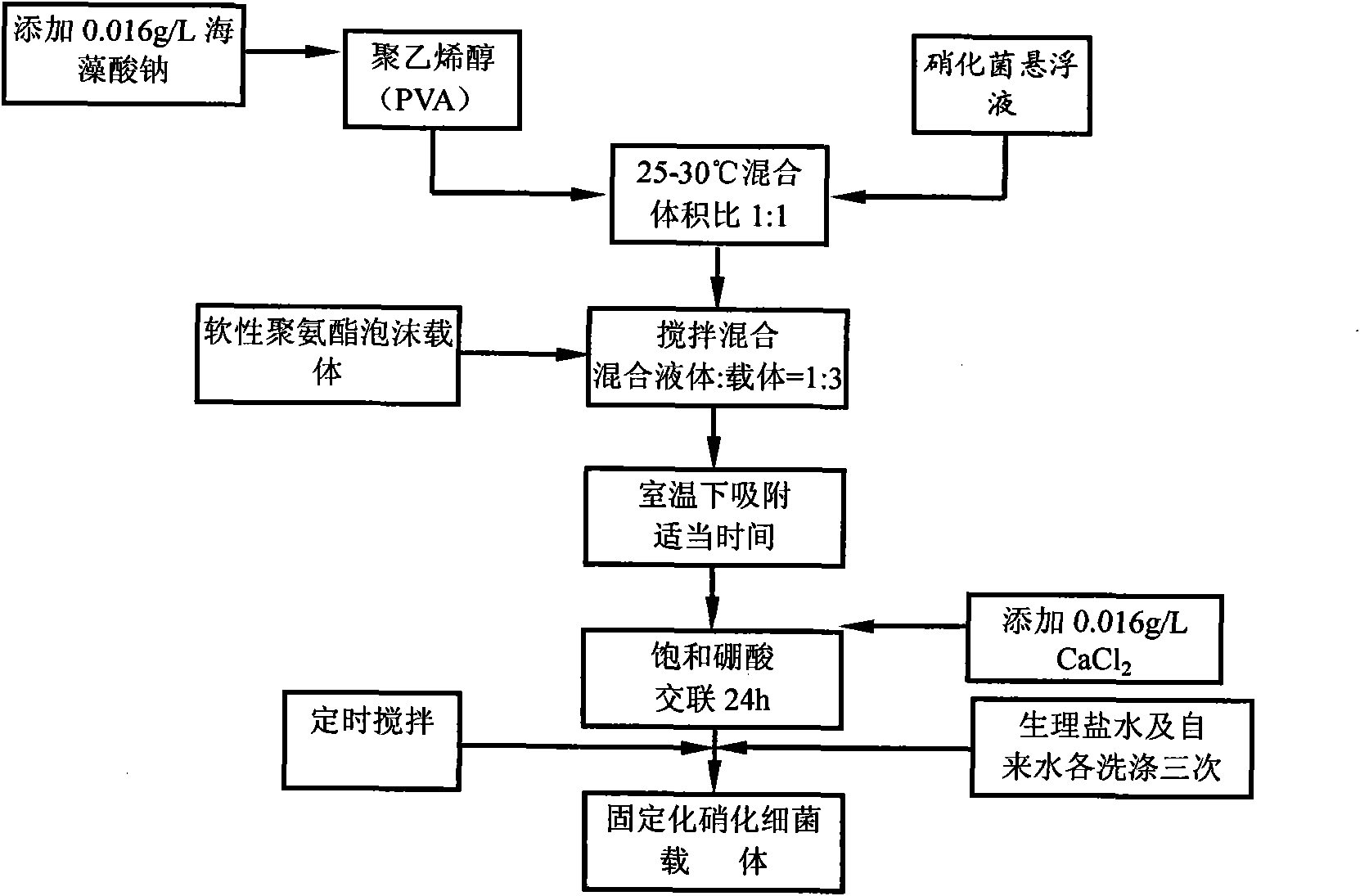
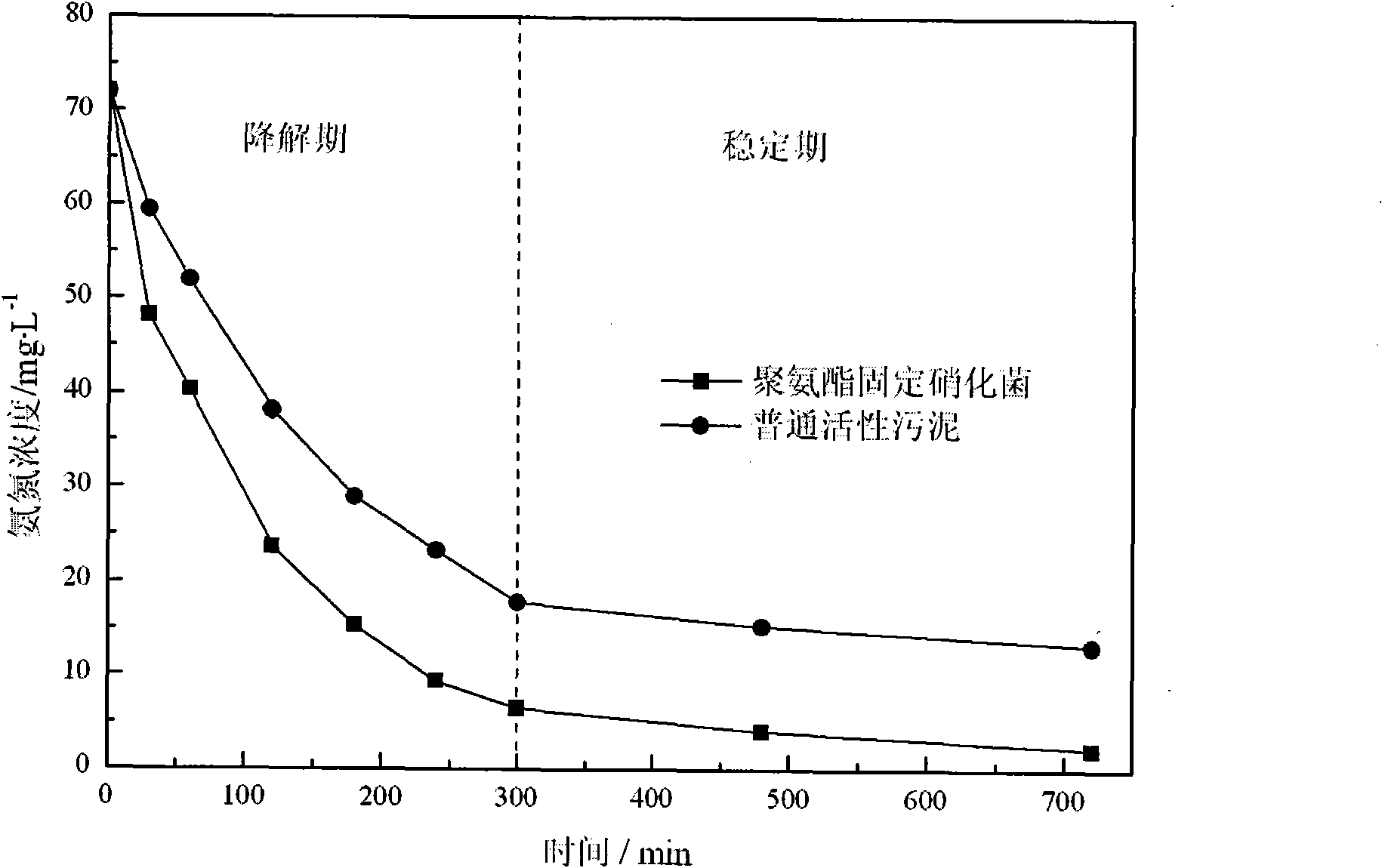
Method for treating nitrogen-containing wastewater from power plants by nitrifying bacteria immobilized on polyurethane
InactiveCN101941758AImprove nitrogen removal efficiencyImprove hydrophilicitySustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentPolyvinyl alcoholNitrifying bacteria
The invention discloses a method for treating nitrogen-containing wastewater from power plants by nitrifying bacteria immobilized on polyurethane, comprising the following steps: (1) separating and screening high-efficiency dominant nitrifying bacteria from a nitrogen removed sewage treating system which runs for more than 1 year and domesticating and carrying out enlarge culture on the dominant nitrifying bacteria; (2) immobilizing the nitrifying bacteria on soft polyurethane foam packing by the immobilization technology combining embedding and adsorption and adding the nitrifying bacteria to a fluidized bed reactor, wherein the volume of the added nitrifying bacteria accounts for 25-35% of the active volume of the reactor and the bacteria addition is 1g of wet strains per 150mL of packing; and (3) adopting intermittent culture at the early stage of running of the reactor, ensuring the inlet water to be the domestic sewage and adding nutrient substances, controlling the mass ratio of C:N:P to be 100:15-20:1, after intermittent running for 10d, the sewage treating system beginning normal running to carry out sewage denitrification when less polyvinyl alcohol in water is dissolved out (less foam or nearly no foam exists on the liquid level). The method of the invention improves the sewage denitrification efficiency.
Owner:STATE NUCLEAR ELECTRIC POWER PLANNING DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD
Method and system for direct rendering of multi-volume data
ActiveUS20090027382A1Ensure correct executionImprove accuracyCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage generationArray data structureComputer graphics (images)
A method for performing direct rendering of a multi-volume data, having the steps of determining whether a volume of the multi-volume data is one of active and inactive via interaction with a ray for the multi-volume data, recording in triplicate a starting point and an end point of the ray for an eyespace, repeating the determining whether the volume is one of active and inactive via interaction with a ray for the multi-volume data and the recording in triplicate a starting point and an end point of the ray for an eyespace for all volumes of the multi-volume data, providing triples from all volumes to an array, sorting the array to create a sorted triples list array, breaking the ray into a plurality of segments using the sorted triples list array, determining which volumes are active for each of the segments via an active volume list, and sampling each segment of the ray to acquire an accumulated result.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
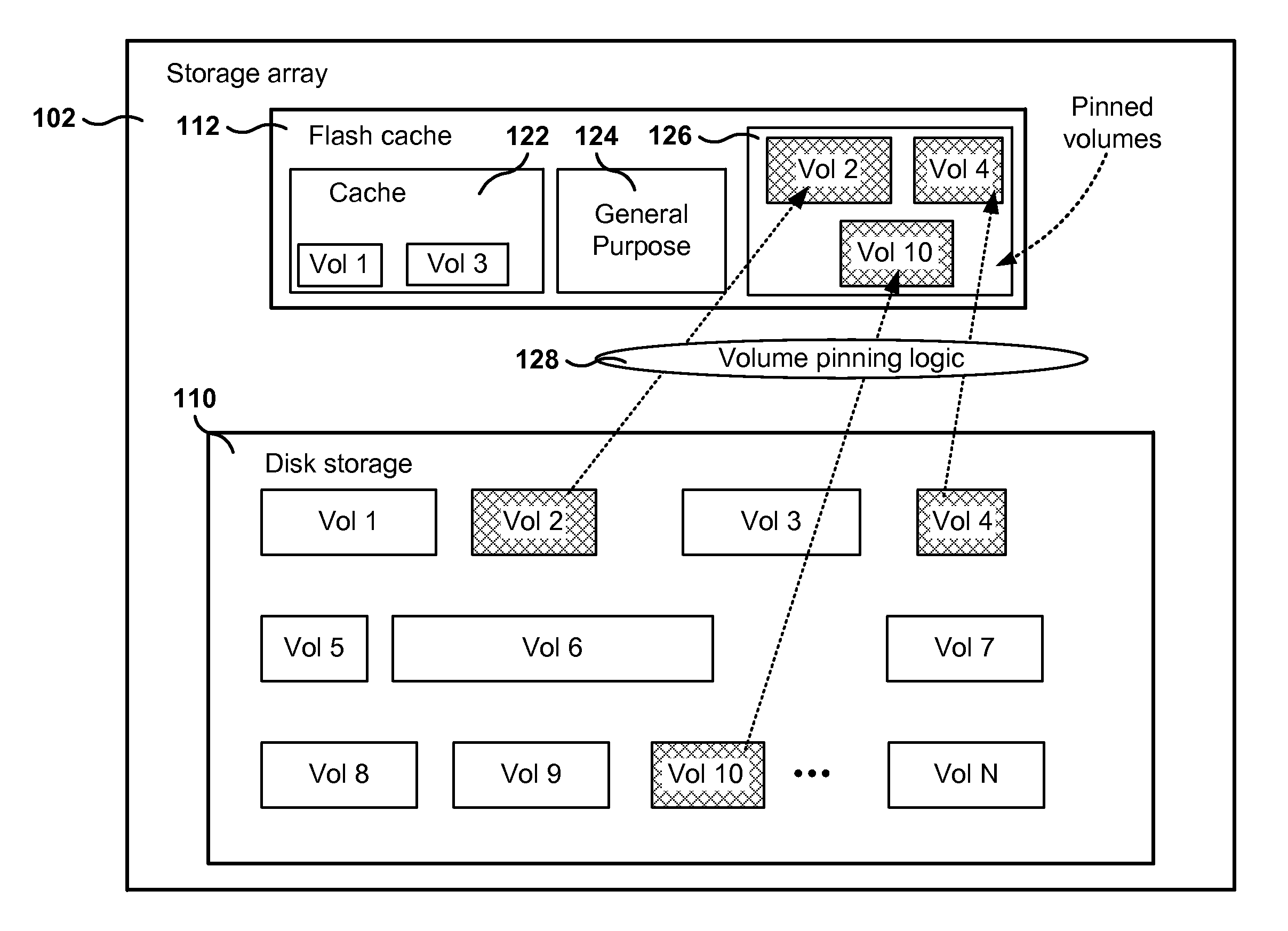
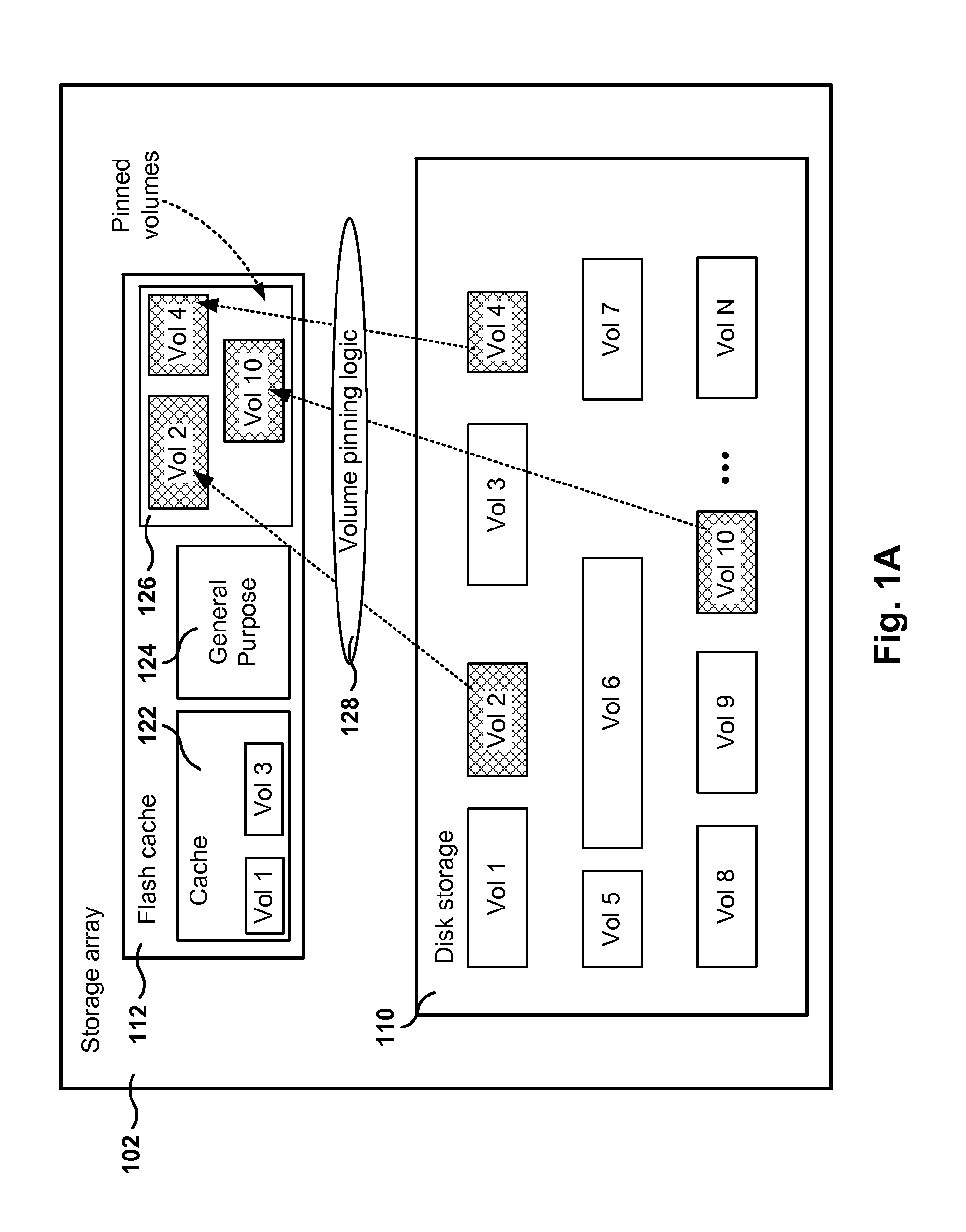
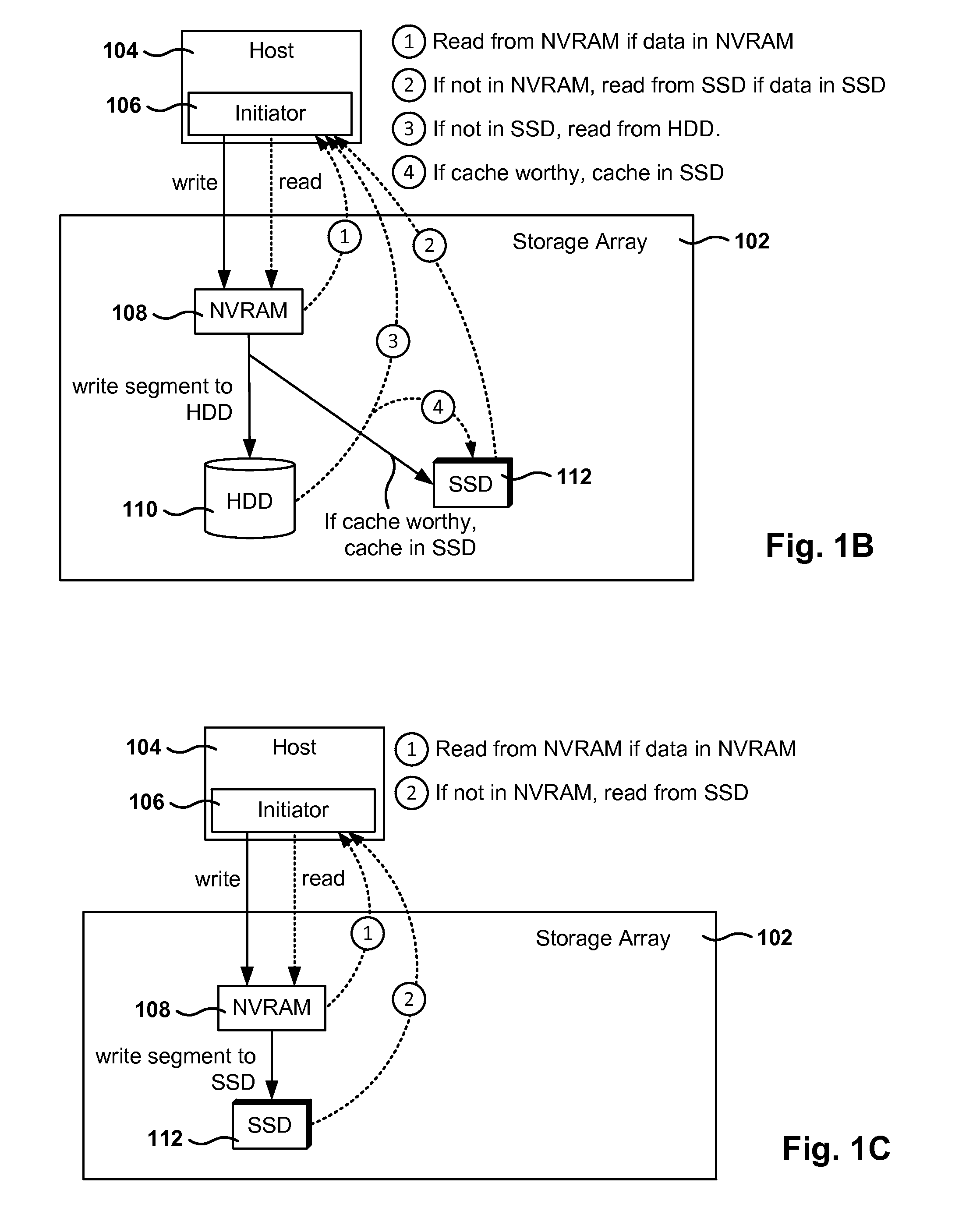
Management of pinned storage in flash based on flash-to-disk capacity ratio
ActiveUS20160342357A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersRatio methodSolid-state drive
Methods, systems, and programs are presented for managing a storage device memory. One method includes an operation for receiving a request to pin a volume stored in the storage device. The device includes disk storage and a solid state drive (SSD) cache, where pinned volumes in the storage device have all active volume data in the SSD cache. Further, the method includes an operation for determining the maximum amount of pinnable space in the SSD cache, the maximum amount of pinnable space being calculated based on the sizes of the disk storage and the SSD cache. Further, the method includes operations for determining the available pinning space, which is the maximum amount of pinnable space minus the current amount of pinned data in the SSD cache, and for granting the request to pin the volume when the available pinning space is greater than or equal to a size of the volume.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method of estimating the volumetric carrying capacity of a truck body
A method for estimating the effective volumetric capacity of a truck body is provided. The method includes the step of establishing a side-to-side profile of a generic load model. A front-to-rear profile of the generic load model is also established. Load plateau lines having predetermined dimensions are established in the front-to-rear and side-to-side profiles and the height of the plateau lines are determined. A top profile of the generic load is then created and the shape of the load plateau is adjusted into a closed curve shape. The front, rear and side load lines below the final outer boundary of the load plateau are then contoured into a generally conical shaped surface. The final three-dimensional generic load model is formed by where this generally conical shaped surface intersects the sides walls, front and floor of the truck body. The volume of the final three-dimensional generic load model can then be calculated.
Owner:HAGENBUCH LEROY G
Rotor for a generator
ActiveUS20080211339A1Large outside diameterReduce mechanical stressTurbinesMagnetic circuit rotating partsWeld seamElectric generator
A rotor (10) for a generator, especially for a turbogenerator, is assembled from a plurality of separate rotor elements (11, 12) which are arranged one behind the other in the rotor axis (18), wherein the rotor elements (11, 12) abut on connecting faces and are welded to one another, forming circular weld seams (17) which concentrically encompass in each case an annular central gap (37) with a predetermined gap width. In order to achieve a maximum magnetically active volume with mechanical stresses which are as low as possible, on the outer circumference of the gap (37) the gap merges into a widening cavity (38) which is adjacent to the weld seam (17).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Rapid vacuum desorption device and rapid vacuum desorption method for collecting volatile gas components in sample
InactiveCN103940640AFast desorptionLow boiling pointWithdrawing sample devicesDesorptionAir cleaning
The invention discloses a rapid vacuum desorption device and a rapid vacuum desorption method for collecting volatile gas components in a sample. The device comprises an air suction cylinder (2), an air suction piston (7), a piston handle (3) and a locking hanger (4), wherein the air suction piston (7) is arranged in the air suction cylinder (2), the piston handle (3) is arranged at the extended part of the air suction piston, and the locking hanger (4) is arranged between the air suction piston (7) and the piston handle (3); an air inlet (10) of an air inlet electromagnetic valve (9) is connected to the bottom of the air suction cylinder (2), a sample bottle is rotatably connected to the lower part of the air inlet electromagnetic valve (9), an air cleaning hole (16) and an air outlet (17) connected with an air-cleaning electromagnetic valve (8) and an air outlet electromagnetic valve (13) are respectively formed in the side face of the bottom of the air suction cylinder (2), and the air-cleaning electromagnetic valve (8) and the air outlet electromagnetic valve (13) are respectively connected with the air cleaning hole (16) and the air outlet (17) which are formed outside a shell; a display screen (15) and a main control board (1) are connected to the interior of the shell. The rapid vacuum desorption device is small in volume and is convenient to carry; the sample does not need to be subjected to complex pretreatment; the active volume of the volatile gas of the sample can be automatically calculated.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Method for measuring electroactive area of three-dimensional porous membrane electrode
InactiveCN101710058AFast electrochemical responseHigh precisionElectrical/magnetic thickness measurementsPermeability/surface area analysisPotassium cyanideInner membrane
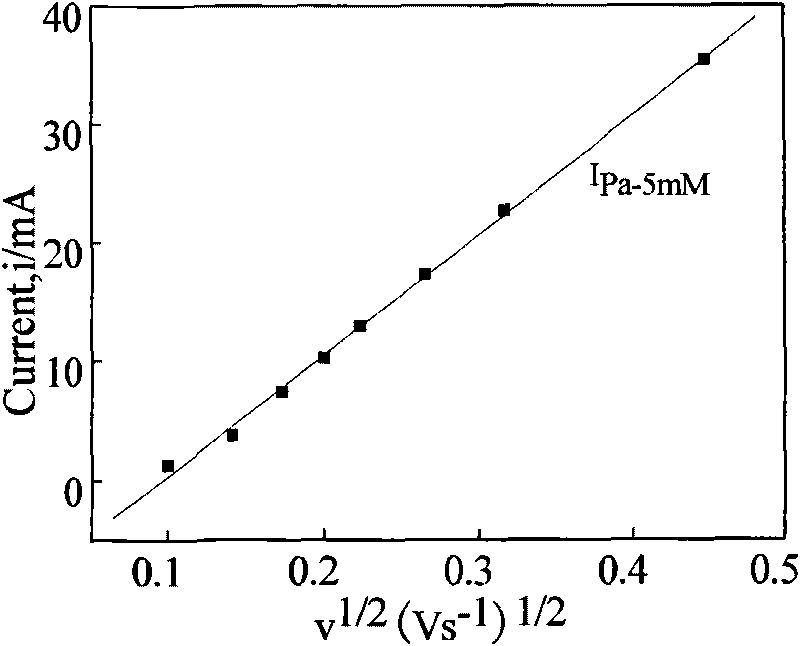
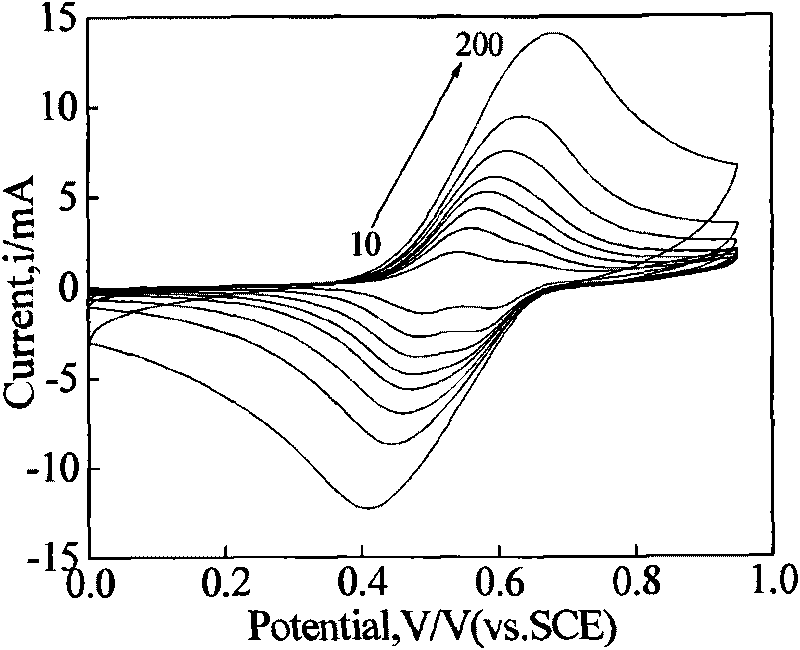
The invention provides a method for measuring the electroactive area of a three-dimensional porous membrane electrode, which comprises the steps of: respectively measuring cyclic voltammetry curves under different scanning speeds in potassium cyanide-containing and potassium cyanide-free kali salt or sodium salt solution with a three-electrode system and a potentiostat by taking a three-dimensional porous electrode or the three-dimensional porous membrane electrode which is deposited with a transition element ferricyanide semiconductor membrane, and measuring the electroactive area and the cover degree thereof with the reversibility of the redox reaction of the membrane electrode in different solution systems; and obtaining the active volume and the average membrane depth of the inner membrane of the three-dimensional porous membrane electrode by combining with the chronocoulometry. The method is simple and reliable, and has strong practicability.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Welded multipartite rotor for a generator
ActiveUS8513841B2Reduce mechanical stressLarge diameterTurbinesMagnetic circuit rotating partsWeld seamEngineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
System and method for transferring data between different raid data storage types for current data and replay data
ActiveUS9489150B2Low costImprove efficiencyInput/output to record carriersRedundant data error correctionRAIDStorage type
The present disclosure relates to a data storage system including a RAID subsystem having a first and second type of RAID storage. A virtual volume configured to accept I / O is stored on the first type of RAID storage, and snapshots of the virtual volume are stored on the second type of RAID storage. A method of the present disclosure includes providing an active volume that accepts I / O and generating read-only snapshots of the volume. In certain embodiments, the active volume is converted to a snapshot. The active volume includes a first type of RAID storage, and the snapshots include a second type of RAID storage. The first type of RAID storage has a lower write penalty than the second type of RAID storage. In typical embodiments, the first type of RAID storage includes RAID 10 storage and the second type of RAID storage includes RAID 5 and / or RAID 6 storage.
Owner:DELL INT L L C
Hybrid catalyst radiant preheating system
InactiveCN102242659AInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusProcess engineeringRadiant heating
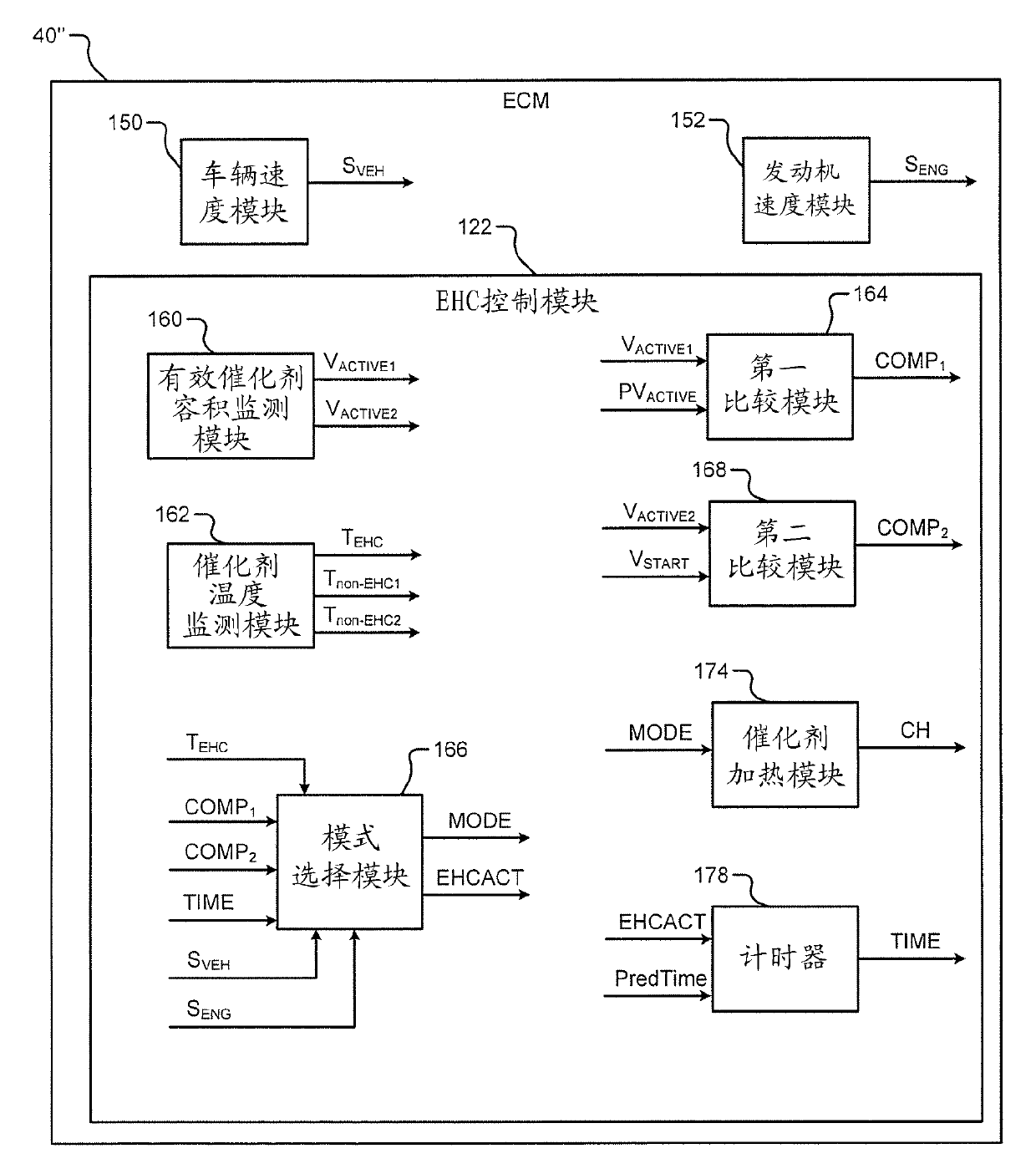
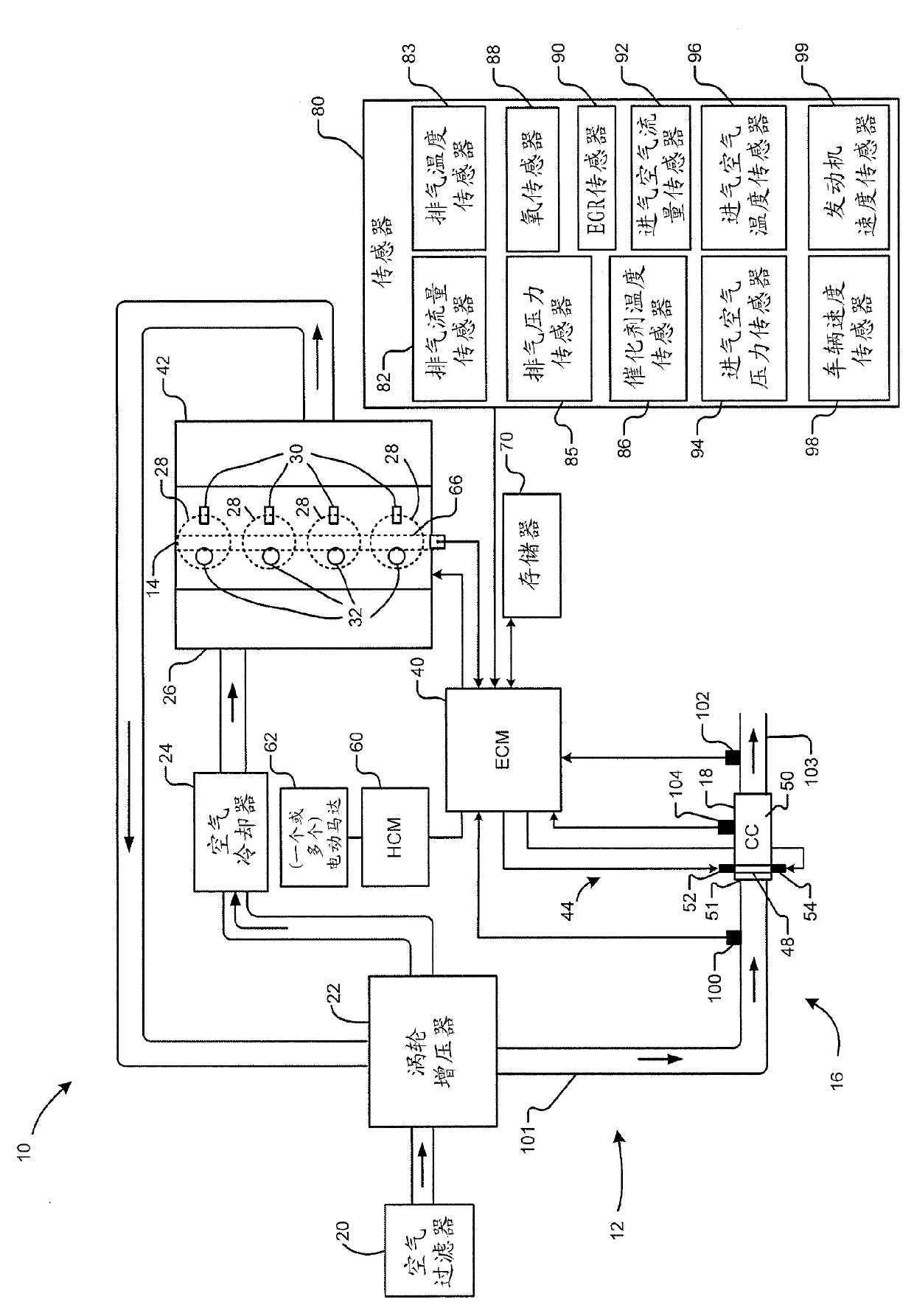
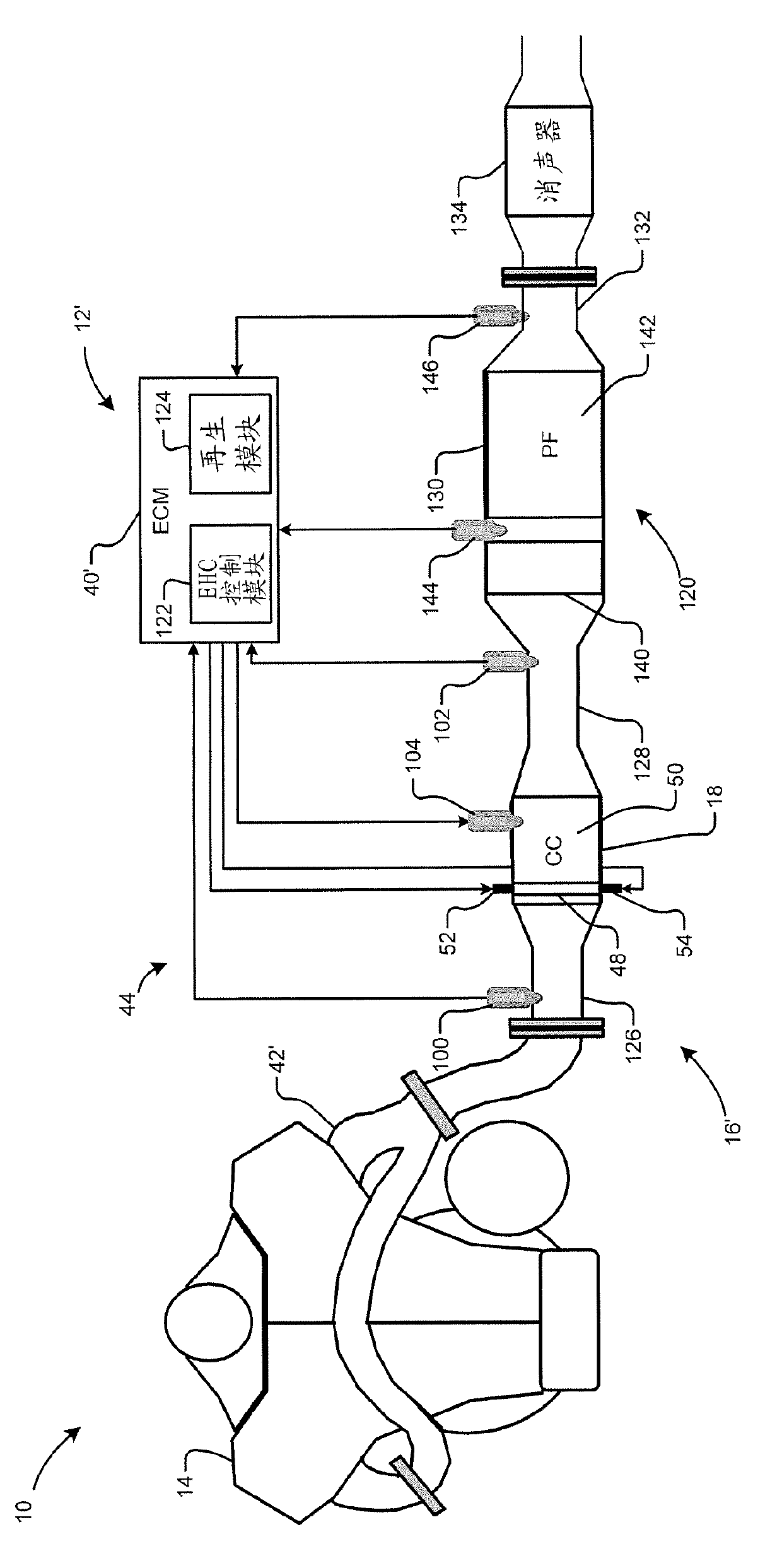
The present invention relates to a hybrid catalyst radiation preheating syste, in particular, a catalyst heating system which includes a monitoring module, a mode selection module and an electrically heated catalyst (EHC) control module. The monitoring module monitors at least one of (i) a first active volume of a catalyst assembly in an exhaust system of an engine and (ii) a first temperature of a non-EHC of the catalyst assembly. The mode selection module is configured to select a non-EHC radiant heating mode and generate a mode signal based on the at least one of the first active catalyst volume and the first temperature. An EHC control module increases temperature of the EHC to an elevated temperature that is greater than a stabilization temperature based on the mode signal. The stabilization temperature is greater than a catalyst light off temperature.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for confirming stress distribution for Y-shaped ventilation gob stratum
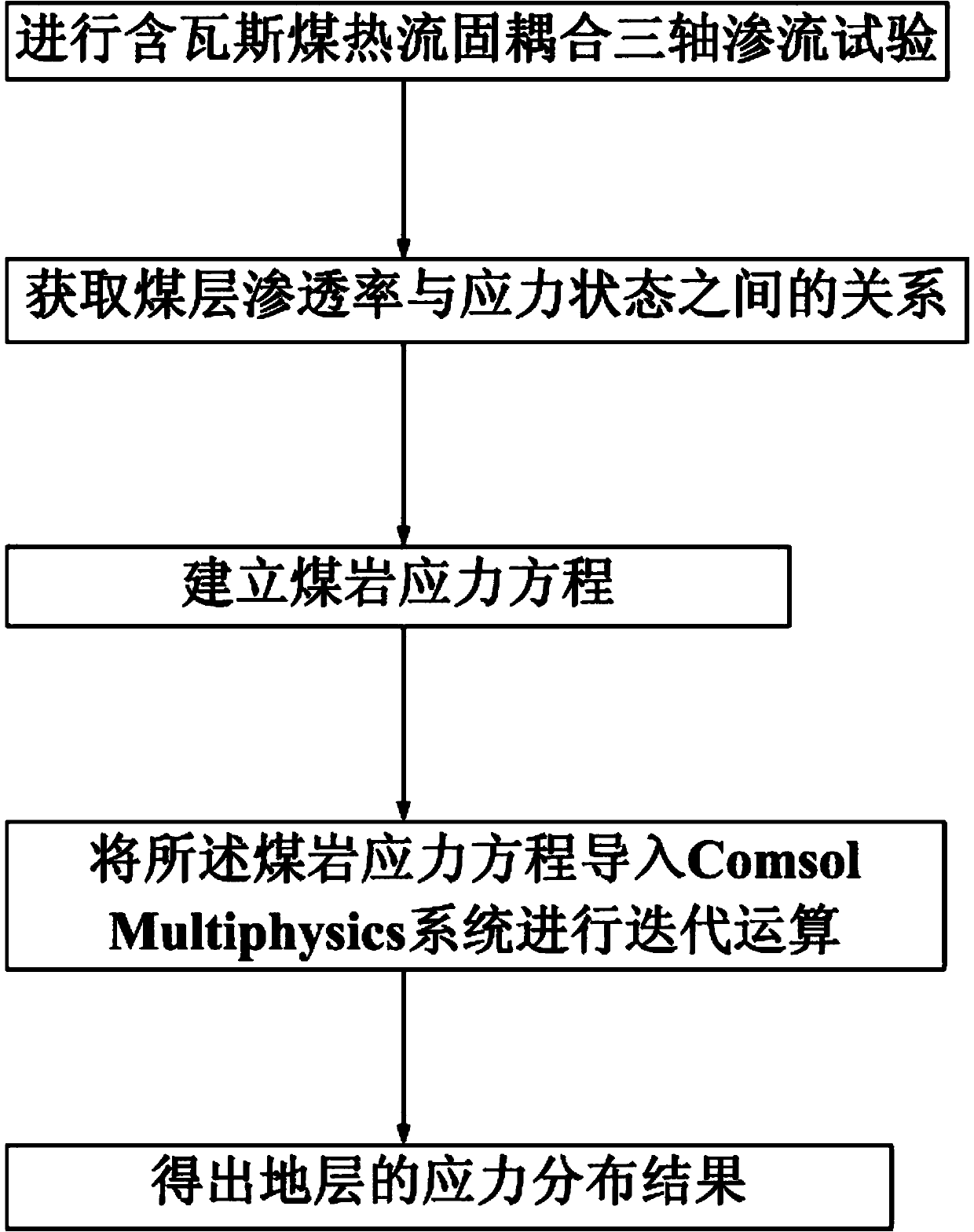
InactiveCN103809214APrecise positioningAccurate measurement of formation stress distributionPermeability/surface area analysisGeological measurementsStress distributionMultiphysics
The invention discloses a method for confirming stress distribution for Y-shaped ventilation gob stratum, and the method belongs to the gas extraction field, the method comprises the steps of doing the coal containing methane heat-fluid-solid coupling triaxial seepage test according to the working conditions on site to obtain the permeability of the coal sample during the stress-strain process, building the active volume stress intensity equation for coal, the coal stress balanced equation, geometric equation for coal containing methane and elastoplastic constitutive equation, importing the Comsol Multiphysics system and inputting the corresponding stratum material parameter to obtain the stress distribution result of the stratum through the iterative operation. The method can measure the stress distribution of the stratum for the Y-shaped ventilation gob more accurately, locate the enrichment region for Y-shaped ventilation gob more accurately and provide more specific guide for the drilling distribution during the gas extraction.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Shimming procedure that includes determination of the target field by optimization in a parameter space of reduced dimensionality
ActiveUS20150102809A1Simple wayReduce the numberMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceDimensionality reduction
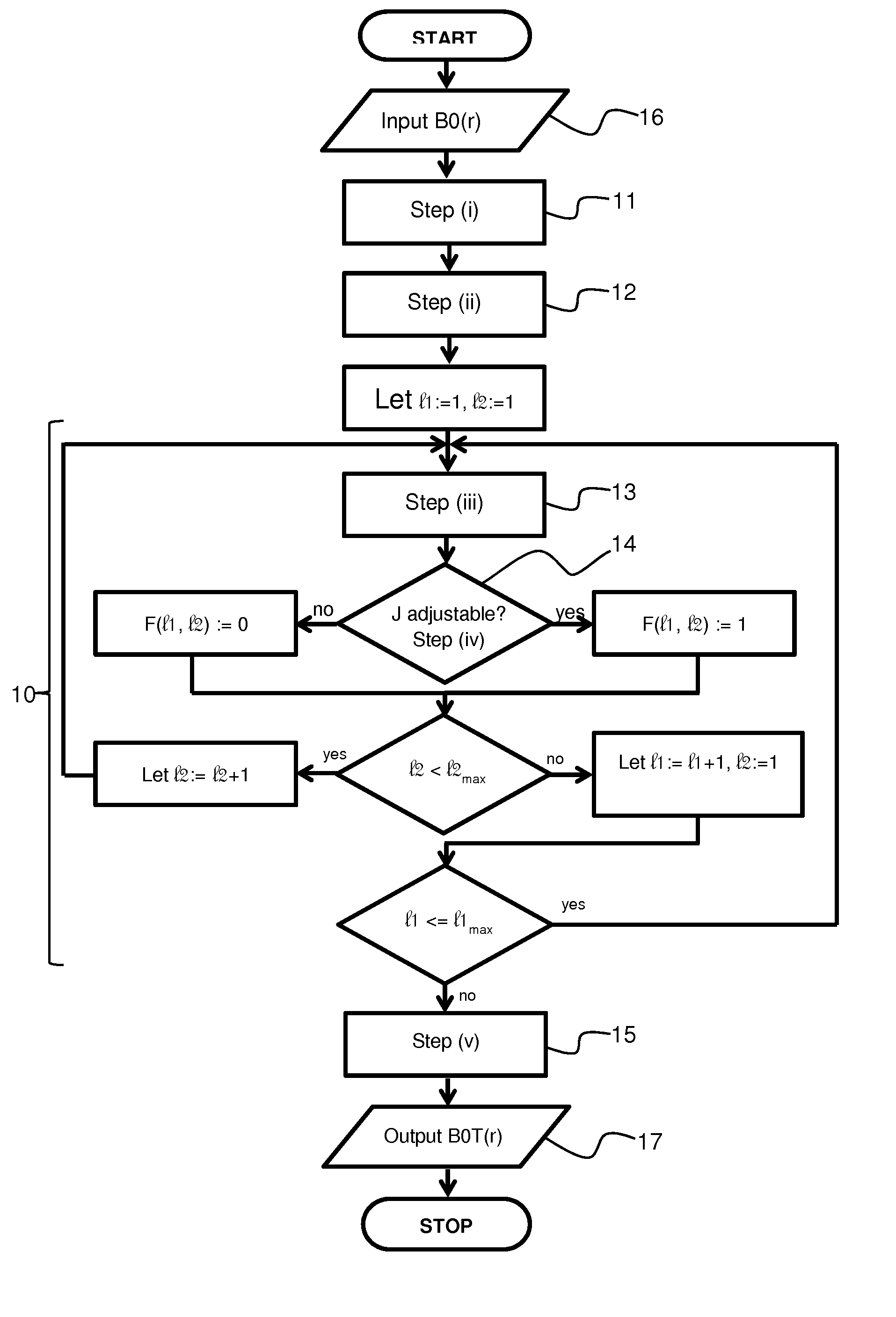
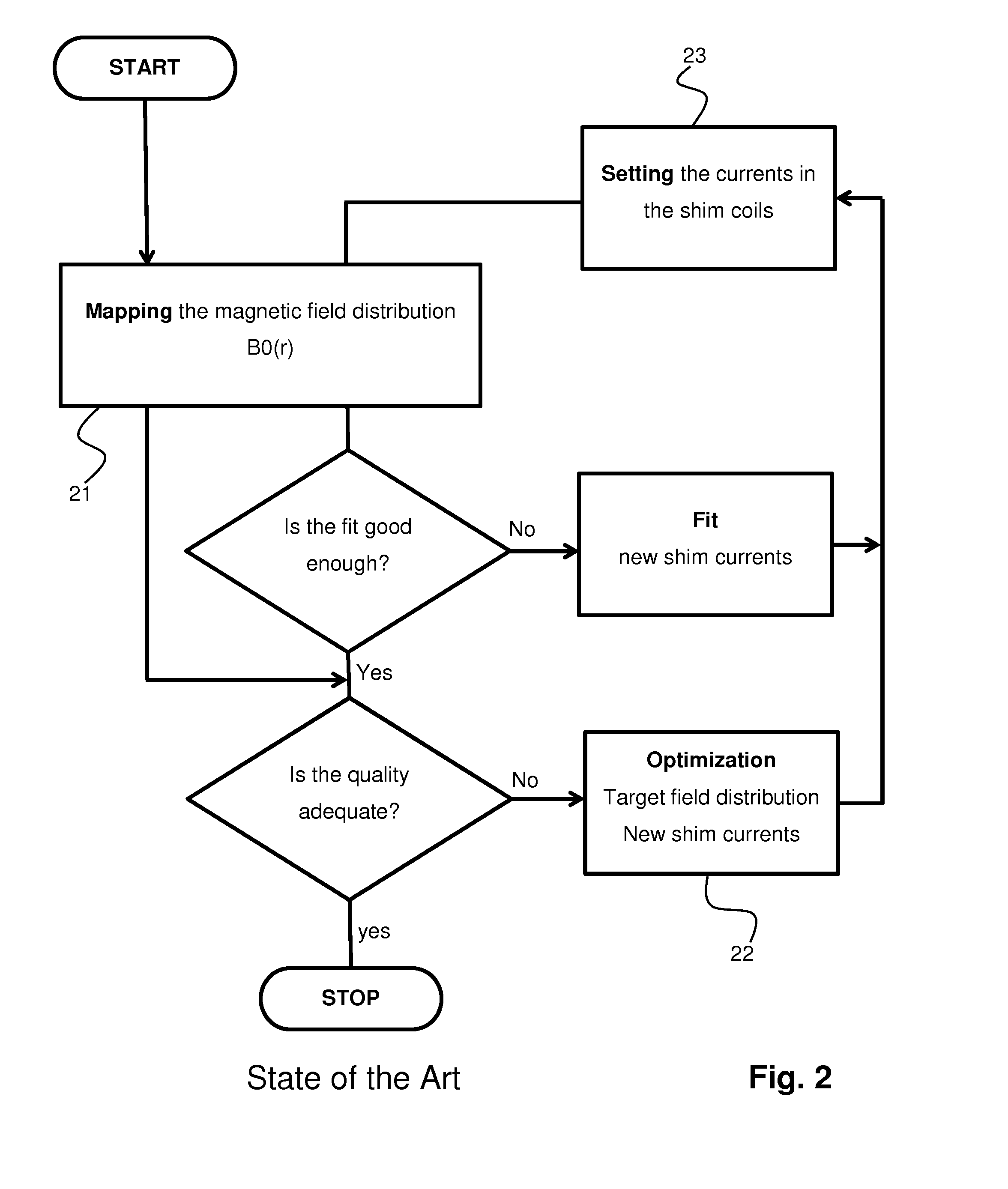
A method for homogenizing the static magnetic field with a distribution B0(r) in the active volume of a magnetic resonance apparatus having a number N of shim coils defines a target field distribution B0T(r) using a filter method in which a norm of the shim currents is influenced by means of filter factors. An optimization procedure works in a parameter space having M control parameters, wherein 2≦M<N. One of the control parameters is used as a weighting parameter for modification of a spatial weighting function and another control parameter is used to control the filter factors. Using this method the hardware limitations can be taken into account when determining the target field distribution, without a significant increase in the computational effort to determine the target field distribution during optimization.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Method of operating an MRI imaging system, while also controlling graadient and shim sub-systems along with the MRI imaging system
ActiveUS8633690B2Data augmentationQuality improvementDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSequence controlControl signal
In an imaging system having a number of subsystems and a control device that controls the subsystems in a coordinated manner to implement a measurement sequence and an operating method therefor, sequence control data that define different functional sub-sequences of the measurement sequence are transmitted to the control device. Different active volumes are associated with the functional sub-sequences. In addition to the sequence control data, active volume position data are provided to the control device that define bearing and extent of the active volumes associated with the different functional sub-sequences. Control signals to implement the measurement sequence for the different subsystems are generated automatically by the control device based on the sequence control data and the active volume position data so that the individual functional sub-sequences are locally optimized at least with regard to a sub-region of their associated active volume.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Amino benzene analog waste water biological treatment method
InactiveCN1769206AHigh mechanical strengthPolymers have the following advantages: (1) mechanically strong mechanical strengthWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentBenzeneProcess conditions
The invention discloses a method for strengthening amino benzenes production wastewater SBR biological treatment with synthesized macroporous high-molecular polymer as immobilization microbe. For the drawback of the prior microbe carrier, the invention provides a kind of synthesized high-molecular polymer as immobilization microbe, and applies it to strength amino benzenes production wastewater SBR biological treatment. Compared with prior SBR technique, when microbe carrier used is 2-10% of active volume of the reactor, and the technique condition such as aeration volume, reaction time and temperature equals, with the method, the clearance of amino benzenes materials improves by 35-60% and the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in water outlet decreases by 5-15mg / L. The invention can be applied for modifying the prior wastewater treatment device, or building new wastewater treatment device, having good economic profit and environmental benefit.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Viable disc regenerative composition and method of manufacture and use
ActiveUS20190191694A1High viscosityIncrease vitalityDead animal preservationTissue regenerationCellular componentBiology
A viable disc regenerative composition has a micronized material of nucleus pulposus and a biological composition made from a mixture of mechanically selected allogeneic biologic material derived from bone marrow having non-whole cellular components including vesicular components and active and inactive components of biological activity, cell fragments, cellular excretions, cellular derivatives, and extracellular components; and wherein the mixture is compatible with biologic function and further includes non-expanded whole cells. The biological composition is predisposed to demonstrate or support elaboration of active volume or spatial geometry consistent in morphology with that of disc tissue. The viable disc regenerative composition extends regenerative resonance that compliments or mimics disc tissue complexity.
Owner:VIVEX BIOLOGICS GRP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com