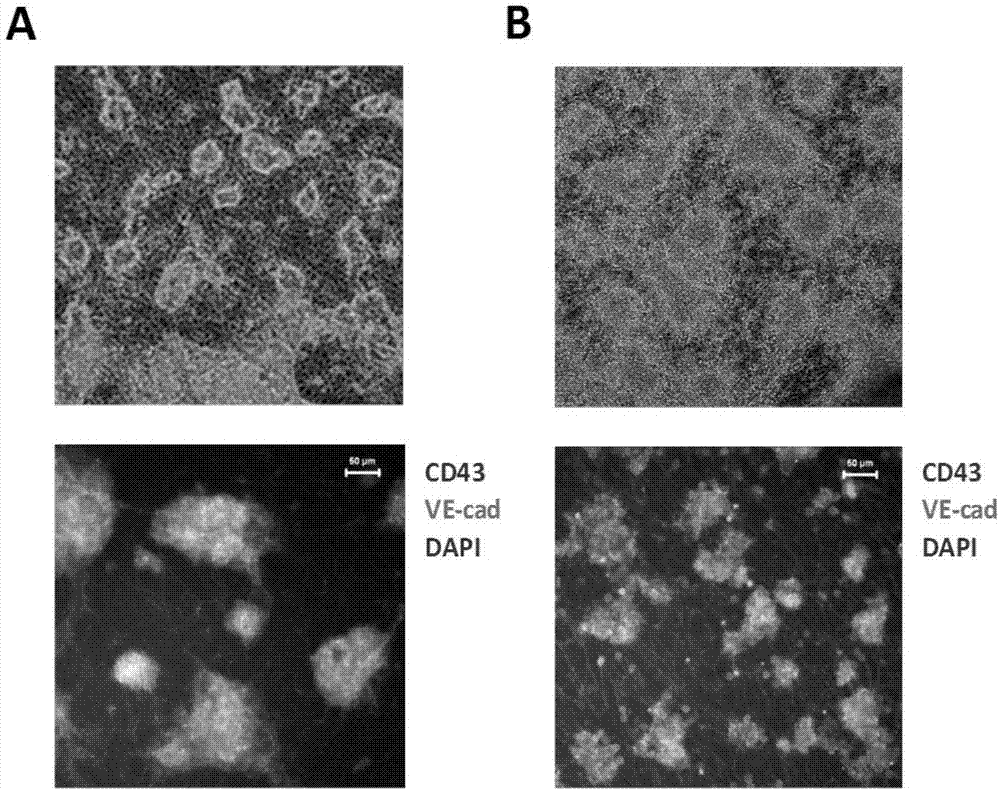
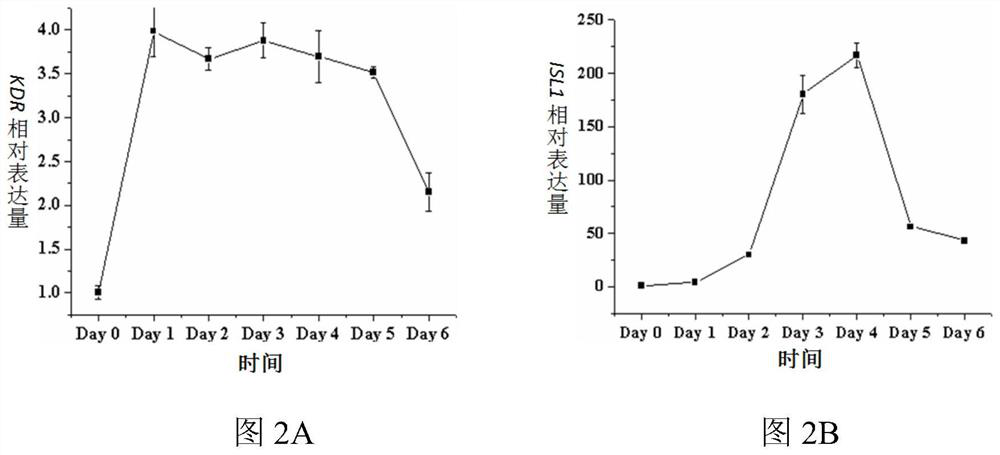
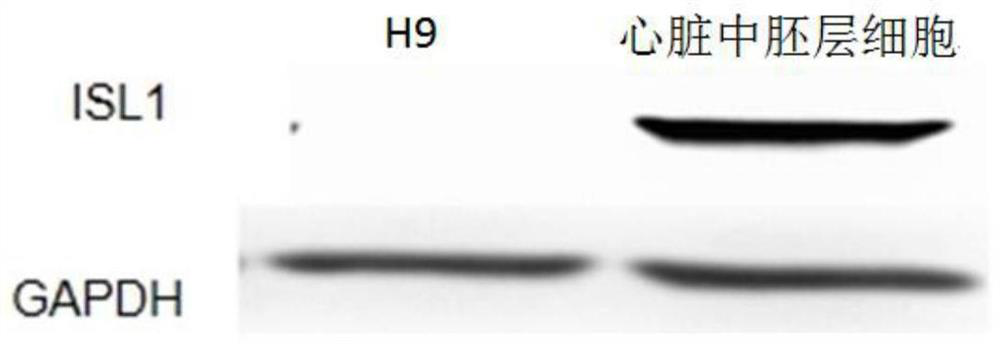
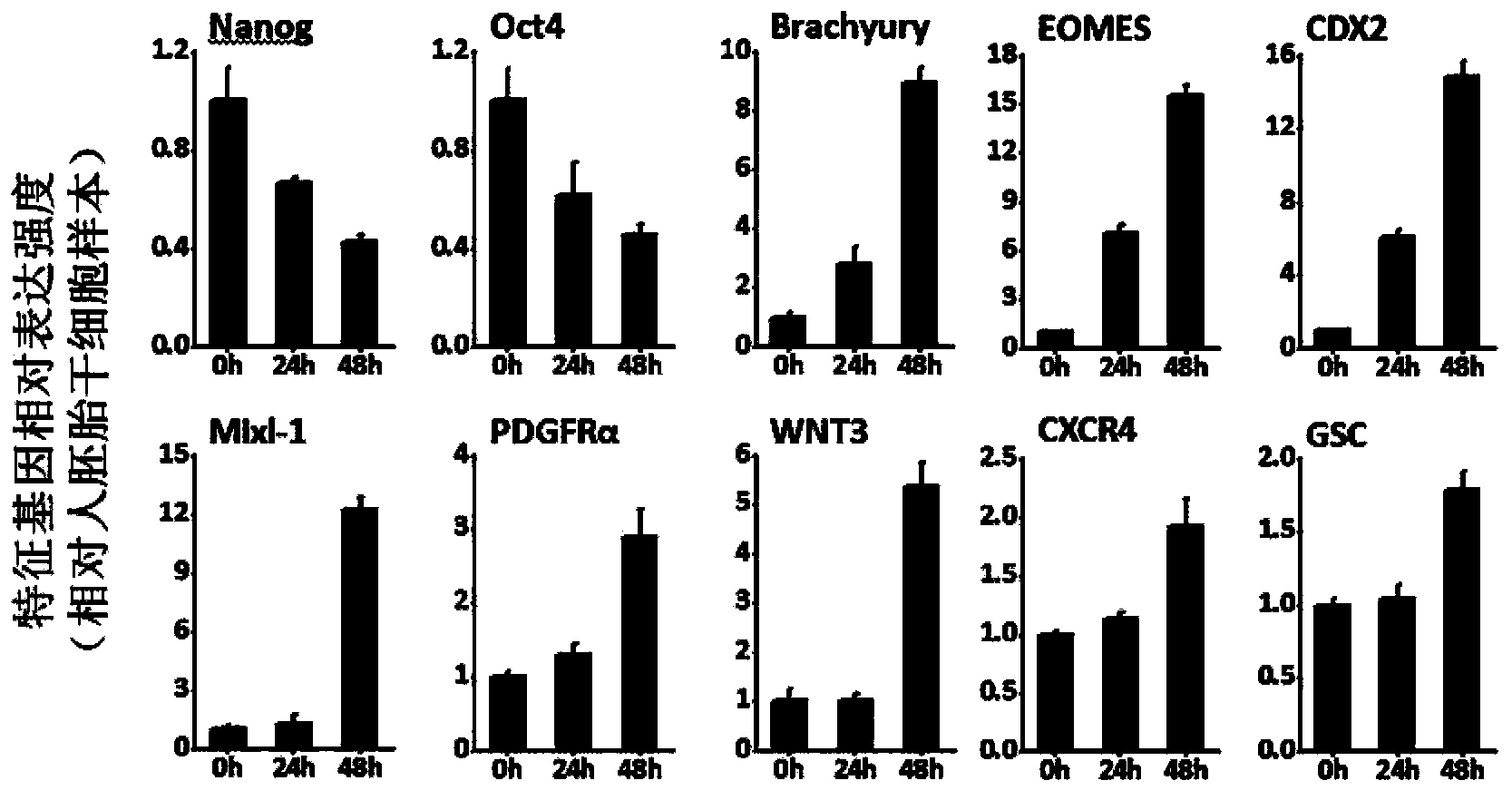
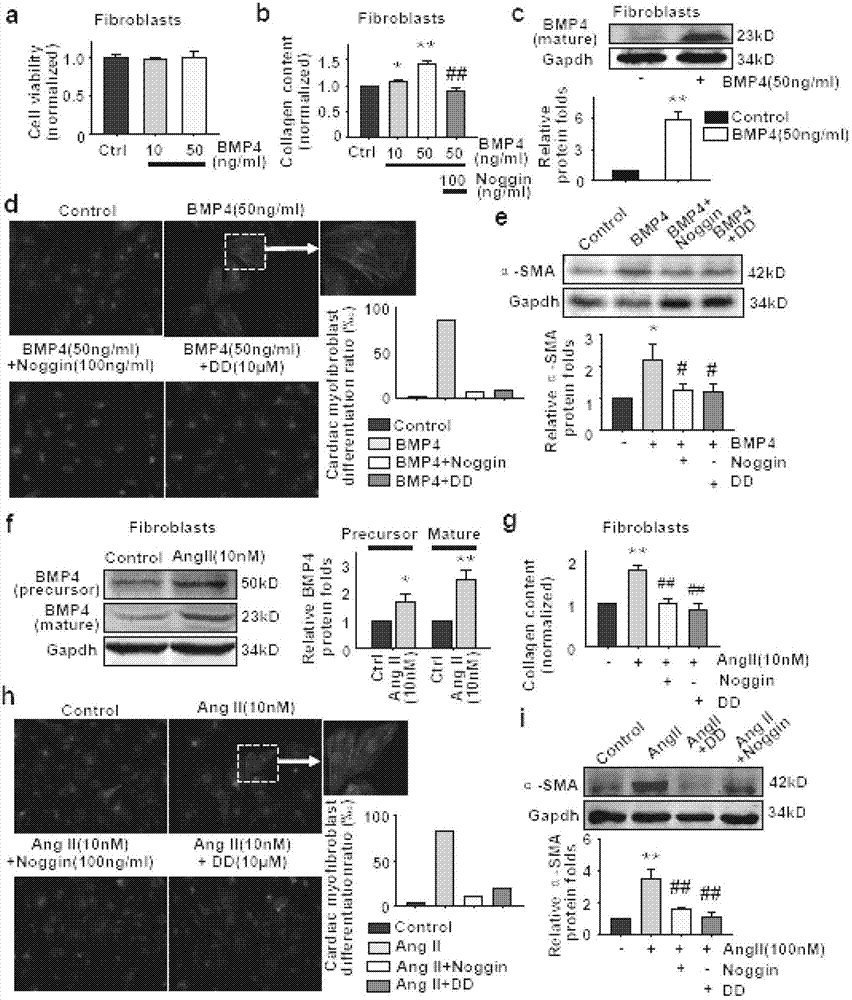
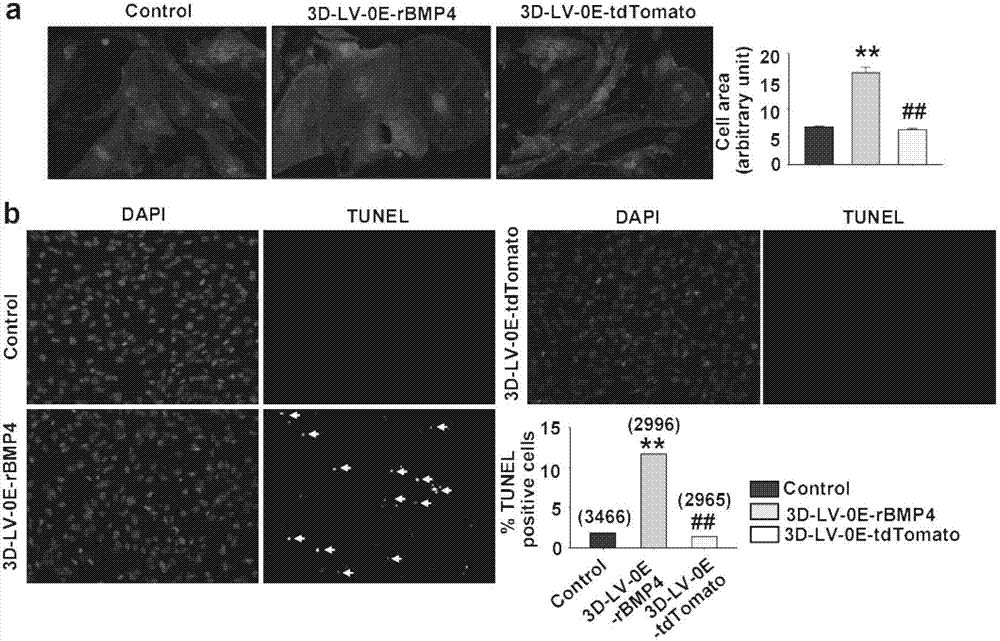
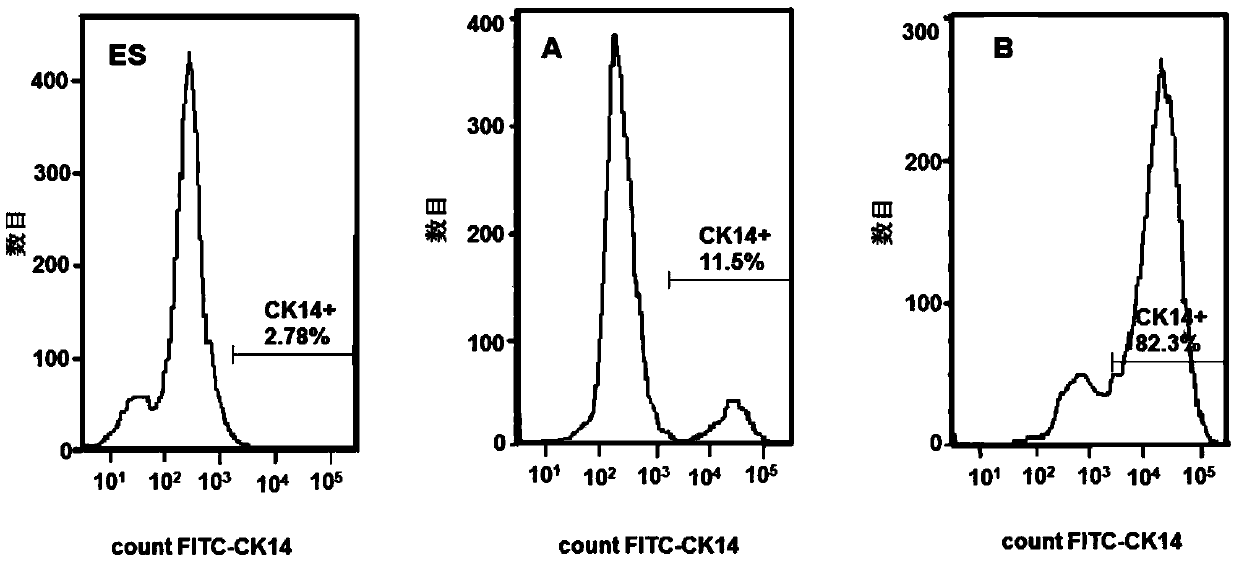
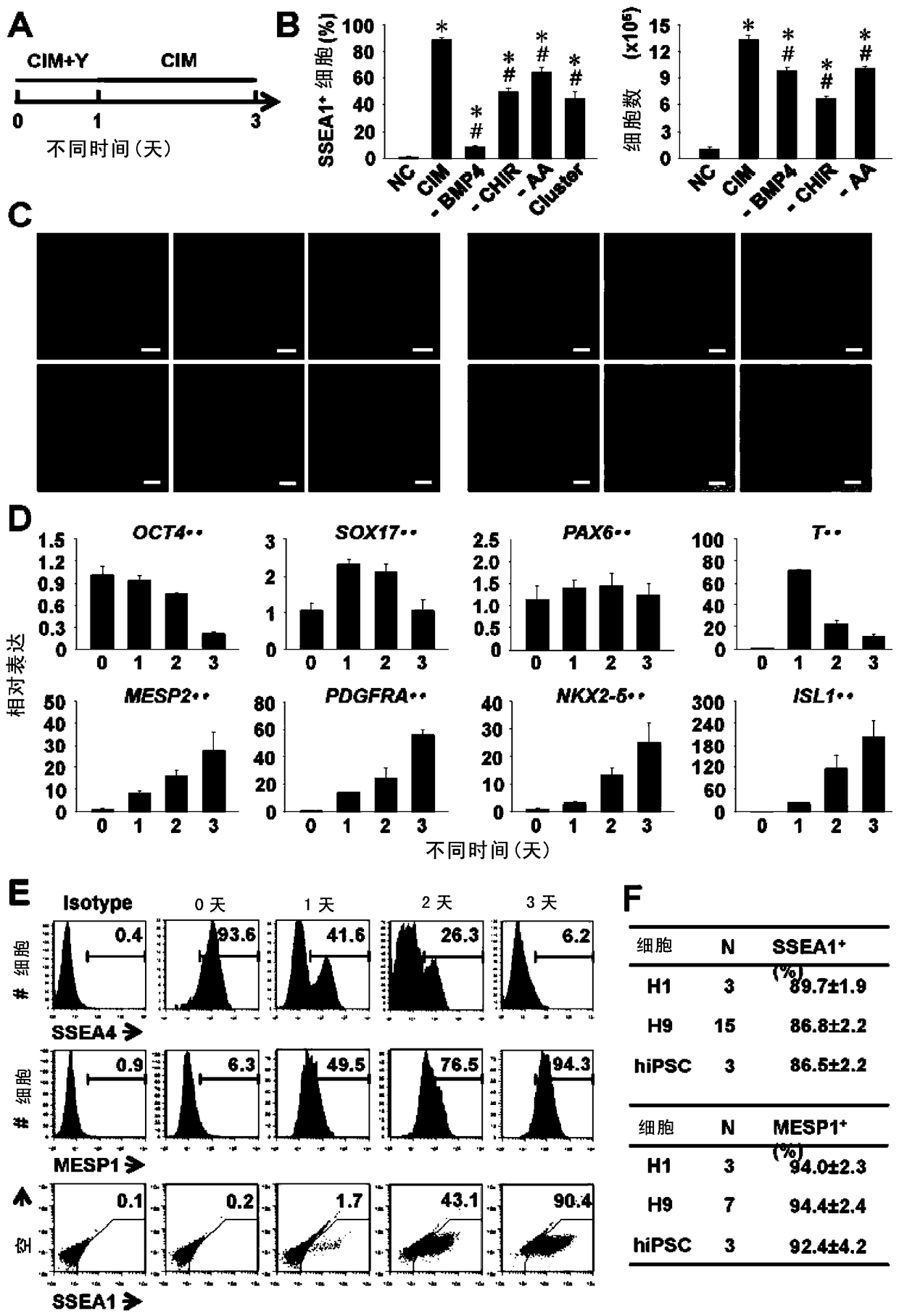
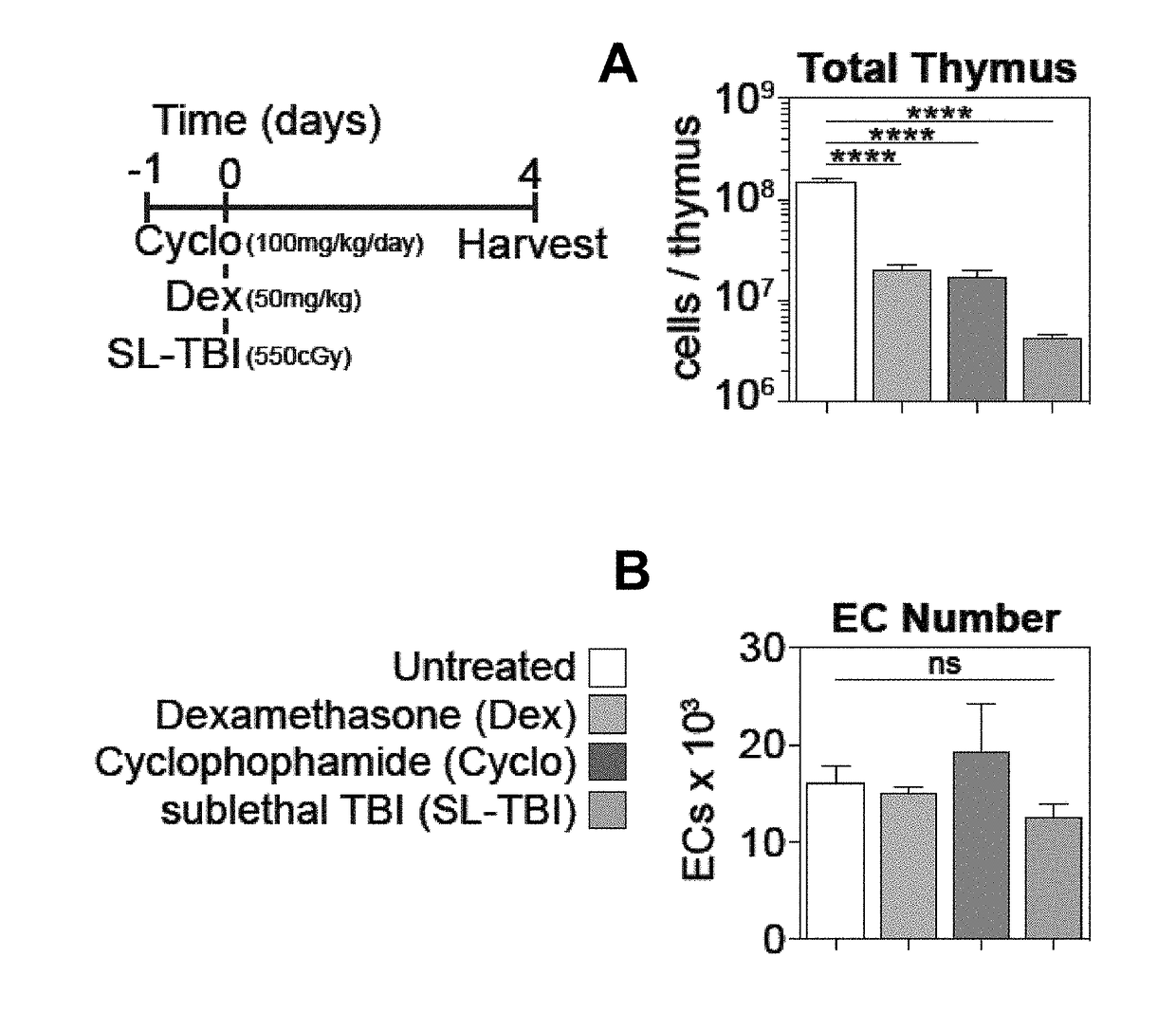
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Bone morphogenetic protein 4" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
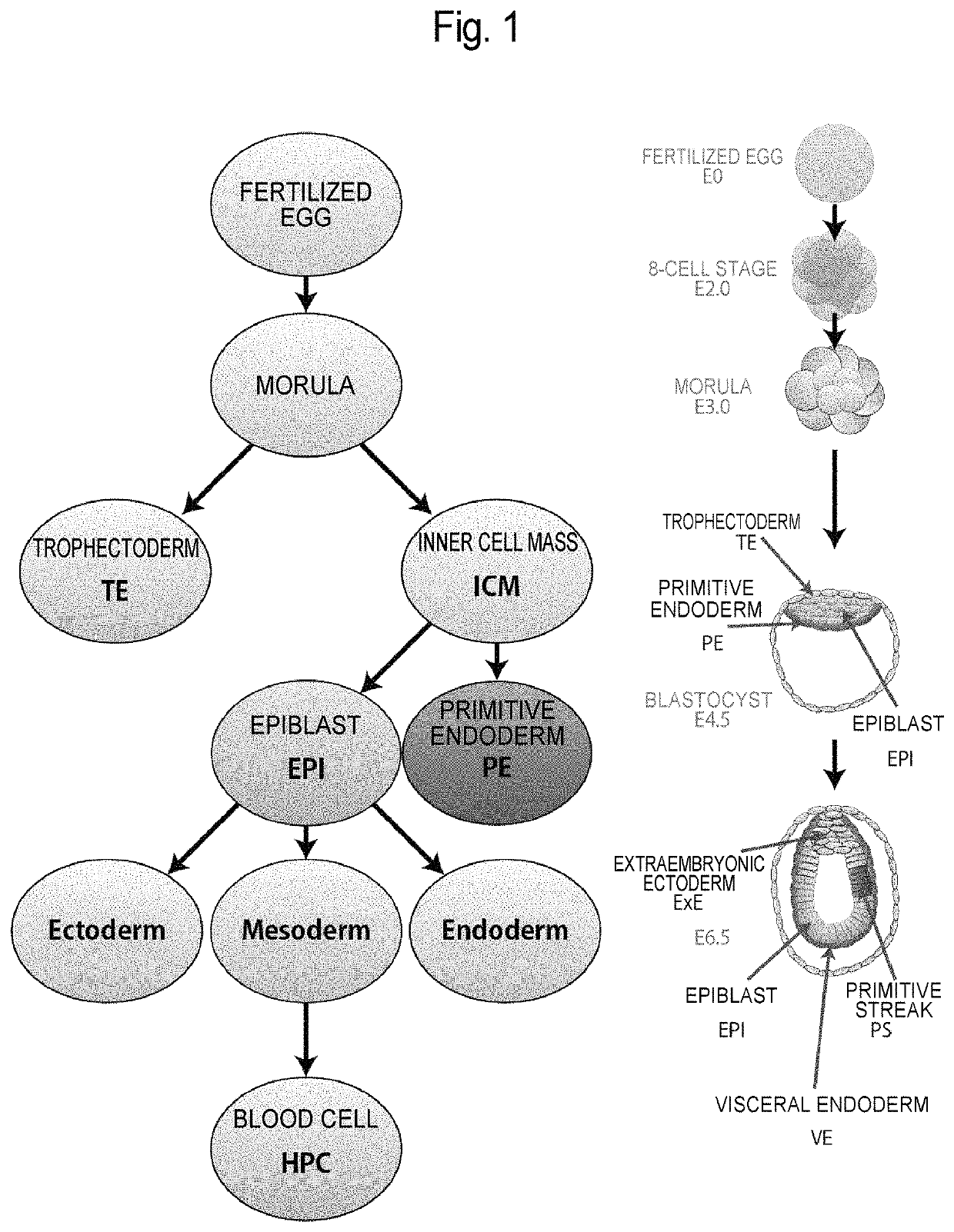
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by BMP4 gene. BMP4 is a member of the bone morphogenetic protein family which is part of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. The superfamily includes large families of growth and differentiation factors. BMP4 is highly conserved evolutionarily. BMP4 is found in early embryonic development in the ventral marginal zone and in the eye, heart blood and otic vesicle.
Method for generating primate trophoblasts
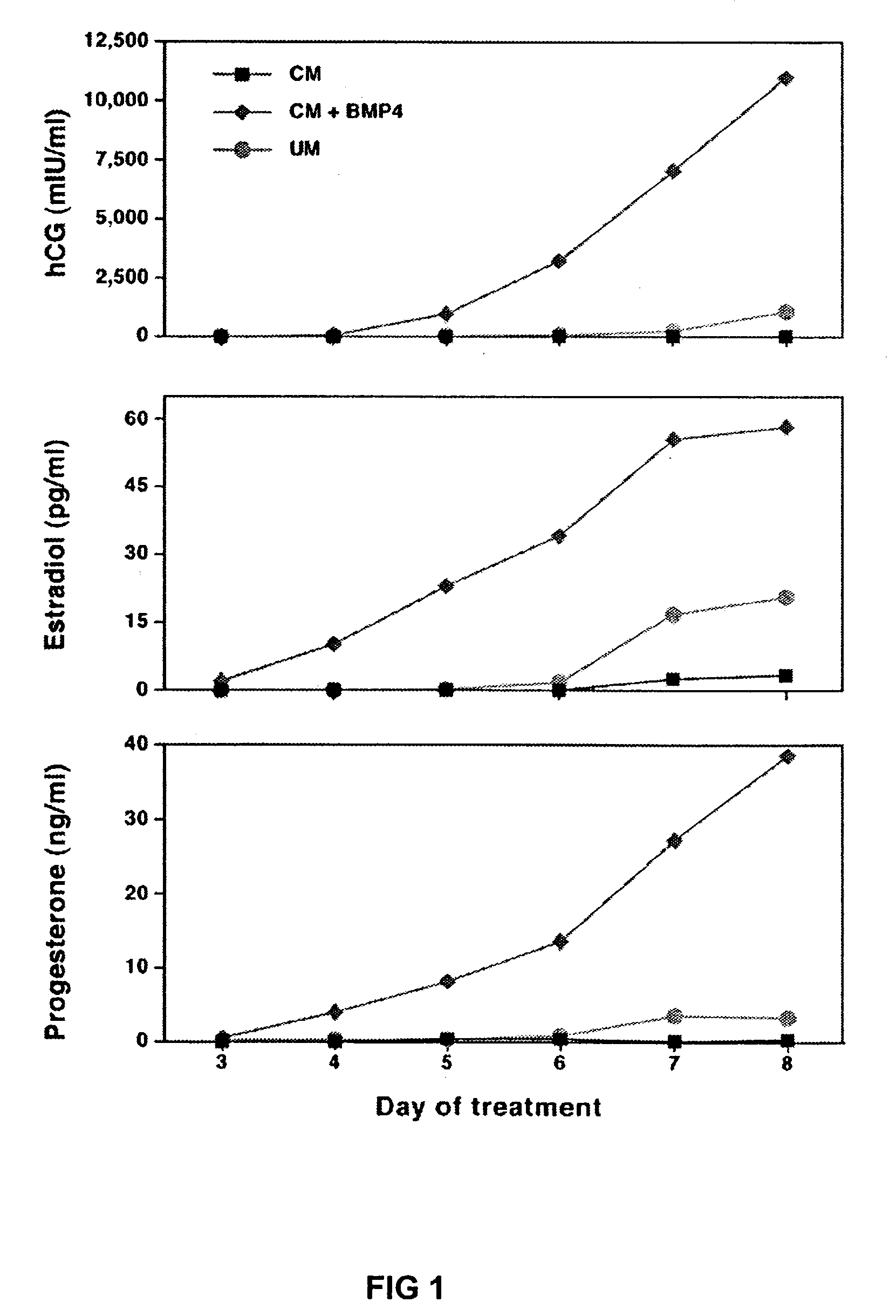
The first method to cause a culture of human and other primate stem cells to directly and uniformly differentiate into a committed cell lineage is disclosed. Treatment of primate stem cells with a single protein trophoblast induction factor causes the cells to transform into human trophoblast cells, the precursor cells of the placenta. Several protein factors including bone morphogenic protein 4 (BMP4), BMP2, BMP7, and growth and differentiation factor 5 can serve as trophoblast-inducting factors.
Owner:WICELL RES INST
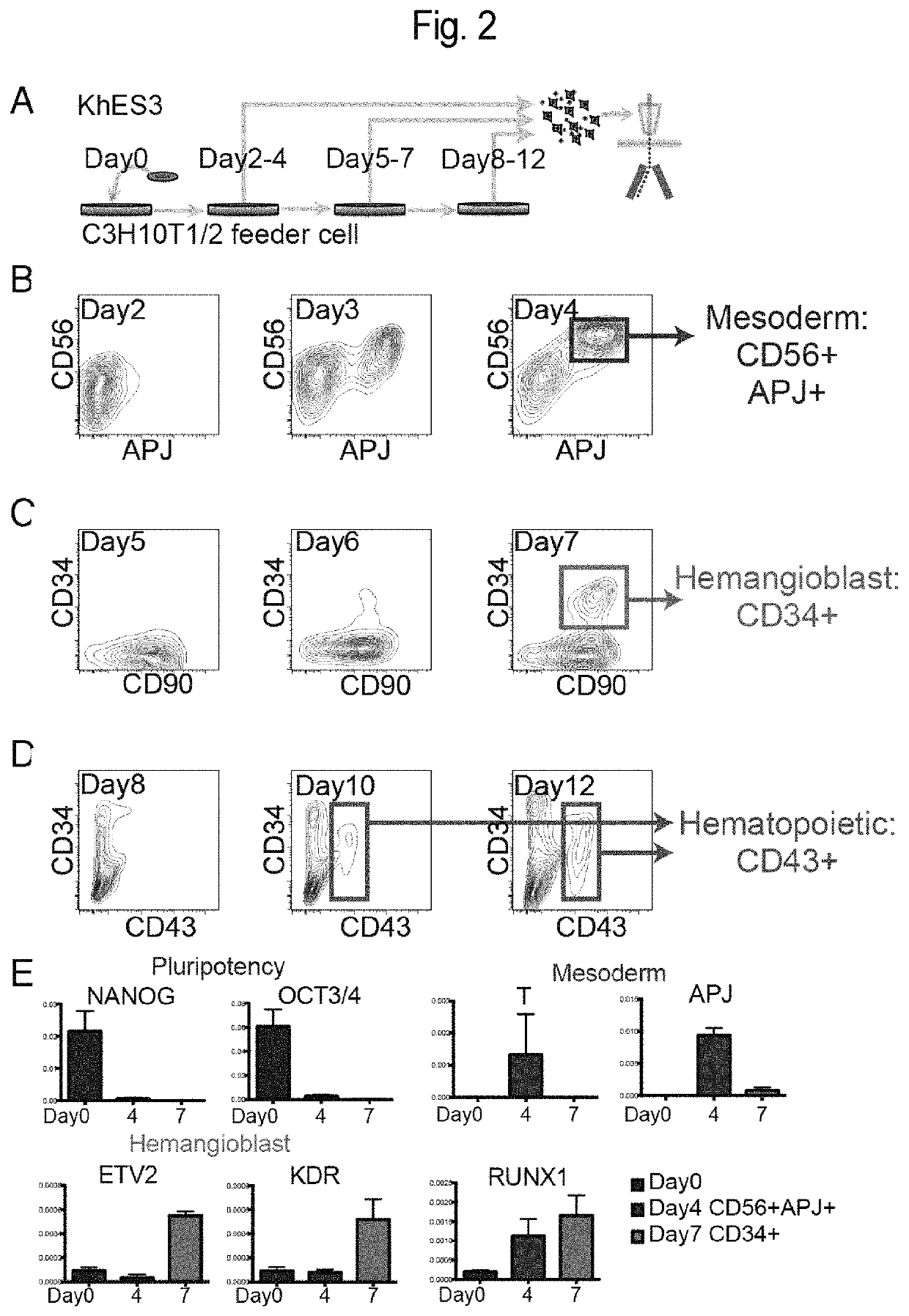
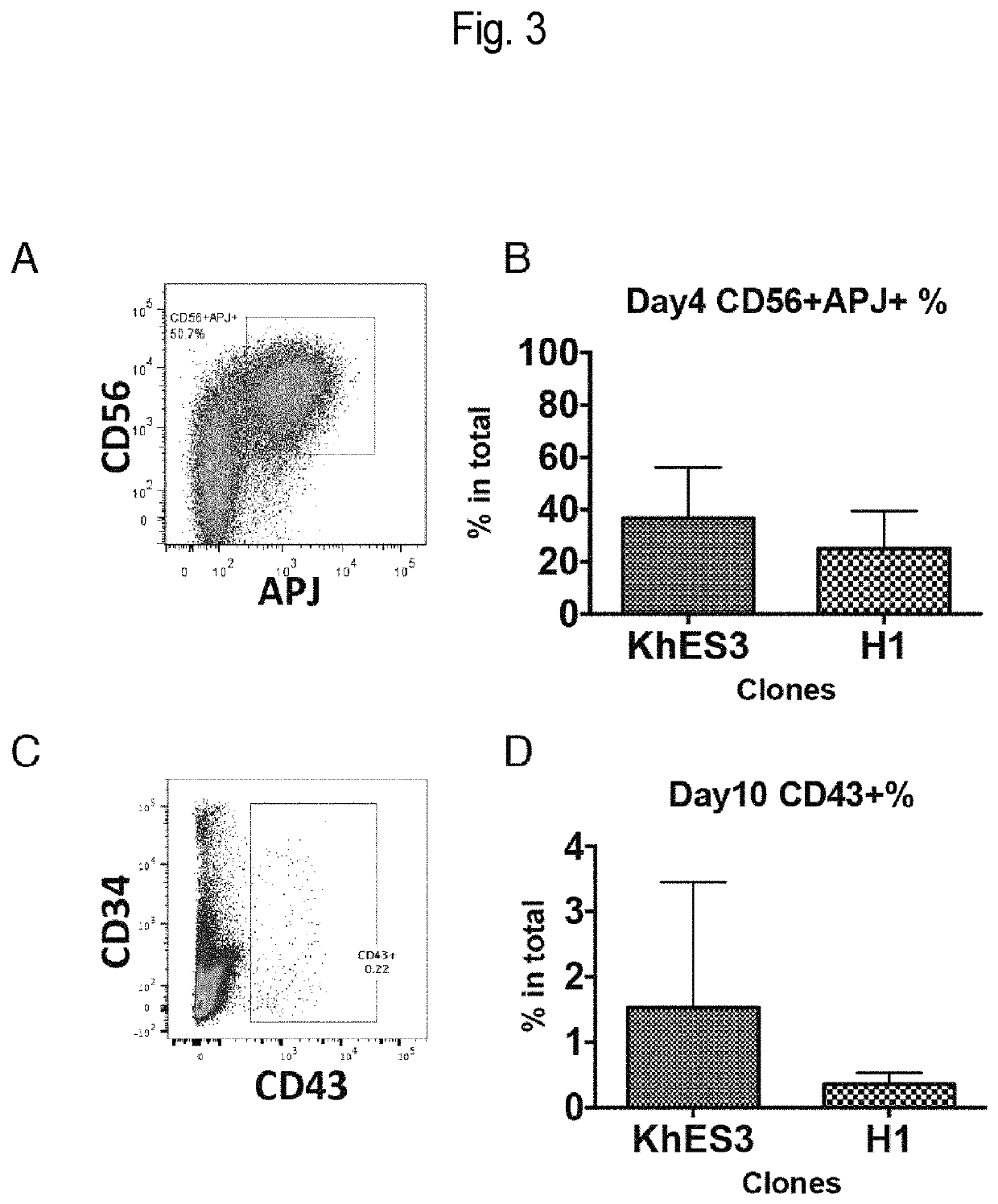
Mesoderm induction method having high blood cell differentiation capacity
ActiveUS11136547B2Efficient inductionPromote differentiationPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsPluripotential stem cellMedicine
Provided is a method for inducing mesoderm, comprising a step of bringing pluripotent stem cells into contact with bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) or CHIR for at least 3 days.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Serum-free cryoprotectant, and application thereof in cryopreservation of mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN107494517AImprove survival rateIncreased clinical allergen riskDead animal preservationUmbilical cordResuscitation
A serum-free cryoprotectant includes: 8-15 v / v% of DMSO, 85-92 v / v% of a DMEM basic culture medium, and a nutritional additive. The nutritional additive includes: fibroblast growth factors, insulin, growth hormone, transferrin, bone morphogenetic protein 4, glutamine, sodium pyruvate, beta-mercaptoethanol, human epidermal growth factor, sodium selenite, and various amino acids and vitamins. The cryoprotectant is free of animal sourced serum and avoids pollution and risk of allergen, and has better clinical safety. The serum-free cryoprotectant is suitable for cryopreservation of human placenta sourced, umbilical cord sourced and cord blood sourced mesenchymal stem cells; compared with common serum cryoprotectants, perinatal mesenchymal stem cells preserved in the cryoprotectant have high cell survival rate after resuscitation, have excellent adherence growth status and maintain biological characters well.
Owner:章毅 +7
Adult regulatory T cell in-vitro amplification culture medium and application method thereof
ActiveCN104278012AHigh amplification rateReduce oxidative damageBlood/immune system cellsDiseaseImmunologic disorders
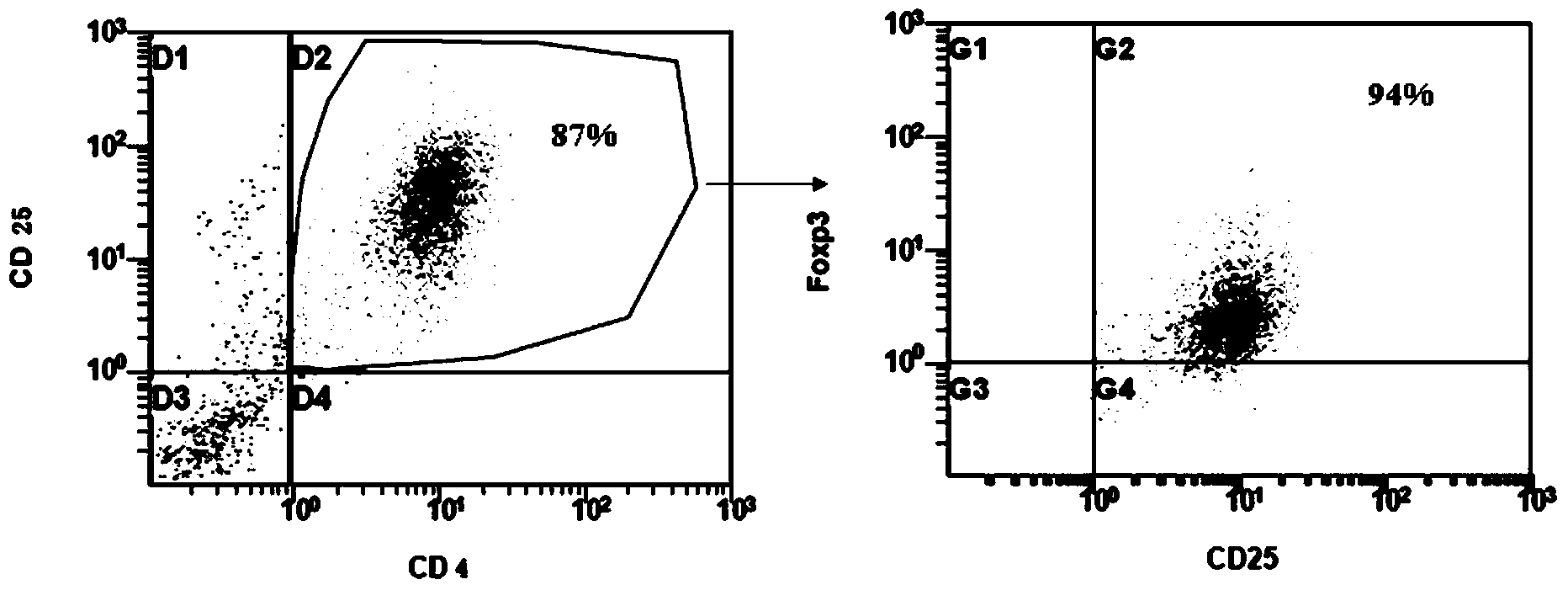
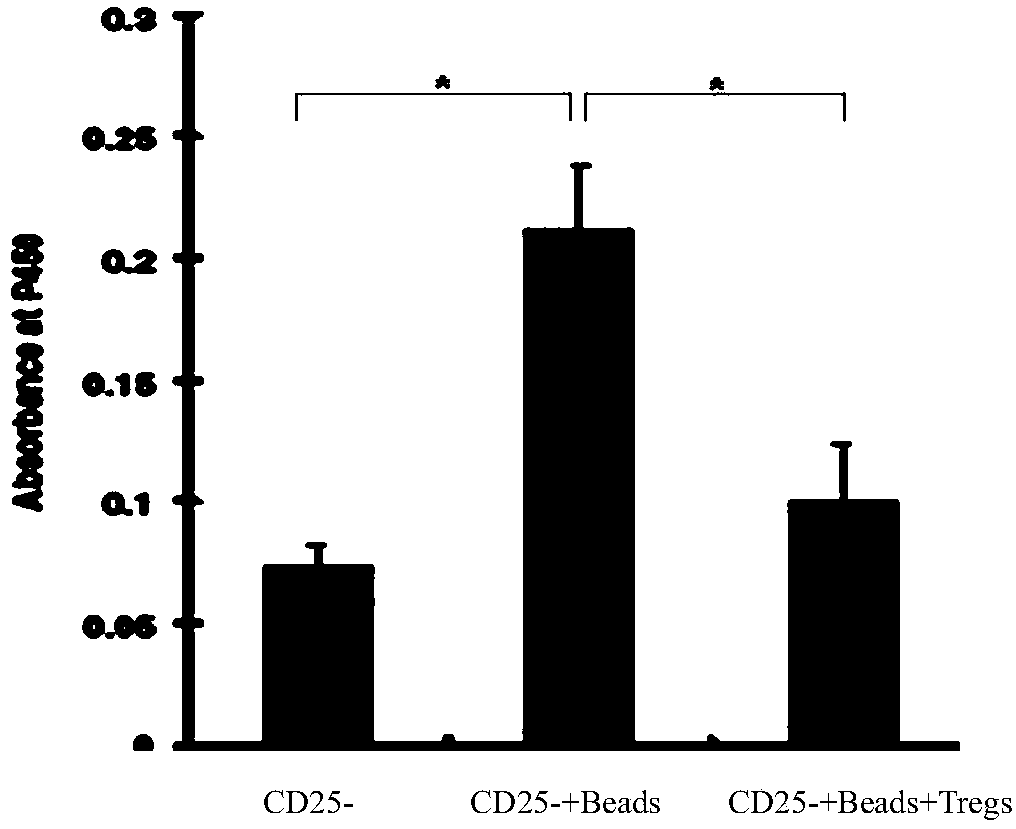
The invention provides an adult regulatory T cell in-vitro amplification culture medium and an application method thereof. The adult regulatory T cell in-vitro amplification culture medium comprises transform growth factor-beta (1-4 ng / ml), bone morphogenesis protein 4 (8-12 ng / ml), recombinant human interleukin-2 (300-500U / ml), rapamycin (80-100nM / ml), al-trans vitamin A acid (1-4 uM / mL), 4-hydroxyethylpiperazinoethylsulfonic acid (20-30mM / ml), L-glutamine (2mM / ml), 2-mercaptoethanol (40-50uM / ml), 5% human AB type serum, CD3CD28 magnetic bead, penicillin (50U / ml) and streptomycin (50ug / ml). When being used for performing amplification culture and induced differentiation on regulatory T cells, the culture medium can shorten the amplification and differentiation time of the regulatory T cells, and can obtain the high-purity Foxp3CD4+CD25+CD127-regulatory T cells. Therefore, the regulatory T cells can be used in the aspect of clinical treatment of anti-transplantation immunity rejection, autoimmune disease, allergic disease and the like to perform a novel clinical cell therapy.
Owner:HUNAN XENO LIFE SCI
Methods for preparing pleuripotent cardiovascular progenitor cells and maintaining cardiovascular differentiation capacity
ActiveCN103834613AUniform non-tumorigenicityArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProgenitorNODAL
The invention relates to methods for preparing pleuripotent cardiovascular progenitor cells and maintaining cardiovascular differentiation capacity and discloses a method for inducing and differentiating pluripotent stem cells into the pleuripotent cardiovascular progenitor cells for the first time. The method comprises the step of carrying out induction by utilizing ascorbic acid, a bone morphogenetic protein 4 and a glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor. The invention further provides a method for stably culturing the pleuripotent cardiovascular progenitor cells. The method comprises the steps of enabling the pleuripotent cardiovascular progenitor cells to stably grow and carry out generation transfer by utilizing a BMP (bone morphogenetic protein) signal channel inhibitor, an activin / Nodal signal channel inhibitor and a glycogen synthase kinase-3 signal channel inhibitor. The pleuripotent cardiovascular progenitor cells prepared by utilizing the method can be further differentiated into cells including myocardial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells or vascular endothelial cells in a cardiovascular pedigree and can be applied to the treatment and myocardial regeneration research of heart diseases, the pharmaceutical cardiovascular cytotoxicity detection and the development of heart medicaments.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vascular endothelial cell culture method
ActiveCN104928230AExcellent self-renewal abilityAvoid uncertaintyArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsProgenitorSodium bicarbonate
The invention discloses a vascular endothelial cell culture method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) differentiating pluripotent stem cells into mesendoderm precursor cells in a culture medium A; 2) differentiating the mesendoderm precursor cells into progenitor cells of vascular endothelial cells in a culture medium B; 3) differentiating the progenitor cells of the vascular endothelial cells into the vascular endothelial cells in a culture medium C. The culture medium A contains a DMEM, an F12 culture medium, sodium selenate, sodium bicarbonate, vitamin C, insulin, an activin A , bone morphogenetic protein-4 and a glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor; the culture medium B contains a DMEM, an F12 culture medium, sodium selenate, sodium bicarbonate, vitamin C, insulin, a vascular endothelial growth factor and a transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway inhibitor; the culture medium C contains a DMEM, an F12 culture medium, sodium selenate, sodium bicarbonate, vitamin C, insulin, a vascular endothelial growth factor, an epidermal growth factor and a fibroblast growth factor. According to the method, the pluripotent stem cells can be differentiated into the vascular endothelial cells.
Owner:宁波医诺生物技术有限公司
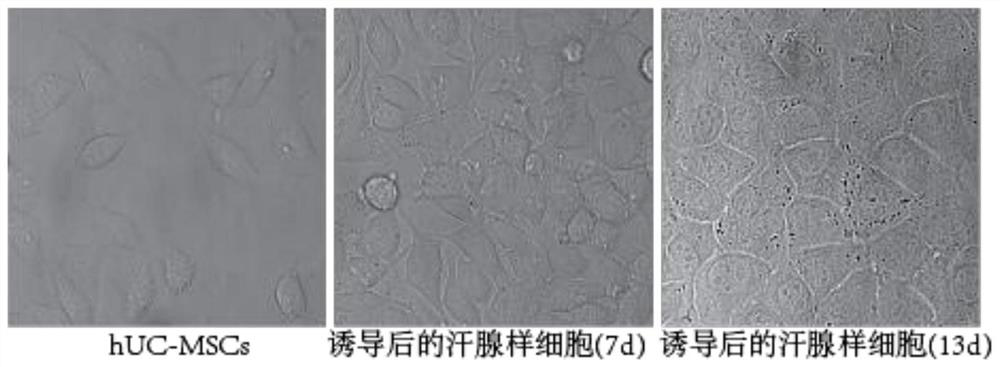
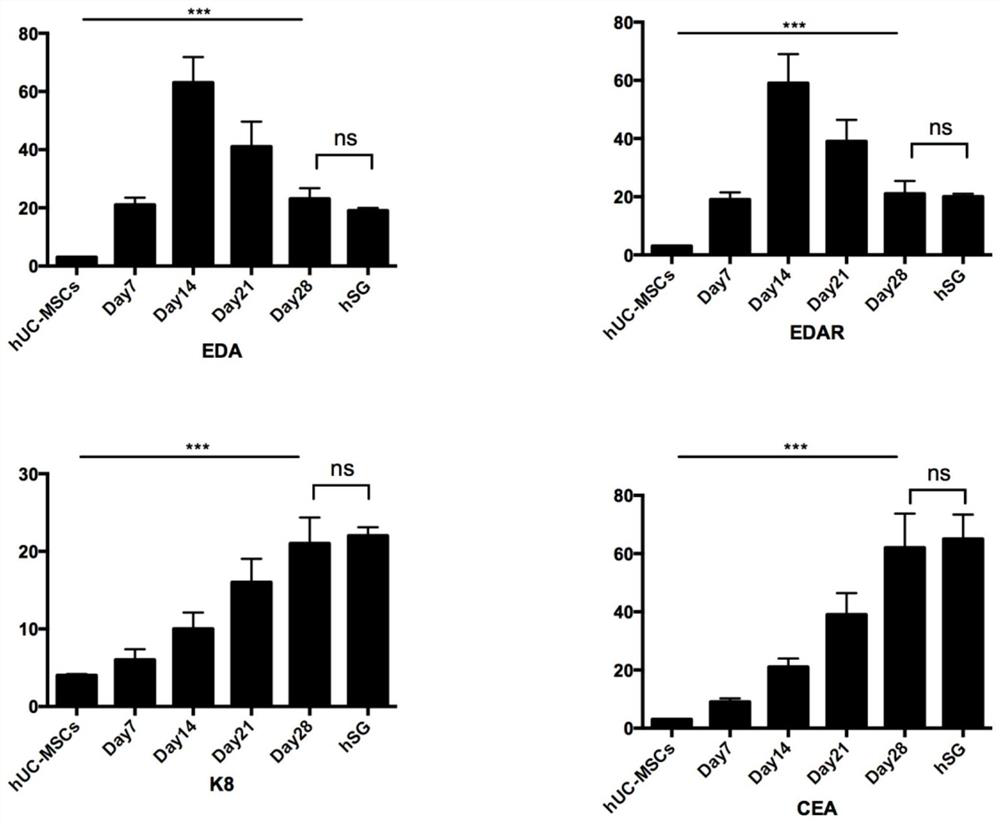
Eccrine sweat gland cell induction medium and application thereof
ActiveCN104450606AEffective differentiationEasy to operateArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsLife qualityPenicillin
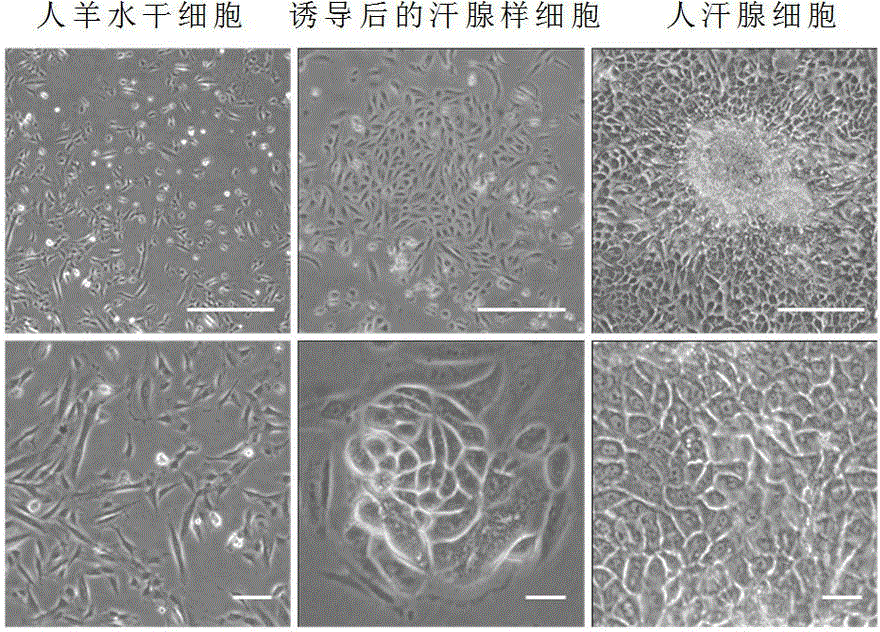
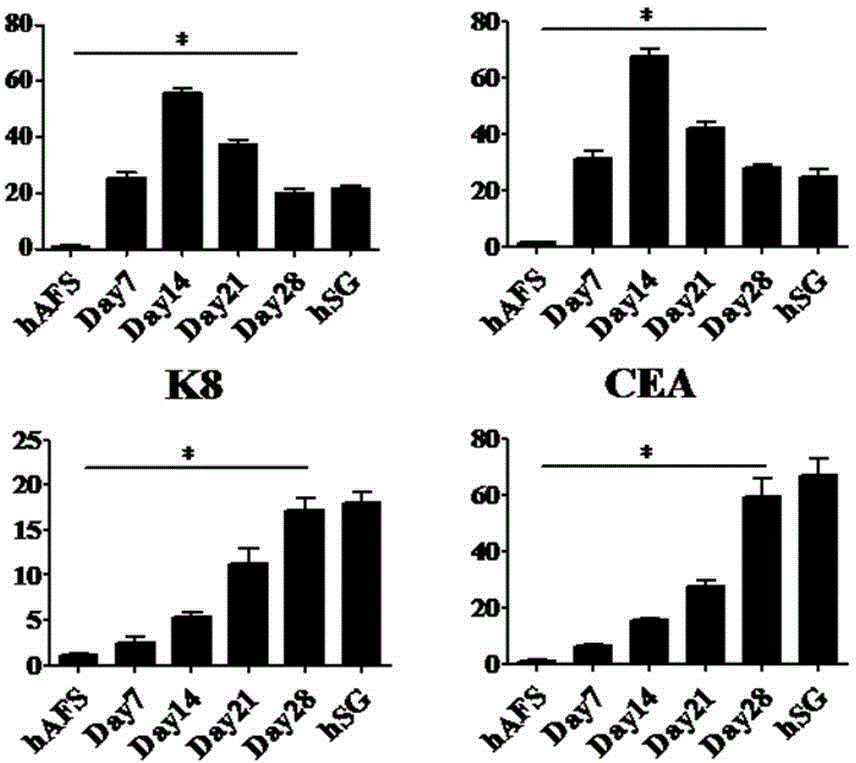
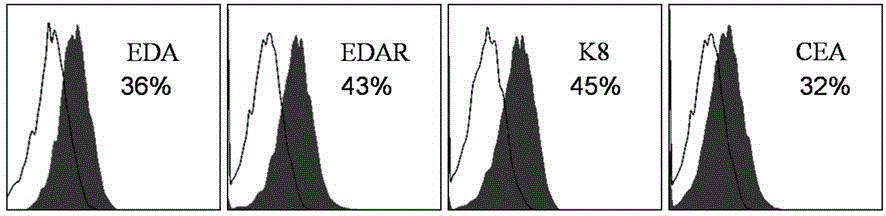
The invention discloses an eccrine sweat gland cell induction medium and an application thereof. The eccrine sweat gland cell induction medium comprises a DMEM / F12 cell medium, a keratinocyt medium, fetal calf serum, an epidermal growth factor, triiodothyronine, hydrocortisone, insulin-transferrin-sodium selenite, L-glutamine, penicillin, streptomycin, a hepatocyte growth factor and a bone morphogenetic protein 4. The eccrine sweat gland cell induction medium disclosed by the invention can be used for successfully inducing stem cells to be directionally differentiated to eccrine sweat gland-like cells so as to provide sufficient eccrine sweat gland cells for treating extensive burn patients, so that the living quality of the patients is greatly improved. The medium further provides a theoretical basis for researching differentiated development of the sweat gland, so that the medium has a potential clinical application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Application of bone morphogenetic protein 4 in cancer inhibition
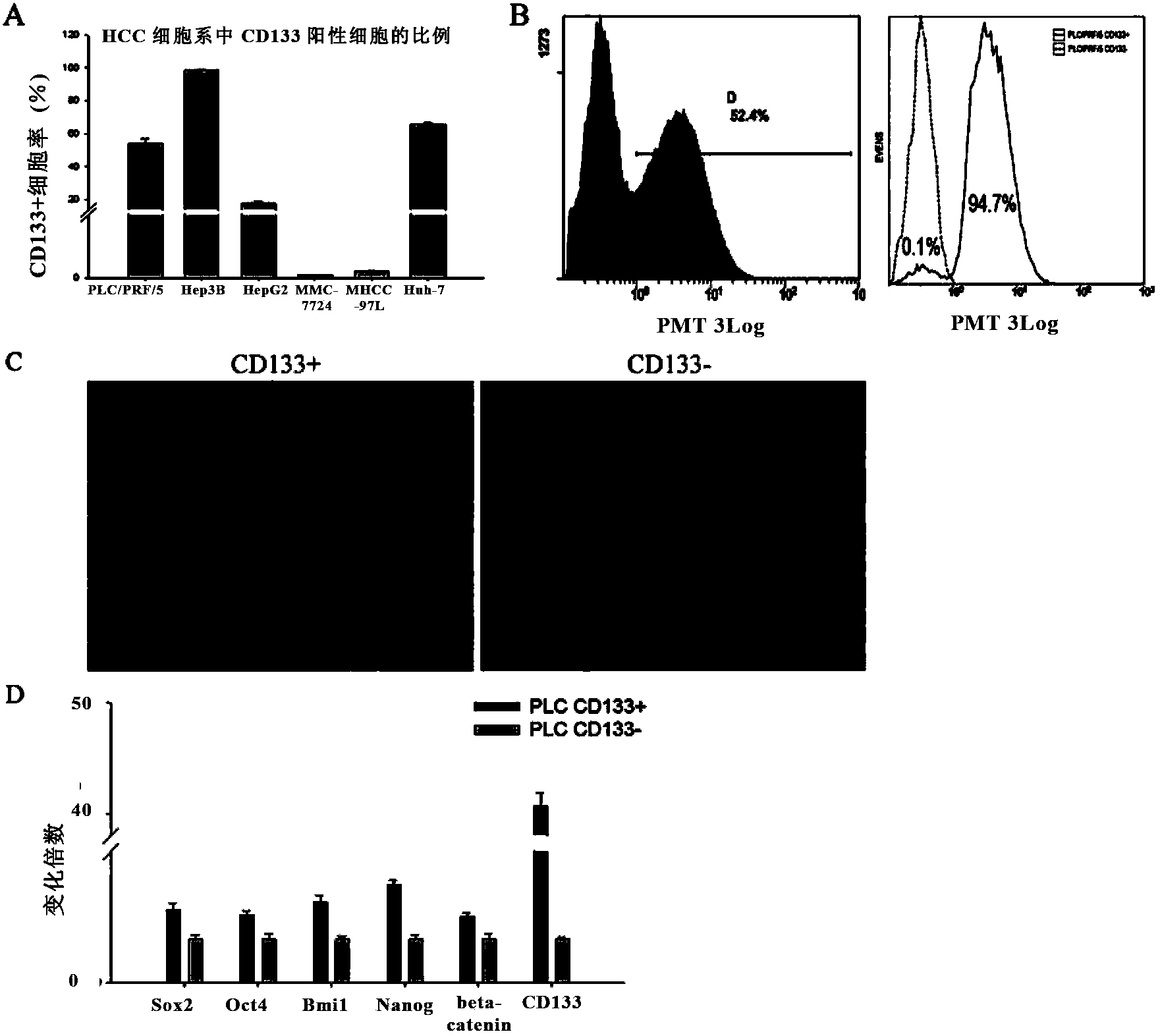
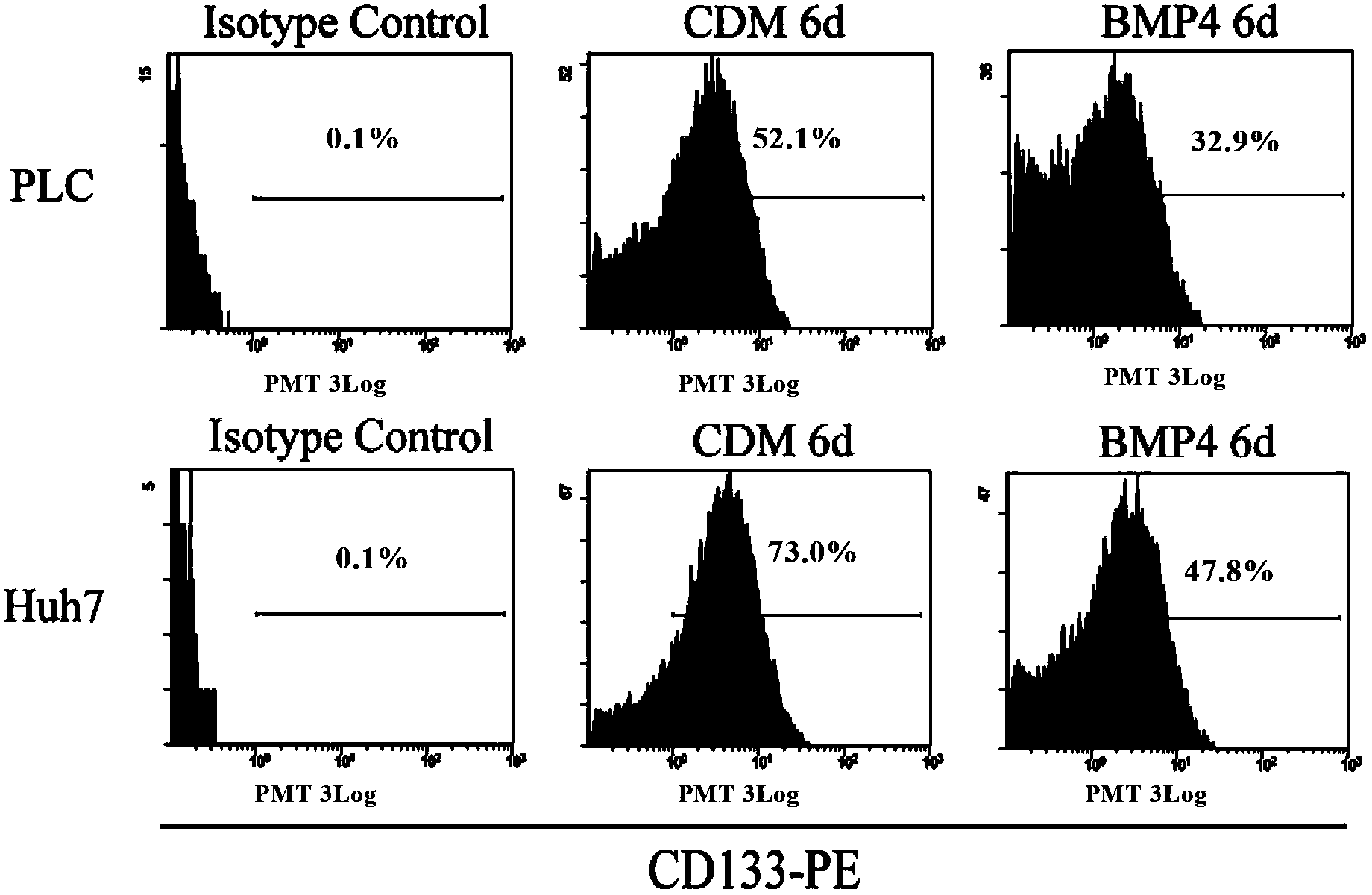
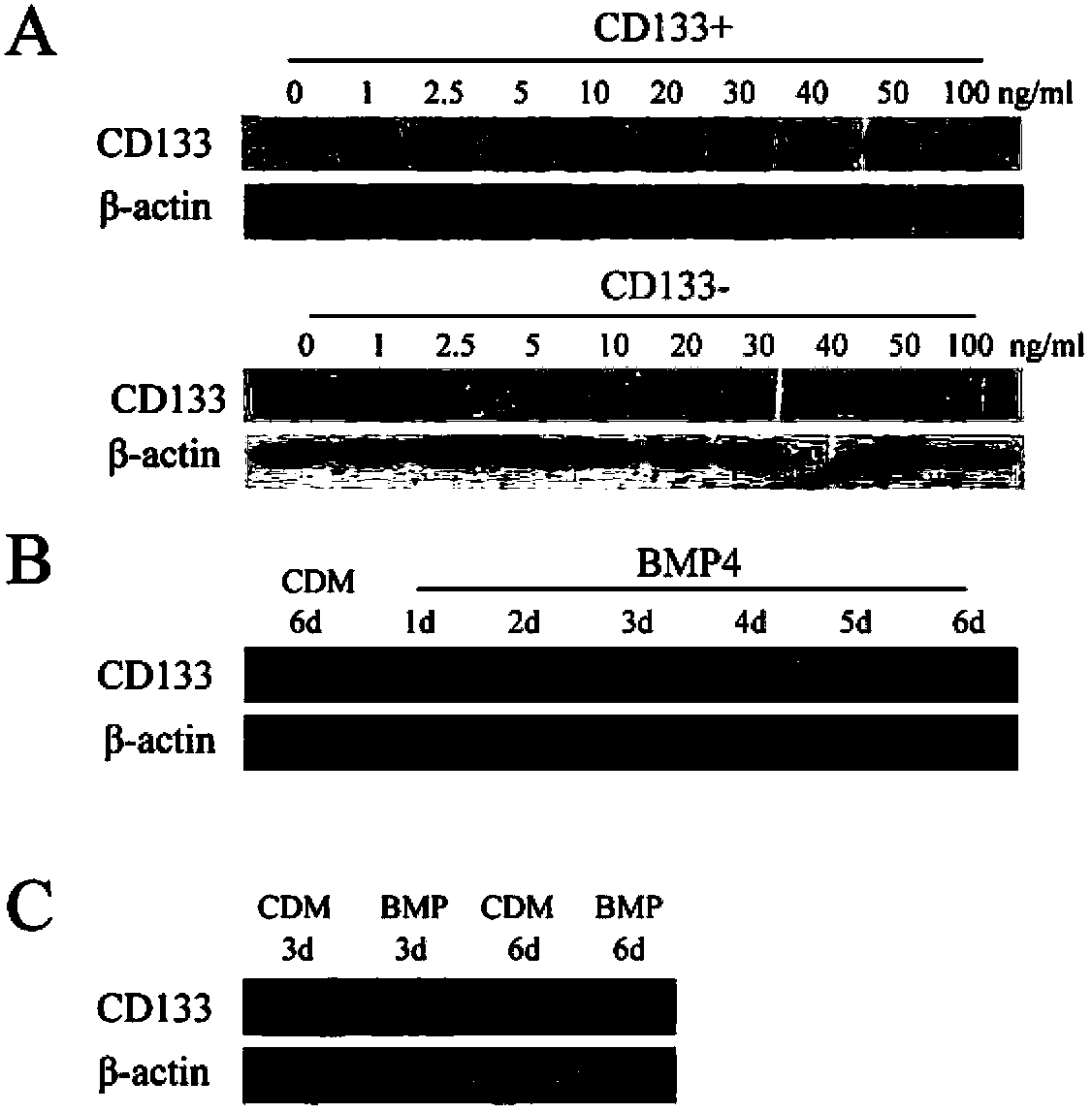
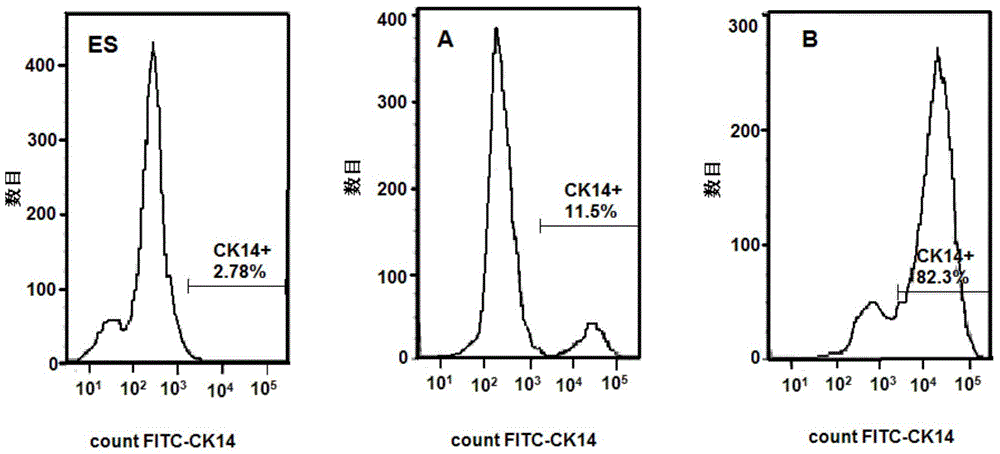
The present invention relates to an application of bone morphogenetic protein 4 in cancer inhibition. Specifically bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) has a liver cancer stem cell differentiation induction effect, wherein CD133 protein expression of liver cancer cell lines can be down-regulated and liver cancer cell line CD133+ liver cancer stem cell differentiation can be promoted with BMP4, and BMP4 can further be provided for inhibiting in vitro proliferation and self-renewal of liver cancer cell lines and inhibiting tumorigenicity of immune-deficient mice. The present invention further provides BMP4-induced liver cancer stem cell differentiation action mechanism.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Pharmaceutical composition containing sodium alginate and preparation method of pharmaceutical composition
InactiveCN104667348AImproved prognosisImprove the quality of lifeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTMechanical property
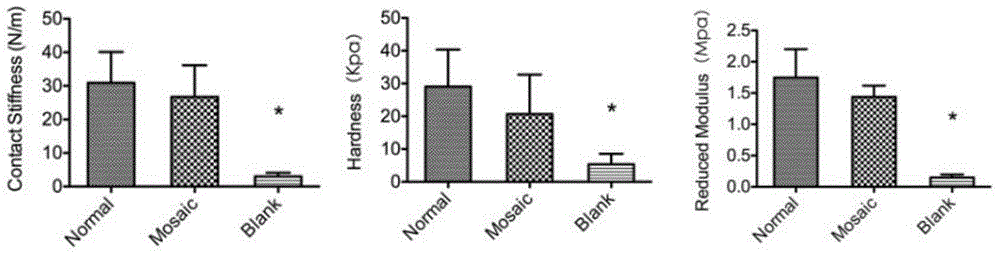
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition containing sodium alginate for cartilage tissue repairing. As an active ingredient of the composition, bone morphogenetic protein-4 transfected fat is derived from stem cells, sodium alginate and calcium chloride; by virtue of the composition, gaps filled between cartilage rods as well as between the cartilage rods and peripheral cartilages and subchondral bones are completely filled by regenerated tissues and mechanical properties similar to that of normal cartilage are guaranteed; full fusion of mosaic bones and cartilages with peripheral cartilages and subchondral bones is achieved, and joint function improvement and level recovery in postoperative patients are significantly improved; in addition, the invention also provides a preparation method of the pharmaceutical composition.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL +1
Inducing agent and medium for inducing directional differentiation of embryonic stem cell into keratinocytes
InactiveCN104651298AImprove efficiencyArtificial cell constructsEmbryonic cellsBone morphogenetic protein 4Mucous membrane
The invention provides an inducing agent for inducing directional differentiation of an embryonic stem cell into keratinocytes. The inducing agent comprises bone morphogenetic protein 4, retinoic acid and ascorbic acid. Preferably, in the inducing agent, the bone morphogenetic protein 4, retinoic acid and ascorbic acid are in a content ratio of (1-50g):(0.1-5 mol):(50-600mol). The inducing agent for inducing directional differentiation of the embryonic stem cell into keratinocytes combines the bone morphogenetic protein 4, retinoic acid and ascorbic acid, can effectively improve the efficiency for induced directional differentiation of hESC into keratinocytes (as high as 77.93%, and far higher than other formula inducing agents), provides an approach for efficiently inducing differentiation of hESC into keratinocytes, and provides seed cells for constructing tissue engineered oral mucosas.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Pluripotent stem cells directional differentiation method
InactiveCN107488629AIncrease productionQuality improvementCulture processCell culture supports/coatingGerm layerProcess mechanism
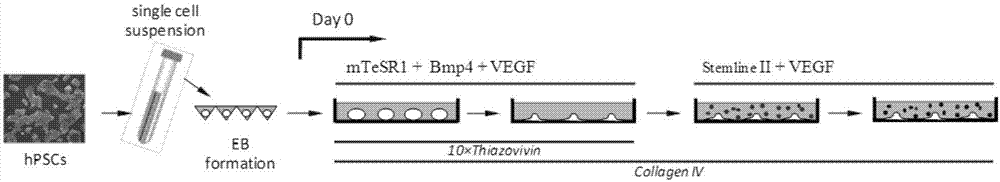
The invention discloses a pluripotent stem cells directional differentiation method. The method is characterized in that pluripotent stem cells are cultured under cell culture environment of non exogenous hematopoietic cytokines, non serum, non matrix cells and clear component, after embryoid is formed, a vascular endothelial growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein 4 are added, the embryoid is attached on the surface spread with collagen IV, mesoderm differentiation is induced, and hemopoietic progenitor cells and blood corpuscles are generated. The cell culture system with determined component enables directional differentiation on the pluripotent stem cells, has the advantages of low cost, simple operation, high repeatability and ordered differentiation process, can massively generate hemopoietic progenitor cells and blood corpuscles, and has important meaning for researching a blood growth process mechanism.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
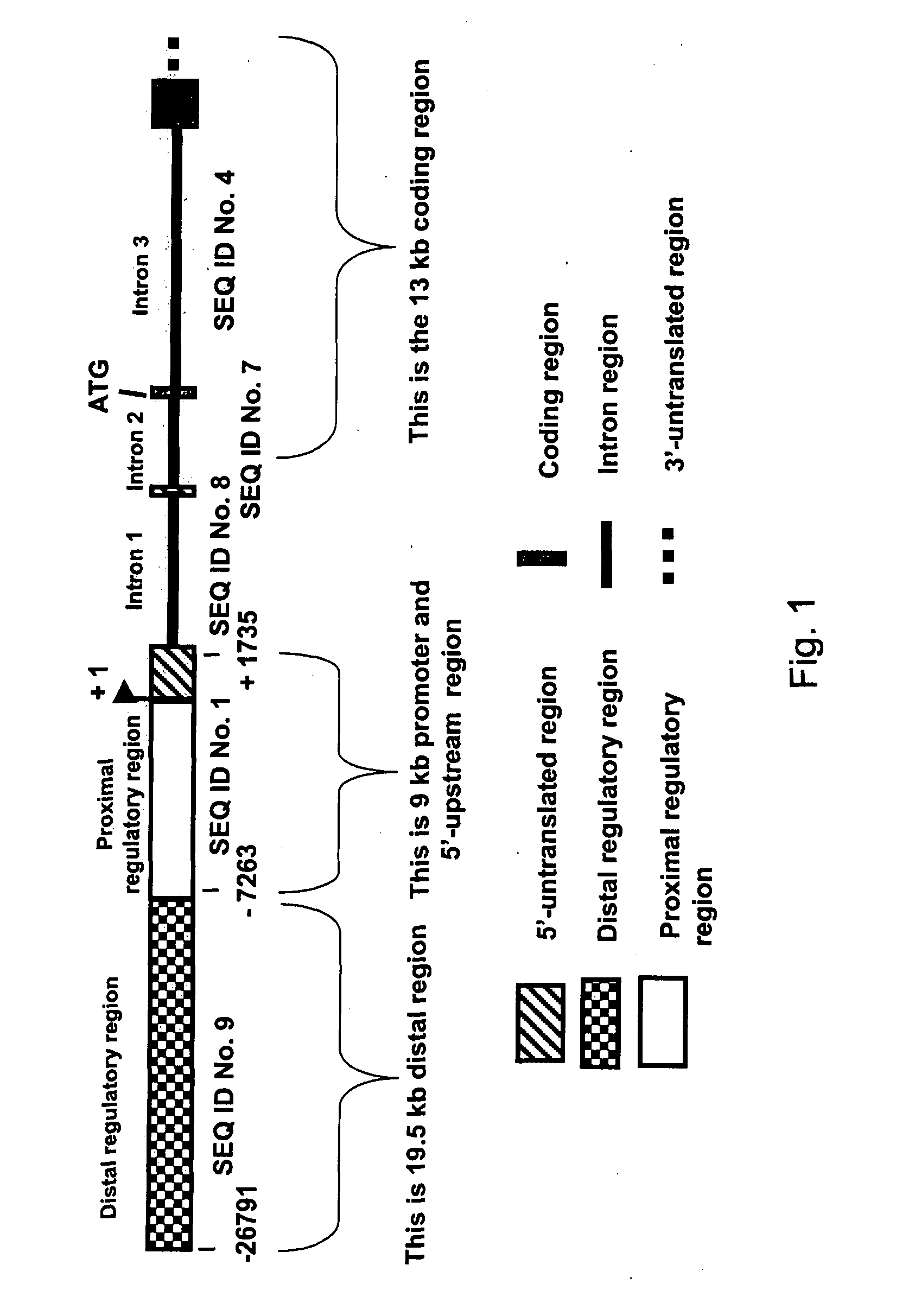
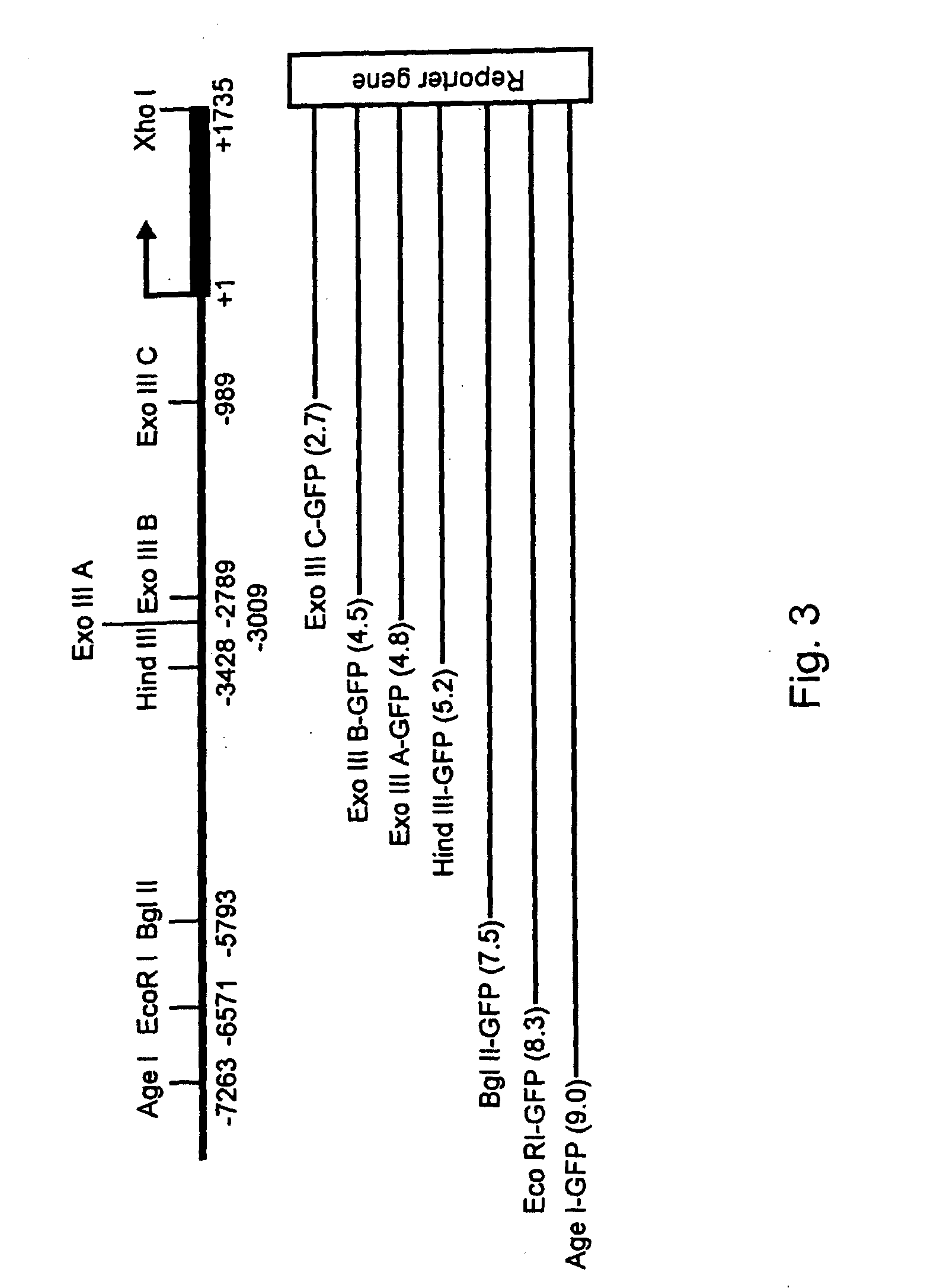
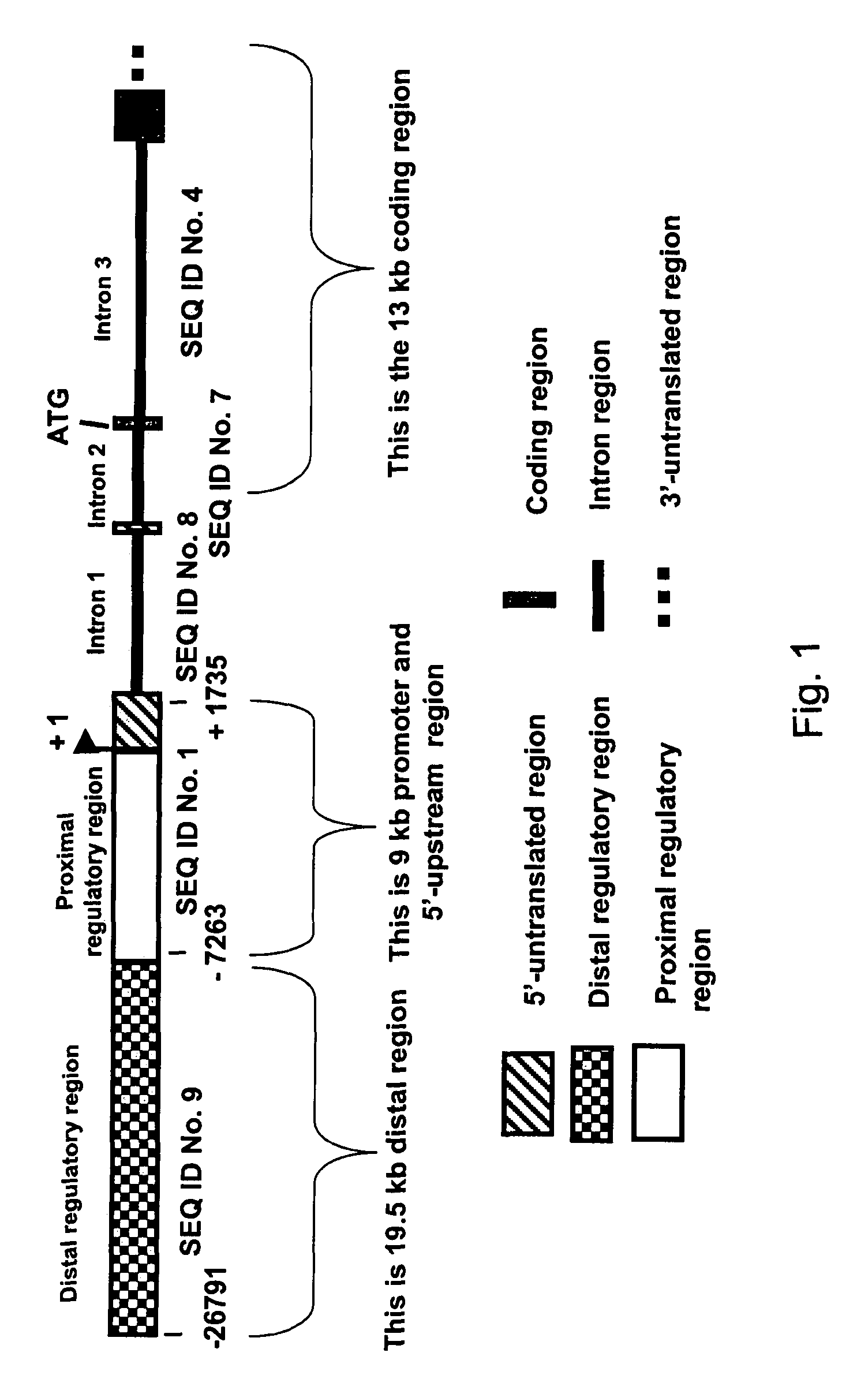
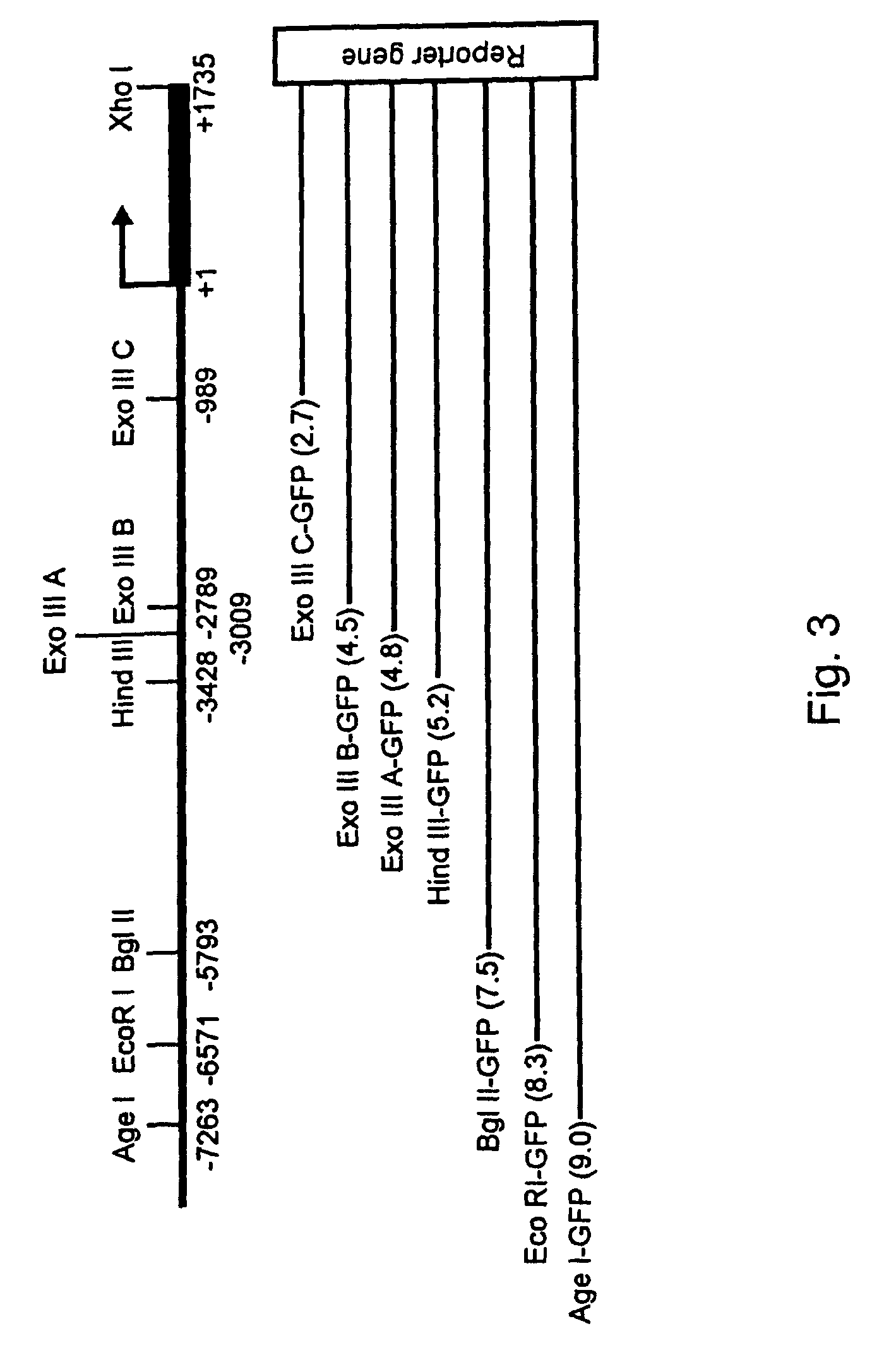
Expression of zebrafish bone morphogenetic protein 4
InactiveUS20050005317A1Tissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionRegulation of gene expressionBone morphogenetic protein 6
Embodiments of the invention generally provide isolated DNA molecules, tissue-specific expression sequences, and promoter and regulatory DNA sequences involved in the regulation of bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4). More specifically, the invention relates to regulation of gene expression in a tissue-specific manner. In one aspect, the invention provides zebrafish BMP4 gene, its structural organization, its promoter, and proximal and distal regulatory regions. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for identifying potential compounds / agents, potential molecular regulators, and the expression pattern for the expression of BMP4 gene.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Method for preparing heart valve endothelial cells by inducing pluripotent stem cell differentiation, and application of heart valve endothelial cells
ActiveCN112359012ADifferentiation is simpleShort timeSkeletal/connective tissue cellsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsPluripotential stem cellInduced pluripotent stem cell
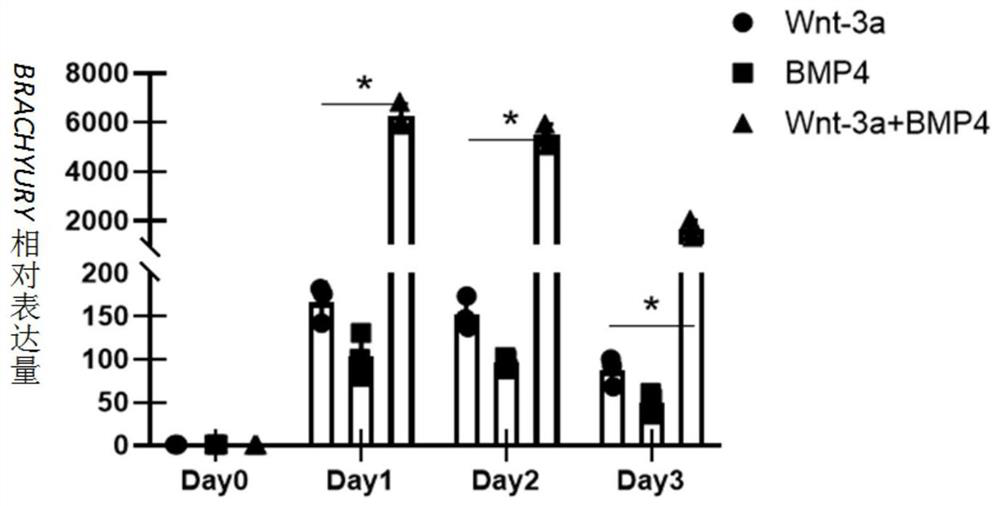
The invention discloses a method for preparing heart valve endothelial cells by inducing differentiation of pluripotent stem cells, and application of the heart valve endothelial cells. The method comprises the following steps: planting pluripotent stem cells in a culture dish coated with matrix glue in a tiled manner, and culturing the pluripotent stem cells by using Essential 8 to enable the pluripotent stem cells to be attached to the wall of the culture dish; and culturing the pluripotent stem cells in a differential medium Essential 6 containing Wnt3a and bone morphogenetic protein 4, culturing the pluripotent stem cells in a differential medium Essential 6 containing epidermal growth factors and bone morphogenetic protein 4, digesting mesoderm cells of the heart, and putting the cardiac mesoderm cells in the culture dish into a differential medium Essential 6 containing bone morphogenetic protein 4, transforming growth factors and endothelial growth factors for continuous cultureto obtain heart valve endothelial cells. The method disclosed by the invention is high in differentiation efficiency, and more than 80% of valvular endothelial cells can be obtained under the condition that flow sorting is not carried out, so that sufficient seed cell sources can be guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA +1
Culture medium, kit and application thereof
The invention discloses a culture medium, a kit, a method for preparing early stage mesoderm ancestral cells and a method for preparing hematogenesis endothelial cells by using the kit, wherein the culture medium contains a basic culture medium namely an SFDM (serum-free differentiation medium), PGE2 (prostaglandin E2) and BMP4 (bone morphogenetic protein 4). By using the culture medium disclosed by the invention, a large amount of early stage mesoderm ancestral cells can be prepared efficiently and quickly.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
Expression of zebrafish bone morphogenetic protein 4
InactiveUS7427677B2Tissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionRegulation of gene expressionBone morphogenetic protein 6
Embodiments of the invention generally provide isolated DNA molecules, tissue-specific expression sequences, and promoter and regulatory DNA sequences involved in the regulation of bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4). More specifically, the invention relates to regulation of gene expression in a tissue-specific manner. In one aspect, the invention provides zebrafish BMP4 gene, its structural organization, its promoter, and proximal and distal regulatory regions. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for identifying potential compounds / agents, potential molecular regulators, and the expression pattern for the expression of BMP4 gene.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Application of bone morphogenetic protein-4 in screening drugs for resisting cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure or cardiac fibrosis
The invention discloses an application of bone morphogenetic protein-4 in screening drugs for resisting cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure or cardiac fibrosis and belongs to the field of biomedicine. Screened drug types comprise: bone morphogenetic protein-4 formation inhibitor, bone morphogenetic protein-4 antagonistic, bone morphogenetic protein-4 receptor antagonists and bone morphogenetic protein-4 downstream signal antagonistic. The invention also relates to an application of the drugs in preparation of medicines for resisting cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure and arrhythmia. Researches have found that bone morphogenetic protein-4 can induce myocardial hypertrophy, apoptosis and cardiac fibroblast collagen secretion increase, lead to occurrence of cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure and arrhythmia. However, drugs for antagonism of bone morphogenetic protein-4 and its cell signaling pathway can be used to inhibit occurrence of cardiac hypertrophy, inhibit cardiac fibrosis and minimize occurrence of cardiac cell death and arrhythmia. The invention provides a theoretical basis for realizing high-flux medicine screening, and is of practical guiding significance.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Culture medium and method for inducing directional differentiation of embryonic stem cells into keratinocytes
InactiveCN104651298BImprove efficiencyArtificial cell constructsEmbryonic cellsBone morphogenetic protein 4Ascorbic acid
The invention provides an inducing agent for inducing directional differentiation of an embryonic stem cell into keratinocytes. The inducing agent comprises bone morphogenetic protein 4, retinoic acid and ascorbic acid. Preferably, in the inducing agent, the bone morphogenetic protein 4, retinoic acid and ascorbic acid are in a content ratio of (1-50g):(0.1-5 mol):(50-600mol). The inducing agent for inducing directional differentiation of the embryonic stem cell into keratinocytes combines the bone morphogenetic protein 4, retinoic acid and ascorbic acid, can effectively improve the efficiency for induced directional differentiation of hESC into keratinocytes (as high as 77.93%, and far higher than other formula inducing agents), provides an approach for efficiently inducing differentiation of hESC into keratinocytes, and provides seed cells for constructing tissue engineered oral mucosas.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for efficiently obtaining beating functional cardiomyocytes from mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN105950548AImprove technical effectEasy to operateSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsCardiac muscleMesenchymal stem cell
The invention discloses a method for efficiently obtaining beating functional cardiomyocytes from mesenchymal stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: reprogramming the mesenchymal stem cells into pluripotent stem cells through mRNA reprogramming, and then adding an activin A and a bone morphogenetic protein 4 by adopting a matrix sandwich method to obtain the beating functional cardiomyocytes with differentiation efficiency of more than 80%. The differentiation efficiency of cardiomyocytes can be greatly improved by the method provided by the invention. The in vitro multiplication capacity of the cardiomyocytes is limited in the prior art, so the requirement for establishing the myocardium of tissue engineering in vitro cannot be met. The method provided by the invention can provide important experimental data for the research of cell therapy of ischemic cardiovascular diseases, and has a good clinical application prospect.
Owner:NANJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Culture medium for sweat gland cells and preparation method of culture medium
ActiveCN106834211AProliferate fastImprove securityEpidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsSweat glandCulture mediums
The invention relates to a culture medium for sweat gland cells and a preparation method of the culture medium. The culture medium comprises a basic culture solution and an additive, wherein the basic culture solution is an SGDM culture solution; the additive comprises the following components, by the addition amount in the basic culture solution, nerve growth factors, transforming growth factors-beta, epidermal growth factors, HEPG (heparin sulfate proteoglycan) and bone morphogenetic protein 4. The culture medium can increase the probability at which ips cells are induced into sweat gland cells, stable passage can be guaranteed, the cell proliferation speed is increased, and a source of seed cells is provided for skin tissue engineering. Additionally, no serum is used in the whole process, risks caused by animal origin pathogens are effectively avoided, and the clinical application safety is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RAINHOME PHARM&TECH CO LTD
Tooth Regeneration Method
InactiveUS20100093080A1Difficult to developArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInsulin-like growth factorMammal tooth
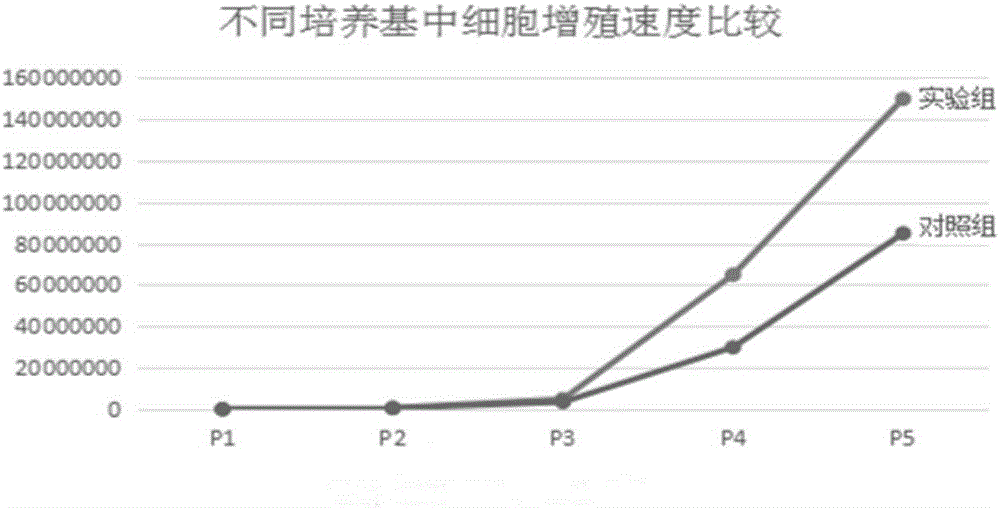
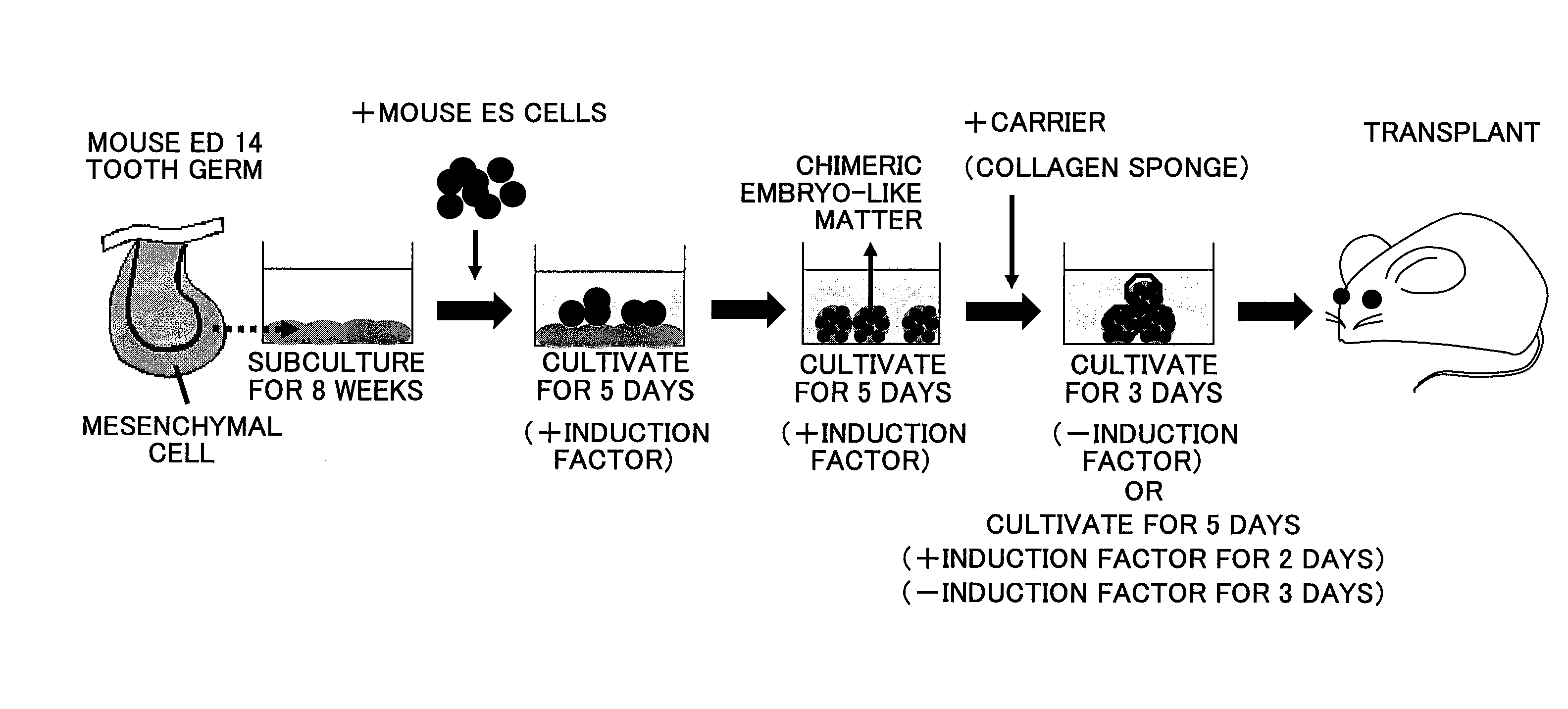
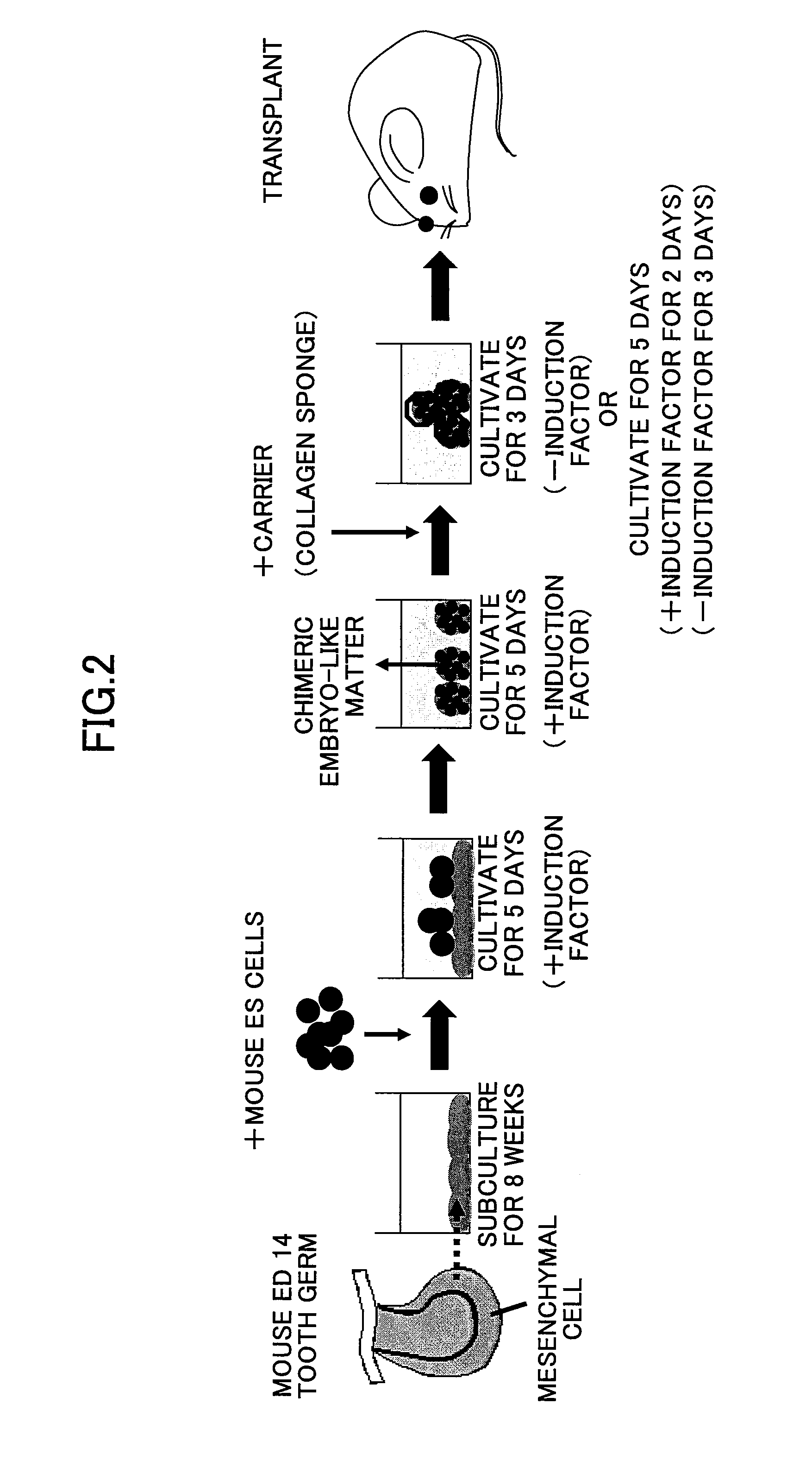
Disclosed is a novel method for formation of a tooth by producing a chimera embryoid body using an undifferentiated cell and a dental mesenchymal cell derived from a mammal of the same species as that of the target mammal and then cultivating the chimera embryoid body on a three-dimensional matrix. A tooth is formed by co-cultivating an undifferentiated cell and a dental mesenchymal cell derived from a mammal of the same species as that of the target mammal in the presence of an induction factor to produce a chimera embryoid body, and then cultivating the chimera embryoid body on a three-dimensional matrix. The cultivation of the chimera embryoid body on the three-dimensional matrix is performed either by cultivating the chimera embryoid body in a serum culture medium without the induction factor for three days; or cultivating the chimera embryoid body in a culture medium supplemented with the induction factor for two days, and further cultivating the chimera embryoid body in a serum culture medium without the induction factor for three days. The undifferentiated cell is at least one cell selected from all stem cells including an ES cell. The mammal is one selected from all mammals. The induction factor is activin, bone morphogenic protein 4, insulin growth factor 1, fibroblast growth factor 2, or transforming growth factor β1.
Owner:MATSUMOTO DENTAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing pluripotent cardiovascular precursor cells and maintaining their cardiovascular differentiation ability
ActiveCN103834613BUniform non-tumorigenicityArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsDiseaseInduced pluripotent stem cell
The present invention relates to methods for preparing pluripotent cardiovascular precursor cells and maintaining their cardiovascular differentiation ability. For the first time, a method for efficiently inducing the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into pluripotent cardiovascular precursor cells was revealed, including induction with ascorbic acid, bone morphogenic protein 4 and glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors. The present invention also provides a method for stably cultivating multipotential cardiovascular precursor cells, including using BMP signaling pathway inhibitors, Activin / Nodal signaling pathway inhibitors and glycogen synthase kinase 3 signaling pathway inhibitors to enable stable growth and passage. The multipotential cardiovascular precursor cells obtained by the present invention can be further differentiated into some cells of cardiovascular lineage such as cardiomyocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells or vascular endothelial cells, which can be used for the treatment of heart diseases and research on myocardial regeneration, drug cardiovascular cytotoxicity Testing, cardiac drug development.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
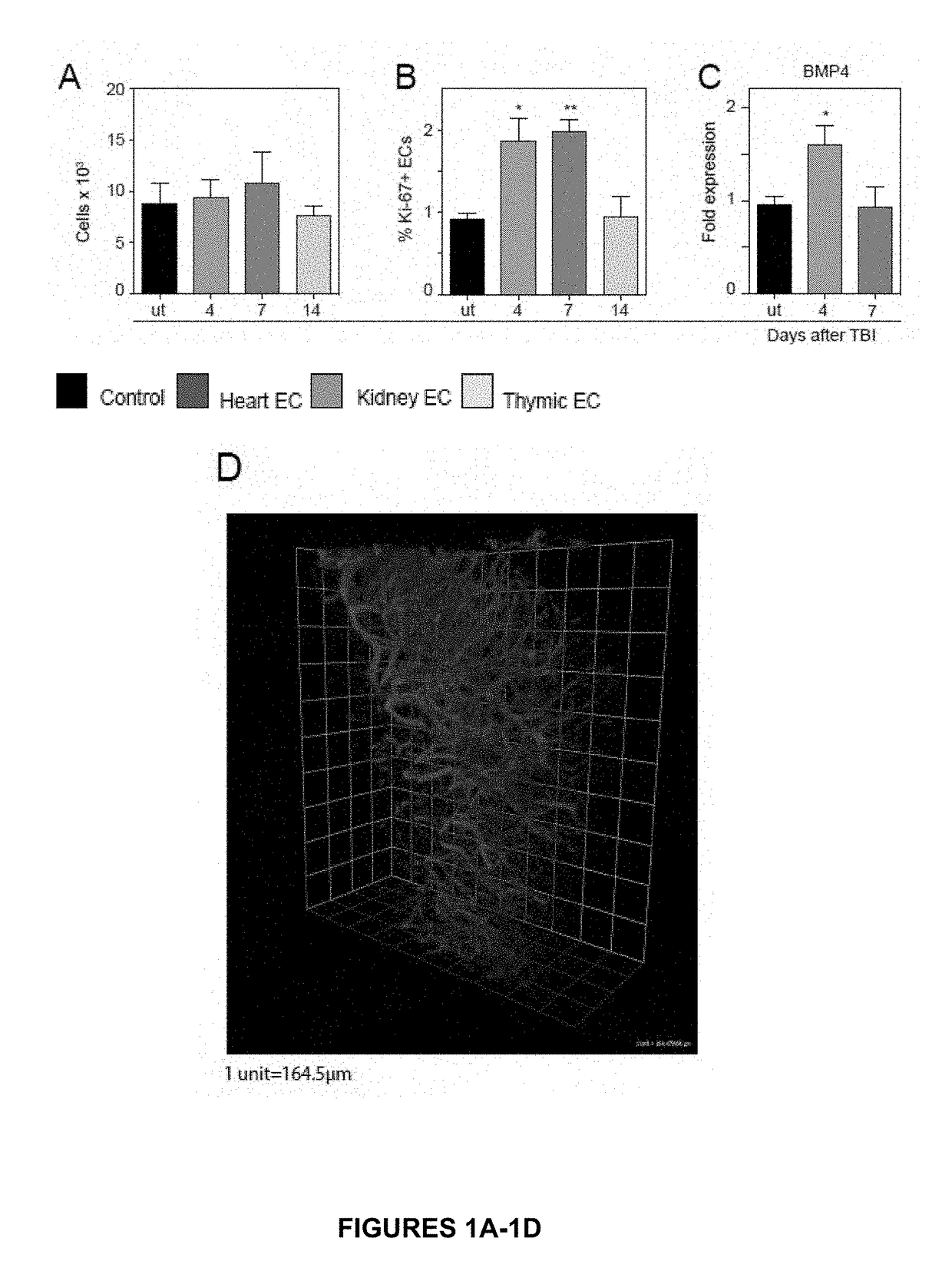
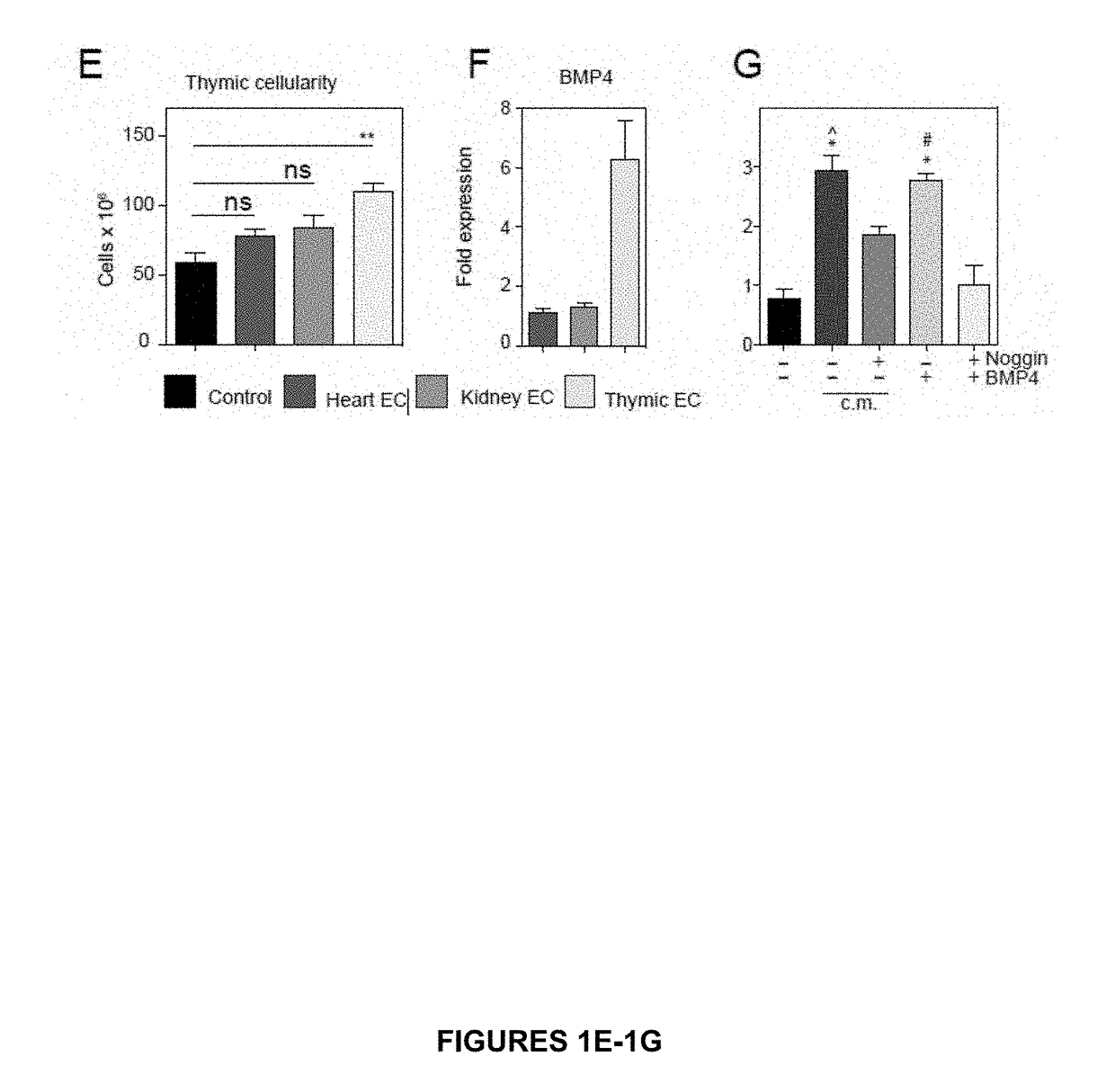
Use of bmp4 for thymic regeneration
ActiveUS20170292111A1Function increaseEnhancement of thymic epithelial cell functionPeptide/protein ingredientsBone-inducing factorEndothelial NOSBone morphogenetic protein 4
The present disclosure describes methods to promote thymic regeneration following injury or damage to the thymus by administering to the thymus an effective amount of (1) bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4), (2) thymus-derived endothelial cells that express BMP4 or (3) a combination of BMP4 and BMP4-secreting thymus-derived endothelial cells.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
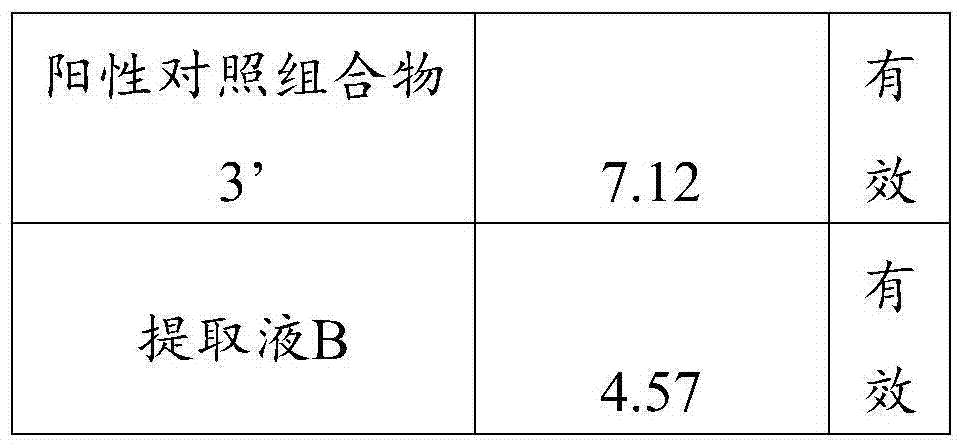
Application of extract composition of natural variform arsenite
ActiveCN103768583AInhibit drug actionHigh drug effectPeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsWilms' tumorCamptothecin
The invention provides application of an extract composition of natural variform arsenite. The extract composition comprises extract of natural variform arsenite and at least one of the following anti-tumor medicines: camptothecin, vincaleukoblastinum, vincristine, taxol, tumor necrosis factor, interleukin, interferon, transforming growth factor-beta, lipopolysaccharide, phorbol ester, adenylate cyclase activating agent andbone morphogenetic protein 4, wherein the weight of the extract of the natural variform arsenite accounts for 0.001-99.9 percent of the total weight of the prepared medicine. The extract composition of natural variform arsenite can be used for preparing anti-tumor stem cells, anti-hepatitis B and anti-AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) virus medicines, can be used for inhibiting hepatitis B and resisting AIDS and other viruses, and expands the application range to development and utilization of natural arsenite preparations.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
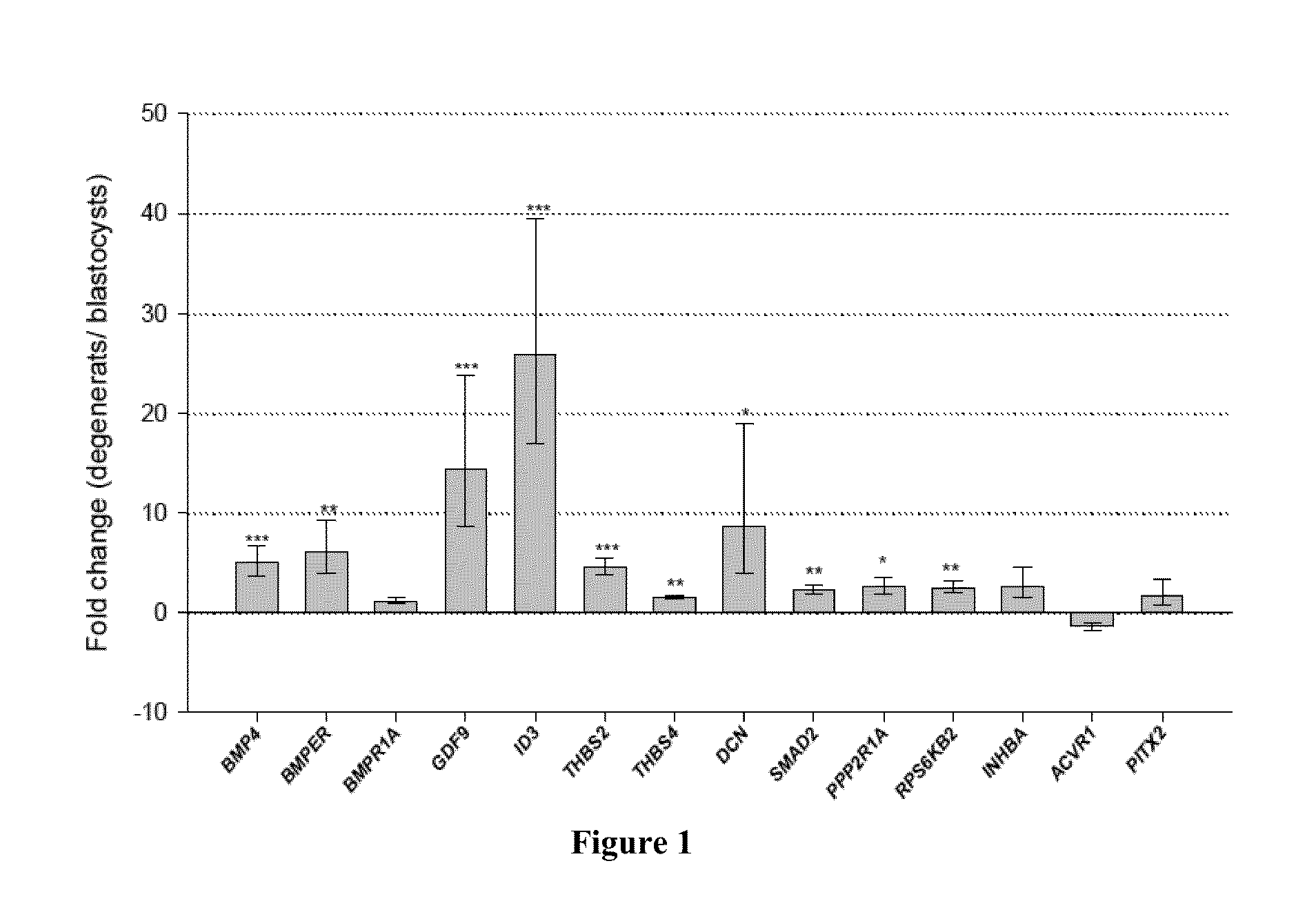
Genetic testing for improved cattle fertility
ActiveUS20160237508A1Preserve viabilityAnimal reproductionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyBone Morphogenetic Protein Gene
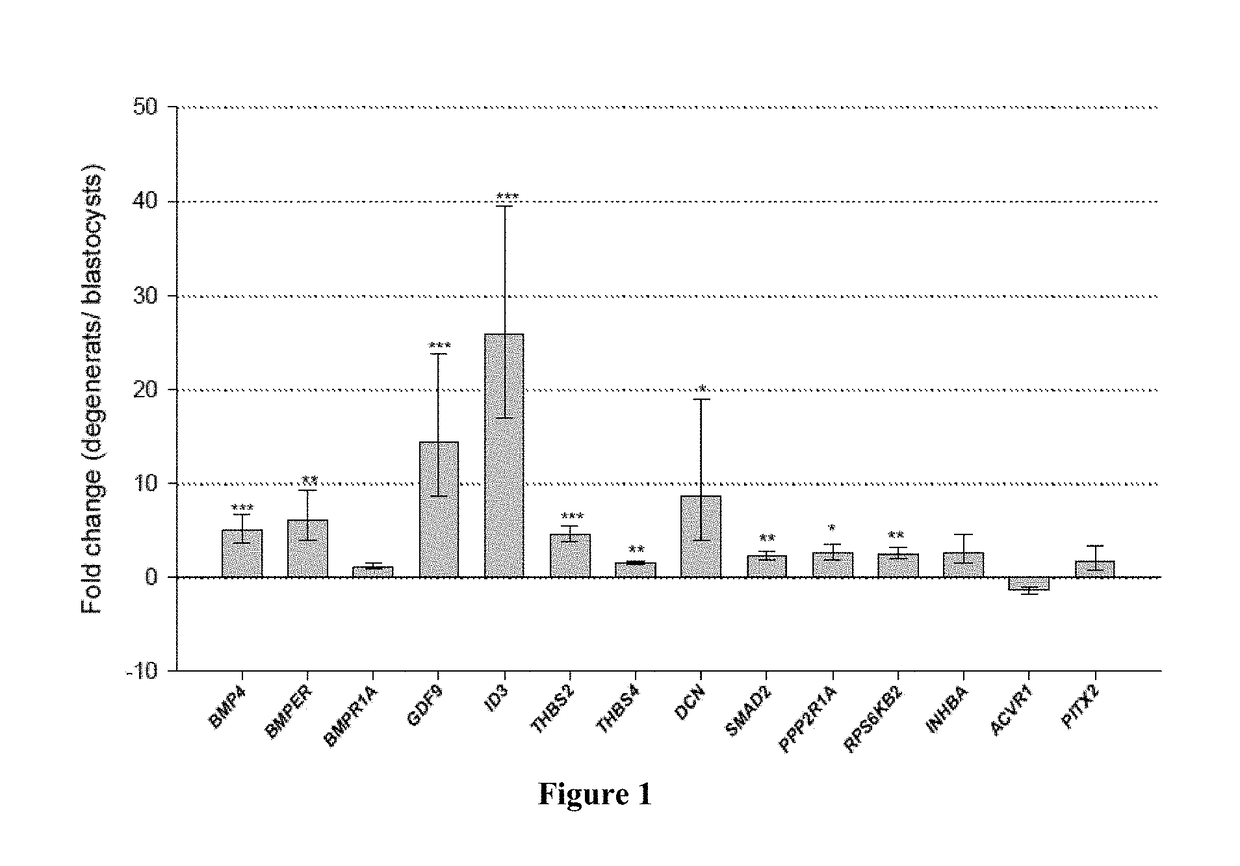
Arrays of nucleic acid molecules, kits, methods of genotyping and marker assisted bovine breeding methods based on novel SNPs on genes of the bovine transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling pathway for improved bovine fertilization rate. The methods and compositions of the present invention are related to SNPs in the DNA-binding protein inhibitor 3 (ID3) gene, and in the bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) gene corresponding to position 2702 of SEQ ID NO: 2. Also disclosed are methods for determining viability of developing bovine embryos by measuring the expression level of one or more target genes in the TGF-signaling pathway, and selecting for implantation only embryos whose target gene expression level is not up-regulated.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Induction medium and induction method for stem cell differentiation into sweat gland-like cells
ActiveCN112725259AAvoid demandEasy to operateEpidermal cells/skin cellsCulture processCell phenotypePenicillin
The invention discloses an induction medium for differentiating stem cells into sweat gland-like cells, and belongs to the technical field of stem cells. A induction culture medium is a DMEM / F-12 cell culture medium containing fetal bovine serum, an epidermal growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor, a recombinant human ectoderm dysplasia A1 protein, a recombinant human Wnt3a protein, a bone morphogenetic protein 4, a hepatocyte growth factor, triiodothyronine and hemisuccinyl hydrocortisone. The composition is prepared from insulin- transferrin-sodium selenite, L-glutamine and penicillin / streptomycin double antibiotics. The sweat gland induction culture medium can effectively induce stem cells, especially mesenchymal stem cells, to be differentiated into sweat gland-like cells with sweat gland-like cell phenotypes in vitro, the sweat gland-like cells can form a tubular structure similar to a sweat gland structure in glue, and the requirement for sweat glands in the treatment process of large-area burn patients can be met.
Owner:福州市皮肤病防治院
Genetic testing for improved cattle fertility
ActiveUS20190002992A9Animal reproductionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyBone Morphogenetic Protein Gene
Arrays of nucleic acid molecules, kits, methods of genotyping and marker assisted bovine breeding methods based on novel SNPs on genes of the bovine transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling pathway for improved bovine fertilization rate. The methods and compositions of the present invention are related to SNPs in the DNA-binding protein inhibitor 3 (ID3) gene, and in the bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) gene corresponding to position 2702 of SEQ ID NO: 2. Also disclosed are methods for determining viability of developing bovine embryos by measuring the expression level of one or more target genes in the TGF-signaling pathway, and selecting for implantation only embryos whose target gene expression level is not up-regulated.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Culture medium of sweat gland cells and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106834211BPromote growthProliferate fastEpidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsCulture fluidSweat gland
Owner:GUANGZHOU RAINHOME PHARM&TECH CO LTD
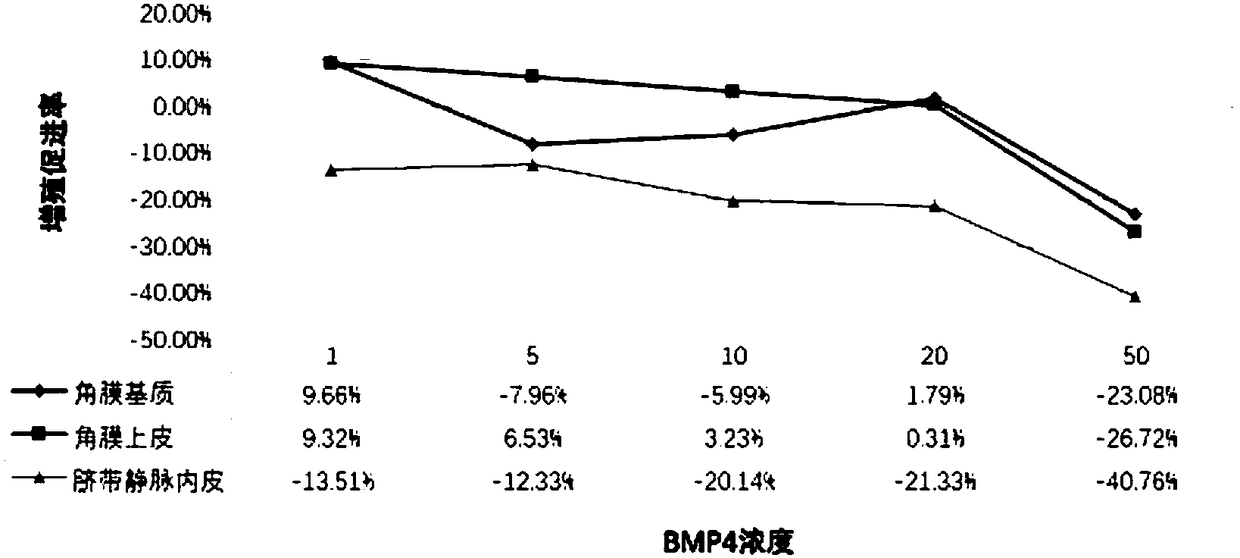
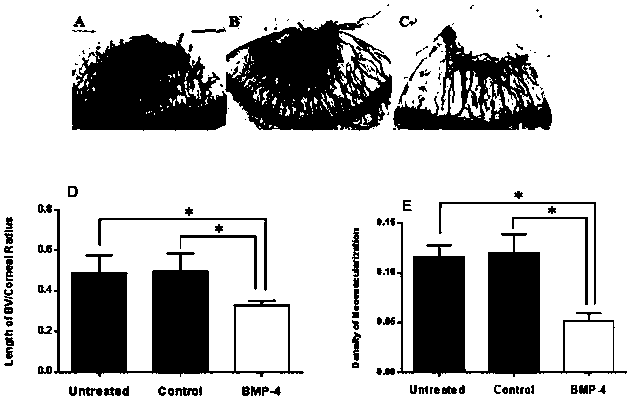
Application of bone morphogenetic protein-4 in drug for treating keratonosus
PendingCN108379556AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove growth performanceSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth promotingKeratitis
The invention belongs to the field of bio-pharmaceuticals, and particularly relates to application of bone morphogenetic protein-4 in a drug for treating keratonosus. The BMP4 has a mild growth-promoting effect on corneal epithelia and stromata, and treats CNV caused by epithelial damage; the BMP4 can serve as a drug for repairing damaged epithelia; the BMP4 is used for inhibiting keratitis reactions, and plays an important effect in the corneal injury repairing process, and the delivery way of t he BMP4 is convenient without trauma, and the BMP4 is easy to popularize.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Media, kits and their uses
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
Anti foot-and-mouth disease drug and ID1 protein and BMP4 (bone morphogenetic protein 4) protein in preparation of the same
ActiveCN108619489ATo achieve the purpose of treating foot-and-mouth diseasePeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsBone morphogenetic protein 4Bioinformatics
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, and discloses an anti-foot-and-mouth disease drug and an application of ID1 protein and BMP4 (bone morphogenetic protein 4) protein in preparation of the same. An embodiment of the invention initially discover the relation of ID1 protein and the replication of the foot-and-mouth disease, which includes that the cure of the foot-and-mouth disease is realized through upregulating the expression of Id1. According to the function of the ID1 protein, the ID1 protein can be utilized in the preparation of the anti foot-and-mouth disease drug, and an important theoretical basis is provided in the development of new anti foot-and-mouth disease drug.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com