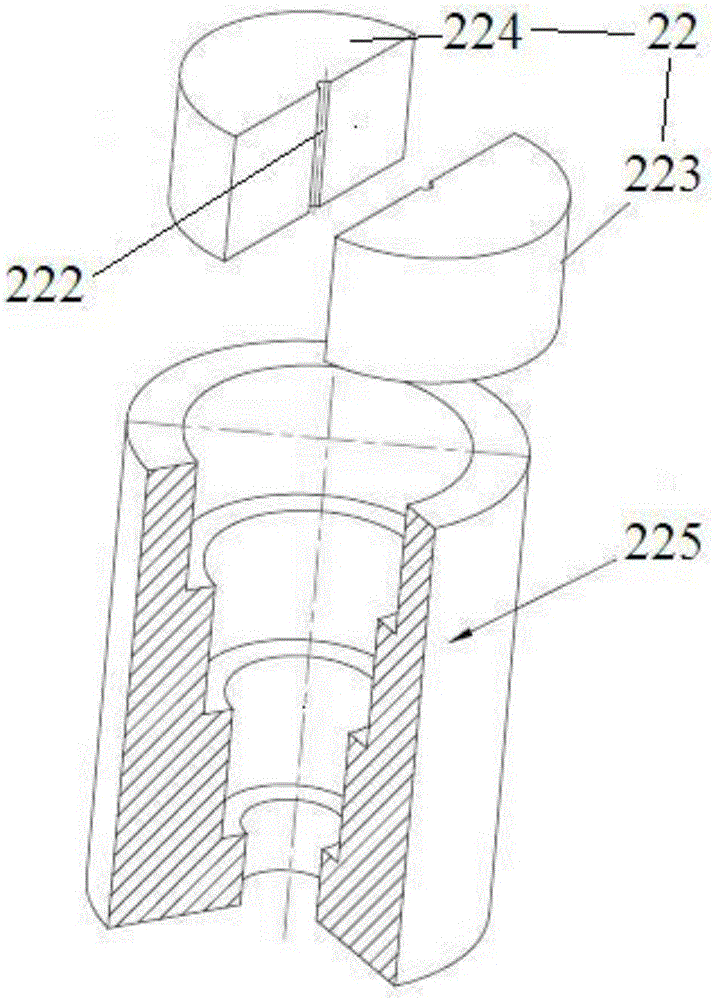
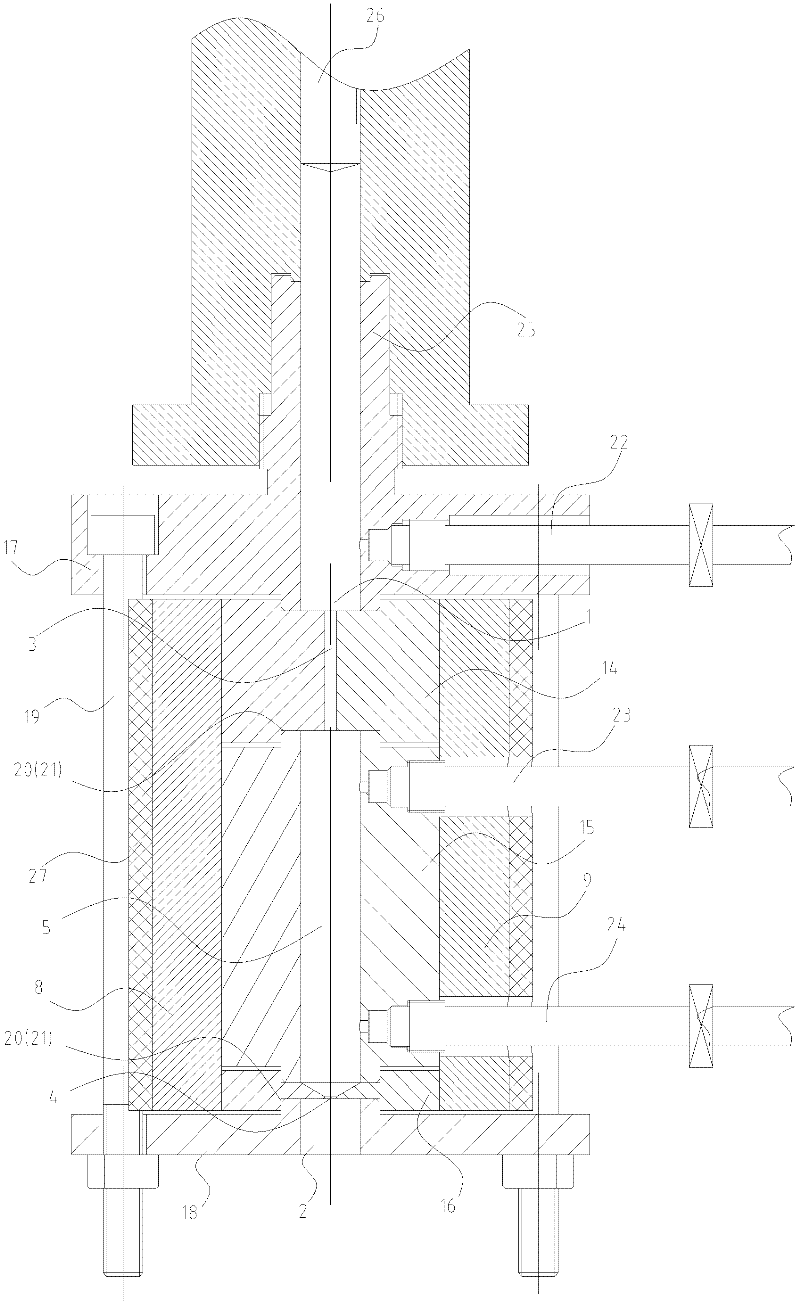
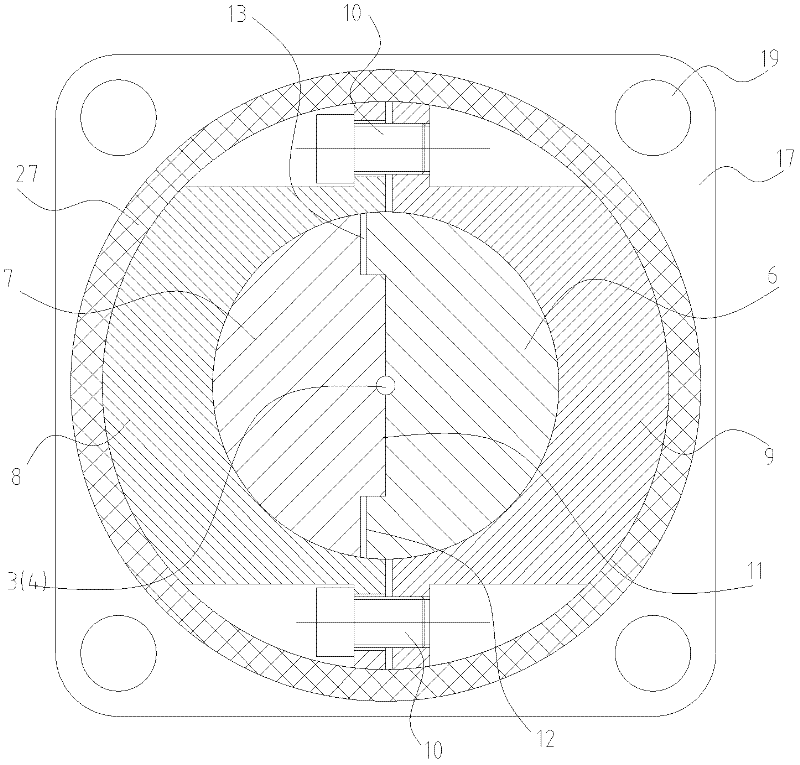
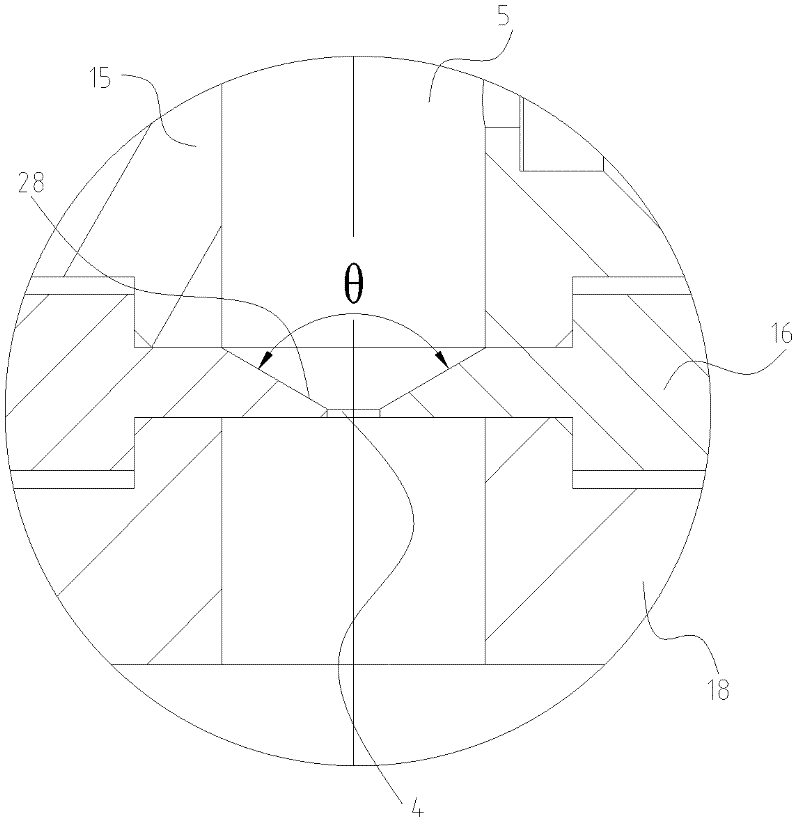
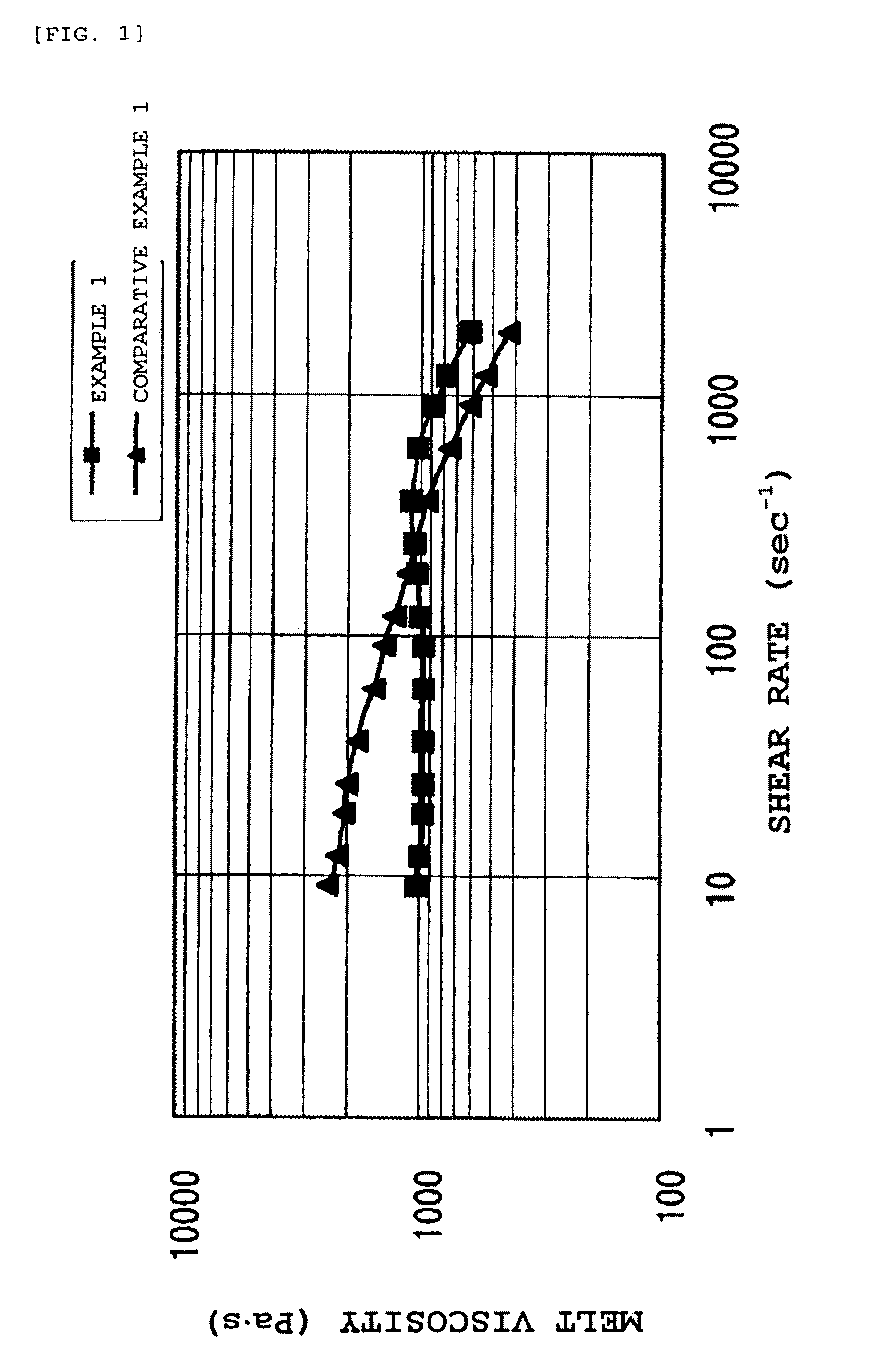
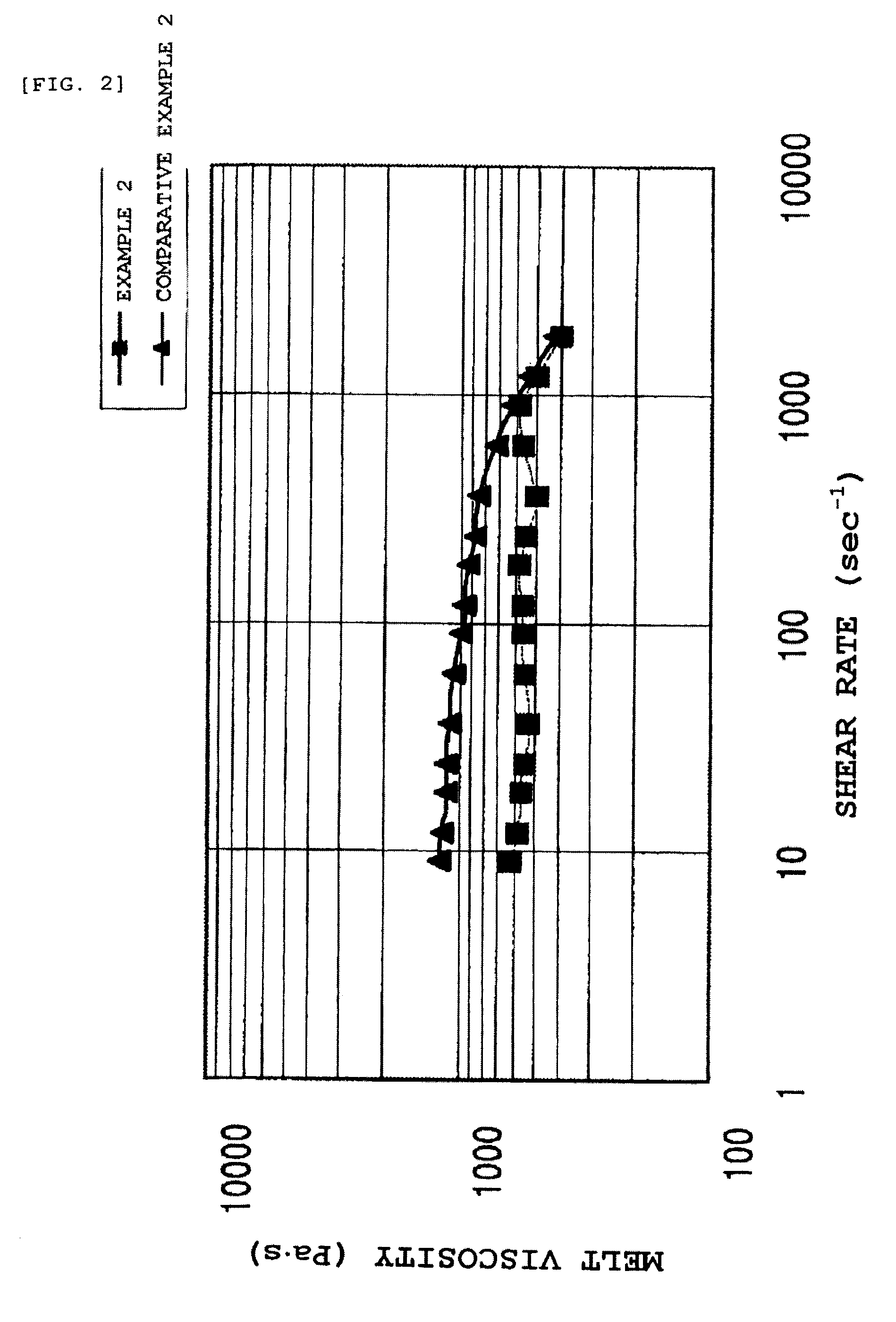
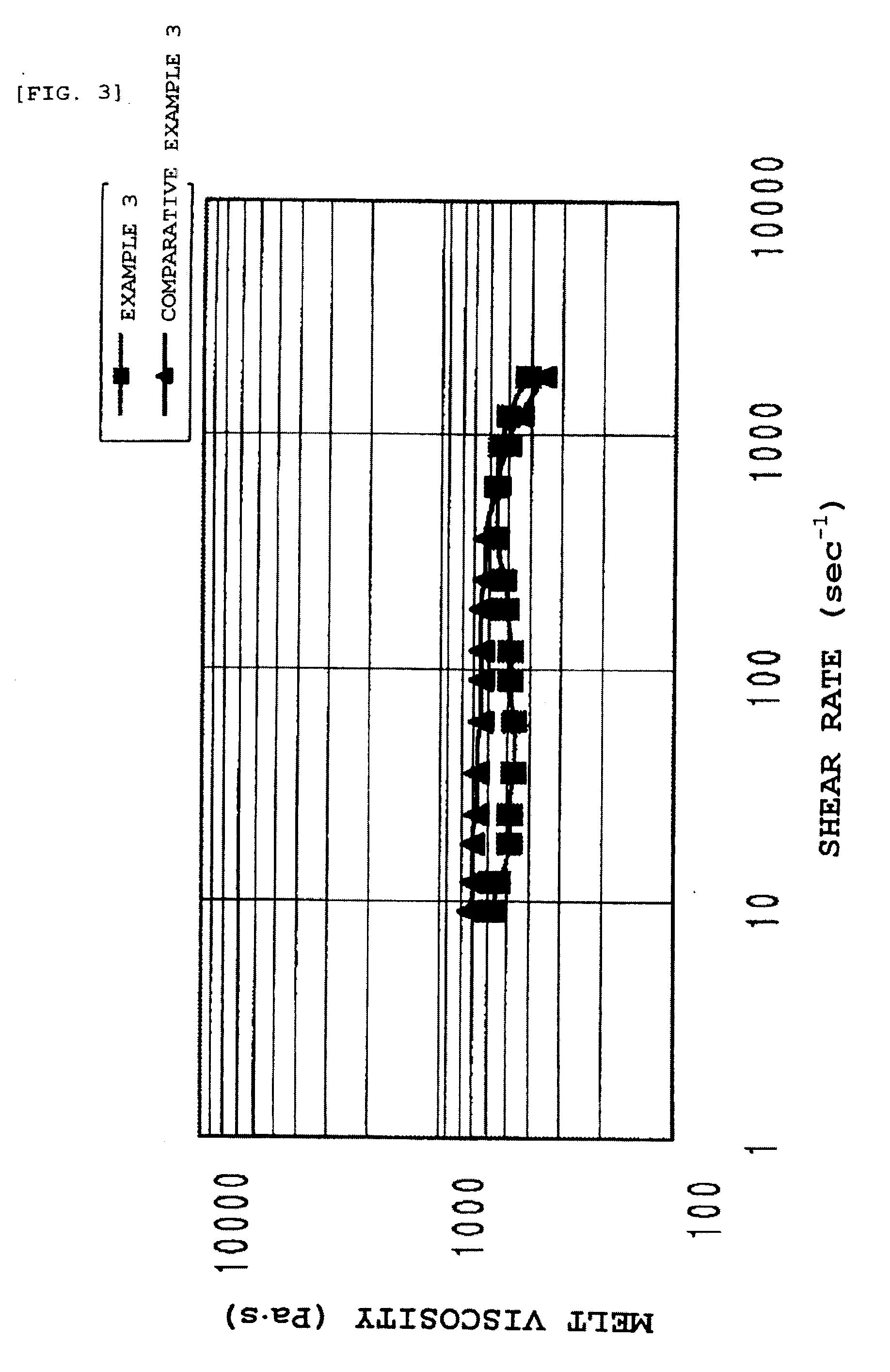
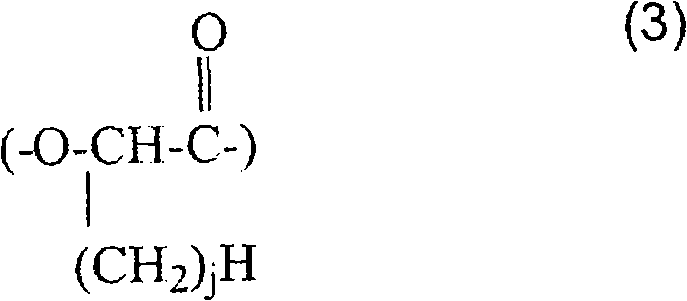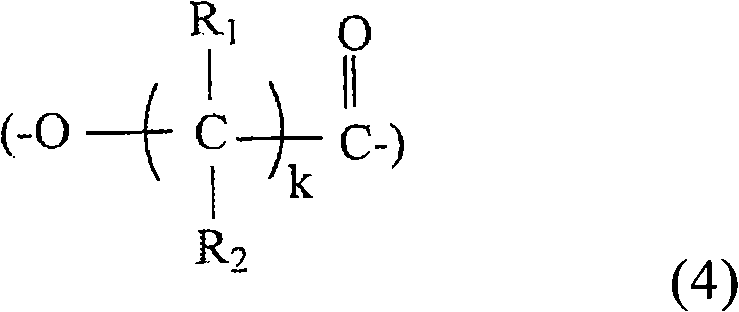Patents
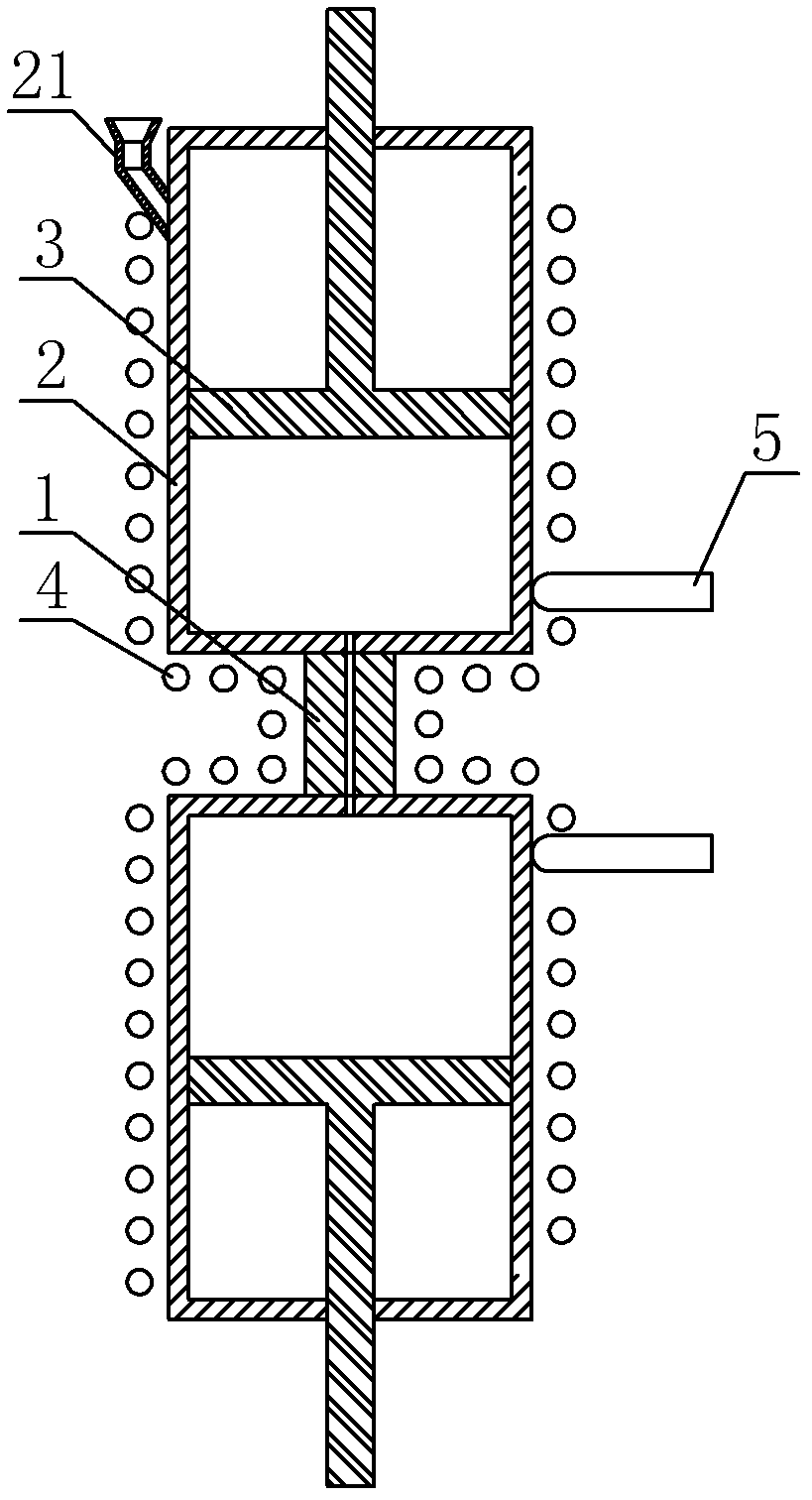
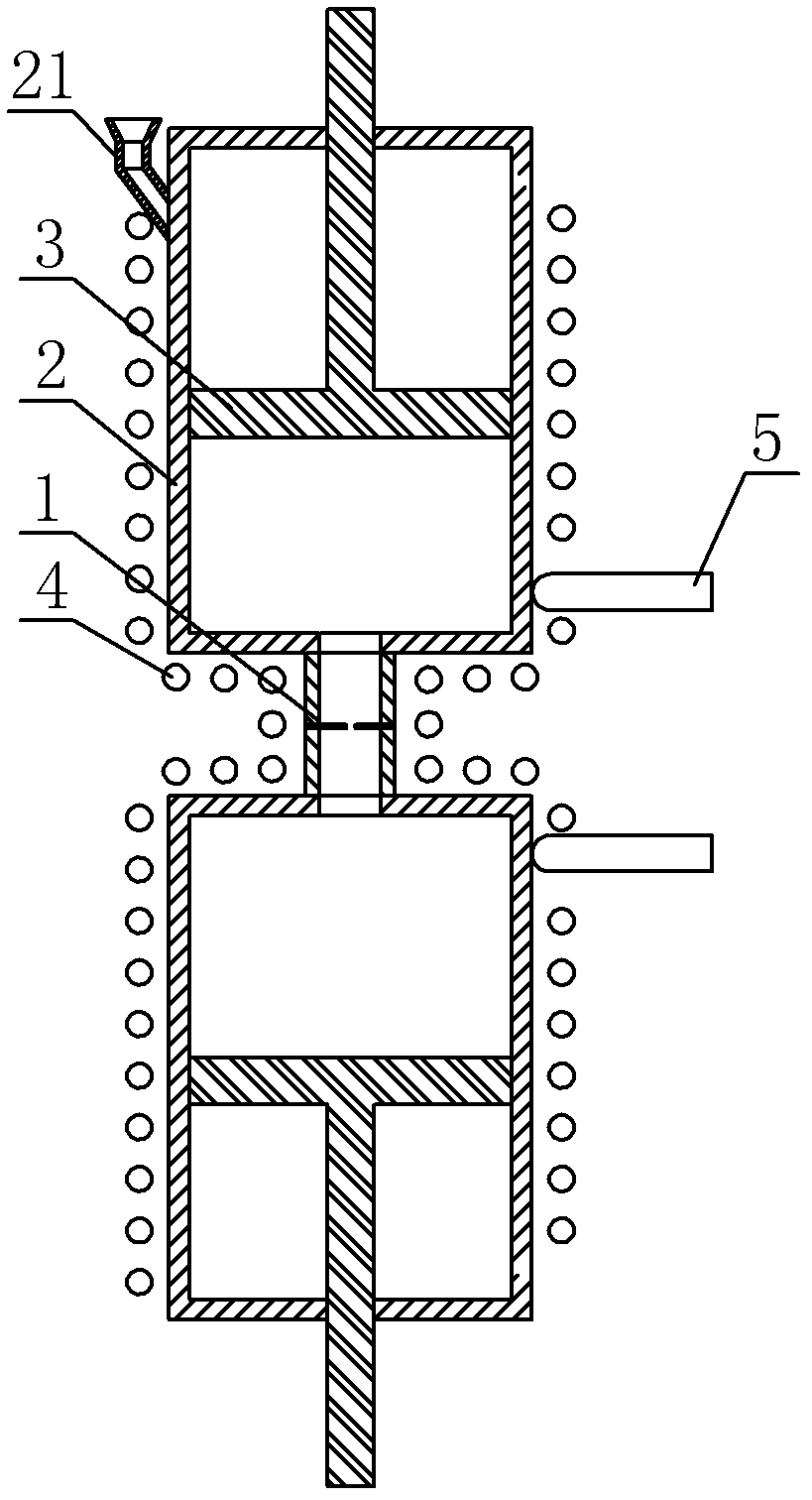
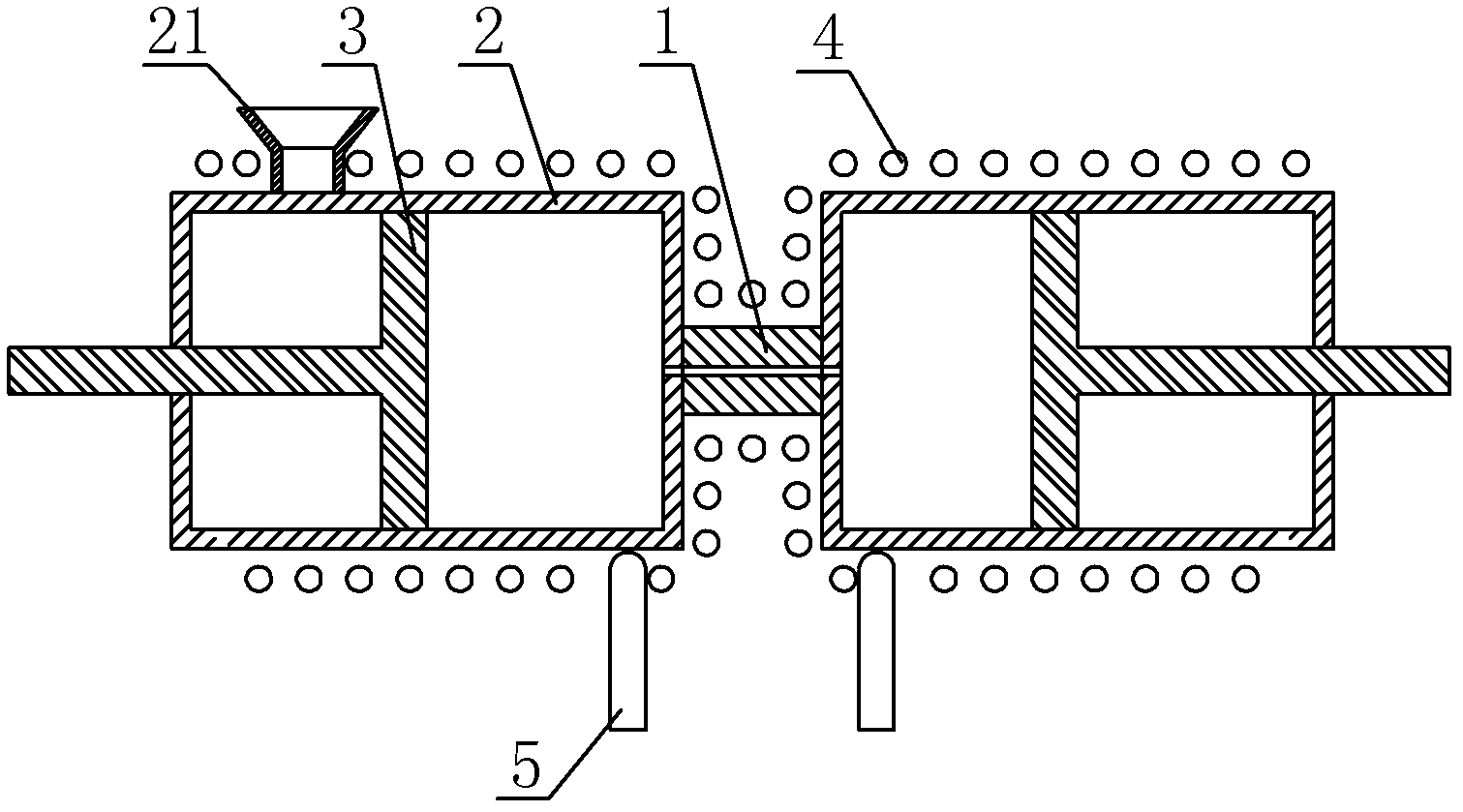
Literature
76 results about "Capillary rheometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Composition for polyolefin resin foam, foam of the same, and process for producing foam
InactiveUS20050049322A1Good flexibilityGood cushioning propertiesOther chemical processesMixingExtensional viscosityPolymer science
A composition for polyolefin resin foam, which comprises a polymer component comprising a polyolefin resin and a rubber and / or thermoplastic elastomer, and a powder particle, wherein the composition has an extensional viscosity as measured with a capillary rheometer (temperature, 200° C.; shear rate, 5,000 [1 / s]) of from 20 to 100 kPa·s.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
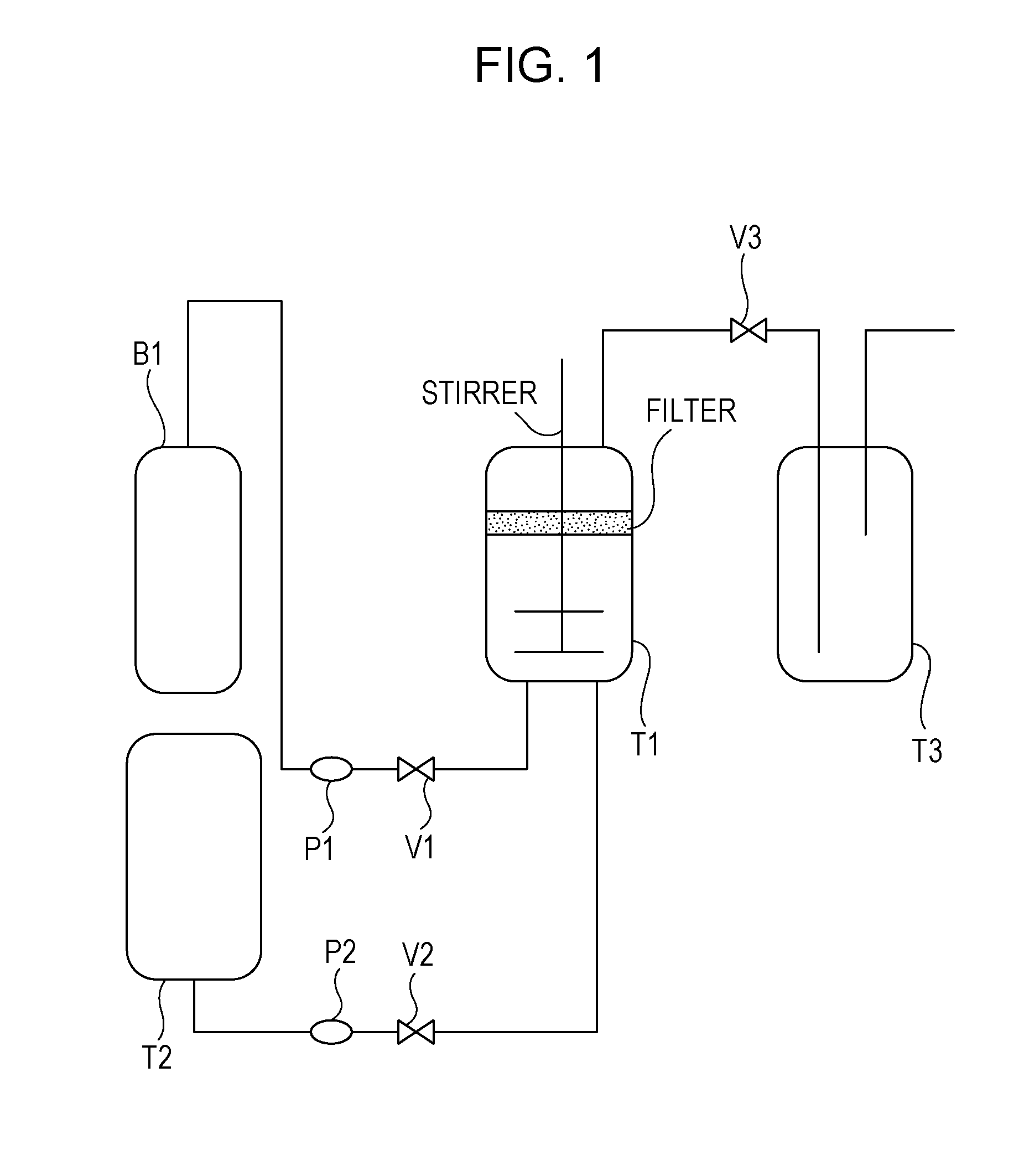
Method and apparatus for measuring drilling fluid properties
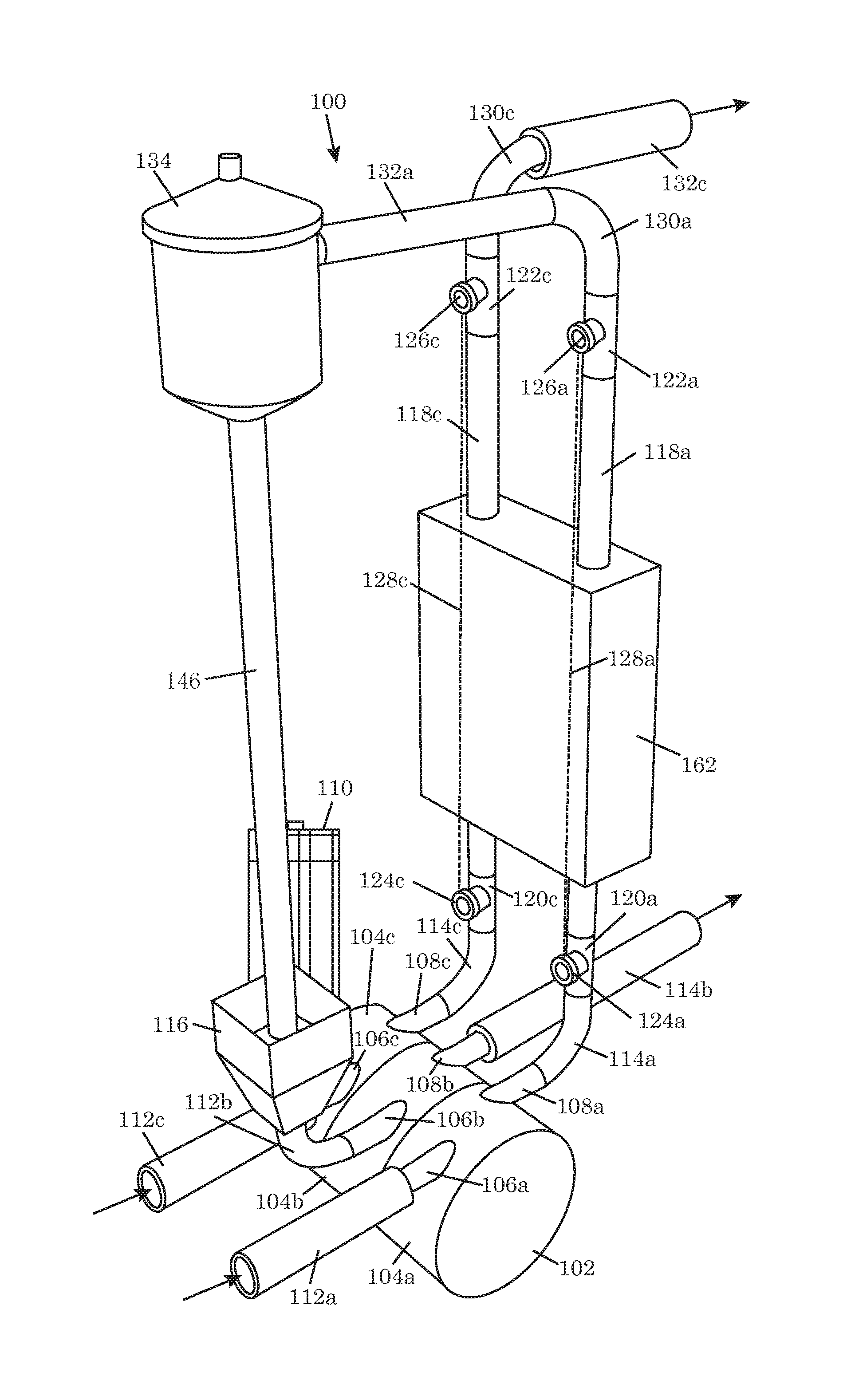
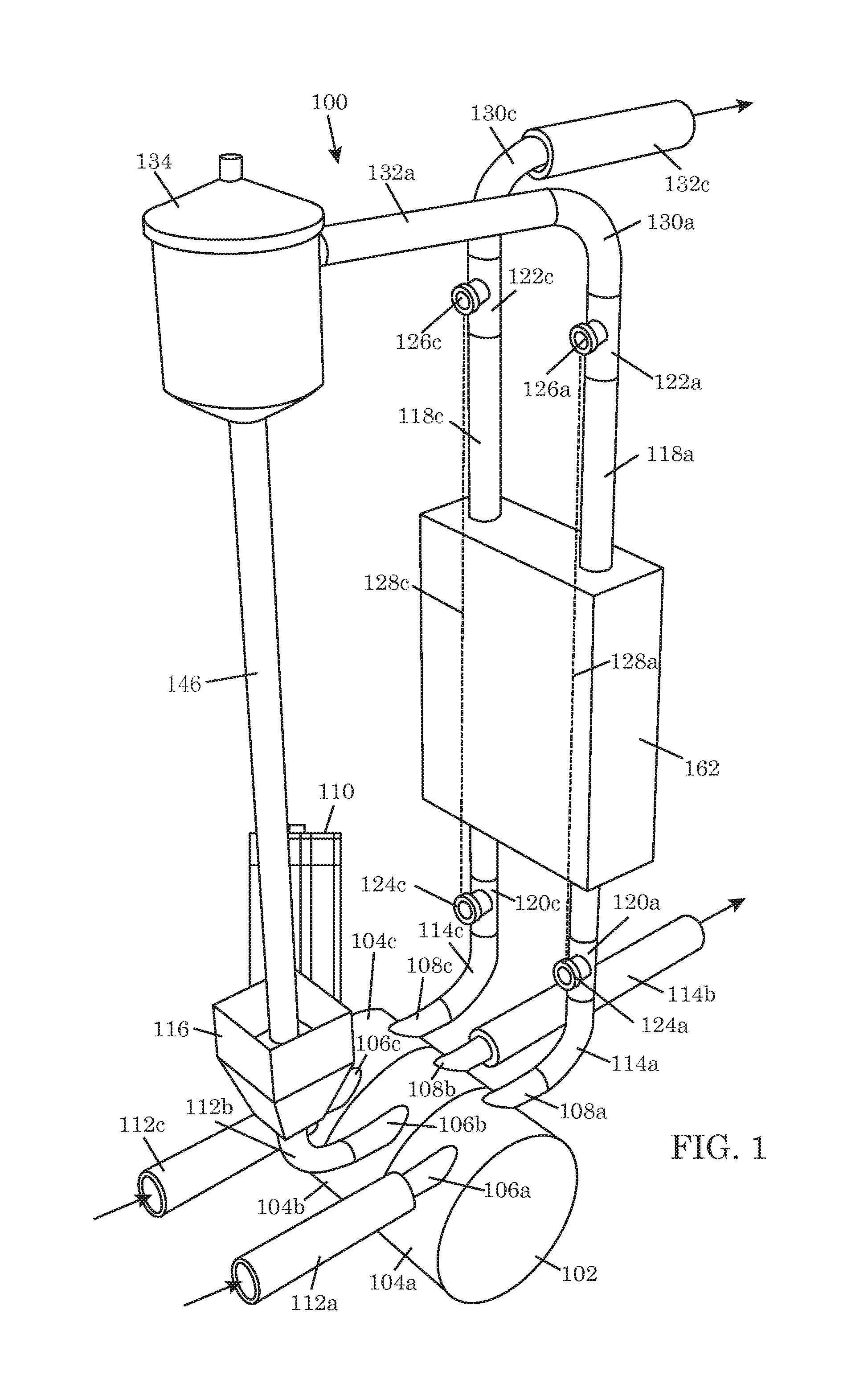
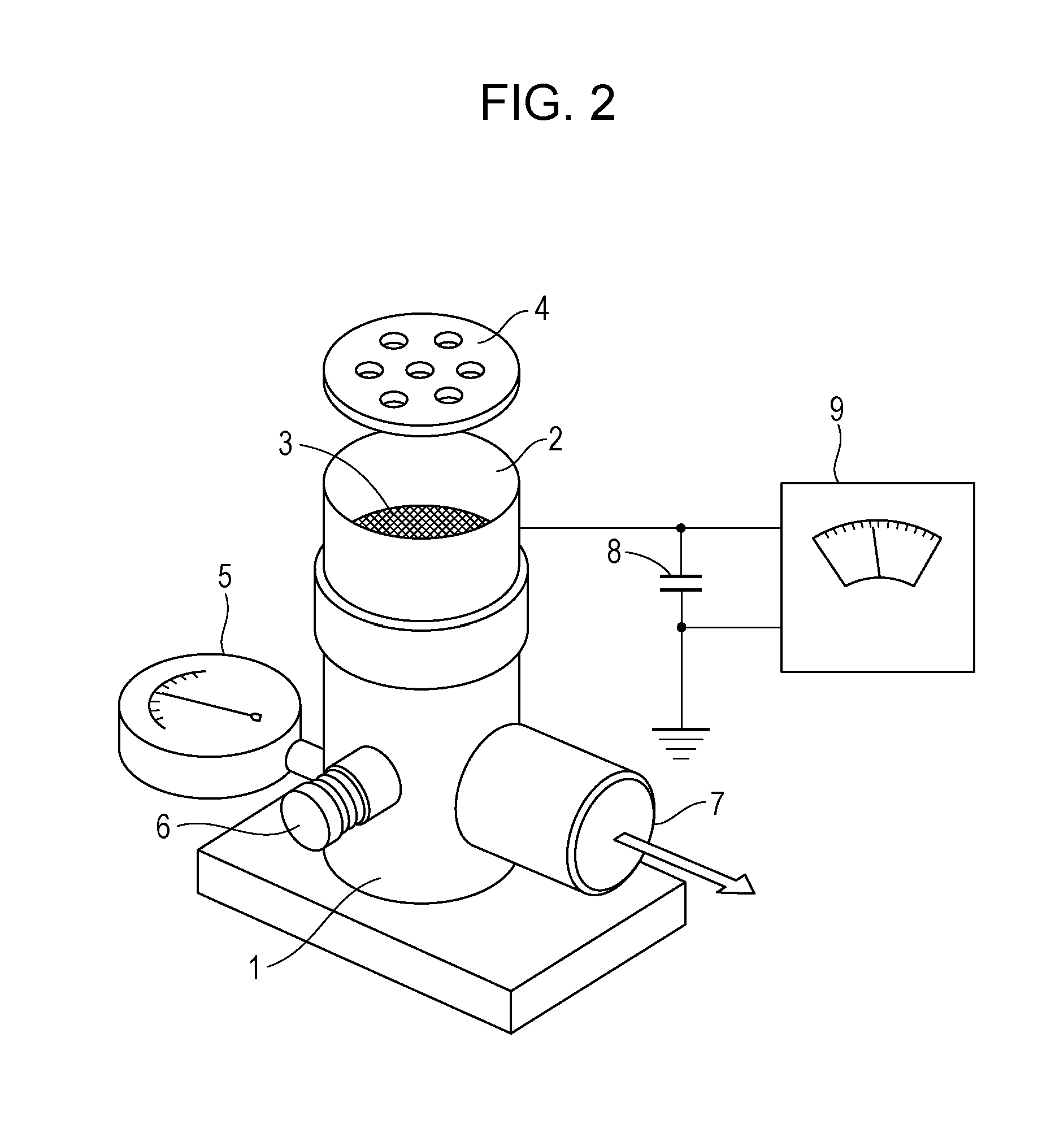
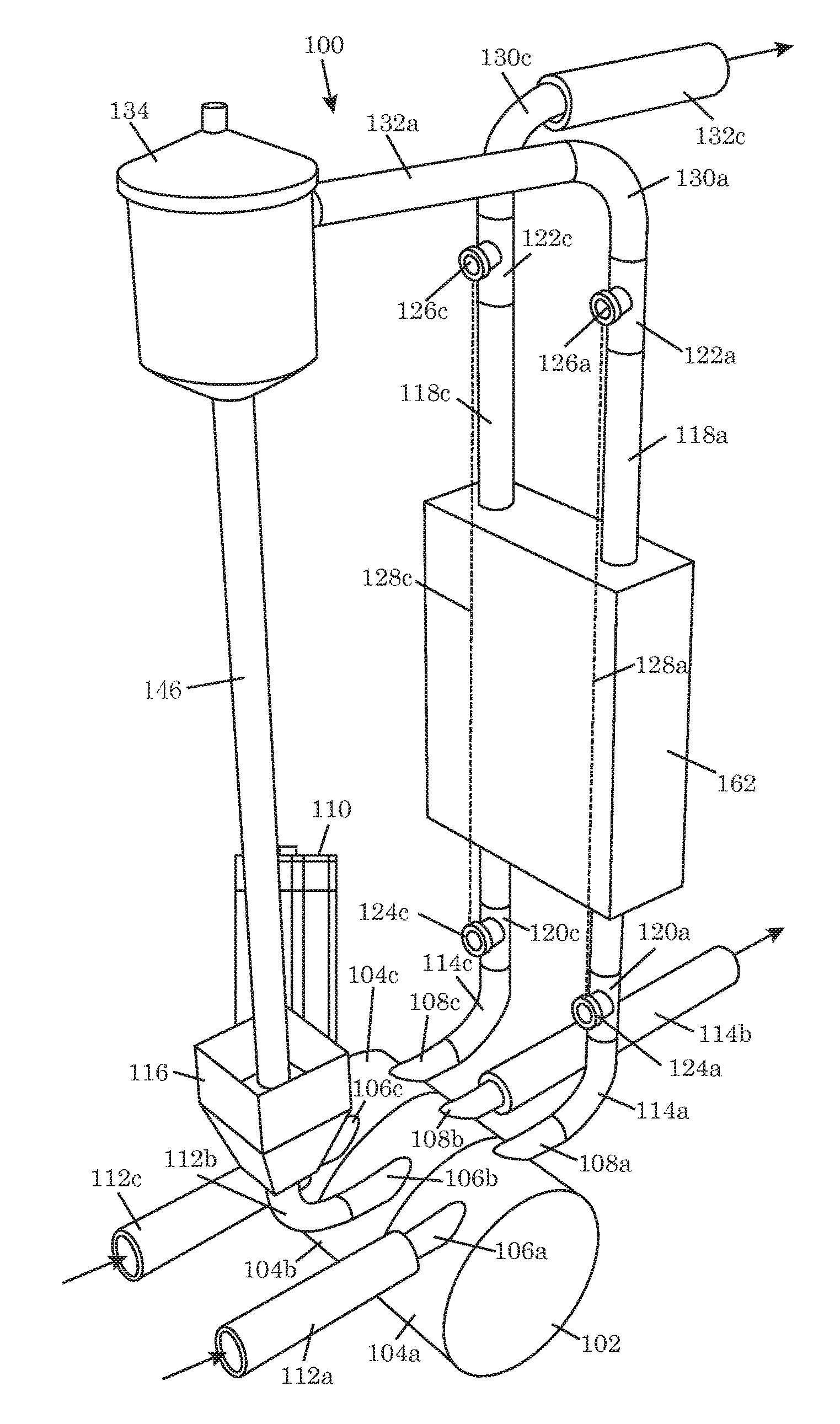
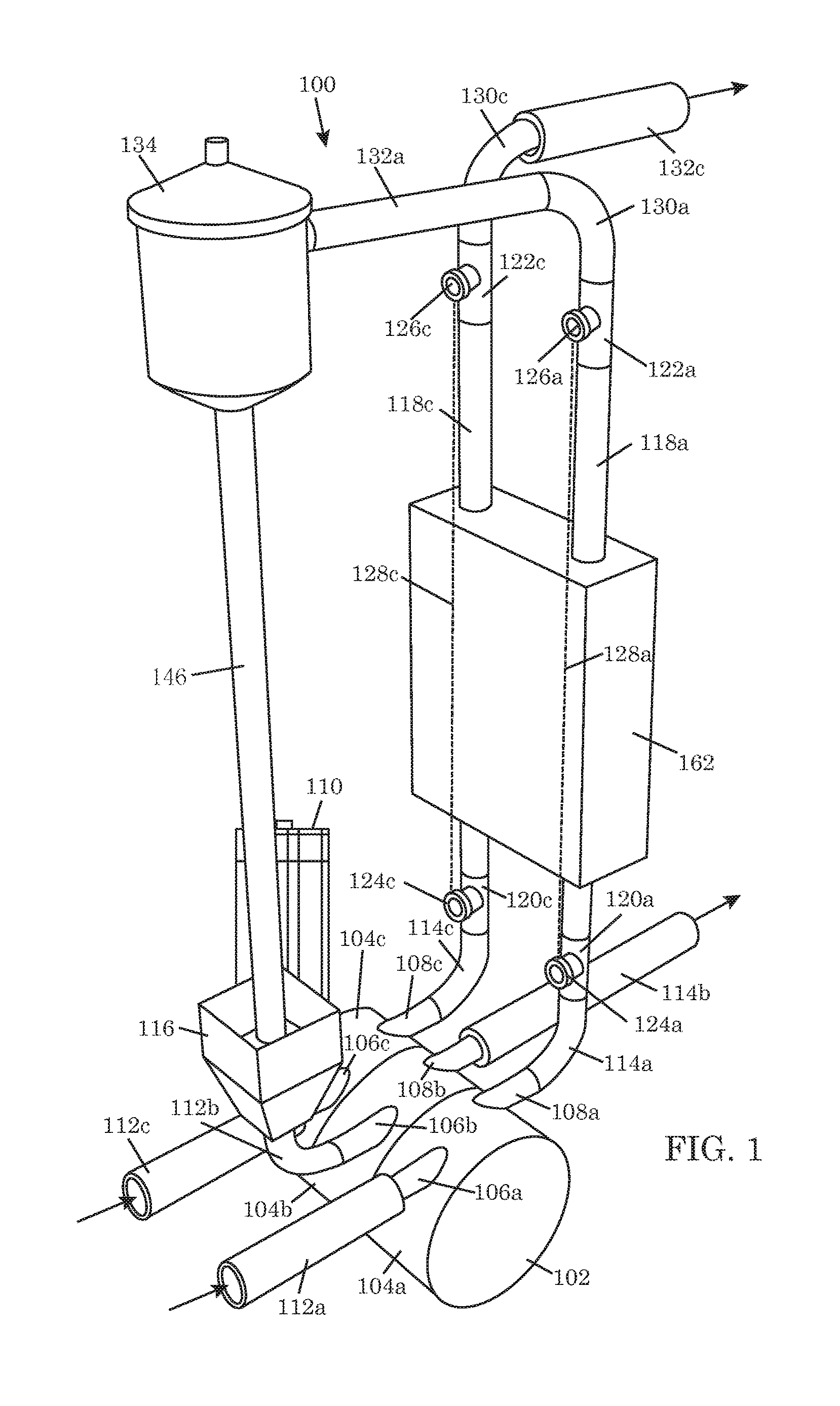
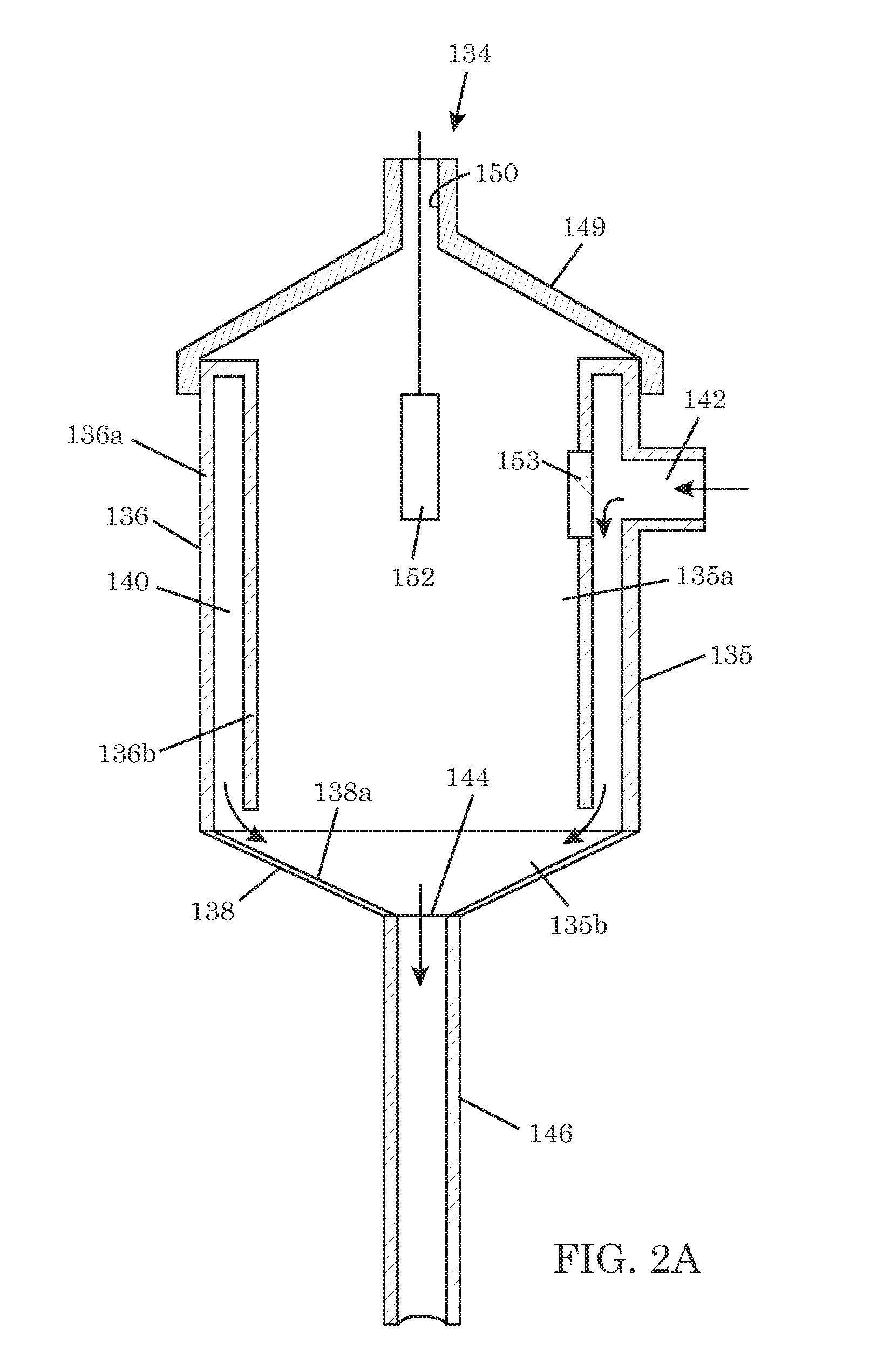
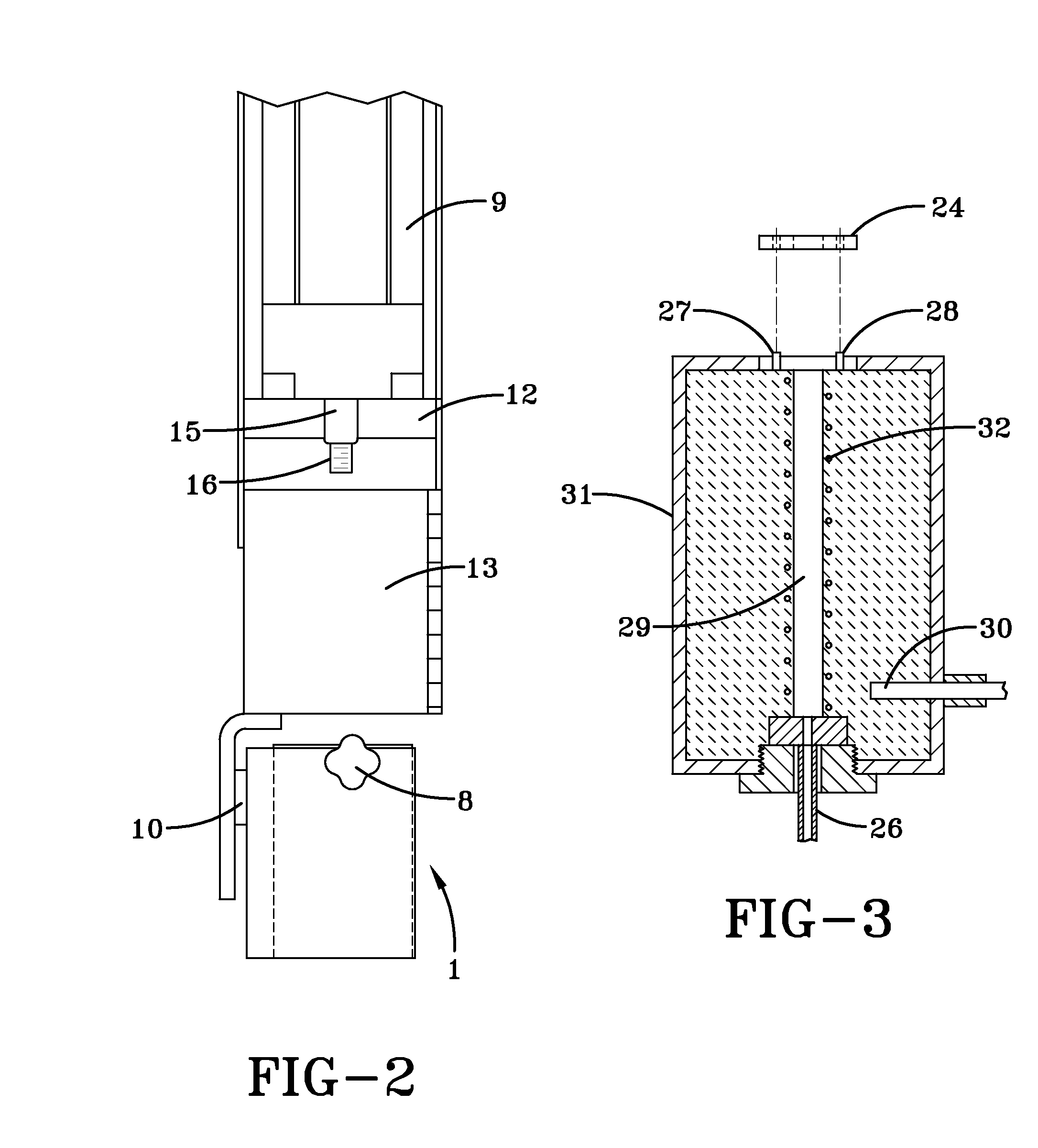
As system for measuring drilling fluid properties includes a capillary rheometer that is adapted to measure viscosity parameters of drilling fluid. The capillary rheometer includes a feed chamber, the feed chamber having a cavity, at least a first drain port for draining fluid out of the cavity, a double wall defining an annulus that opens to the cavity, and a feed port in an outer portion of the double wall that is in fluid communication with the annulus. The capillary rheometer also includes at least a first capillary tube coupled to at least the first drain port. Additionally, the disclosed system further includes a pump that is adapted to pump fluid to the feed port.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
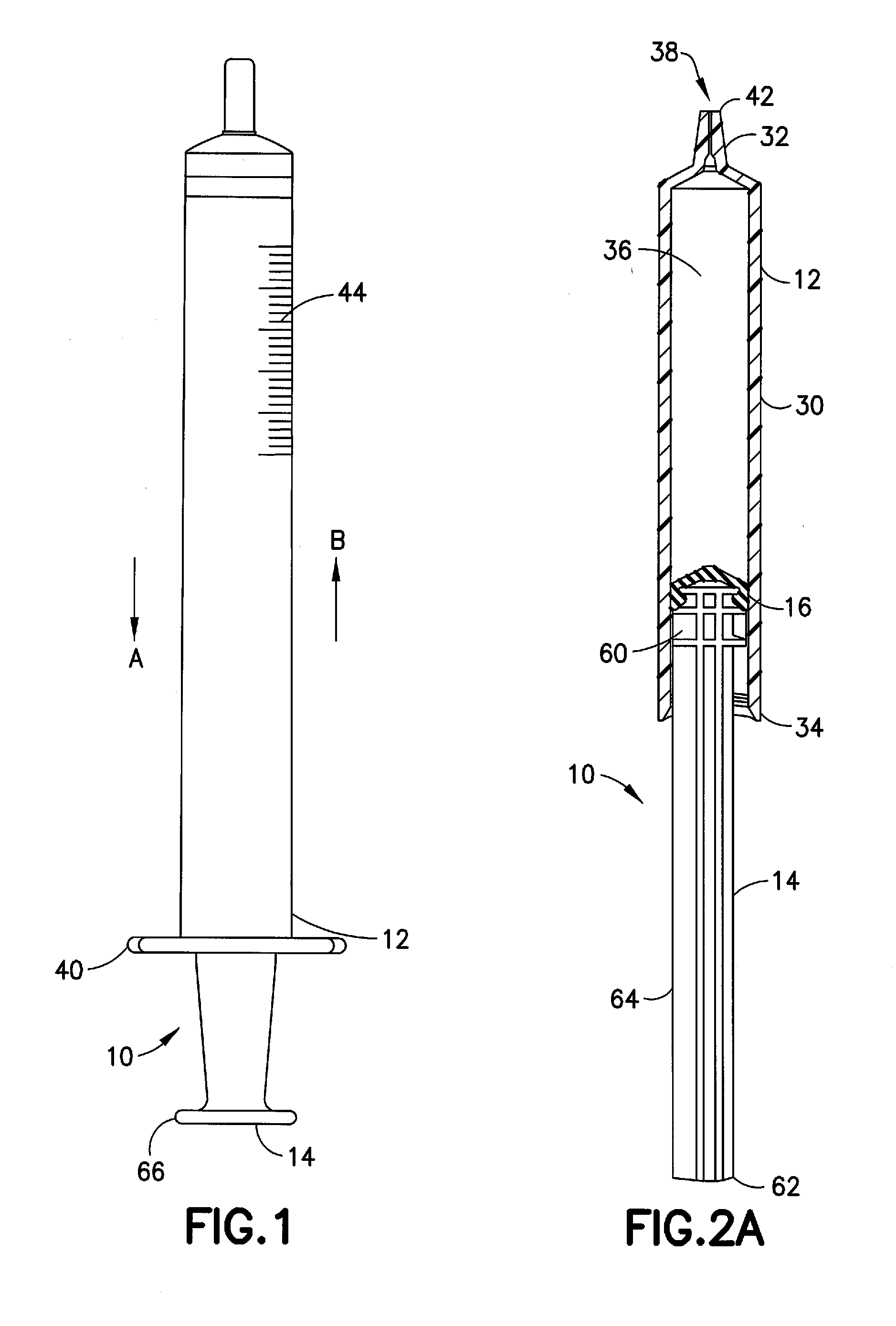
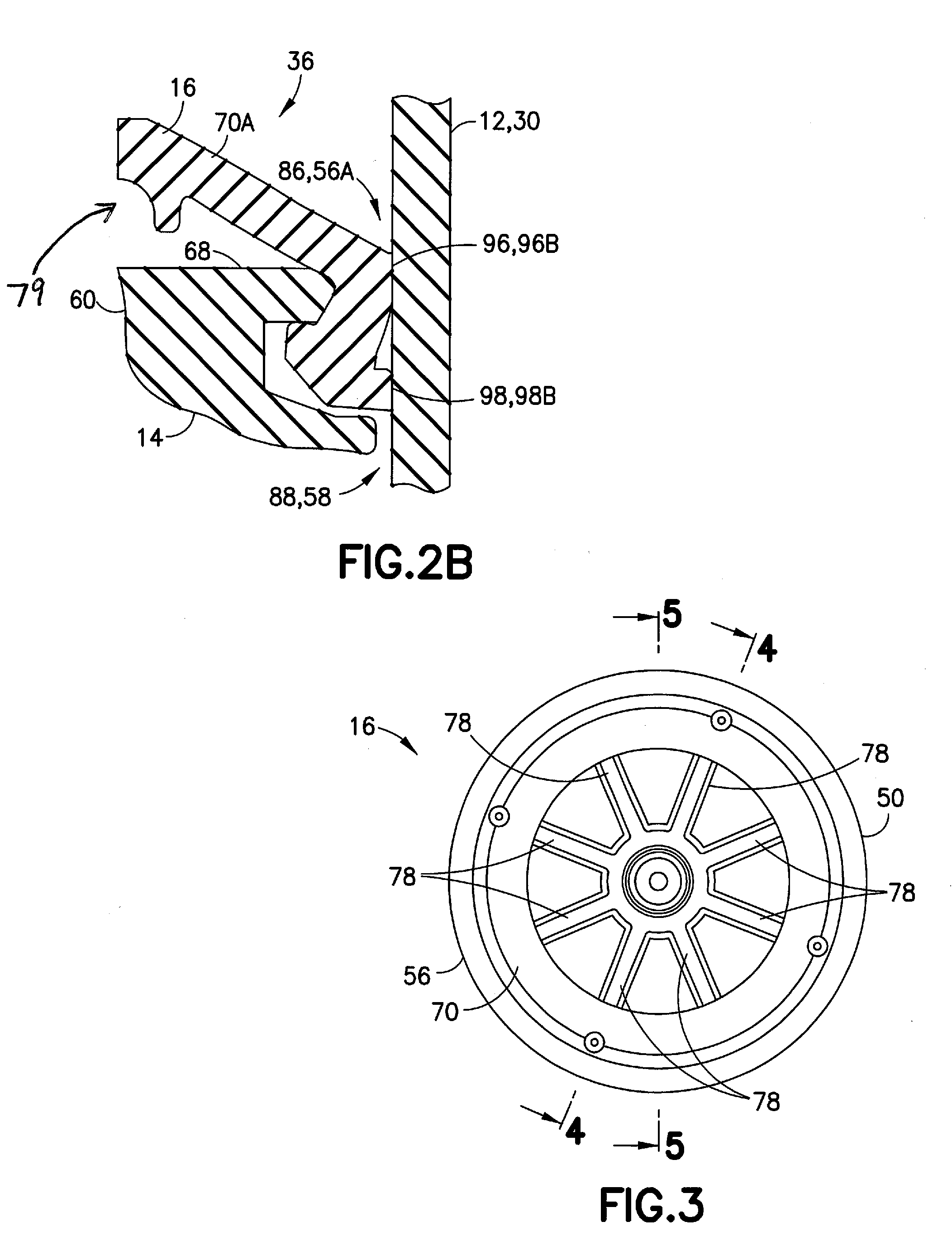
Leak-Free Stopper Having Low Breakloose and Sustaining Forces
ActiveUS20150119817A1Increase contact pressureLow breakoutInfusion syringesIntravenous devicesThermoplastic elastomerEngineering
A thermoplastic elastomer stopper that meets the desired material properties of a stopper for a syringe assembly is disclosed. The compression set of the thermoplastic elastomer stopper of the present disclosure is ≦50% when measured at 25% compression for 22 hrs at 70 degree C. The hardness of the thermoplastic elastomer stopper of the present disclosure is 40-70 Shore A. The viscosity of a thermoplastic elastomer stopper of the present disclosure is ≧70 Pa·s at 1,000 s−1 shear rate, ≧12.0 Pa·s at 10,000 s−1 shear rate, and ≧3.0 Pa·s at 50,000 s−1 shear rate when measured using a capillary rheometer at 205 degree C. (Die: Roundhole 20 mm length / 1 mm diameter / 180 degree inlet, Piston: d=15 mm, and melting time=7 min). The present non-lubricated stopper exhibits the required functional performance of a lubricated stopper.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Toner and method for producing toner
Provided is a toner that is excellent in terms of low-temperature fixability and hot offset resistance, has a wide fixing temperature range from a low-temperature region to a high-temperature region, and has high thermal storability.When the toner is measured with a capillary rheometer,t(1) is 60 seconds or more and t(5) is 30 seconds or less andthe toner satisfies the following formulae (1) and (2)65.0[° C.]≦T(5)≦90.0[° C.] (1)4.5≦t(1) / t(5)≦10.0 (2).
Owner:CANON KK
Device and method for measuring steady-state extrusion viscous dissipation of micro-scale polymer fused mass
InactiveCN101532939AAccurate temperature controlEasy loading and unloadingDirect flow property measurementTemperature controlViscous dissipation
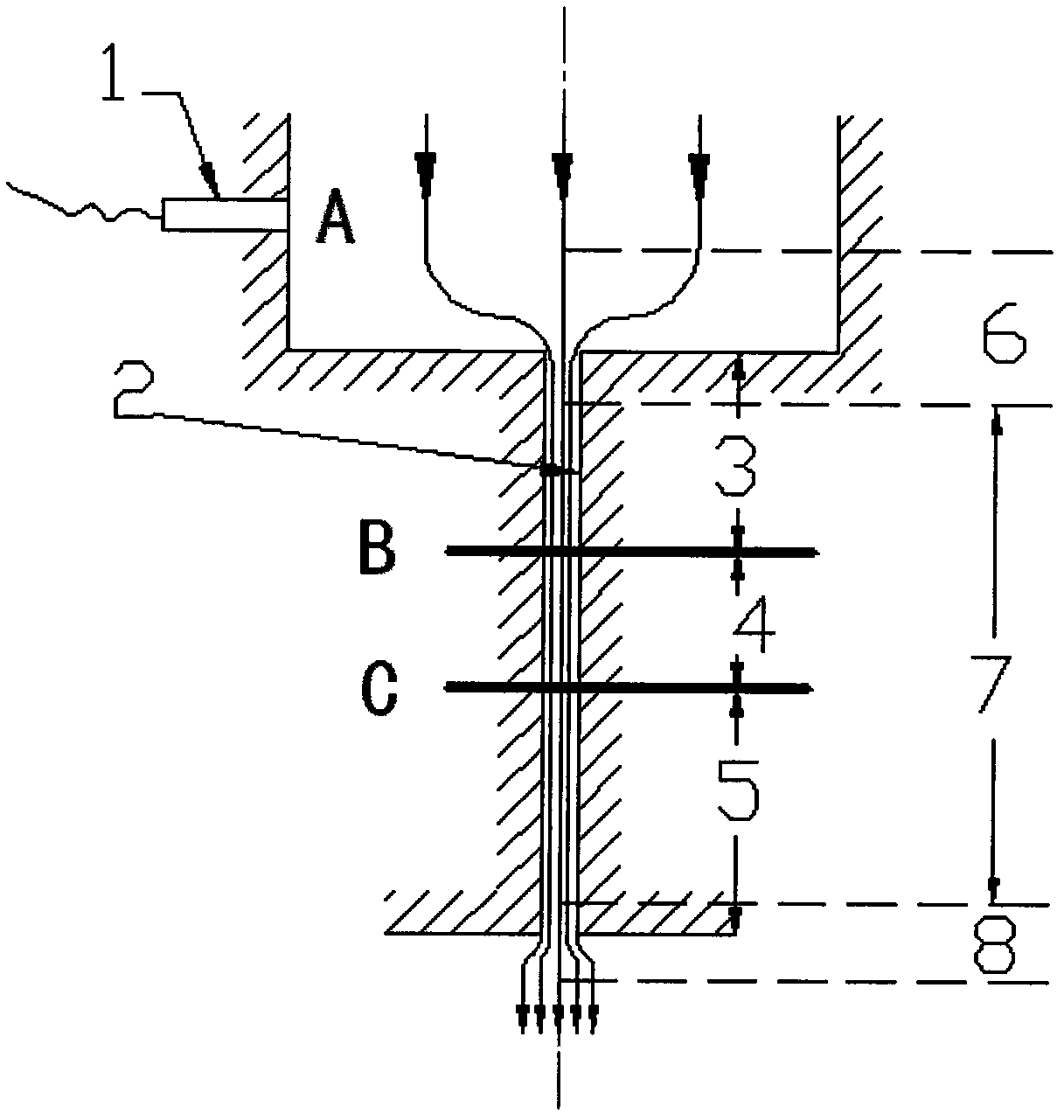
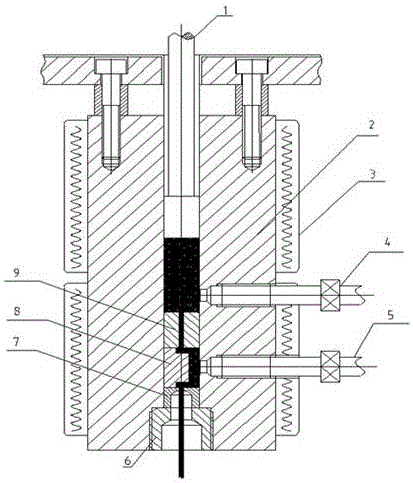
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring steady-state extrusion viscous dissipation of a micro-scale polymer fused mass. The device and the method are characterized in that on the basis of a capillary rheometer with two material barrels, a temperature sensor is arranged at an outlet of a neck ring mold of a capillary tube in the material barrel through a fixing device, the outlet of the neck ring mold of the capillary tube is aligned with a measuring part of the temperature sensor, and the distance between the neck ring mold of the capillary tube and the sensor is adjusted by additionally mounting a spacer; and the other temperature sensor is arranged at the outlet of the other material barrel through the fixing device for the convenience of measuring the temperature of the fused mass simultaneously by the two sensors. The flow parameters of the fused mass are set on the rheometer, the fused mass flows out of the neck ring mold at certain shearing rate through by the extrusion action of a plunger, and the sensors measure the temperature of the extruded fused mass directly. The temperature difference of the two sensors is calculated out so that the temperature rise of the fused mass caused by the viscous dissipation can be measured. The device and the method has the advantages and benefits that the temperature control of the fused mass is constant, the temperature is measured accurately and quickly, the fixing device is easy to assemble and disassemble, the neck ring mold is convenient to replace, and the range of measuring the shearing rate is higherwider.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Ultrasonic plasticizing capillary rheometer and viscosity test method
ActiveCN106124362AImprove liquiditySimplify the delivery pathIndirect flow property measurementEngineeringPolymer
An ultrasonic plasticizing capillary rheometer comprises a frame, a rheological test unit, an ultrasonic vibration apparatus, and a tool head moving and loading unit. The ultrasonic vibration apparatus is provided with an ultrasonic tool head capable of extending into a plasticizing chamber along an axial direction, providing extrusion force for polymer in the plasticizing chamber, and providing ultrasonic wave energy required by the polymer for fusion from a solid state to a liquid state. In the ultrasonic plasticizing capillary rheometer, three steps including heating fusion, ultrasonic vibration for fluidity increase, and material extrusion are completed through the ultrasonic tool head and in the plasticizing chamber, thereby simplifying the conveying path. A heating ring providing the required initial temperature for the plasticizing process sleeves a material canister, provides a constant material canister temperature for the rheometer, and reduces the test error. A filter screen is arranged in the material canister, centralizes fused polymer, and improves the test accuracy. During a test process, a viscosity test method is accurate in heating, short in fusion time, and wide in application range, is slightly affected by the external environment, and can provide viscosity data high in accuracy.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
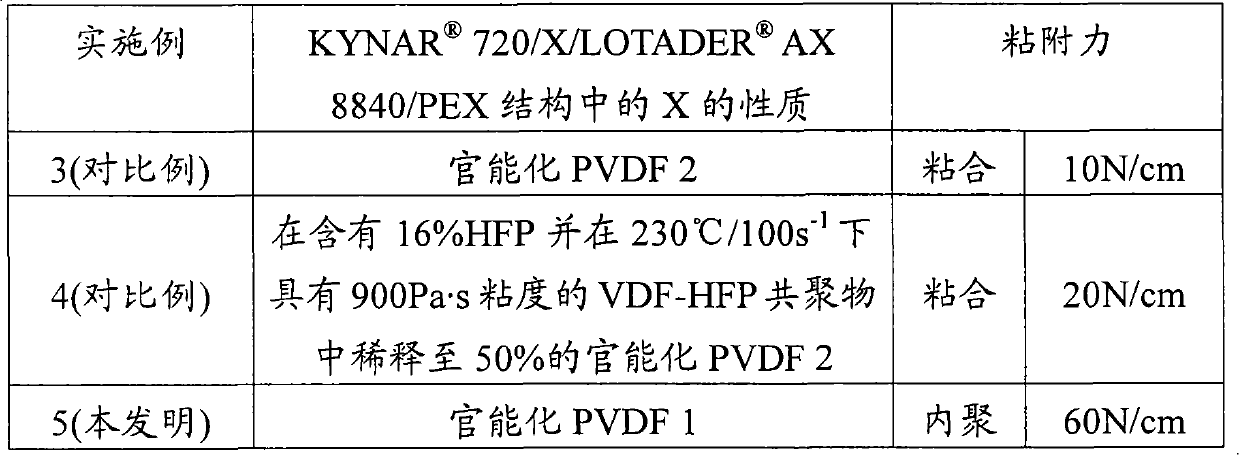
Vinylidene fluoride copolymer functionalized by radiation grafting of an unsaturated polar monomer
InactiveUS20100255378A1Increase line speedSynthetic resin layered productsFlexible pipesElastomerCrystallization temperature
The invention relates to a copolymer of VDF and at least one monomer that is copolymerizable with VDF, having a VDF weight content of at least 50%, preferably at least 75%, onto which at least one unsaturated polar monomer is radiation grafted, characterized in that the VDF copolymer has, before grafting, the following characteristics:a crystallization temperature Tc (measured by DSC according to the standard ISO 11357-3) ranging from 50 to 120° C., preferably from 85 to 110° C.;a yield strength σY ranging from 10 to 40 MPa, preferably from 10 to 30 MPa; anda melt viscosity η (measured with a capillary rheometre at 230° C. and 100 s−1) ranging from 100 to 1500 Pa·s, preferably from 400 to 1200 Pa·s.The invention also relates to a blend comprising this modified copolymer and a PVDF.This modified copolymer or the blend may be combined with a thermoplastic polymer, an elastomer or an inorganic material.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Composite processing adjuvant for polyolefin and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN1482167AReduce extrusion pressureReduce torqueLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
The composite processing assistant for polyolefin is prepared with polymer lubricating agent in 10-100 portions and inorganic stuffing in 10-100 portions and through stirring and mixing in high speedkneading machine or double-roller mixer at 70-80 deg. For 10-30 min. The composite processing assistant and polyolefin are molten and mixed homogeneously at 120-200 deg.c, and the mixture is then extruded in an extruder. The measurement with constant-rate type high pressure capillary rheometer at 190-200 deg.c shows that the composite processing assistant can lower the extrusion pressure, torque and melt viscosity obviously and raise the quality of extruding formation. The composite processing assistant is especially suitable for forming of metallocene linear low-density polyethylene and polyolefin.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Capillary rheometer and method for measuring rheological properties of polymer materials
ActiveCN102507383AEliminate biasImprove comparabilityDirect flow property measurementCapillary channelEngineering
The invention discloses a capillary rheometer and a method for measuring rheological properties of polymer materials. The capillary rheometer comprises a charging barrel, wherein the front end of the charging barrel is provided with a feed port, and the rear end of the charging barrel is provided with a discharging port. A first capillary channel, a material flowing pipeline and a second capillary channel are arranged in the charging barrel, and the feed port is communicated with the discharging port sequentially through the first capillary channel, the material flowing pipeline and the second capillary channel. The cross-sectional area of the material flowing pipeline is larger than that of the first capillary channel and the second capillary channel. The method can simultaneously measure shearing rheological parameters and extensional rheological parameters of the polymer materials. During measuring polymer composite materials, the method can avoid the influence of artificial factors, reduce the errors in measurement for several times, and increase the accuracy of measurement.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Toner for electrostatic image development and method of producing the same
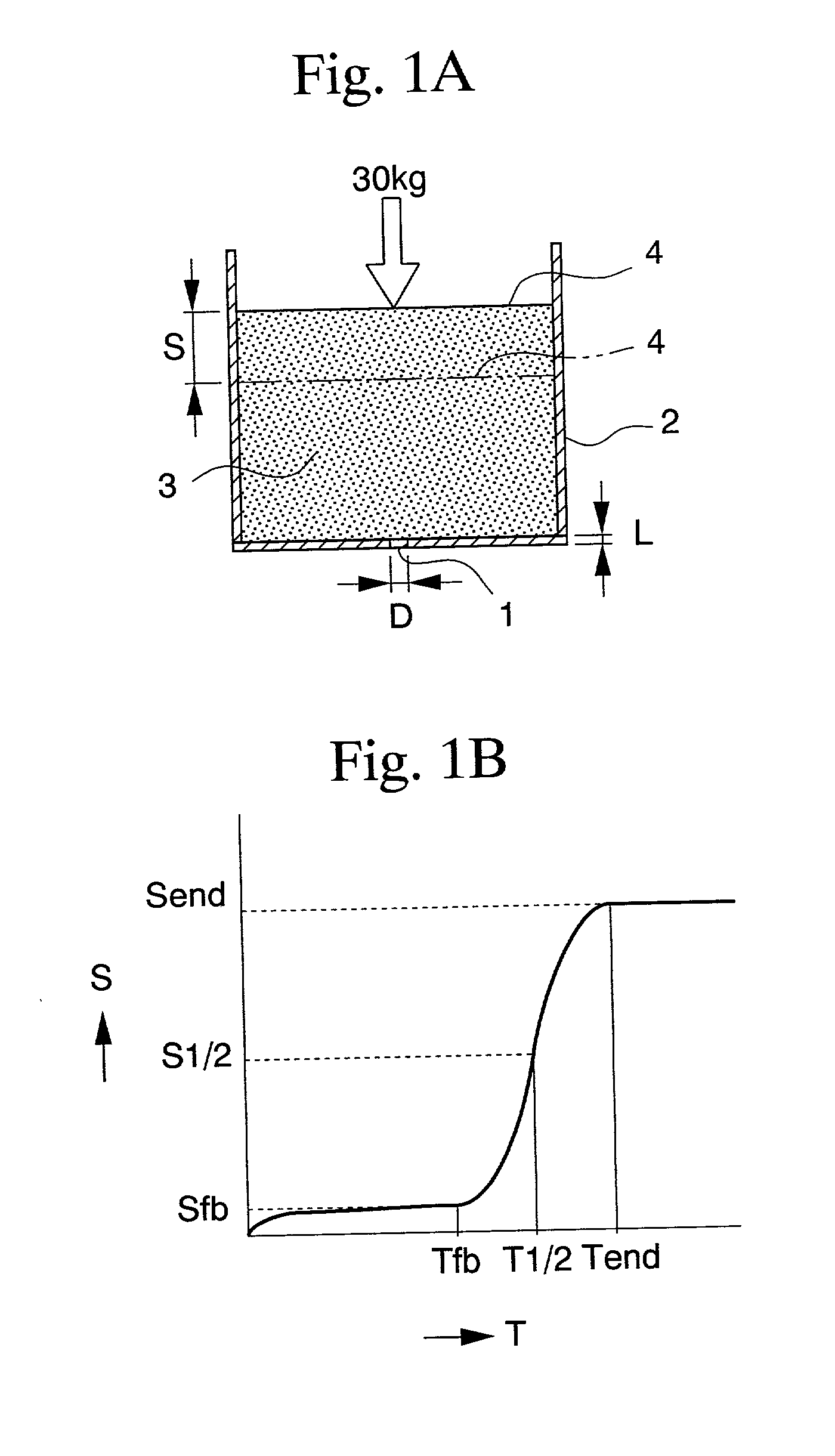
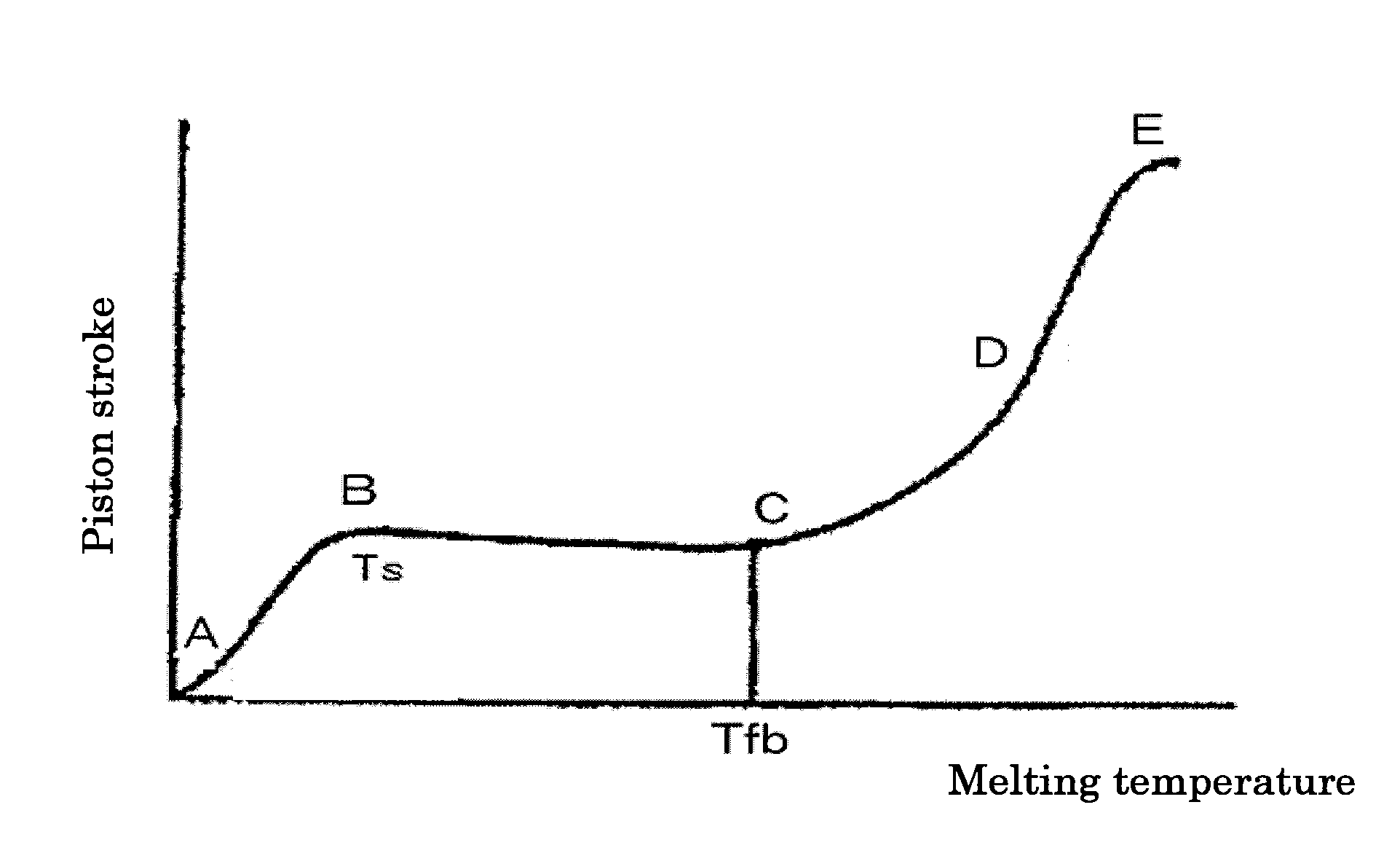
The present invention provides a toner for electrostatic image development made of a polyester resin having a spherical or generally spherical shape, which allows the use of a so-called oilless fixation system capable of fixing, without employing an anti-offset solution as a heat roller fixation system, and which also provides a developed image having excellent quality, and a method of producing the same. The toner for electrostatic image development comprises at least a binder resin and a colorant. The binder resin is made of a polyester resin. The flow beginning temperature Tfb of the toner, as measured by a constant load extrusion type capillary rheometer, is 90° C. or higher and 120° C. or lower, the T½ temperature exceeds 120° C. and is 160° C. or lower, and the flow ending temperature Tend is 130° C. or higher and 170° C. or lower. Also the toner has a spherical or generally spherical shape having an average roundness (the average value of roundness is defined by (the perimeter of a circle having the same area as that of a projected area of the particles) / (the perimeter of a projected image of particles)) of 0.97 or more. The toner having these properties can be preferably produced by phase inversion at a low shear within a range of 0.2-5 m / second employing an added alcohol solvent.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Mesophase pitch raw material used for preparing high-modulus high-thermal-conductivity carbon fiber, and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a mesophase pitch raw mateiral for preparing high-modulus high-thermal-conductivity carbon fiber, and a preparation method thereof. With a polarizing microscope measuring method, a mesophase content of the mesophase pitch raw material is 100%. With a capillary rheometer measuring method, a softening point of the mesophase pitch raw material is 220-260 DEG C. With an X-ray diffraction measuring method, an aromatic hydrocarbon macromolecule average sheet piling thickness Lc of the mesophase pitch raw material is larger than 8nm. According to the invention, a naphthalene series compound such as methylnaphthalene is adopted as a raw material; hydrogen fluoride-boron trifluoride is adopted as a catalyst; and through controlling a catalyst dose, polymerization conditions and low-boiling-point product separation conditions, the mesophase pitch is prepared. Compared with prior arts, the mesophase pitch provided by the invention has excellent spinnability, such that spinning process controlling and operation are facilitated. The mesophase pitch has good molecular orientation, such that high-modulus high-thermal-conductivity carbon fiber with high orientation degree can be prepared under a relatively low graphitization temperature. Therefore, the production cost of high-performance carbon fiber is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for measuring fluid shear stress in capillary and device
InactiveCN102323186AEliminate systematic errorsImprove test accuracyDirect flow property measurementMeasurement deviceTest sample
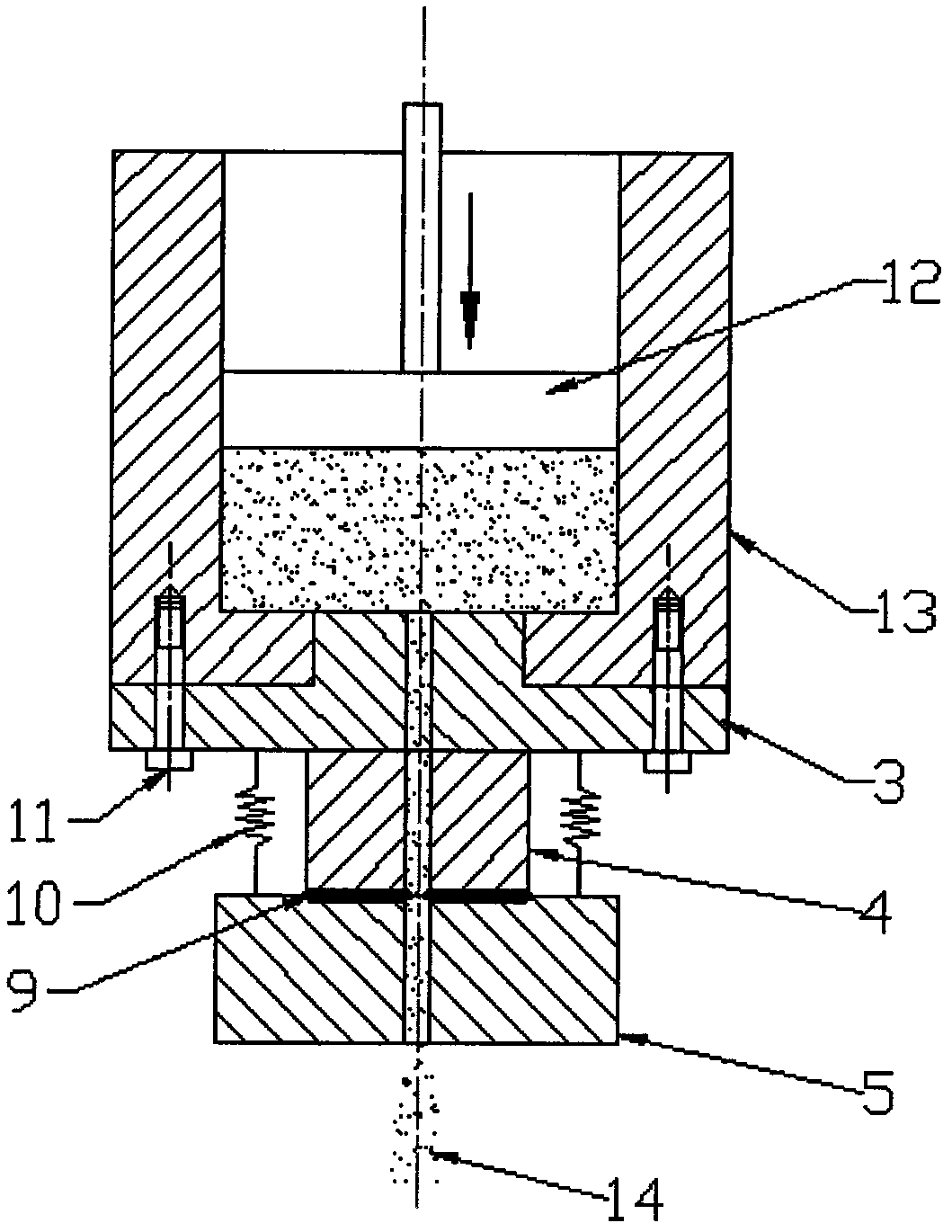
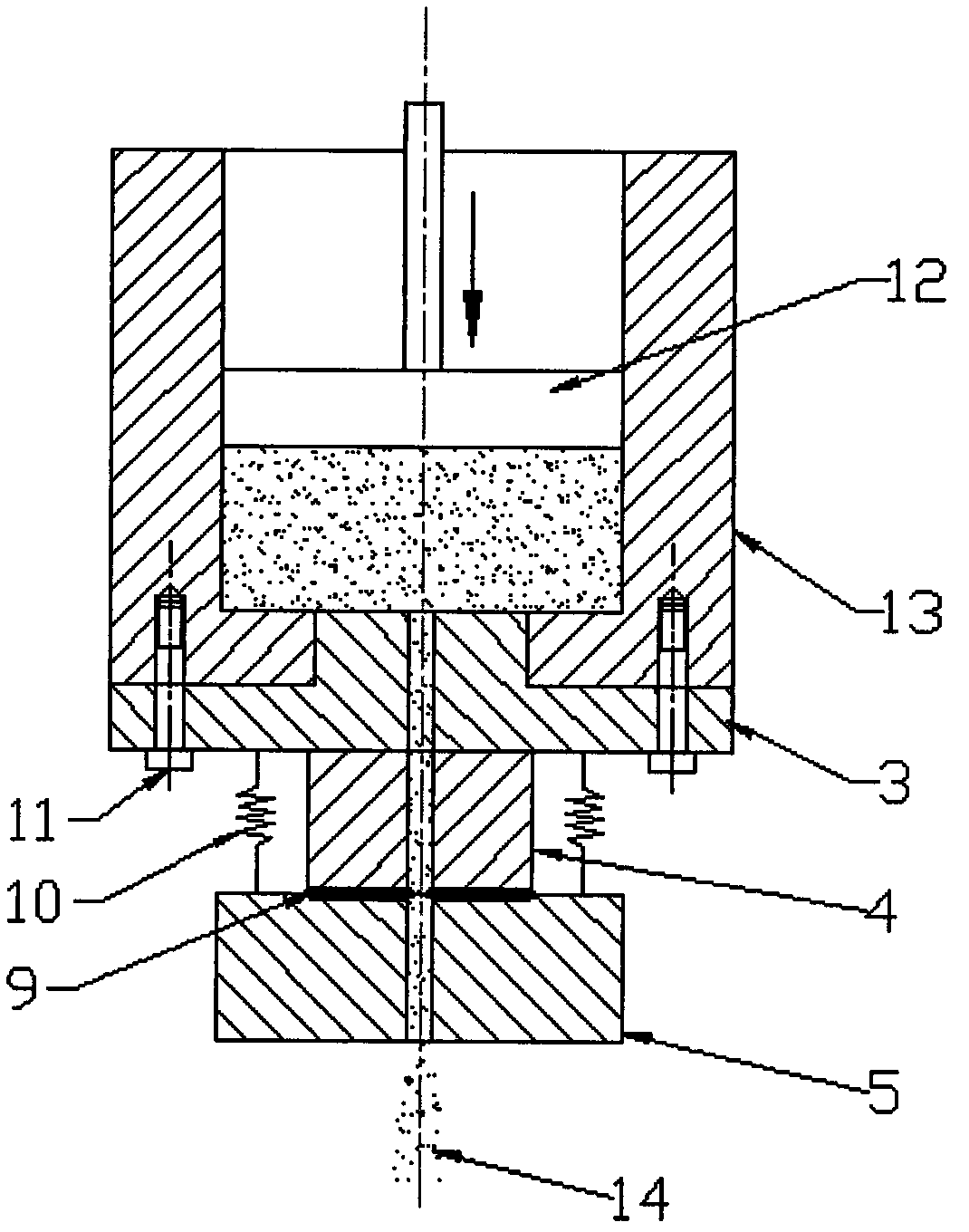
The invention discloses a method for measuring the fluid shear stress in a capillary and an implementing device thereof, and belongs to the field of material testing. The method comprises the following steps of: slicing a capillary die into at least three sections, i.e. an inlet section, a middle section and an outlet section, along the axial direction according to differences of test sample fluid in the capillary in the flow condition; and only measuring the stress of a test sample at the position of the middle section so as to calculate the shear stress of the test sample in the capillary. The measuring device for implementing the method comprises a charging barrel, a plunger rod, the capillary die and a force measuring element. The force measuring element is arranged in the middle section of the die and can be used for measuring an acting force between the middle section and the outlet section. In the testing process, the test sample in the charging barrel outflows through the capillary under the squeezing action of the plunger rod. The change of a force value measured in the middle section of the die corresponds to the shear force applied to the capillary wall of the middle section of the die. Due to the adoption of the method and the implementing device thereof, the influence of a pressure drop of an inlet region and an outlet region in a capillary rheometer on the measurement of the fluid shear stress in the capillary is completely eliminated, and the testing accuracy of the capillary rheometer is promoted.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Rheological in-situ online test system integrating scattering and microscopy
ActiveCN104931388AStable rheological parametersSolve the problem of optical distortionDirect flow property measurementMicroscopic observationOnline test
A rheological in-situ online test system integrating scattering and microscopy is disclosed. Aimed at the problems that a general capillary rheometer cannot realize in-situ online observation and a microscopic rheological test system and a light scattering rheological test system cannot realize intuitive observation of sample microstructure, the invention designs an integrated flat capillary rheological in-situ online test system capable of performing laser scattering and microscopic observation while performing rheological performance testing. A stable shear flow field and rheological parameters related with macroscopic properties of a material can be provided through a rheological system, the in-situ internal microscopic structure of the polymer material can be detected and observed through an optical technology, a microimaging system, a laser scattering system and a capillary rheological system are organically combined, and the relationship between the microstructure and the macroscopic properties of the material can be researched more conveniently. The rheological in-situ online test system is suitable for macromolecular polymer processing application labs.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mesophase pitch material for preparing high-performance carbon fibers and preparation method of mesophase pitch material
InactiveCN104195676AImprove spinnabilityNarrow molecular weight distributionFibre chemical featuresFiberCarbon fibers
The invention relates to a mesophase pitch material for preparing high-performance carbon fibers and a preparation method of the mesophase pitch material. Measured by use of a polarizing microscope, the mesophase content of the mesophase pitch material is 100%; measured by use of a capillary rheometer, the softening point of the mesophase pitch material is 190-270 DEG C and the temperature difference between the flow point and the softening point of the mesophase pitch material is lower than 28 DEG C. The mesophase pitch material is prepared from naphthalene compounds such as methylnaphthalene in the presence of a hydrogen fluoride-boron trifluoride as a catalyst under the control of polymerization conditions and low-boiling point product separation conditions. Compared with the prior art, the mesophase pitch material has the characteristics of excellent spinnability, narrow molecular weight distribution, and good orientation property depending on good melt fluidity, and is advantageous for the control and the operations of a spinning process and also advantageous for preparing the high-performance pitch-based carbon fibers.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Toner for electrostatic charge development
InactiveUS8778588B2Good colorSmall particle sizeDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusDyneViscoelasticity
To provide a toner, which contains a binder resin, a colorant, and a releasing agent, wherein the binder resin contains a low molecular weight resin component, where the low molecular weight resin component has a resin softening coefficient (A), represented by the following formula (1), satisfying A>0.165, and has storage elastic modulus (dyne / cm2) G′(Tfb) satisfying G′(Tfb)≦1×104 where Tfb is a flow onset temperature (° C.) of the low molecular weight resin component as measured by a capillary rheometer:A=|[(r1)−ln G′(r2)] / (T1−T2)| Formula (1)(where T1 is temperature (° C.) at which storage elastic modulus G′(r1) is 1×105 (dyne / cm2) and T2 is temperature (° C.) at which storage elastic modulus G′(r2) is 1×103 (dyne / cm2) as measured by means of a viscoelasticity measuring device with measuring frequency of 1 Hz, and measuring distortion of 1 deg; and | | represents an absolute value.).
Owner:RICOH KK
Toner and method for producing toner
Owner:CANON KK
Resinous composition with improved resistance to plate-out formation, and method
InactiveCN101072829AGood physical propertiesFouling formation reduced or eliminatedChemical recyclingLinear low-density polyethyleneElastomer
Disclosed are compositions comprising: (i) a rubber modified thermoplastic resin comprising a discontinuous elastomeric phase dispersed in a rigid thermoplastic phase, wherein at least a portion of the rigid thermoplastic phase is grafted to the elastomeric phase; (ii) at least two additives selected from the group consisting of glass beads; fluoropolymers; ethylene bis-stearamide; a mixture of at least one metal salt of a fatty acid and at least one amide; a homopolymer comprising structural units derived from at least one (C1-C12)alkyl(meth)acrylate monomer; and mixtures thereof; and optionally (iii) at least one additive selected from the group consisting of a silicone oil and a linear low density polyethylene; wherein said composition has a critical shear rate value of greater than about 50 reciprocal seconds as measured at 190 DEG C. in a capillary rheometer with 10 mm length and 1 mm diameter. In other embodiments the present invention comprises a method to reduce or eliminate plate-out formation in compositions comprising rubber modified thermoplastic resins. In still other embodiments the present invention comprises articles made from said compositions.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Method and apparatus for measuring drilling fluid properties
As system for measuring drilling fluid properties includes a capillary rheometer that is adapted to measure viscosity parameters of drilling fluid. The capillary rheometer includes a feed chamber, the feed chamber having a cavity, at least a first drain port for draining fluid out of the cavity, a double wall defining an annulus that opens to the cavity, and a feed port in an outer portion of the double wall that is in fluid communication with the annulus. The capillary rheometer also includes at least a first capillary tube coupled to at least the first drain port. Additionally, the disclosed system further includes a pump that is adapted to pump fluid to the feed port.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
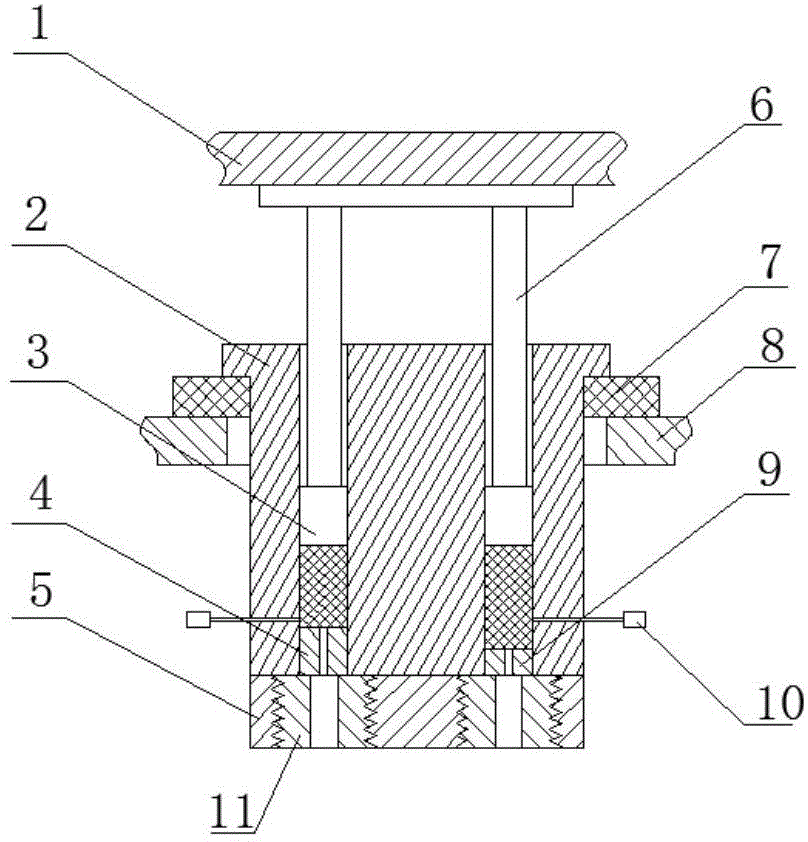
Double-charging barrel capillary pipe rheometer
The invention relates to a double-charging barrel capillary pipe rheometer, and belongs to the technical field of high polymer rheological measurement. The core component double capillary pipe orifice die of the rheometer is designed into a long capillary pipe orifice die and a short capillary pipe orifice die, and the design of a zero long capillary pipe orifice die of the traditional conventional double-charging barrel capillary pipe rheometer is changed. The double-charging barrel capillary pipe rheometer drives and controls a plunger to extrude high polymer fluid in two charging barrels with the same internal diameters at the same rate through a servo motor and a screw, then the fluid enters two capillary pipes with the same internal and external diameters and different lengths, pressure is respectively measured through a pressure sensor, and after the pressure is subtracted, pressure drop of fluid flowing through inlets and outlets of the capillary pipes can be conveniently eliminated; meanwhile, compared with a zero long capillary pipe, the fluid in the short capillary pipe orifice die with certain length is provided with a completely developed flowing region with certain length, and flowing conditions of the fluid in long and short capillary pipes are more similar, so that the pressure drop measured finally is more accurate and closer to the practical situation.
Owner:李振中
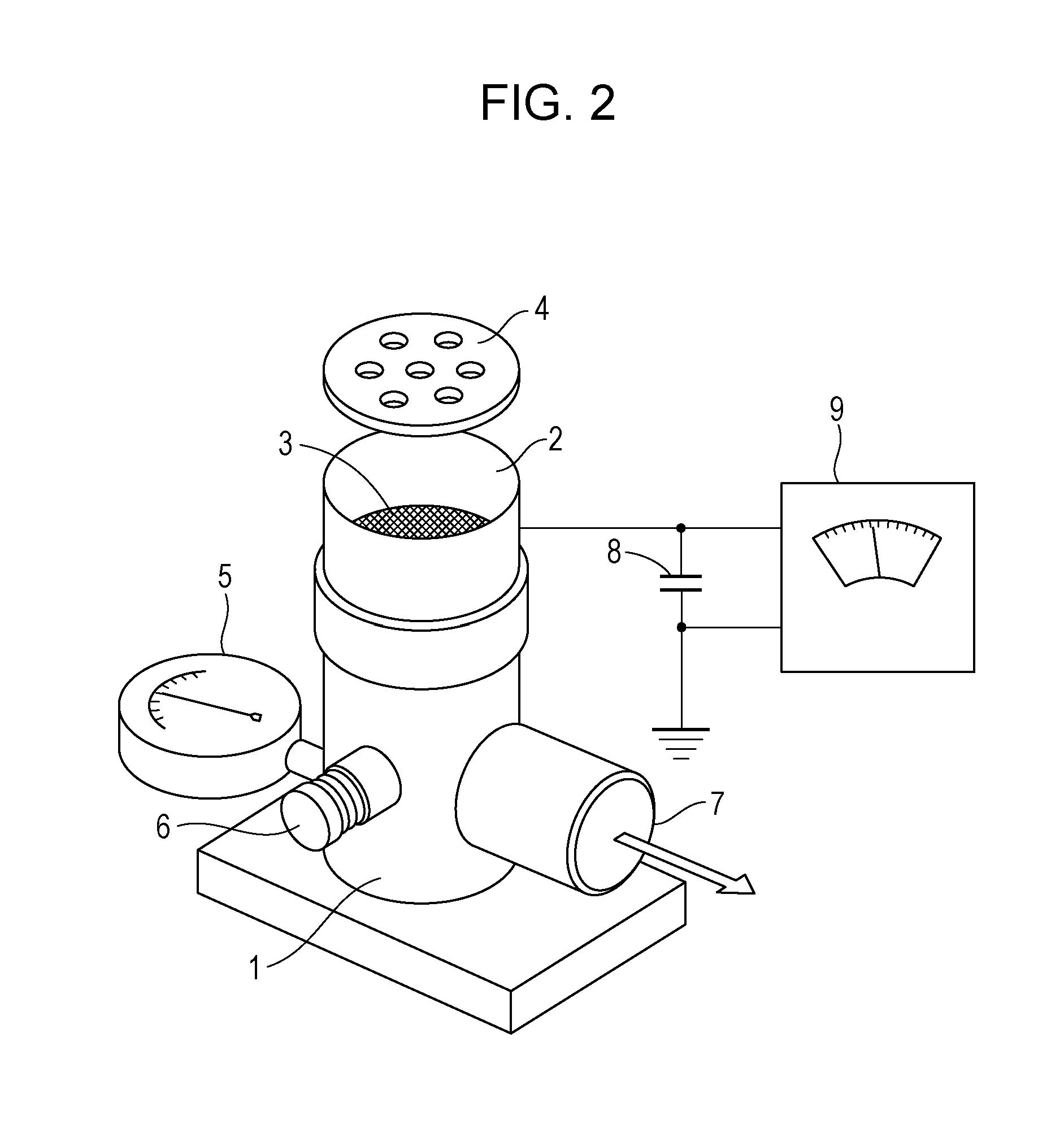
Capillary rheometer with instrumented cleaning and packing device
InactiveUS20080110246A1Quick cleanViscometer maintainanceDirect flow property measurementLinear motionEngineering
The present invention is a capillary rheometer cleaning and packing device comprising: (a) a linear motion device for creating controlled linear motion in a linear motion rod, wherein the linear motion rod is adapted to receive a cleaning / packing rod; (b) a housing securing means wherein the securing means is adapted to secure an existing capillary rheometer housing to the cleaning and packing device such that a barrel mounted concentrically within the capillary rheometer housing is positioned coaxially below the linear motion rod; and (c) a means of attaching the capillary rheometer cleaning and packing apparatus to an existing capillary rheometer.
Owner:TICONA LLC
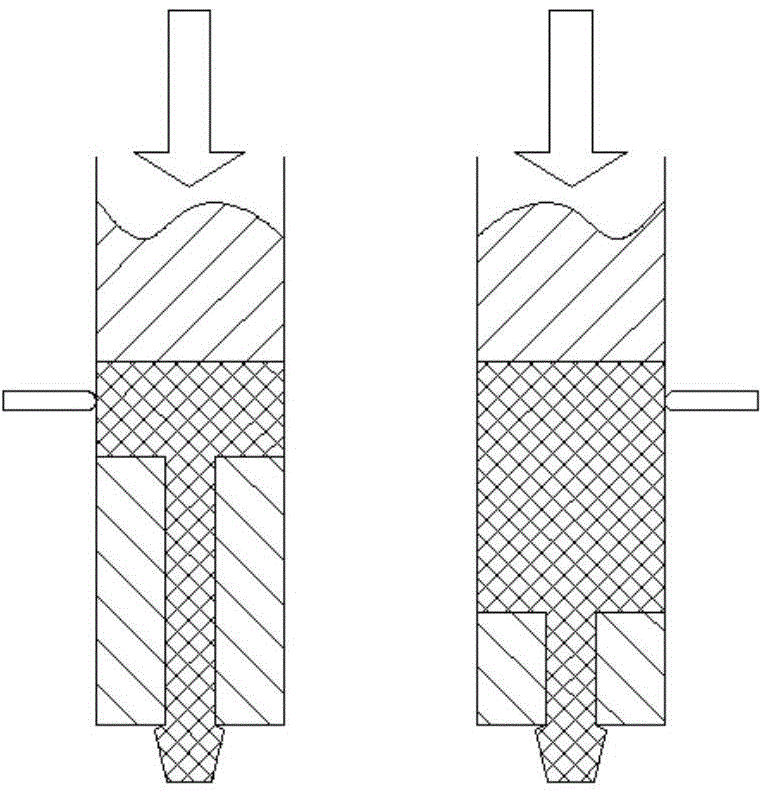
Single-feed-cylinder capillary rheometer
InactiveCN105675443AEliminate pressure dropHigh precisionDirect flow property measurementEngineeringShear flow
The invention discloses a single-feed-cylinder capillary rheometer. A feed cylinder of the capillary rheometer is a single feed cylinder; the front end of the feed cylinder is provided with a plunger, the rear end of the feed cylinder is provided with a traveling nut, an electric heater is arranged around the feed cylinder, a long capillary die, a support part and a zero-length capillary die / short capillary die are arranged in the feed cylinder, and the outer diameter of the long capillary die, the outer diameter of the zero-length capillary die / short capillary die and the outer diameter of the support part all are matched with the inner diameter of the feed cylinder. The single-feed-cylinder capillary rheometer can be used for measuring extensional flow and shear flow parameters of polymer melt simultaneously, can eliminate entry pressure drop well, has the same function as a double-feed-cylinder capillary rheometer, and also has the advantages of saving raw materials, facilitating dismounting, purging easily, reducing artificial influences, realizing higher precision, and the like.
Owner:TAIYUAN INST OF TECH
Bidirectional extrusion capillary rheometer and parallel bidirectional extrusion capillary rheometer
ActiveCN102519839AWork lessSimplify manual laborDirect flow property measurementTest efficiencyPhysical hard work
The invention relates to a bidirectional extrusion capillary rheometer. The capillary rheometer comprises two charging barrels and a capillary tube arranged between the two charging barrels in a detachable mode, wherein a charging device is arranged on one charging barrel; two ends of the capillary tube are communicated with inner cavities of the two charging barrels; and a plunger which is matched with each charging barrel and used for extruding a material to be tested and a driving system for driving the plunger to move are arranged in each charging barrel. By the bidirectional extrusion capillary rheometer, the two charging barrels are arranged at the two ends of the capillary tube, so that the aim of one-time charging and multi-time testing is fulfilled, complicated physical labor is simplified, testing efficiency is improved, the material is saved, and the cleaning work of the charging barrels and the capillary tube is eliminated; and different capillary tubes can be selected fordifferent materials to be tested, so that the different materials to be tested are tested.
Owner:如东文园投资开发有限公司
Multilayer tube for transporting water or gas
InactiveCN101583491AImprove toleranceTolerance hasLighting and heating apparatusChemical industryMolten statePolyolefin
The invention relates to a multilayer tube comprising (in the order starting from the inside to the outside of the tube) layers arranged one on top of the other: an optional layer L1 comprising at least one fluorinated polymer, preferably a PVDF; a layer L2 comprising at least one functionalized PVDF, obtained by radiation grafting of at least one unsaturated polar monomer onto a PVDF; an optional layer L3 of an adhesive binder; a layer L4 comprising at least one polyolefin optionally mixed with at least one functionalized polyolefin; an optional barrier layer L5; an optional layer L6 comprising at least polyolefin, optionally in a mixture with at least one functionalized polyolefin; characterized in that the PVDF onto which the unsaturated polar monomer is grafted is a VDF copolymer whose weight content is at least 50%, preferably at least 75% and at least one monomer copolymerisable with the VDF, having the following characteristics: a crystallization temperature Tc (measured by DSCas per the ISO Standard 11357-3) ranging from 50 to 120 DEG C, preferably from 85 to 110 DEG C; a constraint to the Theta Y threshold ranging from 10 to 40 MPa, preferably from 10 to 30 MPa; a viscosity Eta in the molten state (measured with a capillary rheometer at 230 DEG C at 100 s<-1>) ranging from 100 to 1,500 Pa s, preferably from 400 to 1200 Pa s.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Testing machine with broadband amplitude vibration test/rheological measurement integrated function
The invention discloses a testing machine with a broadband amplitude vibration test / rheological measurement integrated function. The testing machine comprises a mold assembly, a broadband amplitude vibration assembly and a rheological measurement assembly. High-amplitude and low-frequency mechanical vibration and high-frequency and low-amplitude ultrasonic vibration jointly act to form a broadband amplitude vibration field, the shear viscosity of melt is measured based on the principle of a capillary rheometer, and the broadband amplitude vibration test / rheological measurement integrated function is integrated for the manufacturing process of a polymer fine structure. The testing machine plays an important role in systematically researching the orientation and disentanglement action rule and mechanism of a composite vibration synergistic external field condition on a polymer microstructure, and can be used for online obtaining the polymer structure and rheology under broadband amplitude vibration in a fine-scale viscoelastic non-Newtonian chaotic flow field; and mutual competition and synergistic effect rules of a plurality of vibration modes in micro motion of polymer molecules are disclosed. The shearing vibration frequency applied by the testing machine is wide, the processing time is short, and the processing efficiency and the mechanical property of the polymer can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
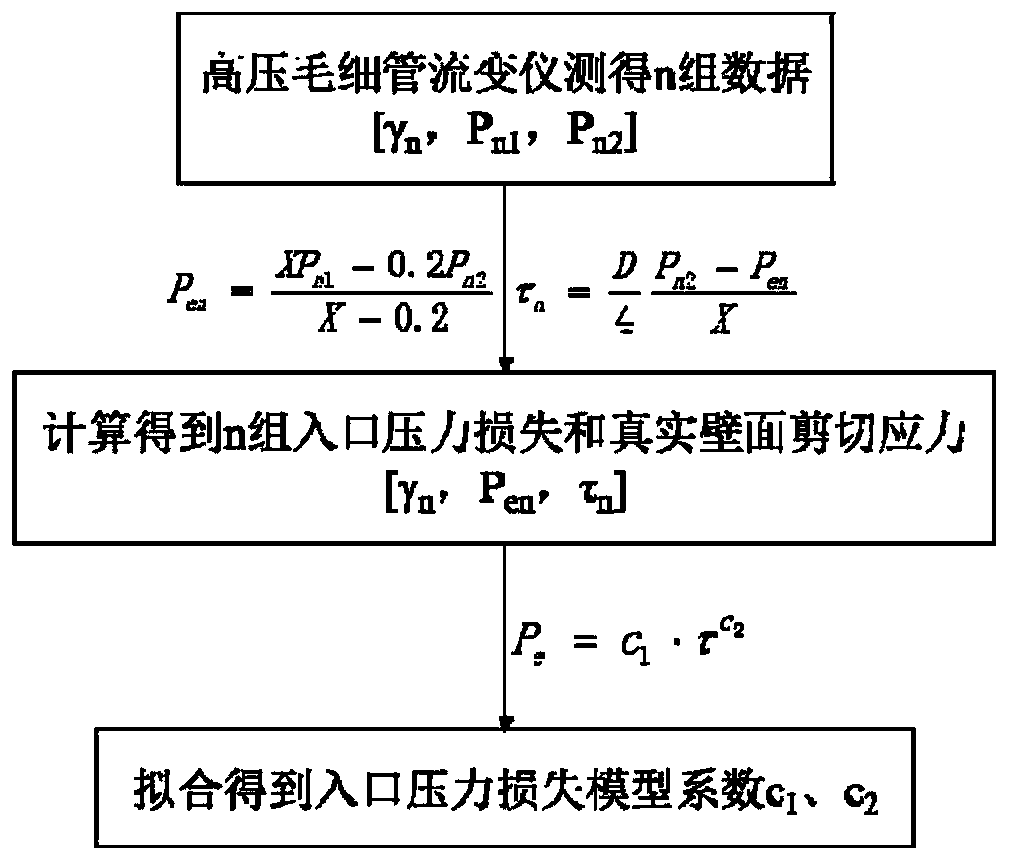
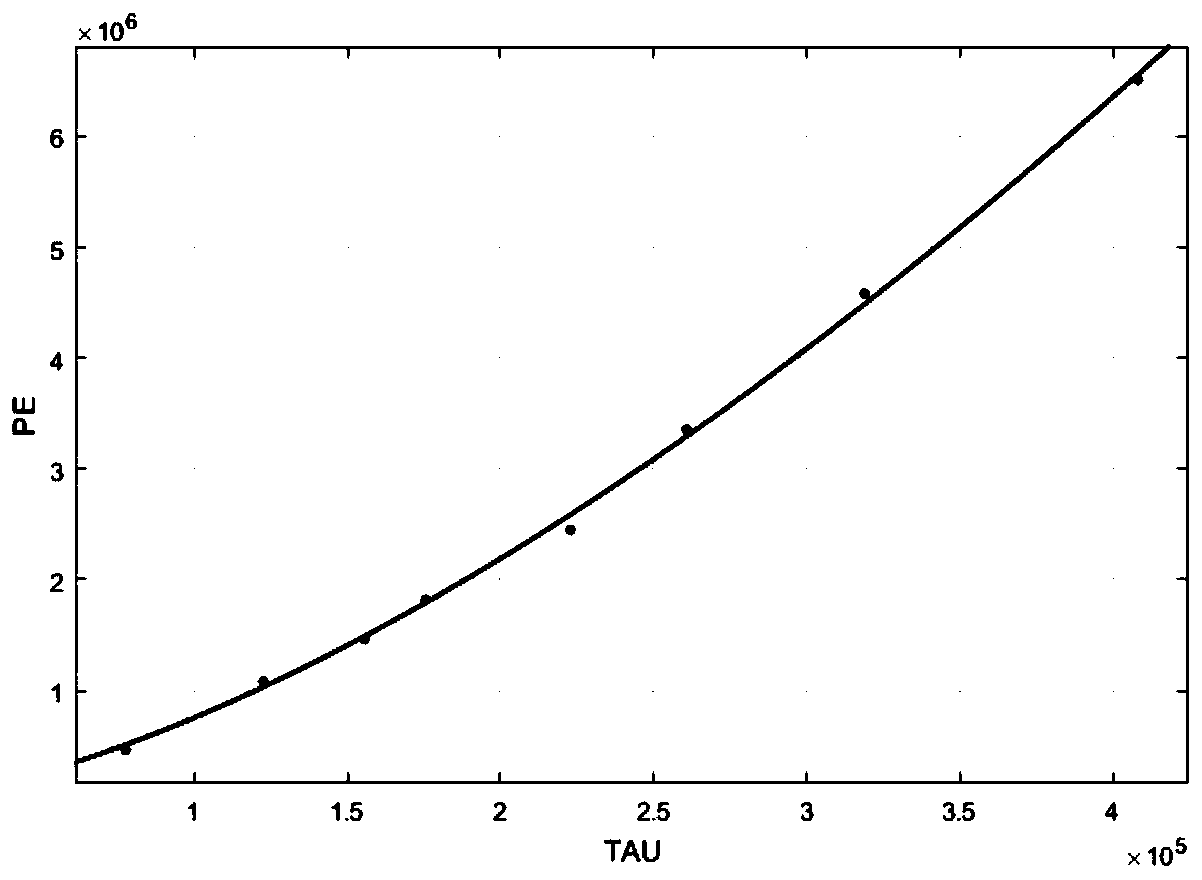
Method for obtaining inlet pressure loss model coefficient through metering
PendingCN111475968AReduce dosageAvoid wastingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWall shearCapillary Tubing
The invention provides a method for obtaining an inlet pressure loss model coefficient through metering. Inlet pressure loss and real wall shear stress can be obtained through test and calculation ofa high-pressure capillary rheometer, and two parameters c1 and c2 of an inlet pressure loss model are obtained by fitting. Specifically, the inlet pressure P of a polymer melt at different shearing rates is tested by using two capillary orifice molds respectively, so that the inlet pressure loss Pe and the real wall surface shearing stress tau are calculated and substituted into the inlet pressureloss model, and two parameters c1 and c2 of the inlet pressure loss model can be obtained by fitting regression. The method has the advantages that the single-time test sample consumption is low, theinfluence of shearing heat generation does not need to be corrected, results more accurate, and data processing is simple and easy to operate. The method has guiding significance for finding out a balance point of material fluidity and mechanical properties, selecting an injection molding machine matched with required injection pressure and designing a mold runner with a proper size, and can solve the problem of pressure distortion caused by change from coarse to fine in injection molding, so that the mold opening success rate and the qualified product yield are improved.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD
Polycarbonate resin
The object of the present invention is to provide a polycarbonate resin having an extremely narrow molecular weight distribution, good flowability when melting, and particularly extremely good flowability when melting that does not depend on shear rate. The present invention relates to a polycarbonate resin, characterized in that a value obtained by dividing difference between a logarithmic value log MV9.12 of a melt viscosity (Pa·s) measured at shear rate of 9.12 sec−1 and a logarithmic value log MV1824 of a melt viscosity (Pa·s) measured at shear rate of 1824 sec−, with a capillary rheometer having a die diameter of 1 mmφ and an effective length of 30 mmL, by a viscosity average molecular weight Mv calculated by the following equations, viscosity difference / molecular weight ratio, is 2.0×10−5 or less.ηsp / C=[η]×(1+0.28ηsp)[η]=1.23×10−4×Mv0.83 (In the above equations, ηsp is a specific viscosity measured at 20° C. with respect to a methylene chloride solution of a polycarbonate resin, C is a polycarbonate resin concentration of the methylene chloride solution, and C=0.6 g / dl).
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
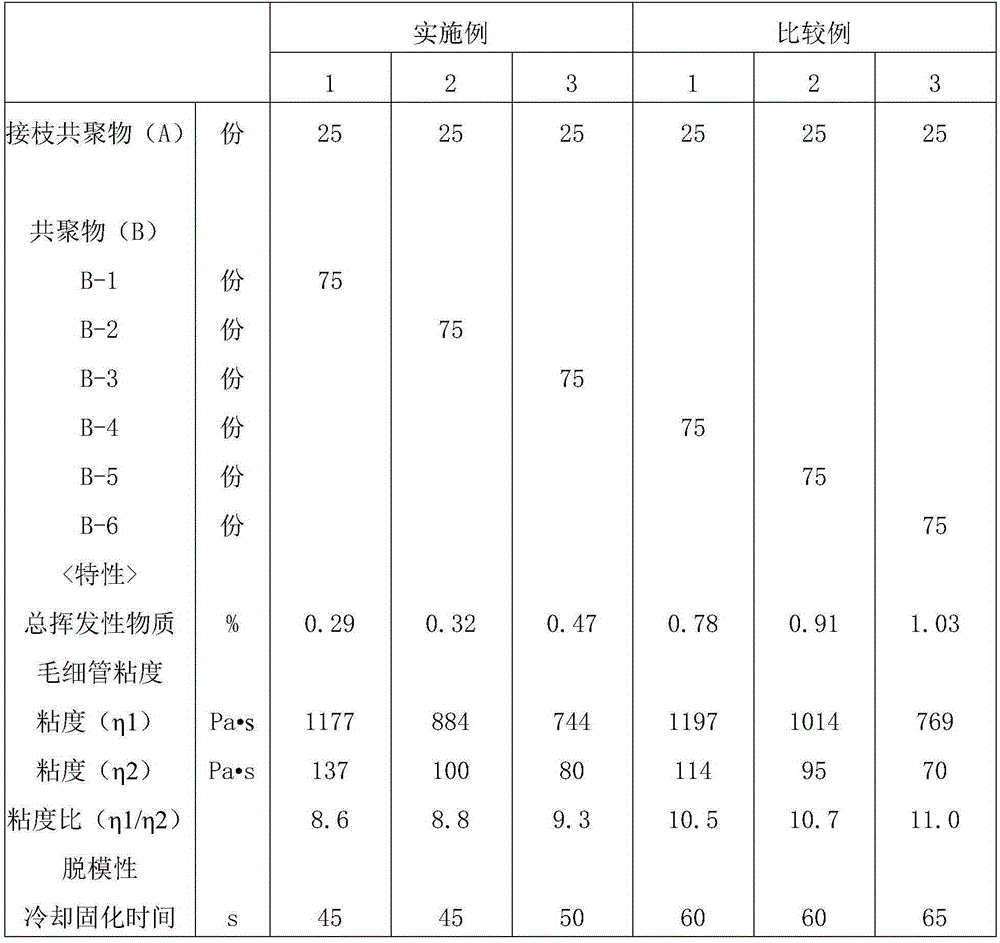
Rubber-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition and resin molded article
A rubber-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition comprising: a graft copolymer (A) forming a dispersion phase and obtained by graft copolymerization, in the presence of a rubber-like polymer (a), of at least one type of monomer (b) selected from a group comprising an aromatic vinyl-based monomer, a vinyl cyanide monomer, a (meth) acrylate ester-based monomer, and other copolymerizable monomers; and a copolymer (B) forming a continuous phase and being a copolymerization of at least one type of monomer (b) selected from a group comprising an aromatic vinyl-based monomer, a vinyl cyanide monomer, a (meth) acrylate ester-based monomer, and other copolymerizable monomers. The rubber-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition is characterized by the viscosity ratio (eta 1 / eta 2), between the viscosity (eta 1) at a shear rate of 1 * 101 / sec and the viscosity (eta 2) at a shear rate of 1 * 103 / sec, being no more than 10 as measured using a capillary rheometer having a 1 mm [phi]bore diameter.
Owner:NIPPON A & L INC
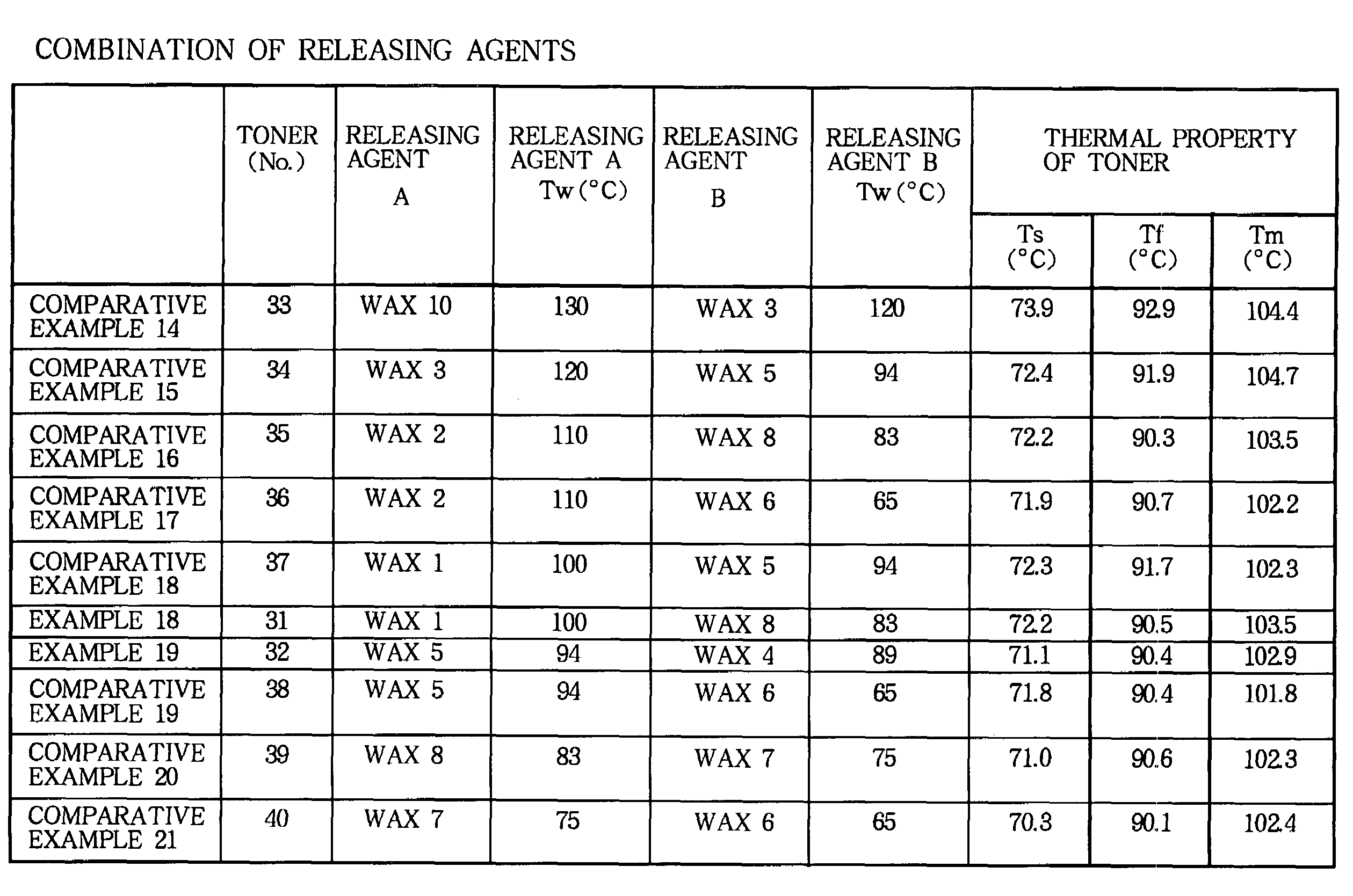
Developer, image forming method and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS7286781B2Increase speedHigh speed printingDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusShear stressLatent image
A toner for developing a latent image includes, at least, a binder resin, a releasing agent, a coloring agent and a fluidizing agent. A melting point Tw of the releasing agent is higher than or equals to a softening temperature Ts of the developer measured by a capillary rheometer of a constant shear stress type. The melting point Tw of the releasing agent is lower than or equals to a melting temperature Tm of the developer measured by ½ method. Using the above described toner, it becomes possible to print a full color image at a high speed without causing an offset phenomena or sheet jam.
Owner:OKI DATA CORP
Die assembly for double-stage differential pressure type capillary rheometers
InactiveCN107219152AIncrease pressureViscosity adjustmentFlow propertiesDifferential pressureEngineering
The invention provides a die assembly for double-stage differential pressure type capillary rheometers. The die assembly comprises a first barrel and a second barrel, the end of the first barrel is provided with a cylindrical socket, the socket is concentric with the cavity of the first barrel, and moreover, the diameter of the socket is greater than the diameter of the cavity; the top end of the second barrel is provided with a cylindrical boss, the boss is concentric with the cavity of the second barrel, the boss matches the diameter of the socket of the first barrel, and the boss of the second barrel is inserted in the socket of the first barrel; a first die is arranged in the end of the cavity of the first barrel, a first pressure sensor is arranged on the barrel wall close to the first die, and the first pressure sensor runs through a first heating jacket and the wall of the first barrel to communicate with the cavity. The die assembly not only can increase the pressure of the inlet of the first die, but also can test the viscosity of high polymer melt under two different pressures each time, so that the efficiency of an experiment is greatly increased, and the die assembly can also compare the viscosity changes of the high polymer melt under different pressures at the same time.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Composition for polyolefin resin foam, foam of the same, and process for producing foam
InactiveUS7803862B2Excellent in softness and cushioning propertyAvoid insufficient thicknessOther chemical processesExtensional viscosityPolyolefin
A composition for polyolefin resin foam, which comprises a polymer component comprising a polyolefin resin and a rubber and / or thermoplastic elastomer, and a powder particle, wherein the composition has an extensional viscosity as measured with a capillary rheometer (temperature, 200° C.; shear rate, 5,000 [1 / s]) of from 20 to 100 kPa·s.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com