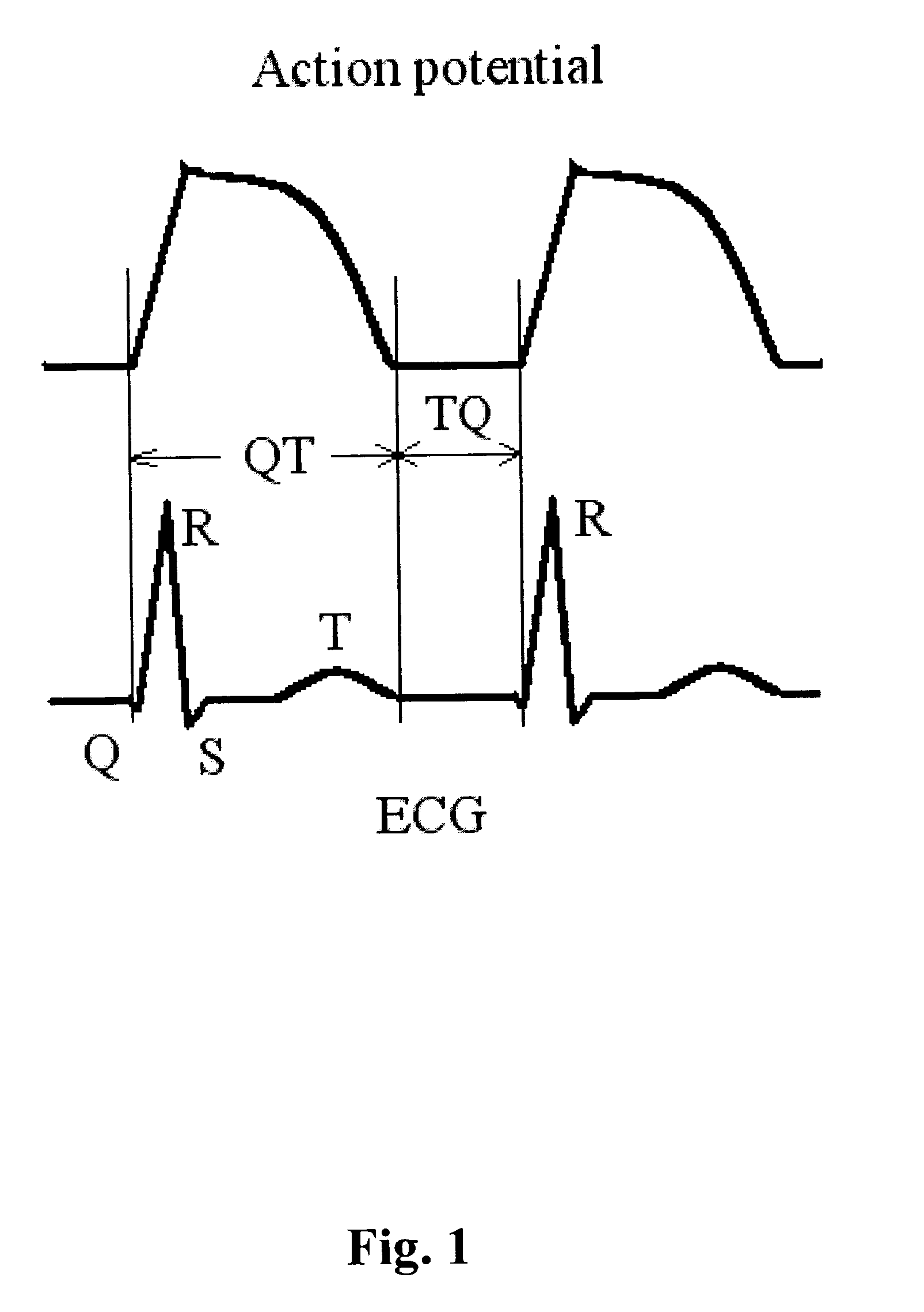
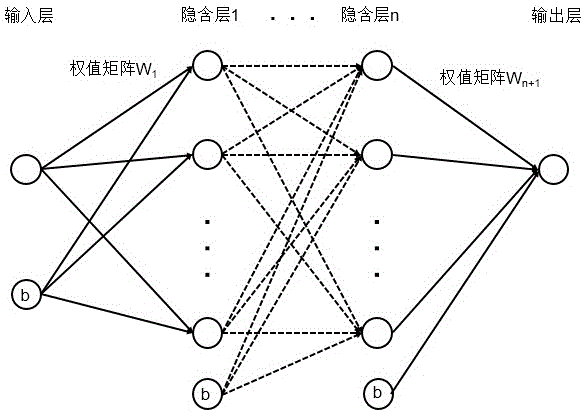
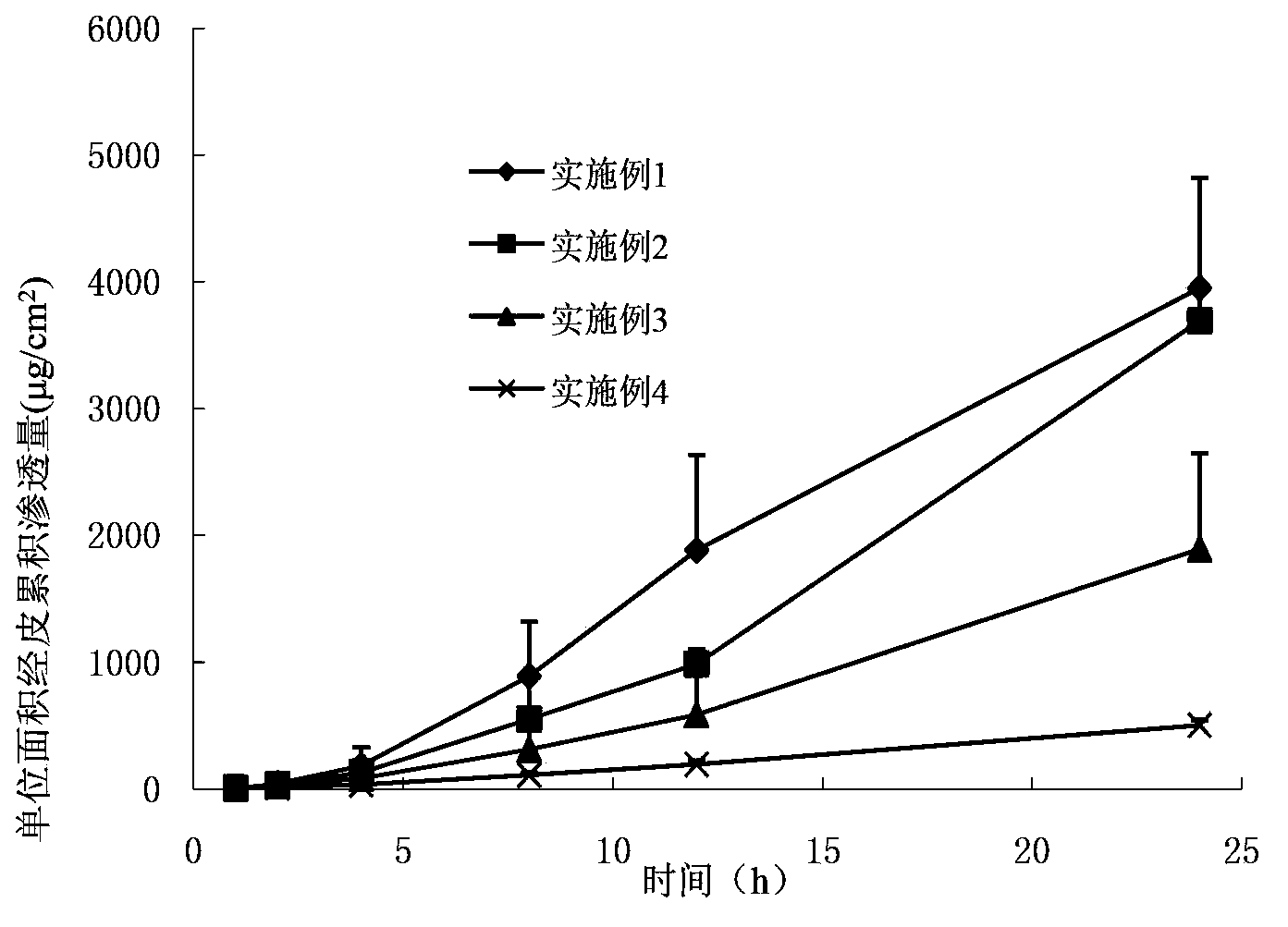
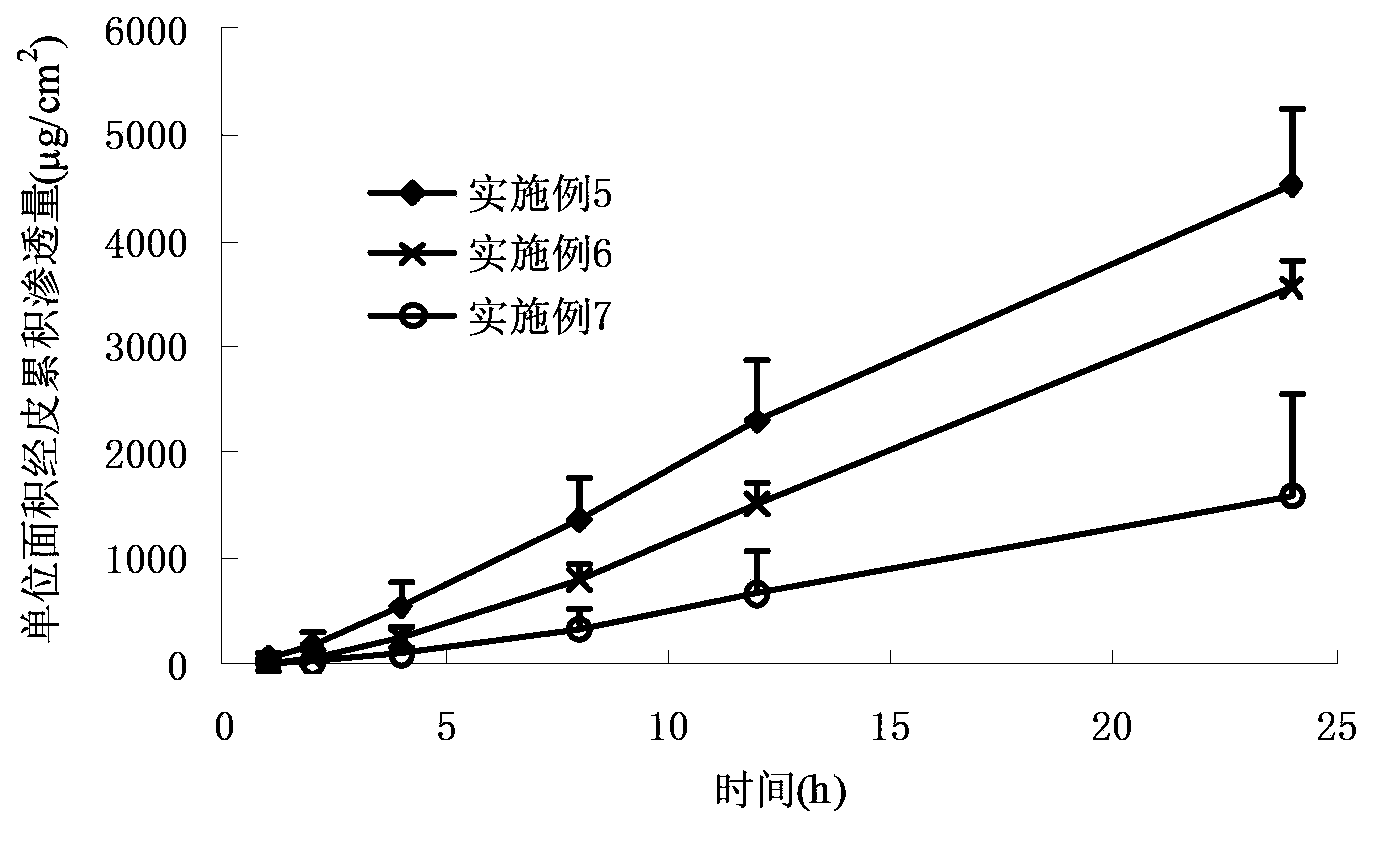
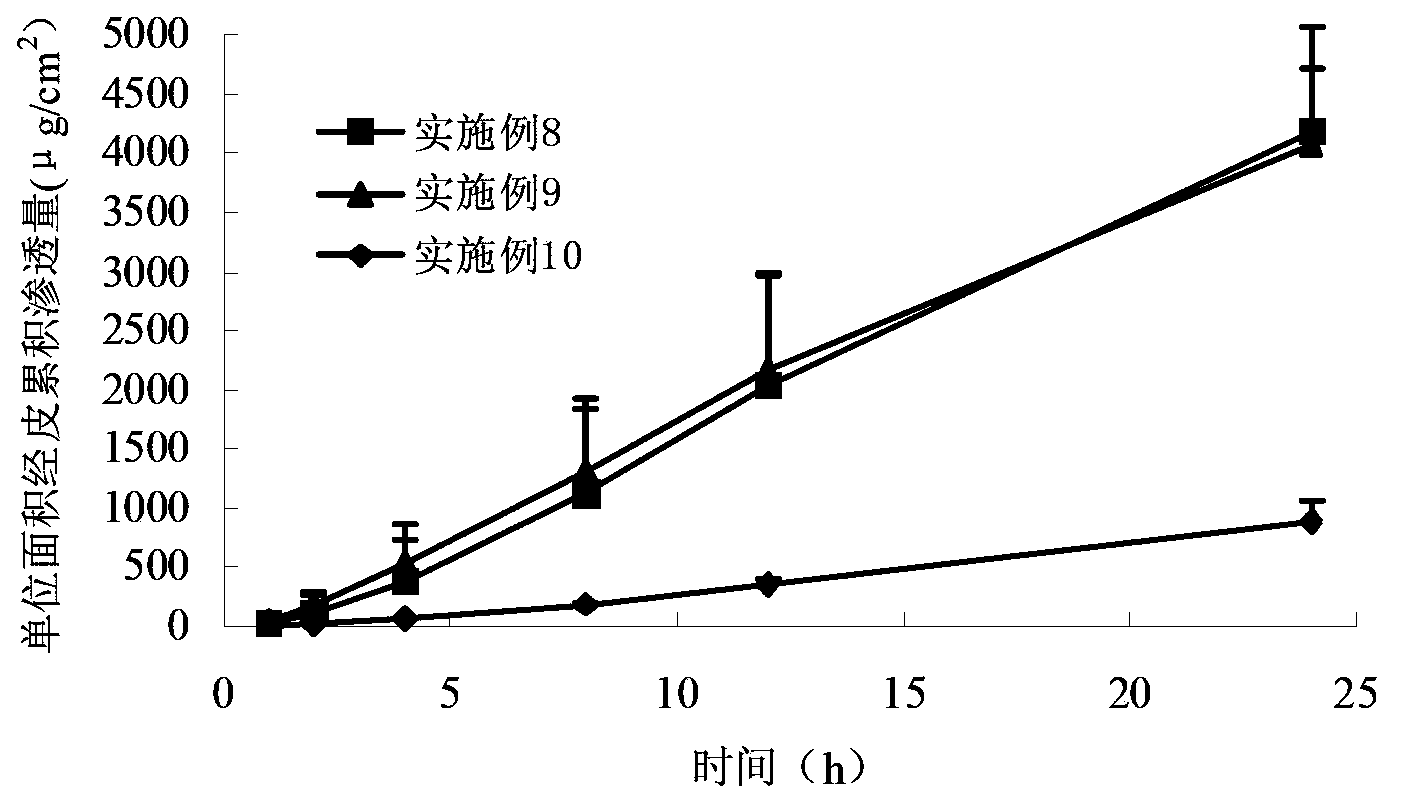
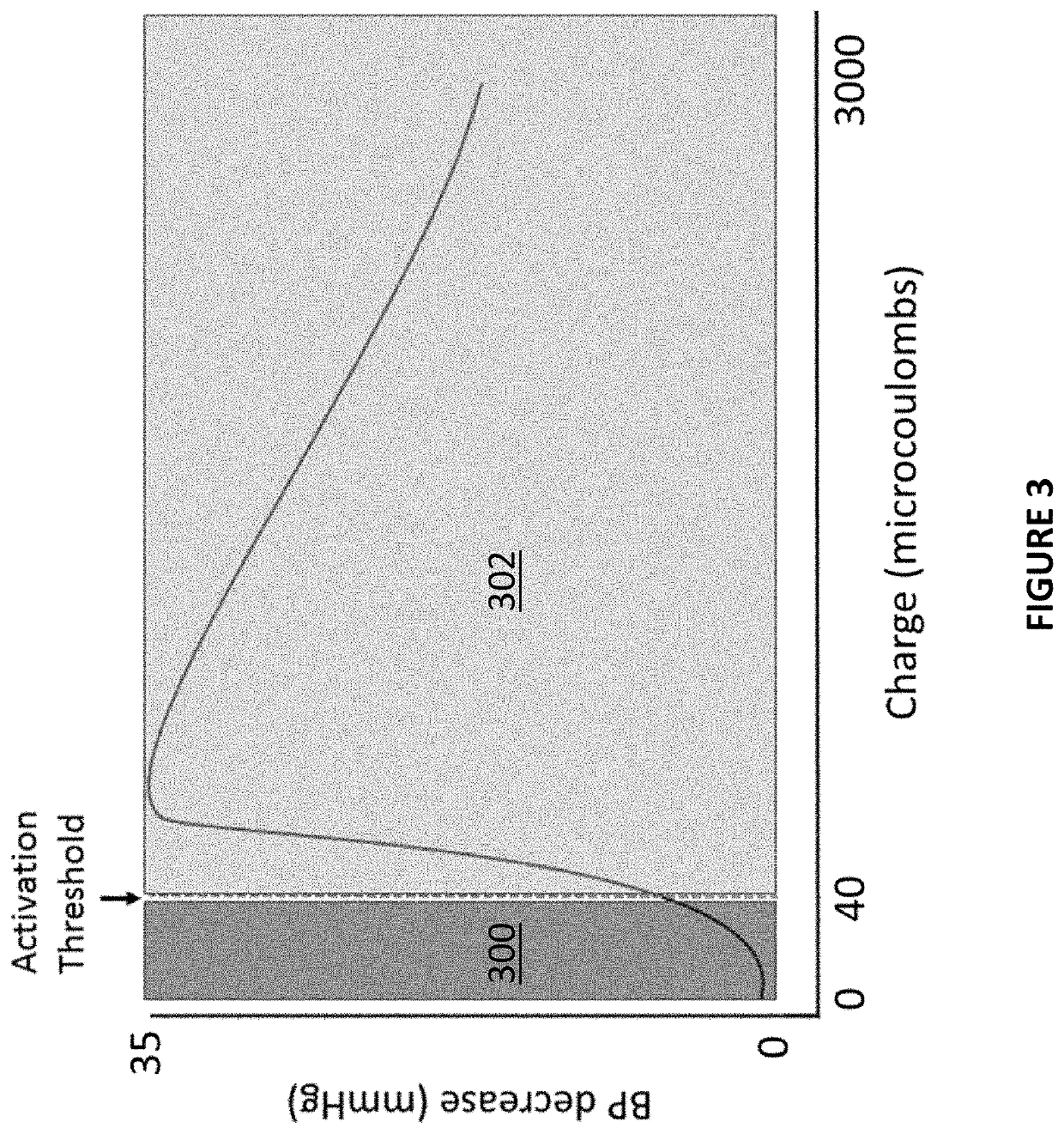
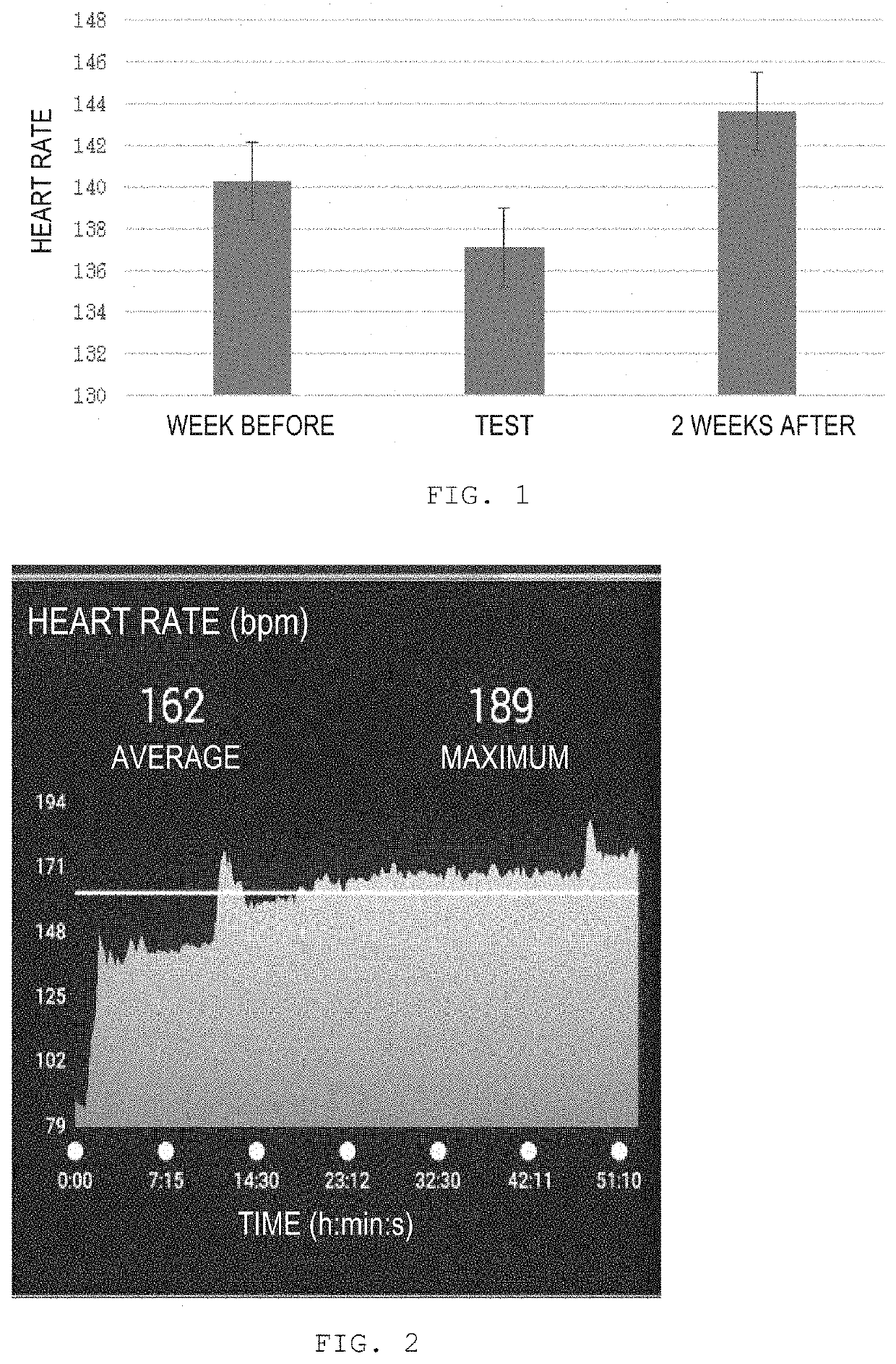
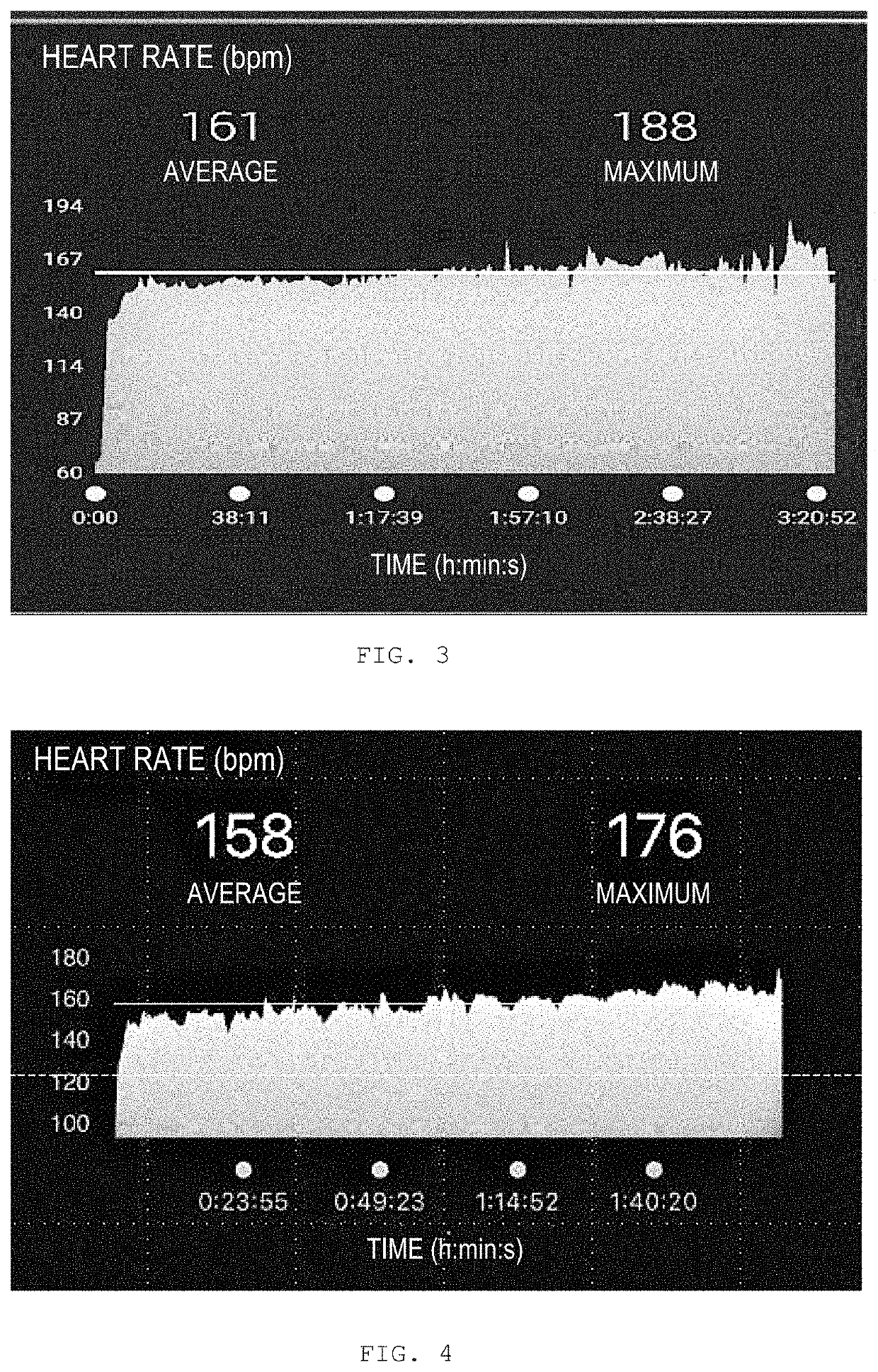
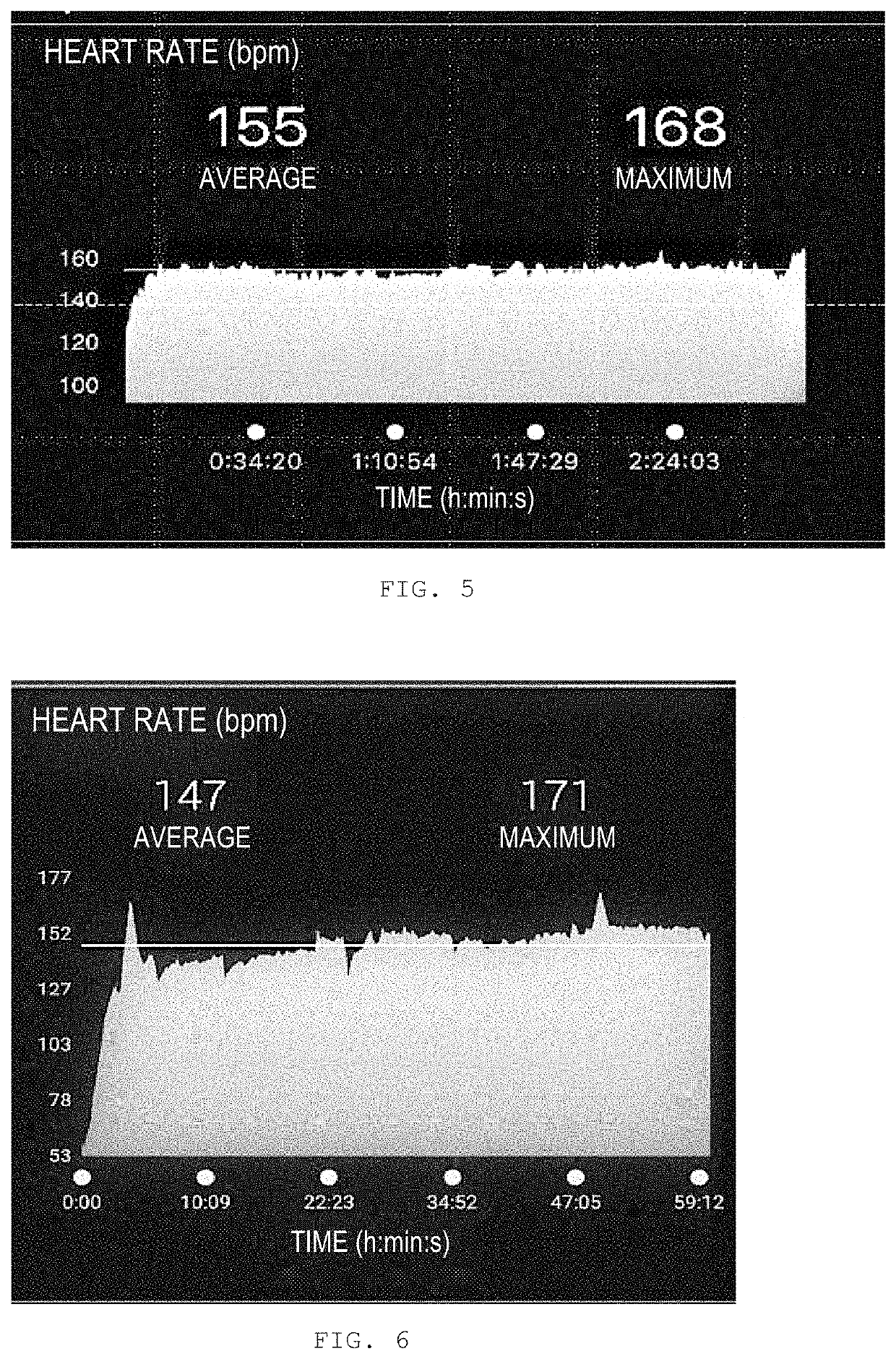
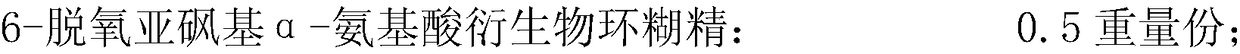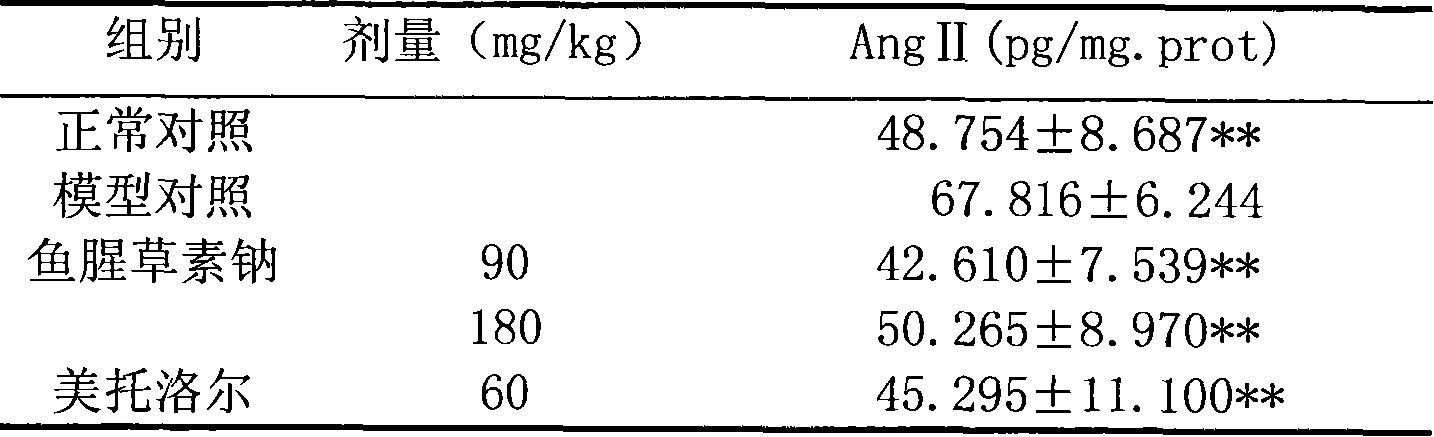Patents
Literature
33 results about "Decreased heart rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The most common causes of decreased heart rate are sinus bradycardia, heart failure, and high blood pressure. Within all the people who go to their doctor with decreased heart rate, 54% report having shortness of breath, 42% report having dizziness, and 34% report having fainting.
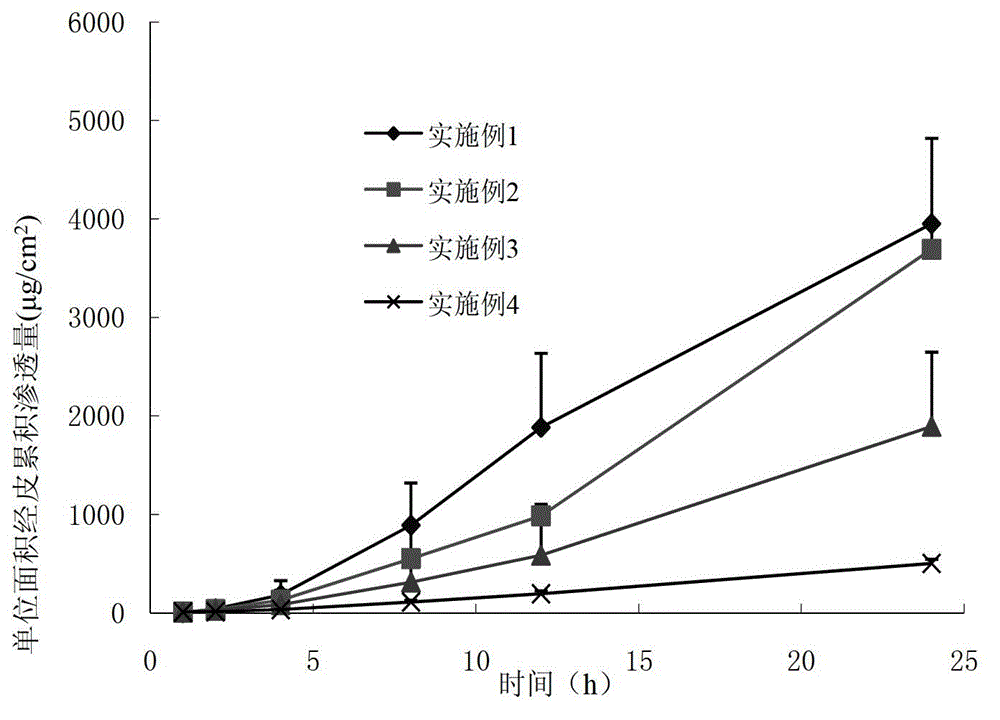
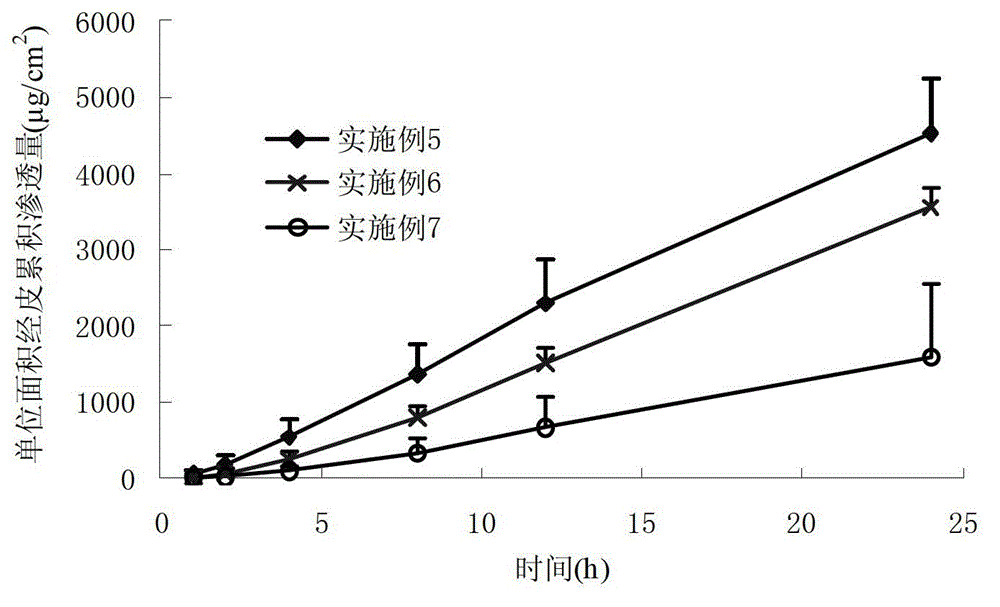
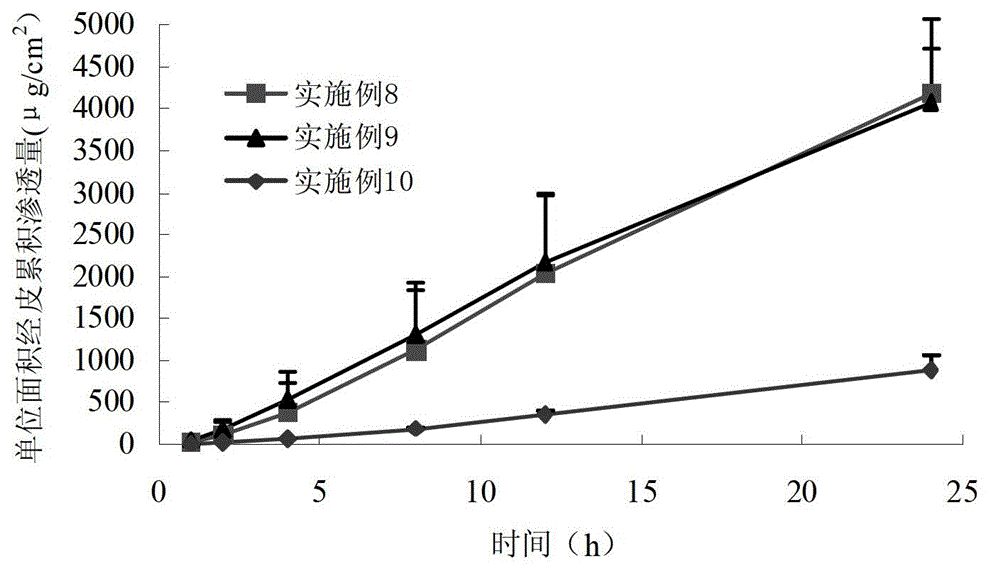
Propranolol hydrochloride gel for treating infant superficial hemangioma
ActiveCN102871956AEasy to makeLow costOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryDecreasing heart rateGranular Leukocytes
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and provides a propranolol hydrochloride (PPL.HCL) gel which can be externally used for treating infant superficial hemangioma. The propranolol hydrochloride gel is mainly prepared from propranolol hydrochloride, gel matrix, a percutaneous penetration enhancer, a preservative, a humectant and the like. By using the propranolol hydrochloride gel, adverse reactions such as decreased heart rate, cyanosis, airway hyperresponsiveness, shortage of granular leukocytes, diarrhoea, sleep change and blood sugar reduction caused by orally taking propranolol by hemangioma patients can be reduced and even avoided, and the problems that oral dosage is not easy to control, infants inconveniently take medicines and the like are solved.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
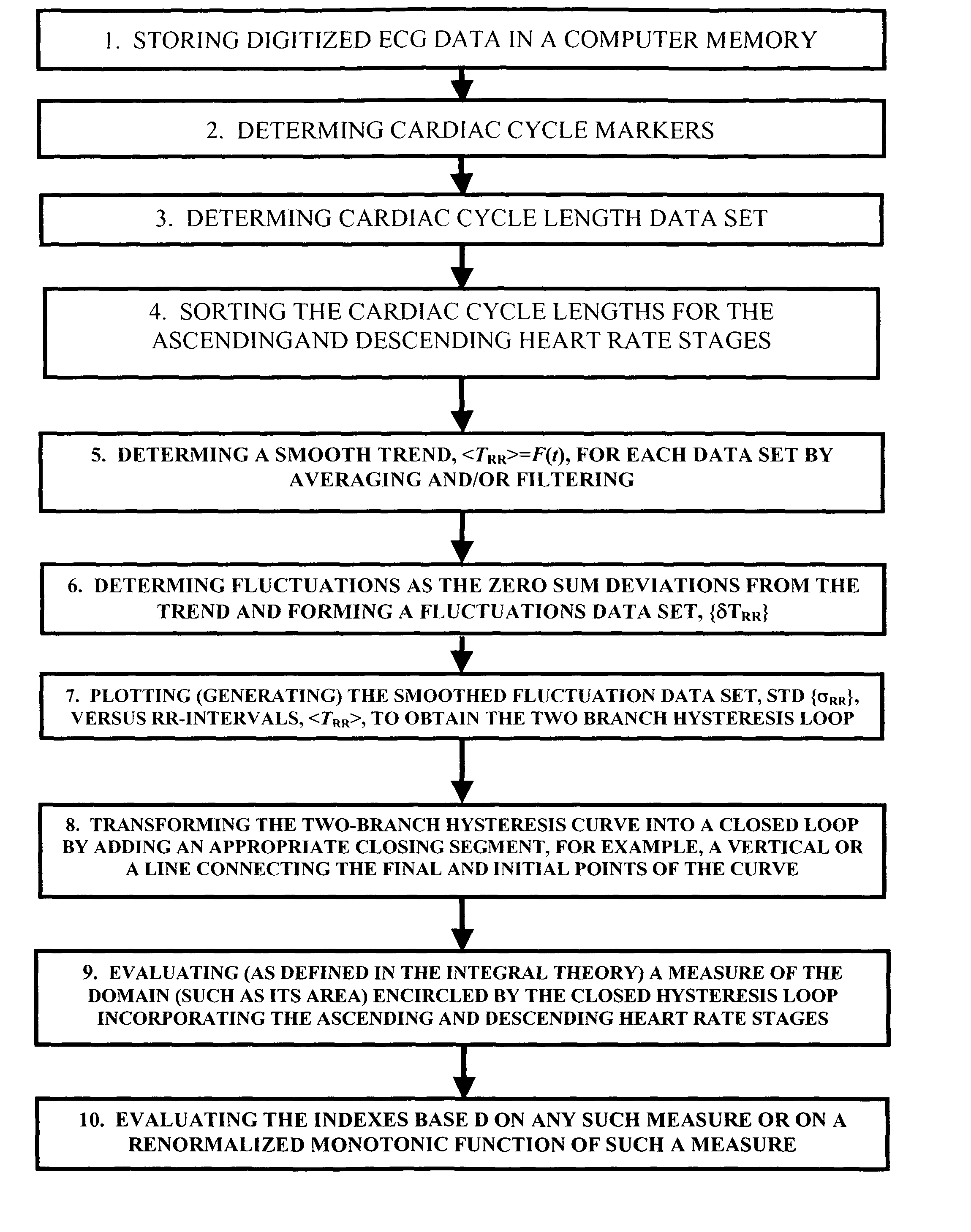
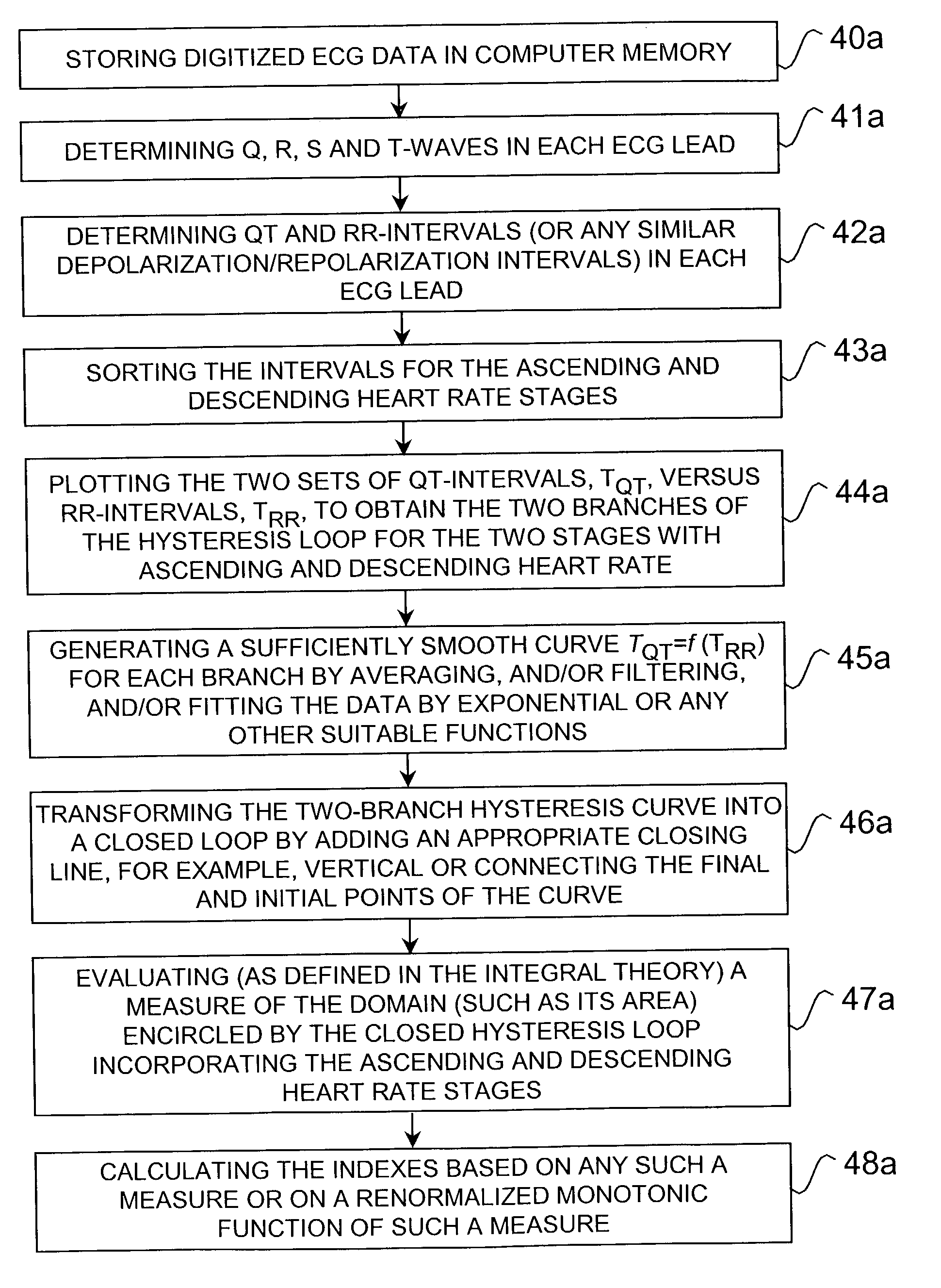
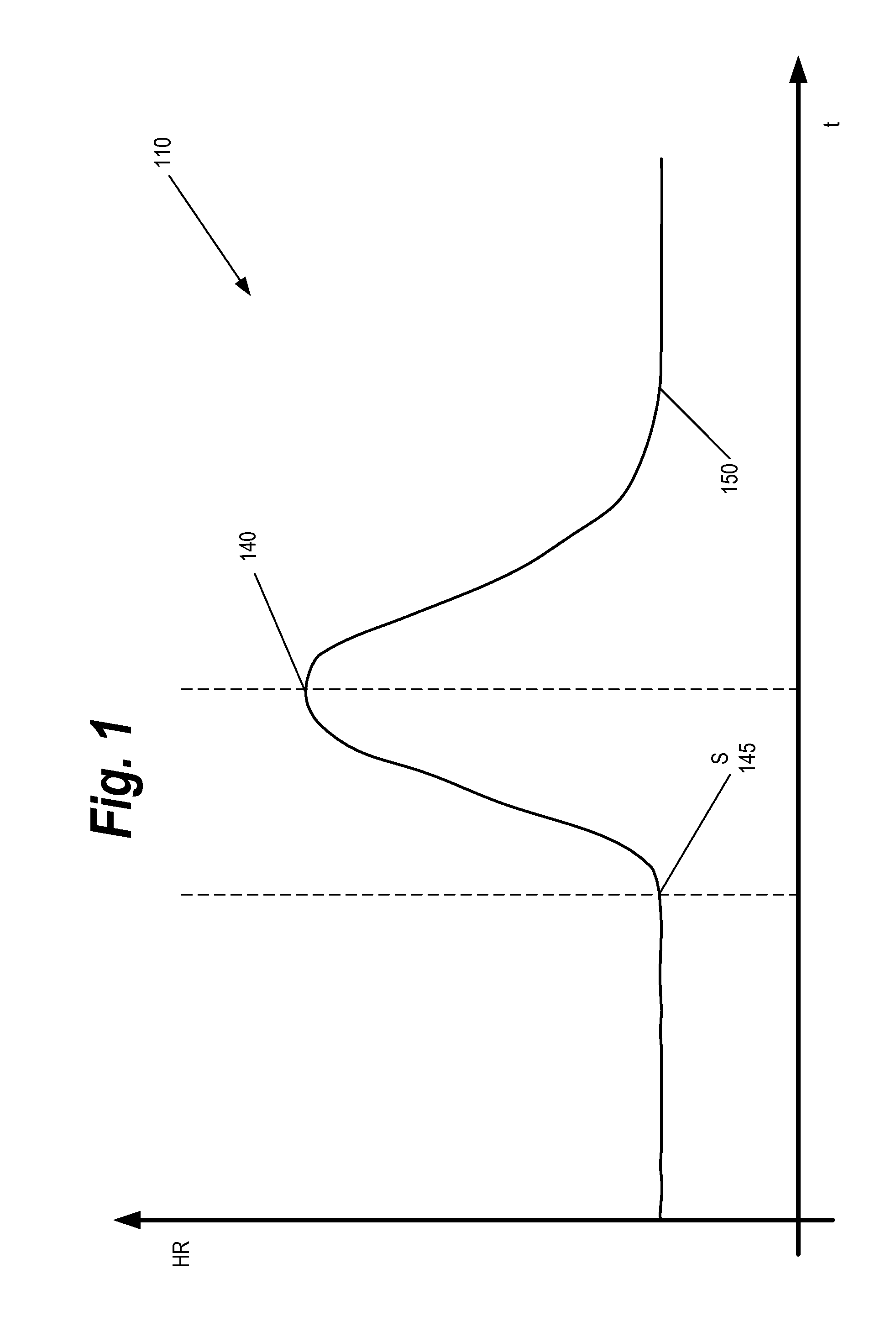
Method and system for evaluating cardiac ischemia based on heart rate fluctuations
InactiveUS20050038351A1Increase pulse rateReduce load levelElectrocardiographySensorsDecreasing heart rateData set
A method of assessing cardiac ischemia in a subject to provide a measure of cardiovascular health in that subject is described. In general, the method comprises the steps of: (a) collecting a first RR-interval data set from the subject during a stage of gradually increasing heart rate; (b) collecting a second RR-interval data set from the subject during a stage of gradually decreasing heart rate (e.g., after an abrupt stop in exercise; during a stage of gradually decreasing exercise load; etc.); (c) separating fluctuations from a slow trend in the first RR-interval data set; (d) separating fluctuations from a slow trend in the second RR-interval data set; (e) comparing the fluctuations of the first RR-interval data set to the fluctuations of the second RR-interval data set to determine a difference between the fluctuation data sets; and (f) generating from the comparison of step (e) a measure of cardiac ischemia during stimulation in the subject, wherein a greater difference between the first and second data sets indicates greater cardiac ischemia and lesser cardiac or cardiovascular health in the subject.
Owner:MEDIWAVE STAR TECH
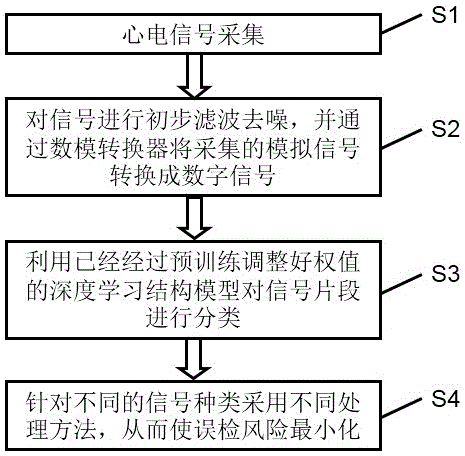
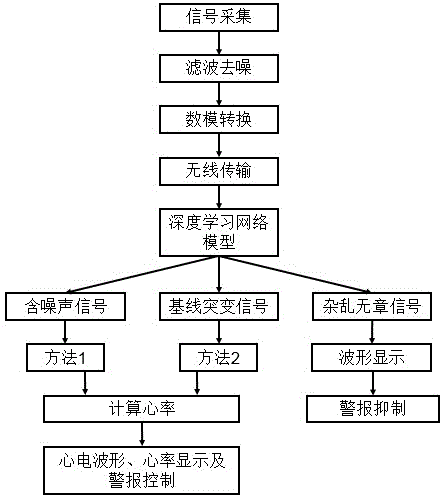
Intelligent electrocardio monitoring method and device
ActiveCN105125206AImprove performanceReduce false alarm rateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFalse detectionVIT signals
The embodiment of the invention discloses an intelligent electrocardio monitoring method and device. The method includes the steps that a probe is utilized to collect human electrocardiosignals; the signals are converted to digital signals through a digital analog converter, and primary denoising processing is conducted on the signals; signal segments are classified through a trained deep learning structure model; different processing methods are adopted according to different signals, and the false detection risk is minimized. According to the intelligent electrocardio monitoring method and device, through a signal collection mode with less interference to a patient and a signal classification means, the heart rate can be detected more accurately, the false alarm rate of clinical equipment is lowered, the rehabilitation process of the patient can be better guaranteed, the work efficiency of the medical staff can be further improved, the workload of the medical staff is reduced, and the sensibility to the alarm of the intelligent electrocardio monitoring device is improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method of early detection of Duchenne muscular dystrophy and other neuromuscular disease
InactiveUS6875418B2Compounds screening/testingDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseDecreasing heart rate
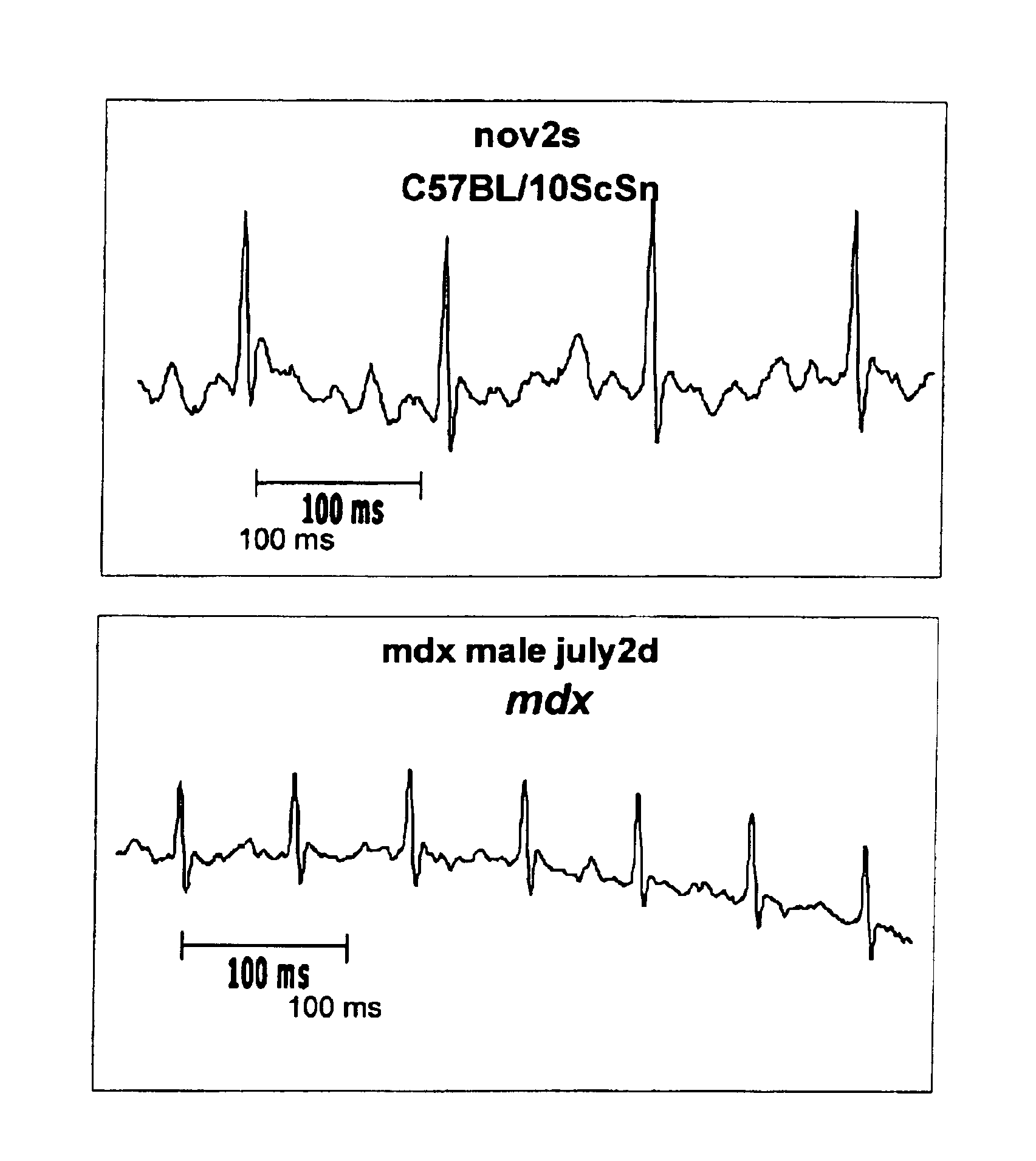
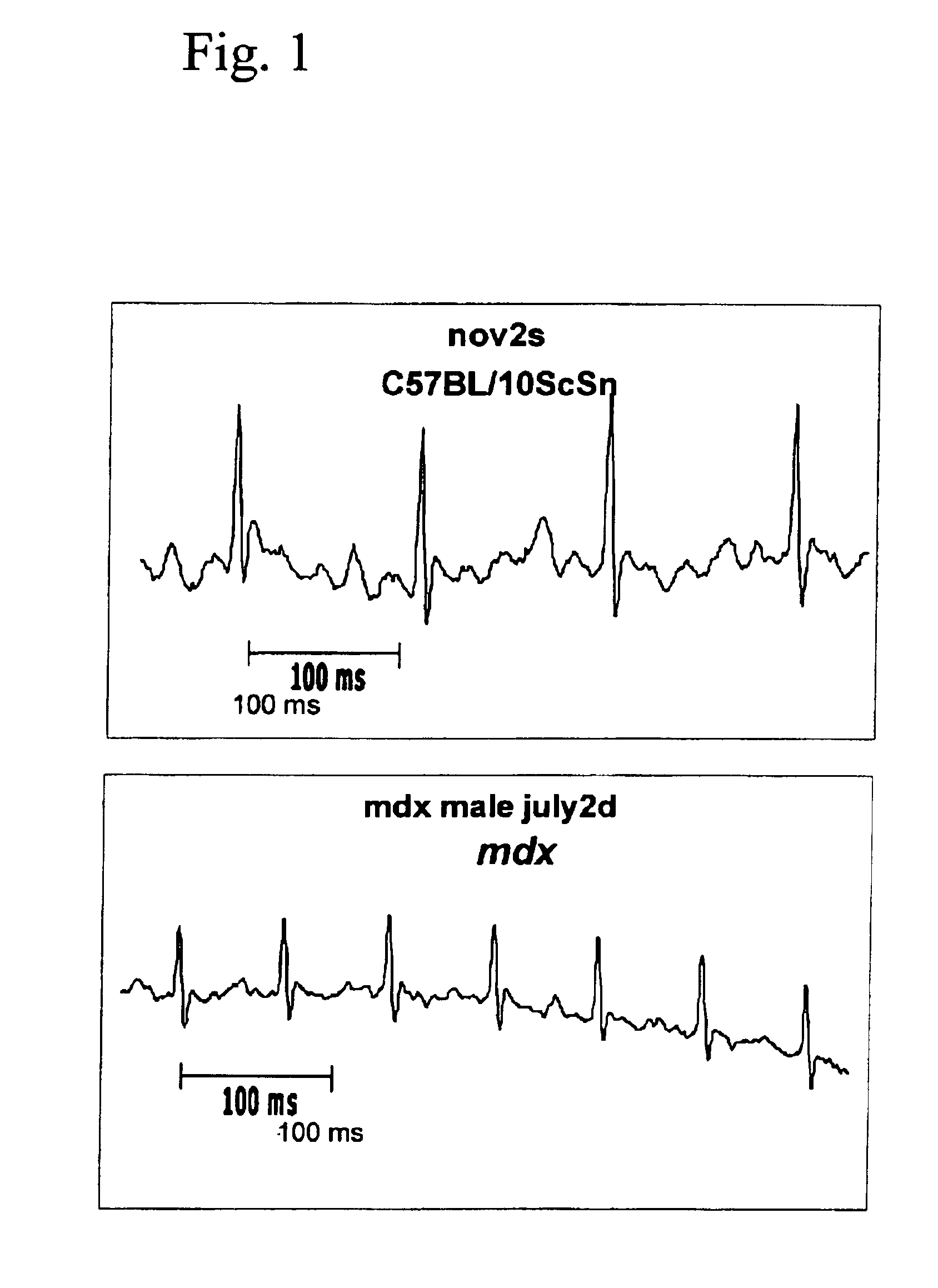
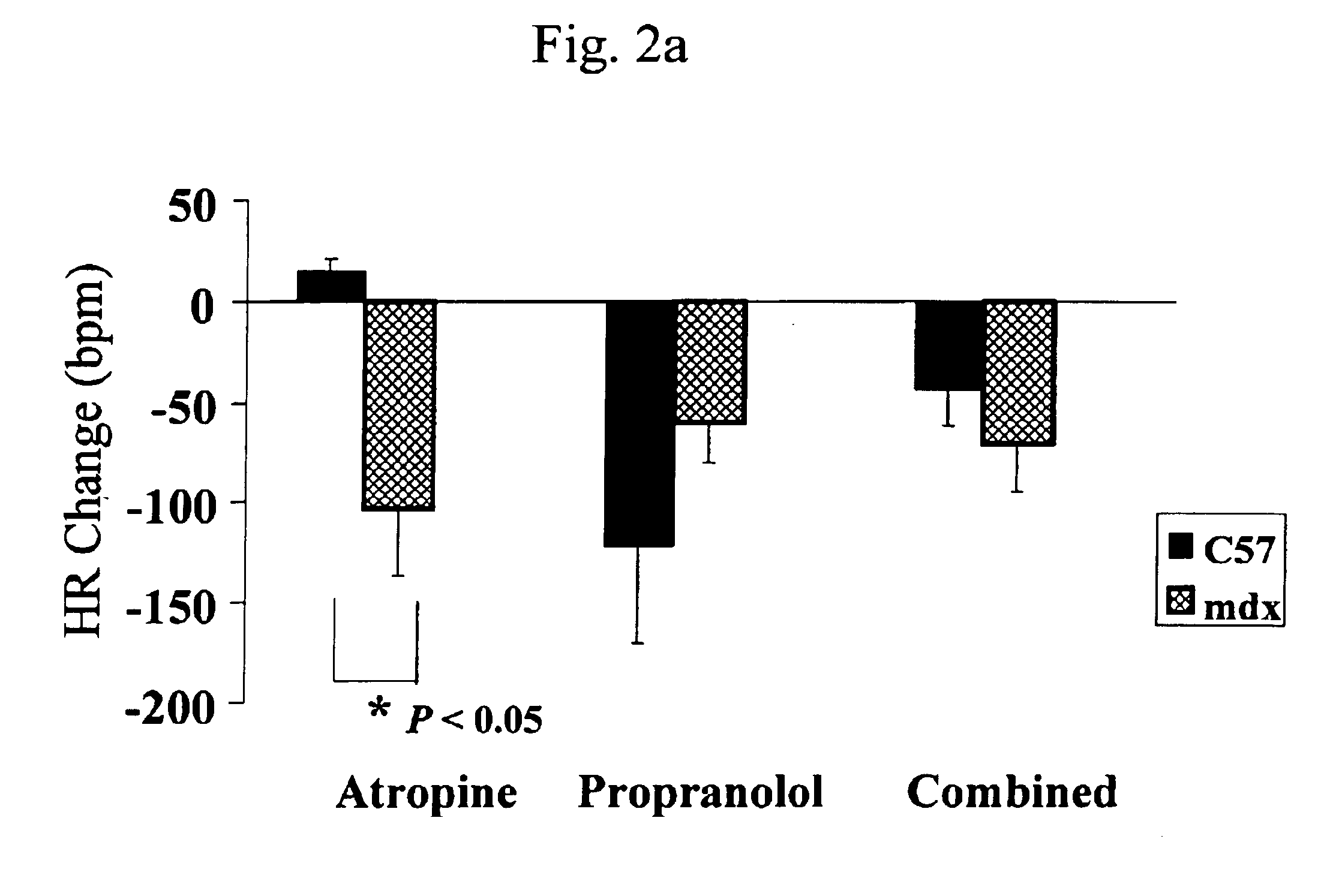
The mdx mouse is a model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The present invention describes that mdx mice exhibited clinically relevant cardiac phenotypes. A non-invasive method of recording electrocardiograms (ECGs) was used to a study mdx mice (n=15) and control mice (n=15). The mdx mice had significant tachycardia, consistent with observations in patients with muscular dystrophy. Heart-rate was nearly 15% faster in mdx mice than control mice (P<0.01). ECGs revealed significant shortening of the rate-corrected QT interval duration (QTc) in mdx mice compared to control mice (P<0.05). PR interval duration were shorter at baseline in mdx compared to control mice (P<0.05). The muscarinic antagonist atropine significantly increased heart-rate and decreased PR interval duration in C57 mice. Paradoxically, atropine significantly decreased heart-rate and increased PR interval duration in all mdx mice. Pharmacological autonomic blockade and baroreflex sensitivity testing demonstrated an imbalance in autonomic nervous system modulation of heart-rate, with decreased parasympathetic activity and increased sympathetic activity in mdx mice. These electrocardiographic findings in dystrophin-deficient mice provide new bases for diagnosing, understanding, and treating patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Owner:MOUSE SPECIFICS
Propranolol hydrochloride gel for treating infant superficial hemangioma
ActiveCN102871956BGood percutaneous penetrationAchieving local therapeutic concentrationsOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryDecreasing heart rateBlood sugar
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and provides a propranolol hydrochloride (PPL.HCL) gel which can be externally used for treating infant superficial hemangioma. The propranolol hydrochloride gel is mainly prepared from propranolol hydrochloride, gel matrix, a percutaneous penetration enhancer, a preservative, a humectant and the like. By using the propranolol hydrochloride gel, adverse reactions such as decreased heart rate, cyanosis, airway hyperresponsiveness, shortage of granular leukocytes, diarrhoea, sleep change and blood sugar reduction caused by orally taking propranolol by hemangioma patients can be reduced and even avoided, and the problems that oral dosage is not easy to control, infants inconveniently take medicines and the like are solved.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Identifying seizures using heart rate decrease
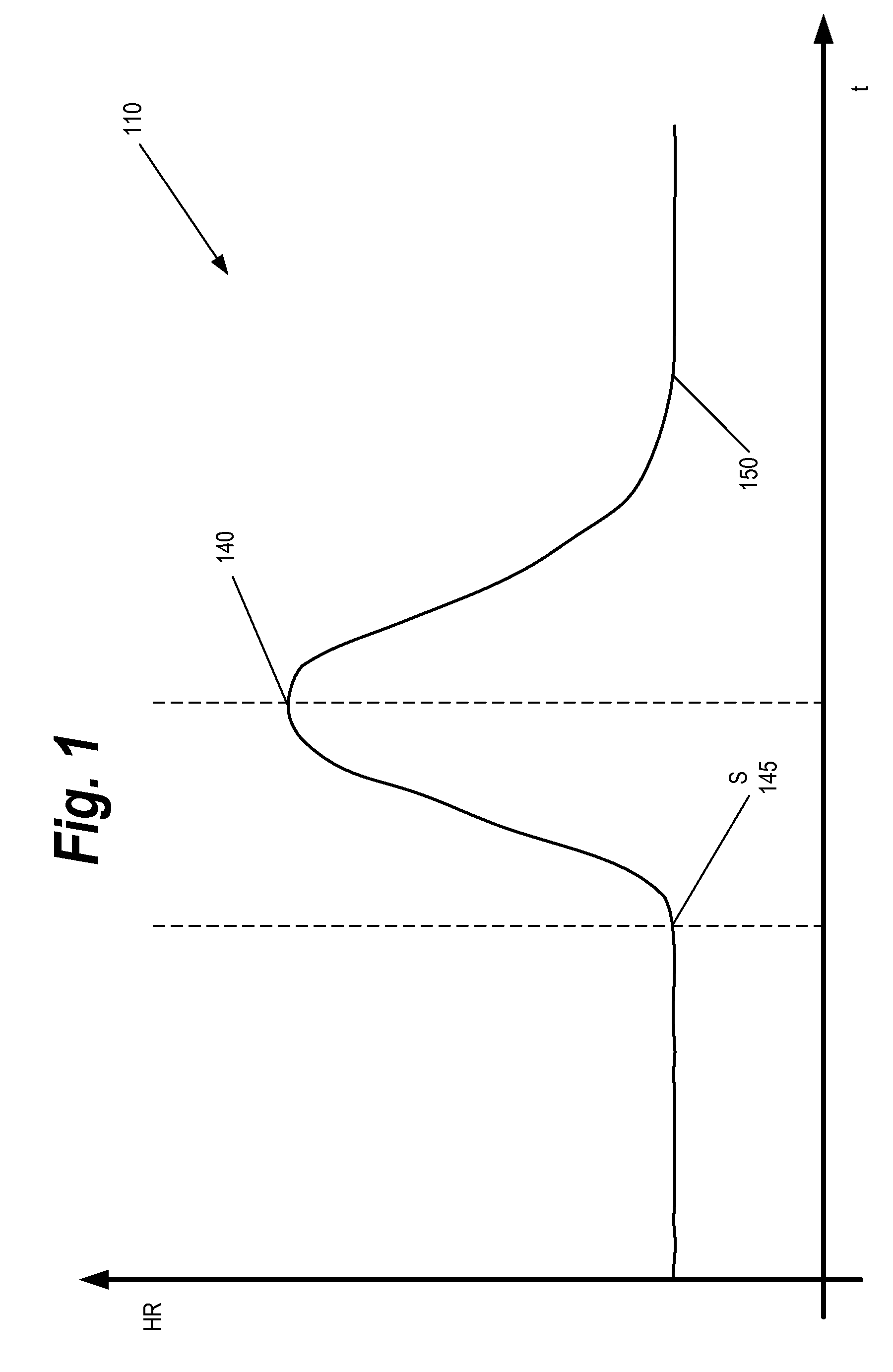
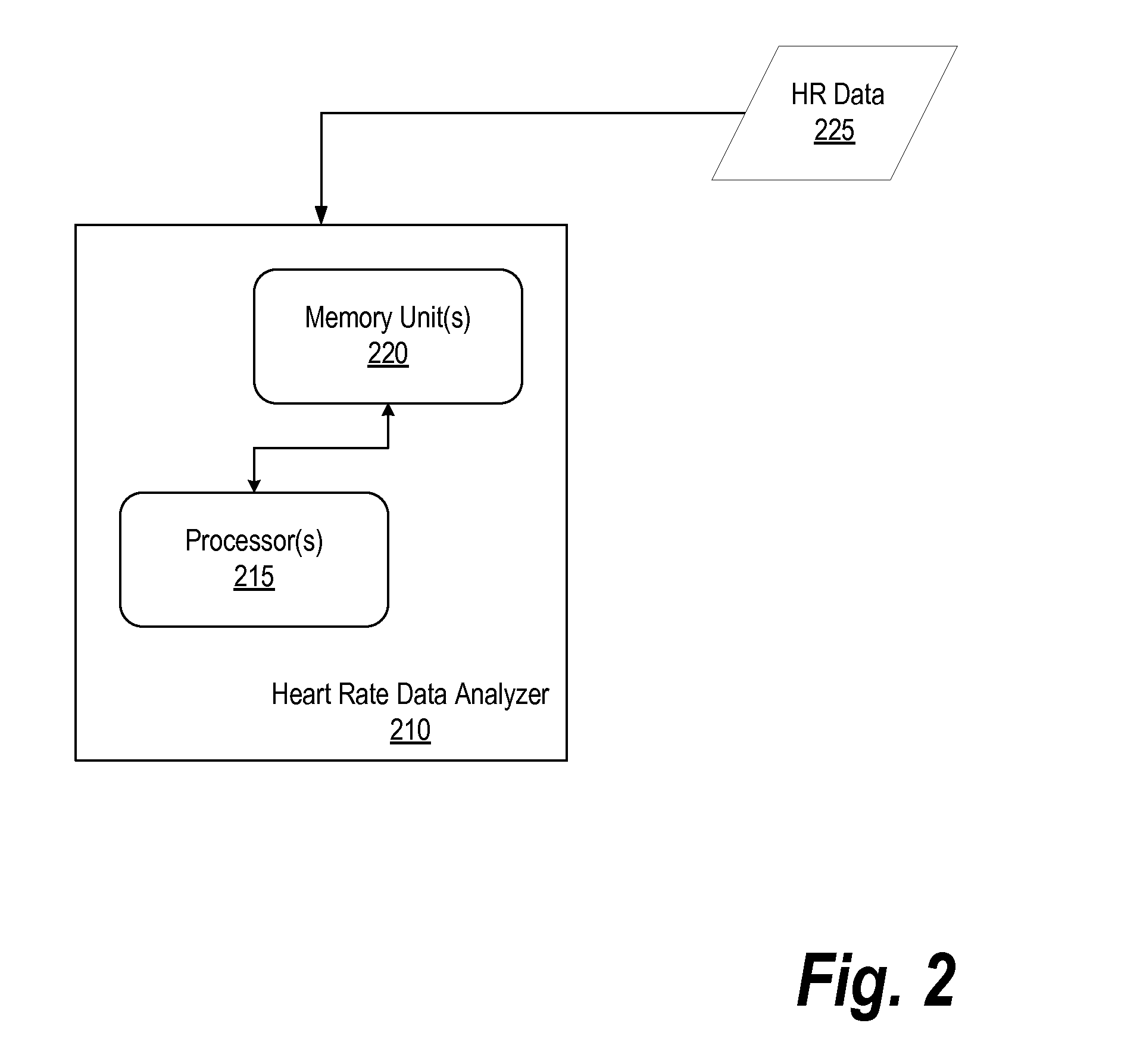
Methods and systems for detecting a seizure event, including receiving heart beat data versus time for a patient, detecting an increase in the heart rate of a patient from a baseline heart rate to an elevated heart rate, detecting a decrease in heart rate from the elevated heart rate, for a time interval occurring during said decrease in heart rate, determining at least one of a) a rate of decrease in heart rate and b) a rate of change in a rate of decrease in heart rate, and detecting a seizure event in response to determining at least one of a) a rate of decrease in heart rate greater than a threshold rate of decrease, and b) a rate of change in the rate of decrease less than a threshold rate of change in a rate of decrease.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
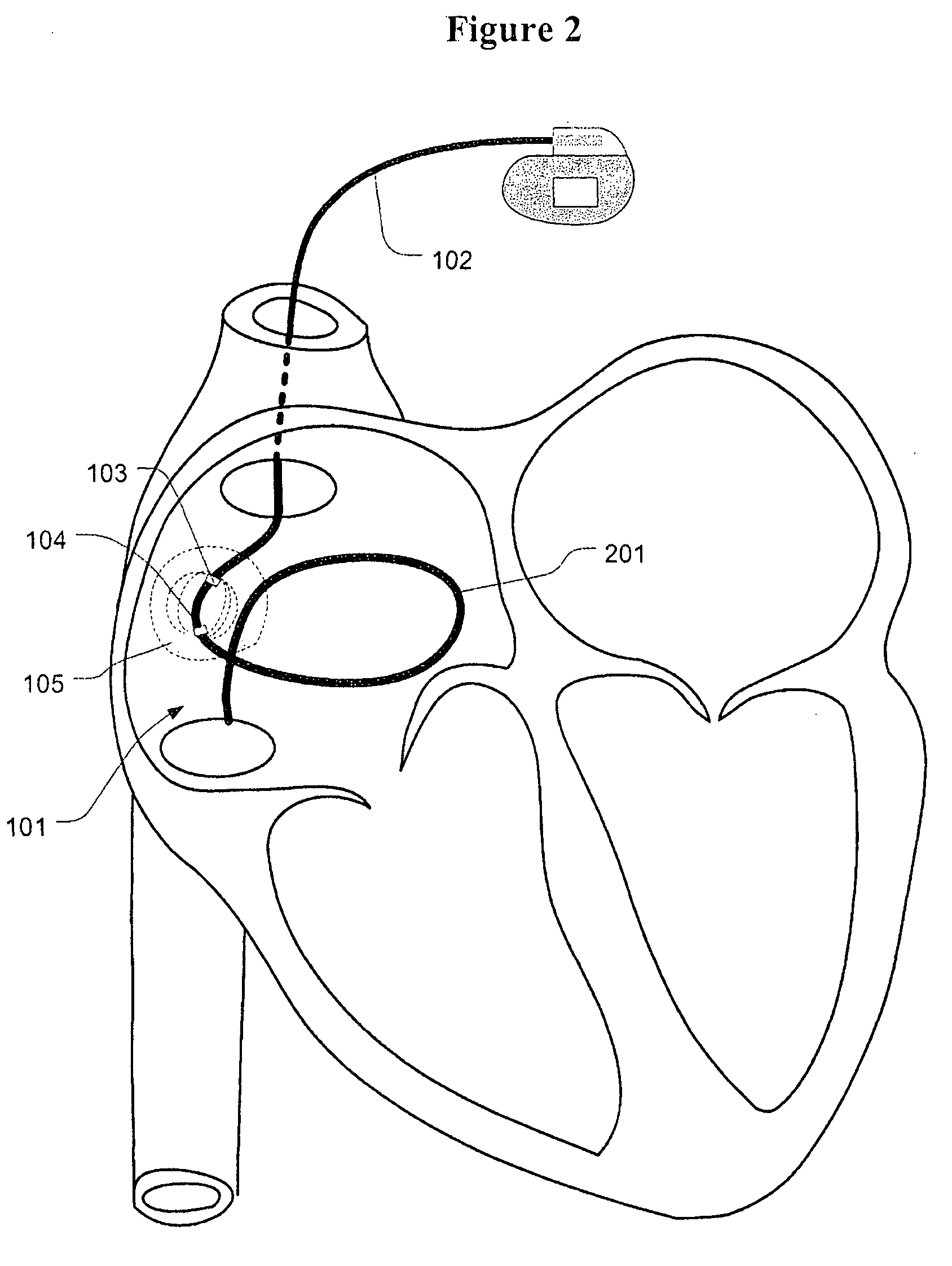
Heart rate reduction method and system
InactiveUS20080188900A1Faster intrinsic rateEnhanced cholinergic activityTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesDecreased heart rateSpecific time
A method and apparatus to slow a heart rate with subthreshold electric stimulation of the SA node. Stimulation is applied at a specific time in the cardiac cycle and at a specific subthreshold level. To control the heart rate, the stimulating signal may be modified automatically based on physiologic feedbacks. Stimulation may be applied using an implantable pulse generator directly to the SA node of the heart.
Owner:G&L CONSULTING
Chinese medicinal composition for treating coronary disease, stenocardia, arrhythmia, hyperlipemia and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101342207AAmphibian material medical ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseAntagonism
The invention provides a Chinese medicine composition used for curing coronary heart disease, angina, arrhythmia and high blood fat and a preparation method thereof. The Chinese medicine composition consists of components as follows: 5 to 20 weight percentage of musk, 12 to 50 weight percentage, 60 to 250 weight percentage of sodium taurocholate, 12 to 50 weight percentage of toad venom, 30 to 120 weight percentage of pearl, 40 to 160 weight percentage of borneol, 1500 to 15000 weight percentage of panax pseudo-ginseng wallich, 150 to 600 weight percentage of ginseng and 50 to 200 weight percentage of the dry extract of buffalo horn. The Chinese medicine composition of the invention can improve blood circulation, dilate coronary arteries, enhance myocardial ischemia, decrease crown arteries resistance, regulate cardiac rate, lower blood pressure, reduce myocardium metabolism, decrease consumed oxygen of myocardium and relieve or eliminate angina via the synergistic and beneficial antagonistic effect of the medicine. As a great amount of the sodium taurochlate is adopted, product cost is reduced while drug effect is ensured as much as possible, thus reducing the economic burden of a patient.
Owner:广东宏兴集团股份有限公司宏兴制药厂
Method and system for evaluating cardiac ischemia with an exercise protocol
InactiveUS7104961B2Easy to detectHigh peak heart rateElectrocardiographyCatheterDecreasing heart rateData set
A method of assessing cardiac ischemia in a subject to provide a measure of cardiac or cardiovascular health in that subject is described herein. The method comprises the steps of: (a) collecting a first RR-interval data set from said subject during a stage of gradually increasing heart rate up to a predetermined heart rate of at least 130 beats per minute; (b) collecting a second RR-interval data set from said subject during a stage of gradually decreasing heart rate; (c) comparing said first RR-interval data set to said second RR-interval data set to determine the difference between said data sets; and (d) generating from said comparison of step (c) a measure of cardiac ischemia during stimulation in said subject, wherein a greater difference between said first and second data sets indicates greater cardiac ischemia and lesser cardiac or cardiovascular health in said subject.
Owner:MEDIWAVE STAR TECH
Composite injection for treating or preventing anesthesia hypotension and preparation method of composite injection
InactiveCN108354899AImprove stabilityNo precipitationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsStimulantAtropine sulfate
The invention relates to the field of medicines and provides a composite injection for treating or preventing anesthesia hypotension. 1000 mL of the composite injection comprises 0.1-2g of atropine sulfate, 2-5g of methoxamine hydrochloride, 10-15g of medicinal auxiliary materials and the balance of injection water, and the pH value of the composite injection is adjusted to 4.5+ / -0.3. According tothe composite injection provided by the invention, the atropine sulfate and the methoxamine hydrochloride are adopted as active components, the methoxamine hydrochloride and the atropine sulfate arecompounded, and by virtue of the property that an alpha1-adrenergic receptor stimulant can be antagonized by atropine, reflective decreased heart rates caused by methoxamine hydrochloride can be antagonized. After the two components are compounded, a blood pressure boosting effect which is not inferior to that of independently used methoxamine hydrochloride can be achieved, the probability of reflective decreased heart rates can be reduced, and thus the composite injection provided by the invention is relatively safe and effective when being used for treating or preventing anesthesia hypotension.
Owner:AFFILIATED RENHE HOSPITAL OF CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
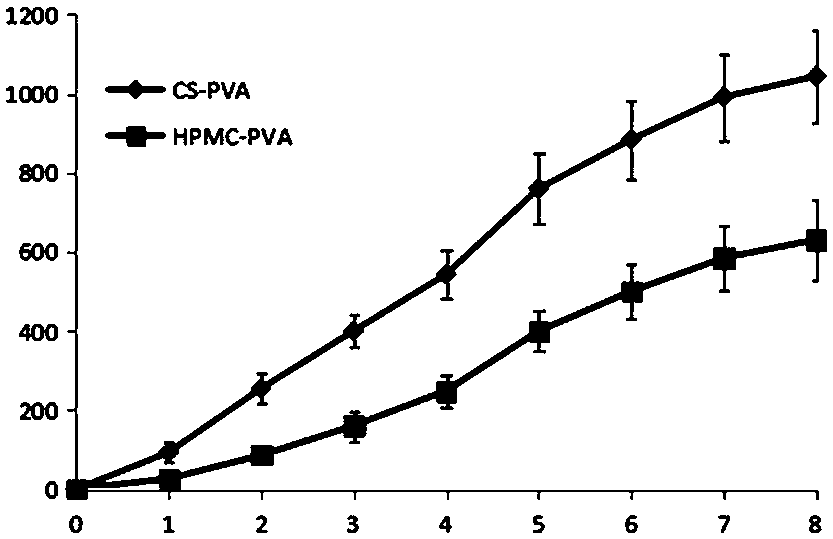
Propranolol hydrochloride-polyvinyl alcohol porous hydrogel preparation as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108451897AImprove use complianceAvoid first pass effectOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryDecreased heart rateChemistry
The invention provides a propranolol hydrochloride-polyvinyl alcohol porous hydrogel preparation as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The propranolol hydrochloride-polyvinyl alcohol porous hydrogel is prepared from 1 to 10 percent of propranolol hydrochloride, 3 to 10 percent of gel matrix, and 3 to 20 percent of pore forming agent. The gel has good transdermal performance andair permeability, and after the gel is locally applied, a great amount of drug can remain on the skin to form a drug deposit. The propranolol hydrochloride-polyvinyl alcohol porous hydrogel preparation has a significant curative effect for treating angioma of babies, the adverse effect such as first-pass effect, sleep disorders, decreased heart rate and the like of the oral propranolol can be avoided, and the convenience and compliance in use can be improved.
Owner:FUZHOU GENERAL HOSPITAL OF NANJING MILITARY COMMAND P L A
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating chronic cardiac insufficiency
InactiveCN103417861AImprove blood supplyImprove aggregation rateHydroxy compound active ingredientsCapsule deliveryMonkshoodsDecreasing heart rate
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating chronic cardiac insufficiency, which is prepared by matching of the traditional Chinese medicines as follows: radix pseudostellariae, radix ophiopogonis, schisandra chinensis, astragalus membranaceus, the root of fangji, pepperweed seed, fructus trichosanthis, monkshood, poria cocos, pseudo-ginseng, bighead atractylodes rhizome, root of common peony, the root of red-rooted salvia, cortex acanthopanacis, Chinese-date, borneol, perillaseed, almond, pinellia ternate, caulis bambusae in taeniam and honey-fried licorice root. Aiming to the pathogenesis of heart failure: depletion of spleen and kidney, insufficient heart yang, blocking of blood vessel, damage of vital energy and blood, evil hydrops and pneuma rushing upwards to the chest, water and pneuma reversing upward and blocking of lung, the traditional Chinese medicine composition, disclosed by the invention, has the treatment rules of benefiting vitality and warming yang, purging the lung of pathogenic fire and promoting diuresis, promoting coronary circulation, improving blood supply of coronary artery, reducing blood pressure, purging the lung of pathogenic fire and regulating qi by alleviation of mental depression, clearing heat and eliminating phlegm, promoting diuresis and alleviating edema, enhancing systole, decreasing heart rate, reducing peripheral resistance, increasing cardiac output, improving microcirculation, relieving smooth muscle spasm and reducing blood platelet gathering rate.
Owner:周国典
Composition with heart rate reducing properties
InactiveCN1802093ASlow down heart rateHydrolysed protein ingredientsHydrolasesLactic acid bacteriumDecreasing heart rate
Use of a composition obtainable by a process comprising fermenting a food material, comprising animal milk or vegetable proteins, with a lactic acid bacterium to obtain a fermented food material which comprises active components with heart rate reducing properties for the manufacture of a product for reducing the heart rate and / or the fluctuations in the heart rate of a mammalian.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
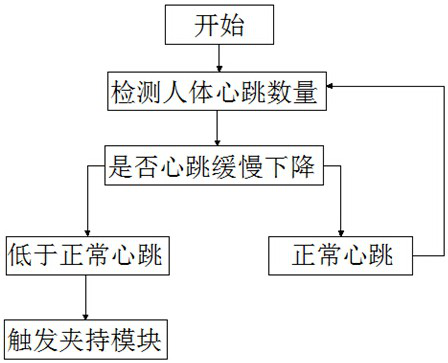
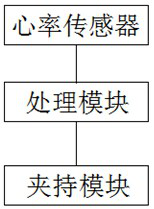
Method and system for preventing fatigue driving based on smart bracelet
InactiveCN112017405ASimple structureImprove securitySensorsAlarmsHuman bodyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses a method and system for preventing fatigue driving based on a smart bracelet. The smart bracelet is provided with a heart rate sensor and a clamping module, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, setting a normal heartbeat range of a human body; S2, detecting the heartbeat of a human body, and checking whether the heartbeat is buffered and reduced or not; S3, when it is detected that the heartbeat of the human body is reduced, starting timing, and after a period of time, triggering the clamping module; and S4, when it is detected that the heartbeat of the human body does not decrease, continuing detection. The system is simple in structure, whether a person is in a sleepiness state or not is judged by detecting the heartbeat of the human body according tothe characteristic that the heartbeat of the person is reduced before sleep, when fatigue driving occurs, an arm is clamped through the clamping module, a driver is reminded and stimulated through stabbing pain, the driver is sober, and the driving safety is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN LINWEAR INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
Identifying seizures using heart rate decrease
Methods and systems for detecting a seizure event, including receiving heart beat data versus time for a patient, detecting an increase in the heart rate of a patient from a baseline heart rate to an elevated heart rate, detecting a decrease in heart rate from the elevated heart rate, for a time interval occurring during said decrease in heart rate, determining at least one of a) a rate of decrease in heart rate and b) a rate of change in a rate of decrease in heart rate, and detecting a seizure event in response to determining at least one of a) a rate of decrease in heart rate greater than a threshold rate of decrease, and b) a rate of change in the rate of decrease less than a threshold rate of change in a rate of decrease.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Medicinal composition containing mongolian snakegourd and notoginseng
InactiveCN101190253AActive ingredients are clearIncrease contentMetabolism disorderCardiovascular disorderDiseaseDecreasing heart rate
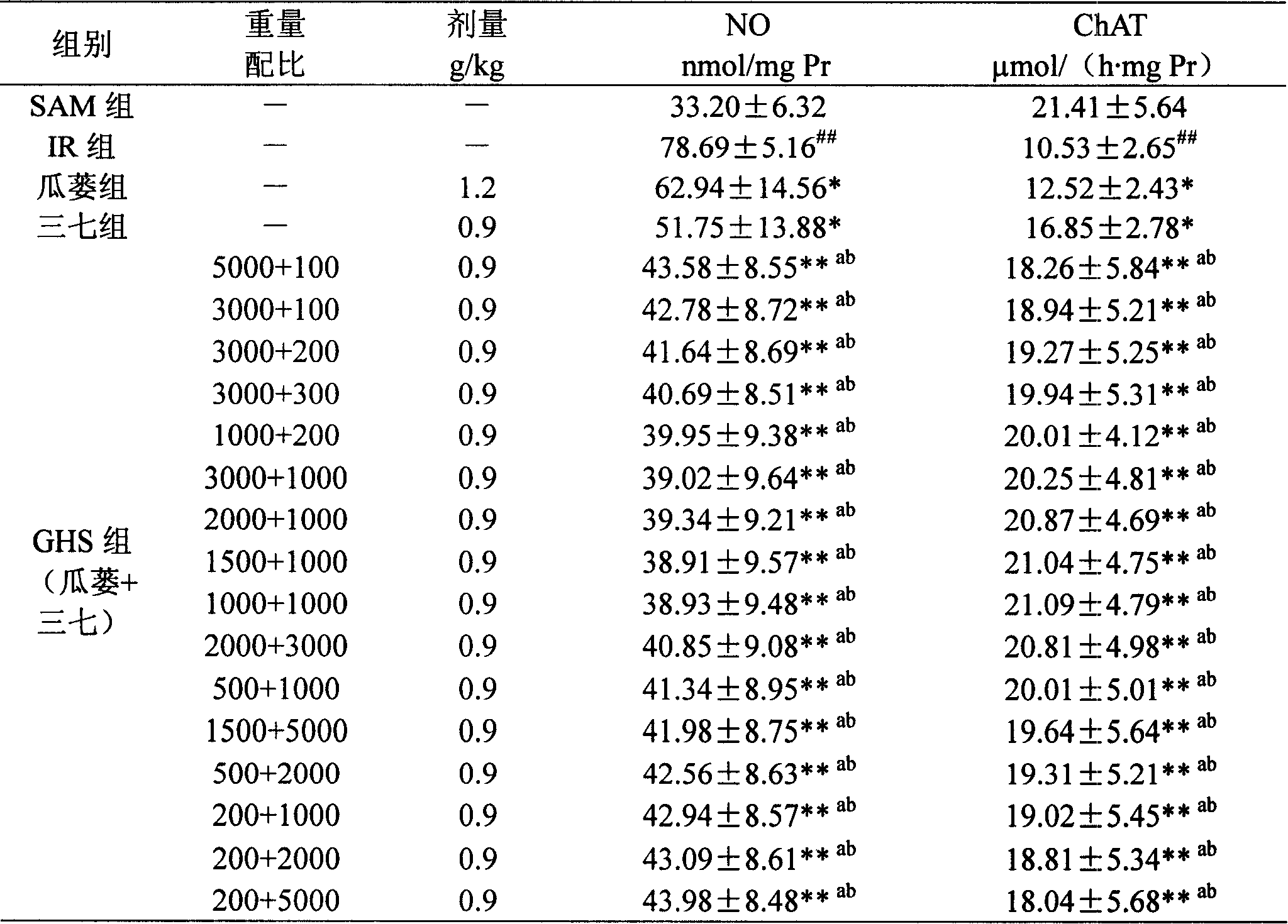
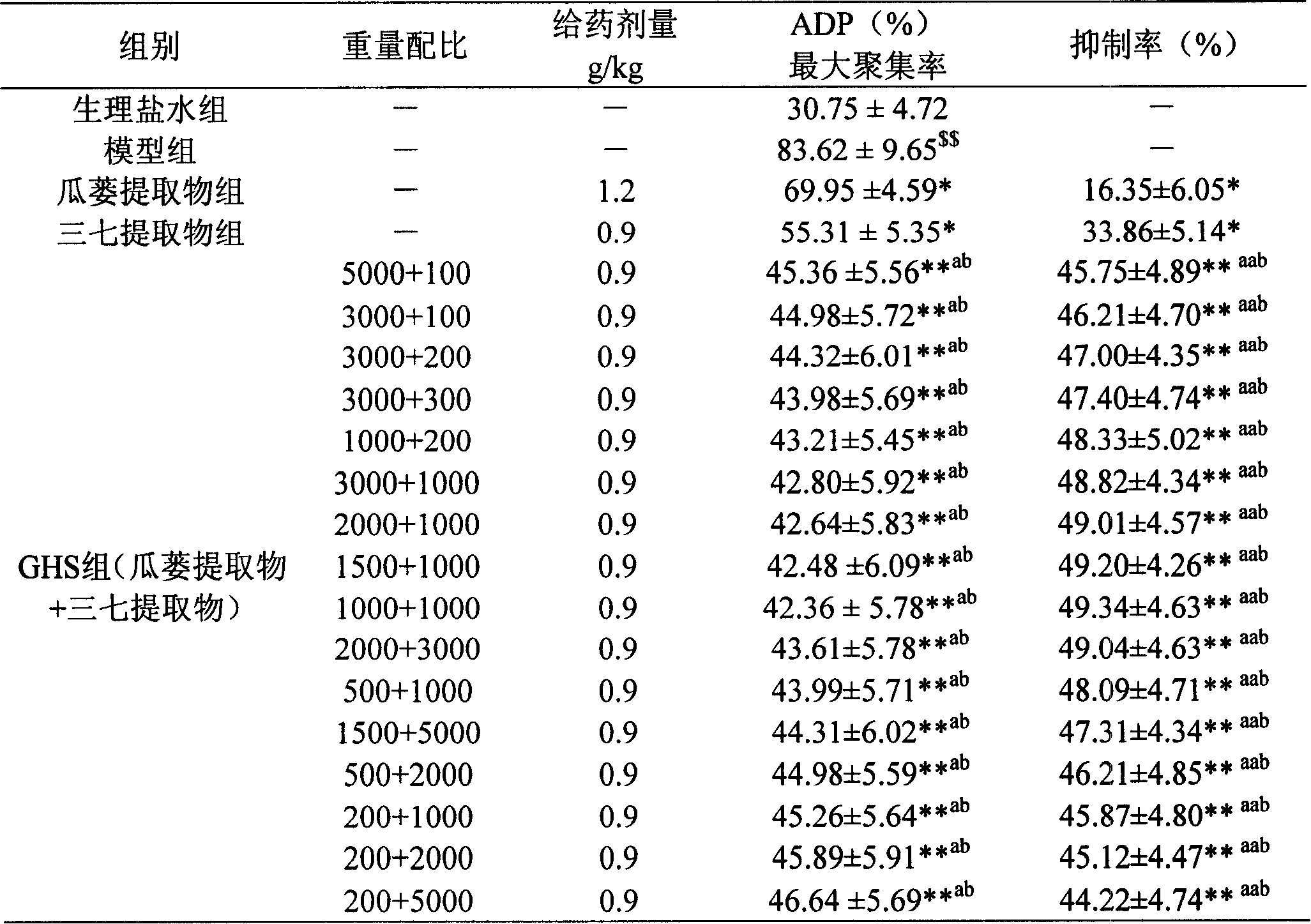
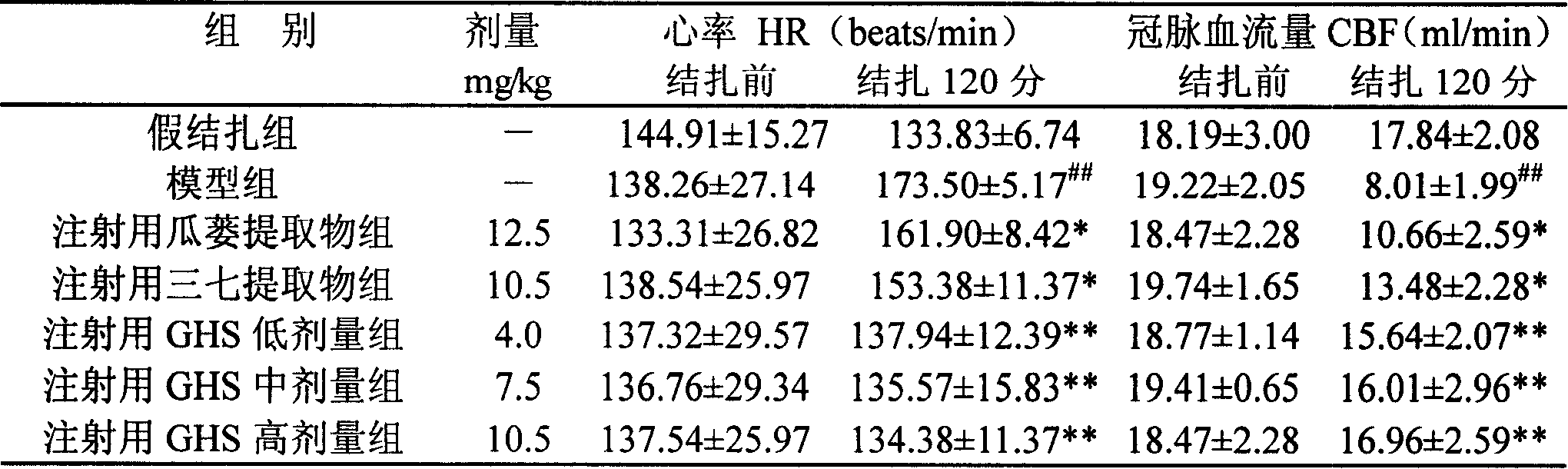
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical technology. The invention discloses a medicine combination of snakegourd fruit or the extract thereof and pseudoginseng or the extract thereof as well as the preparation method thereof; the invention also discloses the application of the medicine combination on the medicines for treating cerebrovascular diseases and the preparations containing the medicine combination. The effective ingredients of the medicine combination are prepared by the following raw medicines by weight: 200-5000 parts of snakegourd fruit and 100-5000 parts of pseudoginseng, or 4-400 parts of snakegourd fruit extract and 4-250 parts of pseudoginseng extract. The invention can be prepared into any dosage forms acceptable in clinical or pharmacy, and the preferred preparation is oral preparation or injection. The two medicines in the invention have synergistic function and achieve the functions of anti-myocardial ischemia, anti-platelet aggregation, reducing myocardial infarct size and decreasing heart rates together. The invention has significantly increasing curative effect than single administration of snakegourd fruit, the extract thereof, pseudoginseng and the pseudoginseng thereof.
Owner:海安江理工技术转移中心有限公司
Heart rate detection method and device, wearable equipment and storage medium
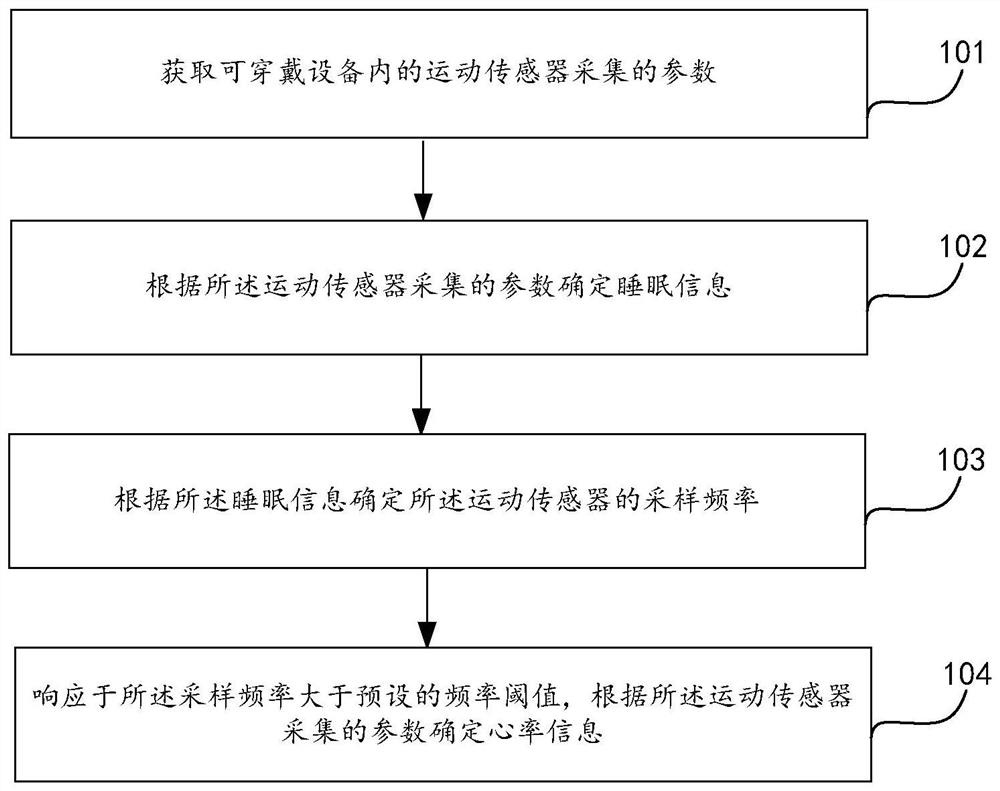
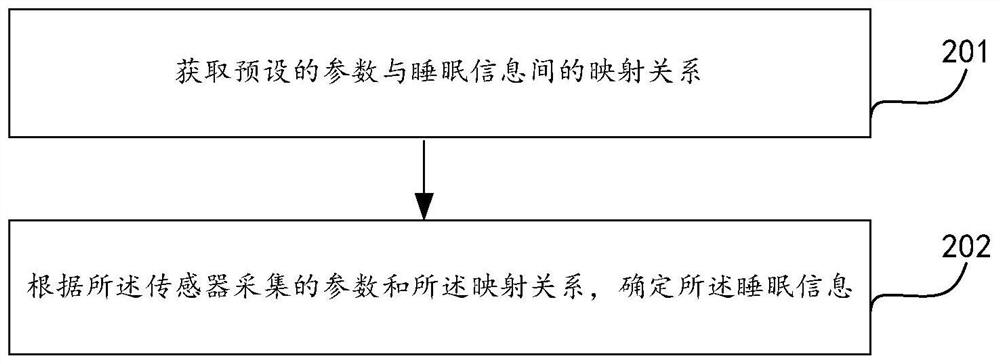
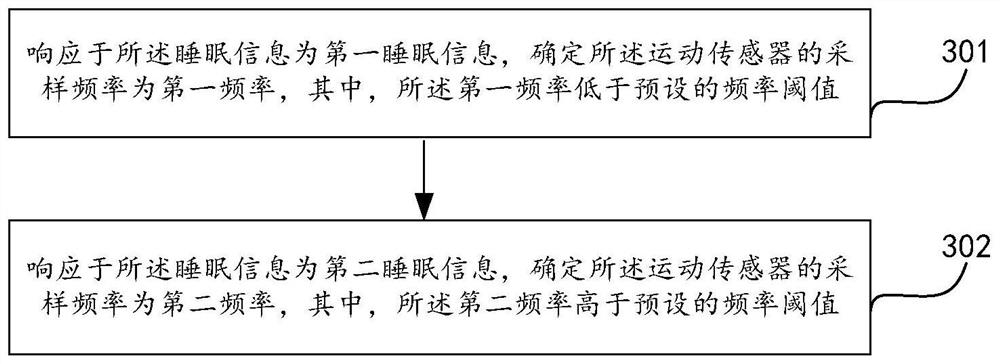
PendingCN113749626AGuaranteed accuracyReduce in quantityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSleep stateEmergency medicine
The invention provides a heart rate detection method and device, wearable equipment and a storage medium, and the heart rate detection method is applied to the wearable equipment and comprises the following steps: obtaining parameters collected by a motion sensor in the wearable equipment; determining sleep information according to the parameters collected by the motion sensor; determining the sampling frequency of the motion sensor according to the sleep information; and in response to the fact that the sampling frequency is larger than a preset frequency threshold value, determining heart rate information according to the parameters collected by the motion sensor. The sampling frequency is increased only in the sleep state to detect the heart rate, power consumption is reduced, the service time of the wearable equipment is prolonged, the use of the whole night sleep time can be met, and the high sampling rate ensures the accuracy of heart rate detection; and the parameters collected by the same motion sensor can be used for sleep analysis and heart rate detection, the number of sensors in the wearable device is reduced, and the size and power consumption of the wearable equipment are reduced at the same time.
Owner:ANHUI HUAMI INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Auxiliary device for interventional therapy of cardiovascular department
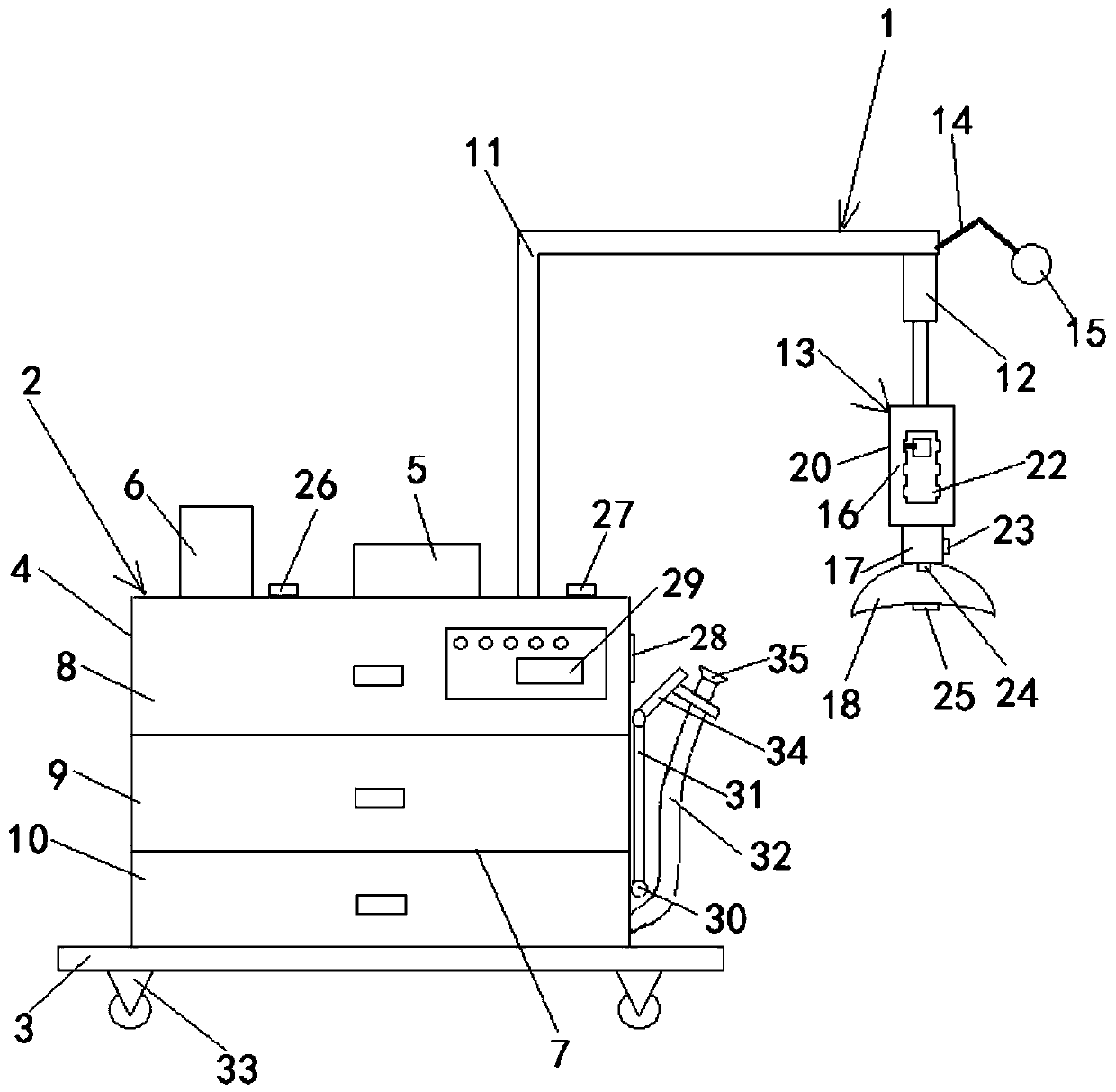
ActiveCN110811742AReduce the burden onConvenient remote observationSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringDecreasing heart rateIncreased heart rate
The invention relates to the technical field of medical appliances and particularly relates to an auxiliary device for interventional therapy of a cardiovascular department. The auxiliary device comprises a bleeding arresting device, a monitoring device and a base, wherein the monitoring device is arranged on the base and is fixedly connected with the bleeding arresting device; the monitoring device comprises a monitoring frame, an electrocardiogram monitor and a dynamic blood pressure monitor are arranged at the top of the monitoring frame, the interior of the monitoring frame is partitionedinto a medicine placement groove, an appliance groove and a refuse chute by a plurality of transverse plates, and the medicine placement groove is partitioned into a normal-temperature area and a low-temperature area by a longitudinal plate; and the bleeding arresting device comprises an inverse-L-shaped rod, an electric telescopic rod and a pressing assembly, the inverse-L-shaped rod is fixedly connected with a fixed end of the electric telescopic rod, a telescopic end of the electric telescopic rod is fixedly connected with the pressing assembly, the inverse-L-shaped rod is further connectedwith a universal rod, and the universal rod is fixedly connected with a monitoring camera. According to the auxiliary device for the interventional therapy of the cardiovascular department, remote observation by medical personnel is achieved, an alert can be issued in time after increased heart rate and decreased heart rate phenomena occur, and the medical personnel can conveniently handle in time.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chinese medicinal composition for treating coronary disease, stenocardia, arrhythmia, hyperlipemia and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101342207BAmphibian material medical ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseAntagonism
The invention provides a Chinese medicine composition used for curing coronary heart disease, angina, arrhythmia and high blood fat and a preparation method thereof. The Chinese medicine composition consists of components as follows: 5 to 20 weight percentage of musk, 12 to 50 weight percentage, 60 to 250 weight percentage of sodium taurocholate, 12 to 50 weight percentage of toad venom, 30 to 120 weight percentage of pearl, 40 to 160 weight percentage of borneol, 1500 to 15000 weight percentage of panax pseudo-ginseng wallich, 150 to 600 weight percentage of ginseng and 50 to 200 weight percentage of the dry extract of buffalo horn. The Chinese medicine composition of the invention can improve blood circulation, dilate coronary arteries, enhance myocardial ischemia, decrease crown arteries resistance, regulate cardiac rate, lower blood pressure, reduce myocardium metabolism, decrease consumed oxygen of myocardium and relieve or eliminate angina via the synergistic and beneficial antagonistic effect of the medicine. As a great amount of the sodium taurochlate is adopted, product cost is reduced while drug effect is ensured as much as possible, thus reducing the economic burden of a patient.
Owner:广东宏兴集团股份有限公司宏兴制药厂
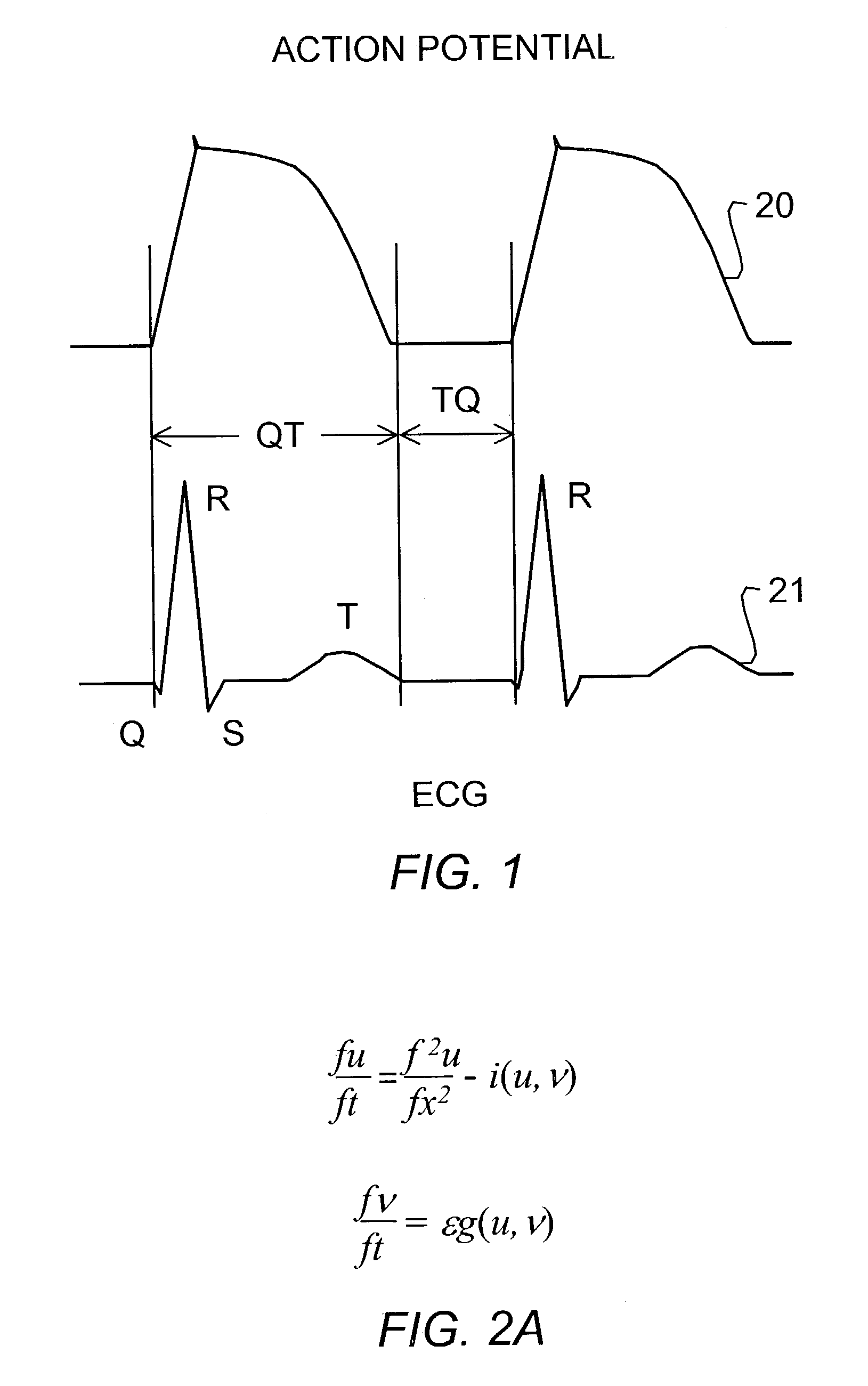
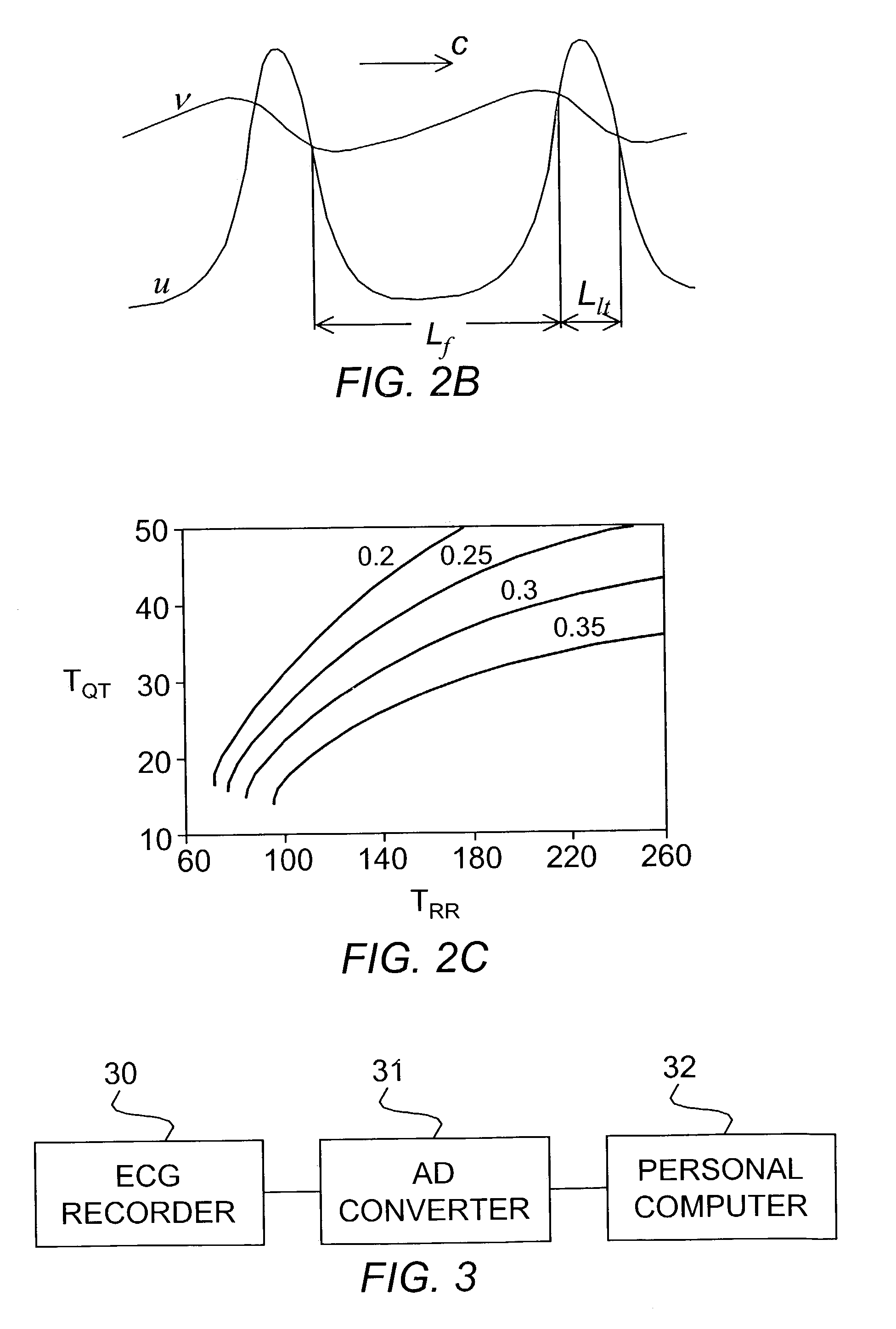
Method and system for evaluating stability of cardiac propagation reserve
InactiveUS20140243695A1Prevents accurate of instabilityLowering indexElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsDecreasing heart rateData set
A method of determining the susceptibility to ventricular arrhythmias in a subject, comprises the steps of: (a) collecting (e.g., by surface EKG or intracardiac EKG) at least one QT and DI interval data set from the subject during a stage of gradually increasing heart rate or a stage of gradually decreasing heart rate; (b) determining (e.g., by applying low- and high pass filtering) low-frequency QT-DI interval trends and high-frequency QT-DI fluctuation signals in said at least one QT and DI interval data set; (c) finding a plurality of correlated and anti-correlated portions between said high-frequency QT-DI fluctuation signals; (d) determining corresponding regression lines for said correlated and anti-correlated portions; (e) finding a plurality of (or in some embodiments all) steady state QT-DI points designated by intersections between said low frequency QT-DI trends and said corresponding regression lines; (f) fitting action potential durations computed from a rate dependent reaction-diffusion model to corresponding ones of said steady state QT-DI points to give (i) a model excitation threshold and (ii) a minimal level of refractoriness at a plurality of (or in some embodiments all of) said steady state QT-DI points; (g) at the steady state QT-DI point corresponding to the highest heart rate in said QT and DI interval data set, determining the difference between said minimal level of refractoriness and a model critical excitation threshold for a stable solitary pulse corresponding to the rate dependent reaction diffusion model of step (f) to give a reserve of refractoriness (RoR); (h) fitting action potential durations computed from a rate dependent reaction-diffusion model to said correlated and anti-correlated portions to give a rate of adaptation of each model excitation threshold to a corresponding steady state value at a plurality of (or in some embodiments all of) said steady state QT-DI points; (i) at the steady state QT-DI point corresponding to the highest heart rate in said QT and DI interval data set, determining the inverse of said rate of adaptation to give a reserve of memory (RoM); (j) combining said reserve of refractoriness (RoR) and said reserve of memory (RoM) to produce a metric of stability-of-propagation reserve (SoPR) in said subject, a higher value of SoPR indicating lower susceptibility to ventricular arrhythmias in said subject. Systems and apparatus for carrying out the method are also described.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
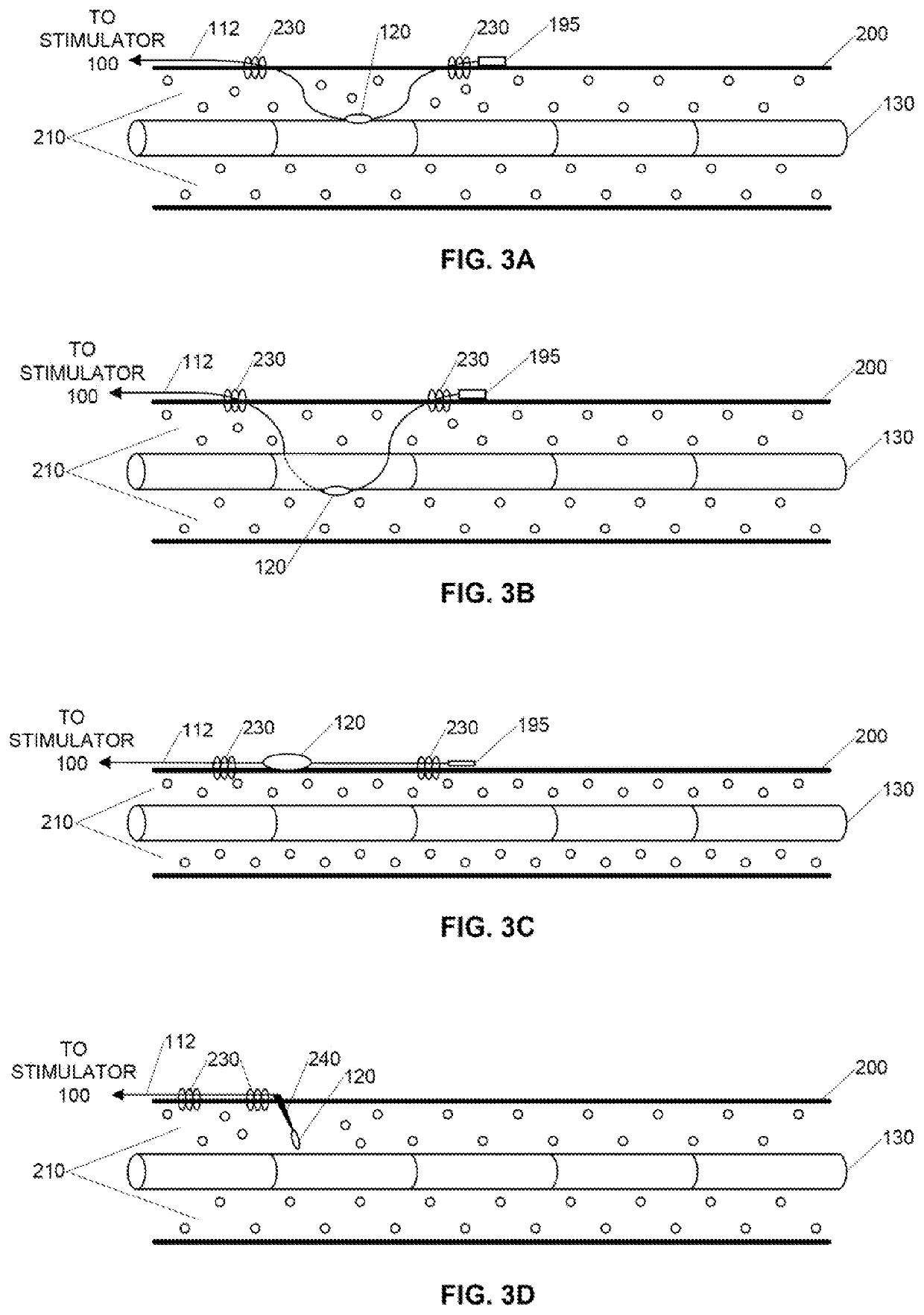
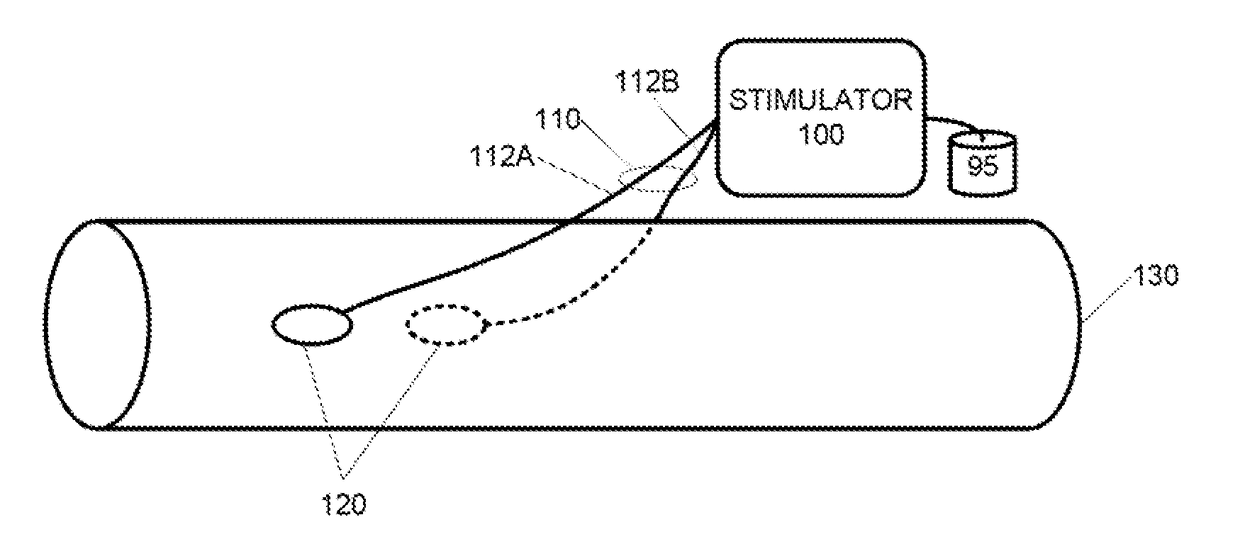
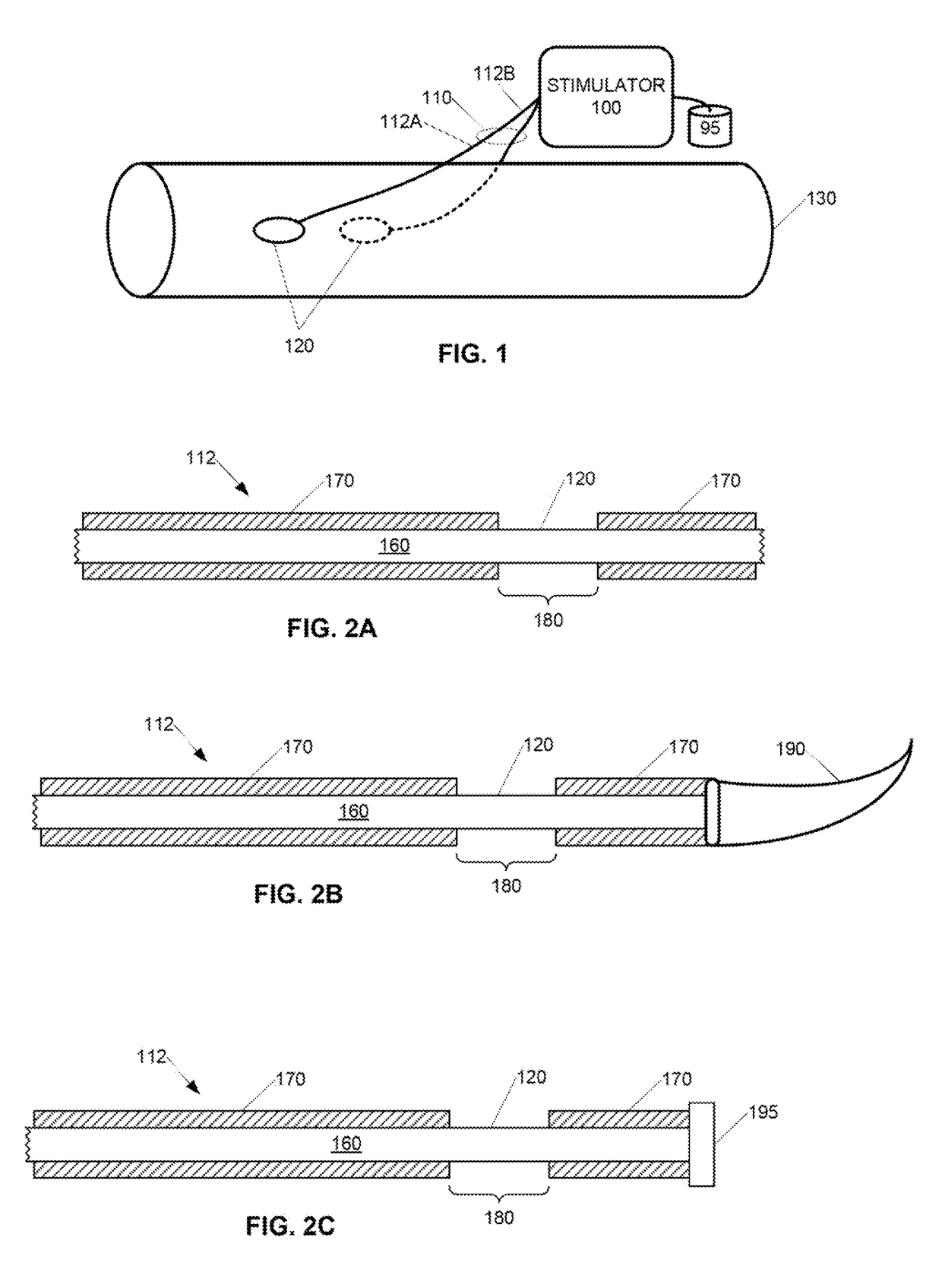
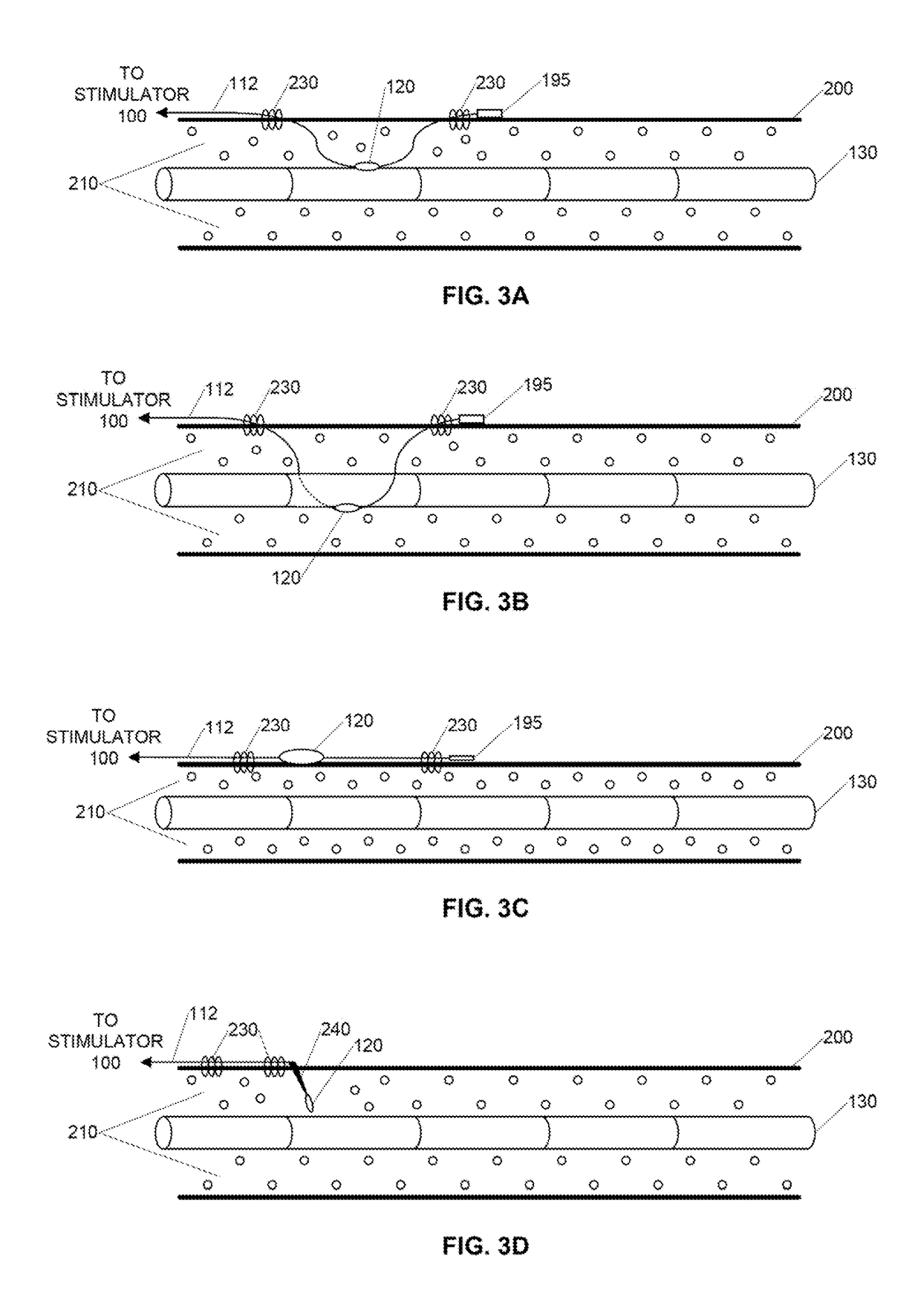
Parasympathetic activation by vagus nerve stimulation
ActiveUS10646715B2Reduce decreaseAvoid side effectsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesDecreasing heart rateSympathetic nerve
The vagus nerve and branches of the vagus nerve are stimulated below the laryngeal nerve branch bifurcation in order to induce desired parasympathetic responses, such as decreased heart rate, without also triggering any adverse sympathetic responses. Stimulating surfaces of an open field bipolar electrode are positioned on or inserted through the pleural membrane overlying the vagus nerve at a location having substantially no cardiac sympathetic fibers adjacent to the vagus nerve. The open field bipolar electrodes can be securable-wire, needle, plate, or any other type of electrode suitable for being secured to the pleural membrane using one or more fastening mechanisms. Electrical stimuli are generated by a stimulator connected to the stimulating surfaces of the open field bipolar electrode by one or more leads.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
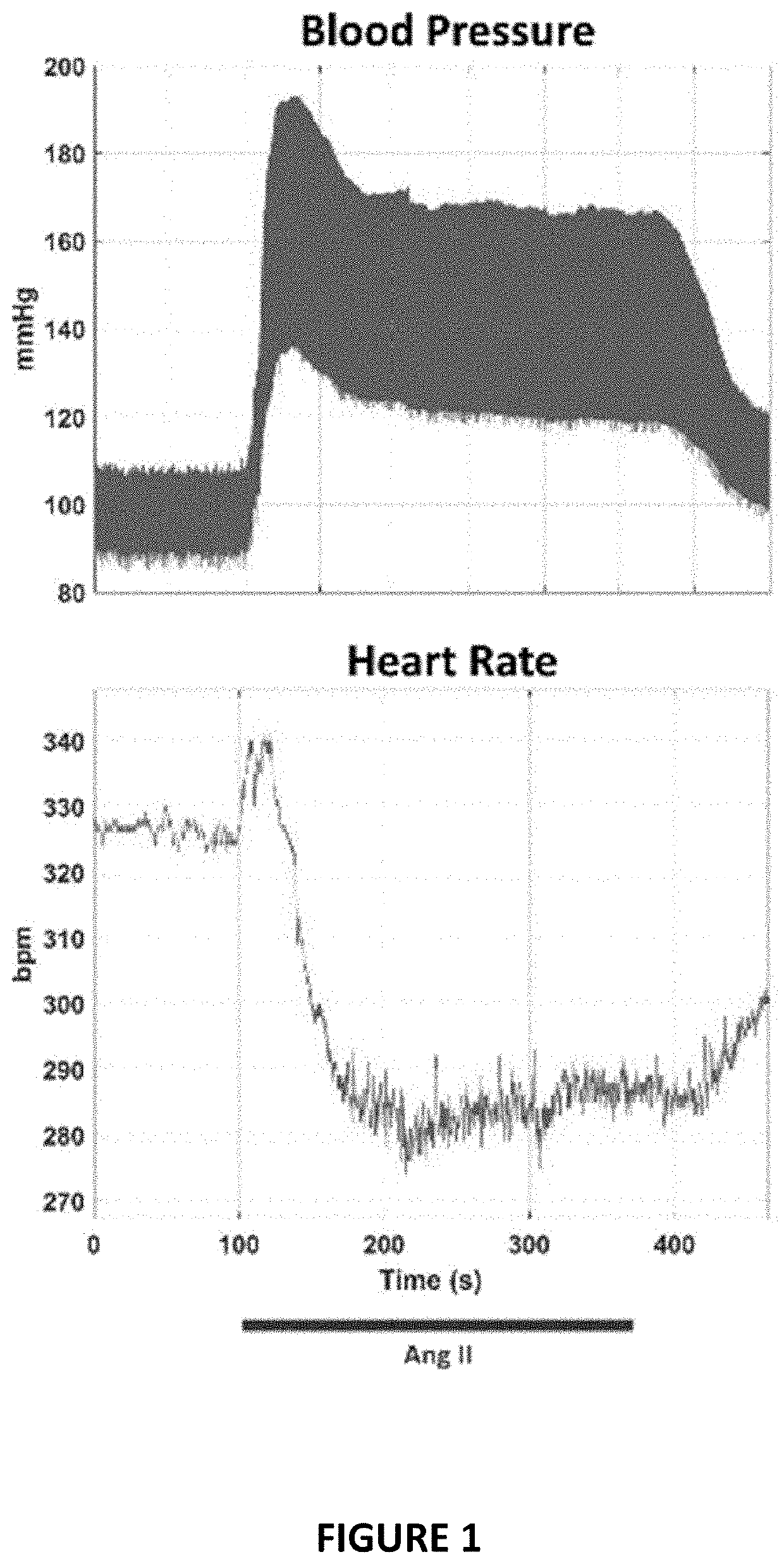
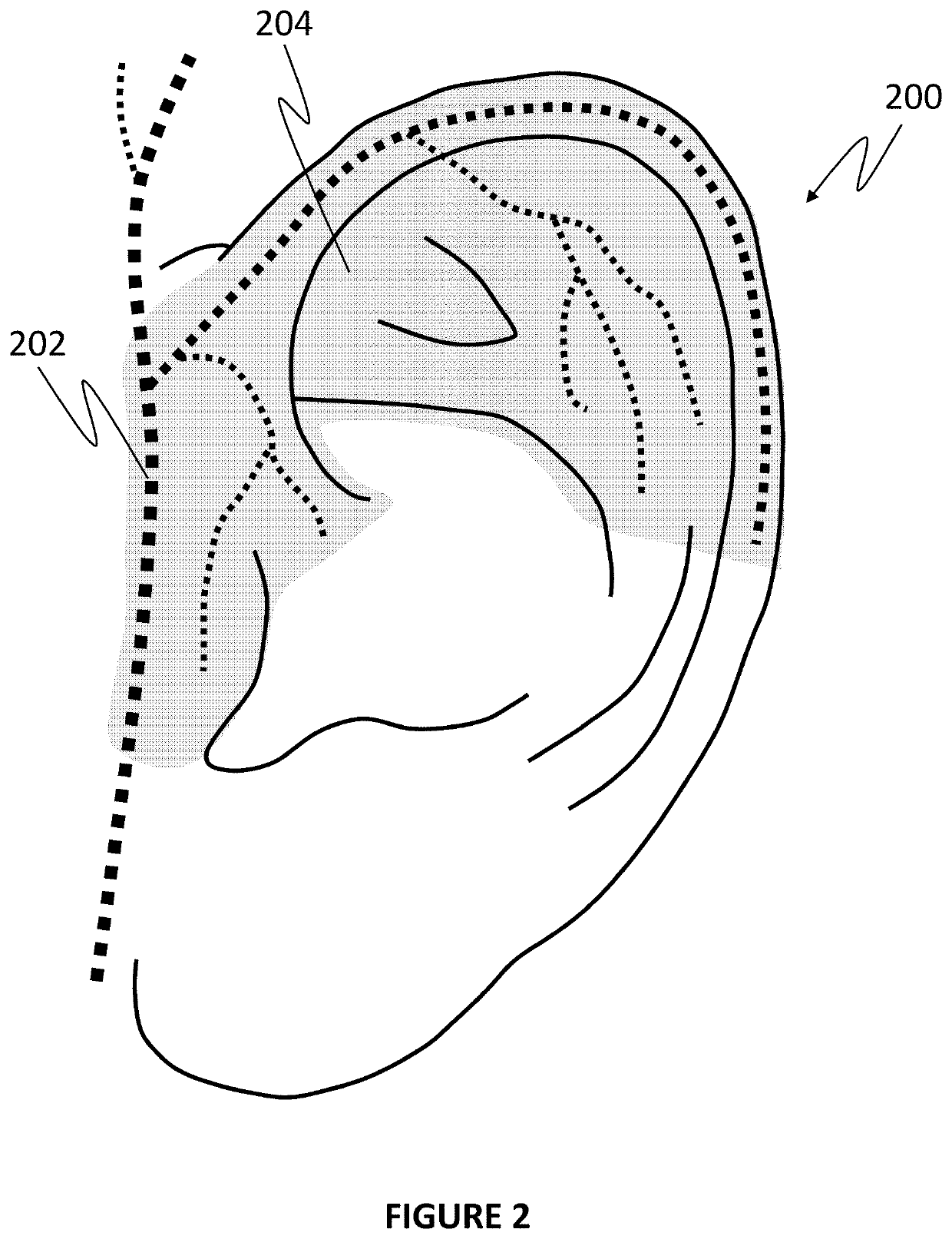
Non-invasive and selective bioelectronic control of blood pressure
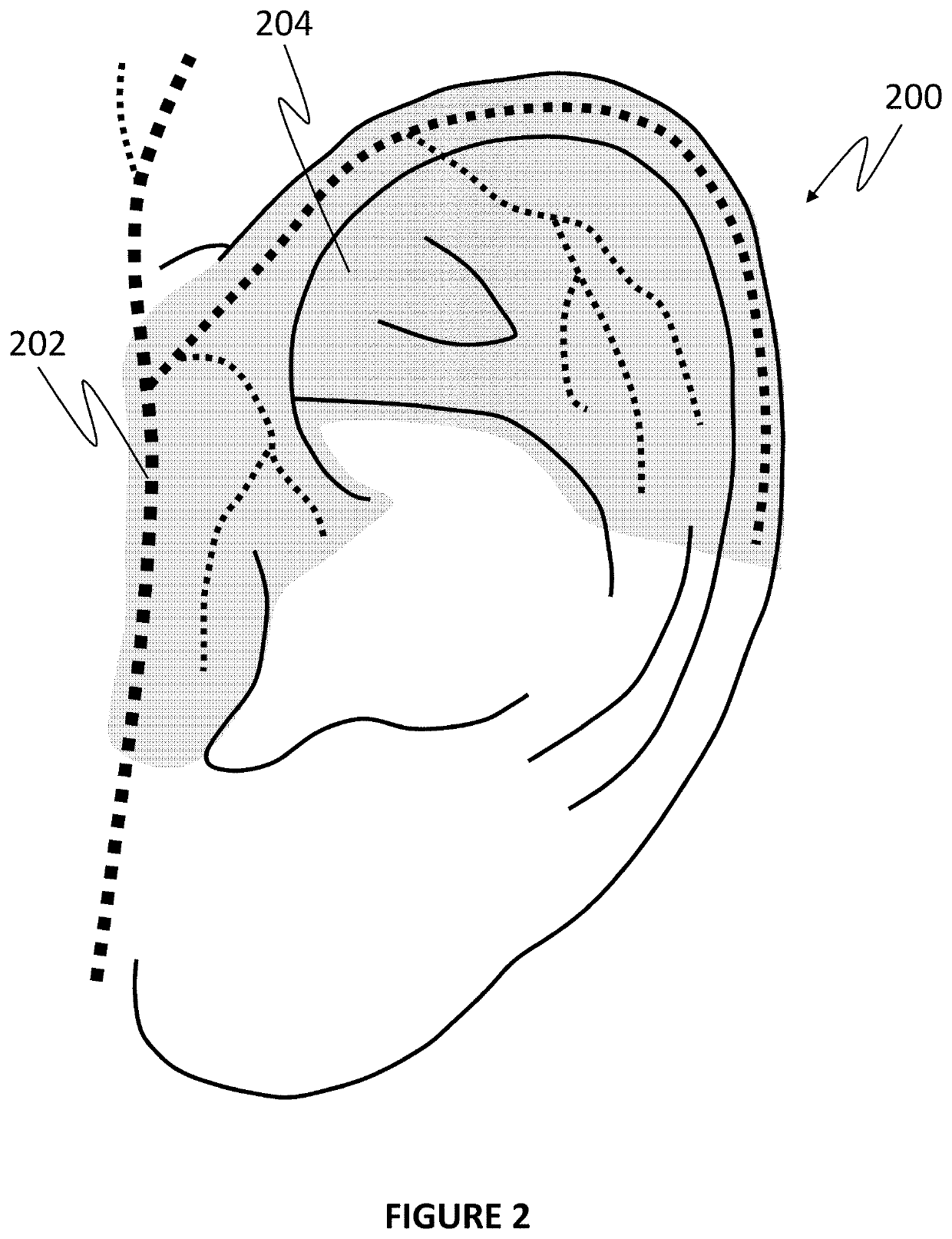
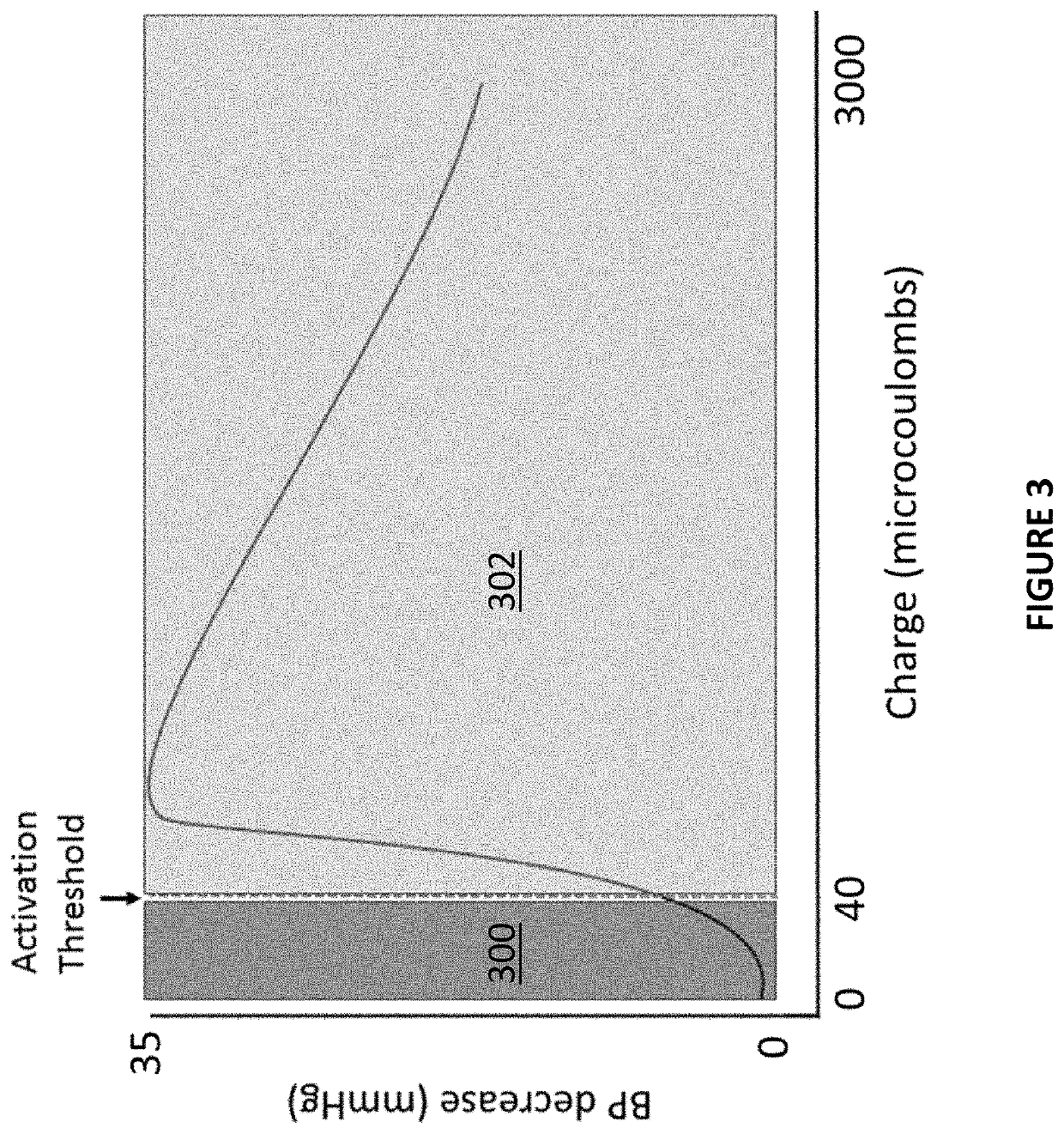
ActiveUS10806920B2Increase ratingsLower blood pressureEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsDecreasing heart rateNon invasive
Methods and systems for non-invasive selective control of blood pressure are described. For example, noninvasive stimulation of the auriculotemporal nerve (on the surface of the ear) facilitates a decrease in blood pressure without a corresponding decrease in heart rate or breathing rate, as occurs in stimulation of the cervical vagus and trigeminal nerves. Such a therapy may be particularly beneficial during hypertensive crises or like events where the body naturally decreases heart rate and breathing rate to compensate for an increased blood pressure.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Heart Rate Decreasing Agent
PendingUS20220016114A1Safely and efficiently decrease heart rateImproved prognosisOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderDecreasing heart rateIncreased heart rate
The present invention addresses the problem of providing an agent for decreasing heart rate having fewer side effects, or a novel agent for suppressing an increase in heart rate during exercise. The heart rate can be decreased, in particular, palpitation, shortness of breath or fatigue associated with an increased heart rate can be prevented or ameliorated, and the increase in heart rate during exercise can be suppressed by ingesting a preparation containing orotic acid or a salt thereof as an active ingredient.
Owner:FURUKAWA RES OFFICE CO LTD
Steroids non-depolarization muscle relaxant antagonistic pharmaceutical composition
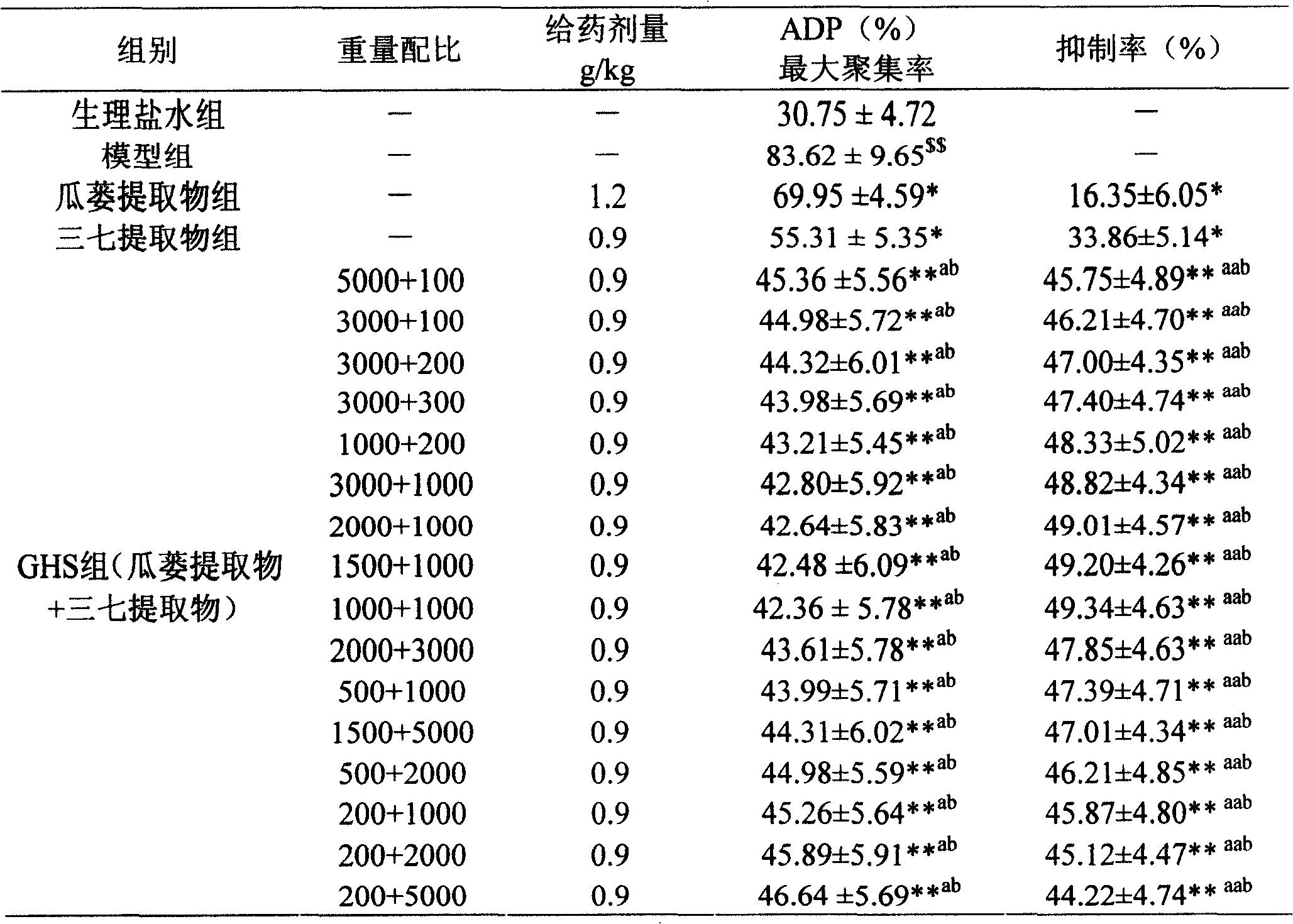
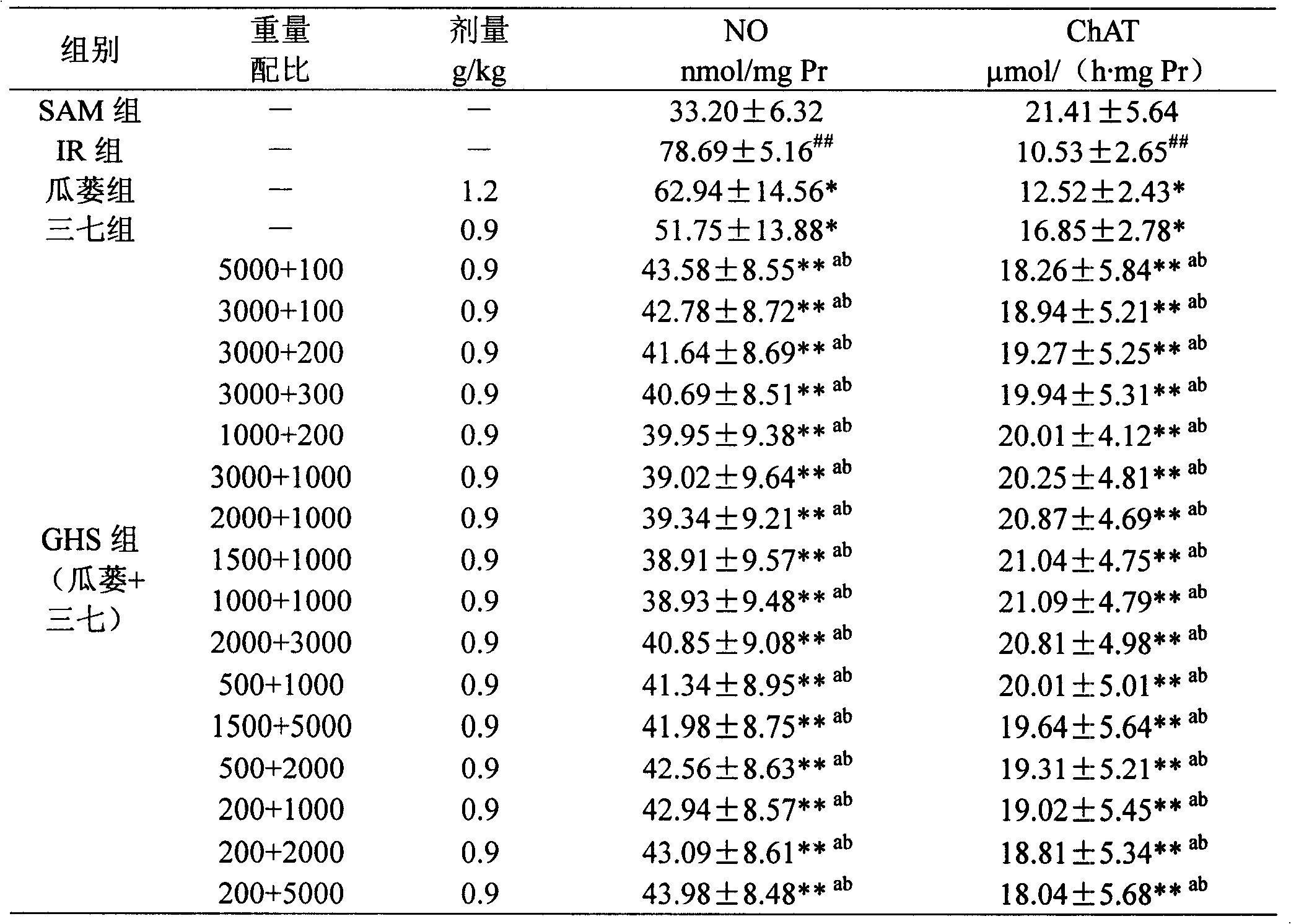
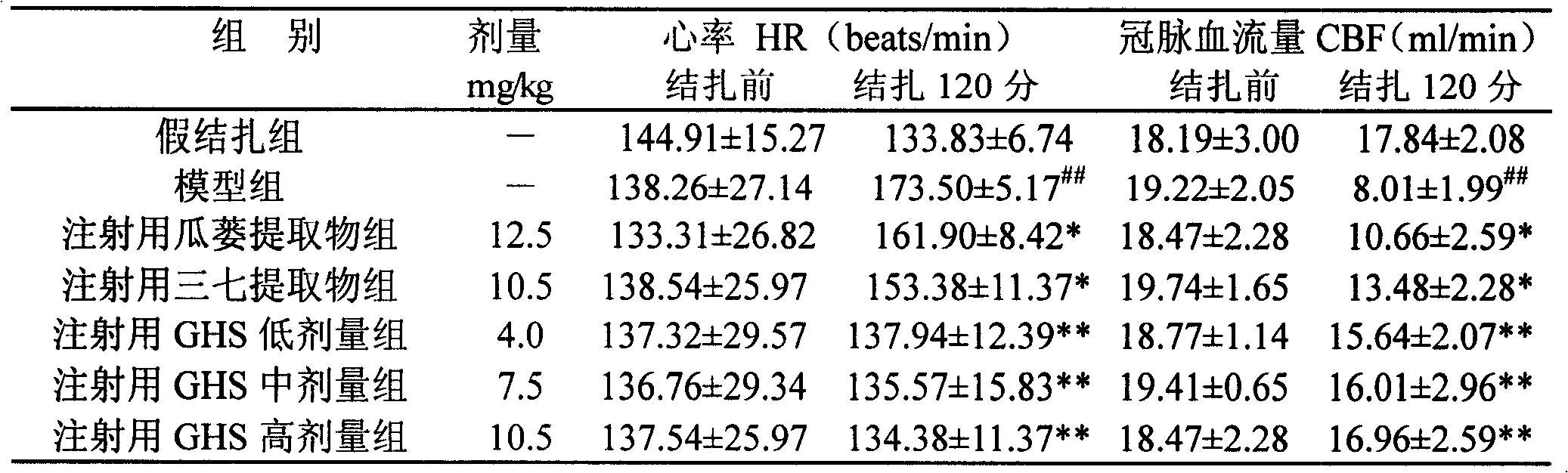
InactiveCN108392623ARelieve nauseaReduce adverse symptoms of vomitingOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDecreasing heart rateSodium bisulfate
The invention discloses a steroids non-depolarization muscle relaxant antagonistic pharmaceutical composition. The composition comprises 6-deoxy alpha-amino acid derivative cyclodextrin, metoclopramide, angiotensin II, anhydrous sodium acetate, sodium bisulfate, and citric acid. The 6-deoxy alpha-amino acid derivative cyclodextrin is a main component of the pharmaceutical composition; metoclopramide is an antiemetic, anhydrous sodium acetate and sodium bisulfite are added for assisting, and are co-effected on a dopamine receptor in a medulla oblongata chemoreceptor trigger zone, so that a threshold of the chemoreceptor trigger zone is increased; the angiotensin II is one of vaso-excitor active substances, and whole body arteriole contraction and arterial blood pressure rise can be realized; and the adverse symptoms such as decreased heart rate and drop of blood pressure of the steroids muscle relaxant antagonistic pharmaceutical composition can be effectively solved while in use, the pharmaceutical composition realizes combined action, and the steroids non-depolarization muscle relaxant antagonistic pharmaceutical composition capable of effectively reducing vomit and reducing adverse symptoms such as blood pressure can be provided.
Owner:SUZHOU SCI&TECH TOWN HOSPITAL
Medicinal composition containing mongolian snakegourd and notoginseng
InactiveCN101190253BProlong survival timeMetabolism disorderCardiovascular disorderDiseaseDecreasing heart rate
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical technology. The invention discloses a medicine combination of snakegourd fruit or the extract thereof and pseudoginseng or the extract thereof as well as the preparation method thereof; the invention also discloses the application of the medicine combination on the medicines for treating cerebrovascular diseases and the preparations containing the medicine combination. The effective ingredients of the medicine combination are prepared by the following raw medicines by weight: 200-5000 parts of snakegourd fruit and 100-5000 parts of pseudoginseng, or 4-400 parts of snakegourd fruit extract and 4-250 parts of pseudoginseng extract. The invention can be prepared into any dosage forms acceptable in clinical or pharmacy, and the preferred preparation is oral preparation or injection. The two medicines in the invention have synergistic function and achieve the functions of anti-myocardial ischemia, anti-platelet aggregation, reducing myocardial infarct size and decreasing heart rates together. The invention has significantly increasing curative effect than single administration of snakegourd fruit, the extract thereof, pseudoginseng and the pseudoginseng thereof.
Owner:海安江理工技术转移中心有限公司
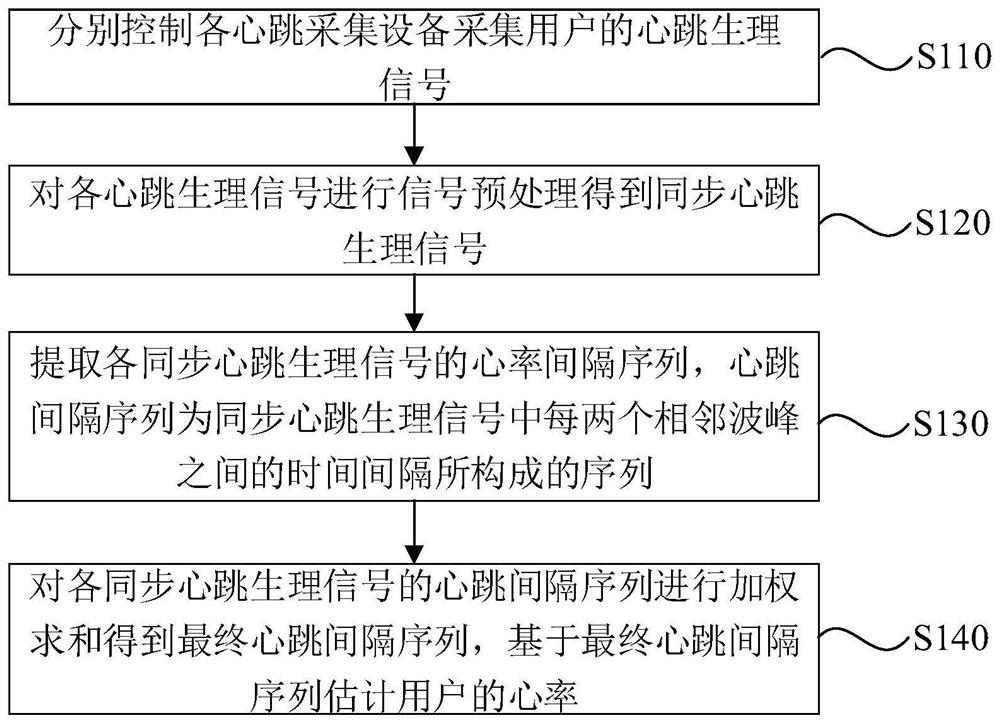
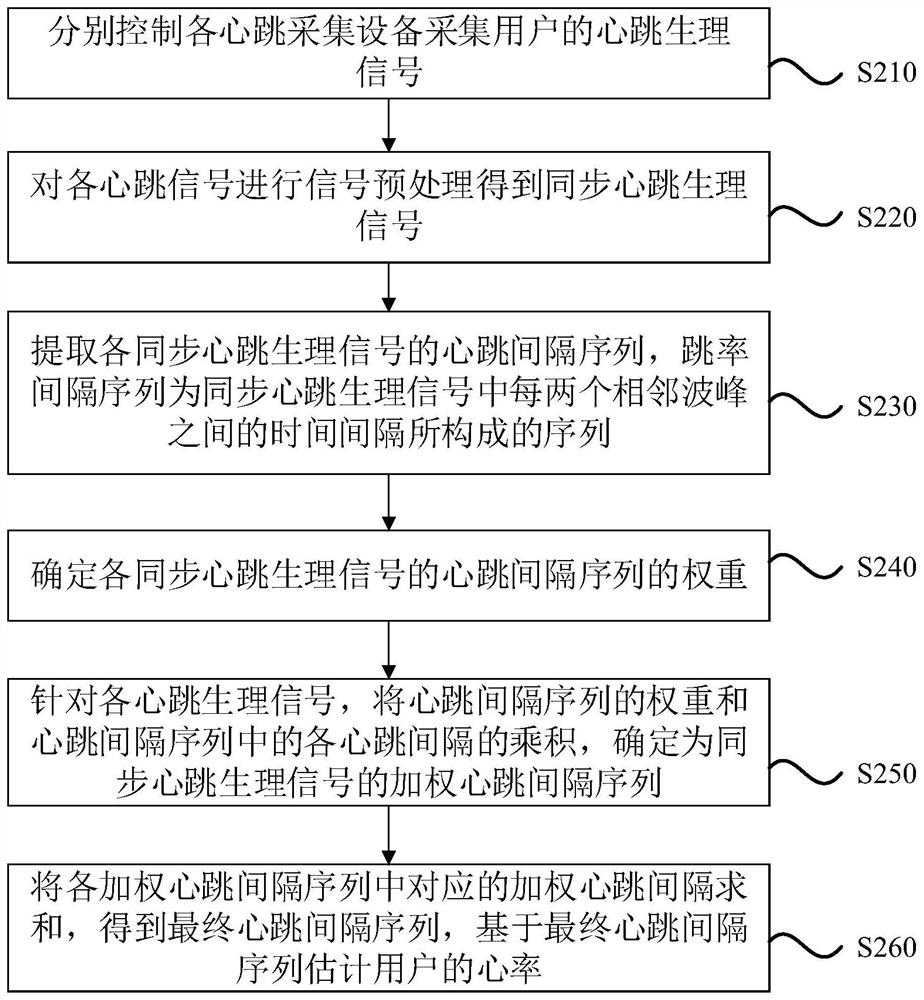
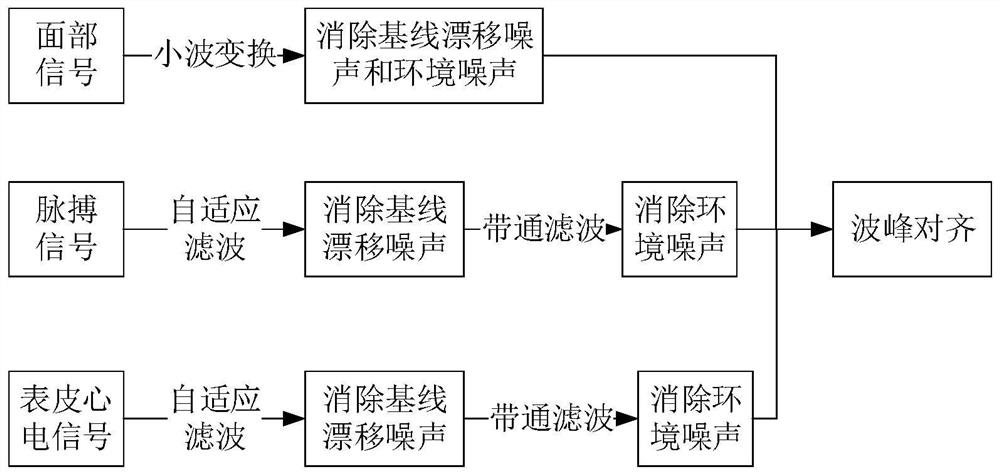
Heart rate estimation method, device, equipment, system and storage medium
PendingCN113693578AReduce detection errorImprove accuracySensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateAcquisition apparatusEngineering
The invention discloses a heart rate estimation method, device, equipment and system and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: respectively controlling each heartbeat acquisition device to acquire a heartbeat physiological signal of a user; performing signal preprocessing on each heartbeat physiological signal to obtain a synchronous heartbeat physiological signal; extracting a heartbeat interval sequence of each synchronous heartbeat physiological signal, wherein the heartbeat interval sequence is a sequence formed by a time interval between every two adjacent wave crests in the synchronous heartbeat physiological signals; and performing weighted summation on the heartbeat interval sequences of the synchronous heartbeat physiological signals to obtain a final heartbeat interval sequence, and estimating the heart rate of the user based on the final heartbeat interval sequence. According to the technical scheme, the heart rate of the user can be estimated by combining the heartbeat physiological signals, collected by an image collecting device, a wearable device and an electrode patch, of the user, the detection error caused by untight attachment of a single sensor is reduced, and the accuracy of heart rate detection in the vehicle driving scene is improved.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
Non-invasive and selective bioelectronic control of blood pressure
ActiveUS20200094040A1Lower blood pressureIncrease heart rateEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsDecreasing heart rateNon invasive
Methods and systems for non-invasive selective control of blood pressure are described. For example, noninvasive stimulation of the auriculotemporal nerve (on the surface of the ear) facilitates a decrease in blood pressure without a corresponding decrease in heart rate or breathing rate, as occurs in stimulation of the cervical vagus and trigeminal nerves. Such a therapy may be particularly beneficial during hypertensive crises or like events where the body naturally decreases heart rate and breathing rate to compensate for an increased blood pressure.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Application of sodium houttuyfonate in preparing medicament for preventing and treating myocardial hypertrophy and/or ventricular hypertrophy
InactiveCN101618032BIncrease dosageIncrease biological functionOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDecreasing heart rateRight ventricular hypertrophy
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Parasympathetic activation by vagus nerve stimulation
ActiveUS20170209700A1Reduce and to avoid side effectSlow heart rateSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesDecreasing heart rateAnesthesia
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
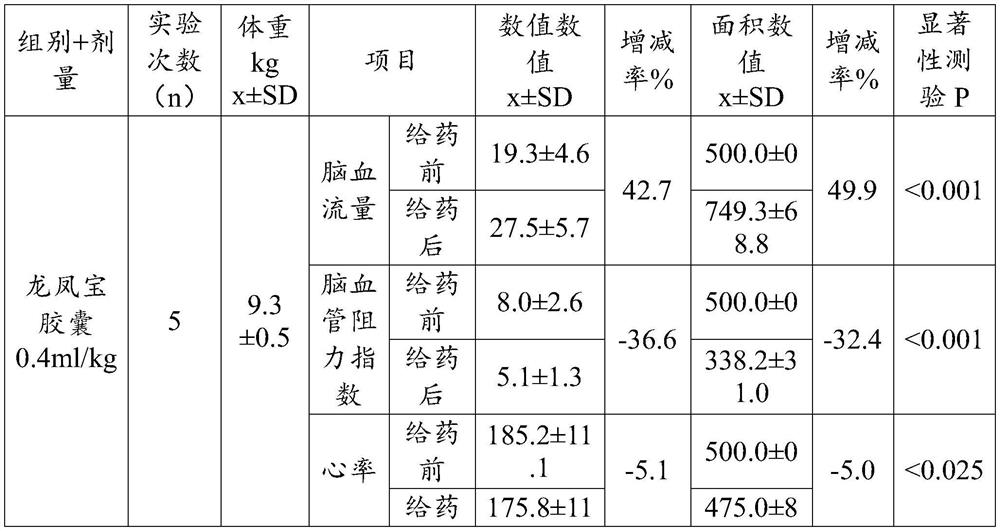
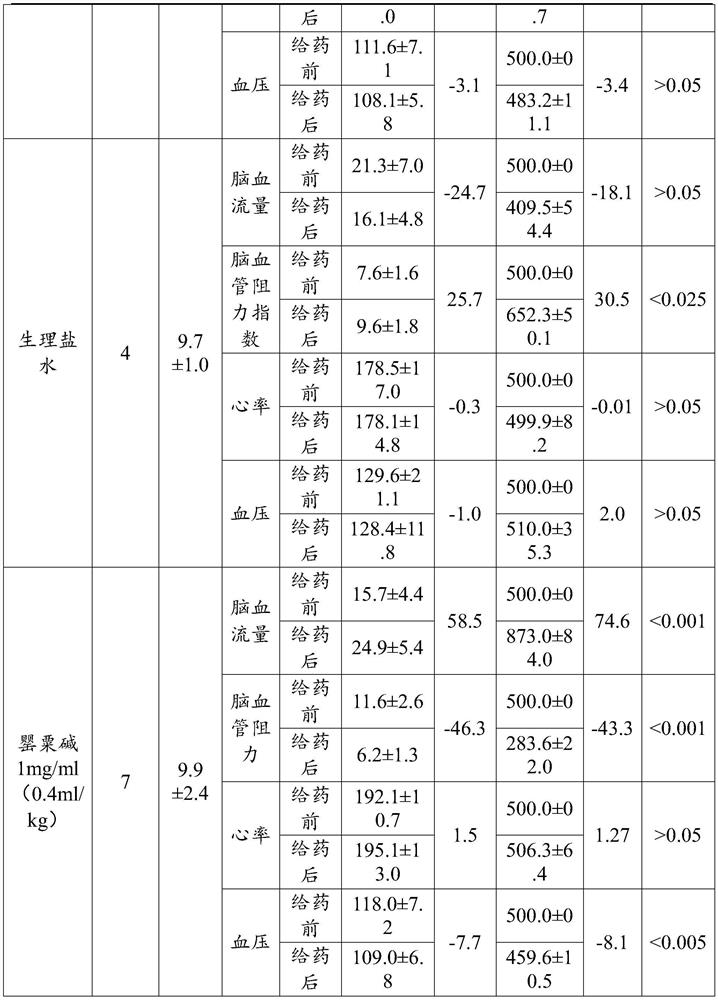
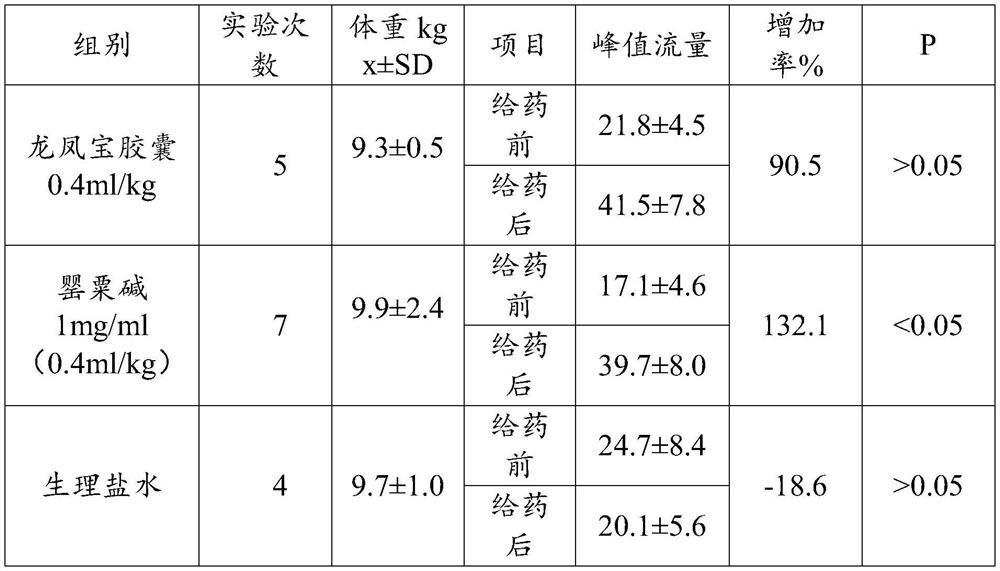
Use of Longfengbao capsule in preparing medicine for preventing and treating cerebral arteriosclerosis and related diseases thereof
InactiveCN113117019AReduce resistanceIncrease cerebral blood flowNervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseAnimal testing
The invention relates to use of a Longfengbao capsule in preparing a medicine for preventing and treating cerebral arteriosclerosis and related diseases thereof. Animal experiments prove that the Longfengbao capsule has very good effects of increasing cerebrovascular flow, reducing cerebral blood resistance, reducing heart rate and reducing cerebral blood pressure. Clinical test results prove that the Longfengbao capsule has good relieving effects on headache, dizziness, lassitude, fatigue and insomnia of patients with cerebral arteriosclerosis, and also has effects of reducing blood fat, reducing blood pressure and improving memory.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIYUNSHAN QIXING PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com