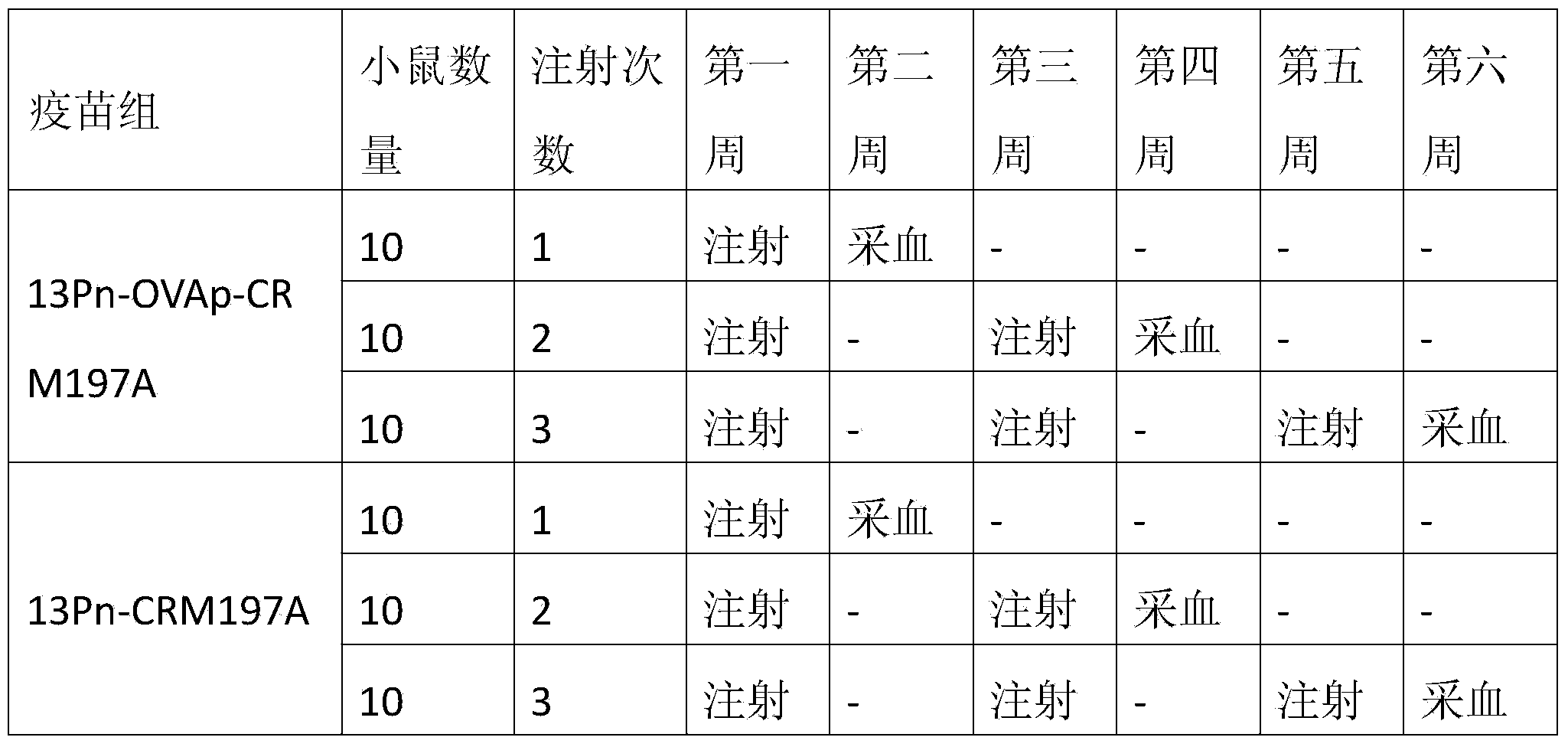
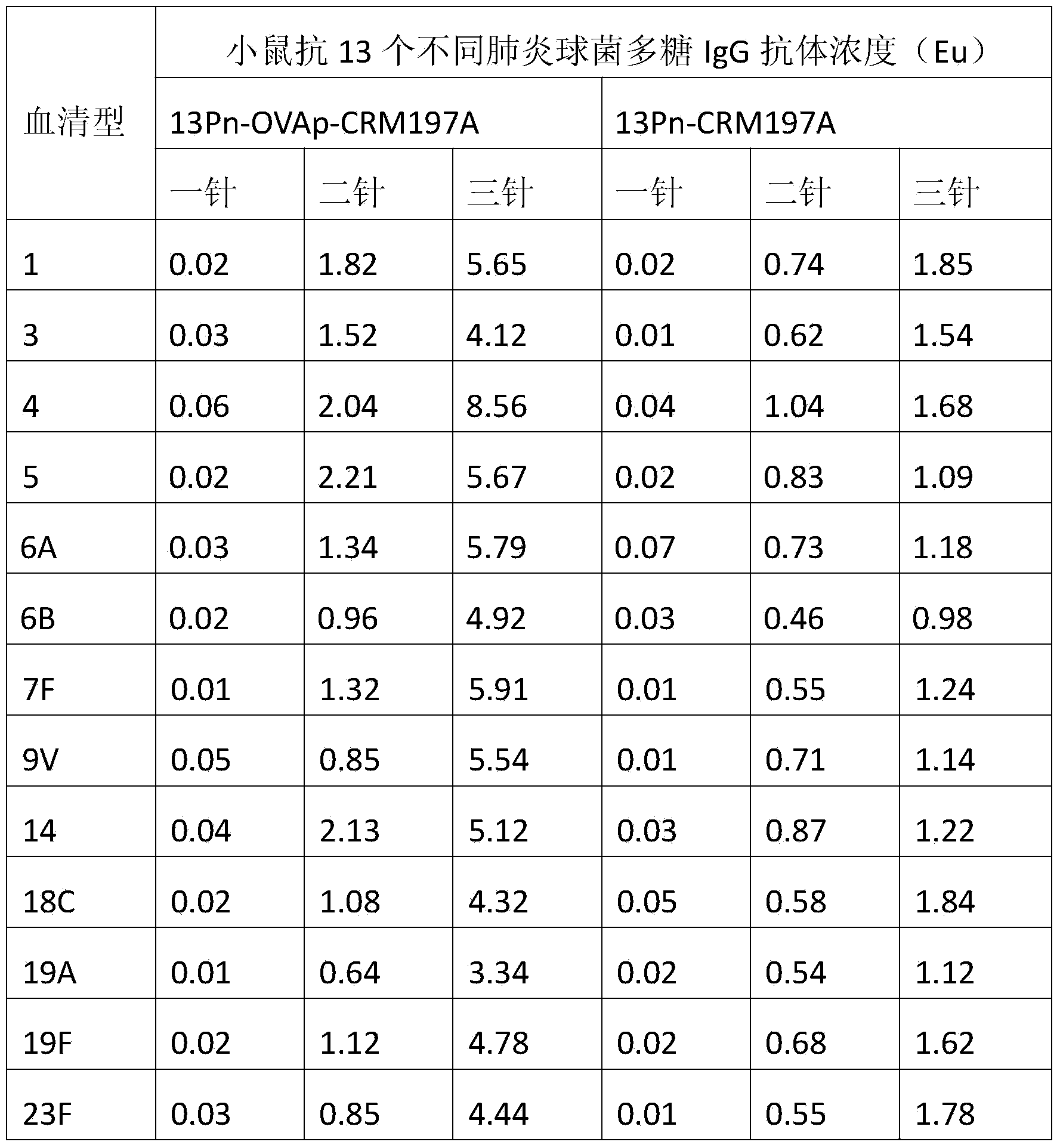
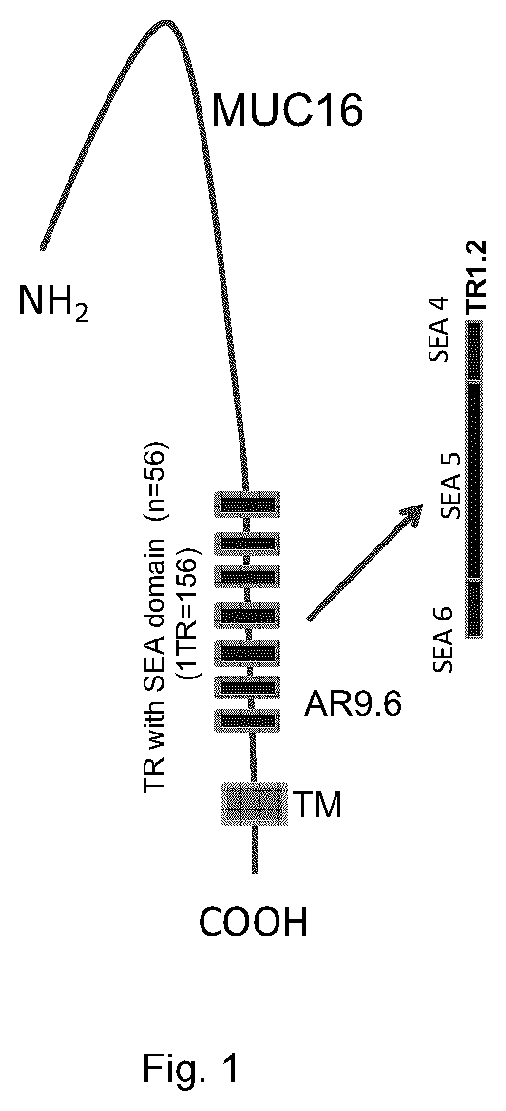
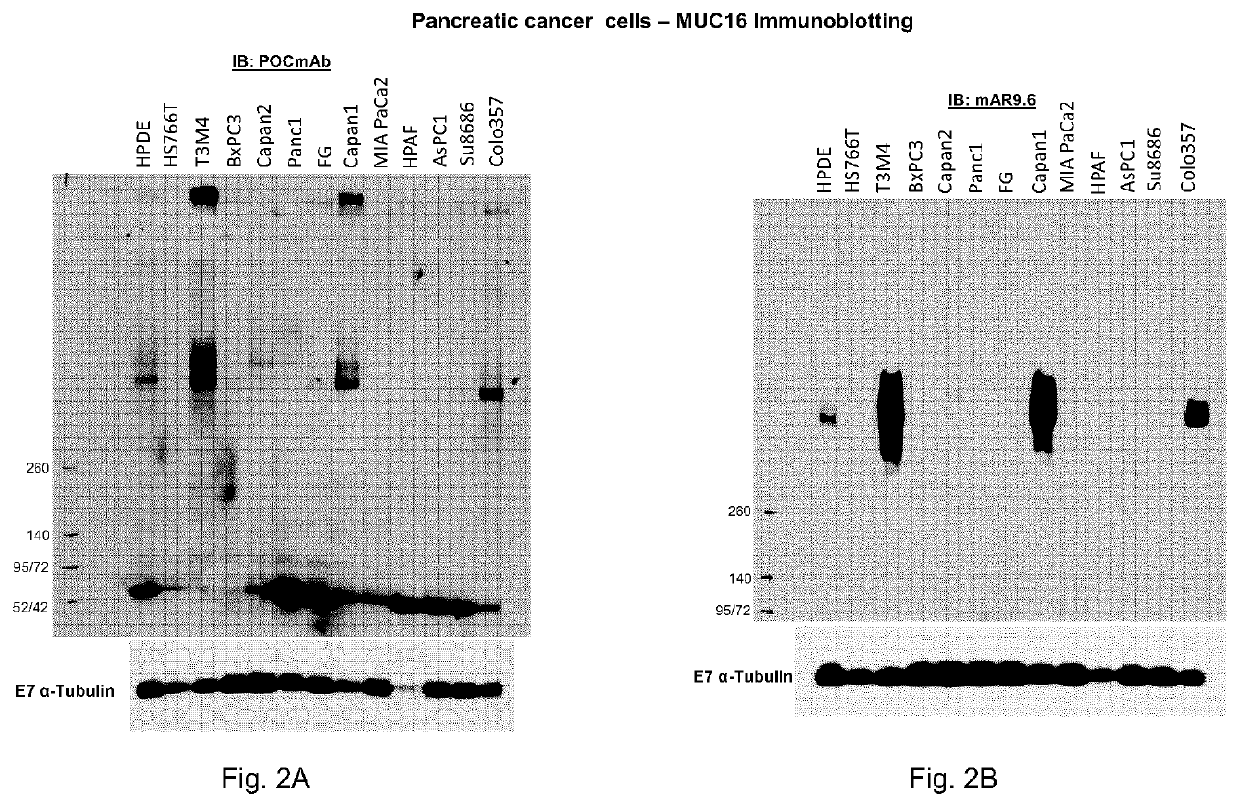
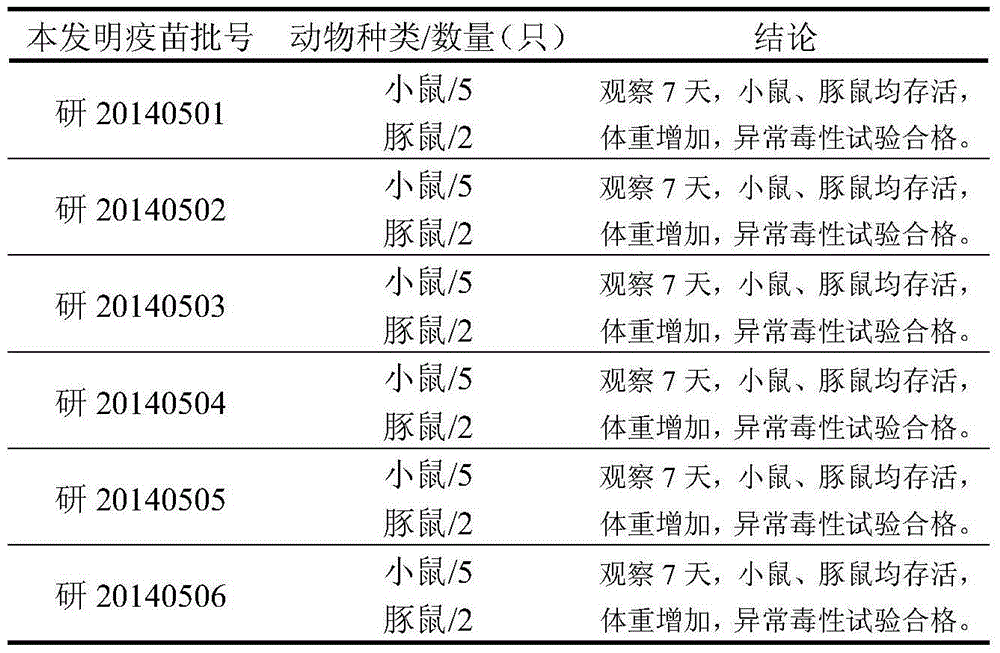
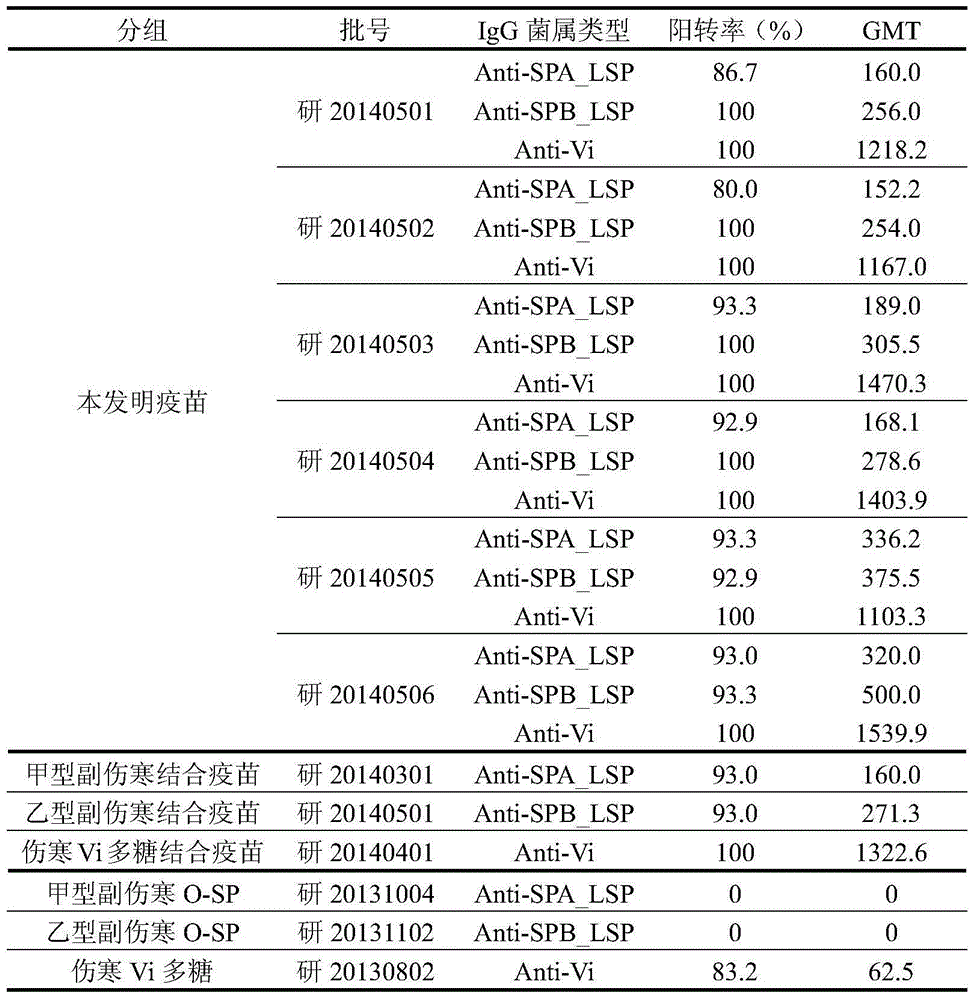
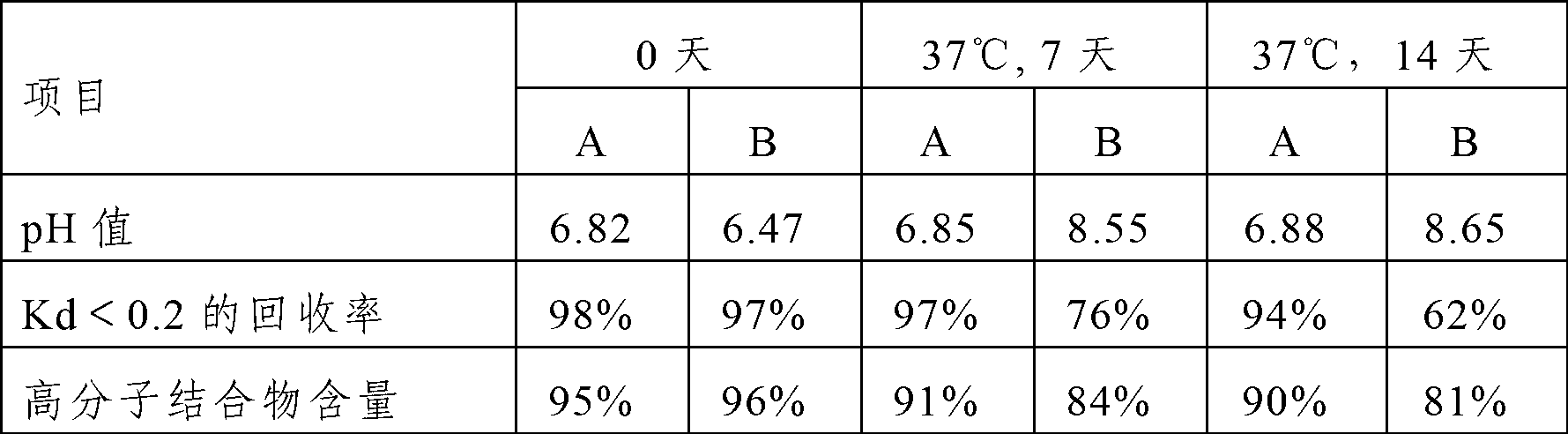
Patents
Literature
49 results about "Glycoprotein binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a glycoprotein, a protein that contains covalently bound glycose (monosaccharide) residues. These also include proteoglycans. [GOC:hjd, ISBN:0198506732]
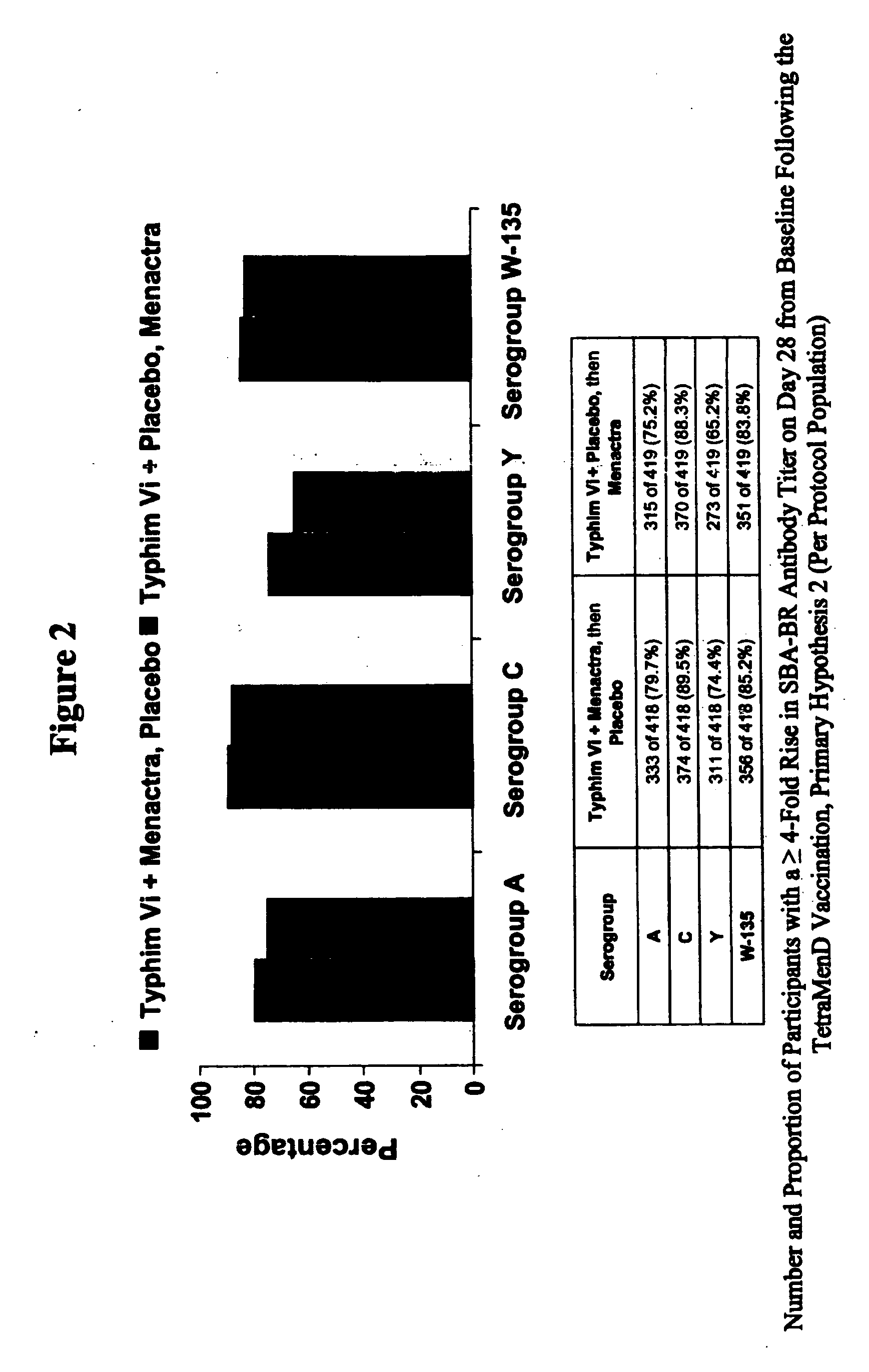
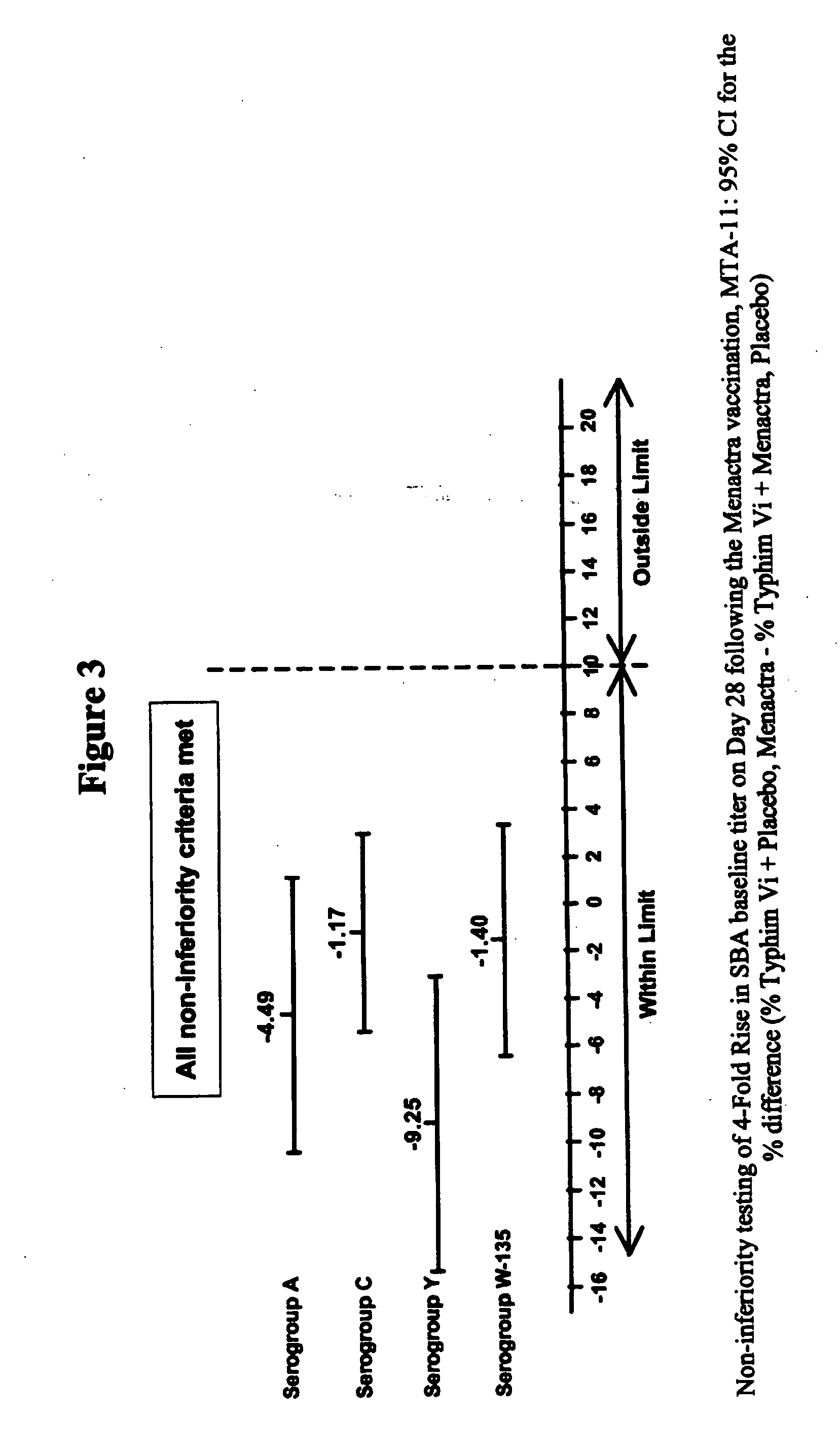
Multivalent meningococcal derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates and vaccine
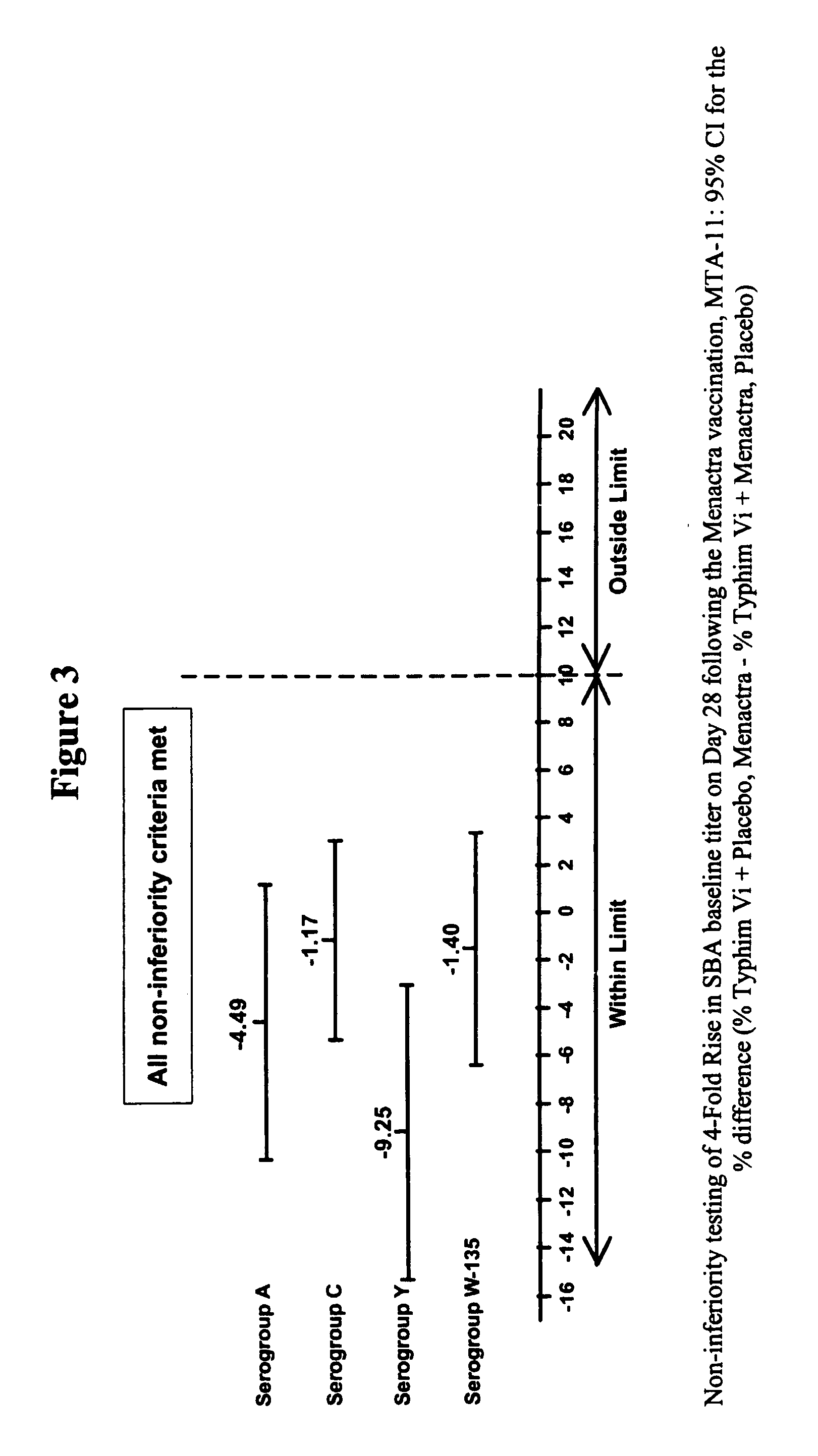
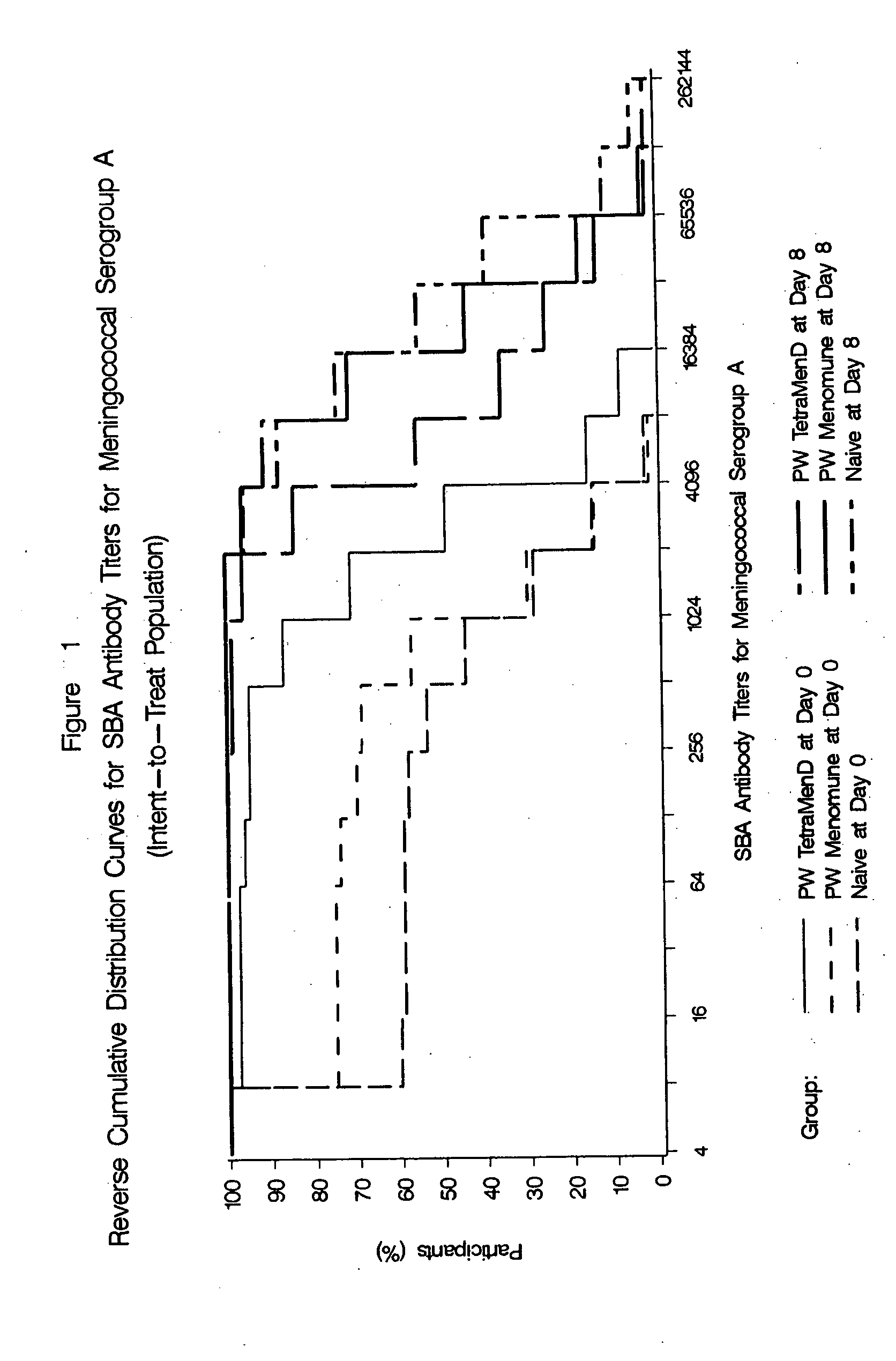
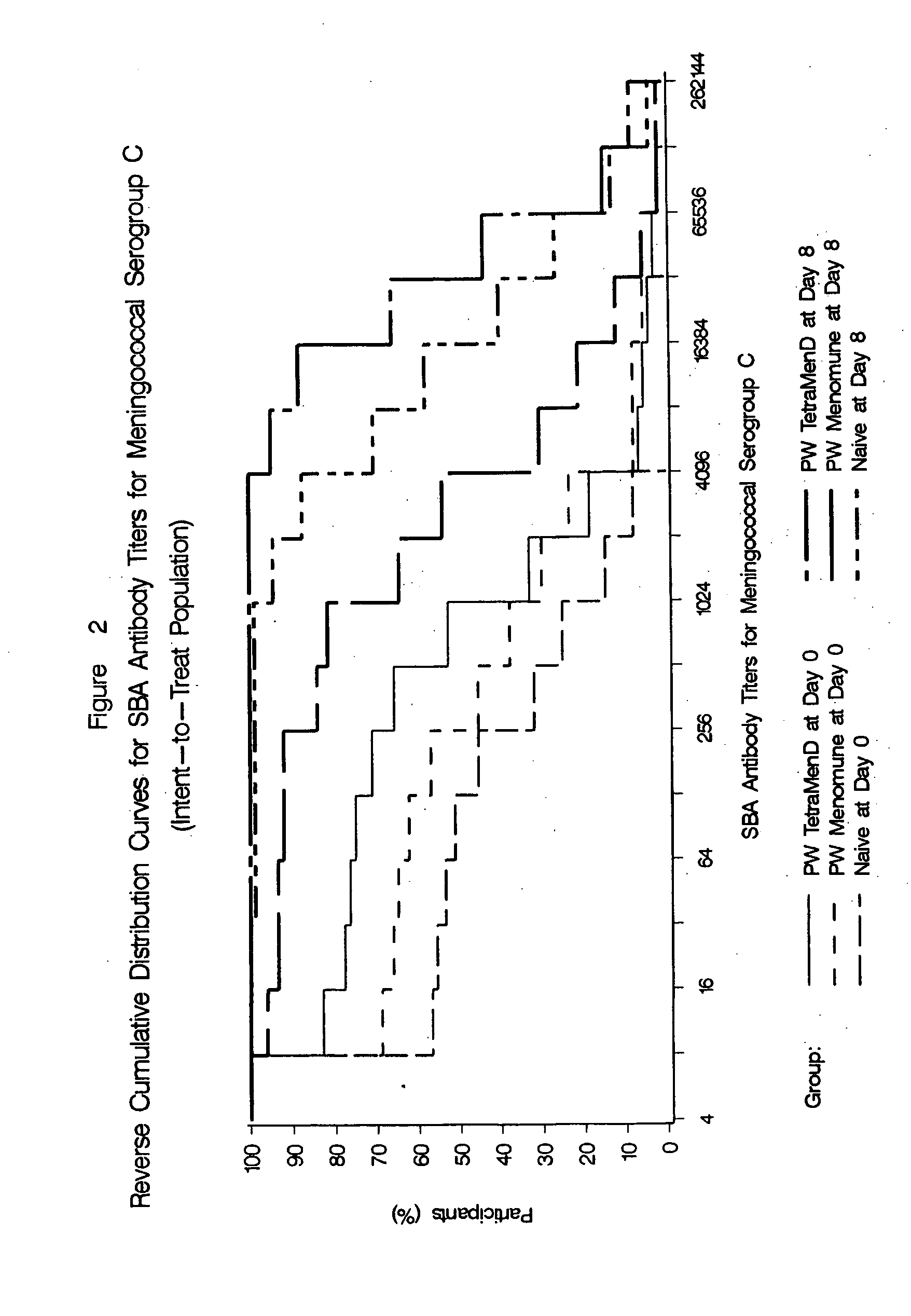
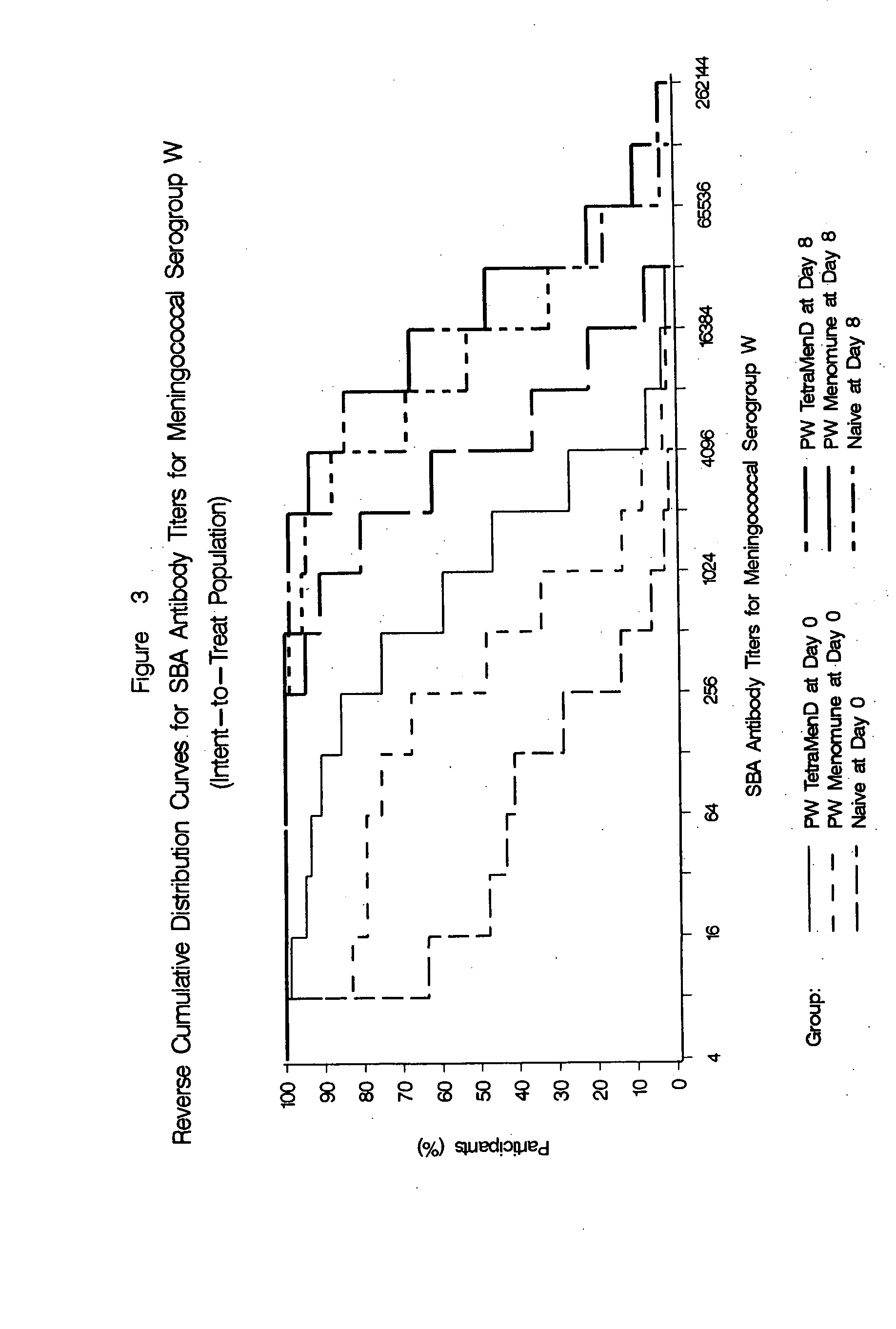
The present invention describes derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates, a composition comprising one or more of such derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates and methods of immunizing human patients with the same. The derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates are purified capsular polysaccharides from Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, W-135, and Y, derivatized chemically activated and selectively attached to a carrier protein by means of a covalent chemical bond, forming polysaccharide-protein conjugates capable of eliciting long-lasting immunity to a variety of N. meningitidis strains.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR INC
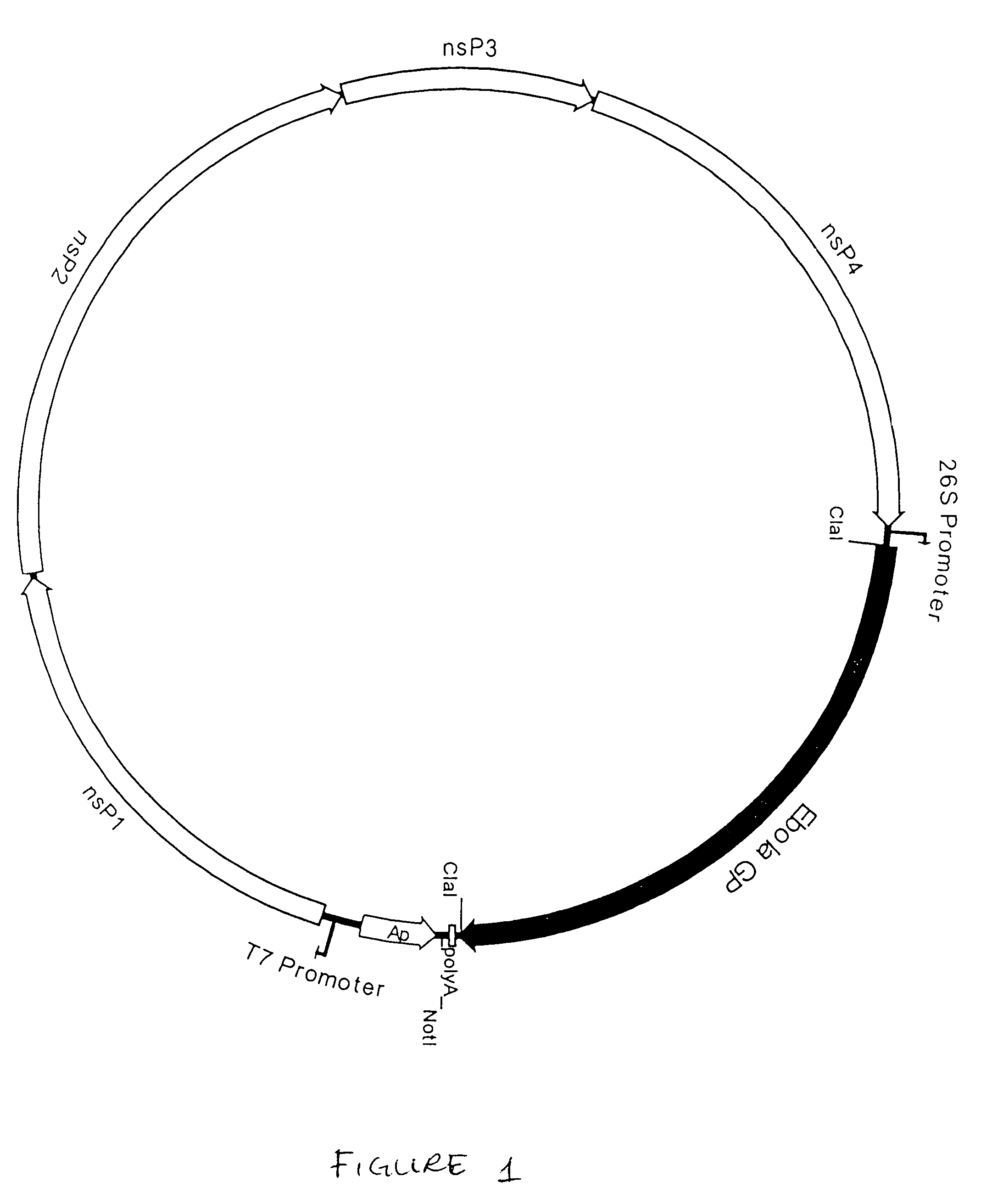
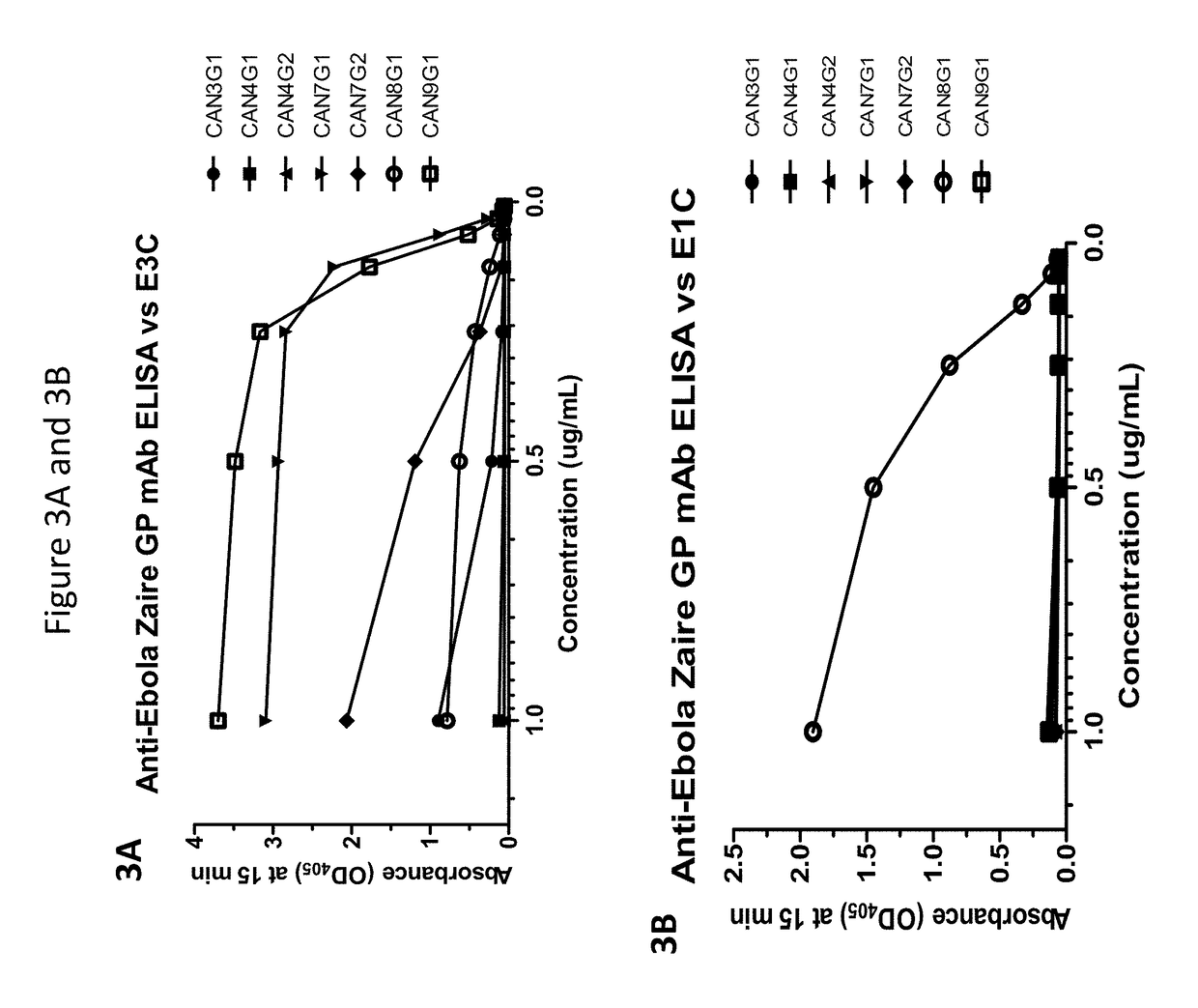
Monoclonal antibodies and complementarity-determining regions binding to Ebola glycoprotein
InactiveUS7335356B2Animal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitopeComplementarity determining region
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Multivalent meningococcal derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates and vaccine
InactiveUS20070065462A1IndiciaAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseGlycoprotein binding
The present invention describes derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates, a composition comprising one or more of such derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates and methods of immunizing human patients with the same. The derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates are purified capsular polysaccharides from Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, W-135, and Y, derivatized chemically activated and selectively attached to a carrier protein by means of a covalent chemical bond, forming polysaccharide-protein conjugates capable of eliciting long-lasting immunity to a variety of N. meningitidis strains.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR INC
Nanoparticles for controlling bleeding and drug delivery
InactiveUS20140242180A1Shorten bleeding timeEffective amountPowder deliveryTetrapeptide ingredientsNanoparticleWater soluble
A temperature stable nanoparticle is provided comprising a core, a water soluble polymer and a peptide, the water soluble polymer attached to the core at a first terminus of the water soluble polymer, the peptide attached to a second terminus of the water soluble polymer, the peptide comprising an RGD amino acid sequence, the water soluble polymer of having sufficient length to allow binding of the peptide to glycoprotein lib / Ilia (GPIIb / llla). In one aspect, the nanoparticle has a melting temperature over 35° C. In various aspects, the nanoparticle has a spheroid shape and a diameter of less than 1 micron.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Anti-tumor prodrug with P-glycoprotein inhibition function and preparation method
ActiveCN108245683AImprove solubilityAvoid effluxOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolyethylene glycolTumor cells
The invention discloses an anti-tumor prodrug with a P-glycoprotein inhibition function and a preparation method. The prodrug comprises a part formed by covalently connecting an anti-tumor drug and polyethylene glycol vitamin E succinate through a connecting arm, wherein the connecting arm comprises a sensitive bond; the sensitive bond is a chemical bond which is broken in an oxidization or reduction environment. The free polyethylene glycol vitamin E succinate and the active anti-tumor drug are dissociated; the polyethylene glycol vitamin E succinate is combined with P-glycoprotein; the expression of a P-glycoprotein efflux pump is inhibited, the activity of the P-glycoprotein is inhibited, the excretion of the anti-tumor drug is reduced and the intracellular concentration of the drug isimproved, so that the multi-drug drug resisting property of tumor cells is inhibited, the intracellular concentration of the active anti-tumor drug is greatly improved and a remarkable anti-tumor effect is obtained. The released active drug can be combined with a specific target spot in the cells and the growth of the tumor cells is inhibited.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for reducing sialic acid loss in bird's nest treatment process
InactiveCN110140955ARetention contentGreat tasteFood preservationFood dryingIce waterGlycoprotein binding
The invention discloses a method for reducing sialic acid loss in a bird's nest treatment process, and belongs to the field of health-care foods. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, steaming bird's nest to be treated by steam; then, soaking the steamed bird's nest by using an ice water mixture for a set time; and then, carrying out feather picking treatment on the soaked bird's nestto obtain a finished product. According to the invention, the bird's nest protein is denatured by high-temperature denaturation before feather picking, so that sialic acid combined with the protein in the bird's nest is retained. The sialic acid in the bird's nest does not exist in a monomer form and is combined with the glycoprotein in the bird's nest. When the protein is not easy to dissolve inwater after being denatured, the sialic acid in the bird's nest is not easy to dissolve in water, so that the content of the sialic acid is retained in the wet picking process. Therefore, the sialicacid in the bird's nest is completely retained in the feather picking treatment and the later product processing.
Owner:华东川峰(厦门)生物科技有限公司
Multivalent meningococcal derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates and vaccine
InactiveUS20060088554A1IndiciaAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseGlycoprotein binding
The present invention describes derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates, a composition comprising one or more of such derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates and methods of immunizing human patients with the same. The derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates are purified capsular polysaccharides from Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, W-135, and Y, derivatized chemically activated and selectively attached to a carrier protein by means of a covalent chemical bond, forming polysaccharide-protein conjugates capable of eliciting long-lasting immunity to a variety of N. meningitidis strains.
Owner:SANOFI PASTCUR
Gene clone of and expression Japan lamprey oral cavity gland KGD model protein possessing anti thrombotic action
A gene clone and expression of the oral gland KGD pattern protein of Japanese lamprey with anti-thrombosis is disclosed. Its cDNA sequence and clone, its relative protein sequence, its expression in colibacillus and Piohia yeast, its combination with the glucoprotein gpó�b / IIIa on cell membrane of platelet to suppress the platelet coagulation, and its application in developing the anti-thrombosis medicines are disclosed.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
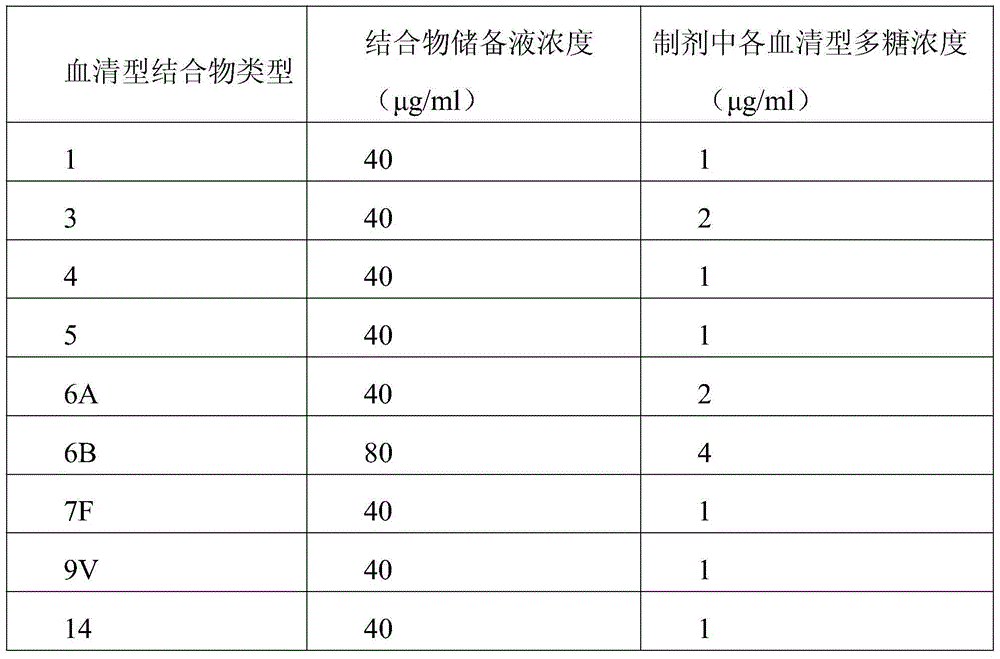
Prescription and preparation method of multi-valent pneumococcal conjugate combined vaccine
InactiveCN108245674AHigh titerNo immune interferenceAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPneumococcal serotypesCoccidia
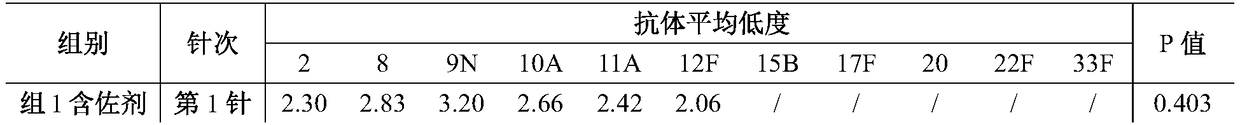
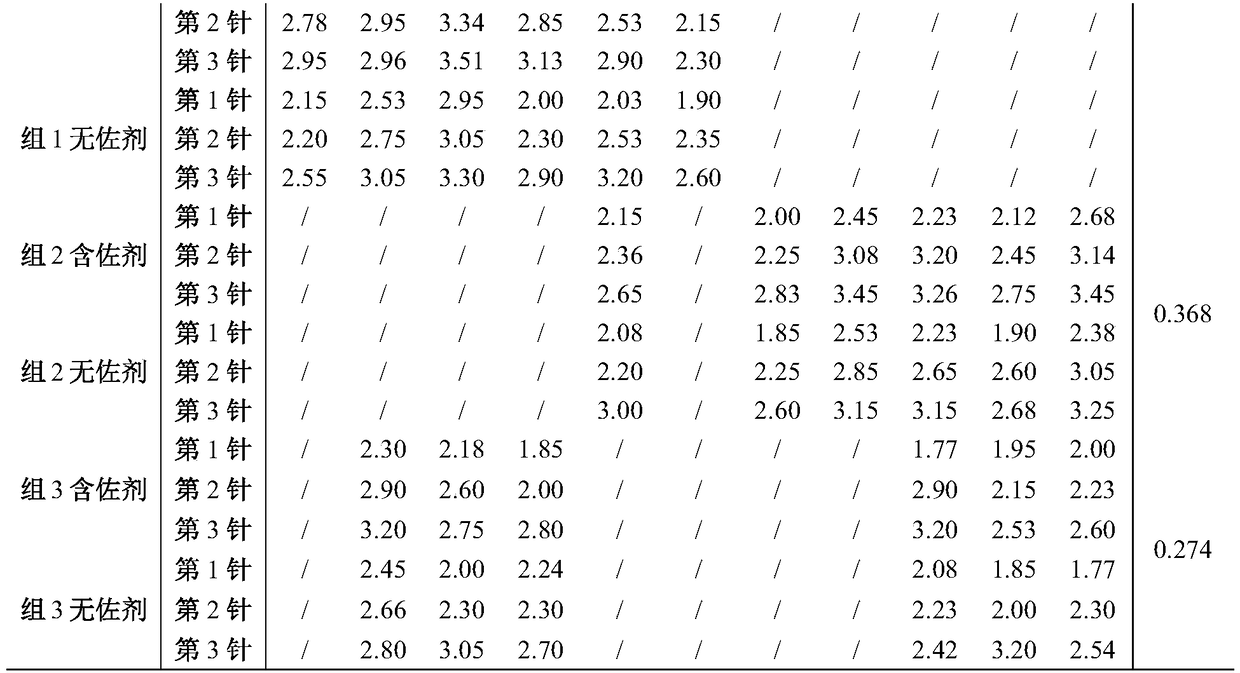
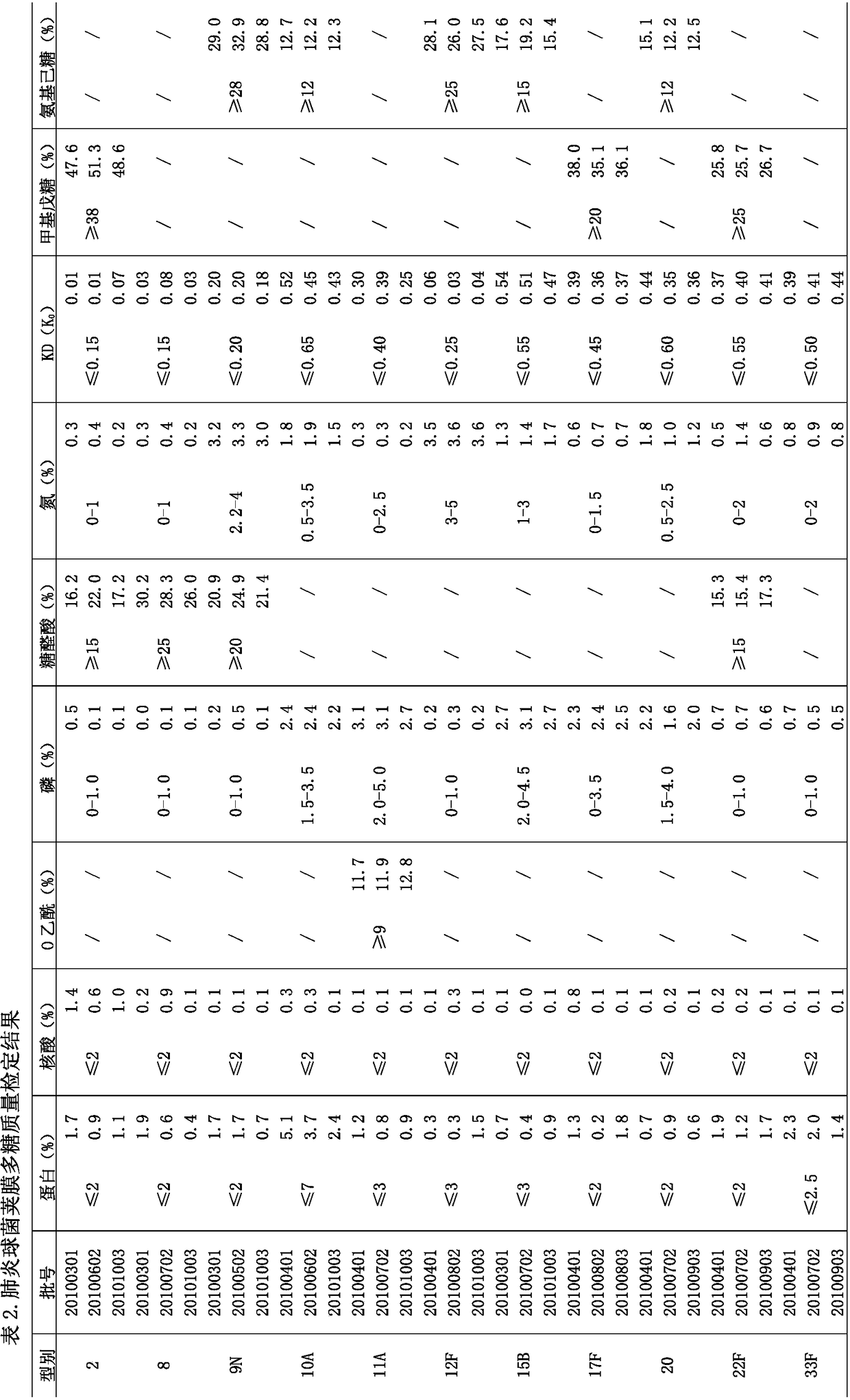
The invention relates to a prescription and a preparation method of a multi-valent pneumococcal conjugate combined vaccine. The combined vaccine is prepared by pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides selecting from pneumococcal serotypes 2, 8, 9N, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B, 17F, 20, 22F and 33F and biologically-acceptable carrier proteins. The prescription and the preparation method provided by the invention have the benefits that a polysaccharide protein conjugate stock solution is prepared by selecting a binding method suitable for the different types of pneumococcal polysaccharides, and the different types of pneumococcal polysaccharides are combined to prepare the vaccine. The combined vaccine is used for preventing infectious diseases caused by unlisted pneumococcal polysaccharide protein-binding vaccine serotype pneumococci.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIFEI LVZHU BIOPHARM +2
Absorbable haemostatic material prepared based on rat tail collagen and preparation method of same
InactiveCN102526796AIncrease productivityAvoid rising costsPeptide/protein ingredientsAerosol deliveryPolyvinyl alcoholFreeze-drying
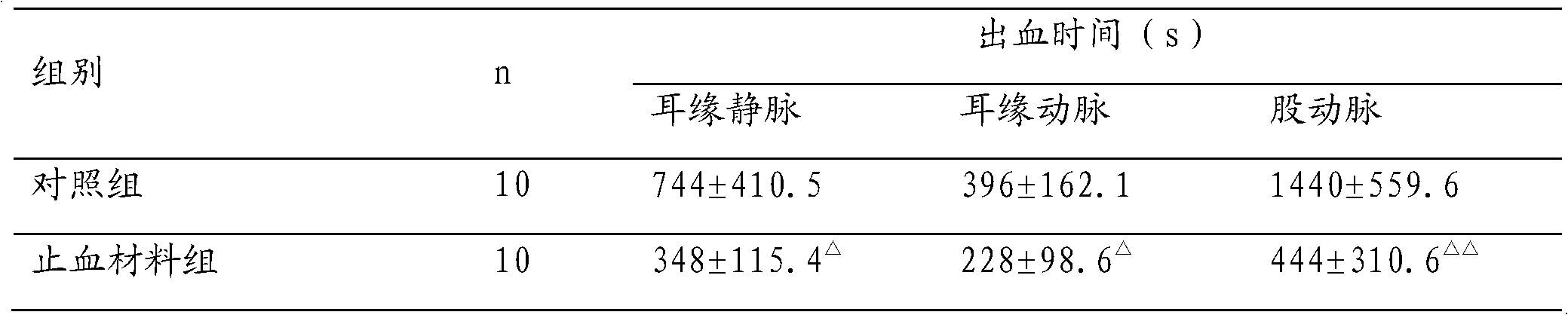
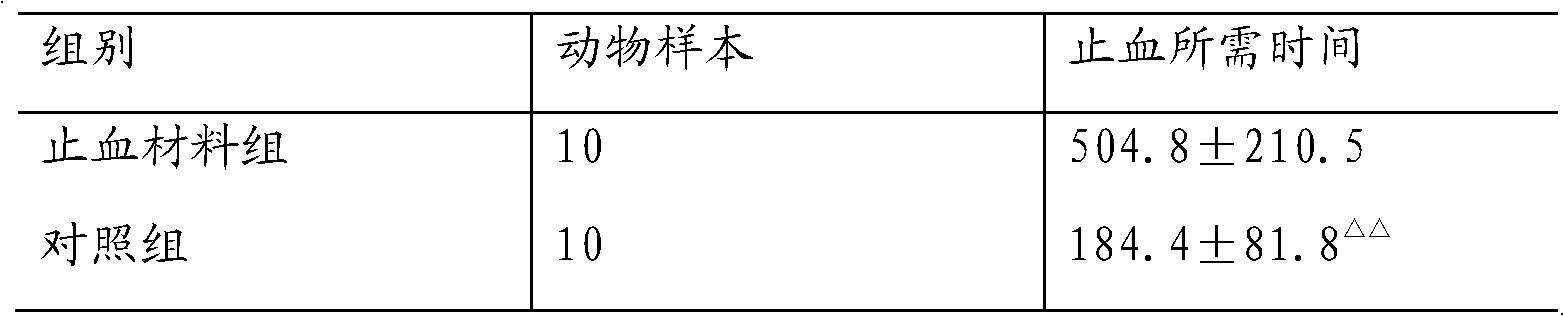
The invention relates to an absorbable haemostatic material prepared based on rat tail collagen and a preparation method of the absorbable haemostatic material. The absorbable haemostatic material is prepared from the rat tail collagen, polyvinyl alcohol and chitosan with respective weight percentages of 1%-10%, 0.2%-5% and 0.2%-2%, and the balance of water by a freeze-drying technology. The haemostatic material of the invention is mainly prepared with the rat tail collagen; compared with disadvantages that the conventional haemostatic material is unabsorbable, body allergy is easily caused, the haemostatic effect is poor, and the like, the haemostatic material prepared by the invention is absorbable in a human body, good in biocompatibility, quick in hemostasis and strong in hydrophilia; platelet aggregation can be activated to form a thrombus, thereby promoting the plasma agglomeration and stopping blood flowing; and a specific region on the surface of the collagen can be bound with glycoprotein similar to fibronectin on the surface of a cell, so that the haemostatic material has a function of preventing intestinal adhesion.
Owner:广东省医学实验动物中心
Method for improving immunogenicity of 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide-protein conjugate
ActiveCN104107428AImproving immunogenicityEffective stimulationAntibacterial agentsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsGlycoprotein bindingSerotype
The invention discloses a method for improving immunogenicity of a 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide-protein conjugate. The method comprises the following steps of 1, adding ISQAVHAAHAEINEAGR OVAp into CRM197A and producing OVAp-containing CRM197A protein carrier (OVApCRM197A), and 2, connecting 13 different serotypes of polysaccharides to the OVApCRM197A by a covalent bond so that a 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide-OVApCRM197A conjugate is obtained. Compared with a 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide-CRM197A conjugate prepared from corresponding OVAp-less CRM197A, the 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide-OVApCRM197A conjugate improves immunogenicity by 3-5 times.
Owner:KANVAX BIOPHARM
Muc16 monoclonal antibody and uses thereof
ActiveUS20210101994A1Improve heat resistanceIncrease resistanceOrganic active ingredientsBiological material analysisAntigenComplementarity determining region
The present document describes an antibody or an antigen-binding fragment that bind to O-glycan mucin-type glycoprotein MUC16 comprising three variable heavy domain complementarity determining regions (CDR)(CDR H1, H2 and H3), and three variable lighy domain CDR (CDR L1, L2 and L3). The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions, nucleic acid vectors, cells comprising the nucleic acid vectors, and methods of inhibiting tumor growth of a tumor expressing O-glycan mucin-type glycoprotein MUC16.
Owner:QUEST PHARMATECH INC
Preparation method of type B haemophilus influenzae capsular polysaccharide and combined vaccine
InactiveCN105646726AHigh purityLess impuritiesAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseTetanus toxoids
The invention discloses a preparation method of a type B haemophilus influenzae capsular polysaccharide. The preparation method comprises the steps of fermentation culture, sterilization and precipitation, polysaccharide extraction and purification, polysaccharide derivatization and polysaccharide protein conjugate preparation. The invention further discloses a multivalent combined vaccine which is prepared through the steps that an acellular pertussis stock solution, refined diphtheria toxoid and refined tetanus toxoid are added into aluminum hydroxide to be adsorbed and then added into a type B haemophilus influenzae capsular polysaccharide stock solution, and the mixed solution is diluted with normal saline. According to the preparation method, the prior art is optimized, and the high-purity low-impurity-content type B haemophilus influenzae capsular polysaccharide can be obtained; meanwhile, the type B haemophilus influenzae capsular polysaccharide is combined with multiple component vaccines to form the multivalent vaccine, the multivalent vaccine can be immune to multiple diseases simultaneously, the inoculating times are decreased, the medical risk is reduced, and the better immune effect can be obtained through one-time inoculating.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHUA BIOLOGICAL PROD
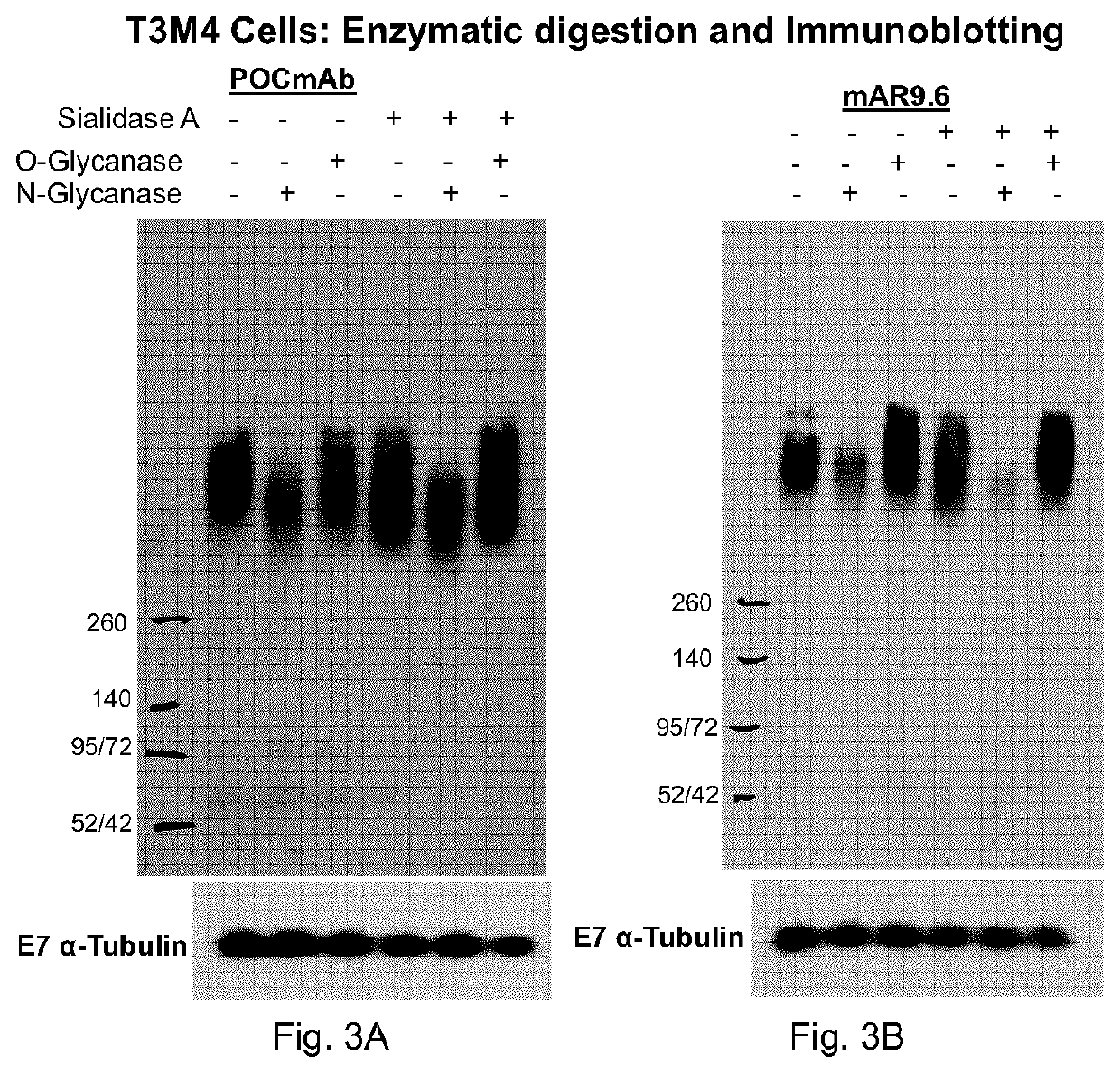
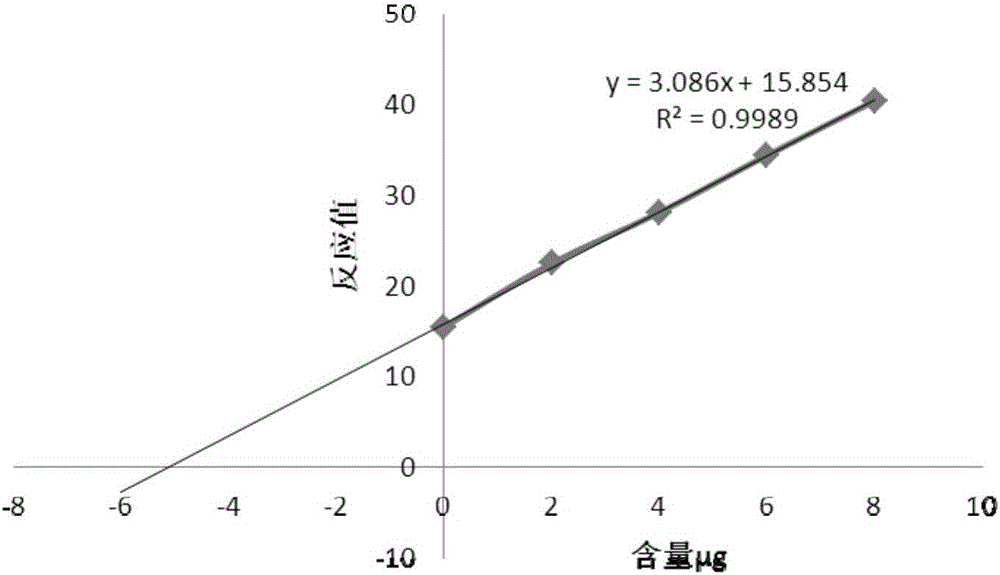
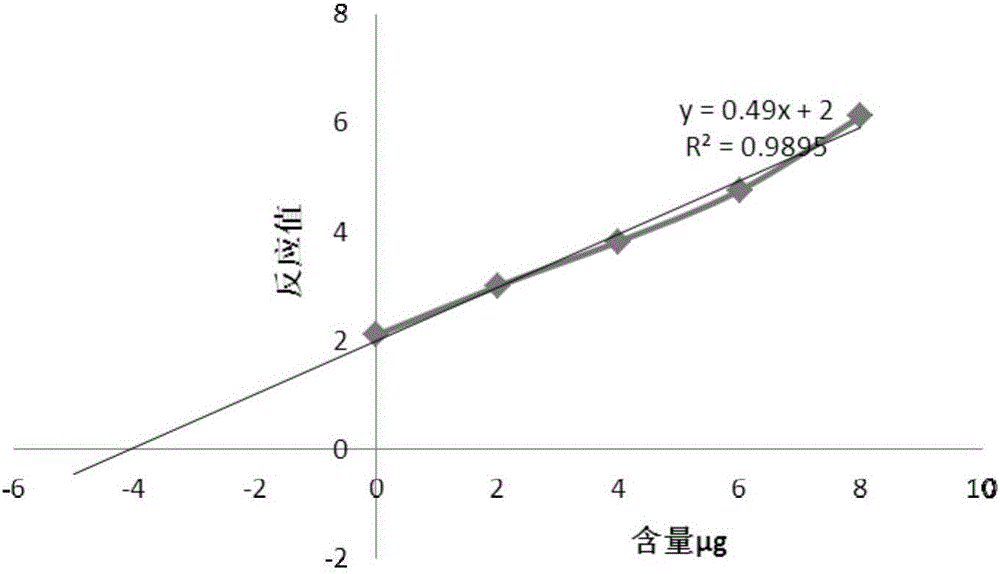
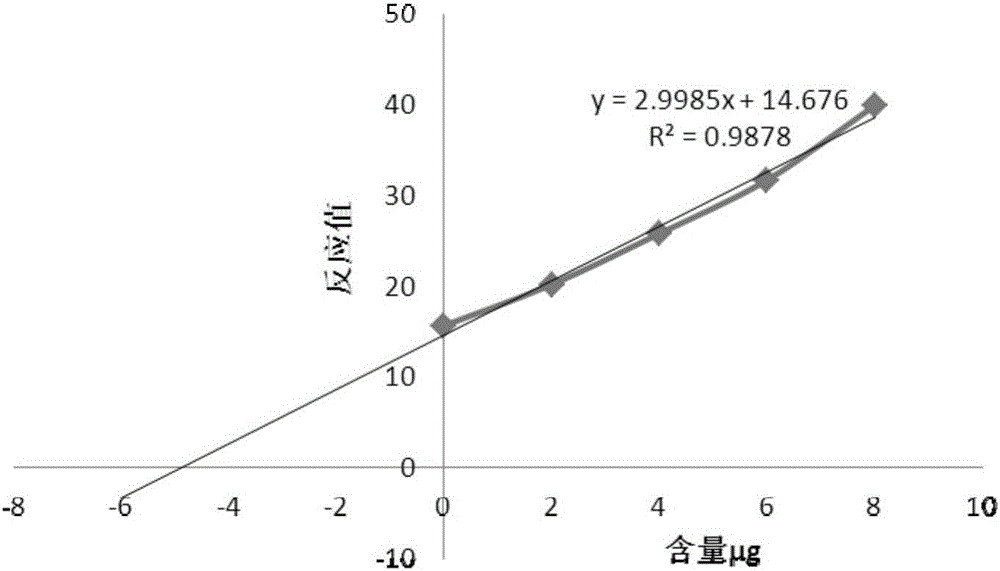
Method for detecting contents of various types of specific sugar in polyvalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
ActiveCN106018832AImprove signal-to-noise ratioLower background requirementsScattering properties measurementsBiological testingGlycoprotein bindingDesorption
The invention relates to a method for detecting the contents of various types of specific sugar in polyvalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. The method comprises the following steps: step I: preparing solutions of certain concentrations from various types of monovalent capsular polysaccharide-protein conjugates according to sugar concentrations; step II: taking several parts of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, adding the conjugate solutions obtained in the first step into the parts of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine except the first part, and diluting all the samples with a solvent to the same volume, wherein the volumes of the conjugate solutions added into the parts of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine increase from the second art to the last part in sequence; step III: adding alkali into each sample for desorption, and then adding acid for neutralization to obtain standards; step IV: carrying out reactions between the standards and a detection reagent, and drawing a standard curve by taking the sugar contents of the conjugate solutions as horizontal coordinates and taking reacting values as vertical coordinates; step V: pushing the standard curve outwards to the content axis, and taking the intercepts on the content axis as the sugar contents of monovalent capsular polysaccharide-protein conjugates in the polyvalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIFEI LVZHU BIOPHARM +2
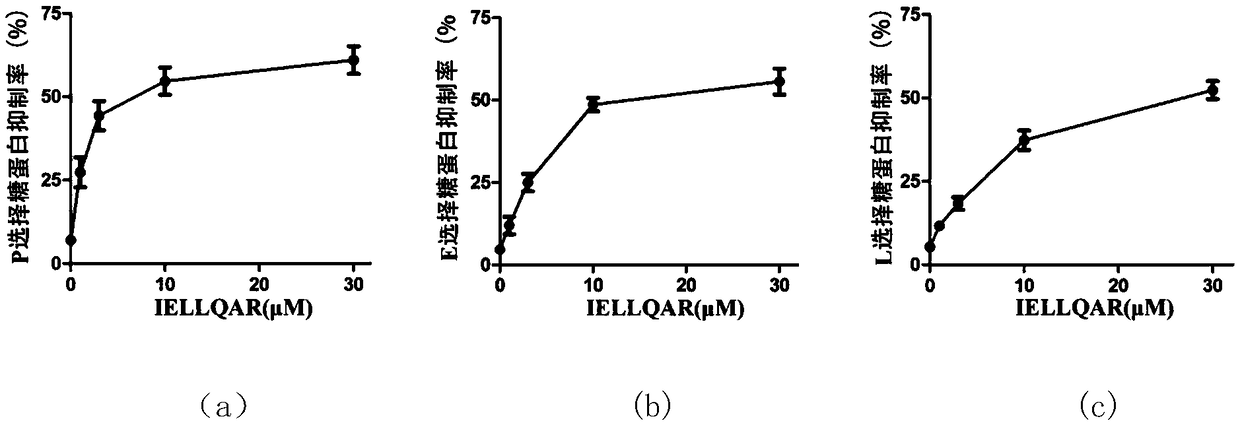
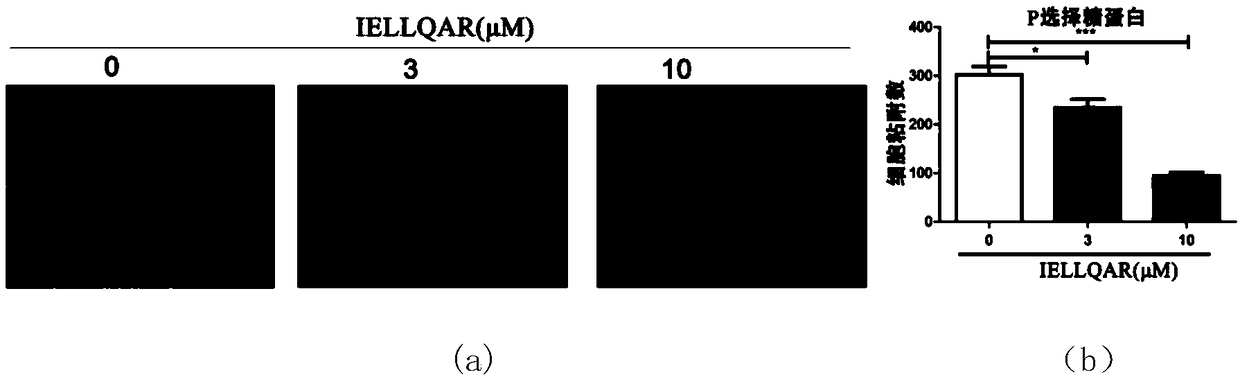
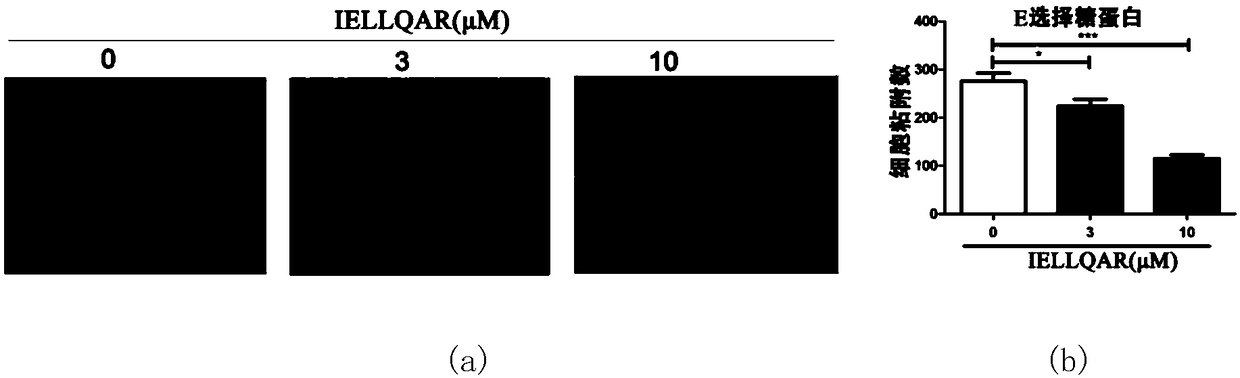
Application of IELLQAR as medicine for preventing and treating atherosclerosis diseases
ActiveCN109106940ADelay progressReduce infiltrationPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderInflammatory factorsAtheroma
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF DALIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Multivalent meningococcal derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates and vaccine
The present invention describes derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates, a composition comprising one or more of such derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates and methods of immunizing human patients with the same. The derivatized polysaccharide-protein conjugates are purified capsular polysaccharides from Nesseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, W-135, and / or Y, derivatized chemically activated and selectively attached to a carrier protein by means of a covalent chemical bond, forming polysaccharide-protein conjugates capable of eliciting long-lasting immunity to a variety of N. meningitidis strains.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR INC
Method for determining binding rate of proteoglycan protein binding site in proteoglycan protein binding vaccine
The invention discloses a method for determining a binding rate of a proteoglycan protein binding site in a proteoglycan protein conjugate vaccine. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out enzymolysis on a standard substance; (2) carrying out solid-phase extraction to enrich a target peptide fragment; (3) performing high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry analysis; (4) drawing a standard curve to obtain a standard working curve equation; (5) detecting a sample, and calculating to obtain the concentration of each characteristic peptide fragment in the sample; and (6) calculating a proteoglycan binding rate of each characteristic peptide fragment and a protein residue rate of each site. According to the method, the multi-site quantitative monitoring of the proteoglycan protein binding rate of the proteoglycan protein conjugate vaccine is achieved, the tetanus protein relates to 20 monitoring sites, and the CRM197 relates to 16 monitoring sites; the method not only can detect the residual protein content, but further can evaluate the binding rate of the proteoglycan protein binding site of the proteoglycan protein conjugate vaccine, can beused for researching polysaccharide or proteoglycan protein conjugate vaccines with the same protein residual rate but different activity and toxicity, and can provide a direct monitoring method for improving a proteoglycan protein binding process.
Owner:SHIMADZU (CHINA) CO LTD +1
Sialic acid extracting equipment
ActiveCN108970167AAffect qualityIncrease productionSolid solvent extractionGlycoprotein bindingSialic acid
The invention relates to sialic acid extracting equipment, which comprises a main body and a material inlet, wherein a debris removing mechanism and an extracting mechanism are arranged in the main body; the debris removing mechanism comprises a dissolving unit, a scraping unit and a filtering unit; the dissolving unit comprises a motor, a debris removing box and a plurality of paddles; the filtering unit comprises a falling pipe, a first valve, a second valve, a material inlet pipe, a filter net and a telescopic assembly; the extracting mechanism comprises an extracting box, a storage box anda pressurizing unit; the pressurizing unit comprises a power assembly, a push plate, a compression pipe, a third valve and a fourth valve. Through the debris removing mechanism, the sialic acid extracting equipment can clear away a large amount of debris in a cubilose raw material and prevent the debris from affecting the quality of extracted sialic acid or blocking a pipeline in the extracting equipment; furthermore, the extracting mechanism can hydrolyze cubilose glycoprotein in a pressurized high-temperature stewing manner to allow sialic acid combined with the cubilose glycoprotein to beconverted into free sialic acid.
Owner:一燕生(福建)生物工程有限公司
Combinations of receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an a1-acidic glycoprotein binding compound
This invention relates to combinations of an abl-, PDGF-Receptor- and / or Kit receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an organic compound capable of binding to α1-acidic glycoprotein (AGP), as well as to pharmaceutical preparations and / or therapies, in relation to disease states which respond to inhibition of abl-, PDGF-Receptor- and / or Kit-receptor tyrosine kinase. In particular, the invention relates to products or combinations comprising an abl-, PDGF-Receptor- and / or Kit receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an organic compound capable of binding to AGP, either in fixed combination or for chronologically staggered or simultaneous administration, and the combined use of both classes of compounds, either in fixed combination or for chronologically staggered or simultaneous administration, for the treatment of proliferative diseases, especially tumor diseases, especially those that can be treated by inhibition of abl-, PDGF-Receptor- and / or Kit receptor-tyrosine kinase activity.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
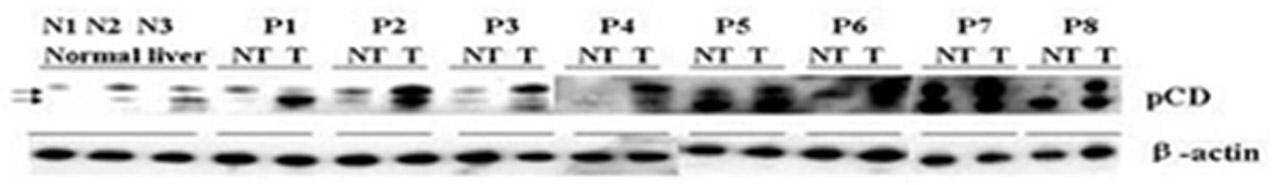
Cathepsin D proenzyme ConA-pCD specifically combined with concanavalin A in serum and application thereof
The invention relates to a cathepsin D proenzyme ConA-pCD specifically combined with concanavalin A in serum and application thereof. The ConA-pCD is prepared by the following method: (1) preparing a concanavalin A affinity chromatography column for standby; (2) taking serum, centrifuging, taking a supernatant and adding glycoprotein bind buffer to reach a final volume of 0.5-5 ml; transferring the mixture into the prepared concanavalin A affinity chromatography column, incubating at room temperature for at least 2 h in a rotating shaking table; centrifuging, abandoning an effluent and adding a glycoprotein bind buffer containing methyl-alpha-D mannopyranoside; incubating in a rotating shaking table, centrifuging and collecting an eluate; and (3) adding acetone into the eluate to reach a concentration of 80%, staying overnight at -20 DEG C, abandoning a supernatant, drying at room temperature and dissolving by a protein lysate, so as to detect ConA-pCD. Results confirm that serum ConA-pCD is a potential and novel serum marker, with clinic application prospect, for diagnosing liver cancer.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
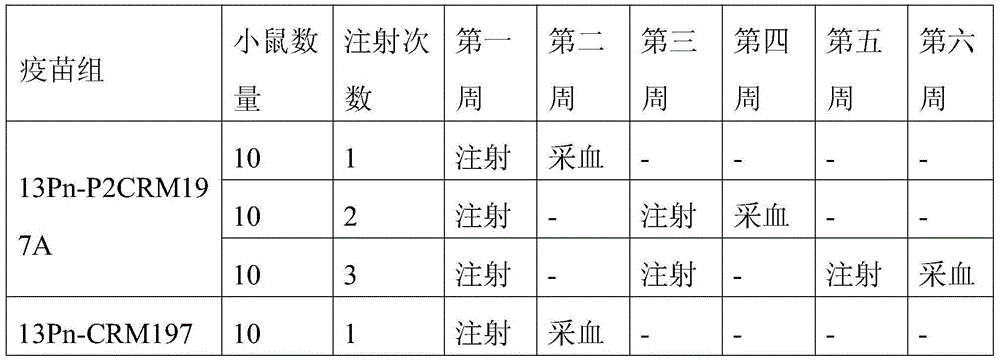
Method for enhancing 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide protein bonder immunogenicity
ActiveCN104096225AImproving immunogenicityEffective stimulationAntibacterial agentsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsEpitopeGlycoprotein binding
The invention discloses a method for enhancing 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide protein bonder immunogenicity, and the method is as follows: adding all-powerful epitope peptide (P2) into CRM197A (A chain of diphtheria toxin variant 197), using genetic recombinant Escherichia coli to produce a P2-containing protein carrier P2CRM197A of the A chain of the diphtheria toxin variant 197 (CRM197); and connecting 13 different serotype polysaccharides with the P2-containing protein carrier P2CRM197A by covalent bonds to form a 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide-P2CRM197A bonder; compared with a 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide-CRM197A bonder obtained by a corresponding protein carrier CRM197A which does not contain the all-powerful epitope peptide (P2), the immunogenicity of the 13-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide-P2CRM197A bonder obtained by the method is increased by 3-5 times than that of a contrast.
Owner:KANVAX BIOPHARM
Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for synthesizing glycoprotein conjugate vaccines for neonatal meningitis escherichia coli and application
ActiveCN108774628AImproving immunogenicityStrong specificityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliAntigen
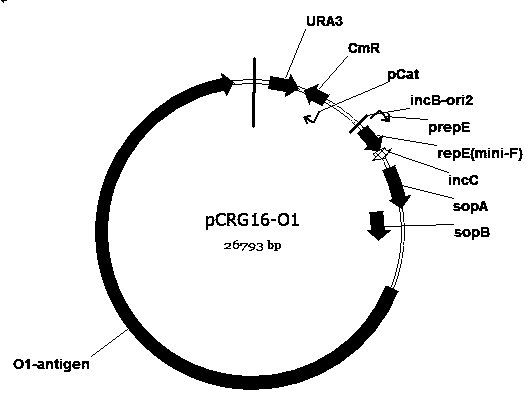
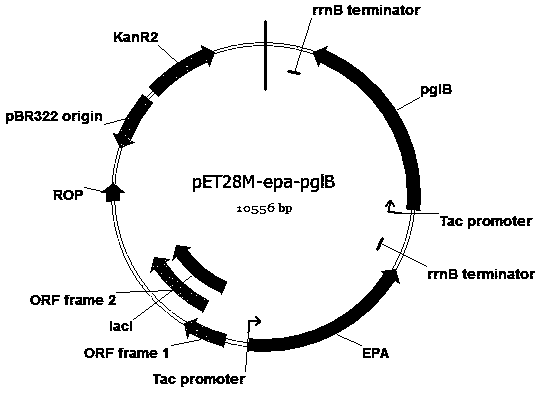
The invention discloses an escherichia coli engineering bacterium for synthesizing glycoprotein conjugate vaccines for neonatal meningitis escherichia coli and application, and relates to a method forconstructing a cell factory for synthesizing O1 serum type glycoprotein conjugate vaccines for neonatal meningitis escherichia coli. O1 antigens are constructed based on a DNA Assembler method by utilizing efficient homologous recombination efficiency of saccharomyces cerevisiae so as to synthesize gene cluster plasmids; the O1 antigens are converted in escherichia coli JM109 to synthesize gene cluster shuttle plasmids, and the plasmids are identified by virtue of lipopolysaccharide extraction, gel electrophoresis and silver staining; waaL and wecA in the JM109 are deleted with the aid of FLP-FRT so as to eliminate the interference of original incomplete O antigens; and pET28a(+) plasmids are reconstructed and induced to synthesize the glycoprotein conjugate vaccines, the glycoprotein ispurified by virtue of an AKTA Primeplus protein purification workstation, and the glycoprotein is identified by virtue of western-blotting. The constructed recombinant escherichia coli provides a novel idea for synthesizing the glycoprotein conjugate vaccines by a biological method.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Electrochemical aptamer detection method of glycoprotein
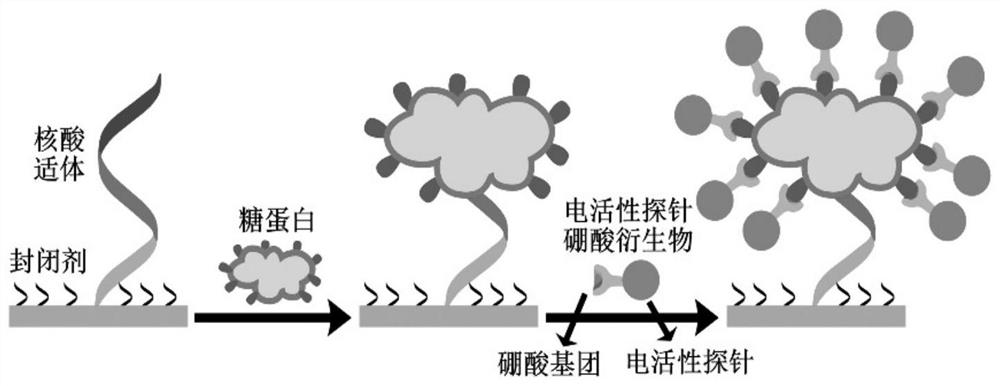
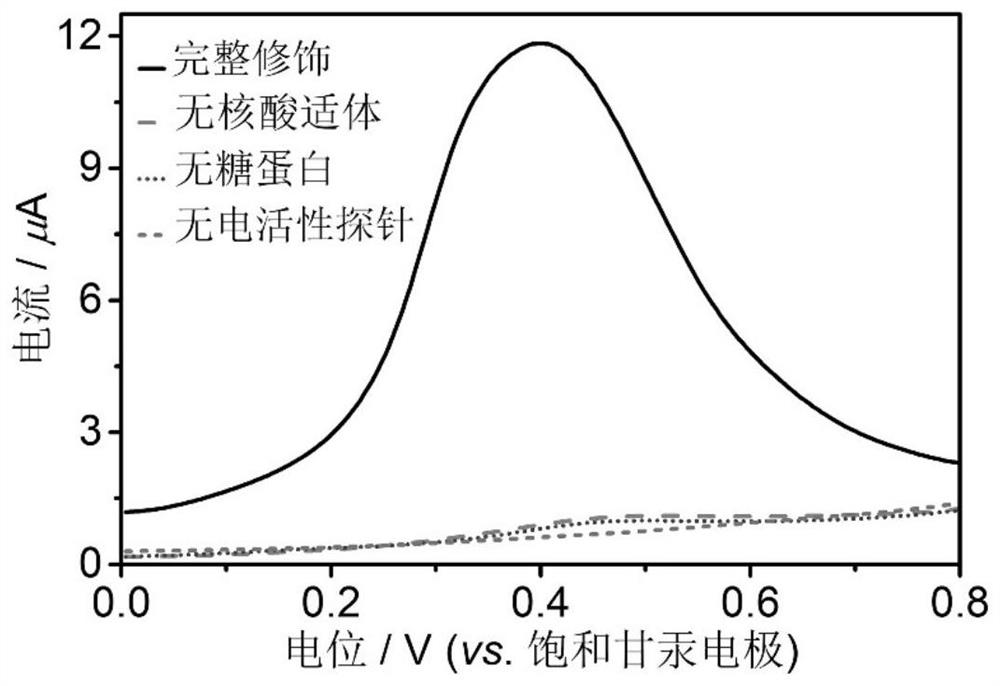
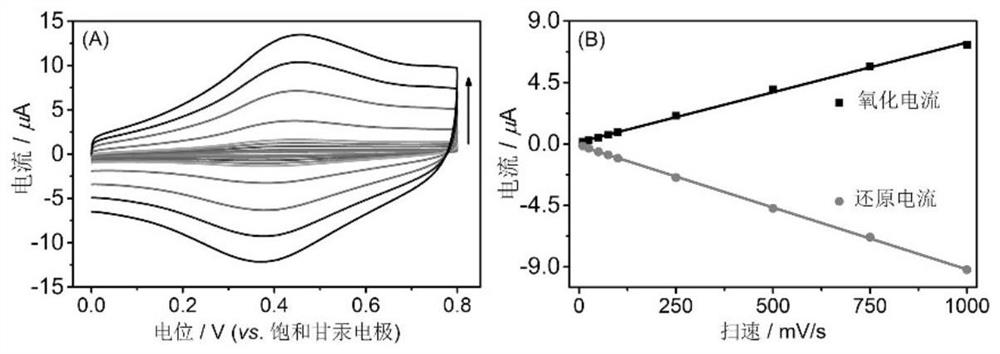
PendingCN114720527ASimple and fast operationLow costAssay labelsMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerGlycoprotein binding
The invention relates to the technical field of electrochemistry, in particular to an electrochemical aptamer detection method of glycoprotein, which comprises the following steps: immobilizing a nucleic acid aptamer for specific recognition and capture of glycoprotein, adding a boric acid derivative of an electroactive probe after the nucleic acid aptamer is combined with target glycoprotein, quantitative analysis of the content of the target glycoprotein can be realized by measuring an oxidation-reduction signal of the electroactive probe. According to the electrochemical aptamer detection method of the glycoprotein, the electroactive probe site is labeled on the glycoprotein captured by the aptamer in a targeting manner by virtue of the affinity recognition interaction of the borate, and the electrochemical aptamer detection method can be used for high-sensitivity and high-selectivity electrochemical detection of other glycoproteins or sugar-containing substances only by replacing the sequence of the used aptamer; the method has the excellent characteristics of simplicity and convenience in operation, low cost, short detection time, high sensitivity, good selectivity and the like, and high-sensitivity electrochemical detection of glycoprotein can be realized without adopting an additional signal amplification strategy.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
HLA binding peptides and their uses
The present invention provides means and methods for selecting immunogenic peptides and immunogenic peptides capable of specifically binding to glycoproteins encoded by HLA alleles and inducing T cell activation in T cells restricted by the alleles combination. These peptides can be used to elicit an immune response against the desired antigen.
Owner:埃皮缪纳股份有限公司
Ebola monoclonal antibodies
InactiveUS20170183396A1Ameliorating and treating and preventing EBOV infectionHigh potencyViral antigen ingredientsBiological material analysisAntigen Binding FragmentAntigen binding
The present disclosure provides antibodies, and antigen-binding fragments thereof that bind to EBOV glycoprotein. The present disclosure further provides hybridoma cell lines and methods for making and using the compositions provided herein.
Owner:INTEGRATED BIOTHERAPEUTICS LLC
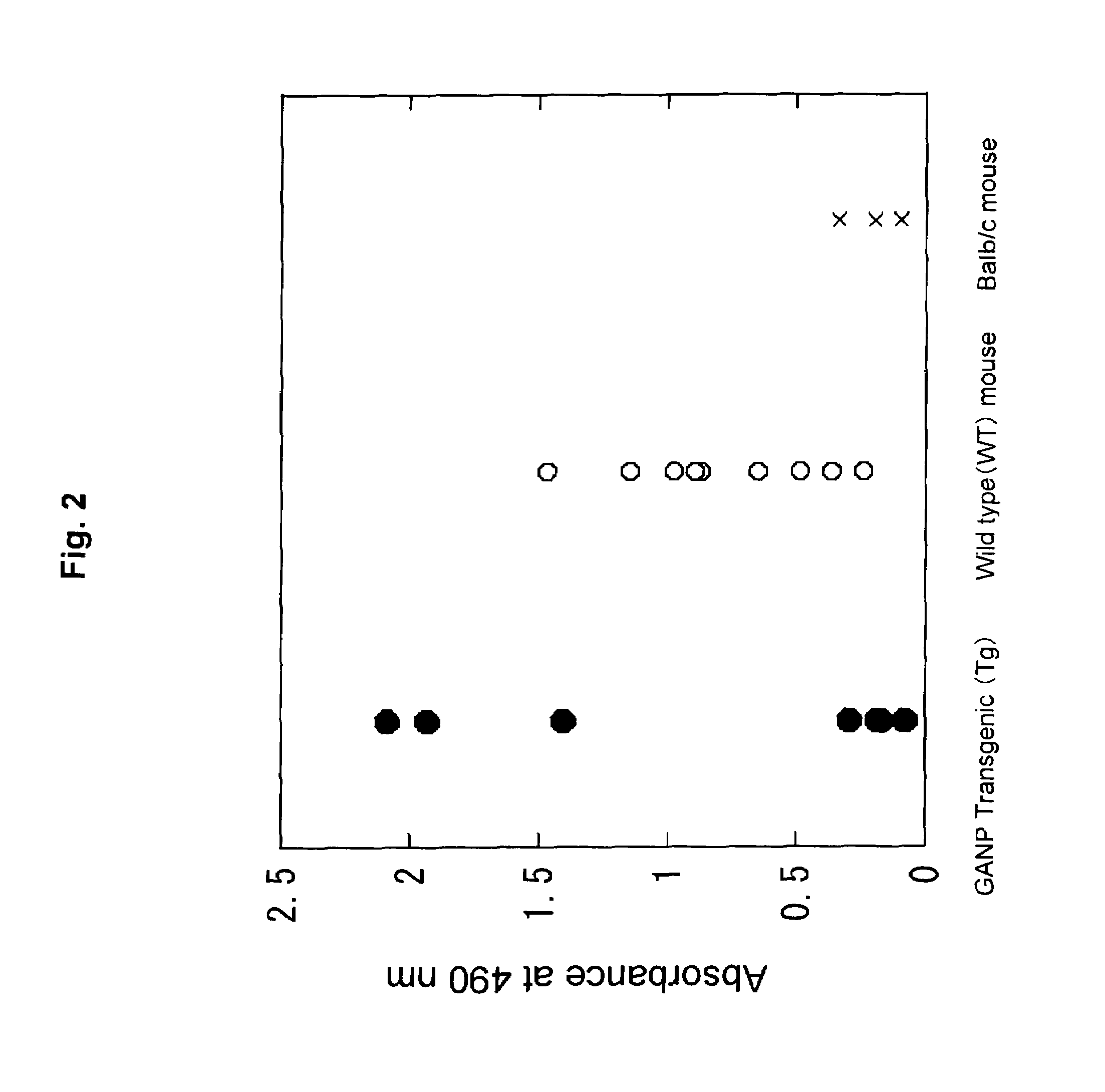
Anti-HIV antibody
The present invention aims at providing a high affinity anti-HIV antibody. According to the present invention, there are provided an antibody or a fragment thereof that binds to the gp12 glycoprotein of HIV and has a dissociation constant (KD) value of 1.0×10−9 (M) or less; a pharmaceutical composition comprising the antibody or fragment thereof; and a method of producing an anti-HIV antibody or a fragment thereof, comprising immunizing a GANP transgenic non-human mammal or a progeny thereof with a polypeptide consisting of the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 6 as an antigen and collecting the antibody from the resultant mammal or progeny.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP KUMAMOTO UNIV
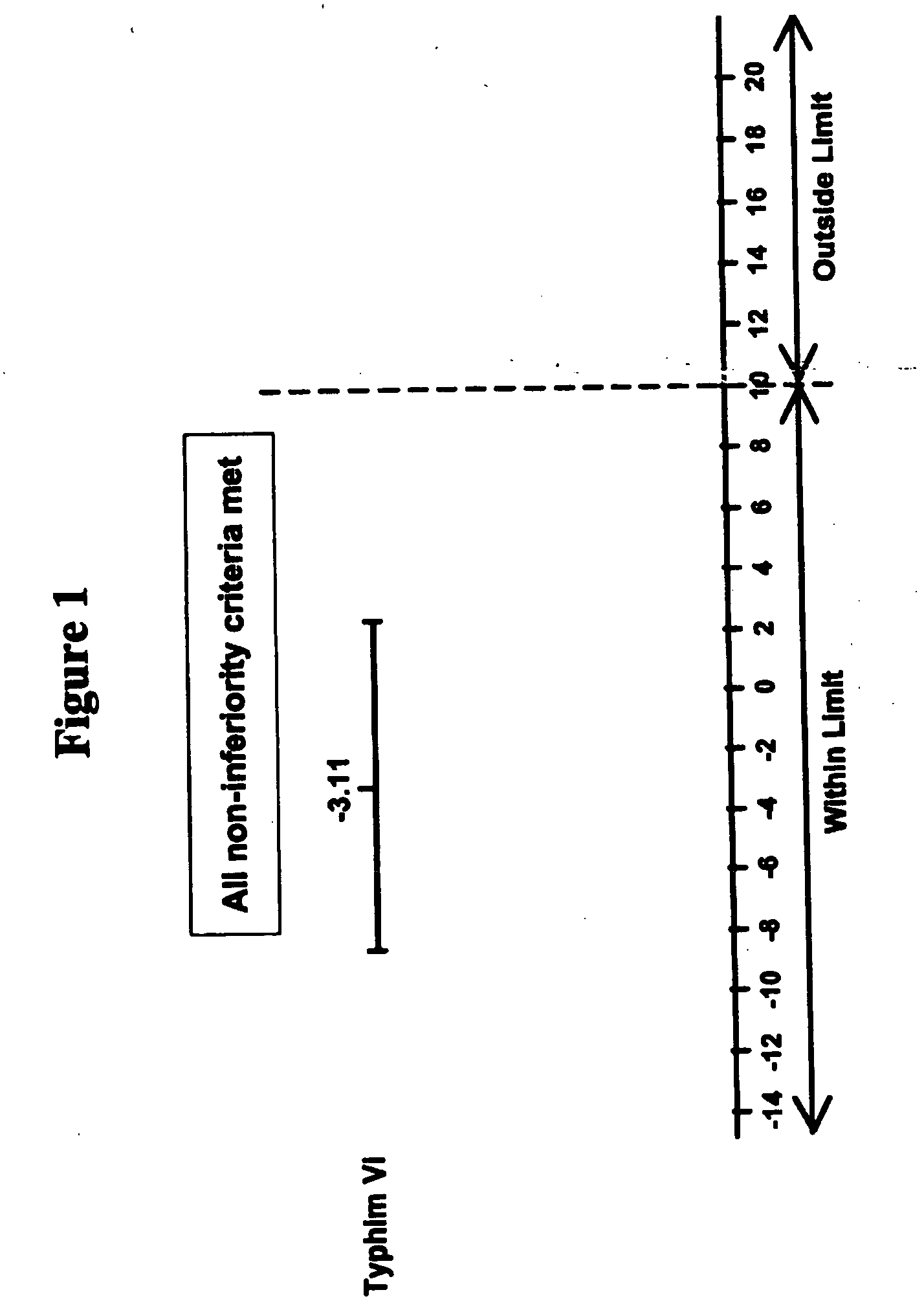
Typhoid and paratyphoid A and B polysaccharide-protein conjugated polyvalent combined vaccine
InactiveCN104587461AHigh active ingredientLarge range of protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsGenus OrthobunyavirusCarrier protein
The invention discloses a typhoid and paratyphoid A and B polysaccharide-protein conjugated polyvalent combined vaccine. The active ingredients of the vaccine include typhoid Vi polysaccharide, paratyphoid A O-SP and paratyphoid B O-SP of salmonella as well as corresponding carrier proteins to form a conjugate. The preparation of the polyvalent combined vaccine comprises preparation combination of the polysaccharide-protein conjugate of three bacteria, dosage selection and preparation of a finished product. The results of animal experiments show that the polyvalent combined vaccine, after being injected to tested animals, can promote the tested animals to generate a high-level anti-paratyphoid A and anti-paratyphoid B lipopolysaccharide antibody (Anti-LPS IgG) and an anti-typhoid Vi polysaccharide (Anti-Vi IgG), and after boosting immunization, the vaccine has immunologic memory response and immune persistence. Meanwhile, upon vaccine safety evaluation, animal abnormal toxicity test, animal allergy test and heat source detection prove the safety and the effectiveness of the polyvalent combined vaccine.
Owner:云南沃森生物技术股份有限公司
Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN103007264AHigh recovery rateImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsConjugate vaccineGlycoprotein binding
The invention relates to a haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine and application thereof. The haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine comprises a haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate, of which the pH value is 7.2 to 7.5. A TRIS-HCI buffer solution system is adopted during the process of purifying a haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide protein conjugate, so that the recovery rate of the purifying process of the polysaccharide protein conjugate is remarkably improved, the stability of the products in the subsequent process can be improved, and the pH value of the product is maintained within the neutral range so as to avoid potential change of the product quality due to change of the pH value.
Owner:BEIJING MINHAI BIOTECH
A method for enhancing the immunogenicity of a 4-valent meningococcal polysaccharide-protein conjugate
ActiveCN104096227BAntibacterial agentsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsEscherichia coliMENINGOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE
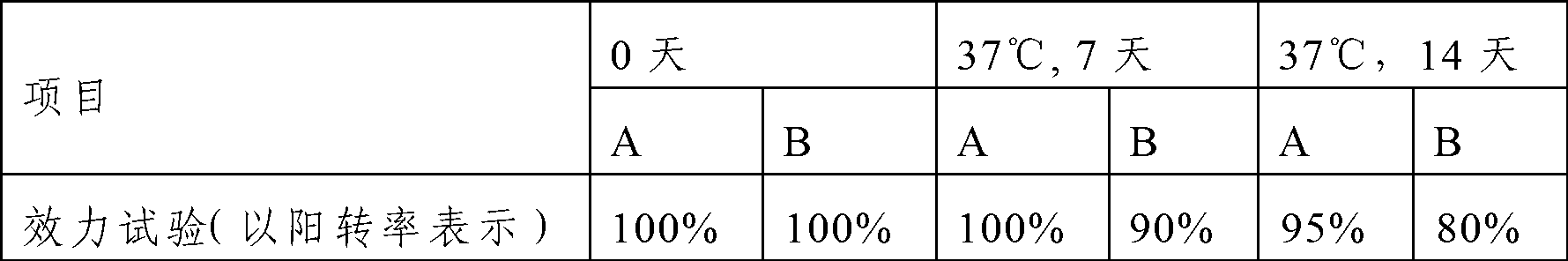
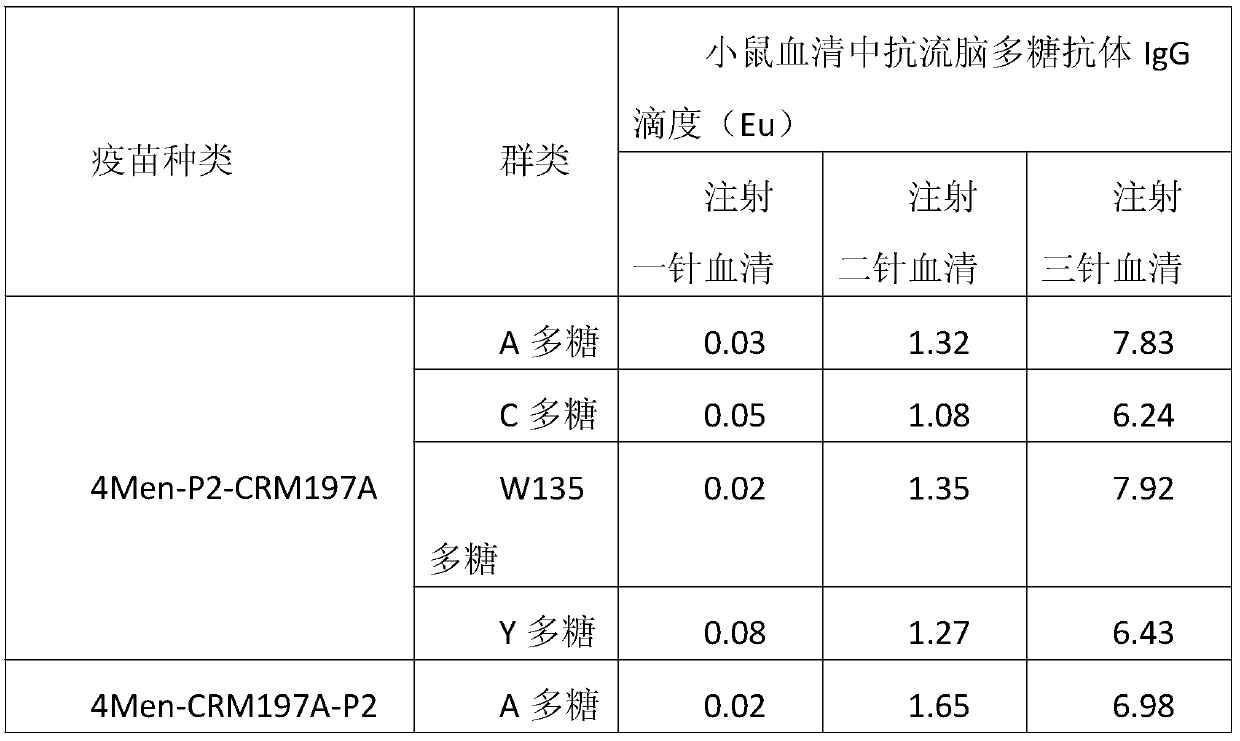
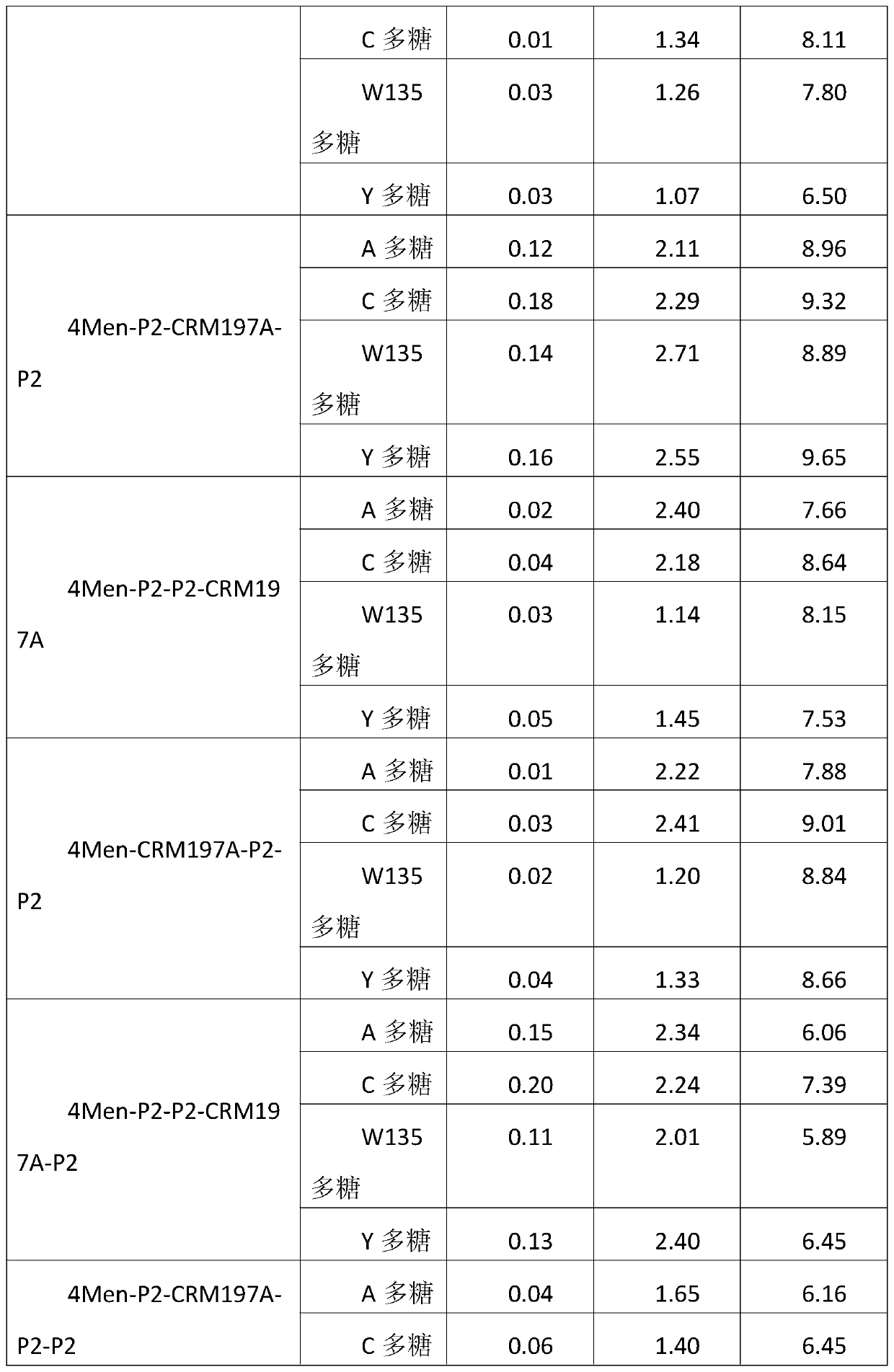
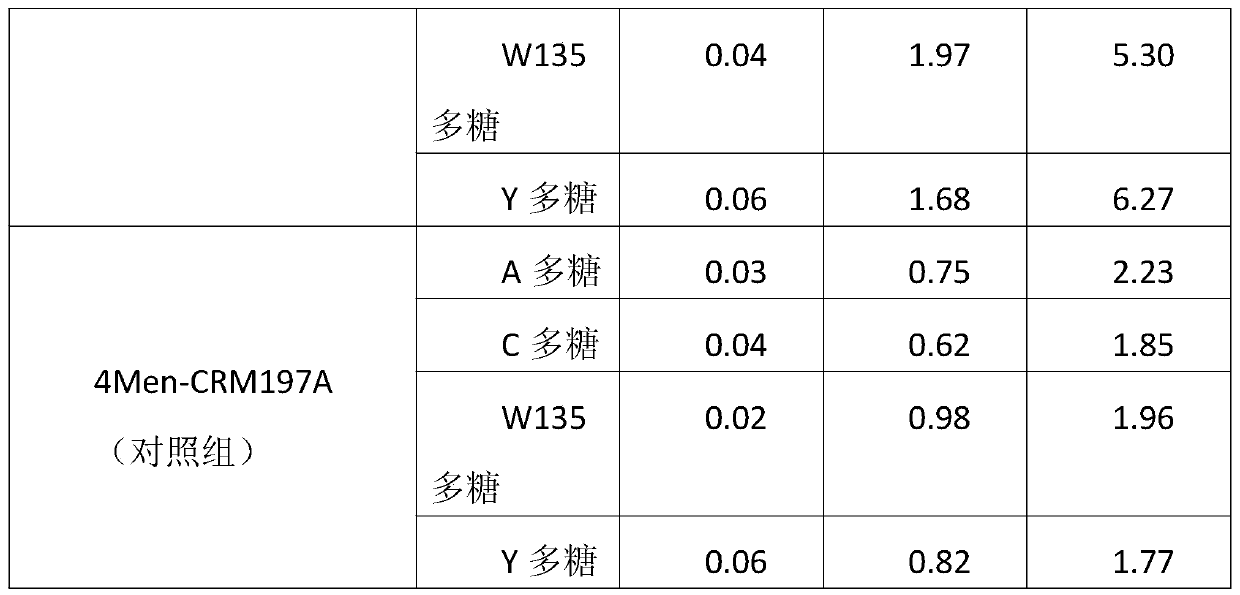
The invention discloses a method for enhancing 4-valent epidemic meningococcal polysaccharide protein bonder immunogenicity, and the method is as follows: adding all-powerful epitope peptide (P2) into CRM197A (A chain of diphtheria toxin variant 197), using genetic recombinant Escherichia coli to produce a P2-containing protein carrier P2CRM197A of the A chain of the diphtheria toxin variant 197 (CRM197); and connecting 4 different serogroups (comprising A, C, W135 and Y) capsular polysaccharides to the P2-containing protein carrier P2CRM197A by covalent bonds to form a 4-valent epidemic meningococcal polysaccharide-P2CRM197A bonder; compared with a 4-valent epidemic meningococcal polysaccharide-CRM197A bonder obtained by a corresponding protein carrier CRM197A which does not contain the all-powerful epitope peptide (P2), the immunogenicity of the 4-valent epidemic meningococcal polysaccharide-P2CRM197A bonder obtained by the method is increased by 3-5 times than that of a contrast.
Owner:KANVAX BIOPHARM
Combinations of receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with a1-acidic glycoprotein binding organic compound
This invention relates to combinations of an abl-, PDGF-Receptor-and / or Kit receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an organic compound capable of binding to alpha 1-acidic glycoprotein (AGP), as well as to pharmaceutical preparations and / or therapies, in relation to disease states which respond to inhibition of abl-, PDGF-Receptor- and / or Kit-receptor tyrosine kinase. In particular, the invention relates to products or combinations comprising and abl-, PDGF-Receptor- and / or Kit receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an organic compound capable of binding to AGP, either in fixed combination or for chronologically staggered or simultaneous administration, and the combined used of both classes of compounds, either in fixed combination or for chronologically staggered or simultaneous administration, for the treatment of proliferative diseases, especially tumor diseases, especially those that can be treated by inhibition of abl-, PDGF-Receptor- and / or Kit receptor-tyrosine kinase activity.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com