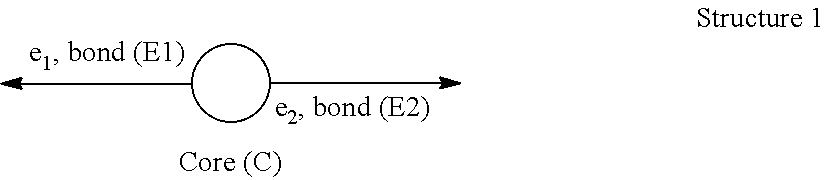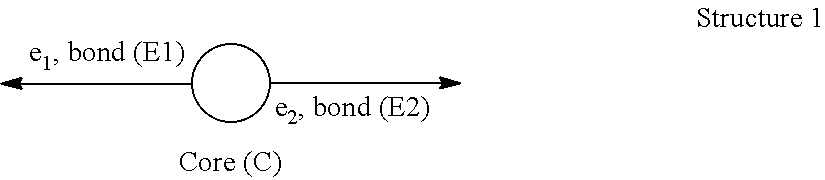Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Low foam density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for making a flexible polyurethane foam
Process for preparing a flexible polyurethane foam comprising reacting at an isocyanate index of 70 to 130, 1) 40-65 parts by weight of a polyisocyanate composition comprising a) 80-100% by weight of a diphenylmethane diisocyanate component comprising, based on 100 parts by weight of the diphenylmethane diisocyanate component, i) 75-100 parts by weight of diphenylmethane diisocyanate comprising 15-75 parts by weight of 4,4′-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, and 25 to 85 parts by weight of 2,4′-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, and 2,2′-diphenylmethane diisocyanate and / or a liquid variant of such diphenylmethane diisocyanate, and ii) 0 to 25 parts by weight of homologues of diphenylmethane diisocyanates having an isocyanate functionality of 3 or more; and b) 20-0% by weight of toluene diisocyanate; 2) 20 to 45 parts by weight of a polyether polyol having an average molecular weight of 4500-10000, an average nominal functionality of 2-6 and comprising oxypropylene and optionally oxyethylene groups, the amount of oxypropylene groups being at least 70% by weight calculated on the weight of this polyol; 3) 3 to 20 parts by weight of a polyether polyol having an average molecular weight of 700-4000, an average nominal functionality of 2-6 and an hydroxyl value of at most 225 mg KOH / g and comprising oxyethylene and optionally oxypropylene groups, the amount of oxyethylene groups being at least 70% by weight calculated on the weight of this polyol; and 4) 2-6 parts by weight of water, wherein the amount of the polyisocyanate composition, polyol 2), polyol 3), and water being 100 parts by weight.
Owner:HUNTSMAN INT LLC +1
Foamable polymeric composition
Owner:TEKNOR APEX
Polybutylene foam material and preparing method thereof
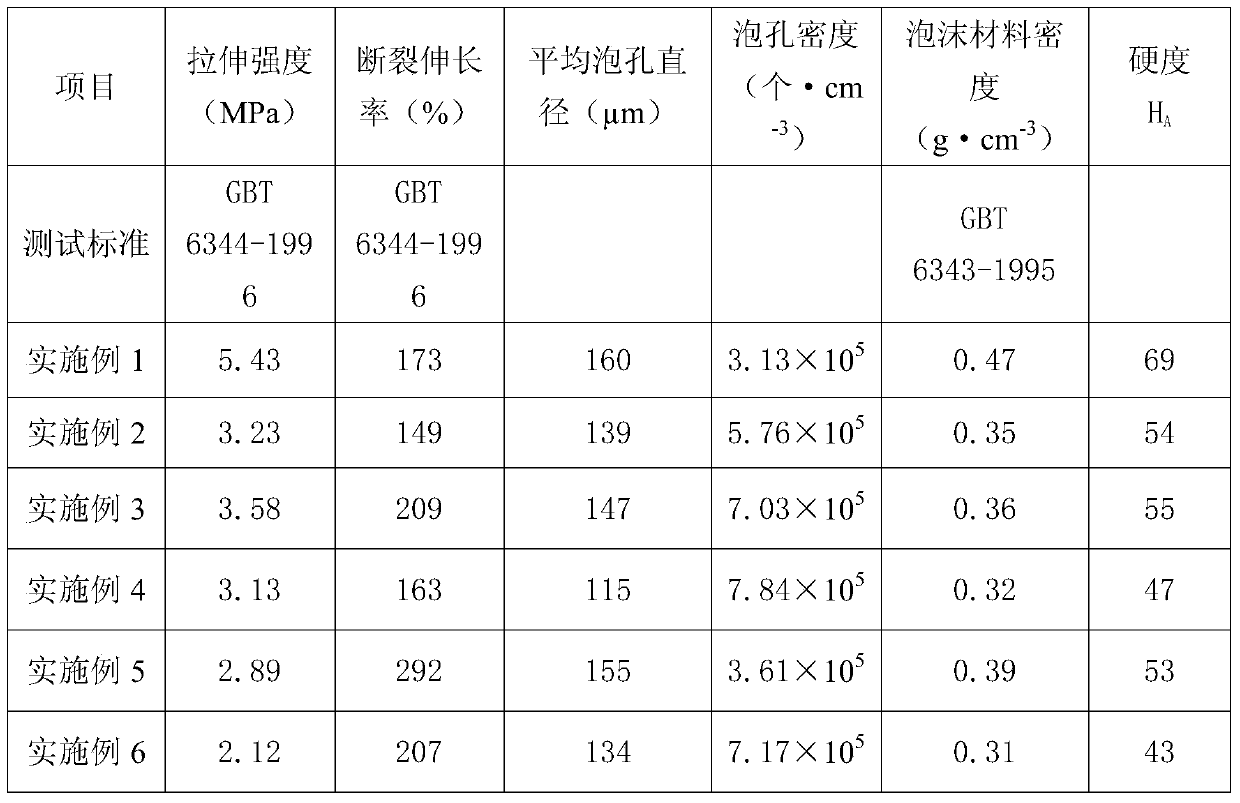
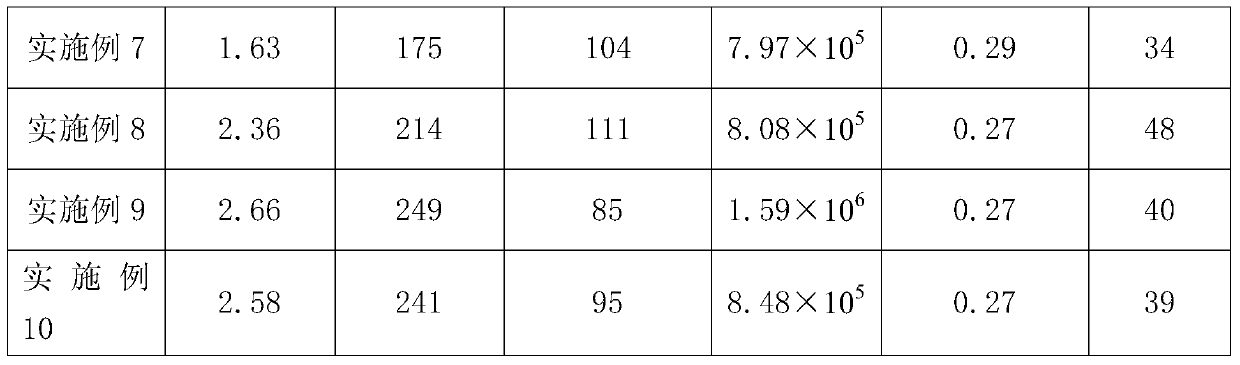
The invention provides a polybutylene foam material and a preparing method thereof. According to the foam material, by means of a chemical foaming method, an extruder is used for carrying out extruding foaming, an injection molding machine is used for carrying out injection molding foaming, and a double-roller mixing mill is used for carrying out mould pressing foaming after blending. The situation that melt indexes and melt strength corresponding to polybutylene of different and identical contents are different is taken into consideration, and the influence on the foaming behavior from polybutylene of the different and identical contents is explored. The influence on the cellular structure and mechanical properties of the foam material from different addition quantities of foaming agents is studied. The influence on the polybutylene cross-linking degree and the material melt strength from different addition quantities of cross-linking agents is studied, so that the foam material with cells distributed uniformly and good mechanical properties is obtained. In addition, different kinds of nucleating agents and the addition quantity of the different nucleating agents are considered according to the classic nucleating theory, and a balance point is found between the cellular structure and the mechanical properties of the foam material. The foam material can be applied to automotive upholstery parts, food packages, biological medicine materials and pipe heat insulation and heat preservation cannulas.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Styrenic polymer composition
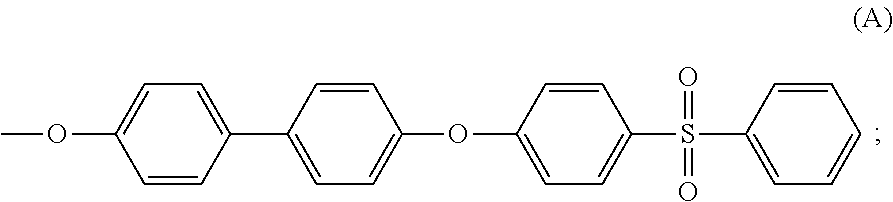
InactiveUS20120123007A1Desirable flame resistance and thermal stabilityElevated melting pointPhosphorus organic compoundsPhosphoric acidBrominated flame retardant
There is provided herein a styrenic polymer composition comprising a styrenic polymer and a flame retardant effective amount of a mixture comprising (a) at least one brominated flame retardant; and, (b) at least one solid phosphate ester that has a melting temperature of at least 80 degrees Celsius.
Owner:ICL IP AMERICA INC
Composition for polyurethane foaming, polyurethane foam and use thereof
A composition for polyurethane foaming, a polyurethane foam and a use thereof. The composition contains two different polyols with a polyethylene oxide ether structure and a polypropylene oxide ether structure, and a specific type of catalyst, flame retardant and water are added thereto; at the same time, the composition contains a small amount of a surfactant and other small molecular alcohols. The traits of the product are that it is pale yellow and transparent, and the product is not layered during long-term storage. The above-mentioned composition and polyphenylpolymethylene polyisocyanate (PAPI) produce a low-density polyurethane foam by means of a foaming machine. The foam has a good thermal insulation effect and a high rate of yield, and the foam has a flame retardant property, that is to say, same can be used for construction insulation, and can also be used for packaging a buffer material, has a good thermal insulation, adhesion and dimensional stability, and has a low odor during the process of construction, the foaming agents all use water, and do not contain chlorofluorocarbon substances that destroy the ozone layer and climate.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM NINGBO RONGWEI POLYURETHANE
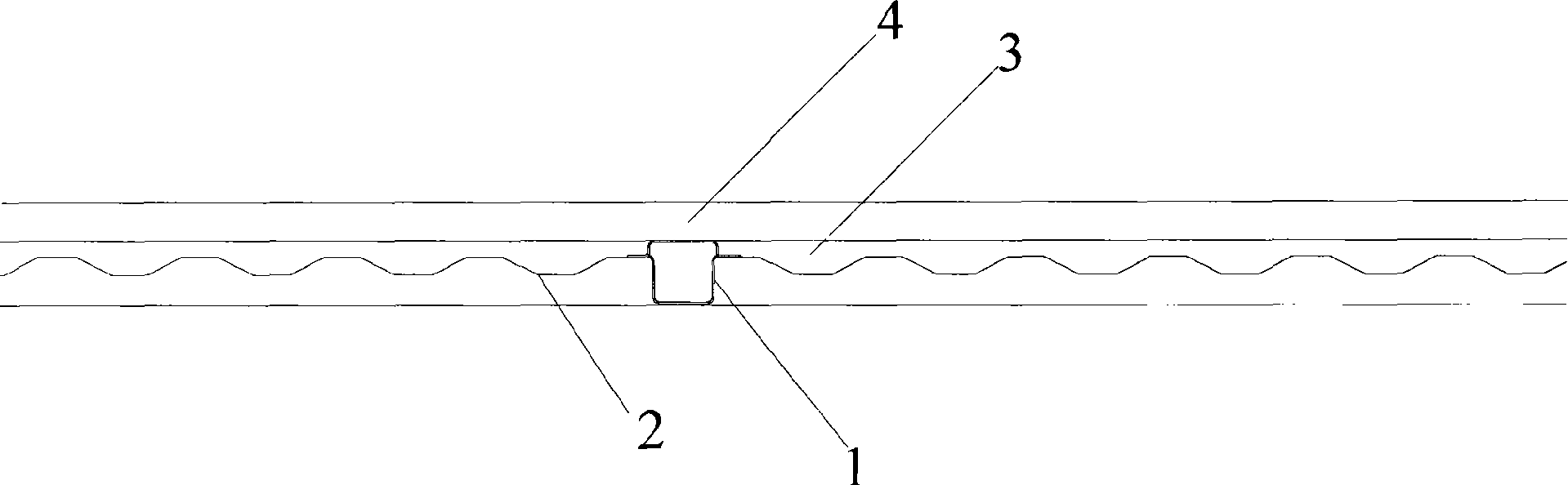
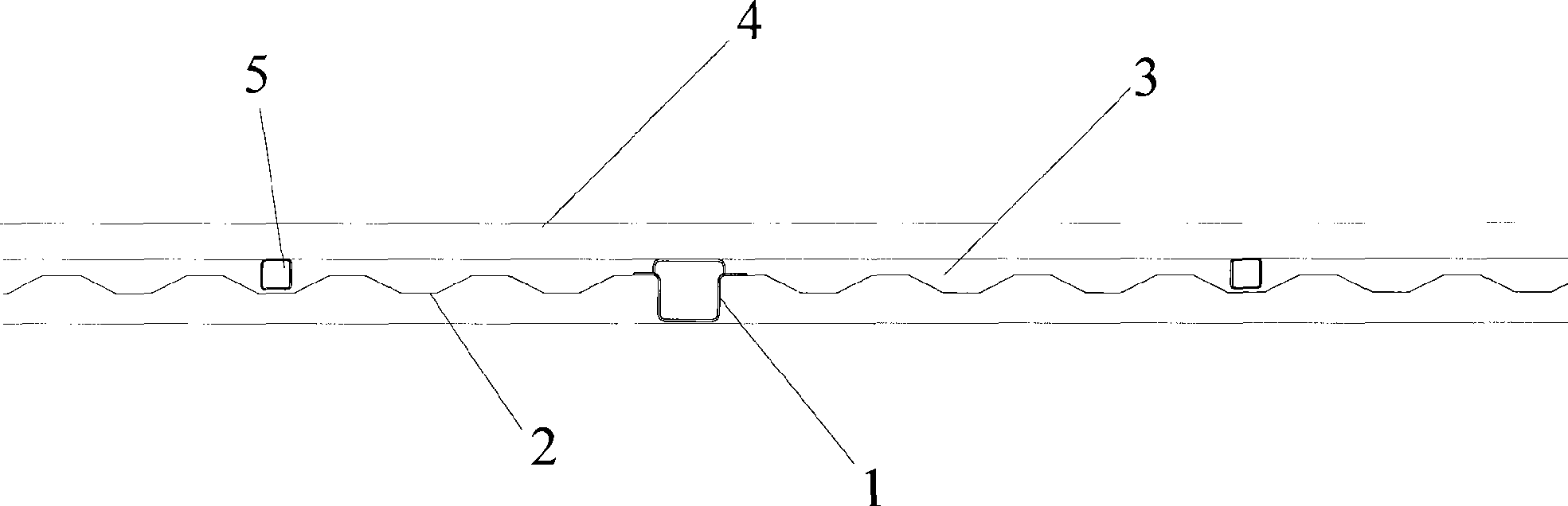
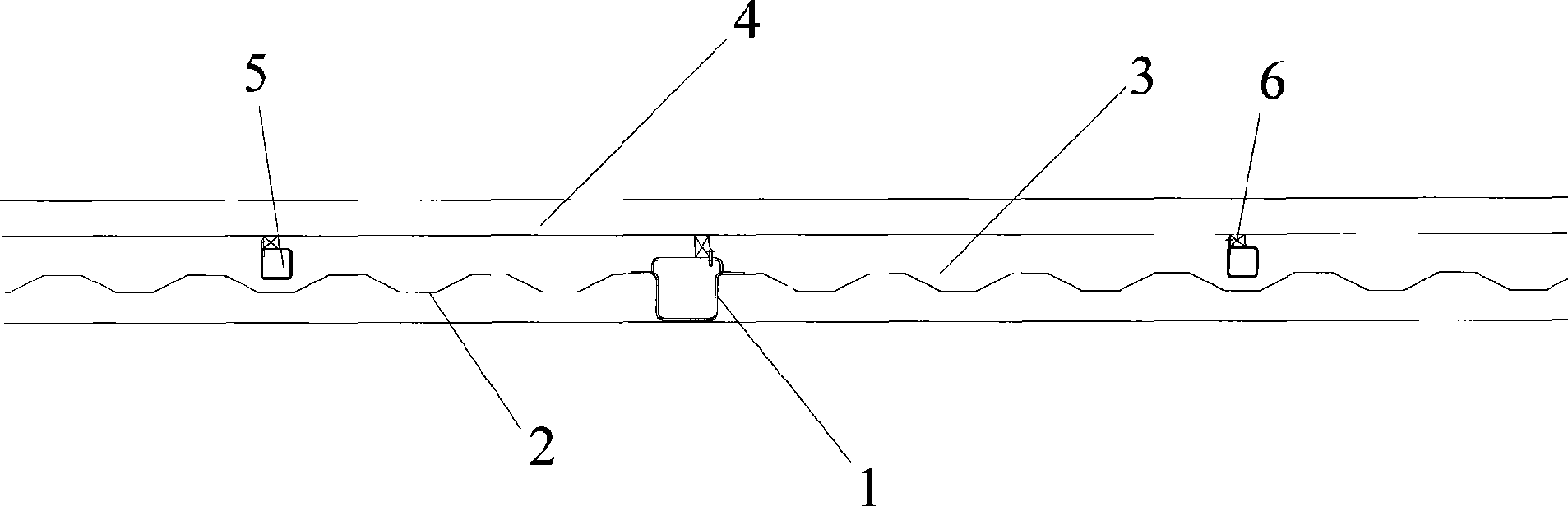
Refrigerated container underframe structure and refrigerated container using the under-frame structure
ActiveCN101423140AMeet the requirementsReduce load capacityLarge containersTank wagonsMaterial consumptionEngineering
The invention provides a chassis structure used for a refrigerated container, comprising two vertically-arranged bottom side beams, a plurality of main bottom cross beams which are arranged to be vertical to the bottom side beams and a corrugated sub floor which is connected with the bottom side beams and the main bottom cross beams. Two ends of the main bottom cross beam are welded onto the bottom side beams and the corrugated sub follow is arranged on the main bottom cross beams. The invention is characterized in that the structure also comprises a plurality of small bottom cross beams and each small bottom cross beam is arranged between the trough of the corrugated sub floor and a T floor inside the container and two ends of the small bottom cross beam are also vertically welded onto the bottom side beams. The invention also provides a refrigerated container adopting the chassis structure. For the chassis structure of the invention, the weight of goods inside the container is mainly borne by the main bottom cross beams and the small bottom cross beams so as to reduce the bearing strength of the corrugated sub floor and enhance the rigidity and strength of the chassis of the refrigerated container, and simultaneously to reduce the corrugated sub floor materials and corrugated height and the foam density of a foam layer so as to reduce the consumption of structure materials and foam material and reduce the heat-leakage rate.
Owner:TAICANG CIMC REEFER LOGISTICS EQUIP CO LTD +2
Expandable polystyrene particles with high foaming ratio and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to expandable polystyrene particles with high foaming ratio and a preparation method thereof, and particularly relates to raw materials for producing cushion packaging materials for electronics, building insulation materials and ocean floating products and a preparation method thereof. The expandable polystyrene particles with high foaming ratio are characterized by being prepared from styrene, soft water, nucleating agent, calcium phosphate, benzoyl peroxide, tert-butyl perbenzoate, white oil, a molecular chain acting force regulating agent, pentane, a surface lubricant and the like as raw materials by the steps of mixing, reacting, filtering and drying. The foam plastic prepared from the expandable polystyrene particles has low production cost; and used as a packaging material, the foam plastic is hard to break and can prevent the packed material from being damaged.
Owner:无锡兴达泡塑新材料股份有限公司 +5
Foamable polyvinyl halogenated resin mass, use of polymerizates thereof as processing aids and objects formed therefrom
InactiveUS6043293ALow foam densitySurface quality is not negativelyProcedure AgentsPolymer chemistry
There are provided foamable, foamable polyvinyl halide resin masses containing: A) 1 to 25 parts relative to 100 parts of polyvinyl halide, of a polymerizate obtainable through the emulsion polymerization of i) up to 20 to not more than 75 parts of methylmethacrylate, ii) 25 to 80 parts of one or more C2-C18 alkylmethacrylates, iii) 0 to 5 parts of one or more vinyl unsaturated monomers copolymerizable with (i) and / or (ii, wherein the components (i)-(iii) together yield 100 parts and are polymerized with up to a further 100 parts of usual additives for emulsion polymerization, wherein the emulsion polymerizate is single stepped and has a viscosity number of >700 cm3 / g and wherein copolymers are excluded which contain iv) MMA per se, or less than 20 or more than 75 parts of MMA together with either v) one or more acrylic acid esters, and / or vi) ethyl methacrylate, n-butyl-methacrylate, or ethylhexyl methacrylate. The resin mass further includes: B) 0.1-10 parts based on 100 parts of the polyvinyl halide of one or more foaming materials, C) 0-100 parts based on 100 parts polyvinyl halide of the usual additives. This polyvinyl halide resin mass, after foaming, yields a resin mass which, as well as of good surface properties, has a foam density of <0.7 g / cm3.
Owner:KANEKA BELGIUM
Use of highly branched polyols for the preparation of polyurethane foams, two-component foam systems containing these polyols, and their use
Described are the use of highly branched and / or dendritic polyols with a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 500 to 100,000 g / mole and preferably of 1,000 to 10,000 g / mole and an average hydroxy functionality per molecule of 10 to 1000 and preferably of 25 to 100, as polyol for the preparation of polyurethane foams with a higher ratio of compressive strength to density, a two-component foam system for the preparation of polyurethane foams with a higher ratio of compressive strength to density, with a polyisocyanates component (A) and a component (B) (polyol component) containing compounds having reactive hydrogen atoms, which are present in separate containers and, for use, can be caused to react by being mixed, which is characterized in that the polyol component (B) contains 1 to 50% by weight and preferably 2 to 30% by weight, based on the weight of the compounds of the polyol component (B) having reactive hydrogen atoms, at least one highly branched and / or dendritic polyol (B1) with a number average molecular weight (Mn) of 500 to 100,000 g / mole and preferably of 1000 to 10,000 g / mole and an average hydroxy functionality per molecule of 10 to 1000 and preferably of 25 to 100, as well as the use of this two-component foam system as installation foam, especially for the installation of door and window frames or of staircases and / or as fire protection foam for sealing openings and / or wall bushings and / or ceilings of buildings.
Owner:HILTI AG
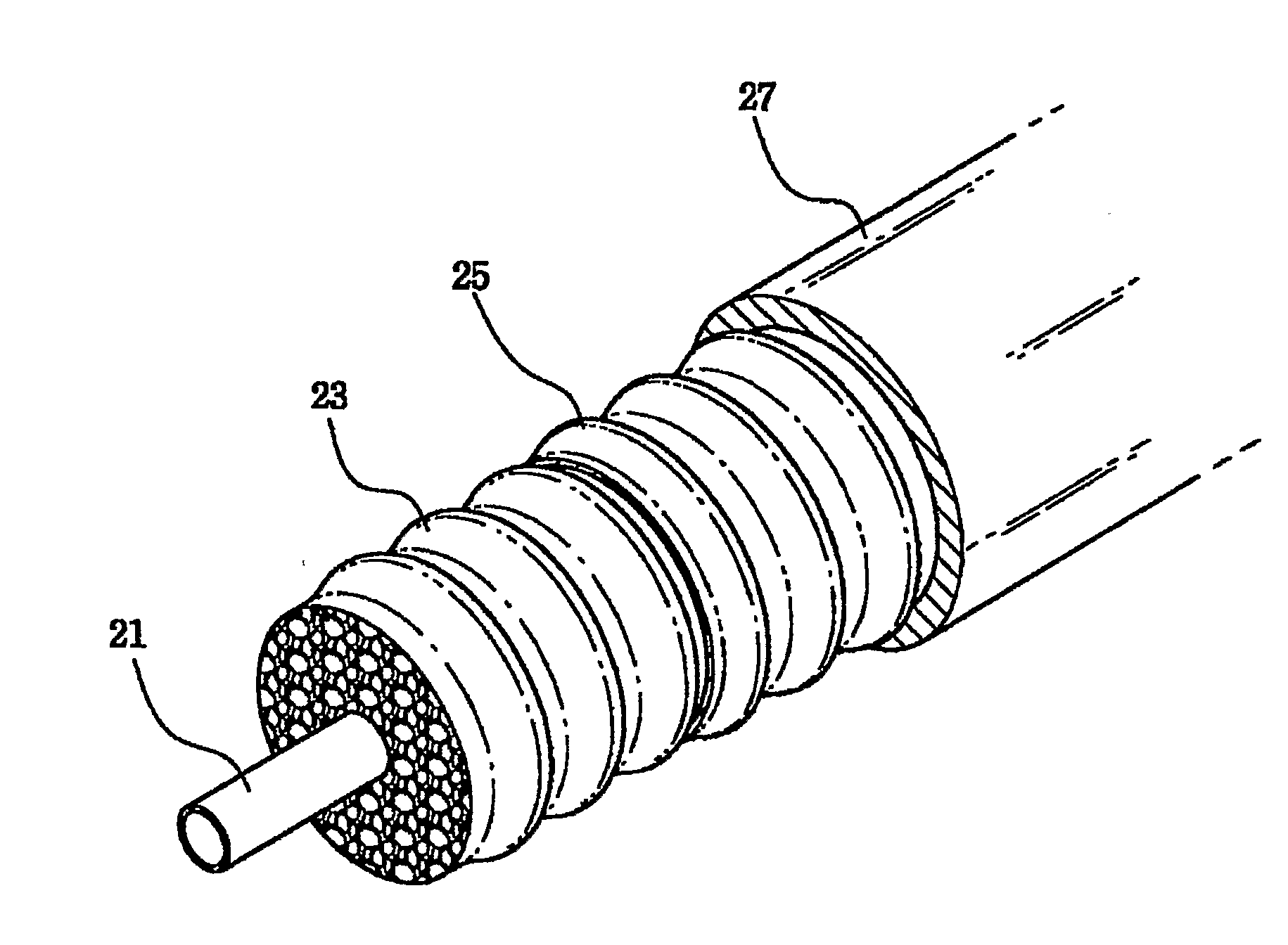
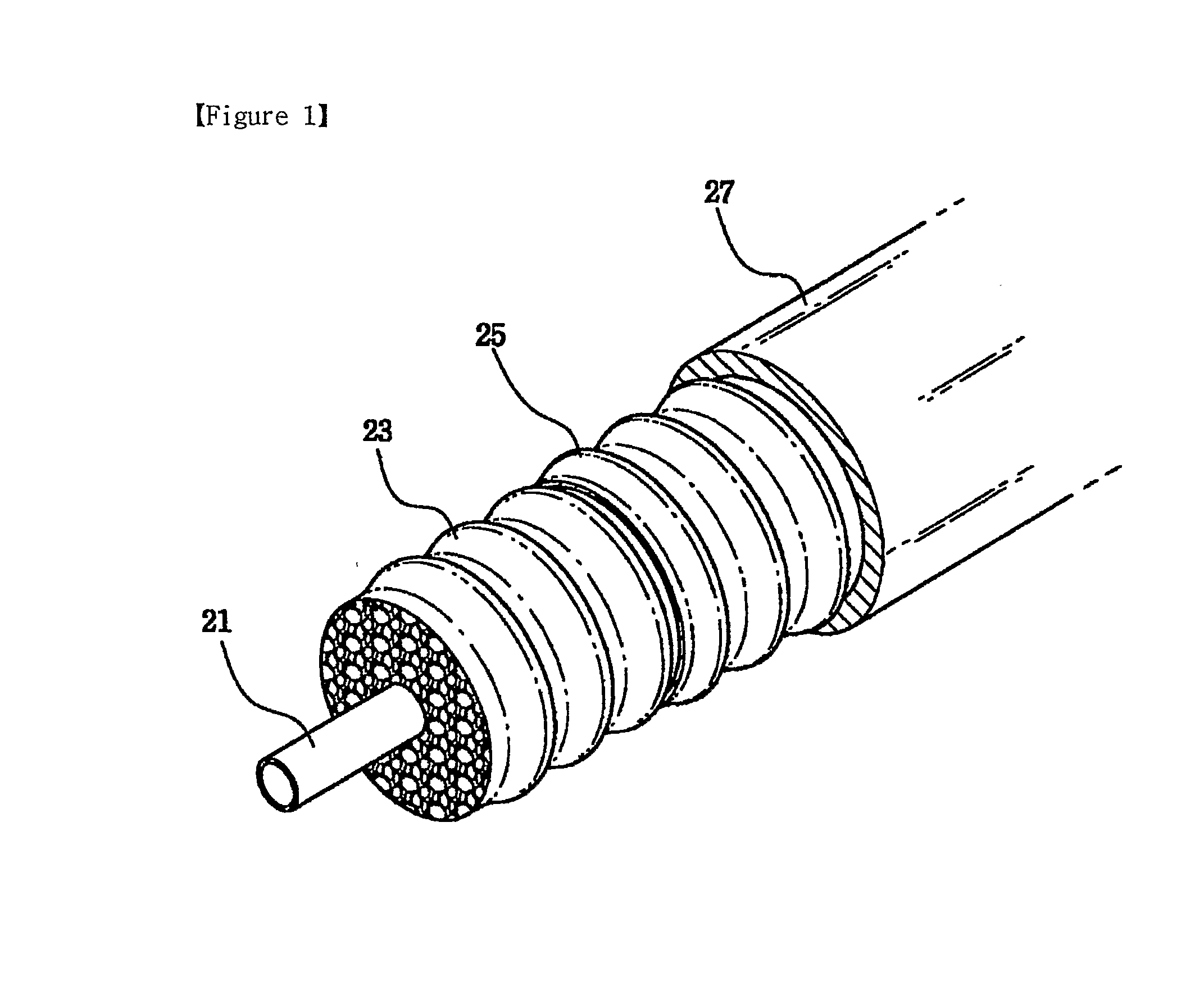
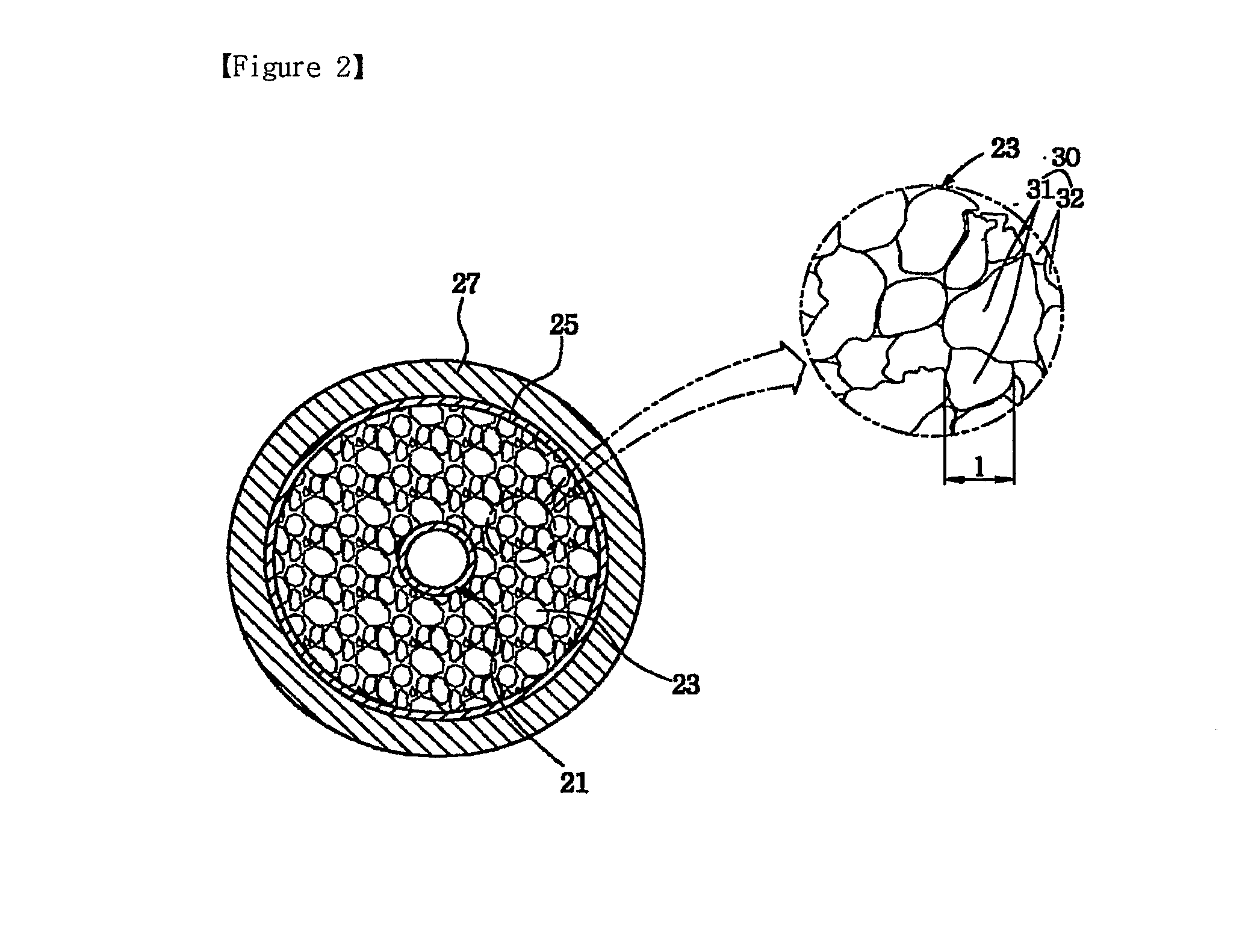
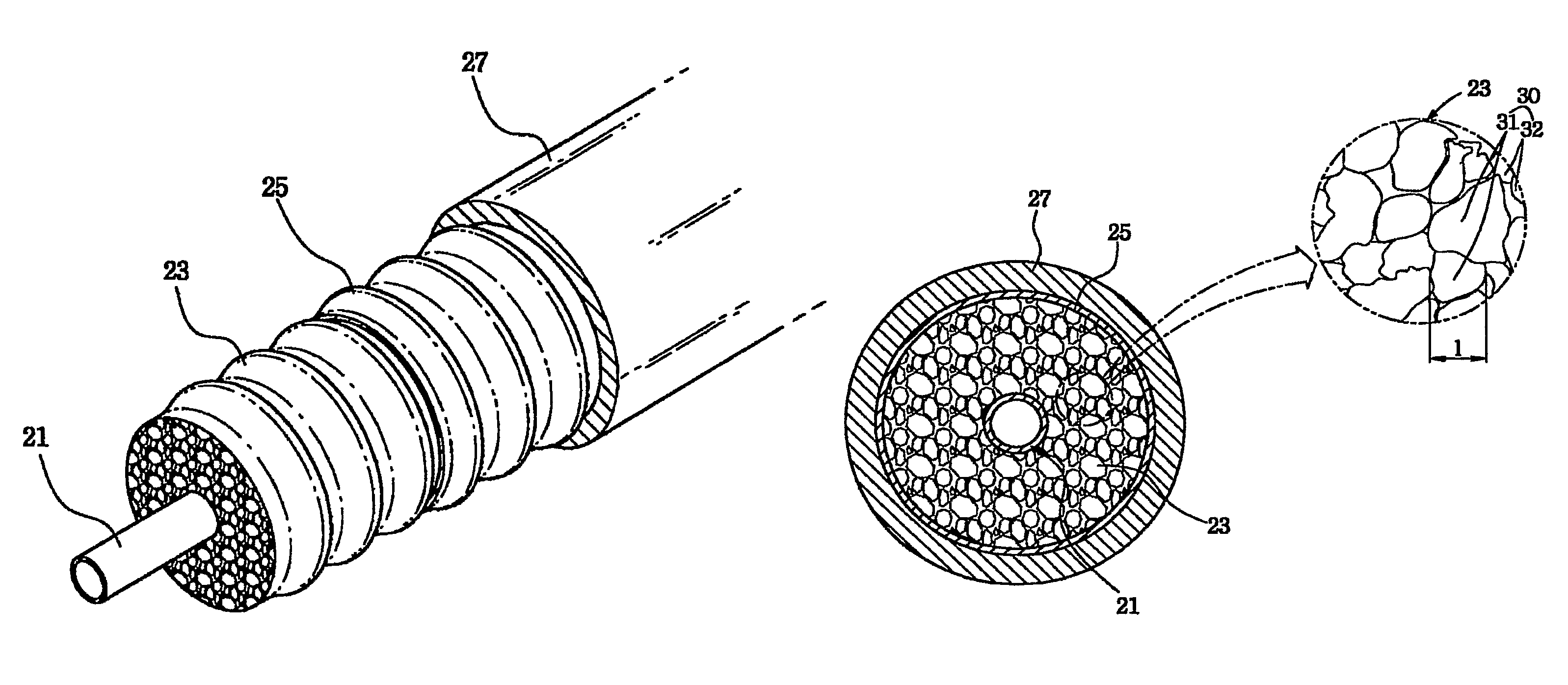
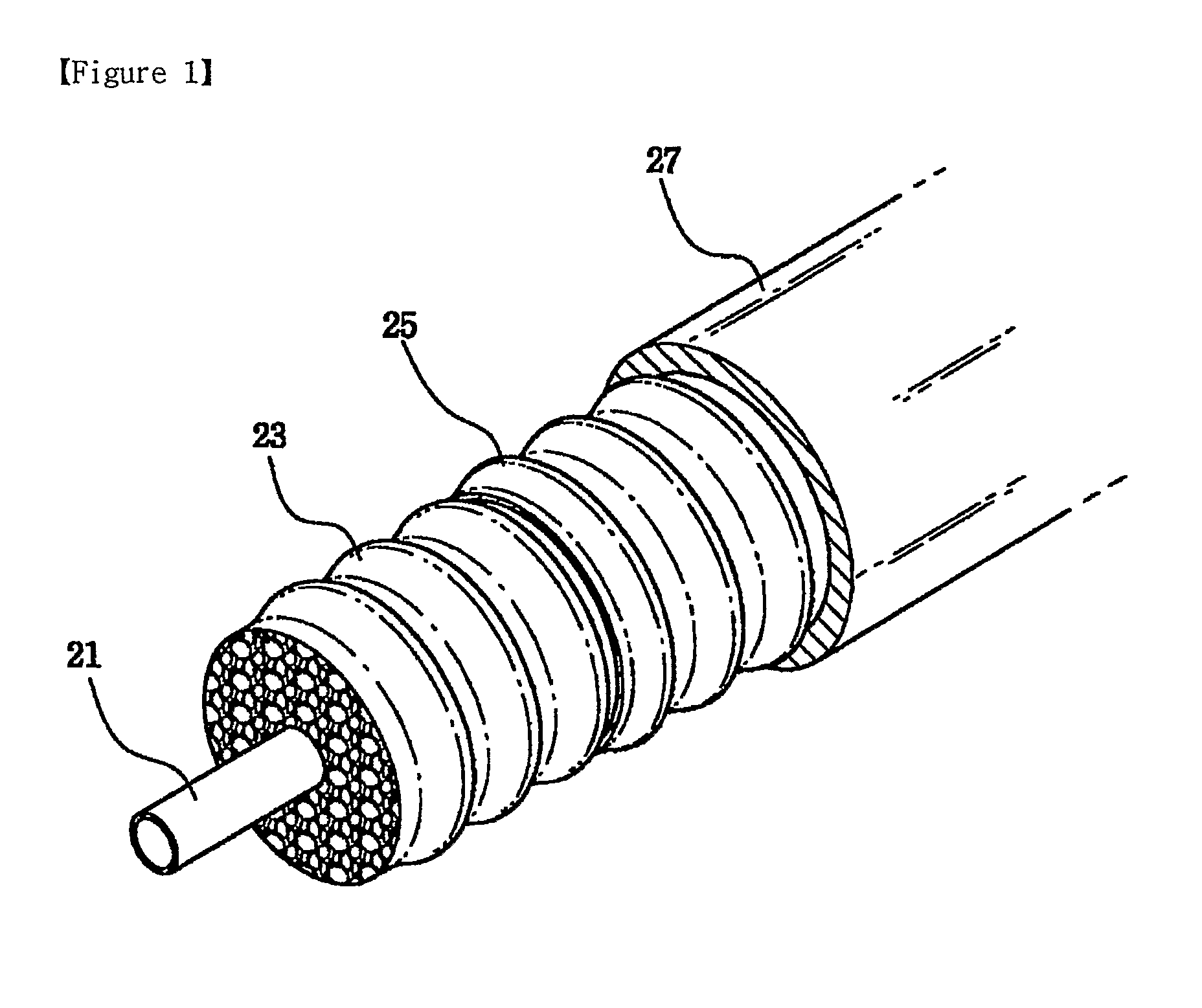
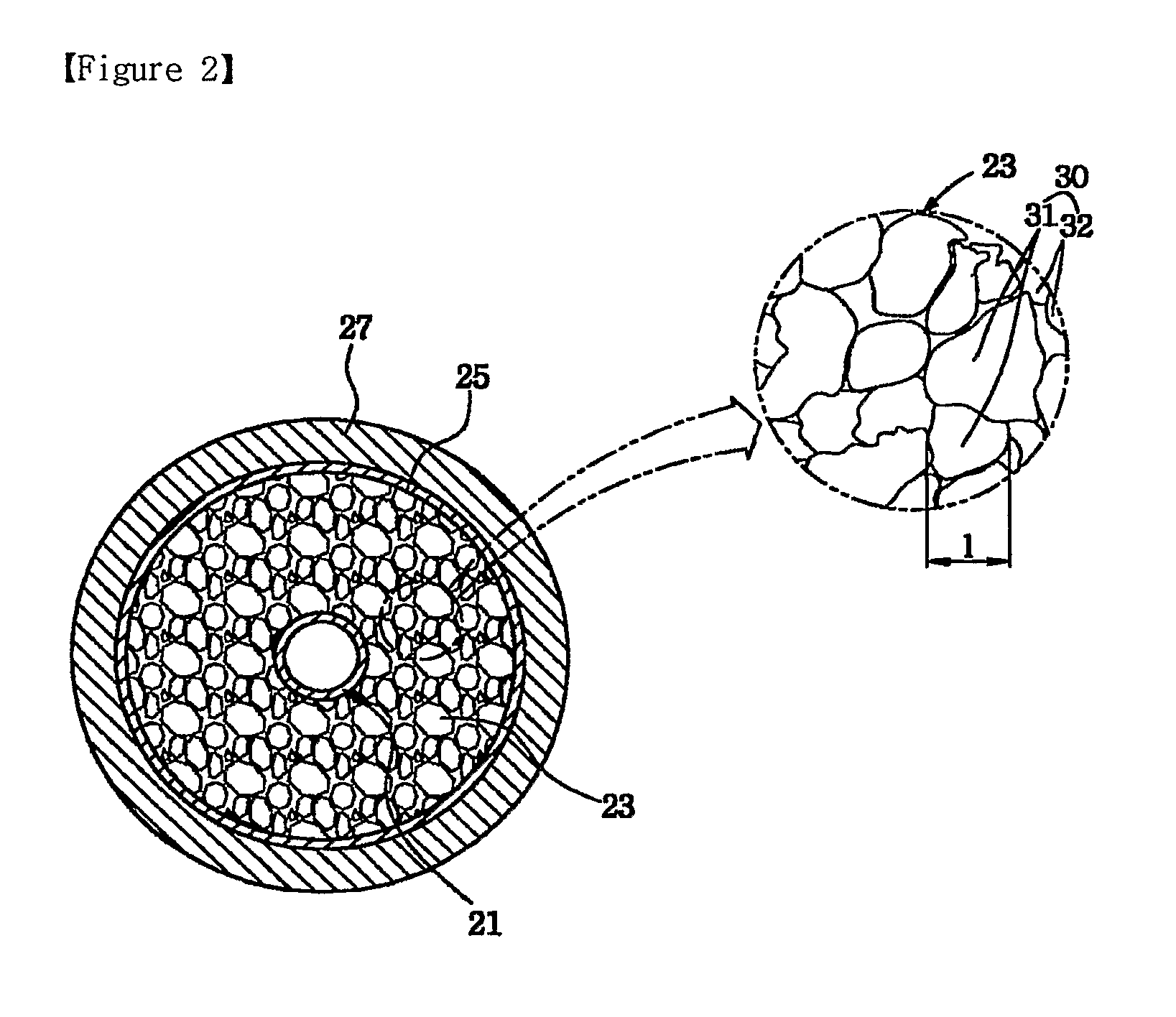
Highly foamed coaxial cable
ActiveUS20100212935A1Low foam densityHigh foaming rateCable conductor constructionCable insulation constructionElectrical conductorCoaxial cable
A highly foamed coaxial cable comprising, an inner conductor disposed in the cable, and a foamed insulator comprising porous cells and surrounding the inner conductor, and an outer conductor surrounding said insulator, and a sheath surrounding said outer conductor, and in said insulator, the total area of macro cell which has a diameter of at least 300 / M is larger than the total area of micro cell which has a diameter smaller than 300 / M at cross section of cable.
Owner:LG CABLE LTD (KR)
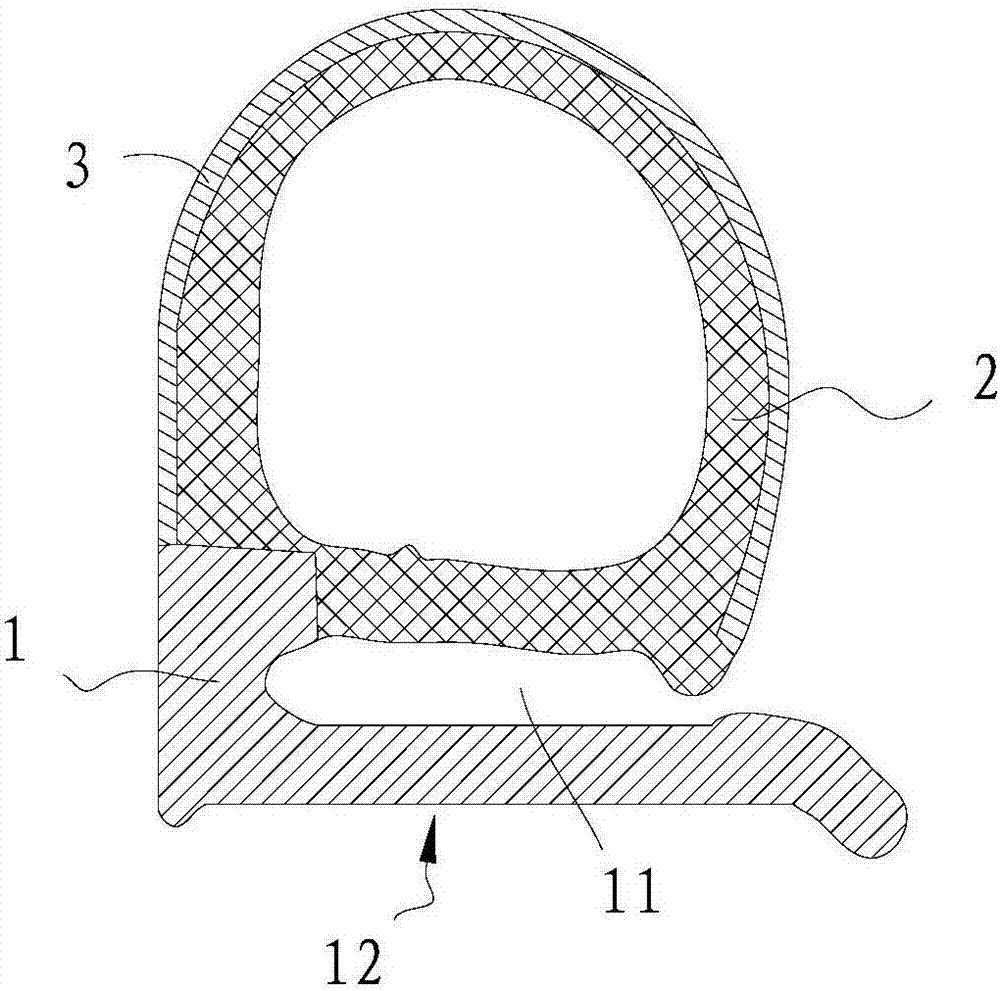
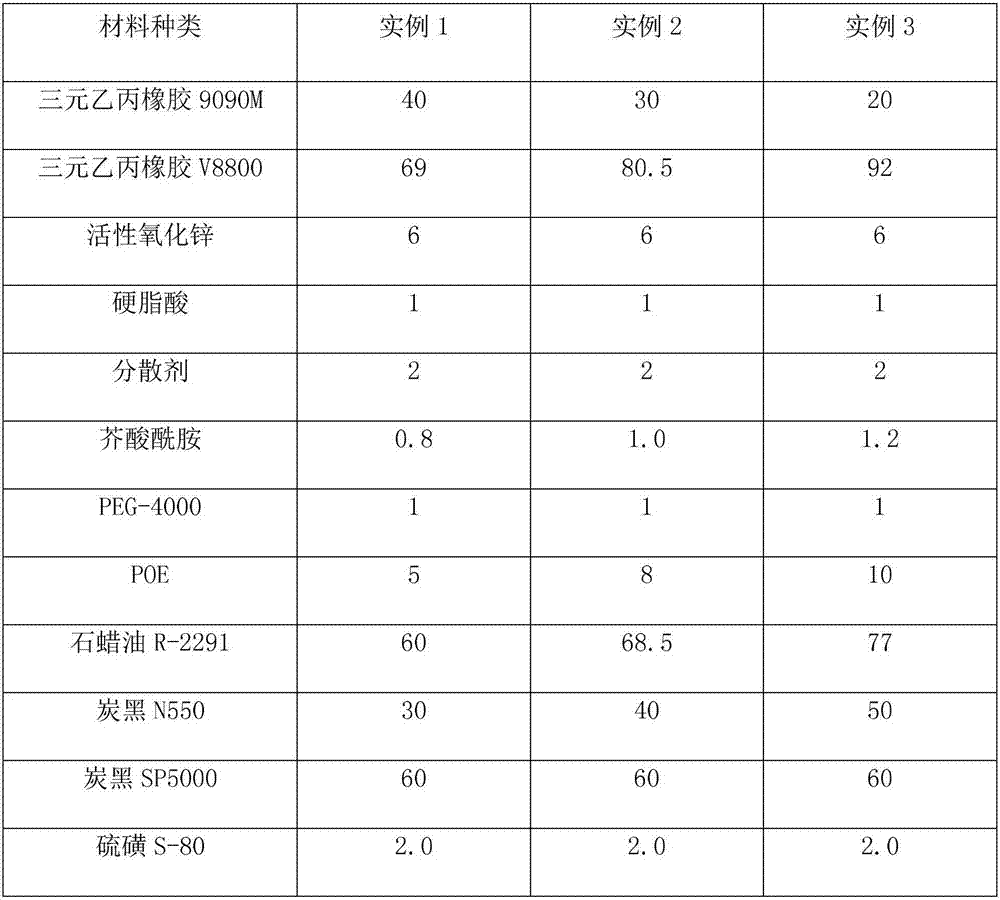
Sponge foaming rubber for car door sealing strip and preparation method thereof, car door sealing strip and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107418061ALow viscosityConducive to lightweight designEngine sealsVehicle sealing arrangementsElastomerPolyolefin
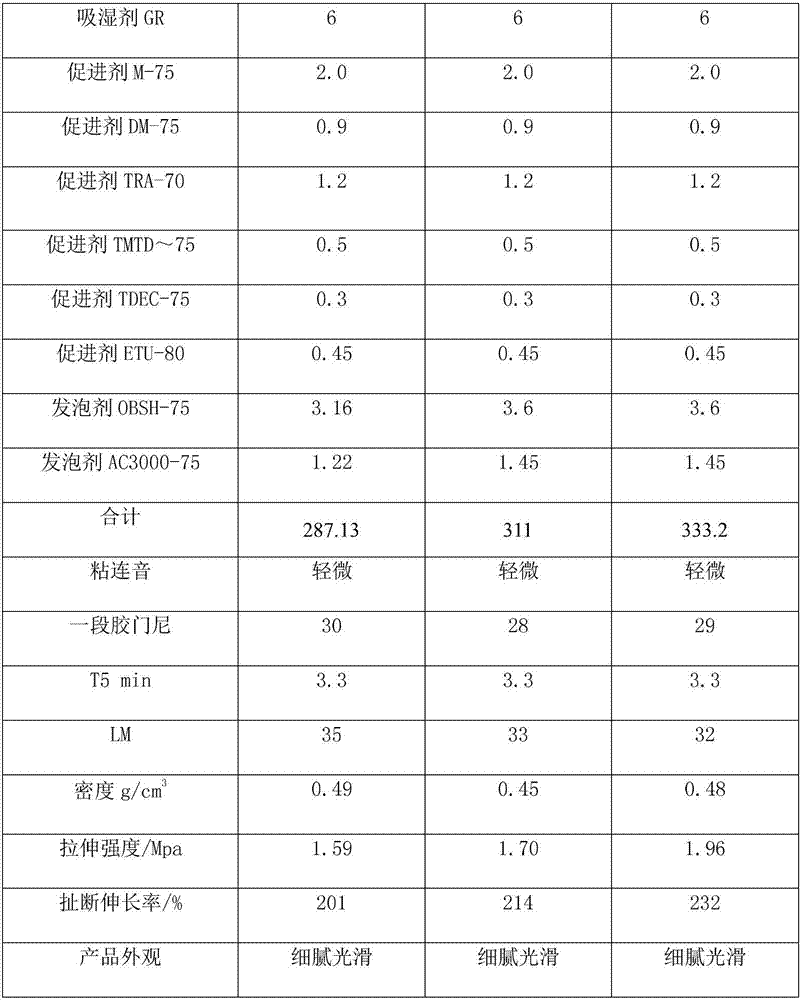
The invention provides sponge foaming rubber for a car door sealing strip and a preparation method thereof, a car door sealing strip and a preparation method thereof. The sponge foaming rubber for the car door sealing strip, provided by the invention, is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 20 to 40 parts of ethylene-propylene-diene monomer 9090M, 69 to 92 parts of ethylene-propylene-diene monomer V8800, 5 to 7 parts of active zinc oxide, 1 to 2 parts of stearic acid, 1 to 3 parts of a dispersant, 0.8 to 1.4 parts of erucamide, 1 to 2 parts of PEG-4000 (Polyethylene Glycol-4000), 5 to 10 parts of POE (Polyolefin Elastomer), 60 to 77 parts of paraffin oil R-2291, 30 to 50 parts of carbon black N550, 50 to 70 parts of carbon black SP5000, 1.5 to 2.5 parts of sulfur S-80, 6 to 10 parts of a moisture absorbent GR, 3 to 6.4 parts of an accelerant, 3 to 3.6 parts of a foaming agent OBSH-75 (Oxydibenzenesulfonyl Hydrazide-75) and 1.1 to 1.5 parts of a foaming agent AC3000-75. By adopting a formula of the sponge foaming rubber for the car door sealing strip, provided by the invention, the prepared sponge rubber has relatively low density and can meet a lightweight design; meanwhile, the obtained rubber also can have relatively good physical performance, so that the utilization quality of the car door sealing strip utilizing the sponge foaming rubber can also be improved.
Owner:NUOBO RUBBER PRODION
Flame-resistant vinyl benzene polymer foam plastic
The invention relates to a flame-retardant styrene polymer foam plastics, which comprises styrene polymer and flame-retardant agent compound. The weight of phosphorus-containing compound takes up 2 percent to 4 percent of the total weight of the styrene polymer. The weight of HBCD takes up at least 5 percent to 8 percent of the total weight of the styrene polymer. The weight of antimony oxide compound takes up at least 2 percent of the total weight of the styrene polymer; the weight of expansion flame-retardant compound takes up at least 6 percent to 12 percent of the total weight of the styrene polymer. The invention, by recycling the styrene polymer foam plastics and through the extrusion production technique of common styrene polymer foam plastics, gets the styrene polymer foam plastics with good flame-retardant performance (the flame-retardant performance meets the requirement on heat insulation foam plastics of GB8624). The extruded type flame-retardant styrene polymer foam plastics the invention gets has low coefficient of thermal conductivity ( high energy saving efficiency), high intensity, and the flame retardance which can meet the requirement of national building fireproof standard, replaces molded type styrene polymer foam plastics and has good prospect on building insulation and pipe sandwich heat thermal insulation, etc.
Owner:TIANJIN FIRE RES INST
Polymer foam and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20170029589A1Good foaming effectReduced melt strengthFlat articlesPolymer scienceFoaming agent
Polymer foam and a method for preparing the same are disclosed. In the present disclosure, the method sequentially comprises the following steps: providing a polymer body; performing a pressure-induced flow (PIF) process on the polymer body at a first predetermined temperature and a first predetermined pressure for a pressure holding time, to obtain a polymer sheet; and performing a foaming process on the polymer sheet by using a foaming agent at a second predetermined temperature and a second predetermined pressure for a saturation time, to obtain polymer foam.
Owner:LEE CHANG YUNG CHEM IND CORP +1
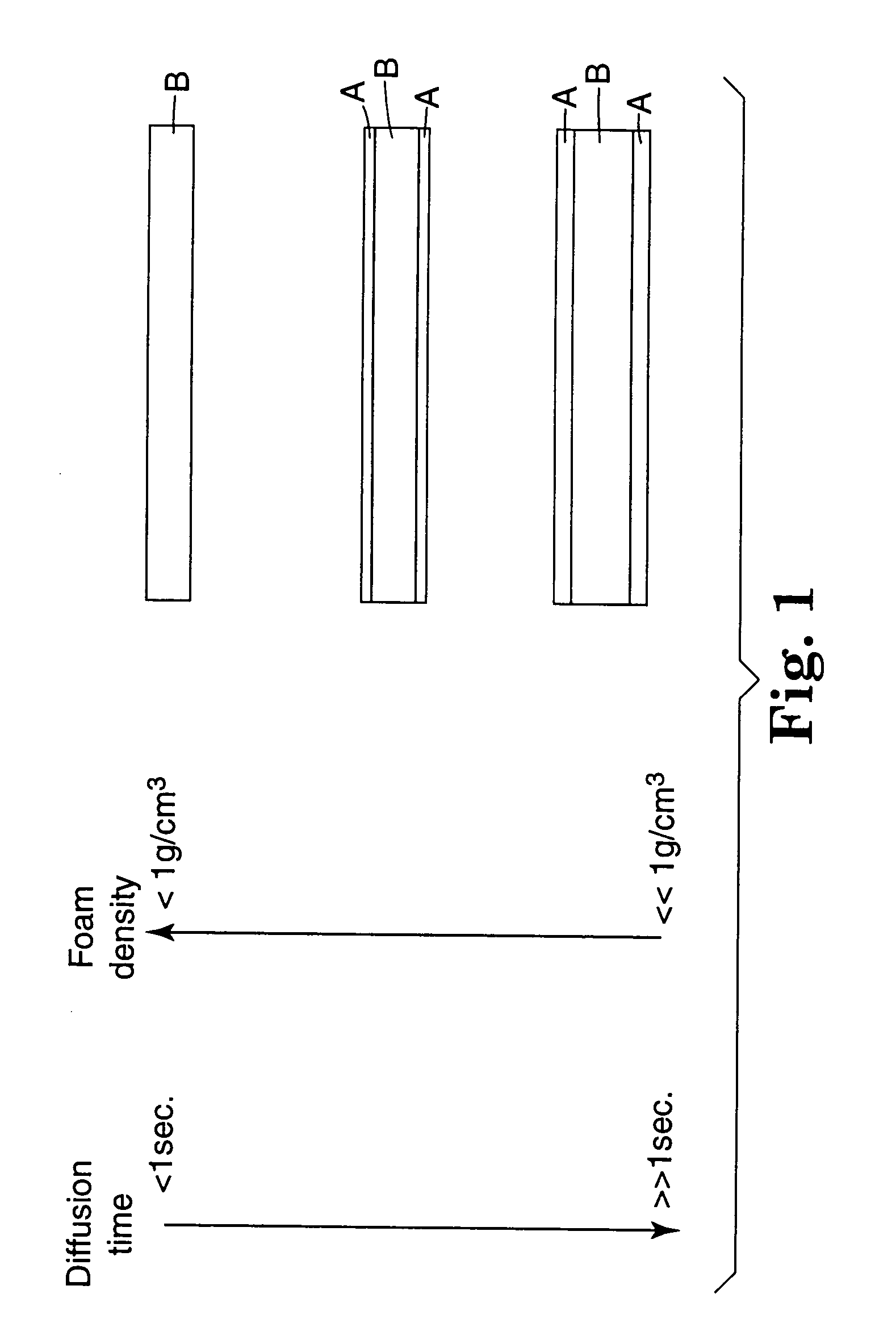
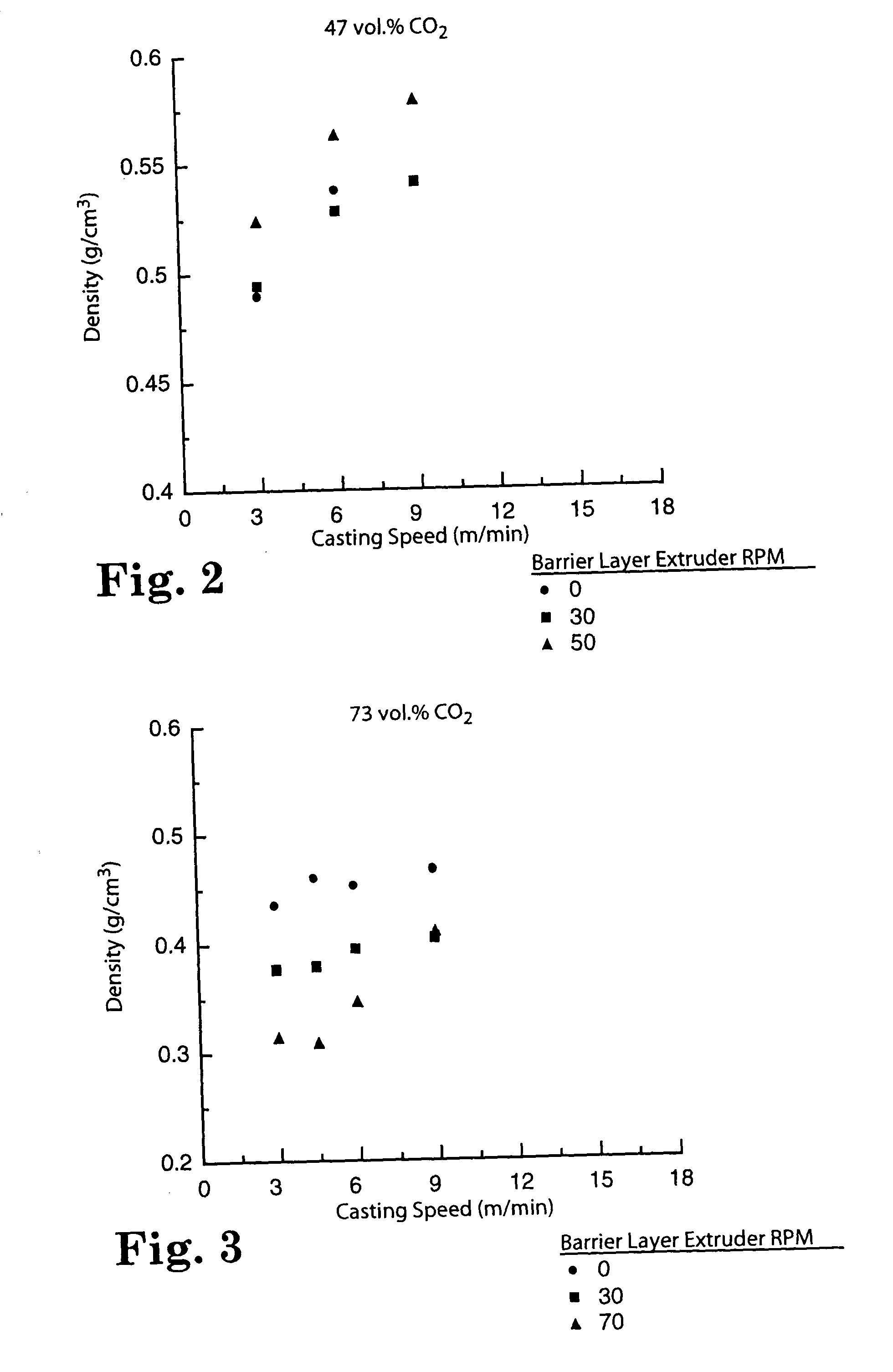
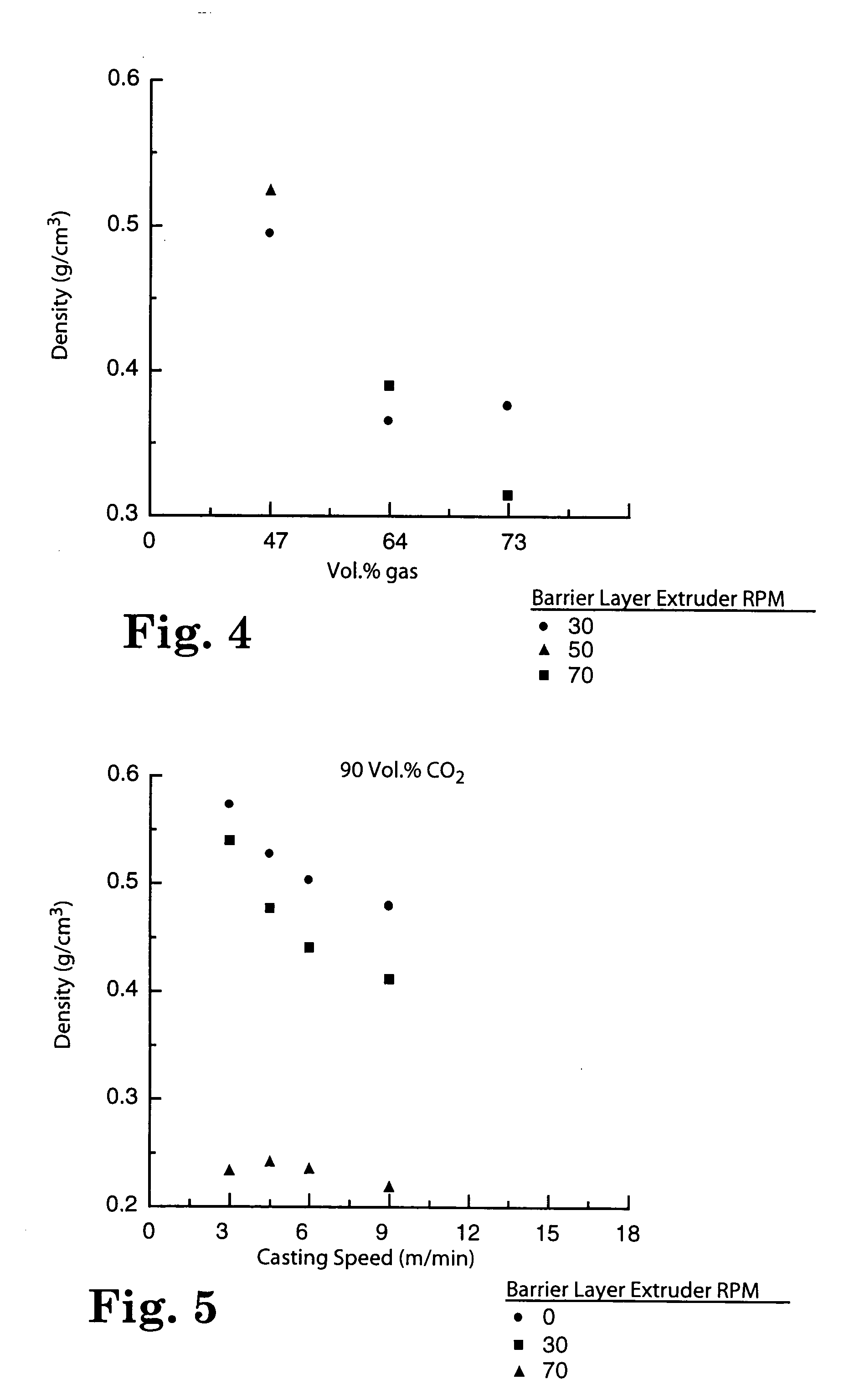
Reduced density foam articles and process for making
InactiveUS20040033350A1Low densityChanges the diffusional characteristics of a fugitive gasFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsVolumetric Mass DensityLow density
The invention discloses reduced density foams and methods of making the foams by applying or creating a nonfoaming barrier layer on a foamable layer, which barrier layer inhibits the escape of fugitive gases during the foaming process.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Preparation method of light-weight wall board and multilayer light weight wall board
ActiveCN109516773AHigh foam densityLow foam densityCeramic materials productionCeramicwareFoaming agentPolymer science
The invention discloses a preparation method of a light-weight wall board and a multilayer light weight wall board, and relates to the technical field of a building material. The preparation method ofthe light-weight wall board uses a multi-time material distribution mode; a first material and a second material are respectively subjected to material distribution and firing, wherein each of the first material and the second material comprises a base material and a foaming agent; the amount of the foaming agent in the first material is 0.1 to 0.2 percent; the amount of the foaming agent in thesecond material is 0.25 to 0.35 percent. Preferably, the material distribution times is 2 to 3 times. The multilayer light-weight wall board is prepared by the preparation method of the light-weight wall plate. The preparation method has the advantage that the sound isolation, heat isolation and mechanical performance of the finally formed multilayer light-weight wall board are improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG KITO CERAMICS GROUP CO LTD +2
High molecular weight processing modifier for polyvinyl chloride low-foaming pipe
The invention relates to high molecular processing modifier used in a polyvinyl chloride low foaming tube, which is characterized in that: the total weight of polymeric monomer is calculated as 100 percent, which comprises 12-72 percent of methyl methacrylate, 21-66 percent of styrene and 7-22 percent of acrylonitrile. Chain extender is added into the compositions to carry out emulsion polymerization in redox system. The invention is characterized in that: the invention can improve plasticizing and the plasticizing can become more even, can improve melt strength to promote extending property, can improve surface quality to reduce melting pulsation and increase surface gloss and can improve processing property to reduce blooming and crazing, decrease the foaming density of the product and increase elongation and pulling speed. Because of higher relative molecular mass, the invention can greatly improve the melt strength. The invention is used for producing PVC foaming products which have dense and even stomata structure and lower density.
Owner:SHANDONG RUIFENG CHEM
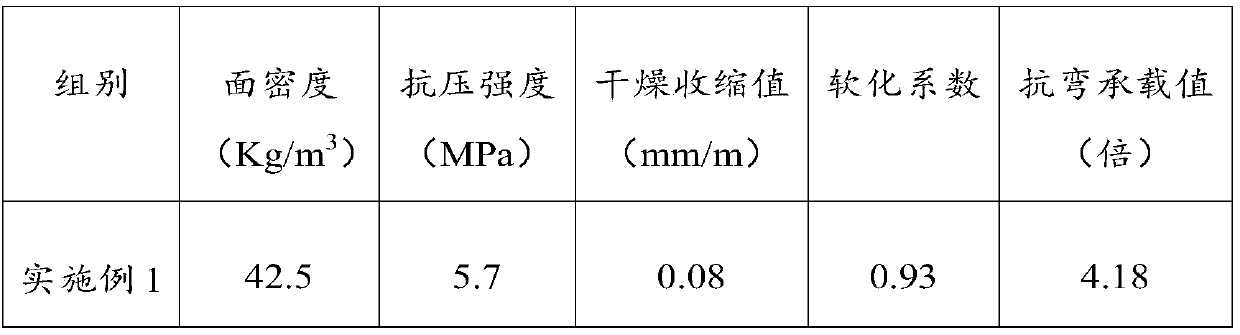
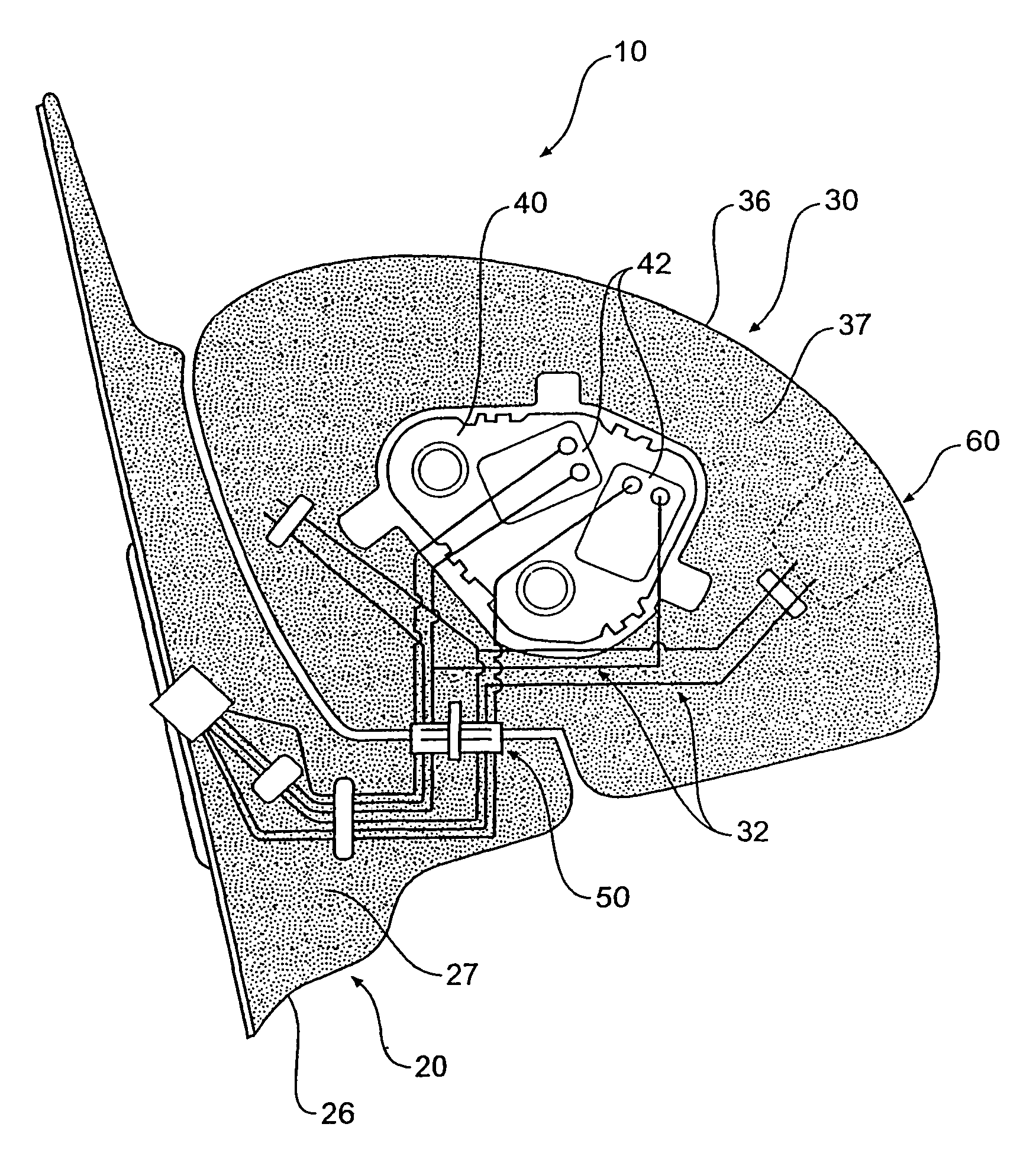
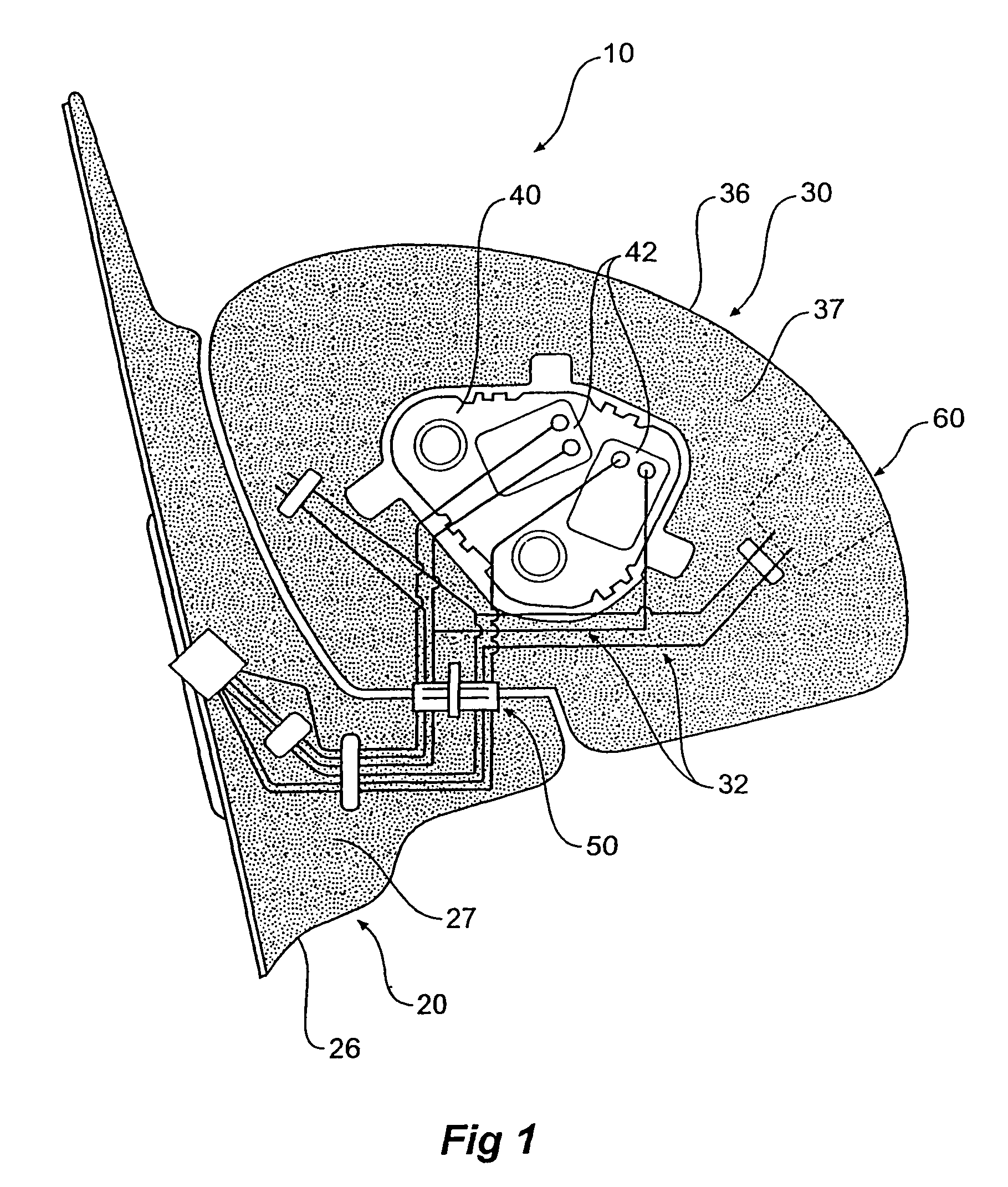
Vehicle external mirror wiring integration
InactiveUS6994443B2Reduce complexityRelieve pressurePicture framesDomestic mirrorsElectrical conductorEngineering
A vehicle external mirror assembly (10) comprising a mirror head (30) adapted to support a mirror, the mirror head (30) having an external shell (36), a first foam core (37) providing support for the shell (36), a mirror base (20) adapted for mounting to a vehicle, the mirror base (20) connected to the mirror head (30) or integral with the mirror head (30) and a plurality of electrical conductors (32) disposed within the first foam core (37), the conductors (32) are arranged and constructed to diffuse stress within the foam core (37).
Owner:SCHEFENACKER VISION SYST AUSTRALIA
Highly foamed coaxial cable
ActiveUS8017867B2Low foam densityLow dielectric constantPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsCable conductor constructionCoaxial cableElectrical conductor
A highly foamed coaxial cable having an inner conductor disposed in the cable, a foamed insulator having porous cells surrounding the inner conductor, an outer conductor surrounding the insulator, and a sheath surrounding the outer conductor and the insulator, wherein the total area of macro cell which has a diameter of at least 300 / M is larger than the total area of micro cell which has a diameter smaller than 300 / M at cross section of cable.
Owner:LG CABLE LTD (KR)
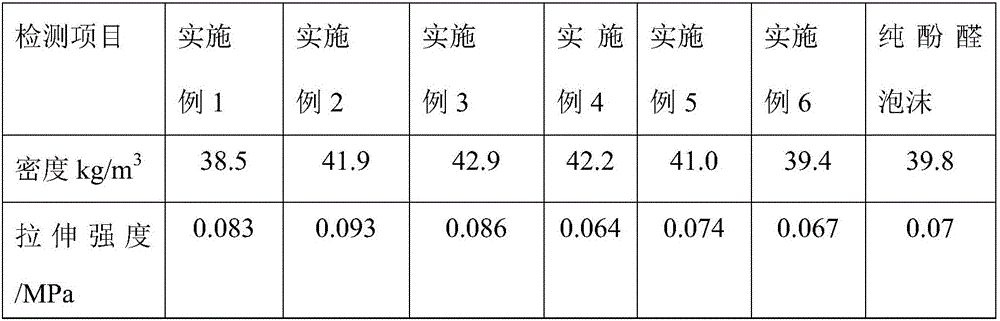
High-weight high-strength phenol formaldehyde foam and preparation method thereof
The invention provides high-weight high-strength phenol formaldehyde foam and a preparation method thereof. The foam is mainly prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of high-viscosity phenolic resin, 4 to 6 parts of silica sol, 3 to 5 parts of pH regulators, 2 to 4 parts of potassium silicate, 7 to 10 parts of foaming agents, 5 to 10 parts of emulsifiers and 10 to 16 parts of curing agents. The preparation method of the foam has the advantages that nanometer silicon dioxide particles are introduced into formaldehyde foam by using silica sol / potassium silicate; Si-O-C chemical bonds are generated by using the effects of nanometer silicon dioxide and high-viscosity phenolic resin; an interface enhancing effect is generated. Concretely, in a container with a stirring function, the raw materials are added according to the proportion ratio; after the materials are uniformly stirred, the materials are fast poured into a mold; foaming is performed at 65 to 70 DEG C; the heat insulation is performed for 20 to 30 min; demoulding is performed. The mechanical intensity is improved; the production cost is reduced; the heat resistance is improved; the operation is simple; the method is suitable for industrialized operation.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Sponge sofa or sponge stool structure
The invention discloses a sponge sofa or sponge stool structure which comprises a low-density sponge foaming forming sofa base or low-density sponge foaming forming stool base with the foaming density of 10-35 kg / m<3>, wherein a high-density sponge cladding layer with the foaming density of 35-60 kg / m<3> is integrally foamed on the outer surface of the base; the hardness of the sponge sofa base or the sponge stool base is Share A 20+; the hardness of the sponge cladding layer is 30-80 Kgf. The sponge sofa structure has the characteristics of simple manufacturing process, shape controllability, high production efficiency and low manufacturing cost. In addition, a low-density sponge of the sponge sofa base or the sponge stool base is relatively low in price and light in weight and has certain supporting strength and supporting toughness. Therefore, the consumption of a high-density sponge can be reduced, and the material cost and weight of a whole sponge sofa or stool can be further reduced. Moreover, the sponge cladding layer is integrally foamed on the outer surface of the sponge sofa base or the sponge stool base, is firmly attached to the surface of the base and is unlikely to loosen, and thus the service life of the sponge sofa or stool is guaranteed.
Owner:ZINUS (XIAMEN) INC
Polyol composition for rigid polyurethane foam and production method for rigid polyurethane foam
A polyol composition for a rigid polyurethane foam, which comprises polyol compounds, and water as a blowing agent, and which is mixed with a polyisocyanate component to react therewith, and thereby forming the rigid polyurethane foam, wherein the polyol compounds comprise a polyether polyol (A) which is a polymer made from an alkylene oxide and has an average functional group number of 2 to 4 and a weight-average molecular weight of 3000 to 8000, and a short glycol (B) having a molecular weight less than 250, and the water is contained in an amount of 20 to 100 parts by weight for 100 parts by weight of the polyol compounds.
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
Polyarylene foam materials
ActiveUS20150307677A1Well defined and fine and homogeneous cell structureImprove uniformitySynthetic resin layered productsVehicle componentsPolymer scienceGlass transition
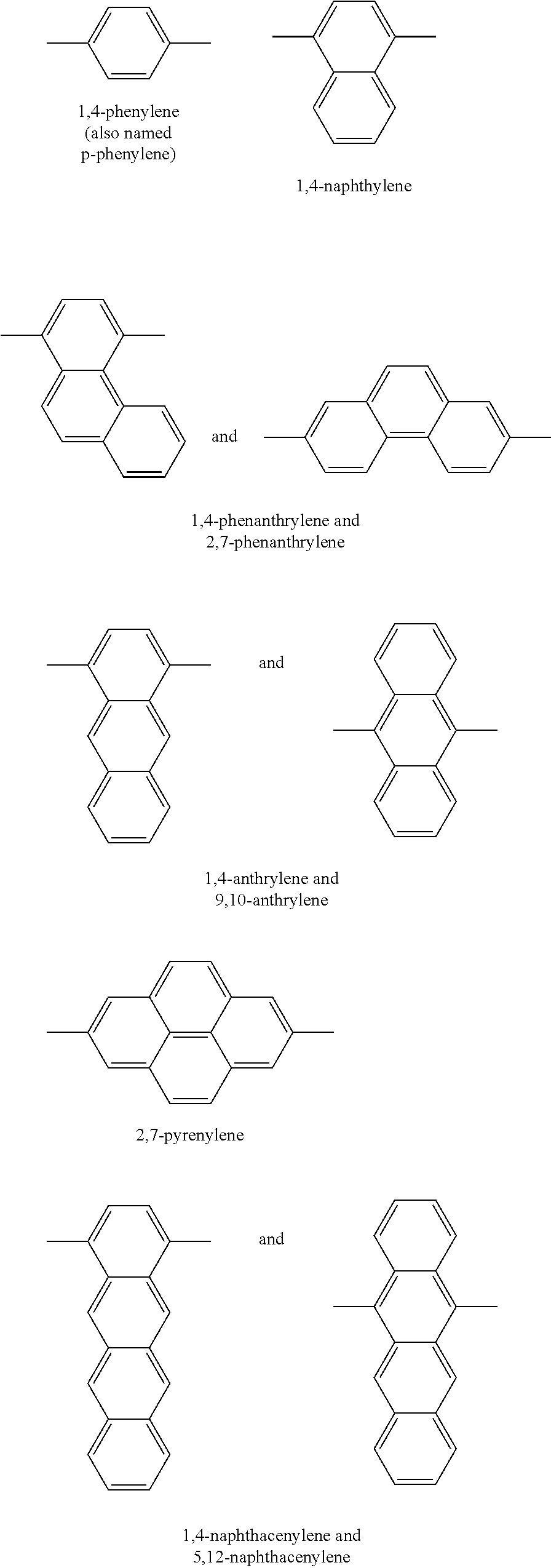
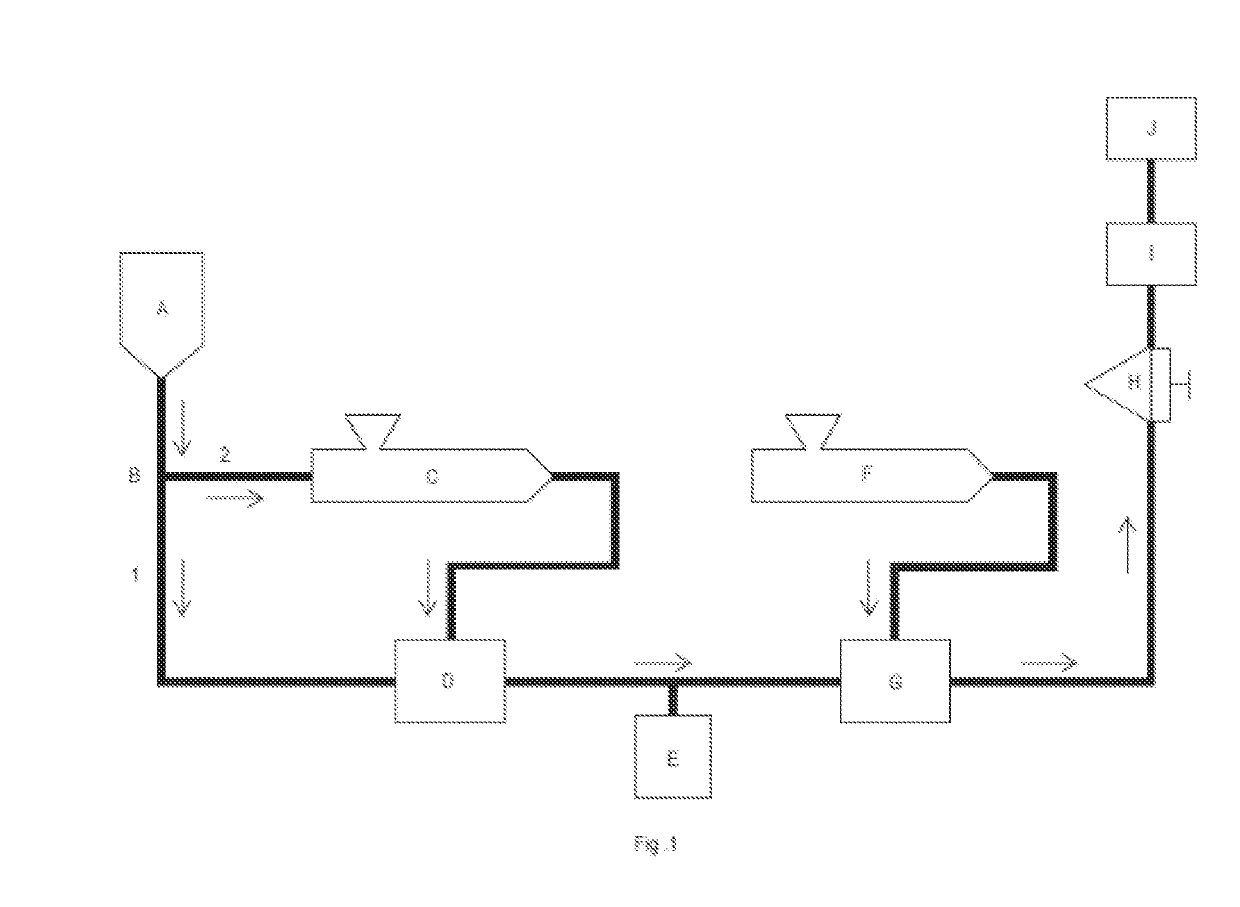
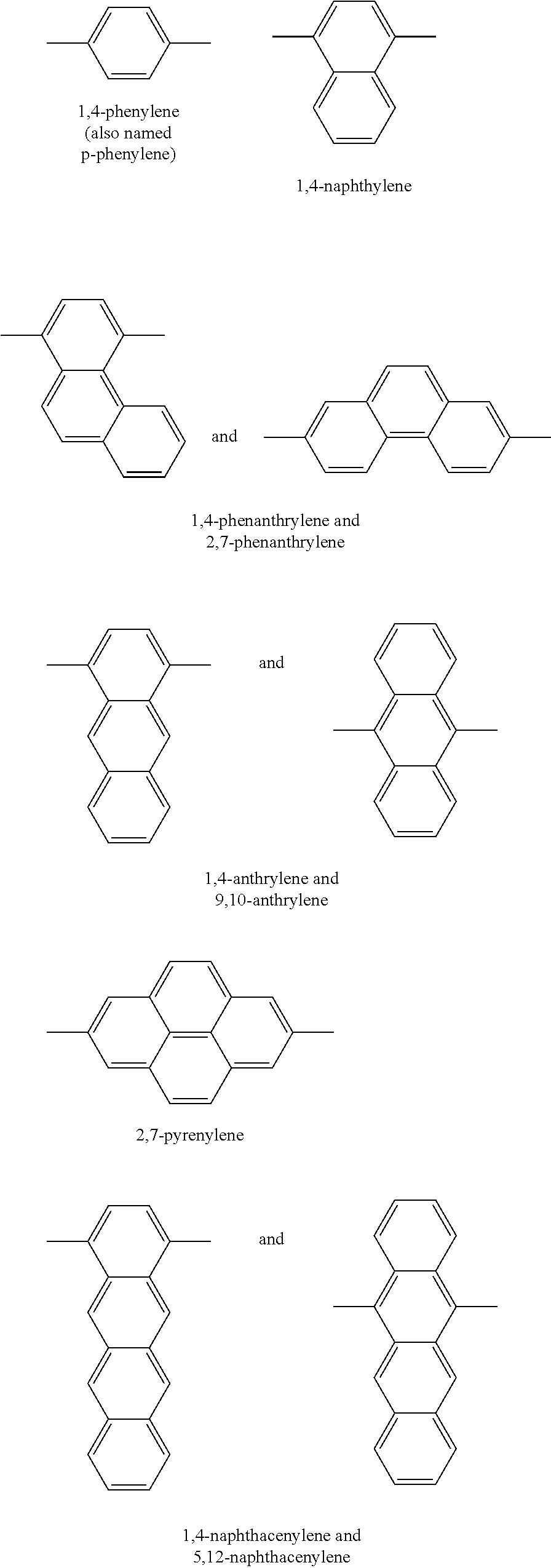
A foam material having one glass transition temperature (Tg) and made from an immiscible composition having at least two glass transition temperatures (Tg) by an extrusion process wherein said composition (C) comprises at least one polyarylene (P1) polymer, wherein more than 50% by moles (moles %) of the recurring units of said (P1) polymer are recurring units (R1) consisting of an arylene group, wherein said arylene group is a hydrocarbon divalent group consisting of one core composed of one benzene ring or of a plurality of benzene rings fused together by sharing two or more neighboring ring carbon atoms, said benzene ring being optionally substituted, wherein each of said arylene group is bound to two other arylene groups of neighboring recurring units (R1) through a first C—C bond (E1) and a second C—C bond (E2), wherein at least 20 moles % of recurring units (R1) are kink-forming arylene units (R1-b), the remainder being rigid rod-forming arylene units (R1-a) different from aryleneR1<sub2>—< / sub2>b units, wherein in said aryleneR1<sub2>—< / sub2>a units the bond (E1) and the bond (E2) are co-linear and anti-parallel towards each other, said (P1) polymer being present in composition (C) in an amount of below 75% by weight (wt. %) and above 10 wt. % based on the total wt. % of (P1) polymer and (PPSU) polymer, and (ii) at least one polyphenylsulfone polymer, said (PPSU) polymer being present in composition (C) in an amount of below 90 wt. % and above 25 wt. % of based on the total wt. % of polyarylene (P4) polymer and (PPSU) polymer.
Owner:SOLVAY SPECIALTY POLYMERS USA LLC
Bedding Product Comprising a Foamed Latex Layer, Slab of Such Foamed Latex Layer for Cutting a Bedding Product Therefrom and Method of Manufacturing Thereof
InactiveUS20150289668A1Improve performanceAdapt quicklyUpholstery manufactureStuffed mattressesVulcanizationEngineering
A method for producing a bedding product is disclosed which has at least a foamed latex layer. The method includes pouring liquid latex foam on a conveyor belt. The liquid latex foam is vulcanized in a vulcanization station to obtain a vulcanized latex foam slab. The vulcanized latex foam slab is cut to a desired length and / or width. Electromagnetic waves with a frequency ranging between 1 and 50 Mhz are used for at least partially vulcanizing the liquid latex foam.
Owner:LATEXCO
A preparation method of light-weight wallboard and multi-layer light-weight wallboard
ActiveCN109516773BHigh foam densityLow foam densityCeramic materials productionCeramicwareFoaming agentProcess engineering
The invention discloses a preparation method of a light-weight wallboard and a multilayer light-weight wallboard, and relates to the technical field of building materials. The preparation method of the light-weight wallboard adopts the method of distributing the first batch and the second batch separately, and then fires them; wherein, both the first batch and the second batch include a base material and a foaming agent, The amount of the foaming agent in the first batch is 0.1%-0.2%, and the amount of the foaming agent in the second batch is 0.25-0.35%; preferably, the number of times of distributing is 2-3 times. The multi-layer light wallboard is prepared by applying the above-mentioned preparation method of the light wallboard. The preparation method of the invention improves the sound insulation, heat insulation and mechanical properties of the finally formed multi-layer lightweight wallboard.
Owner:GUANGDONG KITO CERAMICS GROUP CO LTD +2
Refrigerated container underframe structure and refrigerated container using the under-frame structure
ActiveCN101423140BMeet the requirementsReduce load capacityLarge containersTank wagonsUltimate tensile strengthHeat leakage
The invention provides a chassis structure used for a refrigerated container, comprising two vertically-arranged bottom side beams, a plurality of main bottom cross beams which are arranged to be vertical to the bottom side beams and a corrugated sub floor which is connected with the bottom side beams and the main bottom cross beams. Two ends of the main bottom cross beam are welded onto the bottom side beams and the corrugated sub follow is arranged on the main bottom cross beams. The invention is characterized in that the structure also comprises a plurality of small bottom cross beams and each small bottom cross beam is arranged between the trough of the corrugated sub floor and a T floor inside the container and two ends of the small bottom cross beam are also vertically welded onto the bottom side beams. The invention also provides a refrigerated container adopting the chassis structure. For the chassis structure of the invention, the weight of goods inside the container is mainly borne by the main bottom cross beams and the small bottom cross beams so as to reduce the bearing strength of the corrugated sub floor and enhance the rigidity and strength of the chassis of the refrigerated container, and simultaneously to reduce the corrugated sub floor materials and corrugated height and the foam density of a foam layer so as to reduce the consumption of structure materials and foam material and reduce the heat-leakage rate.
Owner:TAICANG CIMC REEFER LOGISTICS EQUIP CO LTD +2
Freezer foaming layer
The invention discloses a freezer foaming layer, and relates to the technical field of freezer manufacturing. The freezer foaming layer is prepared from a high-viscosity black material, combined polyether and a foaming agent through a reaction. The viscosity of the high-viscosity black material at 25 DEG C is 300 to 700 mPa.s; wherein the high-viscosity black material is a mixture consisting of isocyanate with higher functionality and diphenylmethane diisocyanate. The flowability of the foaming liquid is improved through the combined polyether, so that the problem of insufficient foam flowability caused by the use of a high-viscosity black material is solved; the prepared polyurethane foam has the effects of zero ODP value and low GWP value; besides, the prepared foam is low in foaming density, the using amount of foaming materials is reduced, the foaming cost is reduced, the heat conductivity coefficient of the foam is low, and it is guaranteed that the heat preservation performance of the foam is not affected.
Owner:CHANGHONG MEILING CO LTD
Bedding Product Comprising a Foamed Latex Layer, Slab of Such Foamed Latex Layer for Cutting a Bedding Product Therefrom and Method of Manufacturing Thereof
ActiveUS20190328148A1Improve performanceAdapt quicklyUpholstery manufactureStuffed mattressesVulcanizationEngineering
A method for producing a bedding product comprising at least a foamed latex layer, said method comprising the steps of: —pouring liquid latex foam on a conveyor belt; —vulcanizing said liquid latex foam in a vulcanization station to obtain u vulcanized latex foam slab; —cutting said vulcanized latex foam slab to a desired length and / or width, characterized in that for at least partially vulcanizing said liquid latex foam electromagnetic waves with a frequency ranging between 1 and 50 Mhz are used.
Owner:LATEXCO
Improved Expandable Vinyl Aromatic Polymers
The present invention is related to expandable vinyl aromatic polymers comprising from 1 to 10% by weight of homogeneously dispersed coke particles having a volume median particle diameter (D50) comprised between 0.5 and 8.5 μm and from 0.1 to 5% by weight of a halogenated block copolymer. The invention further is related to a method for producing said expandable vinyl aromatic polymers and to the expanded foams.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH BELGIUM
Polyarylene foam materials
ActiveUS10233299B2Well defined and fine and homogeneous cell structureImprove uniformitySynthetic resin layered productsVehicle componentsPolymer scienceGlass transition
Owner:SOLVAY SPECIALTY POLYMERS USA LLC
A kind of polybutene foam material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a polybutylene foam material and a preparing method thereof. According to the foam material, by means of a chemical foaming method, an extruder is used for carrying out extruding foaming, an injection molding machine is used for carrying out injection molding foaming, and a double-roller mixing mill is used for carrying out mould pressing foaming after blending. The situation that melt indexes and melt strength corresponding to polybutylene of different and identical contents are different is taken into consideration, and the influence on the foaming behavior from polybutylene of the different and identical contents is explored. The influence on the cellular structure and mechanical properties of the foam material from different addition quantities of foaming agents is studied. The influence on the polybutylene cross-linking degree and the material melt strength from different addition quantities of cross-linking agents is studied, so that the foam material with cells distributed uniformly and good mechanical properties is obtained. In addition, different kinds of nucleating agents and the addition quantity of the different nucleating agents are considered according to the classic nucleating theory, and a balance point is found between the cellular structure and the mechanical properties of the foam material. The foam material can be applied to automotive upholstery parts, food packages, biological medicine materials and pipe heat insulation and heat preservation cannulas.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com