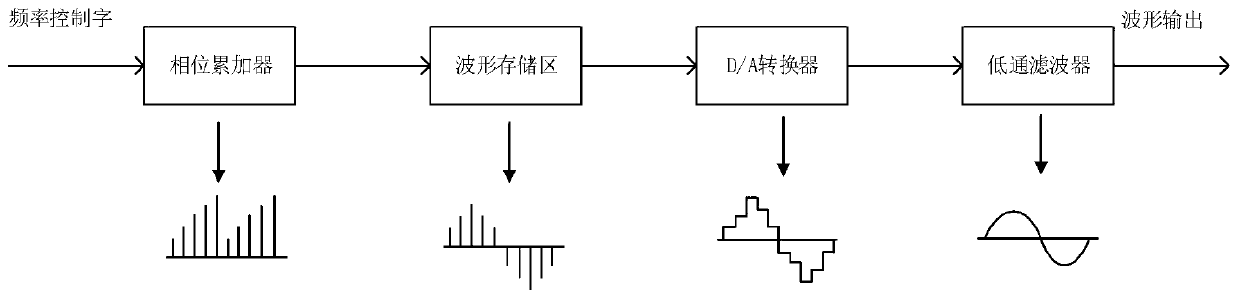
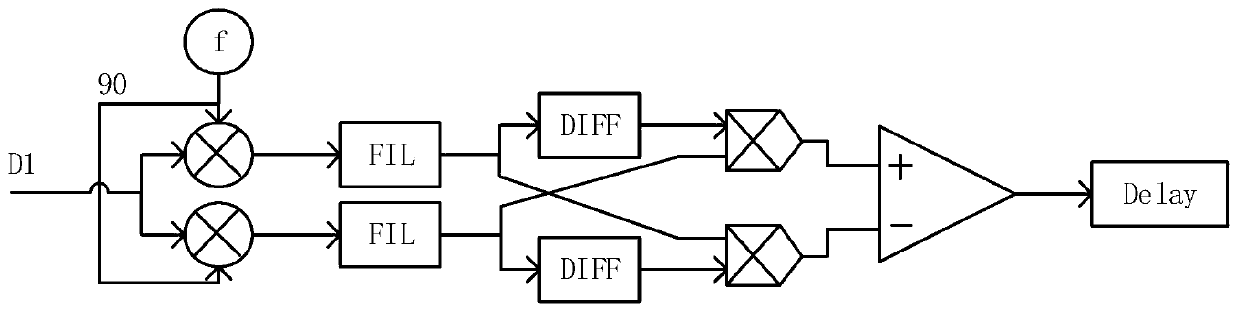
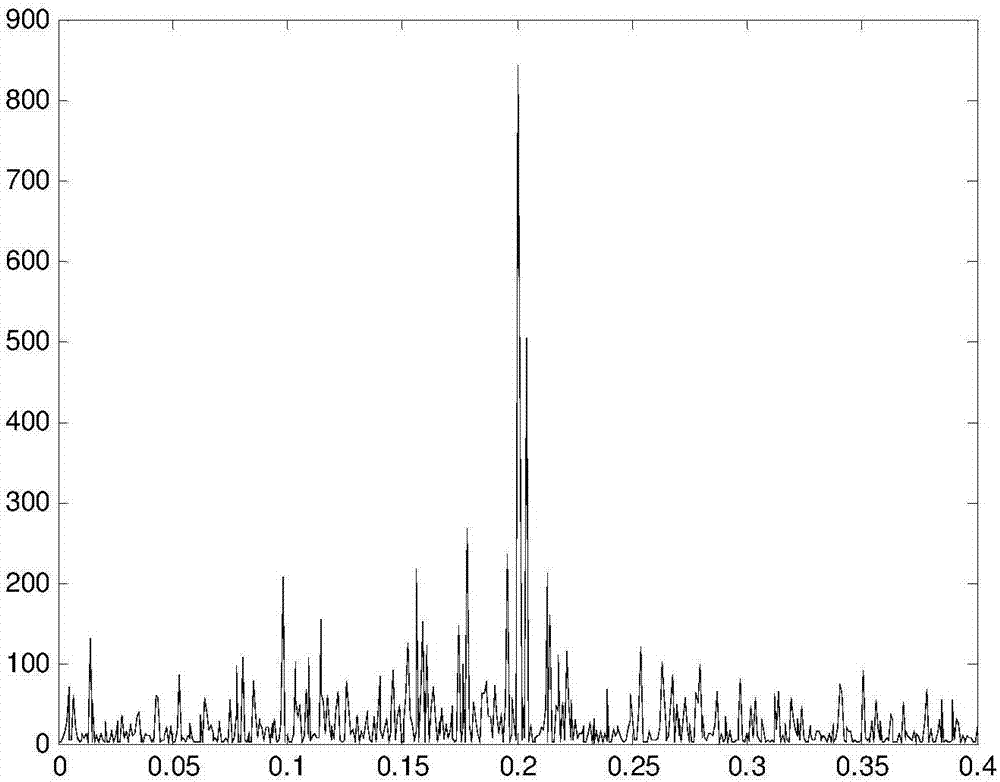
Patents
Literature
64 results about "Chirp rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
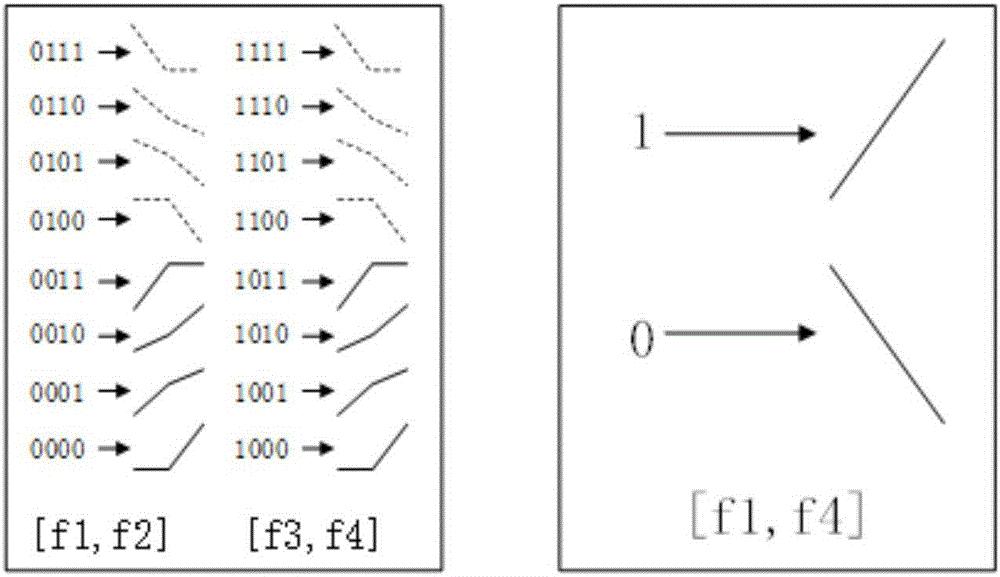
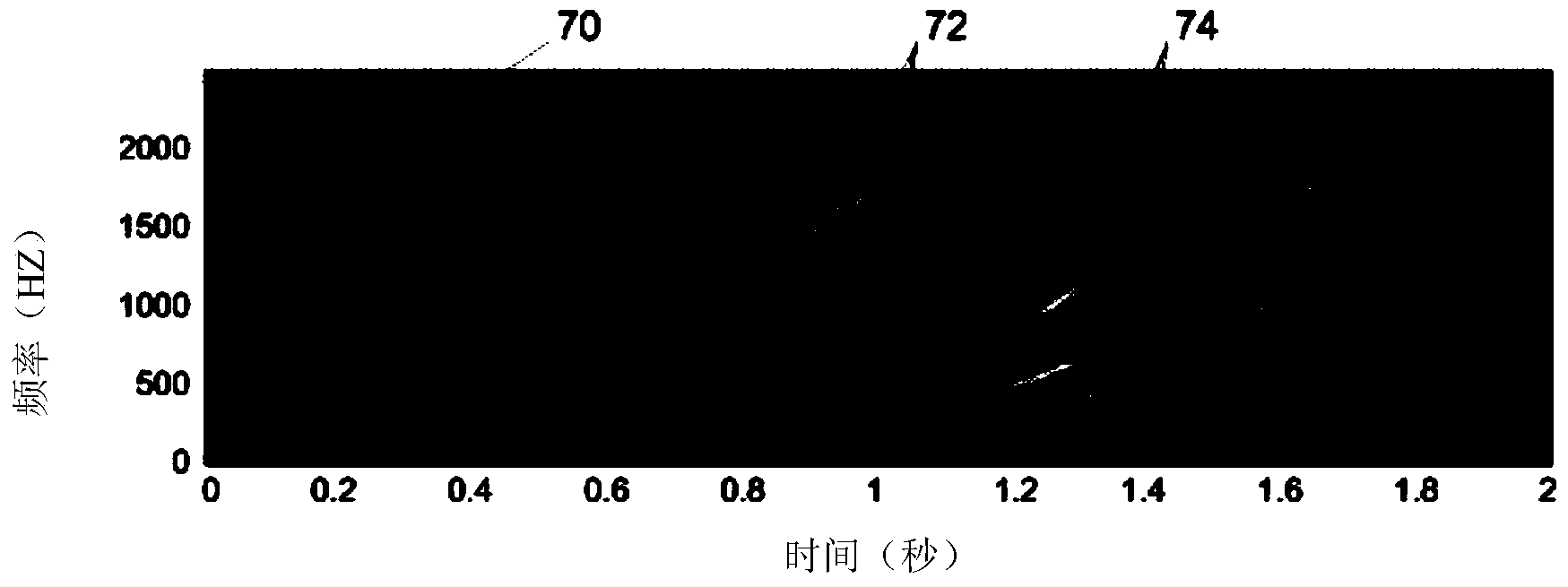
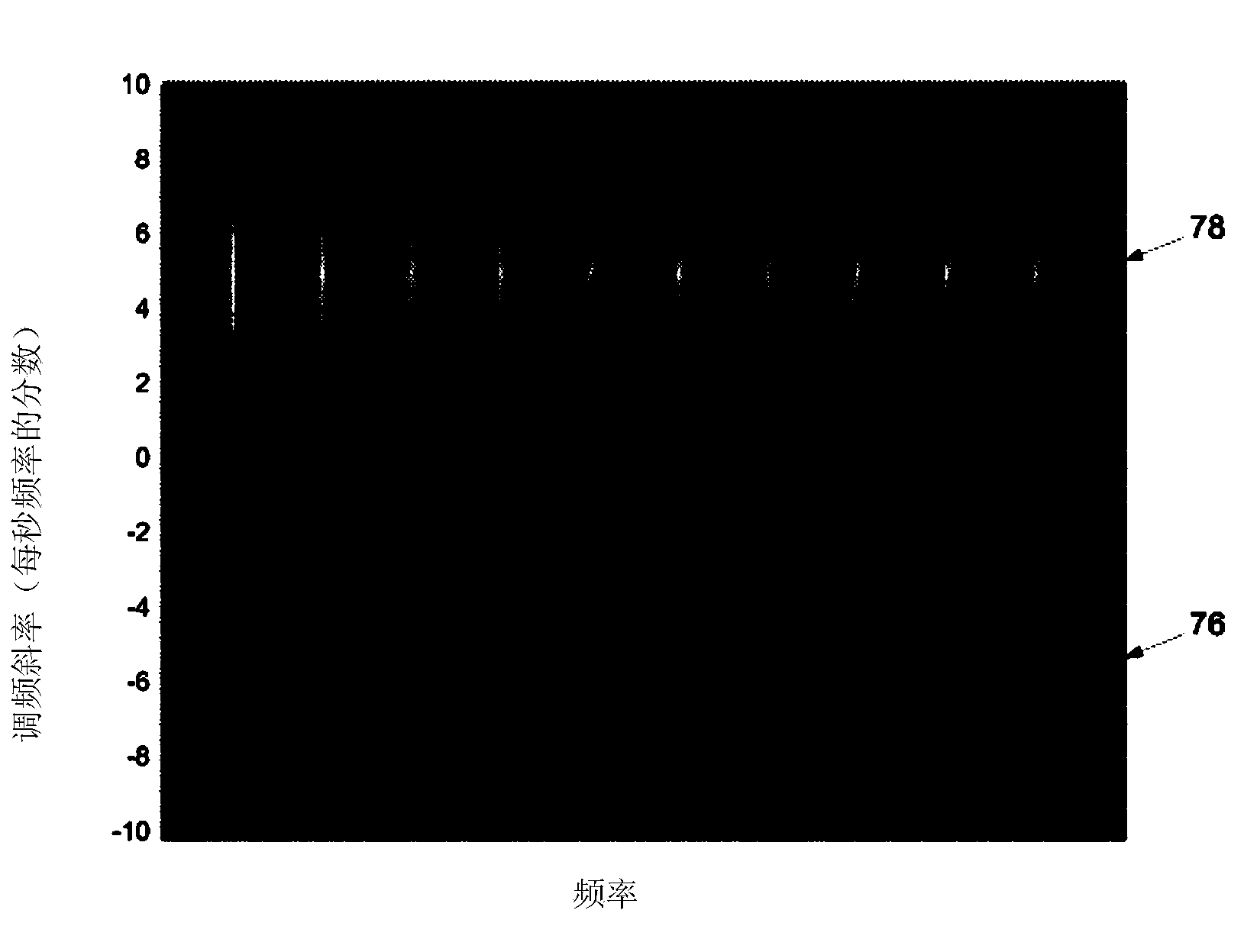
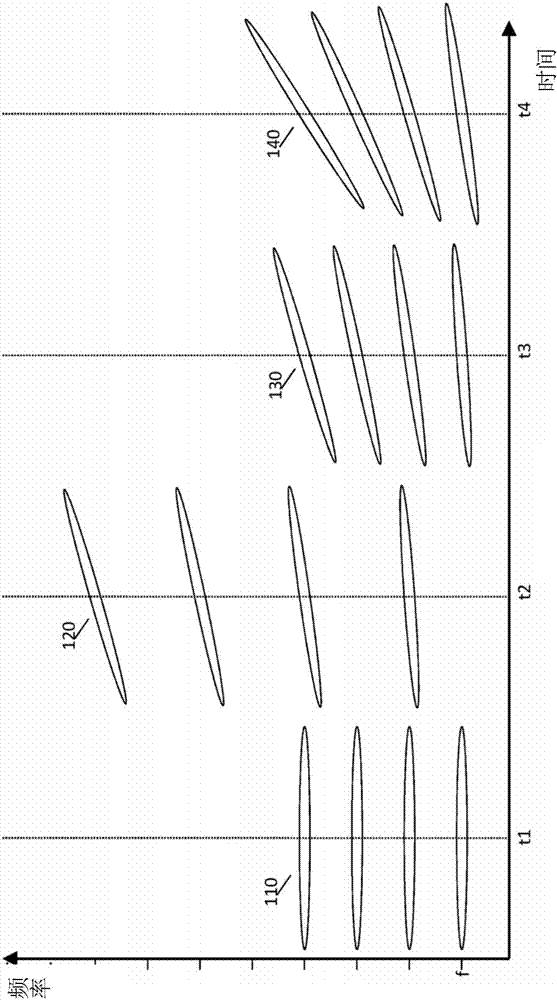
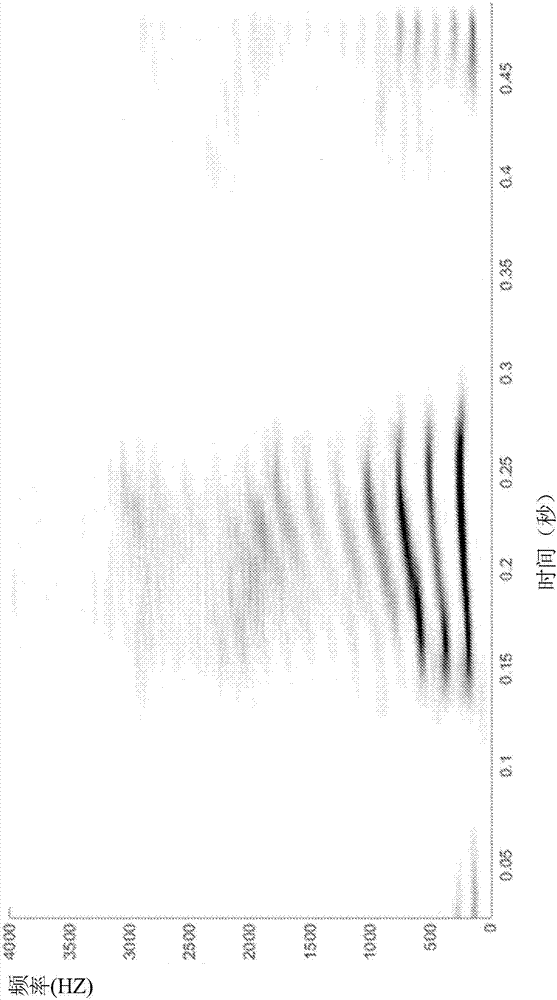
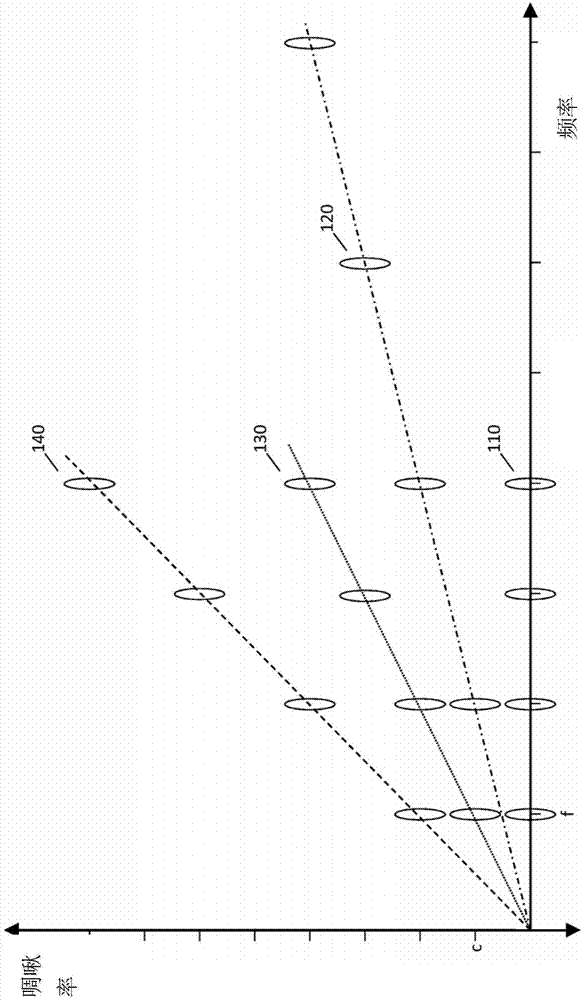
Hence the rate at which their frequency changes is called the chirp rate. In binary chirp modulation, binary data is transmitted by mapping the bits into chirps of opposite chirp rates. For instance, over one bit period "1" is assigned a chirp with positive rate a and "0" a chirp with negative rate −a.
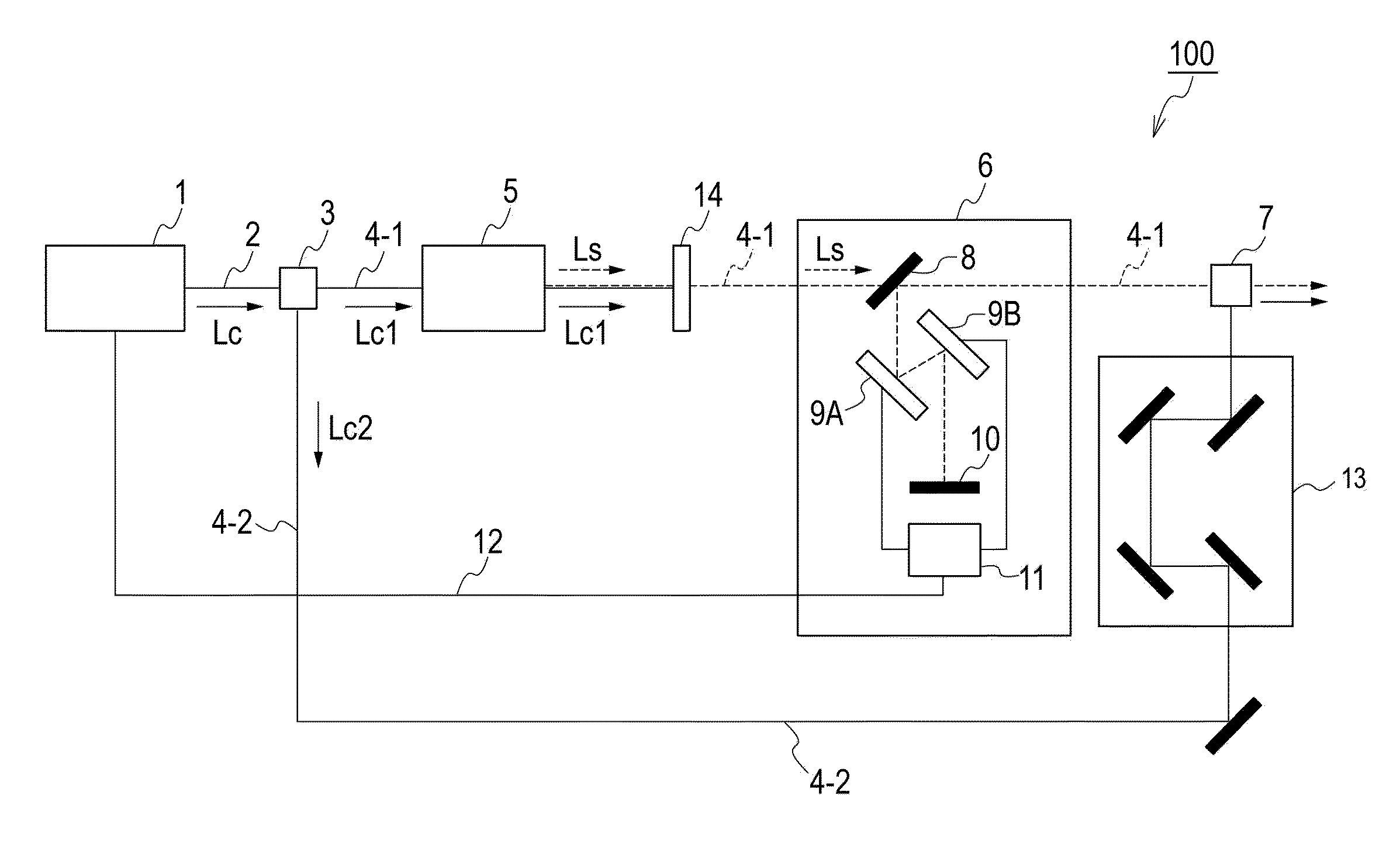
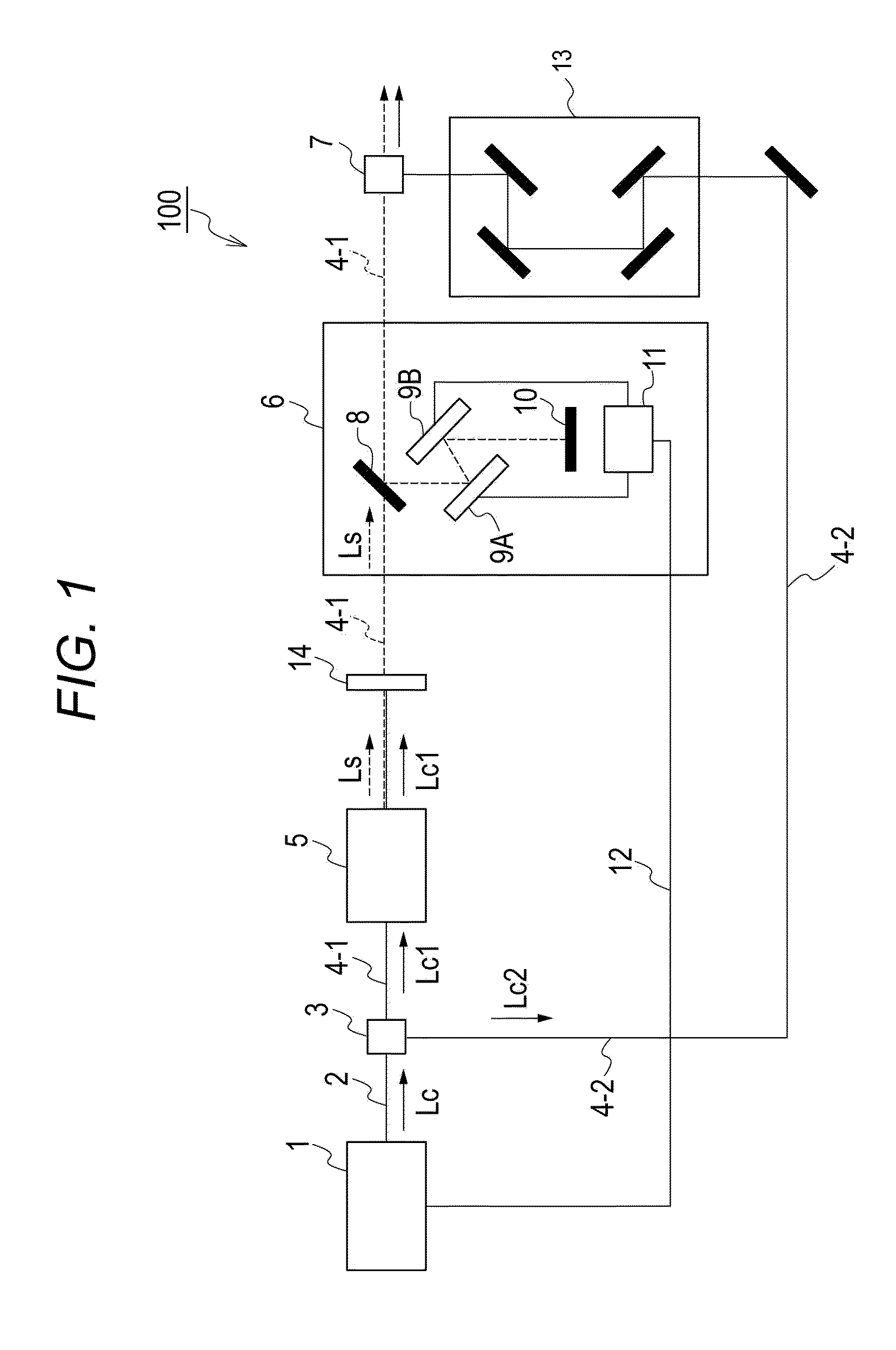
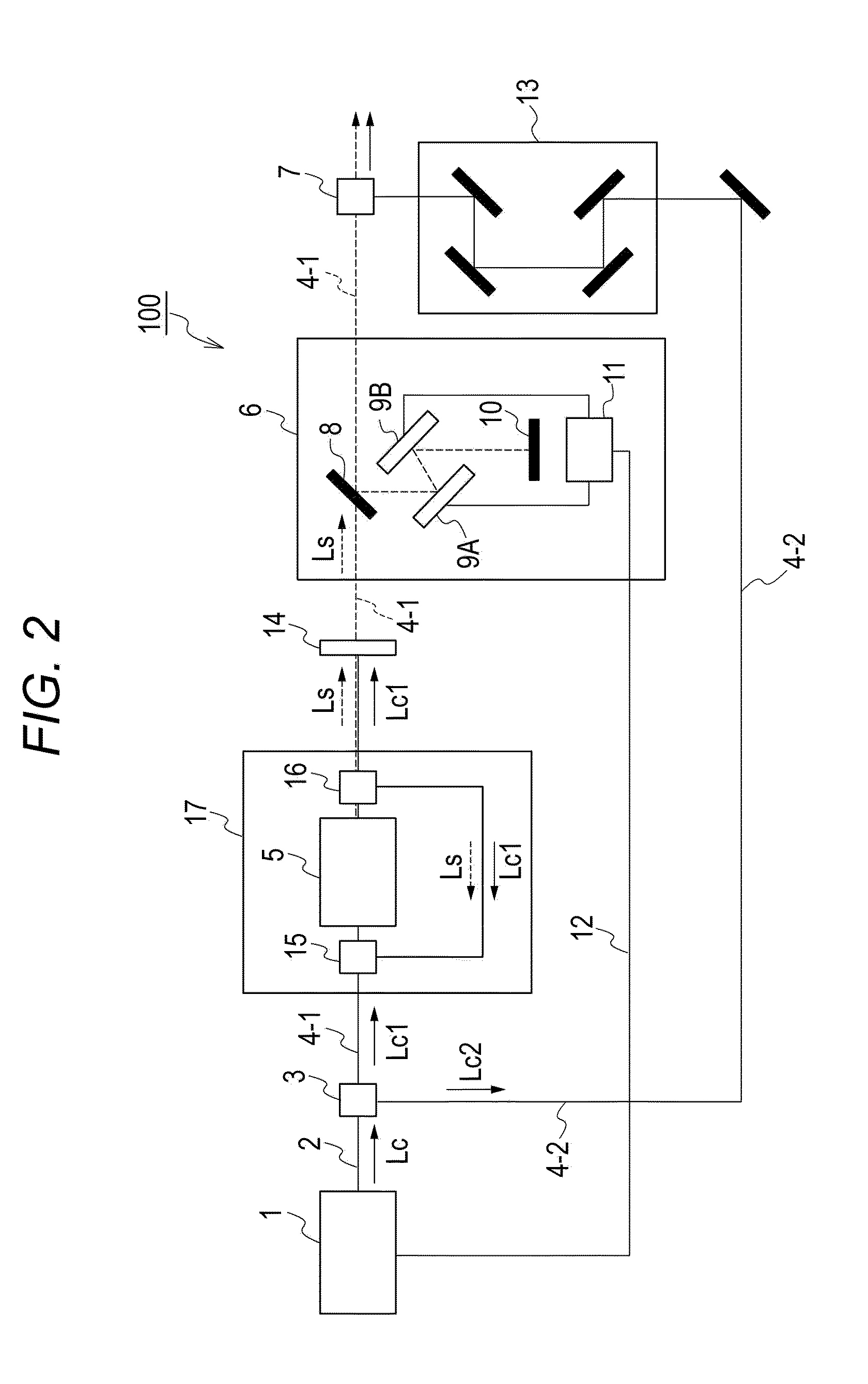
System and method of processing a sound signal including transforming the sound signal into a frequency-chirp domain
ActiveUS20130041658A1Improve classificationElectrical apparatusDigital computer detailsHarmonicAudio frequency
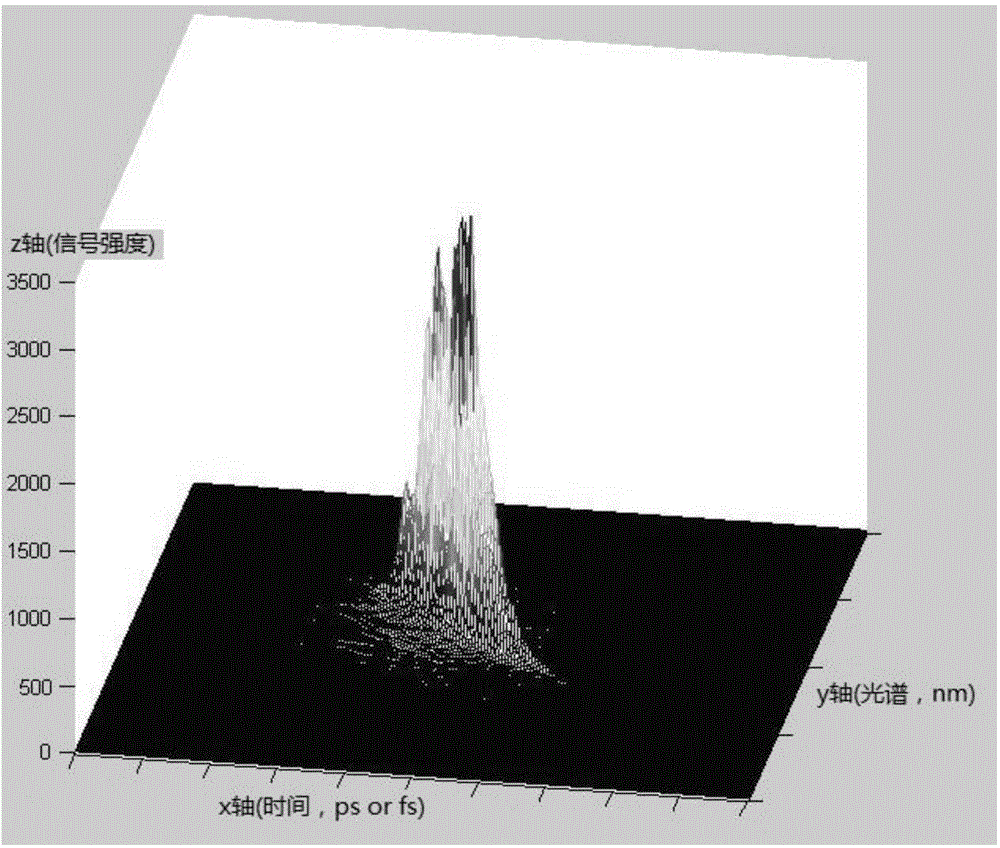
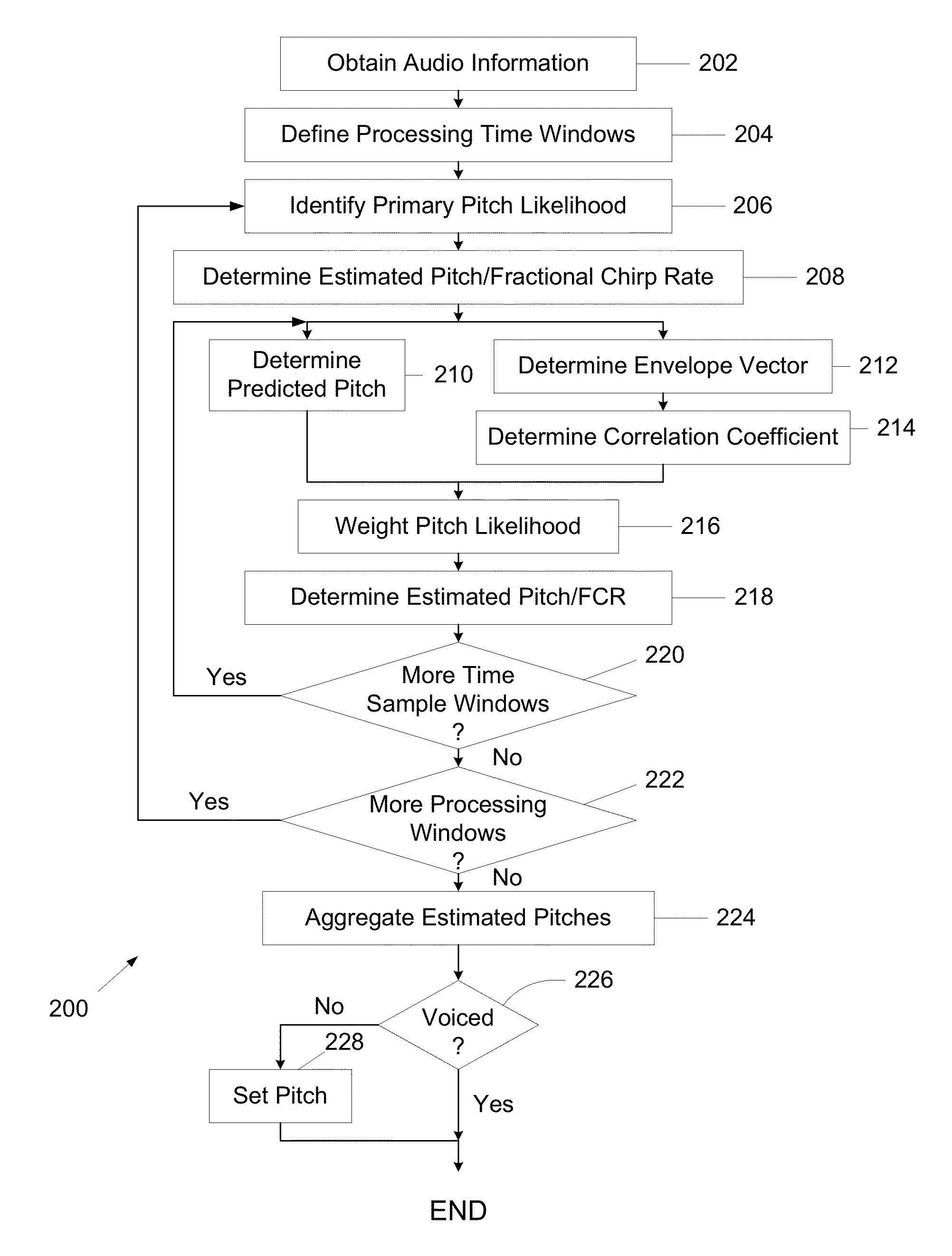
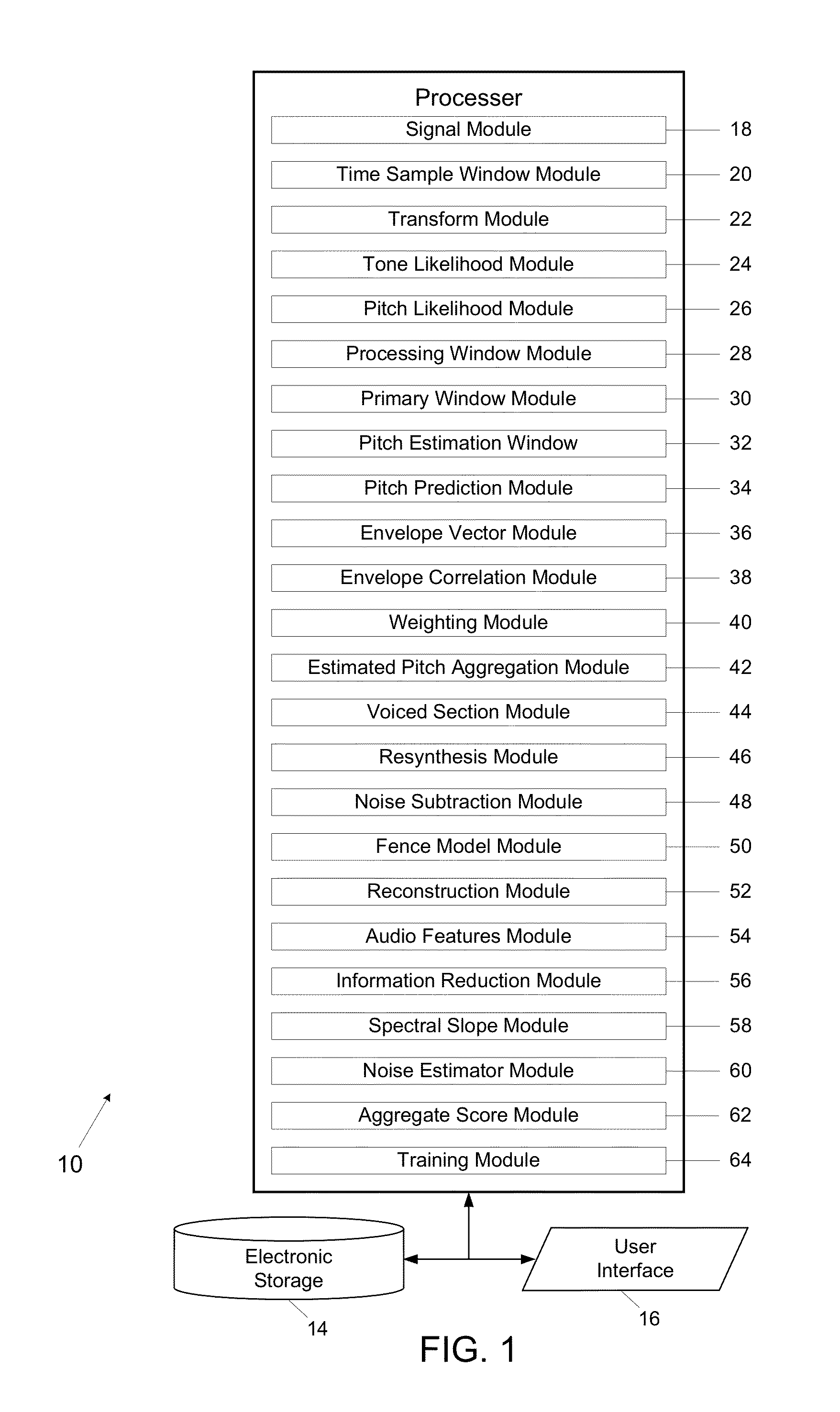
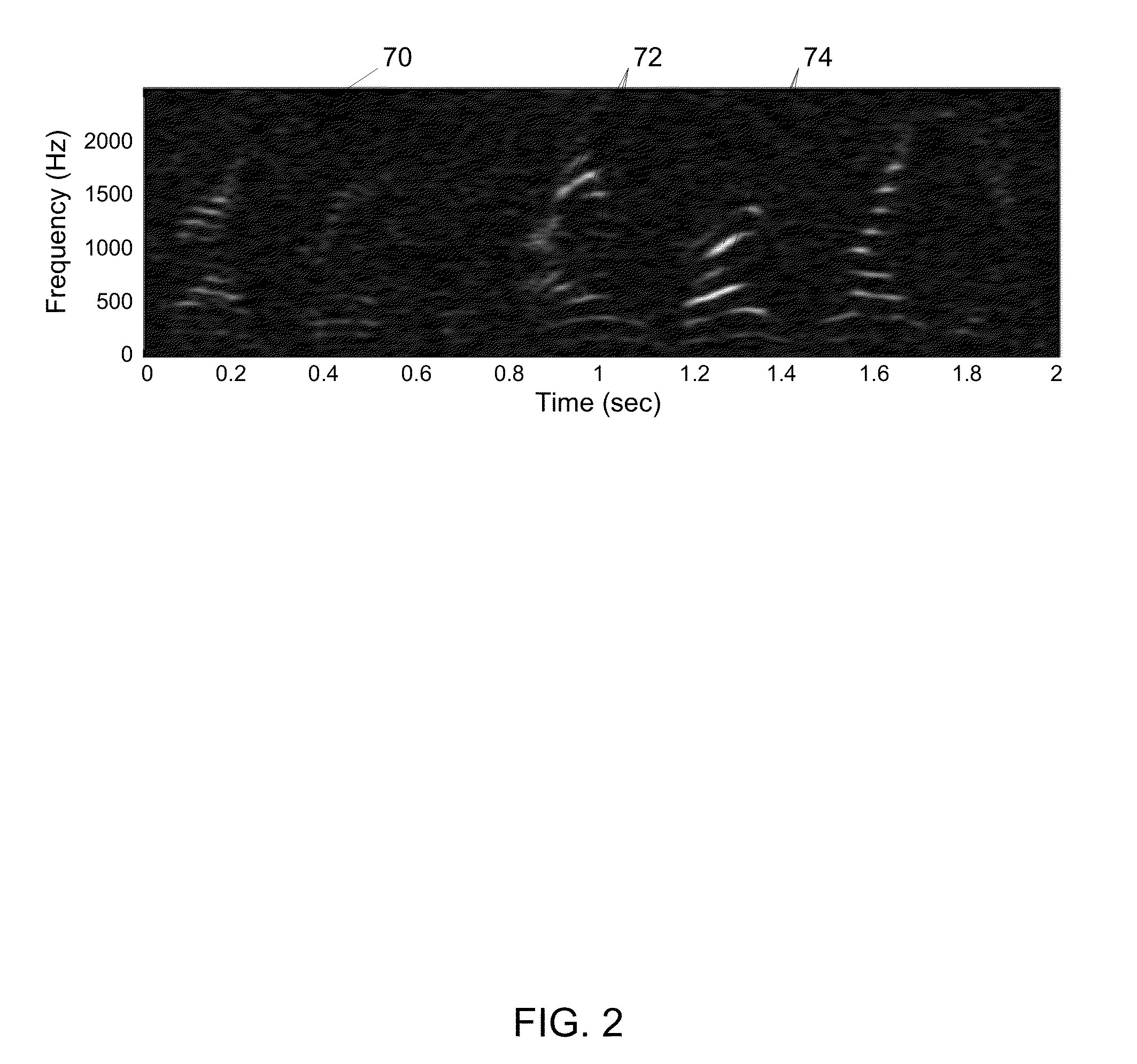
A system and method may be configured to process an audio signal. The system and method may track pitch, chirp rate, and / or harmonic envelope across the audio signal, may reconstruct sound represented in the audio signal, and / or may segment or classify the audio signal. A transform may be performed on the audio signal to place the audio signal in a frequency chirp domain that enhances the sound parameter tracking, reconstruction, and / or classification.
Owner:FRIDAY HARBOR LLC
Low-repetition-rate ring-cavity passively mode-locked fiber laser
InactiveUS20090003391A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionMode locked fiber laserFiber disk laser
A ring-cavity, passively mode locked fiber laser capable of producing short-pulse-width optical pulses at a relatively low repetition rate. The fiber laser uses a one-way ring-cavity geometry with a chirped fiber Bragg grating (CFBG) at its reflecting member. The CFBG is part of a dispersion compensator that includes an optical circulator that defines a one-way optical path through the ring cavity. A doped optical fiber section is arranged in the optical path and serves as the gain medium. A pump light source provides the pump light to excite the dopants and cause the gain medium to lase. A saturable absorber is operable to effectuate passive mode-locking of the multiple modes supported by the ring cavity. The ring cavity geometry allows to achieve mode locking with single pulse operation in a longer cavity length than conventional linear cavities. Furthermore, the longer cavity length reduces the constraints on the chirp rate of the CFBG. This, in turn, allows the CFBG to have a relatively high reflectivity, which provides the necessary dispersion compensation and cavity loss for generating short optical pulses at a low repetition rate.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method and apparatus for detecting optical spectral properties using optical probe beams with multiple sidebands
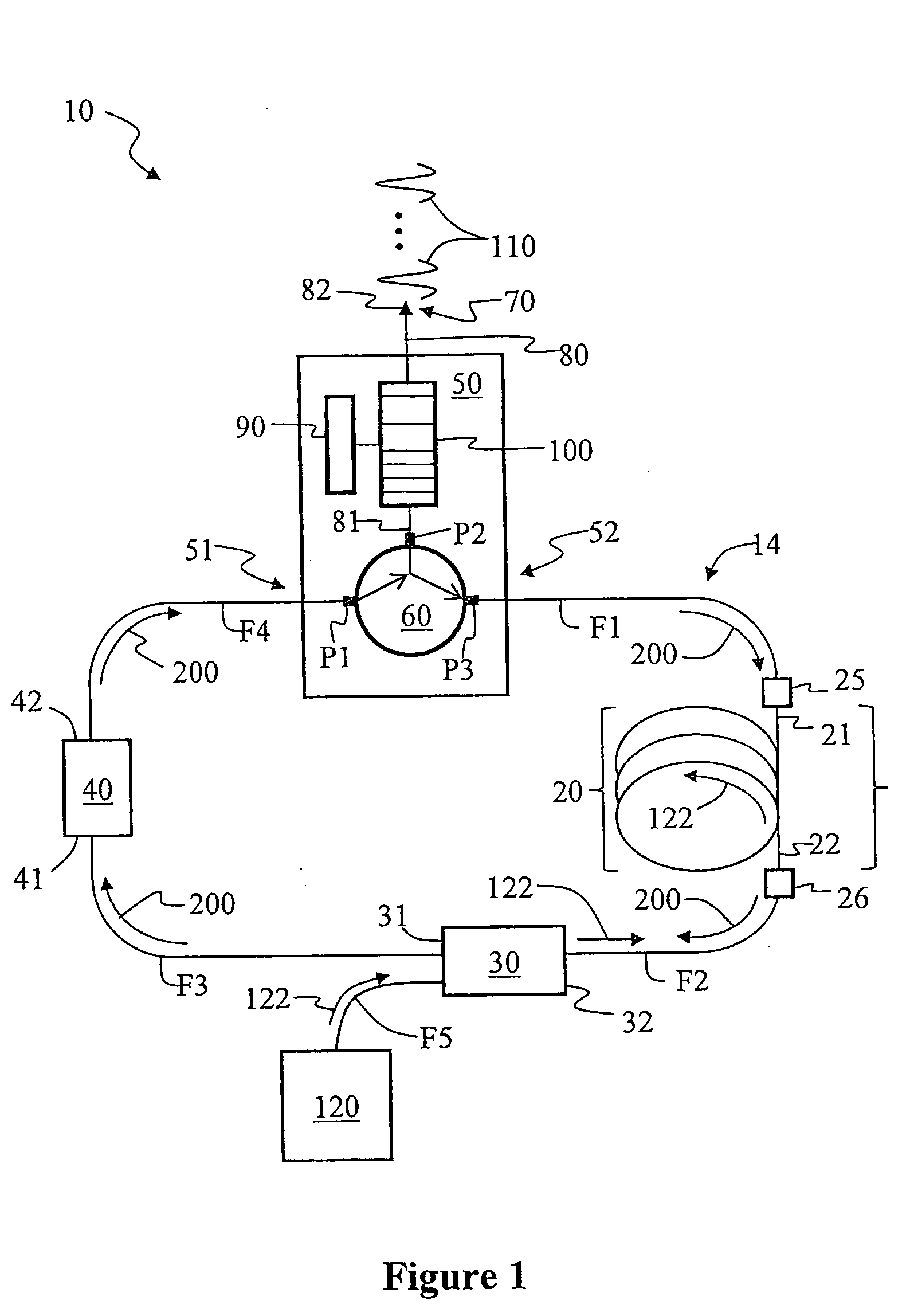
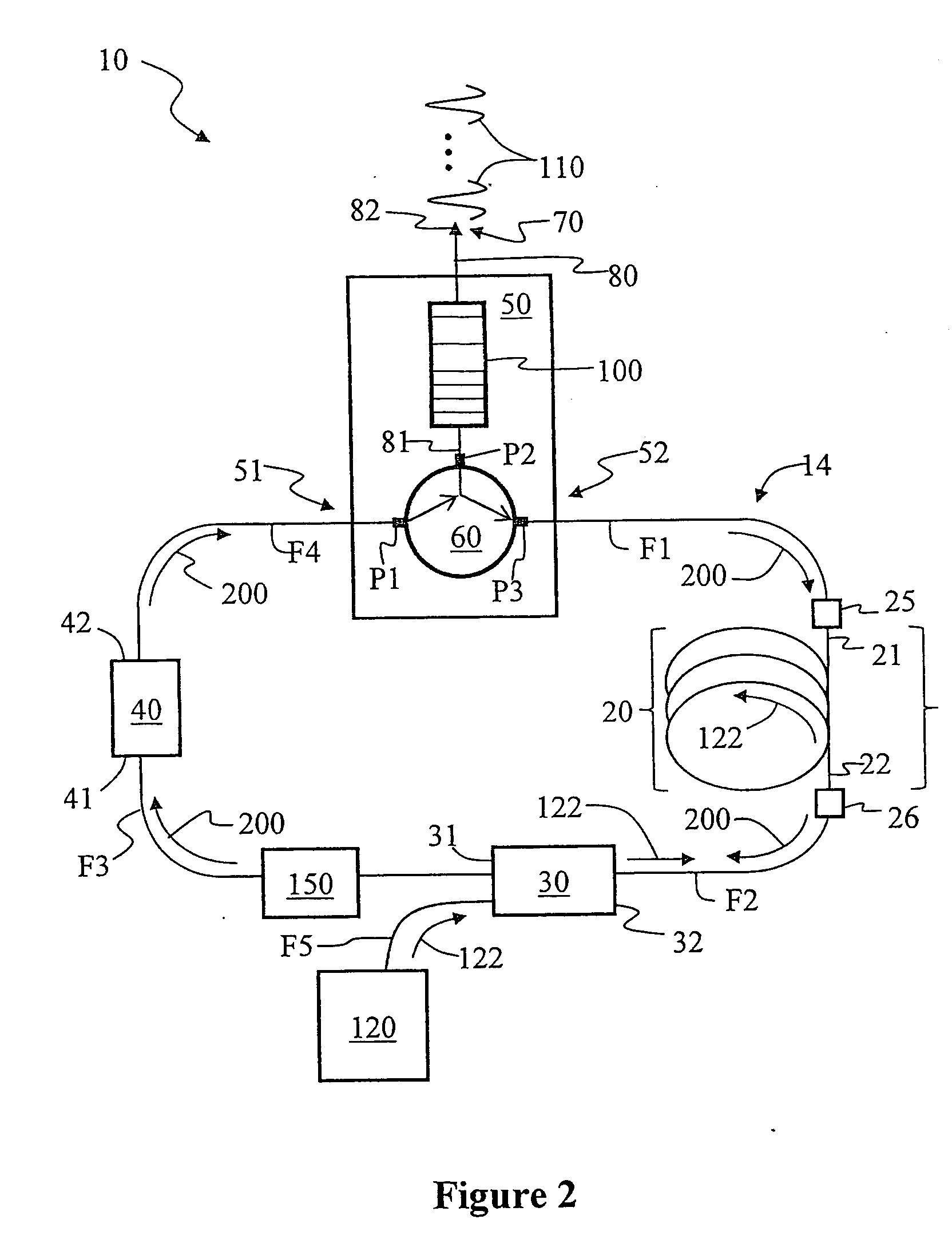
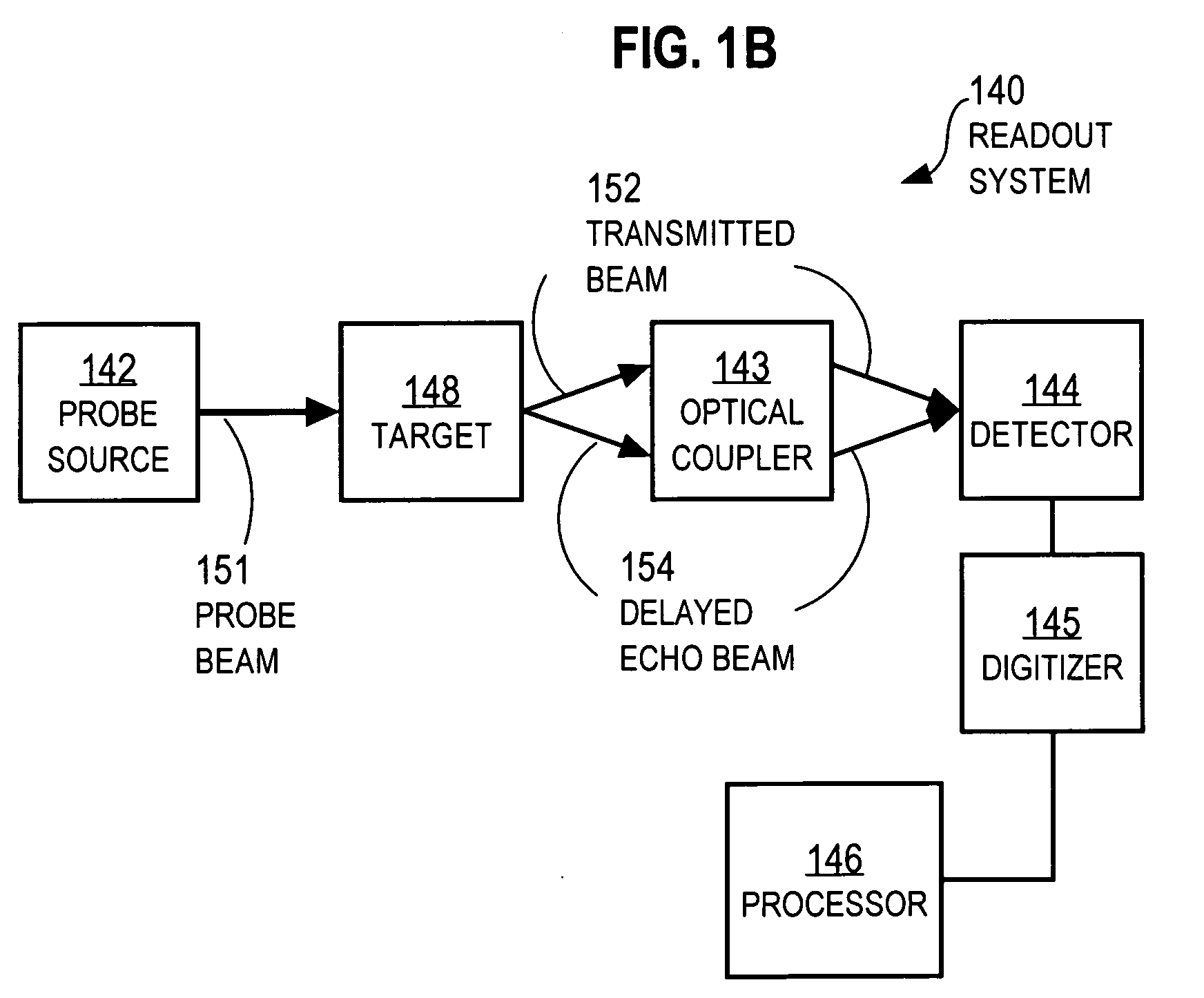
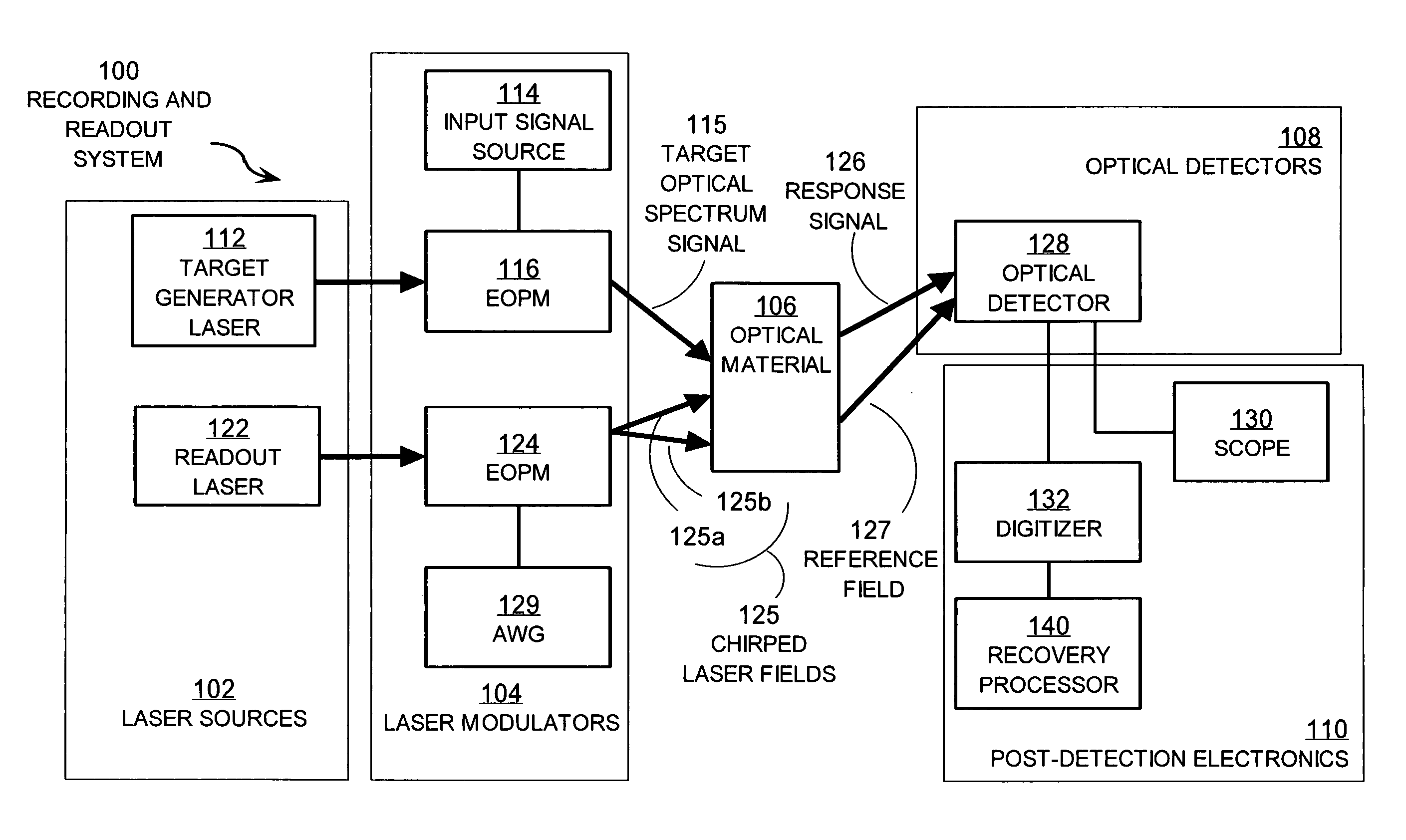
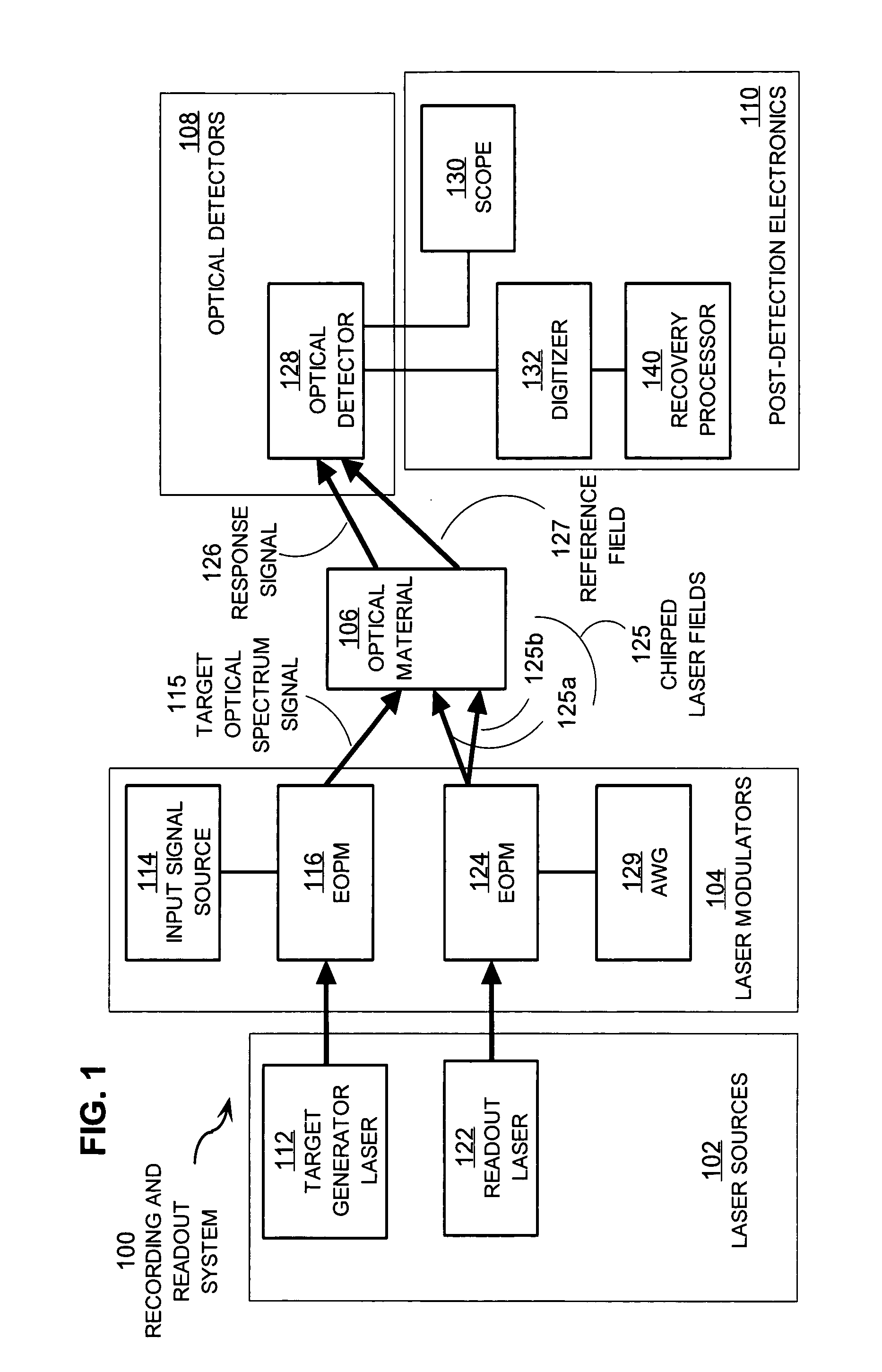
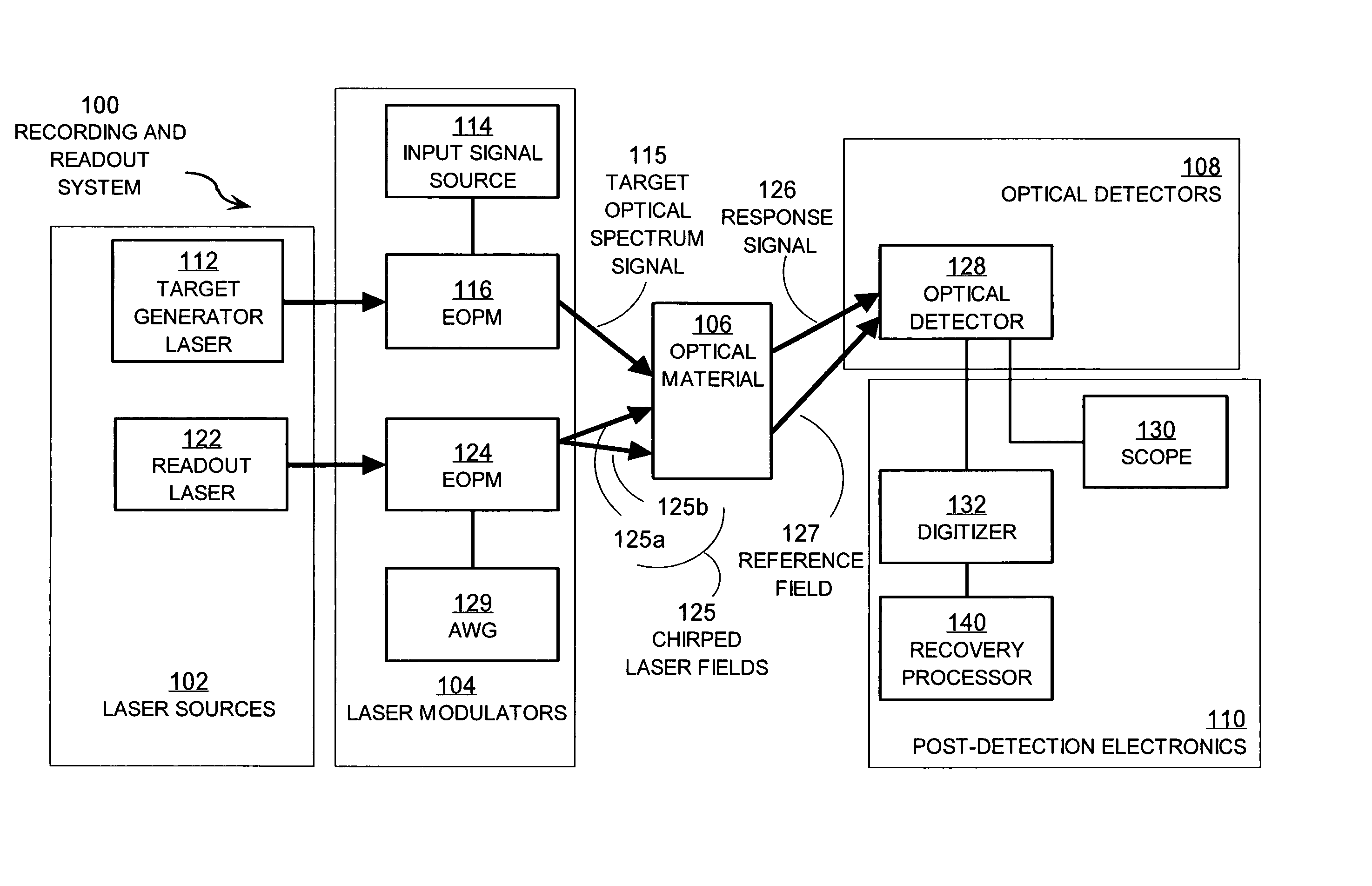
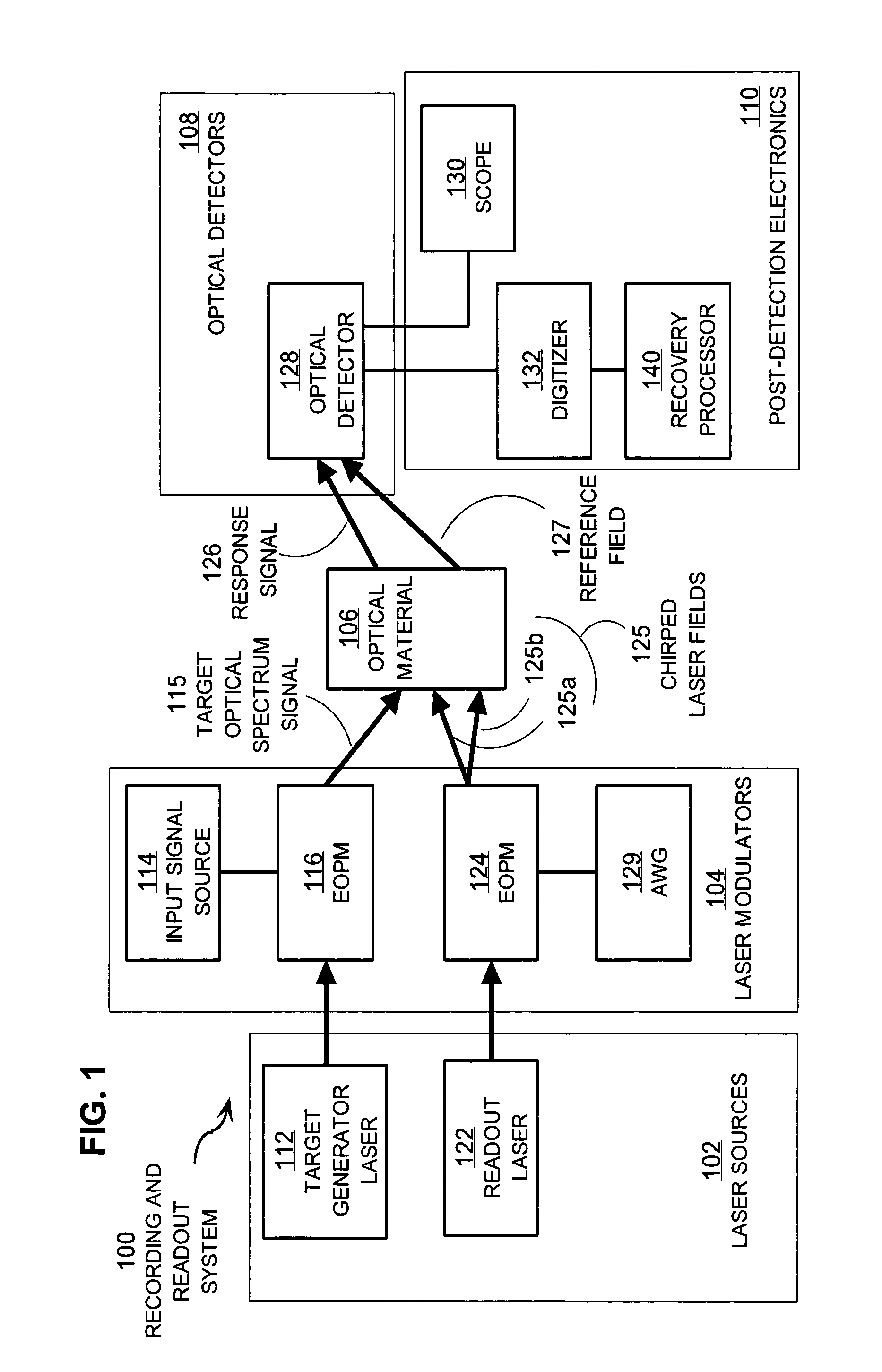
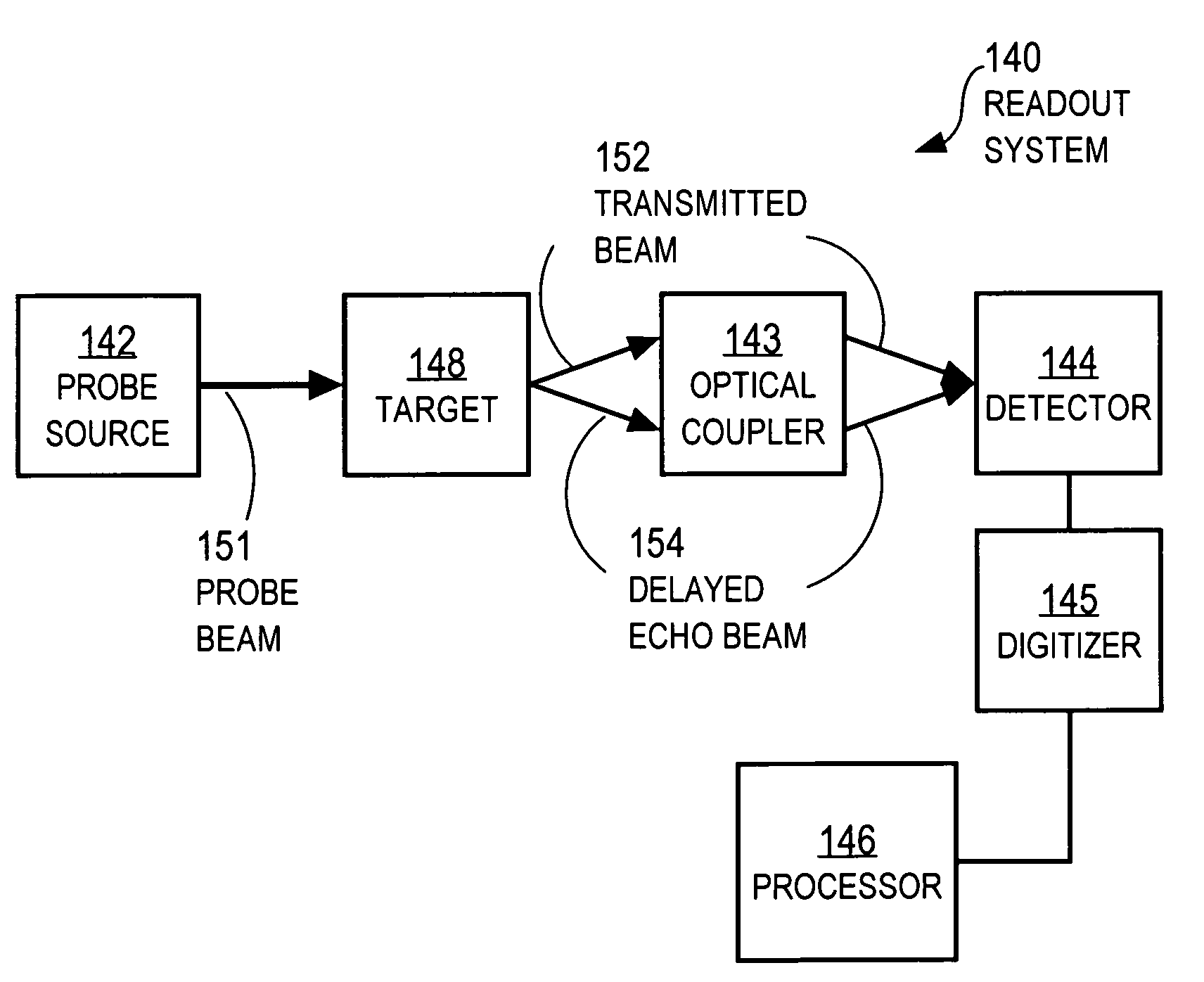
Techniques for detecting optical spectral properties of a target are described. The technique includes providing an optical carrier which has an optical frequency bandwidth which is narrow compared to the width of the narrowest spectral feature of the target to be determined. This optical carrier is then electro-optically modulated with an RF frequency chirp, creating an optical chirp probe beam with a frequency chirped optical spectrum having upper and lower frequency chirped sidebands that have amplitudes sufficient to be detected at a detector. The sidebands are frequency bands arranged symmetrically around the optical carrier frequency. The attributes of a sideband include a start frequency, bandwidth and chirp rate. A probe beam is generated with the sidebands and directed onto a target having a physical property with optical frequency dependence. An optical response signal resulting from an interaction between the probe beam and the target is detected. The optical frequency dependence of the physical property of the target is determined based on the optical response signal and the attributes of the sidebands.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for processing TOPS (Terrain Observation by Progressive Scan)-SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar)-Raw Data
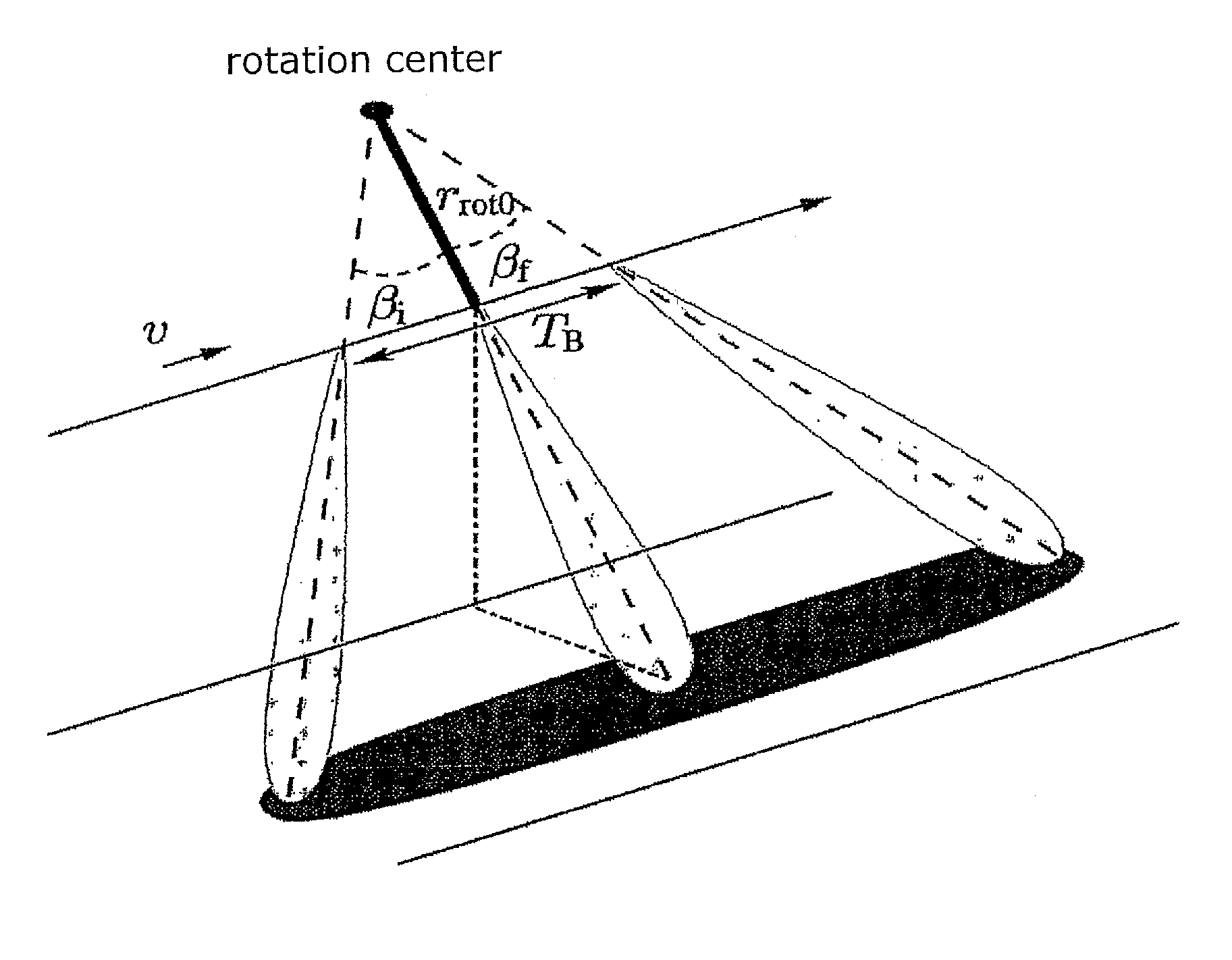
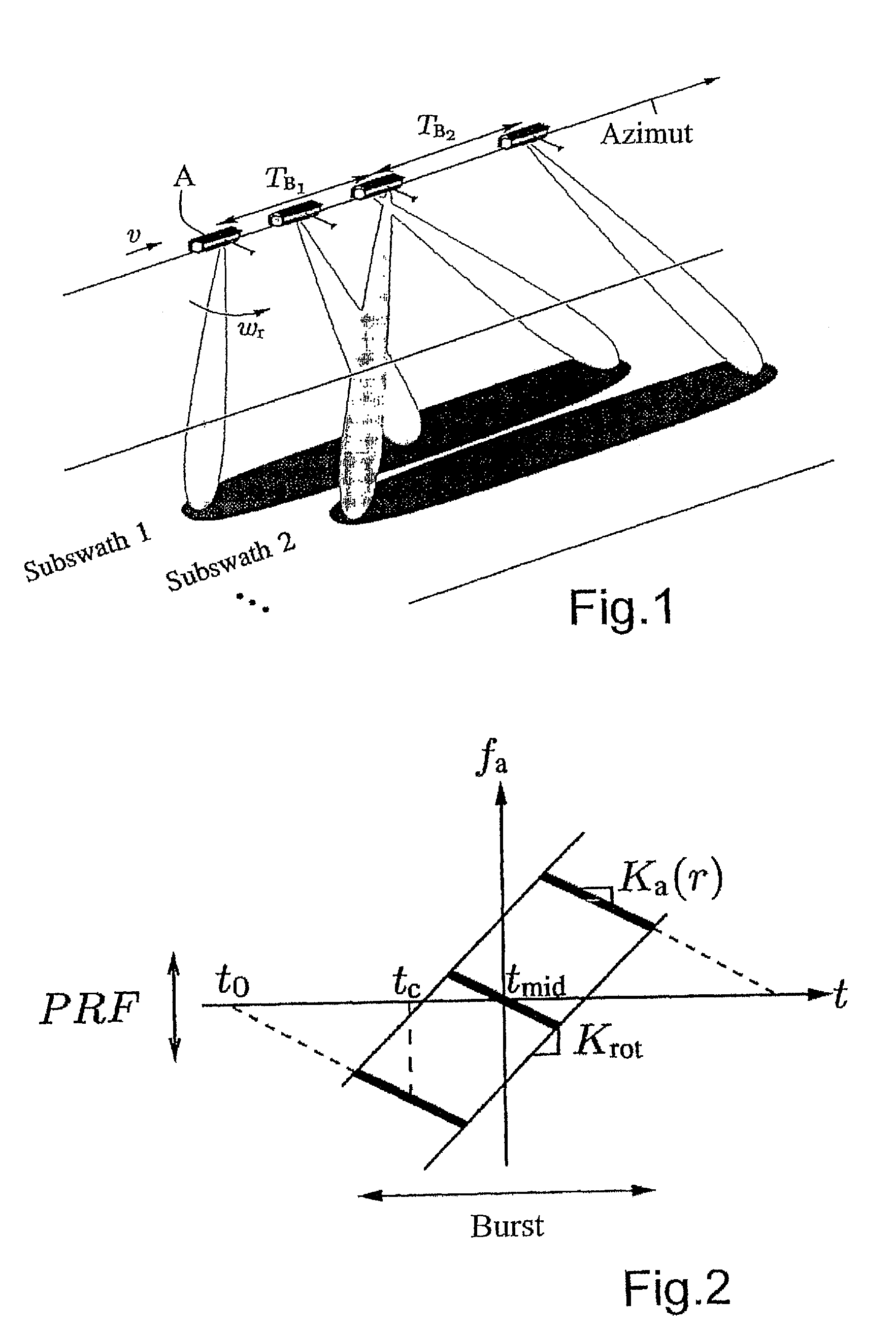
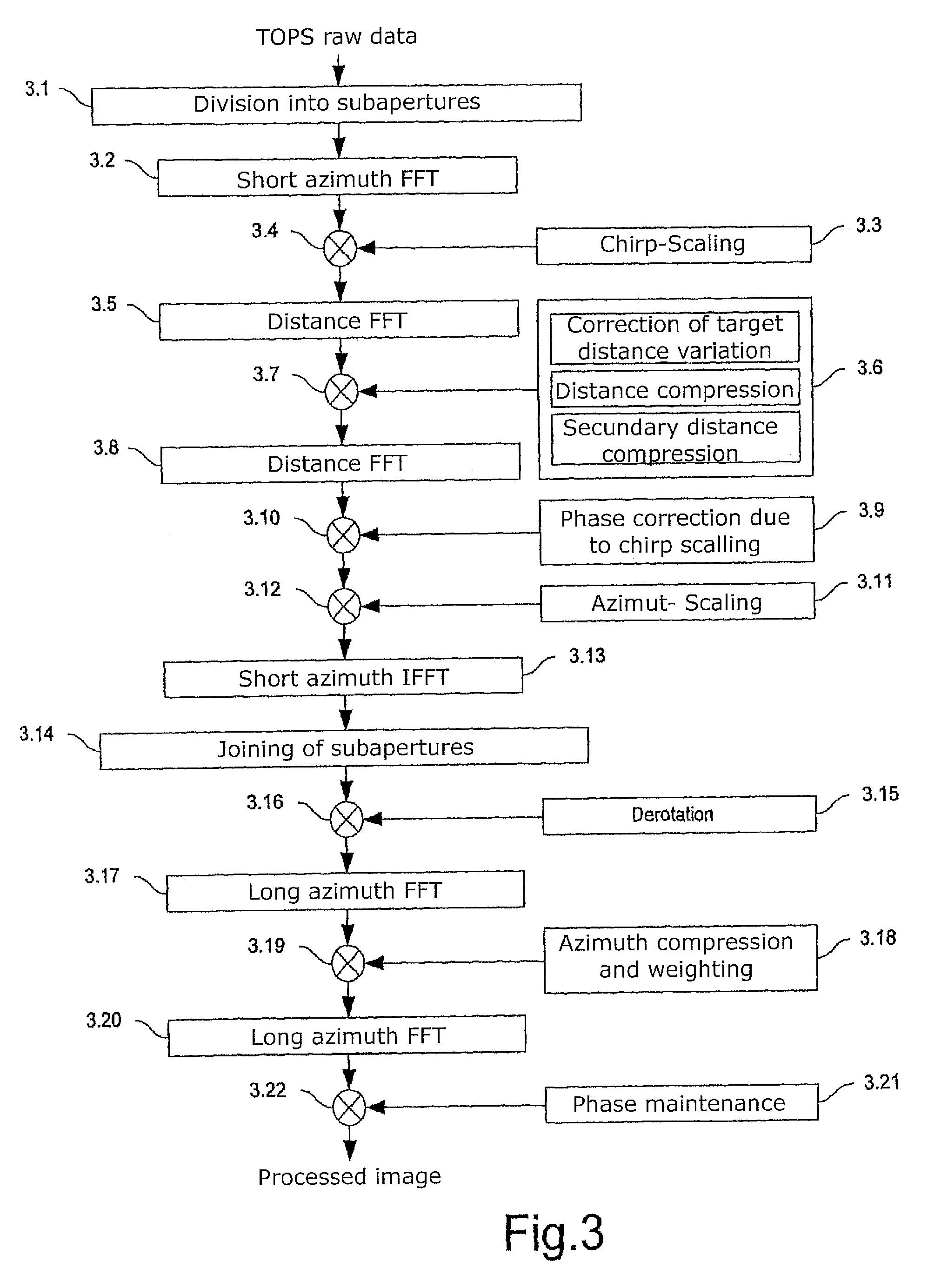
ActiveUS20100207808A1Improve accuracyAvoiding azimuth aliasing (backfoldingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEuclidean vectorLandform
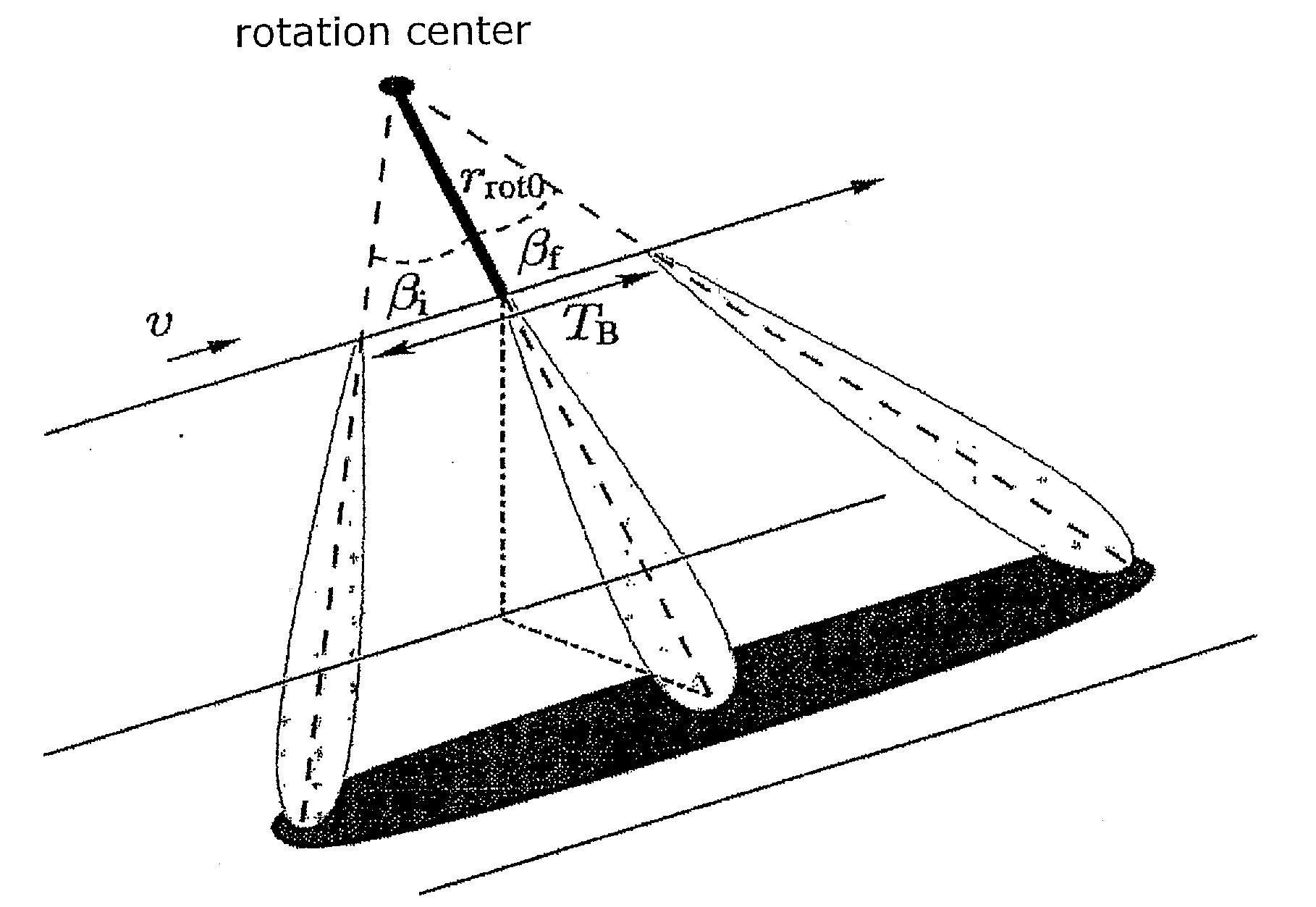
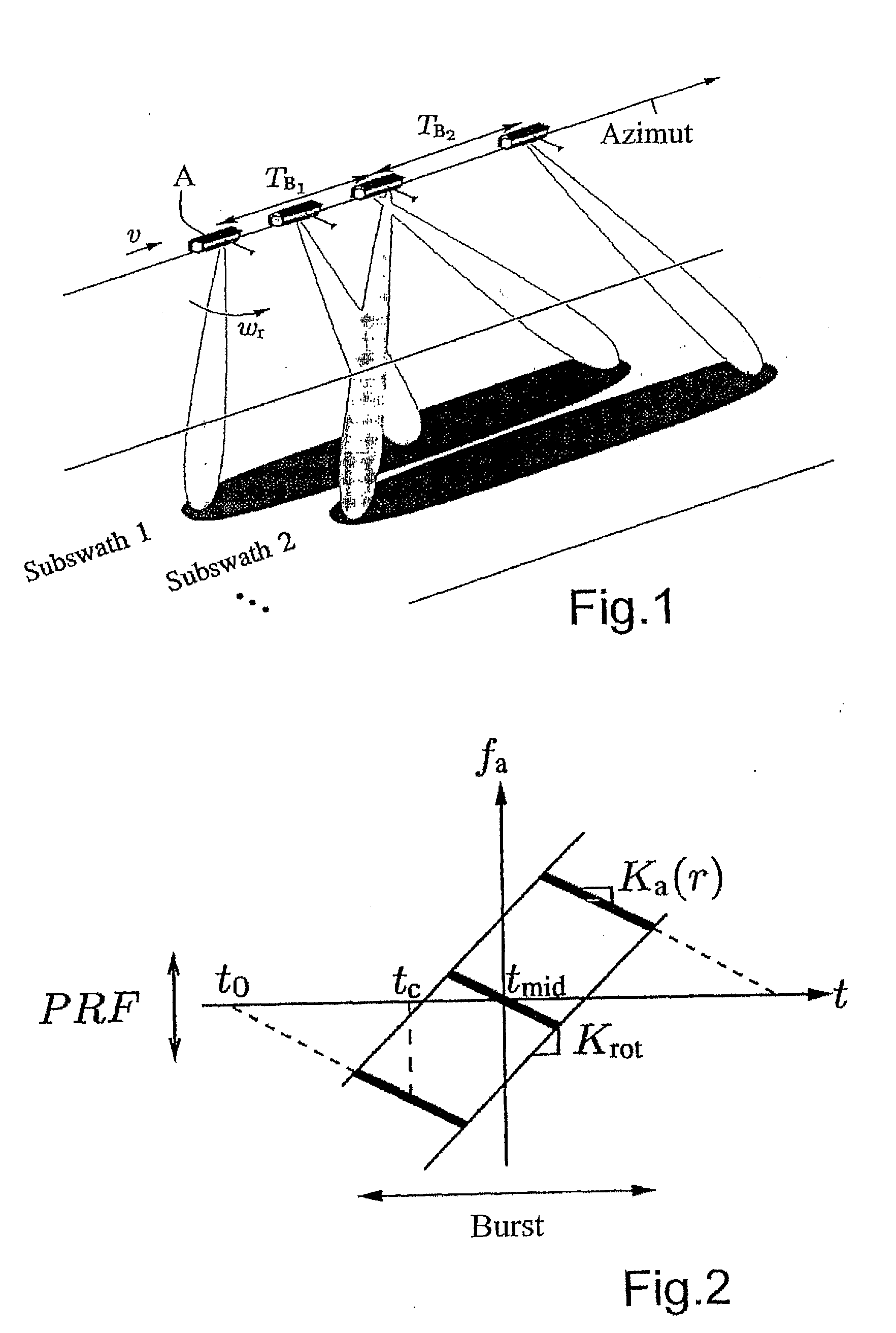
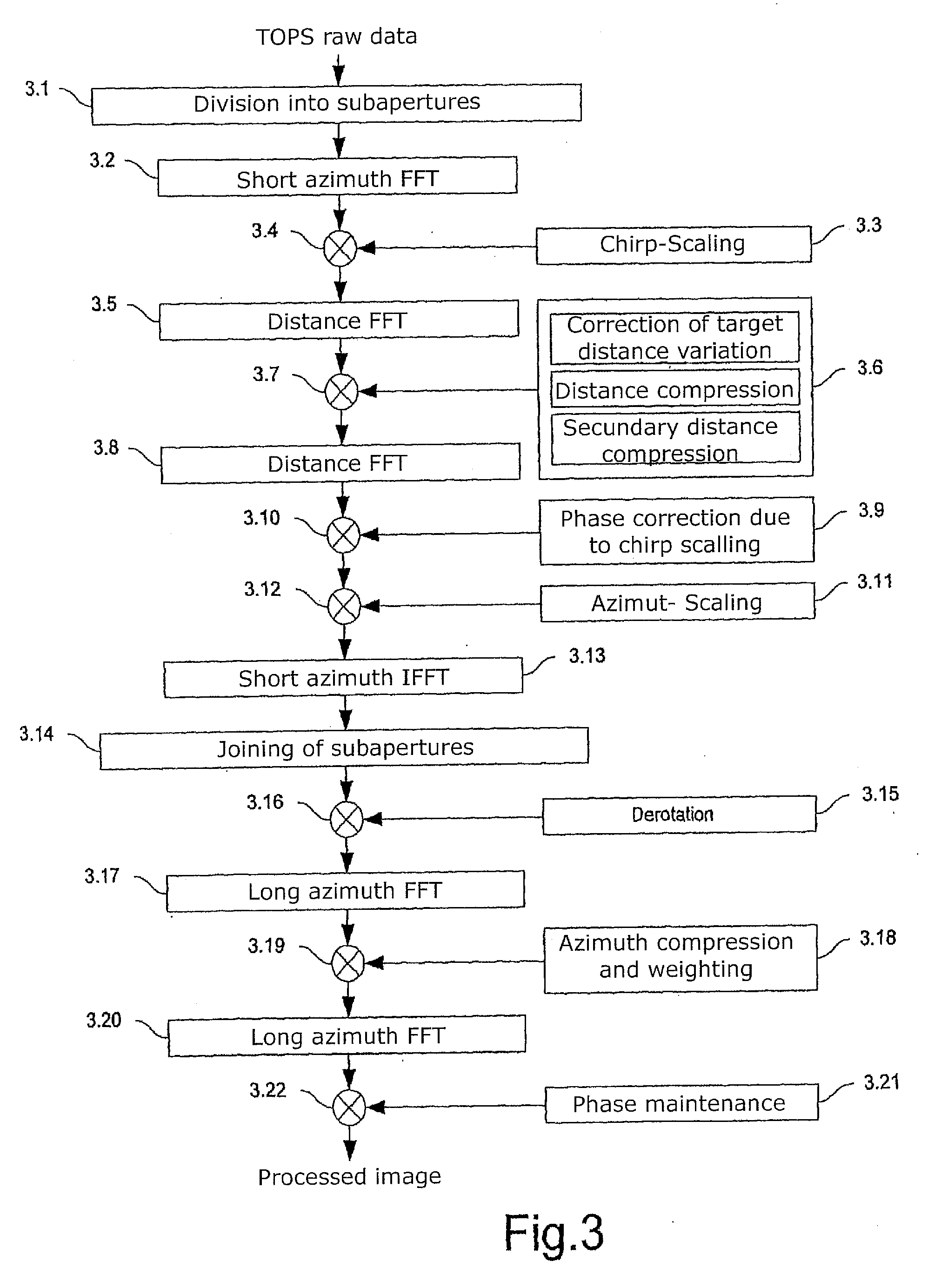
Sub-aperture processing is carried out. Within each sub-aperture, range compression and a correction for the target range variation are carried out. Baseband azimuth scaling is used for processing the azimuth signal, wherein a long azimuth reference function and thus a wide azimuth dimension are prevented. The scaling range is not constant and depends on the range, which is not equal to the original range vector. It is calculated such that, in combination with a subsequent derotation step, constant azimuth scanning is achieved for all ranges. The selected derotation function, which is applied in the azimuth time domain, makes it possible for all the targets to be in base band, in this way varying the effective chirp rate. Since the phase is purely quadratic because of the azimuth scaling step, it is thus possible to use an optimal filter which takes account of the effective chirp rate. IFFT results in a focused image, and a final phase function in the time domain allows phase maintenance. Application for SAR, SONAR and seismic raw data processing in the TOPS mode, as well as other modes which make use of the antenna polar diagram being scanned in the azimuth and / or elevation direction.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Microwave photon MIMO radar detection method and microwave photon MIMO radar system
ActiveCN108287349AEasy to operateHigh radar range resolutionElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsIntermediate frequency
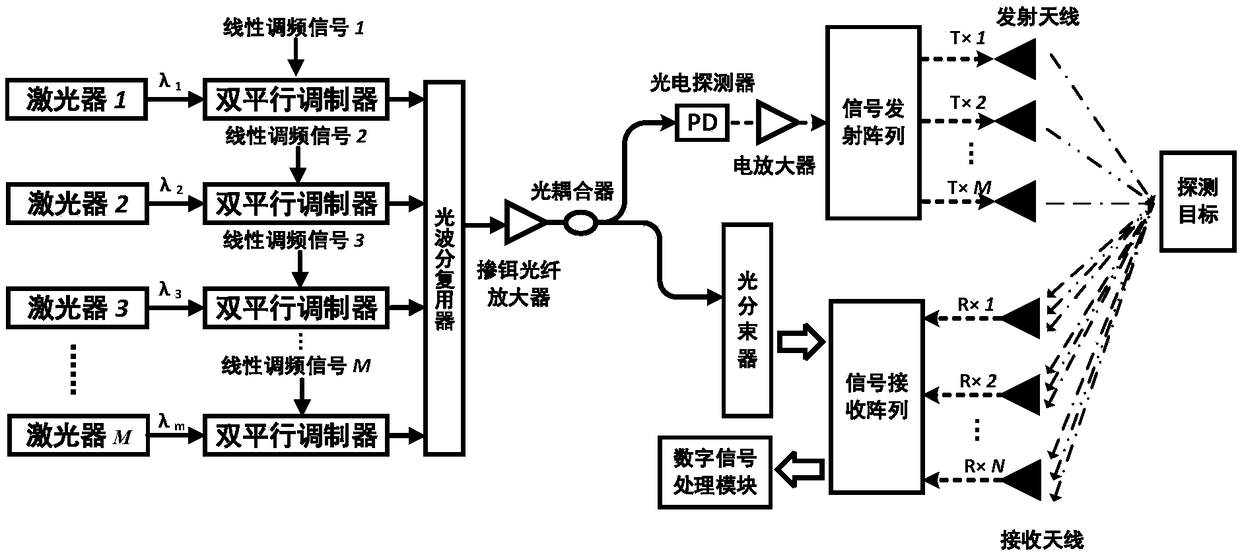
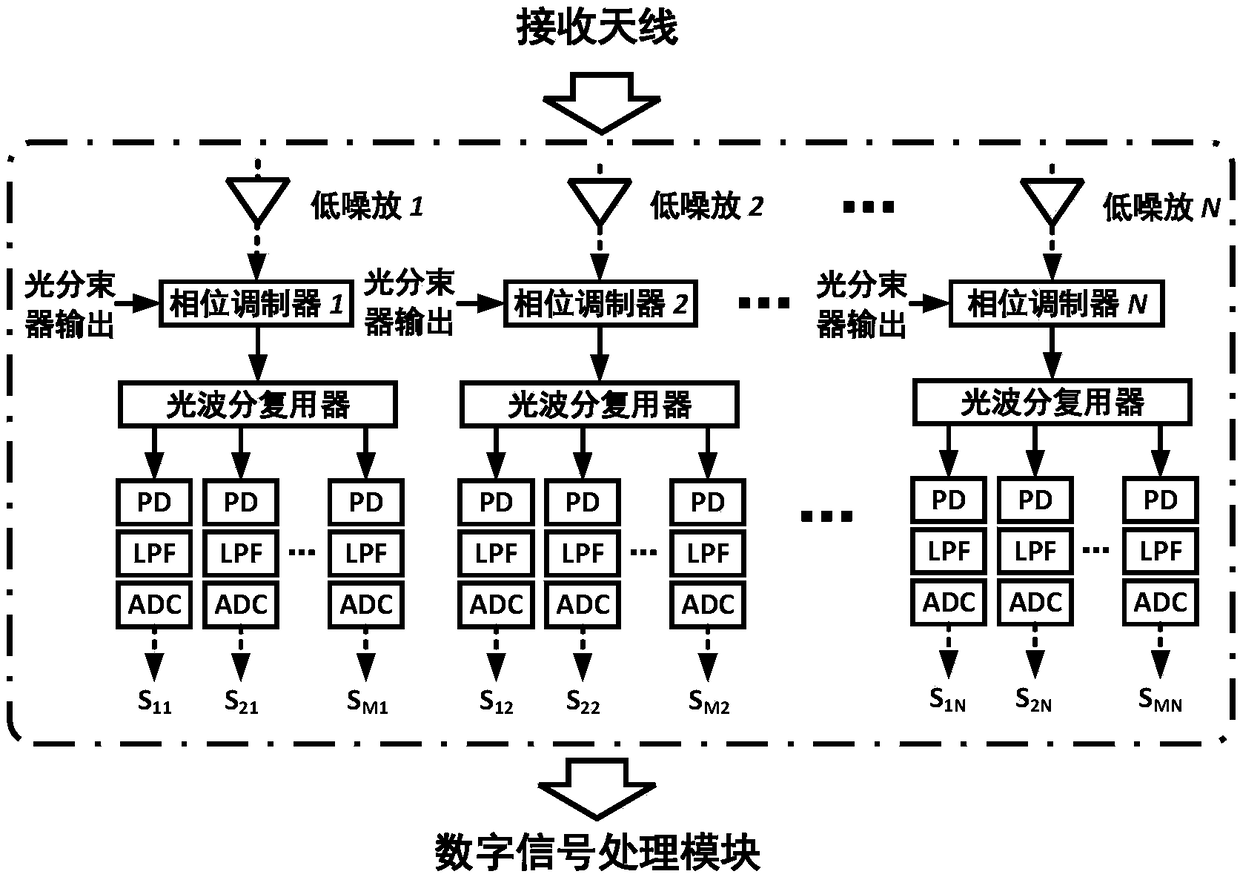
The invention discloses a microwave photon MIMO radar detection method comprising modulating M intermediate-frequency linear frequency-modulated signals with the same bandwidth and chirp rate and non-overlapped frequency on M optical carriers with different wavelengths to generate M optical signals where only the positive and negative second-order sidebands are retained; merging the M optical signals by an optical wavelength division multiplexer and then dividing a combined optical signal into two channels; dividing the optical signal in one channel into N reference light beams; subjecting theoptical signal in the other channel to photoelectric conversion and separating and transmitting M orthogonal linear frequency-modulated signals therein; receiving, by N receiving antennas, the targetreflected signals, performing de-chirp processing and wavelength demultiplexing, and subjecting the obtained M optical signals to photoelectric conversion, low-pass filtering and analog-to-digital conversion to obtain M*N digital signals, processing the digital signals to obtain a target detection result. The invention also discloses a microwave photon MIMO radar system. The method can greatly improve the range resolution and azimuth resolution of the radar system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Techniques for recovering optical spectral features using a chirped optical field
ActiveUS20060012797A1Quick measurementHigh resolutionInterferometric spectrometryUsing optical meansFrequency spectrumOptical frequencies
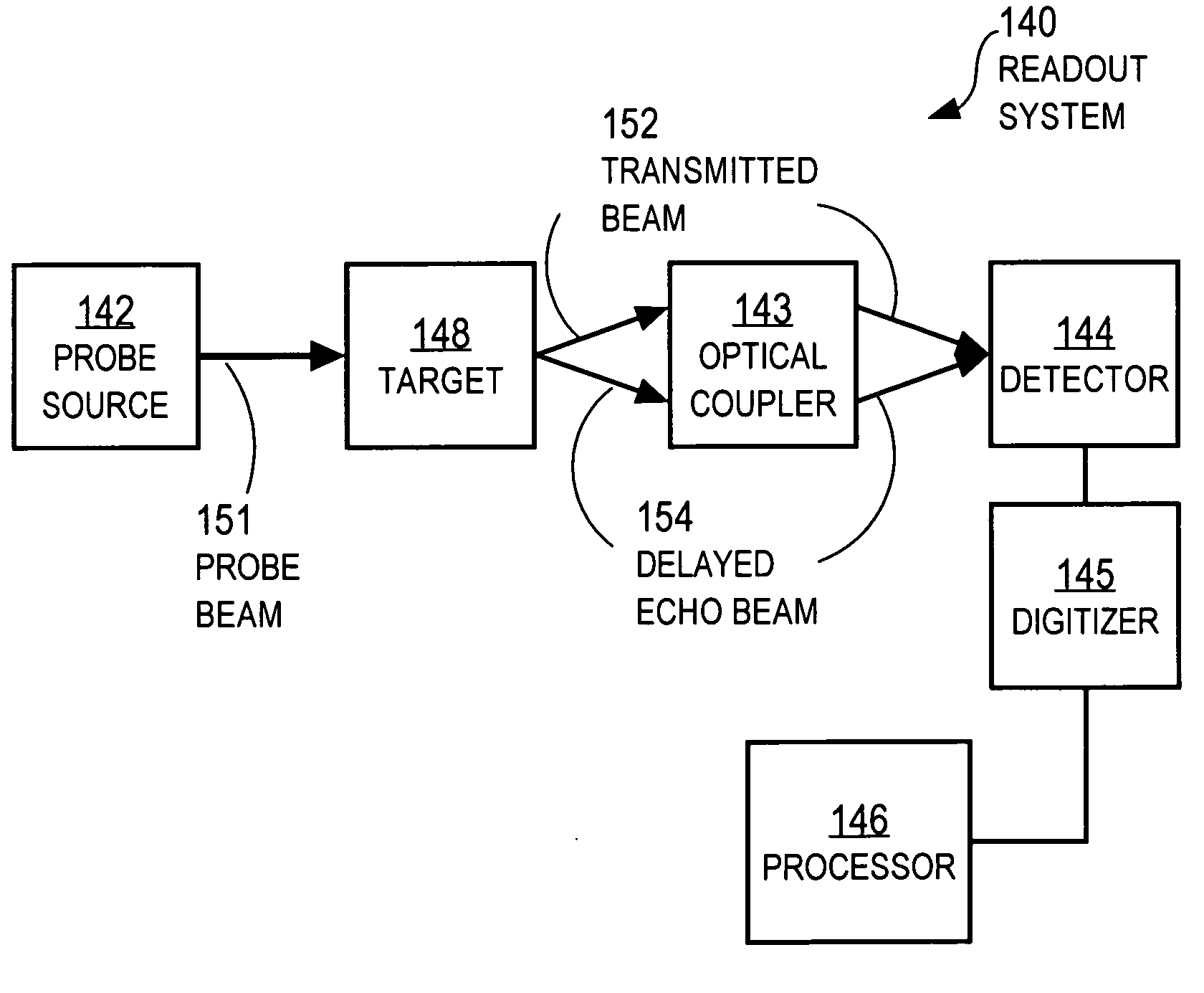
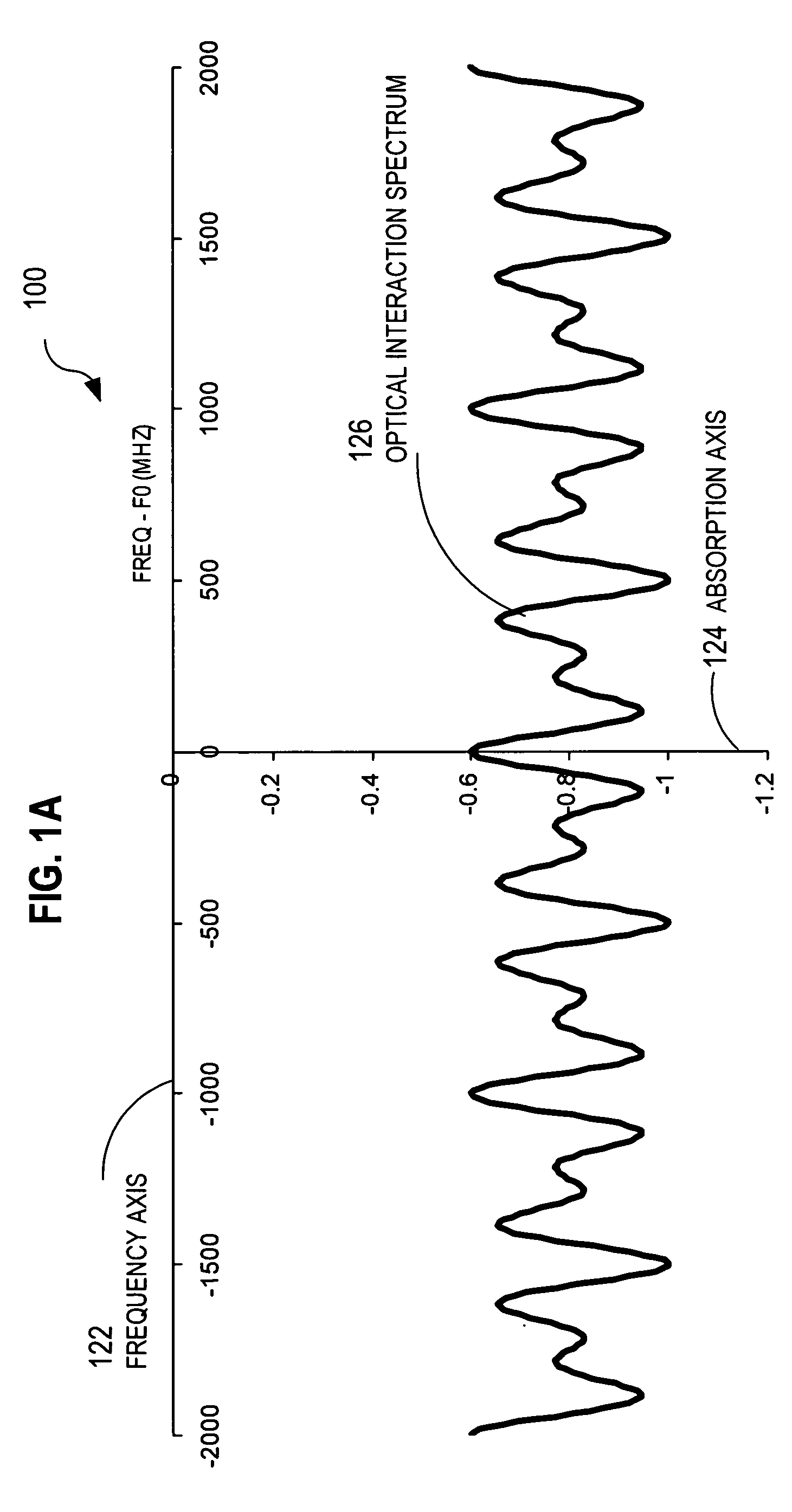
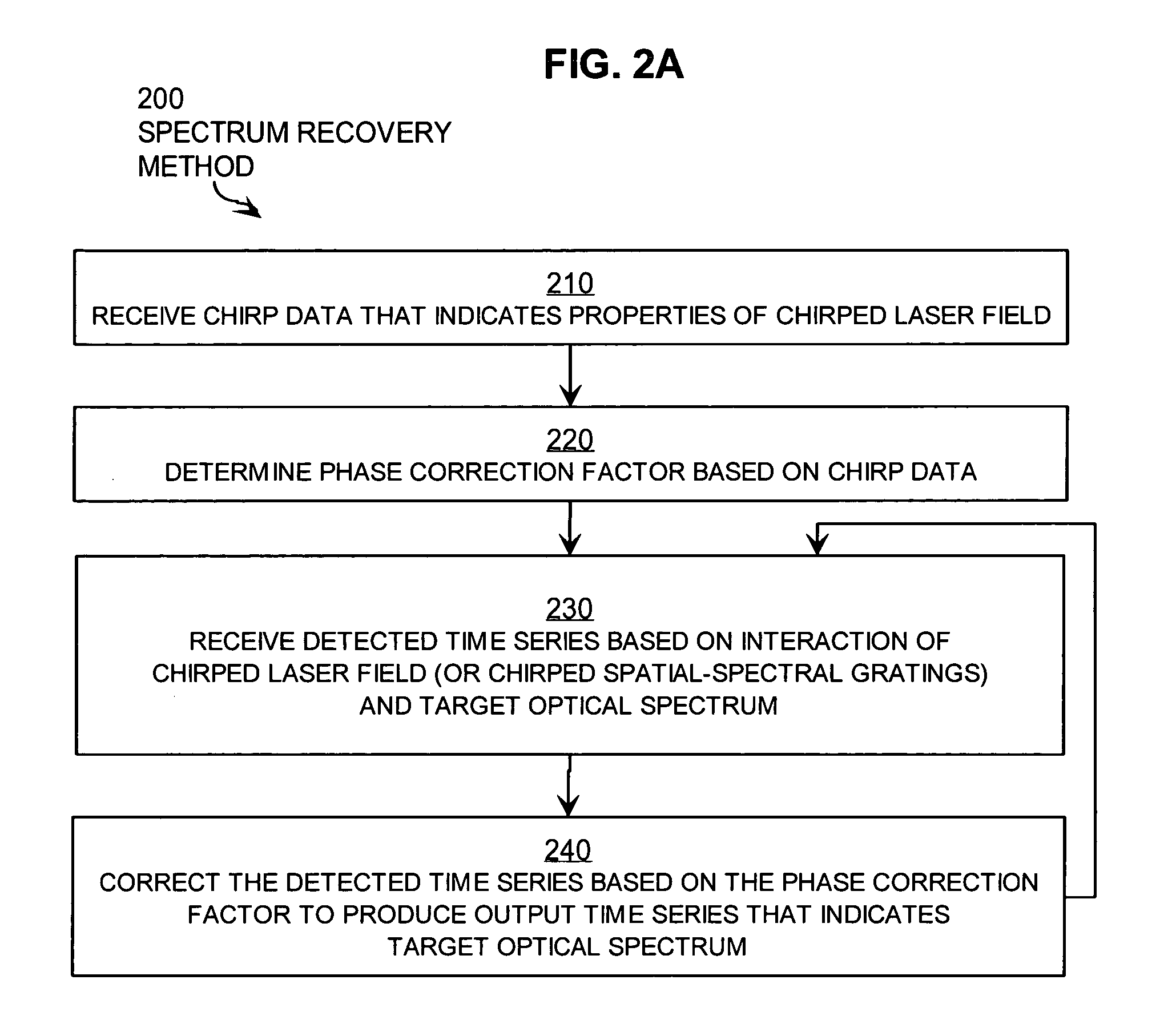
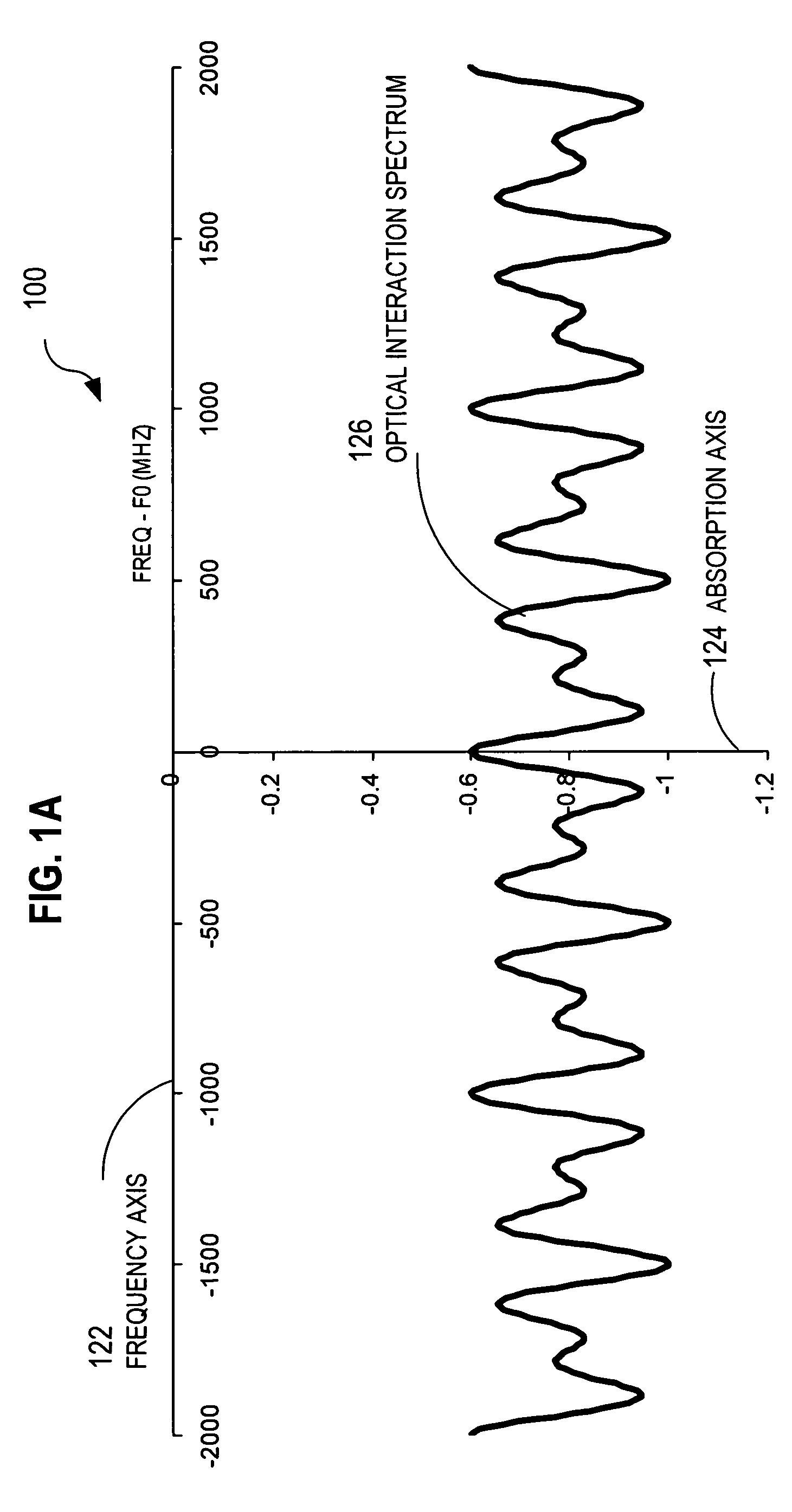
Techniques for recovering optical spectral features include receiving a detected time series that represents a temporally varying intensity of an optical signal. The optical signal is formed in response to an interaction between a target optical spectrum and a chirped optical field. The chirped optical field is an optical field that has a monochromatic frequency that varies in time. The target optical spectrum is an optical frequency dependent optical property of a material or device. A phase correction factor is determined based only on one or more properties of the chirped optical field. The detected time series is corrected based on the phase correction factor to produce an output time series that reproduces in time a shape of the target spectrum in frequency. These techniques allow for fast measurement of spectral features and eliminate the need for prior knowledge of the target optical spectrum to adjust the chirp rate.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
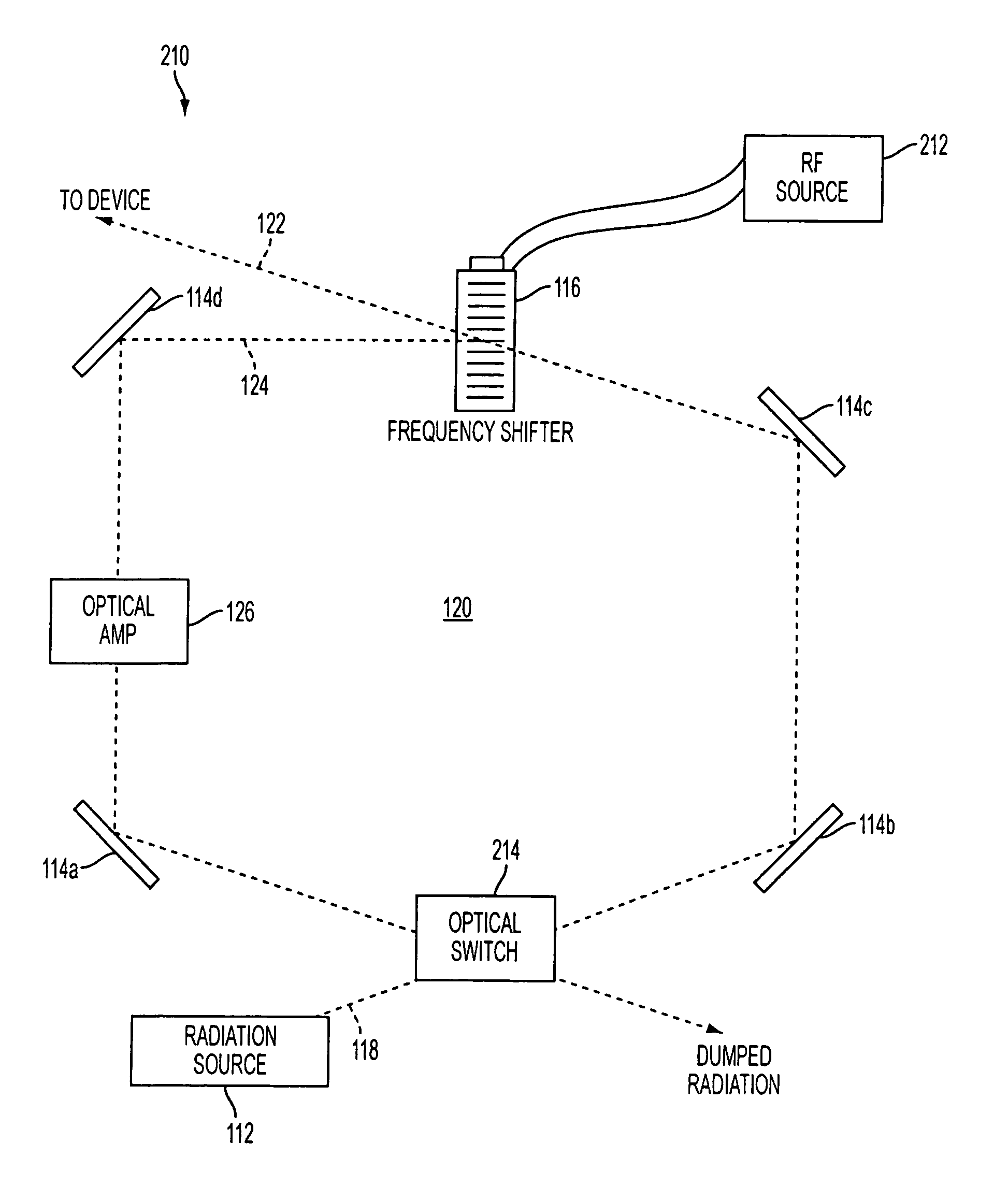
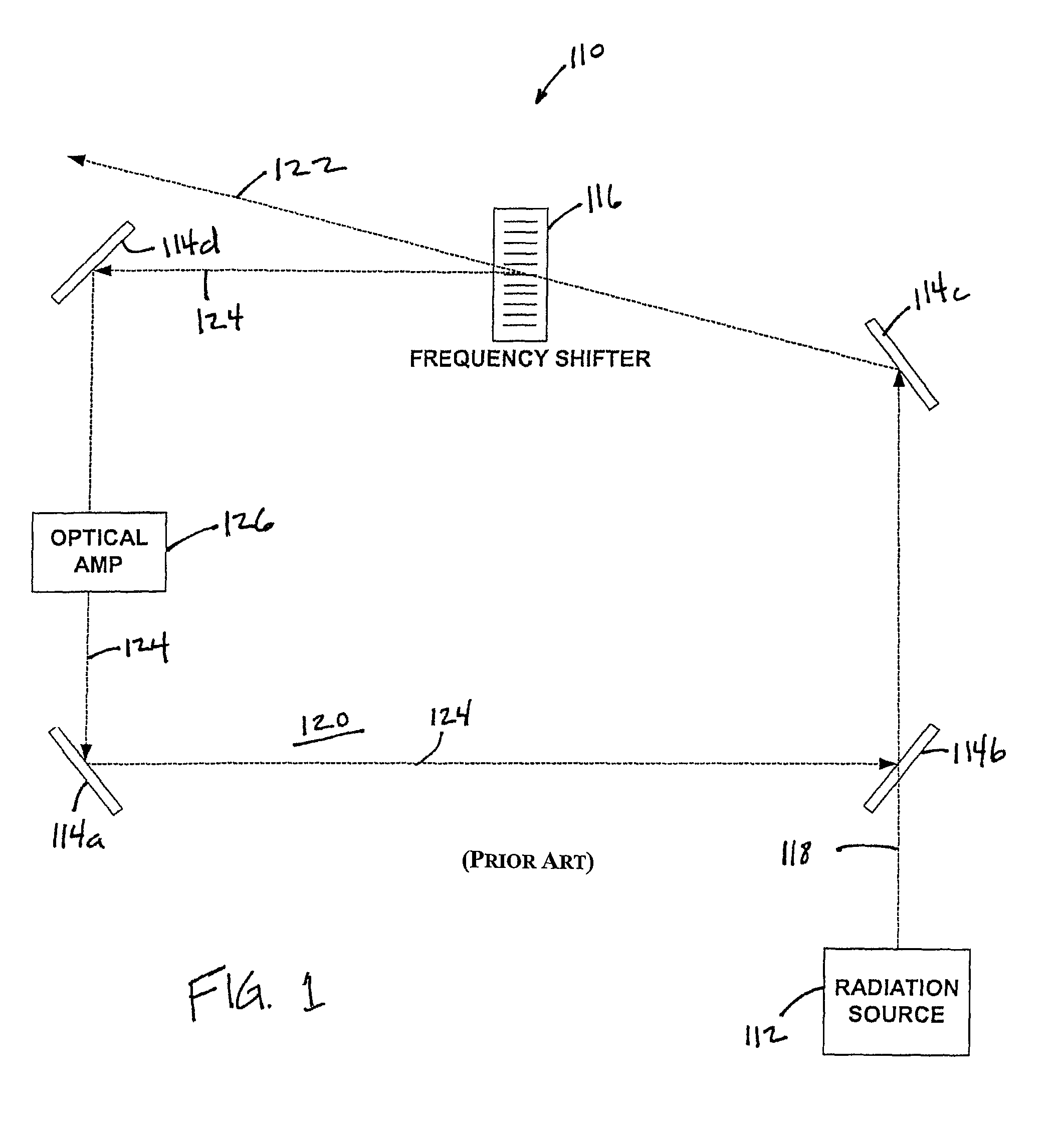
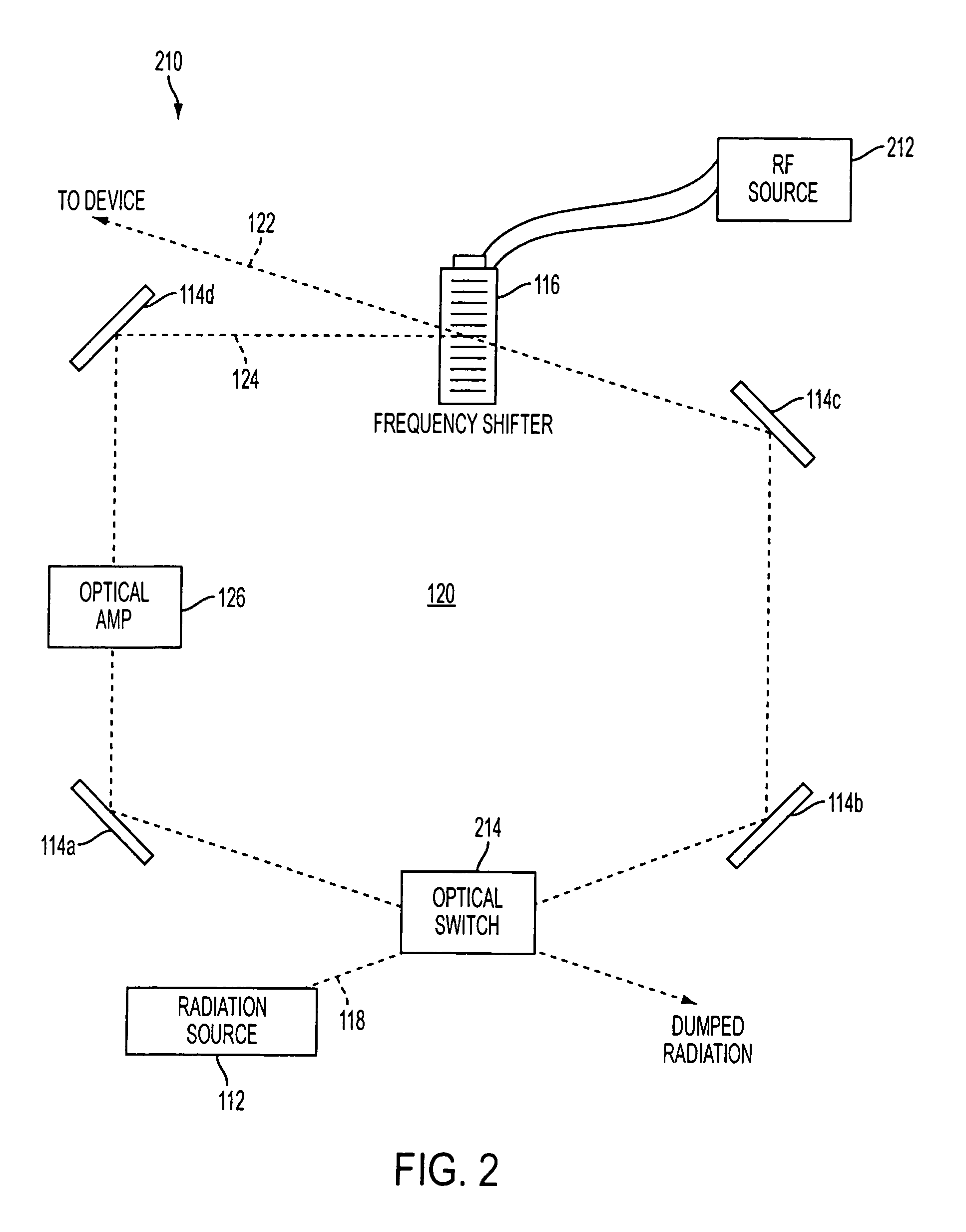
System and method for providing chirped electromagnetic radiation
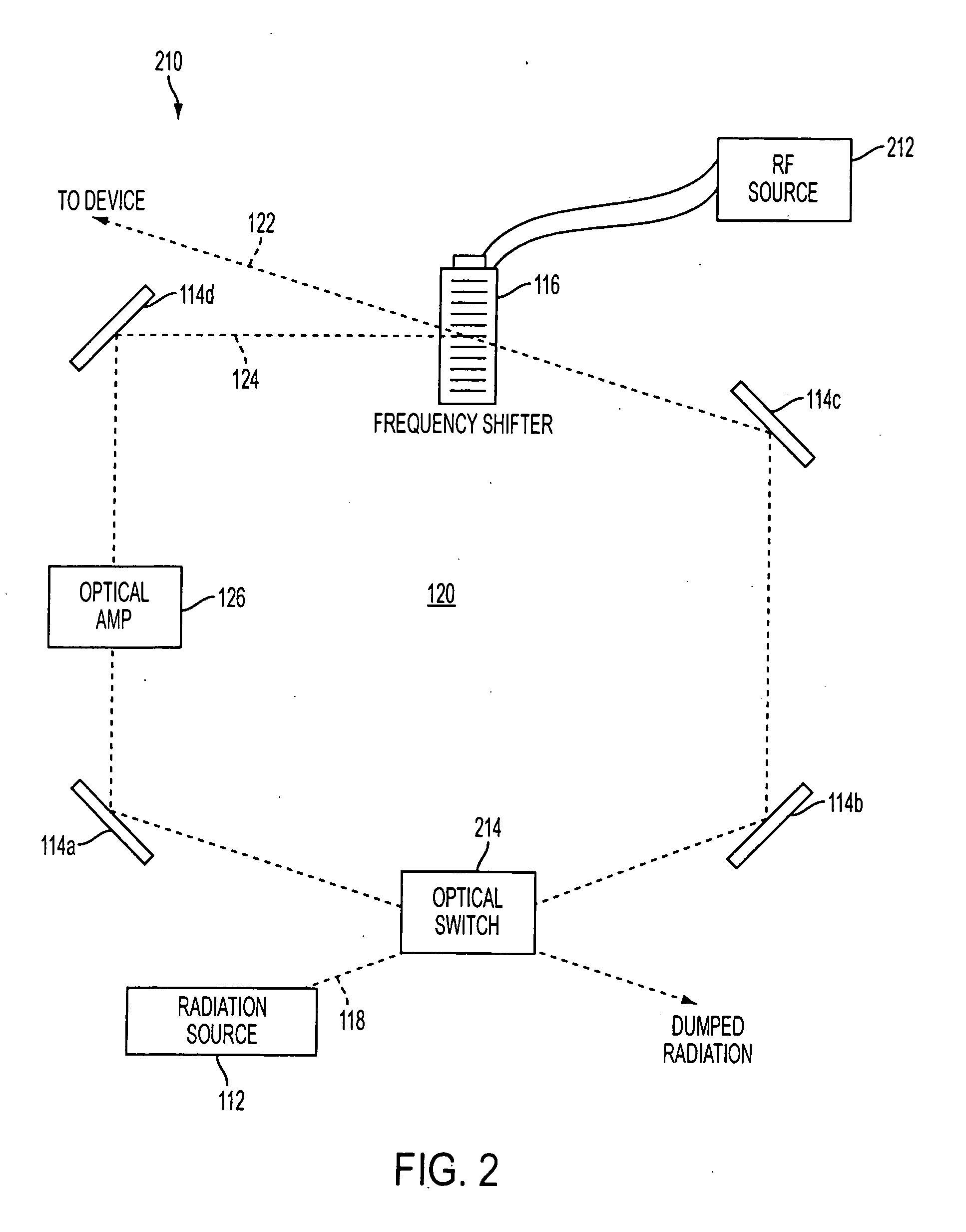
ActiveUS20070189341A1Increase in coherence lengthIncrease the lengthLaser detailsElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsOptical cavity
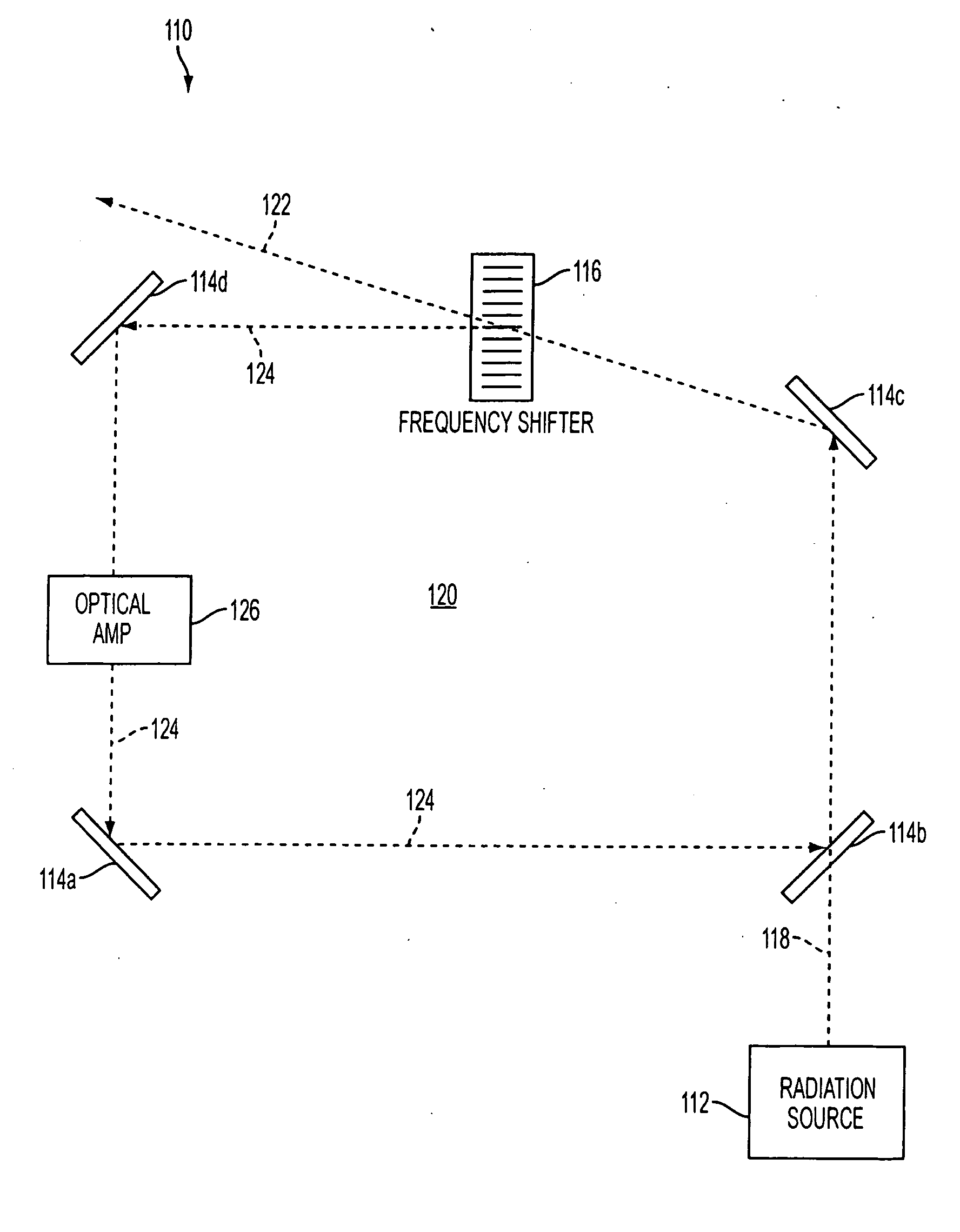
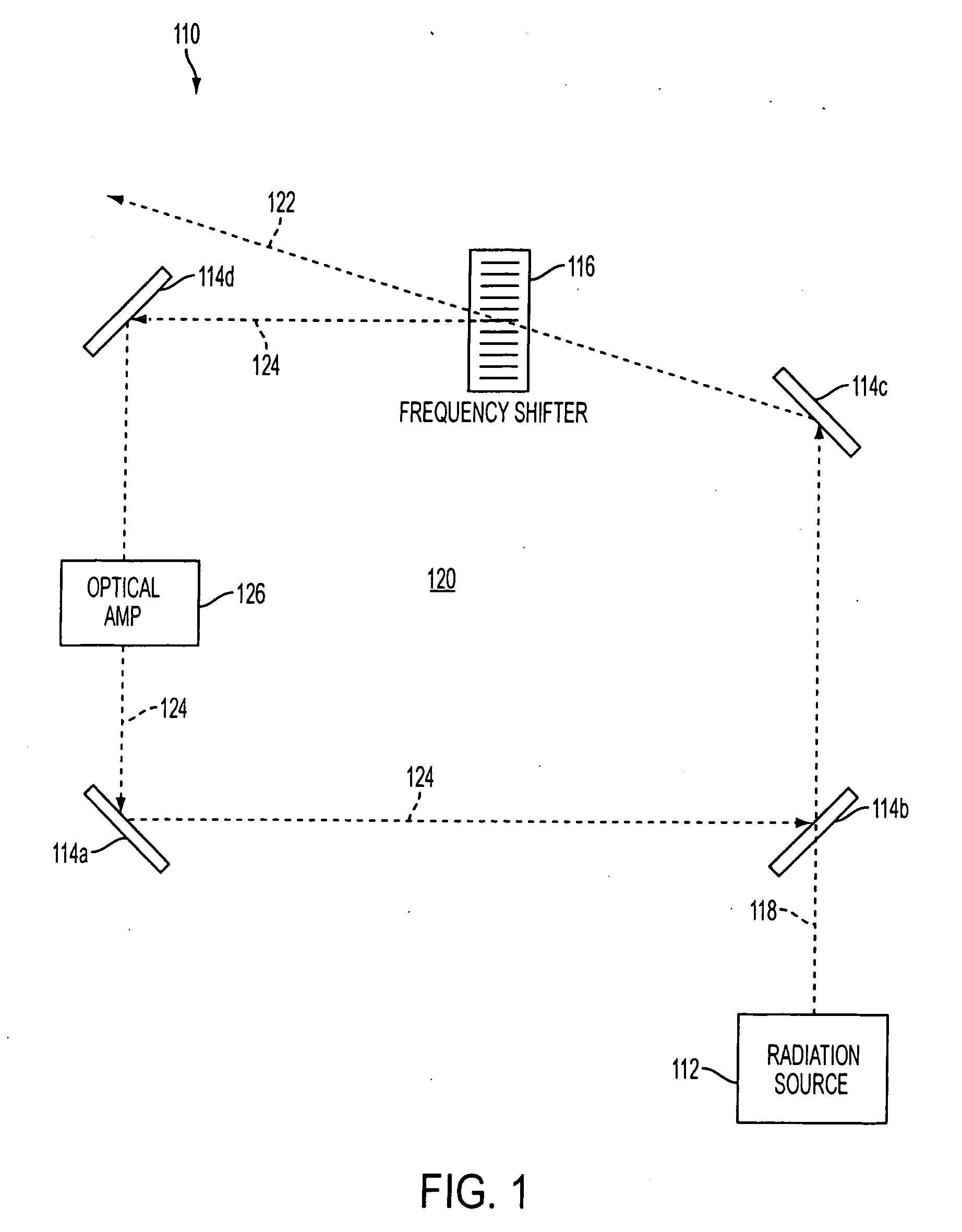
A system and method for controllably chirping electromagnetic radiation from a radiation source includes an optical cavity arrangement. The optical cavity arrangement enables electromagnetic radiation to be produced with a substantially linear chirp rate and a configurable period. By selectively injecting electromagnetic radiation into the optical cavity, the electromagnetic radiation may be produced with a single resonant mode that is frequency shifted at the substantially linear chirp rate. Producing the electromagnetic radiation with a single resonant mode may increase the coherence length of the electromagnetic radiation, which may be advantageous when the electromagnetic radiation is implemented in various applications. For example, the electromagnetic radiation produced by the optical cavity arrangement may enhance a range, speed, accuracy, and / or other aspects of a laser radar system.
Owner:AEVA INC
Radar echo processing with partitioned de-ramp
The spurious-free dynamic range of a wideband radar system is increased by apportioning de-ramp processing across analog and digital processing domains. A chirp rate offset is applied between the received waveform and the reference waveform that is used for downconversion to the intermediate frequency (IF) range. The chirp rate offset results in a residual chirp in the IF signal prior to digitization. After digitization, the residual IF chirp is removed with digital signal processing.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method for processing TOPS (terrain observation by progressive scan)-SAR (synthetic aperture radar)-raw data
ActiveUS8049657B2Improve accuracyAvoiding azimuth aliasing (backfoldingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLandformReference function
Sub-aperture processing is carried out. Within each sub-aperture, range compression and a correction for the target range variation are carried out. Baseband azimuth scaling is used for processing the azimuth signal, wherein a long azimuth reference function and thus a wide azimuth dimension are prevented. The scaling range is not constant and depends on the range, which is not equal to the original range vector. It is calculated such that, in combination with a subsequent derotation step, constant azimuth scanning is achieved for all ranges. The selected derotation function, which is applied in the azimuth time domain, makes it possible for all the targets to be in base band, in this way varying the effective chirp rate. Since the phase is purely quadratic because of the azimuth scaling step, it is thus possible to use an optimal filter which takes account of the effective chirp rate. IFFT results in a focused image, and a final phase function in the time domain allows phase maintenance. Application for SAR, SONAR and seismic raw data processing in the TOPS mode, as well as other modes which make use of the antenna polar diagram being scanned in the azimuth and / or elevation direction.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Orthogonal chirp modulation in multipath environments
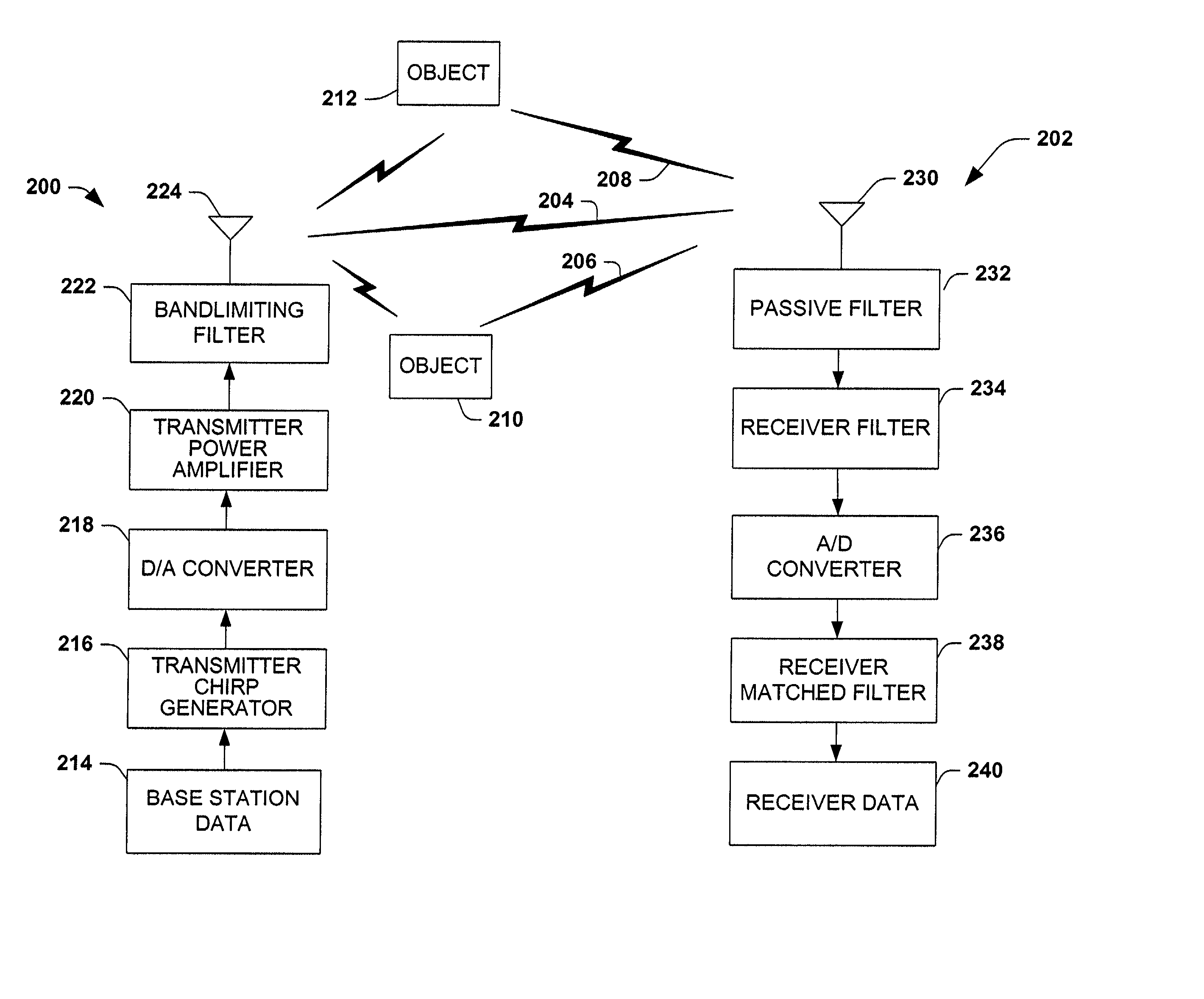
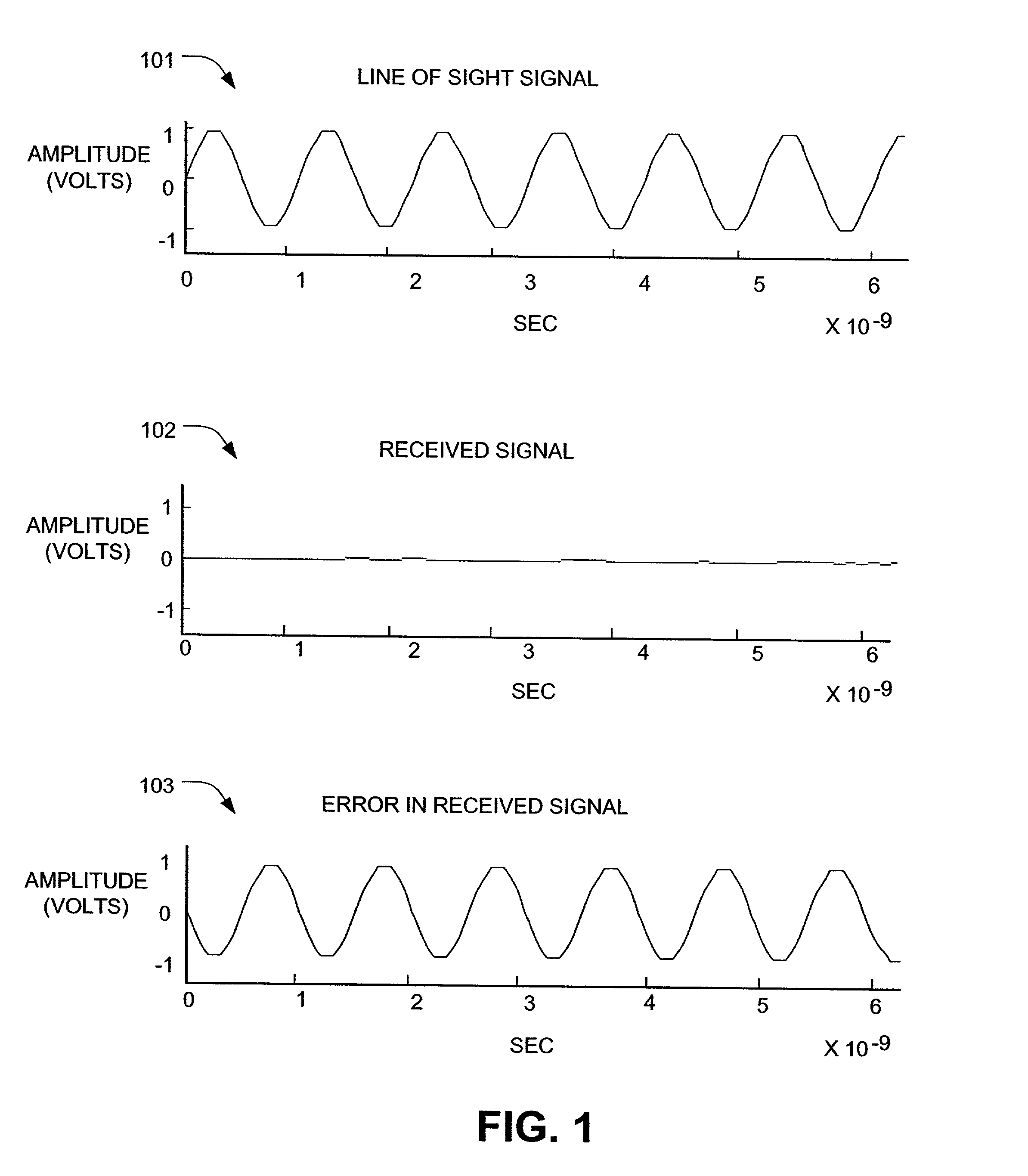
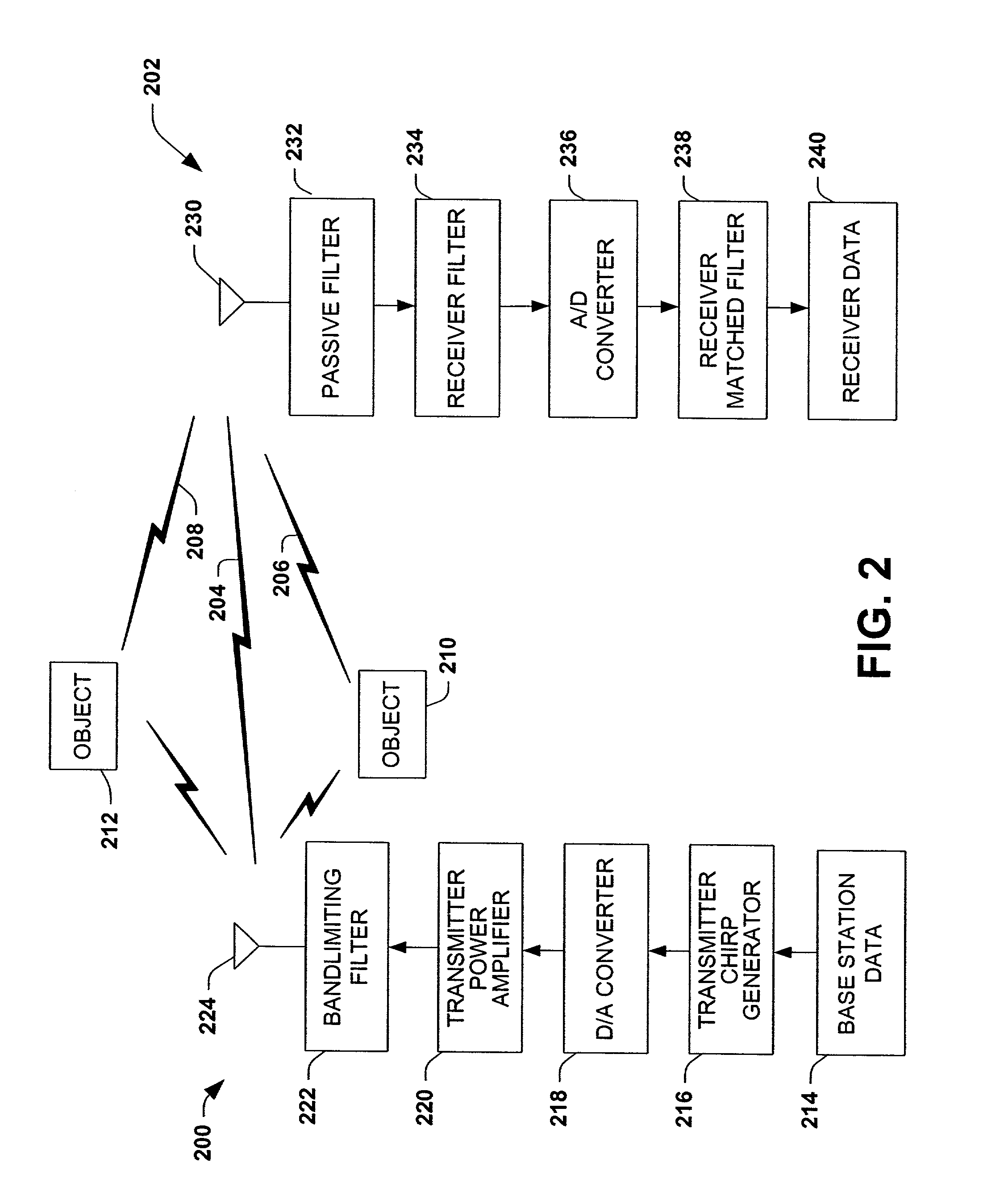
ActiveUS7110432B2Good orthogonalityReduce transmission errorsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationAngle modulationCommunications systemChirp rate
Methods and systems for communication systems are disclosed. Chirp signals generated according to a chirp rate and carrier frequency are used for communication. The chirp rate can be determined by solving integrals or by simulation of transmission parameters. A chirp signal is transmitted from a base station and delayed versions of the chirp signals are created. The delayed versions are generated by the chirp signal reflecting off of reflectors. A receiving station receives an incoming signal. The incoming signal includes the LOS signal plus delayed versions, noise and / or interference. Unwanted signals, either LOS or delayed versions, noise and / or interference are removed from the incoming signal to obtain the desired chirp signal. Using the chirp rate, the chirp signal is converted to a corresponding digital signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Techniques for recovering optical spectral features using a chirped optical field
ActiveUS7145713B2Quick measurementHigh resolutionInterferometric spectrometryUsing optical meansPhase correctionFrequency spectrum
Techniques for recovering optical spectral features include receiving a detected time series that represents a temporally varying intensity of an optical signal. The optical signal is formed in response to an interaction between a target optical spectrum and a chirped optical field. The chirped optical field is an optical field that has a monochromatic frequency that varies in time. The target optical spectrum is an optical frequency dependent optical property of a material or device. A phase correction factor is determined based only on one or more properties of the chirped optical field. The detected time series is corrected based on the phase correction factor to produce an output time series that reproduces in time a shape of the target spectrum in frequency. These techniques allow for fast measurement of spectral features and eliminate the need for prior knowledge of the target optical spectrum to adjust the chirp rate.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
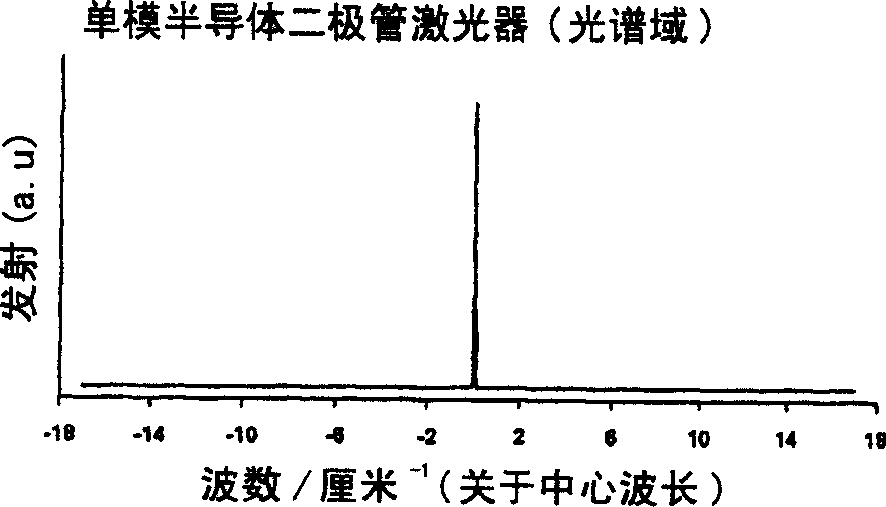
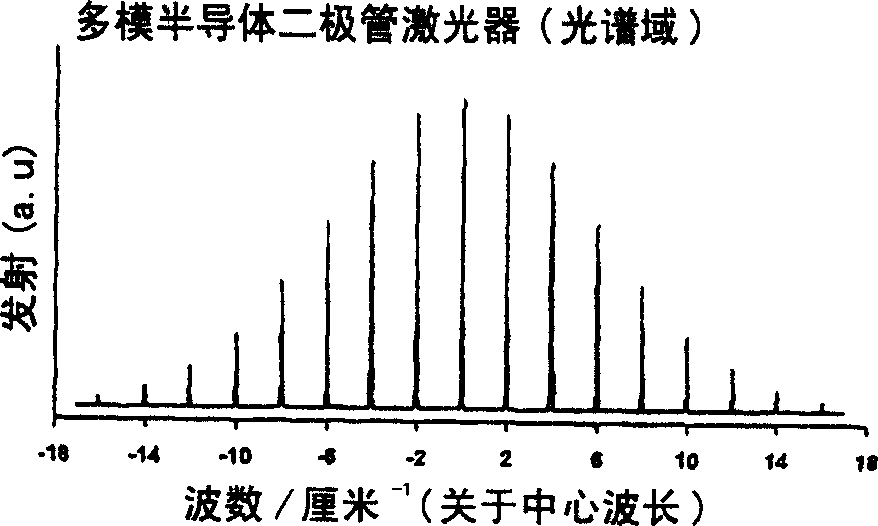
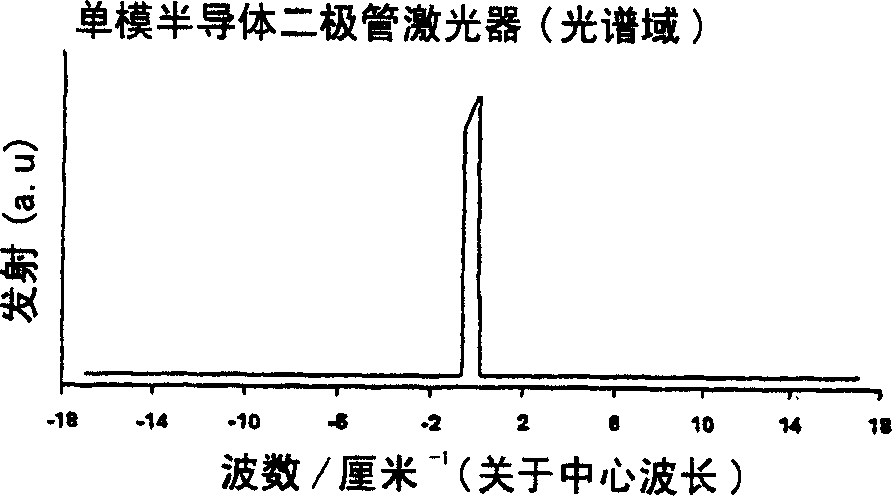
Semiconductor diode laser spectrometer arrangement and method
InactiveCN1659429AAvoid light interferenceAvoid fringe effectsLaser detailsSamplingElectrical impulseLength wave
A method apparatus for sensing gases using a semiconductor diode laser spectrometer, the method comprising: introducing a sample gas into a non-resonant optical cell ( 17 ); applying a step function electrical pulse ( 19 ) to a semiconductor diode laser ( 20 ) to cause the laser ( 20 ) to output a continuous wavelength chirp for injecting ( 16 a) into the optical cell ( 17 ); injecting ( 16 a) the wavelength chirp into the optical cell ( 17 ); using the wavelength variation provided by the wavelength chirp as a wavelength scan, and detecting ( 23 ) light emitted from the cell ( 17 ), wherein a chirp rate is selected to substantially prevent light interference occurring in the optical cell ( 17 ).
Owner:艾默生过程管理有限公司
Fast estimation method for non-uniform rotating target motion parameter
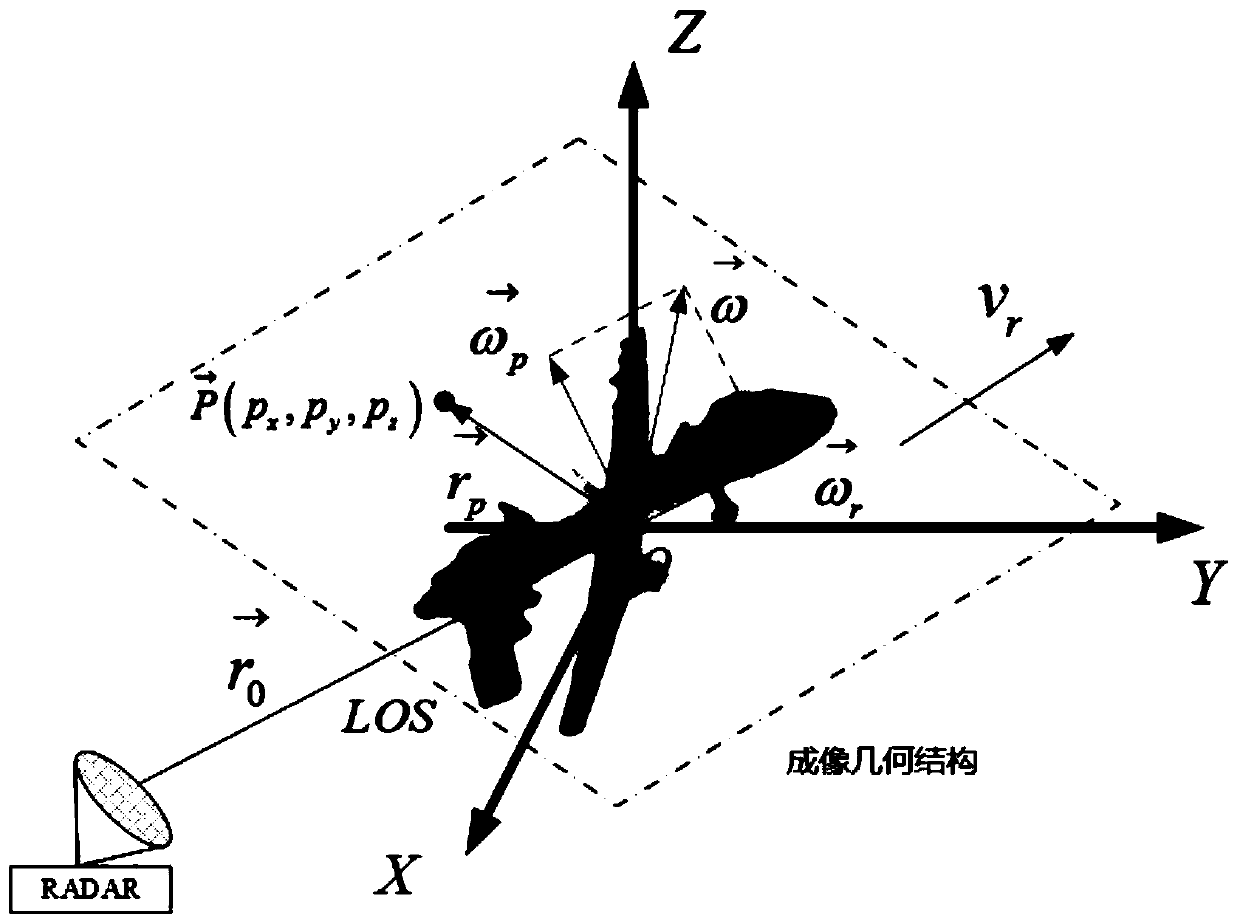
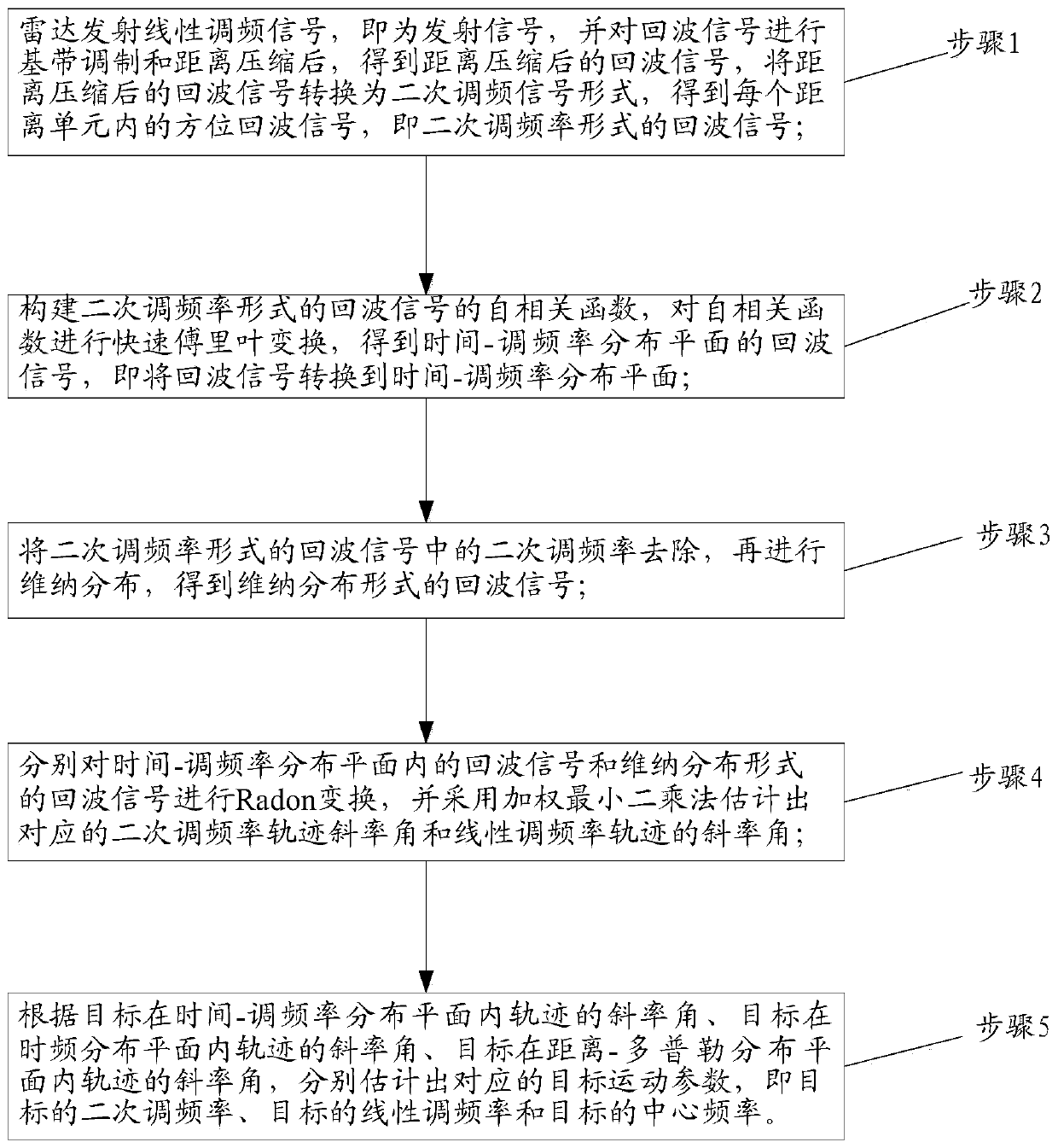
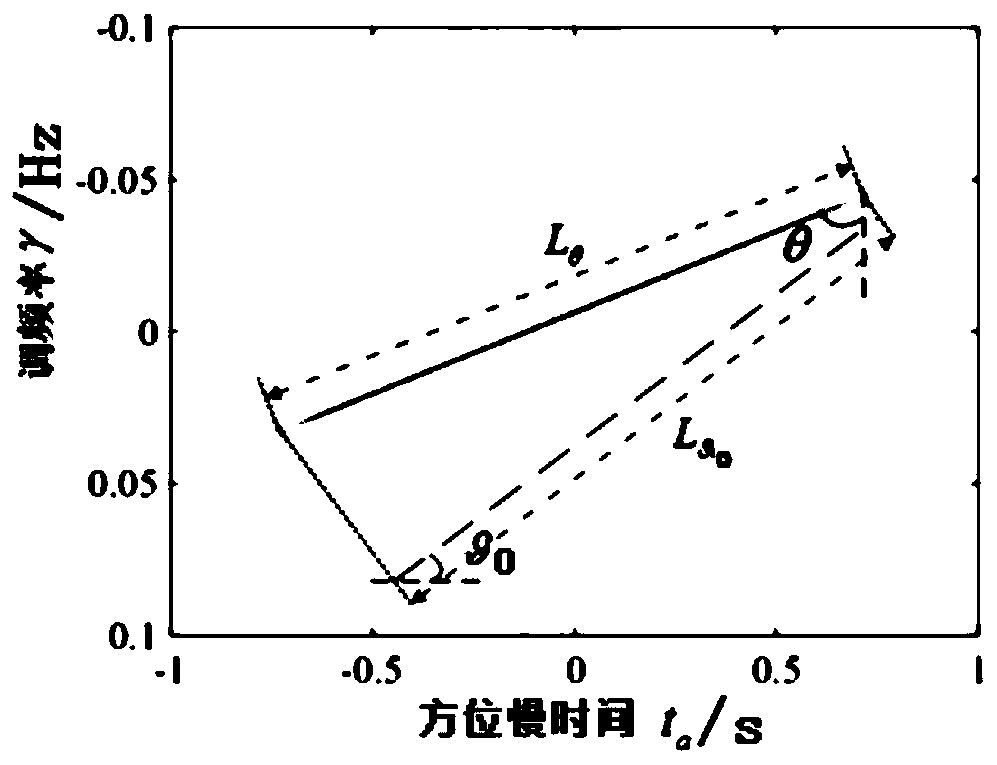
PendingCN110146886AHigh precisionImprove robustnessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmImaging quality
The invention discloses a fast estimation method for a non-uniform rotating target motion parameter. The method comprises specific steps: an echo signal in a single distance unit is modeled into a QFMsignal; a correlation function is constructed, the QFM signal is converted to a time-chirp distribution plane, and minimum entropy criterion-based weighted least squares Radon transform is adopted toestimate secondary chirp; the estimation accuracy and the robustness of the algorithm in a low signal-to-noise ratio environment are improved effectively at the same time; TFD-based weighted least squares Radon transform is adopted to estimate linear chirp, and through filtering, cross-term interference is eliminated; and according to the geometric information in a distance-Doppler domain, the center frequency is directly estimated. The calculation amount of the target motion parameter estimation process can be significantly reduced, the influences of transmission errors on estimation of eachmotion parameter are effectively avoided, and the final target parameter estimation precision and the ISAR imaging quality are ensured.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
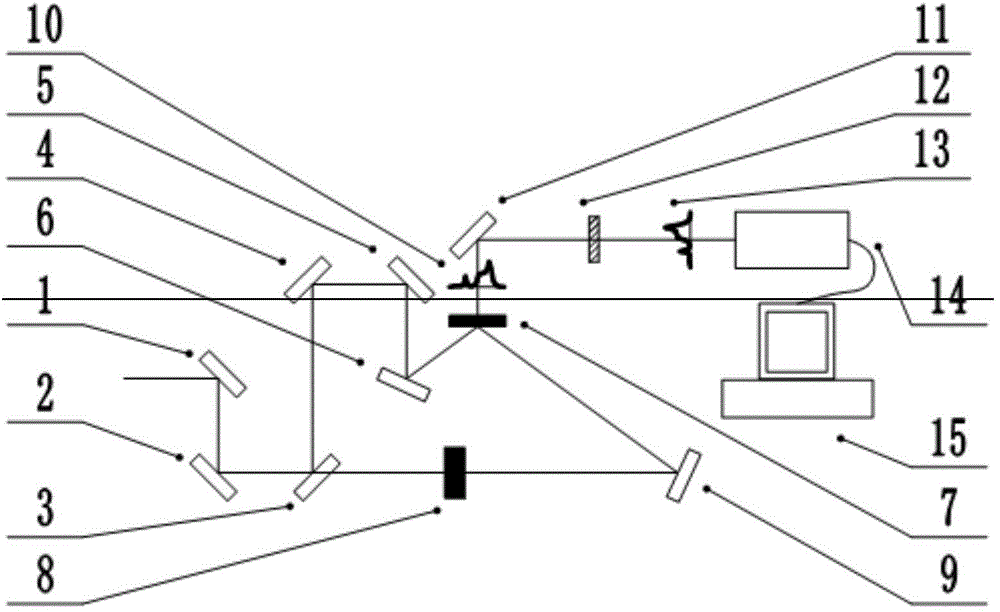
Ultra-short pulse time waveform and chirp rate measuring device and method
ActiveCN104697647AAchieve resolutionRealize analysisInstrumentsMeasurement devicePhotovoltaic detectors
An ultra-short pulse time waveform and chirp rate measuring device comprises a first coupling mirror, a second coupling mirror, a spectroscope, a first reflecting mirror, a second reflecting mirror, a third reflecting mirror, a cross-correlation crystal, a frequency doubling crystal, a fourth reflecting mirror, a fifth reflecting mirror, a diffraction element, a photoelectric detector and a computer. Front-edge and rear-edge high-resolution ratio measuring of ultra-short pulses is achieved through a cross-correlation method to obtain time waveforms and pulse widths. Ultra-short pulse spectrum measuring is achieved through diffraction elements orthogonal to the time axis to obtain the spectrum width, and accordingly, the chirp rate of measured pulses can be obtained based on the pulse width and the spectrum width, the requirement of physical experiments for the time waveform measuring and the requirement of an Ultra-short pulse laser system for measuring of the chirp rate are met conveniently.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-order dynamic adjustable dispersion compensation equipment and dispersion compensation method thereof
ActiveCN101800607ARealize dynamic adjustmentConvenient for dynamic adjustmentCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionFiber couplerGrating
The invention relates to high-order dynamic adjustable dispersion compensation equipment and a dispersion compensation method thereof. In the prior art, the chirp rate of fiber grating can only be linearly changed. In the equipment, the fiber grating and a II port of a fiber circulator are in light connection; a III port of the fiber circulator and a single-port of a fiber coupler are connected; one port of a dual-port of the fiber coupler is in light connection with the input end of a dispersion detector; the input end of the dispersion detector is in signal connection with the input end of a controller; the output end of the controller is in signal connection with the input end of a controllable power supply; and the output end of the controllable power supply is in electrical connection with a semiconductor refrigeration element. The method comprises the following steps: the dispersion compensation equipment is accessed to two ends of the fiber communication network; the controllerperforms analysis feedback according to the measurement parameters of the dispersion detector, and changes the injection current of each semiconductor refrigeration element so as to change the temperature field distribution in a V-shaped groove and realizing the aim of dispersion compensation. The equipment has small module dimension, and can achieve high-order and dynamic adjustment of dispersion.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Sound wave communication method and system based on multi-system chirp-rate keying modulation
ActiveCN106375023AIncrease transfer rateReduce bit error rateSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsInformation transmissionAcoustic wave
The invention is applicable to the field of communication, and provides a sound wave communication method based on multi-system chirp-rate keying modulation. The method comprises signal transmission and signal reception, and comprises the steps of generating a modulated signal by performing channel coding and chirp-rate keying modulation on a digital signal needing to be sent, and inserting a synchronization head before the modulated signal to form a transmission signal; and acquiring the original digital signal by performing synchronization processing on the received signal and demodulating the signal subjected to synchronization processing, wherein the synchronization processing comprises frame synchronization processing and / or code element synchronization processing. According to the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, the signal is modulated by using chirp-rate keying modulation, so that an information transmission rate is high; the received signal is subjected to frame synchronization and / or code element synchronization, and thus signal synchronization accuracy is improved to a certain extent, and signal receiving efficiency is further improved.
Owner:TP-LINK
Method and apparatus for detecting optical spectral properties using optical probe beams with multiple sidebands
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
System and method of processing a sound signal including transforming the sound signal into a frequency-chirp domain
A system and method may be configured to process an audio signal. The system and method may track pitch, chirp rate, and / or harmonic envelope across the audio signal, may reconstruct sound represented in the audio signal, and / or may segment or classify the audio signal. A transform may be performed on the audio signal to place the audio signal in a frequency chirp domain that enhances the sound parameter tracking, reconstruction, and / or classification.
Owner:弩锋股份有限公司
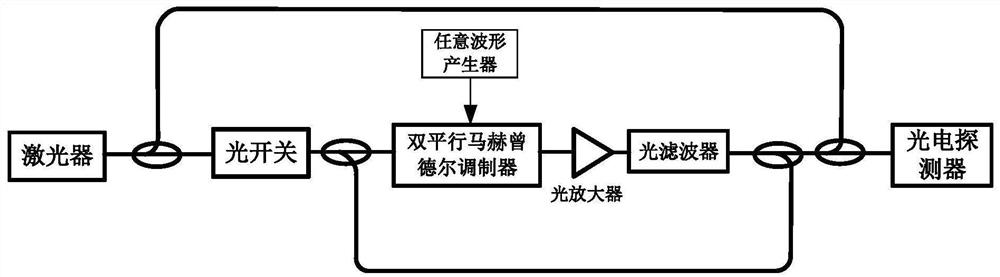
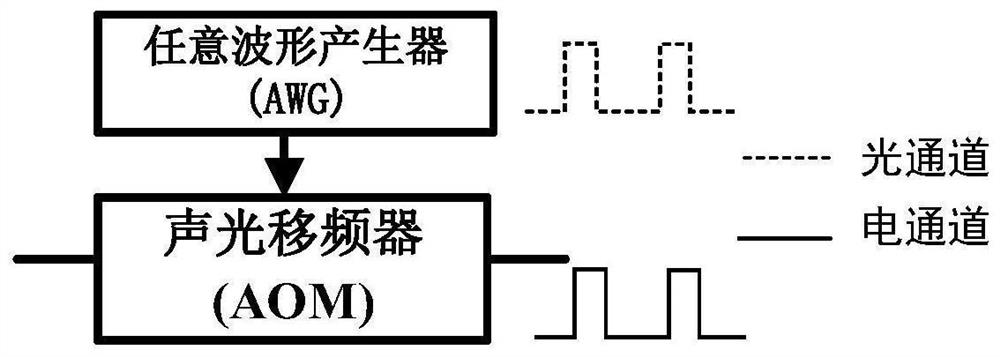
Radio frequency multi-chirp linear frequency modulation stepping signal generation method and device
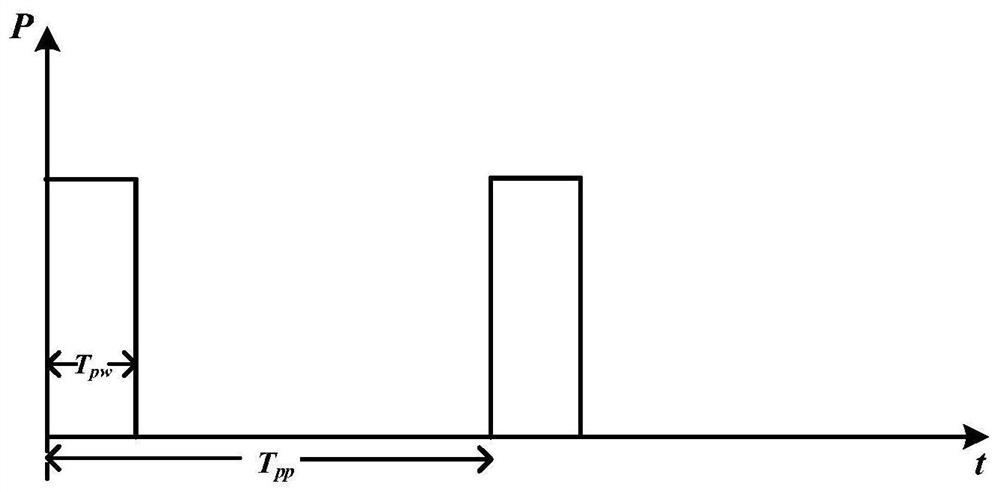
The invention discloses a radio frequency multi-chirp linear frequency modulation stepping signal generation method, which comprises the steps: converting a single-frequency continuous optical carrierinto a periodic optical pulse signal by utilizing an optical switch and then inputting the periodic optical pulse signal into a cyclic frequency shift loop; inputting the linear frequency modulationelectric pulse signal into an electro-optical modulator which is arranged in the cyclic frequency shift loop and is set to be in a mode of suppressing carrier single-sideband modulation, and letting the following conditions shown in the specification be met, wherein Tpw and Tpp are the pulse width and the period of the periodic optical pulse signal respectively, TOFSL is the time delay introducedwhen the optical signal is circulated once in the loop, and N is an integer greater than 1 and represents the number of times of circulation of the optical signal in the loop in one pulse period; andcombining the loop output signal with the beam splitting optical signal of the single-frequency continuous optical carrier, and then performing coherent detection to obtain a radio frequency multi-chirp linear frequency modulation stepping signal of which the chirp rate and the bandwidth are periodically increased. The invention further discloses a radio frequency multi-chirp linear frequency modulation stepping signal generation device. The chirp stepping parameters and bandwidth are controllable, and the signal bandwidth range is large.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
High-speed distributed optical fiber sensing system and method based on fractional Fourier transform
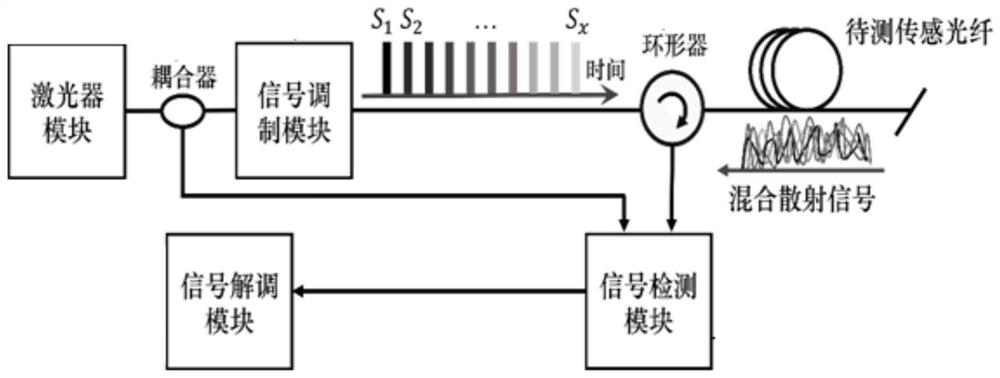
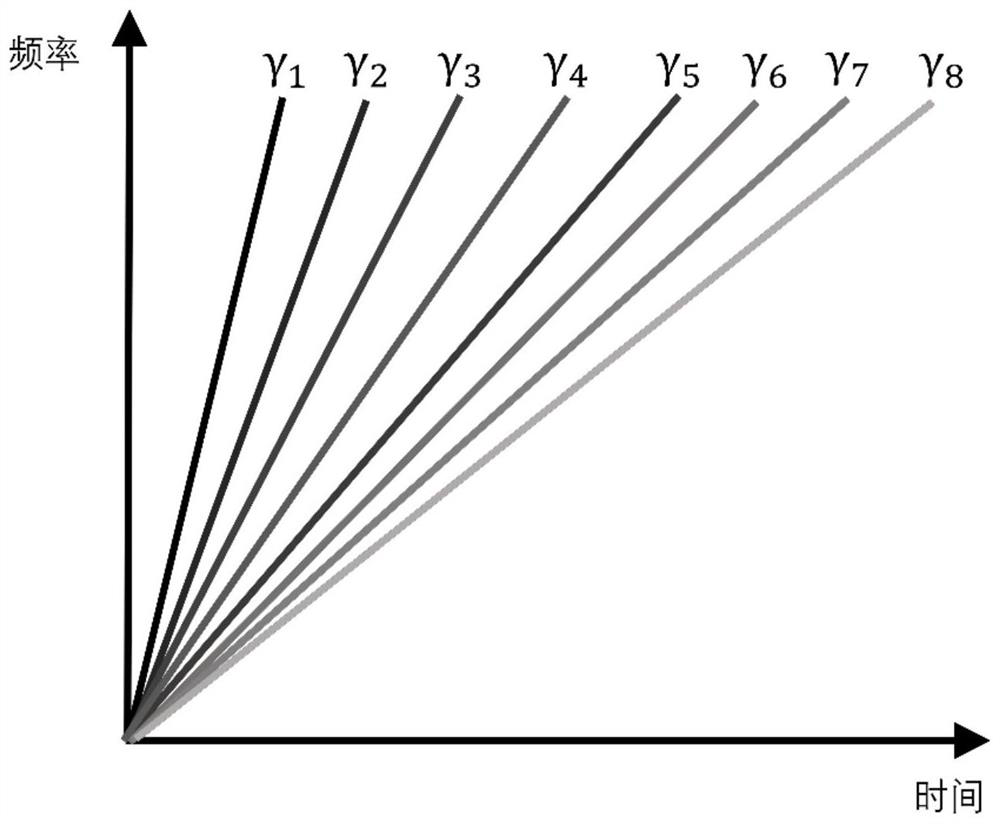
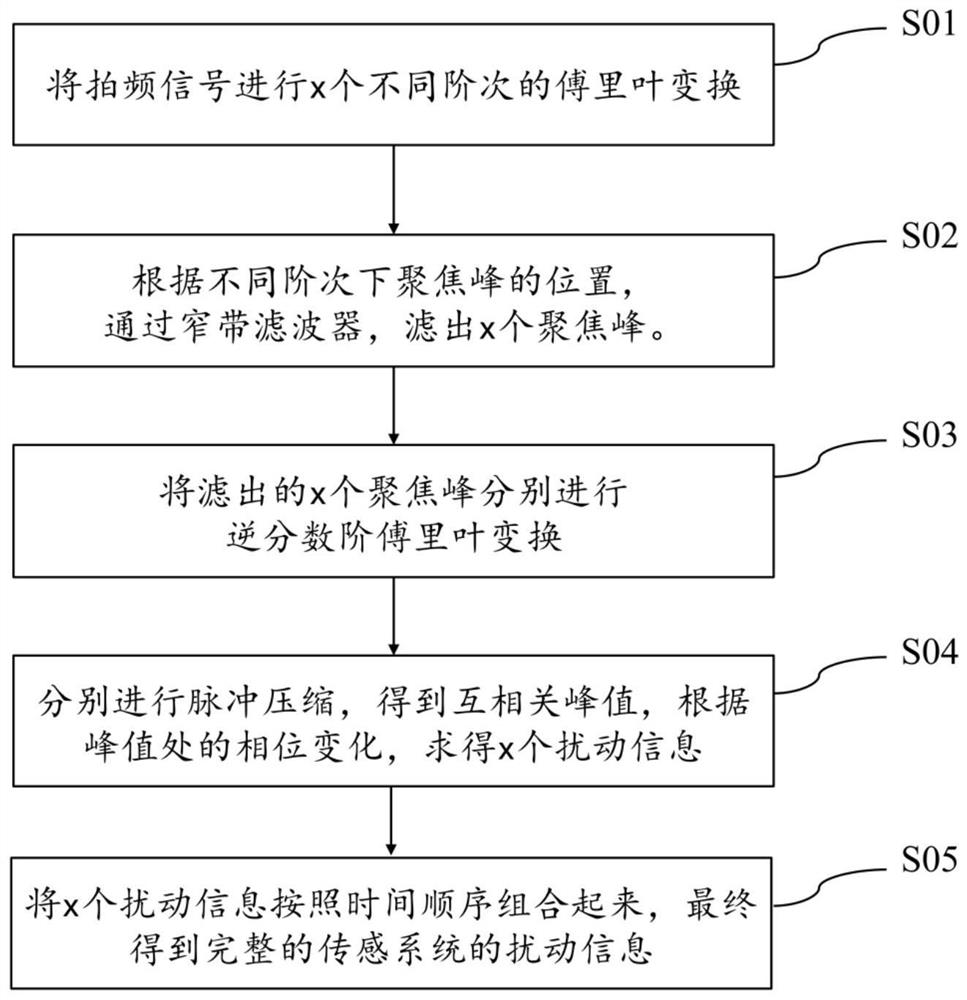
ActiveCN111854815AFast measurementReduce complexityConverting sensor output opticallyFrequency spectrumErbium lasers
The invention discloses a high-speed distributed optical fiber sensing system and method based on fractional Fourier transform. A laser module generates an optical signal, a coupler inputs the opticalsignal into an optical signal modulation module and a signal detection module, and the optical signal modulation module modulates the optical signal into x chirped pulse optical signals with different chirp rates and sends the x chirped pulse optical signals to a to-be-detected sensing optical fiber; after passing through the sensing optical fiber to be detected, mixed scattered light signals generated by x chirped pulse light signals with different chirp rates are sent to the signal detection module; the signal detection module obtains a beat frequency signal by using the optical signal sentby the coupler and the mixed scattered light signal, and the signal demodulation module demodulates the beat frequency signal and then outputs a result. According to the invention, different chirp rates can be set under the same sensing bandwidth, the occupied system sensing bandwidth is reduced, the spectrum utilization rate is increased, the measurement speed is increased by x-1 times, measurement can be completed only through a single channel, and the system complexity is reduced.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ECONOMIC RES INST
Light source apparatus and information-obtaining apparatus using the same
A light source apparatus emitting two pulse lights of which center wavelengths are different from each other, and an information-obtaining apparatus for use with a light source apparatus, are provided. In at least one embodiment, the light source apparatus may include a light source configured to emit a first pulse light of which a center wavelength is variable, a nonlinear optical medium configured to generate a second pulse light having a center wavelength different from the first pulse light in response to incidence of the first pulse light, and a wavelength dispersion adjustment device configured to give a wavelength dispersion to the second pulse light, wherein a wavelength dispersion amount given by the wavelength dispersion adjustment device to the second pulse light is variable. In one or more embodiments, a light source apparatus may include an adjustment unit to adjust a chirp rate of the second pulse light.
Owner:CANON KK
Determining features of harmonic signals
Features that may be computed from a harmonic signal include a fractional chirp rate, a pitch, and amplitudes of the harmonics. A fractional chirp rate may be estimated, for example, by computing scores corresponding to different fractional chirp rates and selecting a highest score. A first pitch may be computed from a frequency representation that is computed using the estimated fractional chirp rate, for example, by using peak-to-peak distances in the frequency distribution. A second pitch may be computed using the first pitch, and a frequency representation of the signal, for example, by using correlations of portions of the frequency representation. Amplitudes of harmonics of the signal may be determined using the estimated fractional chirp rate and second pitch. Any of the estimated fractional chirp rate, second pitch, and harmonic amplitudes may be used for further processing, such as speech recognition, speaker verification, speaker identification, or signal reconstruction.
Owner:弩锋股份有限公司
Filter with variable bandwidth or wavelength interval based on chirp rate tuning of fiber bragg grating
InactiveCN101551516AHigh precisionLarge chirp rate tuning rangeCoupling light guidesGratingFiber network
The invention provides a filter with variable bandwidth or wavelength interval based on chirp rate tuning of fiber bragg grating belongs to optical fiber filter technology field, relates to fiber bragg grating and multiplex optical fiber communication system field. The filter applies strength cantilever girder (2) turning structure of right triangle, the cantilever girder (2) is fixed through splint (1), chirp fiber bragg grating or sampling chirp fiber bragg grating (3) is sticked on side surface of right angle edge in the cantilever girder (2) inclining for 3 to 45 DEG. Applying force or deflection along the vetical direction of free end of the cantilever girder (2), to make the cantilever girder (2) bend for changing chirp rate of the chirp fiber bragg grating (3), and finally reflection peak interval of the sampling chirp fiber bragg grating or reflection spectrum bandwidth of the chirp fiber bragg grating is changed, so as to achieve effect of selecting reflection filter of specific wavelength or wavelength range. The filter has advantages of large bandwidth turning range, high precision, simple structure, low cost, and the filter is siutable for various optical fiber network system especially wavelength division multiplexing system.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Techniques for using chirped fields to reconfigure a medium that stores spectral features
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
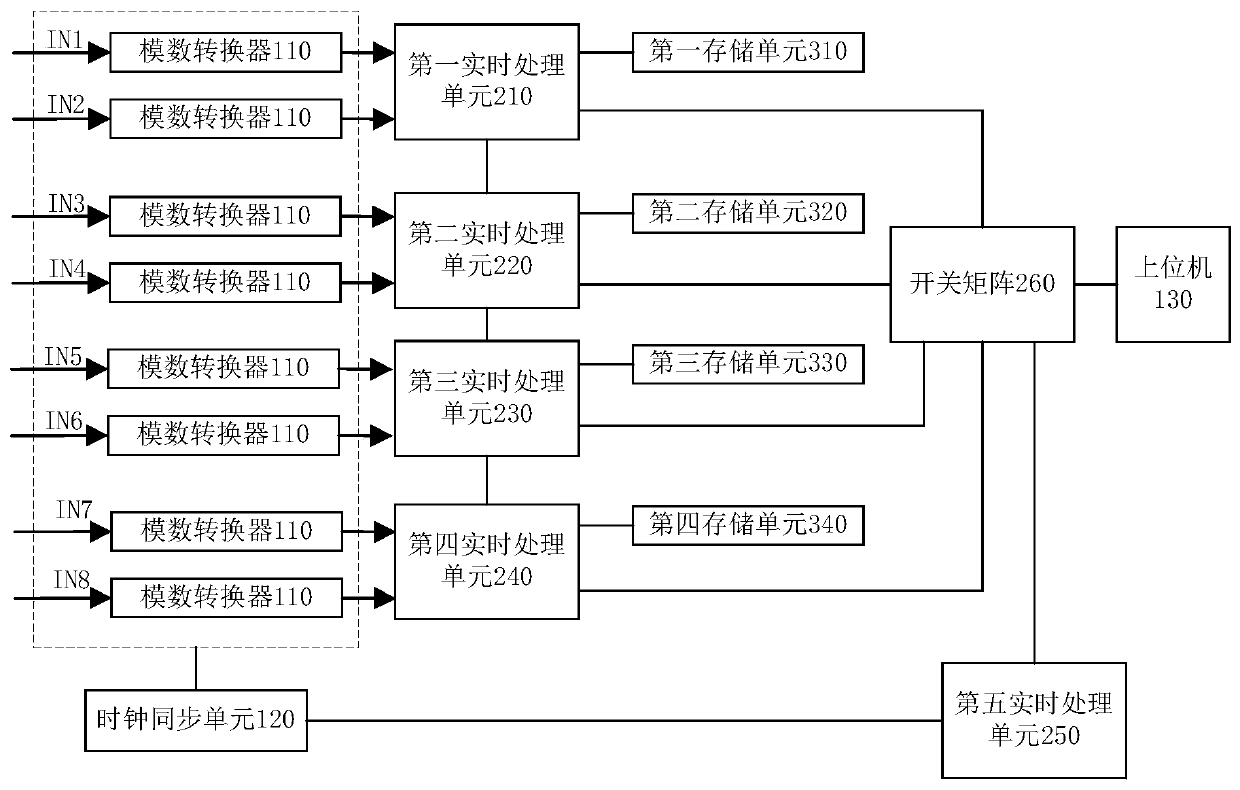
Radar multi-channel data acquisition and real-time processing device
InactiveCN110196416AConvenient verificationFacilitate data analysisWave based measurement systemsTarget signalData acquisition
The invention provides a radar multi-channel data acquisition and real-time processing device, belonging to the field of radar signal acquisition and processing. Functions such as parallel multi-channel acquisition, target ranging and angle measurement are completed, and the on-chip real-time data processing problem of the existing multi-channel data acquisition device is solved. Eight channels ofinput signals are subjected to data sampling, digital down-conversion, target direction-of-arrival estimation and other processing, and estimation on parameters such as the linear chirp rate, the distance and the azimuth of target signals is completed. The device comprises an eight-channel analog-to-digital converter, five FPGA real-time processing units, a clock synchronization unit and four storage units, wherein the FPGAs from the first to the fourth complete data parallel acquisition and real-time processing of the eight channels; an IFDL high-speed interface is adopted between adjacent FPGAs for data transmission; and the fifth FPGA controls the clock synchronization unit and exchange data to an upper computer. As only a data processing result is outputted through a PCIE high-speed serial bus, the data transmission amount is reduced, and the system processing efficiency is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for providing chirped electromagnetic radiation
ActiveUS8081670B2Increase the lengthIncrease rangeLaser detailsElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical cavityRadar systems
Owner:AEVA INC
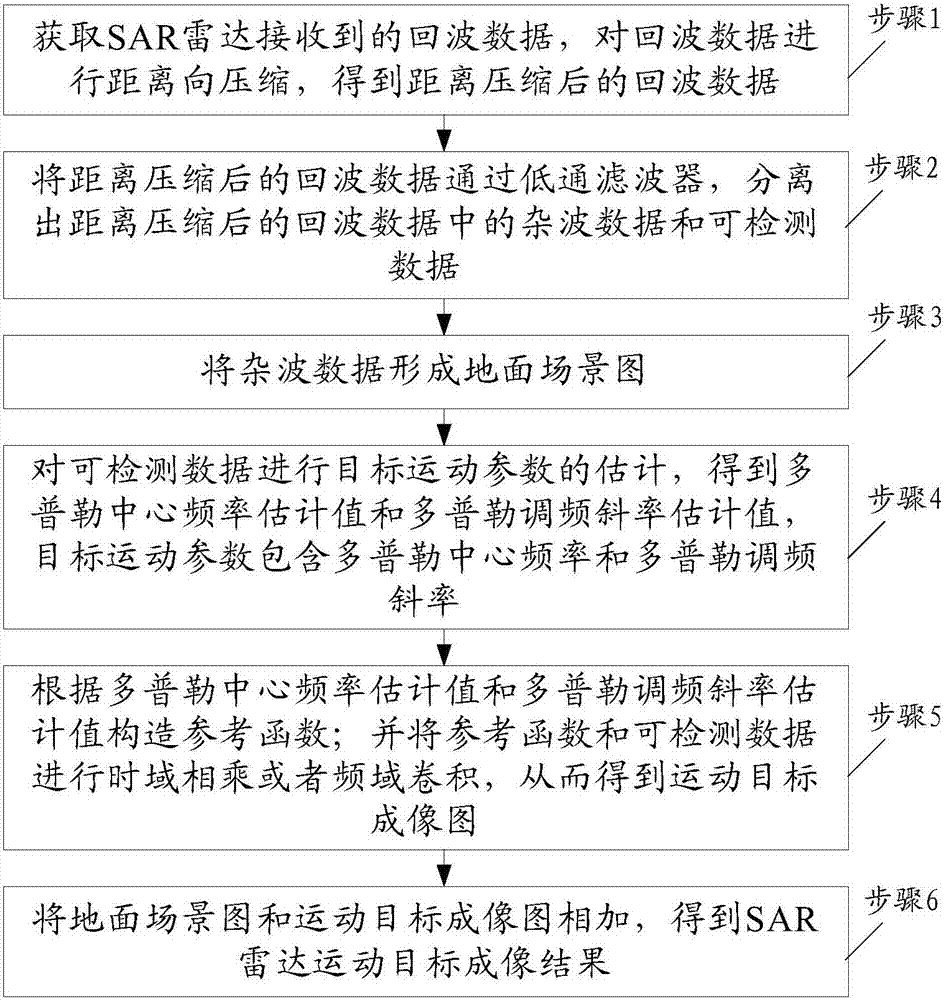
SAR radar moving object imaging method
ActiveCN105699971AEasy to filterEasy to detectRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainLow-pass filter
The invention belongs to the field of radar signal processing, and discloses an SAR radar moving object imaging method. The SAR radar moving object imaging method comprises the steps of acquiring echo data which are received by an SAR radar, performing distance direction compression on the echo data, making the echo data after distance direction compression pass through a low pass filter, and separating clutter data and detachable data in the echo data after distance direction compression; forming a ground scene picture from the clutter data; performing moving object parameter estimation on the detachable data, obtaining a Doppler central frequency estimated value and a Doppler chirp rate estimated value, and constructing a reference function according to the Doppler central frequency estimated value and the Doppler chirp rate estimated value; performing time domain multiplication or frequency domain convolution on the reference function and the detachable data, thereby obtaining a moving object imaging picture; and adding the ground scene picture with the moving object imaging picture, thereby obtaining an SAR radar moving object imaging result. The SAR radar moving object imaging method can be used for performing fine imaging on the moving object.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Chirp spectral pattern cavity-less optical fiber Fabry-Perot filter and manufacturing method thereof
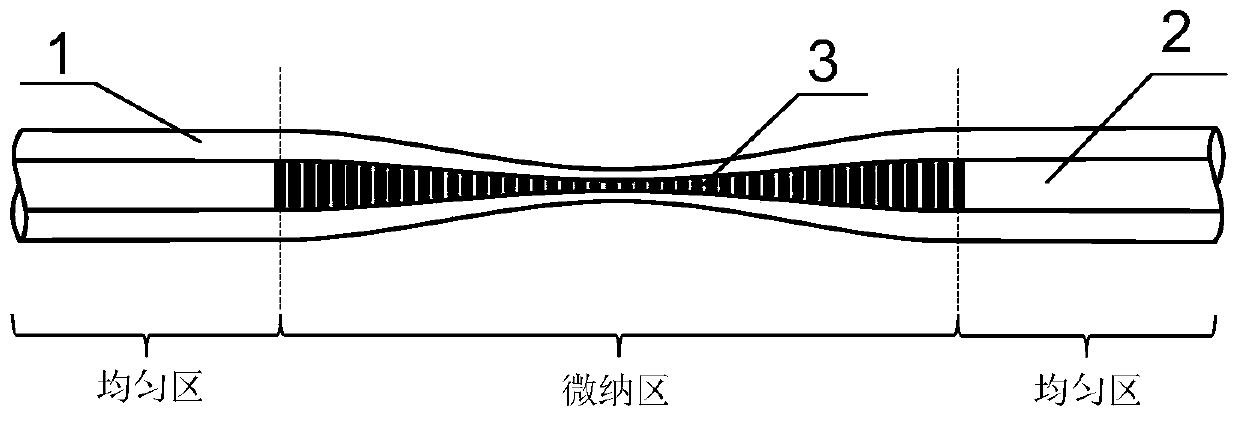
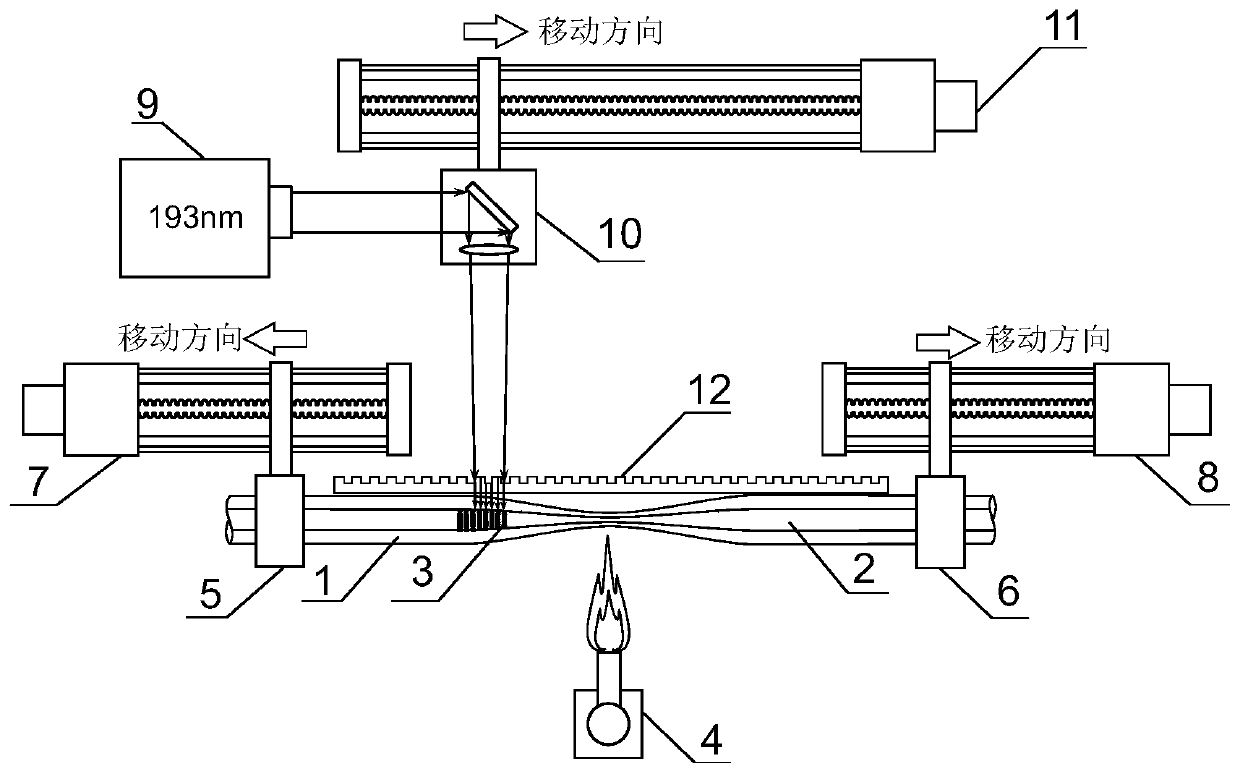
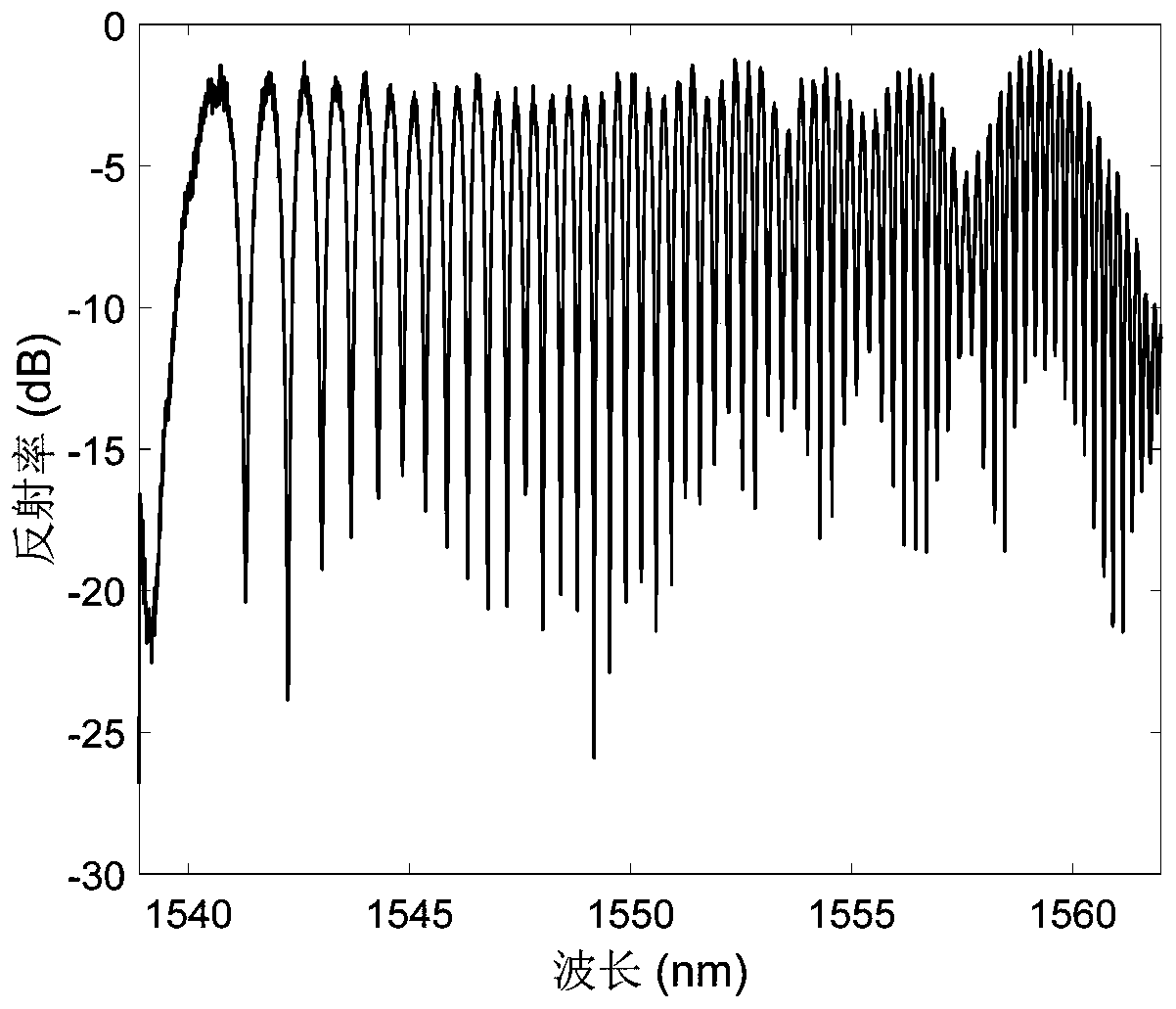
ActiveCN110412689ALarge Chirp Rate of ChangeNo phase mismatchOptical light guidesMicro nanoSpectral pattern
The invention discloses a chirp spectral pattern cavity-less optical fiber Fabry-Perot filter. The filter is characterized in that the filter comprises a multi-mode micro-nano optical fiber cladding,a multi-mode micro-nano optical fiber core and a Bragg grating; the multi-mode micro-nano optical fiber cladding is an outermost layer. According to the along-axis cross section of the multi-mode micro-nano optical fiber cladding, transition is realized from a uniform region with a constant radius to a micro-nano region with a gradually-changed radius, and again transition is realized from the micro-nano region with the gradually-changed radius to the other uniform region with a constant radius. The multi-mode micro-nano optical fiber core is an inner layer and is covered by the multi-mode micro-nano optical fiber cladding. According to the along-axis cross section of the multi-mode micro-nano optical fiber core, transition is realized from a uniform region with a constant radius to a micro-nano region with a gradually-changed radius, and again transition is realized from the micro-nano region with the gradually-changed radius to the other uniform region with a constant radius. The Bragg grating is a continuously-inscribed and equal-period Bragg grating which covers all the micro-nano region of the multi-mode micro-nano optical fiber core. With the chirp spectral pattern cavity-less optical fiber Fabry-Perot filter provided by the invention adopted, a chirp spectral pattern which can change in a free spectral range can be realized within a relatively large wavelength range, anda relatively large chirp rate can be realized. The chirp spectral pattern cavity-less optical fiber Fabry-Perot filter has the advantages of compact structure and easiness in manufacture.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Radio frequency time delay rapid measurement device based on chirp signal quadrature demodulation
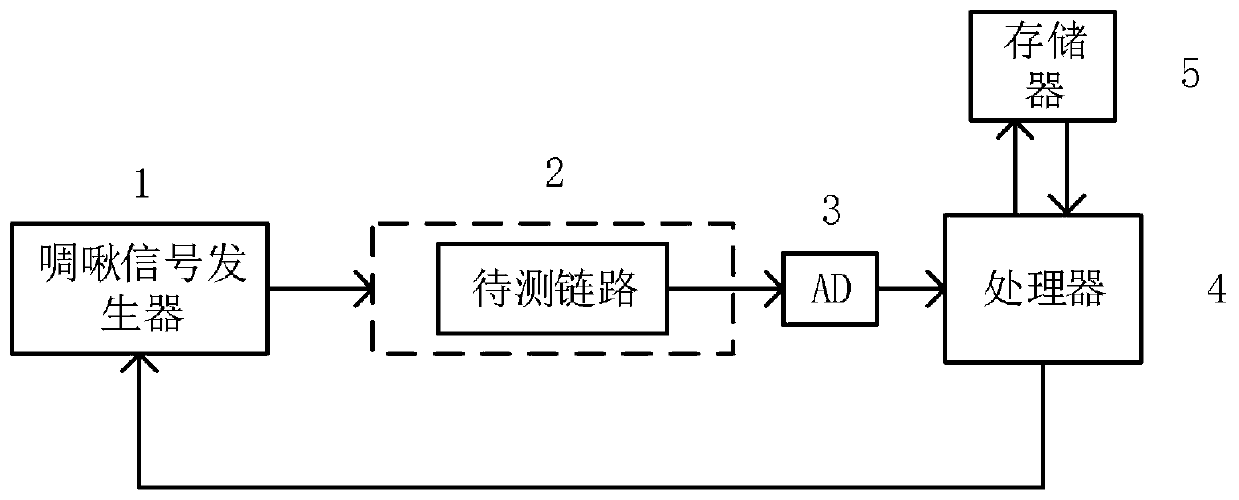
ActiveCN111082834AQuick measurementLarge measuring rangeTransmitters monitoringAnti jammingFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a radio frequency time delay rapid measurement device based on chirp signal quadrature demodulation. The device comprises a chirp signal generator, a to-be-measured device, ananalog-to-digital converter, a processor and a memory; the chirp signal generator adopted by the device emits chirp signals with adjustable frequency ranges and adjustable chirp rates, so the rapid measurement of time delay in different frequency ranges is achieved, and the measurement range of the system is large; meanwhile, the time delay of the frequency converter is measured, and extra reference signals are not needed; the system structure is simple, and the anti-jamming capability is high; moreover, the method achieves the extraction of the time delay through the quadrature demodulation technology, avoids the phenomena of phase ambiguity and spectrum leakage in a conventional time delay detection process, and greatly improves the time delay detection precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A SAR radar moving target imaging method
ActiveCN105699971BEasy to filterEasy to detectRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainLow-pass filter
The invention belongs to the field of radar signal processing, and discloses an SAR radar moving object imaging method. The SAR radar moving object imaging method comprises the steps of acquiring echo data which are received by an SAR radar, performing distance direction compression on the echo data, making the echo data after distance direction compression pass through a low pass filter, and separating clutter data and detachable data in the echo data after distance direction compression; forming a ground scene picture from the clutter data; performing moving object parameter estimation on the detachable data, obtaining a Doppler central frequency estimated value and a Doppler chirp rate estimated value, and constructing a reference function according to the Doppler central frequency estimated value and the Doppler chirp rate estimated value; performing time domain multiplication or frequency domain convolution on the reference function and the detachable data, thereby obtaining a moving object imaging picture; and adding the ground scene picture with the moving object imaging picture, thereby obtaining an SAR radar moving object imaging result. The SAR radar moving object imaging method can be used for performing fine imaging on the moving object.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com