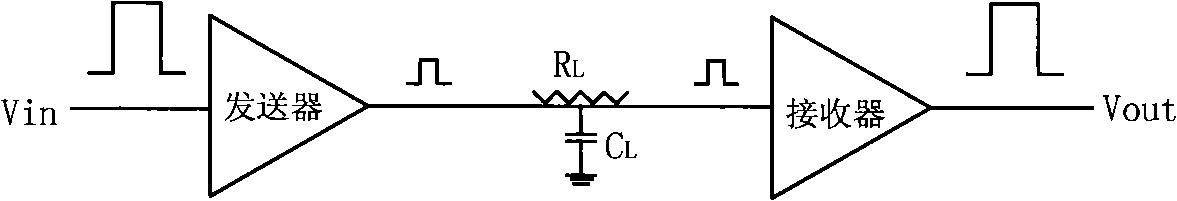Patents
Literature
160 results about "Current-mode logic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
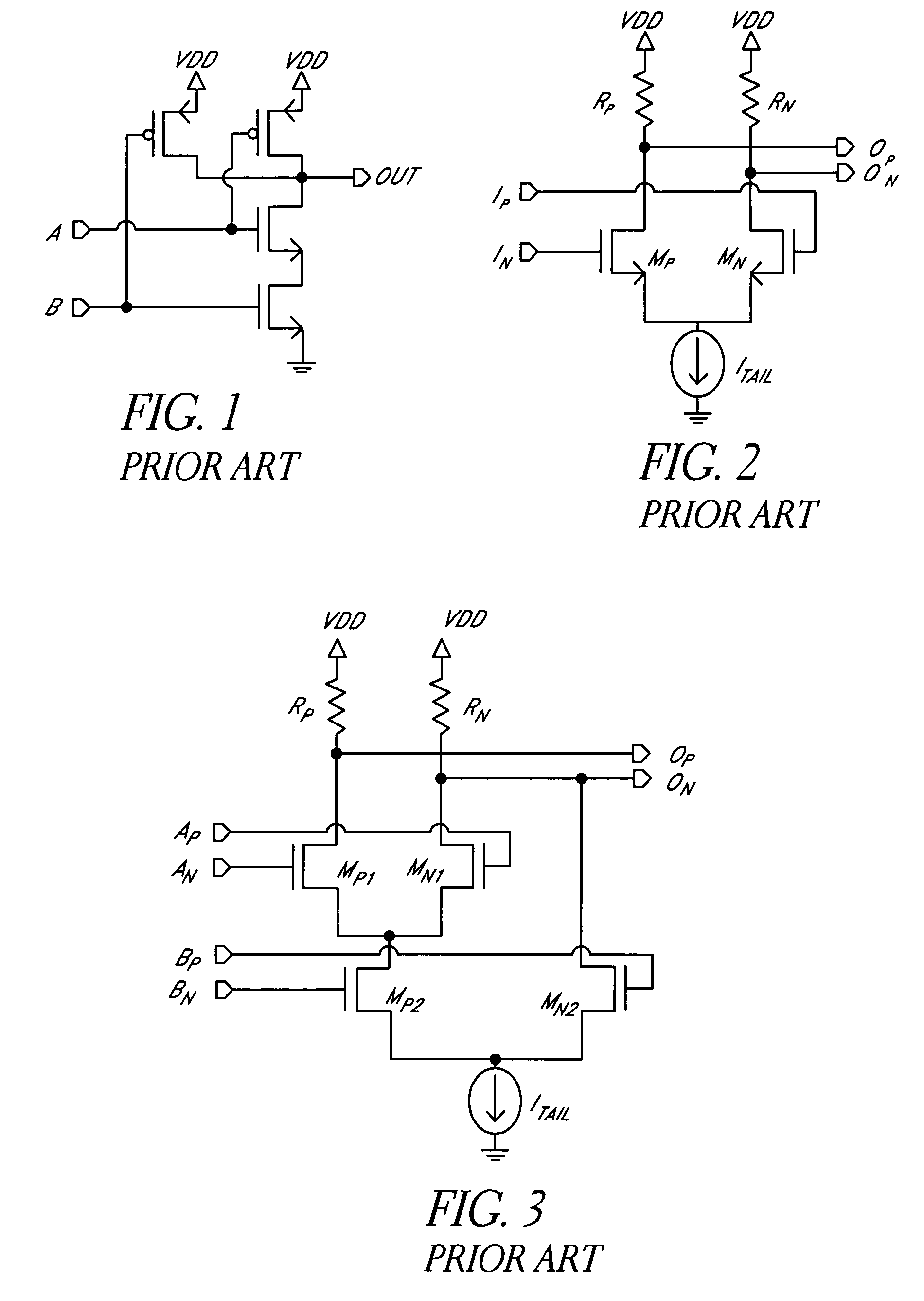
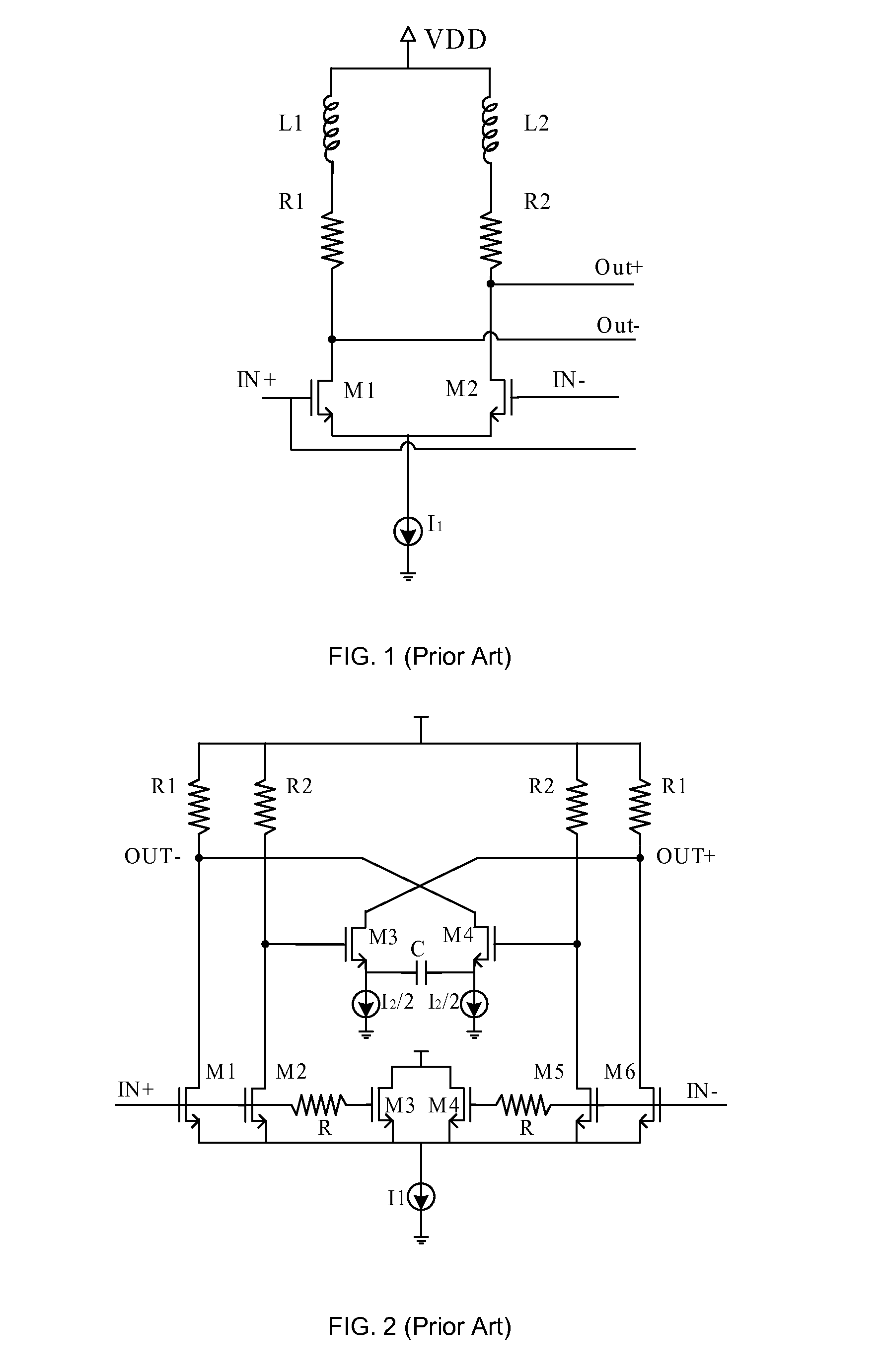
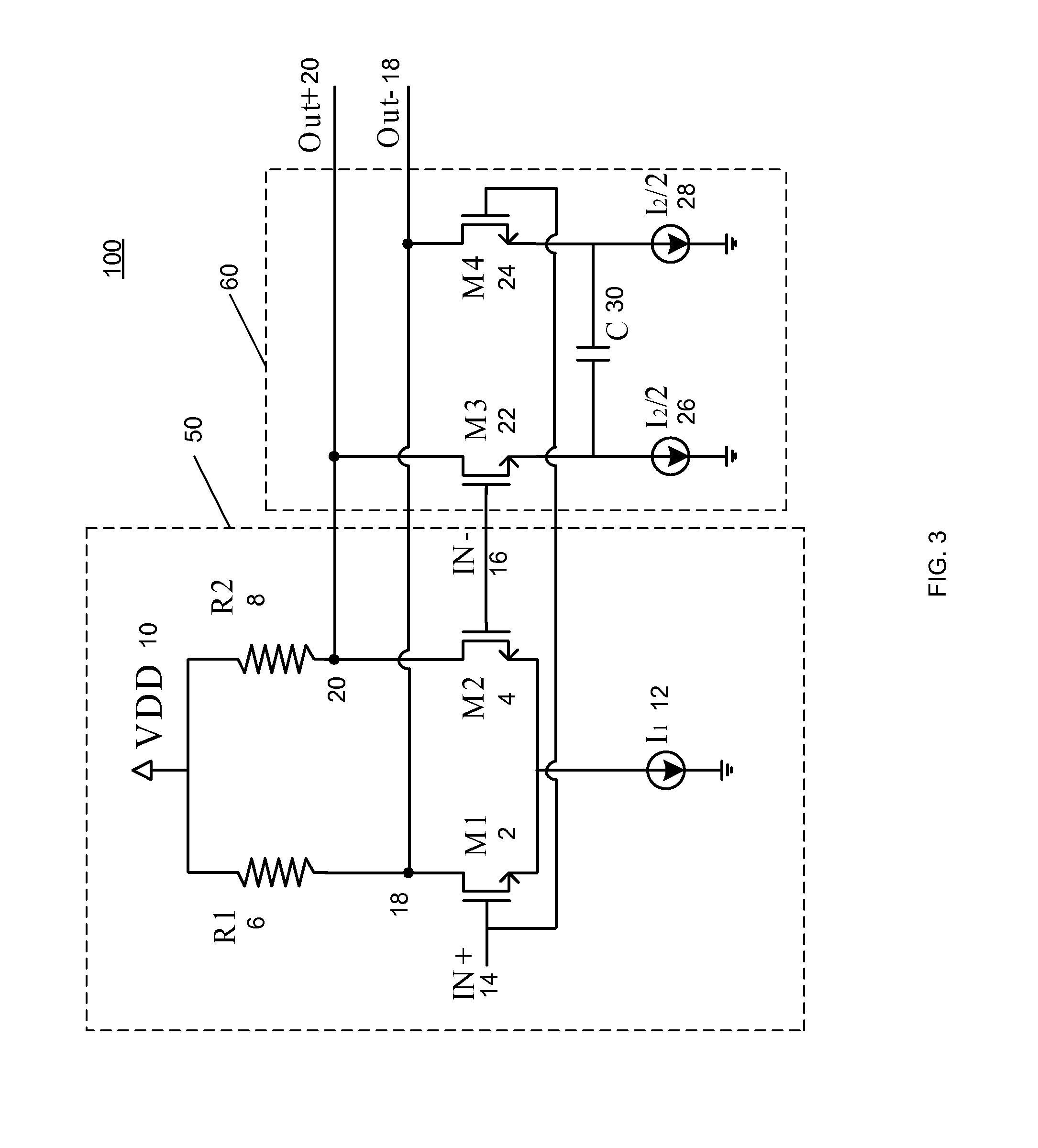
Current mode logic (CML), or source-coupled logic (SCL), is a differential digital logic family intended to transmit data at speeds between 312.5 Mbit/s and 3.125 Gbit/s across standard printed circuit boards.
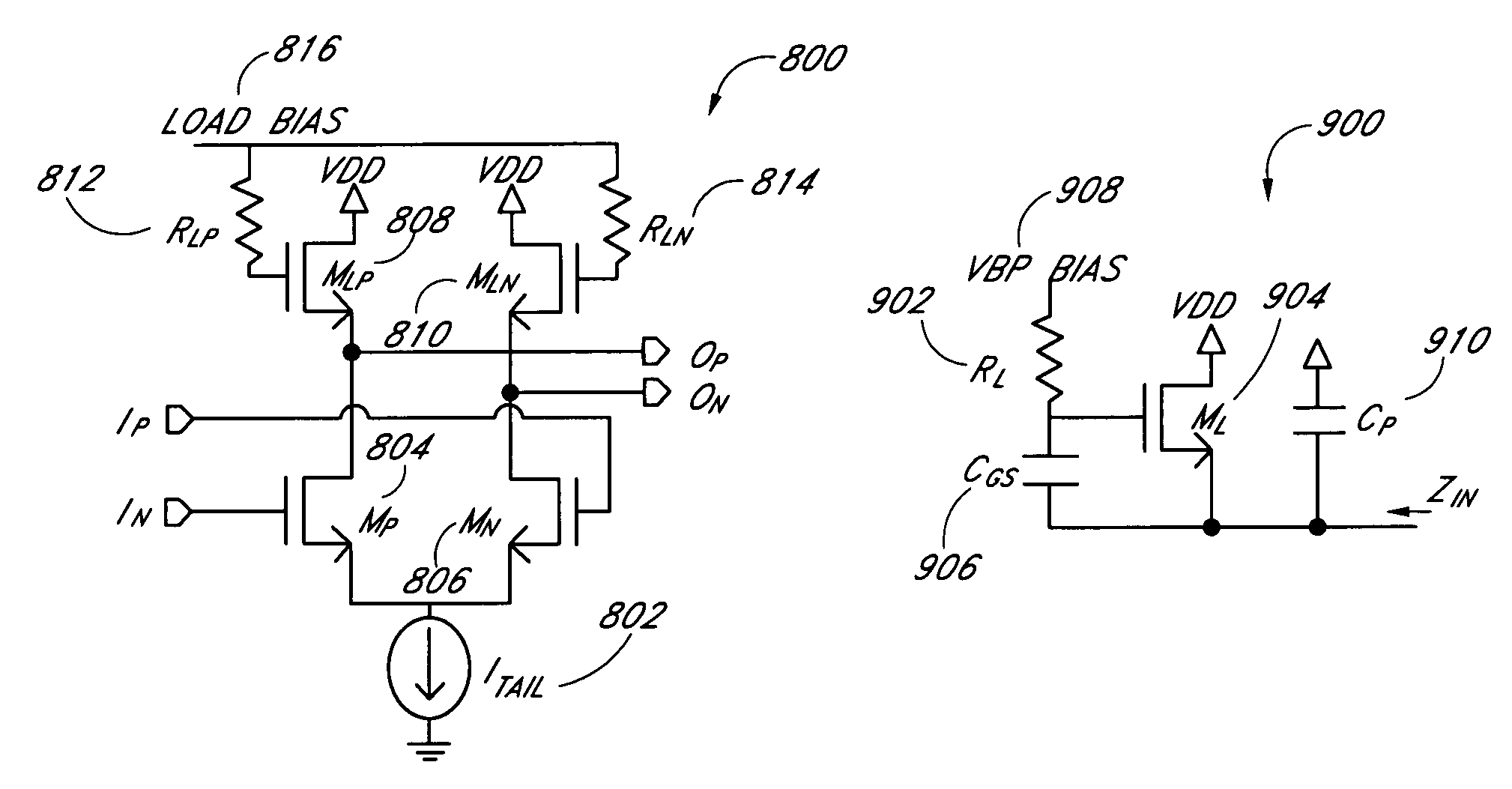
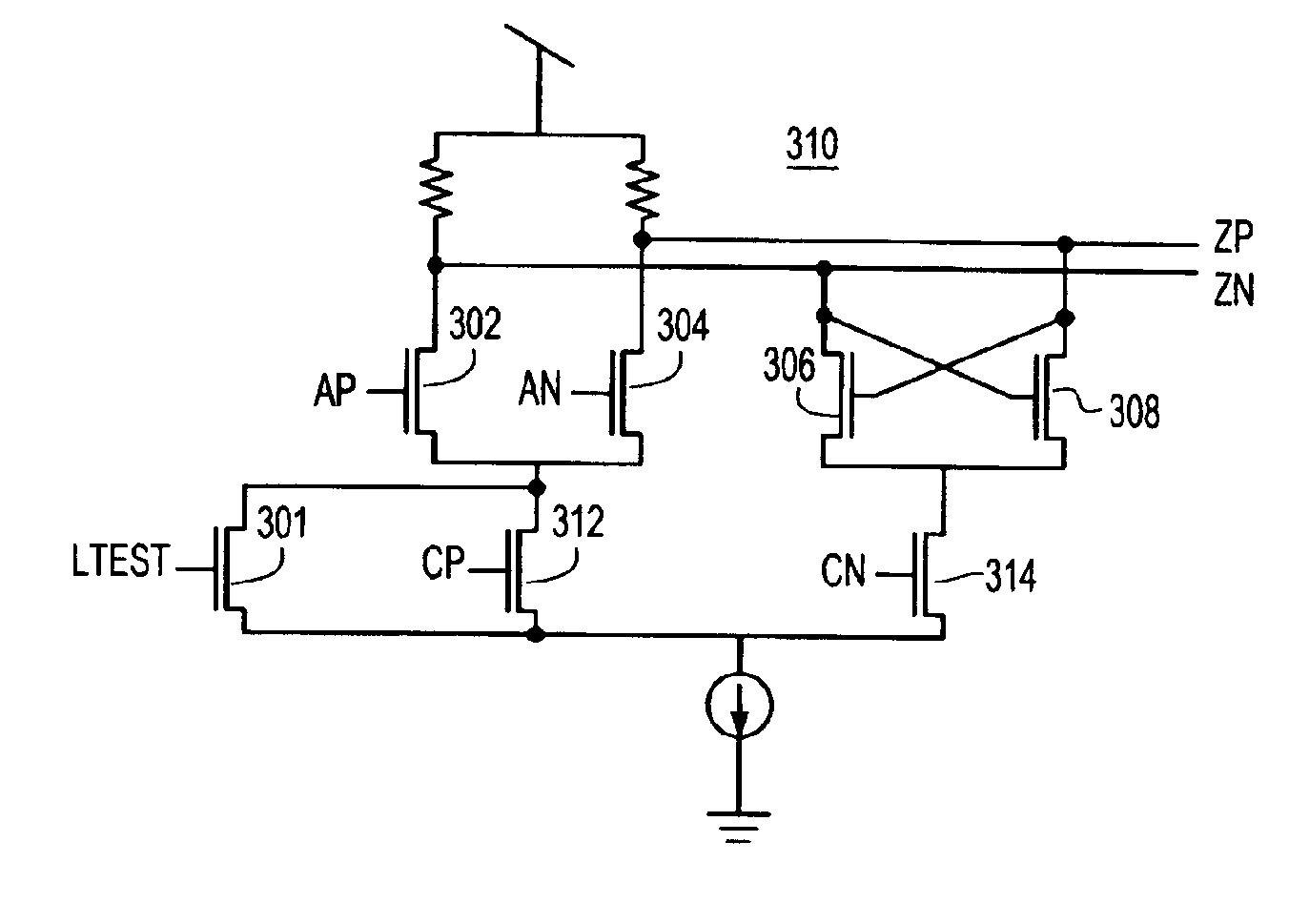
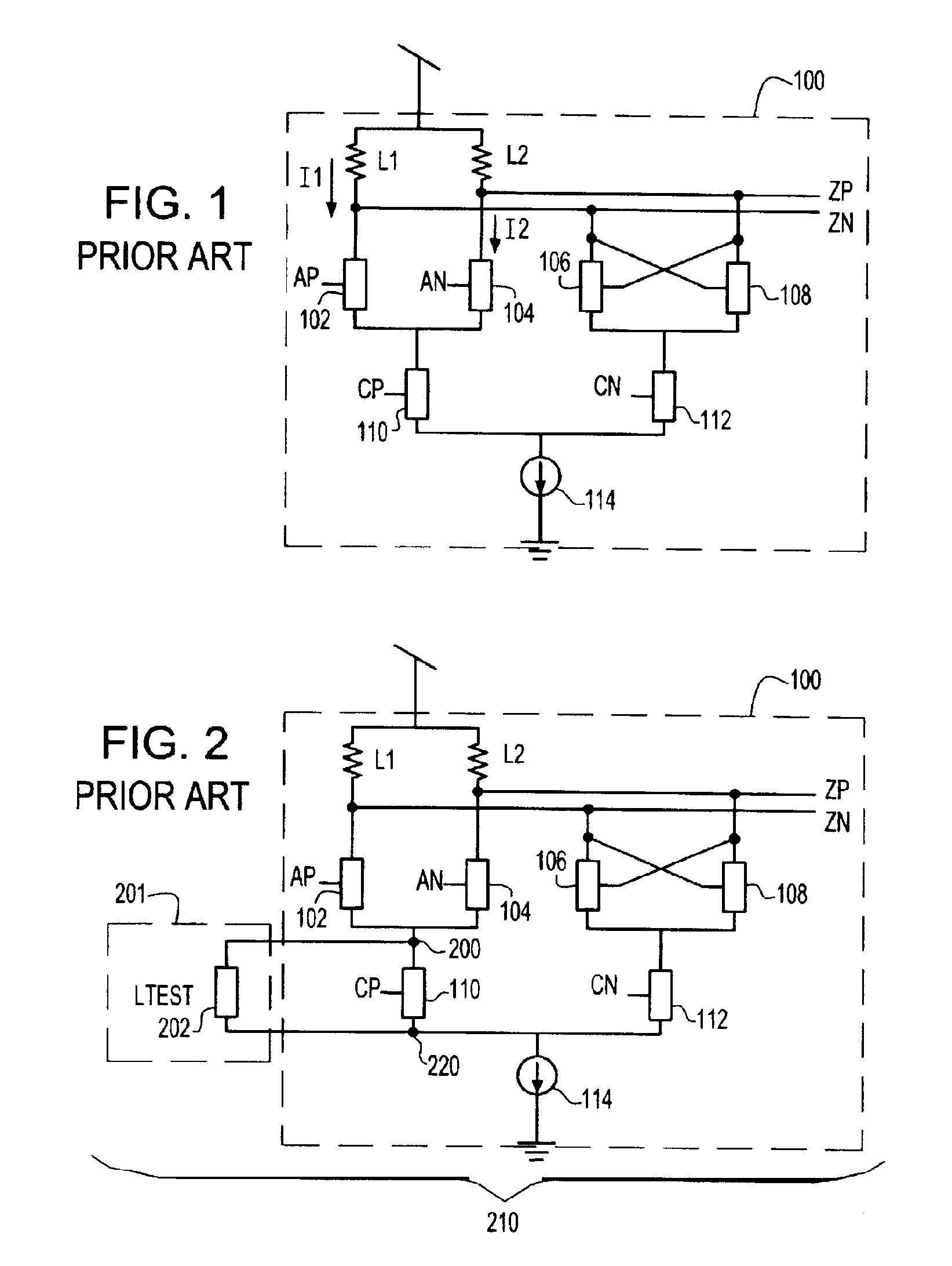
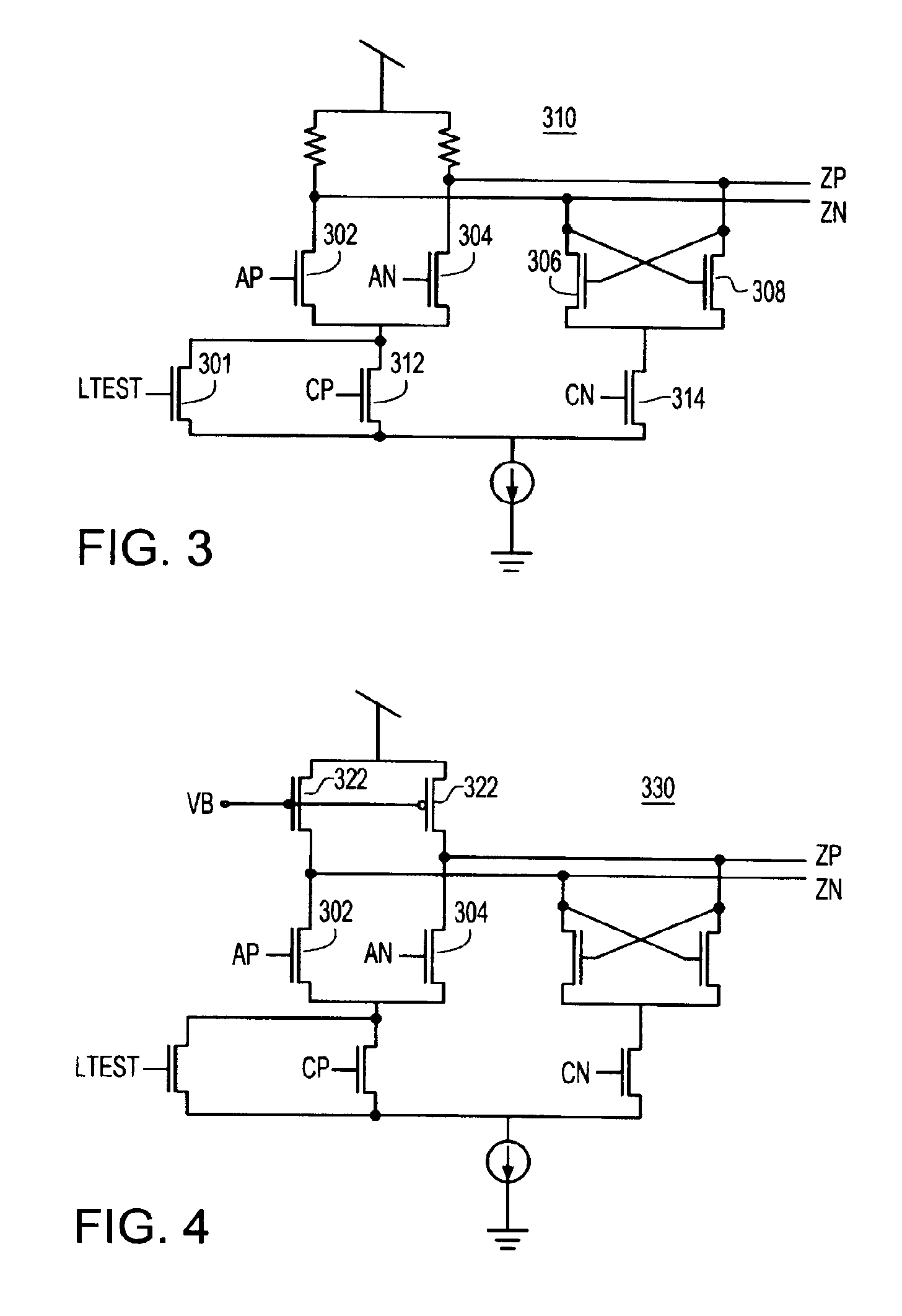
Systems and methods for actively-peaked current-mode logic
ActiveUS7202706B1Minimal costLess cost-effectiveSwitching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectrical resistance and conductanceLogic cell
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Method and system for a feedback transimpedance amplifier with sub-40khz low-frequency cutoff
ActiveUS8471639B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifiers controlled by lightPhotodetectorTransimpedance amplifier
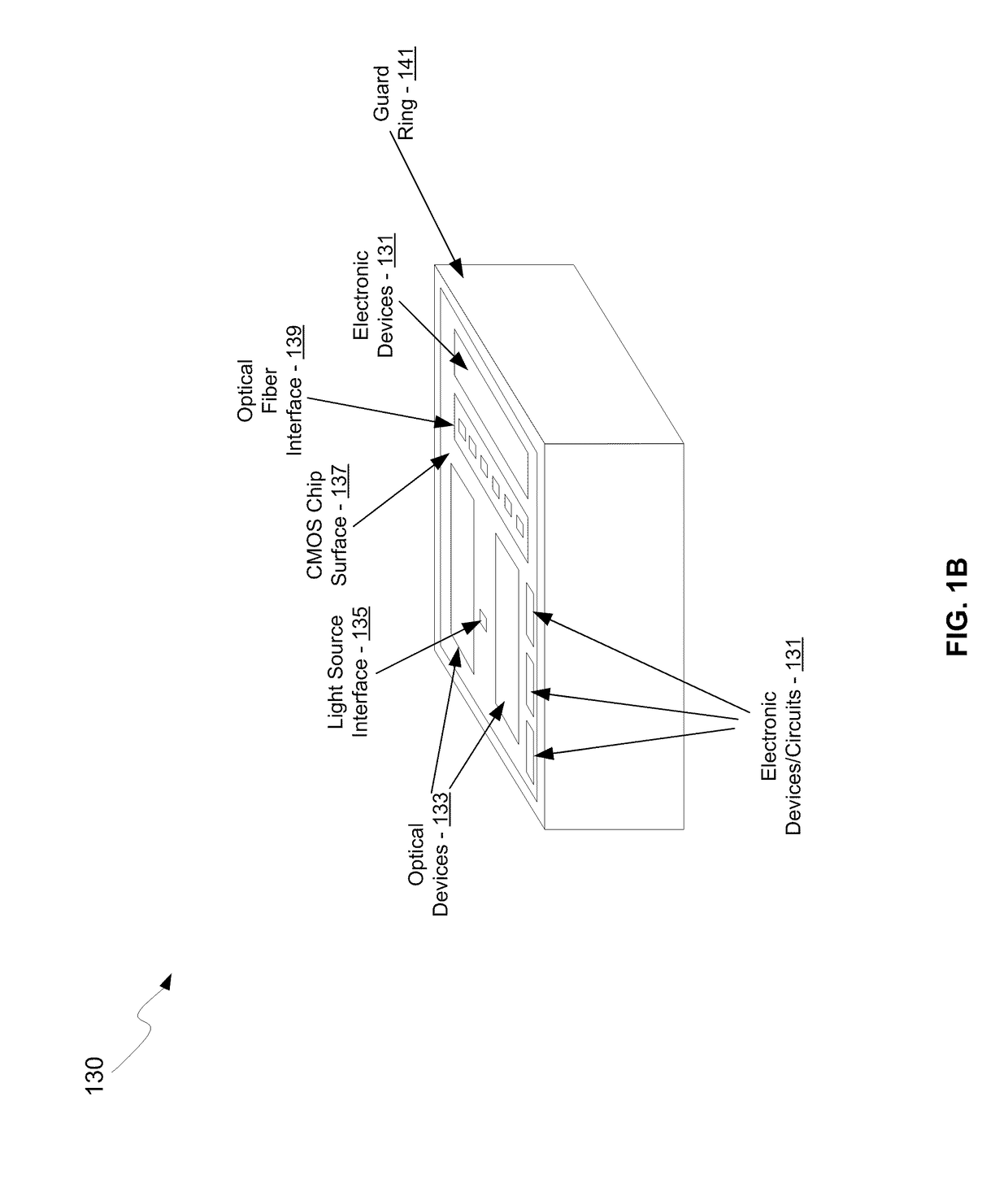
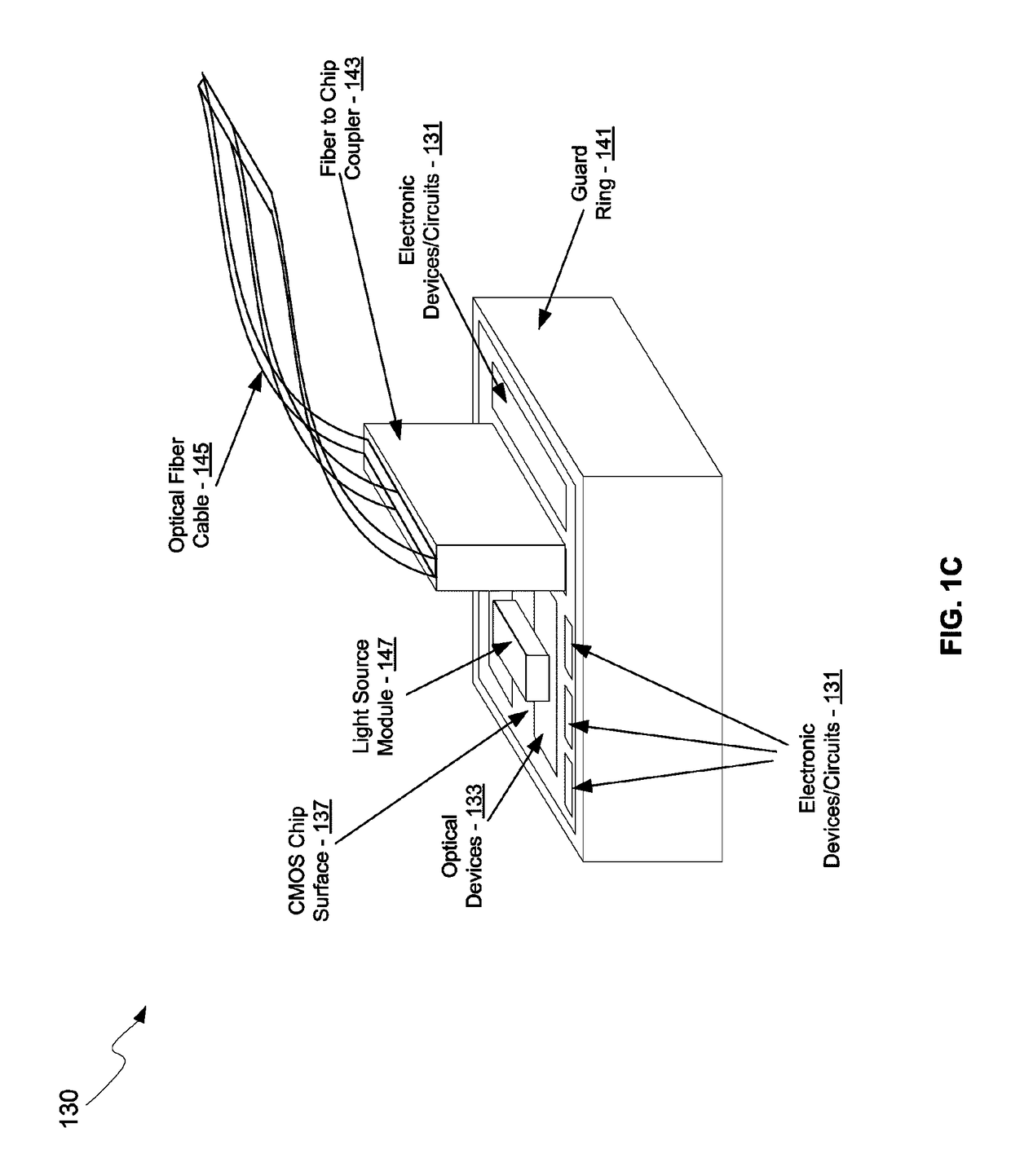
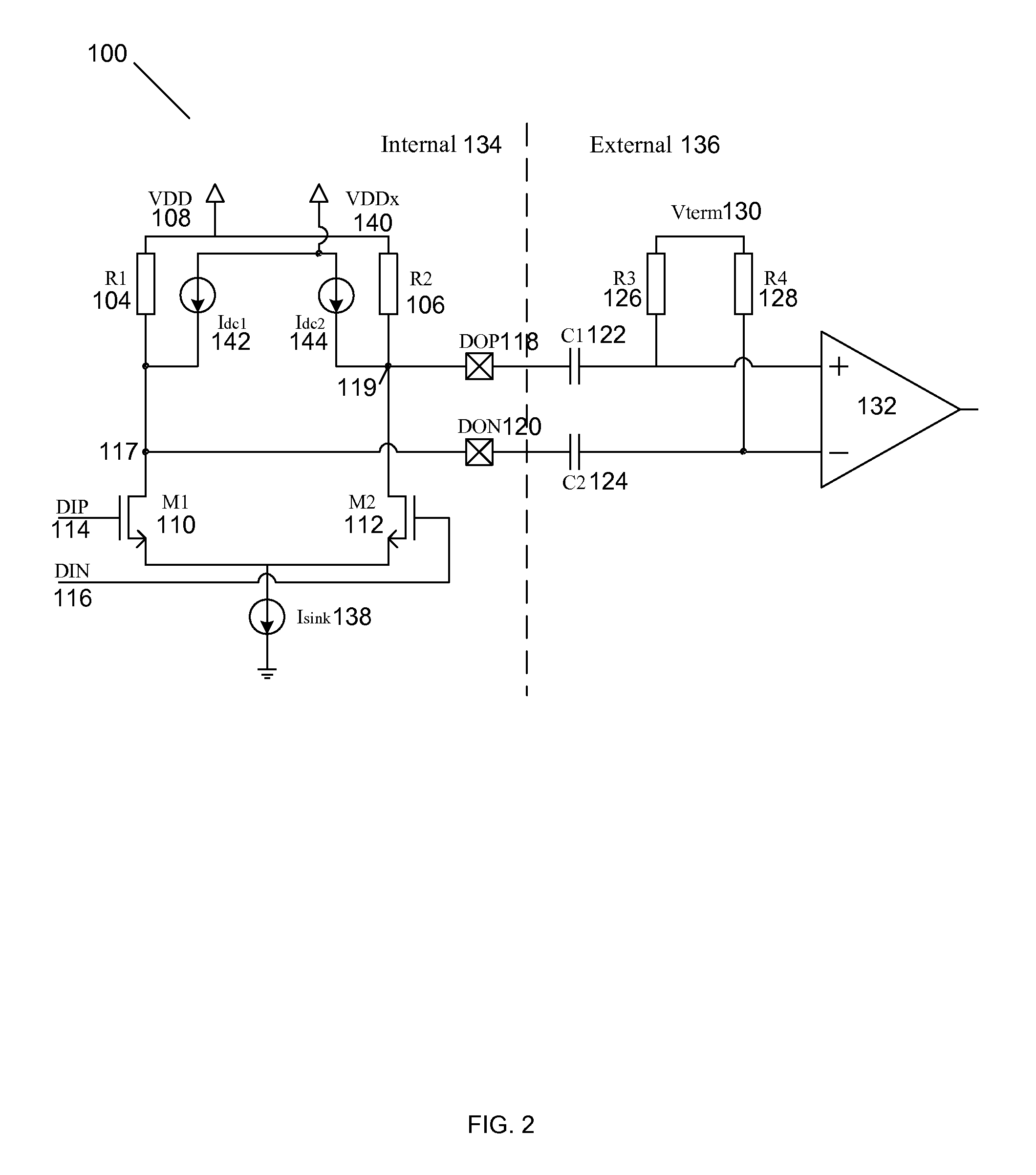
A system for a feedback transimpedance amplifier with sub-40 khz low-frequency cutoff is disclosed and may include amplifying electrical signals received via coupling capacitors utilizing a transimpedance amplifier (TIA) having feedback paths comprising source followers and feedback resistors. The feedback paths may be coupled prior to the coupling capacitors at inputs of the TIA. Voltages may be level shifted prior to the coupling capacitors to ensure stable bias conditions for the TIA. The TIA may be integrated in a CMOS chip and the source followers may comprise CMOS transistors. The TIA may receive current-mode logic or voltage signals. The electrical signals may be received from a photodetector, which may comprise a silicon germanium photodiode and may be differentially coupled to the TIA. The chip may comprise a CMOS photonics chip where optical signals for the photodetector in the CMOS photonics chip may be received via one or more optical fibers.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
High-speed CML circuit design
ActiveUS7560957B2Switching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsInductorEngineering
A current mode logic digital circuit is provided comprising a logic circuit component having at least one data input node and at least one output node. A load is coupled between a power supply node and the output node. The load comprises a folded active inductor coupled to the output node.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Systems and methods for actively-peaked current-mode logic
ActiveUS7288971B1Reduce power consumptionReduce areaSwitching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectrical resistance and conductanceLogic cell
A method and apparatus for creating high speed logic circuits in a CMOS environment using current steering logic cells with actively-peaked NMOS or PMOS loads and the biasing of these logic cells is disclosed. The logic cells can include, for example, buffers, AND gates, OR gates, flip-flops, and latches. The current steering cells with actively-peaked loads can provide benefits such as reduced power consumption, smaller area, and higher speed performance over conventional devices. This performance boost is preferably achieved using NMOS followers with resistively degenerated gates to create frequency peaked transfer function of current-mode logic cells. These logic cells with actively-peaked loads can advantageously be used in circuits in which relatively good power area and performance are desired for state machine logic, parallel to serial conversions, serial to parallel conversions, and the like.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Multifunctional output drivers and multifunctional transmitters using the same
InactiveUS20090174439A1Reduce consumptionLow costPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorTransfer modeEngineering
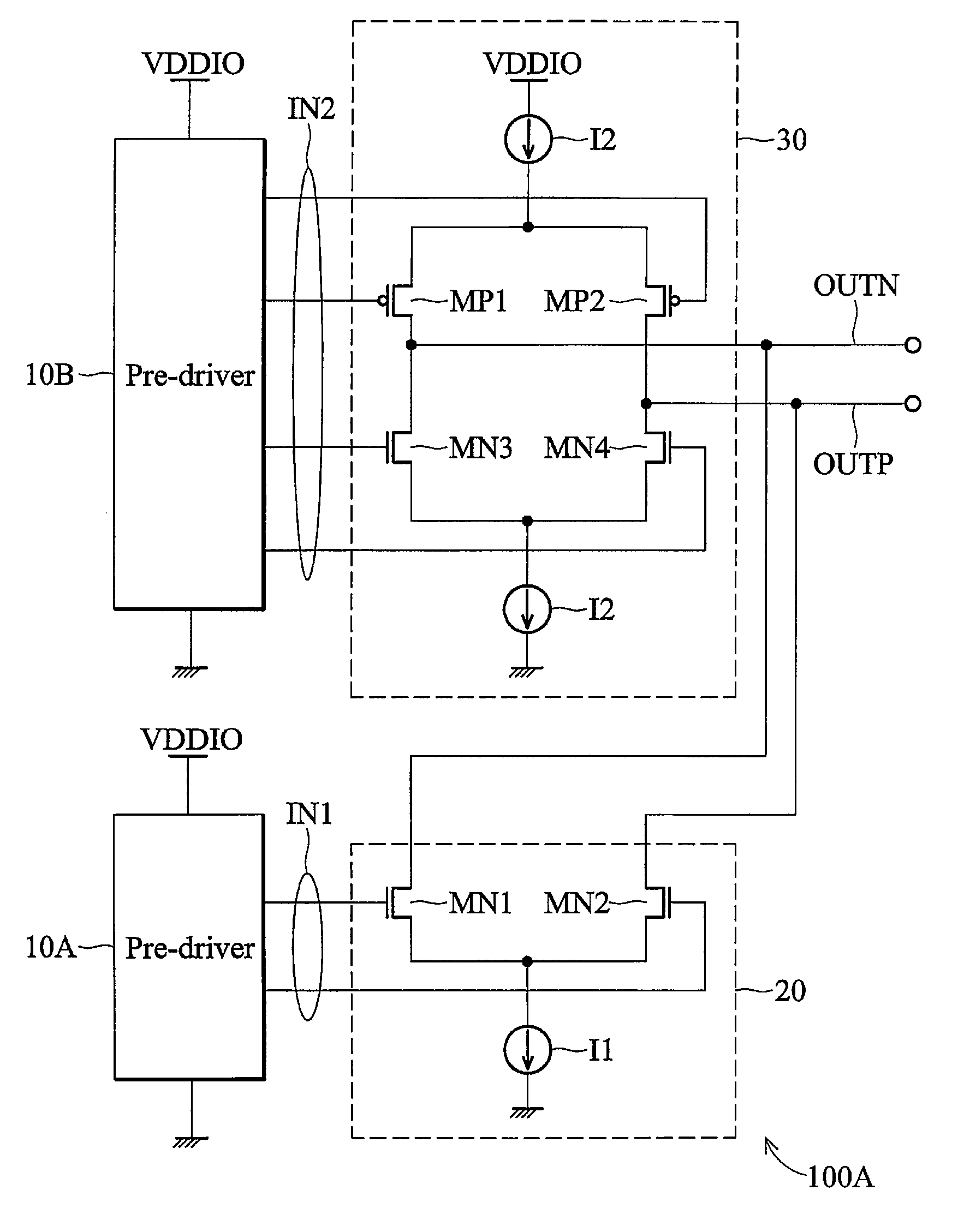
A multifunctional output driver capable of transmitting signals of different interfaces in different modes is provided, in which first and second current sources are provided, and first to fourth switching devices are coupled between the first and second current sources, and the first and second current source and the first to the fourth switching devices act as a current steering circuit. In a first transmission mode, the first and second switching devices are turned off, and the third and fourth switching devices and the first current source act as a current mode logic circuit to provide an output signal compatible with a first transmission interface according to an input signal from a pre-driver. In a second transmission mode, the current steering circuit outputs an output signal compatible with a second transmission interface according to the input signal from the pre-driver.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
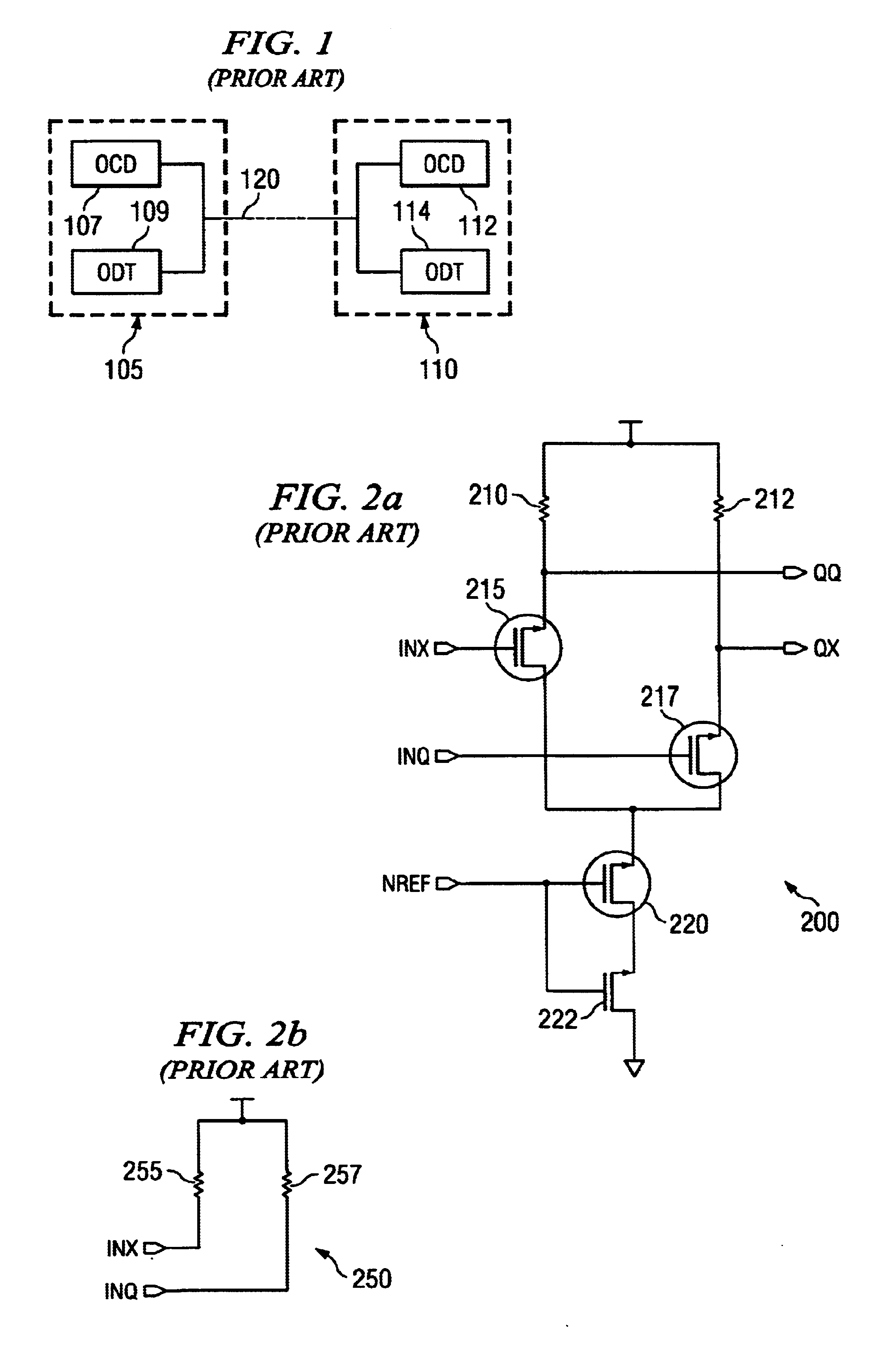
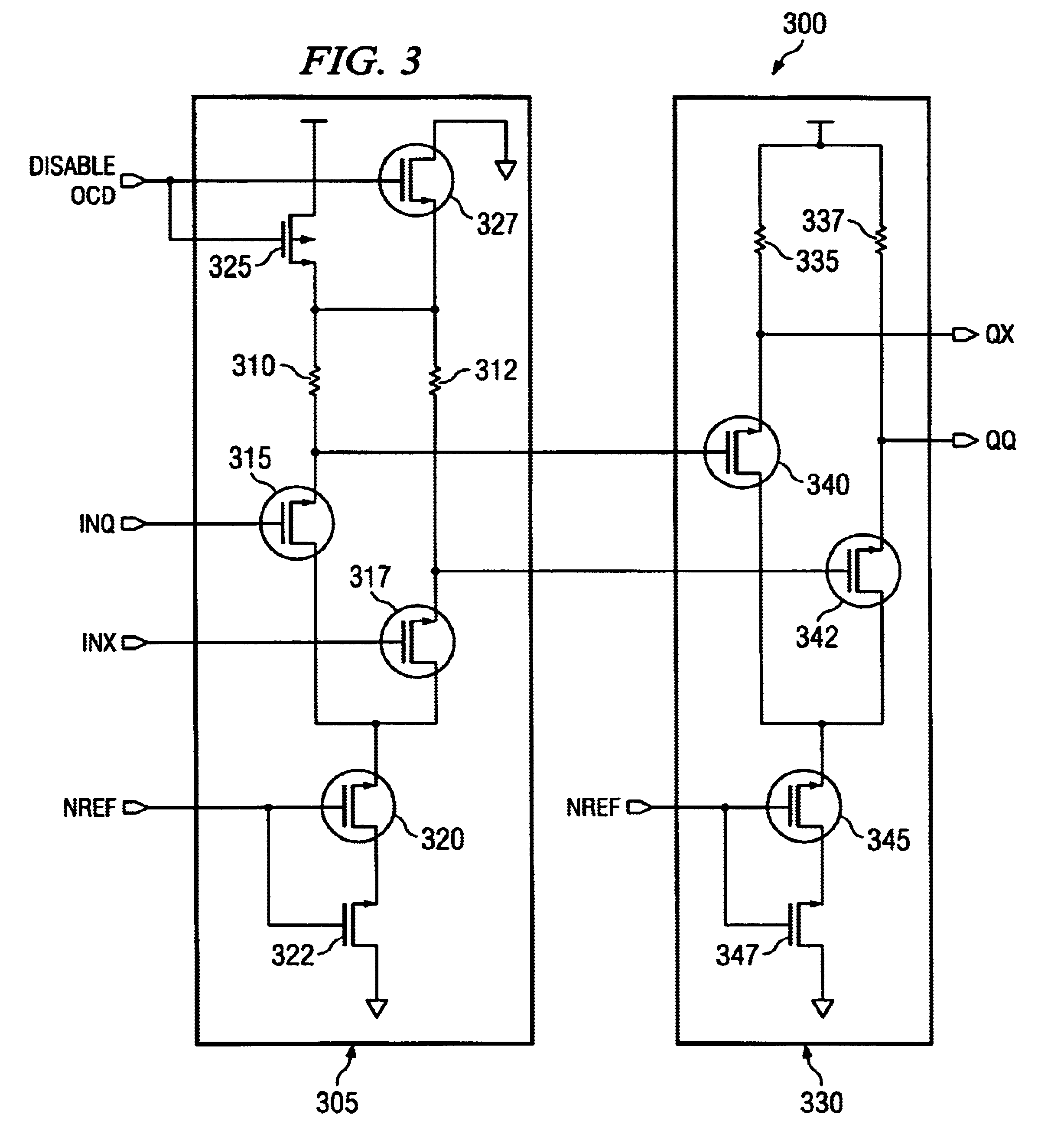
CML (current mode logic) OCD (off chip driver)-ODT (on die termination) circuit for bidirectional data transmission
InactiveUS6847225B2Easy to routeEasy to placeReliability increasing modificationsBaseband system detailsSignal onControl circuit
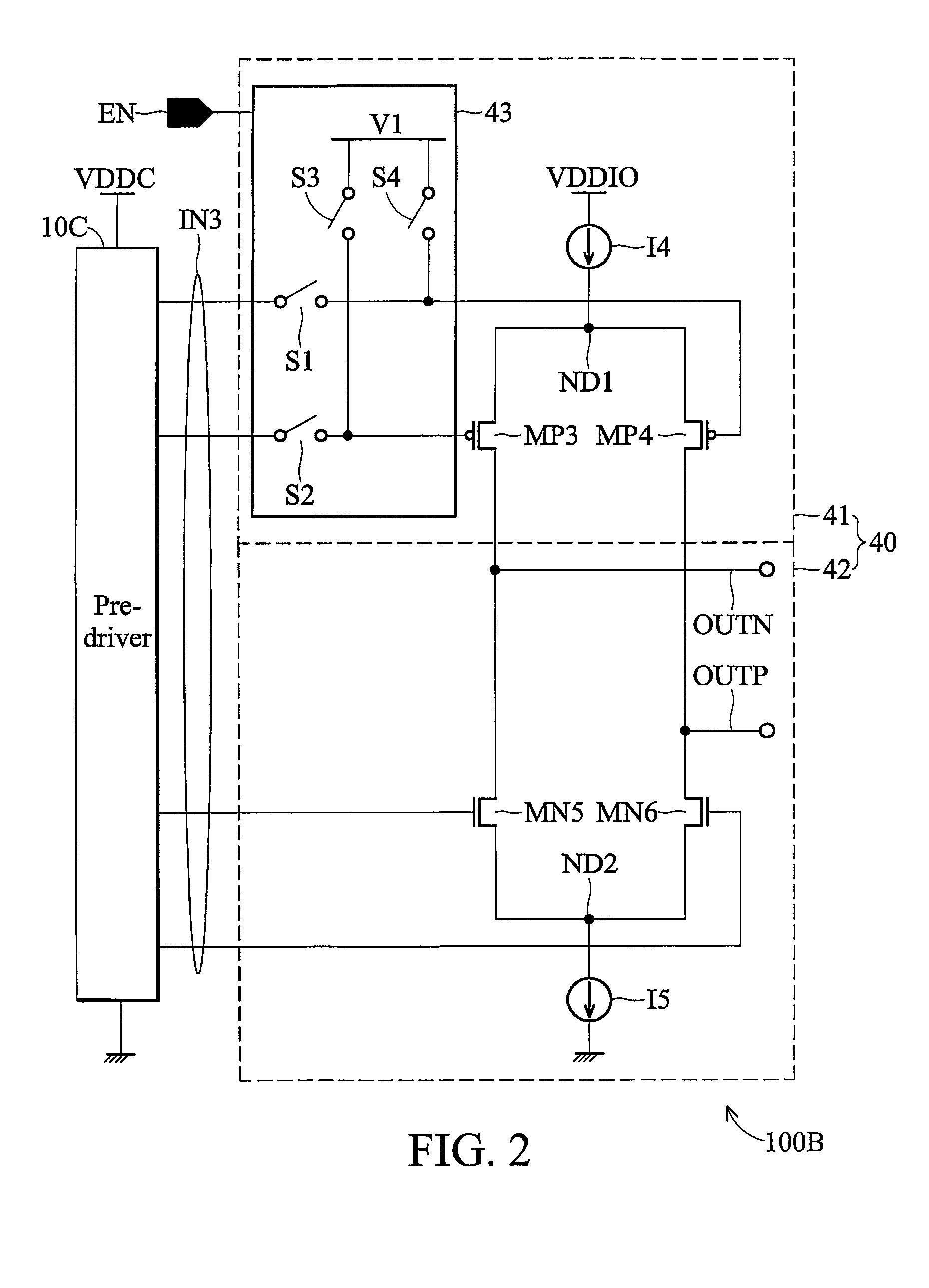
An apparatus for use as both an off chip driver (OCD) and an on die termination (ODT) circuits. A preferred embodiment comprises a control circuit (for example, control circuit 305) coupled to a dual function OCD / ODT circuit (for example, OCD / ODT circuit 330) with an enable line coupled to the control circuit. The control circuit may be used to selectively choose OCD and ODT functionality based on a value on the enable line. With the control circuit choosing OCD, the dual function OCD / ODT circuit functions as an OCD circuit, placing signals provided through the control circuit onto a transmission line. With the control circuit choosing ODT, the dual function OCD / ODT circuit becomes terminating resistors for incoming signals on a transmission line. The use of a single circuit for both OCD and ODT functions can save both integrated circuit real-estate and implementation costs due to a reduction in use of circuit elements.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
High-speed cml circuit design
ActiveUS20070018694A1Switching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsInductorLogic circuitry
A current mode logic digital circuit is provided comprising a logic circuit component having at least one data input node and at least one output node. A load is coupled between a power supply node and the output node. The load comprises a folded active inductor coupled to the output node.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multiple signal format output driver with configurable internal load
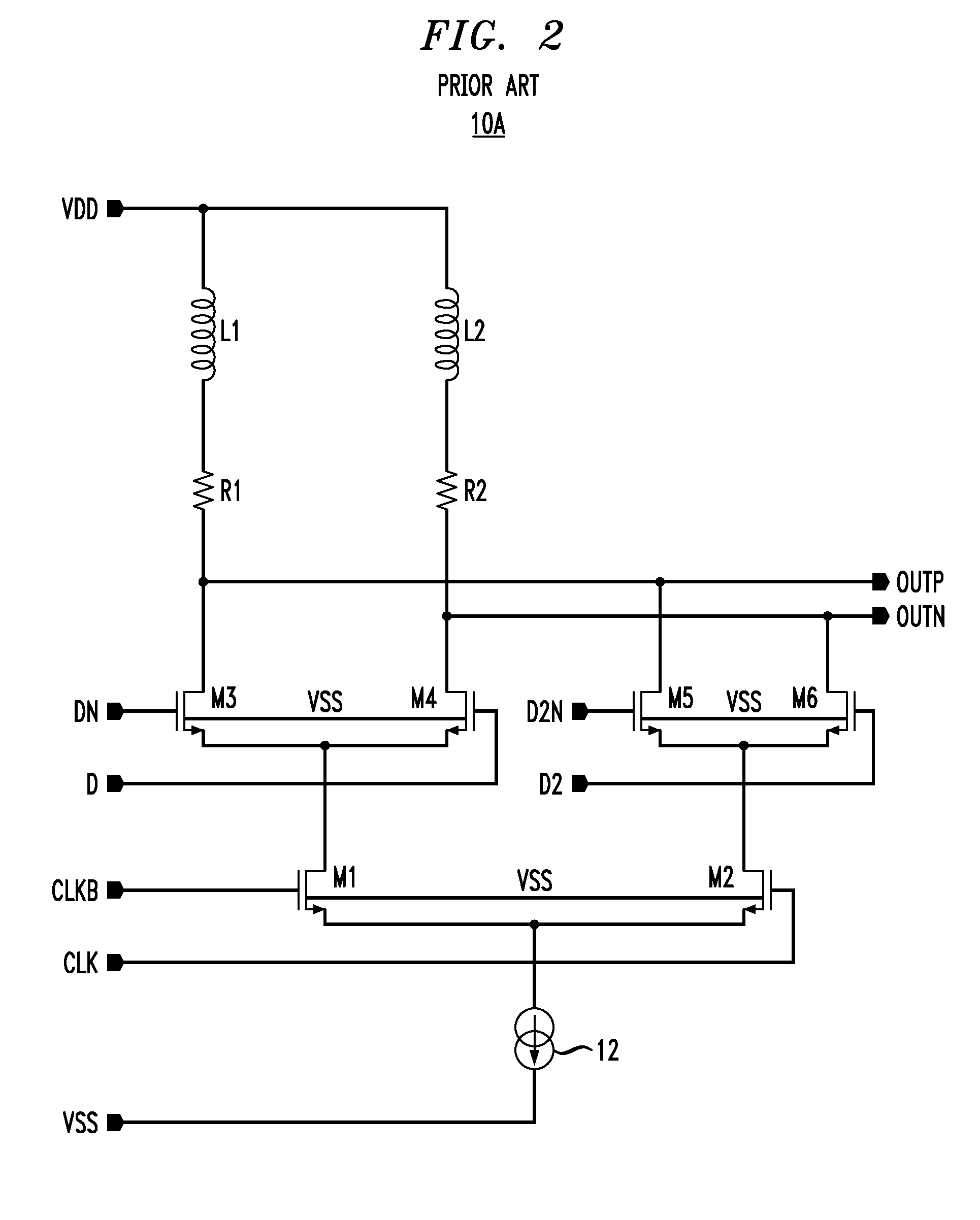
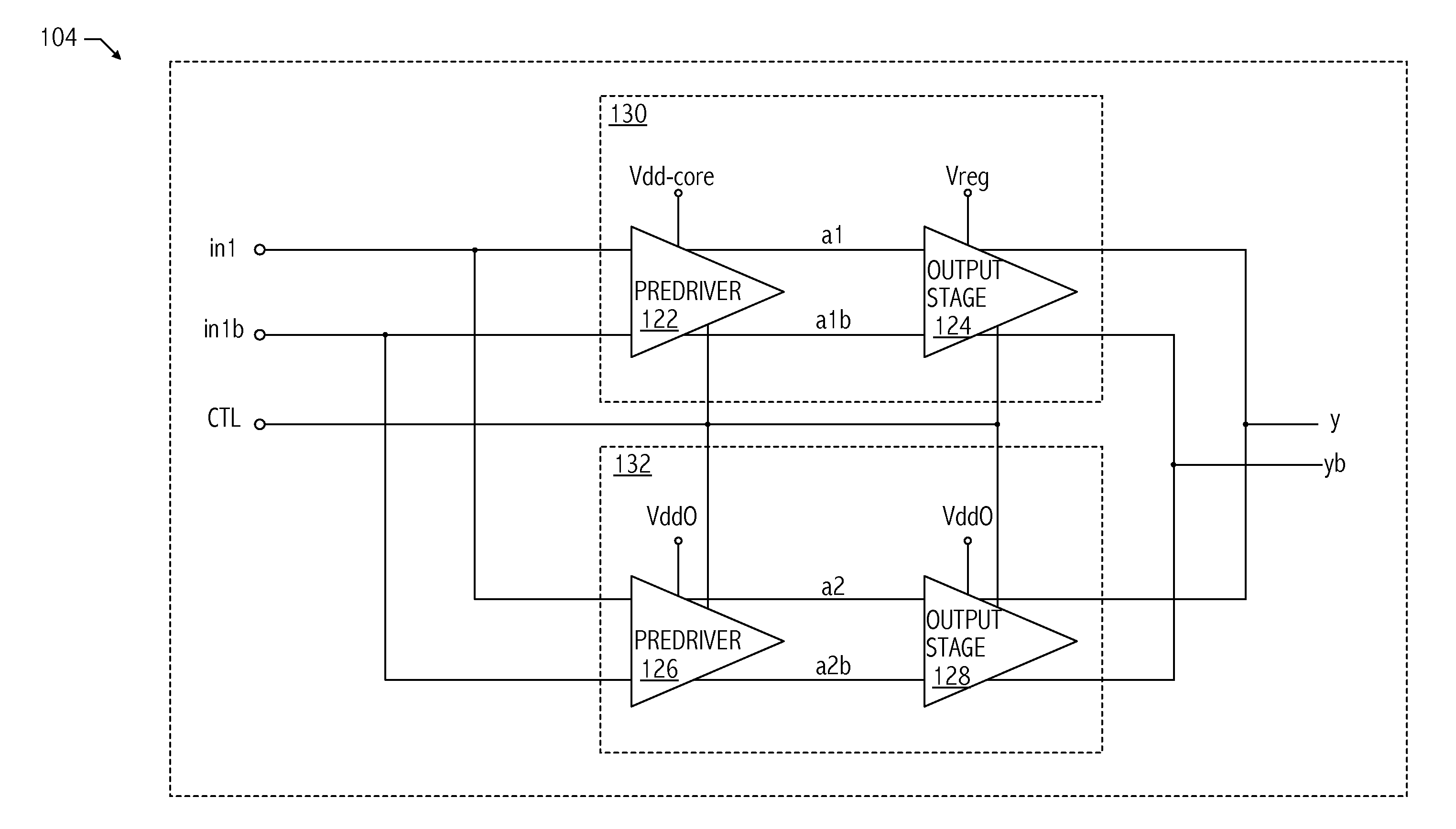
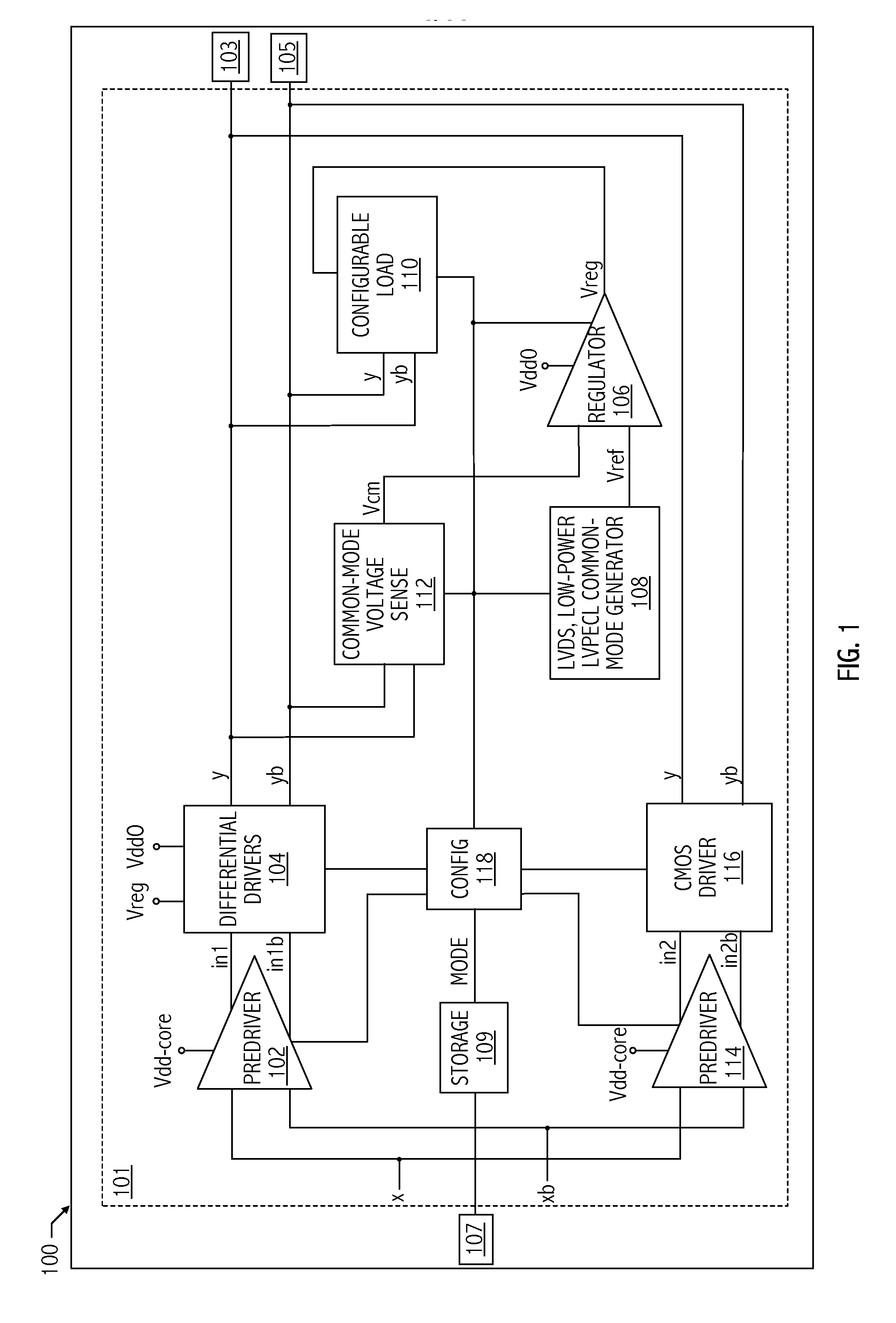
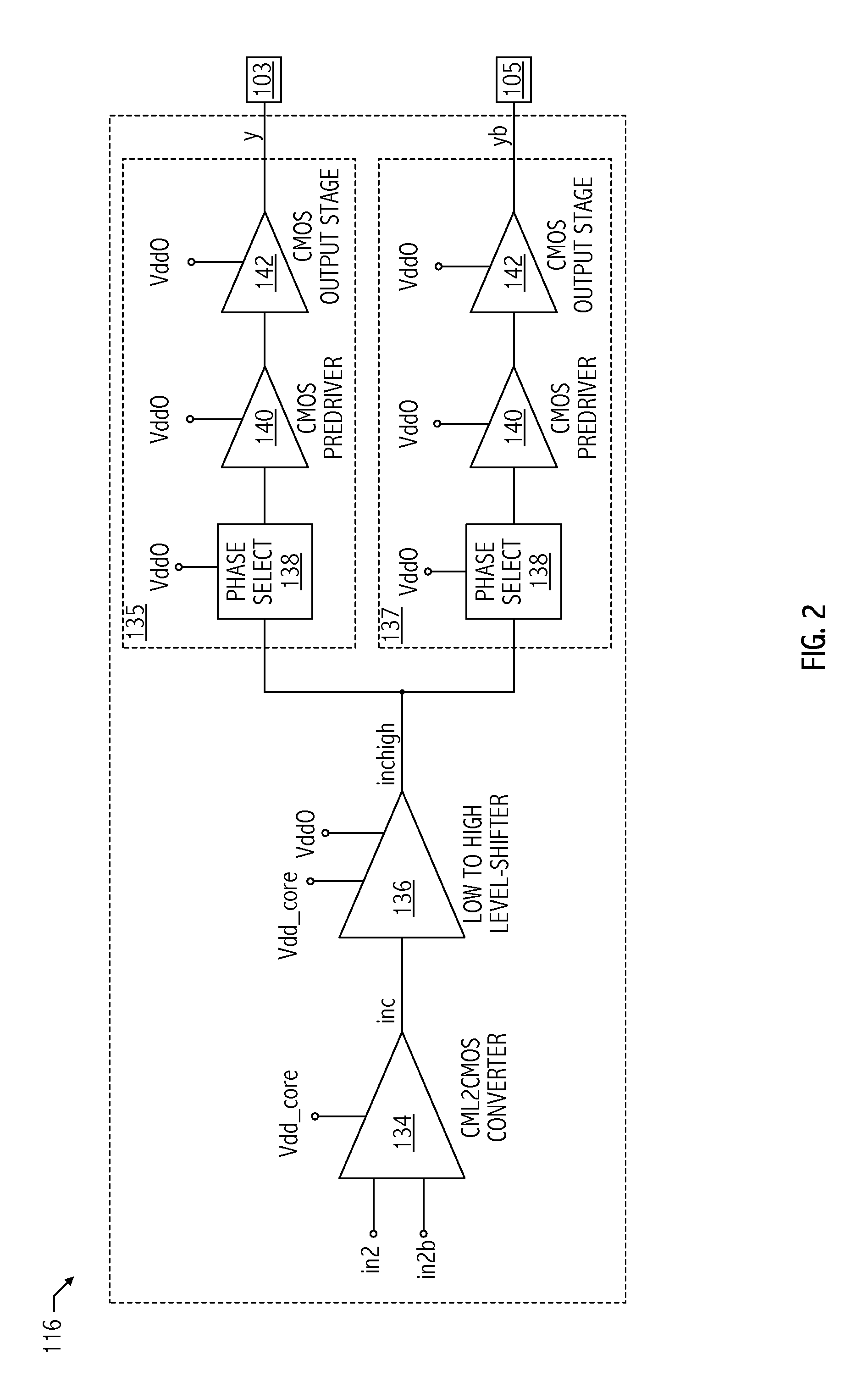
A multiple signal format output driver is configurable to provide a current-mode logic (CML) output signal in response to a CML value of one or more first values of the control signal. The output driver is configurable to provide a low-power, low-voltage positive emitter-coupled logic (low-power LVPECL) output signal in response to a low-power LVPECL value of the one or more first values of the control signal. The output driver is configurable to provide a low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) output signal in response to an LVDS value of the one or more first values of the control signal. The output driver may be configurable to provide a LVPECL output signal in response to a second value of the control signal. The output driver may be configurable to provide a high-speed current steering logic (HCSL) output in response to a third value of the control signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
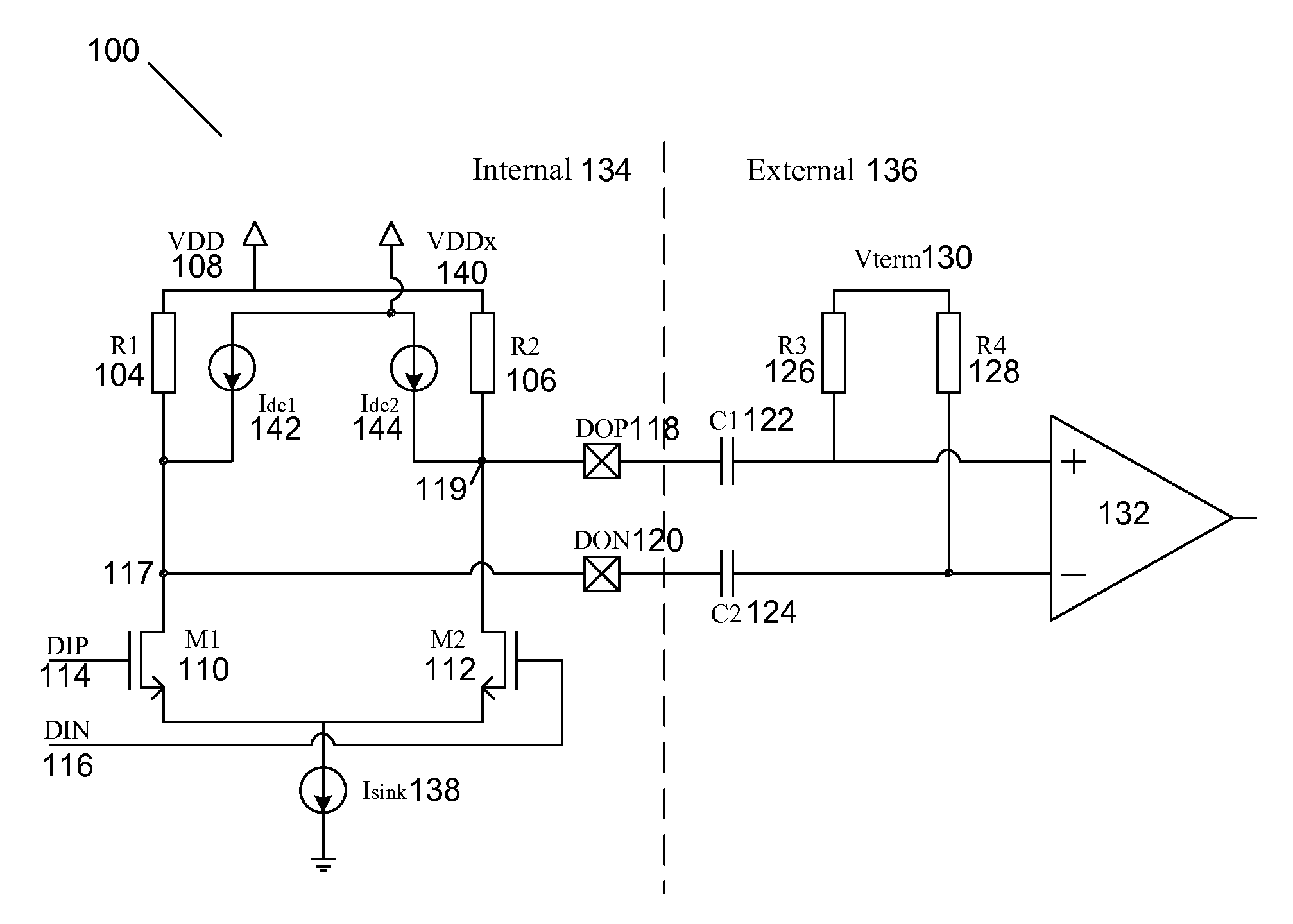
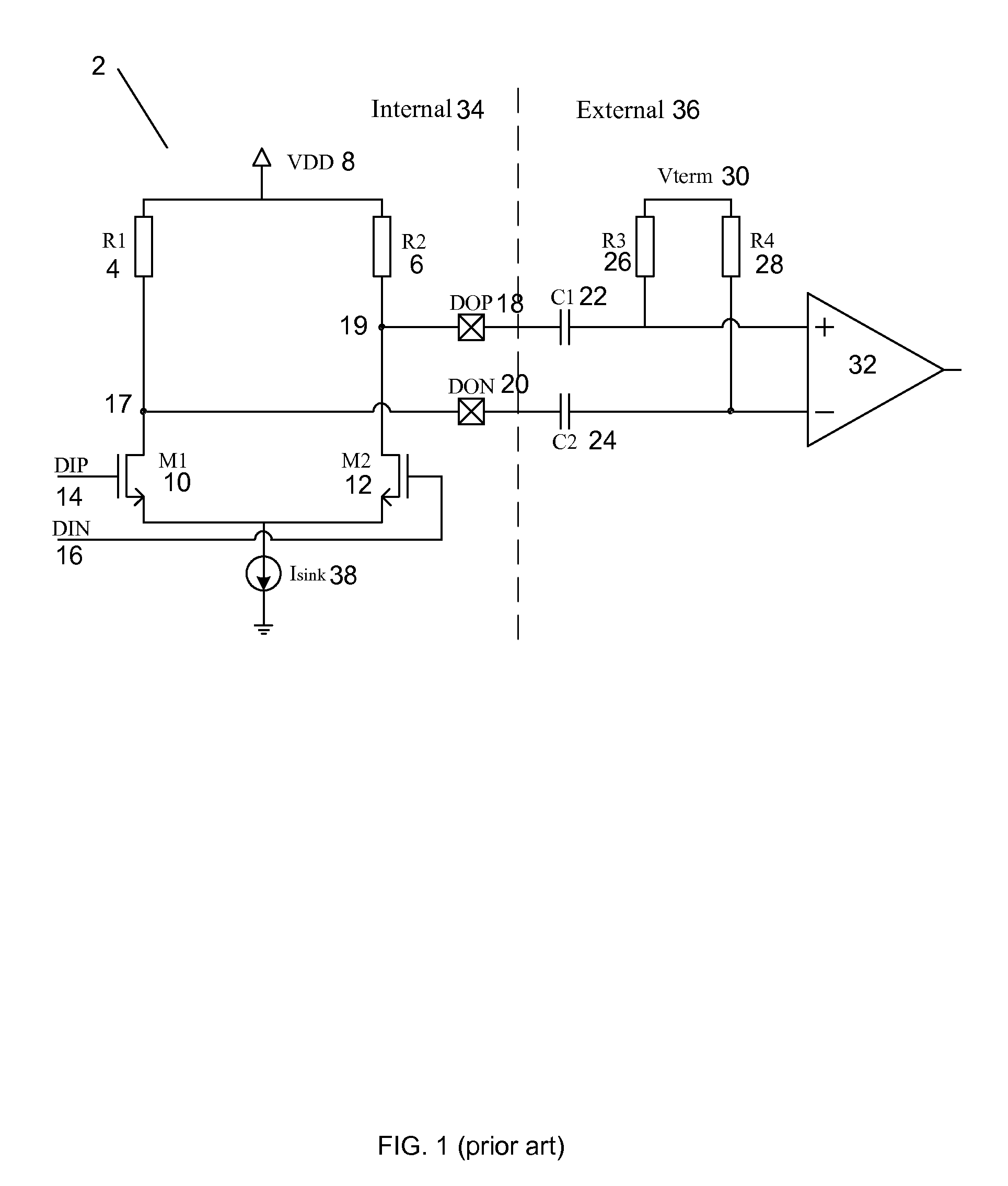
Input stage threshold adjustment for high speed data communications
InactiveUS20050160327A1Improve reliabilityReduce eliminateDigital circuit testingError detection/correctionDecision circuitCommunications system
Systems and methods for correcting distortions in transmitted signals are provided. More particularly, systems and methods for correcting the asymmetry that may occur between a receiver's signal-eye and a distorted signal are provided. One technique centers the signal-eye, with respect to the received signal, by adjusting the voltage threshold of the signal-eye in the receiver's clock and data recovery decision circuit. Another technique centers the signal-eye, with respect to the received signal, by shaping the voltage of the received signal. A current-mode logic circuit is provided to shape the voltage of the received signal by sinking current from the received signal.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Low Power Bias Compensation Scheme Utilizing A Resistor Bias
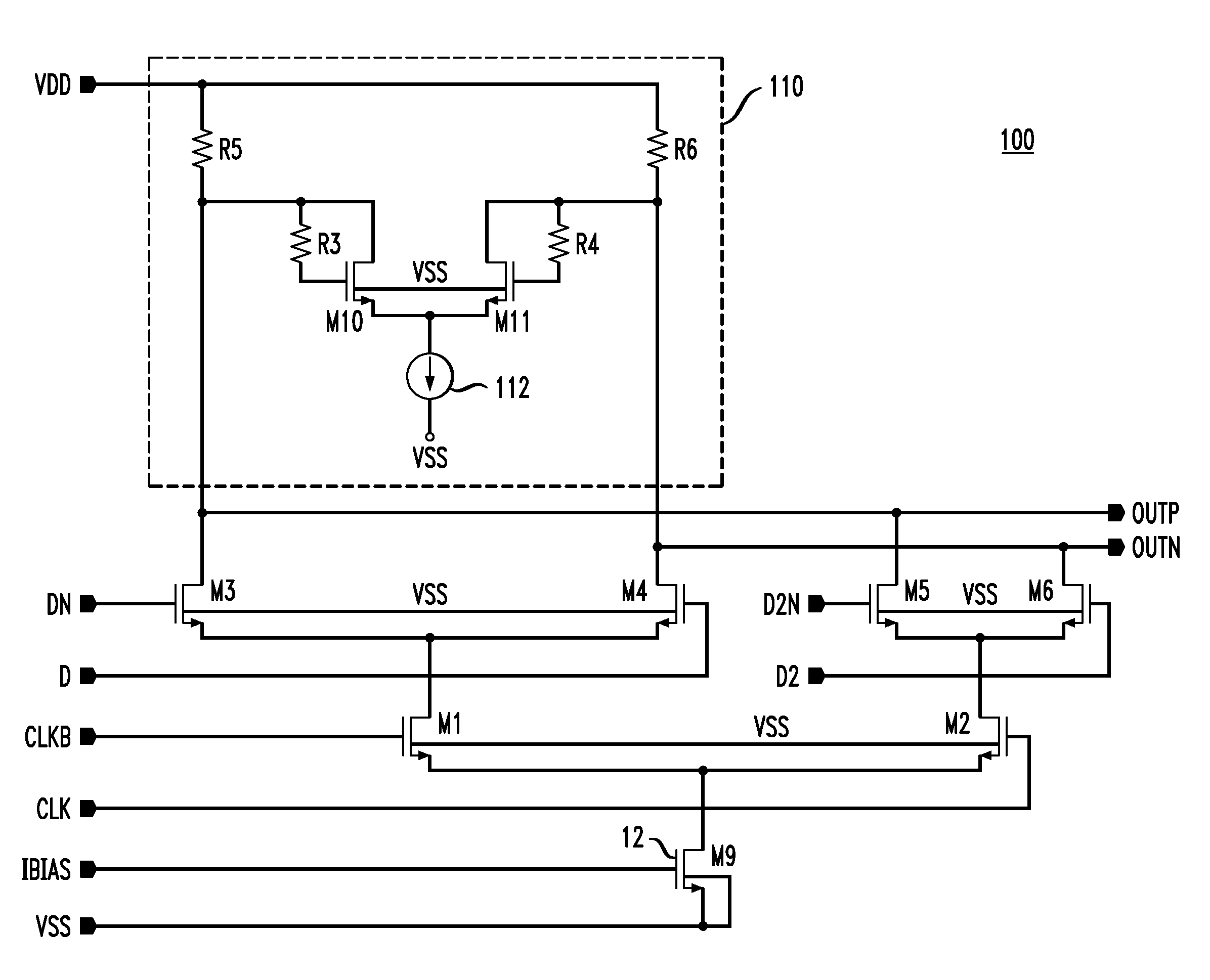
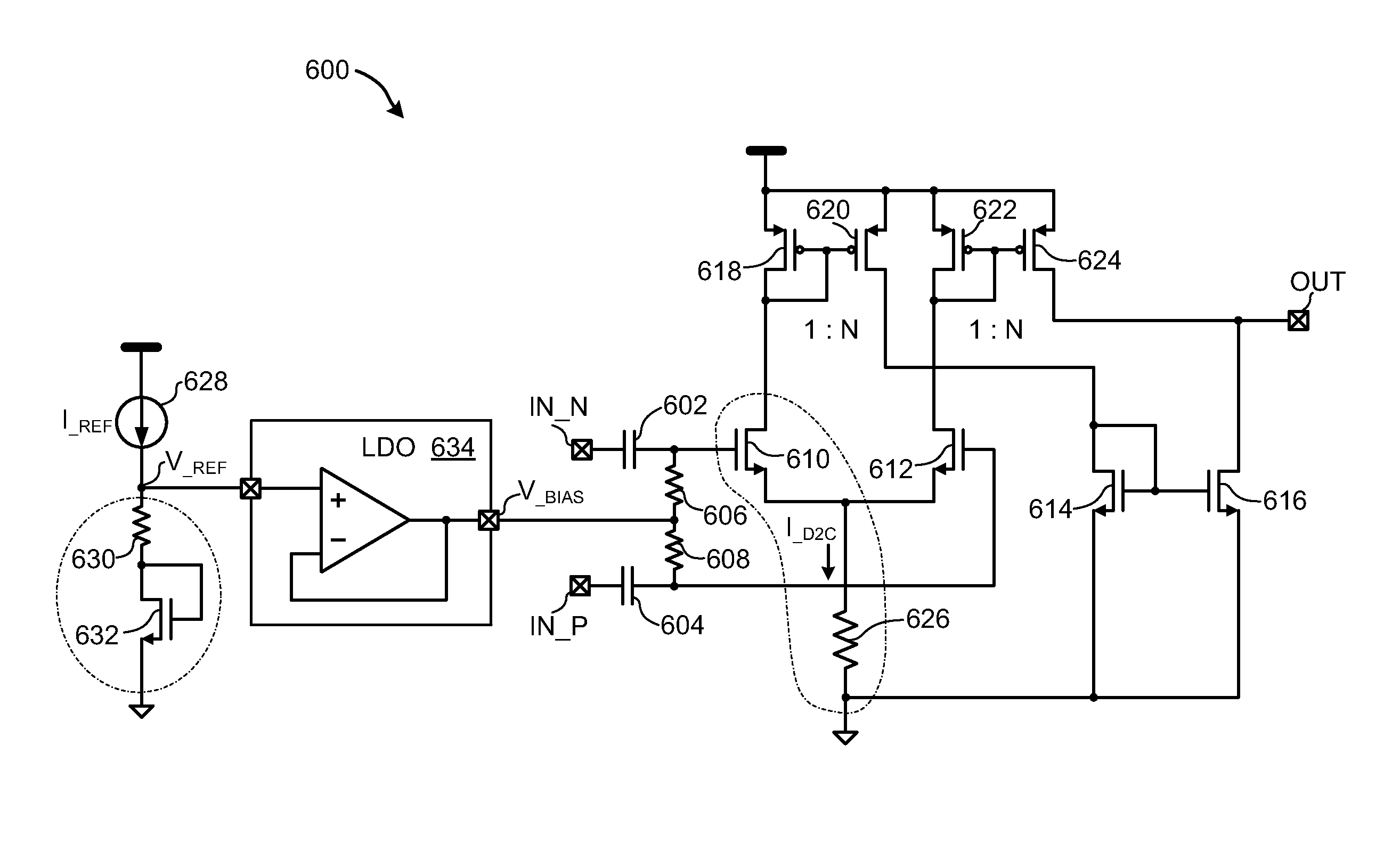
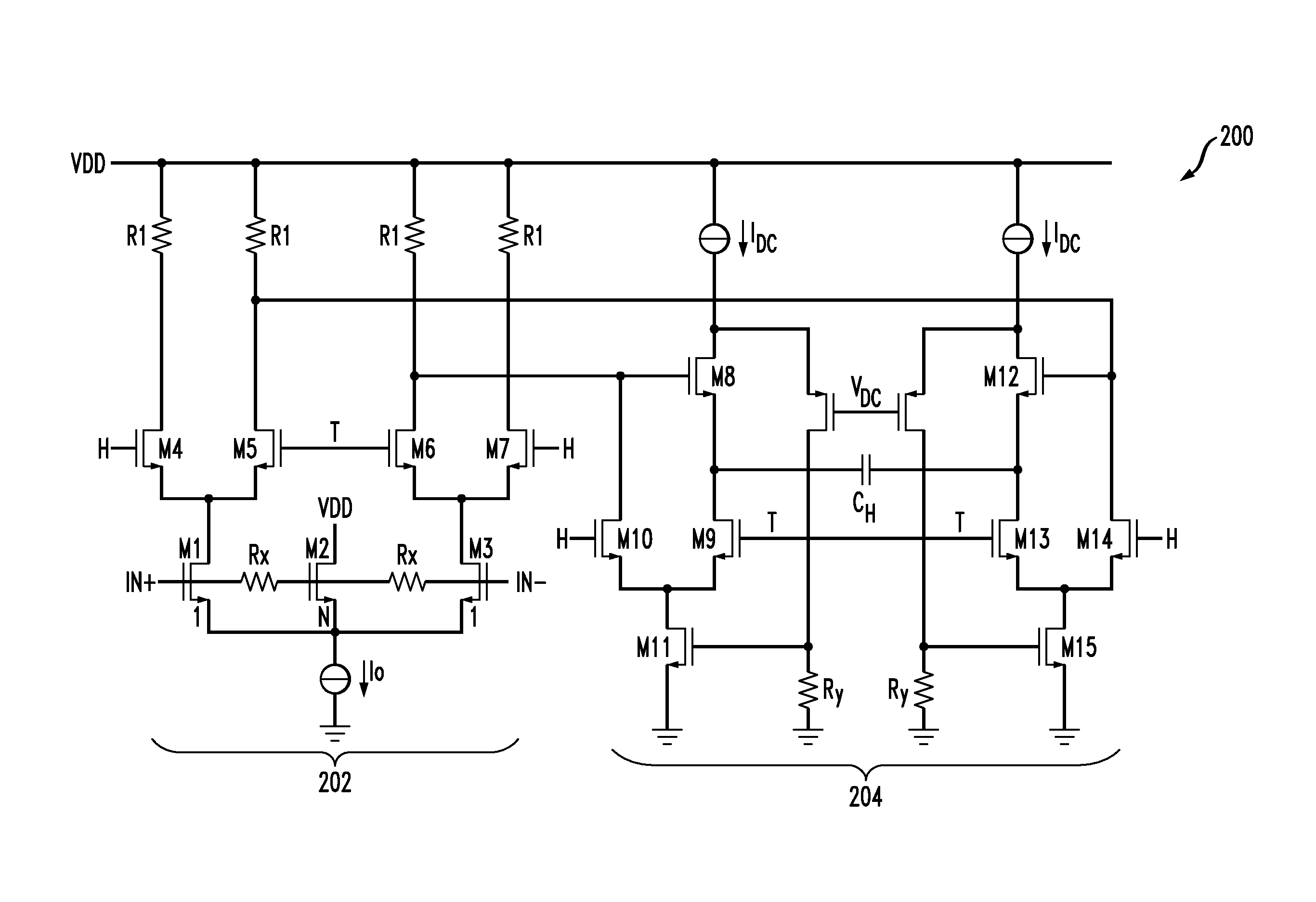
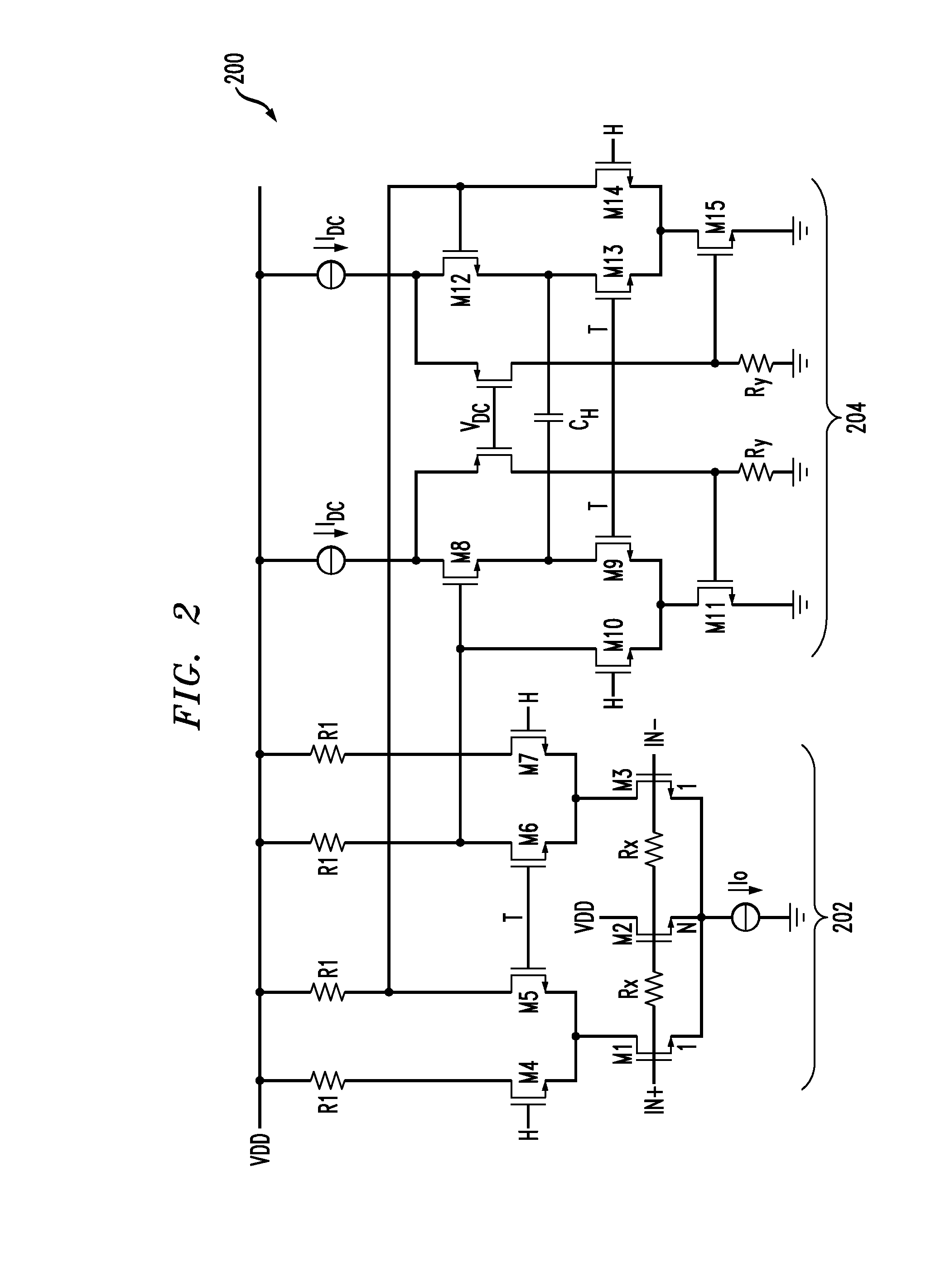
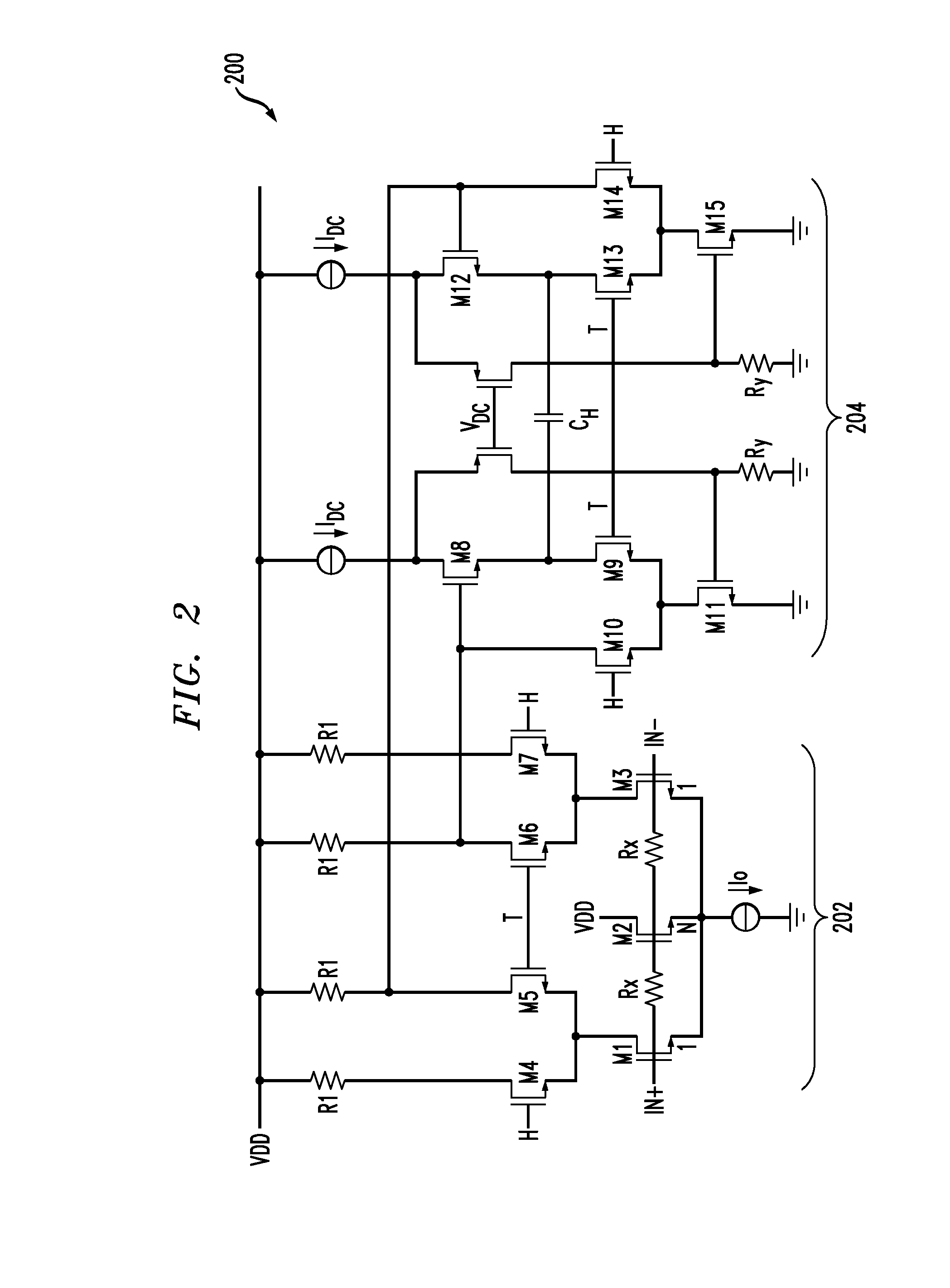
Compensation circuitry includes a resistor and transistor coupled in series with a reference current source to generate a variable reference voltage that is provided, via a voltage regulator, to bias elements of a core circuit in order to establish an operating current in the core circuit. In one embodiment, the resistor and transistor of the compensation circuitry are of similar construction to the bias elements of the core circuit, such that fluctuations in the ratio of the reference current and the operating current of the core circuit are minimized over process, supply voltage and temperature variations. The voltage regulator may be a low dropout regulator. In various embodiments, the core circuit may comprise a resistor biased voltage controlled oscillator, a differential current mode logic (CML) input to single CMOS output circuit, or like circuitry that may be sensitive to phase noise or requires low power operation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
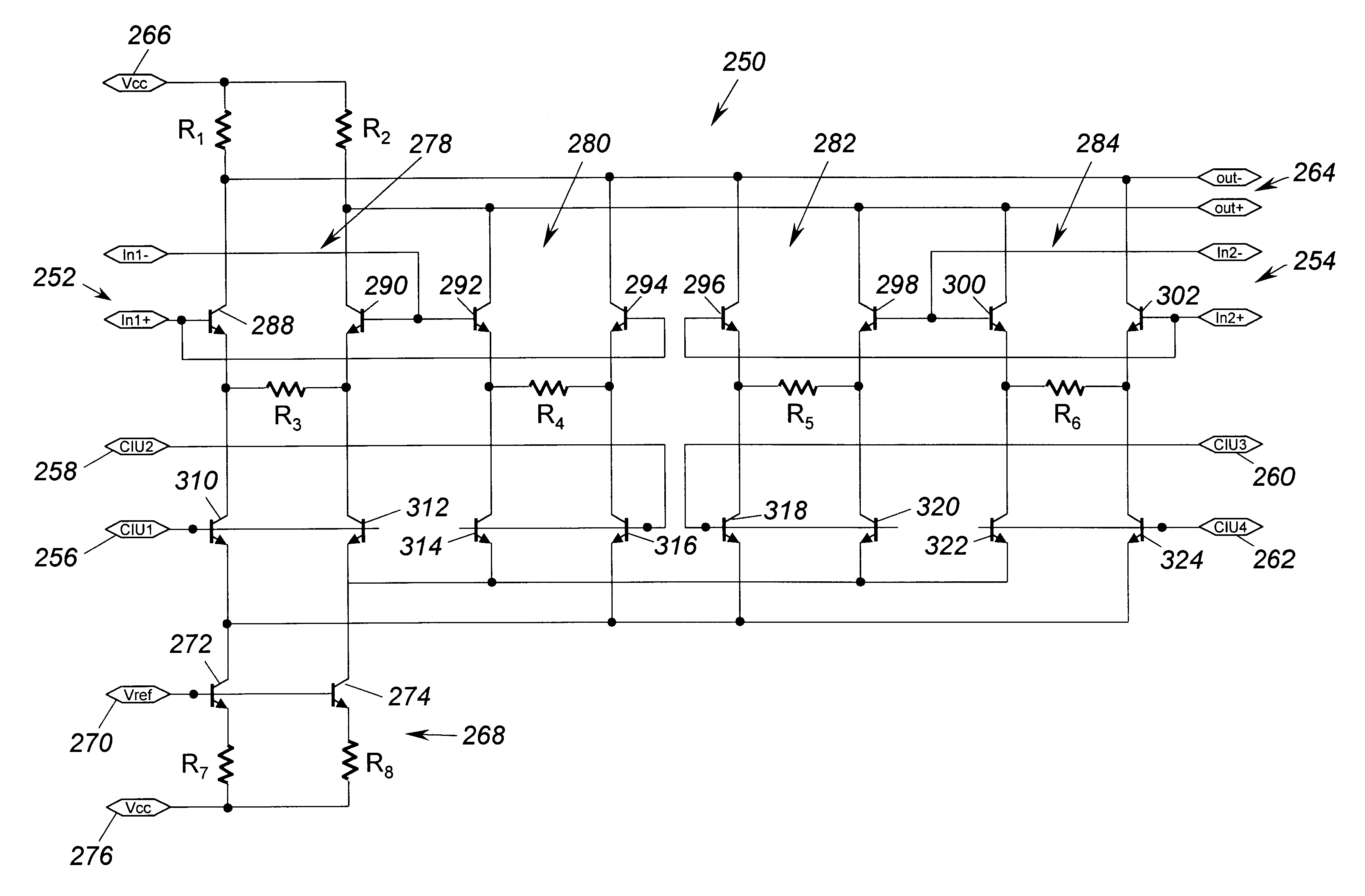
Combined multiplexer and switched gain circuit
A combined multiplexer and switched gain circuit (250) that selectively multiplexes differential analog signals from a primary channel (20) and a diversity channel (22) in a diversity receiver system (10) to a single output. The circuit (250) is based on a current mode logic design where a plurality of separate conduction paths (278-284) are provided between a voltage line (266) and a current source (268). An output line (264) of the circuit (250) is coupled to each conduction path (278-284) so that the differential analog signals from the primary channel (20) and the diversity channel (22) can be selectively outputted to the circuit (250). Each conduction path (278-284) includes a gain device, such as degenerative resistor, that provides signal gain or no signal gain for that conduction path (278-284). Control signals are selectively applied to switching devices (310-324) and each conduction path (278-284) so that the conduction path (278-284) can be independently selected to provide the multiplexing.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Serializer architecture for serial communications
InactiveUS7864084B2Reduce designReduce power consumptionParallel/series conversionPulse manipulationPhase shiftedMultiplexer
A serializer includes a first stage configured to convert m-bit-wide parallel data into n-bit-wide parallel data, where n is 2x, m≧2x+y, x is an integer of at least 1, and y is an integer of at least 1, where the first stage includes a memory unit configured to store the m-bit-wide parallel in response to a timing signal and a first multiplexer configured to output the n-bit-wide parallel data in response to a frequency-multiplied derivative of the timing signal, and a current mode logic (CML) multiplexer stage configured to convert the n-bit-wide parallel data into serial data on successive transitions of n phase-shifted versions of the frequency-multiplied derivative of the timing signal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
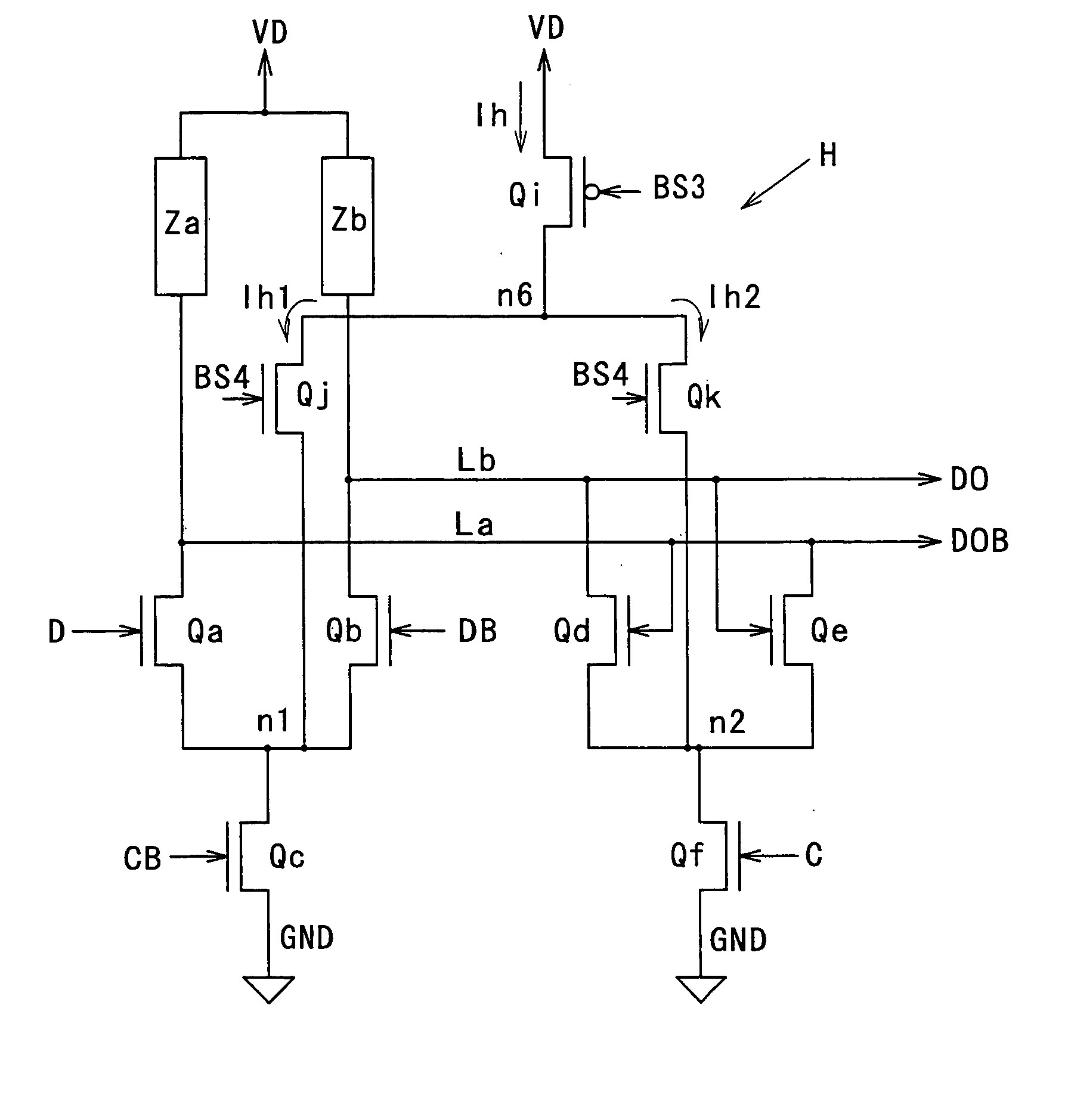
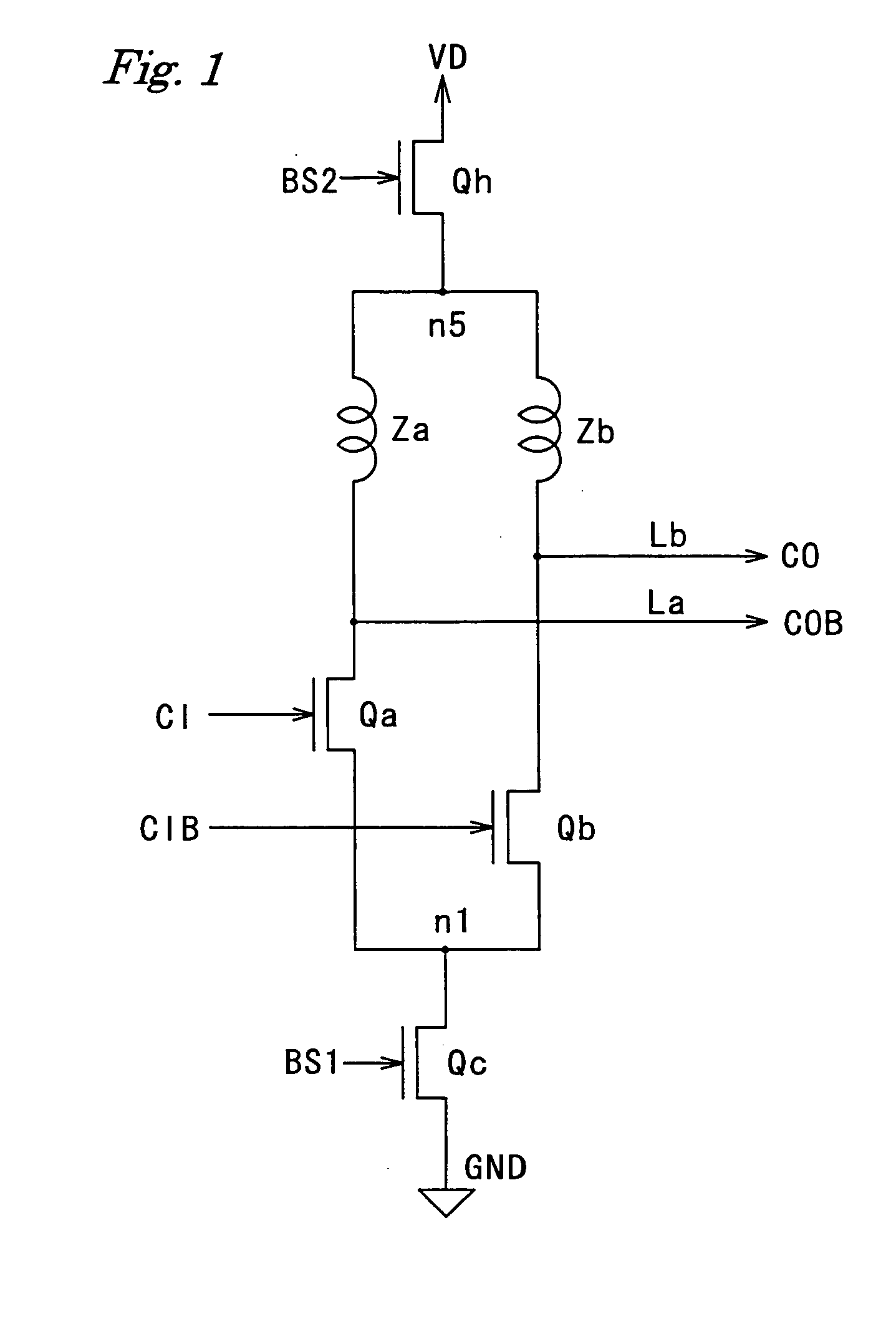
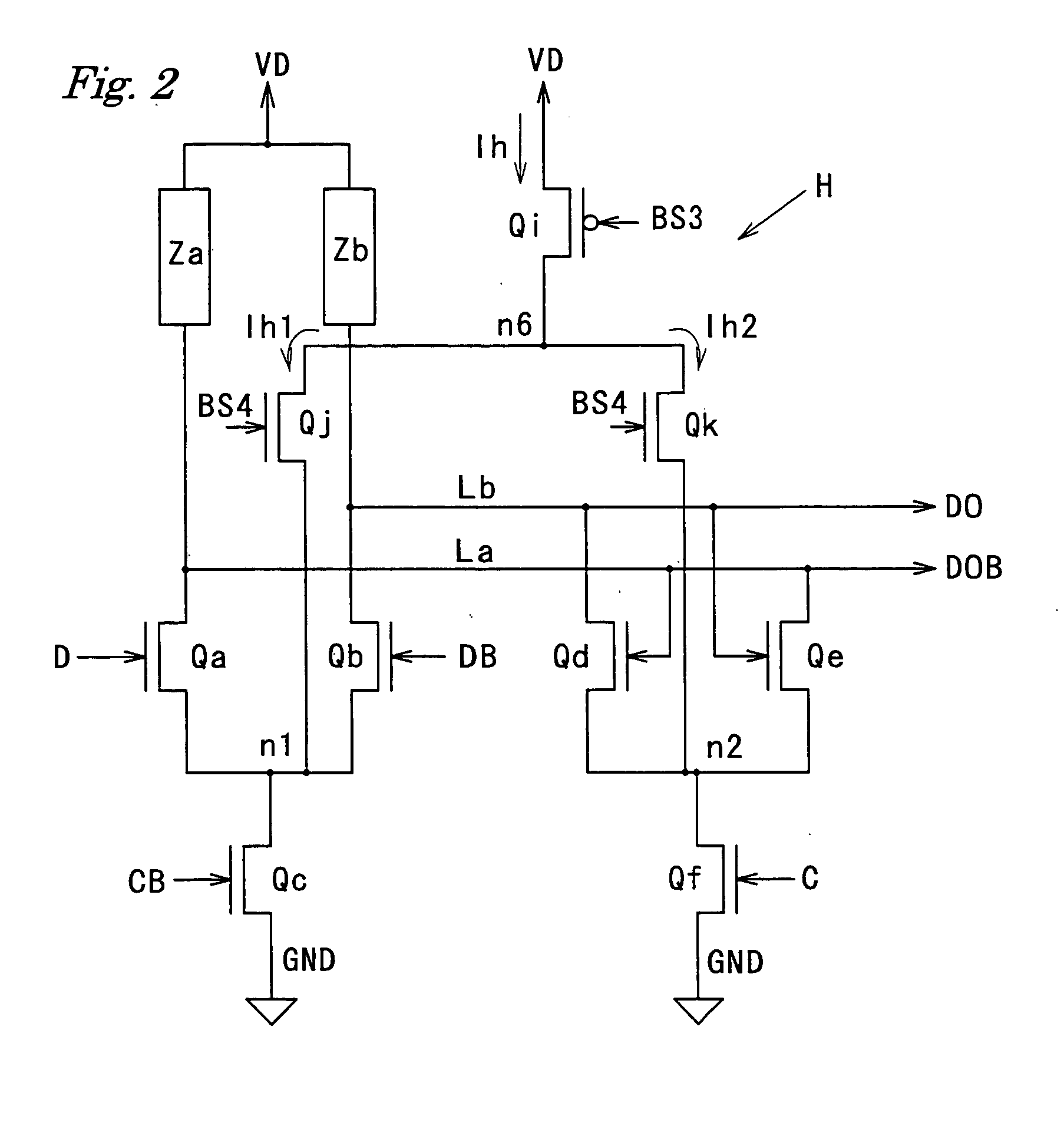
Current-mode logic circuit
InactiveUS20050110525A1Guaranteed uptimeAvoid Voltage FluctuationsTransistorLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLoad circuitLow voltage
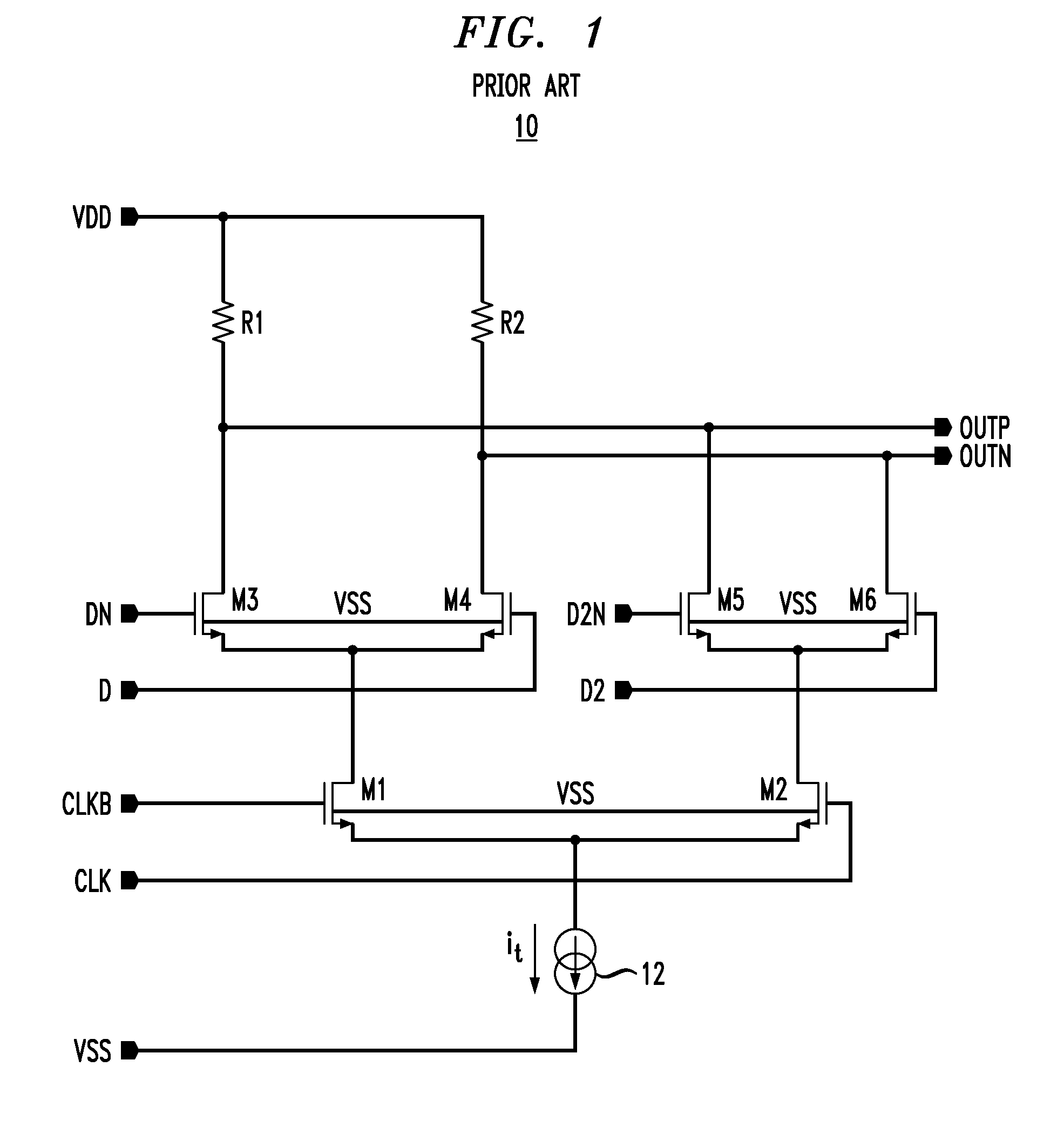
A current-mode logic (CML) circuit includes: a first field effect transistor (FET) operable based on a digital signal; a second FET operable based on an inverted digital signal; a first load circuit connected to the drain of the first FET; a second load circuit connected to the drain of the second FET; a first current limiter circuit connected between a ground line and a source node, at which the sources of the first and second FETs are connected in common; and a second current limiter circuit connected between a power supply line and a drain node, at which power line sides of the first and second load circuits are connected in common, so that the CML circuit can operate stably even with low voltage power supply.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
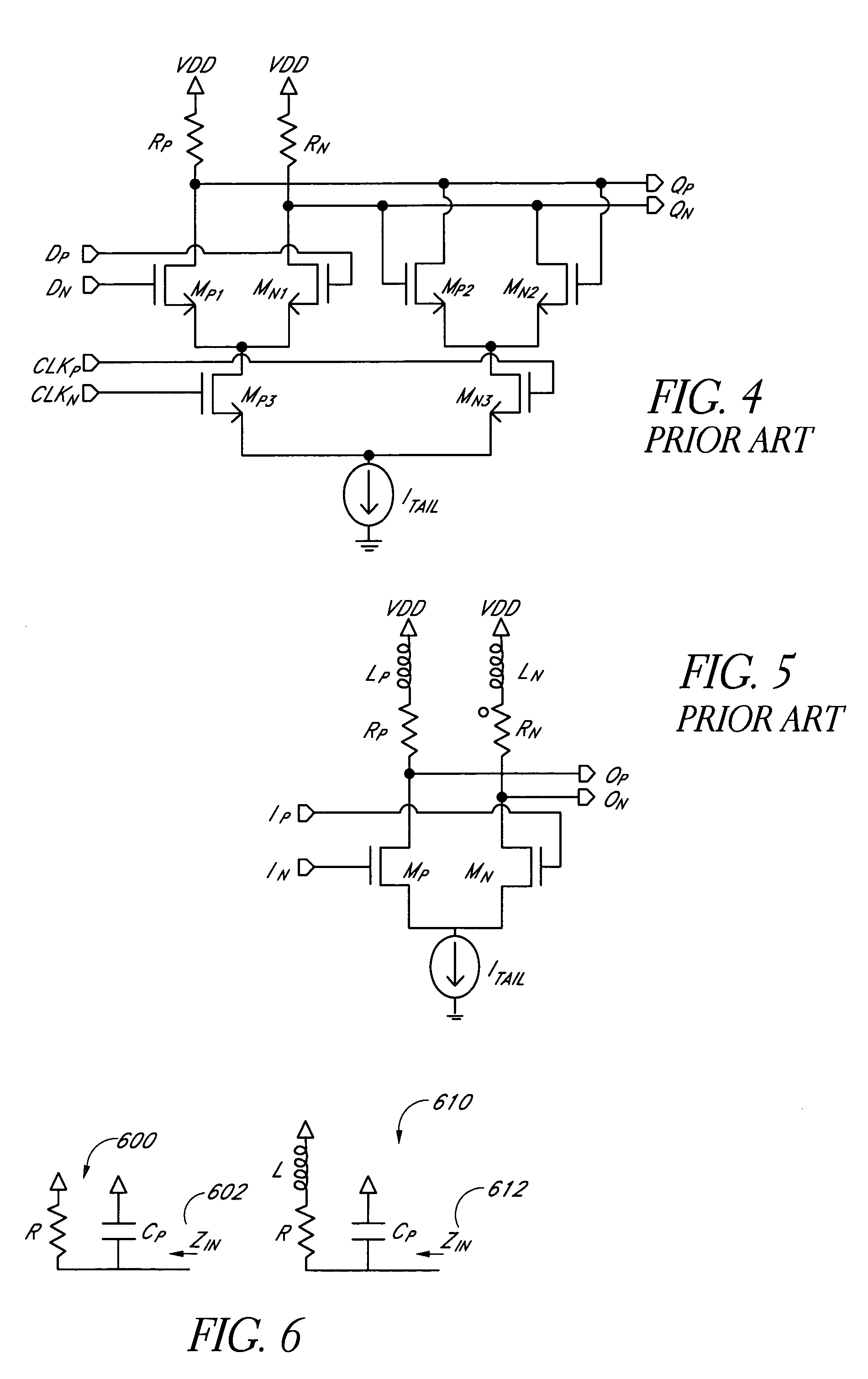
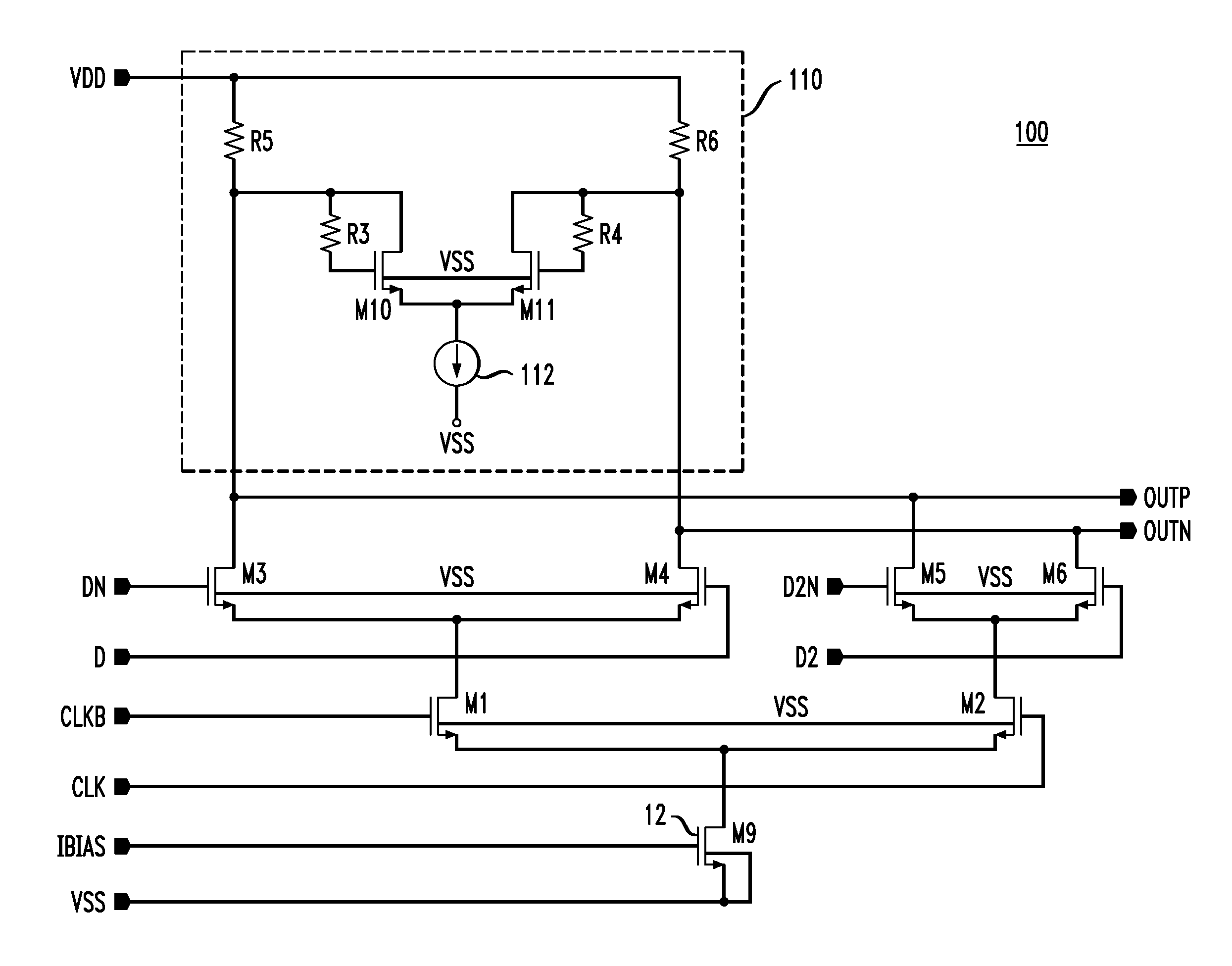
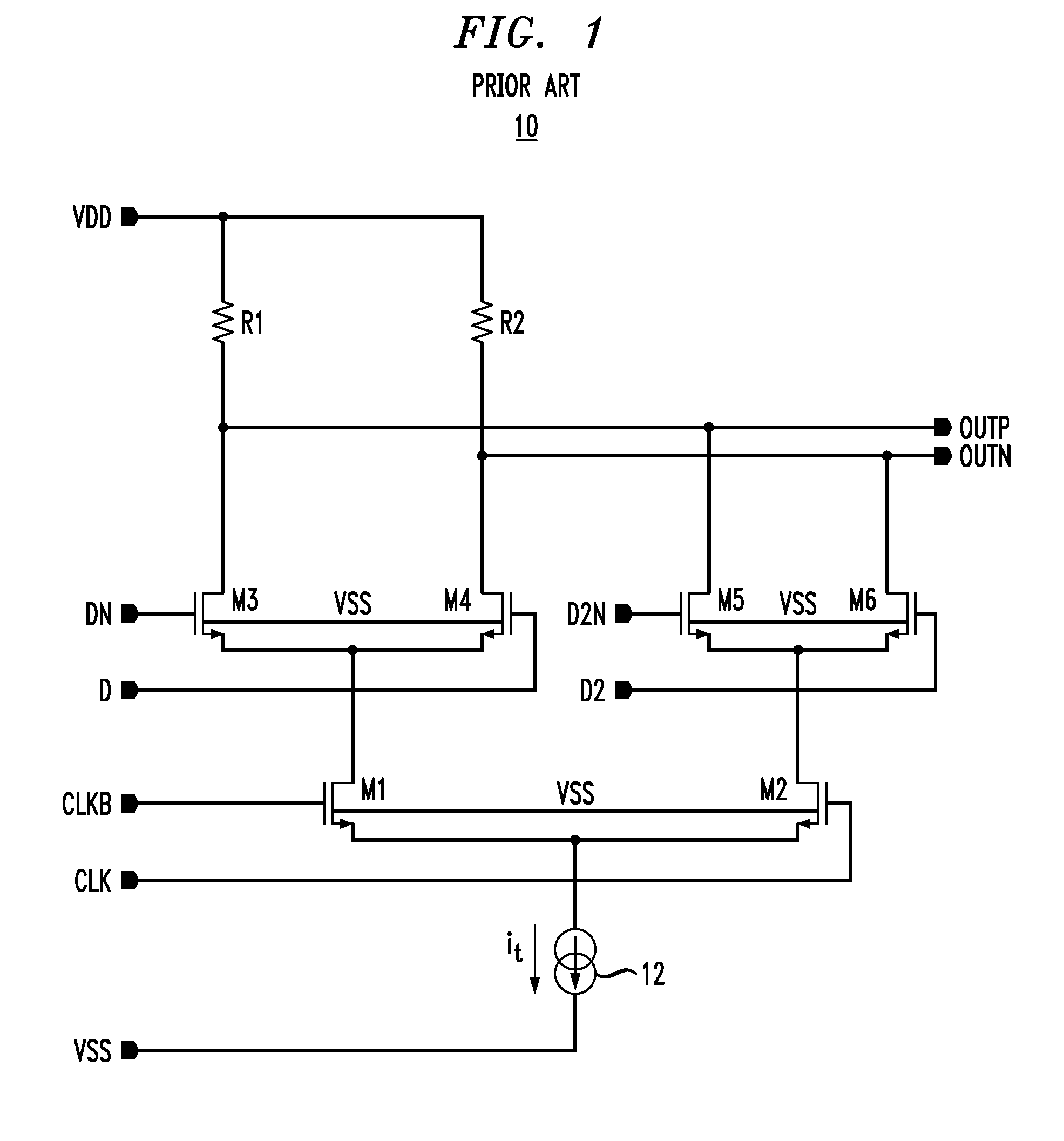
Actively Compensated Buffering for High Speed Current Mode Logic Data Path
InactiveUS20080024172A1Switching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLoad resistanceDatapath
An actively compensated CML circuit includes a CML buffer circuit and a bandwidth expansion circuit. The CML buffer circuit includes a first MOS transistor and a second MOS transistor in a differential pair configuration. A first load resistor is coupled to a first MOS transistor drain at a first output terminal and a second load resistor is coupled to a second MOS transistor drain at a second output terminal. The bandwidth expansion circuit is coupled to the CML buffer circuit in a source follower configuration. The bandwidth expansion circuit includes a third MOS transistor and a fourth MOS transistor. A capacitor is coupled across a third MOS transistor source and a fourth MOS transistor source. The fourth MOS transistor and the third MOS transistor generate a high pass function at the first output terminal and the second output terminal.
Owner:PARADE TECH
Low Supply Voltage, Large Output Swing, Source-Terminated Output Driver for High Speed AC-coupled Double-Termination Serial Links
A current mode logic circuit includes a current mode logic driver circuit and a transistor biasing improvement circuit. The transistor biasing improvement circuit includes a first current source coupled to a first output node of the current mode logic driver circuit and a second current source coupled to a second output node of the current mode logic driver circuit. The first current source and the second current source raise a common mode voltage at the first output node and the second output node.
Owner:PARADE TECH
Phase detection and starting circuit used in multiphase clock generating circuit of high-speed serial interface
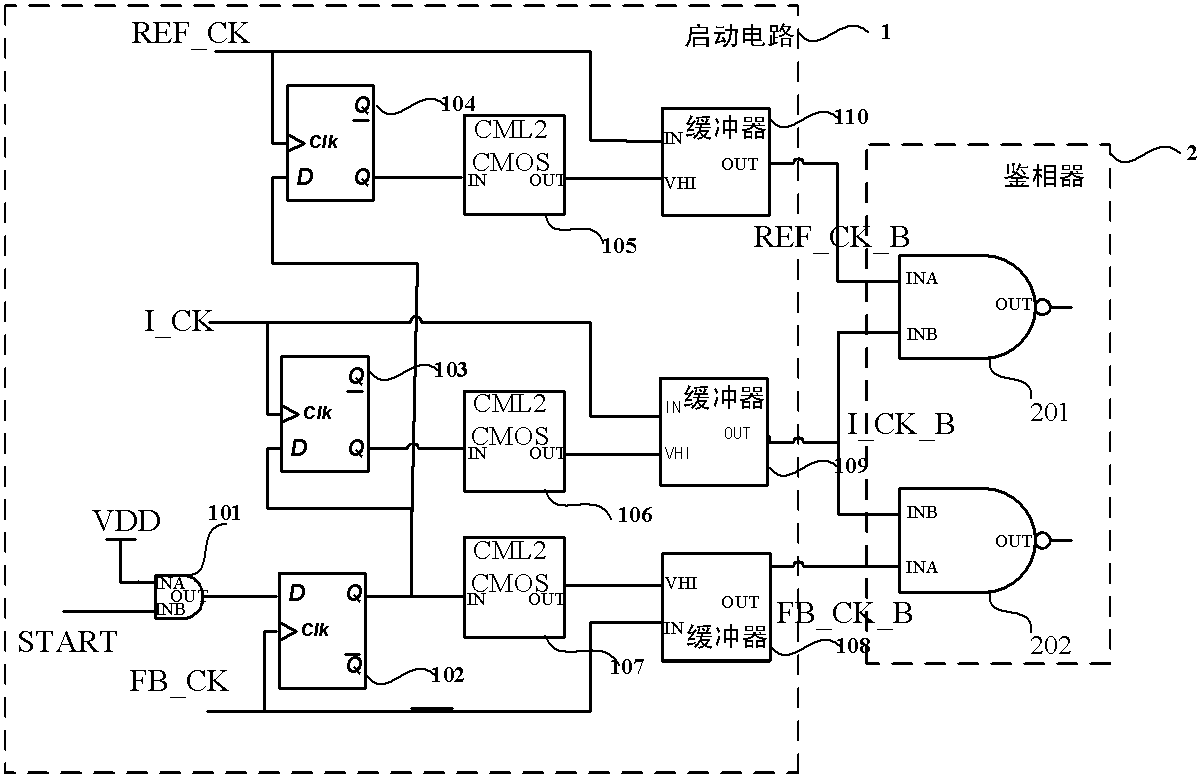
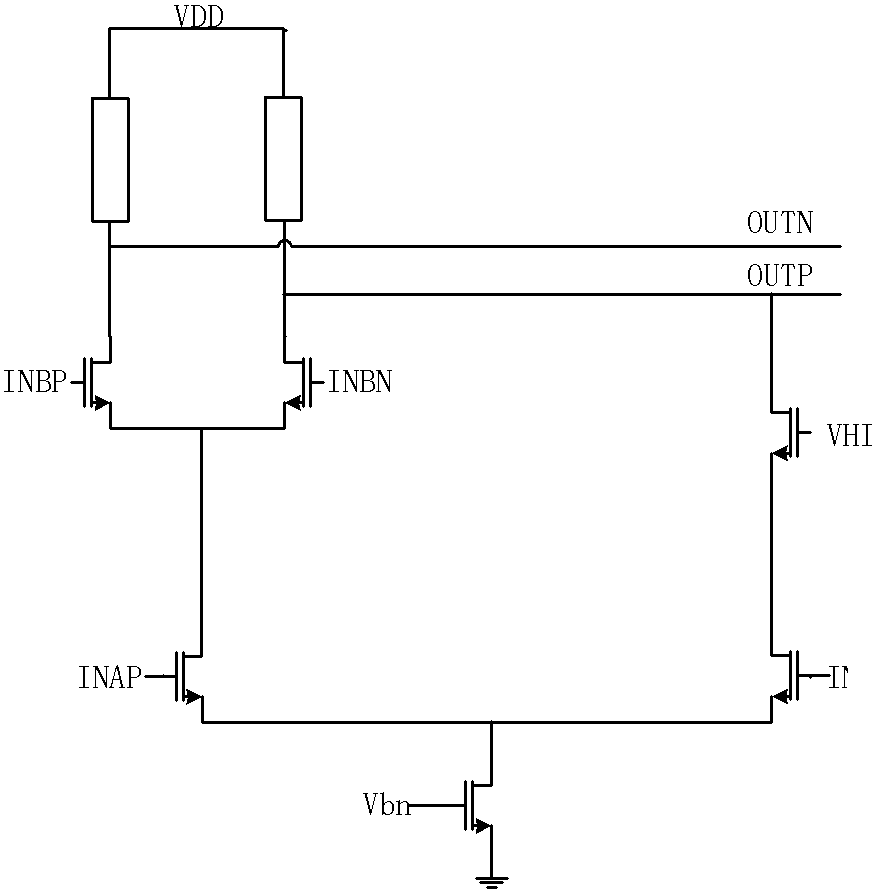
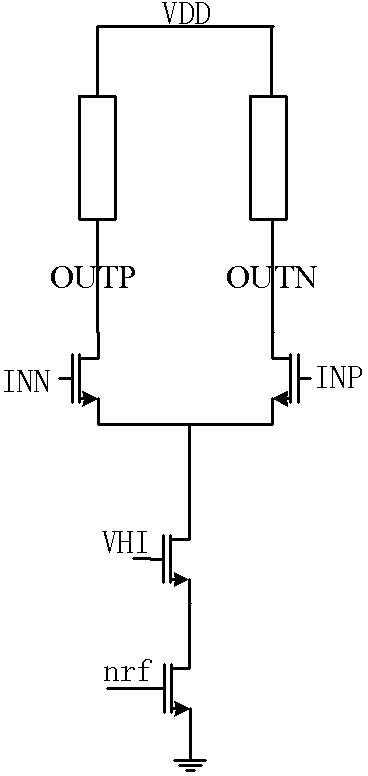
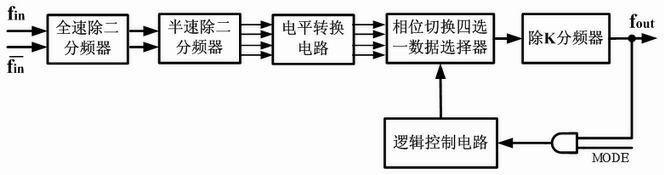
A phase detection and starting circuit used in a multiphase clock generating circuit of a high-speed serial interface comprises a phase detector and a starting circuit, wherein the phase detector is provided with three input ends and two output ends, the starting circuit is connected with the input end of the phase detector, and the starting circuit comprises an AND gate, a first D trigger, a second D trigger, a third D trigger, a first CML2CMOS circuit, a second CML2CMOS circuit, a third CML2CMOS circuit, a first buffer, a second buffer and a third buffer. The circuit controls initial states of clock signals entering the phase detector when the multiphase clock generating circuit starts working, so that the wrong locking and the harmonic locking of the multiphase clock generating circuit can be effectively prevented, the phase detector adopts the current mode logic technology, the working efficiency is high, and the incoming mismatching jittering is low.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Serializer Architecture for Serial Communications
InactiveUS20090259781A1Reduce Design ComplexityReduce power consumptionParallel/series conversionElectric digital data processingMultiplexingComputer architecture
Methods, algorithms, circuits, and / or systems for serializing parallel data are disclosed. In one embodiment, a serializer can include a first stage configured to convert m-bit-wide parallel data into n-bit-wide parallel data, where n is 2x, m≧2x+y, x is an integer of at least 1, and y is an integer of at least 1, where the first stage includes a memory unit configured to store the m-bit-wide parallel in response to a timing signal and a first multiplexer configured to output the n-bit-wide parallel data in response to a frequency-multiplied derivative of the timing signal, and a current mode logic (CML) multiplexer stage configured to convert the n-bit-wide parallel data into serial data on successive transitions of n phase-shifted versions of the frequency-multiplied derivative of the timing signal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Difference interface circuit for on-chip long lines interlinkage
InactiveCN101304251AAvoid it happening againReduce complexityLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsSignal onEngineering
The invention discloses a differential interface circuit used in the interconnection of long on-chip wires, which is mainly solves the power consumption problem of the interconnection of the long on-chip wires. The structure of the circuit comprises a transmitter, a long interconnection wire and a receiver; wherein, the transmitter consists of an inverter (A1) and an MOS current-mode logic circuit, the transmitter used for converting the full-swing signals on chips into low-swing signals; the receiver is formed by connecting a sensitive amplifier (G), a second inverter (A2) and a third inverter (A3), the receiver is used for restoring the low-swing signals on the longer interconnection wires to the full-swing signals. The differential interface circuit of the invention can effectively reduce the power consumption of interconnection of the long on-chip wires without under the condition of introducing the external reference voltages and can be used in the long wire interconnection of system on chip (SOC) of the integrated circuit design.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
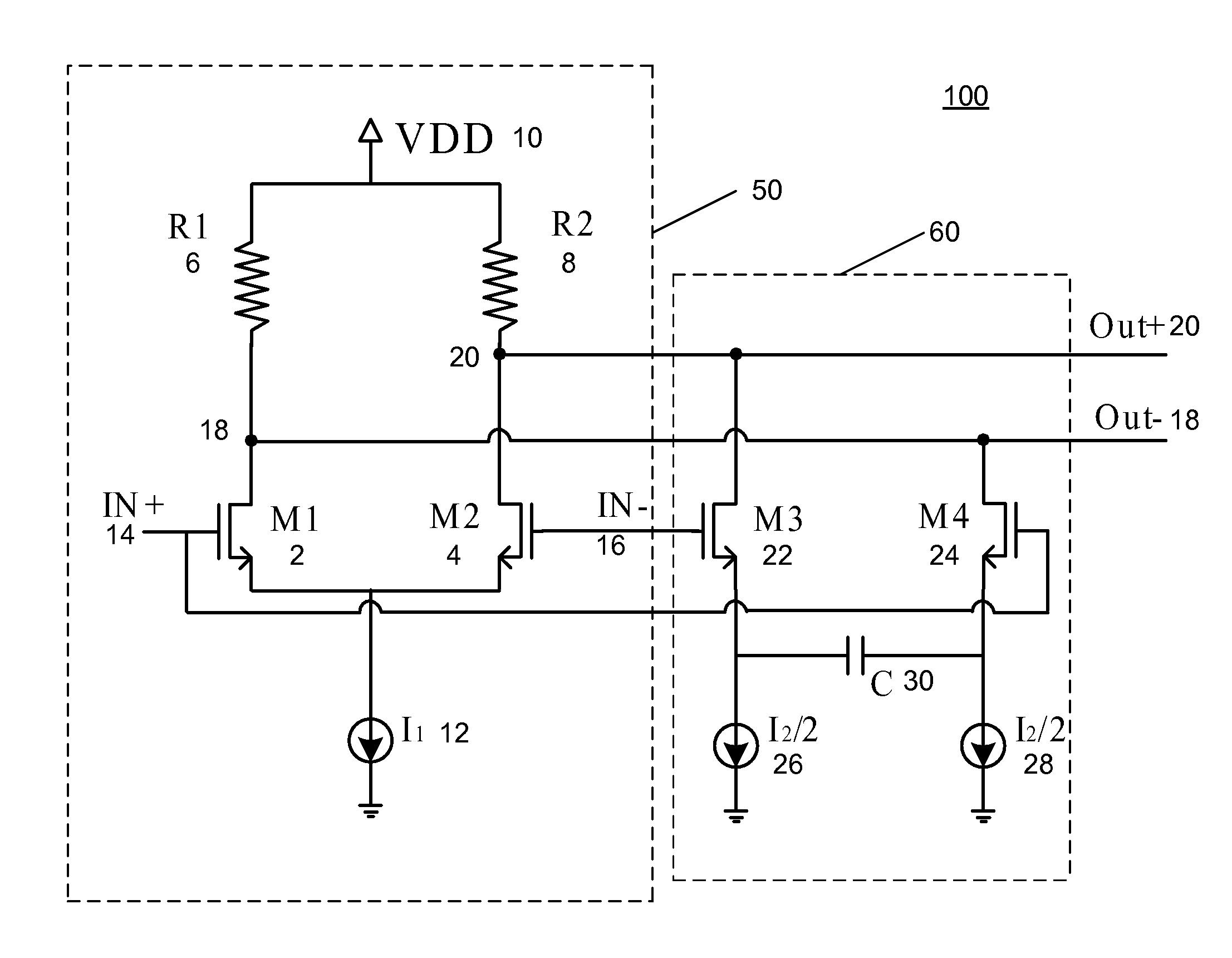
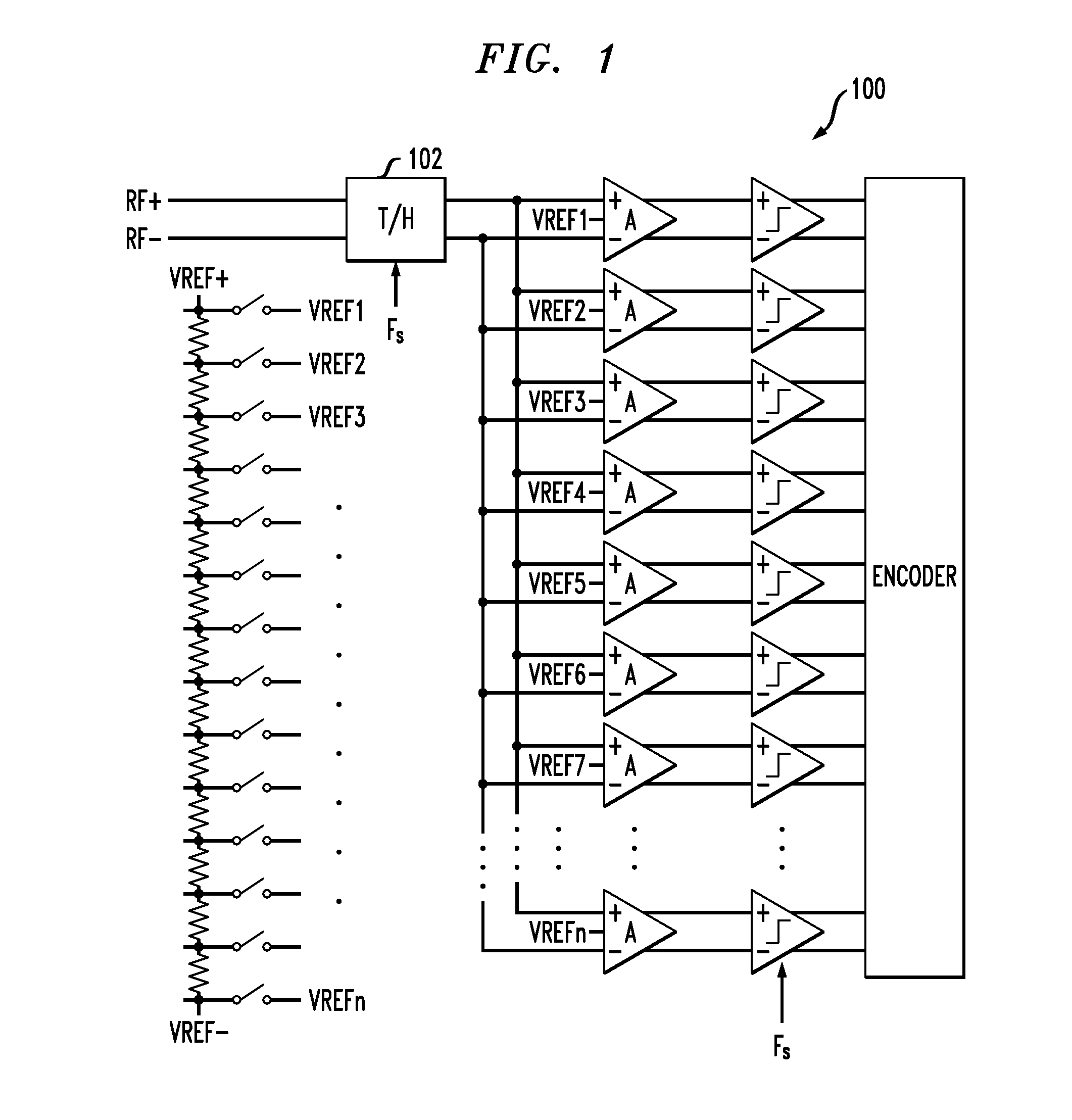
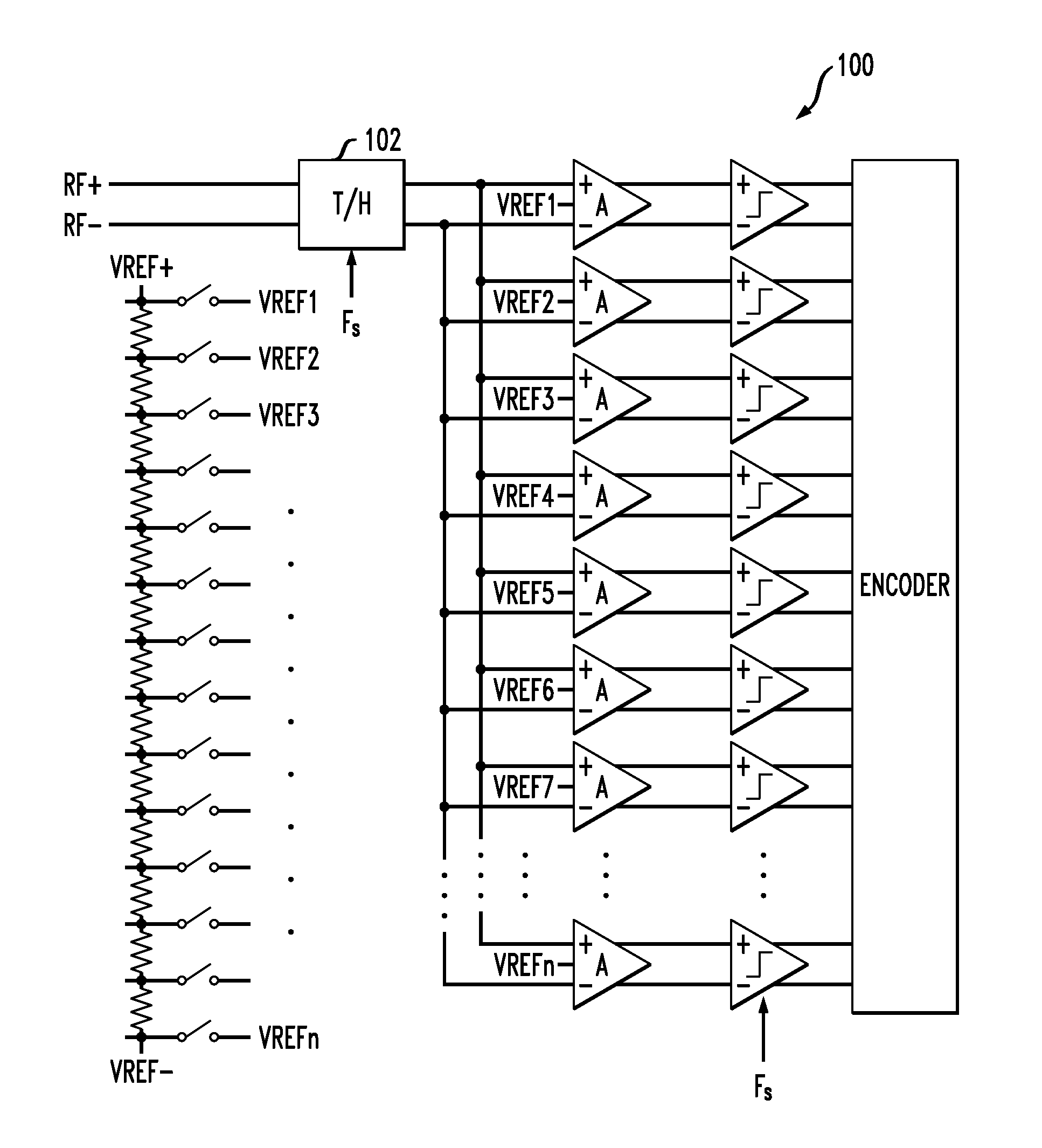
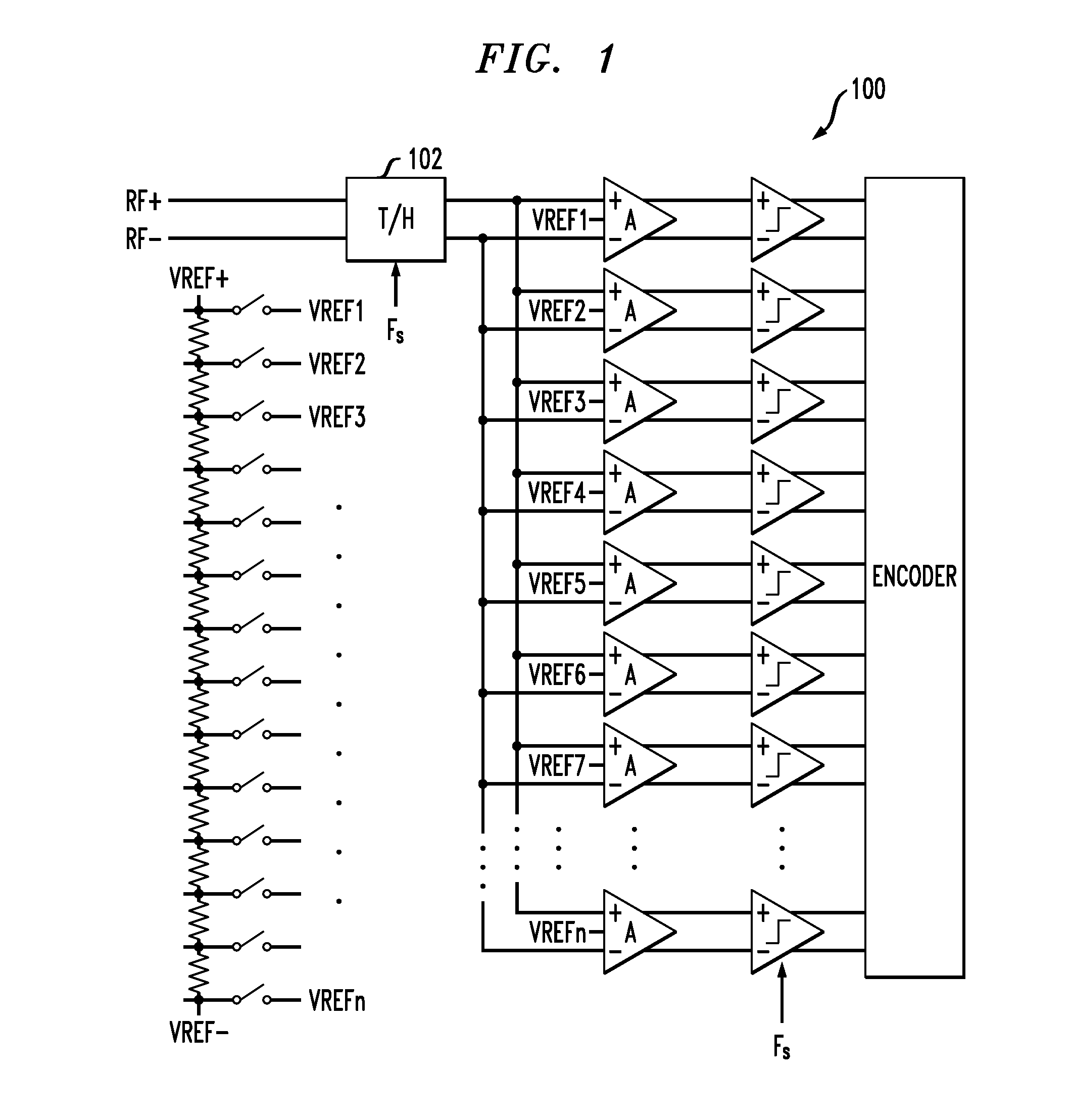
Track and hold amplifiers and digital calibration for analog-to-digital converters
ActiveUS8350738B2Electric signal transmission systemsElectric analogue storesDigital down converterAnalog-to-digital converter
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
System and method for providing a low jitter data receiver for serial links with a regulated single ended phase interpolator
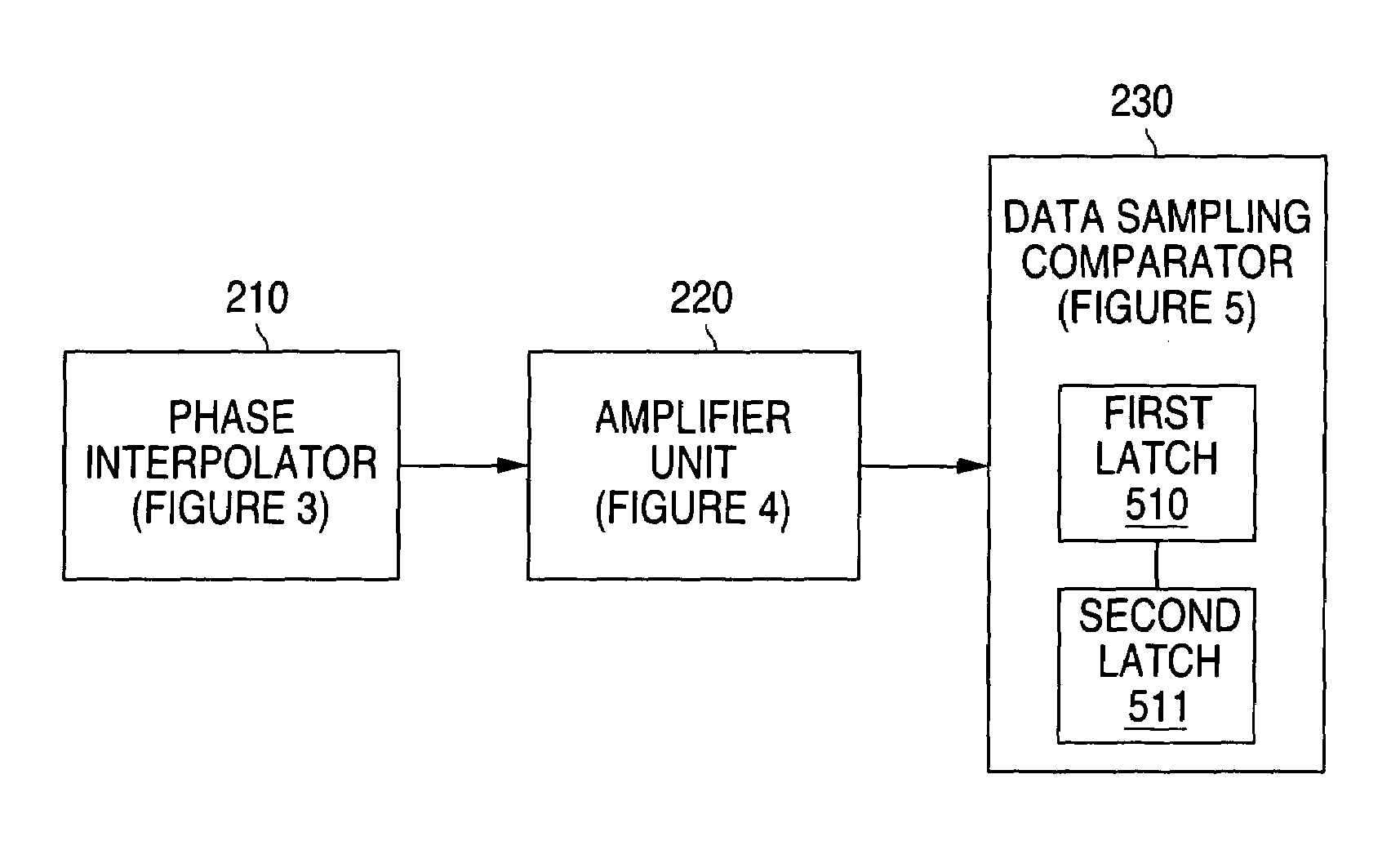
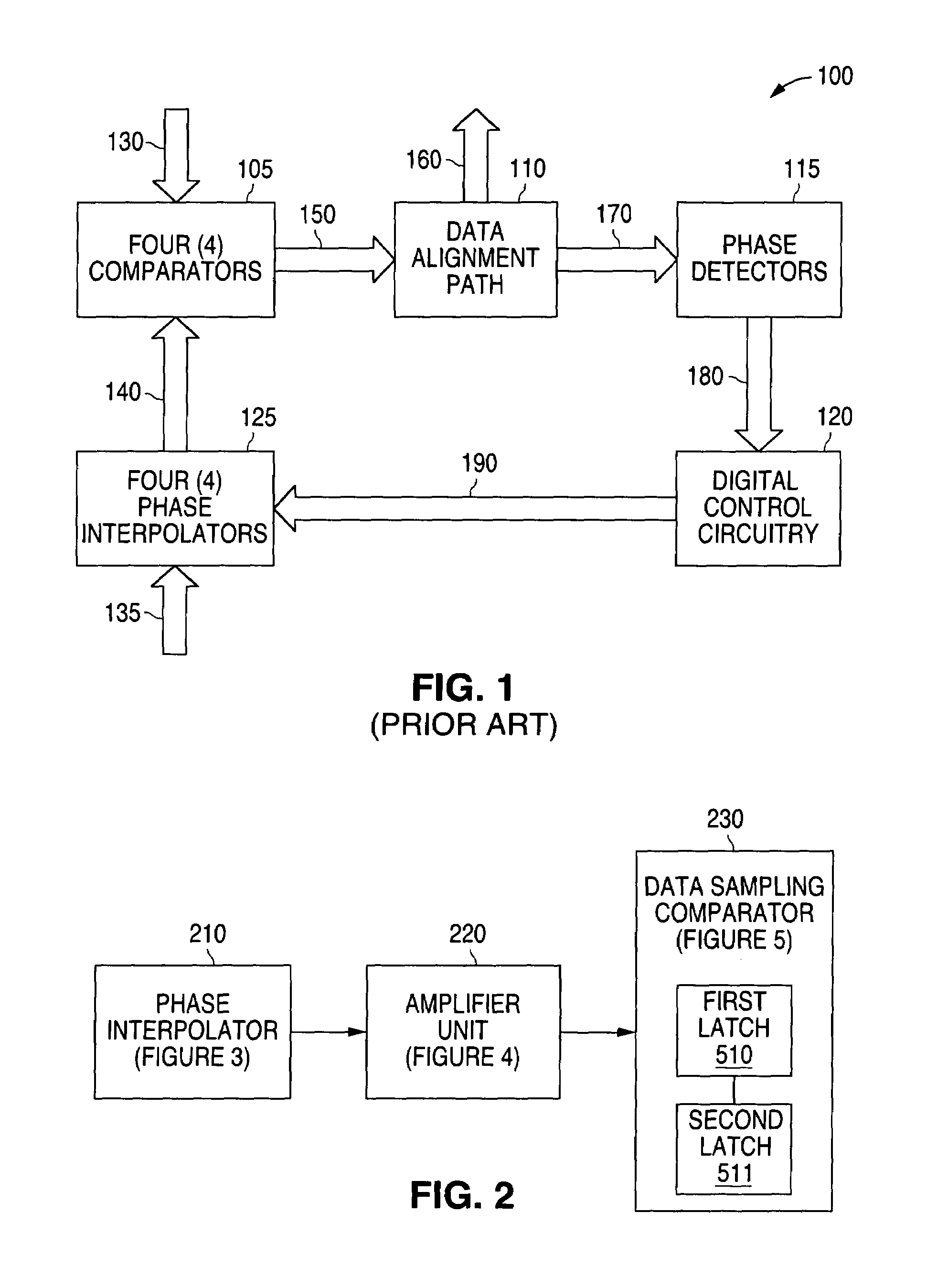
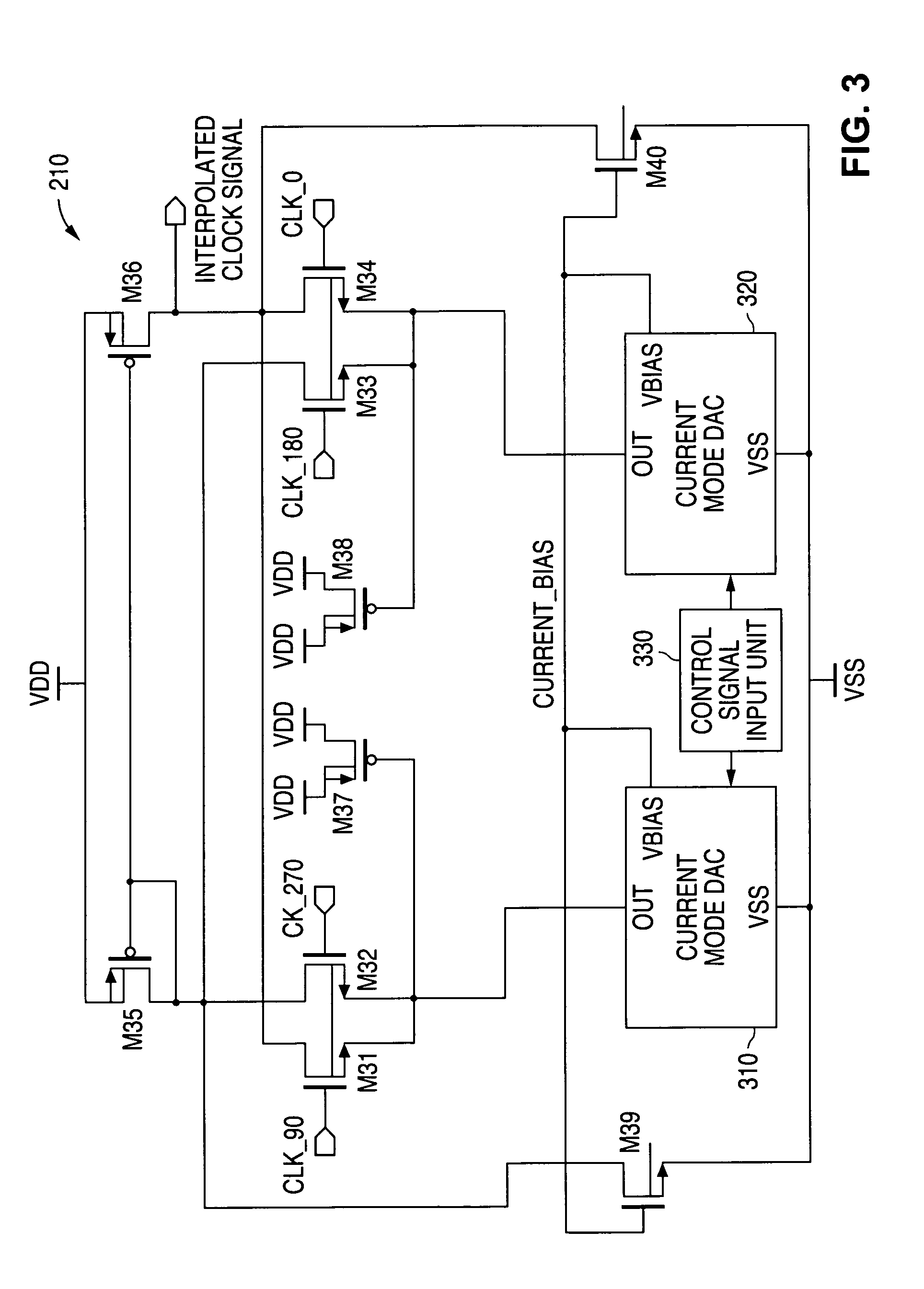
ActiveUS7233173B1Low power supply noiseMinimal jitterMultiple input and output pulse circuitsCurrent/voltage measurementData streamAudio power amplifier
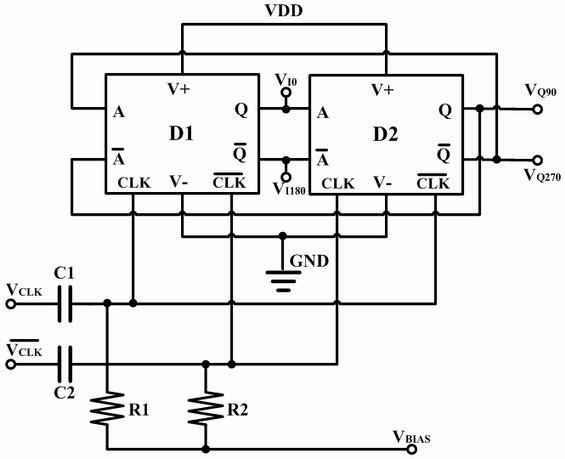
A system and method is disclosed for providing a clock and data recovery circuit that comprises a low jitter data receiver. The low jitter data receiver comprises a phase interpolator, an amplifier unit and a data sampling comparator. The phase interpolator and the amplifier unit provide the data sampling comparator with a single ended clock signal that is relatively immune to power supply noise. The data sampling comparator samples an input data stream with minimal jitter due to power supply noise. The data sampling comparator consumes less static power than a current mode logic D flip flop and also has output levels that are compatible with complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) logic.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Phase-switching prescaler based on injection-locking
InactiveCN101800541AChoose flexibleReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlInjection lockedControl signal
The invention discloses a phase-switching prescaler based on injection-locking, comprising a multi-phase generator, a multi-channel selector, a true single-phase clock module and a state machine. The multi-phase generator is used for primarily scaling the signal to be scaled and generating N signals with equal phase difference; the multi-channel selector is used for selecting one branch of signal from the N signals with equal phase difference; the true single-phase clock module is used for secondarily scaling the branch of signal selected from the N signals with equal phase difference by the multi-channel selector to obtain the output signal of the phase-switching prescaler; and the state machine is used for transforming the scaling-ratio control signal of the phase-switching prescaler into the control signal of the multi-channel selector. Avoiding adopting the current mode logic, the phase-switching prescaler keeps consuming low power when working at high frequency. An even number of signals with equal phase difference can be generated, thus the scaling-ratio can be selected flexibly when the system is designed. The phase-switching prescaler has better ability of resisting the common-mode noise.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Serializer and data serializing method
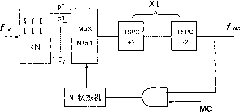
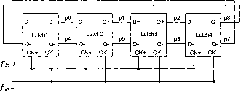
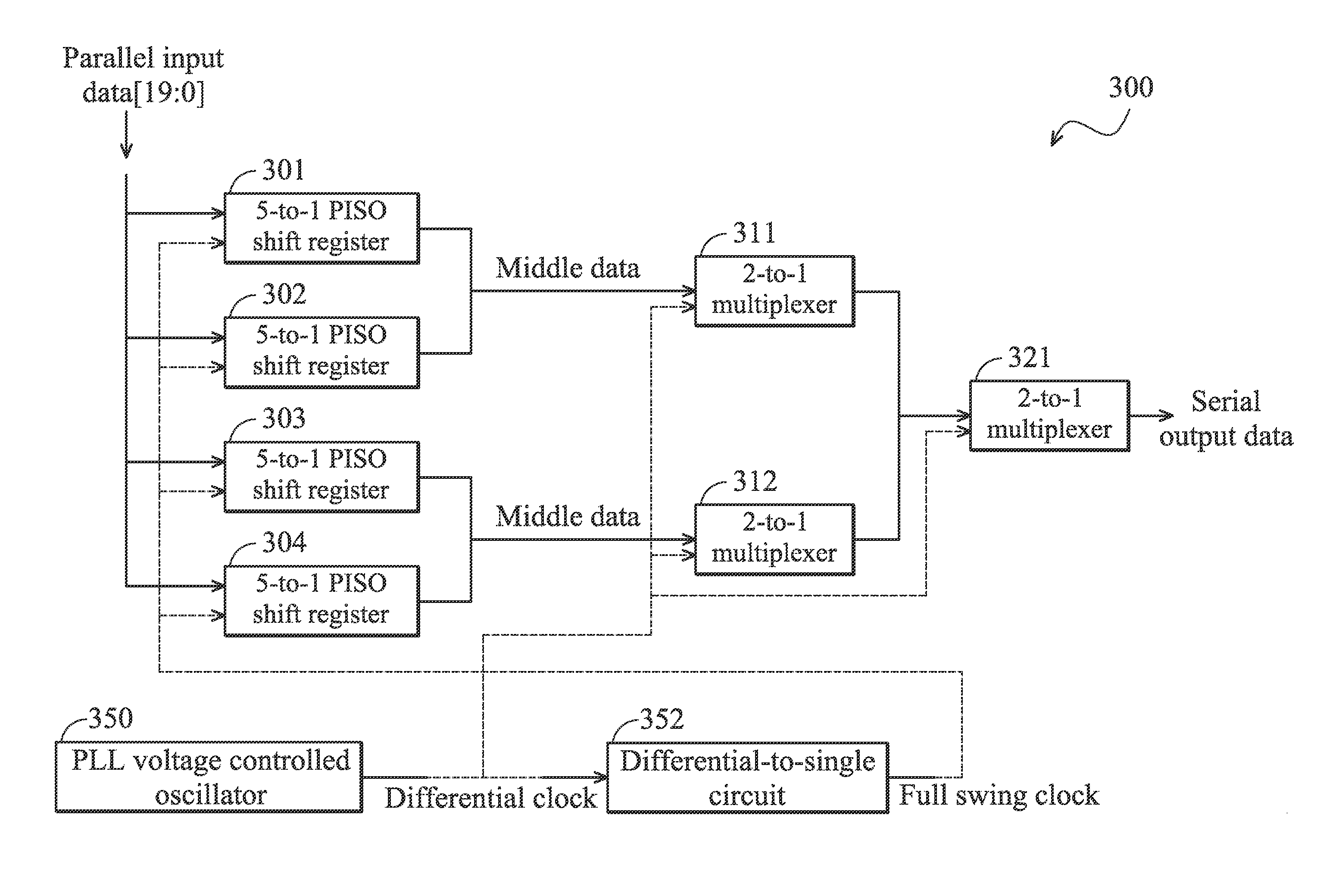
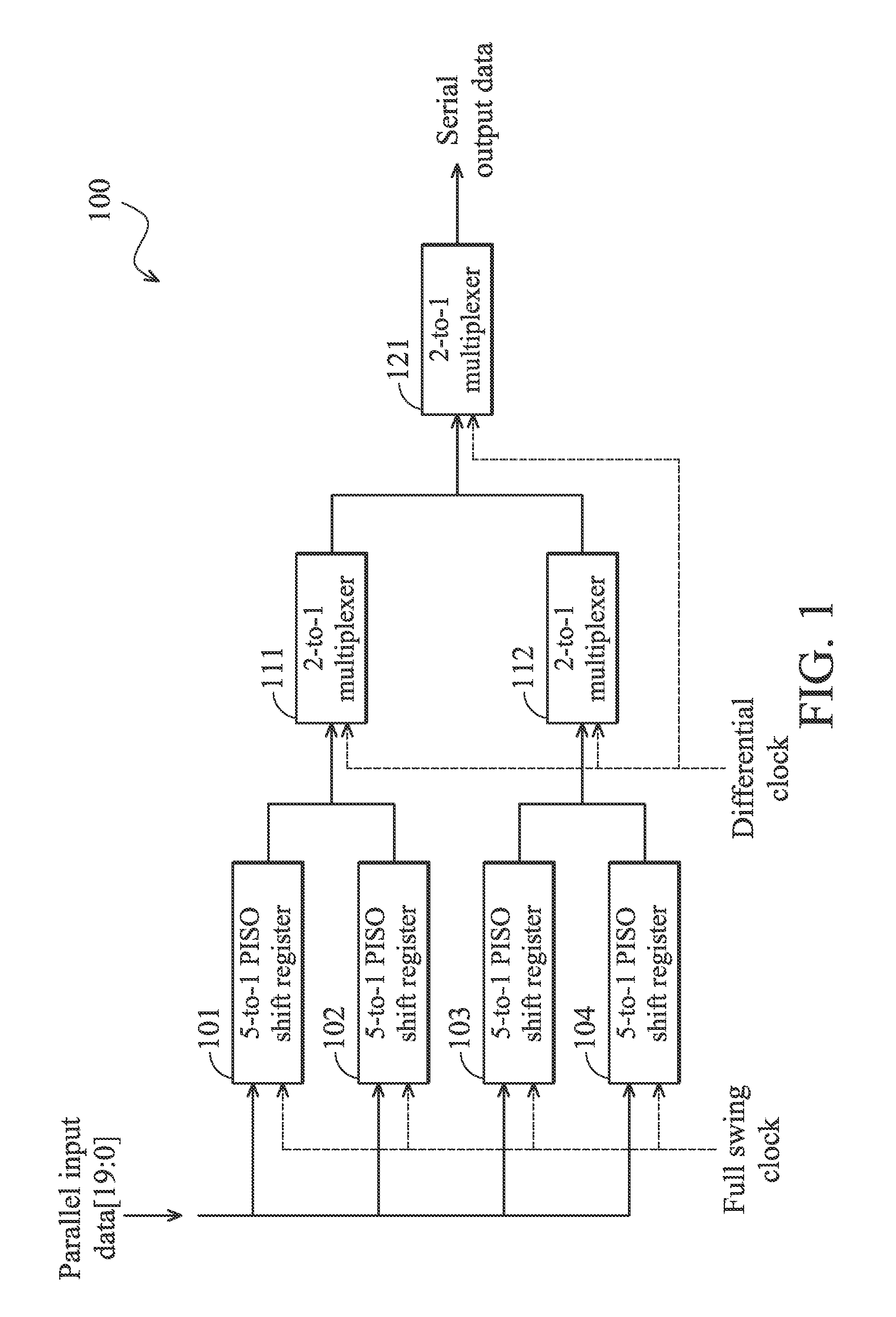
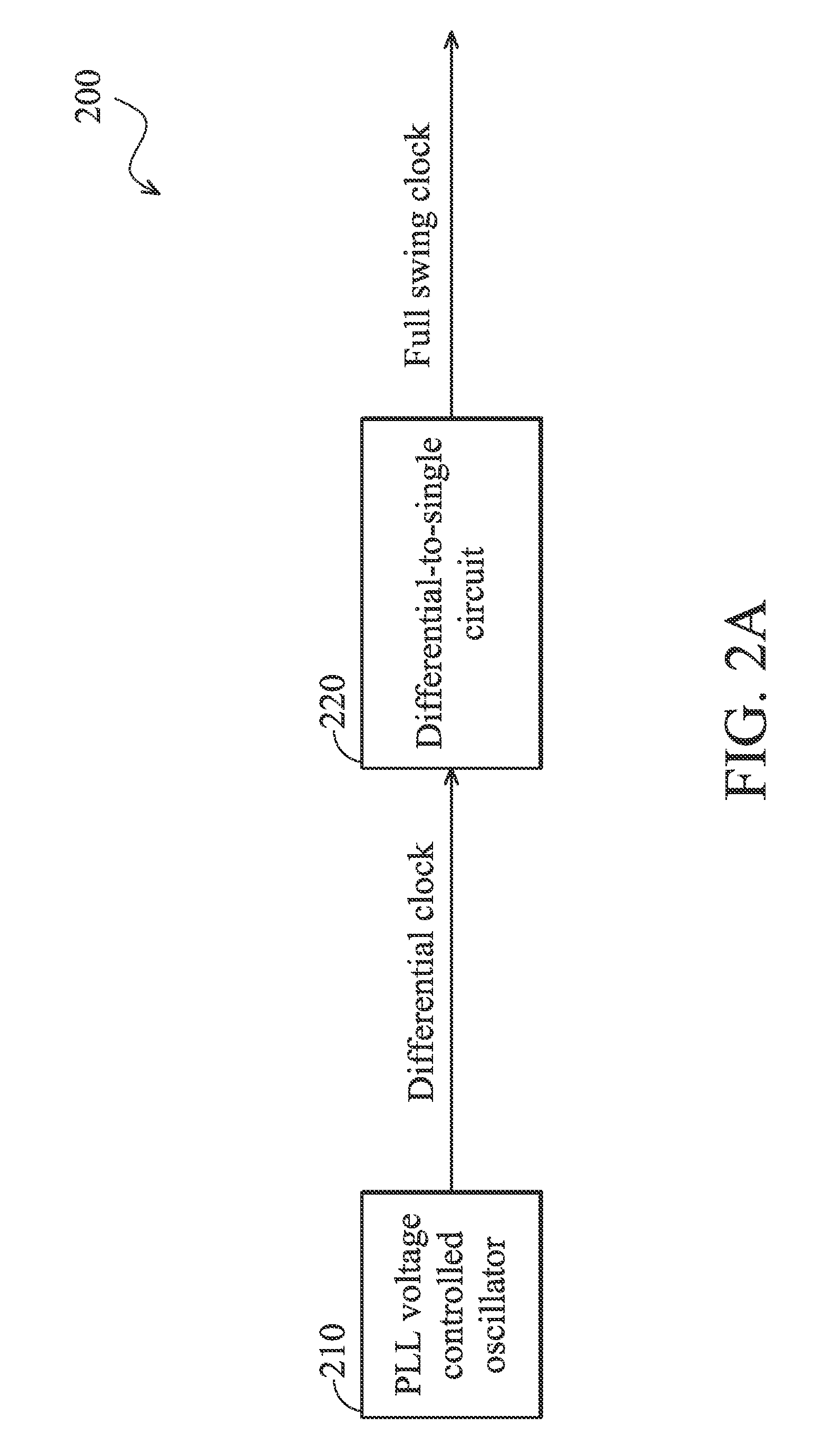
The invention provides a serializer. In one embodiment, the serializer converts parallel input data into serial output data according to a full swing clock and a noiseless differential clock, and comprises a plurality of parallel-input-serial-output (PISO) shift registers, a plurality of current-mode-logic (CML) D flip-flops, and at least one multiplexer. The PISO shift registers respectively selects a plurality of received input bits from the input bits of the parallel input data, and respectively serializes the received input bits according to the full swing clock to generate a plurality of first middle data signals. The CML D flip-flops respectively latches the first middle data signals to generate a plurality of second middle data signals. The at least one multiplexer receives the second middle data signals, and interleaves the second middle data signals according to the noiseless differential clock to generate the serial output data.
Owner:SILICON MOTION INC (TW)
Method for browsing current-mode logic (CML) files on low-end equipment
ActiveCN102831190AEasy to parseSimple renderingSpecial data processing applicationsImage resolutionTerminal equipment
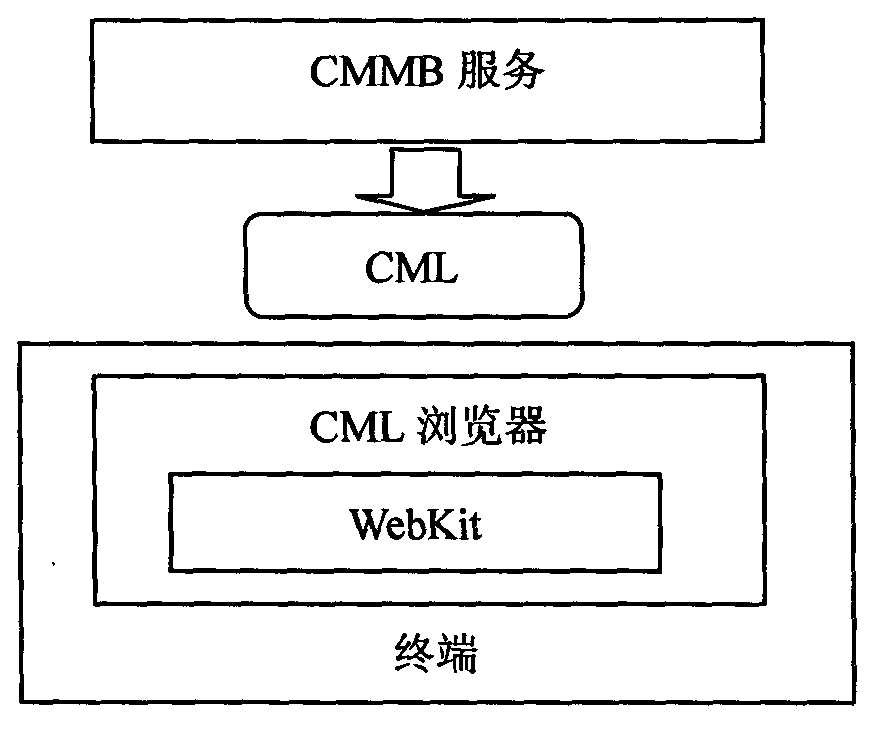
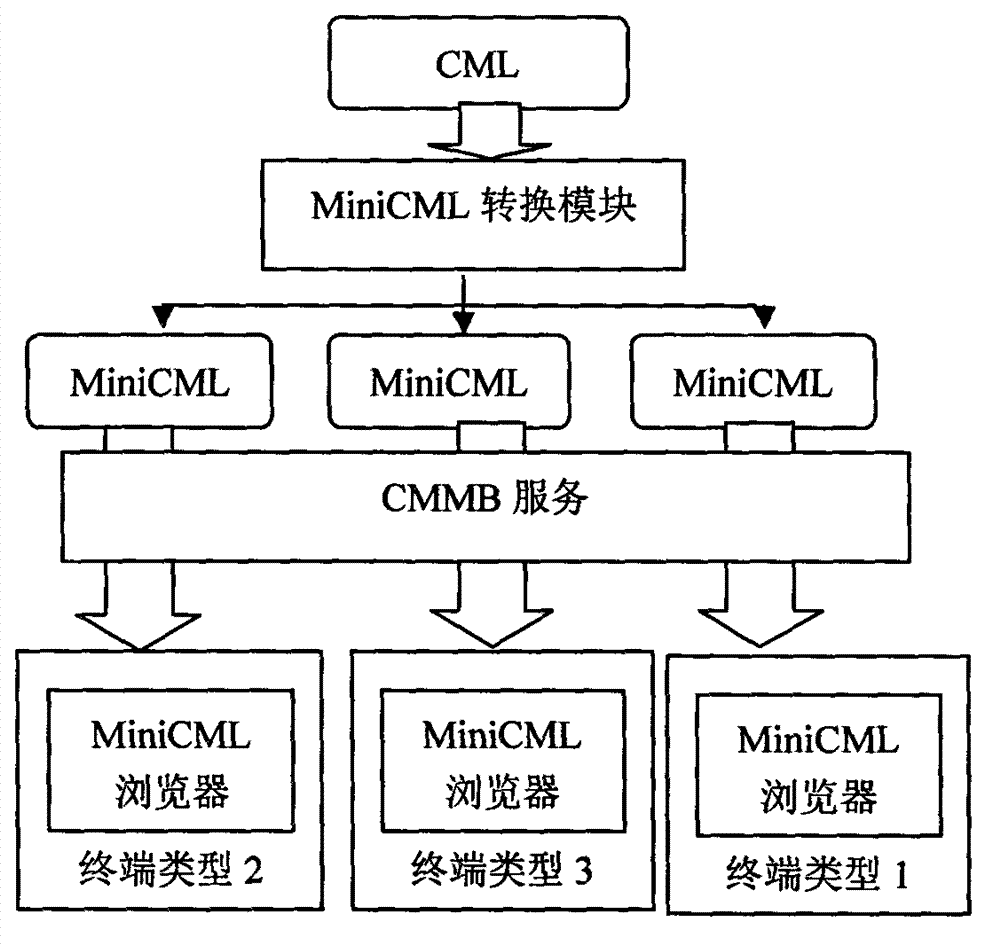
The invention relates to a method for browsing current-mode logic (CML) files on low-end equipment. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: generating different static-state composing positions for CML webpage label content based on the resolution ratio of different types of terminal equipment through a WebKit render engine in advance at a server end, and rewriting in the webpage to generate a webpage based on the resolution ratio of different types of terminal equipment; issuing the webpage based on the resolution ratio of different types of terminal equipment generated in step one to the corresponding type of terminal equipment through a china mobile multimedia broadcasting (CMMB) channel; and carrying out render display on image-text in the webpage by the terminal equipment according to the static-state composing positions in the webpage. The terminal equipment is simple in analysis and rendering, and the technical structure for browsing rich text content by the terminal is greatly simplified, so that the resource expenditure is greatly reduced.
Owner:北京中广睛彩文化传媒有限公司
Low swing current mode logic family
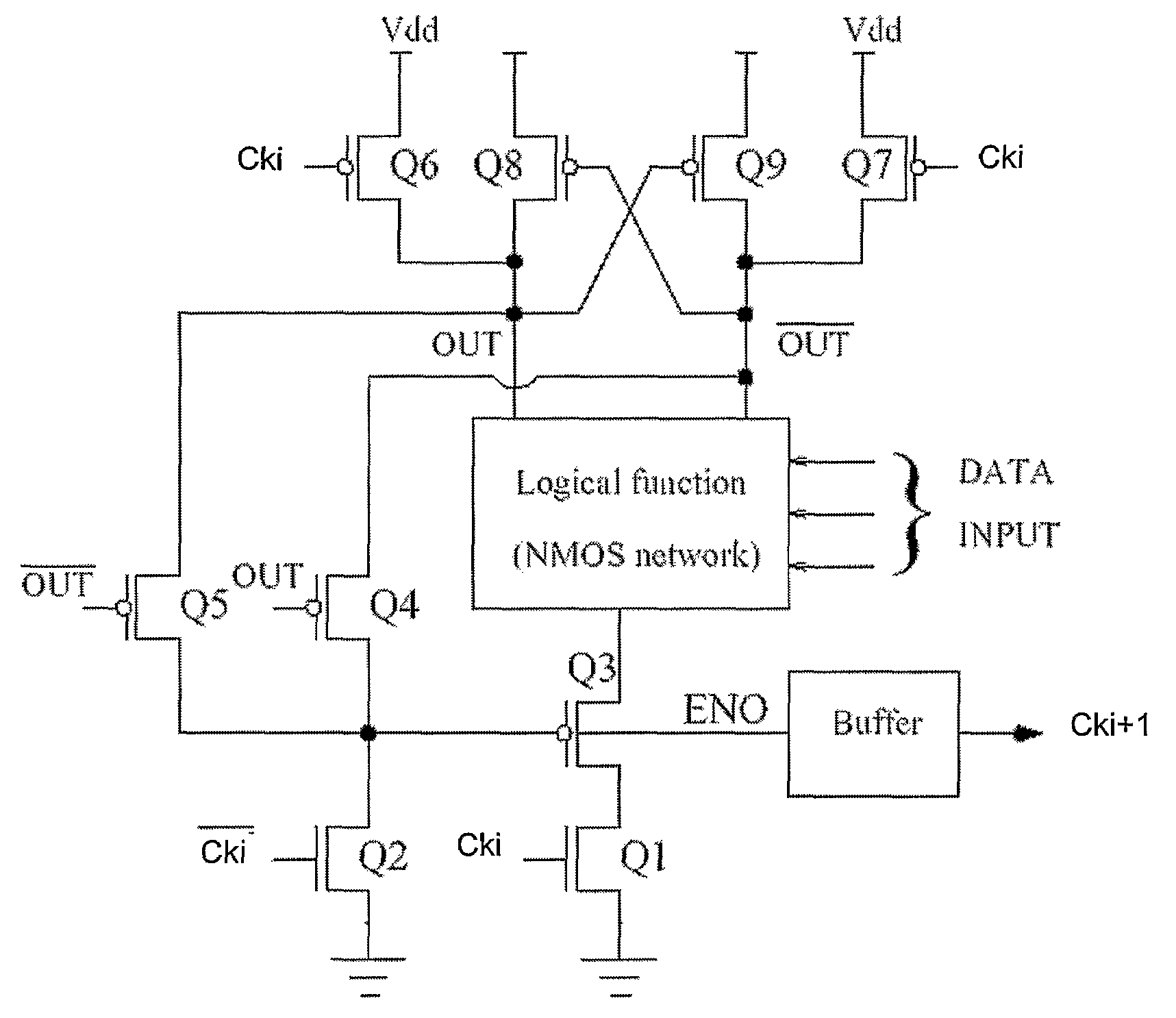
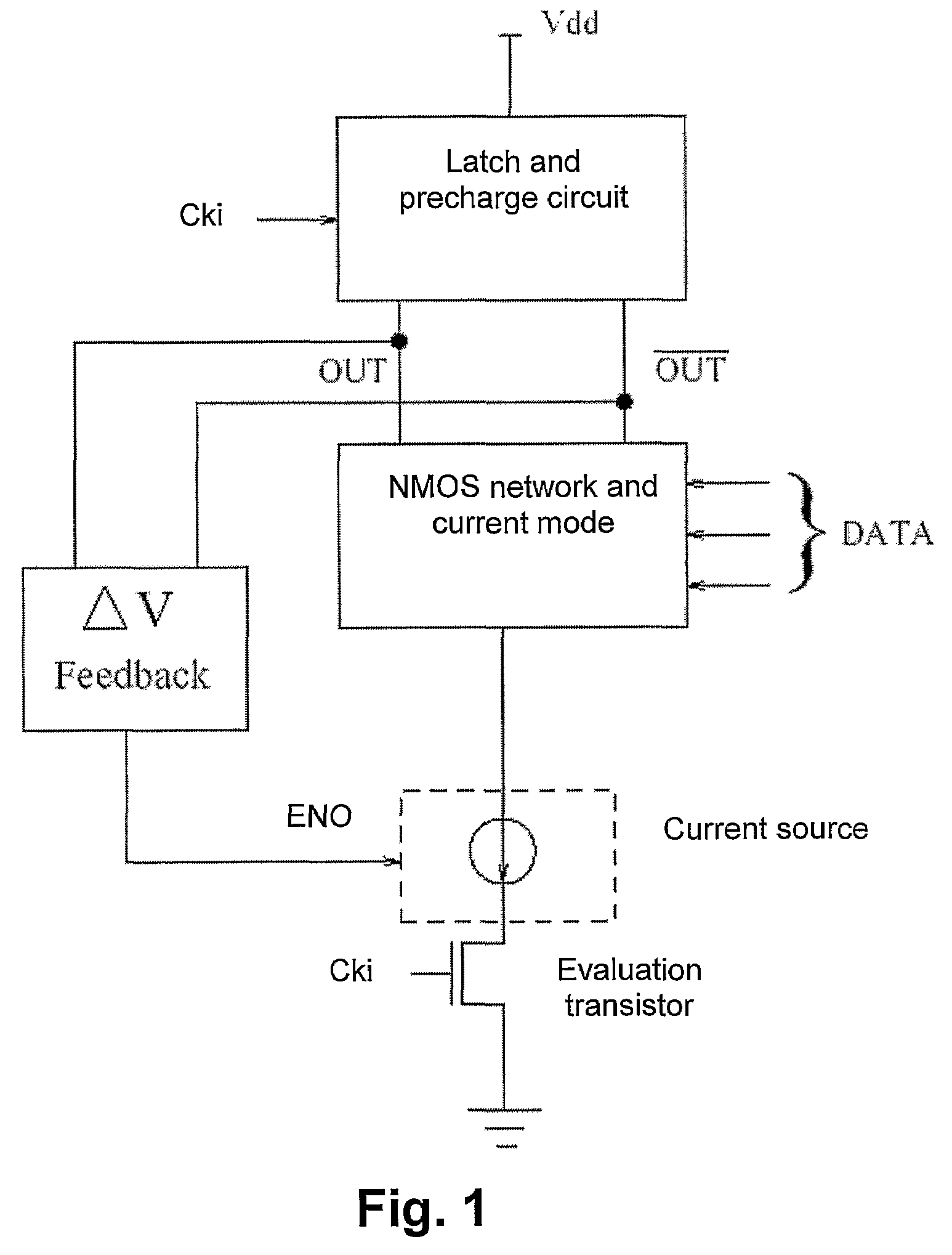
InactiveUS7362140B2Slow changeResist attackReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionPre-chargeEngineering
The present invention provides a low swing current mode logic circuit including: a current mode logic block having data inputs and outputs; a pre-charging circuit for pre-charging the outputs; a dynamic current source; an evaluation circuit for evaluating the logic block during an evaluation phase; and, a feedback path arranged between the outputs and the dynamic current source which is responsive to a difference between the outputs. The simplicity of generating the low swing, achieved by the feedback which may be implemented by only two transistors, is in contrast with the complexity introduced by some methods used by other logic styles for achieving low swing.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Current integrating decision feedback equalizer used in high-speed serial interface
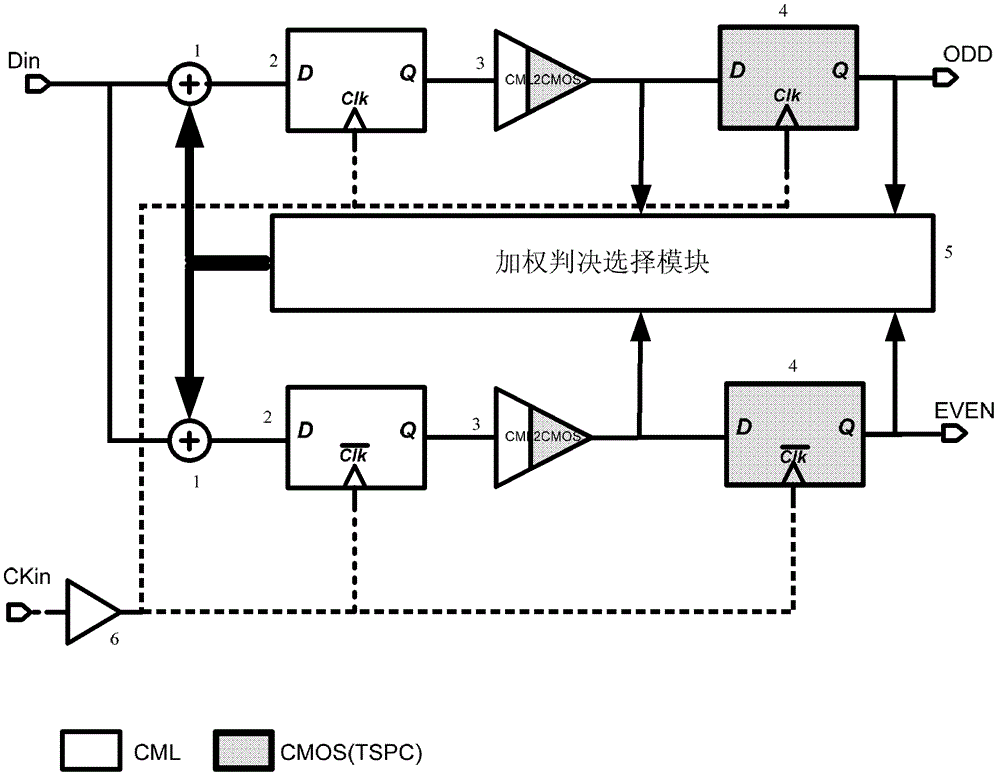
InactiveCN102801667AEasy to handleSimple structureEnergy efficient ICTTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFeedback controlHigh-Speed Serial Interface
The invention discloses a current integrating decision feedback equalizer used in a high-speed serial interface, belonging to the field of integrated circuits. The current integrating decision feedback equalizer comprises two branches, wherein each branch is formed as follows: a signal input end orderly passes through an analogue weighting device, a CML(Current-Mode Logic) D trigger and a CML to CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) level switching circuit to be connected with a TSPC (True Single Phase Clock) D trigger; the input end of a weighting decision selecting module is respectively connected with the output ends of the two branches and the output ends of the CML to CMOS level switching circuits in the two branches, and the output end of the weighting decision selecting module is respectively connected with the feedback control ends of the analogue weighting devices in the two branches; the output end of one input clock buffer module is respectively connected with the clock control input ends of the CML D triggers and the clock control input ends of the TSPC D triggers in the two branches; and the clock signal of the input clock buffer module is an anti-phase half-speed differential clock signal. The current integrating decision feedback equalizer has the advantages of low error rate, simple structure, low power consumption, and so on.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
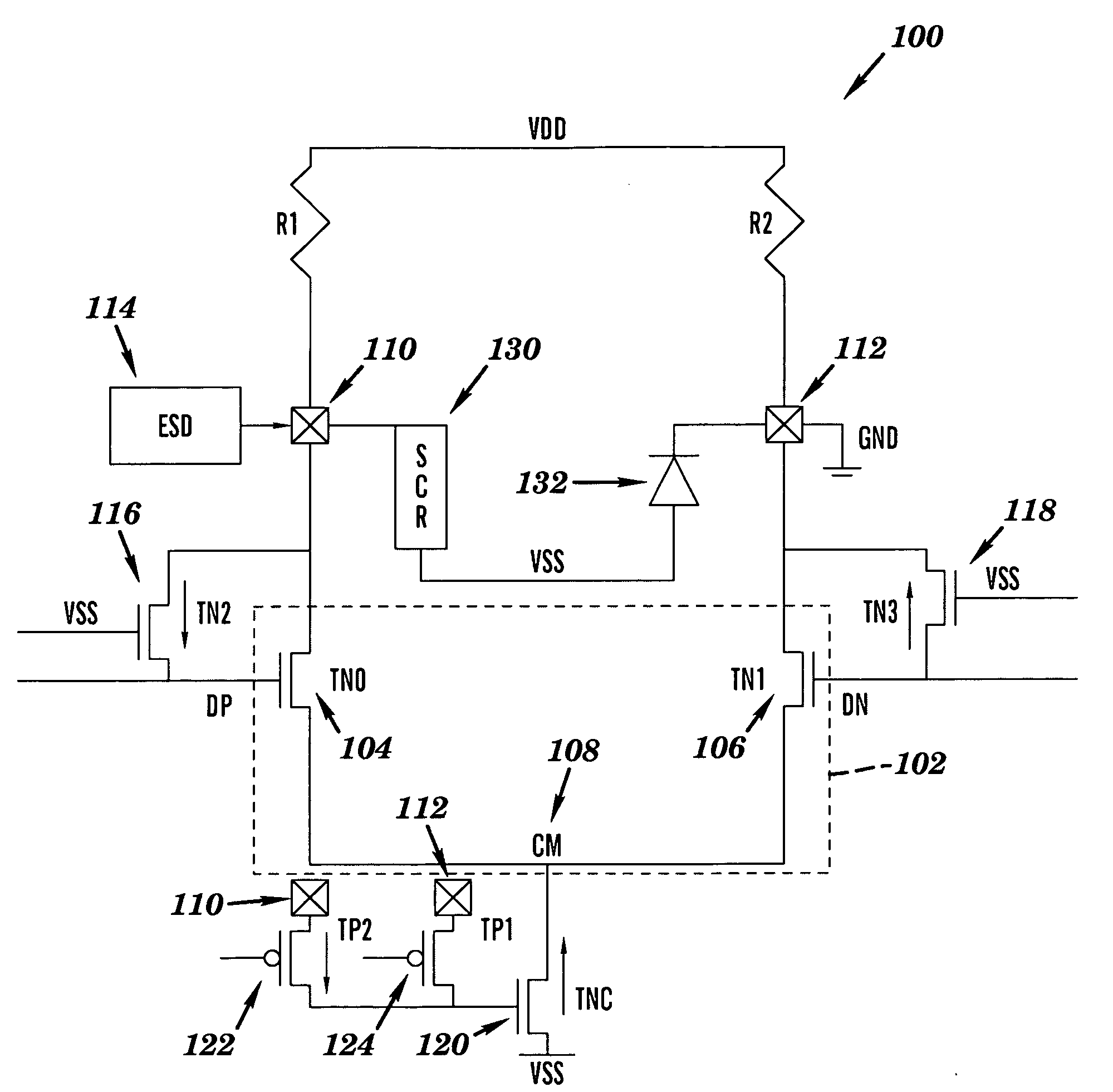
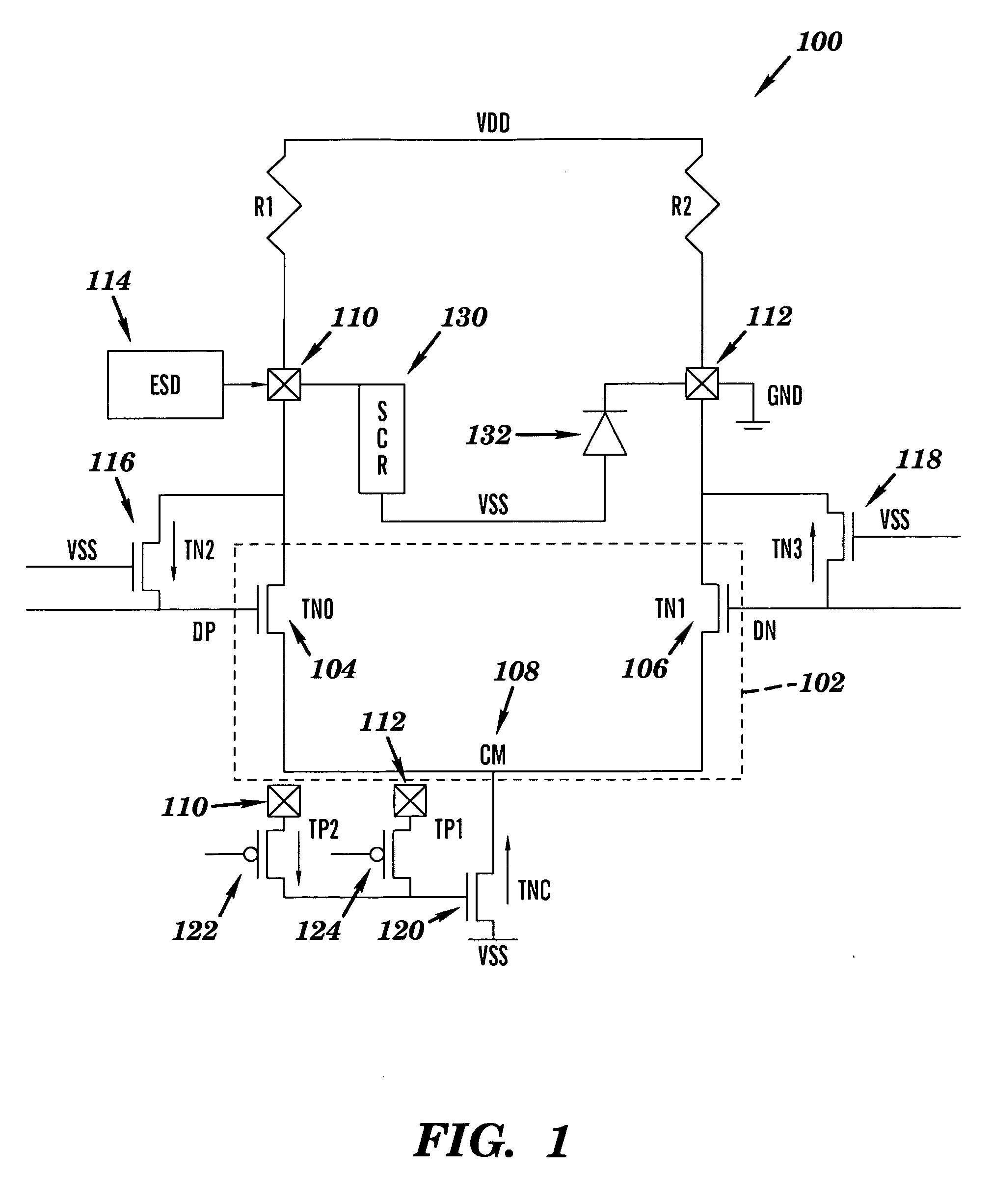
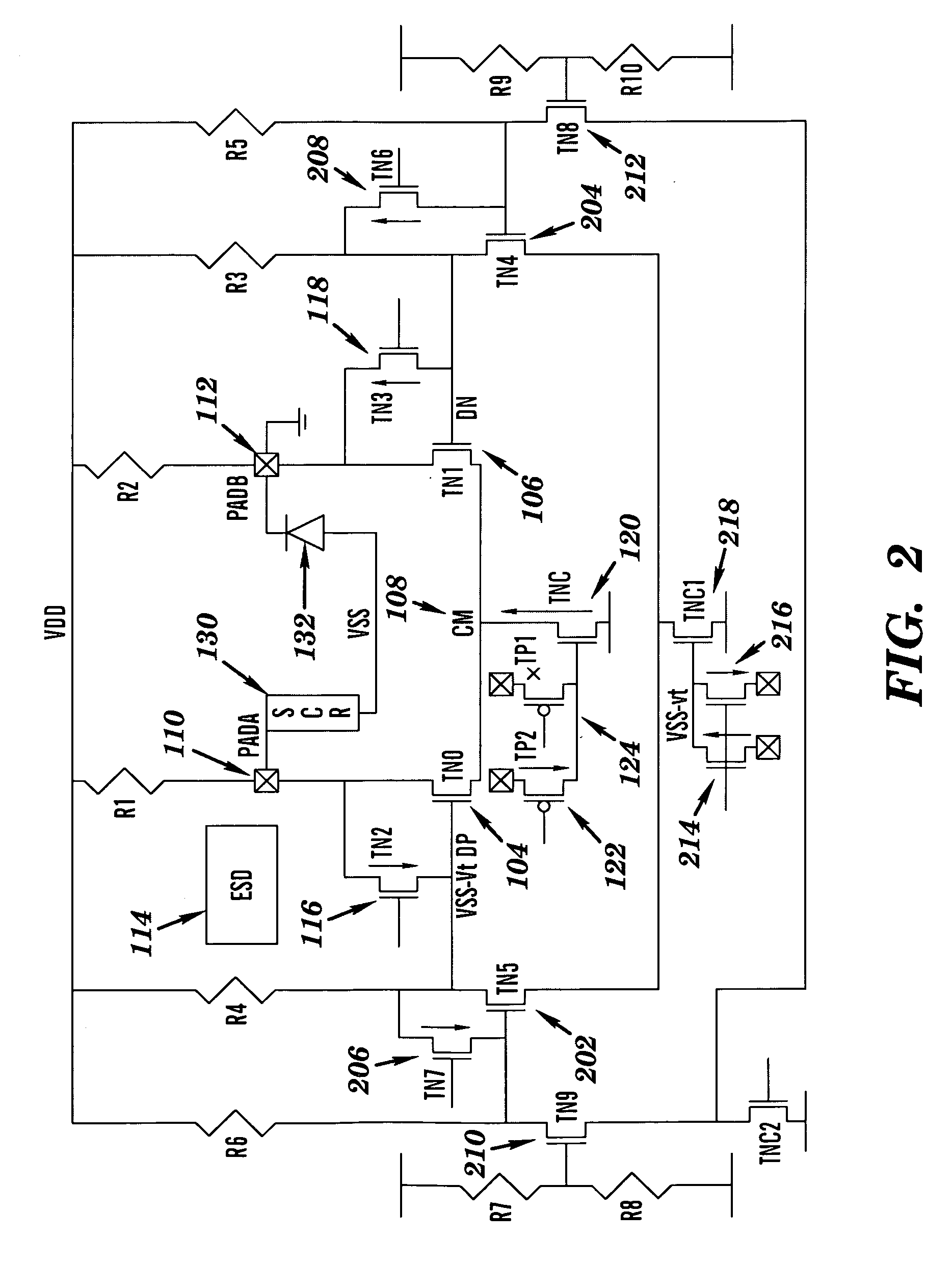
Method, design structures, and systems for current mode logic (CML) differential driver ESD protection circuitry
InactiveUS20090310267A1Solid-state devicesAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesComputer Aided DesignVoltage source
A hardware description language (HDL) design structure encoded on a machine readable data storage medium, the HDL design comprising elements that when processed in a computer aided design system generates a machine executable representation of a device for implementing dynamic refresh protocols for DRAM based cache. The HDL design structure further comprises an integrated circuit having a differential driver, comprising: a first driver and a second driver forming the differential driver, the drivers are coupled in parallel between a first voltage source and a second voltage source; a first switch coupled to the first driver and configured to turn off the first driver during an ESD event such that the first driver sustains stress during the ESD event; and a second switch coupled to the second driver and configured to turn off the second driver during the ESD event such that the second driver sustains stress during the ESD event.
Owner:IBM CORP
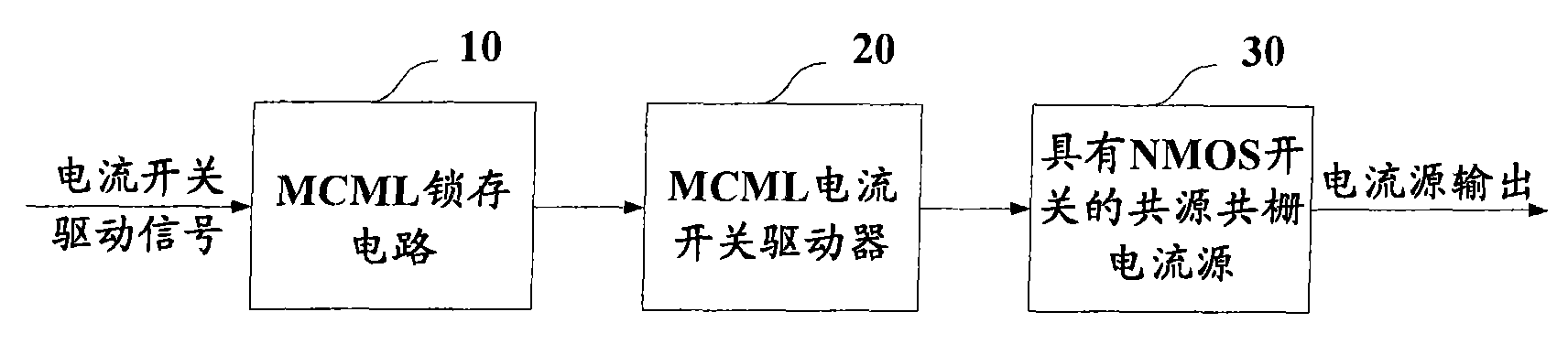
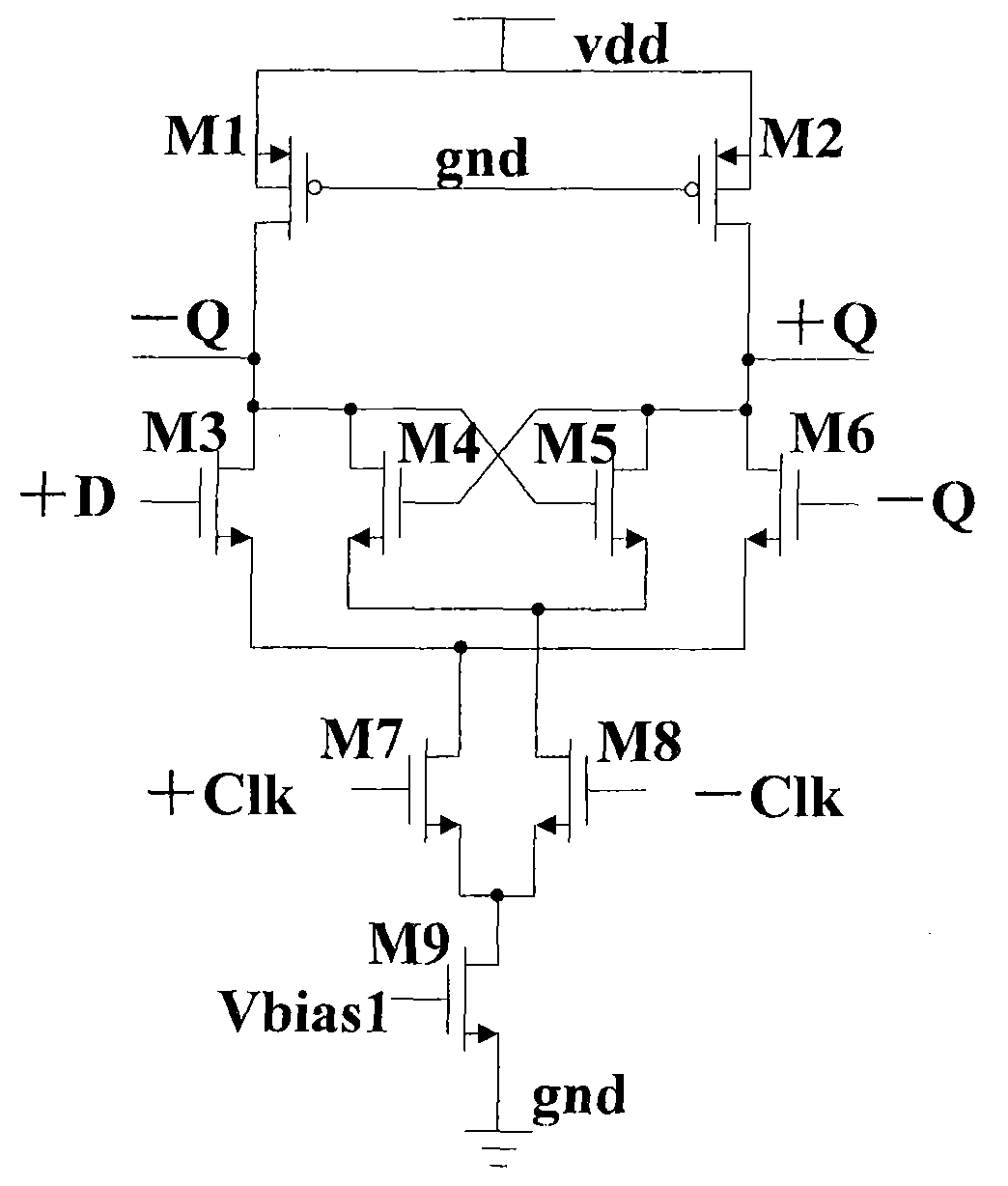
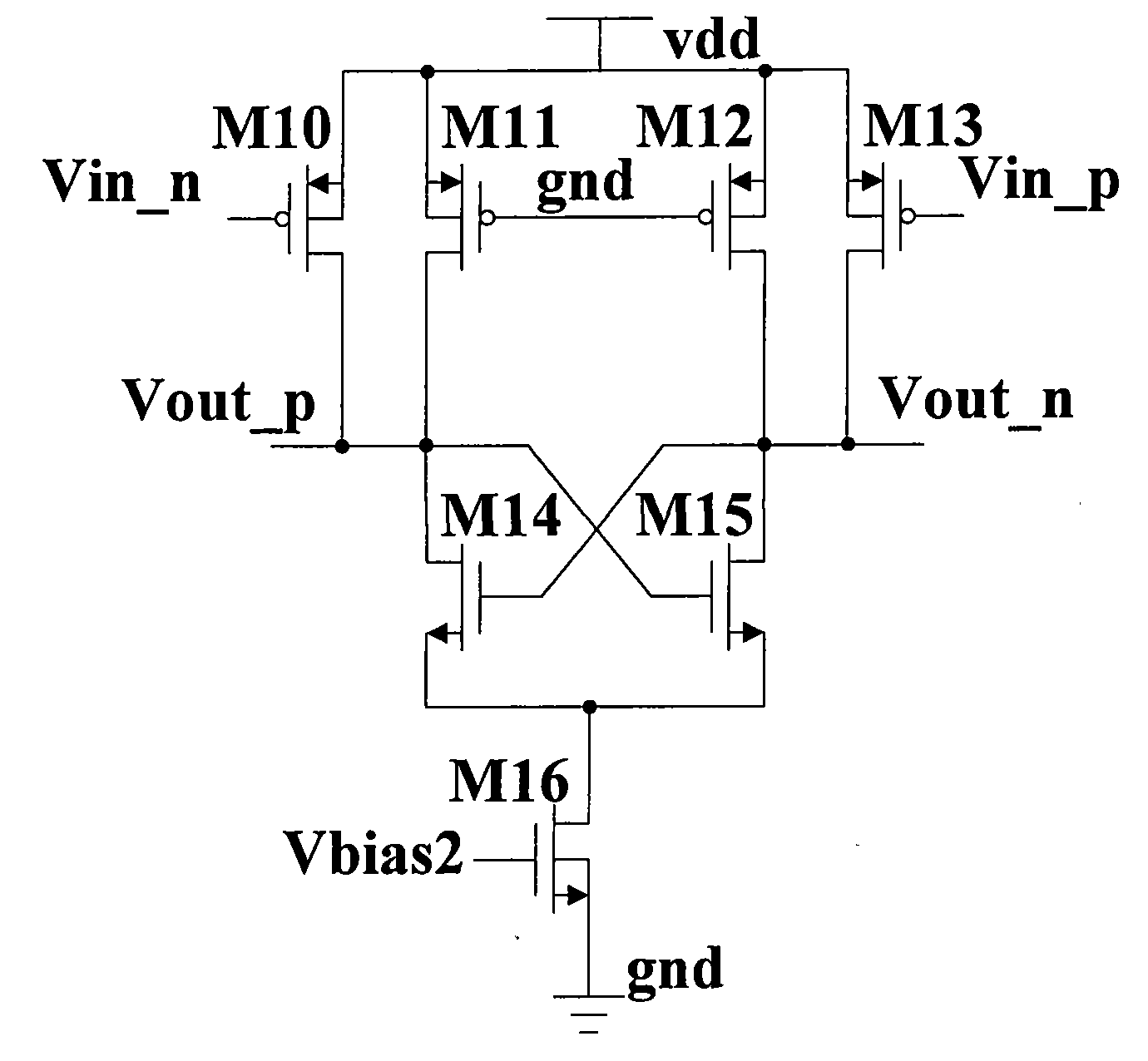
High-speed current switch driver based on MOS current-mode logic
ActiveCN101562449ASmall swingPrevent simultaneous shutdownLogic circuitsLow distortionCurrent switch
The invention provides a high-speed current switch driver based on MOS current-mode logic. The driver comprises: a MOS current-mode logic latch circuit for receiving current switch drive signals, and performing latching and amplitude limiting on the current switch drive signals so as to synchronize the current switch drive signals; a MOS current-mode logic current switch for receiving signals processed by the MOS current-mode logic latch circuit, generating current source drive signals with amplitude limited and adjusting crossing points of the current switch drive signals; and a common-source and common-gate current source with a NMOS switch for receiving the current switch drive signals processed by the MOS current-mode logic current switch and outputting low-distortion current signals, thus synchronizing the current switch drive signals and reducing feed-through effect.
Owner:陕西光电子先导院科技有限公司
A high-speed large-swing divide-by-two frequency divider circuit based on current-mode logic
InactiveCN102291132AImprove anti-interference abilityReduce noisePulse automatic controlDual modeP channel
The invention discloses a high speed high-oscillation amplitude divide-by-two frequency divider circuit, which belongs to the technical fields of integrated circuit designing and signal processing. Specifically, the circuit mainly comprises two high speed high-oscillation amplitude D triggers which are cascaded. The D trigger of each stage eliminates the bias of a tail current source based on theconventional D trigger having a current-mode logic (CML) structure, and adopts a P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) transistor as a load; and simultaneously, a PMOS and N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) complementary cross coupling pair structure and the like are adopted by the output stage of the circuit to finally achieve the aims of increasing the oscillation amplitude of an output signal and making the oscillation amplitude of the output signal approximate to full oscillation amplitude under the condition of ensuring the high speed working of the circuit. The circuit not only can directly drive a post circuit, reduces system power consumption to a certain extent, compensates for the shortcomings of a conventional divide-by-two frequency divider, and is suitable for a high speed frequency divider part in a low-power consumption preposed dual-mode prescaler front-end without any additional level conversion amplification circuit.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Track and Hold Amplifiers and Digital Calibration for Analog-to-Digital Converters
ActiveUS20120188109A1Electric signal transmission systemsElectric analogue storesAnalog-to-digital converterLinearity
An exemplary differential track and hold amplifier includes a track stage including first and second linearized pairs connected in series at their respective inputs and in parallel at their respective outputs. The differential track and hold amplifier also includes a hold stage selectively coupled to the outputs of the first and second linearized pairs. The hold stage includes a unity gain buffer with feedback having a hold capacitor interconnected across its outputs. The differential track and hold amplifier also includes an output buffer coupled to the outputs of the hold stage. An exemplary analog-to-digital converter includes a differential track-and-hold amplifier, a voltage ladder, and a plurality of slices. Each of the slices in turn includes a differential preamplifier coupled to the track-and-hold amplifier and to a corresponding location on the voltage ladder; a current mode logic latch comparator coupled to the differential preamplifier; a large-swing latch coupled to the current mode logic latch comparator; a complementary metal oxide semiconductor latch having a dummy load; a calibration digital to analog converter connected across outputs of the differential preamplifier to inject calibration currents; and a register coupled to the calibration digital to analog converter and storing calibration values for use thereby. The analog-to-digital converter also includes a multiplexer which multiplexes outputs of the complementary metal oxide semiconductor latches down to a predetermined number of outputs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
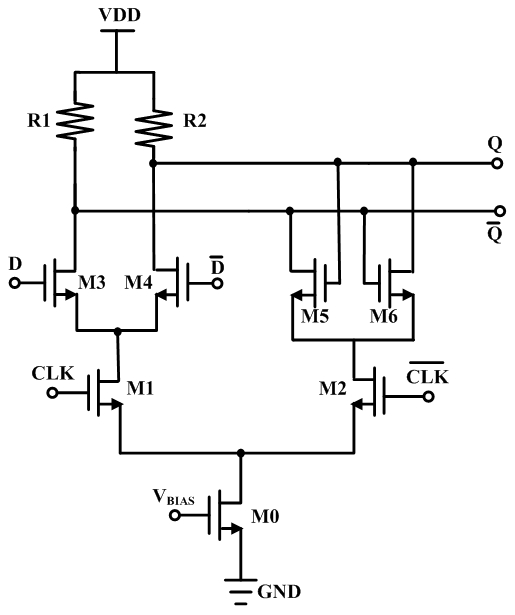
Dual operational mode CML latch
A dual purpose current mode logic (“CML”) latch circuit is provided which includes a CML latch operable to receive at least a pair of differential input data signals and at least one clock signal. The CML latch is operable to generate at least one output signal in accordance with the states of the pair of input differential data signals. A mode control device is operable to receive a mode control signal to operate the CML latch as a buffer or as a latch. In such way, when the mode control signal is inactive, the CML latch generates and latches the output signal at a timing determined by the at least one clock signal, and when the mode control signal is active the CML latch generates the output signal such that the output signal changes whenever the states of the pair of differential input data signals change.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com