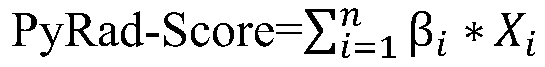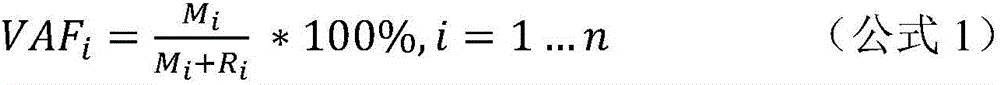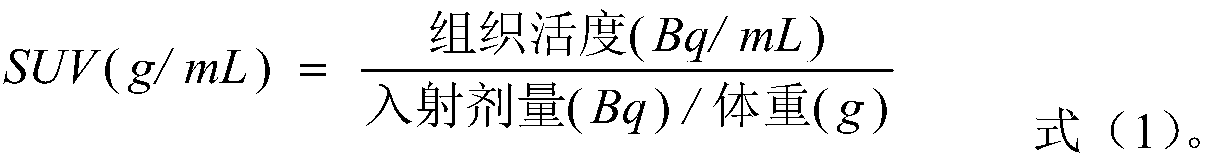Patents
Literature
49 results about "Heterotaxy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An abnormality in which the internal thoraco-abdominal organs demonstrate abnormal arrangement across the left-right axis of the body. [HPO:probinson, PMID:21731561]
Method and apparatus for monitoring and quantitatively evaluating tumor perfusion
InactiveUS20030211036A1Deeper understandingNo adverse effect on general well-beingImage analysisIn-vivo radioactive preparationsVoxelResonance
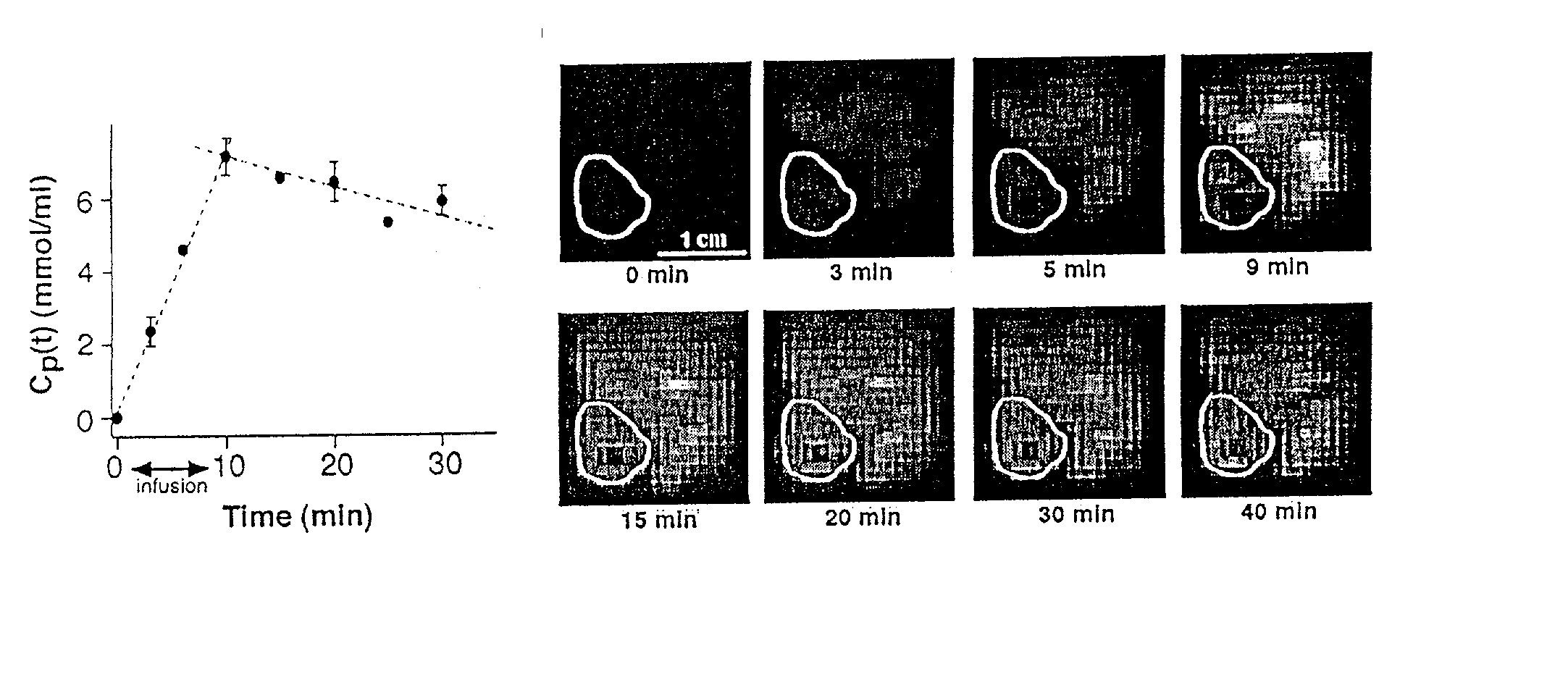
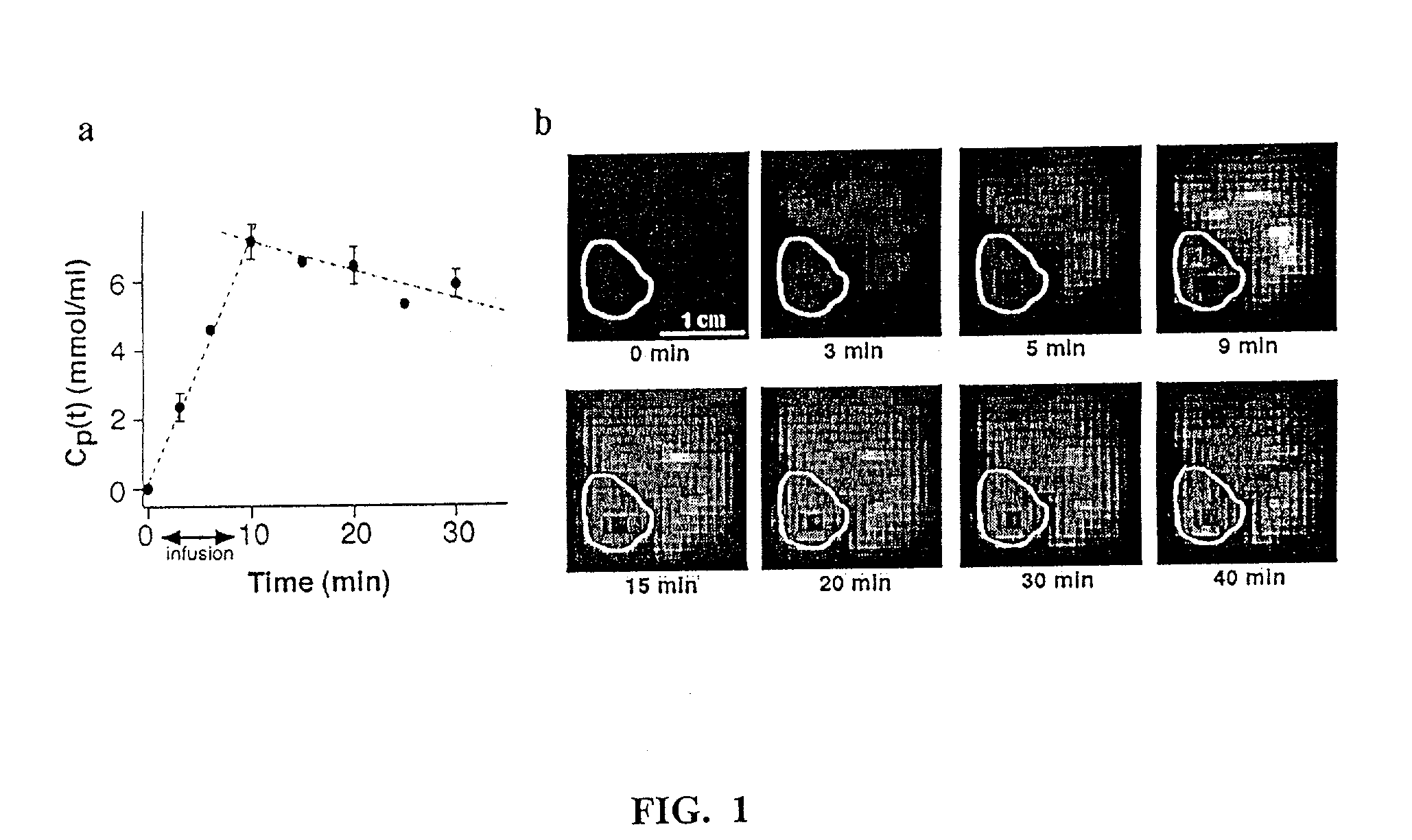
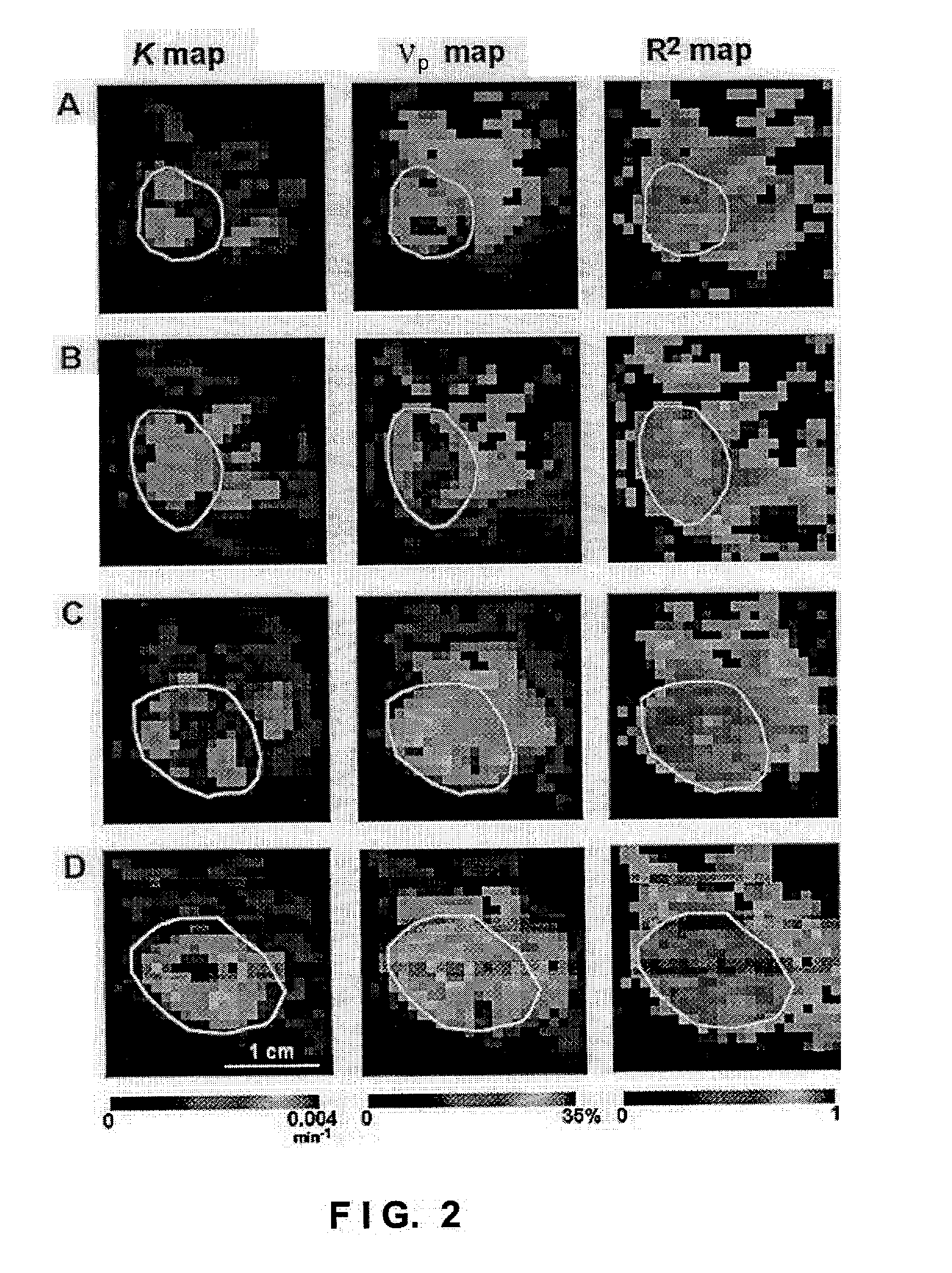
Method and apparatus for monitoring a patient having a tumor to determine perfusion tumor heterogeneity wherein a solution containing a tracer, preferably a <2>H-saline solution is infused into the patient's bloodstream at a predetermined slow rate to effect perfusion into the tumor. An MRI machine is adjusted to acquire a set of dynamic <2>H magnetic resonance images of the tumor. The <2>H-images are obtained before infusion, during infusion and post infusion. First, the obtained images are processed to quantitatively determine perfusion per voxel of the images. Next, maps of perfusion parameters are generated to indicate spatial distribution of tumor perfusion. The maps are displayed in color code and analyzed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD AT THE WEISZMANN INST OF SCI
Method and apparatus for detecting vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque
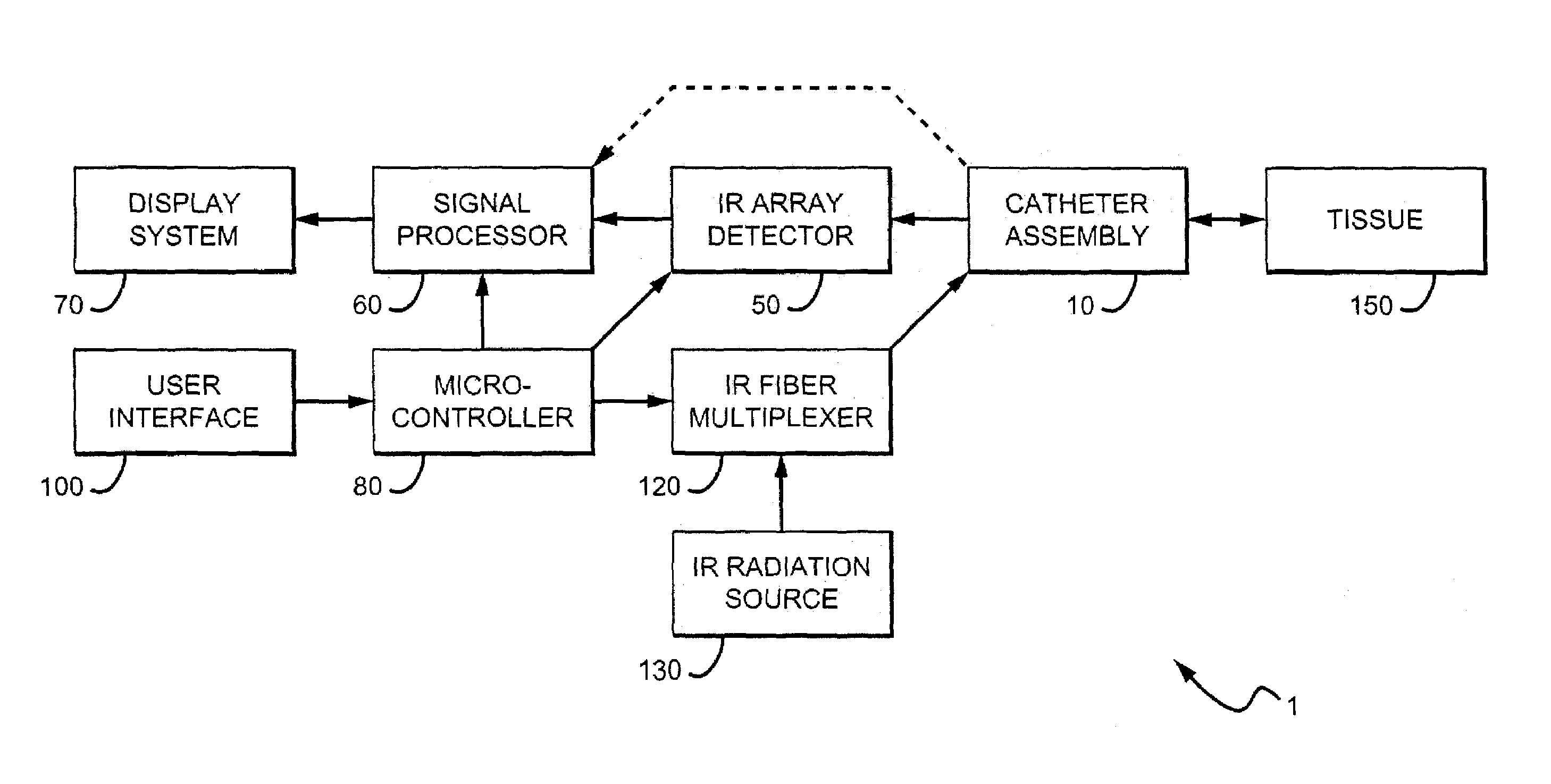
Methods and devices are disclosed for detecting vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque, or plaque at risk of reducing blood flow in a vessel, by identifying a region of elevated temperature along a living vessel wall. The disclosure that human atherosclerotic plaque with measurable temperature heterogeneity has the morphological characteristics of plaque that is likely to ulcerate provides a new and sensitive technique for detecting and treating these dangerous plaques before myocardial infarction and its consequences occur. The disclosed methods are advantageous over conventional plaque detection techniques because they are capable of differentiating between those plaques that are at great risk of rupture, fissure, or ulceration, and consequent thrombosis and occlusion of the artery, and those that are not presently at risk. Infrared heat-sensing catheters useful for identifying potentially fatal arterial plaques in patients with disease of the coronary or other arteries are also described. In some embodiments a coherent infrared fiber optic bundle is employed to radially and longitudinally explore a luminal wall to identify inflamed, heat-producing, atherosclerotic plaque. Certain other methods and devices are disclosed which are particularly suited for non-invasively identifying and then monitoring the progression or amelioration of an inflamed plaque in a patient, and for monitoring for onset of inflammation in an implanted arteriovenous graft. Also disclosed are thermocouple basket catheters and thermistor basket catheters which are also capable of detecting temperature heterogeneity along a vessel wall.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method and apparatus for high resolution spatially modulated fluorescence imaging and tomography
An improvement in a method for quantitative modulated imaging to perform depth sectioned reflectance or transmission imaging in a turbid medium, such as human or animal tissue is directed to the steps of encoding periodic pattern of illumination preferably with a fluorescent excitation wavelength when exposing a turbid medium to the periodic pattern to provide depth-resolved discrimination of structures within the turbid medium; and reconstructing a non-contact three dimensional image of the structure within a turbid medium. As a result, wide field imaging, separation of the average background optical properties from the heterogeneity components from a single image, separation of superficial features from deep features based on selection of spatial frequency of illumination, or qualitative and quantitative structure, function and composition information is extracted from spatially encoded data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
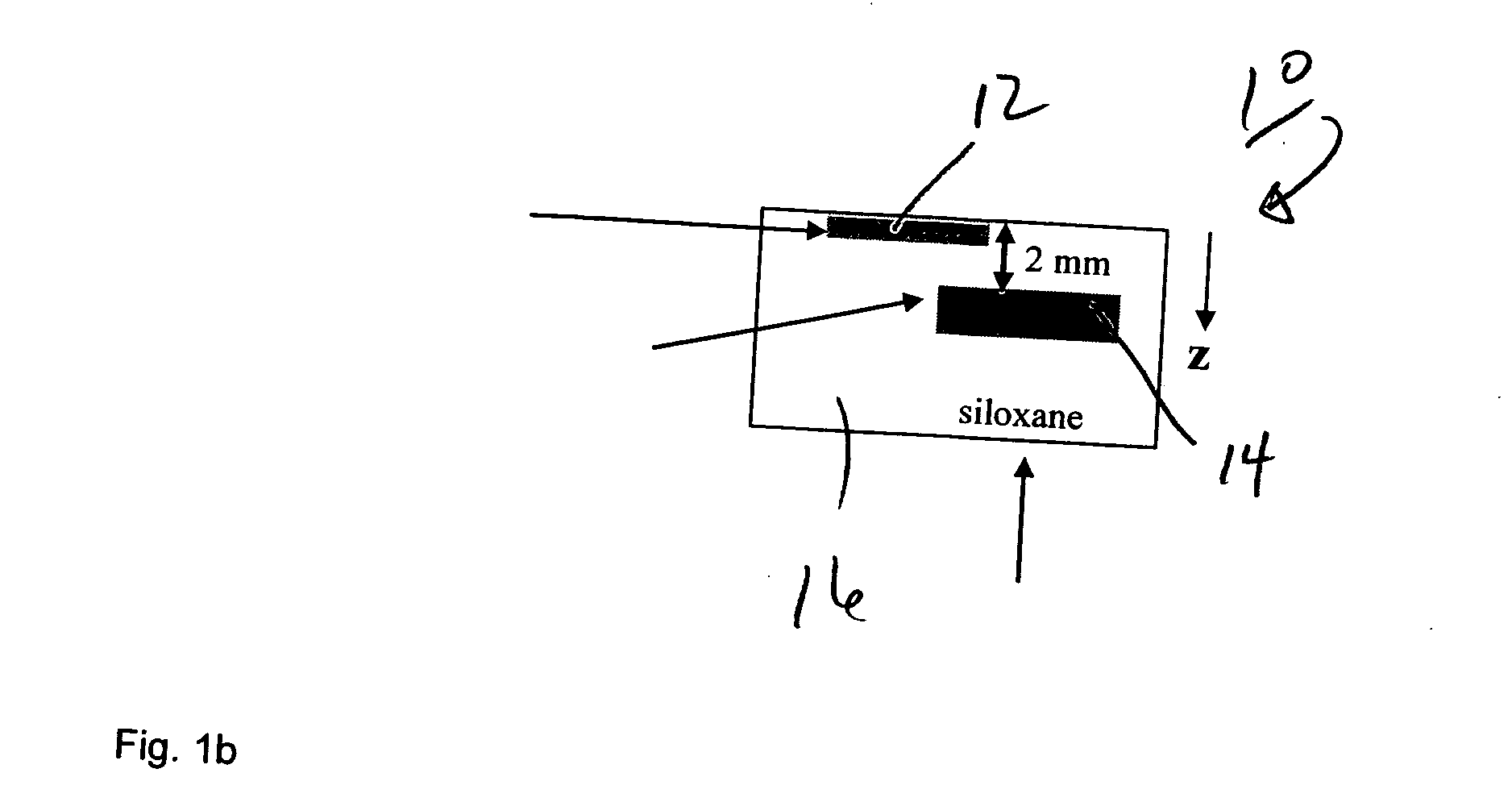
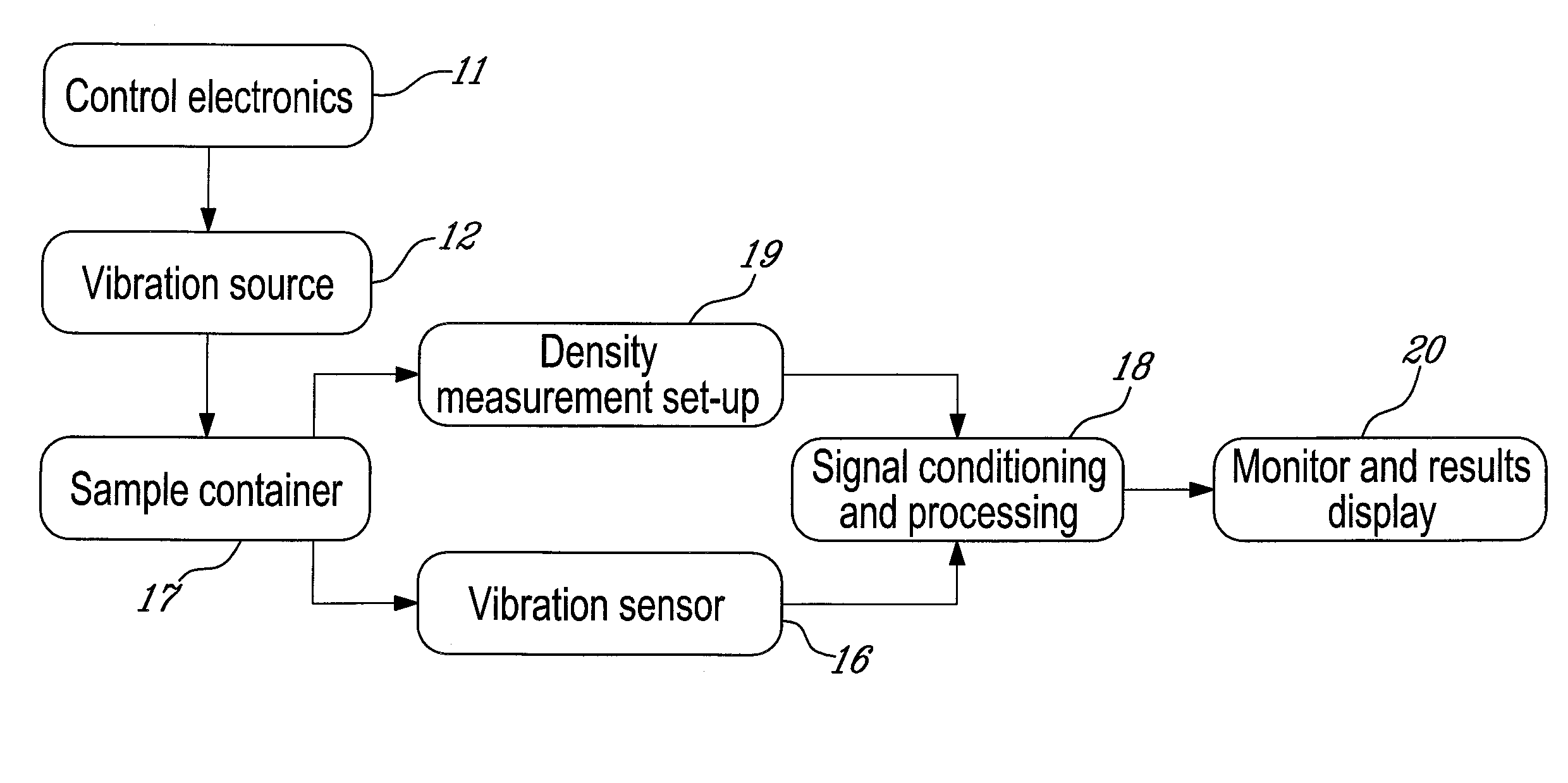
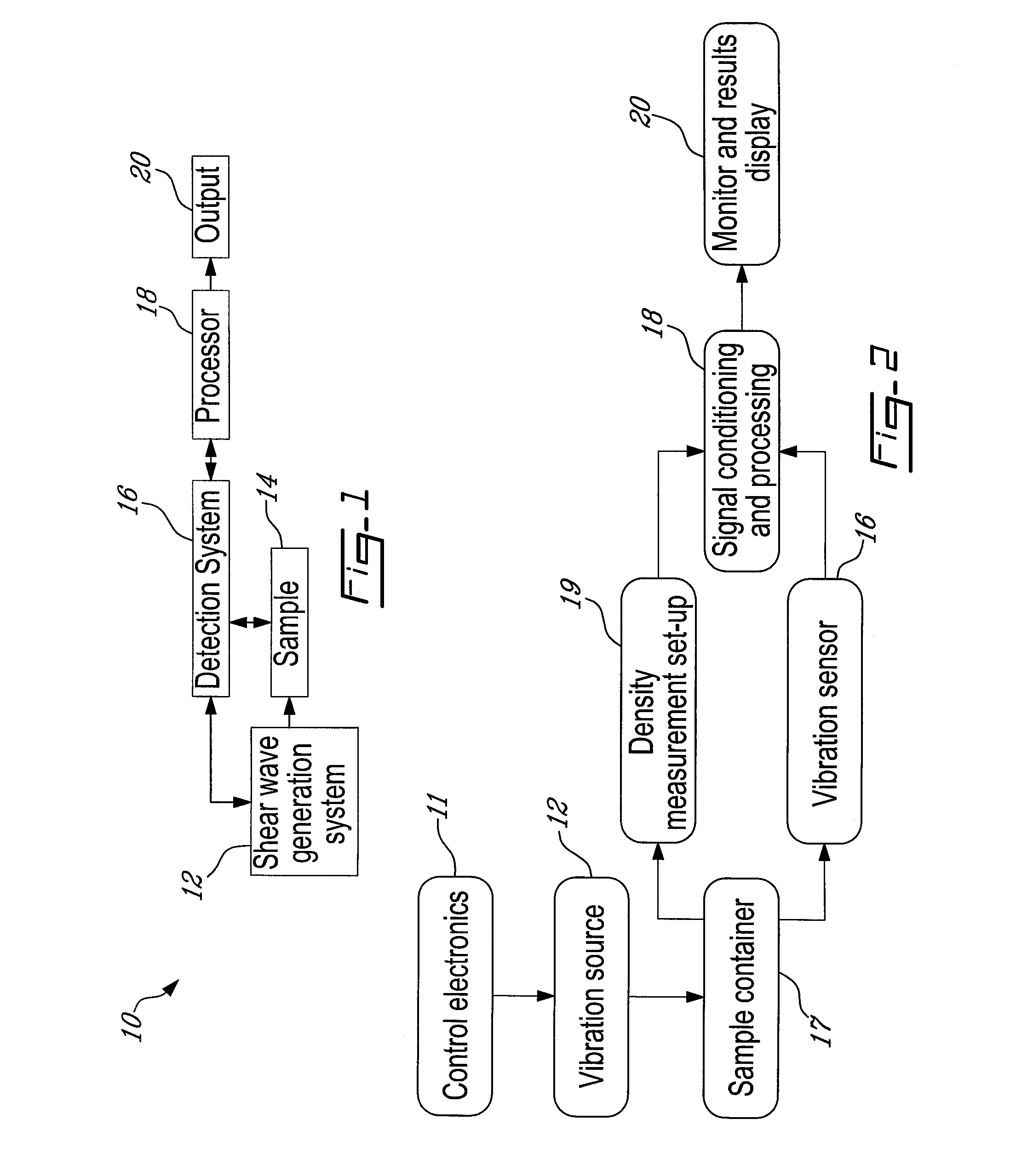
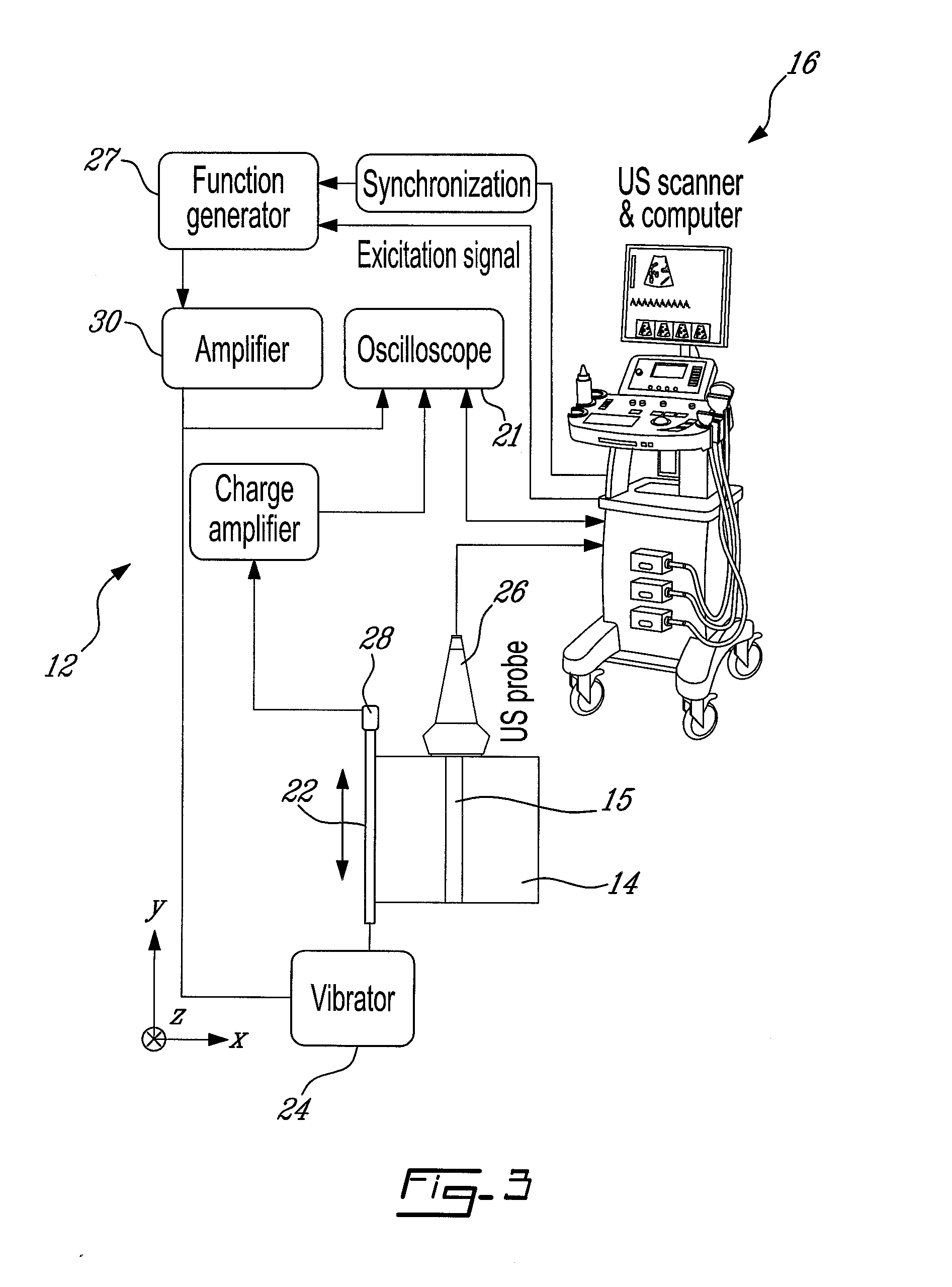
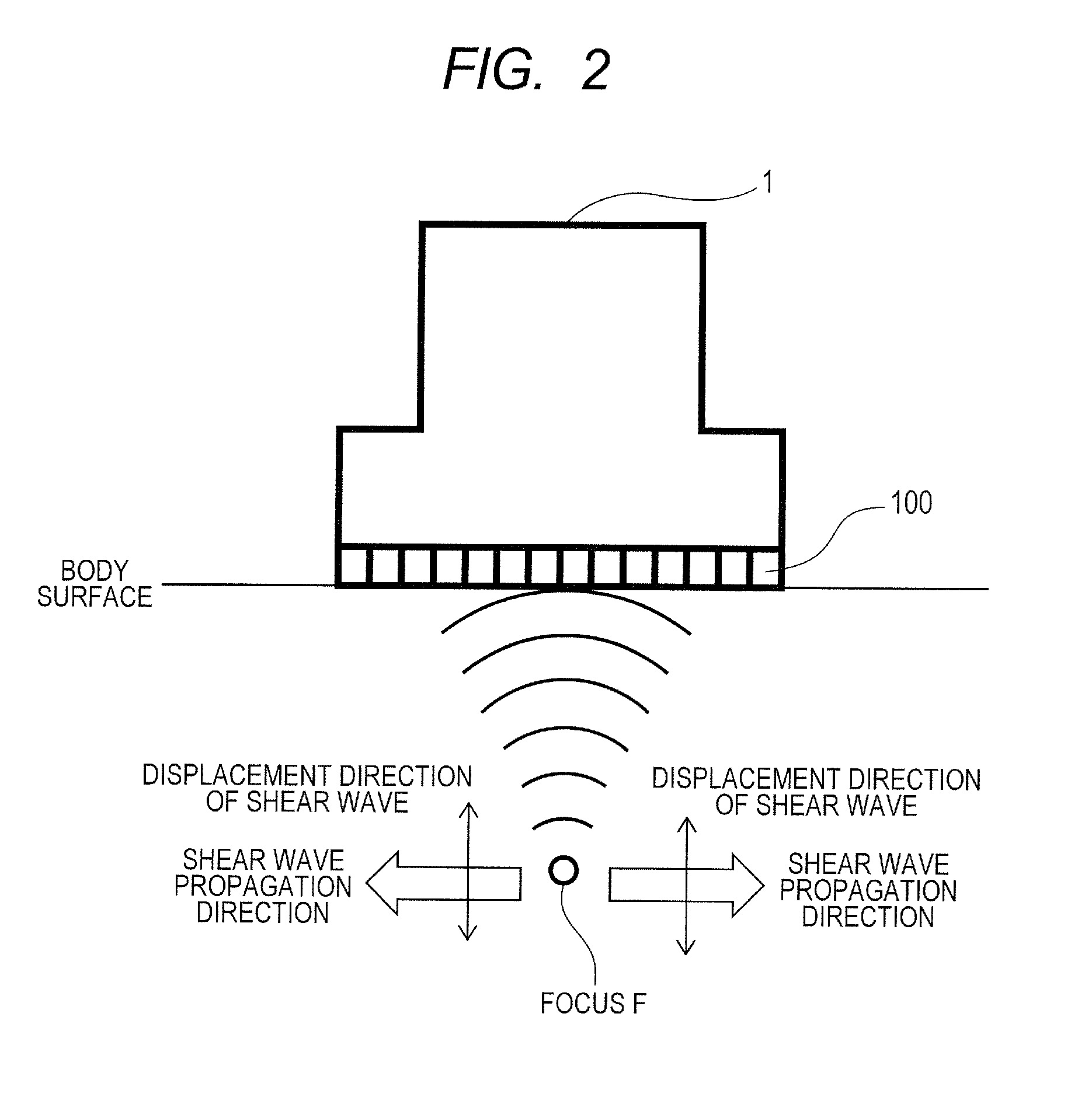
System and method for detection, characterization and imaging of heterogeneity using shear wave induced resonance
InactiveUS20110130660A1Ultrasound therapyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical resonanceAcoustics
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP
System for assessing tissue substance extraction
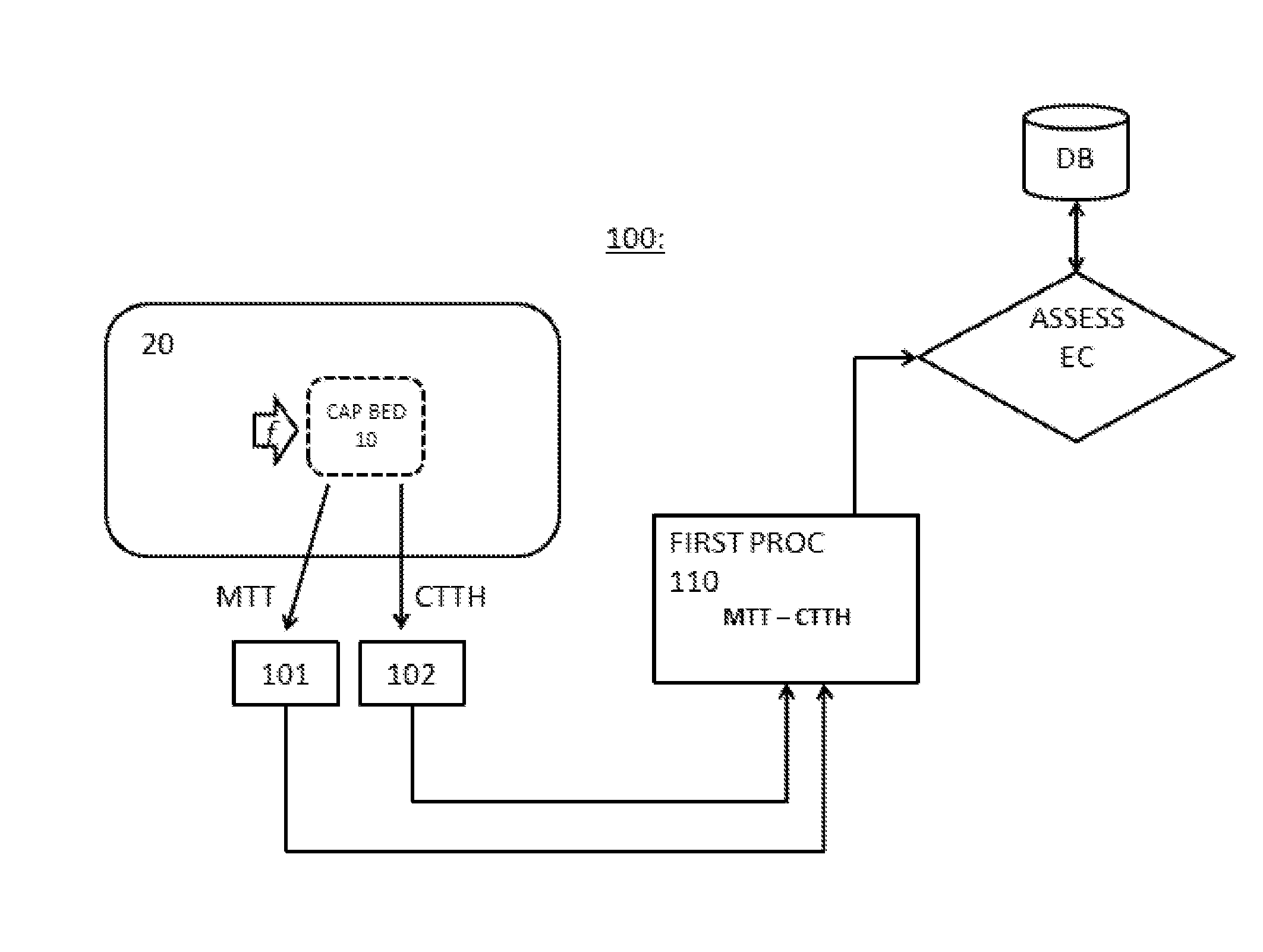
The present invention relates to a system for measuring a micro-vascular flow distribution of a tissue portion of a mammal comprising means (101) for measuring a first indicator (MTT) for the blood flow through a capillary bed, means (102) for measuring a second indicator (CTTH) of heterogeneity of the blood flow in said capillary bed, and a first processor (110) arranged for using the first and the second indicator to estimate an extraction capacity (EC) of a substance from the blood in said capillary bed.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV +1
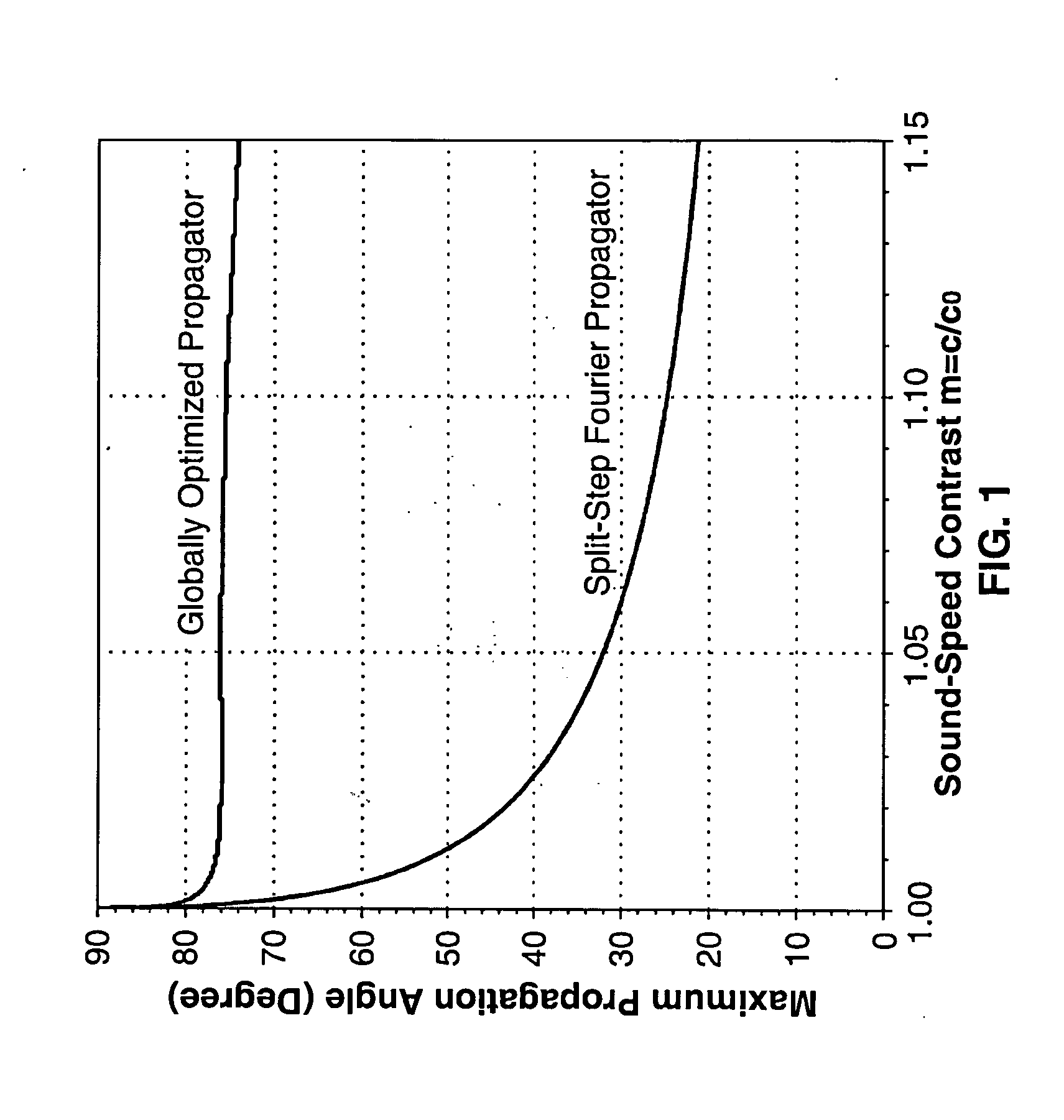
High-resolution wave-theory-based ultrasound reflection imaging using the split-step fourier and globally optimized fourier finite-difference methods
InactiveUS20130251222A1Quality improvementImprove resolutionVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFrequency waveImaging quality
Methods for enhancing ultrasonic reflection imaging are taught utilizing a split-step Fourier propagator in which the reconstruction is based on recursive inward continuation of ultrasonic wavefields in the frequency-space and frequency-wave number domains. The inward continuation within each extrapolation interval consists of two steps. In the first step, a phase-shift term is applied to the data in the frequency-wave number domain for propagation in a reference medium. The second step consists of applying another phase-shift term to data in the frequency-space domain to approximately compensate for ultrasonic scattering effects of heterogeneities within the tissue being imaged (e.g., breast tissue). Results from various data input to the method indicate significant improvements are provided in both image quality and resolution.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
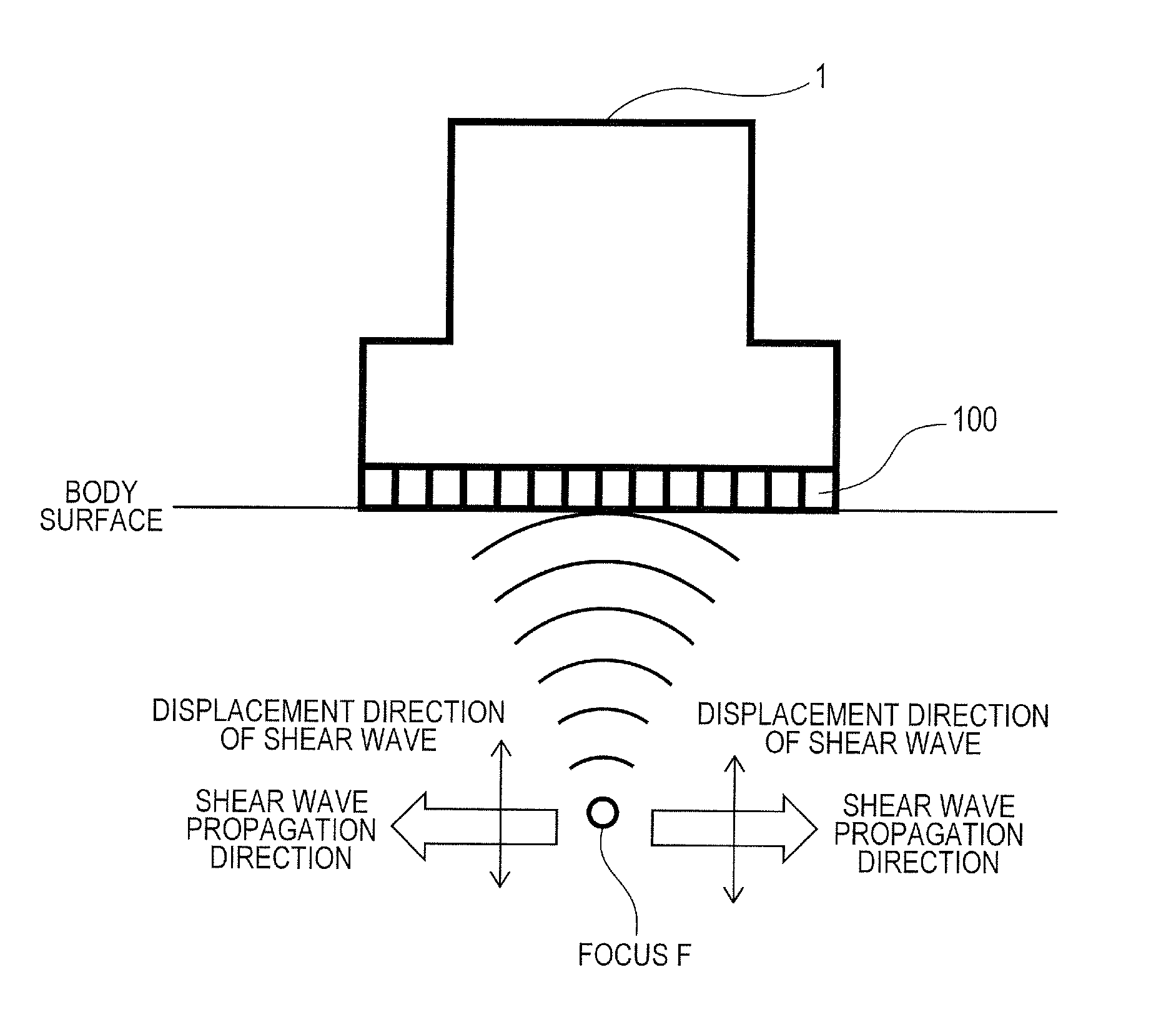
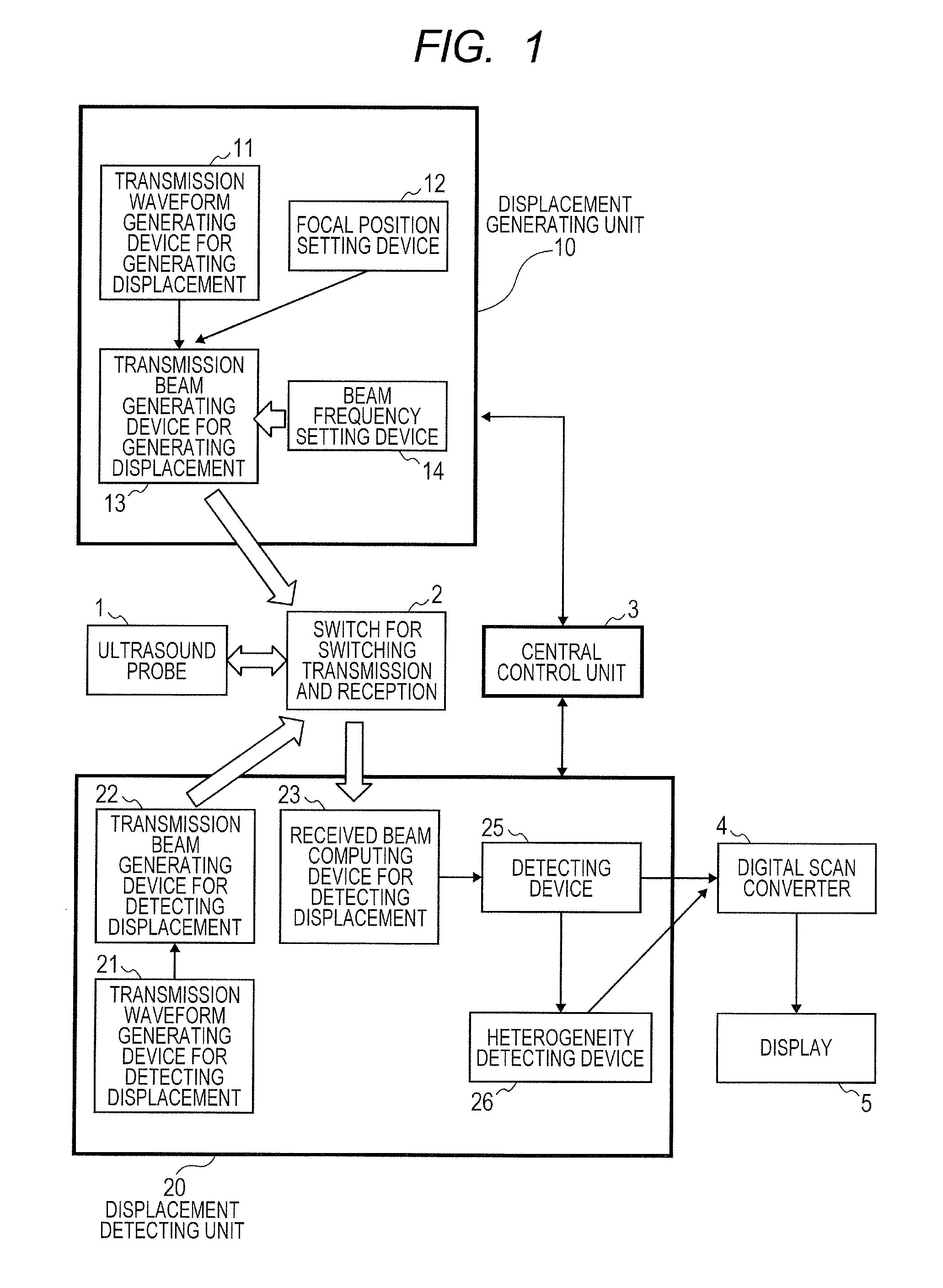
Ultrasound diagnosis apparatus
ActiveUS20130289402A1Higher-precision evaluationEnabling diagnosisWave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionDisplay deviceUltrasound probe
When multiple tissues having differing speeds of sound are intermixed in the viewing field of a measured subject such as a living body, the invention measures hardness, such as modulus of elasticity or viscosity, with high precision. As a means for detecting heterogeneity of sound speed in the tissues of a subject, a displacement-generating transmission beam is applied from a displacement generating beam-generating device (13) of a displacement-generating unit (10) on an ultrasound probe (1) to irradiate a focused ultrasonic wave into the living tissue and generate a shear wave. From the displacement-time waveforms of multiple positions of the shear wave detected using the displacement detection transmission beam-generating device (22) and the displacement detection received beam-computing device (23) of a displacement-detecting unit (20), at least two pieces of information, such as the integrated value and the maximum amplitude value, are obtained. On the basis of the two pieces of information, a heterogeneity-detecting device (26) of the displacement-detecting unit (20) detects the physical magnitude associated with the heterogeneity in sound speed arising from the tissue structure and displays same on a display (5).
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Method for treating neurological disorders, including tumors, with electroporation
ActiveUS20190232048A1Accurate and precise mannerAvoiding undesired electroporation of surroundingHead electrodesSurgical needlesAbnormal tissue growthImaging quality
This disclosure describes the methods, devices, and systems of treating diseased tissue with integrated nanosecond pulse irreversible electroporation. Methods and systems as disclosed provide MRI compatible shielded electrodes and electrode leads to prevent emanating radiofrequency noise and improve image quality, disconnecting the electrode from the cable linkage to the pulse generator reduce electromagnetic interference and image artifacts, placing electrodes strategically within a guide cannula to minimize distortion from heterogeneities or maximize ablation within the tissue, utilizing conductive fluids, innate or external, such as cerebral spinal fluid or grounding pads to provide a pathway for current return, and for timing of the electrical waveforms with inherent brain electrical activity.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Computer aided pulmonary nodule classification method based on migratable multi-model integration
ActiveCN107180426AImprove training effectImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleData set
The invention discloses a computer-aided pulmonary nodule classification method based on migratable multi-model integration to solve the technical problem of low accuracy of an existing pulmonary nodule classification method. The technical scheme includes the steps of training three pre-trained deep convolutional neutral networks (Pre-trained DCNN), describing the textural heterogeneity, shape heterogeneity and global characteristics of pulmonary nodules respectively, performing weighted average for results of the deep convolutional neutral networks, and subjecting the weight of each network to adaptive learning through an error back propagation mechanism so as to improve the accuracy of the pulmonary nodule classification method, wherein, the Pre-trained DCNN migrates the good image characterization capability of the deep convolutional neutral network on a large data set onto a pulmonary nodule classification task so that the training performance of the deep convolutional neutral networks on small pulmonary nodule data is effectively improved. The invention overcomes the technical problem of low accuracy of a classification method based on single type of information, and the accuracy rate can be up to 93%.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
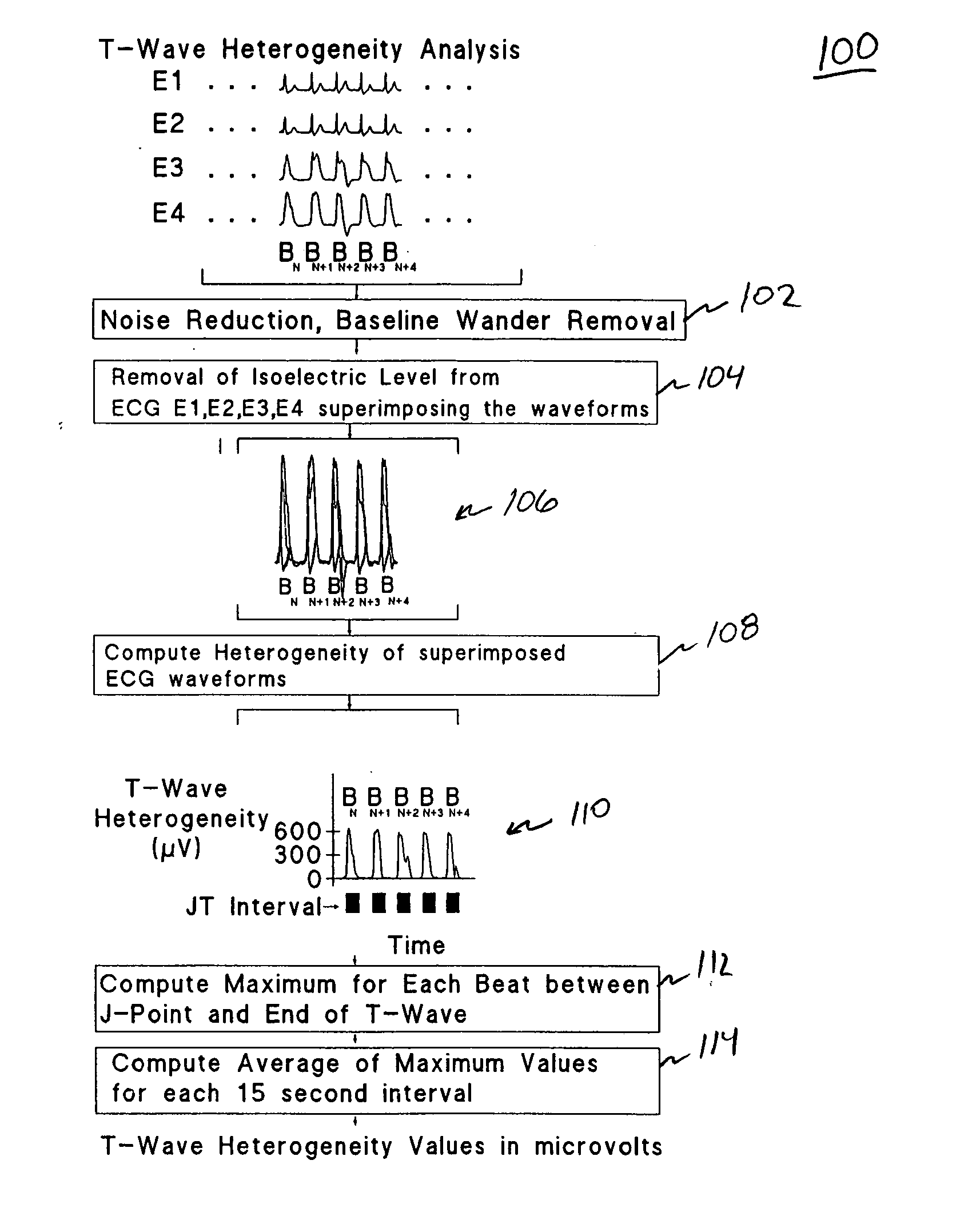
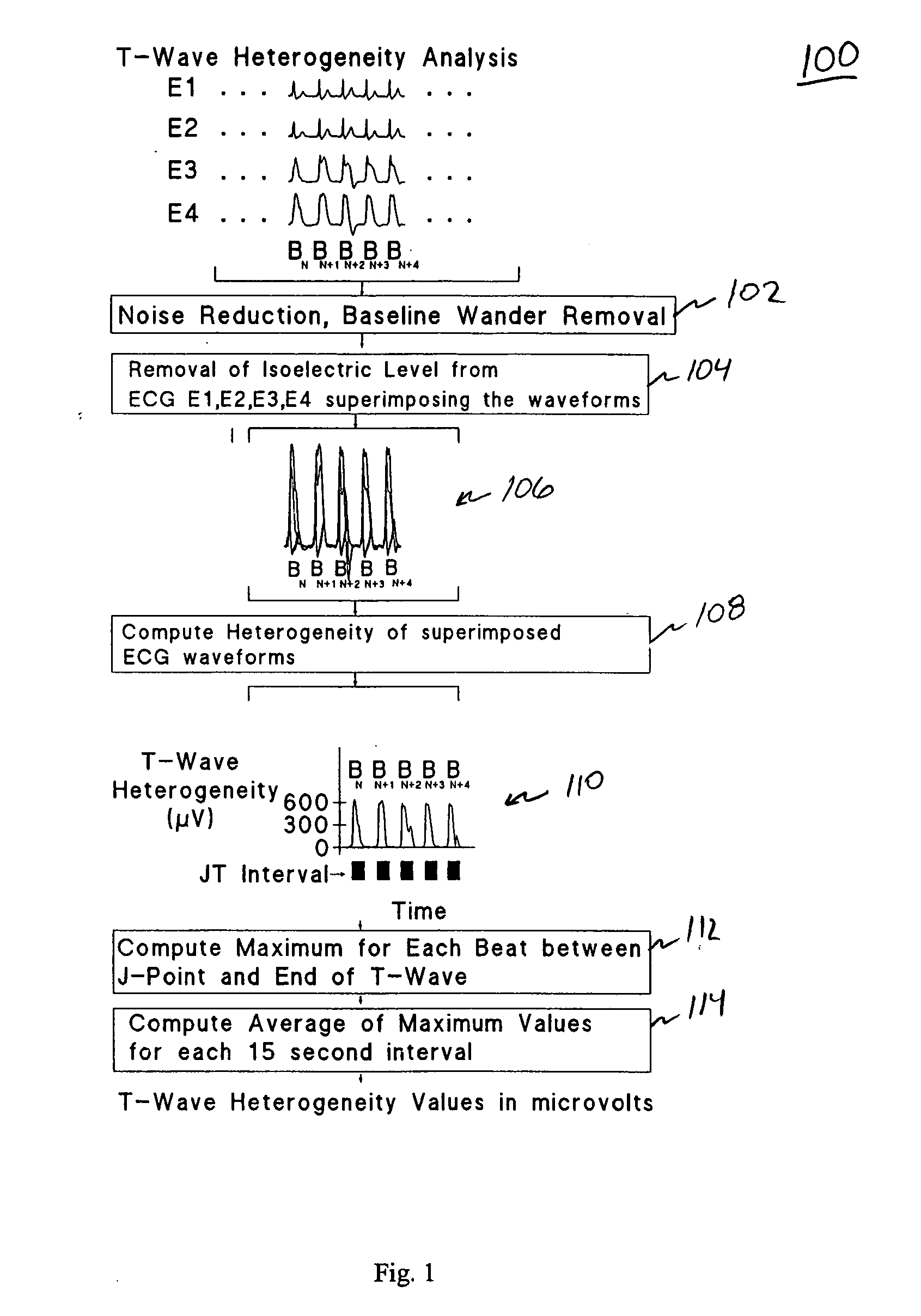
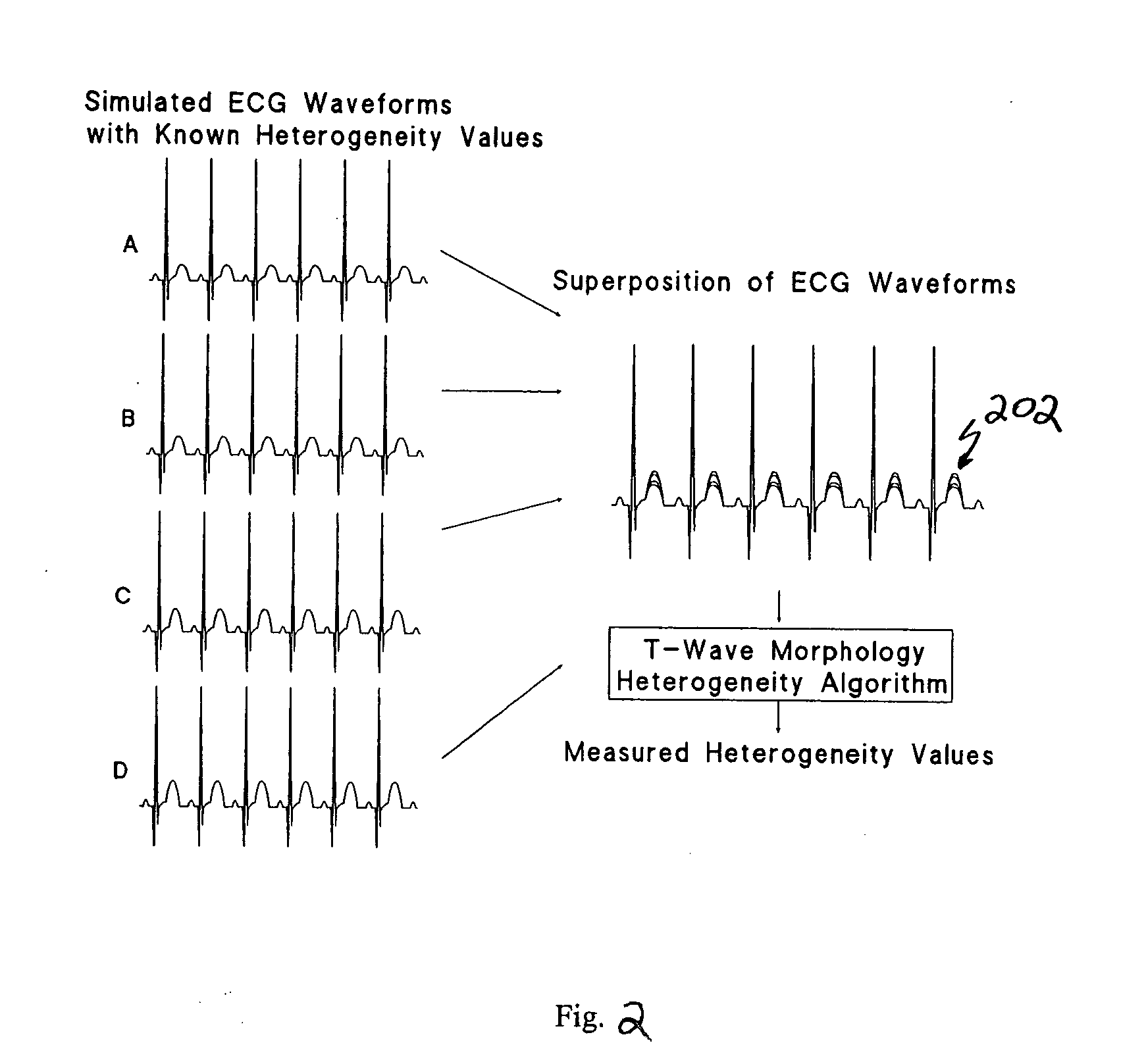
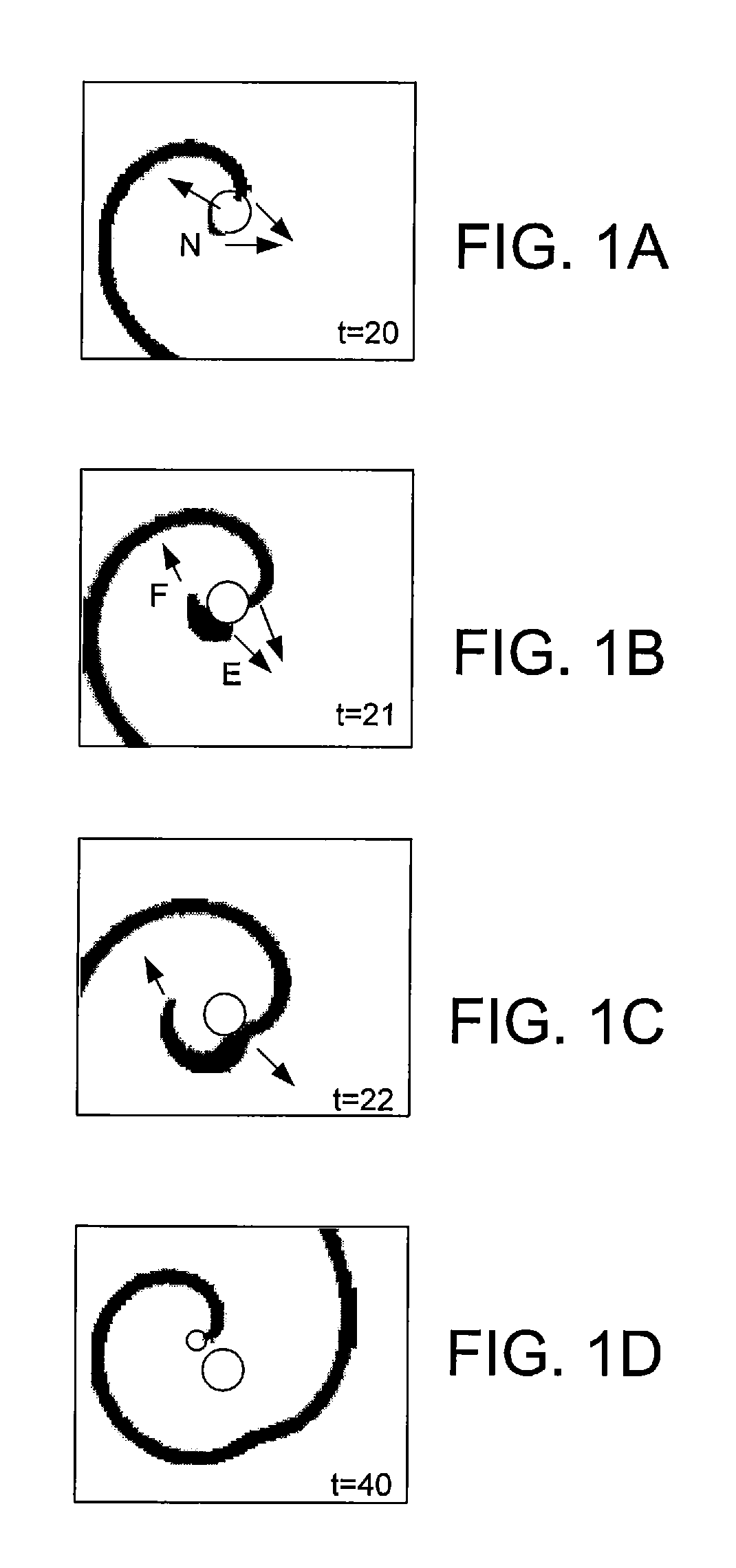
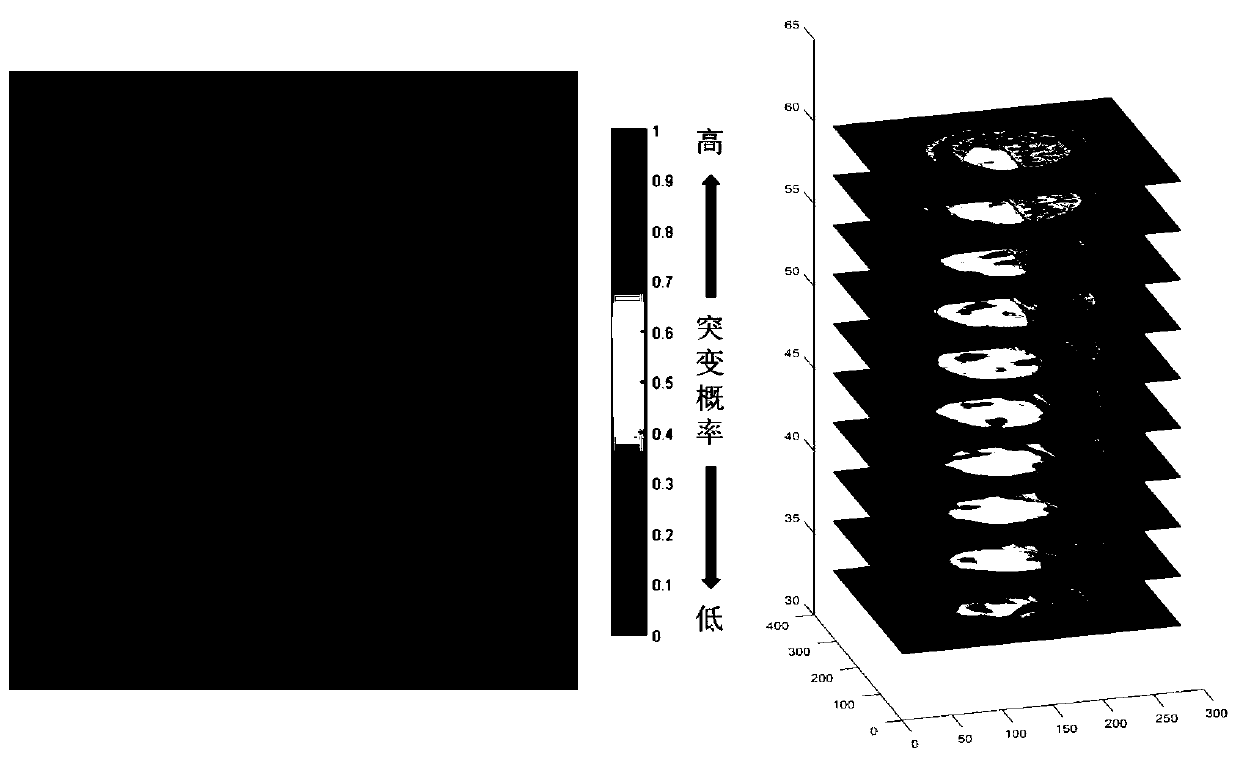
Spatial heterogeneity of repolarization waveform amplitude to assess risk of sudden cardiac death
Exercise-induced T-wave alternans (TWA) in coronary artery disease patients reflects significant levels of spatial heterogeneity of repolarization, which may underlie the predictive utility of TWA in estimating risk of sudden cardiac death. A method for assessing spatial heterogeneity of repolarization of a heart of a patient includes the following steps: simultaneously sensing an ECG signal from each of a plurality of spatially separated leads attached to the patient; for a plurality of N beats in each of the ECG signals, identifying a JT interval of each beat; and for corresponding ones of the JT intervals of the ECG signals, calculating a second central moment indicative of spatial heterogeneity of repolarization.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Method for identifying cancer molecular subtype based on spectral clustering algorithm of sparse similar matrix
InactiveCN106529165AEfficient removalImprove forecast accuracyMedical data miningBiostatisticsSpectral clustering algorithmAlgorithm
The invention discloses a method for identifying a cancer molecular subtype based on a spectral clustering algorithm of a sparse similar matrix. The method is characterized in that based on the spectral clustering algorithm of the sparse similar matrix, a cancer molecular subtype prediction model is built by utilizing cancer gene expression profile data as a training set sample; and the prediction model is used for predicting a cancer modular subtype of an independent test set sample, and a cancer sample set is divided into multiple types of molecular subtypes. According to the method, various patients with different prognosis effects are effectively distinguished for high heterogeneity of cancer molecular expression level, and different individual treatment schemes can be made for various cancer patients respectively.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Apparatus and method for quantitative noncontact in vivo fluorescence tomography using a priori information
InactiveUS20130023765A1Accurate recoveryPrecise positioningDiagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic Radiology ModalityOptical tomography
An apparatus for providing an integrated tri-modality system includes a fluorescence tomography subsystem (FT), a diffuse optical tomography subsystem (DOT), and an x-ray tomography subsystem (XCT), where each subsystem is combined in the integrated tri-modality system to perform quantitative fluorescence tomography with the fluorescence tomography subsystem (FT) using multimodality imaging with the x-ray tomography subsystem (XCT) providing XCT anatomical information as structural a priori data to the integrated tri-modality system, while the diffuse optical tomography subsystem (DOT) provides optical background heterogeneity information from DOT measurements to the integrated tri-modality system as functional a priori data. A method includes using FT, DOT, and XCT in an integrated fashion wherein DOT data is acquired to recover the optical property of the whole medium to accurately describe photon propagation in tissue, where structural limitations are derived from XCT, and accurate fluorescence concentration and lifetime parameters are recovered to form an accurate image.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
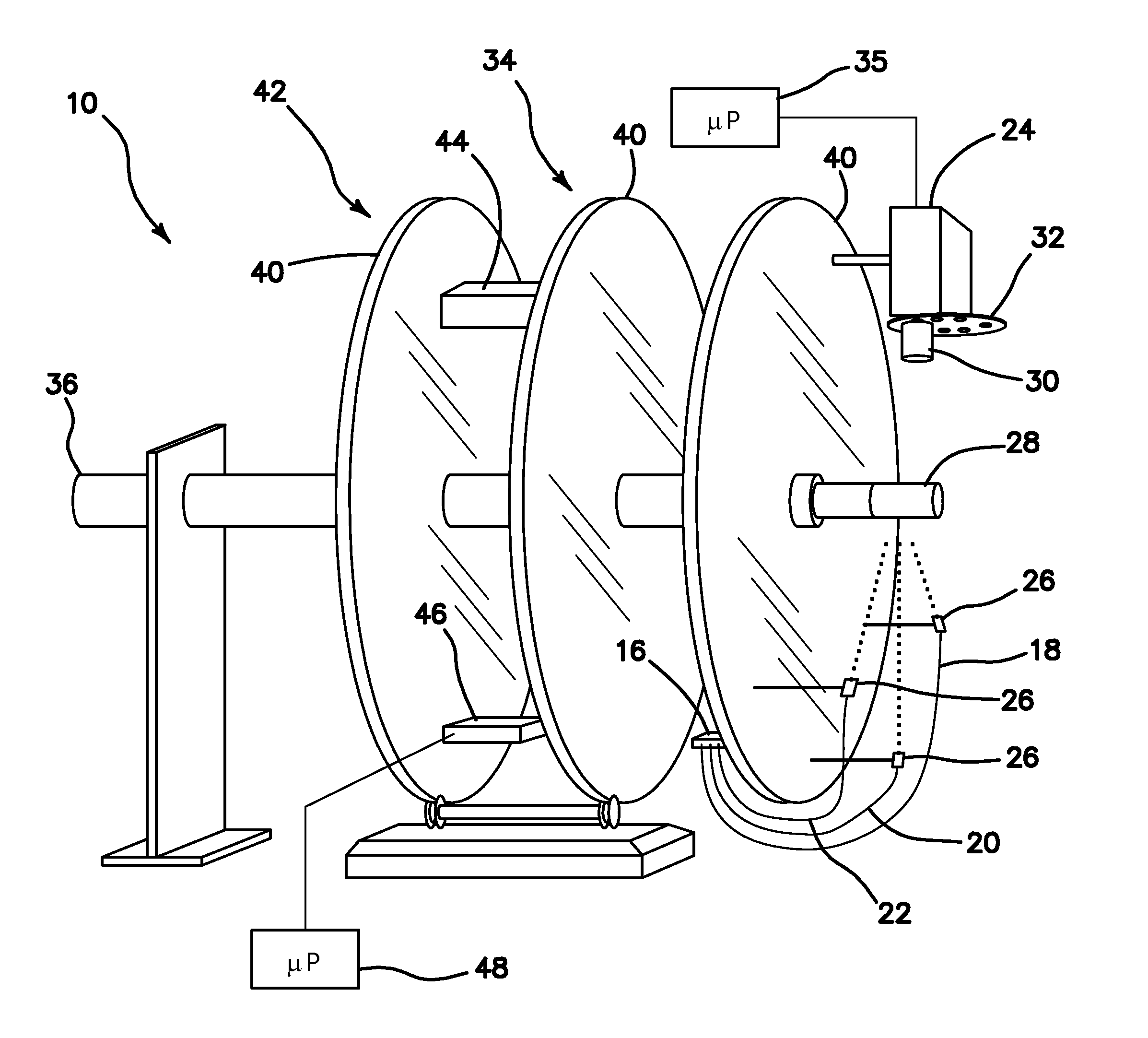
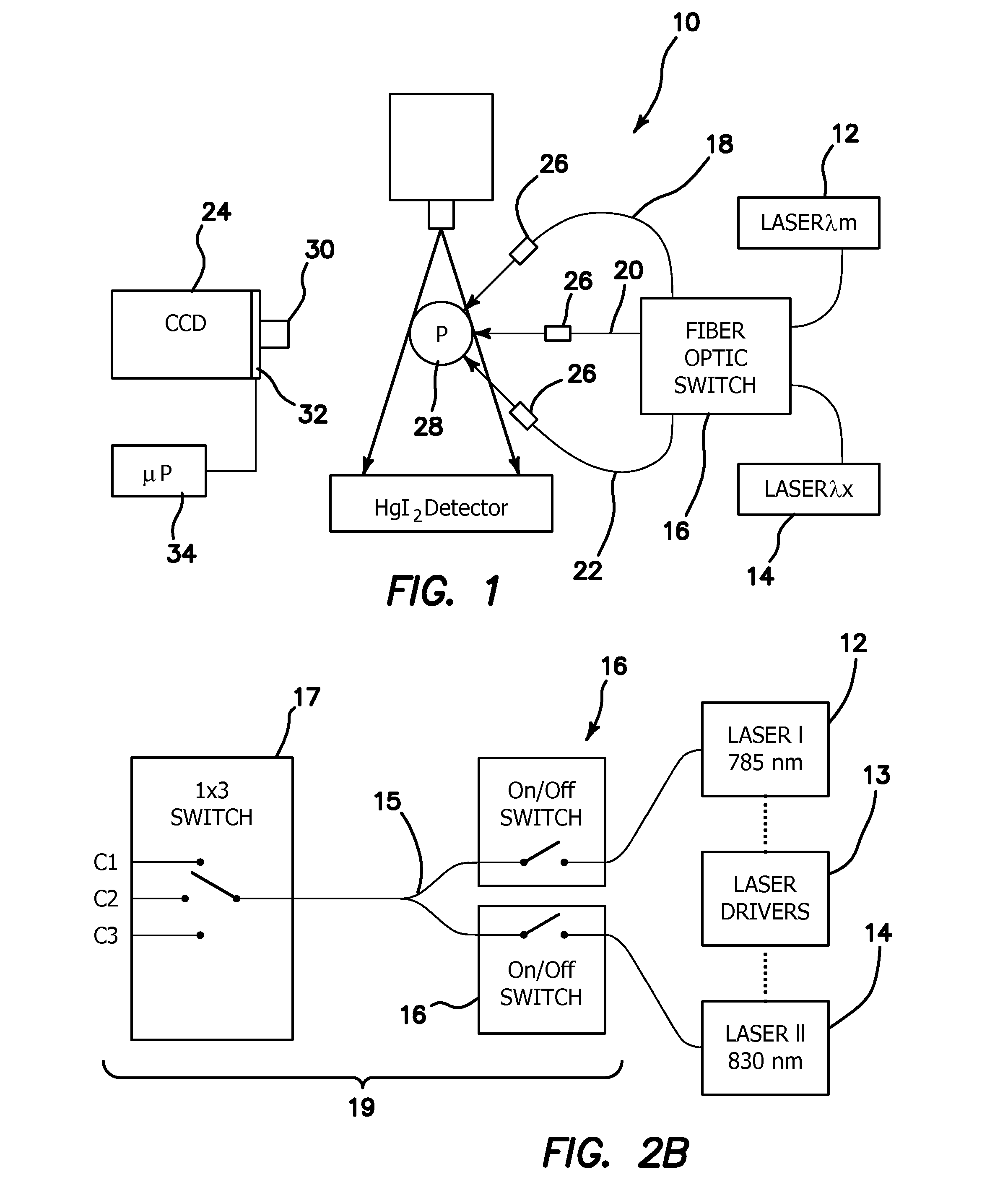
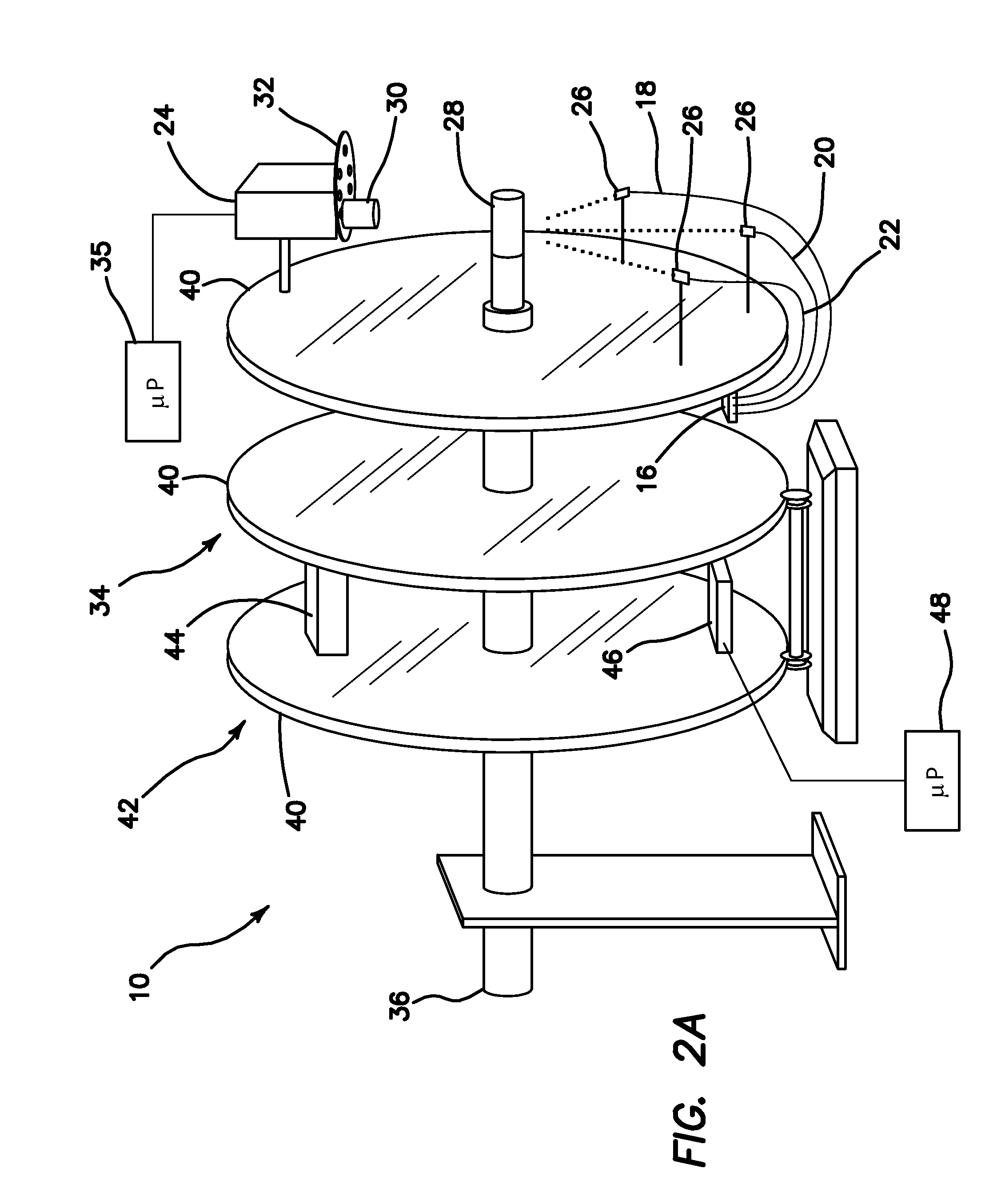
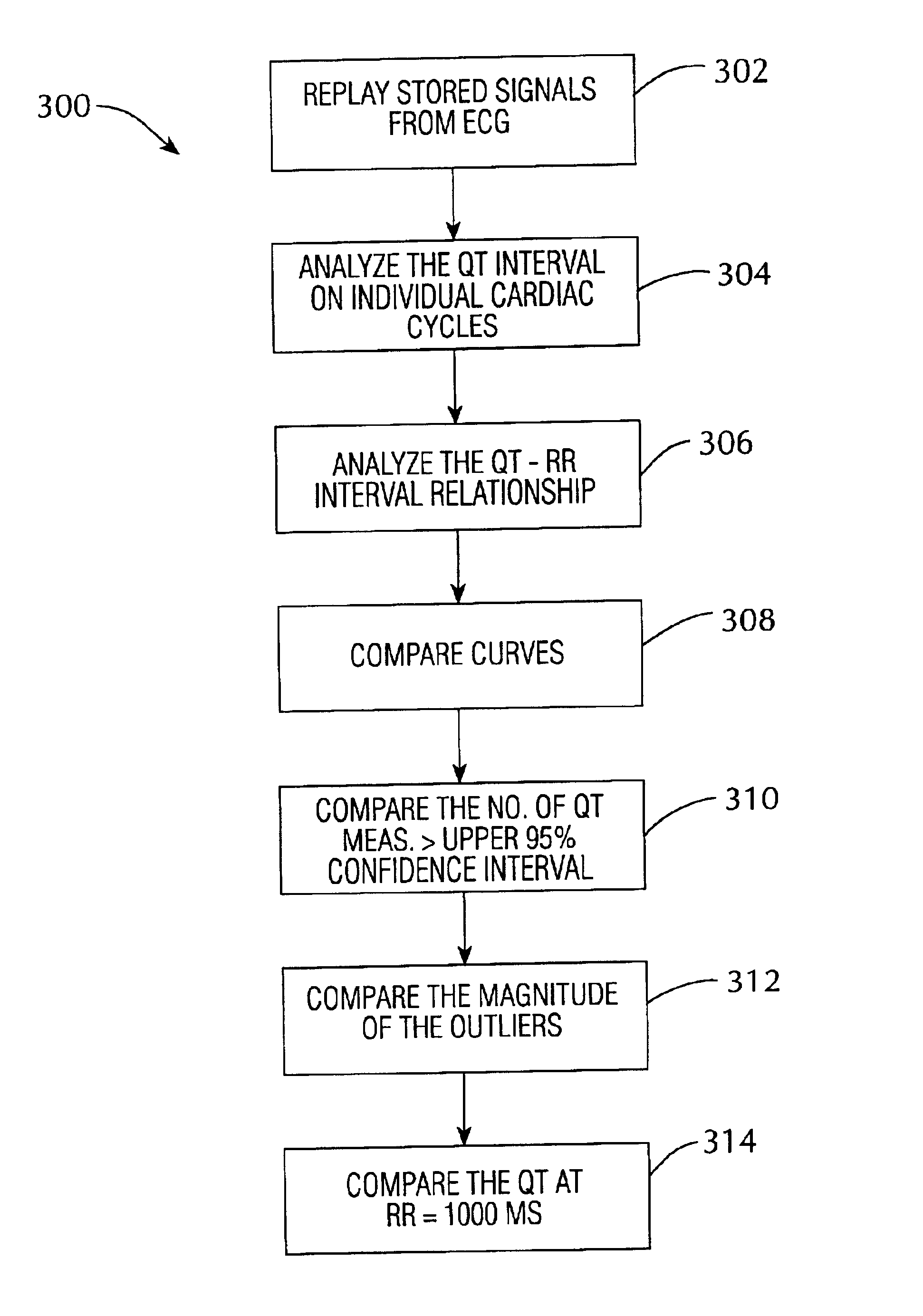
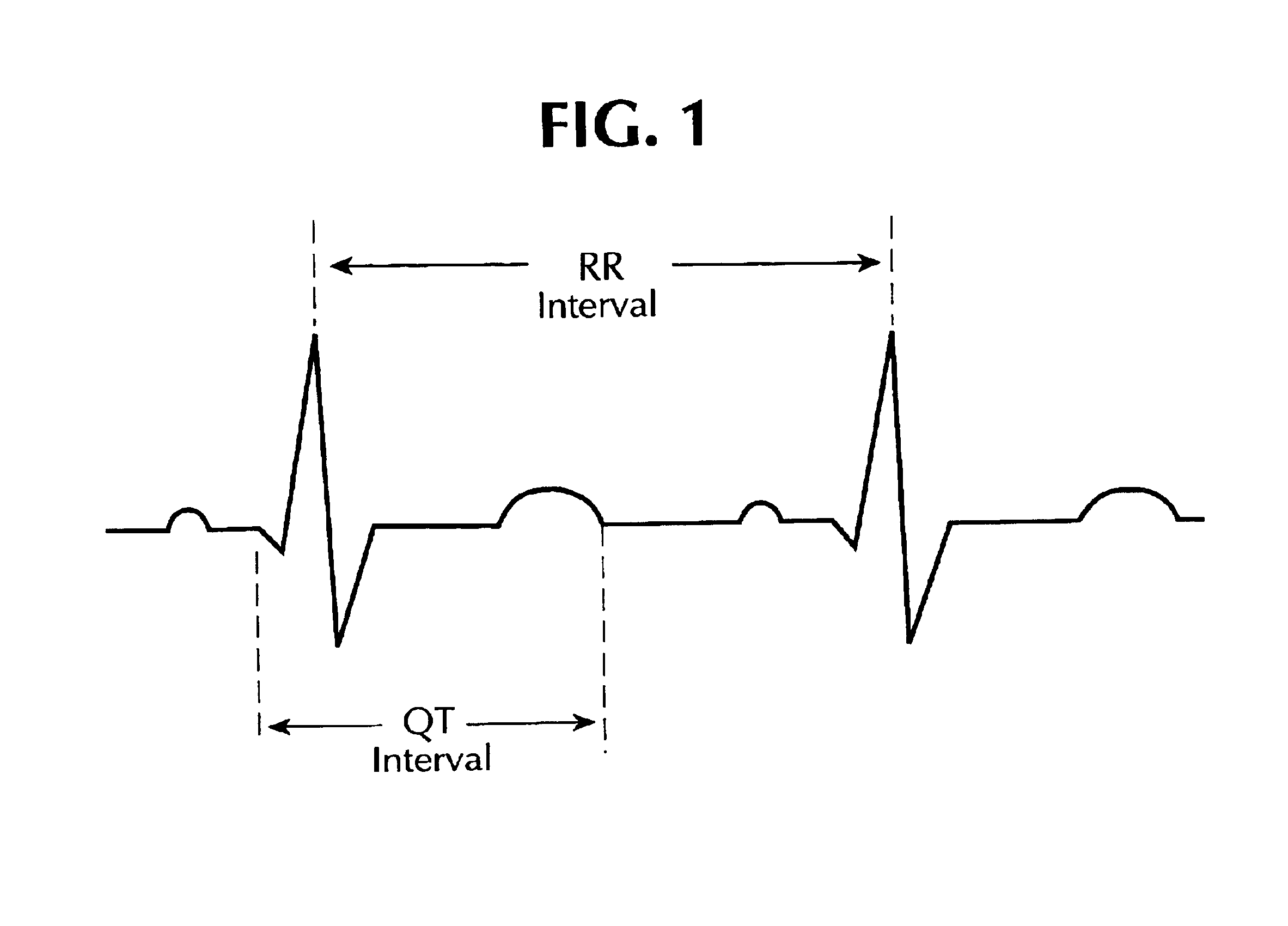
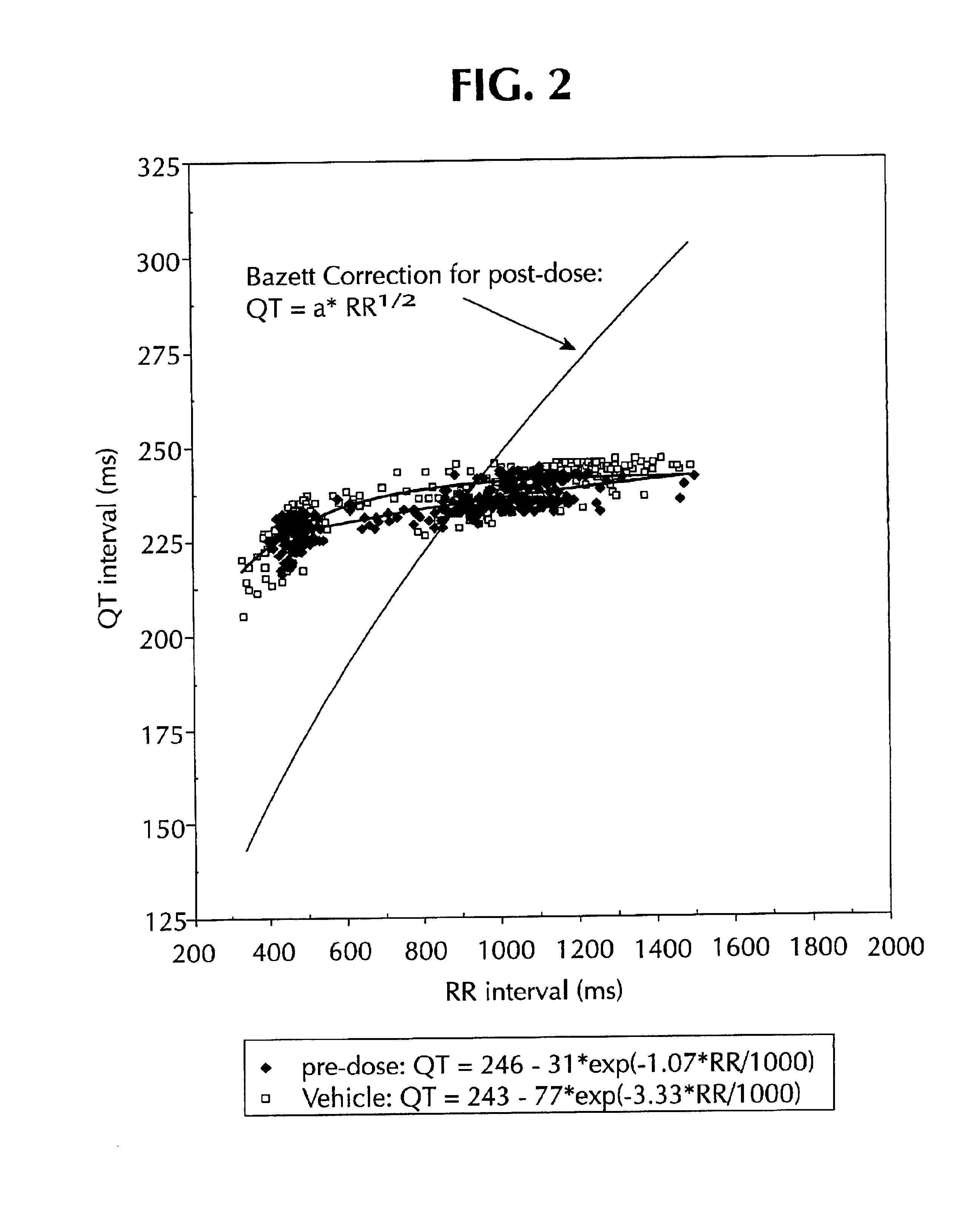
System and method for statistical analysis of QT interval as a function of changes in RR interval
A system and method for statistically analyzing QT interval as a function of changes in the RR interval. The system and method utilize three statistical comparisons to fully characterize the QT response: (1) the comparison of curves to give an overall effect; (2) the incidence of points exceeding a baseline upper 95% single-point prediction bound to reflect the degree of heterogeneity of ventricular repolarization; and (3) the magnitude of these points to provide a quantitative assessment of treatment-induced changes in the QT-RR relationship. The system and method use the relationship between the QT interval and heart rate (RR interval) to reference a control baseline response. Data from mammals such as humans and dogs, and pharmacological maneuvers using both cardiac and non-cardiac therapeutic agents, may be used with this multi-parameter statistical system and method. Additionally, the system and method quantifies the incidence and magnitude of points lying outside the upper 95% single-point prediction limit of the regression analysis for vehicle versus treatment.
Owner:ERESTECH
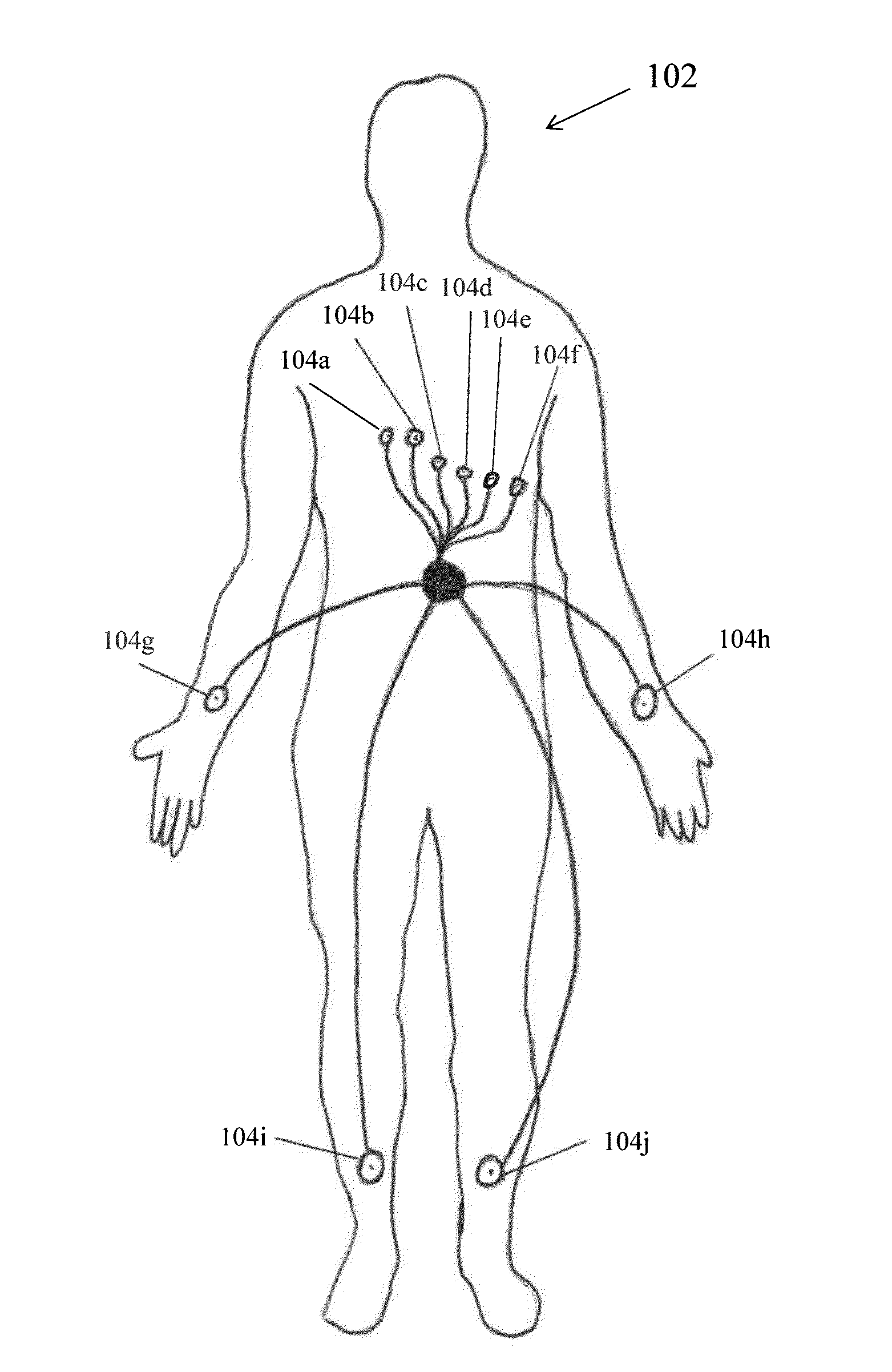
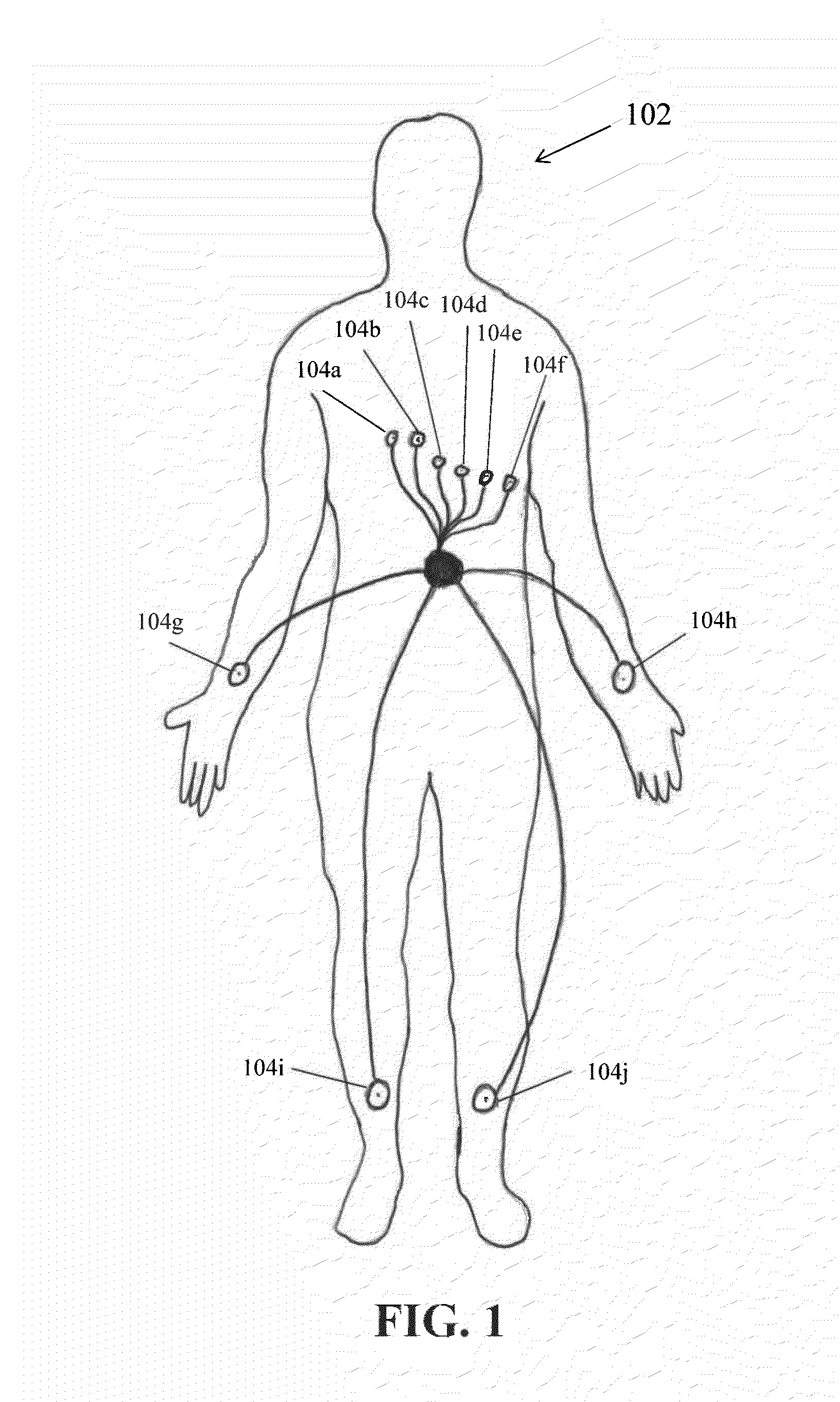
Multilead ECG template-derived residua for arrhythmia risk assessment
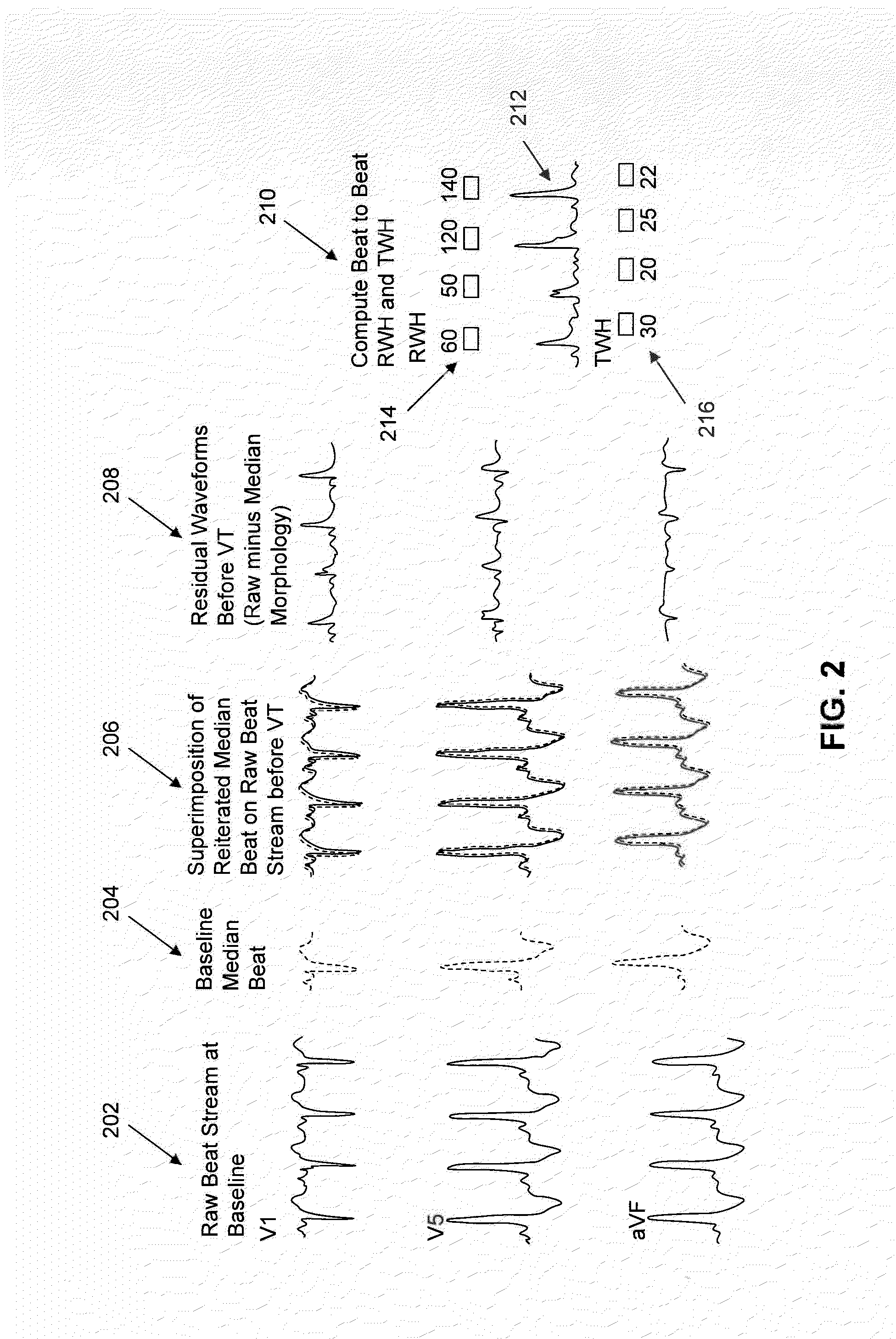
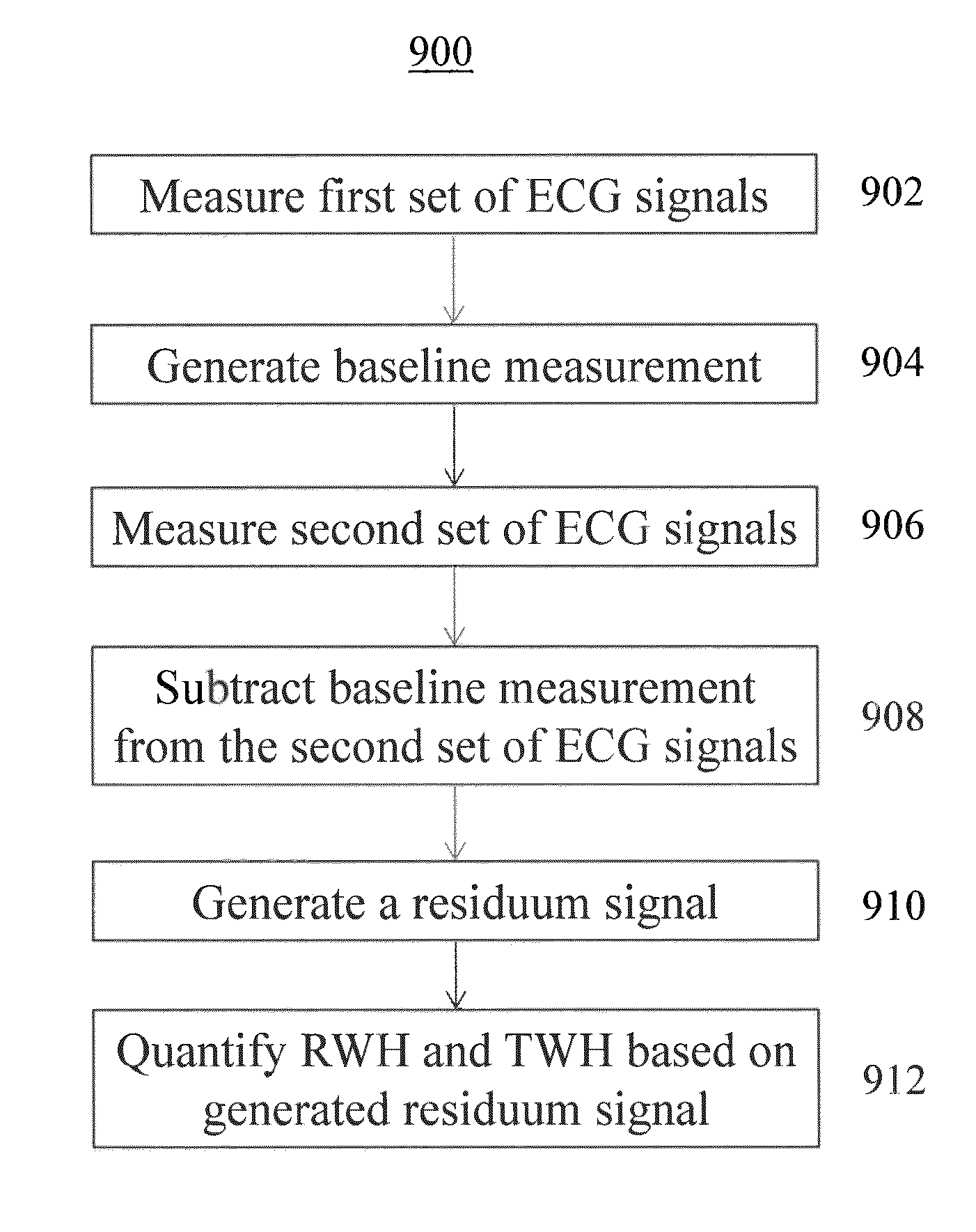
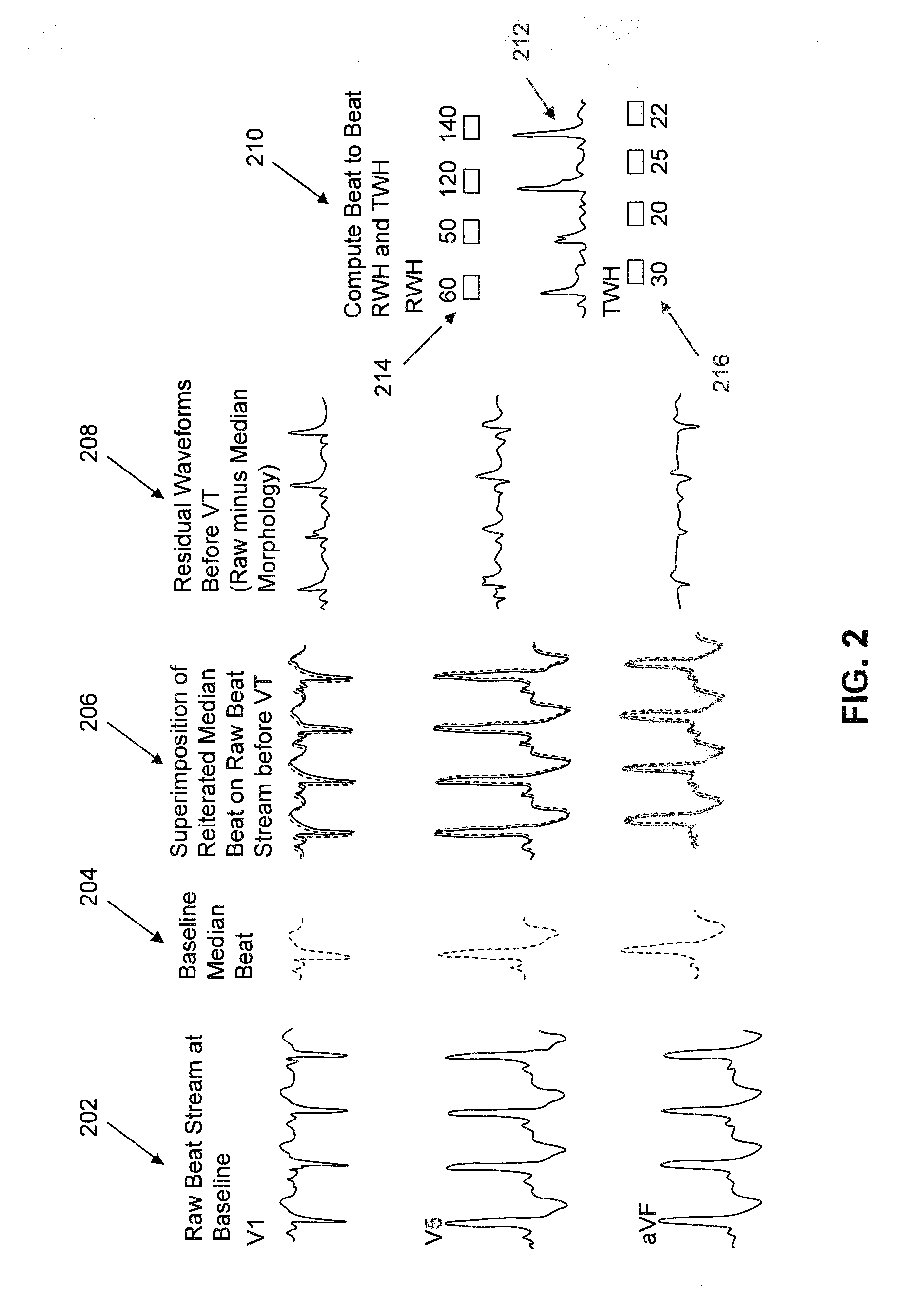
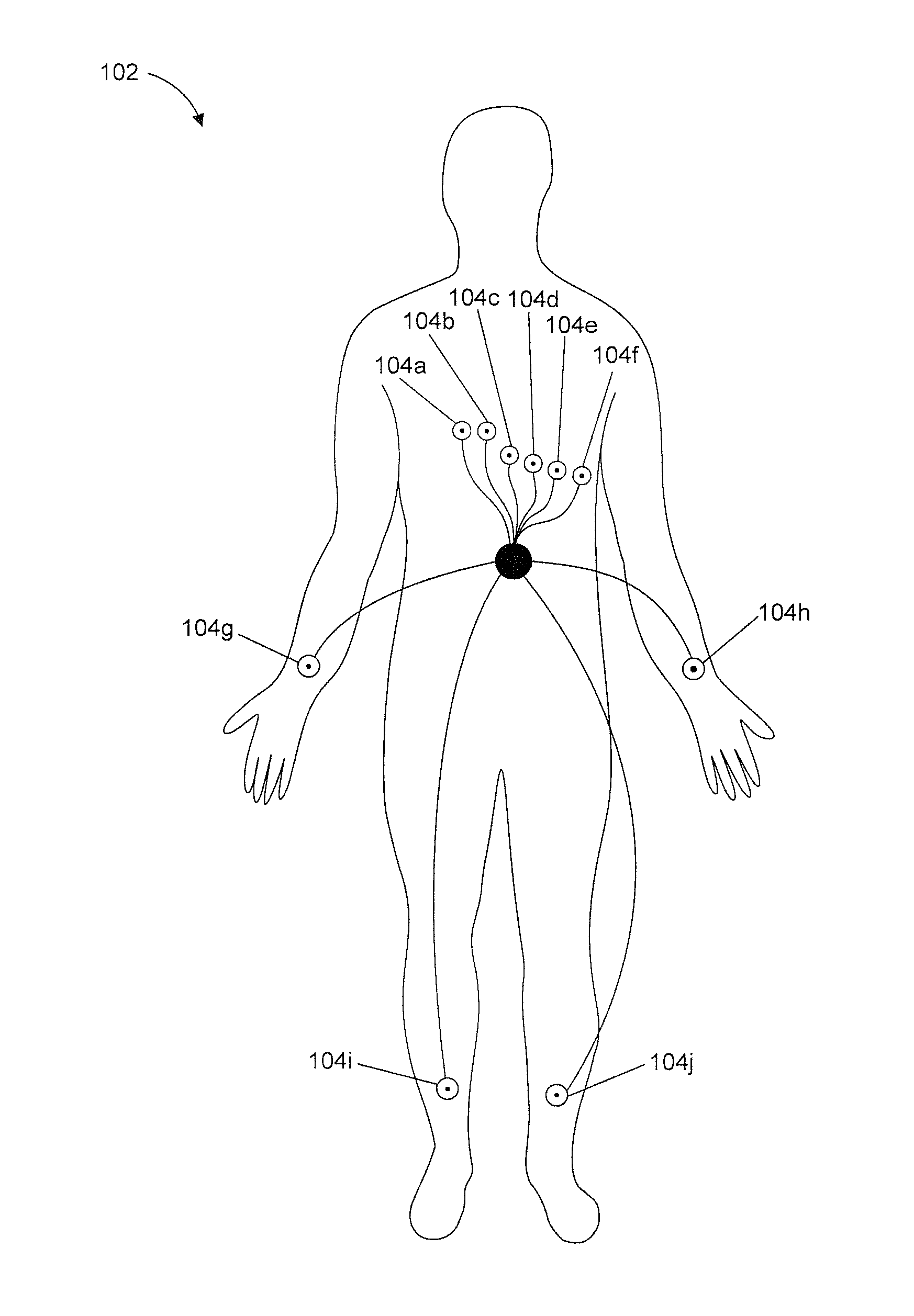
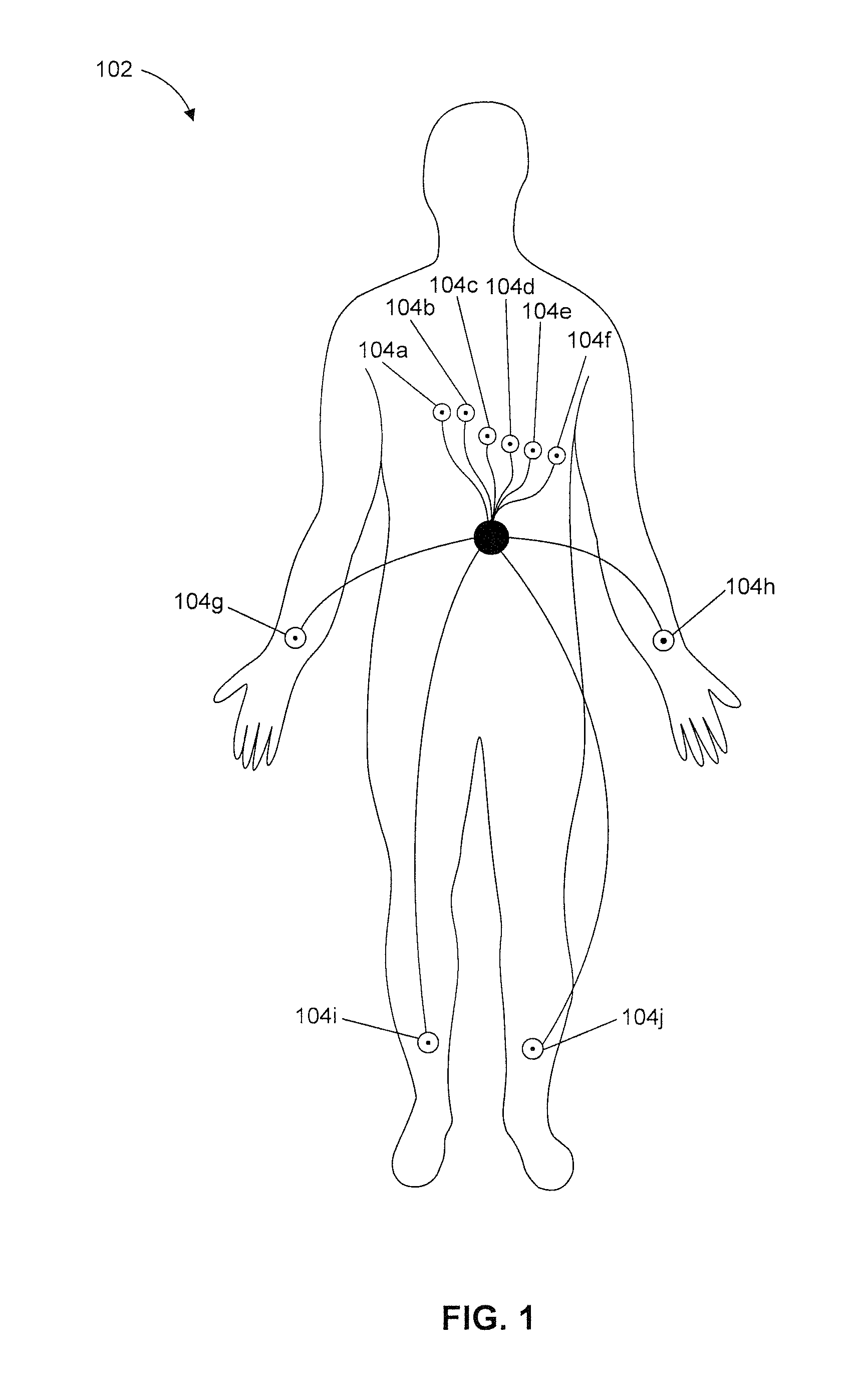
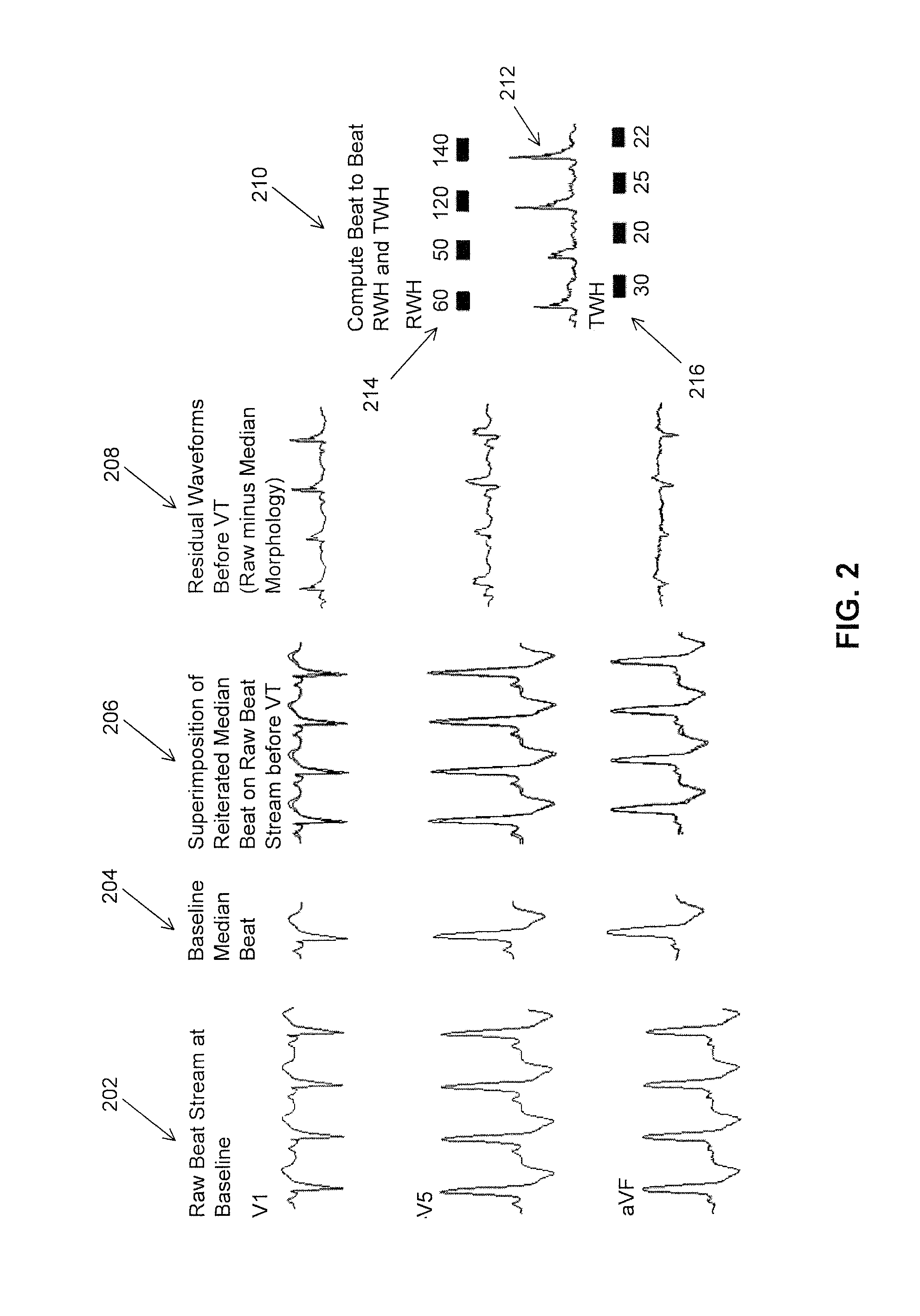
A method and system for predicting the onset of heart arrhythmias more accurately observes trends in abnormal or pathologic morphology of the electrocardiogram (ECG). A first set of ECG signals is monitored from a patient. A baseline measurement is generated from the monitored first set of ECG signals to contain nonpathologic ECG morphologies in each lead. A second set of ECG signals is monitored from the patient and the baseline measurement is subtracted from the second set of ECG signals on a beat-to-beat basis. Afterwards, a residuum signal is generated for each lead based on the subtraction. R-wave heterogeneity, T-wave heterogeneity, P-wave heterogeneity, or ST-segment heterogeneity or other indicators of arrhythmia risk or myocardial ischemia are quantified based on the generated residuum signals.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Method for stabilization of cardiac tissue contractions using limit cycles
InactiveUS20130296959A1Regularized contractilityHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaPoincaré plot
Electrical stimulation to cardiac tissue stabilizes atrial and ventricular arrhythmia when timed to stabilize a limit cycle structure in a Poincare map. Disclosed are methods and apparatus, operational internally or externally, for removing the reentrant effects of heterogeneity present in a diseased heart and returning the heart to an improved metabolic status allowing removal of support. The methods and apparatus disclosed are also useful in the chronic surveillance and maintenance of regularized contractility in an aged or diseased heart.
Owner:TECH INNOVATION LLC
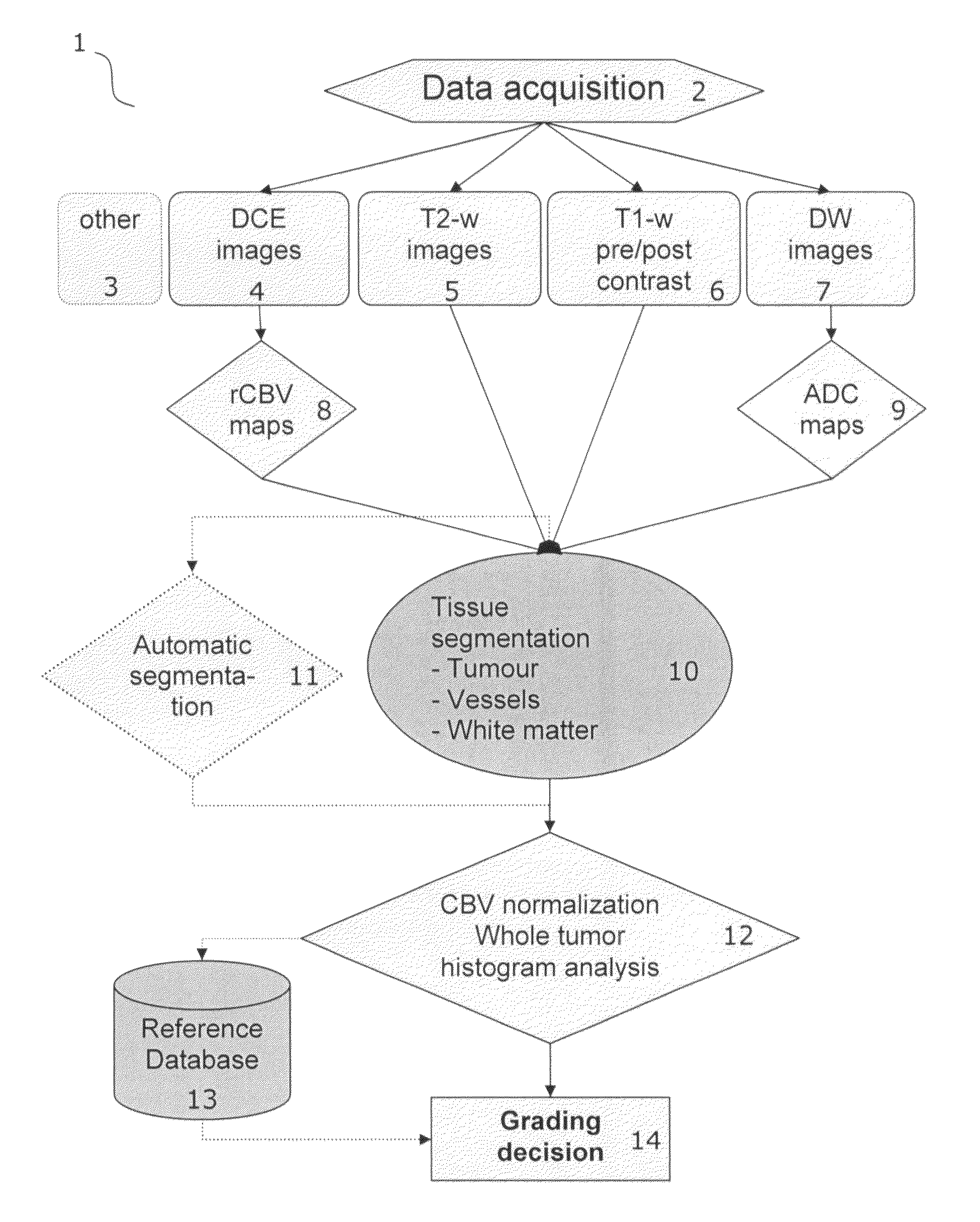
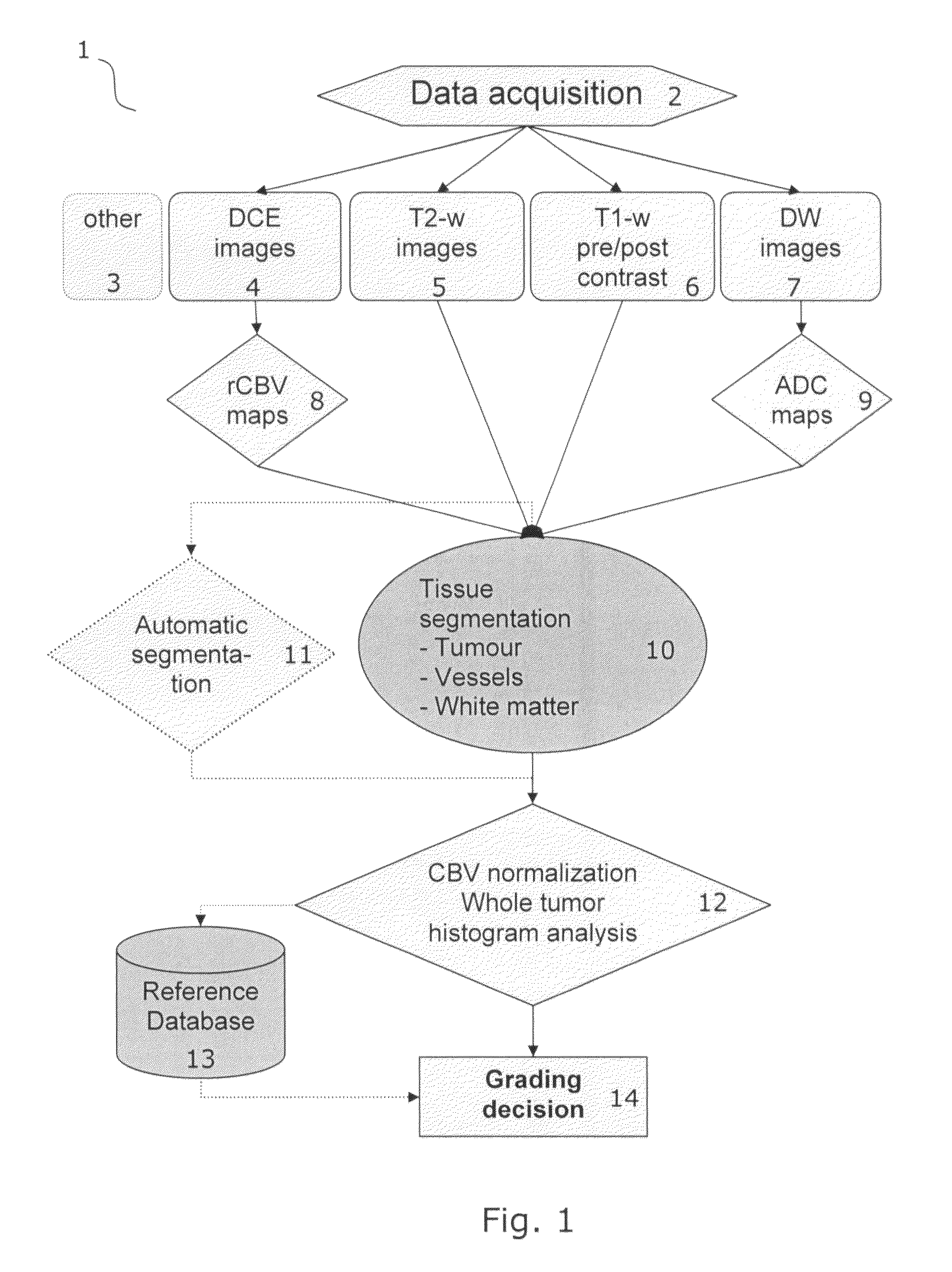
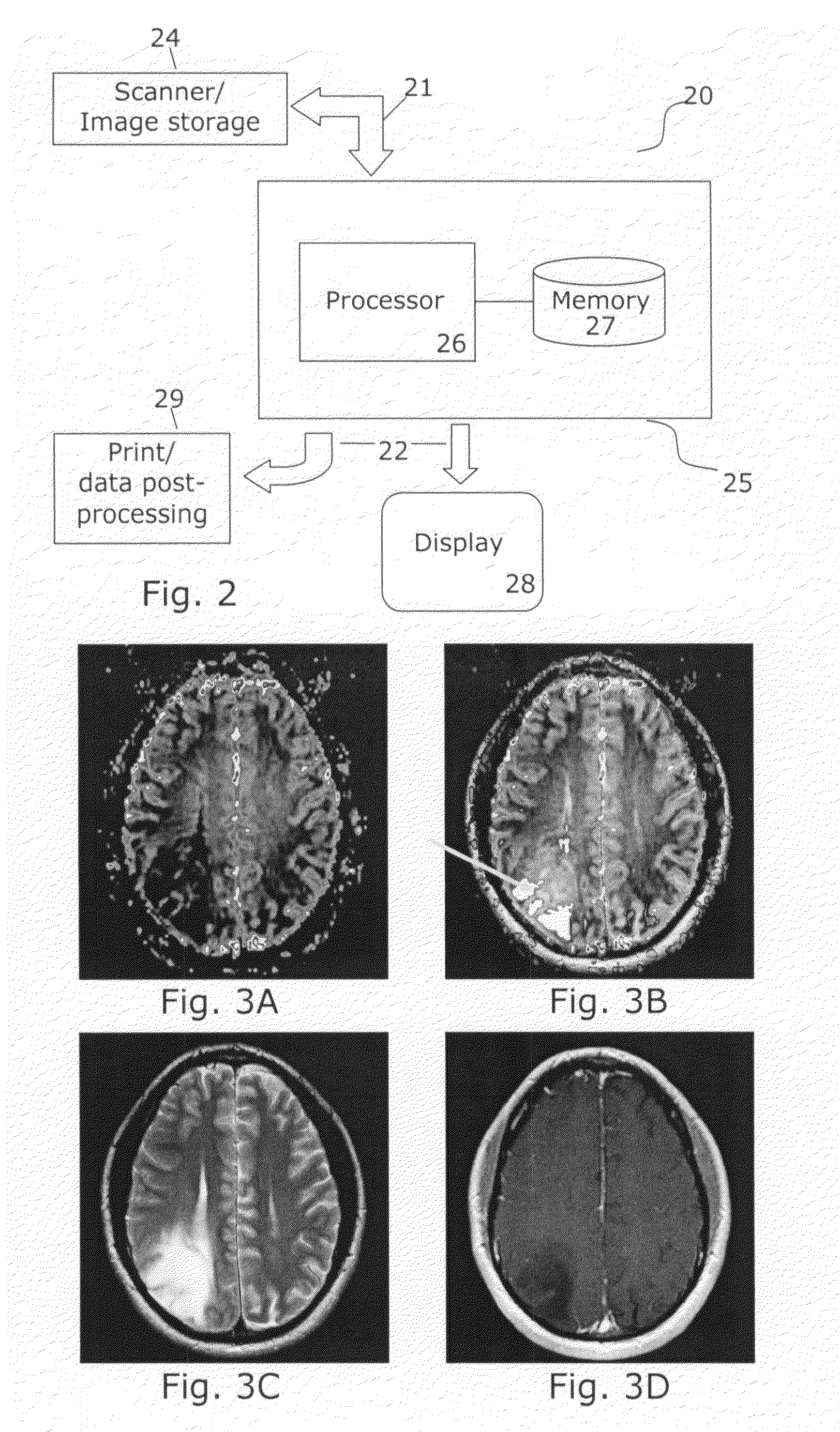
Tumor grading from blood volume maps
An embodiment of the invention is to make possible a non-invasive grading of a tumor based on parameters determined from a frequency distribution (histogram) of values in a map representing cerebral blood volume (CBV) or cellular metabolism in the tumor. The method is especially applicable to brain tumors such as gliomas where histological grading is difficult. The invention provides a precise and consistent grading since it relies on values selected from the whole tumor (not just from hot spots); since it takes the diversity or heterogeneity of the vascularization into account by analyzing the frequency distribution (not just a mean value); and since it involves and allows for a more automated procedure wherein any subjective contributions from human operators is not critical to the resulting grading. CBV maps may be obtained by perfusion imaging using MRI or CT scanning. Cellular metabolism maps may be obtained from a glucose metabolism map obtained by positron emission tomography (PET).
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
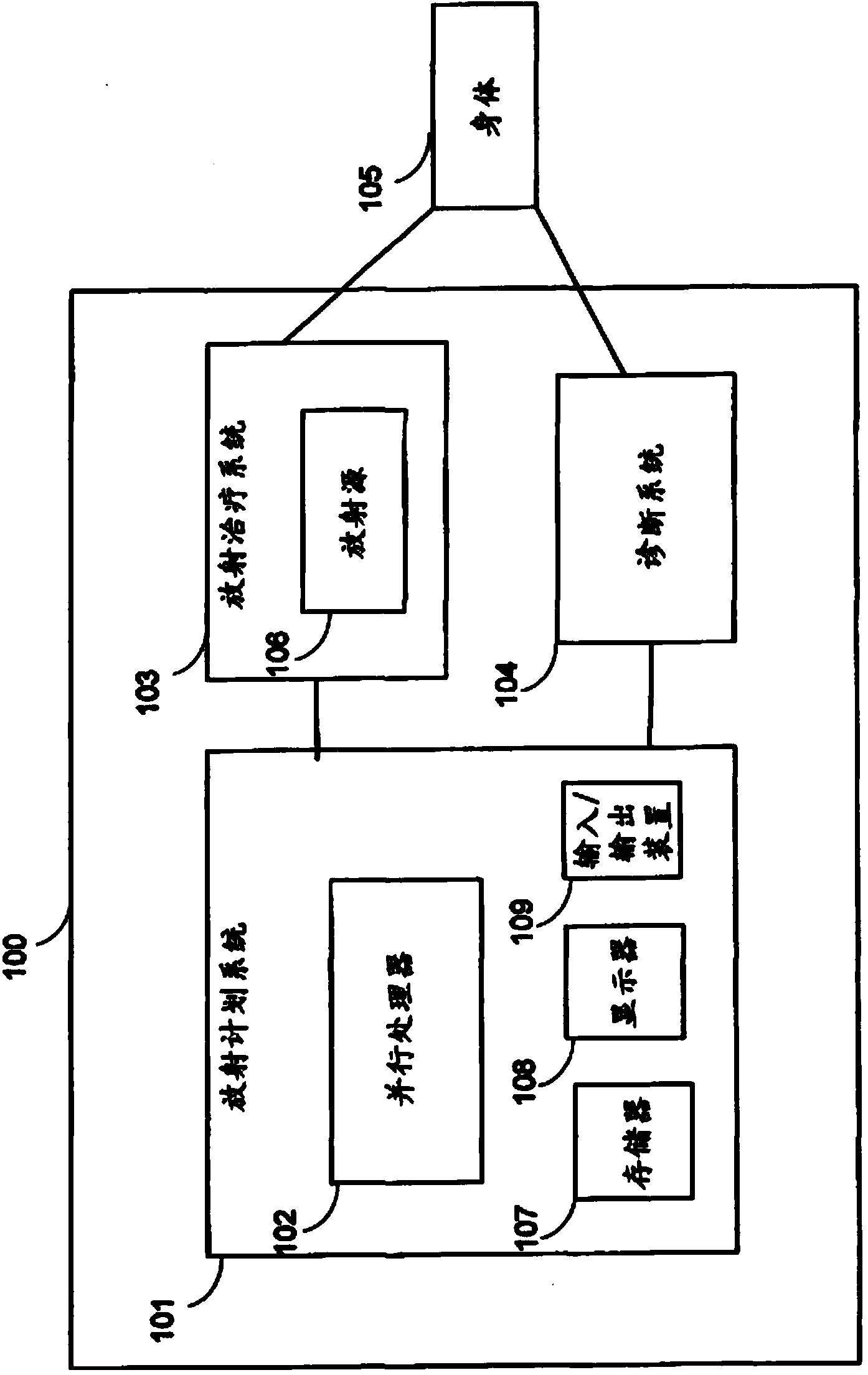
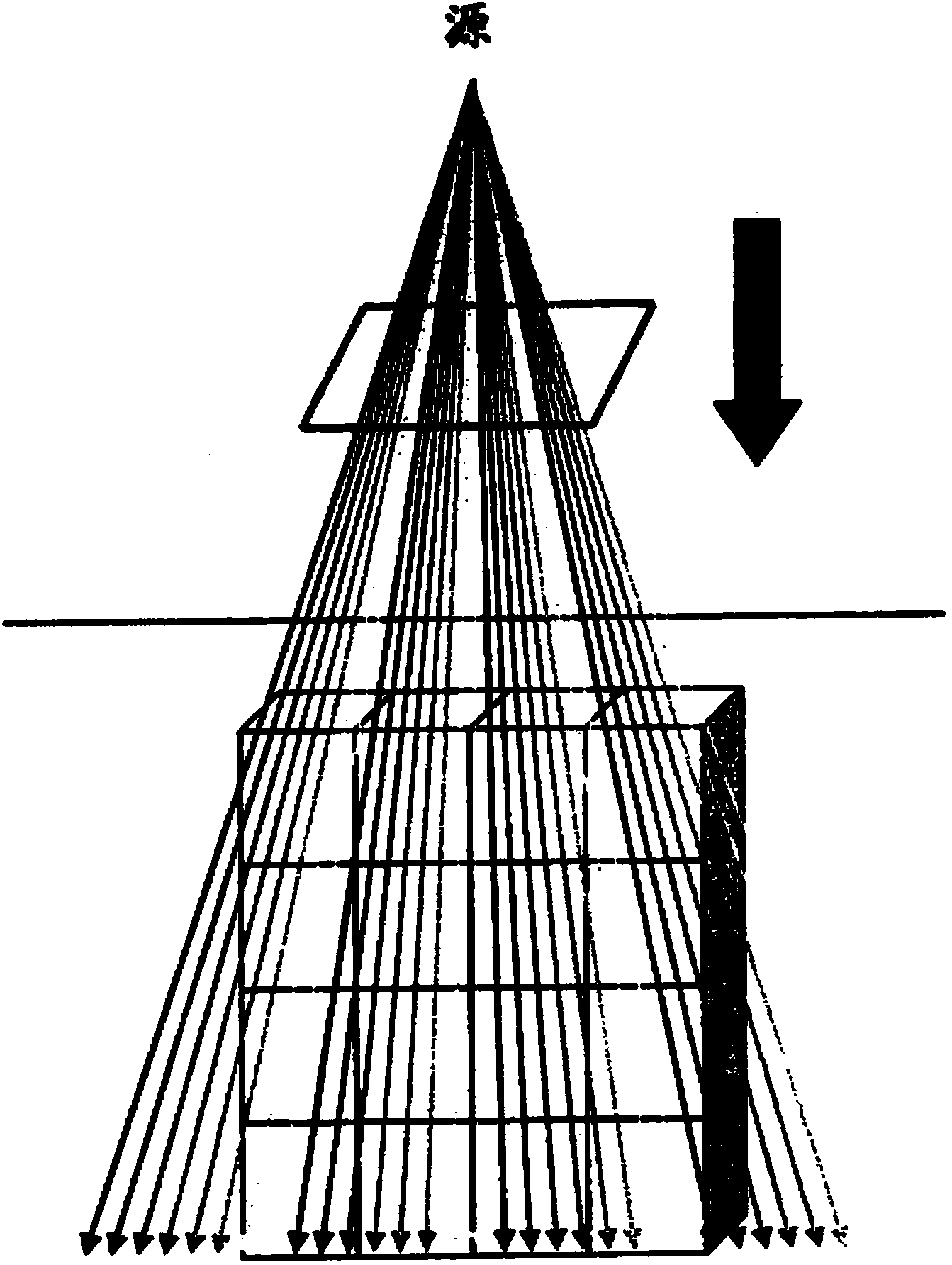
Dose computation for radiation therapy using heterogeneity compensated superposition
ActiveCN104066479AMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesRadiation diagnostics testing/calibrationRadiation planningUnit mass
A system for radiation therapy includes a radiation planning system. The radiation planning system includes a data processor that is adapted to receive information concerning an intended radiation treatment region of a body, receive a calculated initial energy released per unit mass for a plurality of locations within the body, compute a radiation dose at a plurality of locations within the radiation treatment region based on the calculated initial energy released per unit mass and including radiation dose contributions due to scattering from other locations within the body, and determine radiation therapy parameters for providing radiation treatment to the intended radiation treatment region based on the radiation dose computed at the plurality of locations within the radiation treatment region.; Including radiation dose contributions due to scattering from other locations within the body take into account density discontinuities in the body.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Liver cancer image omics data processing method, system and device and storage medium
ActiveCN110175978AStable evaluation effectOvercoming the disadvantage of not considering tumor heterogeneityImage enhancementImage analysisUpper abdomenOmics data
The invention discloses a liver cancer image omics data processing method, system and device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining an upper abdomen CT image of a liver cancer patient, calculating image omics data corresponding to the upper abdomen CT image, calculating a linear combination of the plurality of image omics characteristic values, and dividing the liver cancer patient into a hepatic artery chemoembolization reaction group or a hepatic artery chemoembolization reaction-free group according to a magnitude relation between the predicted value and a presetthreshold value. The used imaging omics technology can extract the tumor feature information contained in the CT image from the three-dimensional perspective in an omnibearing mode, and the defect that tumor heterogeneity is not considered in an existing method is overcome; and patients are divided into a reaction group and a non-reaction group according to scores of the imaging characteristics ofpatients, so that the clinical guiding significance is good, and a better decision reference is provided for clinical workers. The method is widely applied to the technical field of data processing.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
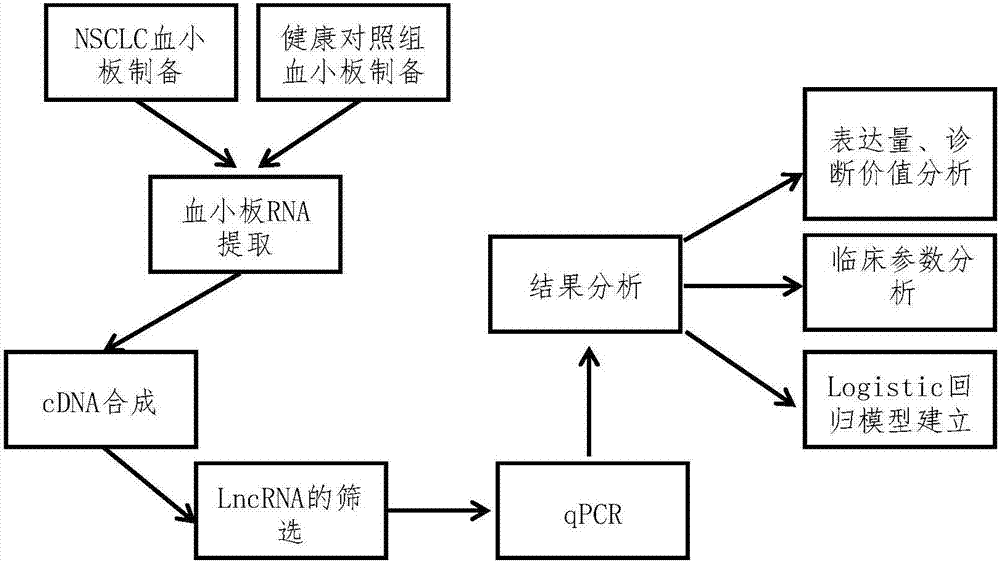
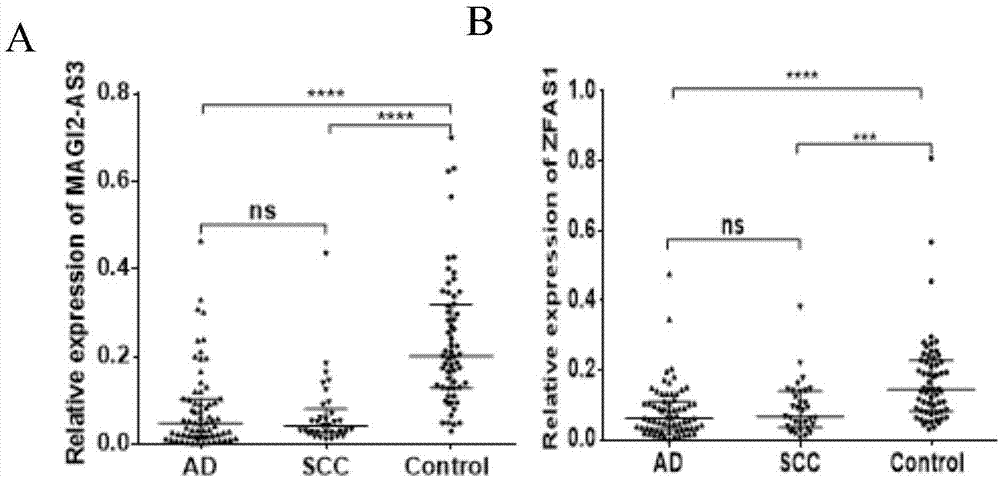
Blood platelet LncRNA quantitative determination method for non-small cell lung cancer diagnosis
ActiveCN107326090AImprove diagnostic capabilitiesIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationOncologyWilms' tumor
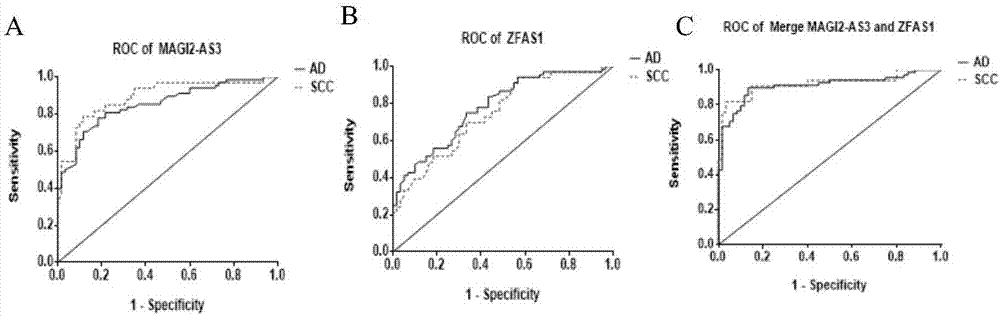
The invention discloses a blood platelet LncRNA quantitative determination method for non-small cell lung cancer diagnosis, and belongs to the field of oncomolecularbiology. Currently, lung cancer diagnosis mainly depends on traumatic tumor tissue clinical symptoms, radioautography, biochemical detection, pathological test and other aspects, and tissue heterogeneity exists. In order to solve the problems, it is proved that expression of platelet long-chain non-coding RNA MAGI2-AS3 and ZFAS1 of an NSCLC patient is lower than that of a normal person; on the basis, a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR kit for non-small cell lung cancer diagnosis is prepared. Through expression quantity data obtained by MAGI2-AS3 and ZFAS1 combined real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR amplification, a logistic regression fit data model of non-small cell lung cancer diagnosis is established, and the model has high diagnosis efficiency and sensitivity to a non-small cell lung cancer and has deep clinical significance and generalization performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
System and method for tumor heterogeneity assessment
ActiveCN106676178ARich in featuresAccurate and Reasonable AssessmentMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsCirculating tumor DNATumor heterogeneity
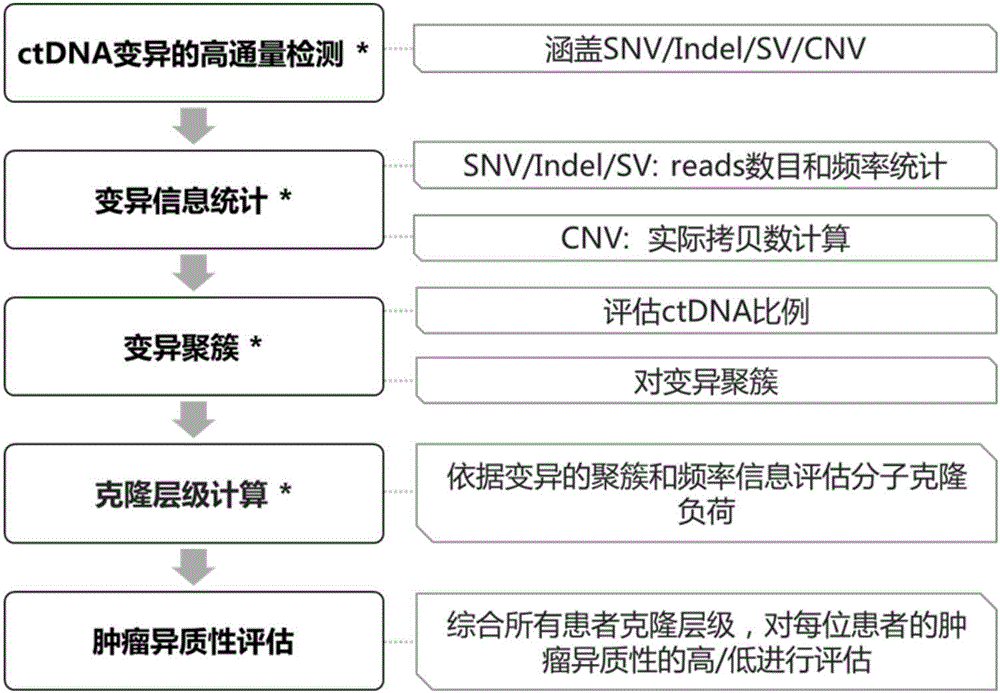
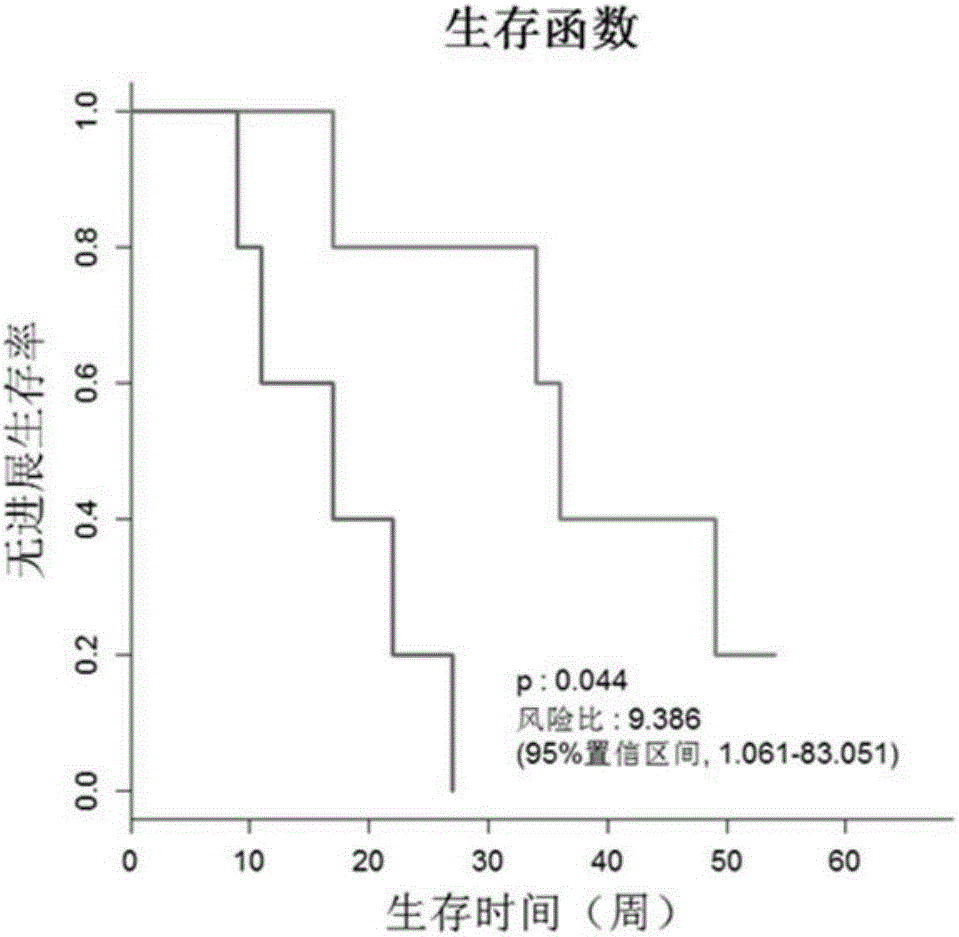
The invention discloses a system and a method for tumor heterogeneity assessment and particularly provides a molecular clone analysis method. On the basis of various types of variation detection results of high-throughput sequencing in circulating tumor DNA, all variations are divided into different molecular clones to realize tumor heterogeneity assessment by molecular clone levels. By adoption of the method, tumor heterogeneity assessment based on ctDNA high-throughput variation detection is realized to effectively assist in making of tumor prognosis and treatment schemes.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH +1
Method and device for constructing brain disease classification model and intelligent terminal
ActiveCN110263880AIncrease diversityImprove learning effectCharacter and pattern recognitionDiseaseFunctional connectivity
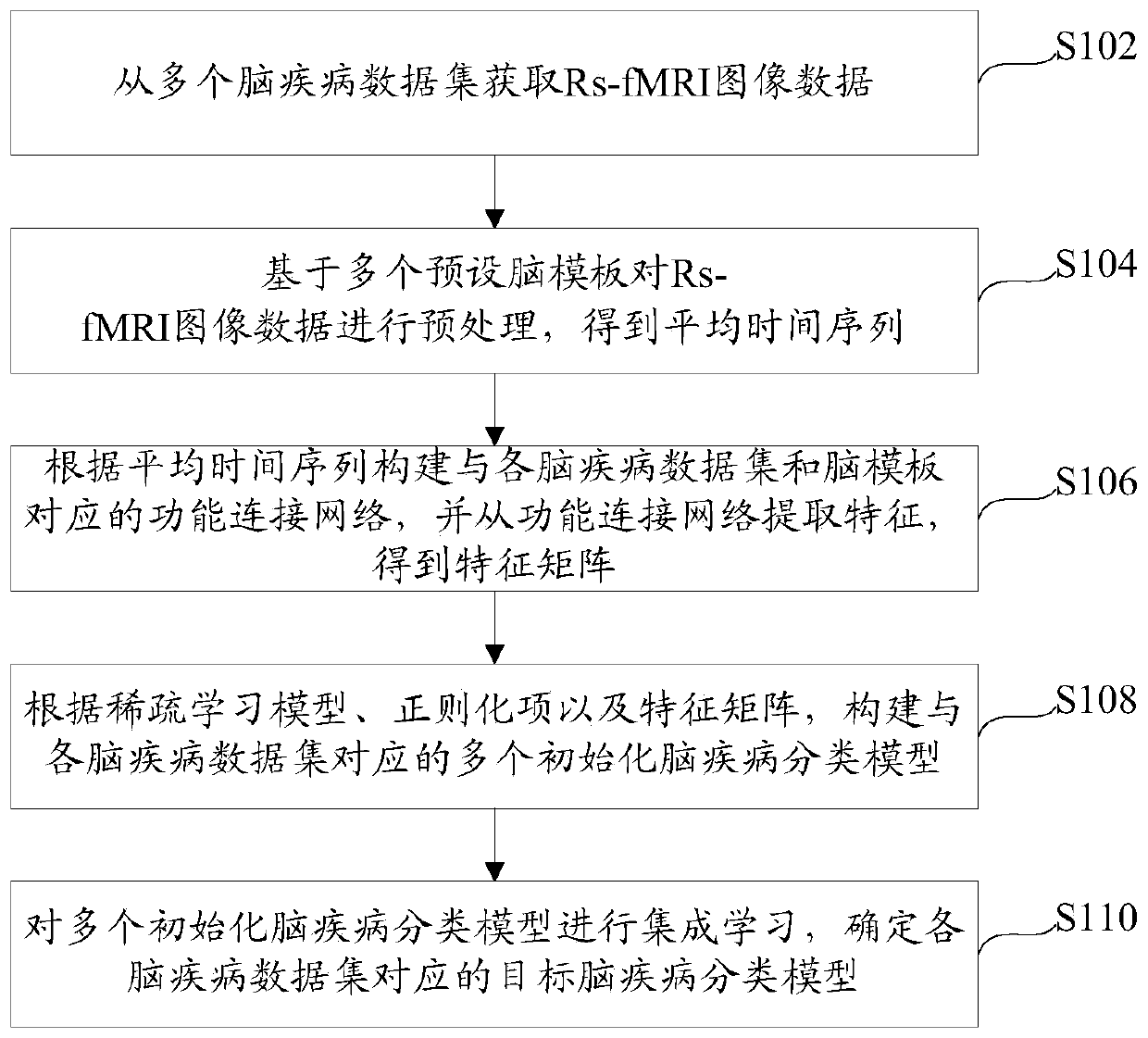
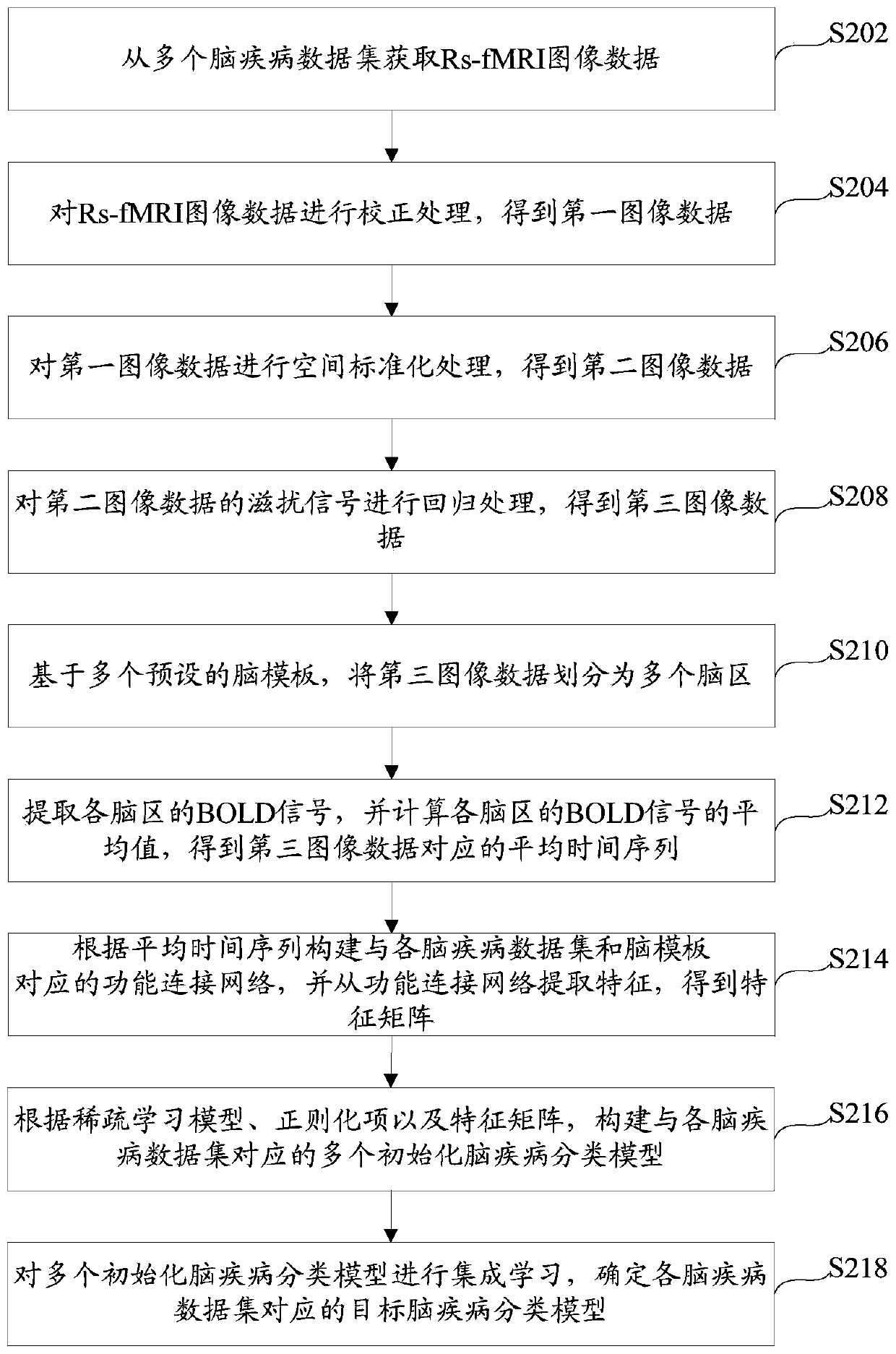
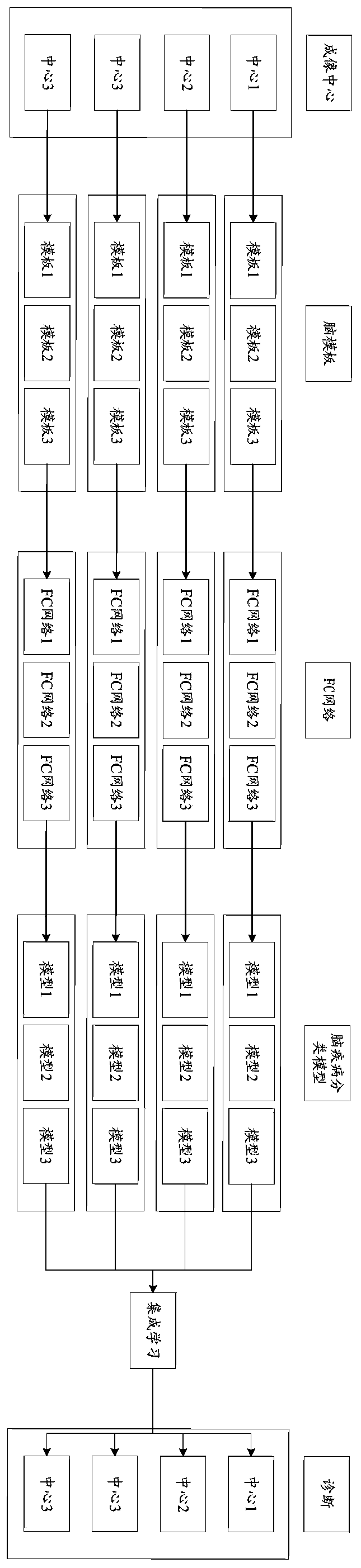
The invention provides a method and device for constructing a brain disease classification model, and an intelligent terminal. The brain disease classification model construction method comprises the steps of obtaining Rs-fMRI image data from multiple brain disease data sets; based on a plurality of preset brain templates, preprocessing the Rs-fMRI image data to obtain an average time sequence; constructing a functional connection network corresponding to each brain disease data set and the brain template according to the average time sequence, and extracting features from the functional connection network to obtain a feature matrix; constructing a plurality of initialized brain disease classification models corresponding to each brain disease data set according to a preset sparse learning model, a regularization item and a feature matrix; and performing integrated learning on the plurality of initialized brain disease classification models, and determining a target brain disease classification model corresponding to each brain disease data set. According to the method, the constructed brain function connection network has more physiological significance, the problem of high heterogeneity in data can be effectively solved, and the universality of a brain disease classification model is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Method for stabilization of cardiac tissue contractions using limit cycles
Electrical stimulation to cardiac tissue stabilizes atrial and ventricular arrhythmia when timed to stabilize a limit cycle structure in a Poincare map. Disclosed are methods and apparatus, operational internally or externally, for removing the reentrant effects of heterogeneity present in a diseased heart and returning the heart to an improved metabolic status allowing removal of support. The methods and apparatus disclosed are also useful in the chronic surveillance and maintenance of regularized contractility in an aged or diseased heart.
Owner:TECH INNOVATION LLC
Multilead ECG template-derived residua for arrhythmia risk assessment
A method and system for predicting the onset of heart arrhythmias more accurately observes trends in abnormal or pathologic morphology of the electrocardiogram (ECG). A first set of ECG signals is monitored from a patient. A baseline measurement is generated from the monitored first set of ECG signals to contain nonpathologic ECG morphologies in each lead. A second set of ECG signals is monitored from the patient and the baseline measurement is subtracted from the second set of ECG signals on a beat-to-beat basis. Afterwards, a residuum signal is generated for each lead based on the subtraction. R-wave heterogeneity, T-wave heterogeneity, P-wave heterogeneity, or ST-segment heterogeneity or other indicators of arrhythmia risk or myocardial ischemia are quantified based on the generated residuum signals.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
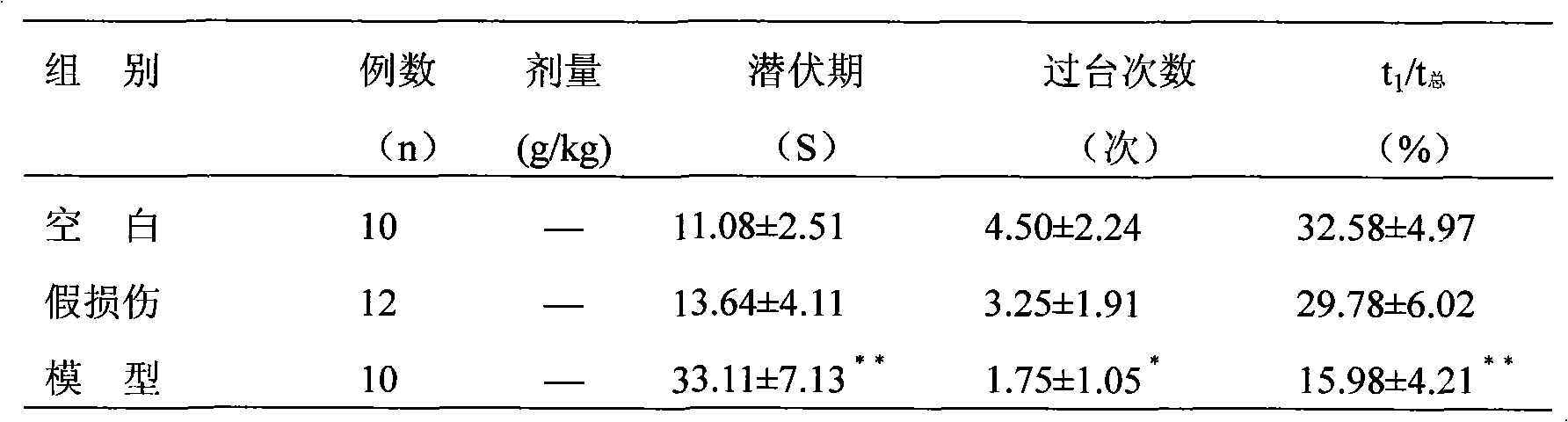
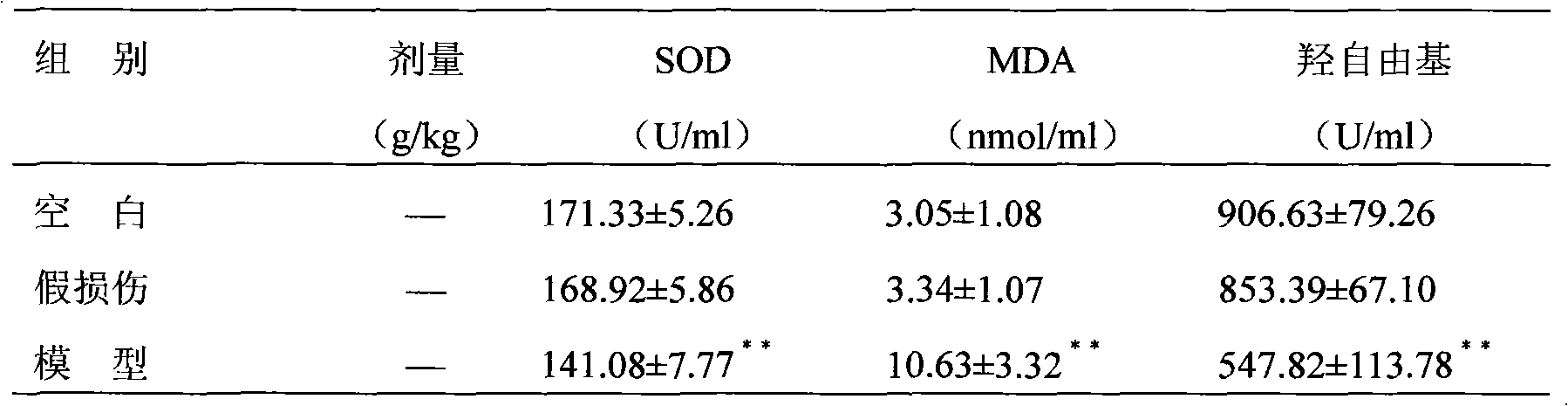
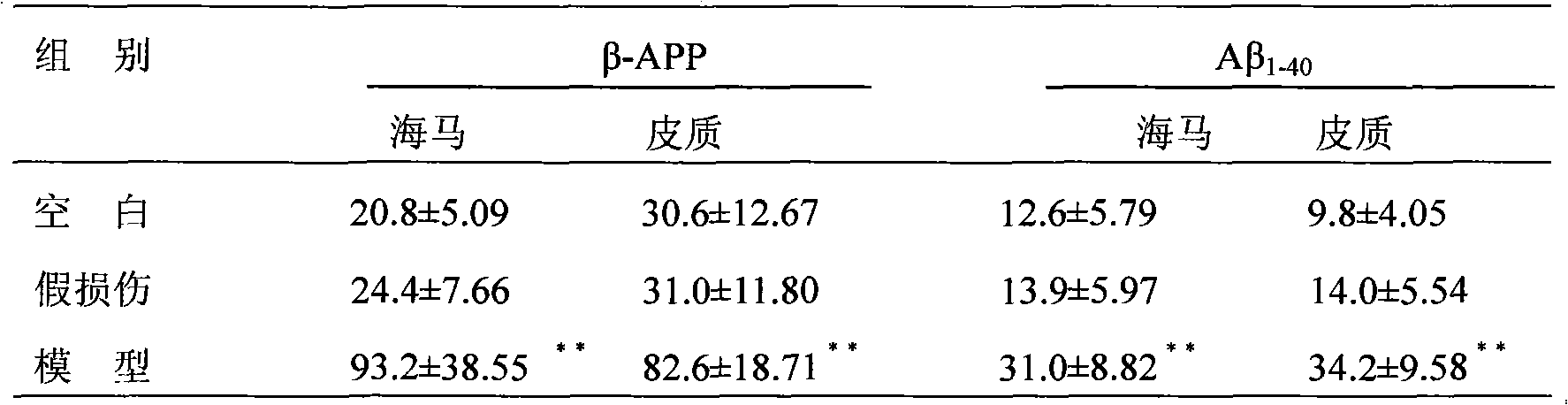
Establishment and application of model for screening medicaments for resisting heterogeneous and multi-reason senile dementias
The invention relates to the establishment of a model for screening medicaments for resisting heterogeneous and multi-reason senile dementias, which is characterized in that the common carotid arteries on two sides of each group of aging rats are ligated repeatedly to block blood flow, the rats are fed for three days after operations, and the alive rats in good condition are intracerebrally injected with Abeta1-40 (incubated 1 W at a temperature of 37 DEG C) which is diluted to be 5 micrograms per microliter by sterile normal saline. The establishment has the following advantages: by using the model, a damage model of the aging rats with declined learning and memory functions is provided for the studies on the nosogenesis of old age AD, VD and mixed dementias and the correlative curative effect of medicaments, and the model can reflect the actual brain pathology damage conditions of senile dementia patients.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Gene heterogeneity visual quantification method in glioma based on pyradiomics and system
ActiveCN110097921AAccurate Gene PredictionJudging the prognosisMedical imagesHybridisationTreatment effectImage segmentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical treatment and pyradiomics, and particularly relates to a gene heterogeneity visual quantification method in glioma based on pyradiomics and a system. The method of the invention comprises the steps of segmenting a glioma magnetic resonance image by means of an image segmenting network 3D U-net; performing predictive modeling on the integral glioma IDH (isocitrate dehydrogenase), namely performing high-flux characteristic extraction and characteristic screening on the image, and screening a characteristic combination which is most sensitive and most effective to gene expression; performing heterogeneous modeling on the glioma IDH based on an image block, extracting a multi-dimensional data block of the glioma image, obtaining the IDH expression strength of each data block based on the integral predicting model; and finally forming the IDH distribution visualization and quantitative expression of the whole tumor. The method and thesystem have advantages of more accurately determining the prognosis and radiotherapy and chemotherapy sensitivity of the patient, realizing surgery resection and targeting treatment in heterogeneous atlas navigation, and realizing high clinical value in improving treatment effect of the patient and improving survival prognosis.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
High Throughput Arrhythmia Risk Assessment Using Multilead Residua Signals
A method and system for high-throughput prediction of the onset of heart arrhythmias observes trends in abnormal or pathologic morphology of the electrocardiogram (ECG). A first set of ECG signals is monitored from a patient. A baseline measurement is generated from the monitored first set of ECG signals to contain nonpathologic ECG morphologies in each lead. A second set of ECG signals is monitored from the patient and a second baseline measurement is generated from the second set of ECG signals. A residuum signal is generated for each lead based on the baseline measurement and the second baseline measurement. The residuum signals are averaged across the leads. R-wave heterogeneity, T-wave heterogeneity, P-wave heterogeneity, or ST-segment heterogeneity or other indicators of arrhythmia risk or myocardial ischemia are quantified based on the generated residuum signals and the averaged residuum signal.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Method for detecting heterogeneity in triple-negative breast cancer
InactiveCN105717082AImprove consistencyReduce mistakesWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationImmunofluorescenceMedicine
The invention discloses a method for detecting intratumoral heterogeneity of triple-negative breast cancer. The method solidifies tissue samples from different parts of the same patient on the same tissue chip, and then performs immunohistochemistry on the tissue chip. , immunofluorescence, fluorescence in situ hybridization and other detection. Effectively reduce the cost of experiments, save time and manpower, and also reduce errors caused by batch experiments, improve the consistency of experimental results, and achieve better quality control. This method uses multi-probe combined with fluorescence in situ hybridization technology to evaluate the intratumoral heterogeneity of triple-negative breast cancer, which reduces the dependence on expensive equipment and investment costs, and is easy to be widely promoted. The invention quantitatively detects intratumoral heterogeneity of triple-negative breast cancer, and provides a clear evaluation index for accurately predicting postoperative recurrence and metastasis risk of patients.
Owner:管晓翔
Quantitative in situ characterization of heterogeneity in biological samples
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Quantitative description method of PET image nasopharyngeal carcinoma intra-tumor heterogeneity
InactiveCN108805892ARealization of quantitative characterizationRichness and sufficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionNasopharyngeal carcinoma
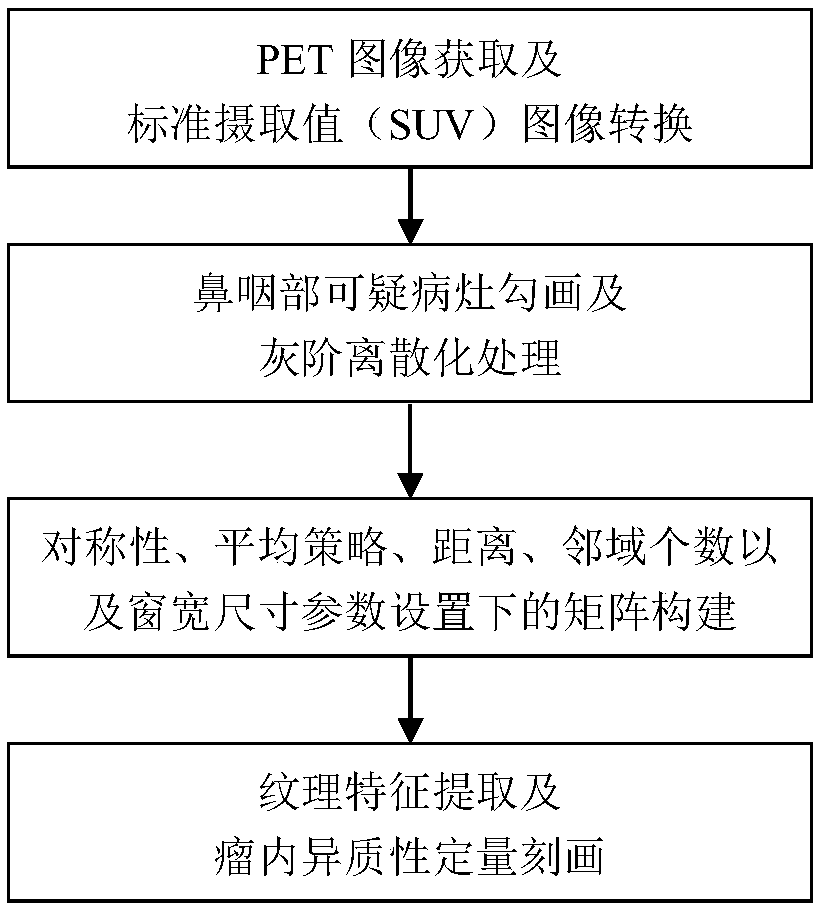
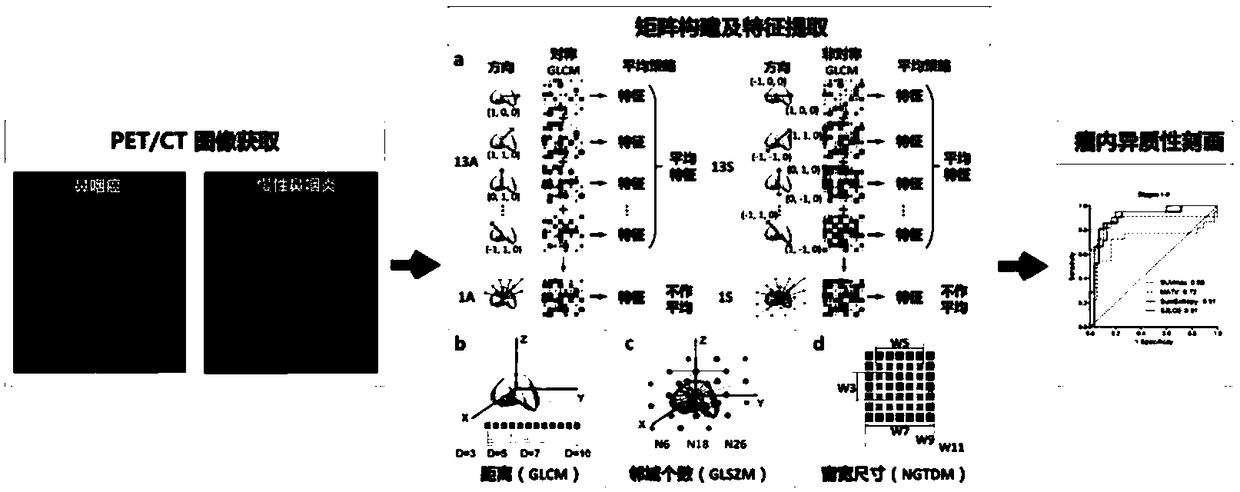
The invention belongs to the field of the medical image analysis, specifically a quantitative description method of PET image nasopharyngeal carcinoma intra-tumor heterogeneity. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring PET / CT scanning data of a patient, and converting the PET / CT scanning data into a standard SUV image; performing three-dimensional segmentation on the primary focus at the nasopharynx; performing discretization processing on the focus, and constructing four image omics matrixes for the processed focus, and comprehensively considering five parameter settings of symmetry, the average policy, the distance, the neighborhood number and window width size in the matrix construction process; extracting 415 texture features from the constructed matrix, and realizing the quantitative description of the intra-tumor metabolic heterogeneity by combining five traditional SUV features. The intra-tumor metabolic heterogeneity is described more comprehensively by sufficientlymining the information contained in the non-invasive PET image, thereby providing the quantitative evaluation index for precisely identifying the nasopharyngeal carcinoma by the doctor.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
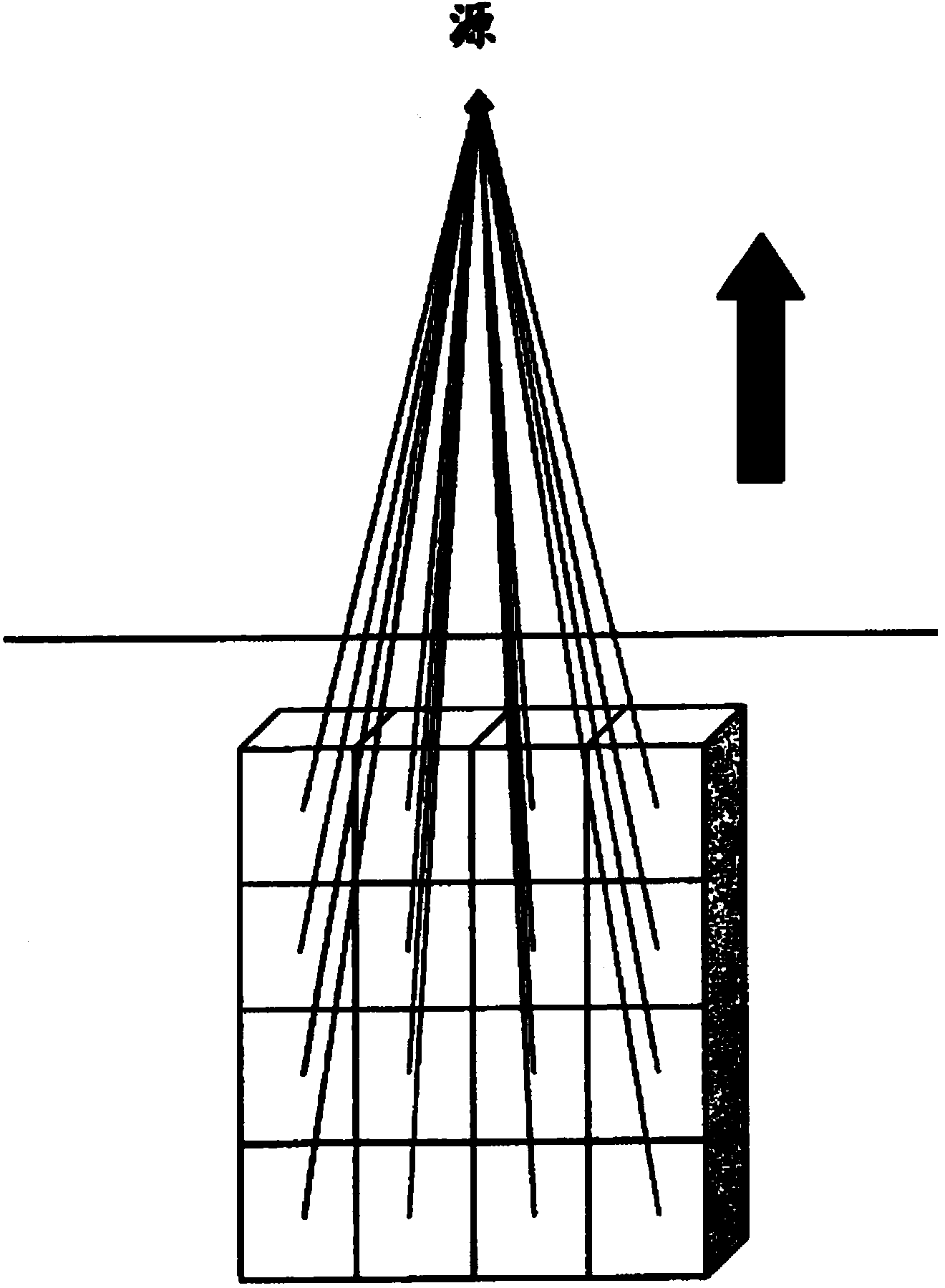
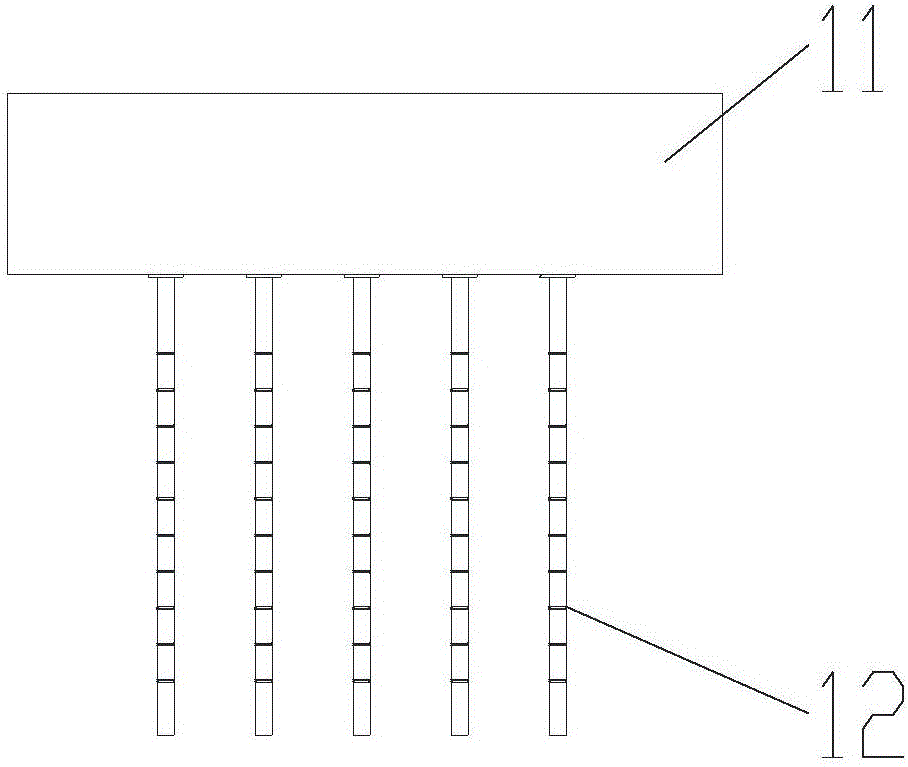
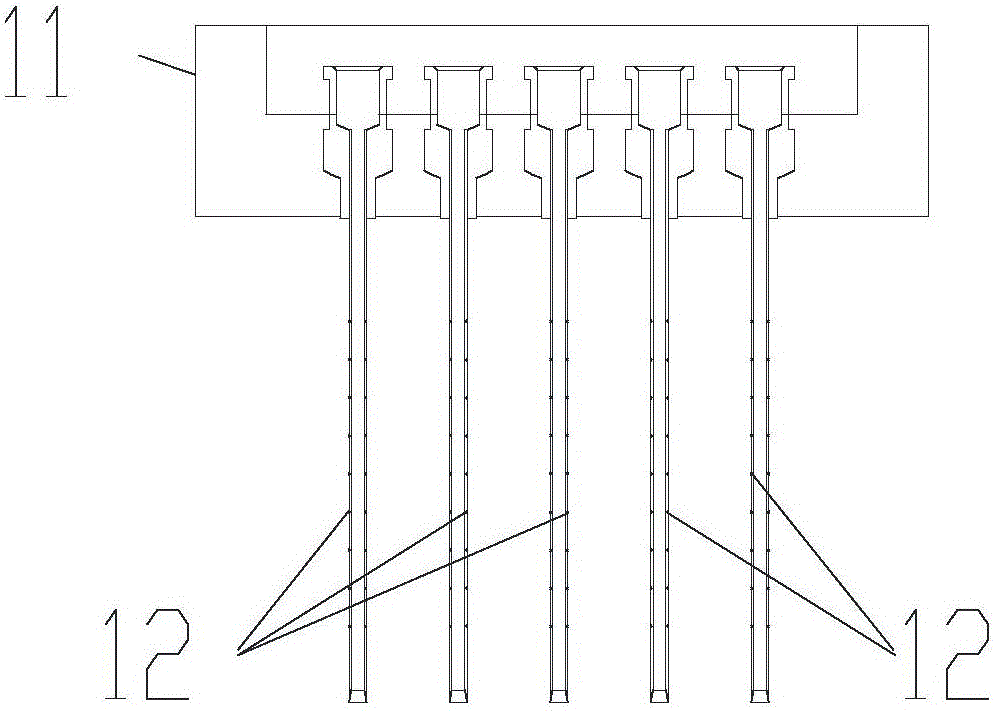
Tumor tissue three-dimensional space sampler and sampling method thereof
PendingCN106556526AShort timeConvenient researchWithdrawing sample devicesMedicineThree-dimensional space
The invention relates to a tumor tissue three-dimensional space sampler and a sampling method thereof, and relates to the technical field of tumor sampling. The main purpose of the invention is to improve the space sampling efficiency. The sampling method comprises the following steps: 1, sampling: aligning a plurality of sampling syringes loaded on a sampling platform at a tissue sample, and inserting the sampling syringes into the tumor tissue sample to make the sampling channels of the sampling syringes filled with a part of the tissue sample; and 2, dividing the sample: using a breaker to align at the interception ring marks of the sampling syringes, cutting the sampling syringes to segment the sampling syringes, carrying out segmented sampling on the different sampling syringes, and carrying out numbering sample dividing according to the spatial positions of the segmented sampling syringes in the sampling syringes to conveniently correspond to the spatial positions in tumors. Compared with existing manual single-point sampling technologies, the method disclosed in the invention has the advantages of short time, realization of obtaining of a plurality of samples from the three-dimensional space of the tumors at one time, and facilitation of the study of tumor space heterogeneity.
Owner:志诺维思(北京)基因科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com