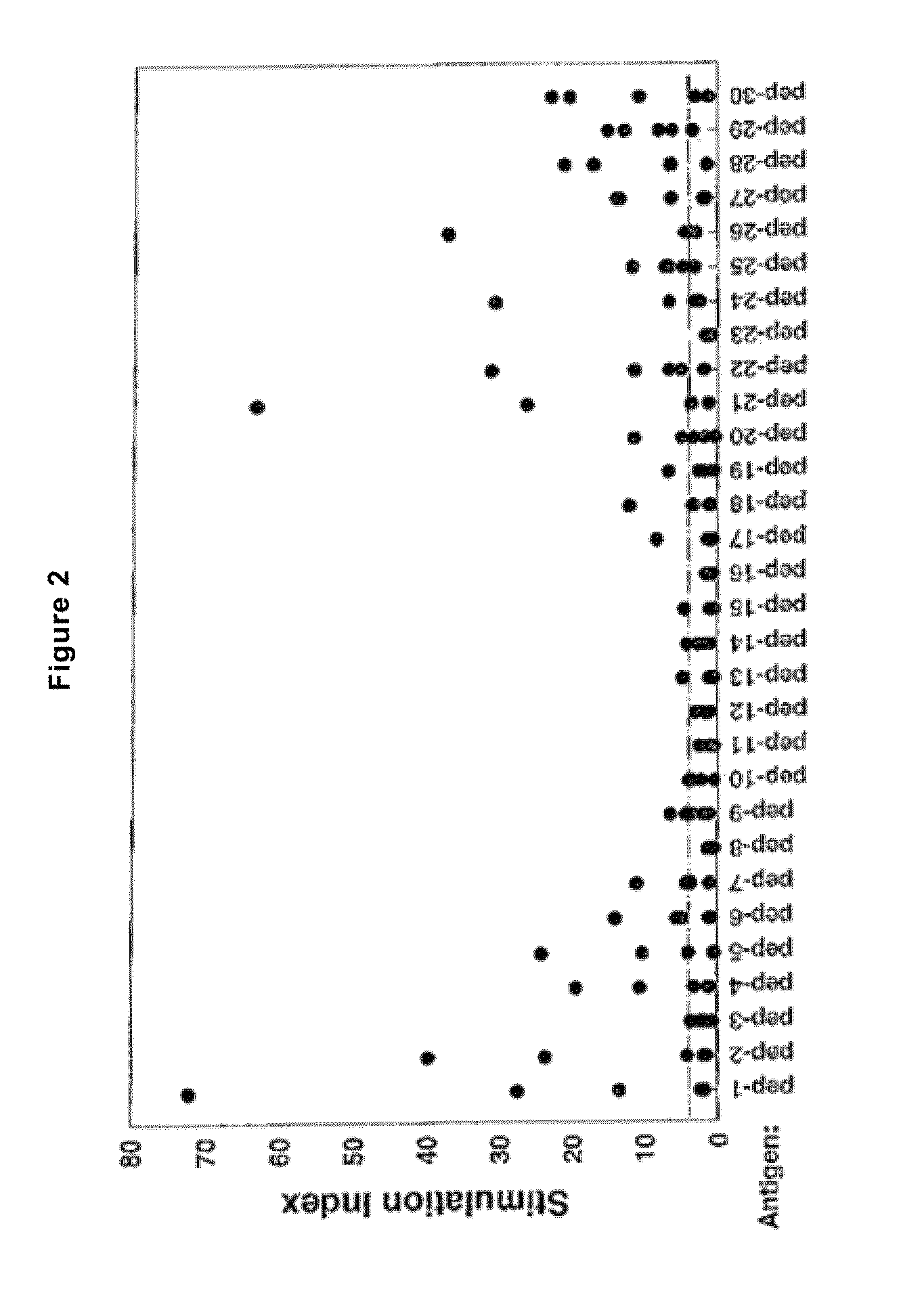
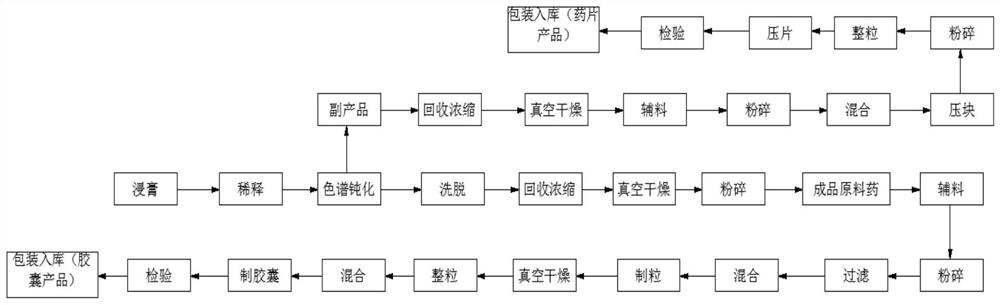
Patents
Literature
121 results about "TB - Tuberculosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
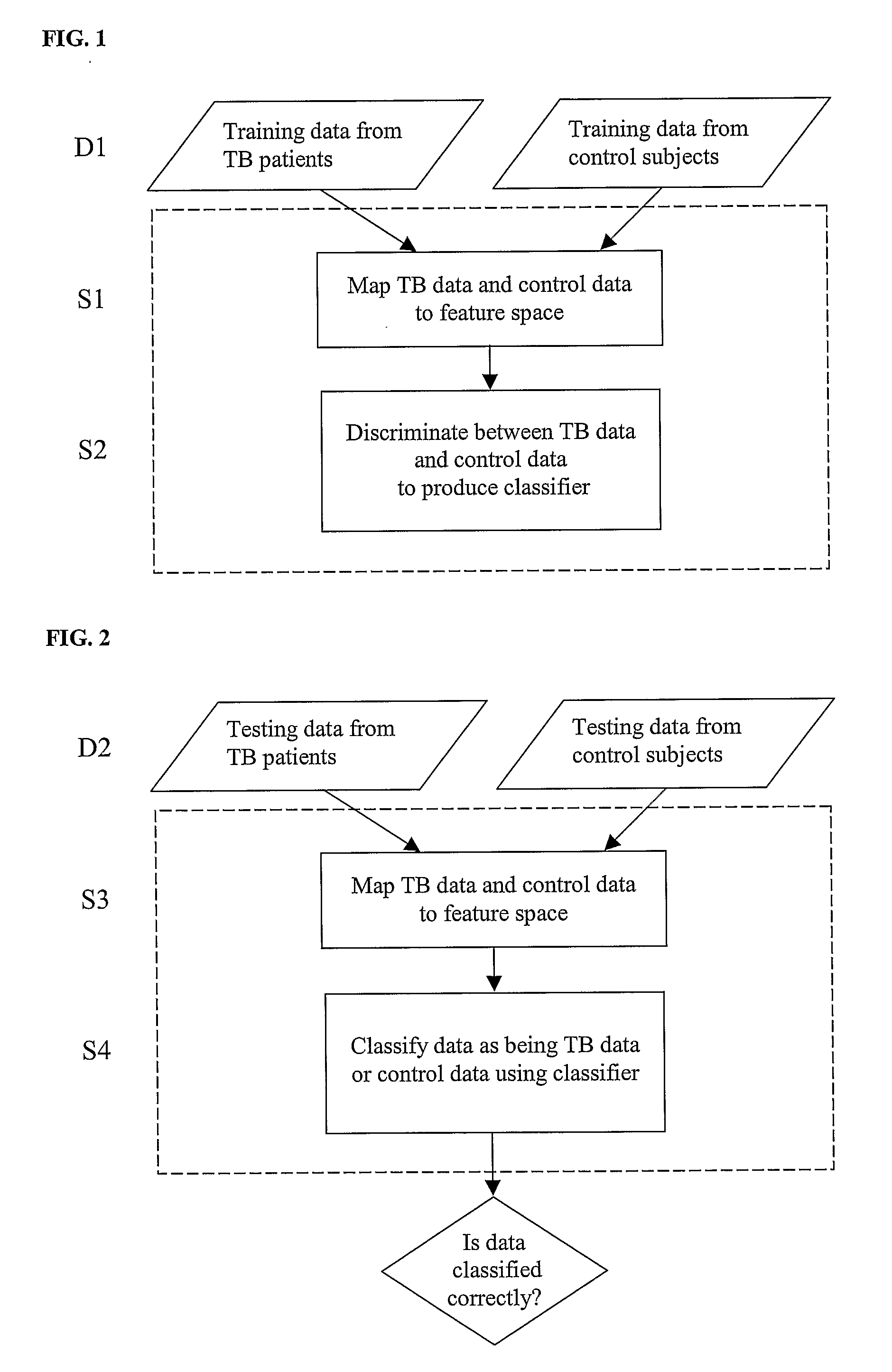
Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by germs that are spread from person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body, such as the brain, the kidneys, or the spine.
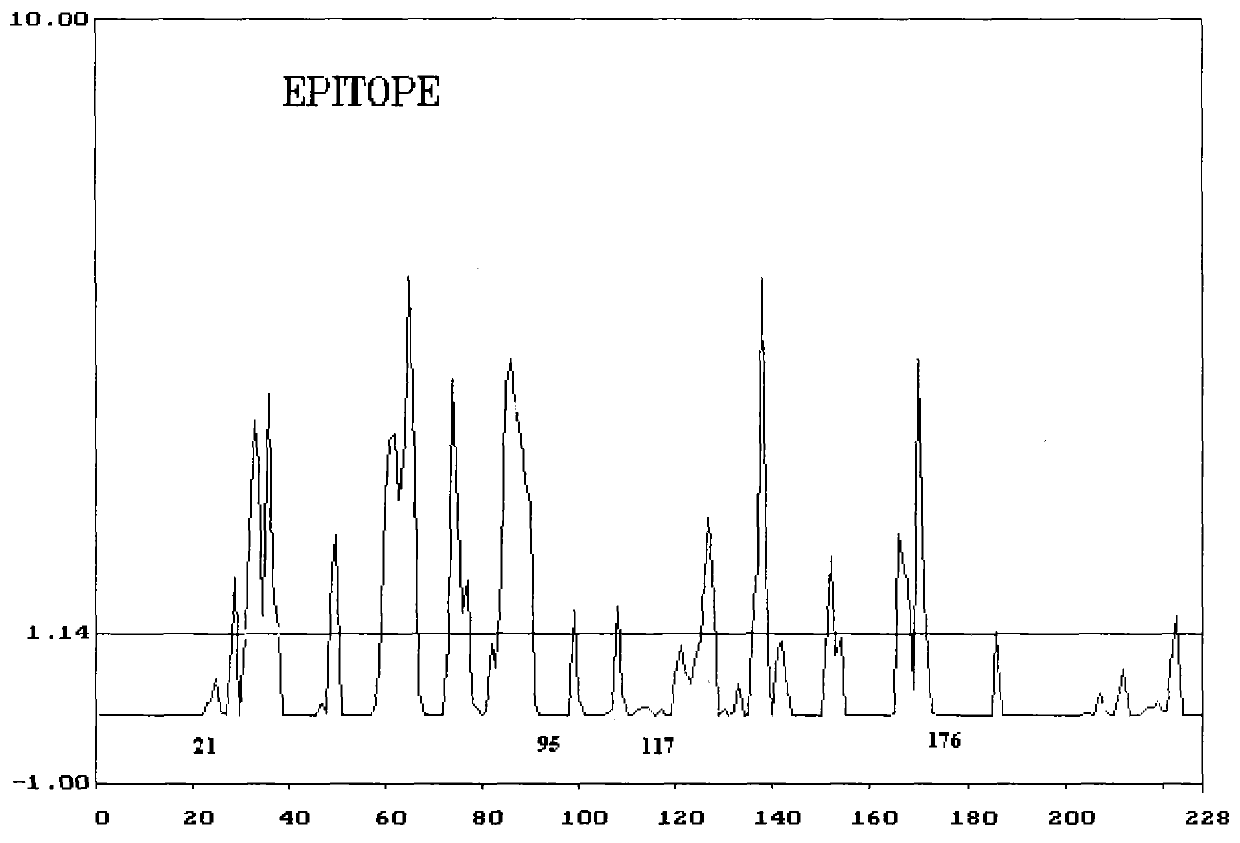
Antigen epitope for exciting human anti-tubercle bacillus protective immunoreaction and its use
InactiveCN1858059AHelp preventAids in healingAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMolecular ImmunologyBCG vaccine
The present invention relates to molecular immunology technology, and aims at screening out antigen epitope molecular simulation peptide capable of exciting human body's protective immunoreaction against tubercle bacillus, researching protective immunoreaction mechanism against tuberculosis, and further developing new type of concatenate polyepitope tuberculosis vaccine. The present invention provides one kind of antigen epitope molecular simulation peptide capable of exciting human body's protective immunoreaction against tubercle bacillus, and the peptide contains the amino acid sequence selected from SEQ ID Nos. 2, 5, 10, 12, 14 and 15. The present invention also provides the screening process and use of the peptide. The present invention may be used in preventing and controlling tuberculosis.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
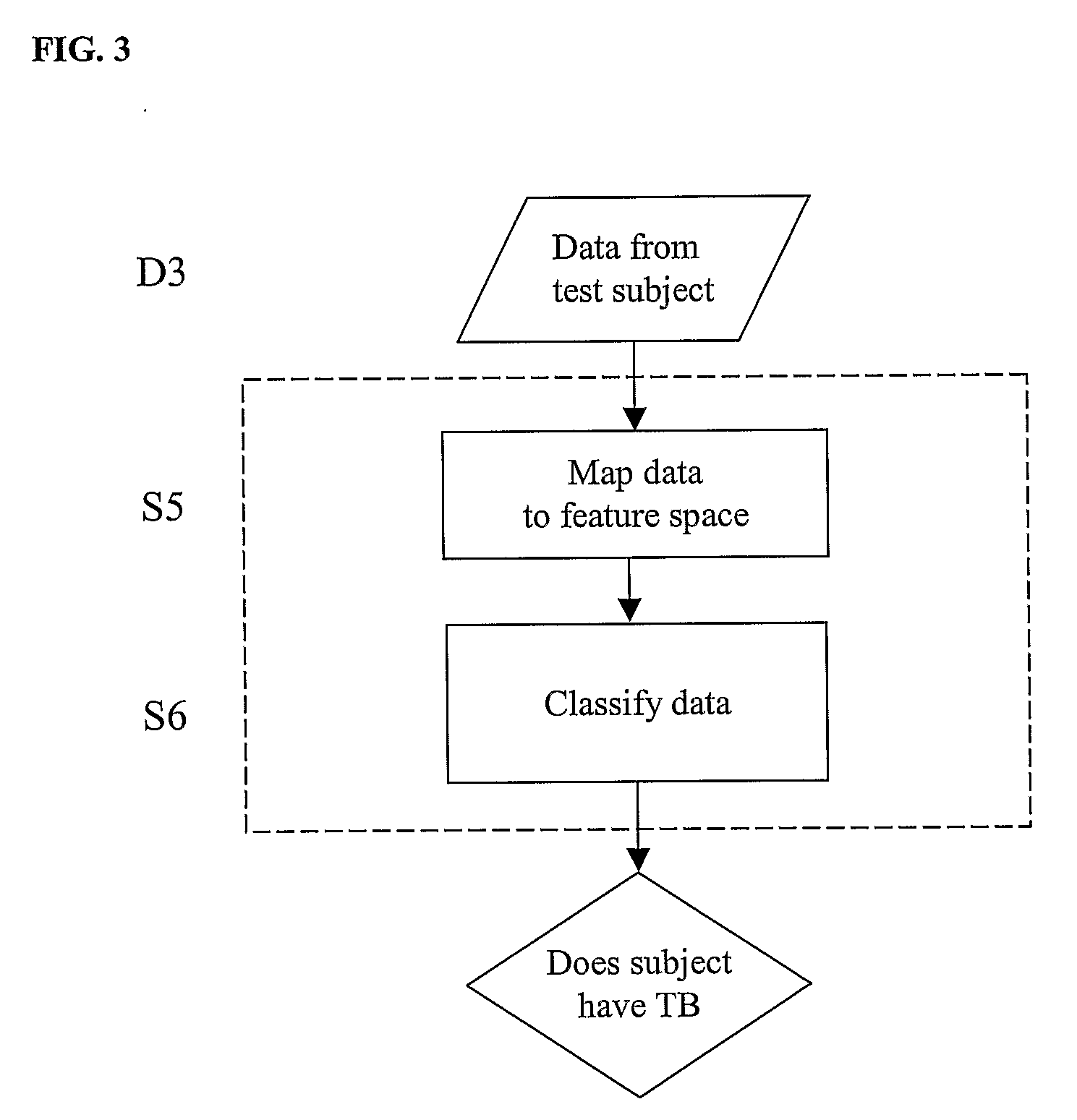
Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
InactiveUS20090104602A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisSerum protein albuminApolipoproteins E
The invention provides a method of diagnosing tuberculosis (TB) in a test subject, said method comprising: (i) providing expression data of two or more markers in a subject, wherein at least two of said markers are selected from transthyretin, neopterin, C-reactive protein (CRP), serum amyloid A (SAA), serum albumin, apoliopoprotein-A1 (Apo-A1), apolipoprotein-A2 (Apo-A2), hemoglobin beta, haptoglobin protein, DEP domain protein, leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein (A2GL) and hypothetical protein DFKZp667I032; and (ii) comparing said expression data to expression data of said marker from a group of control subjects, wherein said control subjects comprise patients suffering from inflammatory conditions other than TB, thereby determining whether or not said test subject has TB.
Owner:FERNANDEZ REYES DELMIRO +3
Polypeptide composition and application thereof in detecting tuberculosis antibody
ActiveCN101735321AHigh sensitivityStrong complementarityHybrid peptidesAnimals/human peptidesAntigenPolypeptide composition
The invention discloses a polypeptide composition which is formed by combining an antigen Mtb16.3, an antigen 38kD, ESAT-6, CFP 10, MPT 64, Mtb 8 and Mtb 8.4. The antigens Mtb 16.3, 38kD, ESAT-6, CFP 10 and MPT 64 have excellent complementarities in serological detection. The sensitivity for diagnosing tuberculosis is obviously promoted by combining antigen Mtb16.3 with at least one of antigen 38kD, ESAT-6, CFP 10 and MPT 64.
Owner:SHANGHAI RONGSHENG BIOLOGICAL PHARM CO LTD +1
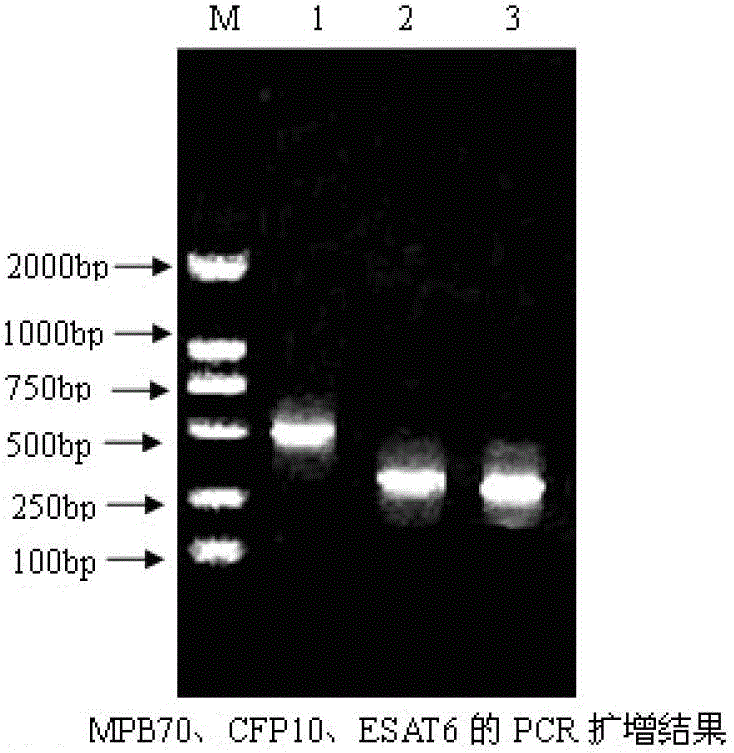
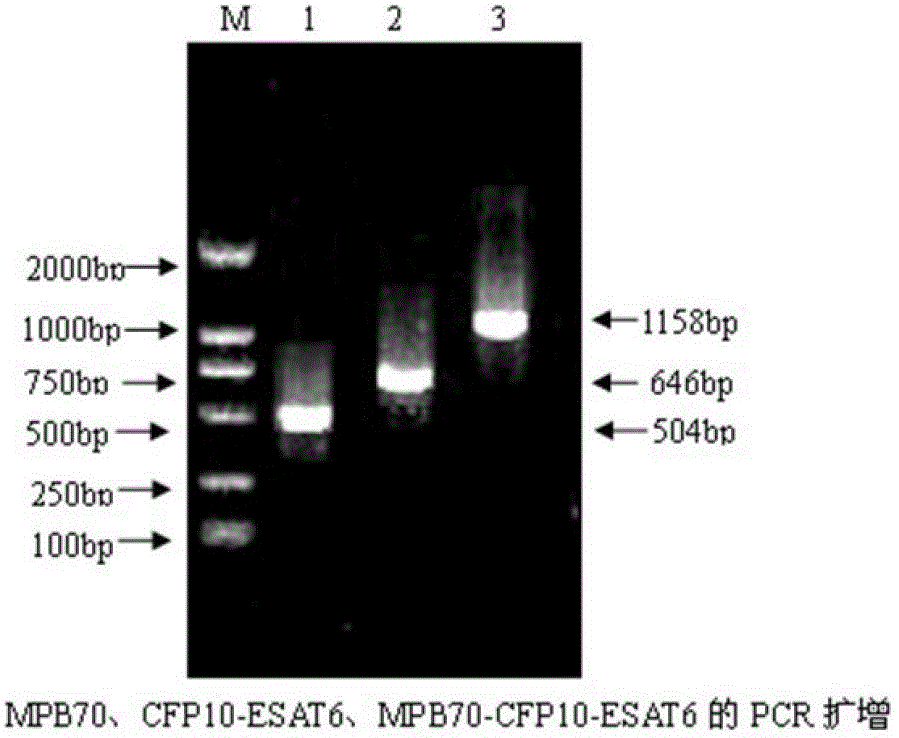
Gamma-interferon sandwich ELISA detection method based on recombinant fusion antigen protein
ActiveCN103333251AImprove stabilityImprove accuracyMicroorganism based processesBiological testingMedical testingTuberculosis diagnostics
The present invention relates to a gamma-interferon sandwich ELISA detection method based on recombinant fusion antigen protein, further relates to a recombinant fusion antigen protein preparation method and a gamma-interferon monoclonal antibody preparation method, and belongs to the technical field of medical examination determination. According to the present invention, the recombinant fusion antigen protein is formed by linking secretory antigen protein MPB70, antigen protein CFP10 and antigen protein ESAT6 through peptide bonds, the gamma-interferon monoclonal antibody is prepared through immunization of animals, cell fusion, hybridoma cell screening, cloning and purification, and the recombinant fusion antigen protein and the gamma-interferon monoclonal antibody are adopted to establish a sandwich ELISA detection method; and the recombinant fusion antigen protein can rapidly stimulate a bovine blood sample to secret gamma-interferon, and the gamma-interferon monoclonal antibody can quickly and specifically identify bovine gamma-interferon, such that strong sensitivity and strong specificity are provided, and broad application prospects are provided in the field of buffalo tuberculosis diagnosis.
Owner:常州同泰生物药业科技股份有限公司
Biomarkers and combinations thereof for diagnosising tuberculosis
ActiveCN107075569AAccurate TB PredictionAccurate diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicineTuberculosis
This invention relates to the detection and diagnosis of tuberculosis. More specifically, the invention relates to new biomarkers and combinations thereof that enable the accurate detection and diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Owner:SEC OF STATE FOR HEALTH & SOCIAL CARE
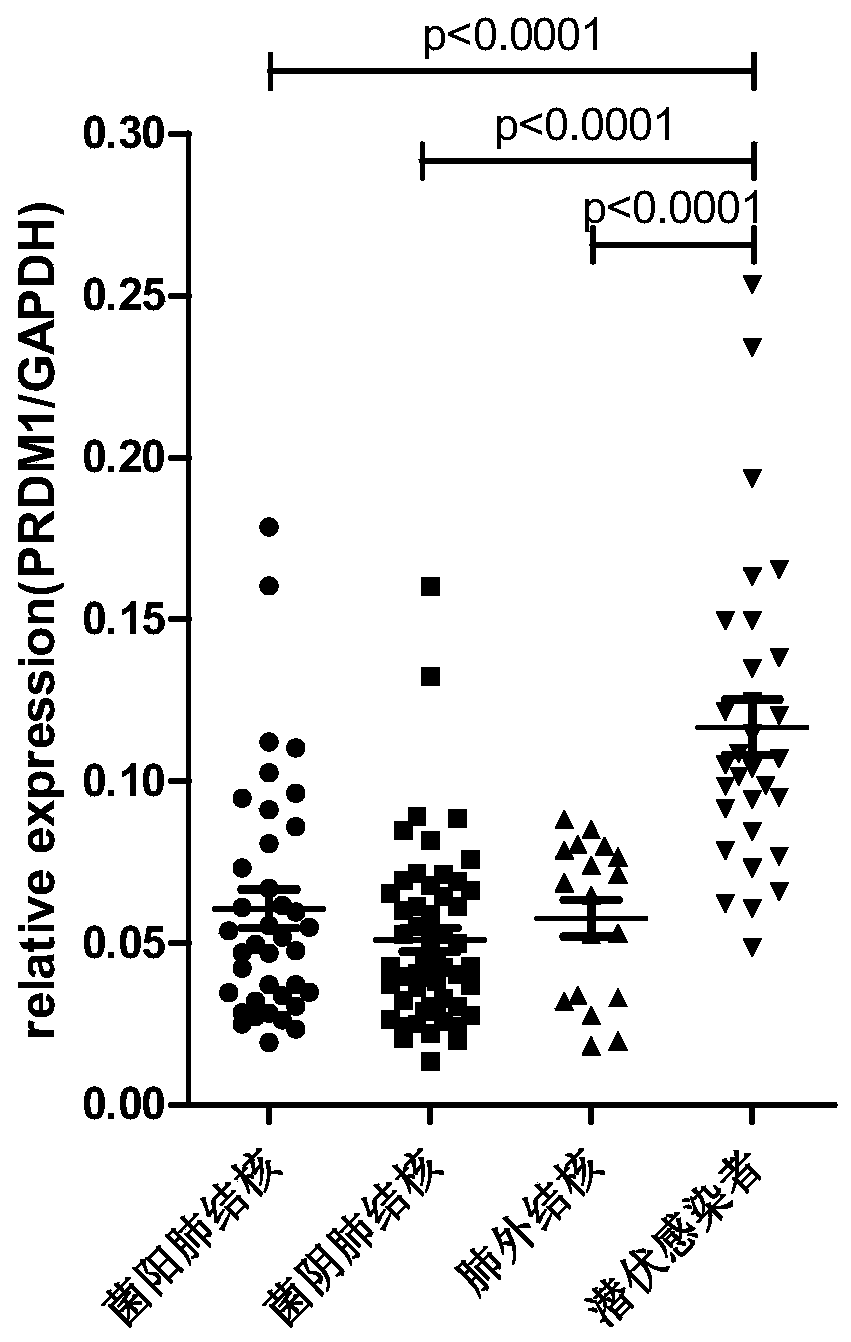
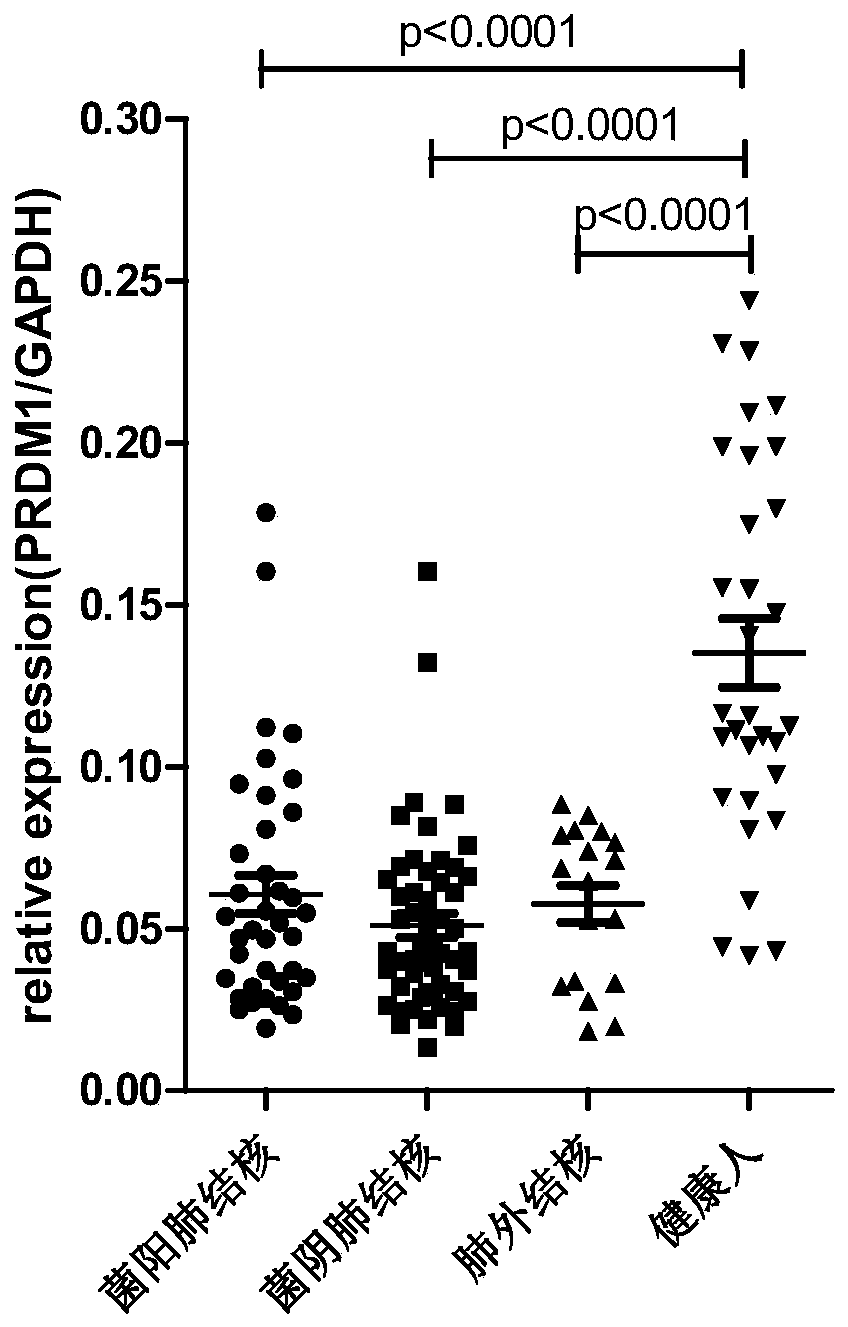
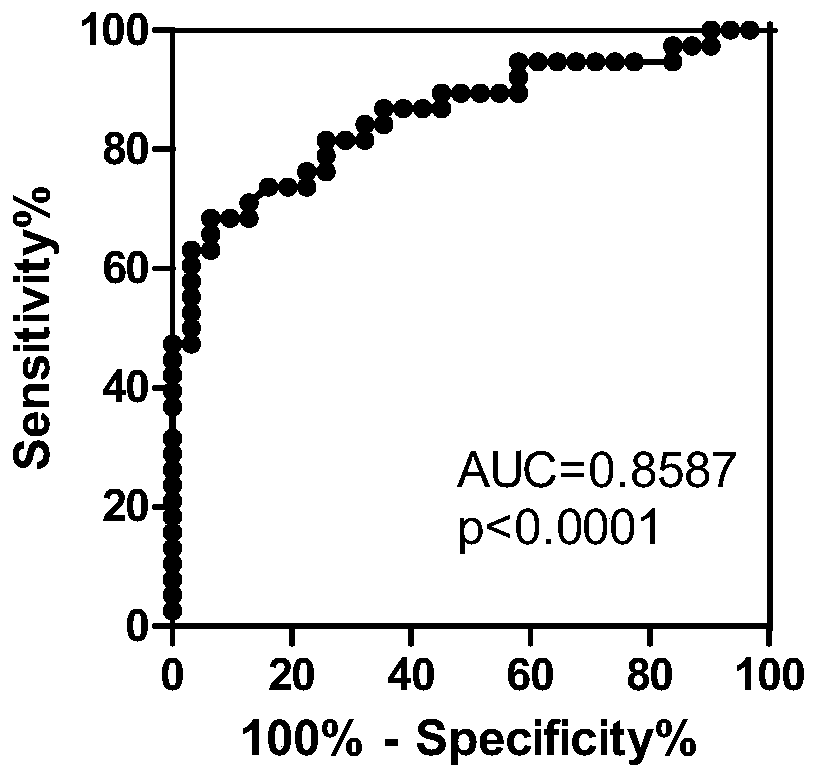
Application of PRDM1 as marker for preparing product for diagnosing active tuberculosis
InactiveCN110295229AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisFluorescenceLatent tuberculosis
The invention discloses application of PRDM1 as a marker for preparing a product for diagnosing active tuberculosis. Fluorescence quantitative PCR is adopted for detecting expression quantity of a PRDM1 gene in a tuberculosis patient PBMCs. A result shows that the relative expression quantity of PRDM1 in smear positive tuberculosis patients, smear negative tuberculosis patients and extrapulmonarytubereulosis patients PBMCs is remarkably lowered that that of latent tuberculosis infected persons and healthy control. A subject working characteristic curve analysis result shows that PRDM1 can distinguish active tuberculosis and latent tuberculosis infection, and becomes the diagnosis target for diagnosing the active tuberculosis.
Owner:中国人民解放军总医院第八医学中心
Pulmonary tuberculosis variation activity marker, kit, method and model construction method
PendingCN113178263AGood clinical valueOvercoming low diagnostic detection ratesMedical simulationProteomicsLung tuberculosisBlood plasma
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
Application of RETN and KLK1 serving as tuberculosis detecting markers
ActiveCN107653313AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisNormal tissueLatent tuberculosis
The invention discloses application of RETN and KLK1 serving as tuberculosis detecting markers. Experiments prove that the RETN gene and the KLK1 gene have evident expression differences in normal tissue, the tissue of a person with latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) and the tissue of a patient with tuberculosis (TB), the expression level of the RETN gene in the tissue of the patient with tuberculosis (TB) is much higher than that in the normal tissue or in the tissue of the person with latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI), and the expression level of the KLK1 gene in the tissue of the patient with tuberculosis (TB) is much lower than that in the normal tissue or in the tissue of the person with latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI). Therefore, the RETN gene and the KLK1 gene can be usedas the markers for detecting or diagnosing the tuberculosis, and the occurrence and development of the tuberculosis can be monitored.
Owner:BEIJING CHEST HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV +1
Catechu extract composition for resisting tubercle bacillus, preparation method of catechu extract composition, pharmaceutical preparation containing catechu extract composition, and application of catechu extract composition
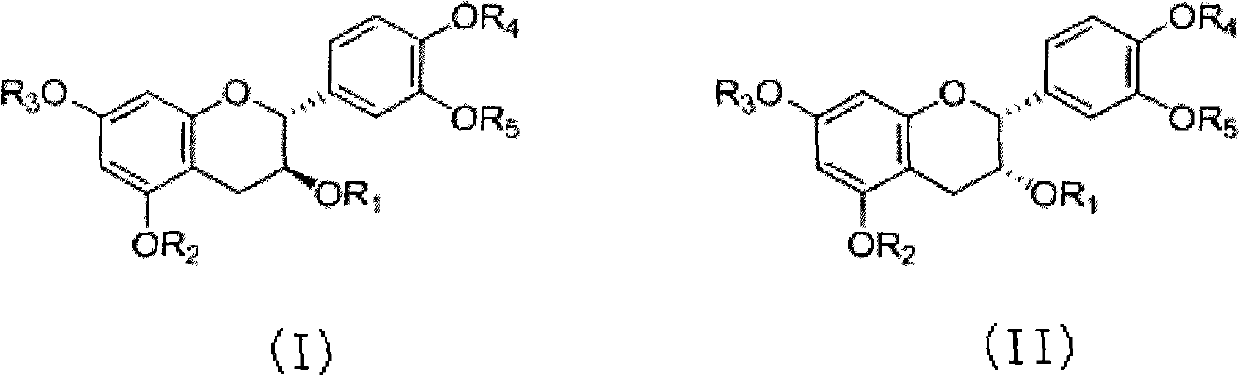
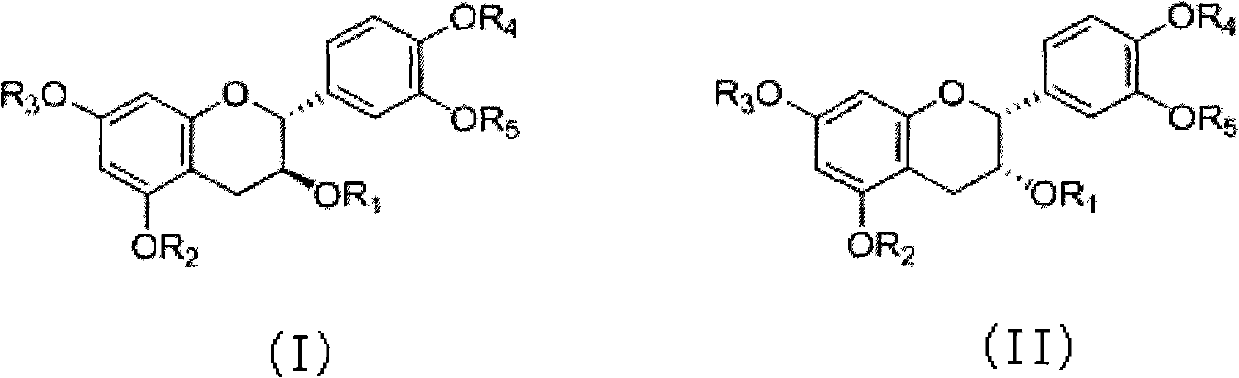
InactiveCN102526170AHigh effective contentGood treatment effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTherapeutic effectStructural formula
The invention discloses a catechu extract composition for resisting tubercle bacillus, a preparation method of the catechu extract composition, a pharmaceutical preparation containing the catechu extract composition, and application of the catechu extract composition. The catechu extract composition contains a flavanoid compound of which the purity is more than 50%, and the flavanoid compound takes catechin and / or epicatechin as main components. The main structural formulas (I) and (II) of the flavanoid compound are shown in the specifications, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, beta-D-glucopyranesyl, SO3 or PO3. By adopting a chromatographic process for refining and purifying the catechu extract composition disclosed by the invention, the effective content is as high as 99.5%. The catechu extract composition and the pharmaceutical composition thereof have excellent effects on improving or treating pulmonary tuberculosis, treating ulcerative bone tuberculosis and AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) complicated by tuberculosis, treating drug resistant tuberculosis, and especially treating drug resistant tuberculosis and AIDS complicated by tuberculosis.
Owner:许学志
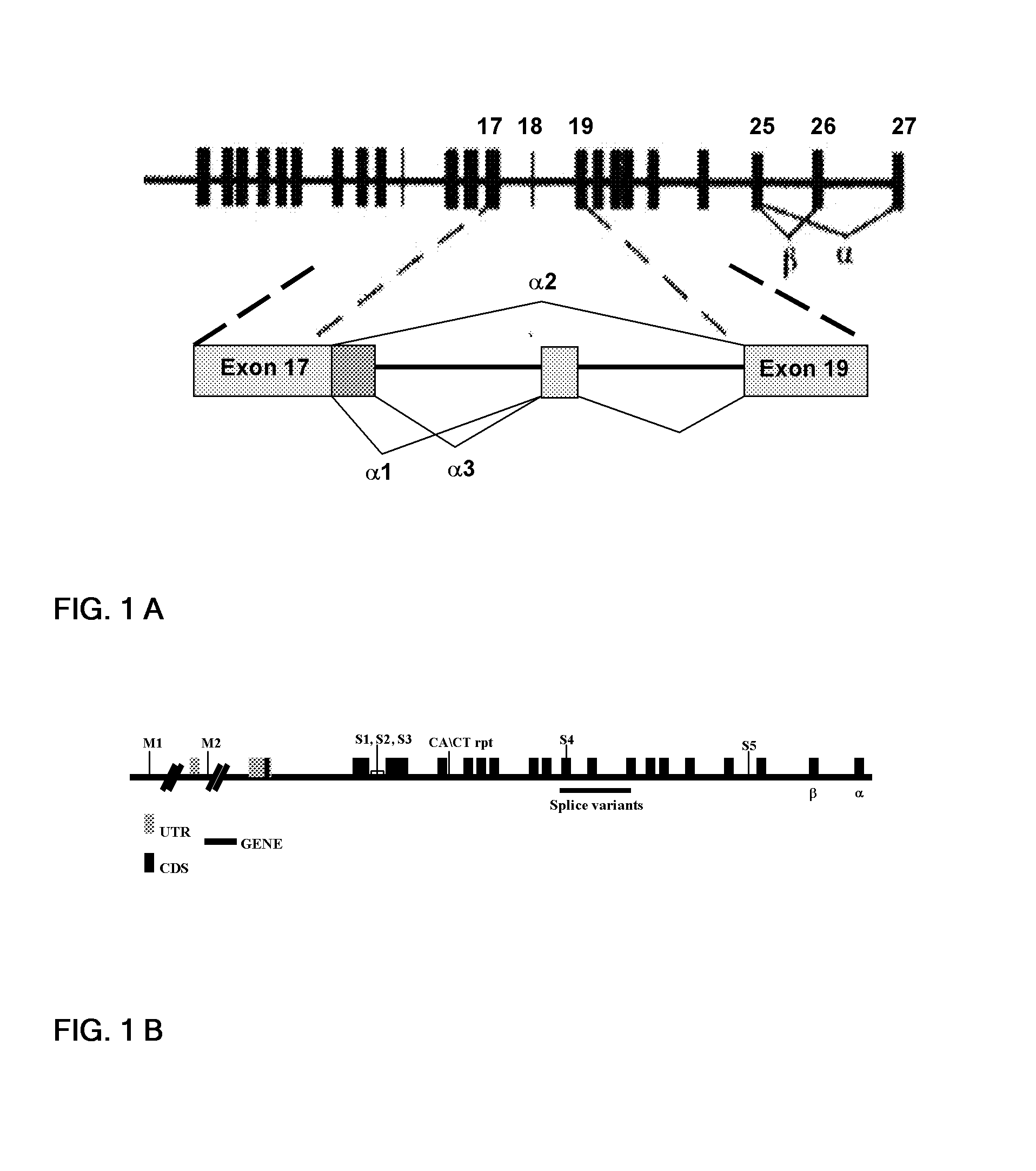
Genetic variants of human inositol polyphosphate-4-phosphatase, type i (INPP4a) useful for prediction and therapy of immunological disorder
Atopic asthma is a chronic, inflammatory lung disease characterized by recurrent breathing problems in response to an allergen. Platelets play an important role in this allergic inflammatory process, by releasing preformed mediators like platelet factor 4 (PF4) and regulated upon activation in normal T cells expressed and secreted (RANTES) upon activation causing eosinophil chemotaxis. The present invention relates to allelic variants of the human Inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase (INPP4A) gene and splice variants of the coding sequence, which encodes INPP4A enzyme known to be an important regulator of platelet activation; and provides primers and methods suitable for the detection of these allelic variants for applications such as molecular diagnosis, prediction and prevention of an individual's disease susceptibility, and / or the genetic analysis of the INPP4A gene in a population. The invention also provides an association with the expression profile of INPP4A protein in the mouse model of asthma. Specifically, the invention provides a method for detection of predisposition to atopic disorders / other immunological disorders such as, autoimmune disorders, inflammatory disorders, cancer, multiple sclerosis, fibrosis, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, hypertension and disorders developing due to hypertension, diabetes and disorders developing due to diabetes, alcohol abuse, anxiety, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cholecystectomy, degenerative joint disease (DJD), seizure disorder, arthritis, etc. where human Inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase (INPP4A) might play an important role due to its involvement in platelet action.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
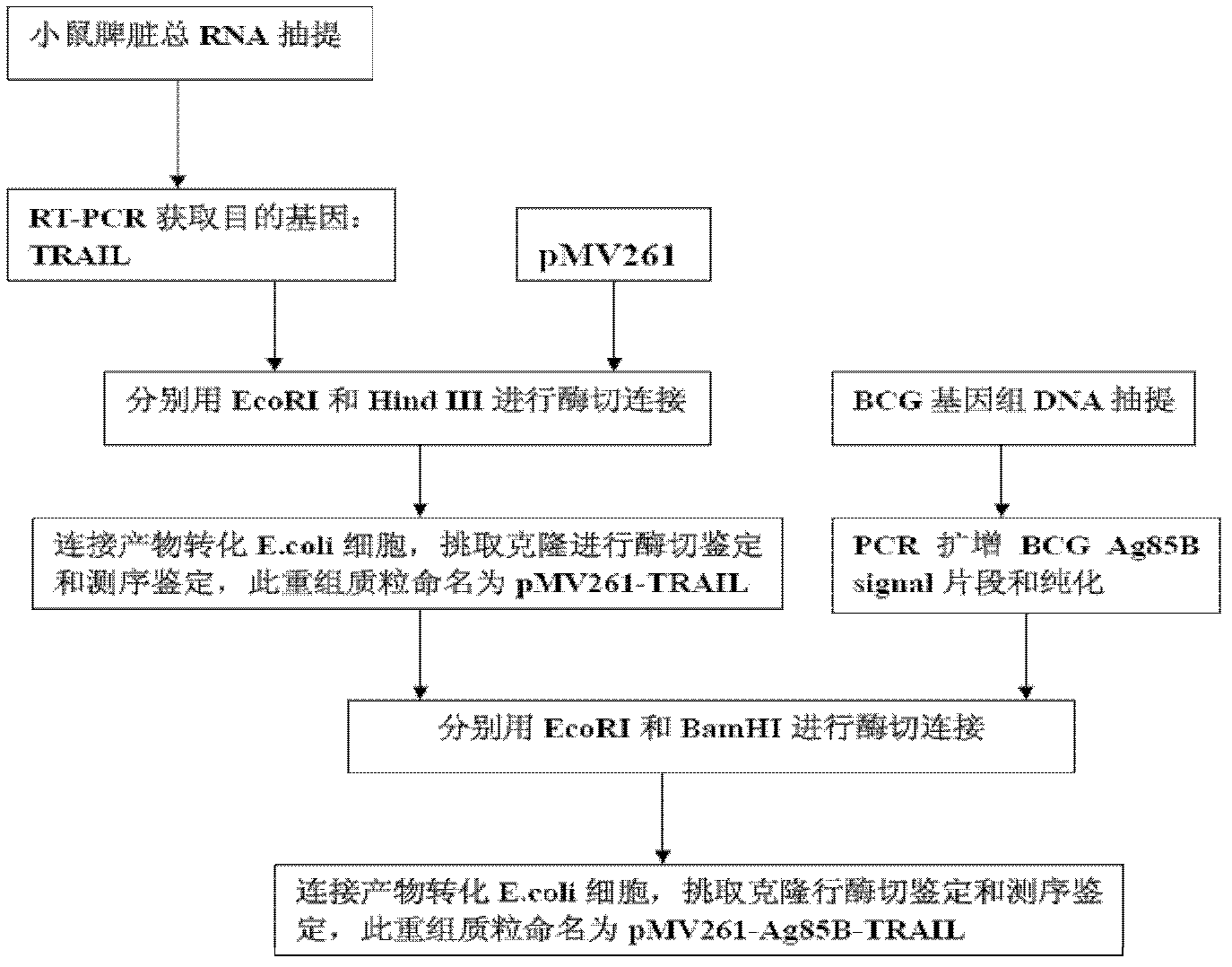
Construction and application of TRAIL (Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand) recombinant bacille calmette guerin (rBCG)
InactiveCN102327604AConnection direction is correctMeet the design requirementsAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenSide effect
The invention provides construction of TRAIL (Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand) recombinant bacille calmette guerin (rBCG), and relates to a shuttle expression vector comprising a signal peptide fragment of a major secretory antigen Ag85B of BCG and a gene fragment of a TRAIL and a construction method thereof. The obtained shuttle expression vector pMV261-Ag85B-TRAIL is used for constructing rBCGTRAIL, and can be applied to preparation of TRAIL rBCG for treating superficial bladder tumors, preventing postoperative recurrence thereof and preventing tuberculosis. The rBCG has dual functions of TRAIL and BCG, so that cooperative and synergistic actions of the TRAIL and BCG can be better brought into play; rBCG-TRAIL can secrete TRAIL, and the using amount of the rBCG-TRAIL can be lower than that of the BCG under the condition that the same or better immune effect is achieved, so that the toxic or side effect is reduced; and the rBCG-TRAIL can directly secrete TRAIL efficiently on a certain part, so that tumor cells can be killed in cooperation with the rBCG-TRAIL, and high cost caused by the use of a foreign cell factor is avoided.
Owner:沈周俊
Chinese traditional medicine soup composition and method of making the same
InactiveCN101095851APromote recoveryGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsMetabolism disorderDiseaseBletilla striata
The invention relates to a Chinese medicinal soup for treating tuberculosis, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, as well as kidney diseases, which is prepared from Siberian solomonseal rhizome, fleece-flower root, bletilla striata, spatholobus stem and glutinous rice through mincing. The soup can be used for breakfast.
Owner:戴光凯
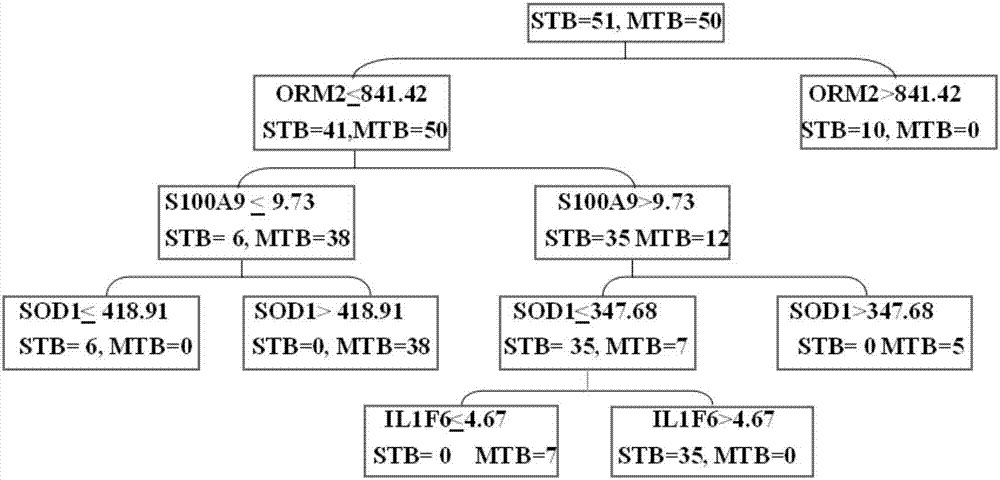
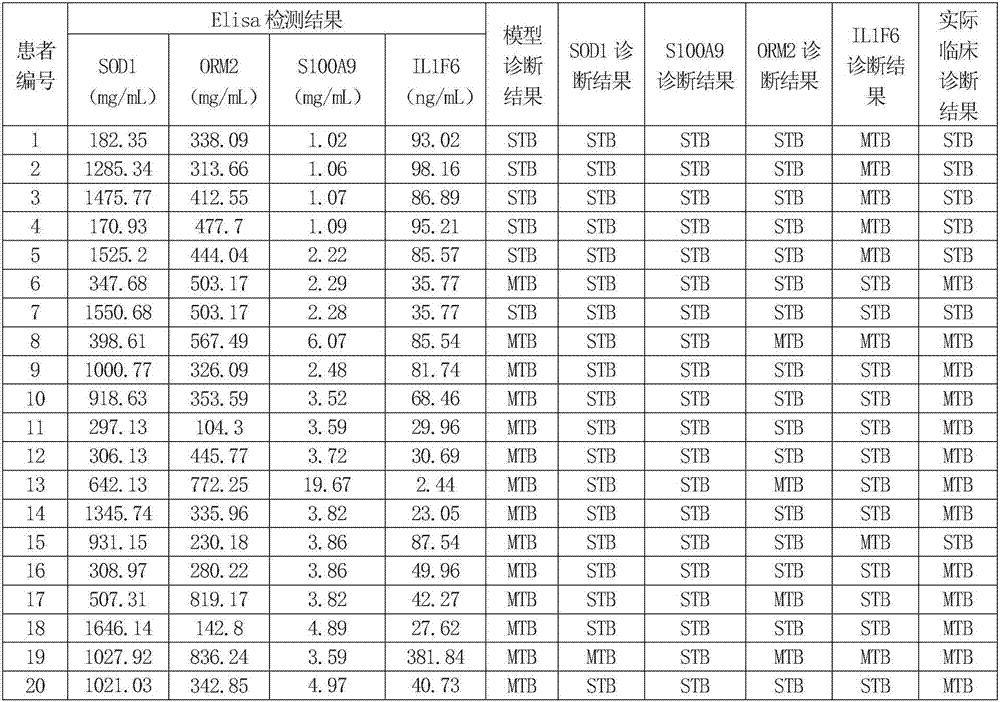
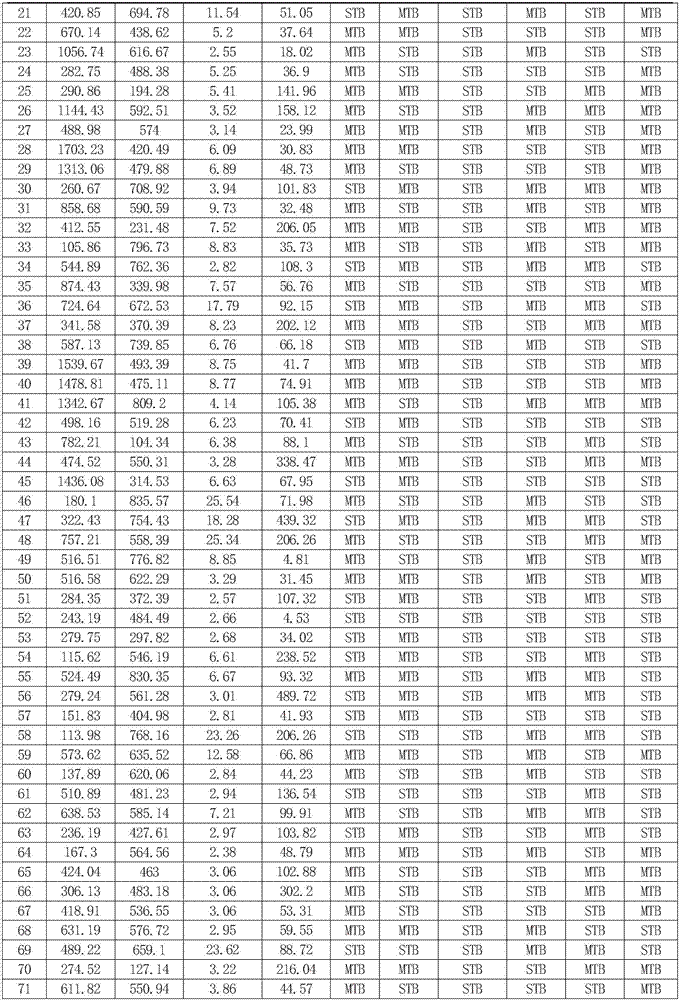
Protein markers assisting diagnosis of severe secondary pulmonary tuberculosis
The invention discloses protein markers assisting diagnosis of severe secondary pulmonary tuberculosis. The invention provides applications of a product for detecting SOD1 protein, a product for detecting S100A9 protein, a product for detecting ORM2 protein and a product for detecting IL1F6 protein in preparation of a kit used for assisting diagnosis of severe secondary pulmonary tuberculosis. The four protein markers (S100A9, ORM2, IL1F6 and SOD1) assisting diagnosis of the severe secondary pulmonary tuberculosis are found, and a model for assisting diagnosis of the severe secondary pulmonary tuberculosis by utilizing the four protein markers is built. The protein markers provide basis for further explanation of developing and aggravating mechanisms of the secondary pulmonary tuberculosis, provide a novel method and novel indexes for disease development, aggravation early warning, and forecast evaluation, lays a foundation for reasonable treatment and cure of the severe secondary pulmonary tuberculosis, and provides technical supports for reducing the death rate of pulmonary tuberculosis.
Owner:BEIJING CHEST HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
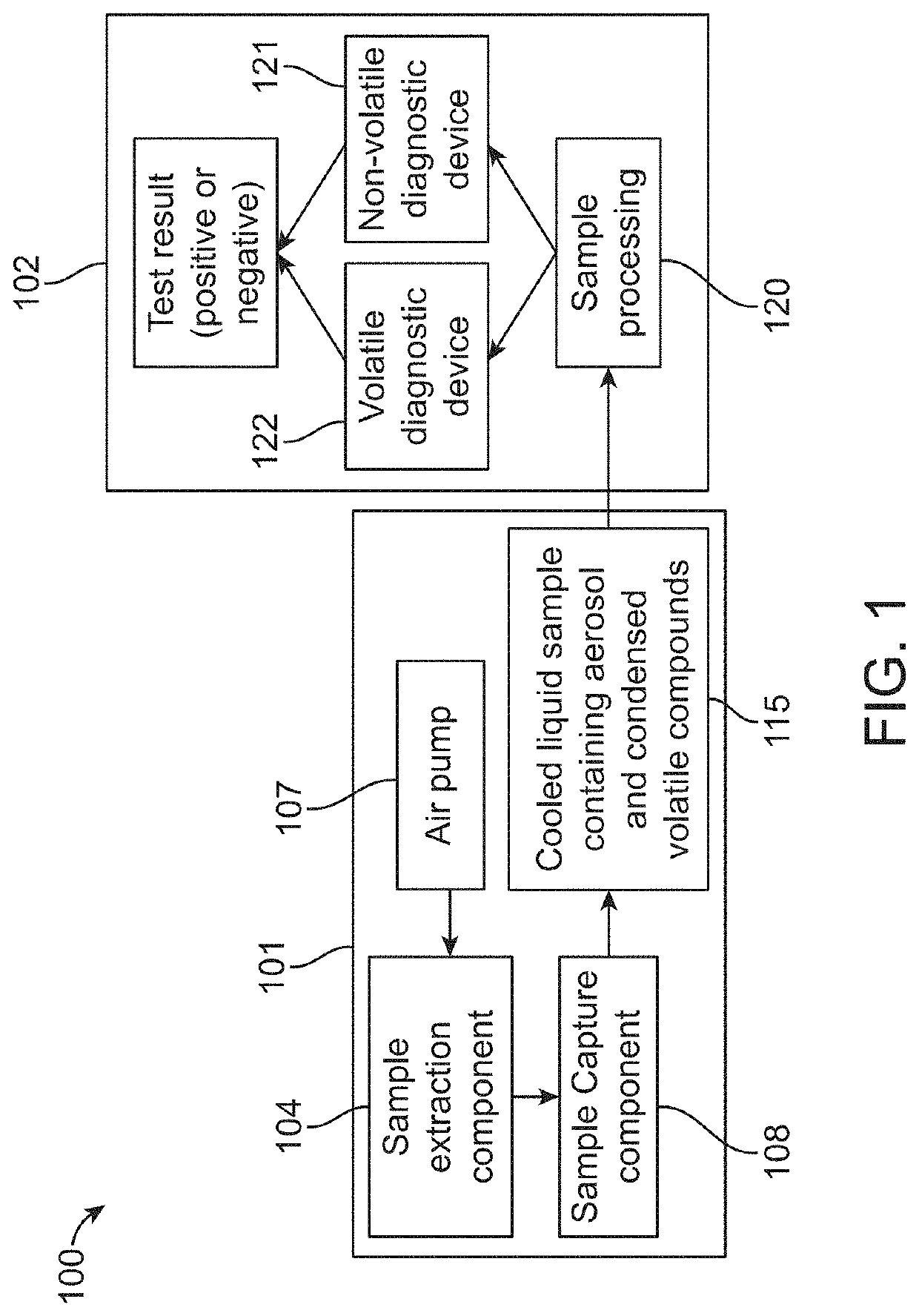
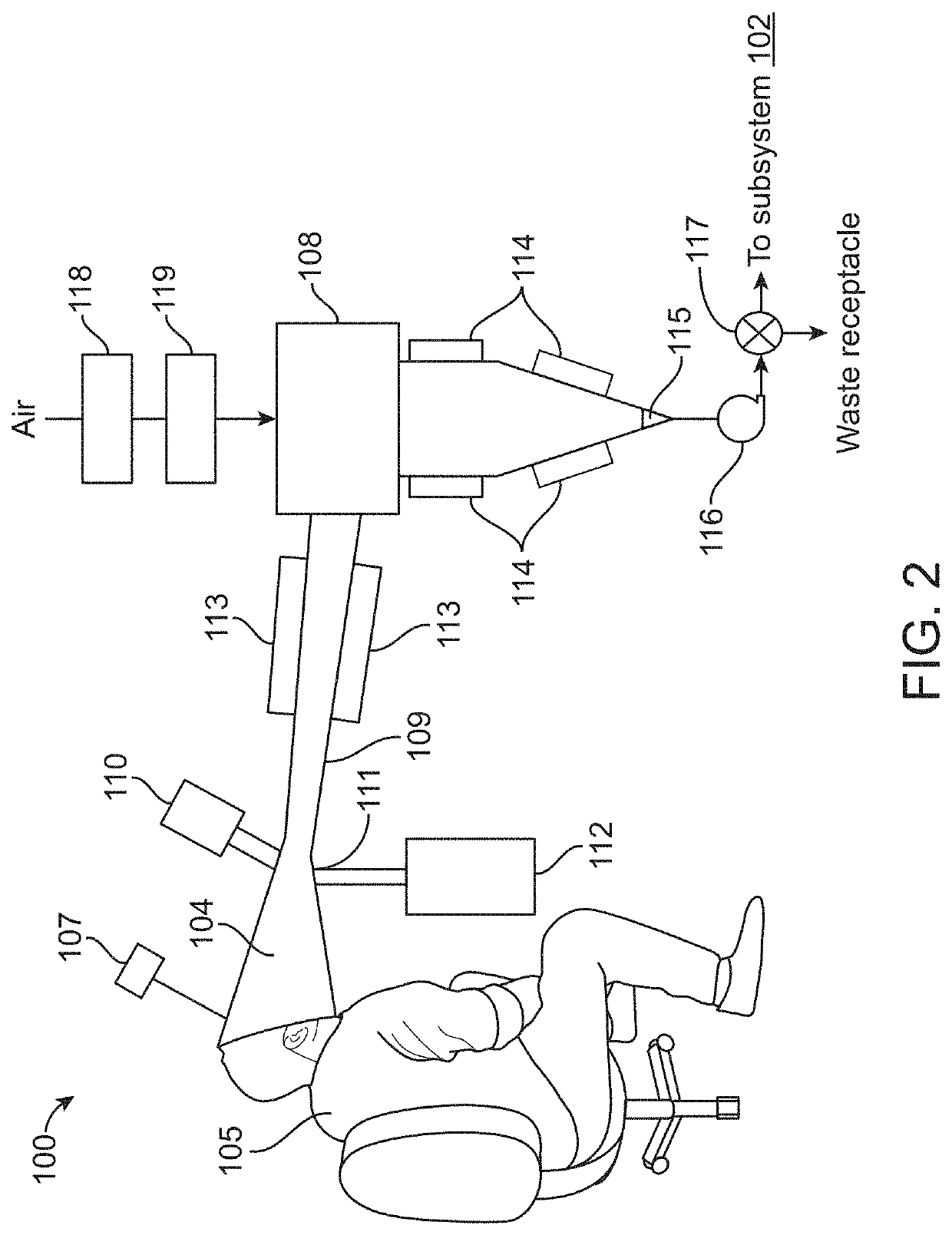
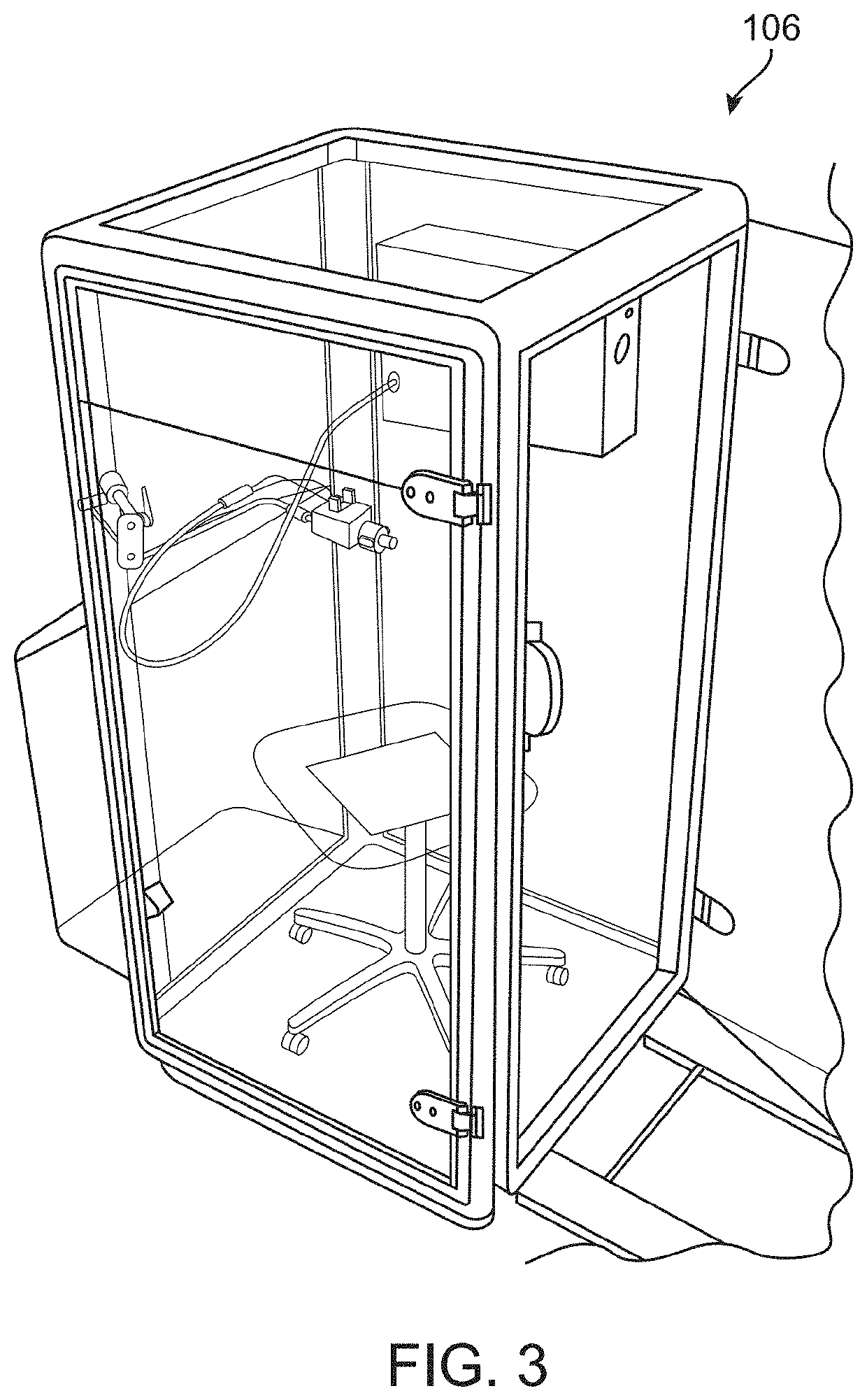
Device and methods for detection and monitoring of tuberculosis
PendingUS20210282678A1Fast and reliable diagnosingAccuracy of diagnosisRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsTest sampleMicrobiology
Methods of diagnosing and / or monitoring tuberculosis (TB) in a subject by analyzing a test sample comprising at least one volatile organic compound (VOC) or semi-volatile organic compound (SVOC) emitted or excreted from the skin of the subject. The test sample can be analyzed by a sensing unit comprising nanomaterials- and / or polymer-based sensors. Further provided is a skin-mountable device comprising a fixing unit and said sensing unit. Also discloses a method of diagnosing and / or monitoring tuberculosis, comprising analyzing specific skin-emitted VOCs or SVOCs, which are indicative of tuberculosis in a subject.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
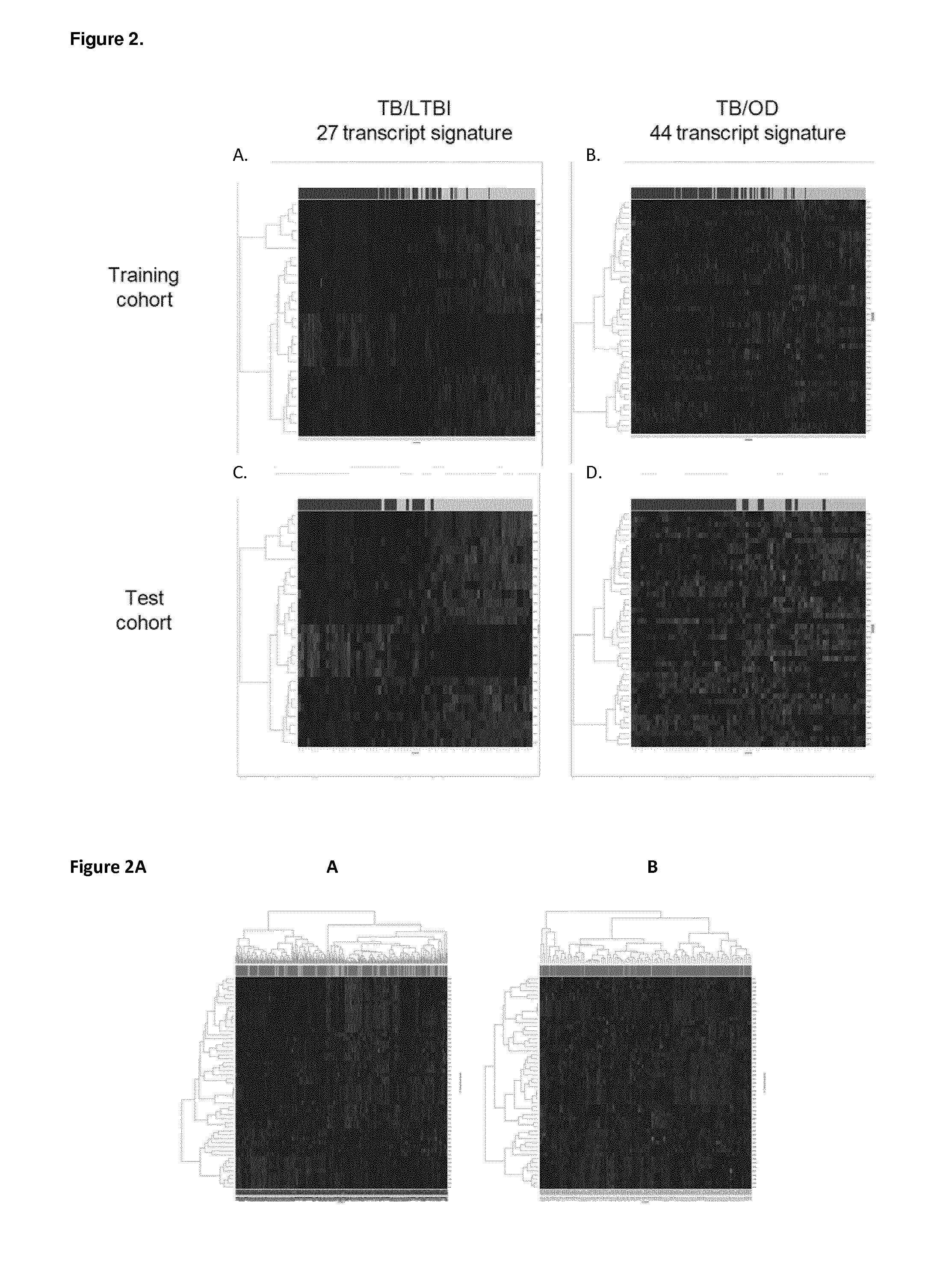
Diagnosis of active tuberculosis by determining the mRNA expression levels of marker genes in blood
InactiveUS20150203899A1Robust and accurate identificationAppropriate treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDiseaseLatent tuberculosis
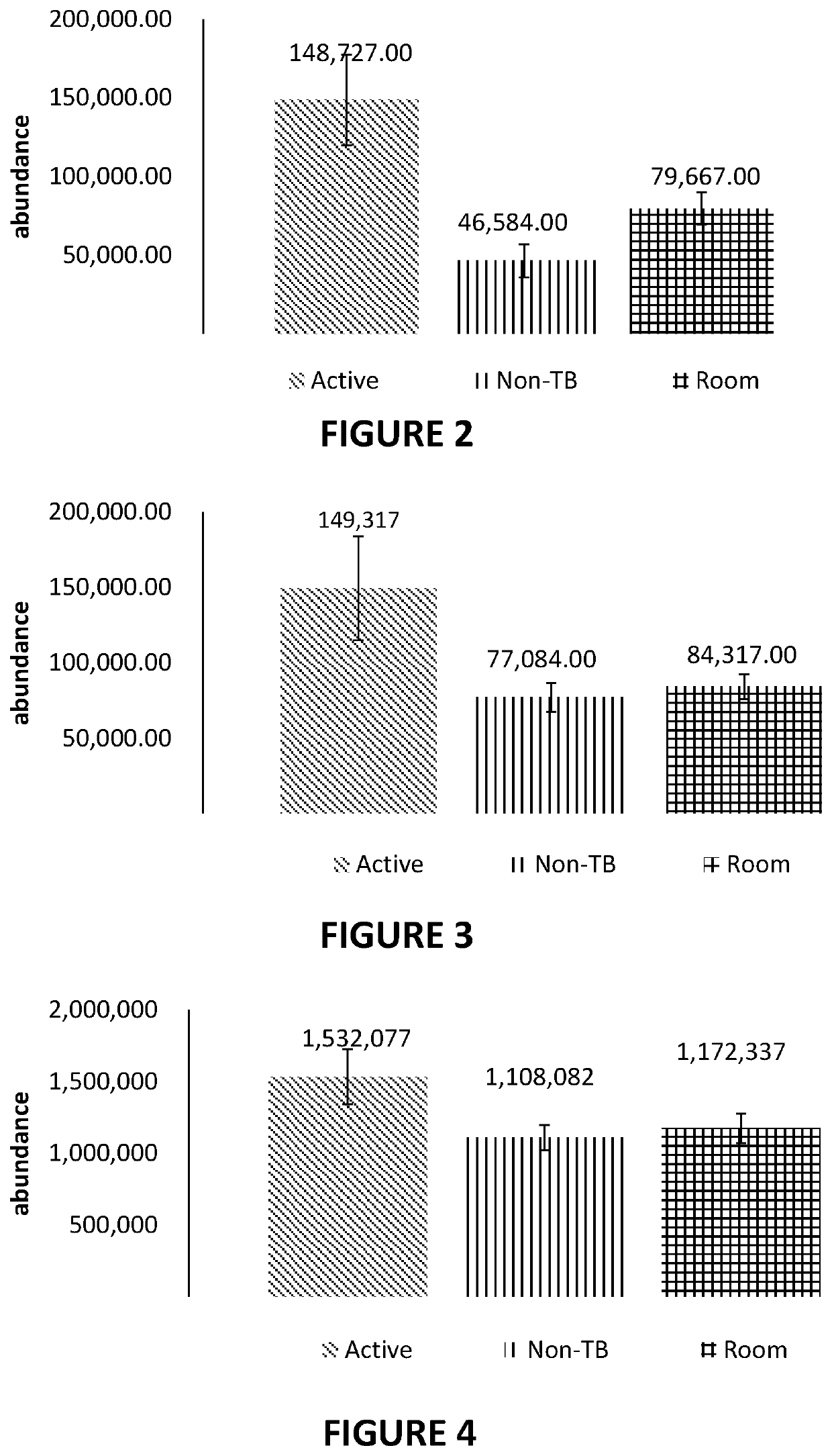
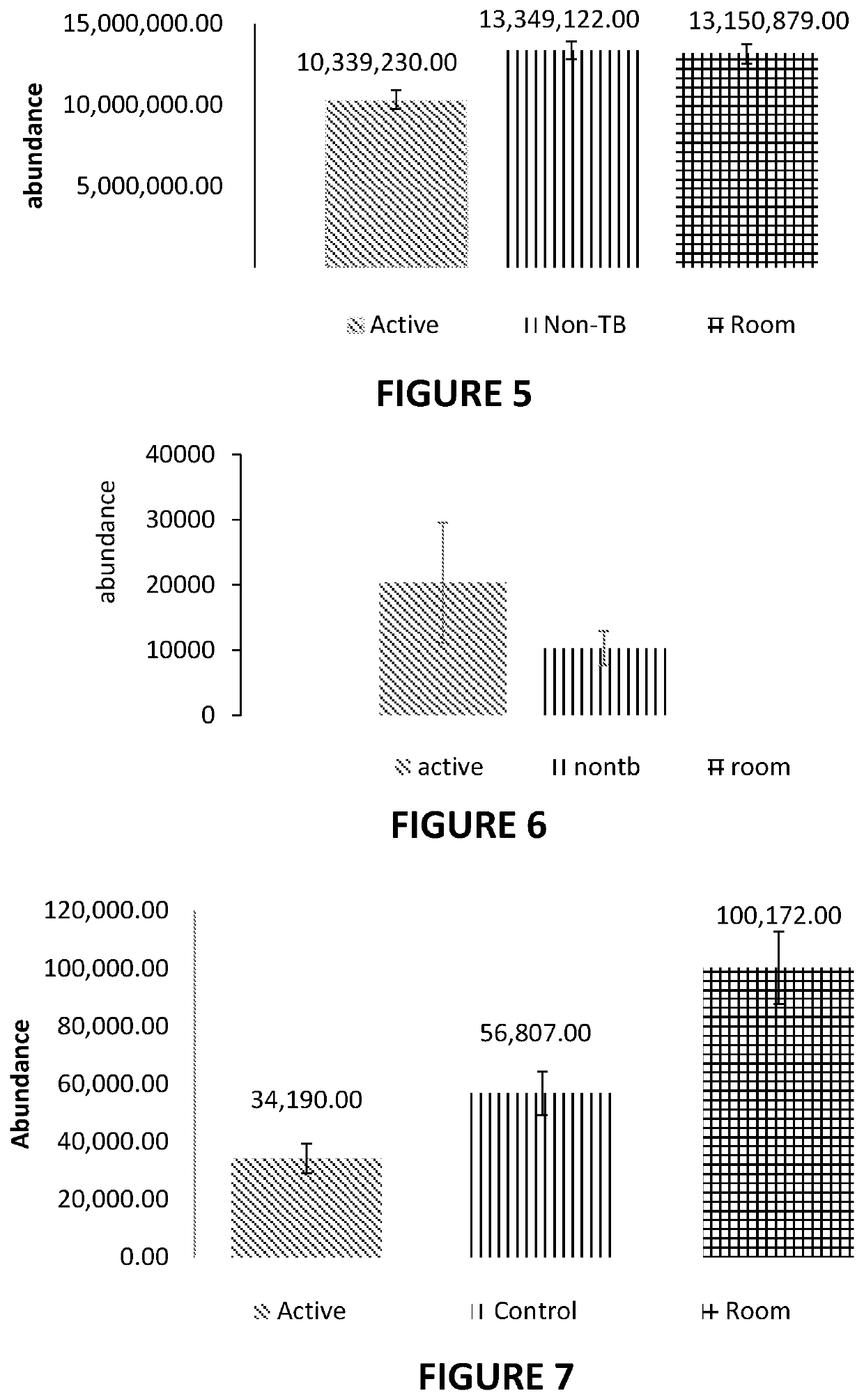
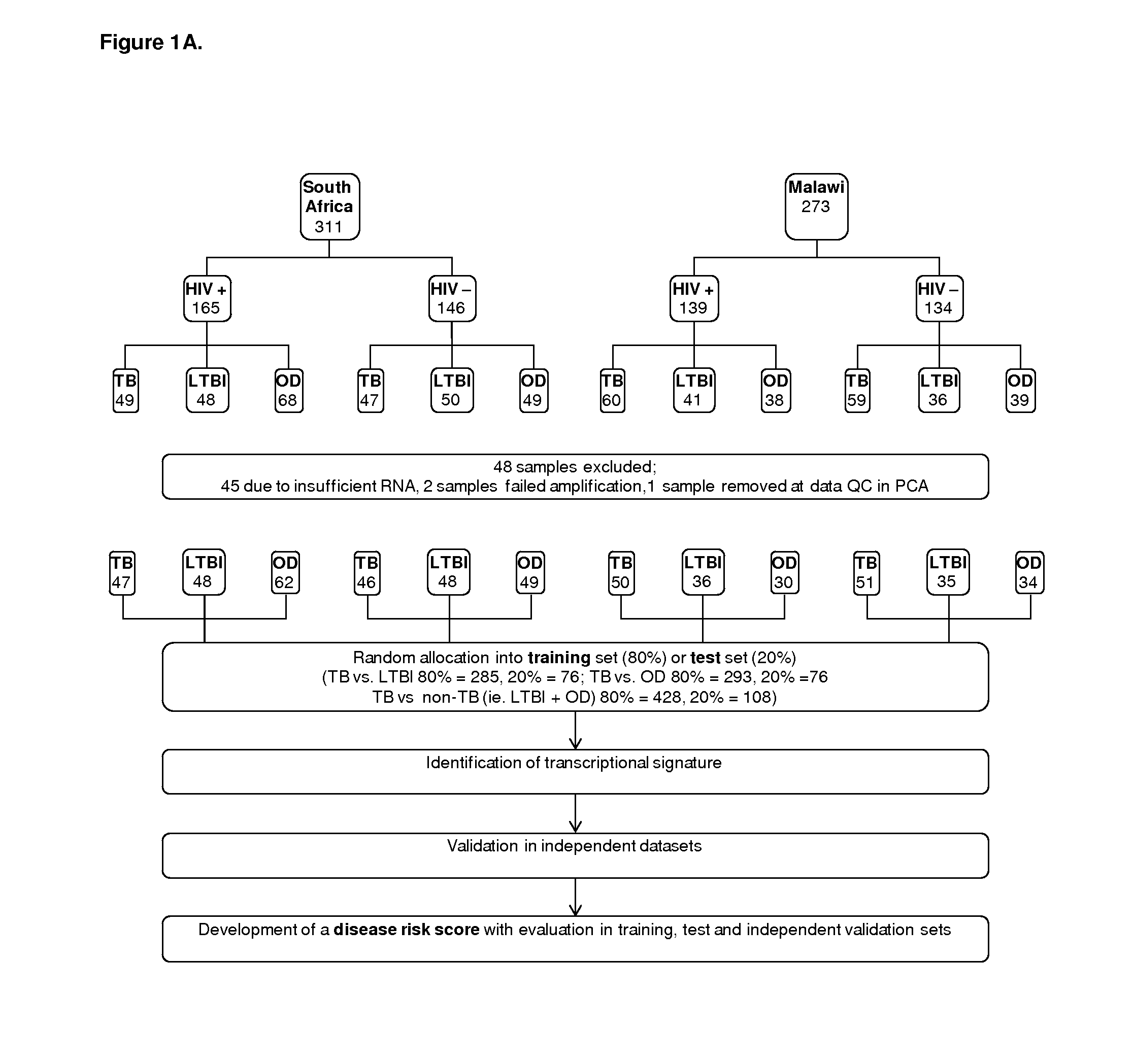
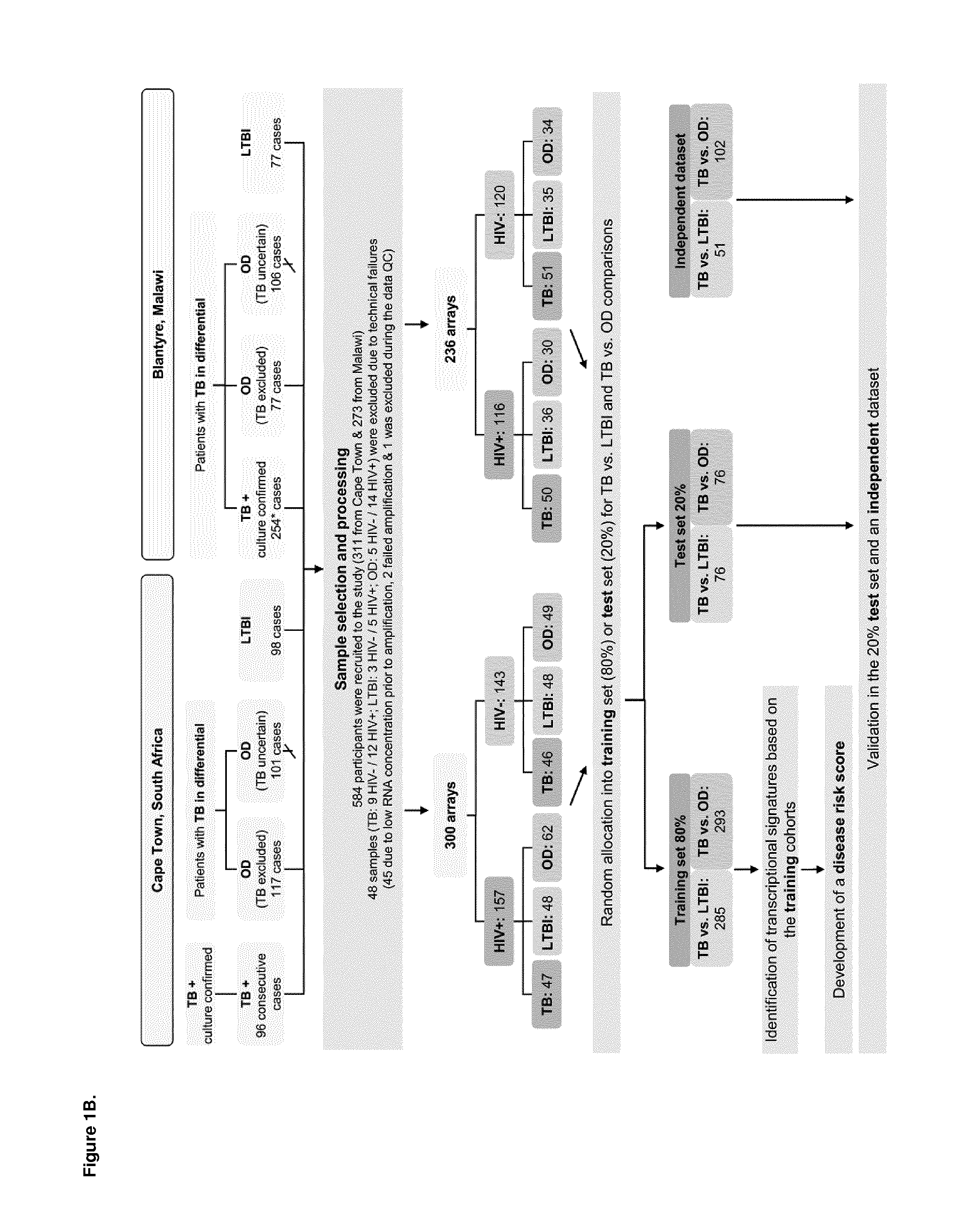
The present disclosure relates to a method of distinguishing active TB in the presence of a complicating factor, for example, latent TB and / or co-morbidities, such as those that present similar symptoms to TB, such as HIV. The method employs a 27 gene signature to distinguish active tuberculosis from latent TB infection, a 44 gene signature to distinguish active TB from other diseases such as HIV and / or a 53 gene signature to discriminate active TB from latent TB and other diseases. The disclosure also relates to a gene signature employed in the method, a bespoke gene chip for use in the method and a disease risk score obtainable from the method.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Tuberculosis resistance Chinese medicine, special adjuvant and method of preparing the same
InactiveCN101249105AReduce dosageSignificant effectAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryYolkPulmonary tuberculoses
The invention relates to an anti-tuberculosis Chinese medicine, a special adjuvant medicine and a preparation method thereof. Pharmaceutically-effective raw materials of the anti-tuberculosis Chinese medicine comprise blister beetle, drgon's bone, oyster, chicken gizzard-membrane, pumice and egg white of 10 eggs (yolk removed). The adjuvant medicine is water soaking liquid or water decoction of one or more selected from milkvetch root, licorice root, ginseng, radix codonopsis, milkvetch root, red jujube and wine-processed twotoothed achyranthes root. The medicine has the effects of removing blood stagnation and eliminating pathogenic accumulation, and is mainly used to treat pulmonary tuberculosis, tuberculous pleurisy, pyogenic osteomyelitis, bone tuberculosis, tuberculosis of thoracic and lumbar vertebra, lymphoid tuberculosis, tuberculous peritonitis, silicosis complicated with tuberculosis, and acute lymphadenitis.
Owner:朱天柱
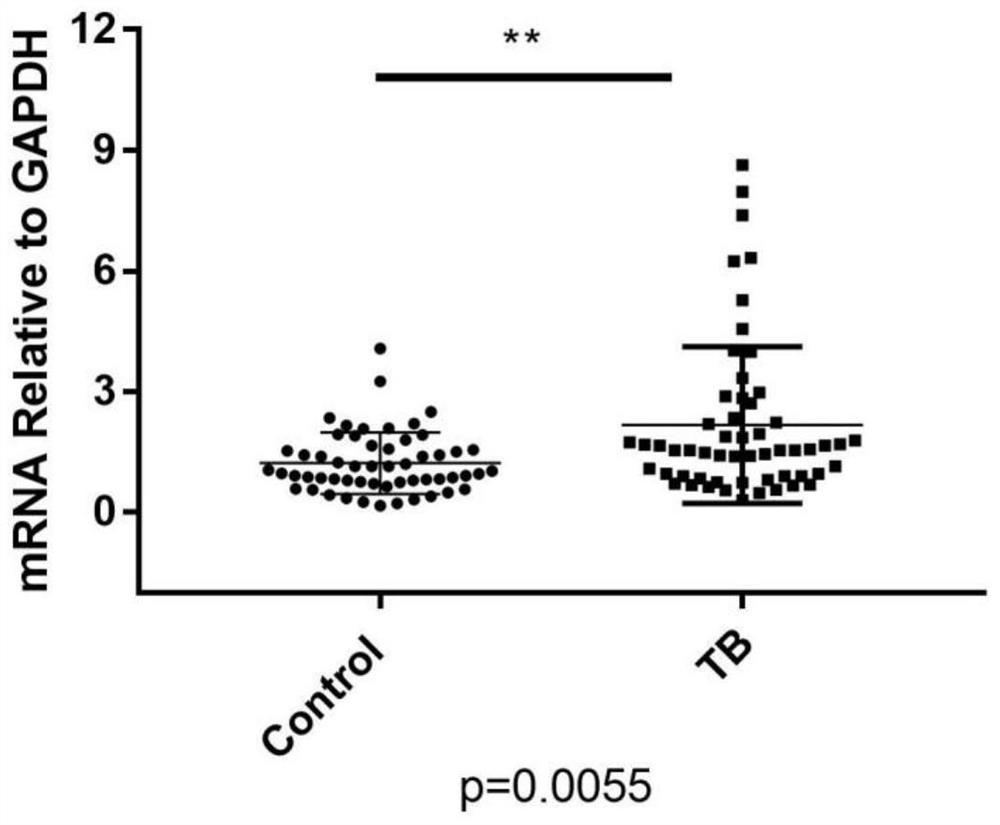
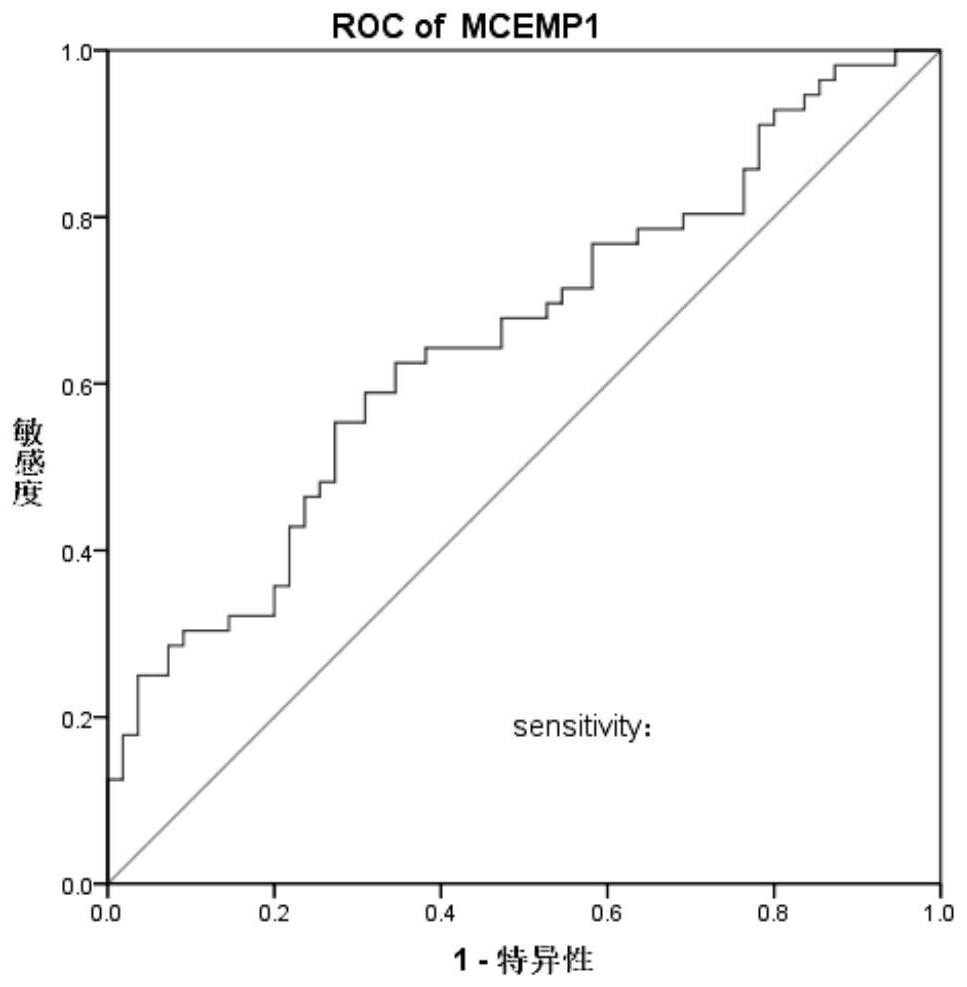
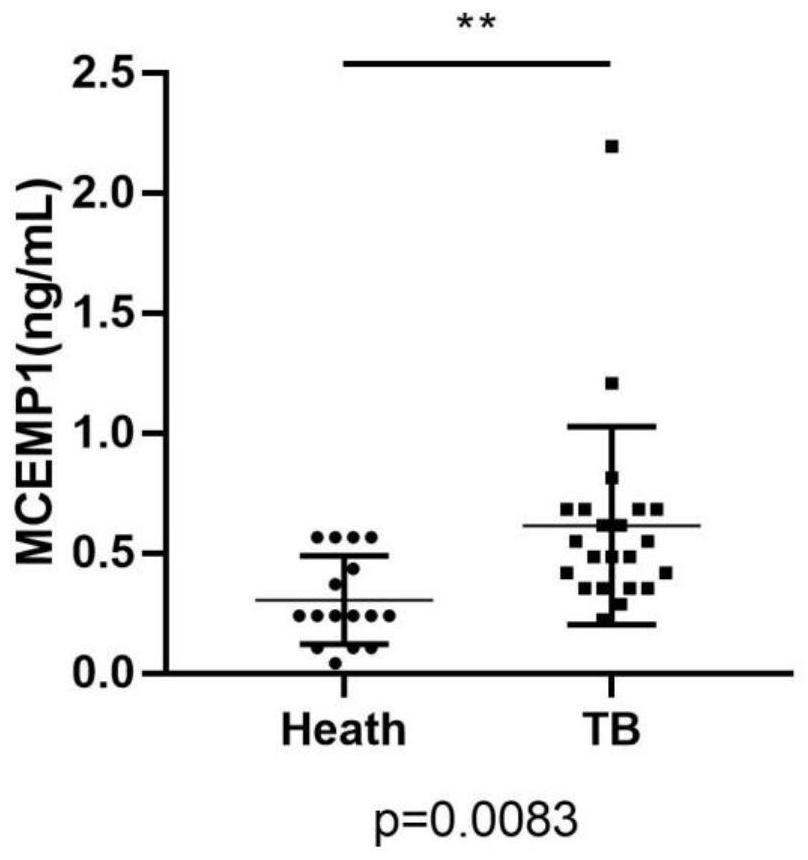
Active tuberculosis diagnostic marker, kit and application thereof
PendingCN112094896AStrong specificityOvercoming low diagnostic detection ratesMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisTotal rnaBlood biomarkers
The invention provides an active tuberculosis diagnostic marker, a kit and application thereof. The diagnostic marker is characterized by comprising a blood biomarker MCEMP1 protein in a blood sample,the amino acid sequence of the MCEMP1 protein is as shown in the SEQ ID NO:1. The invention further provides the kit capable of rapidly detecting whether a subject suffers from active tuberculosis ornot. The kit comprises a total RNA extraction related reagent in a whole blood sample, a quantitative PCR related reagent and an ELISA related reagent. According to the active tuberculosis diagnosticmarker, the MCEMP1 is adopted as a biomarker for active tuberculosis detection for the first time, is used for clinical diagnosis and differential diagnosis of tuberculosis, and provides a new direction for clinical diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
Diagnosis of tuberculosis and other diseases using exhaled breath
PendingUS20220034854A1Increase the burdenLimited accessComponent separationHumidity sensorsDiseaseRespiratory tract disease
Disclosed are methods and devices for analyzing aerosol particles in exhaled breath using diagnostic tools that enable rapid, low cost and autonomous point of care assays for several diseases including respiratory tract diseases. Disclosed are methods and devices for capturing exhaled breath aerosols in a packed bed column and analyzing exhaled captured breath aerosols for tuberculosis diagnosis.
Owner:ZETEO TECH INC
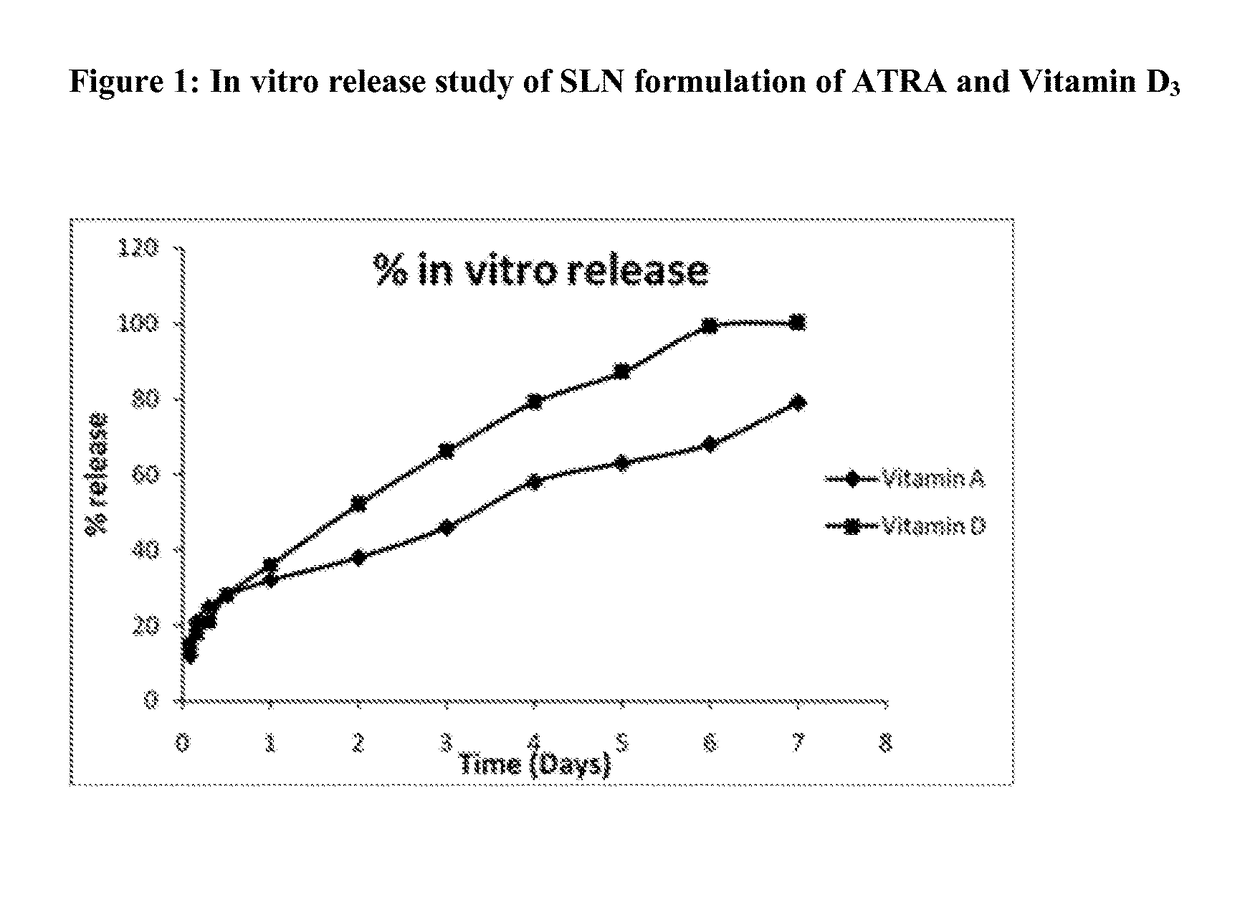
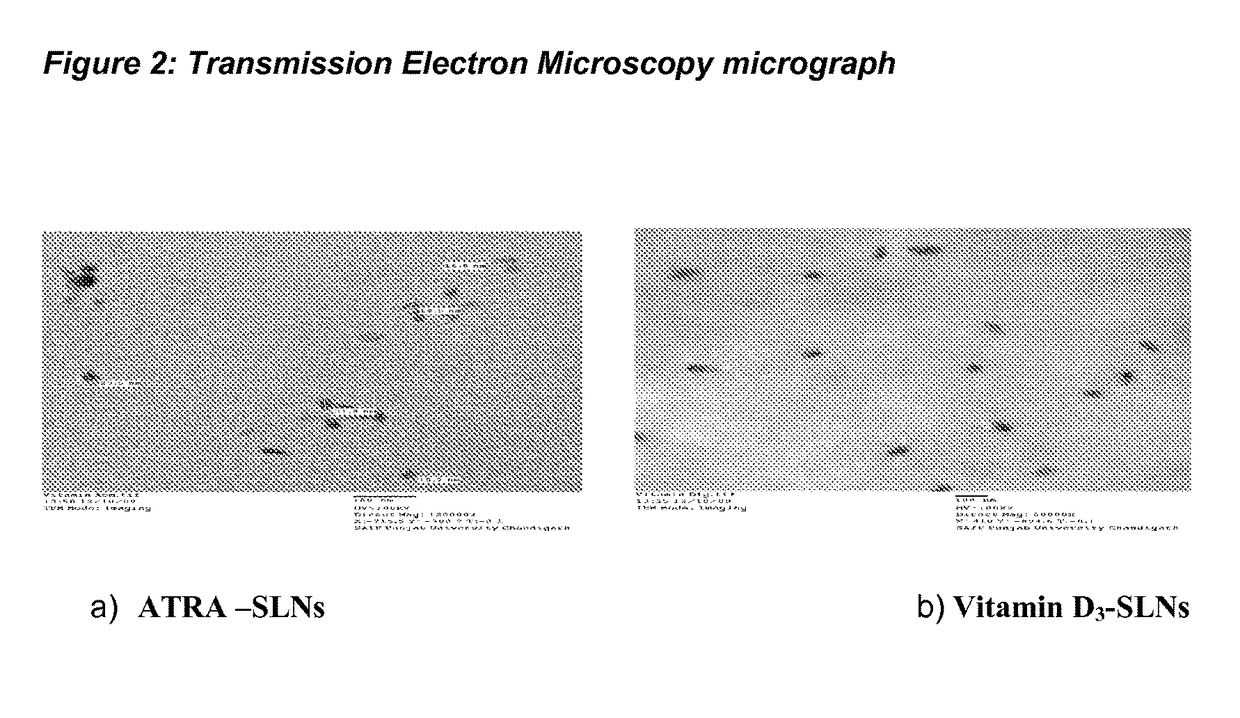
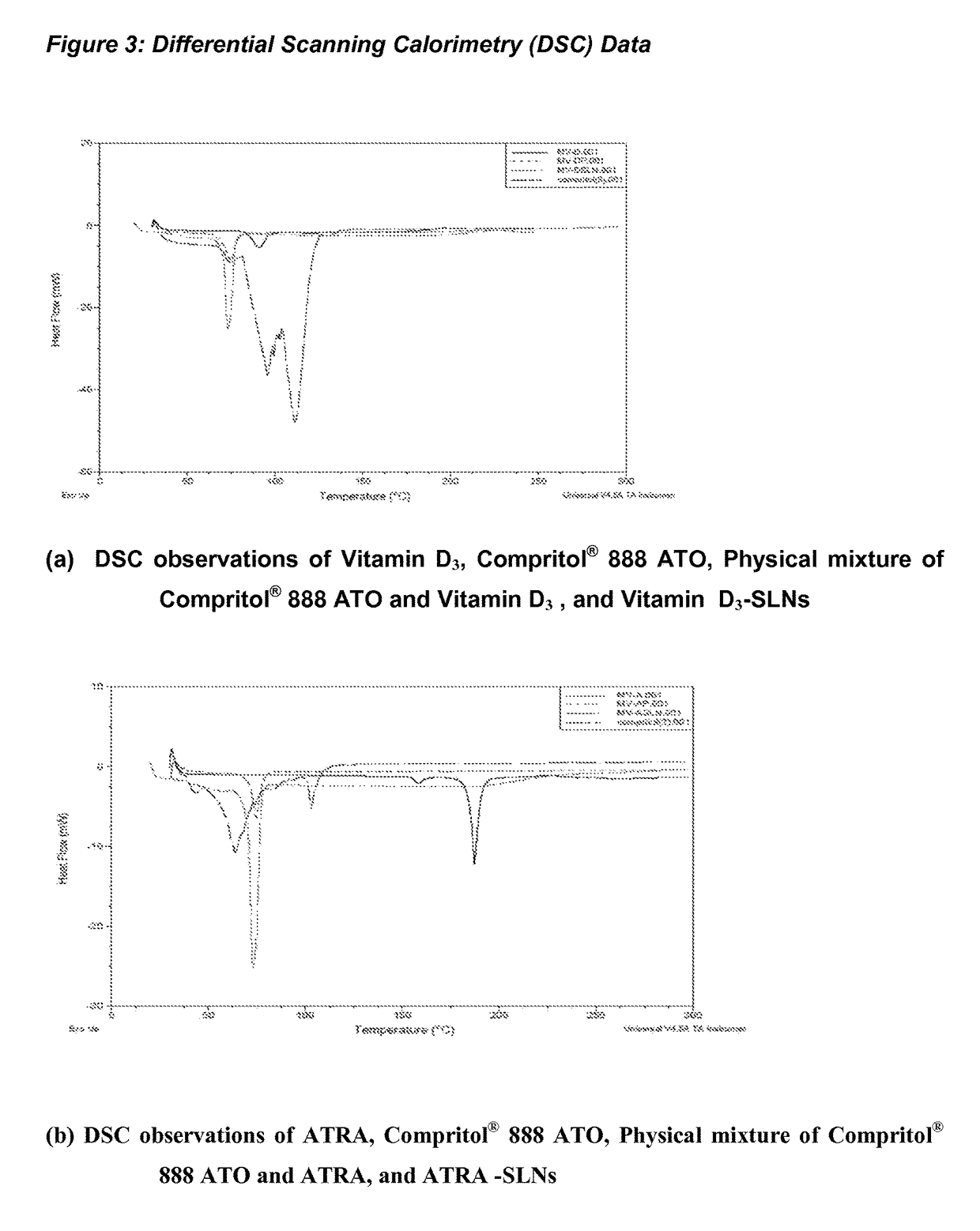
Process for preparing solid lipid sustained release nanoparticles for delivery of vitamins
The present invention relates to a simple and convenient process for preparing solid lipid sustained release nanoparticles for delivery of drugs / vitamins, preferably fat soluble vitamins and more specifically Vitamin D3 and retinoic acid (RA). The process involves microemulsion technique. The nanoparticles of Vitamin D3 and RA obtained by the process of the present invention have utility in treatment of diseases like tuberculosis. Use may be extended to other diseases like AMD, diabetic retinopathy, cancers, hyperpigmentation, acne, and osteoporosis.
Owner:DEPT OF BIOTECHNOLOGY MINIST OF SCI & TECH GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
Method of detecting cancer and/or tuberculosis
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Tb biomarkers
InactiveUS20190062812A1Avoid manipulationAvoid stimulationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCut off valueBlood plasma
The invention relates to a method for the diagnosis of TB in a subject, the method comprising (a) providing a sample from said subject, said sample being selected from the group consisting of: blood, serum and plasma; (b) determining the concentration in said sample of the following biomarkers: IL-1ra, IL6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-12p70, FGF-basic, IP-10, and VEGF; (c) converting each biomarker concentration determined in (b) into a decile value; and (d) converting each decile value into a binary presence or absence by comparing the decile values of (c) to the following specific quantile cut off values wherein a decile value matching or exceeding the specific quantile cut-off value is converted into the binary presence of the biomarker, and a decile value lower than the specific quantile cut-off value is converted into the binary absence of the biomarker; wherein detecting the presence of each of said biomarkers indicates that the subject has TB. The invention also relates to uses, kits and devices.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD +1
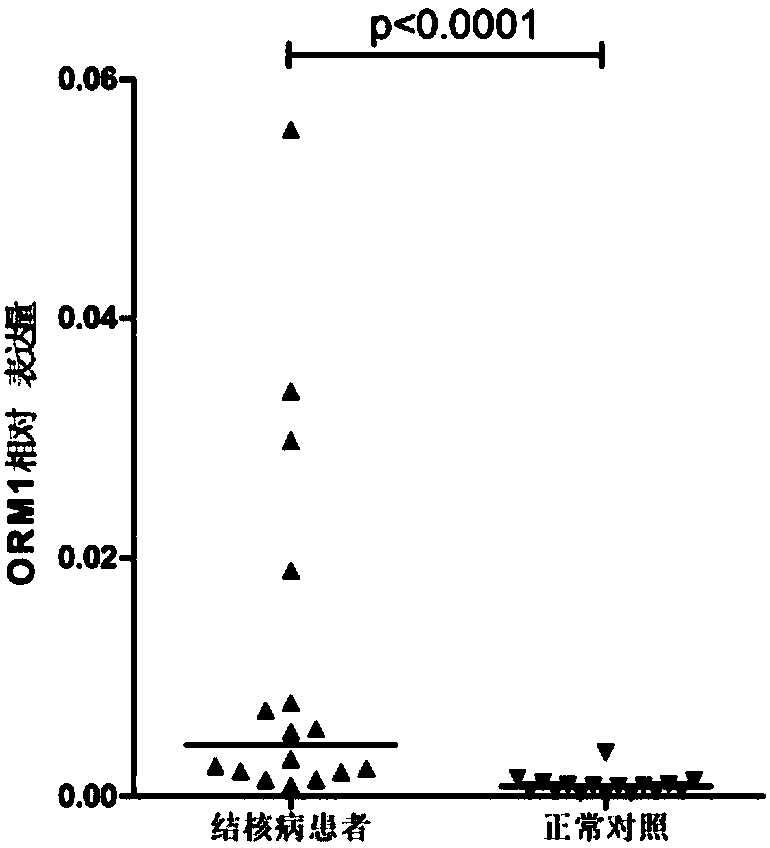
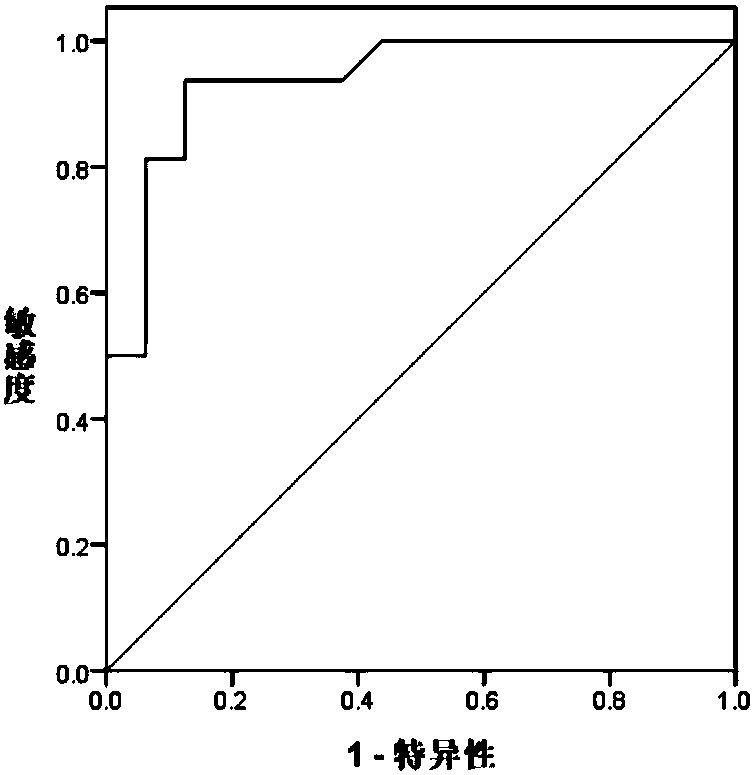
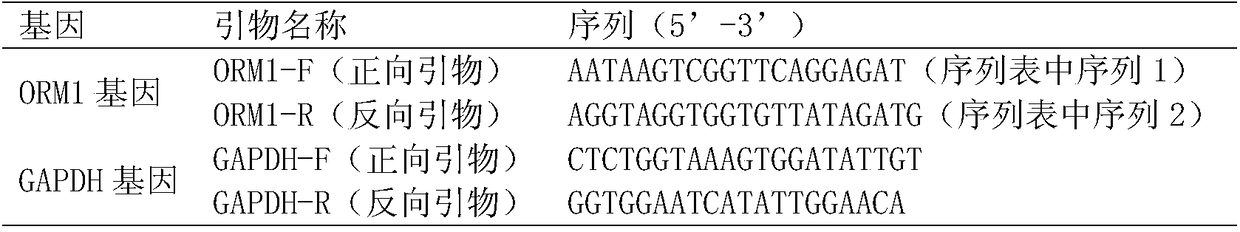
Application of system for detecting ORM1 (orosomucoid 1) gene expression quantity for diagnosing tuberculosis
InactiveCN108504736AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementTrue positive rateTuberculosis
The invention discloses an application of system for detecting an ORM1 (orosomucoid 1) gene expression quantity for diagnosing tuberculosis. The application discovers that the ORM1 gene expression quantity has an obvious difference in tuberculosis patients and healthy people; an analysis result of a subject job characteristic curve indicates that the ORM1 gene expression quantity is used for distinguishing that the tuberculosis patients and the healthy people have high sensitivity and specificity, which explains that the tuberculosis can be diagnosed through the detection of the ORM1 gene expression quantity of an object to be detected.
Owner:中国人民解放军第三0九医院
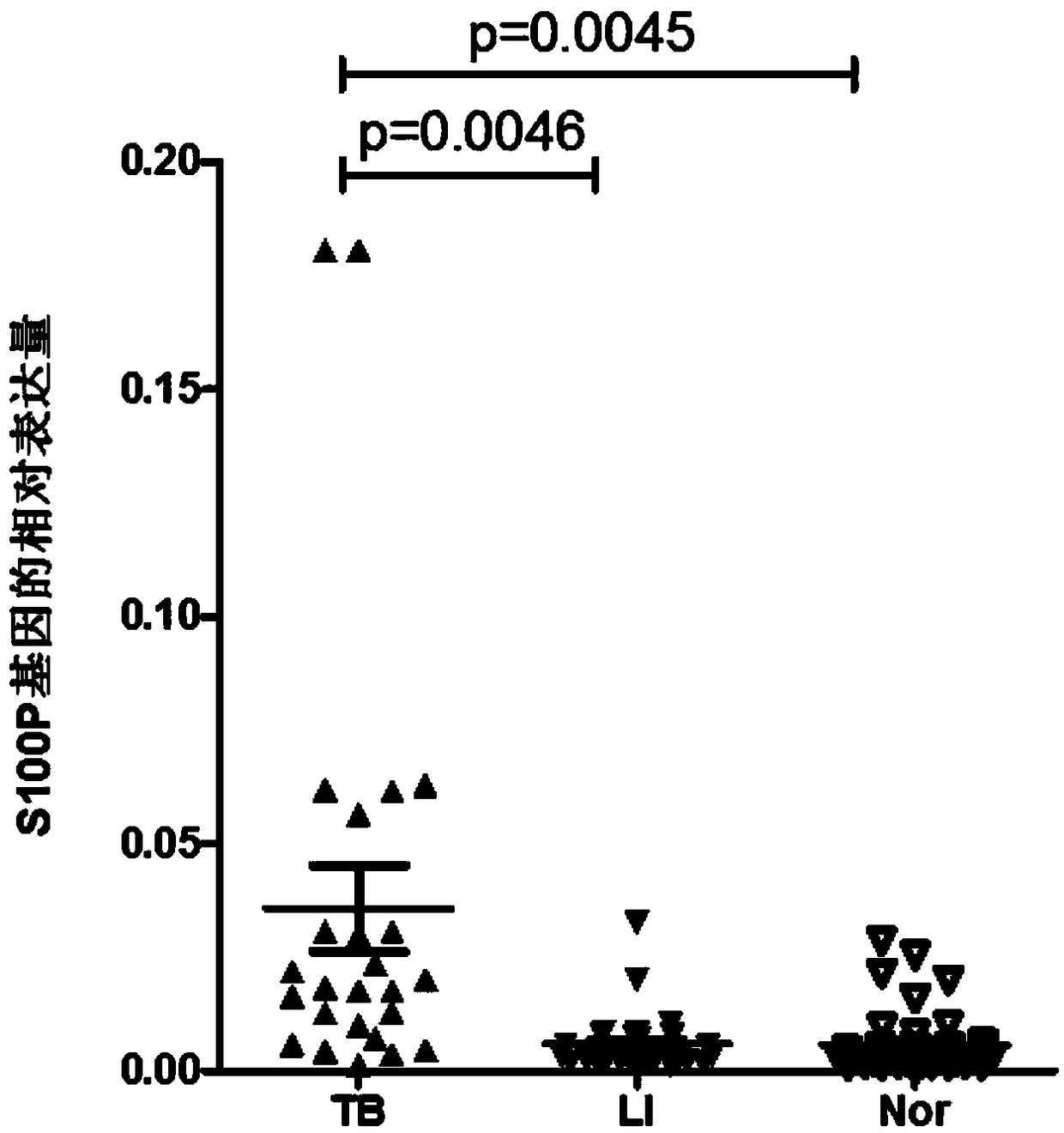
Application of S100P protein as marker in diagnosing active tuberculosis
The invention discloses application of S100P protein as a marker in diagnosing active tuberculosis. Compared with a healthy human and a tuberculosis latent infected person, the expression quantity ofS100P gene in PBMCs of an active tuberculosis patient is remarkably increased; the expression quantity of the S100P gene can be used for distinguishing the active tuberculosis patients and the tuberculosis latent infected persons; and the expression quantity of the S100P gene can be used for distinguishing the active tuberculosis patients and the healthy people. Therefore, the S100P protein and / orthe S100P gene can be used as the marker for diagnosing the active tuberculosis. The application has a great application value.
Owner:THE 309TH HOSPITAL OF CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Combination therapy for tuberculosis
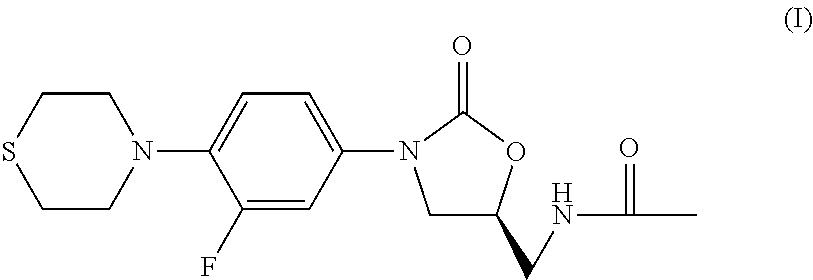
InactiveUS20170368070A1Prevent relapseAntibacterial agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsPharmaceutical medicineLatent tuberculosis
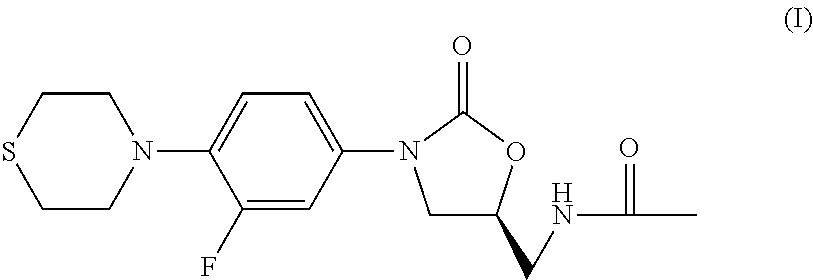
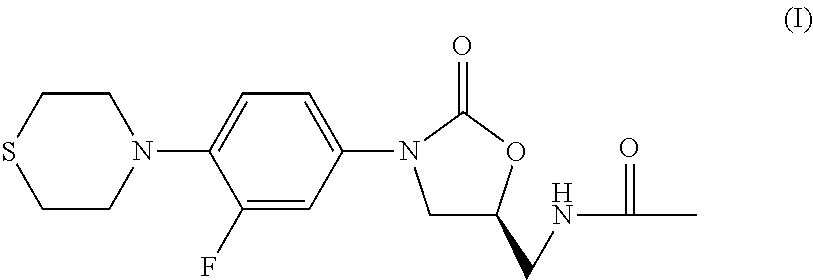
The present invention relates to methods of treating tuberculosis, including multidrug resistant varieties and latent tuberculosis. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of treating tuberculosis in a mammal comprising administering to said mammal in need thereof an effective amount of a compound of formula (T), (S)—N-[[3-[3-fluoro-4-(4-thiomor-pholinyl)phenyl]-2-oxo-5-oxazolidinyl]methyl]acetamide, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in combination with at least two agents useful in the treatment of tuberculosis. The present invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, (ii) a therapeutically effective amount of at least one agent useful in the treatment of tuberculosis and (iii) one or more pharmaceutically acceptable carriers or vehicles.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
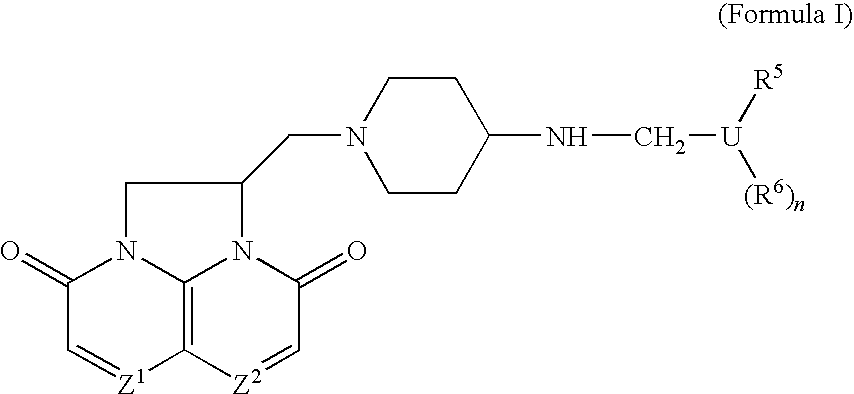
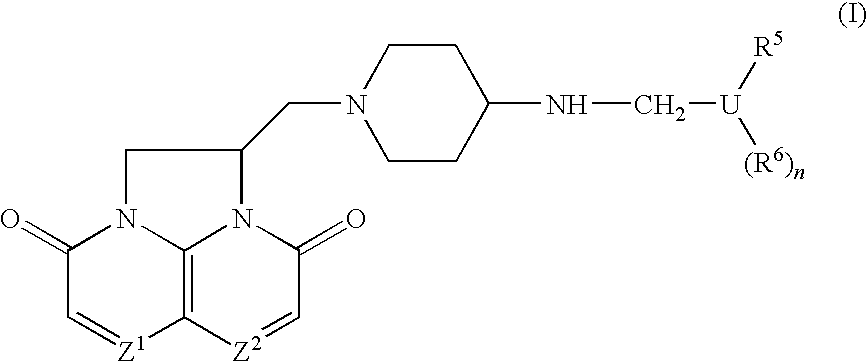
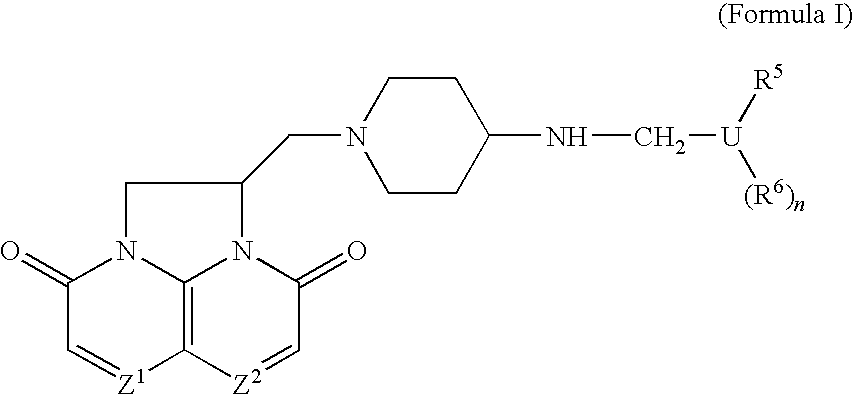
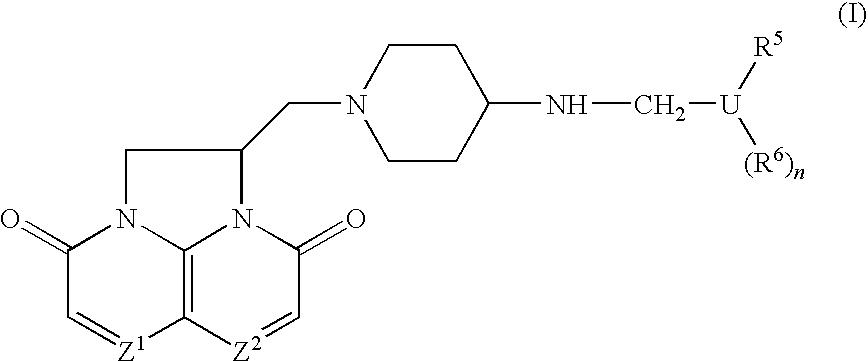
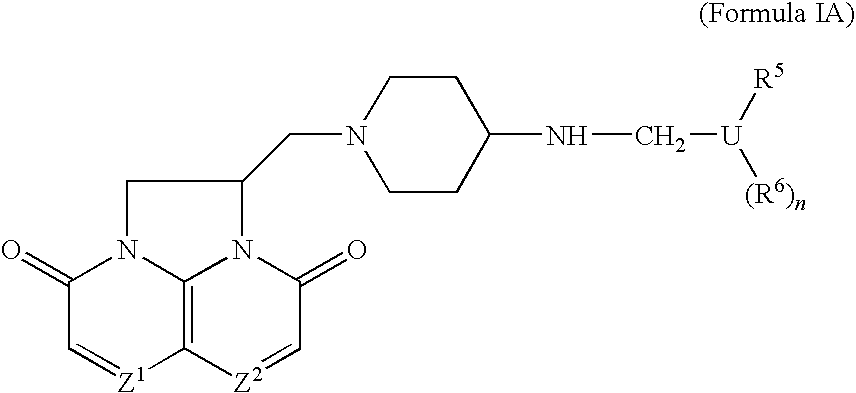
Compounds
Compounds of Formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salts or N-oxides thereof:(relative chemistry shown) pharmaceutical compositions comprising them, their use in therapy especially against tuberculosis, and methods of preparing them are described.
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
Medicine used for treating recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis
InactiveCN103006673AShorten the duration of treatmentHigh cure rateAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRifabutinPyrazine
The invention provides a medicine used for treating recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis. The medicine comprises, by weight, 5-12 parts of moxifloxacin, 18-24 parts of p-aminobenzoic isoniazid salicylate, 5-12 parts of rifabutin, 36-45 parts of pyrazinamide, and 18-24 parts of ethambutol. As a result of clinical verification, with the recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis medicine provided by the invention, recurrent pulmonary tuberculosis treatment period can be shortened, and a cure rate can be greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI PULMONARY HOSPITAL
Modified antigens
Modified Rv3616c proteins and their use as medicaments, particularly for the prevention of reactivation of tuberculosis.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA +1
Arsenic compound recipe for treating tuberculosis and dermatopathy
InactiveCN1546060ADefinite curative effectShort course of treatmentAntibacterial agentsInorganic active ingredientsPulmonary tuberculosisTreating tuberculosis
The invention discloses a compound arsenical preparation for treating tuberculosis and dermatosis, wherein the weight ratio of the raw materials is orpiment : aresenolite = (0.5-1.5) : (3-5), the preparation also contains right amount of medicinal carrying agent.
Owner:SHENYANG JINCHANG PHARMA
Compound paclitaxel anti-tuberculosis capsule tablet preparation method and process
PendingCN113101352AEfficient and safe treatmentNo damageAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellTuberculosis bacillus
The invention discloses a compound paclitaxel anti-tuberculosis capsule tablet preparation method and process, and the process comprises the following steps: step 1, taking a certain amount of paclitaxel extract for dilution, and carrying out separation and passivation treatment on the diluted paclitaxel extract; step 2, carrying out elution treatment on the separated and passivated paclitaxel extract, and carrying out recovery and concentration on the eluted paclitaxel. The paclitaxel anti-tuberculosis capsule tablet has the beneficial effects that the prepared paclitaxel anti-tuberculosis capsule tablet directly kills tubercle bacillus and cancer cell tissues by adopting toxic attack, protects normal cells, is free of toxic reaction, high in curative effect, short in medication time, free of damage to the liver. Meanwhile, the paclitaxel anti-tuberculosis capsule tablet can stimulate and adjust the immune defense function in vivo, enhance the digestion and absorption functions and improve the overall defense function while treating, so that the treatment of tuberculosis is more efficient and safer.
Owner:庞中龙
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com