Patents
Literature
52results about How to "Improve data transmission distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
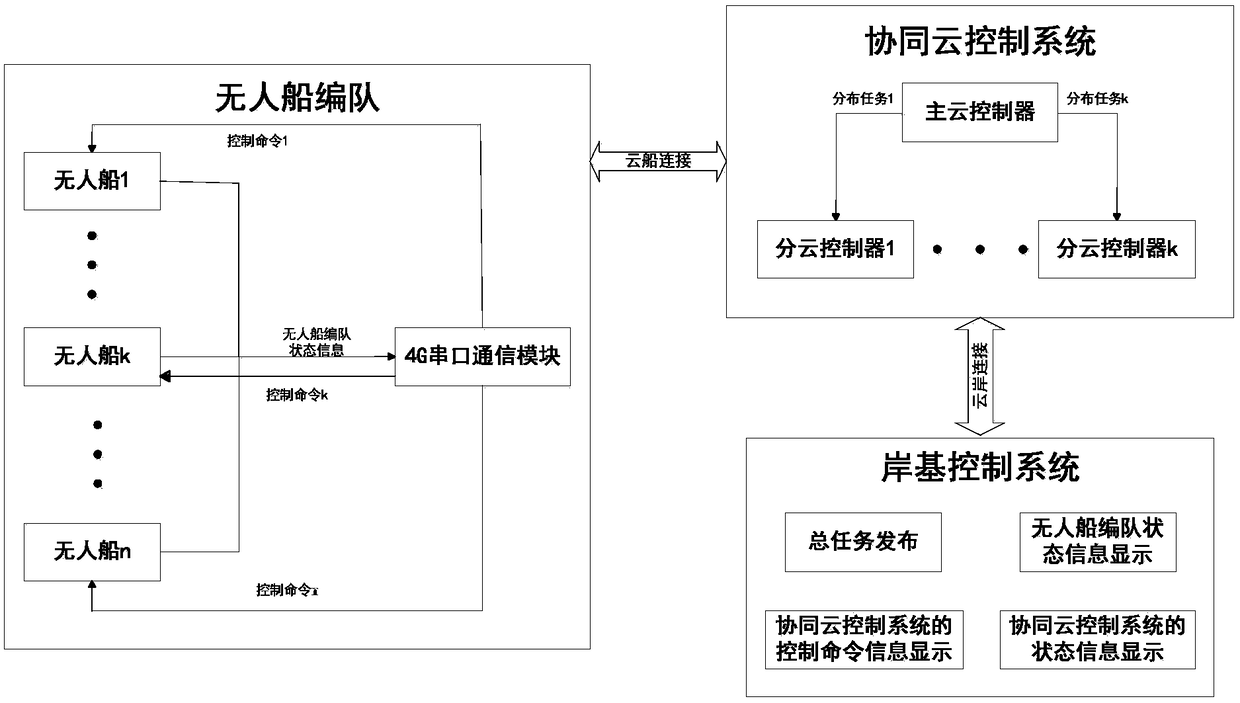
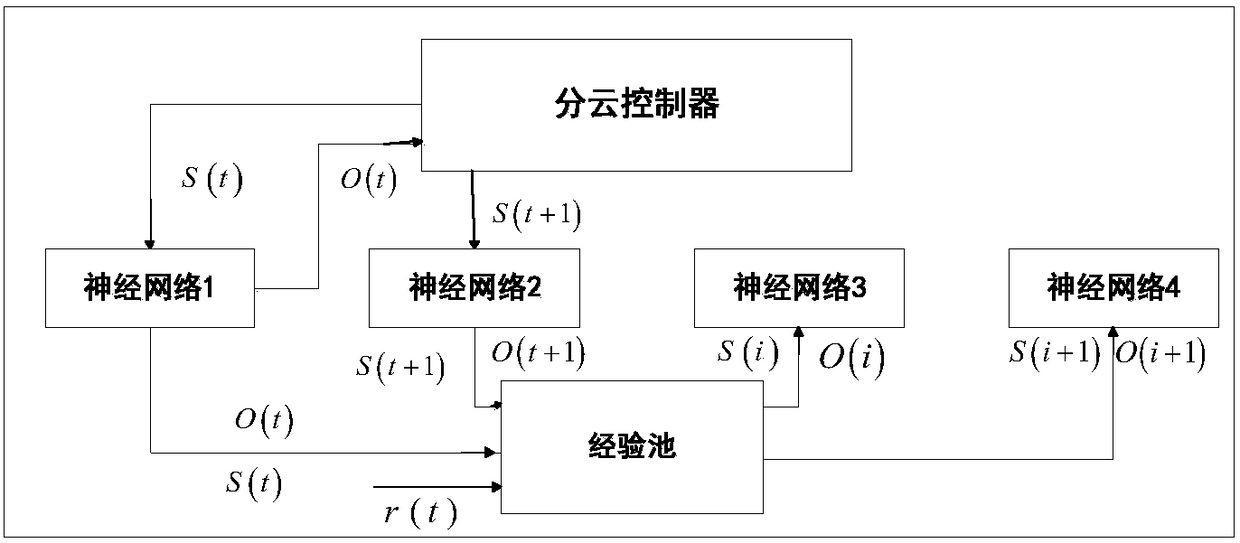
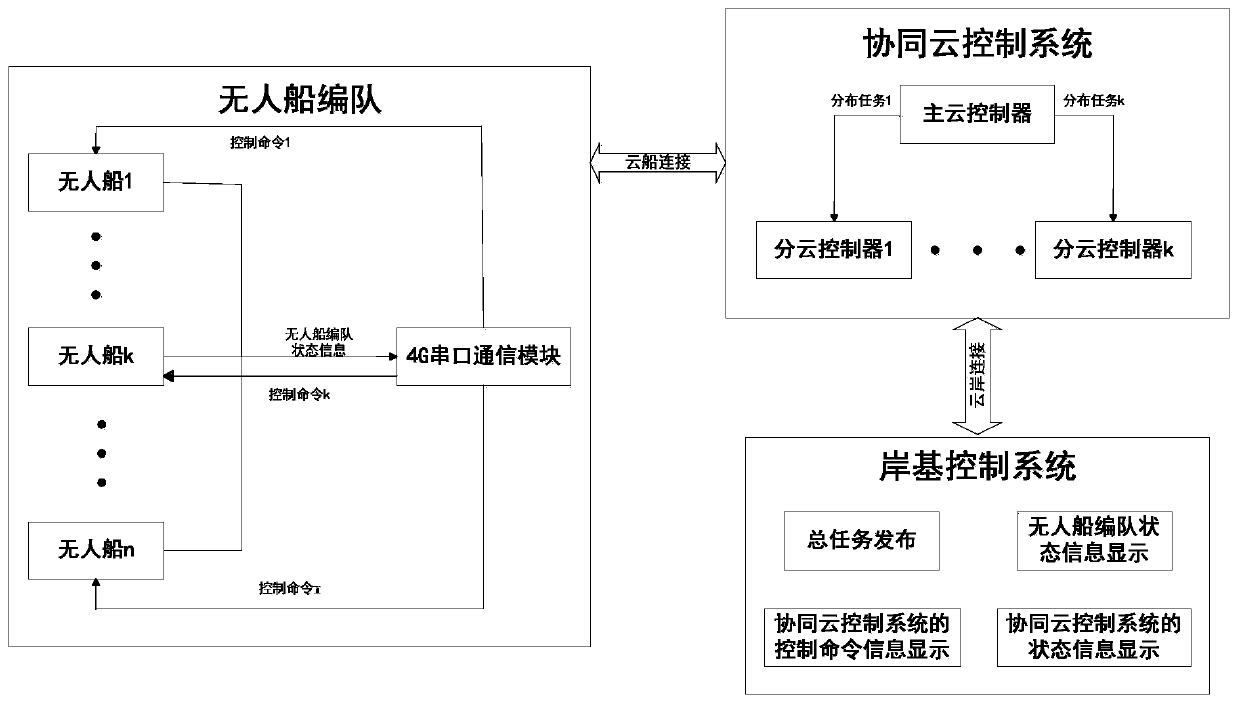
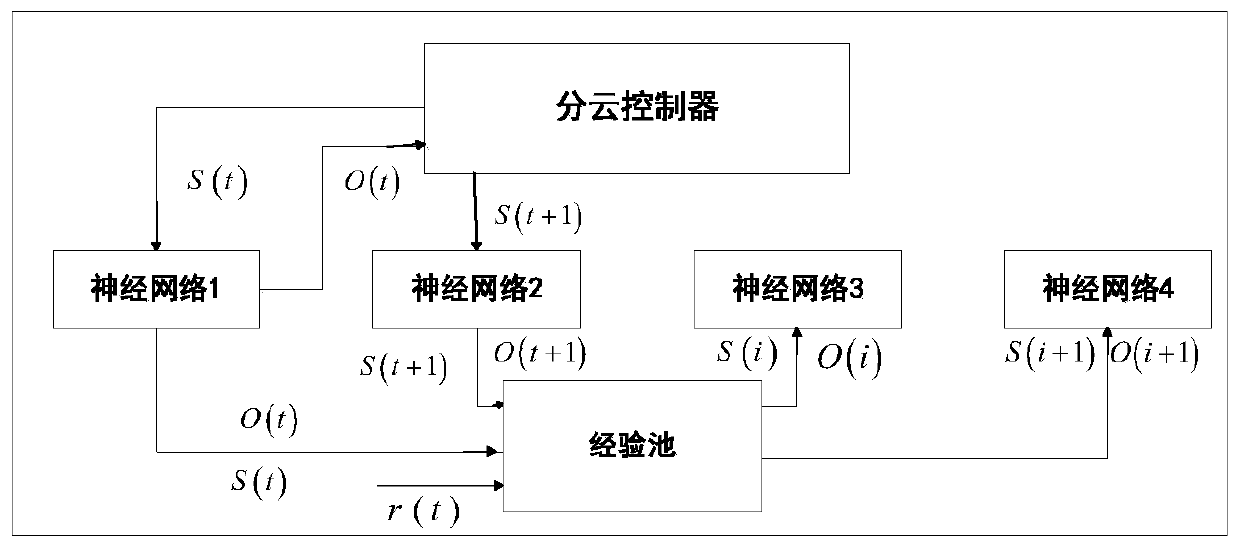
Cooperative cloud control-based multi-unmanned-ship fleet cooperative control system and method
ActiveCN108200175AAvoid collisionImprove accuracyWaterborne vesselsTransmission systemsControl systemShore
The invention relates to a cooperative cloud control-based multi-unmanned-ship fleet cooperative control system and method. The method comprises the following steps: building cloud-shore connection through a shore-based control system and a cooperative cloud control system, and enabling the shore-based control system to communicate with the cooperative cloud control system based on the cloud-shoreconnection, so as to acquire control information of the shore-based control system for an unmanned ship fleet and unmanned ship fleet state information; and building cloud-ship connection through thecooperative cloud control system and the unmanned ship formation, and sending a control instruction of the cooperative cloud control system for the unmanned ship fleet based on the cloud-ship connection, so as to acquire state information of the unmanned ship fleet. According to the cooperative cloud control-based multi-unmanned-ship fleet cooperative control method disclosed by the invention, based on the cooperative cloud control system, a distributed calculation method is adopted, multiple cloud servers are called, and effective resources are fully used, so that the calculation capacity isimproved; the precision and the timeliness of unmanned ship fleet scheduling control are improved; collision of the unmanned ship fleet is effectively prevented; and furthermore, multiple unmanned ships work at the same time, so that the working speed and the working efficiency are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
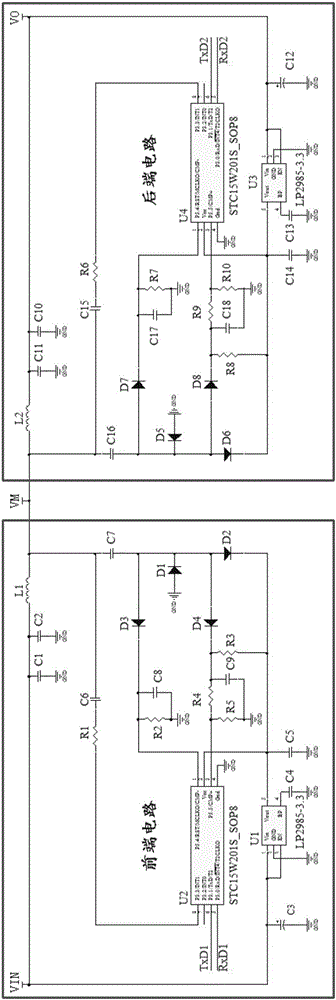
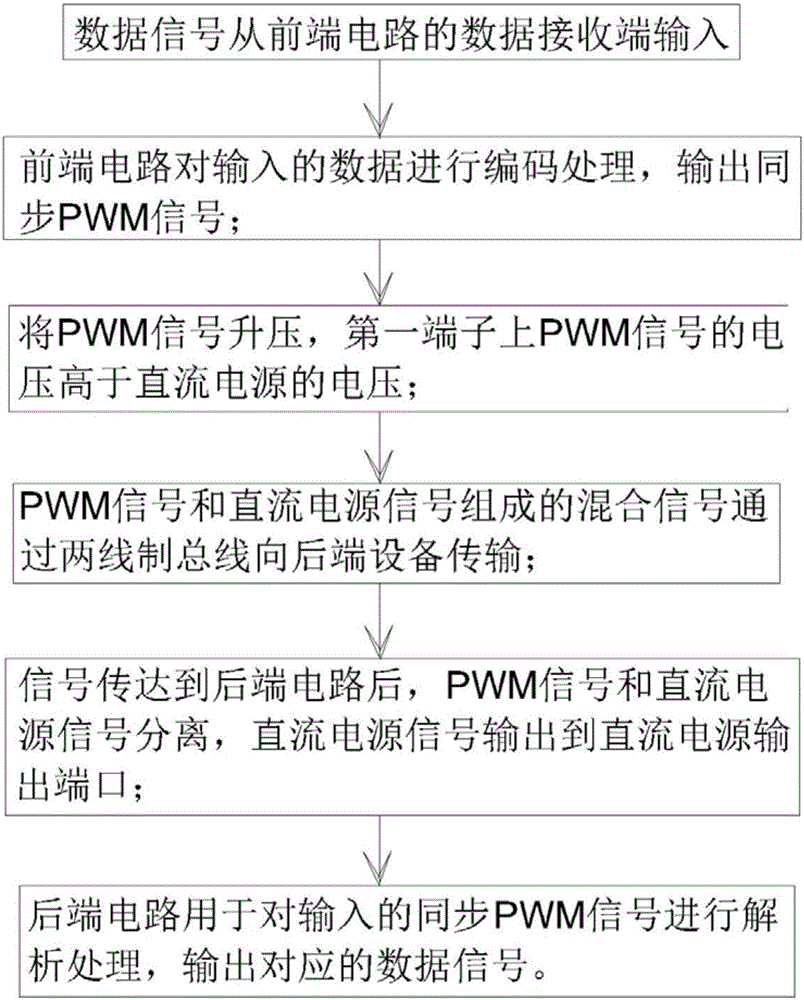
Data signal and DC power source collinear transmission system and method
ActiveCN106331563ARealize collinear transmissionReduce the number of layingClosed circuit television systemsElectrical cable transmission adaptationData signalMonitoring and control
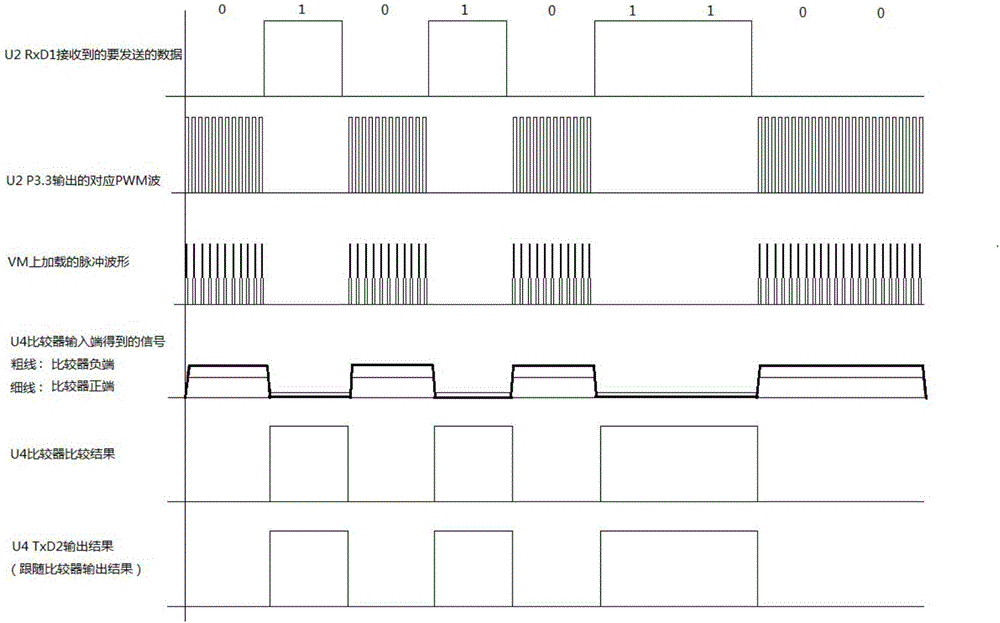
The invention discloses a data signal and DC power source collinear transmission system and method. When the front equipment will send data to the rear equipment, data signals are input into the data receiving end of the front circuit; the front circuit encodes the data input and outputs synchronous PWM signals, to boost PWM signals so that the voltage of PWM signals on the first terminal is higher than that of DC power source; the mixed signals composed of PWM signals and DC power source signals are transmitted to the rear equipment through two-wire system bus; after signals are transmitted to the rear circuit, PWM signals and DC power source signals separate, and DC power source signals are output to DC power source output interface; the rear circuit conducts analysis treatment of synchronous PWM signals input and outputs corresponding data signals. In the invention, the whole system has a centralized power supply and collinear transmission of DC power source and high-speed data signals is realized in the two-wire system, which reduces the quantity of laid cables and system cost in monitoring and control of the system.
Owner:LUMLUX CORP
RAW image radiation temperature measuring apparatus and method
ActiveCN104180908ALarge dynamic response rangeAccurate calculationTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryRgb imageImage detection
The invention discloses a RAW image radiation temperature measuring method. The method comprises the following steps: a CCD camera outputting image data in a RAW format, and storing the data as a true color RGB image after linearity interpolation; arranging the exposure time of the CCD camera through RAW image gray scale signals obtained from the image data in the RAW format; and extracting a spectral color value of each channel from the true color RGB image; obtaining image detection data from ratios of the spectral color values to the exposure time; taking a conversion proportion coefficient, calibrated through a black-body furnace, between the image detection data and incident radiation intensity, as a calibration constant; through the CCD camera, continuously acquiring radiation images, and extracting spectral color signals and exposure time signals of any two channels in pixels R, G or B; and performing correction through the calibration constant to form correspondingly extracted monochromatic radiation intensity signals under the condition of two primary wavelengths, and according to a colorimetric temperature measurement principle, obtaining an image temperature and a radiation ratio. The temperature measuring apparatus provided by the invention comprises the CCD camera, a stiff rod endoscope, a network switch and a background server.
Owner:HUANENG POWER INTERNATIONAL +1
Fiber grating force-measuring anchor rod device
InactiveCN103207037AGood anti-lightning performanceStrong anti-electromagnetic interferenceForce measurement by measuring optical property variationData transmissionElectromagnetic interference
The invention relates to a fiber grating force-measuring anchor rod device. The fiber grating force-measuring anchor rod device comprises an optical fiber, a rod beam and a hollow anchor rod, wherein at least one grating is arranged on the optical fiber, gratings are adhered onto the rod beam, the rod beam penetrates through the hollow anchor rod, a limiting block is arranged at one end of the rod beam and is clamped on one side of the hollow anchor rod, a fastening nut and an end nut are in threaded connection with the rod beam, the hollow anchor rod is connected with an optical fiber base through welding, the optical fiber base is in threaded connection with an optical fiber base cover, the optical fiber base cover is provided with an optical fiber connection flange and is in threaded connection with a protective cover, and an optical fiber outlet is arranged on the protective cover. According to the fiber grating force-measuring anchor rod device, deformation data of the anchor rod device are collected through fiber gratings, and the optical fiber has the advantages of being good in lightning stroke resistance, high in anti-electromagnetic interference capability and capable of achieving remote measurement, so that the reliability and the measurement precision of the fiber grating force-measuring anchor rod device are improved, and the data transmission distance of the fiber grating force-measuring anchor rod device is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI KNP CHEM +3
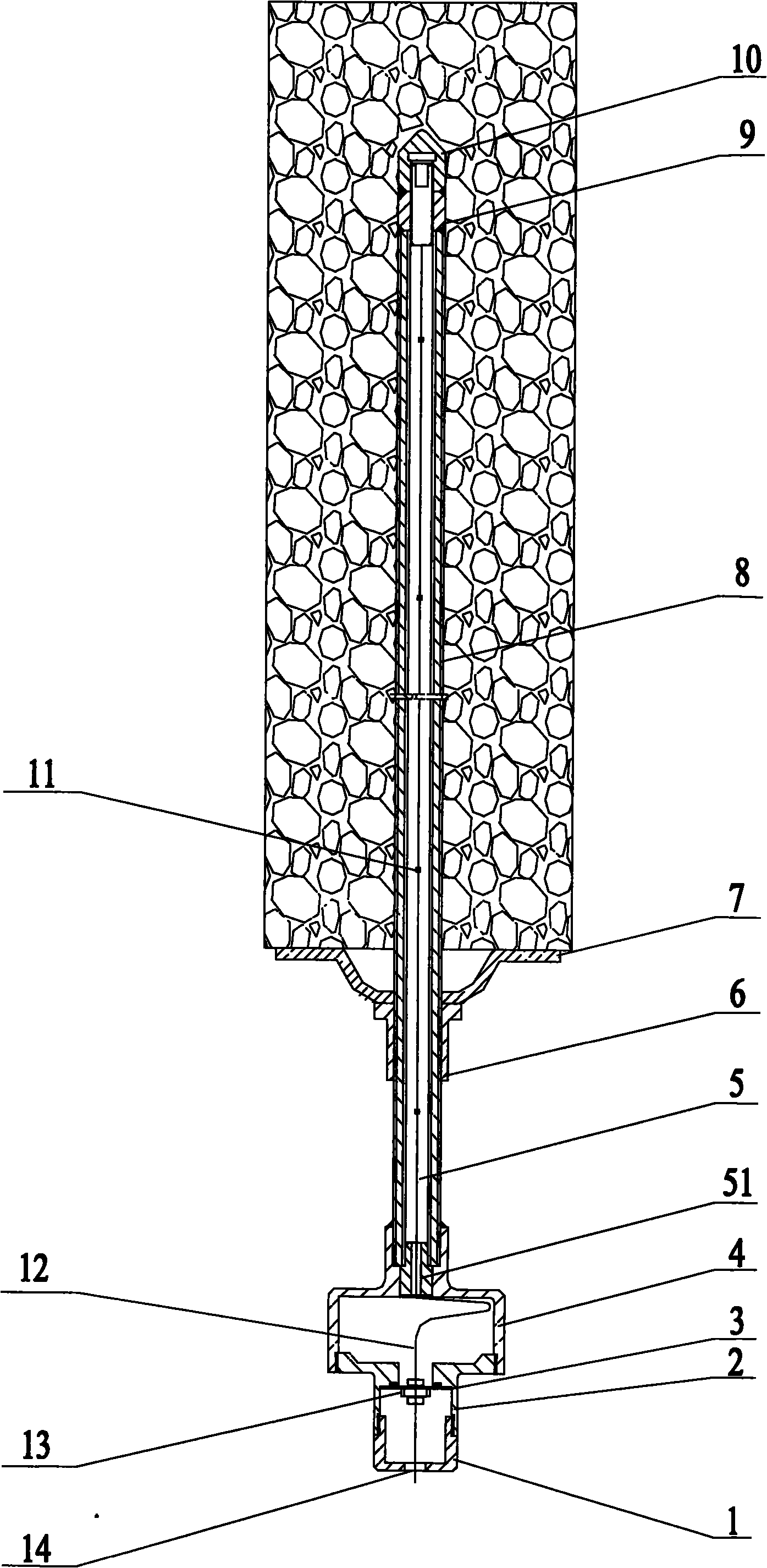
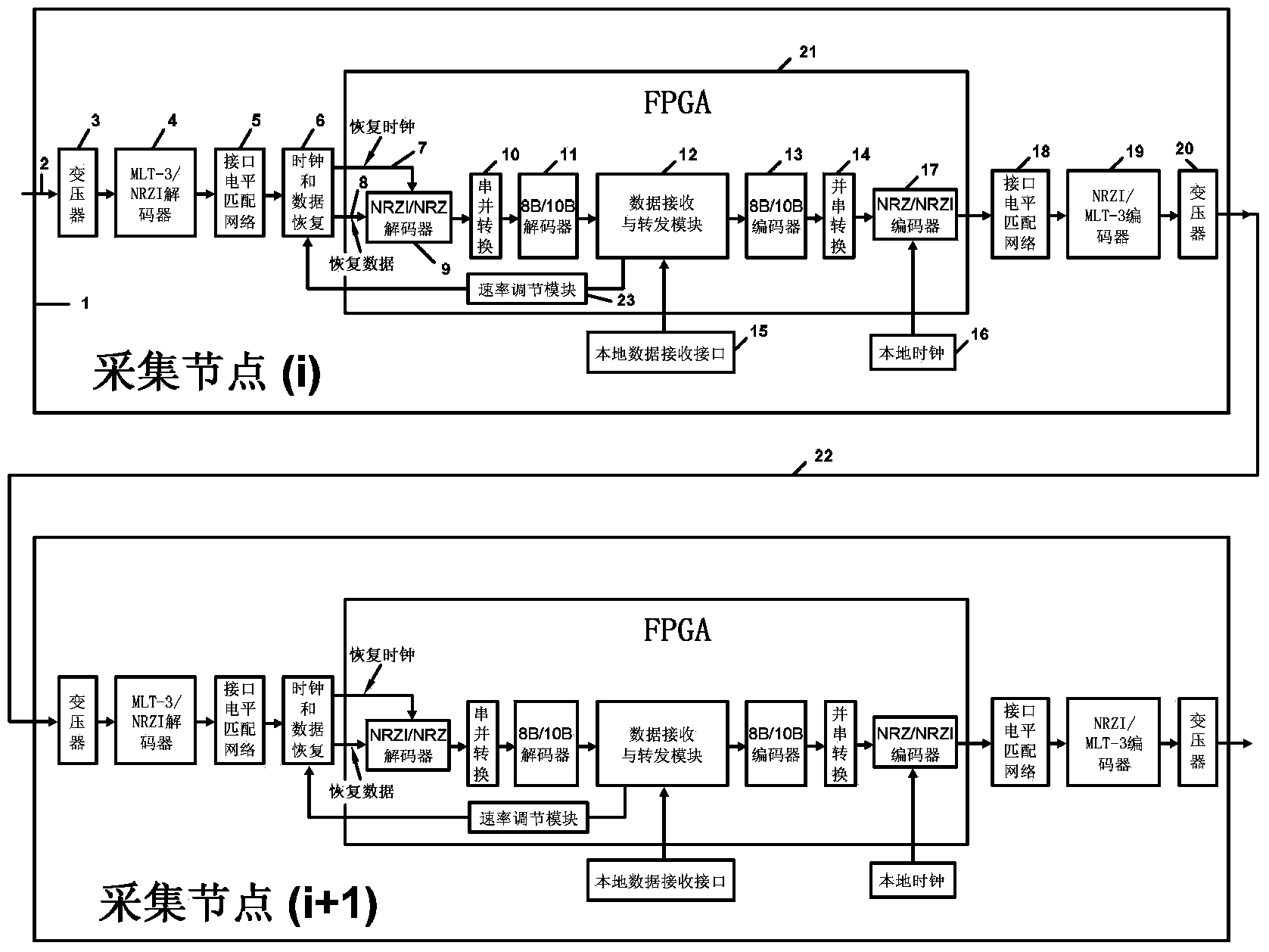
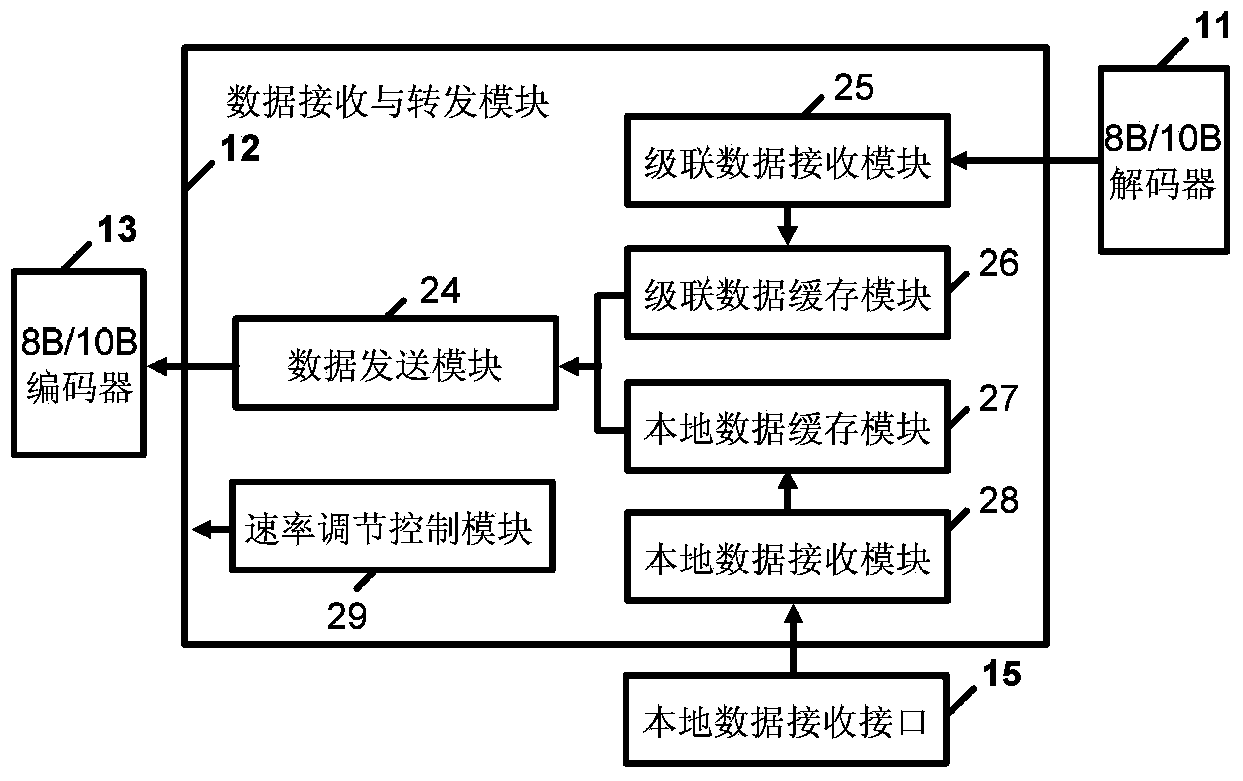
Long-distance wire data transmission device with adjustable transmission rate as needed
ActiveCN103516483ASave transmission bandwidthReliable transmissionTransmission control/equlisationError preventionReliable transmissionTransformer
The invention belongs to the field of geophysical exploration. (1) A general transmission method is provided, wherein transmission rate between collection nodes can be adjusted in an optimal mode according to the actual application requirements; (2), the transmission technology is provided, wherein the encoding efficiency is higher and the transmission bandwidth is lower; (3), a device which can achieve longer-distance data reliable transmission can be achieved under the situation of the same effective data transmission. According to the technical scheme, the long-distance wire data transmission device with the adjustable transmission rate as needed is composed of a data receiving interface, a data receiving and forwarding module and a data sending interface, wherein the data receiving interface is mainly composed of a transformer, an MLT-3 / NRZI decoder, an interface level matching network, a clock and data recovery, an NRZI / NRZ decoder, a staticizer and an 8B / 10B decoder. The device is mainly applied to the geophysical exploration.
Owner:善测(天津)科技有限公司
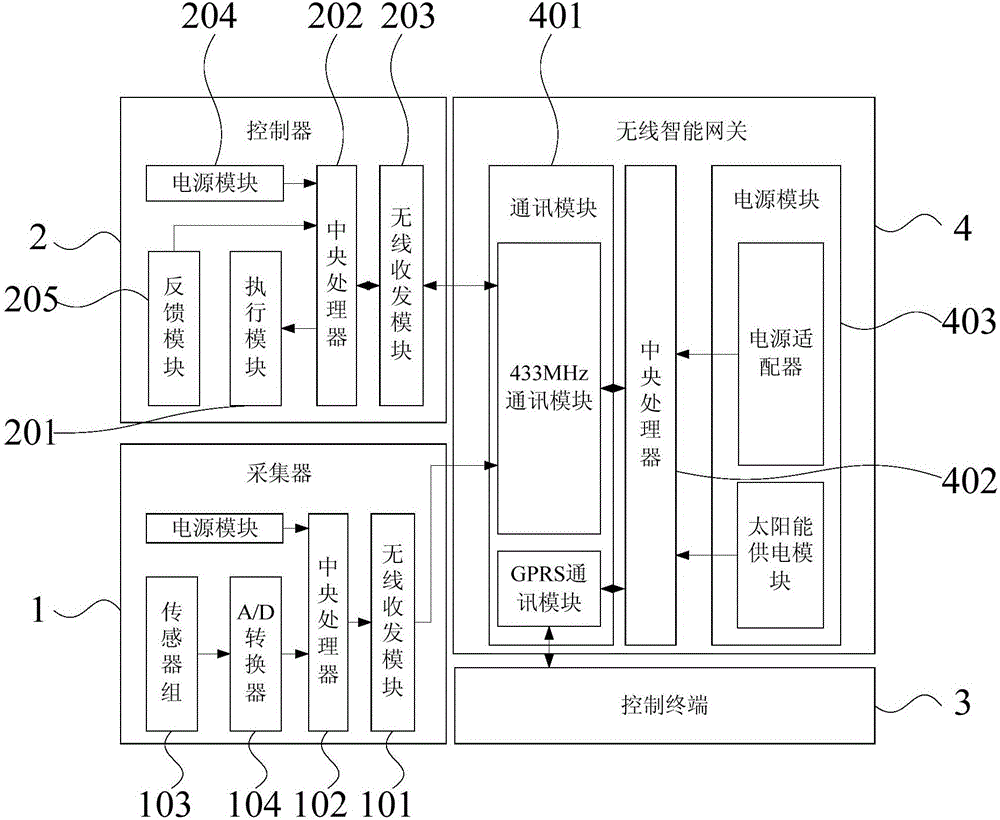
Wireless intelligent irrigation system and method
InactiveCN106804391AEasy to installEasy maintenanceWatering devicesCultivating equipmentsMaterial resourcesComputer terminal
The invention discloses a wireless intelligent irrigation system and method. The wireless intelligent irrigation system comprises a collector, a controller and a control terminal, and also comprises a wireless intelligent gateway. The wireless intelligent gateway comprises a communication module, a central processor and a power module. The collector converts collected analog environment factors into digital environment factors, the digital environment factors are transmitted to the central processor through the communication module and then are transmitted to the control terminal for monitoring planting environment through the communication module, and the control terminal sends execution commands to the controller to control soil humidity according to the soil humidity in environment factor signals received by an agricultural cloud platform. By the adoption of the structure of the wireless intelligent irrigation system and method, users can manage their farms by mobile phones or computers at any time and in any place, the installation of the device is simple, the maintenance is convenient, manpower and material resources are saved, the expandability is strong, and the data transmission distance is prolonged.
Owner:河北知时新农科技有限公司
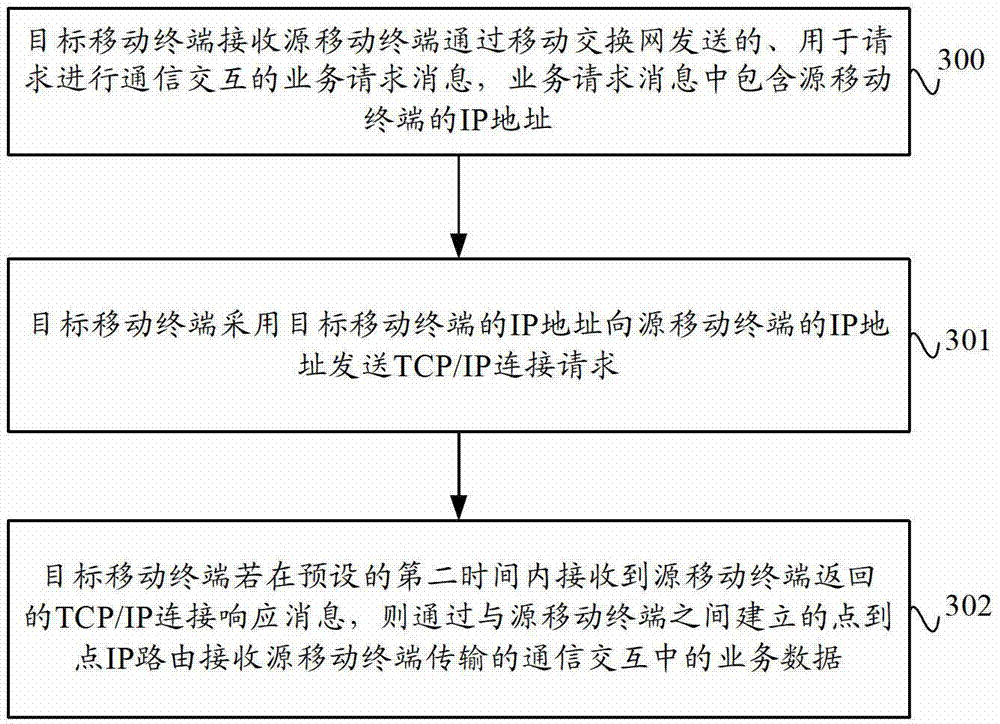
Data transmission method and system based on mobile terminal and mobile terminal
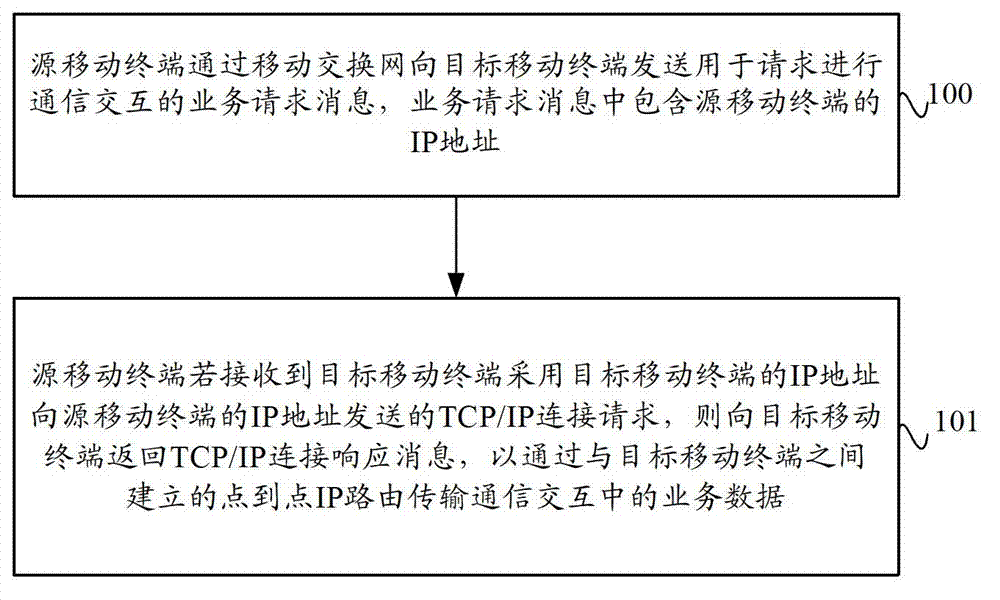
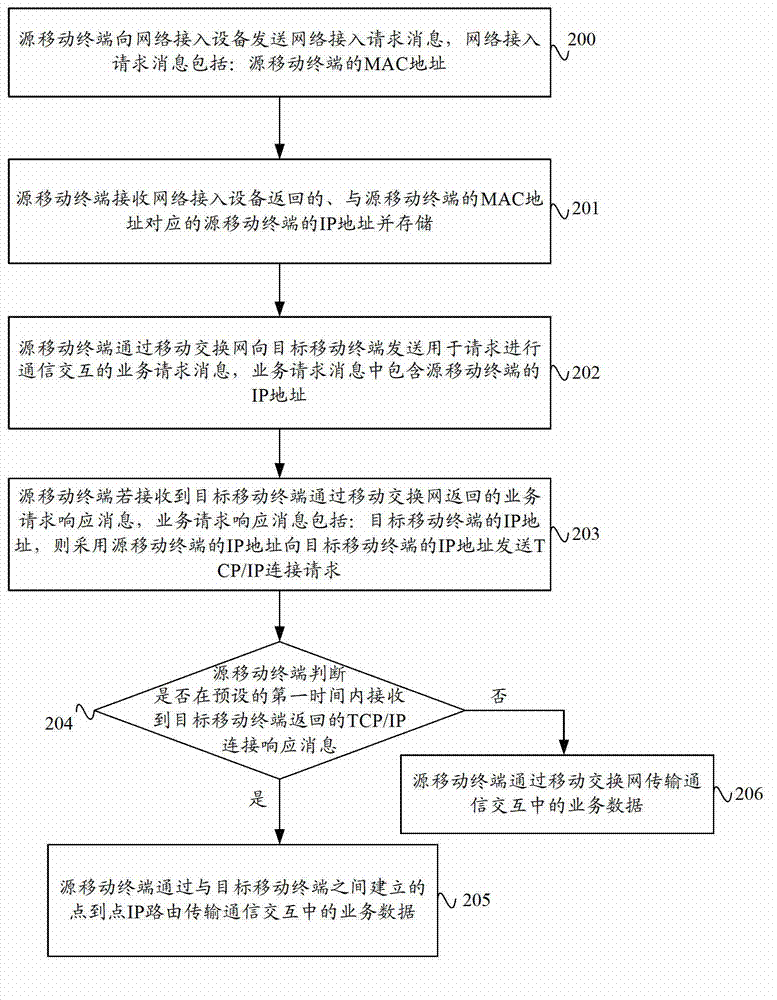
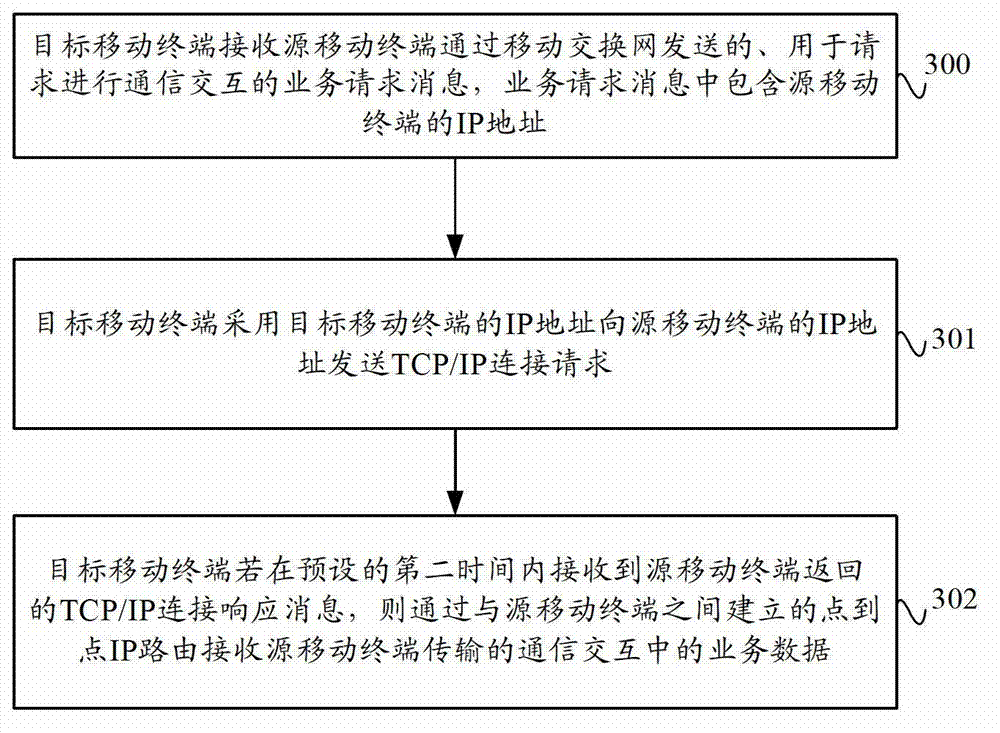
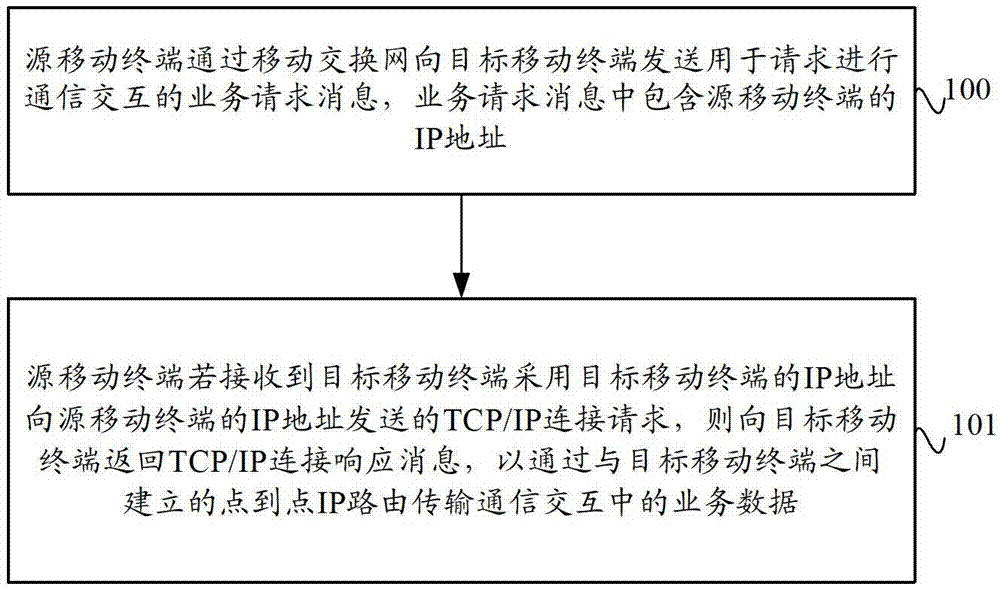
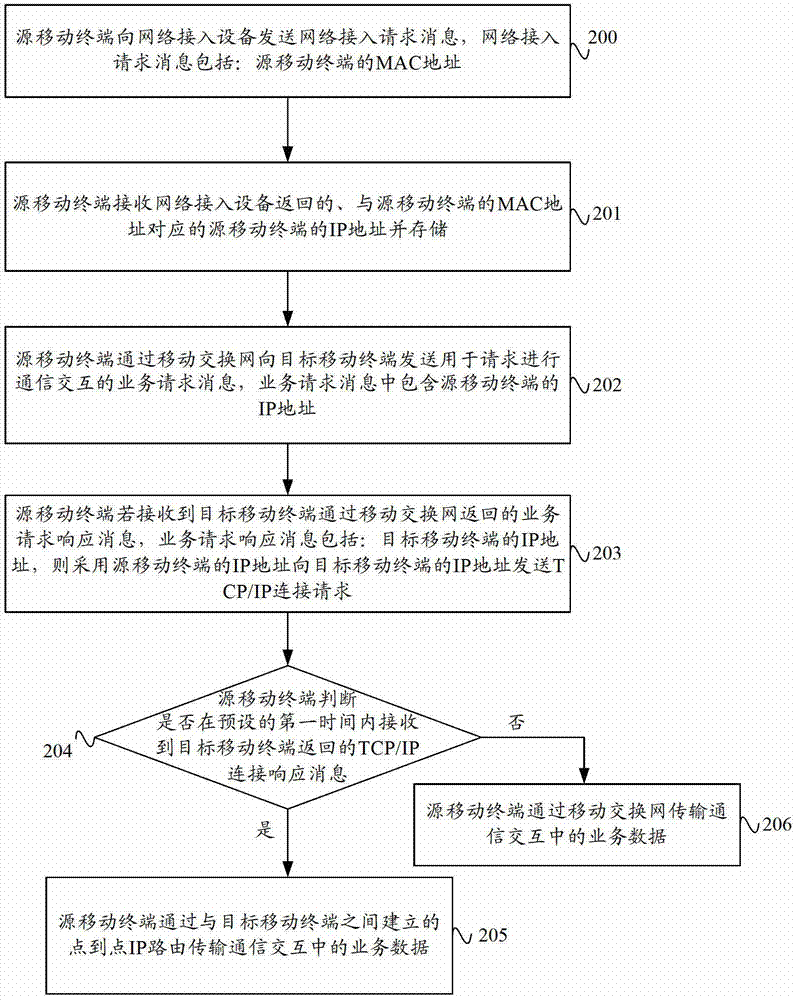
ActiveCN102769844AImprove data transmission distanceReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTHigh level techniquesIp addressData transmission
The invention provides a data transmission method and system based on a mobile terminal and a mobile terminal. The data transmission method comprises the following steps: a source mobile terminal transmits a service request message, which contains the IP (Internet Protocol) address of the source mobile terminal, to an objective mobile terminal through a mobile switch network, and if a TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) / IP connection request transmitted by the object mobile terminal, which adopts an IP address per se, to the source mobile terminal is received, the source mobile terminal returns the TCP / IP connection request to the objective mobile terminal, and service data in communication interaction is transmitted by point-point IP routing, which is established by the source mobile terminal and the objective mobile terminal. The data transmission method and system based on the mobile terminal and the mobile terminal, provided by the invention, can achieve the communication interaction between the source mobile terminal and the objective mobile terminal through the point-point IP routing so as to improve the distance between mobile terminals and reduce the power consumption of mobile terminals, and is conducive to the transmission of large quantities of data.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
Symmetric cross-protocol communication method and device for asymmetric channel
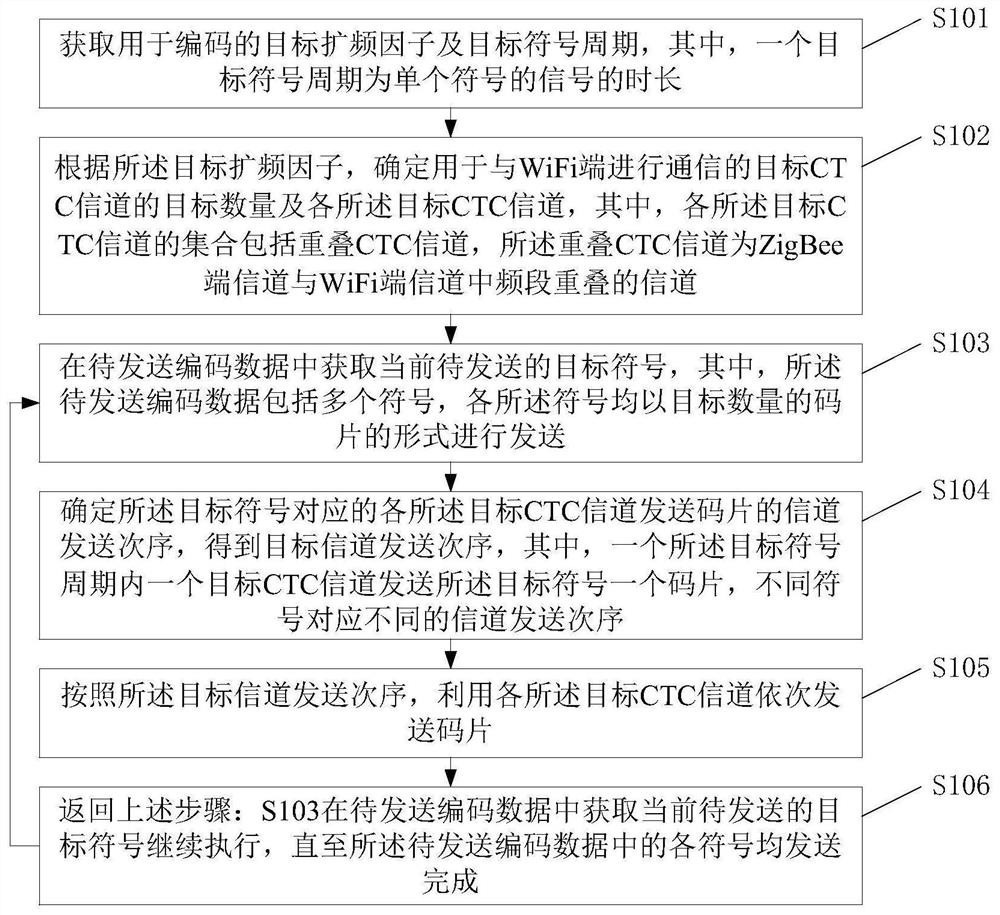
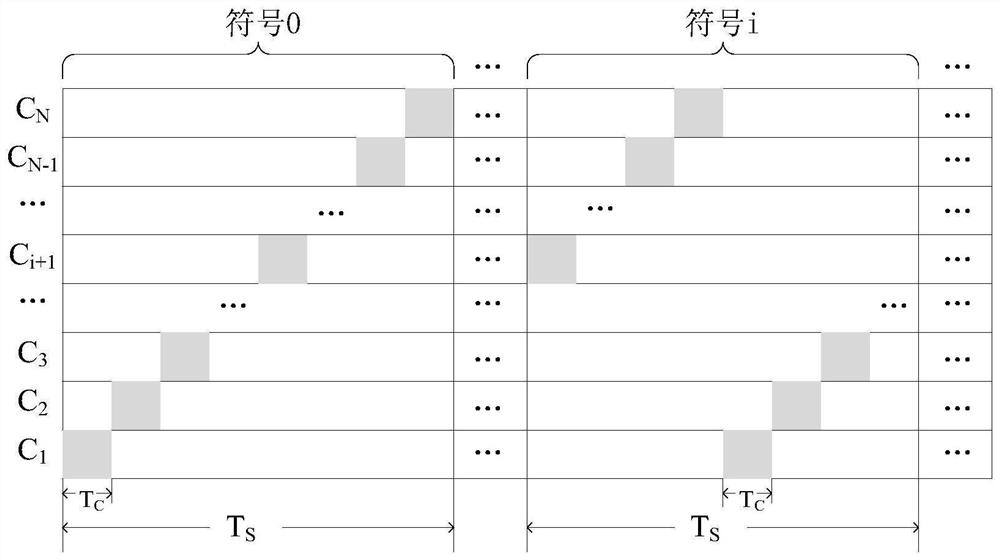
ActiveCN111835492AIncrease profitImprove data transmission distanceNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsData transmissionTotal frequency
The embodiment of the invention provides a symmetric cross-protocol communication method and device for an asymmetric channel. A set of target CTC channels comprises overlapped CTC channels, namely, the total frequency band range of all the target CTC channels covers the frequency band range of the overlapped CTC channels; in cooperation with a chip sending mode of the method, data is sent by using four overlapped channels of a ZigBee end and a WiFi end; even if the data noise of part of channels is very high, data identification can also be carried out through data in other channels; CTC communication from the ZigBee end to the WiFi end is achieved, the utilization rate of overlapped CTC channels can be increased, the data transmission distance from the ZigBee end to the WiFi end is increased, and it is possible to establish symmetric CTC on asymmetric CTC channels.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Process and structure of 2 nanosecond data line
InactiveCN101714422AImprove data transmission distanceImprove video qualityCable/conductor manufactureCables with twisted pairs/quadsPolyesterVideo transmission
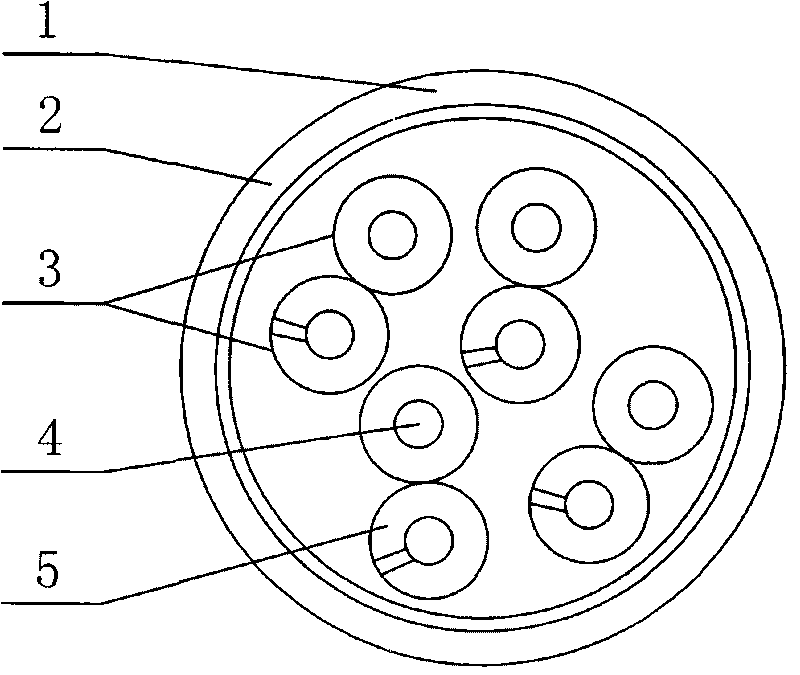
The invention relates to a 2 nanosecond data line. The process comprises the following steps of: drawing and annealing a Phi 2.6mm copper bar; coating membrane high-density polyethylene during extrusion for insulation and generating a single insulating copper wire line; carrying out pair twisting on the insulating single line without conglutination; leading a plurality of pair twisting lines to form a cable core line by a formed cable; extruding the cable core line and forming a sheath at the periphery by extruding. The sheath comprises a PVC low-smoke halogen-free outer layer and an inside polyester band. The 2 nanosecond data line produced by the process realizes long data transmission distance, high video quality, regular pixel arrangement, clear edge and picture and less vertical black spot and double image in the process of video transmission. The invention also discloses a structure of the 2 nanosecond data line.
Owner:ANHUI TIANXING OPTICAL FIBER COMM EQUIP
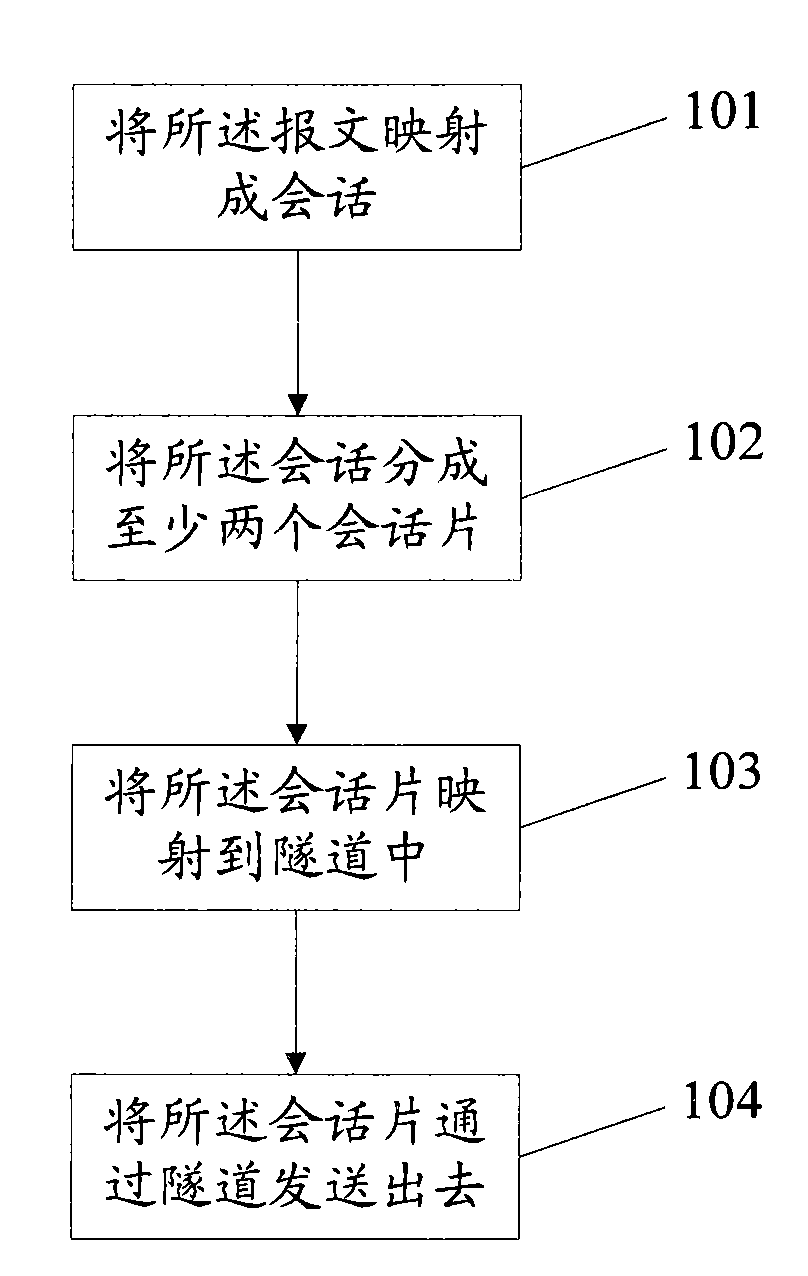
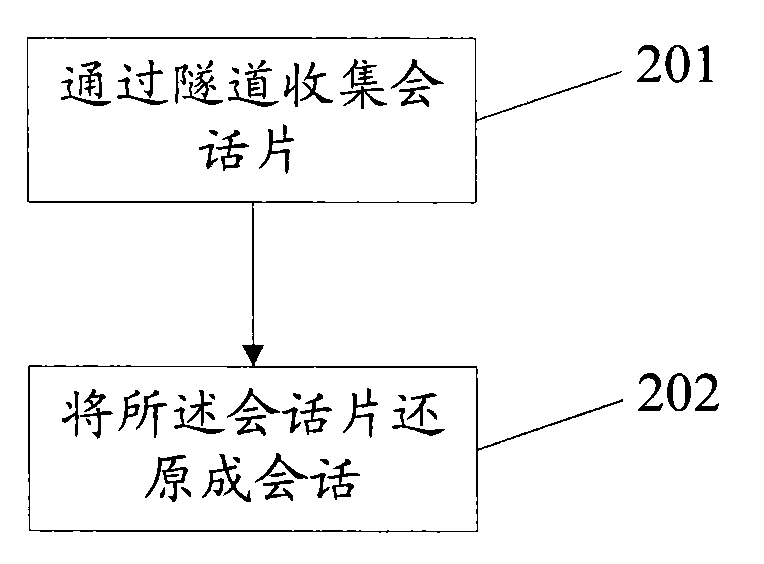
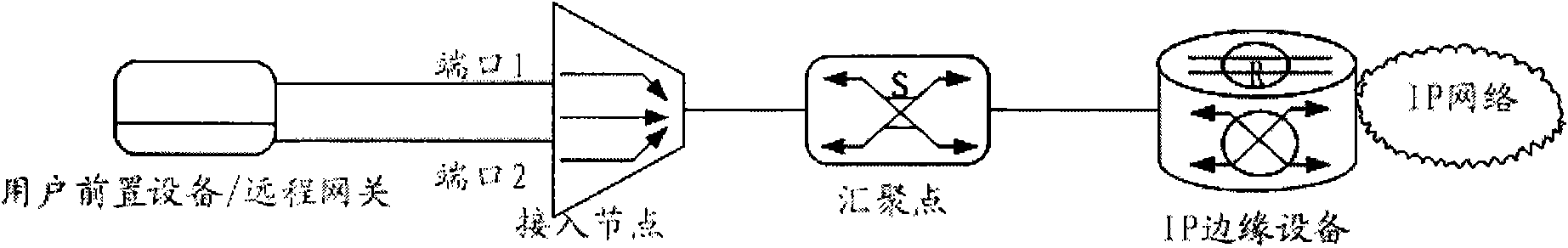
Methods and devices for transmitting and receiving messages in network
InactiveCN101651610ARealize bundlingHigh bandwidthNetworks interconnectionTelecommunicationsTunneling protocol
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
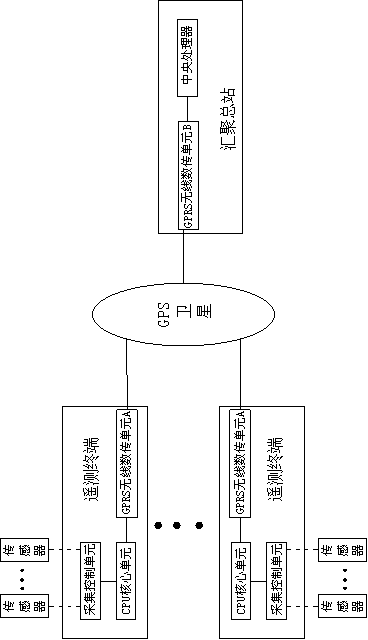
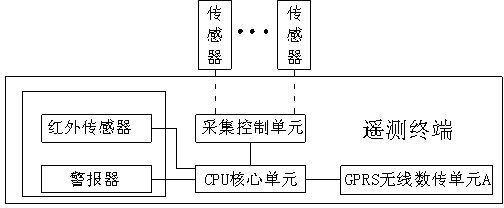
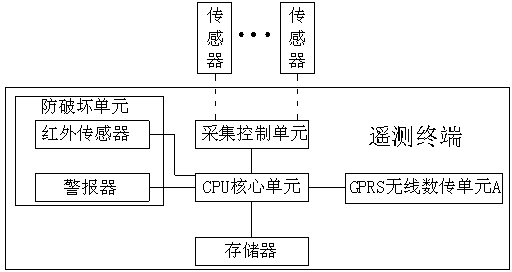
Telemetry terminal system adopting GPS satellite
InactiveCN103323057AReduce in quantityImprove data transmission distanceMeasurement devicesTransmission systemsData transmissionGps satellites
The invention discloses a telemetry terminal system adopting a GPS satellite. The telemetry terminal system adopting the GPS satellite comprises a collection master station and at least one telemetry terminal, the telemetry terminal system is connected to the collection master station through the GPS satellite, the telemetry terminal comprises a CPU core unit, a GPRS wireless data transmission unit A and a collection controlling unit, the collection controlling unit and the GPRS wireless data transmission unit A are both connected to the CPU core unit, a sensor is externally connected with the collection controlling unit, and the collection master station comprises a GPRS wireless data transmission unit B and a central processor. The telemetry terminal system adopting the GPRS satellite has the advantages that the GPS satellite is adopted to be used as a relay to carry out data transmission, data transmission distance is prolonged, the number of collection master stations is reduced, and a large amount of manpower and material resources are saved.
Owner:CHENGDU HANKANG INFORMATION IND
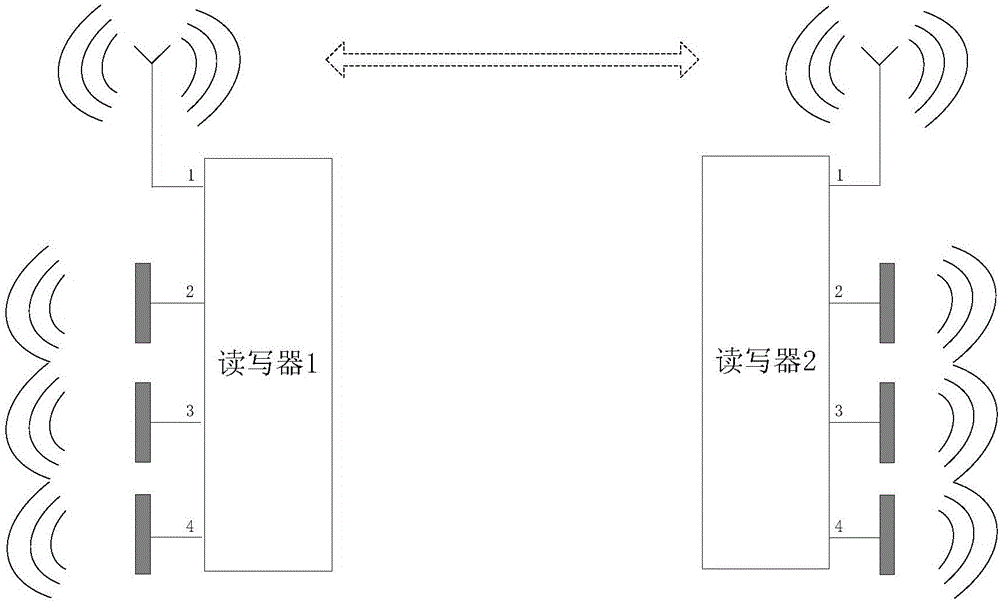
Method employing ultrahigh frequency RFID reader-writer for ad-hoc network communication
ActiveCN105117744AQuick buildResolve interferenceNetwork topologiesCo-operative working arrangementsNetwork deploymentNetwork communication
A method employing ultrahigh frequency RFID reader-writer for ad-hoc network communication is provided. On the basis that a traditional hardware frame is not changed, channel monitoring, frequency division, time division and code division technologies are employed integratedly, an inquiry / response mechanism of a network is established with an inquiry / response principle in an ultrahigh frequency RFID identification technology as a reference, the mutual interference problem of reader-writers in a multi-reader-writer ad-hoc network is solved, and thus the data transmission distance and the network deployment region area are increased greatly.
Owner:JIANGSU JUNYI INTERNET OF THINGS +1
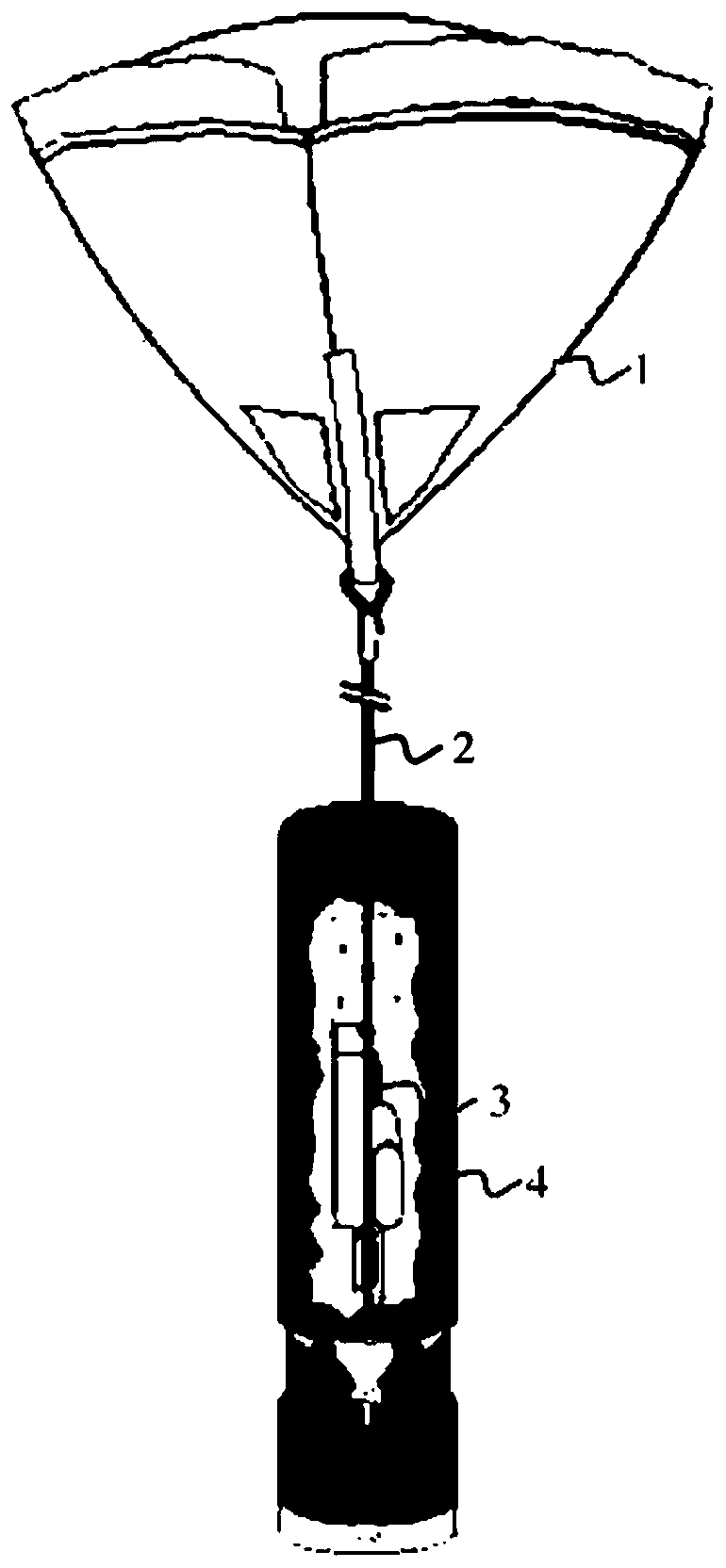
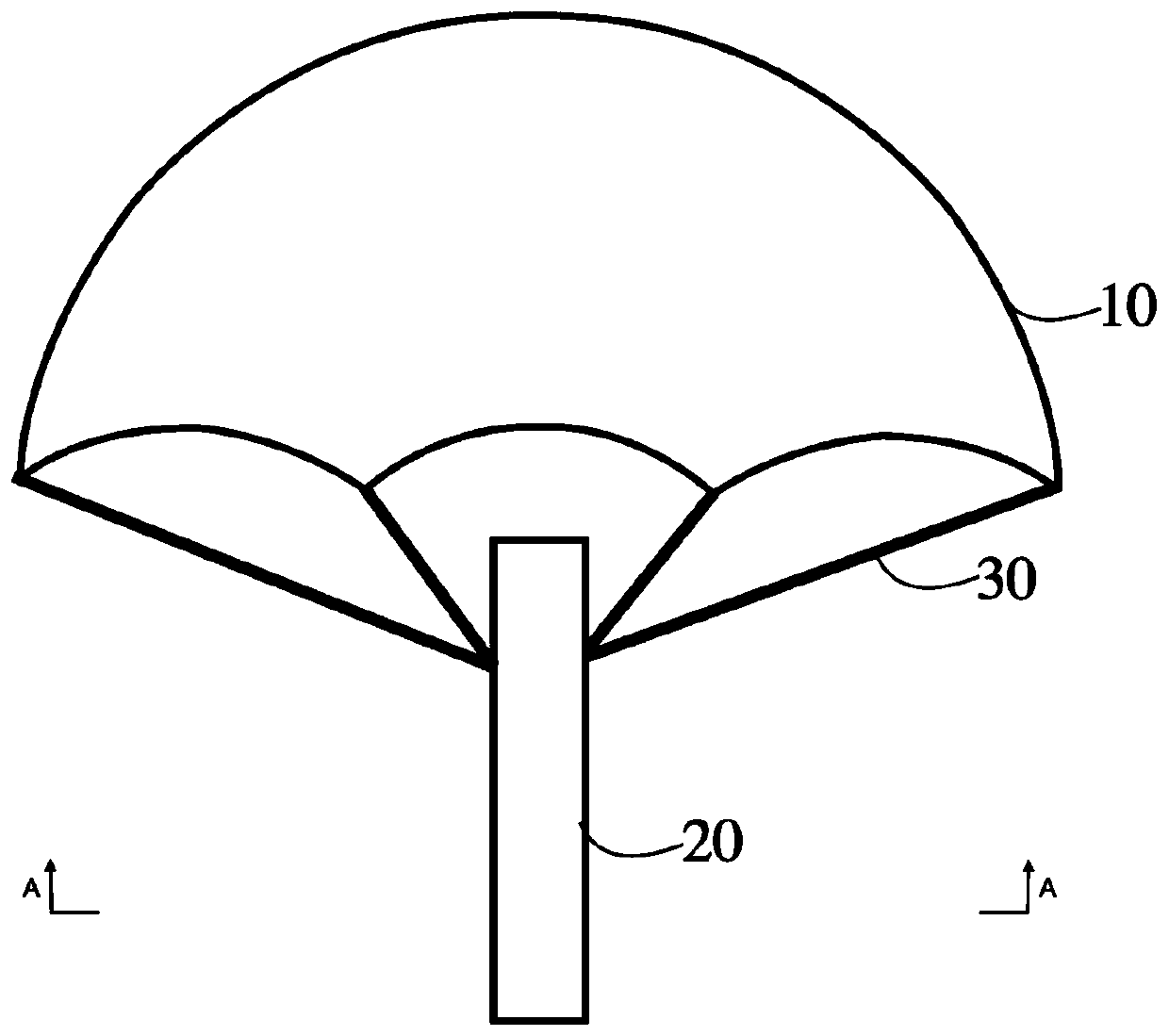
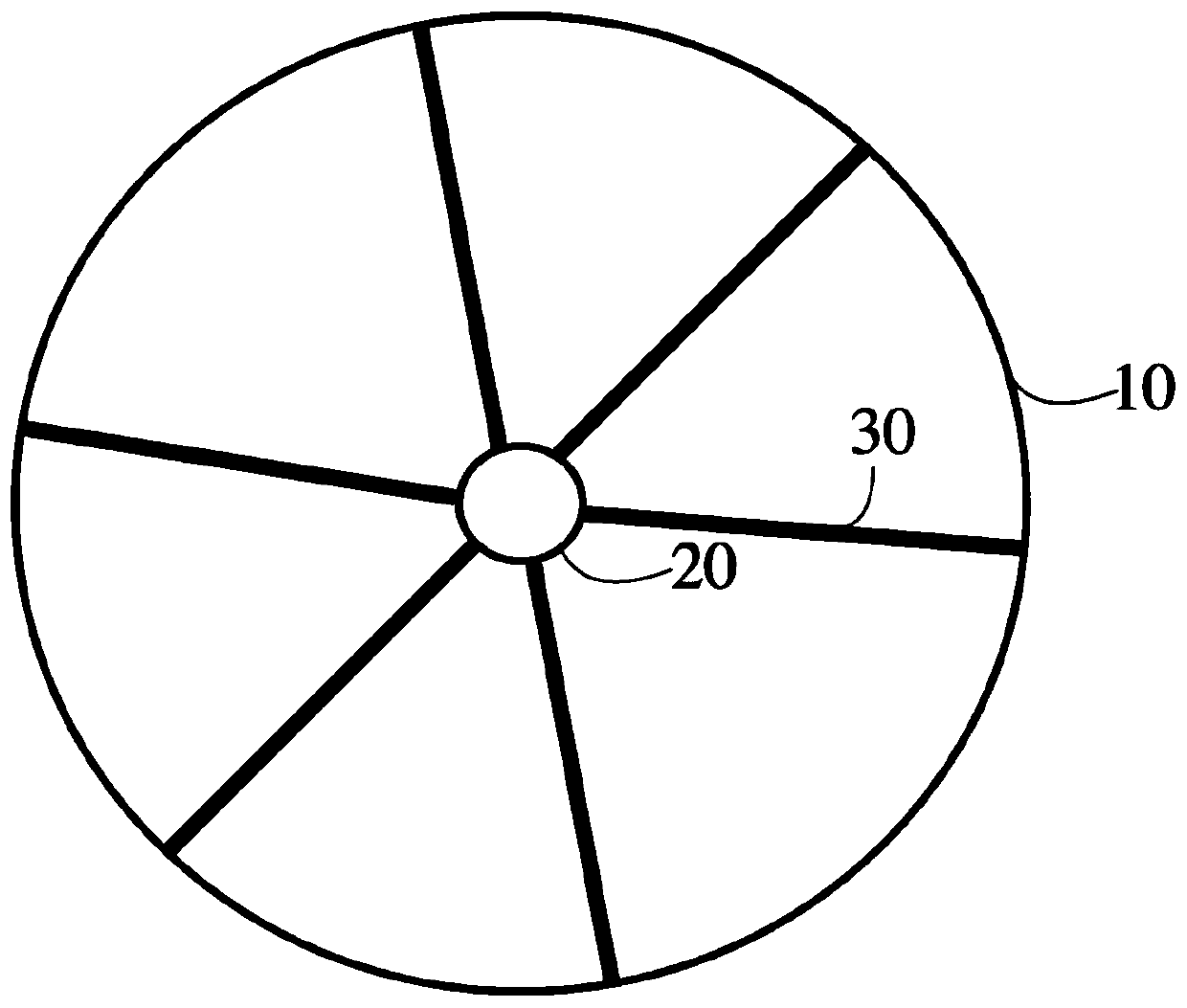
Drop-down detector and detection system
ActiveCN111487694AImprove wind resistanceImprove data transmission distanceIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesData transmissionMeteorology
The invention provides a drop-down detector and a detection system, and relates to the field of high-altitude meteorological detection. The detector comprises a first umbrella cover, a main body part,and a plurality of communication antennas, wherein the main body part is cylindrical, and a meteorological information acquisition and processing device is arranged in the main body part; the plurality of communication antennas are electrically connected with the meteorological information acquisition and processing device, a first end of each of the plurality of communication antennas is movablyconnected with a periphery of the main body part at the same interval, and the second ends of the plurality of communication antennas are connected to an inner edge of the first umbrella cover at thesame interval; and after the detector is put in, the plurality of communication antennas are unfolded towards the periphery by taking the main body part as a center and are fixed at positions forminga first angle with an axis of the main body part so as to support the first umbrella cover. According to the drop-down detector provided by the invention, wind resistance of the detector can be improved, and a data transmission distance of the detector is increased.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
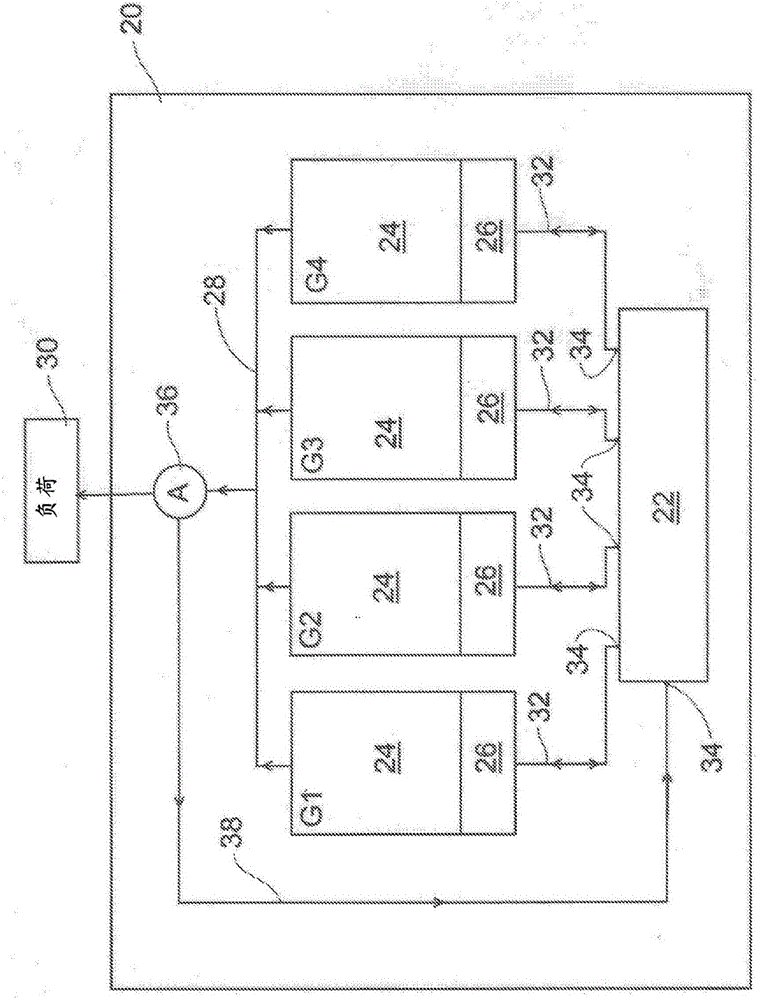
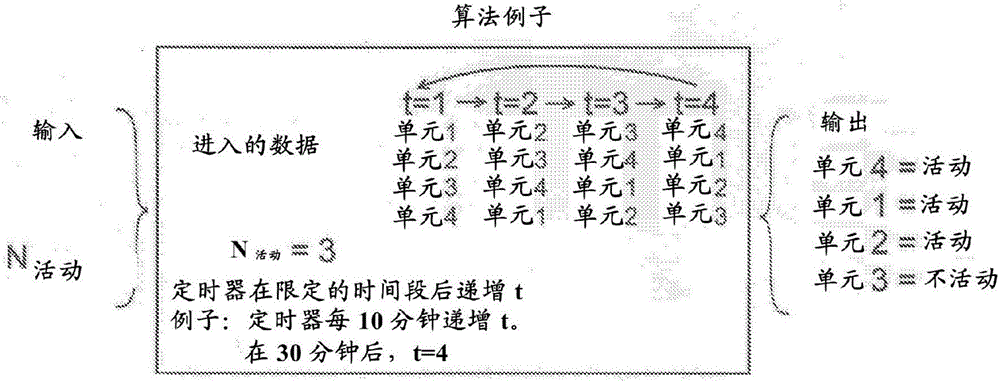
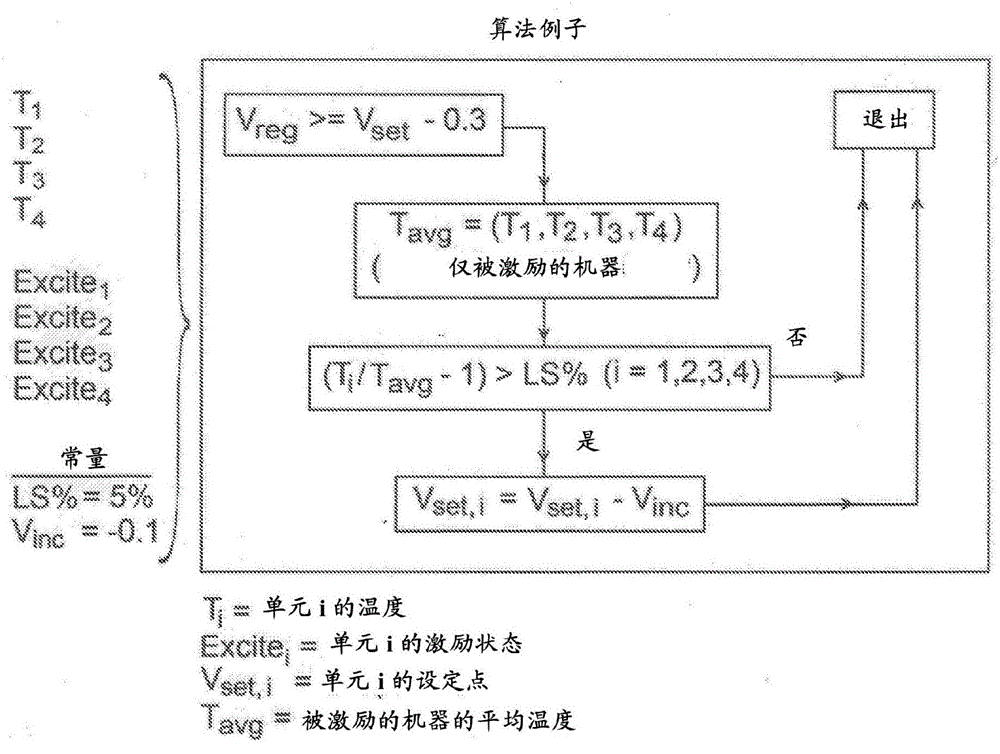
Method for load share balancing in a system of parallel-connected generators using selective load reduction
InactiveCN106165232AEfficient use ofImprove reliabilityComputer controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsParallel computingLoad following power plant
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
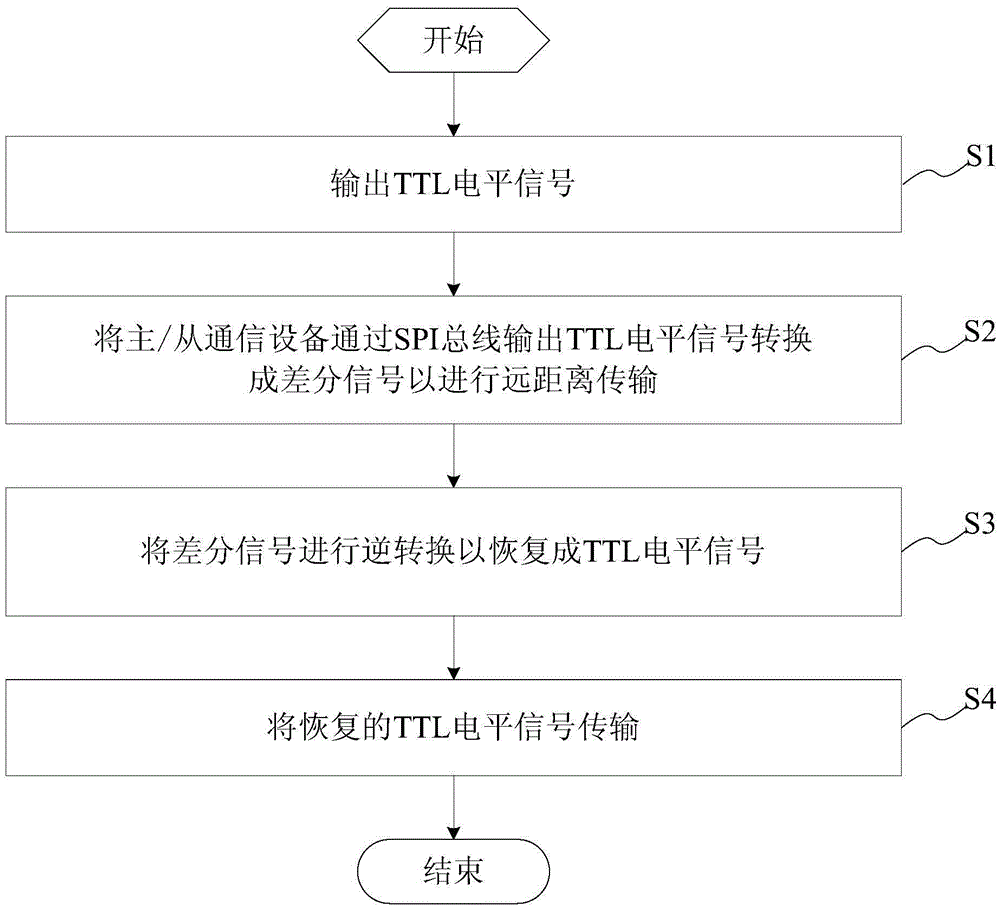
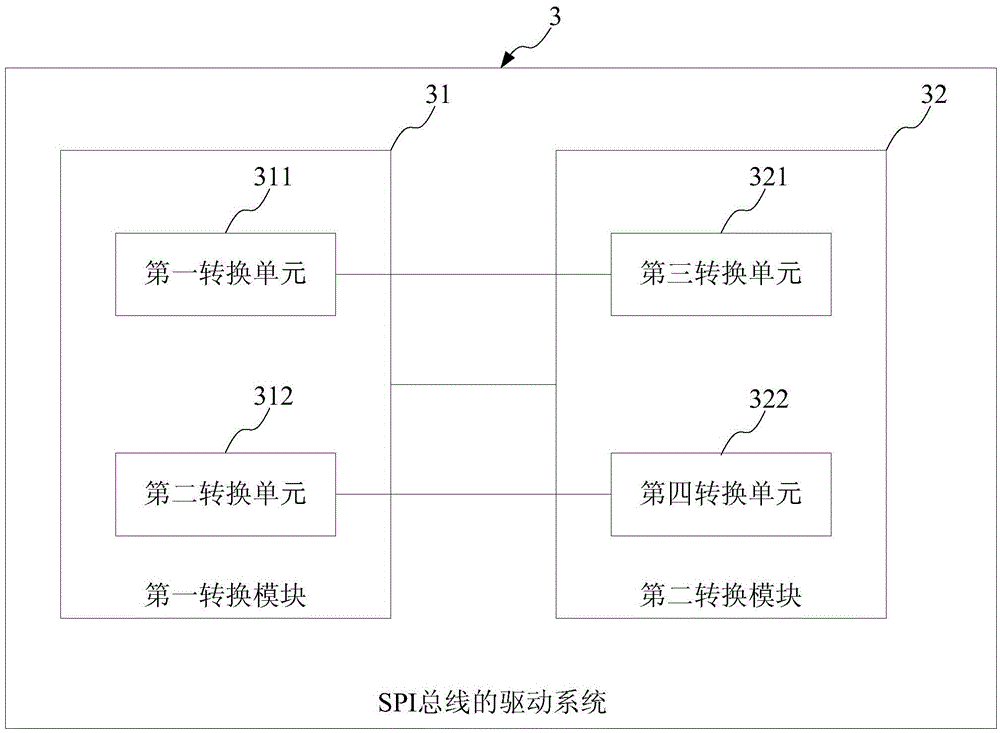
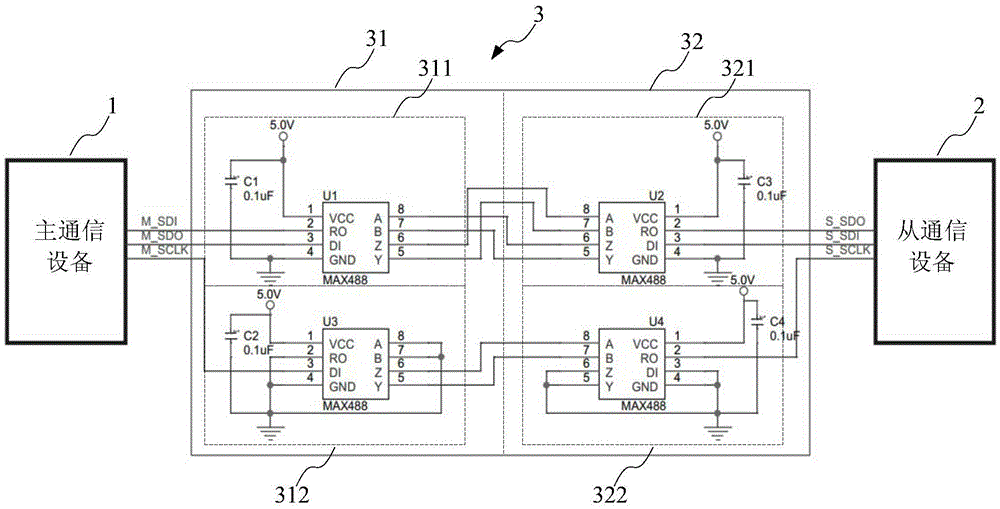
SPI (serial peripheral interface) bus driving method and system and electronic equipment
InactiveCN105512078ANo increased workloadImprove driving abilityElectric digital data processingTransistor–transistor logicDifferential signaling
The invention provides an SPI (serial peripheral interface) bus driving method and system and electronic equipment. The SPI bus driving system is applied to communication through an SPI bus, is a communication network comprising a master communication device and at least one slave communication device and comprises a first conversion module and a second conversion module, wherein the first conversion module is used for converting TTL (transistor-transistor logic) level signals output by the master / slave communication device through the SPI bus into differential signals for long-distance transmission; the second conversion module is used for inversely conversing the differential signals into the TTL level signals and transmitting the recovered TTL signals to the master / slave communication device. The SPI bus driving system has the advantages that the signal output driving capacity and anti-interference of the SPI bus are improved while the workload of a central processing unit is not increased, and the data transmission distance is lengthened.
Owner:PHICOMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Wireless paddy field water level and soil temperature and humidity sensor
PendingCN113494937ACompact designNot easy to damageThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansMicrocontrollerAgricultural engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of water level and temperature and humidity detection, and relates to a wireless paddy field water level and soil temperature and humidity sensor. The sensor comprises a cylinder cover, a control cylinder and a core sensing module, the cylinder cover comprises an antenna and a switch, and the core sensing module comprises a water level sensing probe, a humidity sensing probe and a temperature sensing probe. The control cylinder comprises a circuit board and a battery, and the center is provided with a water level conduit channel; and the circuit board comprises a main control chip, a wireless communication module and a sensing circuit module. The main control chip adopts an 8-bit single-chip microcomputer with ultra-low power consumption; the wireless communication module adopts a Zigbee wireless network for transmission; and the sensor circuit module comprises a humidity acquisition part, a temperature acquisition part and a water level acquisition part. The sensor has the advantages of low cost, high precision, good reliability and the like, can realize the long-term real-time online monitoring of temperature, humidity and water level, improves the agricultural planting efficiency, and has the better application prospect.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Differential frequency multiplication rotary coder
InactiveCN101886936AHigh measurement accuracyAchieve precisionMitigation of undesired influencesConverting sensor outputInterference resistanceRotary encoder
The invention relates to a differential frequency multiplication rotary coder which has the advantages of simple structure, convenient use, long service life, strong interference resistance, stable performance, and the like. The differential frequency multiplication rotary coder structurally comprises a shell, wherein a connecting shaft is arranged in the shell; one end of the connecting shaft is installed in a bearing, and the other end is connected with a pulse code disk; a double-channel Hall chip and a differential conditioning circuit are also arranged in the shell; and the circuit is connected with an aviation plug, and the double-channel Hall chip corresponds to the pulse code disk.
Owner:JINAN WISDOM INTELLIGENT TECH
Data communication method, device and system
InactiveCN103841203AImprove data transmission distanceNear-field transmissionConnection managementComputer terminalFile sharing
An embodiment of the invention provides a data communication method, device and system and relates to the communication field. By means of the data communication method, device and system, long-distance file sharing among a plurality of mobile terminals can be achieved. The data communication method comprises the steps that when a sensing device obtains trigger information, a communication server receives the sensing information sent by the sensing device, establishes a first communication channel and a second communication channel respectively corresponding to a first terminal and a second terminal according to the sensing information, and transmits interactive data between the first terminal and the second terminal through the first communication channel and the second communication channel. The data communication method, device and system is applicable to data communication.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
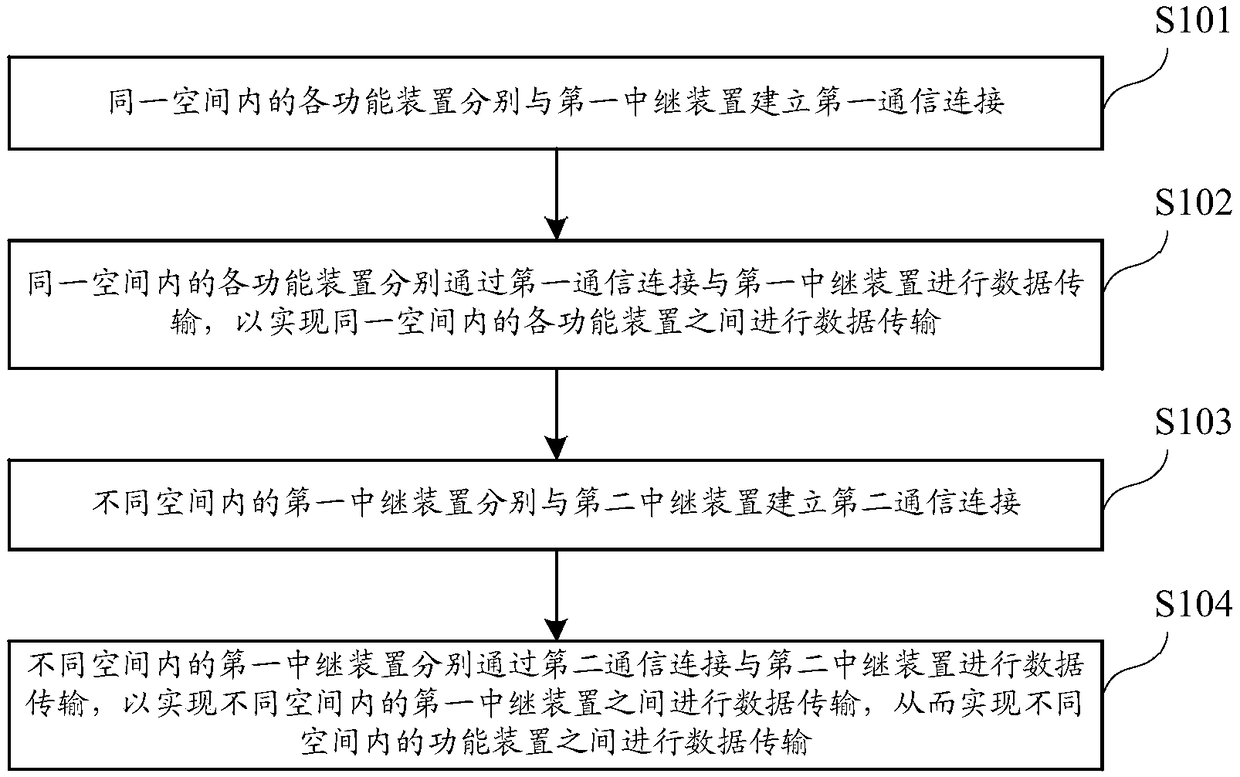
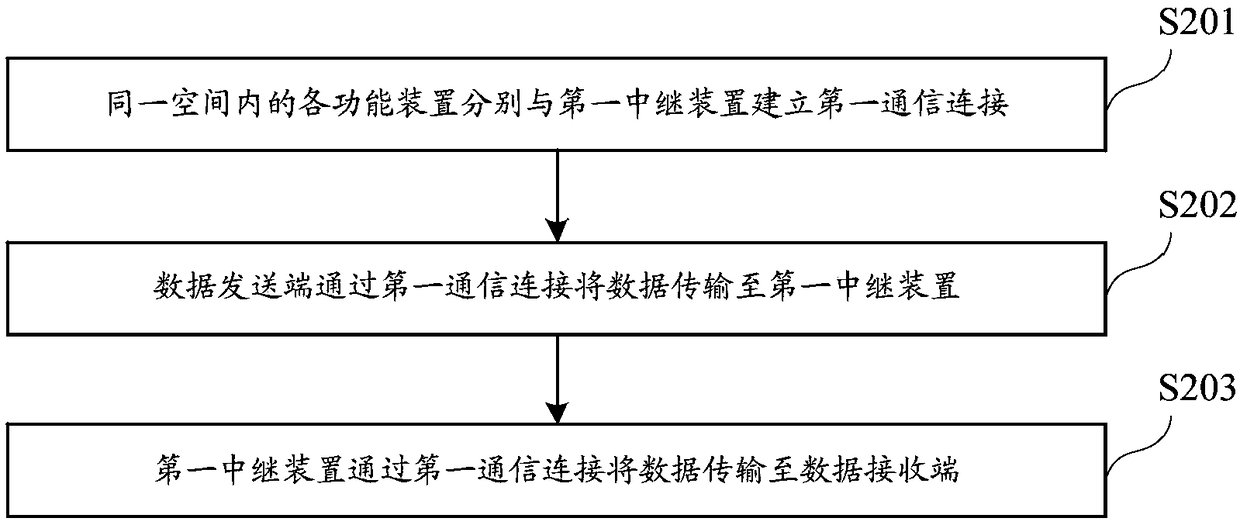
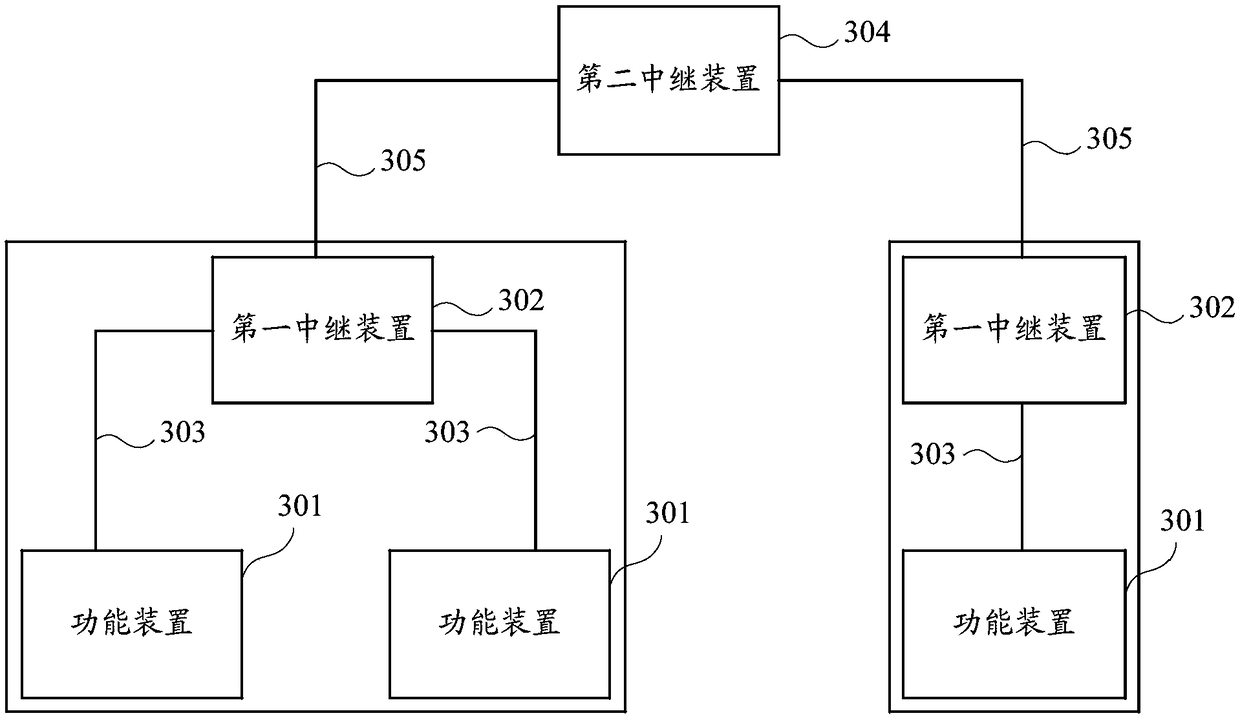
Data transmission method and relay device
ActiveCN108768488AImprove data transmission distanceImprove data transfer efficiencyActive radio relay systemsConnection managementData transmissionComputer science
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, and discloses a data transmission method and a relay device. The data transmission method comprises the steps that functional devices in the same space respectively establish first communication connection with a first relay device; the functional devices in the same space perform data transmission with the first relay devicethrough the first communication connection so as to realize data transmission among the functional devices in the same space; the first relay devices in different spaces respectively establish secondcommunication connection with a second relay device; and the first relay devices in the different spaces respectively perform data transmission with the second relay device through the second communication connection so as to realize data transmission among the first relay devices in the different spaces, so that data transmission among the functional devices in the different spaces is realized. The data transmission distance and the data transmission efficiency can be improved according to the method.
Owner:SHENZHEN JAGUAR WAVE TECH LTD +2
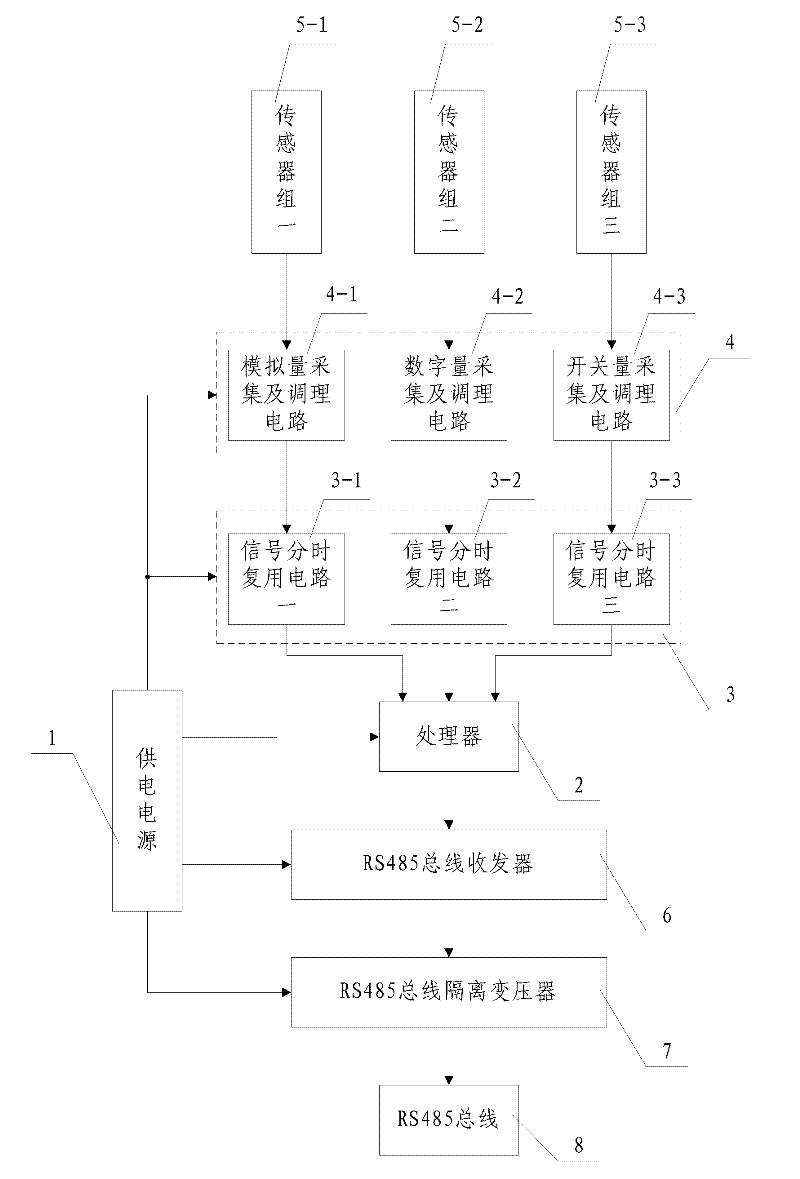
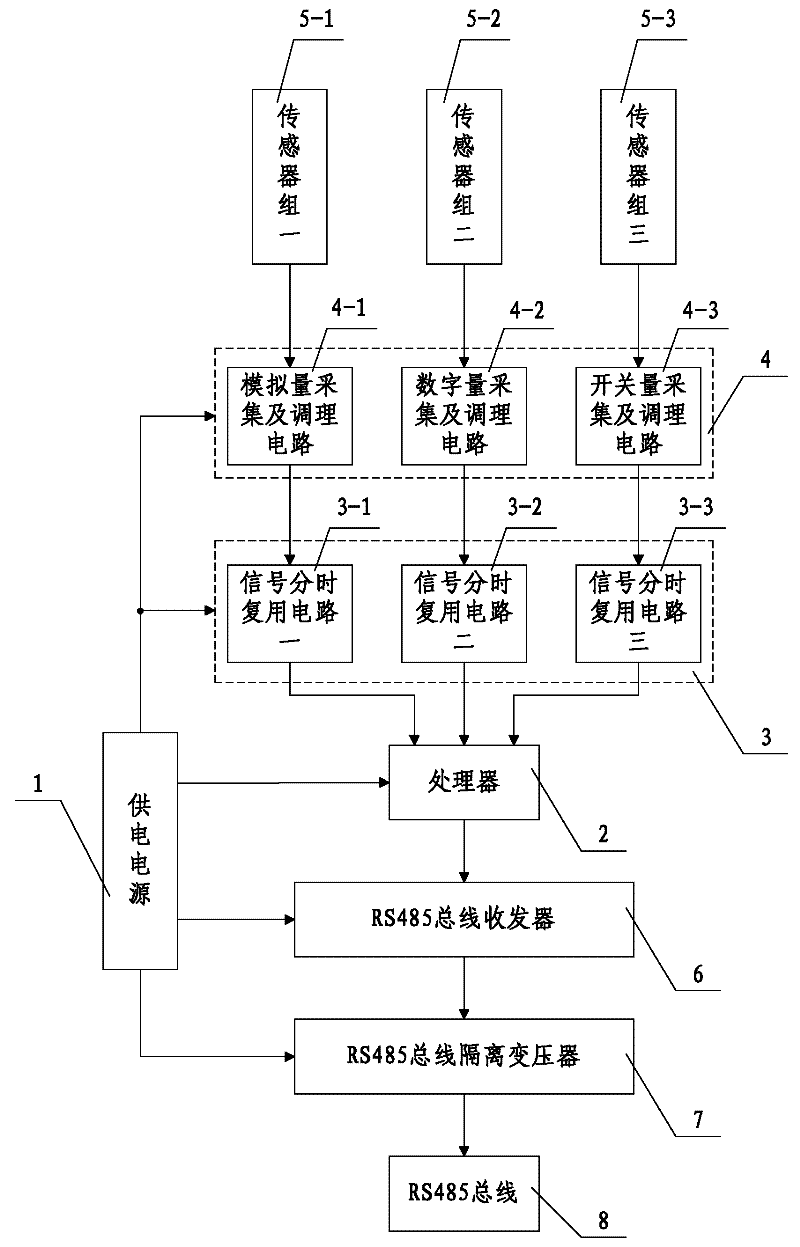
Data acquisition system convenient for realizing RS (Remote Sensing) 485 bus networking
The invention discloses a data acquisition system convenient for realizing RS (Remote Sensing) 485 bus networking, which comprises a power supply and a processor, wherein the input end of the processor is connected with a signal time-sharing multiplexing circuit, and the input end of the signal time-sharing multiplexing circuit is connected with a signal acquisition and conditioning circuit. The signal acquisition and conditioning circuit is composed of an analog quantity acquisition and conditioning circuit, a digital quantity acquisition and conditioning circuit and a switching value acquisition and conditioning circuit. The input end of the analog quantity acquisition and conditioning circuit is connected with a sensor group 1, the input end of the digital quantity acquisition and conditioning circuit is connected with a sensor group 2, and the input end of the switching value acquisition and conditioning circuit is connected with a sensor group 3. The output end of the processor is connected with an RS485 bus transceiver, and the output end of the RS485 bus transceiver is connected with an RS485 bus isolation transformer used for connecting an RS485 bus. The data acquisition system has reasonable design and is simple and convenient for use and operation, and the data acquisition system is convenient for realizing RS485 bus networking. According to the data acquisition system, deployments of field acquisition equipment can be reduced, difficulty of field operation can be reduced, and manpower and material costs can be saved.
Owner:XIAN CENTN TECH
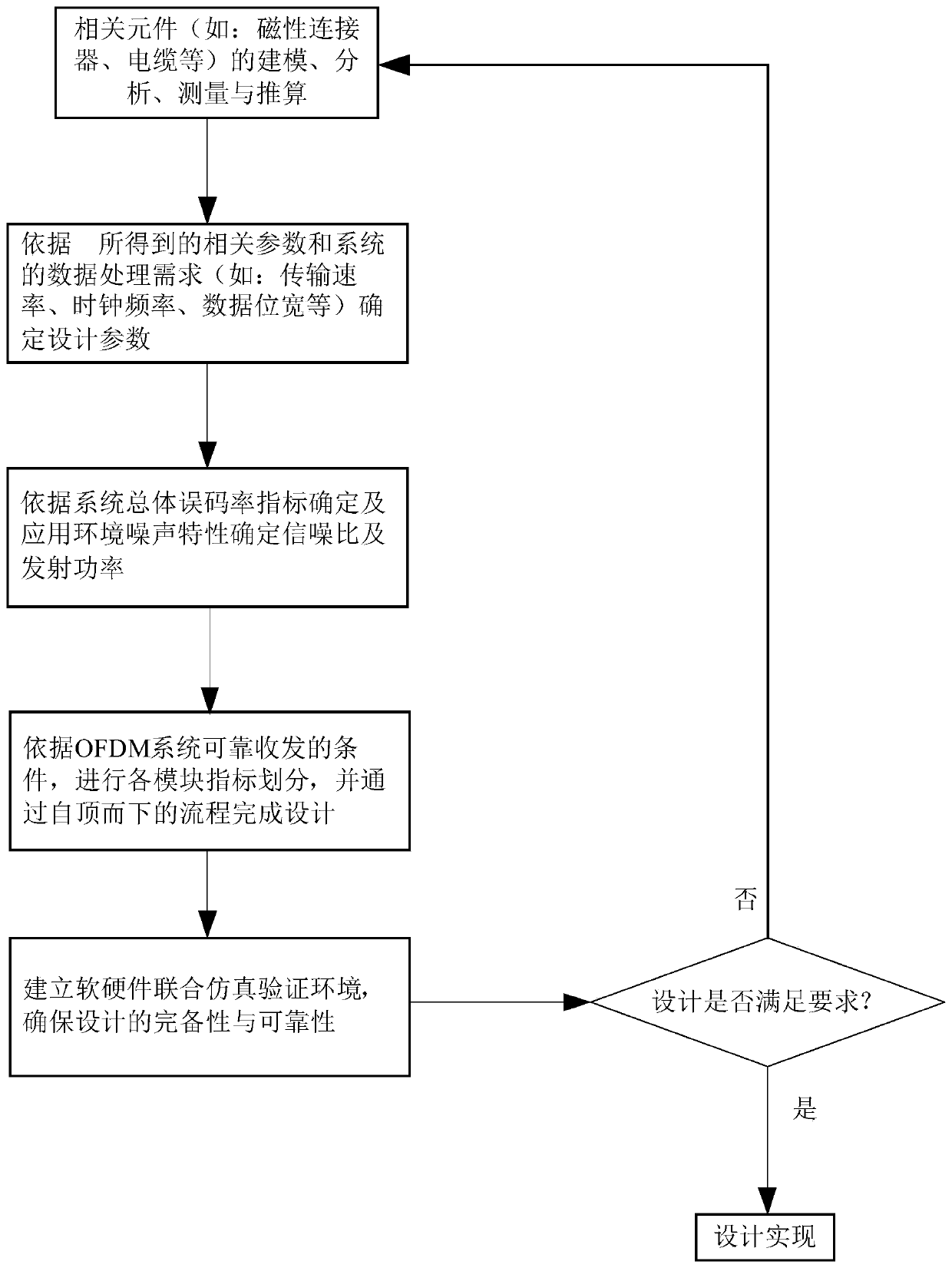
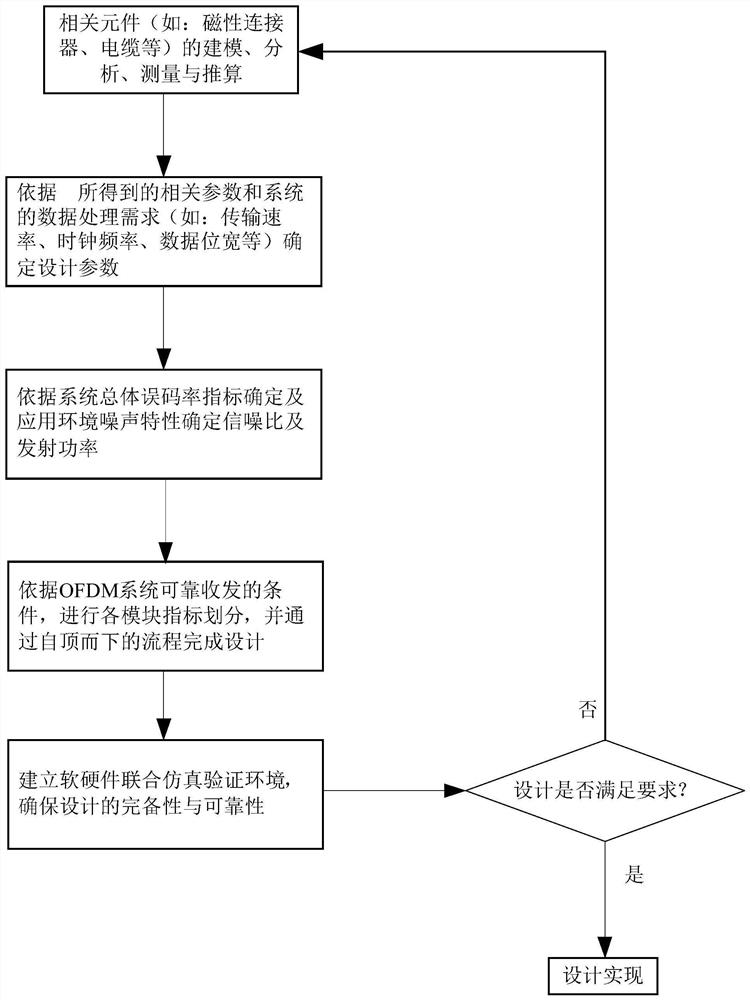
Wired signal transmission design method based on orthogonal frequency division multiplexing
ActiveCN111327348AIncrease data transfer rateImprove data transmission distancePower distribution line transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitted powerPhysical layer
The invention discloses a wired signal transmission design method based on orthogonal frequency division multiplexing. The method comprises the steps of modeling, analyzing, measuring and parameter reckoning of related elements. And determining design parameters according to the extracted related parameters and data processing requirements, determining a signal-to-noise ratio and transmitting power according to a total bit error rate index of the system and noise characteristics of an application environment, performing system index decomposition and design implementation, and ensuring designreliability through joint simulation verification. The method can be suitable for different wired medium channels, can unify physical layer implementation architectures of different protocol buses, can also be used for improving the physical layer transmission rate of a low-speed bus, and realizes reliable long-distance transmission; moreover, the software and hardware joint simulation verification platform performs simulation verification on system modeling, verification system architecture and design codes, and performs index verification by building a physical prototype system, so that thedesign reliability is improved.
Owner:XIAN MICROELECTRONICS TECH INST
Submersible electric pump downhole data acquisition device
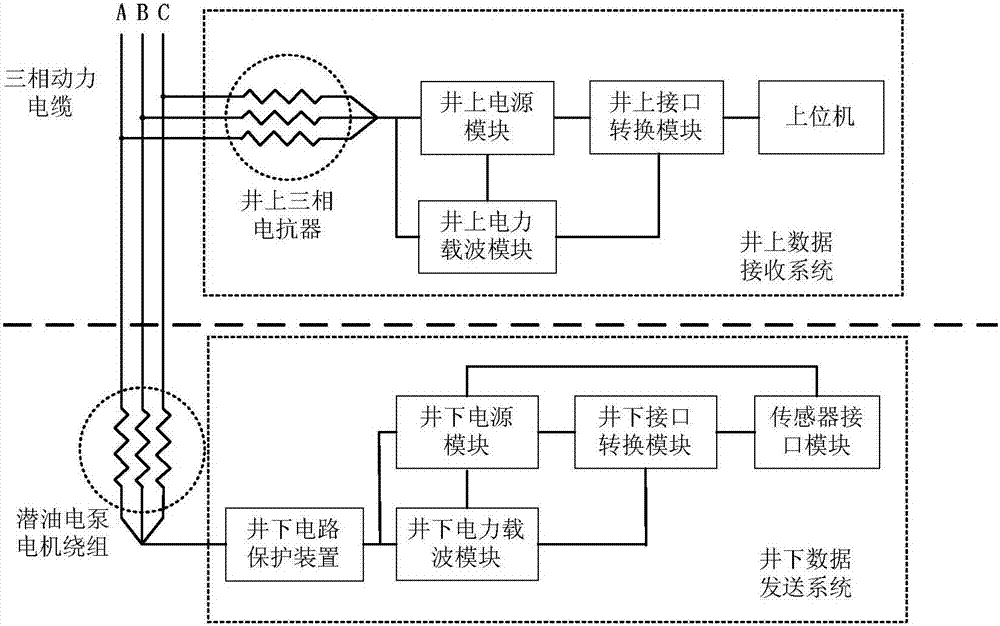
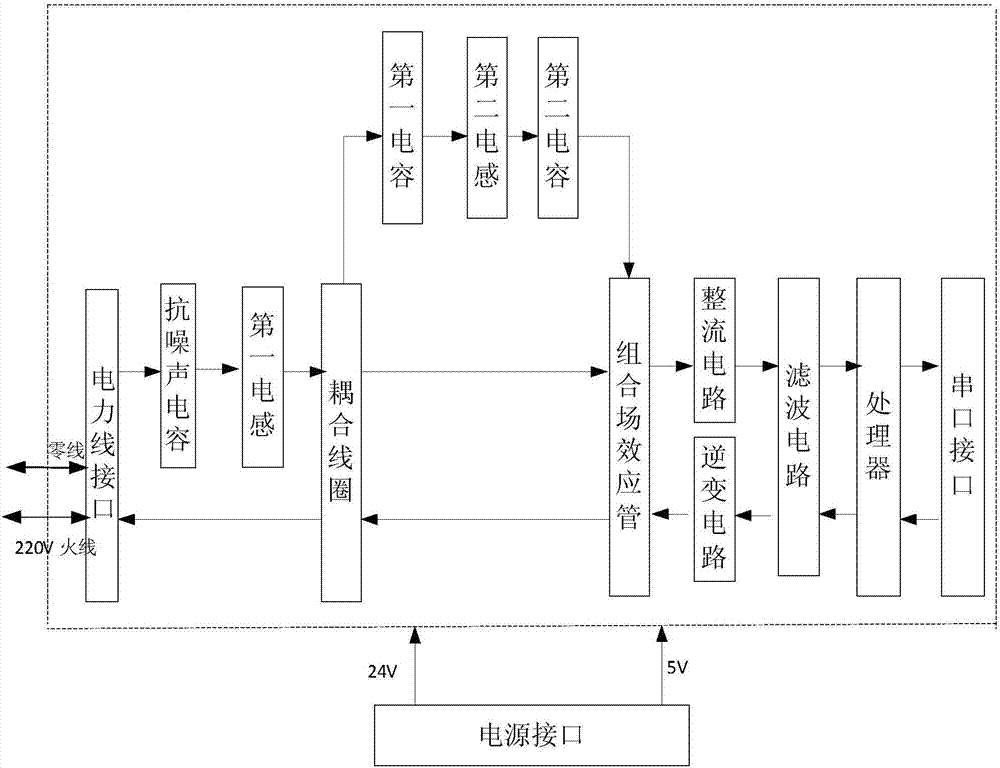
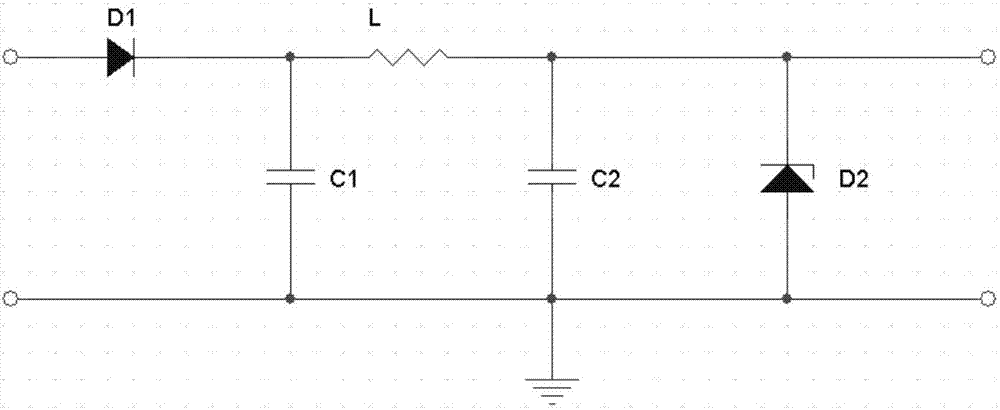
InactiveCN106930750ASmall attenuationIntegrity guaranteedSurveyConstructionsCapacitanceFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a submersible electric pump downhole data acquisition device for solving the problem that transmission of an existing data acquisition device is interfered. The submersible electric pump downhole data acquisition device comprises an on-well data receiving system and a downhole data transmission system; the on-well data receiving system is connected with the downhole data transmission system through an on-well three-phase electric reactor and a three-phase power cable, and the on-well data receiving system exchanges the data with the downhole data transmission system through an on-well power line carrier module; and the downhole data transmission system exchanges the data with a sensor interface module through the downhole power line carrier module, and the downhole data transmission system exchanges data with the on-well data receiving system through a submersible electric pump motor winding assembly. According to the submersible electric pump downhole data acquisition device, the power line carrier module adopts power supply lines of the submersible electric pump as carriers, communication is conducted through power line carrier, a spread spectrum technology is combined, a sensor signal is conducted frequency conversion under the same transformer, a signal spectrum is moved to a plurality of frequency bands, then the signal is coupled to the power lines through a coupling capacitor, and data transmission is realized.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV +1
A Design Method for Wired Signal Transmission Based on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
ActiveCN111327348BIncrease data transfer rateImprove data transmission distancePower distribution line transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitted powerPhysical layer
A design method for wired signal transmission based on OFDM, including modeling, analysis, measurement and parameter calculation of relevant components, determining design parameters based on the extracted related parameters and data processing requirements, and determining the design parameters based on the overall bit error rate of the system Determine the signal-to-noise ratio and transmit power according to the indicators and the noise characteristics of the application environment, decompose the system indicators and realize the design, and ensure the reliability of the design through co-simulation verification. The present invention can be applied to different wired medium channels, can unify the physical layer implementation architecture of different protocol buses, can also be used to improve the physical layer transmission rate of low-speed buses, and realize reliable long-distance transmission; in addition, the software-hardware joint simulation verification platform Through simulation verification of system modeling, verification system architecture and design code, and index verification by building a physical prototype system, the reliability of the design is improved.
Owner:XIAN MICROELECTRONICS TECH INST
Wireless sensing system based on radio frequency energy awakening
PendingCN113691890AReduce energy consumptionRealize differentiated managementParticular environment based servicesNetwork topologiesRadio frequency energyEngineering
The invention relates to a wireless sensing system based on radio frequency energy awakening. The invention relates to the technical field of wireless sensing. The system comprises a plurality of clusters, an awakening source and a cloud server, wherein each cluster comprises a plurality of intra-cluster nodes and a cluster head node, information collected by the intra-cluster nodes is gathered to the cluster head node and is forwarded to a cloud server through data fusion, and the intra-cluster nodes and the cluster head node are awakened to work by an awakening source. A load switch is controlled through the MCU, so that differentiated management of a high-energy-consumption module and a low-energy-consumption module is realized; in a dormant state, the high-energy-consumption wireless communication module and the DTU are powered off by the load switch; and when needed, the device is powered on. By means of the fine management of energy, the energy consumption is lower, and the service life of the wireless sensing system is longer.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
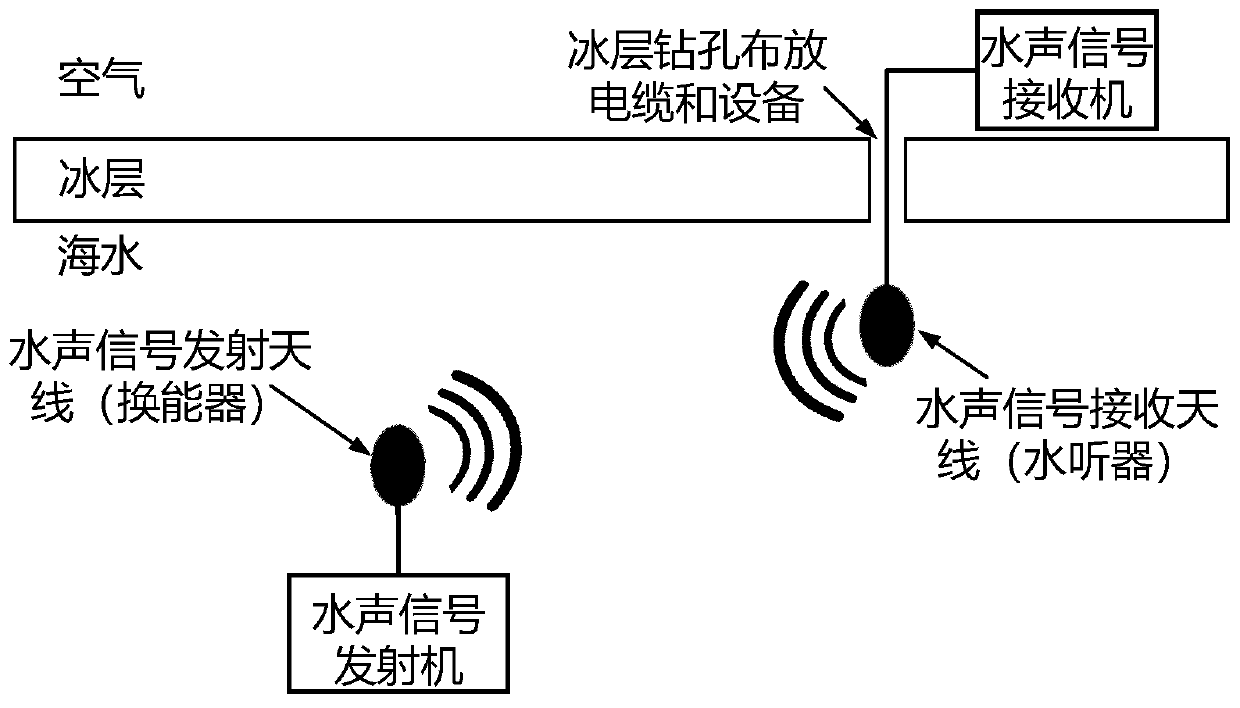
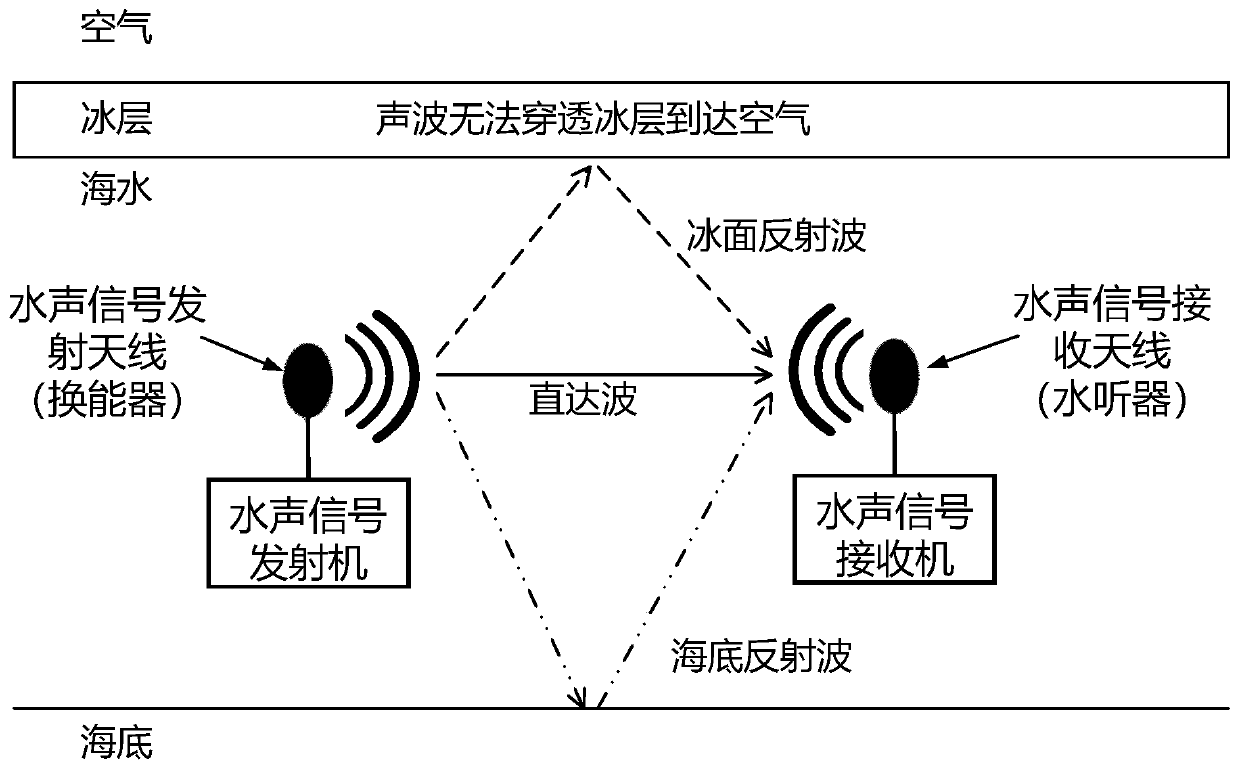
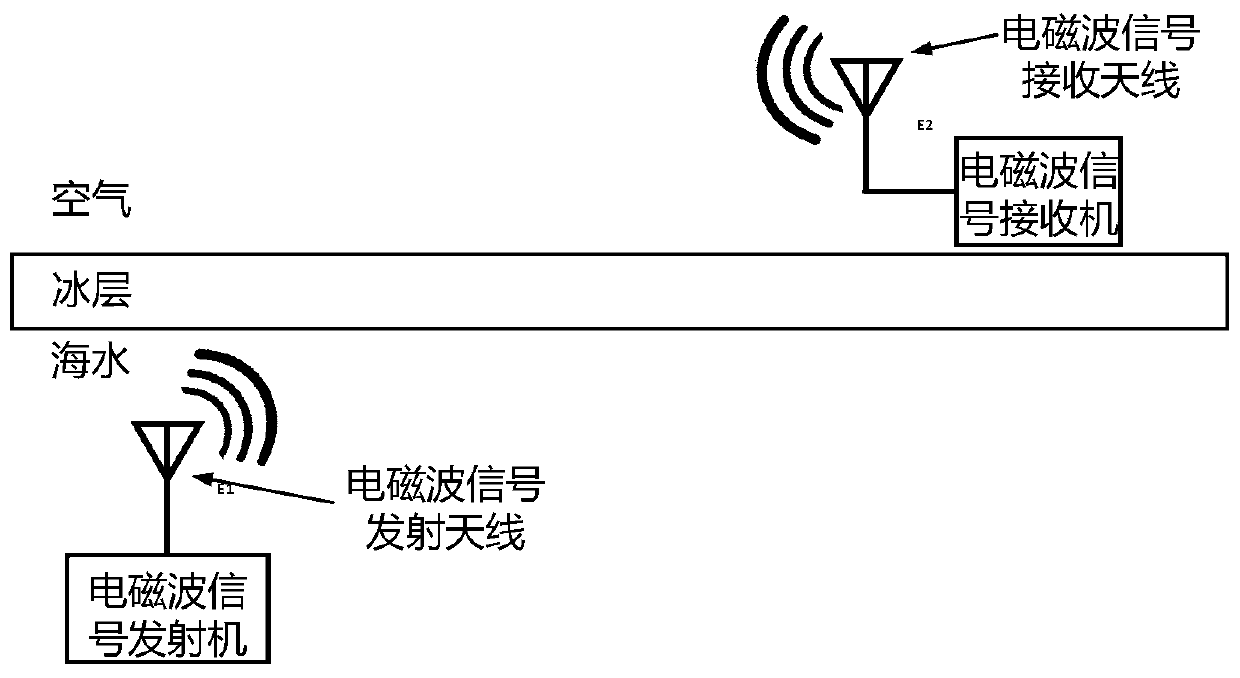
Cross-ice-layer data wireless transmission method
ActiveCN110224765ALong transmission distanceIncrease electric dipole momentTransmissionAntenna feed intermediatesDipole antennaSeawater
The invention relates to a cross-ice-layer data wireless transmission method, the frequency of an electromagnetic wave signal is low frequency and lower frequency, the frequency range is 0.5 kHz to 50kHz, and data terminals are respectively located at the depth within 10m in seawater below an ice layer and at an air layer above the ice layer. And the transmitting antenna adopts an electric dipoleantenna. And the receiving antenna adopts a magnetic antenna. The electric dipole antenna needs to be subjected to sealing and seawater corrosion prevention treatment, and seawater is prevented fromdirectly contacting with the metal part of the antenna. Electromagnetic wave signals are transmitted into the air after crossing the ice layer underwater, so that an electromagnetic wave-based data wireless transmission link in the underwater-ice layer-air is constructed, and data in seawater below the ice layer can be wirelessly transmitted into the air above the ice layer based on the link. Thereceiving antenna adopts a magnetic antenna, so that the detection sensitivity of electromagnetic wave signals can be improved, and the data transmission distance is increased. In addition, the electric dipole moment of the transmitting electric dipole antenna in seawater below the ice layer is increased, and the transmission distance in the air can be increased.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
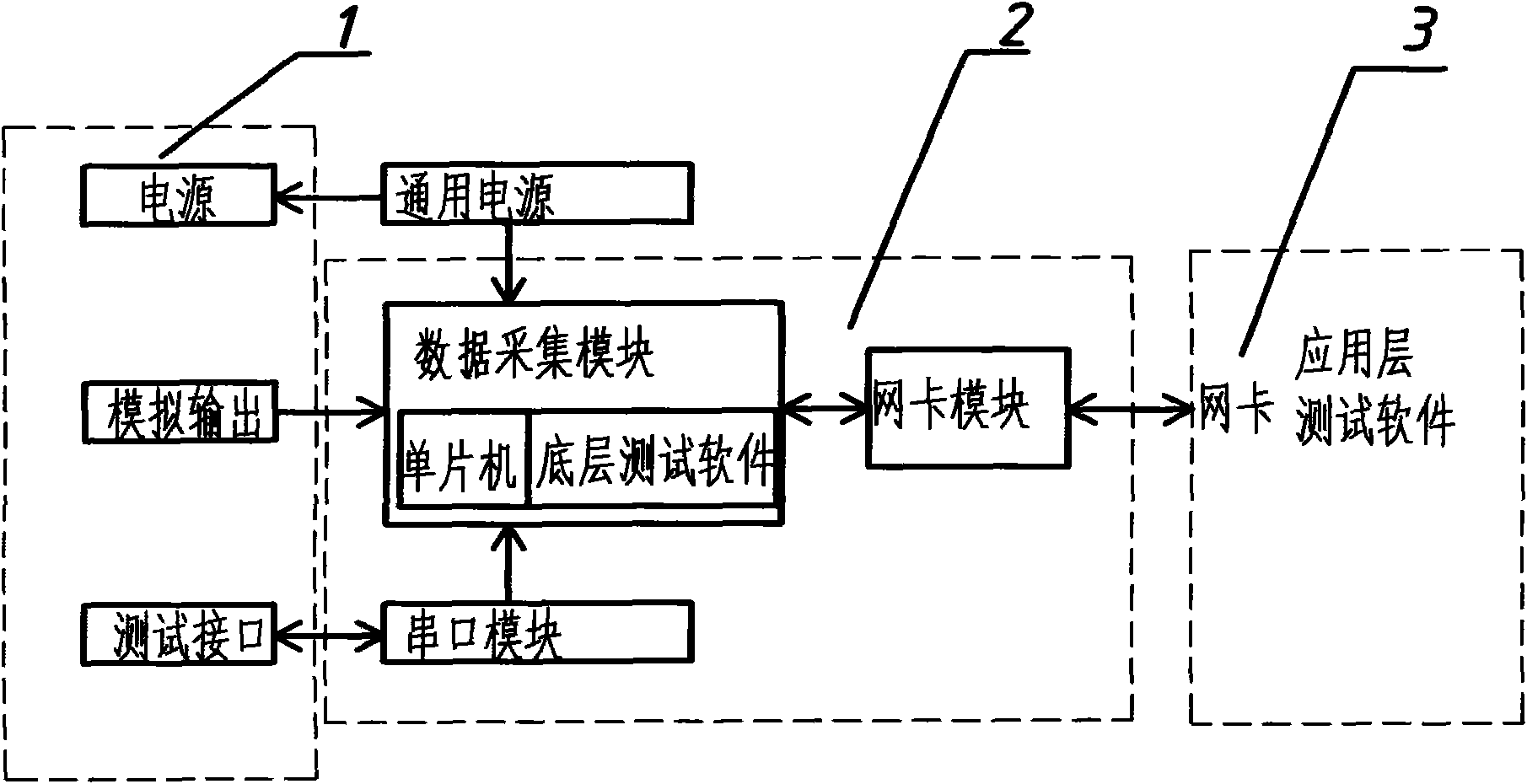
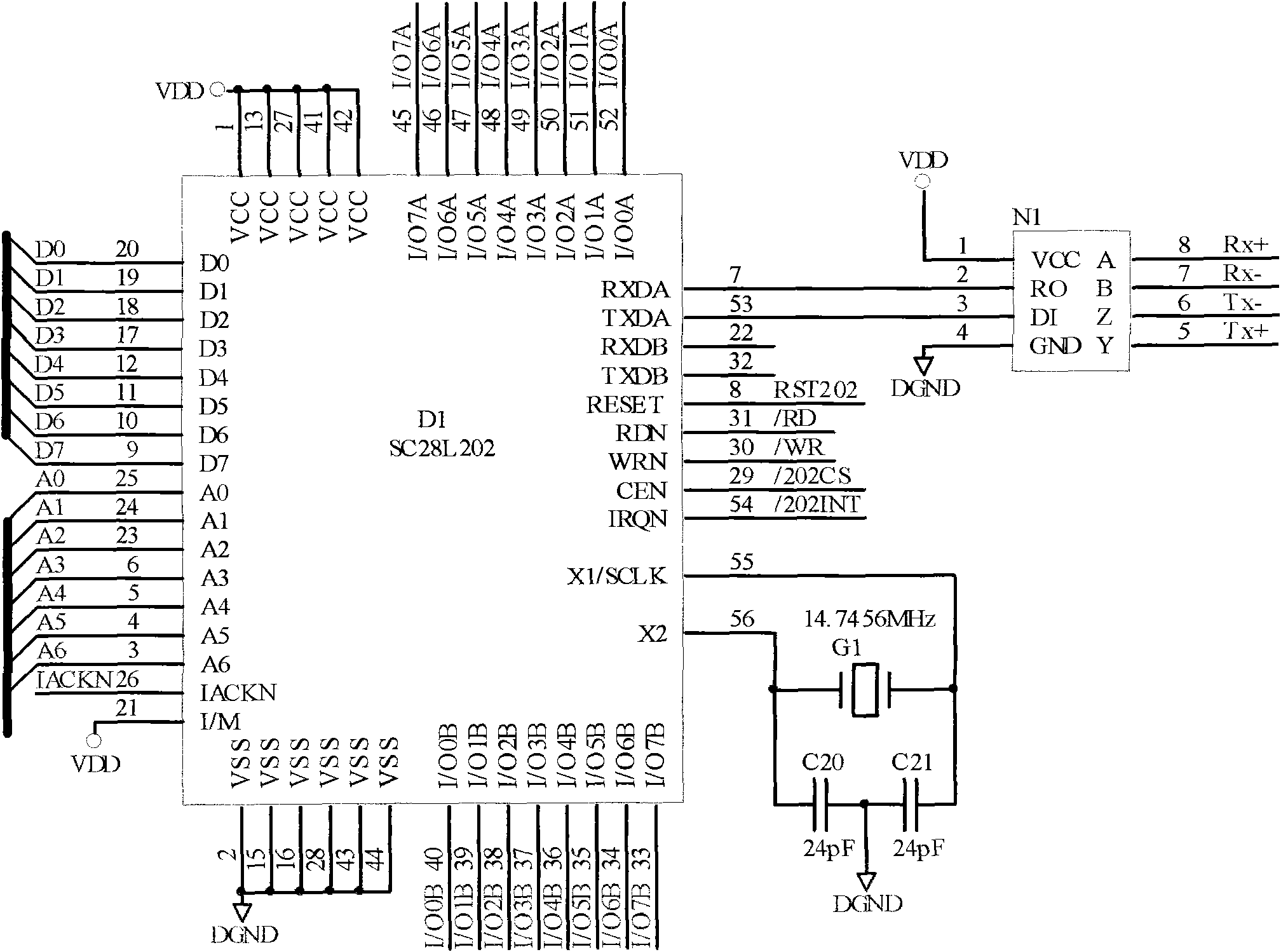
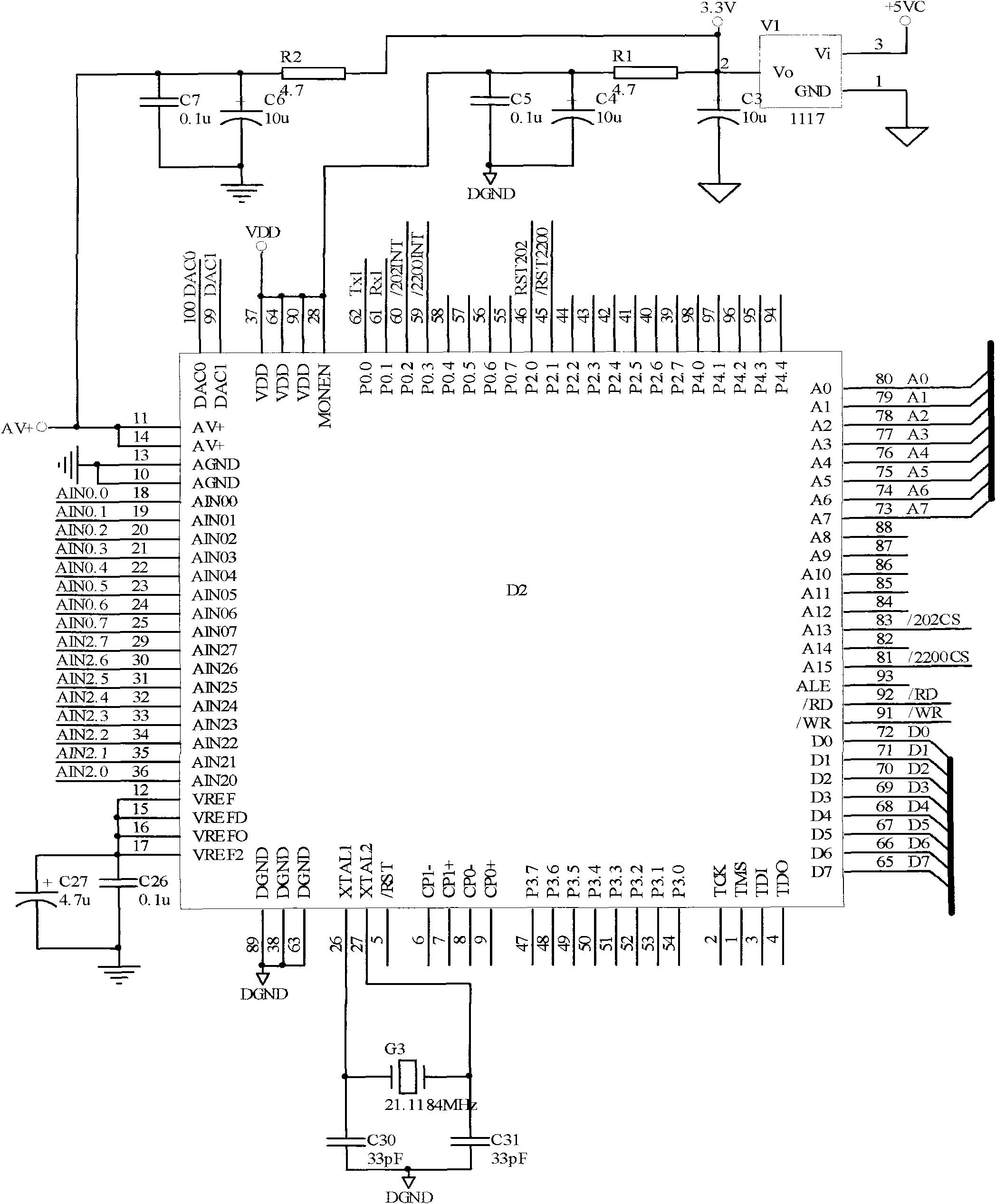
Universal serial port conversion and data acquisition card (DAC)
InactiveCN102081836AImprove versatilityImprove reliabilityElectric signal transmission systemsTransmissionNetwork packetComputer module
The invention provides a universal serial port conversion and data acquisition card (DAC), mainly comprising a serial port module, a data acquisition module and a network card module. A tested product is connected with the serial port module by a test port, which is used for receiving the test data packets of the tested product; the serial port module sends the received test data packets to the data acquisition module by a serial port of the serial port module; and the data acquisition module collects analog quantity and self-power analog quantity output by the product through a built-in A / D chip of the data acquisition module, sends the data packets transmitted by the serial port module to a personal computer (PC) by the network card module, and receives instruction protocol packets from the PC as well as sends the decoded instruction protocol packets to the serial port module. The universal serial port conversion and data acquisition card provided by the invention is used to solve the problems of short transmission range, low reliability of data transmission, low transmission speed and the like when the product performs data exchange with the PC.
Owner:贵州航天控制技术有限公司
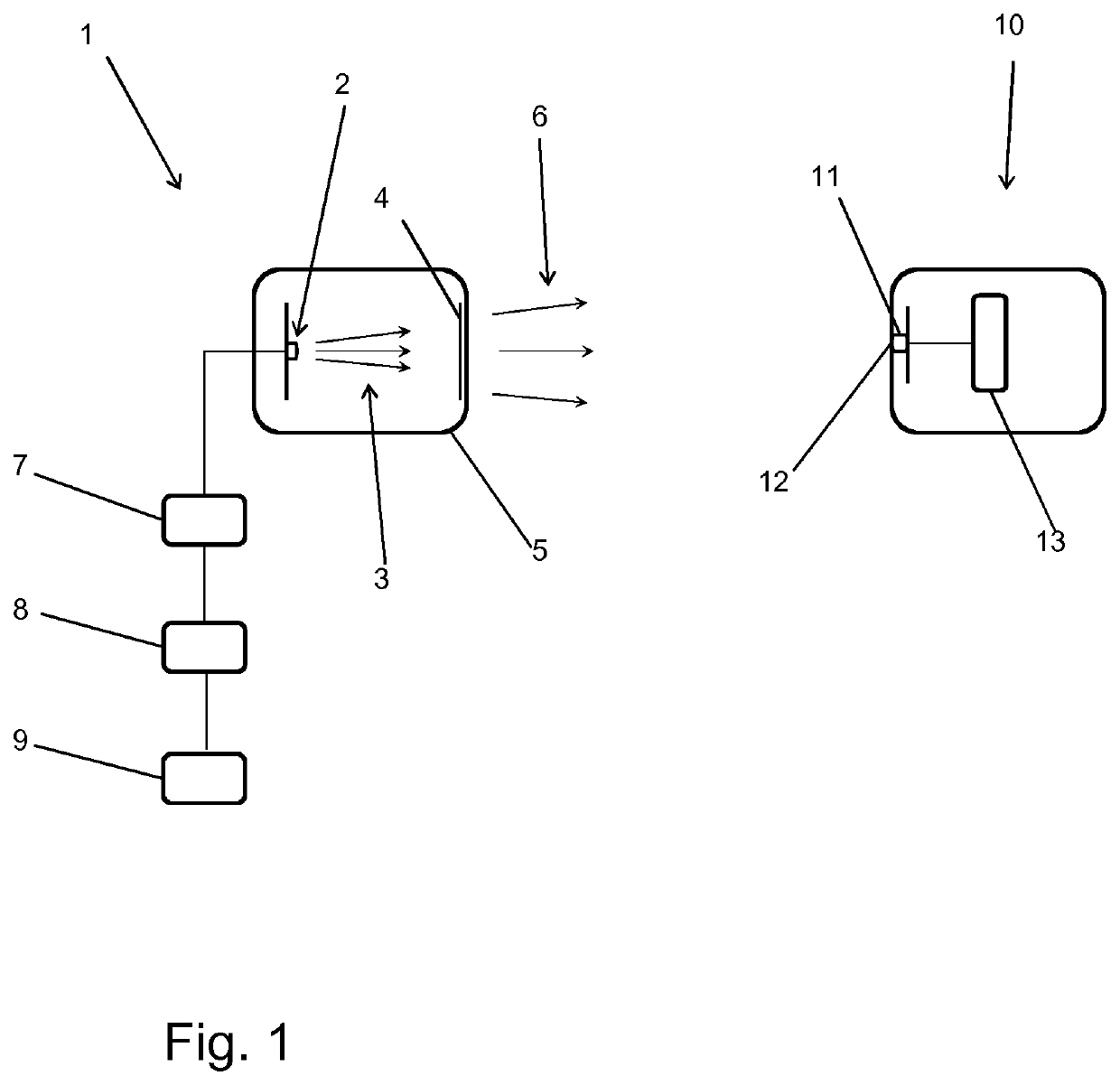
Transmitter for transmitting data and for emitting electromagnetic radiation in the visible spectral range and data transmission system
ActiveUS20200259567A1Increase distanceImprove data transmission distanceElectromagnetic transmittersAnthracene dyesLight equipmentFluorescence
The present invention relates to a transmitter for transmitting data and for emitting electromagnetic radiation in the visible spectral range, wherein the transmitter comprises a) a radiation source for generating and emitting first electromagnetic radiation, b) a modulator being adapted to modulate the first electromagnetic radiation depending on the data to be transmitted generating modulated first electromagnetic radiation, and c) a frequency converter for converting at least a part of the modulated first electromagnetic radiation into modulated second electromagnetic radiation, said modulated second electromagnetic radiation being different from the modulated first electromagnetic radiation, wherein the frequency converter comprises a polymeric matrix material comprising at least one organic fluorescent colorant. Furthermore, the invention relates to an illumination device comprising such transmitter. Moreover, the invention relates to a data transmission system comprising such a transmitter as well as a receiver and a data analyzer.
Owner:BASF AG
Data transmission method and system based on mobile terminal and mobile terminal
ActiveCN102769844BImprove data transmission distanceReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTHigh level techniquesTelecommunicationsIp address
The invention provides a data transmission method and system based on a mobile terminal and a mobile terminal. The data transmission method comprises the following steps: a source mobile terminal transmits a service request message, which contains the IP (Internet Protocol) address of the source mobile terminal, to an objective mobile terminal through a mobile switch network, and if a TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) / IP connection request transmitted by the object mobile terminal, which adopts an IP address per se, to the source mobile terminal is received, the source mobile terminal returns the TCP / IP connection request to the objective mobile terminal, and service data in communication interaction is transmitted by point-point IP routing, which is established by the source mobile terminal and the objective mobile terminal. The data transmission method and system based on the mobile terminal and the mobile terminal, provided by the invention, can achieve the communication interaction between the source mobile terminal and the objective mobile terminal through the point-point IP routing so as to improve the distance between mobile terminals and reduce the power consumption of mobile terminals, and is conducive to the transmission of large quantities of data.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
Multi-unmanned ship formation cooperative control system and method based on collaborative cloud control
ActiveCN108200175BAvoid collisionImprove accuracyWaterborne vesselsTransmission systemsMarine engineeringControl system
The invention relates to a multi-unmanned ship formation cooperative control system and method based on collaborative cloud control. The method includes: establishing a cloud-shore connection through a shore-based control system and a collaborative cloud control system, and connecting the shore-based control system and collaborative cloud control based on the cloud-shore System communication to obtain the control information of the shore-based control system for the unmanned ship formation and the status information of the unmanned ship formation; establish a cloud ship connection with the unmanned ship formation through the collaborative cloud control system, and send the cooperative cloud control system to the unmanned ship formation based on the cloud ship connection. Control instructions of the unmanned ship formation and obtain status information of the unmanned ship formation. The present invention is based on a collaborative cloud control system, adopts a distributed computing method, calls multiple cloud servers, makes full use of effective resources, and improves computing capabilities; improves the accuracy and timeliness of unmanned ship formation scheduling control, and effectively prevents unmanned ship formation Collision occurs; and multiple unmanned ships operate at the same time, which improves the operating speed and efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
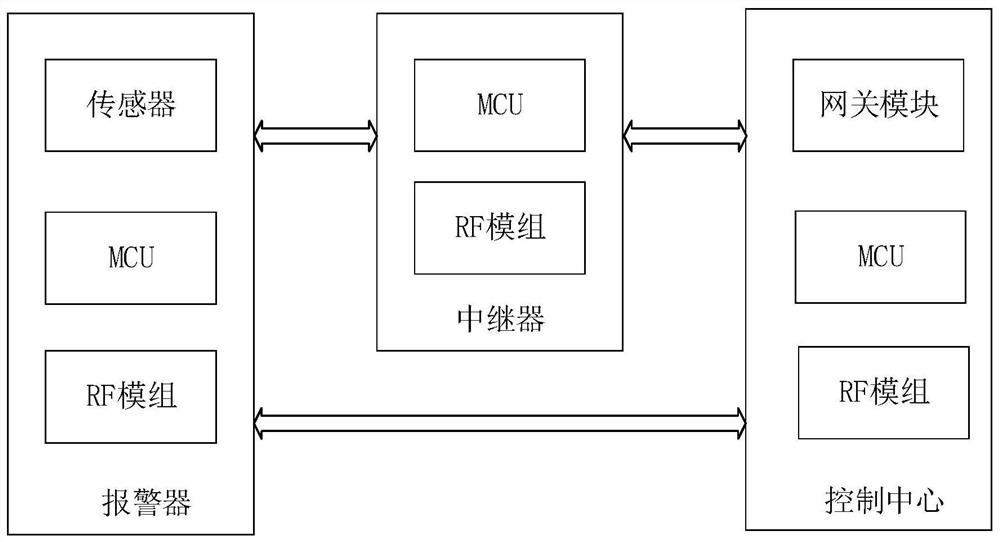
Alarm topology transmission method and related products
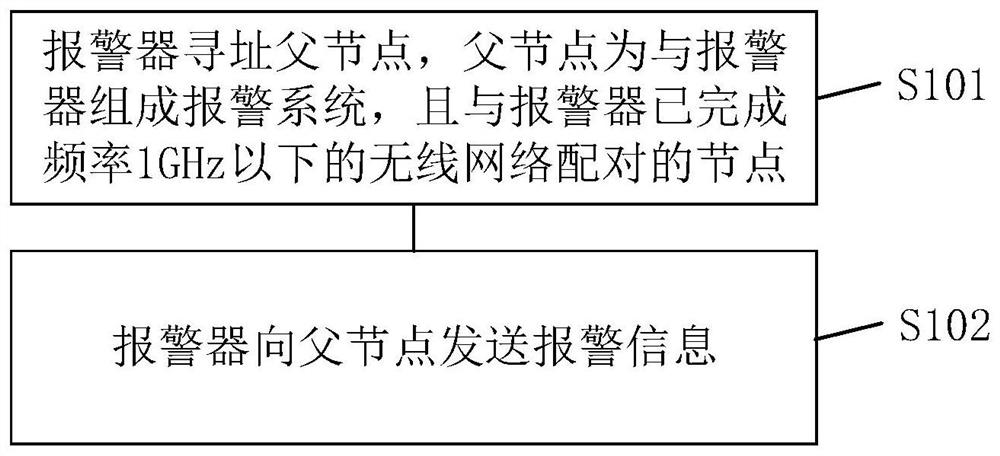
ActiveCN112396814BImprove data transmission distanceImprove response efficiencyAlarmsEmbedded systemData transmission
The embodiment of the present application discloses an alarm topology transmission method and related products, wherein the method includes: the alarm addresses the parent node, the parent node forms an alarm system with the alarm, and the alarm has been completed A node paired with a wireless network with a frequency below 1 GHz; the alarm device sends alarm information to the parent node. In the embodiment of the present application, by addressing the parent node of the alarm device that has been paired with the wireless network below 1 GHz, and then performing network connection and data transmission, the transmission distance of the alarm device is extended and the data transmission delay is shortened.
Owner:深圳市安室智能有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com