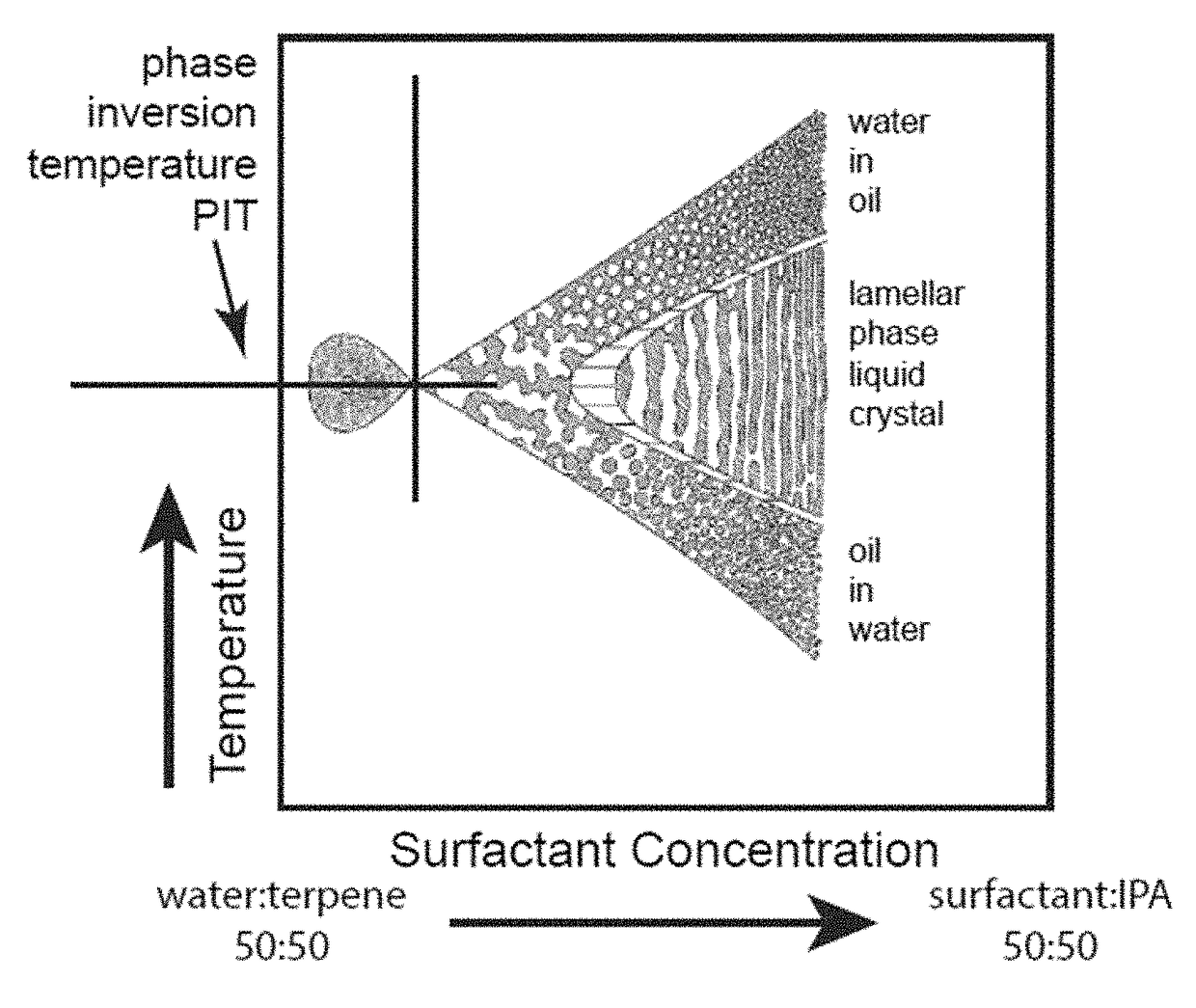
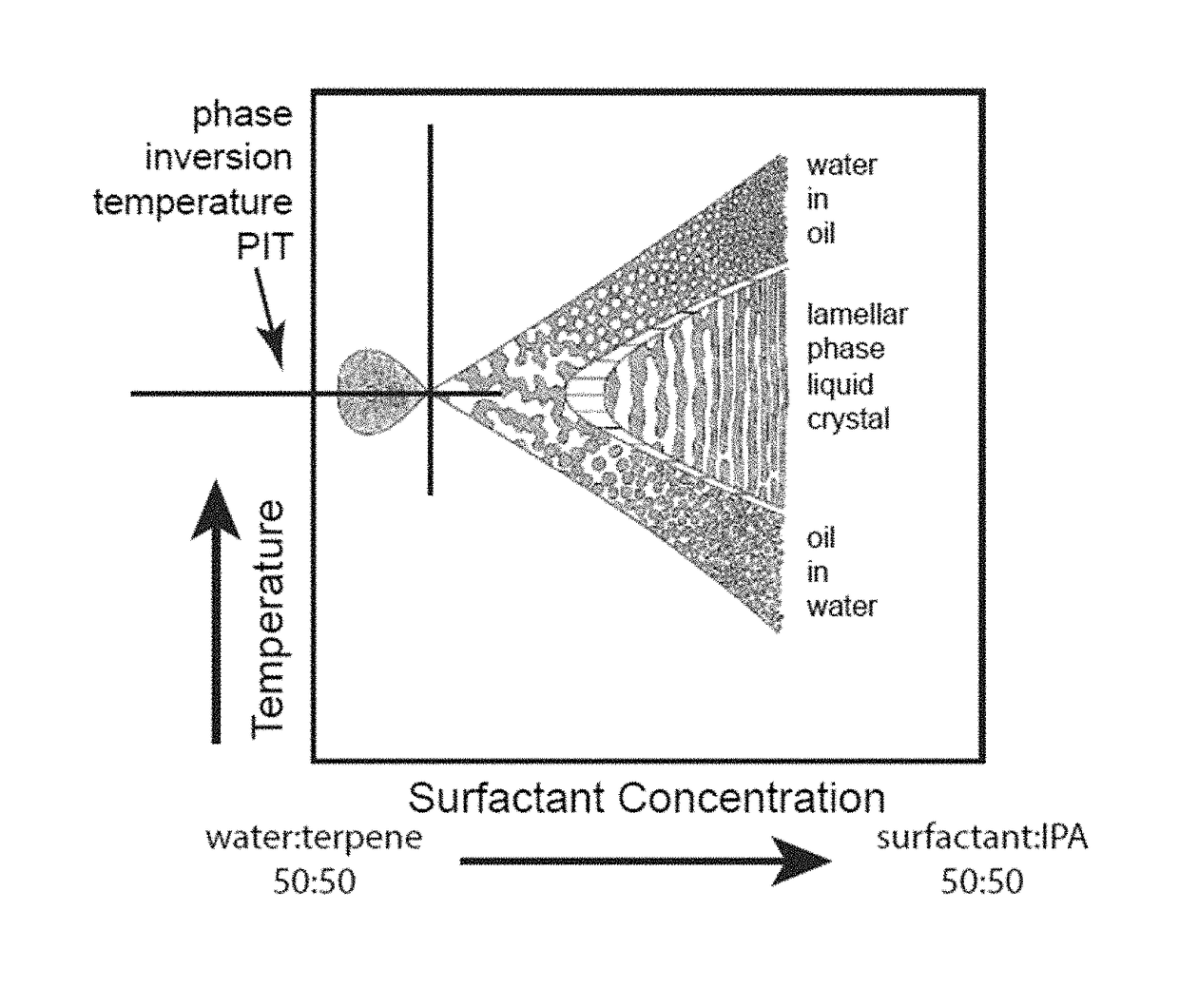
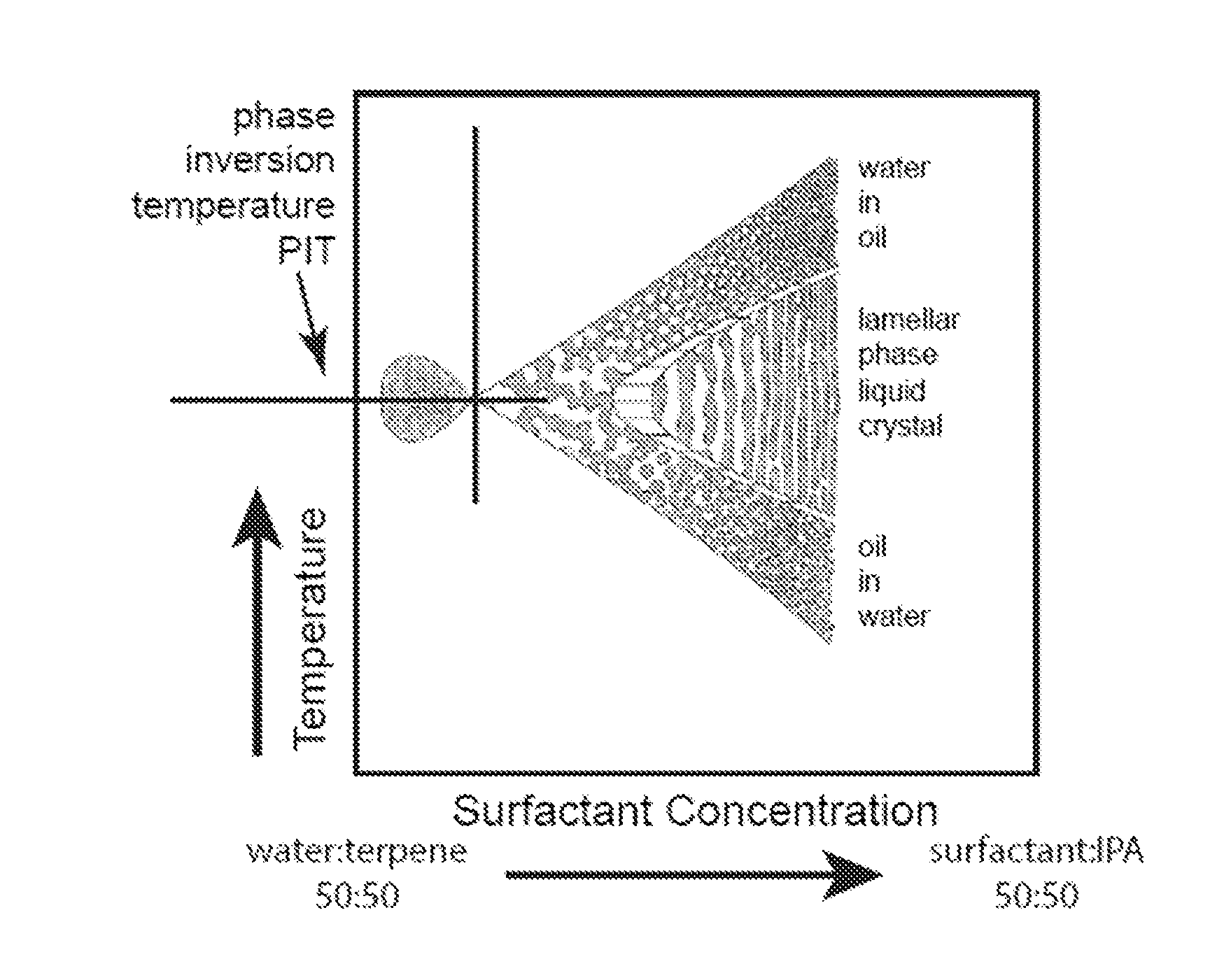
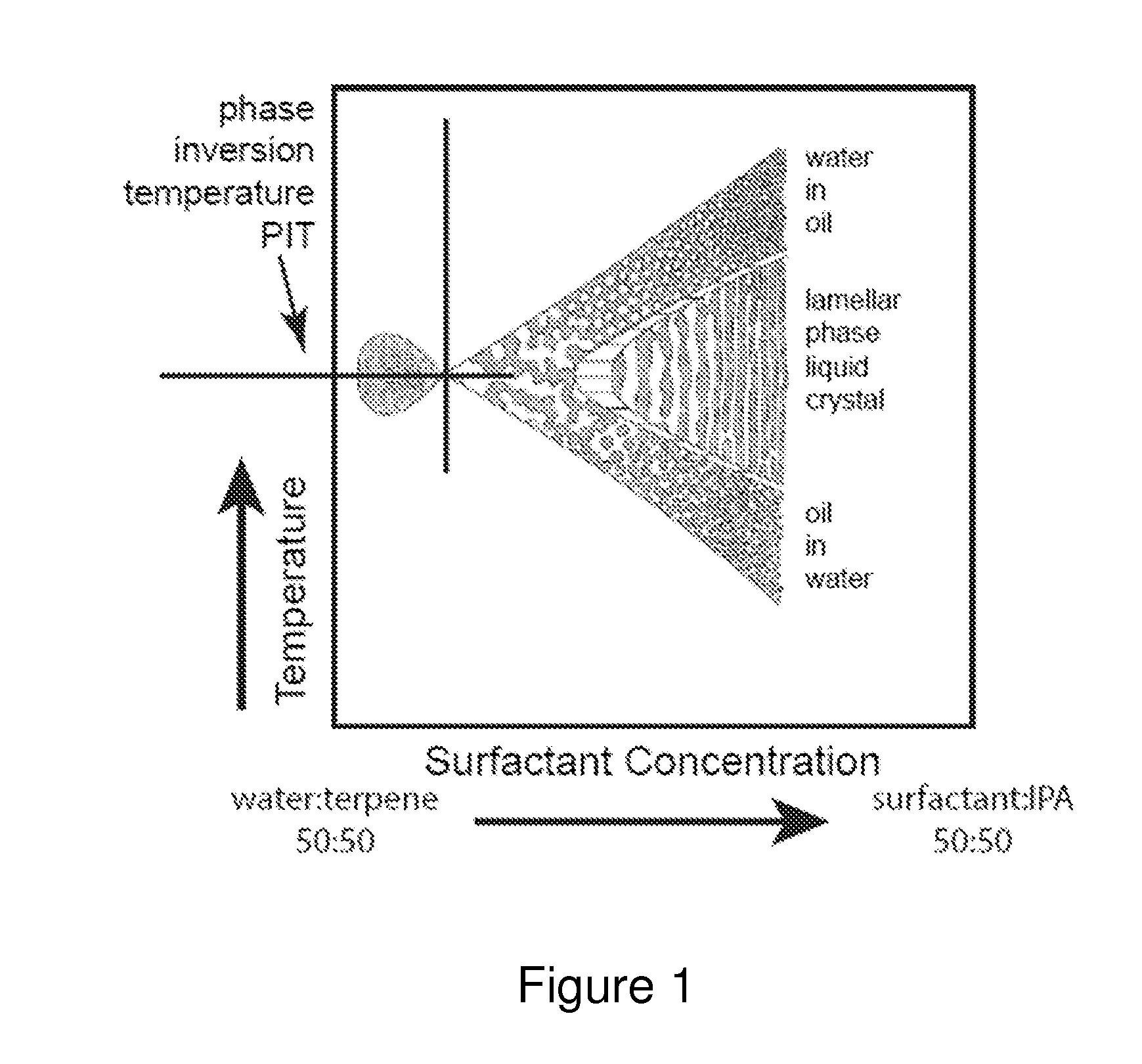
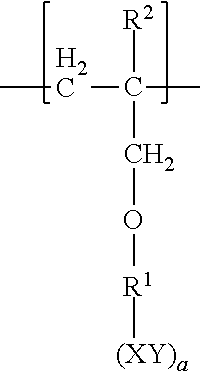
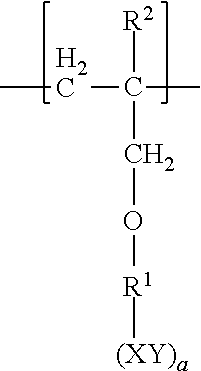
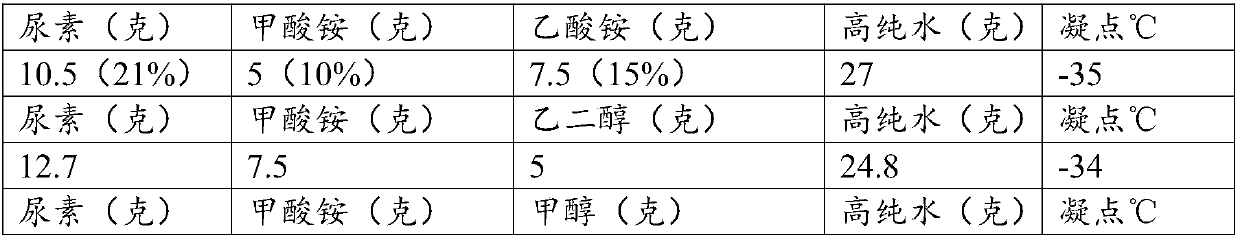
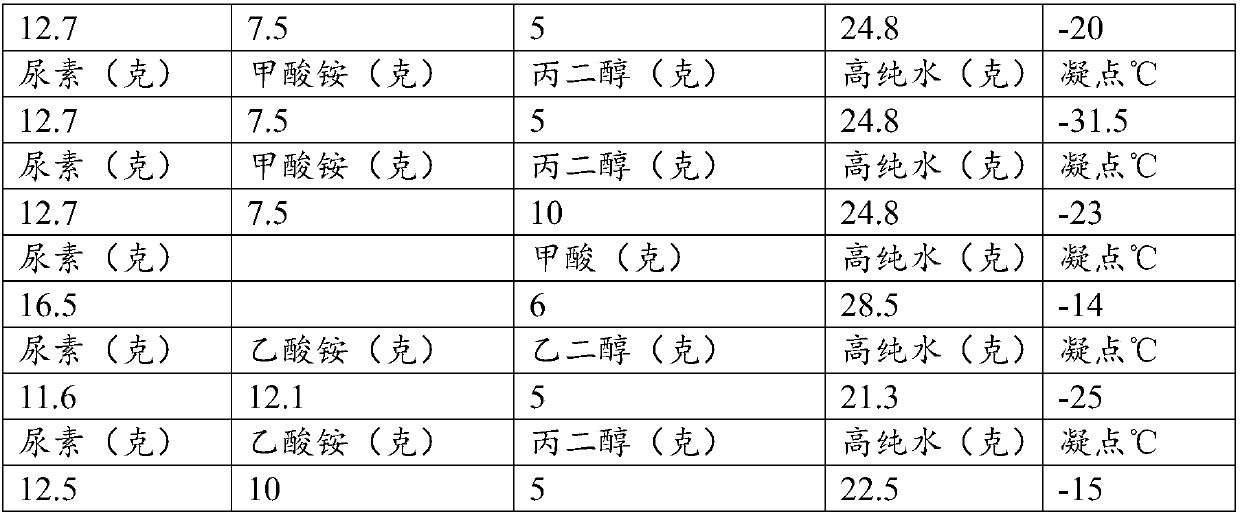
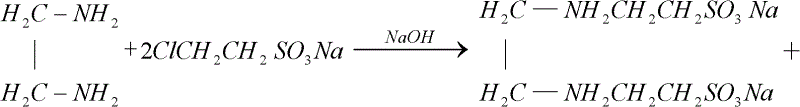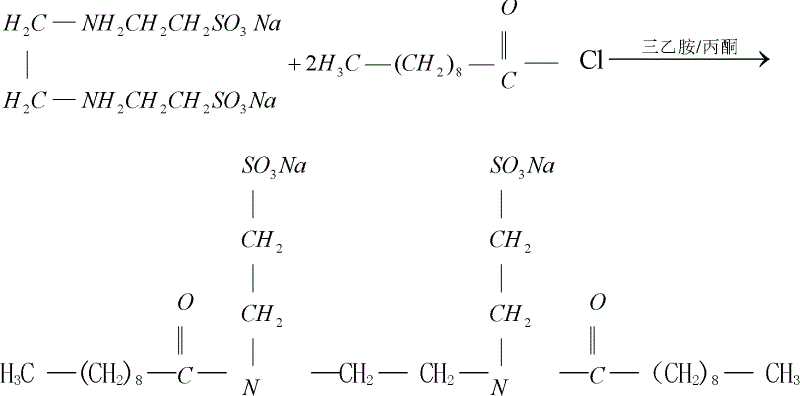Patents
Literature
60 results about "Freezing-point depression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
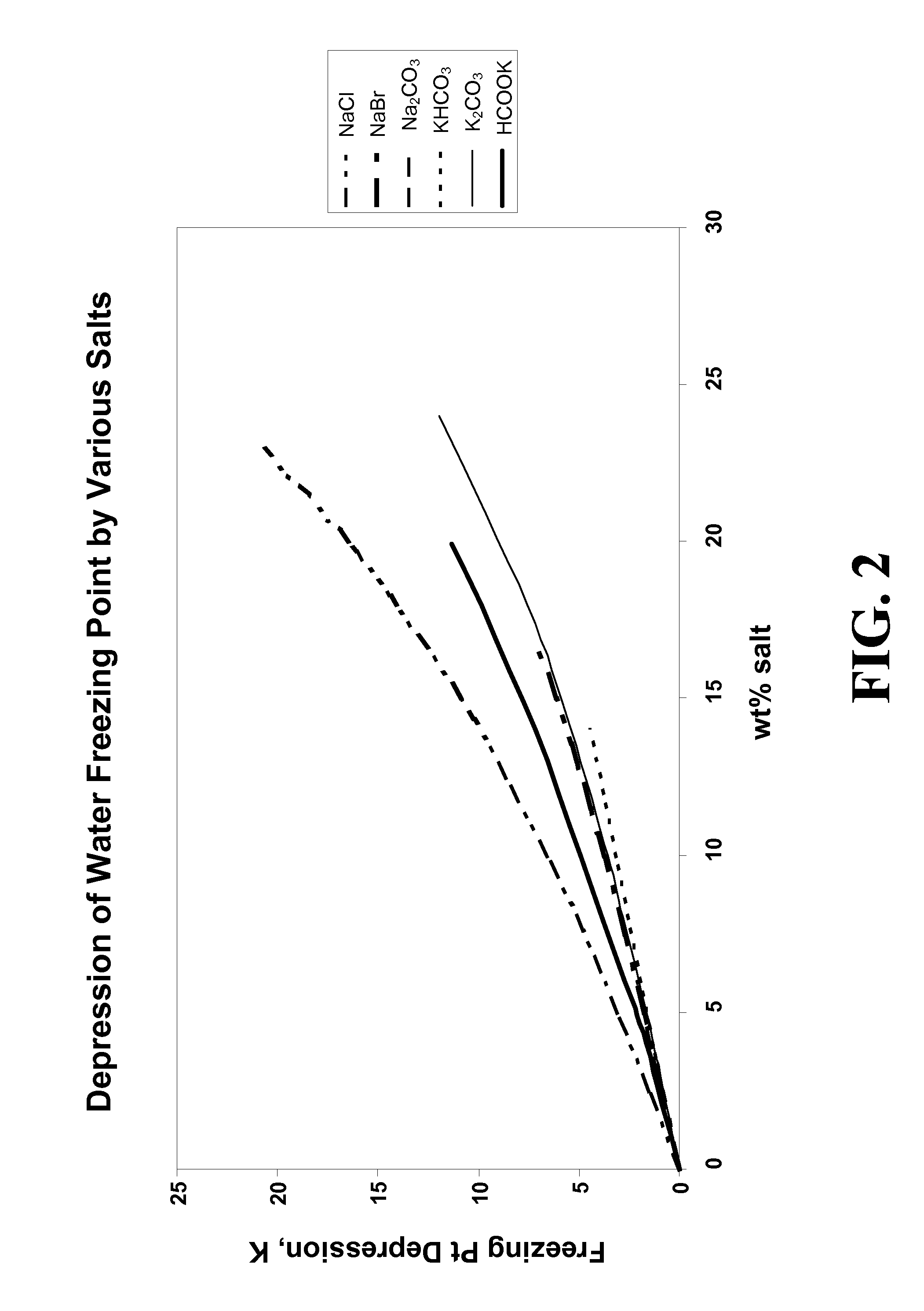
Freezing-point depression is the decrease of the freezing point of a solvent on the addition of a non-volatile solute. Examples include salt in water, alcohol in water, or the mixing of two solids such as impurities into a finely powdered drug. In all cases, the substance added/present in smaller amounts is considered the solute, while the original substance present in larger quantity is thought of as the solvent. The resulting liquid solution or solid-solid mixture has a lower freezing point than the pure solvent or solid because the chemical potential of the solvent in the mixture is lower than that of the pure solvent, the difference between the two being proportional to the natural logarithm of the mole fraction. In a similar manner, the chemical potential of the vapor above the solution is lower than that above a pure solvent, which results in boiling-point elevation. Freezing-point depression is what causes sea water, (a mixture of salt [and other things] in water) to remain liquid at temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F), the freezing point of pure water.
Reduced-carbohydrate and nutritionally-enhanced frozen desserts and other food products
InactiveUS20060286248A1Mitigate laxation effectReduce impactFrozen sweetsConfectioneryTagatoseMaltitol
A reduced carbohydrate ice cream or other frozen dessert product that contains a low-digestible sweetener system and a fermentable fiber material. The a low-digestible sweetener system consists of one or more low-digestible sweeteners having a molecular weight of from about 90 to about 190; and is typically a low molecular weight saccharide or a polyol. Typical low-digestible sweeteners include mannitol, maltitol, sorbitol, lactitol, erythritol, xylitol, isomalt, glycerin, talitol, mannose, tagatose, fructose, arabinose, fucose, lycose, ribose, sorbose, talose, and xylose, and mixtures thereof. The low-digestible sweetener replaces the digestible sugars to provide the appropriate freezing point depression of the product. The level of fermentable fiber is sufficient to mitigate a Taxation effect that can be caused by ingestion of the amount of the low-digestive sweetener. The fermentable fiber can be an inulin, a maltodextrin resistant to human digestion, an oligofructose, a fructooligosaccharide, a high water binding fermentable fiber, and a mixture thereof.
Owner:TECHCOM GRP LLC
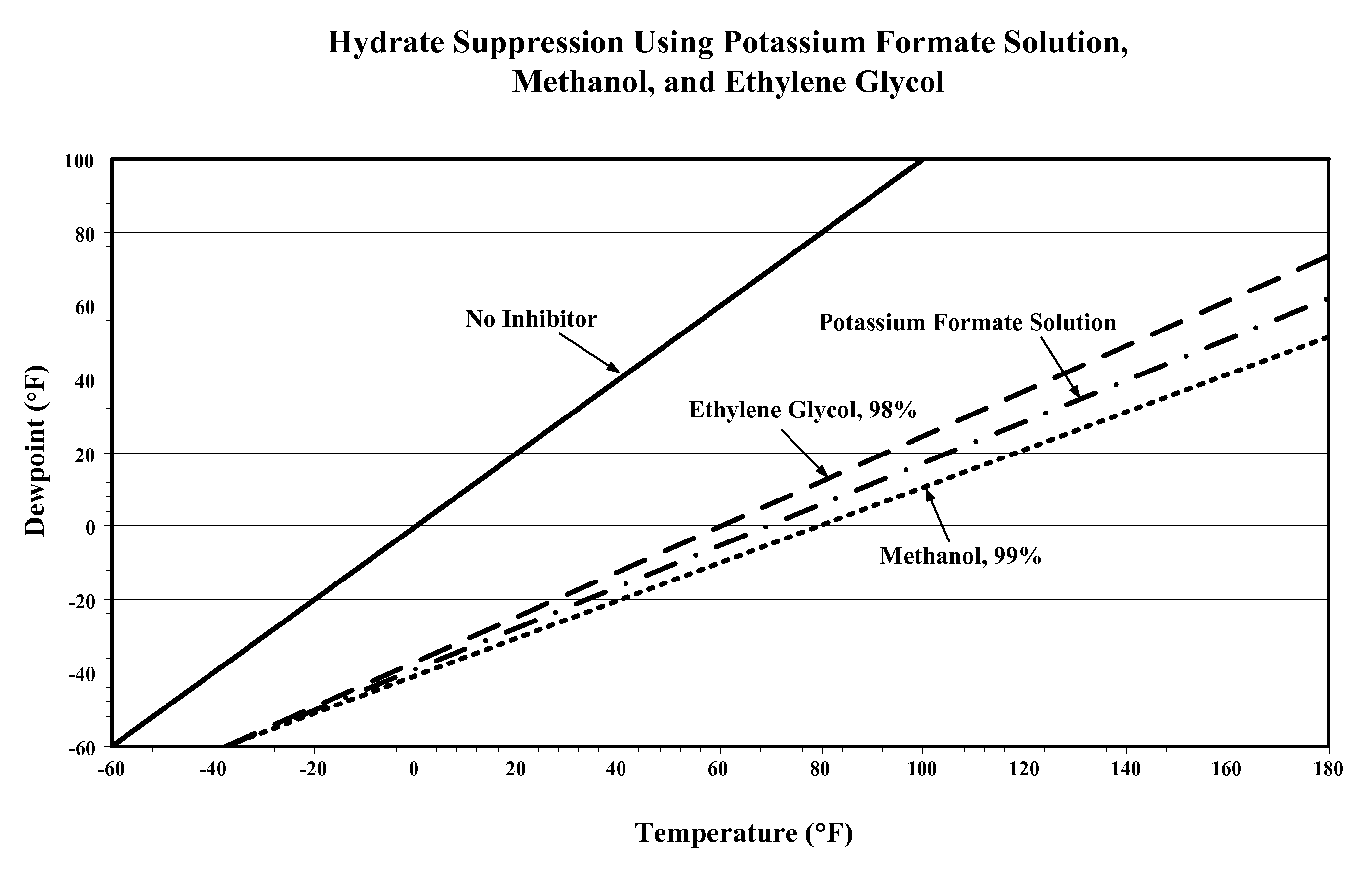
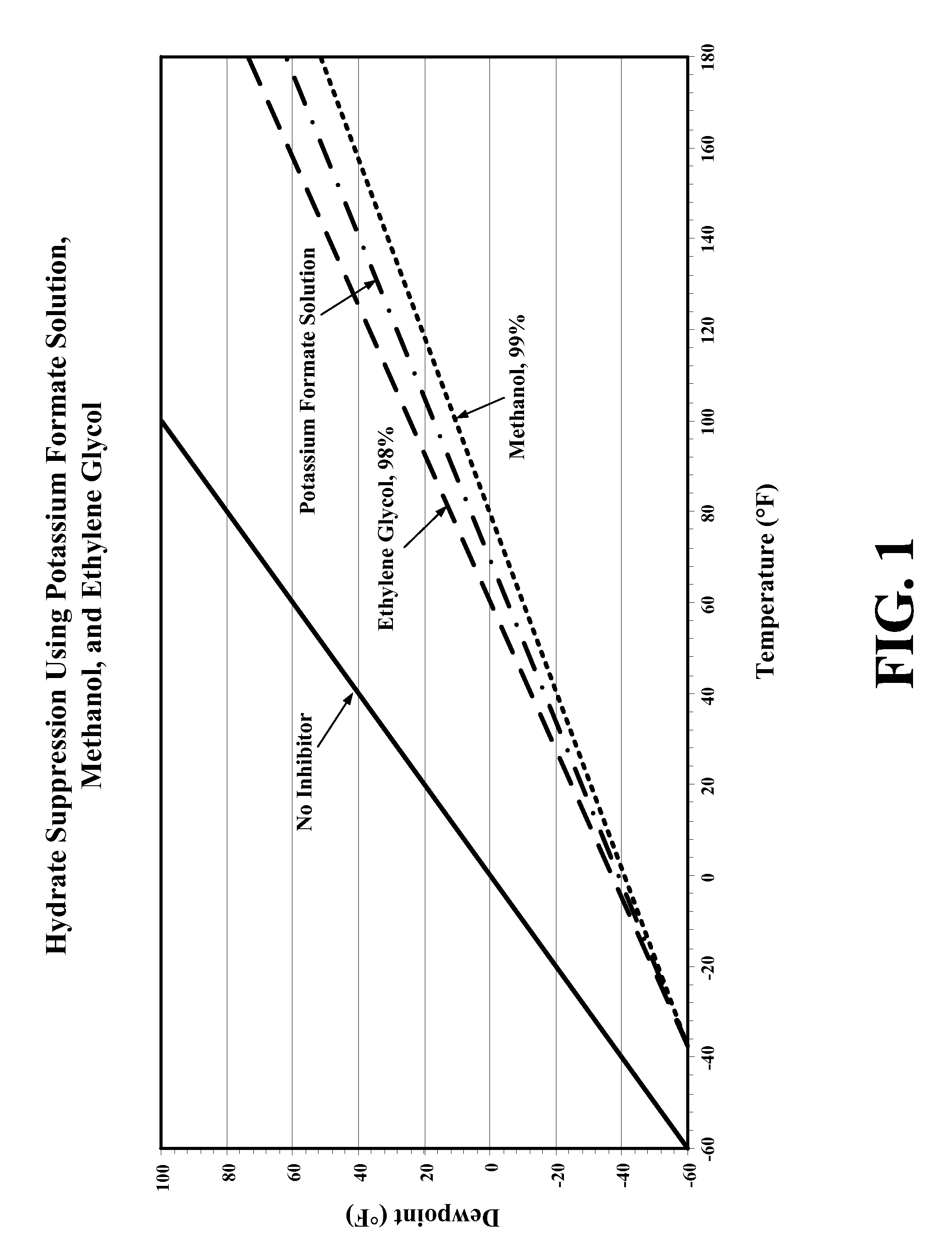
Composition and method for pipeline conditioning & freezing point suppression
InactiveUS20080314124A1Reduce and eliminate hydrate formationSufficiently reducedDetection of fluid at leakage pointHollow article cleaningSolubilityFormate
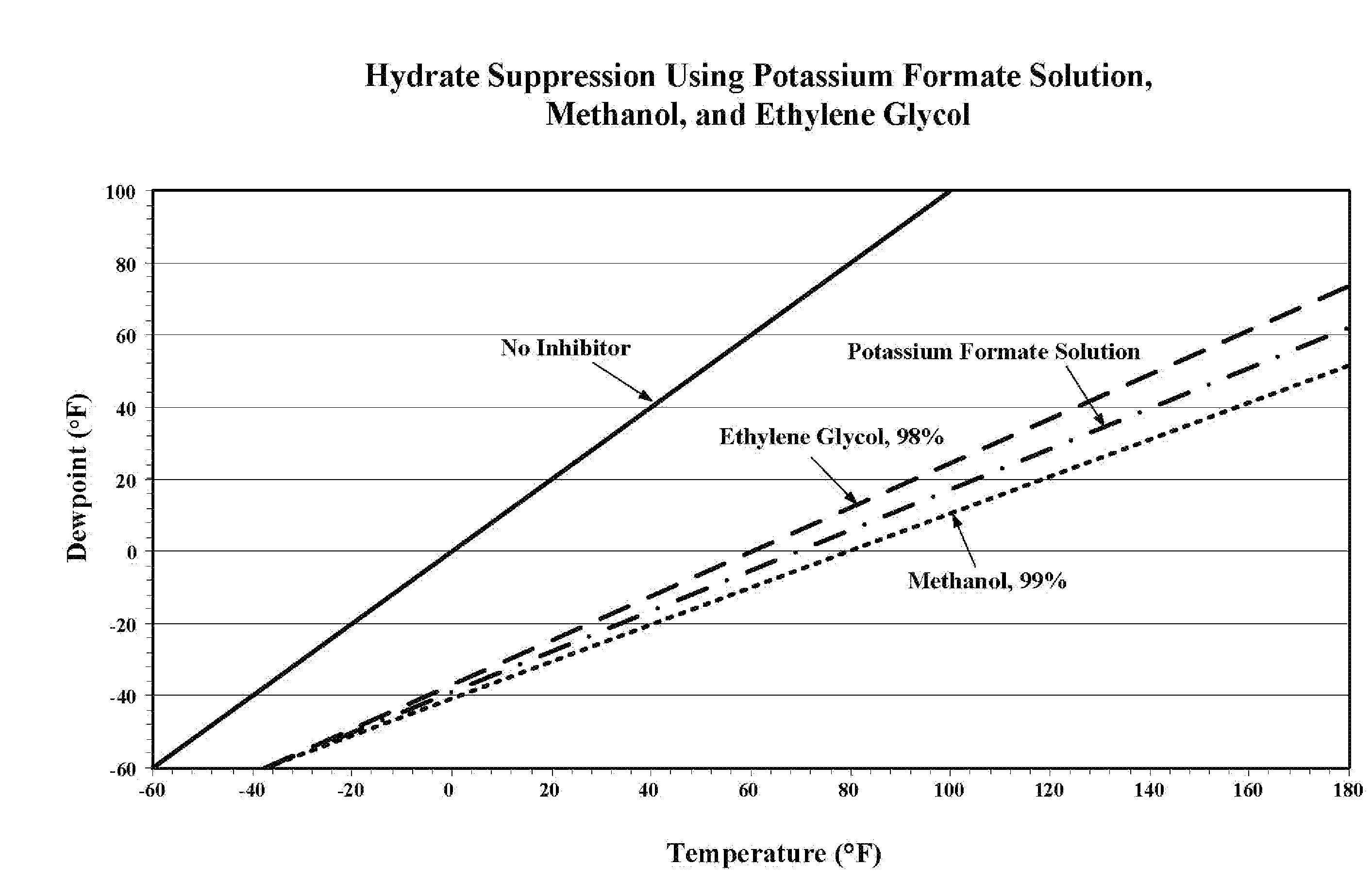
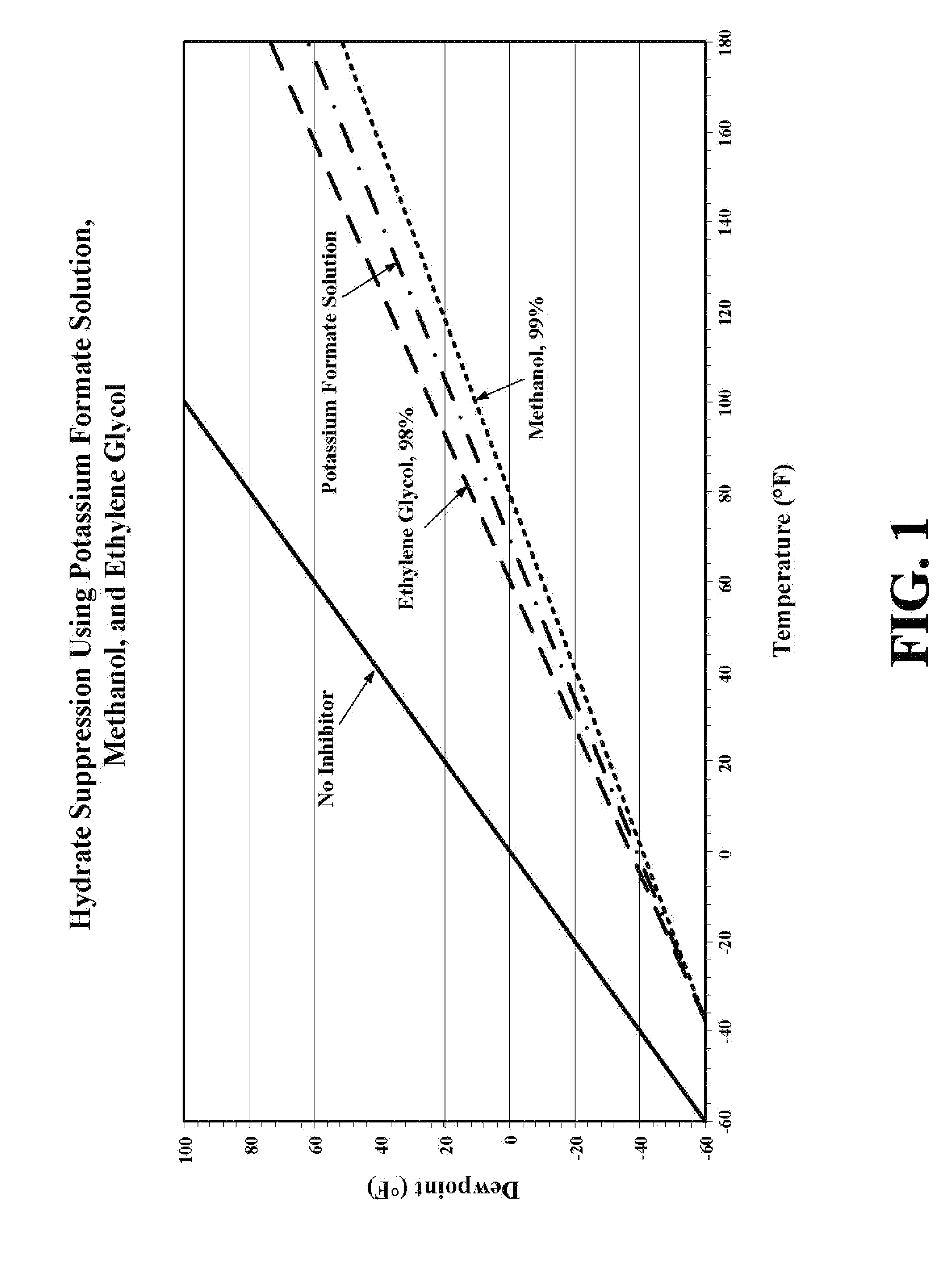
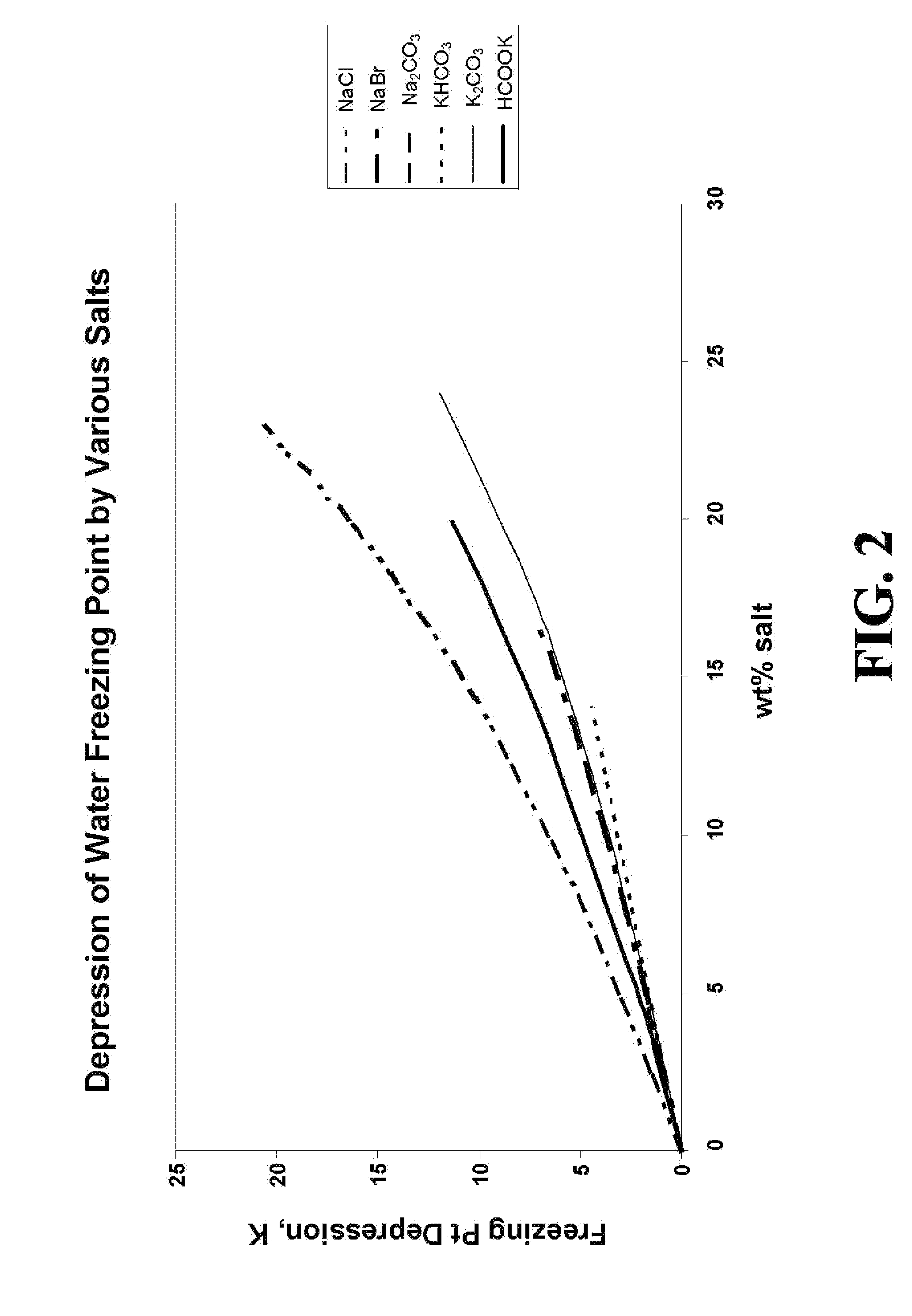
Method for dewatering, pressure testing, hydrotreating, suppressing methane hydrate formation and suppressing solution freezing point in pipeline operations have been disclosed, where the solution used in the operations includes an effective amount of a metal formate salt. The metal formate salt solutions have a low viscosity, have a high density, have a low metals corrosivity, are non-volatile, have a low solubility in hydrocarbons, are readily biodegradable, have a low toxicity, are non-hazardous, have a low environmental impact, have a freezing point depression property forming water / formate eutectic point mixtures, and have a water-structuring and water activity modification property.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC +1
Polyurethane compositions for golf balls
Polyurethane and polyurea compositions for golf balls with improved stability of the curative blend, wherein the curative blend includes a pigment, a curing agent, and a compatible freezing point depressing agent so that the curative blend has a lower freezing point than the curing agent by itself and the blend does not lose pigment dispersion upon solidification and subsequent thawing.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Vapor permeable barrier coating applicable at low temperature
InactiveUS20120231170A1Low temperature applicationPromote formationSynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialWater vaporLiquid water
Disclosed is a coating composition that includes an aqueous emulsion of a hydrophobic acrylic polymer, a water-soluble polymer, and an inorganic filler, and further includes a freezing-point lowering component to permit low temperature application. The freezing-point lowering component will preferably include a water-soluble, corrosion inhibiting salt. The coating composition will also optionally and preferably include an evaporation enhancing component to promote faster drying and skin formation at low temperatures. The coating composition may be coated onto a construction surface (e.g., by spraying) where, after drying, it will form a fully adhered barrier membrane that is water-vapor permeable, but air and liquid-water impermeable. Such membrane will preferably have sufficient coating thickness and sufficiently high elongation that it will bridge joints and cracks.
Owner:GCP APPL TECH INC
Method for reducing wear of steel elements in sliding-rolling contact
InactiveUS7244695B2Quantity minimizationConvenient amountOrganic chemistryWork treatment devicesAntioxidantMetallurgy
According to the invention there is provided a method of reducing wear of one or both of two steel elements having surfaces in sliding or sliding-rolling contact. The method involves applying an HPF friction control composition to one, or more than one contacting surface of one or both of the two steel elements. In a particular example, the HPF friction control composition comprises a rheological control agent, a lubricant, a friction modifier, and one, or more than one of a retentivity agent, an antioxidant, a consistency modifier, and a freezing point depressant.
Owner:KELSAN TECH
Method and apparatus for desolvating flowing liquid
ActiveUS20100000943A1Quick releaseAvoid contactLiquid degasificationComponent separationTemporal resolutionSolvent vapor
Methods and apparatus for desolvating flowing liquid streams while retaining temporal resolution of dissolved substrates are disclosed. A novel small-scale self-regulating spray dryer preserves temporal resolution while desolvating a liquid chromatography eluent stream and depositing the solute onto an optical surface for infrared spectrographic analysis. The liquid eluent is pumped through a heated nebulizer to create a high-speed jet of solute containing liquid and solvent vapor. This jet is directed circumferentially inside a hot cylindrical cavity. Centrifugal force causes the larger liquid droplets to travel along the outer diameter of the cavity. The cavity surface is heated to cause the droplets to film boil. Film boiling reduces droplet contact with the cavity surface thereby retaining the solute in the droplets. The solute temperature is limited by controlling the pressure into which the solvent evaporates from the droplets. When the droplets are sufficiently small, Stokes drag from the exiting solvent vapor carries the droplets out through the center of the cylindrical cavity. After exiting, the superheated solvent vapor further dries the droplets. Solvent vapor is removed by condensation onto a cooled surface. A freezing point reducing agent may be added to improve removal of solvent condensate. Stokes drag from a non-condensable gas maintains the dried droplets in suspension. This suspension travels through an orifice that focuses the impaction of the dried droplets onto the optical surface for infrared analysis. The deposition surface is in an evacuated chamber and is temperature controlled to freeze liquid solutes yet allowing sublimation of residual solvent.
Owner:SPECTRA ANALYSIS INSTR
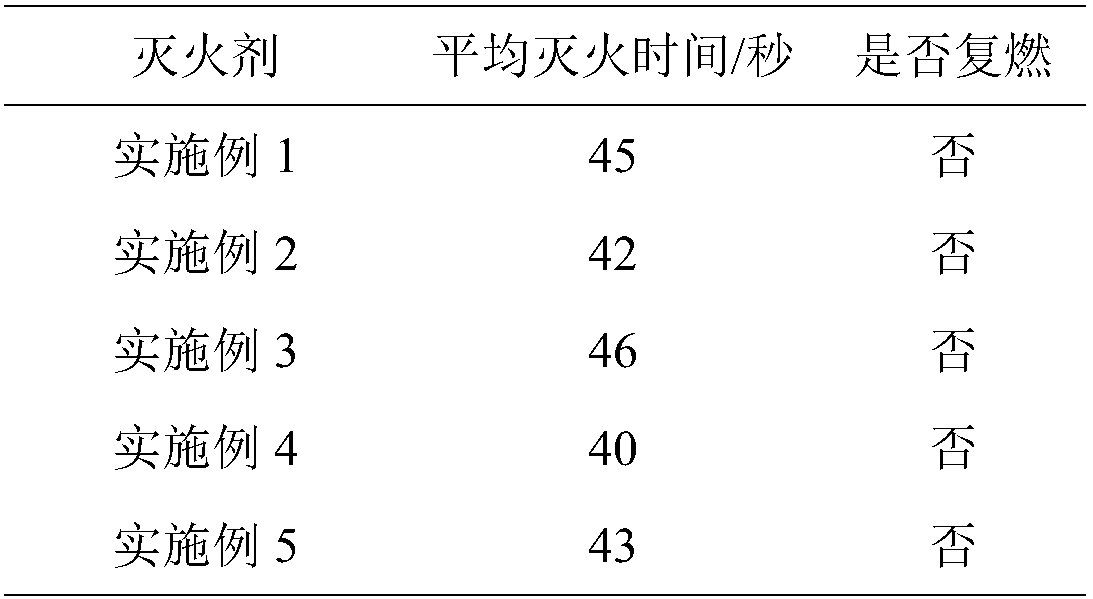
Anti-reburning environment-friendly power transmission line forest fire extinguishing agent
The invention discloses an anti-reburning environment-friendly power transmission line forest fire extinguishing agent. The anti-reburning environment-friendly power transmission line forest fire extinguishing agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5-20 parts of ammonium carbonate, 10-45 parts of ammonium polyphosphate, 10-30 parts of sodium silicate, 1-10 parts of a foaming agent, 0.5-5 parts of polyethylene glycol, 1-5 parts of a thickening agent, 4-10 parts of a composite anti-freezing agent and 55-80 parts of water, wherein the foaming agent is selected from one of alkylethoxylate carboxylate, an imidazoline amphoteric surfactant and a biological surfactant; the composite anti-freezing agent is a compound which is prepared by compounding inorganic salt and polyhydric alcohol according to a mole ratio of (1 to 3)-(1 to 9). All the raw materials of the anti-reburning environment-friendly power transmission line forest fire extinguishing agent are environment-friendly materials, so that the fire extinguishing agent is free of fluorine compound, toxicity, smell and pollution; a fire retardant is added into the fire extinguishing agent, so that the fire extinguishing agent is capable of effectively preventing the fire from spreading and is high in fire extinguishing efficiency; the environment-friendly surfactant serves as the foaming agent, so that the fire extinguishing agent is high in foaming performance and is capable of effectively isolating contact between the combustion material and the air and accelerating the fire extinguishing speed; the anti-freezing agent is compounded by the inorganic salt and polyhydric alcohol, so that the freezing point of the fire extinguishing agent is reduced to be -30 DEG C.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Anti-reflash environmental protection water-based extinguishing agent
InactiveCN107812340AImprove water retentionAvoid spreadingFire extinguisherWater basedPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses anti-reflash environmental protection water-based extinguishing agent. The water-based extinguishing agent is composed of the components, by weight, 5-20 parts of ammonium carbonate; 10-45 parts of ammonium polyphosphate; 10-30 parts of sodium silicate; 1-10 parts of foaming agent; 0.5-5 parts of polyethylene glycol; 1-5 parts of thickening agent; 4-10 parts of compound antifreeze and 55-80 parts of water. The foaming agent is selected from one of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether carboxylate, an imidazoline amphoteric surfactant and a biosurfactant. The compound antifreeze is a compound compounded by inorganic salt and polyhydric alcohols, wherein the molar ratio of inorganic salt to polyhydric alcohols is 1:3-1:9. According to the anti-reflash environmental protection Water-based extinguishing agent, all raw materials are made of environmental protection materials; the water-based extinguishing agent is free in fluorine compound and are non-poisonous, odorless and non-polluting; a fire retardant is added so that fire spreading can be effectively prevented, and fire extinguishing effectiveness is high; the green surfactant is adopted as the foaming agent;foaminess is good; the contact between comburent and air is effectively isolated; the fire extinguishing speed is improved; and the compound antifreeze of inorganic salt and polyhydric alcohols is adopted, so that the freezing point of the extinguishing agent is reduced to be -30 DEG C.
Owner:微普安全科技(徐州)股份有限公司
Methods and compositions related to gelled layers in oil and/or gas wells
Methods and compositions for the prevention of the formation, breakdown, and / or removal of gelled layers in an oil and / or gas well are provided. In some embodiments, the compositions and methods comprise a concentrate, as described in more detail herein, where the concentrate comprises two or more surfactants. In certain embodiments, the compositions and methods comprise an emulsion or a microemulsion. The emulsion or microemulsion may include a surfactant, optionally a solvent, and optionally a freezing point depression agent or other components.
Owner:FLOTEK CHEM LLC
Fire suppression fluid containing a carboxylate salt
InactiveUS20140138105A1Low viscosityInhibit flammabilityFire rescueHeat-exchange elementsCarbon numberFire sprinkler
An aqueous fire sprinkler fluid containing low carbon number carboxylate salts for freezing point depression is described. The salts may be used in conjunction with glycols. The salts decrease the combustibility of the glycol containing fluids and give lower viscosity than higher glycol fluids, both benefitting fire sprinkler systems. These salt solutions are friendly to metal and CPVC pipes and are thus useful for fire sprinkler systems by not causing environmental stress cracking of the CPVC components and not being corrosive to the metal parts.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Deicing/anti-icing fluids
A nontoxic deicing / anti-icing fluid includes a freezing point depressant selected from short chain polyols having 3 to 5 carbons atoms, and mixtures thereof, a wetting agent, an antioxidant / preservative, and water. The fluid has an LD50 greater than about 10,000 mg / L. Another deicing / anti-icing fluid includes the freezing point depressant, a vinylpyrrolidone polymer having a molecular weight between about 10,000 and about 700,000, and water. A runway deicing fluid includes glycerol, a buffer, an antioxidant / preservative, and water. Another deicing / anti-icing fluid includes a freezing point depressant having hydrophobic character, a wetting agent comprising an organophosphorus compound capable of producing an organic wettable surface, and water.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Methods and compositions related to gelled layers in oil and/or gas wells
Methods and compositions for the prevention of the formation, breakdown, and / or removal of gelled layers in an oil and / or gas well are provided. In some embodiments, the compositions and methods comprise a concentrate, as described in more detail herein, where the concentrate comprises two or more surfactants. In certain embodiments, the compositions and methods comprise an emulsion or a microemulsion. The emulsion or microemulsion may include a surfactant, optionally a solvent, and optionally a freezing point depression agent or other components.
Owner:FLOTEK CHEM LLC
Methods and compositions related to gelled layers in oil and/or gas wells
Methods and compositions for the prevention of the formation, breakdown, and / or removal of gelled layers in an oil and / or gas well are provided. In some embodiments, the compositions and methods comprise a concentrate, as described in more detail herein, where the concentrate comprises two or more surfactants. In certain embodiments, the compositions and methods comprise an emulsion or a microemulsion. The emulsion or microemulsion may include a surfactant, optionally a solvent, and optionally a freezing point depression agent or other components.
Owner:FLOTEK CHEM LLC
Composition and method for pipeline conditioning and freezing point suppression
InactiveUS8065905B2Reduce and eliminate hydrate formationSufficiently reducedDetection of fluid at leakage pointHollow article cleaningSolubilityFormate
Method for dewatering, pressure testing, hydrotreating, suppressing methane hydrate formation and suppressing solution freezing point in pipeline operations have been disclosed, where the solution used in the operations includes an effective amount of a metal formate salt. The metal formate salt solutions have a low viscosity, have a high density, have a low metals corrosivity, are non-volatile, have a low solubility in hydrocarbons, are readily biodegradable, have a low toxicity, are non-hazardous, have a low environmental impact, have a freezing point depression property forming water / formate eutectic point mixtures, and have a water-structuring and water activity modification property.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC +1
Vapor permeable barrier coating applicable at low temperature
InactiveUS8748528B2Low temperature applicationPromote formationNon-fibrous pulp additionCoatingsWater vaporLiquid water
Disclosed is a coating composition that includes an aqueous emulsion of a hydrophobic acrylic polymer, a water-soluble polymer, and an inorganic filler, and further includes a freezing-point lowering component to permit low temperature application. The freezing-point lowering component will preferably include a water-soluble, corrosion inhibiting salt. The coating composition will also optionally and preferably include an evaporation enhancing component to promote faster drying and skin formation at low temperatures. The coating composition may be coated onto a construction surface (e.g., by spraying) where, after drying, it will form a fully adhered barrier membrane that is water-vapor permeable, but air and liquid-water impermeable. Such membrane will preferably have sufficient coating thickness and sufficiently high elongation that it will bridge joints and cracks.
Owner:GCP APPL TECH INC
Ultralow temperature discharge electrolyte of novel lithium ion battery
InactiveCN103647110AImprove electrochemical stabilityLow freezing pointSecondary cellsAcid electrolytesOrganic solventIon transfer
The invention relates to ultralow temperature discharge electrolyte of a novel lithium ion battery. The electrolyte comprises the following raw materials in percent by weight: component A, namely 10-15 percent of conductive lithium salt, component B, namely 80-90 percent of organic solvent and component C, namely 2-8 percent of additive. The electrolyte has extremely high electrochemical stability. The freezing point is lowered, the ion migration capability is improved, the electrical conductivity is improved, the lithium ion transfer resistance is reduced, and the wettability of the electrolyte on a diaphragm under low-temperature conditions and the penetrability of the lithium ion to the diaphragm are improved. Therefore, the electrolyte has the characteristics of being capable of normally working in an environment with temperature of 50 DEG C below zero and being stable in performance and excellent in cycle indicators.
Owner:HUARUI XINXIANG CHEM
Environmentally-friendly deicing/anti-icing solution
InactiveCN101967367AHarm reductionOther chemical processesNatural productNaturally occurring surfactants
The invention discloses environmentally-friendly deicing / anti-icing solution, which belongs to the technical field of eliminating and preventing ice covering of a transportation tool by using a physical method. The environmentally-friendly deicing / anti-icing solution comprises a freezing point depression compound, water, a surfactant and a thickening agent, wherein the freezing point depression compound is at least one of propanediol and polybasic alcohol; the surfactant is a natural surfactant; and the thickening agent is a natural product. The components of the environmentally-friendly deicing / anti-icing solution can be degraded by microbes; and the environmentally-friendly deicing / anti-icing solution generates small hazard to the environment, and is environmentally-friendly.
Owner:丁颖
Method for reducing the freezing point of aminated aviation gasoline by the use of tertiaryamylphenylamine
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Polyurethane compositions for golf balls
A method of forming golf balls with at least a portion formed from polyurethane and polyurea compositions employing a curative blend that includes a pigment, a curing agent, and a compatible freezing point depressing agent so that the curative blend has a lower freezing point than the curing agent by itself and the blend does not lose pigment dispersion upon solidification and subsequent thawing.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Polyurethane compositiones for golf balls
InactiveUS20060205913A1Improve adhesionIncreased durabilityInksGolf ballsFirming agentPigment dispersion
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Method and apparatus for desolvating flowing liquid
ActiveUS8695813B2Quick releaseAvoid contactParticle separator tubesIon-exchanger regenerationTemperature controlTemporal resolution
Methods and apparatus for desolvating flowing liquid streams while retaining temporal resolution of dissolved substrates are disclosed. A novel small-scale self-regulating spray dryer preserves temporal resolution while desolvating a liquid chromatography eluent stream and depositing the solute onto an optical surface for infrared spectrographic analysis. The liquid eluent is pumped through a heated nebulizer to create a high-speed jet of solute containing liquid and solvent vapor. This jet is directed circumferentially inside a hot cylindrical cavity. Centrifugal force causes the larger liquid droplets to travel along the outer diameter of the cavity. The cavity surface is heated to cause the droplets to film boil. Film boiling reduces droplet contact with the cavity surface thereby retaining the solute in the droplets. The solute temperature is limited by controlling the pressure into which the solvent evaporates from the droplets. When the droplets are sufficiently small, Stokes drag from the exiting solvent vapor carries the droplets out through the center of the cylindrical cavity. After exiting, the superheated solvent vapor further dries the droplets. Solvent vapor is removed by condensation onto a cooled surface. A freezing point reducing agent may be added to improve removal of solvent condensate. Stokes drag from a non-condensable gas maintains the dried droplets in suspension. This suspension travels through an orifice that focuses the impaction of the dried droplets onto the optical surface for infrared analysis. The deposition surface is in an evacuated chamber and is temperature controlled to freeze liquid solutes yet allowing sublimation of residual solvent.
Owner:SPECTRA ANALYSIS INSTR
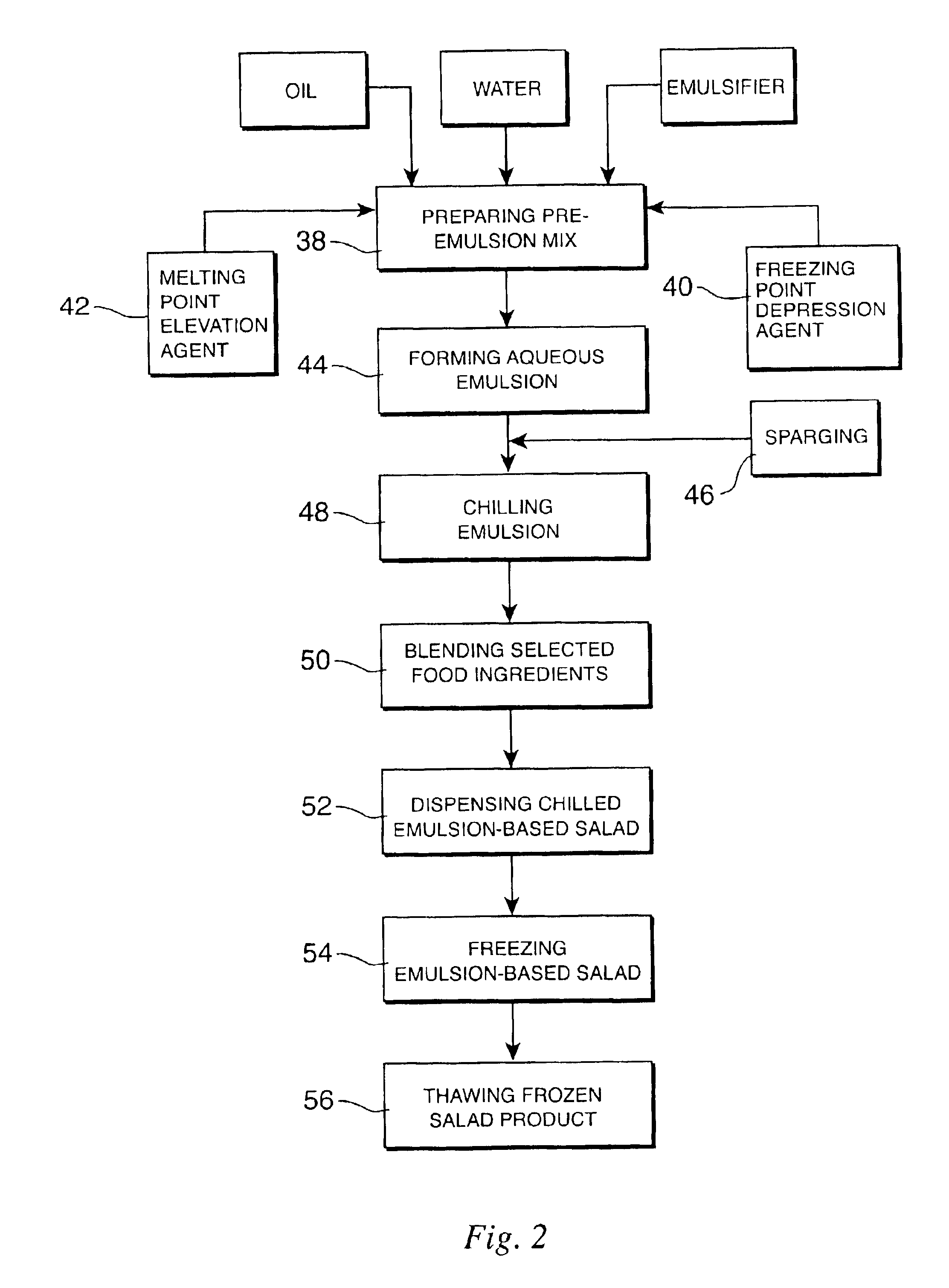
Process for preparing an emulsion based food salad having freeze-thaw stability
InactiveUS6838112B1Reduce microbial activityMilk preservationWort preparationEmulsionFreezing thawing
A process for making a freezably stable emulsion based food salad. A freezing point depression agent, such as propylene glycol, is added to a water component of the emulsion to prevent the formation of ice crystals during freezing of the non-aqueous salad components and to prevent oil separation upon thawing. A hardenable oil such as partially hydrogenated soybean oil, provides an elevated emulsion melt point. Microbial control is maintained during processing by oxygenating the water component. The frozen food salad may be-containerized for shipping or used as a frozen sandwich filling.
Owner:ENDICO FELIX W
Yeast cell cracking method
ActiveCN101195808AImprove solubilityImprove completenessFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastMicrowave
The invention provides a method for yeast cell wall breaking. The method comprises the steps that yeast paste with water added is prepared into live bacterial suspension; cysteine or cysteine hydrochloride and neutral protease are added, the pH value is controlled to 6 to 8, thermal retardation hydrolyzing is performed for 6 to 48 hours under 40 to 60 DEG C, and yeast digest is obtained; yeast deposition is obaitned through centrifuging being performed to the yeast digest, water is added to prepare yeast cell suspending liquid, and the wall breaking ratio reaches above 95 percent through multi times freezing and microwave tempering. The invention integrates the cysteine promoting dissolution, gradient freezing point depression freezing and microwave repaid tempering, and therefore greatly improves the wall breaking ratio of the yeast cell. The cell wall breaking process of the invention has the advantages that the operation is simple, the facility request is low, and the cell wall breaking process is very suitable for the cell wall breaking of the beer yeast or the bakery yeast.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PROSYN BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Corrosion Prevention and Friction Reduction Coating and Low Temperature Process
InactiveUS20110036262A1Enough mass productionUse a lotRail switchesPretreated surfacesFriction reductionCrystalline materials
This invention relates to a structural coating comprising a liquid carrier (e.g., paint), a borate-based additive, and a dynamic stabilization material. The borate-based additive provides corrosion protection through electrochemical binding of active surface corrosive sites, lubrication enhancement through the creation and re-supply to a surface where friction contact occasionally occurs of a weak slip lane crystalline material which may be a locally formed product utilizing local atmospheric humidity, and a material for reaction with an initiator to provide for freezing point depression during coating application. The dynamic stabilization material creates a balance of stabilized material for supply of corrosion protection product, lubrication reduction product, and freezing point depression product.
Owner:ADVANCED LUBRICATION TECH
Oil-displacing agent for low condensate oil
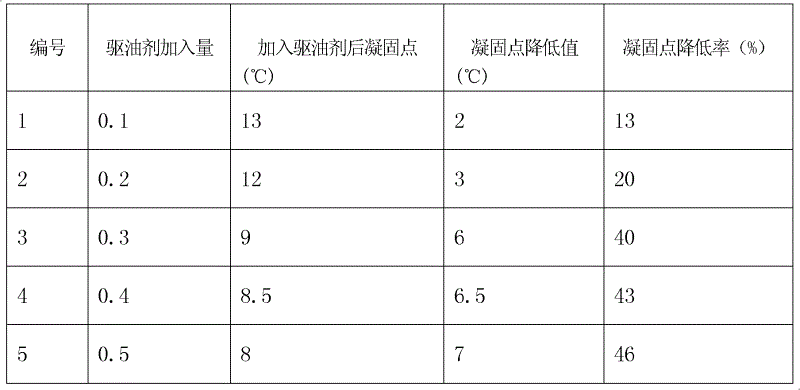
InactiveCN102618241ALow freezing pointSolve unmineable puzzlesSulfonic acids salts preparationDrilling compositionEthanesulfonic acidSURFACTANT BLEND
The invention provides an oil-displacing agent for low condensate oil, which is a Gemini surfactant and ethylene-double (N-ethanesulfonic acid-ten amide) sodium salt. The oil-displacing agent for the low condensate oil can lead the freezing point of the low condensate oil to reduce, so that the low condensate oil is led to be in a flow state at existing oil layer temperature and can be easily extracted with an existing oil extraction method.
Owner:SHAANXI HAIAN IND
Composition for cleaning a heat transfer system having an aluminum component
ActiveUS20150152365A1Prevent leaching and corrosionReduce heat transferInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsOxalic acidChemistry
Disclosed herein is a cleaner concentrate comprising: greater than 10 weight percent of a freezing point depressant, 0.5 to 35 weight percent of oxalic acid, and an azole compound, wherein weight percent is based on the total weight of the cleaner concentrate.
Owner:PRESTONE PROD CORP
Composition for cleaning a heat transfer system having an aluminum component
ActiveUS20120216834A1Prevent leaching and corrosionReduce heat transferInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOxalic acidCleanser
Disclosed herein is a cleaner concentrate comprising: greater than 10 weight percent of a freezing point depressant, 0.5 to 35 weight percent of oxalic acid, and an azole compound, wherein weight percent is based on the total weight of the cleaner concentrate.
Owner:PRESTONE PROD CORP
Ultralow-temperature urea solution for automobile and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107587922ALow freezing pointEasy to storeExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusThermal insulationFiltration
Owner:锦西天然气化工有限责任公司
Multiphase liquid composition for low voltage electrowetting device
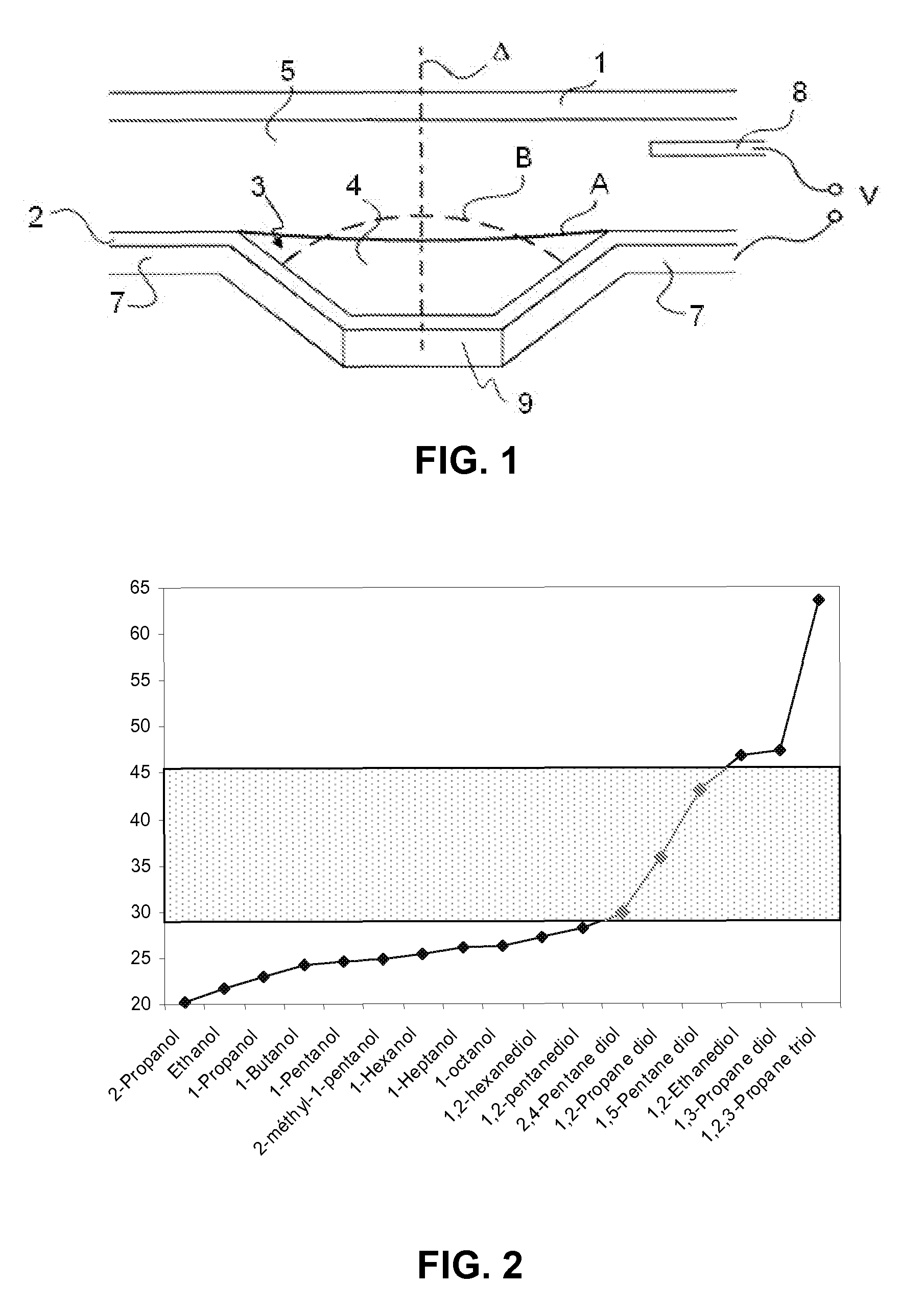
ActiveUS9074168B2Good optical performanceImprove solubilityNon-ionic surface-active compoundsConductive materialLow voltageMulti phase
A multi-phase liquid composition comprising a conductive liquid and a non-conductive liquid, said liquids being non miscible, wherein the conductive liquid comprises more than 90% up to 99.9% by weight of a first component having a surface tension above 45 mN / m and comprising water, salt and at least one freezing point lowering agent, and from 0.01% to less than 10% by weight of a second component having a surface tension below 30 mN / m and comprising at least one first compound, wherein said at least one first compound is a non ionic surfactant.
Owner:INVENIOS FRANCE SAS
Corrosion Prevention and Friction Reduction Coating and Low Temperature Process
InactiveUS20070021310A1Sufficient productionUse a lotAdditivesCoatingsFriction reductionPolymer resin
This invention relates to a structural coating comprising a polymeric resin, a borate-based additive, and a dynamic stabilization material. The borate-based additive provides corrosion protection through electrochemical binding of active surface corrosive sites, lubrication enhancement through the creation and re-supply to a surface where friction contact occasionally occurs of a weak slip lane crystalline material which may be a locally formed product utilizing local atmospheric humidity, and a material for reaction with an initiator to provide for freezing point depression during coating application. The dynamic stabilization material creates a balance of stabilized material for supply of corrosion protection product, lubrication reduction product, and freezing point depression product.
Owner:CHARLES FOSCUE NOTES COLLATERAL AGENT FOR SECURED PARTY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com