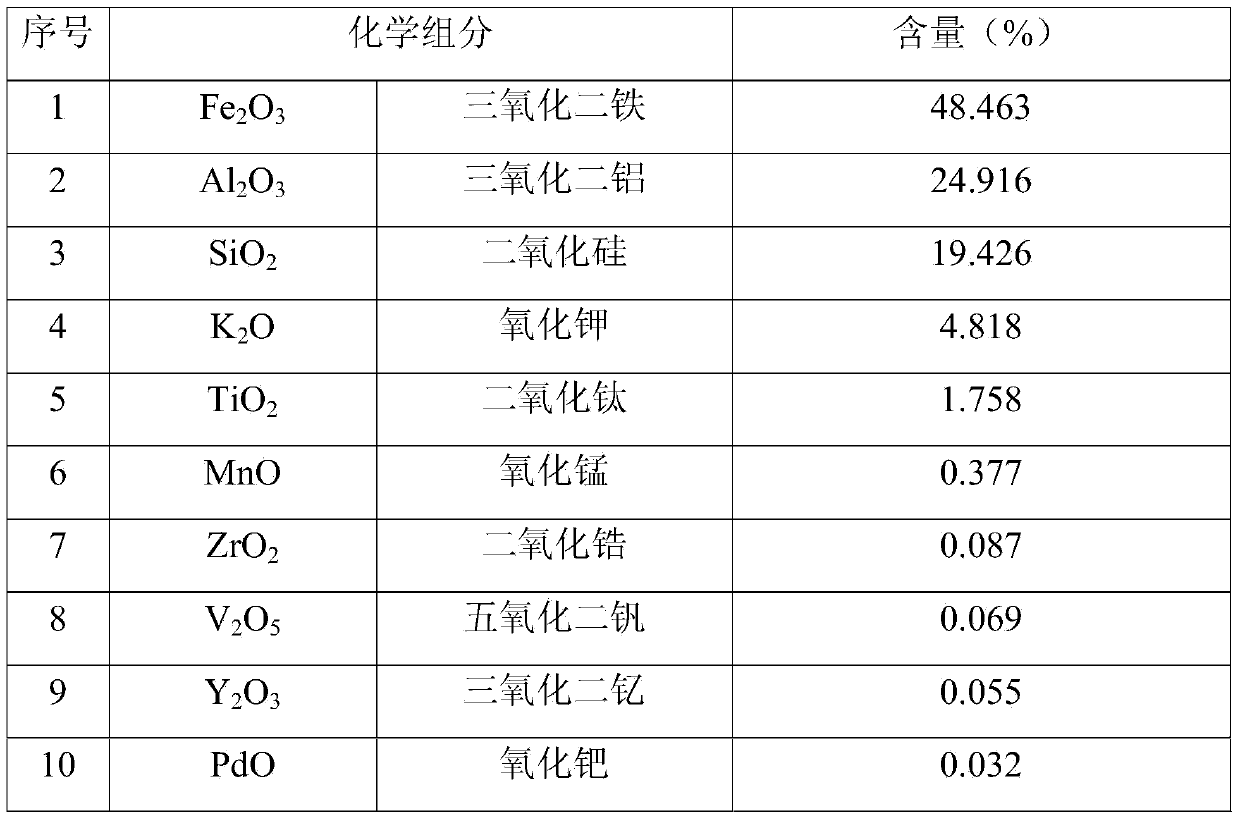
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Ironwork" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ironwork is any weapon, artwork, utensil or architectural feature made of iron especially used for decoration. There are two main types of ironwork: wrought iron and cast iron. While the use of iron dates as far back as 4000BC, it was the Hittites who first knew how to extract it (see iron ore) and develop weapons. Use of iron was mainly utilitarian until the Middle Ages, it became widely used for decoration in the period between the 16th and 19th century.
Longquan celadon iron glaze and method for manufacturing celadon iron glaze product by using same
The invention relates to the field of ceramic arts and crafts and specifically discloses a Longquan celadon iron glaze and a method for manufacturing a celadon product by using the same. The glaze comprises the following ingredients in percentage by weight: 35-45% of Baoxi glaze clay, 6-9% of limestone, 6-9% of quartz, 18-20% of large kiln Zijin clay, 23-25% of iron ore and 1.2-2% of Badu fluorite. The celadon iron glaze product manufactured by using the celadon iron glaze and the method thereof provided by the invention combine the advantages of the traditional celadon product and an iron product, can not only inherit the advantage of fine texture of the traditional celadon, but also release divalent iron ions from water which is boiled out and similar to the water boiled out by an iron pot and has the effect of preventing and reducing hypertension. The water which is boiled out by the celadon iron glaze product is similar to the temperature of the water boiled by the iron pot, so that the effect of softening water quality is realized; the water becomes sweet and smooth, has thick and full taste and is particularly suitable for infusing old tea or boiling Puer tea.
Owner:LONGQUAN LUYAO PORCELAIN FACTORY
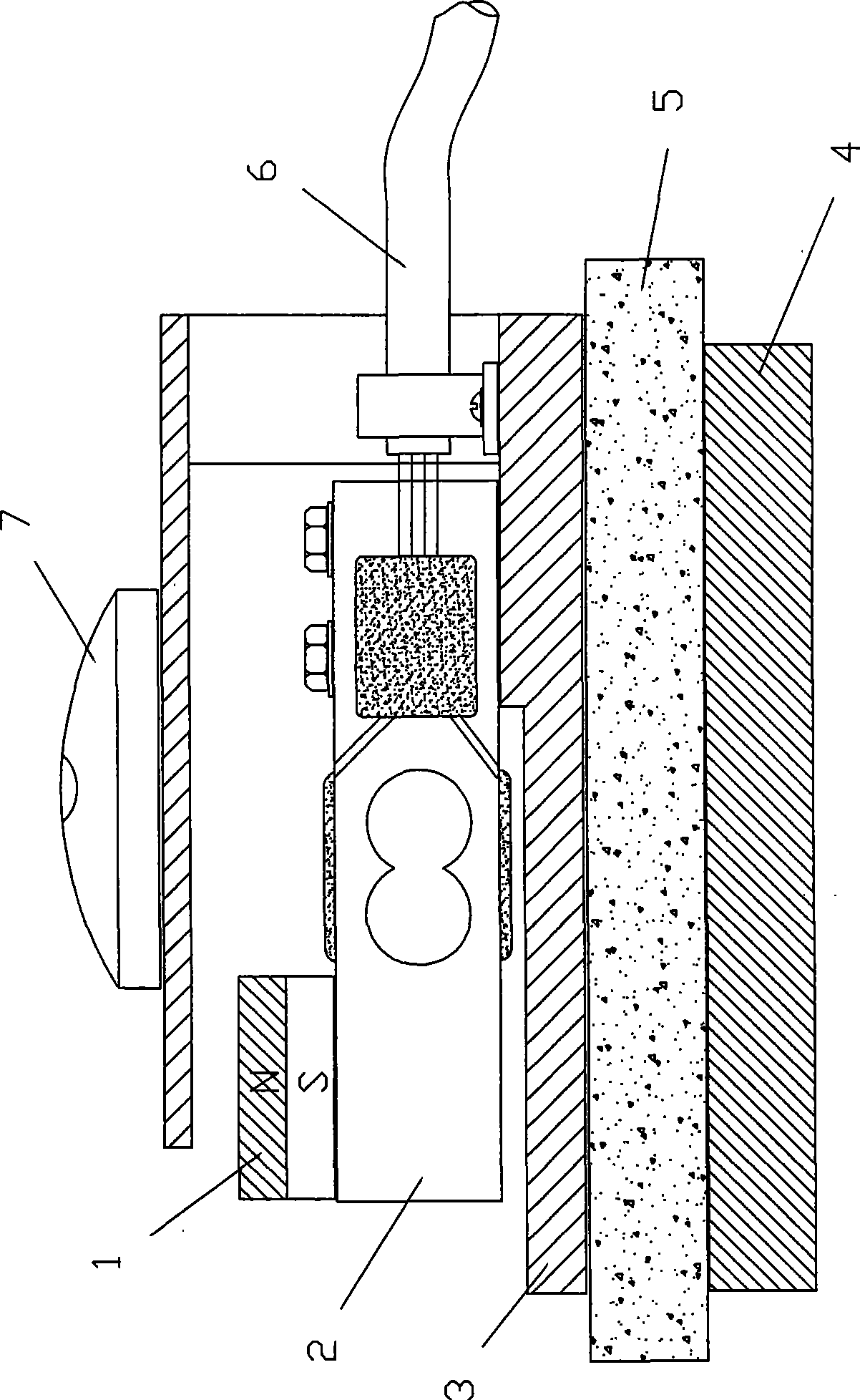
Instrument for measuring thickness of non-ferromagnetic material and surface coating of ironwork
InactiveCN101398286ARealize measurementElectrical/magnetic thickness measurementsIncline measurementSuction stressMeasuring instrument
The invention discloses an instrument for measuring the thickness of nonferrous magnetic materials and the thickness of a coating layer on the surface of ironworks, which comprises a probe, a measuring circuit and a reference iron plate, wherein, the probe is a strain transducer that is arranged on a base made of the nonferrous magnetic materials, a magnet is arranged on the strain transducer, the reference iron plate is arranged under feet of the base and used for pressing a measured substance between an iron plate and a bottom foot surface of the base during measurement, and the strain transducer is electrically connected with the measuring circuit. The thickness of the substance affects the attraction force between the magnet and the reference iron plate, and the thickness of the substance can be reflected through the strain transducer and the measuring circuit. The measuring instrument can be further used for measuring the thickness of the coating layer on the surface of the ironworks. As the clamping foot contact measurement such as with a caliber rule is not needed, the measuring instrument can be placed at any position, is not limited by substance area and shape, and can consequently realize the measurement of wall thickness of substances with large area and complex shapes.
Owner:王洋
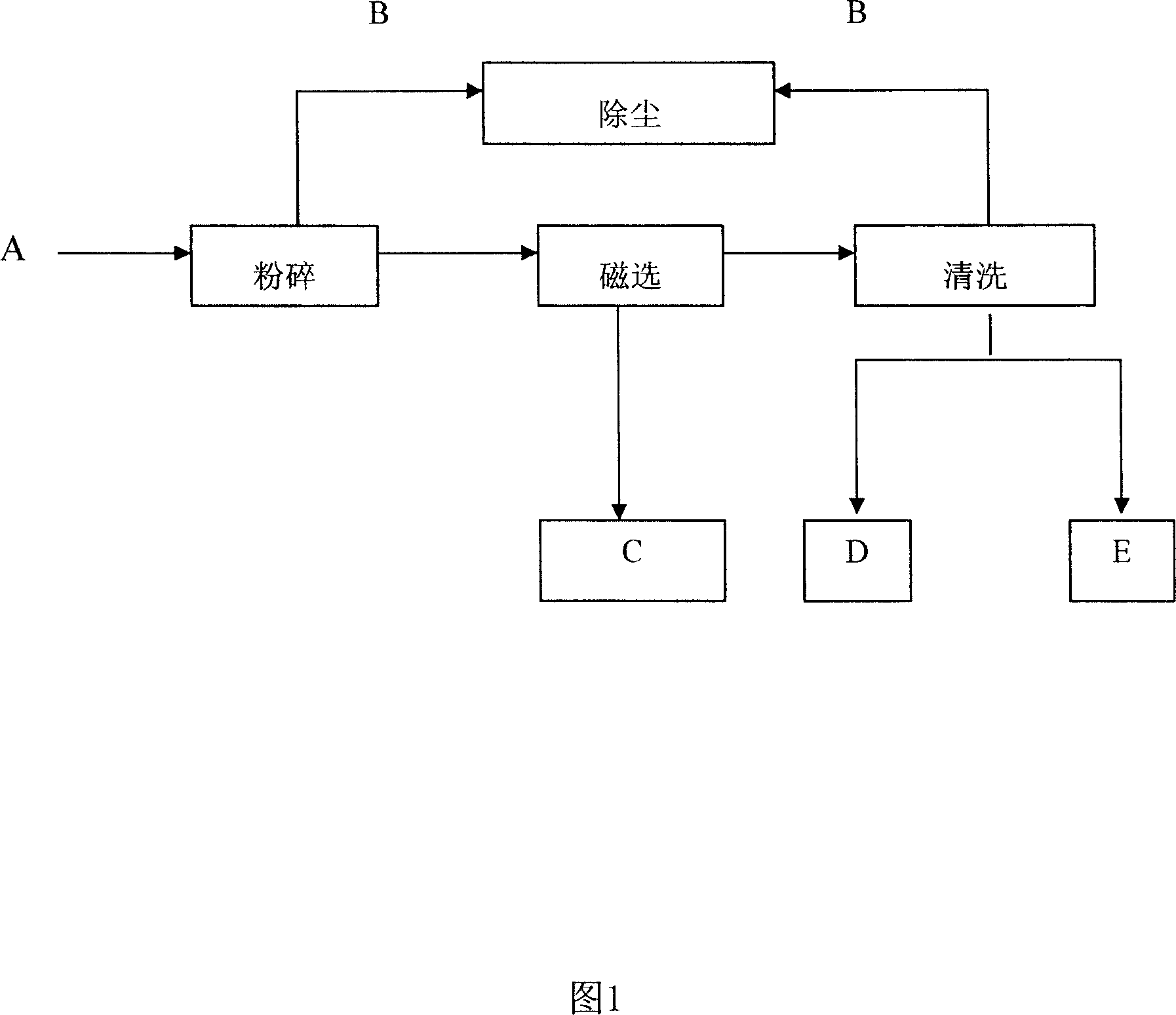
Waste and old se-drum reclaiming and processing technique
InactiveCN101109925AImplement resourcesAchieving processing powerElectrography/magnetographyAir cleaningPulp and paper industry
The utility model discloses a technique used for the recovery processing of the discarded selenium drum. The entire recovery processing is conducted under the suction pressure and includes the processing steps as below: (1) The old and useless selenium drum is shattered into the particles with the uniform sizes and the dust remover is used for collecting the organic ink powder; (2) the shattered materials are delivered into the magnetic sliding pulley, so that the ironwork can be sorted out through the magnetic separation; (3) the remained organic ink powder could be removed via the air cleaning machine and collected through the dust remover. The remained materials are processed via the artificial disintegration so as to obtain the plastics and the copper. This utility model realizes the regeneration of the resource and solves the disposal of the old and useless selenium drum soundly. Meanwhile, the utility model has the advantages of good separating effect, safety, environment protection and practicability.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINJINQIAO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
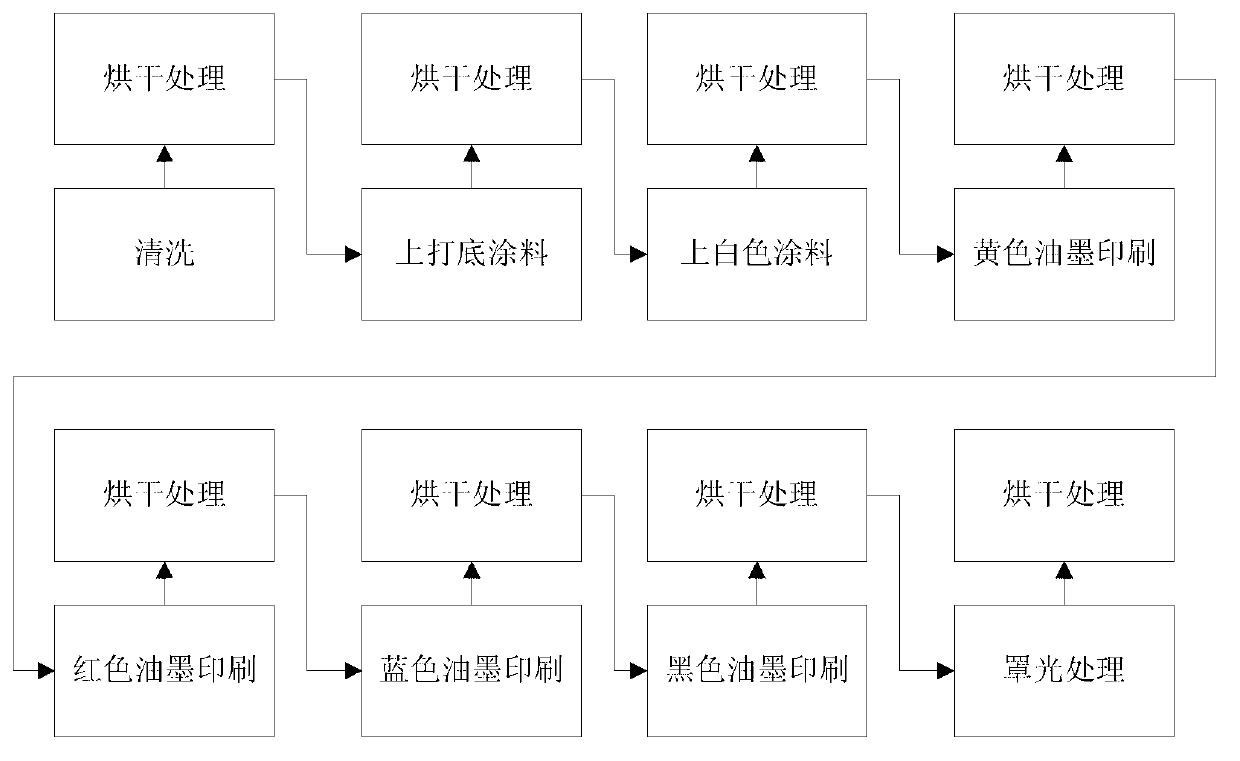
Metal decorating machining technique
InactiveCN103129199AEfficient removalNo yellowingOther printing apparatusPrinting after-treatmentOrganic solventPrinting ink
The invention relates to the field of ironwork printing, in particular to a metal decorating machining technique. The technique includes the following steps: cleaning tinplate with water, and then wiping the tinplate with organic solvent to remove dust; arranging bottoming coating material on the tinplate, and then treating the tinplate in a drying mode; and then respectively arranging white coating material on the tinplate and treating the tinplate in a drying mode, carrying out yellow printing ink printing operation and treating the tinplate in a drying mode, carrying out red printing ink prinking operation and treating the tinplate in a drying mode, carrying out blue printing ink prinking operation and treating the tinplate in a drying mode, carrying out black printing ink prinking operation, treating the tinplate in a drying and vanishing mode, and sending the tinplate into a drying room for drying treatment after the vanishing treatment. According to the metal decorating machining technique, not only can dust be effectively removed through cleaning, but also the organic solvent which is insoluble in water can be effectively cleaned up, the investment in equipment is effectively reduced, the coloring materials can not yellow, and the glossiness is better.
Owner:GUIZHOU ZHONGYUAN METAL DECORATING CANNER
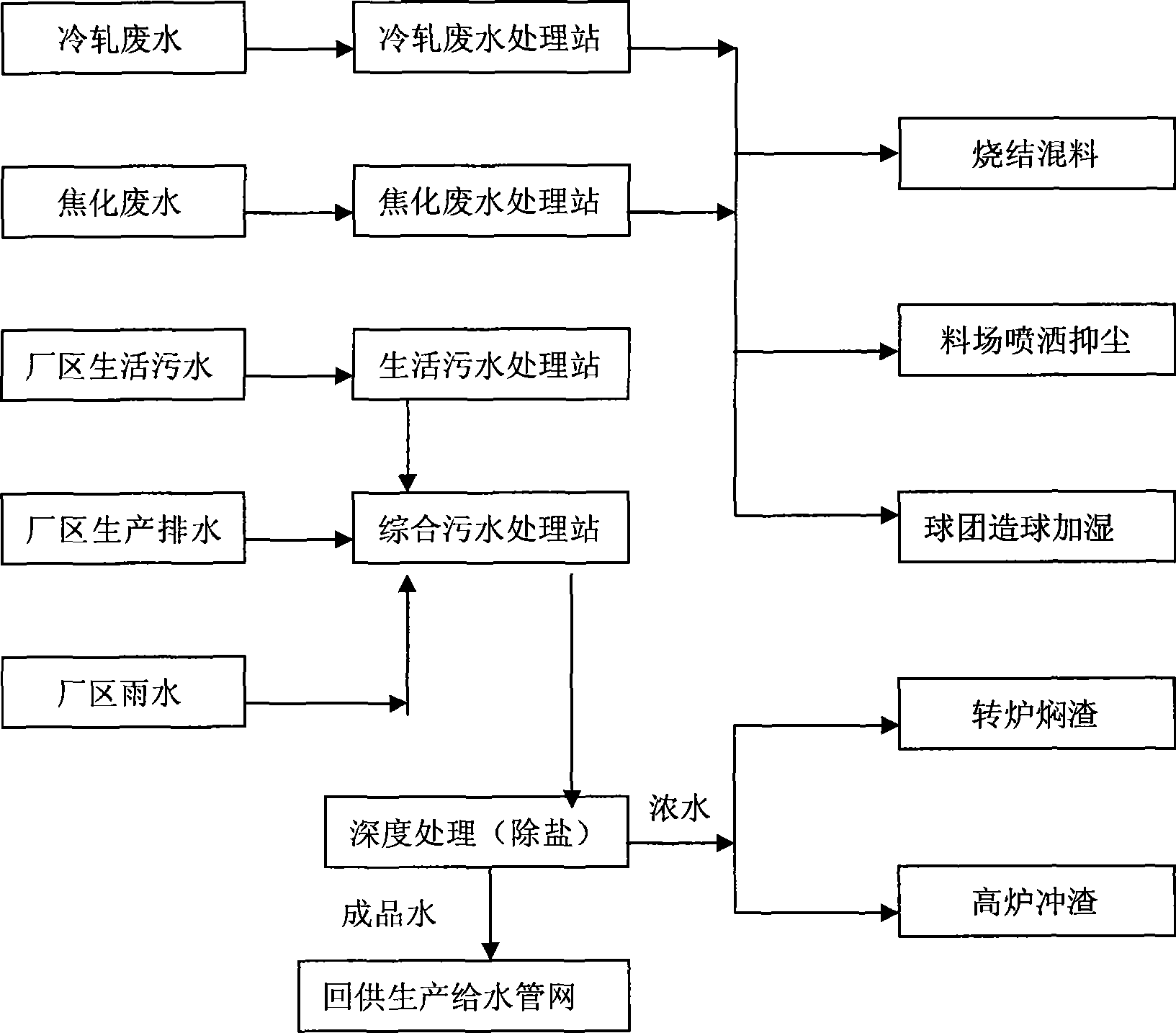
Comprehensive recovery and utilization method of various waste waters in iron and steel plant
InactiveCN101386457AFulfil requirementsGuarantee water qualityWaste water treatment from metallurgical processTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSocial benefitsWater resources
Owner:BEIJING SHOUGANG INT ENG TECH
Screening equipment for ironware in decoration garbage
ActiveCN113769849AAvoid turning stuckDoes not affect workGrain treatmentsStructural engineeringRaw material
The invention relates to the technical field of screening, in particular to screening equipment for ironware in decoration garbage. The screening equipment comprises a stock bin, first grinding plates, second grinding plates, a crushing cutter and a main shaft, wherein the main shaft is rotatably arranged in the stock bin, the first grinding plates and the second grinding plates are sequentially and alternately connected end to end in a hinged mode to form a grinding and crushing wheel coaxial with the main shaft, the grinding and crushing wheel is driven by the main shaft to rotate, in the rotating direction of the grinding and crushing wheel, the rear ends of the first grinding plates and the rear ends of the second grinding plates interact with the inner wall of the stock bin to crush raw materials, a plurality of crushing cutters are arranged, each crushing cutter is rotatably installed on one first grinding plate and is attached to the first grinding plate when the grinding and crushing wheel works normally,s and when the rear end of the second grinding plates are extruded by the raw materials to rotate inwards, the crushing cutters are driven by a connecting rod transmission assembly to rotate by a preset angle relative to the first grinding plates, so that the crushing cutters crush the raw materials at the position when rotating along with the first grinding plates, and the crushed raw materials are sieved by a screen to obtain ironware in the decoration garbage.
Owner:SUZHOU CONSTR MATERIAL RECYCLING APPL
Ironwork electronickelling rust-proof liquid and preparing method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal surface treatment, and particularly relates to ironwork electronickelling rust-proof liquid. The ironwork electronickelling rust-proof liquid is composed of water, strong acid, boric acid and citrate, wherein the strong acid, the boric acid and the citrate are dissolved into water; according to the ironwork electronickelling rust-proof liquid,all ingredients which are wide in raw material source and low in cost are mixed according to a certain proportion, the ironwork nickel layer yellowing phenomenon can be quickly solved, a matrix and aplating layer are not corroded, use at the room temperature can be achieved, power consumption is reduced, and the electroplating cost is reduced; and in addition, the ironwork electronickelling rust-proof liquid can be used for plugging places existing surface seepage repairing, rusting again after rust on the surface layer of a plating piece is prevented, the using reliability of a gold platingpart is improved, and the service life of the gold plating part is prolonged.
Owner:GUIZHOU AEROSPACE NANHAI SCI & TECH
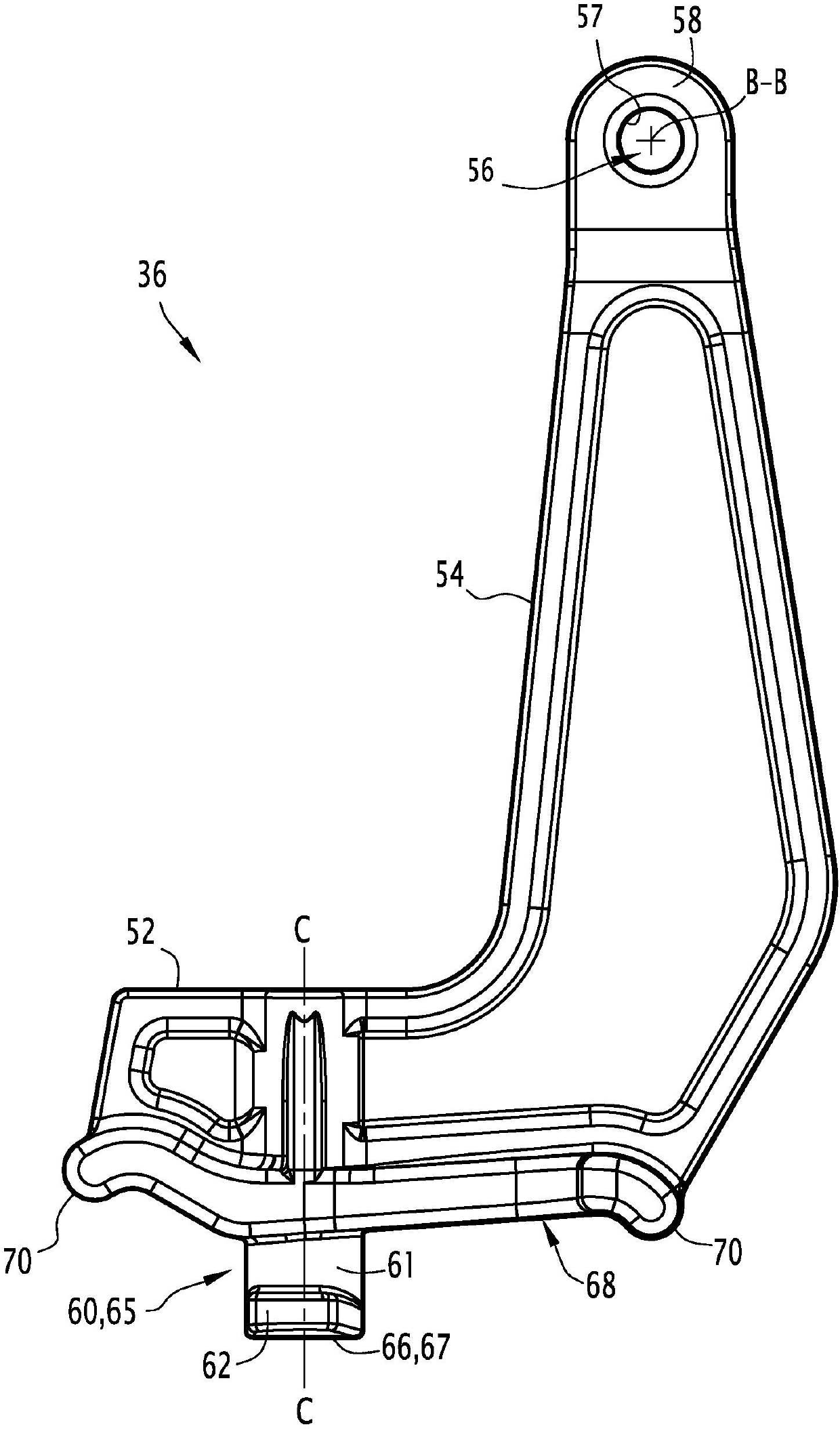
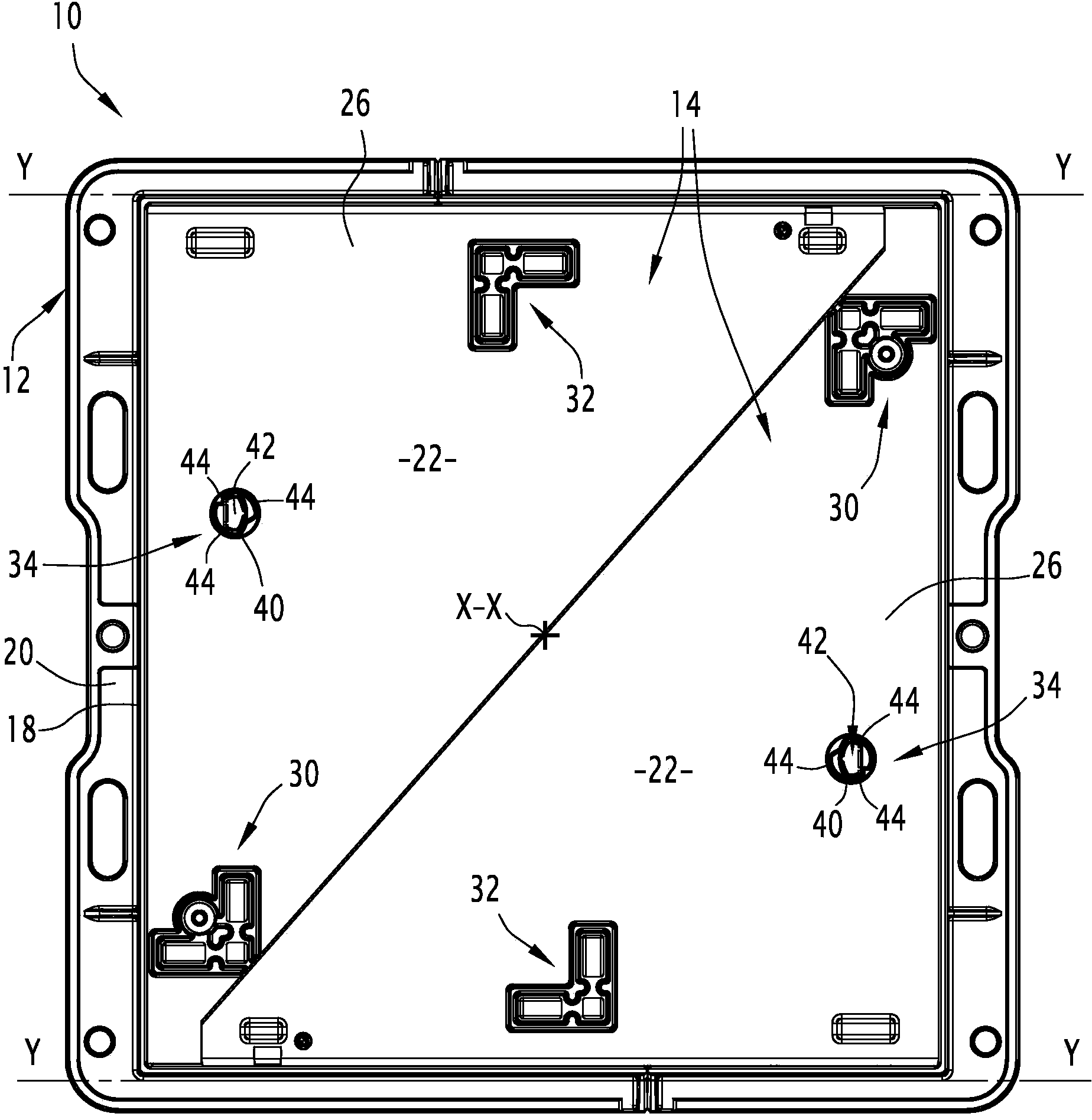
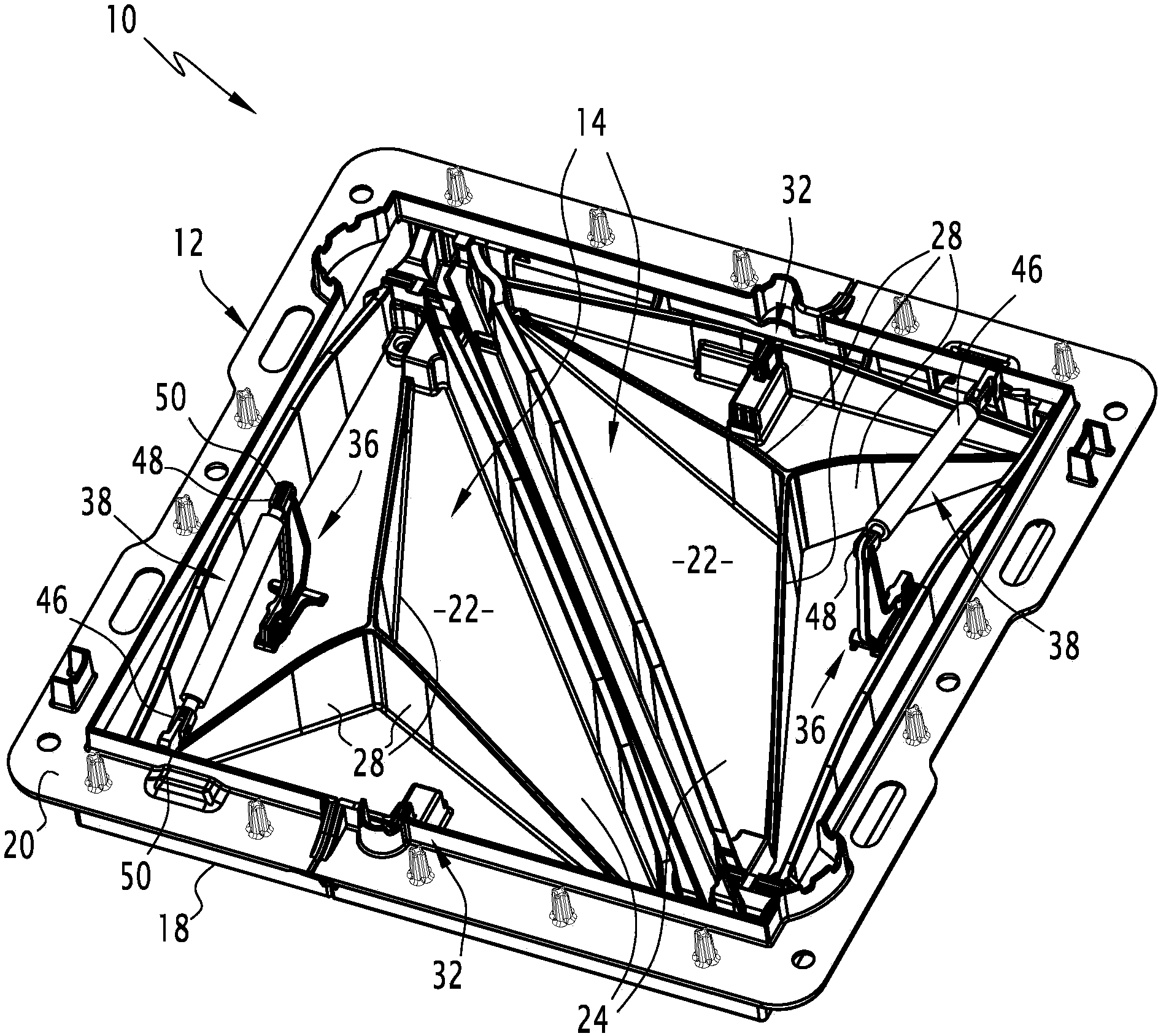
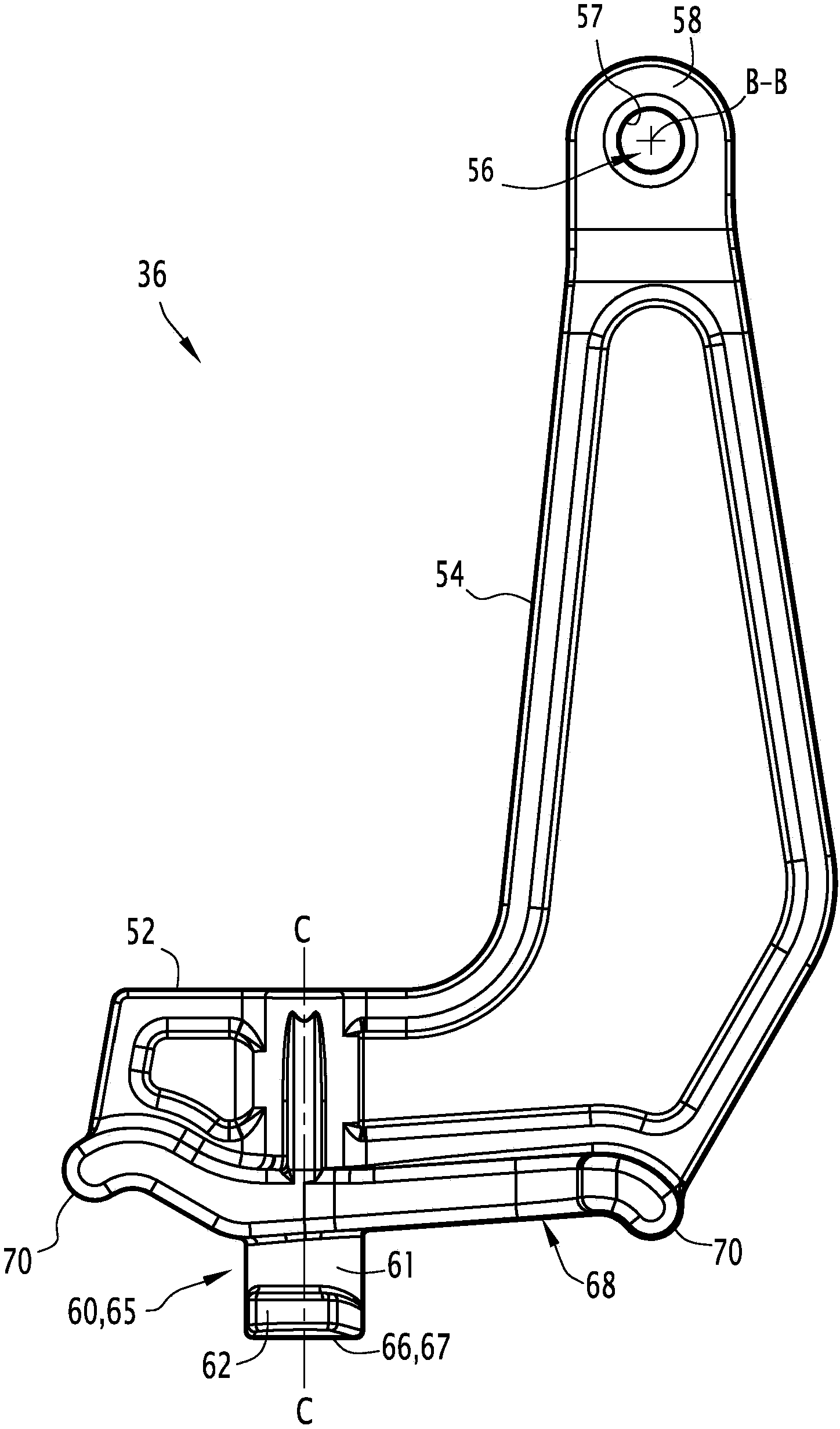
Fastener for street ironwork, assembly, street ironwork and corresponding method
The present fastener (36) for street ironwork includes a fastening or locking means (56). The fastener (36) includes a retaining foot (60) suitable for removably connecting the fastener (36) to a member of the street ironwork, via a receiving cavity (40) made in the member of the street ironwork by means of a shape-matching connection. The invention further relates to the use in attaching jacks to man hole covers.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PAM SA
Rust removing process for steel plate surface
InactiveCN108580238AQuick fixShorten the timeLiquid surface applicatorsSpraying apparatusEngineeringDrying time
The invention provides a rust removing process for a steel plate surface. By means of the rust removing process for the steel plate surface, the technical problems that in an existing rust removing method, manual work is needed for repeatedly turning faces of ironwork, and rust removing is not convenient are solved. The rust removing process for the steel plate surface comprises the following steps that a, by weight, 15-25 parts of polyglutamic acid, 22-28 parts of a complexing agent, 10-16 parts of sodium carbonate, 10-15 parts of sodium chloride, 8-16 parts of vinegar and 8-12 parts of waterare weighed and put into a mixer to be mixed and stirred to be uniform, and an antirust agent is prepared; b a steel plate is vertically put on a clamping plate in a spraying device; c, the antirustagent is evenly sprayed to the two surfaces of the steel plate through the spraying device; and d, the sprayed steel plate is put into an oven, the drying temperature is 120 DEG C-140 DEG C, and the drying time is 2 min-5 min. The rust removing process has the beneficial effect that rust removing is convenient.
Owner:海宁鑫墨香印刷有限公司
Preparation method of zinc-nickel coating for ironwork
InactiveCN102766865AHigh strengthIncrease stiffnessHeat inorganic powder coatingWorking environmentOxidation resistant
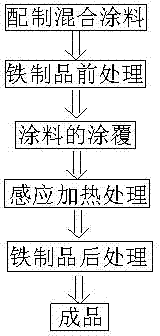
The invention discloses a preparation method of zinc-nickel coating for ironwork. The preparation method includes the following steps: a, preparing and mixing coating; b, pre-processing the ironwork; c, applying the coating; d, performing an induction heating process; and e, post-processing the ironwork. The preparation method is reasonable in process arrangement and moderate in preparation cost, the ironwork is remarkable in performances of strength, rigidity, toughness, corrosion resistance and anti-oxidation due to the zinc-nickel coating, the bonding strength of the zinc-nickel coating and the ironwork is high, the ironwork is durable, and requirements of severe working environments for performances of the ironwork are satisfied.
Owner:KUSN QIAORUI METAL PRODS
Clamping anchor for fastening ironwork to hollow profile of window or door
The invention relates to a clamping anchor for fastening ironwork to a hollow profile of a window or door, whereby the clamping anchor essentially consists of an L-shaped body with a first leg and a second leg, whereby the first leg is short in proportion to the second leg, the second leg of which is provided with an internal thread for securing the clamping anchor via a screw, which internal threads extends lengthways of the second leg, whereby the first leg is provided with a clamping surface for an internal wall surface of the profile, characterized in that at the free end of the second leg, a supporting surface is provided for the ironwork, whereby the clamping surface and the supporting surface are located at both sides of the thread of the second leg, whereby a stable balance of forces is created on the clamping anchor when tightening the screw. The invention also relates to a method for fastening ironwork to a hollow profile of a window or door by means of said clamping anchor.
Owner:埃马纽埃尔迪德里希卡米尔范帕里斯
Method for extracting zinc oxide from iron-smelting blast furnace fly ash
The invention discloses a method for extracting zinc oxide from iron-smelting blast furnace fly ash. Compared with the commonly used rotary furnace process at present, the method has the following advantages that 1, the used fly ash index is wide: the iron content required by the fly ash used by the rotary furnace process is below 20% and the zinc content is above 20%, and iron content required by the fly ash used by the method is not limited and the zinc content is above 6%; 2, fuel addition is not required: 0.45 ton of anthracite or 0.35 ton of coke powder is required to be added in each ton of fly ash in the rotary furnace, and the method does not require fuel addition; 3, the operation cycle is long: the operation cycle of the rotary furnace is 60 days and the operation period of the enclosed furnace in the method is longer than one year; 4, the fireproof material in the furnace is low in cost: the high-temperature wear-resistant fireproof brick used by the rotary furnace costs ** yuan per ton, and the common fireproof brick used in the enclosed furnace costs ** yuan per ton; and 5, the tailing recycle is convenient: the tailings of the rotary furnace process flow out in a liquid state and need to be continuously cooled by water, and contain less iron so that the value in use is low, and the tailings in the method are discharged in a solid state, the tailings with iron content higher than 50% can be directly used in ironworks and the tailings with iron content lower than 50% can be used in cement plants.
Owner:王全生
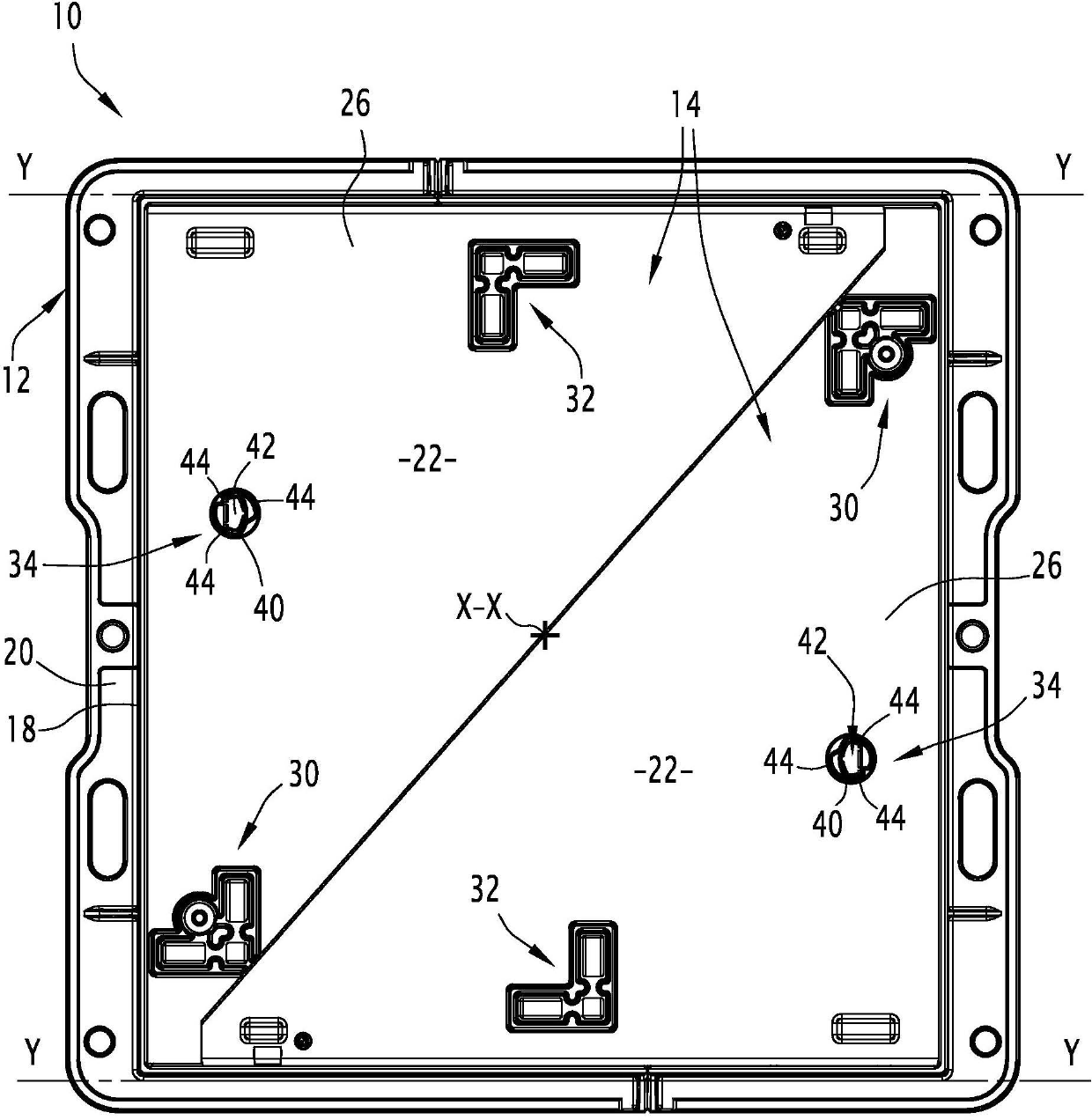
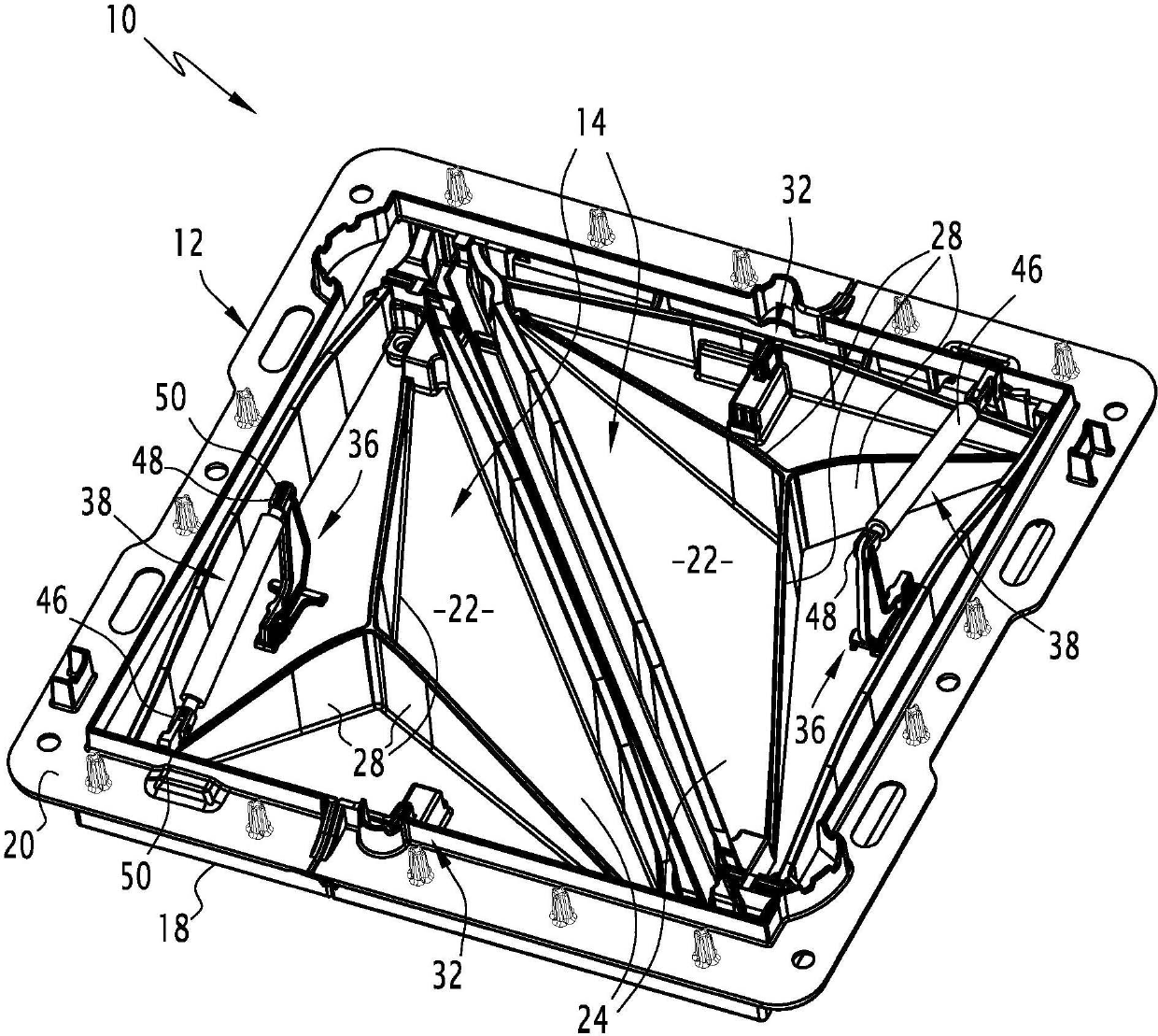
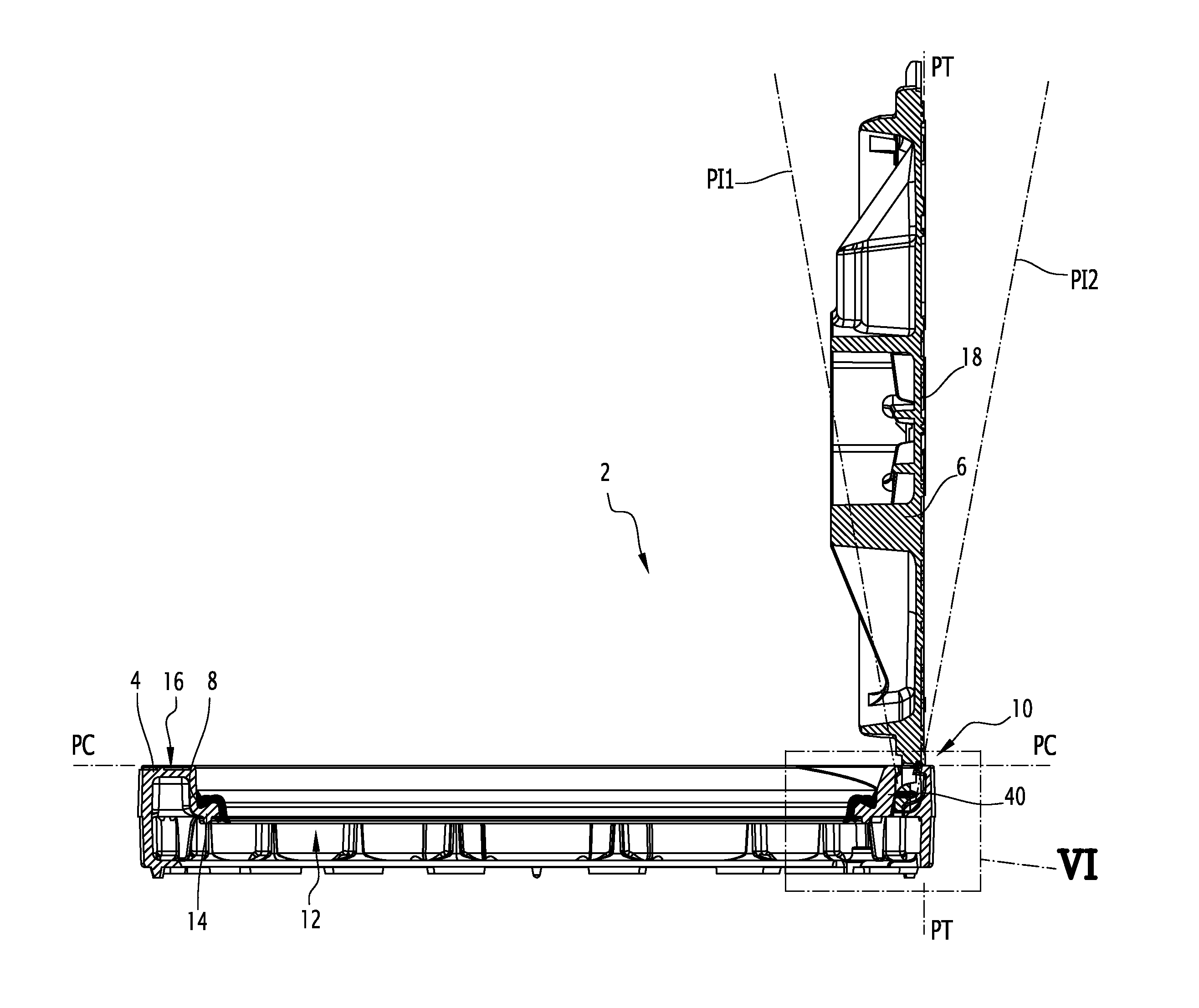
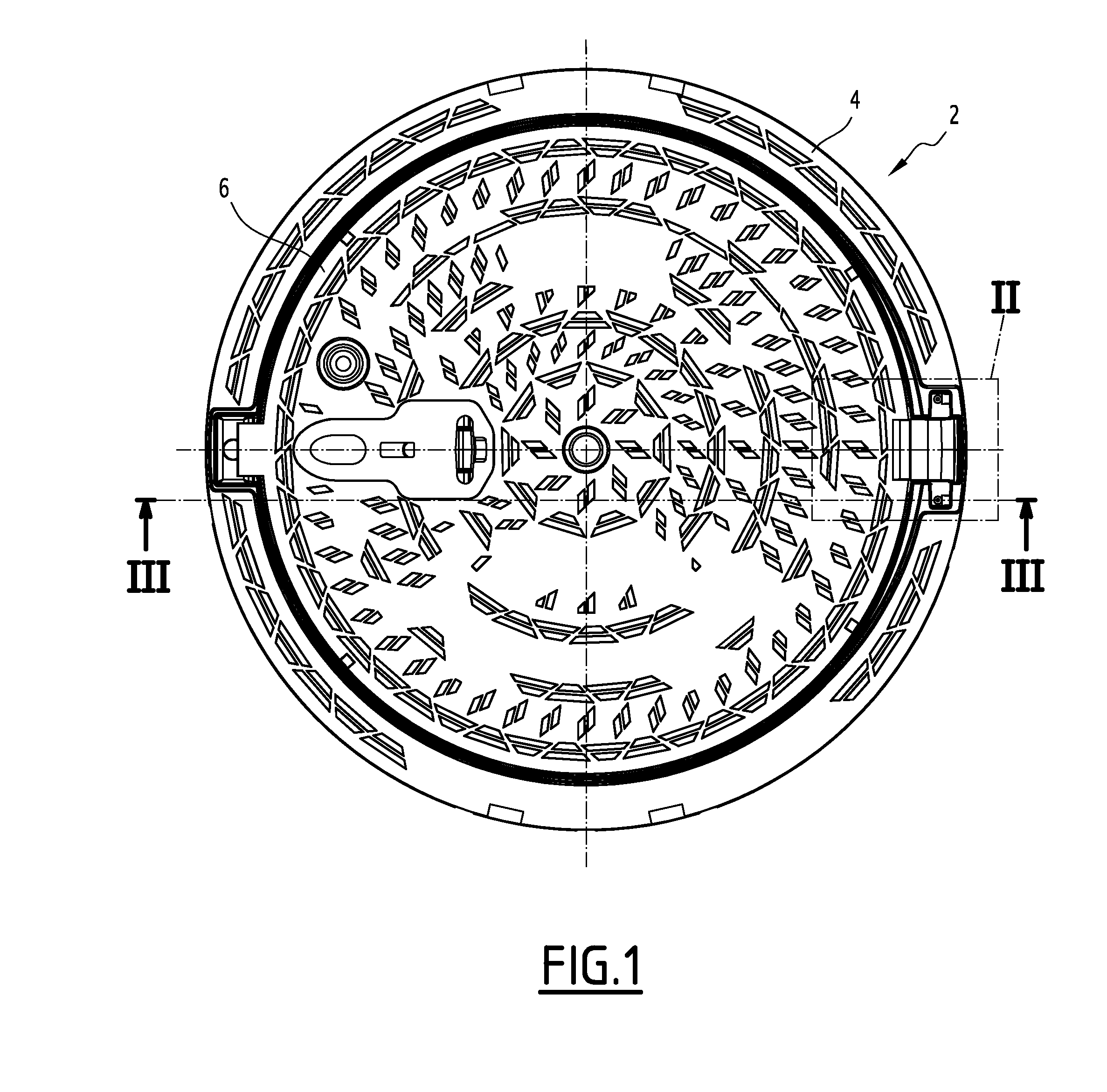
Street ironwork
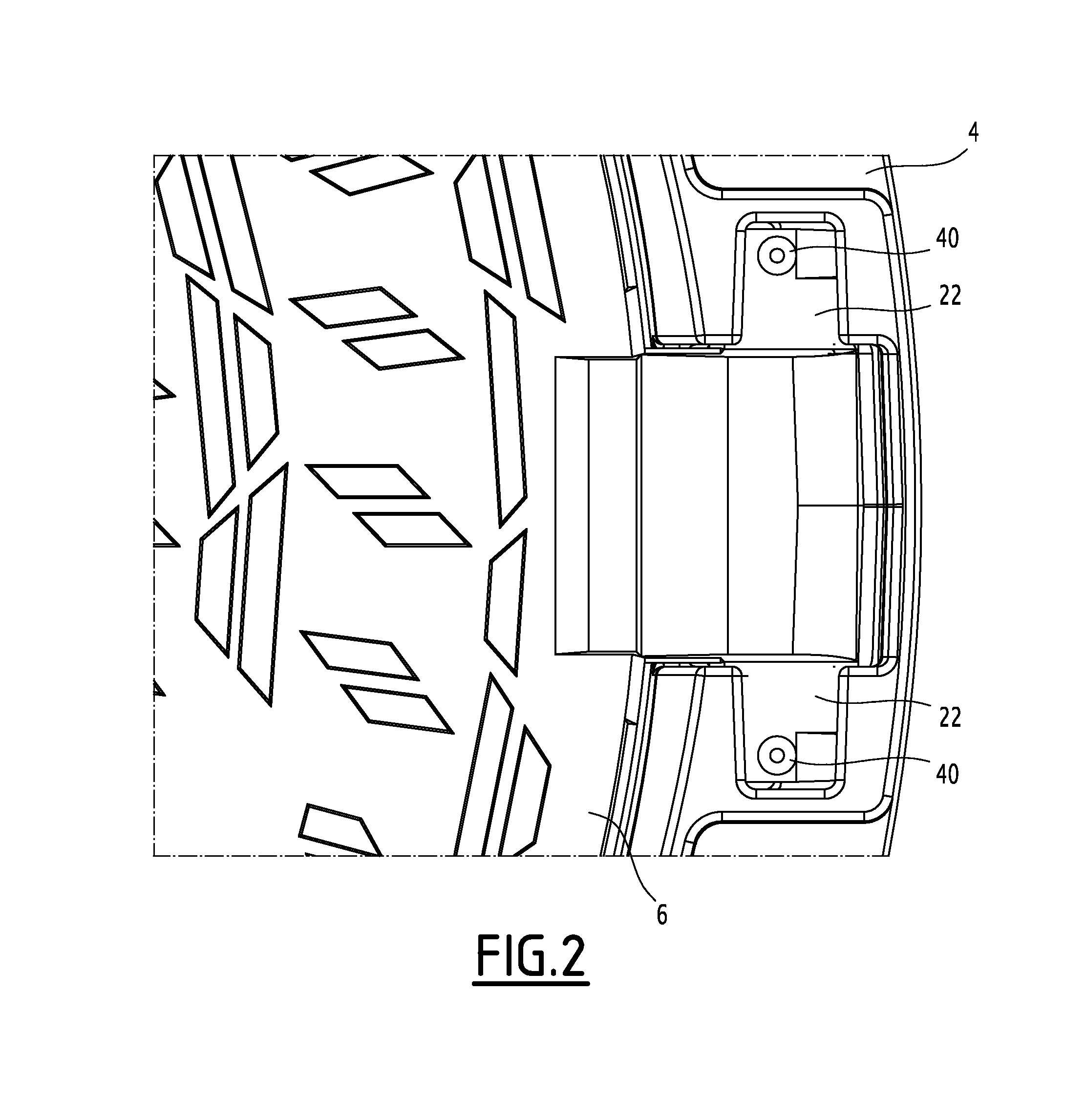
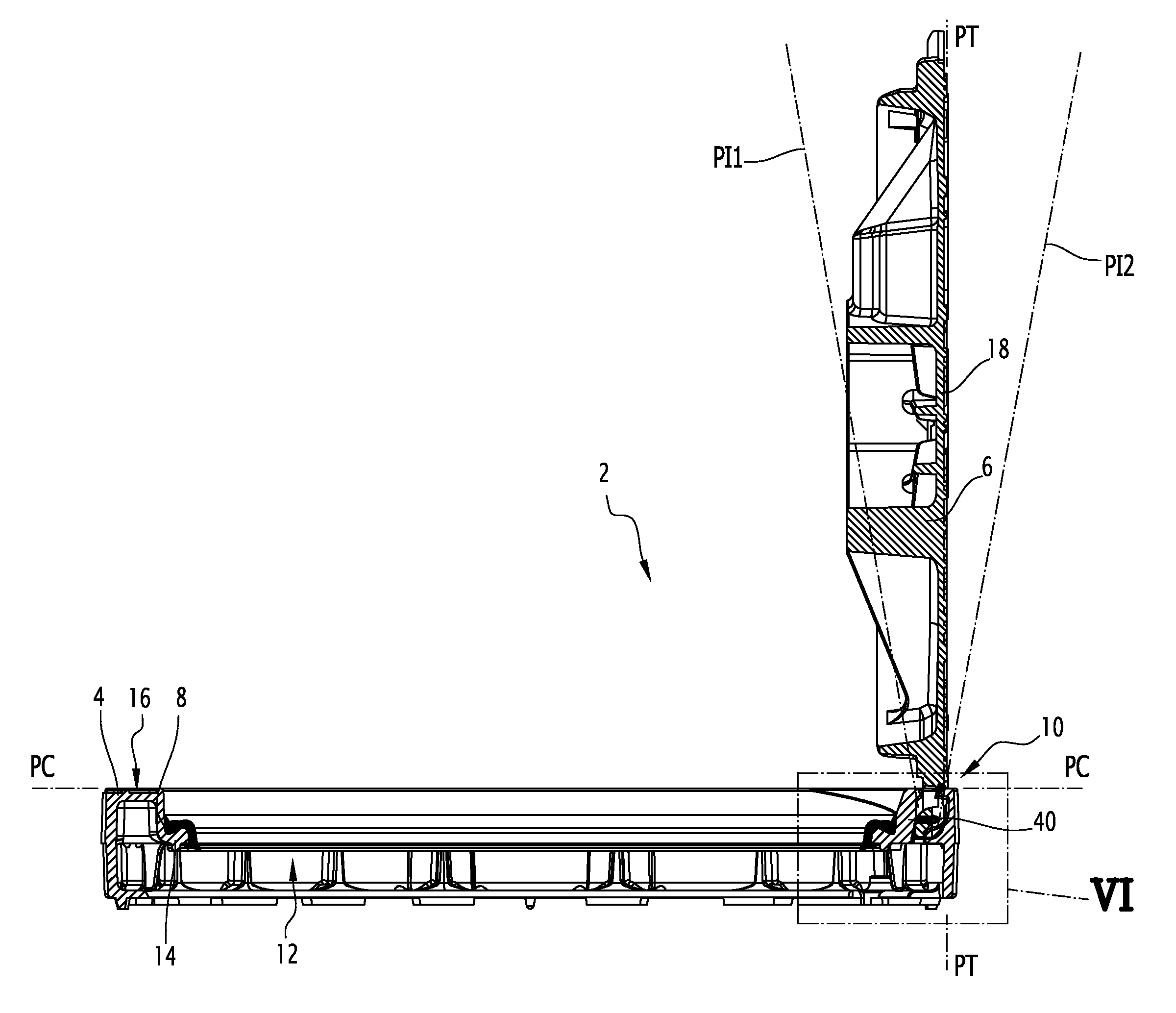
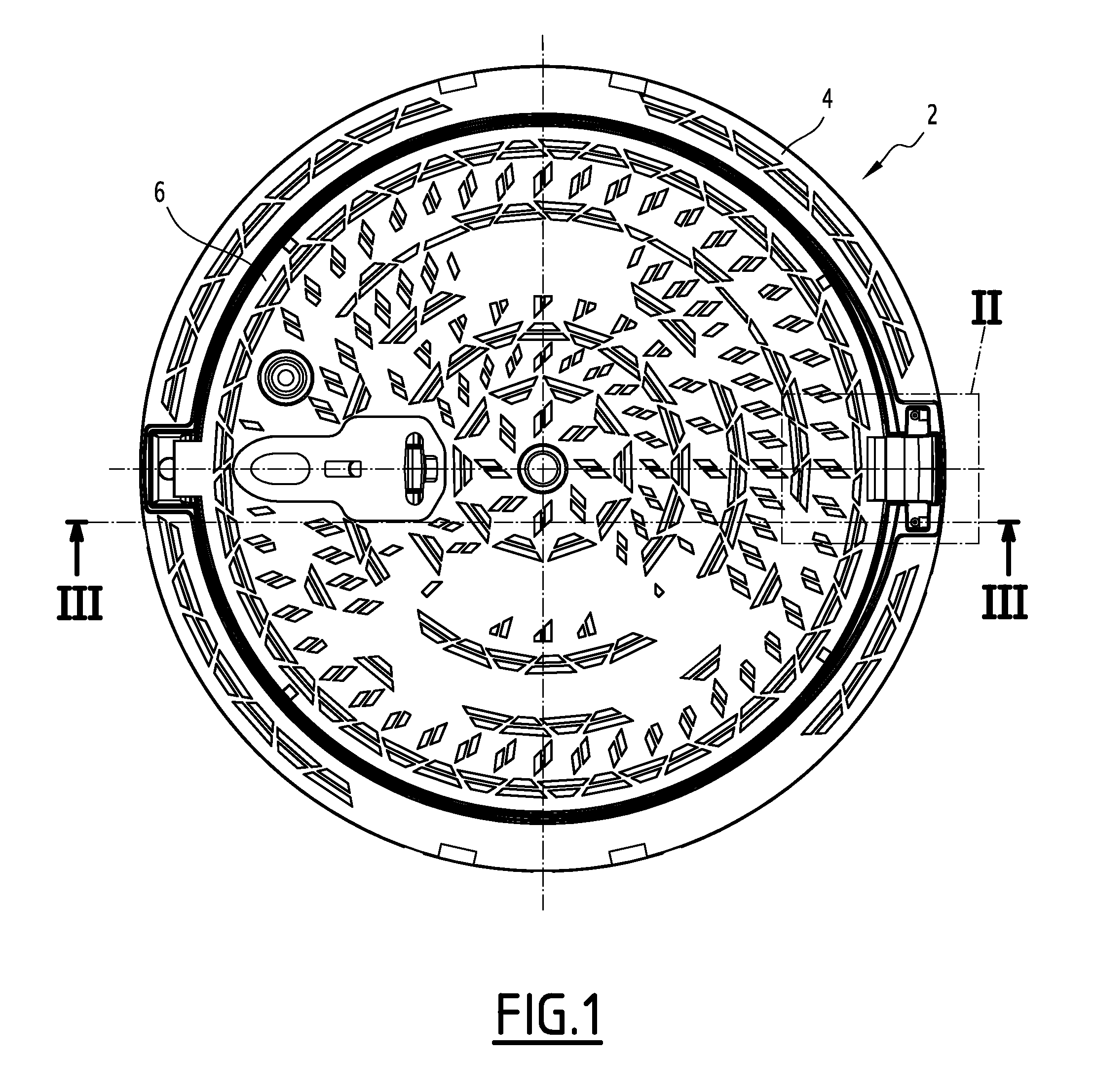
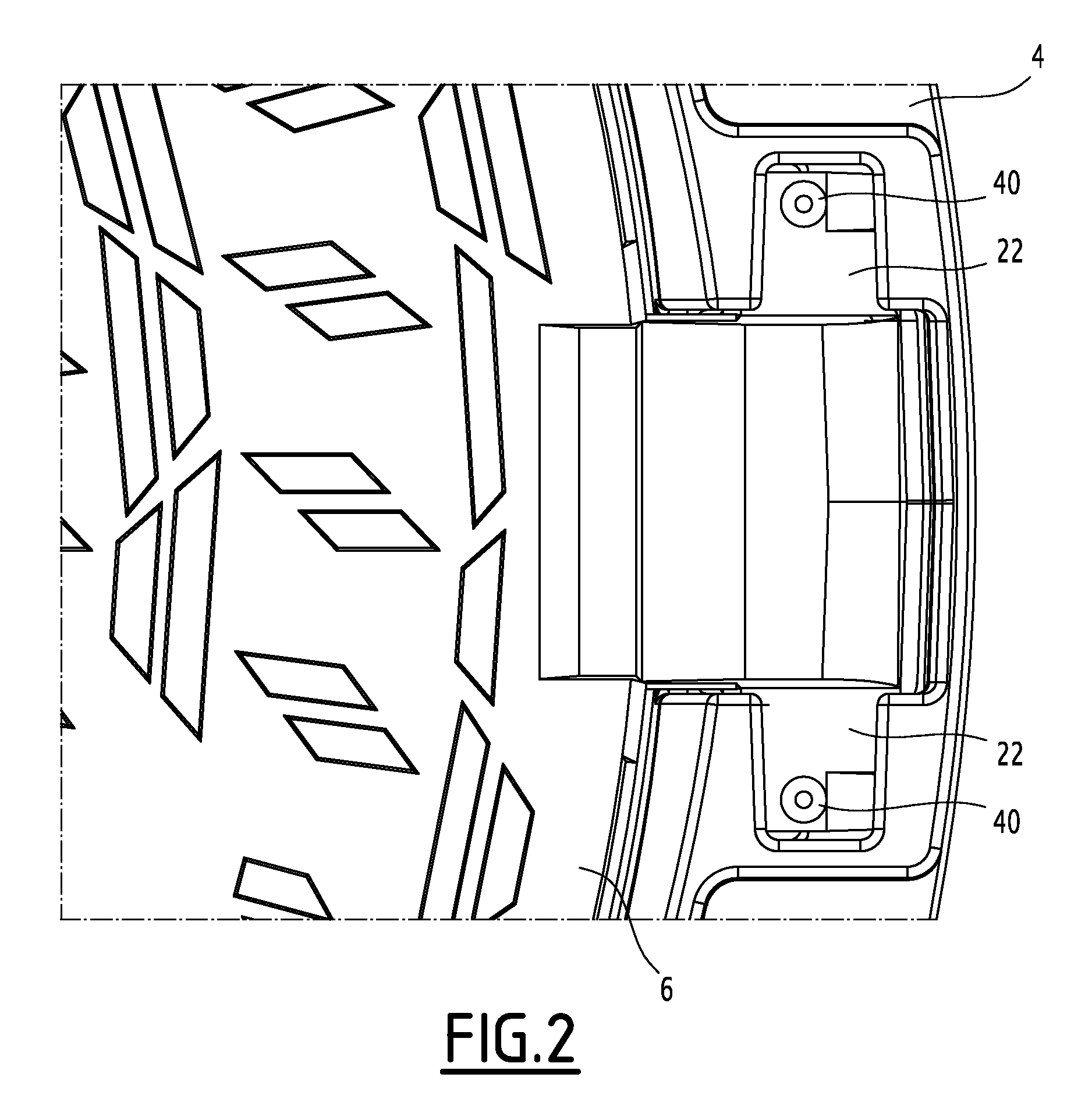
ActiveUS20140123560A1Inhibition releaseArtificial islandsBuilding locksMechanical engineeringIronwork
The street ironwork according to the invention includes a frame (4), a manhole cover (6), a hinge (10) for pivotably connecting the covering element relative to the frame between a closed position and an open position, the hinge including a frame knuckle (20) and a covering element knuckle (22).The street ironwork includes a locking element (40) attached to the covering element knuckle and suitable for preventing the covering element knuckle from being released from the frame knuckle in at least one of the open positions of the covering element relative to the frame or in the closed position.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PAM SA
Street ironwork
The street ironwork according to the invention includes a frame (4), a manhole cover (6), a hinge (10) for pivotably connecting the covering element relative to the frame between a closed position and an open position, the hinge including a frame knuckle (20) and a covering element knuckle (22).The street ironwork includes a locking element (40) attached to the covering element knuckle and suitable for preventing the covering element knuckle from being released from the frame knuckle in at least one of the open positions of the covering element relative to the frame or in the closed position.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PAM SA
Blackening treatment process for surface of ironwork
InactiveCN105349935AOvercoming brittlenessPrevent decarbonizationSolid state diffusion coatingStrong acidsOperation safety
The invention discloses a blackening treatment process for the surface of ironwork. The blackening treatment process comprises the following steps that firstly, a nitriding furnace is warmed to 620-650 DEG C; secondly, the surface of the ironwork is cleaned; thirdly, the cleaned ironwork is placed in the nitriding furnace; fourthly, 900 ml of alcoholic solution is dropped in the nitriding furnace; fifthly, constant temperature is kept for 120 min; sixthly, the nitriding furnace stops heating, and natural cooling is carried out; and seventhly, the ironwork is taken out of the nitriding furnace and cooled to normal temperature. The steps of the blackening treatment process are reasonable, strong-acid-free ironwork surface blackening treatment is achieved through the steps, cost is low, and operation safety is high.
Owner:河北兴康汽车部件制造有限公司
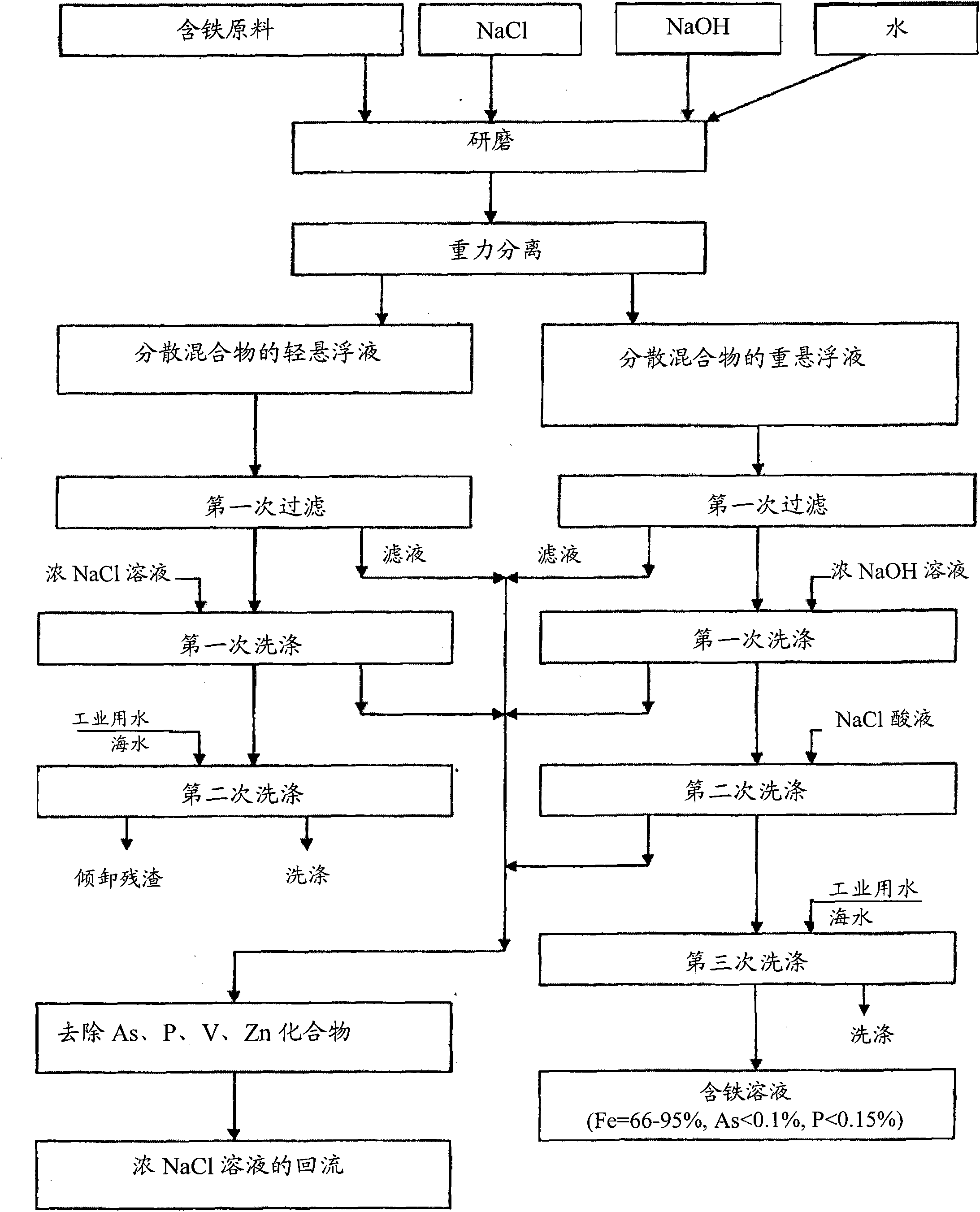
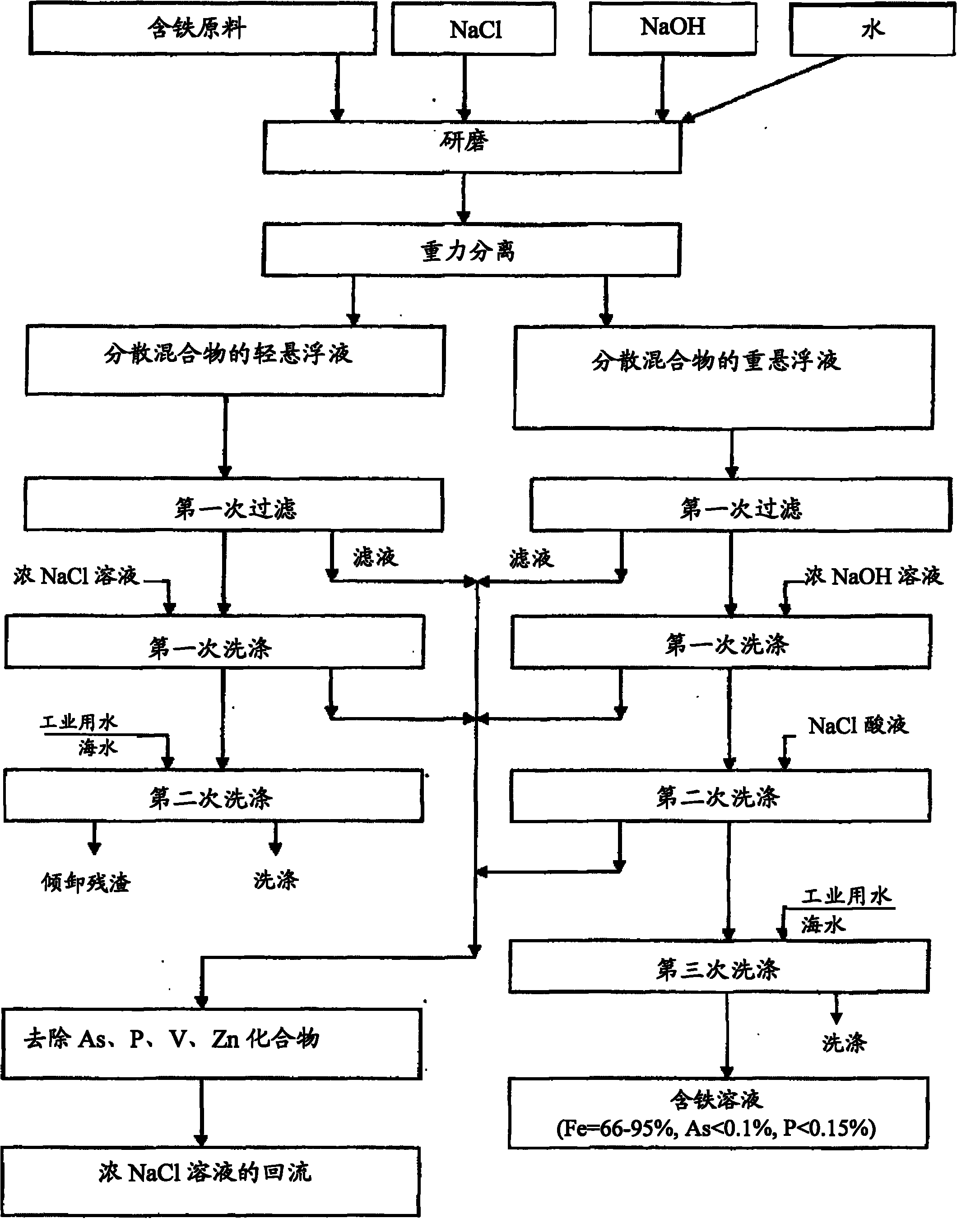
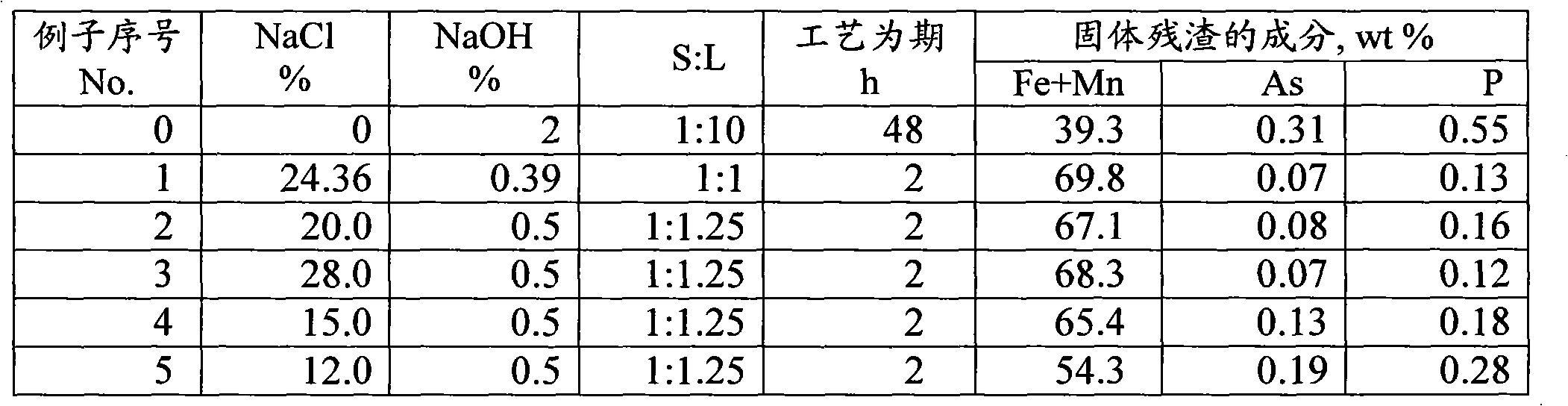
Method for arsenic removal and phosphorous removal out of iron-containing materials
InactiveCN101956072AHigh in ironLower arsenic and phosphorous levelsProcess efficiency improvementIronstoneFerrochrome
The invention relates to a method for arsenic removal and phosphorous removal out of iron-containing materials and belongs to the metallurgy and mining field and the metallurgy field. Particularly, the invention relates to a method for treating iron ore, ferromanganese ore, ferrotitanium ore, ferrochrome ore, manganese ore and other ores, solution, sponge iron, pre-reduction ball and ironwork block. The method comprises the steps of increasing the iron content in the iron-containing materials, removing the unwanted impurities (firstly, arsenic and phosphorus), and separating the valuable impurities (firstly, vanadium) so as to increase the quality. The invention aims to increase the iron content in the products, decrease the arsenic and phosphorus contents to a preset value, decrease the technical period, reduce the dosage of alkali agent and lower the cost.
Owner:顿涅茨克钢铁制品私营股份公司
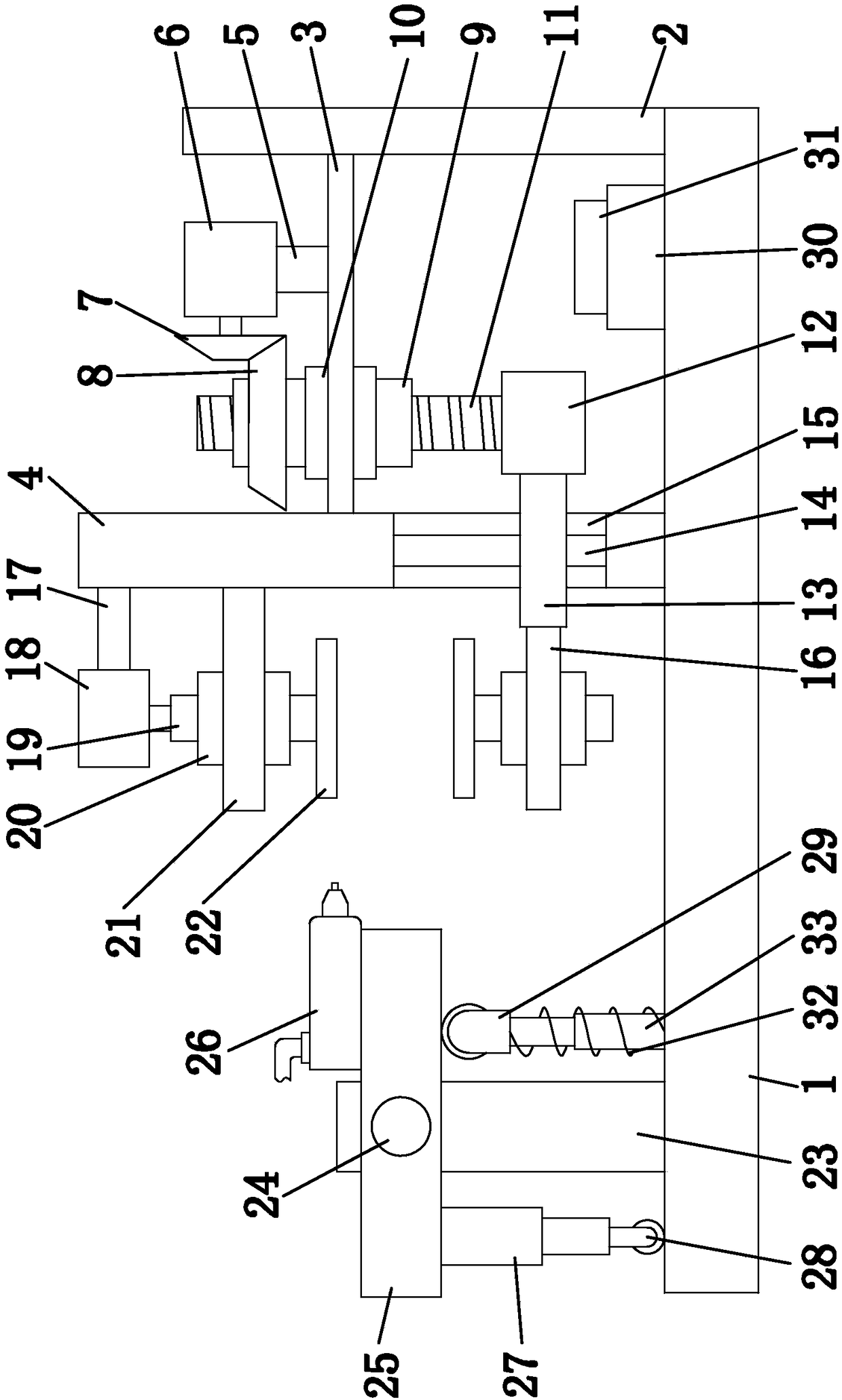
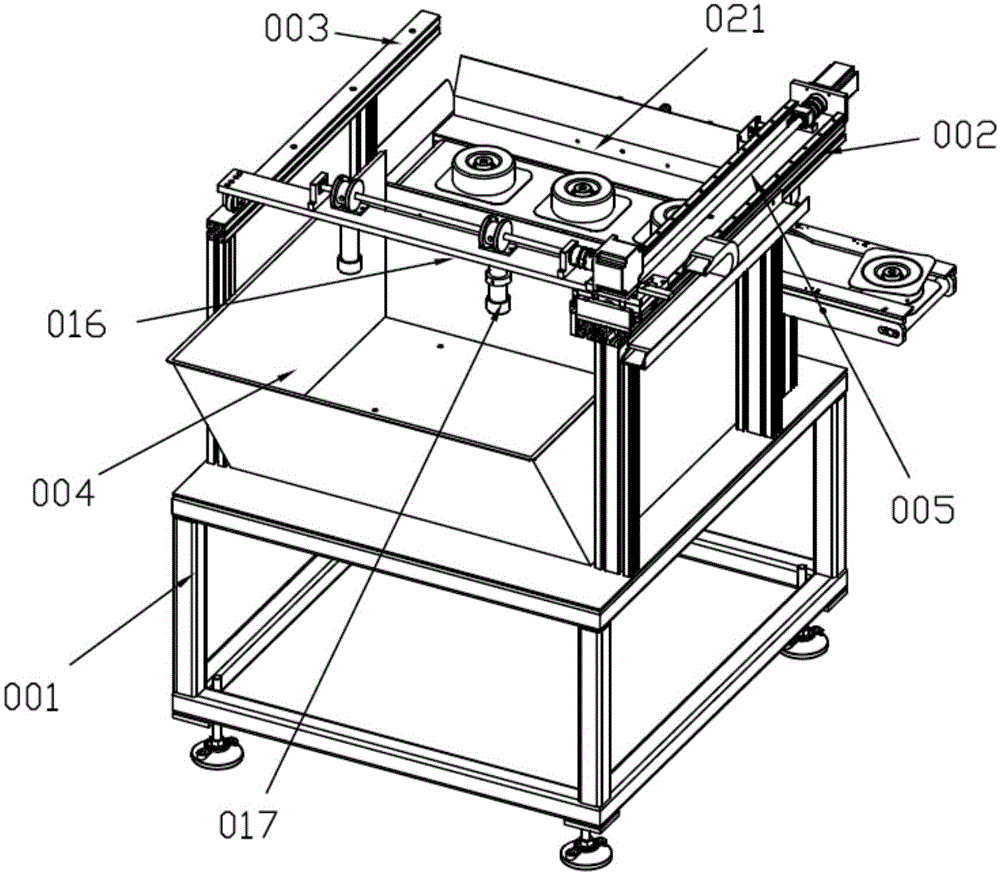
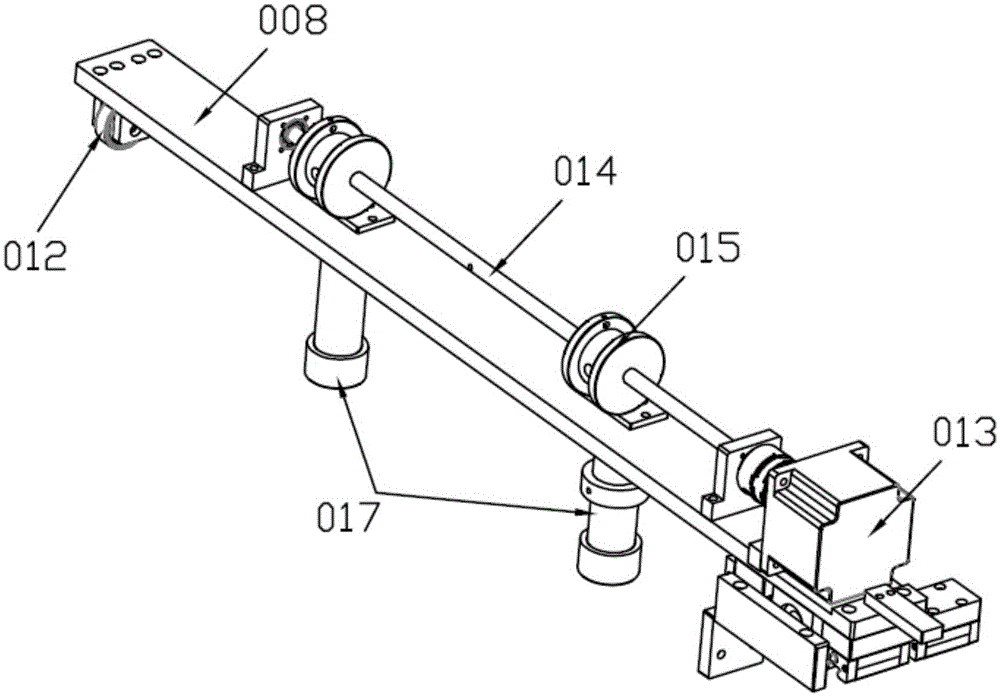
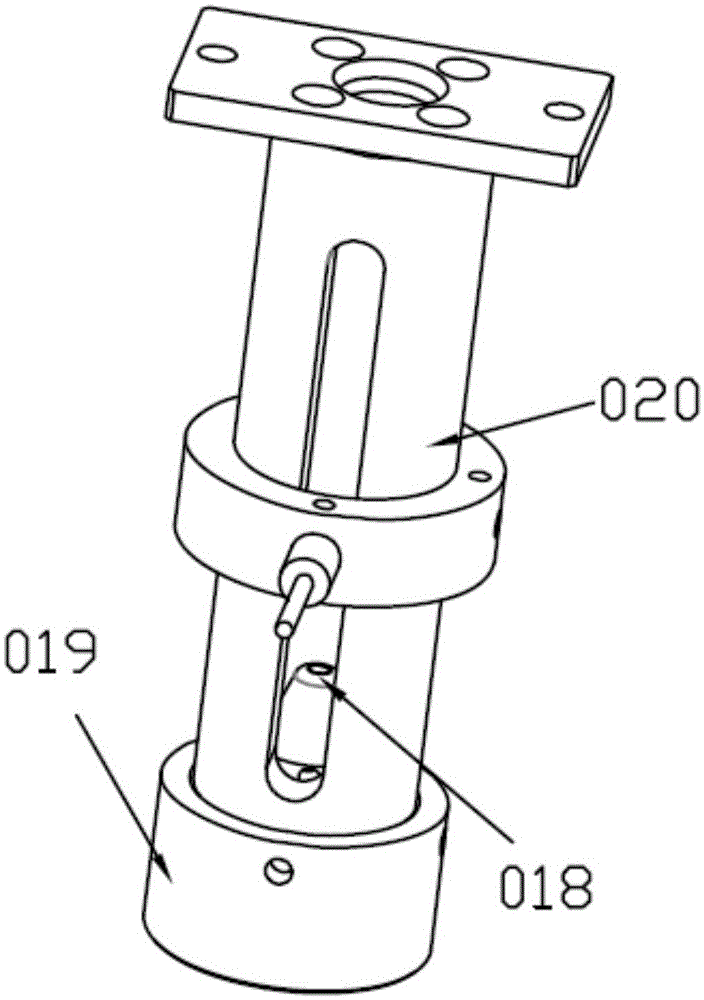
Ironwork feeding mechanism
The invention discloses an ironwork feeding mechanism which comprises a feeding machine frame; a first cross beam and a second cross beam, which are arranged symmetrically, are arranged on the feeding machine frame; a loading frame is arranged below a space between the first cross beam and the second cross beam; a front-back servo movement mechanism is arranged on the first cross beam; a feeding mechanism is arranged on the feeding machine frame, and is arranged below the tail ends of the two cross beams; the front-back servo movement mechanism is connected with a product taking mechanism; the product taking mechanism is transversally arranged between the first cross beam and the second cross beam; and a taking magnet attraction jig is arranged on the product taking mechanism. The ironwork feeding mechanism has the advantages that the working efficiency can be improved, the working intensity of personnel can be reduced, the product quality can be ensured, damage to ironwork can be avoided, and the product appearance can be effectively prevented from being damaged; and in addition, through the adoption of the manner of magnet attraction, noise is small, so that the working environment of staffs can be improved effectively, and the working efficiency of the staffs is further improved.
Owner:DONGGUAN DELONG AUTOMATION TECH
Cabin water-leakage alarm apparatus
The prior iron products of thousands of tons float on the water surface by buoyancy. When vessels operate on the water or are anchored, water leakage caused by the quality of electric welding, the quality of steel materials, etc. can cause risk and pose a threat to the safety of the vessels and the personnel. The invention provides a vessel water leakage and seepage alarm, which is designed to automatically detect water seepage on the bottom or in some positions of the vessel. The alarm is composed of a single channel, a multiple channel, a probe, and a main frame of the alarm. As long as the water exists where water should not appear, electrical water resistance is transferred to the main frame following the water, and an alarm action is conducted, thereby solving the problem of alarming about water leakage.
Owner:NANTONG FENGSHI LIGHT SOURCE ELECTRONICS APPL TECH INST
Modification method of ironwork for petroleum field
InactiveCN113151816AImprove corrosion resistanceLow crude oil adhesionMetallic material coating processesHydrophilic polymersPetroleum oil
The invention discloses a modification method of ironwork, and belongs to a metalwork processing technology. According to the method, various hydrophilic polymers are utilized to modify the ironwork, so that the ironwork is endowed with certain corrosion resistance, and the ironwork has extremely low crude oil adhesion. The technology is expected to be popularized in the petroleum field, so that ironwork used in the petroleum field has relatively low crude oil adhesion and corrosion resistance. The preparation process comprises the following steps: preparing different modification liquids, alternately modifying the to-be-modified ironwork by using the different modification liquids in a certain manner, and treating the modified ironwork to obtain the modified ironwork with excellent oil stain resistance and corrosion resistance.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
A method for extracting zinc oxide from ironmaking blast furnace dust
The invention discloses a method for extracting zinc oxide from iron-smelting blast furnace fly ash. Compared with the commonly used rotary furnace process at present, the method has the following advantages that 1, the used fly ash index is wide: the iron content required by the fly ash used by the rotary furnace process is below 20% and the zinc content is above 20%, and iron content required by the fly ash used by the method is not limited and the zinc content is above 6%; 2, fuel addition is not required: 0.45 ton of anthracite or 0.35 ton of coke powder is required to be added in each ton of fly ash in the rotary furnace, and the method does not require fuel addition; 3, the operation cycle is long: the operation cycle of the rotary furnace is 60 days and the operation period of the enclosed furnace in the method is longer than one year; 4, the fireproof material in the furnace is low in cost: the high-temperature wear-resistant fireproof brick used by the rotary furnace costs ** yuan per ton, and the common fireproof brick used in the enclosed furnace costs ** yuan per ton; and 5, the tailing recycle is convenient: the tailings of the rotary furnace process flow out in a liquid state and need to be continuously cooled by water, and contain less iron so that the value in use is low, and the tailings in the method are discharged in a solid state, the tailings with iron content higher than 50% can be directly used in ironworks and the tailings with iron content lower than 50% can be used in cement plants.
Owner:王全生
Fastener for street ironwork, assembly, street ironwork and corresponding method
The present fastener (36) for street ironwork includes a fastening or locking element (56). The fastener (36) includes a retaining foot (60) suitable for removably connecting the fastener (36) to a member of the street ironwork, via a receiving cavity (40) made in the member of the street ironwork by element of a shape-matching connection. The invention further relates to the use in attaching jacks to man hole covers.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PAM SA
Environment-friendly healthy anti-aging paint for ironwork surfaces
InactiveCN105860679AImprove adsorption capacityImprove air qualityCoatingsHazardous substanceFlexural strength
The invention discloses an environmentally friendly, healthy and aging-resistant paint for the surface of iron products, which comprises component A and component B, and the weight ratio of component A to component B is 6-10:2-5; wherein, component A The raw materials include by weight: 10-20 parts of negative ion powder, 20-40 parts of composite magnetic particles, 10-30 parts of tourmaline powder, 20-40 parts of chrysotile, 10-20 parts of sepiolite, 10-20 parts of vermiculite powder , 2-8 parts of quartz powder, 5-15 parts of calcined clay, 20-40 parts of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer; component B is water. The invention can release negative ions for a long time to improve air quality, has strong adsorption capacity for harmful substances, has excellent adhesion to iron product bases, is resistant to aging, has good heat resistance, and has extremely high bending strength.
Owner:ANHUI KAILIN ADVANCED MATERIAL CO LTD
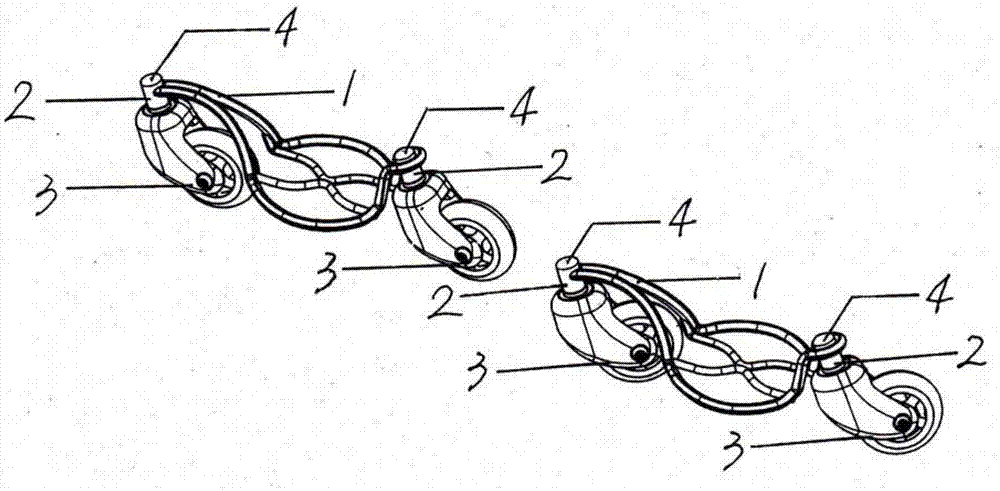
Iron art shaped foot swinging type roller skates made of metal round bar material
The present invention relates to a roller skate, and particularly relates to a rocker-type roller skate made of ironwork of metal circular rod material, comprising omni-directional wheels, and further comprising an ironwork frame made of metal circular rod material. One of these omni-directional wheels is mounted on both the front end and the rear end of the frame. The present invention incorporates an ironwork technique into the rocker-type roller skate, enabling the rocker-type roller skate made of ironwork of metal circular rod material to both have very good playability and provide ornamental ironwork rocking members, while increasing the structural strength of the roller skate.
Owner:TAICANG CHEZHONGBAO LEISURE ARTICLES +1
Cable clamp capable of driving nails
InactiveCN107453183AEasy to useLine/current collector detailsDispensing apparatusEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:ZHUGELIANG MIDDLE SCHOOL
Method for discriminating ancient cast iron and block ironmaking products
ActiveCN112986302AFar-reaching research valueAccurate discriminationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNon-metallic inclusionsAlloy
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for discriminating ancient cast iron and block ironmaking products, and belongs to the technical field of methods for discriminating ancient steel products. The method comprises two parts of metallographic analysis and non-metallic inclusion analysis of ancient cast iron and block ironmaking products. Wherein the metallographic analysis is used for distinguishing according to different room-temperature equilibrium structures of the ancient cast iron and the block ironmaking product, and the non-metallic inclusion analysis is used for the quantity, composition, morphology and distribution of non-metallic inclusions of the ancient cast iron and the block ironmaking product. Through collaborative analysis of alloy phase structures and inclusions, the method for accurately distinguishing ancient cast iron and block ironmaking products is obtained, and large-scale popularization and application are facilitated.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Equipment capable of quickly taking out iron products in decoration waste
The invention discloses equipment capable of quickly taking out iron products in decoration waste. The equipment comprises a separator, the separator is internally provided with an input cavity, a rotating mechanism can smash the decoration waste into small blocks, so that subsequent treatment is facilitated, a fishing mechanism is arranged on the right side of the rotating mechanism, a long cavity with a leftward opening is formed in the right end wall of the input cavity, a transmission mechanism is arranged on the lower side of the fishing mechanism, the transmission mechanism can fish outthe waste, sinking in water, in the decoration waste and take out the iron products for simple classification, the equipment is easy to operate, after a certain amount of water is added into the equipment, the equipment is started, the decoration waste is put into the equipment, after the decoration waste is smashed, the decoration waste falls into the water, light objects float on the water, theiron products and other heavy objects sink to the water bottom, through the equipment, the light objects floating on the water can be fished out, and the heavy objects can be divided into two kinds, namely non-iron products and the iron products after being conveyed by a conveying belt.
Owner:PUJIANG CIFANG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
A device capable of taking out iron products in decoration waste
The invention discloses equipment capable of quickly taking out iron products in decoration waste. The equipment comprises a separator, the separator is internally provided with an input cavity, a rotating mechanism can smash the decoration waste into small blocks, so that subsequent treatment is facilitated, a fishing mechanism is arranged on the right side of the rotating mechanism, a long cavity with a leftward opening is formed in the right end wall of the input cavity, a transmission mechanism is arranged on the lower side of the fishing mechanism, the transmission mechanism can fish outthe waste, sinking in water, in the decoration waste and take out the iron products for simple classification, the equipment is easy to operate, after a certain amount of water is added into the equipment, the equipment is started, the decoration waste is put into the equipment, after the decoration waste is smashed, the decoration waste falls into the water, light objects float on the water, theiron products and other heavy objects sink to the water bottom, through the equipment, the light objects floating on the water can be fished out, and the heavy objects can be divided into two kinds, namely non-iron products and the iron products after being conveyed by a conveying belt.
Owner:PUJIANG CIFANG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
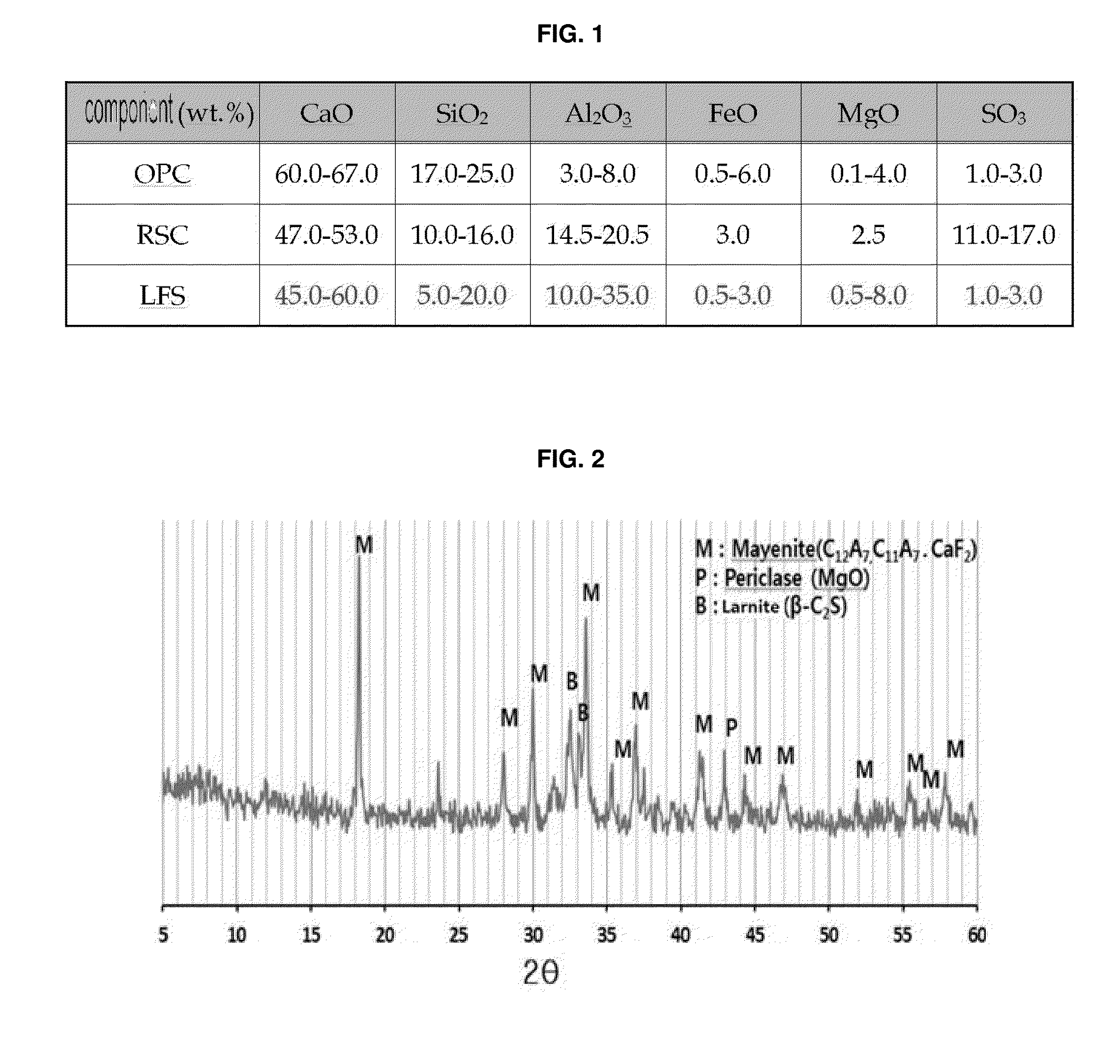
Hydraulic binder composition using rapidly-cooled steelmaking reduced slag powder, and method of preparing the same
Disclosed are a hydraulic binder composition using rapidly-cooled steelmaking reduced slag powder and a method of preparing the same. More particularly, the rapidly-cooled steelmaking reduced slag (RC-LFS) powder is obtained by spraying and scattering gas at a high pressure and high speed onto electric furnace smelting reduction slag, which is one of the by-products generated during iron smelting performed in an ironworks, and quickly cooling and pulverizing the slag. The initial high hydration heat reaction and initial setting of the rapidly-cooled steelmaking reduced slag (RC-LFS) powder are delayed to ensure workability. A retardant and gypsum are mixed into the rapidly-cooled steelmaking reduced slag (RC-LFS) powder so as to activate the generation of needle-shaped ettringite and to thus develop the initial and long-term strength, and therefore the rapidly-cooled steelmaking reduced slag (RC-LFS) powder of the present invention can be used as a substitute for ordinary Portland cement.
Owner:KIM JIN MAN
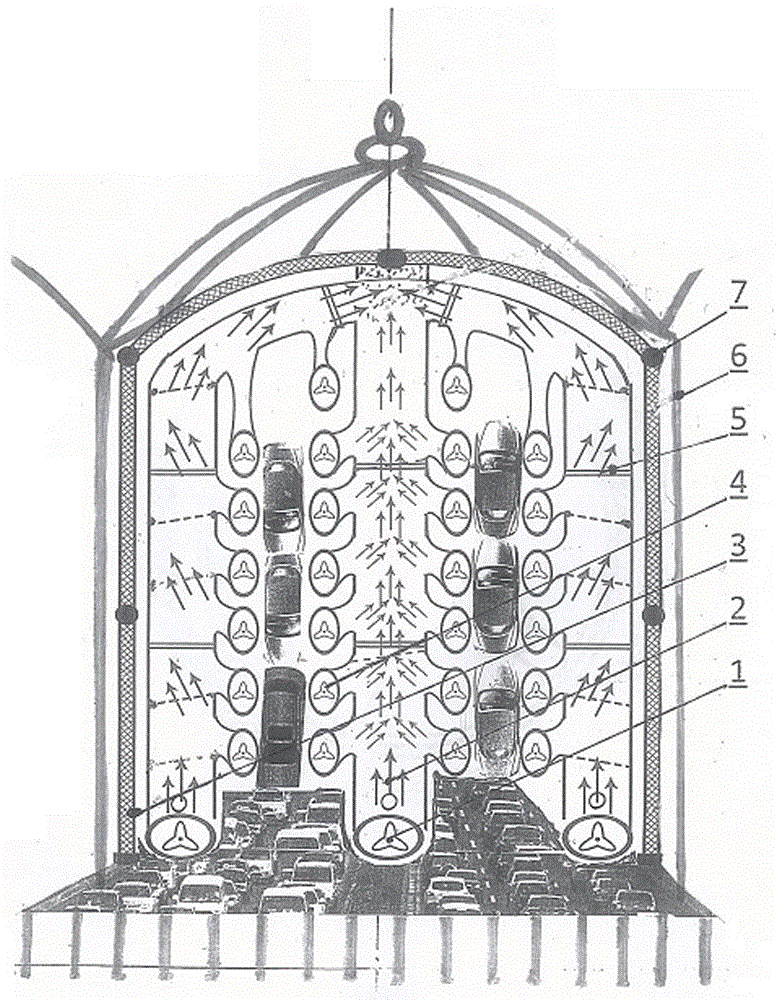
Absorption and water solution flushing and purifying ventilator for chimneys, workshops, shaft pollution and intersection tail gas
InactiveCN106731353AEliminate infectious diseasesPractical appearanceGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentFertilizer plantOxygen
The invention relates to environmental protection equipment, and provides an absorption and water solution flushing and purifying ventilator for chimneys, workshops, shaft pollution and intersection tail gas, comprising a shed-shaped suction hood, wherein a plurality of vertical column type suction machines are arranged in the suction hood, a plurality of suction fans are arranged on the suction machines, the suction machines are connected with waste gas channels at the top, the waste gas channels laterally expand for laterally communicating the suction machines with each other, the tail ends of the waste gas channels are communicated with a purification tank; the purification tank contains a purification solution at the bottom, a waste gas storage cavity is arranged above the purification solution, a plurality of spraying layers are arranged above in sequence, and the purification solution is sprayed from top to bottom through a spraying machine. The ventilator can be arranged in various ironworks, fertilizer plants, cement plants, power plants and large-scale manufacturing and installation workshops for eliminating pollutant dust and noxious gas; and because 80% of carbon compounds, 60% of carbon monoxide and 30% of compounds of nitrogen and oxygen are from the automotive tail gas, the ventilator can be safely and flexibly used in intersections in the wind and rain.
Owner:孙田梓 +1
A Discrimination Method of Ancient Cast Iron and Block Iron Products
ActiveCN112986302BFar-reaching research valueAccurate discriminationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNon-metallic inclusionsAlloy
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for discriminating ancient cast iron and block iron products, which belongs to the technical field of discriminating methods for ancient iron and steel products. The discrimination method includes two parts: metallographic analysis of ancient cast iron and block iron-making products and non-metallic inclusion analysis; wherein: metallographic analysis is aimed at distinguishing the difference in room temperature equilibrium structure of ancient cast iron and block iron-making products, not Metal inclusion analysis is aimed at the quantity, composition, morphology and distribution of non-metallic inclusions in ancient cast iron and block ironworks. The present invention obtains a method for accurately discriminating ancient cast iron and lump iron-making products through synergistic analysis of alloy phase structure and inclusions, which is beneficial to large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com