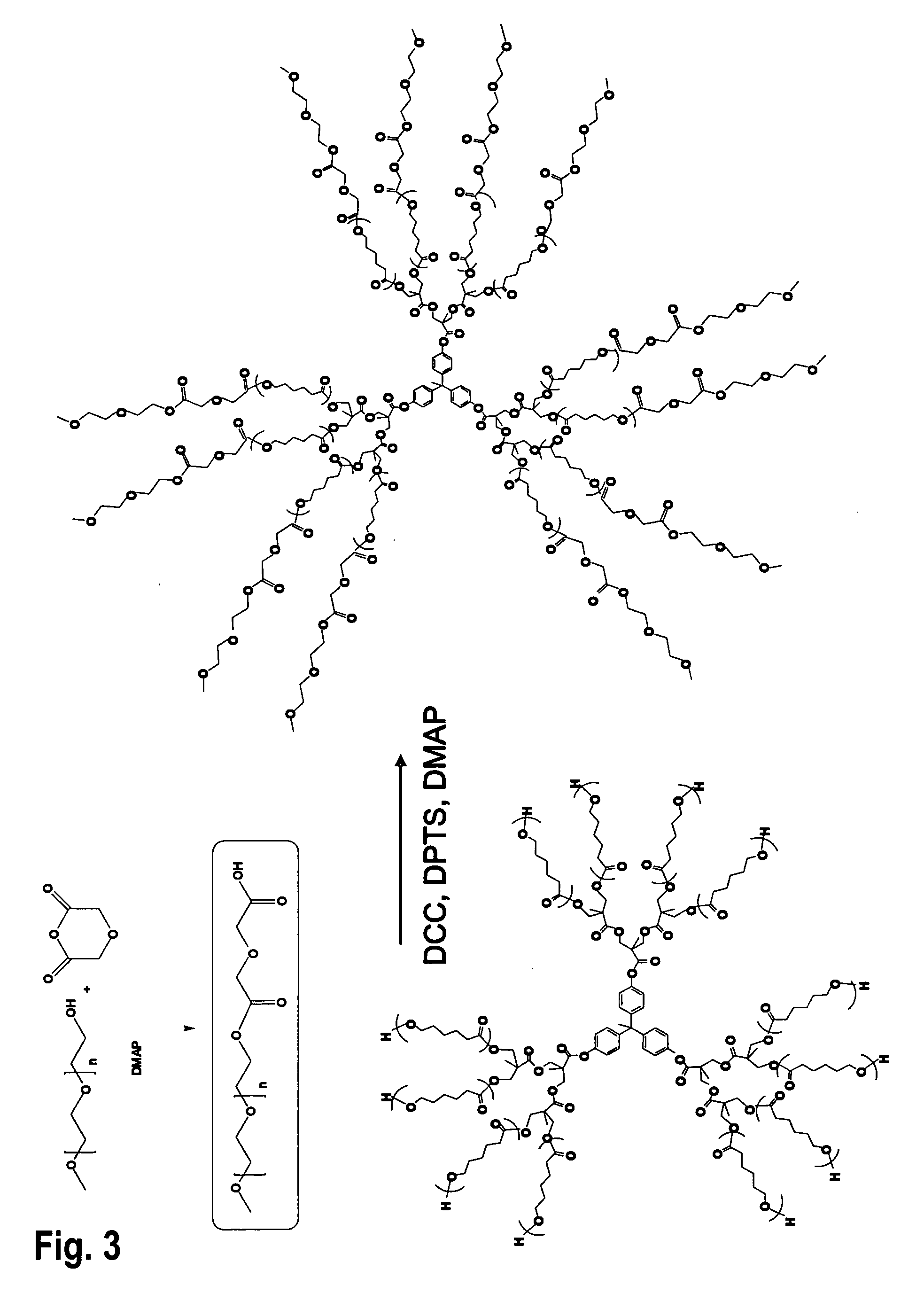
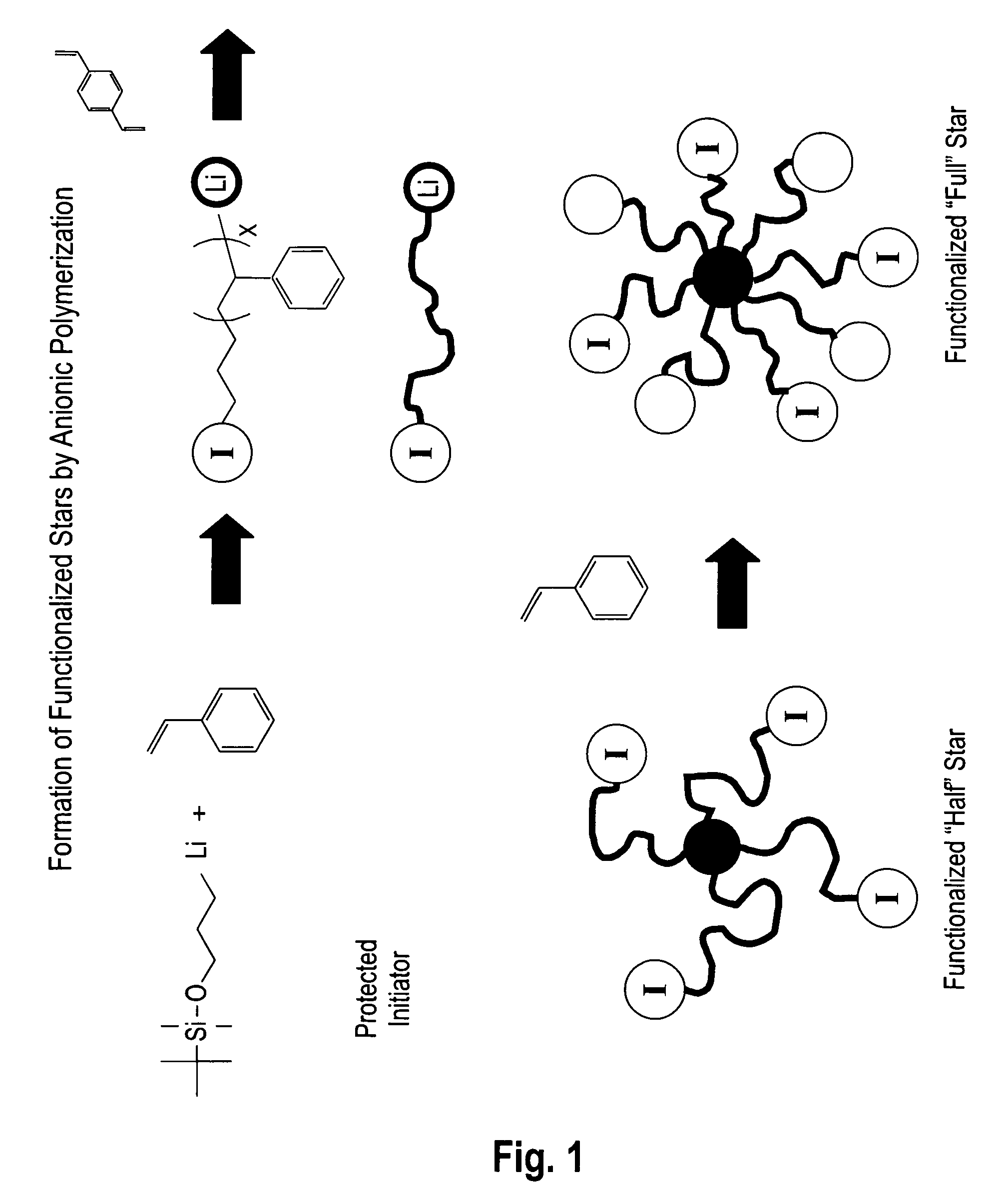
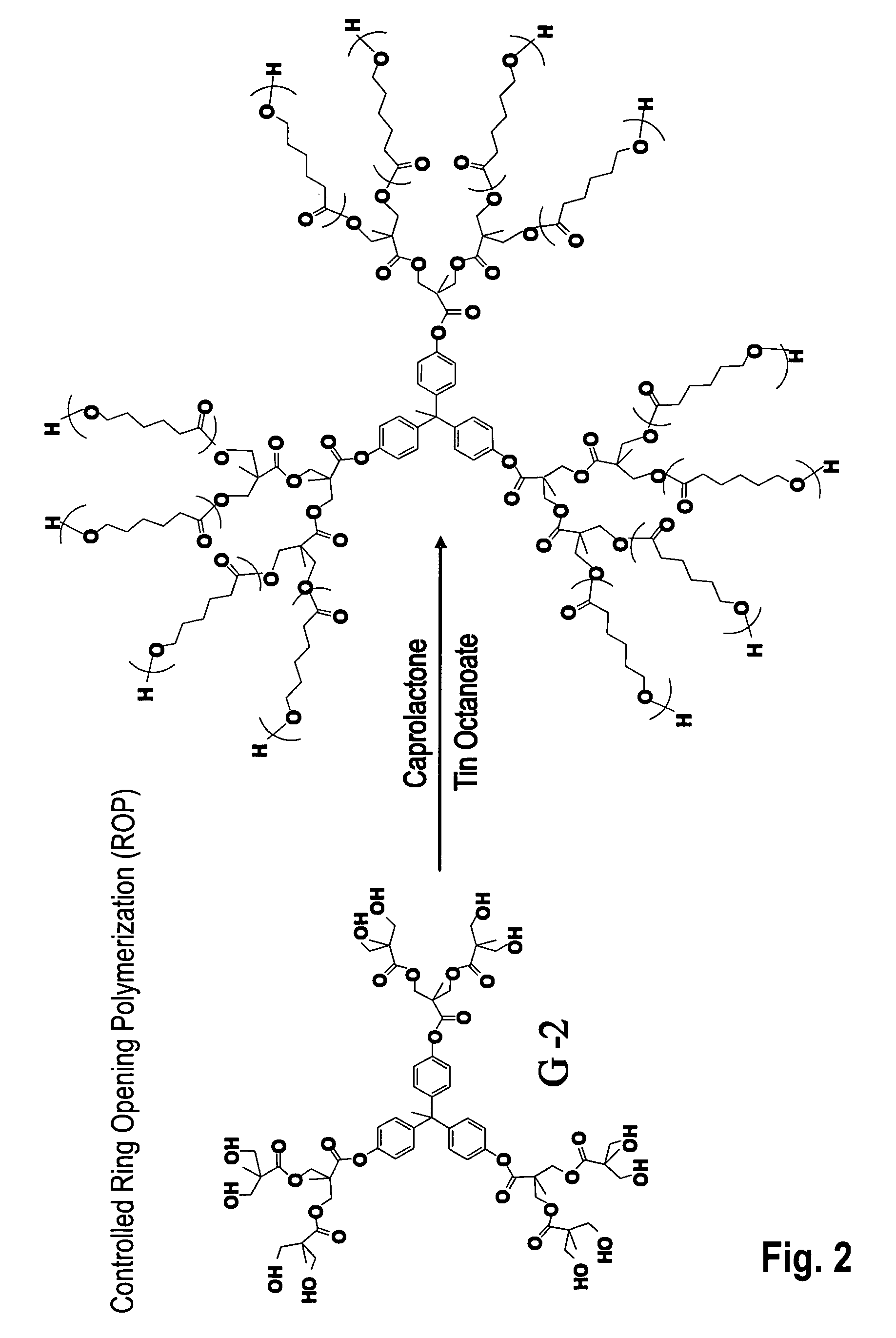
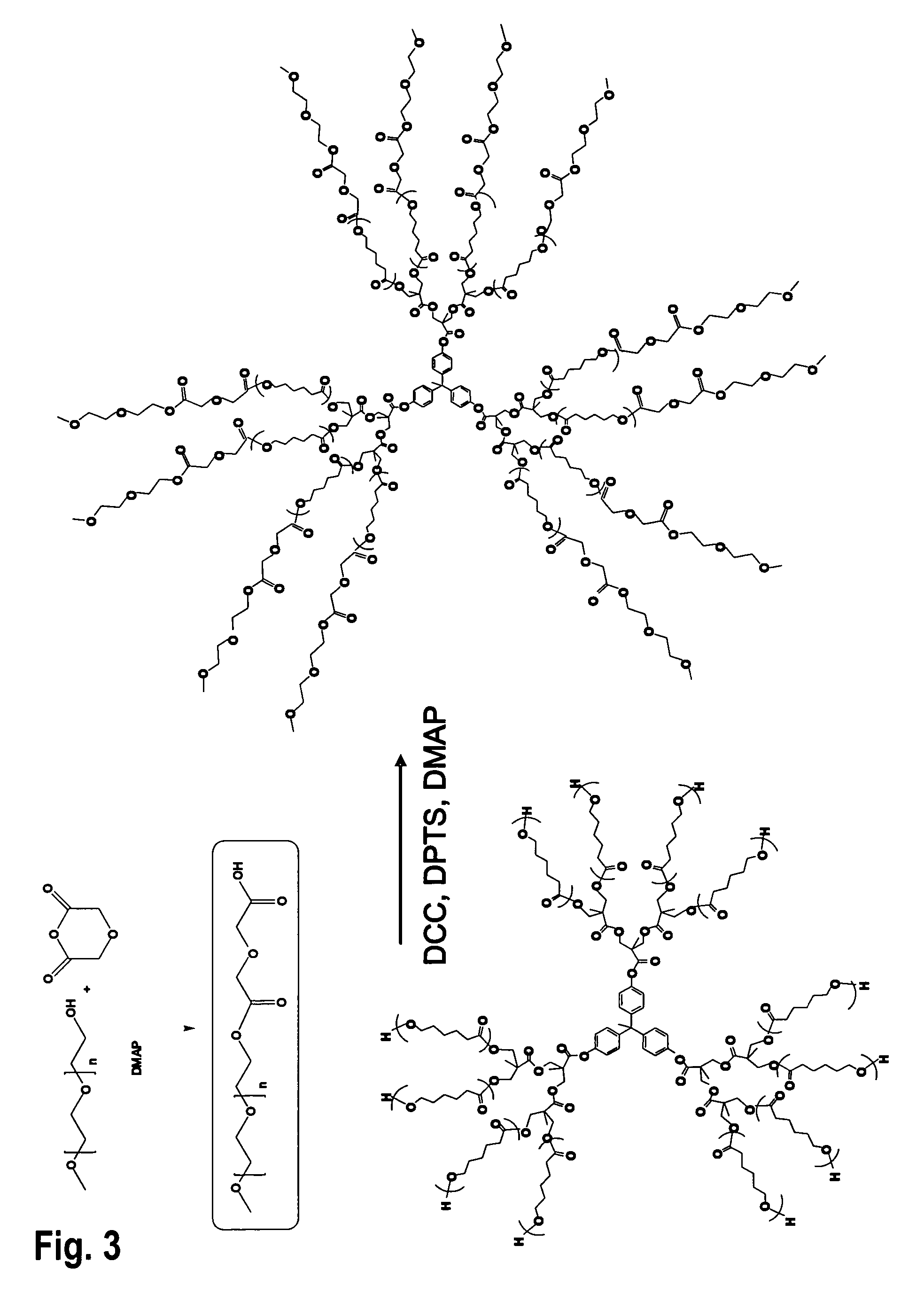
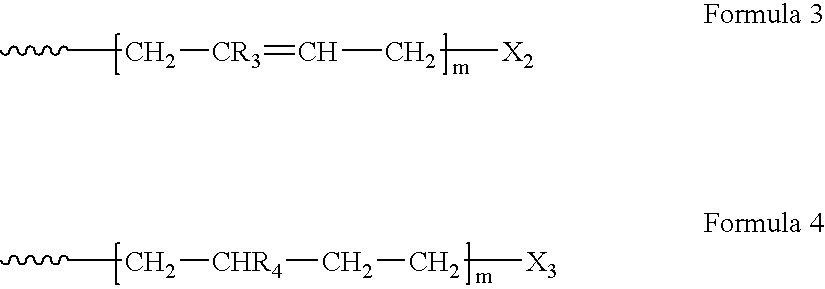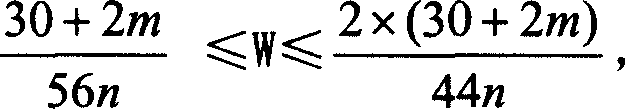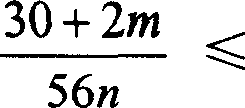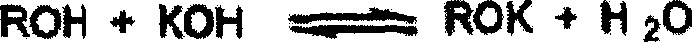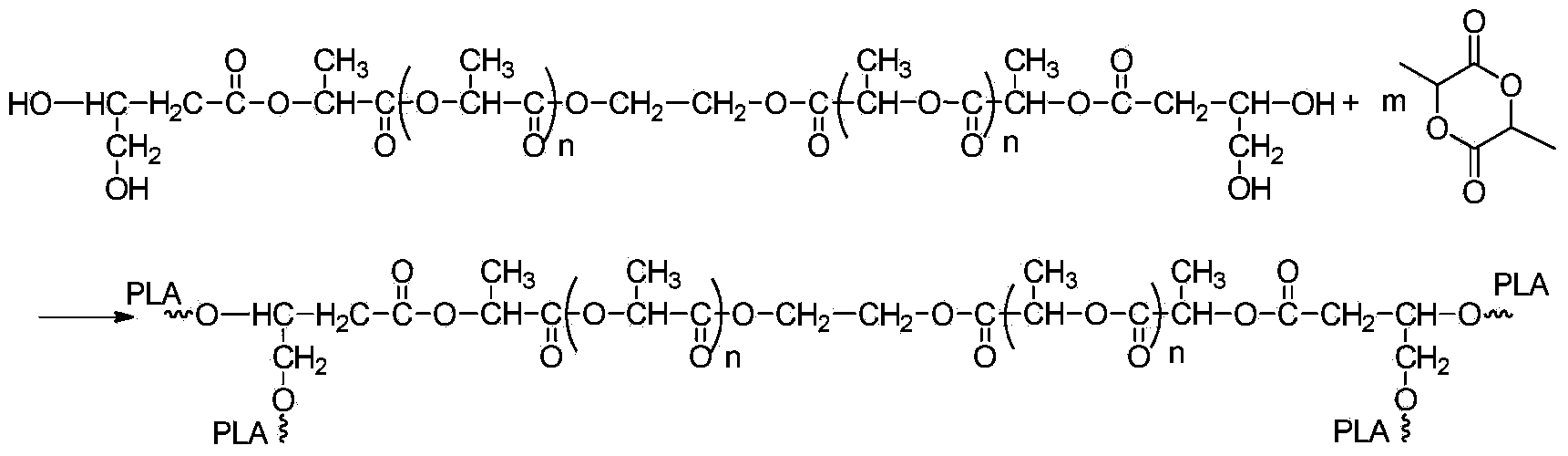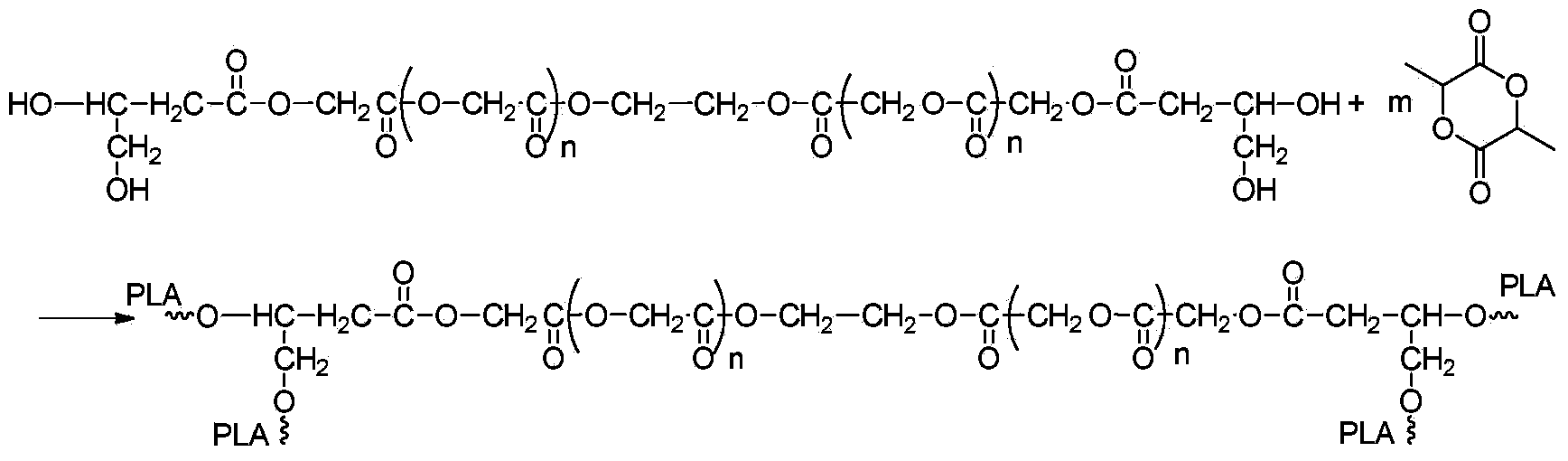Patents
Literature
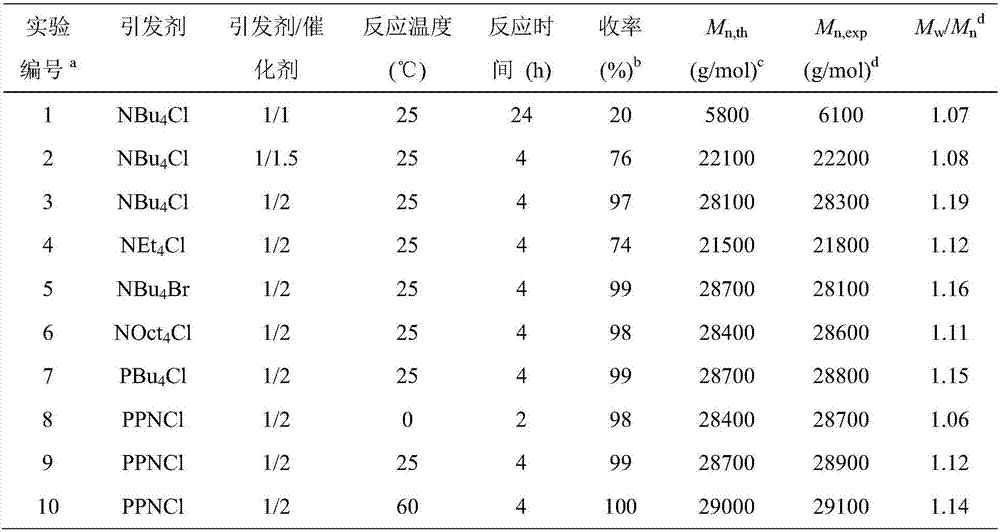
60 results about "Living anionic polymerization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
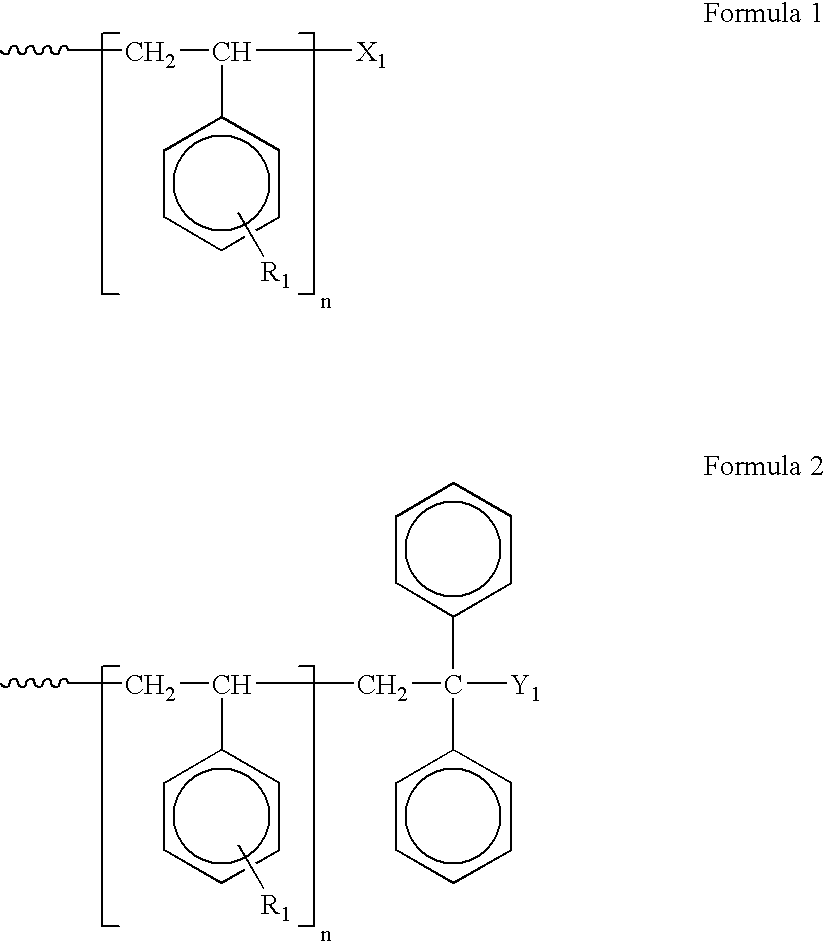
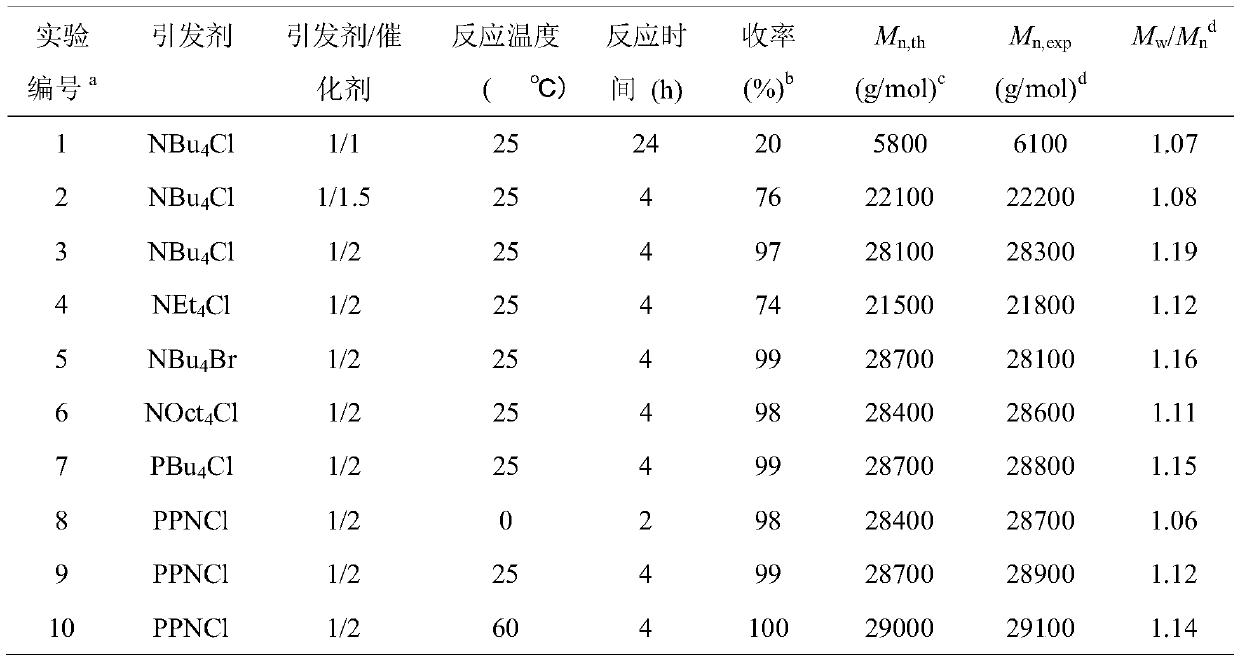
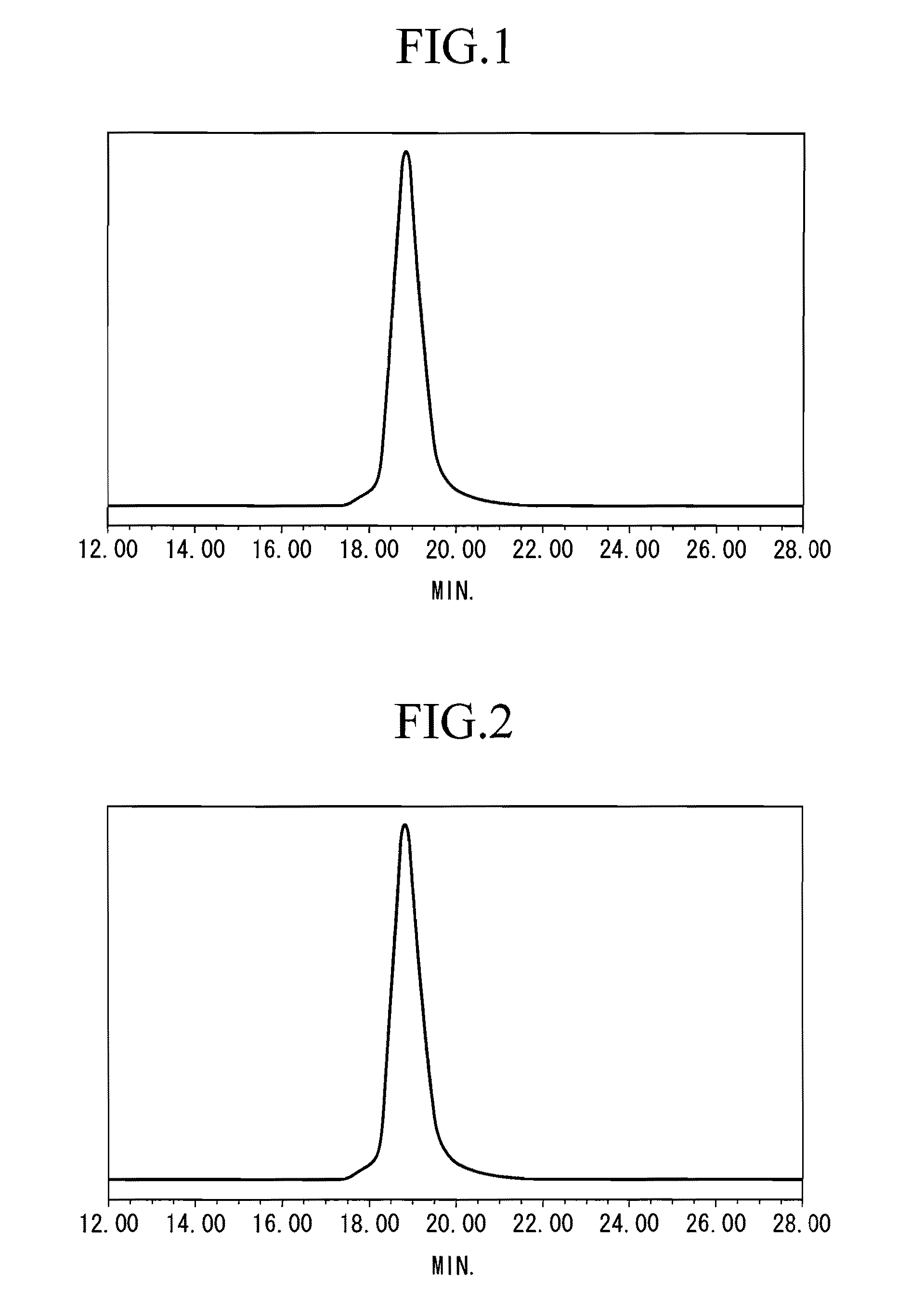
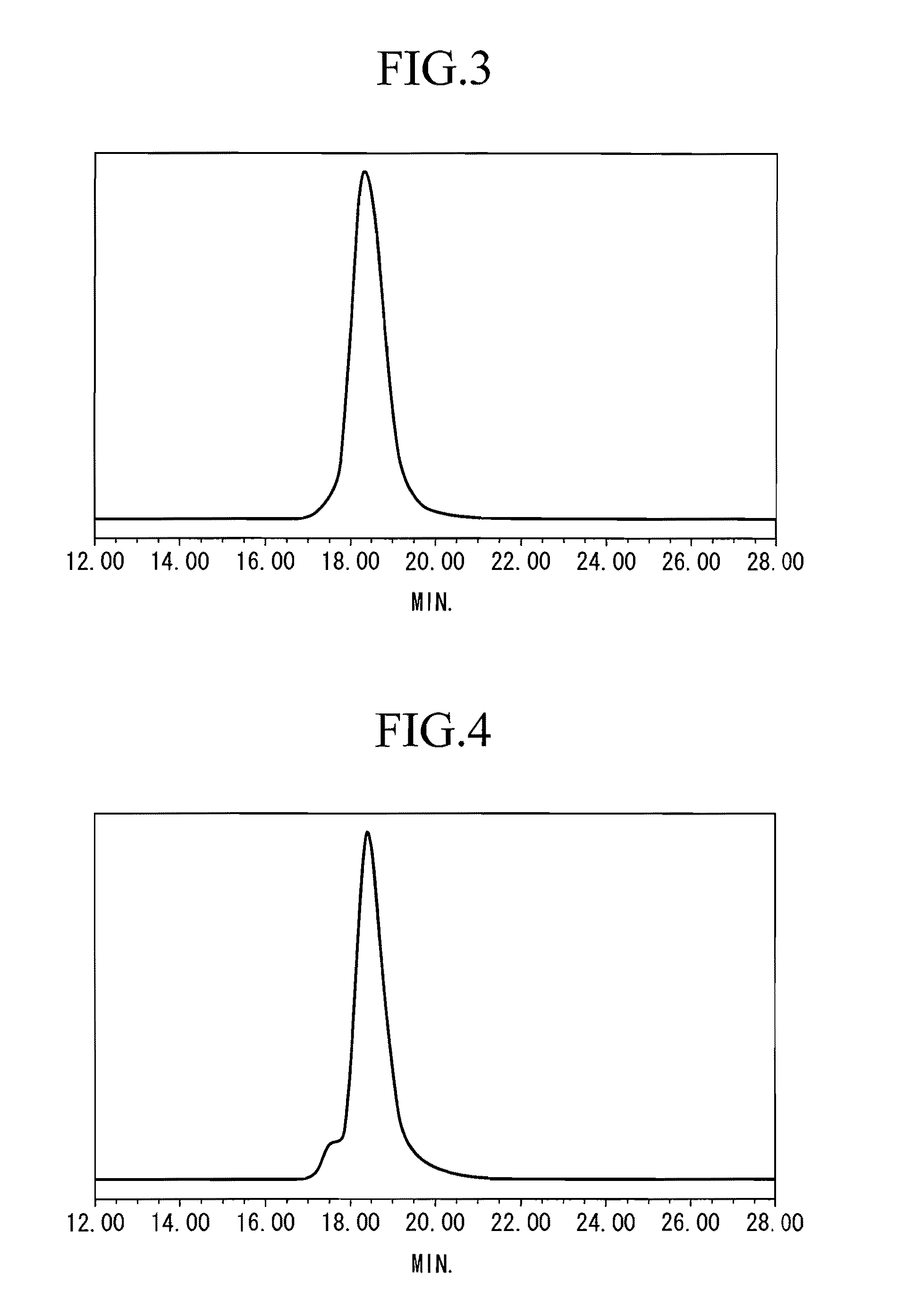
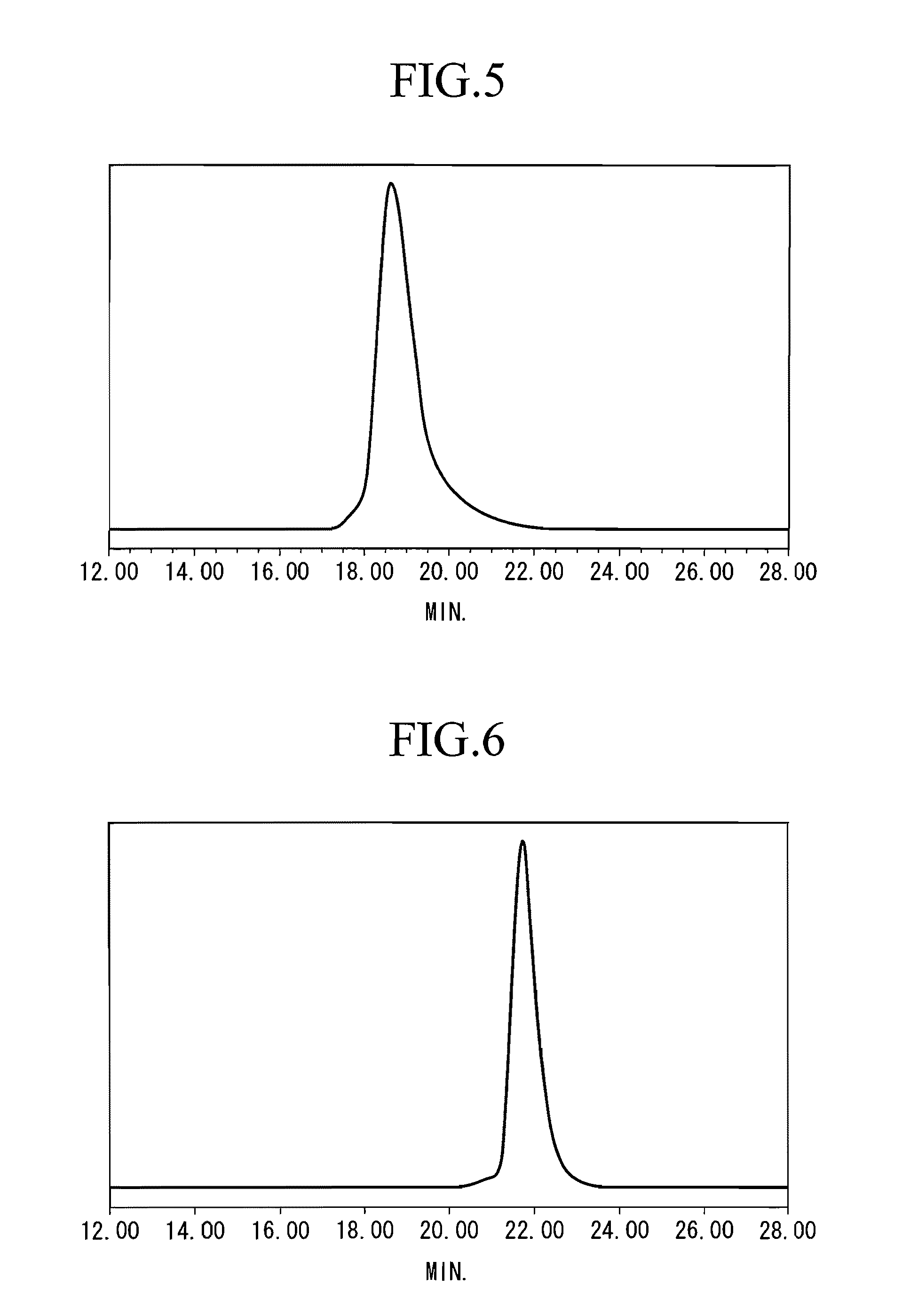
Living anionic polymerization is a living polymerization technique involving an anionic propagating species. Living anionic polymerization was demonstrated by Szwarc and co workers in 1956. Their initial work was based on the polymerization of styrene and dienes. One of the remarkable features of living anionic polymerization is that the mechanism involves no formal termination step. In the absence of impurities, the carbanion would still be active and capable of adding another monomer. The chains will remain active indefinitely unless there is inadvertent or deliberate termination or chain transfer. This gave rise to two important consequences: The number average molecular weight, Mₙ, of the polymer resulting from such a system could be calculated by the amount of consumed monomer and the initiator used for the polymerization, as the degree of polymerization would be the ratio of the moles of the monomer consumed to the moles of the initiator added. , where Mₒ = formula weight of the repeating unit, [M]ₒ = initial concentration of the monomer, and [I] = concentration of the initiator. All the chains are initiated at roughly the same time.
Fabric care composition comprising an epichlorohydrin resin and anionic polymer
InactiveUS6846797B1Improve transmission performanceImprove decontamination abilityOrganic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsAnionic polymersEpichlorohydrin
Fabric care compositions adapted for use in a laundering process such as detergent compositions and laundry rinse compositions, comprise at least one reactive cationic polymer (preferably amine- or amide-epichlorohydrin resin or a derivative thereof), at least one reactive anionic polymer and at least one textile compatible carrier. The compositions have improved dye transfer and stain release properties and may be used in methods of treating fabric as part of a laundering process.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Nano-sized metals or metal salts stabilized by using chain-end functionalized polymers and their synthetic methods
ActiveUS7319127B2Easy to manufactureMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufacturePolymer scienceSynthesis methods
Disclosed are nano-sized metals and metal salts stabilized by using semi-telechelic and telechelic polymers prepared through living anionic polymerization, and their synthetic methods, and a nanostructure wherein the nano-sized particles are self-assembled by mixing block copolymers and film-casting. The present invention provides a new method for preparing nano-sized particles capable of easily accomplishing nanostructure by merely mixing, especially with block copolymers, and having excellent stability.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH +1
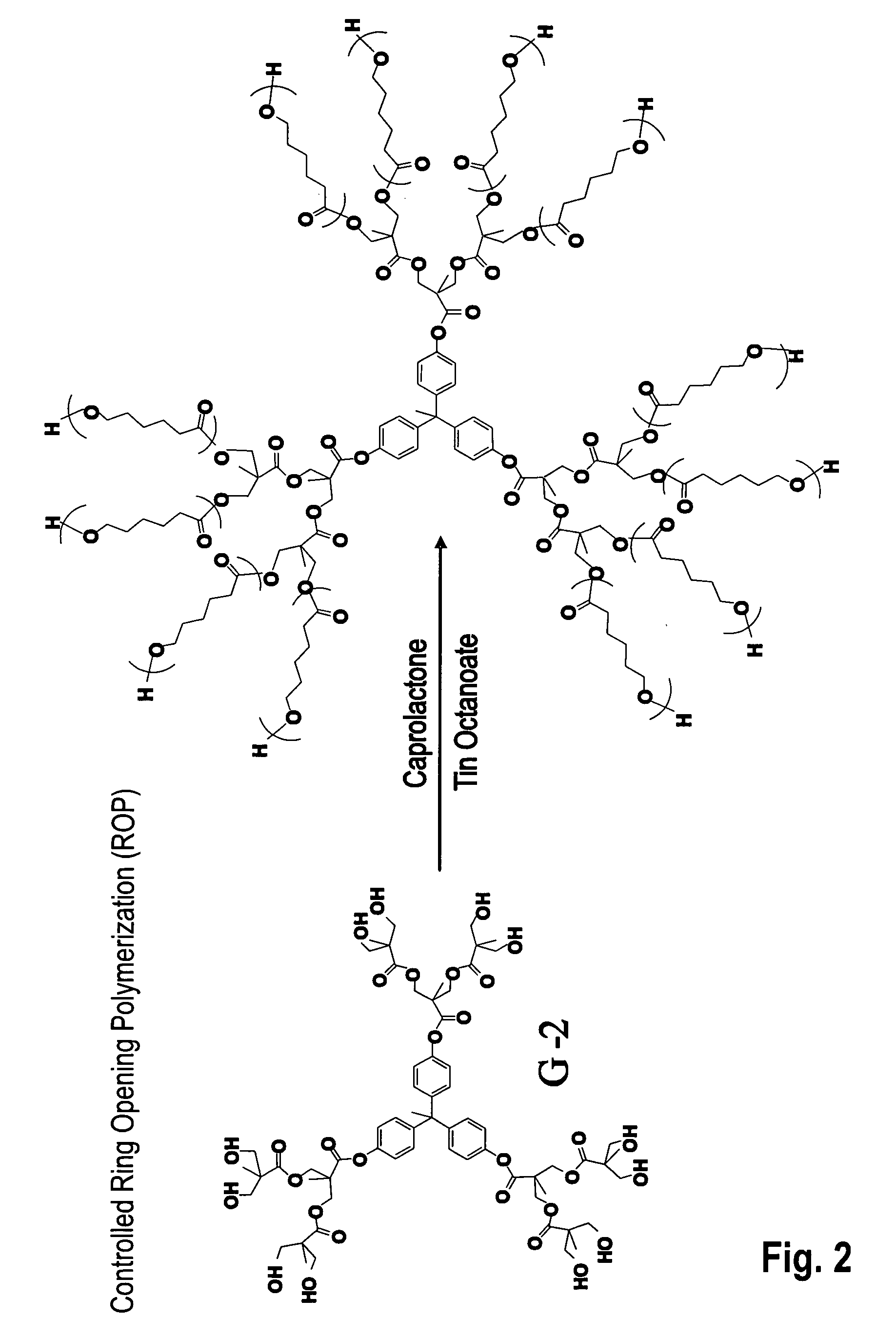
Surface-decorated polymeric amphiphile porogens for the templation of nanoporous materials
A nanoparticle which includes a multi-armed core and surface decoration which is attached to the core is prepared. A multi-armed core is provided by any of a number of possible routes, exemplary preferred routes being living anionic polymerization that is initiated by a reactive, functionalized anionic initiator and ε-caprolactone polymerization of a bis-MPA dendrimer. The multi-armed core is preferably functionalized on some or all arms. A coupling reaction is then employed to bond surface decoration to one or more arms of the multi-armed core. The surface decoration is a small molecule or oligomer with a degree of polymerization less than 50, a preferred decoration being a PEG oligomer with degree of polymerization between 2 and 24. The nanoparticles (particle size ≦10 nm) are employed as sacrificial templating porogens to form porous dielectrics. The porogens are mixed with matrix precursors (e.g., methyl silsesquioxane resin), the matrix vitrifies, and the porogens are removed via burnout. Greater porosity reduces the dielectric constant k of the resulting dielectrics. The porous dielectrics are incorporated into integrated circuits as lower k alternatives to silicon dioxide.
Owner:IBM CORP
Coupled radial anionic polymers
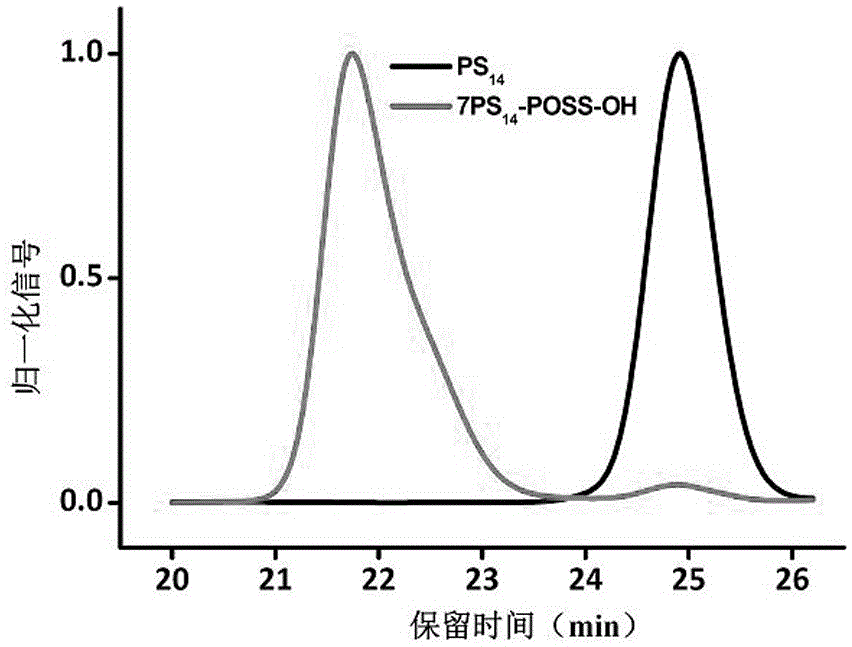
The present invention is a coupled radial anionic polymer comprising a polyhedral oligosilsesquioxane [POSS] of the formula [R—SiO3 / 2]n. POSS compounds having R=vinyl, glycidyldimethyl silyl, and isobutyl have been found effective in coupling anionic living polymers to yield radial polymers having 2 to 10 arms. Radial polymers of the present invention have been formed using POSS octamers and mixtures of POSS octamers, decamers and dodecamers. The present invention also relates to a process for coupling living anionic polymers with POSS compounds.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
Method for preparing terminal carboxyl group polymer through active anionic polymer termination
The invention discloses a method for preparing terminal carboxyl group polymer through active anionic polymer termination, and belongs to the field of anionic polymerization. The method comprises steps as follows: step (1), an active anionic polymer solution is prepared and has the concentration of 5-20g / 100 ml, active anionic polymer comprises homopolymer or copolymer of styrene, butadiene and isoprene; step (2), oxa-cycloalkane is added into the active anionic polymer solution, the mixture reacts for 10-50 minutes at the temperatures ranging from 20 DEG C to 60 DEG C, and a solution of active polymer with an oxygen anion terminal is prepared; and step (3), the solution of active polymer with the oxygen anion terminal is mixed with acid anhydride, the mixture reacts for 20-120 minutes at the temperatures ranging from 20 DEG C to 100 DEG C, and a product is terminated by a methanol solution of HCl or an ethanol solution of HCl. The method is a new terminal carboxyl group functionalization method and is provided for solving problems of excessive side reactions, rigorous reaction conditions and the like of a conventional method for preparing terminal carboxyl group polymer through anionic polymerization; and by means of the method, terminal carboxyl group functionalized polymer with a controllable terminal structure can be obtained under the mild condition, the side reaction is few, and the operation is simple.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Slurry polymerization method for preparing bimodal distribution star-branched butyl rubber by using imino-terminated functionalized macromolecular branching agent
ActiveCN110845650AEnhance the polarity of the molecular chainGood compatibilityPolymer scienceCationic polymerization
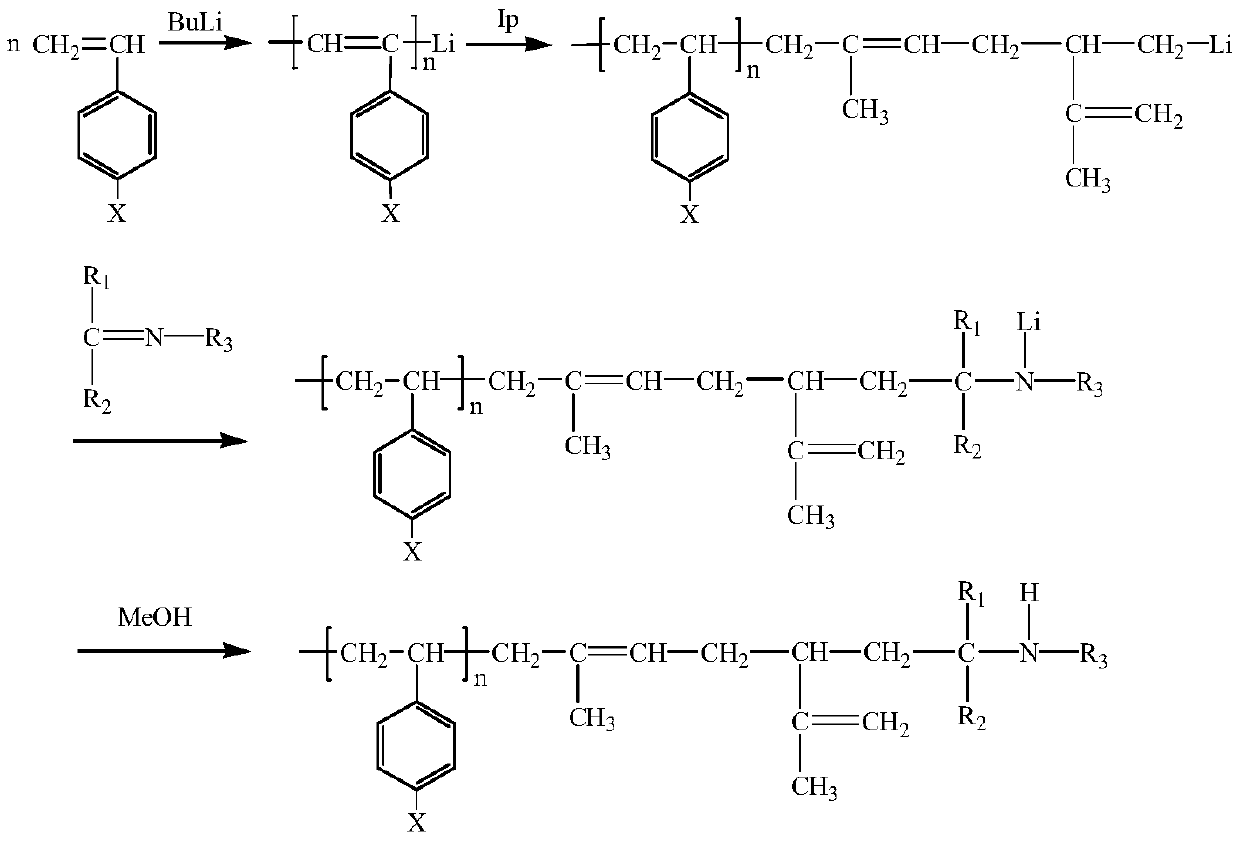
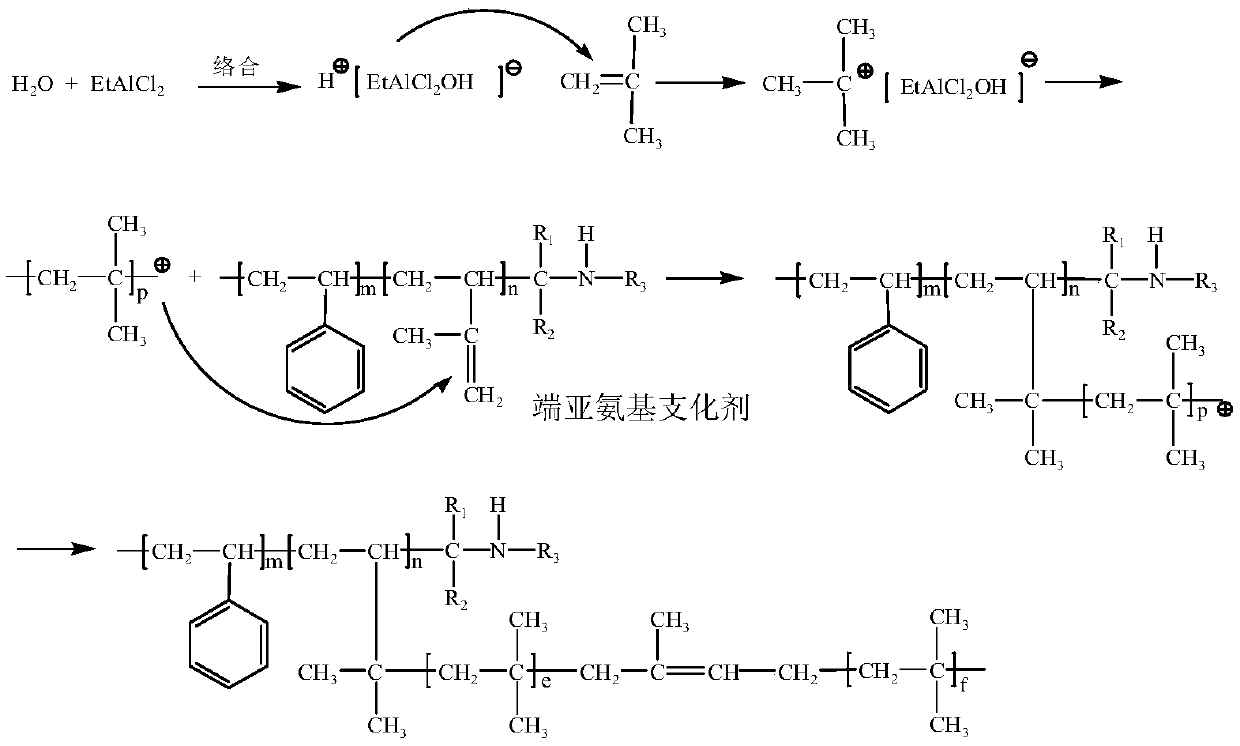
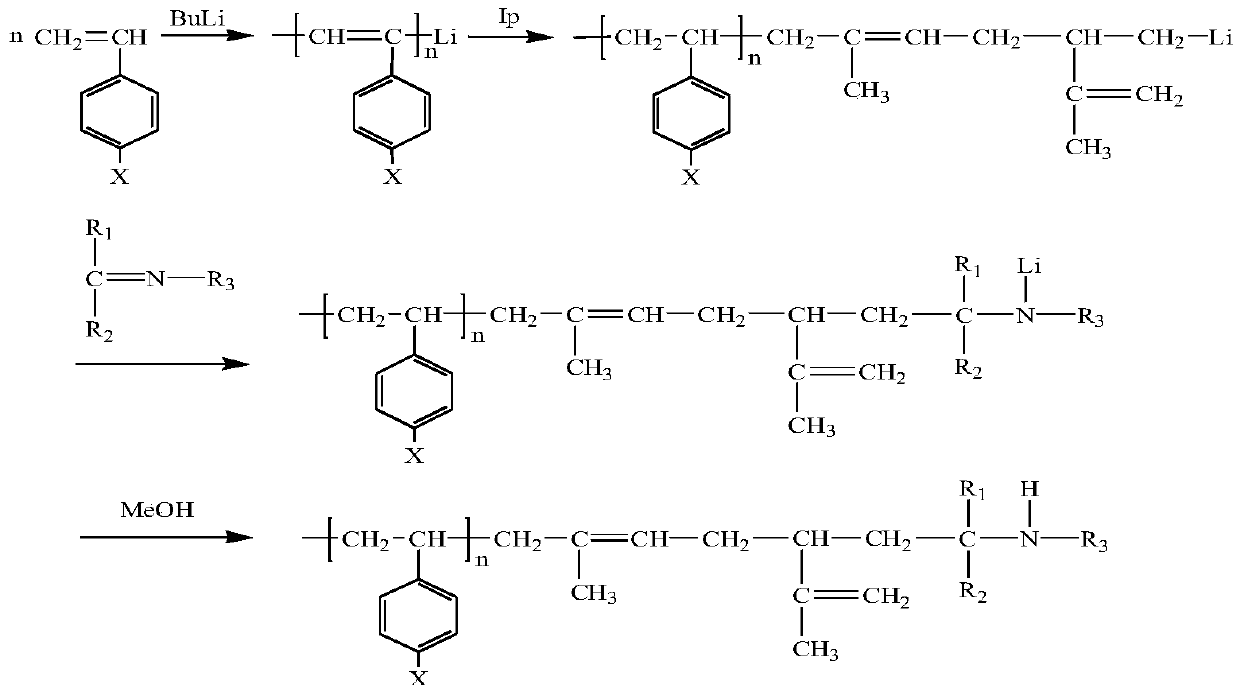
The invention belongs to the technical field of butyl rubber preparation, and relates to a slurry polymerization method for preparing bimodal distribution star-shaped branched butyl rubber by using animino-terminated functionalized macromolecular branching agent. The slurry polymerization method comprises two steps of synthesizing the imino-terminated functionalized macromolecular branching agentand synthesizing the star-branched butyl rubber with amino; a copolymer of styrene and derivatives of styrene, and isoprene is prepared by adopting active anionic polymerization technology, and the imino-containing branching agent macromolecules are obtained by using Schiff base for end capping. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving the branching agent into chloromethane, adding an obtained mixture into a butyl rubber slurry polymerization kettle, and preparing the star-shaped branched butyl rubber with bimodal distribution by taking the branching agent as a cationic polymerization grafting agent and a slurry stabilizer. Lower Mooney stress relaxation and intrinsic viscosity are achieved, and better processability is achieved; the imino groups introduced duringend capping can increase the polarity of the branching agent, so that the dispersion of carbon black in a butyl rubber matrix is facilitated, the compatibility of butyl rubber and carbon black is improved, and the system energy is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
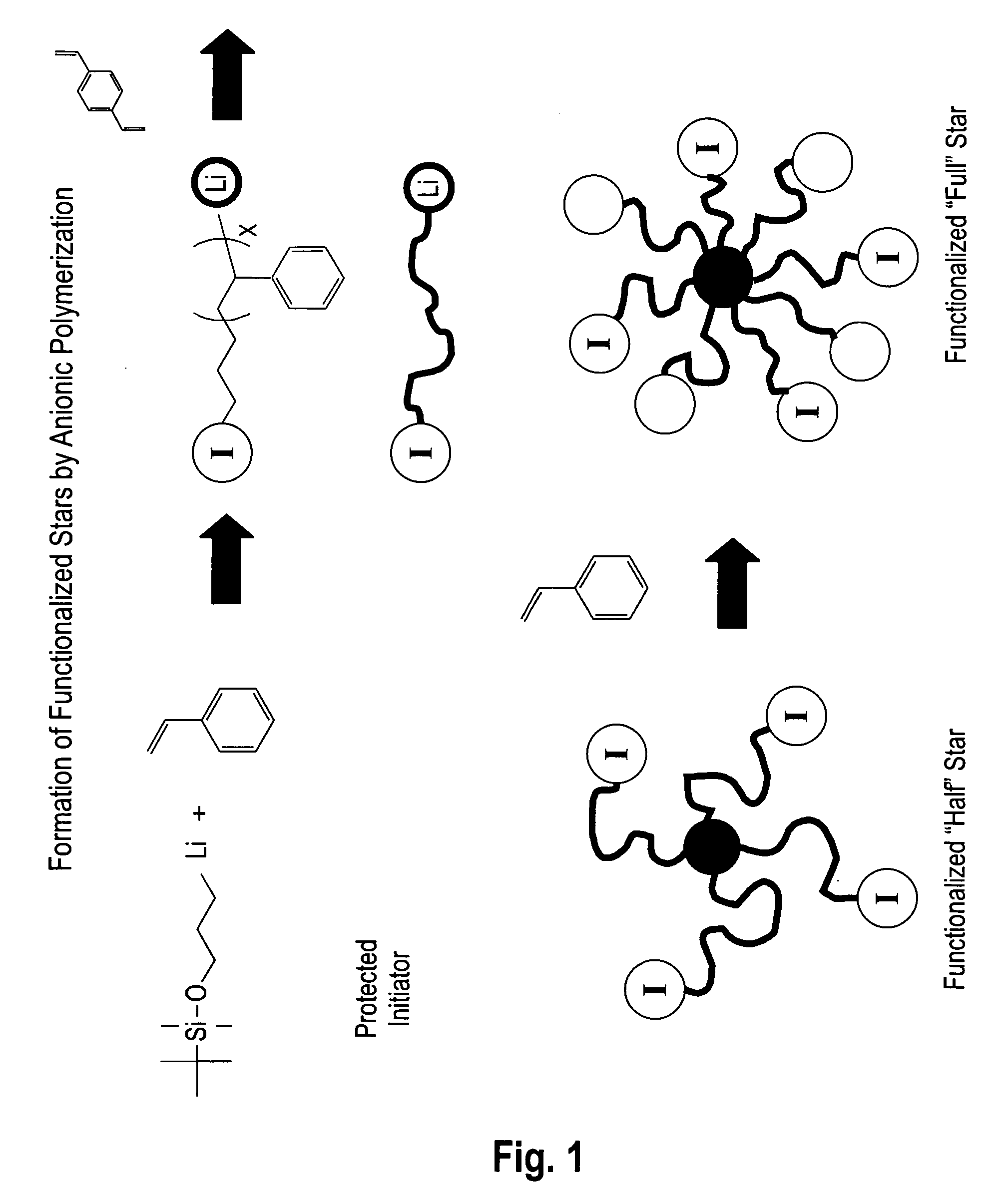
Eight-arm heteroarm star-shaped polymer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of an eight-arm heteroarm star-shaped polymer. A polystyrene lithium compound is synthesized through a living anionic polymerization method, and then subjected to an addition reaction with monohydroxy heptaethylene polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane in benzene to obtain a seven-arm star-shaped polystyrene crude product; slightly excessive low addition products are removed by utilizing a fractional precipitation method, thus pure monohydroxy functional seven-arm star-shaped polystyrene can be obtained, and hydroxyls of the pure monohydroxy functional seven-arm star-shaped polystyrene are subjected to azide modification to obtain seven-arm star-shaped polystyrene containing azide groups. On the other hand, polycaprolactone, polyethylene glycol, polymethylacrylic acid-N, N-dimethylamino ethyl ester, and tert-butyl methacrylate of which the ends contain alkynyls are respectively synthesized, and subjected to cycloaddition reaction with alkynyls and azides at the generating end of the seven-arm star-shaped polystyrene containing the azide groups to obtain the product; the method has the characteristics of high reaction efficiency, mild reaction conditions and few side reactions. The star-shaped polymer prepared by the invention is controllable in structure and molecular weight, and relatively narrow in molecular weight distribution.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Coupled radial anionic polymers
The present invention is a coupled radial anionic polymer comprising a polyhedral oligosilsesquioxane [POSS] of the formula [R—SiO3 / 2]n. POSS compounds having R=vinyl, glycidyldimethyl silyl, and isobutyl have been found effective in coupling anionic living polymers to yield radial polymers having 2 to 10 arms. Radial polymers of the present invention have been formed using POSS octamers and mixtures of POSS octamers, decamers and dodecamers. The present invention also relates to a process for coupling living anionic polymers with POSS compounds.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
Radiation-ray sensitive composition for colour-filtering piece, colour filtering piece and colour liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN1677138AExcellent adhesionGood storage stabilityOrganic chemistryOptical filtersLiquid-crystal displayAcid value
The present invention provides a radiation sensitive composition for a color filter comprising (A) a pigment, (B) a dispersant, (C) an alkali-soluble resin, (D) a polyfunctional monomer, (E) a photopolymerization initiator and (F) a solvent, wherein the dispersant (B) comprises an acrylic copolymer obtained through living anionic polymerization and having an amine value (unit; mgKOH / g) and an acid value (unit; mgKOH / g) each greater than 0.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Catalyst system for preparing polyether material for aviation
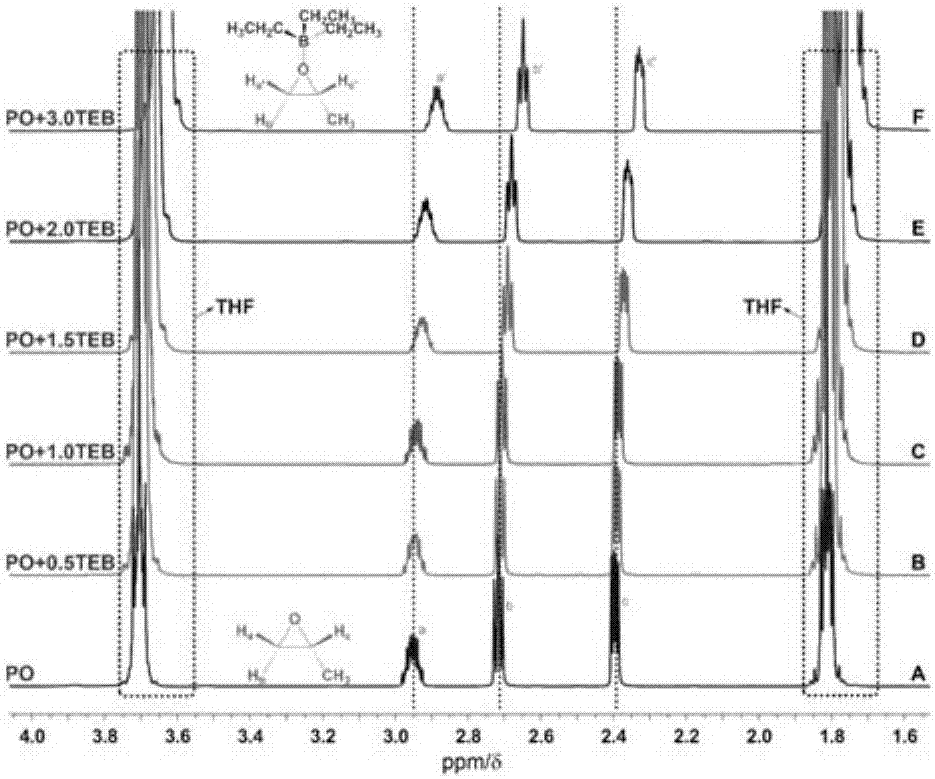
The invention provides a boron alkyl-halogenated onium salt system and an application thereof in living polymerization of epoxy monomers and belongs to the field of an epoxy resin. An epoxy monomer active anion controllable polymerization reaction system provided by the invention contains an initiator, a catalyst, a solvent and epoxy monomers, wherein the halogenated quaternary ammonium salt or halogenated quaternary phosphor salt is taken as the initiator and the boron alkyl is taken as the catalyst. The epoxy monomer polymerization system provided by the invention is capable of efficiently triggering the epoxy monomer controllable anionic polymerization reaction under the conditions of shorter period and room temperature. An epoxypropane / ethane polymer prepared according to the system provided by the invention can be applied to the additives of aviation chemical products.
Owner:THE SECOND RES INST OF CIVIL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION OF CHINA
Detersive compositions containing hydrophobic benefit agents pre-emulsified using sub-micrometer-sized insoluble cationic particles
InactiveUS7569533B2Improve stabilityIncrease depositionInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsPolymer scienceOil emulsion
A cationic oil-in-water emulsion, for addition to detersive compositions, comprising hydrophilic cationic polymers, a surface-active, anionic polymer that is capable of adsorbing at an air-water interface or an oil-water interface and / or is oil-soluble, and a hydrophobic benefit agent in the oil phase made by adding the benefit agent to a hydrophobic liquid; thickening the oil phase with an organophillic smectite clay reacted at clay platelet surfaces to make the clay platelet surfaces hydrophobic while the edge surfaces of the clay remain hydrophilic, such that the organophillic smectite clay is adsorbed at an oil / water interface in the emulsion, and one of the hydrophilic, cationic polymers has a cationic nitrogen content of at least 6% by weight, that is incompatible with anionic surfactants, being insoluble in anionic-surfactant solutions containing an amount of 3% or higher of an anionic surfactant, and another hydrophilic cationic polymer has a cationic nitrogen content of at least 0.1% by weight and has a molecular weight of at least 600,000 Dalton.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Circular polymer and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a circular polymer and a preparation method thereof. The active anion polymerizing and end-capping techniques and the ring-opening polymerization (ROP) are adopted to synthesize a linear polymer with hydroxyls at both ends; sodium hydride (NaH) and propine bromide are adopted to modify chain-end hydroxyls into propargyls; the ROP is adopted to synthesize a linear polymer which is polycaprolactone (PCL) with hydroxyls at both ends; the propiolic acid is adopted to modify chain-end hydroxyls into propargyls; the atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) is adopted to synthesize linear polymer with bromine-based group at two ends; the nitrogen-oxygen free radical compound containing propargyls is adopted to modify chain-end bromine-based groups into propargyls; and the Glaser coupling reaction of the propargyls is adopted to synthesize the circular polymer in the presence of cuprous bromide (CuBr) and N, N, N', N'' and N''-pentamethyl diethylenetriamine (PMDETA).
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Hydrogenated block copolymer and composition containing same
The present invention provides a thermoplastic elastomer composition having excellent fluidity, compression set and flexibility, and a block copolymer which provides the thermoplastic elastomer composition. Specifically disclosed is a hydrogenated block copolymer obtained by hydrogenating a block copolymer which is obtained by reacting a living polymer represented by formula (1): B1-A-B2-X (wherein B1 and B2 each represents a polymer block mainly composed of a structural unit derived from a conjugated diene compound; A represents a polymer block mainly composed of a structural unit derived from a vinyl aromatic compound; and X represents an active end of the living anionic polymer) with a coupling agent. The mass of the polymer block B1 before the hydrogenation reaction relative to the total mass of the polymer blocks B1 and B2 is within the range of 0.10-0.45, and the contained amount of the structural unit derived from a vinyl aromatic compound relative to the mass of the hydrogenated block copolymer is within the range of 25-50% by mass.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Surface-decorated polymeric amphiphile porogens for the templation of nanoporous materials
A nanoparticle which includes a multi-armed core and surface decoration which is attached to the core is prepared. A multi-armed core is provided by any of a number of possible routes, exemplary preferred routes being living anionic polymerization that is initiated by a reactive, functionalized anionic initiator and ε-caprolactone polymerization of a bis-MPA dendrimer. The multi-armed core is preferably functionalized on some or all arms. A coupling reaction is then employed to bond surface decoration to one or more arms of the multi-armed core. The surface decoration is a small molecule or oligomer with a degree of polymerization less than 50, a preferred decoration being a PEG oligomer with degree of polymerization between 2 and 24. The nanoparticles (particle size≦10 nm) are employed as sacrificial templating porogens to form porous dielectrics. The porogens are mixed with matrix precursors (e.g., methyl silsesquioxane resin), the matrix vitrifies, and the porogens are removed via burnout. Greater porosity reduces the dielectric constant k of the resulting dielectrics. The porous dielectrics are incorporated into integrated circuits as lower k alternatives to silicon dioxide.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for producing block copolymer, and block copolymer obtained using same
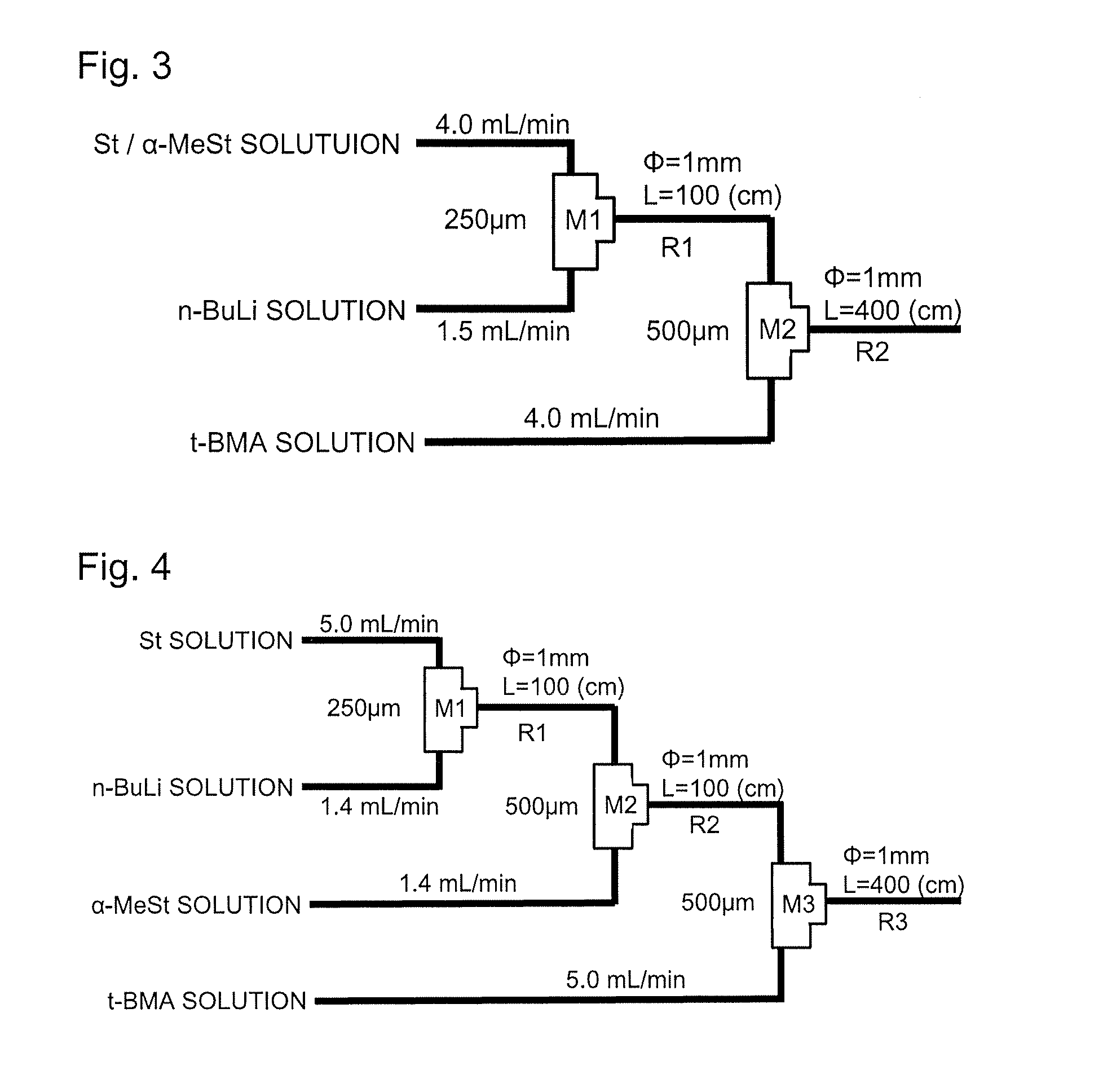
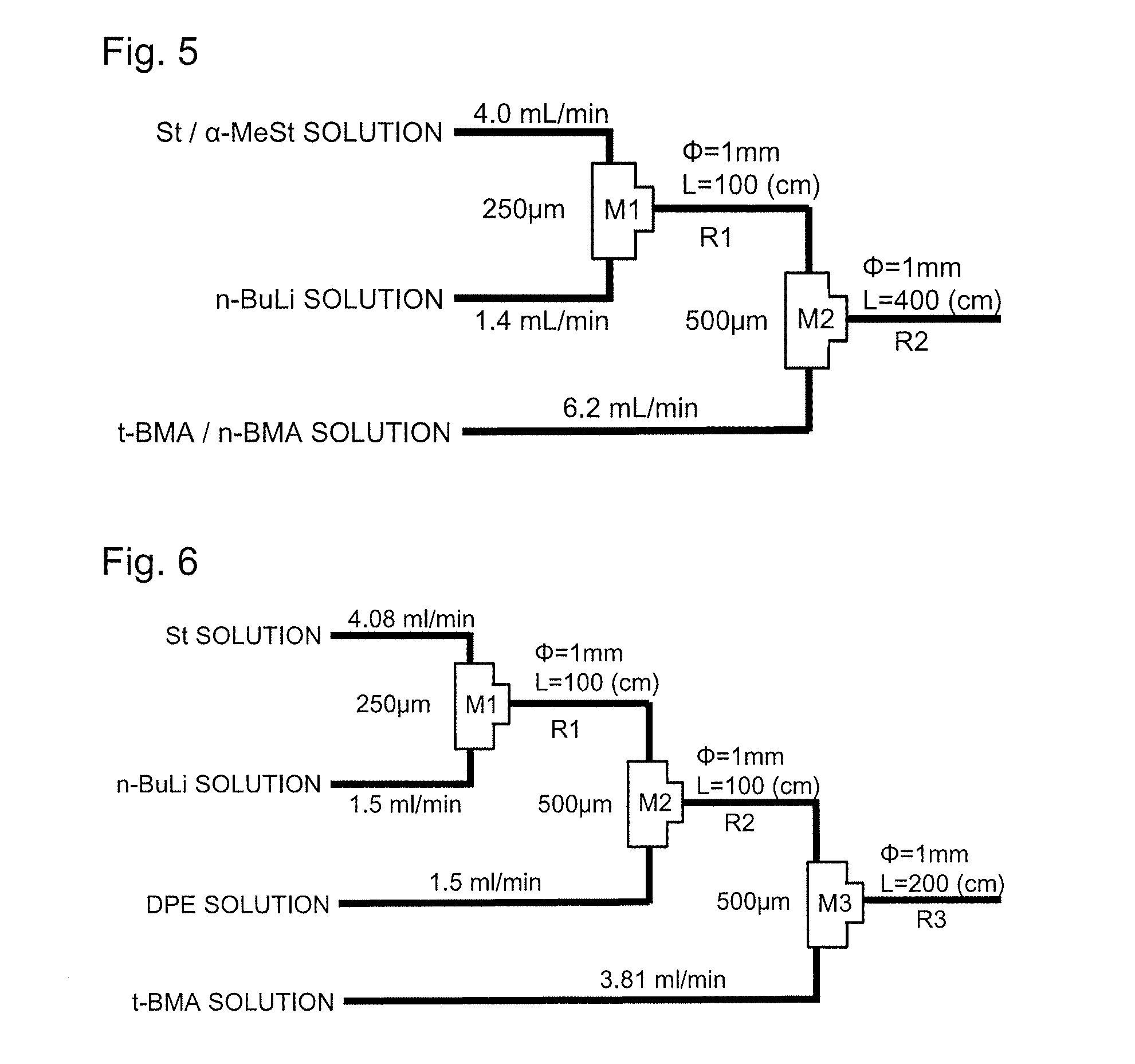
ActiveUS20160229943A1Narrow molecular weight distributionProduced efficiently and smoothlyChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsMicroreactorMethacrylate
The present invention provides a method for producing a block copolymer, which includes subjecting styrene or a derivative thereof (excluding α-methylstyrene) to living anionic polymerization in the presence of a polymerization initiator by means of a microreactor having a channel being capable of mixing a plurality of liquids with each other, reacting a propagation end of the resultant polymer block (A) derived from styrene or a derivative thereof with α-methylstyrene to obtain an intermediate polymer having a polymer unit (B) derived from α-methylstyrene bonded to one end of the polymer block (A), and then subjecting a)meth)acrylate compound (c) to living anionic polymerization in the presence of a polymerization initiator so that the polymer unit (B) derived from α-methyl styrene in the intermediate polymer serves as a propagation end to form a polymer block (C) derived from the)meth)acrylate compound (c)
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Copolymer of conjugated cyclodiene
A cyclic conjugated diene copolymer comprising a main chain comprised of (A) cyclic conjugated diene monomer units, (B) monomer units obtained from vinyl aromatic monomers each having a hydrogen atom at the α-position thereof, and optionally (C) monomer units obtained from commoners which are other than the monomers used for obtaining the monomer units A and B and which are copolymerizable with at least one of the monomers used for obtaining the monomer units A and B, wherein all monomer units A and the monomer units B together form one or more polymer chains each having an A / B random sequence, wherein the one or more polymer chains each having an A / B random sequence contain at least one polymer chain having a number average molecular weight of from 20,000 to 500,000 and contain no polymer chain having a number average molecular weight of more than 500,000. A process for producing the above-mentioned cyclic conjugated diene copolymer by living anionic polymerization.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Process of preparing oxyalkylene-base unsaturated ester polymer
InactiveCN101089028AMeet different performance requirementsSynthesis conditions are easy to controlMolecular sieveCopolymer
The present invention discloses process of preparing polyoxyalkylene-base unsaturated ester. The process is a one-step active anionic polymerization process including three steps of dewatering the reactant with molecular sieve, reaction and separating side product. The polyoxyalkylene-base unsaturated ester has controllable molecular weight for different requirements, and the process has easy control in the synthesis condition, easy application in industrial production and short reaction period. The polyoxyalkylene-base unsaturated ester may be copolymerized with hydrophilic and lipophilic monomer to form amphiphilic graft copolymer with polyoxyalkylene-base long branched chain, with the ratio between the hydrophilic groups and the lipophilic groups being adjustable for obtain products with different performances.
Owner:SHENZHEN OCEANPOWER NEW MATERIALS TECH
Radiation-ray sensitive composition for colour-filtering piece, colour filtering piece and colour liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN1677139AIncrease contrastImprove the development effectOptical filtersPaving detailsSolid componentColor gel
The radiation-sensitive composition for a color filter contains (A) a pigment, (B) a dispersant, (C) an alkali-soluble resin, (D) a polyfunctional monomer, (E) a photopolymerization initiator and (F) solvent. The dispersant (B) essentially comprises an acrylic copolymer obtained by living anion polymerization and having >0 amine value (mgKOH / g) and 0 acid value (mgKOH / g). The use amount (in terms of solid content) of the acrylic copolymer is 3 to 35 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the pigment (A).
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
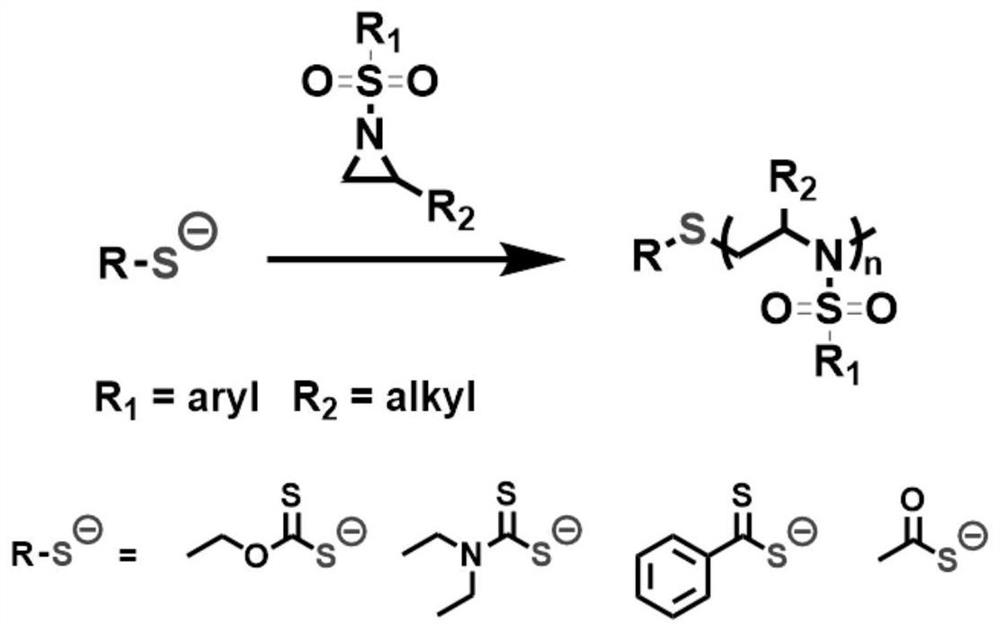
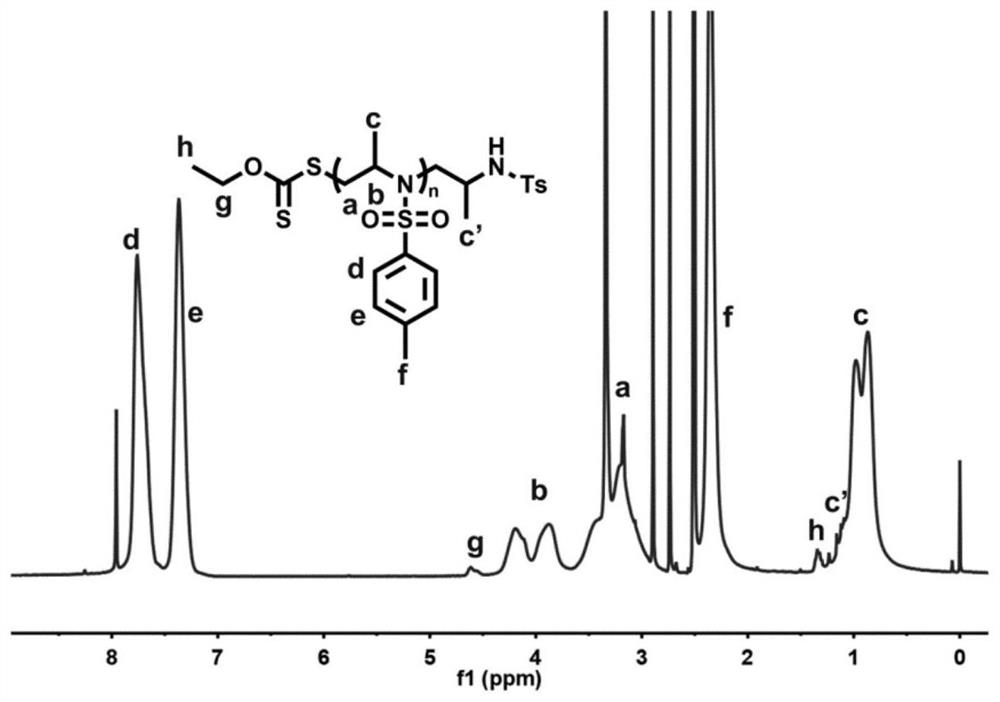
Air atmosphere anion ring-opening polymerization method of N-sulfonyl aziridine derivative
ActiveCN111675806AActive polymerization in air atmosphereVariety and easy to getAir atmosphereAziridine
The invention relates to an air atmosphere anion ring-opening polymerization method of an N-sulfonyl aziridine derivative. The preparation method comprises the following step: by taking sulfur anionswith stable air as an initiator, adding the sulfur anions, an N-sulfonyl aziridine derivative monomer and a solvent according to a stoichiometric ratio in an air atmosphere to carry out active anion ring-opening polymerization, so as to obtain a corresponding polymer. The initiator and the monomer of the polymerization system are insensitive to air and water, air atmosphere active anion polymerization can be achieved, the initiator has numerous varieties and is easy to obtain, the polymerization system is suitable for a wide variety of monomers, and large-scale controllable preparation of homopolymers and copolymers of the N-sulfonyl aziridine derivative can be achieved. Because a high vacuum technology and an inert atmosphere are not needed, the method is suitable for industrial scale-upproduction.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hydrogenated block copolymer and composition containing same
To provide a thermoplastic elastomer composition excellent in fluidity, compression set property, and flexibility, and a hydrogenated block copolymer that provides the composition. The hydrogenated block copolymer is obtained by hydrogenating a block copolymer which is obtained by reacting a living polymer represented by the following formula (1): B 1 - A - B 2 - X wherein B 1 and B 2 each represent a polymer block mainly including a structural unit derived from a conjugated diene compound, A represents a polymer block mainly including a structural unit derived from a vinyl aromatic compound, and X represents an active terminal end of a living anion polymer, with a coupling agent, wherein the ratio of the mass of the polymer block B 1 to the total mass of B 1 and B 2 before hydrogenation is from 0.10 to 0.45; and the content of the structural unit derived from the vinyl aromatic compound is from 25 to 50 mass% based on the mass of the hydrogenated block copolymer.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
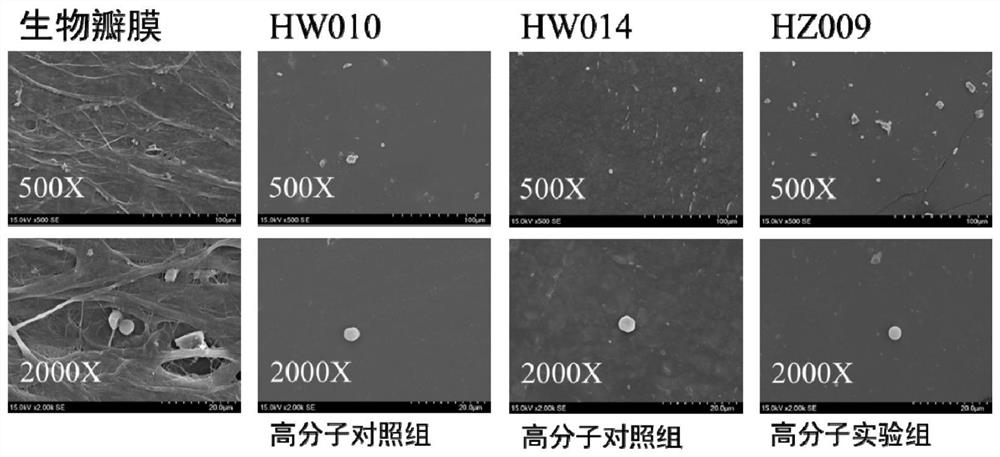
Application of hydrogenated styrene thermoplastic elastomers in preparation of artificial heart valves
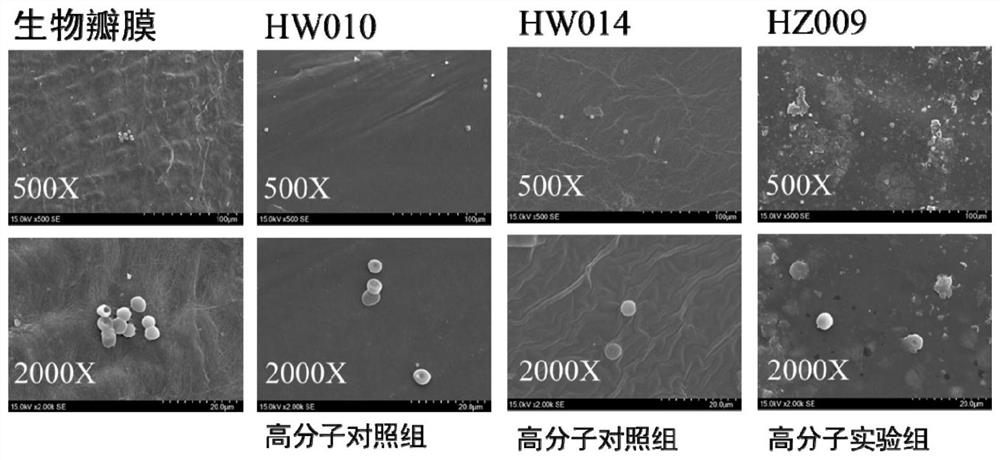
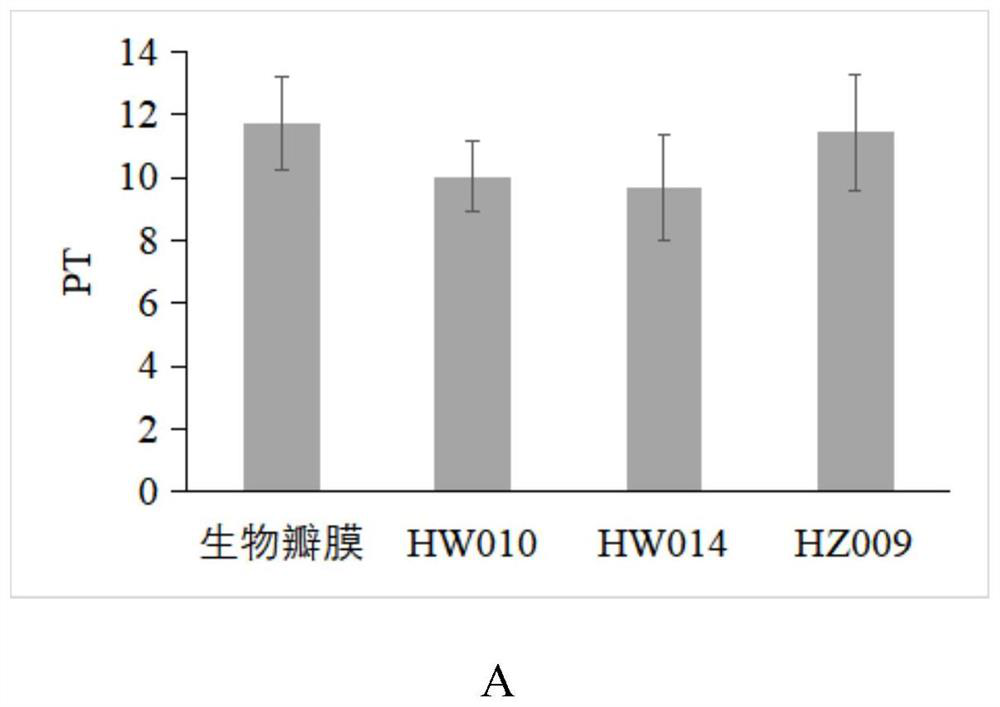
ActiveCN113117139AGood biological stabilityExcellent anticoagulant propertiesHeart valvesTissue regenerationElastomerPolymer science
The invention discloses an application of hydrogenated styrene thermoplastic elastomers in preparation of artificial heart valves. The thermoplastic elastomers are a block polymer synthesized through active anionic polymerization, a solid phase or a dispersed phase is polystyrene, and a rubber phase is a hydrogenated conjugated diene polymer or a hydrogenated conjugated diene and styrene random copolymer. The hydrogenated styrene elastomers used in the invention have excellent biological stability, anti-coagulation performance, anti-calcification performance and mechanical strength, and can be used for preparing the artificial heart valves with more durable performance than that of a bioprosthetic valve.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Radiation-ray sensitive composition for colour-filtering piece, colour filtering piece and colour liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN100376905CExcellent adhesionGood storage stabilityOrganic chemistryOptical filtersLiquid-crystal displayAcid value
The present invention provides a radiation sensitive composition for a color filter comprising (A) a pigment, (B) a dispersant, (C) an alkali-soluble resin, (D) a polyfunctional monomer, (E) a photopolymerization initiator and (F) a solvent, wherein the dispersant (B) comprises an acrylic copolymer obtained through living anionic polymerization and having an amine value (unit; mgKOH / g) and an acid value (unit; mgKOH / g) each greater than 0.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Organic-inorganic nano composite particle as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113337063AHigh solid contentImprove general performancePhotovoltaic energy generationCross linkerVinyl pyridine
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Chain-end functionalized poly(ethykene oxide) and process for the preparation of a nano-sized transition metal or metal salt using the same
InactiveUS20090142268A1Efficient preparationIncrease drug penetrationHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideAnticarcinogenDrug group
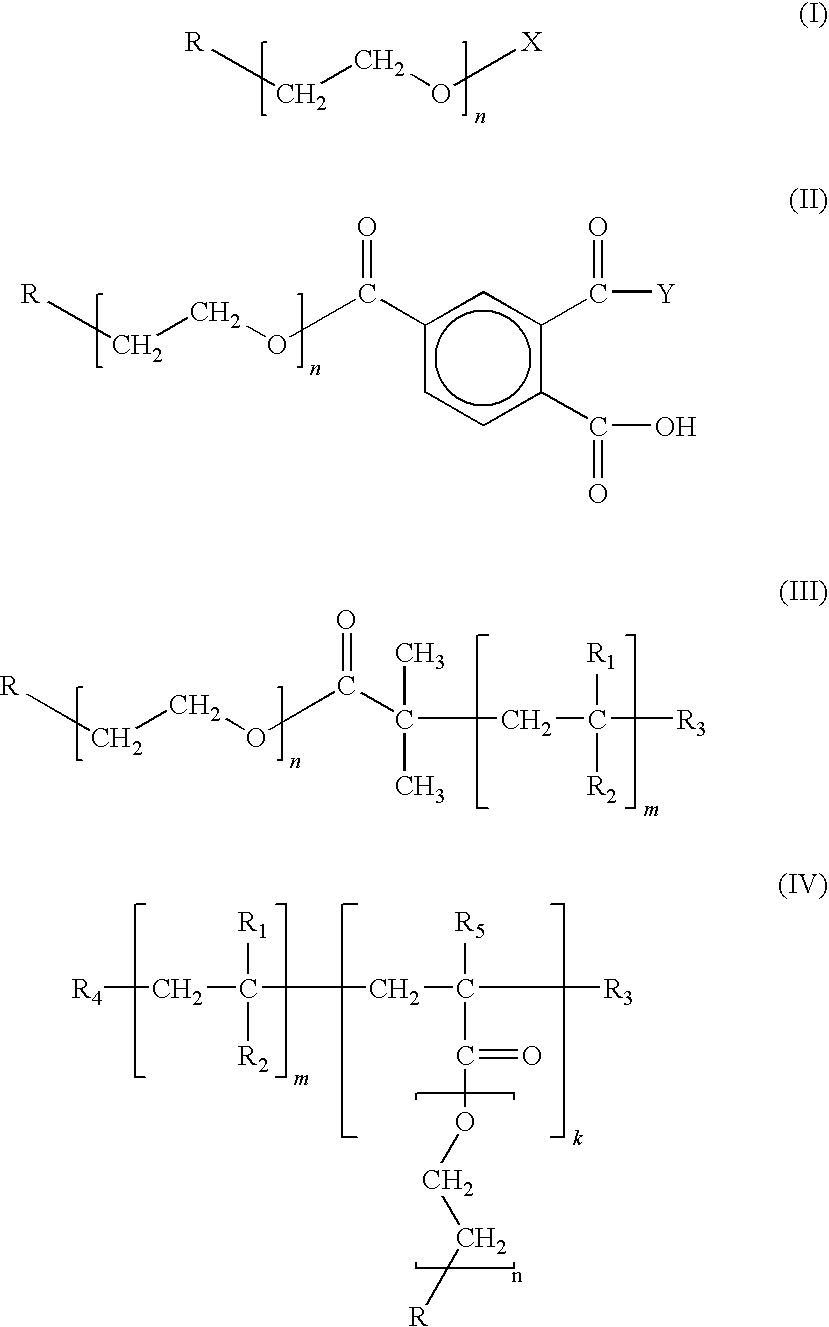
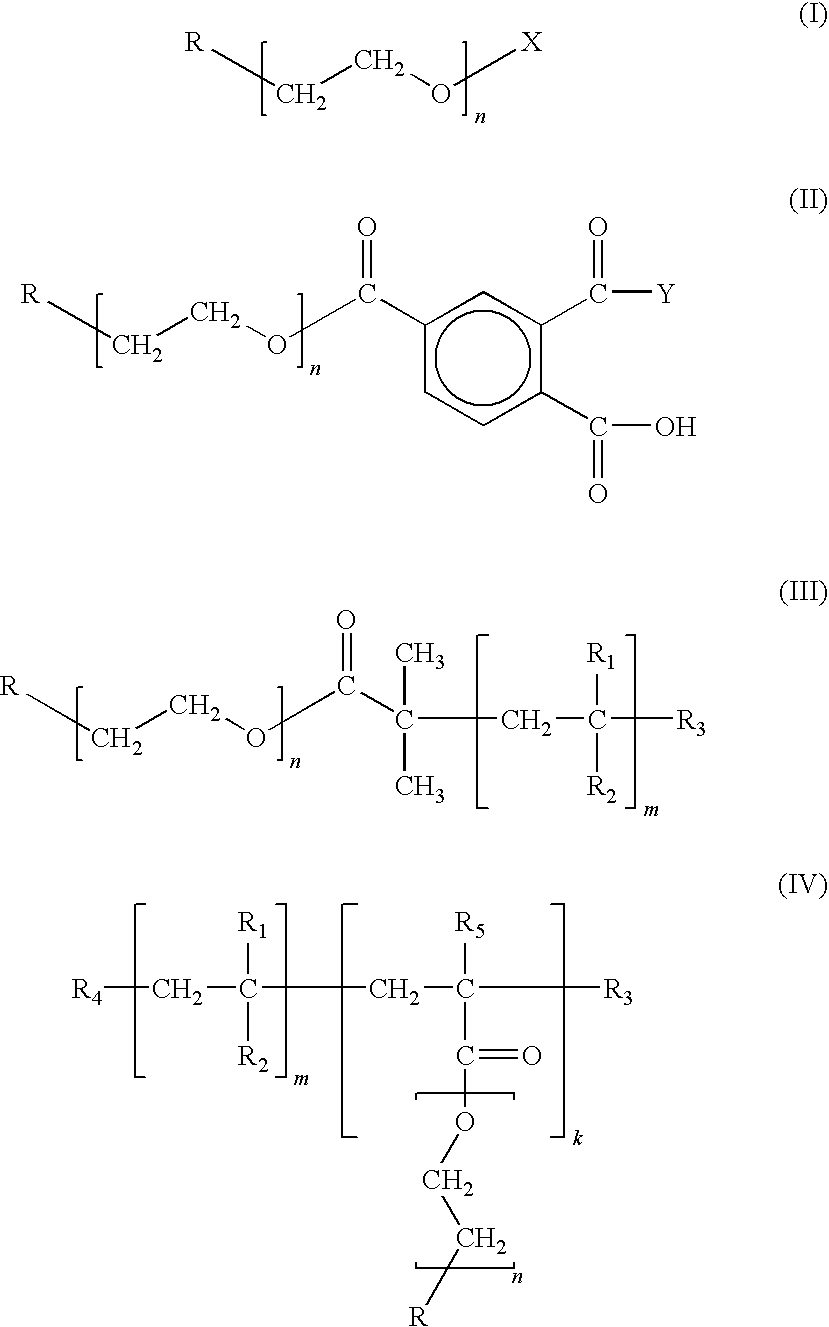
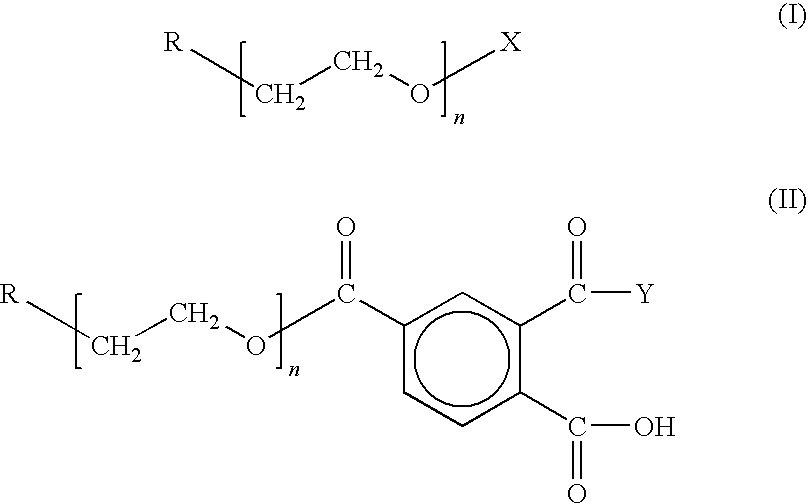
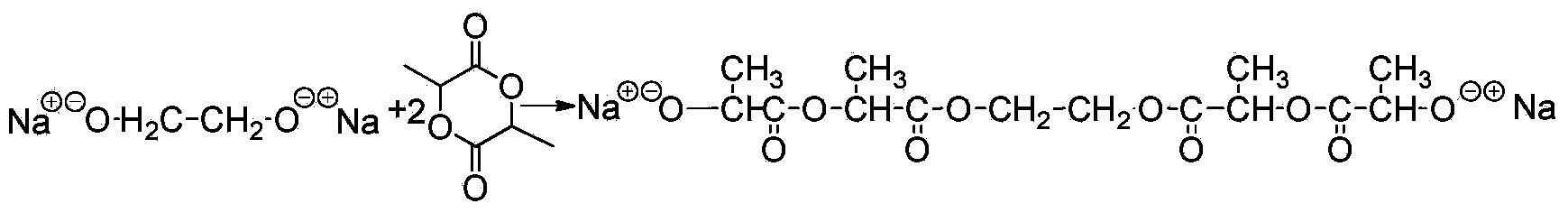
There is provided a novel chain-end functionalized PEO of formulas (I) to (IV) prepared via living anionic polymerization and chain-end functionalization, as well as a simple method of preparing nano-sized transition metal or metal salt particles using the same, which can be readily stabilized even in an aqueous medium. The water-soluble PEO-based polymers having various functional groups (including a drug group such as vitamin and anti-cancer agent) and the process of preparing nano-sized transition metal or metal salt particles using the same can be advantageously used in the development of new materials for drug delivering system and imaging, e.g., a contrast agent and an anti-cancer agent simultaneously.
Owner:YOULCHON CHEM
Synthesis method of bola-like polylactic acid with precise controlled molecular structure
The invention discloses a synthesis path of a bola-like polylactic acid with a precise controlled molecular structure. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a dianion activity center with trigger abilities on two ends; 2, triggering a linear long chain of which the molecular weight is controllable through the dianion activity center, wherein the main chain can be prepared through polymerization of monomers of any degradable polymer suitable for dry anionic polymerization, so that the flexibility of the main chain can be changed and can be used as a connection chain between 'bolas'; 3, carrying out aggregation blocking on active anions to obtain a macromonomer with a double-end polyfunctional group; and 4, carrying out ring opening polymerization on the macromonomer as an initiator and lactide under a proper condition, so as to obtain the bola-like polylactic acid with 'adjustable main chain molecular structures, controllable length and multi-branched double ends' and the precise controlled molecular structure.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for controlling anionic polymerization
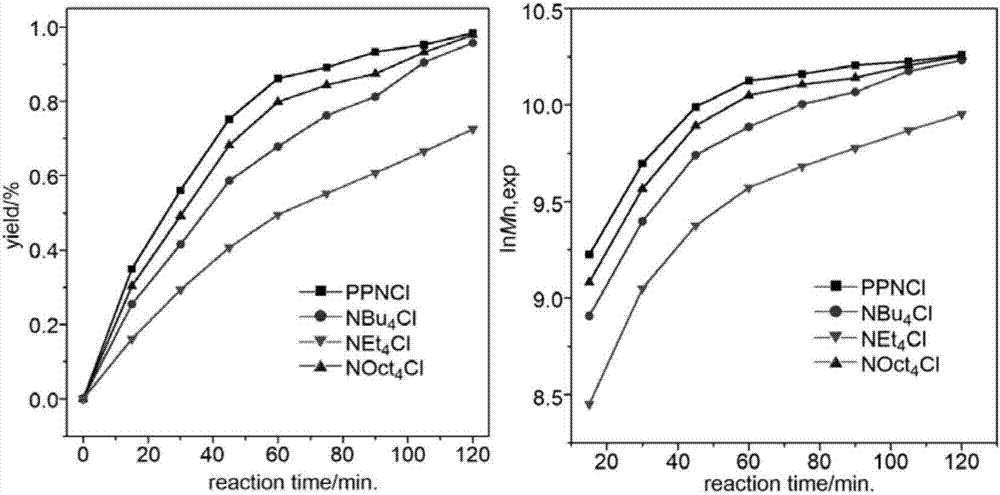
This invention deals with an approach to control anionic polymerization. The anionic polymerization is conducted by adding a kind of initiator ligand compound, directly or in the form of solution into the monomer or initiator at the same or different time, or at different stages. The metal atoms in the ligand can form the association with the initiator cations, while the alkyloxy groups in the initiator ligand can restrict the entering channel of the addition of the monomers due to their relatively large volume or steric hindrance. Therefore, the initiator ligand compound can restrict the rate of anionic polymerization, restrain the side reaction, and make the anionic polymerization possible to be conducted at room or even higher temperature. The molar ratio of initiator ligand compound to initiator is from 0.01:1 to 20:1. Compared with present technologies, the method of this invention can control and adjust the homopolymerization and copolymerization rate, side reactions and the polymerization temperature, and make it possible to industrialize.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Catalyst system for preparing polyether materials for aviation
The invention provides a boron alkyl-halogenated onium salt system and an application thereof in living polymerization of epoxy monomers and belongs to the field of an epoxy resin. An epoxy monomer active anion controllable polymerization reaction system provided by the invention contains an initiator, a catalyst, a solvent and epoxy monomers, wherein the halogenated quaternary ammonium salt or halogenated quaternary phosphor salt is taken as the initiator and the boron alkyl is taken as the catalyst. The epoxy monomer polymerization system provided by the invention is capable of efficiently triggering the epoxy monomer controllable anionic polymerization reaction under the conditions of shorter period and room temperature. An epoxypropane / ethane polymer prepared according to the system provided by the invention can be applied to the additives of aviation chemical products.
Owner:THE SECOND RES INST OF CIVIL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION OF CHINA
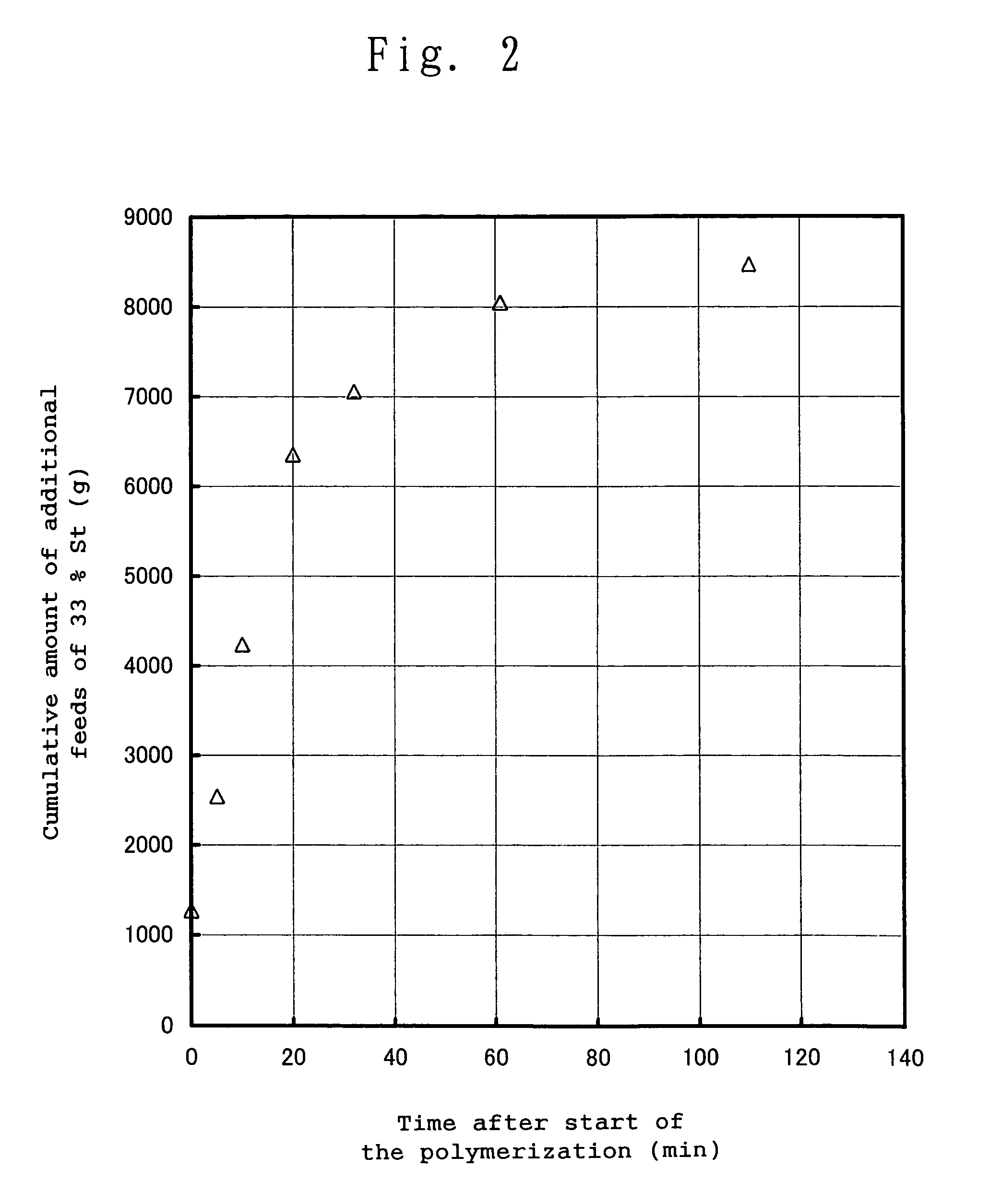
Production method of polymers by using living anionic polymerization method
An anionic polymerizable monomer is added to a reaction system in which an anion species which is incapable of initiating polymerization but may react with polymerization inhibiting substances to convert them into compounds that do not inhibit polymerization is present, and then an anion species capable of initiating polymerization is added thereto. It becomes possible to produce high molecular weight polymers and to precisely control the molecular weight thereof even if polymerization inhibiting substances are present in the system or when polymerization inhibiting substances enter from outside.
Owner:NIPPON SODA CO LTD
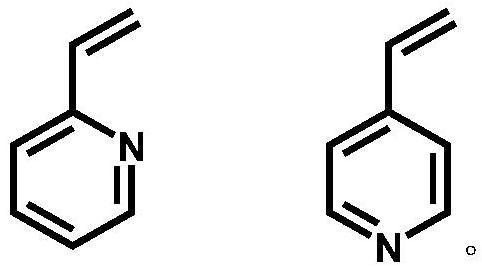
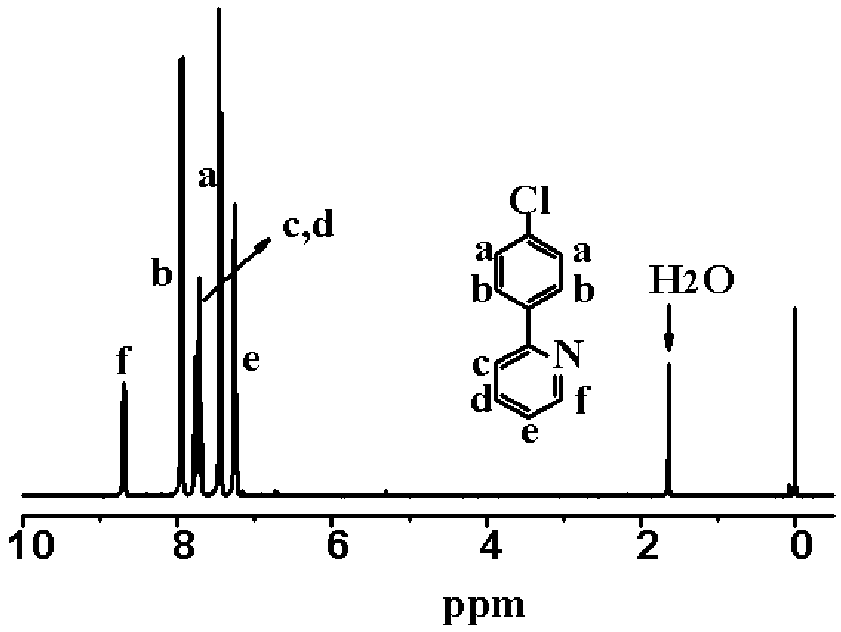
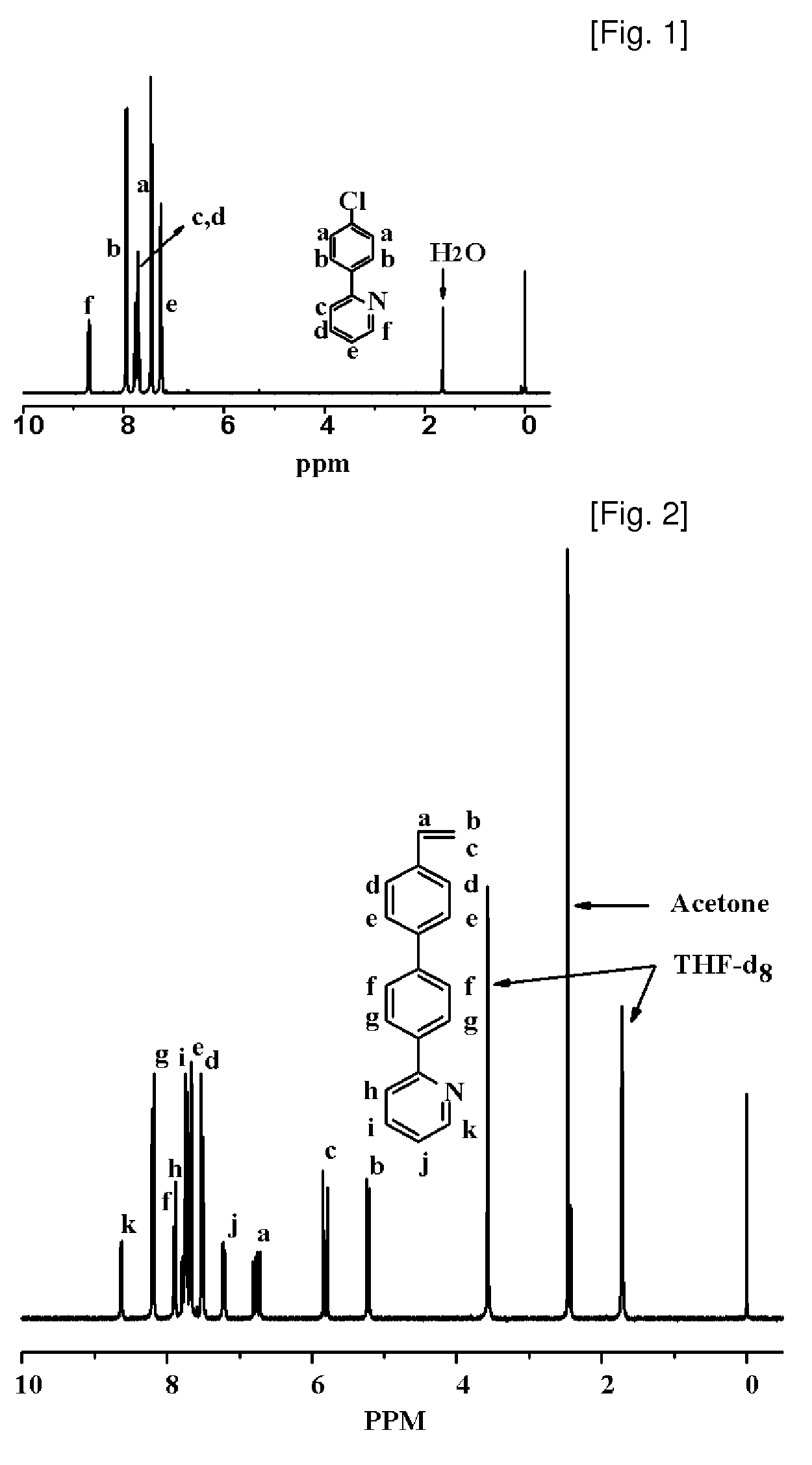
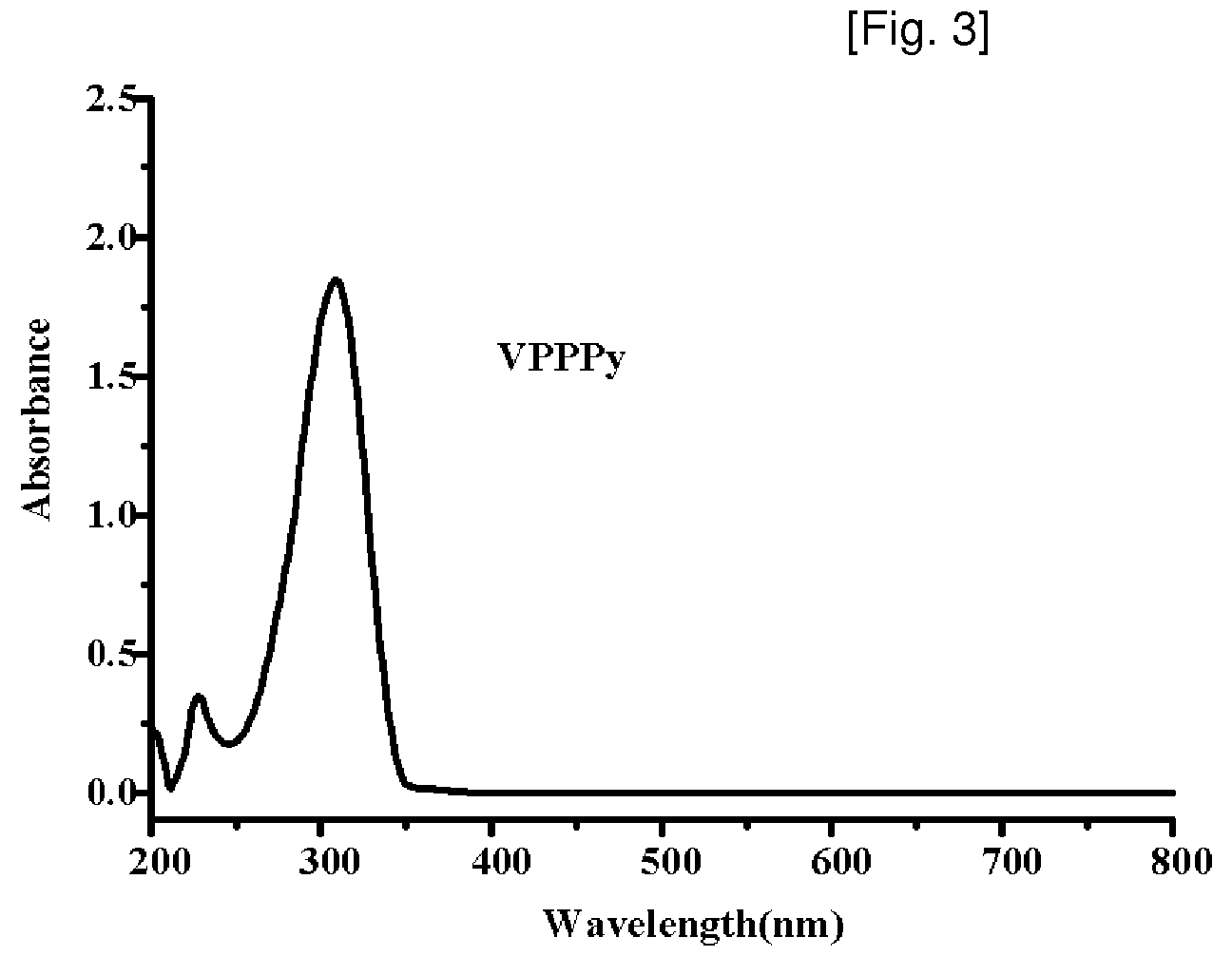
Synthesis of Vinylphenylpyridine and Living Anionic Polymerization
Provided are a vinyl-biphenylpyridine monomer and a polymer thereof. More particularly, the present invention provides a vinyl-biphenylpyridine monomer having a side chain of pyridine or phenylpyridine as a functional group, a homopolymer of which molecular weight and molecular weight distribution are controlled using the monomer, and a block copolymer of which molecular structure and molecular weight are controlled to facilitate synthesis of an organic metal complex. Accordingly, the present invention provides a vinyl-biphenylpyridine monomer and a polymer thereof which are effectively used as nano and optical functional materials.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for controlling anionic polymerization
This invention deals with an approach to control anionic polymerization. The anionic polymerization is conducted by adding a kind of initiator ligand compound, directly or in the form of solution into the monomer or initiator at the same or different time, or at different stages. The metal atoms in the ligand can form the association with the initiator cations, while the alkyloxy groups in the intiator ligand can restrict the entering channel of the addition of the monomers due to their relatively large volume or steric hindrance. Therfore, the initiator ligand compound can restrict the rate of anionic polymerization, restrain the side reaction, and make the anionic polymerization possible to be conducted at room or even higher temperature.The molar ratio of initiator ligand compound to initiator is from 0.01:1 to 20:1. Compared with present technologies, the method of this invention can control and adjust the homopolymerization and copolymerization rate, side reactions and the polymerization temperature, and make it possible to industrialize.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com