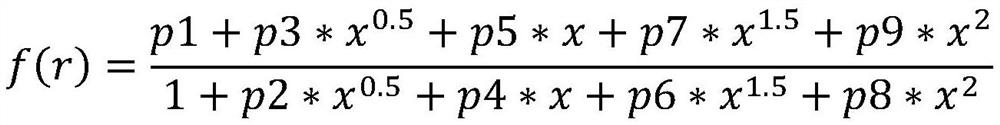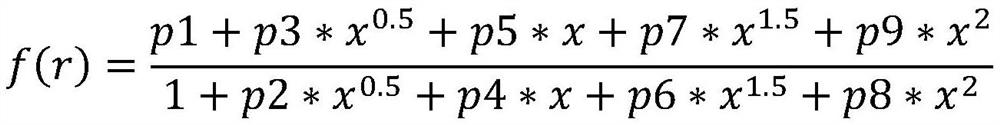Patents
Literature
67 results about "Rock tapaculo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The rock tapaculo or Espinhaço tapaculo (Scytalopus petrophilus) is a species of bird in the Rhinocryptidae family. It is endemic to altitudes of 900–2,100 metres (3,000–6,900 ft) in the central and southern Espinhaço Mountains, and the Mantiqueira Mountains in Minas Gerais, Brazil, though it may also occur in adjacent parts of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. It is found in shrubby and grassy habitats in rocky regions, and in elfin and cloud forests. It closely resembles the Diamantina tapaculo and Planalto tapaculo in appearance and voice (especially song; less so in call).
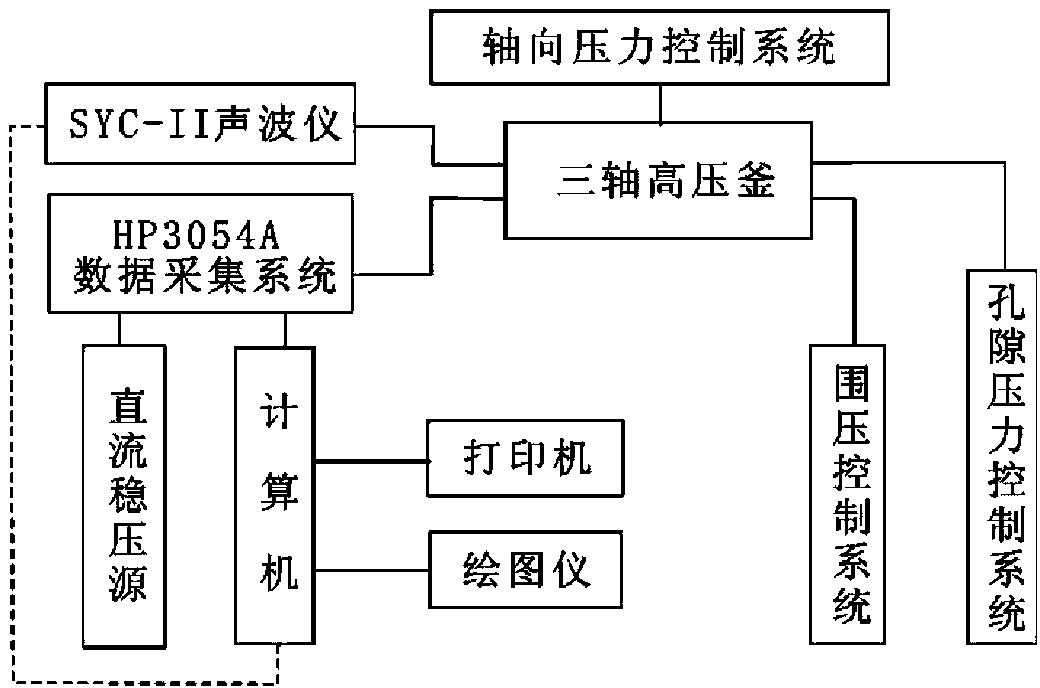
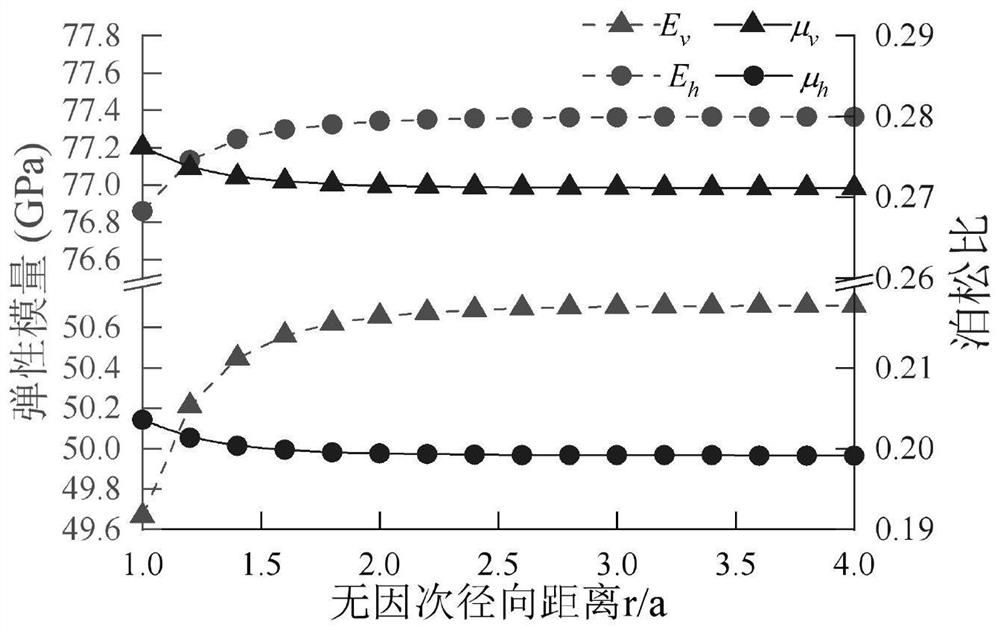
Method for synchronous measurements on dynamic and static elastic parameters of rocks
InactiveCN103278389AGuaranteed validityGuaranteed accuracyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesControl systemAxial pressure
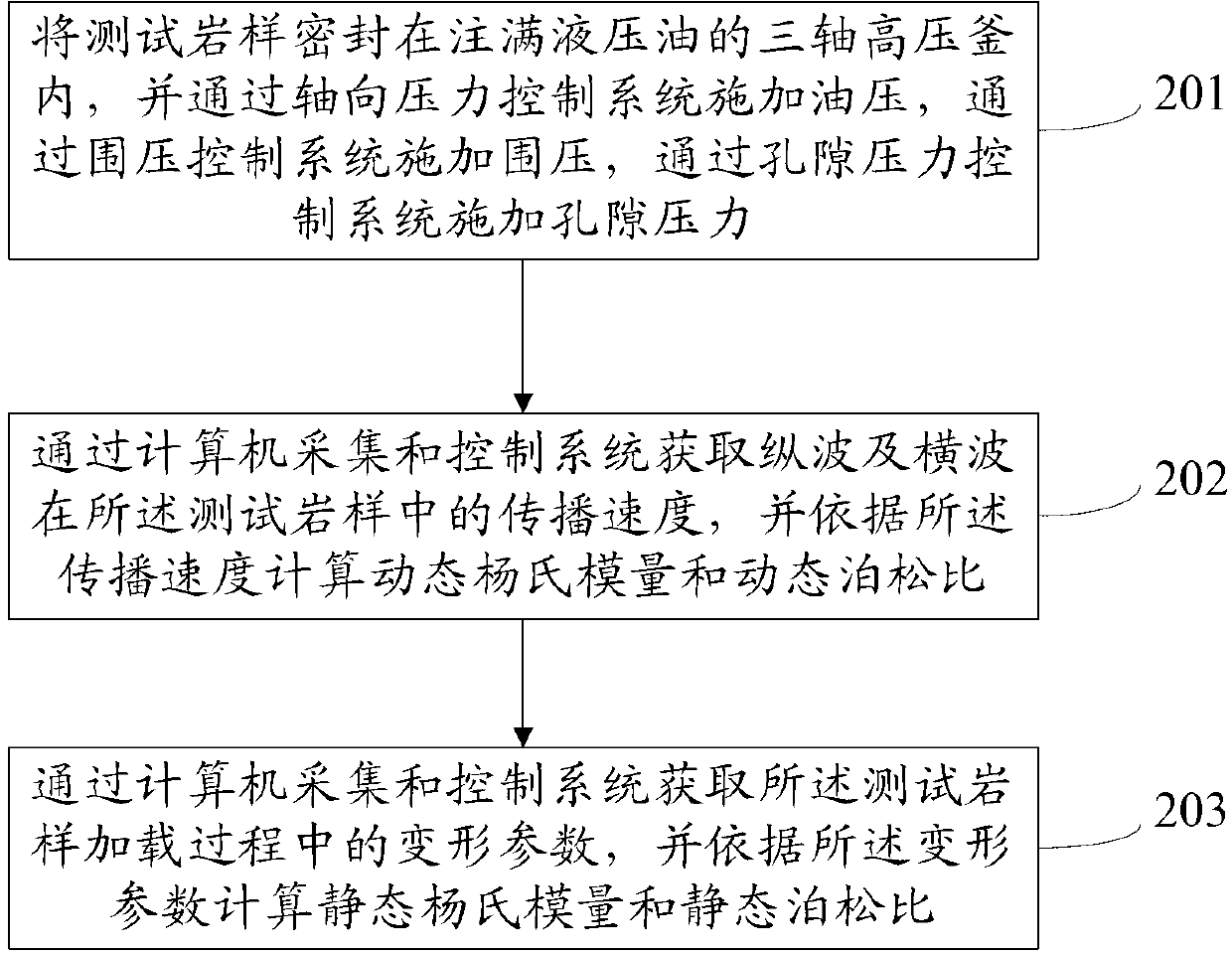
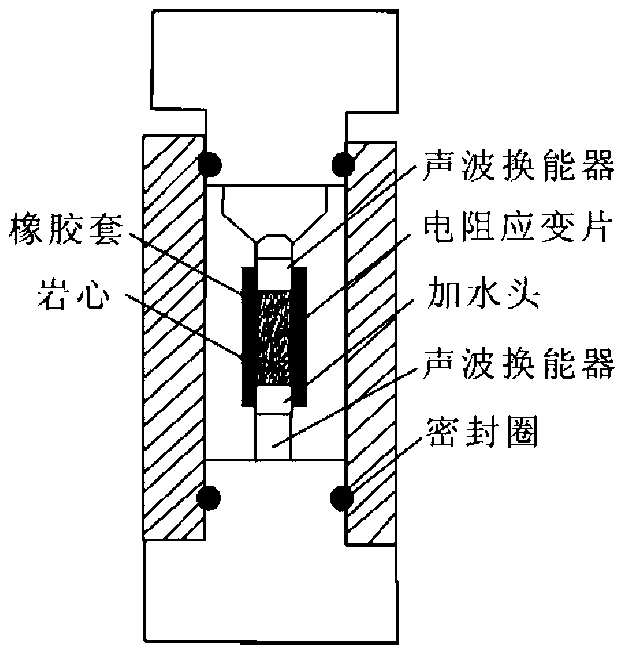
The invention provides a method and a device for synchronous measurements on dynamic and static elastic parameters of rocks by using a rock triaxial anti-compression testing device. The method comprises: sealing a test rock sample in a triaxial autoclave filled with hydraulic oil, applying an oil pressure by an axial pressure control system, applying a confining pressure by a confining pressure control system, and applying a pore pressure by a pore pressure control system; acquiring propagation speeds of longitudinal waves and transverse waves in the test rock sample by a computer acquisition and control system, and calculating the dynamic Young modulus and the dynamic Poisson ratio according to the propagation speeds; and acquiring deformation parameters of the test rock sample during a loading process by the computer acquisition and control system, and calculating the static Young modulus and the static Poisson ratio according to the deformation parameters. The method and the device can ensure validity and accuracy of hydrocarbon reservoir rock mechanical parameter measurements in thousands of meters deep underground and under the conditions of complex confining pressure, high temperature, high pore pressure and polyphase fluid.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Ecological restoration method of bare rock engineering wound-surface vegetation
InactiveCN101491193APreserve flatnessLess investmentCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationVegetationEcological environment
The invention relates to a method for ecologically restoring vegetation on the bare rock engineering wound surface, which belongs to the technical field of vegetation ecological restoration. A similarly natural mode is used to accelerate the restoration of the vegetation ecological environment and landscape. The method comprises the following steps: firstly carrying out the pretreatment on the bare rock engineering wound surface, and retaining the definite natural unevenness and fissure degree of the actual slope line (4) of the bare rock within the range from the low level control line (2) to the high level control line (3) of a designed slope line (1) under the preconditions of keeping a stable rock slope base and removing dangerous and floating stones; and by adhering to the concept of artificial guidance and natural selection, adjusting measures to the local conditions according to the geological, geomorphic and climatic conditions and different target vegetations, and adopting different processes and slurries with different components to carry out the spray sowing on the rock slope. The method has low cost and high efficiency, facilitates the retention of soil and plant seed sources, and completes at one pass the vegetation restoration which needs years of accumulation and multiple superposition of the natural force. The vegetation ecological restoration is similar to the nature, but is far quicker than the nature. The prosperous period or declining period of a single species mutation can never appear. The method is particularly suitable for the large-area application, achieves the landscape and ecological effects in the near term, the medium term and the long term, and has practical and long term significance.
Owner:赵平 +1
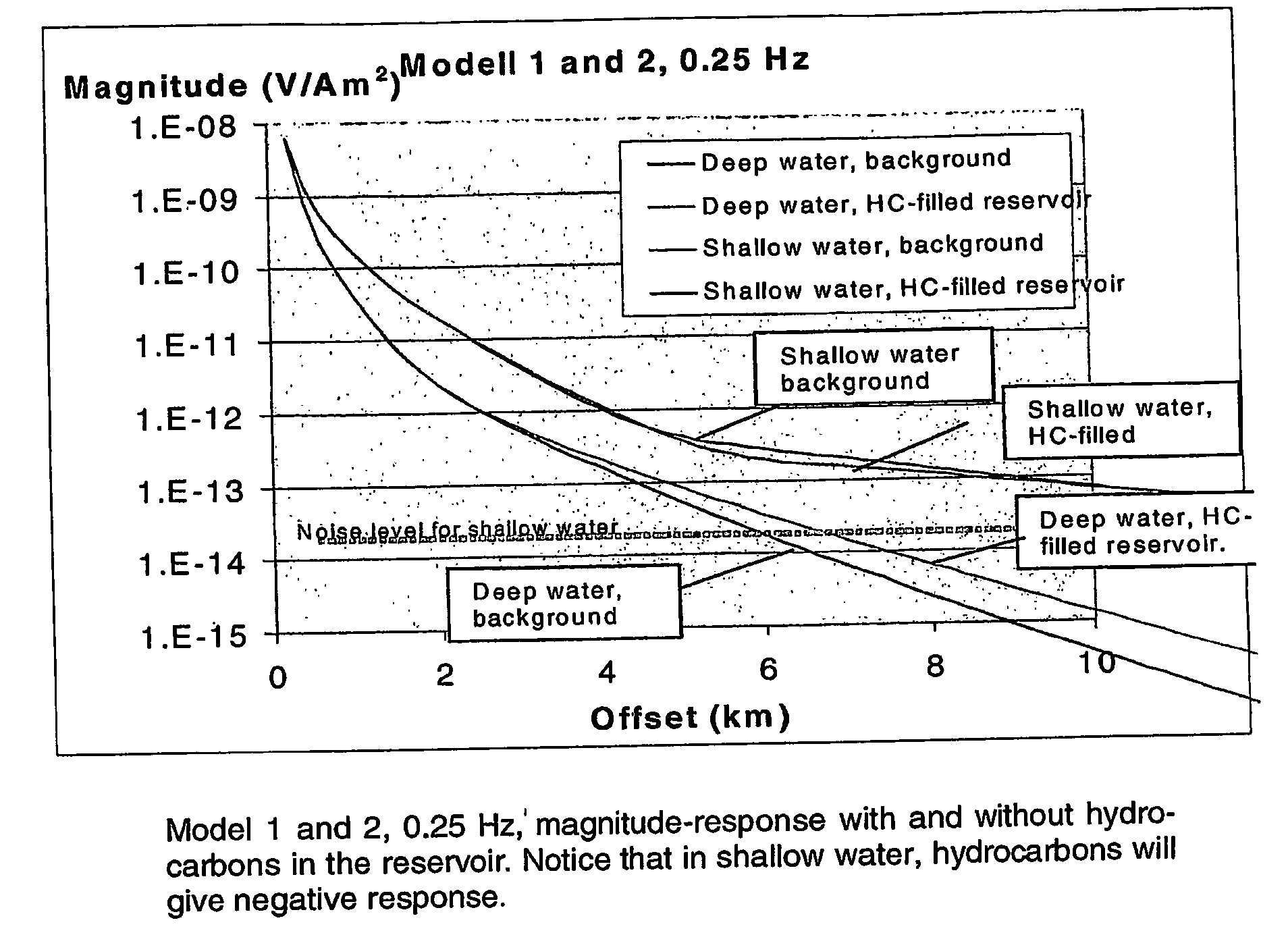
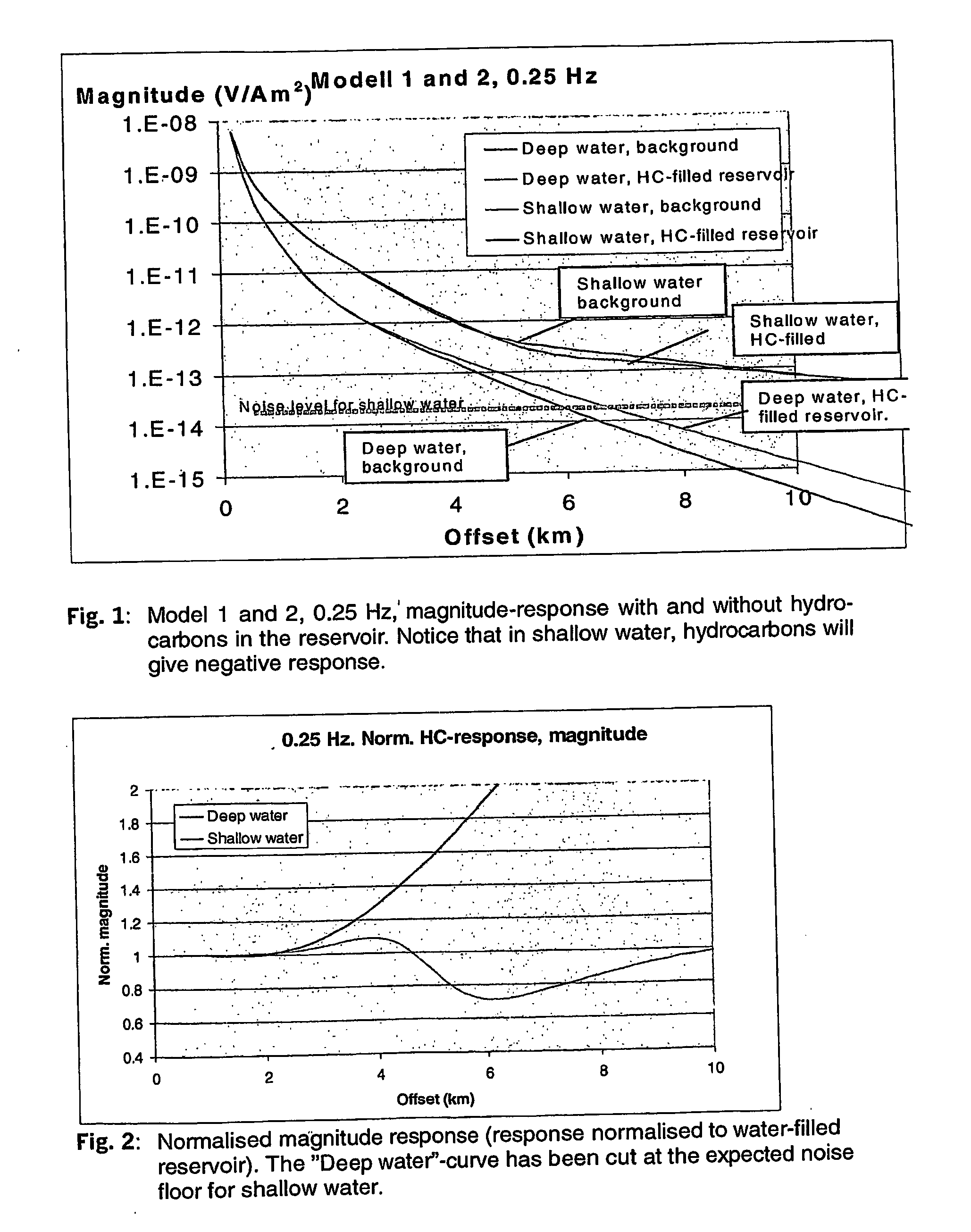
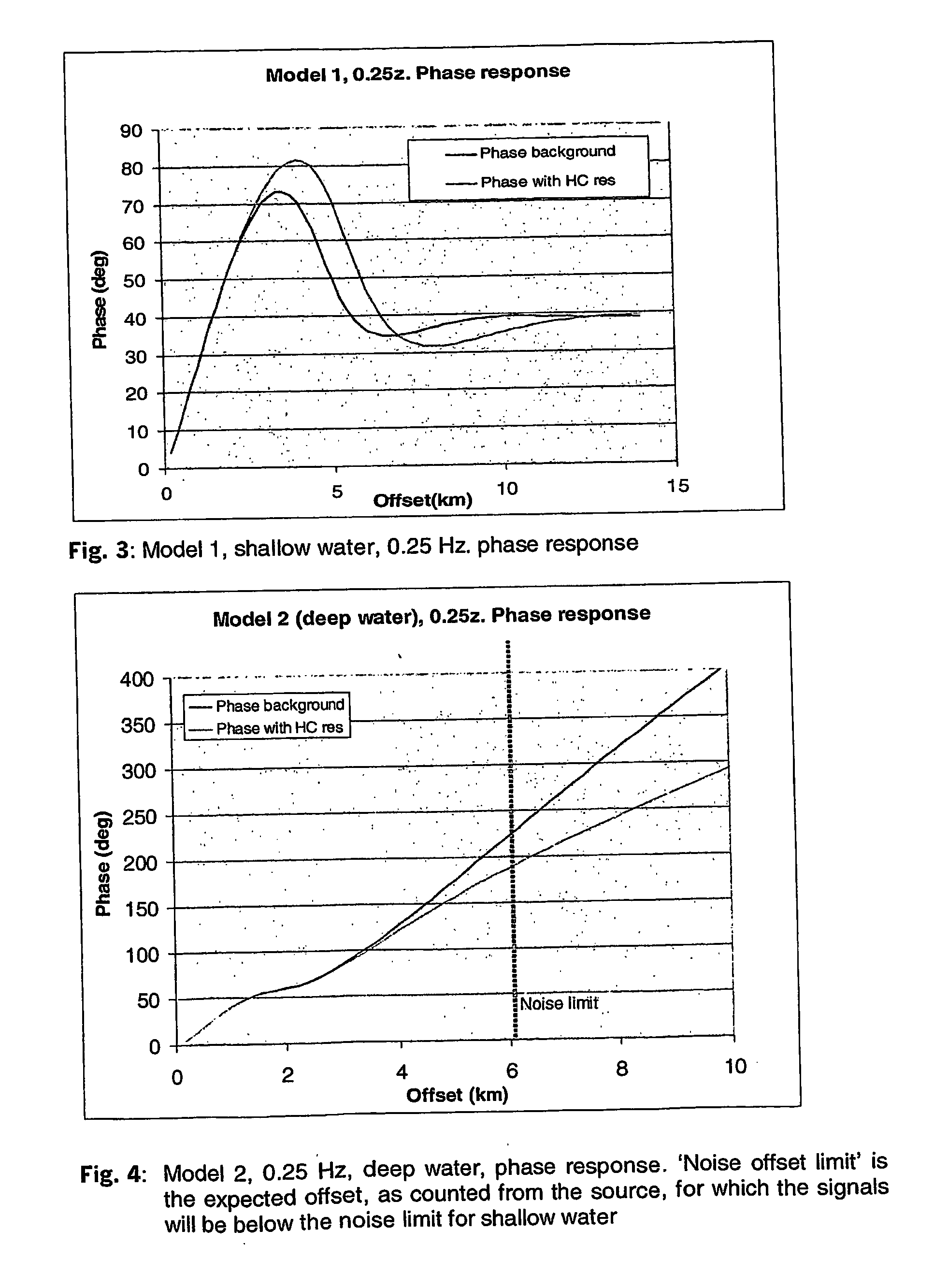
Electromagnetic Method on Shallow Water Using a Controlled Source
InactiveUS20090278541A1High resistivityLow resistivityWater resource assessmentDetection using electromagnetic wavesHigh resistivityPetroleum
Owner:MULTIFIELD GEOPHYSICS
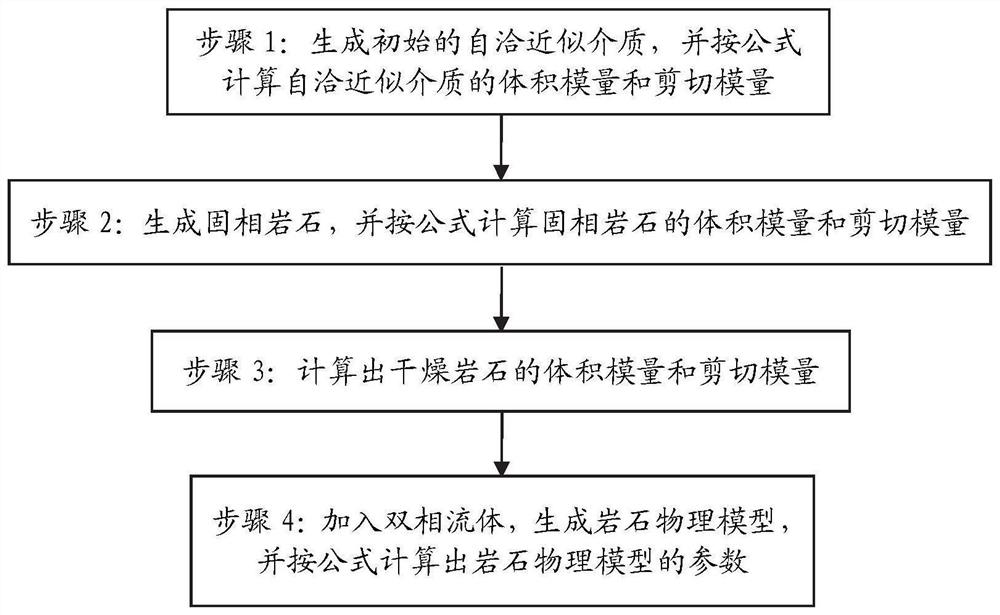
Rock physical model construction method for hydrate reservoir and processing terminal
ActiveCN111859632AEfficiently Conduct Attenuation StudiesGeomodellingDesign optimisation/simulationShear modulusBulk modulus
The invention relates to a rock physical model construction method for a hydrate reservoir and a processing terminal, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, generating an initial self-consistent approximate medium, and calculating the bulk modulus and shear modulus of the self-consistent approximate medium according to a formula; 2, generating a solid-phase rock, and calculating the bulkmodulus and the shear modulus of the solid-phase rock according to a formula; 3, calculating the bulk modulus and the shear modulus of the dry rock; and 4, adding a two-phase fluid to generate a rockphysical model, and calculating attenuation factor parameters of the rock physical model according to a formula. According to the method, the adaptive theory, the equivalent difference theory, the effective medium theory and the spot saturation model are fused and adopted, the rock physical model for the stratum rich in argillaceous natural gas hydrate in the sea area is established, and hydratereservoir attenuation research of a subsequent earthquake frequency band can be effectively carried out according to the rock physical model.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MARINE GEOLOGICAL SURVEY
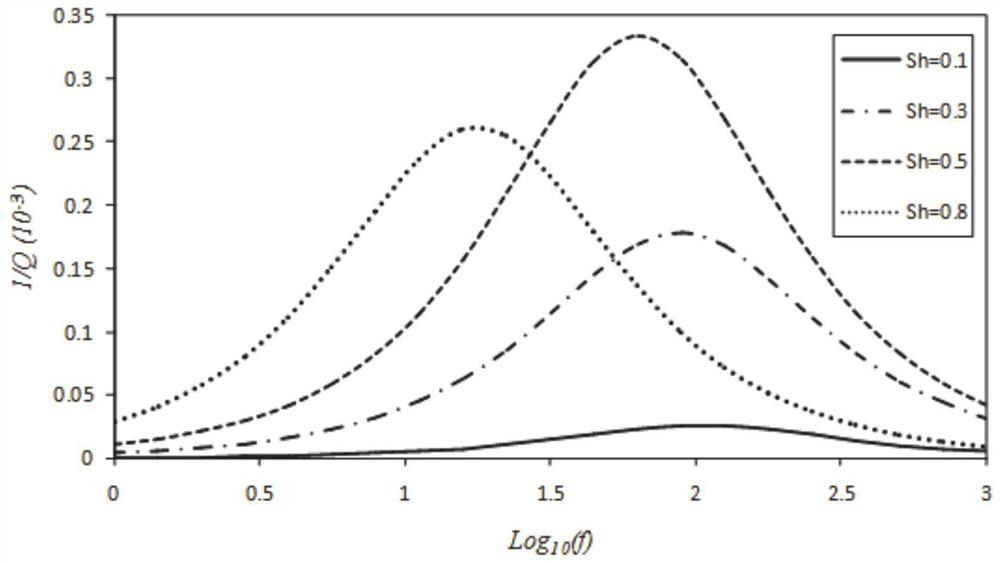
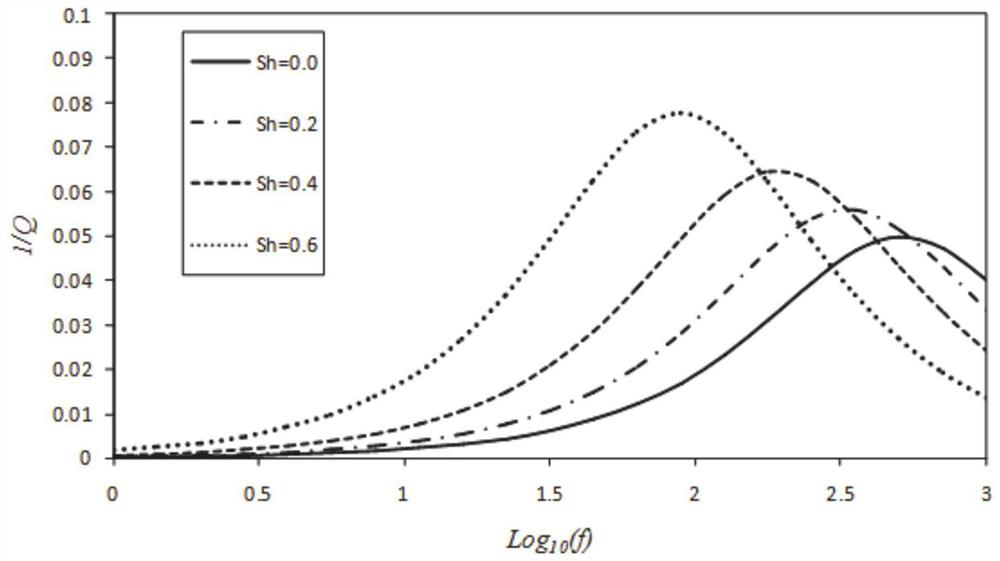
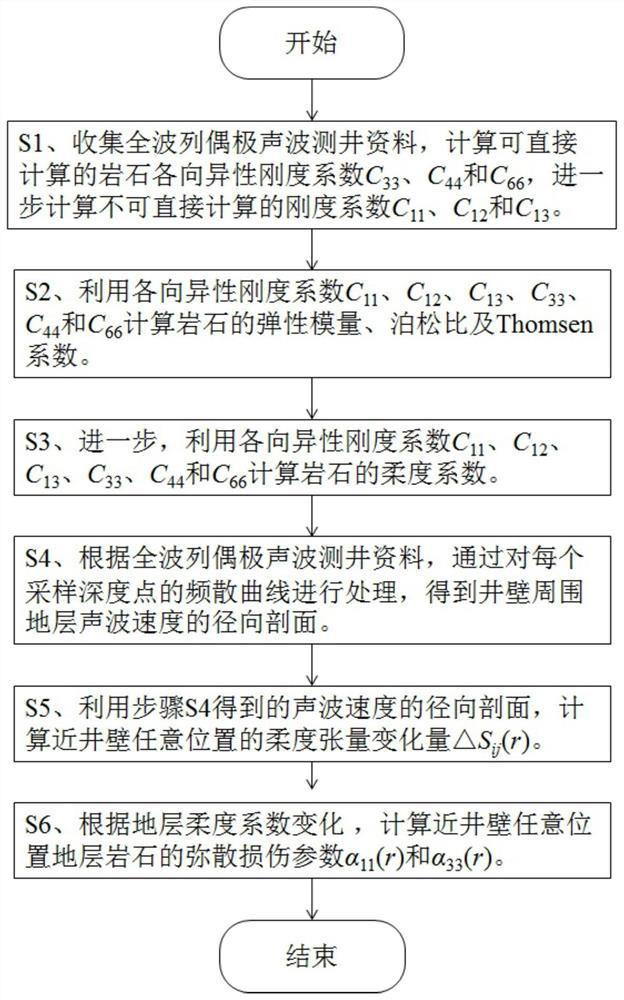
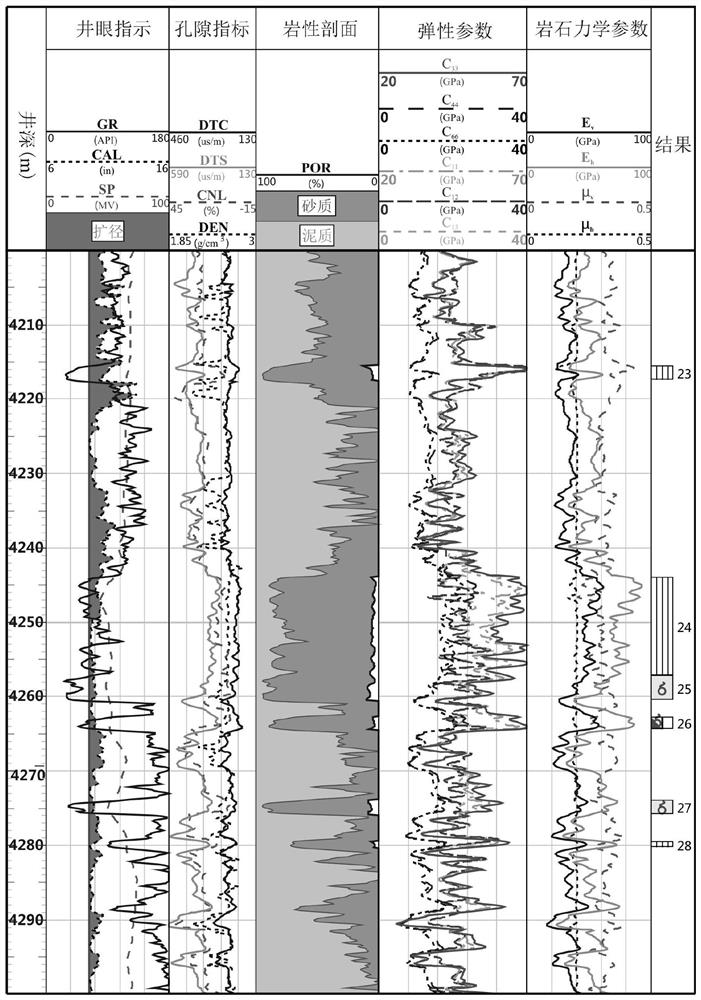
Well-surrounding near-well-wall stratum damage evaluation method based on logging information
The invention discloses a well-surrounding near-well-wall stratum damage evaluation method based on logging information. The method comprises the steps: calculating a rock anisotropic rigidity coefficient according to full-wave-train dipole acoustic logging information; calculating the elastic modulus, Poisson's ratio and Thomsen coefficient of the rock and the flexibility coefficient of the rock; according to the full-wave-train dipole acoustic logging information, obtaining the radial section of the acoustic velocity of the stratum around the well wall; calculating the flexibility tensor variable quantity of any position close to the well wall; and according to the flexibility tensor variable quantity of any position near the well wall, calculating dispersion damage parameters of stratum rocks at any position near the well wall. According to the method, acoustic logging is adopted to evaluate the damage characteristics of the stratum close to the well wall, the stratum is regarded as a transverse isotropic medium, and acoustic logging information is utilized to calculate and analyze rock mechanical parameters, Thomsen anisotropy coefficients and mechanical damage parameters of different lithology and different radial positions; and the method plays a very important role in ground stress evaluation, borehole wall stability analysis, hydraulic fracturing and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
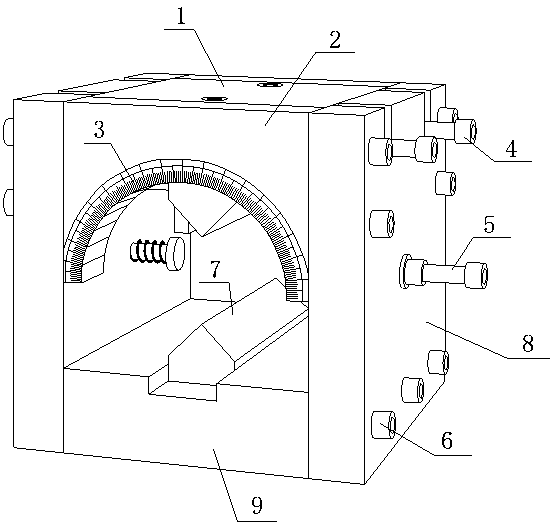
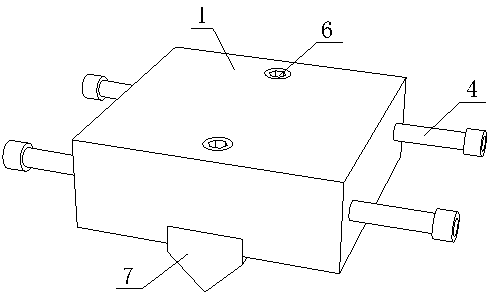
Rock Brazilian test fixture device capable of accurately controlling a layered rock splitting direction
PendingCN111272541AGuaranteed linear loadEasy to put inStrength propertiesProtractorClassical mechanics
The invention relates to an indoor rock mechanics test device, in particular to a rock Brazilian test fixture device capable of accurately controlling a layered rock splitting direction, and belongs to the technical field of geotechnical engineering. The device is composed of an upper pressing plate, a lower pressing plate, a filler strip, a baffle, a protractor, a clamping panel and a telescopicscrew. According to the rock Brazilian test fixture device capable of accurately controlling the layered rock splitting direction, the problems that in a traditional Brazilian splitting fixture device, sample centering is difficult, bedding inclination angle control is inaccurate, and splitting crack angle measurement is inconvenient are solved; the rock Brazilian test fixture device is capable ofaccurately applying the linear load to the sample, conveniently controlling the bedding inclination angle, measuring the stratified rock splitting angle, ensuring the reliability of the result and accurately controlling the stratified rock splitting direction is simple in structure, safe to operate and high in practicability, and can be universally used for assembling and testing the stratified rock Brazilian split sample.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Zoology reconditioning technical method of mountains rock landscape
The invention relates to a treatment technique of ecological landscape restoration, in particular to an ecological restoration technology method of mountain and rock landscape by being treated with utilization of the ecological landscape and waste elements, solving the defect that the mountain and rock without ecological treatment lack in the green landscape. The technical proposal of the invention is that bio1ogical solution is initially prepared with the ingredients of (proportioning by weight) 43-48 portions of waste saw dust, 19-25 portions of tea oil slag, 23-29 portions of human urine, 11-13 portions of bittern and 8-11 proportions of green moss (being rolling into powder); the ingredients are smashed and mixed and added corresponding mineral pigments and ink according to the color situation of rocks to be sprinkled to rocks and mountains so as to produce a natural ecological landscape with primitive simplicity. (The capacity ratio of mineral pigments and water is 9-91 and the capacity ratio of ink and water is 6-94.) The rocks and mountains are moistened according to the situation of rain water and dew and humid conditions; the green moss and plants grow after the rocks arecombined with alkali water, thus the green ecological landscape is resumed and the landscape environment is beautified. The invention is mainly used for ecological landscape restoration of rocks and abandoned mines as well as reclamation of green plants.
Owner:王卿芳
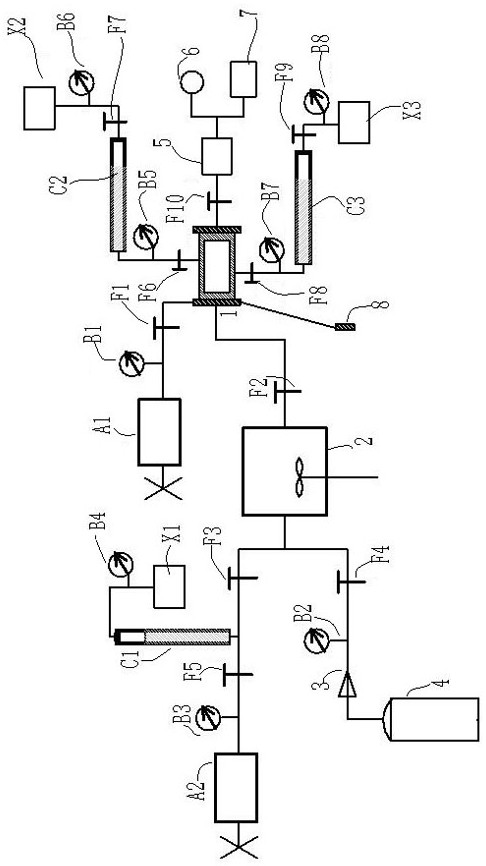
Multifunctional high-temperature high-pressure rock true triaxial experiment system and method
InactiveCN112284923AAchieving associativityImprove scienceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesPermeability/surface area analysisAxial pressureClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a multifunctional high-temperature high-pressure rock true triaxial experiment system and method, which belong to the technical field of rock experiment analysis. The system comprises a true triaxial pressure container, an axial pressure loading device, a confining pressure loading device, a pore pressure loading inlet and a pore pressure outlet; the upper section of the true triaxial pressure container is connected with the pore pressure loading inlet, and the lower end is connected with the pore pressure loading outlet; four external channels are arranged on the outer wall of the true triaxial pressure container and are symmetrically connected with the confining pressure loading system in pairs; the external channels are directly communicated with the confining pressure cavity of the true triaxial pressure container; by adopting the system and the method, gas-liquid single-phase seepage, gas displacement, adsorption and desorption, competitive adsorption andwater-gas two-phase seepage rules can be studied in a rock high-temperature true triaxial loading state, and the radial deformation and anisotropy of a rock sample in a first horizontal direction anda second horizontal direction can be measured at the same time; by coupling the work of each system, the complex geological environment where the rock is located is truly simulated in the experiment process, and the relevance, scientificity and accuracy of detection data are improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
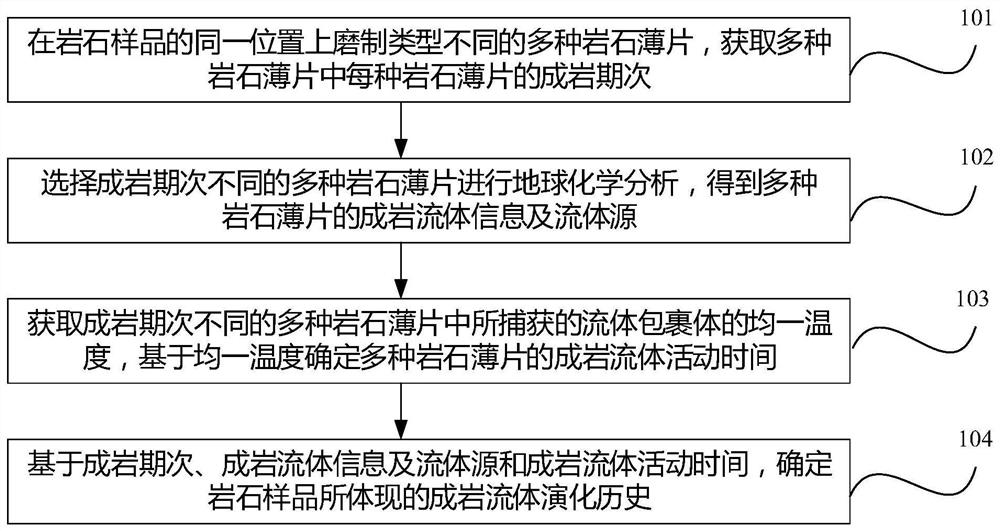
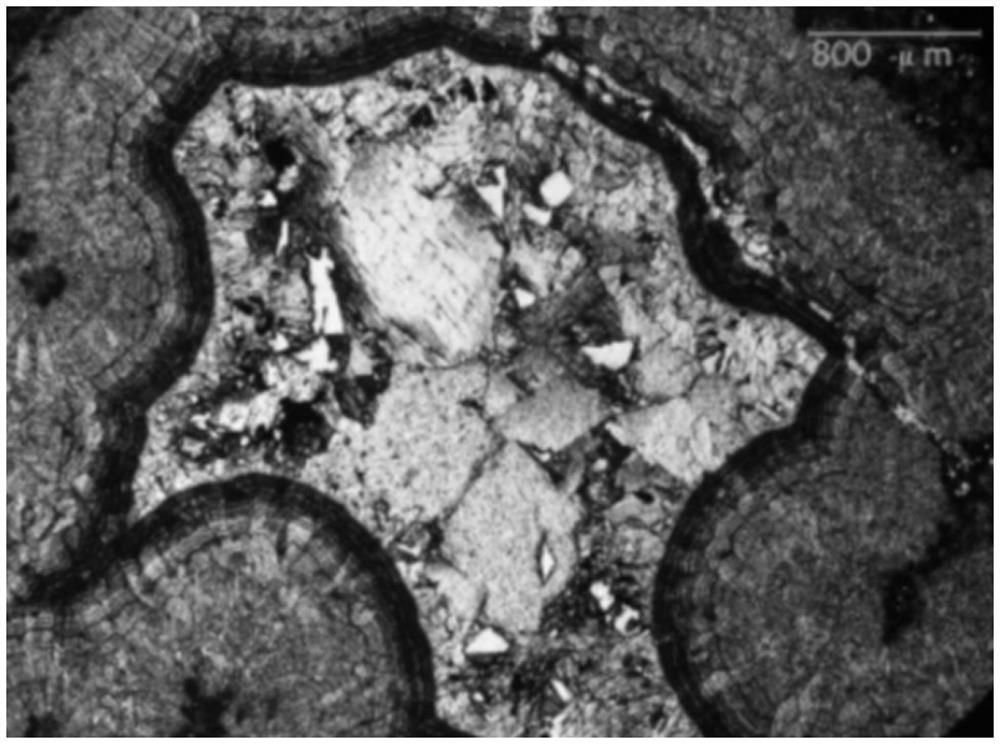
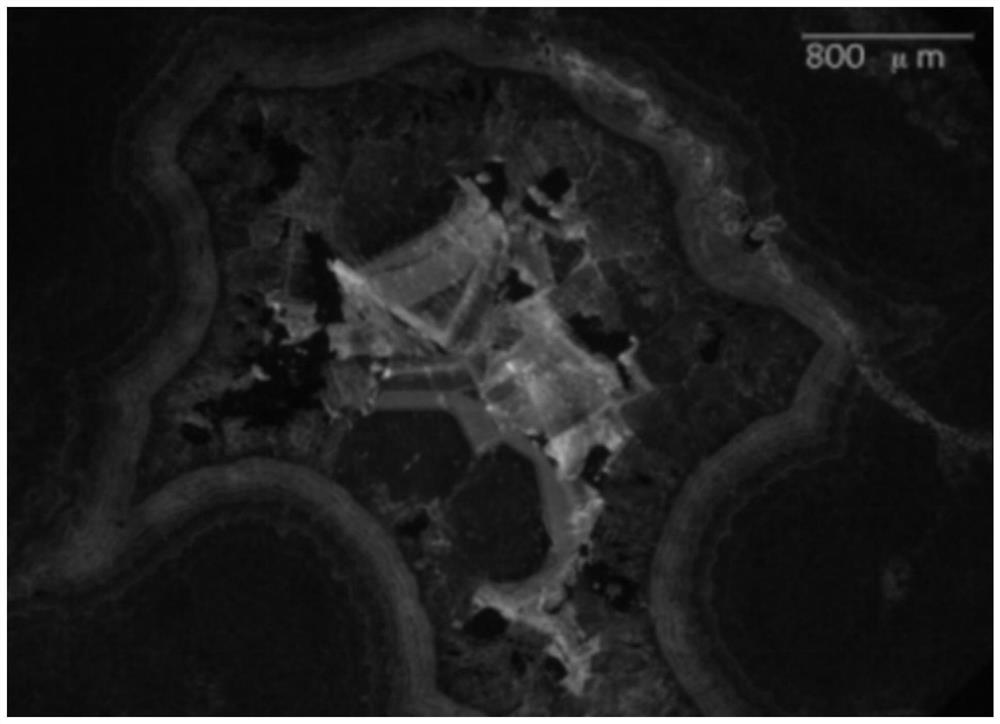
Method for determining diagenesis fluid evolution history
PendingCN113916880AEasy to buildBuild accuratelyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRock samplePetroleum
The invention discloses a method for determining diagenesis fluid evolution history, and belongs to the field of petroleum and natural gas exploration. The method comprises the following steps: grinding a plurality of rock slices with different types at the same position of a rock sample, and obtaining the diagenesis period of each rock slice in the plurality of rock slices; selecting the multiple rock slices with different diagenesis periods for geochemical analysis to obtain diagenesis fluid information and fluid sources of the multiple rock slices; obtaining the uniform temperature of the fluid inclusion captured in the multiple rock slices with different diagenesis periods, and determining the diagenesis fluid activity time of the multiple rock slices based on the uniform temperature; and determining the diagenetic fluid evolution history embodied by the rock sample based on the diagenetic period, the diagenetic fluid information, the fluid source and the diagenetic fluid activity time. Therefore, the diagenetic fluid characteristics and diagenetic fluid evolution history of the marine carbonate rock can be simply, conveniently and accurately constructed.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
A double structural plane direct shear test method for studying the mechanism of sliding rockburst
ActiveCN106323768BReliable experimental methodPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesSquare cross sectionStress conditions
The invention provides a dual-structure plane direct shear test method for studying the mechanism of slip-type rockburst, which includes the following steps: making a rock sample with a square cross-section; and sequentially generating a dual-parallel structure from the rock sample under Brazilian splitting conditions. surface; conduct 3D scanning of the double parallel structural surfaces respectively, obtain the three-dimensional digital model of the double parallel structural surfaces and calculate their roughness; place the rock sample on the shear testing machine, and install the acoustic emission monitoring probe on the bottom side, and test The sample was subjected to a direct shear test under normal normal stress conditions, and the acoustic emission signal of the rock specimen was monitored at the same time; the shear time, shear stress, shear displacement, and acoustic emission signal data during the shear test were summarized and sorted. On this basis, The mechanism of slip-type rockburst in this rock sample is analyzed. The present invention constructs a simplified rock mass system in which structural surfaces and rocks interact and influence each other within the scope of the laboratory, and can provide a more reliable experimental method for mechanism research and early warning prediction of slip-type rock bursts.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Construction method of specialized garden for lithophytes in south China
The invention discloses a construction method of a specialized garden for lithophytes in the south China. According to the construction method, specific landscape stone-Yingde stone in the south Chinais utilized, Taishan stone is assisted, the screened native specific lithophytes are combined, so that the lithophytes can truly and fixedly grow on the rock to form a 'natural, stable, stereoscopicand alternate' lithophytes landscape. The construction method can be applied and popularized to the construction of botanical gardens, specialized rock gardens, garden expos and related rock landscapeengineering.
Owner:东莞植物园
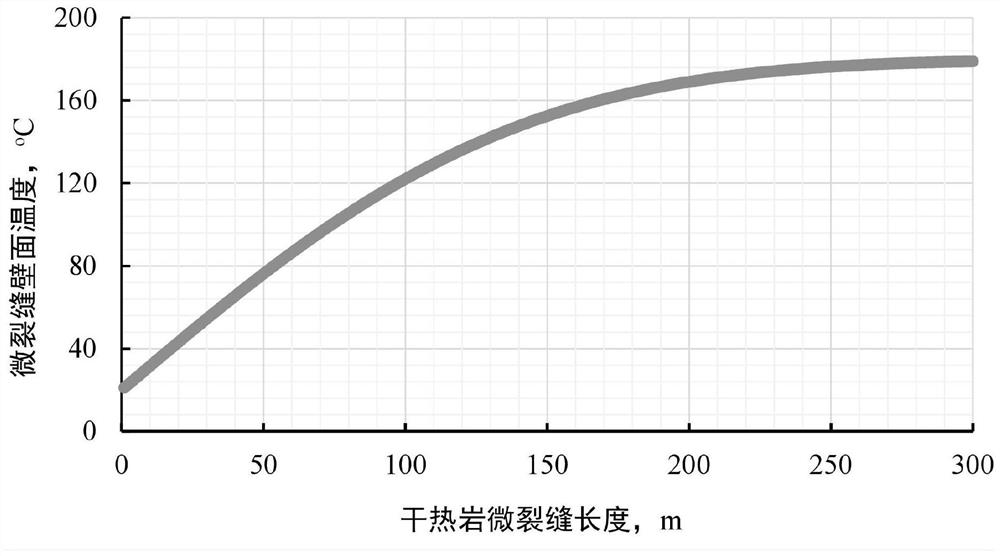
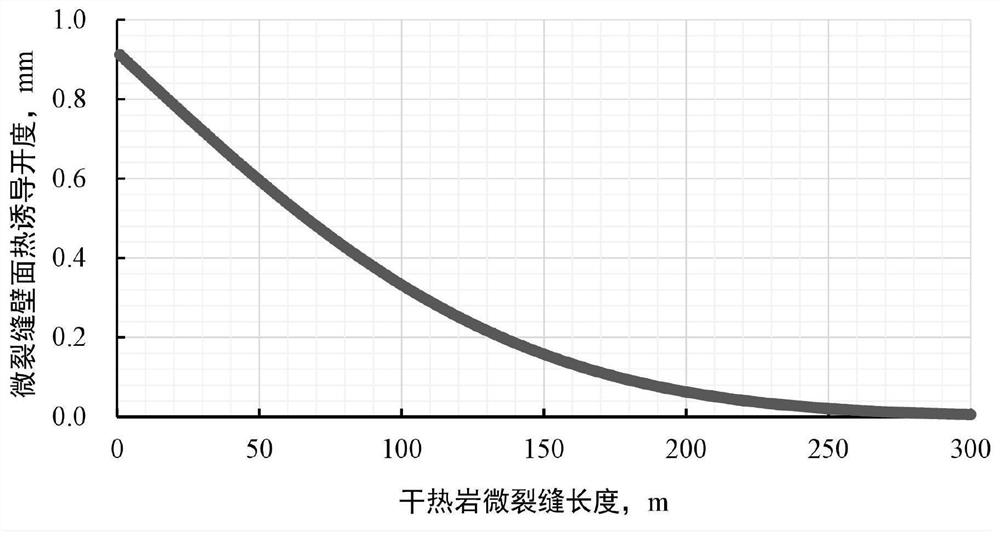
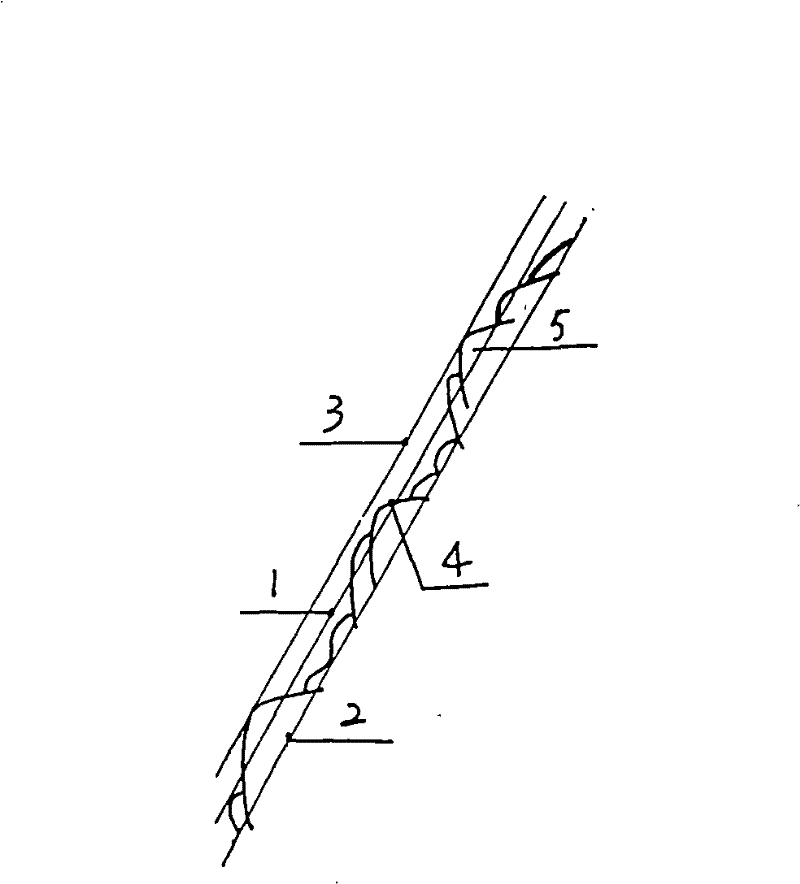
Calculation method for micro-crack thermally induced conductivity of hot dry rock mass
ActiveCN113204928AAccurate comprehensive diversion capacityDesign optimisation/simulationBorehole/well accessoriesThermodynamicsRock core
The invention discloses a calculation method for micro-crack thermally induced conductivity of hot dry rock mass. The method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting a dry hot rock mass reservoir core containing a micro-crack, and carrying out laser scanning to obtain two-dimensional morphology data of the micro-crack, and S2, calculating a roughness coefficient of the micro-crack according to the two-dimensional morphology data; S3, according to the in-situ stress state and the mechanical strength of the hot dry rock mass, calculating the initial mechanical opening degree of the hot dry rock mass micro-crack; S4, calculating the temperature field of the wall surface of the micro-crack in a hydraulic fracturing long-term injection process in combination with rock thermophysical parameters of the dry hot rock mass; S5, according to the temperature drop and mechanical parameters of the wall surface of the micro-crack of the hot dry rock mass, calculating the thermal induction opening degree of the wall surface of the micro-crack in the hydraulic fracturing long-term injection process; and S6, according to the initial mechanical opening degree and the thermal induction opening degree, calculating the flow guide opening degree, the thermal induction flow guide capacity and the micro-crack comprehensive conductivity capability at any position of the dry hot rock mass micro-crack. The method provided by the invention can accurately calculate the comprehensive flow conductivity of the micro-crack after the hot dry rock transformation.
Owner:河北省煤田地质局第二地质队
Ecological restoration method of bare rock engineering wound-surface vegetation
InactiveCN101491193BPreserve flatnessLess investmentCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationVegetationEcological environment
The invention relates to a method for ecologically restoring vegetation on the bare rock engineering wound surface, which belongs to the technical field of vegetation ecological restoration. A similarly natural mode is used to accelerate the restoration of the vegetation ecological environment and landscape. The method comprises the following steps: firstly carrying out the pretreatment on the bare rock engineering wound surface, and retaining the definite natural unevenness and fissure degree of the actual slope line (4) of the bare rock within the range from the low level control line (2) to the high level control line (3) of a designed slope line (1) under the preconditions of keeping a stable rock slope base and removing dangerous and floating stones; and by adhering to the concept ofartificial guidance and natural selection, adjusting measures to the local conditions according to the geological, geomorphic and climatic conditions and different target vegetations, and adopting different processes and slurries with different components to carry out the spray sowing on the rock slope. The method has low cost and high efficiency, facilitates the retention of soil and plant seed sources, and completes at one pass the vegetation restoration which needs years of accumulation and multiple superposition of the natural force. The vegetation ecological restoration is similar to thenature, but is far quicker than the nature. The prosperous period or declining period of a single species mutation can never appear. The method is particularly suitable for the large-area application, achieves the landscape and ecological effects in the near term, the medium term and the long term, and has practical and long term significance.
Owner:赵平 +1
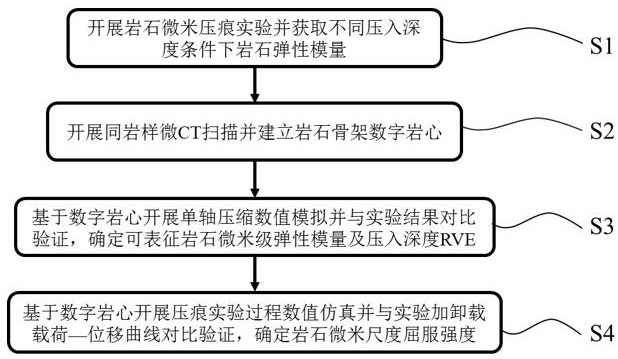
A Method for Obtaining Rock Microscale Elastic Modulus and Yield Strength
ActiveCN109060539BSolve defects that cannot be applied to the micro scaleMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMicron scaleRock sample
The invention discloses a method for acquiring micro-scale rock elastic modulus and yield strength parameters. The method includes: using a micron-scale indenter to carry out a rock micron indentation experiment, obtaining a load-displacement curve during the loading process, and combining the indentation experiment formula to obtain the elastic modulus of the rock under different displacement conditions; carrying out micro-CT on the rock sample Scan to establish a finite element mesh model of the rock skeleton in the indentation area; use the elastic modulus obtained from the micron indentation experiment as an input parameter to simulate the rock uniaxial compression process, obtain the overall elastic modulus of the model and compare it with the core uniaxial compression experiment , determine the indentation depth RVE that effectively characterizes the micron elastic modulus of the rock; then, carry out the numerical simulation of rock sample indentation experiments under different yield strength conditions, and compare and verify the loading and unloading load-displacement curves obtained from the simulation with the indentation experiments , so as to determine the yield strength of the rock at the micron scale.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
A method for ecological restoration of rocky mountain vegetation
ActiveCN113243258BReduce lossGuaranteed growth environmentGeneral water supply conservationHops/wine cultivationMicroorganismVegetation
The invention discloses a rocky mountain vegetation ecological restoration method, which includes a rocky mountain body, and selects a corresponding restoration method by measuring the inclination angle of the rocky mountain body. In the present invention, planting points of drought-resistant plants are arranged on the rocky mountain, and a waterproof cloth that can reduce water loss and collect rain, snow, and dew is laid in the conical tree pit, so that the waterproof cloth can collect water as much as possible in the root of the plant to ensure the growth of vegetation Environment: By laying a straw network or a grass-filled round pipe bag between the conical tree pits, it can greatly increase the water content of the soil around the repair vegetation, reduce water loss, increase the content of humus in rock debris soil, and increase the content of microorganisms As well as tiny organisms, improving the characteristics of rocky soils and improving restoration efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN INVESTIGATION & RES INST
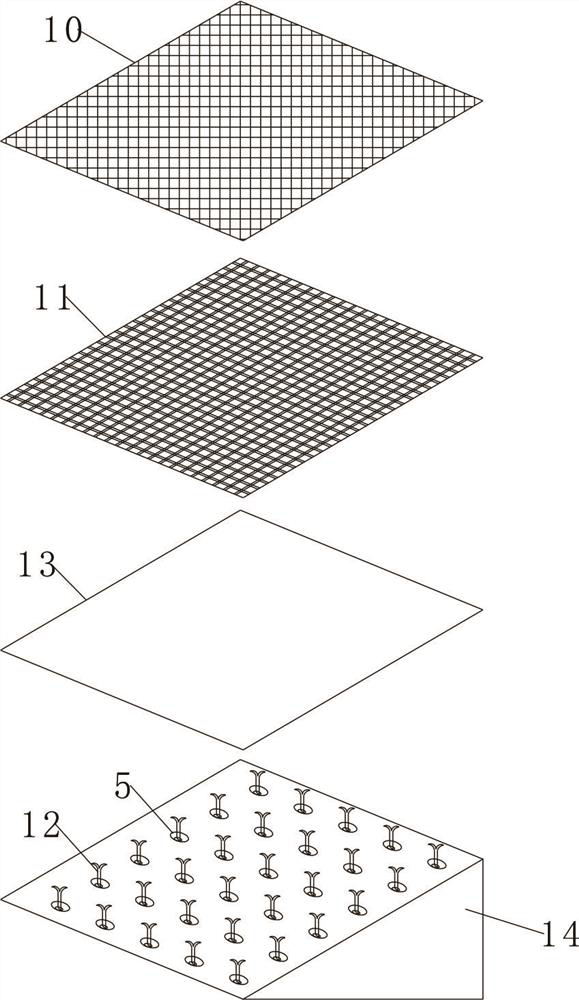
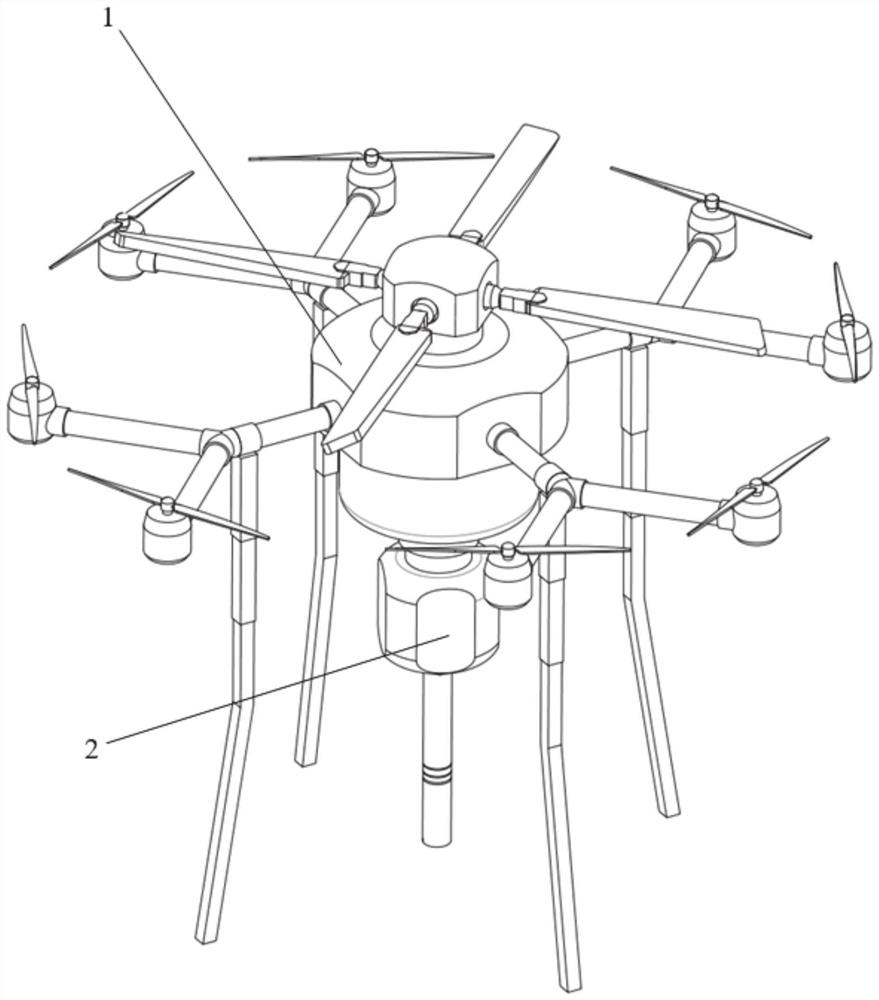
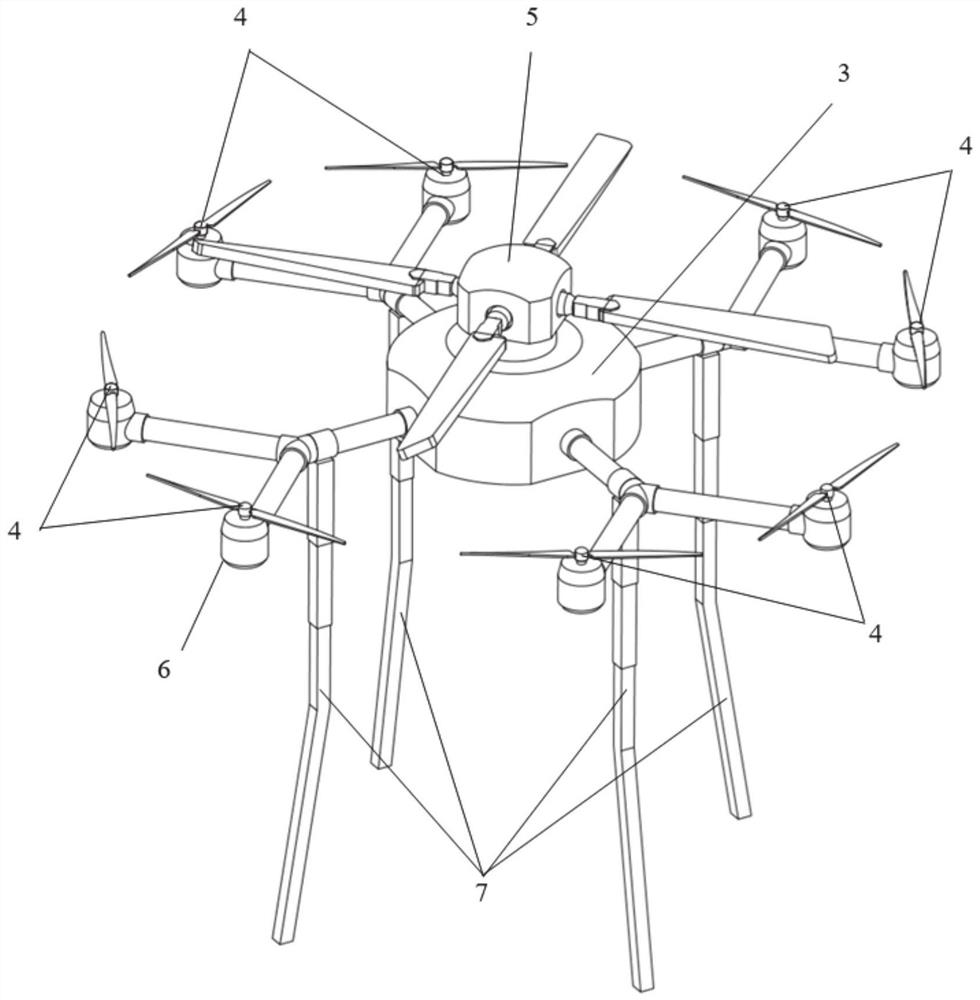
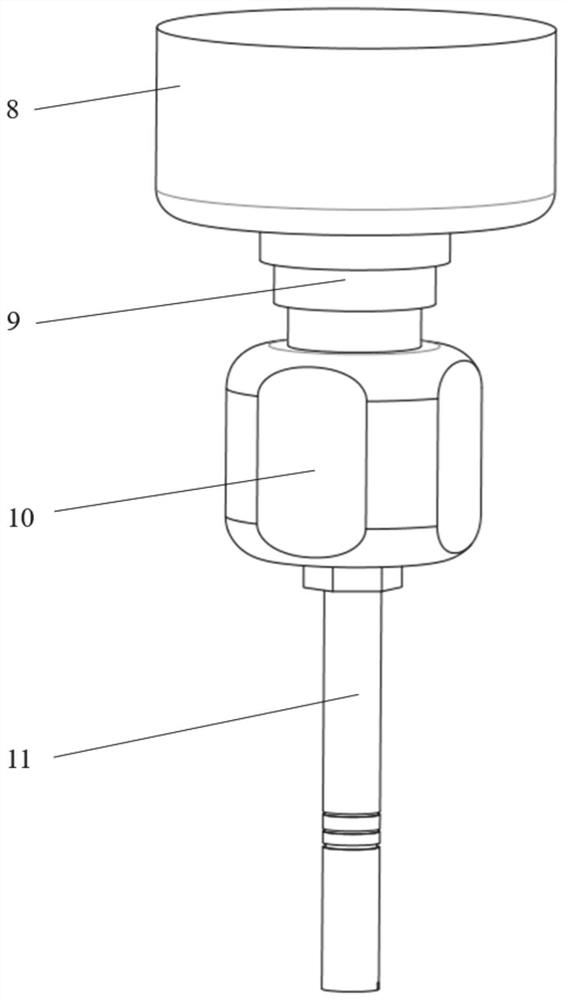
A field rock automatic sampling system and its working method
ActiveCN111562134BReduce work intensityGood effectWithdrawing sample devicesRemote controlled aircraftClassical mechanicsUncrewed vehicle
The invention belongs to the technical field of rock sampling, and provides an automatic field rock sampling system and its working method, which solves the great limitations of sampling work, and at the same time, the obtained samples often have irregular shapes and small volumes that contain information. For limited problems, it has a high degree of automation and can conveniently collect rock samples in various terrain areas. Among them, the field rock automatic sampling system includes a drone and a drilling system, the drilling system is mounted on the lower part of the drone; Man-machine flight, the reaction force propeller is used to provide drilling pressure for the drilling system to sample the target rock in the dangerous zone.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A Method for Evaluation of Leakage Risk Area in the Process of CO2 Geological Storage
ActiveCN109033737BReliable resultsSimple resultComplex mathematical operationsNumerical modelsCarbon sequestration
A kind of CO 2 The evaluation method of the leakage risk area during the geological storage process uses the principle of sedimentary microfacies constraint, how to obtain the rock mechanical parameters of the caprock, and select a suitable fracture pressure prediction model to evaluate the mechanical sealing of the caprock, using fine geological models and numerical values. Model, applying reservoir numerical model theory, and in-depth study of CO through the established storage volume numerical model 2 Injection process until storage for 200 years to store pressure and CO in the body 2 Dynamic changes in saturation. Using the concepts of fluid potential and potential gradient in oil and gas migration theory combined with CO 2 Saturation dynamic distribution analysisCO 2 migration direction and accumulation area, and then according to the CO in the storage body 2 The migration direction and distribution characteristics of the storage body and sand body boundary are combined to conduct lateral CO 2 Leakage risk prediction; Based on the rupture pressure distribution characteristics of the caprock and the dynamic distribution characteristics of the pressure in the storage body, CO is quantitatively studied through the proposed identification formula of the caprock rupture risk area. 2 Possible leakage risk areas longitudinally along the migration path. This method is used in low permeability reservoir CO 2 It has important practical application value to achieve safe and efficient carbon sequestration during oil displacement.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Heat-water-force combined action rock statistical damage calculation method and application thereof
PendingCN113155699AComprehensiveImprove applicabilityPermeability/surface area analysisData acquisitionCurve fitting
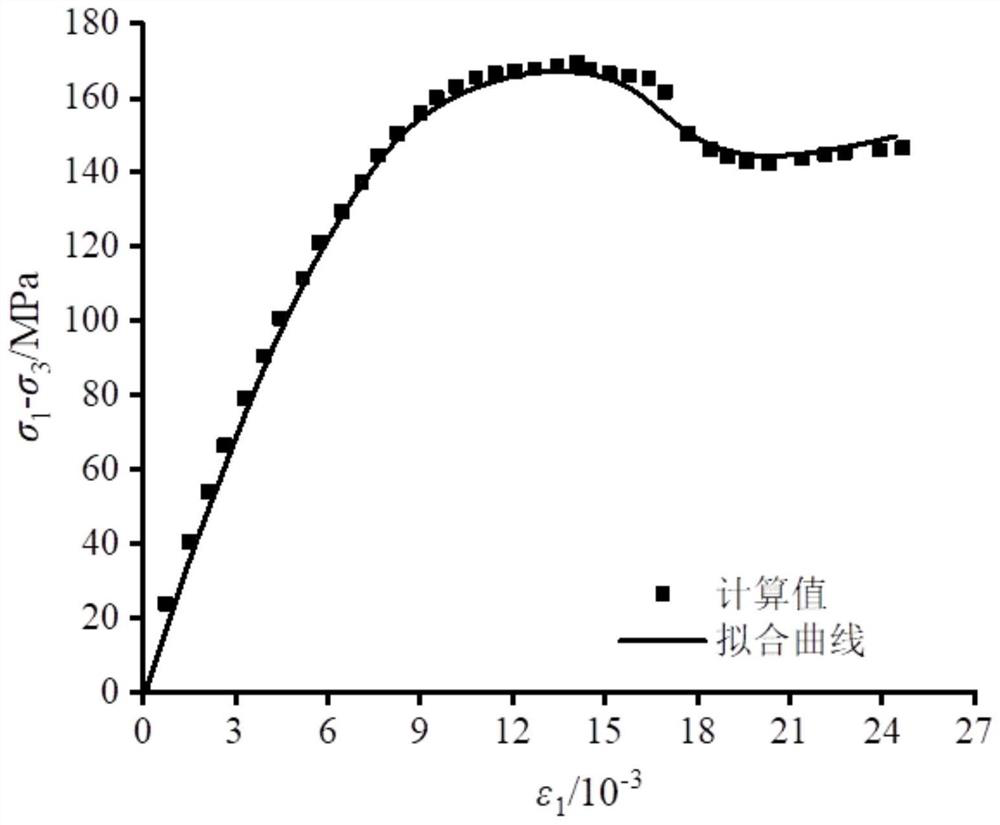
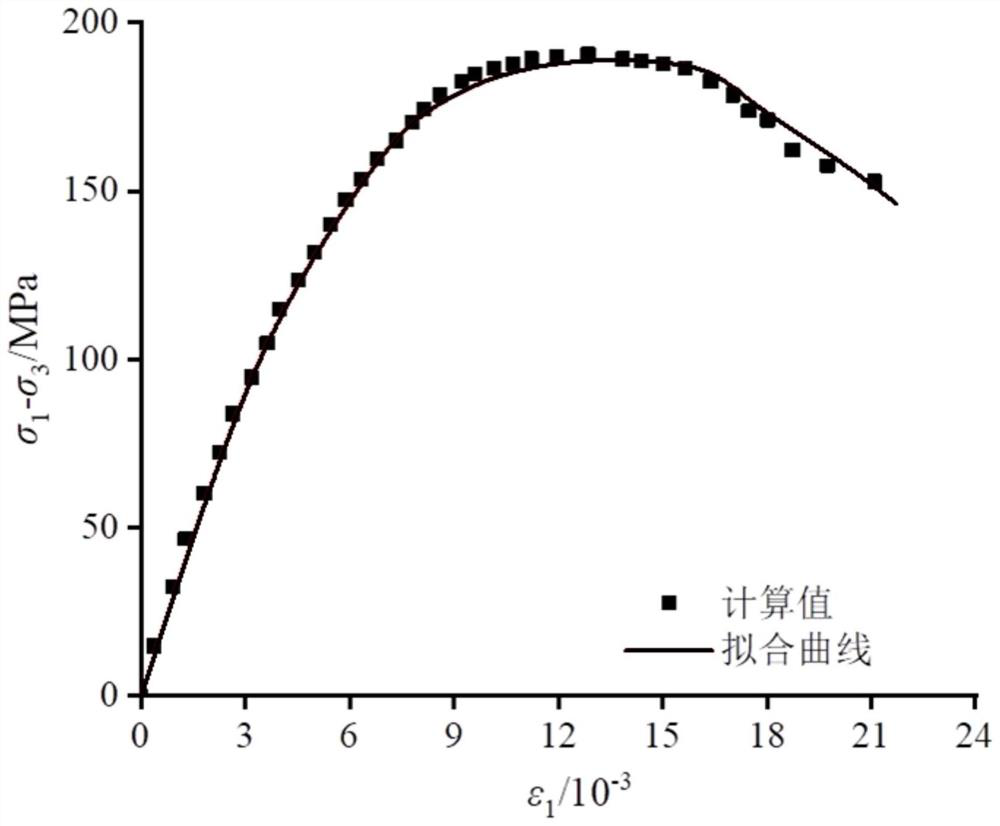
The invention provides a heat-water-force combined action rock statistical damage calculation method, and also provides a test device applying the calculation method. The device comprises a high-temperature heating device (less than 100 DEG C), a seepage device, a pressure chamber, a base test board, a pressure applying element, a top plate, a stress detection element, a strain detection element, a temperature detection element, a water flow detection element and an automatic detection data acquisition device. According to the method, the calculation process is complex, the method has high comprehensiveness, the method is applied to the rock triaxial compression seepage test, compared with an existing model, the provided new model is high in comprehensiveness and applicability, and the fitting degree of a stress-strain curve obtained through the test is high. The deformation and failure characteristics of the rock under the action of different temperatures are reflected, the trend of the post-peak stage is fully reflected, and the stress-strain relationship of the high-temperature rock under the triaxial compression-seepage coupling test condition can be well reflected.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
A method for obtaining unfrozen water content in rocks under freeze-thaw cycle conditions
ActiveCN110806422BEasy to testReduce mistakesMaterial moisture contentWater resource assessmentNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonancePhysical chemistry
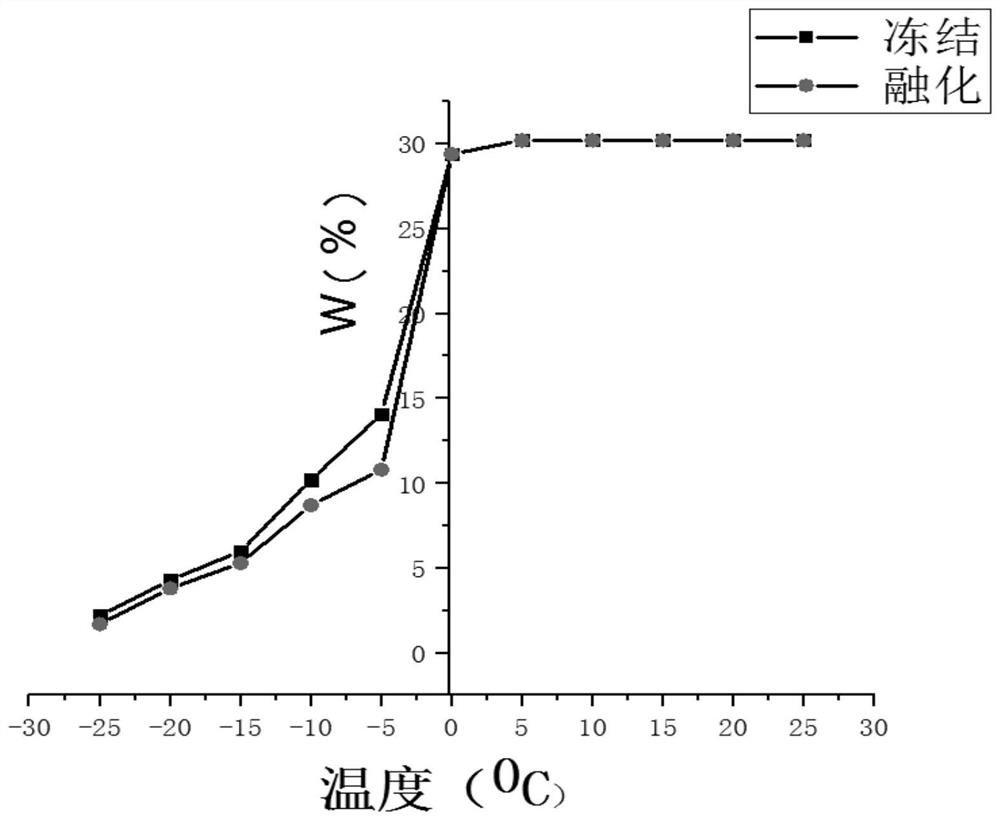
The invention belongs to the technical field of thawing rocks, and discloses a method for obtaining unfrozen water content in rocks under freeze-thaw cycle conditions, and the method comprises the following steps of preparing rock column samples, and saturating the rock column samples with formation water; performing a nuclear magnetic resonance test on the rock column samples of saturated formation water to obtain a T2 spectrum curve; converting the T2 spectrum curve into a nuclear magnetic pore throat distribution curve f(r); bringing the nuclear magnetic pore throat distribution curve f(r)into an integral formula to respectively obtain the relationship curve between unfrozen water content and temperature during melting and freezing. The method for obtaining the unfrozen water content in rocks under the freeze-thaw cycle conditions provided by the invention can achieve high accuracy and high reliability, and is easy to obtain the unfrozen water content.
Owner:INST OF ROCK & SOIL MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A cross-sectional rock formation sampling device for studying biofossil belts
InactiveCN110118668BConvenient researchIntegrity guaranteedWithdrawing sample devicesRock sampleVision sensor
The invention discloses a section rock sampling device for studying biofossil belts, which comprises a base, an elevating ladder and a box body arranged on the top of the elevating ladder, and a power drive mechanism, a drilling mechanism, a sampling mechanism and a visual sensor are mounted in the box body , the base is equipped with a display controller electrically connected with the power drive mechanism, the drilling mechanism, the sampling mechanism and the navigation mechanism. The present invention can accurately sample the mountain section presenting the biofossil belt, and use a small electric drill to excavate a cylindrical rock sample on the rock, and then use the gripper of a manipulator to take it out. For chip samples, the present invention can ensure the integrity of the samples to the greatest extent, and can also obtain larger volume samples, which is more convenient for studying biological fossil belts in rocks. In a word, the rock formation sampling device of the present invention has the advantages of high flexibility, strong adaptability, and high sampling integrity.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
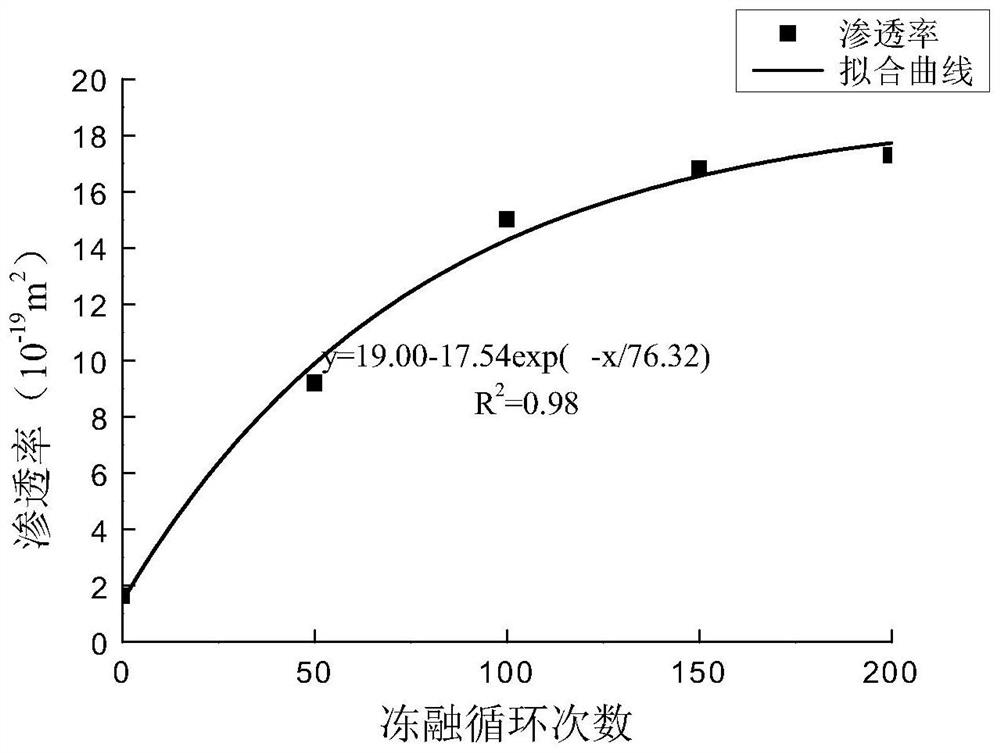
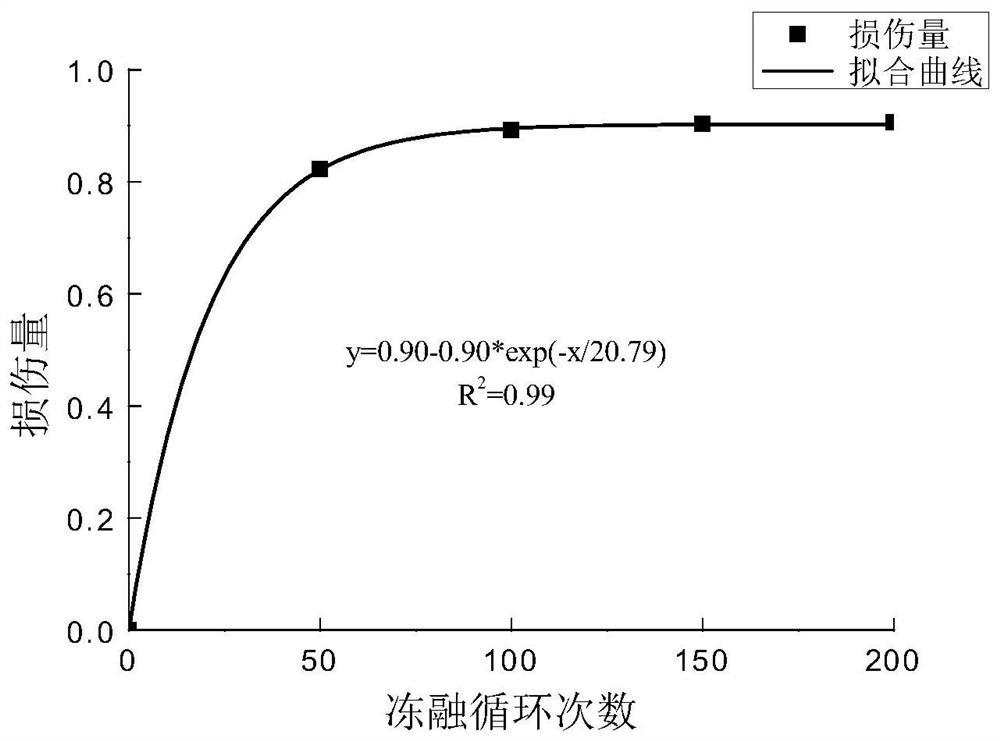
A method to determine the degree of freeze-thaw damage of rocks in high-altitude cold regions
ActiveCN108956412BPredict damageHigh use valuePermeability/surface area analysisFreeze thawingThermodynamics
The invention discloses a method for determining freezing-thawing damage degree of a rock in a high-altitude cold region. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a high-altitude cold region rock sample, drying the sample to a constant weight, cooling the sample, and saturating the sample with water; performing freeze-thaw cycle treatment on the water-saturated sample, measuring the gaspermeability of the sample under the same confining pressure under the same osmotic pressure after different freeze-thaw cycles, drawing a change curve of the gas permeability of the rock with different freeze-thaw cycles, and fitting the curve; defining a calculation formula of a freezing-thawing damage quantity D: D = 1 - (ki / k0),wherein k0 is the gas permeability of the sample before freezingand thawing, ki is the gas permeability of the sample after i freezing-thawing cycles, and i=1, 2, 3, 4...; and drawing a change curve of the freezing-thawing damage quantity of the rock with the number of freezing-thawing cycles, fitting the curve by a function, and determining the according to the degree of rock damages caused by any freezing-thawing cycle according to the fitting function. Themethod defines the freezing-thawing damage quantity of the rock by the gas permeability of the rock, and makes a test result accurate, scientific and reliable.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
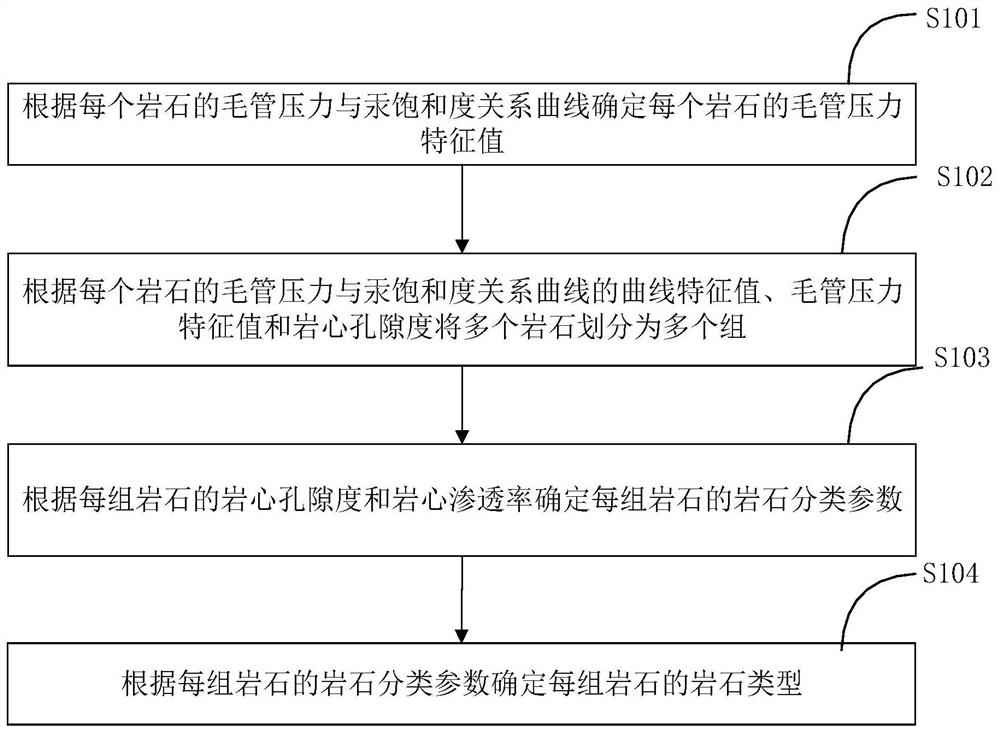
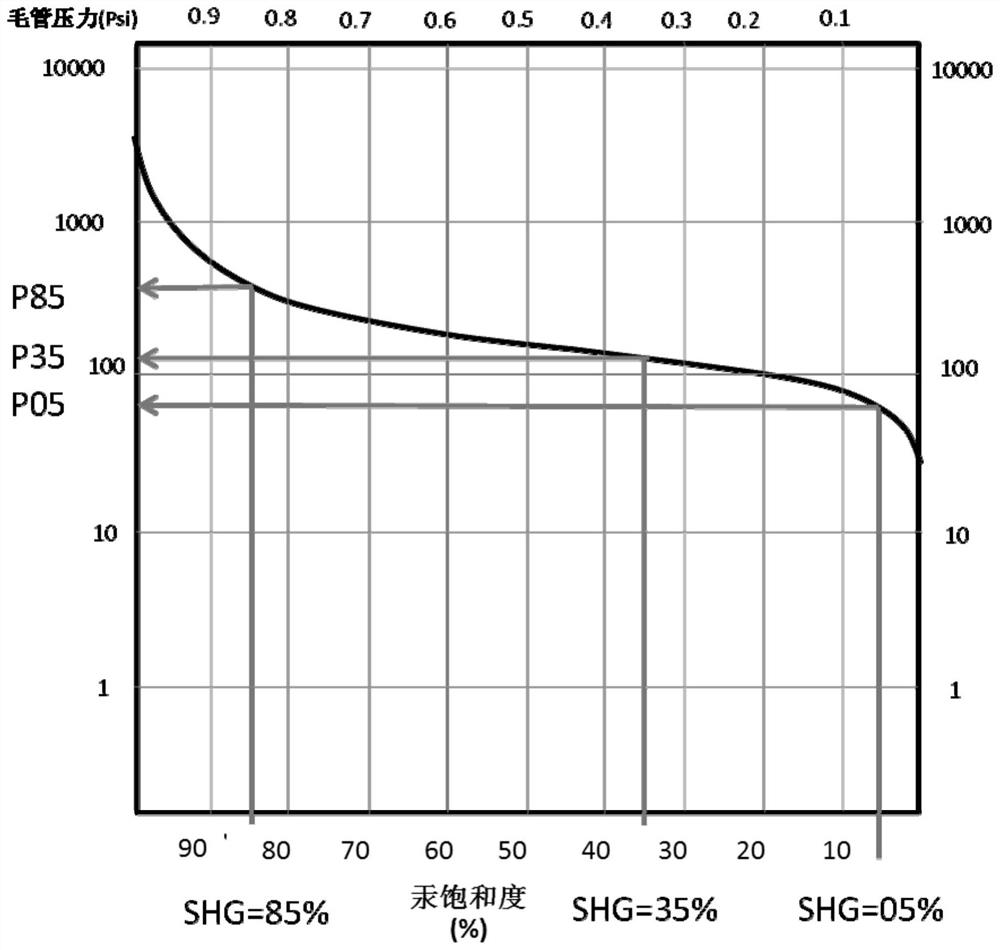
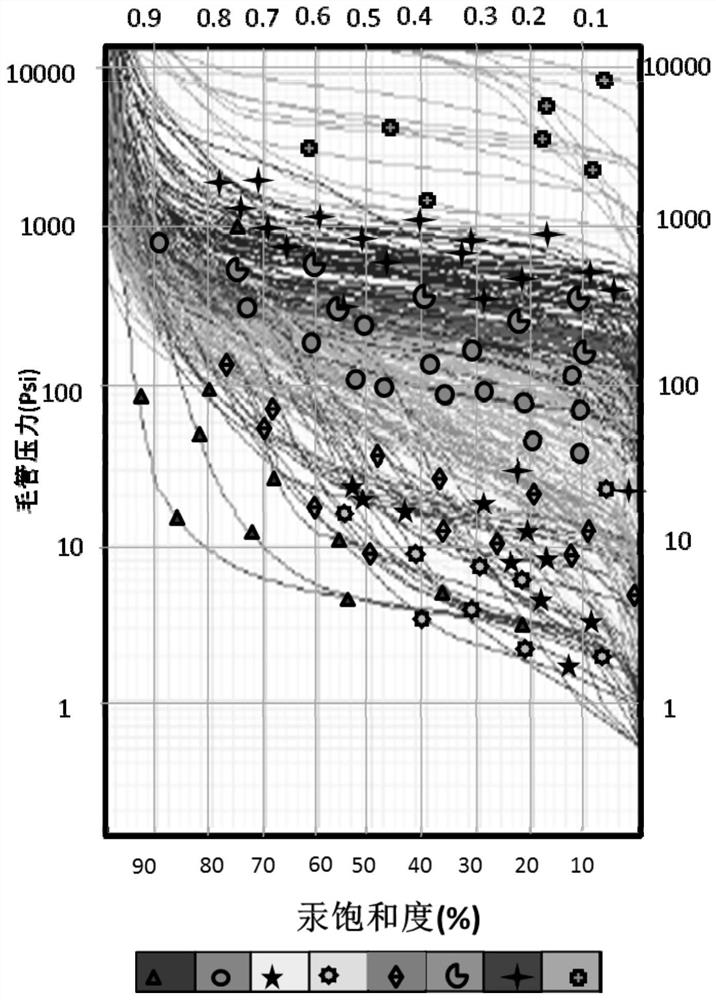
Rock type division method and system
The invention provides a rock type division method and system. The rock type division method comprises the following steps of: determining a capillary pressure characteristic value of each rock according to a capillary pressure and mercury saturation relation curve of each rock; dividing the plurality of rocks into a plurality of groups according to the curve characteristic value of the capillary pressure and mercury saturation relation curve of each rock, the capillary pressure characteristic value and the core porosity; determining rock classification parameters of each group of rocks according to the core porosity and the core permeability of each group of rocks; and determining the rock type of each group of rocks according to the rock classification parameters of each group of rocks so as to quantitatively divide the rock types. The rock type division method and system are high in operability, and point out a direction for the next efficient development of the carbonate rock oil and gas field.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
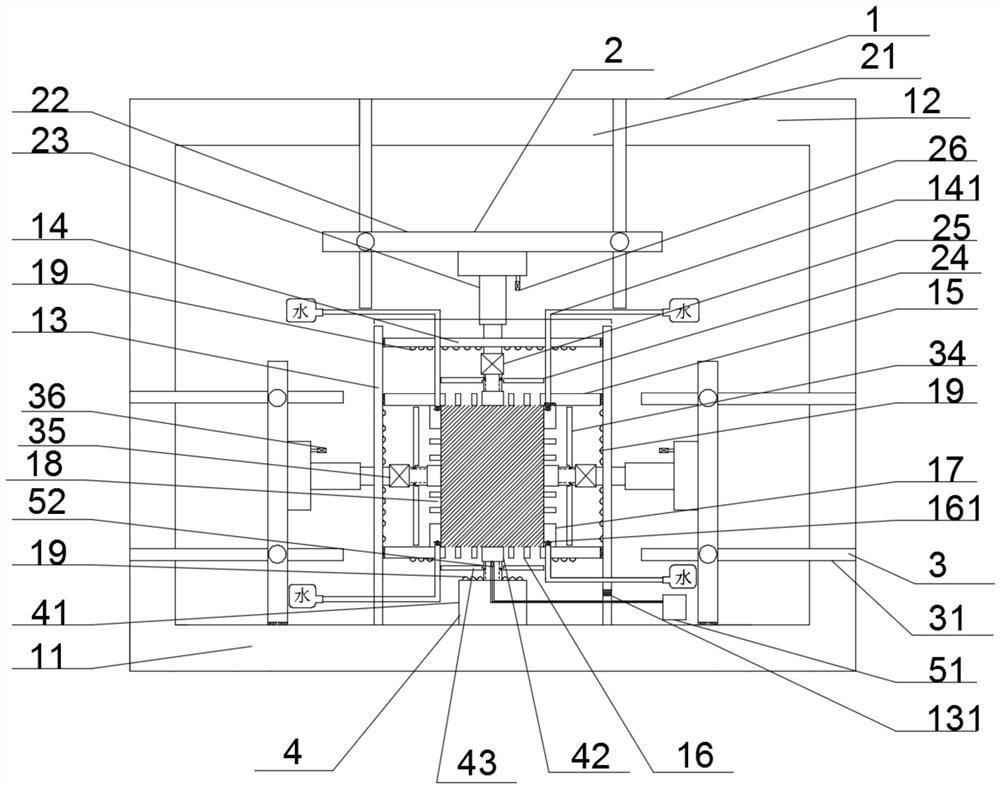
An all-in-one machine suitable for rock true triaxial, dry-wet cycle and acoustic emission tests
ActiveCN110441144BAchieve fixationAid in geological researchMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesAcoustic emissionAxial pressure
The invention relates to an all-in-one machine suitable for rock true triaxial, dry-wet cycle, and acoustic emission tests, including: a test accommodation mechanism, a top lifting mechanism, a lateral telescopic mechanism, a bottom lifting mechanism, an acoustic emission mechanism, and a test accommodation mechanism Including base, bracket, barrel-shaped reaction force thick wall, oven cover, top axial pressure plate, bottom axial pressure plate, several lateral axial pressure plates, top lifting mechanism is fixed with oven cover, top axial pressure plate, lateral The telescopic mechanism is fixed to the lateral axial pressure plate, the bottom lifting mechanism is fixed to the bottom axial pressure plate, and the acoustic emission mechanism is arranged on the bottom lifting mechanism, and sends sound waves into the accommodating space. The invention realizes the fixing of the rock in the three-axis direction, can simulate the dry-wet cycle, detects the rock, and is helpful for geological research.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for placing or excavating cavities in mountains
ActiveCN104271867BImprove efficiencyDisloding machinesUnderground chambersPlasma generatorEngineering
The invention relates to a method for excavating or inserting cavities in mountains, in which method the cavities (2) are melted frontally by means of an electric plasma generator. In order to generate in such a method an energy density sufficient to completely or partially vaporize the existing rock on the front of the cavity (2), the invention proposes that a thermal protection shield (4) is arranged directly on the front of the cavity (2), which heat The protective cover and the front face of the cavity (2) form a dynamic pressure chamber (7), in which the temperature is adjusted to be higher than 2000°C by heating with a plasma generator (8) at a pressure greater than 2 bar. This energy supply is sufficient to melt, completely or partially vaporize and expel the rock located in front of the cavity (2) from the cavity (2).
Owner:约瑟夫·格罗特多斯特
A kind of production method of healthy drinking water
ActiveCN104496097BGreat tasteMeet the requirements of health qualityTreatment involving filtrationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisMountain streamWater source
The invention relates to a production method of healthy drinking water, which comprises (1) setting up a ditch on the hillside, setting a creek trough without a top along the trough, and laying tourmaline and tourmaline-like sand on the bottom of the trough; Rocks, so that when the water flows through, small waterfalls and flat streams are formed like mountain streams; (2) On the hillside, plants that are harmless to the soil and water are planted to form a forest environment, and the forest environment will not block the sunlight at the creek; (3) Flow pure water into the creek, so that the water flows through the entire creek for no less than 20 minutes; (4) Filter and sterilize the water flowing out of the creek in order to obtain healthy drinking water. The drinking water obtained in the invention meets people's requirements on the health quality of drinking water. At the same time, the invention has strong applicability, can be implemented all over the country, can be produced on a large scale, has a wide range of water sources and low cost, has great prospects for popularization and application, and fundamentally solves the problems of drinking water safety and drinking water health.
Owner:广西正一投资有限公司
A Method for Constructing Failure Criterion of Rock Under Triaxial Compression
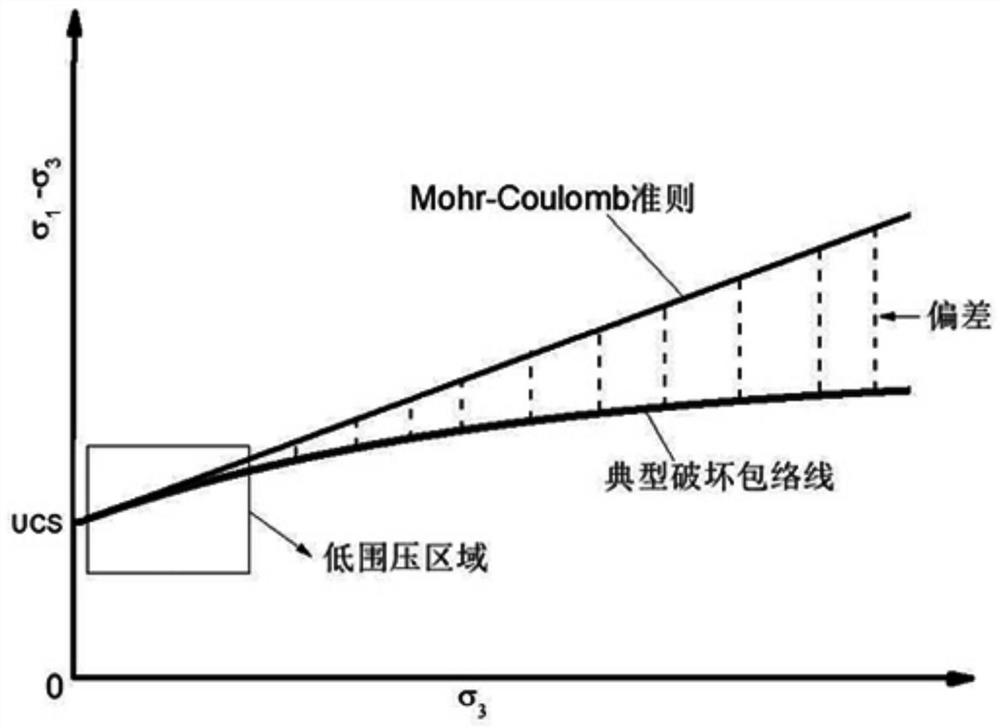
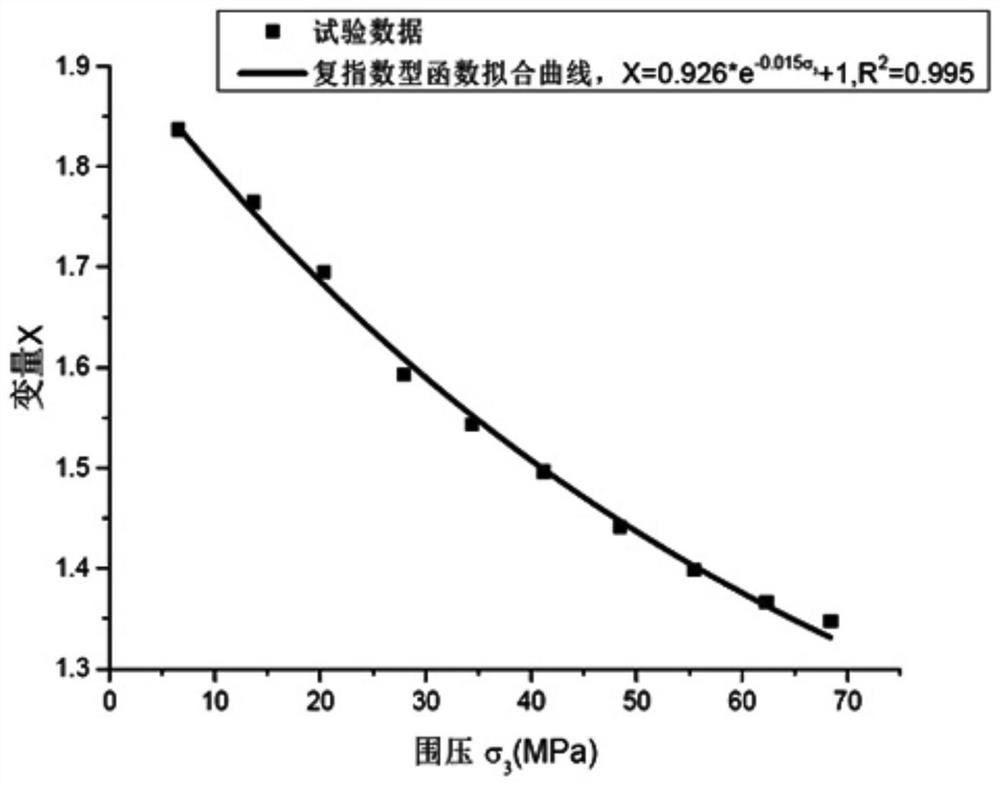
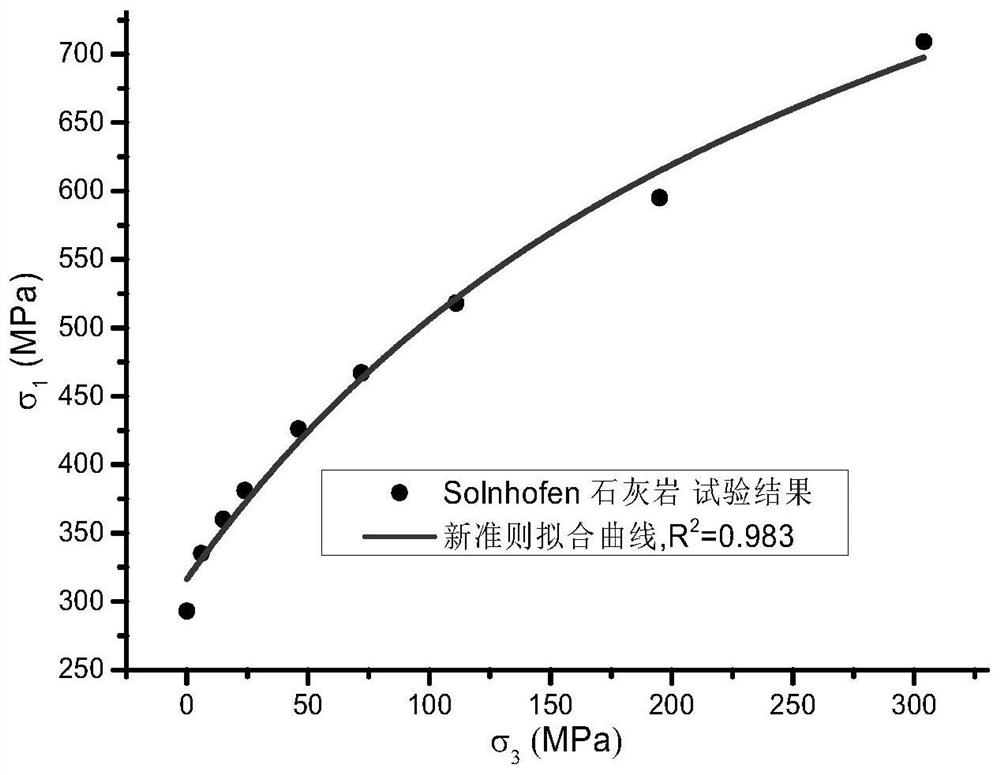
ActiveCN112014213BWell formedParameters are clear and easy to findMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesComplex mathematical operationsFriction angleMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a method for constructing failure criteria of rocks under triaxial compression conditions, comprising the following steps: S1. In view of the fact that the linear Mohr-Coulomb criterion overestimates the peak strength of the low confining pressure section and cannot characterize the rock failure characteristics of the high confining pressure section For the problem of linear characteristics, a new intermediate variable S2 is constructed based on the Mohr-Coulomb criterion and the internal friction angle φ. 3 Reasonable functional expressions for changes; S3. Bring intermediate variables into the Mohr-Coulomb criterion, and obtain a new empirical failure criterion expression for conventional triaxial compression analysis of rocks through parameter substitution; S4. Adopt a variety of rocks The test data of the present invention verifies the criteria established by the present invention, and proves the superiority of the criteria established by the present invention by comparing with the existing five common criteria.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
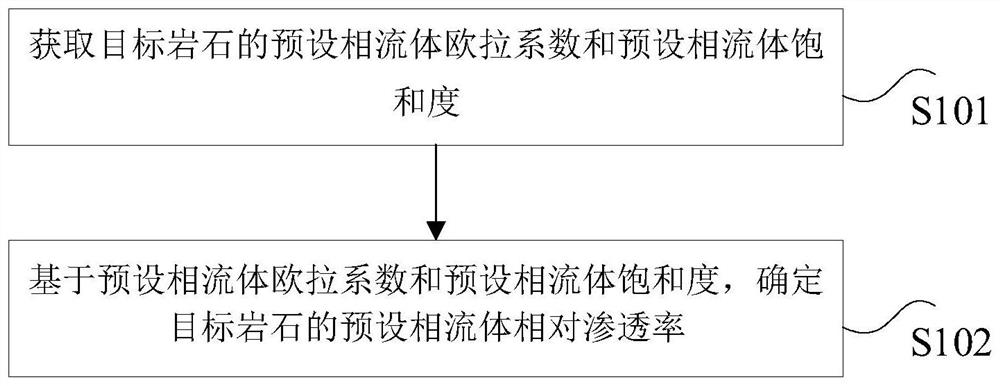
Rock relative permeability determination method and device
ActiveCN112989653ARelative permeability is accurateStrong reliabilityData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationFluid saturationEngineering
The invention provides a rock relative permeability determination method and device. The method comprises the steps that the preset phase fluid Euler coefficient and the preset phase fluid saturation degree of a target rock are obtained, the preset phase fluid Euler coefficient is used for representing the preset phase fluid topological connectivity of the target rock, the preset phase fluid is a wetting phase fluid or a non-wetting phase fluid; and the preset phase fluid relative permeability of the target rock is determined based on the preset phase fluid Euler coefficient and the preset phase fluid saturation. In the scheme, the relative permeability is not only related to the fluid saturation, but also related to the topological connectivity of the fluid, so that the relative permeability of the preset phase fluid of the target rock is determined based on the preset phase fluid Euler coefficient and the preset phase fluid saturation for representing the topological connectivity of the preset phase fluid, and the obtained relative permeability is more accurate; the reliability is high.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Method of predicting parameters of a geological formation
ActiveUS10788598B2Increase probabilityReduce porosityDesign optimisation/simulationProbabilistic networksSi modelComputational physics
Owner:BERGEN TEKNOLOGIOVERFORING AS
A method for automatic identification and classification of rock lithology under deep learning mode
ActiveCN107633255BTo achieve the purpose of automatic identificationReduce the influence of subjective factorsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesNerve networkFeature extraction
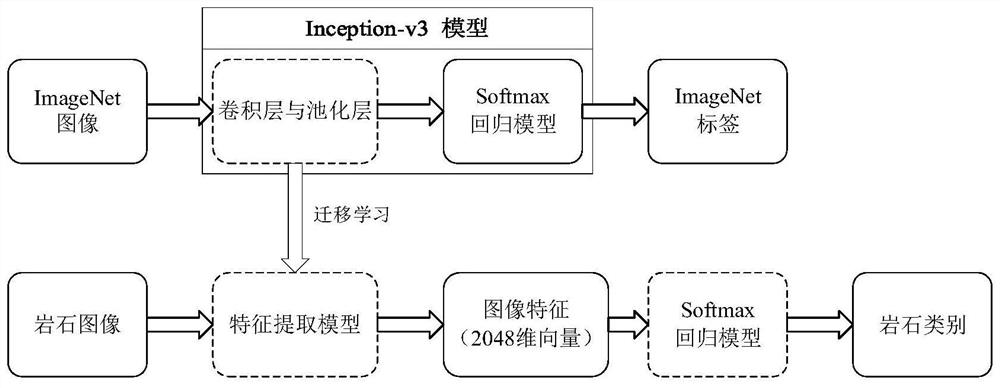
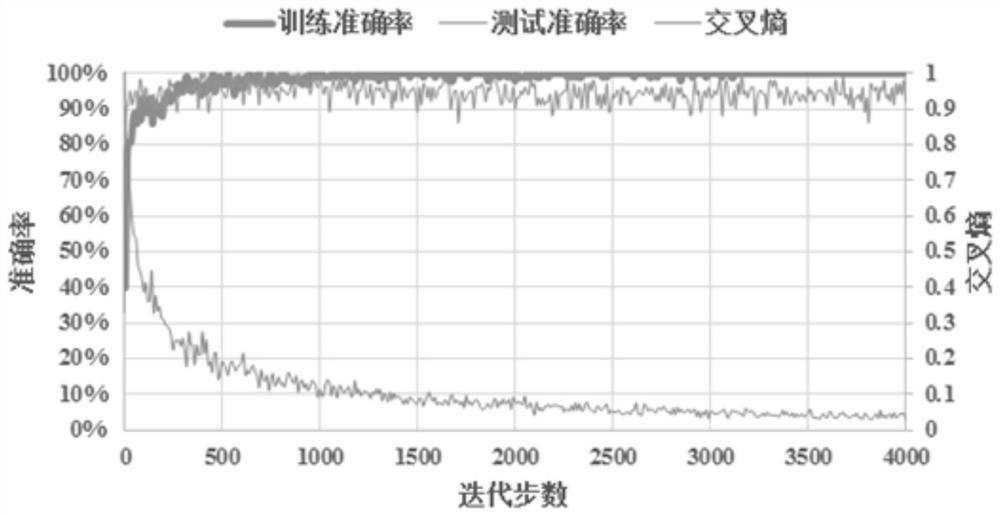
The invention discloses a method for automatic identification and classification of rock lithology in a deep learning mode, which is used to analyze rock lithology in geological engineering, comprising the following steps: step A, collecting different types of rock images according to the required rock types, And divide it into a training set and a test set; Step B, use the convolutional neural network Inception‑v3 model as a pre-training model, and use its feature extraction model to obtain image features; Step C, establish a Softmax regression model; Step D, train rock Image automatic recognition and classification model; Step E, testing the rock image automatic recognition and classification model. The invention can automatically and intelligently analyze the geological conditions in engineering by establishing an automatic recognition and classification model of rock images, greatly saving manpower and material resources, and reducing costs.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
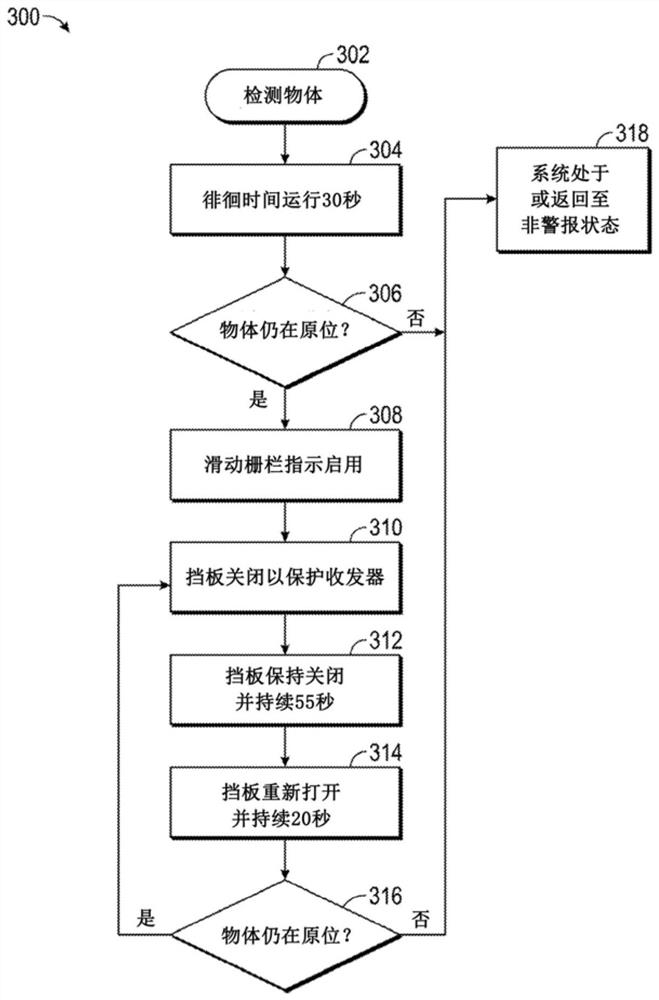
Wireless slide fence system and method
PendingCN113928370ARailway traffic control systemsSignalling indicators on vehicleTrackwaySimulation
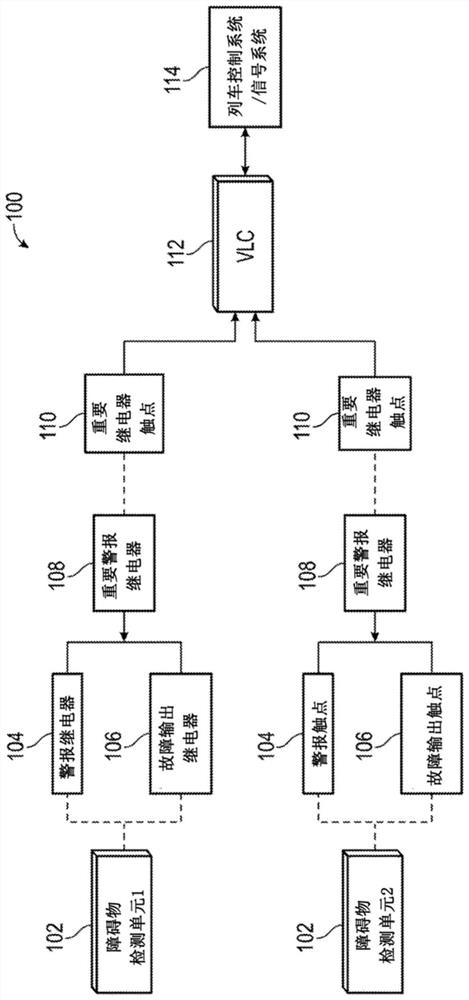
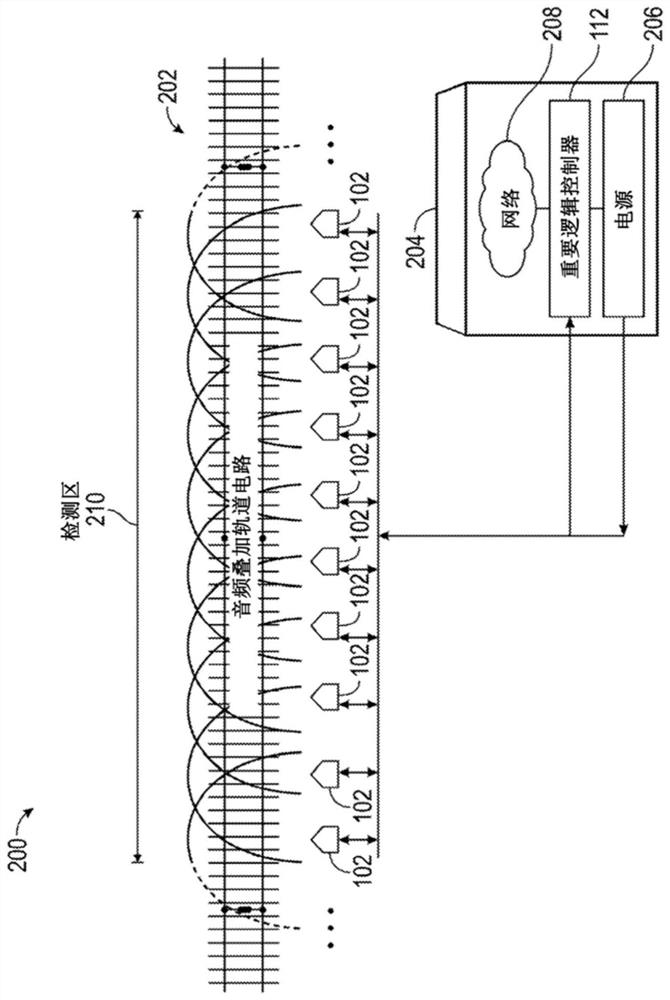
A Wireless Slide Fence utilizing signal reflection technology to detect rockslides and can determine the size and location of fallen rocks / objects impeding travel along a train track is presented. The present disclosure solves the technological problem of determining rock size and location to validate rockslide / fall alarms to reduce false alarms, while minimizing repairs required by conventional systems through the use of obstacle detection units and vital logic controllers. The present disclosure improves the performance of the system by, generating validated alarms when fallen rocks / objects satisfy the size criteria and are located in an area hazardous to train operations. In one exemplary embodiment, a loitering time can be implemented to validate object detections to reduce false positives due to transient objects such as migrating animals.
Owner:北伯林顿铁路公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com