Patents
Literature
98 results about "Wide gap semiconductors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
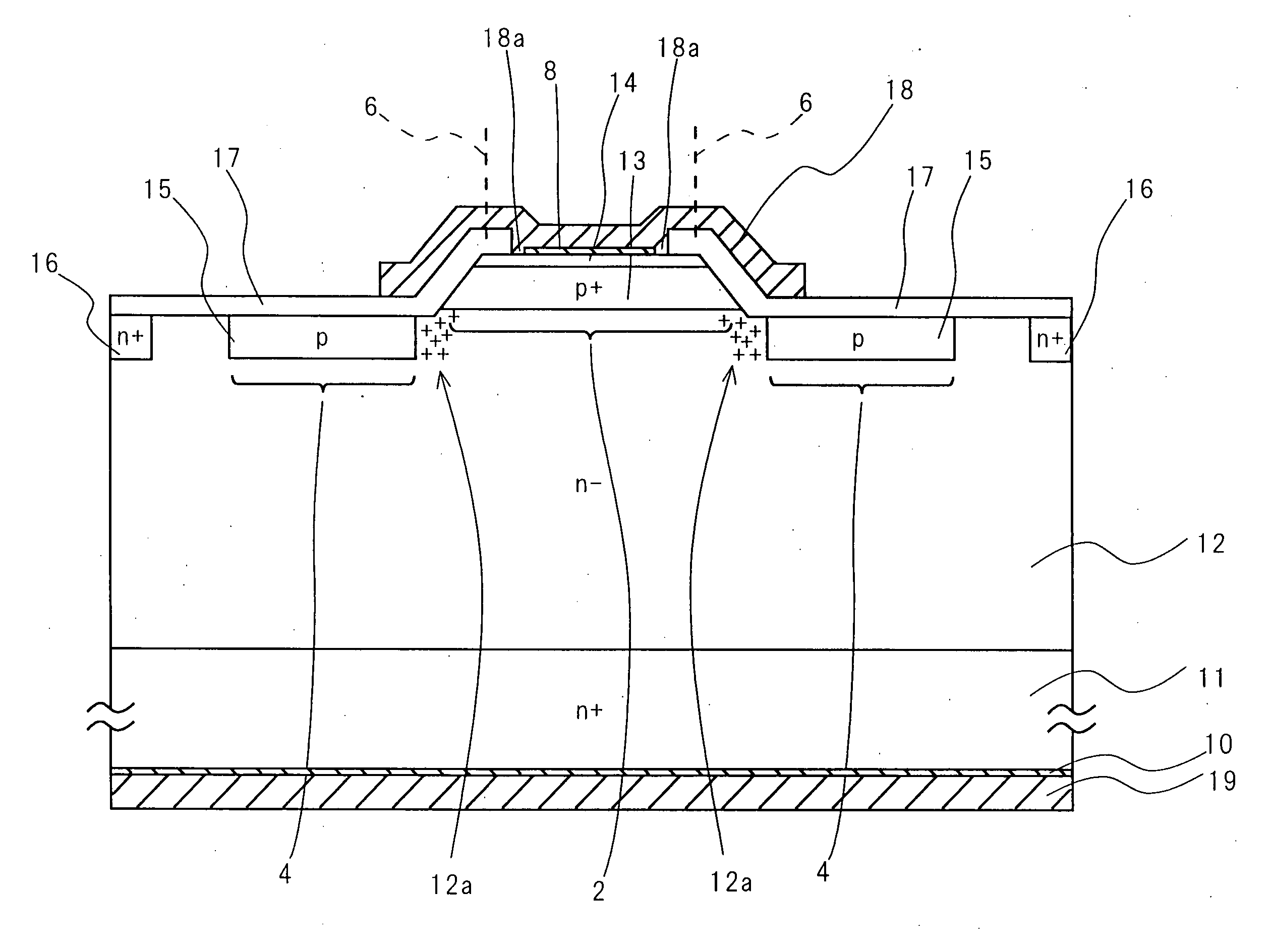
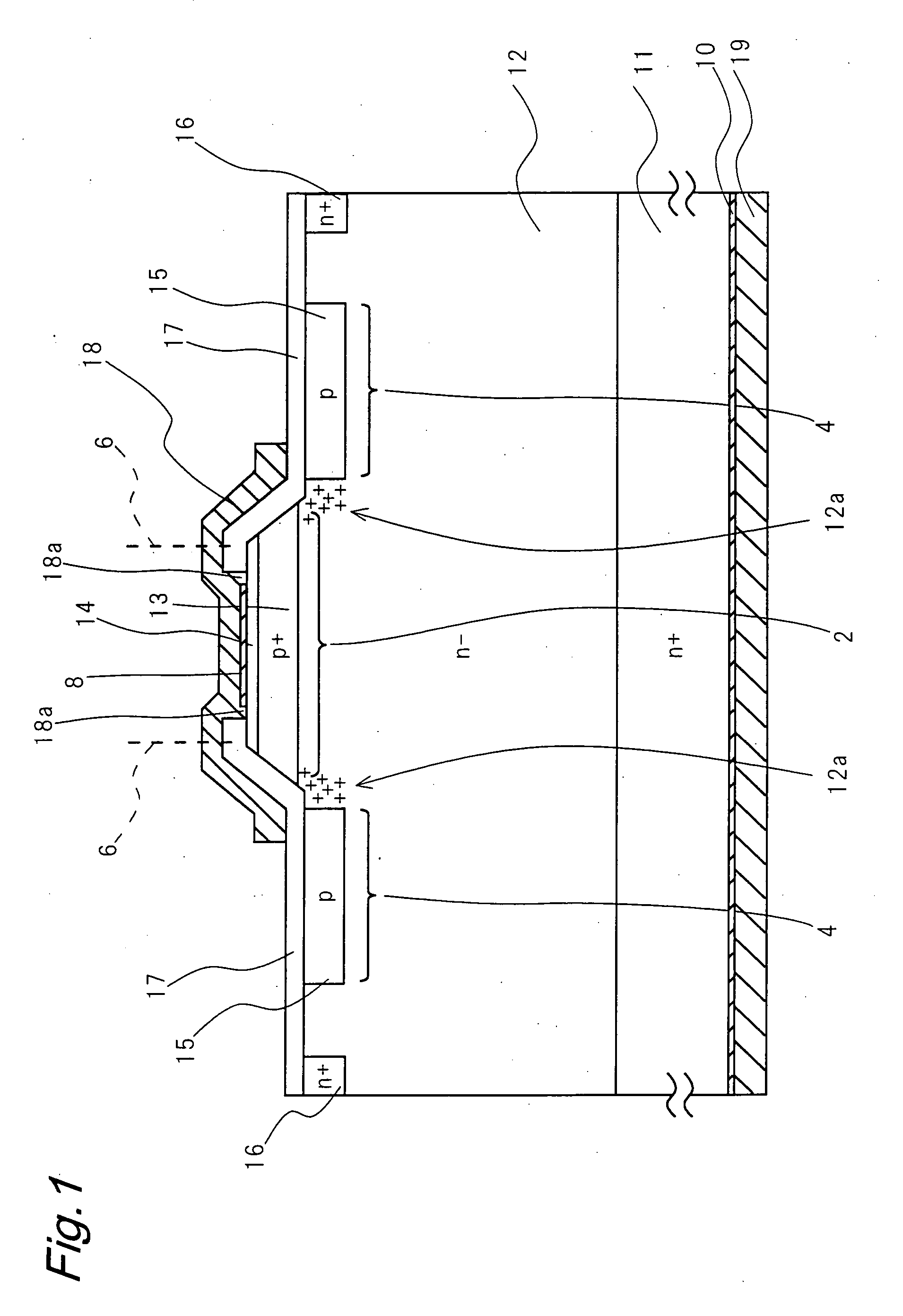
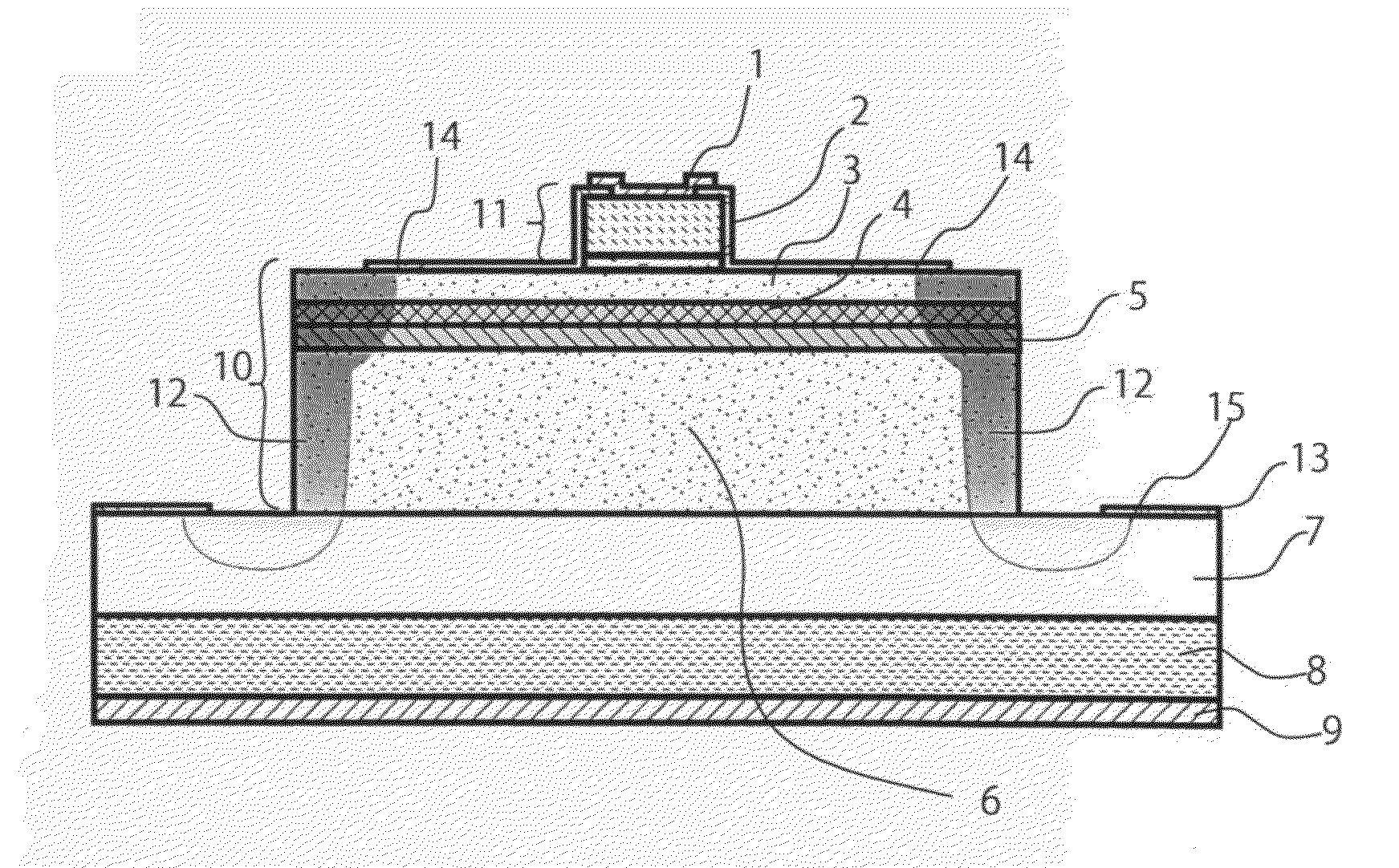
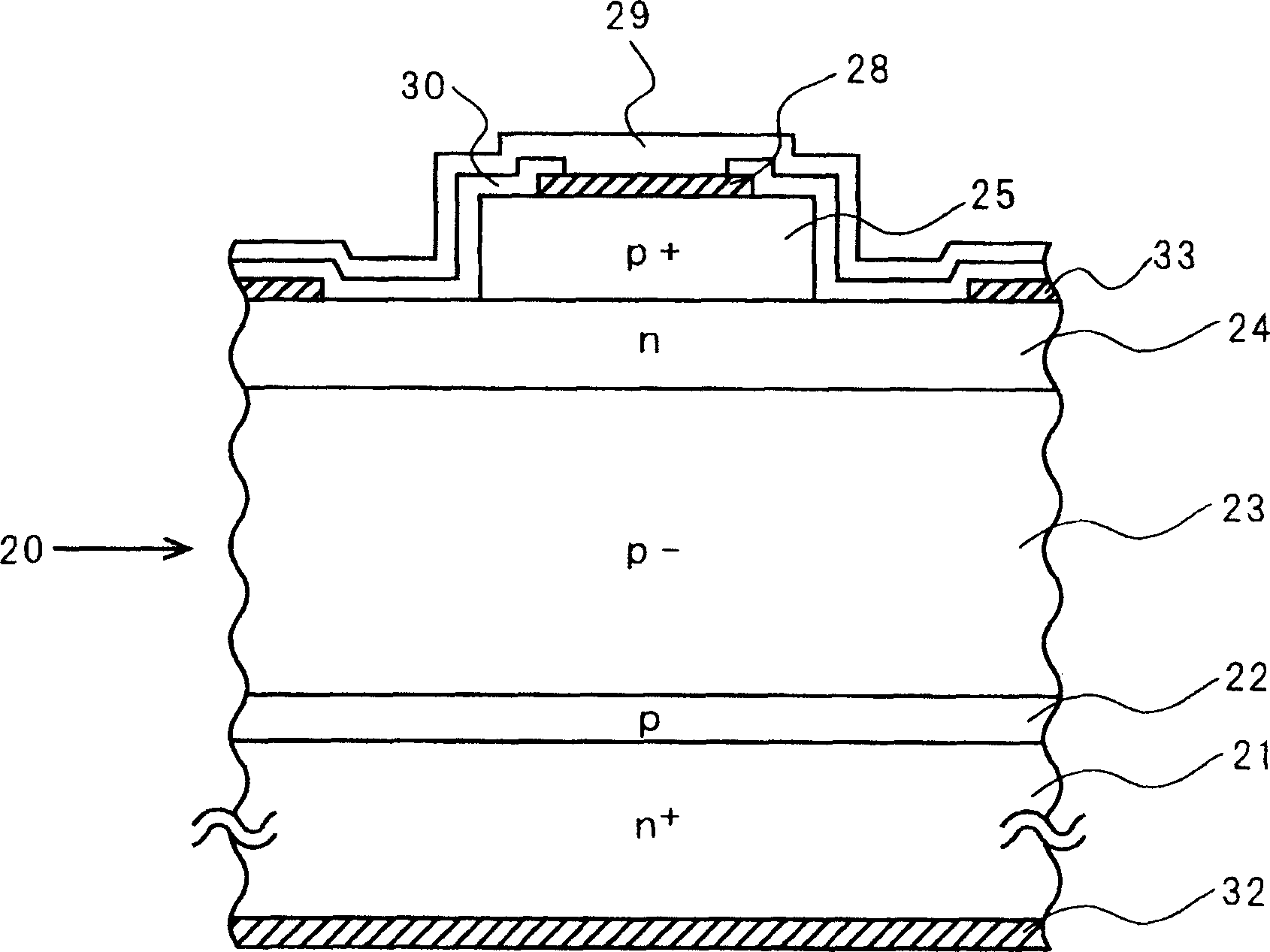
High-withstand voltage wide-gap semiconductor device and power device
InactiveUS20070170436A1Rise in forward-direction voltageExpansion can be suppressedThyristorWide gap semiconductorsBroadband
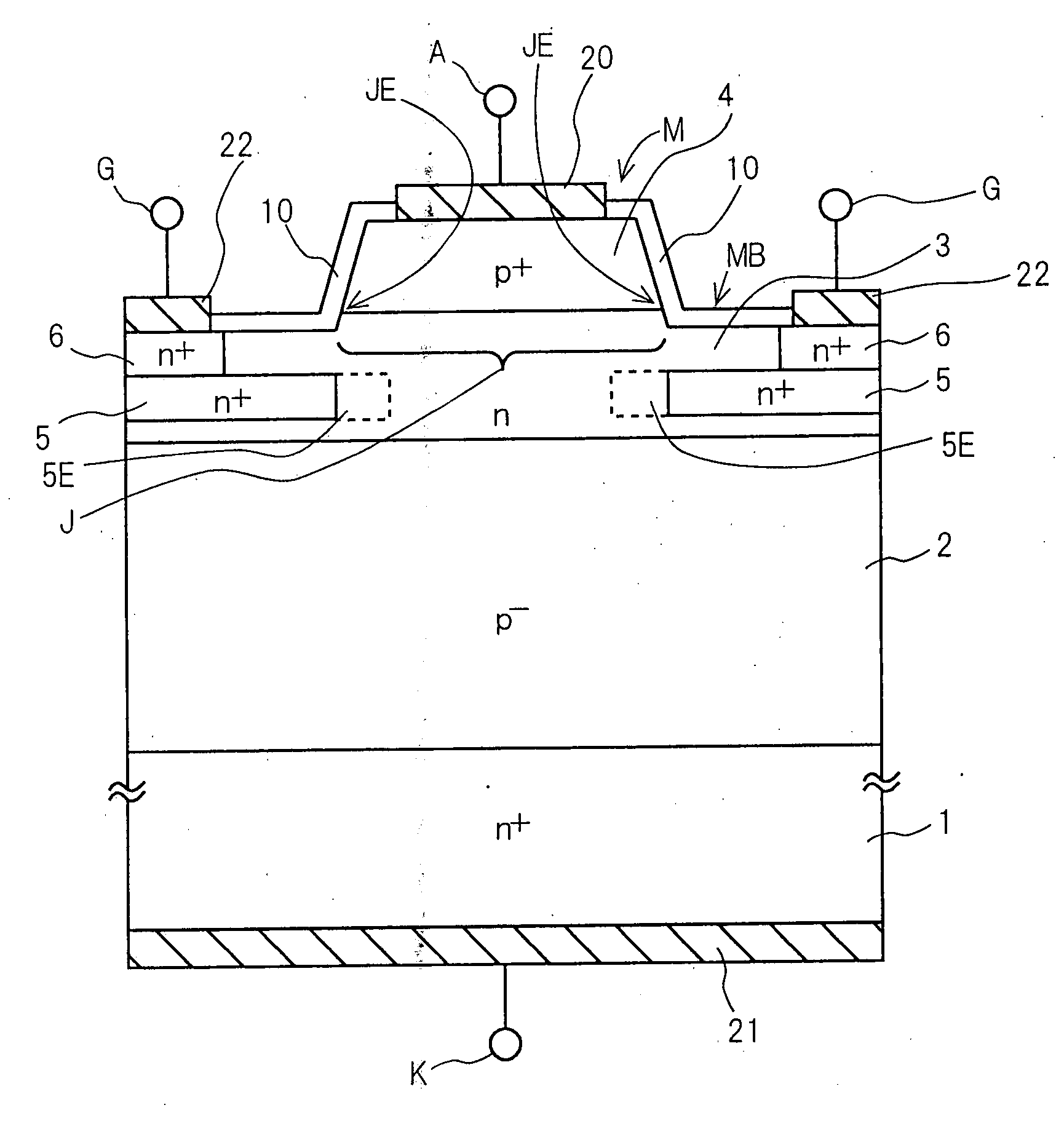
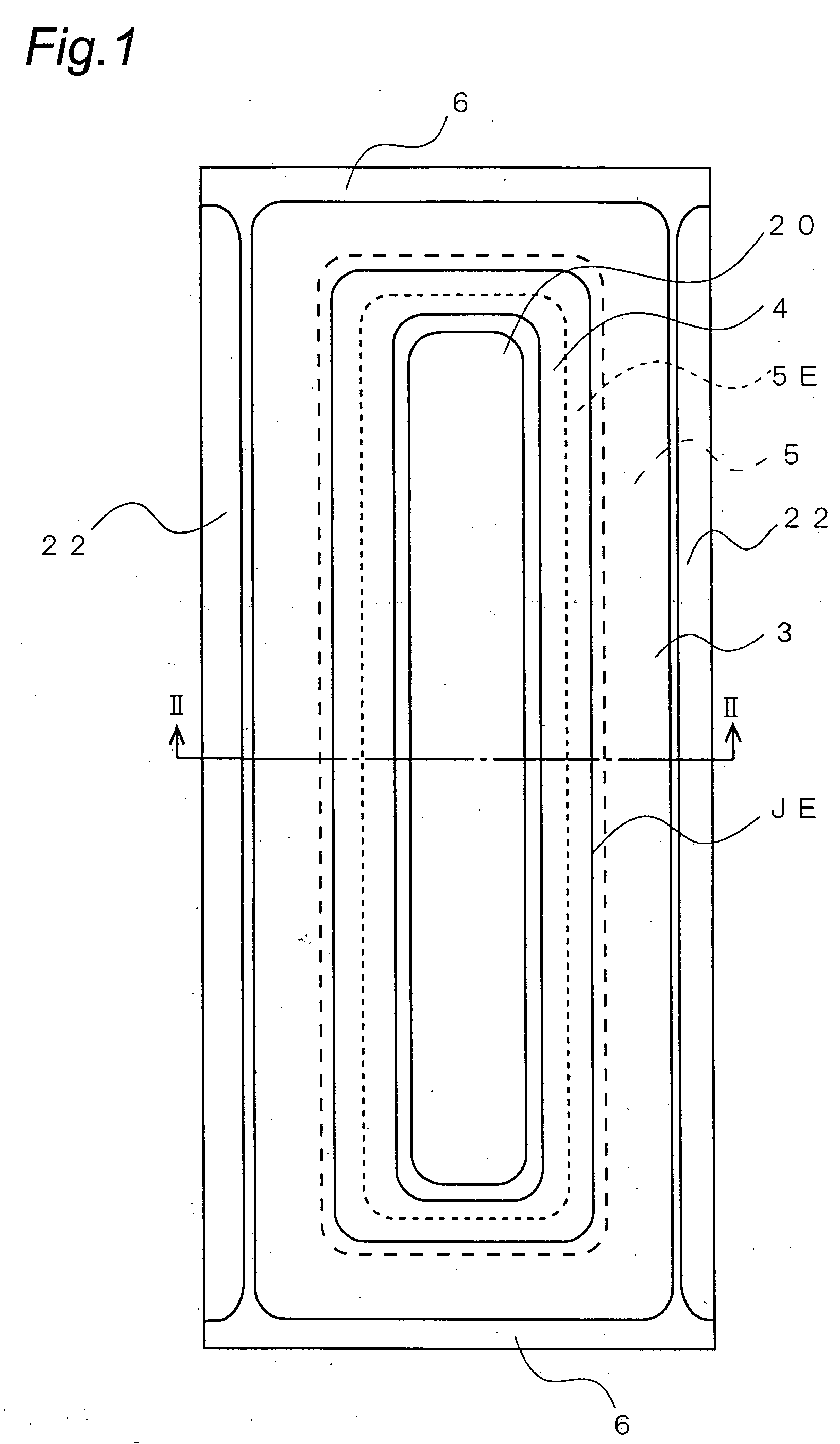
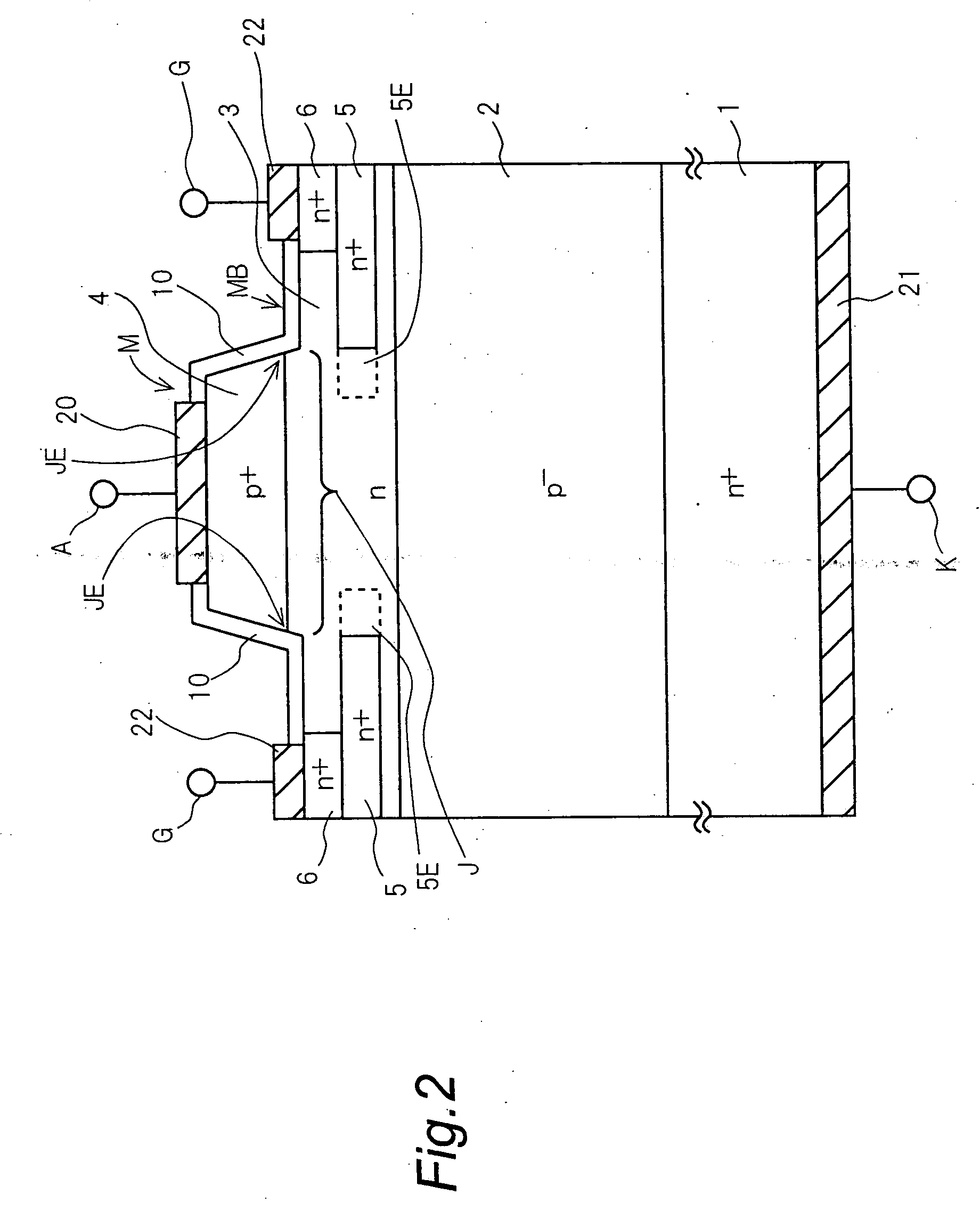
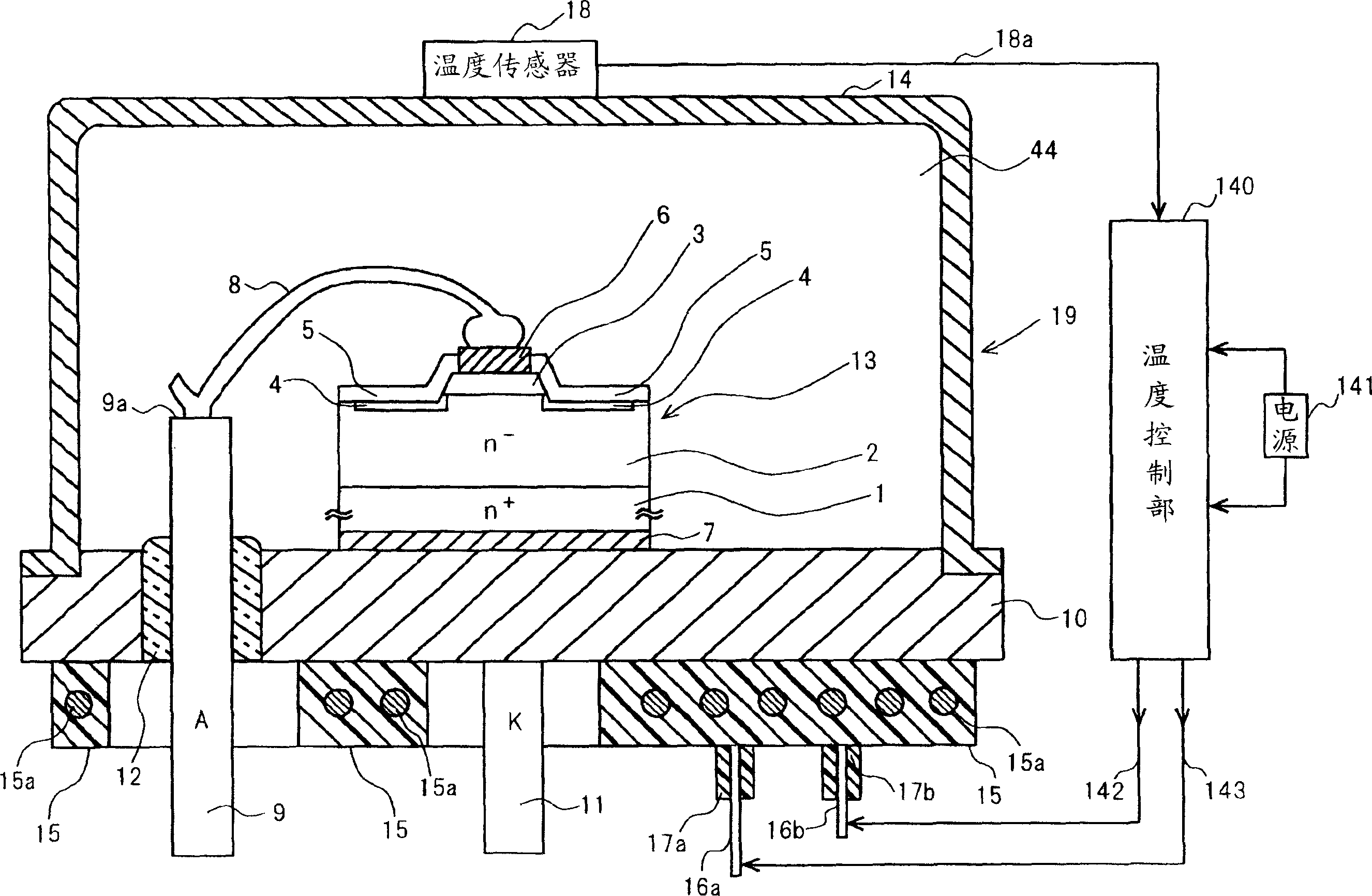
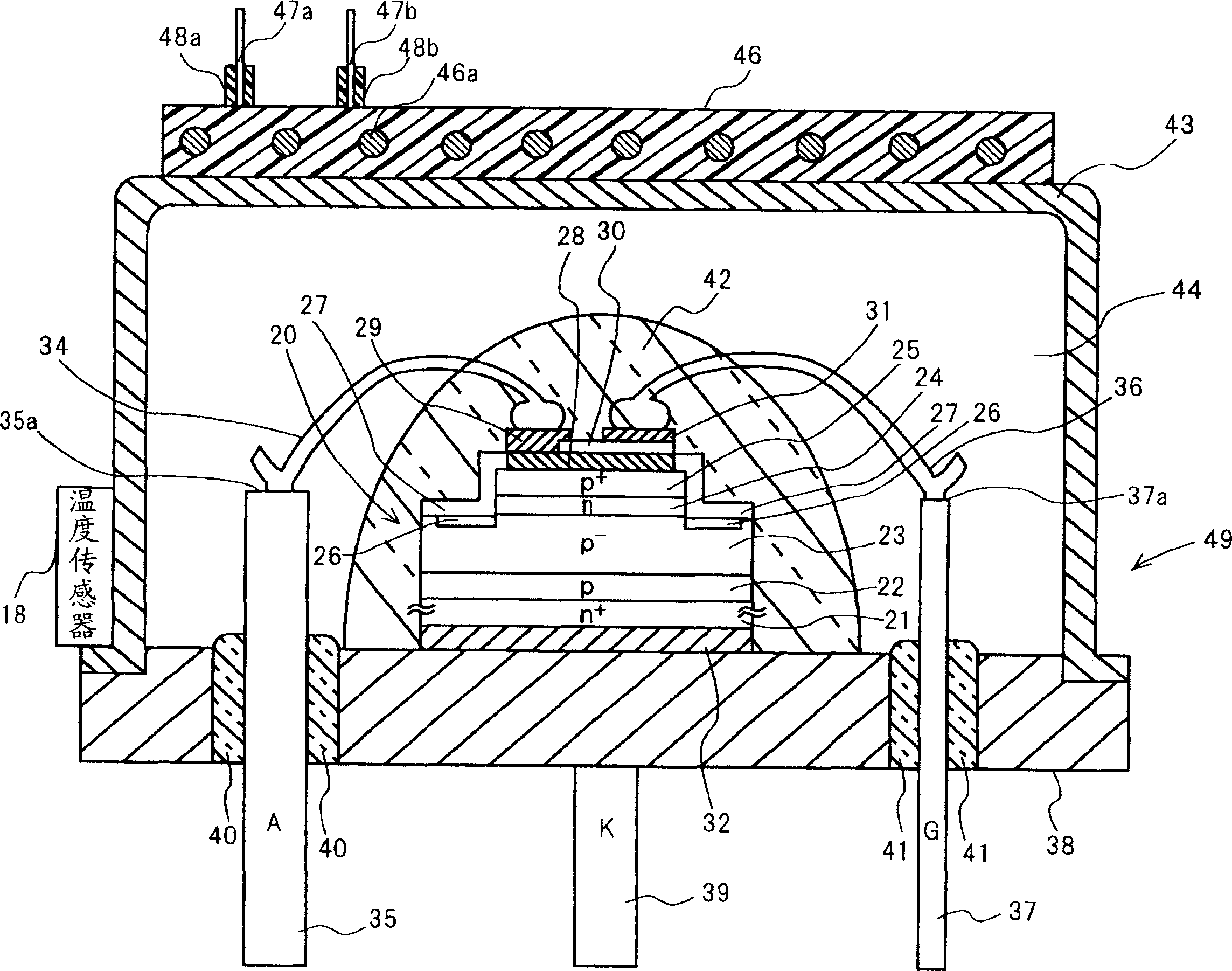
A semiconductor device with high withstand voltage, reduced forward-direction voltage degradation, long lifetime and high reliability, is provided. A junction between the drift layer and anode layer of a bipolar semiconductor device and an electric field relaxation layer are formed at a distance from each other, and an edge portion of the anode is opposed to the semiconductor region between the junction and the electric field relaxation layer, with an insulating film intervening. When reverse-biased, due to the electric field effect imparted to the drift layer between the junction and the electric field relaxation layer from the electrode, with the insulating film intervening, the junction and electric field relaxation layer are electrically connected, and electric field concentration at the junction edge portion is relaxed. When forward-biased, the junction and electric field relaxation layer are electrically isolated, and forward-direction current flows only through the junction.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO
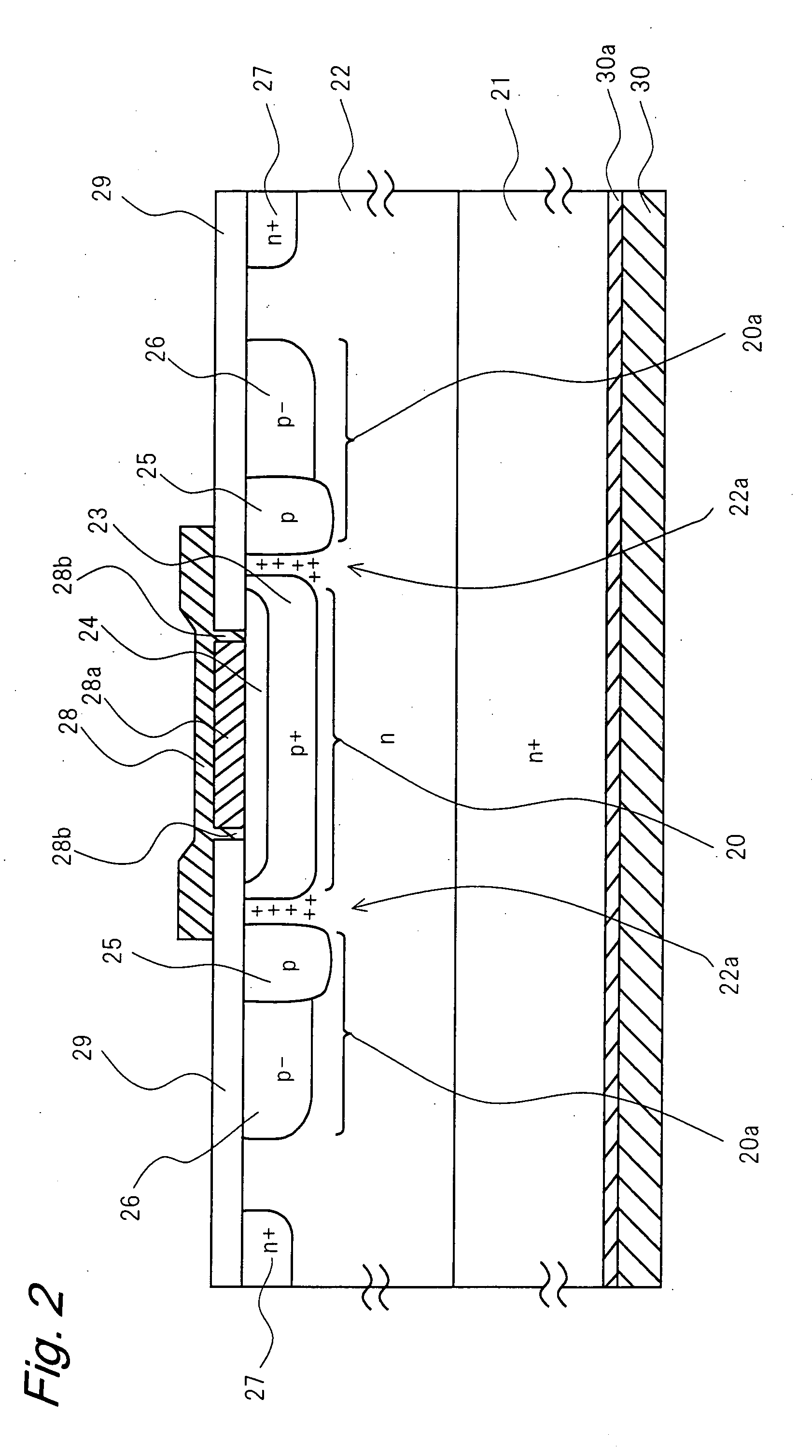
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20120187475A1Occurrence can be suppressedReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTransistor
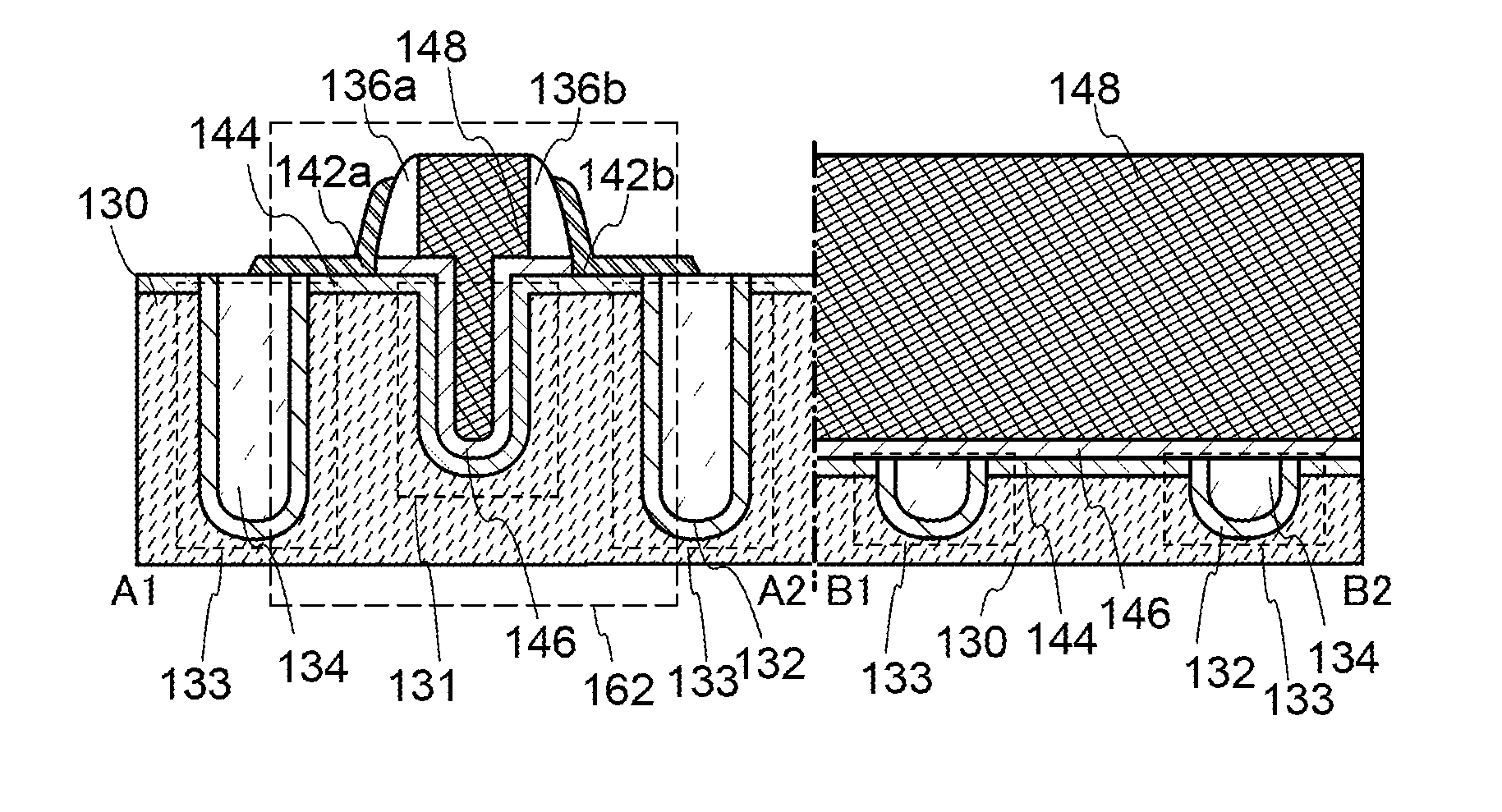
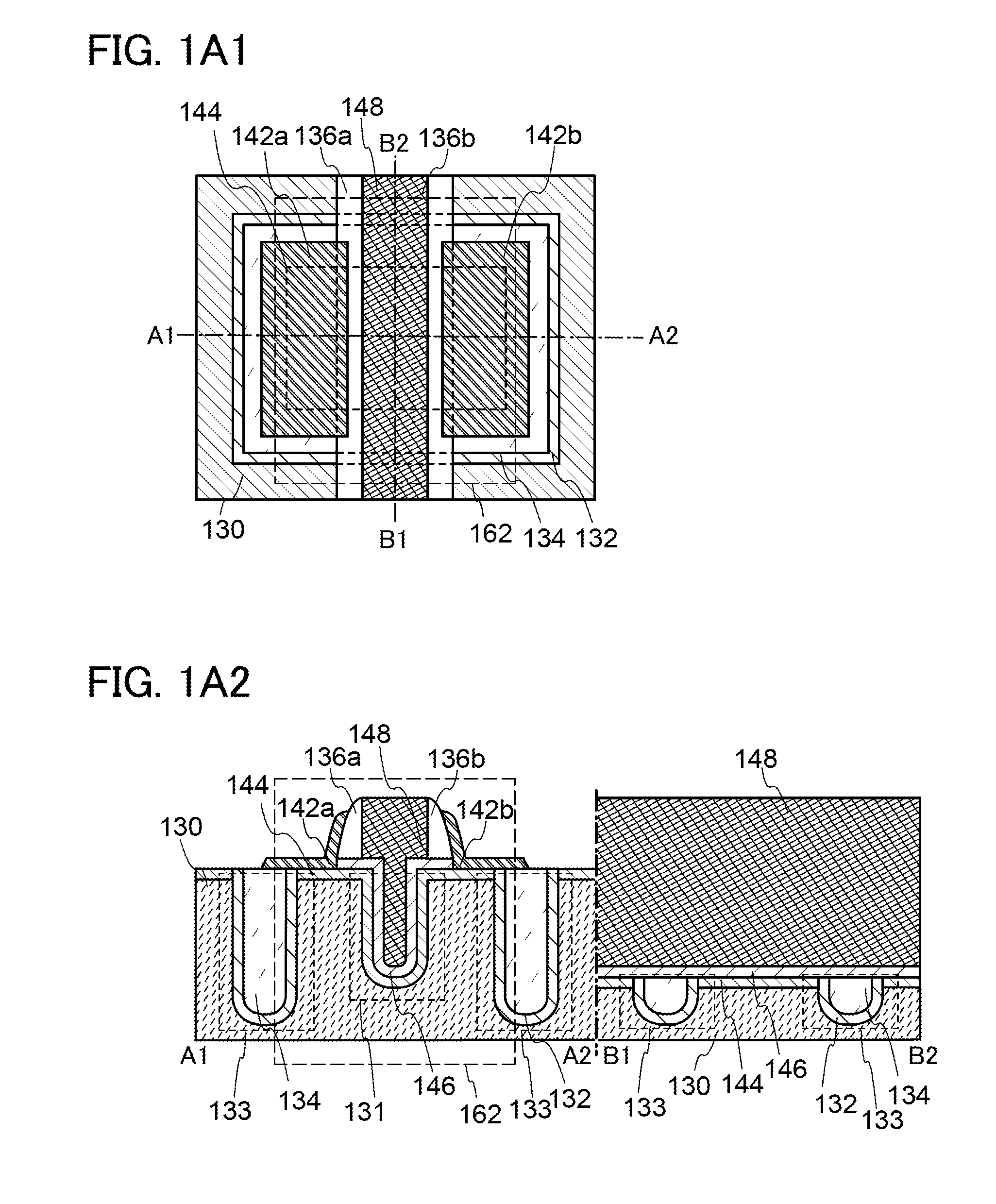
A conventional DRAM needs to be refreshed at an interval of several tens of milliseconds to hold data, which results in large power consumption. In addition, a transistor therein is frequently turned on and off; thus, deterioration of the transistor is also a problem. These problems become significant as the memory capacity increases and transistor miniaturization advances. A transistor is provided which includes a wide-gap semiconductor and has a trench structure including a trench for a gate electrode and a trench for element isolation. Even when the distance between a source electrode and a drain electrode is decreased, the occurrence of a short-channel effect can be suppressed by setting the depth of the trench for the gate electrode as appropriate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Driver circuit for switching device
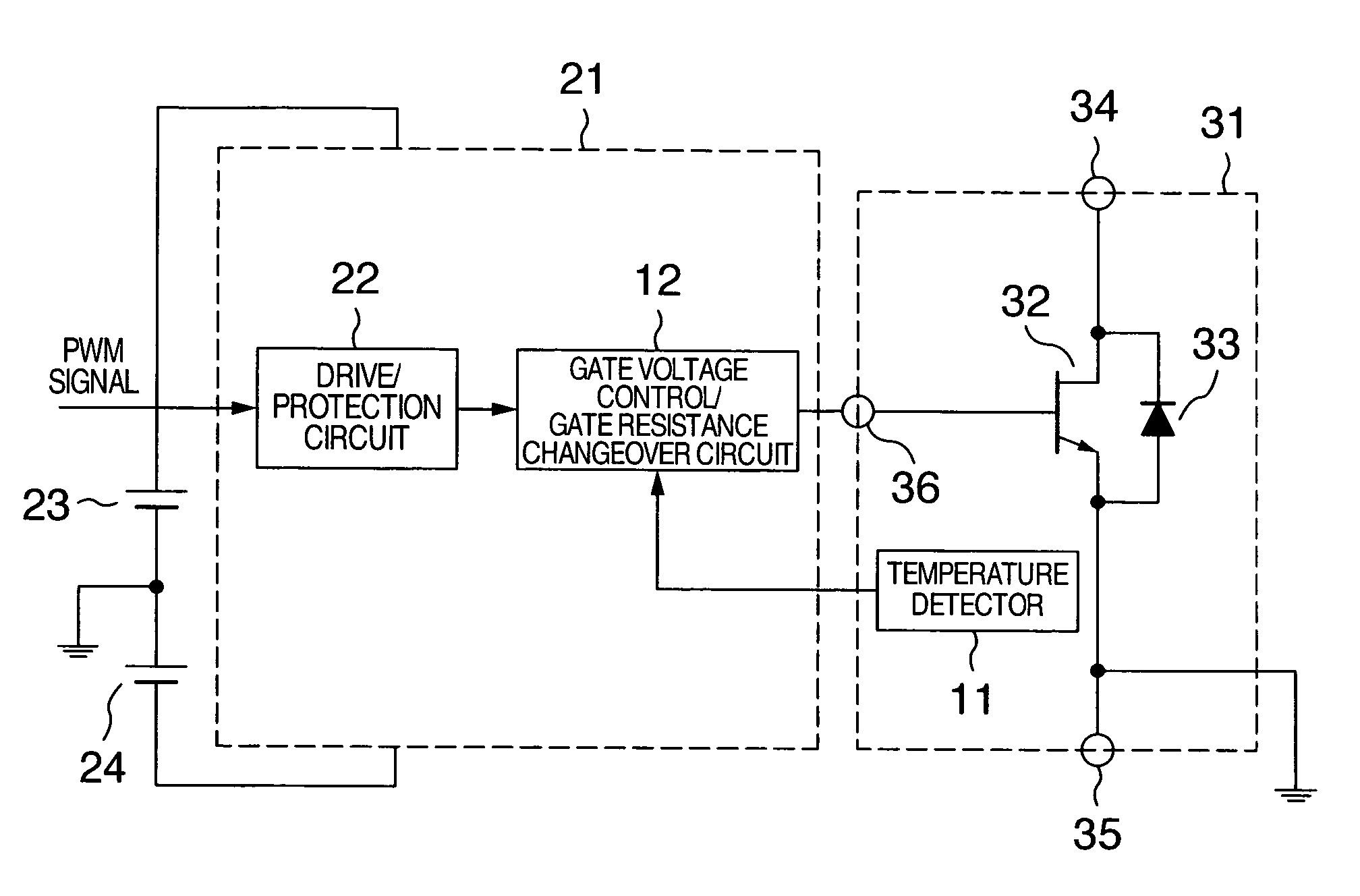
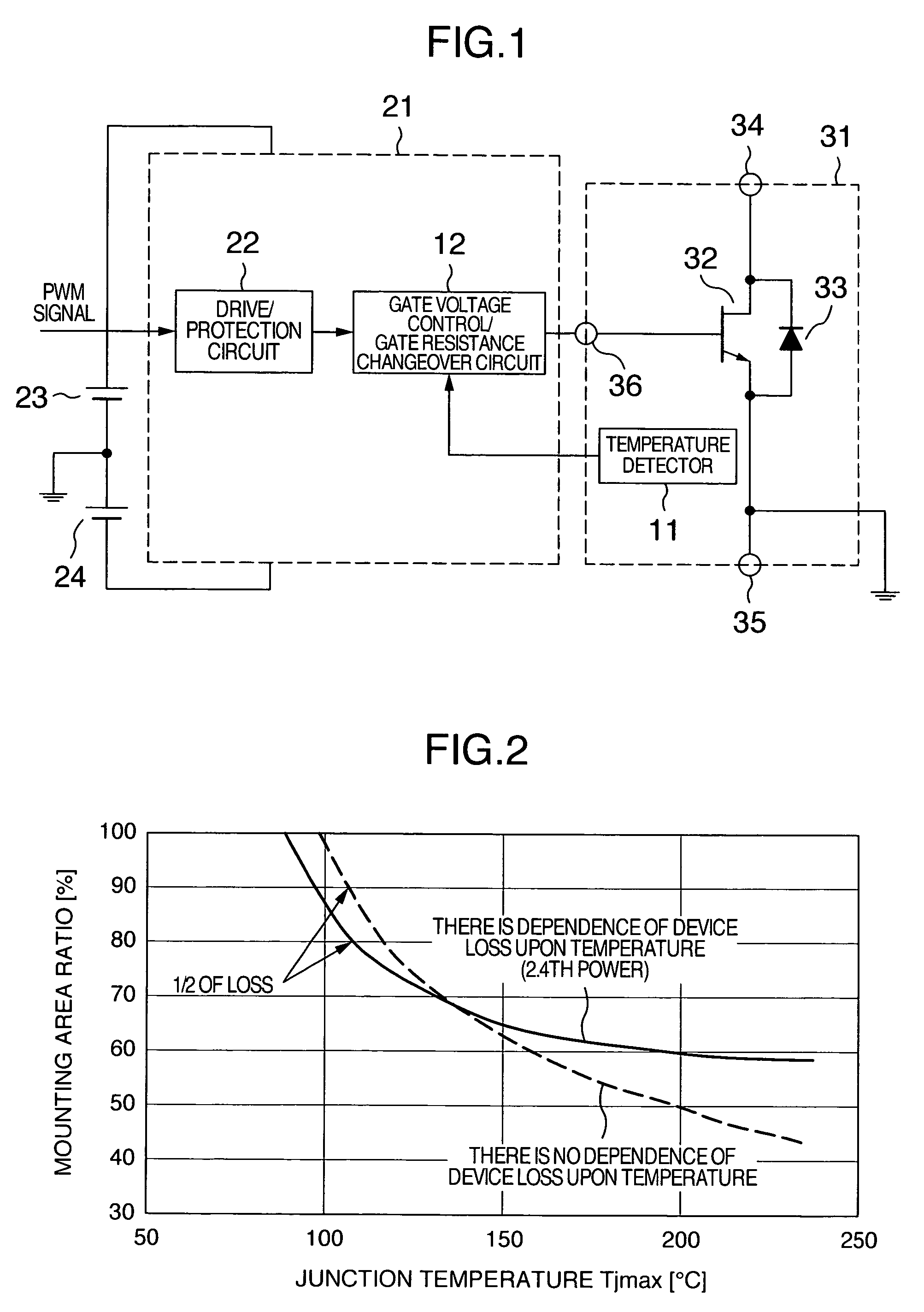
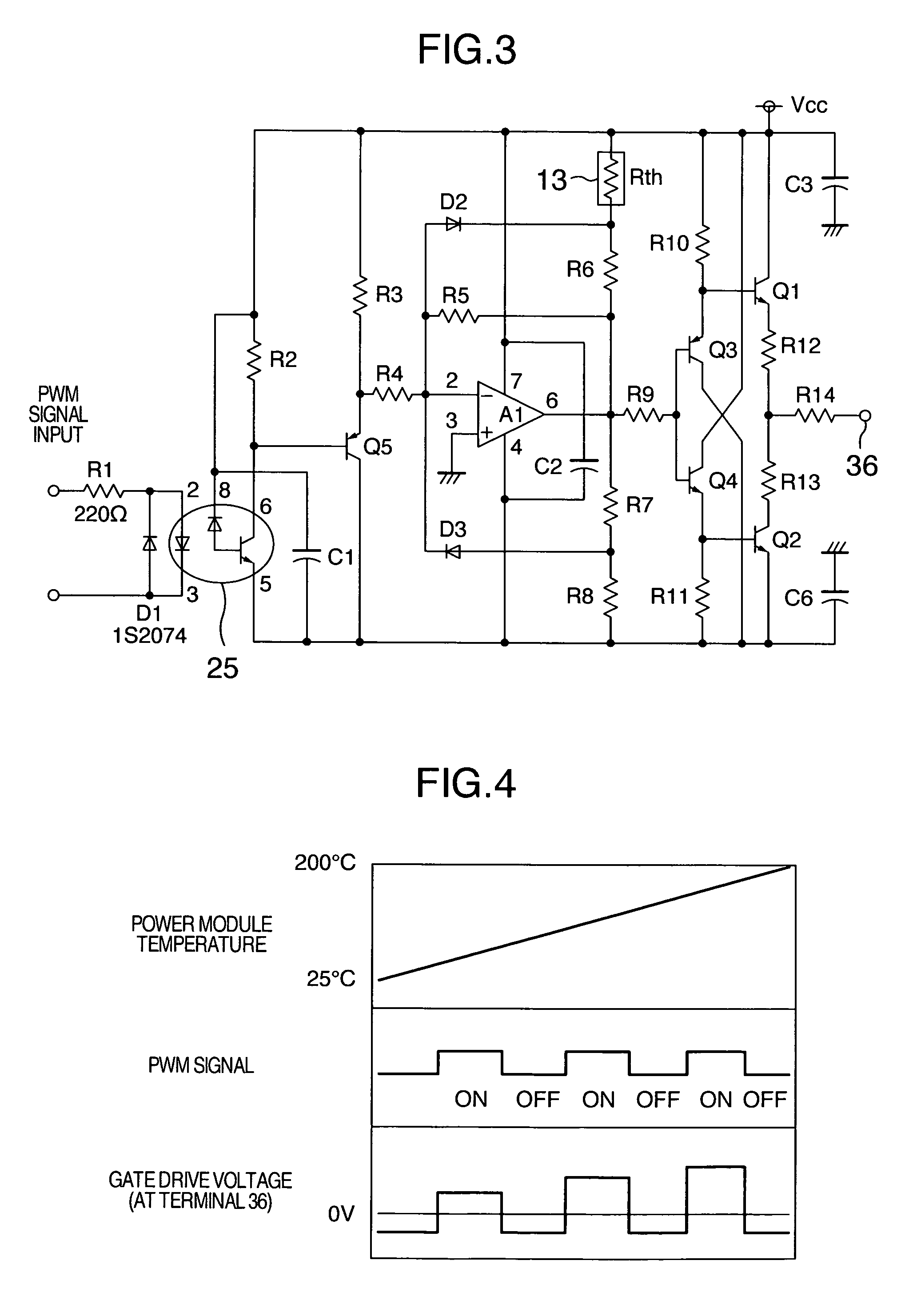
InactiveUS20070221994A1Suppression of increase in mounting areaMade smallSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceDriver circuit
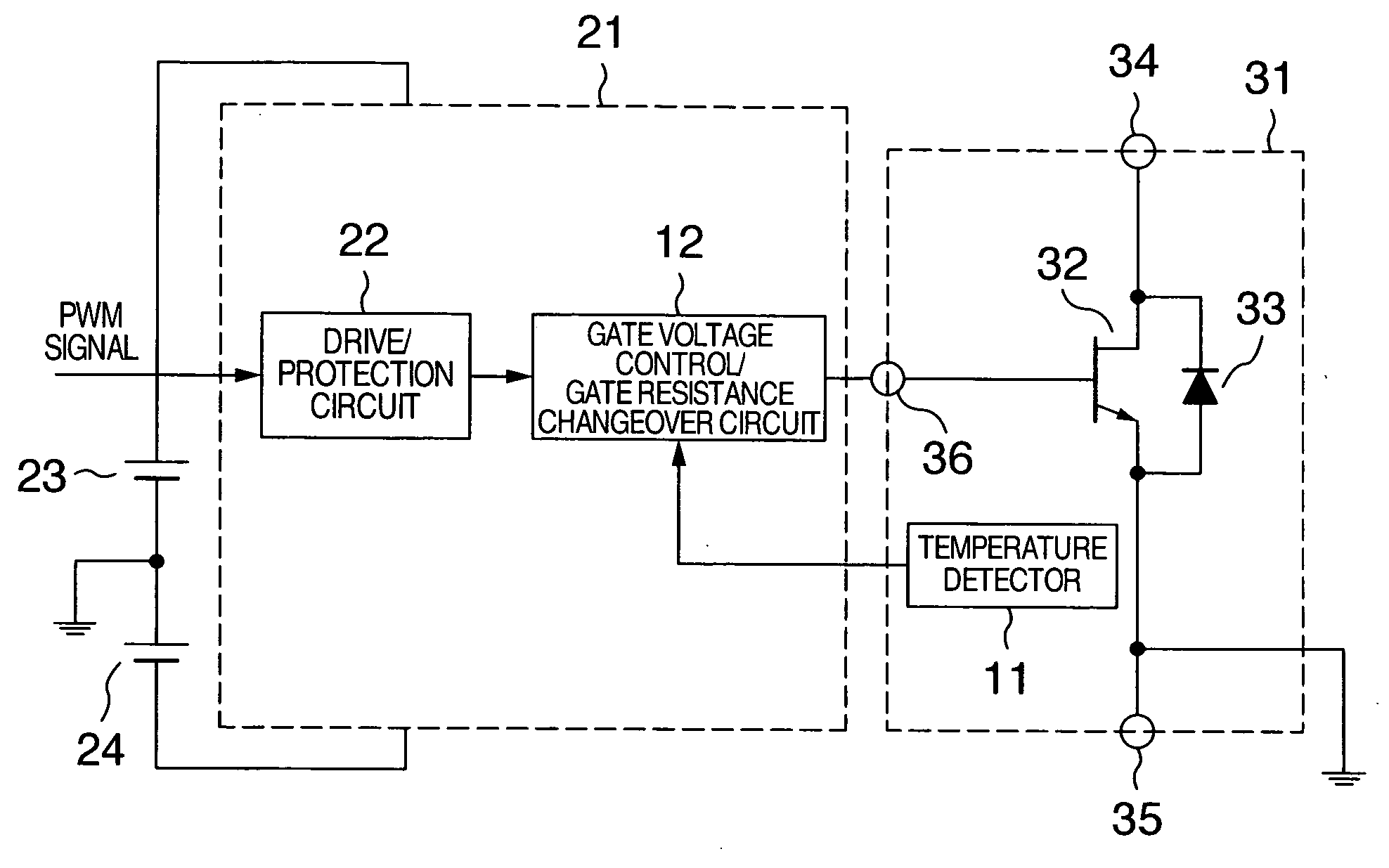
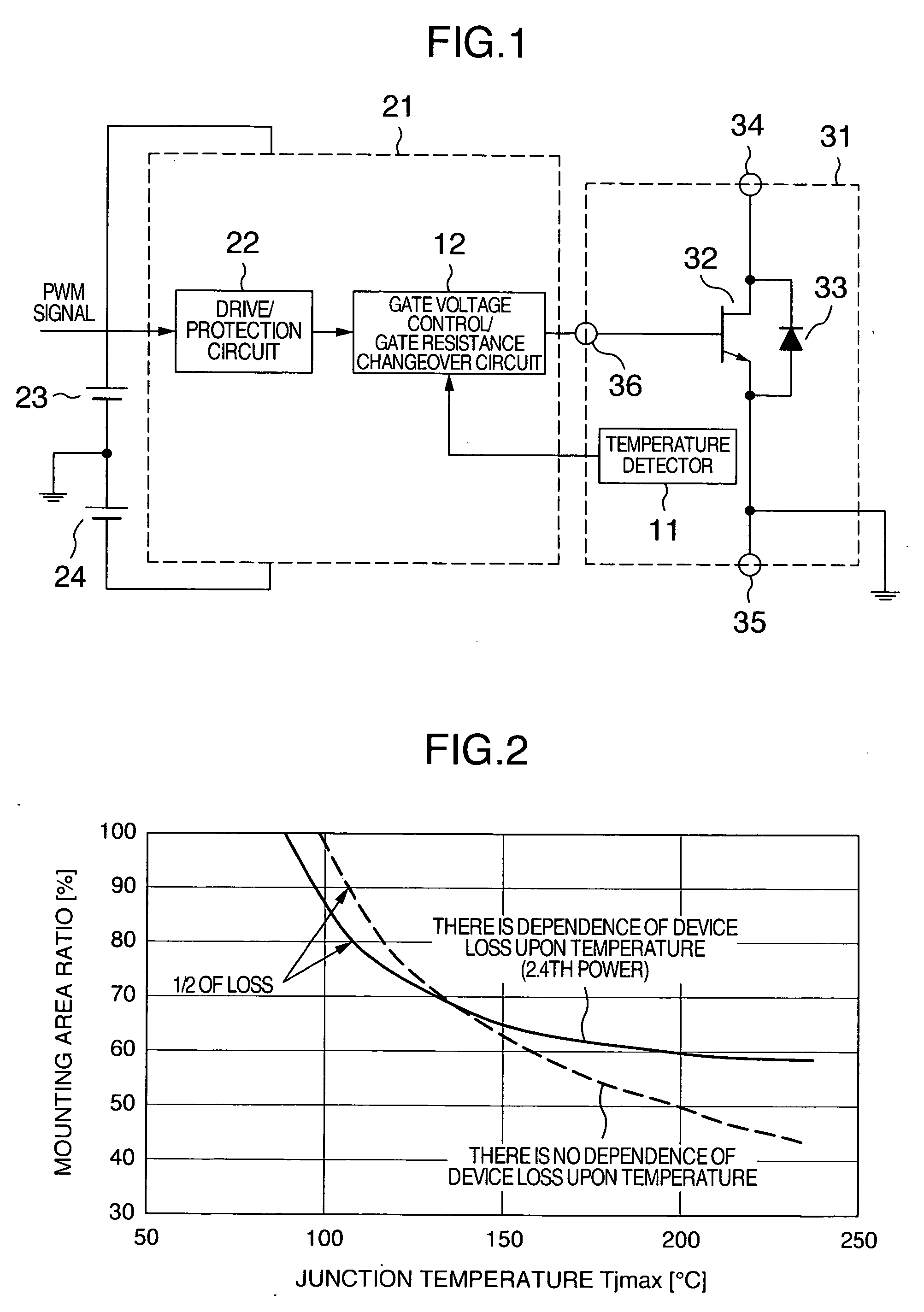
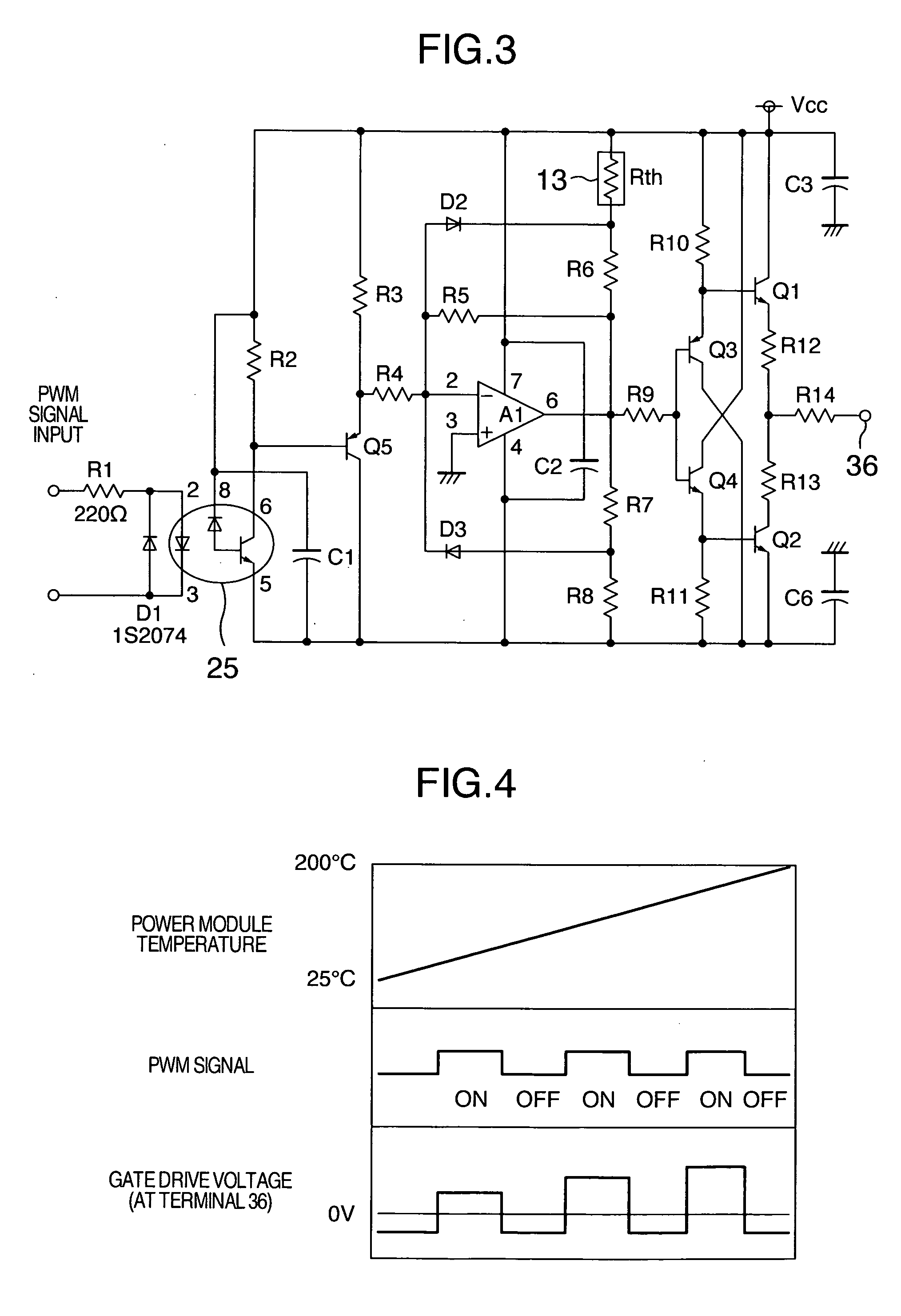
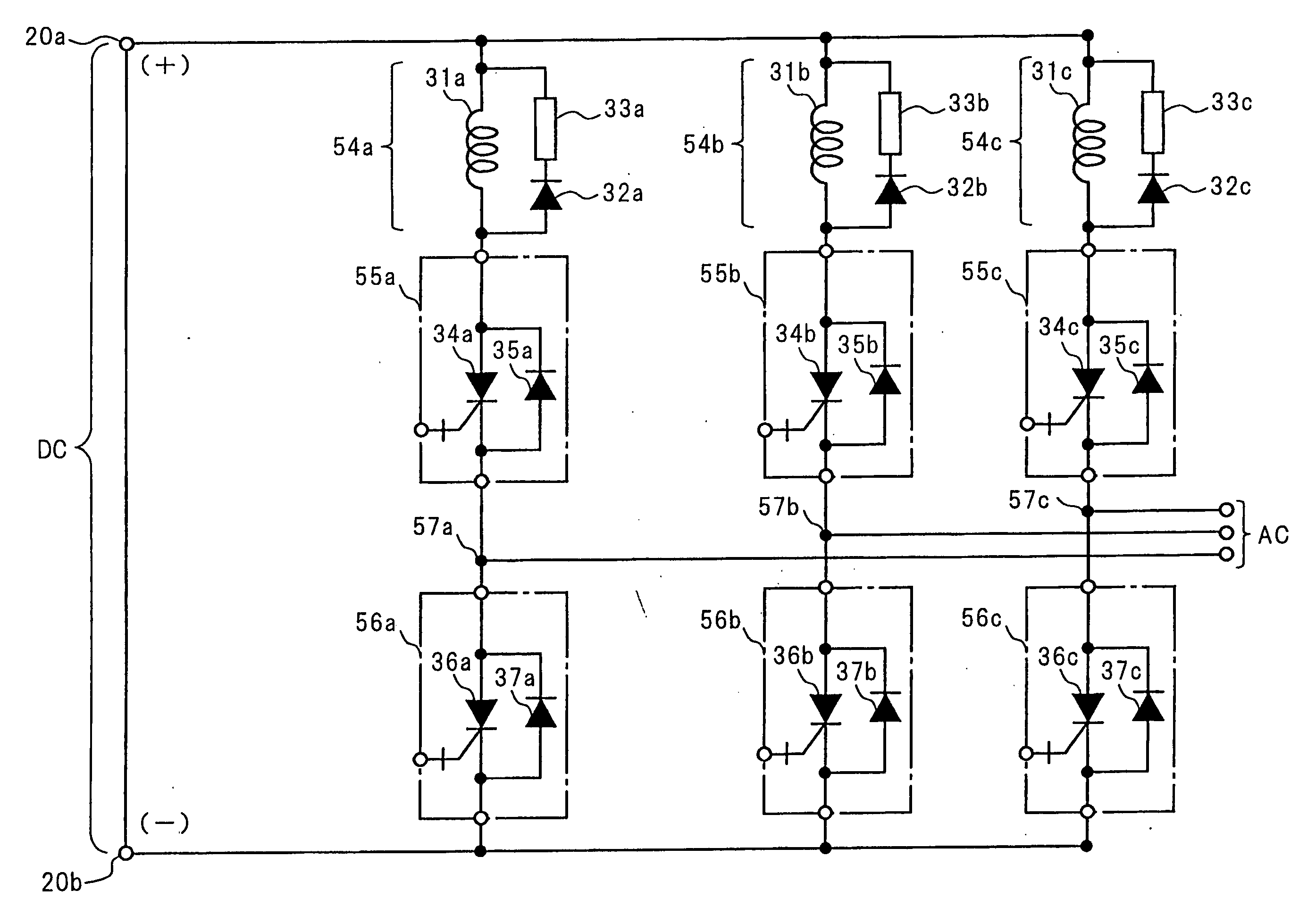
A driver circuit that lowers the dependence of the loss in the wide gap semiconductor device upon the temperature is provided. A gate driver circuit for voltage driven power semiconductor switching device includes a power semiconductor switching device, a driver circuit for supplying a drive signal to a gate terminal of the switching device with reference to an emitter control terminal or a source control terminal of the switching device, and a unit for detecting a temperature of the switching device. The temperature of the power semiconductor switching device is detected, and a gate drive voltage or a gate drive resistance value is changed based on the detected temperature.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Charged particle application apparatus
InactiveUS20090101817A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesLow voltageElectron avalanche
The present invention provides a highly sensitive, thin detector useful for observing low-voltage, high-resolution SEM images, and provides a charged particle beam application apparatus based on such a detector. The charged particle beam application apparatus includes a charged particle irradiation source, a charged particle optics for irradiating a sample with a charged particle beam emitted from the charged particle irradiation source, and an electron detection section for detecting electrons that are secondarily generated from the sample. The electron detection section includes a diode device that is a combination of a phosphor layer, which converts the electrons to an optical signal, and a device for converting the optical signal to electrons and subjecting the electrons to avalanche multiplication, or includes a diode device having an electron absorption region that is composed of at least a wide-gap semiconductor substrate with a bandgap greater than 2 eV.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120032164A1Simple circuit configurationLonger heldSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPower semiconductor devicePower flow
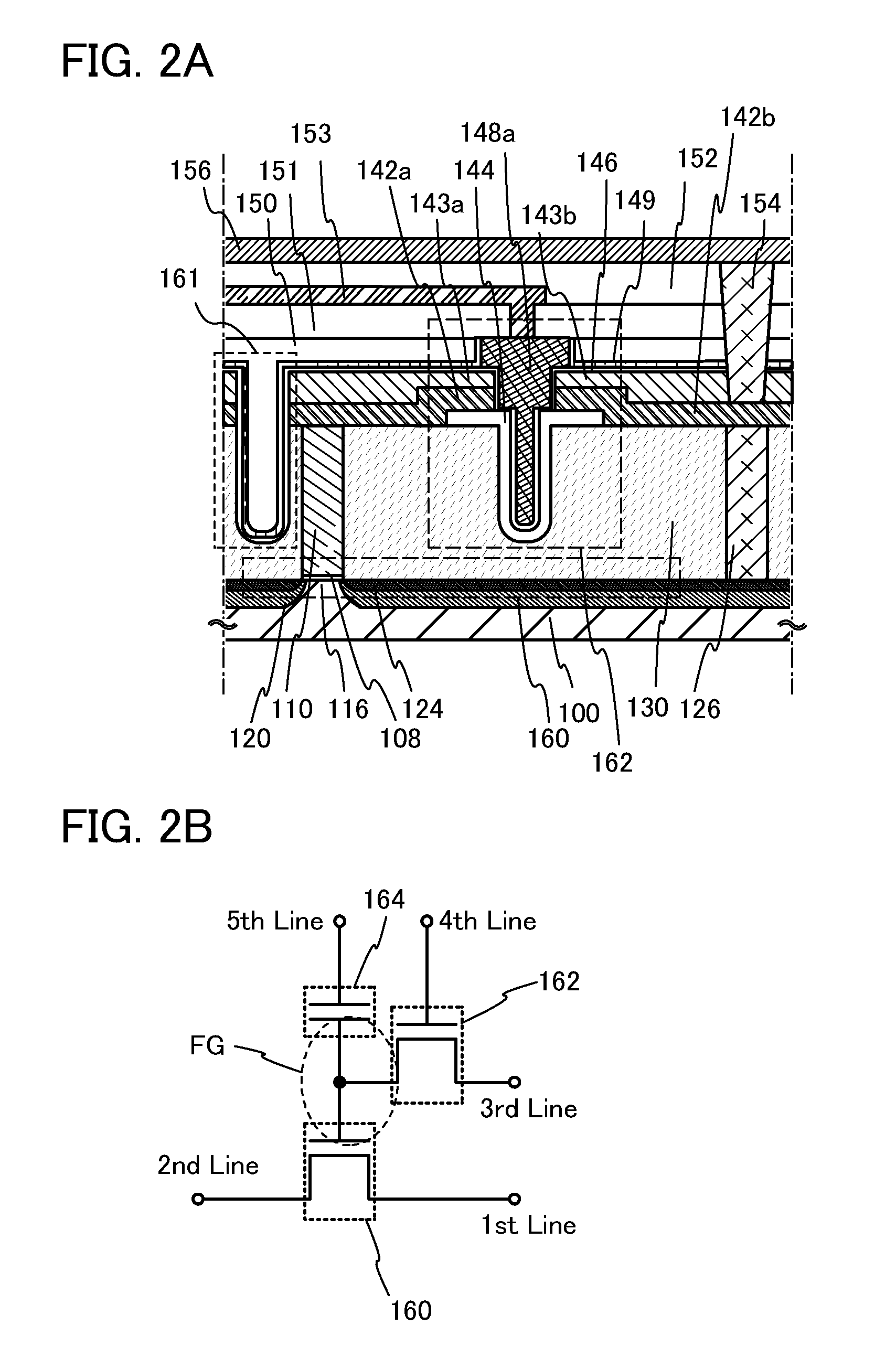
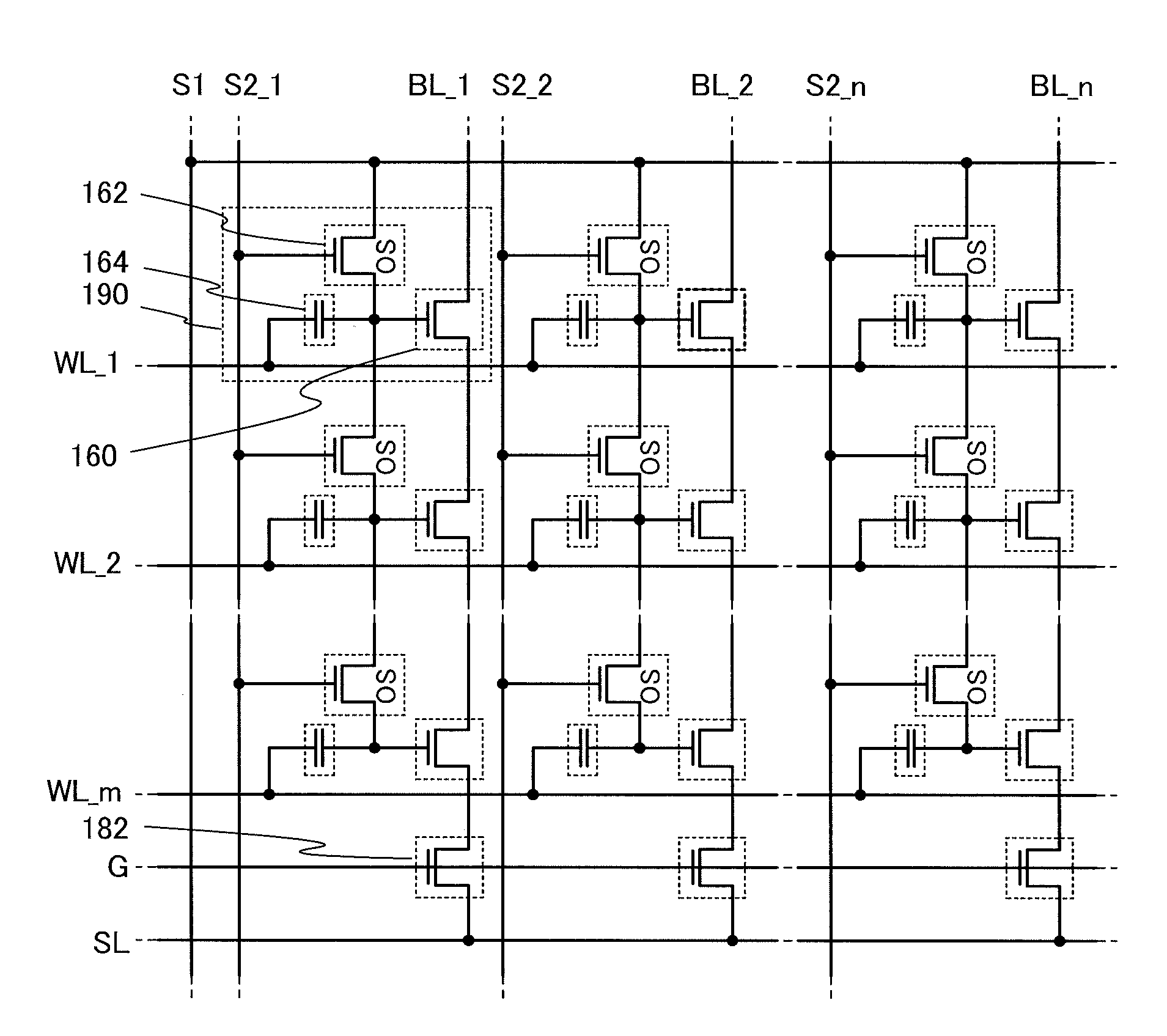
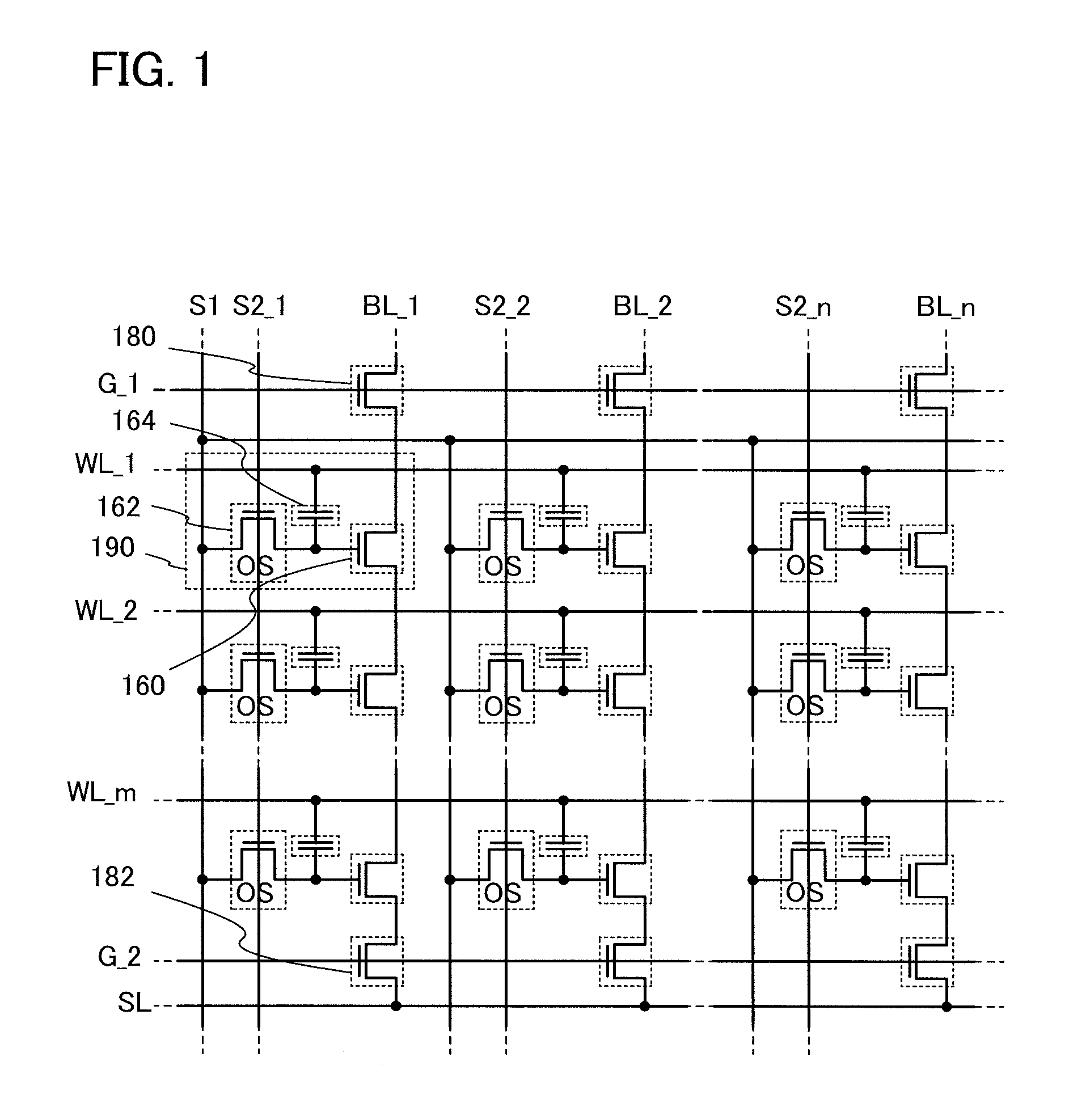
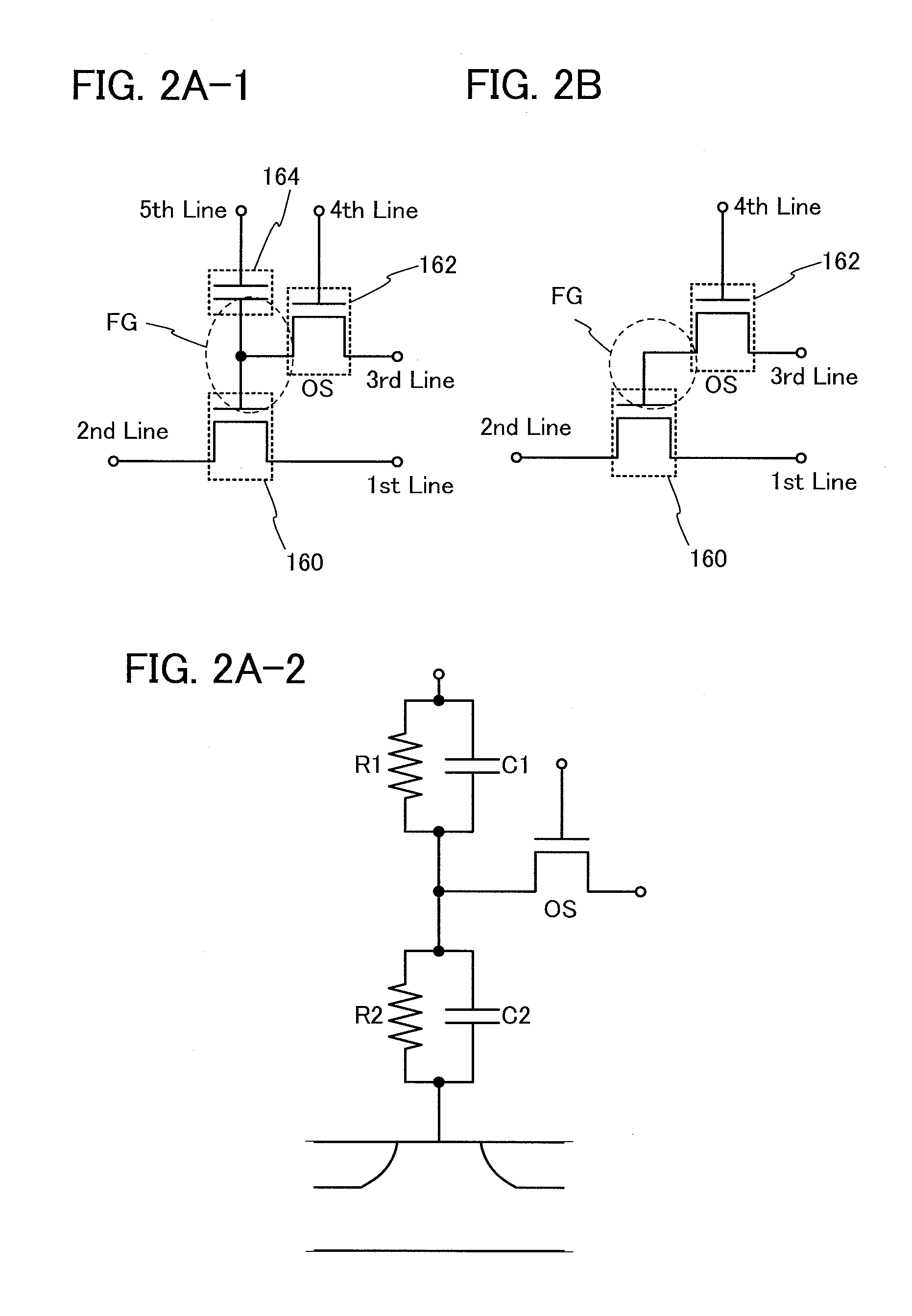
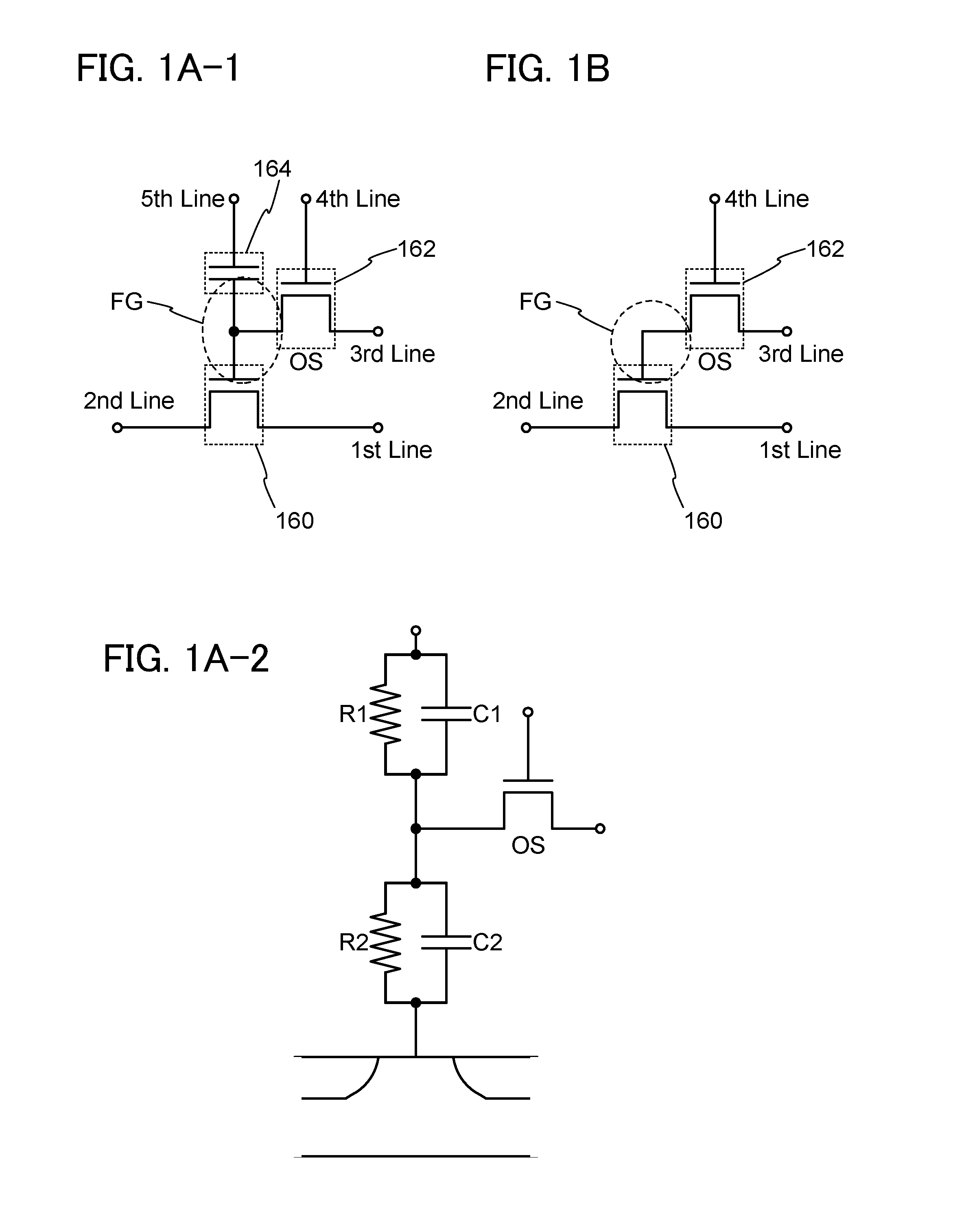
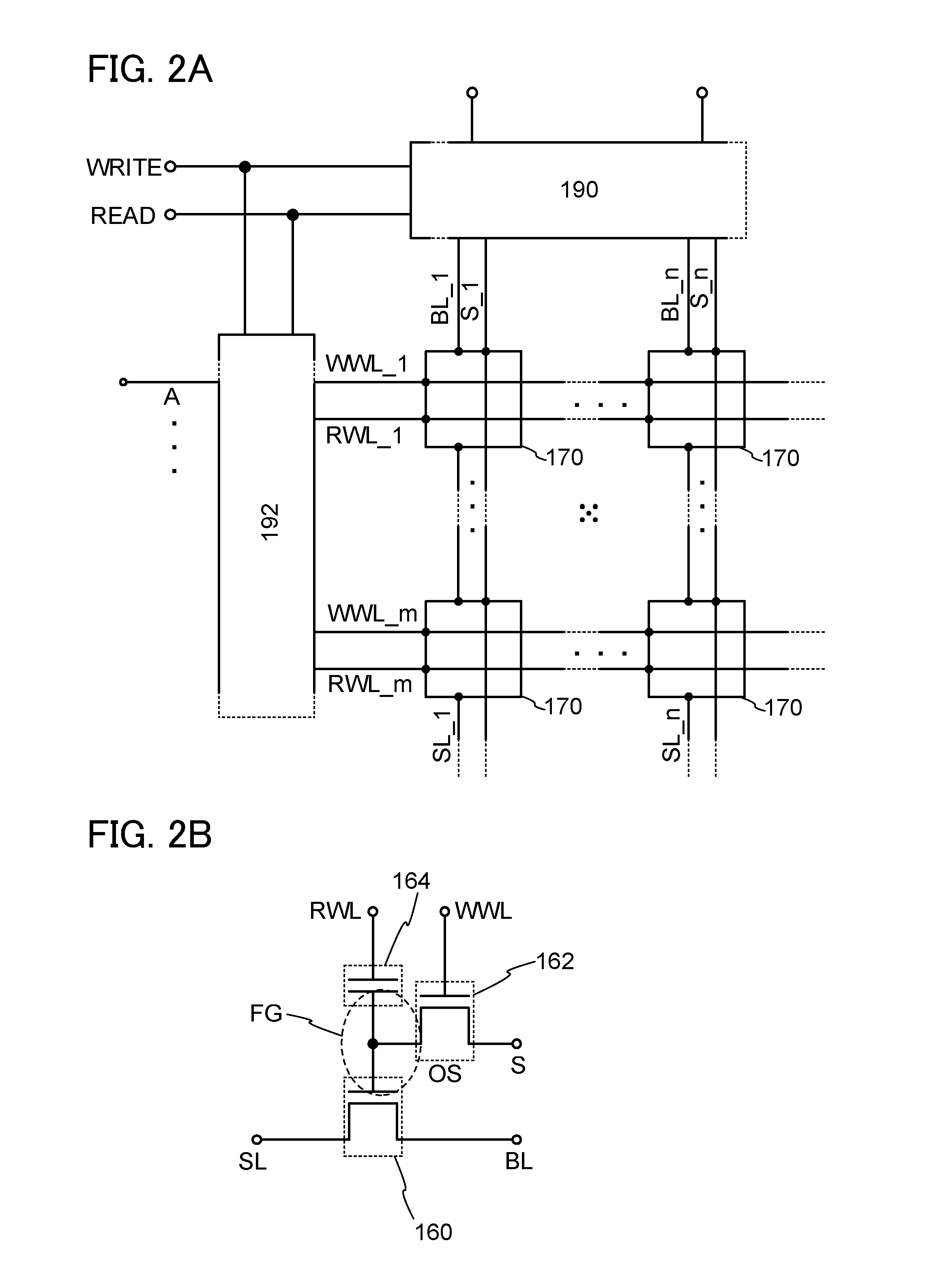
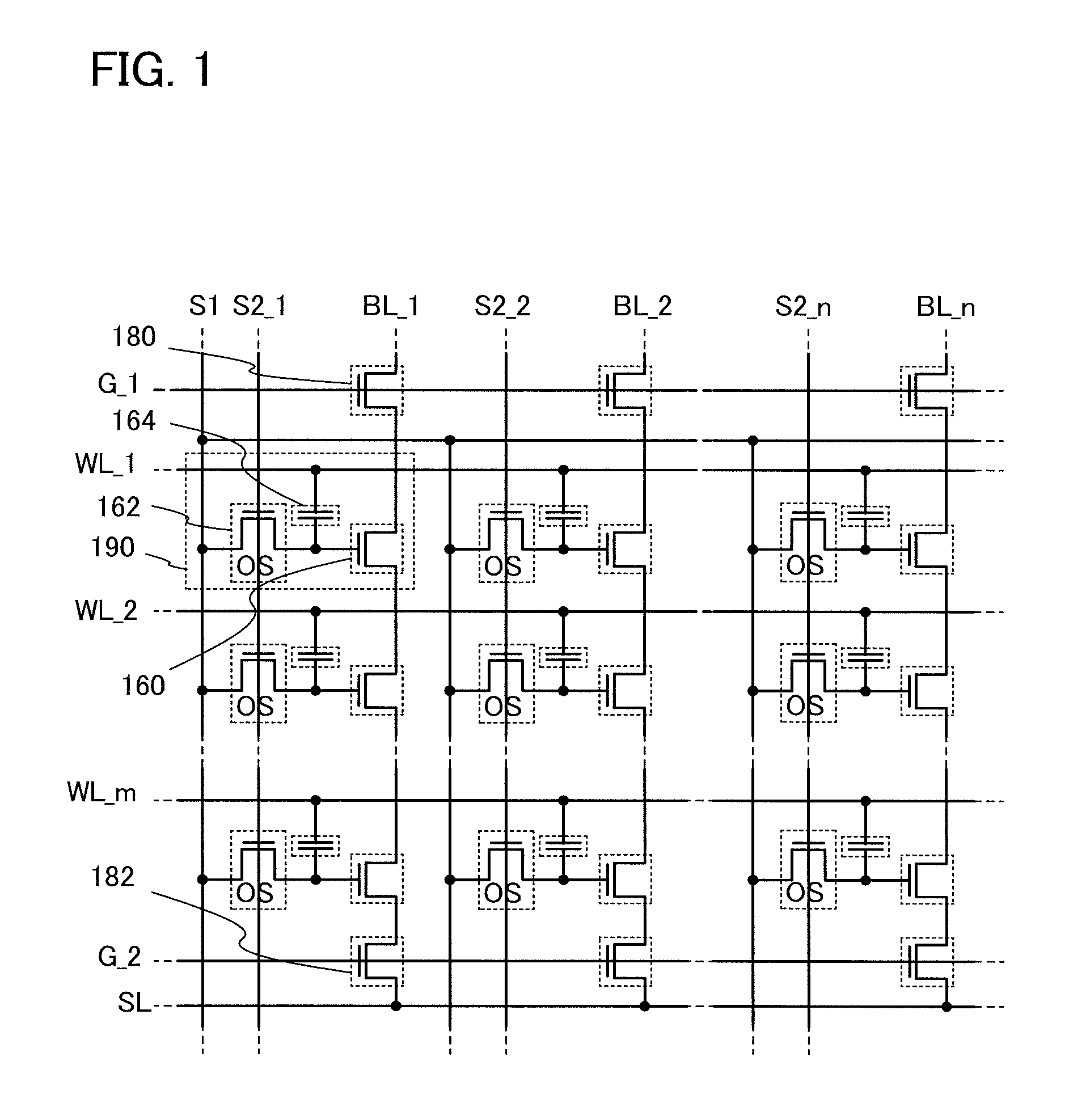
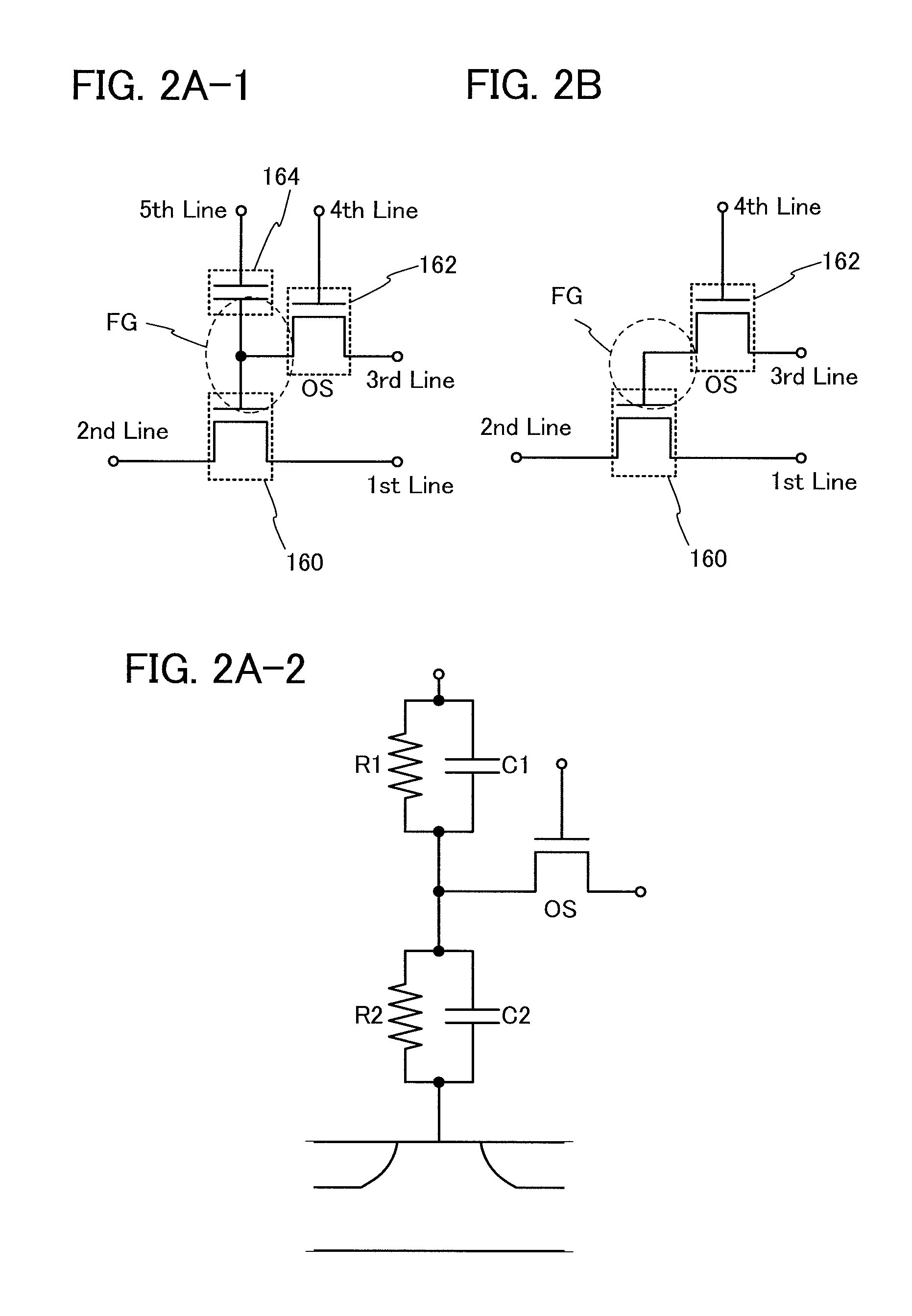
In a semiconductor device which conducts multilevel writing operation and a driving method thereof, a signal line for controlling on / off of a writing transistor for conducting a writing operation on a memory cell using a transistor including an oxide semiconductor layer is disposed along a bit line, and a multilevel writing operation is conducted with use of, also in a writing operation, a voltage which is applied to a capacitor at a reading operation. Because an oxide semiconductor material that is a wide gap semiconductor capable of sufficiently reducing off-state current of a transistor is used, data can be held for a long period.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Snubber Circuit and Power Semiconductor Device Having Snubber Circuit
InactiveUS20080043500A1Improve reliabilityReduce in quantityThyristorEfficient power electronics conversionJunction temperatureVolumetric Mass Density
A snubber circuit as a conventional protection circuit for inverters, which is composed of an anode reactor, a Si diode and a resistance, needs to keep junction temperature of the Si diode at 125° C. or lower during operation and therefore requires mounting of a large-size heat sink, which causes a large number of component parts and difficulty in downsizing. As a diode of a snubber circuit for circulating electomagnetic energy of the anode reactor, a wide gap semiconductor (SiC) diode, which does not need a heat sink or requires only a small-size heat sink, is used. When the current density of SiC diode is made 20 to 30 times larger than the current density during normal temperature operation, ON resistance increases, and therefore it becomes possible to substitute the ON resistance for the resistance of the snubber circuit. The increase in current density increases the temperature of the SiC diode. However, since the SiC diode can operate at temperature near 300° C. without any problems, a large-size heat sink is not necessary.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO
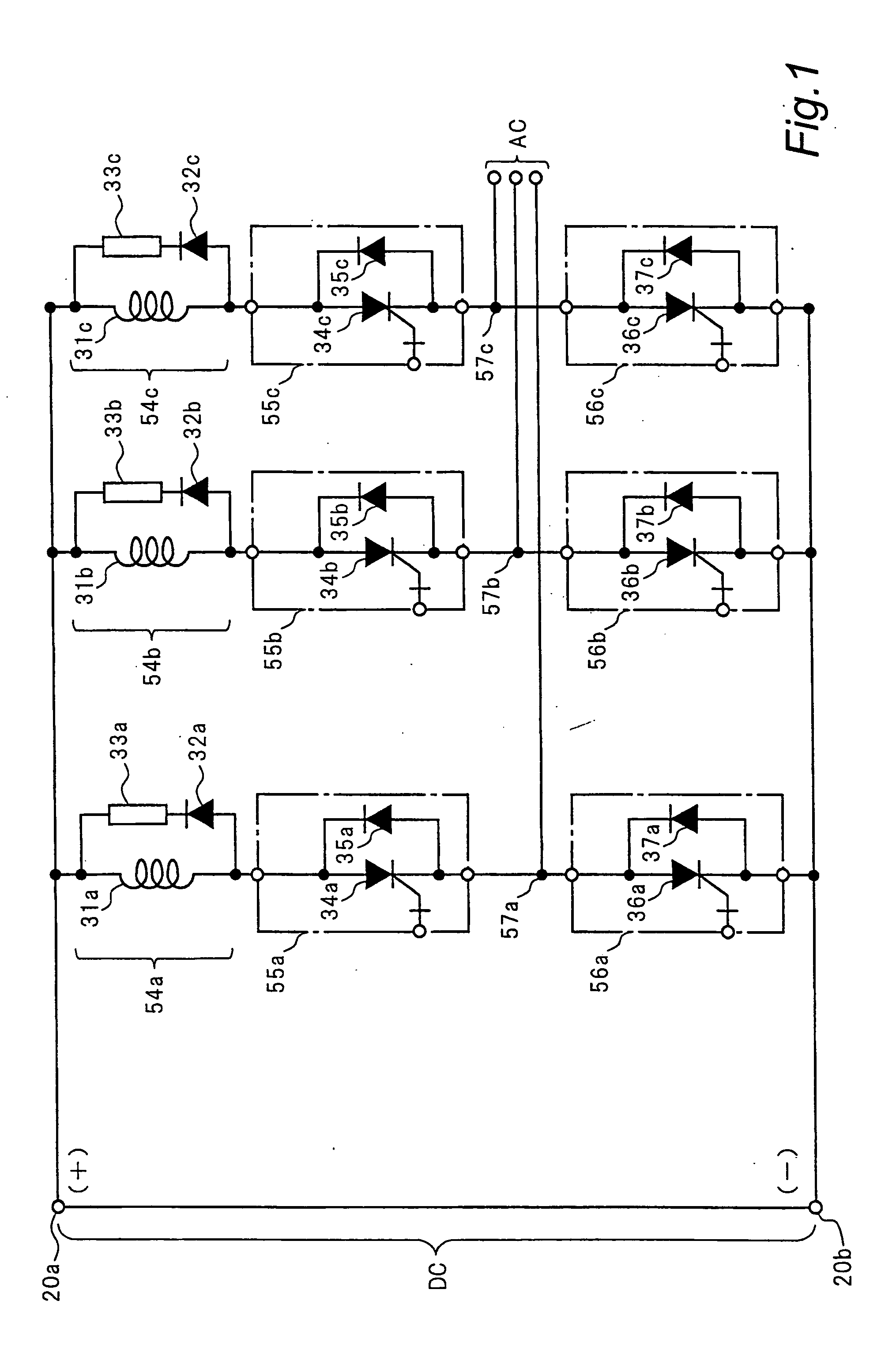
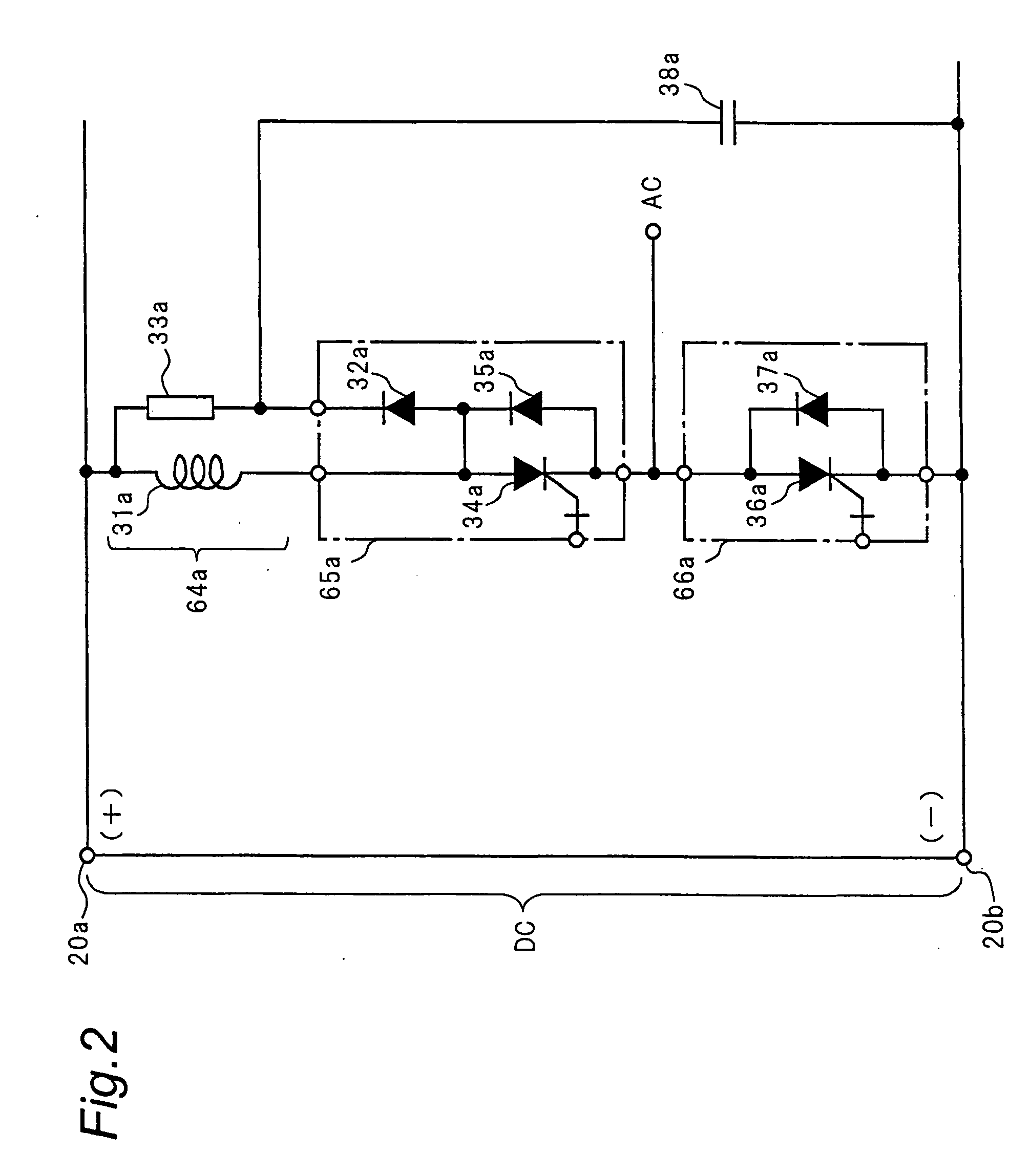
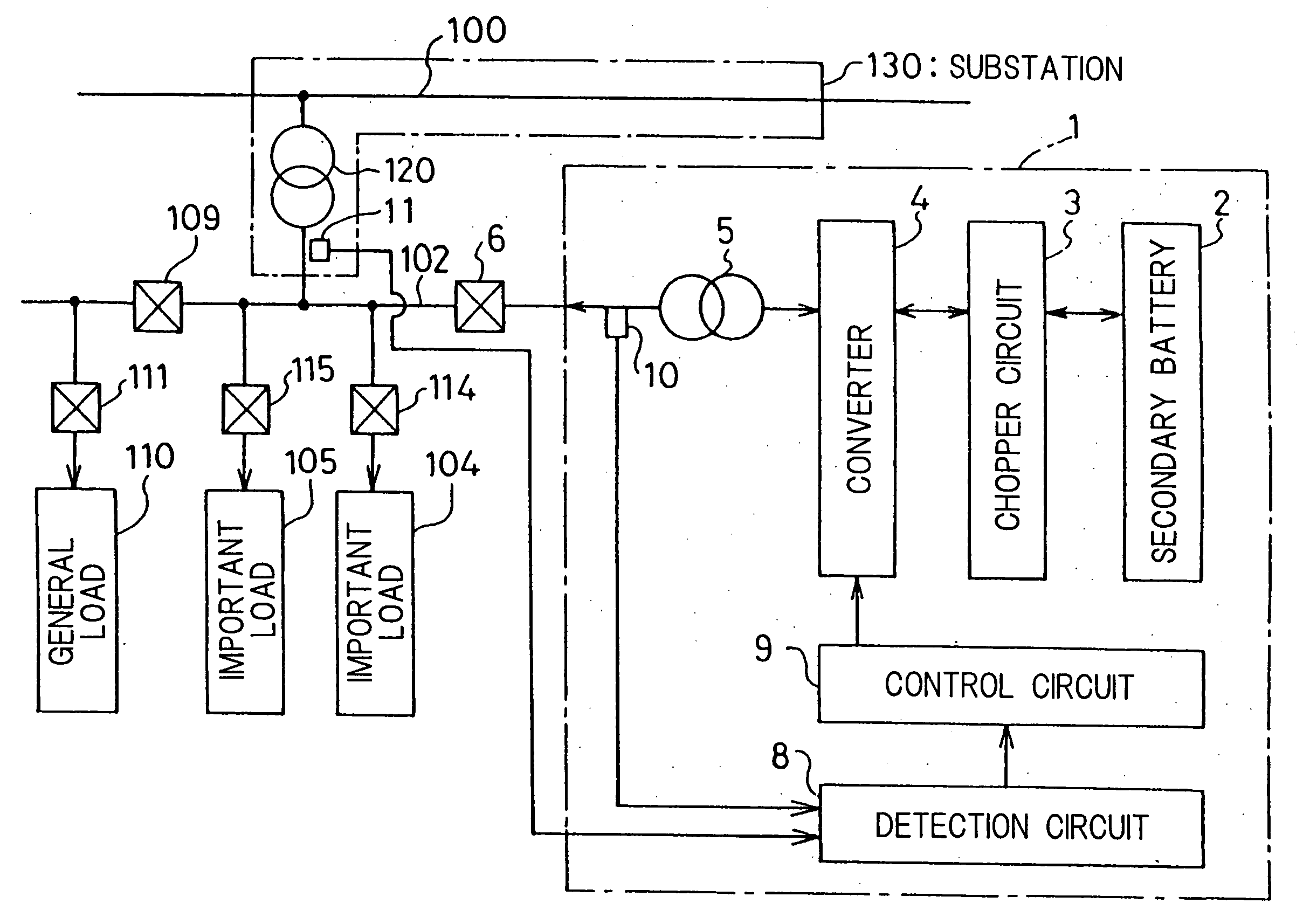
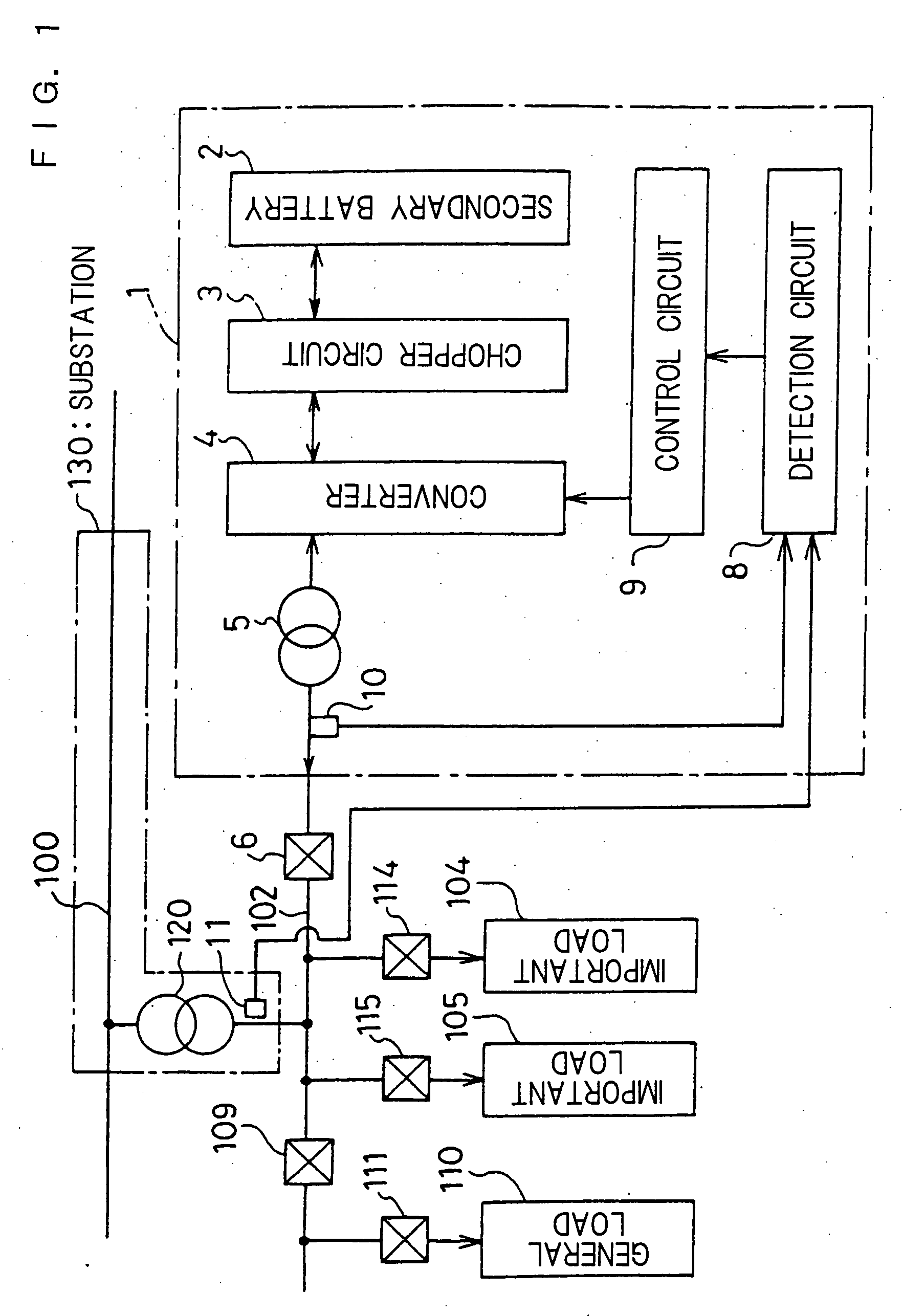
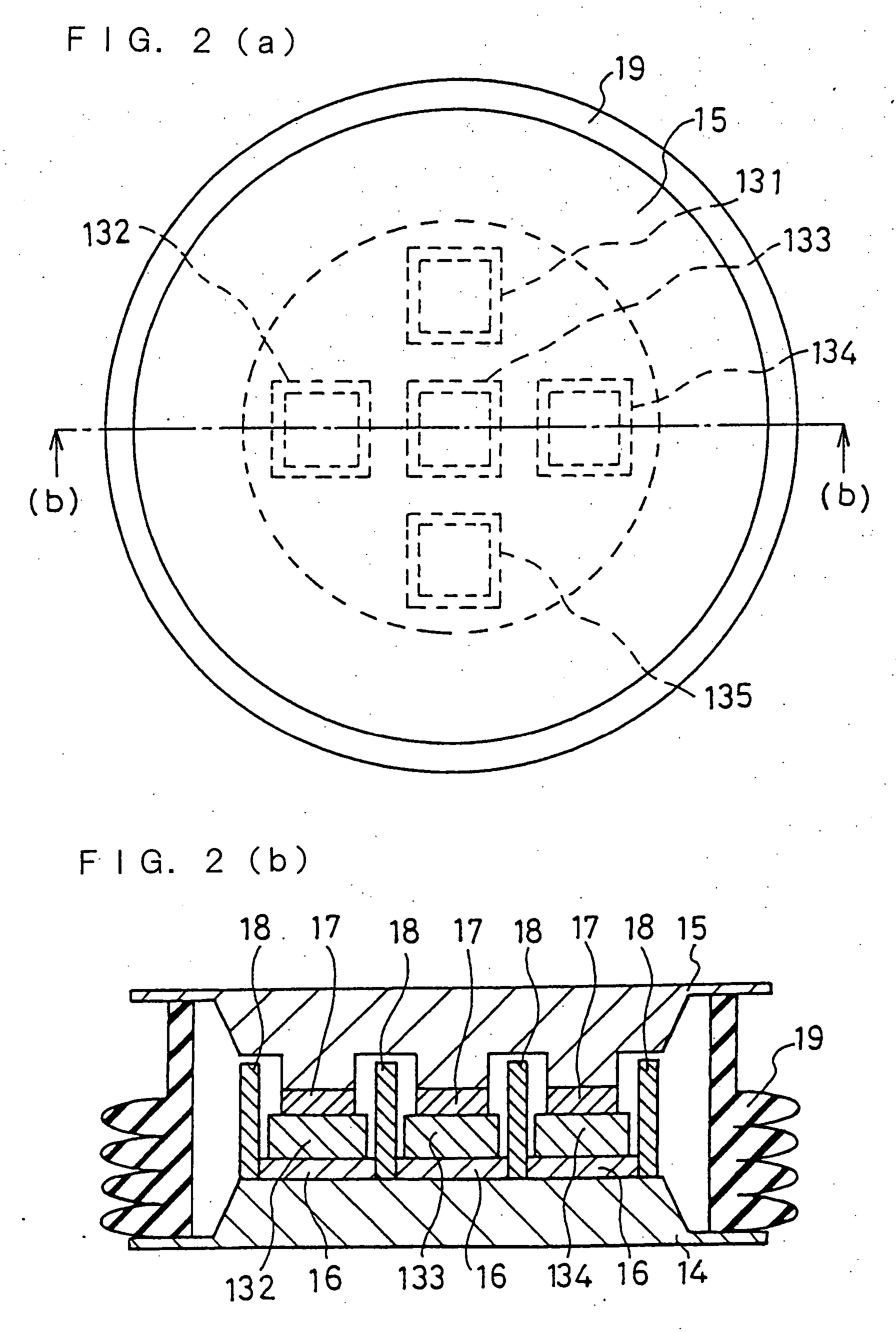
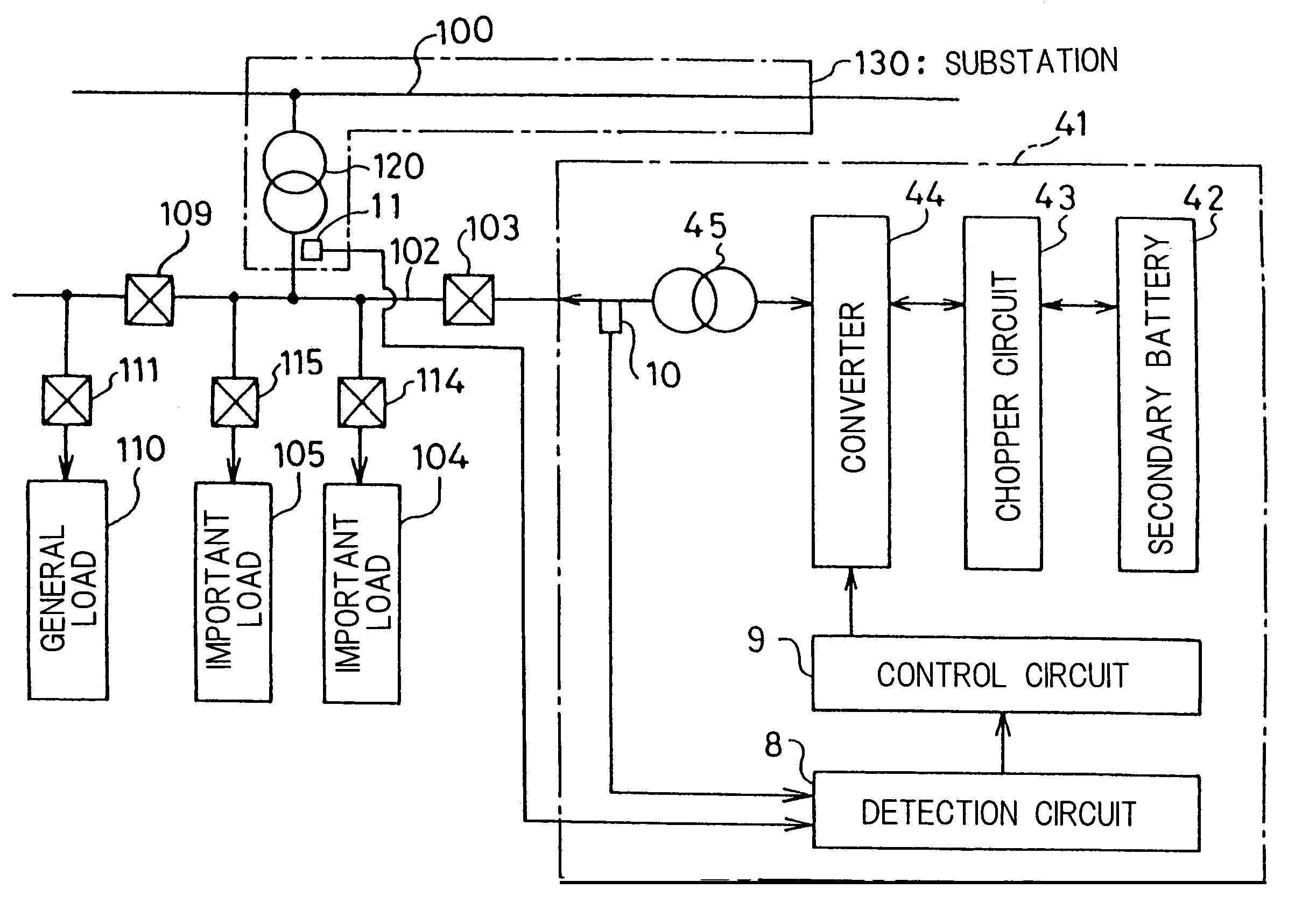
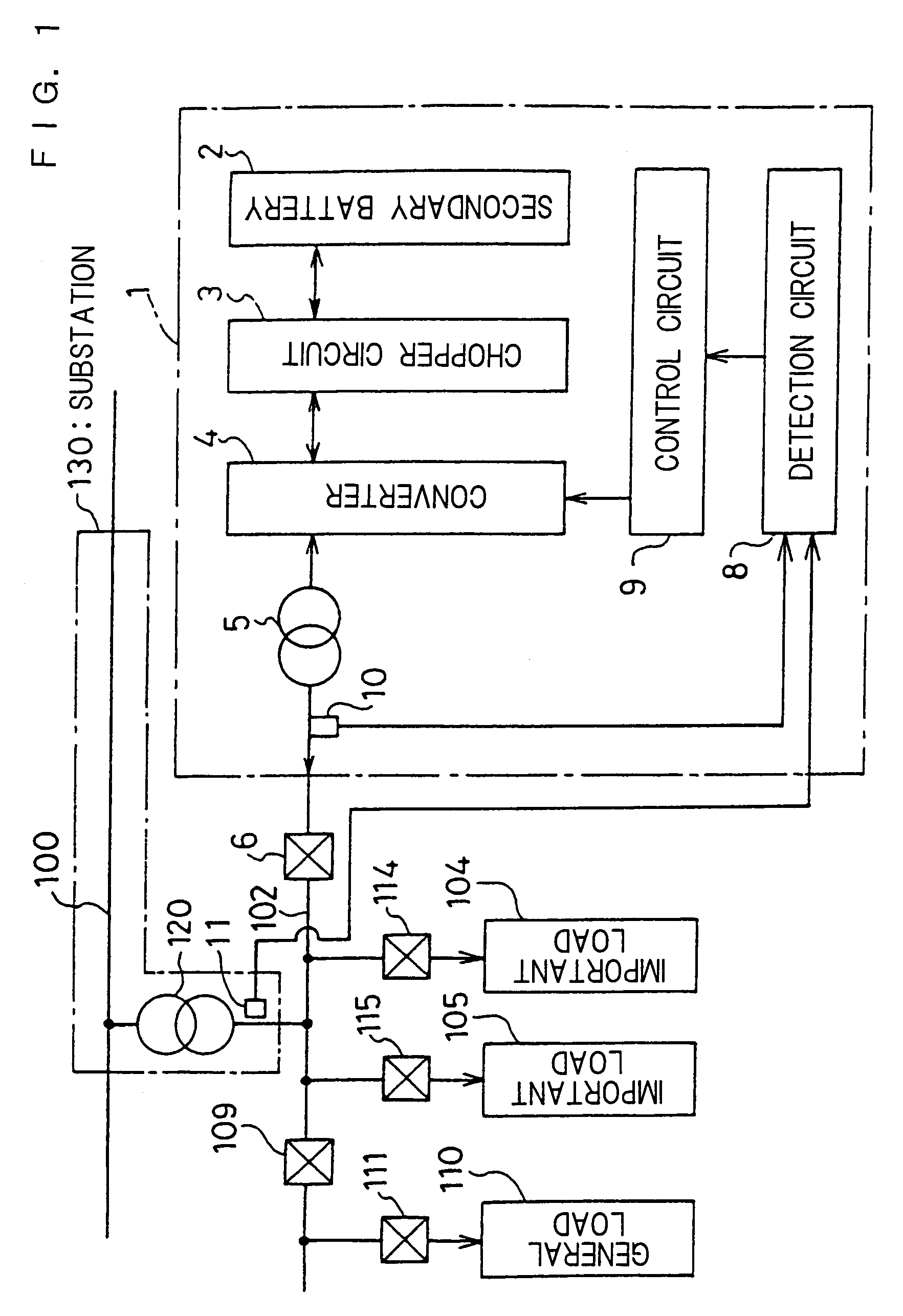
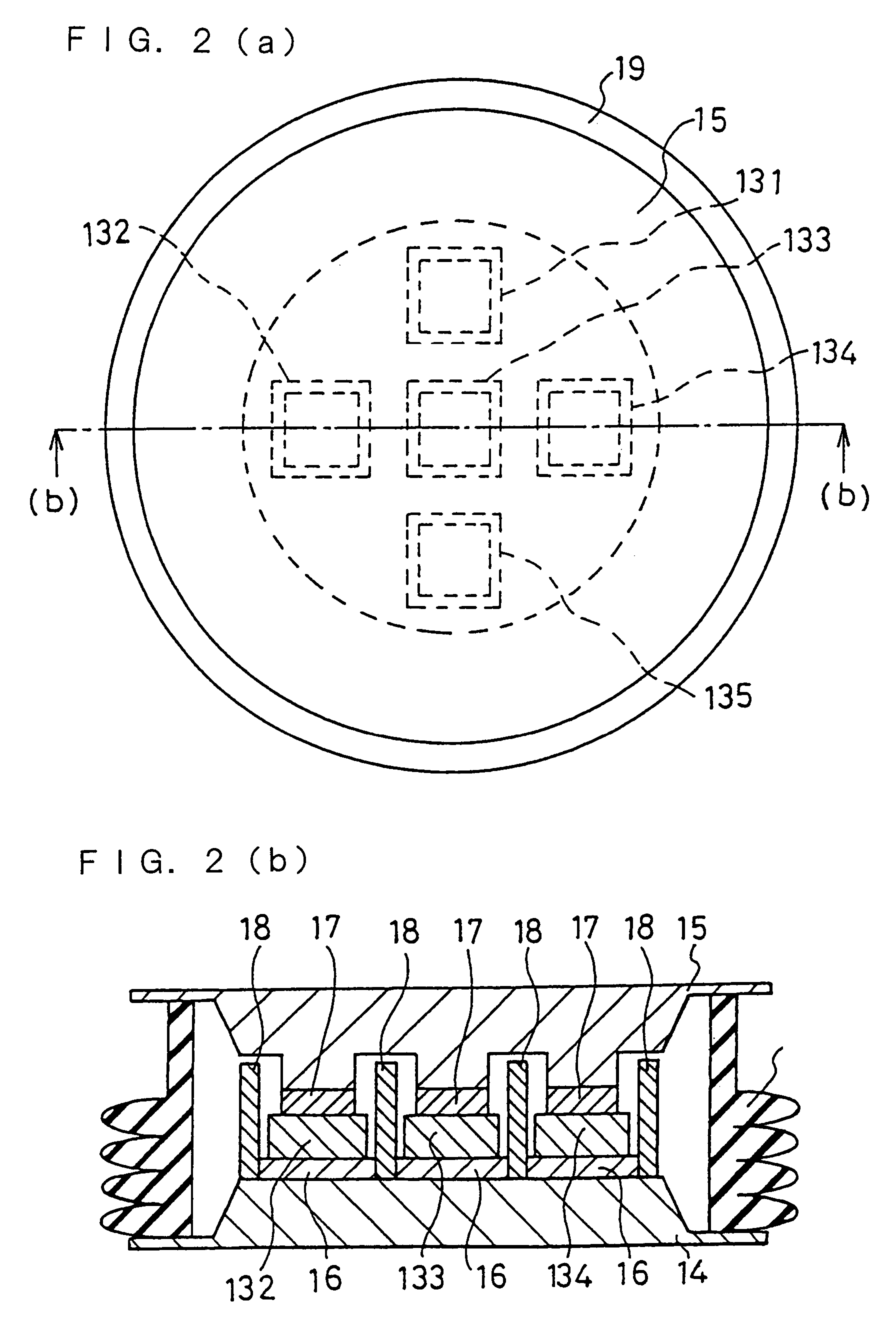
Stable power supplying apparatus
InactiveUS20060014054A1Small sizeLight weightBatteries circuit arrangementsCells structural combinationElectric forceDevice material
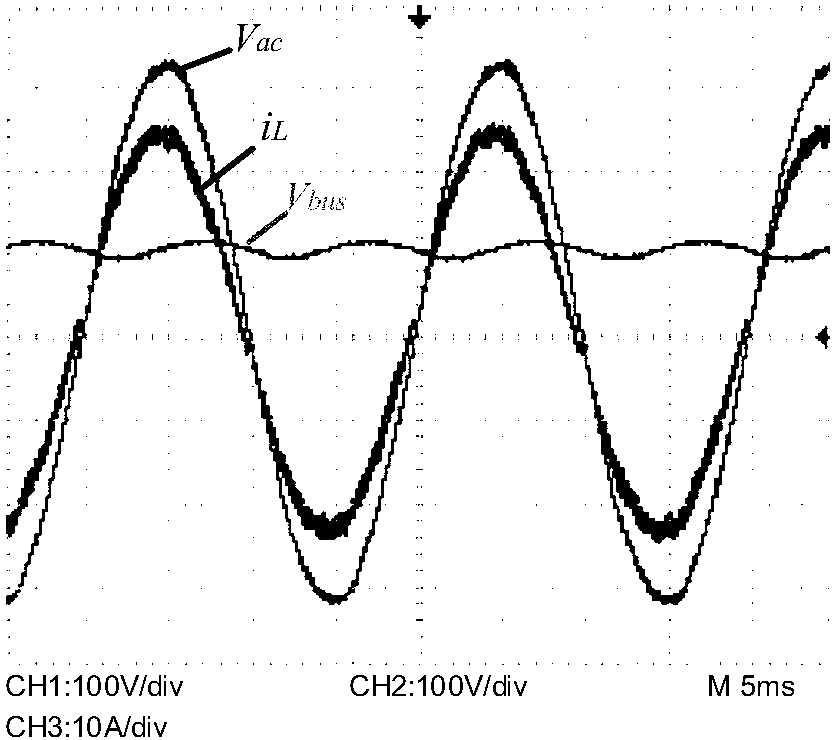
A stable power supply apparatus in accordance with the present invention comprises a secondary battery, a bidirectional chopper circuit and a bidirectional converter, wherein the secondary battery, the chopper circuit and the converter are connected in this order in the direction from the secondary battery side to a system bus line side. The converter is formed of a wide-gap semiconductor device, more particularly, a wide-gap bipolar semiconductor device, and the instantaneous large-power operation capability of the wide-gap bipolar semiconductor device and the instantaneous large-power supplying capability of the secondary battery are utilized. For a short time during which the influence of an instantaneous drop is prevented, the converter is operated as a converter having capability exceeding the instantaneous large-power supplying capability of the secondary battery and having power capacity several times or more the rating of the converter.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO
Stable power supplying apparatus
InactiveUS7554220B2Small sizeLight weightBatteries circuit arrangementsCells structural combinationWide gap semiconductorsEngineering
A stable power supply apparatus in accordance with the present invention comprises a secondary battery, a bidirectional chopper circuit and a bidirectional converter, wherein the secondary battery, the chopper circuit and the converter are connected in this order in the direction from the secondary battery side to a system bus line side. The converter is formed of a wide-gap semiconductor device, more particularly, a wide-gap bipolar semiconductor device, and the instantaneous large-power operation capability of the wide-gap bipolar semiconductor device and the instantaneous large-power supplying capability of the secondary battery are utilized. For a short time during which the influence of an instantaneous drop is prevented, the converter is operated as a converter having capability exceeding the instantaneous large-power supplying capability of the secondary battery and having power capacity several times or more the rating of the converter.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO
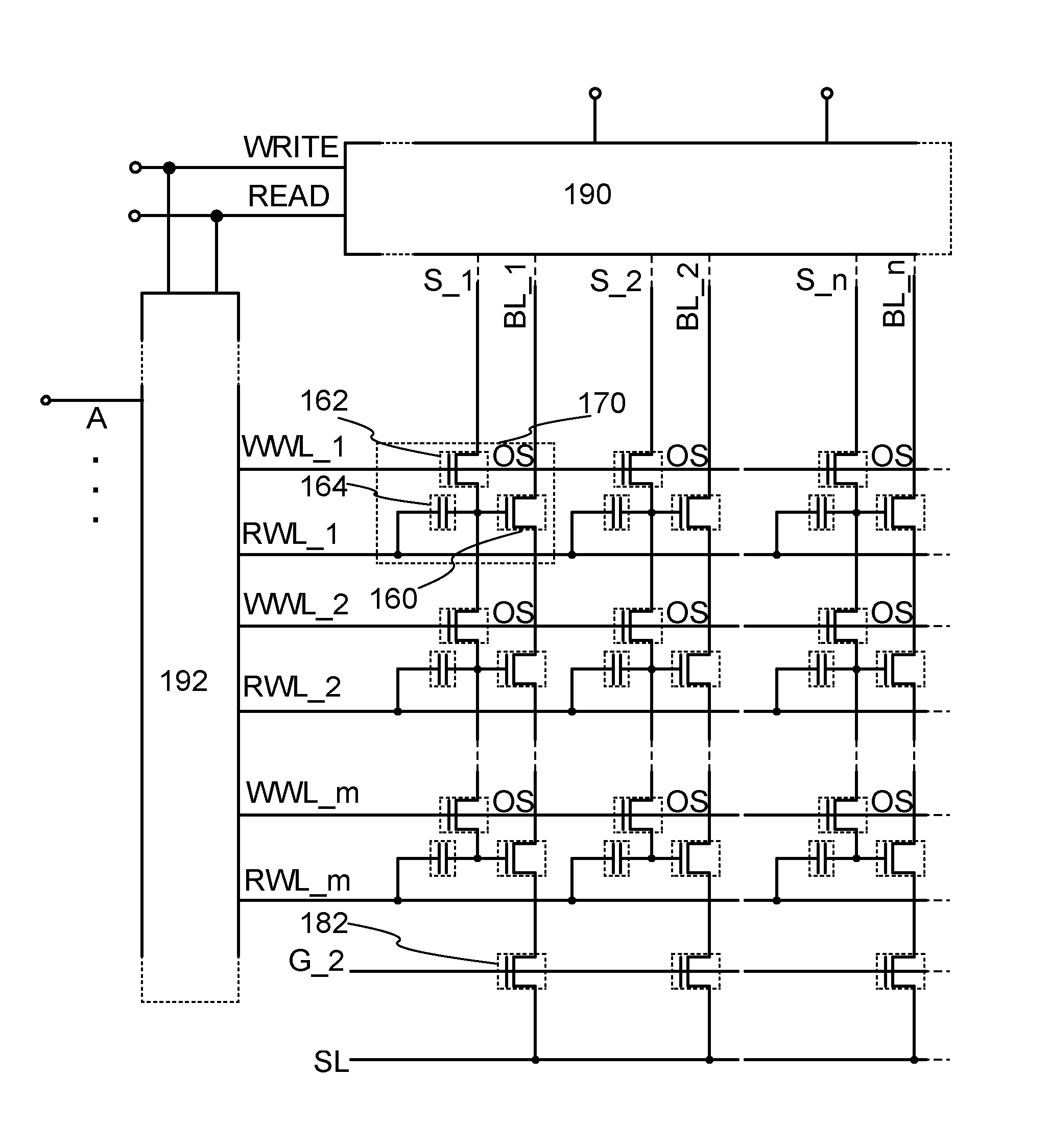
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20130228839A1Reduce leakage currentIncrease cell densityTransistorSolid-state devicesWide gap semiconductorsBroadband
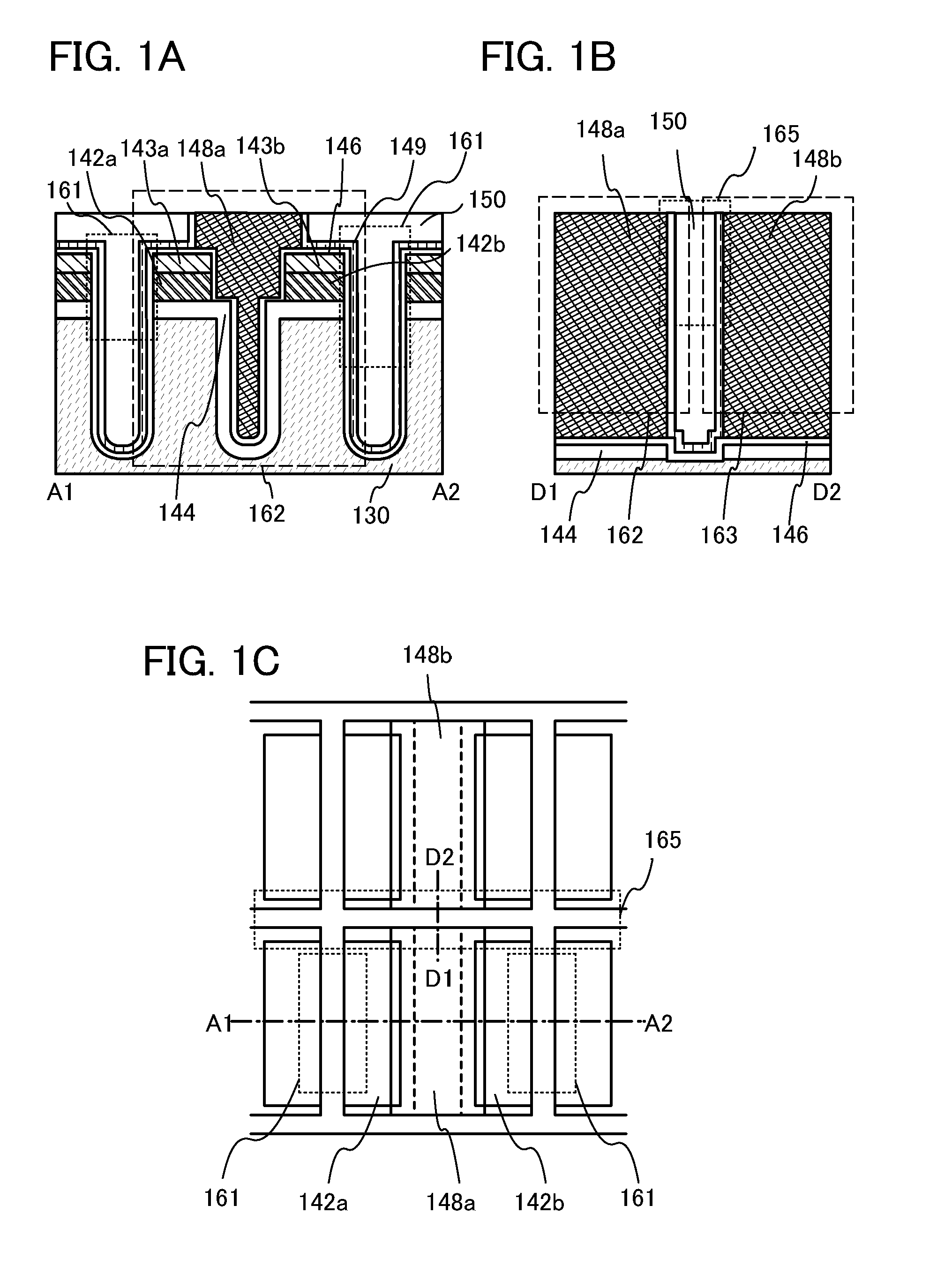
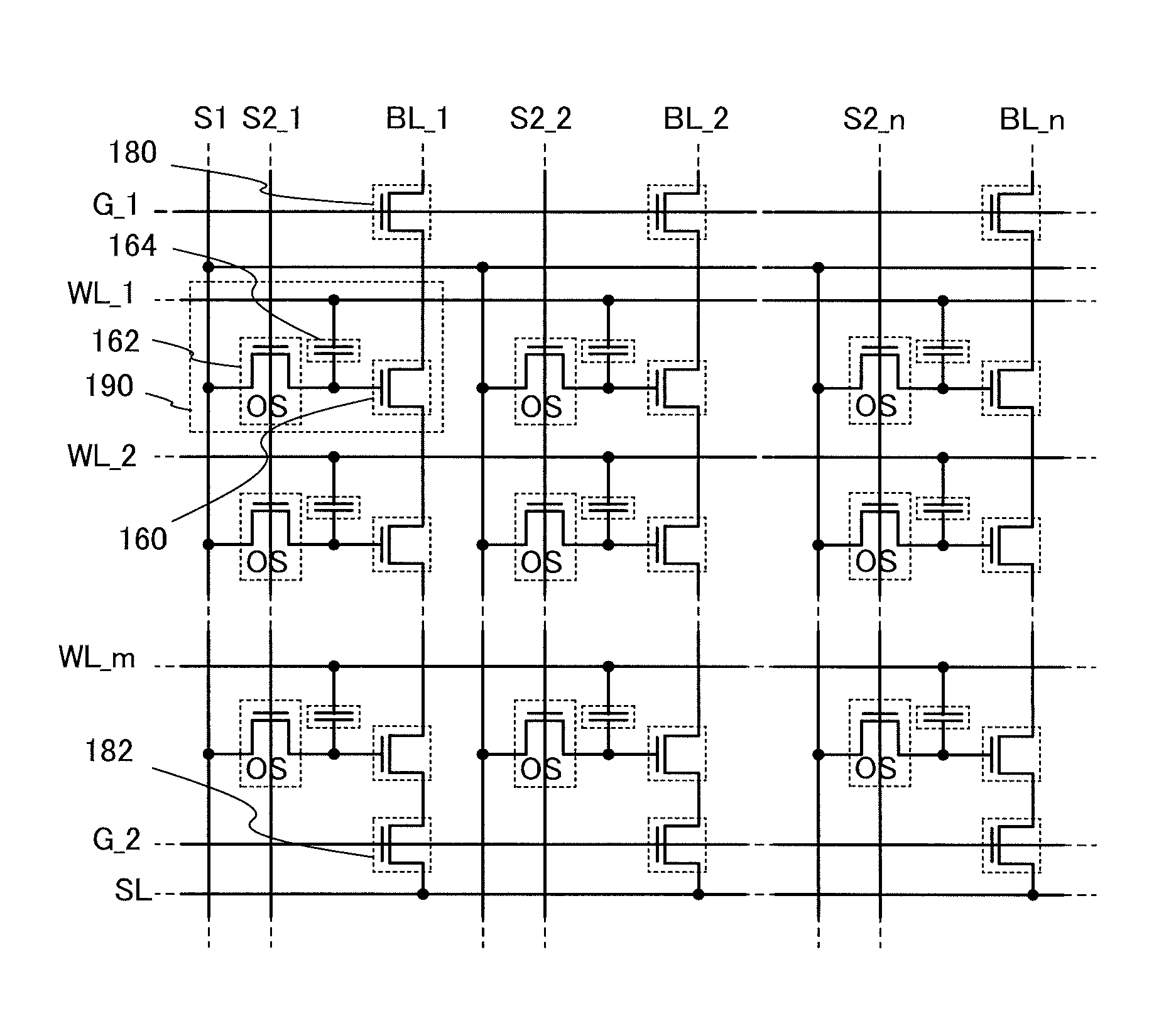
To provide a highly integrated semiconductor memory device. To provide a semiconductor memory device which can hold stored data even when power is not supplied. To provide a semiconductor memory device which has a large number of write cycles. The degree of integration of a memory cell array is increased by forming a memory cell including two transistors and one capacitor which are arranged three-dimensionally. The electric charge accumulated in the capacitor is prevented from being leaking by forming a transistor for controlling the amount of electric charge of the capacitor in the memory cell using a wide-gap semiconductor having a wider band gap than silicon. Accordingly, a semiconductor memory device which can hold stored data even when power is not supplied can be provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
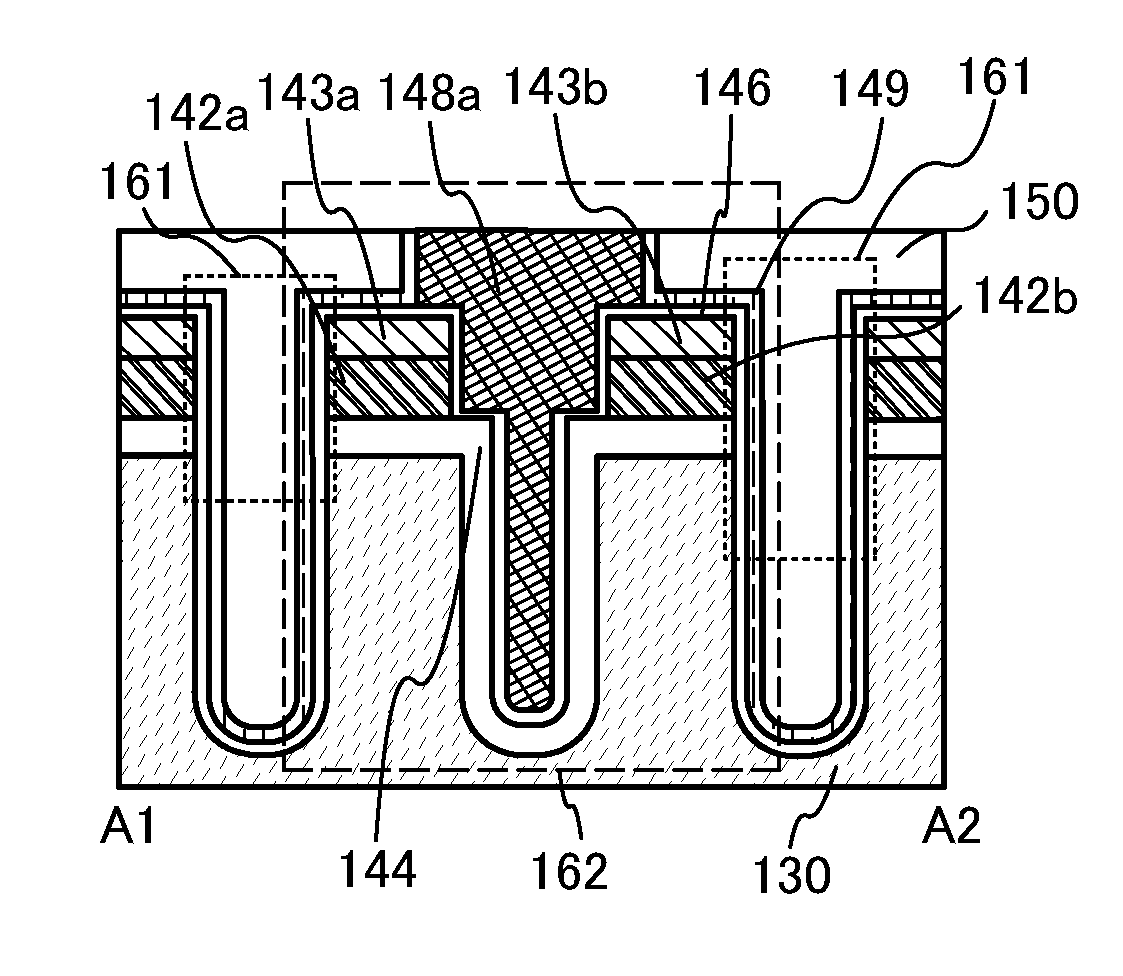
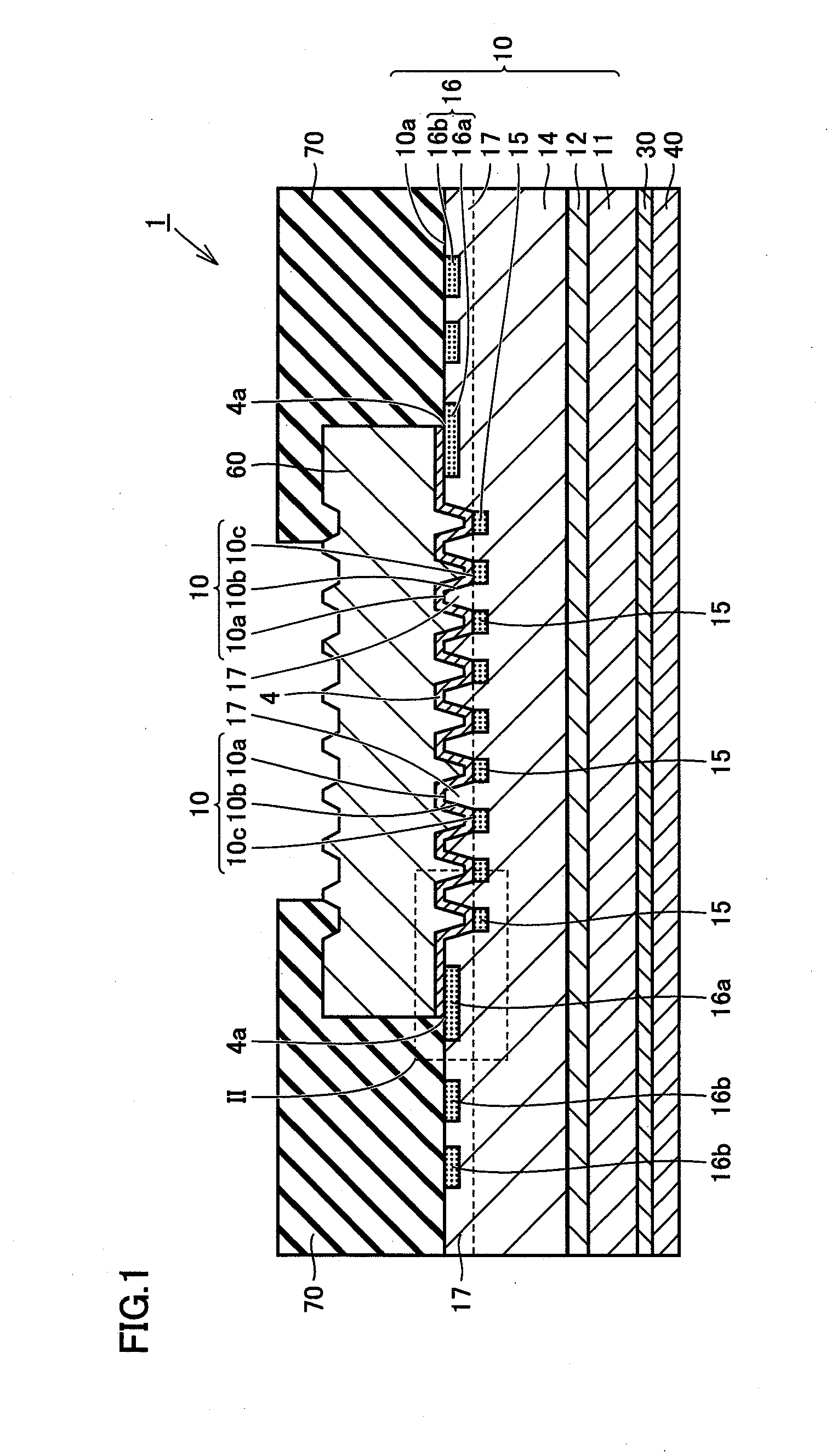
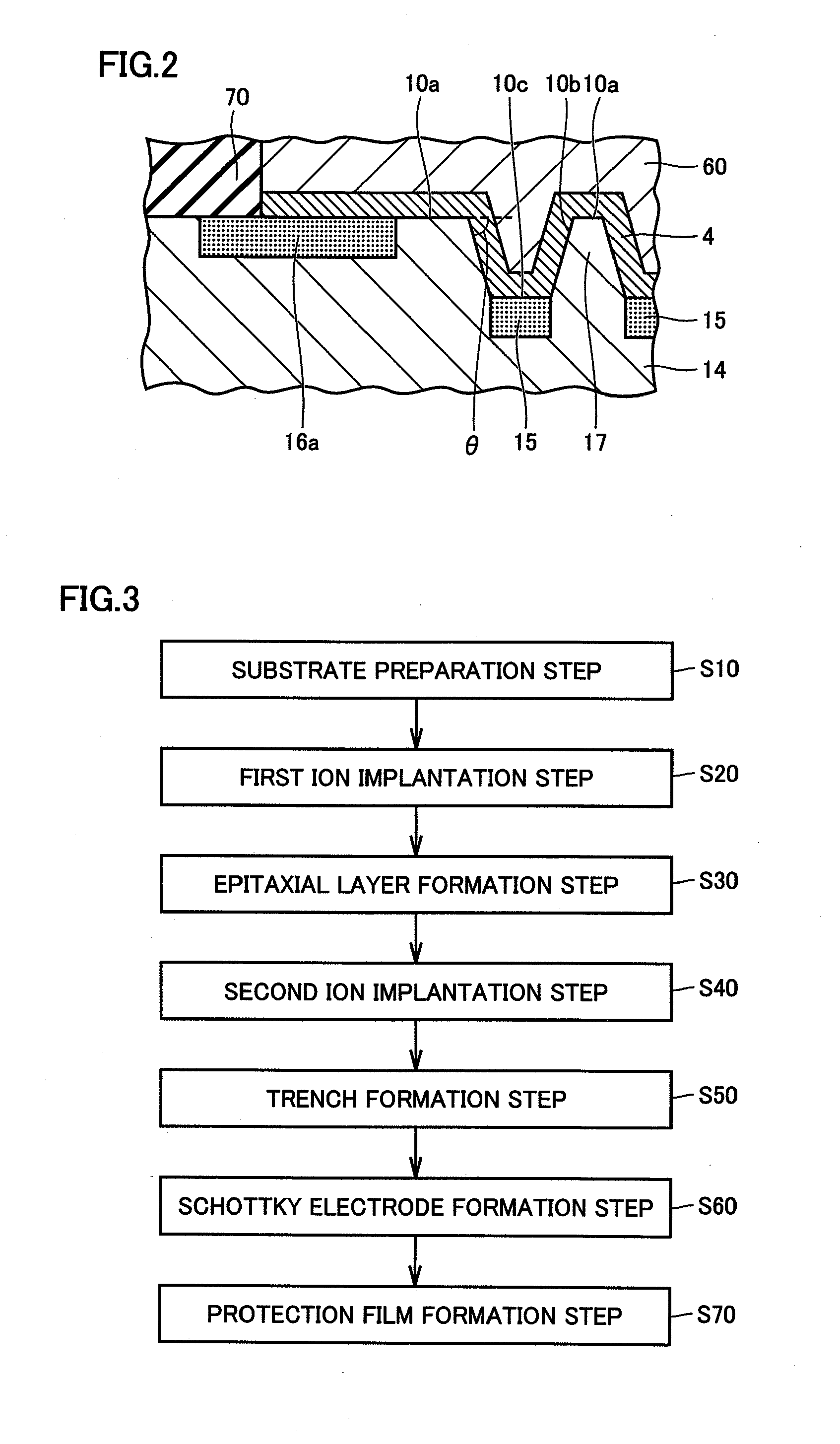
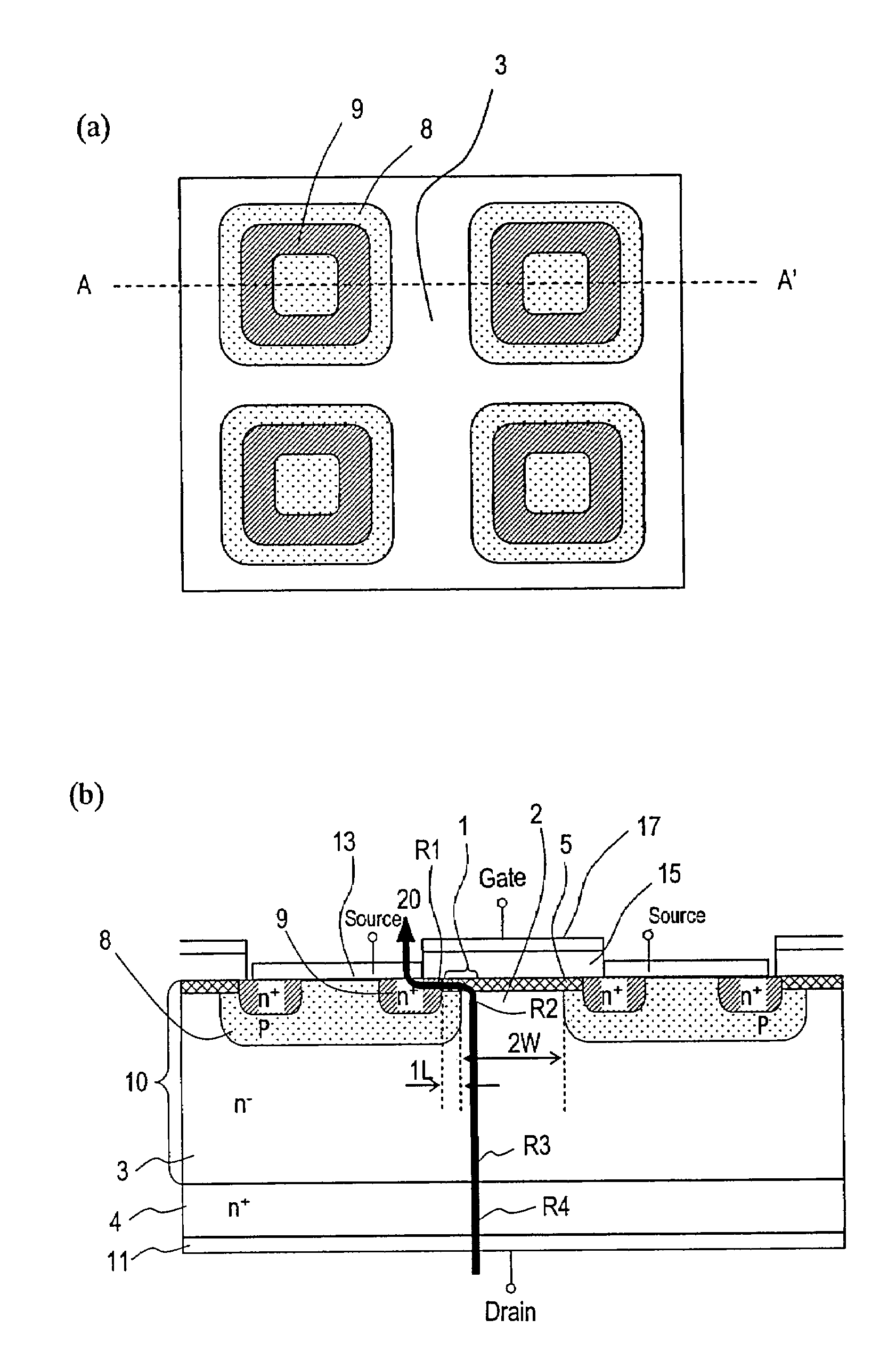
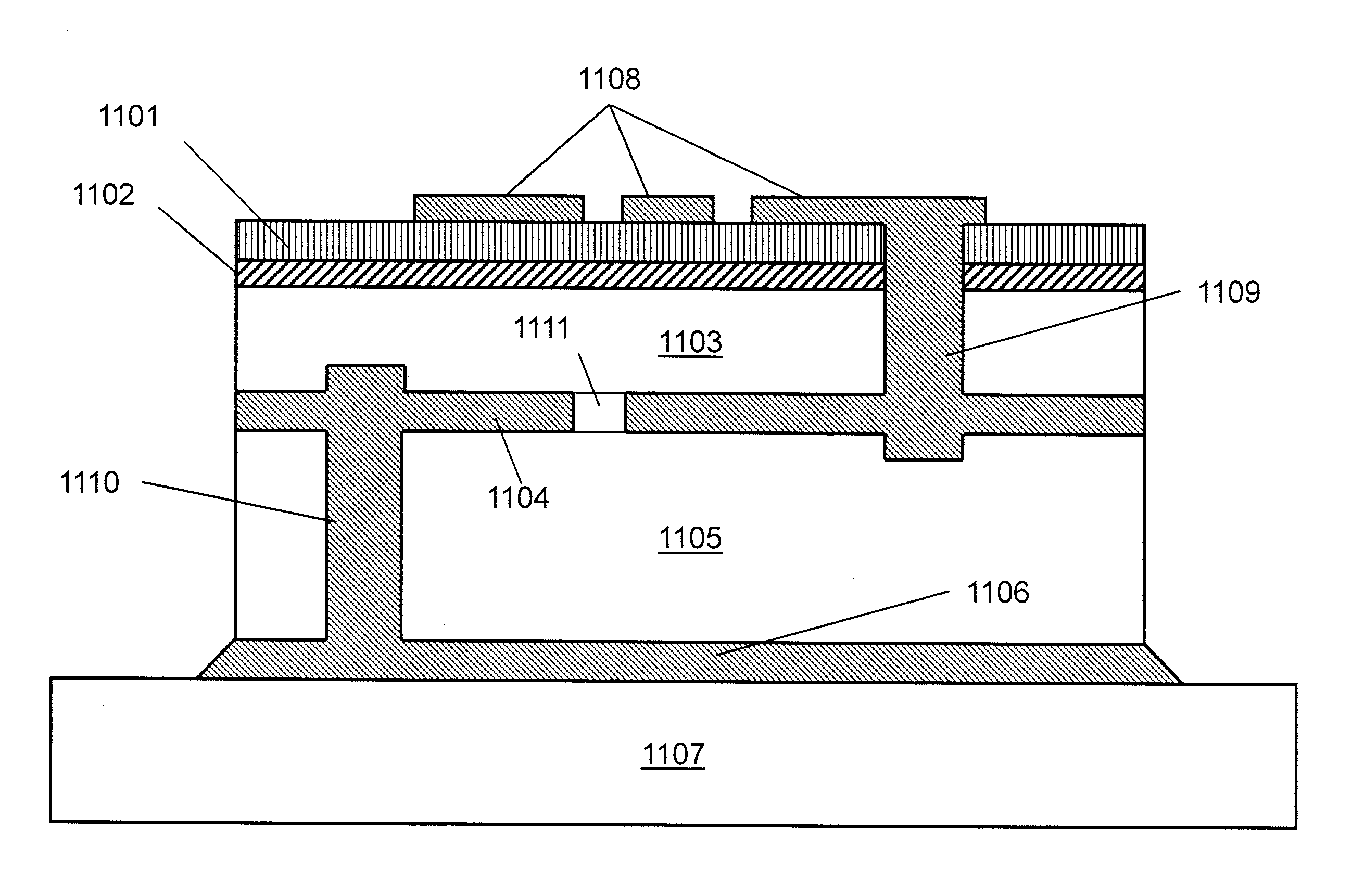
Wide gap semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20140061671A1Fine surfaceEliminate damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeWide gap semiconductorsEngineering
A wide gap semiconductor device includes a substrate and a Schottky electrode. The substrate formed of a wide gap semiconductor material has a main face, and includes a first-conductivity-type region and a second-conductivity-type region. The Schottky electrode is arranged adjoining the main face of the substrate. At the substrate, there is foamed a trench having a side face continuous with the main face and a bottom continuous with the side face. The Schottky electrode adjoins the first-conductivity-type region at the side face of the trench and the main face, and adjoins the second-conductivity-type region at the bottom of the trench. The side face of the trench is inclined relative to the main face of the substrate.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120235150A1Improve propertiesReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsWide gap semiconductors
A semiconductor device in which improvement of a property of holding stored data can be achieved. Further, power consumption of a semiconductor device is reduced. A transistor in which a wide-gap semiconductor material capable of sufficiently reducing the off-state current of a transistor (e.g., an oxide semiconductor material) in a channel formation region is used and which has a trench structure, i.e., a trench for a gate electrode and a trench for element isolation, is provided. The use of a semiconductor material capable of sufficiently reducing the off-state current of a transistor enables data to be held for a long time. Further, since the transistor has the trench for a gate electrode, the occurrence of a short-channel effect can be suppressed by appropriately setting the depth of the trench even when the distance between the source electrode and the drain electrode is decreased.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and driving method of the same
ActiveUS20110199816A1Reduce power consumptionSufficient reduction in off-state currentSolid-state devicesDigital storageBit linePotential change
An object is to provide a semiconductor device with a novel structure in which stored data can be held even when power is not supplied, and the number of times of writing is not limited. The semiconductor device is formed using a wide gap semiconductor and includes a potential change circuit which selectively applies a potential either equal to or different from a potential of a bit line to a source line. Thus, power consumption of the semiconductor device can be sufficiently reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Driver circuit for switching device
InactiveUS8508258B2Lower dependence of lossReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDriver circuitPower semiconductor device
A driver circuit that lowers the dependence of the loss in the wide gap semiconductor device upon the temperature is provided. A gate driver circuit for voltage driven power semiconductor switching device includes a power semiconductor switching device, a driver circuit for supplying a drive signal to a gate terminal of the switching device with reference to an emitter control terminal or a source control terminal of the switching device, and a unit for detecting a temperature of the switching device. The temperature of the power semiconductor switching device is detected, and a gate drive voltage or a gate drive resistance value is changed based on the detected temperature.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
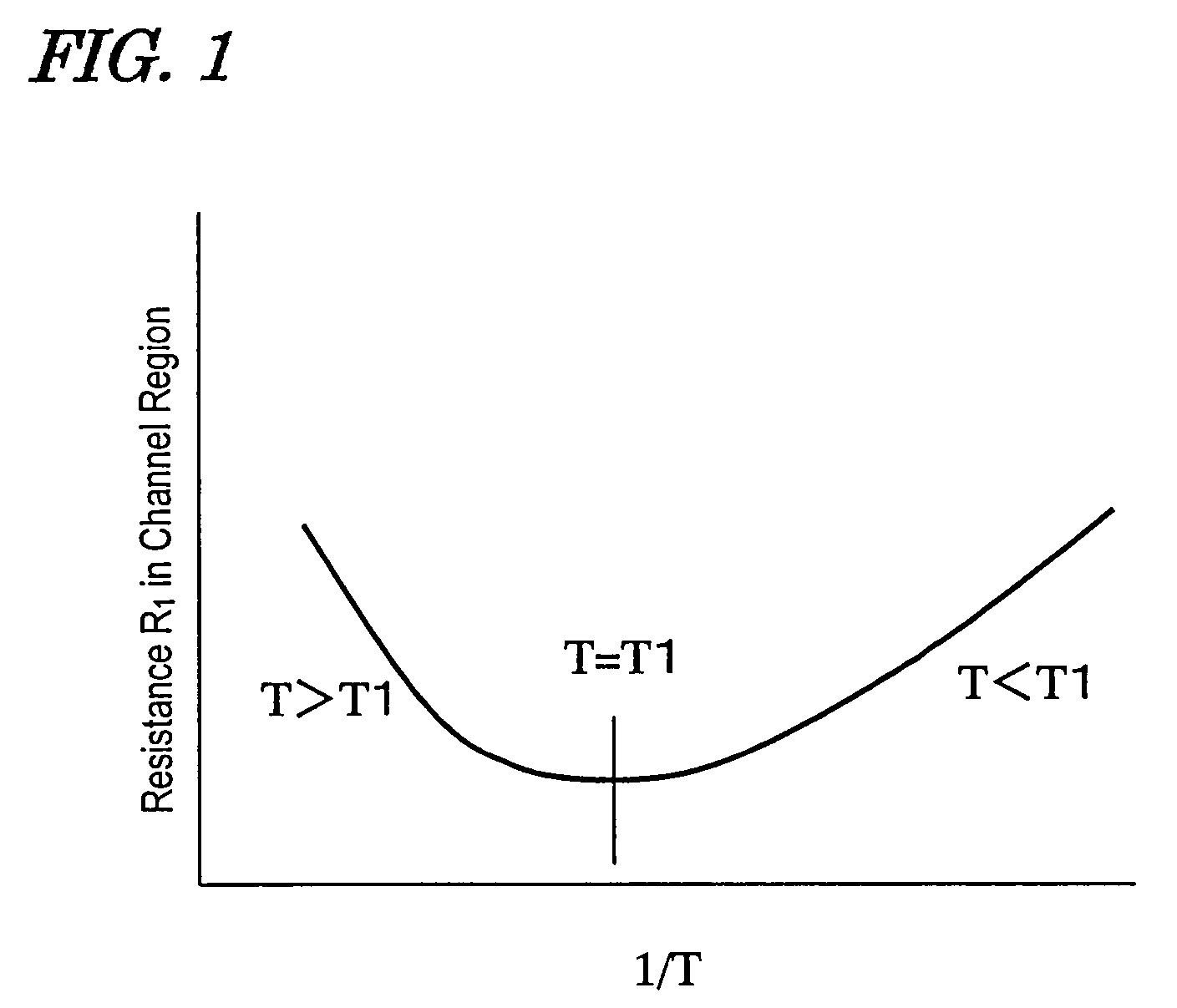
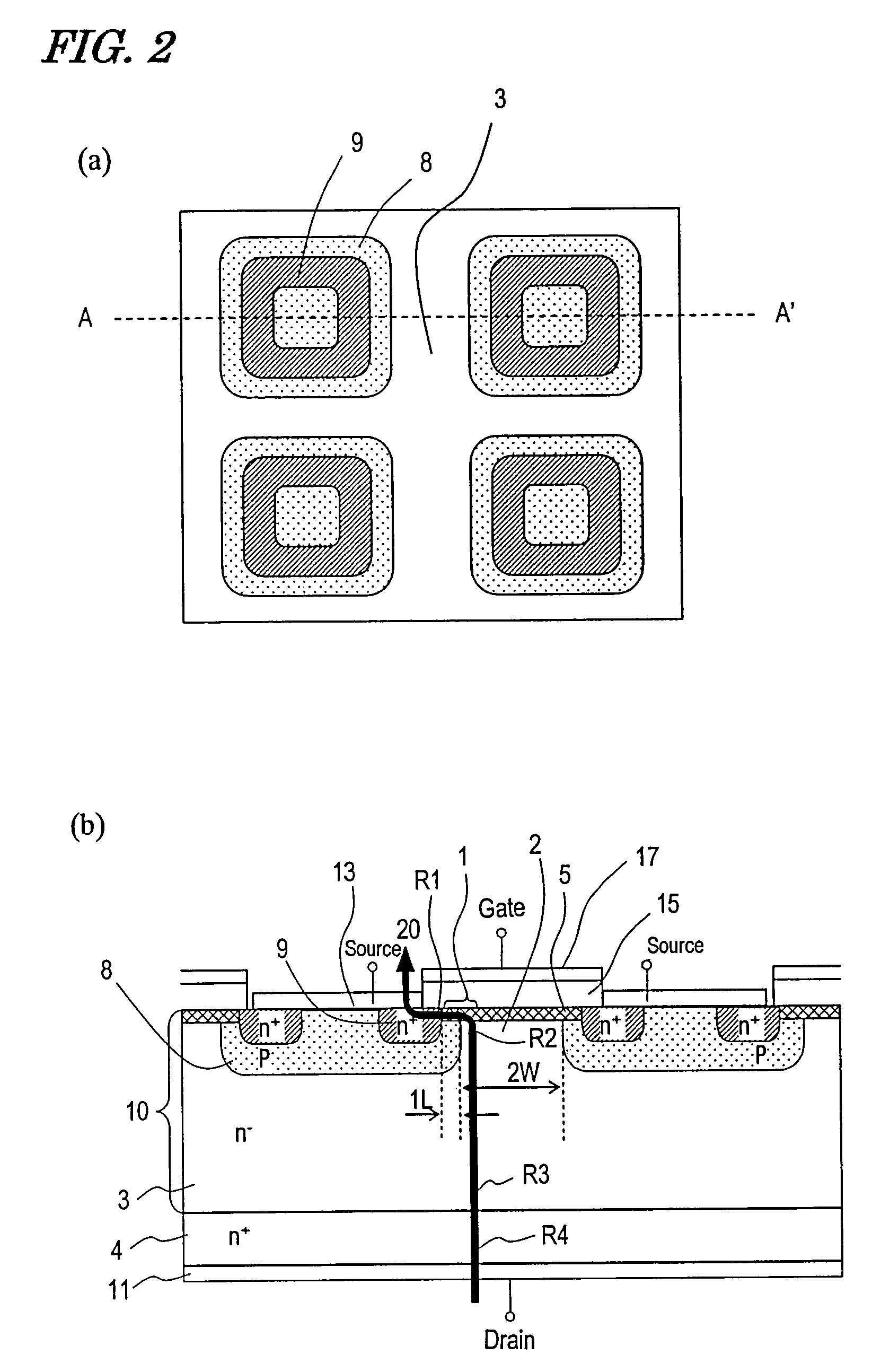
Wide gap semiconductor power device with temperature independent resistivity due to channel region resistivity having negative temperature dependence
ActiveUS7671409B2Highly stable against temperatureSlow changeTransistorForce measurementNegative temperatureWide gap semiconductors
A field-effect transistor power device includes a source electrode, a drain electrode, a wide gap semiconductor including a channel region and a drift region, the channel region and the drift region forming a series current path between the source electrode and the drain electrode, a gate insulating film that covers the channel region, and a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film. In the series current path which is electrically conducting when the field-effect transistor power device is in an ON state, any region other than the channel region has an ON resistance exhibiting a positive temperature dependence, and the channel region has an ON resistance exhibiting a negative temperature dependence. A ratio ΔRon / Ron(−30° C.) is 50% or less.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
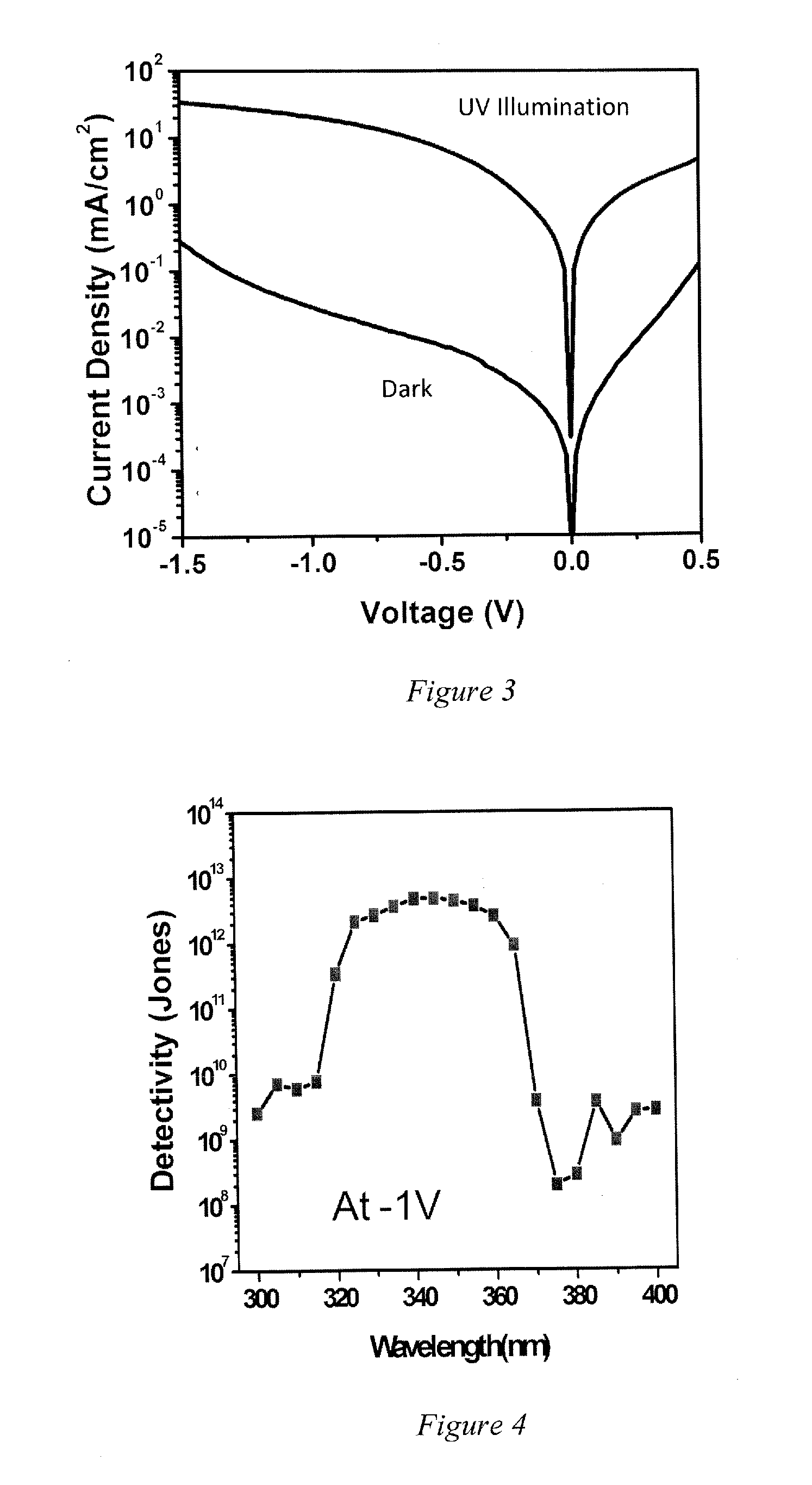
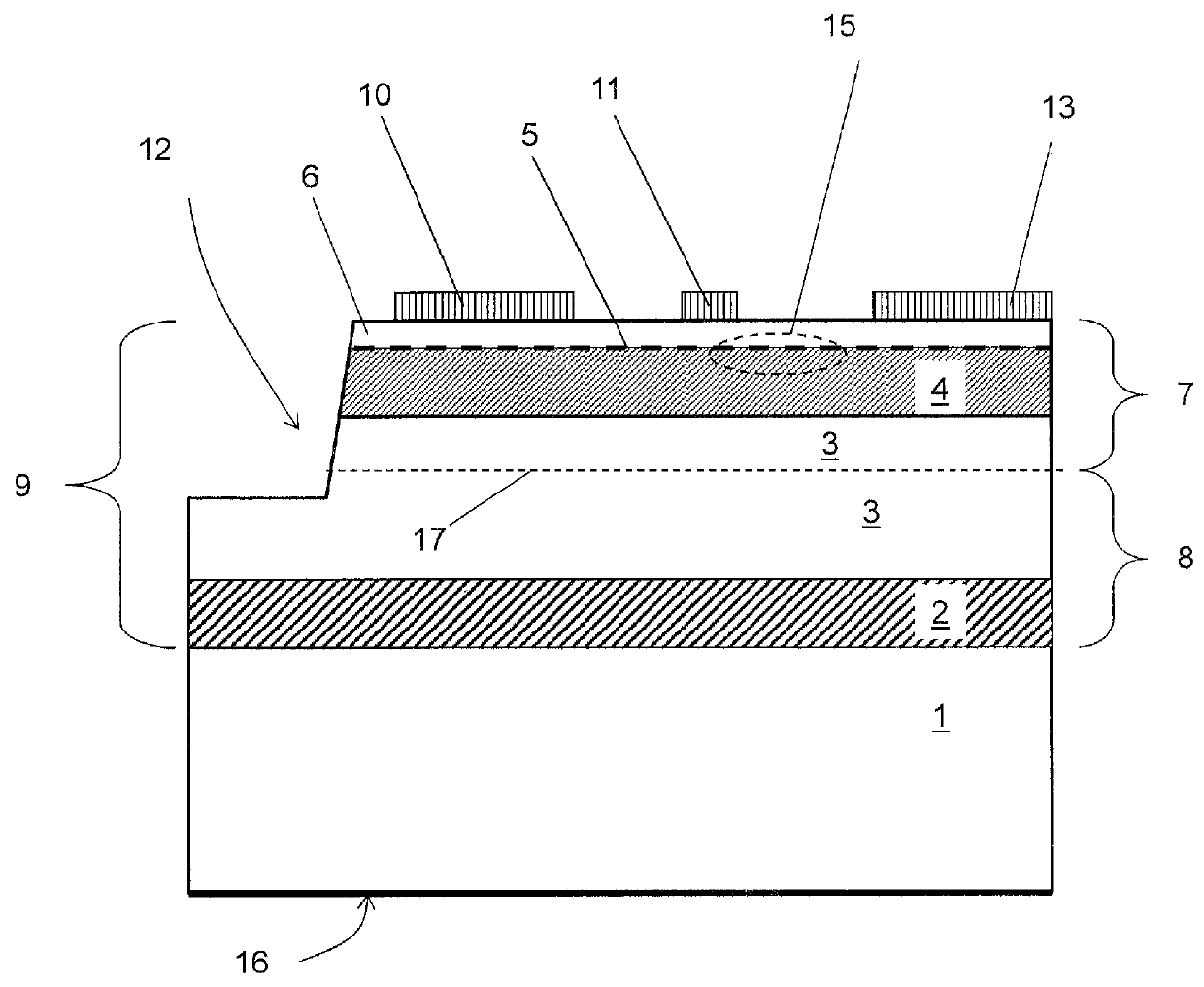
Solution-processed ultraviolet light detector based on p-n junctions of metal oxides
InactiveUS20150287871A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMetal oxide nanoparticlesUltraviolet detectors
An ultraviolet light detector has a pn-junction of wide-gap semiconductors layers, where a p-type semiconductor layer with a polycrystalline metal oxide contacts an n-type semiconductor layer of metal oxide nanoparticles, or the converse. The ultraviolet detector is prepared using solvent based deposition methods and where temperatures can be maintained below 300° C.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
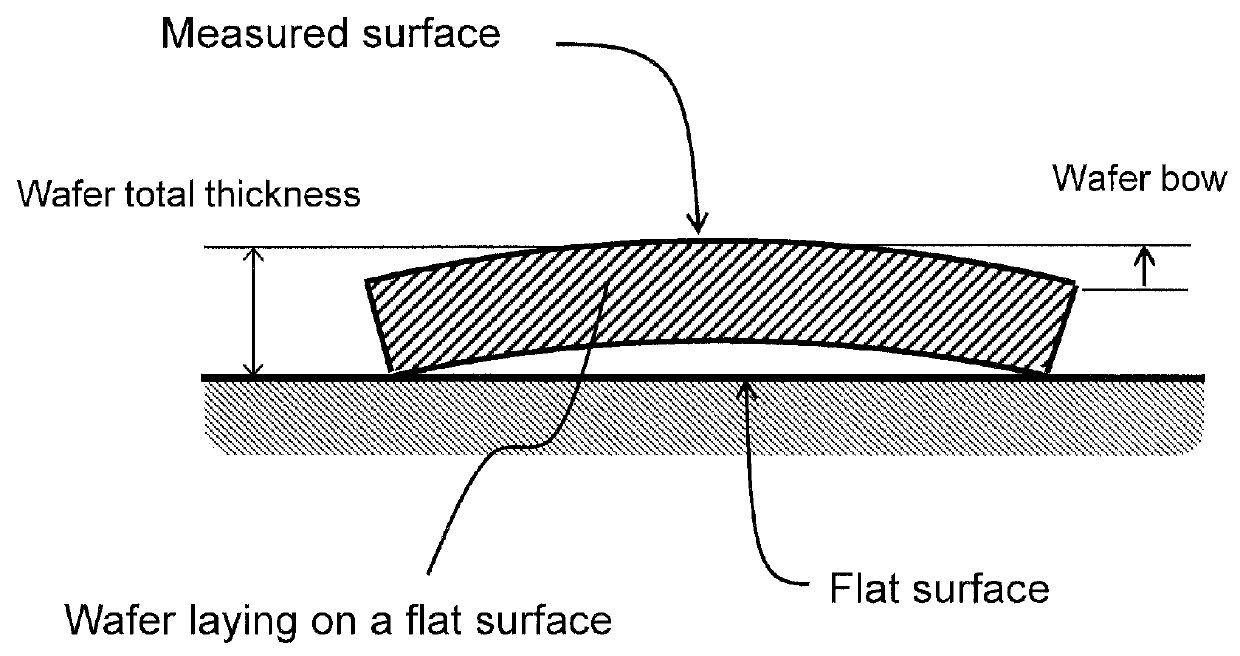
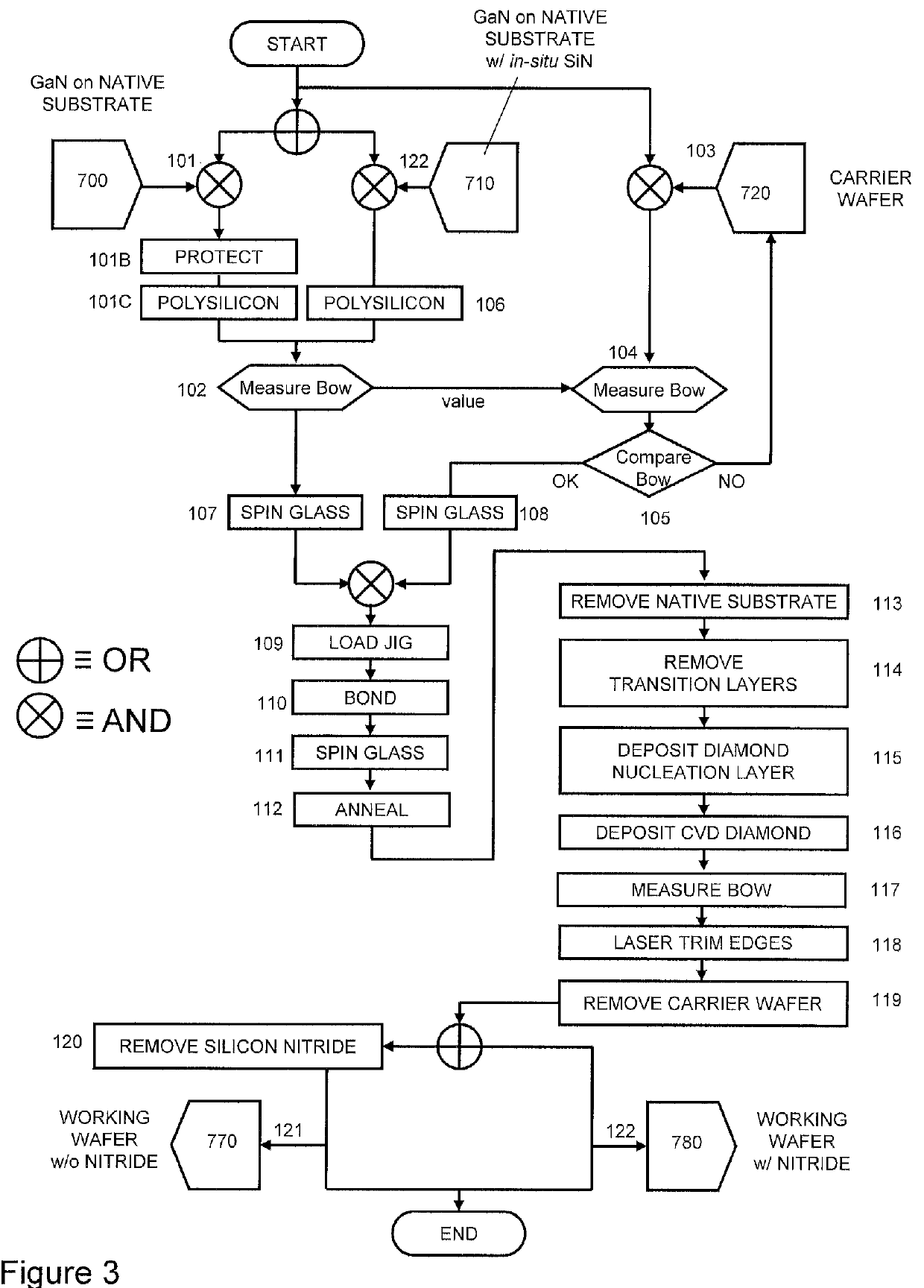
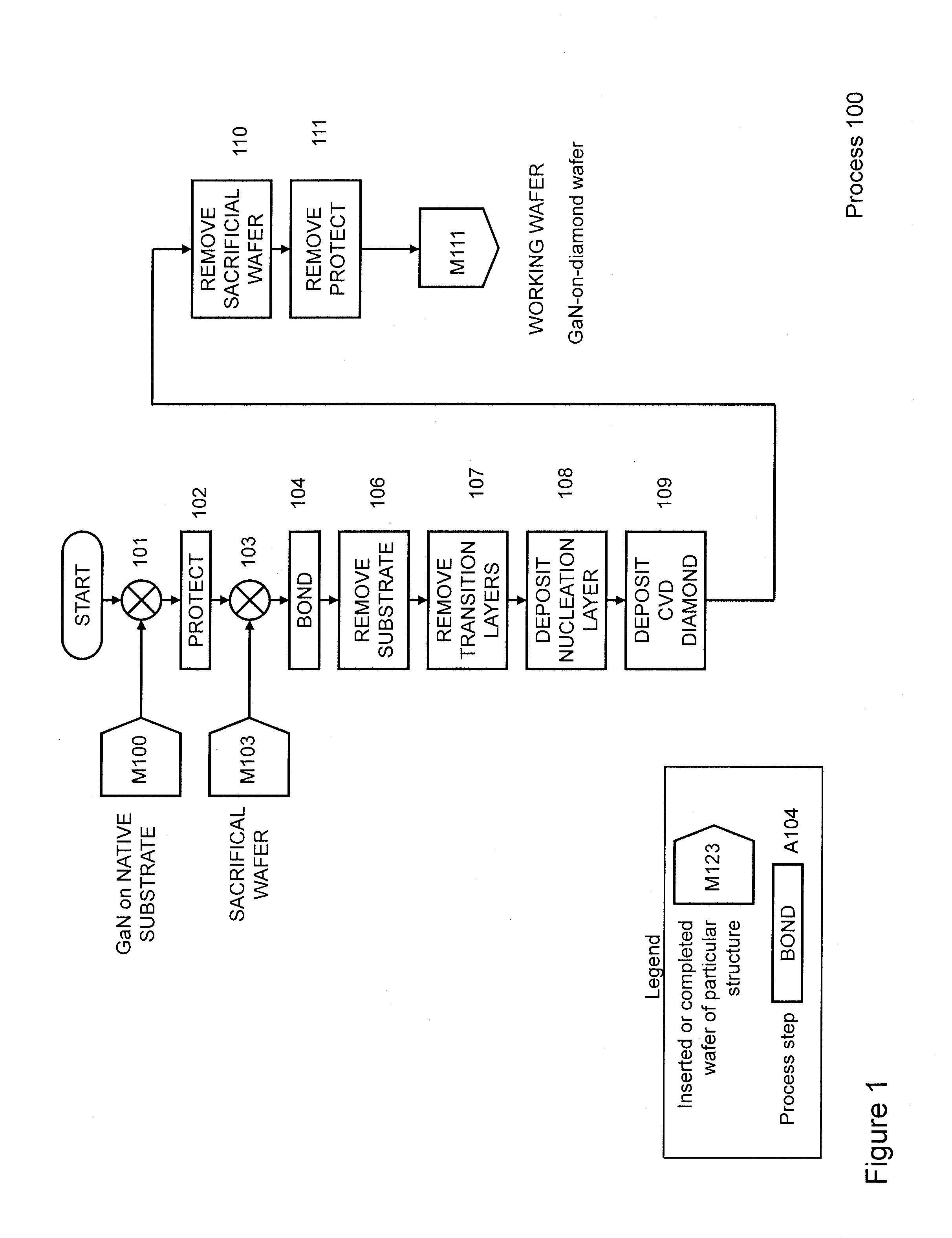
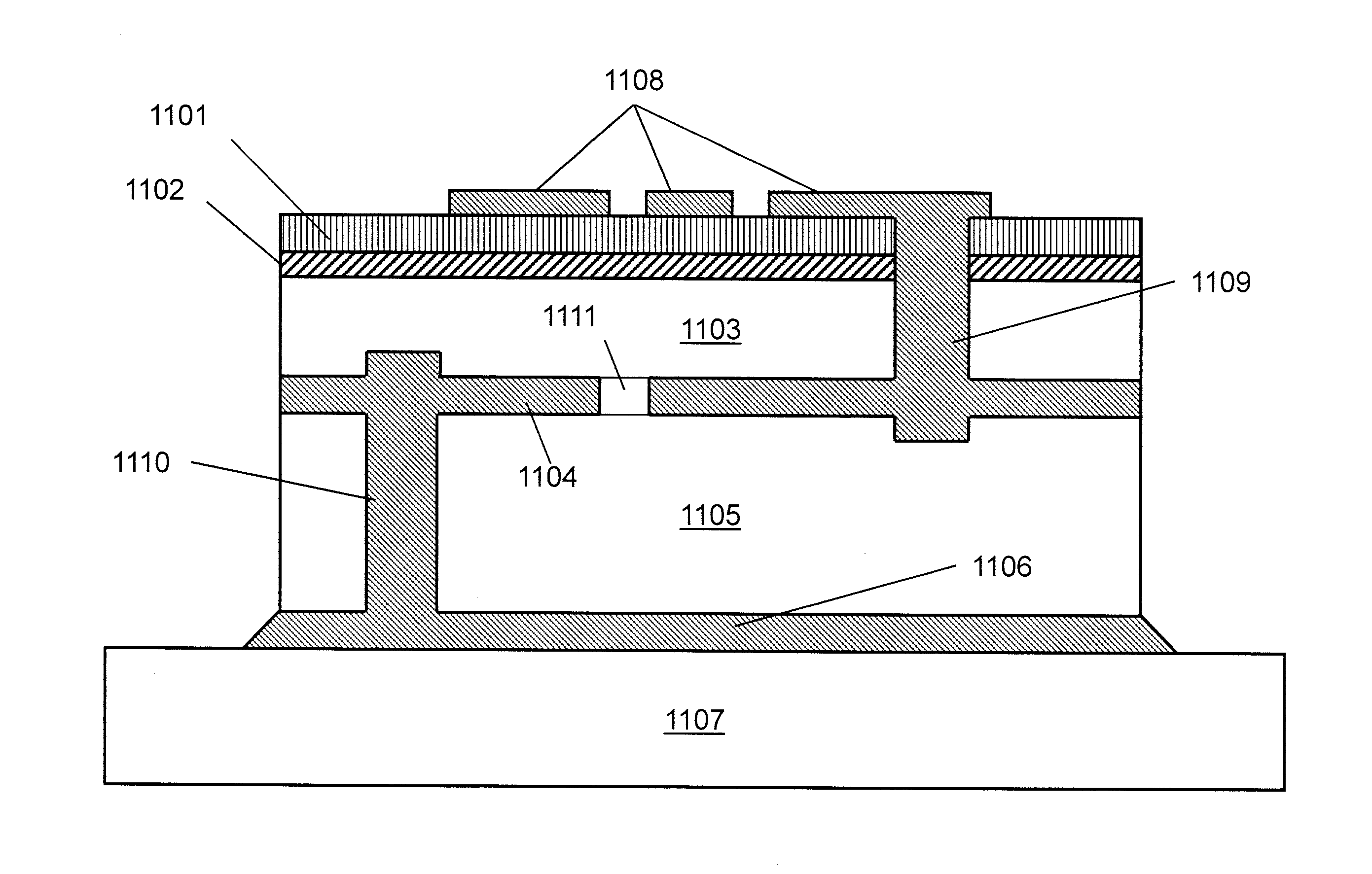
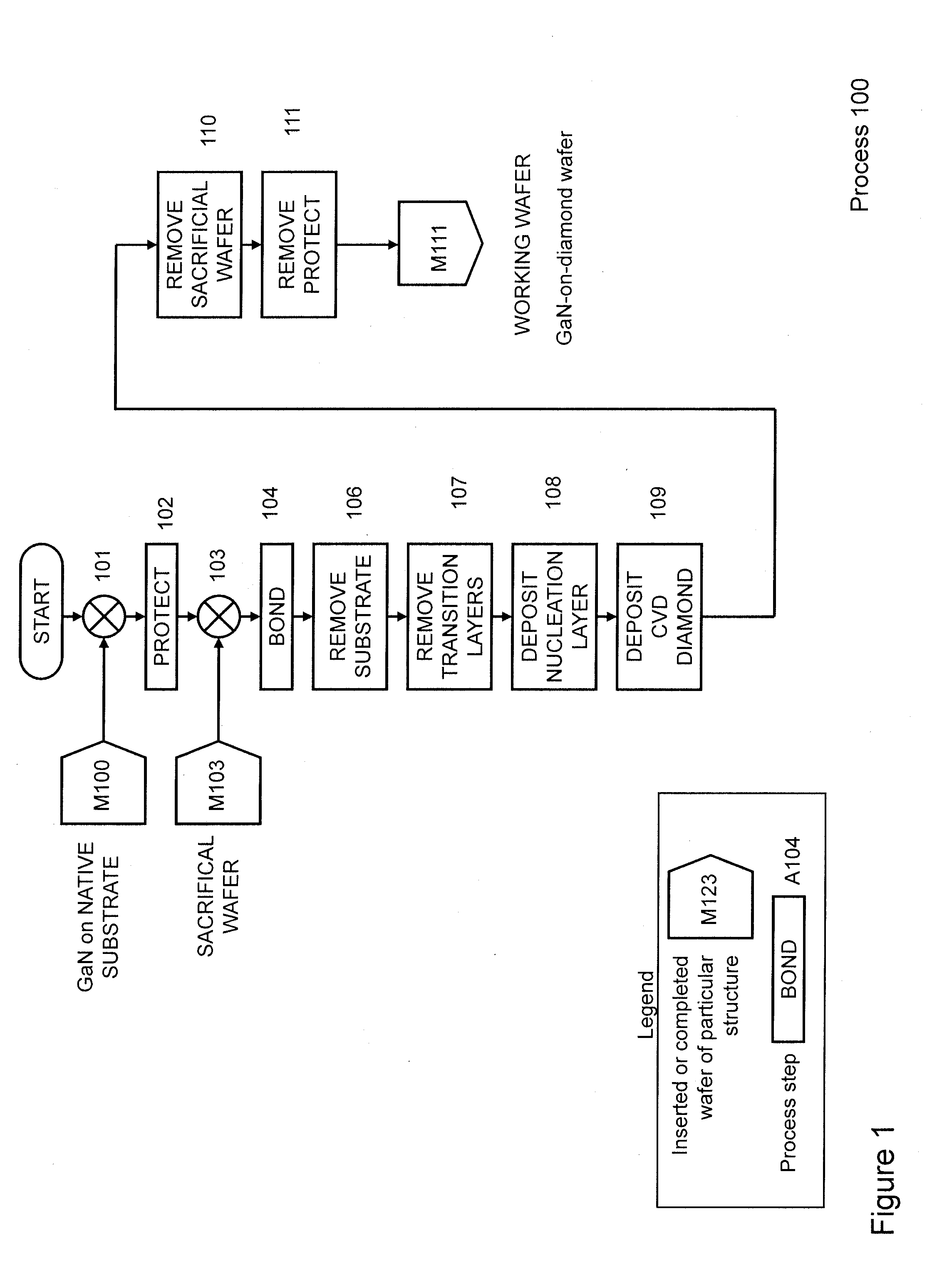
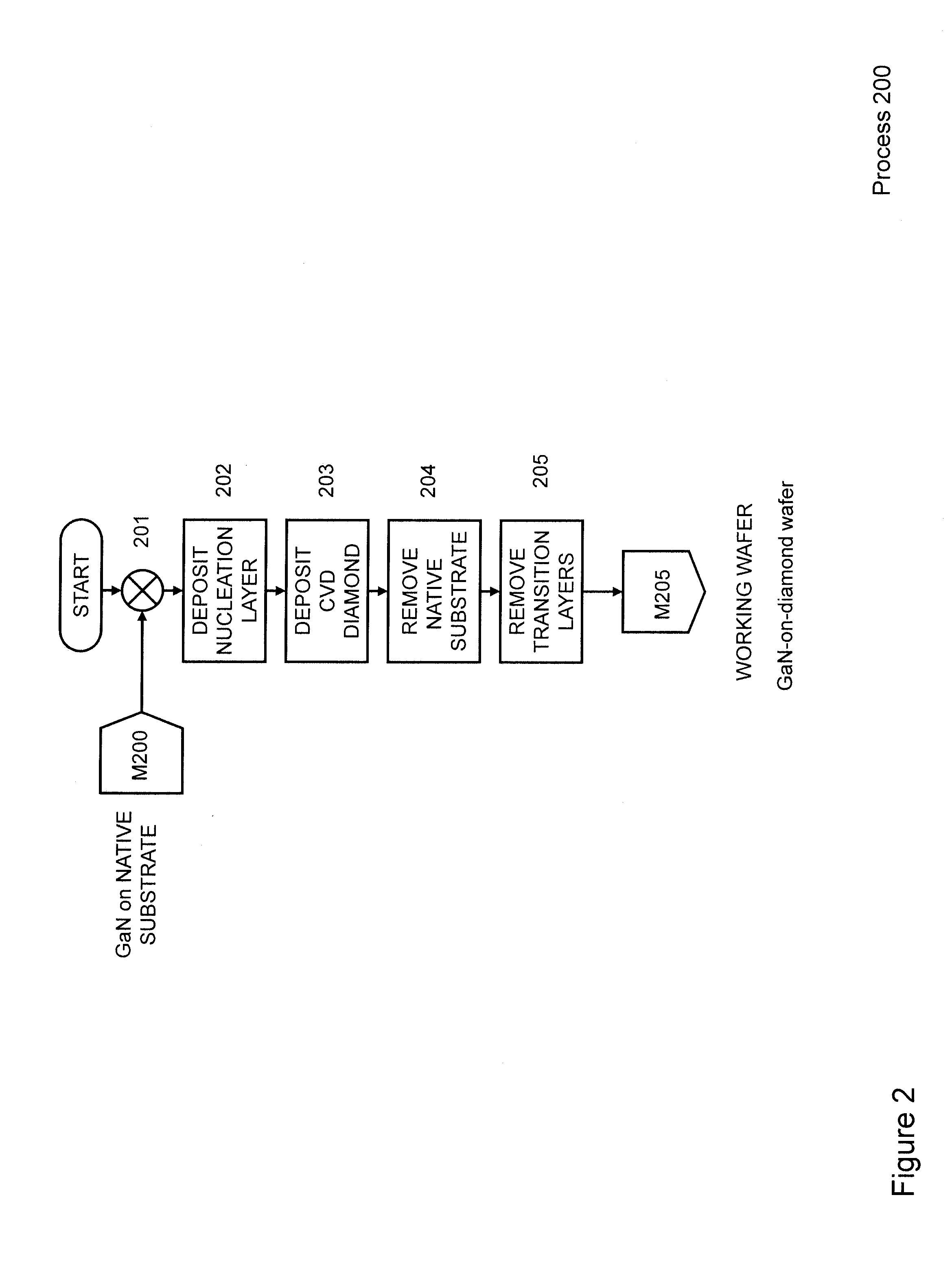
Gallium-nitride-on-diamond wafers and manufacturing equipment and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS9359693B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWide gap semiconductorsGallium nitride
A method for integrating wide-gap semiconductors, and specifically, gallium nitride epilayers, with synthetic diamond substrates is disclosed. Diamond substrates are created by depositing synthetic diamond onto a nucleating layer deposited or formed on a layered structure that comprises at least one layer of gallium nitride. Methods for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers with low bow and high crystalline quality are disclosed along with preferred choices for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers and chips tailored to specific applications.
Owner:AKASH SYST INC
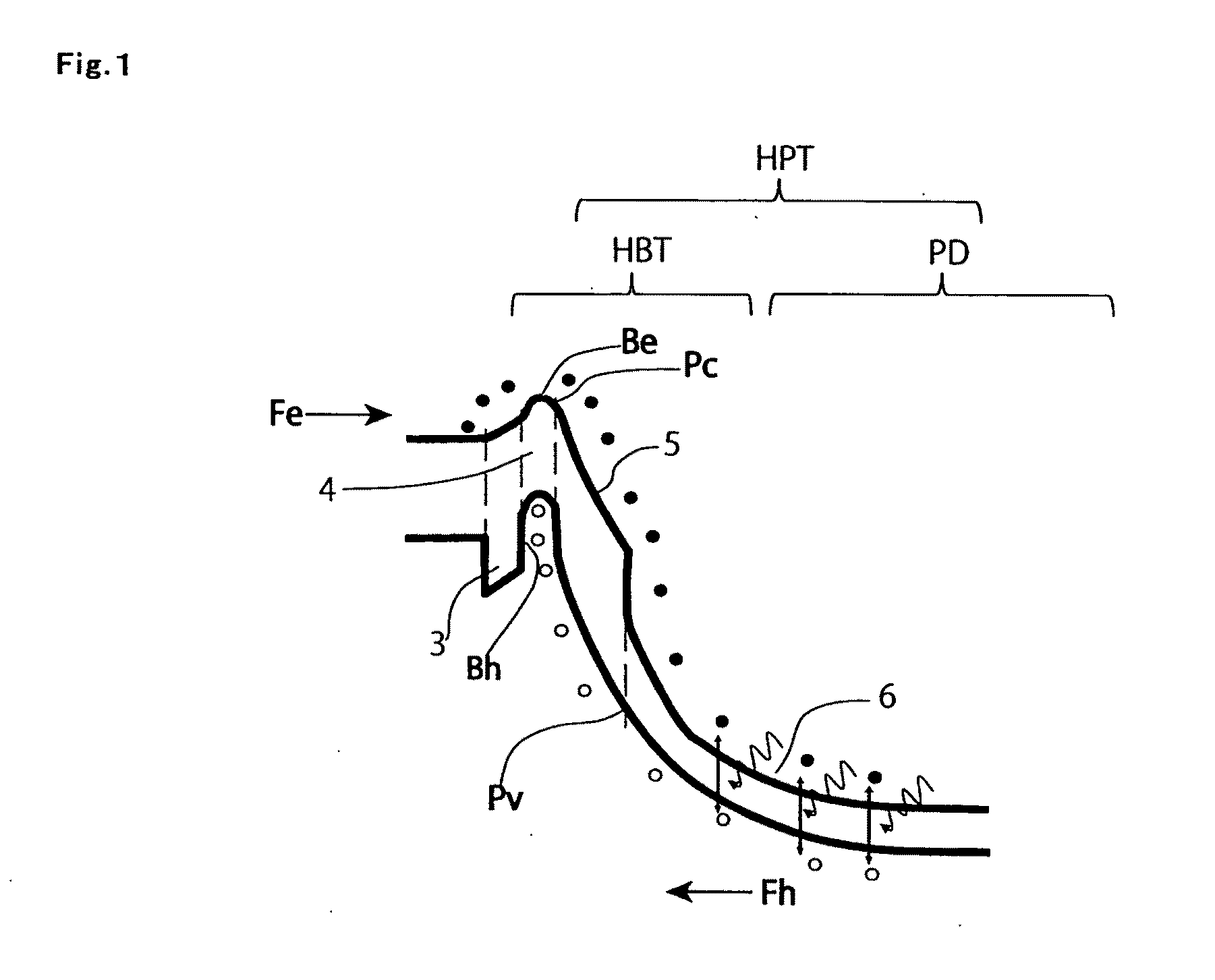
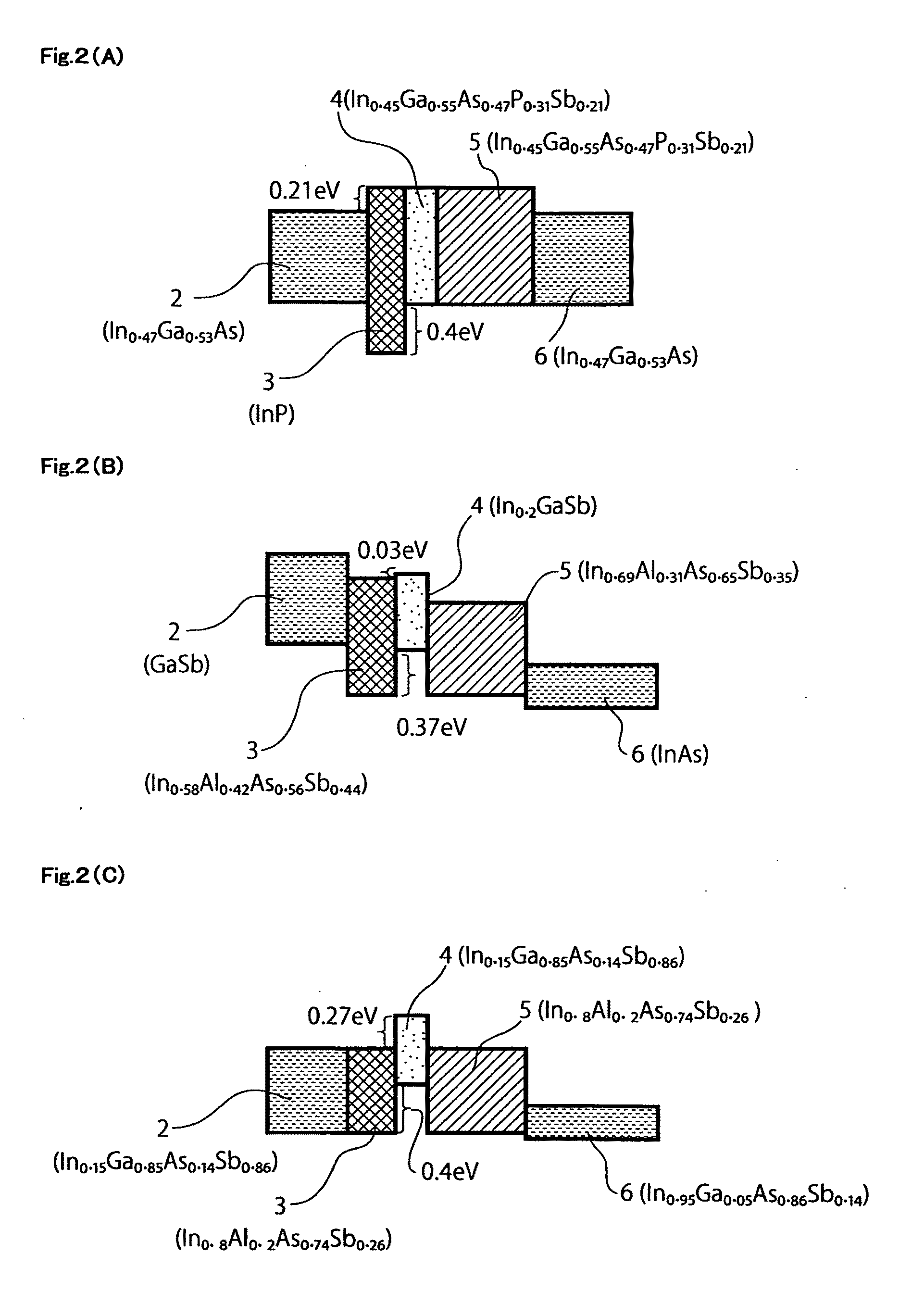
Hetero-junction bipolar phototransistor
InactiveUS20110291158A1Easy to implementPrevent decrease of transistor current gainPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesValence bandConduction band
The present invention provides a HPT having high sensitivity and extensive wavelength band characteristics. The collector and barrier layer (5) is formed on the photo-absorption layer (6), wherein the energy level in the conduction band is higher than that of the photo-absorption layer (6), the energy level in the valence band is almost equal to or higher than that of the photo-absorption layer (6) and is a relatively wider gap semiconductor than the photo-absorption layer. The base layer (4) formed on the collector and barrier layer (5), is a relatively narrow gap as compared with the collector and barrier layer (5), wherein the energy level in the conduction band is equal to or higher than that of the collector and barrier layer (5) in the boundary of the collector and barrier layer (5). The emitter layer (3) formed on a base layer (4) is a relatively wide gap as compared with the base layer (4), and the energy level in the valence band is the first conductivity type semiconductor layer lower than that of the base layer (4).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
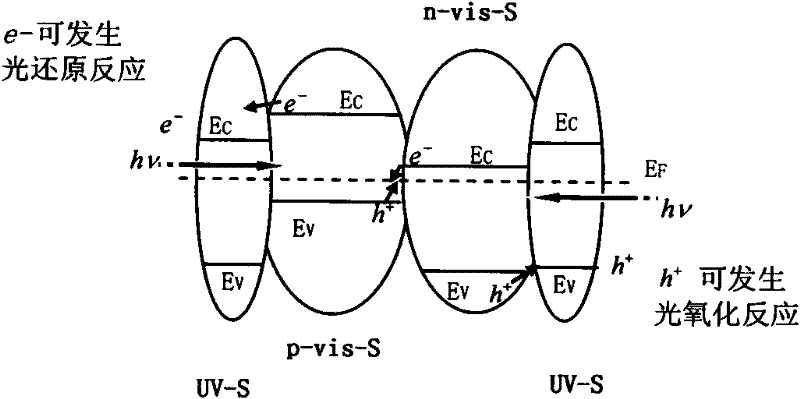
Ternary core-shell composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102188980AEfficient combinationExcellent photocatalytic water splitting hydrogen production performanceHydrogen productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDecompositionWastewater
The invention provides a ternary core-shell composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof. The photocatalyst comprises outer wide-gap semiconductor oxides and inner n-type and p-type narrow bandgap semiconductor oxides. The ratio of them is as follows: the mass ratio of the outer wide-gap semiconductor oxides and the inner n-type and p-type narrow bandgap semiconductor oxides binary assembly is 0.01-0.9:1, the mol ratio of the outer wide-gap semiconductor oxides and the inner n-type and p-type narrow bandgap semiconductor oxides is 0.2-5.0:1. The photocatalyst is used in photocatalysis decomposition water for hydrogen production reaction or photocatalysis dye waste water degradation reaction. The ternary core-shell composite photocatalyst in the invention can resist photochemicalcorrosion, and has good photocatalysis decomposition water for hydrogen production performance and good photocatalysis dye waste water degradation performance.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120012845A1Longer heldReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor materials
A semiconductor device with a novel structure is provided, which can hold stored data even when no power is supplied and which has no limitations on the number of writing operations. A semiconductor device is formed using a material which enables off-state current of a transistor to be reduced significantly; e.g., an oxide semiconductor material which is a wide-gap semiconductor. With use of a semiconductor material which enables off-state current of a transistor to be reduced significantly, the semiconductor device can hold data for a long period. In a semiconductor device with a memory cell array, parasitic capacitances generated in the nodes of the first to the m-th memory cells connected in series are substantially equal, whereby the semiconductor device can operate stably.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Switching converter
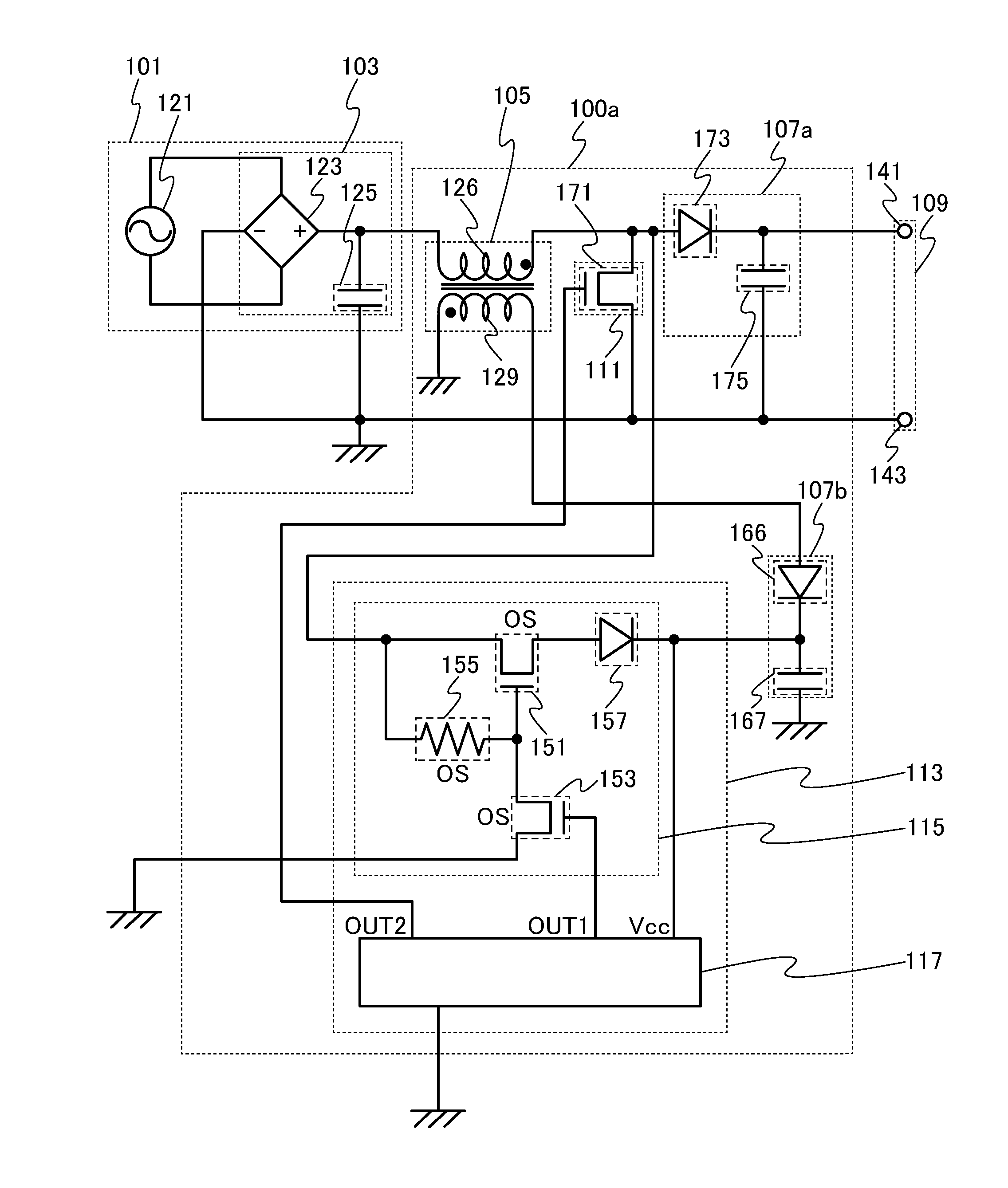
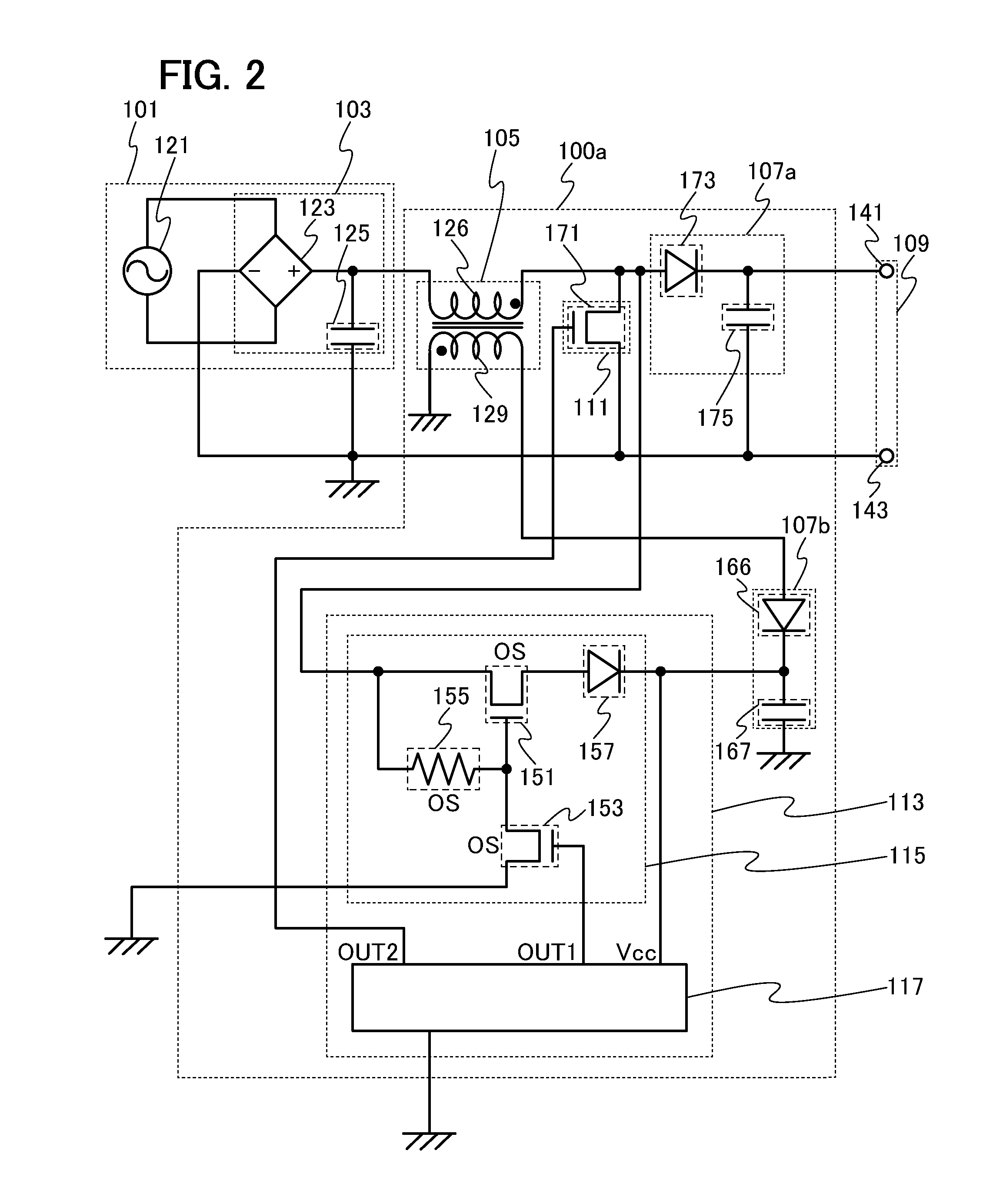
InactiveUS20130294120A1Small sizeSuppress adverse effects of the noise generated in the starterAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionWide gap semiconductorsControl circuit
A switching converter in which deterioration and breakage can be suppressed is provided. A switching converter whose area can be reduced is provided. The switching converter includes a switch connected to a power supply portion; a transformer connected to the power supply portion; a first rectifying and smoothing circuit and a second rectifying and smoothing circuit each connected to at least the transformer; and a switching control circuit which is connected to the first rectifying and smoothing circuit and the second rectifying and smoothing circuit and which controls operation of the switch. The switching control circuit includes a control circuit controlling on / off of the switch and operation of a starter circuit; and the starter circuit controlling startup of the control circuit. The starter circuit includes a transistor and a resistor each including a wide-gap semiconductor.
Owner:SKY SOCKET +1
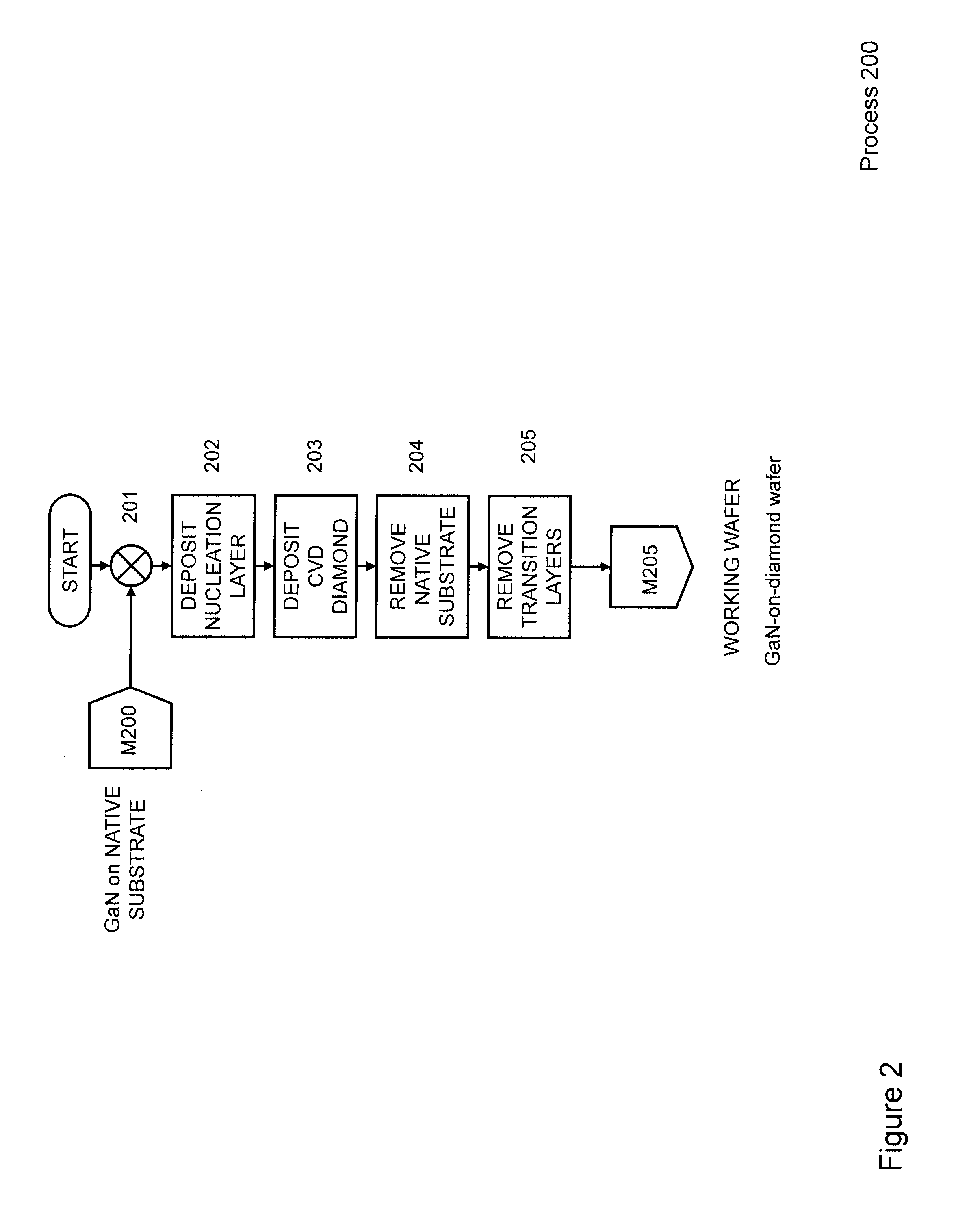
Gallium-nitride-on-diamond wafers and devices, and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS8674405B1Reduce thermal resistanceLower bow of the wafersPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsWide gap semiconductorsGallium nitride
Methods for integrating wide-gap semiconductors, and specifically, gallium nitride epilayers with synthetic diamond substrates are disclosed. Diamond substrates are created by depositing synthetic diamond onto a nucleating layer deposited or formed on a layered structure that comprises at least one layer made out of gallium nitride. Methods for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers with low bow and high crystalline quality are disclosed along with preferred choices for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers and chips tailored to specific applications.
Owner:GROUP4 LABS
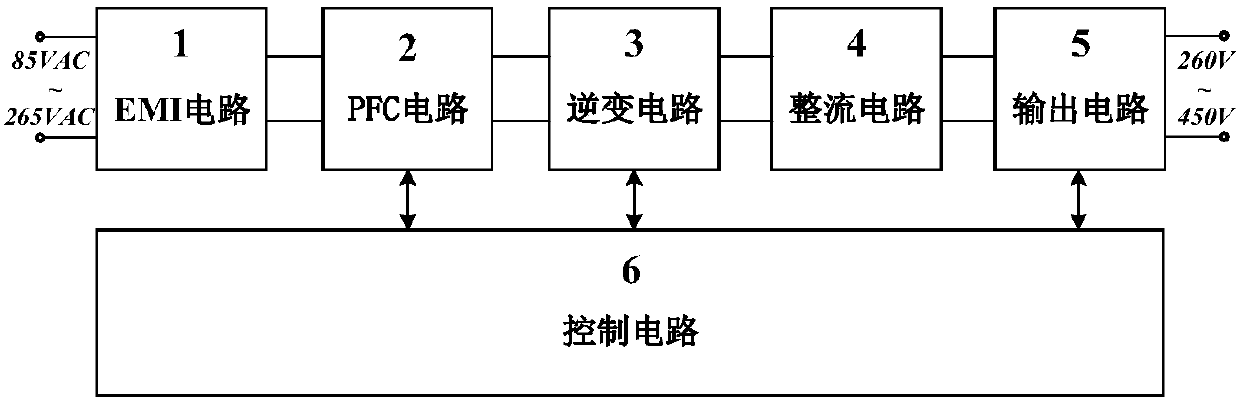
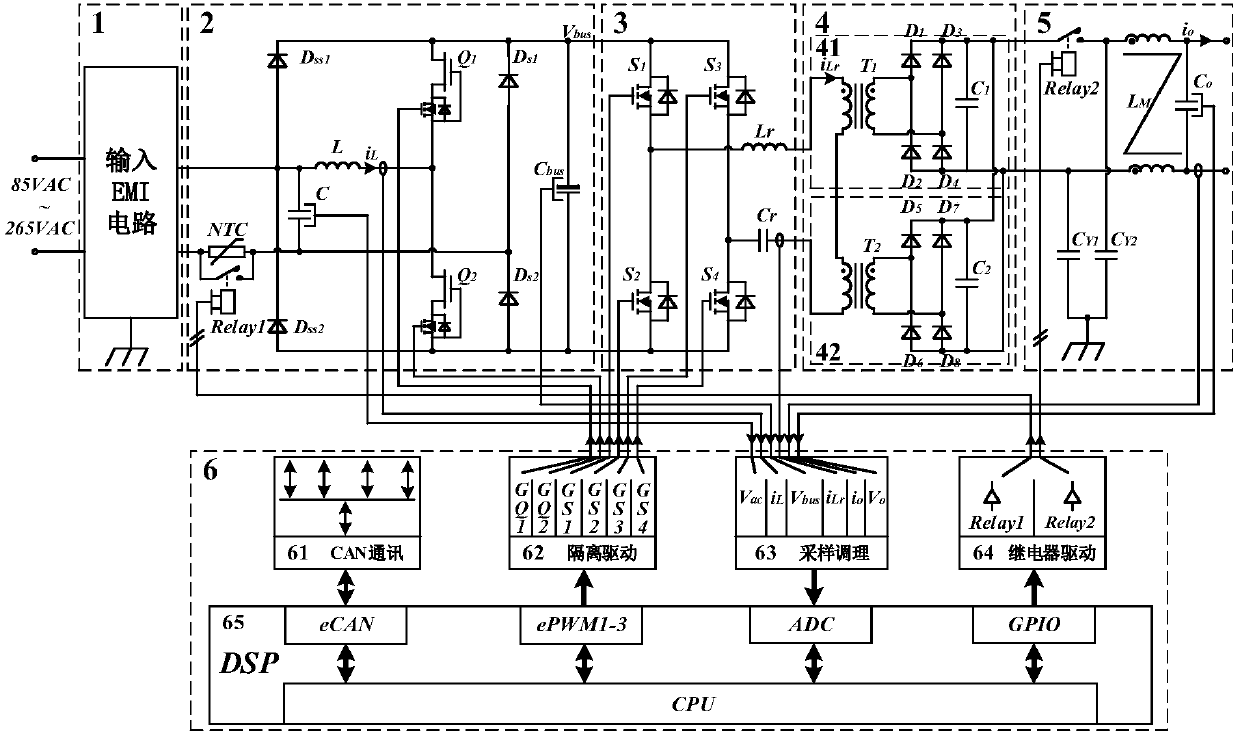
Vehicle charging converter with high efficiency
InactiveCN107846151AReduce current stressAccurate perceptionAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionMOSFETTransformer
The invention discloses a vehicle charging converter with high efficiency. The vehicle charging converter with high efficiency includes successively connected EMI circuit, a PFC circuit, an inversioncircuit, a rectification circuit, an output circuit and a control circuit, wherein the EMI circuit is used for reducing the influence of high frequency noise of the converter on the power grid; on thepremise of guaranteeing the quality of the input current, the PFC circuit can convert the single phase alternating current into the high voltage direct current; the inversion circuit converts the high voltage direct current into high frequency square wave which is adjustable in frequency; the rectification circuit performs rectification after performing transformer isolation of the rectificationcircuit to obtain stable direct current voltage; and finally the high frequency current ripple is filtered and then is output by the output circuit, and the control circuit completes acquisition, calculation and output of the controlled quantity of the converter, and then operating and protection of the vehicle charging converter can be realized. In the vehicle charging converter with high efficiency, the PFC circuit and the inversion circuit respectively use GaN HEMT and Si MOSFET as the main switch devices; by means of combination with the advantages of a wide-gap semiconductor device and atotem PFC topology, the vehicle charging converter with high efficiency has the advantages of being good in the grid side harmonic wave characteristic, being small in volume, being flexible in control, and greatly improving the conversion efficiency of vehicle charging.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gate turn-off thyristor
A mesa-type wide-gap semiconductor gate turn-off thyristor has a low gate withstand voltage and a large leakage current. Since the ionization rate of P-type impurities greatly increases at high temperatures when compared with that at room temperature, the hole implantation amount increases and the minority carrier lifetime becomes longer. Consequently, the maximum controllable current is significantly lowered when compared with that at room temperature. To solve these problems, a p-type base layer is formed on an n-type SiC cathode emitter layer which has a cathode electrode on one surface, and a thin n-type base layer is formed on the p-type base layer. A mesa-shaped p-type anode emitter layer is formed in the central region of the n-type base layer. An n-type gate contact region is formed sufficiently apart from the junction between the p-type anode emitter layer and the n-type base layer, and an n-type low-resistance gate region is so formed in the n-type base layer that it surrounds the anode emitter layer.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO
Gallium-nitride-on-diamond wafers and devices, and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20140141595A1Reduce thermal resistanceLower bow of the wafersPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsWaferingWide gap semiconductors
Methods for integrating wide-gap semiconductors, and specifically, gallium nitride epilayers with synthetic diamond substrates are disclosed. Diamond substrates are created by depositing synthetic diamond onto a nucleating layer deposited or formed on a layered structure that comprises at least one layer made out of gallium nitride. Methods for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers with low bow and high crystalline quality are disclosed along with preferred choices for manufacturing GaN-on-diamond wafers and chips tailored to specific applications.
Owner:AKASH SYST INC
Semiconductor device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS8467231B2Total current dropAvoid dataRead-only memoriesDigital storagePower semiconductor devicePotential change
The semiconductor device is formed using a material which allows a sufficient reduction in off-state current of a transistor; for example, an oxide semiconductor material, which is a wide gap semiconductor, is used. When a semiconductor material which allows a sufficient reduction in off-state current of a transistor is used, the semiconductor device can hold data for a long period. In addition, the timing of potential change in a signal line is delayed relative to the timing of potential change in a write word line. This makes it possible to prevent a data writing error.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Process of preparing anatase crystal phase titanium dioxide film at low temp.
The present invention is low temperature process of preparing anatse type crystalline titania film, and belongs to the field of wide-gap semiconductor photocatalyzing technology. Titania film is deposited on the substrate through reactive magnetically controlled sputtering, and the deposition process has the base with the substrate cooled by a water cooling system, argon flow rate of 30 sccm, the flow rate between argon and nitrogen of 5-10, total gas pressure of 1-4 Pa, power density of 1.4-2.8 W / sq cm, negative voltage applied on the base of 20V-100, and base temperature always lower than 80 deg.c. During the film depositing process, great amount of positive argon ion is driven by the base bias voltage to bombard the deposited titania film so as to form anatse type crystalline titania film on the heat labile substrate.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Semiconductor device, method for manufacturing same, and power converter using such semiconductor device
InactiveCN1701439AImprove reliabilityRapid temperature stabilizationThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceWide gap semiconductors
The temperature of a bipolar semiconductor element using a wide-gap semiconductor is raised using heating means, such as a heater, to obtain a power semiconductor device being large in controllable current and low in loss. The temperature is set at a temperature higher than the temperature at which the decrement of the steady loss of the wide-gap bipolar semiconductor element corresponding to the decrement of the built-in voltage lowering depending on the temperature rising of the wide-gap bipolar semiconductor element is larger than the increment of the steady loss corresponding to the increment of the ON resistance increasing depending on the temperature rising.
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO
RF and milimeter-wave high-power semiconductor device
ActiveUS8796843B1Simple processLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
High-power and high-frequency semiconductor devices require high signal integrity and high thermal conductance assembly technologies and packages. In particular, wide-gap-semiconductor devices on diamond benefit from spatially separate electrical and thermal connections. This application discloses assembly and package architectures that offer high signal integrity and high thermal conductance.
Owner:GROUP4 LABS
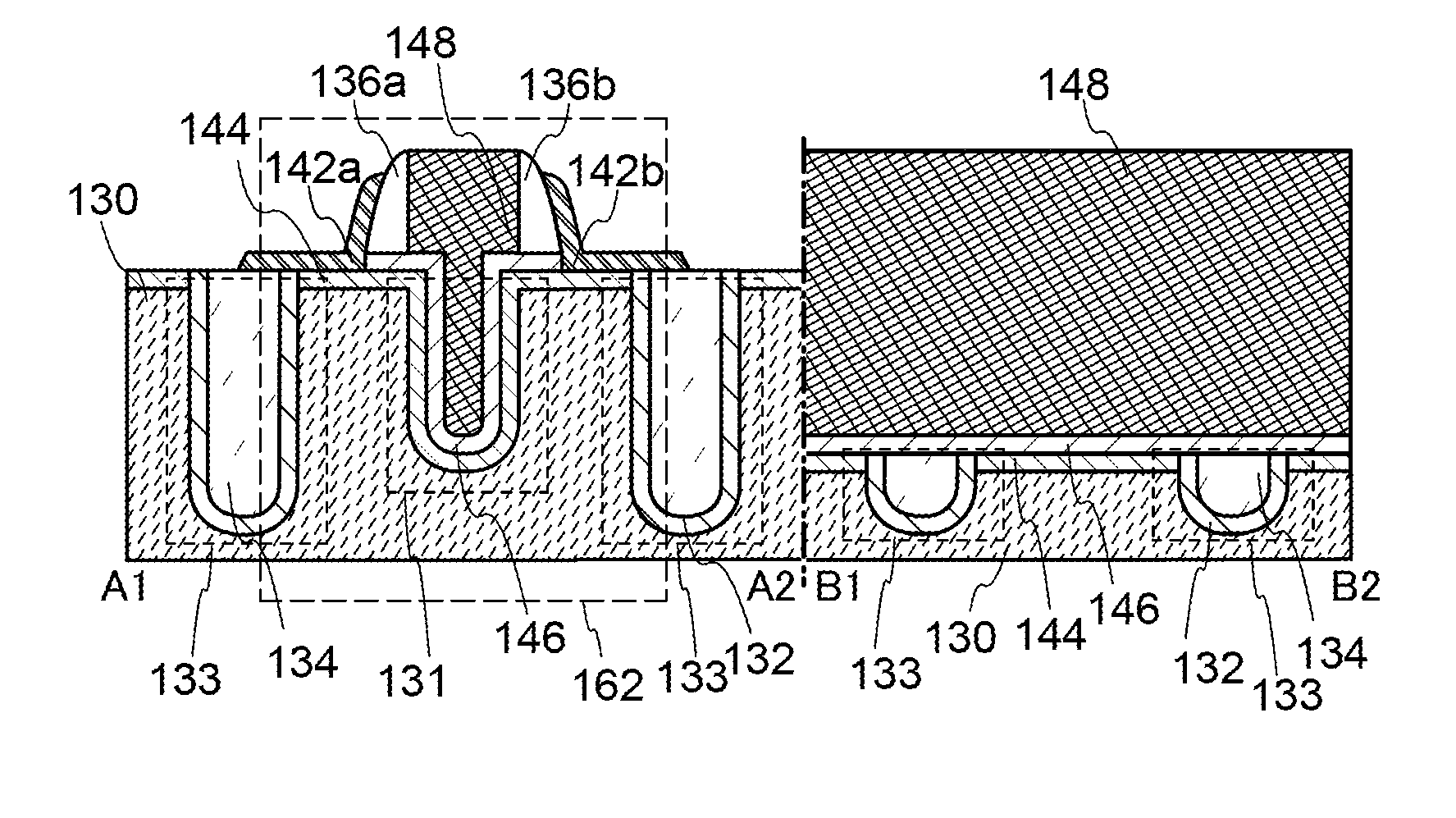
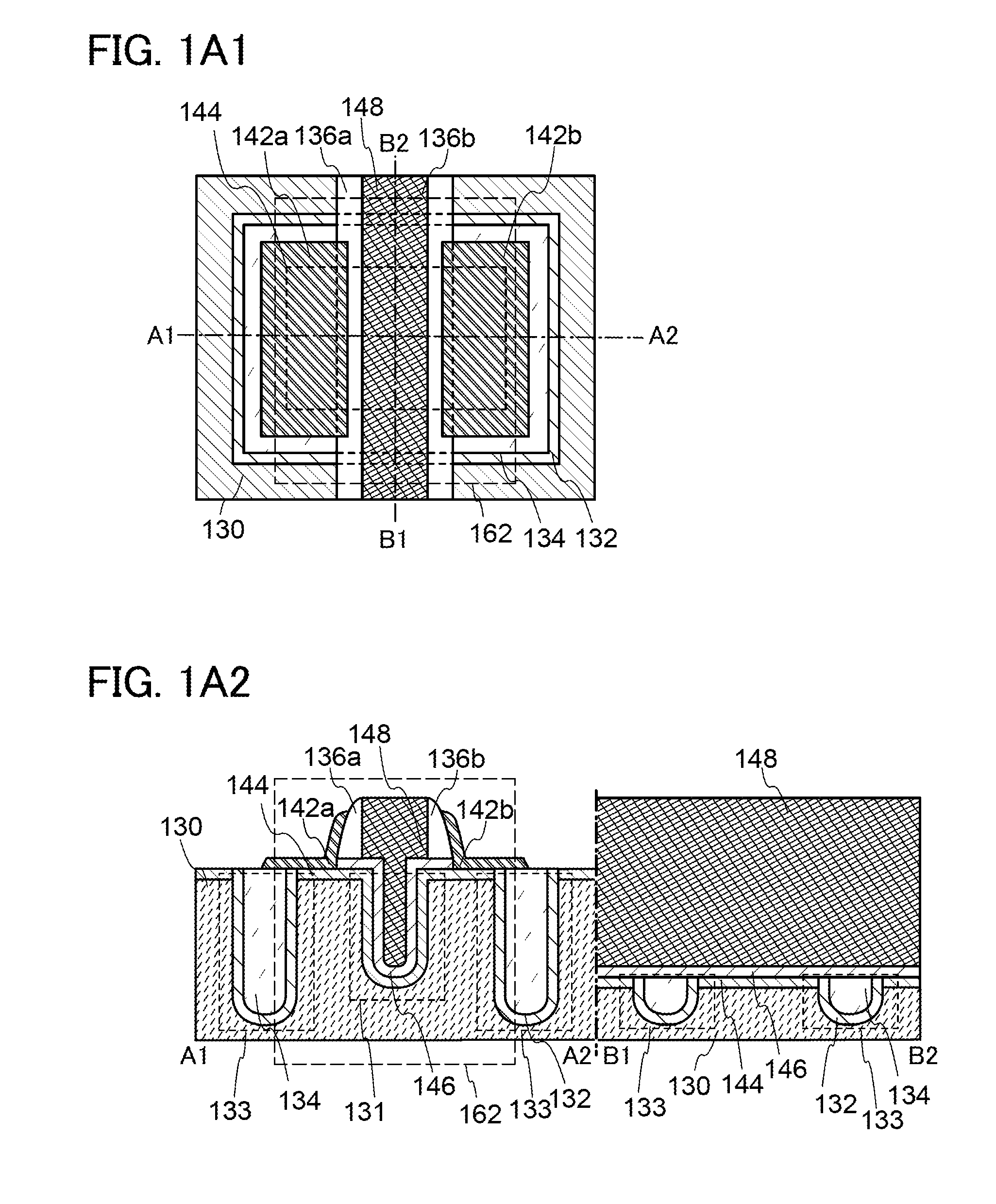
Oxide semiconductor device including gate trench and isolation trench
InactiveUS8766255B2Improve propertiesReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor materials
A semiconductor device in which improvement of a property of holding stored data can be achieved. Further, power consumption of a semiconductor device is reduced. A transistor in which a wide-gap semiconductor material capable of sufficiently reducing the off-state current of a transistor (e.g., an oxide semiconductor material) in a channel formation region is used and which has a trench structure, i.e., a trench for a gate electrode and a trench for element isolation, is provided. The use of a semiconductor material capable of sufficiently reducing the off-state current of a transistor enables data to be held for a long time. Further, since the transistor has the trench for a gate electrode, the occurrence of a short-channel effect can be suppressed by appropriately setting the depth of the trench even when the distance between the source electrode and the drain electrode is decreased.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Oxide semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS8792284B2Increase in sizeSimplify the semiconductor deviceTransistorSolid-state devicesPower flowWide gap semiconductors
In a semiconductor device which conducts multilevel writing operation and a driving method thereof, a signal line for controlling on / off of a writing transistor for conducting a writing operation on a memory cell using a transistor including an oxide semiconductor layer is disposed along a bit line, and a multilevel writing operation is conducted with use of, also in a writing operation, a voltage which is applied to a capacitor at a reading operation. Because an oxide semiconductor material that is a wide gap semiconductor capable of sufficiently reducing off-state current of a transistor is used, data can be held for a long period.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com