Patents
Literature
88results about How to "Component used" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
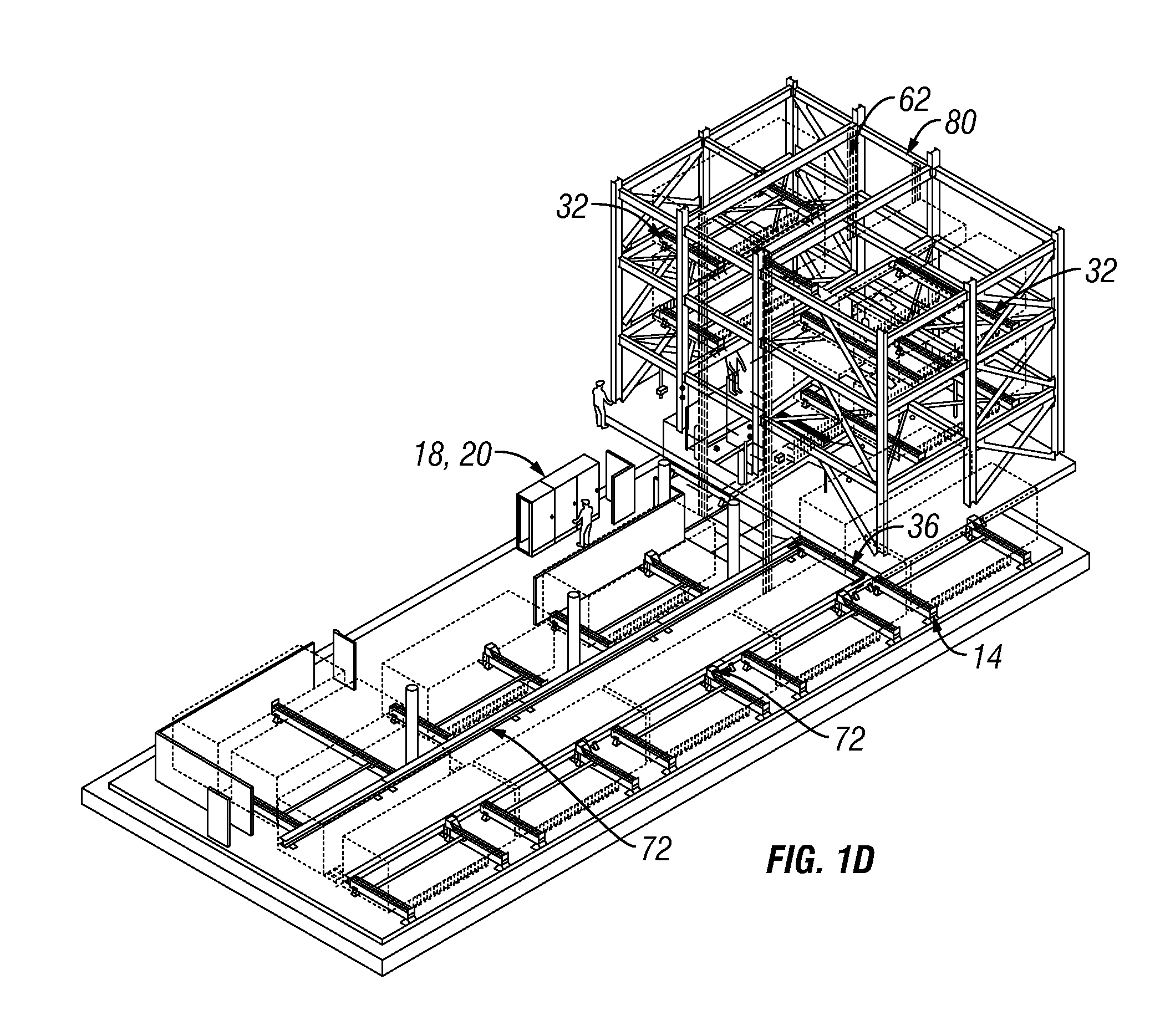
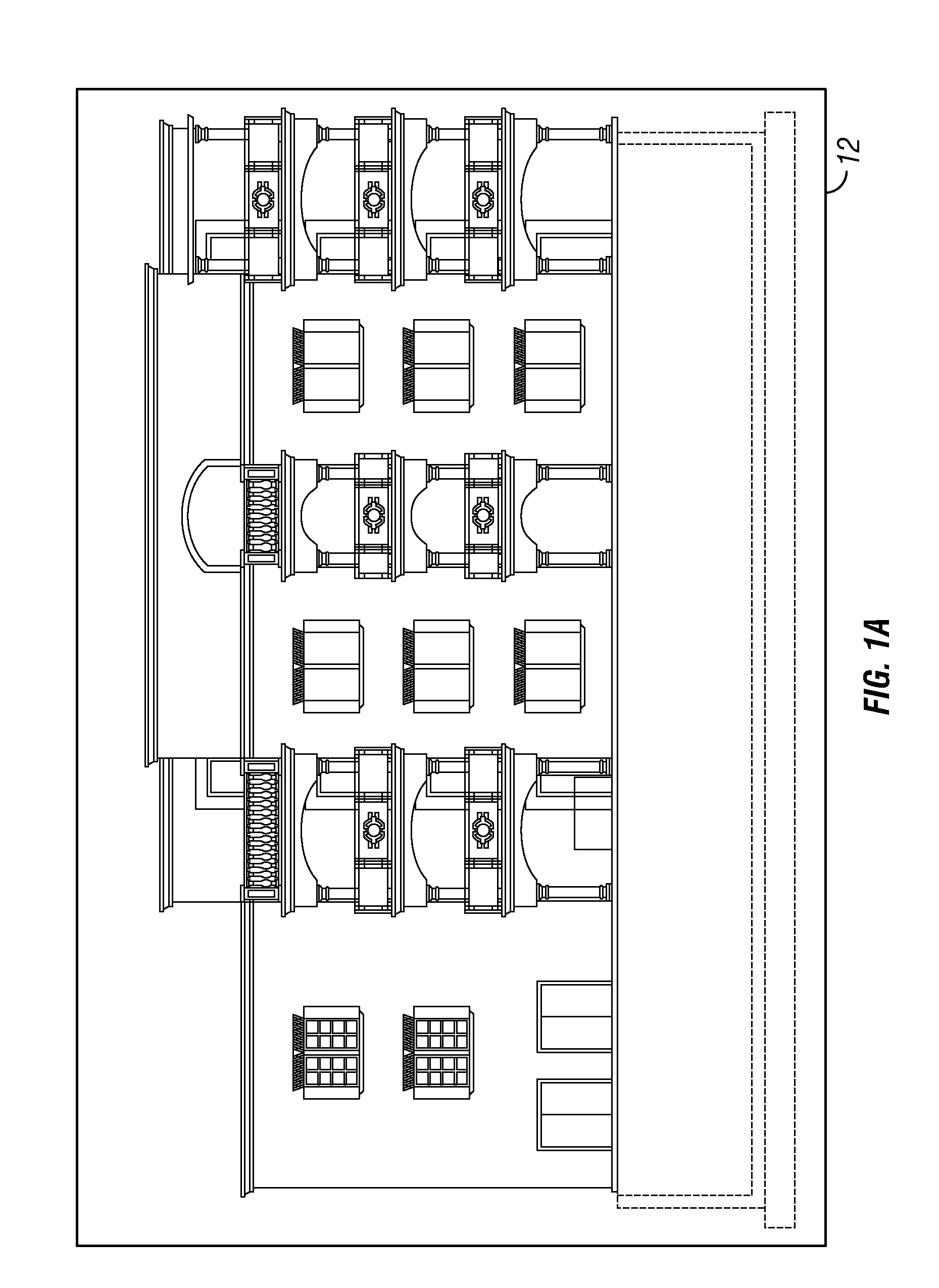
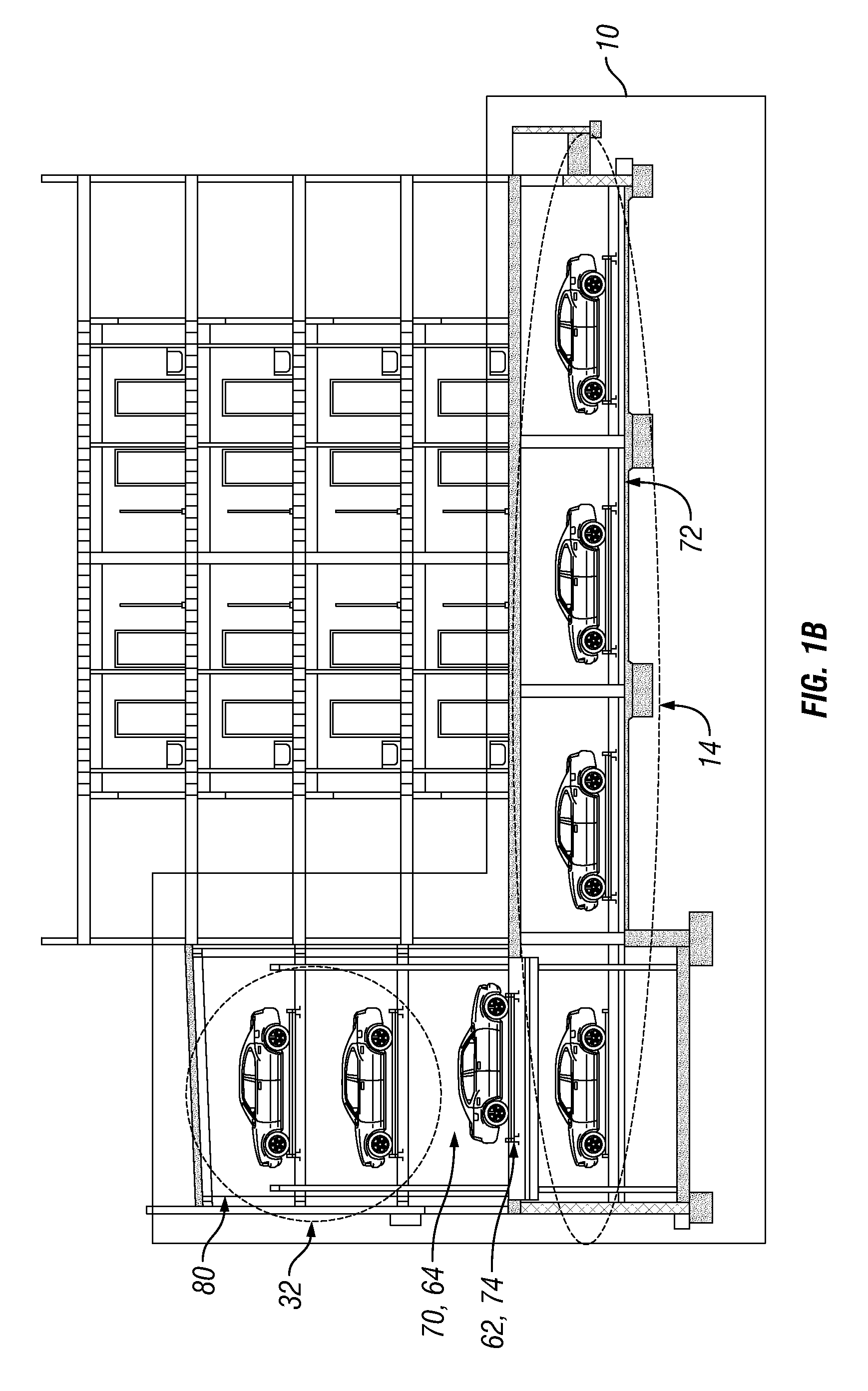
Automated parking system
InactiveUS20110182703A1Component usedDigital data processing detailsParkingsEngineeringHorizontal and vertical
An automated parking system for a parking structure includes a controller which receives a vehicle loading request from a vehicle customer. A loading bay accepts the vehicle and transfers to the parking system. Equipment is provided for transferring the vehicle horizontally and vertically through the parking system. The vehicle parking system includes a rack structure that is integrated as part of the parking structure.
Owner:AUTO PARKIT
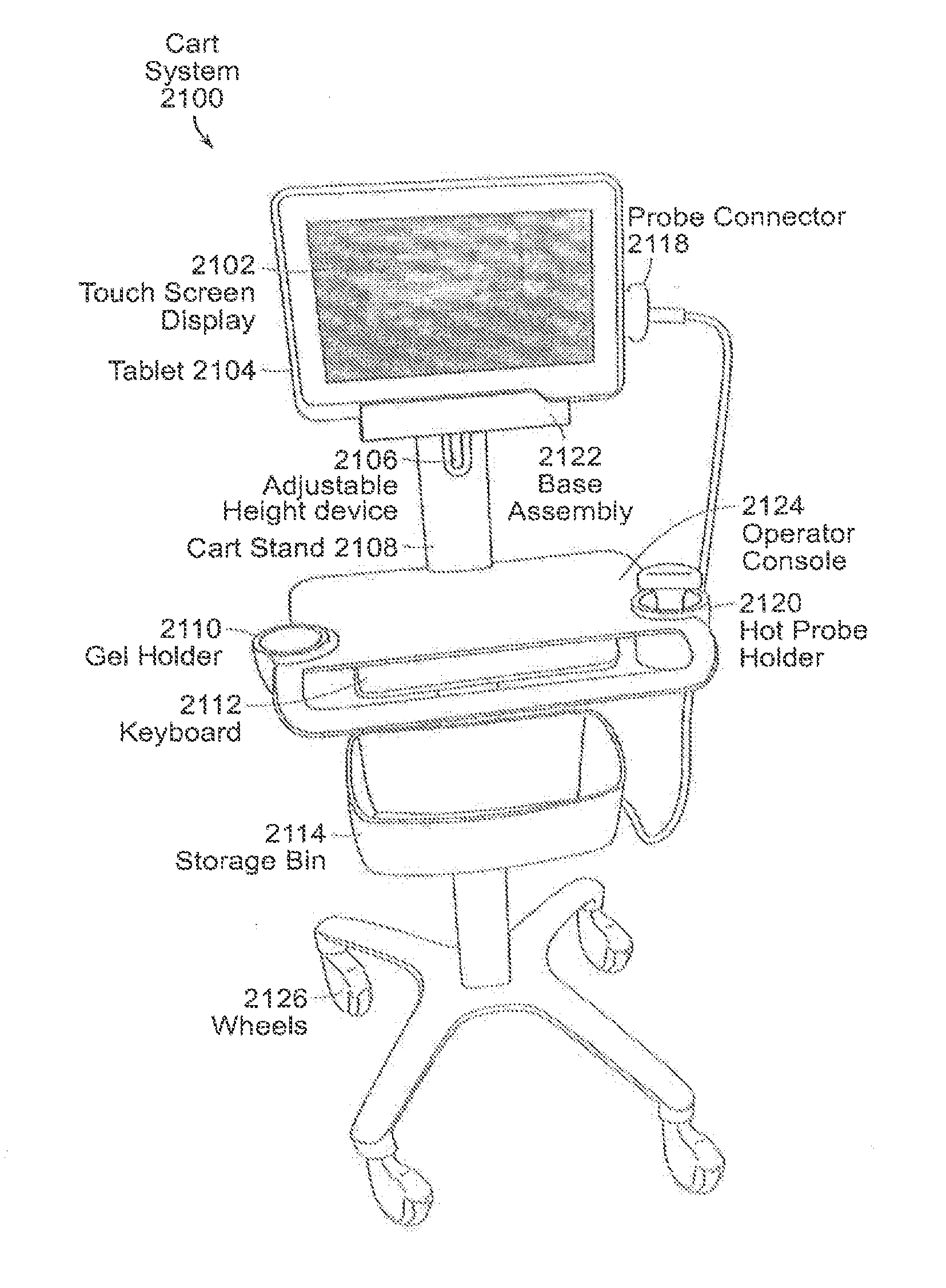
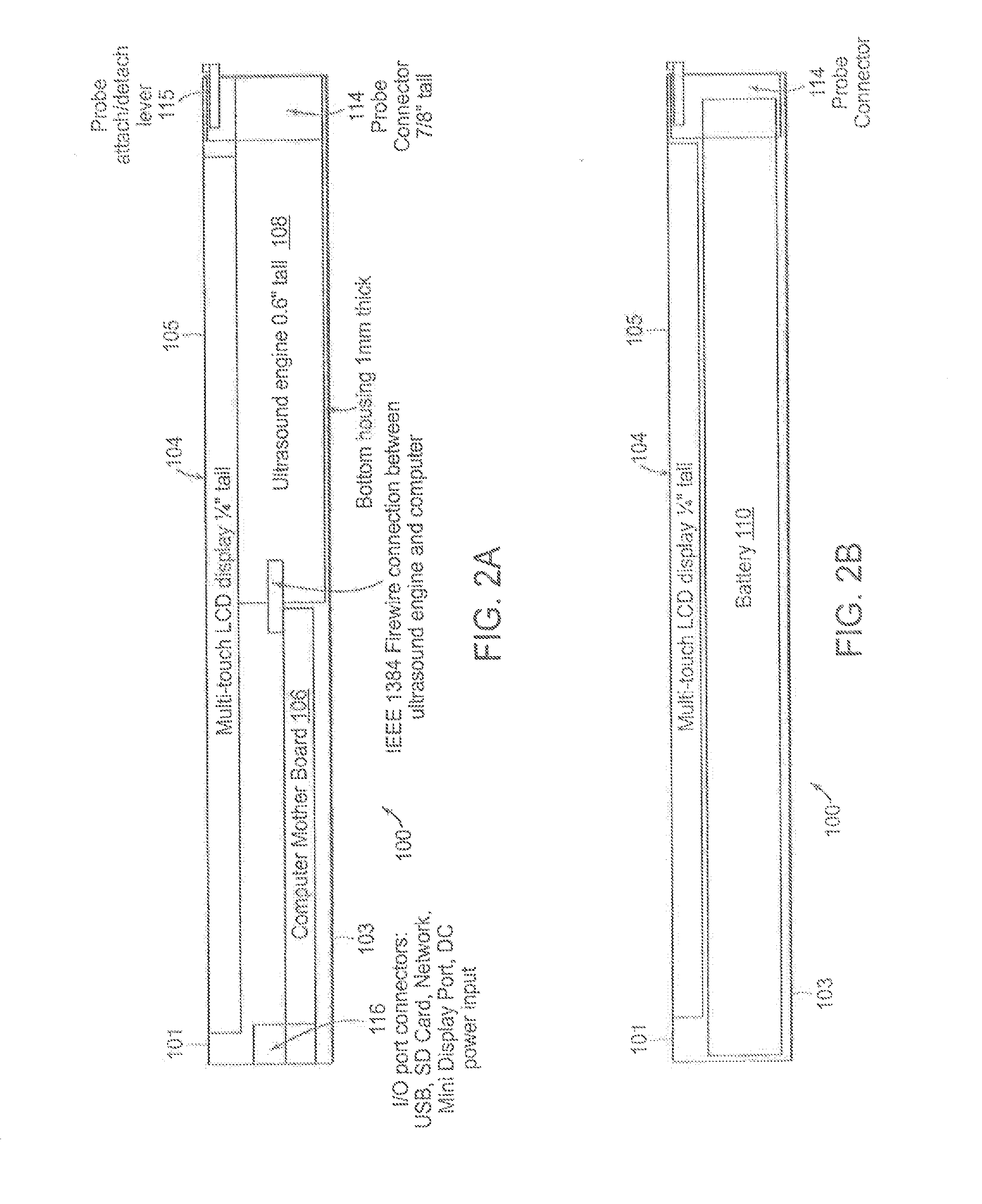
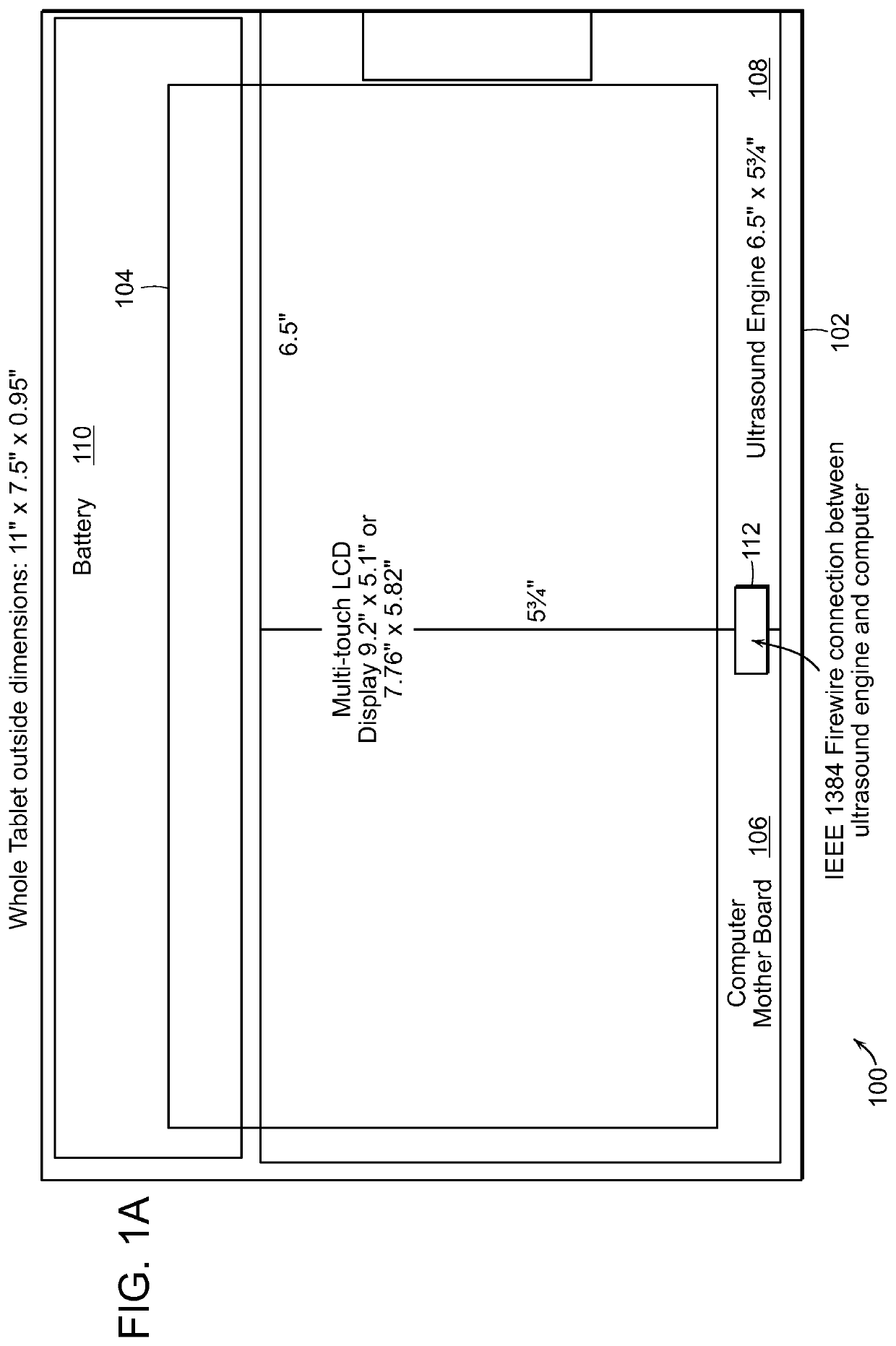
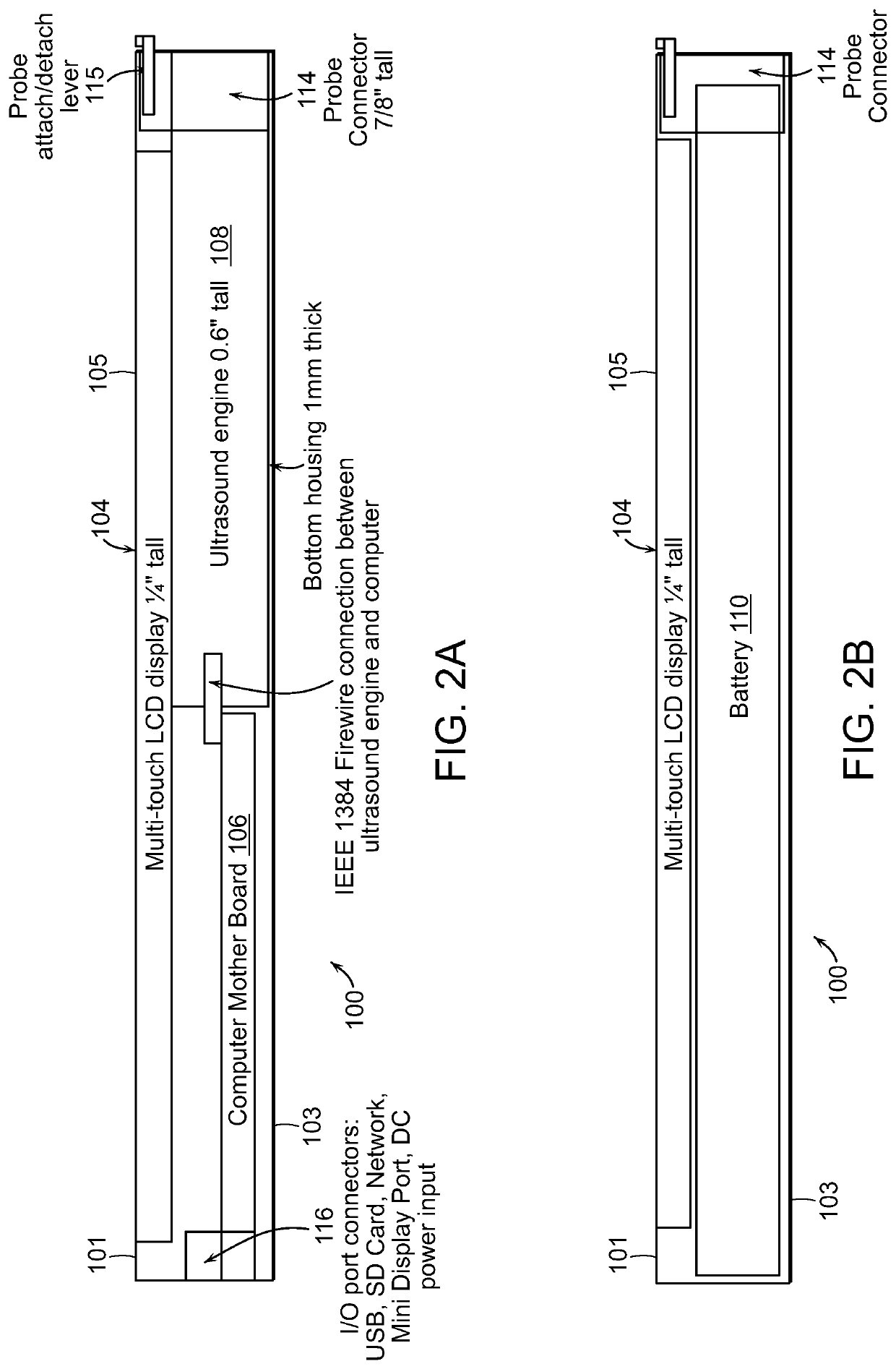
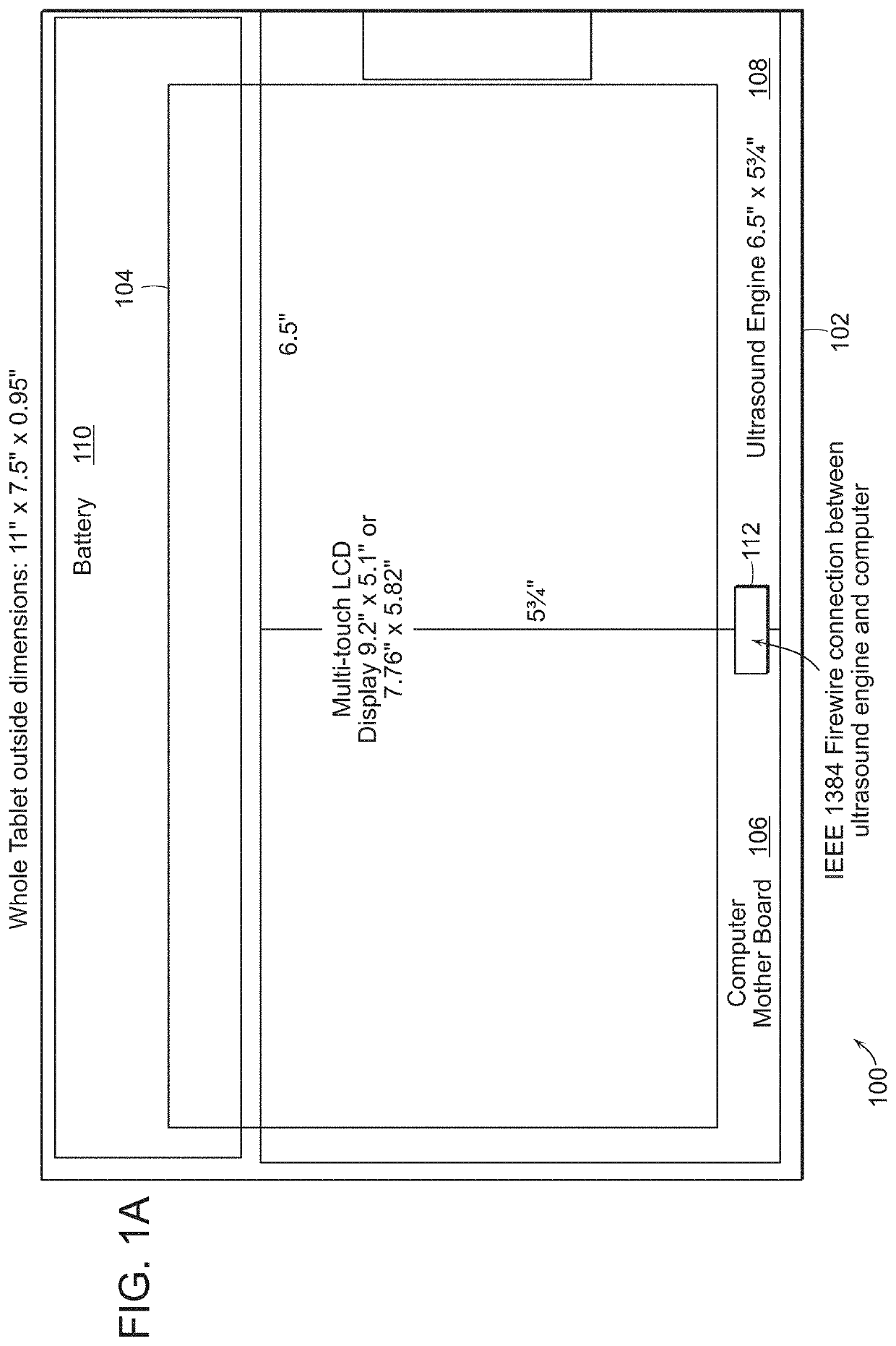
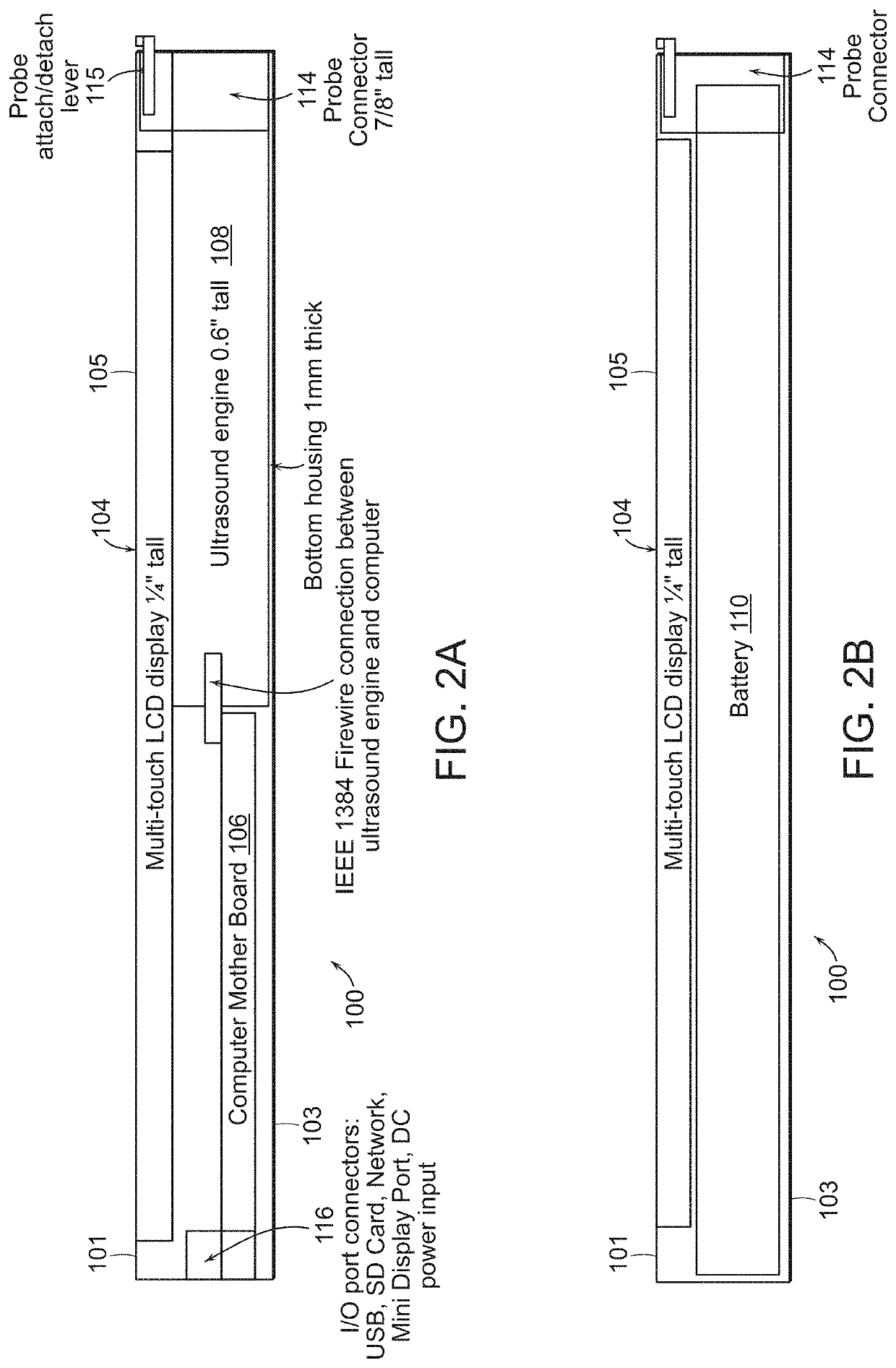
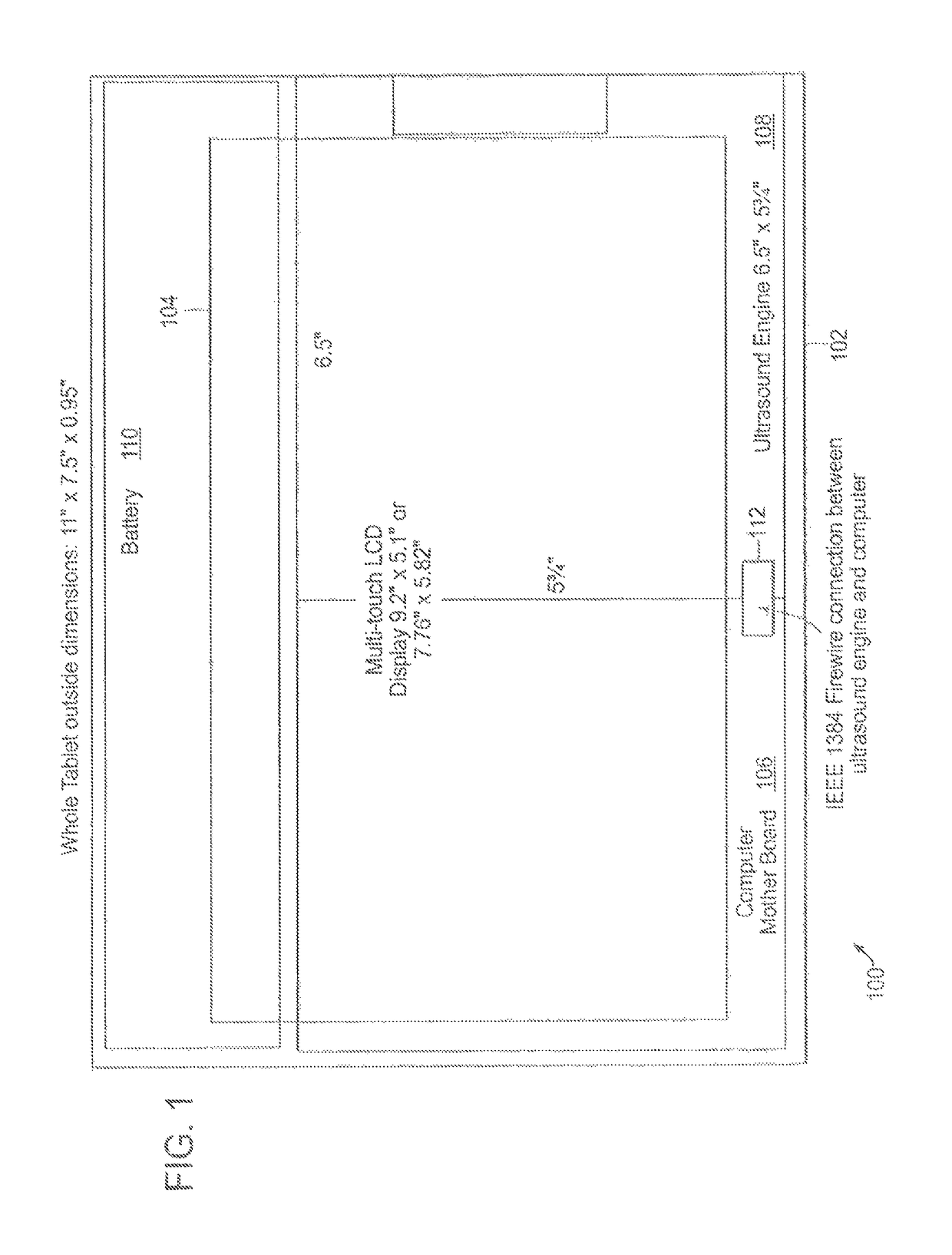
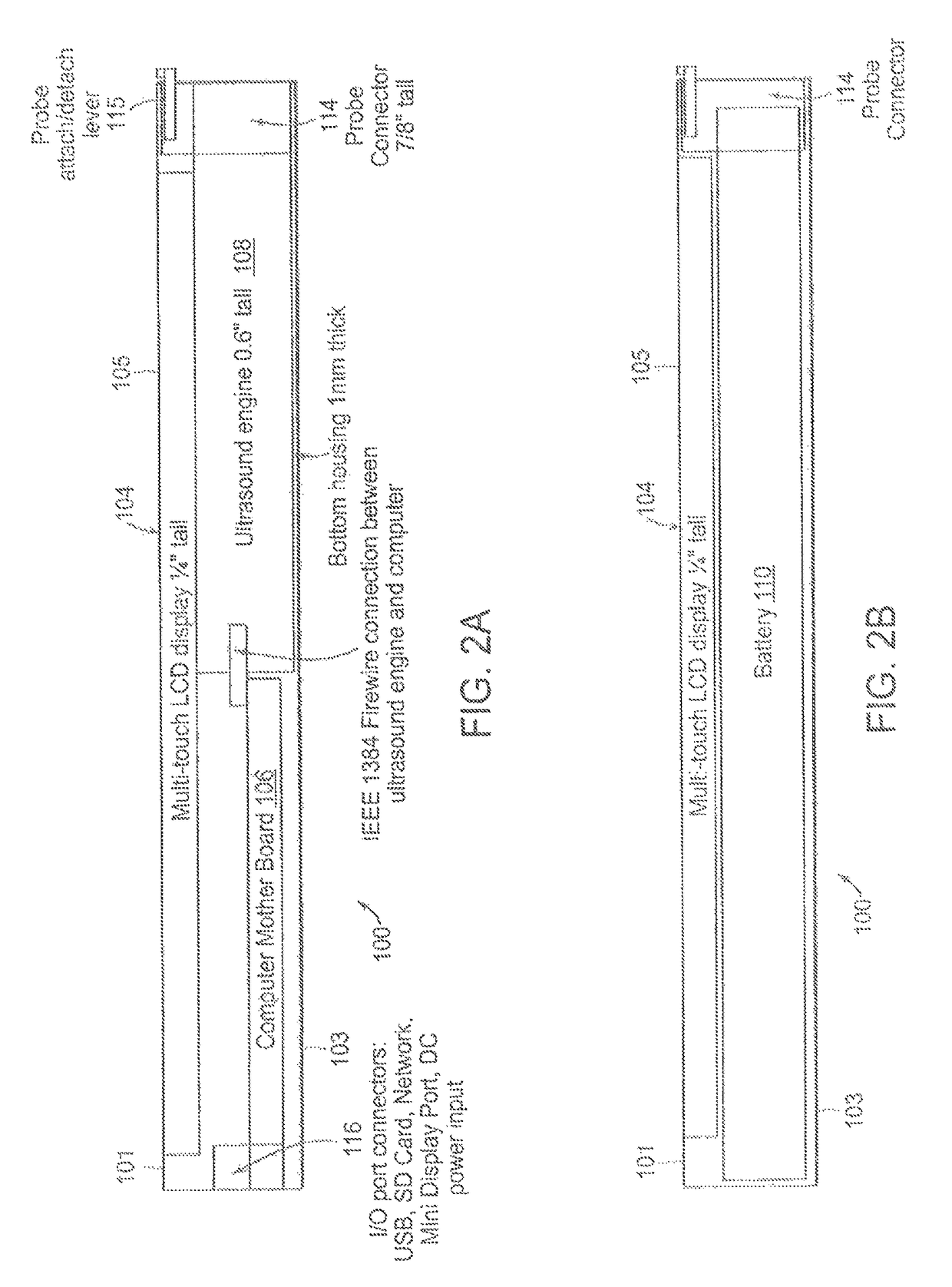
Tablet ultrasound system
ActiveUS20140121524A1Minimize packaging sizeMinimized footprintSolid-state devicesTomographyUltrasonographySonification
Exemplary embodiments provide systems and methods for portable medical ultrasound imaging. Preferred embodiments utilize a tablet touchscreen display operative to control imaging and display operations without the need for using traditional keyboards or controls. Certain embodiments provide ultrasound imaging system in which the scan head includes a beamformer circuit that performs far field sub array beamforming or includes a sparse array selecting circuit that actuates selected elements. Exemplary embodiments also provide an ultrasound engine circuit board including one or more multi-chip modules, and a portable medical ultrasound imaging system including an ultrasound engine circuit board with one or more multi-chip modules. Exemplary embodiments also provide methods for using a hierarchical two-stage or three-stage beamforming system, three dimensional ultrasound images which can be generated in real-time.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
Antioxidant doping of crosslinked polymers to form non-eluting bearing components
InactiveUS20090030524A1Improve wear resistanceGood biocompatibilityBone implantJoint implantsAntioxidantCrosslinked polymers
Methods provide a non-eluting antioxidant doped UHMWPE in the form of an implant bearing component. The process includes the steps of: (a) providing a preform; (b) irradiating the preform with γ-irradiation to crosslink the UHMWPE; (c) doping the crosslinked preform by exposing it to an antioxidant composition at a temperature below the melting point of the UHMWPE; (d) removing the doped material from contact with the antioxidant composition; and then (e) annealing by heating the doped material at a temperature above 30° C. and below the melting point of the UHMWPE; followed by (f) making an implant bearing component from the doped material, wherein at least 1 mm but no more than about 15 mm of material are removed to make the component.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
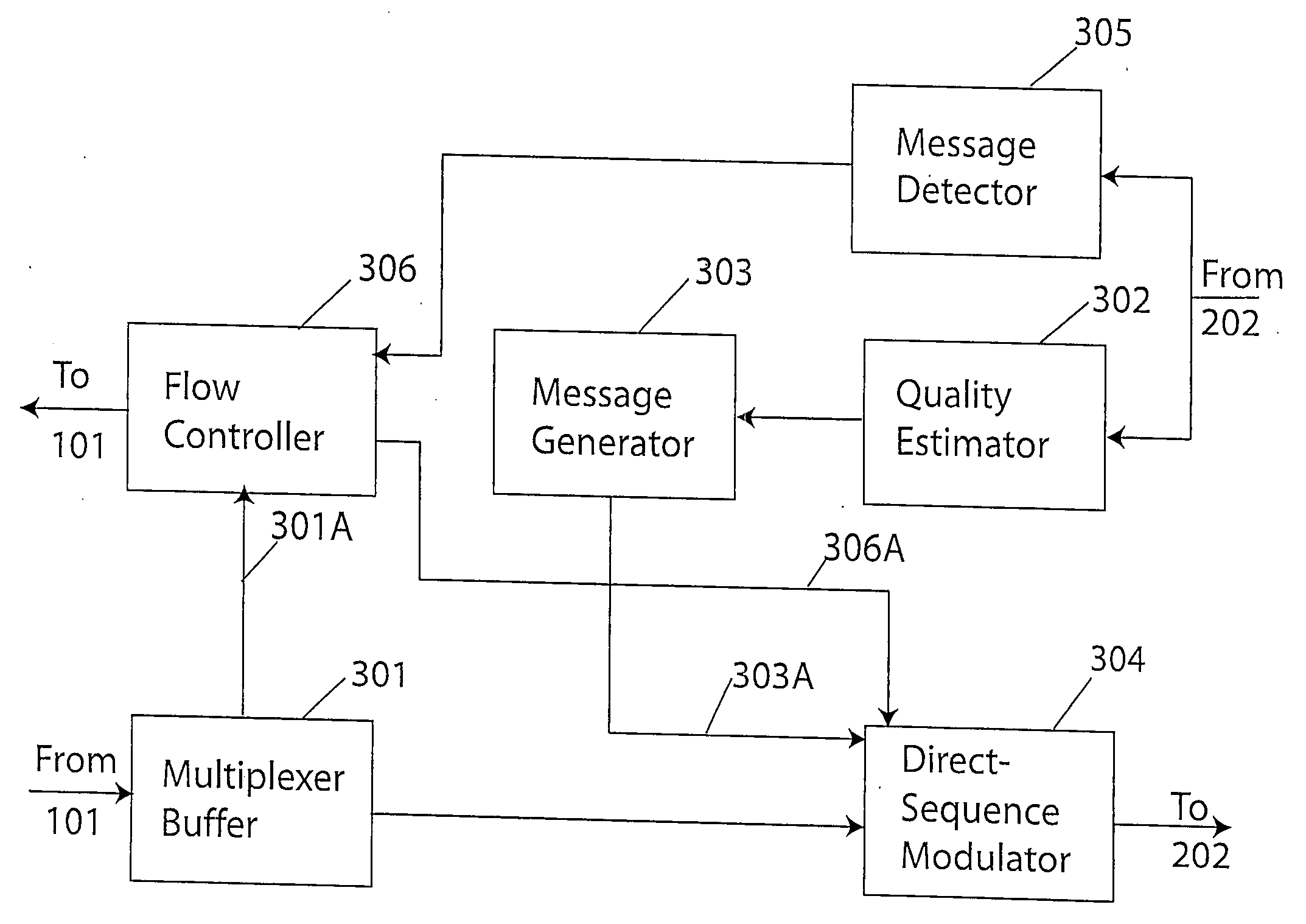
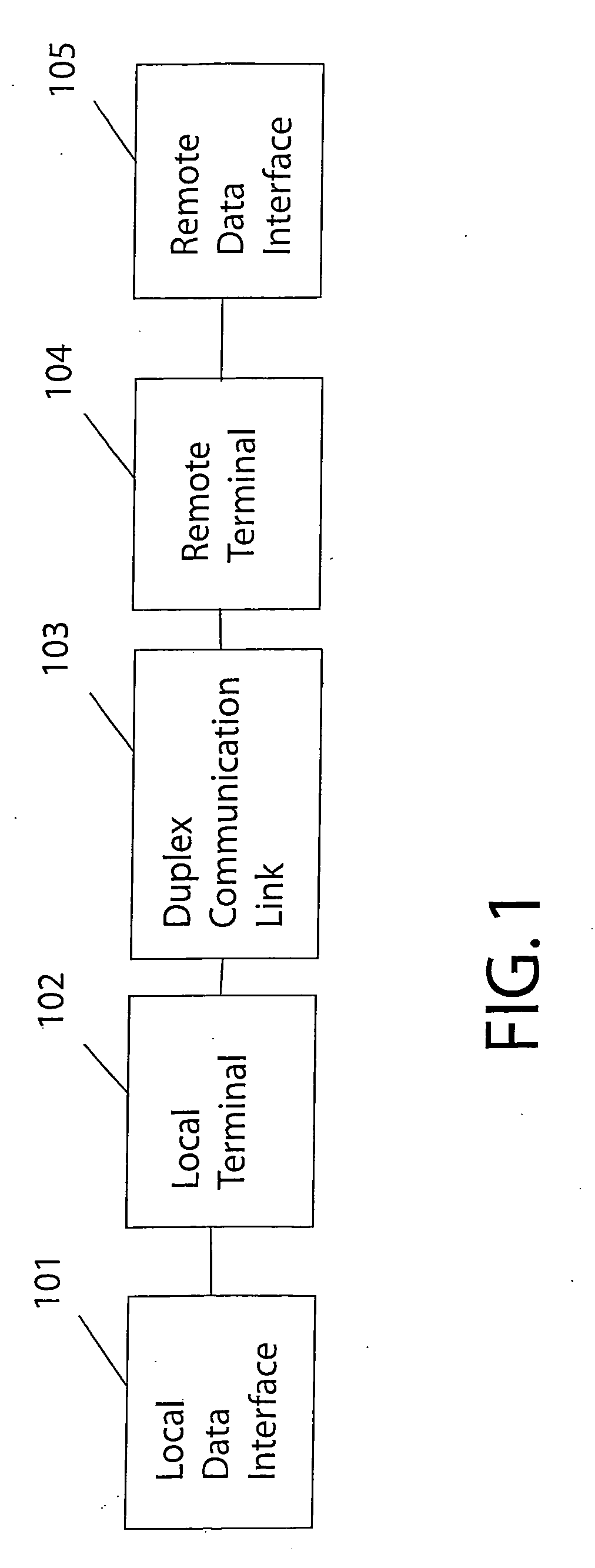
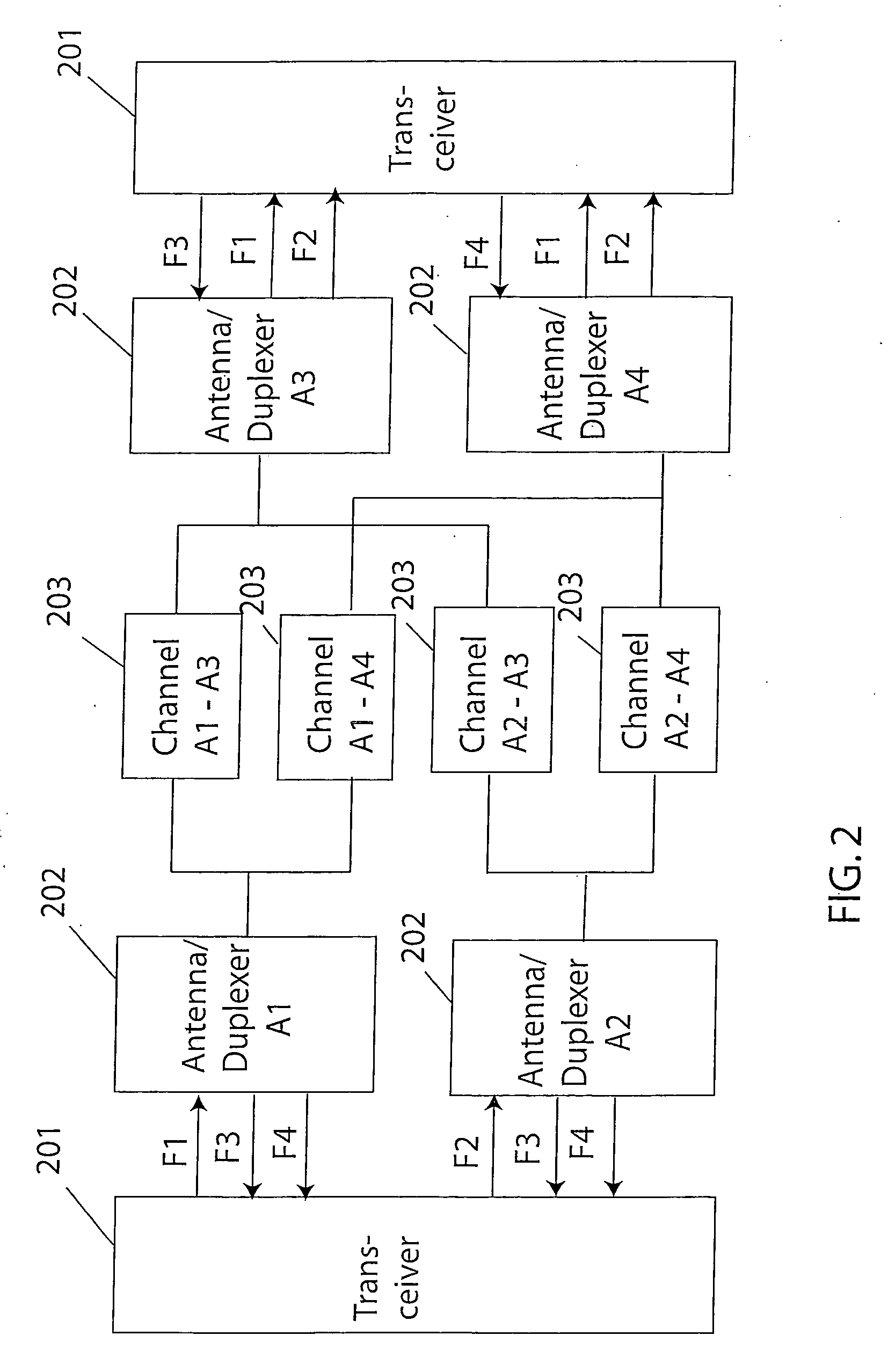
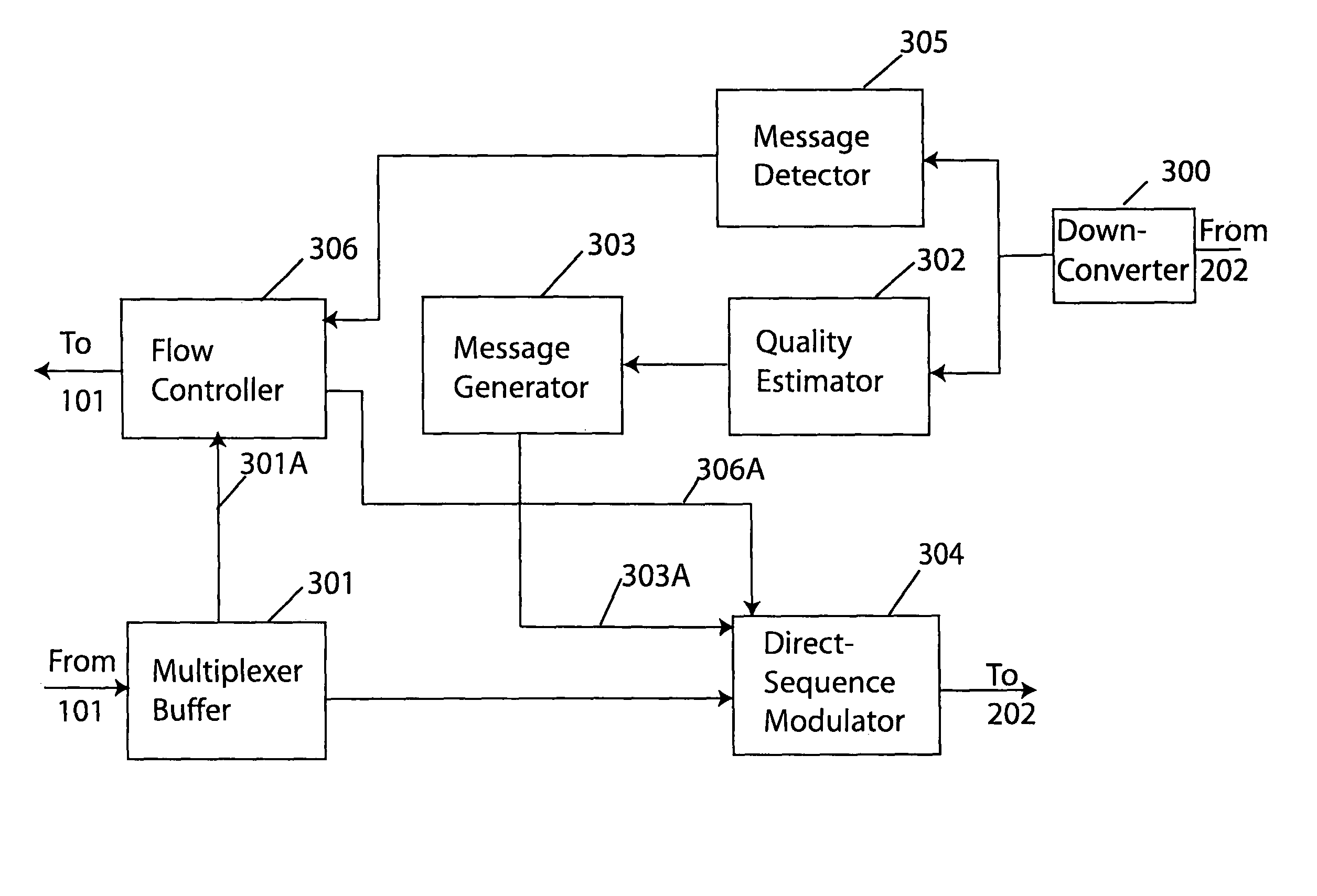
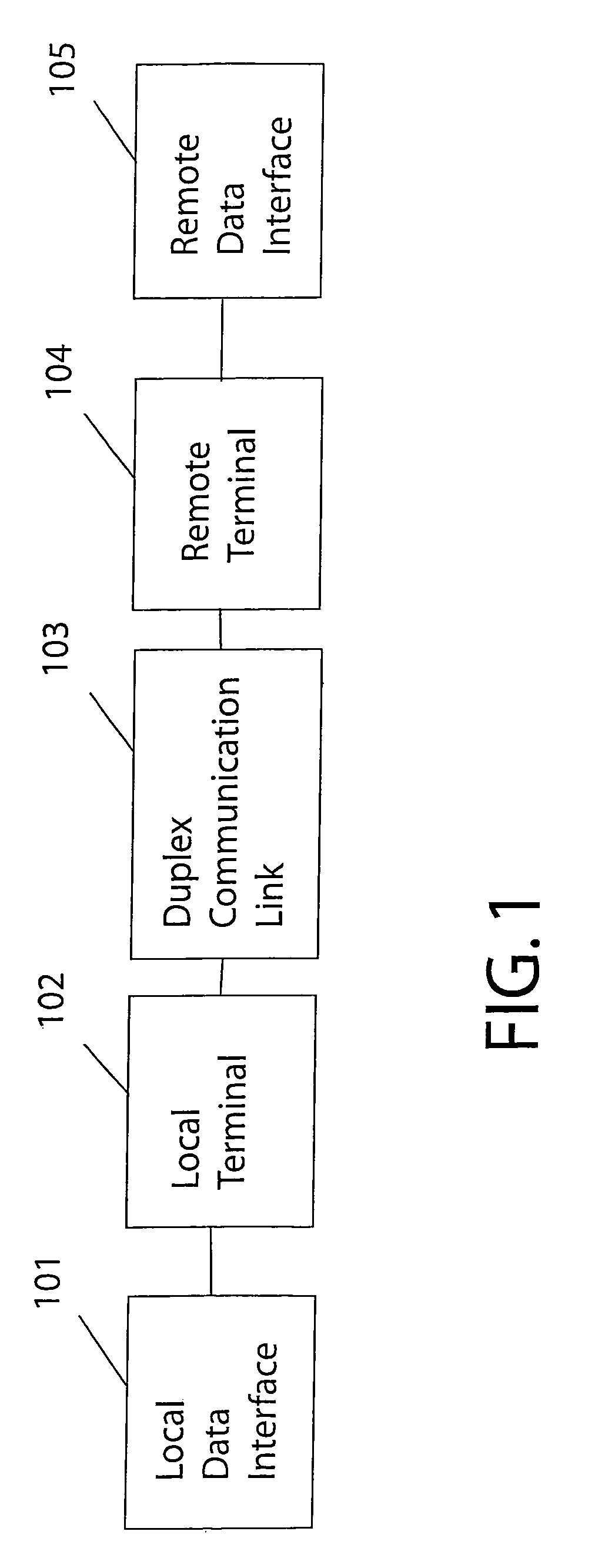
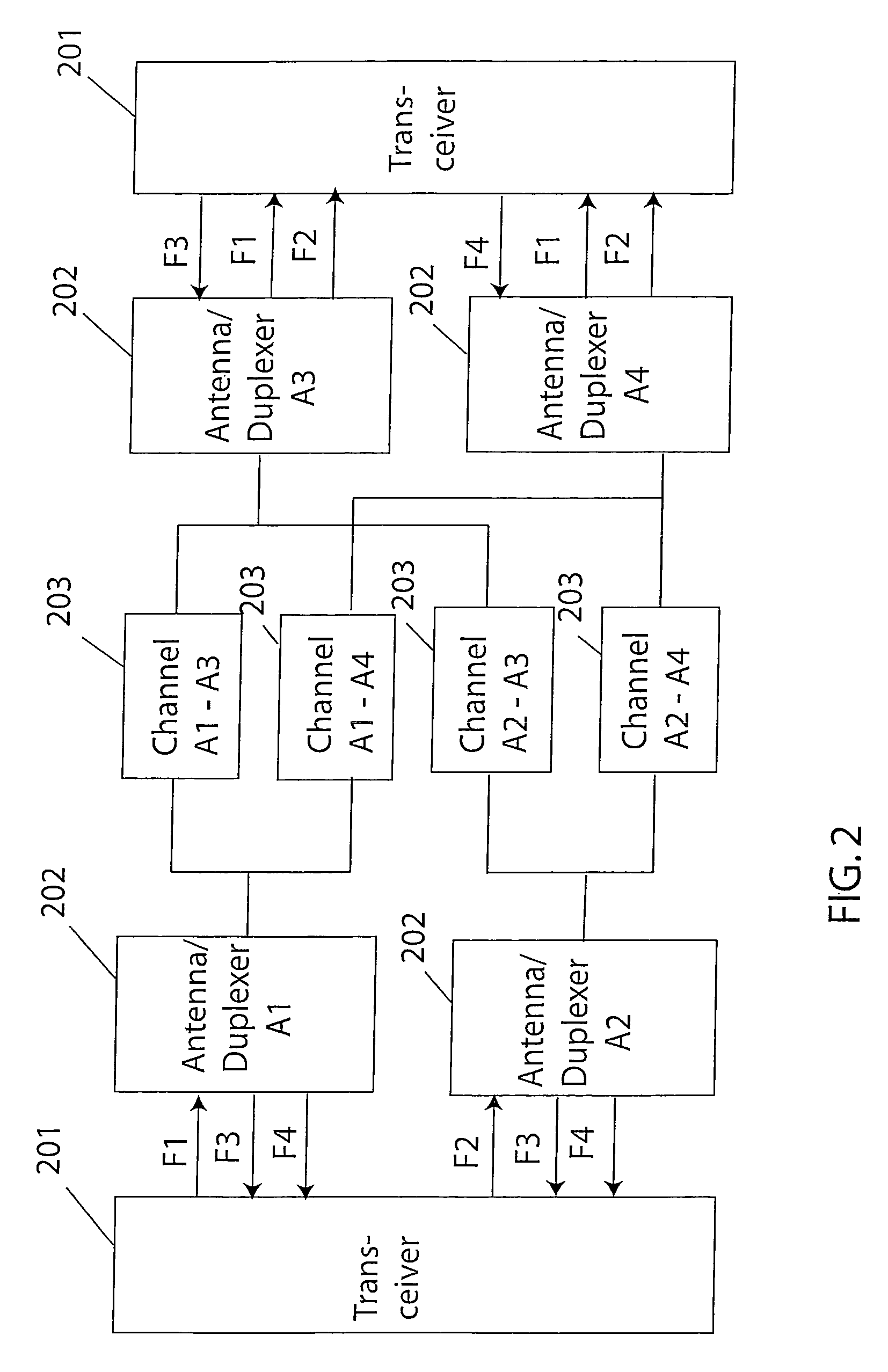
Technique for adaptive data rate communication over fading dispersive channels
ActiveUS20070147251A1Increase capacityMitigate mutual interferenceTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsIndependent dataWave band
In a duplex radio link wherein digital data information from a data interface is transmitted from a local terminal to a remote terminal over fading dispersive channels, a method and transceiver are described that provide for transmission at an adaptive data rate. The transmission is at a constant symbol rate so that the signal bandwidth can be fixed and at the remote terminal receiver the input sampling rate can be fixed. The digital data information is transmitted over a constant data rate interval in accordance with a selected data rate mode that is a function of direct sequence spreading gain, error correction code rate, and signal constellation type. The data rate is adapted by selecting a data rate mode that is a function of the arrival rate of data packets from the data interface and a link quality measure fed back from the remote terminal. The data packet arrival rate is controlled as a function of the link quality measure and the current data packet arrival rate. In systems with multiple transmit diversity channels, independent data is sent over each of the transmit diversity channels. The adaptive data rate technique utilizes both orthogonal transmit diversities such as frequency and troposcatter polarization diversity as well as nonorthogonal transmit diversities in a Multiple-input Multiple-Output (MIMO) configuration. A single antenna troposcatter link using angle diversity and adaptation of data rate by feedback communications is described. In an idealized feedback communication example, the single antenna system in a Ku-band application is shown to have 15.5 times the data rate capability of a conventional two-antenna system at S-band.
Owner:MONSEN PETER
Technique for adaptive data rate communication over fading dispersive channels
ActiveUS7751372B2Improve data throughputImprove transmission conditionsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsPacket arrivalDigital data
In a duplex radio link digital data information is transmitted to a remote terminal at a constant symbol rate in accordance with a selected data rate mode that is a function of direct sequence spreading gain, error correction code rate, and signal constellation type. The data rate is adapted by selecting a data rate mode that is a function of a data packet arrival rate and a link quality measure fed back from the remote terminal. The data packet arrival rate is controlled as a function of the link quality measure and the current data packet arrival rate. In systems with multiple transmit diversity channels, independent data is sent over each of the transmit diversity channels. In an idealized feedback communication example, a single antenna troposcatter system in a Ku-band application is shown to have 15.5 times the data rate capability of a conventional two-antenna system at S-band.
Owner:MONSEN PETER
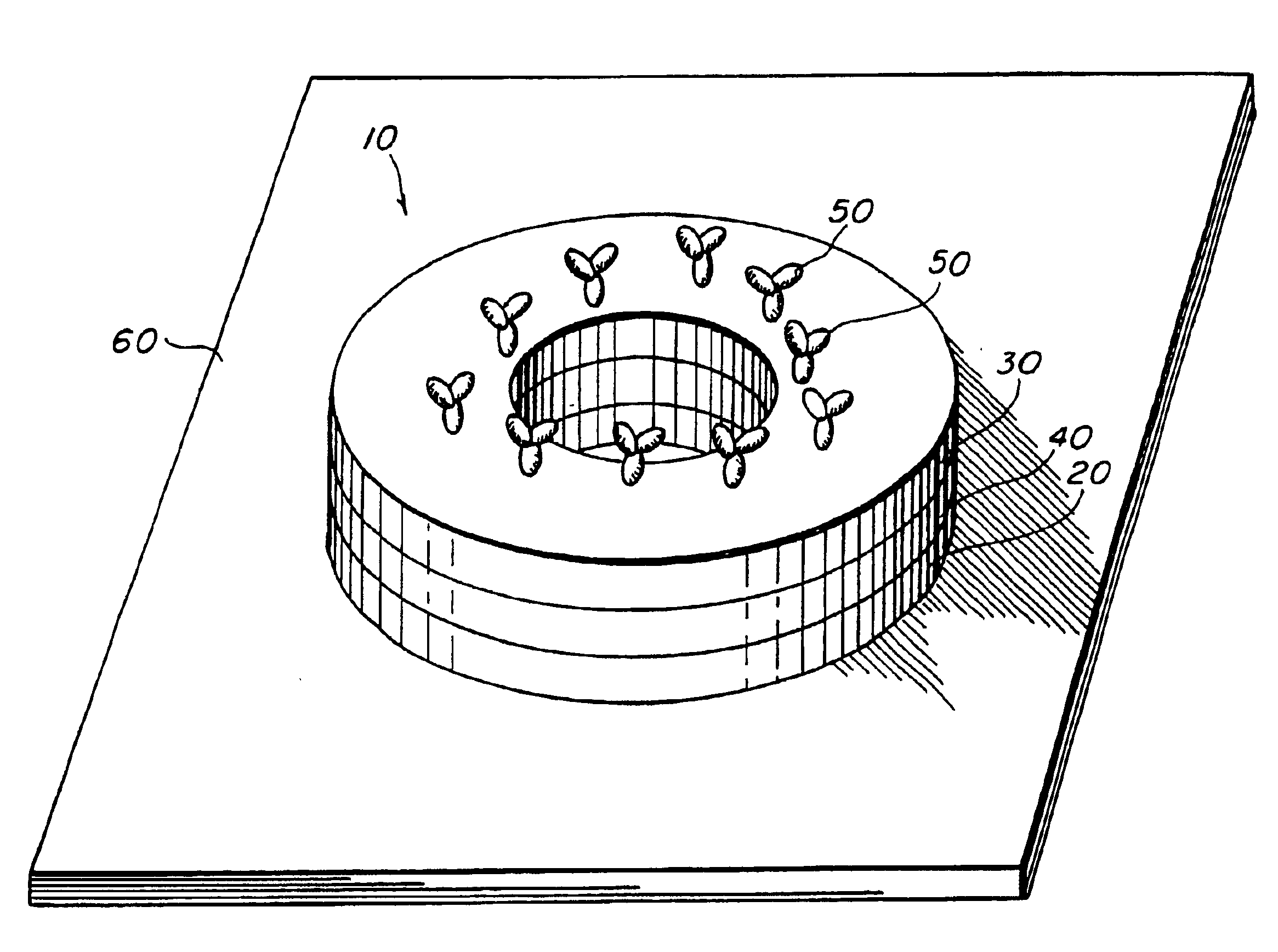
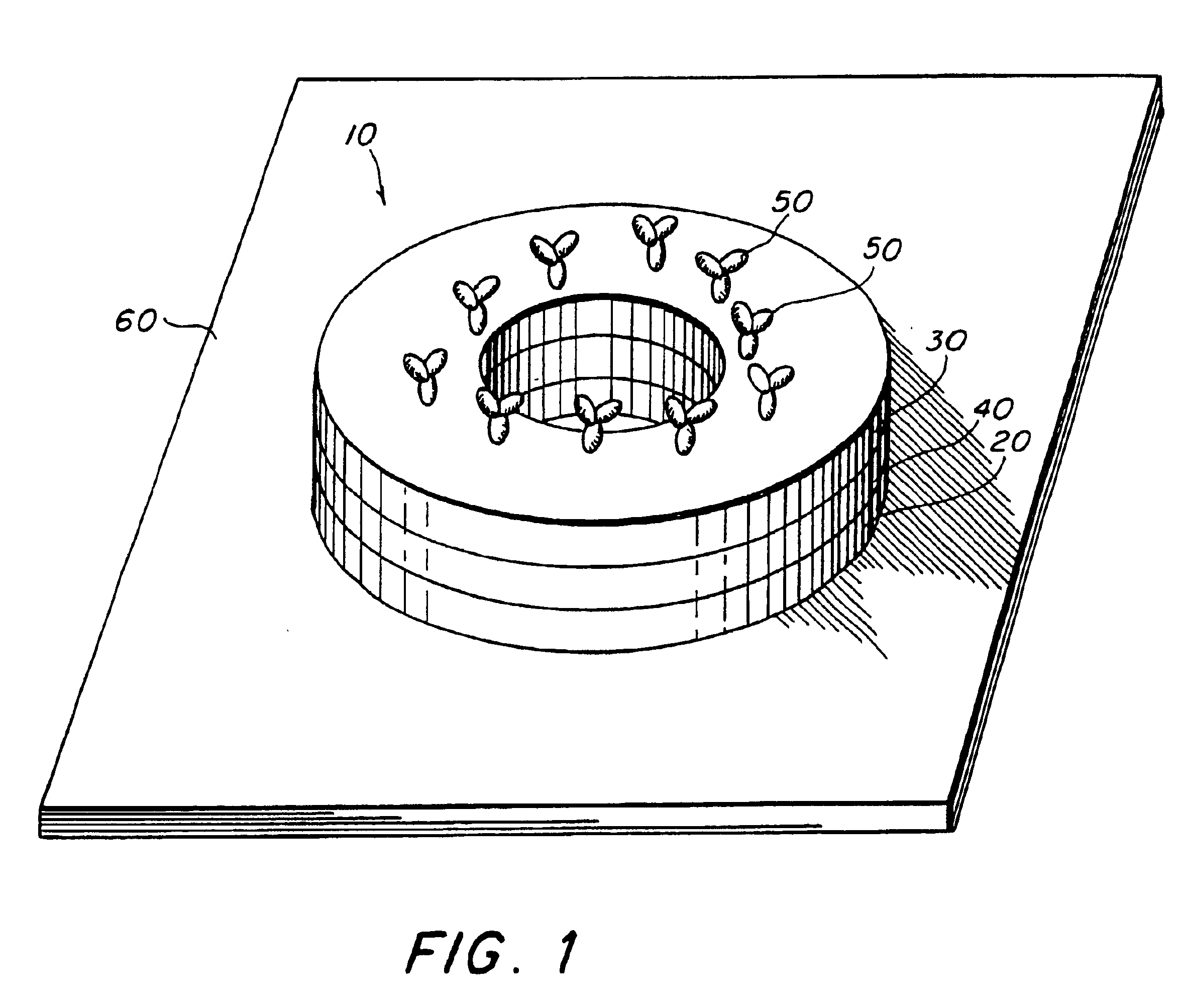
High efficiency magnetic sensor for magnetic particles
InactiveUS6844202B2Maximizing abilityComponent usedMicrobiological testing/measurementWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsAnalyteMagnetic moment
A magnetic sensing element detects the presence of magnetic particles in a binding assay. The magnetic sensing element has at least one planar layer of electrically conductive ferromagnetic material that has an initial state in which the material has a circular magnetic moment within the plane of the layer. The magnetic sensing element has molecules of a first specific binding member attached to it. The device also includes a fluid test medium to which the magnetic sensing element is exposed during the course of a binding assay. The fluid test medium includes magnetizable particles that become immobilized during the assay in relation to the amount of analyte in the test medium. The relative size of the magnetic particle and the magnetic sensing element and the location of the molecules of the first specific binding member on the magnetic sensing element are selected so that when the magnetic particle becomes immobilized with respect to the magnetic sensing element, the radial fringing field of the magnetic particle causes the magnetic moment of at least one layer of electrically conductive ferromagnetic material to shift from circular to radial, thereby causing a detectable change in the electrical resistance of the magnetic sensing element.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
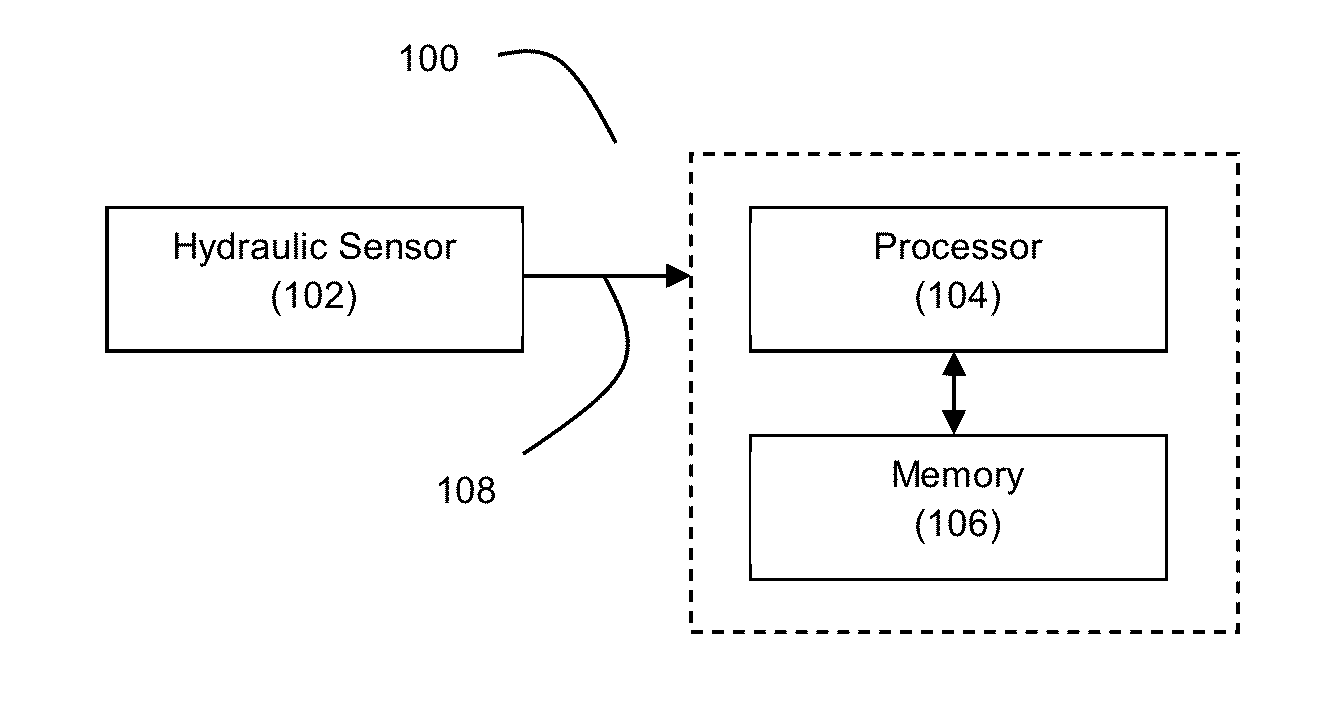
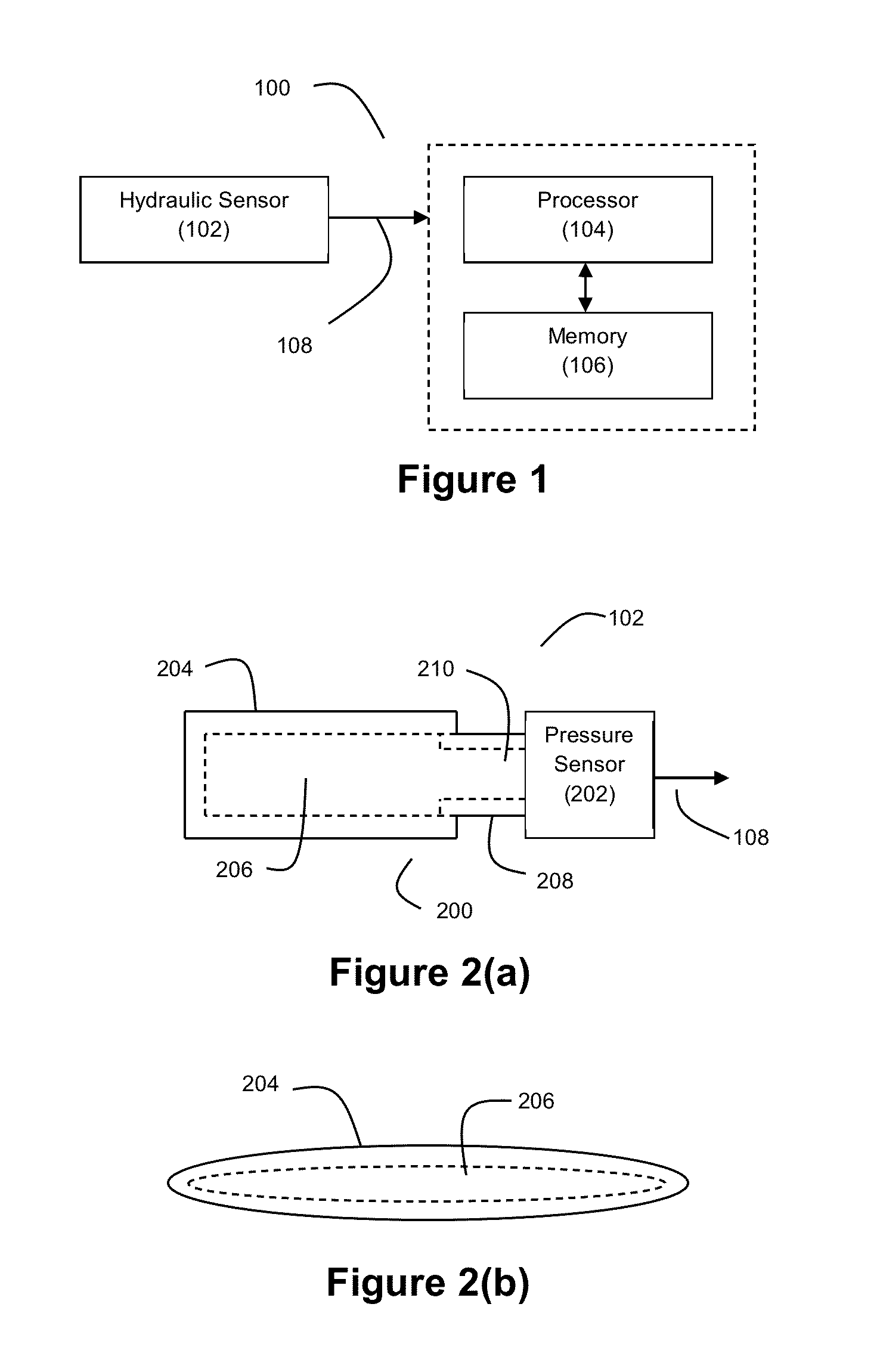
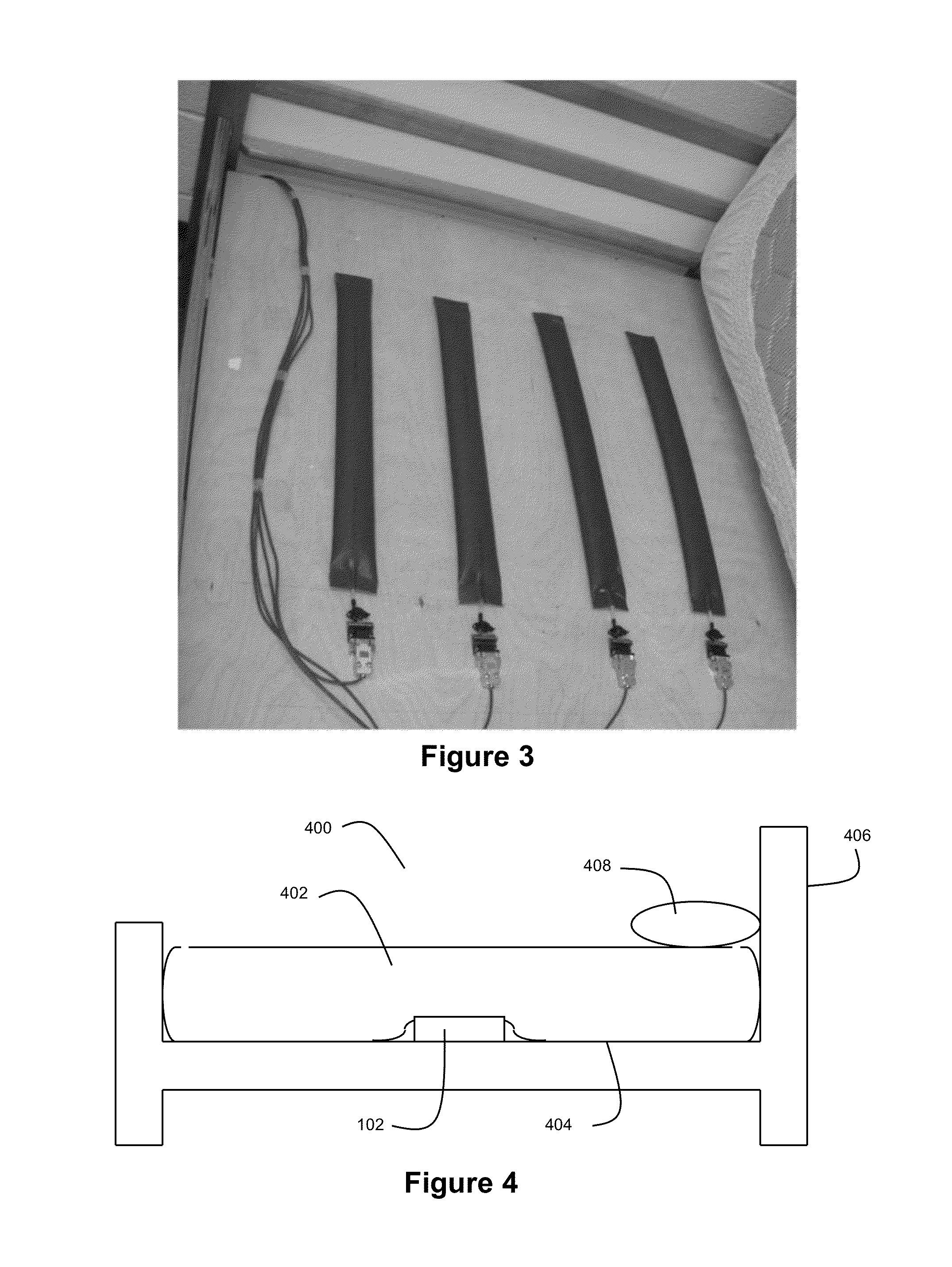
Hydraulic Bed Sensor and System for Non-Invasive Monitoring of Physiological Data
ActiveUS20130197375A1Maintain healthMaintain independenceDiagnostic signal processingPerson identificationShallow breathBiology
Disclosed herein is a new and improved non-invasive bed sensing system for detecting and monitoring physiological movements such as heartbeat and respiration. The system may employ a hydraulic fluid to transduce the physiological pressures to an integrated pressure sensor and a new and improved signal processing method to identify individual cardiac pulses from the electronic signals generated by the hydraulic transducer. The system provides increased sensitivity capable of capturing quantitative pulse and respiration rates with subtle changes, ability to distinguish between instances of low pulse rate and shallow breathing, and improved comfort over existing system.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Orientation sensor for downhole tool
InactiveUS20100175923A1Facilitate communicationLess disturbingSurveyDrilling rodsRotational axisMagnet
A downhole drilling apparatus incorporating an orientation sensor (24) is disclosed. The orientation sensor is mounted to a housing (16) for providing a signal representing the orientation of the housing, and is connected to a first transceiver coil (26). A second transceiver coil (30) and a series of magnets (32) are mounted to a rotary shaft (18). As the shaft rotates relative to the housing, passage of the magnets past the first transceiver coil generates a voltage to provide electrical power to the sensor, and electromagnetic coupling between the first and second transceiver coils enables signals from the sensor to be transmitted to a measurement while drilling tool mounted on the rotary shaft.
Owner:ALLAN VICTOR LAING
Thermoplastic Resin Composition Having Improved Impact Resistance
ActiveUS20080160240A1Improve impact resistanceImprove flame retardant performanceOrganic chemistryLayered productsPolymer sciencePolyester resin
A thermoplastic resin composition with improved impact resistance can include (A) about 30 to about 99 parts by weight of an epoxy group-containing styrenic polymer comprising (A1) about 5 to about 100% by weight of an epoxy group-containing vinyl copolymer containing about 0.001 to about 5.0 mol % of an epoxy compound; and (A2) about 0 to about 95% by weight of a rubber modified styrenic copolymer resin; (B) about 1 to about 70 parts by weight of a polyester resin; (C) about 0.001 to about 10 parts by weight of a silicone oil, per 100 parts by weight of a base resin comprising (A) and (B); (D) about 3 to about 20 parts by weight of a bromine-containing flame retardant, per 100 parts by weight of a base resin comprising (A) and (B); and (E) about 0.1 to about 6 parts by weight of a flame retardant aid, per 100 parts by weight of a base resin comprising (A) and (B).
Owner:LOTTE ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
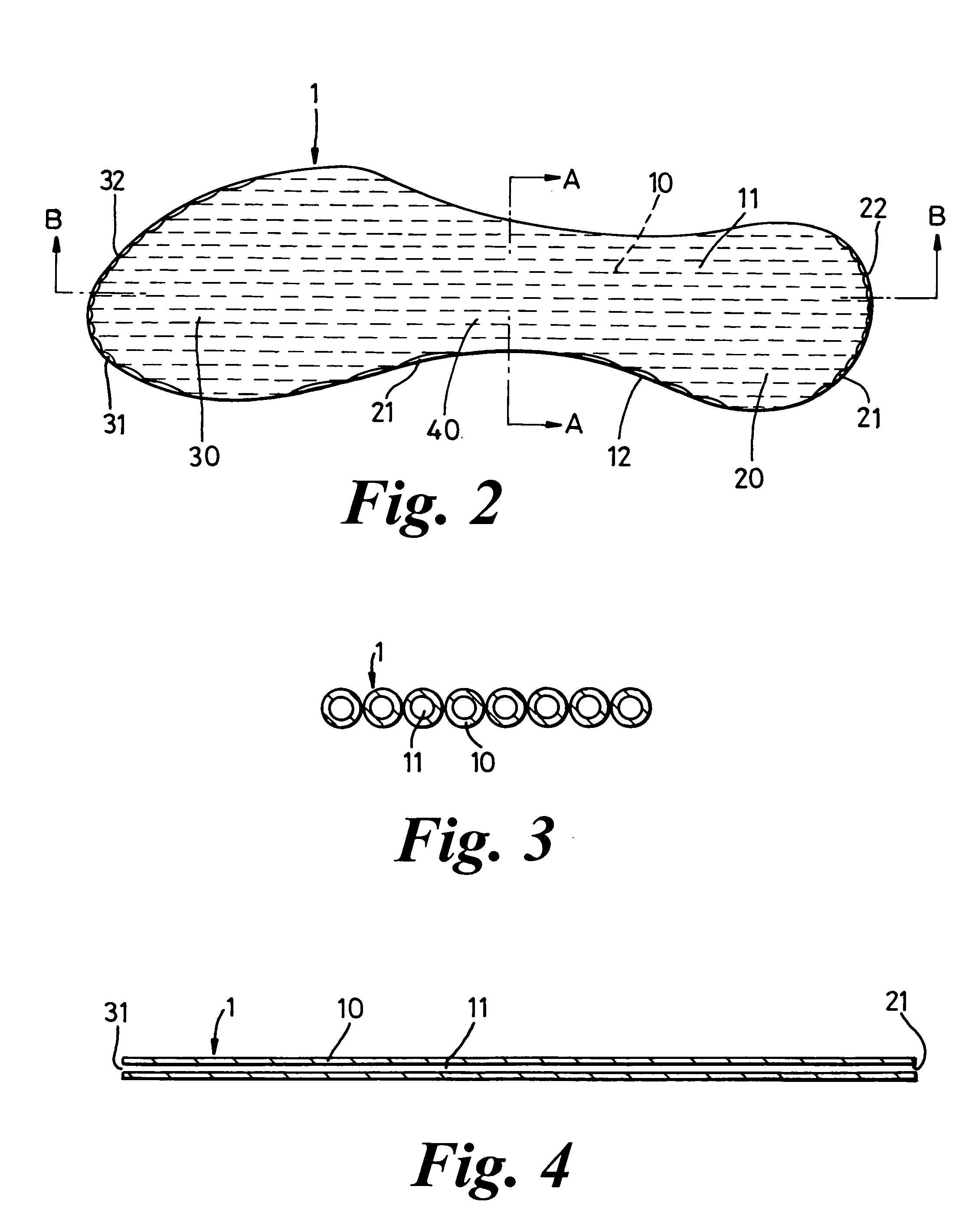
Footwear
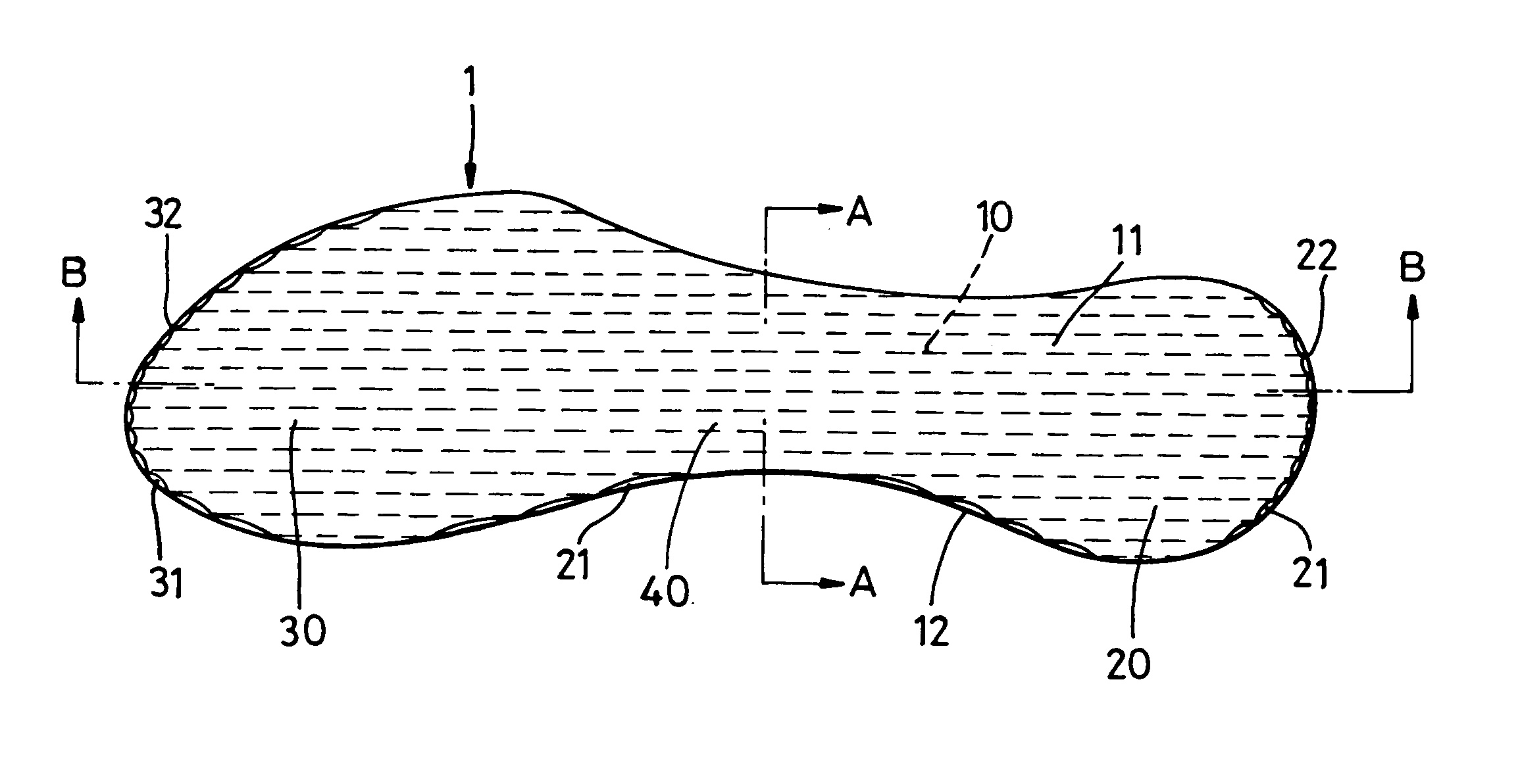
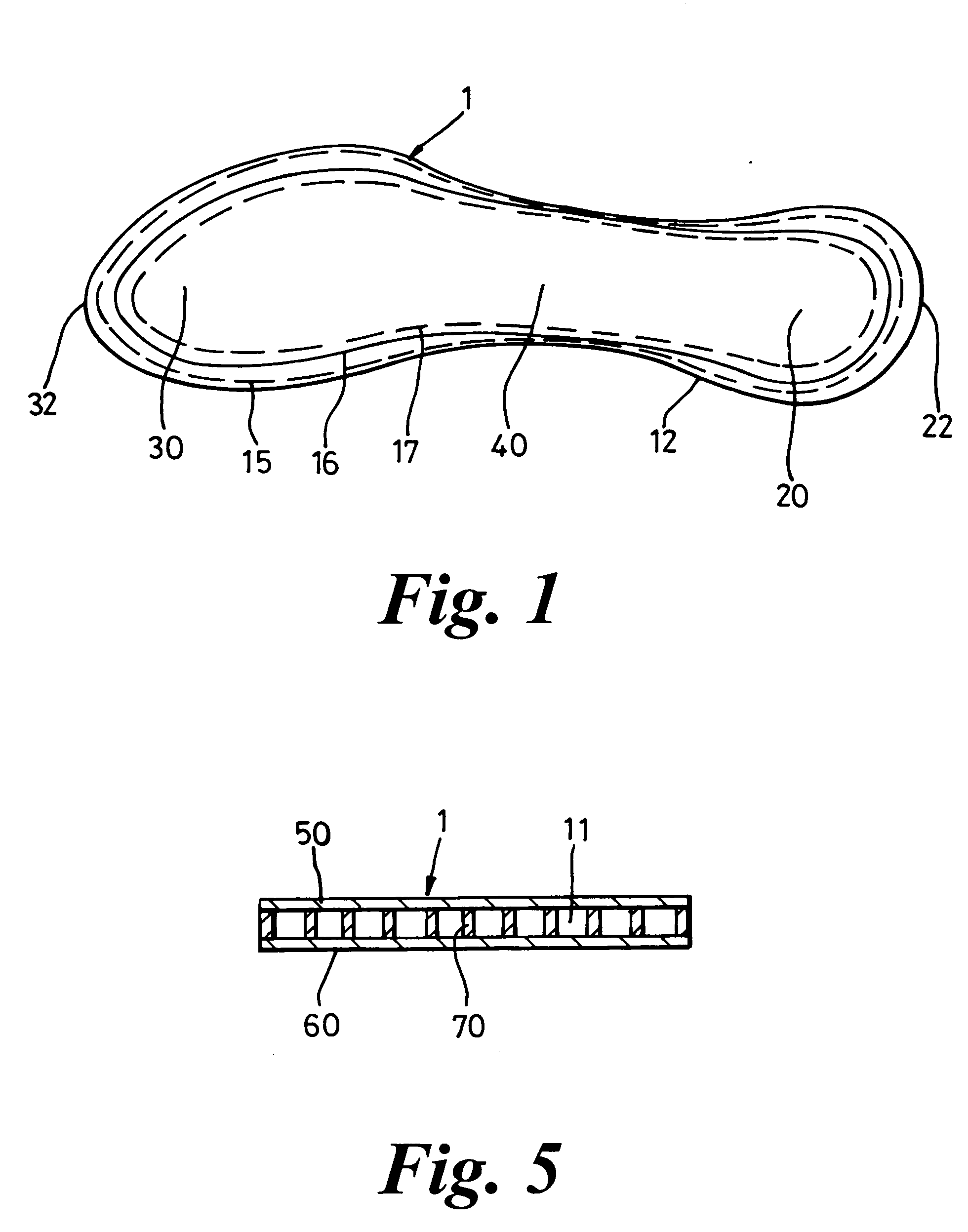
InactiveUS20050120591A1Without adversely affecting a wearer's comfortComponent usedSolesInsolesEngineeringWalking cycle
The invention relates to a footwear sole component and to an article of footwear 2 comprising such a sole component. A sole component is suitably an insole 1 with toe and heel portions 30, 20 connected by an arch portion 40, the sole component being arranged to form part of a sole of a closed article of footwear 2 having a foot chamber 90. The sole component includes at least one compressible passage 11 arranged, in use, to have an opening into a first region of the foot chamber 90 and an opening into a second region of the foot chamber 90 such that air can be caused to travel from passage 11 into a second region of the foot chamber 90, by a pumping effect caused by compression of the passage 11 along at least a part of its extent during a stage of a wearers walking cycle.
Owner:ANDREW TERENCE SIDNEY
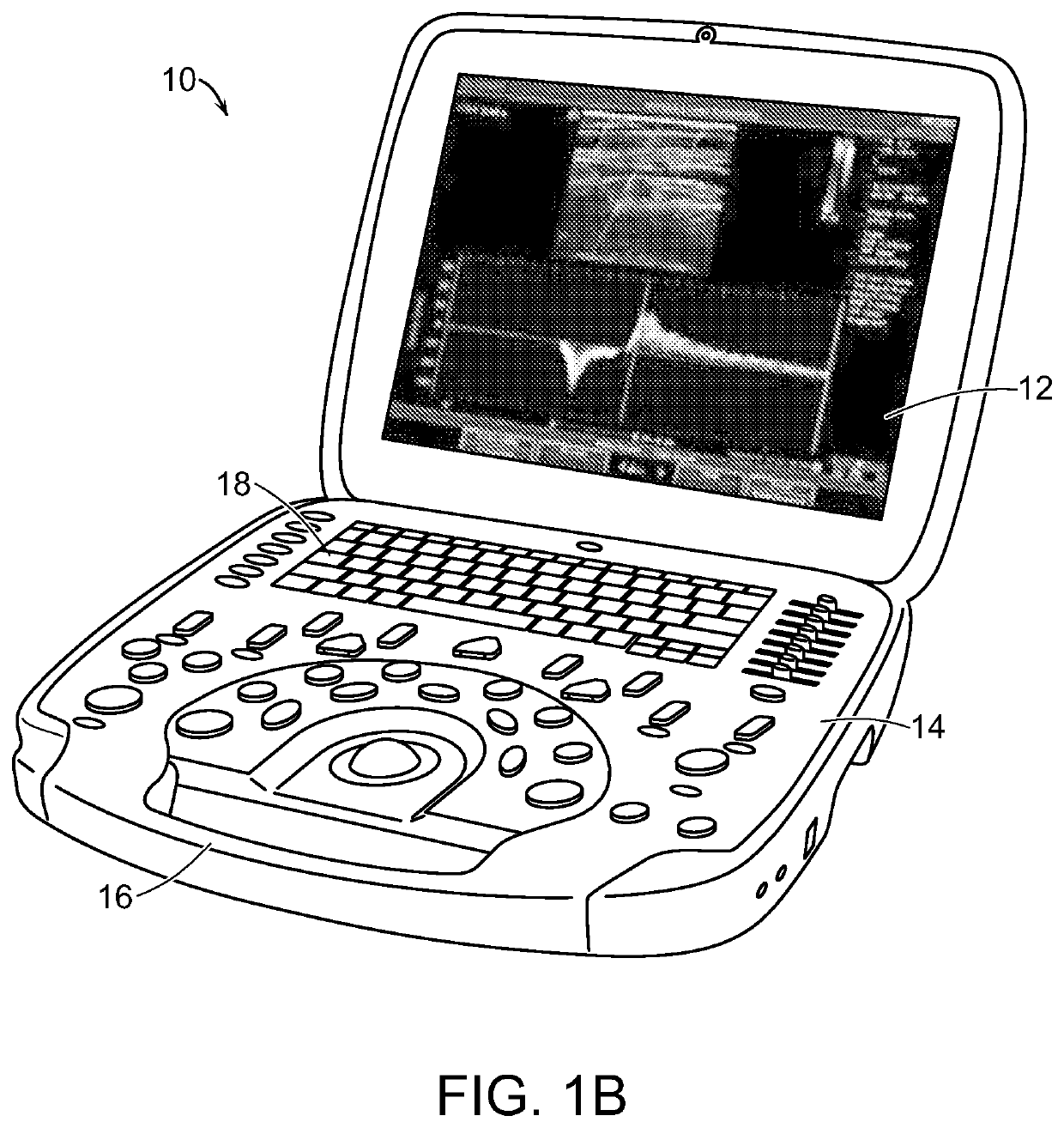
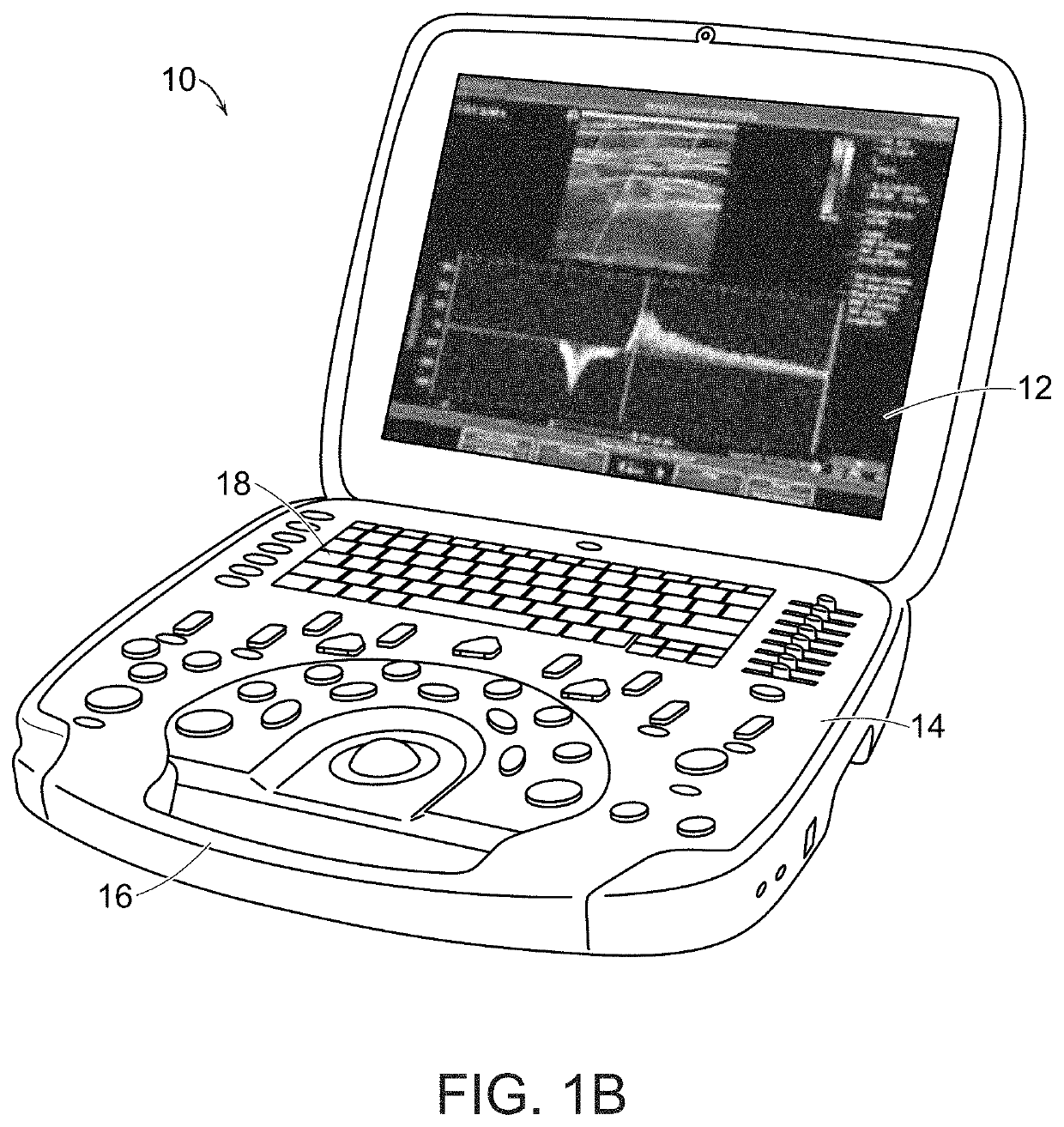
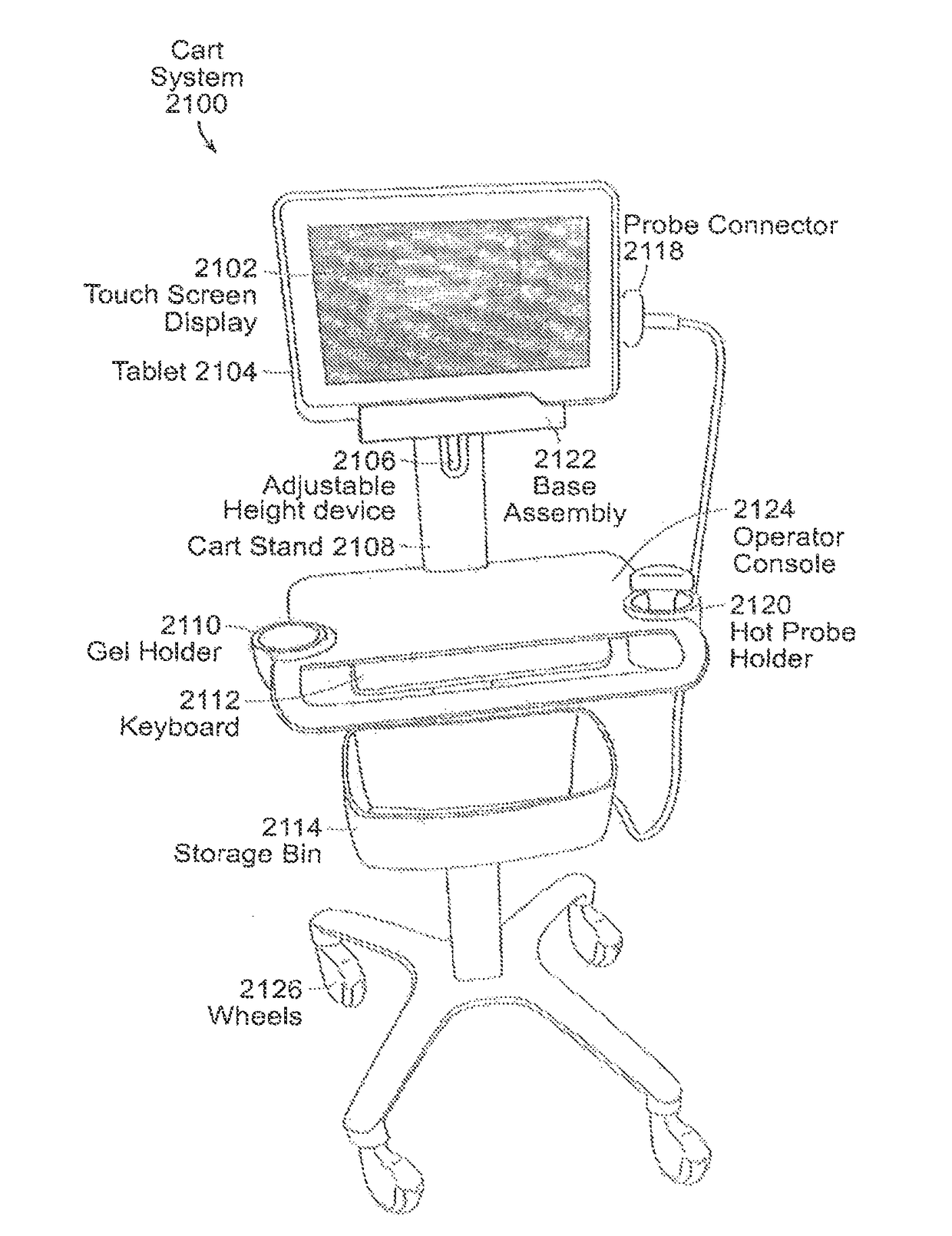
Portable ultrasound system
PendingUS20190365350A1Allow useFunction increaseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSolid-state devicesUltrasonographyGraphics
Exemplary embodiments provide systems and methods for portable medical ultrasound imaging. Preferred embodiments utilize a hand portable, battery powered system having a display and a user interface operative to control imaging and display operations. A keyboard control panel can be used alone or in combination with touchscreen controls to actuate a graphical user interface. Exemplary embodiments also provide an ultrasound engine circuit board including one or more multi-chip modules, and a portable medical ultrasound imaging system including an ultrasound engine circuit board.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
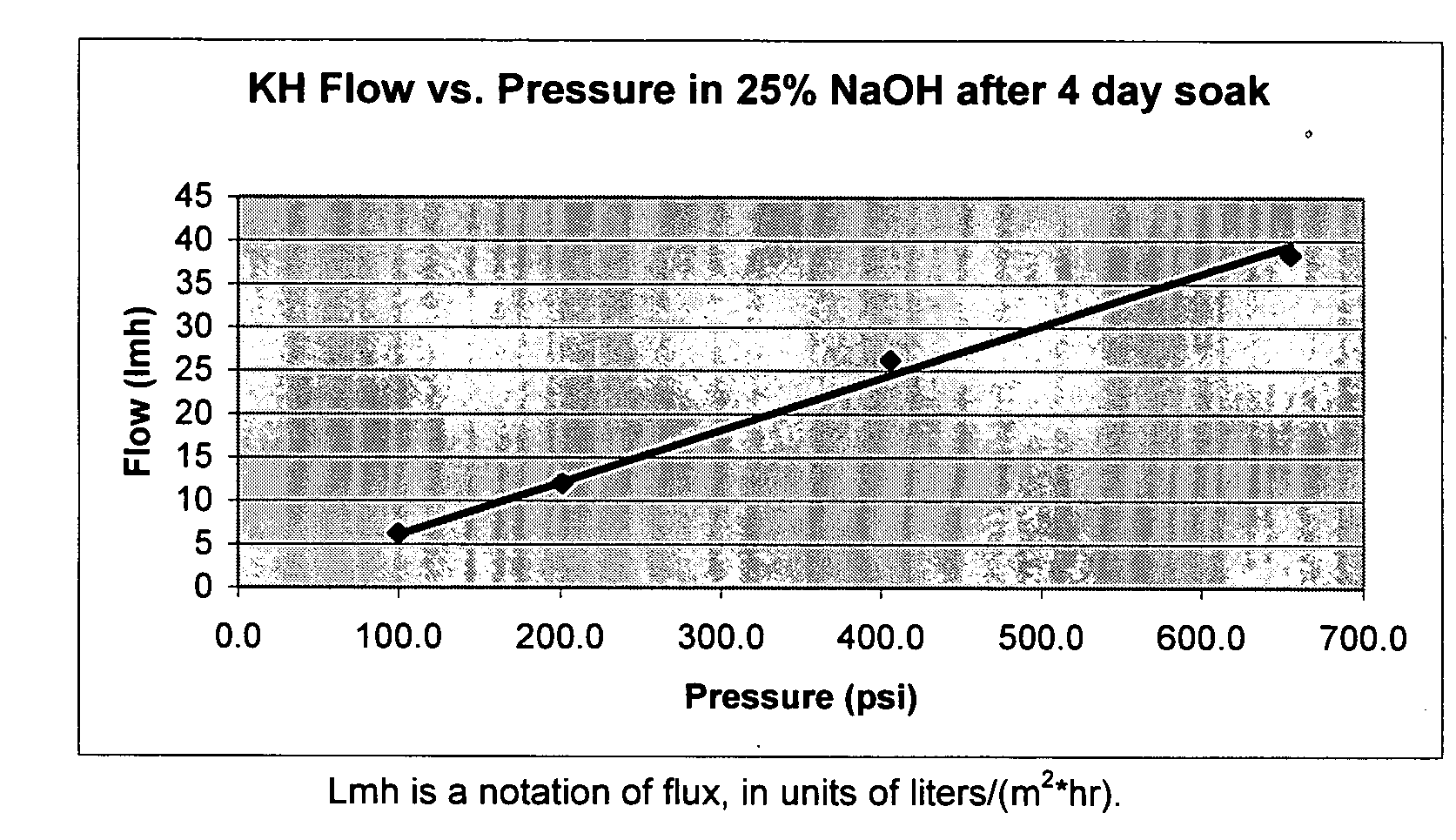
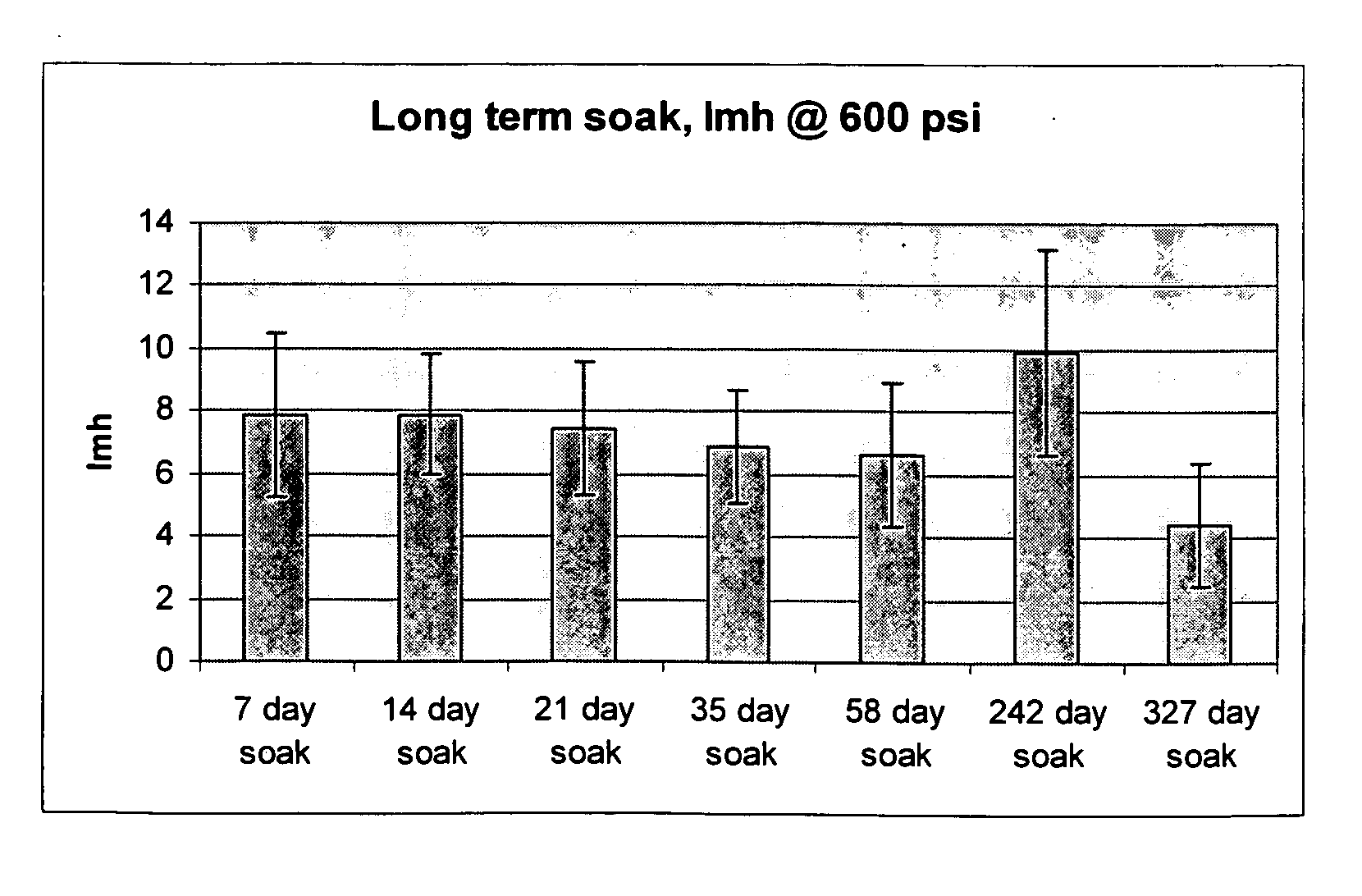
Membranes and methods useful for caustic applications
ActiveUS7575687B2Lower the volumeIncrease volumeGallium/indium/thallium compoundsUltrafiltrationChemistry
Owner:GE OSMONICS INC
Process to produce polyolefins using metallocene catalysts
ActiveUS20080020928A1High yieldHigh qualityOther chemical processesHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionPolyolefinPolymerization catalysts
The invention is directed to a process for producing polyolefins by one or more homogeneous or colloidal polymerization catalyst wherein residual catalyst is removed by using a solid sorbent
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Devices and Methods for Ultrasound Monitoring
PendingUS20210015456A1Allow useFunction increaseOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsComputer hardwareUltrasonography
Exemplary embodiments provide systems and methods for portable medical ultrasound imaging. Preferred embodiments utilize a hand portable, battery powered system having a display and a user interface operative to control imaging and display operations. A keyboard control panel can be used alone or in combination with touchscreen controls to actuate a graphical user interface. The system includes a transducer assembly to image, measure and monitor a condition of a patient
Owner:TERATECH CORP
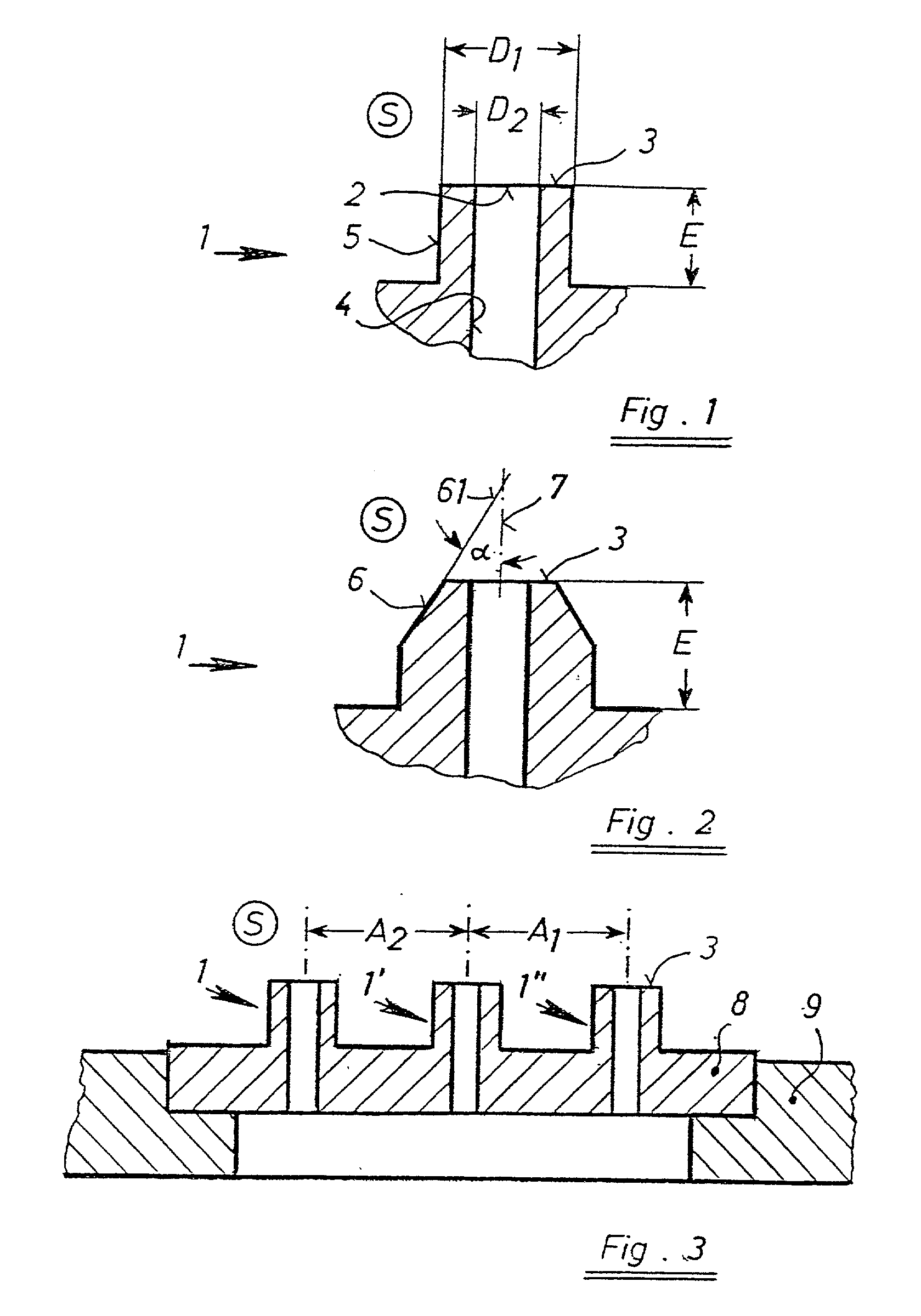
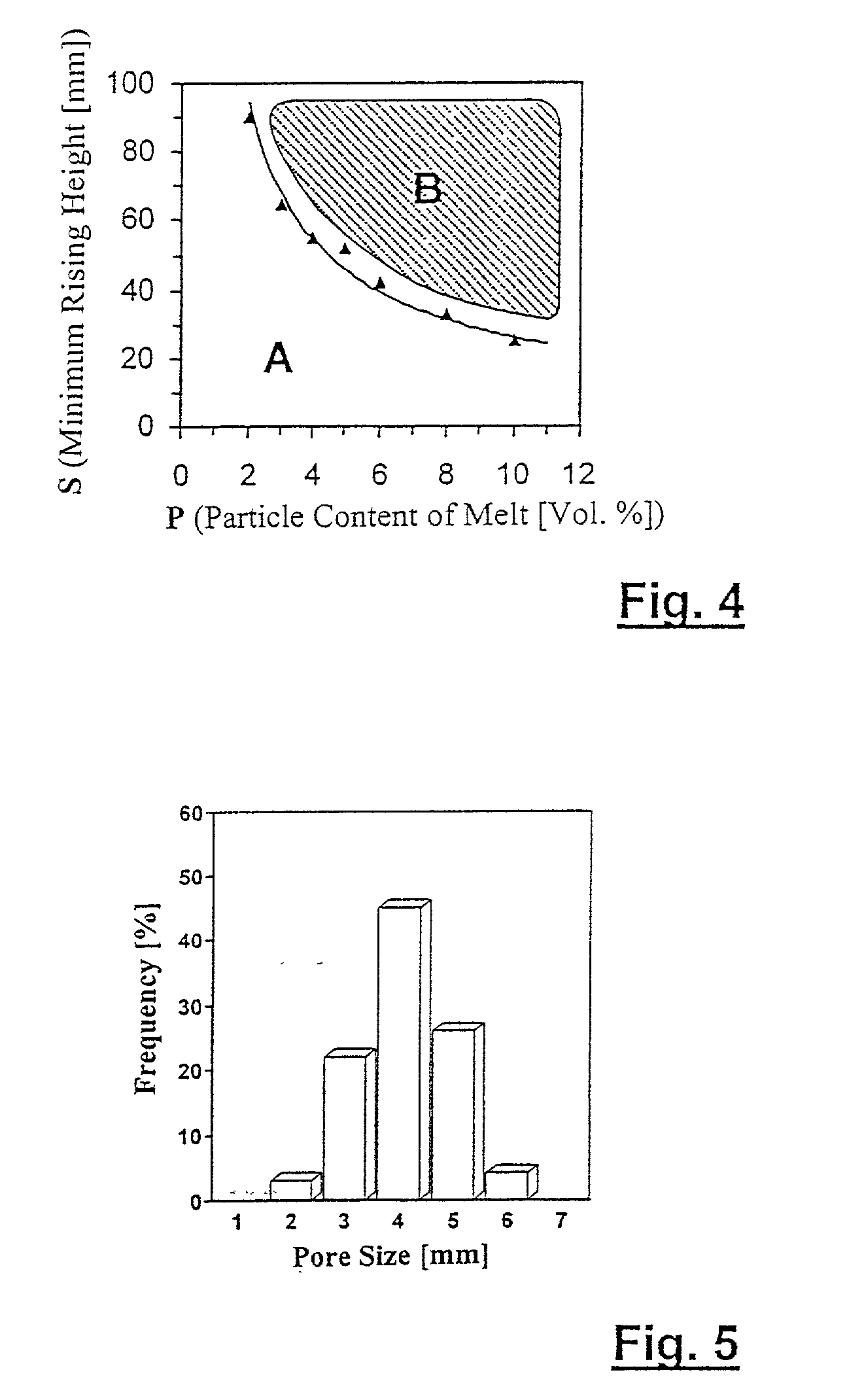
Device and process for producing metal foam
InactiveUS20030047036A1Effective stable separation criterionIncrease load capacityManufacturing convertersPolymer scienceLiquid metal
A device for feeding gas in a melt of foamable metal by means of at least one pipe for producing metal foam. The gas insertion pipe projects inwardly into the melt and at the projecting end has a gas outlet having a cross section of 0.006 to 0.2 mm2 and a pipe face area of less than 4.0 mm2. A flowable metal foam has gas bubbles defined by walls of a liquid metal matrix with solid reinforcing particles, and the diameter of the largest gas bubbles divided by that of the smallest gas bubbles is less than 2.5.
Owner:HUTTE KLEIN REICHENBACH
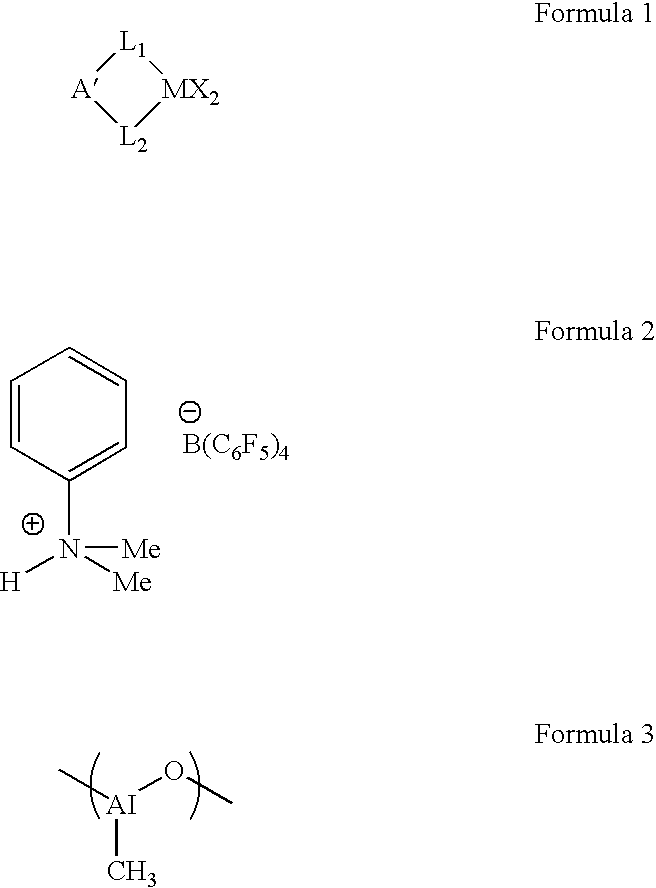
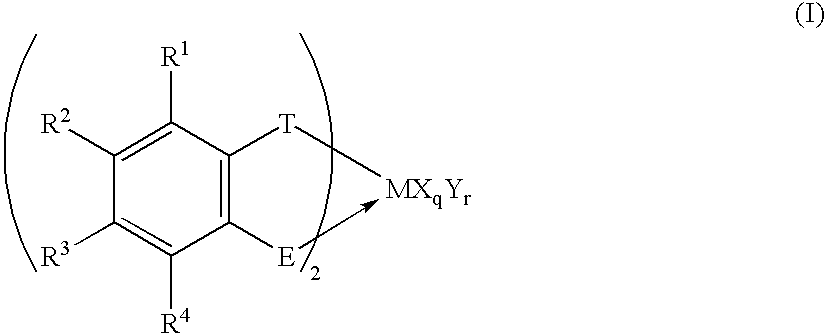
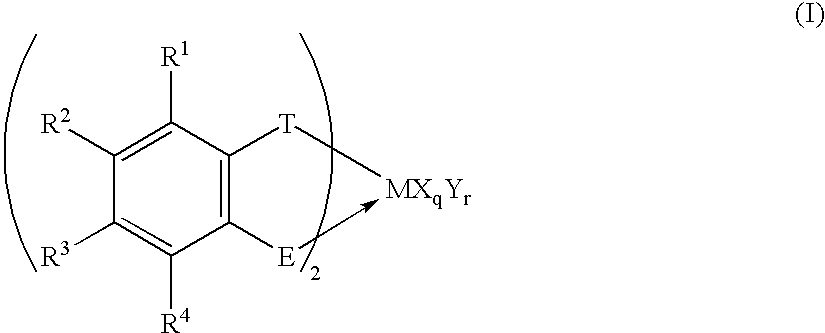
Transition metal compound, polymerization catalysts for olefins, olefin polymers and process for their production
InactiveUS20020193536A1Easy to synthesizeEfficiently provides ethylene (co)polymersGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHalogenHydrogen atom
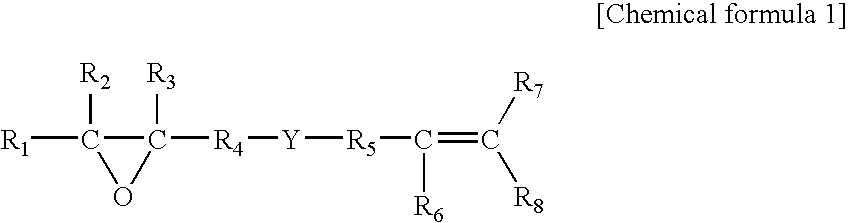
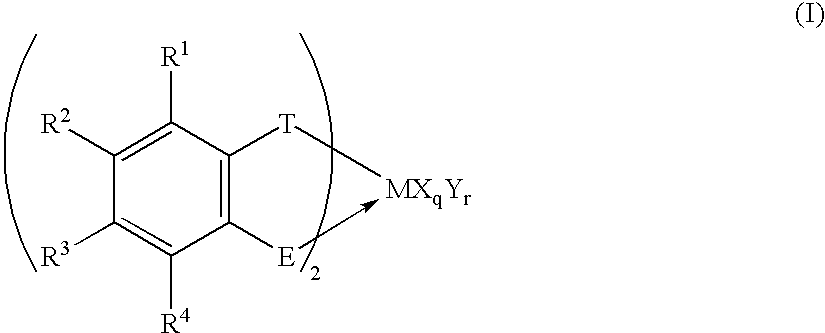
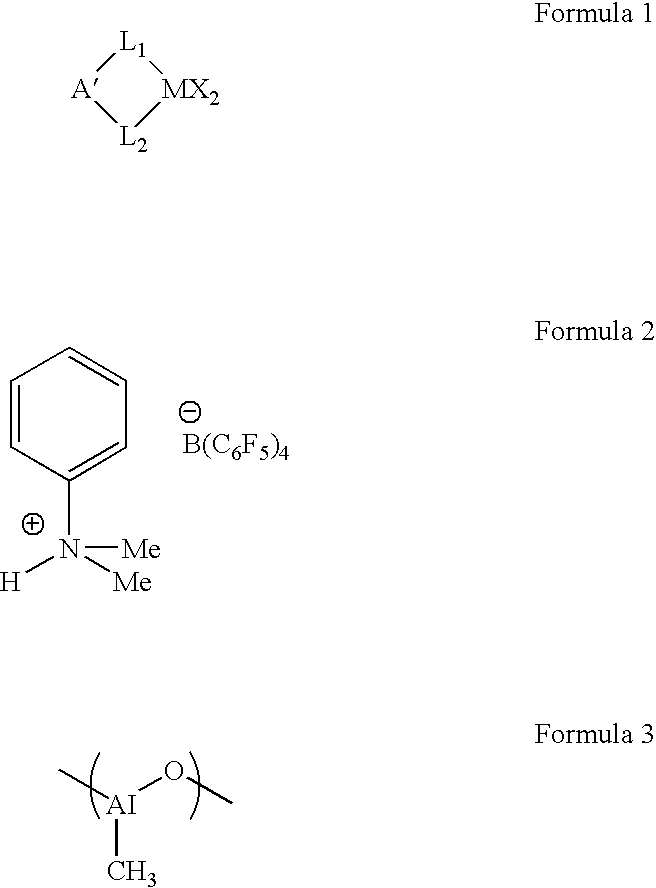
Useful as a catalyst component for polymerizing olefin is the transition metal compound of the present invention represented by Formula (I): wherein M represents a transition metal compound of the fourth group in the periodic table; X represents a sigma bonding ligand; Y represents a Lewis base; T represents a group containing a sigma bonding atom; E is a specific group containing an atom which can coordinate with M via sigma lone pair; q is 1 or 2 and represents [(valency of M)-2]; r represents an integer of 0 to 3; R1 to R4 represent a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a hydrocarbon group, a halogen-containing hydrocarbon group, a silicon-containing group or a hetero atom-containing group.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Polymer based tunneling sensor
InactiveUS7094622B1Reduce noiseComponent usedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAcceleration measurementLithography processPolymer science
A process for fabricating a polymer based circuit by the following steps. A mold of a design is formed through a lithography process. The design is transferred to a polymer substrate through a hot embossing process. A metal layer is then deposited over at least part of said design and at least one electrical lead is connected to said metal layer.
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH UNIV RES FOUND A DIV OF LOUISIANA TECH UNIV FOUND
Positive resist composition, method of forming resist pattern, and polymeric compound
ActiveUS20100297560A1High sensitivitySuppress thickness lossPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCompound aSolubility
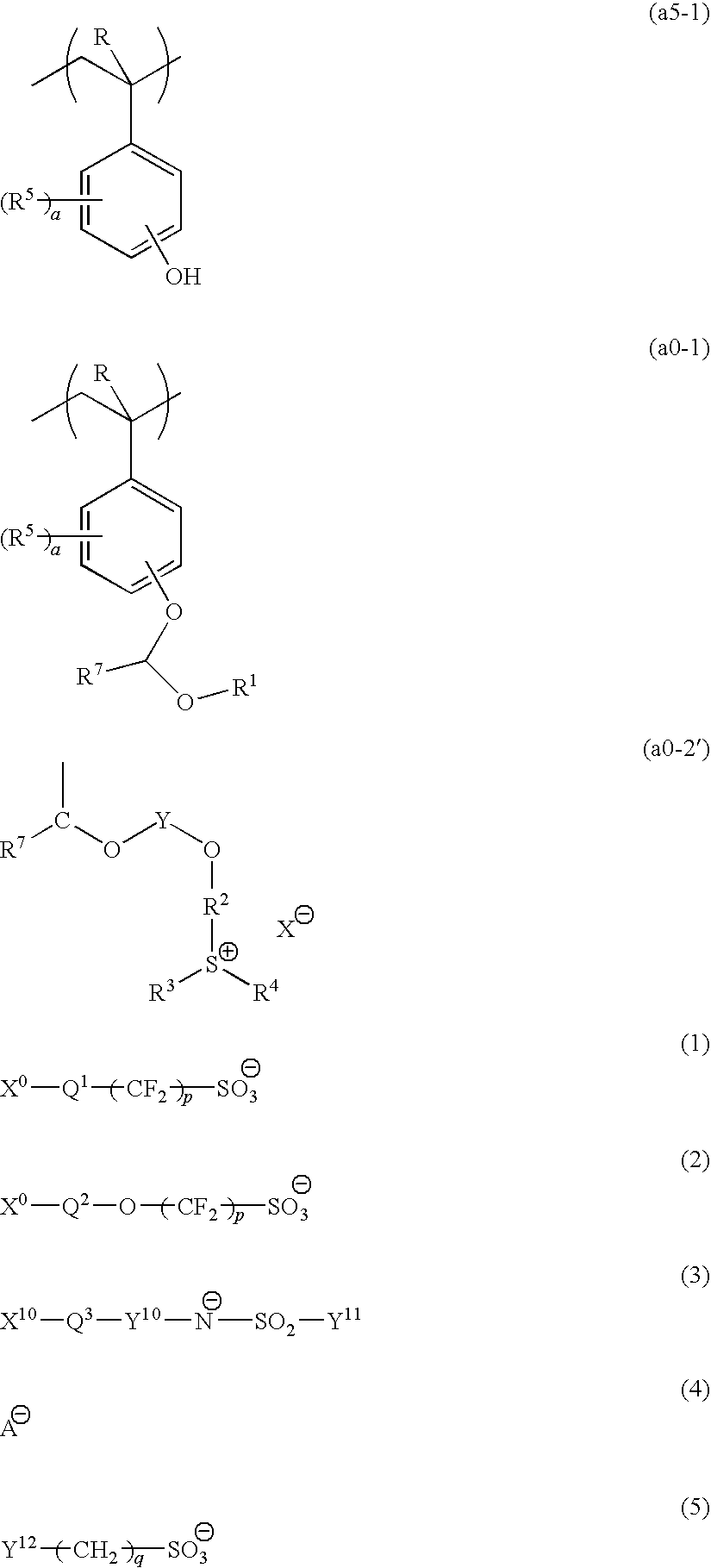
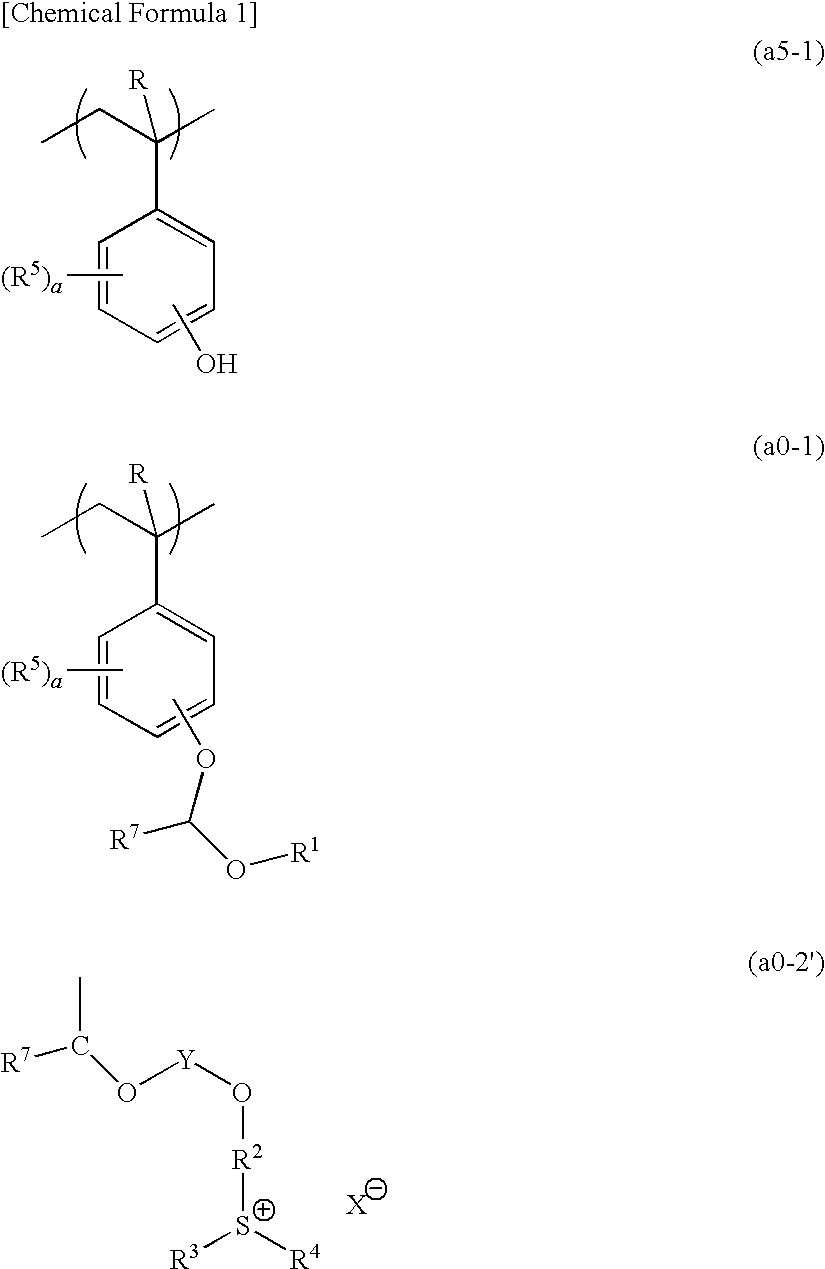
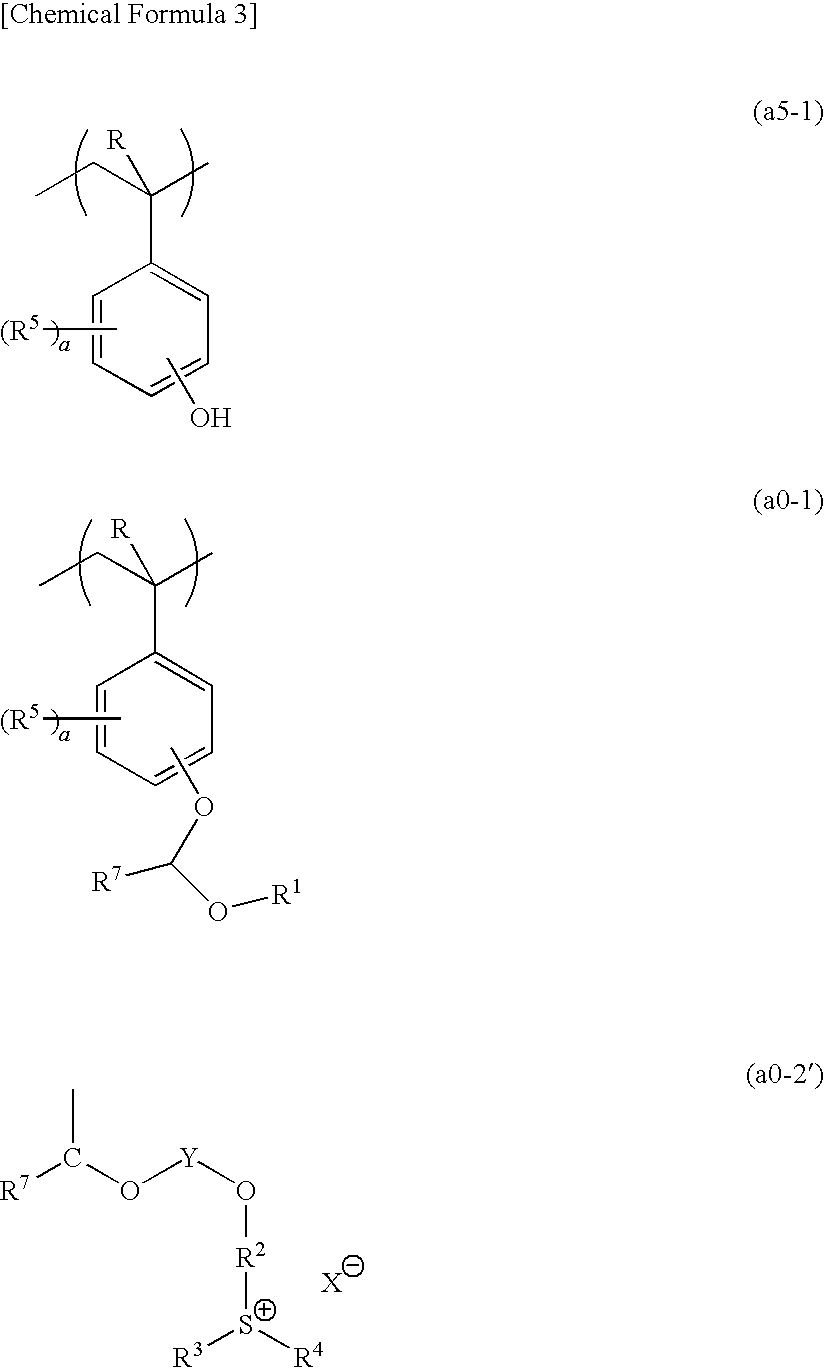
A positive resist composition including a base component (A′) which exhibits increased solubility in an alkali developing solution under action of acid and generates acid upon exposure, the base component (A′) including a polymeric compound (A1′) having a structural unit (a5-1) represented by general formula (a5-1), a structural unit (a0-1) represented by general formula (a0-1) and a structural unit (a0-2) that generates acid upon exposure, the structural unit (a0-2) containing a group represented by general formula (a0-2′) (wherein represents an anion moiety represented by one of general formulas (1) to (5)).
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Membranes and methods useful for caustic applications
ActiveUS20070039885A1Lower the volumeIncrease volumeUltrafiltrationSolid sorbent liquid separationMembrane configurationChemistry
Owner:GE OSMONICS INC
Tablet ultrasound system
ActiveUS9877699B2Function increaseIncrease penetration depthSolid-state devicesTomographyUltrasonographySonification
Exemplary embodiments provide systems and methods for portable medical ultrasound imaging. Preferred embodiments utilize a tablet touchscreen display operative to control imaging and display operations without the need for using traditional keyboards or controls. Certain embodiments provide ultrasound imaging system in which the scan head includes a beamformer circuit that performs far field sub array beamforming or includes a sparse array selecting circuit that actuates selected elements. Exemplary embodiments also provide an ultrasound engine circuit board including one or more multi-chip modules, and a portable medical ultrasound imaging system including an ultrasound engine circuit board with one or more multi-chip modules. Exemplary embodiments also provide methods for using a hierarchical two-stage or three-stage beamforming system, three dimensional ultrasound images which can be generated in real-time.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
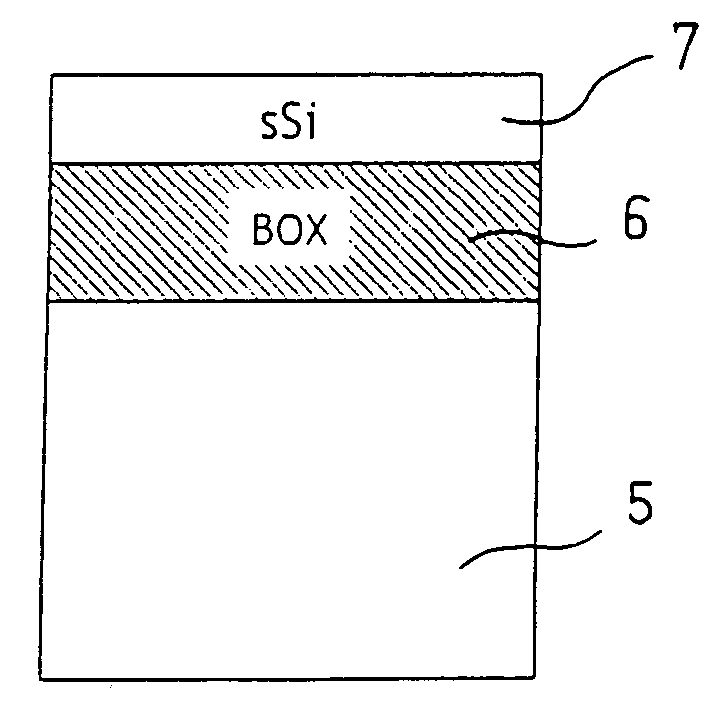
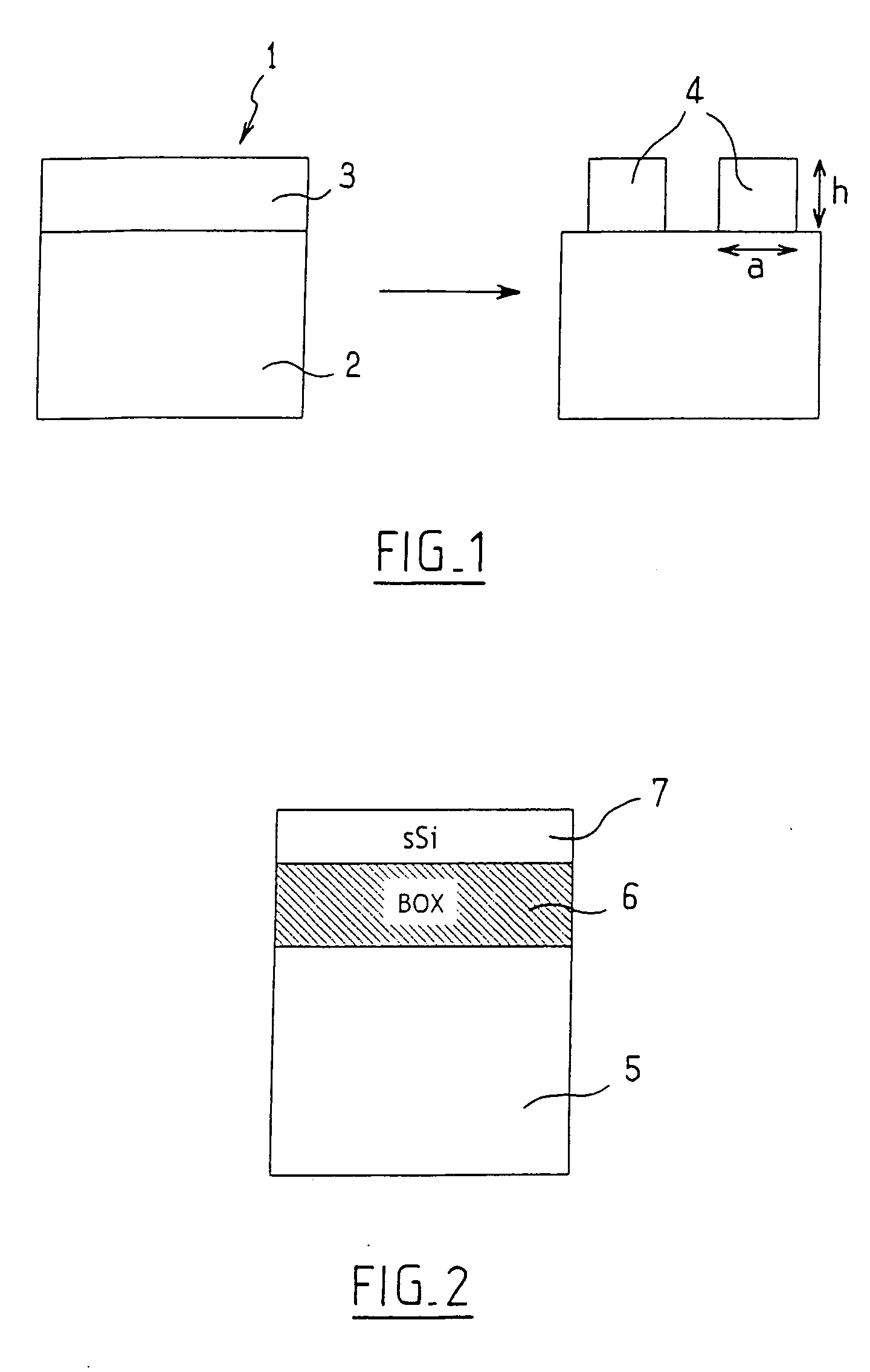
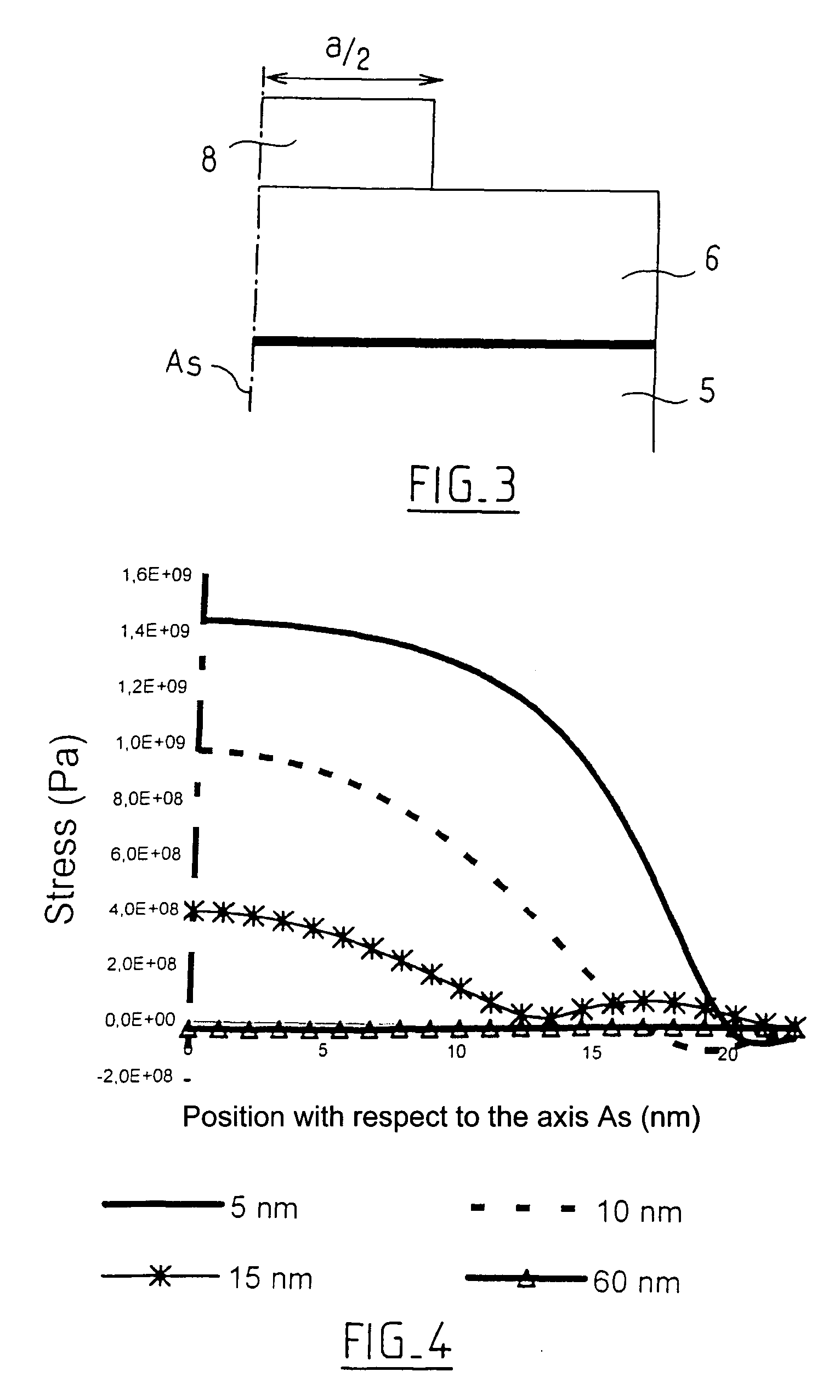
Process for holding strain in an island etched in a strained thin layer and structure obtained by implementation of this process
InactiveUS20060284252A1Relax restrictionsComponent usedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsThin layer
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Process to produce polyolefins using metallocene catalysts
ActiveUS8071835B2Reduce molecular weightComponent usedOther chemical processesHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionPolyolefinSorbent
The invention is directed to a process for producing polyolefins by one or more homogeneous or colloidal polymerization catalyst wherein residual catalyst is removed by using a solid sorbent.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
EMC shield and housing for electronic components
InactiveUS6985366B2Good electrical contactPrecise positioningMagnetic/electric field screeningRack/frame constructionEngineeringElectronic component
An EMC shield is provided for electronic components on a printed circuit board, which has a housing which surrounds the electronic components at least on the sides not facing the printed circuit board and shields them against electromagnetic radiation, with the housing having a number of electrically conductive spring contacts which make electrically conductive contact with the printed circuit board, and the housing being pressed against the printed circuit board by means of at least one pressure contact-making device.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
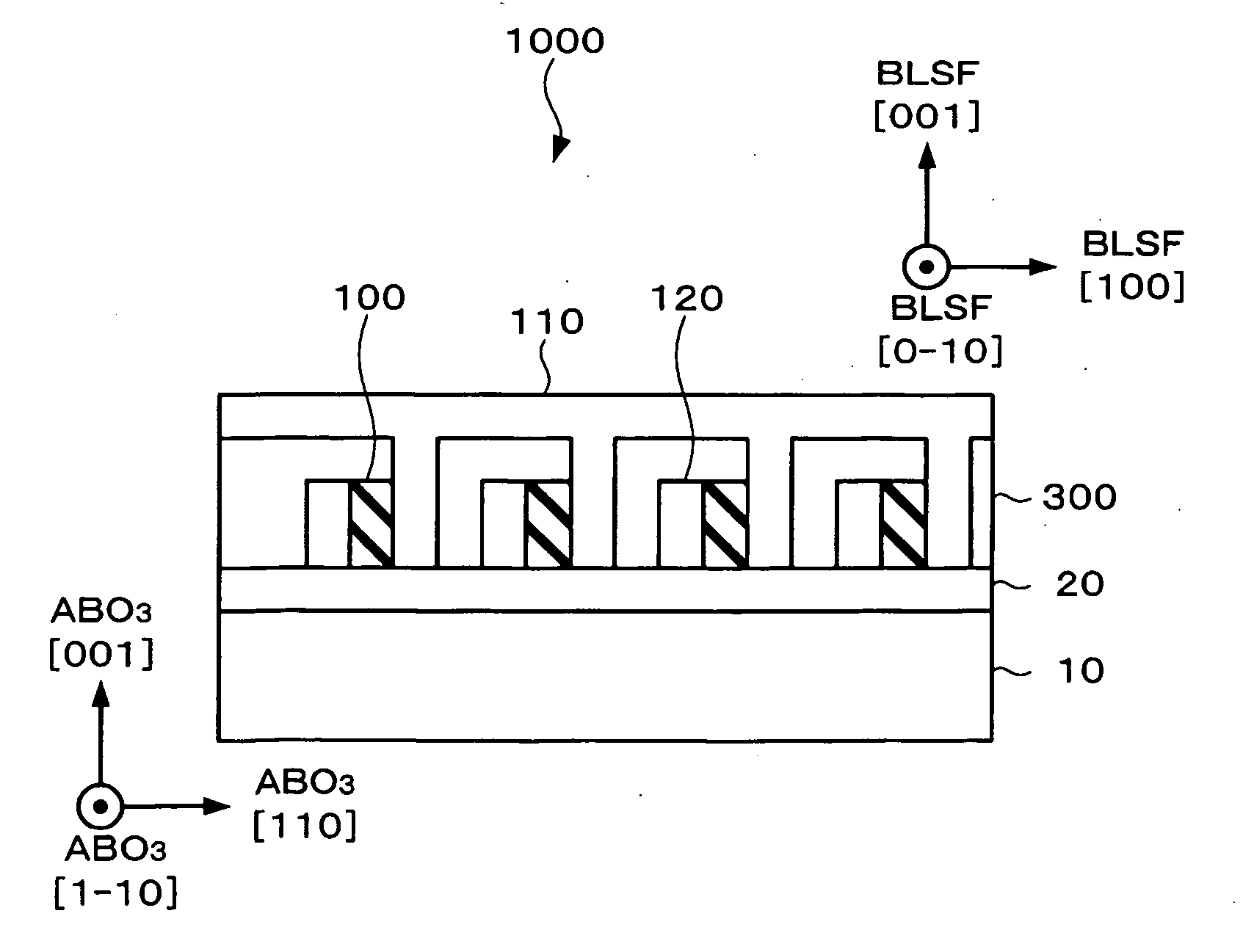
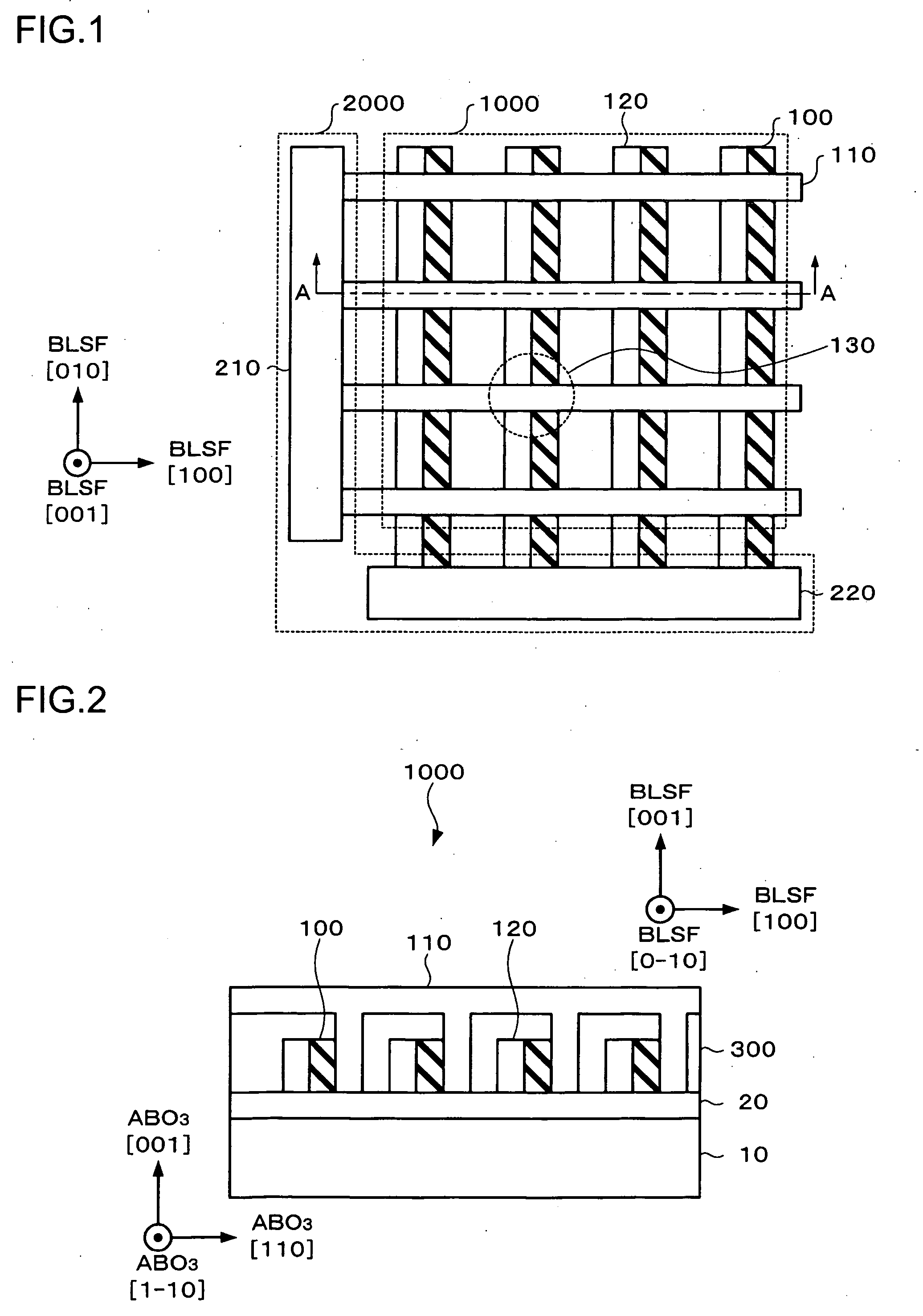
Ferroelectric memory
InactiveUS20050189571A1Broaden your optionsExcellent in angularitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsFerroelectric capacitor
A ferroelectric memory includes a memory cell array in which memory cells having a ferroelectric capacitor are arranged in a matrix shape. The memory cell array includes a ferroelectric layer formed out of a thin film made of a Bi layer-structured ferroelectric single crystal having a (001) orientation and which is patterned such that the ferroelectric layer has two or more side walls perpendicular to a (100) axis of the Bi layer-structured ferroelectrics, first electrodes contacting at least one of the side walls of the ferroelectric layer and which are formed in stripe patterns extending along the one side wall, and second electrodes which contact the other side wall of the ferroelectric layer not contacting the first electrodes and which are formed in stripe patterns to intersect the first electrodes. The memory cells are formed at intersections between the first electrodes and the second electrodes.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Polyamide matrices and methods for their preparation and use
ActiveUS20080277342A1Lower the volumeIncrease volumeSynthetic resin layered productsSolid sorbent liquid separationPolyamidePolymer
Owner:GE OSMONICS INC
Toner and image forming method
InactiveUS20040115553A1Small heat capacityComponent usedDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusWater basedSalting out
A toner includes a resin and a colorant; wherein the toner is obtained by carrying out a step of salting-out / fusing resin particles and colorant particles in a water-base medium, the toner satisfying the following relationship: 0.88<=F25 / F50<=1.0, where F25 represents an adhesive stress at a toner temperature of 25° C., and F50 represents an adhesive stress at a toner temperature of 50° C.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC +1
Microcrystalline cellulose and calcium carbonate compositions useful as recompactible pharmaceutical excipients
ActiveUS8632819B2Reduce the amount requiredLower the volumeBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsParticulatesSlurry
Coprocessed compositions containing microcrystalline cellulose and calcium carbonate, wherein the weight ratio of microcrystalline cellulose to calcium carbonate is relatively high, are useful as excipients in the preparation of solid dosage forms containing active pharmaceutical ingredients, particularly those prepared by processes involving multiple compaction steps. Such compositions may be obtained, for example, by preparing aqueous slurries or wet masses of microcrystalline cellulose and calcium carbonate and drying such slurries or wet masses to produce particulate products. The coprocessed products exhibit improved recompactibility, as compared to coprocessed products having lower microcrystalline cellulose:calcium carbonate weight ratios or as compared to physical dry blends of the two excipients.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION USA INC
Polyamide matrices and methods for their preparation and use
ActiveUS8092918B2Lower the volumeIncrease volumeSemi-permeable membranesSynthetic resin layered productsPolyamidePolymer
Owner:GE OSMONICS INC
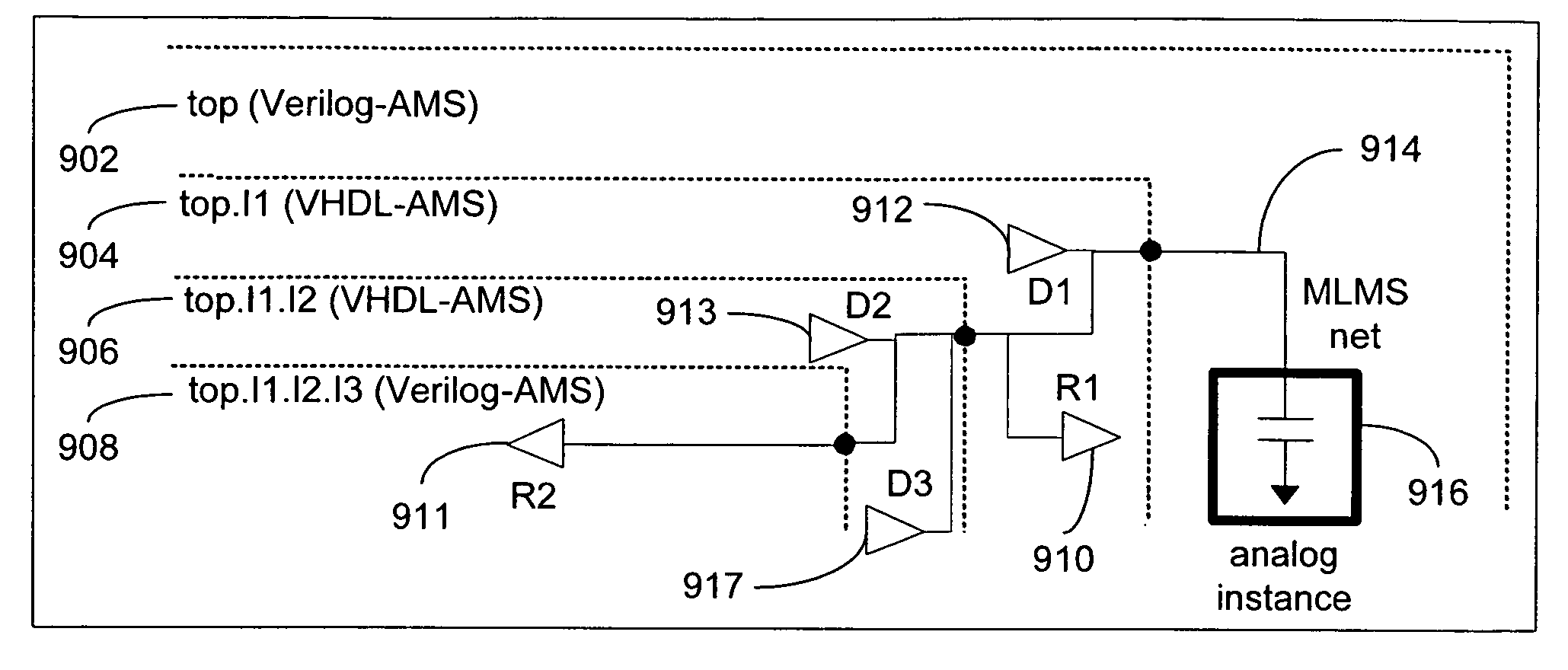
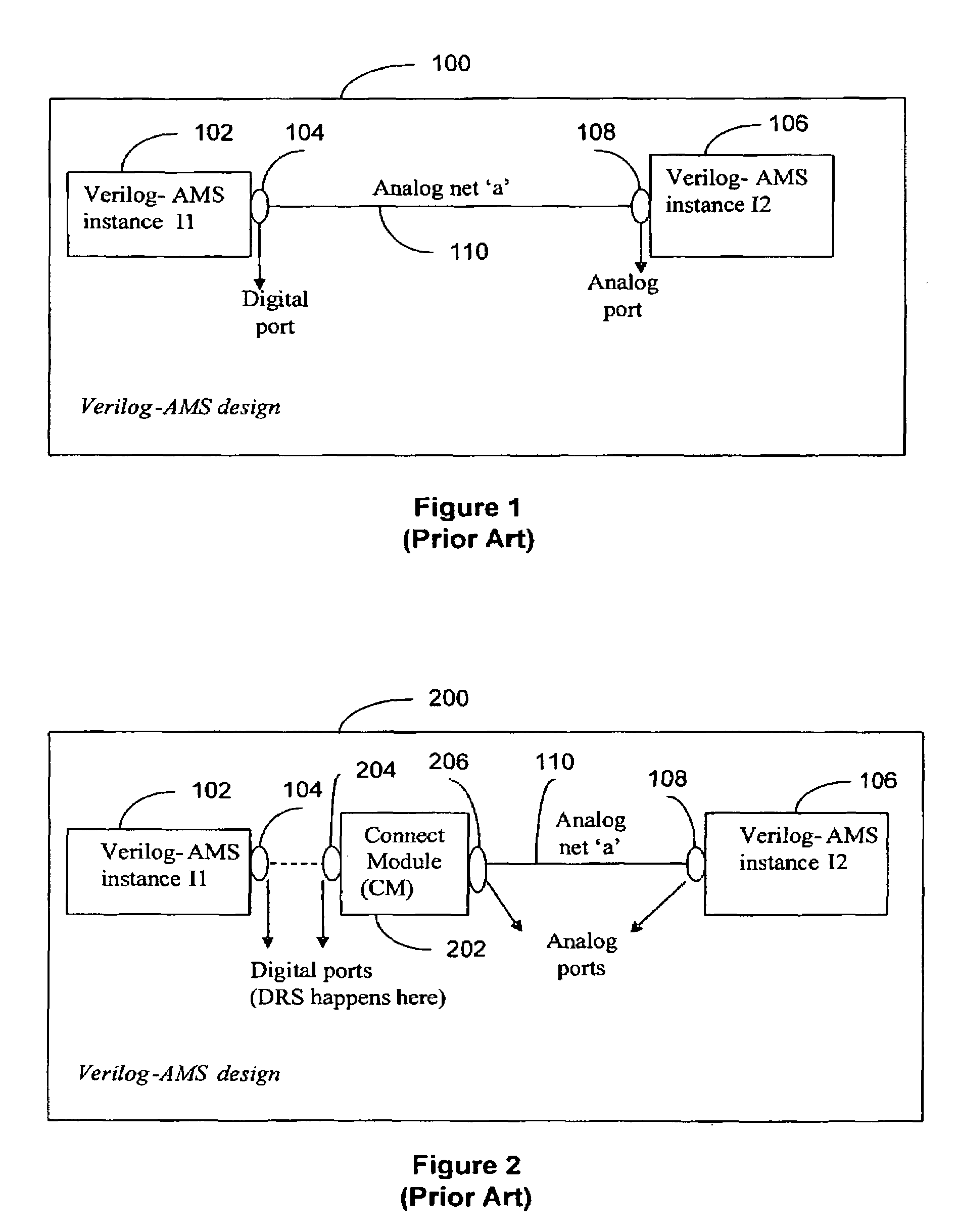
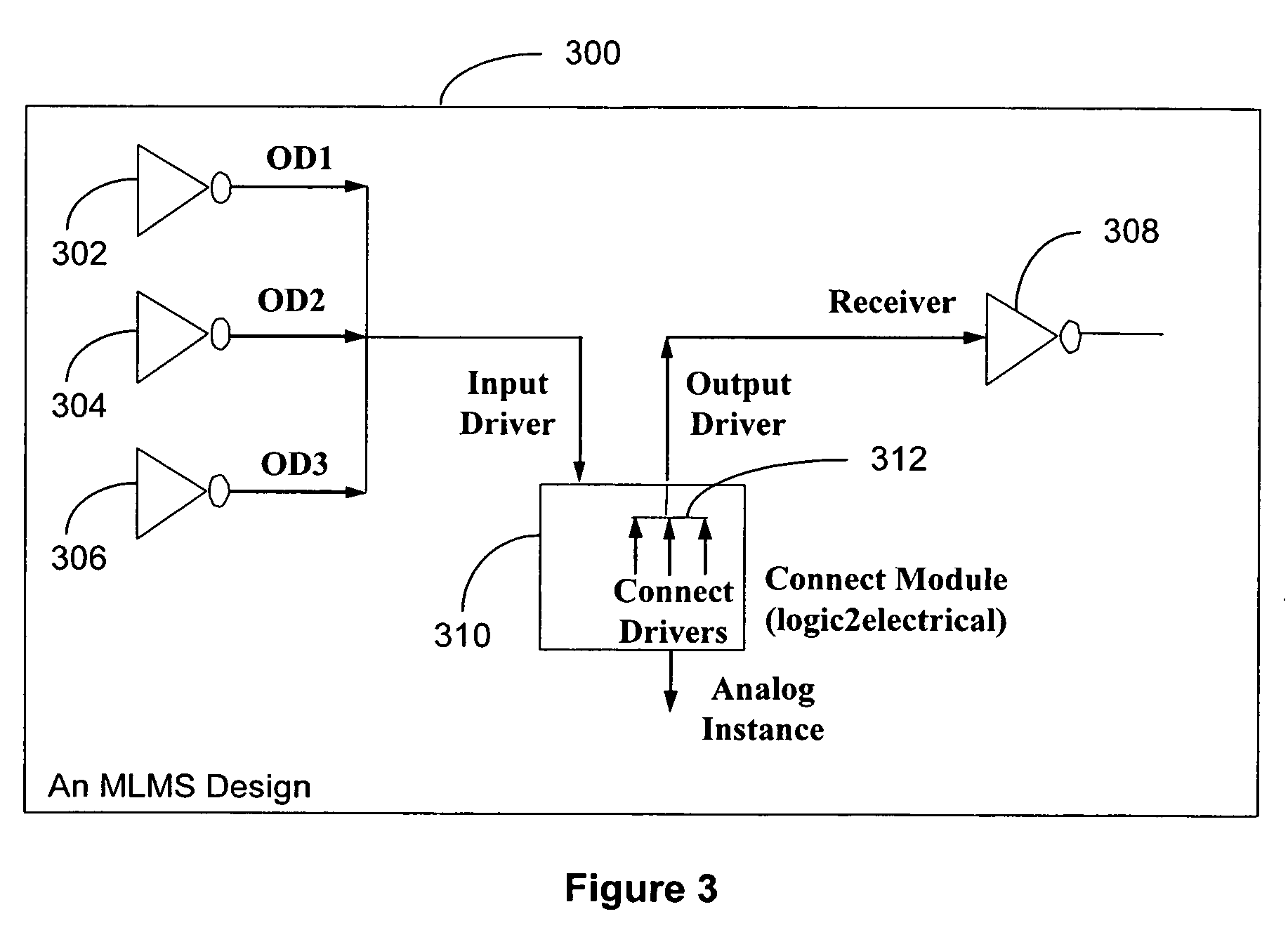
Modeling a mixed-language mixed-signal design
InactiveUS7260792B2Component usedDetecting faulty computer hardwareCAD circuit designSoftware engineeringSignal design
A method for modeling a mixed-language and mixed-signal (MLMS) design is disclosed. The method includes receiving an MLMS design comprising at least a digital driver, a digital receiver, and an analog block connected by an MLMS net in a hierarchical structure and identifying analog-digital boundaries of the MLMS design. For each analog-digital boundary, the method further includes a) selecting a connect module (CM) by using a predetermined discipline resolution procedure; b) determining input driving values of the CM; and c) connecting the digital driver, the digital receiver, and the analog block to the CM. The method repeats steps a), b), and c) on all analog-digital boundaries of the MLMS design.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Microcrystalline cellulose and calcium carbonate compositions useful as recompactible pharmaceutical excipients
ActiveUS20110151014A1Easy to ejectComponent usedPowder deliveryBiocideParticulatesAdditive ingredient
Coprocessed compositions containing microcrystalline cellulose and calcium carbonate, wherein the weight ratio of microcrystalline cellulose to calcium carbonate is relatively high, are useful as excipients in the preparation of solid dosage forms containing active pharmaceutical ingredients, particularly those prepared by processes involving multiple compaction steps. Such compositions may be obtained, for example, by preparing aqueous slurries or wet masses of microcrystalline cellulose and calcium carbonate and drying such slurries or wet masses to produce particulate products. The coprocessed products exhibit improved recompactibility, as compared to coprocessed products having lower microcrystalline cellulose:calcium carbonate weight ratios or as compared to physical dry blends of the two excipients.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com