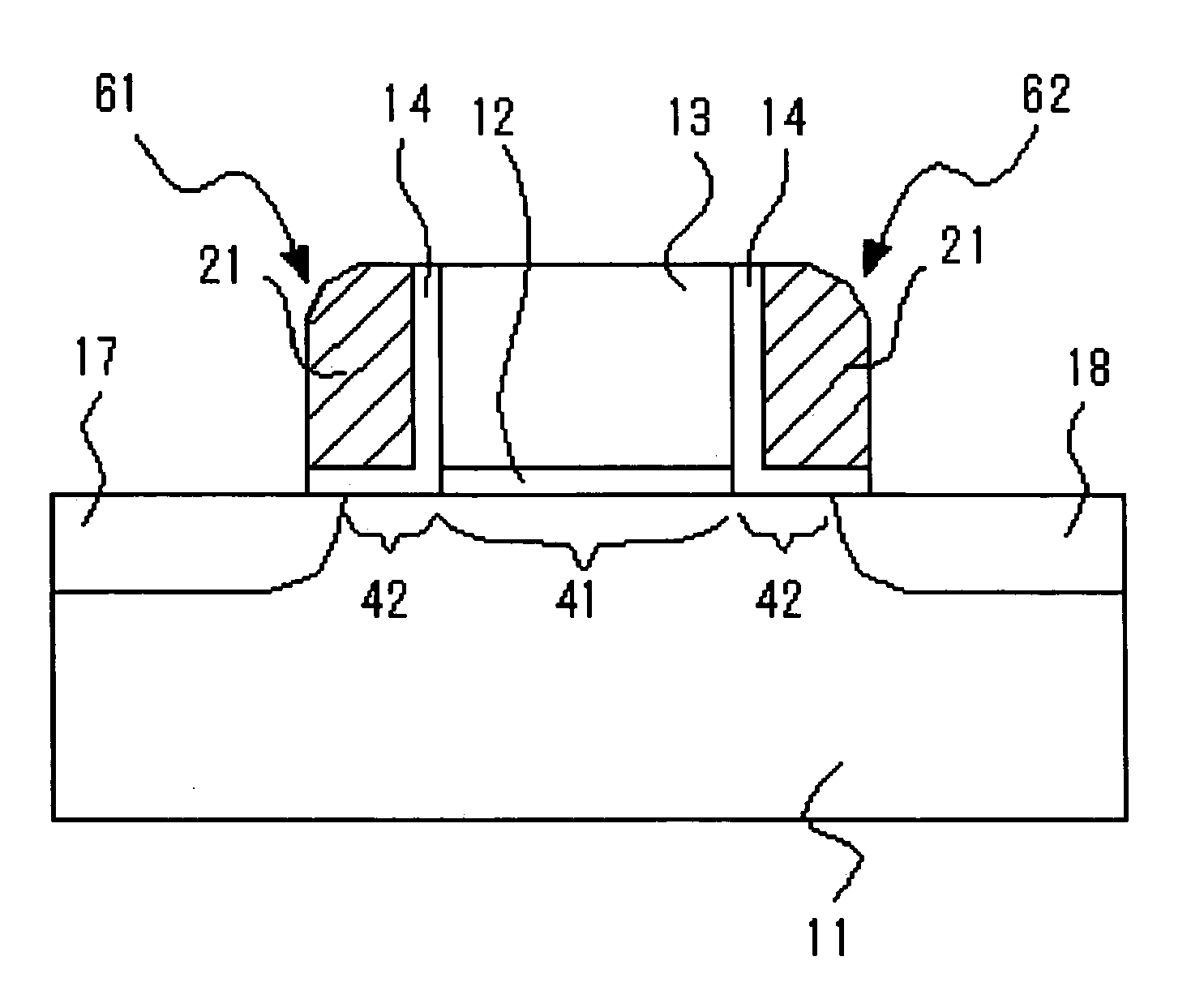
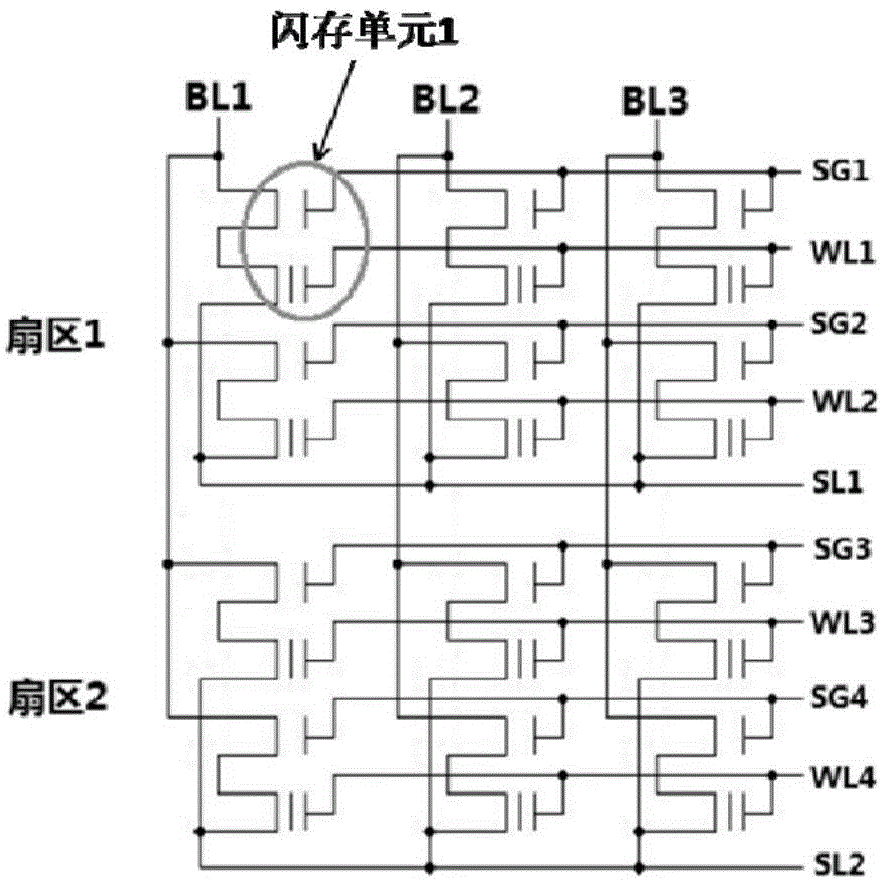
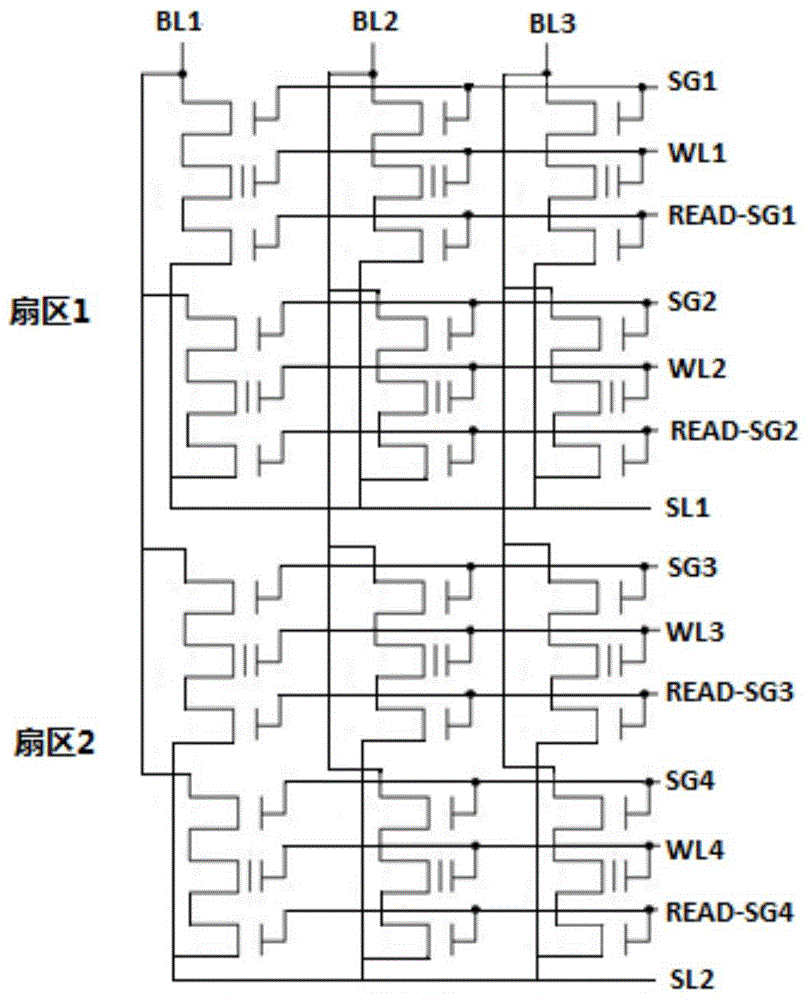
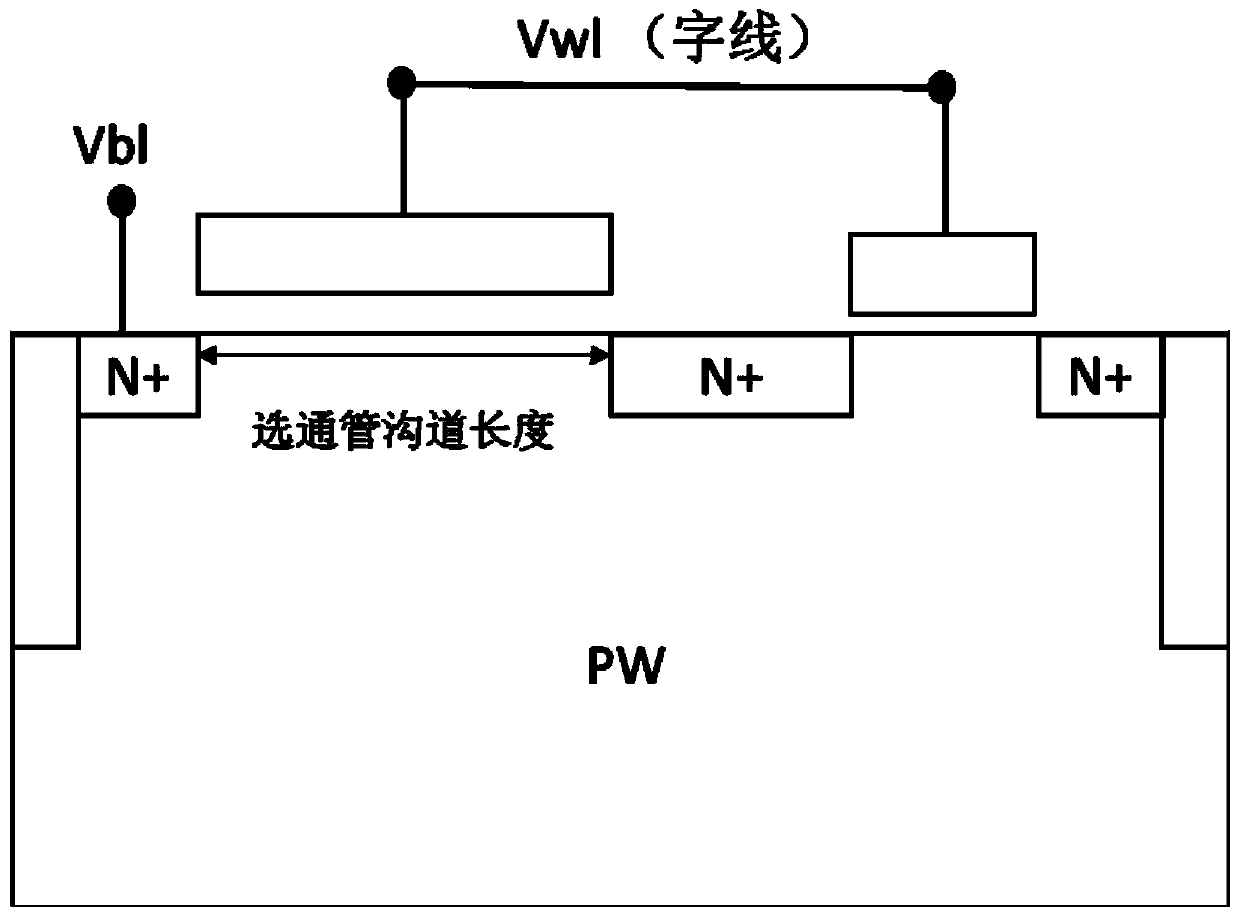
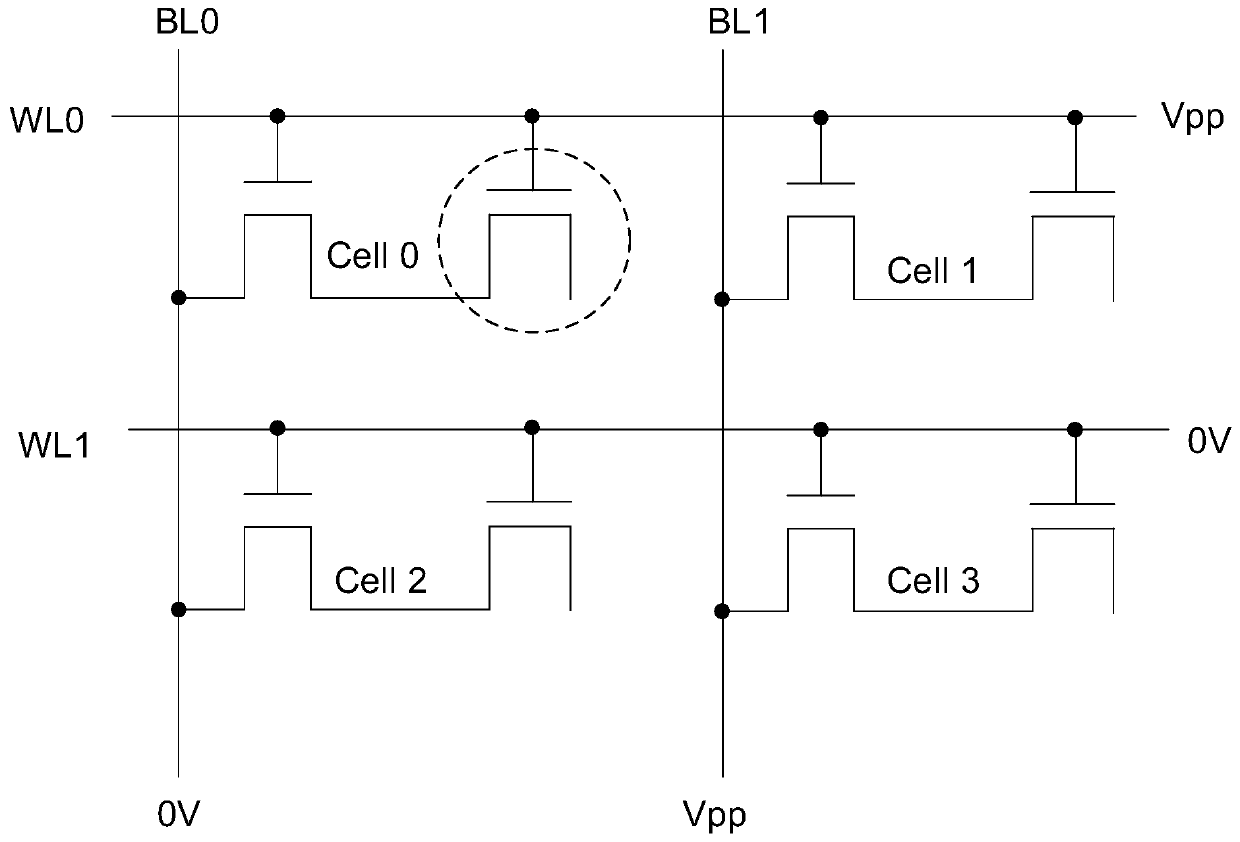
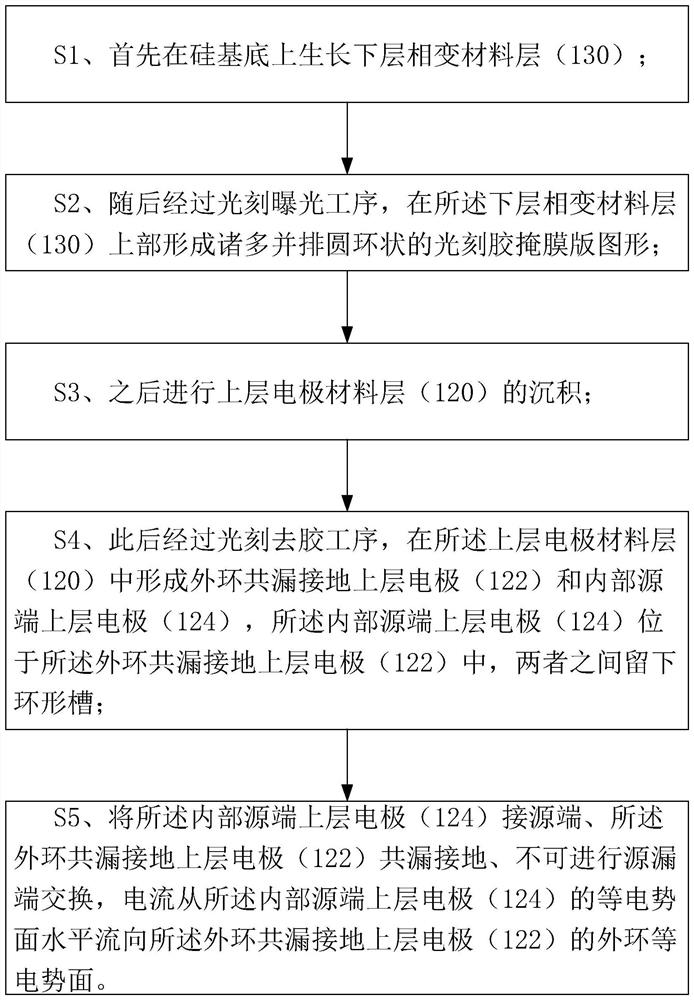
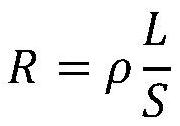Patents
Literature
75results about How to "Increase read current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
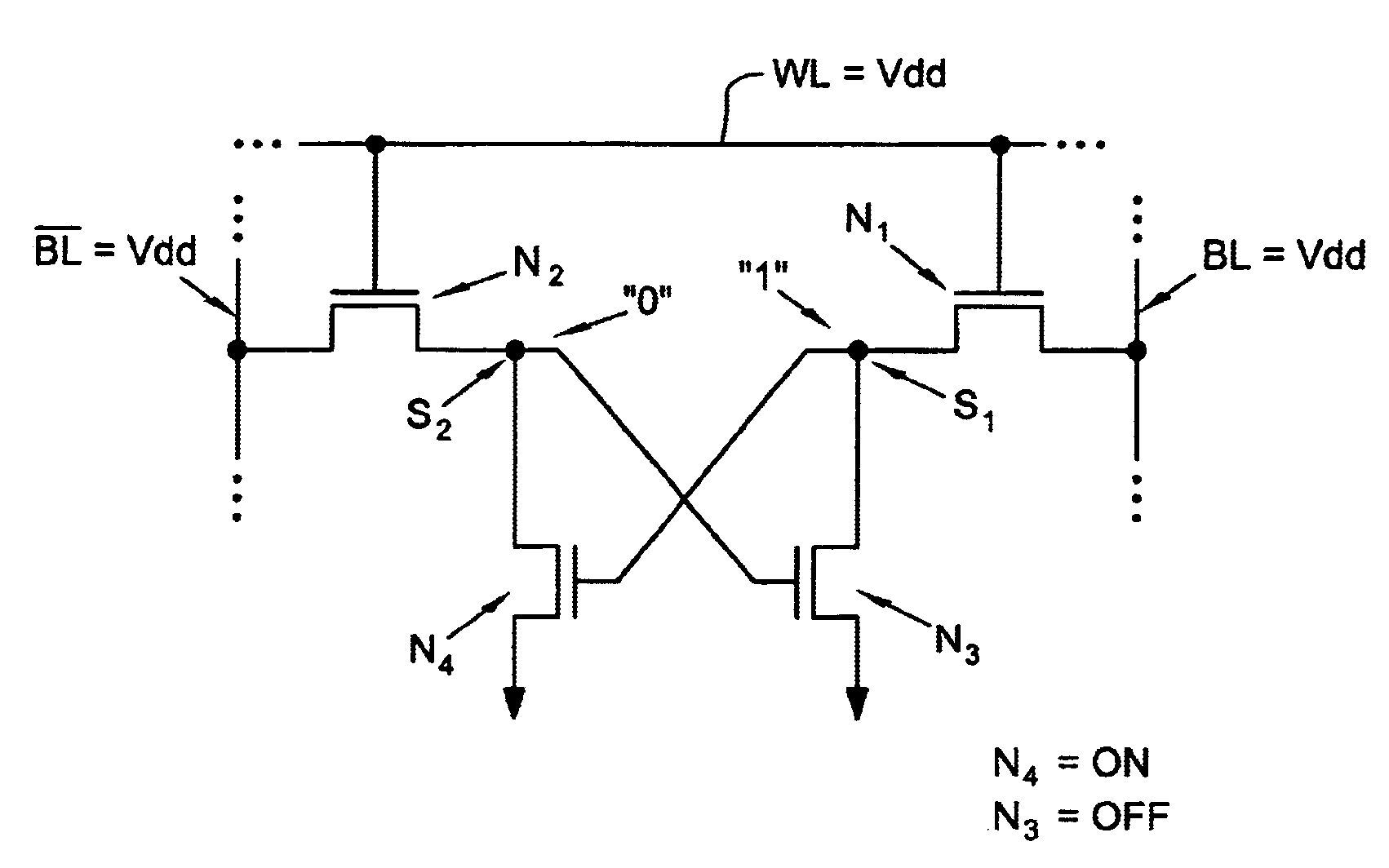
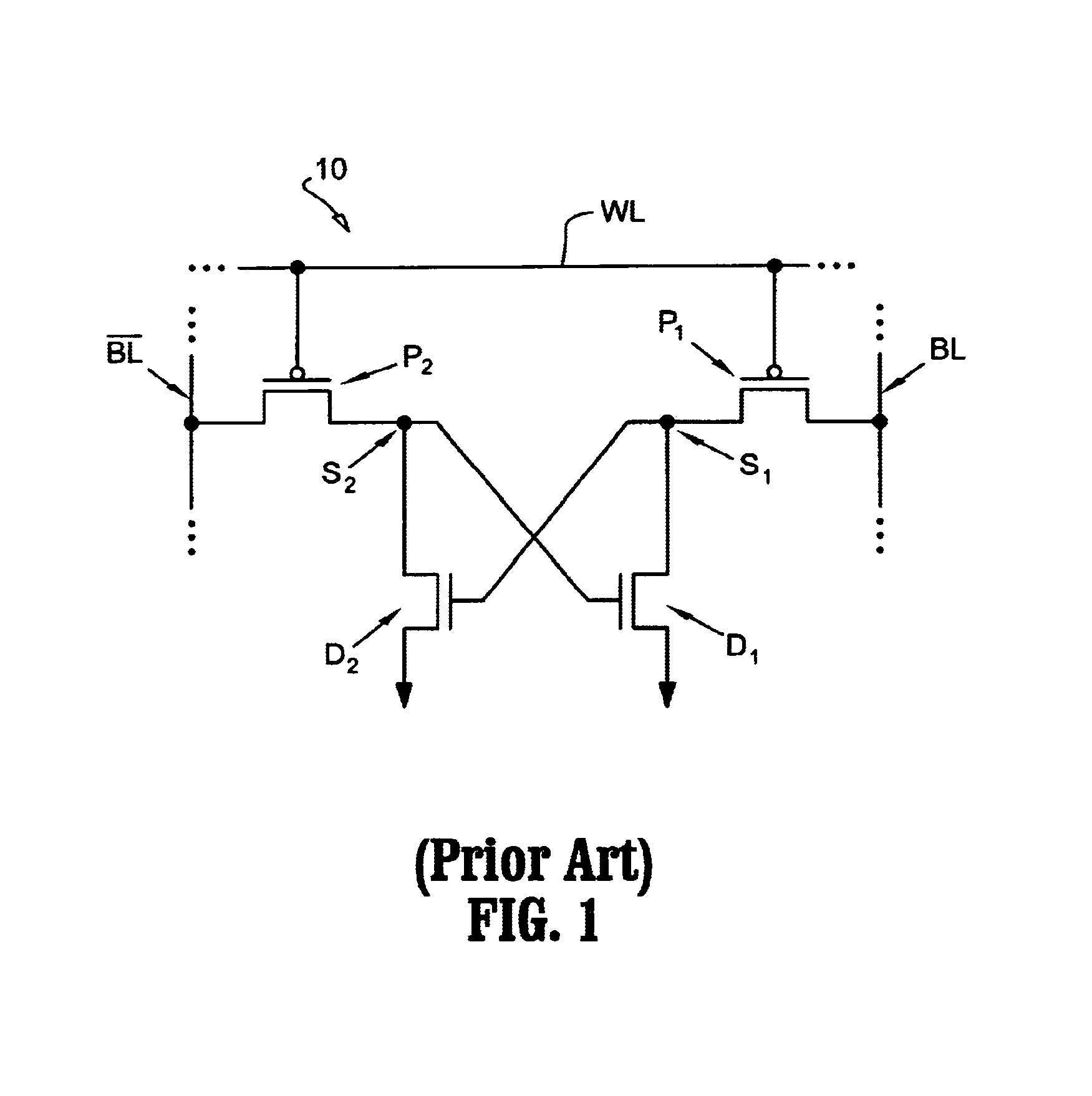
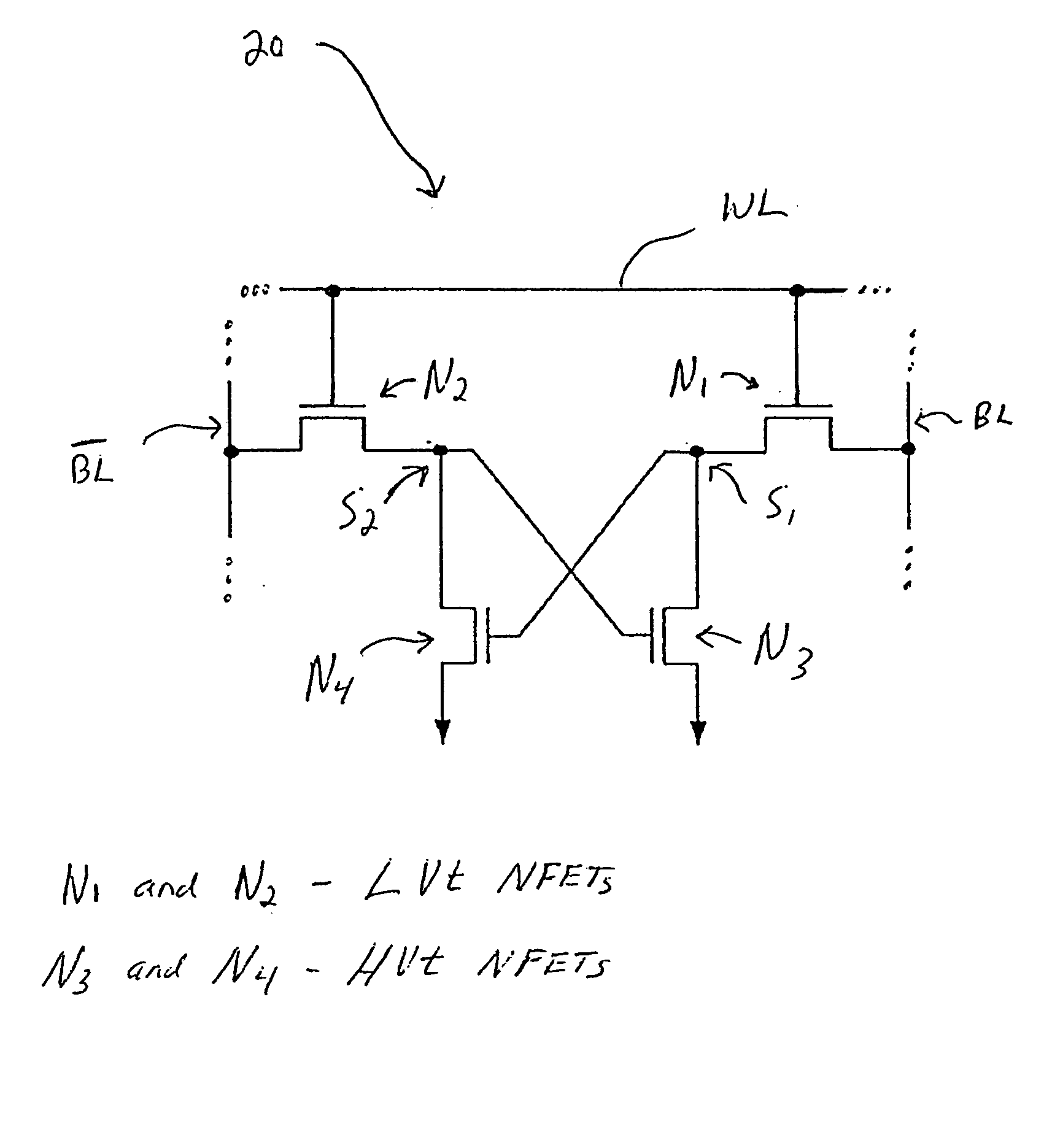
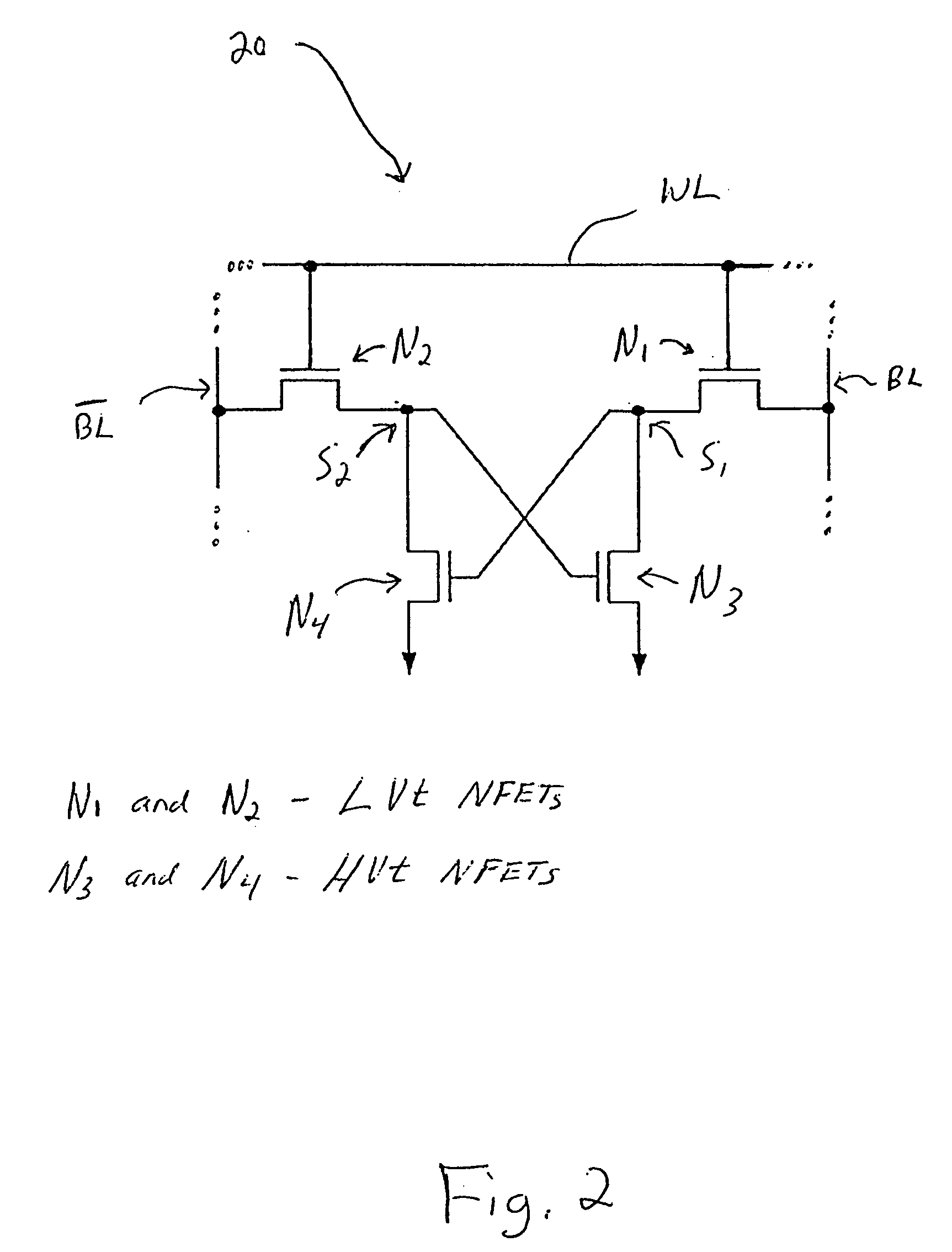
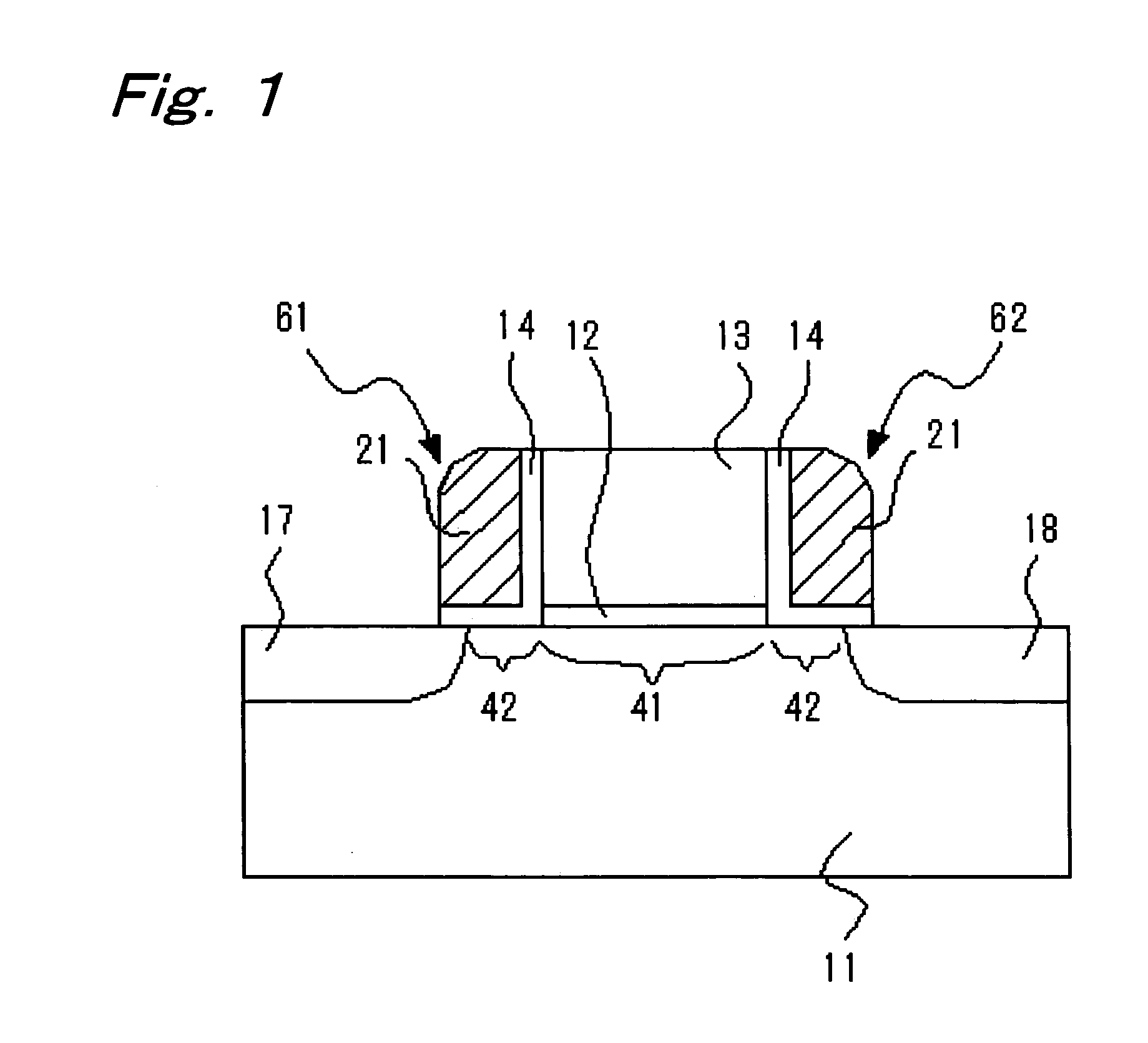
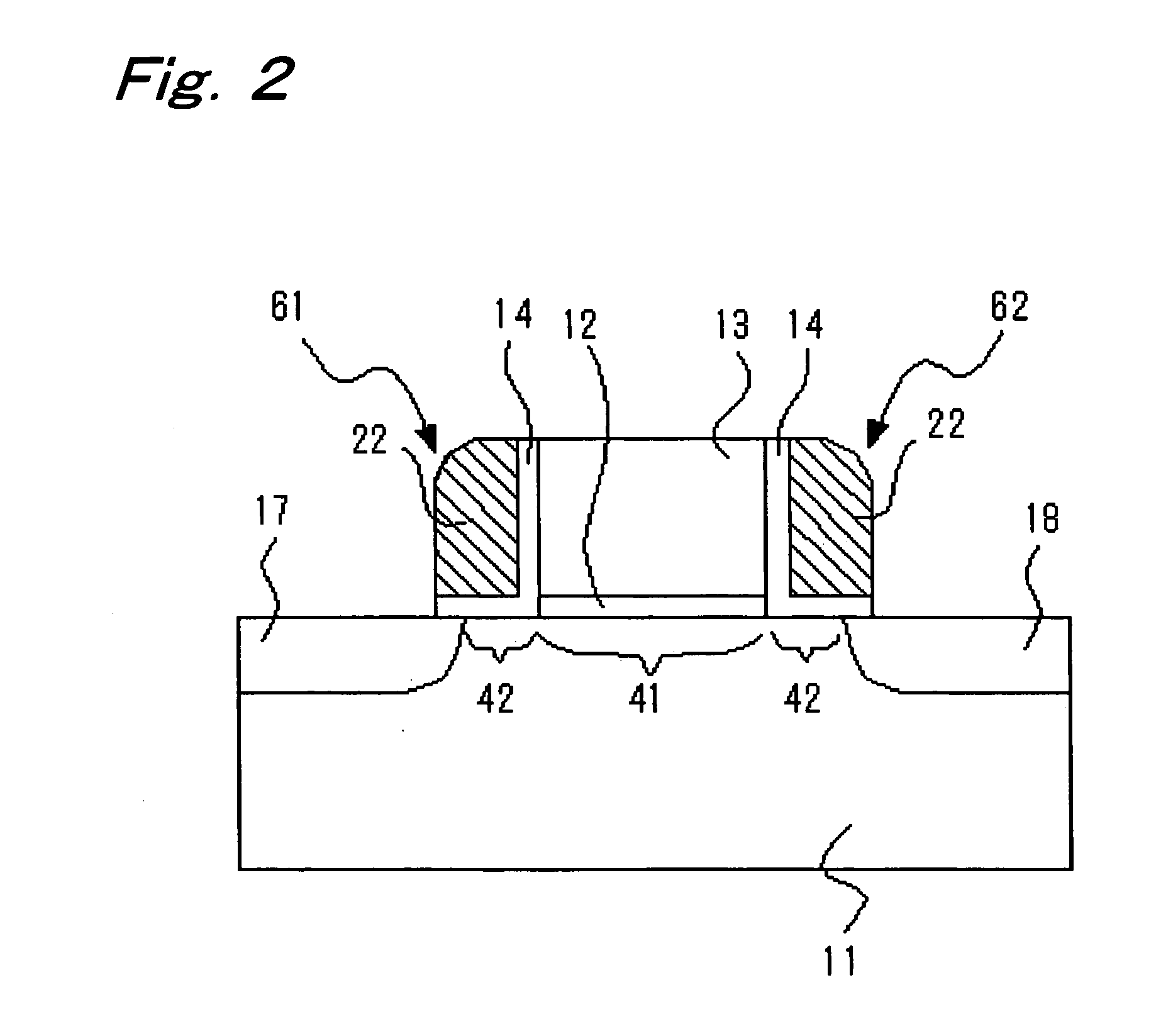
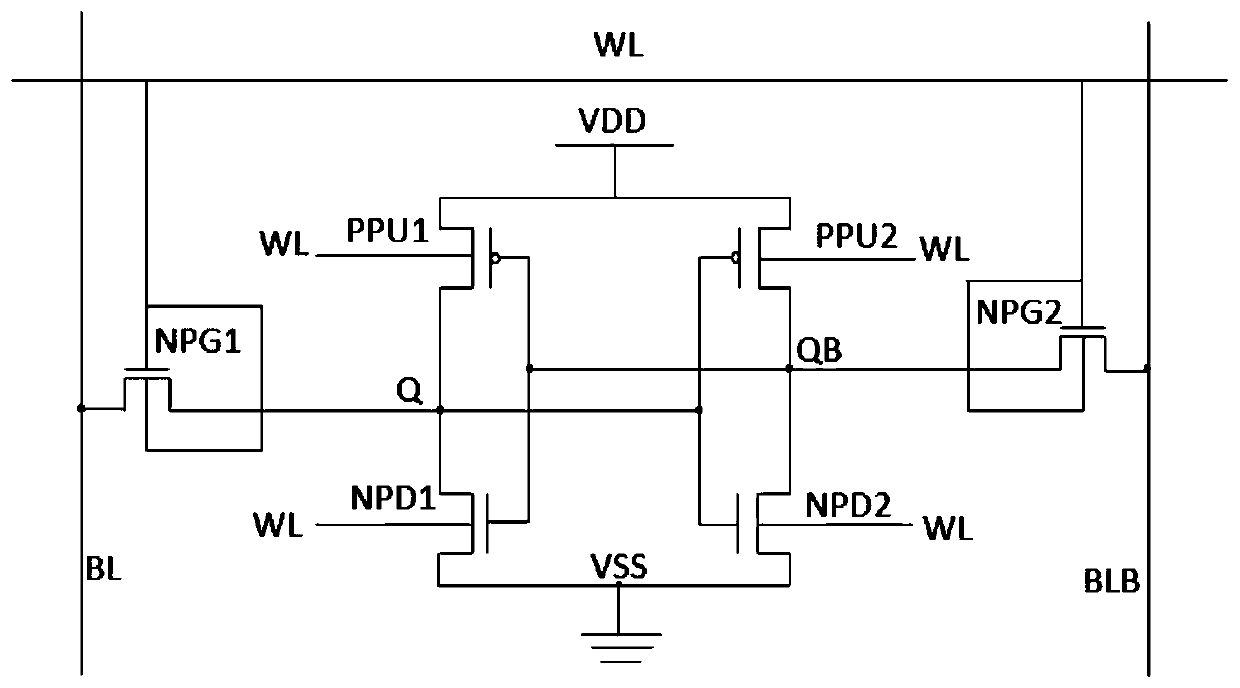
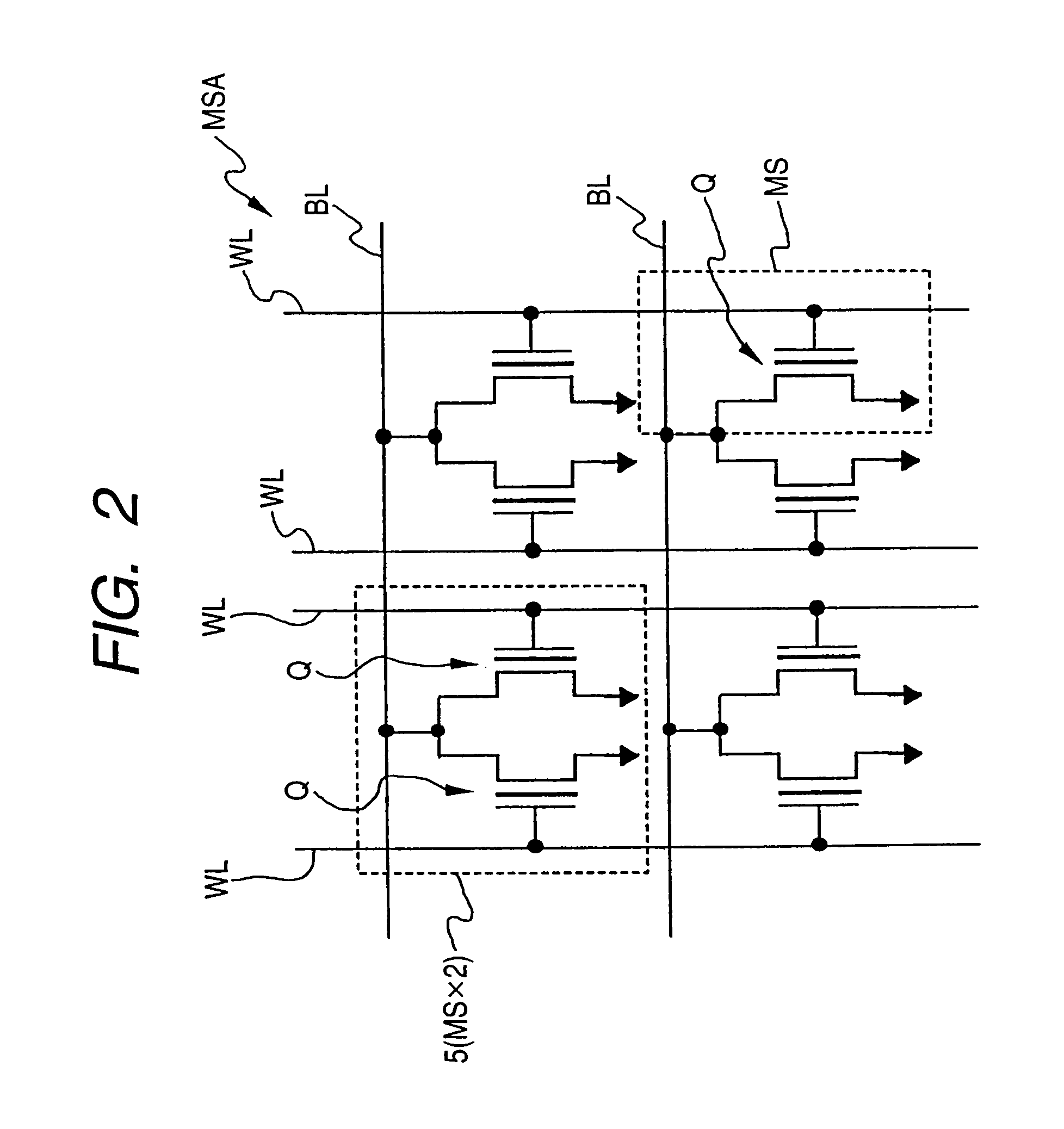
Loadless NMOS four transistor dynamic dual Vt SRAM cell
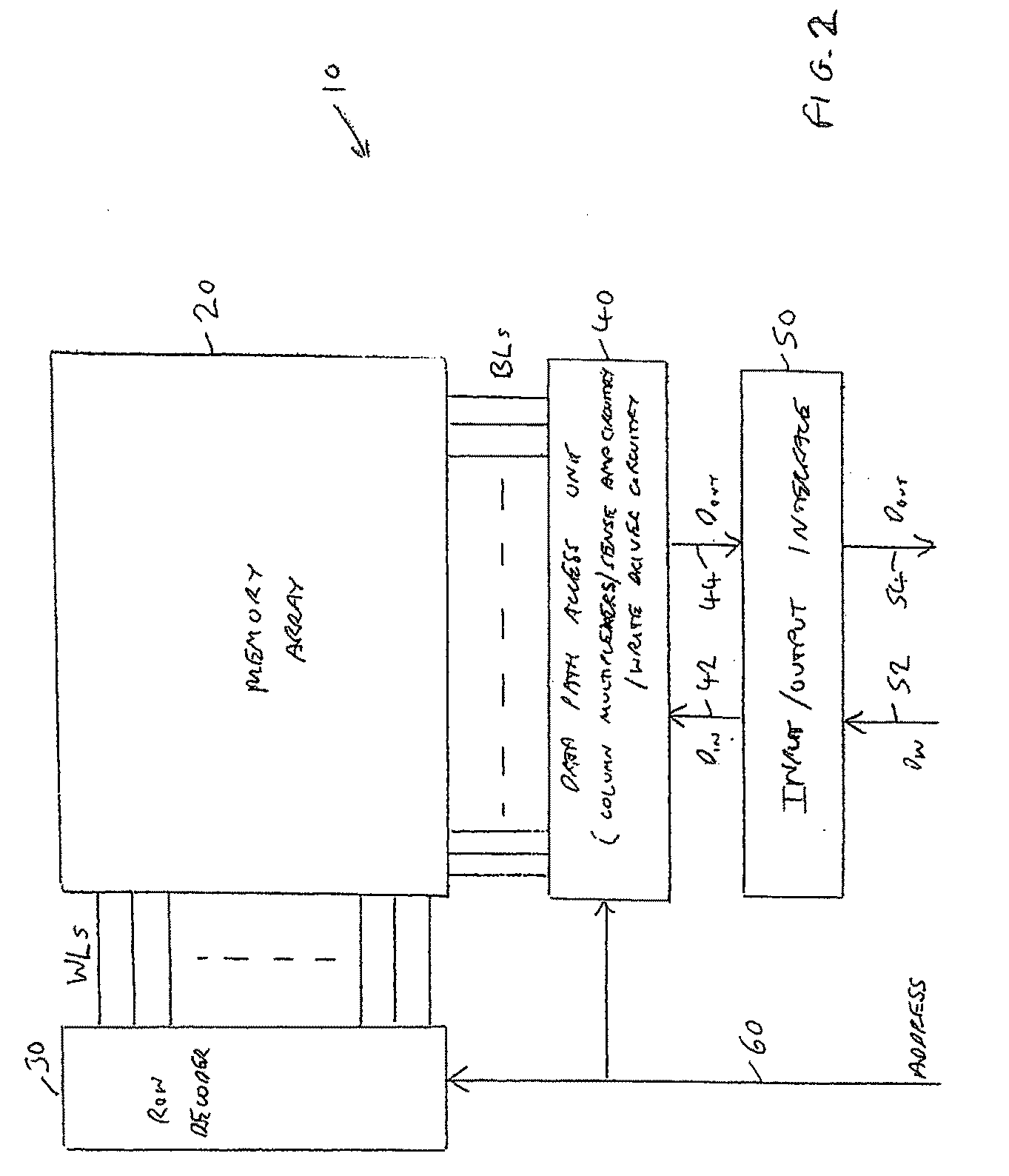
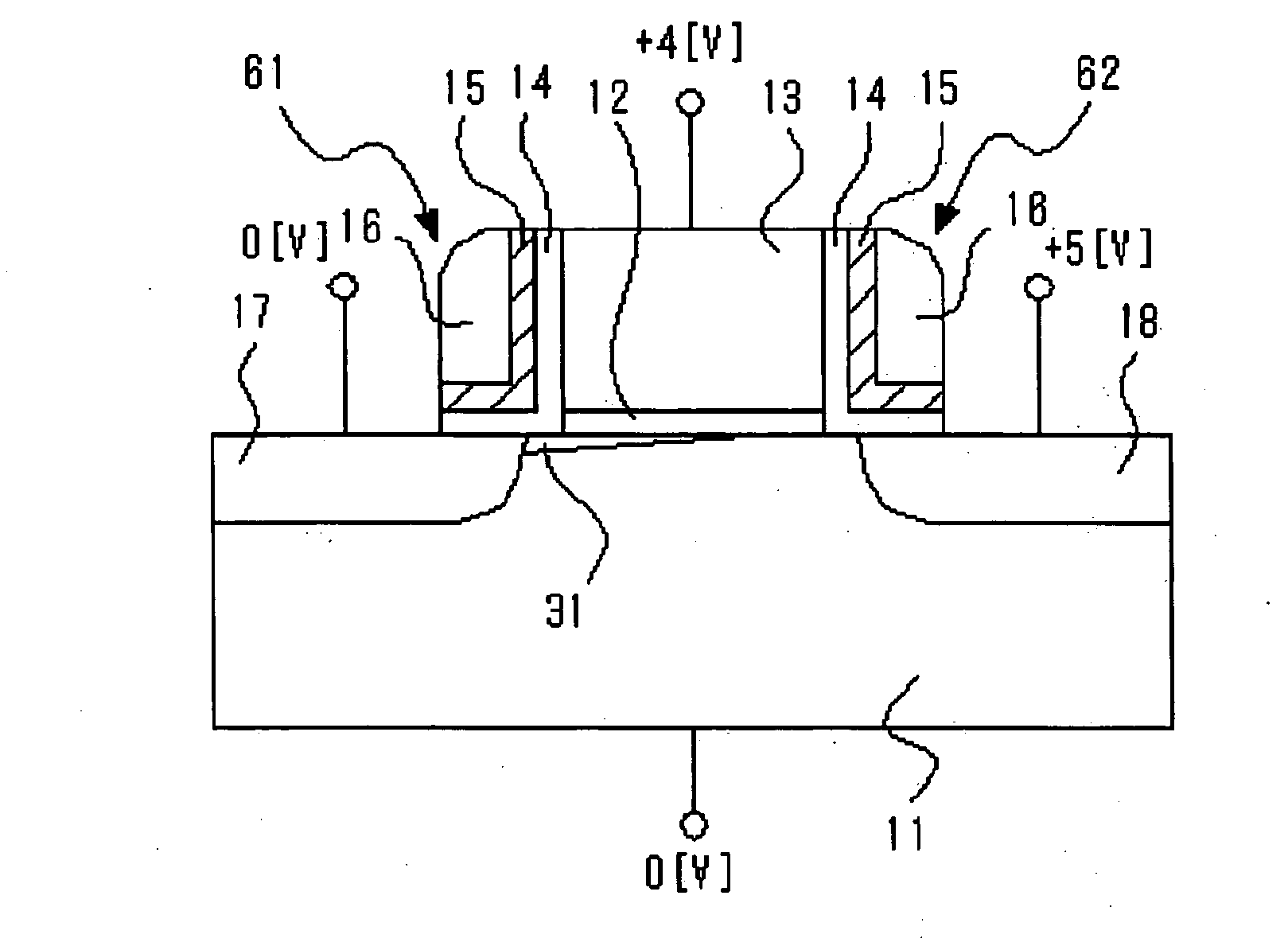
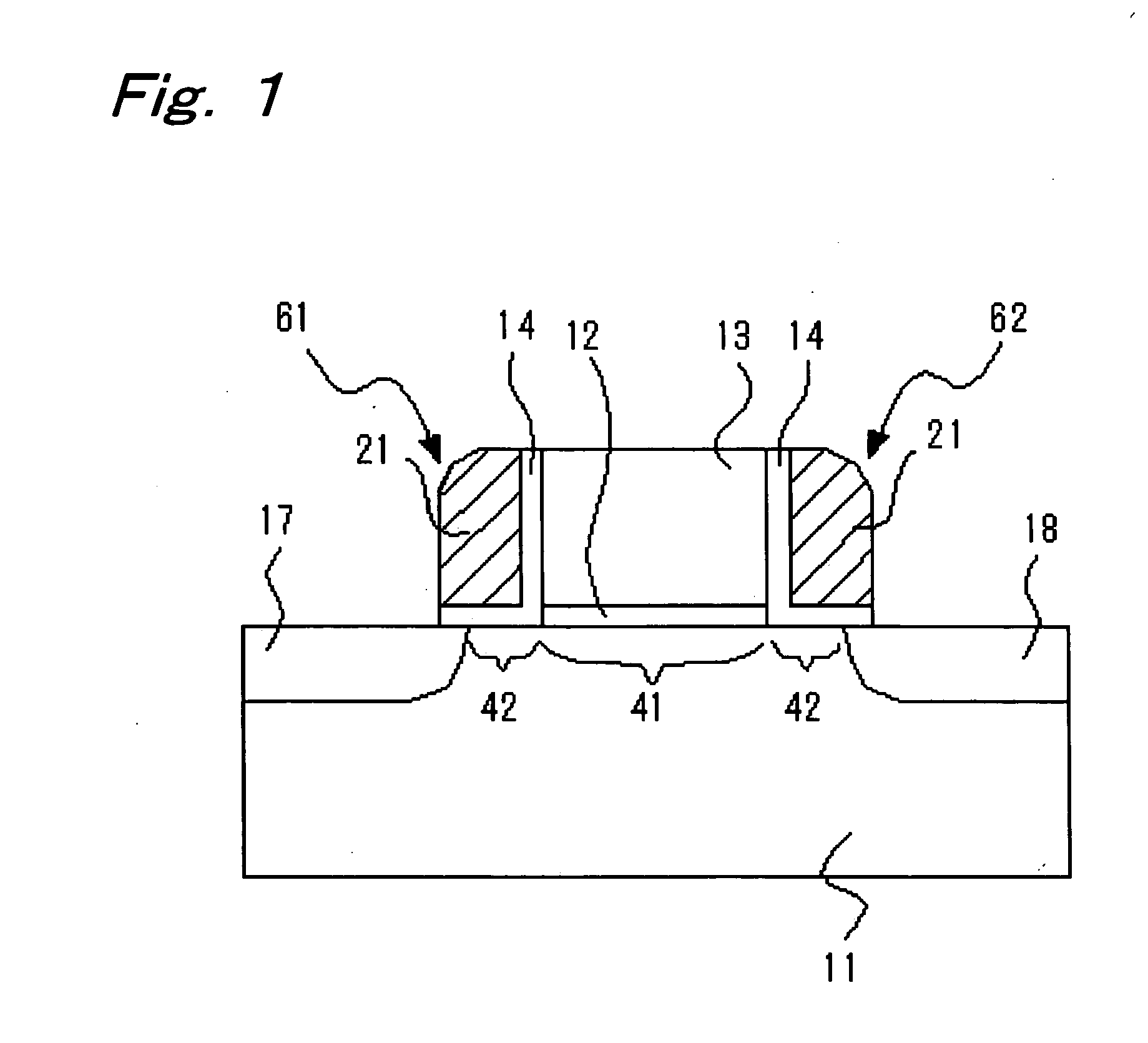
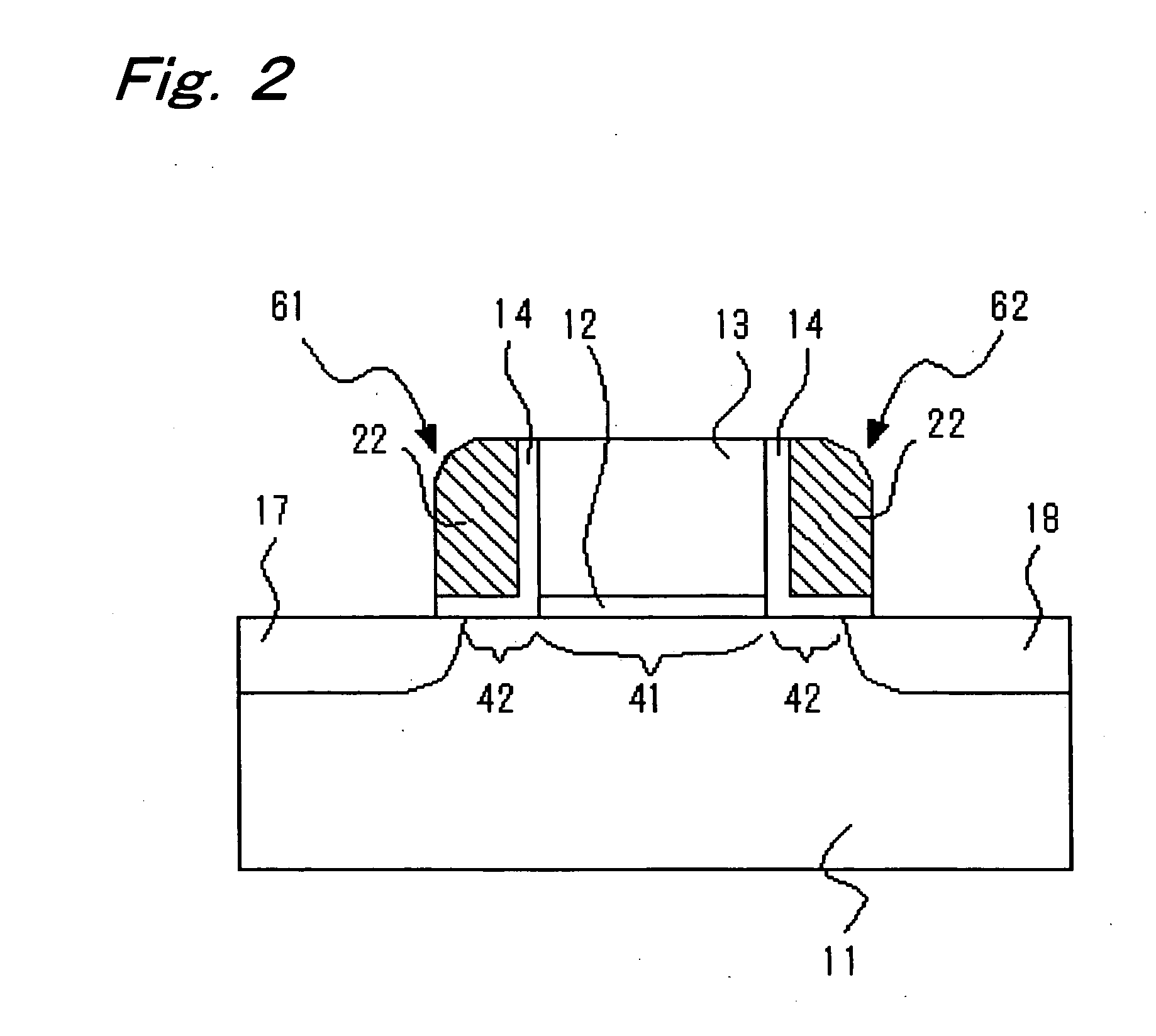
ActiveUS6920061B2Improve performanceHighly integrated semiconductor memorySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesData accessEngineering
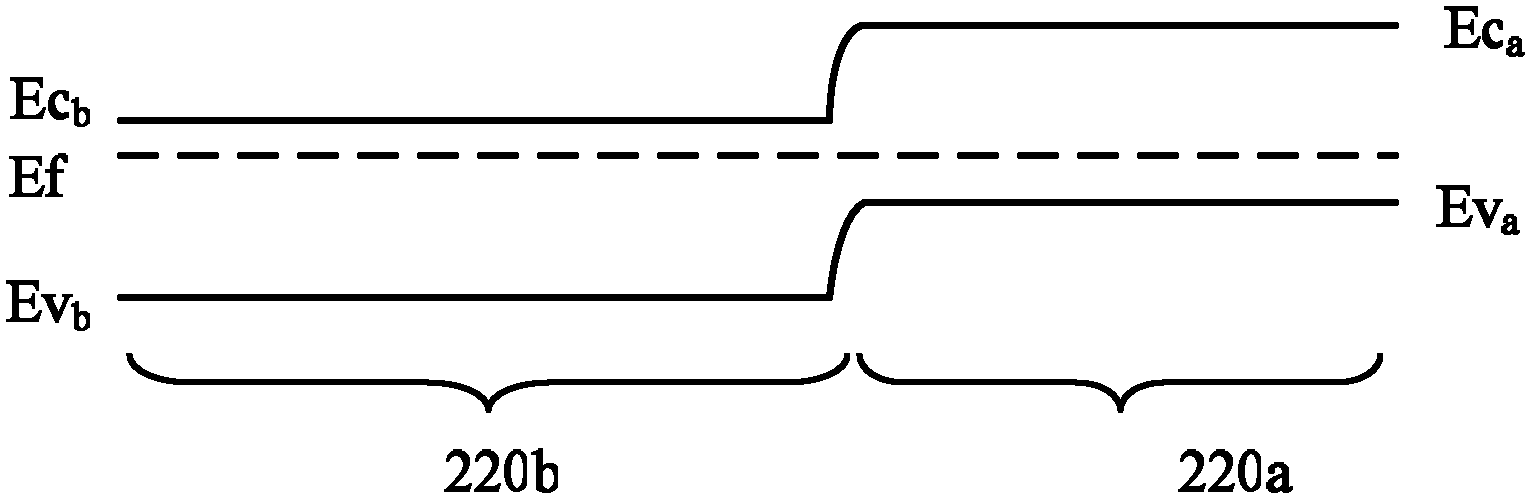
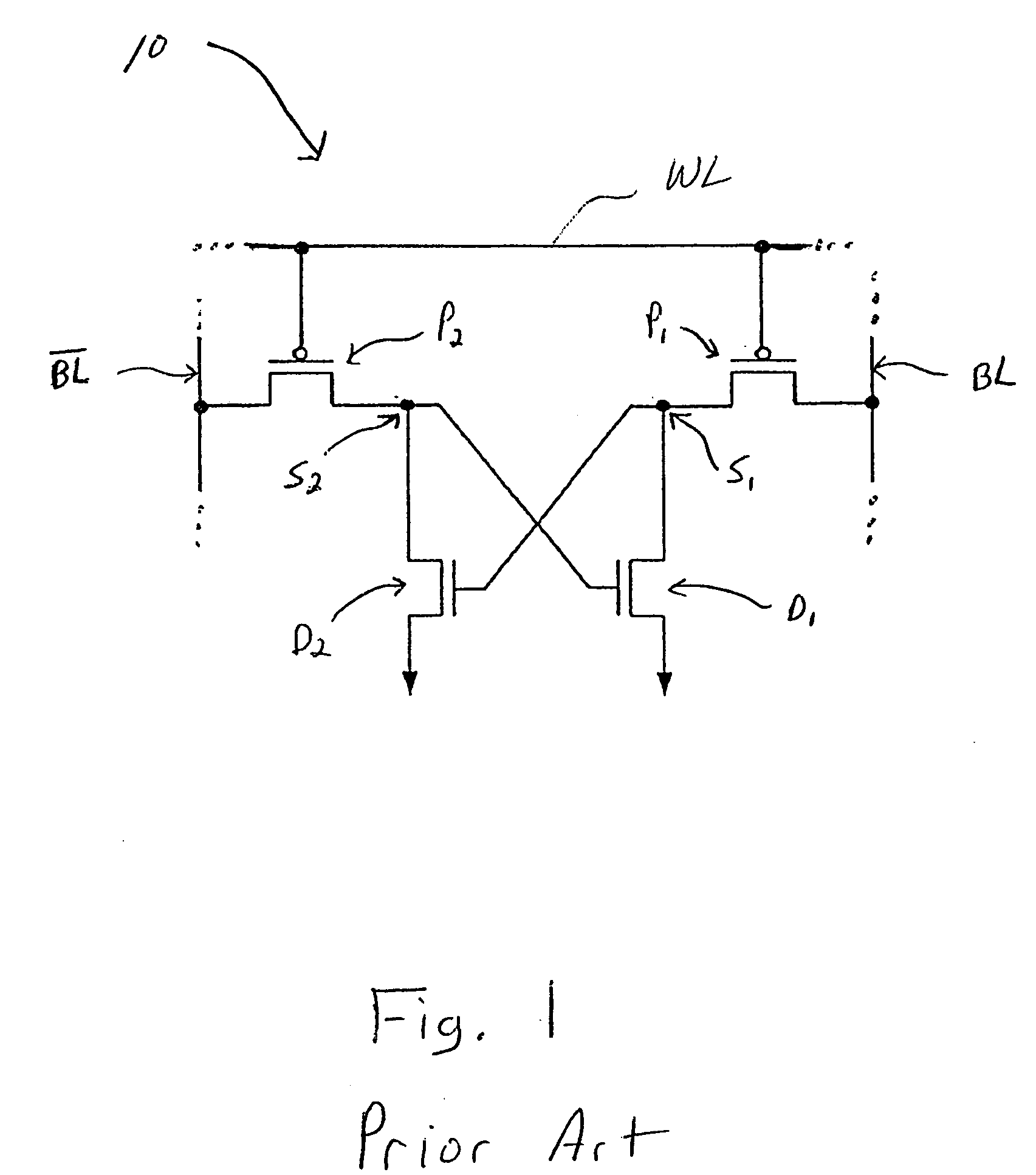
Loadless 4T SRAM cells, and methods for operating such SRAM cells, which can provide highly integrated semiconductor memory devices while providing increased performance with respect to data stability and increased I / O speed for data access operations. A loadless 4T SRAM cell comprises a pair of access transistors and a pair of pull-down transistors, all of which are implemented as N-channel transistors (NFETs or NMOSFETS). The access transistors have lower threshold voltages than the pull-down transistors, which enables the SRAM cell to effectively maintain a logic “1” potential during standby. The pull-down transistors have larger channel widths as compared to the access transistors, which enables the SRAM cell to effectively maintain a logic “0” potential at a given storage node during a read operation. A method is implemented for dynamically adjusting the threshold voltages of the transistors of activated memory cells during an access operation to thereby increase the read current or performance of the accessed memory cells.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
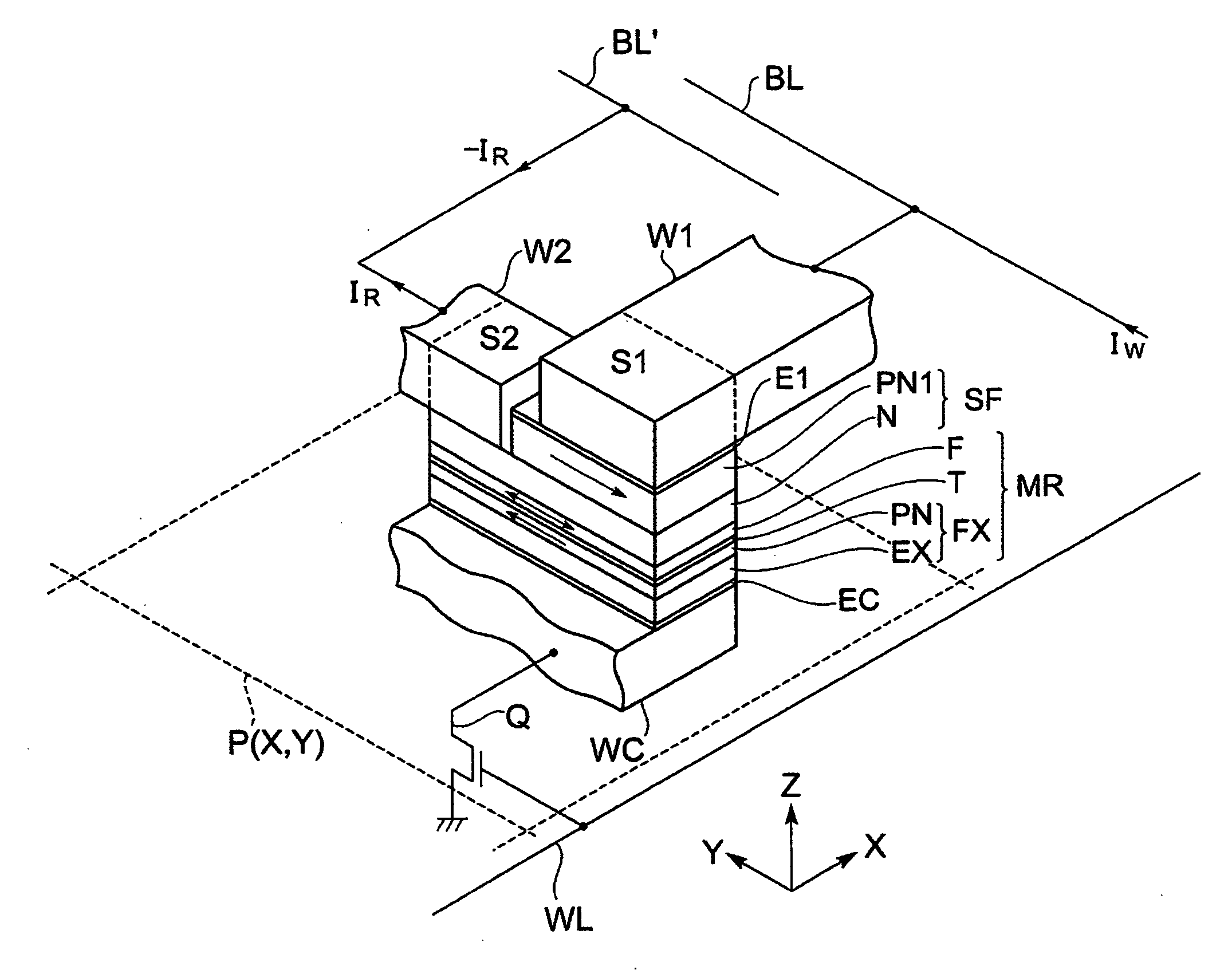
Magnetic memory
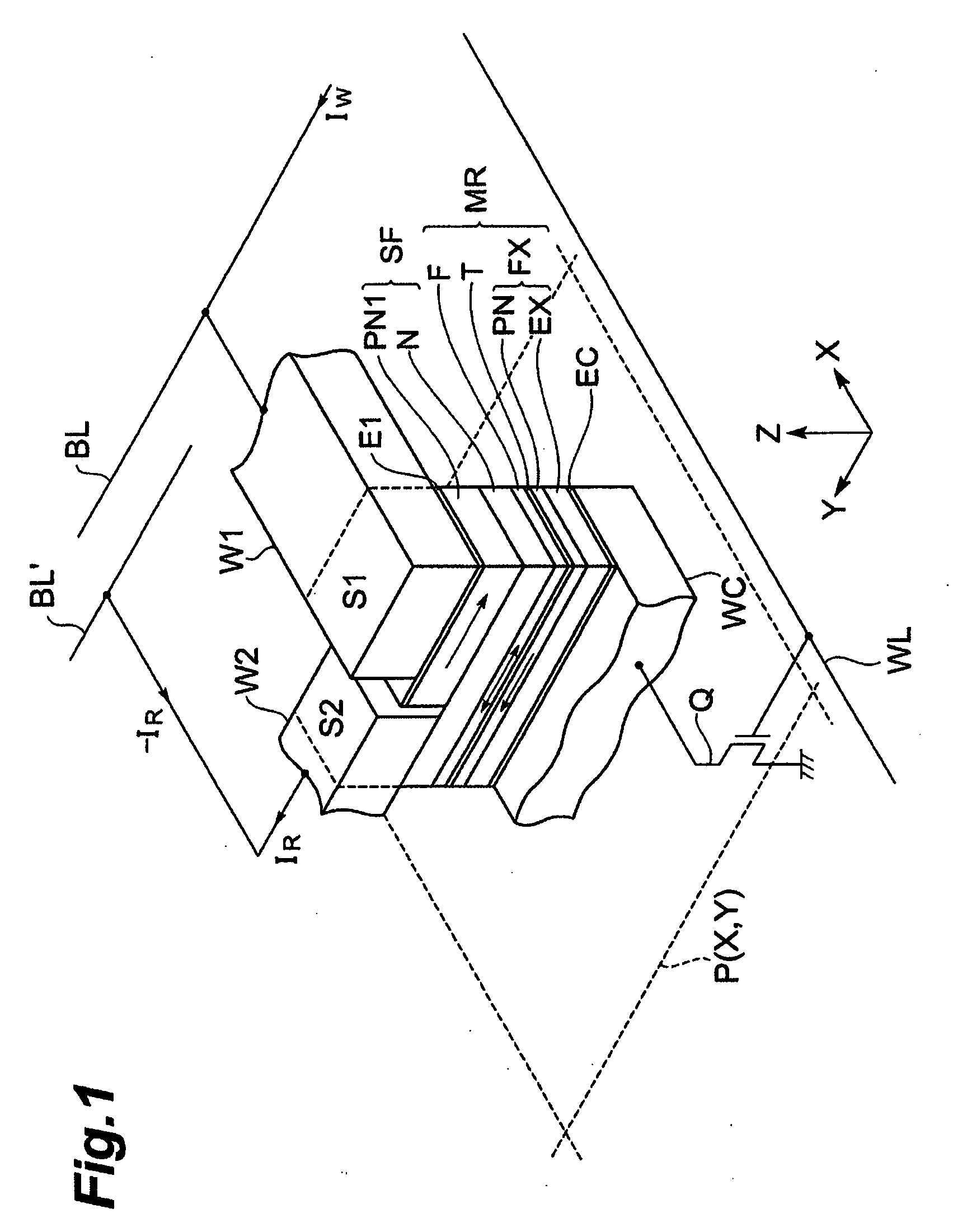
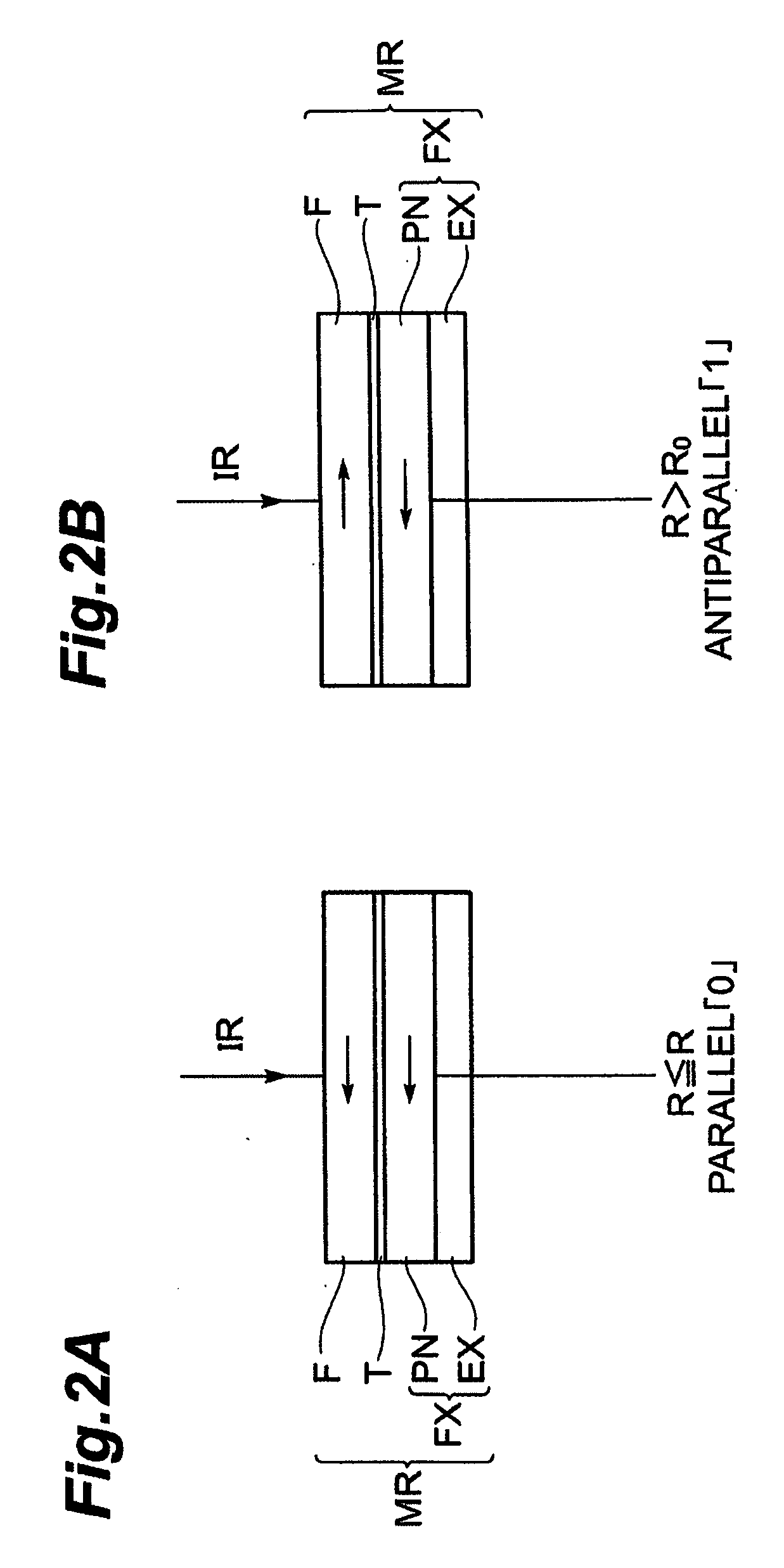
ActiveUS20070195594A1Easily short-circuitedTotal current dropDigital storageSemiconductor devicesElectricityMagnetic memory
A magnetoresistance effect element is also located between second wiring and common wiring. The magnetoresistance effect element is electrically connected to the second wiring without a spin filter. When a reading current is supplied between the second wiring for supplying a reading current and the common wiring, since this is not supplied via a spin filter, no spin polarized current is supplied into the magnetoresistance effect element, so that it becomes difficult to magnetization-reverse a magnetosensitive layer. Even in a structure where, in order to improve recording density, the magnetosensitive layer is reduced in area so as to lower a writing current, no magnetization reversal occurs due to a supply of the reading current, and information can be read out without making the reading current considerably small in comparison with the writing current.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Flash memory unit for shared source line and forming method thereof
ActiveCN102315252AImprove coupling coefficientImproved Stress ReliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
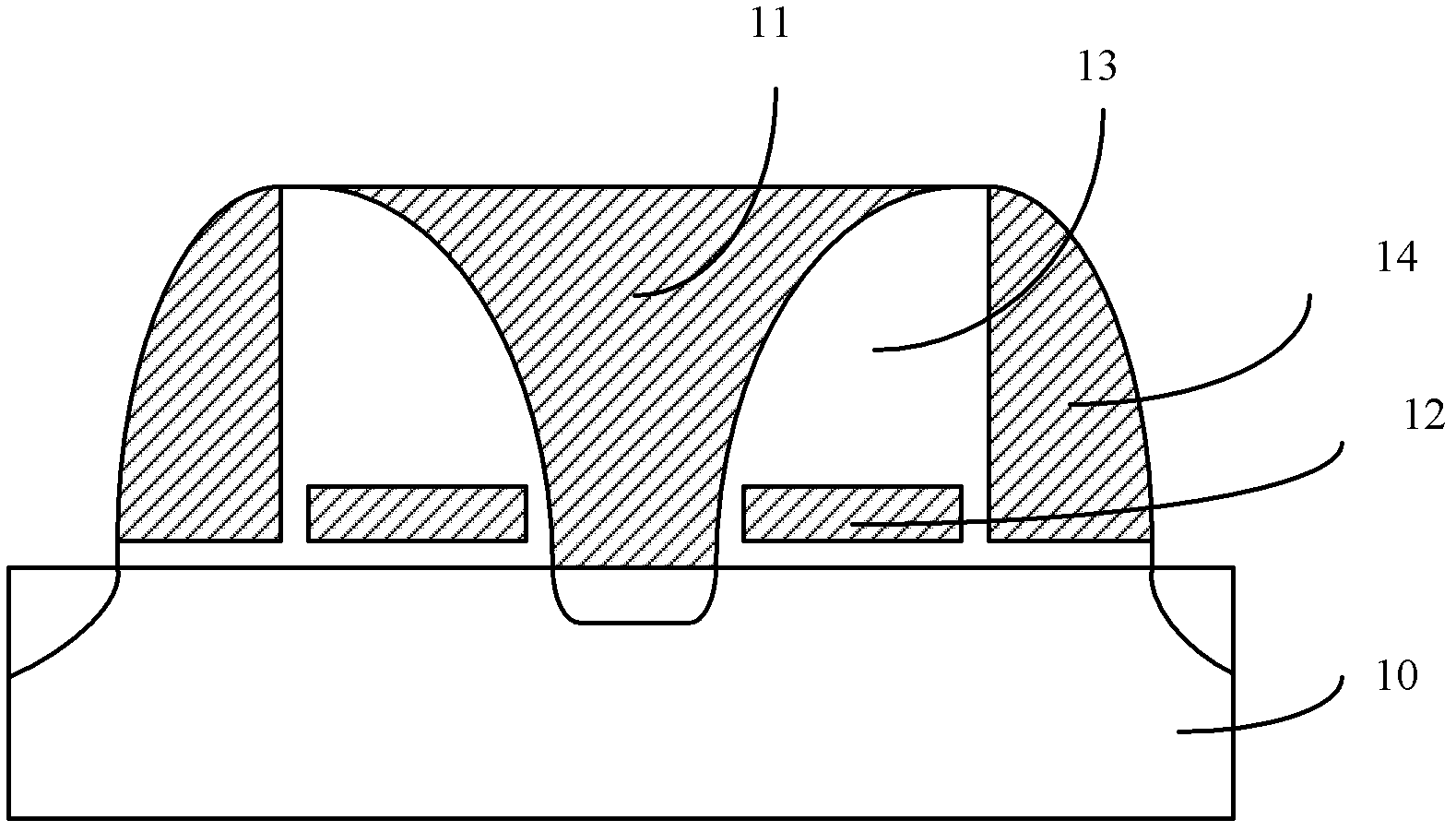
The embodiment of the invention provides a flash memory unit for a shared source line and a forming method thereof. The provided flash memory unit for the shared source line comprises a semiconductor substrate, a source line, a floating gate dielectric layer, a floating gate, a control gate dielectric layer, a control gate, side wall dielectric layers, side walls, a tunneling oxide layer, a word line, a drain electrode and a source electrode, wherein the source line is positioned on the surface of the semiconductor substrate; the floating gate dielectric layer, the floating gate, the control gate dielectric layer and the control gate are sequentially positioned on the surface of the semiconductor substrate on two sides of the source line; the side wall dielectric layers are positioned between the source line and the floating gate as well we between the source line and the control gate; the side walls are positioned on the floating gate and the control gate, which are far from the source line; the tunneling oxide layer is adjacent to the side wall and is positioned on the surface of the semiconductor substrate; the word line is positioned on the surface of the tunneling oxide layer; the drain electrode is positioned in the semiconductor substrate at one side of the word line, which is far from the source line; the source electrode is positioned in the semiconductor substrate which is right opposite to the source line; and the floating gate is provided with a p-type doping end which is close to the source line, wherein the doping type of the floating gate is in a p type and the doping type of other parts is respectively in an n type.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
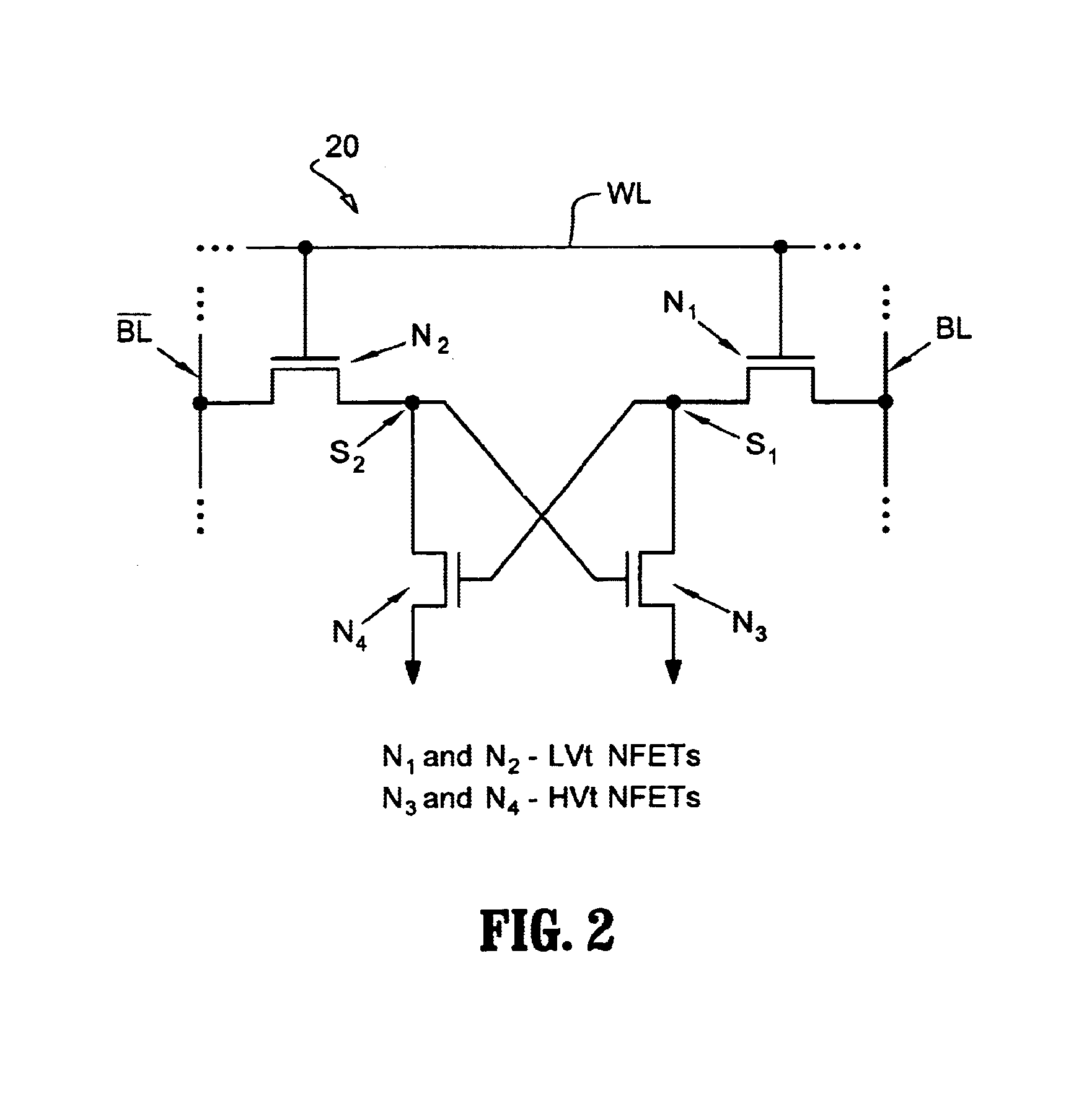
Loadless NMOS four transistor dynamic dual Vt SRAM cell
ActiveUS20050047196A1Increase heightImprove performanceSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesData accessEngineering
Loadless 4T SRAM cells, and methods for operating such SRAM cells, which can provide highly integrated semiconductor memory devices while providing increased performance with respect to data stability and increased I / O speed for data access operations. A loadless 4T SRAM cell comprises a pair of access transistors and a pair of pull-down transistors, all of which are implemented as N-channel transistors (NFETs or NMOSFETS). The access transistors have lower threshold voltages than the pull-down transistors, which enables the SRAM cell to effectively maintain a logic “1” potential during standby. The pull-down transistors have larger channel widths as compared to the access transistors, which enables the SRAM cell to effectively maintain a logic “0” potential at a given storage node during a read operation. A method is implemented for dynamically adjusting the threshold voltages of the transistors of activated memory cells during an access operation to thereby increase the read current or performance of the accessed memory cells.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Three-dimensional semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104393046AImprove efficiencyHigh strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCouplingEngineering
The invention discloses a three-dimensional semiconductor device which comprises a plurality of storage units and a plurality of selection transistors. Each of the plurality of storage units comprises a channel layer which is distributed along a direction perpendicular to the surface of a substrate; a plurality of interlayer insulating layers and a plurality of grid stack structures which are alternately stacked along the side wall of the channel layer; a plurality of floating gates which are arranged between the plurality of interlayer insulating layers and the side wall of the channel layer; a drain electrode which is arranged at the top of the channel layer; and a source electrode which is positioned in the substrate between two adjacent storage units of the plurality of storage units. According to the three-dimensional semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof, the floating gates are arranged at the side walls of the vertical channels, and the starting of the source and drain regions generated on the side walls of the channels due to induction is controlled through the coupling between the gate electrodes and the floating gates, thereby improving induction efficiency and intensity of the source and drain regions, reducing source and drain resistance of the storage units, and improving read current and read speed of a storage array.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor storage
InactiveUS7187588B2Effective restraint of interferenceSolve the lack of functionTransistorSolid-state devicesCharge retentionSemiconductor storage devices
A semiconductor storage device includes a semiconductor substrate, a gate insulating film formed on the semiconductor substrate, a single gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film, two charge holding portions formed on both sides of the gate electrode, source / drain regions respectively corresponding to the charge holding portions, and a channel region disposed under the single gate electrode. A memory function implemented by these two charge holding portions and a transistor operation function implemented by the gate insulating film is separated from each other for securing sufficient memory function as well as easily suppressing short channel effect by making the gate insulating film thinner.
Owner:SHARP KK
Memory device and method of operating such a memory device
ActiveUS20090116308A1Improve stabilityFaster read operationRead-only memoriesDigital storageCapacitanceBit line
A memory device and method of operation is provided, the memory device having a plurality of memory cells arranged in at least one column, with each column having at least one bit line and a supply voltage line associated therewith. A capacitance exists between the supply voltage line and associated at least one bit line for each column. Control circuitry is used to control, for each column, connection of a voltage source to the associated supply voltage line. For a predetermined period during a memory access operation, the control circuitry disconnects the supply voltage line for at least the selected column from the voltage source, such that a voltage level on that supply voltage line changes in response to any change in voltage on the associated at least one bit line. This basic mechanism can be used to provide a variety of assist mechanisms, such as a write assist mechanism, a bit flip assist mechanism and a read assist mechanism. The technique of the present invention provides a particularly simple and power efficient technique for providing such assist mechanisms.
Owner:ARM LTD
Memory array and electronic equipment
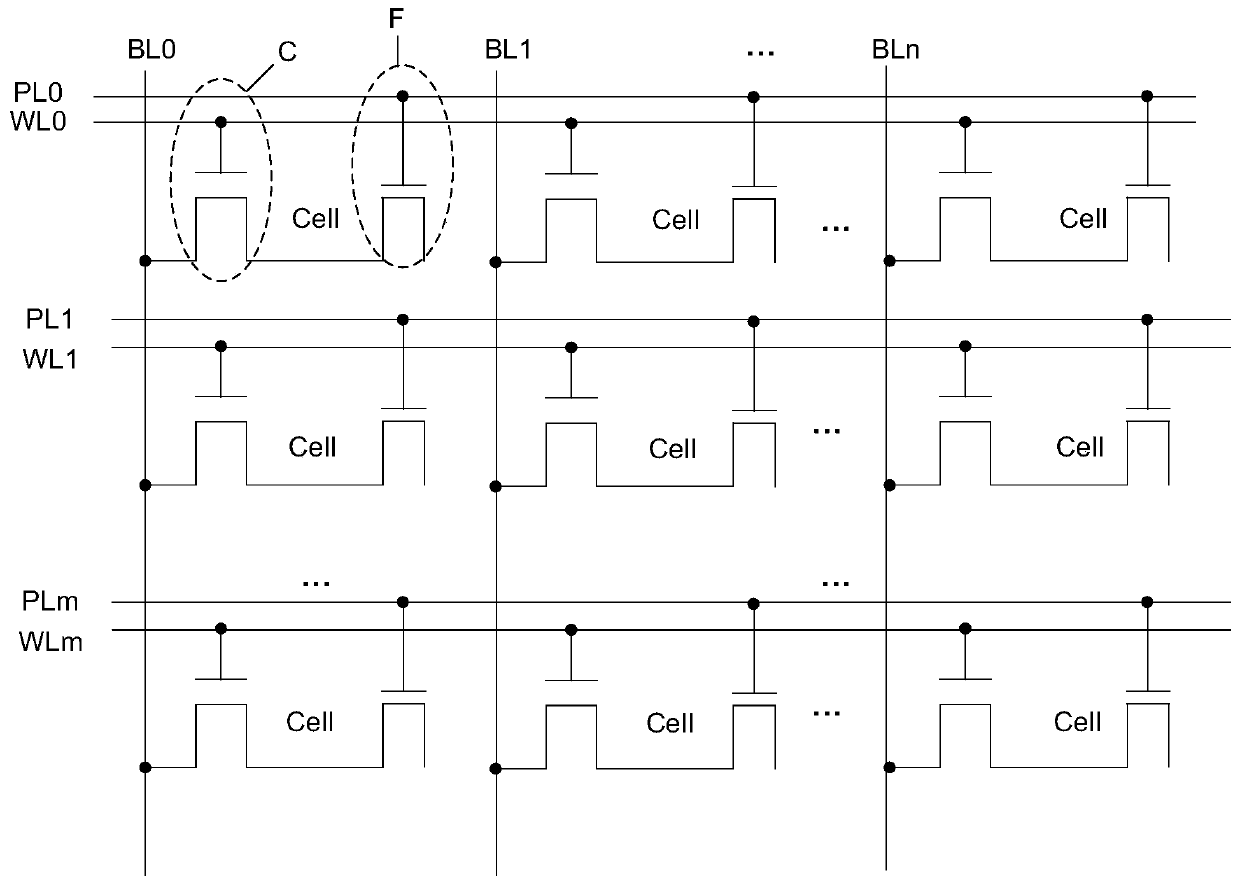
ActiveCN102768855ANo crosstalkIncreased active area widthRead-only memoriesProgrammable read-only memoryParallel computing
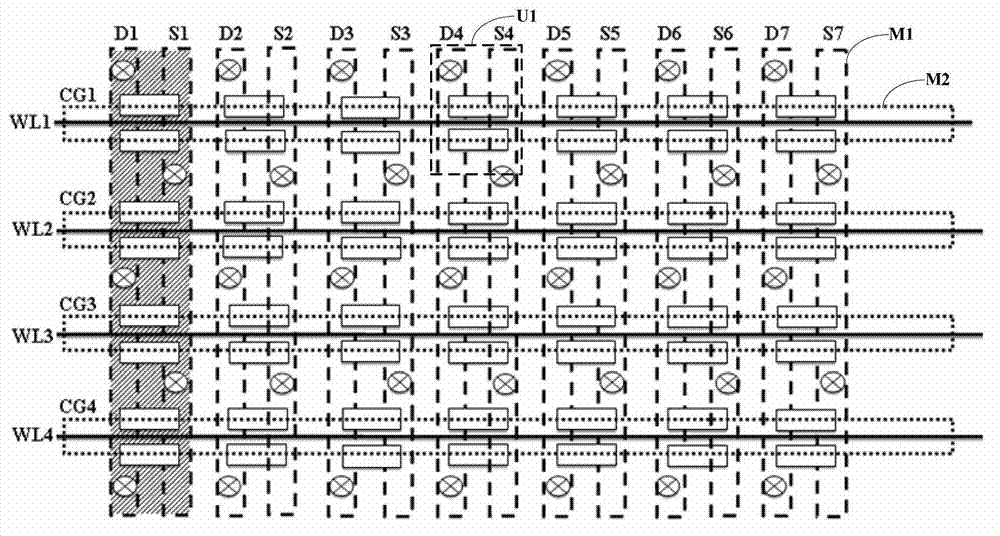
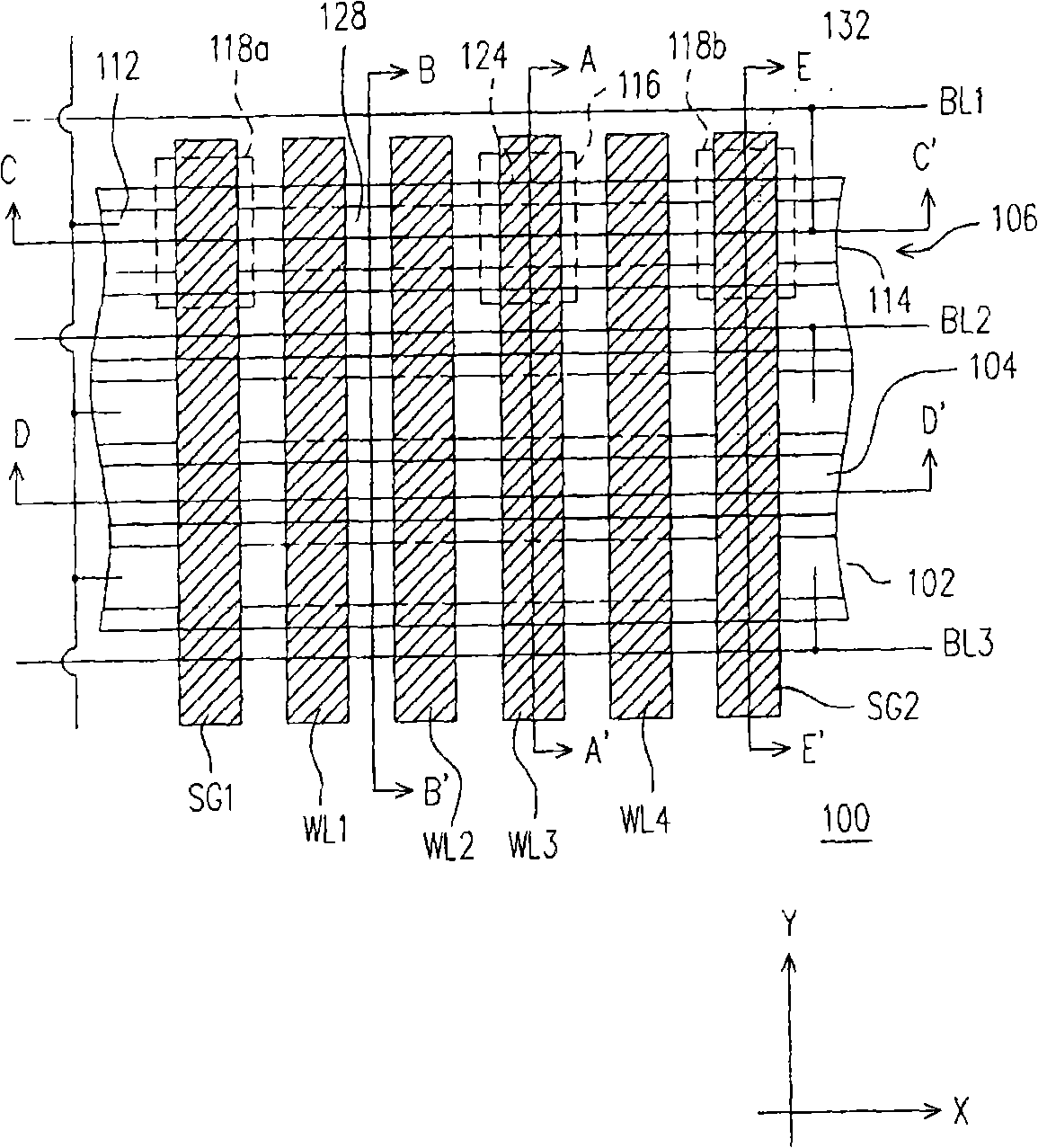
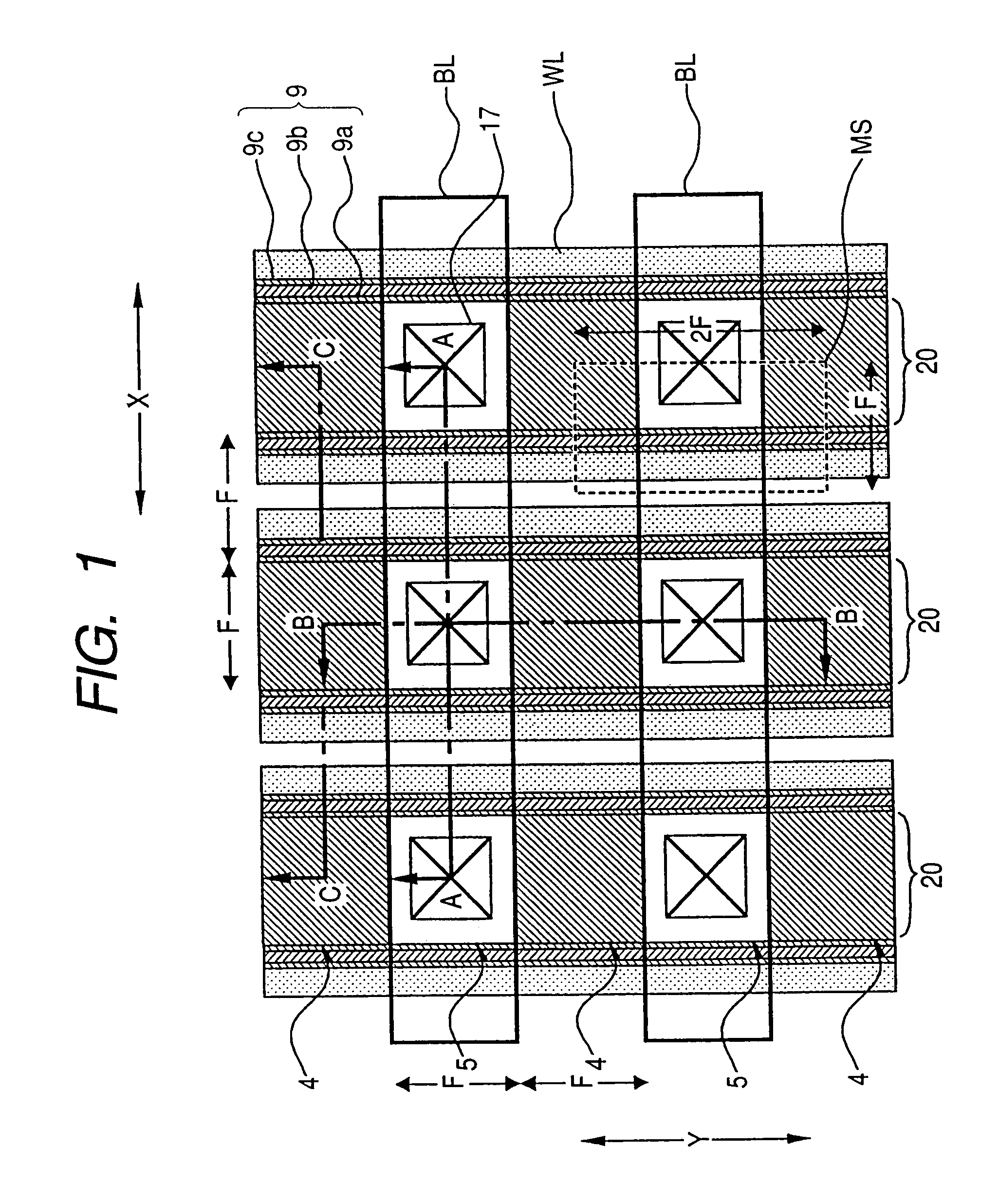
The invention discloses a memory array and electronic equipment. The memory array comprises a plurality of memory units arranged in an array way, wherein each memory unit comprises a plurality of parallel bit lines and word lines which are arranged in parallel on the bit lines and vertical to the bit lines, each bit line is connected with the source electrode or the drain electrode of each memory unit in a column direction, each word line is connected with the grid electrode of each memory unit in a row direction, the grid electrode of each memory unit comprises double grid structures and a selection grid arranged between the double grid structures, and the double grid structures are arranged in parallel on a substrate. The electronic equipment is equipped with the memory array. The memory array and the electronic equipment are designed for an electric erasable programmable read-only memory, so that crosstalk can be prevented from generating on other memory units when operation is carried out on a selected memory unit.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Flash memory and a reading method thereof
ActiveCN104157307AImprove reading efficiencyReduce read power consumptionSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesGate oxideComputer science
The invention relates to a semiconductor device, and discloses a flash memory and a reading method thereof. In the invention, each flash memory unit in the flash memory includes a selection grid PMOS transistor, a control grid PMOS transistor and a reading selection grid PMOS transistor. The selection grid PMOS transistor, the control grid PMOS transistor and the reading selection grid PMOS transistor are in series connection through a first electrode and a second electrode; the absolute values of electrical thickness, channel length and threshold voltage of a grid oxide layer of the reading selection grid PMOS transistor are less than the corresponding values of the selection grid PMOS transistor. The 3T PMOS flash memory provided by the invention is dedicated to the reading select grid PMOS transistor, can improve the reading efficiency overall, effectively reduce the read power, and overcome the defects of long charge and discharge time, high dynamic current and high reading power consumption of the existing 2T PMOS flash memory in reading operations.
Owner:INTEGRATED SILICON SOLUTION SHANGHAI
OTP embedded memory and programming method and reading method thereof
The invention provides an OTP memory and a programming method and a reading method thereof. The OTP embedded memory comprises a plurality of word lines, a plurality of bit lines, and a plurality of programming lines; the programming lines are connected with the control end of the anti-fuse in each storage unit to provide a control voltage for the anti-fuse; a control voltage is provided for the control end of the gating tube by the word lines; therefore, the control voltage of the control end of the anti-fuse is separated from the control voltage of the control end of the gating tube, the control voltage of the gating tube is not limited by the control voltage of the anti-fuse, the control voltage of the gating tube can be further reduced, the channel length of the gating tube can be further reduced, and the area of a storage unit of the OTP embedded memory is reduced. Or, on the basis of not changing the channel length of the gating tube, the control voltage of the antifuse is independently controlled, the channel width of the gating tube can be relatively reduced, and the area of the storage unit of the OTP embedded memory can also be reduced.
Owner:ZHUHAI CHUANGFEIXIN TECH CO LTD
Static random access memory based on back gate structure of FDSOI device
PendingCN111145810ARaise the threshold voltageLower threshold voltageDigital storageStatic random-access memoryEngineering
The invention discloses a static random access memory (SRAM) based on a back gate structure of a FDSOI device, all transistors on the novel static random access memory are FDSOI devices, and back gates of the devices are connected with a word line WL. When the SRAM performs read-write operation, the word line is at a high level, so that the threshold voltage of the PMOS is increased, and the threshold voltage of the NMOS is reduced, thereby enhancing the write-in capability of the SRAM and improving the read current; in the maintaining state, the word line WL is at a low level, and the threshold voltage of the device on the SRAM is not different from the threshold voltage of the device on the traditional FDSOI SRAM, so that the static power consumption is not changed.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Nanocrystal nonvolatile memory based on strained silicon and manufacturing method of memory
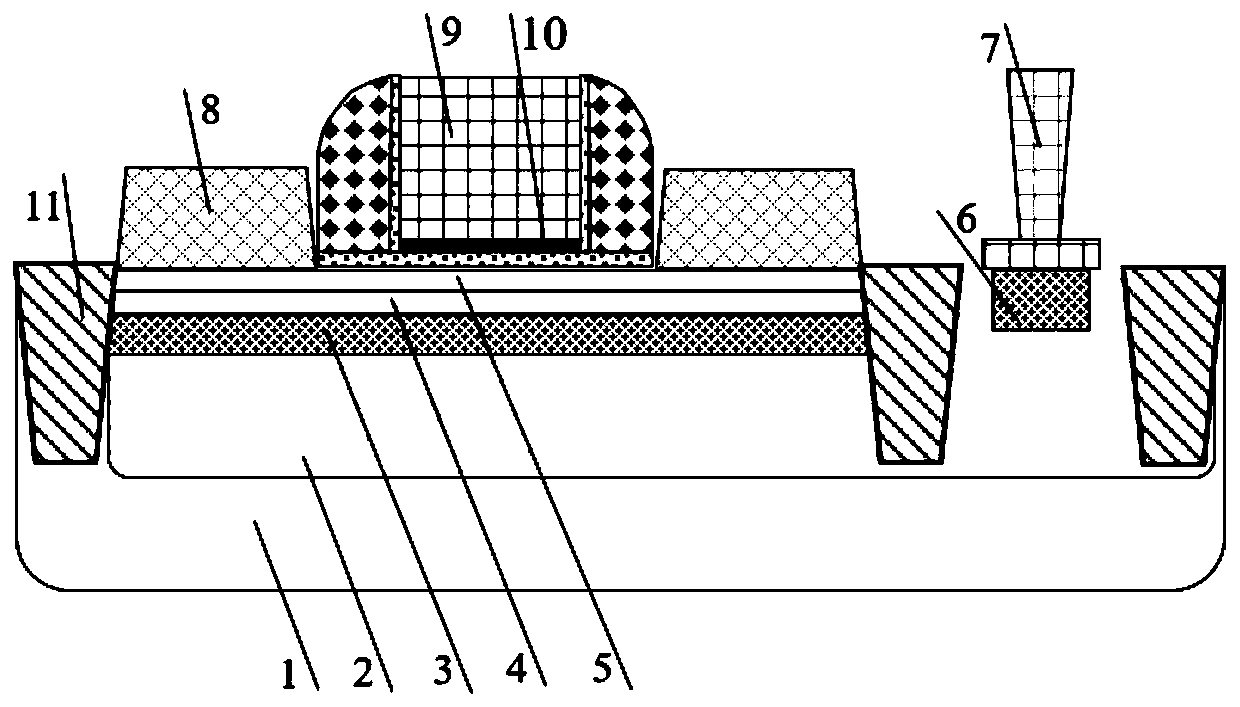
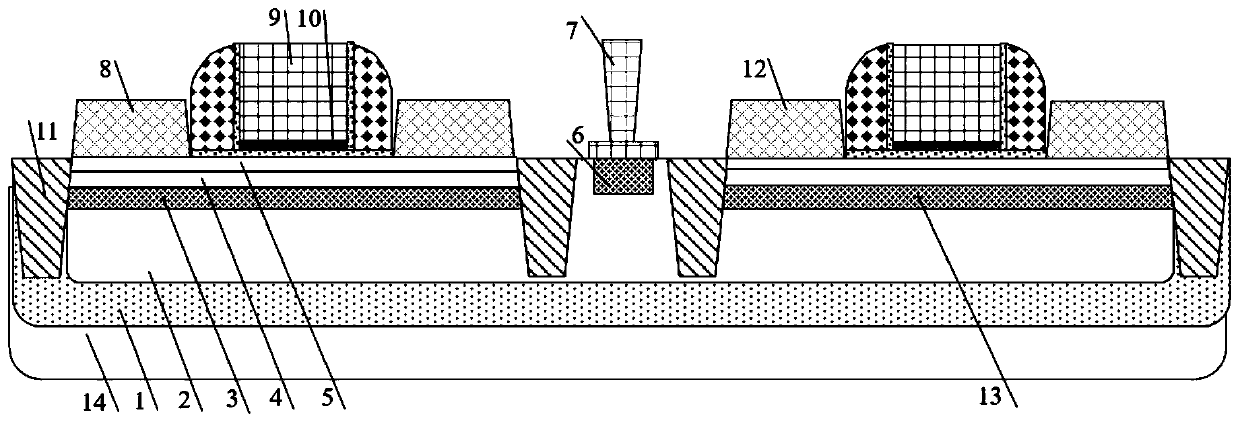
InactiveCN102117812AImprove mobilityIncrease read currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanometreStrained silicon
The invention relates to a nanocrystal nonvolatile memory based on strained silicon in the technical fields of nano electronic components and nano processing. The nanocrystal nonvolatile memory based on strained silicon comprises a silicon substrate, a GeSi gradually-doped buffer layer, a Gel-xSix relieving layer, a strained silicon layer, lightly-doped drain electrodes, a source conduction region, a drain conduction region, a tunneling dielectric layer, a nanocrystal charge storage layer, a control grid dielectric layer and a grid electrode material layer, wherein the GeSi gradually-doped buffer layer, the Gel-xSix relieving layer and the strained silicon layer are deposited on the silicon substrate; the lightly-doped drain electrodes, the source conduction region and the drain conduction region are arranged at two sides in the silicon substrate; the tunneling dielectric layer covers a current carrier channel arranged between the source conduction region and the drain conduction region; the nanocrystal charge storage layer covers the tunneling dielectric layer; the control grid dielectric layer covers the tunneling dielectric layer; and the grid electrode material layer covers the control grid dielectric layer. According to the invention, the mobility is increased by utilizing the strained silicon, thereby increasing the reading current, and simplifying a peripheral circuit; the nanocrystal nonvolatile memory based on strained silicon adopts the nanocrystal as a floating grid material, so that the performance of a storage device is improved, and particularly, the storage performance, such as storage windows, programming / erasing speed, data retention characteristic and the like, is improved comprehensively.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
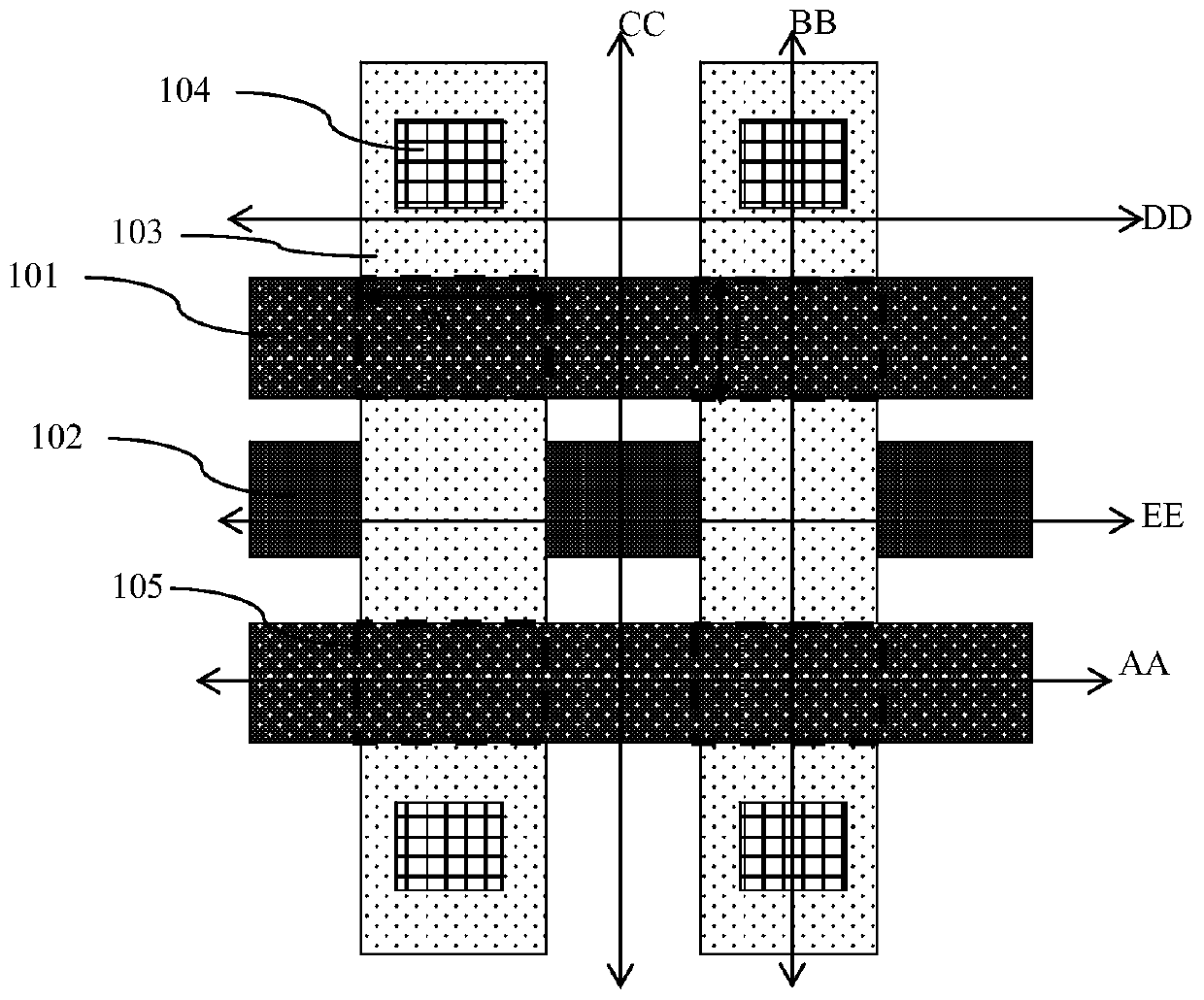
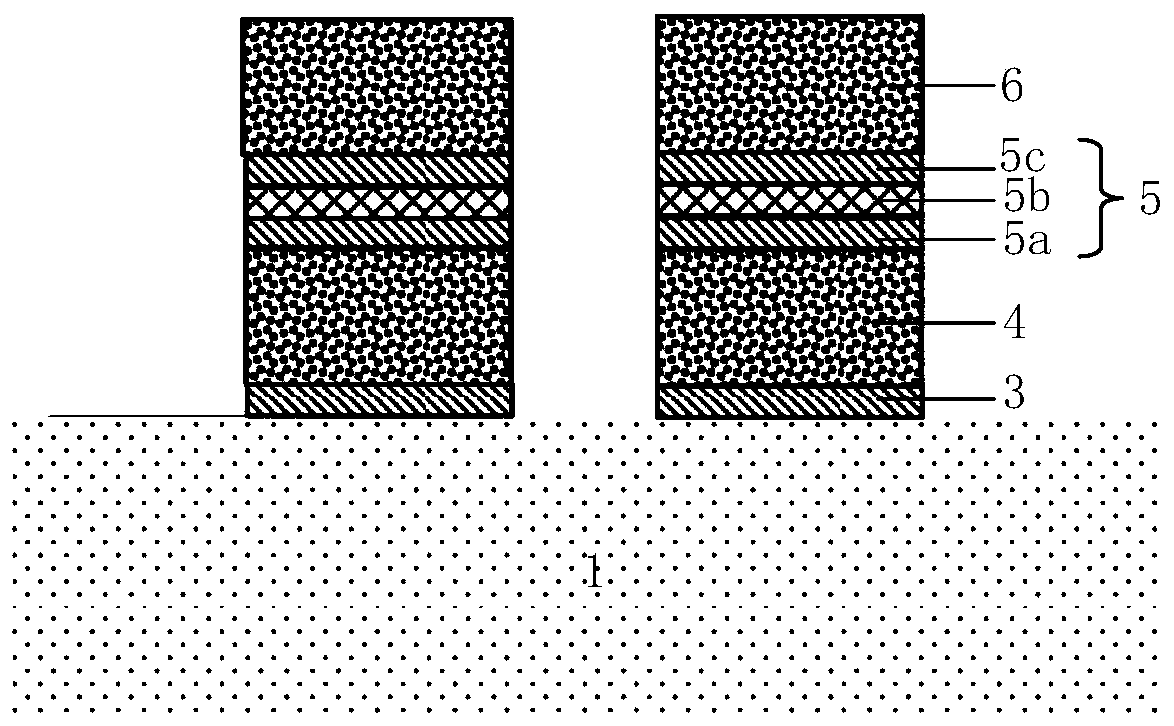
Three-dimensional NAND ferroelectric memory and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111799263ACompact wiringHigh density integrationTransistorSolid-state devicesFerroelectric thin filmsIsolation layer
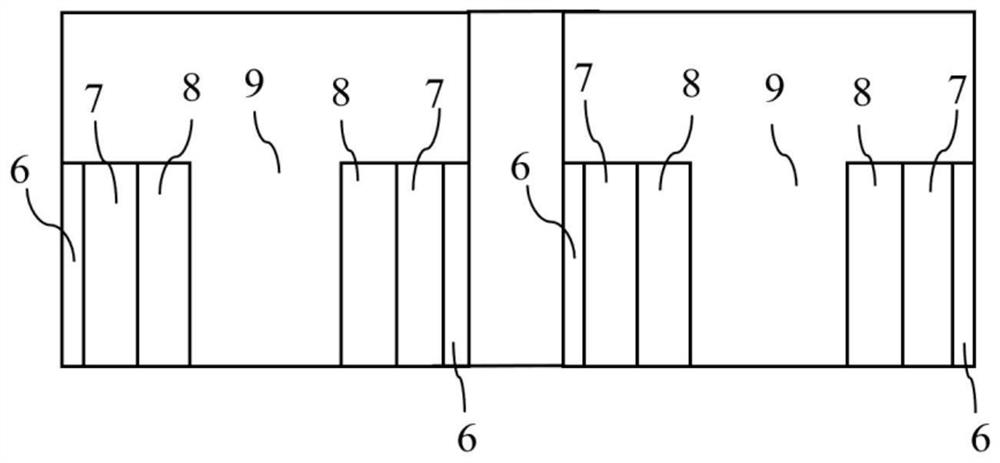
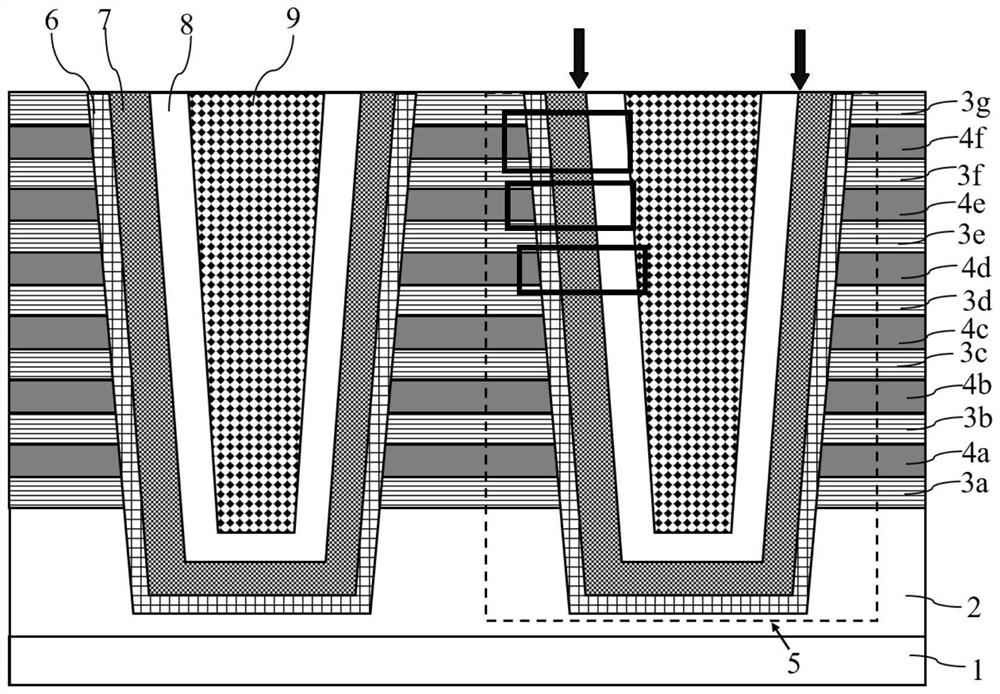
The invention discloses a three-dimensional NAND ferroelectric memory and a preparation method thereof, and the three-dimensional NAND ferroelectric memory comprises a substrate layer (1), a conductive layer (2) and a stacked layer which are sequentially stacked, and the stacked layer comprising a plurality of isolation layers and a plurality of control gate electrode layers which are stacked; anda plurality of channel groups, each channel group in the plurality of channel groups comprising two channels; the two channels being arranged in a manner of penetrating through the laminated layer; the bottom ends of the two channels being embedded into the conductive layer (2). The bottom ends of the two channels are communicated, a separation layer (6) for separating the control gate electrodelayers of the two channels is arranged between the two channels, and a buffer layer (7), a ferroelectric film layer (8), a channel layer (9) and a channel group (5) formed by connecting a plurality offerroelectric field effect transistors (13) in series are sequentially arranged on the inner walls of the channels. More compact wiring can be obtained through channel group arrangement of the memory, higher-density integration is realized, and the reliability is higher.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Forming method for memory cell of flash memory
ActiveCN102637647ASmall sizeImprove mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrier mobilitySemiconductor
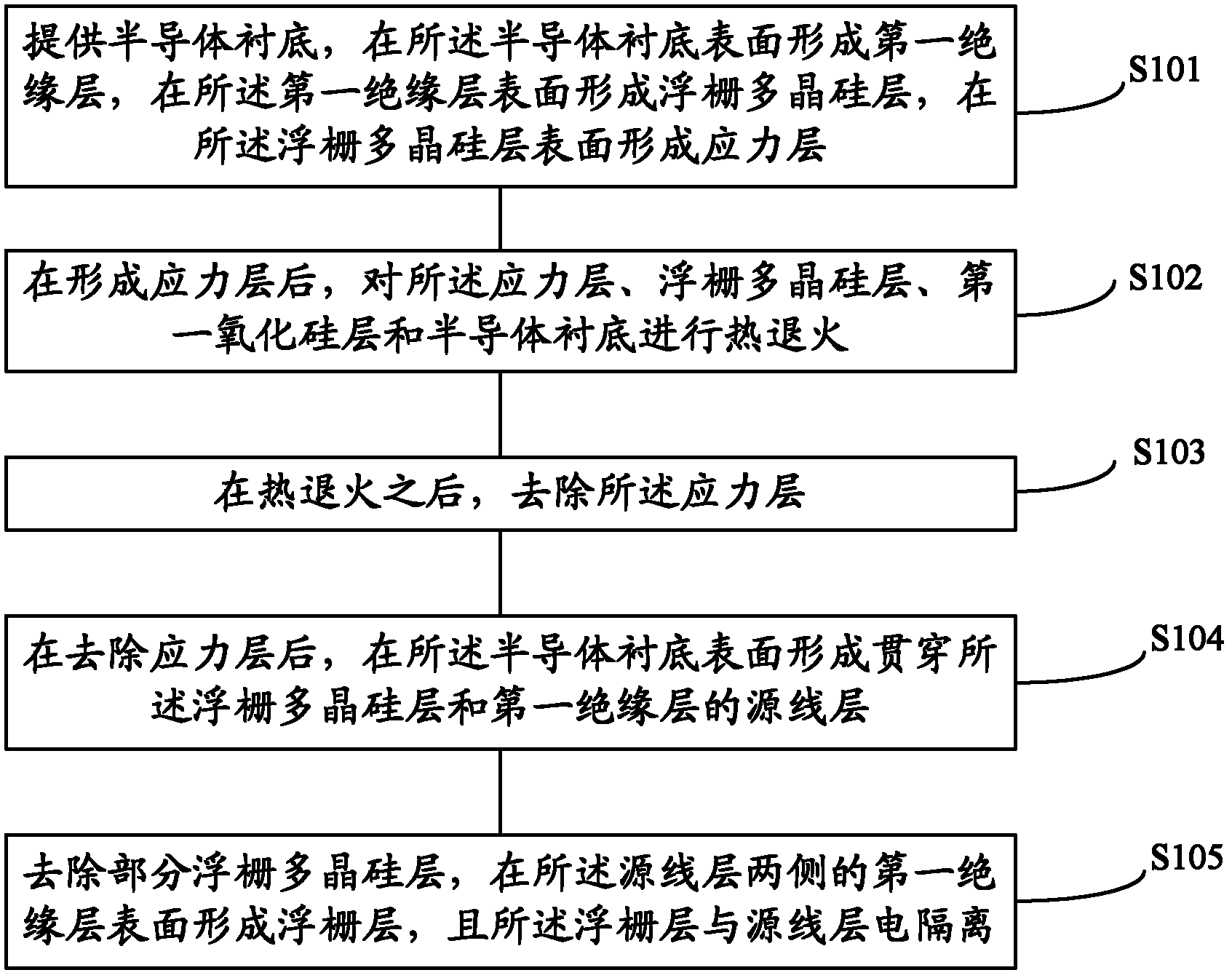
The invention discloses a forming method for a memory cell of a flash memory. The forming method comprises the steps of: providing a semiconductor substrate; forming a first insulating layer on the surface of the semiconductor substrate; forming a floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer on the surface of the first insulating layer; forming a stress layer on the surface of the floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer; after the forming of the stress layer, conducting thermal annealing on the stress layer, the floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer, the first insulating layer and the semiconductor substrate; after thermal annealing, removing the stress layer; after the removal of the stress layer, forming a source line layer passing through the floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer and the first insulating layer on the surface of the semiconductor substrate; and removing part of the floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer and forming a floating gate layer on the surface of the first insulating layer on two sides of the source line layer, wherein the floating gate layer is electrically isolated from the source line layer. The forming method for the memory cell of the flash memory can retain stress inside the floating gate layer, thereby enhancing the channel carrier mobility of the memory cell of the flash memory and reducing the size of the memory cell of the flash memory simultaneously when improving the data retention.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Non-volatile memory and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN101271868AImprove performanceIncrease read currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBiochemical engineeringIsolation layer
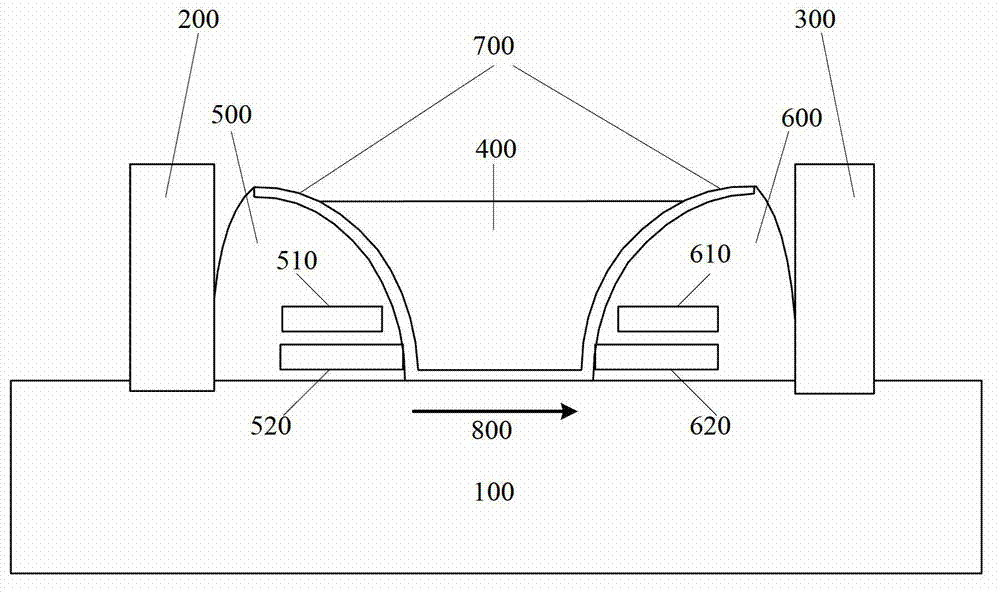
The invention discloses a nonvolatile memory, which includes a basement, an active layer, an element isolation layer and a memory cell. The active layer is arranged on the basement and protrudes from the surface of the basement. A plurality of element isolation layers are arranged on both sides of the active layer, and the surface of the element isolation layer is lower than the surface of the active layer. The memory cell comprises a control grid, a charge storage layer, a roof cover layer and a source electrode / drain electrode region. The control grid is arranged on the basement across the active layer. The charge storage layer is arranged on the lateral wall of the active layer and is located between the control grid and the active layer. The roof cover layer is arranged on the top of the active layer and is located between the control grid and the active layer. The source electrode / drain electrode region is arranged in the active layer at the both sides of the control grid.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
Storage unit and storage array erasing method
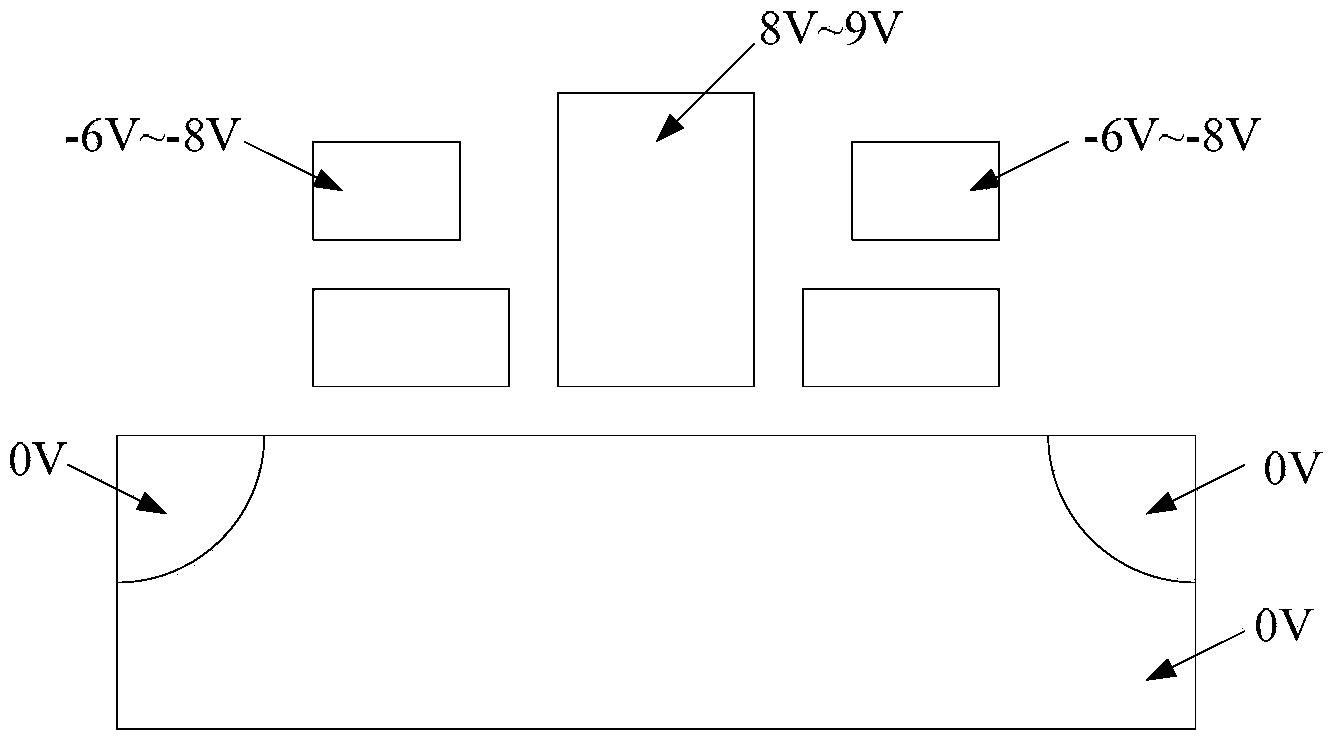
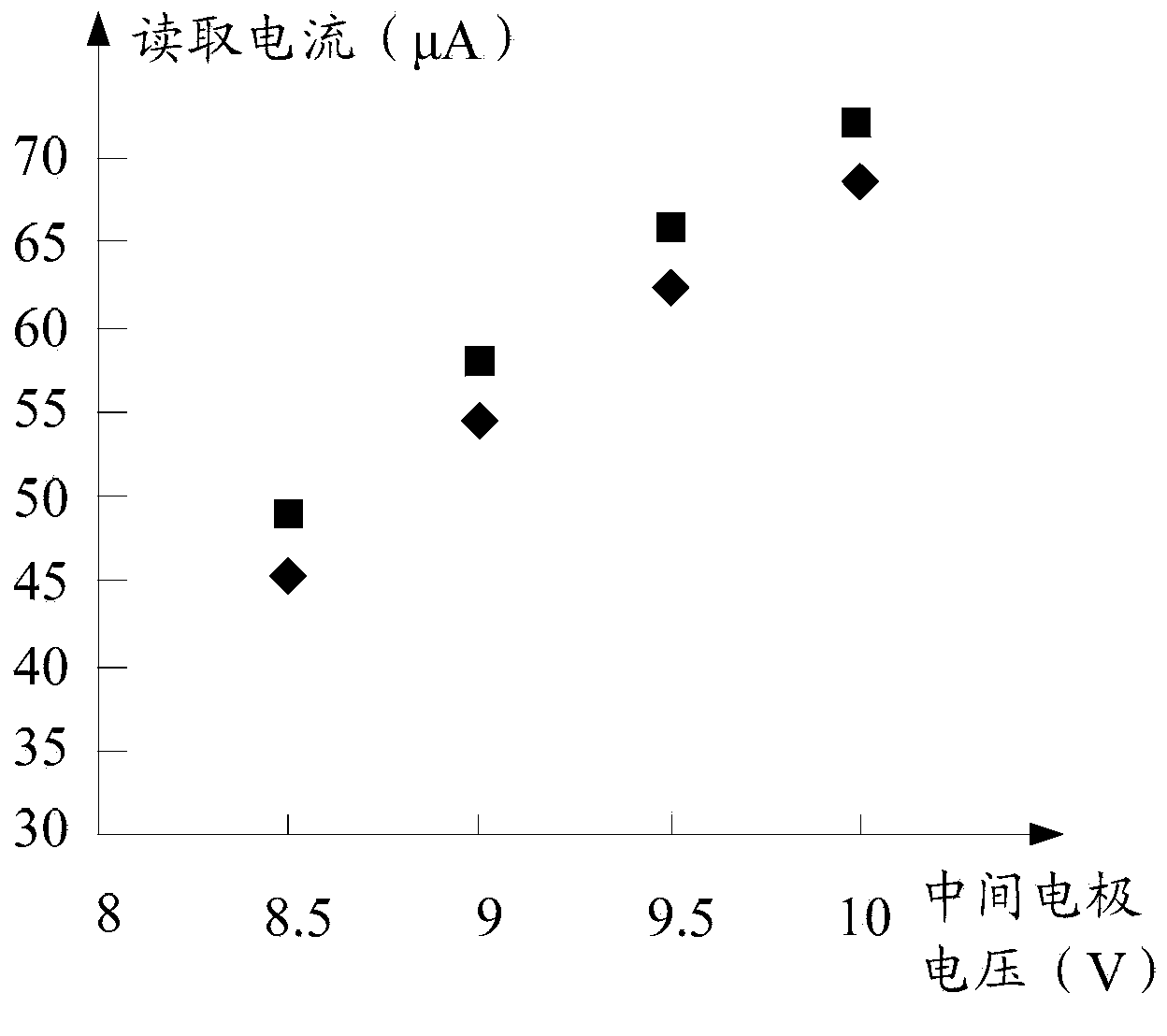
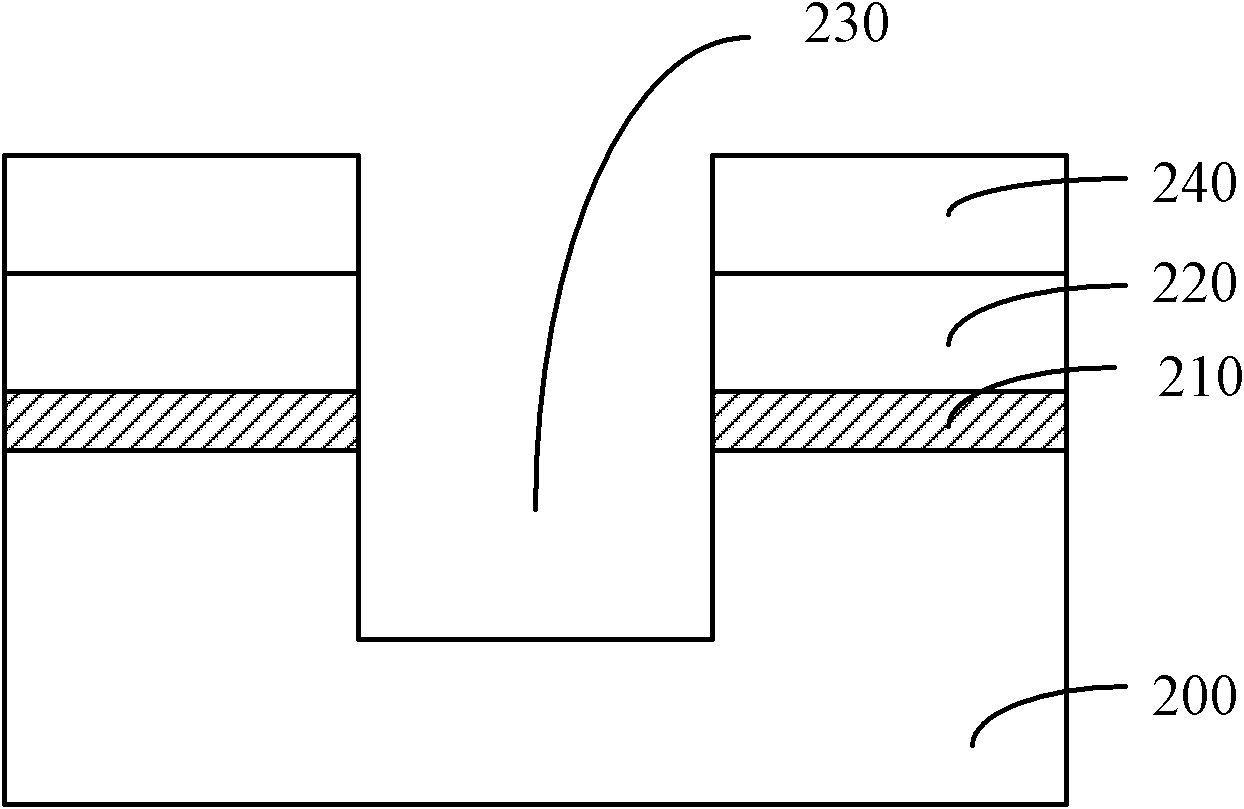
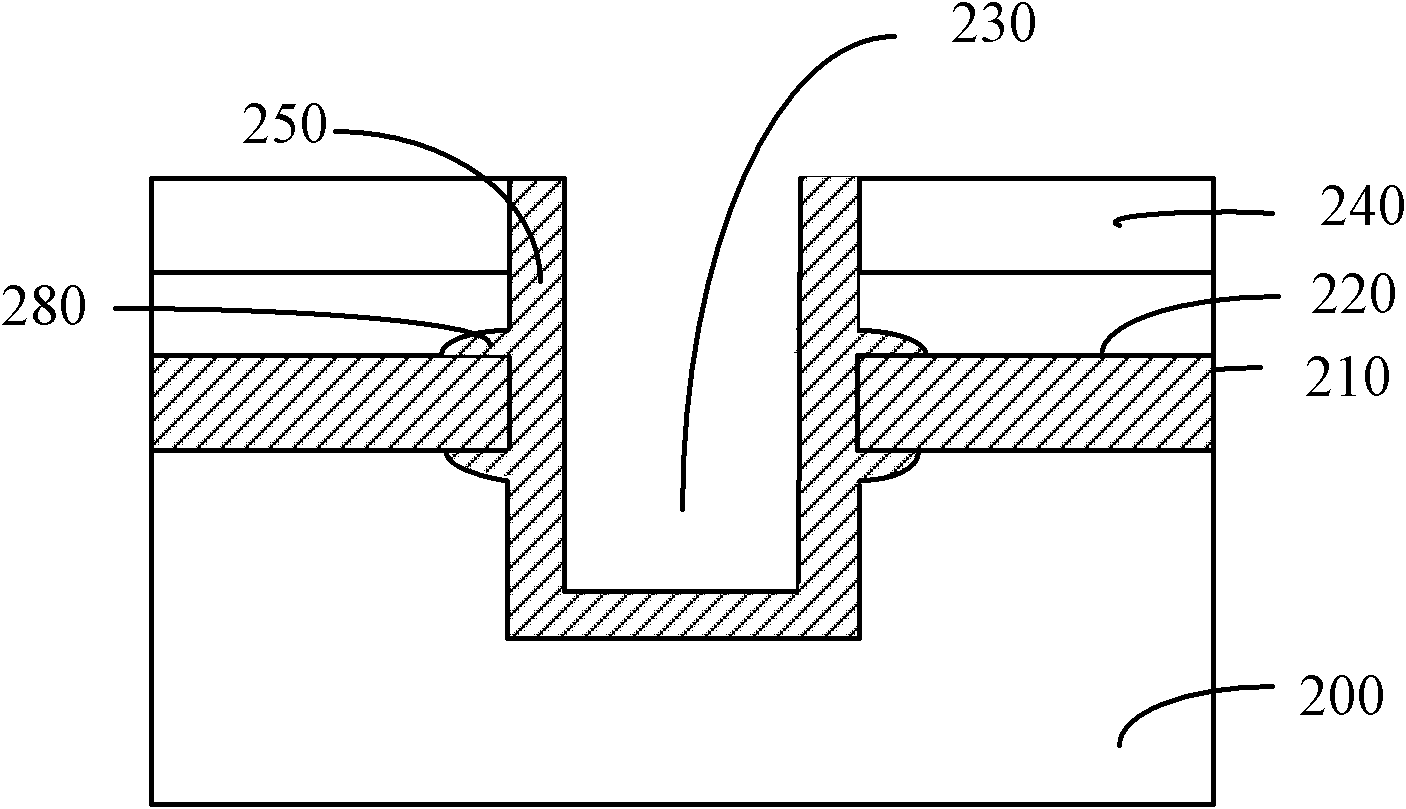
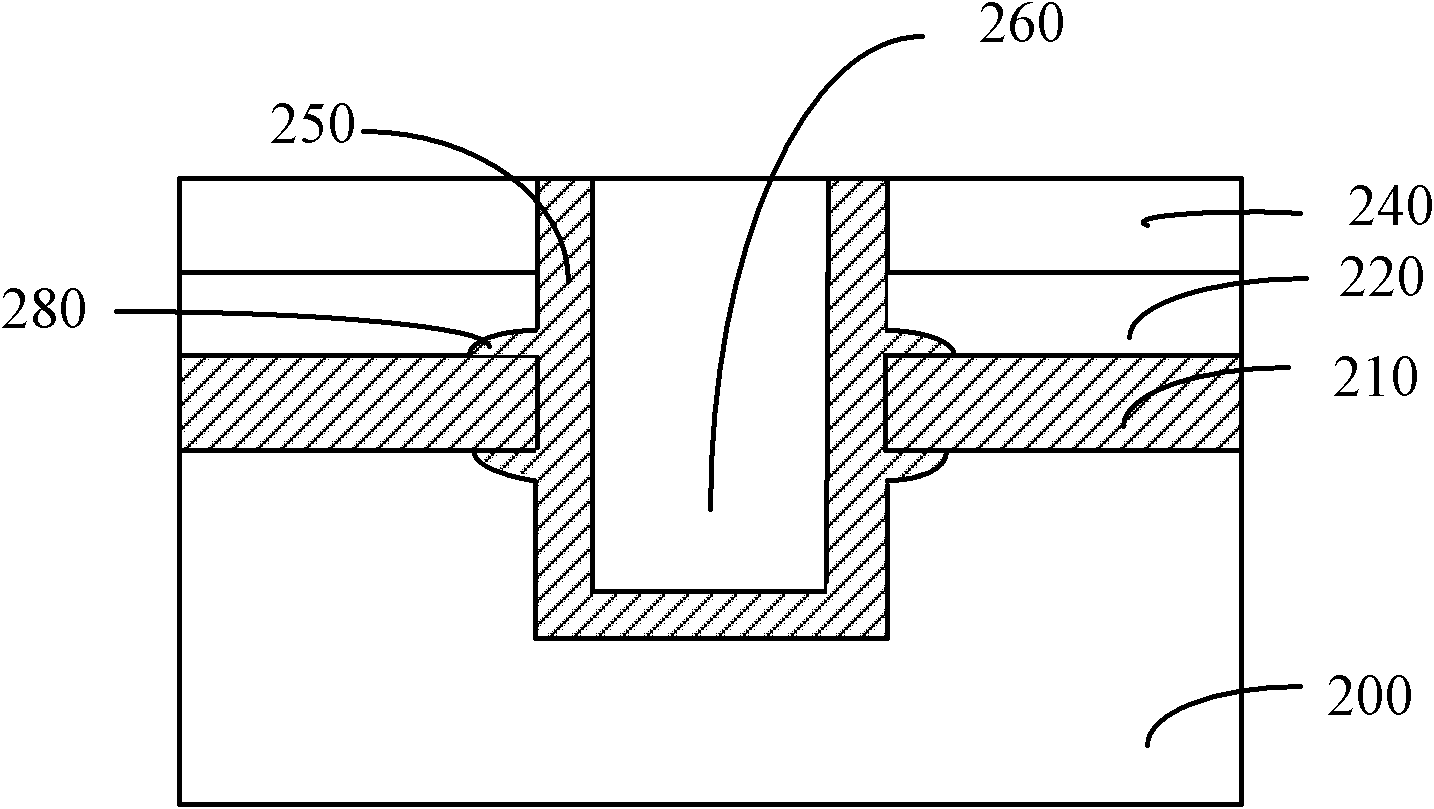
ActiveCN104183274ARaise the voltage differenceIncrease read currentRead-only memoriesStorage cellEngineering
The invention relates to a storage unit and a storage array erasing method. The storage unit comprises a P-type well region, a drain electrode, a source electrode, a first control grid electrode, a second control grid electrode and a middle electrode; the storage array erasing method comprises the following steps: applying first bias voltage to the P-type well region; applying second bias voltage to the drain electrode; applying third bias voltage to the source electrode; applying minus 6V-minus 8V voltage to the first control grid electrode; applying minus 6V-minus 8V voltage to the second control grid electrode; and applying 8V-9V voltage to the middle electrode, wherein the value of the first bias voltage is negative, and the values of the first bias voltage, the second first bias voltage and the third first bias voltage are equal. The storage unit and the storage array erasing method can improve the durability of the storage unit.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Method for forming shallow trench isolation (STI) structure used for flash memory
ActiveCN102184887AFast depositionReduce oxidation reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseChemical vapor deposition
The invention provides a method for forming a shallow trench isolation (STI) structure used for improving the 'smiling face' effect of a flash memory. The method comprises the following steps: providing a semiconductor substrate, wherein a tunneling oxidization layer and a floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer are sequentially formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate; forming a hard mask layer on the surface of the floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer, sequentially etching the hard mask layer, the floating gate polycrystalline silicon layer, the tunneling oxidization layer and the semiconductor substrate, and forming a shallow trench in the semiconductor substrate; adopting in-situ steam generation process to form a liner oxidization layer covering the surface of the shallow trench; and adopting chemical vapor deposition to form an isolation medium layer filling the shallow trench. Through the STI structure forming method for the flash memory, the smiling face problem of the floating gate tunneling oxide caused by the traditional process can be effectively solved, the programming and erasure efficiency of the flash memory can be improved, and the read current of the flash memory in an erasure state can be increased, thus achieving the purpose of increasing a memory window.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
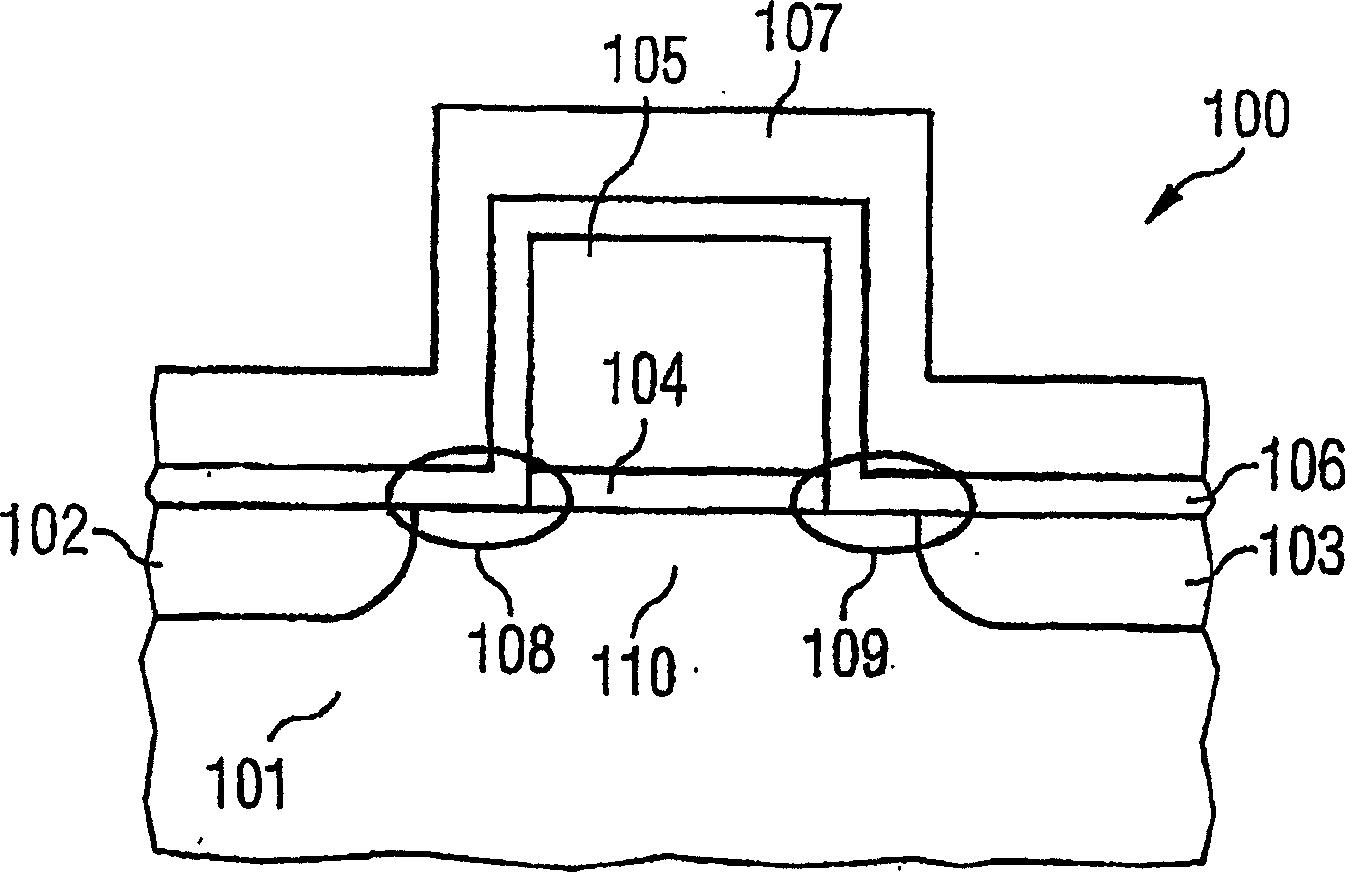
Semiconductor storage
InactiveUS20050226044A1Sufficient memory functionEffective restraint of interferenceTransistorSolid-state devicesCharge retentionSemiconductor storage devices
A semiconductor storage device includes a semiconductor substrate, a gate insulating film formed on the semiconductor substrate, a single gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film, two charge holding portions formed on both sides of the gate electrode, source / drain regions respectively corresponding to the charge holding portions, and a channel region disposed under the single gate electrode. A memory function implemented by these two charge holding portions and a transistor operation function implemented by the gate insulating film is separated from each other for securing sufficient memory function as well as easily suppressing short channel effect by making the gate insulating film thinner.
Owner:SHARP KK
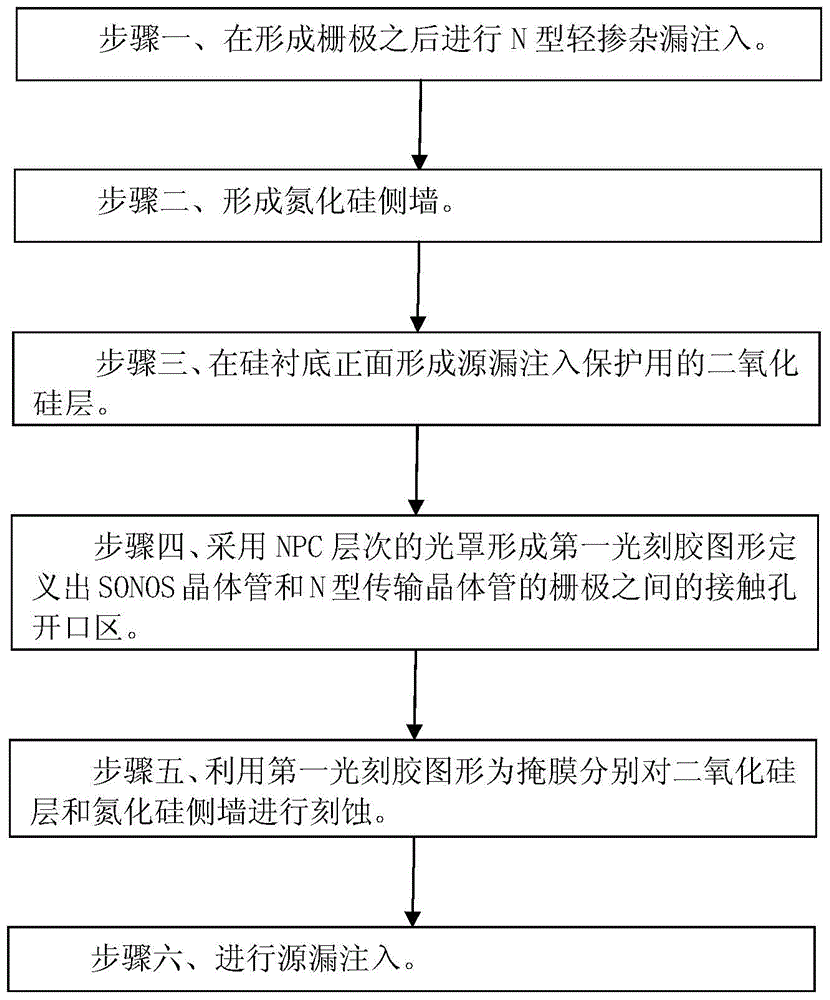
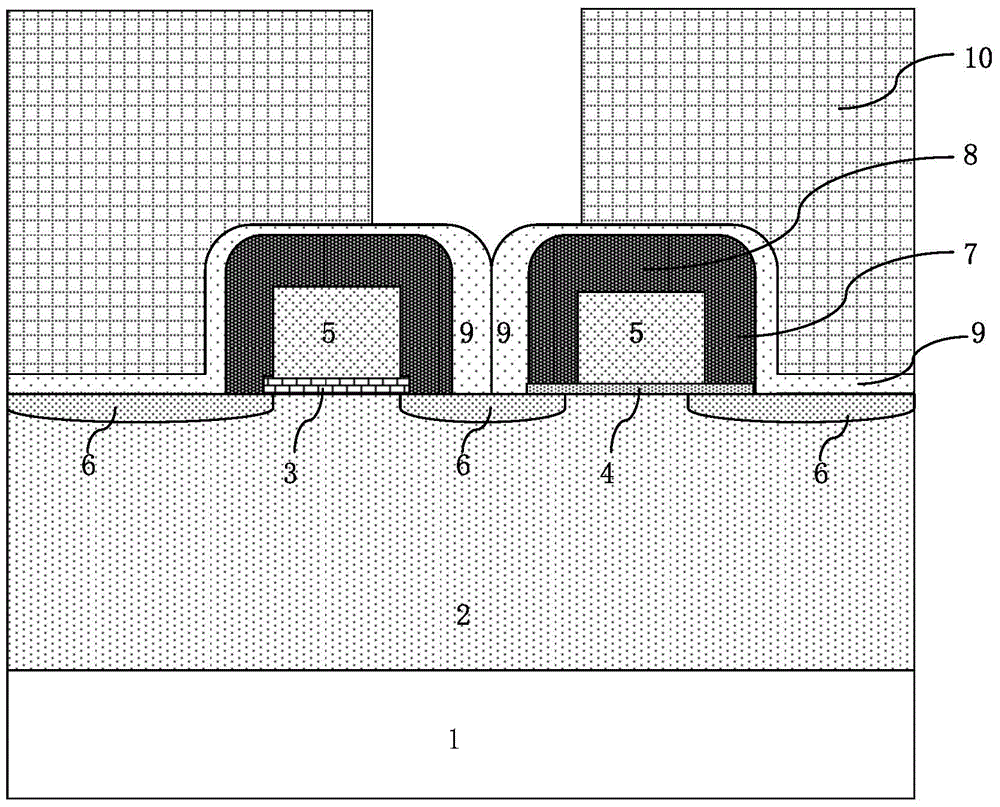
Method for improving SONOS memory reading operation capability
ActiveCN105742249AProtectEfficient dopingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon dioxideTransistor
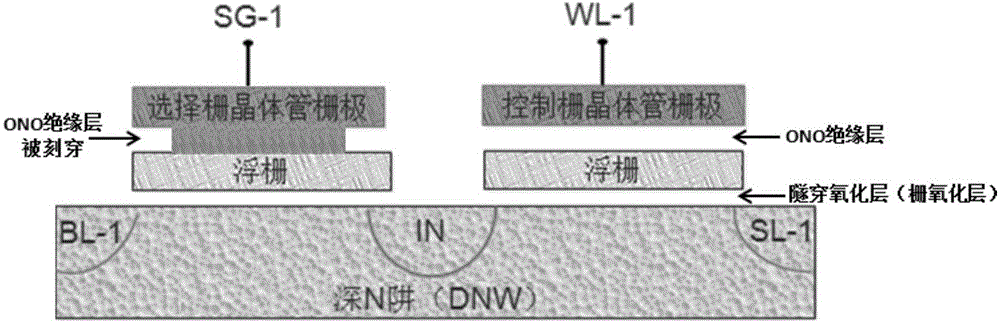
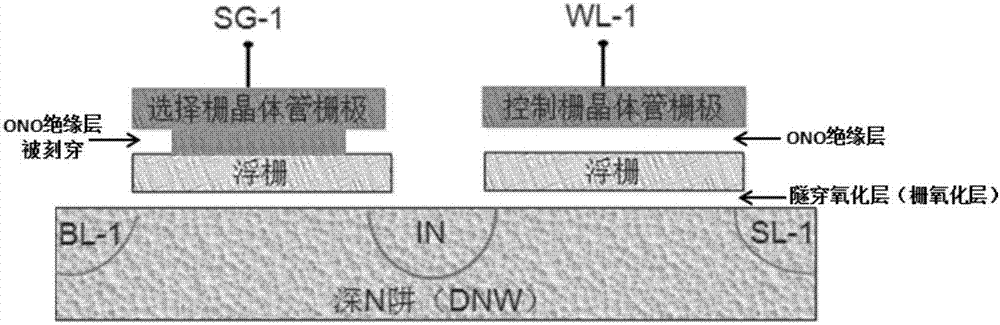
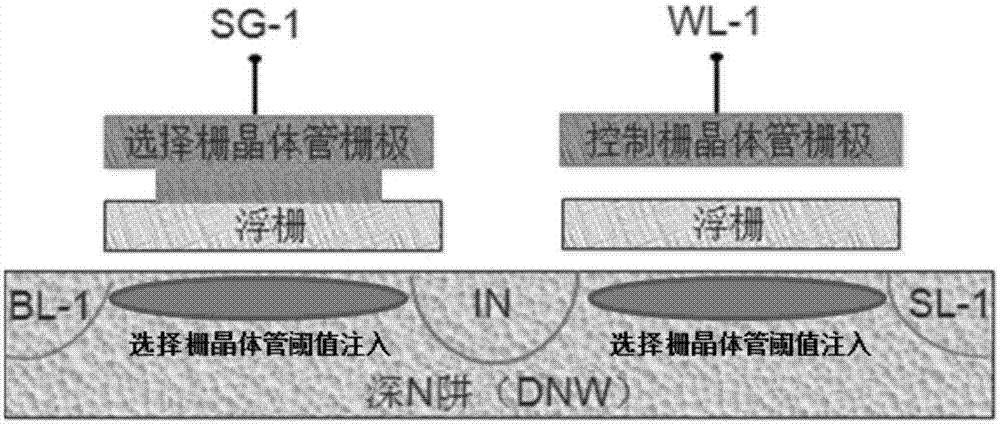
The invention discloses a method for improving SONOS memory reading operation capability. The method comprises steps that N-type light doping drain injection is carried out after formation of a grid electrode; a silicon nitride side wall is formed; a silicon dioxide layer for source and drain injection protection is formed at a front face of a silicon substrate; an NPC-level light cover is employed to from a first photoresist graph to define contact hole opening zones between grid electrodes of an SONOS transistor and an N-type transistor; the first photoresist graph is utilized as a mask layer for respectively etching the silicon dioxide layer and the silicon nitride side wall; source and drain injection is carried out. Through the method, the reading current of devices can be improved, and reading operation capability of the devices is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
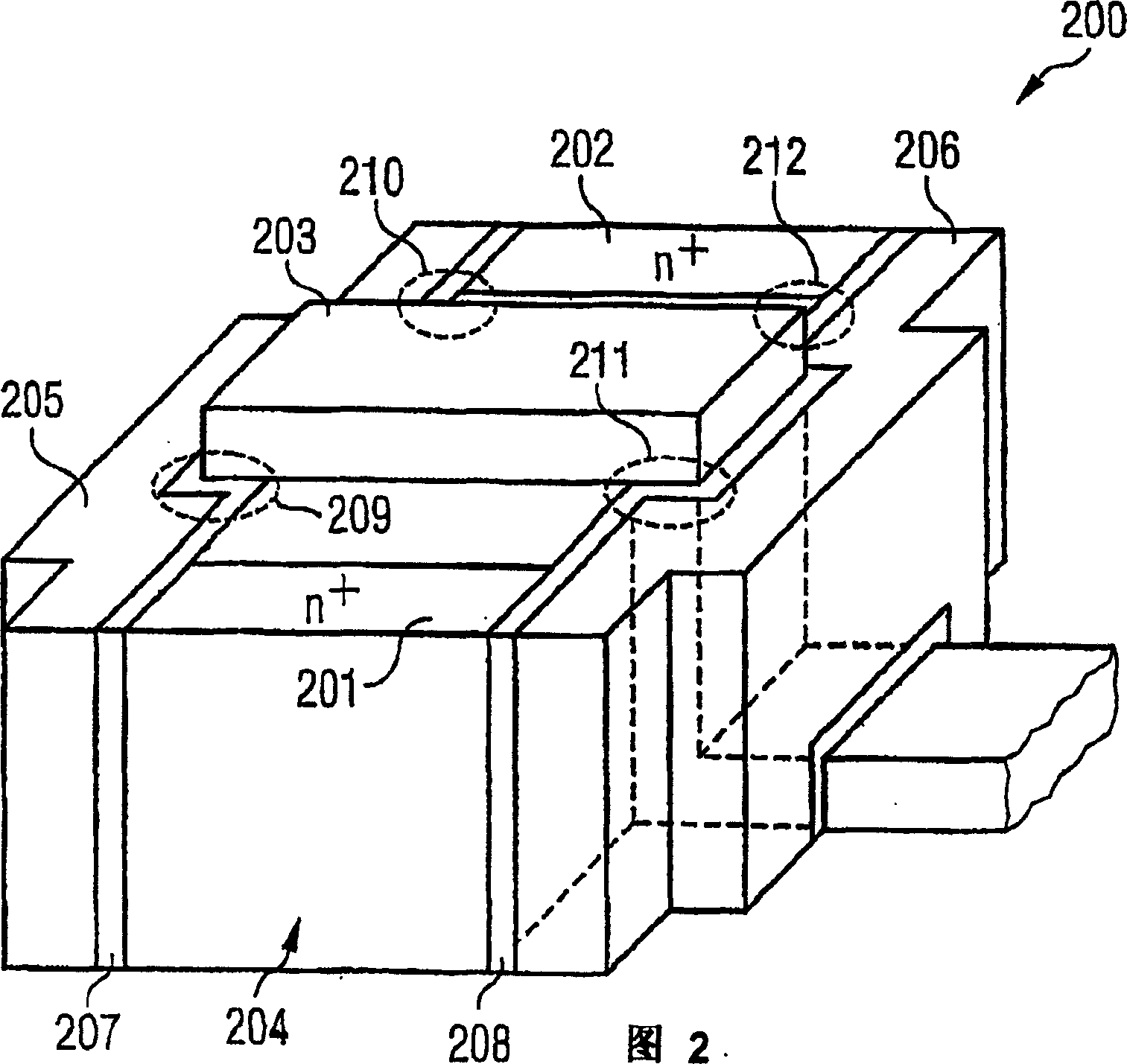
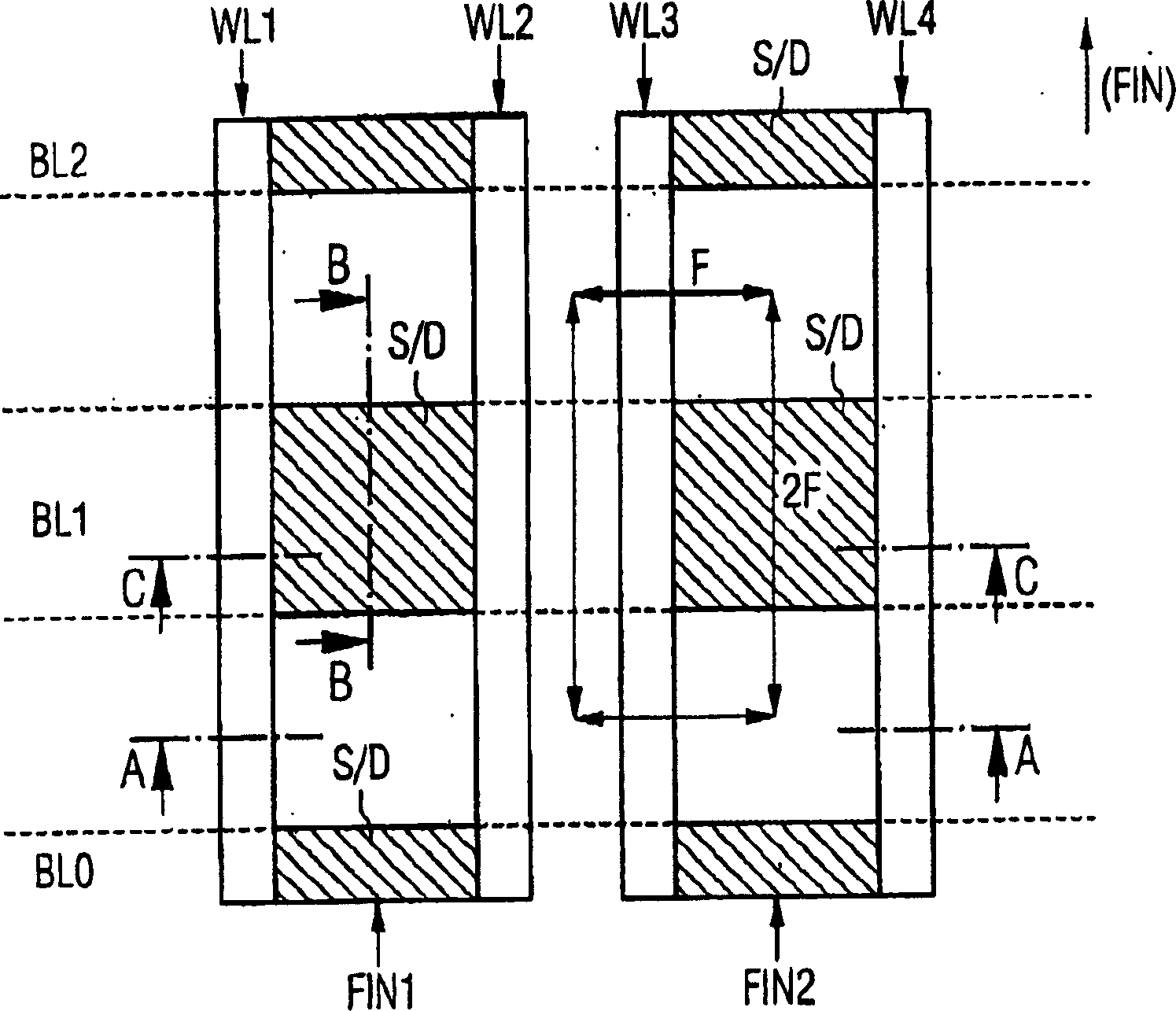
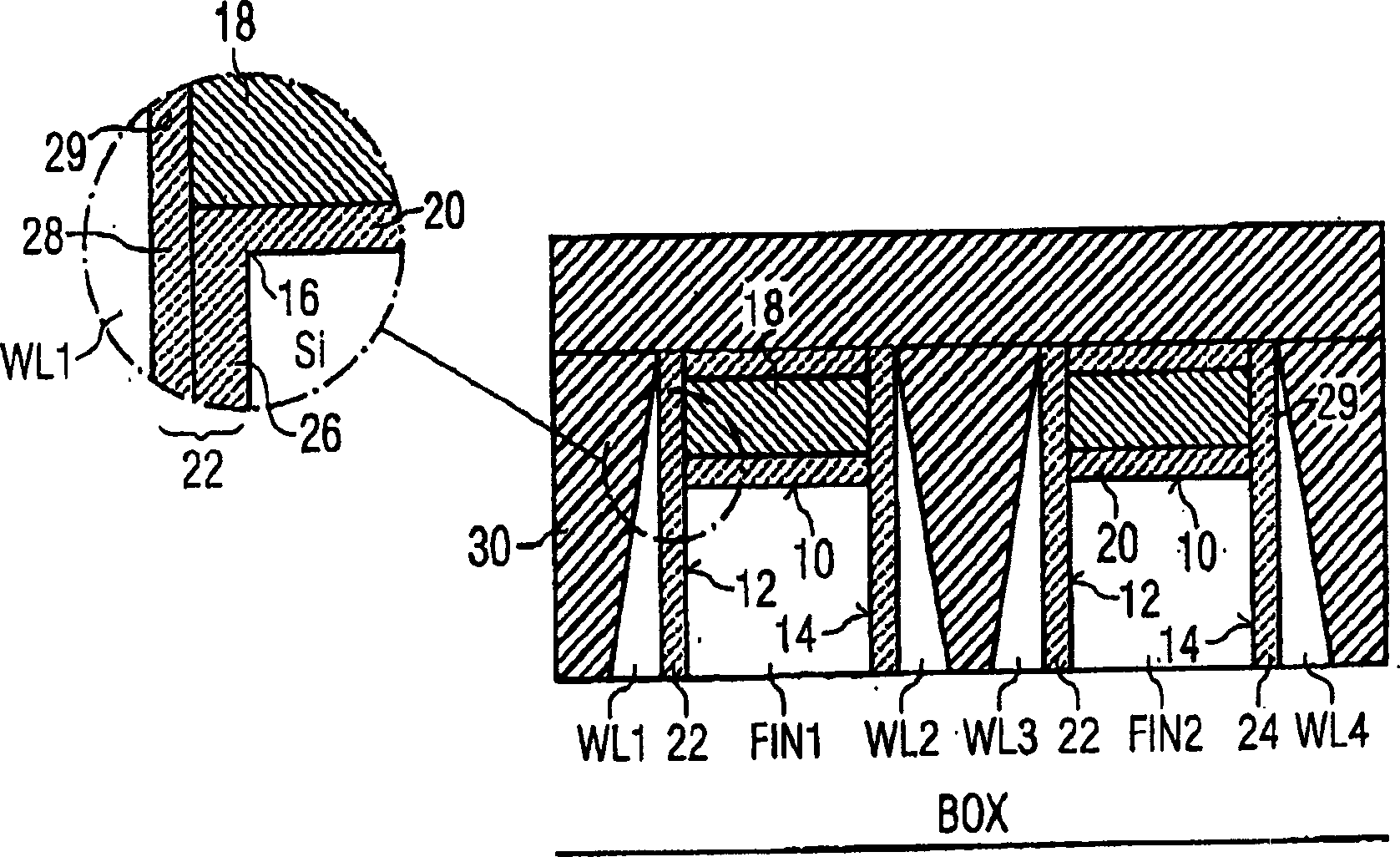
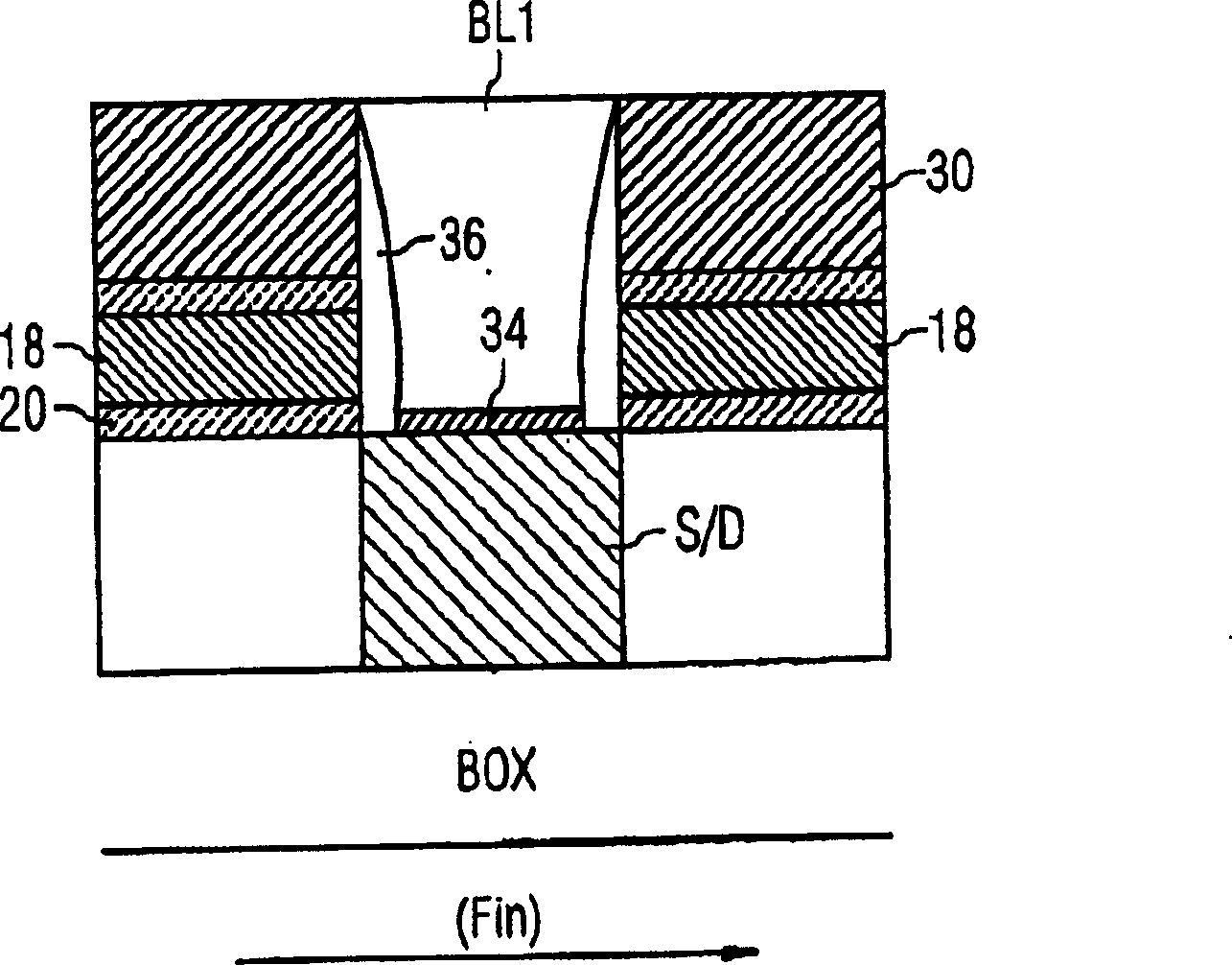
Fin field effect transistor memory cell, fin field effect transistor memory cell arrangement, and method for the production of a fin field effect transistor memory cell
InactiveCN1751392AImprove storage densityLow costTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor
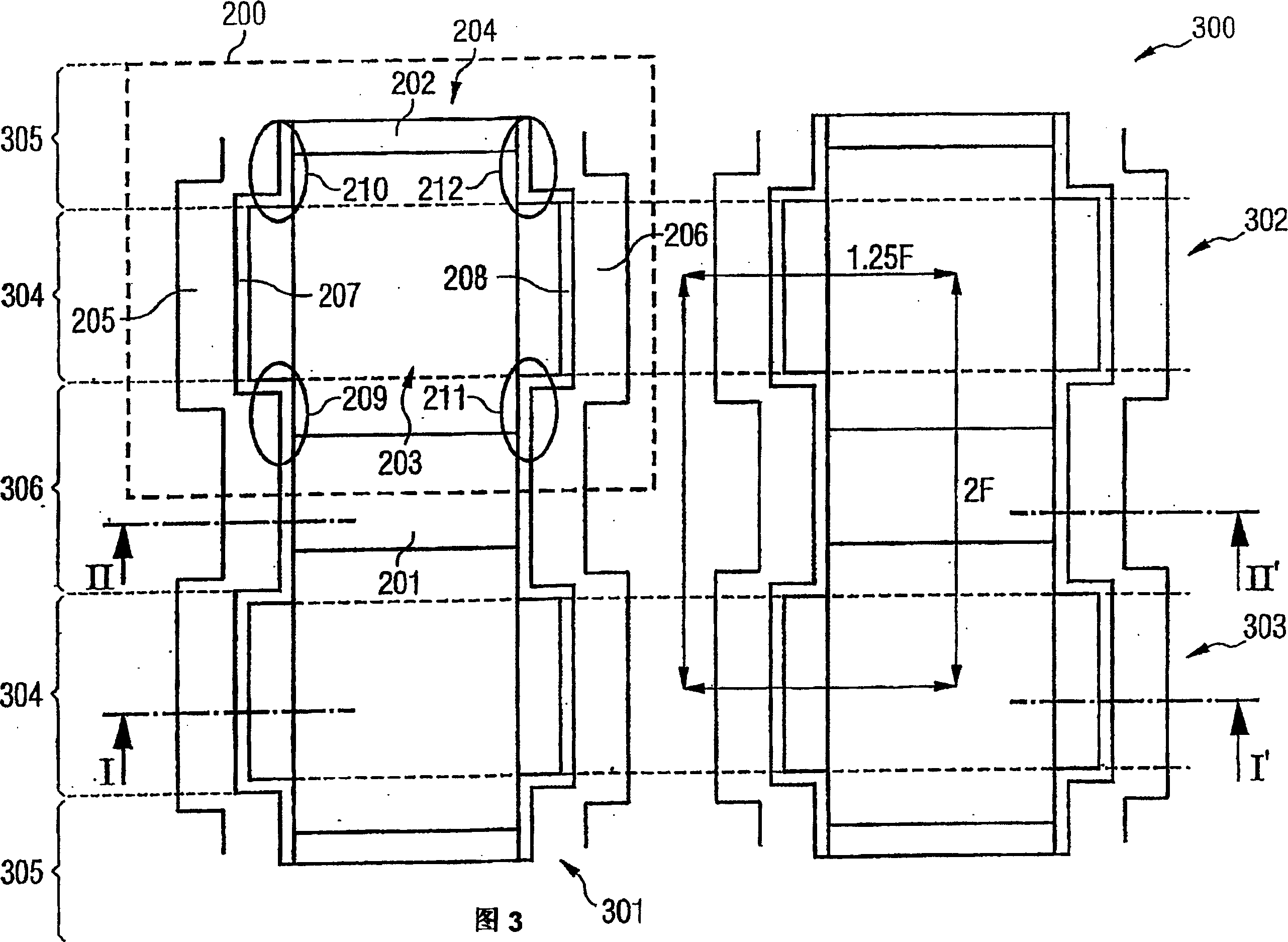
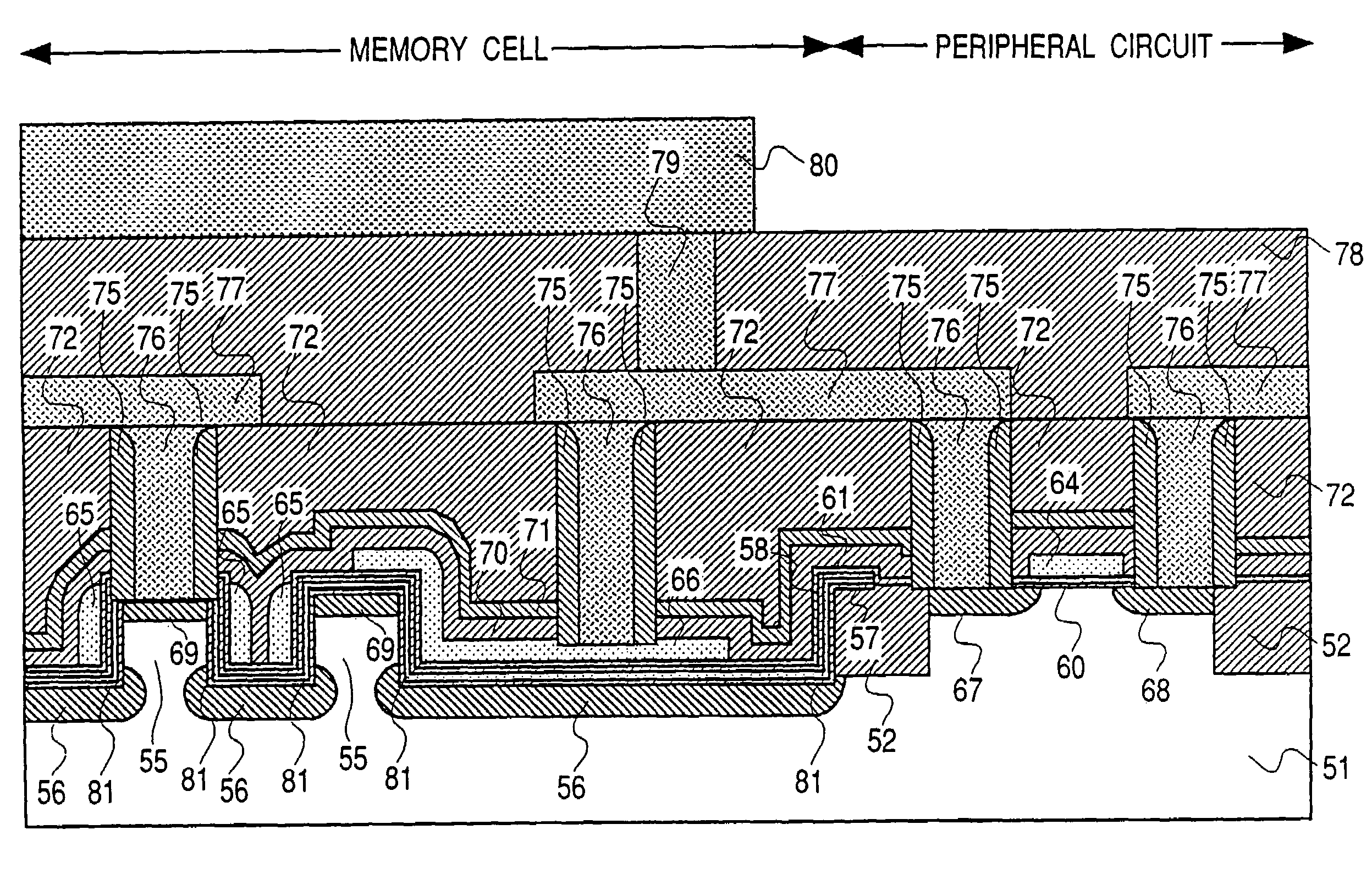
The invention relates to a fin field effect transistor memory cell (200), a fin field effect transistor memory cell arrangement, and a method for producing a fin field effect transistor memory cell. Said fin field effect transistor memory cell comprises a first (201) and a second (202) source / drain area and a gate area. The memory cell further comprises a semiconductor fin (204) encompassing the channel zone between the first and the second source / drain area. Also provided is a charge storage layer (207, 208) that is disposed at least in part on the gate area. A wordline area (205, 206) is arranged in at least one sector of the charge storage layer. The charge storage layer is designed such that electric charge carriers can be selectively introduced into or removed from the charge storage layer by applying predefined electrical potentials to the fin field effect transistor memory cell.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Fabrication method of flash memory unit
ActiveCN106981493AImprove qualityLower resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxide semiconductorEngineering
The invention relates to a fabrication method of a semiconductor device, and discloses a fabrication method of a flash memory unit. According to the fabrication method of the flash memory unit, P-type impurity injected to a logic grate of a select gate P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) transistor region is diffused to an N-type floating gate poly-silicon layer by a subsequent high-temperature process after the logic gate of the select gate PMOS transistor region and a logic gate of a control gate PMOS transistor region are separated, so that an N-type floating gate is changed to a P-type floating gate, a select gate PMOS transistor with a surface channel having a relatively threshold value can be successfully fabricated on the flash memory unit with a size being 55 nanometers, and mass production is achieved. Moreover, by the process of growing the logic gates and the process of separating the logic gates, the floating gate doping of the control gate PMOS transistor cannot be affected as well as the surface channel, having the relatively threshold value, of the select gate PMOS transistor is formed.
Owner:INTEGRATED SILICON SOLUTION SHANGHAI
High-density NROM-FINFET
InactiveCN1689162AReduce areaIncrease read currentTransistorEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsRead-only memoryCharge carrier
Semiconductor memory having memory cells, each including first and second conductively-doped contact regions and a channel region arranged between the latter, formed in a web-like rib made of semiconductor material and arranged one behind the other in this sequence in the longitudinal direction of the rib. The rib has an essentially rectangular shape with an upper side of the rib and rib side faces lying opposite. A memory layer is configured for programming the memory cell, arranged on the upper side of the rib spaced apart by a first insulator layer, and projects in the normal direction of the one rib side face over one of the rib side faces so that the one rib side face and the upper side of the rib form an edge for injecting charge carriers from the channel region into the memory layer. A gate electrode is spaced apart from the one rib side face by a second insulator layer and from the memory layer by a third insulator layer, electrically insulated from the channel region, and configured to control its electrical conductivity.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
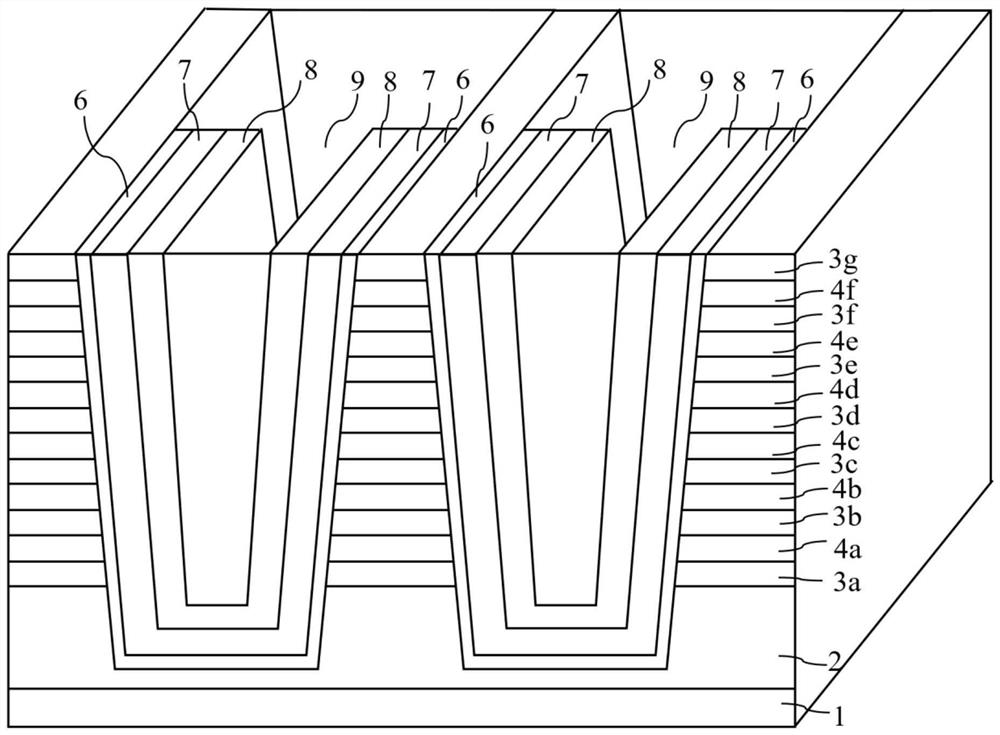
Three-dimensional groove type ferroelectric memory and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111799264ACompact wiringHigh density integrationTransistorSolid-state devicesPhysicsThin membrane
The invention discloses a three-dimensional groove type ferroelectric memory and a preparation method thereof. The three-dimensional groove type ferroelectric memory comprises a substrate (1) and a conductive layer (2) arranged on the substrate (1). A laminated structure arranged on the conductive layer (2) comprises a plurality of horizontal isolation layers (3) and control gate electrodes (4) which are arranged in an overlapping manner. The plurality of trench-type memory cell strings (5) vertically penetrate through the laminated structure, and each trench-type memory cell string (5) comprises a trench hole (11) which vertically penetrates through the laminated structure and has a trench bottom embedded into the conductive layer (2). A buffer layer (6), a ferroelectric film layer (7), achannel layer (8) and a filling layer (9) are sequentially laid on the side wall and the groove bottom of the groove hole (11). The control gate electrode (4), the buffer layer (6), the ferroelectricfilm layer (7) and the channel layer (8) form a plurality of ferroelectric field effect transistors which are connected in series. According to the ferroelectric memory, more compact wiring can be obtained, and higher-density integration can be realized; during preparation, required materials are sequentially deposited, etching is not needed, and the reliability of the ferroelectric memory is ensured.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and its manufacturing method
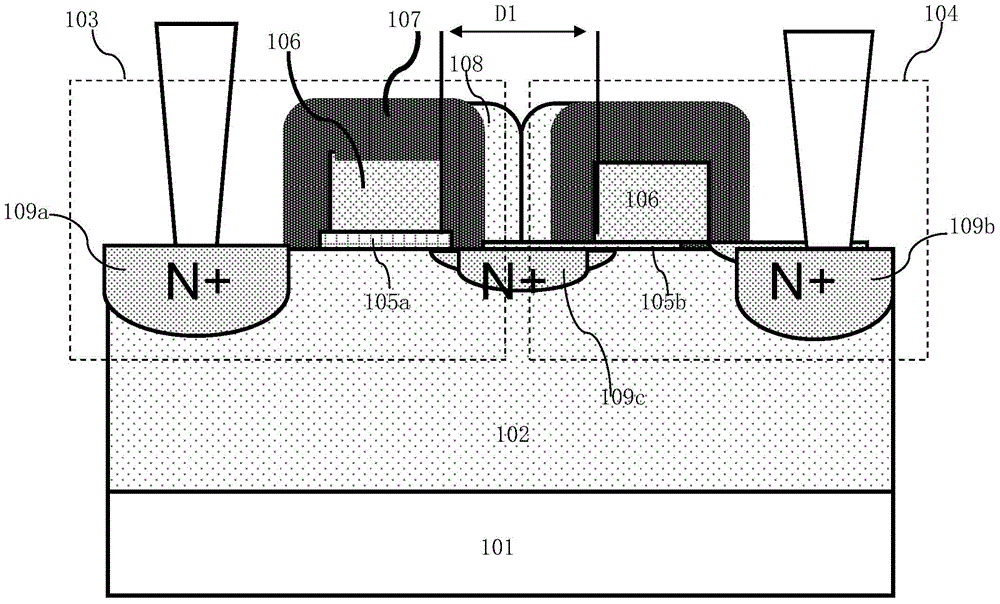
InactiveUS7585731B2Increase read currentEliminate failureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringAnisotropic etching
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor integrated circuit device is provided including providing a substrate with projecting island regions formed in stripes, with first regions of the substrate adjacent the projecting island regions and with a conductive film covering the projecting island regions and first regions. An insulating film is formed between the projecting island regions and conductive film, wherein the projecting island regions extend in a first direction in stripes. The conductive film is anisotropically etched using a mask covering portions of the conductive film to form conductive lines on sides of the projecting island regions and the portions of the conductive film integrated with the conductive lines, which conductive lines serve as common gate electrodes for MISFETs.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
NOR flash memory and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN109727983AIncrease junction areaImprove programming efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEtchingPolycrystalline silicon
The invention discloses a NOR flash memory. In the flash cell array of the storage area of the NOR flash memory, active regions are in strip shapes and are arranged in parallel. The polycrystalline silicon of polycrystalline silicon control gates of the flash cells in the same row are connected together to form a polycrystalline silicon row. A polycrystalline silicon floating gate is on top of theactive region perpendicularly intersecting the polycrystalline silicon row and is isolated by a first gate oxide layer. A drain region comprises a self-aligned conformal injection region extending tothe sides of the active regions. The position of the self-aligned conformal injection region is defined by the self-aligned etched back field oxygen. The self-aligned etch back region of the field oxide is formed by the self-aligned definition of the gate structure and the active region after the gate structure etching. In the source region, a self-aligned conformal injection region is also superimposed. The invention also discloses a method for manufacturing a NOR flash memory. The NOR flash memory can improve the programming efficiency without changing the gate structure, and can also reduce electric leakage and improve the performance of the device.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20060205130A1Increase read currentEliminate failureTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorIntegrated circuit
A semiconductor integrated circuit device has a plurality of rows of pillars, each row being composed of semiconductor pillars and insulator pillars alternately arranged in one direction with no gap therebetween, a plurality of nonvolatile memory elements provided individually in said plurality of semiconductor pillars, said plurality of nonvolatile memory elements having control gate electrodes provided over side surfaces of said semiconductor pillars along said one direction via gate insulating films, drain regions provided in upper surface portions of said semiconductor pillars, and source regions provided in bottom surface portions of said semiconductor pillars, and lines including the respective control gate electrodes of said plurality of nonvolatile memory elements and provided along said one direction over the side surfaces of said rows of pillars along said one direction.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
3D NAND preparation method adopting novel channel hole electric connecting layer material and 3D NAND
ActiveCN107994029AIncrease read currentGood electrical performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesCvd grapheneStructural stability
The invention provides a 3D NAND preparation method adopting a novel channel hole electric connecting layer material and a 3D NAND. The preparation method comprises the steps of depositing a substratestack structure on a substrate; etching the stack structure to form channel holes, wherein the channel holes are connected to the substrate to form a silicon groove of a certain depth; depositing a graphene epitaxial layer in the silicon groove; forming a channel hole side wall stack structure; etching the stack structure; and depositing a graphene connecting layer, wherein the graphene layer inthe channel hole side wall stack structure is connected with the graphene epitaxial layer through the graphene connecting layer. The thin graphene thin film has very high mobility and mechanical strength, so that the read current can be increased and channel hole structural stability can be improved.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
Method for forming shallow trench isolation structure for flash memory
ActiveCN102184887BFast depositionReduce oxidation reactionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower flowGas phase
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Method for manufacturing and using horizontal electrode configuration structure of nanoscale phase change memory unit
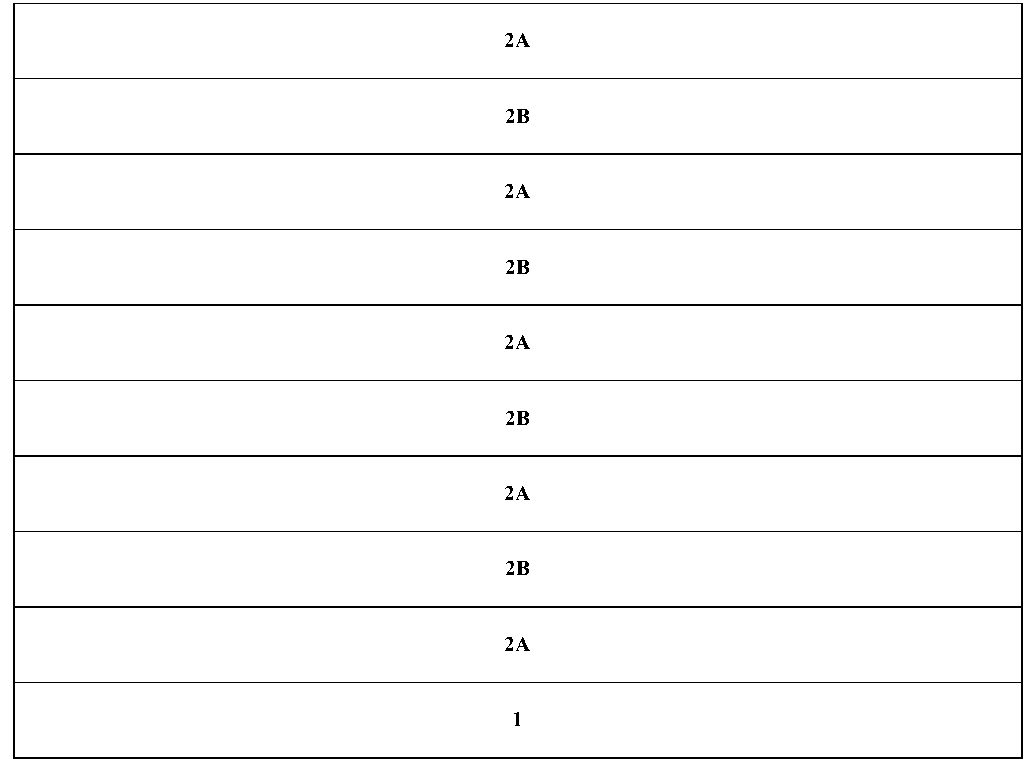
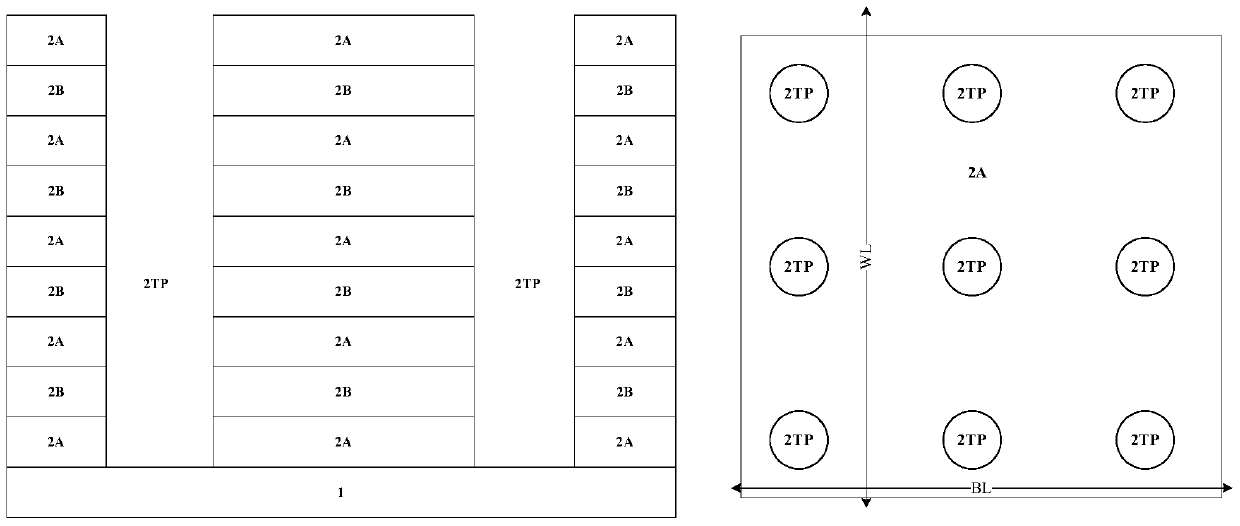
ActiveCN110783455BReduced equivalent resistanceIncrease read currentElectrical apparatusEquipotential surfacePhase-change memory
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing and using a horizontal electrode configuration structure for a nanoscale phase-change memory unit. The lower phase-change material layer and the upper electrode material layer are grown sequentially according to the procedures; during processing, the upper electrode material layer is based on the same process. The photolithography process forms the upper electrode of the outer ring common drain ground and the upper electrode of the inner source end; when in use, the upper layer electrode of the inner source end is connected to the source end, and the upper layer electrode of the outer ring common drain ground is common drain ground, and the source and drain end cannot be exchanged, and the current flows from The equipotential surface of the upper layer electrode at the inner source end flows horizontally to the outer ring equipotential surface of the outer ring common drain grounding upper layer electrode. For the high-resistance amorphous state, compared with the square structure, the equivalent resistance value R is significantly reduced, and the read current is increased, which is convenient for correct reading. Moreover, the horizontal flow of current reduces the current loss of elements connected in series at both ends in a general sense, thereby reducing the threshold current required for the amorphization process and reducing the overall power consumption.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three-dimensional semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104037175BIncrease read currentImprove reading speedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMOSFETPower flow
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com