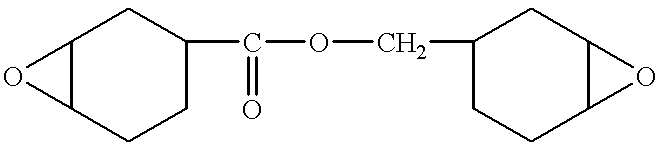
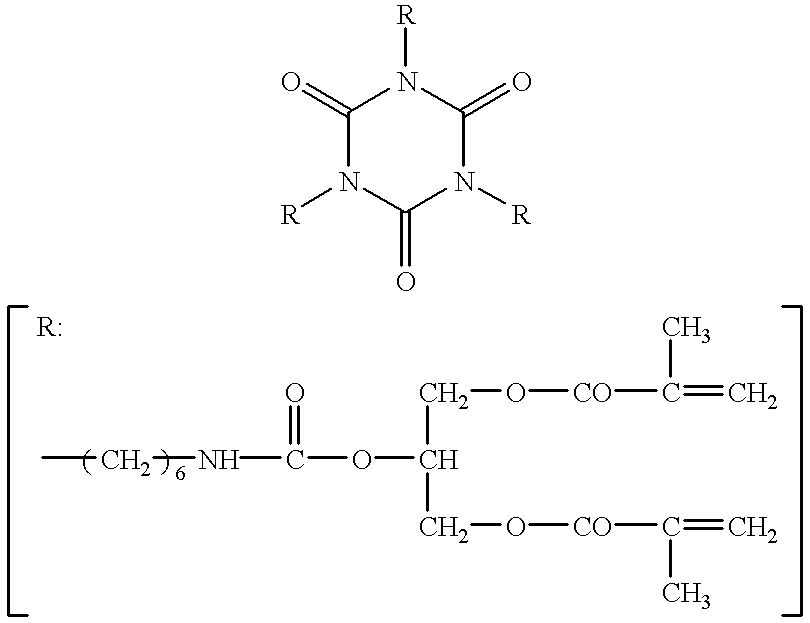
Patents
Literature
200 results about "Cell substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell substrate refers to the cells that are used to produce the desired biotechnological/biological products. Cell substrates may be microbial cells (e.g. yeast) or cells derived from various animal sources. ... Cell substrates differ in the degree to which they can be adapted to grow in defined culture media such as serum-free media. This is desirable for production in order to avoid potential contaminants from serum.
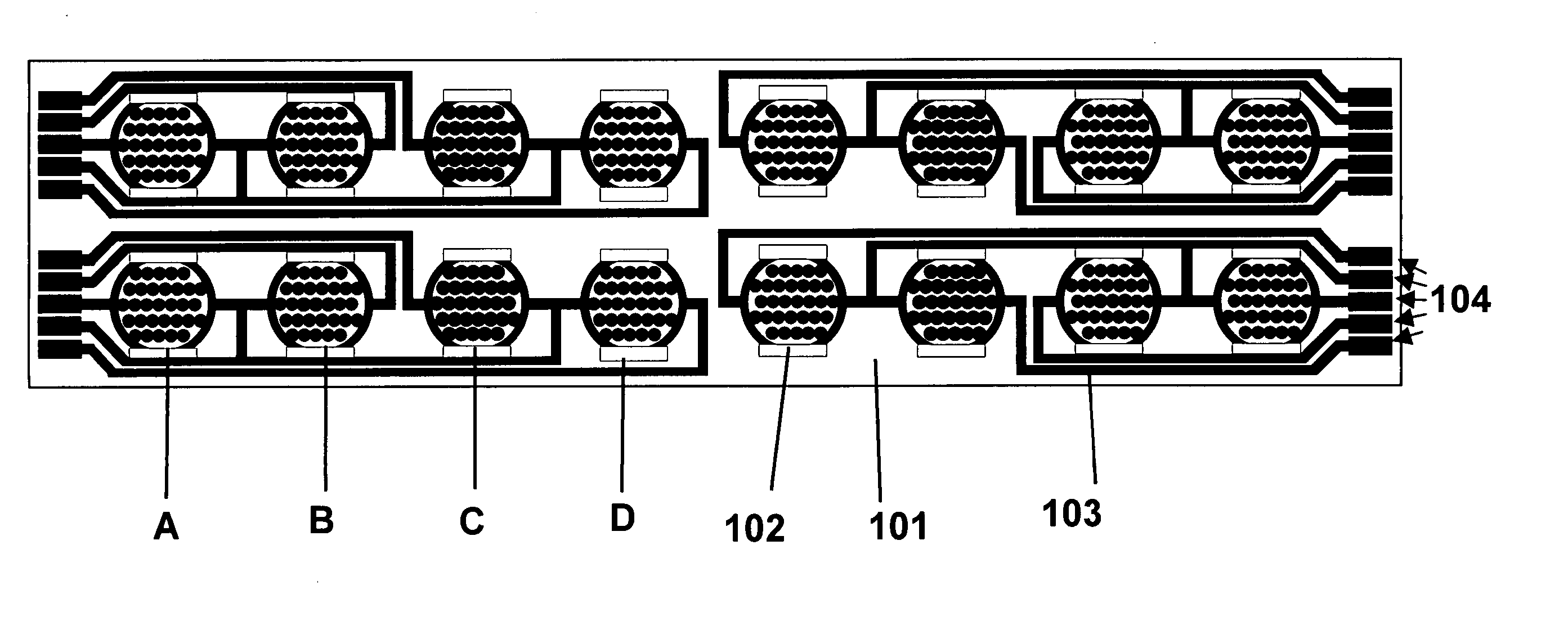
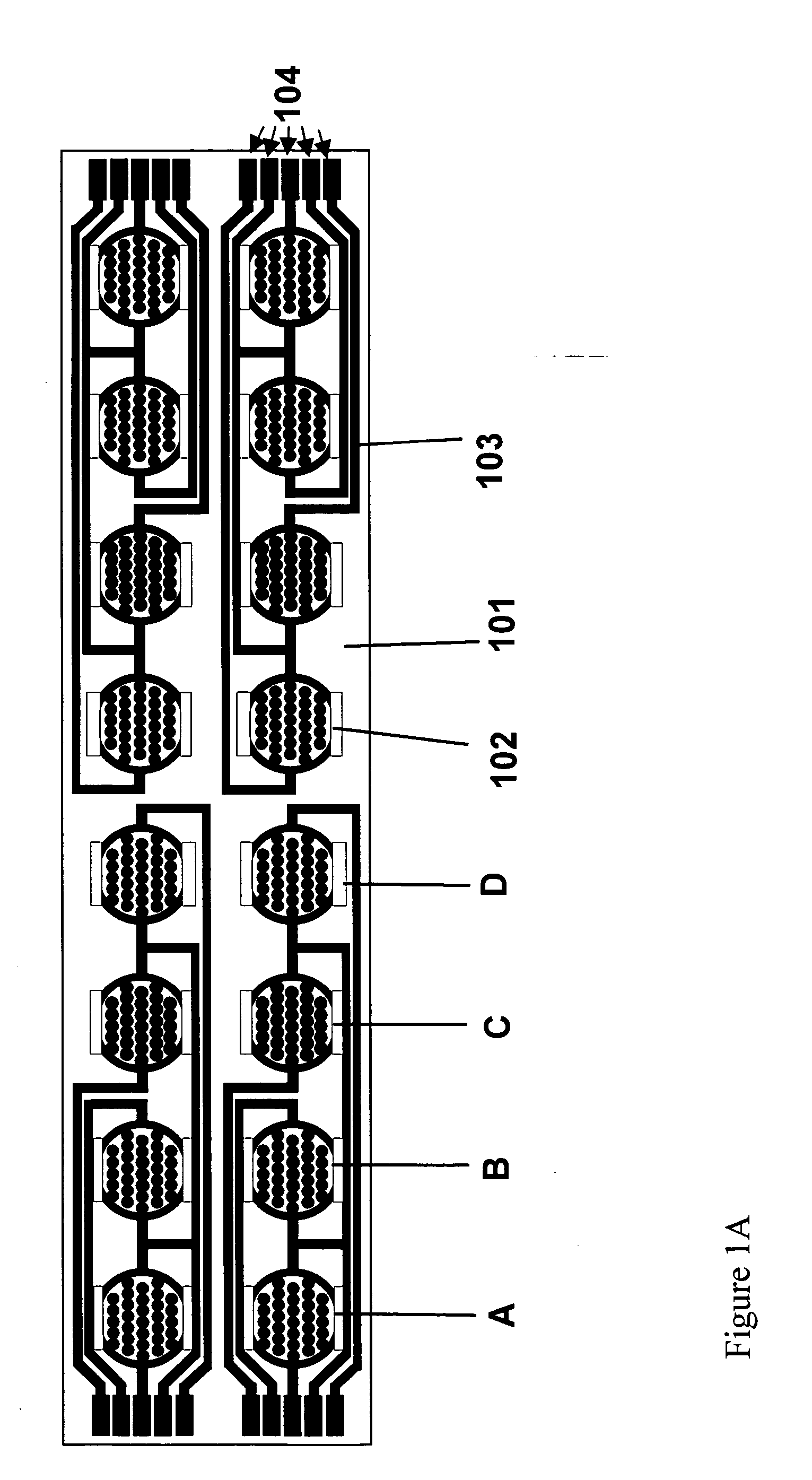
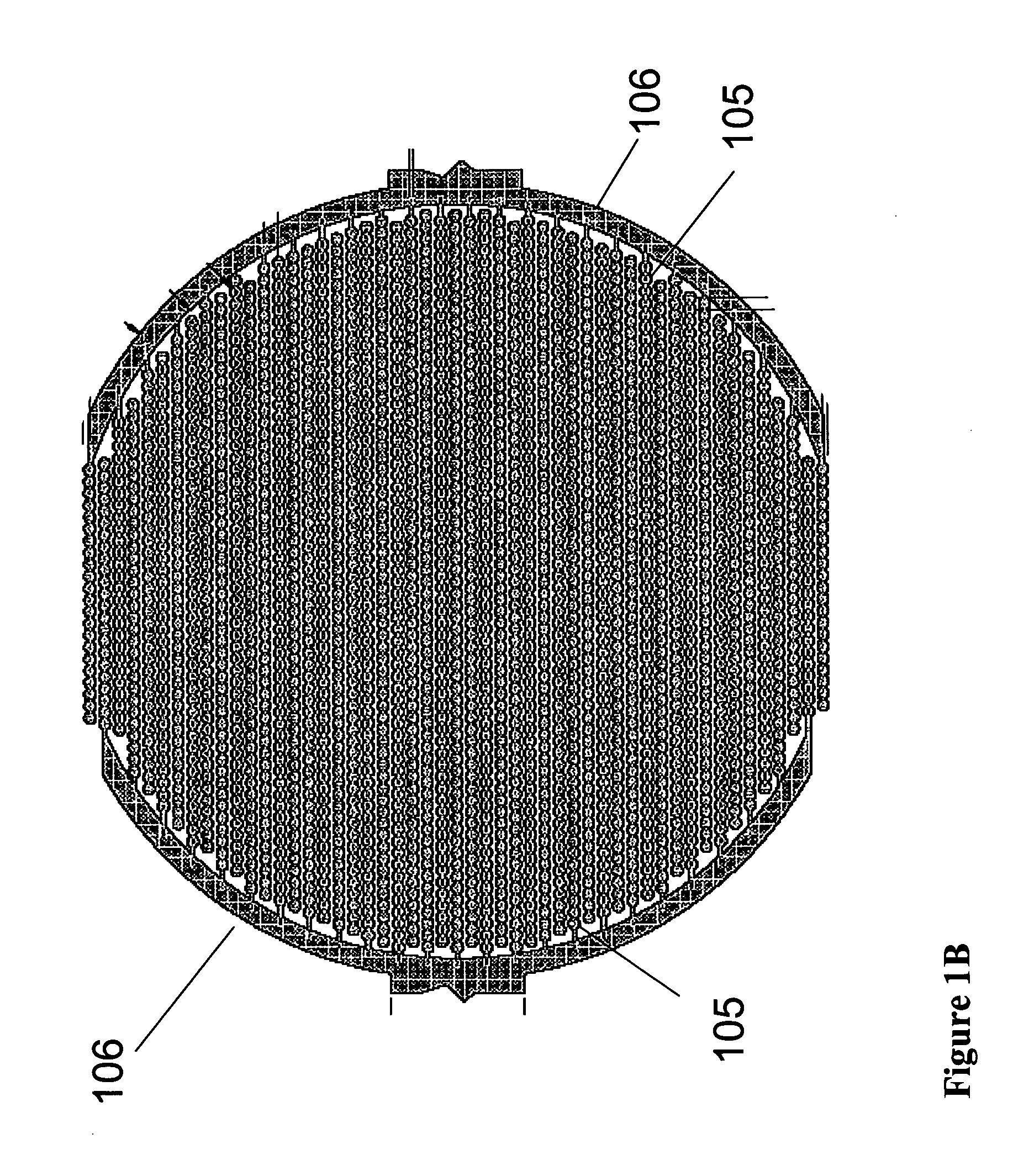
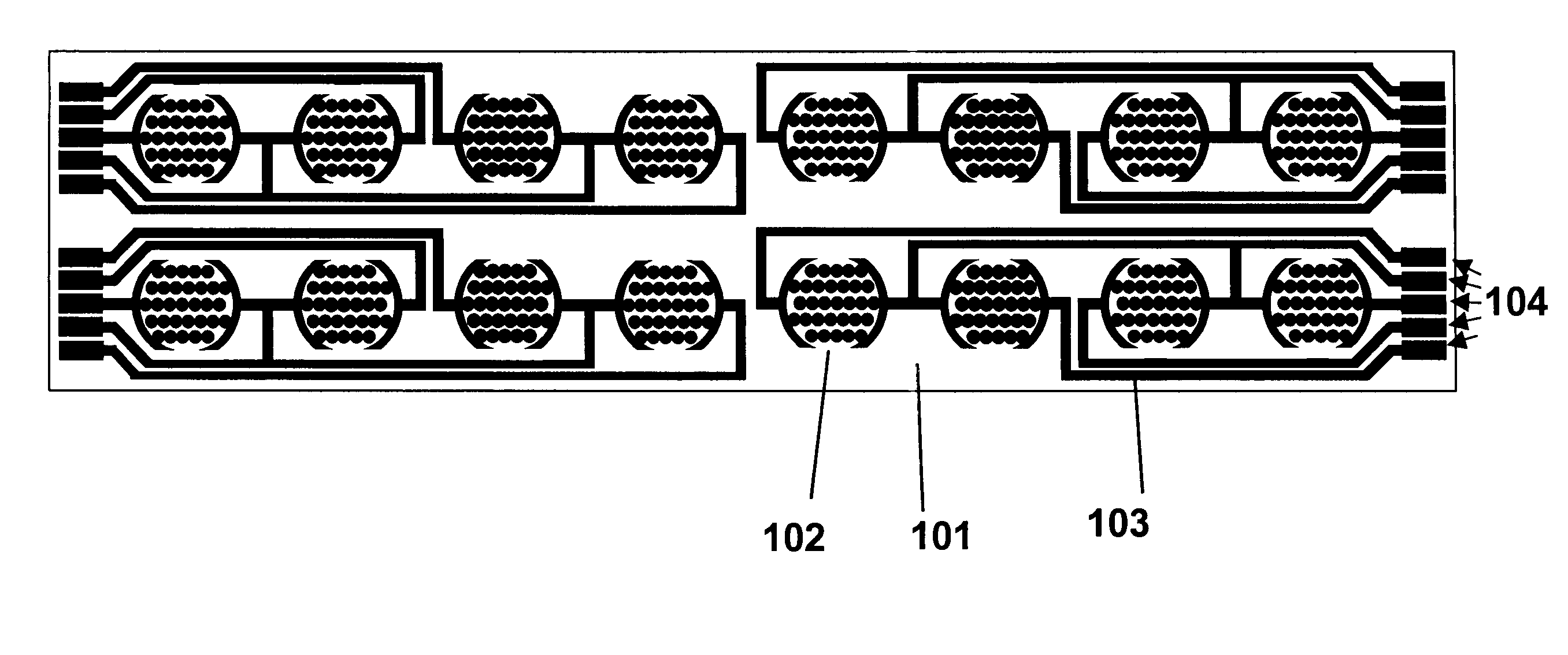
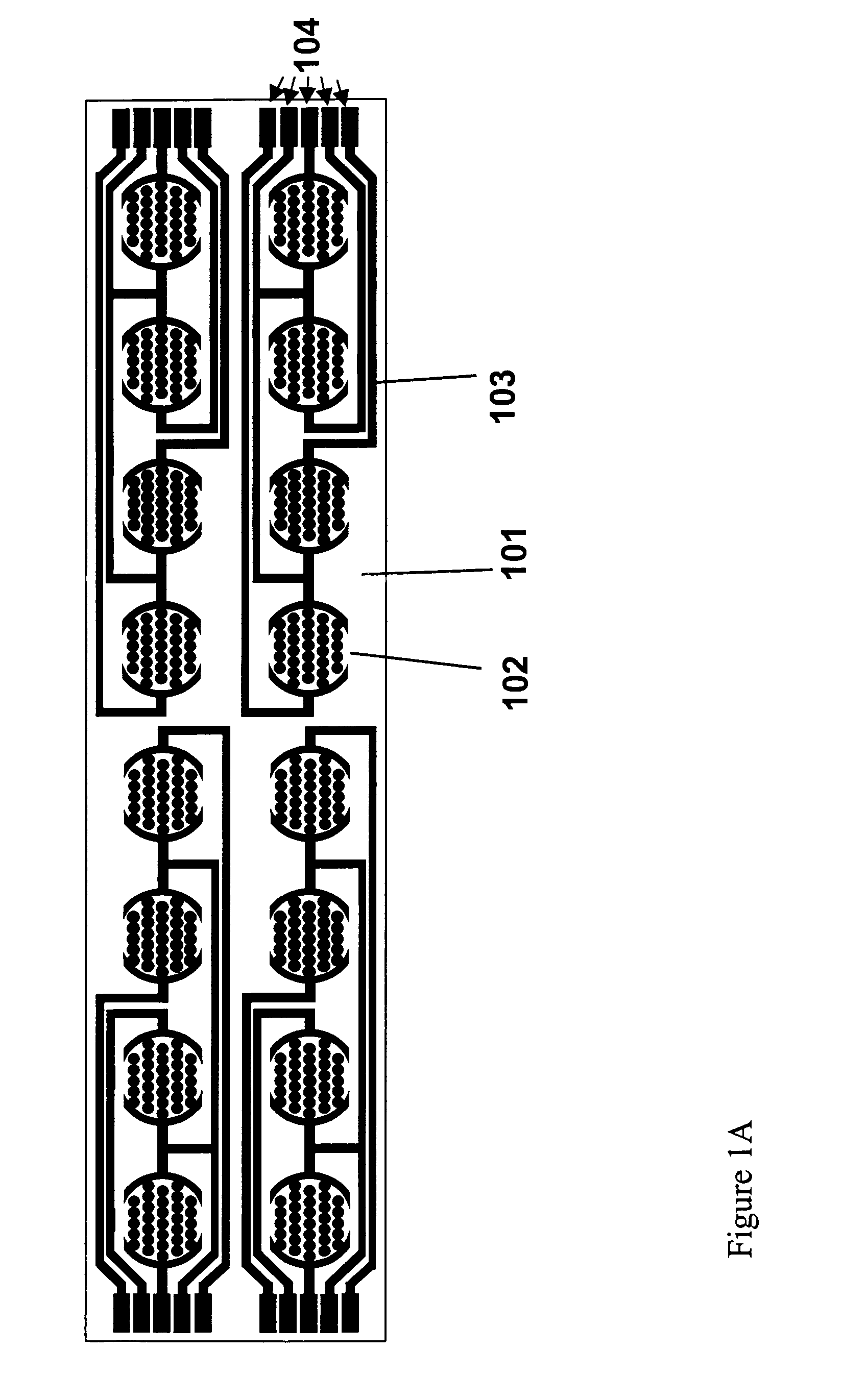
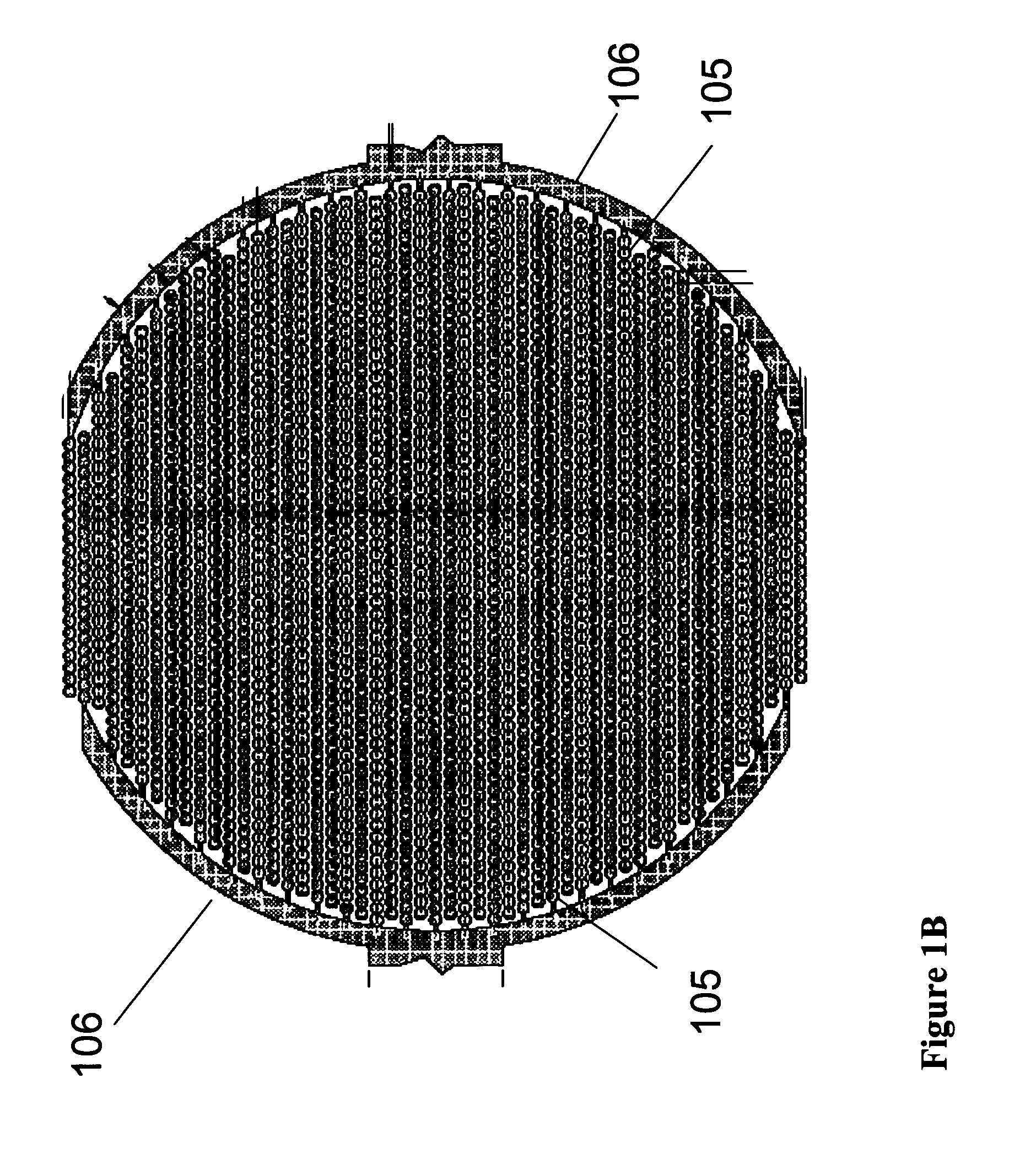
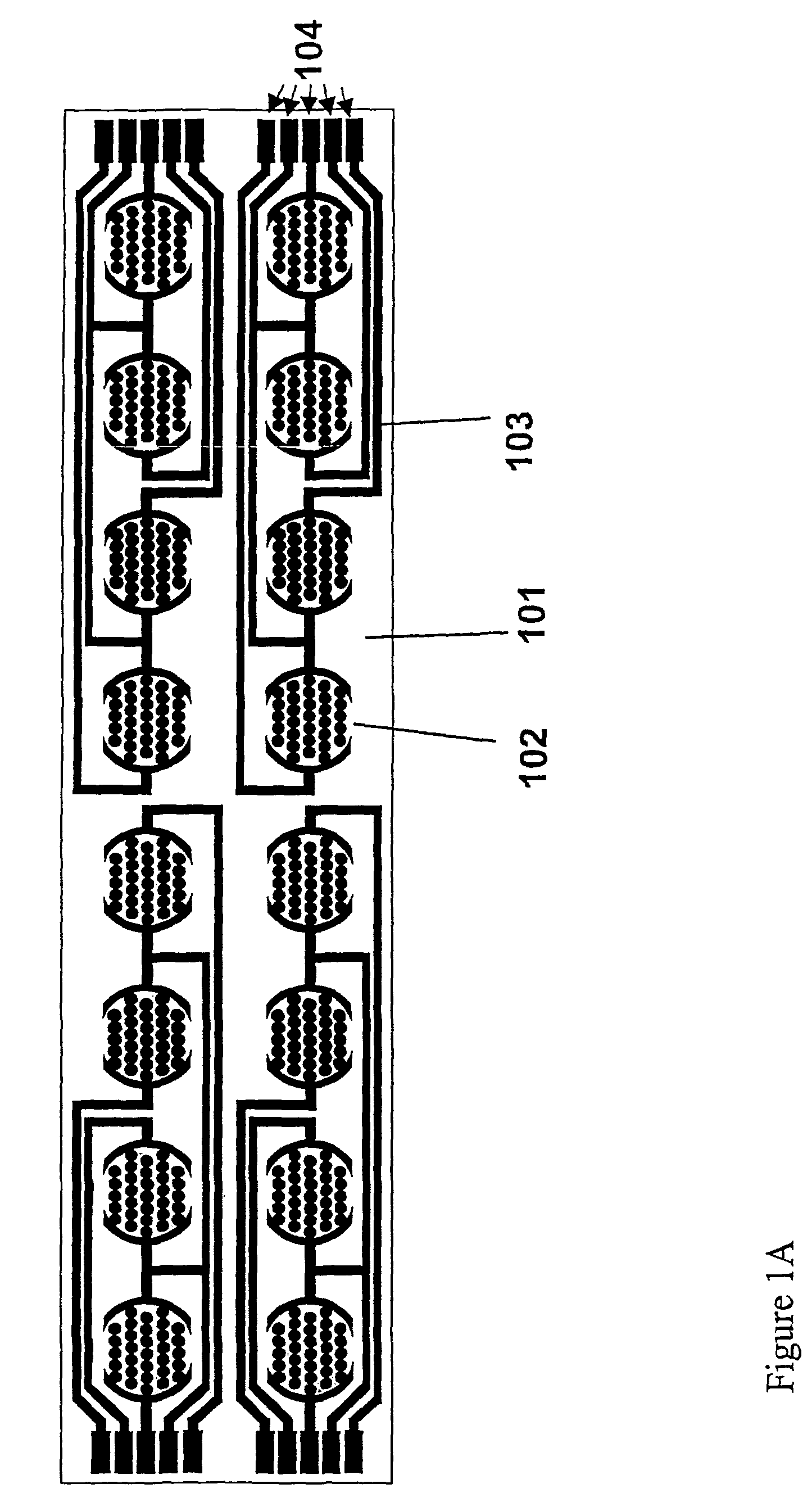
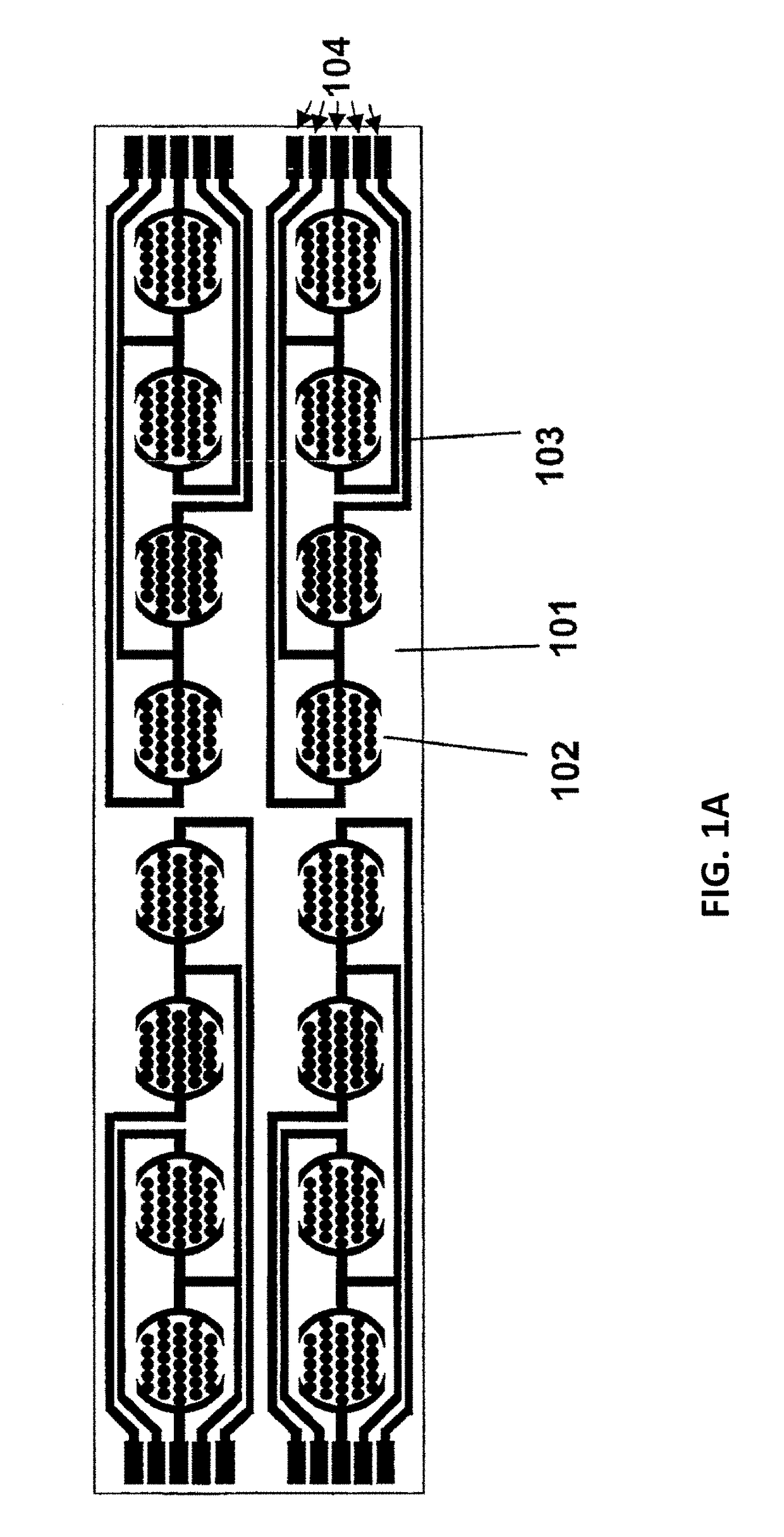
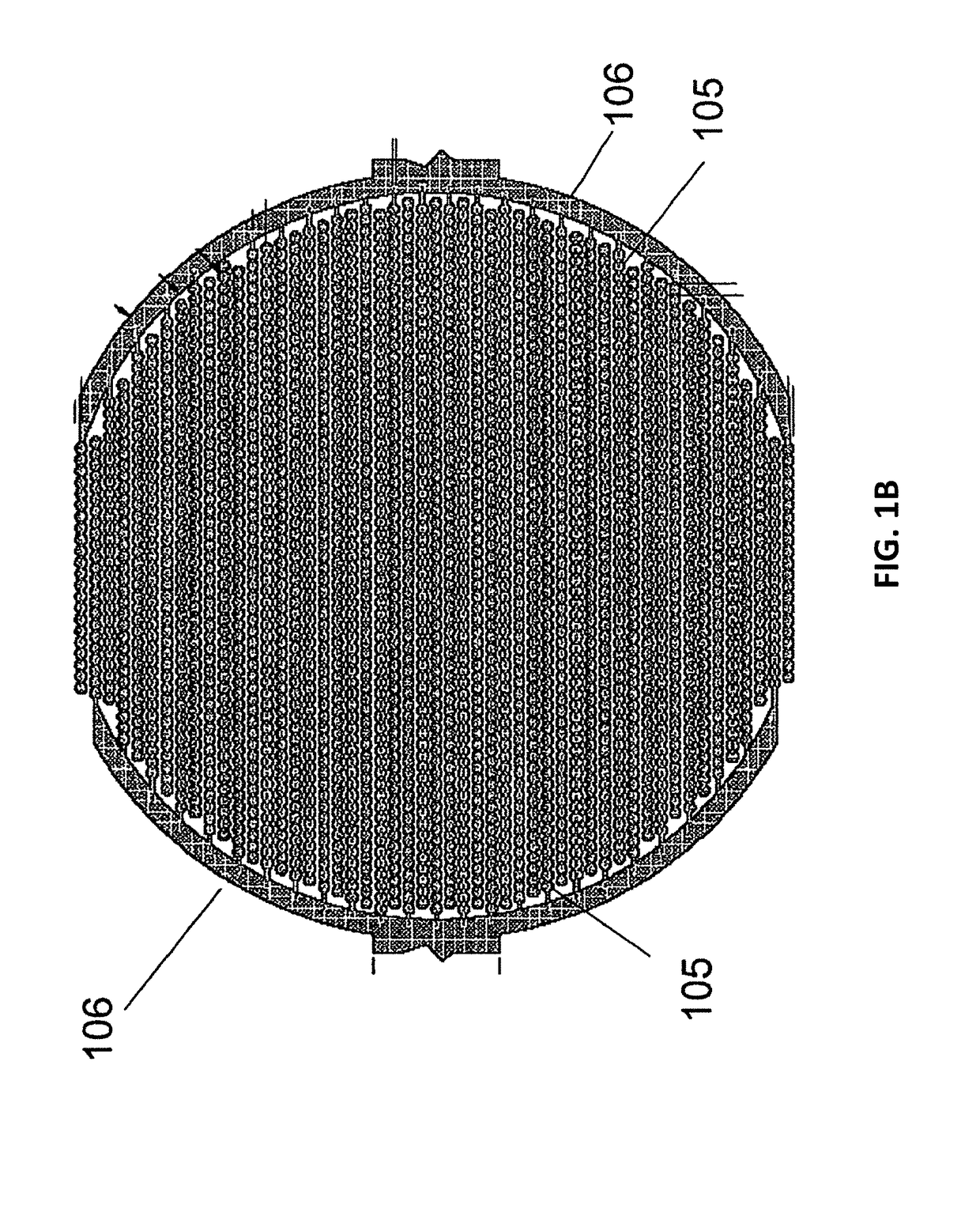
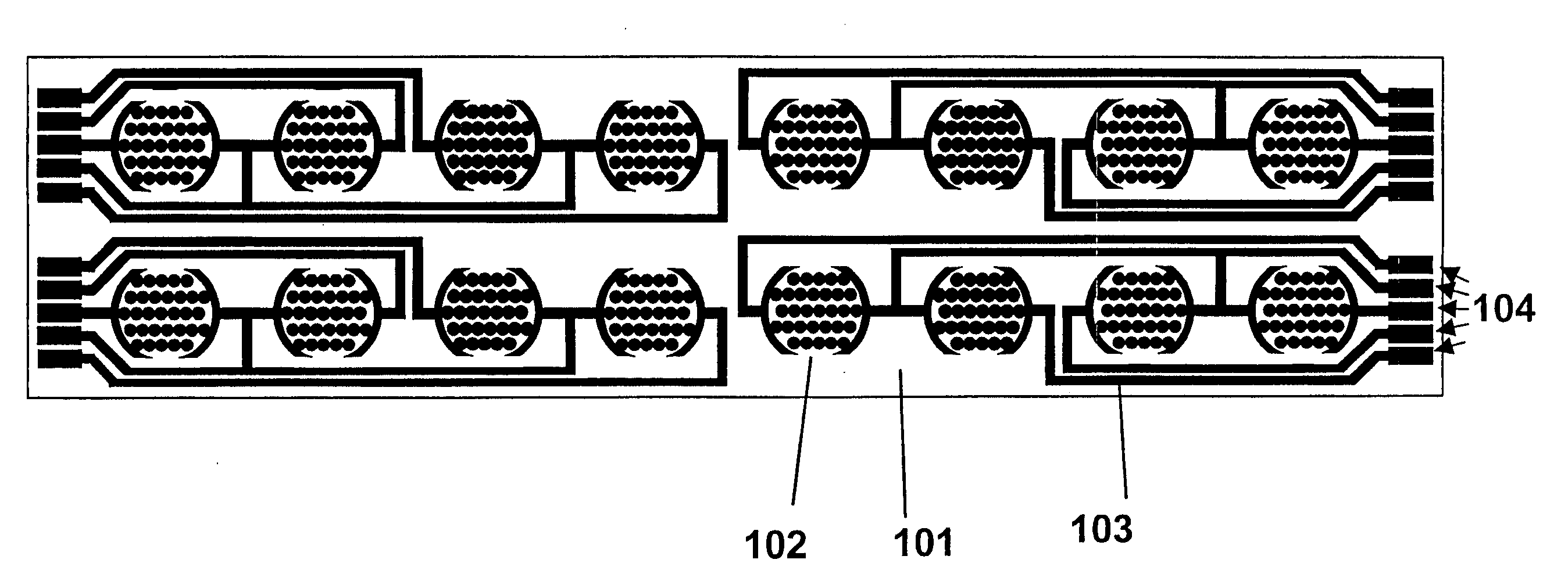
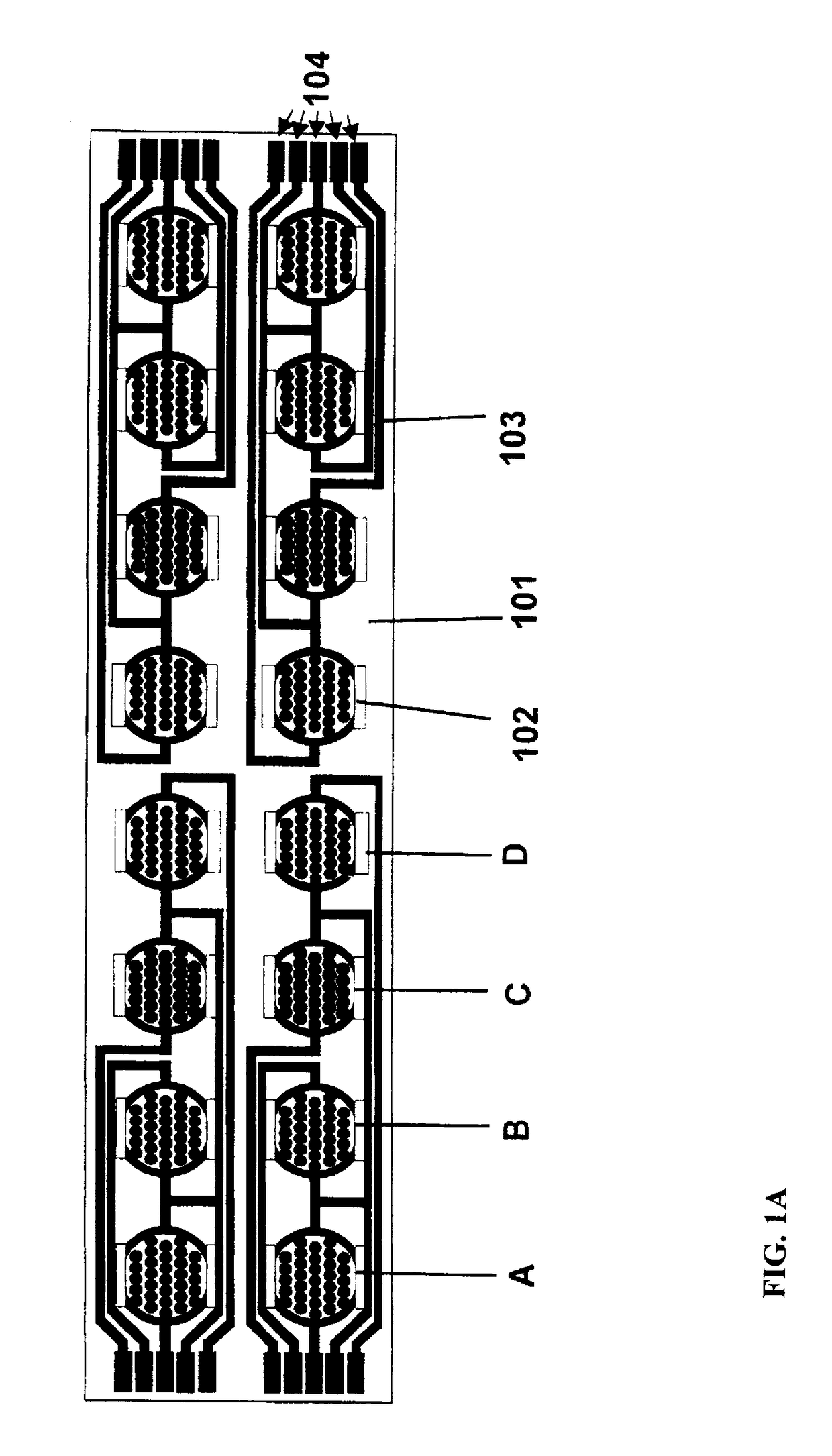
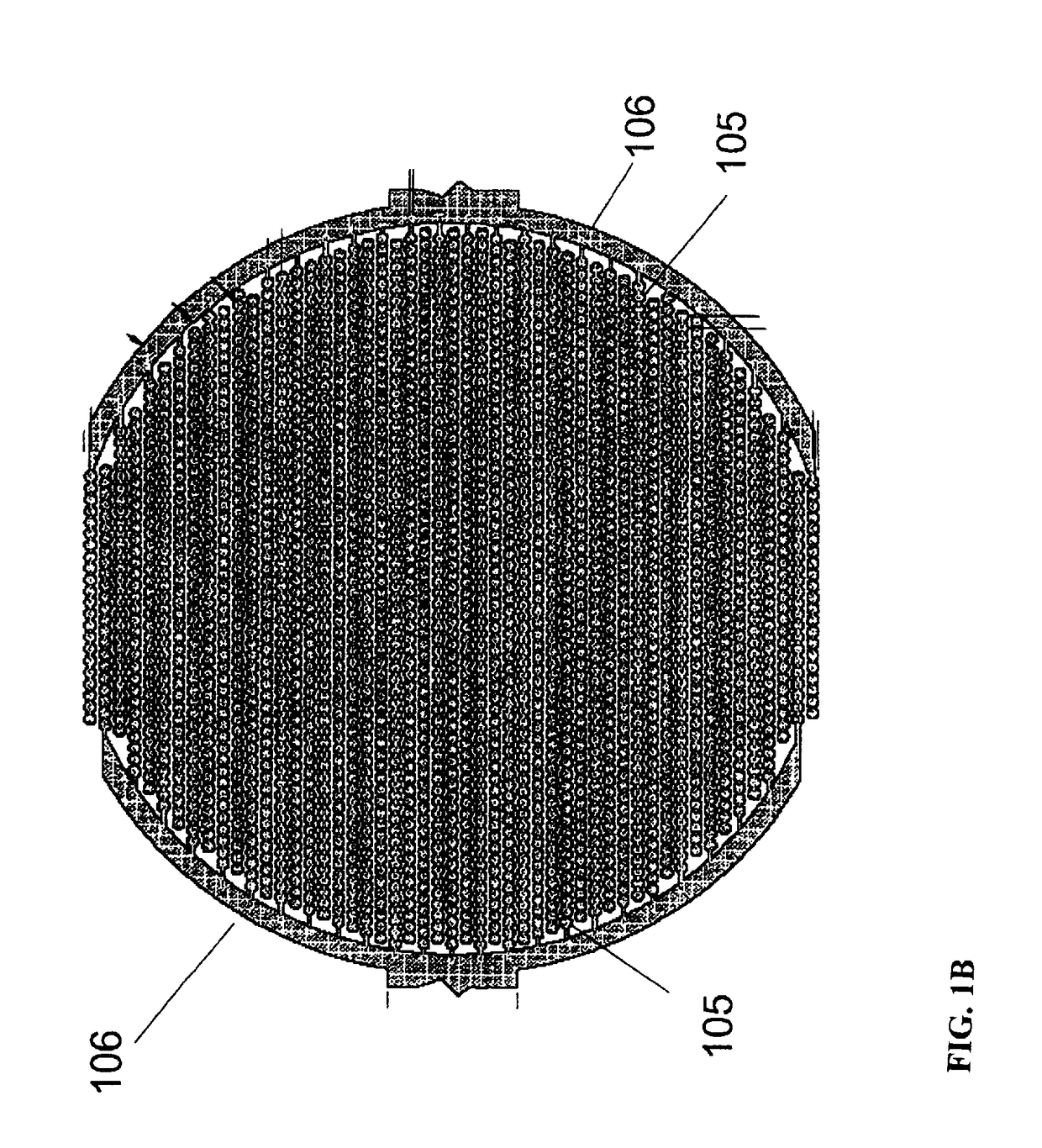
Real time electronic cell sensing systems and applications for cell-based assays
InactiveUS7192752B2Reducing cell-impedance response of cellImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAntigenCytotoxicity
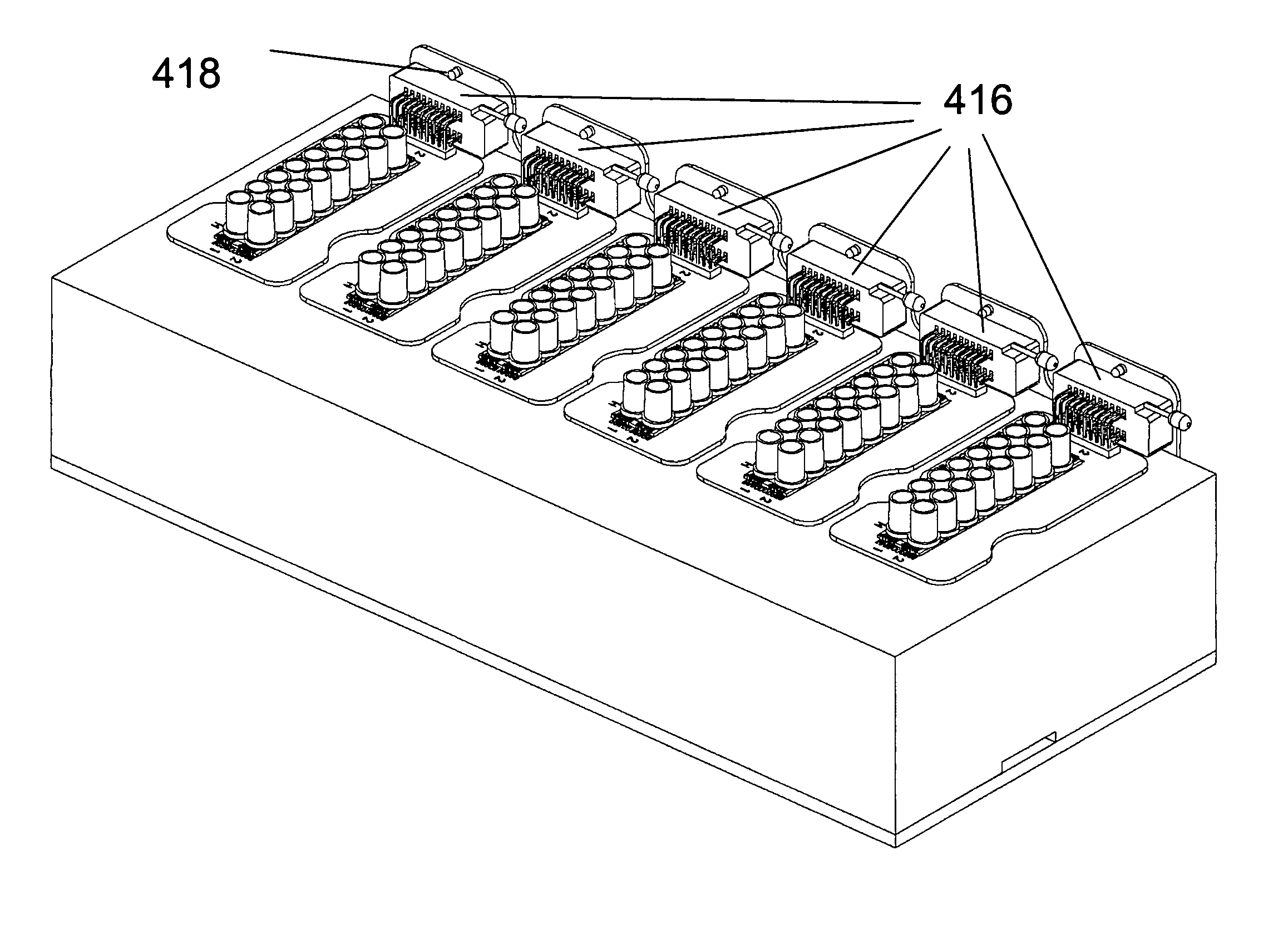
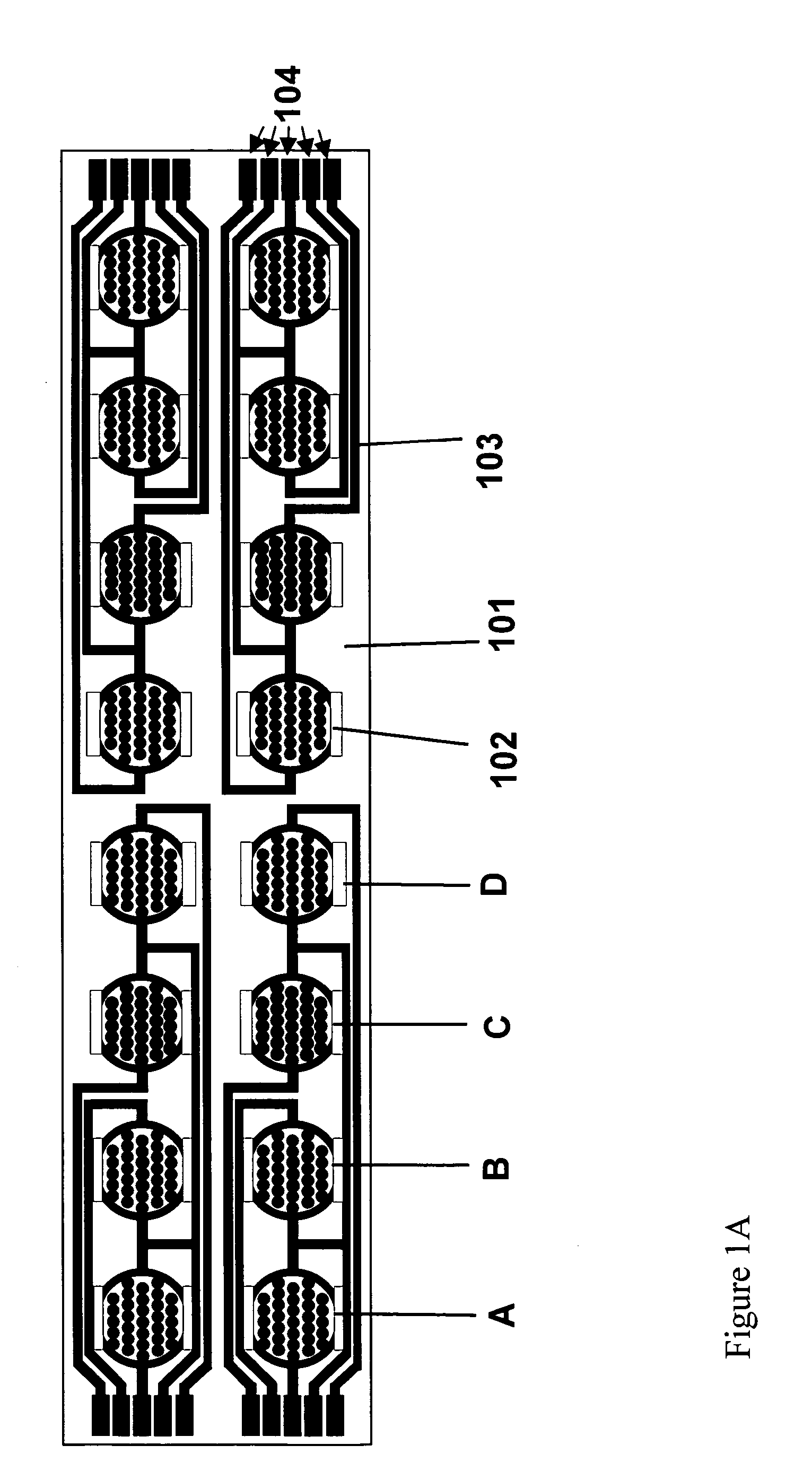
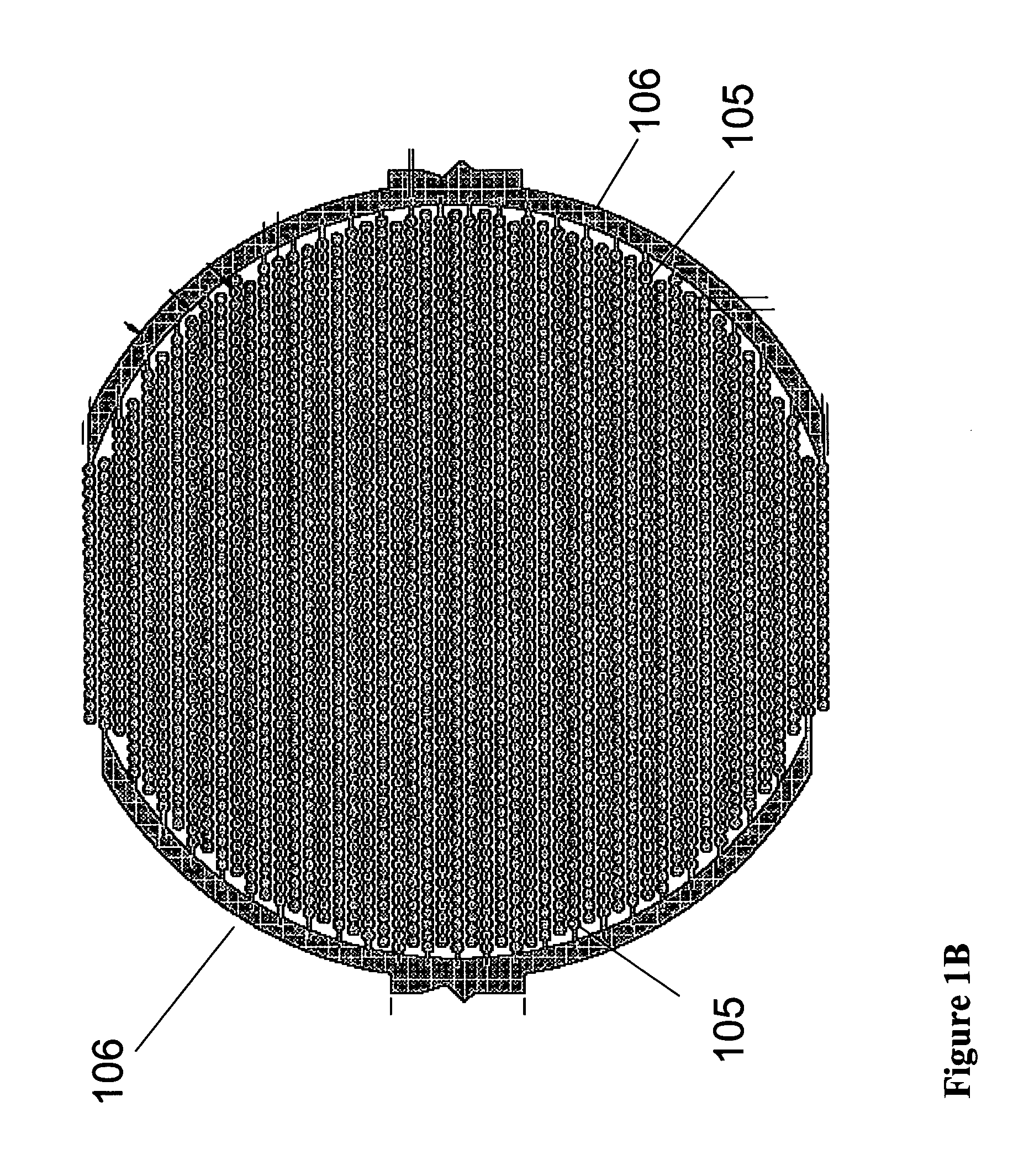
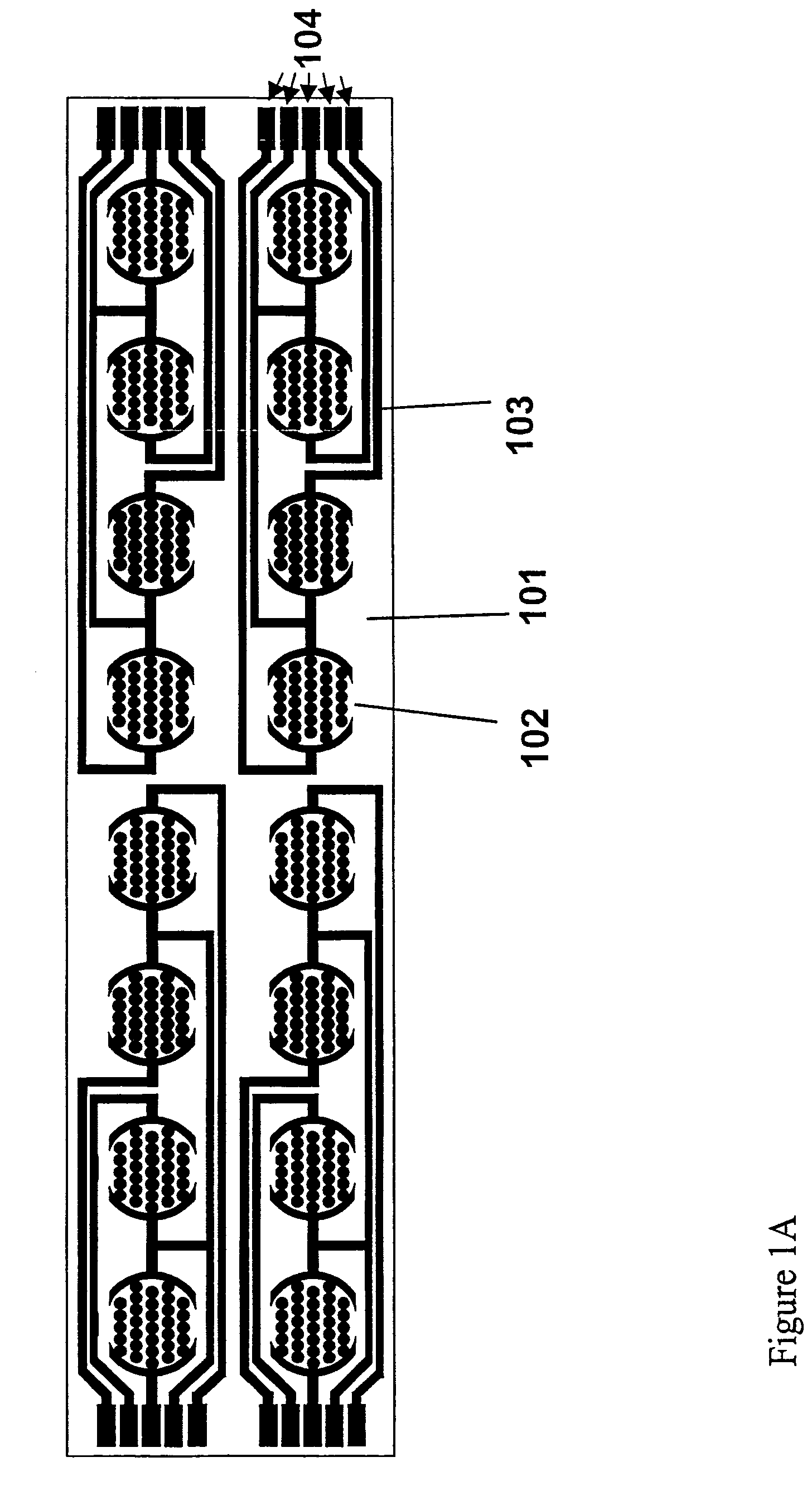
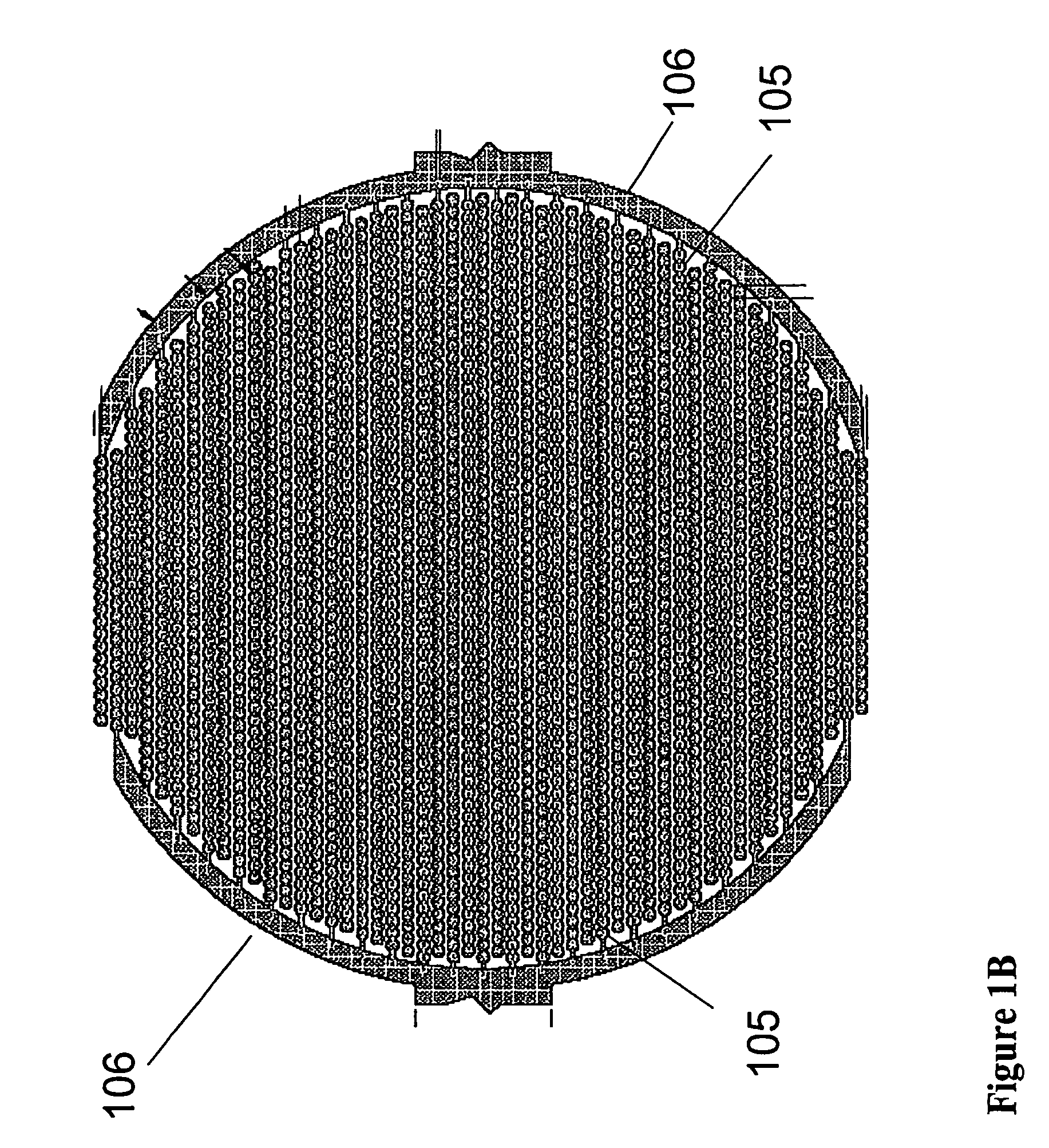
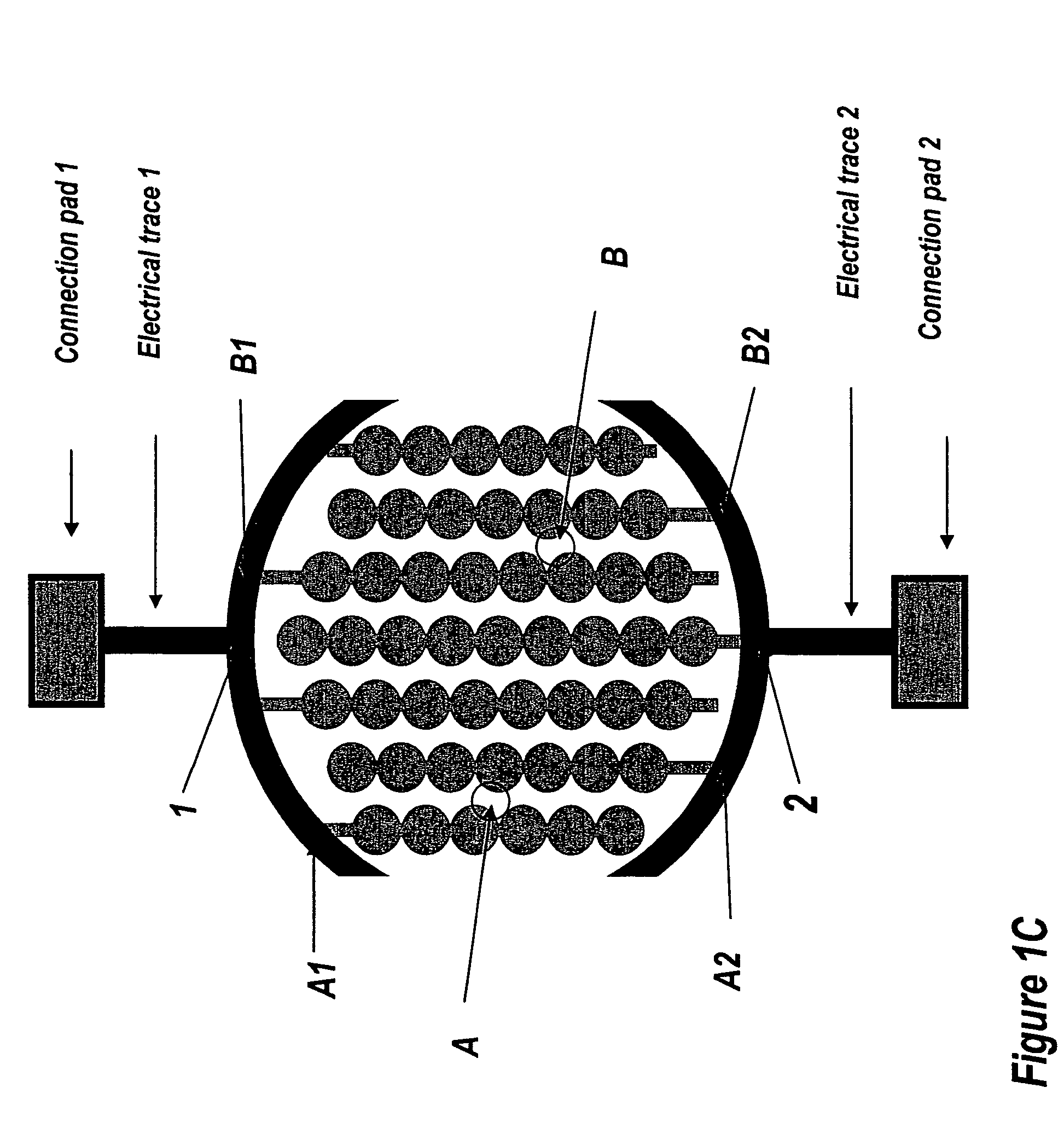
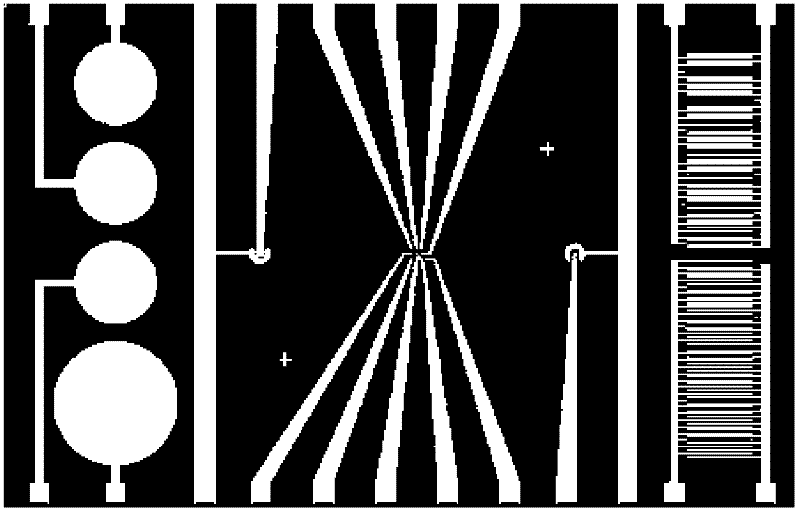
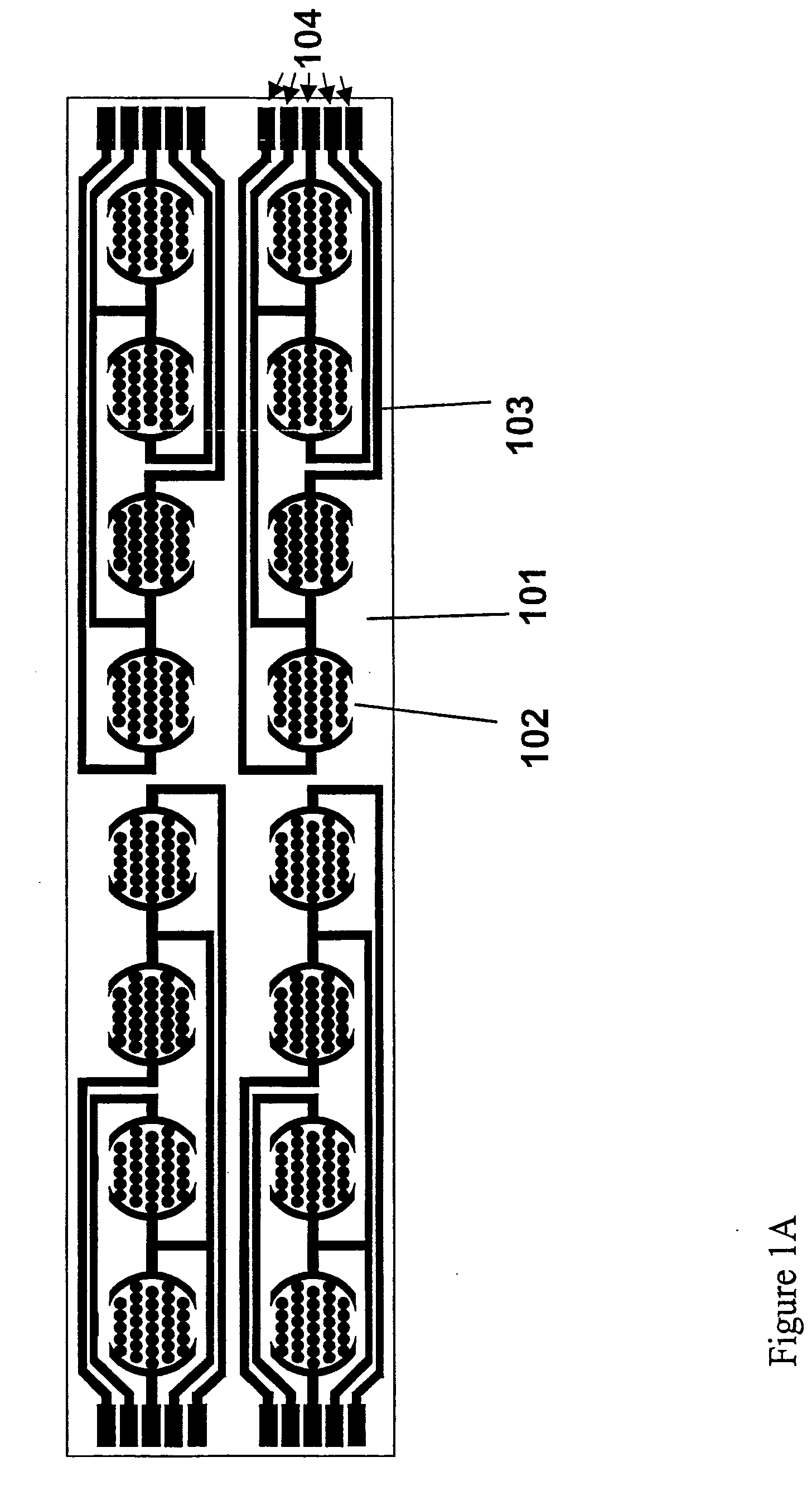
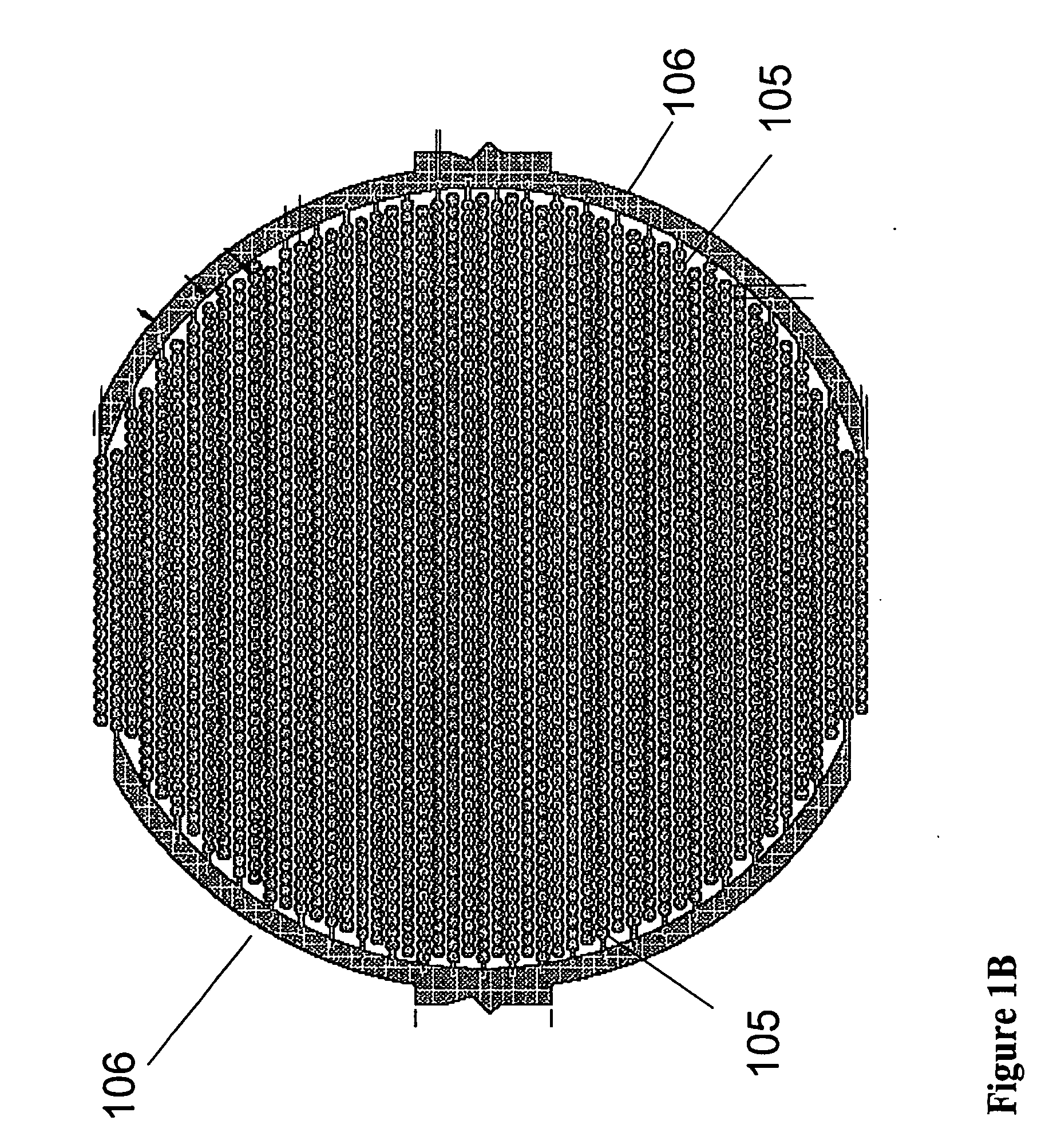
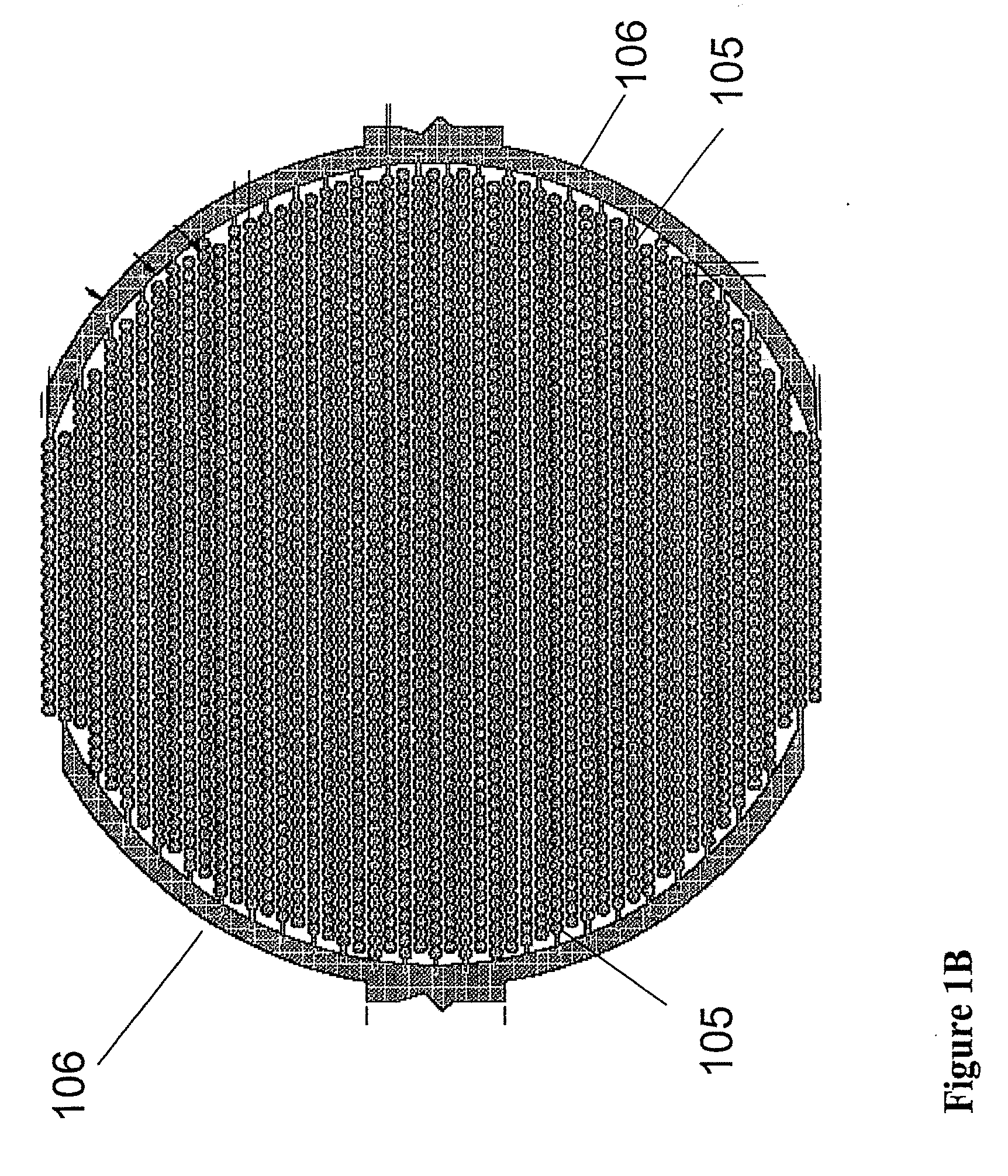
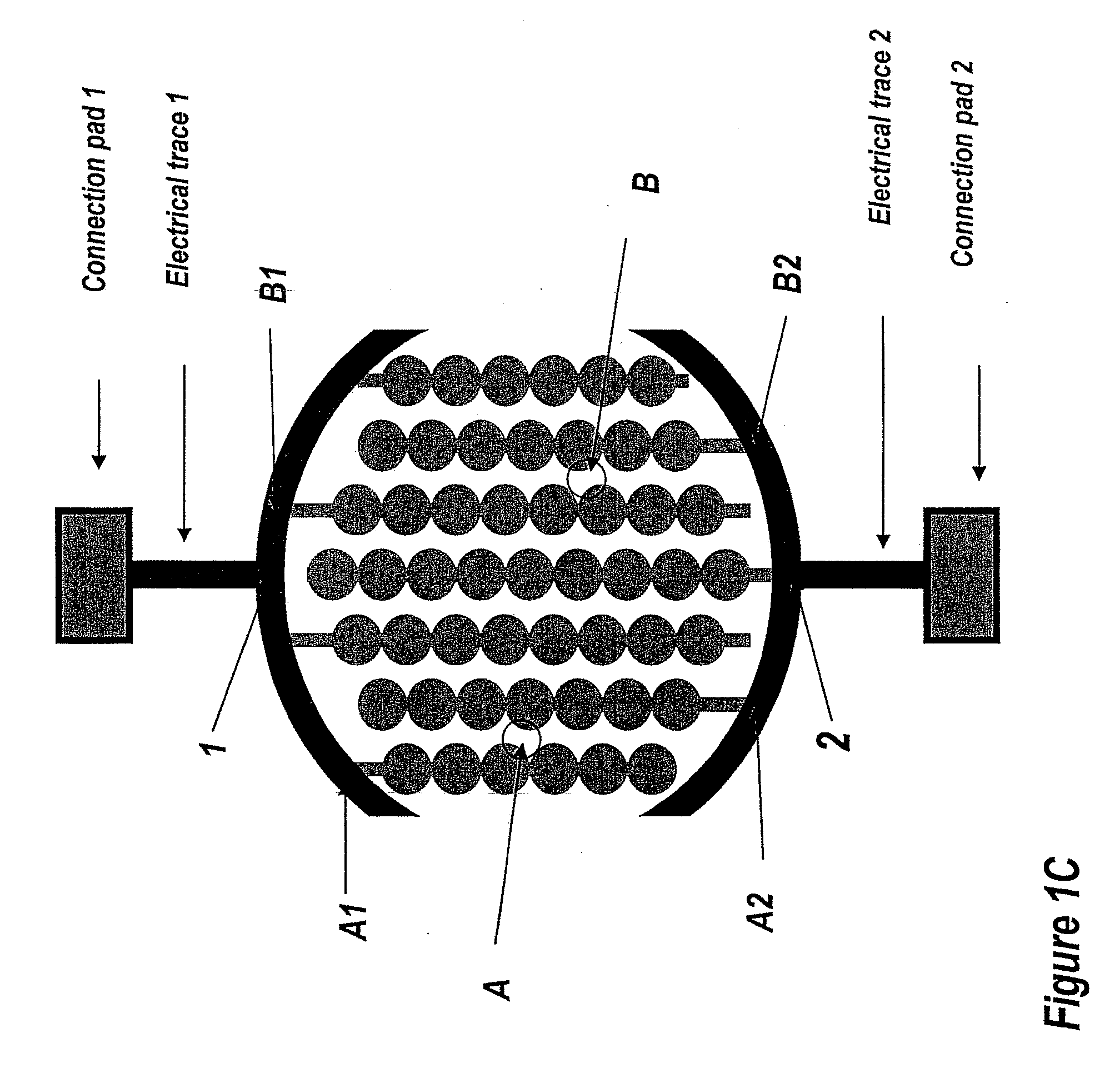
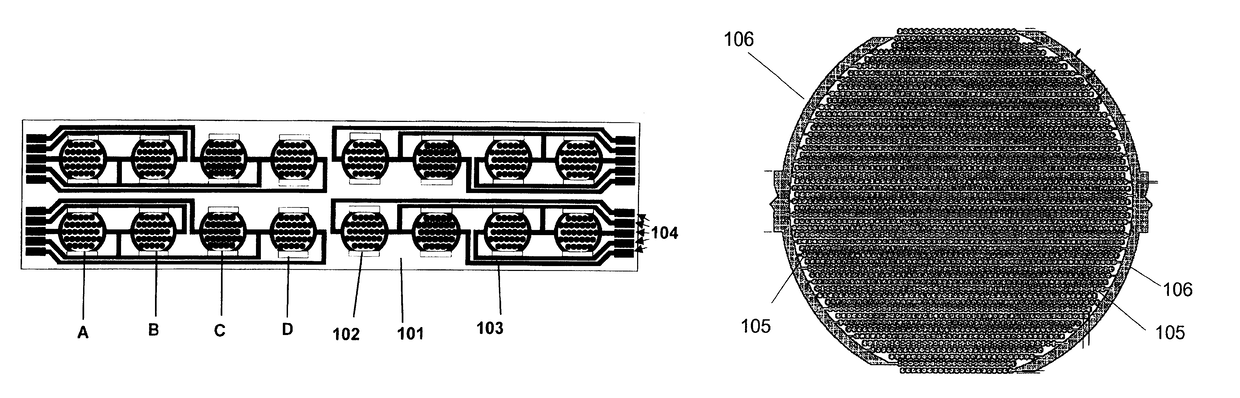
The present invention includes devices, systems, and methods for assaying cells using cell-substrate impedance monitoring. In one aspect, the invention provides cell-substrate impedance monitoring devices that comprise electrode arrays on a nonconducting substrate, in which each of the arrays has an approximately uniform electrode resistance across the entire array. In another aspect, the invention provides cell-substrate monitoring systems comprising one or more cell-substrate monitoring devices comprising multiple wells each having an electrode array, an impedance analyzer, a device station that connects arrays of individual wells to the impedance analyzer, and software for controlling the device station and impedance analyzer. In another aspect, the invention provides cellular assays that use impedance monitoring to detect changes in cell behavior or state. In some preferred aspects, the assays are designed to investigate the affects of compounds on cells, such as cytotoxicity assays. In other preferred aspects, the assays are designed to investigate the compounds that effect IgE-mediated responses of cells to antigens.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Liquid Crystal Display Device
ActiveUS20080259254A1High response rateQuality improvementLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsIn planeDopant
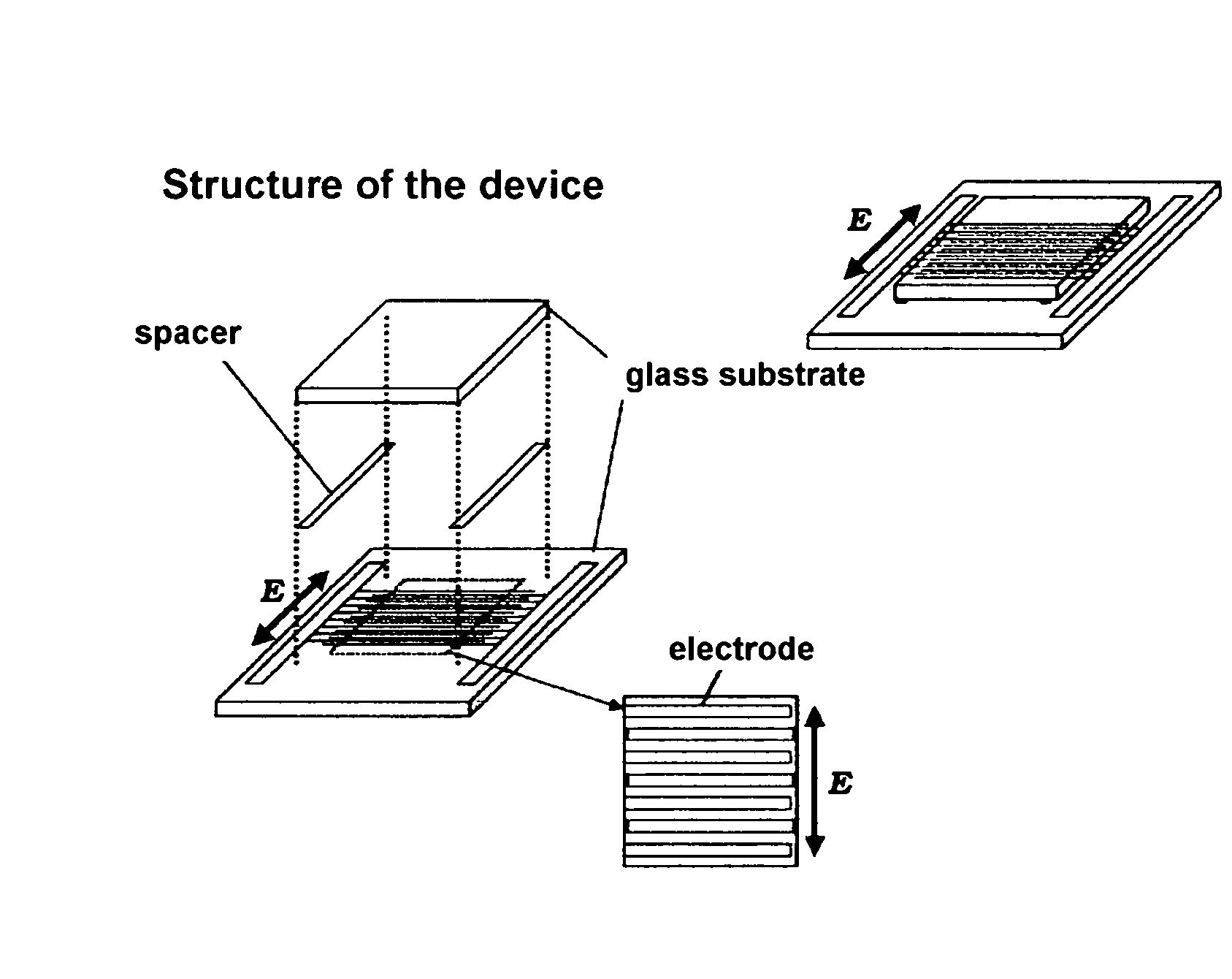
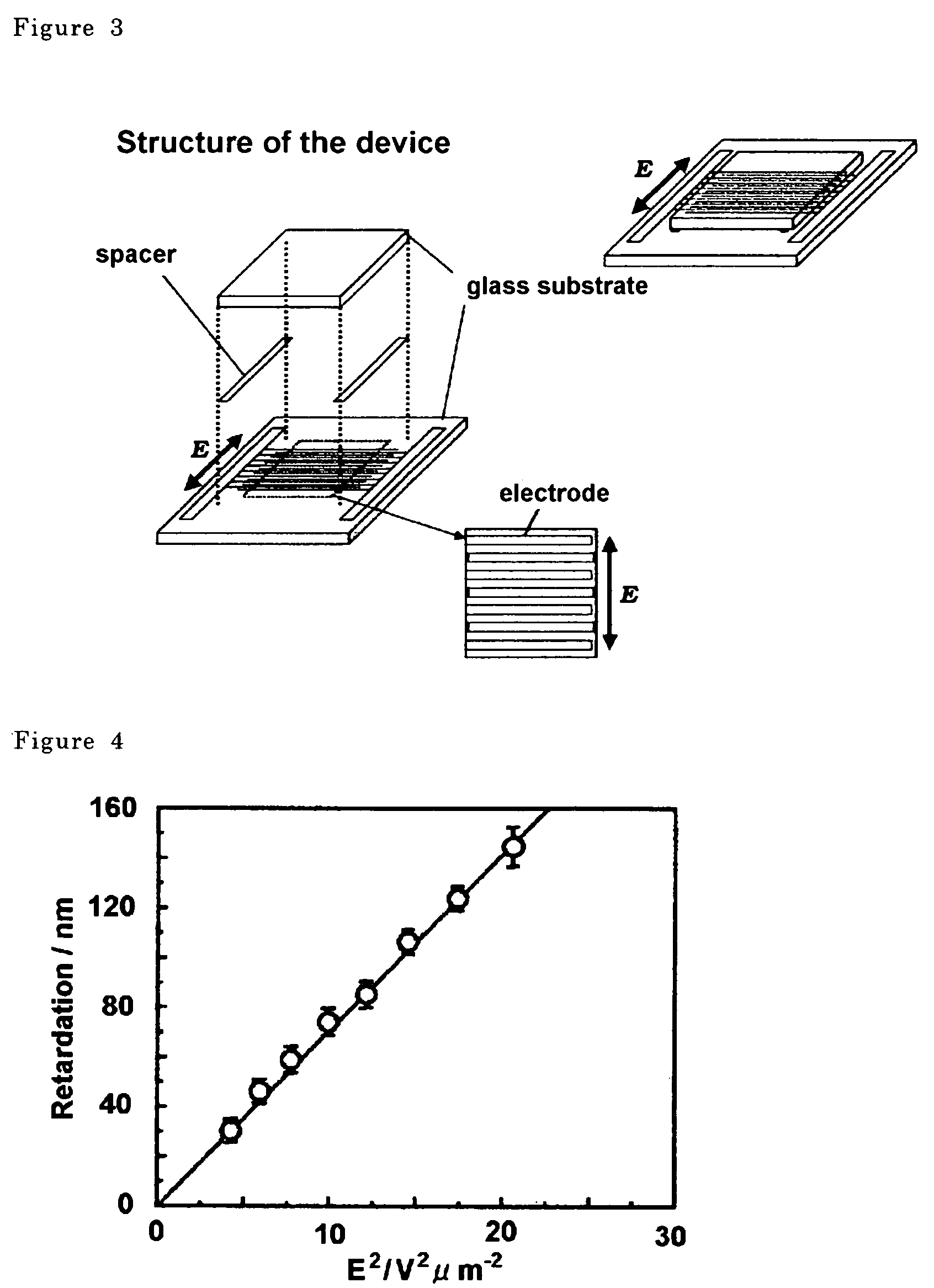
[PROBLEMS] To provide a liquid crystal display device that does not need any surface aligning treatment, realizes striking increase of a response speed of movie display and is free from any light leakage (produce dark field) at black display.[MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] There is provided a liquid crystal display device comprising a pair of transparent substrates and, interposed therebetween, a polymer stabilized blue-phase liquid crystal. The liquid crystal display device utilizing the polymer stabilized blue-phase liquid crystal exhibits a large birefringence change upon application of an electric field to cell substrate in an in-plane direction. The polymer stabilized blue-phase liquid crystal is composed of a low-molecular liquid crystal capable of developing a blue phase between cholesteric phase and isotropic phase and a polymer network created in the low-molecular liquid crystal. Further, by optimizing the type and amount of chiral dopant added to the liquid crystal, there can be provided a liquid crystal display device that is free from any light leakage (produce dark field) at black display.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS7576829B2High response rateQuality improvementLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsIn planeDopant
Presents a liquid crystal display device that does not require a surface orientation treatment, dramatically improves the response rate of dynamic image displays and does not experience light leaks when the display is black, which means to yield a dark field of vision. The liquid crystal display device comprises polymer-stabilized blue phase liquid crystals sandwiched between a pair of clear substrates. The liquid crystal display device obtained using polymer-stabilized blue phase liquid crystals exhibits large double refraction changes when an electrical field is applied in an in-plane direction to the cell substrates. The polymer-stabilized blue phases liquid crystals comprises a low molecular weight liquid crystal that allows a blue phase to appear between cholesteric and isotropic phases and polymer network formed in the low molecular weight liquid crystals. Furthermore, a liquid crystal display device that does not leak light when the display is black (yields a dark field of vision) can be obtained by optimizing the type and amount of a chiral dopant added to the liquid crystals.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method for assaying for natural killer, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte and neutrophil-mediated killing of target cells using real-time microelectronic cell sensing technology
ActiveUS7468255B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEffector cellNeutrophil granulocyte
The present invention includes a method of measuring cytolytic activity including providing a device capable of monitoring cell-substrate impedance operably connected to an impedance analyzer, adding target cells to at least one well of the device, adding effector cells to the at least one well, monitoring impedance of the at least one well and optionally determining a cell index from the impedance, wherein monitoring impedance includes measuring impedance during at least one time point before and at least one time point after adding effector cells, and determining viability of said target cells after adding effector cells by comparing the impedance or optionally the cell index at the at least one time point after adding effector cells to the impedance or optionally the cell index at the at least one time point before adding effector cells.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Real time electronic cell sensing systems and applications for cell-based assays
InactiveUS20050153425A1Reducing cell-impedance response of cellBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningAntigenEngineering
The present invention includes devices, systems, and methods for assaying cells using cell-substrate impedance monitoring. In one aspect, the invention provides cell-substrate impedance monitoring devices that comprise electrode arrays on a nonconducting substrate, in which each of the arrays has an approximately uniform electrode resistance across the entire array. In another aspect, the invention provides cell-substrate monitoring systems comprising one or more cell-substrate monitoring devices comprising multiple wells each having an electrode array, an impedance analyzer, a device station that connects arrays of individual wells to the impedance analyzer, and software for controlling the device station and impedance analyzer. In another aspect, the invention provides cellular assays that use impedance monitoring to detect changes in cell behavior or state. In some preferred aspects, the assays are designed to investigate the affects of compounds on cells, such as cytotoxicity assays. In other preferred aspects, the assays are designed to investigate the compounds that effect IgE-mediated responses of cells to antigens.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Real time electronic cell sensing system and applications for cytotoxicity profiling and compound assays
ActiveUS7560269B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCytotoxicityEngineering
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
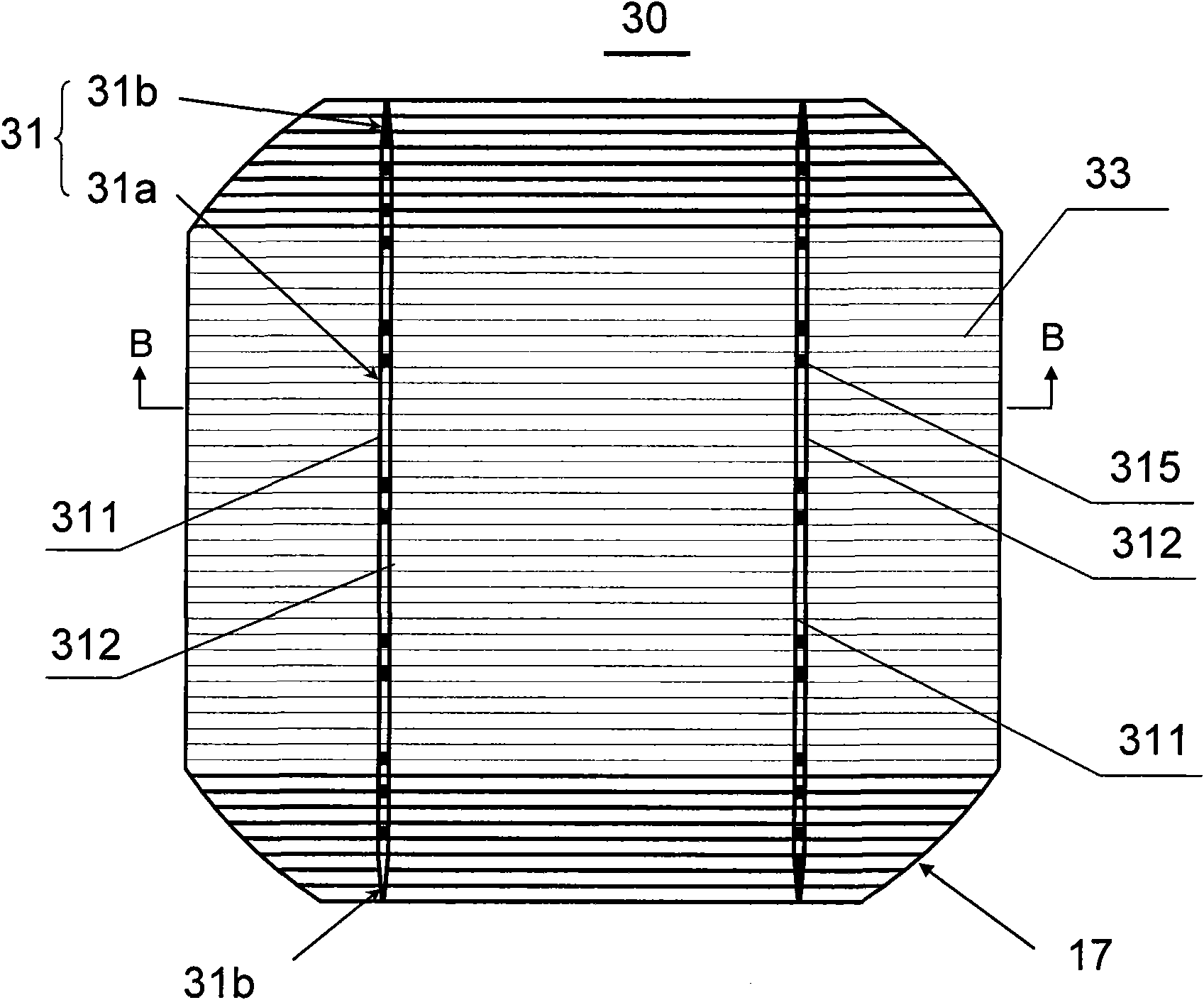
Solar cell, screen printing plate and solar cell module thereof
InactiveCN101826569AReduce stressReduce contact areaPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesScreen printingInterconnector
The invention discloses a solar cell, a screen printing plate and a solar cell module thereof, belonging to the technical field of photovoltaics. The solar cell of the invention comprises a cell substrate and an electrode, wherein the electrode is arranged on the substrate; the electrode comprises a main grid line; the construction of the line area of the main grid line is in a structure comprising at least one thin grid line to reduce the contact area between the main grid line and the substrate; the screen pringting plate provided by the invention is used for manufacturing the electrode of the solar cell of the invention by screen printing; and meshes for composing and forming the main grid line of the electrode are arranged on the screen printing plate. The solar cell module provided by the invention comprises a plurality of the solar cells provided by the invention. The solar cell and the solar cell module have low cost, and because the compound area between the metal electrode and the silicon in the cell structure is reduced, the conversion efficiency is improved, the output power of the module is increased, and in addition, the reliability after an interconnector is welded with a cell plate is good.
Owner:WUXI SUNTECH POWER CO LTD
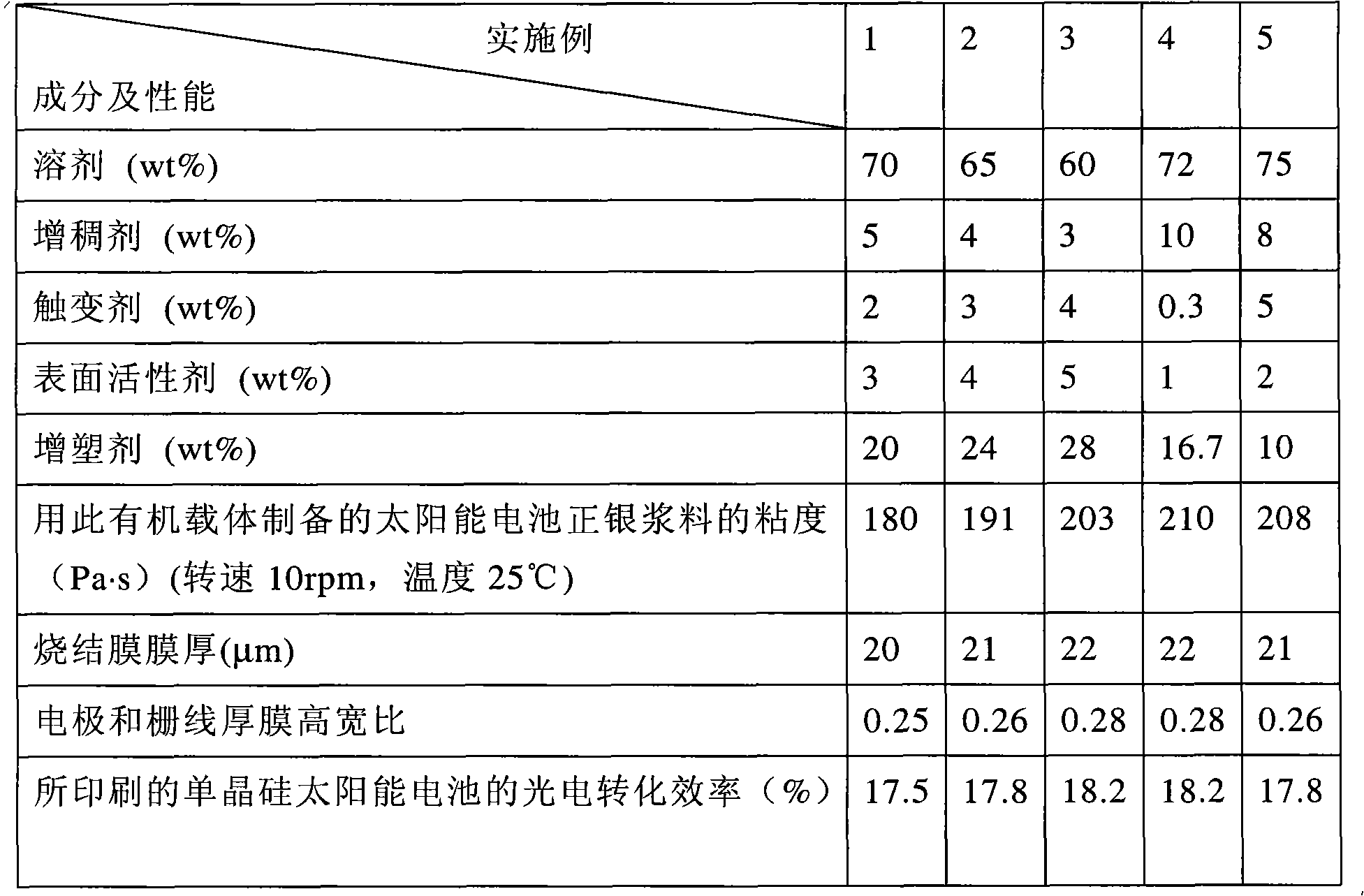
Organic carrier for silver paste and preparation method thereof as well as silver paste containing organic carrier and solar cell manufactured from silver paste
InactiveCN102136308AModerate viscositySuitable ThixotropyNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialSemiconductor devicesSolventChemical stability
The invention discloses an organic carrier for conductive silver paste applied to a front face electrode and a grid line of a solar cell, a preparation method of the organic carrier, silver paste containing the organic carrier and a solar cell manufactured from the silver paste. The organic carrier comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 60-75 percent of solvent, 1-10 percent of thickener, 0.3-5 percent of thixotropic agent, 1-5 percent of surfactant and 10-30 percent of plasticizer. The preparation method of the organic carrier comprises the following steps of: weighing various raw materials; adding various aids into a solvent respectively; and heating and stirring until the aids are dissolved completely. The organic carrier has proper viscosity and a simple preparation process. Paste prepared from the organic carrier has proper viscosity, fineness, leveling property, thixotropy and chemical stability. After the paste is subjected to screen printing and sintering on a cell substrate, the thicknesses of a front face electrode and a grid line thick film of a cell panel can be over 20 micros, and the prepared electrode and the grid line thick film can obtain a higher height-width ratio.
Owner:湖南威能新材料科技有限公司
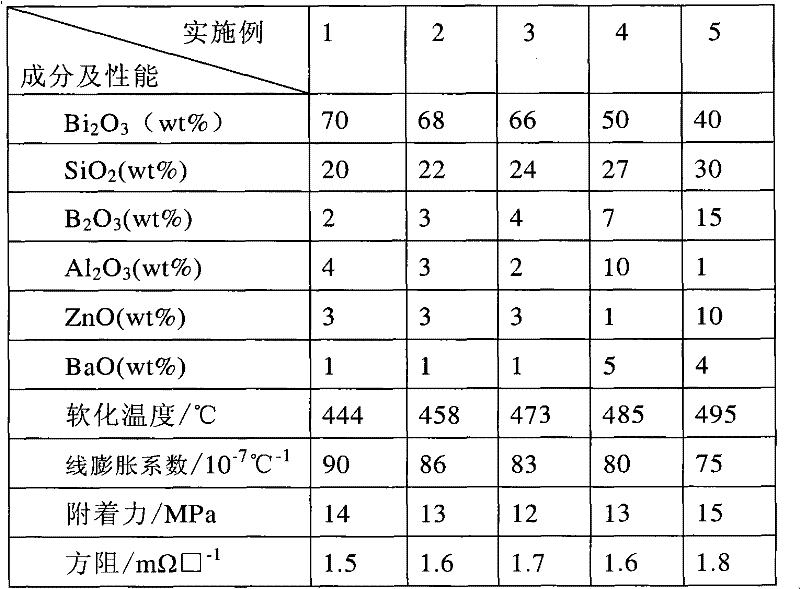
Lead-free glass powder, preparation method thereof, silver paste containing glass powder and crystal silicon solar cell manufactured by using silver paste
InactiveCN102126829AImprove adhesionStrong adhesionNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialSemiconductor devicesSilver pasteScreen printing
The invention discloses lead-free glass powder, a preparation method thereof, silver paste containing the glass powder and a crystal silicon solar cell manufactured by using the silver paste. The lead-free glass powder comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 20-30 percent of SiO2, 2-15 percent of B2O3, 40-70 percent of Bi2O3, 1-10 percent of ZnO, 1-10 percent of Al2O3 and 1-5 percent of BaO. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) weighing the components for preparing a mixture; (2) putting the mixture into a crucible for melting; (3) performing water quenching on molten glass; (4) drying; (5) smashing the mixture into powder by planetary ball milling; and (6) screening. The needed silver paste is prepared from the lead-free glass powder, silver powder, an additive and an organic carrier. A solar panel front face electrode and a grid line are manufactured by performing screen printing and sintering on conductive silver paste on a cell substrate, so that the needed solar cell is obtained. The lead-free glass powder has low melting temperature, low softening temperature and low linear expansion factor.
Owner:湖南威能新材料科技有限公司
Methods of texturing surfaces for controlled reflection
InactiveUS20130295712A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationRemote plasmaNanoparticle
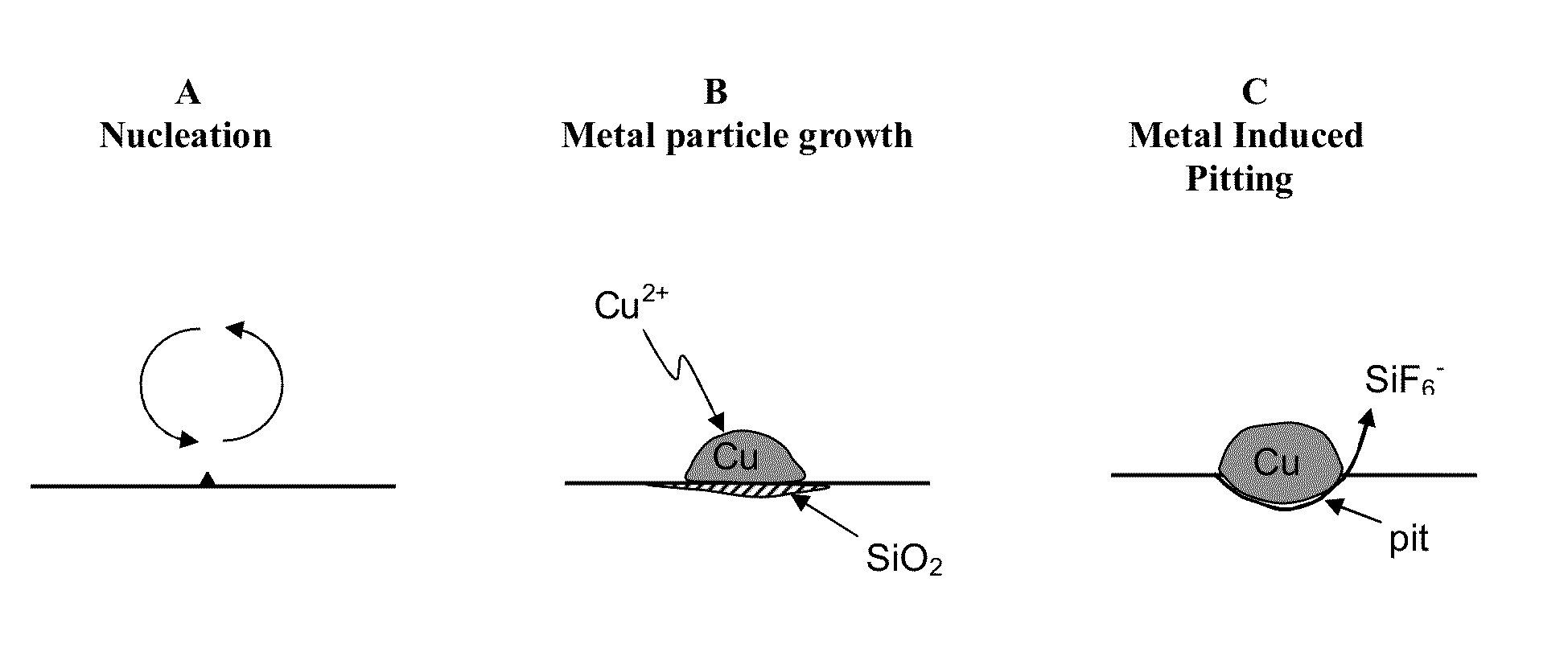
Novel methods for the texturing of photovoltaic cells is described, wherein texturing minimizes reflectance losses and hence increases solar cell efficiency. In one aspect, a microstamp with the mirror inverse of the optimum surface structure is described. The photovoltaic cell substrate to be etched and the microstamp are immersed in a bath and pressed together to yield the optimum surface structure. In another aspect, micro and nanoscale structures are introduced to the surface of a photovoltaic cell by wet etching and depositing nanoparticles or introducing metal induced pitting to a substrate surface. In still another aspect, remote plasma source (RPS) or reactive ion etching (RIE), is used to etch nanoscale features into a silicon-containing substrate.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
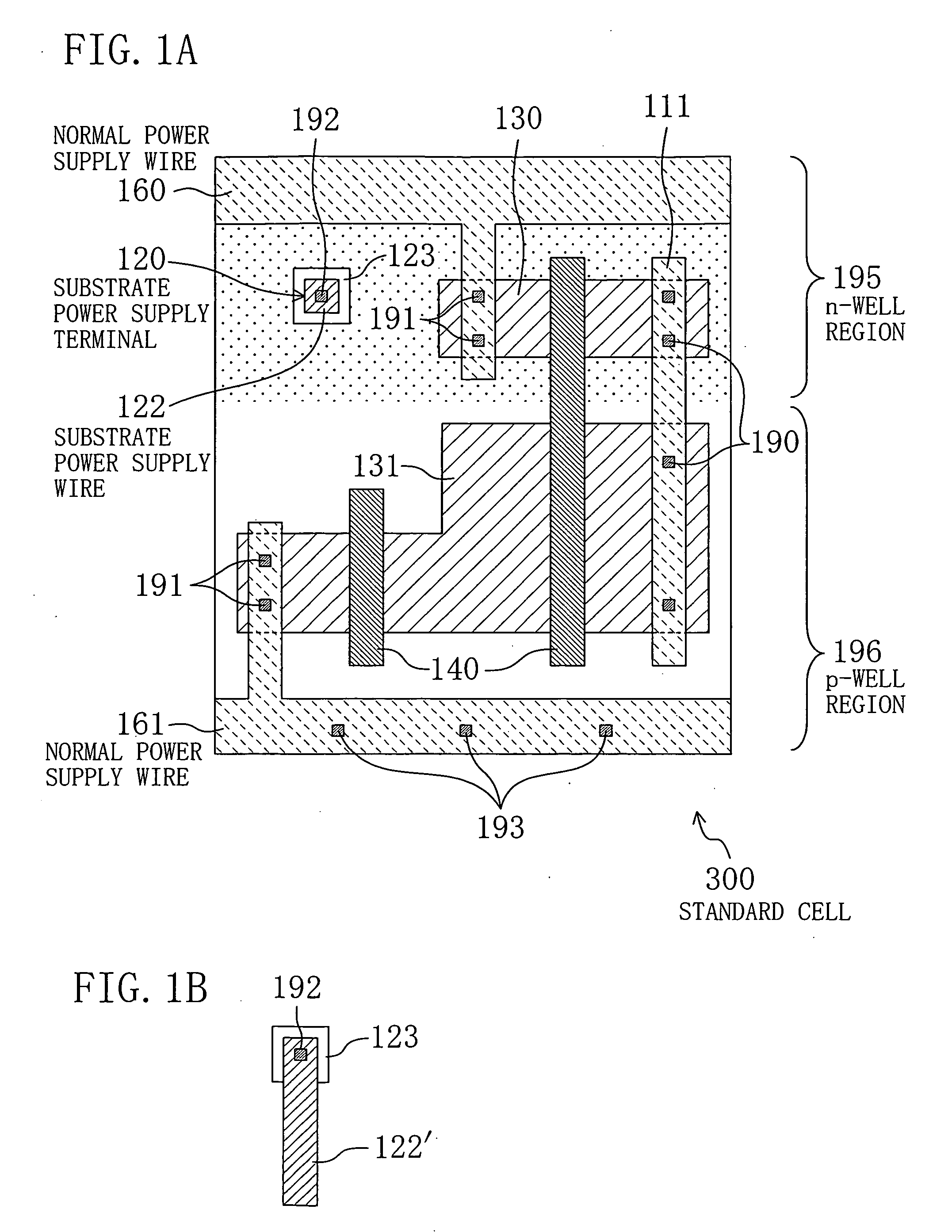
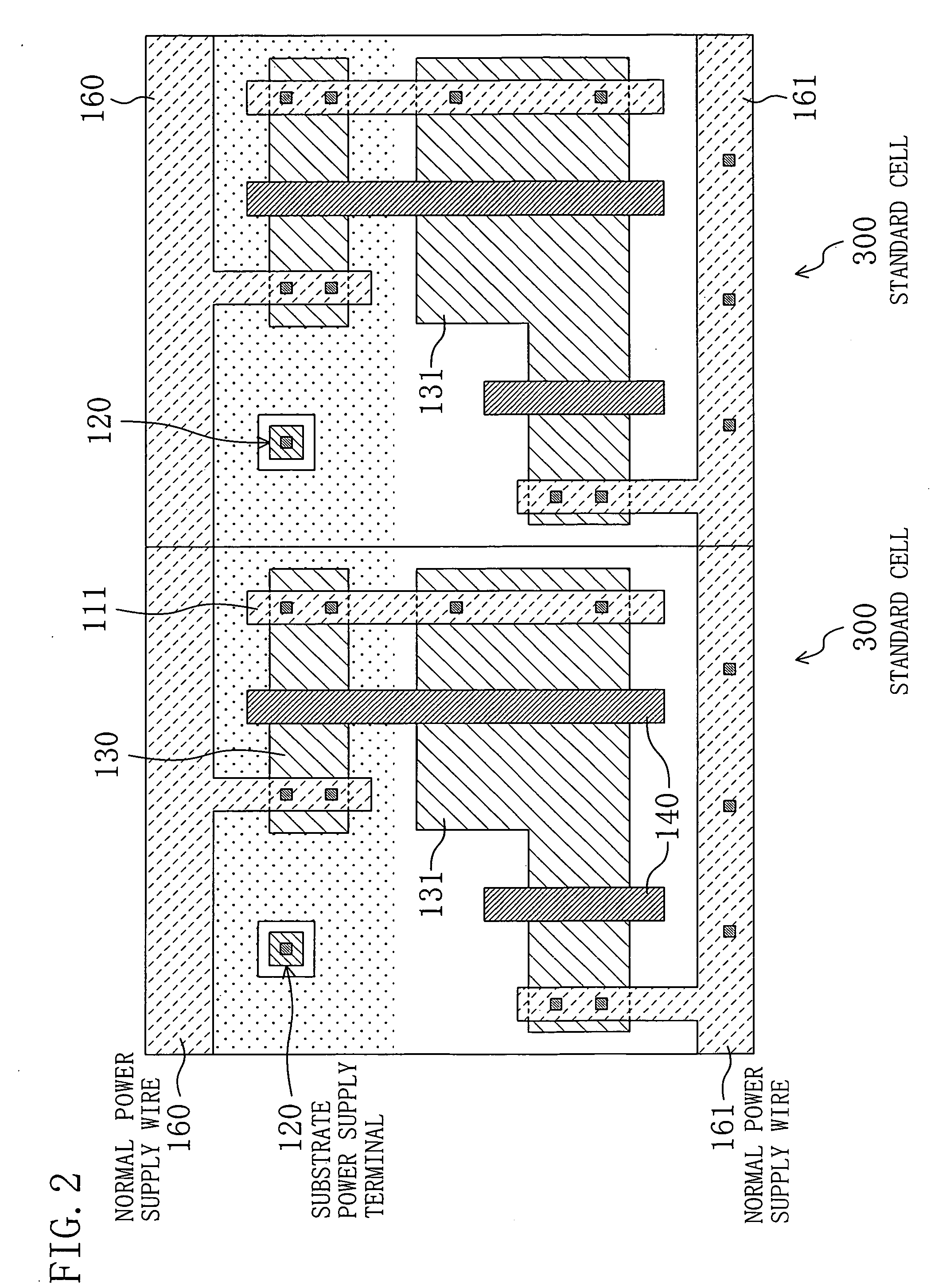
Standard cell
InactiveUS20070096154A1Increase freedomShort timeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVoltage controlSemiconductor
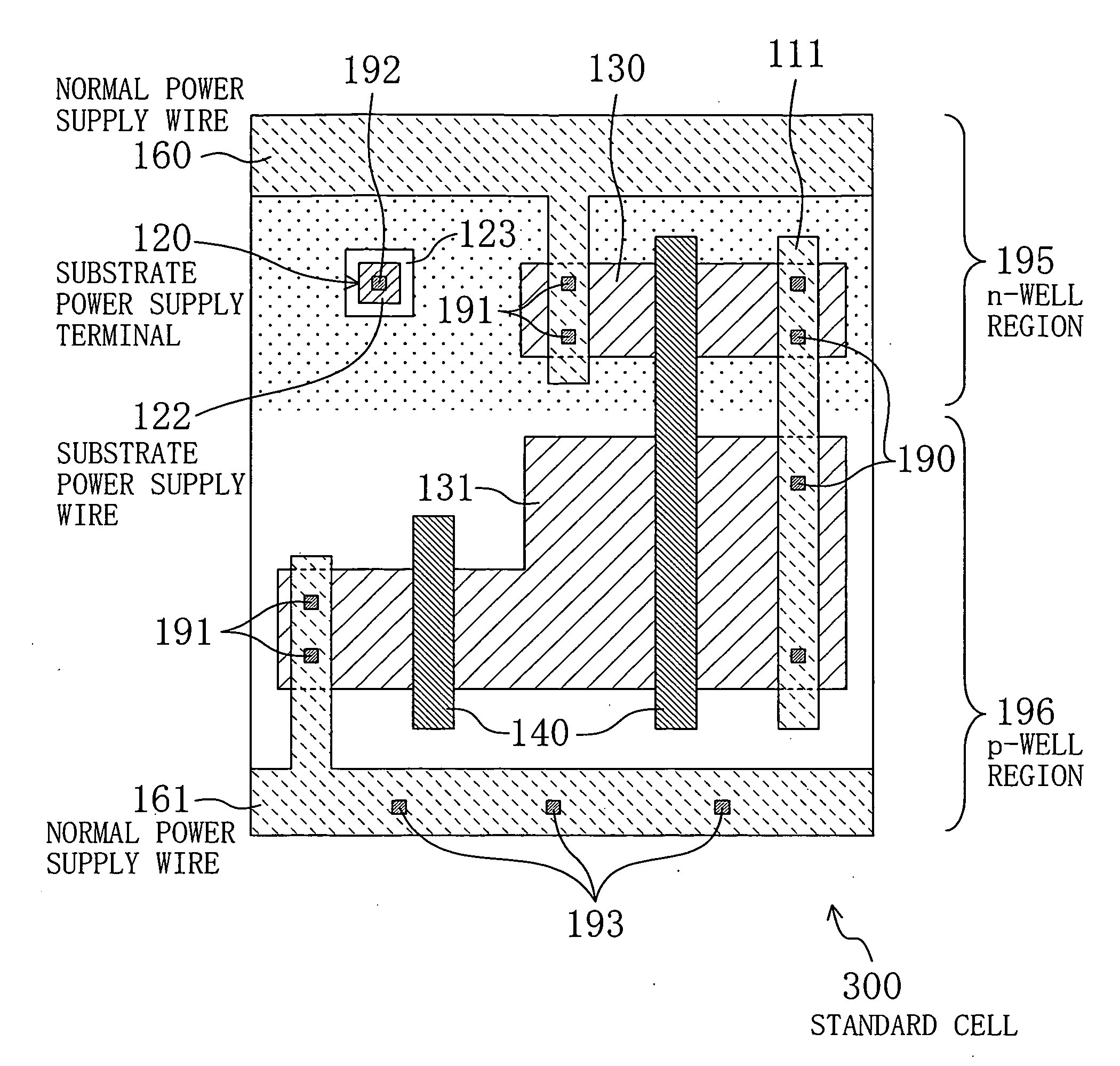
In a standard cell in which a substrate voltage control technique is implemented, a plurality of normal power supply wires are disposed at previously set positions. Therefore, when the standard cell is disposed adjacent to another standard cell having such normal power supply wires, these normal power supply wires are connected to each other. In addition, the standard cell is provided with a substrate power supply terminal which is not connected to that of the other standard cell when the other standard cell is disposed adjacent to the standard cell. Therefore, when a semiconductor integrated circuit is composed of a plurality of the standard cells, a wiring route of an inter-cell substrate power supply wire, or the like can be freely set.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Sub-micrometer gap thermophotovoltaic structure (MTPV) and fabrication method therefor
ActiveUS20100319749A1Reduce manufacturing costPrecise and uniform setting of gap dimensionPV power plantsThermoelectric device detailsEngineeringThermophotovoltaic
An MTPV thermophotovoltaic chip comprising a photovoltaic cell substrate, micron / sub-micron gap-spaced from a juxtaposed heat or infrared radiation-emitting substrate, with a radiation-transparent intermediate window substrate preferably compliantly adhered to the photovoltaic cell substrate and bounding the gap space therewith.
Owner:MTPV POWER CORP
Element interconnection member, photoelectric conversion element and a series of photoelectric conversion elements including the same, and photoelectric conversion module
InactiveUS20100243028A1Poor electrical connectionRelease stressPV power plantsElectrical connection printed elementsInterconnectorDegrees of freedom
An interconnector includes an extending portion extending in one direction and a connection portion fixed to an n electrode or a p electrode formed on a cell substrate of a photoelectric conversion element for connection to this electrode. The connection portion is formed in a comb shape so as to protrude from the extending portion in a direction substantially orthogonal to the one direction. Though the extending portion is in contact with the cell substrate, it is not fixed to the cell substrate. By not fixing the extending portion to the cell substrate, stress involved with heat shrinkage can be released and a degree of freedom in arrangement of the n electrode and the p electrode formed on the photoelectric conversion element can be enhanced.
Owner:SHARP KK
Optical member, cell substrate and liquid-crystal display
InactiveUS6331882B1Increase in sizeEfficient assemblyStatic indicating devicesLayered productsAdhesive bondingLiquid crystal cell
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Label-Free Monitoring of Excitation-Contraction Coupling and Excitable Cells Using Impedance Based Systems with Millisecond Time Resolution
ActiveUS20100029506A1Easy to measureEffective monitoringLibrary screeningMaterial impedanceExcitable cellEngineering
Systems and methods for improved monitoring of excitation-contraction coupling and excitable cells are provided, which provide millisecond time resolution. The system is capable of continuously monitoring excitation-contraction coupling in a relatively high-throughput manner. The system includes a device for monitoring cell-substrate impedance, an impedance analyzer capable of impedance measurements at millisecond time resolution, electronic circuitry that can engage the device and selectively connect two or more electrode arrays of the device to the impedance analyzer and a software program that controls the electronic circuitry and records and analyzes data obtained from the impedance analyzer.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
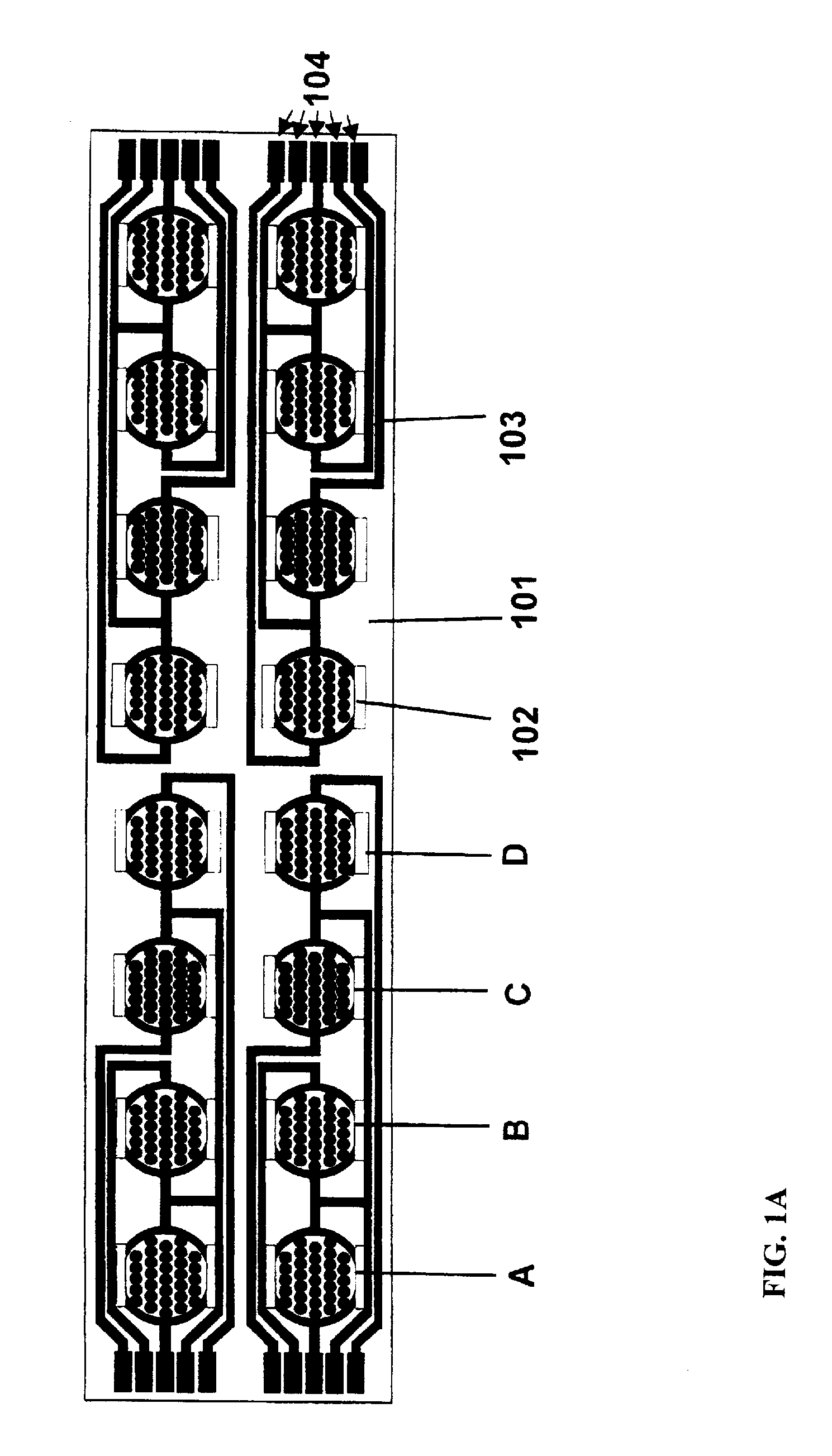
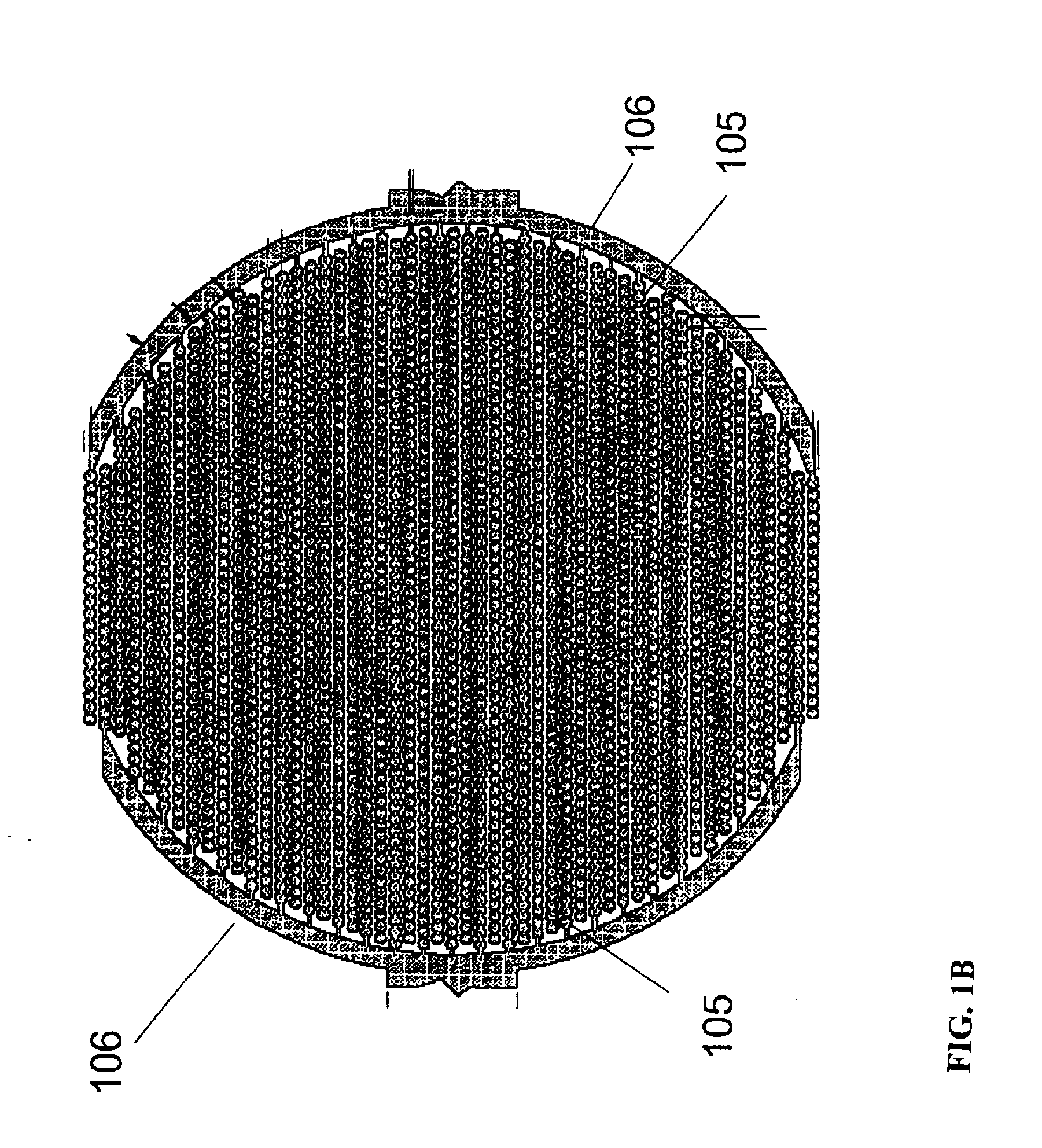
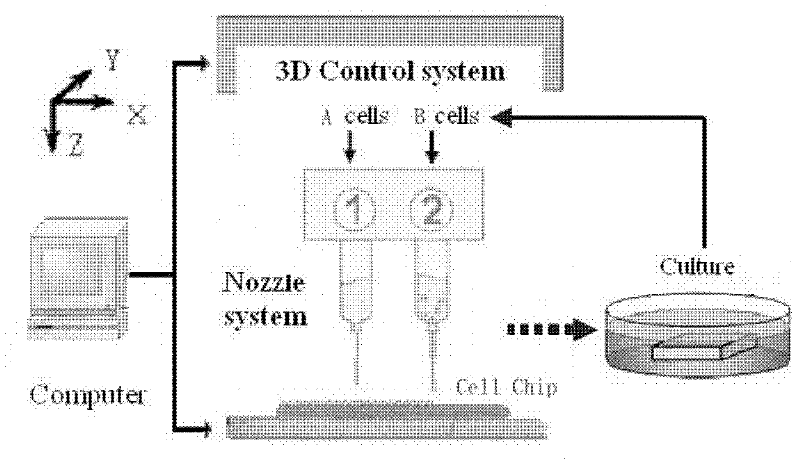
Three-dimensional cell chip based on cell printing and multi-parameter sensing array integrated technology
ActiveCN102382758AReduce development costsReduce riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSensor arrayMulti sensor
The invention relates to a cell chip technology based on cell printing technology and multi-sensor integrated chip technology and application of the cell chip technology in high content medicine screening. An integrated cell MEA (Microelectrode Array) is constructed on glass or a silicon substrate by utilizing micro-electronics processing technology, and an ECIS (Electric Cell-Substrate Impedance System) comprises a disc type ECIS and an IDA (Interdigitated Array). By an arrayed chip of three sensing units, different cells and special imitated extracellular substrate material are mixed, and are positioned and printed at the assigned position in the MEA by a multi-nozzle cell printing device so as to construct the cell chip. A cell sensor on the chip is used for transmitting and recording the static and dynamic parameters such as cell action potential frequency, amplitude, wave form, network signal transmitting speed, cell attaching, moving state and the like. The invention provides a method applying the three-dimensional cell chip for medicine screening.
Owner:REGENOVO BIOTECH
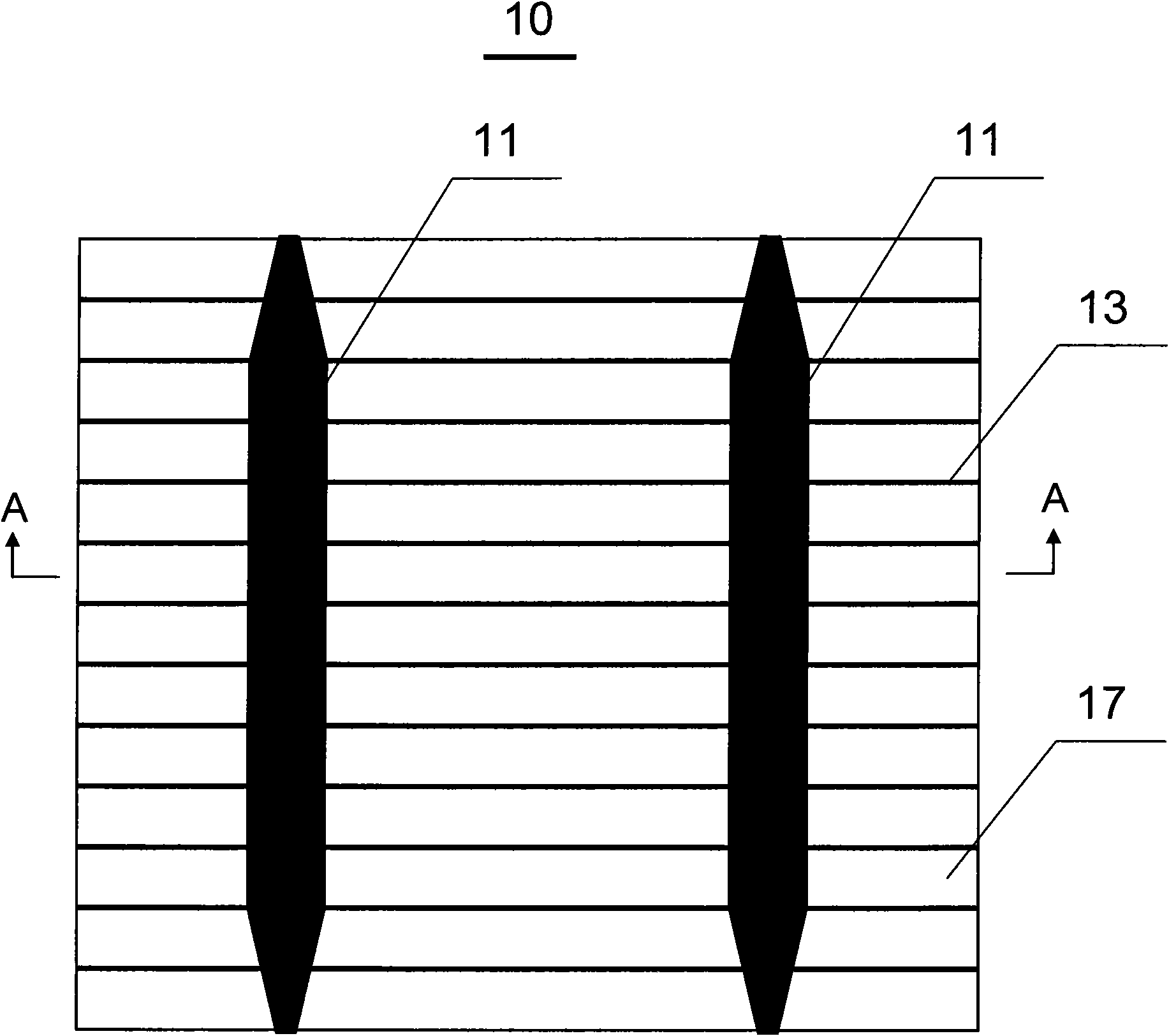
Method to Form a Polysilicon Nanocrystal Thin Film Storage Bitcell within a High K Metal Gate Platform Technology Using a Gate Last Process to Form Transistor Gates
ActiveUS20150054044A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricEngineering
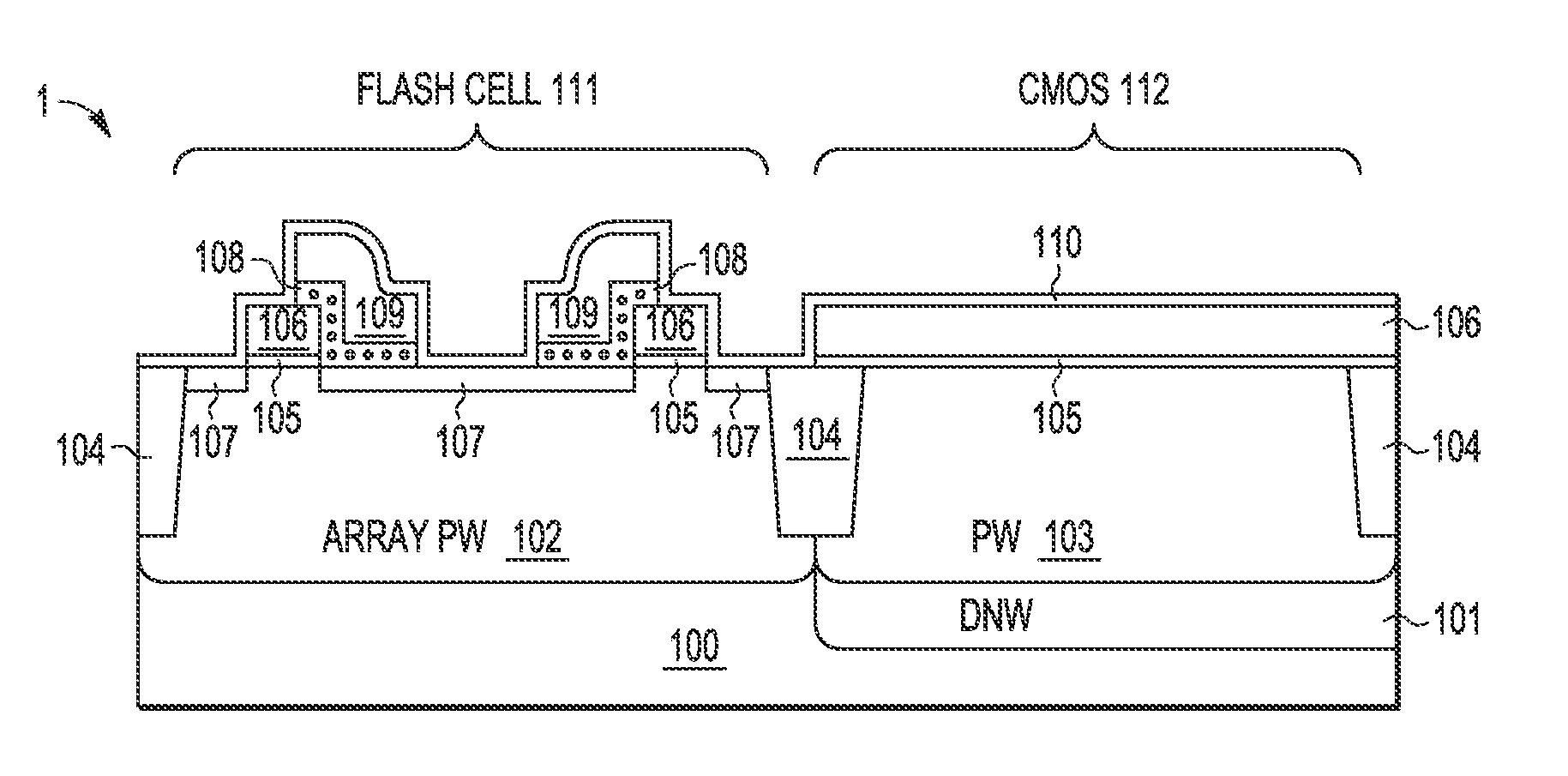
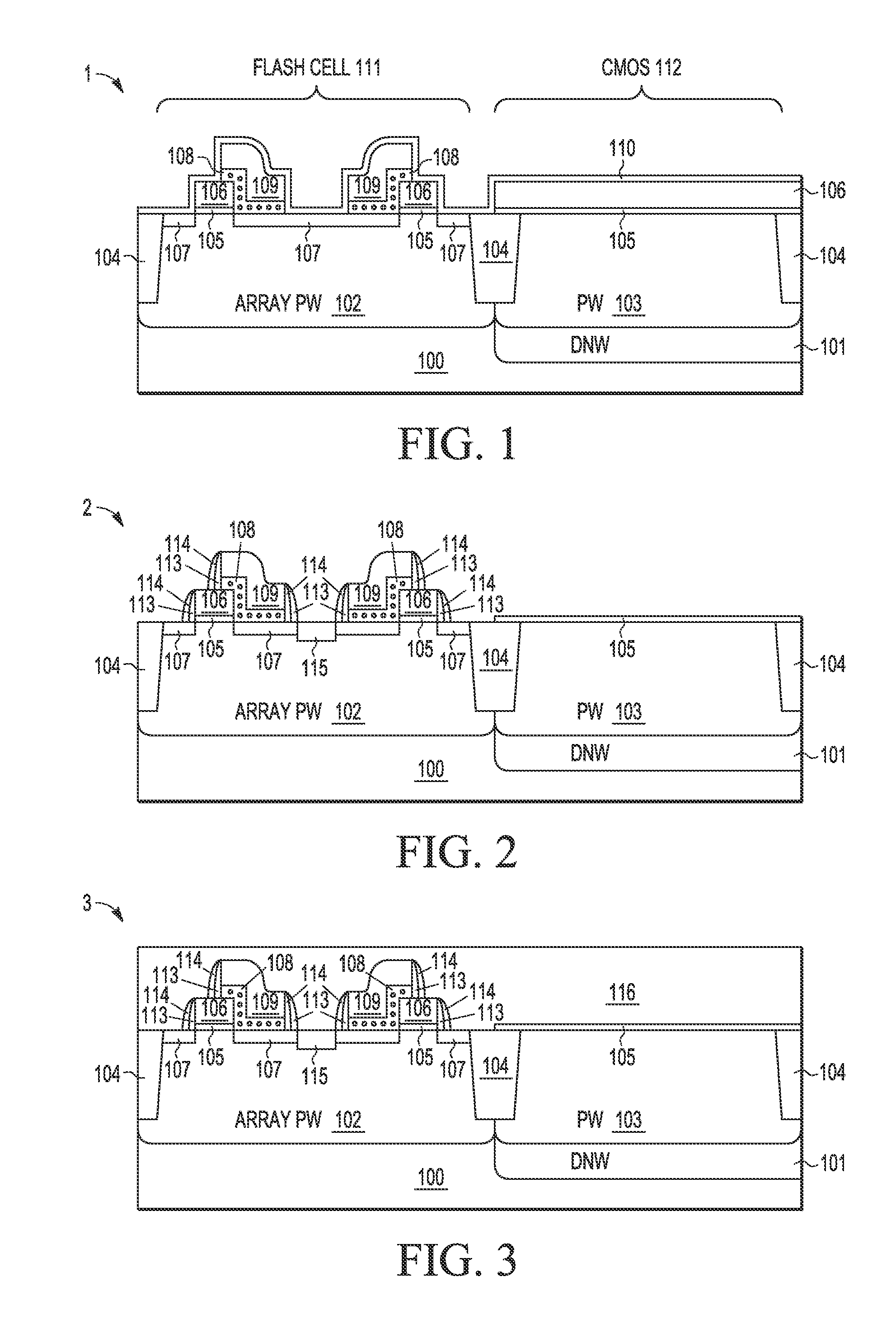
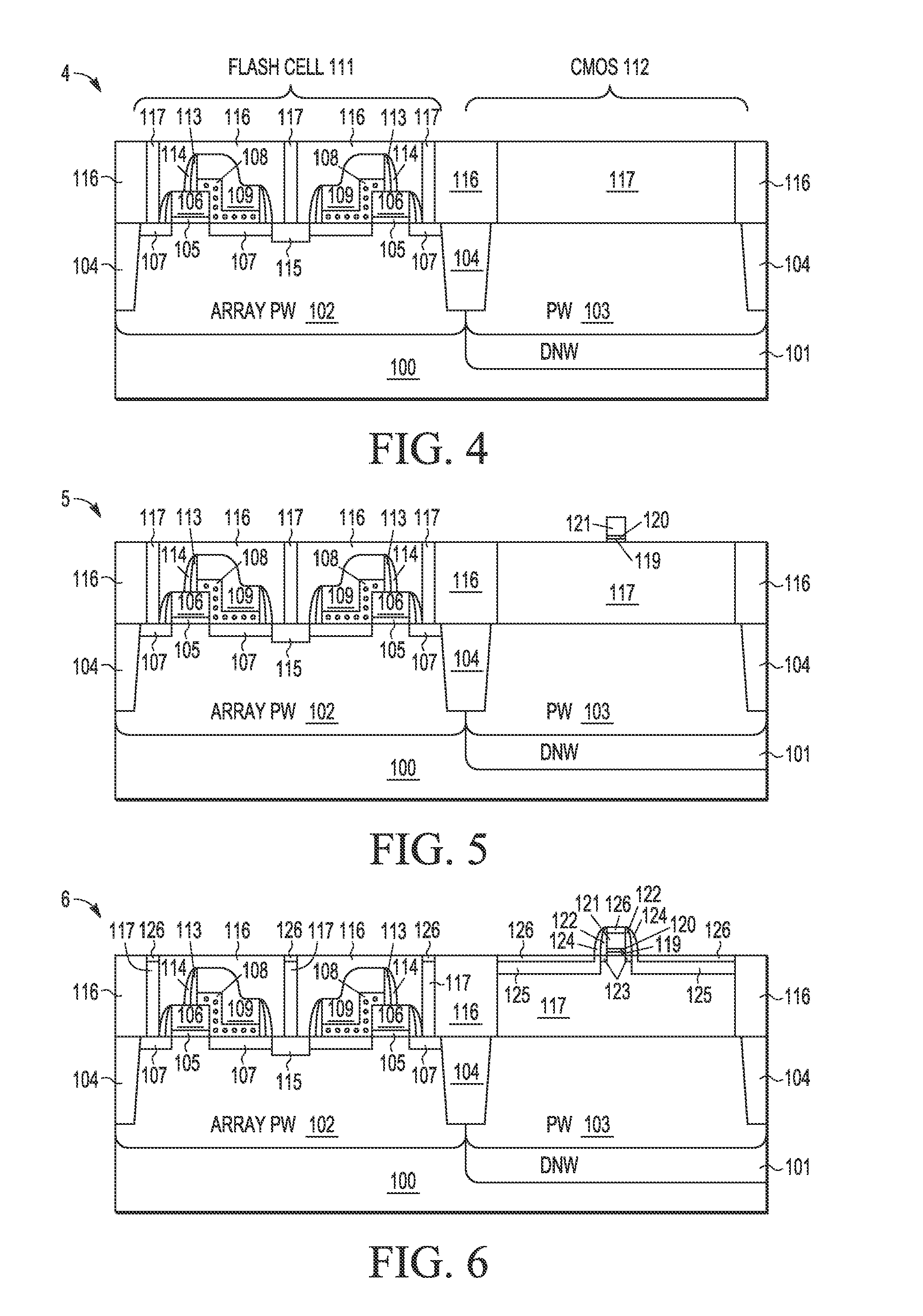
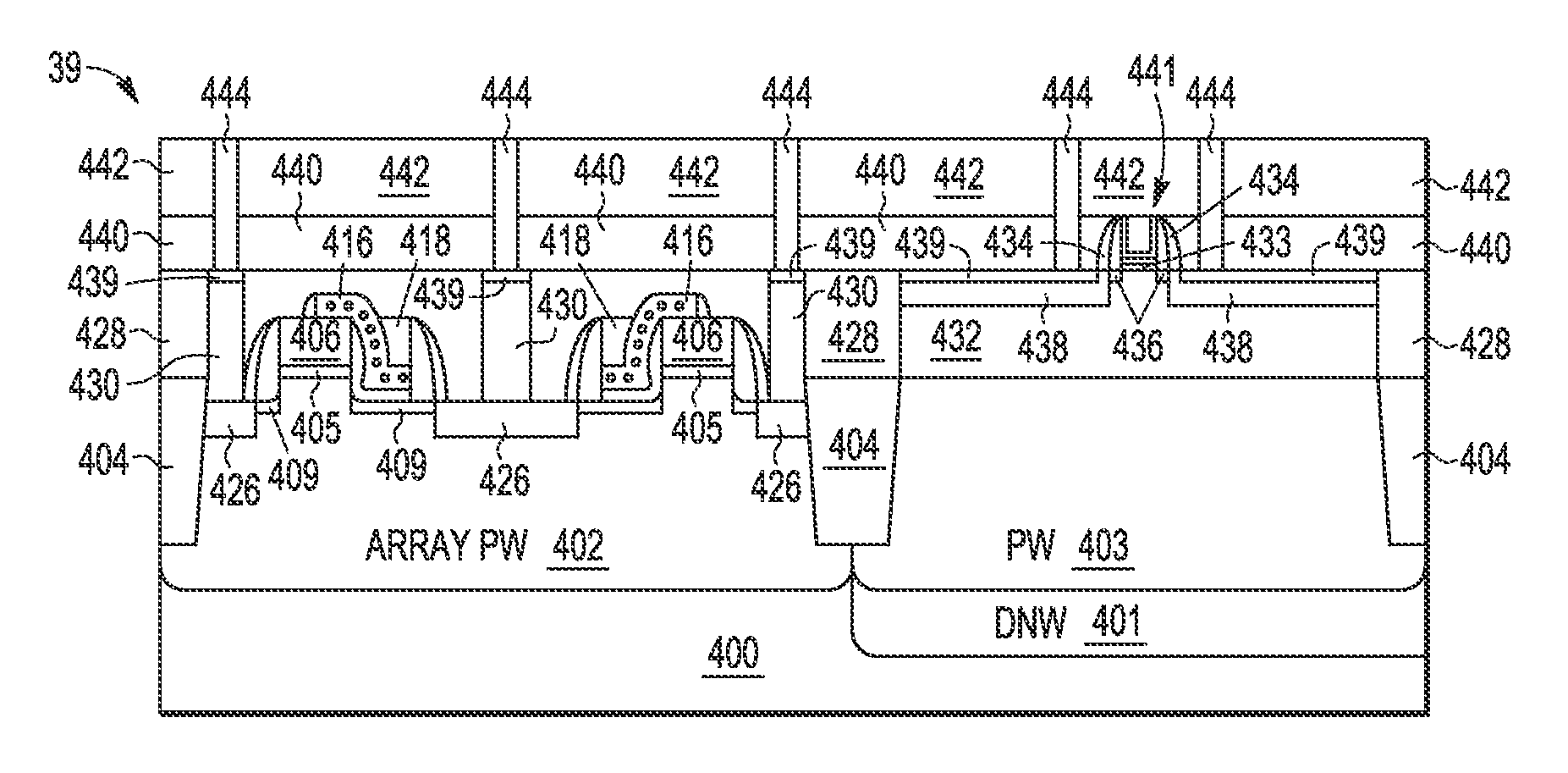
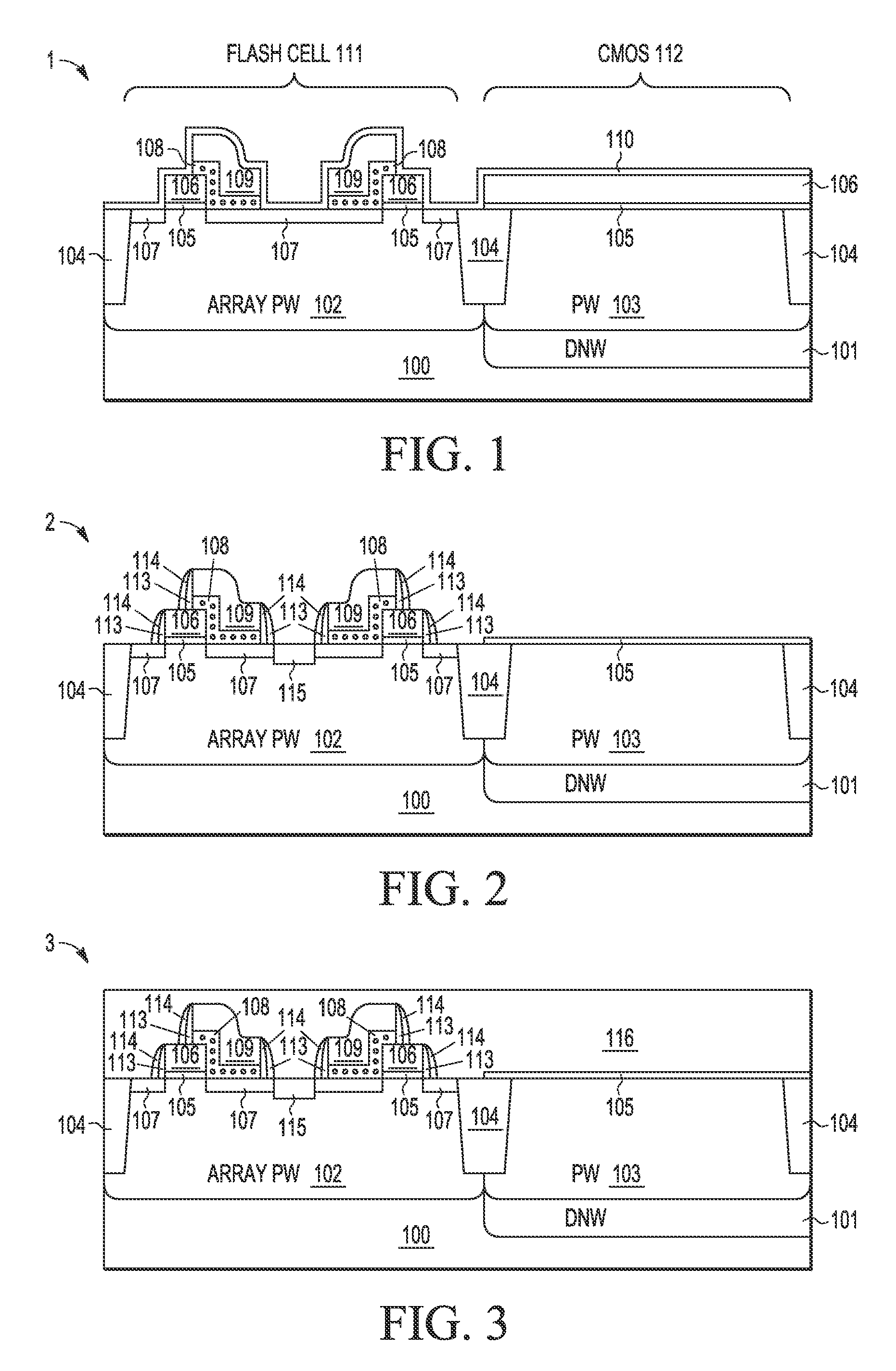
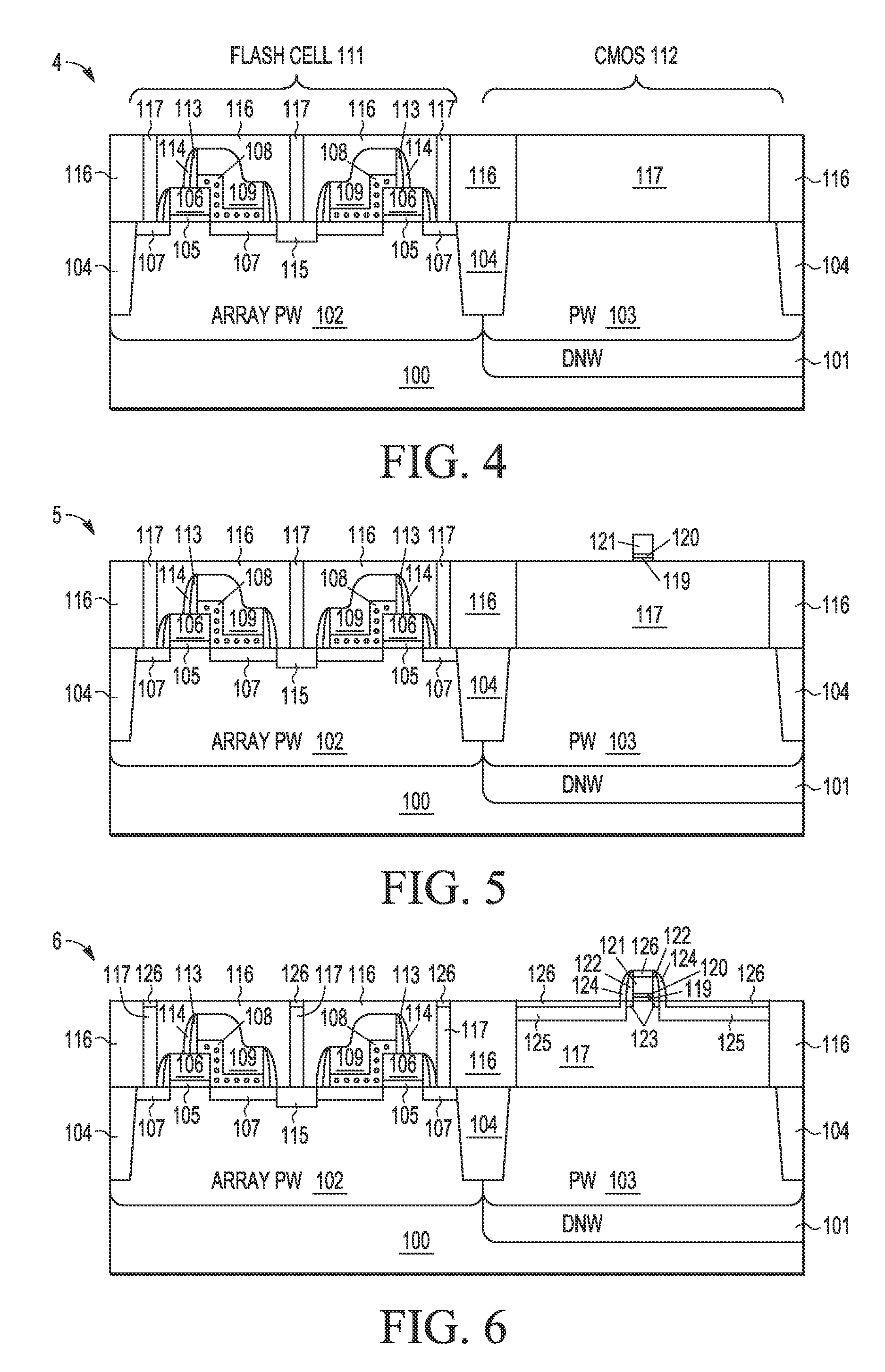
A process integration is disclosed for fabricating non-volatile memory (NVM) cells (105-109, 113-115) on a first flash cell substrate area (111) which are encapsulated in one or more planar dielectric layers (116) prior to forming an elevated substrate (117) on a second CMOS transistor area (112) on which high-k metal gate electrodes (119-120, 122-126, 132, 134) are formed using a gate-last HKMG CMOS process flow without interfering with the operation or reliability of the NVM cells.
Owner:NXP USA INC
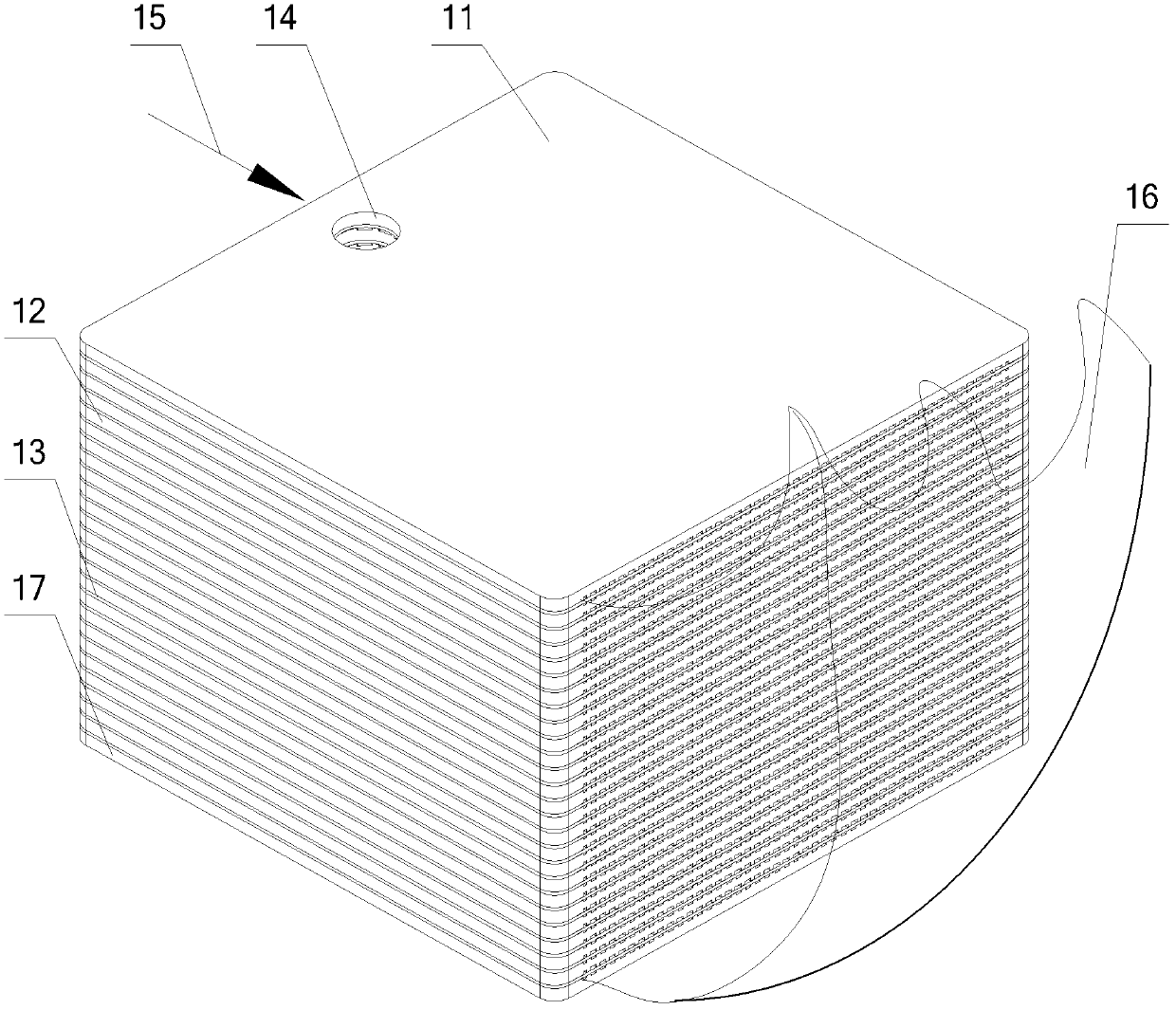
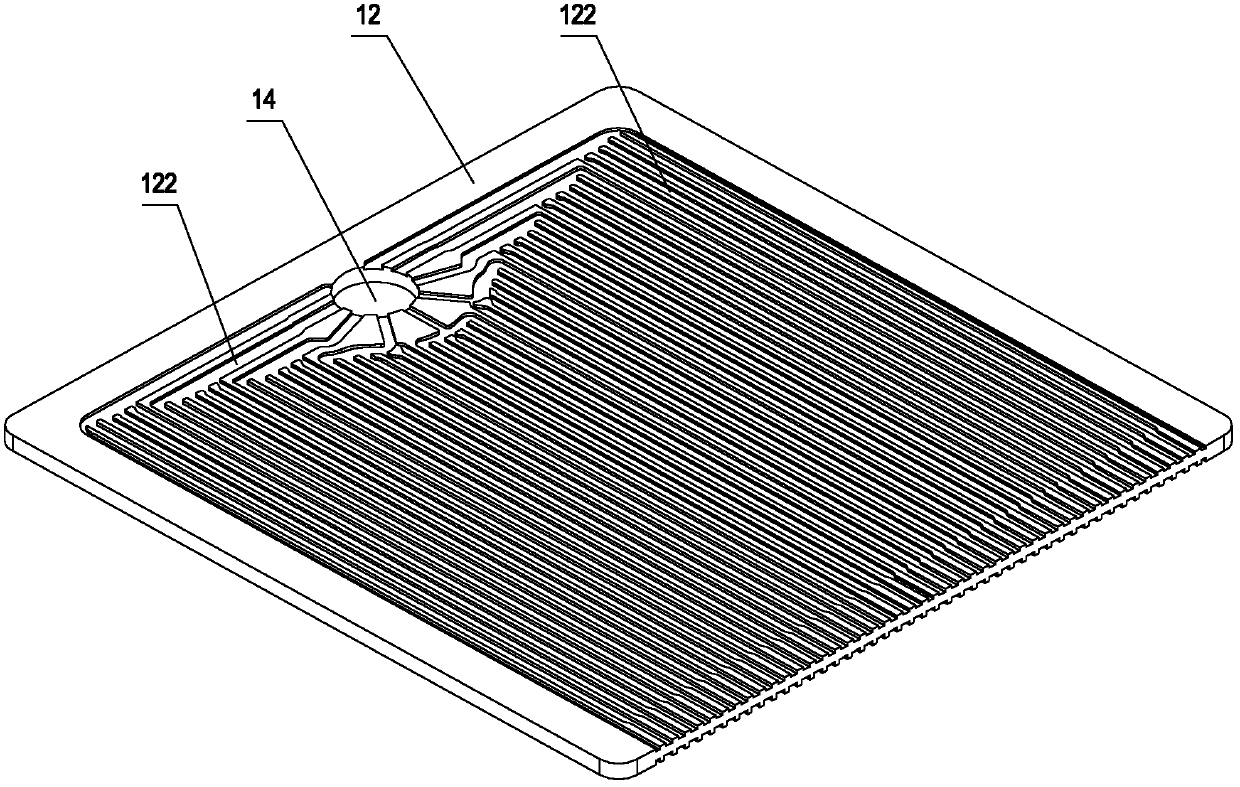
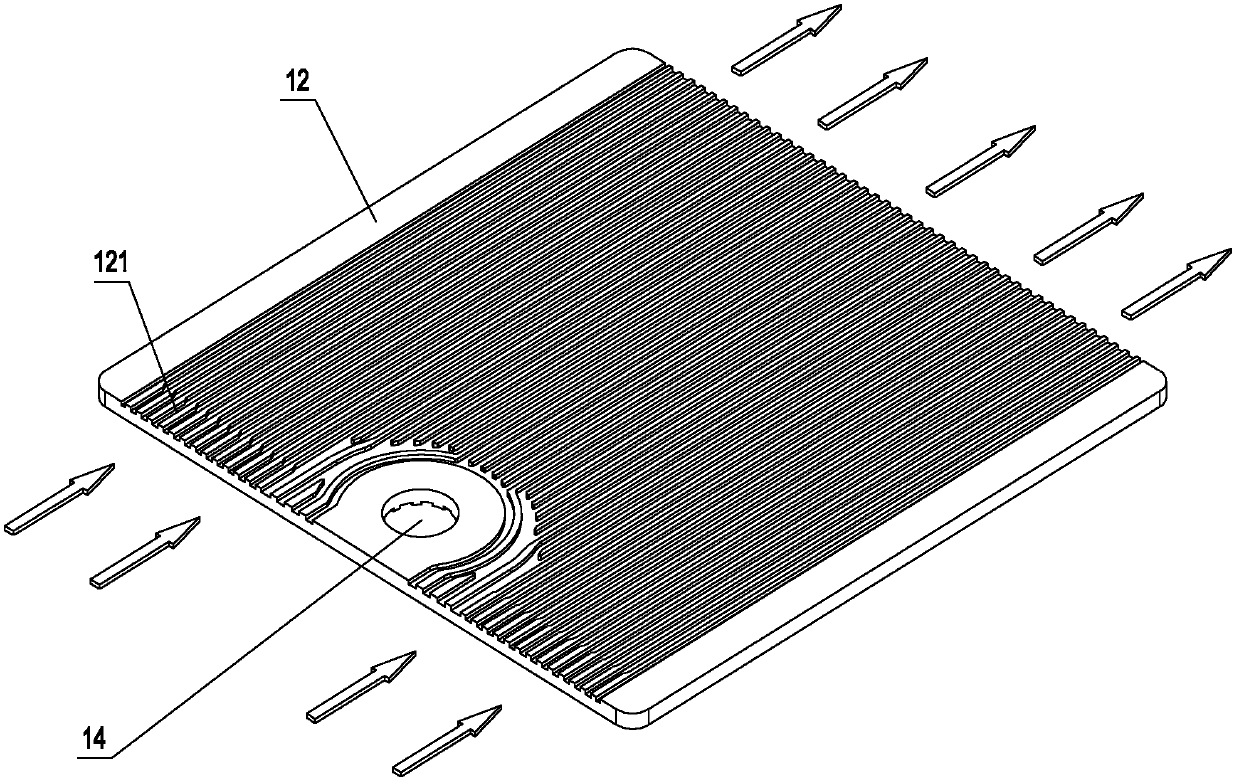
Solid oxide fuel cell power generating system and cell stack thereof
The invention discloses a cell stack. The cell stack comprises double-sided runner plates, cell substrates, an air dispersion cavity and a tail gas mixing burning cavity, wherein the upper surface and the lower surface of each double-sided runner plate are respectively provided with an air runner and a fuel gas runner, the cell substrates and the double-sided runner plates are alternately laminated, one cell substrate is arranged between two adjacent double-sided runner plates, the double-sided runner plates and the cell substrates are respectively provided with a fuel gas inlet penetrating through the double-sided runner plates and the cell substrates, the air dispersion cavity and the tail gas mixing burning cavity are respectively formed on two sides of the double-sided runner plates, the fuel gas runner extends from the fuel gas inlet to the tail gas mixing burning cavity, and the air runner extends from the air dispersion cavity to the tail gas mixing burning cavity. By adopting the cell stack, the structure is simplified, the natural gas inlet resistance is reduced, and the heat radiation loss of a pipeline can be reduced. The invention also discloses a solid oxide fuel cell power generating system with the cell stack.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Dynamic monitoring of activation of G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) and receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) in living cells using real-time microelectronic cell sensing technology
ActiveUS8263375B2Compound screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsG protein-coupled receptorDynamic monitoring
The present application includes systems and methods for identifying a compound capable of interacting with a G-Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR) or Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) including providing a device capable of measuring cell-substrate impedance operably connected to an impedance analyzer, adding test cells expressing a GPCR or a RTK to wells of the device, measuring first impedances of the wells and optionally determining first cell indices from the first impedances, adding a compound to at least one well containing test cells to form at least one compound well and adding a vehicle control to at least another well containing test cells to form at least one control well, measuring second impedances of the compound well and the control well and optionally determining second cell indices from the second impedances, determining the change in the impedance or cell index for the compound well and the one control well, comparing the change in impedance or cell index between the compound well and the control well, and identifying the compound interacts with the GPCR or RTK if the comparison demonstrates a significant difference between the change in impedance or cell index of the compound well and the control well.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
IPS mode liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20050213012A1Increase contrastEasy to viewStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsTectorial membraneIn plane
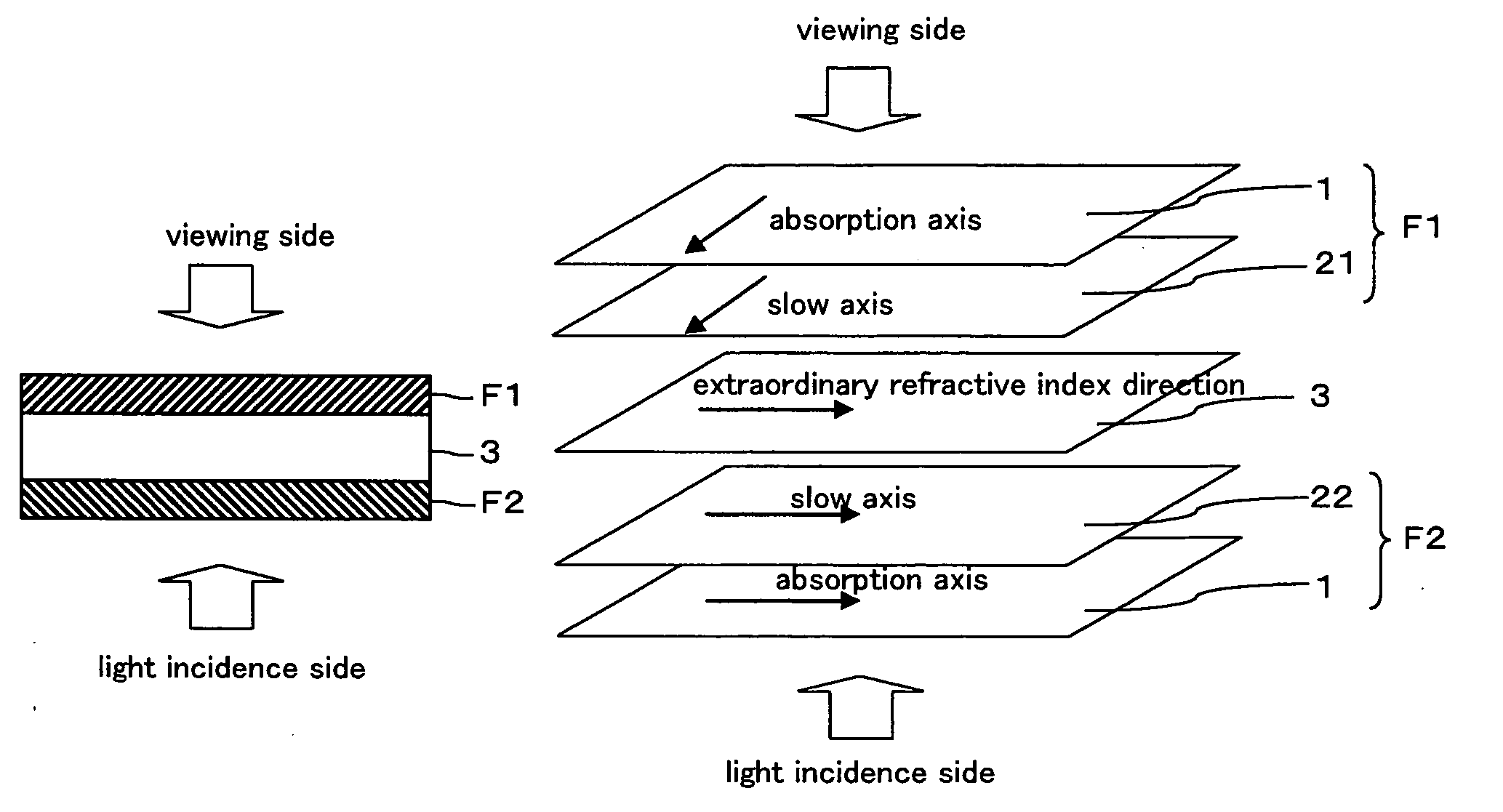
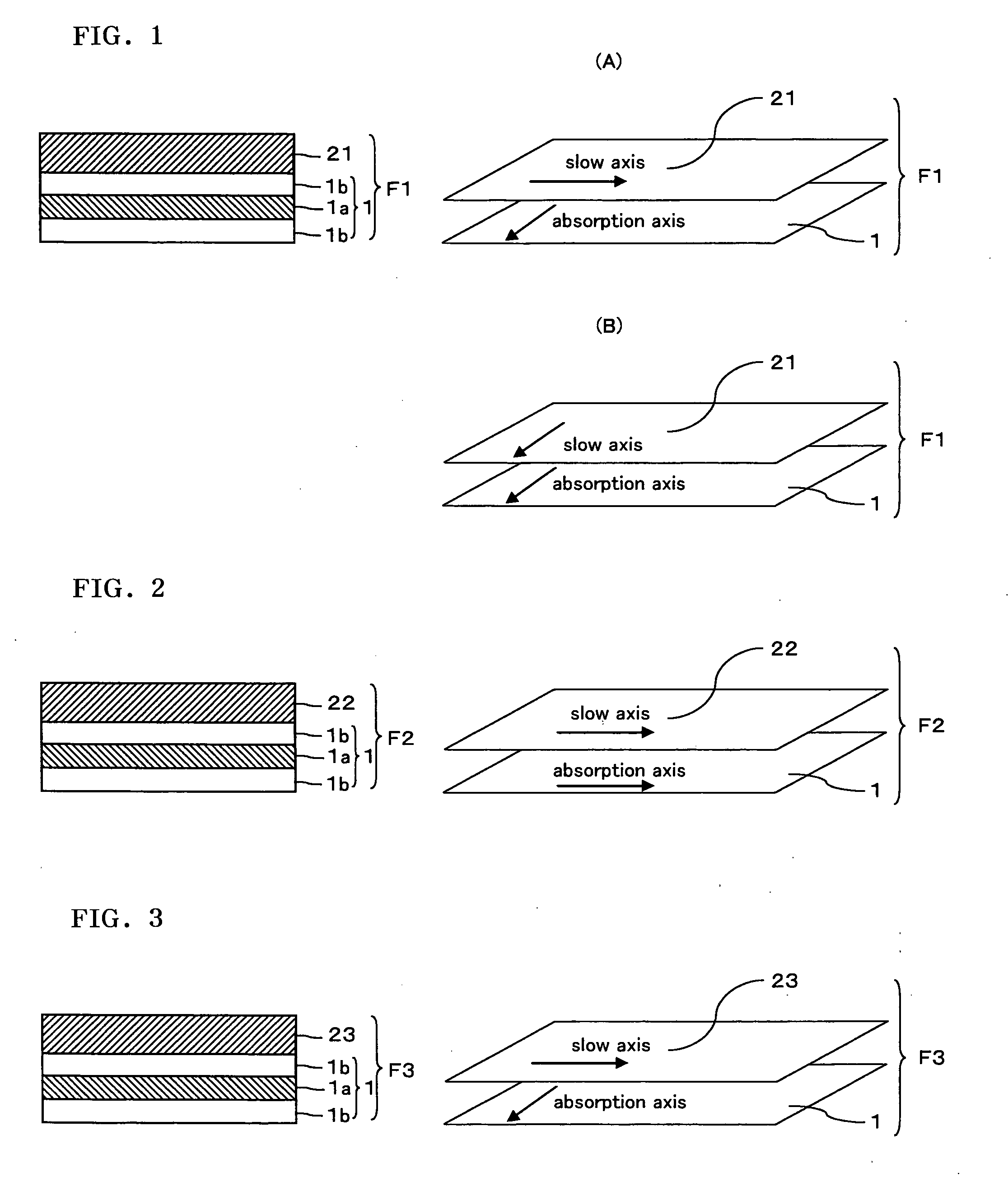
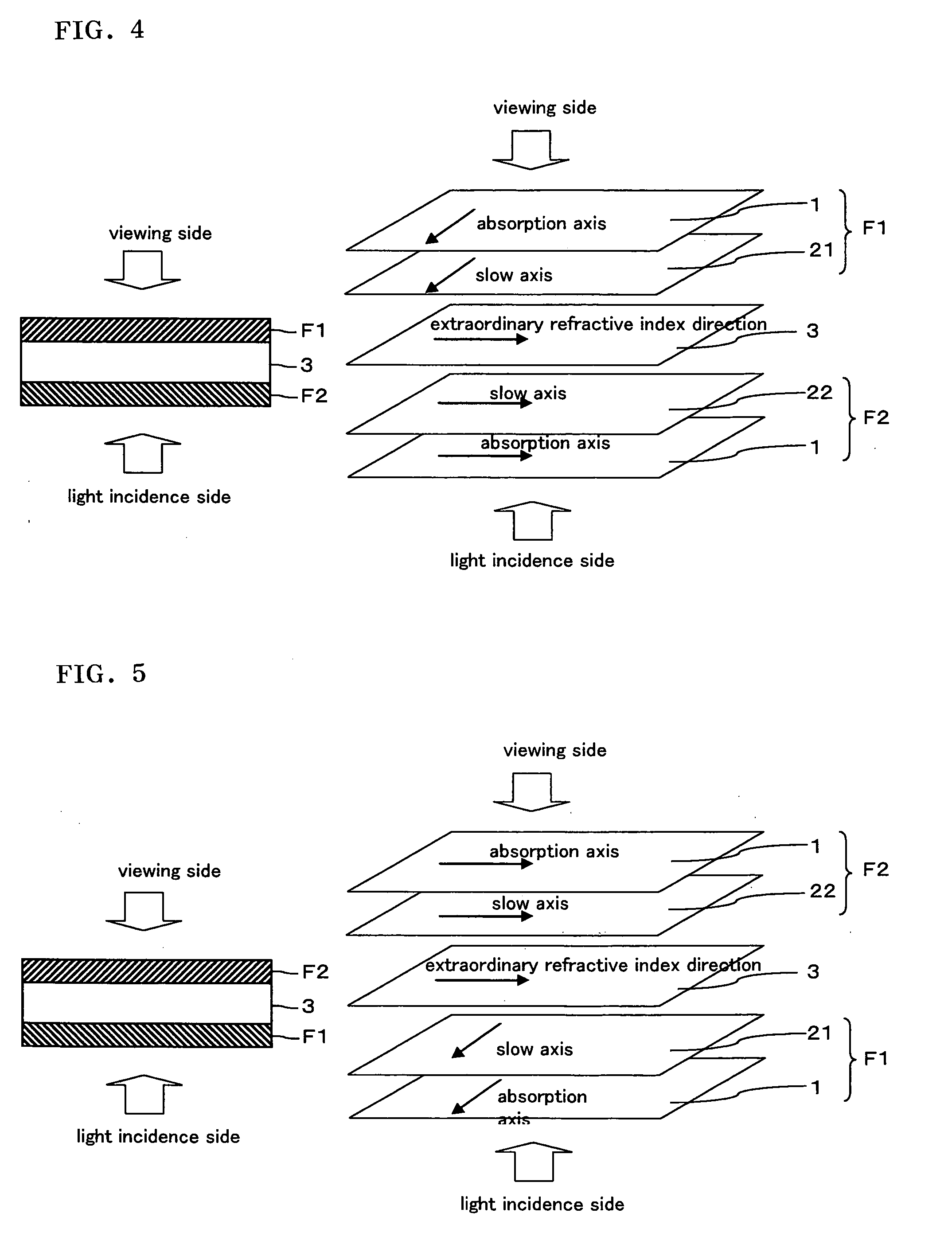
An IPS mode liquid crystal display comprising a liquid crystal cell, an optical film (F1) provided on a cell substrate on one side of the liquid crystal cell and comprises a polarizing plate comprising a transparent protective film having an in-plane retardation Re 10 nm or less and a thickness direction retardation Rth in the range of from 30 to 100 nm, a retardation film having an Nz value in the range of from 0.3 to 0.7 and an in-plane retardation Re1 in the range of from 200 to 300 nm, and an optical film (F2) provided on a cell substrate on the other side of the liquid crystal cell and comprises the polarizing plate and a retardation film having an Nz value in the range of from 0.9 to 1.2 and an in-plane retardation Re2 in the range of from 150 to 280 nm, and the absorption axes of the polarizing plates of the optical film (F1) and the optical film (F2) are perpendicular to each other, and both films are disposed so that the retardation film sides face the liquid crystal cell. The IPS mode liquid crystal display has a high contrast ratio across a wide range, and capable of realizing a better view.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Display device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110149218A1Improve productivityLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentEngineeringParallax barrier
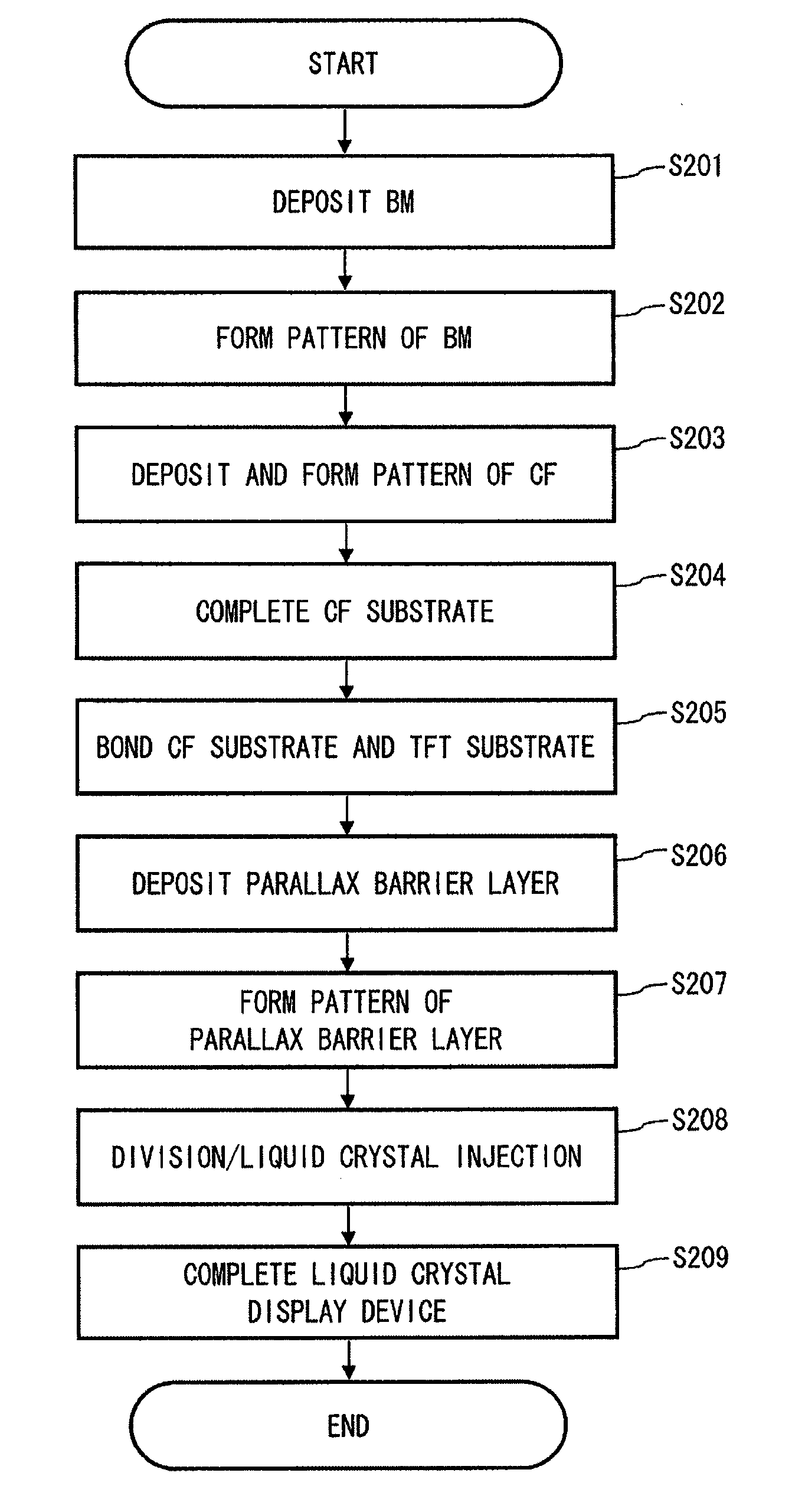
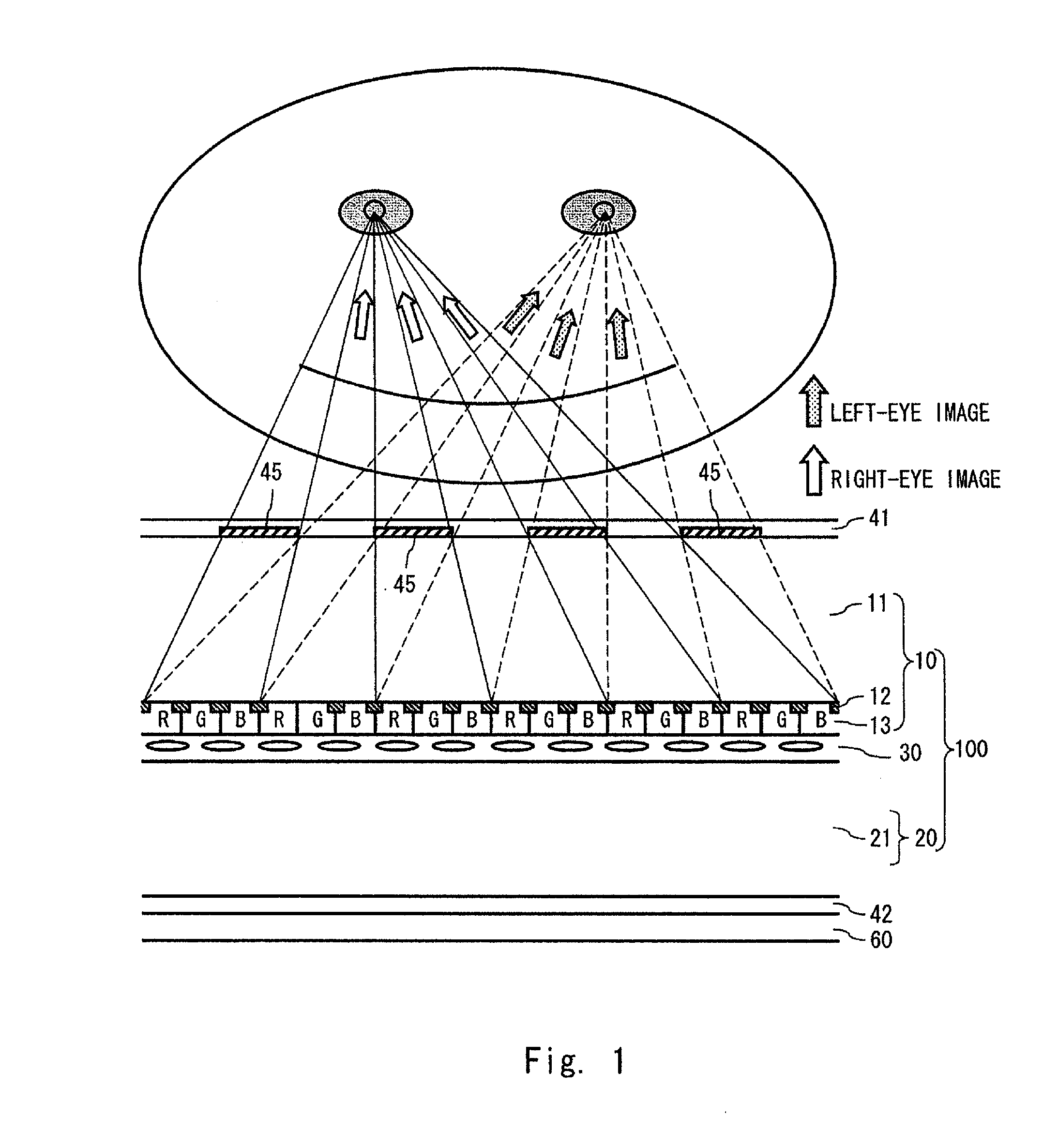
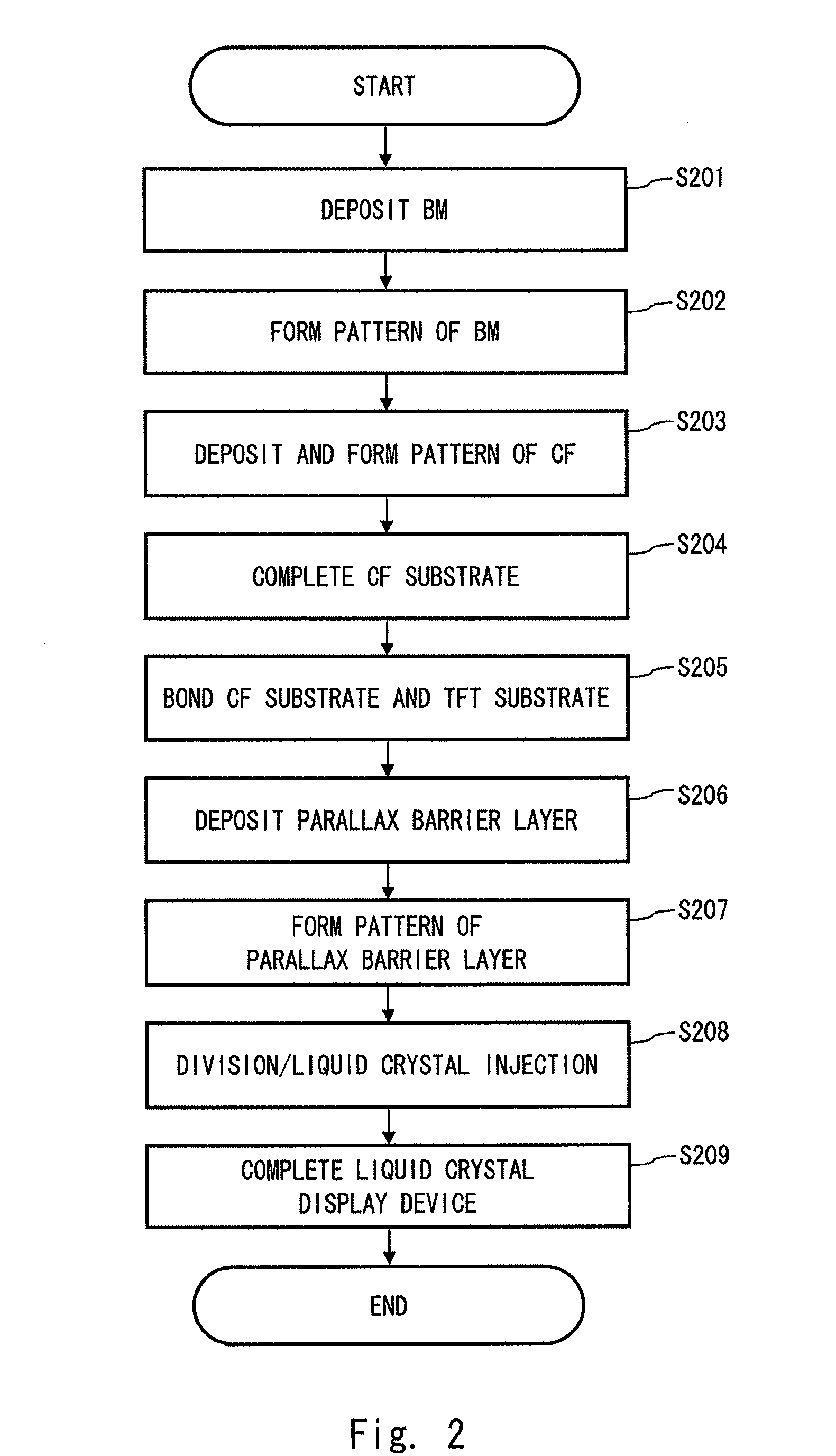
A method of manufacturing a display device according to one aspect of the present invention is a method of manufacturing a display device including a liquid crystal interposed between a CF substrate and a TFT substrate that are opposed to each other, the method including the steps of: bonding the CF substrate and the TFT substrate each having a mother substrate shape to form a cell substrate from which at least one panel is to be cut out; forming, after formation of the cell substrate, a parallax barrier layer for separating a display image on an outer side of the cell substrate at a side of one of the CF substrate and the TFT substrate; and dividing, after formation of the parallax barrier layer, the cell substrate into at least one panel.
Owner:TRIVALE TECH LLC
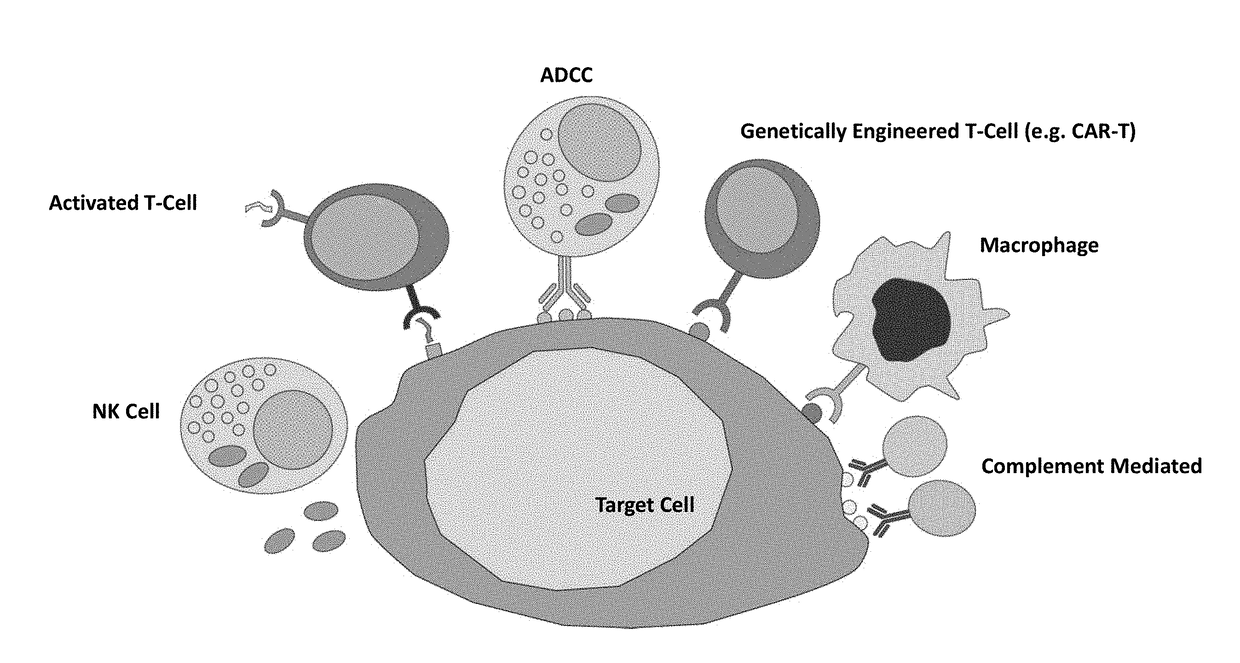
Cell-substrate impedance monitoring of cancer cells
InactiveUS20180246079A1Efficient testingImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCancer cellEffector cell
Methods of assessing cytolysis of cancer cells, including providing a cell-substrate impedance monitoring device operably connected to an impedance analyzer, wherein the device comprises a well for receiving cells and an electrode array at a base of the well; adding target cells characterized as cancer cells to the well; adding effector cells to the well to form a test well, wherein the effector cells are immune cells obtained or derived from a same patient as the target cells; monitoring cell-substrate impedance of the test well before and after adding the effector cells and optionally deriving an impedance-based parameter from the impedance; and determining effectiveness of effector cell killing of the target cells by comparing the impedance or impedance based parameter over time.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method for assaying for natural killer, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte and neutrophil-mediated killing of target cells using real-time microelectronic cell sensing technology
ActiveUS20060023559A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEffector cellT lymphocyte
The present invention includes a method of measuring cytolytic activity including providing a device capable of monitoring cell-substrate impedance operably connected to an impedance analyzer, adding target cells to at least one well of the device, adding effector cells to the at least one well, monitoring impedance of the at least one well and optionally determining a cell index from the impedance, wherein monitoring impedance includes measuring impedance during at least one time point before and at least one time point after adding effector cells, and determining viability of said target cells after adding effector cells by comparing the impedance or optionally the cell index at the at least one time point after adding effector cells to the impedance or optionally the cell index at the at least one time point before adding effector cells
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method and device for dividing brittle substrate
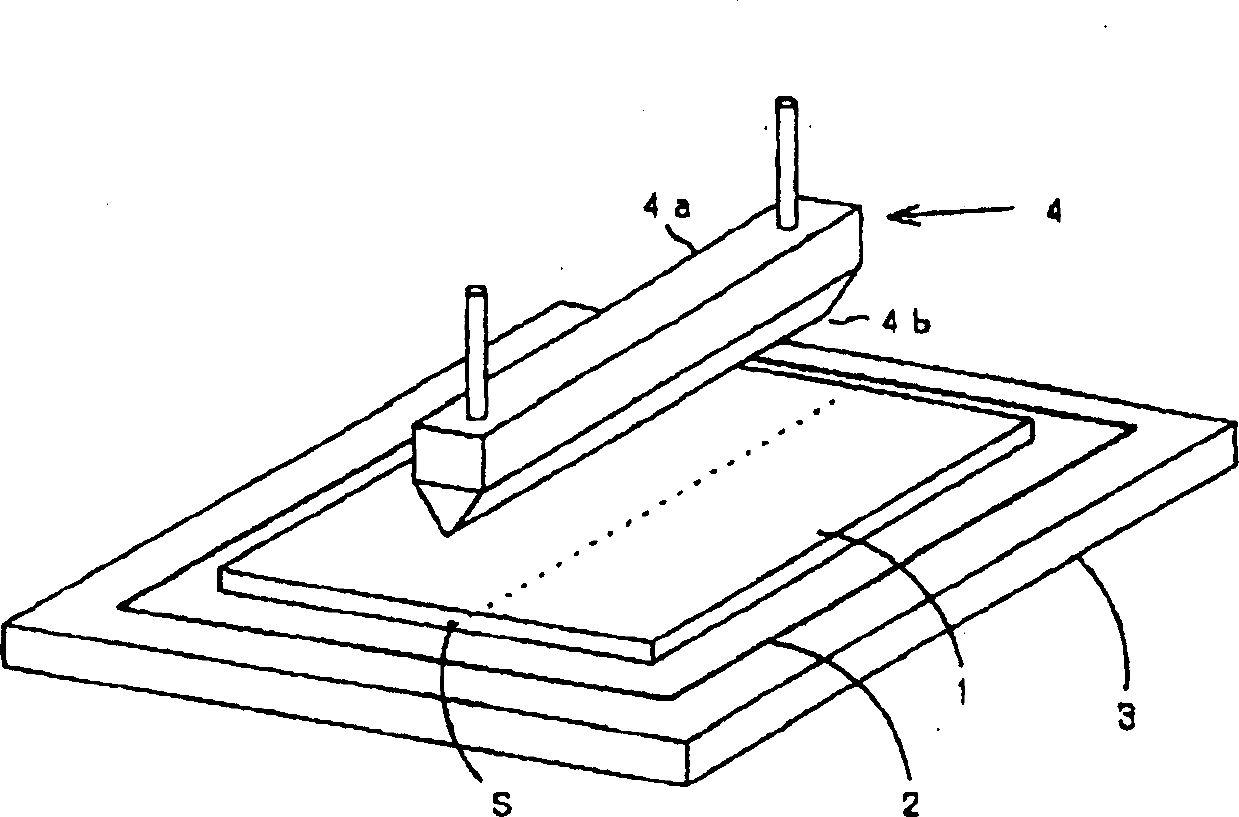
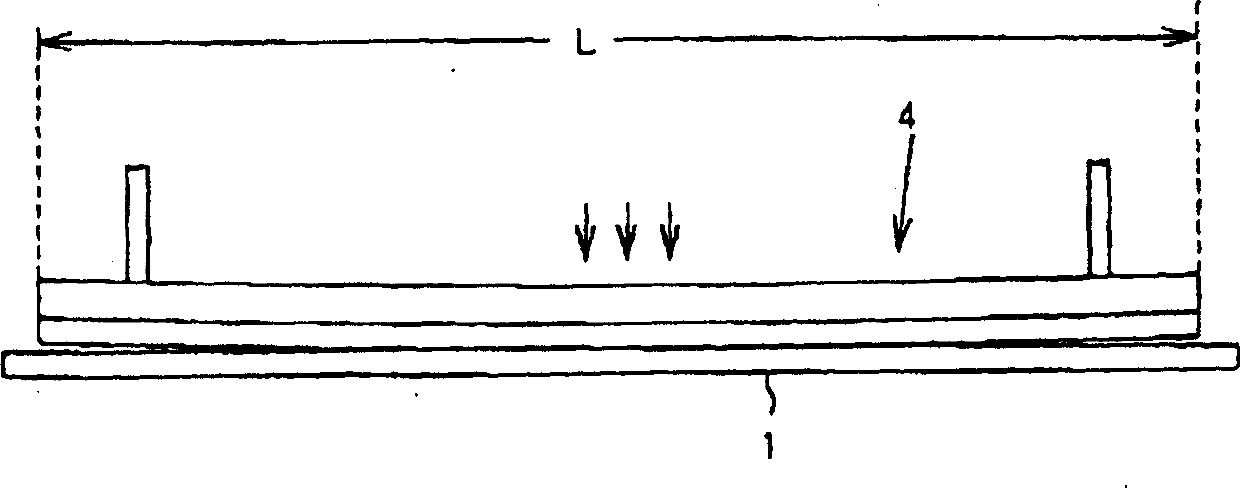
InactiveCN1359784ASuppression of poor segmentationConveyorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingModel methodEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and a device for dividing brittle substrate. The device comprises a splitting pole for pressing the lineate brittle substrate to execute splitting along the scratch. The device is characterized in that the bottom of the splitting pole is provided with a curved shaped pressing part; a pressing control part is provided for bringing the curved shaped pressing part into contact with the surface of the brittle substrate along the splitting predetermined line with respect to the scratch, at the same time horizontally moving along the long edge direction of the splitting pole. The utility model method and apparatus are used where the undesirable parts on the ends of the cell substrates are retained. After cutting of the laminated glass substrate, another device is used to cut off the undesirable parts. Thus in the process of cutting a laminated glass substrate of a large size into a plurality of cell substrate of a small size while cutting off undesirable parts from the glass substrate, the forming of fragments on the glass ends can be prevented.
Owner:MITSUBOSHI DIAMOND IND CO LTD
Method to form a polysilicon nanocrystal thin film storage bitcell within a high k metal gate platform technology using a gate last process to form transistor gates
A process integration is disclosed for fabricating non-volatile memory (NVM) cells (105-109, 113-115) on a first flash cell substrate area (111) which are encapsulated in one or more planar dielectric layers (116) prior to forming an elevated substrate (117) on a second CMOS transistor area (112) on which high-k metal gate electrodes (119-120, 122-126, 132, 134) are formed using a gate-last HKMG CMOS process flow without interfering with the operation or reliability of the NVM cells.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Liquid-based thin-layer cell preservation solution and use thereof
ActiveCN101914483AReduce manufacturing costEfficient separationAnimal cellsDead animal preservationStainingWhite blood cell
The invention discloses liquid-based thin-layer cell preservation solution and use thereof. The preservation solution comprises 5 to 28 volume percent of aldehyde solution, 0.1 to 3 volume percent of acid solution, 0.1 to 6 mass volume percent of chloride, 0.1 to 3 mass volume percent of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane and the balance volume percent of double distilled water. The preservation solution of the invention can remove red blood cells, preserve white blood cells, timely fix the original state of cells of diagnostic value, soften mucilage and epidermal tissues, weaken mucous effect and separate effective cells from mucilage. The microscopic examination piece manufactured by using the preservation solution has clear microscopic examination view field and high cellular staining contrast and is widely suitable for gynecological and non-gynecological exfoliative cytological specimens and manual, semi-automatic or fully-automatic liquid-based cell substrate making processes. The production cost of the preservation solution is low, so the application and promotion of a liquid-based thin-layer cell detection technique are convenient.
Owner:山东龙奥生物技术有限公司
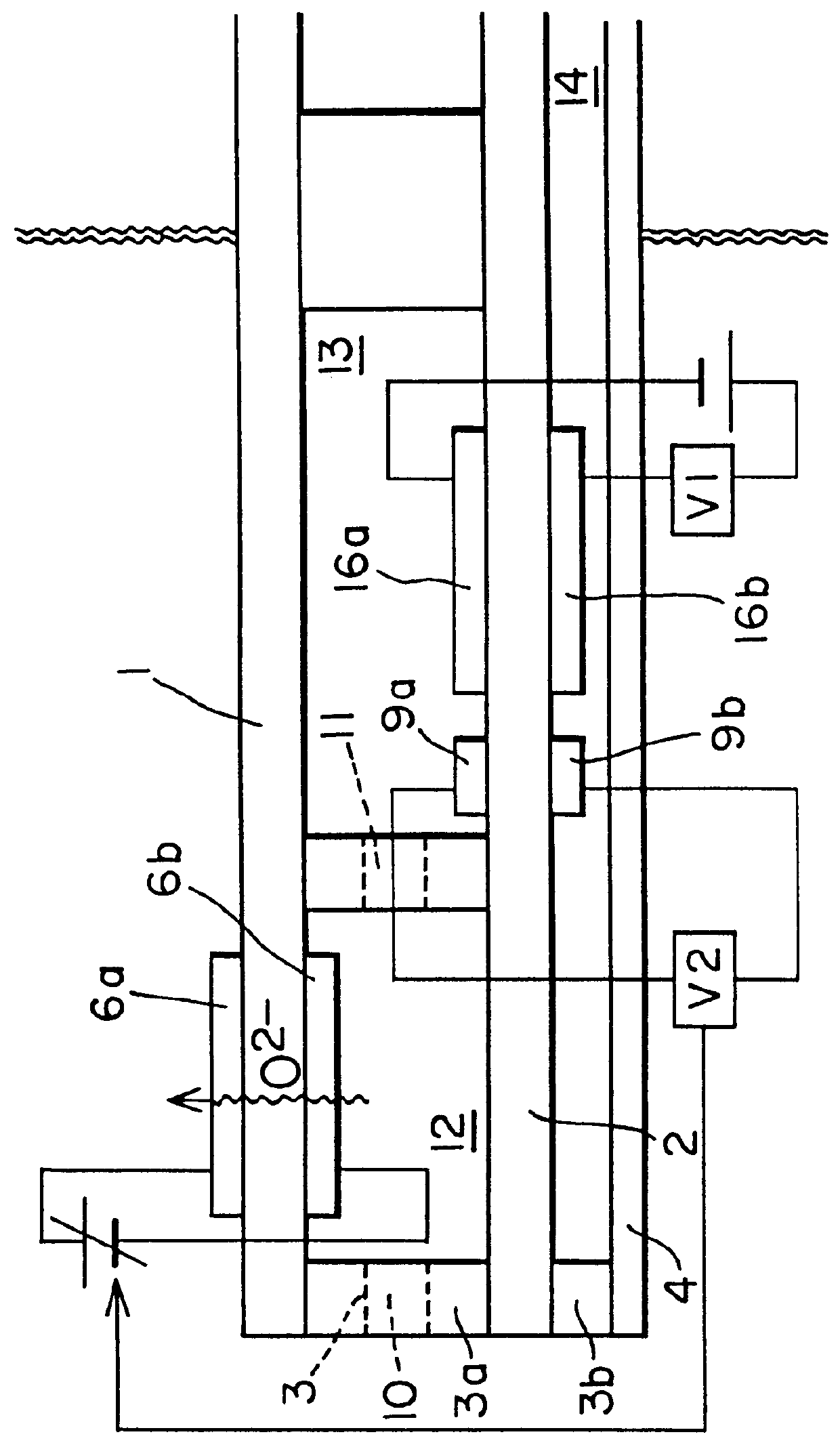
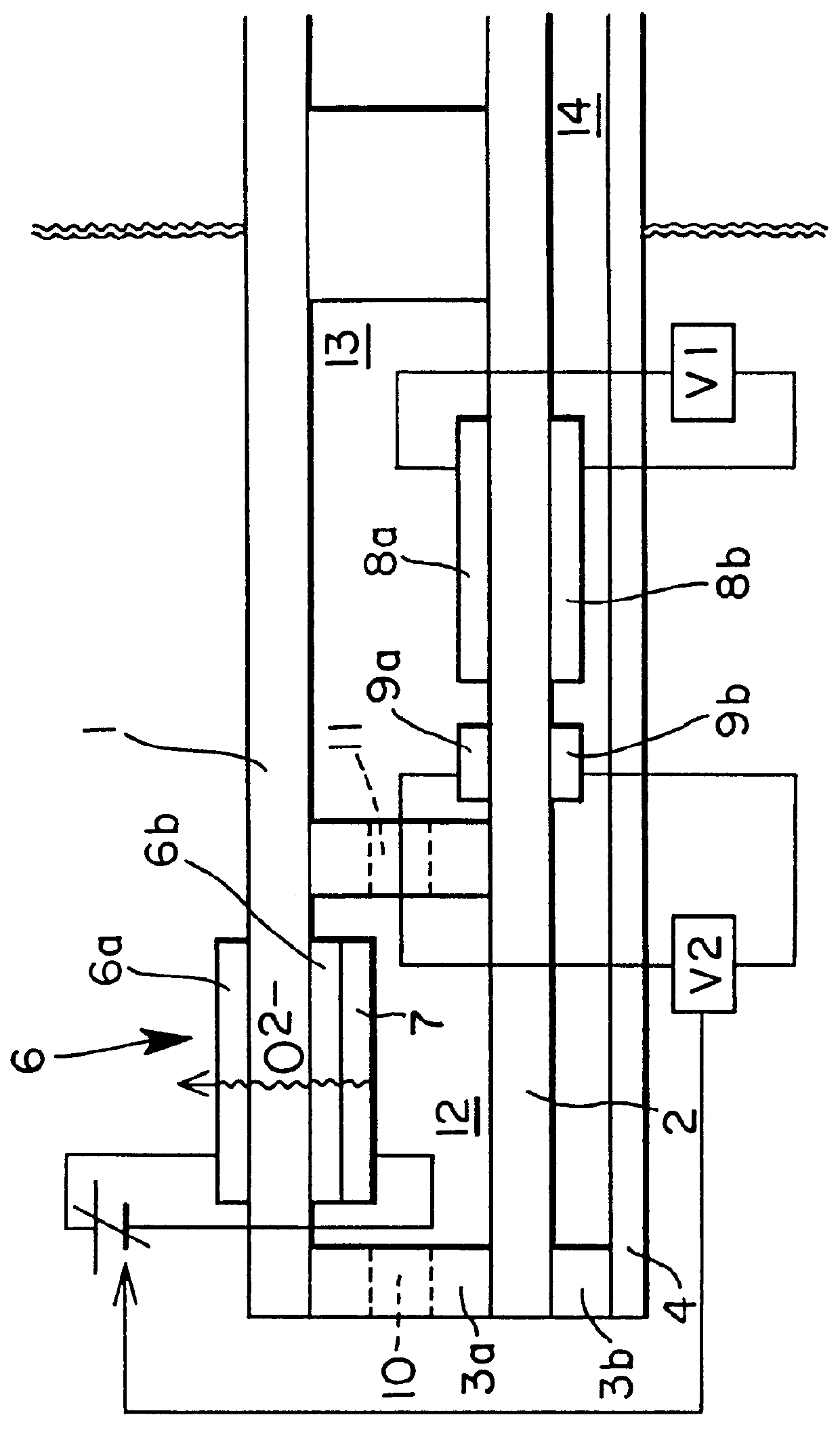
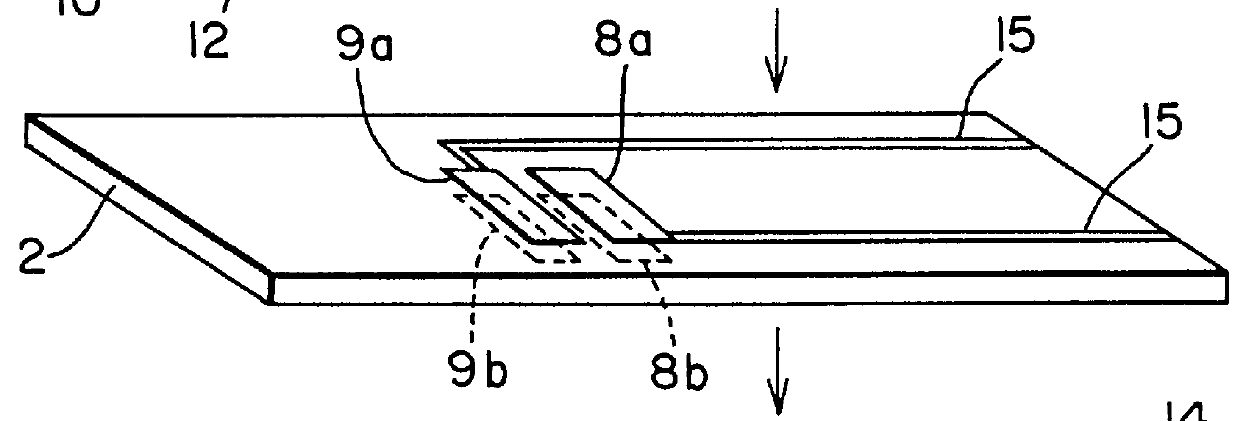
NOx sensor
A stable sensor designed to detect accurately the total NOx concentration under 100 ppm in terms of the NO gas concentration is made up of a first cell and a second cell with a gas diffusion aperture provided between the two cells. The first cell has a partition wall of a substrate of oxygen ion conductor containing zirconia as the main component and permitting a gas to be detected to enter the zirconia substrate; oxygen pumping electrodes are also formed on the first cell substrate which functions to expel oxygen in an atmosphere of the first cell to the outside and to reduce NO2 of the NOx gas to be detected to NO gas. While NO gas entering through a gas diffusion aperture between the two cells flows into the second cell, a measurement is made of an electromotive force between a NO detection electrode formed in the second cell and a counter electrode also formed therein or a counter electrode formed on the reverse side of the zirconia substrate, since such electromotive force corresponds to the level of the NO gas concentration and thus provides the total NOx concentration.
Owner:RIKEN CO LTD
Dynamic Monitoring of Activation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) in Living Cells Using Real-Time Microelectronic Cell Sensing Technology
Methods for identifying a compound capable of interacting with a Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) including providing a device capable of measuring cell-substrate impedance, adding test cells expressing a RTK to the device, measuring first impedances, adding a compound to at least one compound well and adding a vehicle control at least one control well, measuring second impedances of the compound well and the control well, determining the change in the impedance for the compound well and the one control well, comparing the change in impedance between the compound well and the control well, and identifying the compound interacts with the RTK if the comparison demonstrates a significant difference between the change in impedance.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Full-back-electrode solar cell structure and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN105390555AImprove surface passivation effectAvoid recombinationFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSolar cellPolycrystalline silicon
The invention discloses a full-back-electrode solar cell structure and a preparation method therefor. The full-back-electrode solar cell structure comprises a cell substrate, a tunneling passivation layer, and a polycrystalline silicon layer, wherein the tunneling passivation layer is arranged on the back surface of the cell substrate; the polycrystalline silicon layer is arranged on the lower surface of the tunneling passivation layer; and the polycrystalline silicon layer is provided with an N type heavily-doped polycrystalline silicon layer and a P type polycrystalline silicon layer that are arranged side by side. According to the full-back-electrode solar cell structure, the silicon body is good in the surface passivation effect, and carriers can be selectively output, so that the efficiency of the full-back-electrode solar cell is improved.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD
Label-free monitoring of excitation-contraction coupling and excitable cells using impedance based systems with millisecond time resolution
ActiveUS9709548B2Easy to measureEffective monitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningImage resolutionExcitation–contraction coupling
Systems and methods for improved monitoring of excitation-contraction coupling and excitable cells are provided, which provide millisecond time resolution. The system is capable of continuously monitoring excitation-contraction coupling in a relatively high-throughput manner. The system includes a device for monitoring cell-substrate impedance, an impedance analyzer capable of impedance measurements at millisecond time resolution, electronic circuitry that can engage the device and selectively connect two or more electrode arrays of the device to the impedance analyzer and a software program that controls the electronic circuitry and records and analyzes data obtained from the impedance analyzer.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com