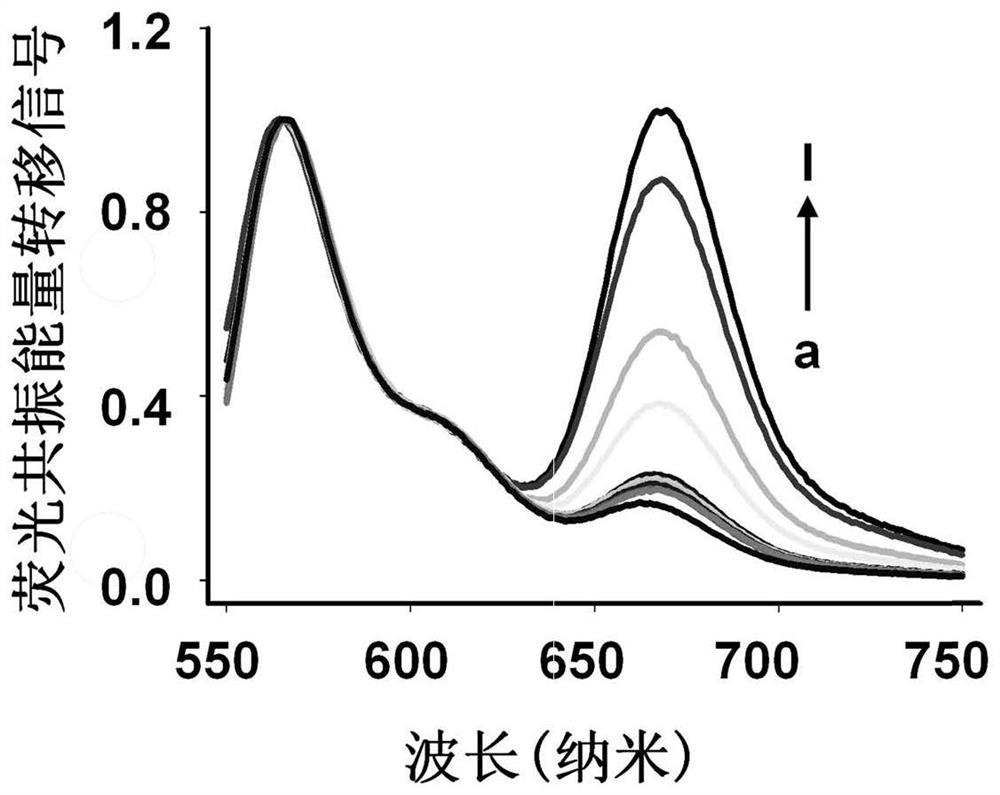
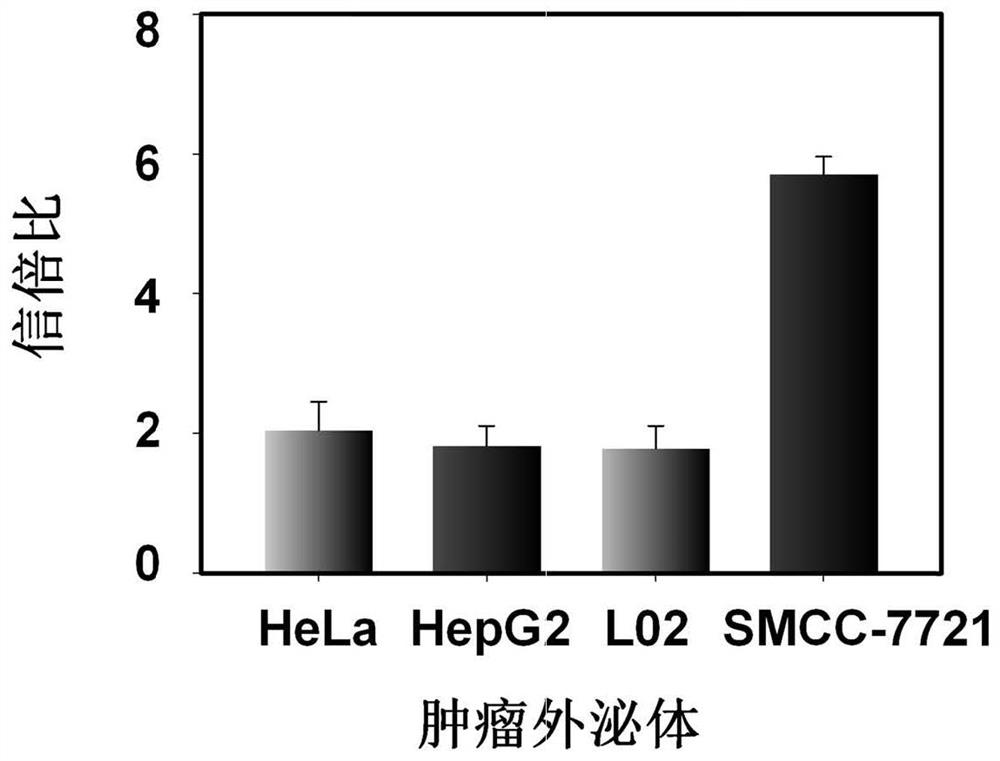
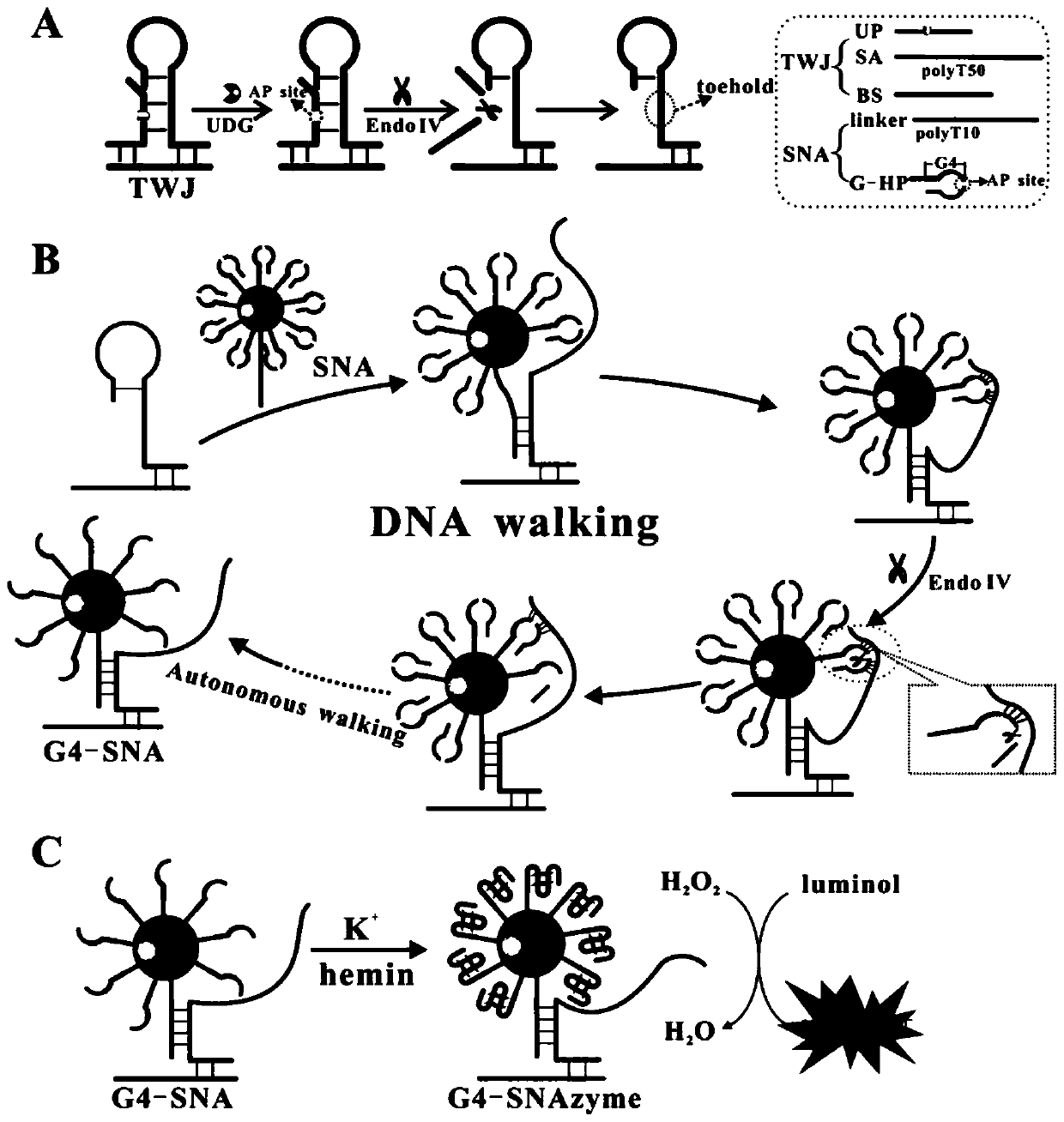
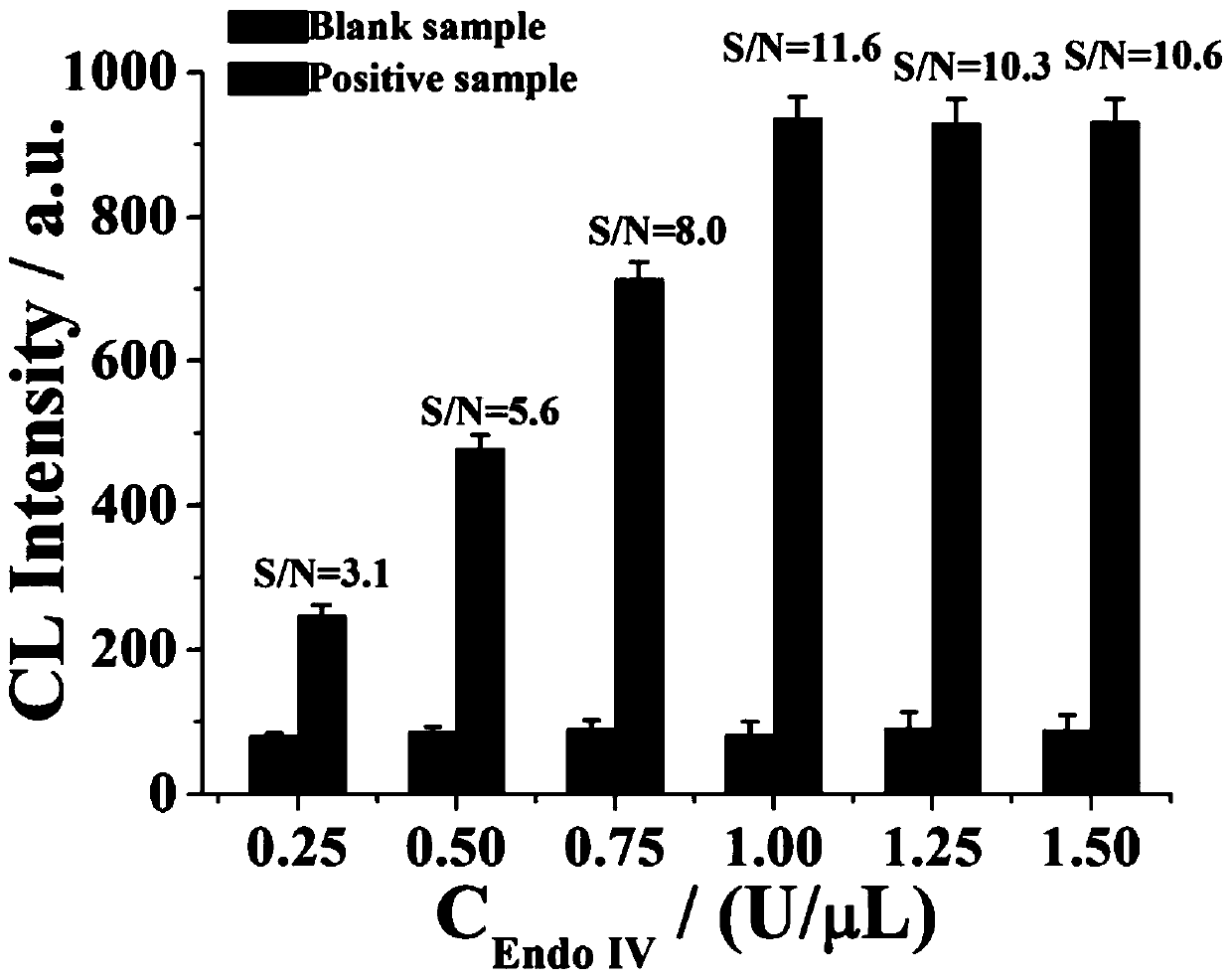
Patents
Literature
38 results about "DNA walker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A DNA walker is a class of nucleic acid nanomachines where a nucleic acid "walker" is able to move along a nucleic acid "track". The concept of a DNA walker was first defined and named by John H. Reif in 2003. In 2004 the first autonomous DNA walkers were experimentally demonstrated .
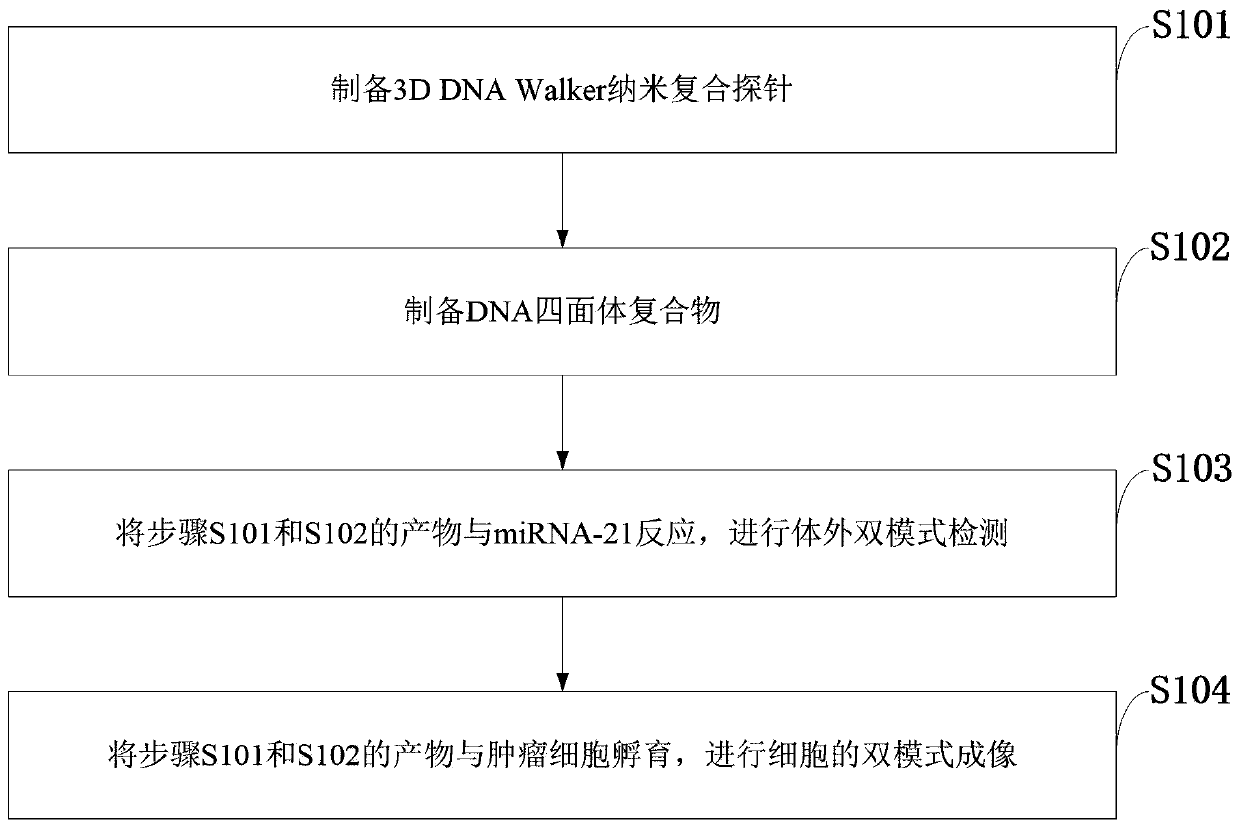
Method for detecting tumor cell marker miRNA-21 and tumor cells
ActiveCN110455764AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityRaman scatteringFluorescence/phosphorescenceIntracellularNanoparti cles
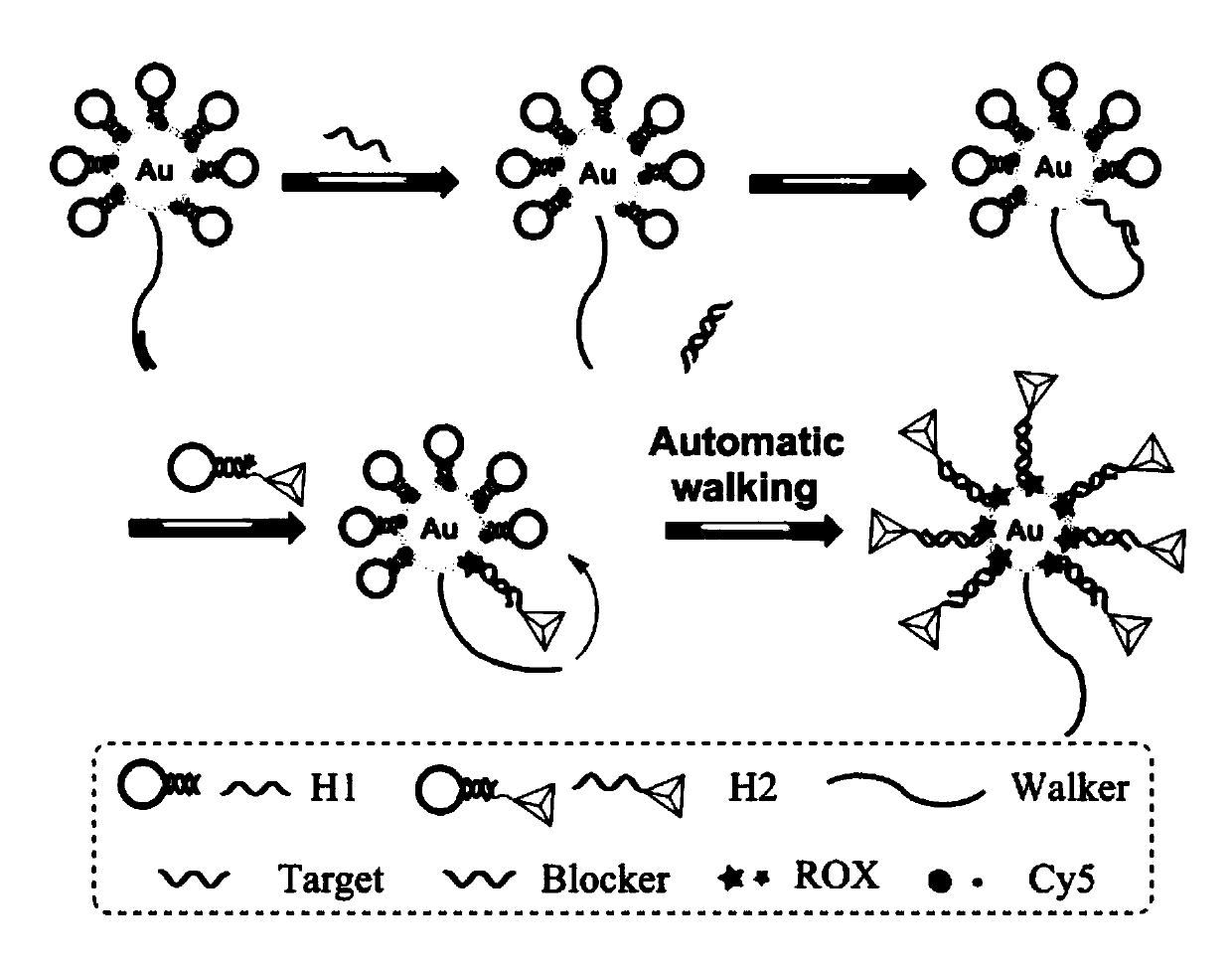
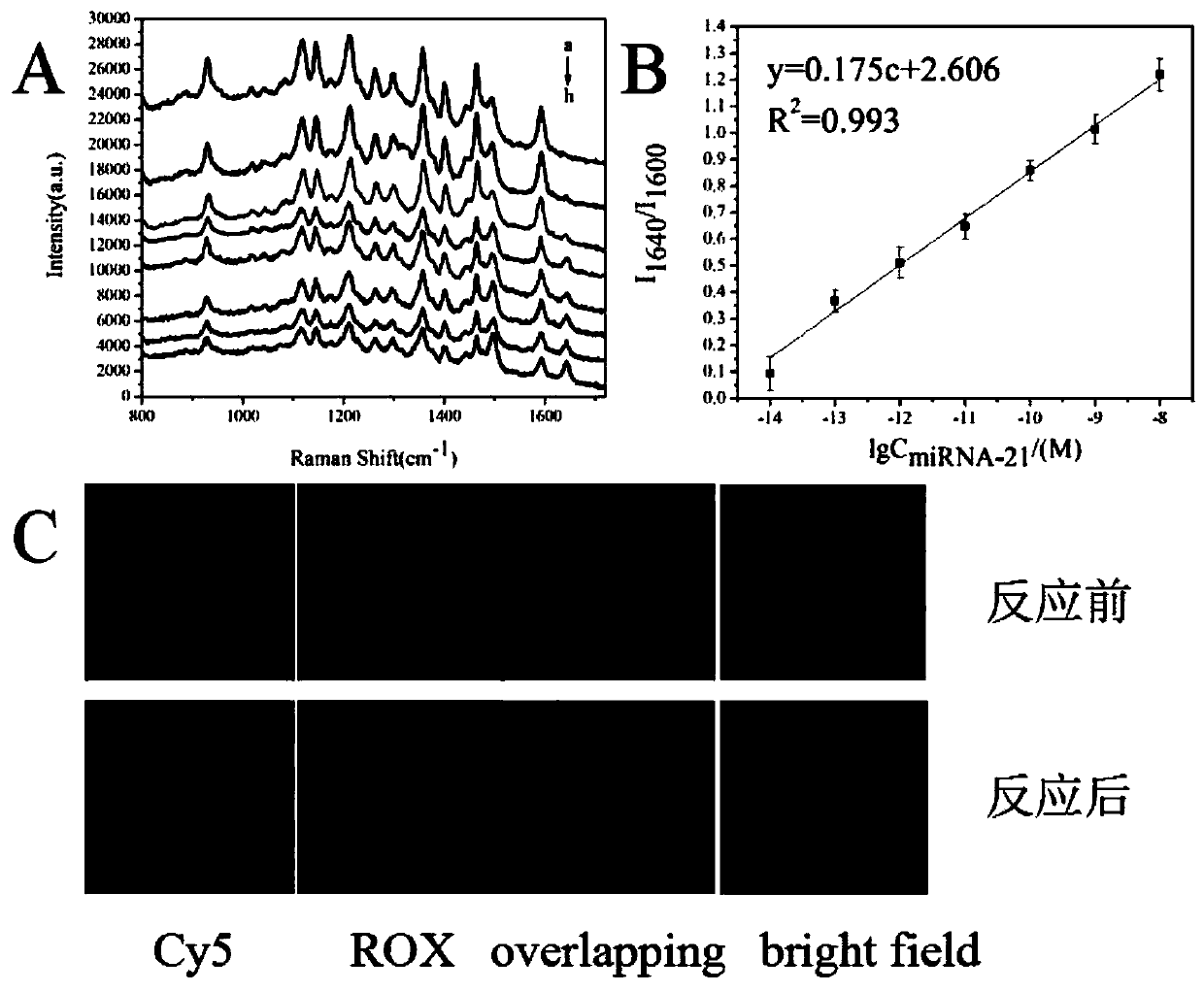
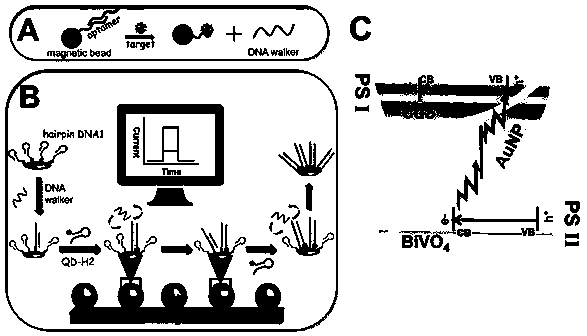
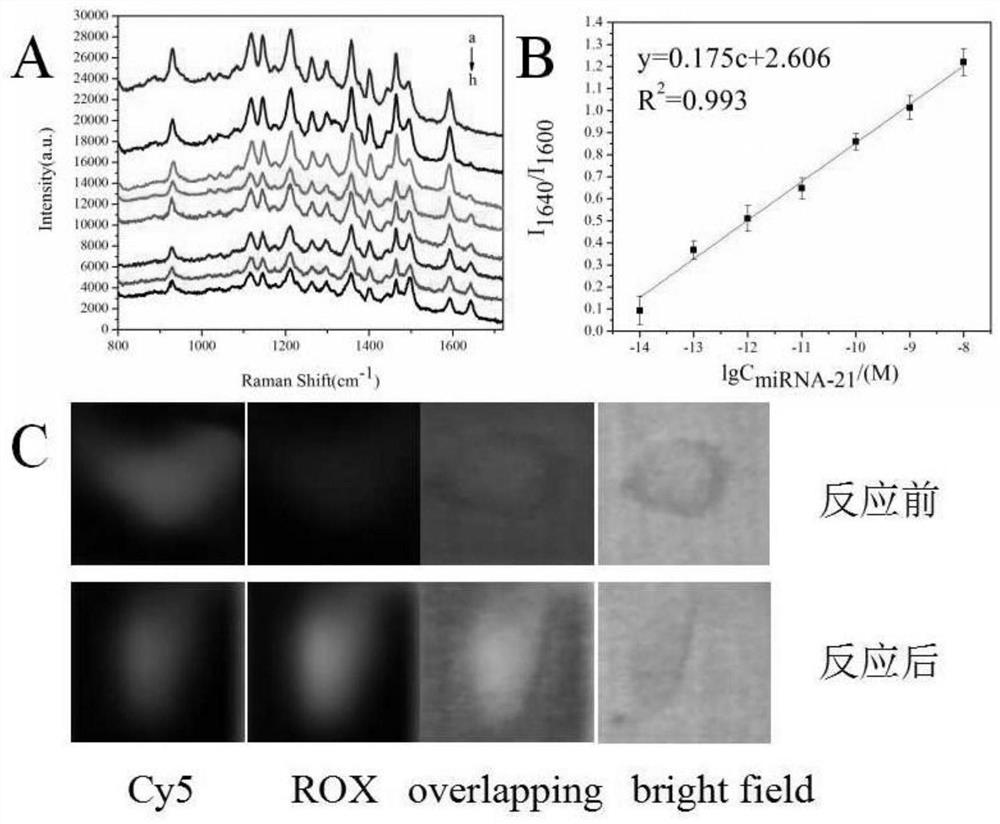
The invention belongs to the technical field of tumor detection and discloses a method for detecting a tumor cell marker miRNA-21 and tumor cells. A composite nano-probe comprises a gold nanoparticlecore, hairpin DNA H1 and swing arm Walker-Blocker; the apex of DNA tetrahedron complex is connected with hairpin DNA H2; miRNA-21 is a 3D DNA Walker activator; by means of DNA walker cycle signal amplification of Walker DNA, H1 and H2, miRNA-21 ratiometricand fluorescence Raman dual-mode detection is achieved; gold nanoparticles and DNA tetrahedral structure enter tumor cells for ratiometric and fluorescence Raman dual-mode imaging detection of tumor cells. 3D DNA Walker nano-machine amplification and the DNA tetrahedral nano-probe are combined for ratiometric and dual-mode detection of the tumor cell marker miRNA-21 and the tumor cells.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
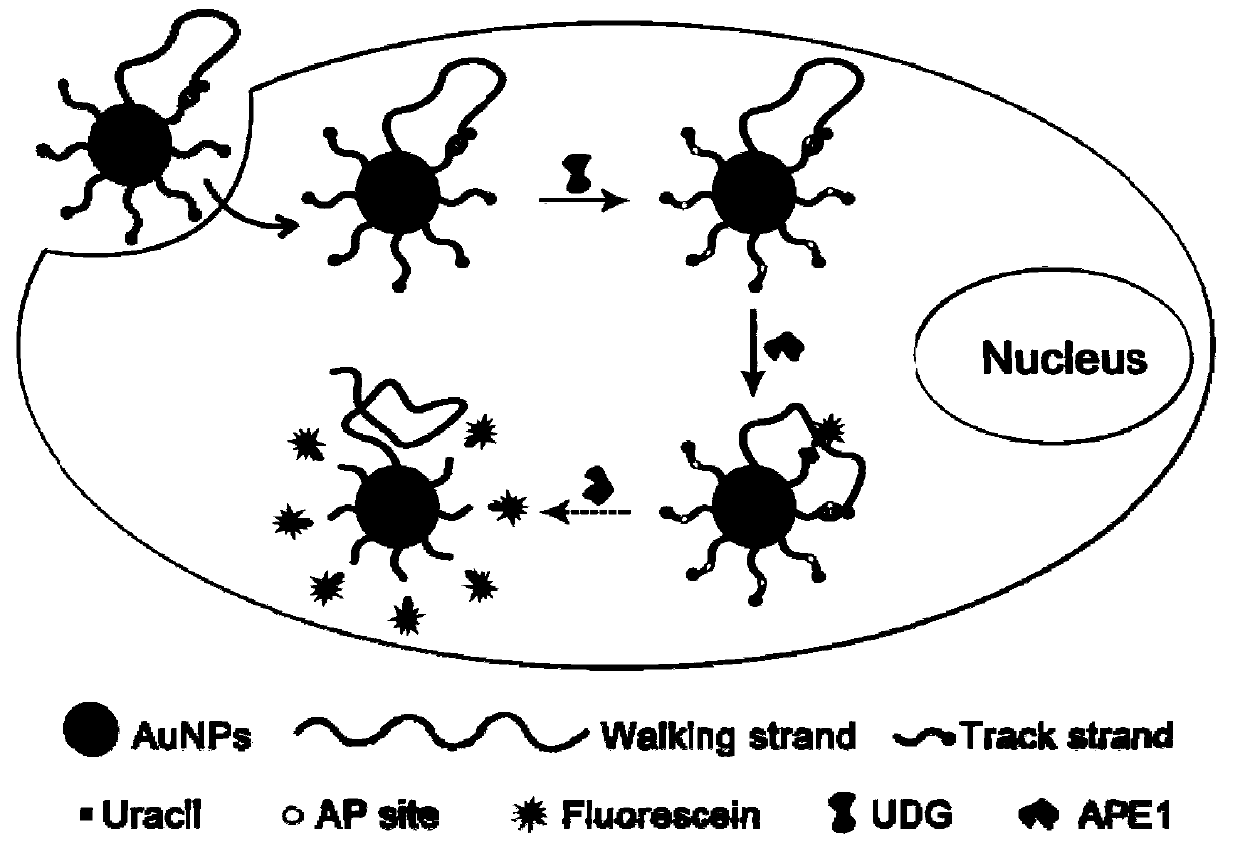
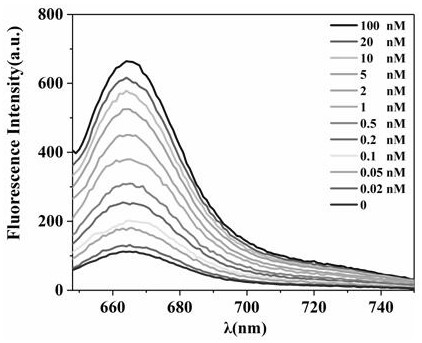
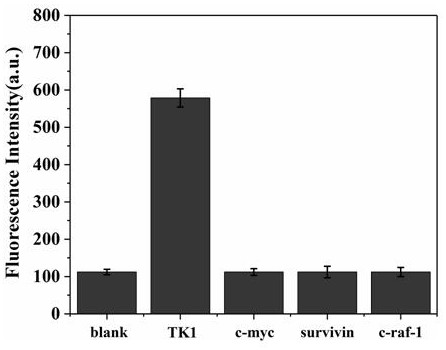
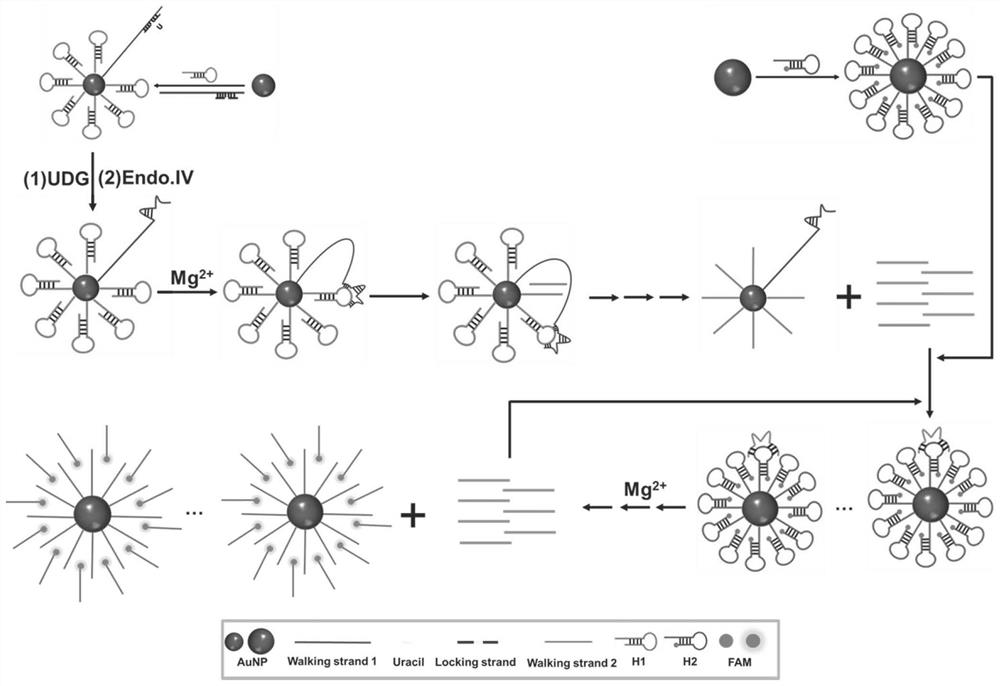
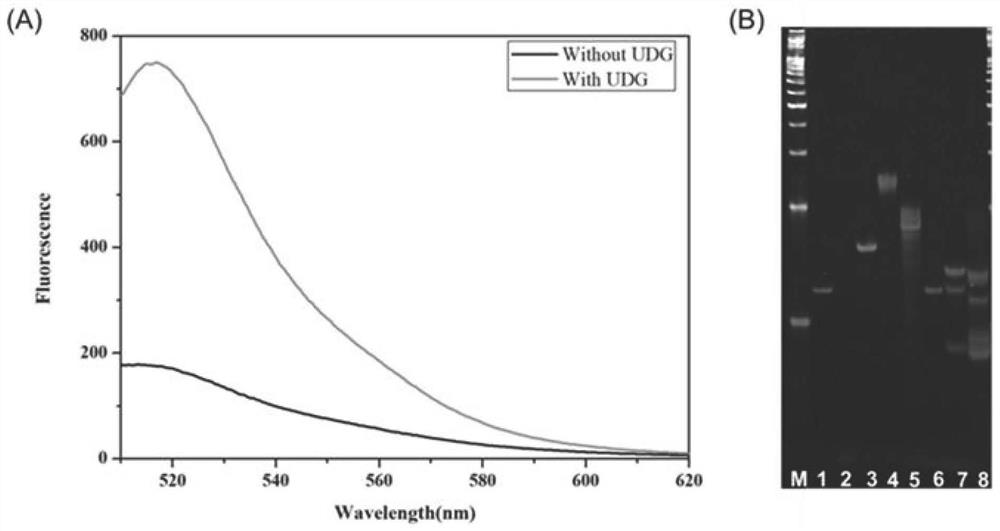
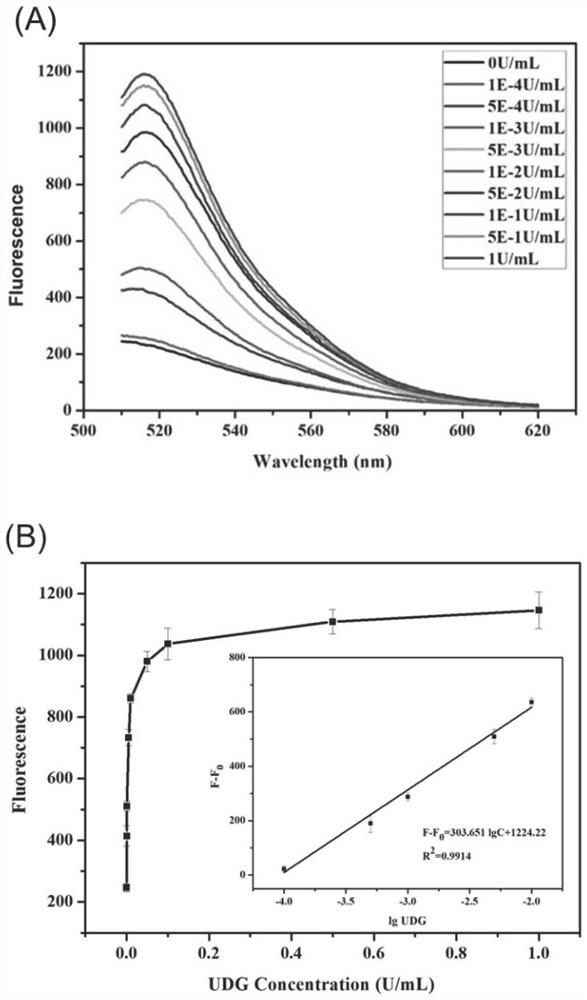
Endogenous enzyme-triggered DNA walker and its application for detecting UDG
ActiveCN110093344AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNanoparticleFluorophore
The present disclosure provides an endogenous enzyme-triggered DNA walker and its application for detecting UDG, The DNA walker comprises gold nanoparticles, at least one walking chain and a pluralityof track chains, wherein the walking chain and the tracks are single-stranded DNA, one end of the walking chain is connected with the gold nanoparticles, one end of each track chain is connected to the gold nanoparticles, the other end of each track chain is connected to fluorophore, the walking chain contains a first sequence, the track chain contains a second sequence, the first sequence is complementary to the second sequence, and one base in the second sequence is a uracil base. The constructed DNA walker is capable of sensitive imaging of UDG activity in cells.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Micro-droplet electrochemical sensor for detecting food-borne microorganisms and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110186975ASolve the problems of long routine detection cycle and complicated operationLow detection limitMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEscherichia coliMicroorganism
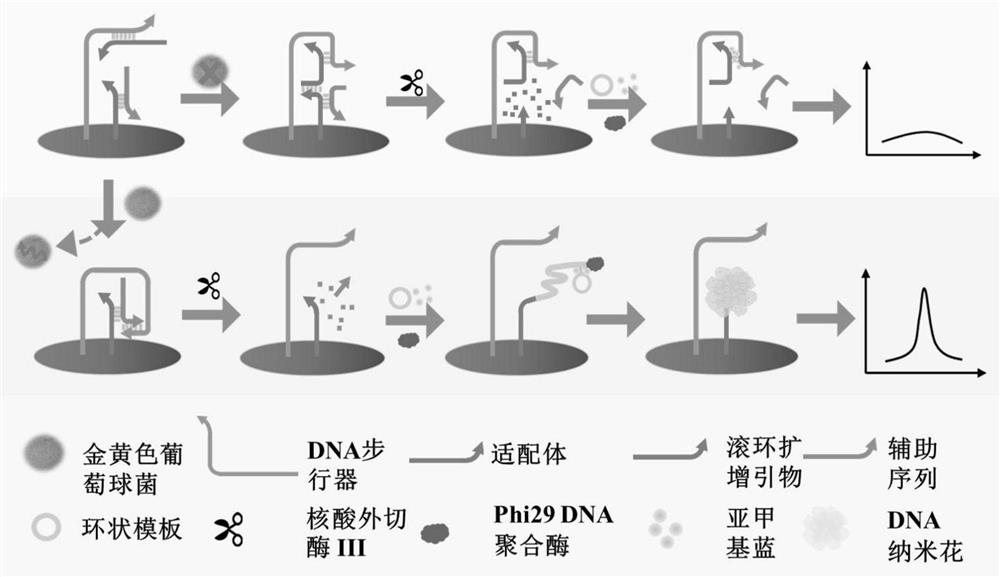
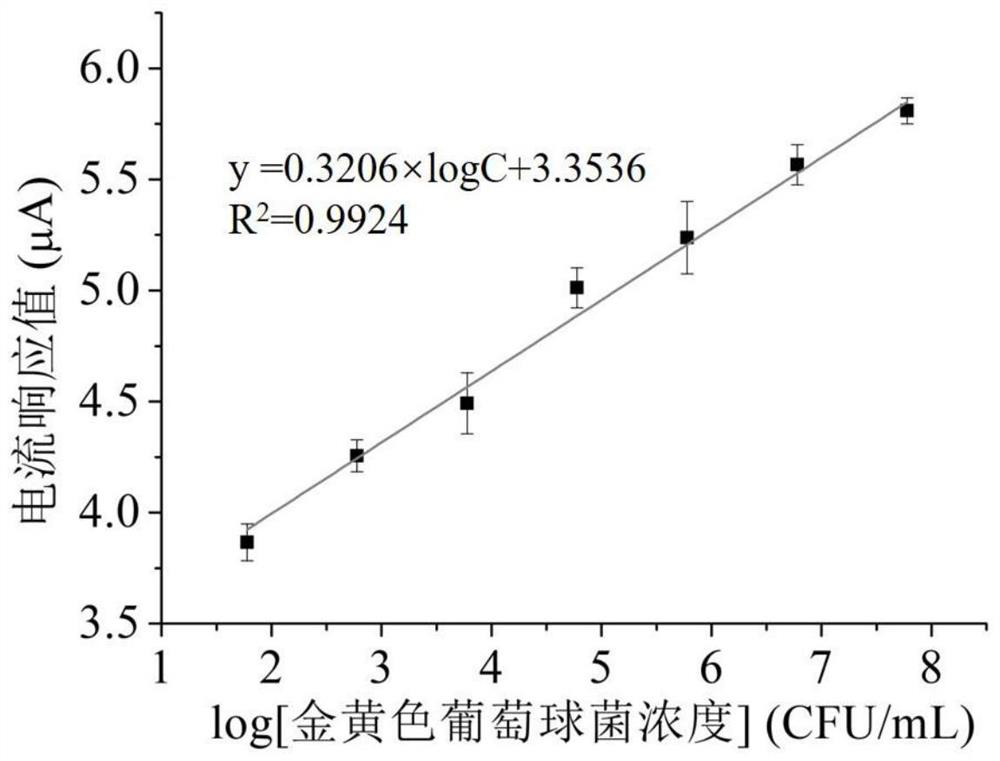
The invention belongs to the field of chemical analysis, in particular to a micro-droplet electrochemical sensor for detecting food-borne microorganisms and a preparation method thereof. Specific genefragments of the food-borne microorganisms are subjected to trace detection by a double-signal amplification system strategy to achieve signal amplification in the first step in the presence of a target gene fragment; a second DNA walker opens a third probe to form double-stranded DNA which is dissociated by a fourth probe modified with ferrocene at one end through two-strand displacement to release the DNA walker for use in the next cycle, thereby achieving signal amplification in the second step. According to the invention, the detection efficiency is improved by a double signal amplification technology, the signal stability is achieved, and the target escherichia coli O157:H7 specific gene fragment detection limit is reduced, the problems of the long period and complicated operation ofthe conventional detection of food-borne pathogens are solved; the detection accuracy is improved, and false positive detection is effectively avoided; and moreover, the electrochemical sensor has asimple production process and a wide application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
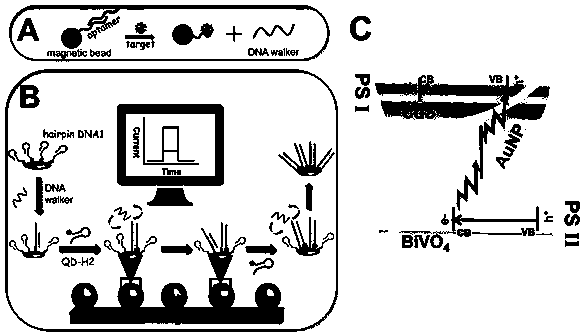
Analysis method of constructed Z-shaped photoelectric adaptor based on DNAWalker signal amplification
InactiveCN108663418ALow costInhibition of hole recombinationMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemistryWorkstation
The invention discloses an analysis method of a constructed Z-shaped photoelectric adaptor based on DNA Walker signal amplification. The method is inspired by plant photosynthesis Z electron transfer,and connects a CdS quantum dot to nanogold deposited to BiVO4 through DNA Walker, and photo-induced electron produced by the BiVO4 is transferred to a valence band of the CdS quantum dot from a conduction band of the BiVO4 through electron transfer effect of nanogold, so that compounding of electrons and electron holes is inhibited, photoelectric current is improved, and signal amplification is realized. The method adopts an electrochemical workstation combined with a xenon lamp, is low in cost, high in detection sensitivity, applies bionics to photoelectrochemistry, and provides a sensitivephotoelectrochemistry detection method with stable performances for the detection of cancer markers.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
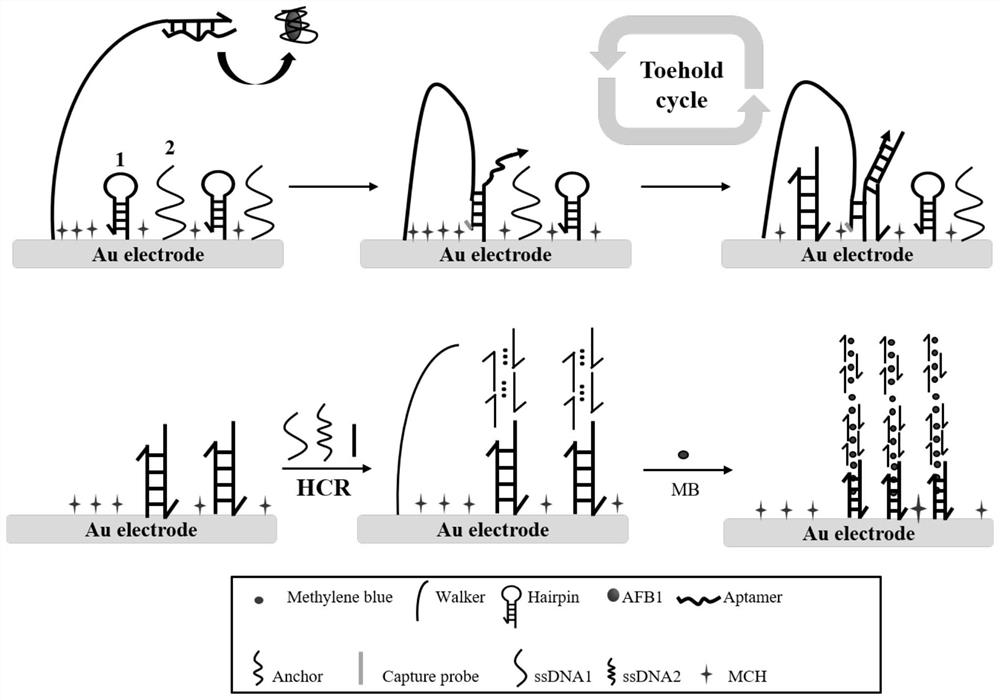
Preparation method and application of electrochemical biosensor based on DNA walker
PendingCN112280831AEasy constructionDoubly magnifiedMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical biosensorA-DNA
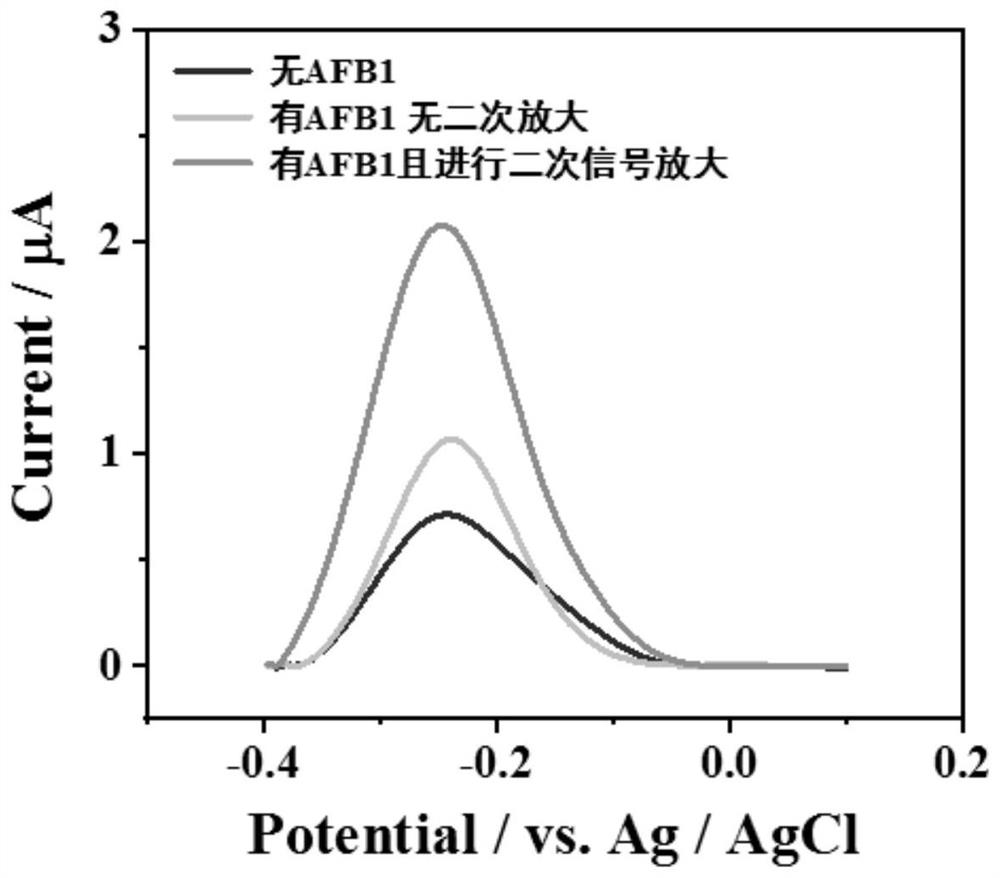
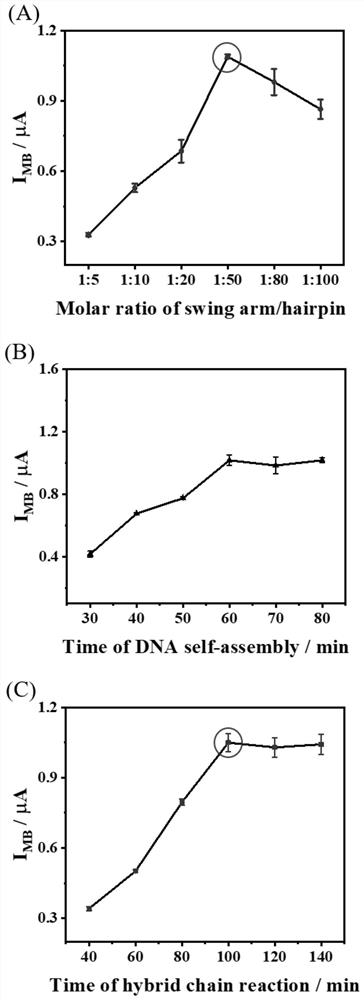
The invention belongs to the technical field of biosensors, and relates to a preparation method and application of an electrochemical biosensor based on DNA walker. The method comprises the followingsteps: firstly, mixing a DNA walkerAFB1 aptamer with hairpin DNA1 and hairpin DNA2, dropwise adding a mixture to the surface of a gold electrode, performing reacting, dropwise adding MCH, and performing incubating at normal temperature to obtain an electrochemical biosensor; then, modifying the surface of the biosensor with AFB1, anchoring a mixed solution of a probe 1, short-chain DNA1 and short-chain DNA 2, soaking the biosensor into a methylene blue solution, and constructing a standard curve by measuring the current value of a sensor and the concentration of the AFB1; and finally, measuring the current value of an unknown sample, and substituting the current value into the constructed standard curve so as to achieve the detection of the AFB1 in the unknown sample. According to the invention, dual signal amplification can be carried out by using an extremely small amount of target AFB1 to obtain a larger methylene blue electrochemical signal, and the method has good detection selectivity, high speed and high sensitivity.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Electrochemical nucleic acid detection method based on DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) walking and rolling circle amplification signal magnification
ActiveCN111172246AHigh sensitivityChanging the electrochemical signal strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionPhysical chemistry
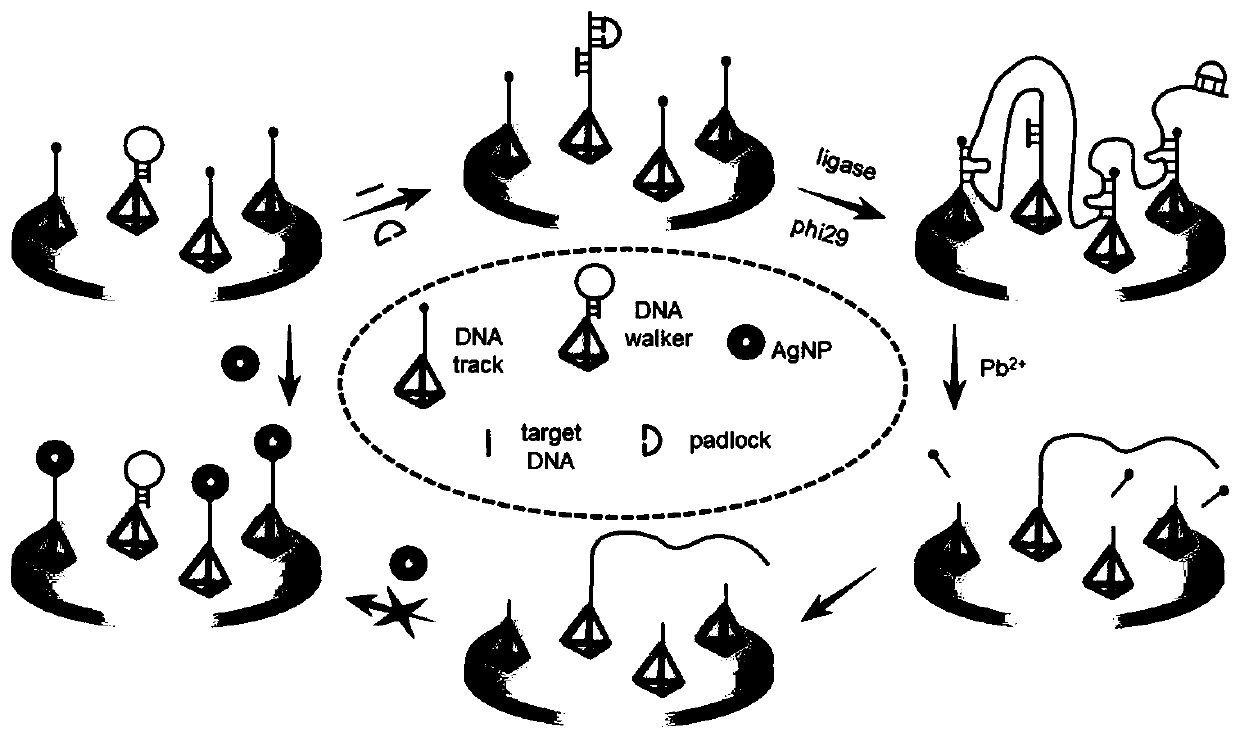
The scheme of the invention relates to an electrochemical nucleic acid detection method based on DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) walking and rolling circle amplification signal magnification. The method comprises the following steps: designing two DNA tetrahedrons, namely DNA walker and DNA track; immobilizing the DNA tetrahedrons on the surface of an electrode; adding a padlock probe into a sample tobe detected, inserting the electrode into the sample to be detected, and performing incubation; continuously adding DNA ligase and DNA polymerase into the sample to be detected, and performing a reaction; taking out the electrode, soaking the electrode into Pb<2+> at room temperature, performing a reaction, and finally performing incubation with silver nanoparticles; by taking the electrode as aworking electrode, and by using an electrochemical working station, recording a linear volt-ampere scanning curve by using a three-electrode system, detecting variation of volt-ampere current signals,and calculating the concentration of target nucleic acid. The detection method provided by the scheme of the invention is high in sensitivity, high in selectivity, simple and convenient to operate and low in detection cost.
Owner:天津国科医疗科技发展有限公司 +1
Preparation method of DNA walker and application of DNA walker in sensing analysis
InactiveCN110542714AAchieve improvementSimplify human operationChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesBiotin-streptavidin complexA-DNA
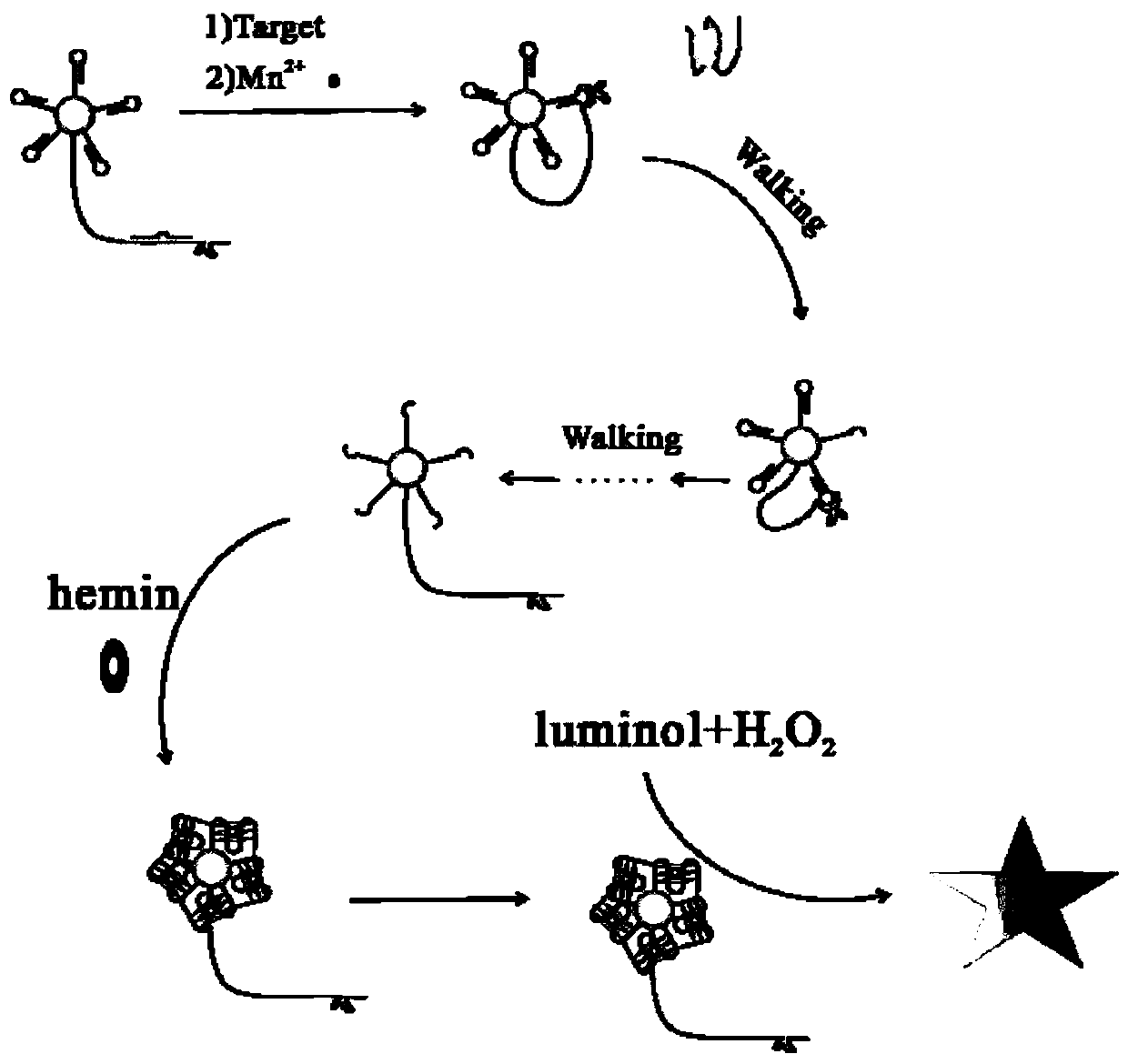
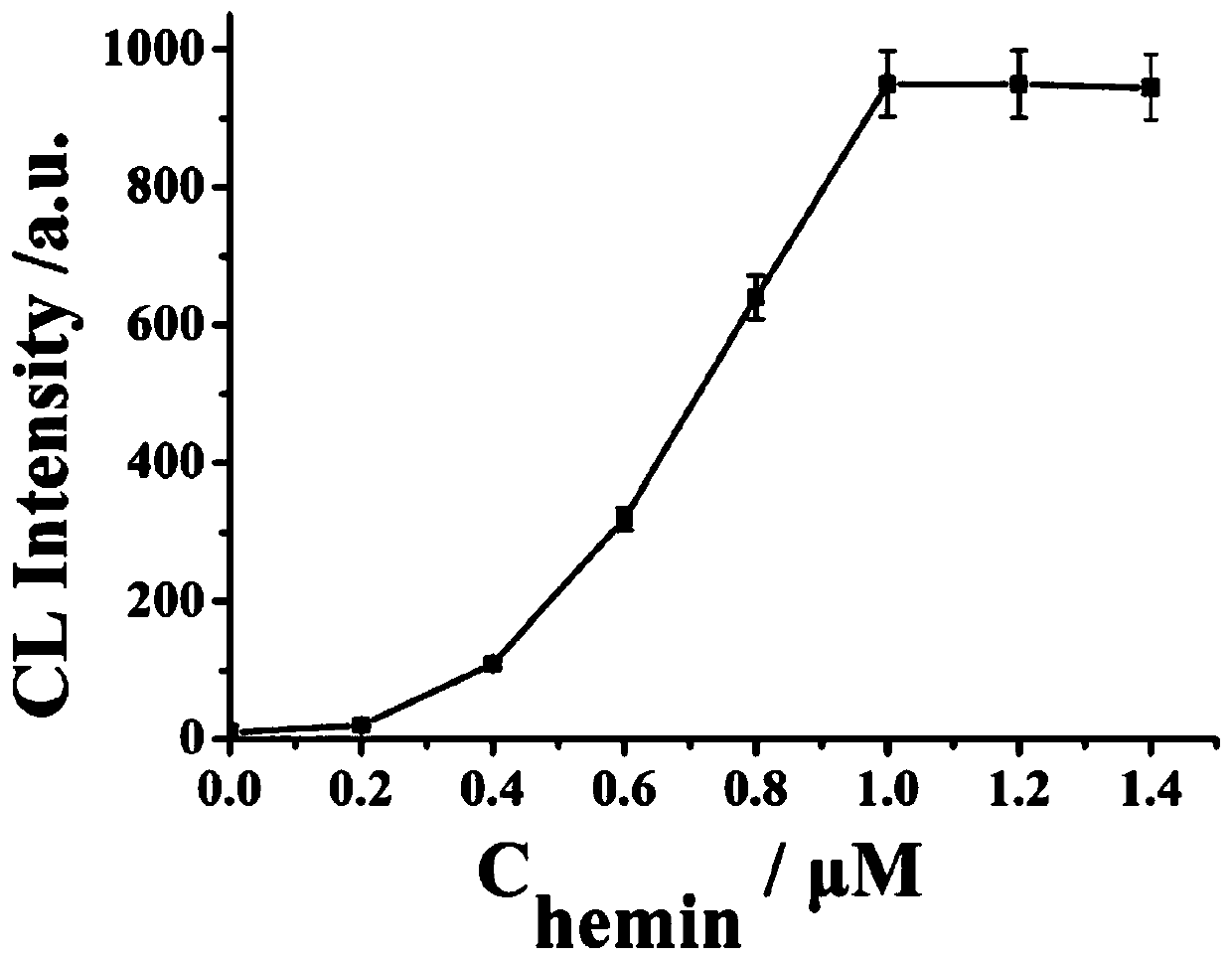
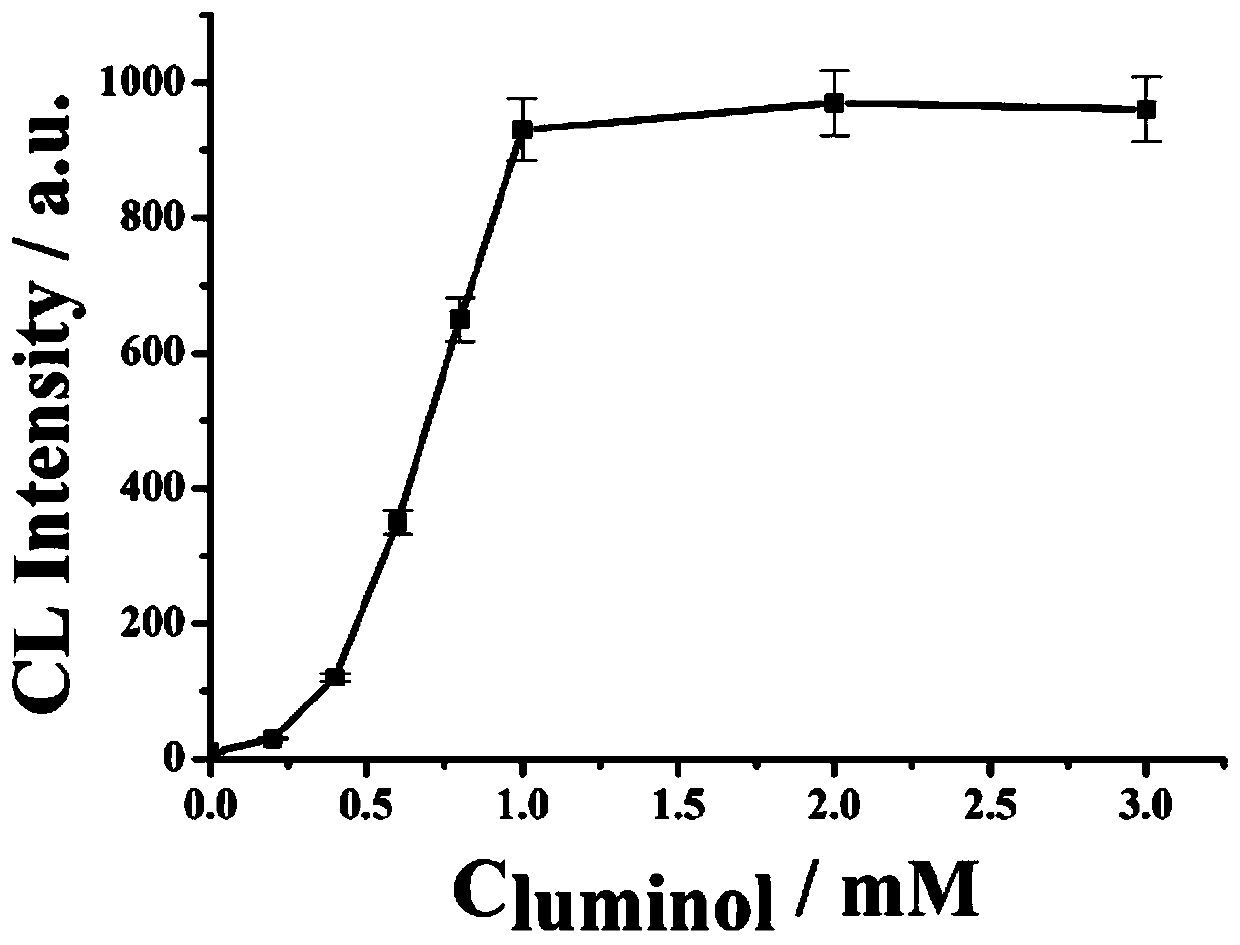
The invention discloses a preparation method of a DNA walker and an application of the DNA walker in sensing analysis. A hydrophobic area, a hydrophilic area, a hollow channel and a fluid channel netare prepared on paper by utilizing wax printing and laser cutting machine technologies to realize automatic cleaning and signal acquisition of a paper electrode. The method comprises steps that streptavidin and a DNA chain modified with biotin are assembled, the multi-foot DNA walker is constructed, the DNA walker is pushed to move on a surface of the electrode by virtue of a chain substitution reaction, so a DNA-platinum-copper nano composite material is fixed on the surface of the electrode, and a luminol light-emitting signal is amplified by virtue of the extremely good catalytic action ofthe platinum-copper nano material on hydrogen peroxide, so ultra-sensitive detection of a to-be-detected object is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
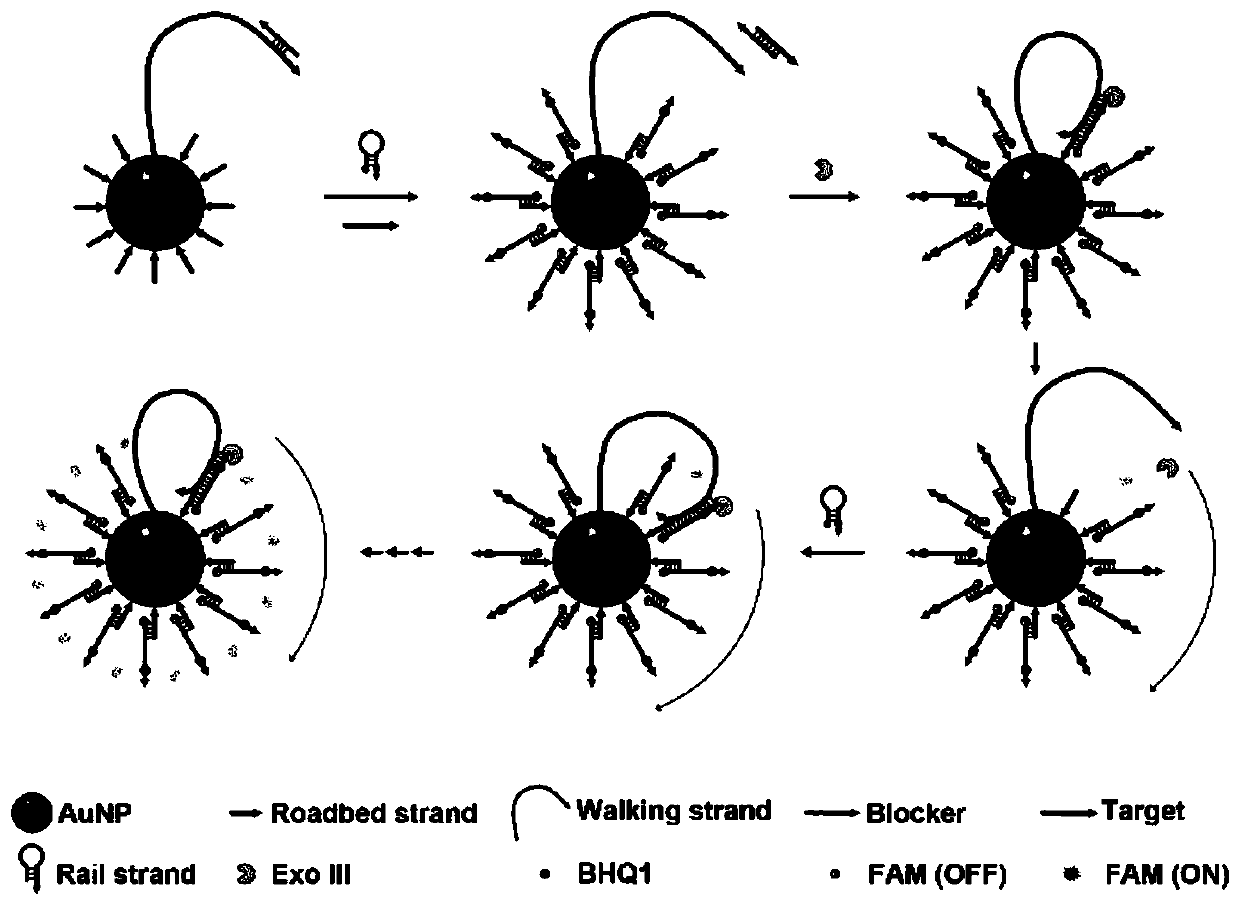
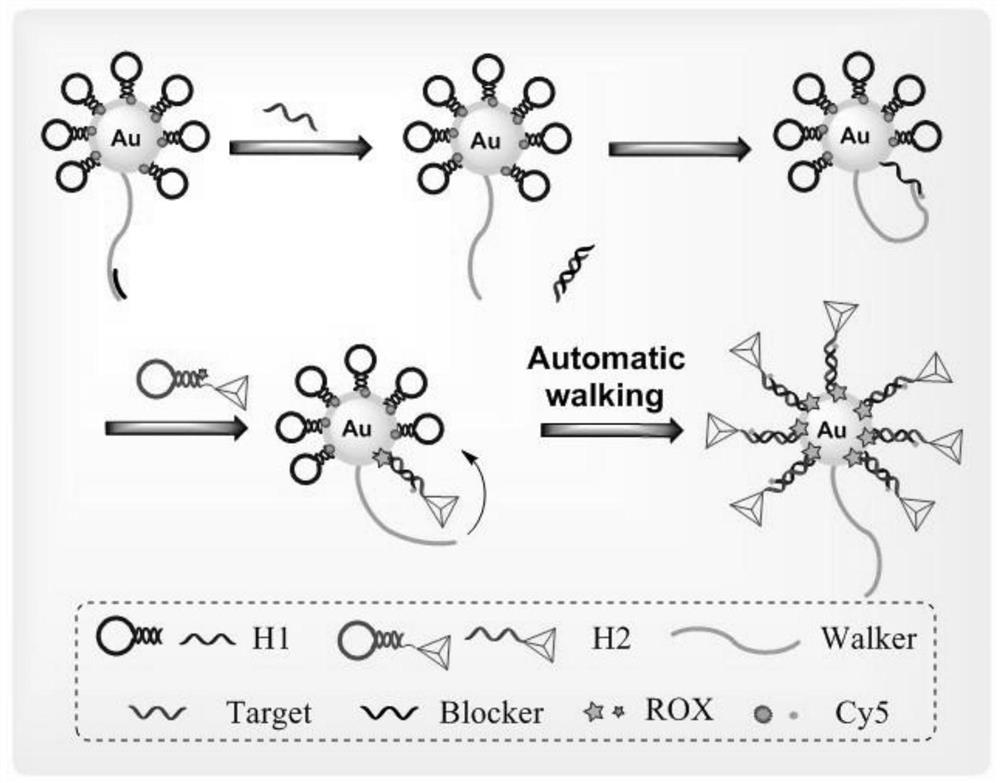
Dual-signal amplification AuNPs-DNA walker based on hairpin structure transformation and preparation method
ActiveCN111808925AAchieving a magnificationDoubly magnifiedMicrobiological testing/measurementTarget signalDNA walker
The invention provides a dual-signal amplification AuNPs-DNA walker based on hairpin structure transformation and a preparation method. Through the transformation of the hairpin structure, the AuNPs-DNA walker is initiated to progressively move and walk, and the primary amplification of the signal is realized; and the replaced DNA strand can replace the target again to participate in the next cycle, thereby further amplifying the signal. Through the detection strategy, dual amplification of the target signal can be realized. Through the detection strategy, dual amplification of the target signal can be realized, and the detection sensitivity is greatly improved; and amplification strategies of the system are all based on conversion of the hairpin structure, and a detection system of the sensor is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Fluorescent biosensor for detecting uracil DNA glycosylase as well as detection method and application of fluorescent biosensor
PendingCN113512579AAchieve improvementHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesUracilUracil-DNA glycosylase
The invention provides a fluorescent biosensor for detecting uracil DNA glycosylase as well as a detection method and application of the fluorescent biosensor, and belongs to the technical field of detection and analysis. According to the method, the activity of the uracil-DNA glycosylase is detected on the basis of a DNAzyme-driven cascade DNA walker signal amplification strategy, specifically, the activity of a walking chain of DNA walker 1 is sealed by adopting a locking chain containing a uracil basic group, and after a target UDG is recognized, operation of the cascade DNA walker is activated, and an amplified fluorescence signal is generated. The detection method successfully realizes cascade signal amplification, has higher sensitivity and specificity, good precision and reproducibility, and good anti-interference capability, can be used for analysis and detection of complex biological samples, and thus has good practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
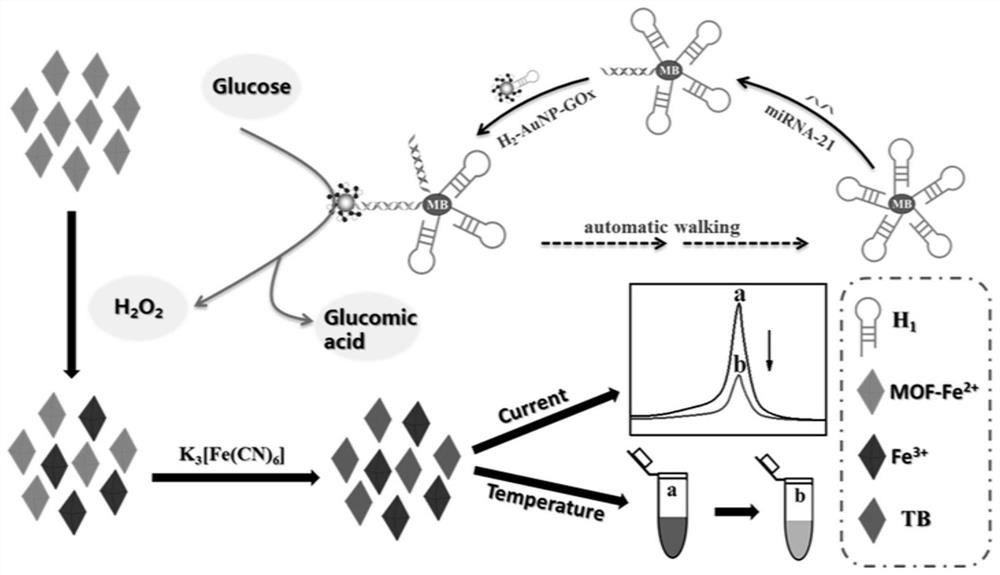
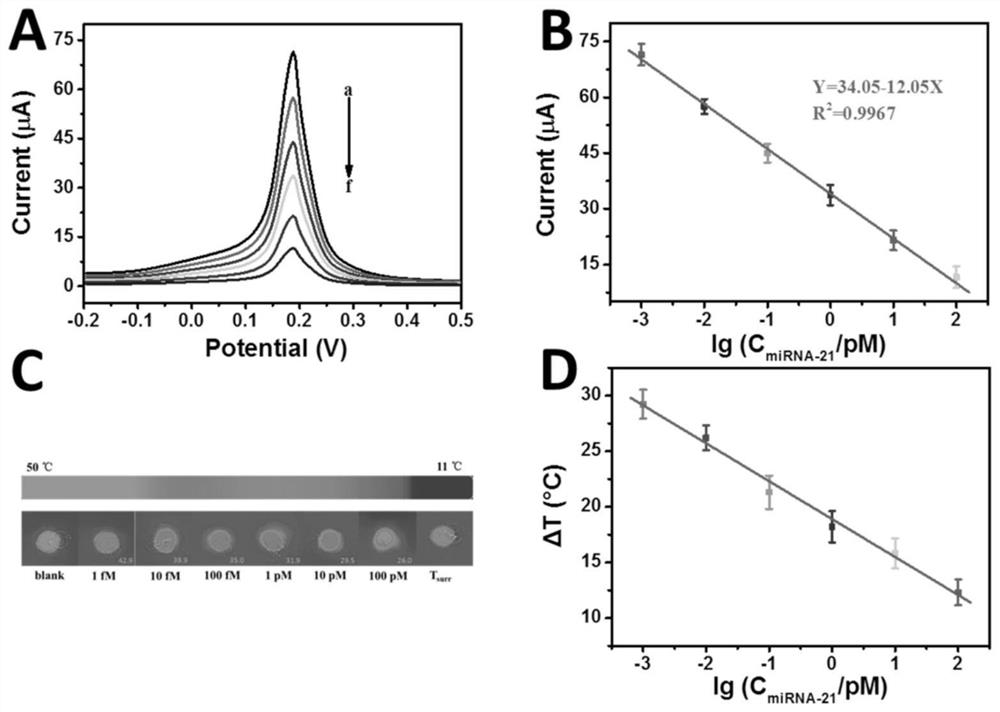
Double-signal miRNA-21 detection method based on three-dimensional DNA Walker and MOF-Fe (II) induced generation of Turnskill blue
ActiveCN113624815AImplementing Dual Signal DetectionEmbody versatilityMaterial electrochemical variablesAgainst vector-borne diseasesA-DNADNA walker
The invention discloses a double-signal miRNA-21 detection method based on three-dimensional DNA Walker and MOF-Fe (II) induced generation of Turnskill blue. The method comprises the following steps: mixing and incubating avidin modified MB and a biotin modified hairpin strand H1, and then mixing and incubating with a hairpin strand H2-Au NP-GOx probe and a miRNA-21 solution, so as to obtain a DNA Walker product; adding the DNA Walker product into a glucose solution to carry out catalytic reaction, and carrying out magnetic separation to obtain a solution containing hydrogen peroxide; and enabling the MOF-Fe (II) to react with a solution containing hydrogen peroxide and induce generation of TB on an electrode to realize electrochemical detection, or enabling the MOF-Fe (II) solution containing hydrogen peroxide to induce generation of TB in the solution to realize photo-thermal detection, so that the method can be used for dual-signal detection of miRNA, and is low in miRNA target object detection lower limit and high in selectivity.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
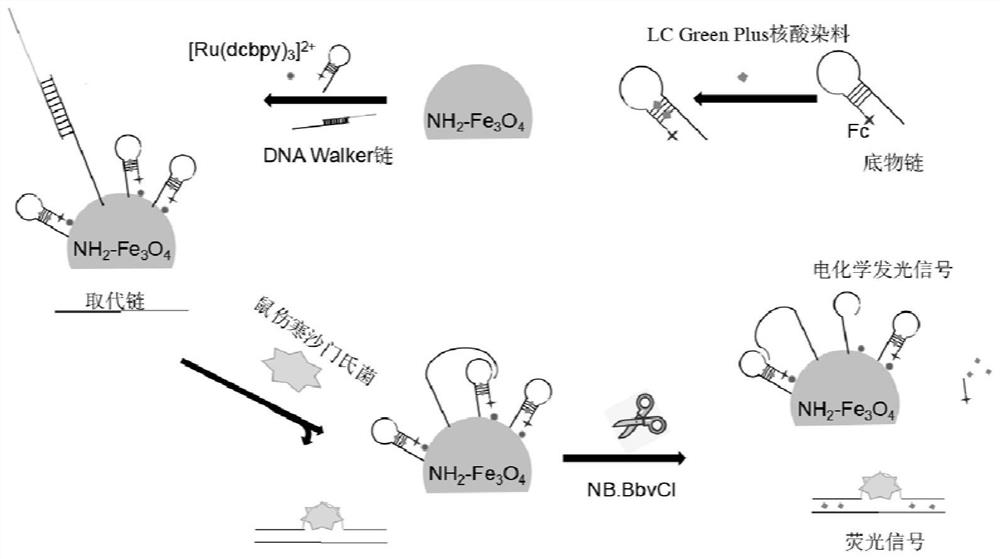
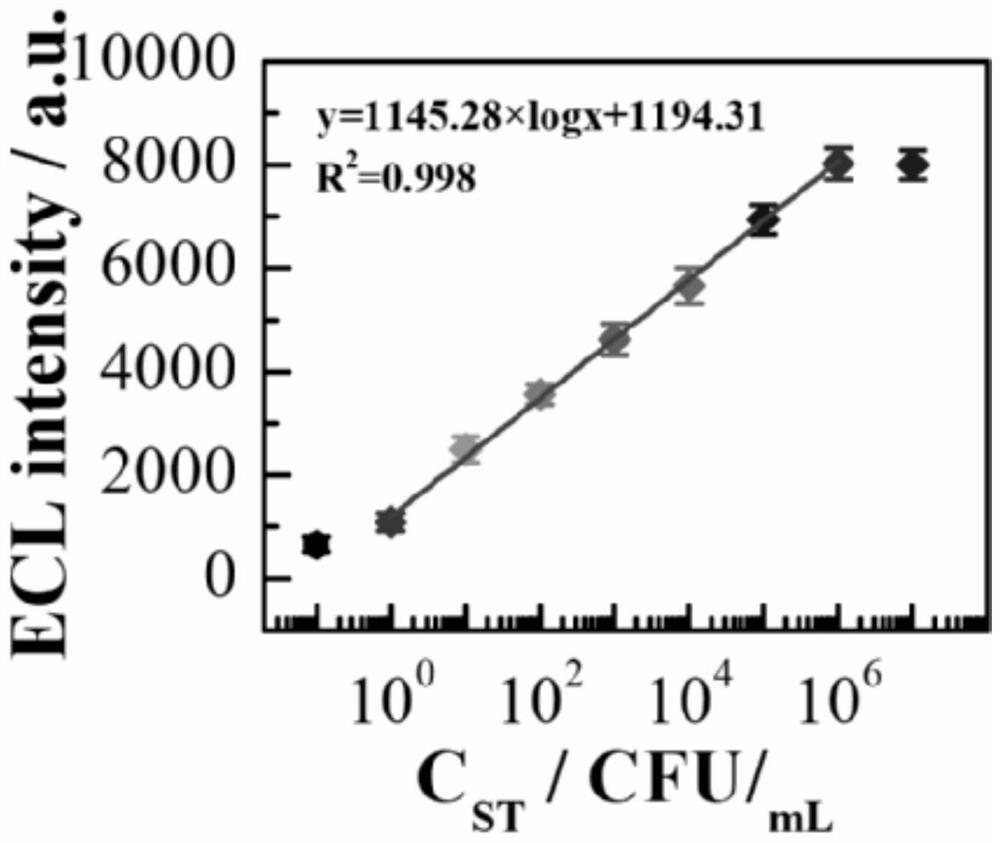
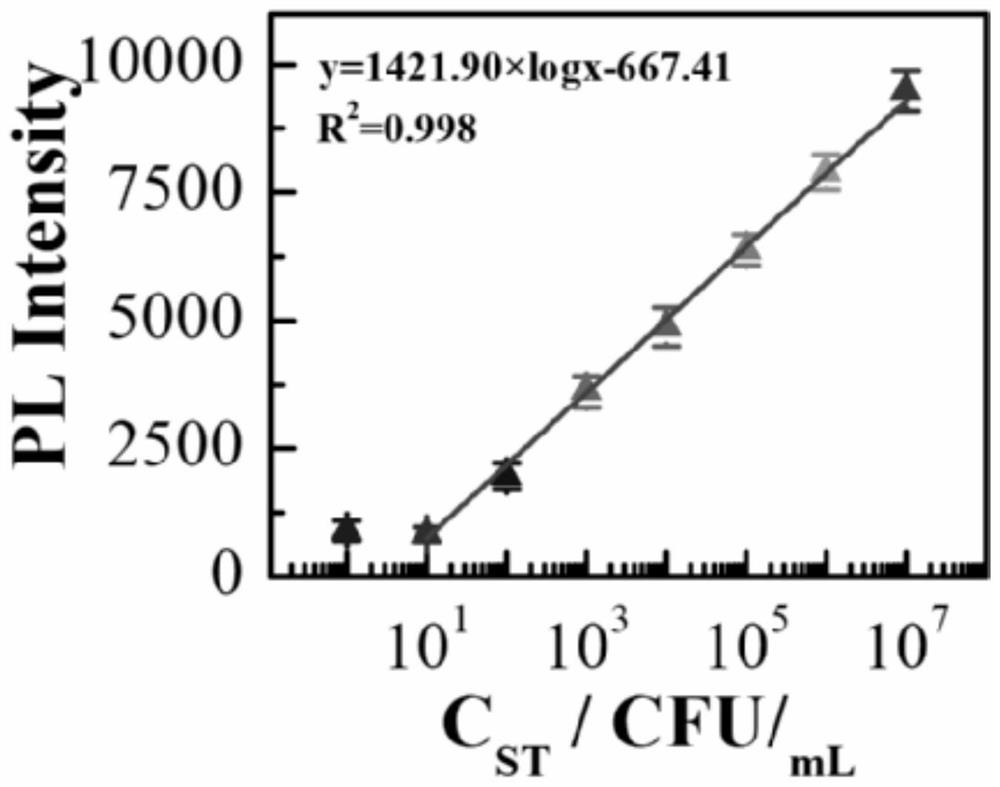
Method for detecting food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on double signals of DNA Walker driven by chain substitution triggered by nucleic acid conformation
ActiveCN112626242ALow detection limitHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiotechnologyA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for detecting food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on double signals of DNA Walker driven by chain substitution triggered by nucleic acid conformation, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: mixing a DNA Walker swing arm chain solution with a protective probe solution containing a to-be-detected food-borne pathogenic bacteria aptamer in an isopyknic, performing reaction, and slowly cooling to room temperature to form a protected DNA Walker chain solution; mixing aminated ferroferric oxide with glutaraldehyde, stirring at room temperature, performing magnetic cleaning, suspending in an oligonucleotide stock solution, adding a Walker chain solution and hairpin substrate chain mixed solution which are fully and uniformly mixed, performing reaction and magnetic cleaning, fixing the volume by using the oligonucleotide stock solution, mixing with a to-be-detected solution, a substitution chain solution and an endonuclease solution for incubation, taking supernatant for fluorescence detection, taking precipitates and dropwise adding the precipitates to a magnetic glassy carbon electrode for electrochemical luminescence detection, and the method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high selectivity and simplicity and quickness in operation.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Track regeneration type DNA walker and application thereof
ActiveCN110904100AAchieve regenerationCut thoroughlyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTrackwayNanoparticle
The invention belongs to the technical field of construction of DNA walkers, and particularly relates to a track regeneration type DNA walker and an application thereof. The concept of the track regeneration type DNA walker is provided and verified. The walker adopts a separable track consisting of a roadbed and a track. The roadbed chain of the walker is functionalized on gold nanoparticles, anda large number of track chains are dissociated in a solution and are hybridized with the roadbed chain to construct the track. As the walker walks along the track, the track chain is digested and releases the roadbed chain at the same time, and the released roadbed chain can be continuously combined with the track chain in the solution to form a new track. The continuous supply of the track enables the walker to keep walking. The walker has great advantages in the aspect of signal enrichment, so that the walker can be used for sensitive detection of Ebola virus gene segments in serum.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
MicroRNA biosensor for triggering 3-D double-leg DNA walker through exponential amplification reaction
PendingCN112251496AHigh sensitivityDevelop sensitiveMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosphereA-DNA
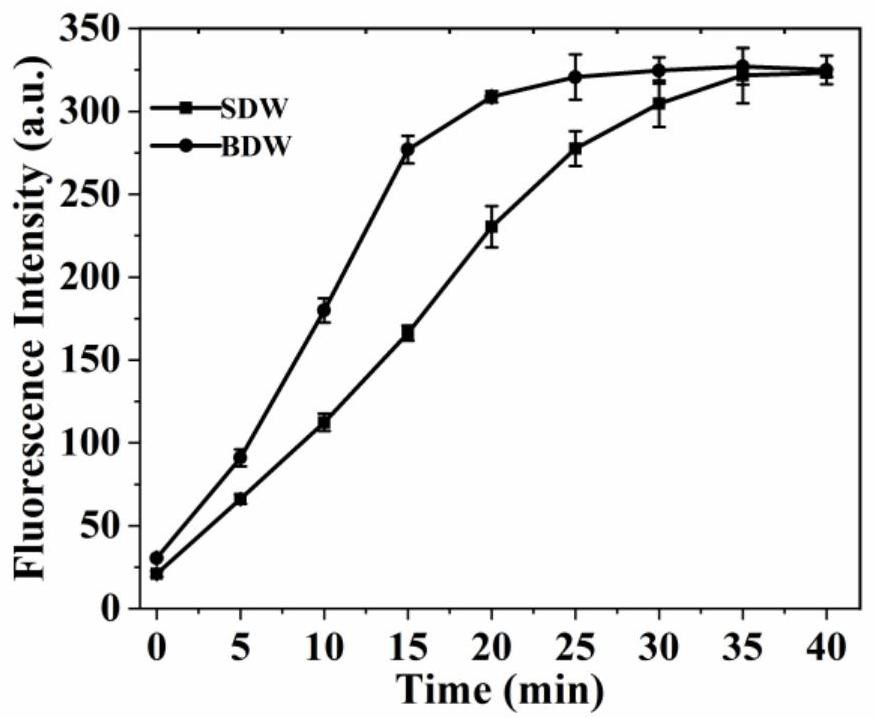
The invention relates to a DNA amplifier which is designed by using an incision enzyme-driven three-dimensional (3-D) DNA walker, wherein a double-leg DNA walker (BDW) can be continuously assembled ona fluorescently-labeled polystyrene microsphere track through an exponential amplification reaction (EXPAR) triggered by target miRNA (micro ribonucleic acid). According to comparative study, the situation that the walking speed of BDW is higher than that of a single-leg DNA walker (SDW) is proved firstly. In view of this, EXPAR is activated by the target miRNA by means of a polymerase and incision endonuclease to produce a large number of BDWs in a solution, so that the walker is activated in the presence of incision endonuclease, an enhanced fluorescence signal is produced in the supernatant. By taking microRNA 21 as a model target, the detection limit of the method under the optimal condition is as low as 5.2 fM, and compared with other DNA walkers, the method has higher sensitivity. The binding of the enzyme-assisted EXPAR in the solution to the enzymatic BDW on the particles can significantly improve signal amplification efficiency and improve detection sensitivity. Therefore, the method has huge potential for the application of biosensors related to BDW.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Visual detection method and detection probe for simultaneously detecting two circulating miRNAs
InactiveCN112795626AReduce background signalHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNanoparti clesCirculating miRNA
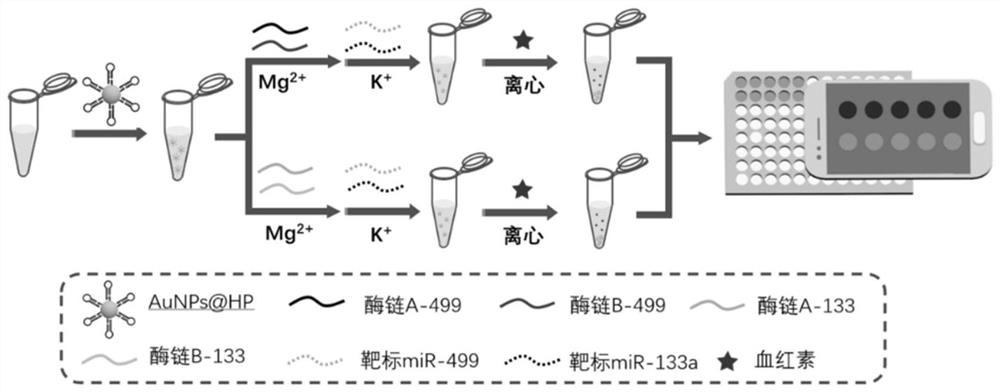
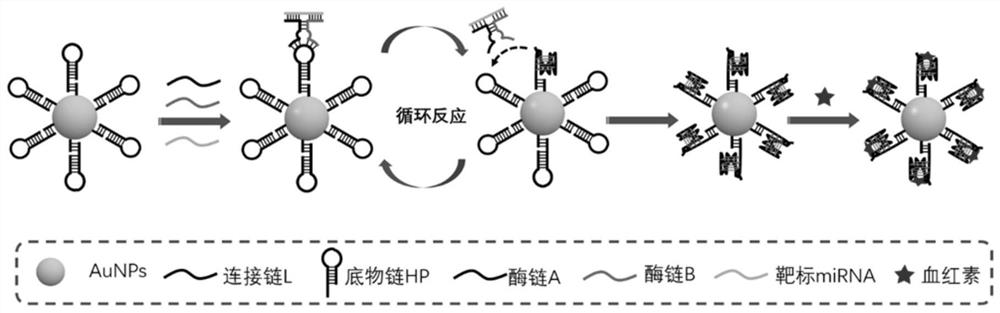
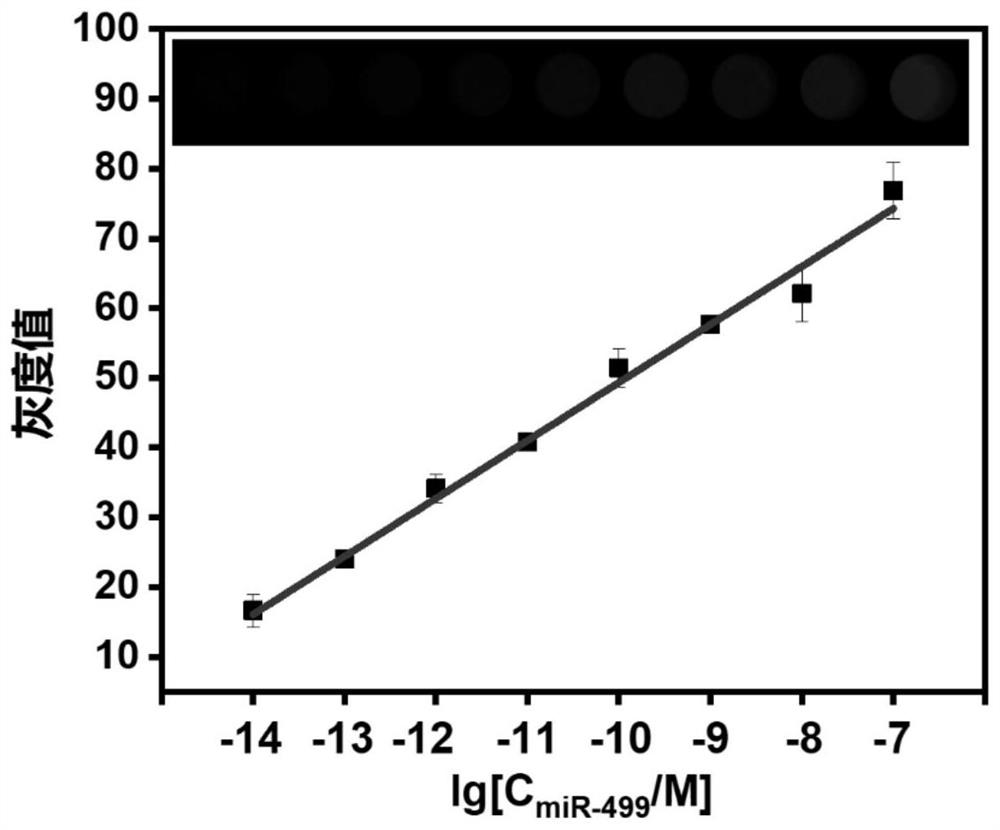
The invention provides a visual detection method and a detection probe for simultaneously detecting two circulating miRNAs. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing gold nanoparticles; step 2, preparing a gold nanoparticle-substrate DNA chain HP compound HP (at) AuNPs, and combining the compound HP (at) AuNPs with enzyme chains A and B to form an AuNPs-DNA walker detection probe; step 3, performing signal amplification reaction on the target miRNA and a detection probe; and step 4, carrying out visual detection on the target miRNA based on chemiluminescence. The detection probe provided by the invention can realize simultaneous quantitative detection of a plurality of samples containing two different circulating miRNAs, and detection results are not interfered with each other. According to the detection method provided by the invention, a chemiluminescence signal is recorded in a mobile phone photographing manner, expensive instruments are not needed, the cost is reduced, the detection operation is simplified, and immediate detection of miRNA can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Chemiluminescence sensor for detecting acetamiprid and preparation method of sensor
ActiveCN111440850APlay the role of signal amplificationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAptamerNanoparti cles
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a chemical biosensor using a DNAzyme based DNA Walker, aims to solve the problems of relatively low specificity and sensitivity and high cost of acetamiprid detection methods in the prior art, and discloses a chemical biosensor for detecting acetamiprid by the DNAzyme based DNA Walker. DNAzyme cracking is used for assisting in realizing circulating amplification and forming a lot of G-quadruplets simulating the horseradish peroxidase activity on gold nanoparticles. A preparation method comprises the following steps ofpreparing the gold nanoparticles; modifying a Walker chain and a Lock chain to the surfaces of the gold nanoparticles; producing a homogeneous reaction of a labeled gold nanoparticle solution; carrying out a DNAzyme cracking reaction, and chemiluminiscence detection; carrying out high-specificity detection on the acetamiprid as a target object by using a nucleic acid aptamer; and realizing the signal amplification effect by utilizing DNAzyme cracking reaction amplification.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Pathogenic bacteria electrochemical detection method based on DNA walker and nanoflower structure
ActiveCN112432980AIncrease the effective areaExpand the scope of detectionMaterial electrochemical variablesA-DNAMicrobiology
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for detecting huanglongbing bacteria based on aPCR and DNA walker
InactiveCN112159853AEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific enzymeNanoparticle
The invention discloses a method for detecting huanglongbing bacteria based on aPCR and DNA walker, and relates to the field of bacterial detection. The method comprises the following steps of selecting a to-be-detected target, reacting the to-be-detected target with a DNA walker probe, drawing a standard curve, reacting the to-be-detected target with a specific enzyme chain DNAzyme, and generating fluorescence by a system, wherein the DNA walker probe comprises nanoparticles, the nanoparticles are modified with the specific enzyme chain DNAzyme and a plurality of substrate chains with FAM fluorophores, and the specific enzyme chain DNAzyme can cut the FAM fluorophores on the substrate chains; extracting total DNA from the to-be-detected sample, carrying out aPCR amplification, and carrying out a mixed reaction on an amplification product and the DNA walker probe for 0.5-2 hours; and comparing a detection result with the standard curve. The method is lower in cost in high-throughput detection, and relates to secondary conversion of signals, so that the accuracy is higher.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method and kit for detecting ricin based on relative DNA walker initiation index amplification of gold nanoprobe constructed by freezing
ActiveCN113151414AEasy to operateOperation time savingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRicinus sanguineusToxin detection
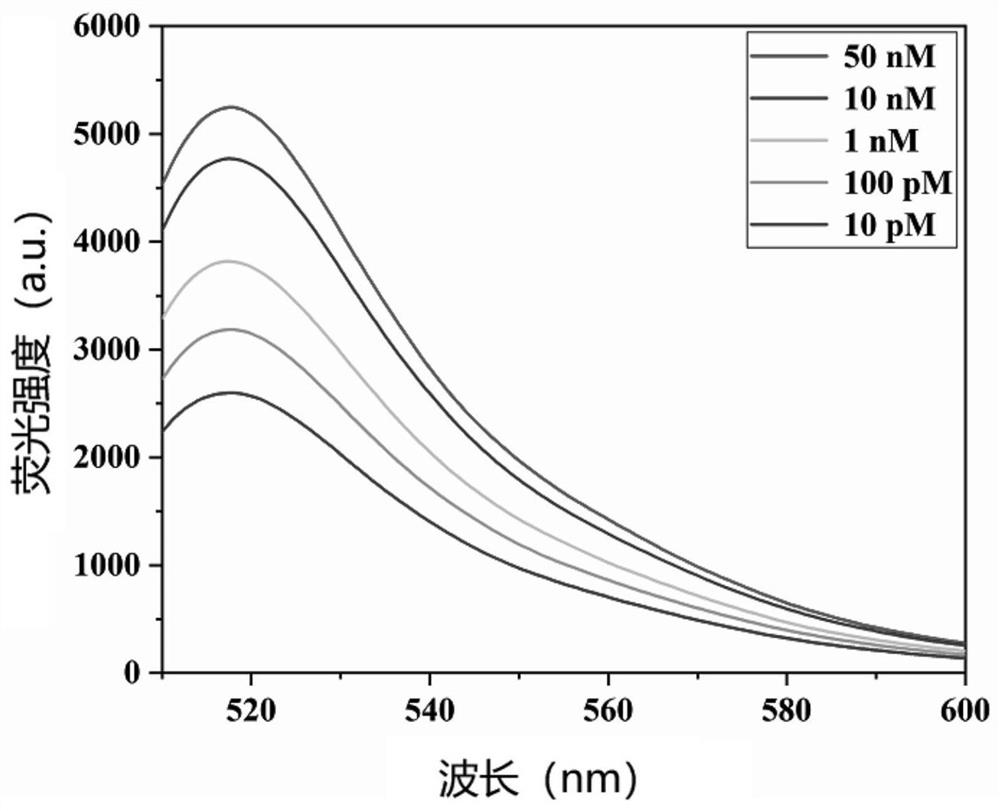
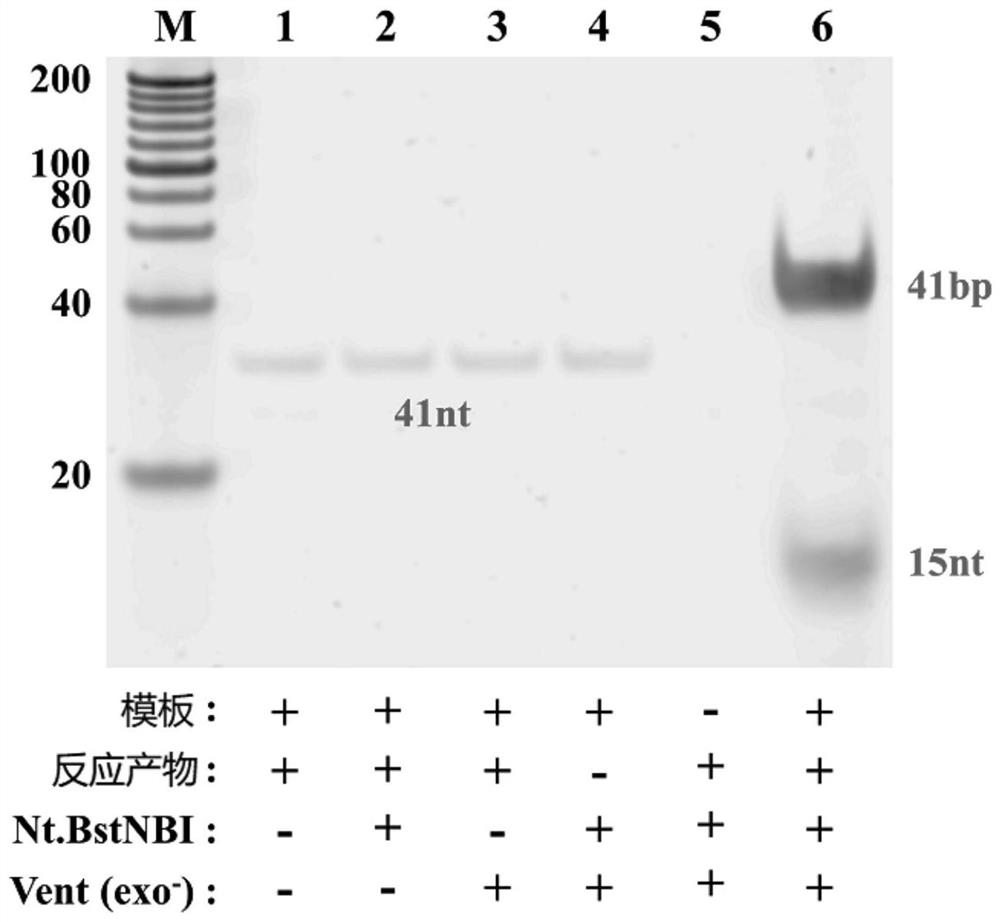
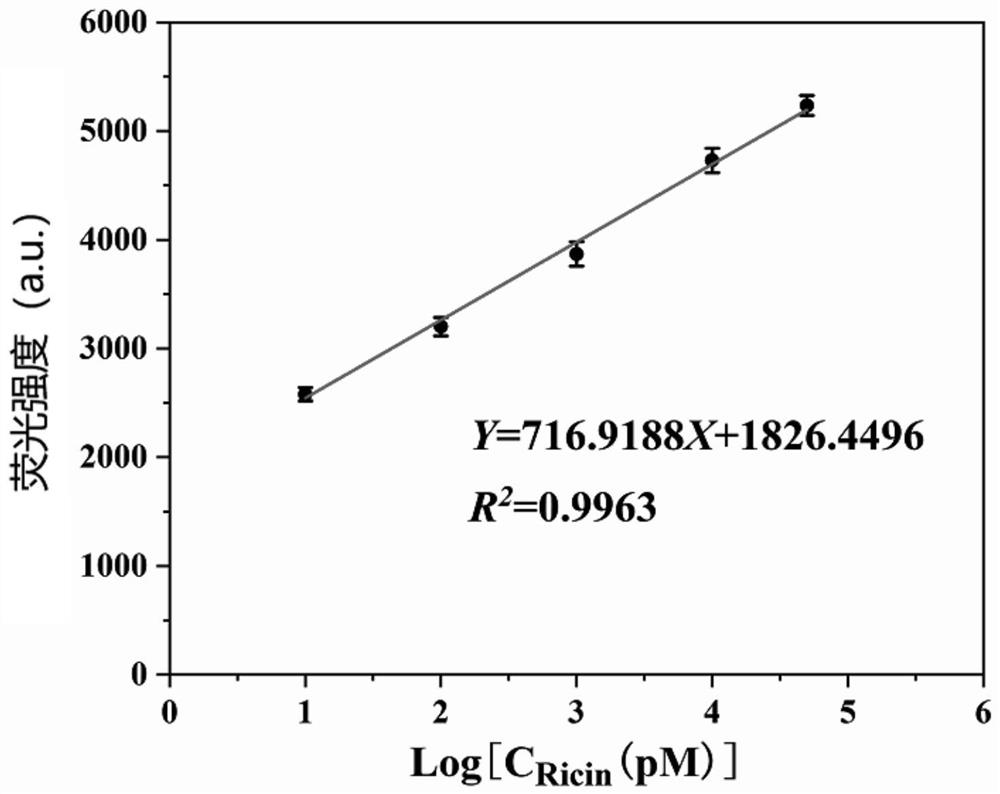
The invention belongs to the field of protein toxin detection, and relates to a method and a kit for detecting ricin based on relative DNA walker initiation index amplification of a gold nanoprobe constructed by freezing. The method mainly comprises the following four processes: performing freezing to construct the gold nanoprobe, competitively combining the ricin and the gold nanoprobe with an aptamer, and carrying out a relative DNA walker and index amplification reaction. The method and the kit can be used for detecting the ricin with relatively high sensitivity, good specificity and excellent stability in practical application.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE & OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
Three-dimensional DNA walker and application thereof in tumor exosome detection
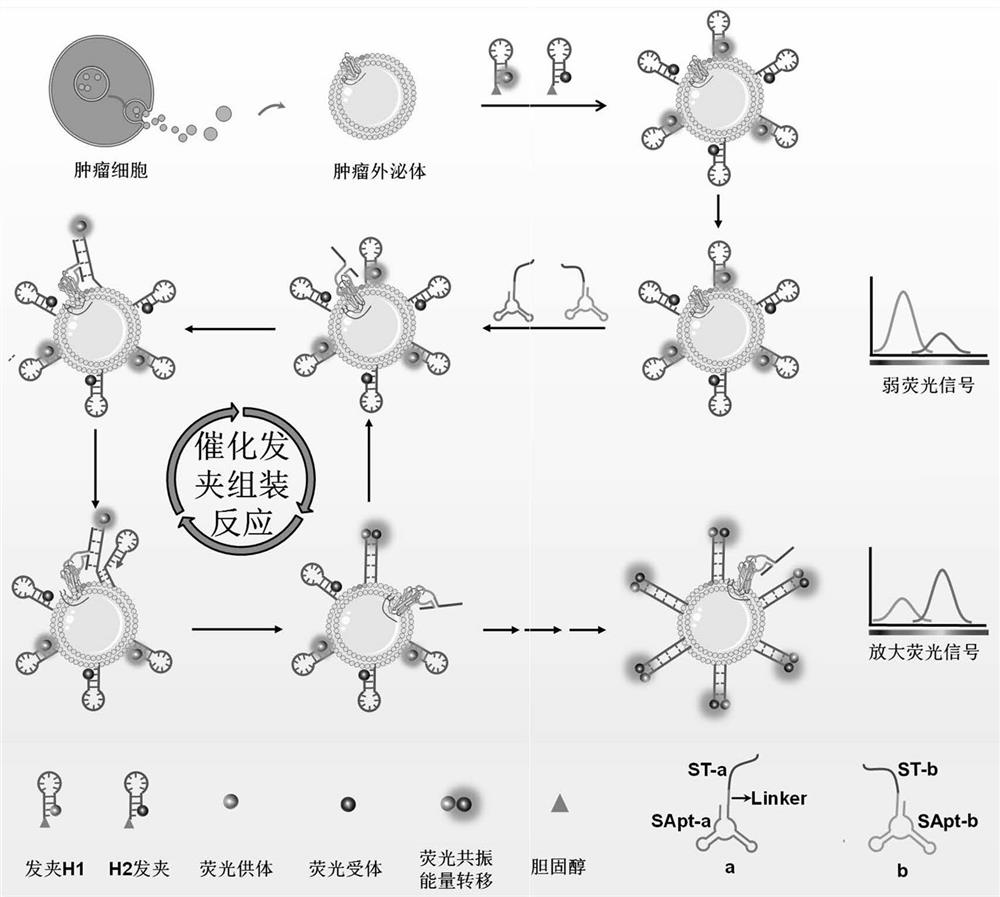
ActiveCN113930482ASynthesis fastEasy to synthesizeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesPhospholipinCholesterol
The invention provides a three-dimensional DNA walker and application thereof in tumor exosome detection. The three-dimensional DNA walker comprises a split probe a, a split probe b, a hairpin H1 and a hairpin H2; the split probe a is formed by connecting a split Aptamer sequence Apt-a and a split trigger sequence Ta, and the split probe b is formed by connecting a split Aptamer sequence Apt-b and a split trigger sequence Tb. According to the invention, the target exosome is used as a three-dimensional orbit carrier, the three-dimensional orbit assembled by the catalytic hairpin can be quickly and conveniently synthesized through the interaction of the cholesterol-phospholipid bilayer, and the experimental operation process is greatly simplified. Beneficial to Aptamer specific recognition performance and low background advantages based on a split trigger chain strategy, the three-dimensional DNA walker can be used for detecting tumor exosomes, and can also realize direct detection of targets in a complex system and even in clinical plasma.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Chemiluminescence biosensor for detecting uracil-DNA glycosylase and preparation method and application of chemiluminescence biosensor
ActiveCN110607351ARealize highly sensitive detectionLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpherical nucleic acidDisplacement reactions
The invention relates to the technical field of a biosensor, in particular to detection of uracil-DNA glycosylase based on a chemiluminescence technique for driving a strand displacement reaction based on a tee structure and driving spherical nucleases based on a DNA walker technique. In order to solve the problems of being complex to operate and low in sensitivity for a method for detecting uracil-DNA glycosylase in the prior art, the invention provides a biosensor based on two nanometer technologies of the tee structure and DNA walker, and spherical nucleases are used for catalyzing luminalto be subjected to a chemiluminescence reaction for detection. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing nano-Au, preparing spherical nucleic acid, and forming spherical nucleases in homogeneous phase for catalyzing the chemiluminescence reaction of the luminal. The uracil-DNA glycosylase is used for performing specific recognition and excision on U alkali, so as to realize target specificity detection. Besides, the DNA walker nanometer technology is used for realizing quick and high-sensitivity detection on targets.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Signal turnover type photoelectrochemical biosensor for detecting cancer markers as well as preparation method and application of signal turnover type photoelectrochemical biosensor
PendingCN114487042AAccurate detectionRealize detectionMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorIndium
The invention provides a preparation method of a signal turnover type photoelectrochemical biosensor for detecting cancer markers. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing an indium tin oxide / titanium dioxide electrode, preparing an indium tin oxide / titanium dioxide / single-chain auxiliary probe electrode, preparing a conjugate Ab1-Fe3O4 (at) Au-DNA, preparing a conjugate Ab2-AuNPs-DNA, constructing an intermediate probe and preparing the sensor. The invention also provides the biosensor prepared by the method and application thereof. The biosensor for detecting the cancer marker is based on the organic combination of a direct contact type photocurrent direction overturning strategy, a targeted induction three-dimensional dual-support DNA walker circulation signal amplification technology and a metal organic framework material adsorption characteristic, and photocurrent signal overturning design is carried out, so that the biosensor can be used for detecting the cancer marker. The biosensor can realize environment-friendly detection of cancer markers, and has the advantages of high sensitivity, high selectivity, good reproducibility, high stability and the like.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Construction of "z"-shaped optoelectronic aptamer analysis method based on dnawalker signal amplification
InactiveCN108663418BLow costInhibition of hole recombinationMaterial electrochemical variablesWorkstationElectron transfer
The invention discloses an analysis method of a constructed Z-shaped photoelectric adaptor based on DNA Walker signal amplification. The method is inspired by plant photosynthesis Z electron transfer,and connects a CdS quantum dot to nanogold deposited to BiVO4 through DNA Walker, and photo-induced electron produced by the BiVO4 is transferred to a valence band of the CdS quantum dot from a conduction band of the BiVO4 through electron transfer effect of nanogold, so that compounding of electrons and electron holes is inhibited, photoelectric current is improved, and signal amplification is realized. The method adopts an electrochemical workstation combined with a xenon lamp, is low in cost, high in detection sensitivity, applies bionics to photoelectrochemistry, and provides a sensitivephotoelectrochemistry detection method with stable performances for the detection of cancer markers.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Tumor cell marker miRNA-21 and tumor cell detection system
ActiveCN110455764BHigh surface sensitivityAchieve sensitive detectionRaman scatteringFluorescence/phosphorescenceIntracellularNanoprobe
The invention belongs to the technical field of tumor detection, and discloses a tumor cell marker miRNA‑21 and a detection method for tumor cells. The nanocomposite probe consists of a gold nanoparticle nucleus, a hairpin DNA H 1 and the swing arm Walker‑Blocker; the apex of the DNA tetrahedral complex connects the hairpin DNA H 2 ; miRNA‑21 is a 3D DNA Walker activator; Walker DNA, H 1 、H 2 DNA walker cycle signal amplification, ratiometric and fluorescence Raman dual-mode detection of miRNA-21; gold nanoparticles and DNA tetrahedral structure enter tumor cells, ratiometric, fluorescence Raman dual-mode imaging detection of tumor cells . The invention combines 3D DNA Walker nano-machine amplification and DNA tetrahedral nano-probes to perform ratiometric and dual-mode detection of tumor cell marker miRNA-21 and tumor cells.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electrochemical detection method of pathogenic bacteria based on DNA walker and nanoflower structure
ActiveCN112432980BIncrease the effective areaExpand the scope of detectionMaterial electrochemical variablesExonuclease IExonuclease III
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
An electrochemical aptamer sensor for ampicillin detection
ActiveCN112378976BMild reaction conditionsQuick responseBiological material analysisBiological testingAptamerAmpicillin
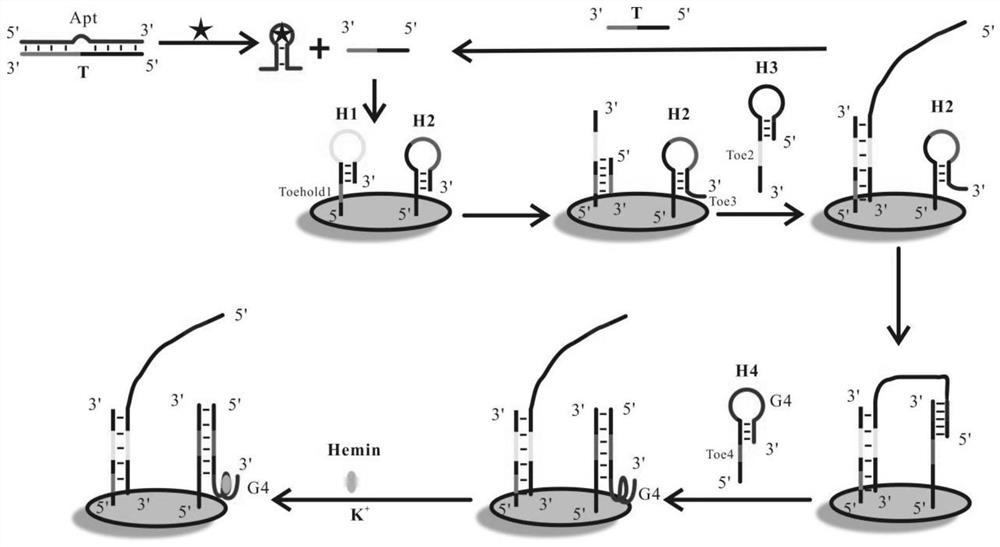
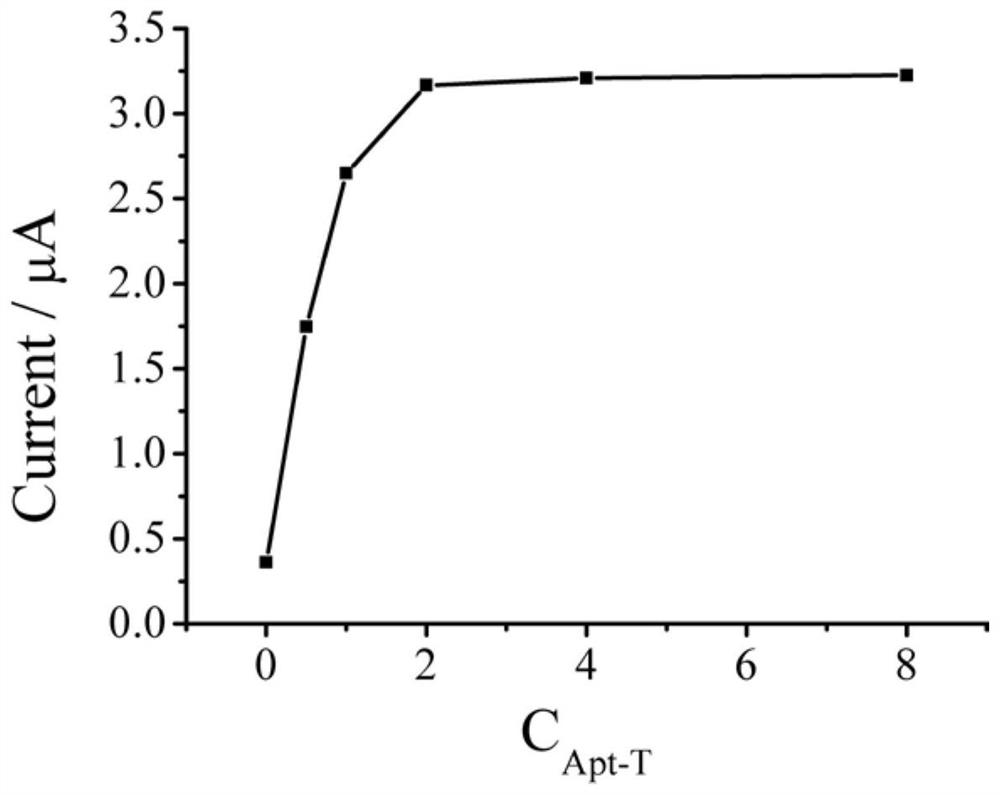
The invention provides an electrochemical aptamer sensor for ampicillin detection, comprising a detection electrode, heme, H3 chain, H4 chain, aptamer Apt, T chain; the detection electrode is a gold electrode with surface modified H1 chain and H2 chain, the H1 chain and H2 chain sequence are shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-2, the 5' end of the H1 chain and the H2 chain The 3' end of the modified sulfhydryl group. The sensor realizes the increase of the signal through the circulation of the T chain and the DNA walker on the electrode, which greatly improves the detection sensitivity and obtains a lower detection limit, which can be used to detect the trace amount of ampicillin in food.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
DNA biosensor for rapidly detecting clostridium perfringens in meat products and detection method thereof
PendingCN114878647AEasy to operateReduce testing costsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerNucleotide
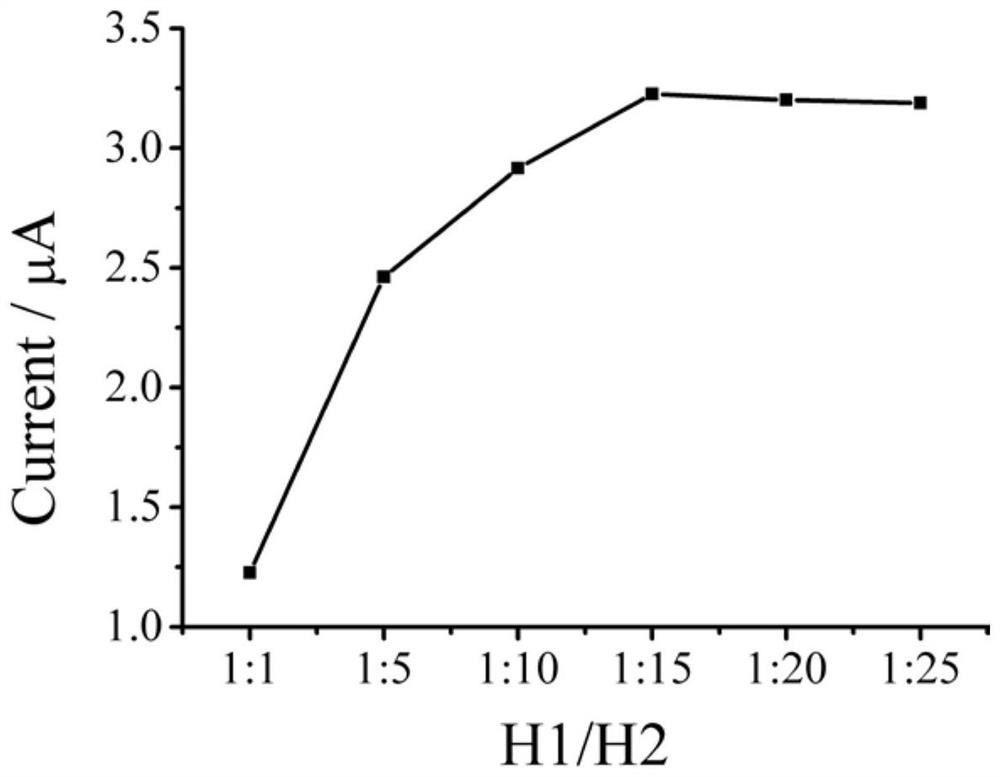
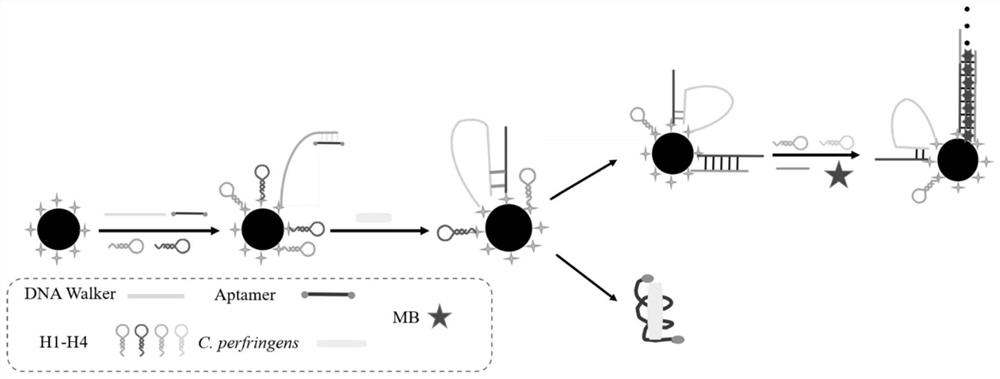
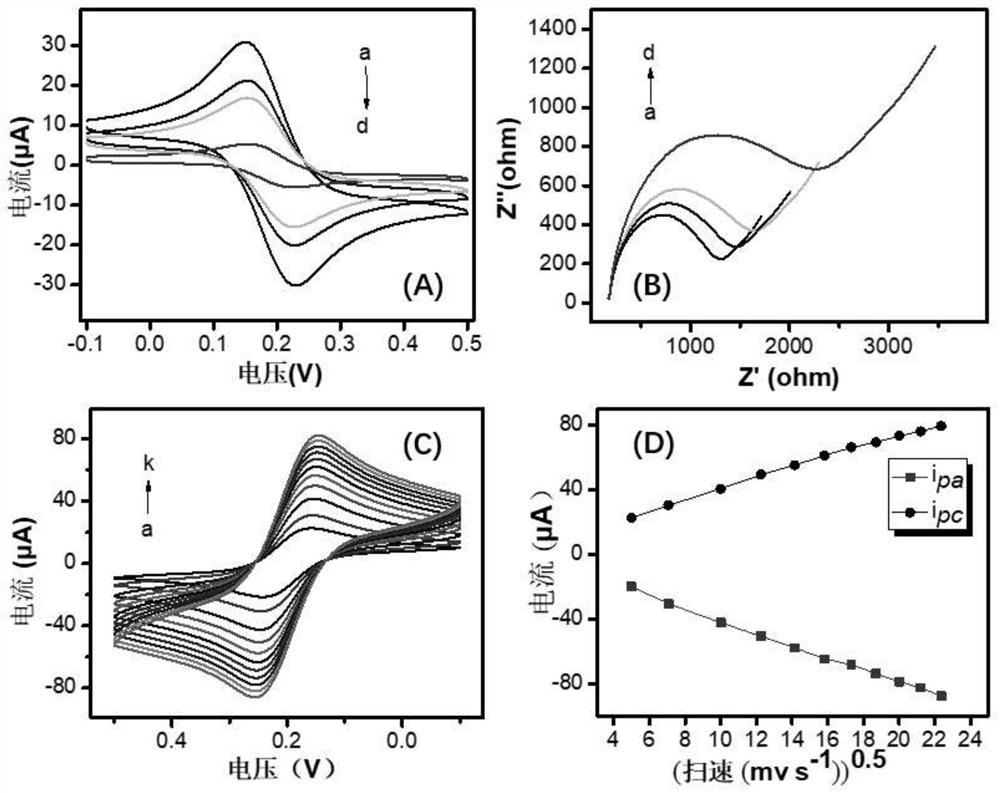
The invention discloses a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) biosensor for rapidly detecting clostridium perfringens in meat products and a detection method of the DNA biosensor. The biosensor comprises nano magnetic beads, DNA walker, DNA Aptamer, DNA H1, DNA H2, DNA Trigger, DNA H3 and DNA H4, wherein carboxyl groups are modified on the surfaces of the nano magnetic beads, and the nucleotide sequences of the DNA walker, the DNA Aptamer, the DNA H1, the DNA H2, the DNA Trigger, the DNA H3 and the DNA H4 are respectively shown as SEQ ID NO: 1-7. By introducing the magnetic nanoparticles and orderly assembling the nucleic acid aptamers on the surfaces of the magnetic nanoparticles, the operation steps in the detection process of the clostridium perfringens are greatly simplified, and the detection cost of the clostridium perfringens is reduced. Meanwhile, the detection method provided by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, low cost, rapidness and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Preparation method of DNA walker-based coupled magnetic nano-composite, and product and application of nano-composite
ActiveCN111218496AReduce non-specific adsorptionIncrease loadMicrobiological testing/measurementBulk chemical productionSignalling moleculesA-DNA
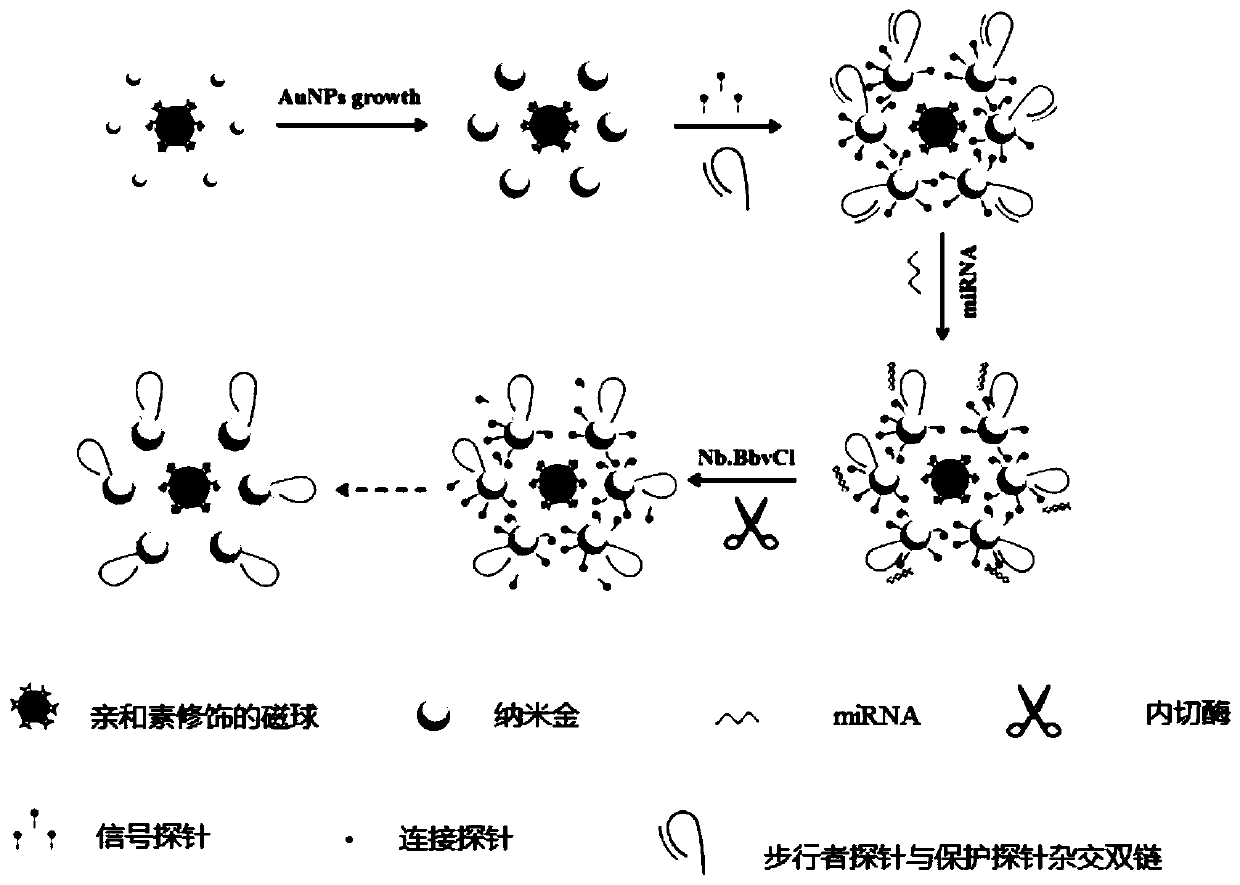
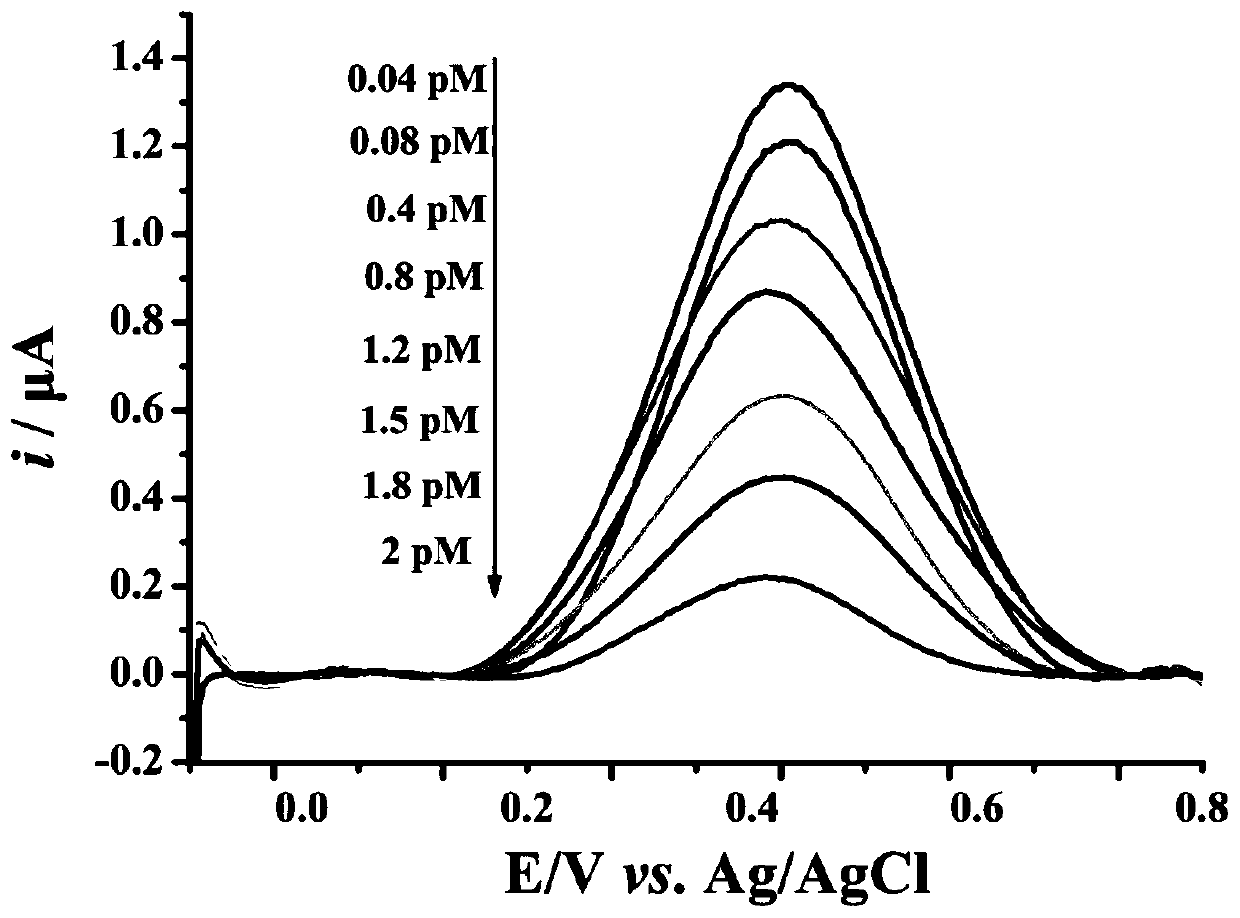
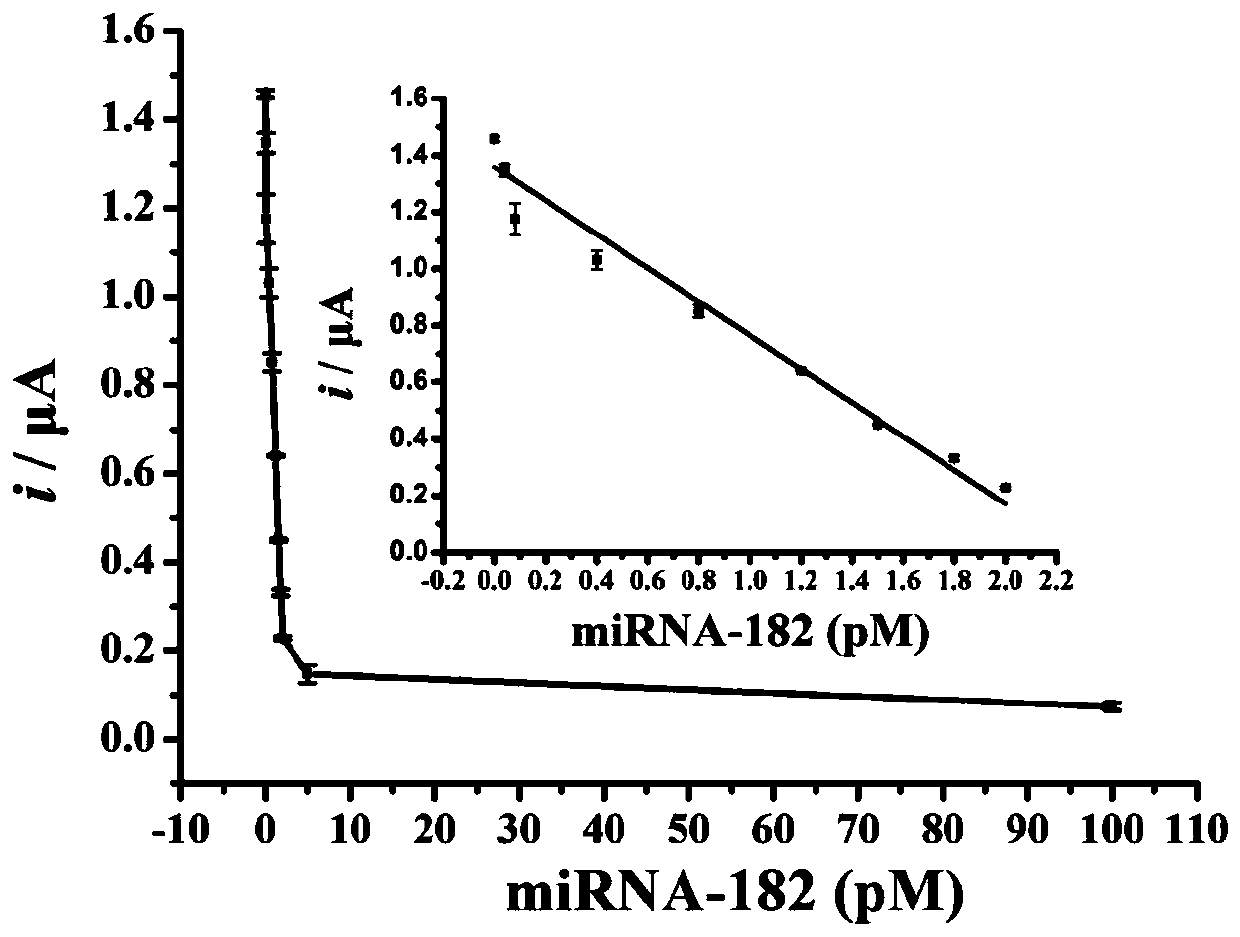
The invention discloses a preparation method of a DNA walker-based coupled magnetic nano-composite, and a product and application of the nano-composite. According to the invention, magnetic spheres easy to separate and enrich, gold nanoparticles with large specific surface area and DNA walkers are combined, the magnetic spheres can reduce the non-specific adsorption of interferents, the gold nanoparticles can increase the load capacity of DNA sequences, and the DNA walkers can gradually cut signal molecules under the action of enzymes to cause the changes of electrochemical signals. Compared with a traditional electrochemical detection method, the method avoids the complex steps of modifying the DNA sequences on the surfaces of electrodes, reducing the non-specific adsorption by using blocking agents, etc., has extremely high sensitivity, and can reach the lowest detection concentration of 1 fM for a target miRNA-182. The method of the invention has a wide detection range, ranging from0.001 to 2 pM. The content of miRNA-182 in a normal serum sample is about 0.2-1 pM, and the content of miRNA-182 in a glioma patient is about 1-2 pM. The method of the invention is feasible for the determination of miRNA-182 in the normal serum sample and the glioma patient serum sample.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
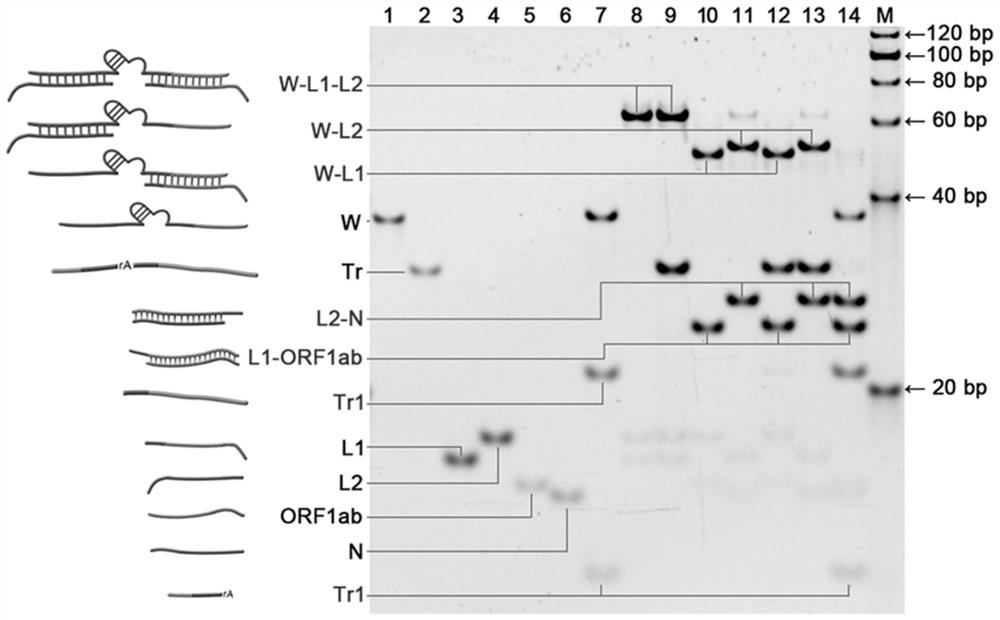
DNA walker for SARS-CoV-2 detection and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114875180ALess distracting factorsLow priceMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNanoparticleViral test
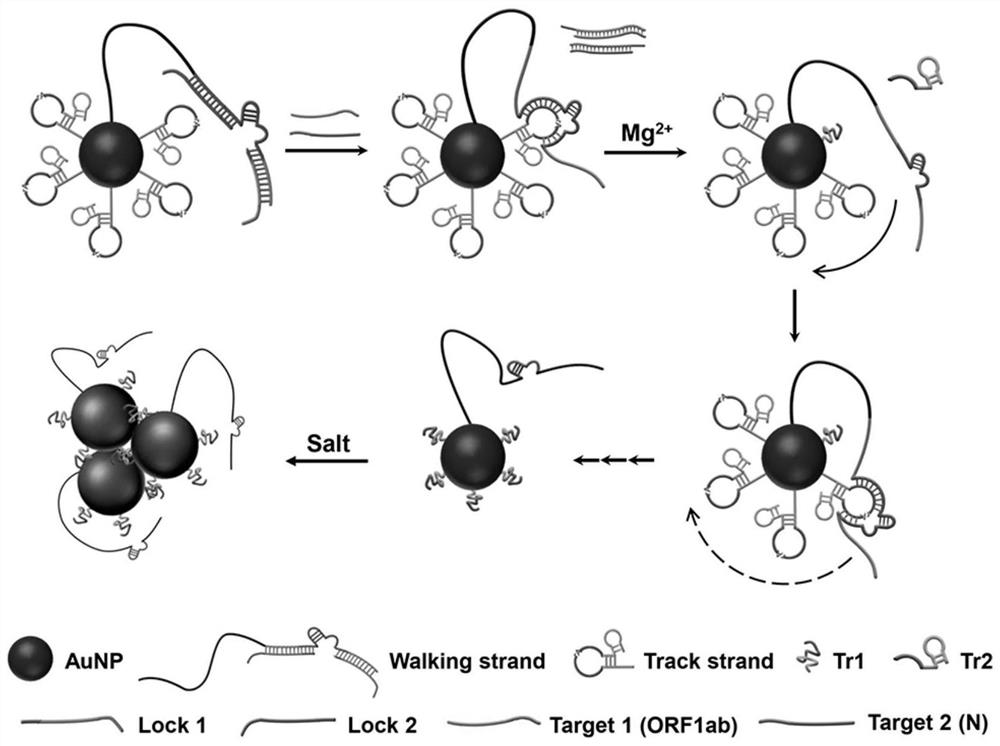
The invention relates to a DNA walker for SARS-CoV-2 detection and a preparation method of the DNA walker. The DNA walker for SARS-CoV-2 detection comprises a walking chain W, a locking chain L1, a locking chain L2, an orbital chain Tr, a target chain T1, a target chain T2 and gold nanoparticles. The invention also provides a preparation method of the DNA walker, and a method for detecting SARS-CoV-2 by using the DNA walker. According to the DNA walker provided by the invention, visual SARS-CoV-2 detection is realized, the DNA walker has the advantages of few interference factors, low price and good stability, and meanwhile, the sensitivity can reach 1nM. When the DNA walker or the kit provided by the invention is used for detection, a reverse transcription step is not needed, the use of enzymes, labels or modifications is avoided, the result is visualized, the requirement on complex equipment is reduced, and a convenient, economical, rapid and reliable method is provided for SARS-CoV-2 virus detection.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Ratio-type ECL biosensor as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113278683AGood receptorMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesA-DNAElectrochemiluminescence
The invention constructs a ratio electrochemical luminescence (ECL) biosensor, which is used for detecting the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) gene of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2). The SARS-COV-2RdRp gene participates in the entropy-driven cyclic amplification reaction, then a piece of Bandage DNA is output, and can be combined with the other two single chains S1 and S2 to form a double-chain DNAWalker, and the next cyclic reaction is started. After the walking process of the double-foot DNA Walker is completed, a hairpin structure at the top of a DNA tetrahedron (TDNAs) is removed. Then, a PEI-Ru@Ti3C2@AuNPs-S7 probe is used for being specifically combined with a TDNAs hairpin part cut off from the surface of Au-g-C3N4, and signal change is achieved through ECL-RET (electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer).
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE
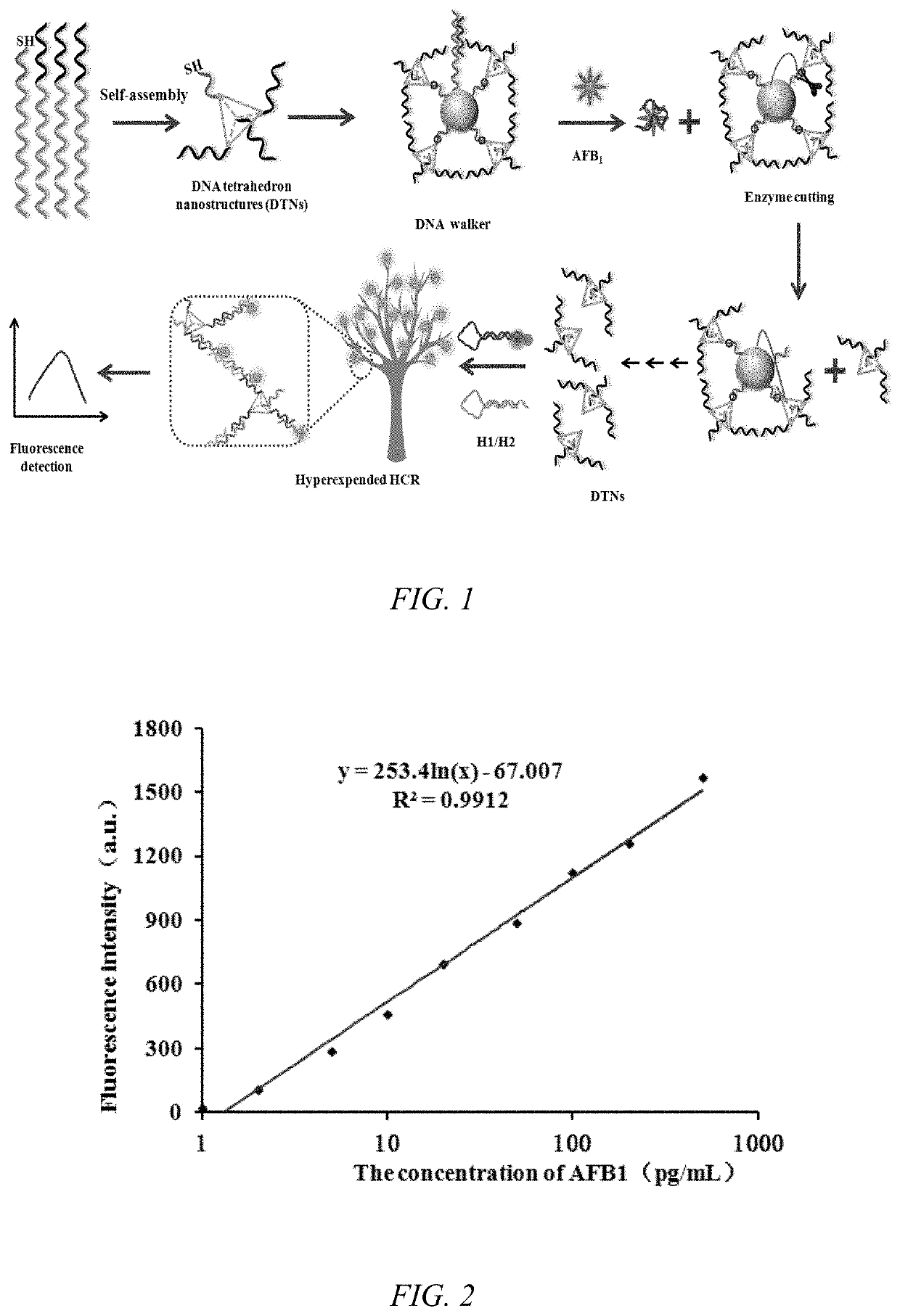
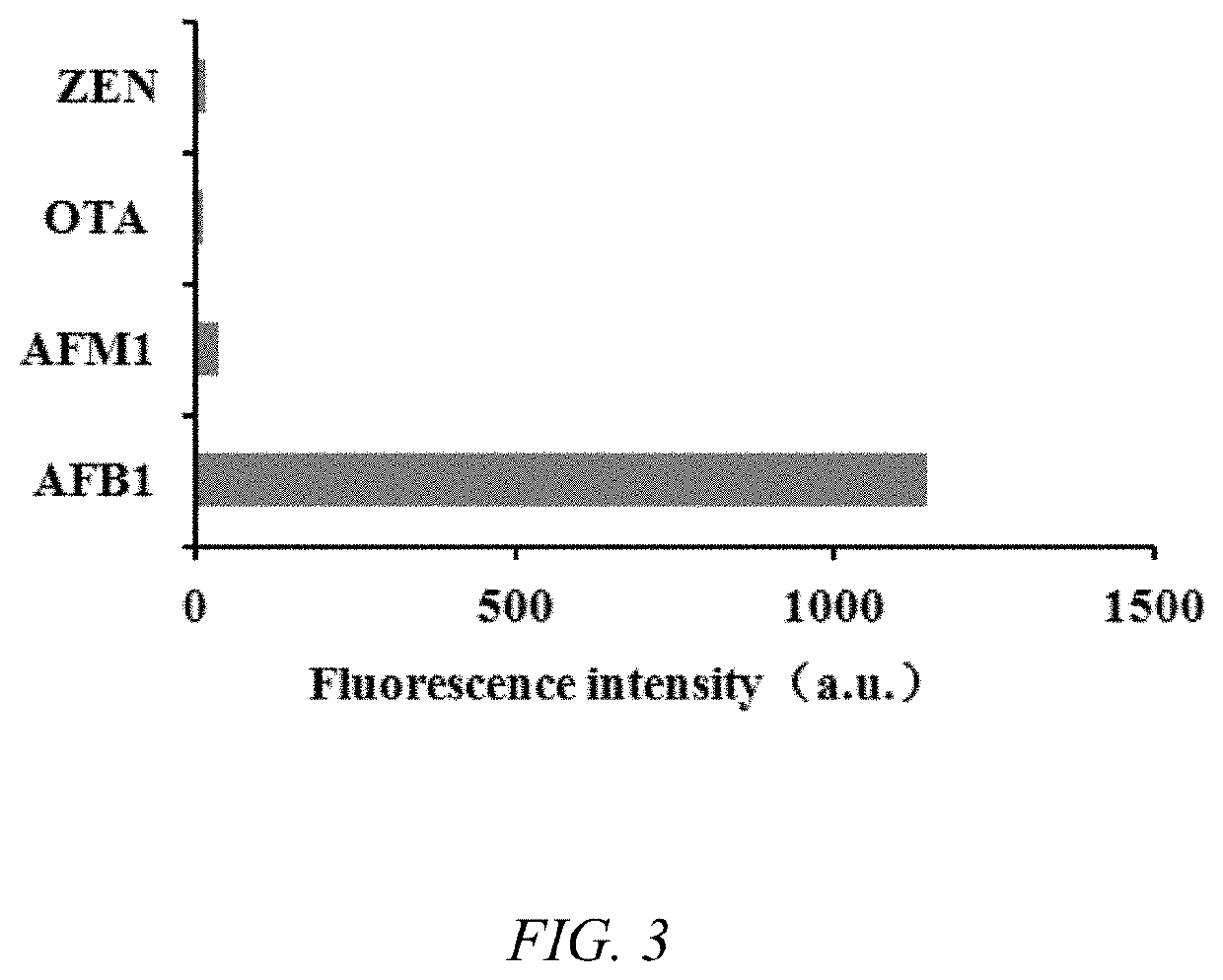
Kit for aflatoxin b1 (AFB1) monitoring
PendingUS20220213545A1Enhanced detection signalImprove reaction speedMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansAflatoxin BToxin
The invention displays aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) detection kit and AFB1 detection method. The invention belongs to the technical field of detecting harmful substances. The AFB1 detection kit was fabricated with DNA walker structure, endonuclease, hairpin H1 and H2. The AFB1 detection kit has benefits of high sensitivity and short detection time based on signal amplification strategy of DNA Walker structure and hyperbranched fluorescent nanotrees. The present invention can realize high sensitive and rapid detection of AFB1.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com