Patents
Literature
339 results about "Lotus japonicus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
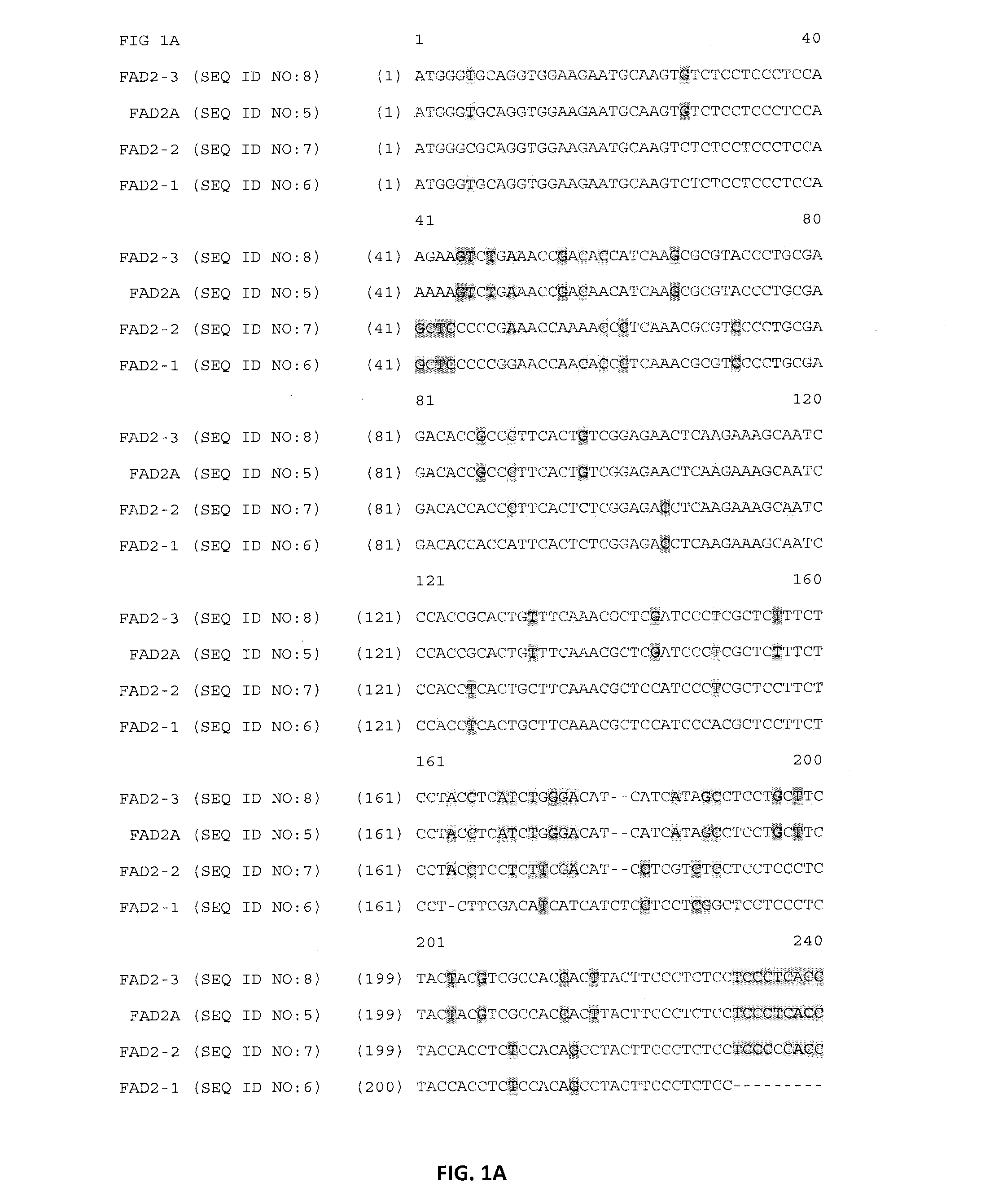
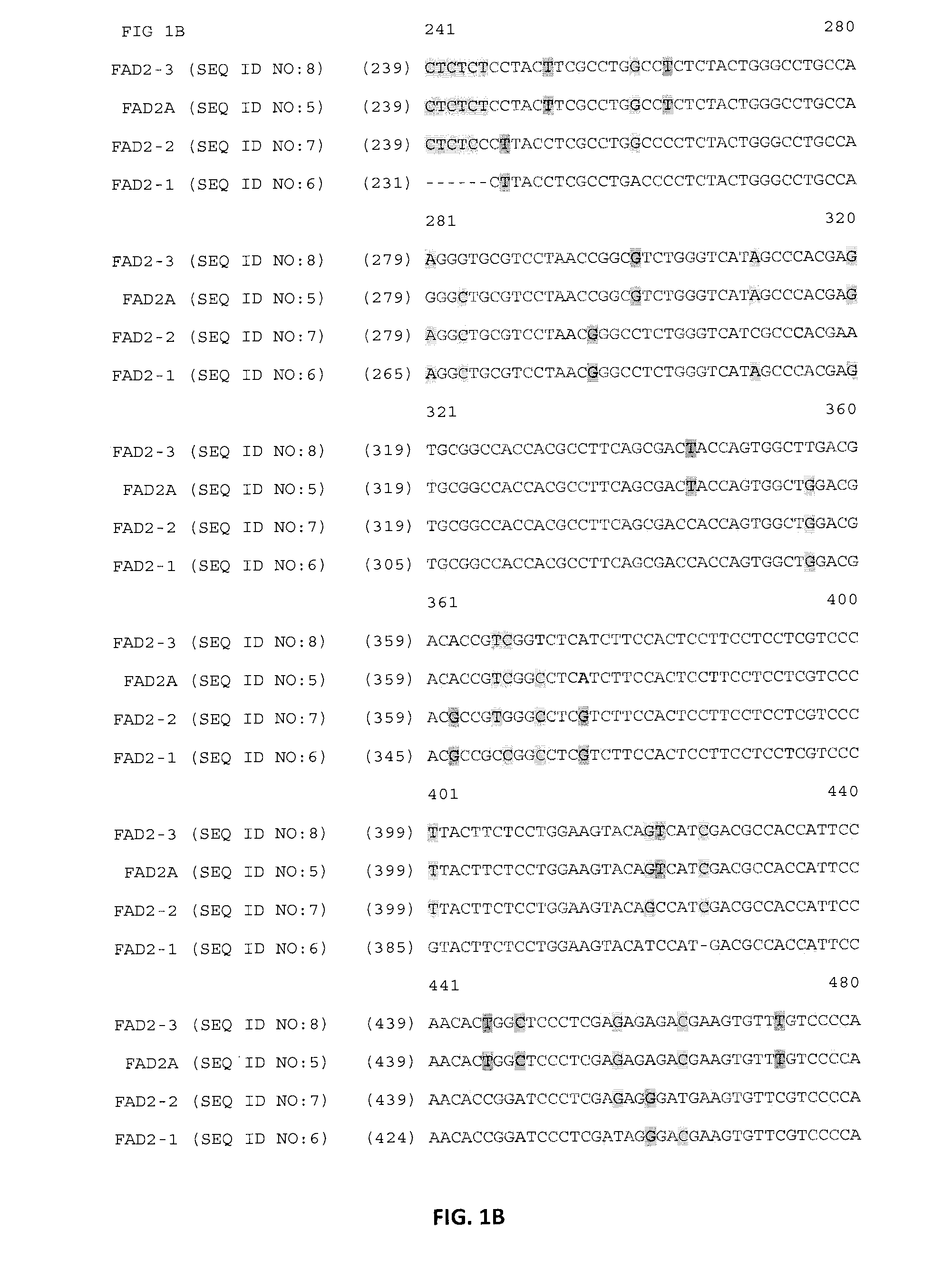
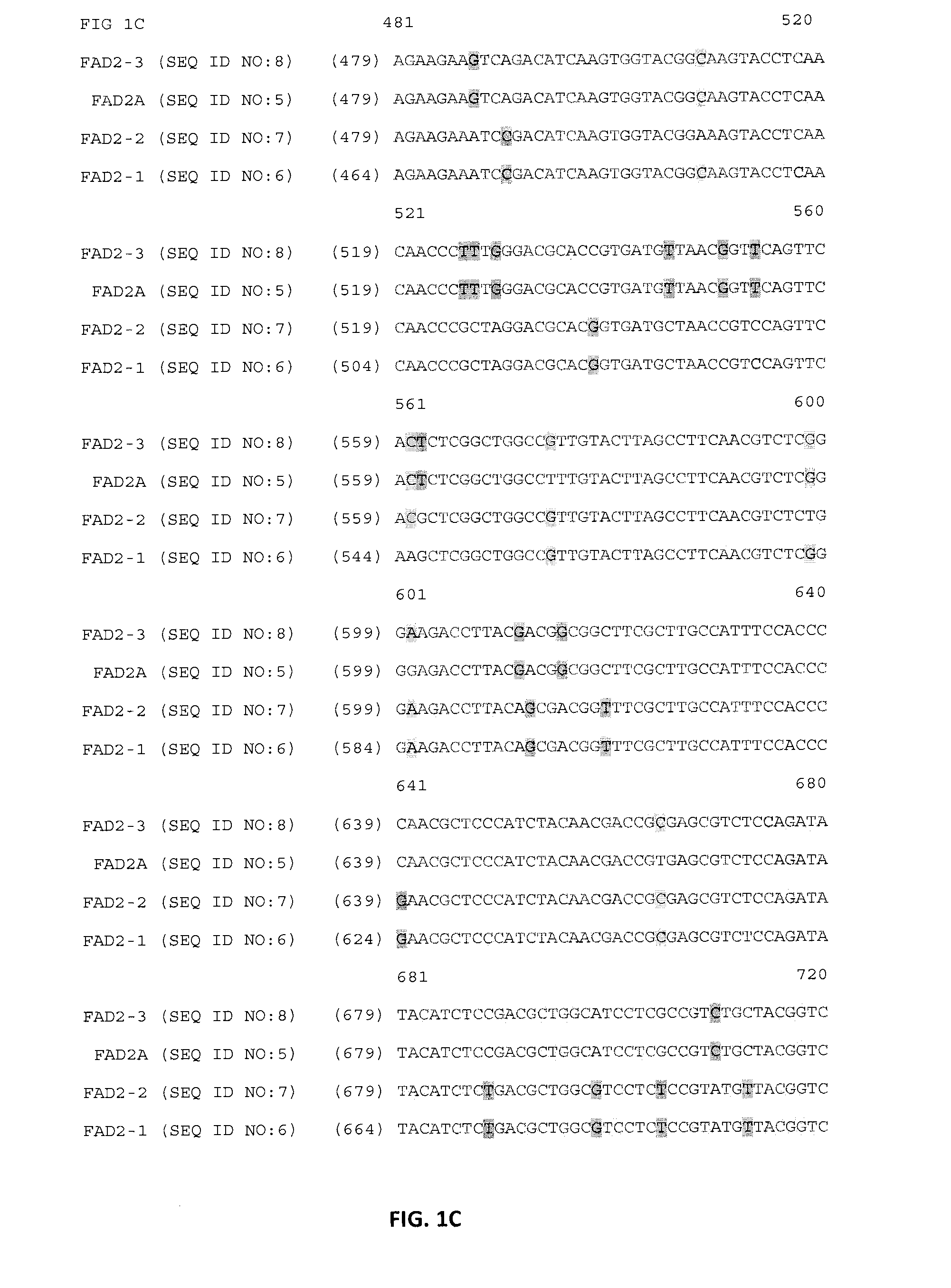
Lotus japonicus is a wild legume that belongs to family Fabaceae. Members of this family are very diverse, constituting about 20,000 species. They are of significant agricultural and biological importance as many of the legume species are rich sources of protein and oil and can also fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Engineered transgene integration platform (ETIP) for gene targeting and trait stacking
An Engineered Transgene Integration Platform (ETIP) is described that can be inserted randomly or at targeted locations in plant genomes to facilitate rapid selection and detection of a GOI that is perfectly targeted (both the 5′ and 3′ ends) at the ETIP genomic location. One element in the subject disclosure is the introduction of specific double stranded breaks within the ETIP. In some embodiments, an ETIP is described using zinc finger nuclease binding sites, but may utilize other targeting technologies such as meganucleases, CRISPRs, TALs, or leucine zippers. Also described are compositions of, and methods for producing, transgenic plants wherein the donor or payload DNA expresses one or more products of an exogenous nucleic acid sequence (e.g. protein or RNA) that has been stably-integrated into an ETIP in a plant cell. In embodiments, the ETIP facilitates testing of gene candidates and plant expression vectors from ideation through Development phases.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
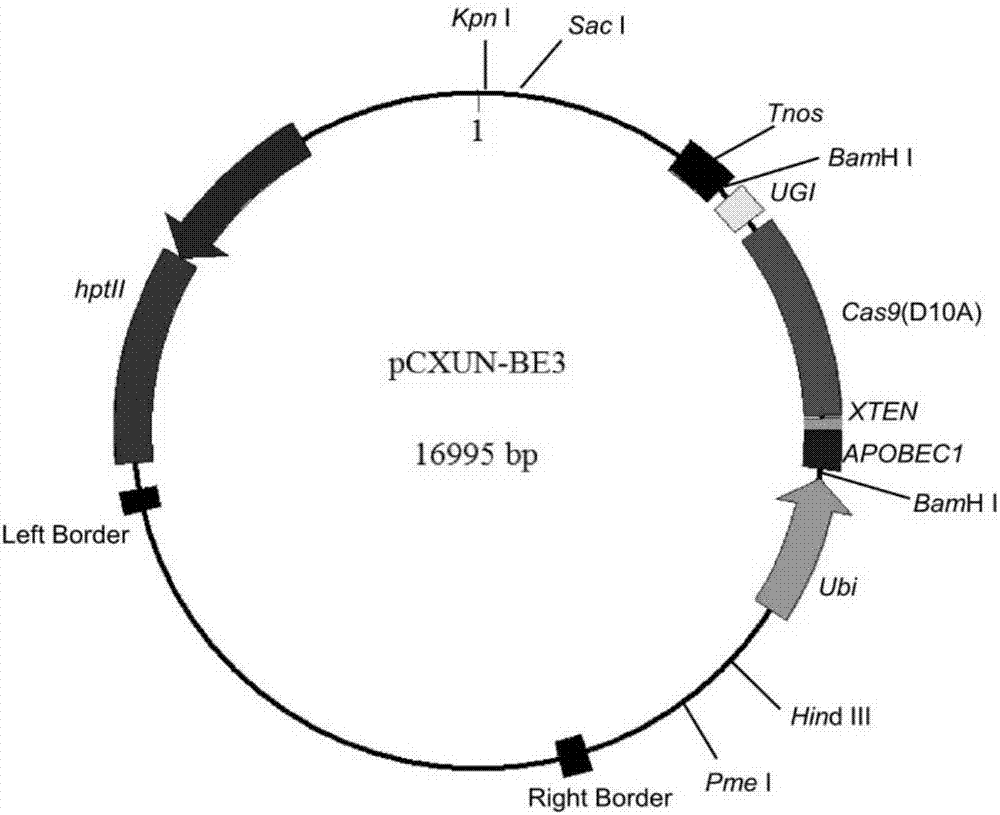
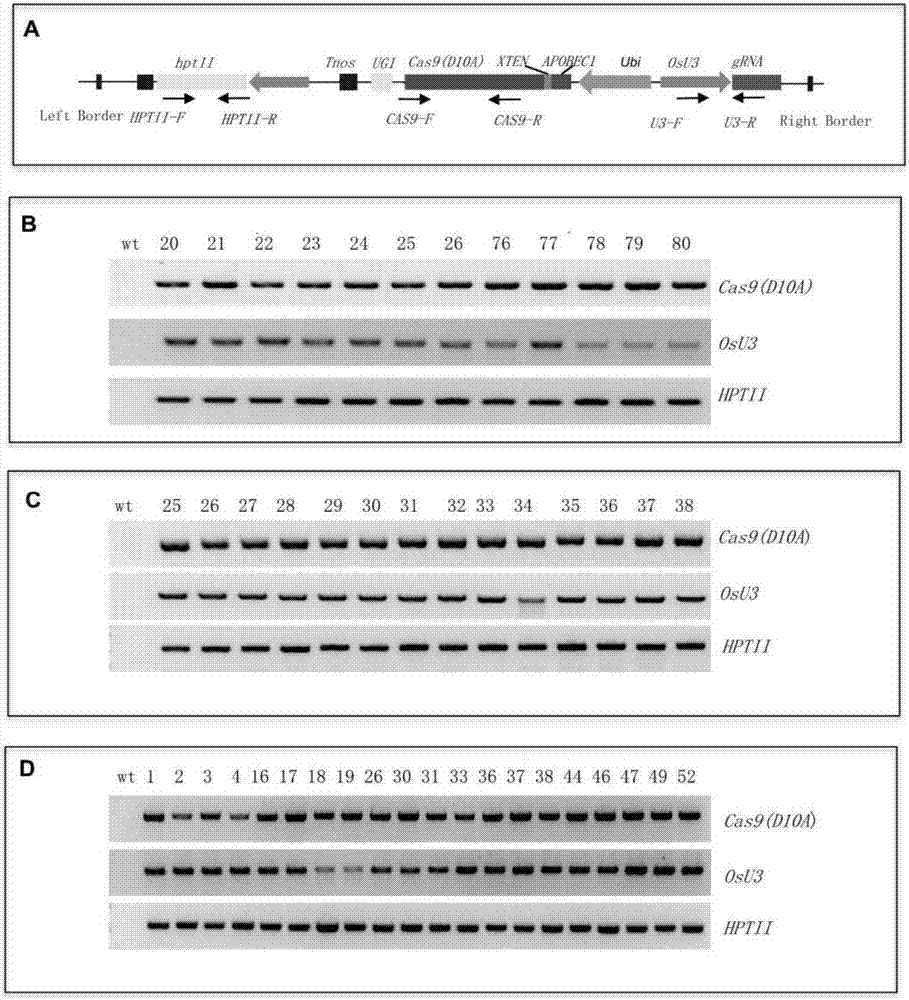
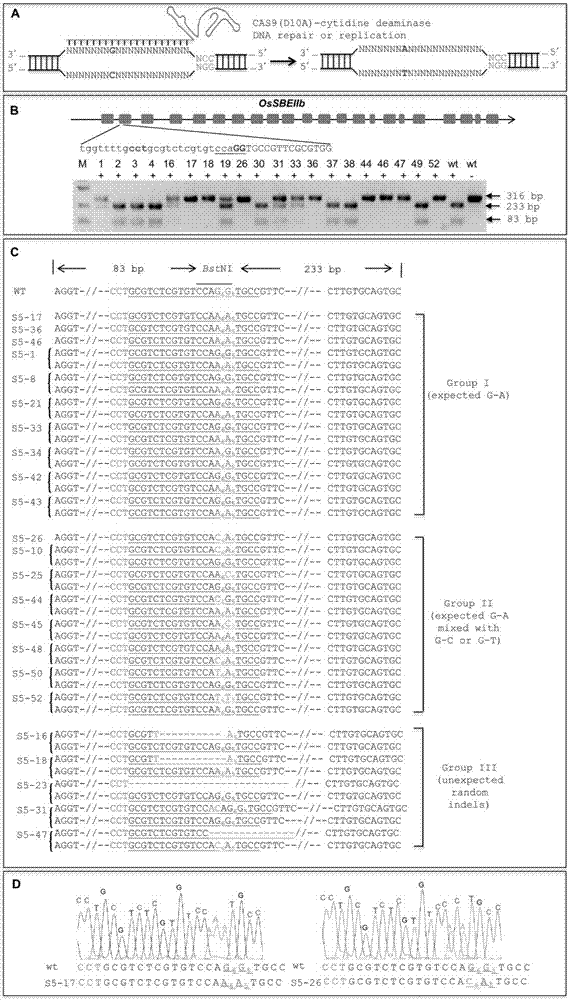
Application of CRISPR/nCas9 mediated site-directed base substitution in plant
ActiveCN107043779ARapid improvement of agronomic traitsImproved agronomic traitsVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionUracil-DNA glycosylaseSubstitution method
The invention discloses application of CRISPR / nCas9 mediated site-directed base substitution in a plant. The invention provides a plant genome site-directed edition system. The system comprises a BE3 plant expression carrier (expressing a fusion protein composed of nCas9(D10A), deaminase and a uracil DNA glycosylase inhibitory protein), and rice OsPDS and OsSBEIIb are taken as target genes for verifying the system. Results show that an expected site-directed mutant plant is respectively obtained in the three selected target spots, accurate site mutation of a base is realized in rice, and the highest efficiency reaches about 20%, so that a feasible and effective base substitution method is provided for crop breeding, the method has strong application potential in the aspect of agricultural breeding, and a foundation is provided for rapidly improving important agronomic traits of crops.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjWRKY1
ActiveCN105087601AIncrease contentHigh expressionGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyGenomics
The invention discloses application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjWRKY1, namely, application in improving the expression quantity of key enzyme genes in the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins, and increasing the content of saponins in panax japonicus callus. The nucleotide sequence of the PjWRKY1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and WRKY transcription factors are coded. Through the adoption of functional genomics and techniques related to metabolic engineering, a panax japonicus PjWRKY1 transcription factor is proved to have the effect of positively regulating the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins; when the panax japonicus PjWRKY1 transcription factor gene disclosed by the invention is established on a plant expression vector and transferred into the panax japonicus callus for over expression, the expression quantity of the key enzyme genes in the synthetic route of panax japonicus saponins is increased, and the yield of panax japonicus saponins is increased.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
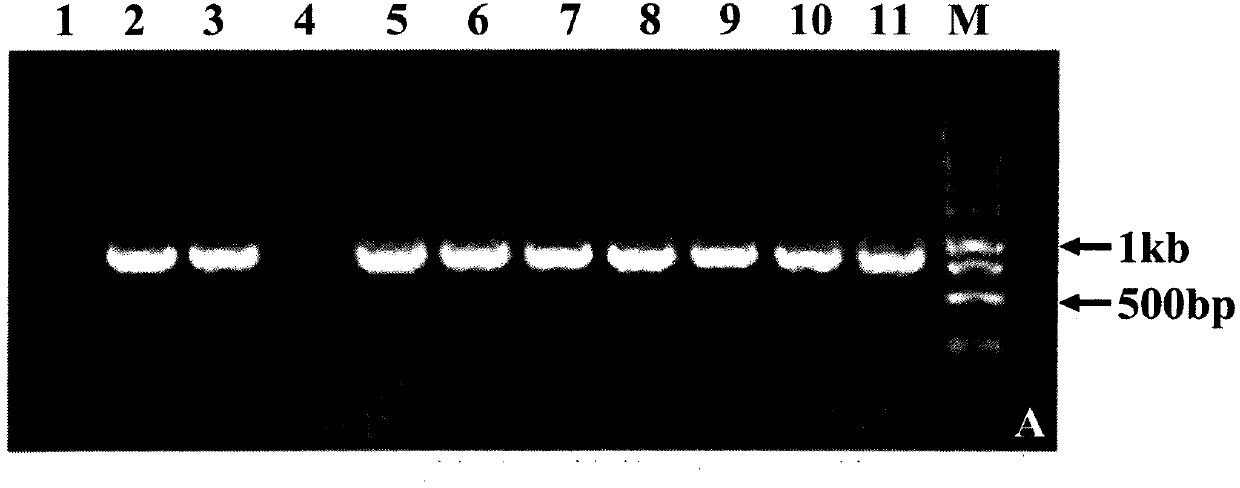
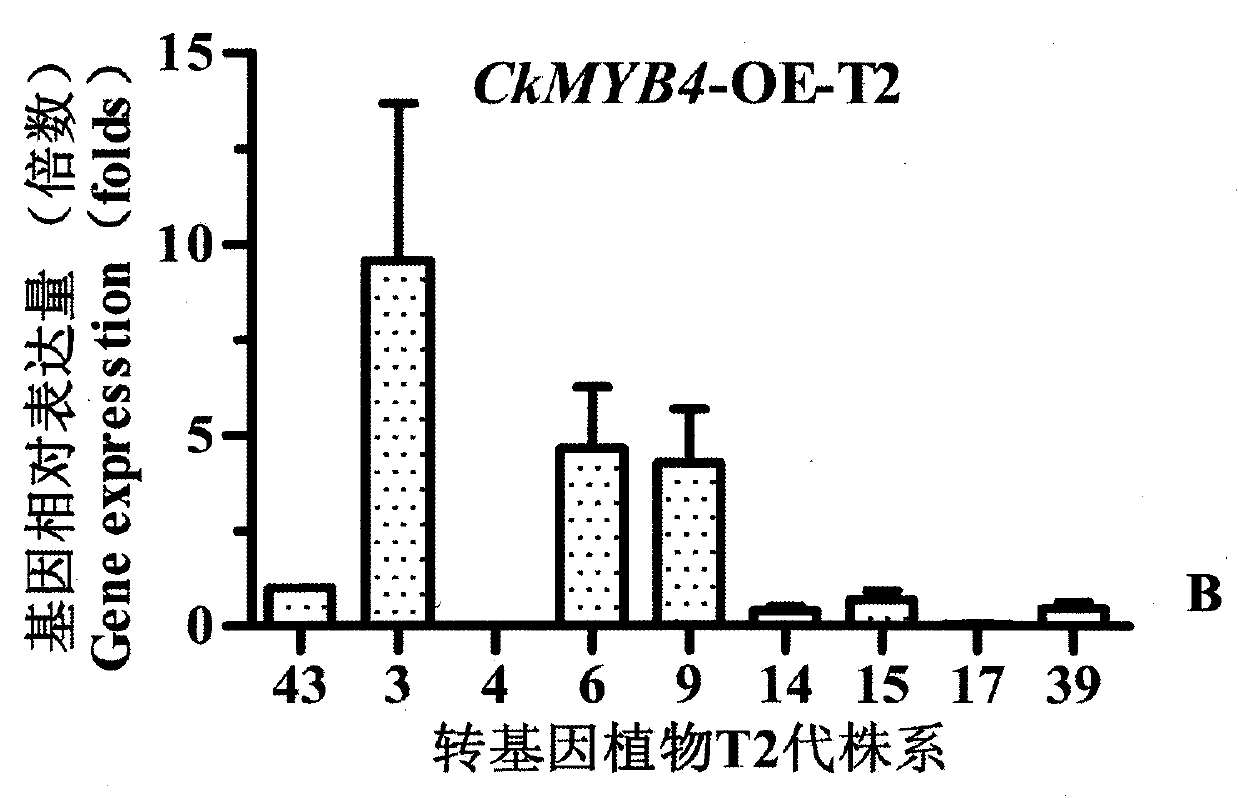
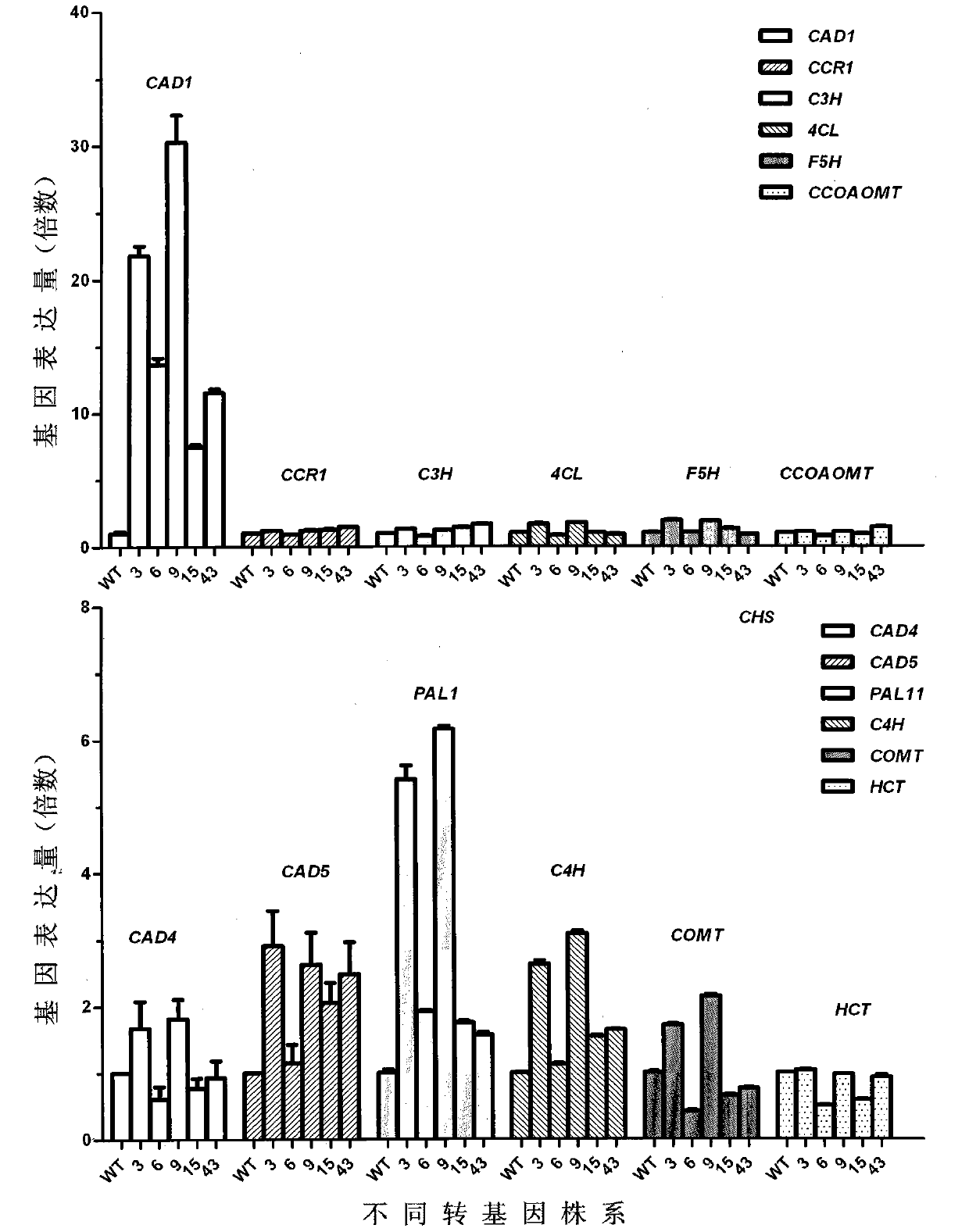
Caragana korshinskii Kom. transcription factor CkMYB4 and its gene
The invention provides a new CkMYB4 transcription factor and its gene. The gene originates from Leguminosae Caragana shrubs Caragana korshinskii Kom., and codes R2R3 MYB transcription factors. The full length cDNA sequence of the gene comprises 1106bps, comprises a 798bp open reading frame, and codes 266 amino acids. The cDNA sequence obtained after cloning is used for constructing a plant expression vector, and the vector is transformed into wild Arabidopis thaliana to obtain a transgenic plant. Transgenic Arabidopis thaliana lignin synthetase gene and lignin content detection results show that the gene provided by the invention can change the expression of the plant lignin synthesis gene and the lignin content.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
New anti-drought and cold-resistant gene CaDHN1 in caragana korshinskii
The invention discloses caragana korshinskii dehydrin and gene thereof. The dehydrin consists of 243 amino acid residues, and comprises two Y stricture regions and a K structure region; and compared with the other dehydrin, the dehydrin is abundant in histidine (H) and glycocoll (G). The whole length of the gene of the dehydrin is 1165bp, the dehydrin is a 731bp opened reading frame from 5'end to 106-837 position, and the dehydrin has intense express under the condition that the plant is stressed by the drought and the cold, so that the dehydrin reduces the damage to plant cells, improves the anti-drought and cold-resistant capability, and is the key element of the anti-drought mechanism of the plant. The similarity between the amino acid sequence of the gene of the caragana korshinskii dehydrin and that of the gene of the pea dehydrin is 34%, and the gene of the dehydrin is a new gene. If the plant expression vector of the gene is built, and the anti-drought gene is leaded into various plants, the anti-drought and cold-resistant capability of the plant can be improved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI & ANIMAL HUSBANDRY SCI
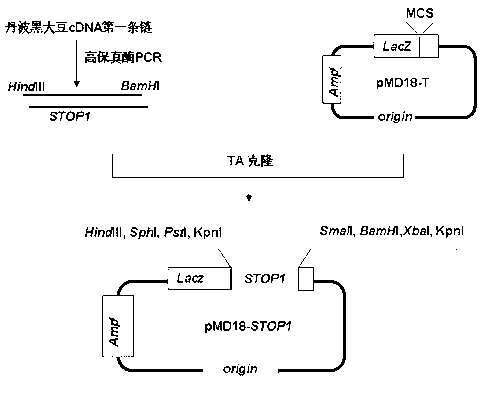
Plant expression vector of Tanba black soybean C2H2 zinc finger protein gene STOP1 and application thereof
InactiveCN102952822AIncrease aluminum resistanceReduce adsorptionVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyCauliflower mosaic virus
The invention discloses a plant expression vector Ppzp-35S-STOP1 of Tanba black soybean C2H2 zinc finger protein gene STOP1 and an application thereof for improving plant aluminum toxicity stress resistance. The vector is the plant expression vector containing constitutive promoter (35S) of cauliflower mosaic virus and C2H2 zinc finger protein gene STOP1 induced by the Tanba black soybean aluminum, the STOP1 gene is amplified from tanba black soybean roots, and the over-expression of the STOP1 gene in tobacco is controlled by utilizing the constitutive promoter, so that the aluminum toxicity resistance of the tobacco can be improved. The STOP1 transgene tobacco forcedly grows in solution containing 30microliters aluminum trioxide (AlCl3) for 24hours, the malic acid and the citric acid secreted from roots of the transgene tobacco as well as the aluminum resistance can be remarkably higher than that of a wild contrast plant, and the aluminum content on the root of the tobacco is remarkably lower than that of the wild plant.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Pesticidal protein encoding gene Cry1Ab-Ma and expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN102094030AHigh expressionEfficient and stable expressionClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesBacillus thuringiensisResistant genes
The invention provides an insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-Material. The synthesis of the gene is as follows: according to the amino acid sequence of the N-terminal of the original Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) protein (Cry1Ab), the preferred codons of monocotyledon (corn) is used to perform human reformation and synthetize a new Cry1Ab DNA sequence; and the prokaryotic expression vector and plant expression vector are constructed, and transformation is performed in the host cells. Vitro tests prove that the transformed and synthetized Bt gene toxic protein has obvious insecticidal effect on Ostrinia nubilalis. The expression of the insect-resistant gene Cry1Ab-Ma in monocotyledon is stable and efficient, thus the gene can be used to produce insect-resistant transgenic plant.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjERF1
ActiveCN105087599AIncrease contentHigh expressionFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjERF1, namely, application in improving the expression quantity of key enzyme genes in the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins, and increasing the content of saponins in panax japonicus callus. The nucleotide sequence of the PjERF1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and AP2 / ERF transcription factors are coded. Through the adoption of functional genomics and techniques related to metabolic engineering, a panax japonicus PjERF1 transcription factor is proved to have the effect of positively regulating the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins; when the panax japonicus PjERF1 transcription factor gene disclosed by the invention is established on a plant expression vector and transferred into the panax japonicus callus for over expression, the expression quantity of the key enzyme genes in the synthetic route of panax japonicus saponins is increased, and the yield of panax japonicus saponins is increased.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY3 and application thereof
ActiveCN110818782AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY3 and a preparation method thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and a protein with an aminoacid sequence shown as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; according to the invention, functional genomics related technical researches prove that the LrWRKY3 gene has the function of improving the antifungal performance of plants; the antifungal LrWRKY3 gene disclosed by the invention is constructed on a plant expression vector and is transferred into tobacco for overexpression; the transgenic tobacco plantshave very strong fungus infection resistance, and experimental results show that transgenic tobacco leaves with over-expression of LrWRKY3 have very strong resistance to infection of five pathogenicfungi such as alternaria oryzae, Botryosphaeria dothidea, fusarium graminearum, Fusarium rotunda and fusarium solani.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Specific expression promoter OsAnth1 for rice anthers
ActiveCN104946649AImprove featuresAvoid wastingVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsPlant genetic engineeringCancer research
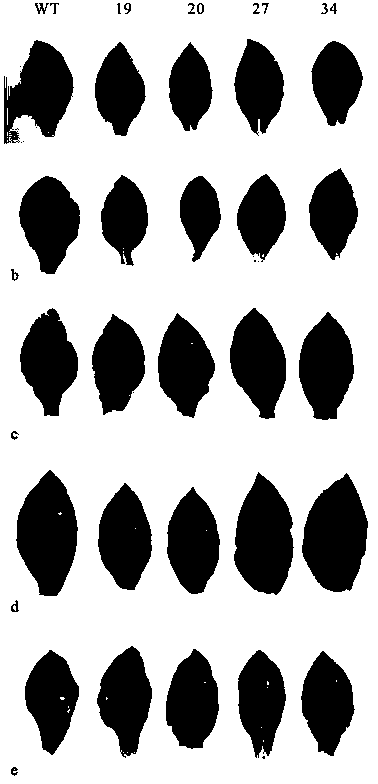
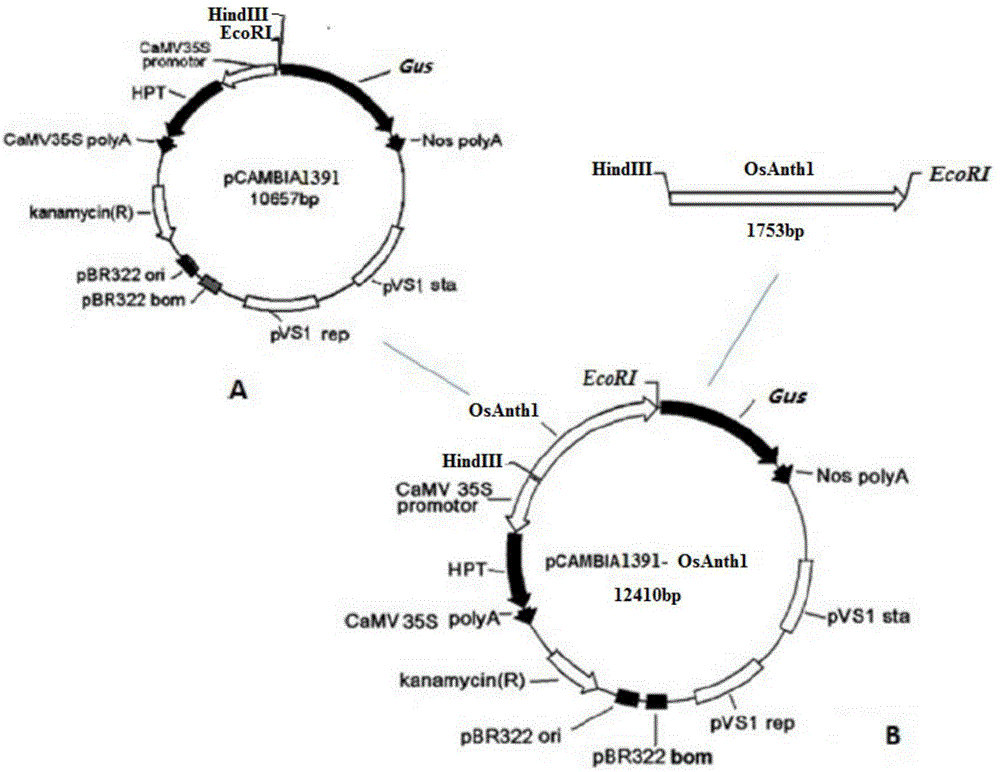
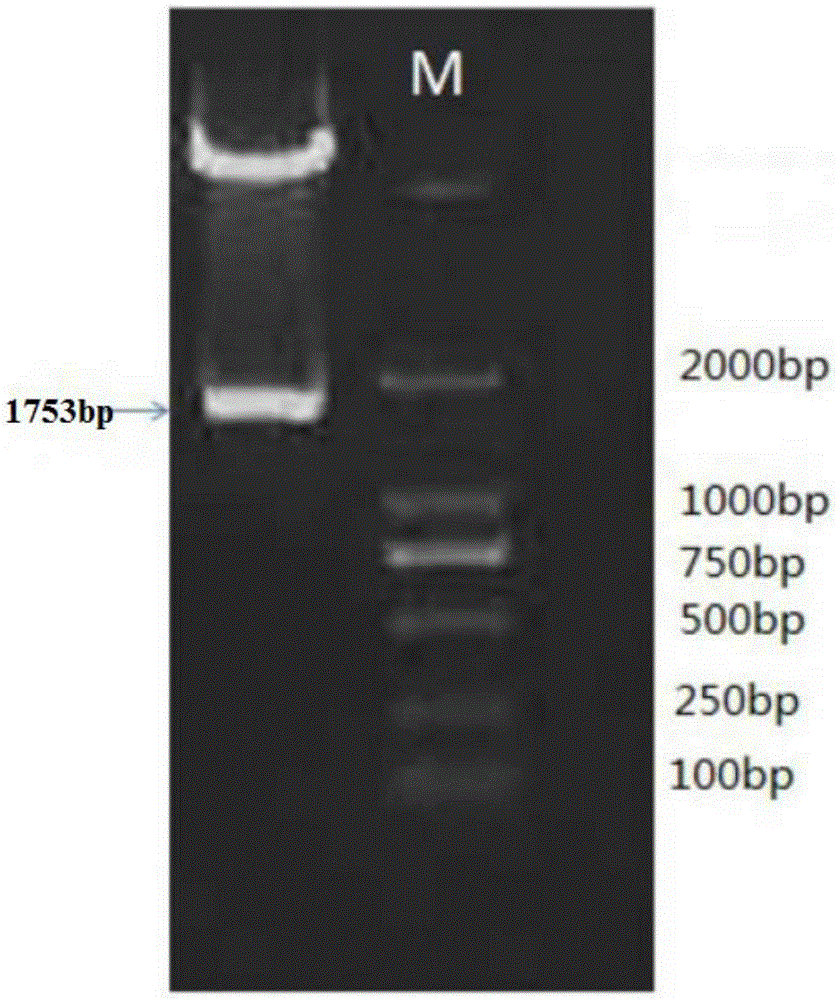
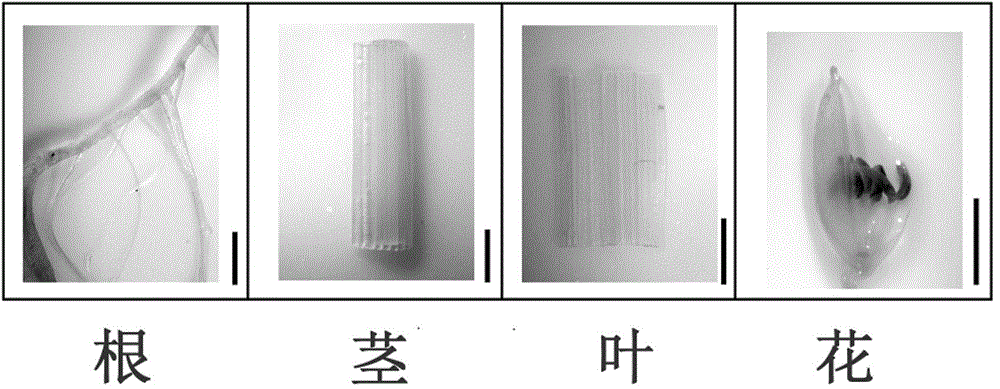
The invention provides a specific expression promoter OsAnth1 for anthers and an application thereof. The promoter which can carry out a specific expression in the plant anthers is departed, and the promoter can guide a target gene to carry out a specific high expression in the plant anthers and carry out a low expression or not express in other issues of a plant. The invention further provides an expression box containing the promoter, a plant expression carrier and a method for obtaining corresponding host bacteria and converters by using the promoter. In addition, the promoter is applied to plant gene engineering. The promoter has a significant theory and an actual meaning for relevant researches about the rice anthers. The wide application and the wide market prospect are going to be obtained in the field of agriculture.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of OsWRKY28 transcription factor gene of rice in improvement of plant disease resistance
ActiveCN102816773AIncrease resistanceFermentationGenetic engineeringDiseaseGenetically modified rice
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering and discloses application of OsWRKY28 transcription factor gene of rice in improvement of plant disease resistance. In research of functions of the WRKY transcription factor gene OsWRKY28 of rice as shown inthe SEQ ID NO.1 by means of a reverse genetics method, the OsWRKY28 transcription factor gene is found to have positive regulation function for resistance to rice banded sclerotial blight. The OsWRKY28 transcription factor gene is planted on a proper plant expressing carrier to convert cells or rice, and resistance of obtained rice with OsWRKY28 excessive-expression transcription factor to the banded sclerotial blight is evidently improved. Accordingly, disease resistance of rice and other crops can be improved by the OsWRKY28 gene, and new varieties of transgenosis plants resistant to the banded sclerotial blight can be cultured.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Artificial reconstruction synthetic pesticidal gene as well as encoding protein and use thereof
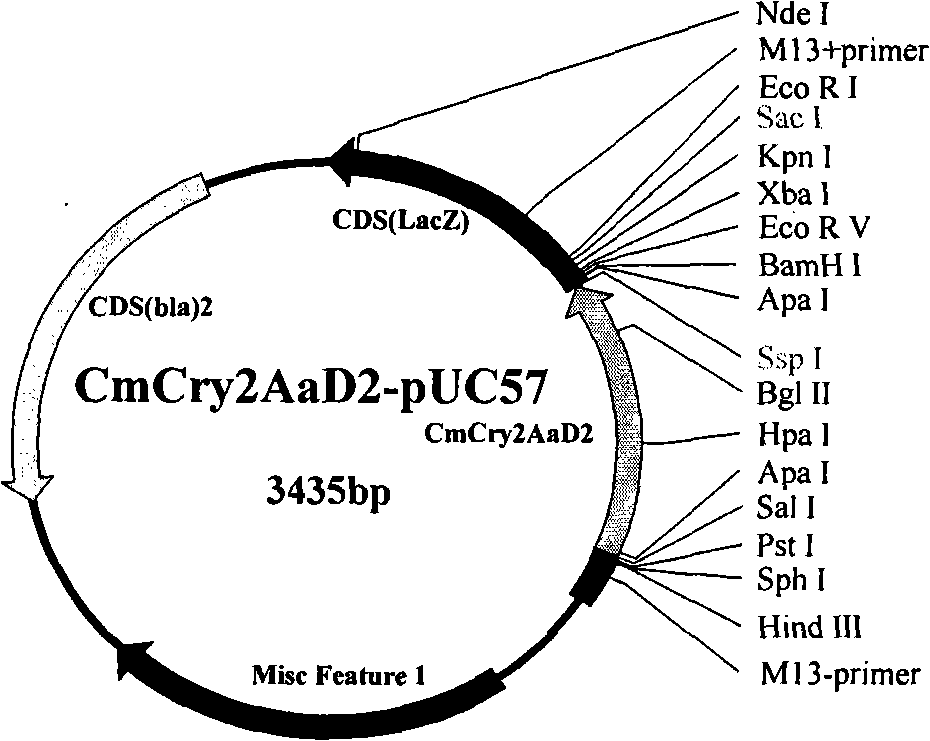
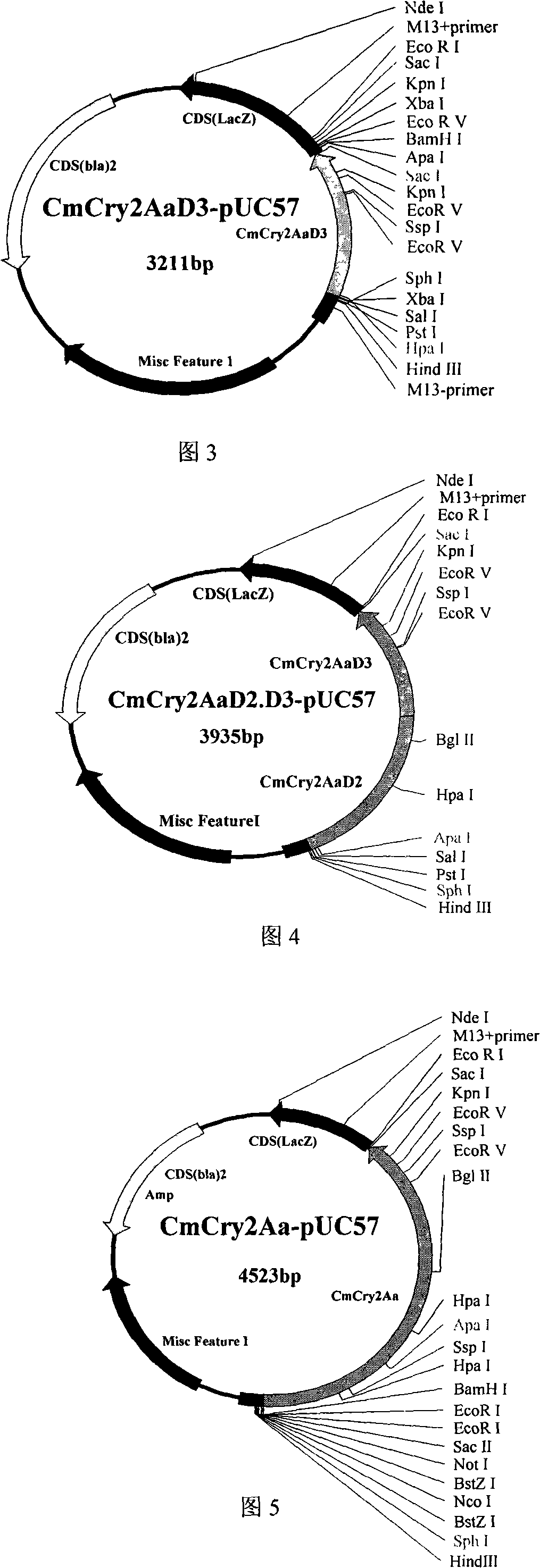
ActiveCN101255432AStrong resistancePromote activationClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesNicotiana tabacumTransgene
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering for plant, which provides an insect killing gene, encoded protein thereof and application of the same. The invention synthesizes CmCry2Aa insect killing protein gene by optimized codon design of cotton, and further obtains Cm1Cry2Aa insect killing protein gene which loses 29 amino acids at N terminal of the encoded protein, and constructs plant expression carrier respectively. Expert evidence of genetic modified tobacco indicates that CmCry2Aa and Cm1Cry2Aa insects killing gene has evident resistance to boll worm.
Owner:BIOCENTURY TRANSGENE CHINA
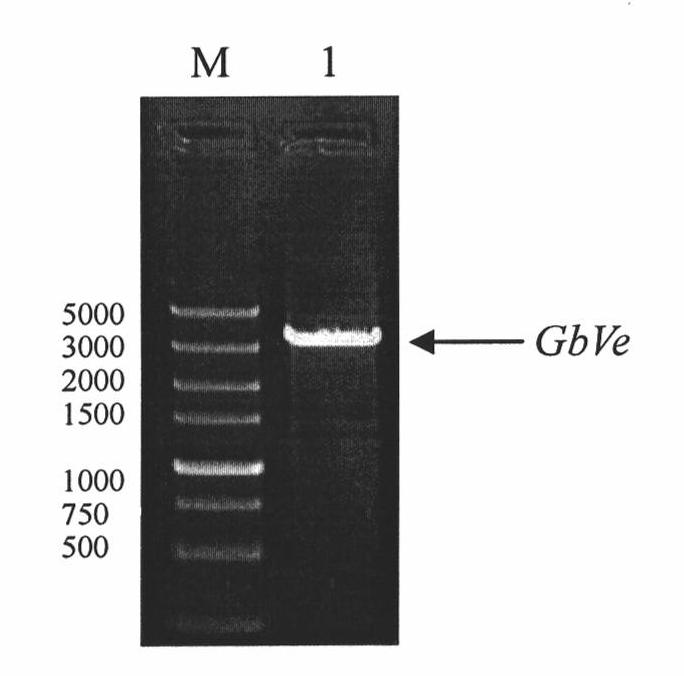
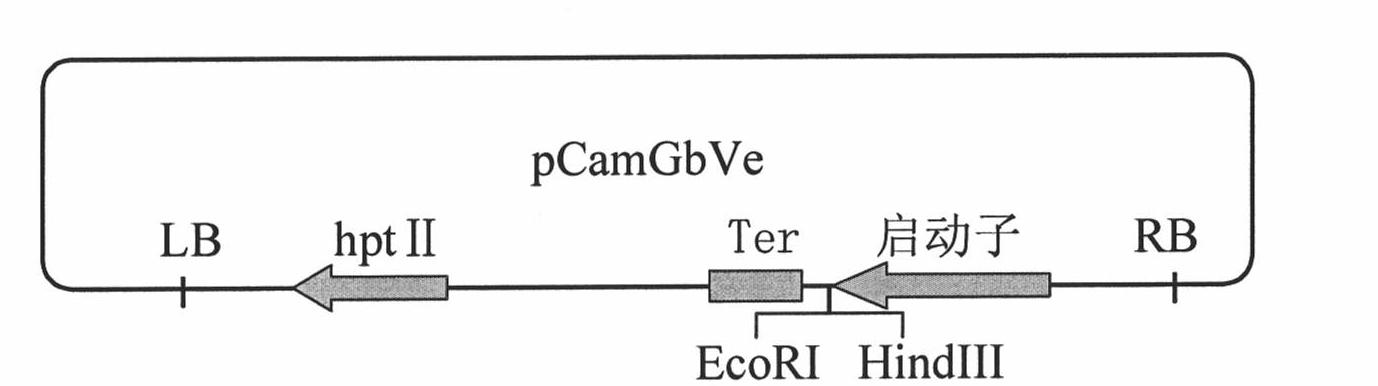
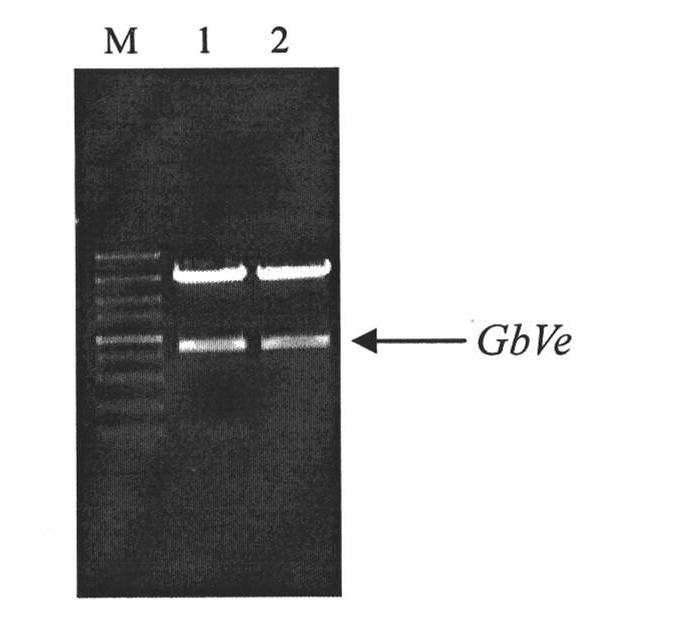
Cotton GbVe gene, protein coded thereby and use thereof in vegetable verticillium wilt resistance
InactiveCN101928338AVerticillium wilt resistance increasedHelps reveal molecular mechanismsFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention relates to cotton GbVe gene and a protein coded thereby. In the invention, a Ve gene associated with verticillium wilt resistance is obtained by cloning in a gossypium barbadense variety having high verticillium wilt resistance; a 5'-terminal GbVe gene fragment and a 3'-terminal GbVe gene fragment, which are obtained by amplification, are spliced; a primer capable of amplifying the full-length GbVe gene is designed and synthesized according to a gene sequence; the sequence of the full-length GbVe gene is obtained by the conventional colony sequencing method according to an RT-PCR technique; and the nucleotide sequence of the full-length GbVe gene is represented by SEQ ID No.1. In the invention; a new and important candidate gen is provided for vegetable verticillium wilt resistant gene project; and the obtained full-length GbVe gene and a vegetable expression vector constructed by the full-length GbVe gene lay a foundation for further transforming important crops for improving the verticillium wilt resistance of transgenic crops and have great economic benefits and application values.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
NAC transcription factor gene GmST2 of soybean holy bean No.9 and application of NAC transcription factor gene GmST2
ActiveCN102676541AImprove salt/drought toleranceImproves salt/drought toleranceGenetic engineeringFermentationSalt resistanceArabidopsis
The invention discloses an NAC (N-acetyl-L-Cysteine) transcription factor gene GmST2 of soybean holy bean No.9 and a plant expression vector of the GmST2. The invention further discloses application of the gene GmST2 in improvement on the salt resistant / drought tolerance in arabidopsis thaliana and soybean plants. Provided by tests, the salt resistance / drought tolerance of a transgenic plant is greatly improved compared with that of a non transgenic plant and theoretical base and practice foundation for improving the salt resistance / drought tolerance of crops through genetic engineering means are provided. The NAC transcription factor gene GmST2 can be widely applied to cultivation of salt-resisting / drought tolerant plant varieties.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
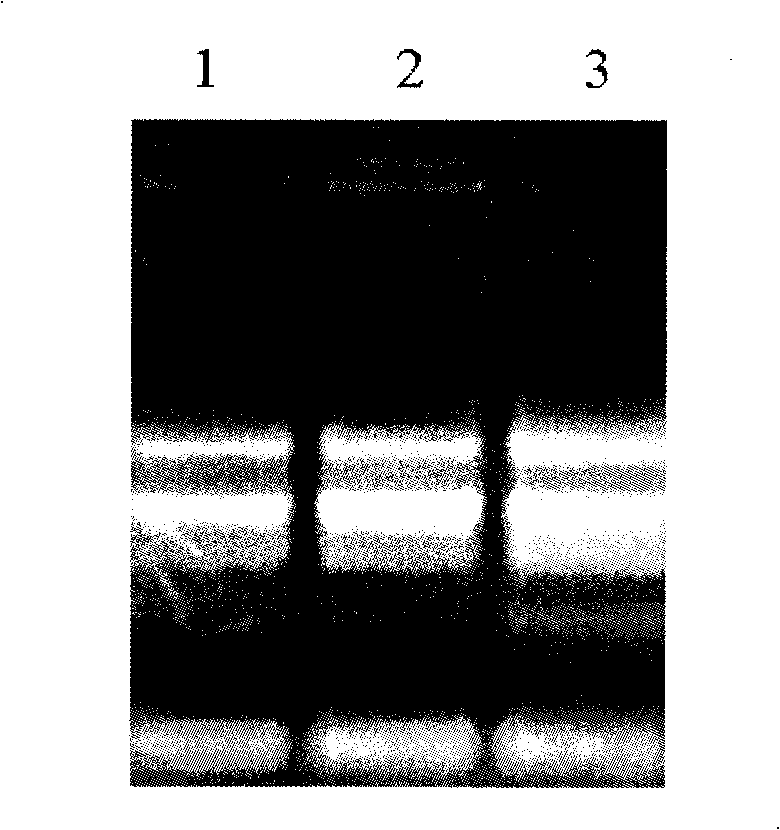
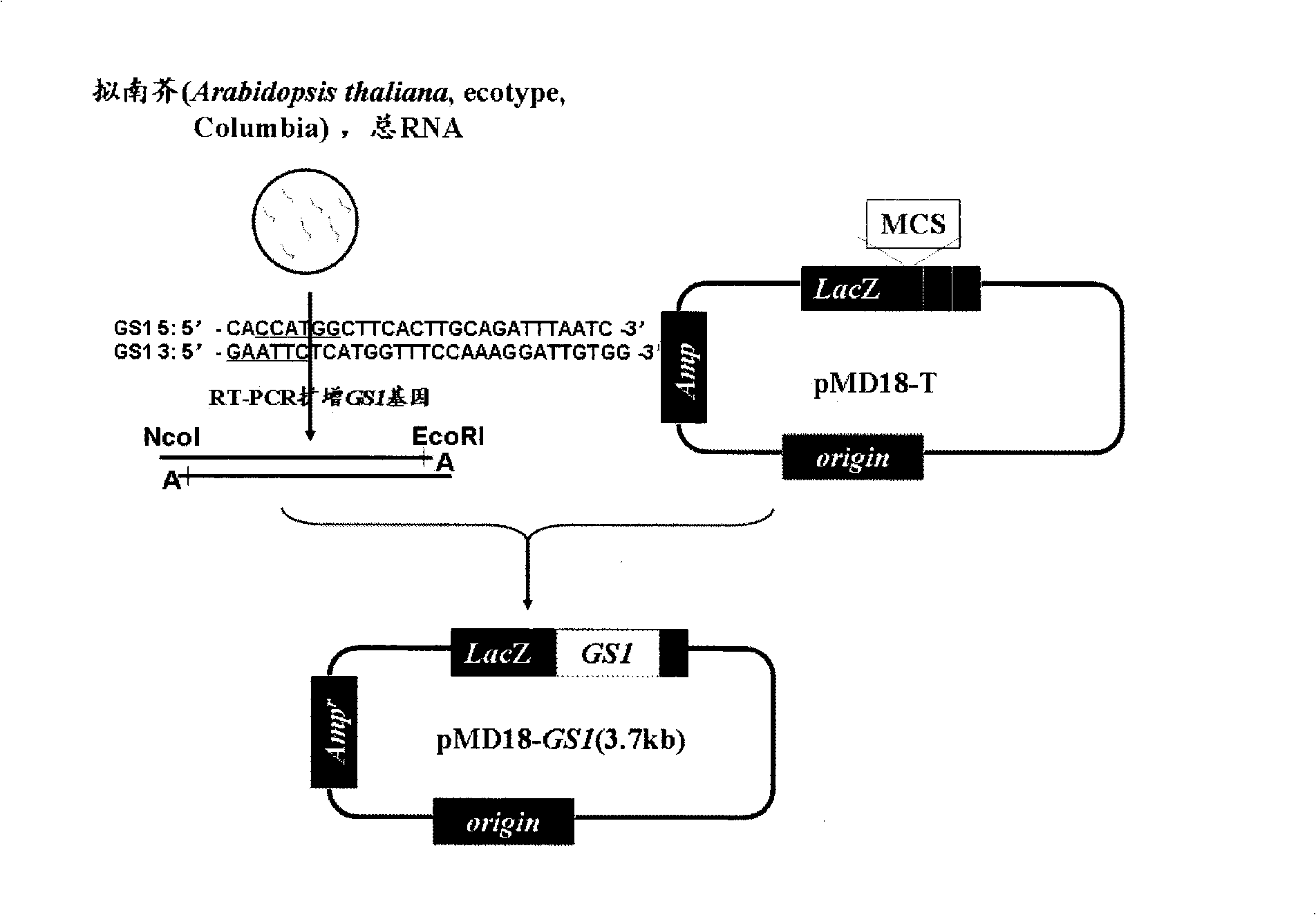
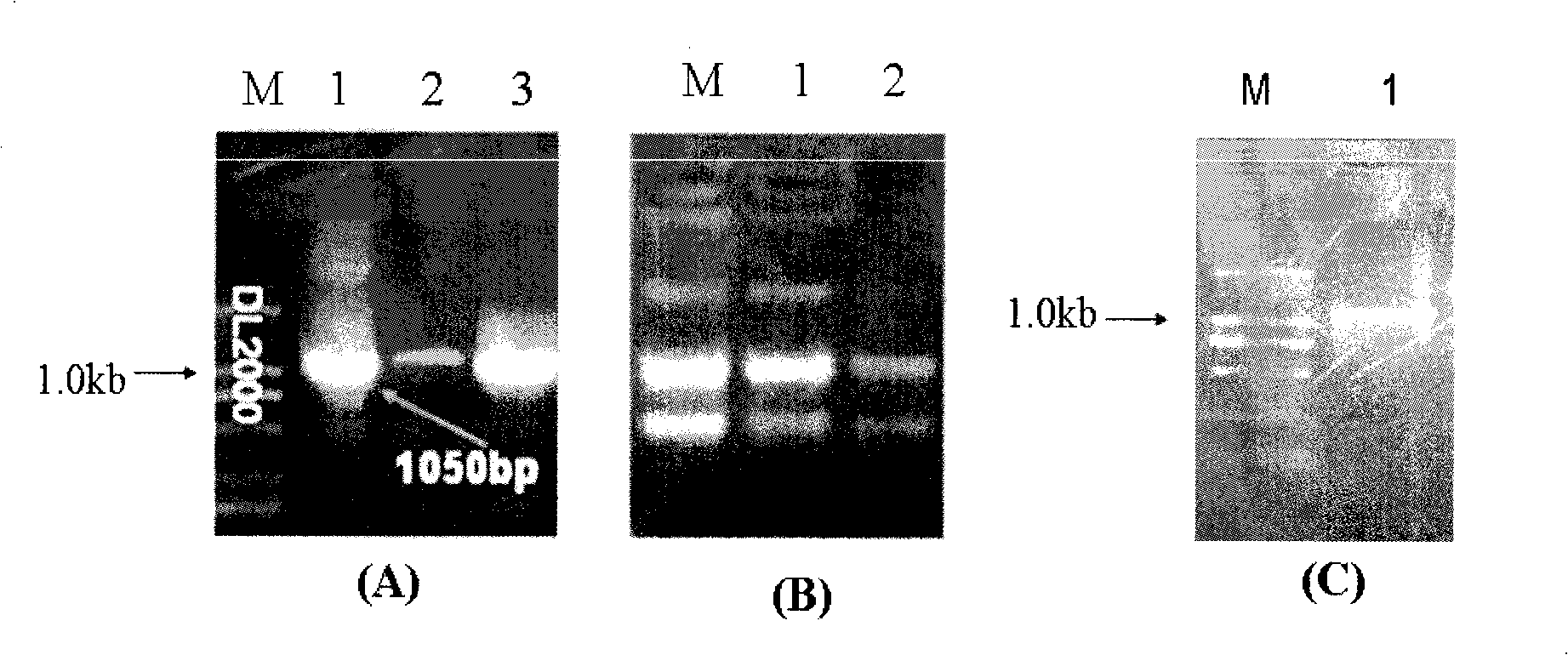
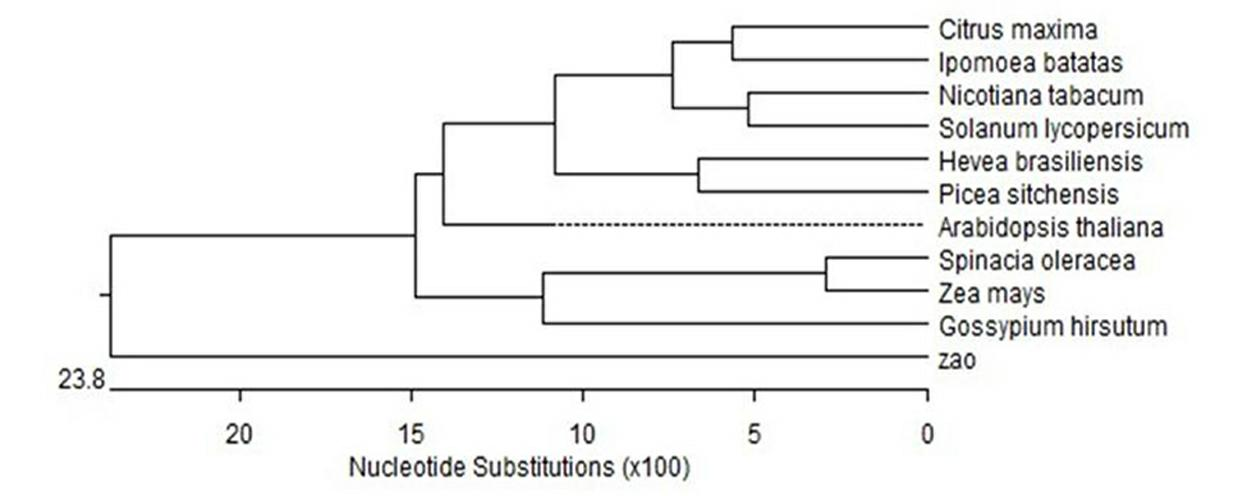
Construction and use of plant expression vector of Arabidopsis thaliana cytoplasm type glutamine synthetase gene
InactiveCN101407824AImprove nitrogen use efficiencyIncreased reassimilation capacityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsNicotiana tabacumLow nitrogen
The invention relates to a special plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-GS1 which comprises an arabidopsis thaliana cytoplasm glutamine synthetase gene GS1 and can improve the utilization rate of a plant nitrogen element. A method of RT-PCR is used for cloning the GS1 gene from the arabidopsis thaliana of a model plant, a photoinduction type promotor (the promotor of a a small subunit Rubisco) is used for controlling the excessive expression of the GS1 gene in a plant leaf and a leaf disc conversion method is used for transferring the GS1 gene into a pPZP221-PrbcS-Dof1 type transgene tobacco. An experiment result shows that the GS1 gene can be normally transferred in the transgene tobacco; under the nutrition condition of low nitrogen and the growing conditions of indoor irradiation for 24 hours of 2000LUX and 25 DEG C, the growing situation of the plant transferred with the single gene of Dof1 is (the expression of the gene is controlled by the photoinduction type promotor Prbcs) is a little better than that of a contrast tobacco (a wild type without transgene); after being transferred under the natural growing condition of a green house, the growing situation of the tobacco which is simultaneously transferred with the GS1 gene and the Dof1 gene shows remarkable growing advantages than that of the contrast plant; and therefore, simultaneously and excessively expressing the GS1 gene and the Dof1 gene, can improve the efficiency of the GS / GOGAT (glutamine synthetase / glutamic acid synthetase) approaches in the leaf more extensively, thereby improving the utilization rate of the plant nitrogen element. The vector can be broadly applied to the molecule breeding of crops, improving the utilization rate of the plant nitrogen element thereof and the durability to the nutrition condition of low nitrogen and being capable of obtaining a higher yield under the conditions of applying less fertilizers and even not applying the fertilizers.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Jujube tree ascorbate peroxidase gene and application thereof in improving stress resistance of plants
InactiveCN102161996AImprove stress resistanceClear molecular structureEnzymesGenetic engineeringEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, in particular relating to a jujube tree ascorbate peroxidase gene and application thereof in improving stress resistance of plants. The nucleotide sequence of the jujube tree ascorbate peroxidase gene and the amino acid sequence of the coding protein of the jujube tree ascorbate peroxidase gene are shown in sequence tables of SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2. In the invention, the jujube tree ascorbate peroxidase gene is obtained to construct a plant expression vector successfully transferred into an arabidopsis strain, and the salt tolerance of the jujube tree ascorbate peroxidase gene is evaluated, thereby proving that the jujube tree ascorbate peroxidase gene can be used for improving the salt tolerance of the plants. In addition, a prokaryotic expression vector constructed by the invention can be used for realizing induction and expression in escherichia coli. According to the invention, the first-time separation of the jujube tree ZjAPX (Ascorbate Peroxidase) gene is realized, and the gene can be used as a target gene transferred to the plants so as to improve the stress resistance, especially the salt tolerance of the plants, and has guiding significance in improving varieties of the plants, thereby providing test data and laying a theoretical basis for sufficiently utilizing the excellent-resistance gene ofjujube trees to improve the stress resistance of the plants.
Owner:AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT OF SHANXI PROVINCE +1
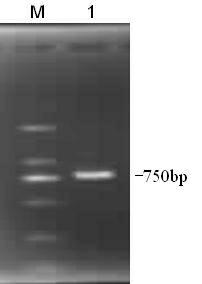
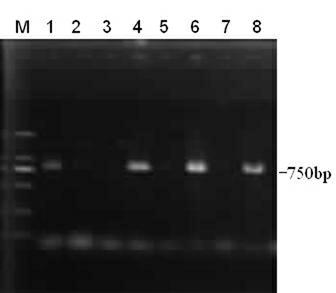
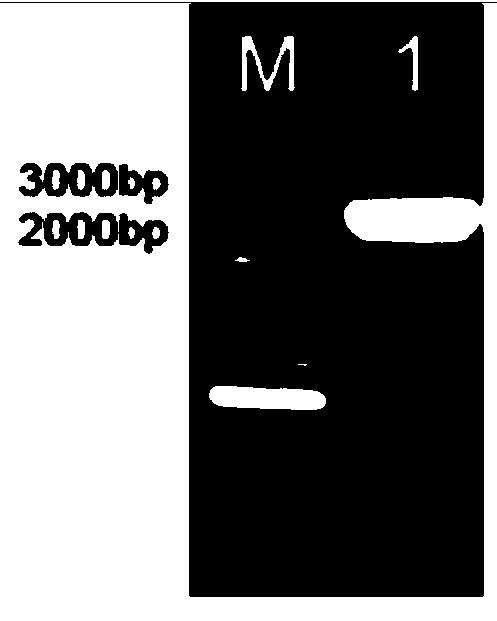
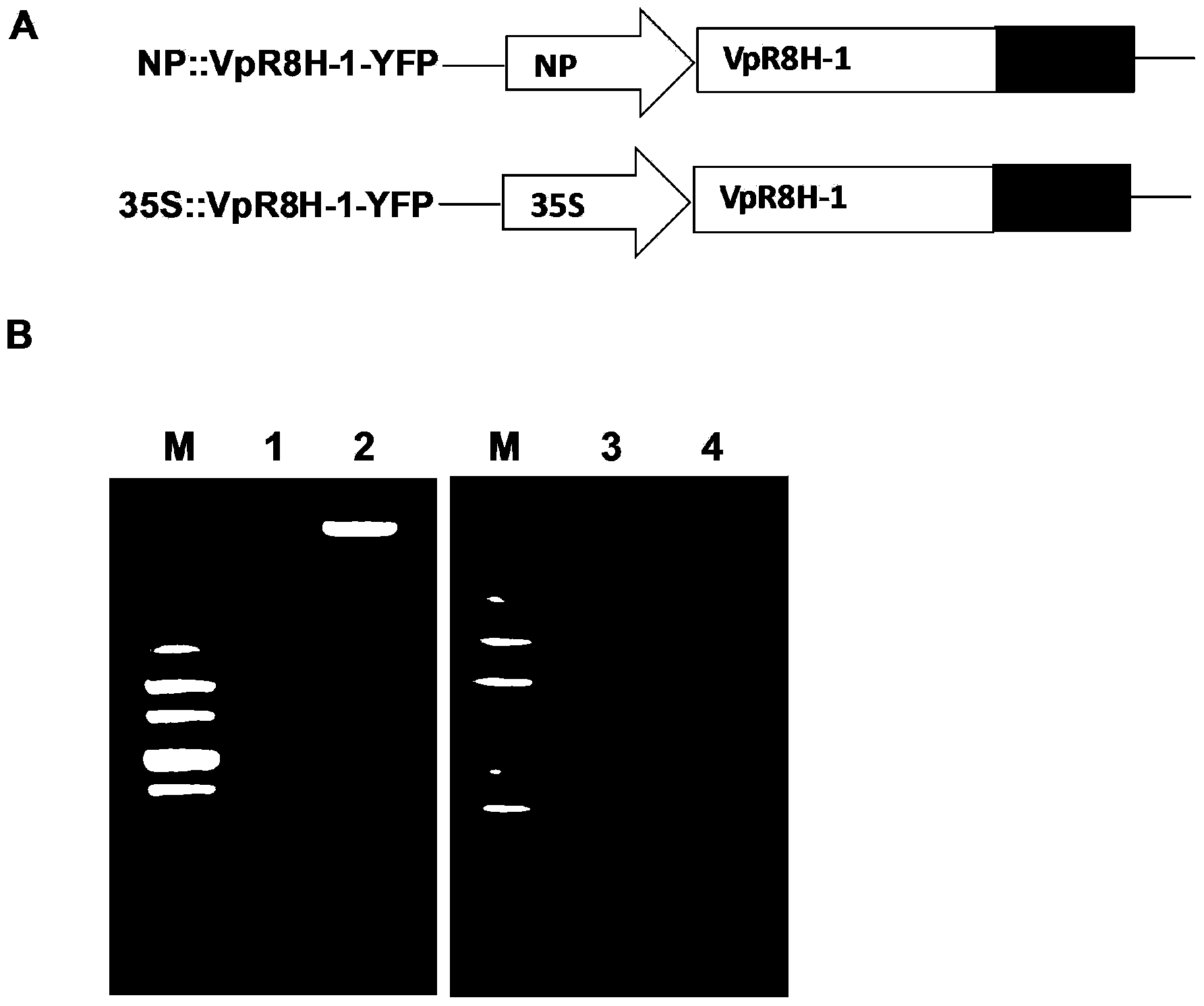
Specific grape powdery mildew resistant gene VpR8H-1 cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence and application of cDNA sequence
InactiveCN104357456AImprove disease resistanceResponsiveFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionOpen reading frameNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a specific grape powdery mildew resistant gene VpR8H-1 cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence and an application of the cDNA sequence. A VpR8H-1 gene is cloned from cDNA of leaves of Chinese wild vitis pseudoreticulata Baihe-35-1, the overall length of gDNA is 3136bp, the overall length of cDNA is 2448 bp, the gene comprises five exons and four introns, 815 amino acid is inferred and coded, an open reading frame sequence of VpR8H-1 is cloned to a plant expression vector, instantaneous conversion of tobaccos is performed, stable conversion of arabidopsis thaliana is performed, powdery mildew is inoculated, and specific positioning expression and disease resistant functions of the gene are verified. Functional analysis proves that the gene has specific positioning expression and disease resistant functions, can be directly applied to improve disease resistance of crops, and can further be indirectly used as a vector to improve the disease resistance of crops; and further, the VpR8H-1 gene has remarkable response to different hormones and biotic and abiotic stress, thereby having positive effects in the aspects of response to hormone treatment, biotic and abiotic stress and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
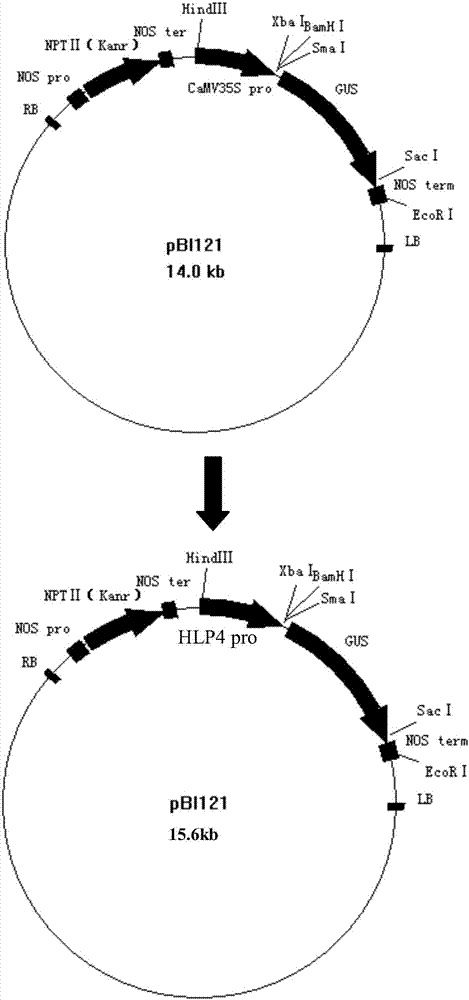
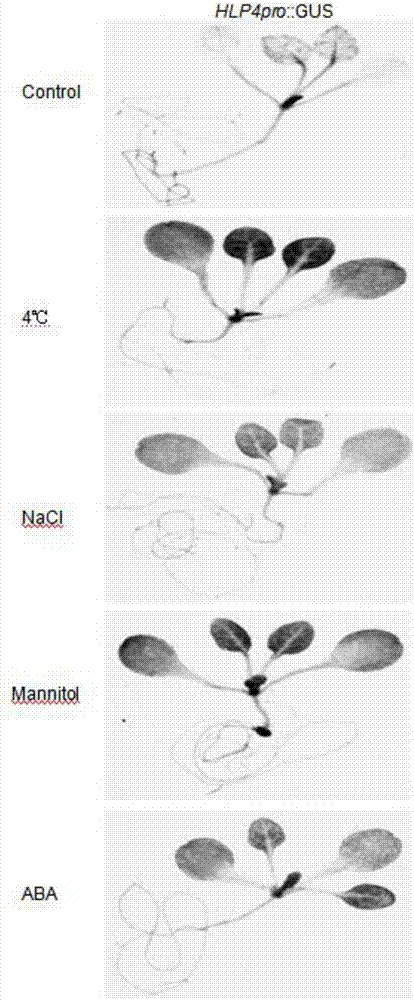
Promoter HLP4 induced by low temperature, high salinity, drought or ABA
ActiveCN107099535AImprove expression levelPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionTransgeneBiology
The invention discloses a promoter HLP4 induced by low temperature, high salinity, drought or ABA of arabidopsis. The nucleotide sequence of the promoter is as shown in SEQ ID No: 1, and the promoter is cloned from an arabidopsis genome by a PCR technology. The invention further discloses application of the promoter HLP4 in research of plant stress resistance genes or stress resistance gene engineering breeding. The promoter HLP4 constructs a plant expression vector of a reporter gene GUS to carry out plant transgenic operation so as to obtain a transgenic plant; and experiments prove that when the transgenic plant is treated under the conditions of low temperature, high salinity, drought and ABA, the expression activity of the reporter gene GUS is remarkably higher than the expression activity of a reporter gene GUS in a contrast group, it shows that the promoter HLP4 is a promoter which is highly induced by adverse situations, and the promoter HLP4 has huge application potential in research of stress resistance genes of plants and crop stress resistance breeding.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Coding hemaagglutinin gene of poultry influenza virus, plant expressing carrier and application thereof
InactiveCN1861793AHigh expressionImproving immunogenicityViral antigen ingredientsFermentationHemagglutininFowl
This invention discloses a new coding fowl influenza hemagglutinin protein gene VAIVHA and the construction, conversion and expression of the plant carrier. This gene can be highly expressed in the plant, and the expression value can be improved more than 40 times than the wild fowl influenza hemagglutinin gene. The gene transfer plant can be directly feed on the animal, or the protein extraction and purified protein immunize the animal, and the protection result of it is good. This shows that the gene plant has the ability to prevent the fowl influenza.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
Application of lilium regale wilson pathogenesis-related protein 10 gene LrPR10-5
InactiveCN104131015AIncrease resistanceReduce usageMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomicsNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses an application of a lilium regale wilson pathogenesis-related protein 10 gene LrPR10-5. A nucleotide sequence of the LrPR10-5 is as shown in SEQIDNO:1, and the pathogenesis-related protein 10 gene is encoded. The research proves that the LrPR10-5 gene has the function of improving the plant antifungal capability by functional genomics-related technologies, the antifungal LrPR10-5 gene is built on a plant expression vector and is switched into tobacco to perform overexpression, the transgenic tobacco plant has strong in-vitro antifungal activity in the result, and the experiment result shows that the transgenic tobacco for overexpression of the LrPR10-5 has an obvious inhibiting effect on growth of a plurality of fungi, such as botrytis cinerea, rhizoctonia solani and sclerotinia sclerotiorum.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
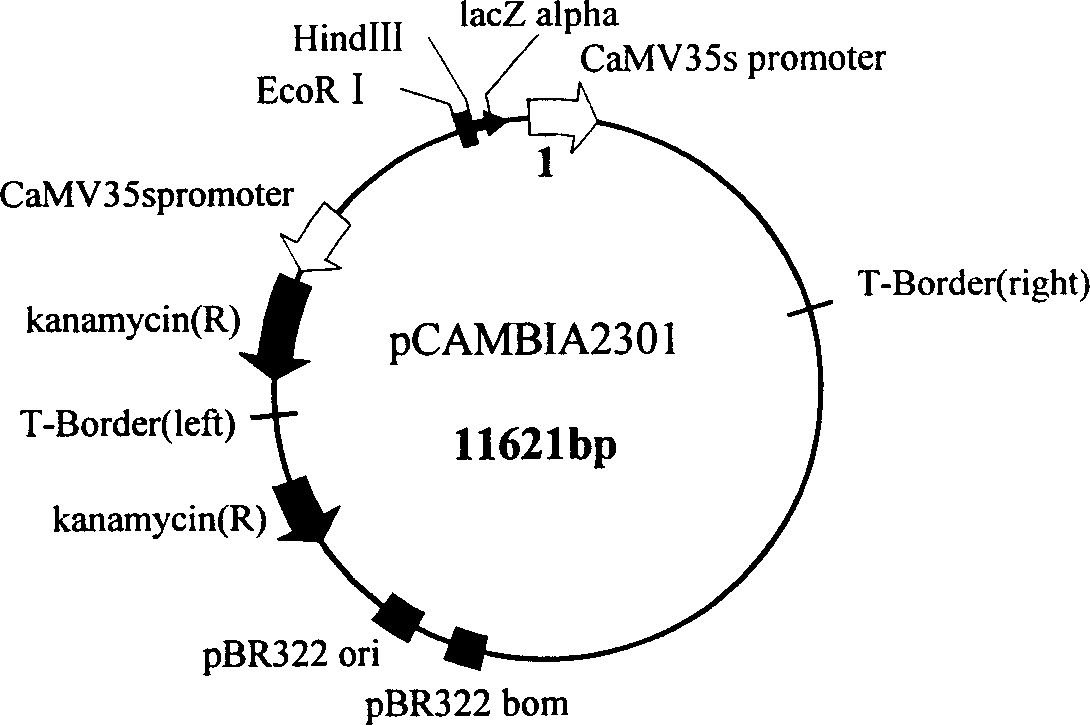
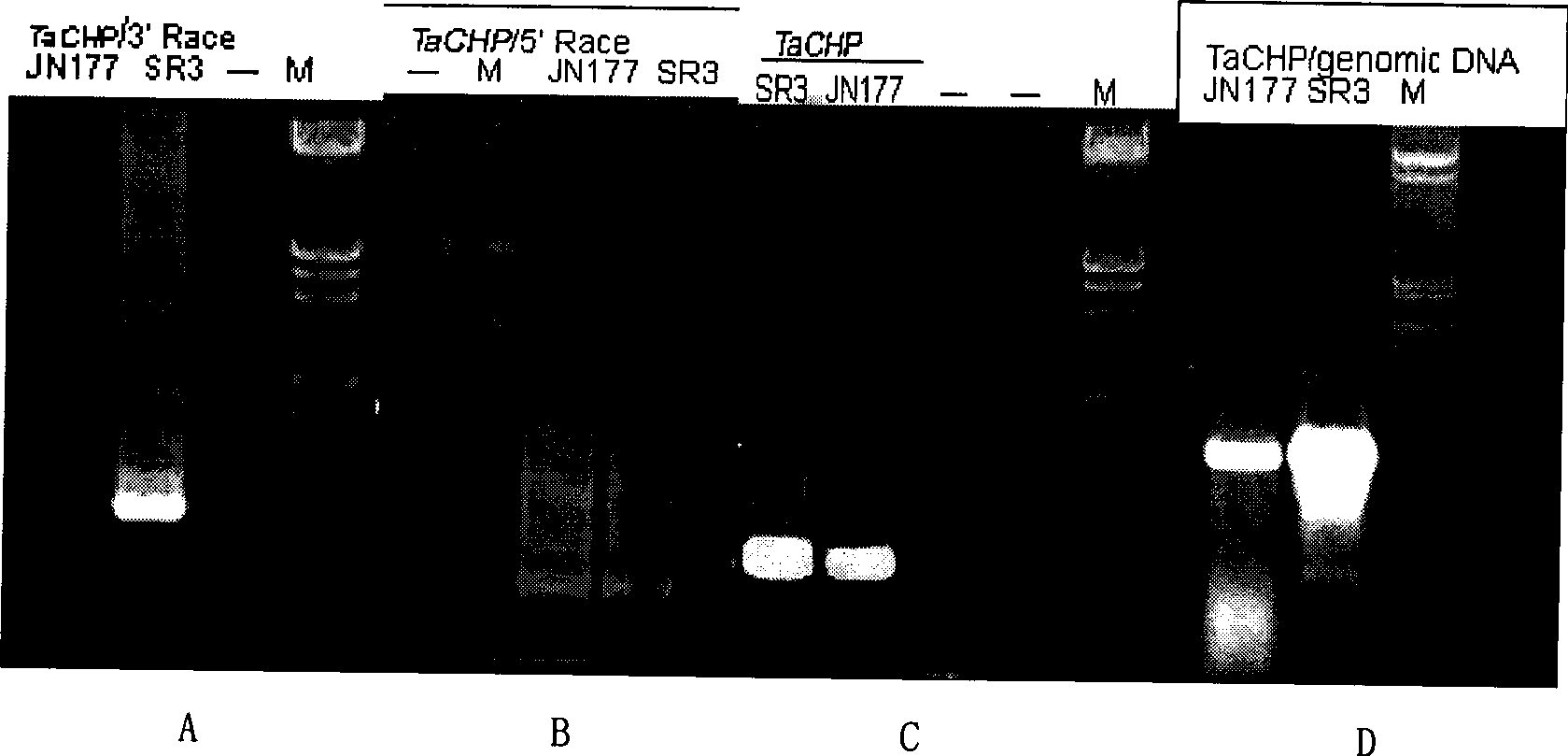
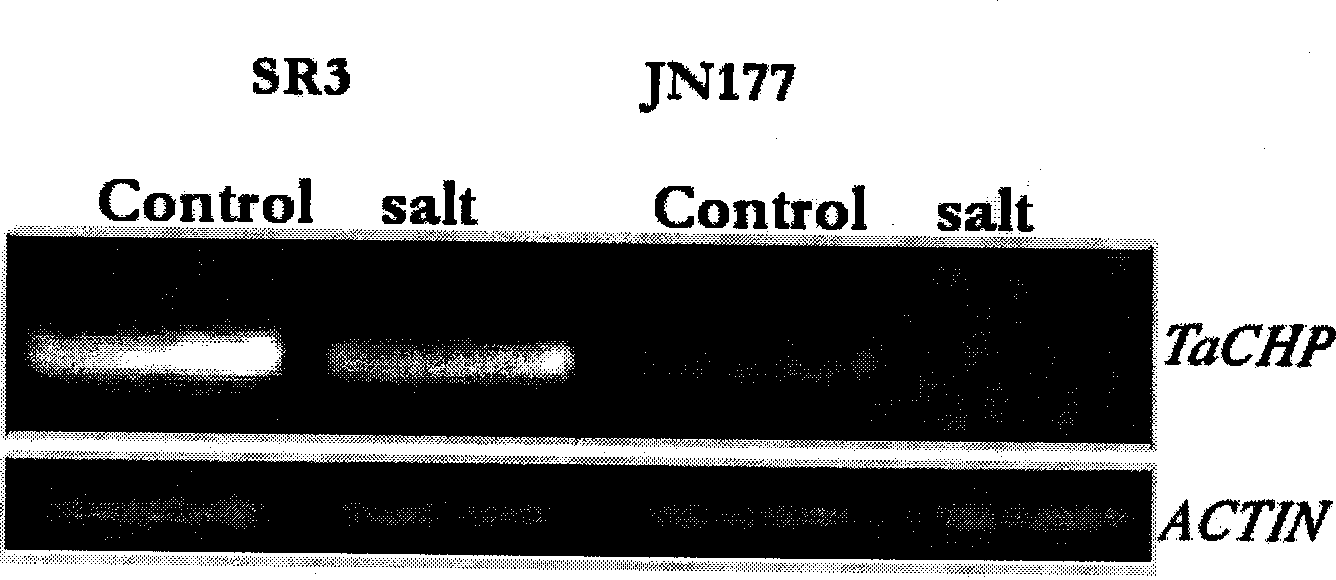
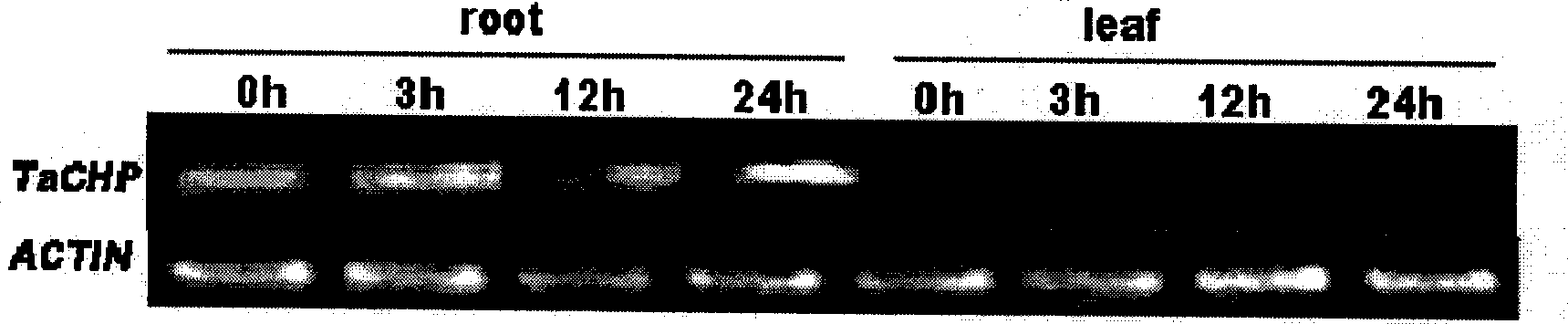
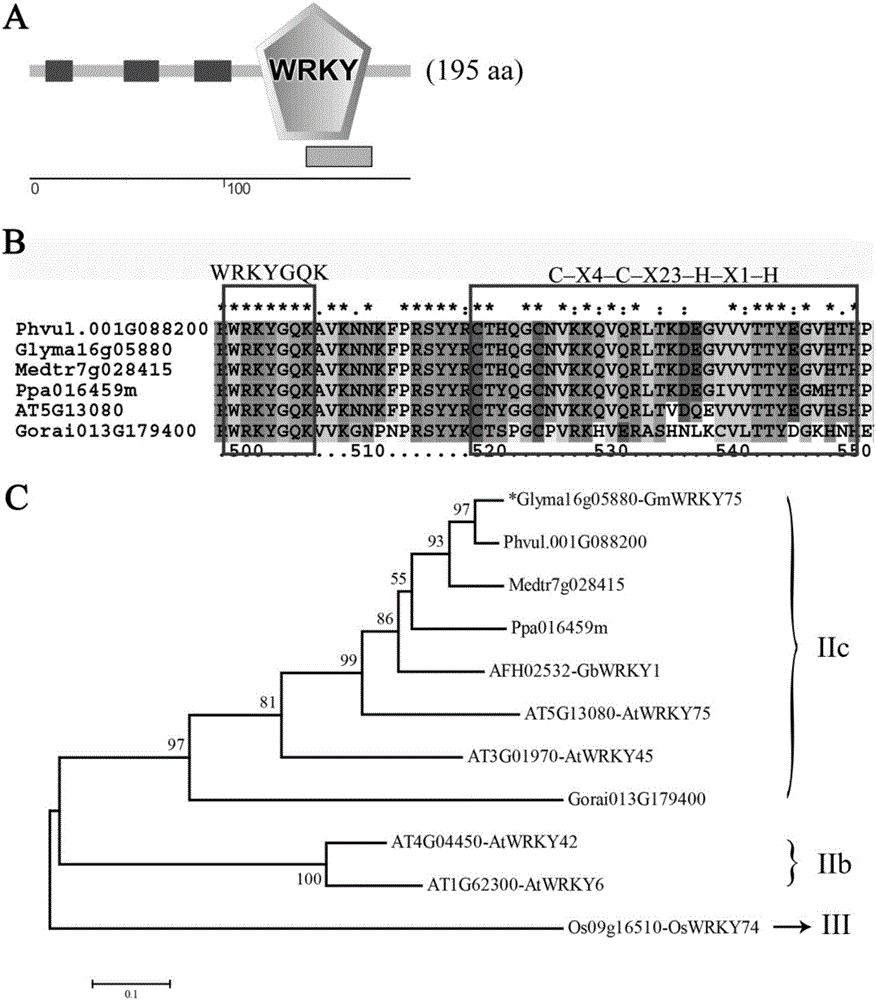
Wheat salt tolerance gene TaCHP and use thereof
InactiveCN101481693AImprove salt toleranceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceSalt Tolerant Plants
The invention discloses a salt tolerant gene of wheat, namely CHP zinc finger protein gene TaCHP of wheat and a plant expression vector containing the gene TaCHP. The invention also discloses an application of the gene TaCHP to culturing a salt tolerant plant, in particular culturing the wheat. Experiments prove that the salt tolerant ability of the transgenic plants of the invention is improved obviously.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
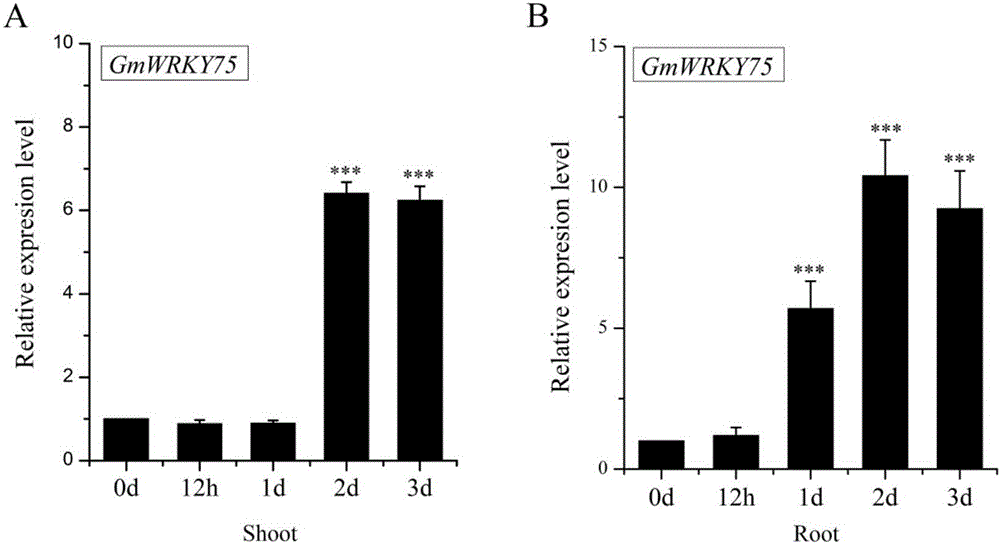
Soybean phosphorus starvation transcription factor GmWRKY75, encoded protein and application of phosphorus starvation transcription factor GmWRKY75
InactiveCN106244594APositive regulationIncreased total phosphorus contentNucleic acid vectorPlant peptidesNucleotideLateral root
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and in particular discloses a phosphorus starvation transcription factor GmWRKY75, an encoded protein and an application of the phosphorus starvation transcription factor GmWRKY75. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is as shown in Seq ID NO.1. According to the invention, it discovers that by transforming plant cells by virtue of any one plant expression vector in which the exogenous gene GmWRKY75 can be imported, a transgenic plant for over-expression of the GmWRKY75 can be obtained, and in comparison with a non-transgenic plant, the total phosphorus content of the transgenic plant is significantly increased and the development of lateral roots and root hair is obviously inhibited. The gene disclosed by the invention, as a target gene, can be imported into plants, so that the absorption of phosphorus element to transgenic plants is enhanced; therefore, the gene has an important significance for breeding a soybean variety which achieves the efficient utilization of phosphorus.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Wheat salt-tolerant gene TaOPR and application thereof
InactiveCN102121008AImprove salt toleranceVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyLotus japonicus
The invention discloses a wheat salt-tolerant gene TaOPR, a plant expression vector pSTART-TaOPR or pXQUbi-TaOPR containing the gene, and application of the gene TaOPR and the expression vector thereof in salt-tolerant plants, particularly arabidopsis thaliana or common wheat. Proved by experiments, the salt tolerance of the transgenic plants is obviously improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for producing meat chicken on a large scale by artificial planting grass and free raising
The present invention discloses meat chicken raising method of artificial planting grass and free raising. The artificial grass land is planted in grass land and through reclamation, land preparation, applying fertilizer, seeding white clover, Lotus japonicus, perennial ryegrass and dayflower, weeding and other measures. After the grass grows to cover 90 % over land and height over 20 cm, meat chicken may be raised freely in the pasture. The present invention has the advantages of low feed cost, high chicken quality, less diseases, good taste of chicken, no problem of disposing chicken manure, etc. and is favorable to maintaining soil and water and protecting environment.
Owner:吴启进 +2
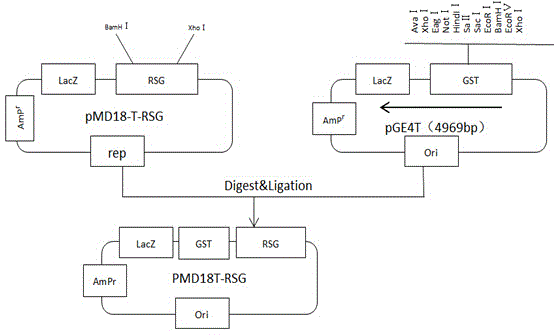
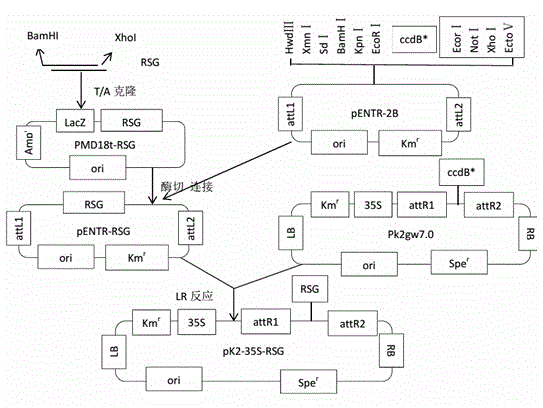
Plant expression vector with nicotiana tabacum gibberellins synthesis transcription regulation factor gene, and application of plant expression vector
ActiveCN104928317AHigh gibberellin contentLow gibberellin contentVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyLotus japonicus
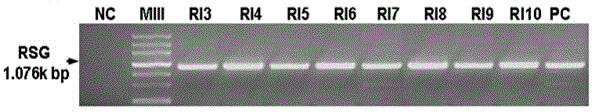
The invention discloses a plant expression vector with a nicotiana tabacum gibberellins synthesis transcription regulation factor gene, and application of the plant expression vector, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The cDNA of the nicotiana tabacum gibberellins synthesis transcription regulation factor gene, namely an RSG gene, is used for constructing the plant expression vector pk2-35S-RSG; agrobacterium tumefaciens are mediated into plants, so that the plant resistance to aluminum stress is improved, and the shortcoming that the aluminum stress resistance of the plants is low is overcome; experimental results show that through overexpressing gibberellins synthesis transcription factor gene, namely, the RSG gene, in nicotiana tabacum, the resistance of nicotiana tabacum to the aluminium stress is improved, relatively higher concentration aluminum stress almost has no influence on the growth of nicotiana tabacum roots; the significant increase of the gibberellins content also illustrates that the aluminium resistance of RSG overexpressed transgenic nicotiana tabacum is higher than that of wild type nicotiana tabacum under high-concentration aluminum stress.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
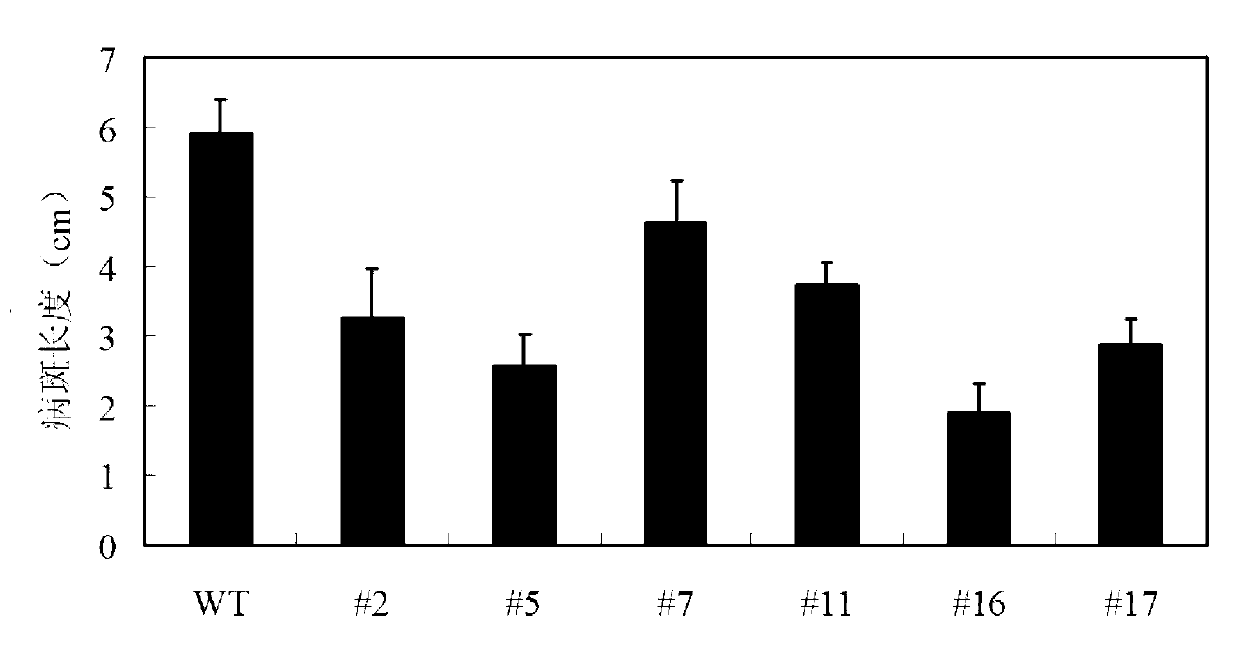
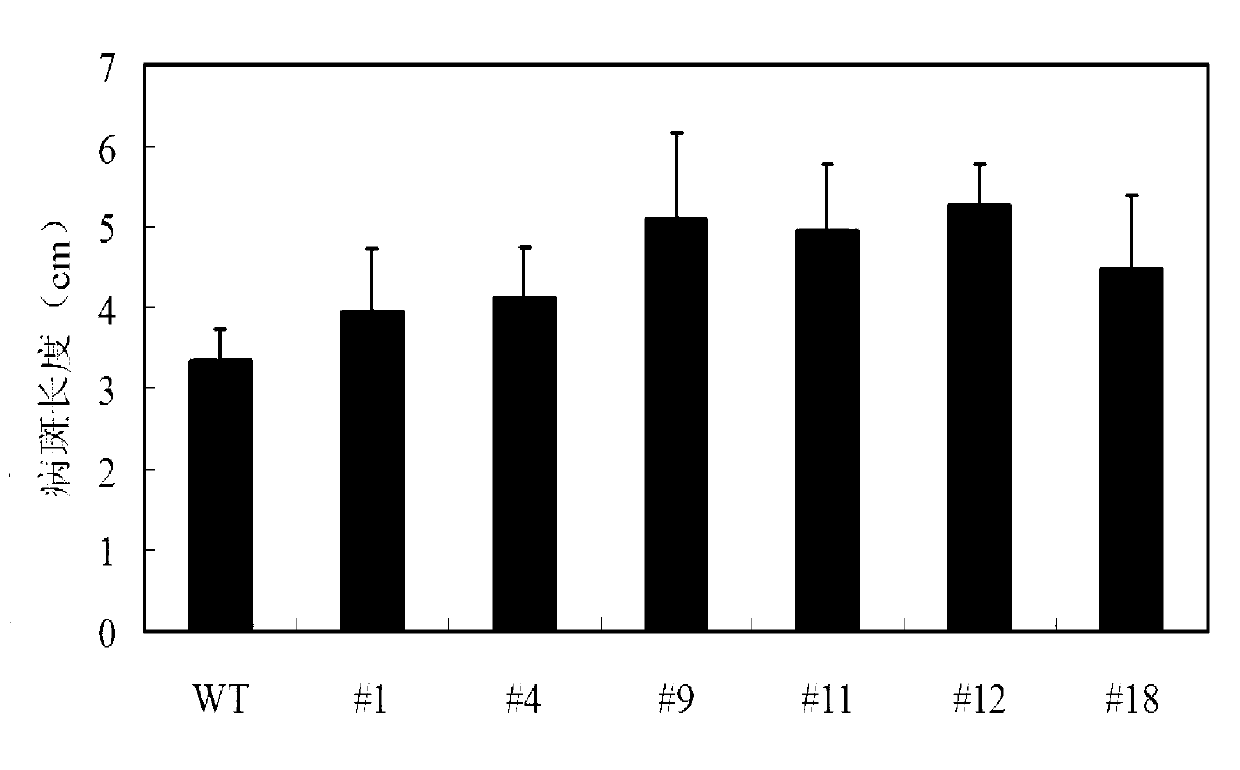
Lotus japonicus ERF transcription factors as well as encoding gent, expression vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a lotus japonicus ERF transcription factors as well as an encoding gent, an expression vector and application thereof. The ERF transcription factor cDNA is obtained by isolating from lotus japonicus and has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The invention also provides the expression vector and a host cell containing the transcription factor cDNA. Functional analysis experiments show that by overexpressing ERF transcription factor cDNA in plants, the resistance of plants against adversity stress comprising high salt, drought, low temperature and the like can be effectively enhanced or improved. The invention further provides the application of the ERF transcription factors in improvement on adversity stress resistance of plants or breeding of new varieties of adversity-stress-resistant transgenic plants. The application is achieved by the following steps: constructing a recombinant plant expression vector containing the ERF transcription factor cDNA; transforming the recombinant plant expression vector into cells of the plants, and breeding and screening to obtain the transgenic plants with improved adversity stress resistance.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Method for Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of sugarcane growth points
ActiveCN111893138AImprove infection abilityAchieve interactionGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyLotus japonicus
The invention discloses a method for Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of sugarcane growth points, and belongs to the technical field of sugarcane cultivation. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a genetically transformed sugarcane material, a strain and plasmid, preparing a callus induction medium M1, a differentiation medium M2, a rooting medium M3, a transformation medium MR and a co-medium M4, inducing and differentiating sugarcane callus, preparing an Agrobacterium engineering bacterial solution, using an Agrobacterium-mediated method to perform genetic transformation on the sugarcane growth points, and testing transgenic plants. The method shortens the time for sugarcane to obtain transformed plants, and improves the transformation efficiency. Through theAgrobacterium-mediated transformation technology, a pCAMBIA3301 plant expression vector is introduced into GT35 sterile seedlings, a total of 353 resistant plants are obtained after screening by a screening medium, the resistant plants are tested by PCR, 333 plants are positive, a positive rate reaches to 94.33%, and thereby the result indicates that the foreign gene is successfully introduced into sugarcane.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
New CkNHX gene and shearing decorative gene CkNHXn, method for cultivating inverse-resistant plant
ActiveCN101037693AStrong salt toleranceImprove salt tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationYeastSalt resistance
The invention provides a novel CkNHX genen and excision adorn gene CkNHXn thereof. The gene stems from Caragana korshinskii Kom, its gene codes Na+ / H+ antiporter gene. The cDNA obtained by clone constructs yeast expression carrier and plant expression carrier. The yeast mutant strain vertifies salt resistance thereof by complament experiment. Moreover, a transgenic plant is also obtained. By testing salt resistance of transformed plant, transformation of the gene can make the transgenic plant with salt resistance.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
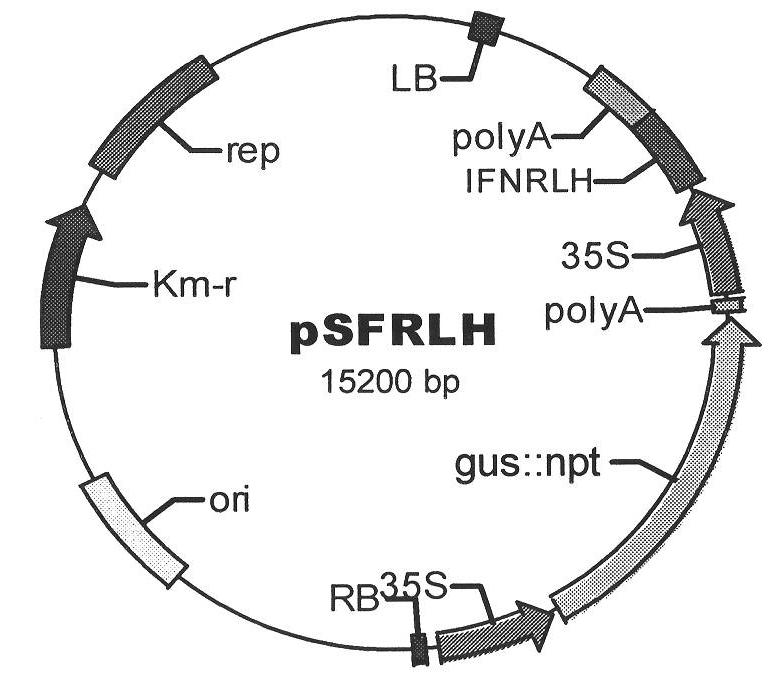
Plant expression vector and construction method thereof, and method for producing chicken alpha interferon by utilizing crowtoe as bioreactor
InactiveCN102121029AExtensive managementLong grass seasonFermentationHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyWestern blot
The invention relates to a plant expression vector and a construction method thereof, and a method for producing chicken alpha interferon by utilizing crowtoe as a bioreactor, belonging to the technical field of biology. The plane expression vector pSFRLH is shown as the figure 1 in the specification. In the invention, main stem sections, rachis stem sections and tender leaves of crowtoe are used as explants, and a constructed plane expression vector chicken alpha interferon gene ChIFN-alpha is subjected to genetic transformation and regeneration and then subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction), Southern blot, Western blot and ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay). Proved by a detection result, the ChIFN-alpha gene is integrated into a crowtoe chromosome genome and correctly transcribed, translated and expressed, and recombinant protein can be neutralized by a ChIFN-alpha antibody. The invention lays the foundation for producing animal medical protein by utilizing crowtoe pasture grass as a bioreactor and provides a new thinking for the control of animal epidemic diseases.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Mutant gene and mutant of corn gibberellin oxidase, expression vector and applications
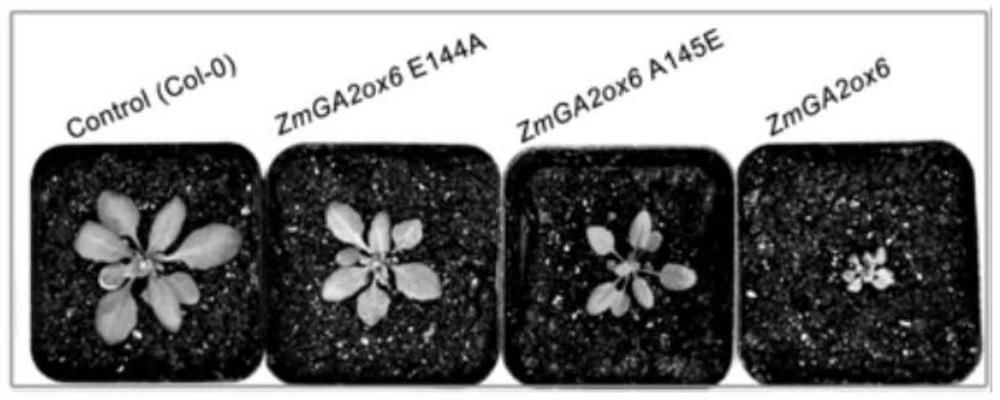
ActiveCN111778265AReduce plant heightImprove drought toleranceOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
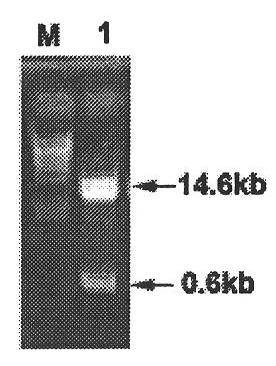
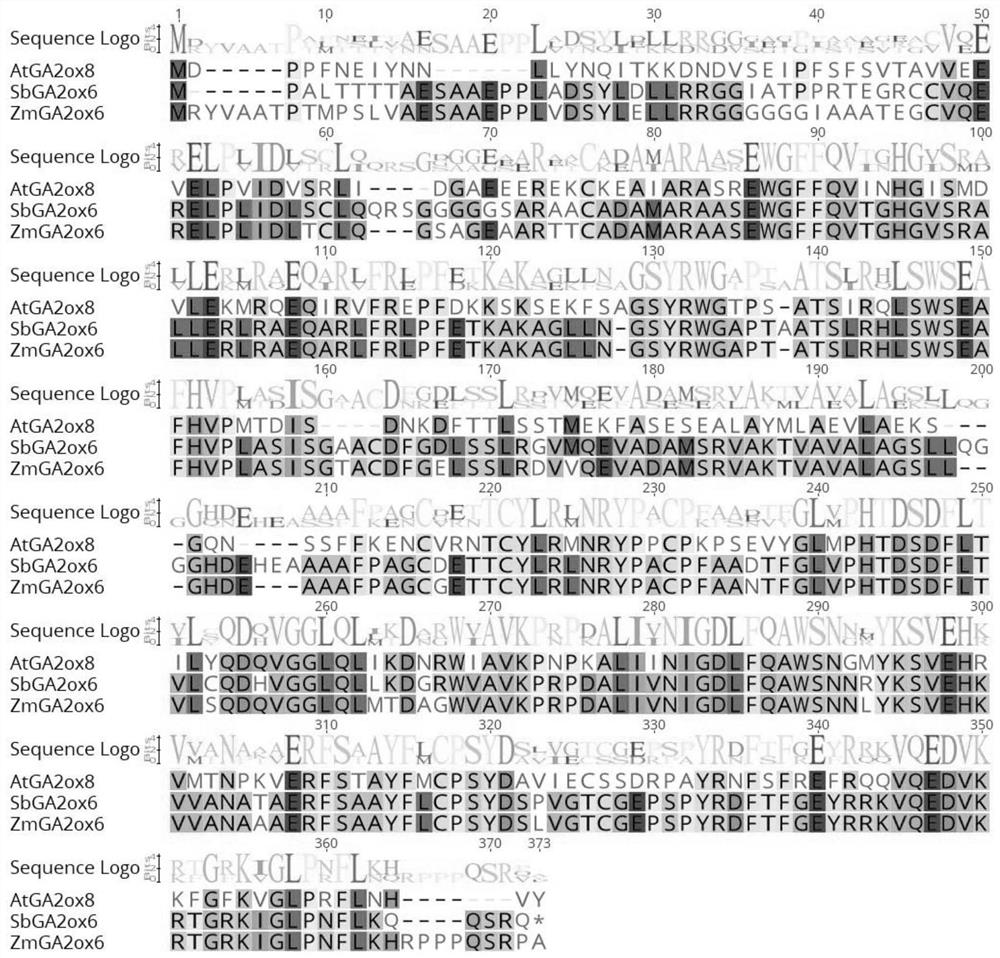
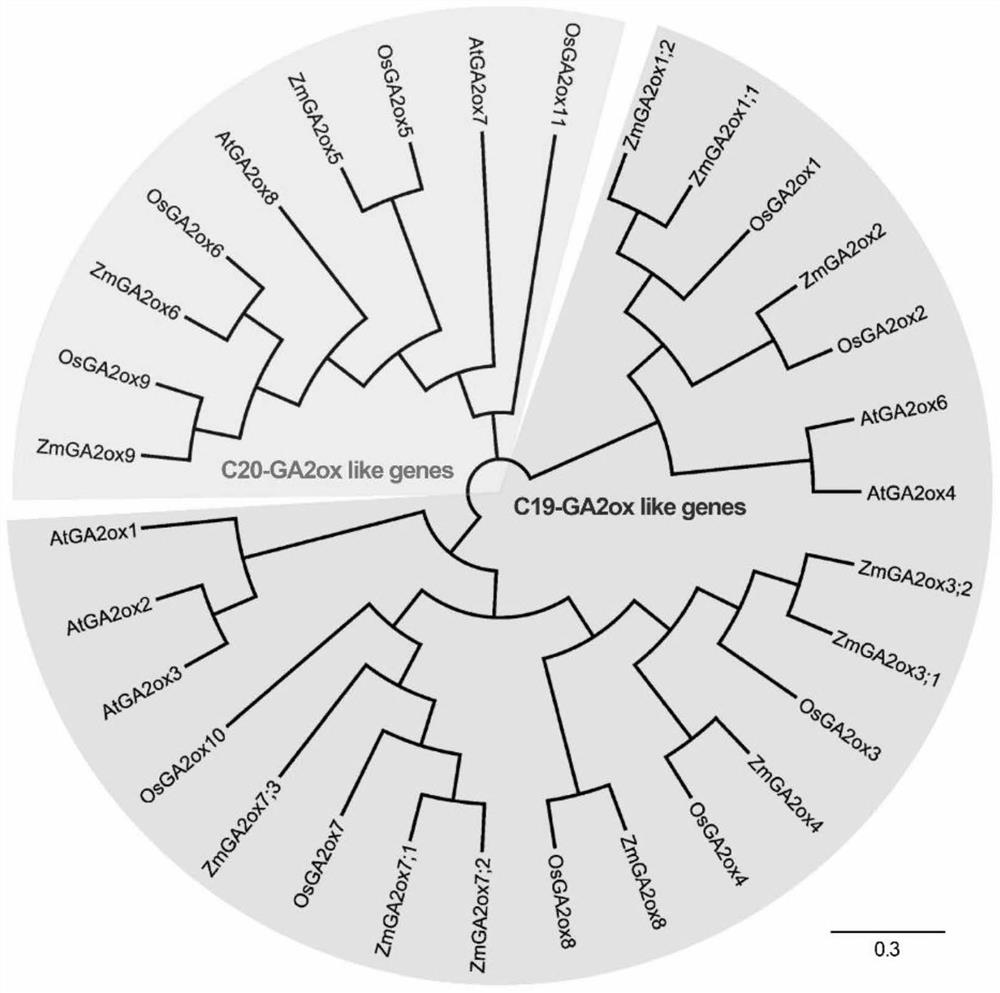
The invention is suitable for the technical field of molecular biology, and provides a mutant gene and mutant of corn gibberellin oxidase, an expression vector and applications. The nucleotide sequence of the original gene of the corn gibberellin oxidase is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 in a sequence table, and the nucleotide sequence of the mutant gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 or SEQ ID NO: 3 in the sequence table. The mutant gene of the corn gibberellin oxidase provided by the embodiments can be used for building the plant expression vector to convert into crops such as arabidopsis thaliana; the life states such as phenotype and survival rates of transgenic arabidopsis thaliana can be observed before and after drought stress treatment; and through the indication of results, the mutant gene of the corn gibberellin oxidase can lower the plant height of plants such as the arabidopsis thaliana and can also enhance the drought tolerance of the arabidopsis thaliana and other plants.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com