Patents
Literature
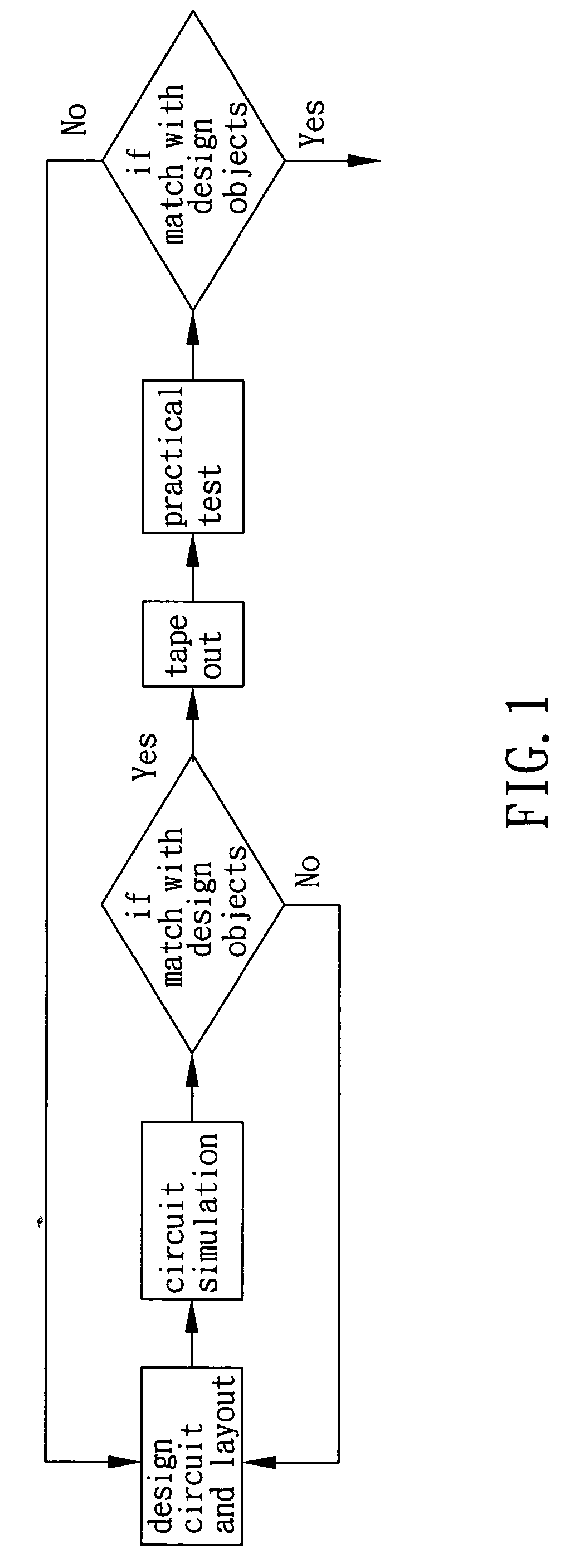
115 results about "Tape-out" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics design, tape-out or tapeout is the final result of the design process for integrated circuits or printed circuit boards before they are sent for manufacturing. The tapeout is specifically the point at which the graphic for the photomask of the circuit is sent to the fabrication facility. A synonym used at IBM is RIT (release interface tape). IBM differentiates between RIT-A for the non-metallic structures and RIT-B for the metal layers.
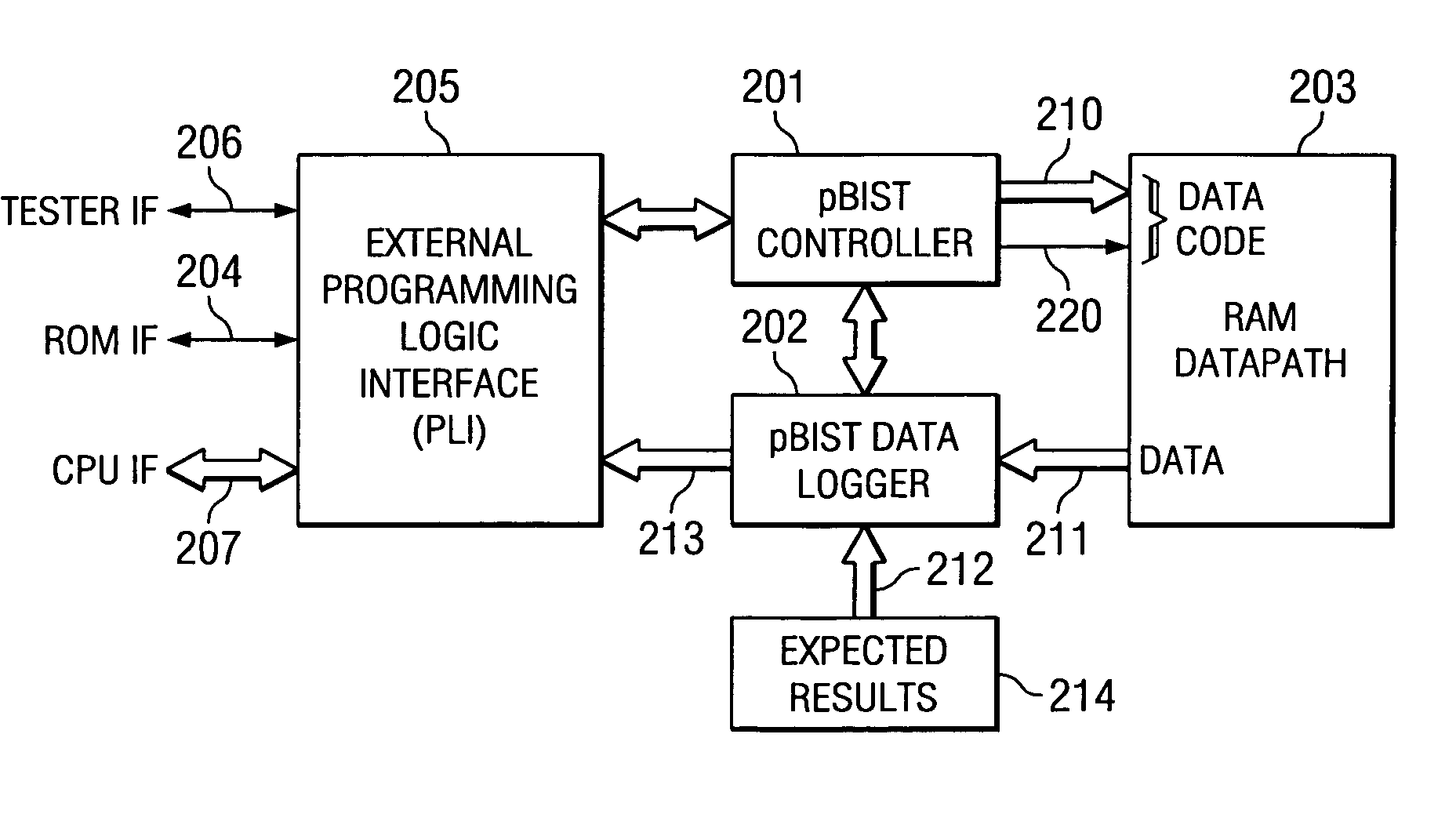
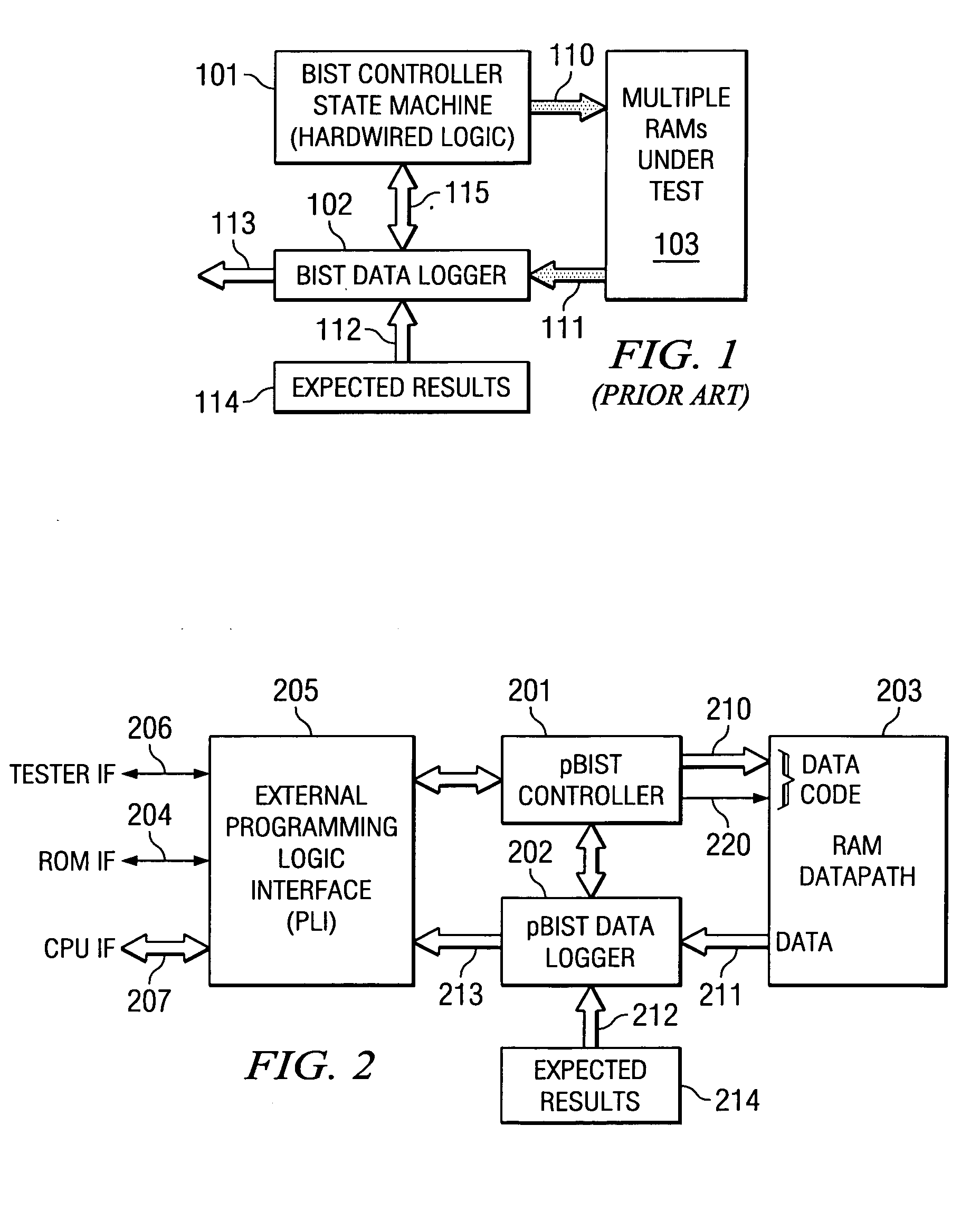
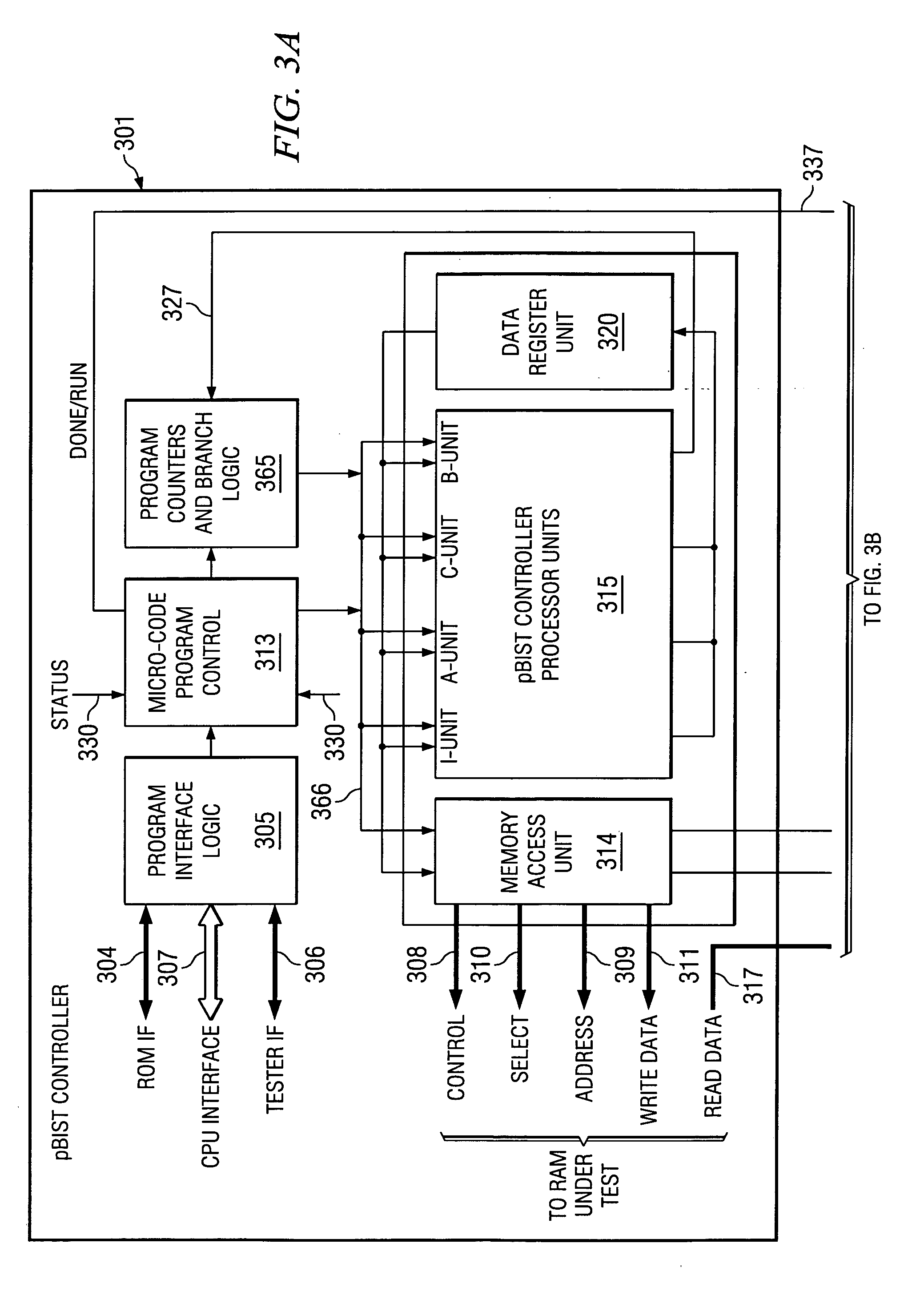
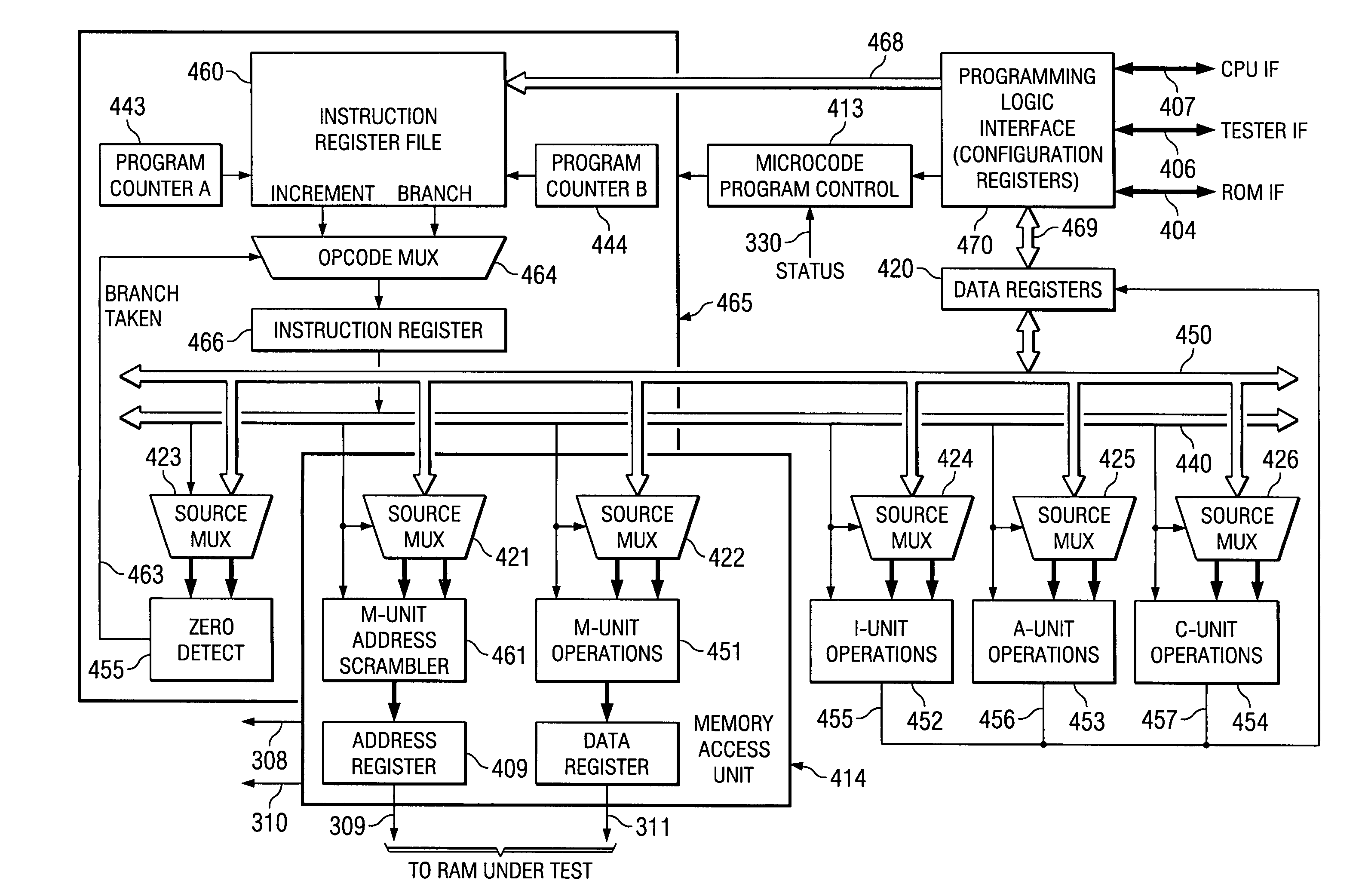
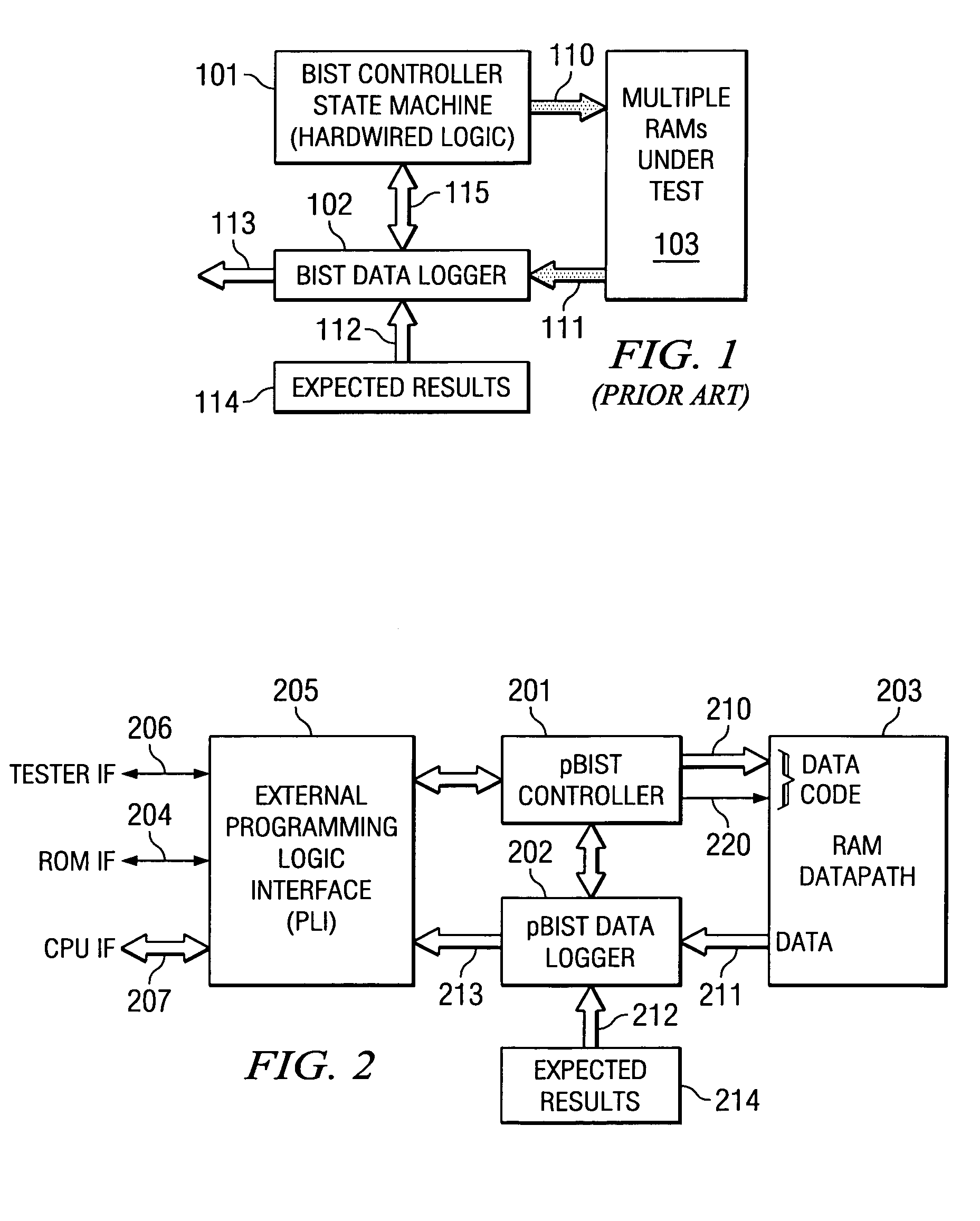
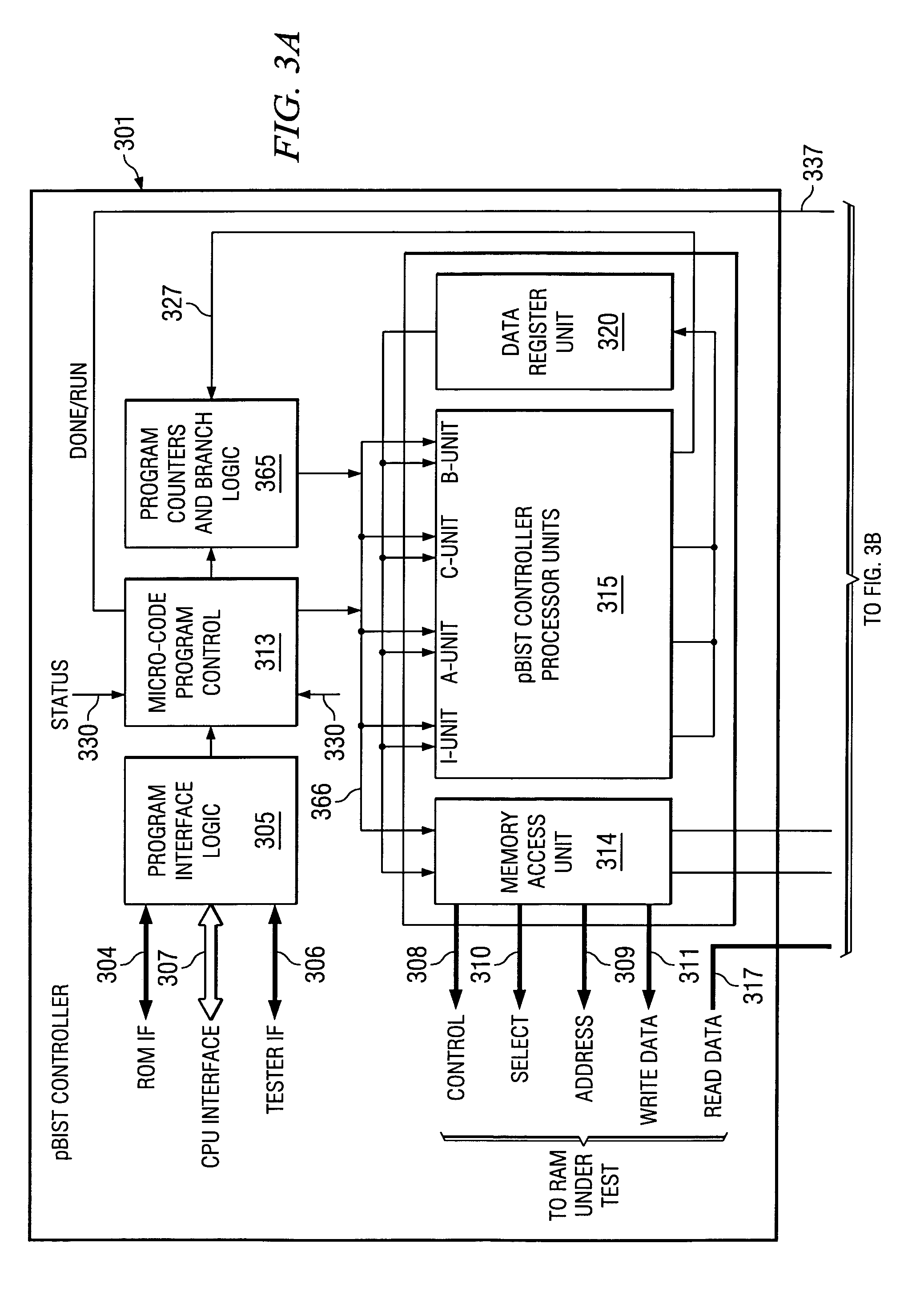
Programmable built in self test of memory
The pBIST solution to memory testing is a balanced hardware-software oriented solution. pBIST hardware provides access to all memories and other such logic (e.g. register files) in pipelined logic allowing back-to-back accesses. The approach then gives the user access to this logic through CPU-like logic in which the programmer can code any algorithm to target any memory testing technique required. Because hardware inside the chip is used at-speed, the full device speed capabilities are available. CPU-like hardware can be programmed and algorithms can be developed and executed after tape-out and while testing on devices in chip form is in process.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
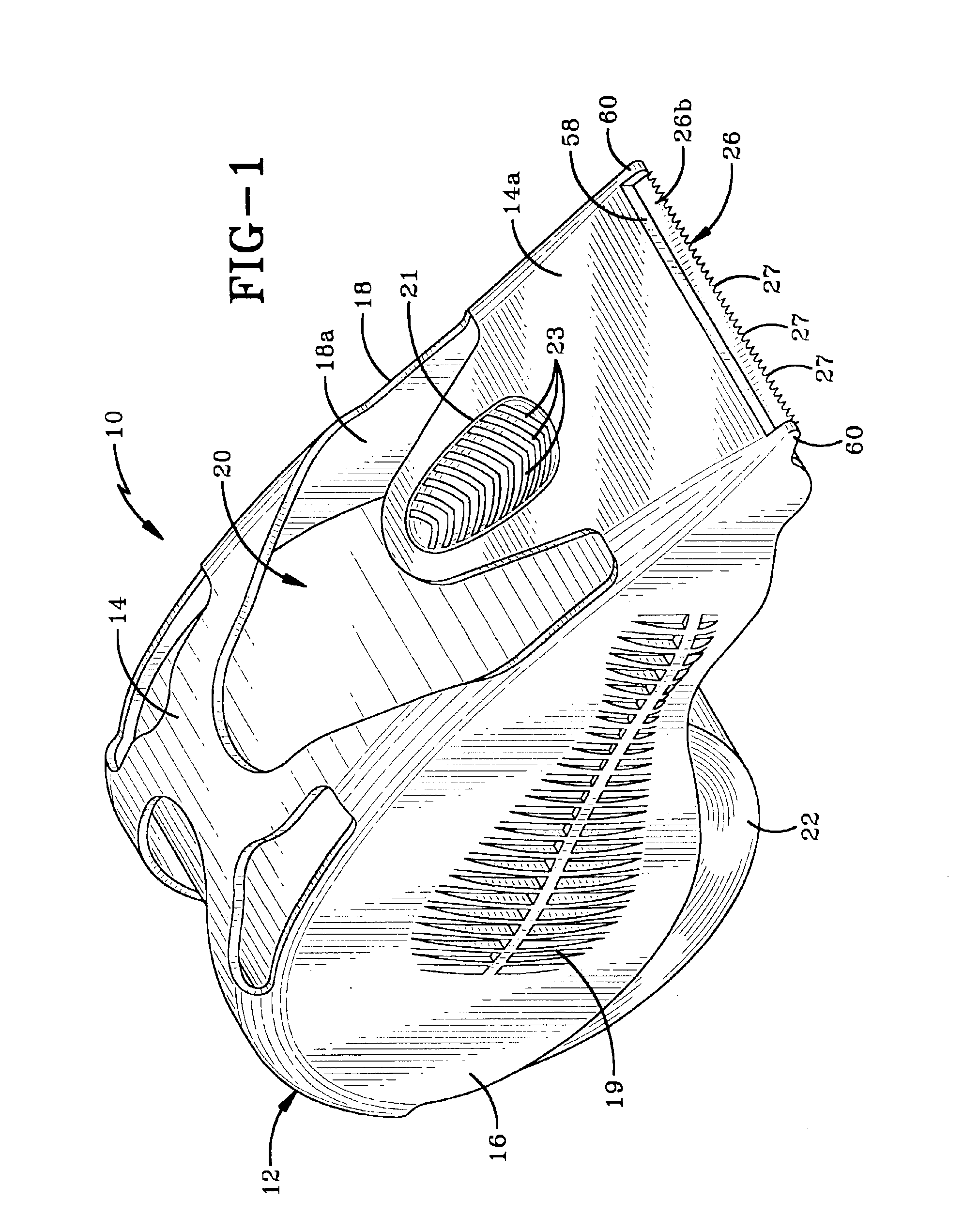
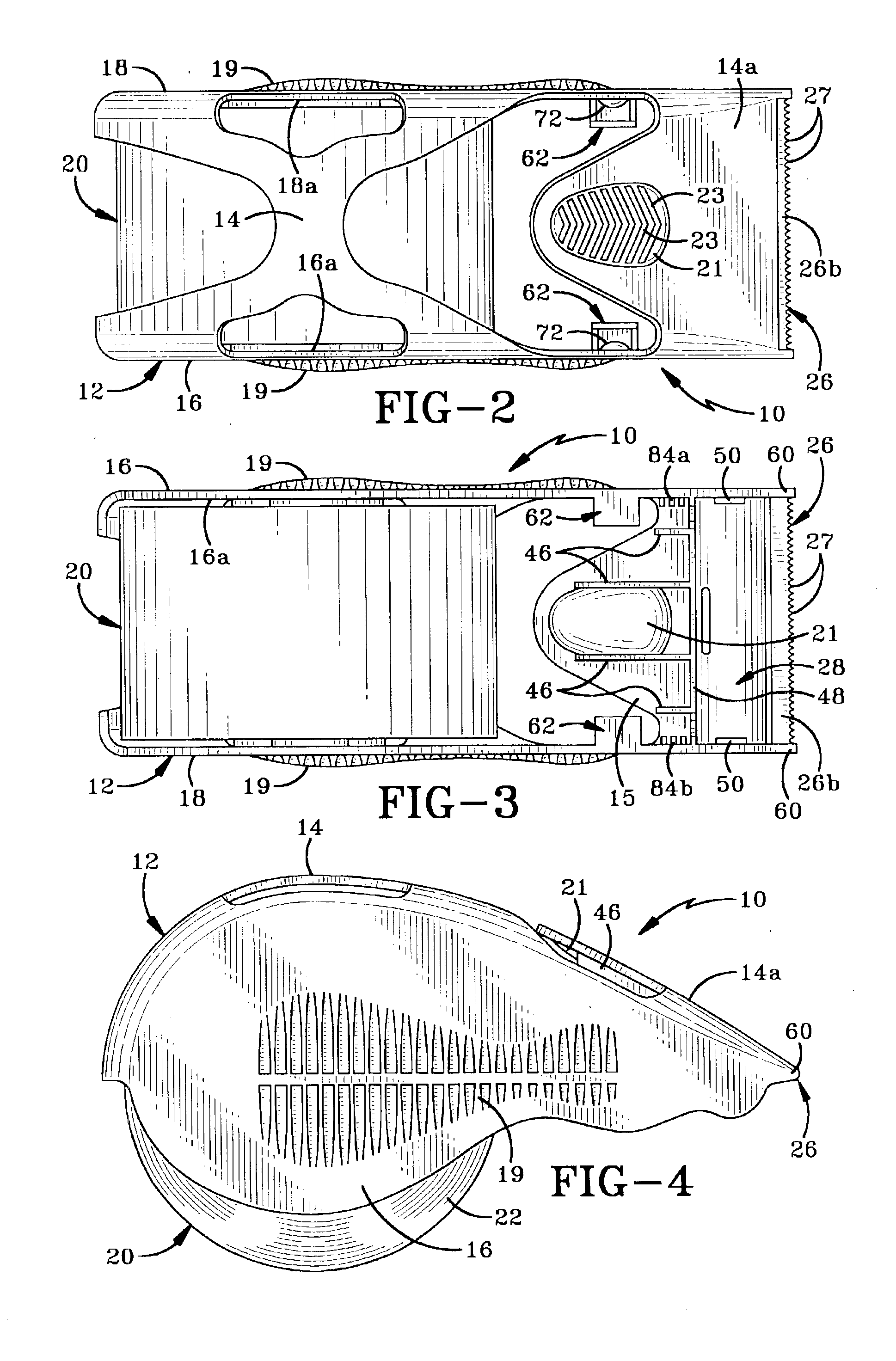
Tape dispenser having a tape retaining and application area
A tape dispenser having a frame, a cutter blade and at least one pair of projections disposed on the opposed interior surfaces of the side walls is disclosed. The distance between the projections is less than the distance between the interior surfaces of the side walls and is also less than the width of the tape held in the dispenser. The tape dispenser may also include a pair of tabs either associated with the projections or positioned between the projections and the tape mount. The dispenser is adapted to hold a roll of adhesive tape therein and because of the decreased distance between the projections, the tape assumes a convex shape when viewed from the front end of the dispenser. The shape of the tape and position of the tabs and projections causes the tape to be biased into contact with the interior of the front end of the dispenser. This helps to keep the free end of the tape out of contact with the roll in the dispenser.
Owner:CONROS +1
Programmable built in self test of memory
The pBIST solution to memory testing is a balanced hardware-software oriented solution. pBIST hardware provides access to all memories and other such logic (e.g. register files) in pipelined logic allowing back-to-back accesses. The approach then gives the user access to this logic through CPU-like logic in which the programmer can code any algorithm to target any memory testing technique required. Because hardware inside the chip is used at-speed, the full device speed capabilities are available. CPU-like hardware can be programmed and algorithms can be developed and executed after tape-out and while testing on devices in chip form is in process.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
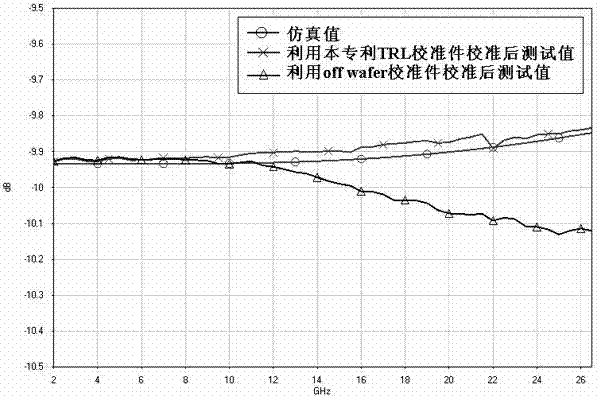
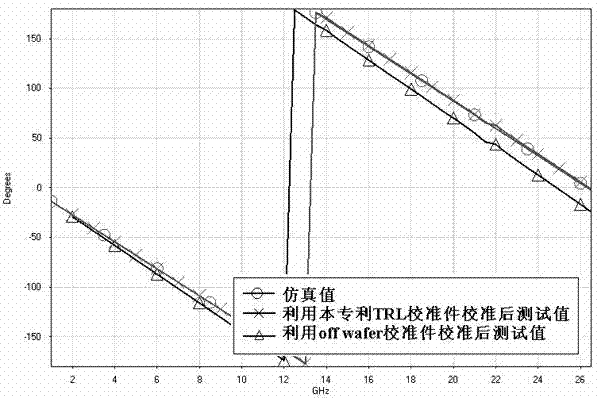
Microwave GaAs substrate on-chip S parameter microstrip line TRL (transistor resistor logic) calibrating member
The invention discloses a microwave GaAs substrate on-chip S parameter microstrip line TRL (transistor resistor logic) calibrating member and relates to the technical field of microwave or millimeter-wave S parameter testing. The microwave GaAs substrate on-chip S parameter microstrip line TRL calibrating member comprises a GaAs substrate layer, the lower surface of the GaAs substrate layer is connected with a metal layer, graph structures of a direct-through standard member Thru, reflection standard members Reflect and a transmission line standard member Line are arranged on the upper surface of the GaAs substrate layer, ground voltage points of the direct-through standard member Thru, the reflection standard members Reflect and the transmission line standard member Line are connected with the metal layer through grounding columns penetrating the GaAs substrate layer respectively, and the GaAs substrate layer is provided with grounding through holes matched with the grounding columns. The microwave GaAs substrate on-chip S parameter microstrip line TRL calibrating member is manufactured by adopting a GaAs tape-out process identical with a tested member. By using the calibrating member when microwave single-chip circuit tube core model parameters are extracted, a reference plane after calibration can be positioned at the root of a tube core, so that model extracting accuracy is improved.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
Tape measure utilizing mechanical decoupling of power tape extension feature for tape retraction
InactiveUS7475842B2Easily and consistently initiate drive mechanismConsistent positionMeasuring tapesGear wheelMagnetic tape
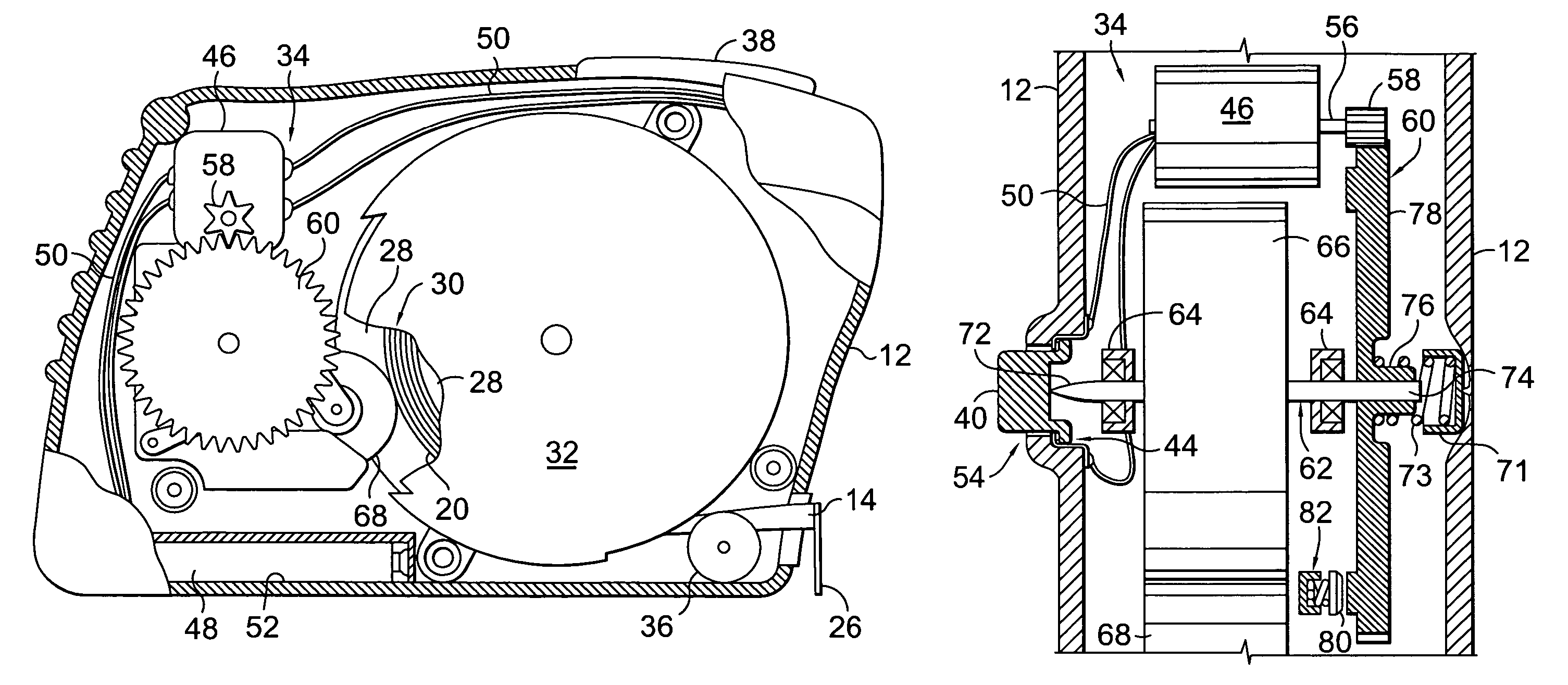
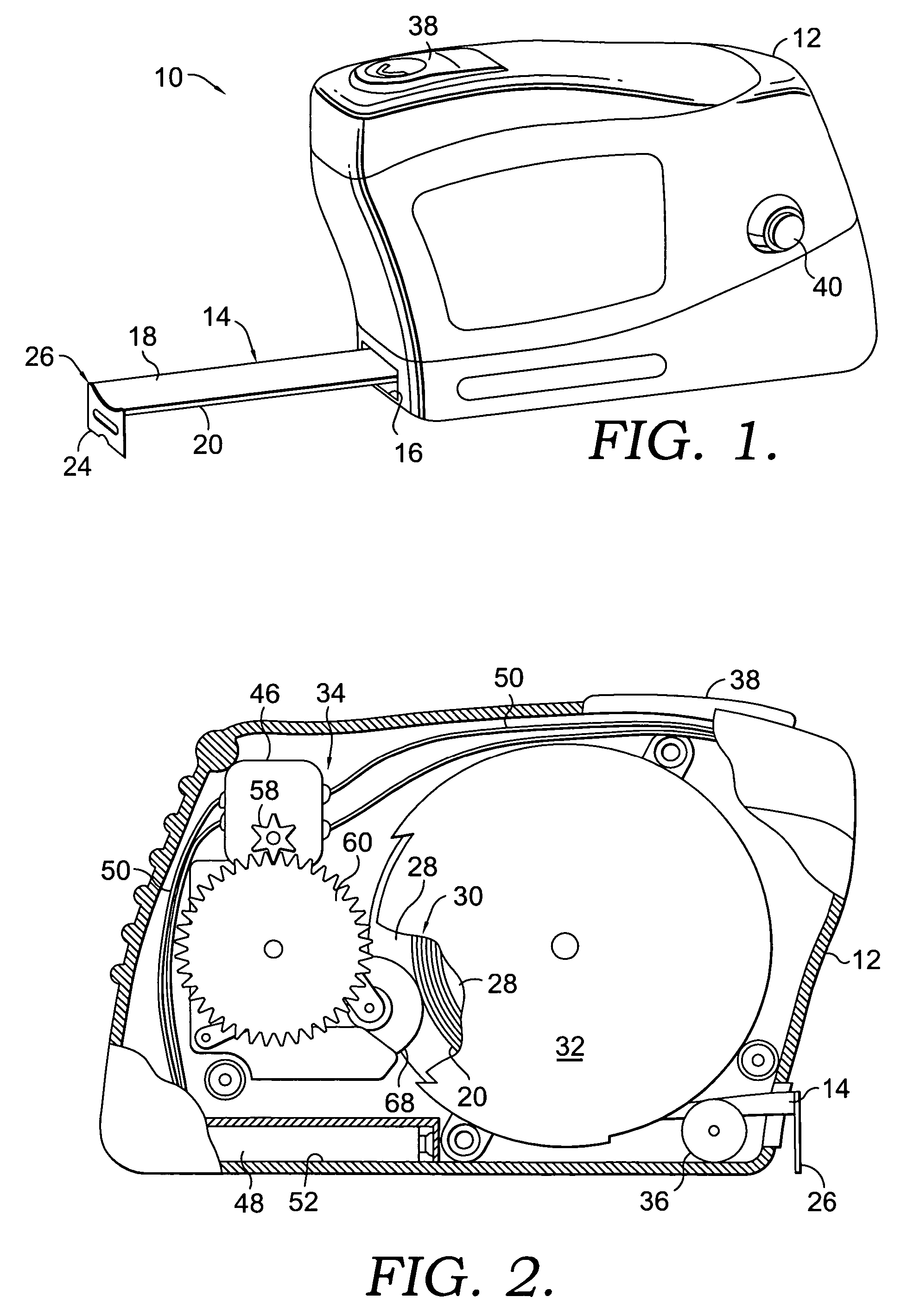
A power operated tape measure enables extension of a tape via a drive mechanism, as well as retraction of the tape through a mechanical decoupling within the drive mechanism. The tape measure has a housing within which is positioned a spring-biased tape assembly, the drive mechanism and a clutch. The spring-biased tape assembly includes an annular reel onto which is wound a tape having indicia for taking length measurements. The drive mechanism includes a driving gear and a driven gear, and is adapted to engage with a bottom surface of the tape to extend the tape out of the housing. The clutch is adapted to displace the driven gear out of engagement with the driving gear and thereby decouple the driving and braking force provided by the drive mechanism from acting upon the bottom surface of the tape to permit the spring-biasing of the tape assembly to retract the tape into the housing.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Apparatus for printing and applying tape and methods of printing and applying tape
InactiveUS6884312B2Improve performanceMinimizing eliminating concernLamination ancillary operationsManual label dispensersEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
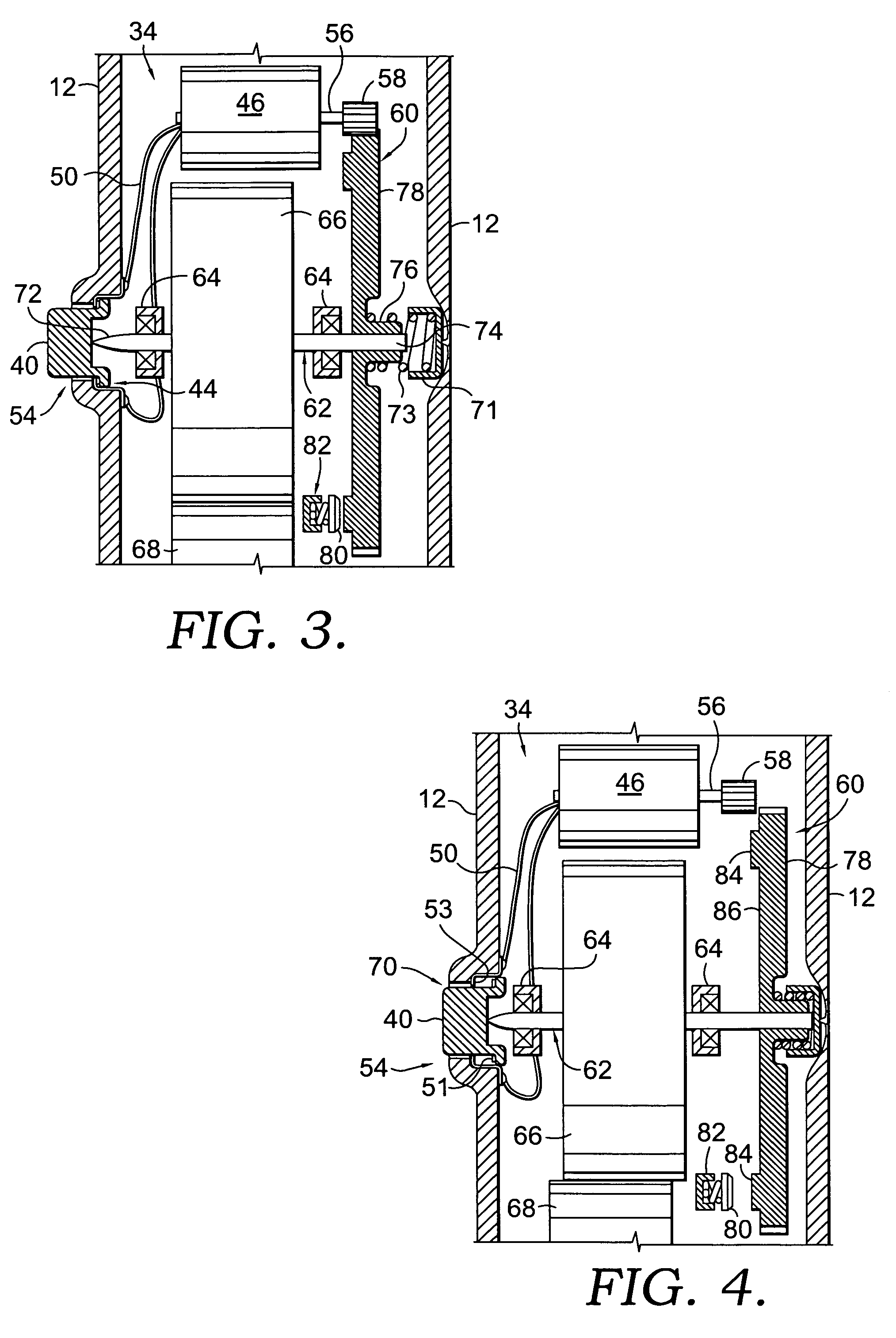
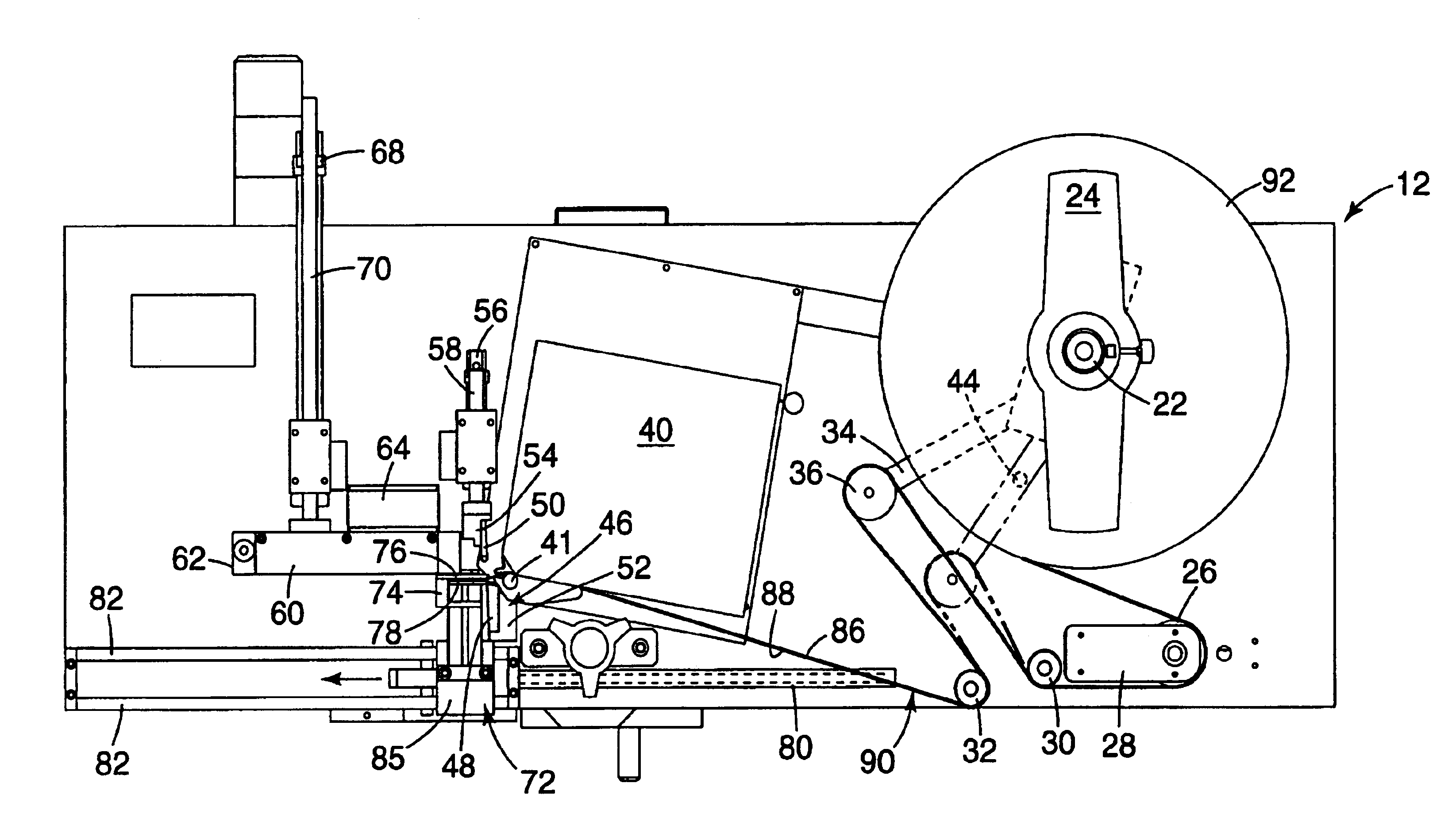
An apparatus for printing and applying tape. A preferred embodiment of the invention provides an apparatus that includes a printer for printing on tape, a tape puller that pulls the printed tape out from the printer, and an applicator that applies the printed tape to an object. The present invention also generally relates to methods of printing and applying tape to objects.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
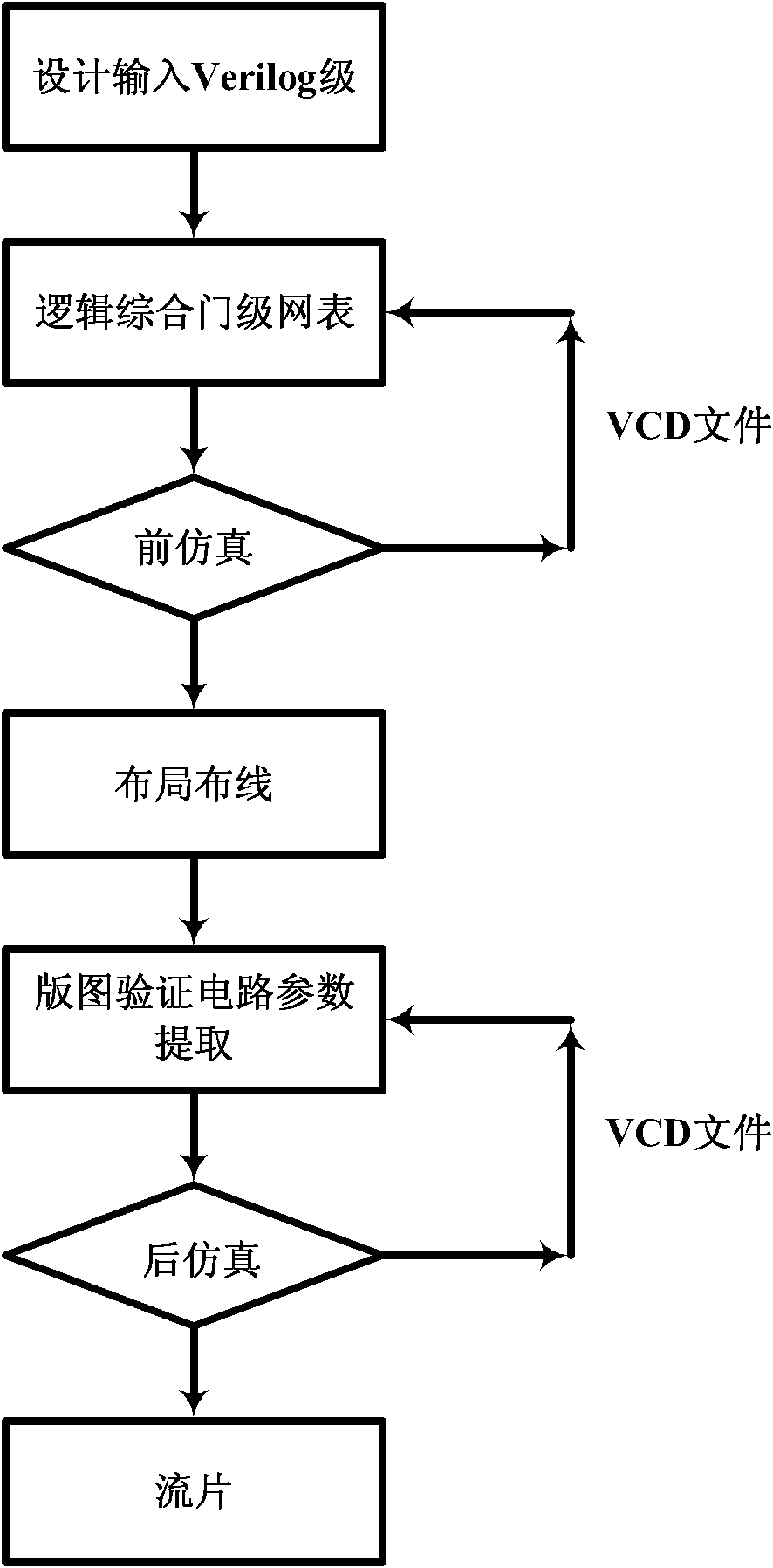
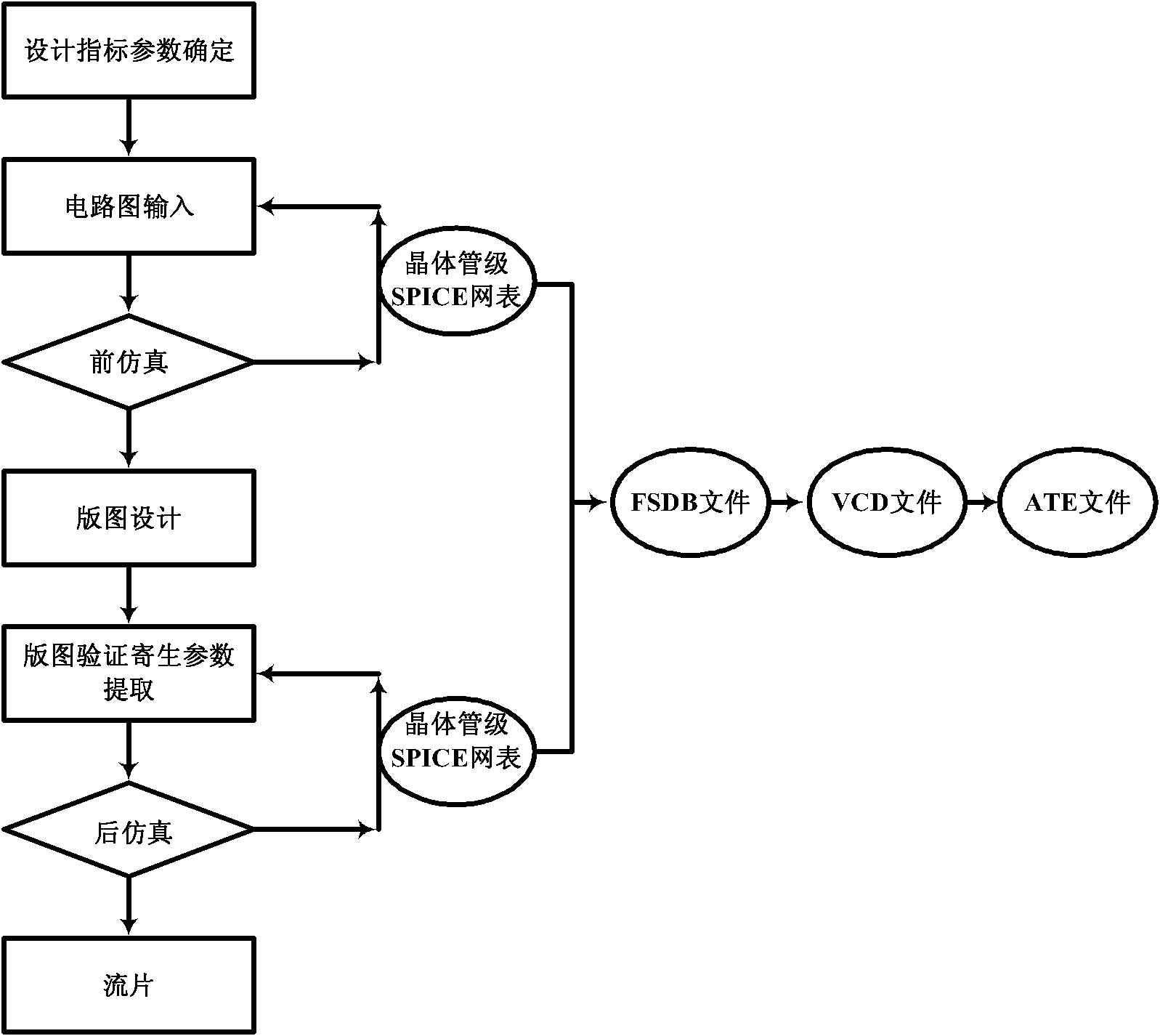
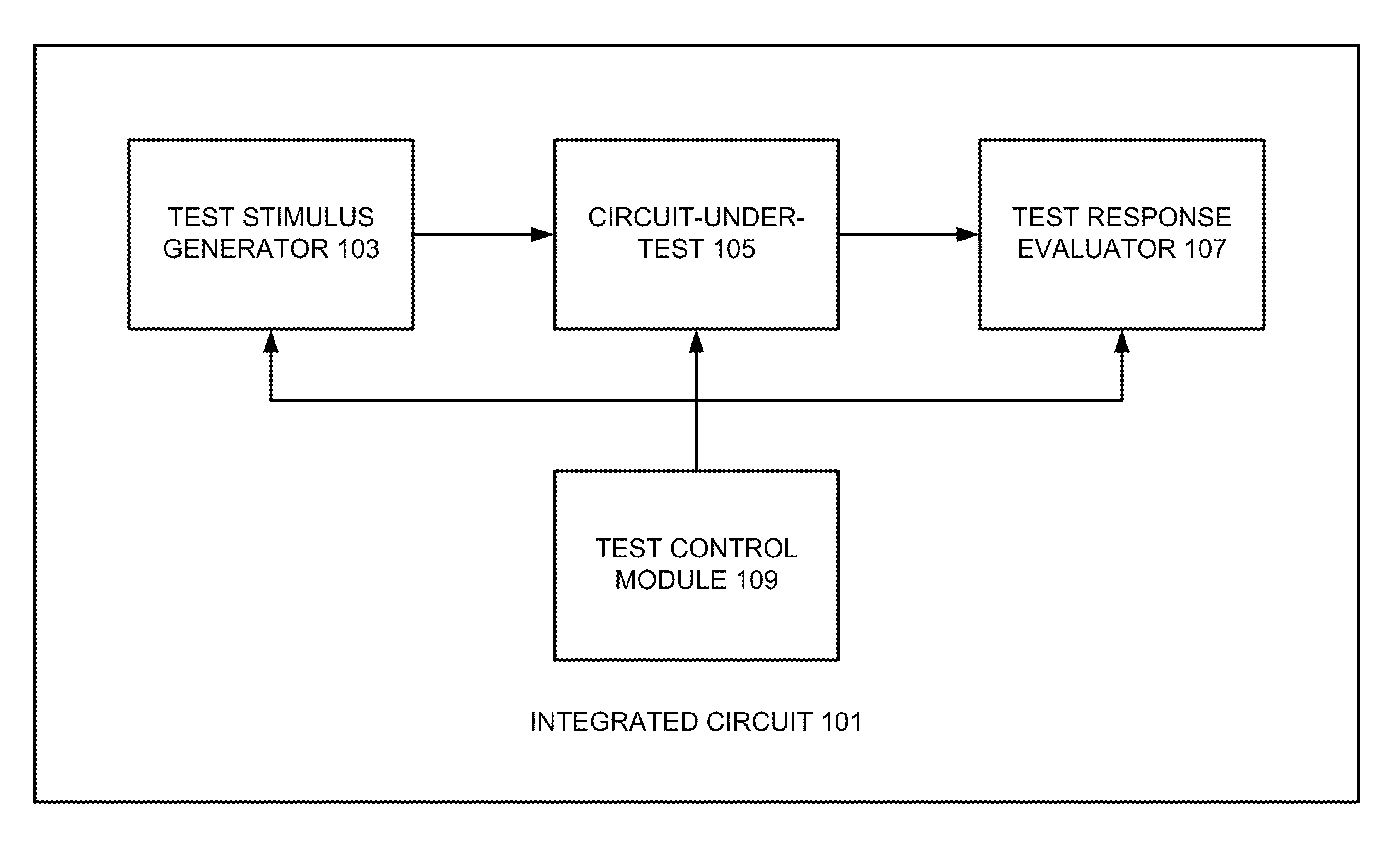
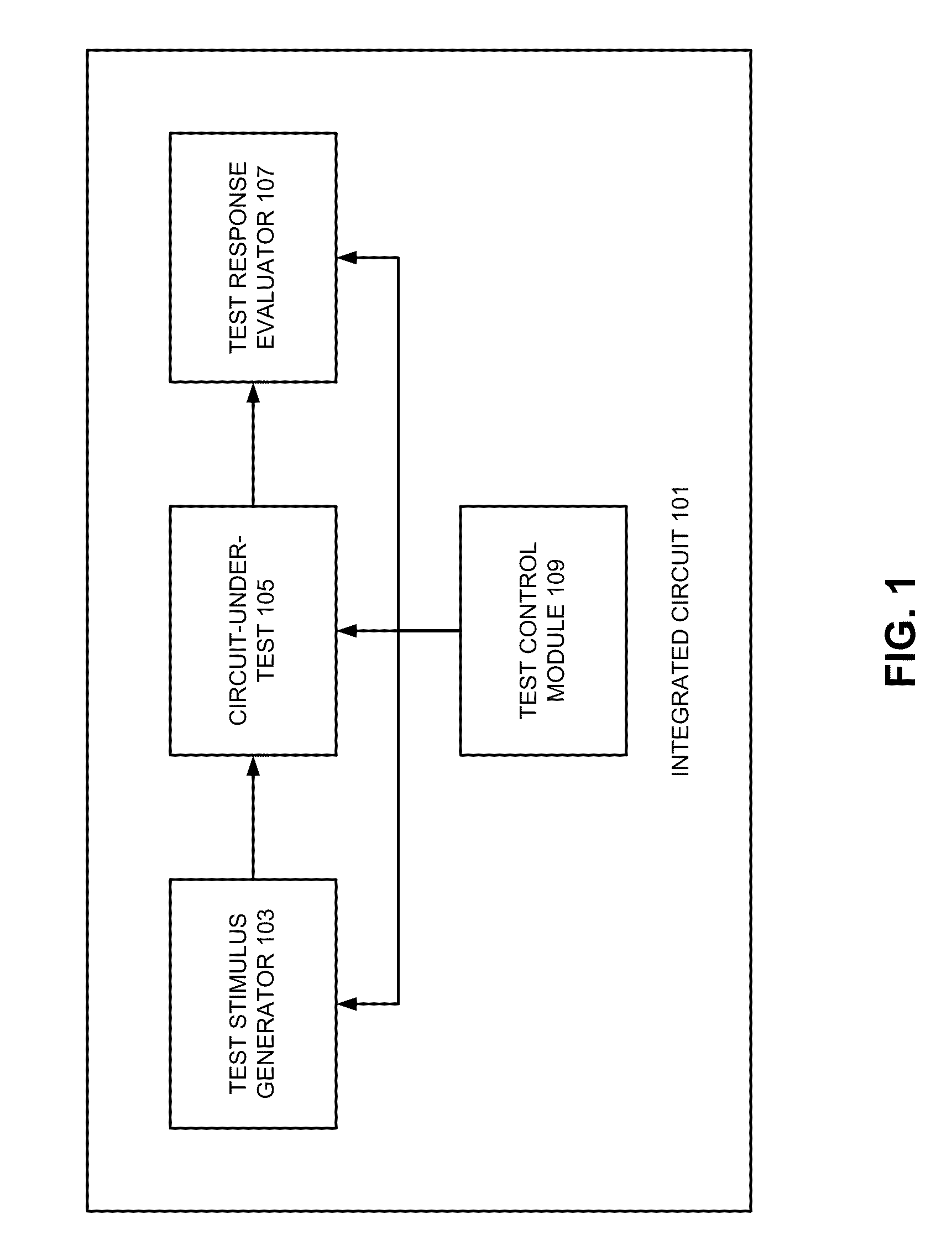
Integrated circuit testing method
ActiveCN102866349ASpeed up testingAvoid misinterpretationElectrical testingTest platformAutomatic testing
The invention provides an integrated circuit testing method, which comprises the steps of design index parameter determination, circuit diagram input, pre-simulation, layout design, layout verification and parasitic parameter extraction, post-simulation and tape-out. The integrated circuit testing method is characterized in that both the pre-simulation and the post-simulation use a transistor-level SPICE netlist, which can be converted to documents required for an automatic testing platform. The testing method provided by the invention can be used to greatly shorten the original test vector writing time for chip testing personnel, speed up the progress of the test, avoid understanding deviation between designers and testers and achieve seamless butting.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
AES (advanced encryption standard) algorithm circuit oriented method for testing differential power attack
InactiveCN103530474ASolve the technical difficulties of power consumption attack testingReduce risk of redesignSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientDesign stage
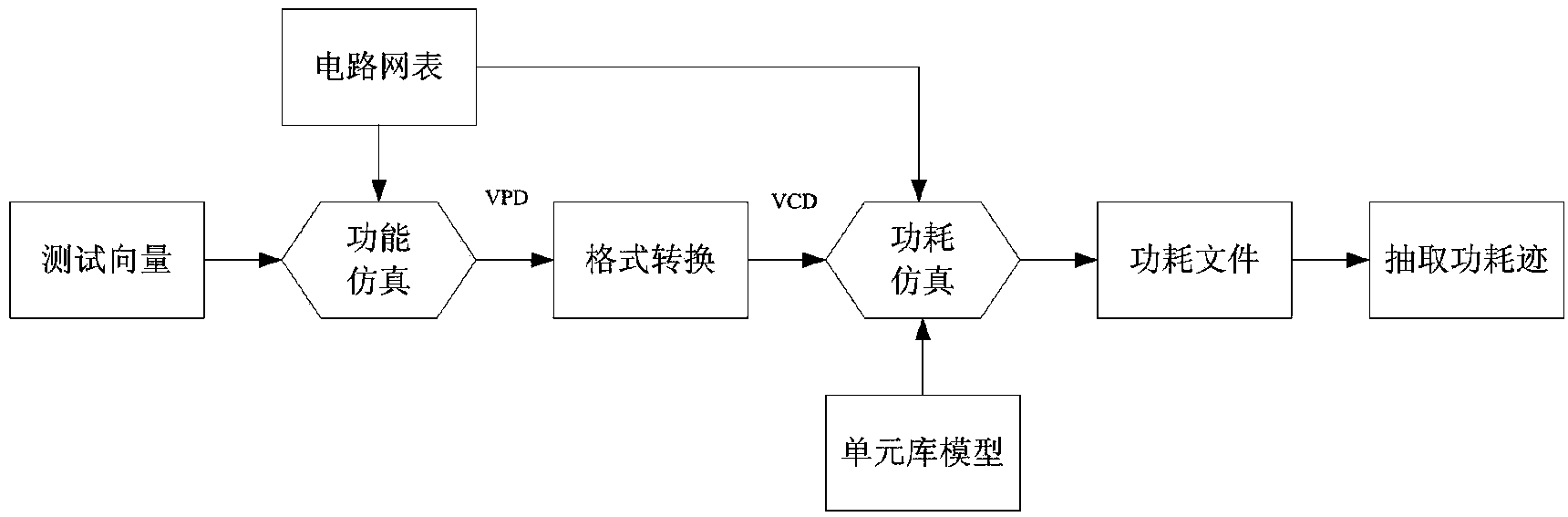
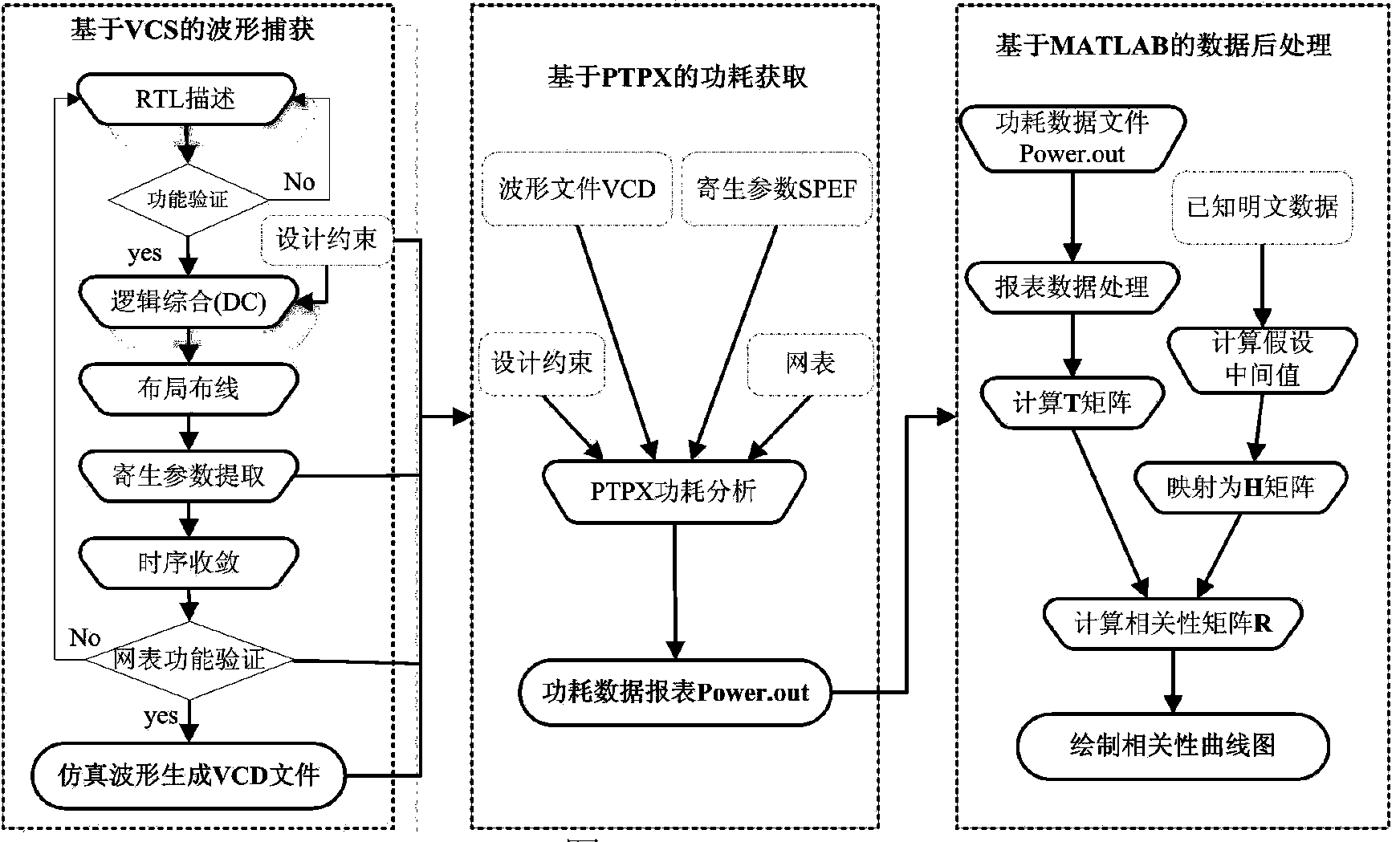
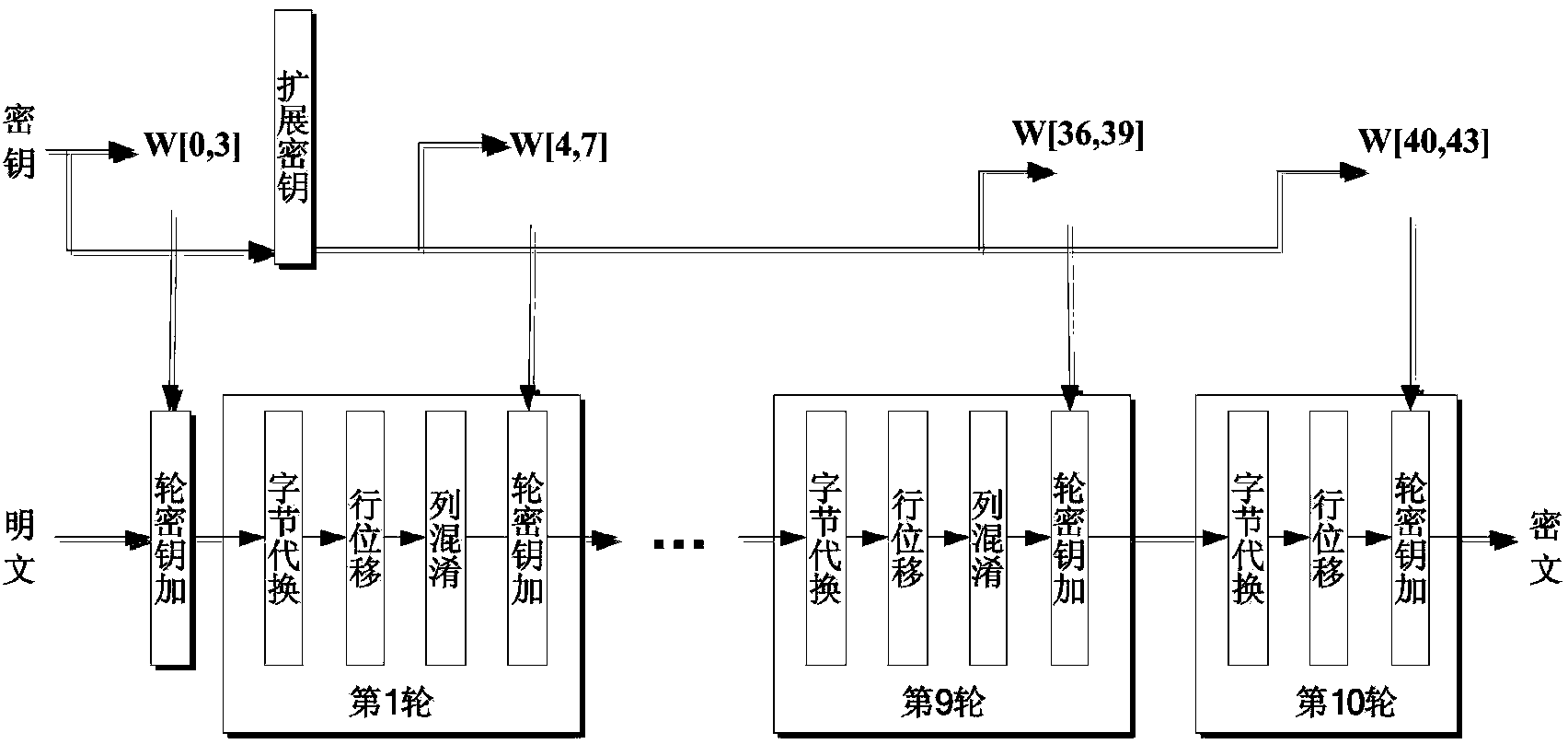
The invention discloses an AES (advanced encryption standard) algorithm circuit oriented method for testing differential power attack. An AES algorithm is a widely applied grouping symmetric cryptographic algorithm. The AES algorithm circuit oriented method is used for acquiring and processing power samples for tests for the differential power attack in a design stage of an AES cryptographic algorithm circuit and includes steps (1), carrying out functional simulation and acquiring power samples; (2), preprocessing the power samples; (3), acquiring hypothetical power samples; (4), computing correlation coefficients and analyzing attack results. The AES algorithm circuit oriented method has the advantages that only varied power points are sampled, so that large quantities of power sample data can be omitted, power attack computational complexity can be greatly reduced, the assess effectiveness and the speed are high, more importantly, the tests for the differential power attack can be carried out in the design stage of the circuit, the attack resistance of the cryptographic circuit can be assessed in advance, and tape-out risks of the AES circuit can be reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
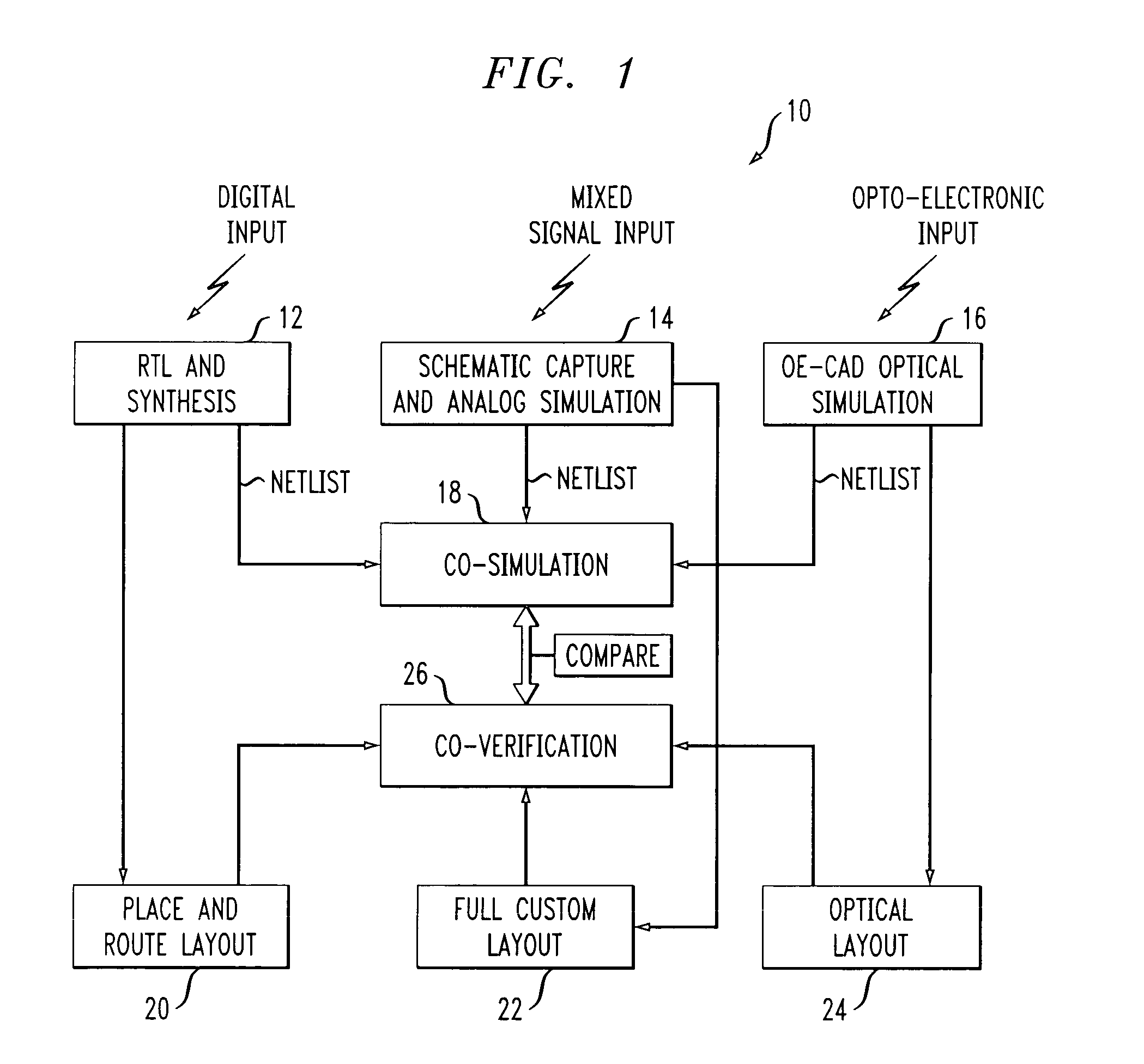
Integrated approach for design, simulation and verification of monolithic, silicon-based opto-electronic circuits
ActiveUS7269809B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer Aided DesignIntegrated design
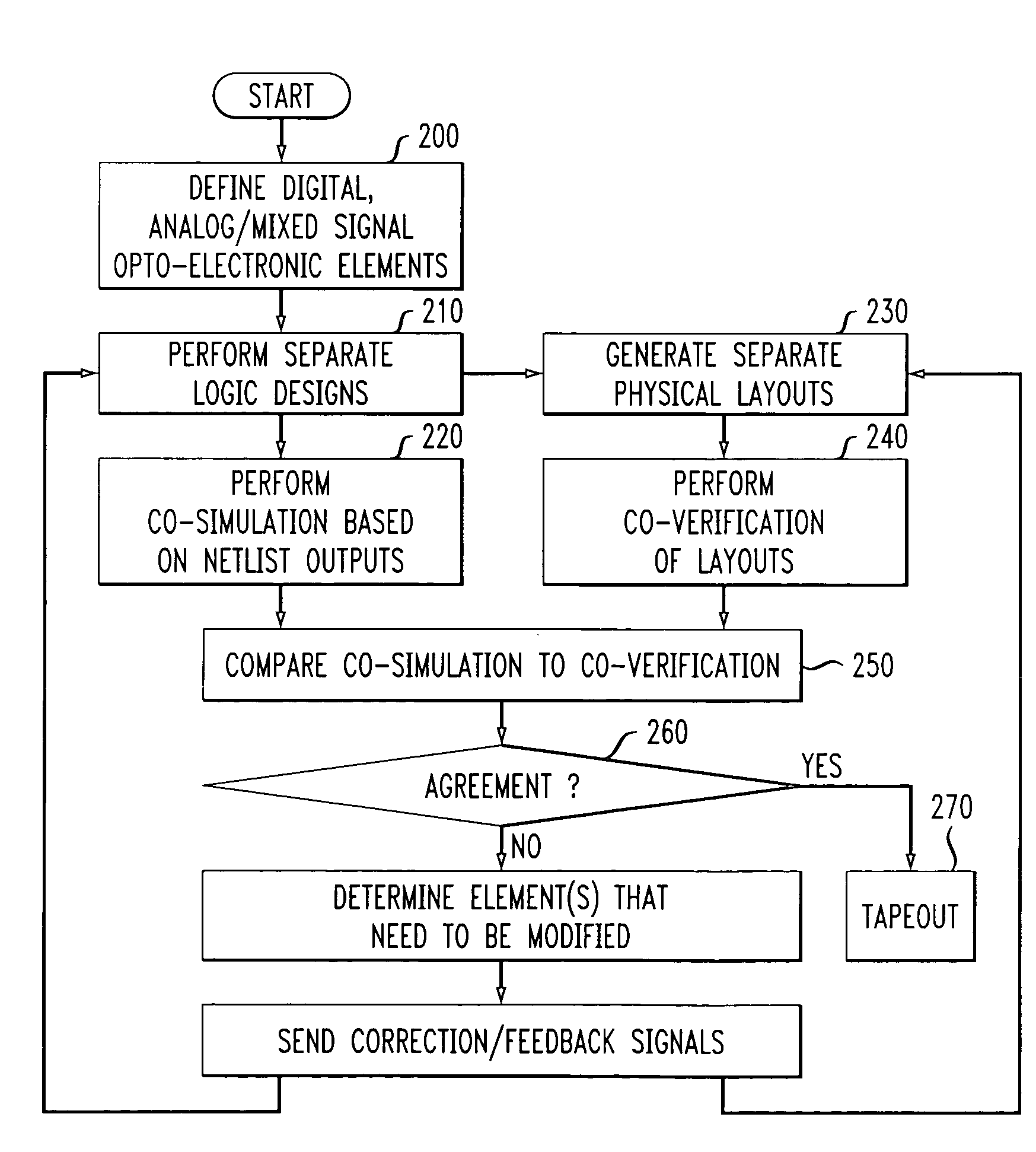
Computer-aided design (CAD) tools are used to perform the integrated design, verification and layout of electrical and optical components in a monolithic, silicon-based electro-optic chip. Separate top-level behavioral logic designs are prepared for the three different types of elements included within the final, silicon-based monolithic structure: (1) digital electronic integrated circuit elements; (2) analog / mixed signal electronic integrated circuit elements; and (3) opto-electronic elements (including passive and active optical elements). Once the behavioral logic design is completed, the results are combined and co-simulated. A physical layout design is developed and verified for each different type of element in the circuit. The separate physical layouts are then co-verified, to assess the properties of the overall physical design. The results of the co-simulation are compared to the results of the co-verification, with alterations made in the logic design and / or the physical layout until the desired operating parameters are obtained. Once the desired results are generated, conventional wafer-level fabrication operations are then considered to provide a final product (“tape out”).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Tape measure utilizing mechanical decoupling of power tape extension feature for tape retraction
InactiveUS20070152091A1Easily and consistently initiate drive mechanismConsistent positionMeasuring tapesMagnetic tapeGear wheel
A power operated tape measure enables extension of a tape via a drive mechanism, as well as retraction of the tape through a mechanical decoupling within the drive mechanism. The tape measure has a housing within which is positioned a spring-biased tape assembly, the drive mechanism and a clutch. The spring-biased tape assembly includes an annular reel onto which is wound a tape having indicia for taking length measurements. The drive mechanism includes a driving gear and a driven gear, and is adapted to engage with a bottom surface of the tape to extend the tape out of the housing. The clutch is adapted to displace the driven gear out of engagement with the driving gear and thereby decouple the driving and braking force provided by the drive mechanism from acting upon the bottom surface of the tape to permit the spring-biasing of the tape assembly to retract the tape into the housing.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
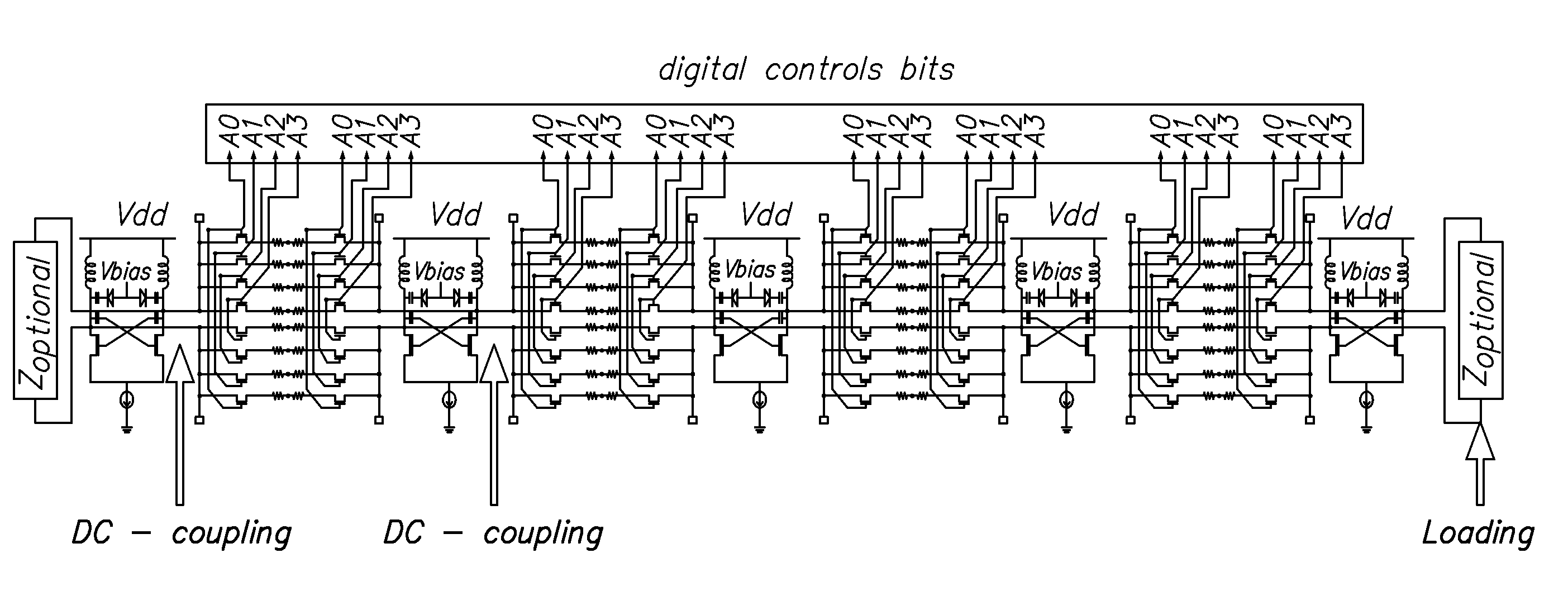
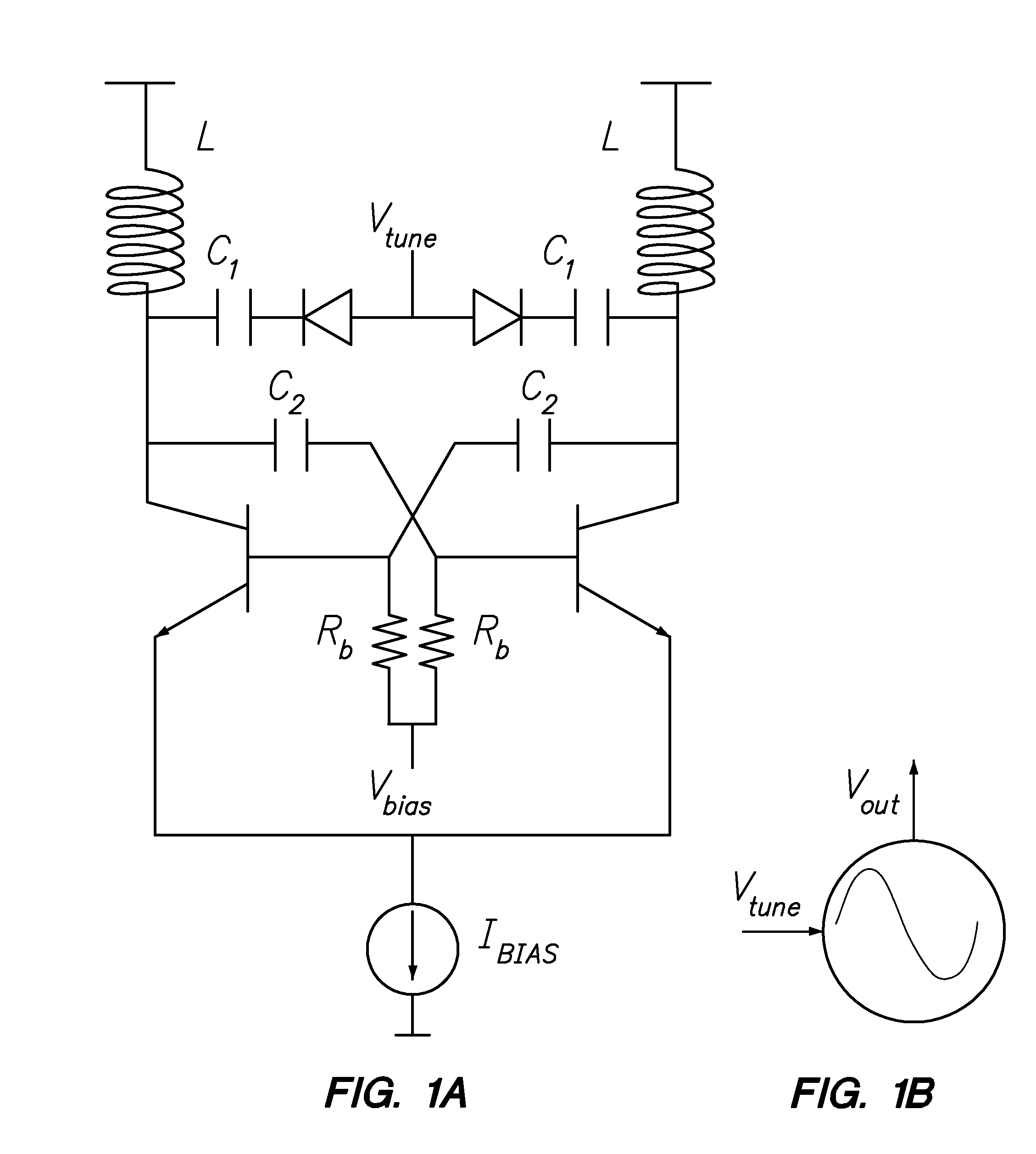
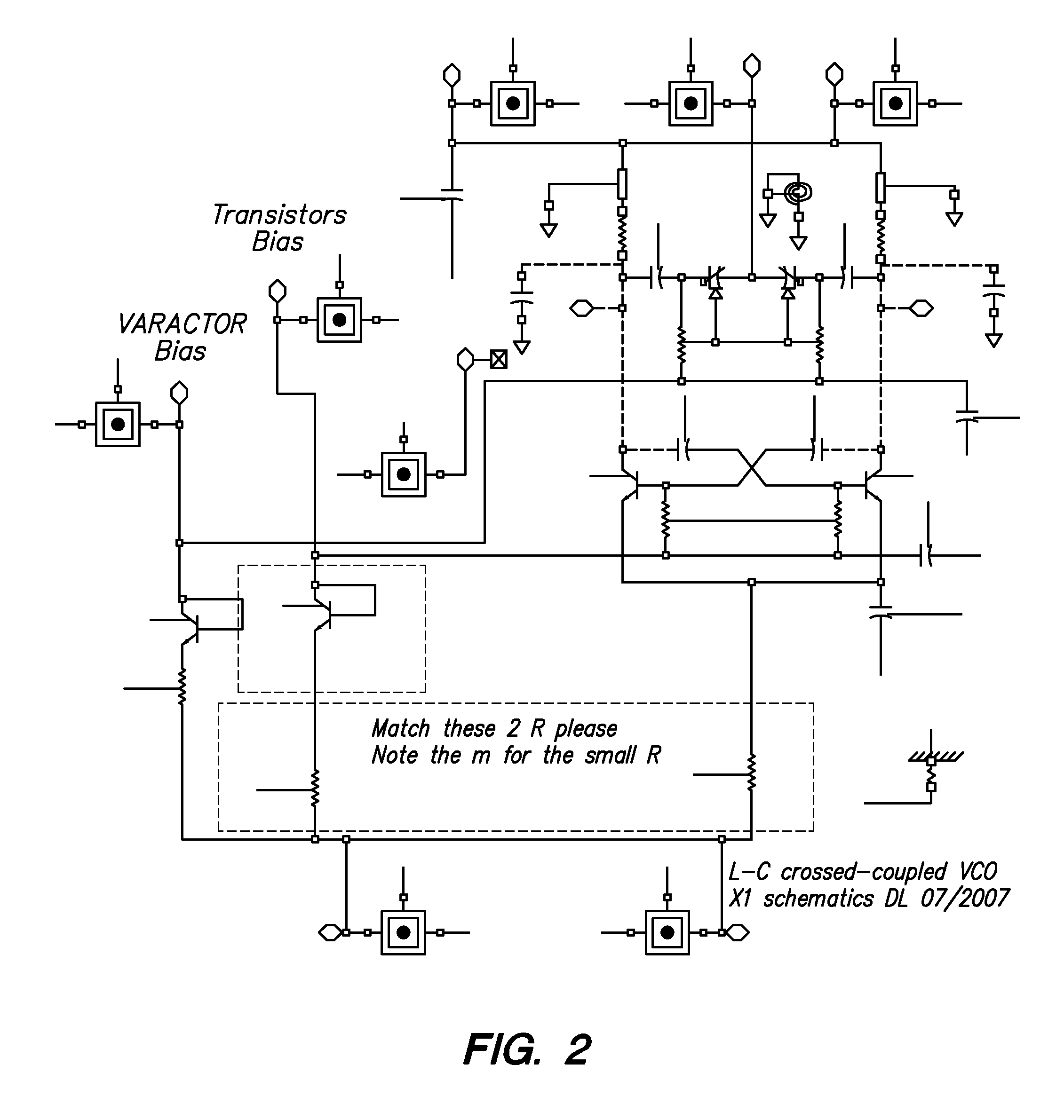
Frequency tuning and phase shifting techniques using 1-dimensional coupled voltage-controlled-oscillator arrays for active antennas
InactiveUS8558625B1Reduce phase noiseLarge tuning rangePulse generation by logic circuitsOscillations generatorsPhase noiseBeam steering
A technique for enhancing the frequency tuning range for monolithic RF source generation using fully-integrated coupled Voltage-Controlled-Oscillator (VCO) arrays that contain an odd number of VCOs. Fully-monolithic SiGe VCO arrays using on-chip inductor and varactor with on-chip bias current sources have been carefully designed and simulated in IBM 7HP 0.18 μm BiCMOS technology and taped out for fabrication. The SPICE simulated frequency and phase tuning of the 1-D VCO×5 array is dependent on the edge VCOs termination impedance, the tuning voltages, and the VCO coupling strength. The simulated data suggests that the enhanced tuning range and beam steering can be accomplished using coupled-VCO arrays without needing complex and bulky phase shifters. This design technique imposes no apparent phase noise penalty but can provide simulated RF frequency tuning range of ˜40% and also ˜+ / −25° beam steering for active antennas applications.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Etching device of organic EL display panel and its method
InactiveCN101170056ASimple structureEasy maintenanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringOrganic electroluminescence
The invention discloses organic electroluminescent display panel etching equipment and a method thereof and relates to display panel etching equipment technical field. The problem to be solved is structure simplification and cost reduction of the panel etching equipment. The display panel etching equipment includes a tape-out opening, a transition unit with an air knife arranged therein, a etching unit used to etch the base plate, a liquid cutting unit arranged on the air knife and used to blow down etching liquid, a rinse unit used to rinse the base plate and an air knife drying unit for cleaning the base plate from an input end to an output end of a base plate in turn. All units are connected by a roller delivery unit used to deliver the base plate. The invention is characterized in that: the etching unit is a cycle etching slot and the rinse unit is a cycle rinse slot. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, easy repair, low manufacture cost, reduced etching time and improved etching effect.
Owner:INESA ELECTRON
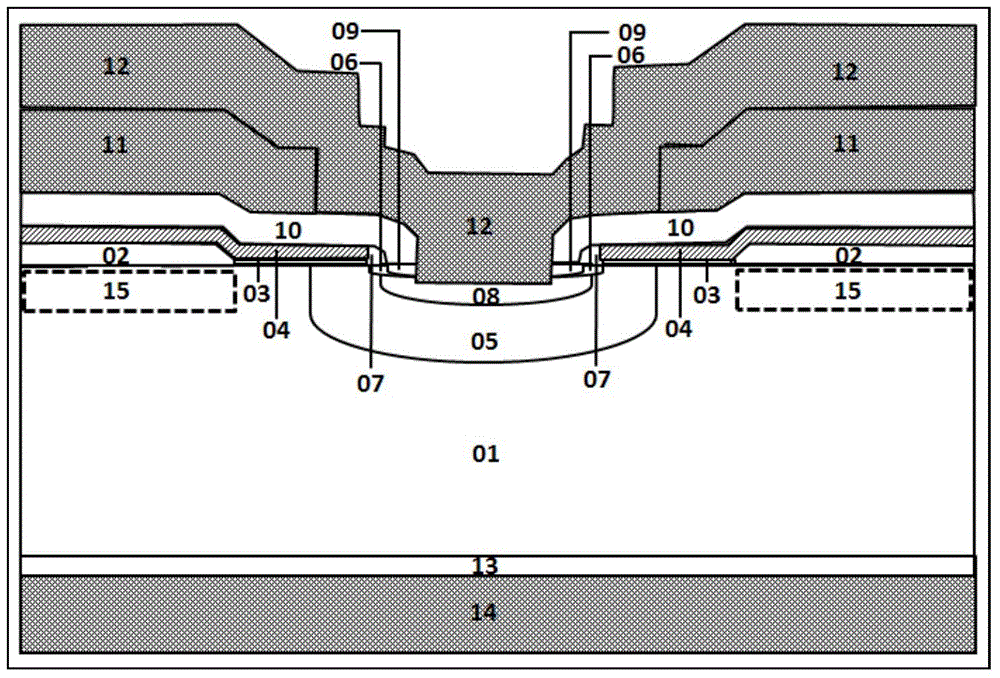
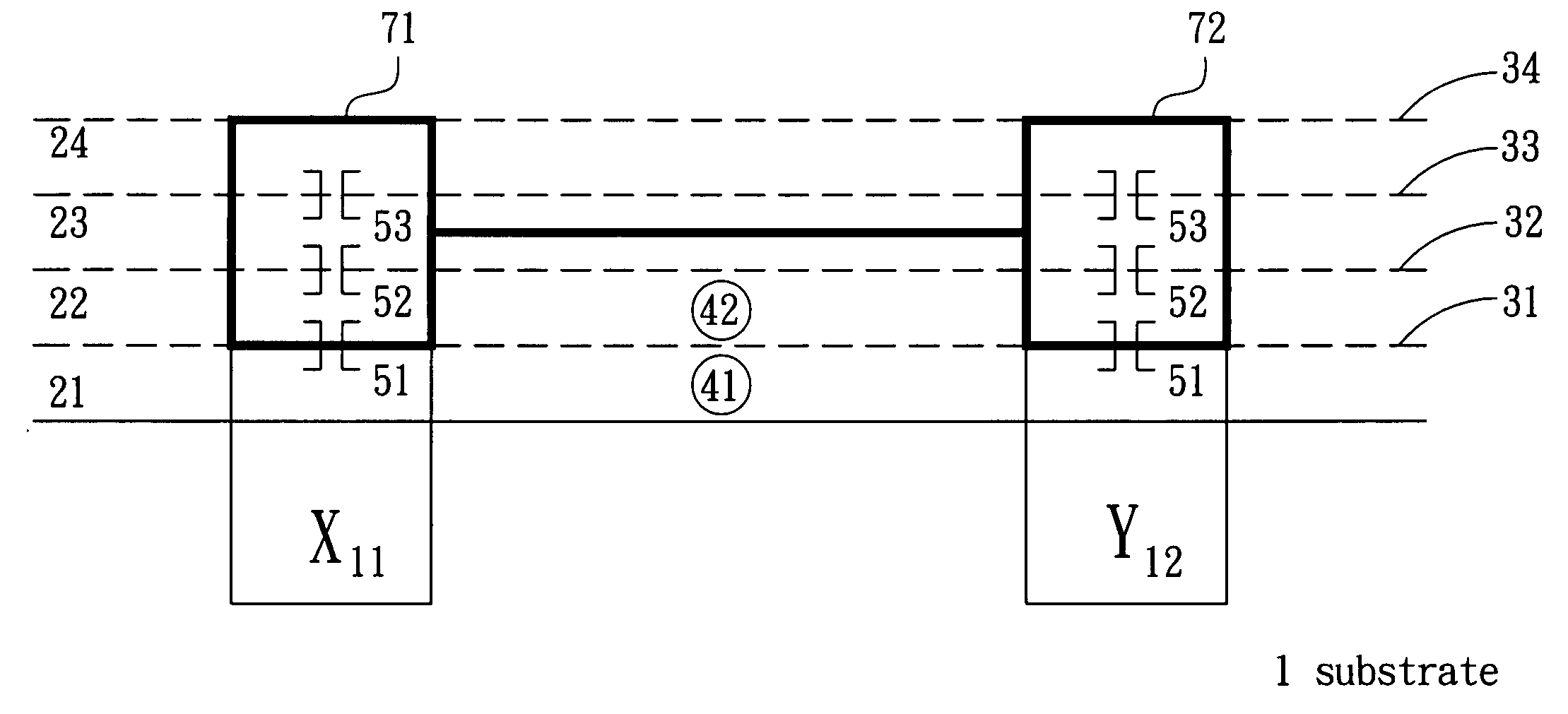
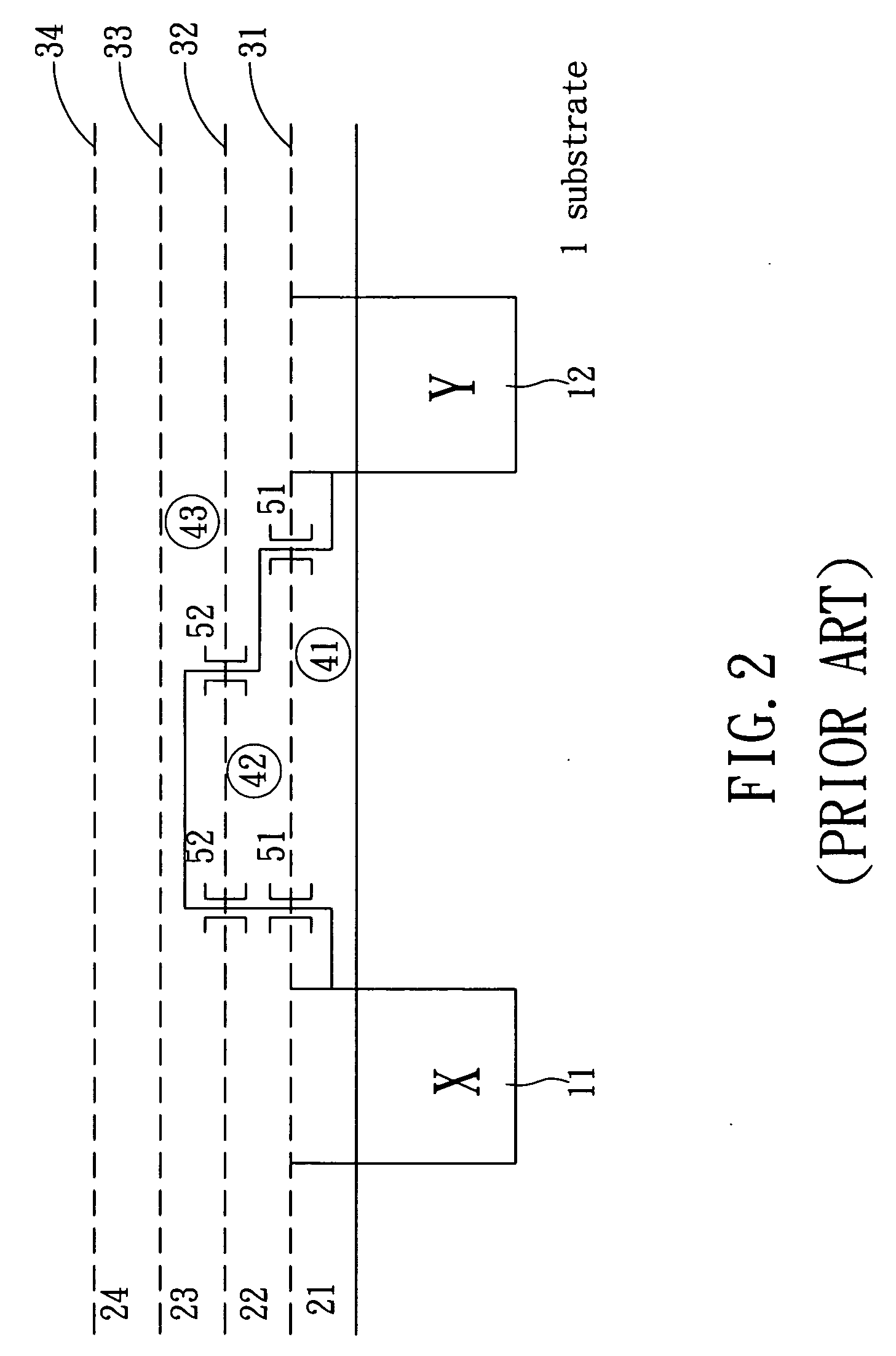
Integrated circuit structure and a design method thereof
ActiveUS7281231B2Minimize changesLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringDesign methods
The present invention discloses an integrated circuit structure and a design method thereof, in which a circuit passageway is arranged at each circuit element terminal in circuit design stage. The arranged circuit passageway does not only increase layout flexibility in circuit simulation stage but also simplify layout difficulty when the circuit layout needs to be modified after taping out stage. Also, the circuit passageway can minimize modified metal layers, i.e. the number of modified masks is minimized. Because the expense of fab is based on the utilized layers and number of masks instead of designs of masks, the present invention will not increase the expense in taping out stage and can save the cost of research and development when modifications are required.
Owner:ALICORP
Method of decomposing integrated circuit layout and computer readable media
ActiveCN102147820AEasy to limitHigh speedComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureIntegrated circuit layout
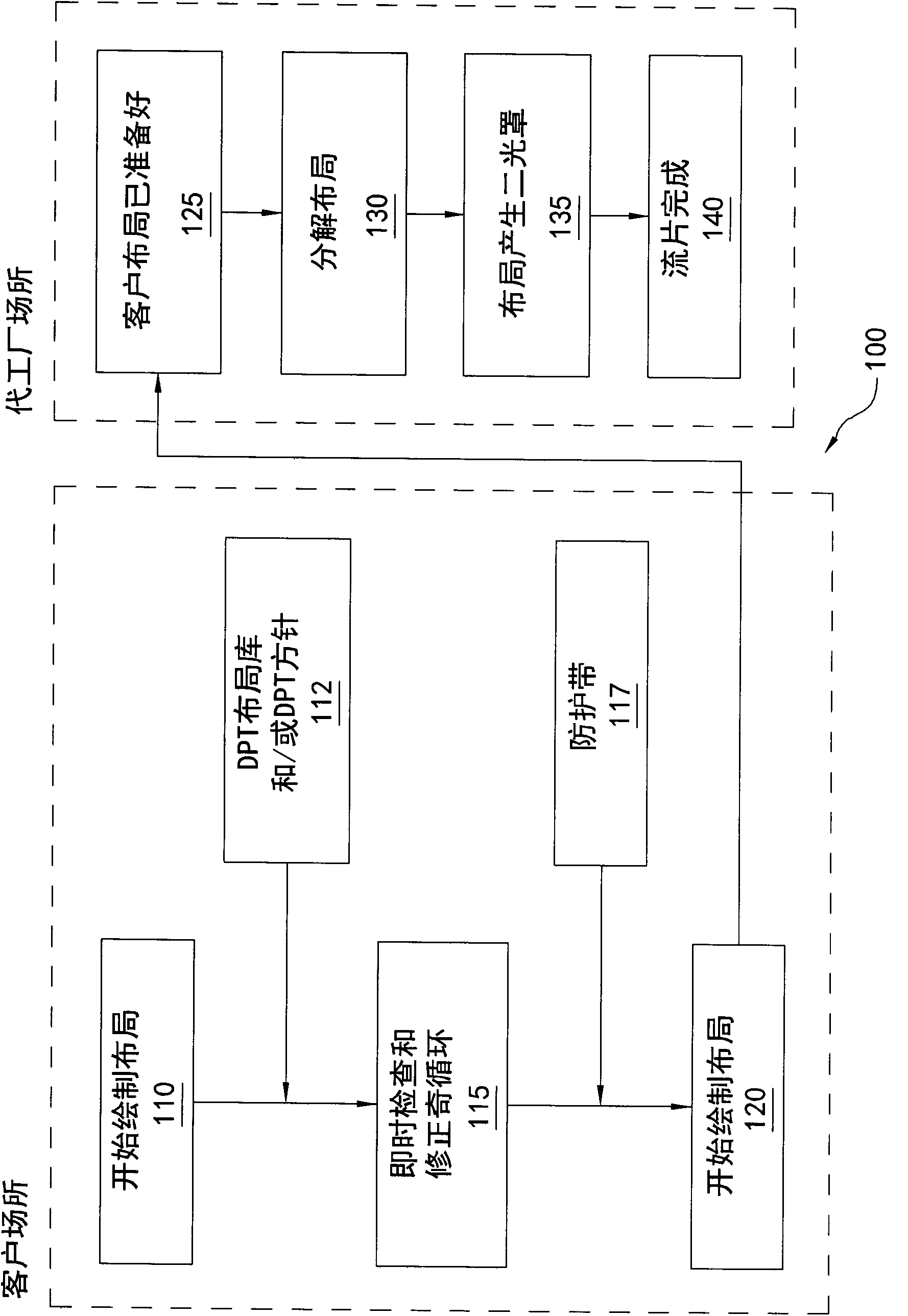
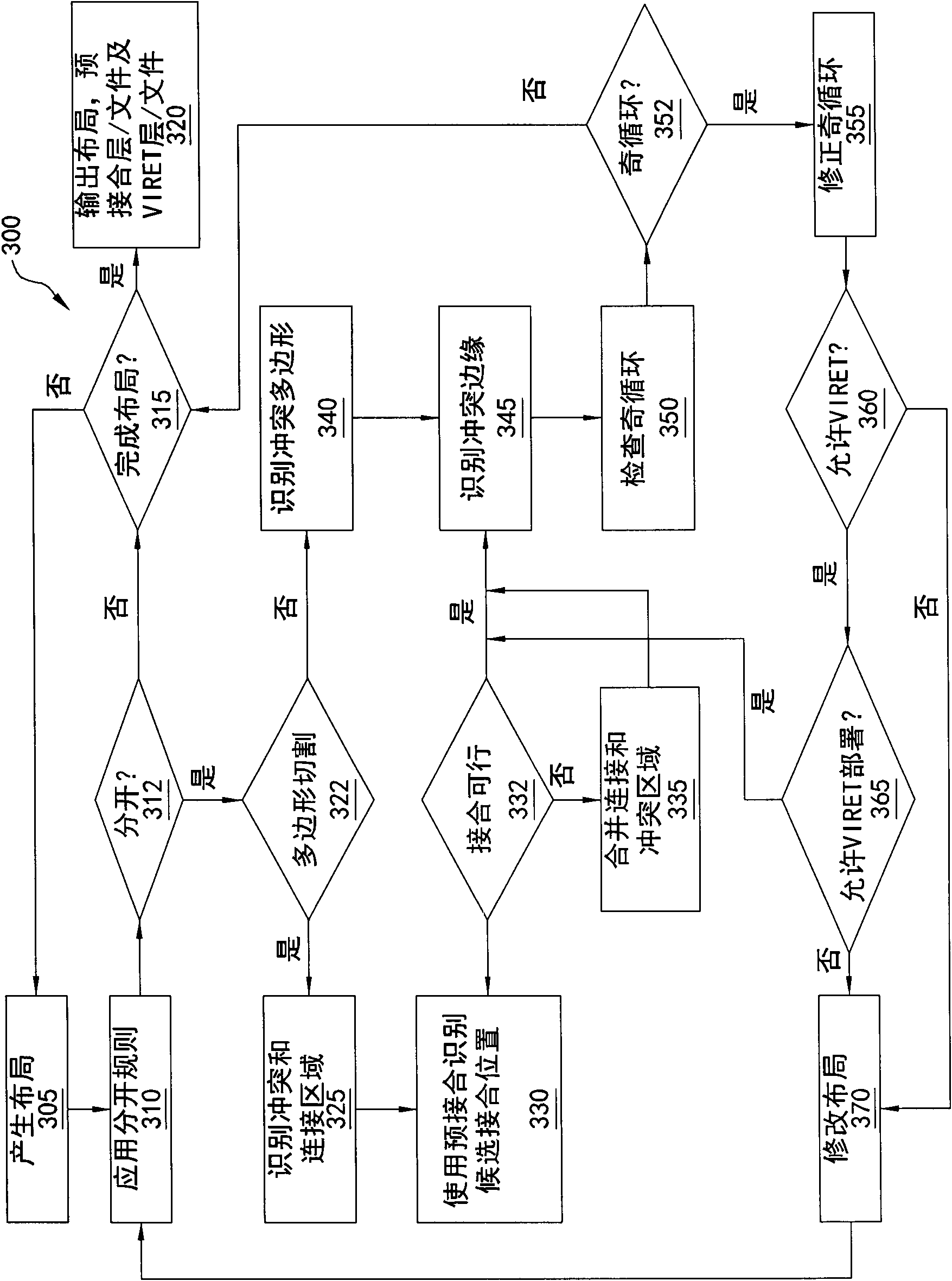
The invention relates to a method of decomposing the integrated circuit layout and the computer readable media storing a plurality of computer instructions. Various embodiments of the invention provide techniques to ensure a layout for an integrated circuit is split-able. In a method embodiment, a layout is generated in a customer site having a layout library as inputs wherein the library provides exemplary layouts that have been verified to be spit-able and that can be used and layouts that can cause conflicts to avoid. A real-time odd cycle checker is also provided in which the checker identifies in real time conflict areas and odd cycles as they arise during layout generation. To reduce memory usage layouts of various devices may be separated so that each individual layout or a small number of layouts, rather than a large layout for the whole application circuit, can be checked against conflicts. Once the layout is ready at the customer site, it is sent to the foundry site to be decomposed into two masks and taped-out. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
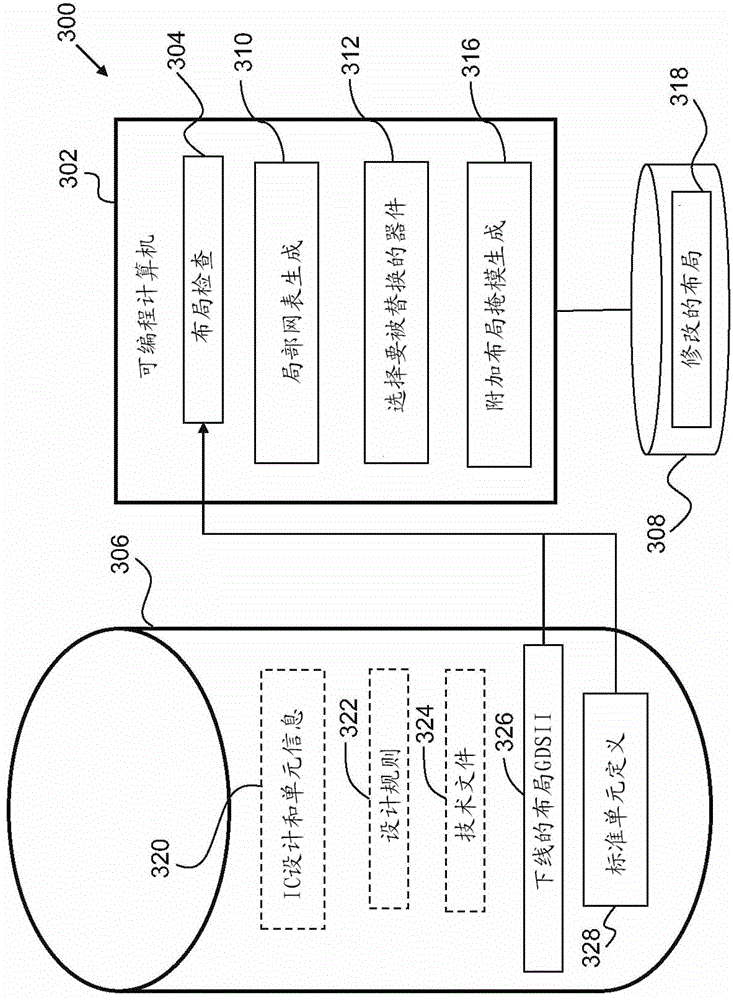
Layout modification method and system
ActiveCN103605817AConfiguration CADSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer architectureModified method
The invention provides a method. The method comprises providing a non-transitory, machine-readable storage medium storing a partial netlist of at least a portion of a previously taped-out integrated circuit (IC) layout, representing a set of photomasks for fabricating an IC having the IC layout such that the IC meets a first specification value. A computer identifies a proper subset of a plurality of first devices in the IC layout, such that replacement of the proper subset of the first devices by second devices in a revised IC layout satisfies a second specification value different from the first specification value. At least one layout mask is generated and stored in at least one non-transitory machine readable storage medium, accessible by a tool for forming at least one additional photomask, such that the set of photomasks and the at least one additional photomask are usable to fabricate an IC according to the revised IC layout. The invention further provides a layout modification method and system.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
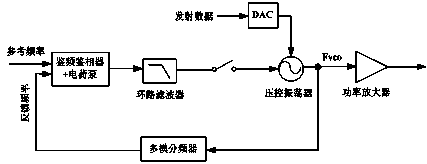
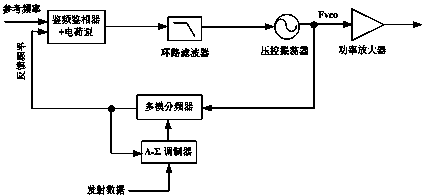
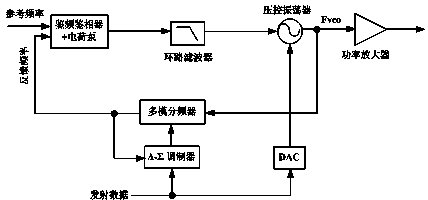
Two-point wireless transmitter and frequency offset correcting method thereof
InactiveCN104242961AReduce noise interferenceAchieve flatnessAngle modulation detailsTransmissionMicrocontrollerEngineering
The invention discloses a two-point wireless transmitter and a frequency offset correcting method of the two-point wireless transmitter. Improvement is conducted based on a circuit structure of a traditional two-point transmitter, and frequency offset correction is achieved by conducting data interaction by means of two wireless communication chips which have the complete functional design and are successfully taped out. During implementation, the two chips are respectively provided with a microcontroller, a register, a transmitting module, a receiving module, an antenna and a change-over switch; transmitted data are input to the wireless transmitter through two paths, one path of data are input to a voltage-controlled oscillator through a branch switch S2 of the first chip and a DAC to be transmitted in an out-band mode, and the other path of data are input to a multi-mode frequency divider through a branch switch S1 of the first chip and a delta-sigma modulator for modulation and frequency division and then are transmitted in an in-band mode. According to the two-point wireless transmitter and the frequency offset correcting method of the two-point wireless transmitter, through the data interaction between the two chips and software processing of the microcontroller of the first chip, the frequency offset of the transmitted data can be corrected effectively, and high-quality smooth transmission of data is achieved; the two-point wireless transmitter and the frequency offset correcting method of the two-point wireless transmitter have the advantages that energy consumption is low, the number of hardware resources is small, cost is low and stability is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI PANCHIP MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
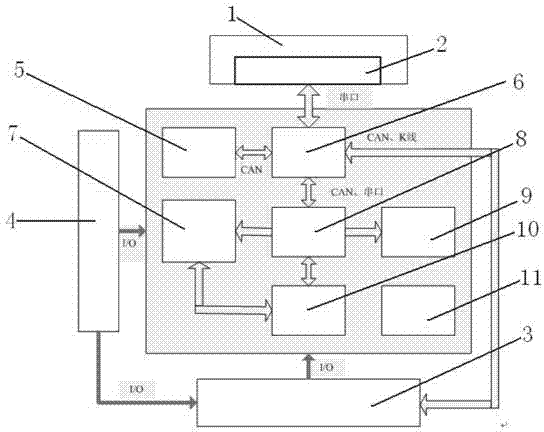
Offline detection device of body control module product based on CAN bus, and test method
InactiveCN110597225AImprove general performanceReduce construction costsElectric testing/monitoringTested timeProduct base
The invention provides an offline detection device of a body control module (BCM) product based on a CAN bus, and a test method. The detection device comprises a programmed power supply, a PCB test board, a test clamp, a load box, a CAN communication tool, a host computer and a load module. According to the device, the university is high, the design of a PCB test board is adopted, the establishment cost of the device can be greatly reduced without adoption of a commercial test board, the offline detection device can perform repeated use, test personnel does not need to participate in operationin a test process, test software of the host computer performs programming modification on a test sequence according to the product difference, the test time is reduced, input and output signals of the tested BCM are automatically tested and determined through the test device, man-made errors are reduced, and the test accuracy is improved.
Owner:CATARC TIANJIN AUTOMOTIVE ENG RES INST CO LTD +1
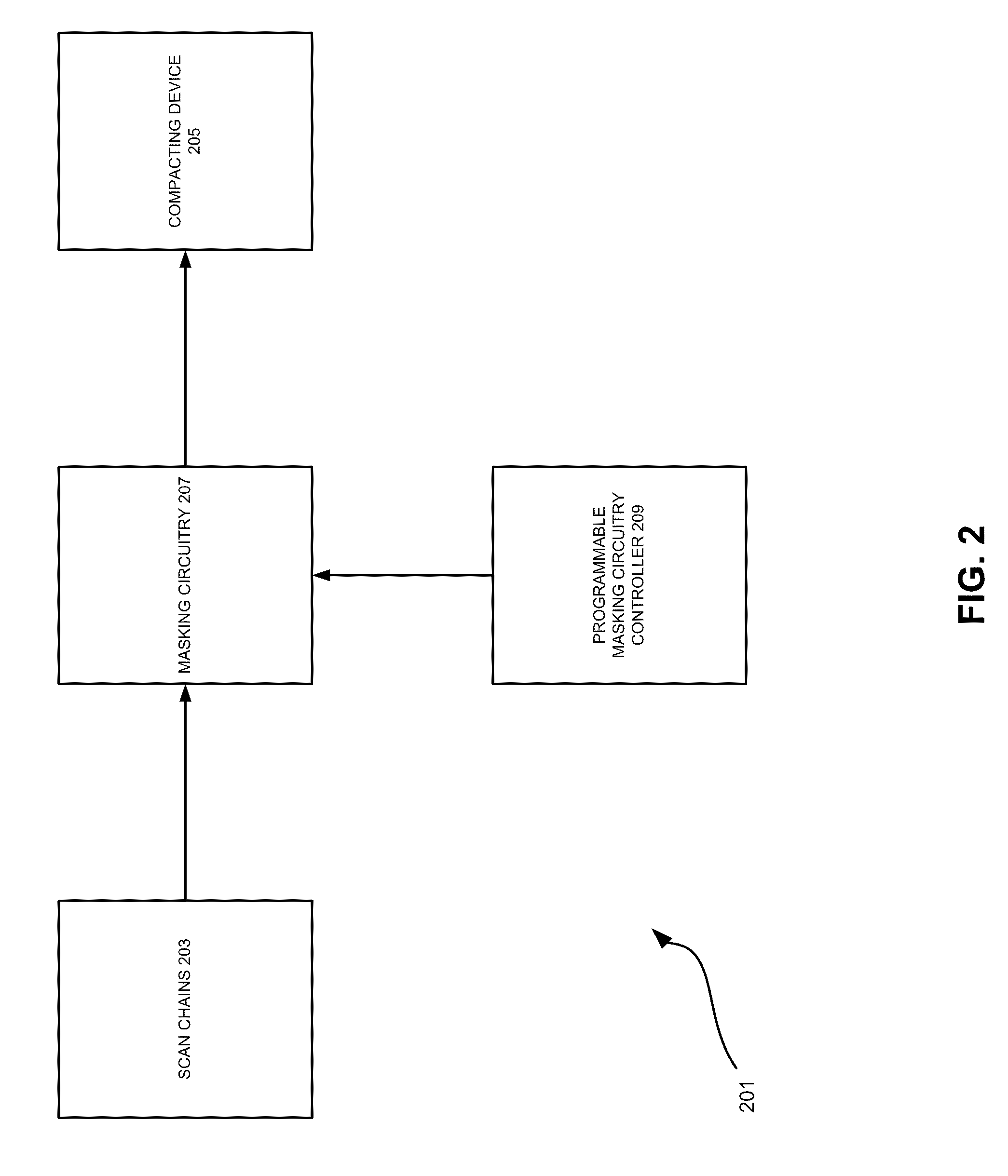
On-Chip Logic To Support In-Field Or Post-Tape-Out X-Masking In BIST Designs
InactiveUS20100253381A1Functional testingIndividual semiconductor device testingData valueEmbedded system
Techniques for masking unknown and irrelevant response values that may be produced by a BIST process. Masking circuitry is provided for selectively masking the response values obtained from a BIST process. The operation of the selective masking circuitry is controlled by a programmable mask circuitry controller that can be programmed after the integrated circuit has been manufactured. A user can analyze an integrated circuit after it has been manufactured to identify irrelevant and unknown data values in a BIST process. After the irrelevant and unknown data values have been identified, the user can program the programmable mask controller to have the selective masking circuitry mask the identified irrelevant and unknown data values.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Off-line detection device and detection method of anti-lock brake system electronic control unit
ActiveCN102890502AValid queryEffective trackingElectric testing/monitoringControl areaRegulated power supply
The invention discloses an off-line detection device and an off-line detection method of an anti-lock brake system electronic control unit. The off-line detection device comprises a computer, an off-line detection software module which is arranged in the computer, an integrated function circuit board and a direct current voltage stabilizing power supply, wherein the function circuit board is connected with the detected anti-lock brake system electronic control unit and the computer through a control area network (CAN) bus and a K line; and the off-line detection software module is connected with the integrated function circuit board through a serial port. During off-line detection of different types of anti-lock brake system electronic control unit products, determination data of off-line detection software are modified, and novel off-line testing equipment is not required to be redeveloped. The invention has the advantages of high expandability, simple structure, high intuitiveness, high practicability, effective failure positioning capacity, high system traceability and the like. Product information is recorded, and unqualified electronic control unit products are effectively searched and traced.
Owner:WUHU BETHEL AUTOMOTIVE SAFETY SYST
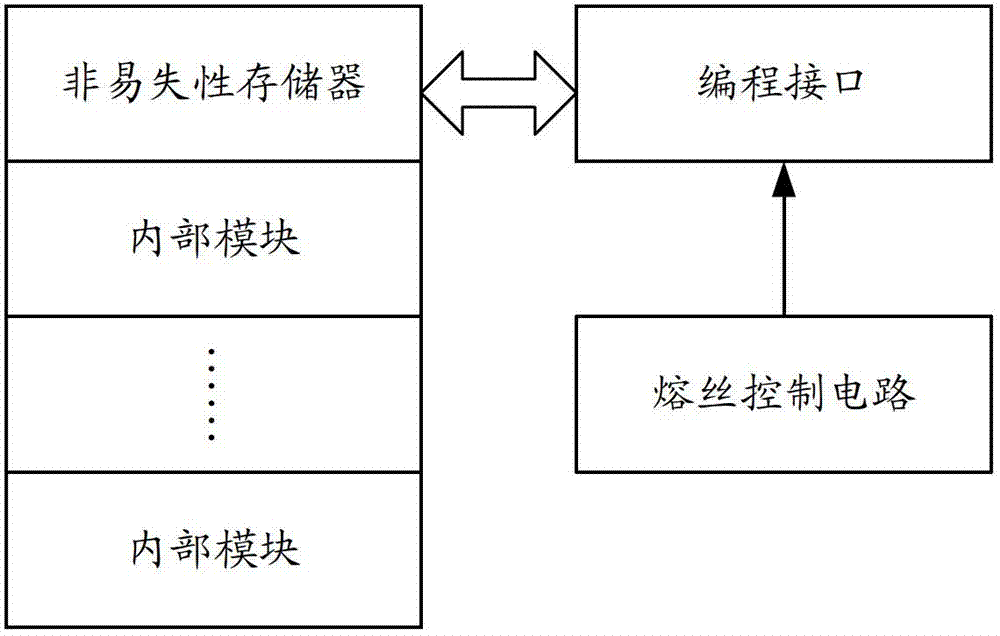
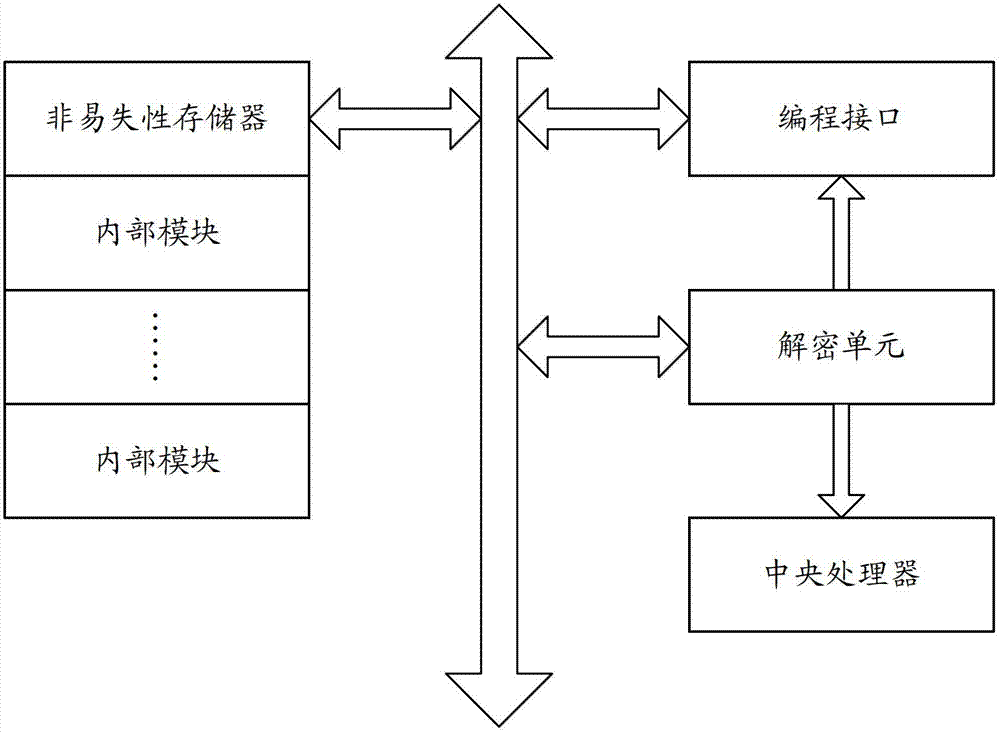
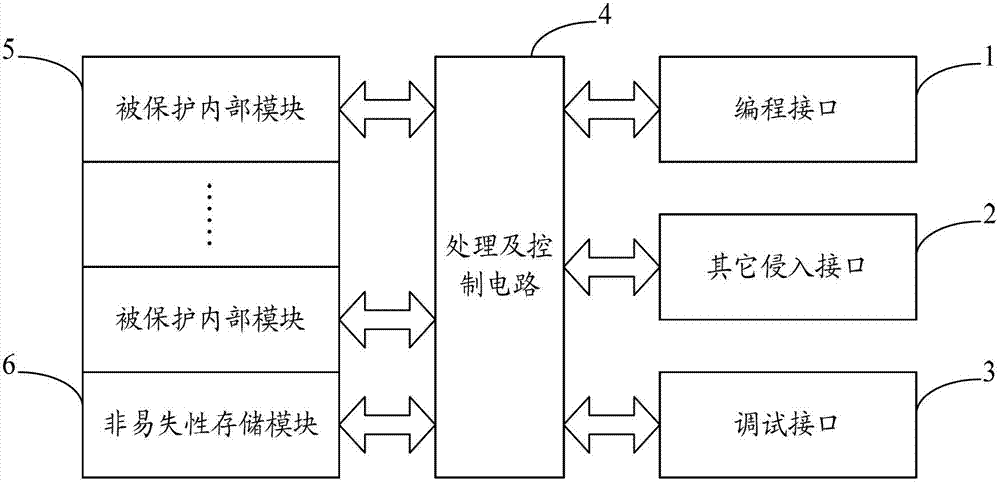
Chip and inner module encryption system thereof
ActiveCN102779254AImprove reliabilityReduced change feesComputer security arrangementsComputer moduleControl circuit
The invention belongs to the technical field of a chip design and provides a chip and inner module an encryption system thereof. The system comprises a nonvolatile storage module and a processing and controlling circuit, wherein the nonvolatile storage module is used for storing an encryption protection policy and a decipherment algorithm; and the processing and controlling circuit is used for reading and analyzing the encryption protection policy stored in the nonvolatile storage module when peripheral equipment is connected with an invasion interface of the chip, and protecting a protected inner module of the chip according to the analyzed encryption protection policy. According to the chip and the inner module encryption system thereof, the decipherment algorithm in a software form and the processing and controlling circuit in a hardware manner are separately realized, so that when the decipherment algorithm needs to be changed, a user can directly change the decipherment algorithm stored in the nonvolatile storage module; the chip does not need to be taped out again, so that the changing cost is extremely reduced and the utilization flexibility is enhanced; and the user can customize the decipherment algorithm and the cracking difficulty is improved, so that the reliability of the chip is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN RENERGY TECH
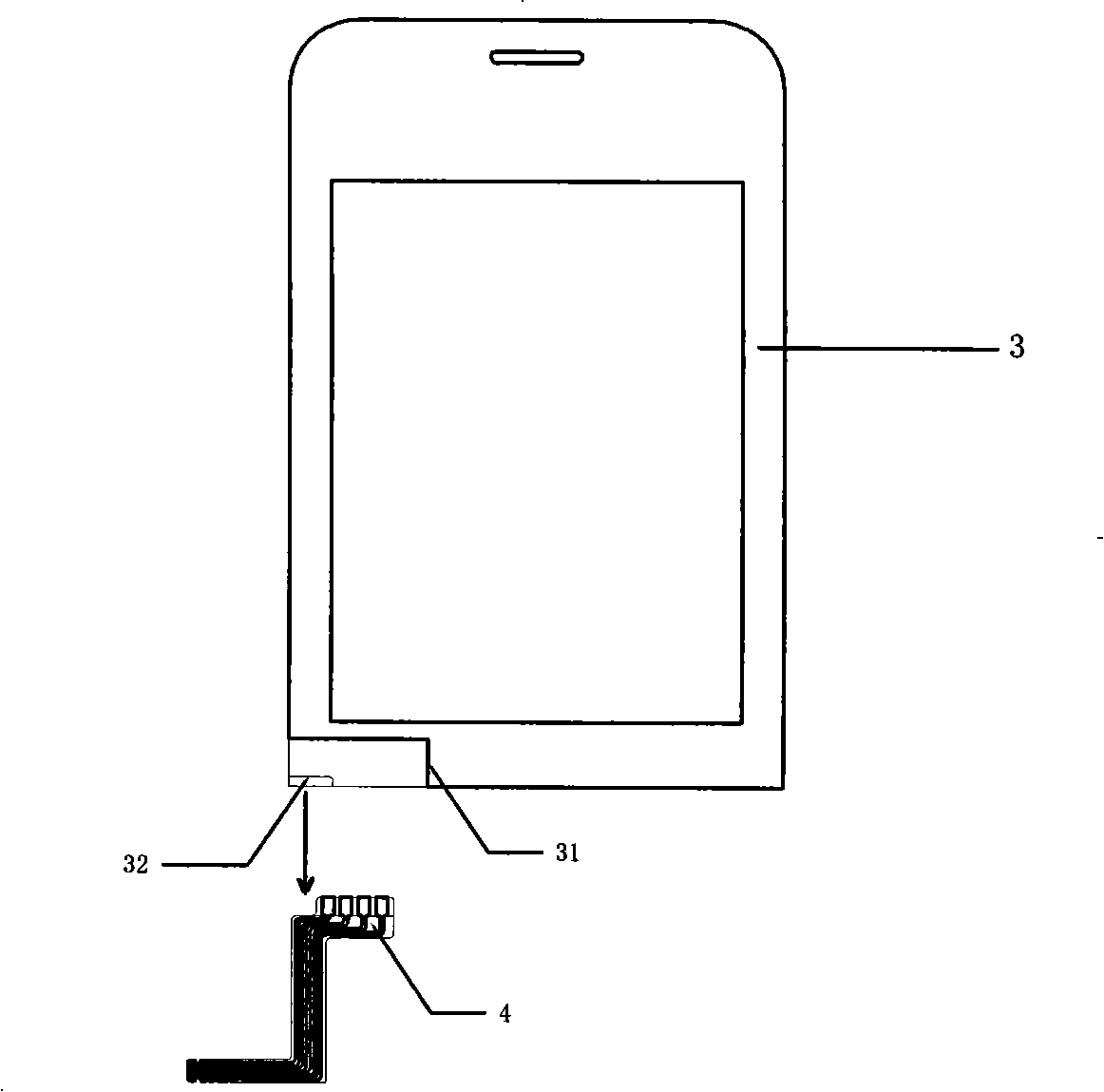
Electric resistance type touch screen and method of manufacture
The invention discloses a resistance-type touch screen, which is characterized in that the resistance-type touch screen comprises a circuit layer, a flexible printed circuit educed from the circuit layer, an upper ITO film integrated on the upper surface of the circuit layer; a mirror integrated on the upper ITO film through adhesive, and a lower conductive PC board integrated on the lower surface of the circuit layer. Correspondingly, the invention also discloses a manufacturing method of the resistance-type touch screen. The invention avoids various shortcomings caused by glass materials used in the prior art, such as poor bending degree, poor pressure resistance and bad anti-attack performance, and also avoids the limitations that only the rectangular and inner-clipping way can be used.
Owner:GANZHOU DPT TECH
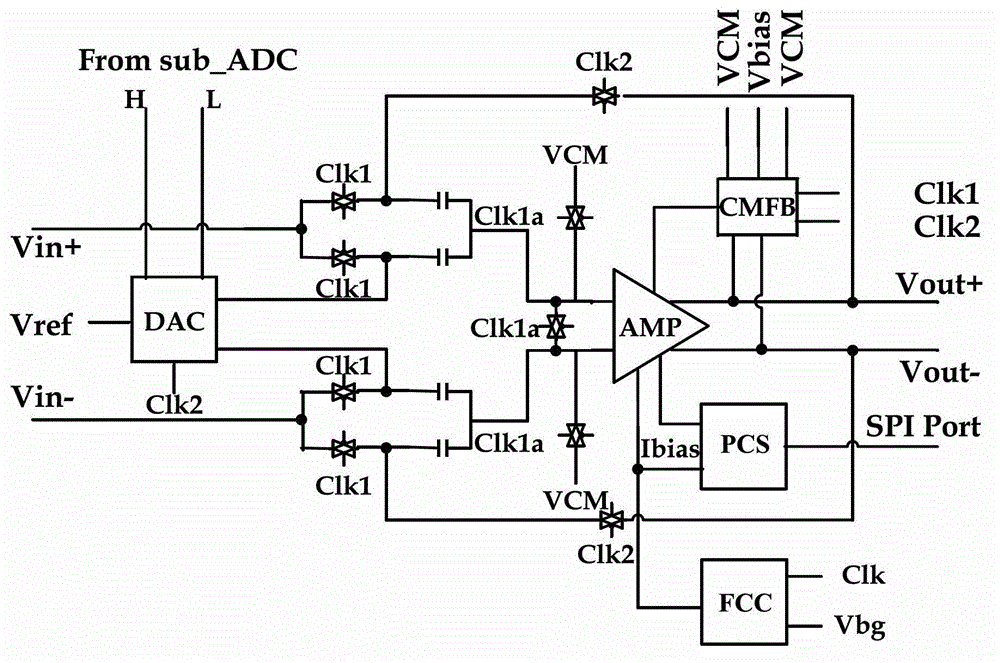
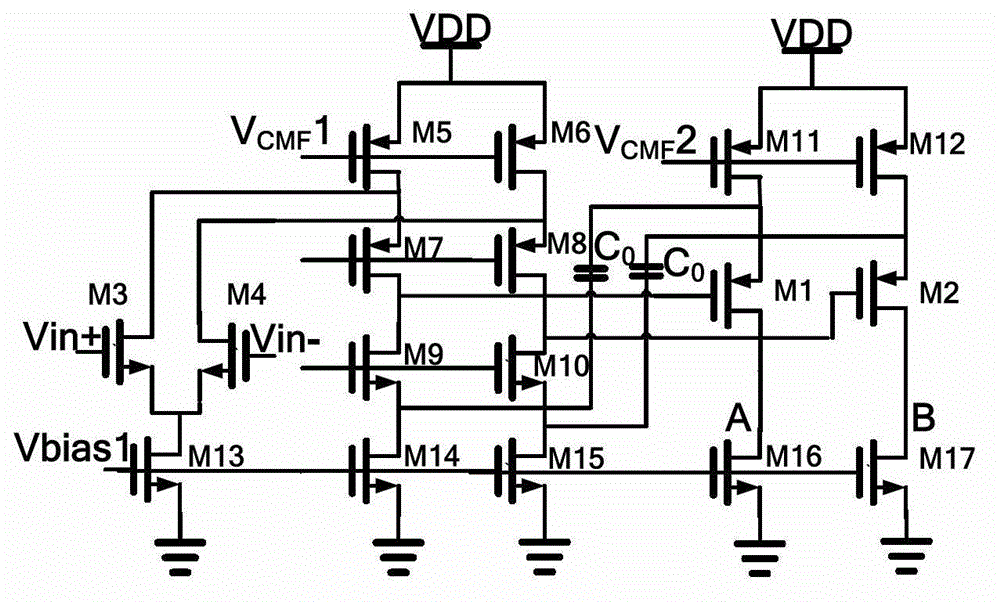
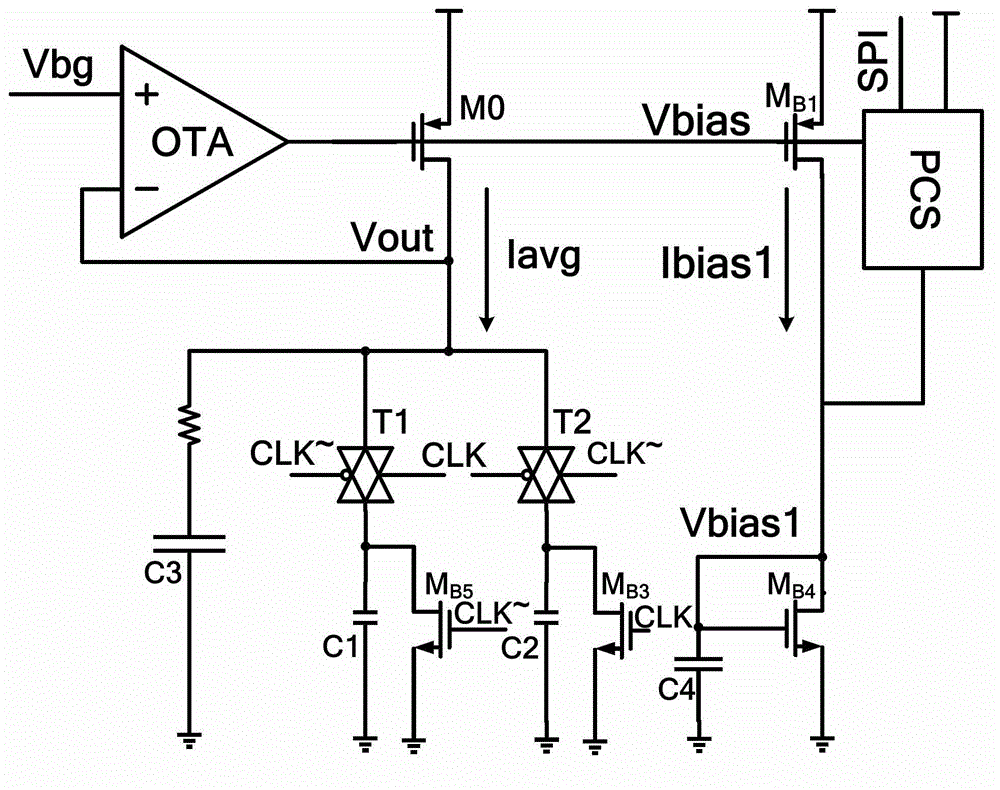
Programmable gain digital-analog unit and analog-to-digital converter
ActiveCN103944570AAvoid the problem of consuming too much energyGain controlAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterLinear relationship
The invention provides a programmable gain digital-analog unit and an analog-to-digital converter and belongs to the field of analog-to-digital converters. The programmable gain digital-analog unit is applied to the analog-to-digital converter, and working current of an operational amplifier of the programmable gain digital-analog unit has a linear relationship with a sampling frequency of the analog-to-digital converter. With the adoption of the technical scheme, the working current of the operational amplifier of the gain digital-analog conversion unit is linearly dependent on the sampling frequency, a purpose of realizing self adaption of the sampling frequency of the analog-to-digital converter to power consumption is achieved, and a programmable current source array controlled by an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) port can adjust and optimize circuit performance after tape-out at the same time.
Owner:西安电子科技大学重庆集成电路创新研究院
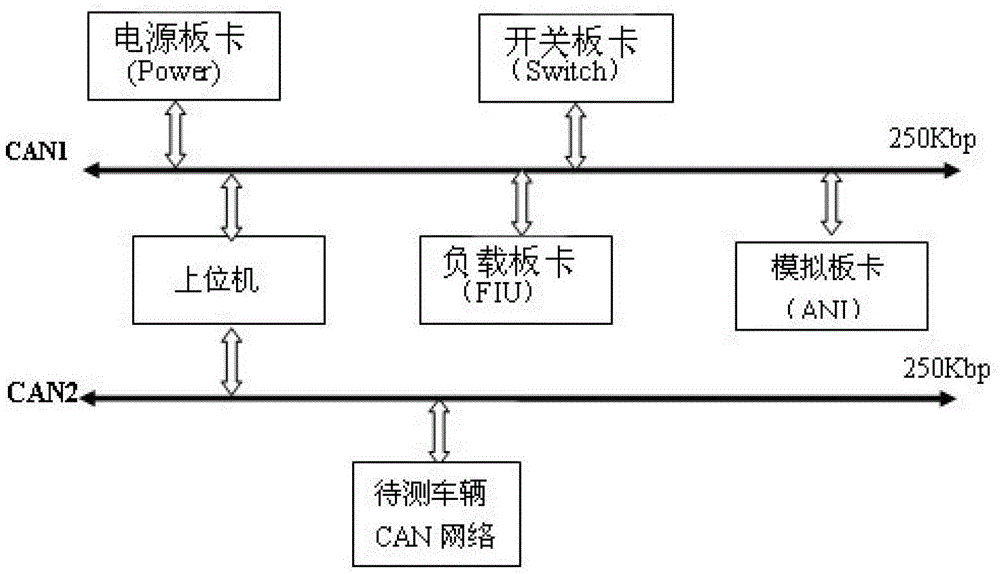
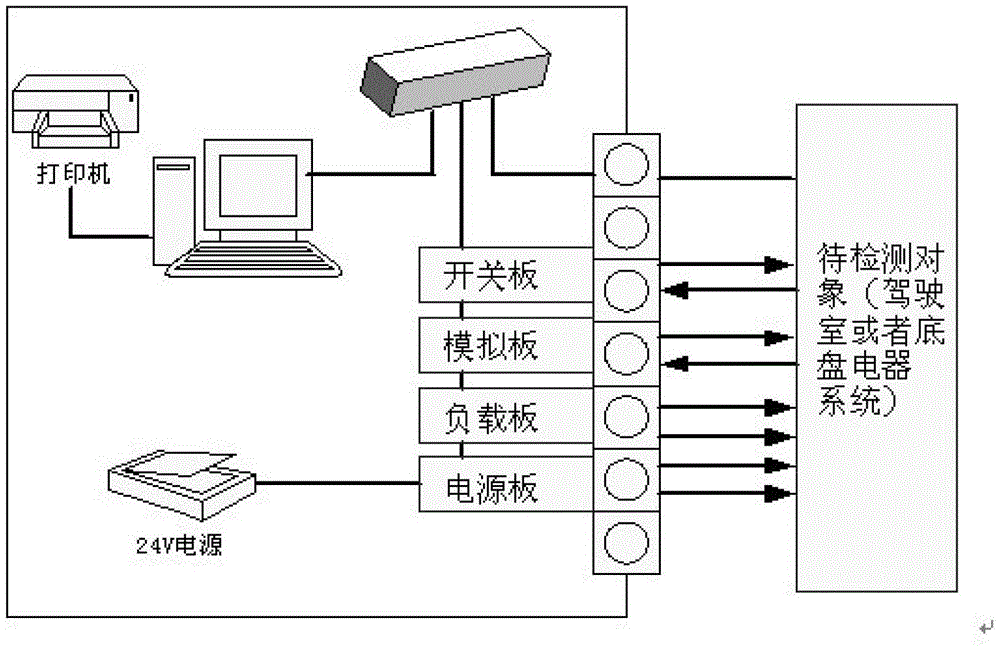
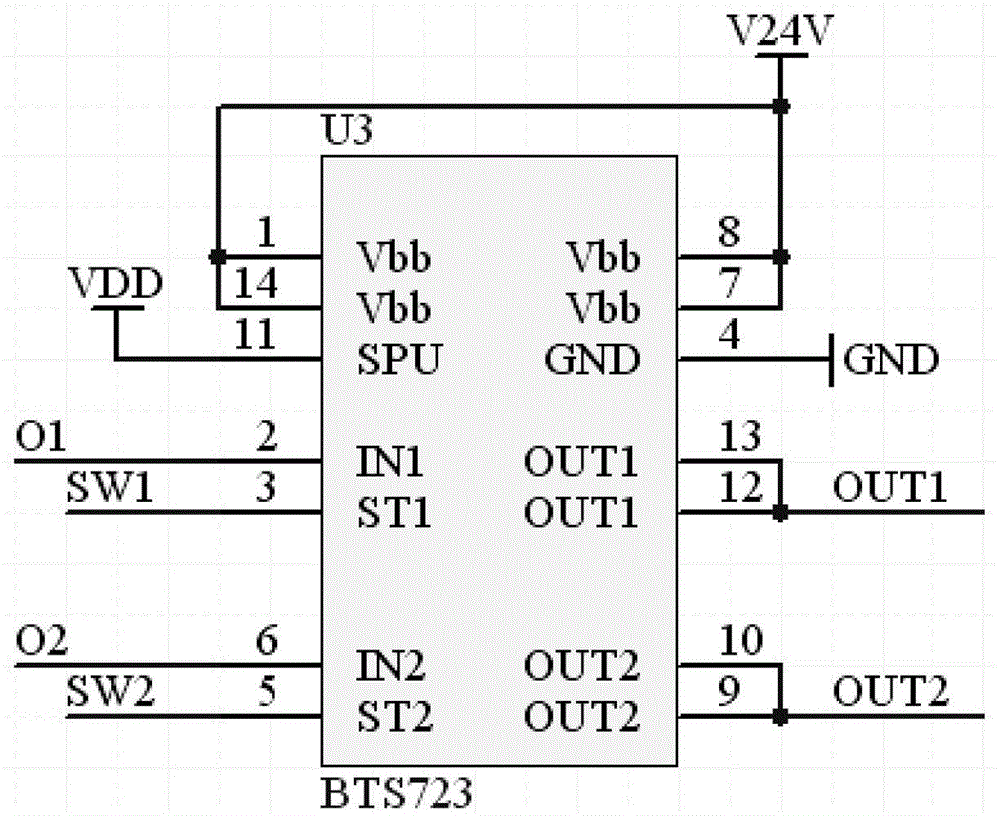
Offline fault detection method for electromobile
InactiveCN103149033AImprove safety and reliabilityQuality improvementVehicle testingElectrical testingArea networkEngineering
The invention relates to an offline fault detection method for an electromobile. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) setting an offline fault detection system for the electromobile comprising an upper computer and a low computer consisting of a switch board card, a power supply board card, a load board card and a simulation board card; 2) connecting a diagnosis interface with a bundle interface in a driver's cab part or a chassis part, wherein the simulation driver's cab part or the simulation chassis part consists of the switch board card, the power supply board card, the load board card and the simulation board card; 3) outputting 24V voltage by the power supply board card to the simulation chassis consisting of the switch board card, the load board card and the simulation board card to supply power; 4) transmitting the detection signals of the driver's cab part to an MCU (Microprogrammed Control Unit) signal collecting terminal in the upper computer through a CAN (Controller Area Network) bus, and converting the received processing information to a control command to the board cards after receiving the processing information by the MCU; and 5) sending the control command to the board cards through the CAN bus by the upper computer and returning the detection signal to the upper computer by each board card, comparing with variables stored in the detected driver's cab part and judging whether faults occur or not to detect the driver's cab part.
Owner:BEIJING RUIRI CHEXIN SCI & TECH
IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) chip manufacturing method for crimped type package
ActiveCN104810283AGood effectLow costTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPolysilicon gate
The invention relates to an IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) chip manufacturing method for crimped type package. The IGBT chip manufacturing method comprises the following steps: selecting a silicon substrate and preprocessing the silicon substrate; carrying out field oxide layer growth on the surface of the silicon substrate, and etching the field oxide layer; manufacturing a gate oxide layer and a polysilicon gate electrode; manufacturing a P well and an N well; manufacturing Spacer, a P+ type doping region and an N+ type doping region; forming a positive electrode EM2 above the polysilicon gate electrode; forming a positive electrode EM1 on the outer side of the positive electrode EM2; forming a P+ collector region on the back surface of the silicon substrate; manufacturing a back electrode C. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the IGBT chip manufacturing method has low requirement on technological precision, and the tape-out cost is reduced.
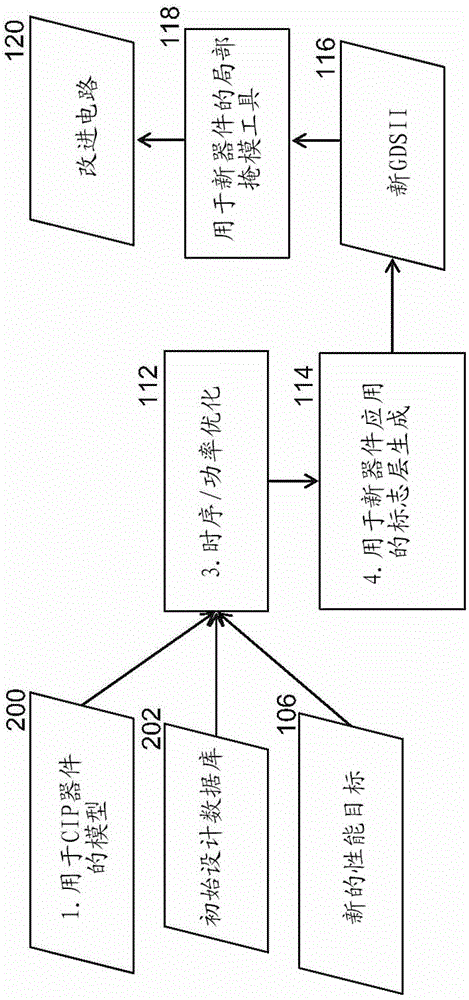
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY INTERCONNECTION RES INST CO LTD +1
Integrated circuit structure and a design method thereof
ActiveUS20050028126A1Minimize changesLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuitTape-out
The present invention discloses an integrated circuit structure and a design method thereof, in which a circuit passageway is arranged at each circuit element terminal in circuit design stage. The arranged circuit passageway does not only increase layout flexibility in circuit simulation stage but also simplify layout difficulty when the circuit layout needs to be modified after taping out stage. Also, the circuit passageway can minimize modified metal layers, i.e. the number of modified masks is minimized. Because the expense of fab is based on the utilized layers and number of masks instead of designs of masks, the present invention will not increase the expense in taping out stage and can save the cost of research and development when modifications are required.
Owner:ALICORP
Circuit structure integrating graphic processor and video codec
ActiveCN102932645AImprove reliabilityIncrease profitTelevision systemsProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsComputer architecture
The invention discloses a circuit structure integrating a graphic processor and a video codec. The circuit structure comprise the graphic processor, wherein the graphic processor comprises a stream processor. The circuit structure is characterized in that the stream processor comprises a graphic processing unit, a video processing unit, a slave controller and a sharing unit. The circuit structure can effectively solve the problems of poor reliability, long data transmission delay, high taping-out cost of chips, low utilization rate of on chip resources and the like due to separate design of a graphic processing chip and a video processing chip in an integrated circuit, the problems in the conventional method of separately designing the graphic processing chip and the video processing chip are solved well, the reliability of the circuit design is improved, the data transmission delay is reduced, the tapping-out cost is lowered, and the utilization rate of the on chip resources is improved to a great extent.
Owner:SHANDONG LINGNENG ELECTRONIC TECH CO LTD
Soft reset device of integrated circuit chip
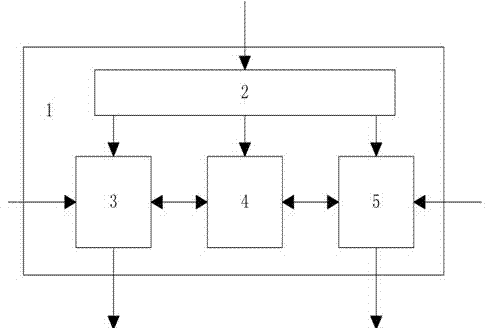
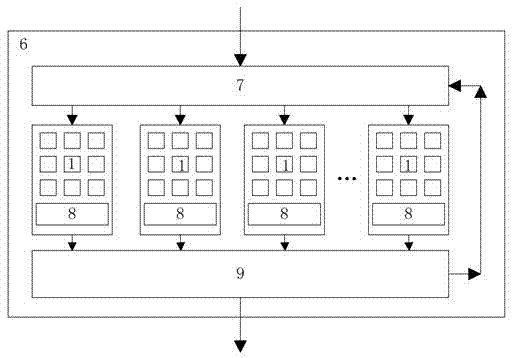
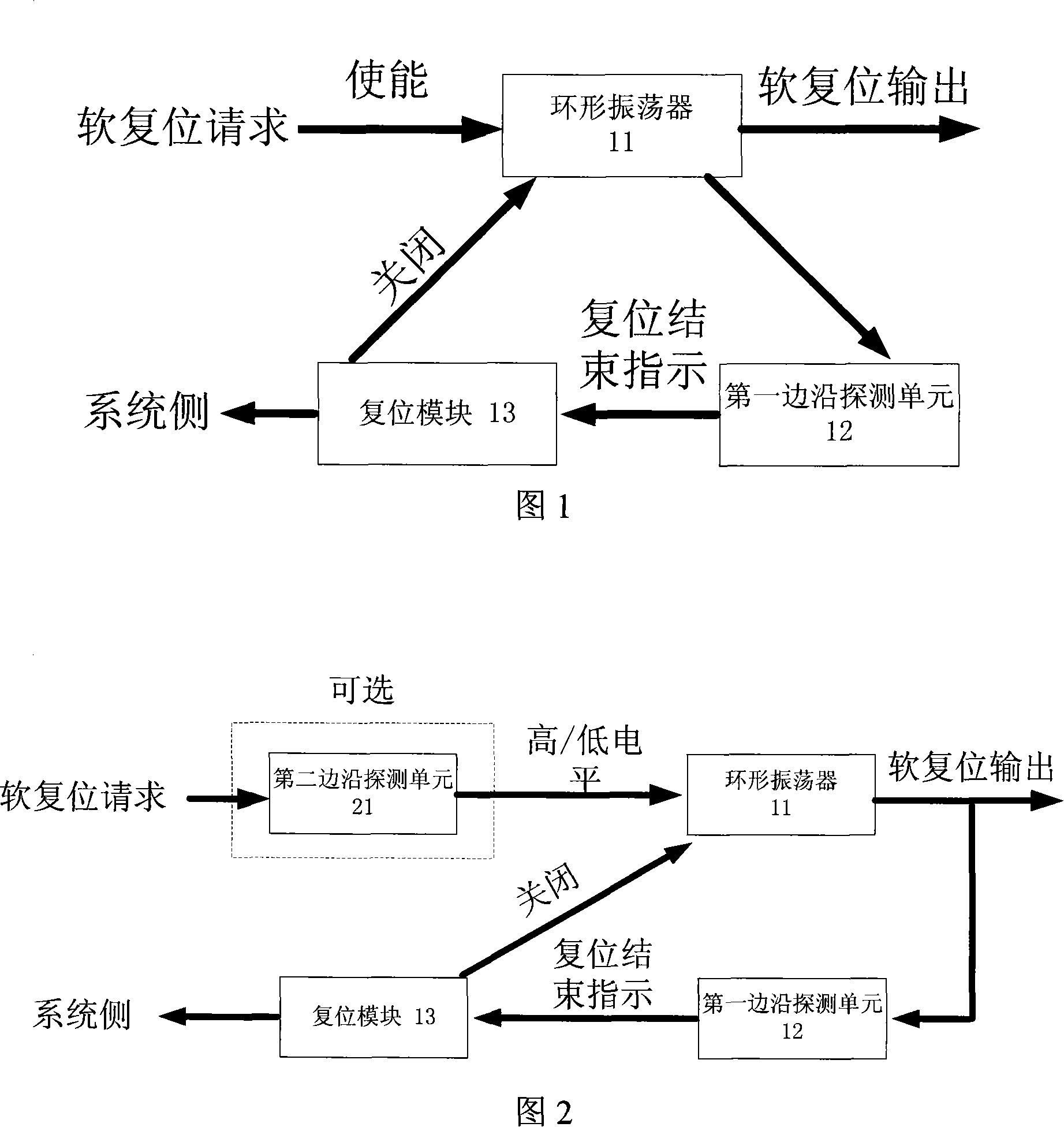
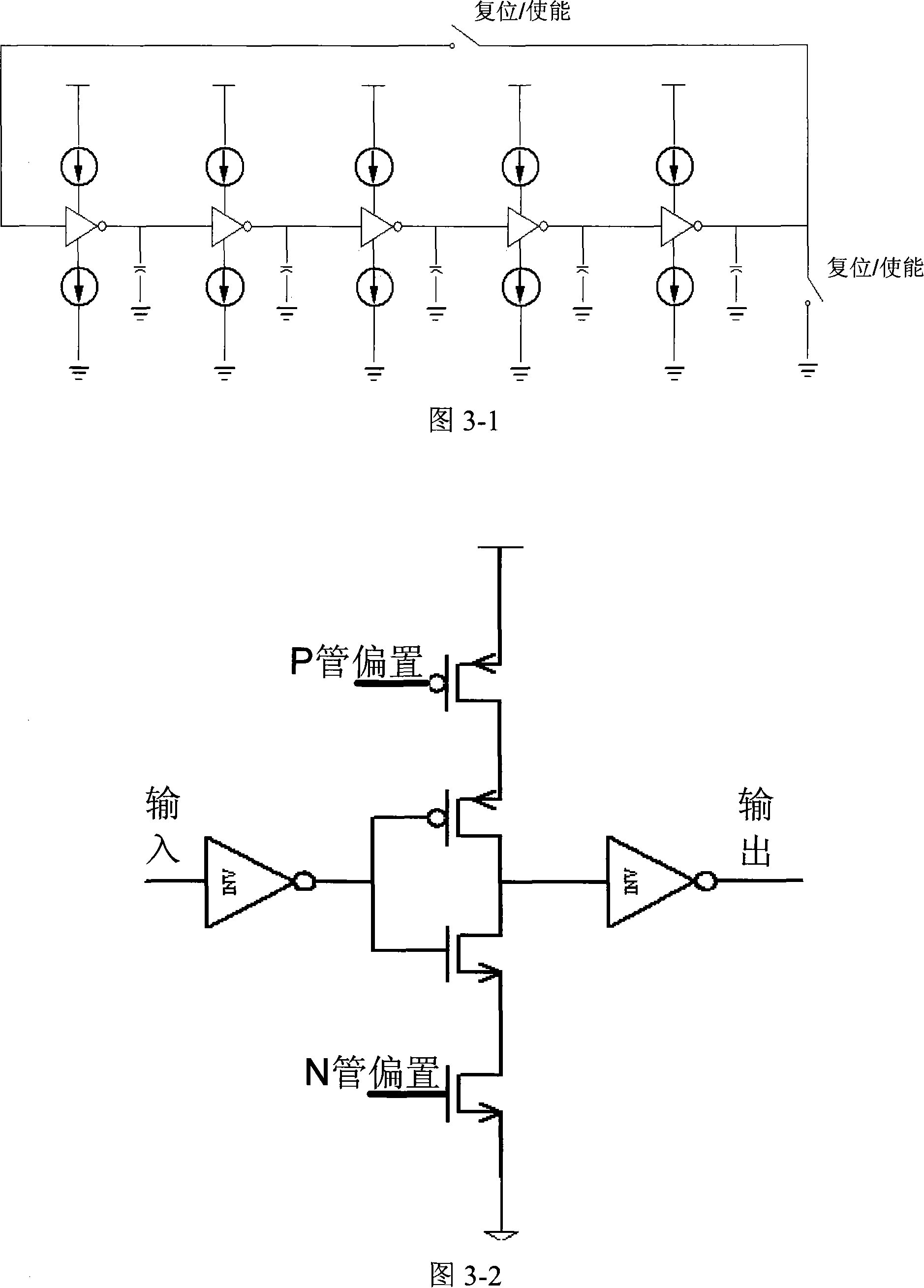
InactiveCN101141126AReduce power consumptionAvoid filteringPulse generation by logic circuitsElectronic switchingEngineeringStart up
The invention relates to a soft reset device for integrated circuit chip and is inserted into the integrated circuit chip. The utility model consists of a ring shape oscillator(11), a reset pulse signal that has certain cycle and meets the reset request under the action of trigger signal according to the software control; a first edge detecting unit(12) that receives the reset pulse signal and outputs reset ending signal, a reset module(13) that receives the reset ending signal and outputs reset signal to start-up reset while outputs reset closing signal to the ring shape oscillator to stop the output of the reset pulse signal. The static power consumption of the module is around zero; the area is small and can prevent the filtering of high frequency input signal caused by the low pass property of the RC; compatible to meet more than one trigger method; clear design concept and can be realized by standard CMOS technique approved by tape-out inspection needless of adding mask.
Owner:ZTE CORP
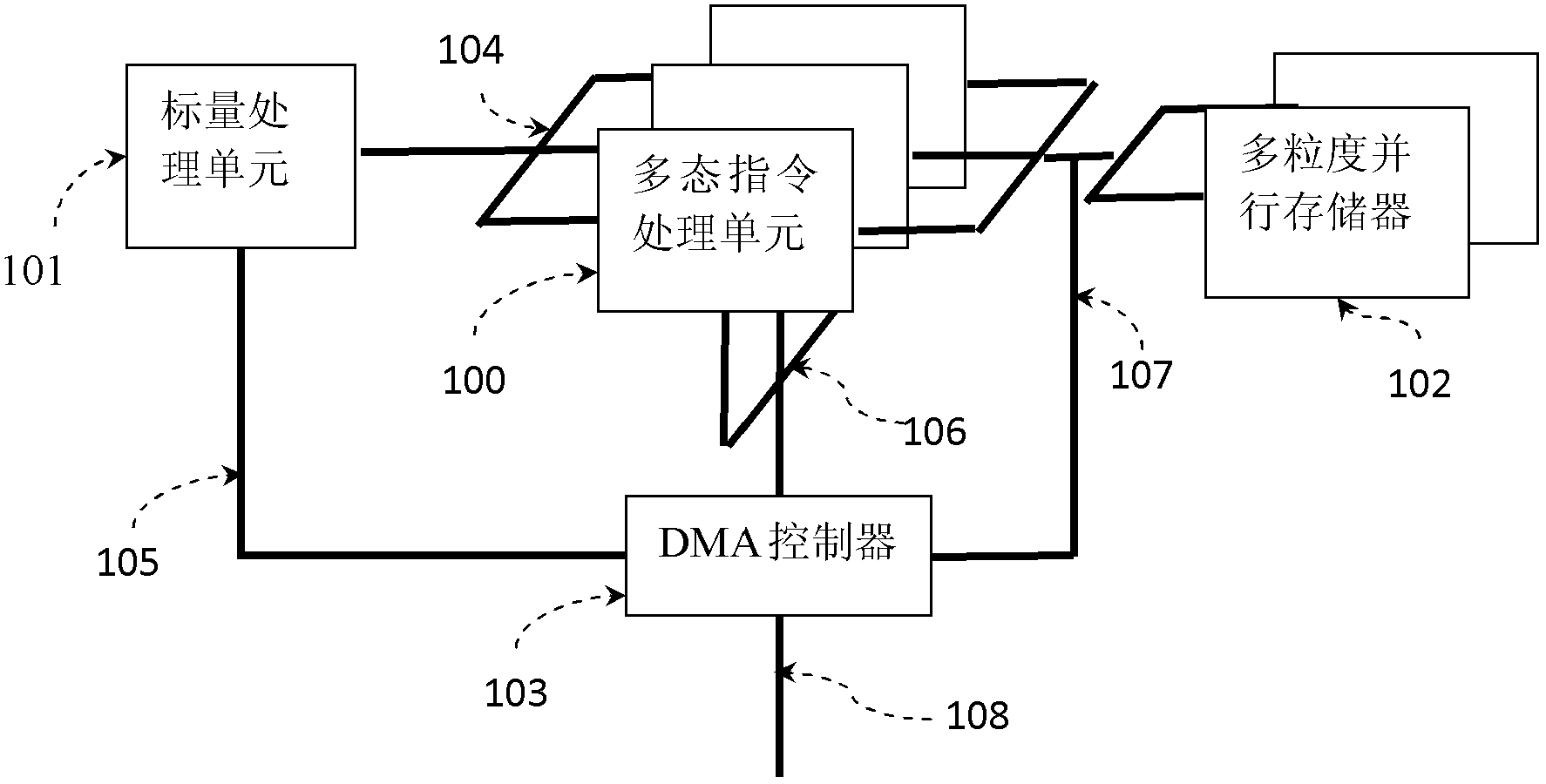
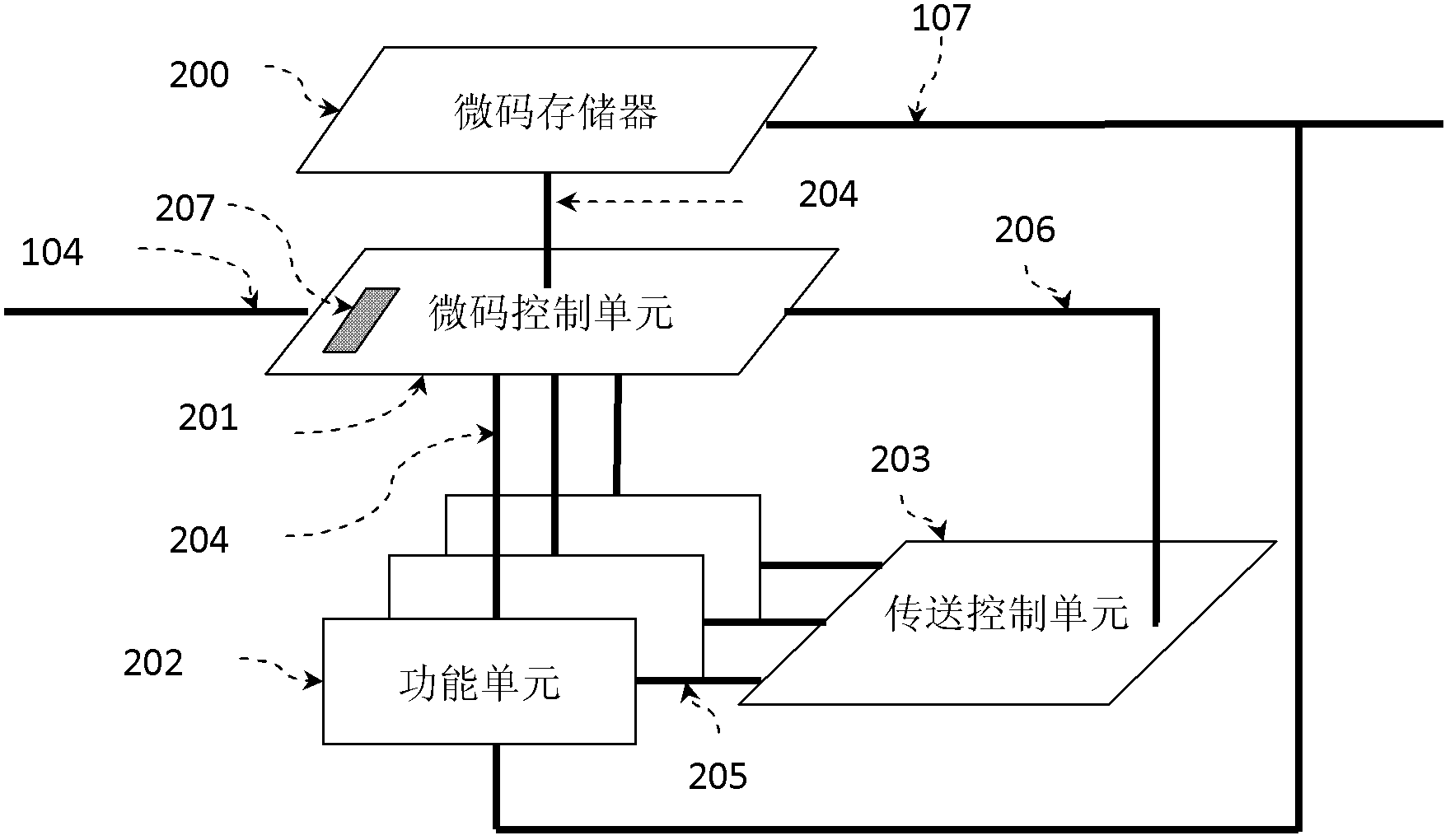
Processor with polymorphic instruction set architecture
ActiveCN103235717AEasy to handleConcurrent instruction executionDirect memory accessInstruction processing unit
The invention provides a processor with a polymorphic instruction set architecture. The processor comprises a scalar processing unit (101), at least one polymorphic instruction processing unit (100), at least one multi-granularity parallel memory (102) and a direct memory access (DMA) controller (103). Each of the polymorphic instruction processing units (100) comprises at least one function unit (202), the polymorphic instruction processing units (100) are used for explaining and executing polymorphic instructions, and the function units (202) are used for executing specific data operation tasks; the scalar processing unit (101) is used for calling the polymorphic instructions and inquiring execution states of the polymorphic instructions; and the DMA controller (103) is used for transmitting configuration information of the polymorphic instructions and transmitting data required by the polymorphic instructions to the multi-granularity parallel memories (102). According to the processor, programmers can still redefine the instruction set of the processor according to characteristics of an application algorithm after tape-out production of the processor.
Owner:BEIJING SMART LOGIC TECH CO LTD
An end-of-line testing tool and detection method of the testing tool
InactiveCN105759776AAchieve traceabilityEnsure downline pass rateElectric testing/monitoringTransmissionInteraction interfaceEngineering
The invention relates to an end-of-line testing tool and a detection method of the testing tool. The end-of-line testing tool comprises a test host, a USBCAN card, a human-computer interaction interface, a scanning device and a printing device. The USBCAN card, the human-computer interaction interface, the scanning device and the printing device are connected with the test host. The end-of-line testing tool sends fault reading, storing and clearing instructions through a CAN bus; a vehicle controller develops corresponding response programs and executes corresponding actions; vehicle key parameters are read according to set content, and are compared with set parameter range to determine whether the vehicle state is normal; action test is carried out on key components and high-voltage relays and the like, feedback result is collected, and result judgment is made; and archives are established for end-of-line vehicles, and traceability of information of the end-of-line vehicles is realized.
Owner:SAIC-GM-WULING AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Jitter tolerance simulation verification method of clock data recovery circuit
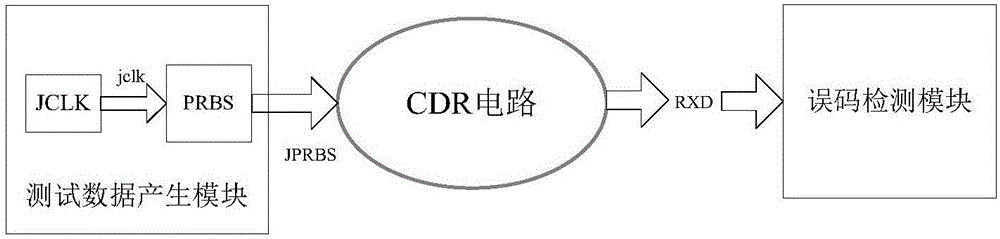
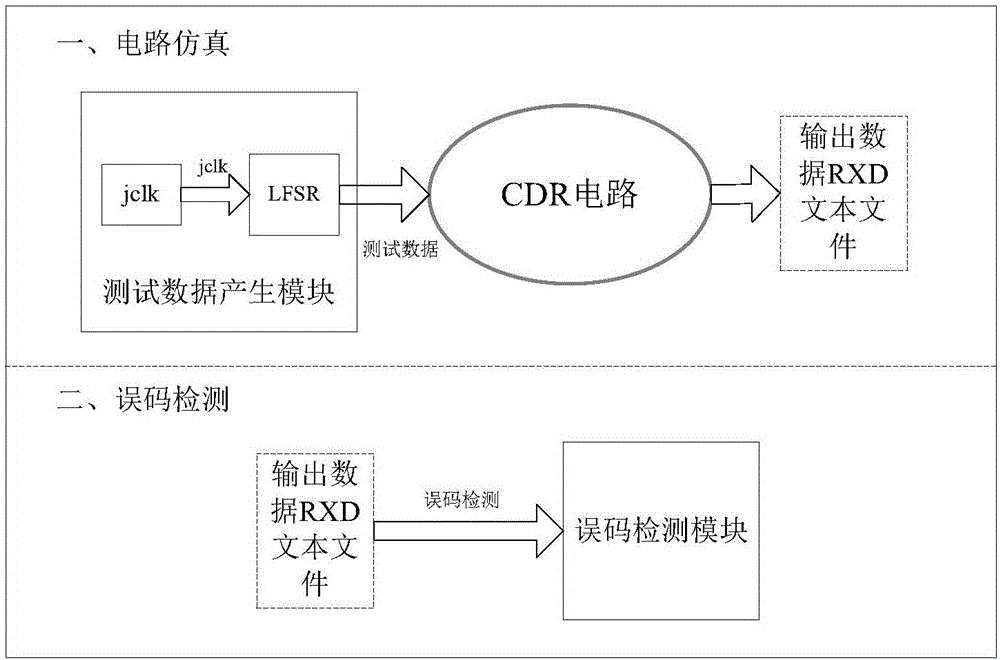
InactiveCN106777506AReduce Tape-out RiskAdjustment rangeCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsData fileComputer module
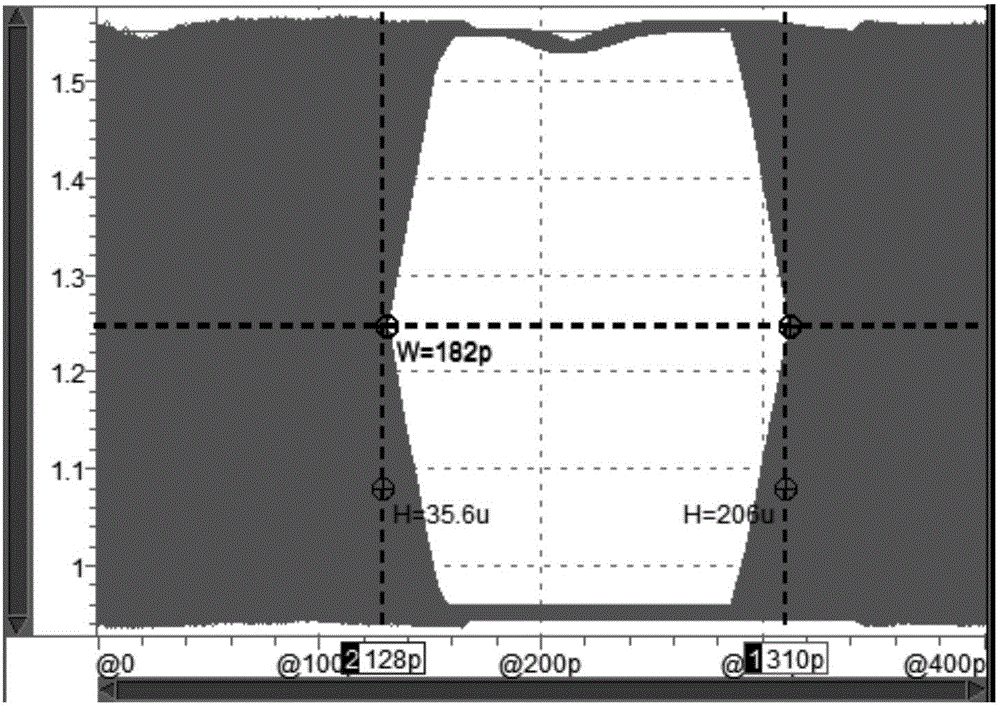
The invention discloses a jitter tolerance simulation verification method of a clock data recovery circuit. The jitter tolerance simulation verification method is implemented through the following three modules: a test data generating module, a clock data recovery (CDR) circuit and an error code detection module, wherein the test data generating module generates a pseudo random sequence superposed with jitter information as an input of the CDR circuit, consists of a jitter modulating clock and a pseudo random code generating module, and is implemented via VerilogA language design; the error code detection module performs an error code detection on an output data file of CDR simulation, and is implemented through Python scripts. The jitter tolerance simulation verification method comprises the following two steps: first, simulating the test data generating module and the CDR circuit to obtain the output data file of the CDR; then, performing the error code detection on the output data file by using the error code detection module. By the jitter tolerance simulation verification method, the jitter resistance of the CDR is evaluated in a design stage, so that tape-out risks are effectively reduced; in addition, the jitter tolerance simulation verification method is easy to implement and short in verification time and has relatively strong practicability.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com