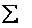Patents
Literature
80results about How to "Quick steps" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
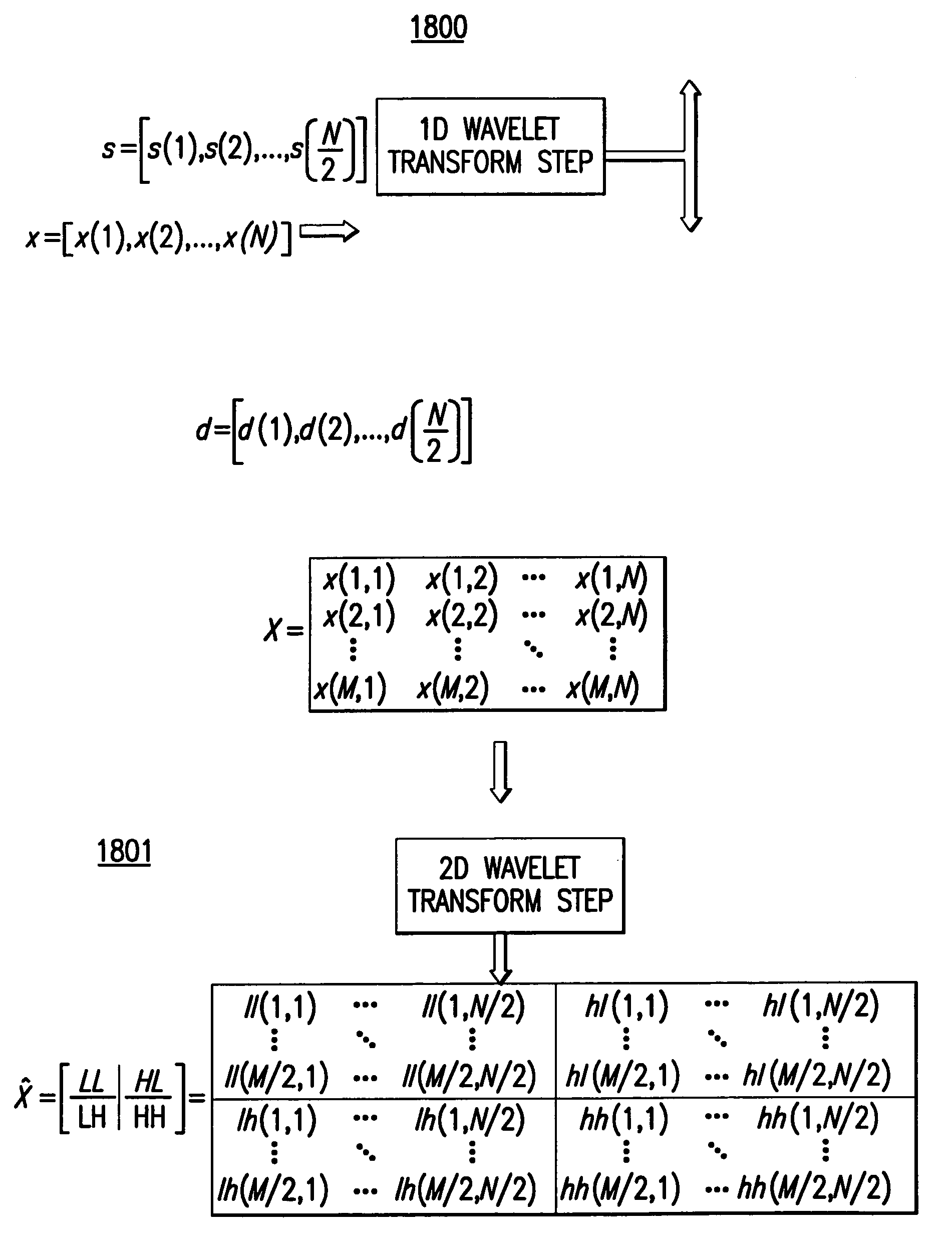
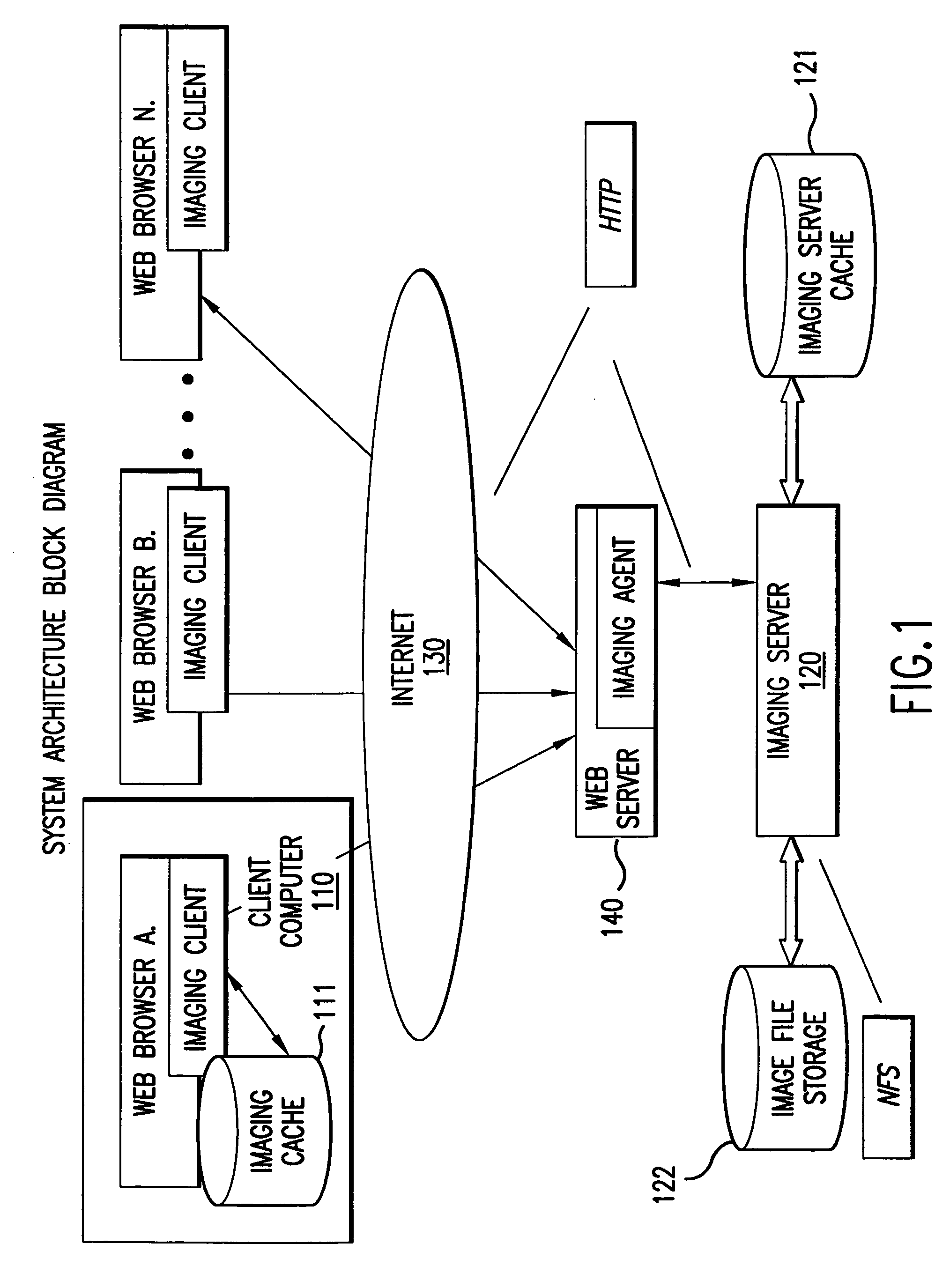
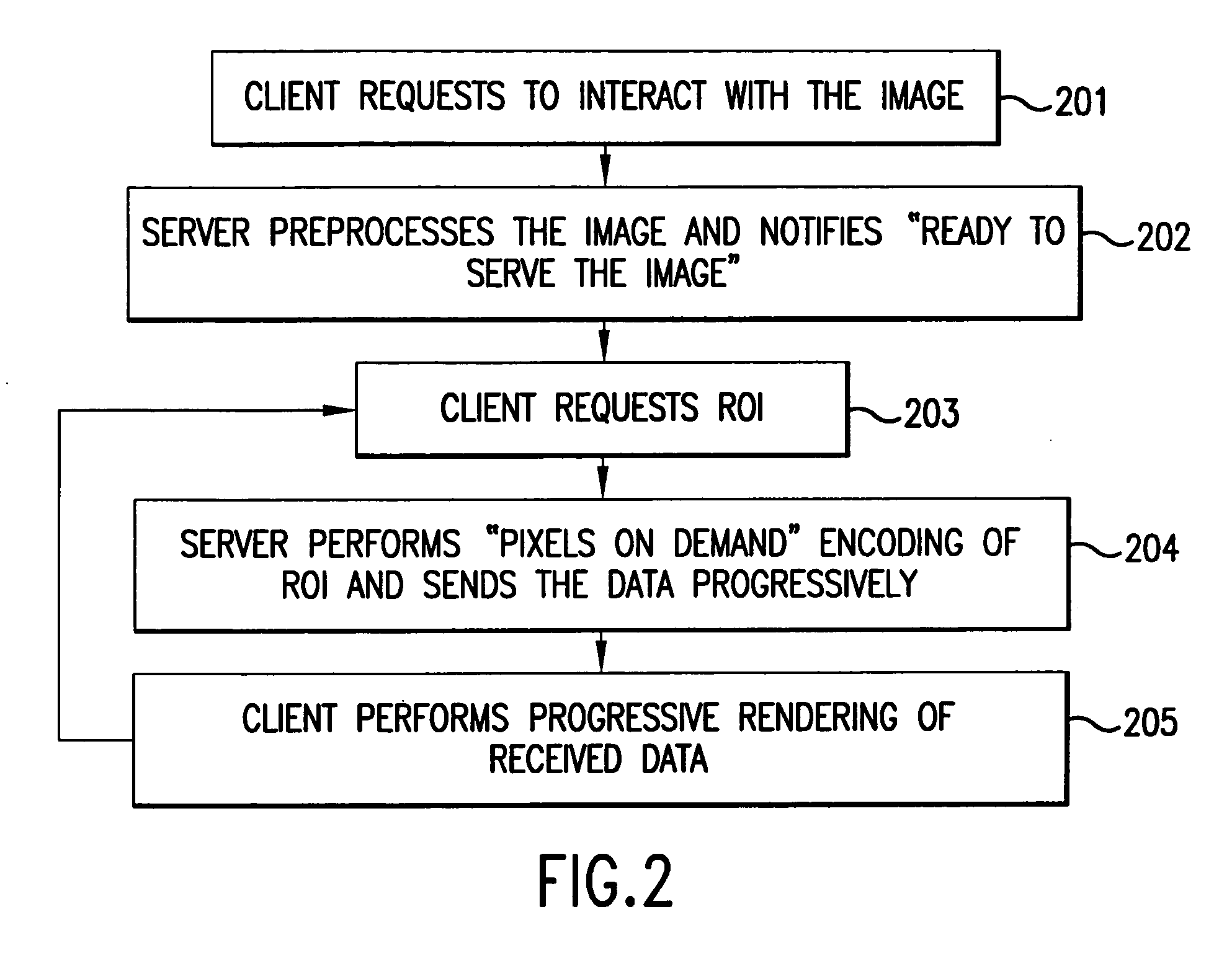
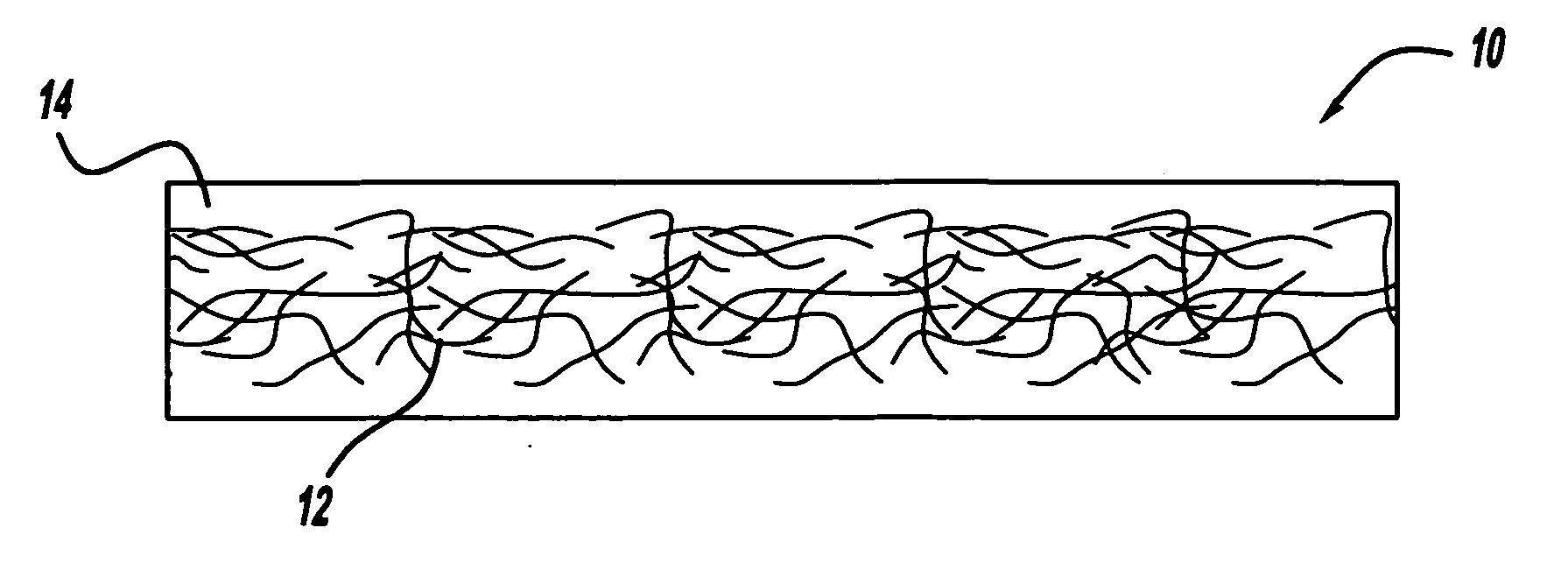
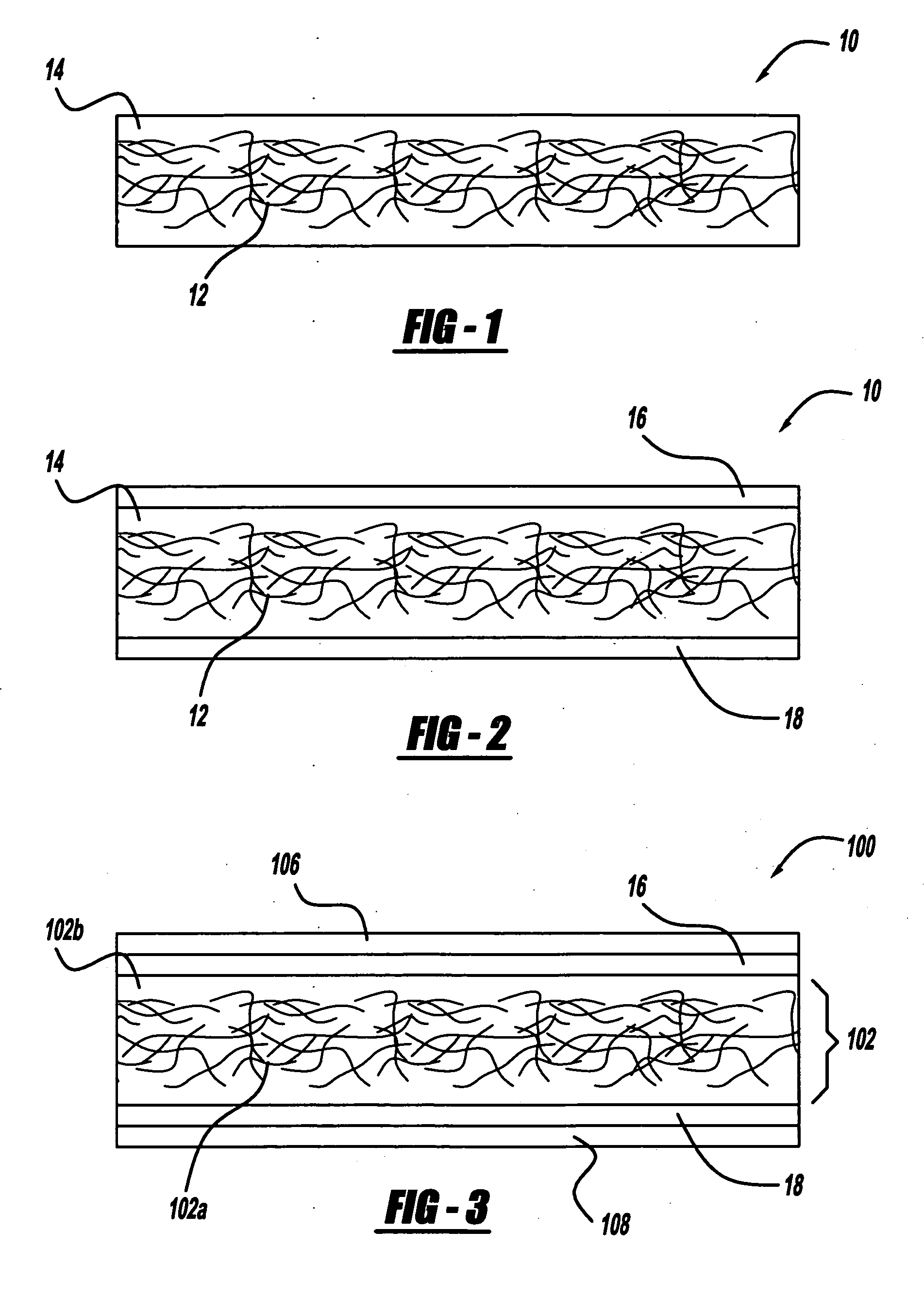
System and method for the lossless progressive streaming of images over a communication network
InactiveUS7024046B2Avoids computationally intensive taskEliminate needPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet ProtocolImage server
Owner:IDX INVESTMENT CORP
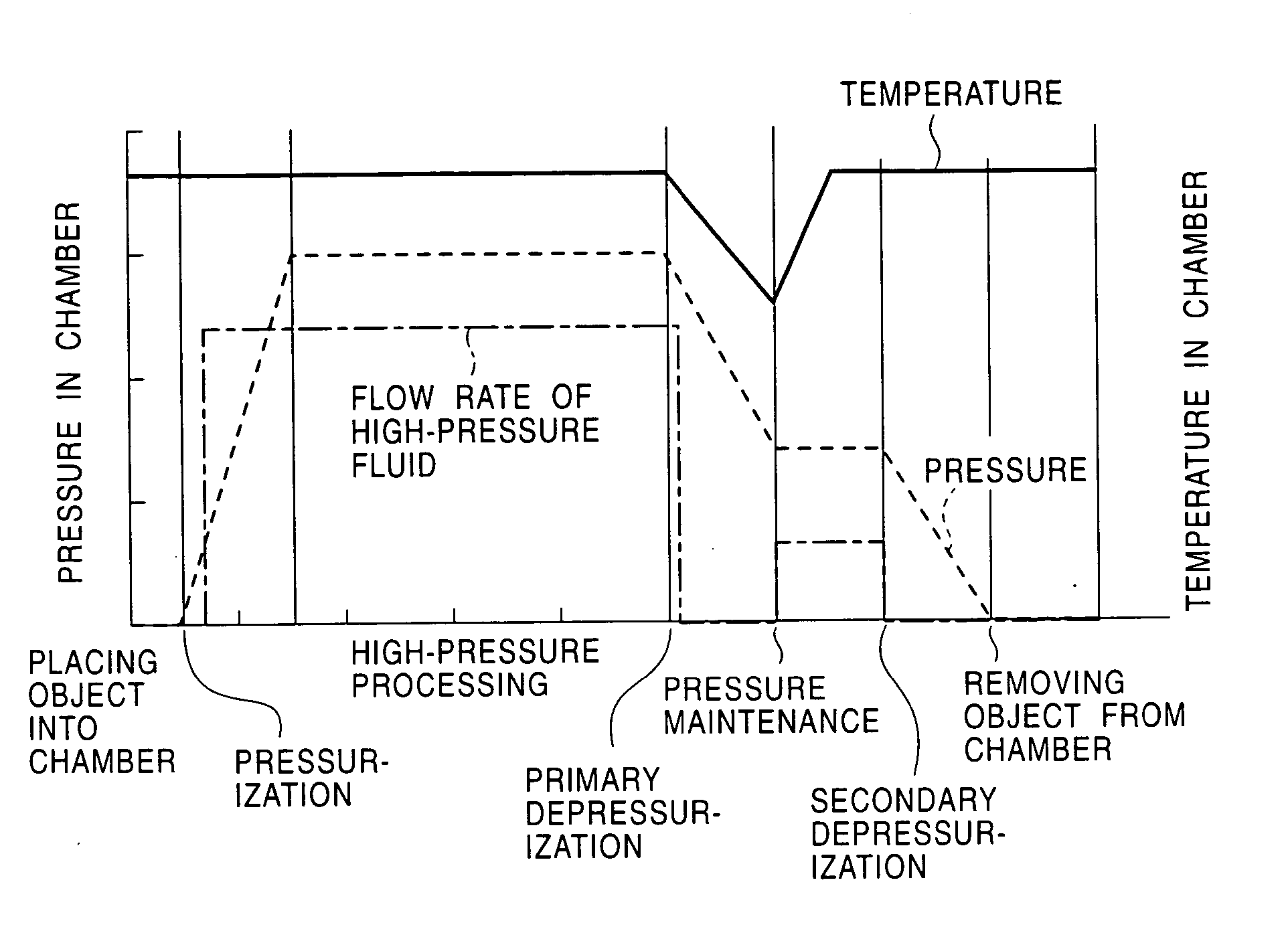
Method for high-pressure processing
InactiveUS20050051194A1Improve production yieldReduce pressureMilk treatmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVapor liquidEngineering
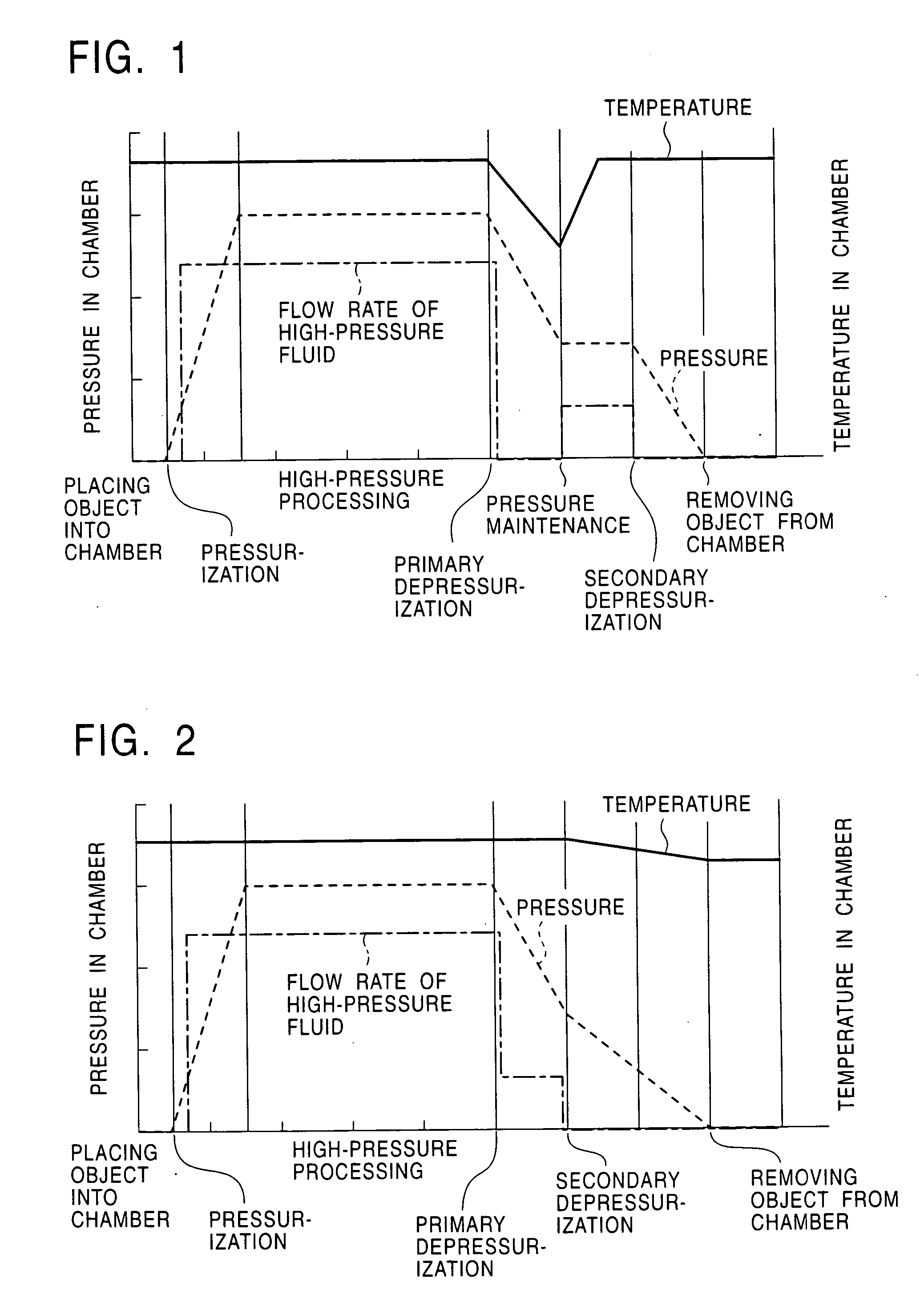
An object is subjected to high-pressure processing by bringing at least a high-pressure fluid into contact with the object under pressure in a high-pressure processing chamber, and then the high-pressure processing chamber is depressurized while the temperature in the chamber is controlled to be maintained above a temperature achieved by an adiabatic expansion, the adiabatic expansion starting from the pressure and temperature at the end of the high-pressure processing step. To control in such a way, the temperature in the high-pressure processing chamber is controlled so as to suppress or recover a temperature descent caused by an adiabatic expansion during the depressurizing step. This solves a problem in which the temperature is decreased to the vapor-liquid phase coexistence region or a region in which a solid is deposited.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
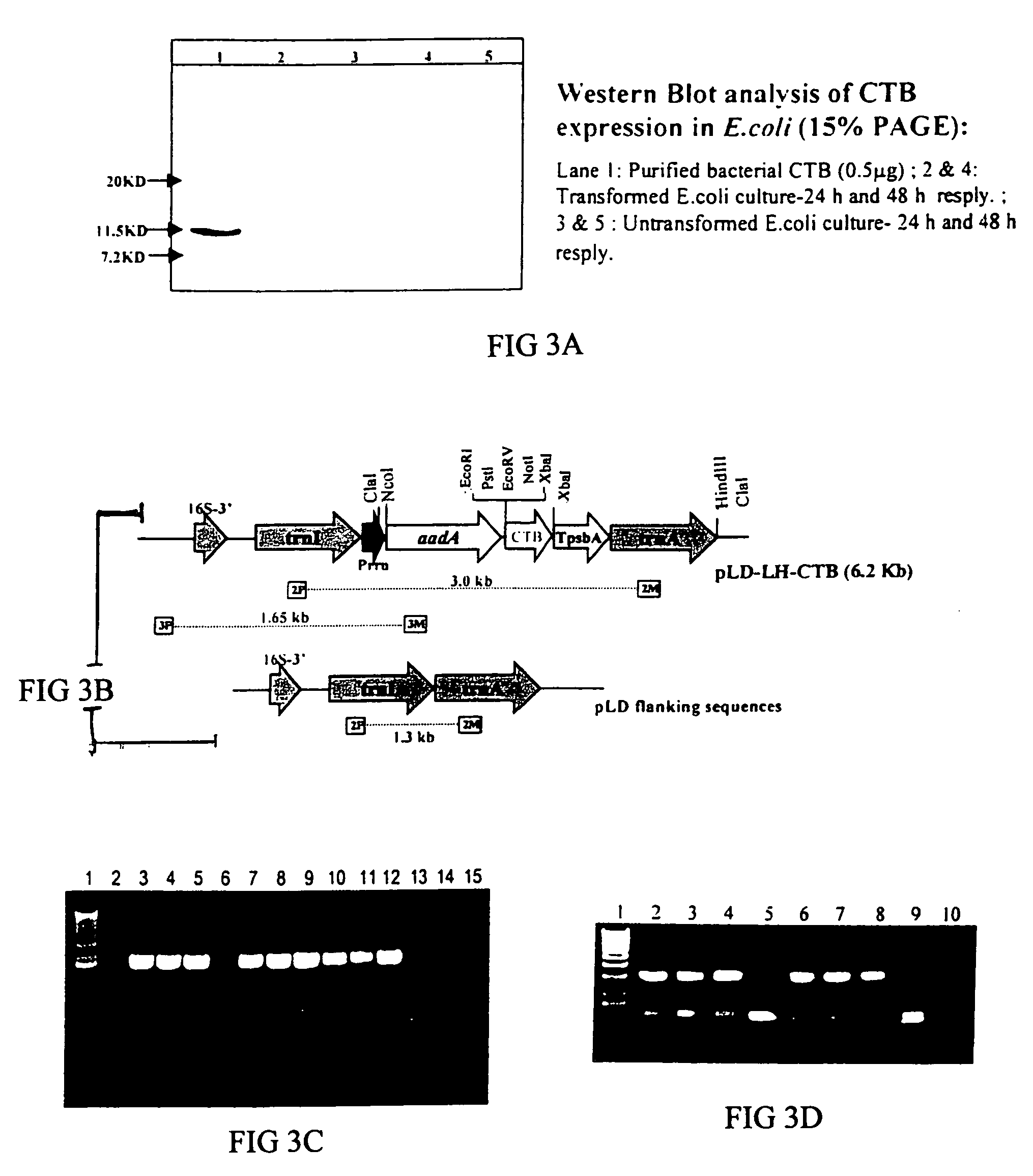
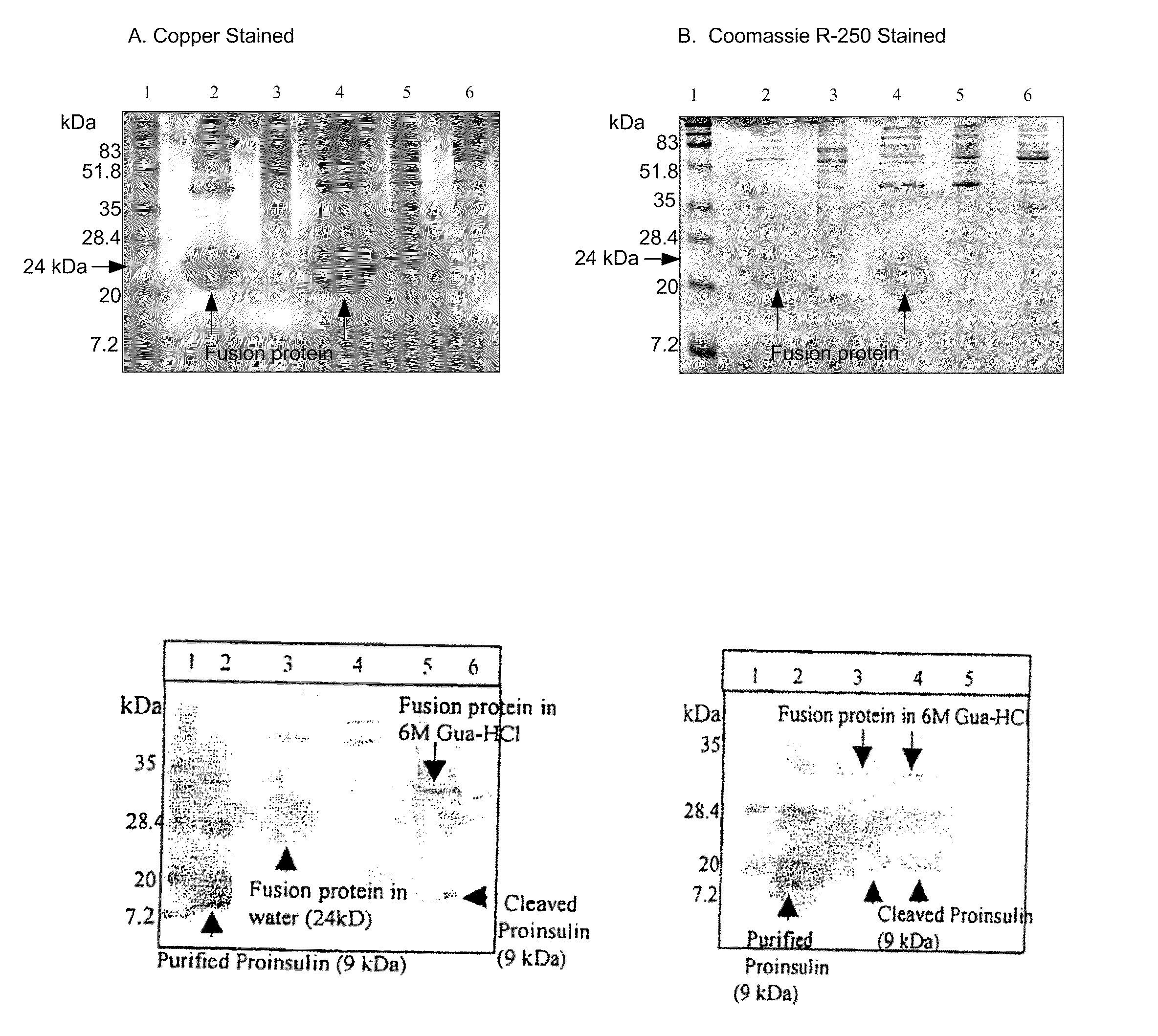
Pharmaceutical proteins, human therapeutics, human serum albumin, insulin, native cholera toxic b submitted on transgenic plastids
InactiveUS20030204864A1Eliminate needLarge biomassBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliInsulin-like growth factor
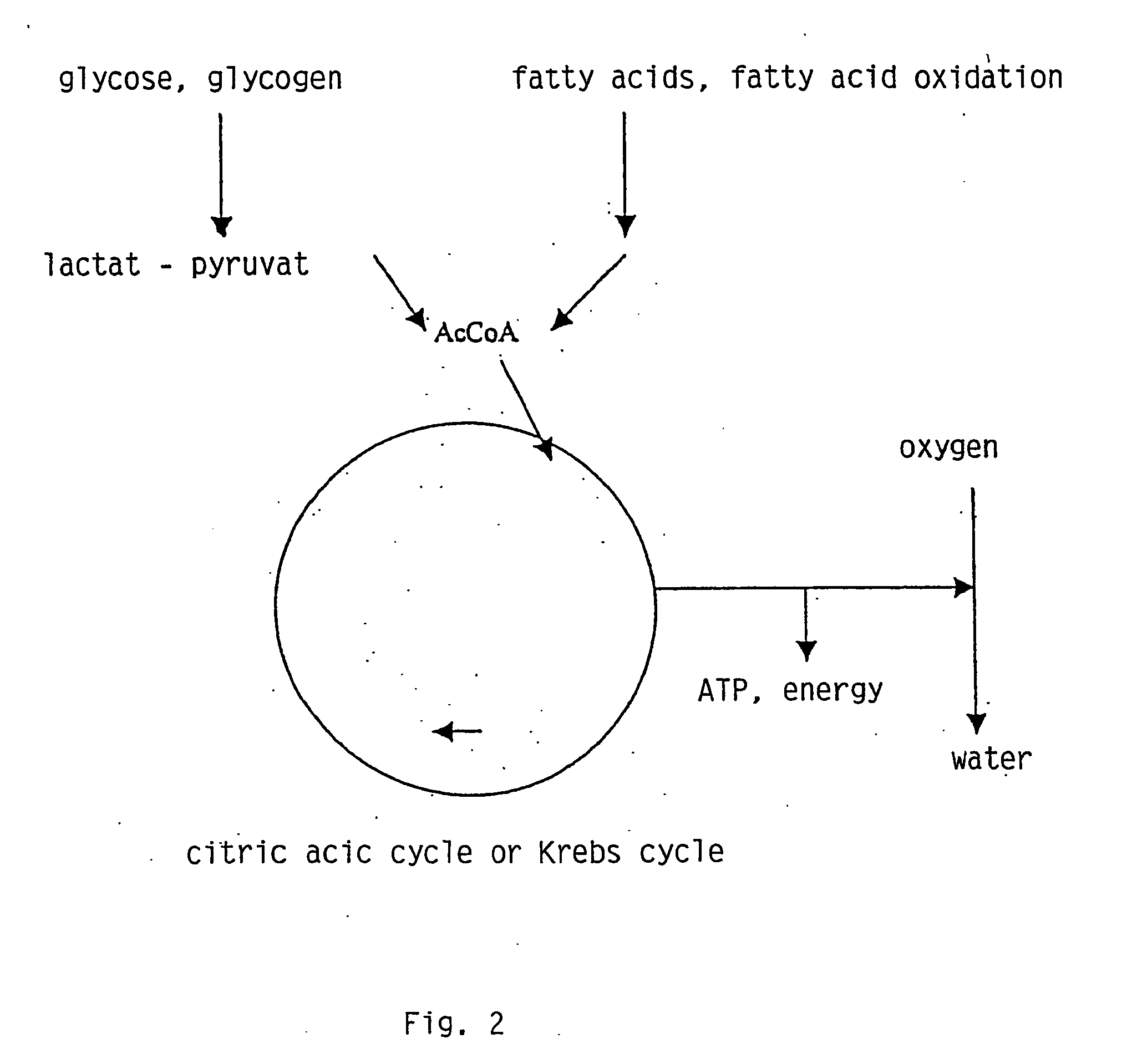
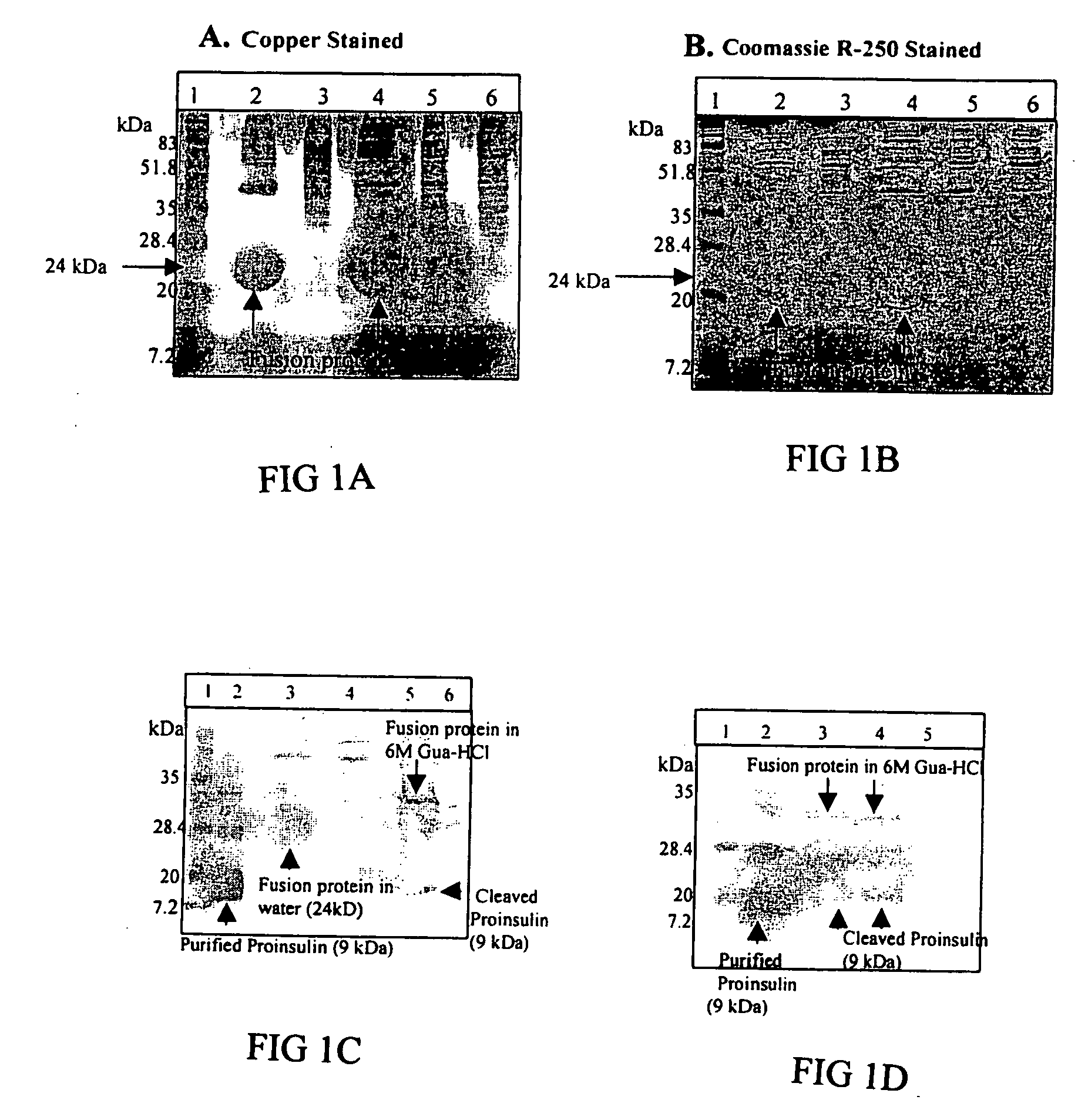
Transgenic chloroplast technology could provide a viable solution to the production of Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I), Human Serum Albumin (HSA), or interferons (IFN) because of hyper-expression capabilities, ability to fold and process eukaryotic proteins with disulfide bridges (thereby eliminating the need for expensive post-purification processing). Tobacco is an ideal choice because of its large biomass, ease of scale-up (million seeds per plant), genetic manipulation and impending need to explore alternate uses for this hazardous crop. Therefore, all three human proteins will be expressed as follows: a) Develop recombinant DNA vectors for enhanced expression via tobacco chloroplast genomes b) generate transgenic plants c) characterize transgenic expression of proteins or fusion proteins using molecular and biochemical methods d) large scale purification of therapeutic proteins from transgenic tobacco and comparison of current purification / processing methods in E. coli or yeast e) Characterization and comparison of therapeutic proteins (yield, purity, functionality) produced in yeast or E. coli with transgenic tobacco f) animal testing and pre-clinical trials for effectiveness of the therapeutic proteins. Mass production of affordable vaccines can be achieved by genetically engineering plants to produce recombinant proteins that are candidate vaccine antigens. The B subunits of Enteroxigenic E. coli (LTB) and cholera toxin of Vibrio cholerae (CTB) are examples of such antigens. When the native LTB gene was expressed via the tobacco nuclear genome, LTB accumulated at levels less than 0.01% of the total soluble leaf protein. Production of effective levels of LTB in plants, required extensive codon modification. Amplification of an unmodified CTB coding sequence in chloroplasts, up to 10,000 copies per cell, resulted in the accumulation of up to 4.1% of total soluble tobacco leaf protein as oligomers (about 410 fold higher expression levels than that of the unmodified LTB gene). PCR and Southern blot analyses confirmed stable integration of the CTB gene into the chloroplast genome. Western blot analysis showed that chloroplast synthesized CTB assembled into oligomers and was antigenically identical to purified native CTB. Also, GM1,-ganglioside binding assays confirmed that chloroplast synthesized CTB binds to the intestinal membrane receptor of cholera toxin, indicating correct folding and disulfide bond formation within the chloroplast. In contrast to stunted nuclear transgenic plants, chloroplast transgenic plants were morphologically indistinguishable from untransformed plants, when CTB was constitutively expressed. The introduced gene was stably inherited in the subsequent generation as confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analyses. Incrased production of an efficient transmucosal carrier molecule and delivery system, like CTB, in transgenic chloroplasts makes plant based oral vaccines and fusion proteins with CTB needing oral administration a much more practical approach.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV +1
Method and Group for the Compression Molding of Preforms for Containers in Polymeric Material
InactiveUS20080026239A1Reduce tensionIncreasing the thicknessConfectioneryWood working apparatusCompression moldingPolymer science
The preform is formed by an upper neck which maintains unchanged its form in the final object and a hollow body, joined to the neck. The method foresees the insertion, within a matrix cavity, of a metered body of polymeric material whose mass is metered according to a reference value, and the subsequent pressure insertion of a punch within the matrix cavity until it closes the mold's molding chamber, the punch conferring the shape to the inner surface of the preform and the matrix having an inner surface which confers the shape to the outer surface of the preform. According to the invention, in the molding of the preform, the error of the mass of the metered body with respect to the reference value is distributed in the hollow body, which undergoes a subsequent hot deformation until it achieves the final shape. In the mold, the matrix comprises at least one deformable wall ( 31 ) whose inner surface defines at least part of the inner surface of the matrix part intended to give form to the hollow body of the preform, said deformable wall ( 31 ) having, at least in part, a relatively thin thickness which permits it to be elastically deformed under the pressure of the polymeric material in the final preform molding step, thereby varying the thickness of the hollow body.
Owner:SACMI COOP MECCANICI IMOLA S C R L
Method for detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus with chromatographic strip test
InactiveUS20080280296A1Improve detection efficiencyQuick stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptasePoint-of-care testing
The present invention discloses a method for detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus with chromatographic strip test. Firstly, the nucleic acid sequence of FMDV NSPs is set up, the nucleic acid sequence is amplified by the reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method, the recombinant vector is constructed and performed through a prokaryotic system to transform and express the recombinant protein, and the purified recombinant protein is mass produced. Design principles of the method are based on immunoassay and chromatographic analysis. The advantages are easy and simple to handle, no need of elaborate equipment, only one drop of body fluid is required to quickly complete the qualitative test in 10-20 minutes, and operating with a portable POCT (Point of care testing) instrument to complete the quantitative detection within 40-50 minutes.
Owner:NAT INST FOR ANIMAL HEALTH COUNCIL AGRI EXECUTIVE YUAN
Method and group for the compression molding of preforms for containers in polymeric material
InactiveUS7939009B2Quick stepsFacilitate heat exchangeConfectioneryWood working apparatusCompression moldingMaterials science
The preform is formed by an upper neck which maintains unchanged its form in the final object and a hollow body, joined to the neck. The method foresees the insertion, within a matrix cavity, of a metered body of polymeric material whose mass is metered according to a reference value, and the subsequent pressure insertion of a punch within the matrix cavity until it closes the mold's molding chamber, the punch conferring the shape to the inner surface of the preform and the matrix having an inner surface which confers the shape to the outer surface of the preform. According to the invention, in the molding of the preform, the error of the mass of the metered body with respect to the reference value is distributed in the hollow body, which undergoes a subsequent hot deformation until it achieves the final shape. In the mold, the matrix comprises at least one deformable wall (31) whose inner surface defines at least part of the inner surface of the matrix part intended to give form to the hollow body of the preform, said deformable wall (31) having, at least in part, a relatively thin thickness which permits it to be elastically deformed under the pressure of the polymeric material in the final preform molding step, thereby varying the thickness of the hollow body.
Owner:SACMI COOP MECCANICI IMOLA SOC COOP A R L
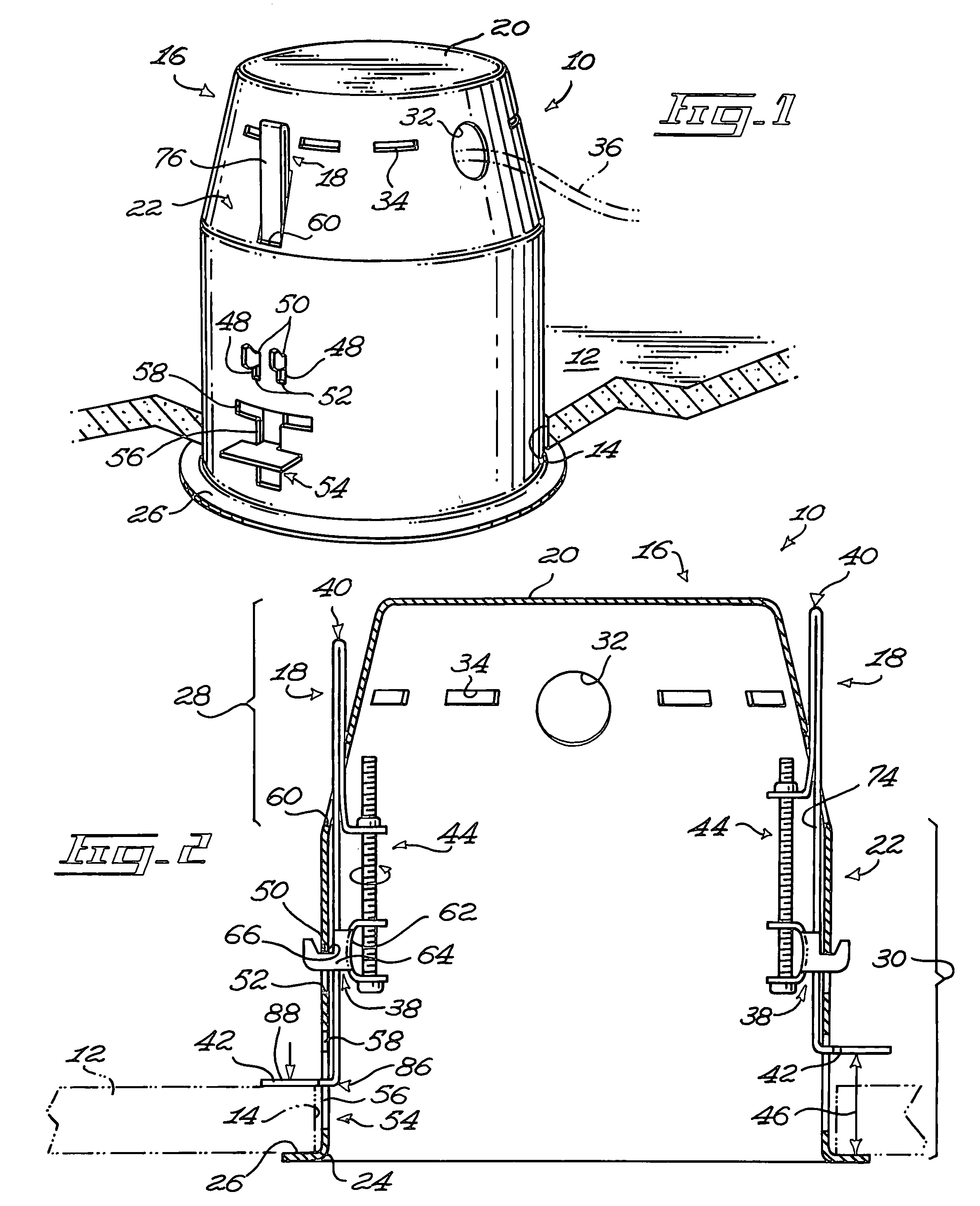
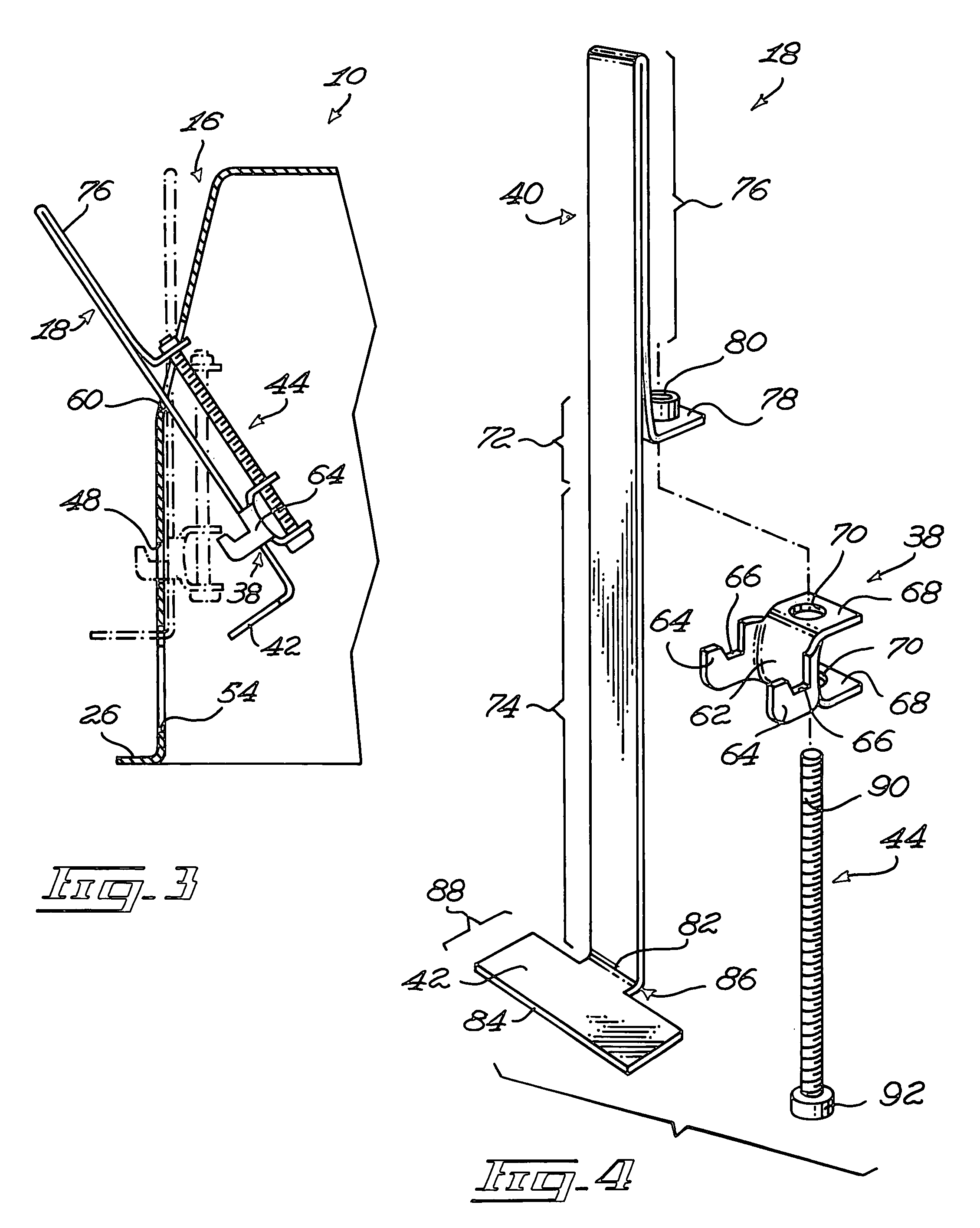
Recessed light fixture
InactiveUS20080068847A1Easy to manufactureQuick stepsLighting support devicesProtective devices for lightingEngineeringActuator
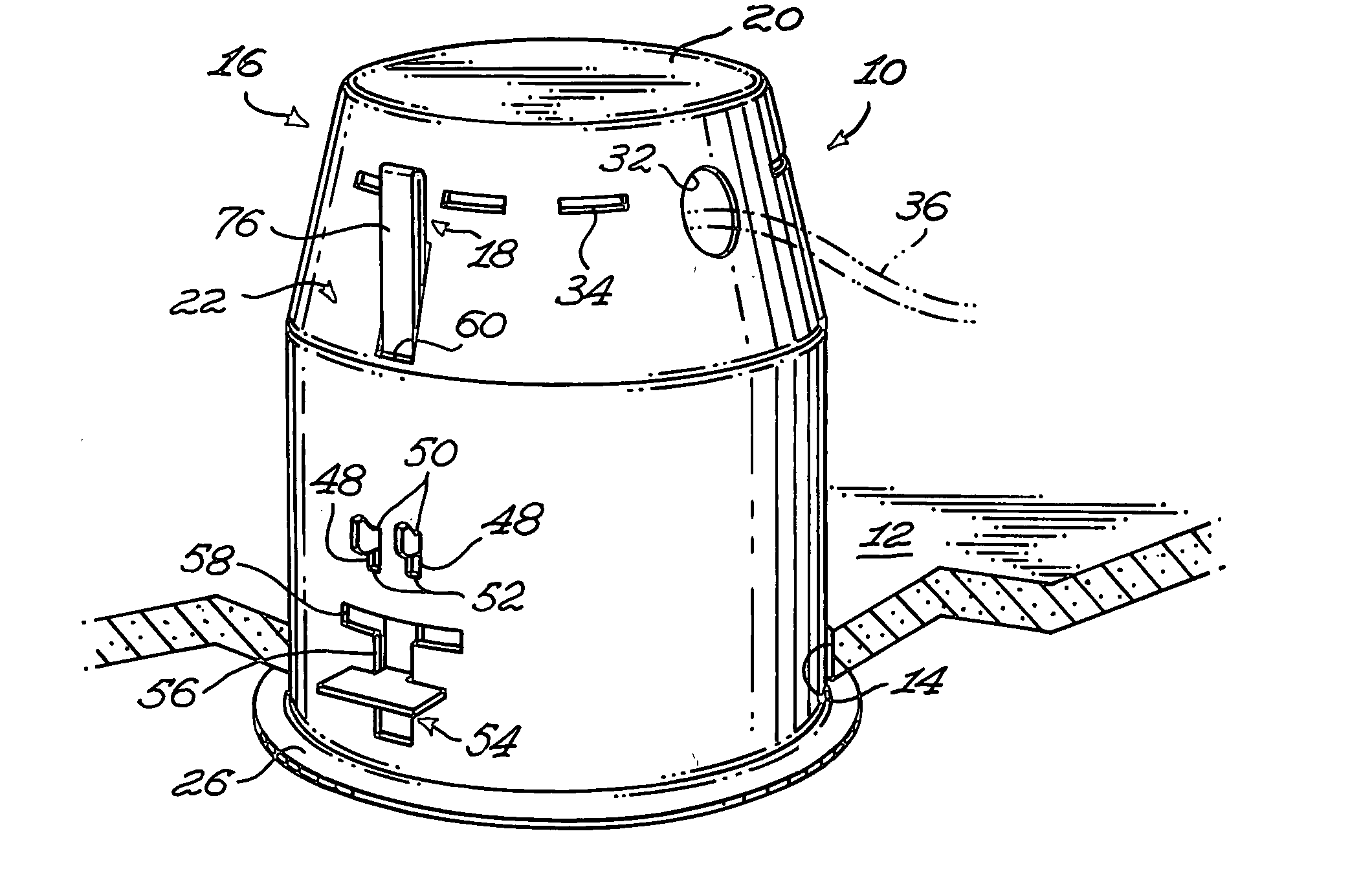
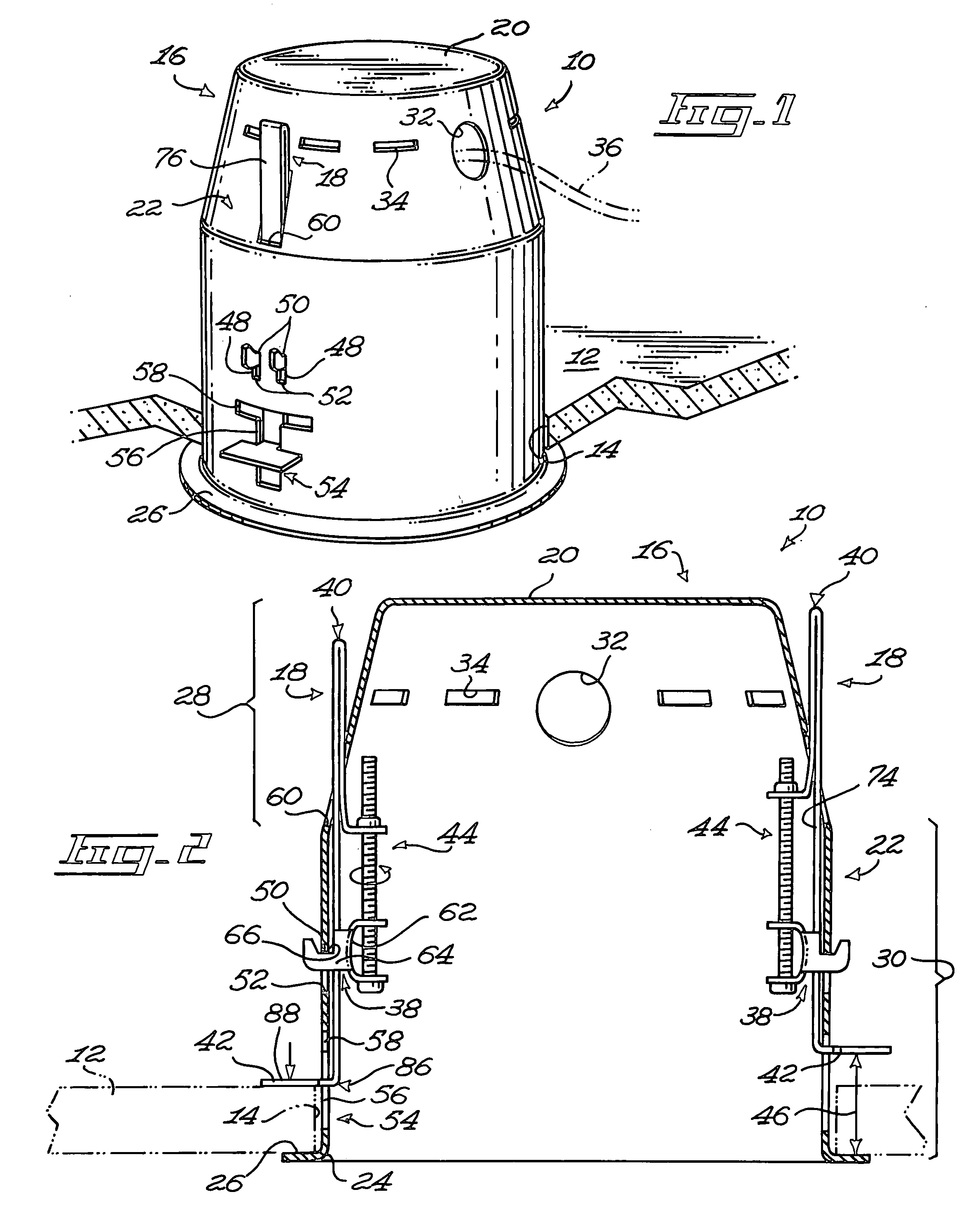
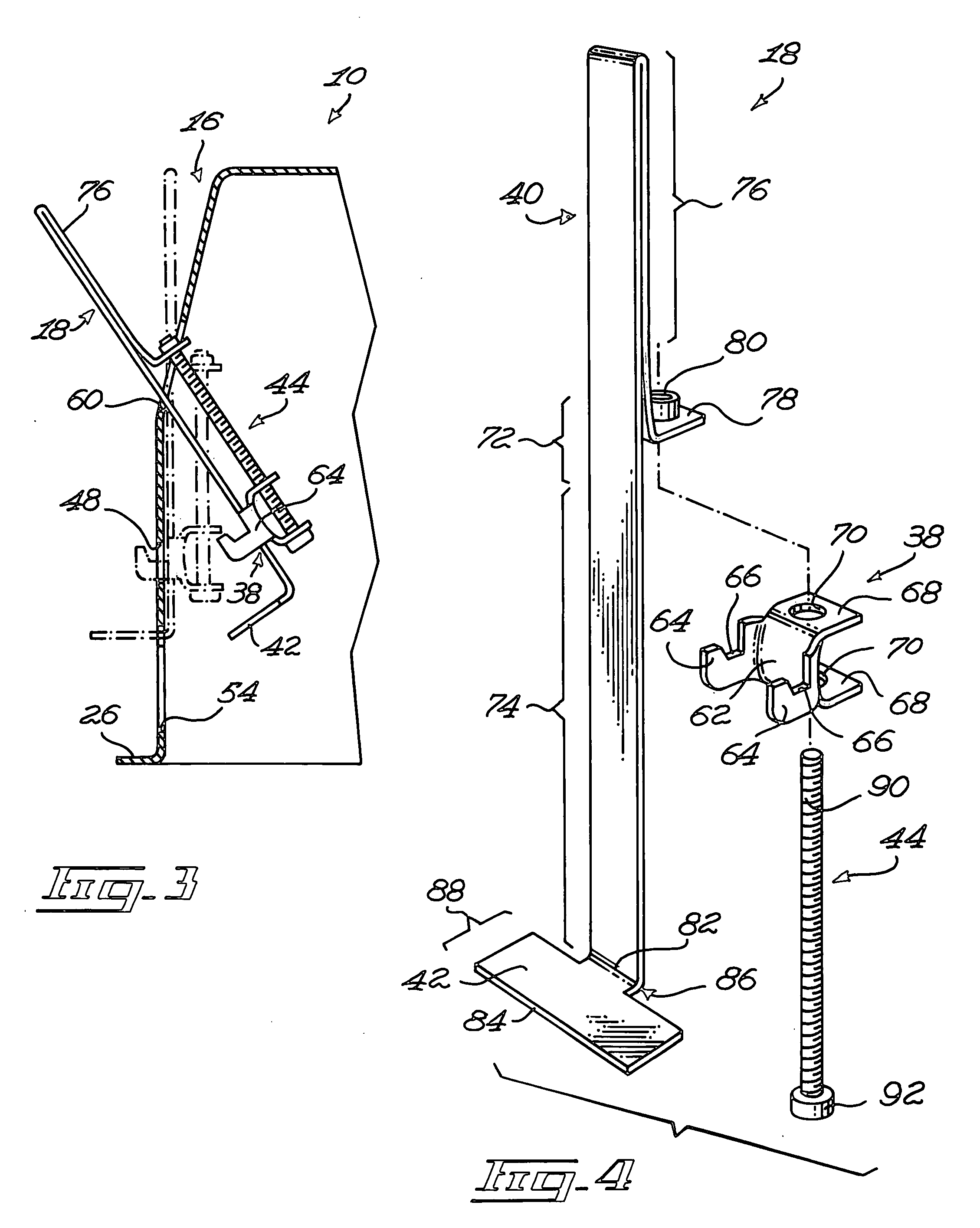
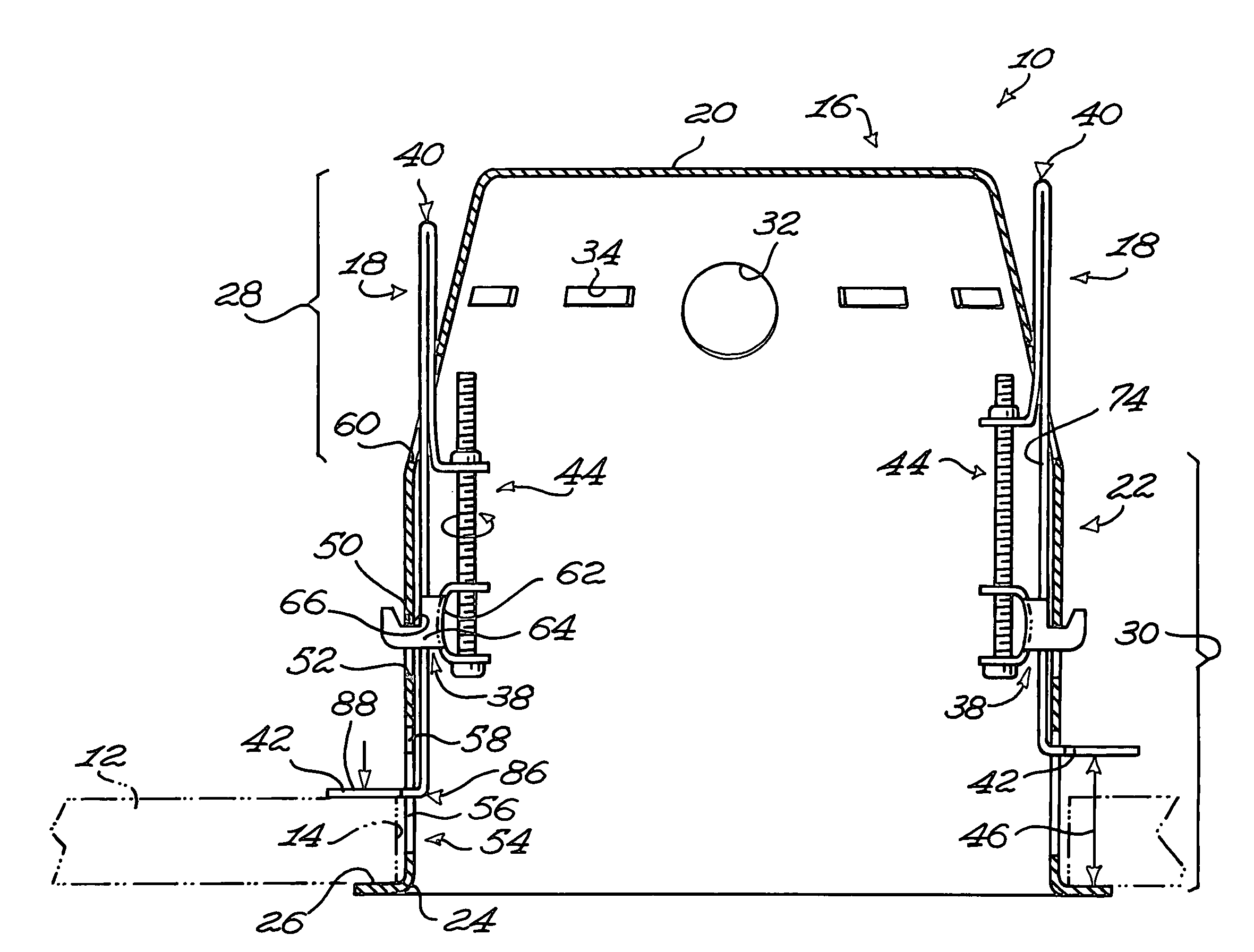
A recessed light fixture mountable to a panel. The panel defines a panel aperture extending therethrough. The recessed light fixture includes a housing, the housing defining an end wall and a side wall extending from the end wall. The side wall defines a side wall edge substantially opposed to the end wall. The housing further defines a housing flange extending substantially peripherally and outwardly from the side wall substantially adjacent the side wall edge. A retaining clip is mounted to the housing. The retaining clip includes a clip mounting element mounted to the housing. A clip body is also included in the retaining clip and defines a retaining flange. The retaining flange is located outside of the housing in a substantially parallel and spaced apart relationship relatively to the housing flange when the retaining clip is mounted to the housing in an operative configuration. An actuator is operatively coupled to the clip mounting element and to the clip body for moving the clip body and the clip mounting element relatively to each other so as to vary a retaining flange-to-housing flange distance between the retaining flange and the housing flange; When the housing is mounted through the panel aperture with the panel positioned between the housing and retaining flanges, using the actuator to move the clip body relatively to the clip mounting element moves the retaining flange relatively to the housing flange to allow the attachment of the light fixture to the panel by pinching the panel between the housing flange and the retaining flange.
Owner:BEDARD SYLVAIN
Recessed light fixture
InactiveUS7618167B2Easy to manufactureQuick stepsLighting support devicesProtective devices for lightingActuatorRecessed light
A recessed light fixture mountable to a panel. The panel defines a panel aperture extending therethrough. The recessed light fixture includes a housing, the housing defining an end wall and a side wall extending from the end wall. The side wall defines a side wall edge substantially opposed to the end wall. The housing further defines a housing flange extending substantially peripherally and outwardly from the side wall substantially adjacent the side wall edge. A retaining clip is mounted to the housing. The retaining clip includes a clip mounting element mounted to the housing. A clip body is also included in the retaining clip and defines a retaining flange. The retaining flange is located outside of the housing in a substantially parallel and spaced apart relationship relatively to the housing flange when the retaining clip is mounted to the housing in an operative configuration. An actuator is operatively coupled to the clip mounting element and to the clip body for moving the clip body and the clip mounting element relatively to each other so as to vary a retaining flange-to-housing flange distance between the retaining flange and the housing flange; When the housing is mounted through the panel aperture with the panel positioned between the housing and retaining flanges, using the actuator to move the clip body relatively to the clip mounting element moves the retaining flange relatively to the housing flange to allow the attachment of the light fixture to the panel by pinching the panel between the housing flange and the retaining flange.
Owner:BEDARD SYLVAIN
Expression of human serum albumin insulin in plastids
InactiveUS20060253935A1Eliminate needLarge biomassSugar derivativesSolid waste disposalNicotiana tabacumSerum albumin
Humans Serum Albumin (HSA) or an HSA fusion protein is expressed in plant plastids. A plastid transformation vector is made which contains an expression cassette that contains regulatory sequences, the coding region for HSA or an HSA fusion protein and a selectable marker coding sequence. The vector is used to transform a plant where the plant expresses the HSA or HSA fusion protein. HSA is isolated and purified from the plant. A preferred plant is tobacco.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Closure apparatus
InactiveUS20100030240A1Safer procedureFacilitate healingSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBiological tissueEngineering
An apparatus for binding together two biological tissue portions with a binding component. The apparatus includes a body defining a body handle for receiving a hand; at least one drum rotatably mounted to the body, the at least one drum including a binding component attachment for attaching the binding component thereto; a drum actuating lever mounted to the body, the drum actuating lever being operatively coupled to the at least one drum for rotating the at least one drum in a predetermined direction when the drum actuating lever is moved; and a crimping assembly operatively coupled to the body for holding a crimp component and selectively crimping the crimp component to the binding component. The body handle, the drum actuating lever and the crimping assembly are configured, sized and positioned in a manner such that the intended user is able to tighten the binding component around the at least one drum by moving the drum actuating lever using one hand; and the intended user is able to operate the crimping assembly to selectively crimp the crimp component to the binding component middle section using another hand while simultaneously holding the body handle with the first hand.
Owner:BRAILOVSKI VLADIMIR +3
Pharmaceutical Proteins, Human Therapeutics, Human Serum Albumin Insulin, Native Cholera Toxin B Subunit on Transgenic Plastids
InactiveUS20110179530A1Eliminate needLarge biomassBryophytesMicroorganismsOral tolerizationInsulin-like growth factor
This invention relates in part to synthesizing high value pharmaceutical proteins in transgenic plants by chloroplast expression for pharmaceutical protein production. We use poly(GVGVP), for example, as a fusion protein to enable hyper-expression of insulin and to accomplish rapid one step purification of fusion peptides utilizing the inverse temperature transition properties of this polymer. We also use insulin-CTB fusion protein in chloroplasts of nicotine free edible tobacco (LAMD 605) for oral delivery. This invention includes expression of native cholera toxin B subunit gene as oligomers in transgenic tobacco chloroplasts which may be utilized in connection with large-scale production of purified CTB, as well as an edible vaccine if expressed in an edible plant, as a transmucosal carrier of peptides to which it is fused to enhance mucosal immunity, and / or to induce oral tolerance of the products of these peptides. The present invention also relates in part to recombinant DNA vectors for enhanced expression of human serum albumin, insulin-like growth factor I, and interferon-α 2 and 5, via chloroplast genomes.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Image graphic system comprising a highly tacky adhesive and method for using same
InactiveUS20030127181A1Efficient use ofImprove adhesionLamination ancillary operationsPicture framesAdhesiveGraphic system
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Preparation method of porous graphene
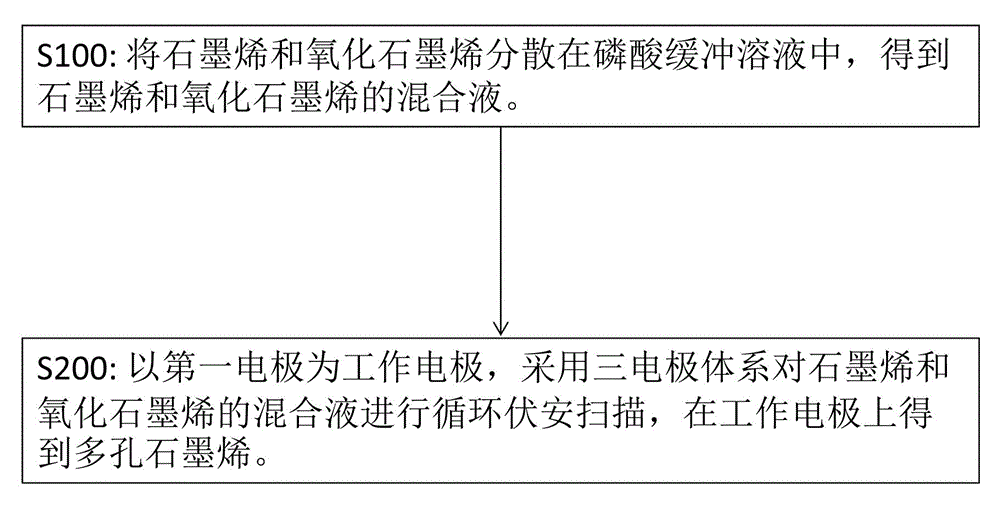
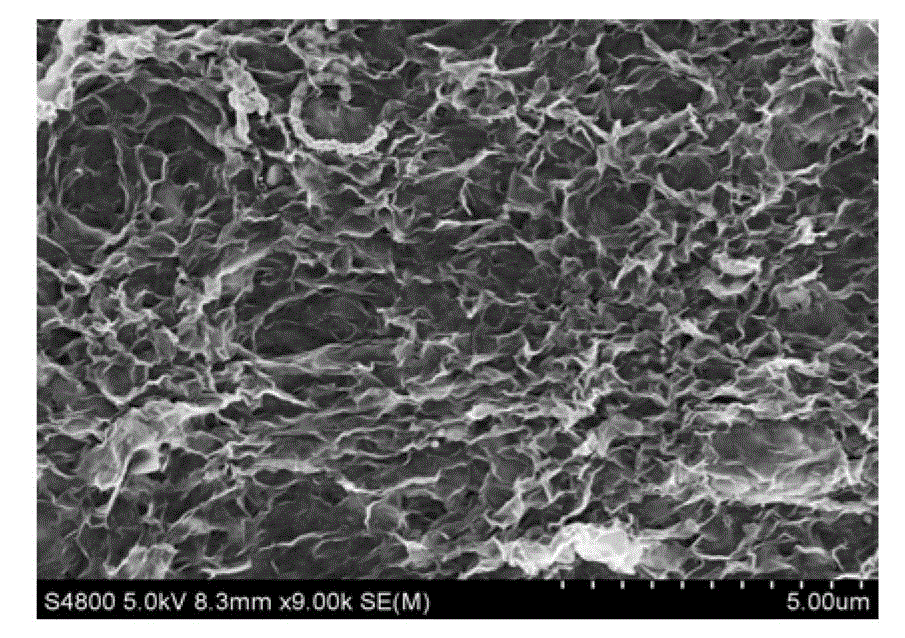
The invention relates to a preparation method of porous graphene. The method includes the steps of dispersing graphene and graphene oxide in a phosphate buffer to obtain a mixture of graphene and graphene oxide, and conducting cyclic voltammetry scan on the mixture of graphene and graphene oxide through a three-electrode system so that a working electrode for decorating the porous graphene can be obtained, that is, the porous graphene can be obtained on the working electrode. The method is easy to operate, few in steps, rapid and low in cost.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Composition comprising phosphate
InactiveUS20050153020A1Short windednessPoorer fitnessInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffSports drinkMedicine
The present invention concerns a composition comprising phosphate wherein phosphate, as the main active ingredient, corrects mammalian phosphate depletion and the use thereof. The composition may be in form of a powder, an infusion solution or a sports drink. Inlet of the sports drink or administration of the infusion solution to an athlete or an animal, or to a patient who suffers from a condition needing extra supply of phosphate is advantageous for the treatment or the prevention of a variety of conditions.
Owner:HAMRE PER +2
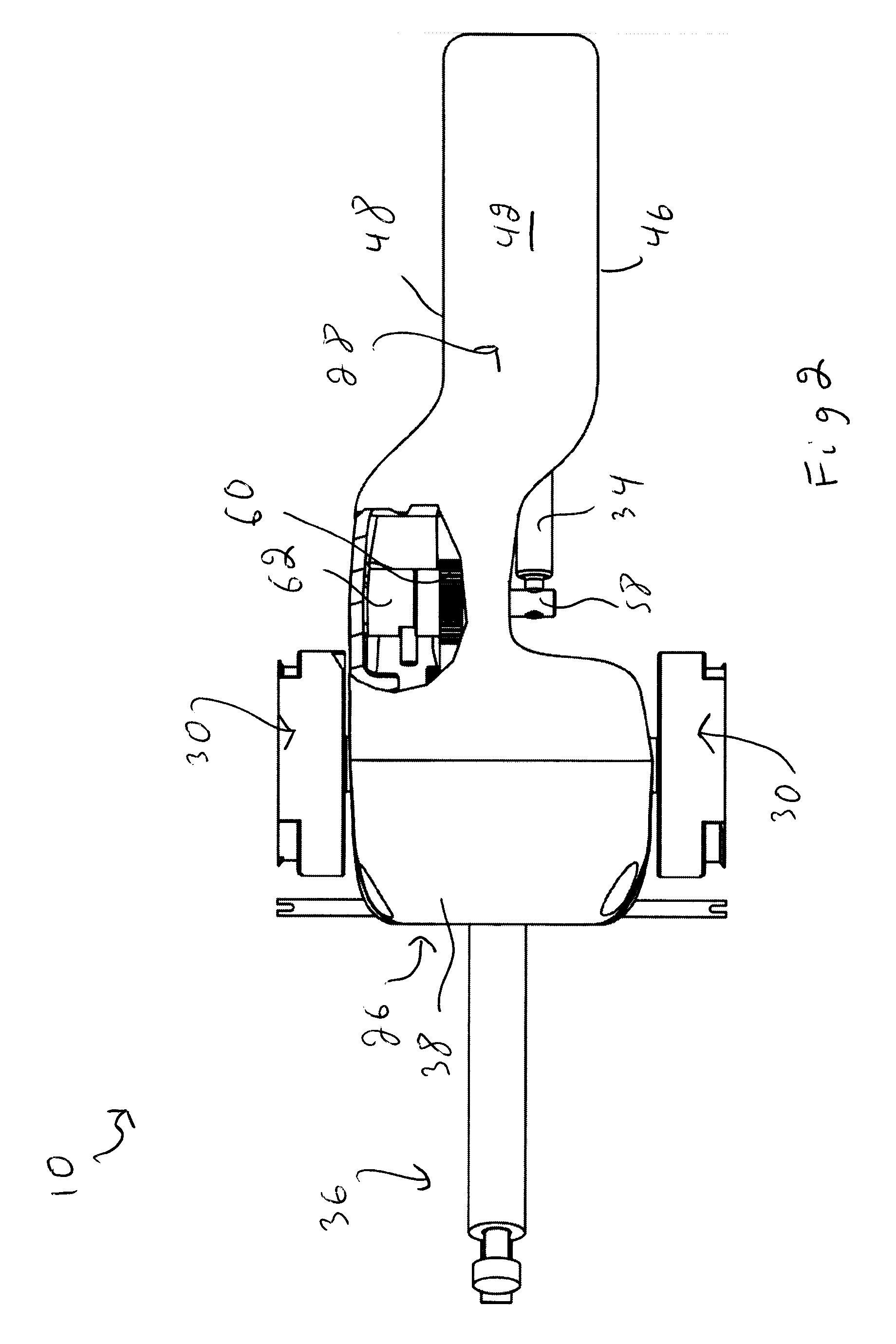
Pharmaceutical proteins, human therapeutics, human serum albumin insulin, native cholera toxic B submitted on transgenic plastids
InactiveUS20060117412A1Eliminate needLarge biomassSerum albuminDepsipeptidesInsulin-like growth factorEscherichia coli
Transgenic chloroplast technology could provide a viable solution to the production of Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I), Human Serum Albumin (HSA), or interferons (IFN) because of hyper-expression capabilities, ability to fold and process eukaryotic proteins with disulfide bridges (thereby eliminating the need for expensive post-purification processing). Tobacco is an ideal choice because of its large biomass, ease of scale-up (million seeds per plant), genetic manipulation and impending need to explore alternate uses for this hazardous crop. Therefore, all three human proteins will be expressed as follows: a) Develop recombinant DNA vectors for enhanced expression via tobacco chloroplast genomes b) generate transgenic plants c) characterize transgenic expression of proteins or fusion proteins using molecular and biochemical methods d) large scale purification of therapeutic proteins from transgenic tobacco and comparison of current purification / processing methods in E. coli or yeast e) Characterization and comparison of therapeutic proteins (yield, purity, functionality) produced in yeast or E. coli with transgenic tobacco f) animal testing and pre-clinical trials for effectiveness of the therapeutic proteins. Mass production of affordable vaccines can be achieved by genetically engineering plants to produce recombinant proteins that are candidate vaccine antigens. The B subunits of Enteroxigenic E. coli (LTB) and cholera toxin of Vibrio cholerae (CTB) are examples of such antigens. When the native LTB gene was expressed via the tobacco nuclear genome, LTB accumulated at levels less than 0.01% of the total soluble leaf protein. Production of effective levels of LTB in plants, required extensive codon modification. Amplification of an unmodified CTB coding sequence in chloroplasts, up to 10,000 copies per cell, resulted in the accumulation of up to 4.1% of total soluble tobacco leaf protein as oligomers (about 410 fold higher expression levels than that of the unmodified LTB gene). PCR and Southern blot analyses confirmed stable integration of the CTB gene into the chloroplast genome. Western blot analysis showed that chloroplast synthesized CTB assembled into oligomers and was antigenically identical to purified native CTB. Also, GM1-ganglioside binding assays confirmed that chloroplast synthesized CTB binds to the intestinal membrane receptor of cholera toxin, indicating correct folding and disulfide bond formation within the chloroplast. In contrast to stunted nuclear transgenic plants, chloroplast transgenic plants were morphologically indistinguishable from untransformed plants, when CTB was constitutively expressed. The introduced gene was stably inherited in the subsequent generation as confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analyses. Incrased production of an efficient transmucosal carrier molecule and delivery system, like CTB, in transgenic chloroplasts makes plant based oral vaccines and fusion proteins with CTB needing oral administration a much more practical approach.
Owner:DANIELL HENRY
Natural fiber as core material in composite sandwich structure
InactiveUS20070149084A1Low costLight weightConstruction materialMagnetic materials for record carriersThermoplasticGlass fiber
A core component includes a natural fiber portion and a binder portion. The natural fiber portion and the binder portion are combined together, either partially or fully, so as to form a substantially homogenous material. Natural fibers can include: (1) bast fibers such as hemp, flax, kenaf, ramie, jute, and / or the like; (2) leaf fibers such as henequen, abaca, and / or the like; and (3) seed fibers such as cotton and / or the like. The core component can be used in conjunction with a composite structure, e.g., after formation of the core component, a reinforcing material (e.g., glass fibers, carbon fibers, aramid fibers and / or the like) can be placed on either side of the core component and injected with a resin material to form the composite structure. The resin material can be comprised of any number of polymeric materials, such as but not limited to thermoplastics, thermosets, and / or the like.
Owner:MAGNA INTERNATIONAL INC +1
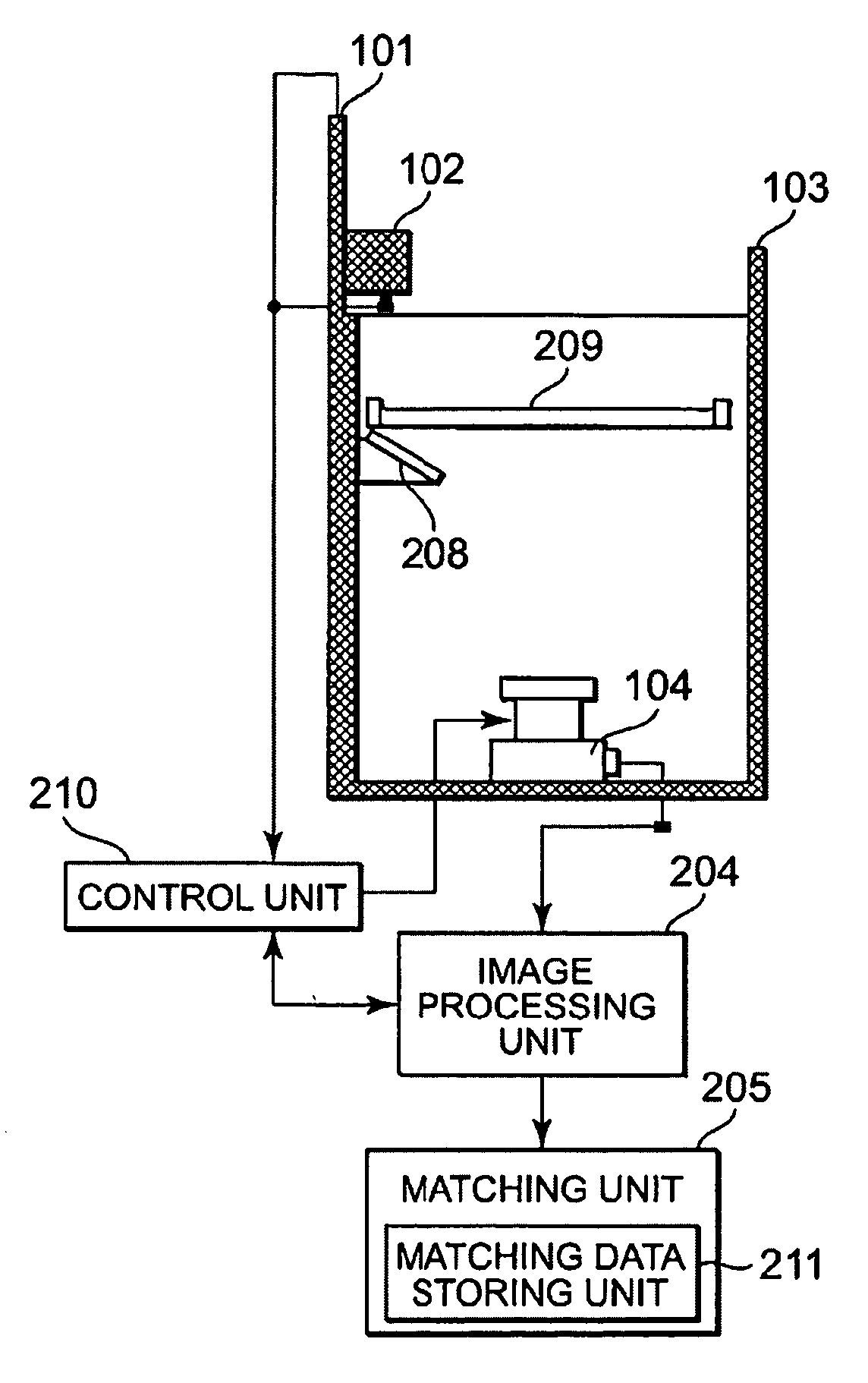
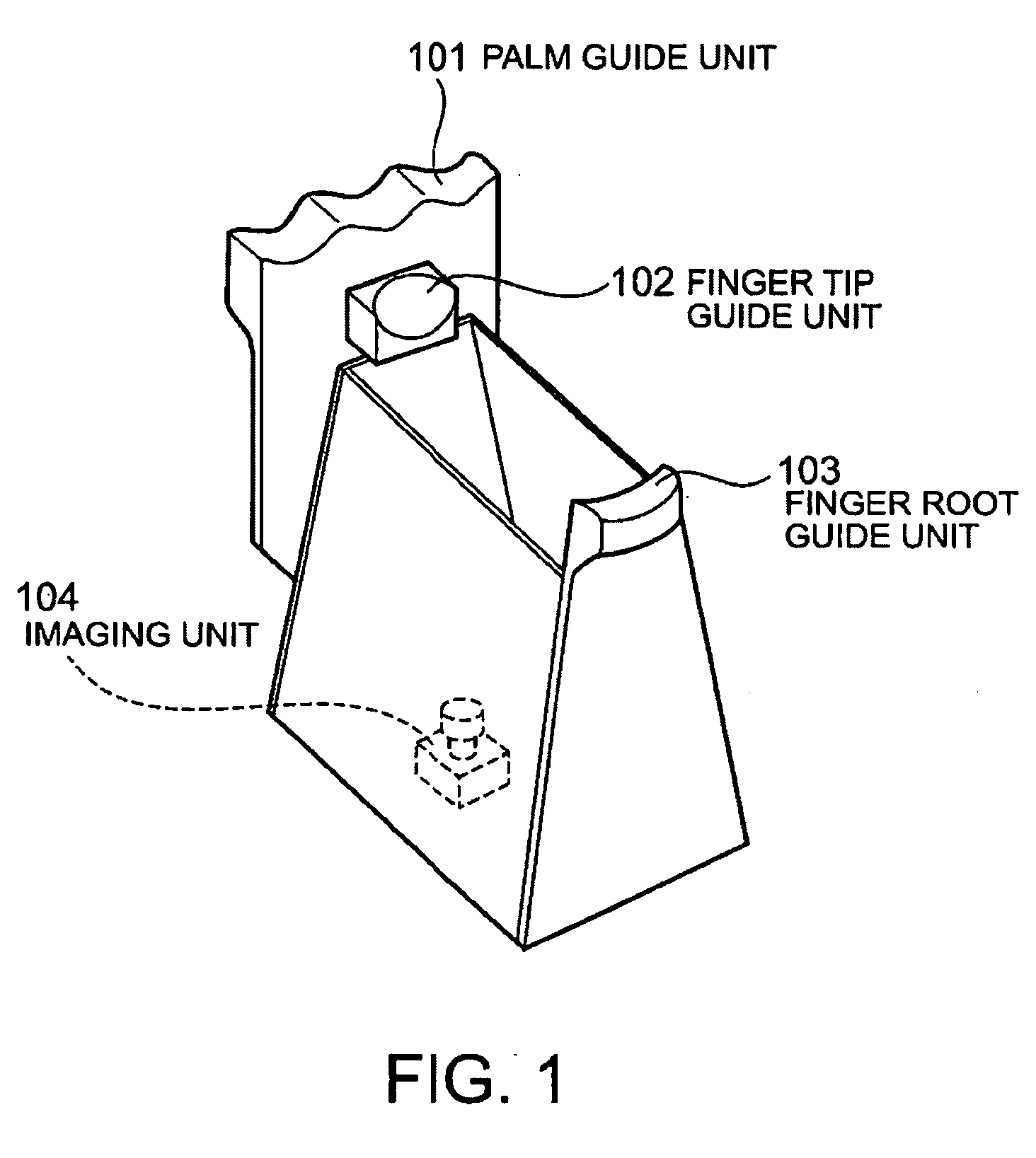
Imaging apparatus and method for authentication of user
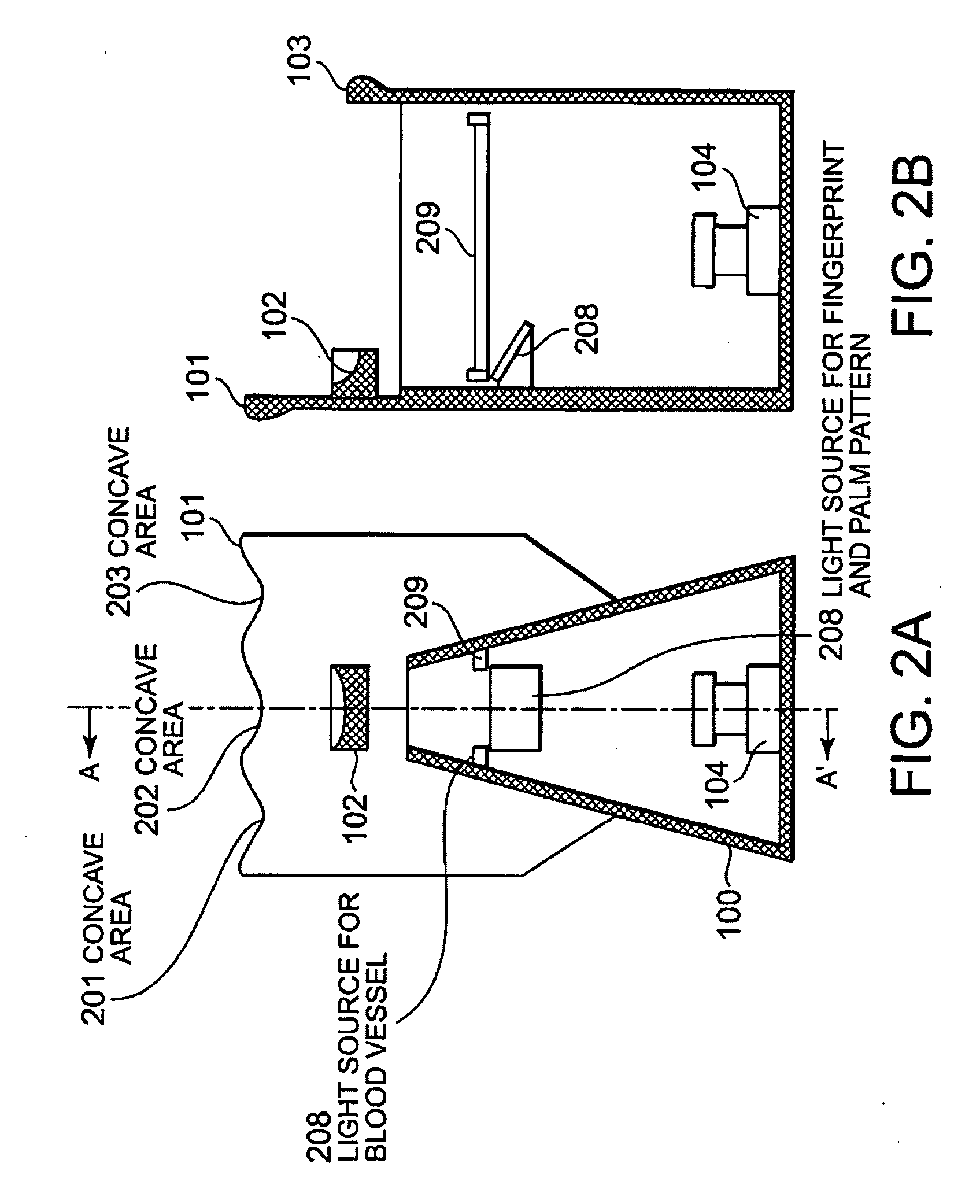
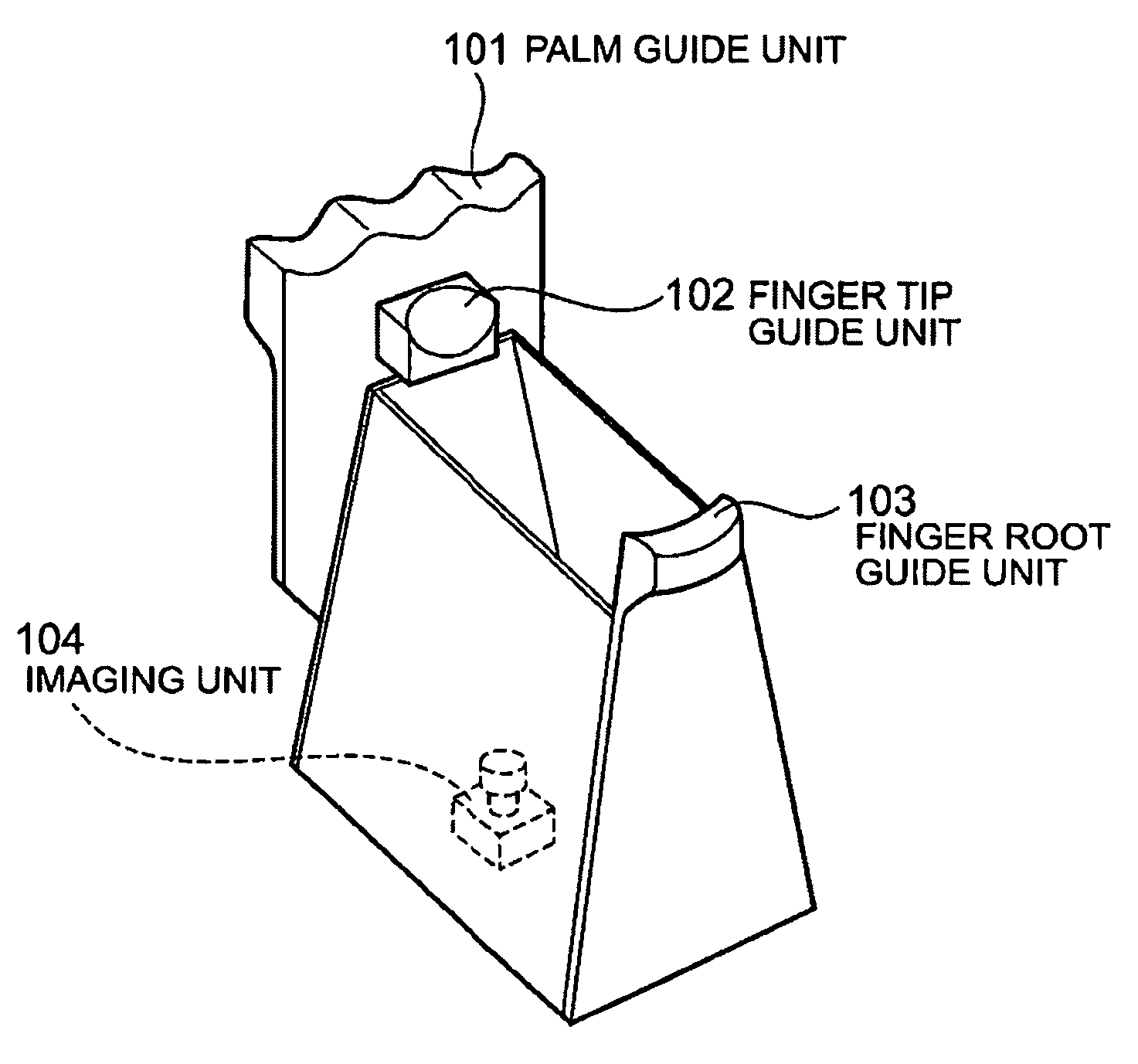
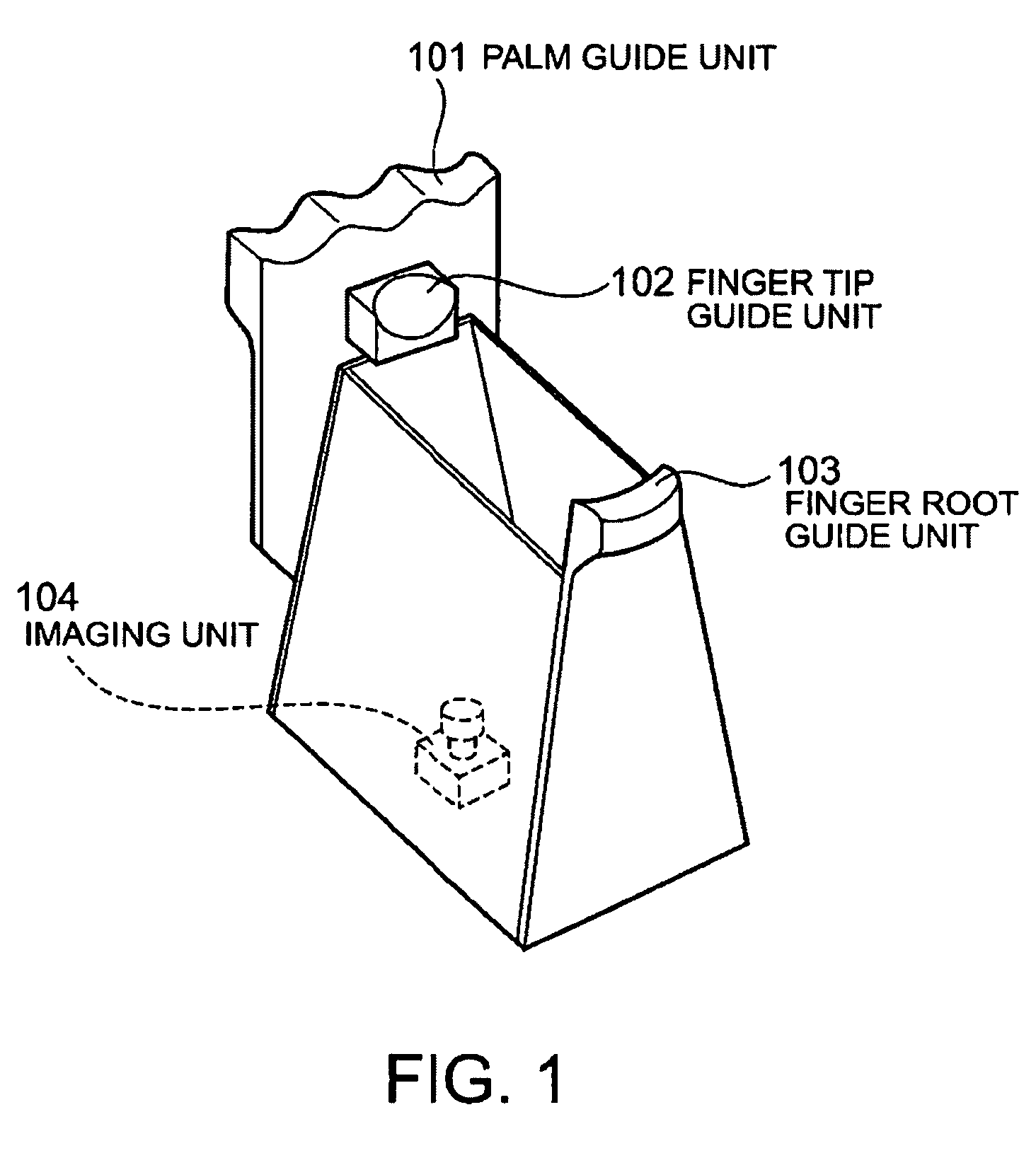
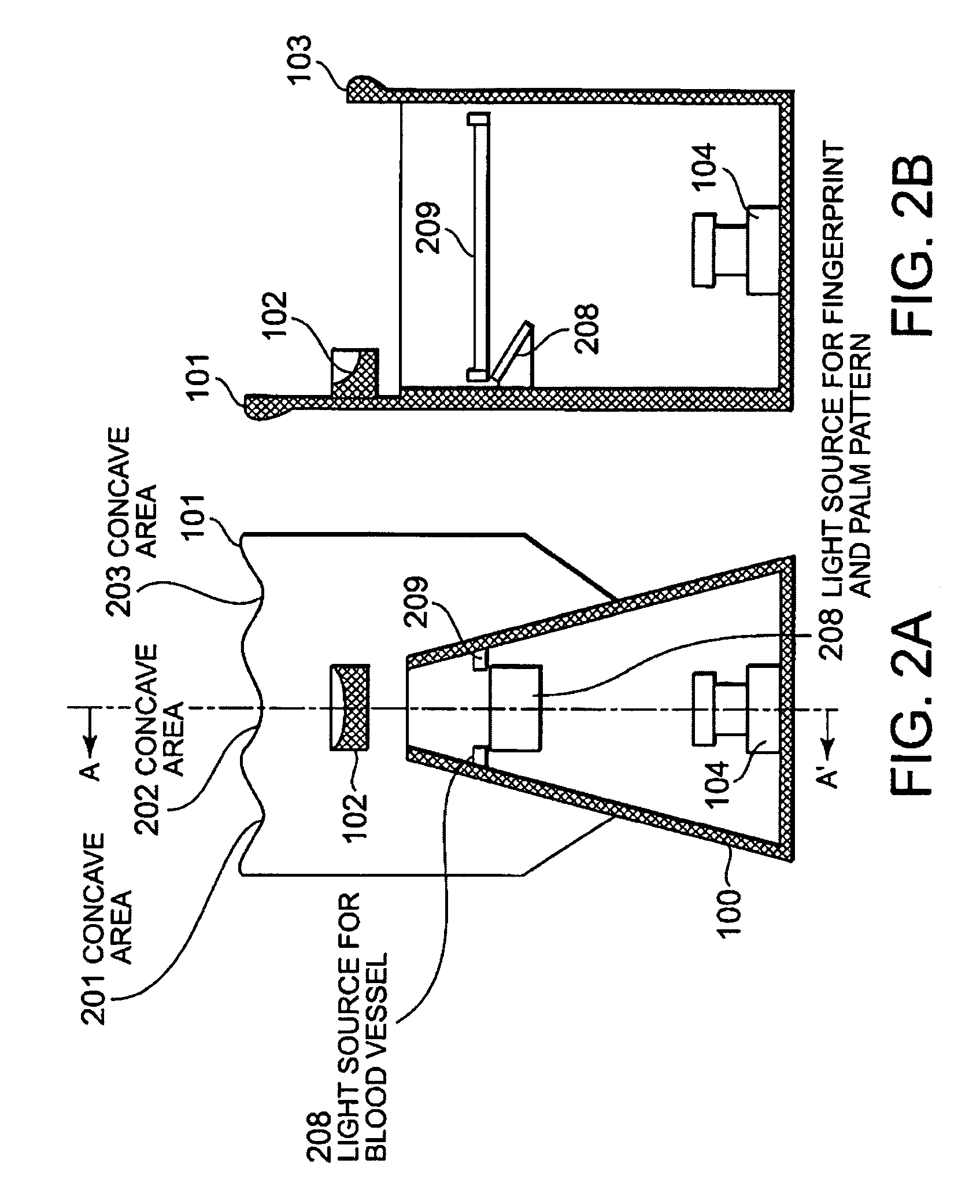
InactiveUS20090252387A1Quick stepsMultiple biometrics useSubcutaneous biometric featuresBiometric dataImaging equipment
The imaging apparatus for authenticating a user can quickly perform matching step of the inputted biometric data. This apparatus for authenticating the user includes an imaging unit for imaging a guided finger and a guided palm, a matching data storing unit for storing the determined finger image and the determined palm image, and a matching unit for matching the imaged finger image and the imaged palm image with the stored finger image and the stored palm image. The matching unit selects the finger image having the similar feature amount based on the imaged finger image and authenticates a user based on the result of matching of the palm image corresponding to the selected finger image with the imaged palm image.
Owner:NEC CORP
Compact Folding Step Stool
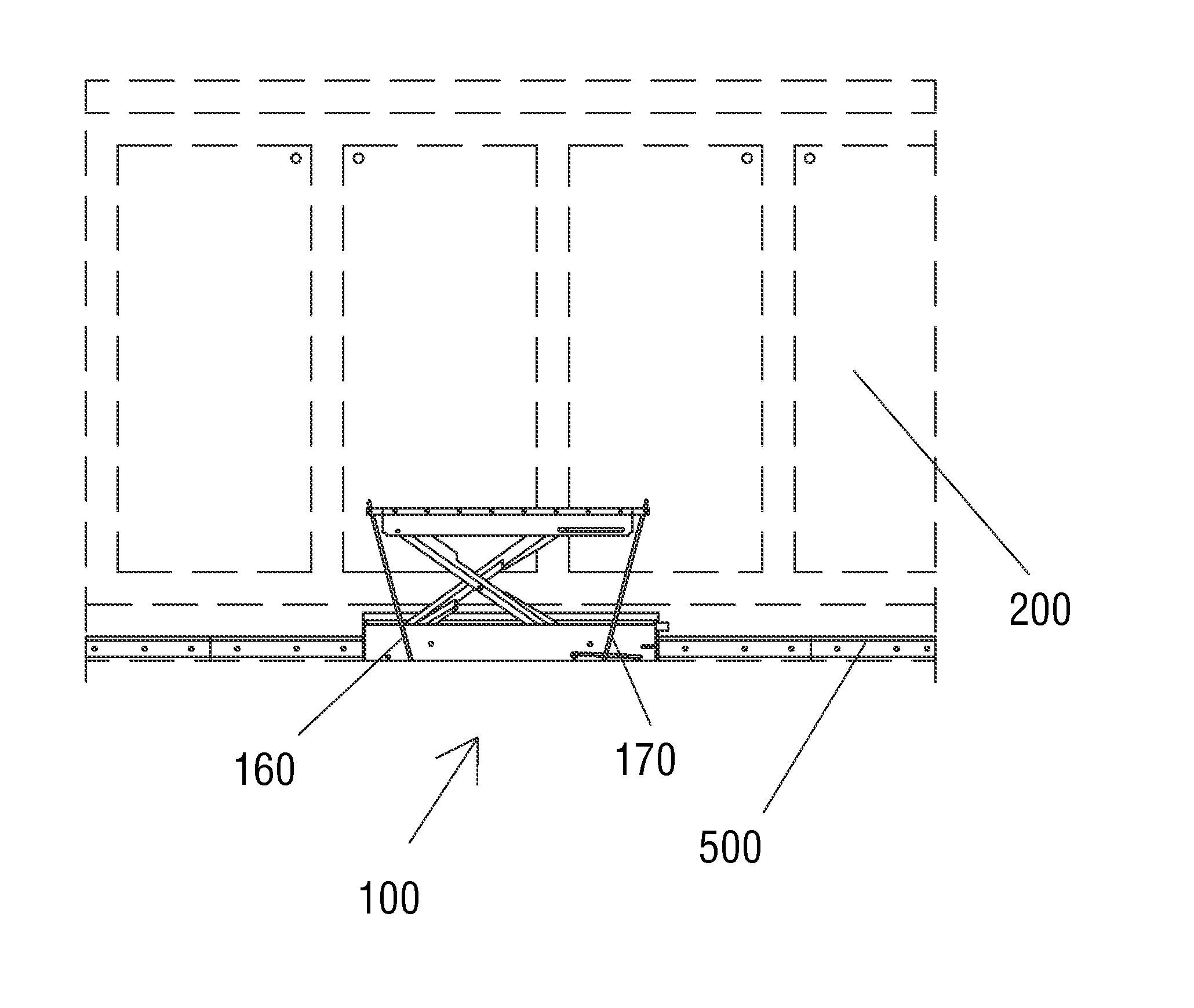
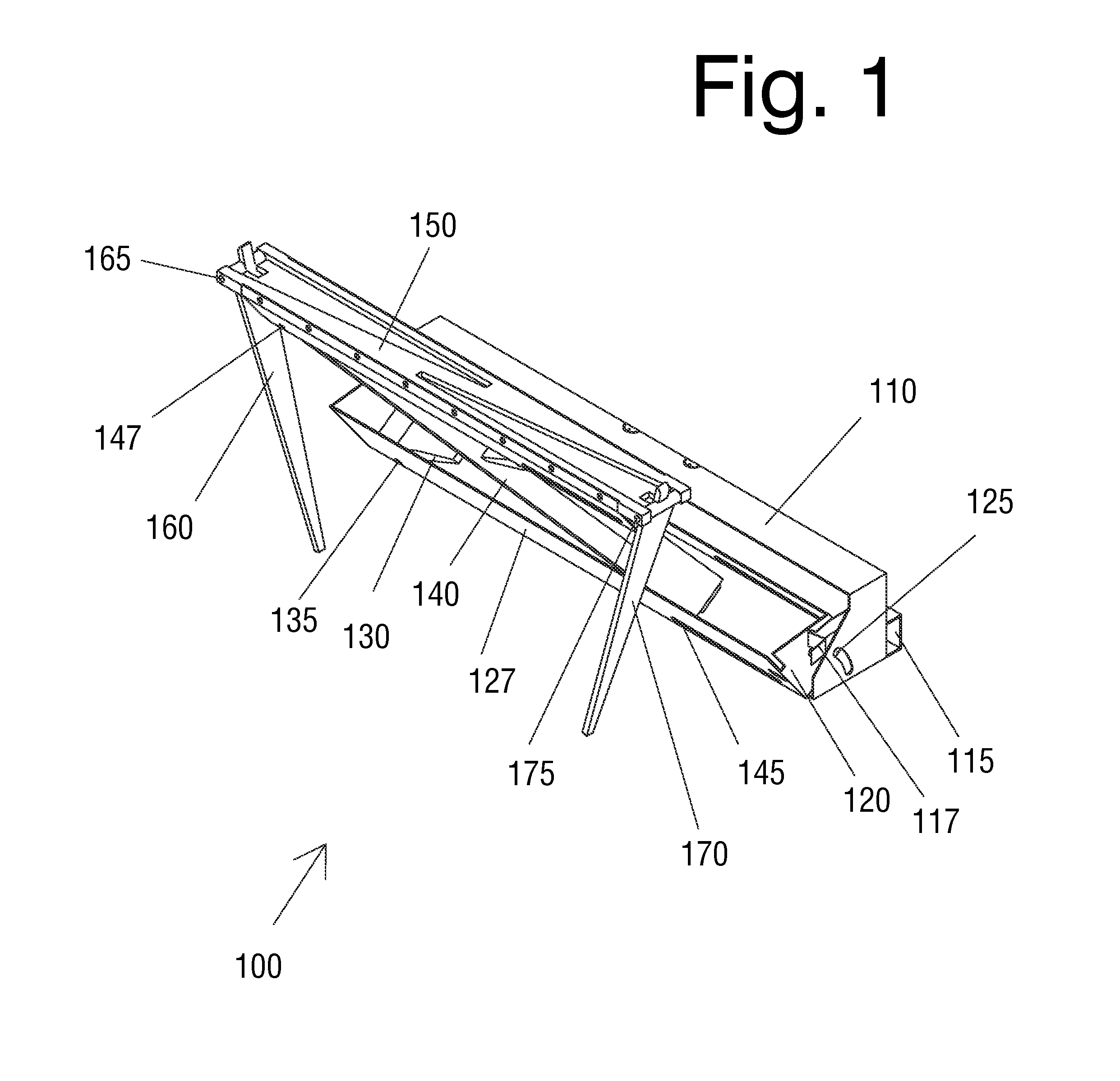
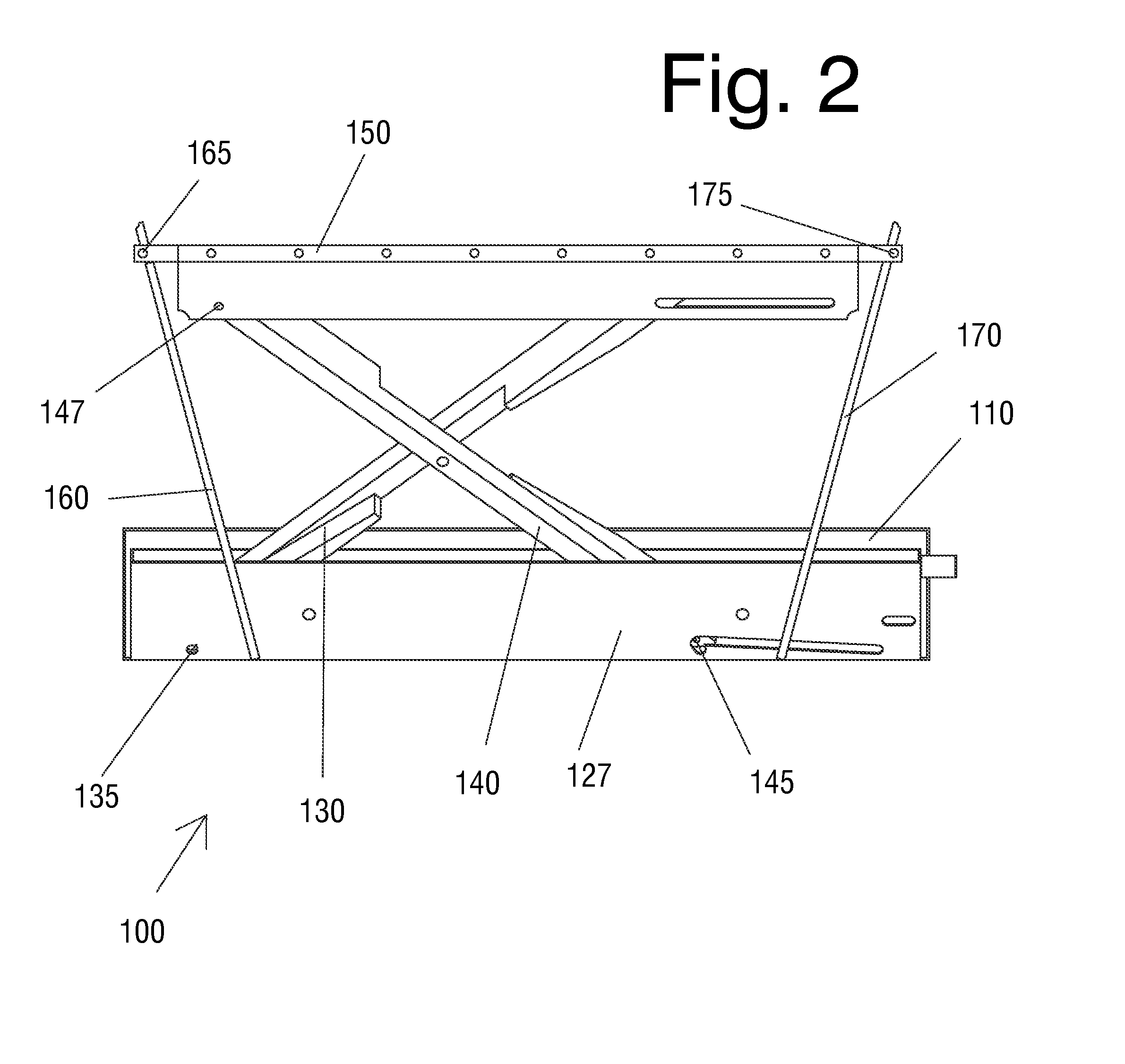
InactiveUS20130213738A1Safer floor environmentEasy accessStep stoolsBuilding support scaffoldsEngineeringCupboard
A quick folding step stool is provided that folds compactly enough to fit in a cabinet toe-kick area while requiring no modifications to existing cabinets. The quick folding step stool can also be mounted on a track to move laterally along a bank of cabinets. The quick folding step stool or the track can also be mounted on a wall, behind a bar, in a work area, or in any other location where occasional access to higher shelves or other features is required.
Owner:SCHROEDER JOHN S
Device for deep driving of tubes having a large diameter
ActiveUS20150259871A1Functional and simple and cost-effectiveImprove verticalityCaissonsBulkheads/pilesEngineeringTower
The invention describes a tubing device of the type operatively connectable to an excavation machine and configured to perform an excavation in the ground contained, at least partially, inside at least one tube segment. The tubing device comprises a base frame, at least one guiding tower for the tube segment, operatively connected to the base frame, and a tube operating unit, operatively connected to the guiding tower. The tube operating unit is slidable along the guiding tower and is provided with engaging means capable of both selectively holding the tube segment, and of transmitting a rotary motion and an axial sliding movement to such a tube segment so as to allow the progressive driving in the ground and subsequent extraction from the ground. The axial sliding movement is guided by the guiding tower and the width of such axial sliding movement is determined by the stroke of the tube operating unit on such a guiding tower and is proportional to at least once the diameter of the tube segment.
Owner:SOILMEC
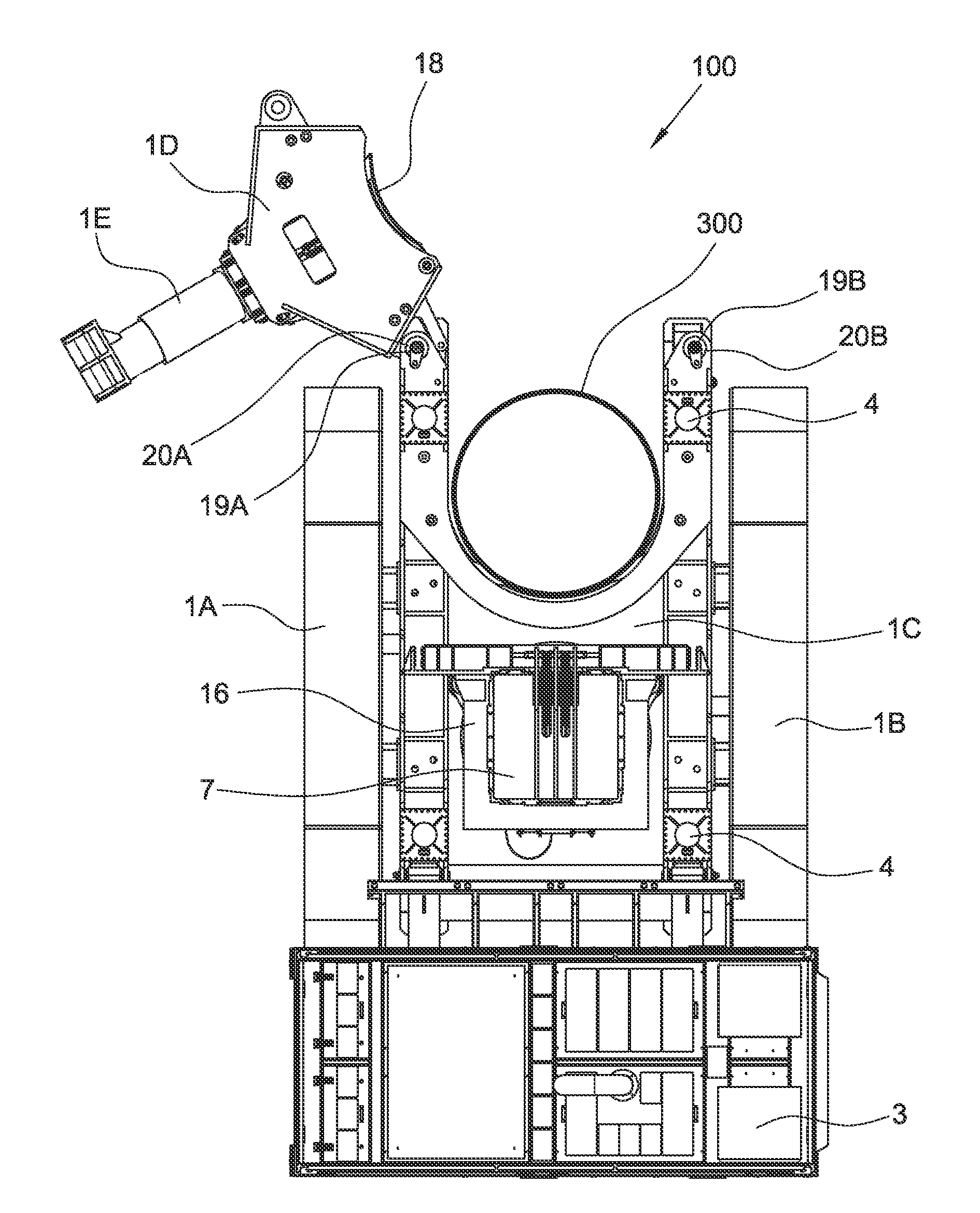
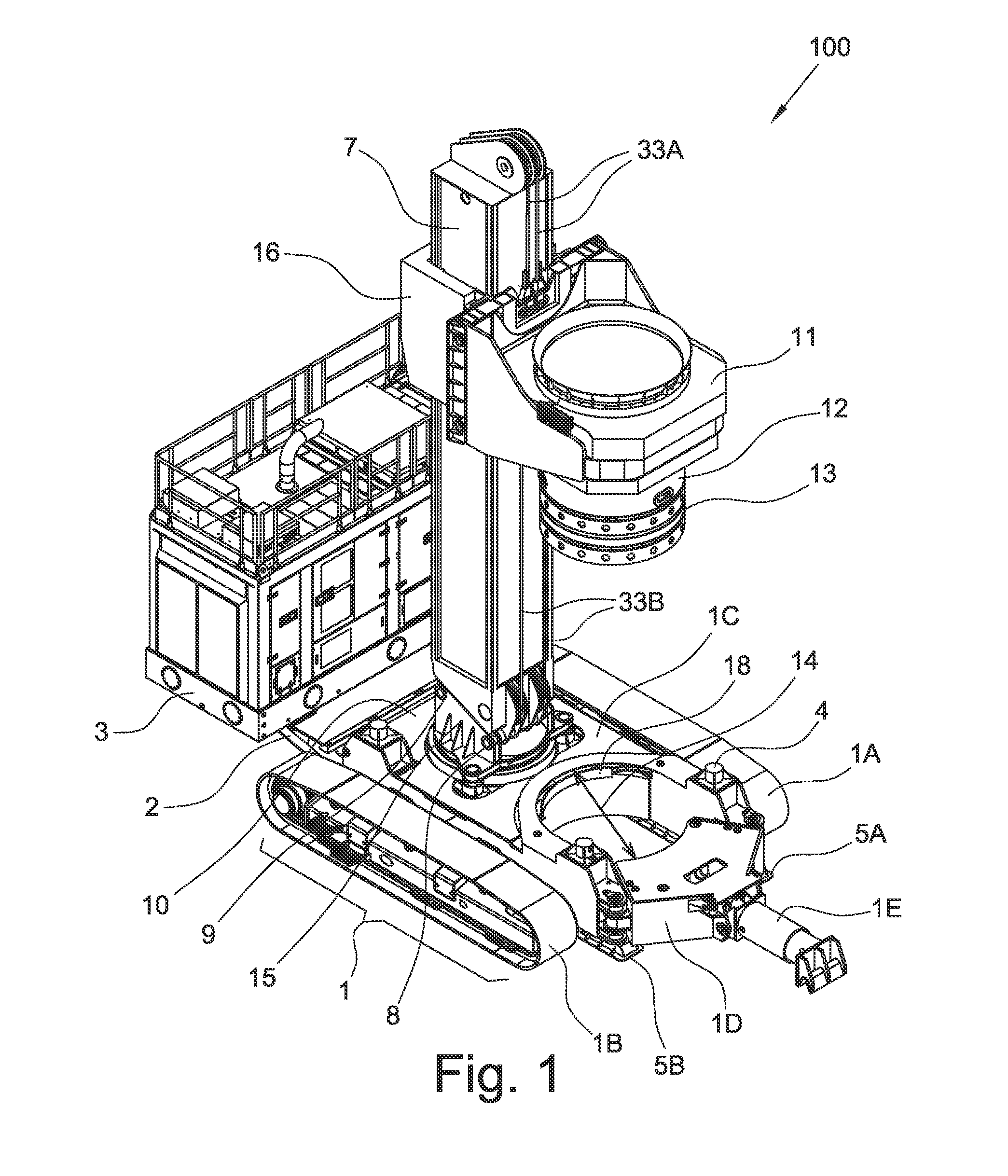
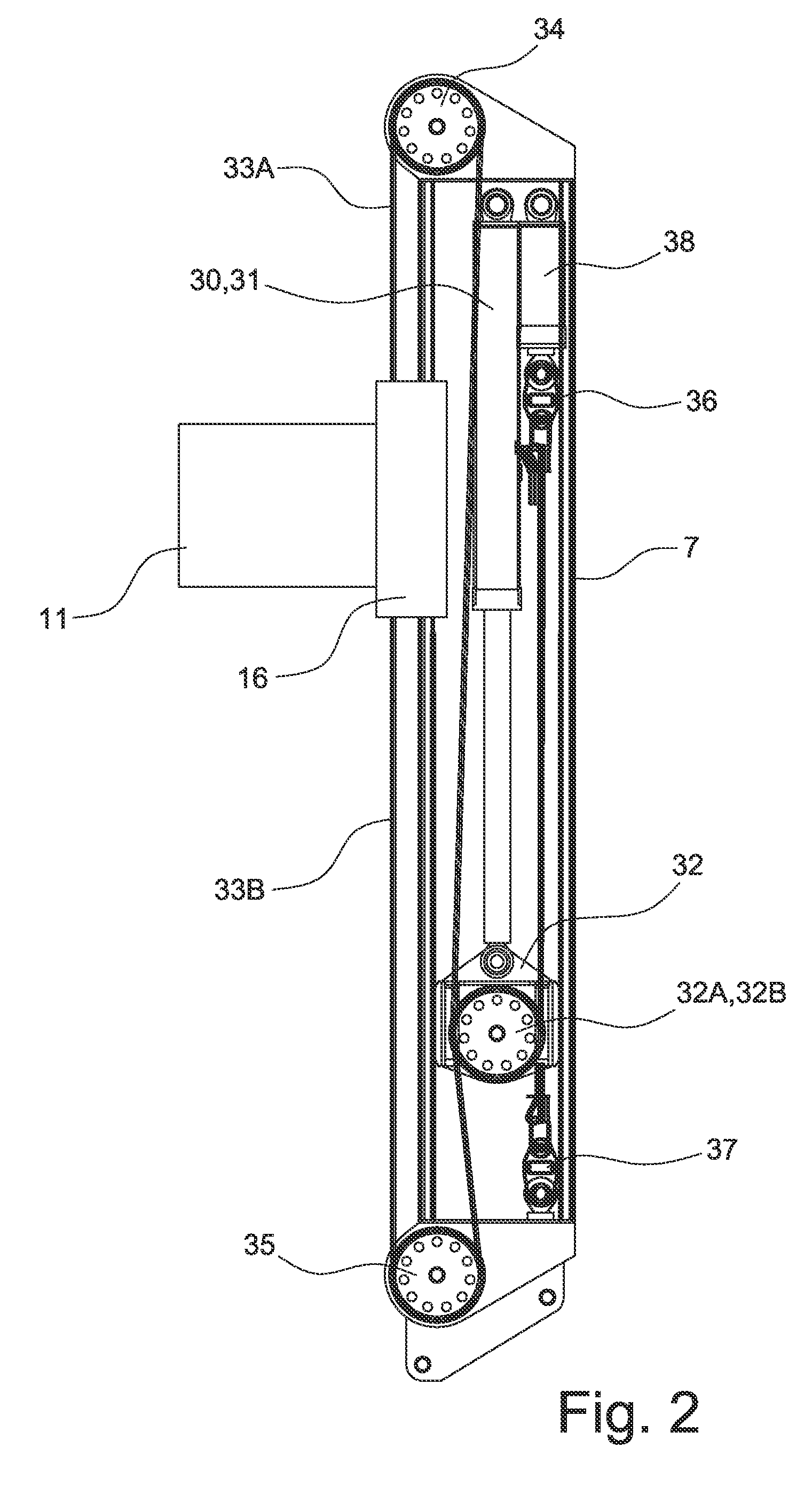
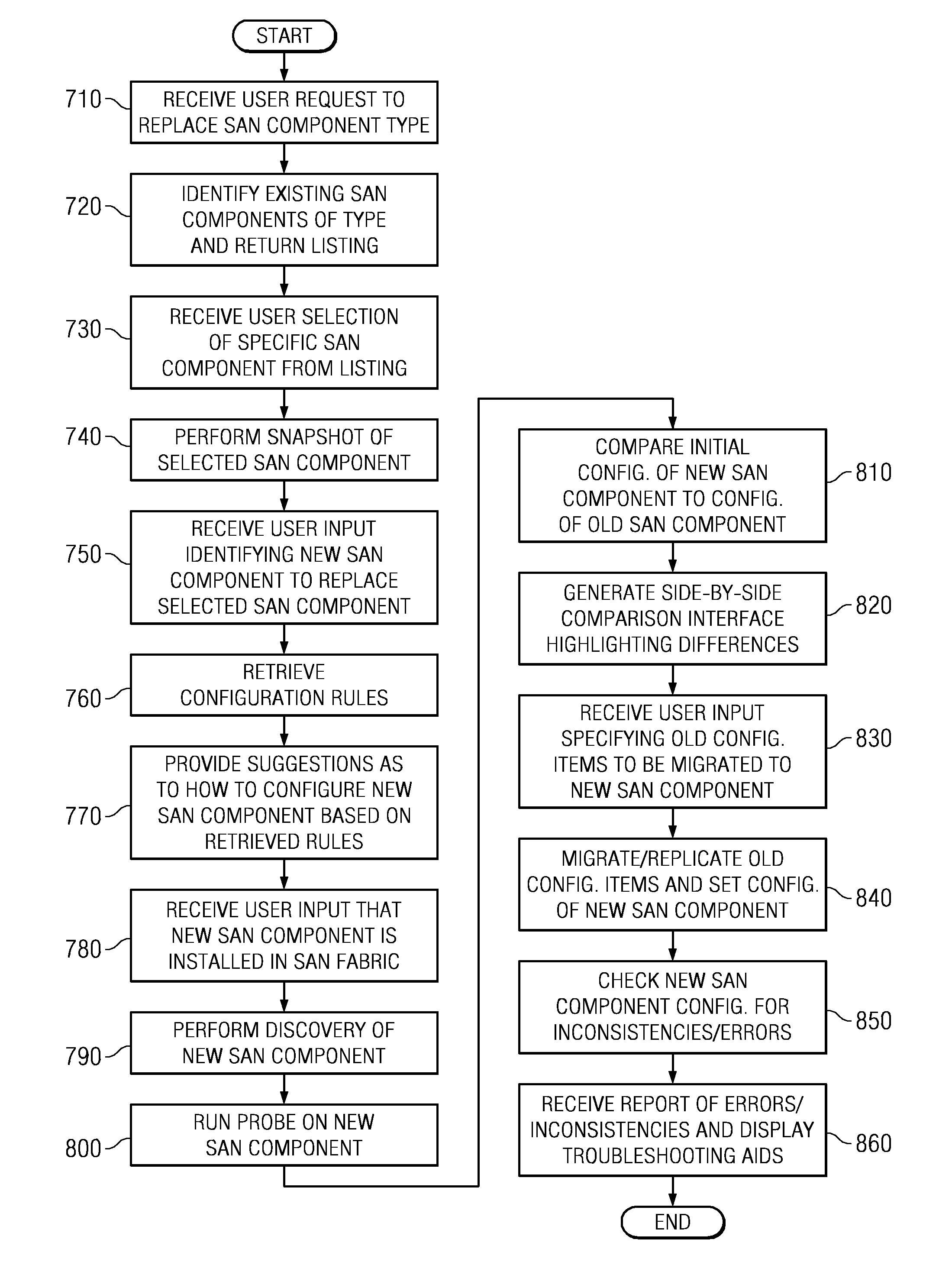
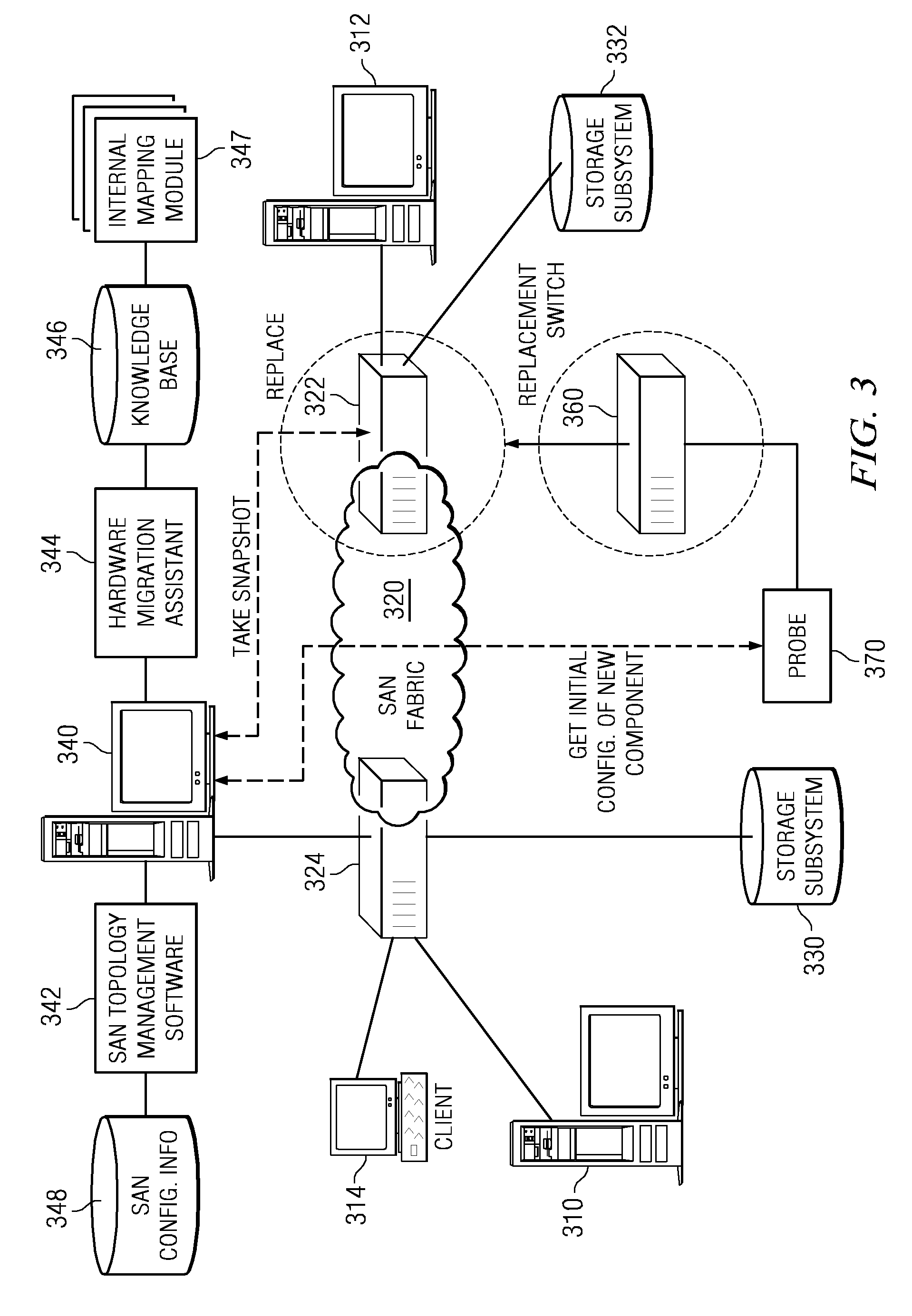
Enabling storage area network component migration
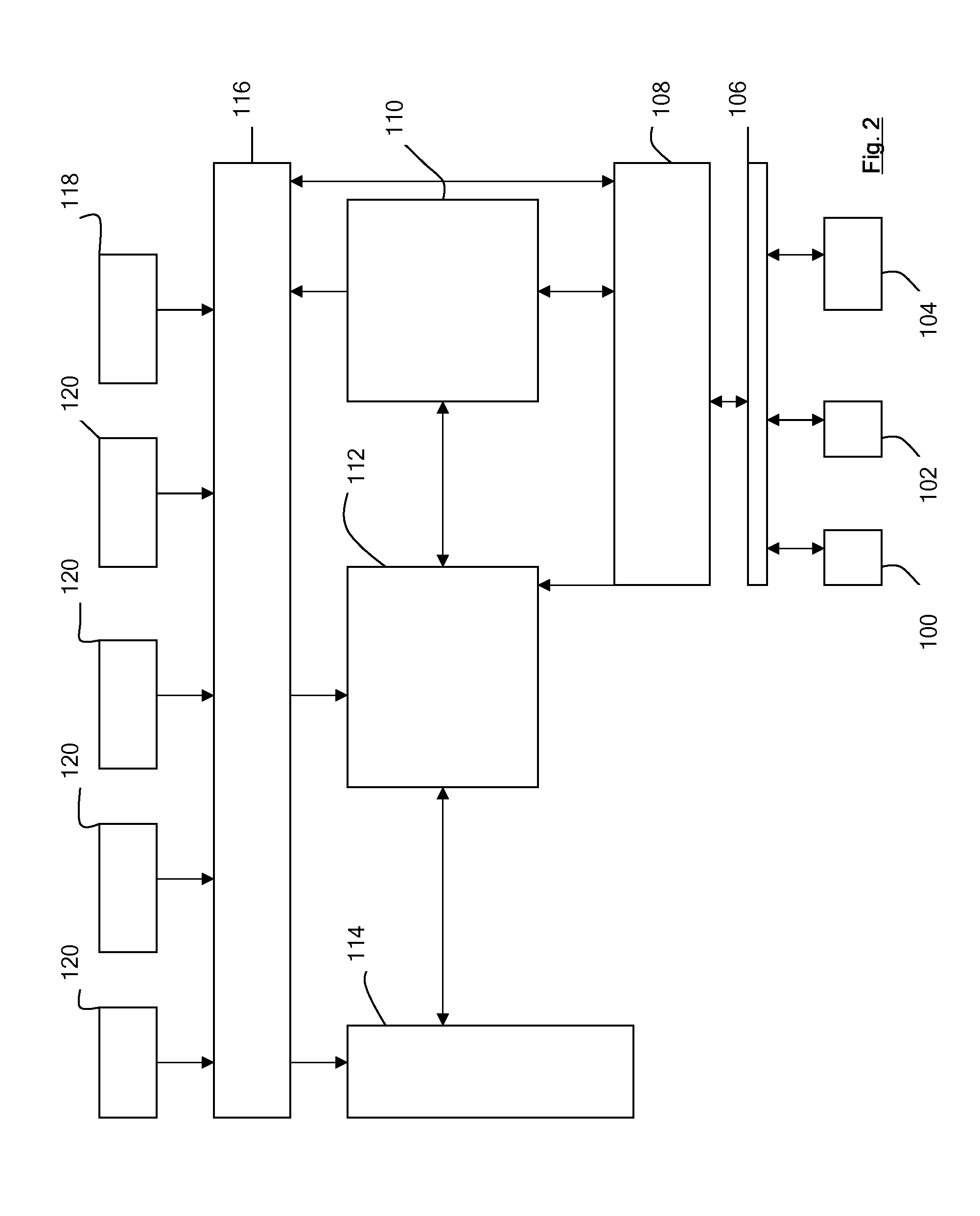
InactiveUS8341251B2Simplify migration stepAvoid excessive errorDigital computer detailsData resettingComponent MigrationStorage area network
Enabling storage area network (SAN) component migration are provided. An end-to-end systems management console, referred to as the hardware migration assistant, is provided to simplify the migration steps for a SAN administrator to replace key SAN components. The hardware migration assistant provides a single interface suitable for stepping the SAN administrator through the reconfiguring task faster and with fewer sources of error than the known distributed manual process. The hardware migration assistant of the illustrative embodiments provides an interface through which a user may specify a type of SAN component that is being replaced and identifies the particular SAN components that are being replaced. The hardware migration assistant provides a knowledge base for guiding the user through the replacement operation and the reconfiguring of the SAN components, including the new SAN components, based on the previous configuration of the replaced components.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
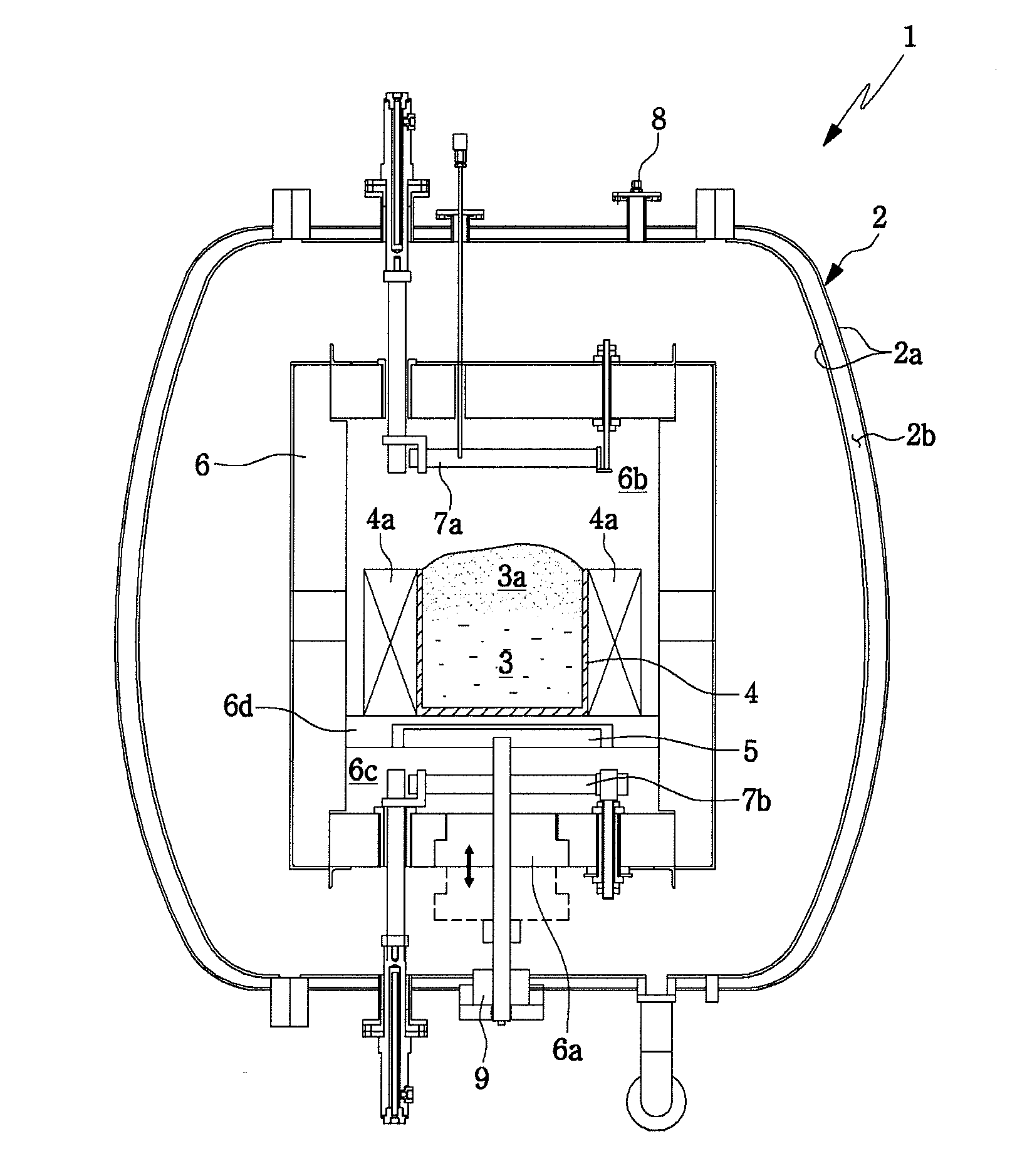
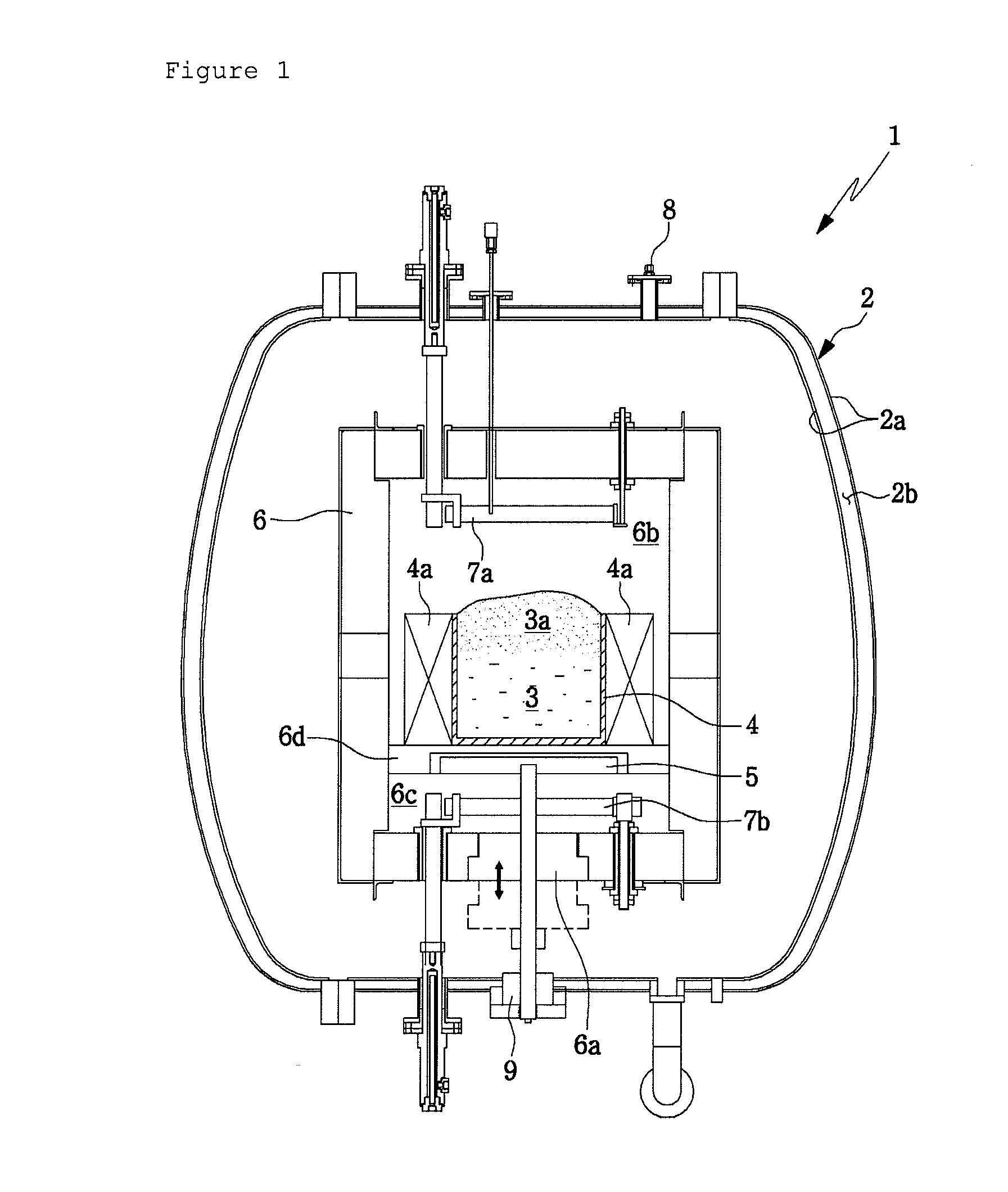
Device for producing a crystallized silicon body for solar cells
InactiveUS20100209319A1Improve melting efficiencyRapidly cooling stepPolycrystalline material growthCrystallization separationActuatorSolar cell
A device is provided for producing a crystallized silicon body for solar cells. The device includes a reaction vessel, a silicon container arranged within the reaction vessel for containing a raw silicon material, an upper heater arranged above the silicon container for heating the raw silicon material contained in the silicon container, a lower heater arranged below the silicon container for heating the raw silicon material contained in the silicon container, and an insulator unit arranged inside the reaction vessel for surrounding the silicon container, the upper heater and the lower heater. The insulator unit is provided with a side insulator which includes a fixed side insulation member, a plurality of movable side insulation members coupled with the fixed side insulation member and a plurality of side actuators operatively connected to the movable side insulation members for moving the movable side insulation members toward or away from the silicon container.
Owner:THERMVAC ENG
Process for the production of a paper or board product and a paper or board produced according to the process
The present invention relates to a process for the production of a paper or paperboard comprising at least two plies wherein microfibrillated cellulose is added to the surface of a first ply and the other ply is attached to the first ply so that the microfibrillated cellulose located in between the plies. The invention further relates to a paper or board produced according to the method.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
Piezoelectric crystal plate resonant frequency measurement method
ActiveCN103063292ALow implementation costHighly targeted and professionalSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing electrical meansFrequency measurementsInterference factor
The invention belongs to the field of aeronautical material performance test, and relates to a piezoelectric crystal plate resonant frequency measurement method. According to the method, a short-term high-voltage pulse method is adopted to excite a piezoelectric crystal plate, the piezoelectric crystal plate generates response vibration, a high voltage pulse is used as wideband excitation, the piezoelectric crystal plate responds selectively to vibration, and the vibrational frequency of the piezoelectric crystal plate is the resonant frequency of the piezoelectric crystal plate. According to the method, a pure time domain algorithm is adopted, the method is direct and simple and convenient, is small in interference factor, and high in accuracy. The piezoelectric crystal plate in a certain shape corresponds to more than one resonant frequency. For example, a round crystal plate has a high-frequency thickness mold vibration resonant frequency and a low-frequency radial mold resonant frequency. The method can totally measure the resonant frequency of mold vibration in different directions.
Owner:CHINA AIRPLANT STRENGTH RES INST
Imaging apparatus and method for authentication of user
InactiveUS7792337B2Quick stepsMultiple biometrics useSubcutaneous biometric featuresBiometric dataImaging equipment
The imaging apparatus for authenticating a user can quickly perform matching step of the inputted biometric data. This apparatus for authenticating the user includes an imaging unit for imaging a guided finger and a guided palm, a matching data storing unit for storing the determined finger image and the determined palm image, and a matching unit for matching the imaged finger image and the imaged palm image with the stored finger image and the stored palm image. The matching unit selects the finger image having the similar feature amount based on the imaged finger image and authenticates a user based on the result of matching of the palm image corresponding to the selected finger image with the imaged palm image.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of forming MIM capacitor electrodes
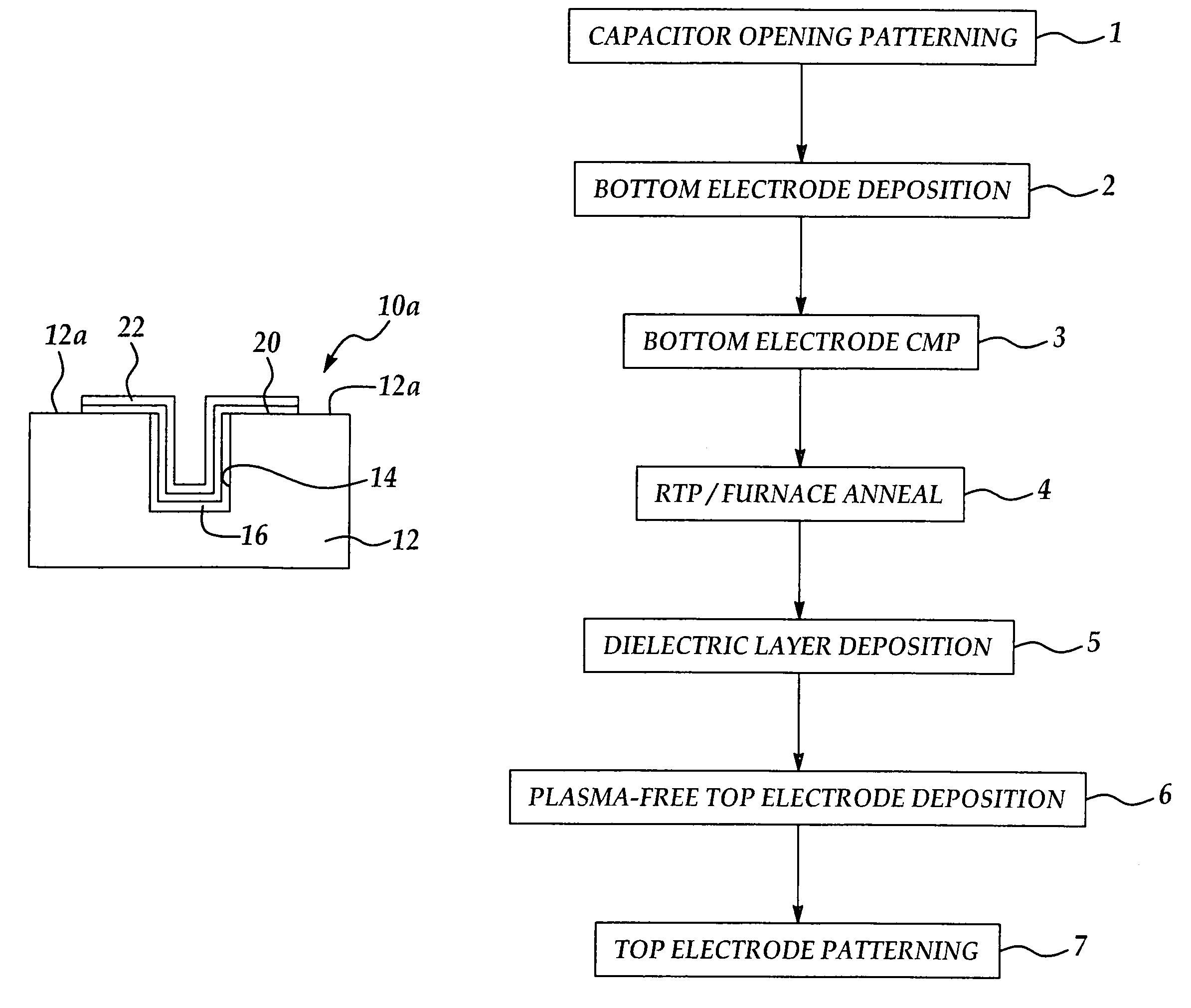
ActiveUS7199001B2Avoid damageImprove performanceFixed capacitor electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetal-insulator-metalEngineering
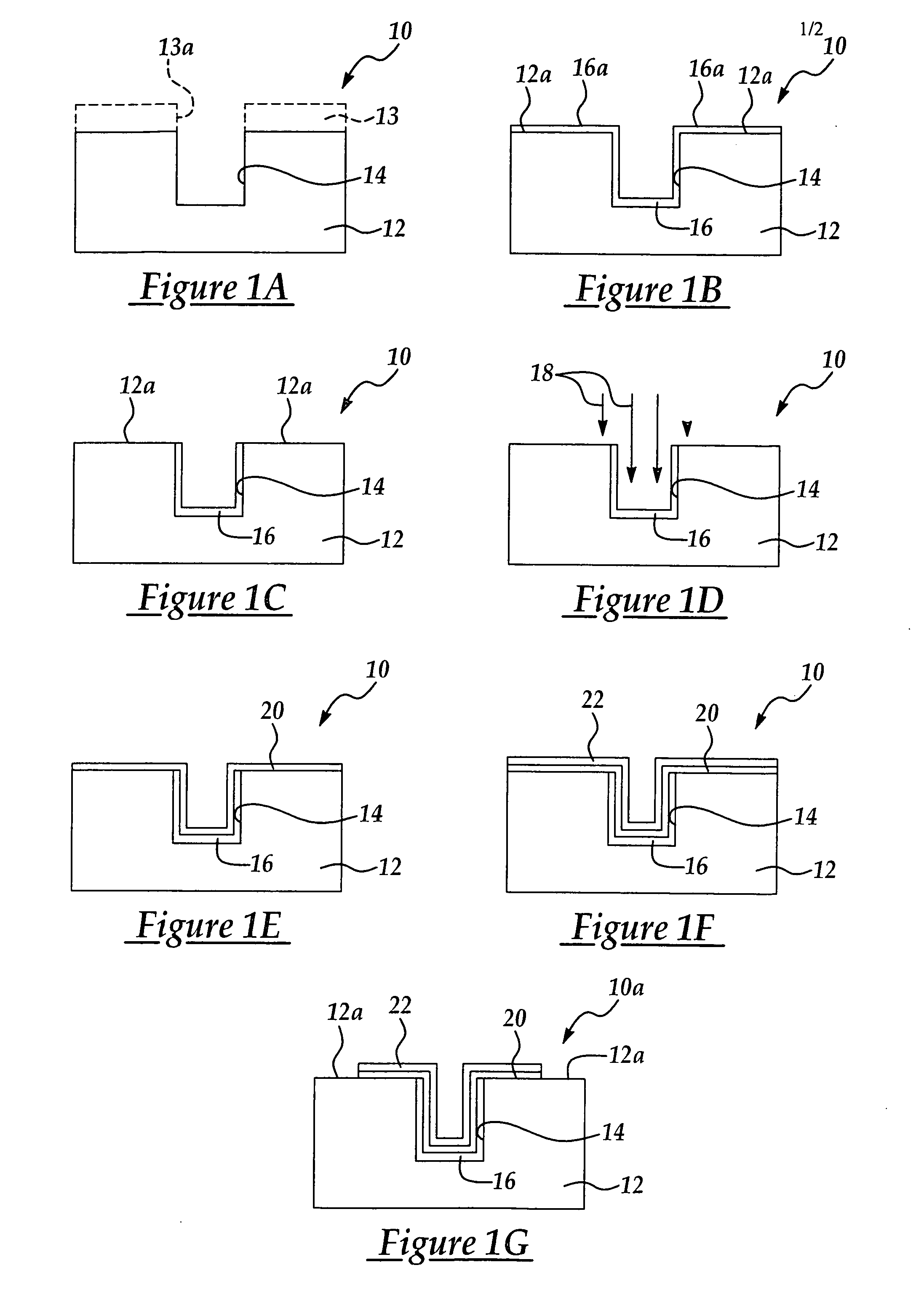
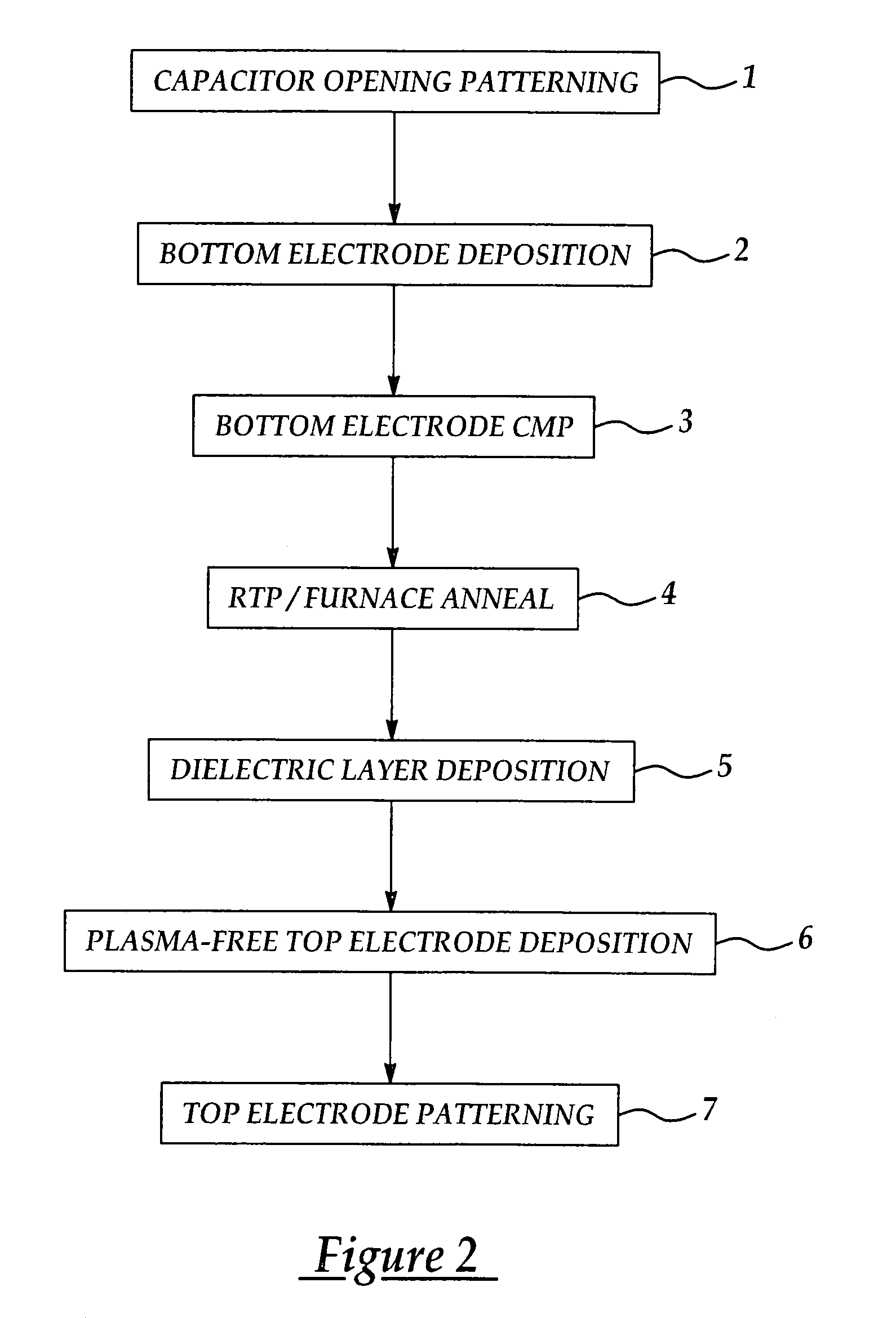
A novel method for forming electrodes in the fabrication of an MIM (metal-insulator-metal) capacitor, is disclosed. The method improves MIM capacitor performance by preventing plasma-induced damage to a dielectric layer during deposition of a top electrode on the dielectric layer, as well as by reducing or preventing the formation of an interfacial layer between the dielectric layer and the electrode or electrodes, in fabrication of the MIM capacitor. The method typically includes the patterning of crown-type capacitor openings in a substrate; depositing a bottom electrode in each of the crown openings; subjecting the bottom electrode to a rapid thermal processing (RTP) or furnace anneal step; depositing a dielectric layer on the annealed bottom electrode; depositing a top electrode on the dielectric layer using a plasma-free CVD (chemical vapor deposition) or ALD (atomic layer deposition) process; and patterning the top electrode of each MIM capacitor.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Nondestructive testing method for pigment content of color wheat grain
ActiveCN102507485ARapid determination of pigment contentIntegrity guaranteedColor/spectral properties measurementsMathematical modelWheat grain
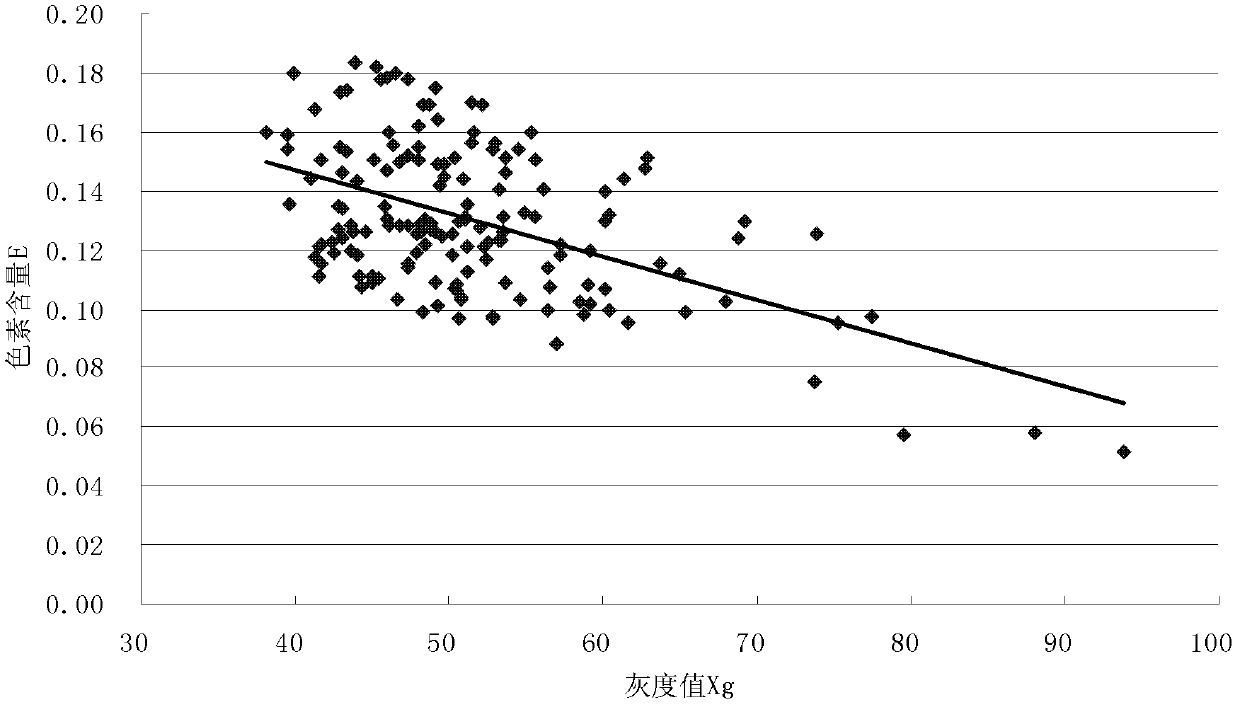
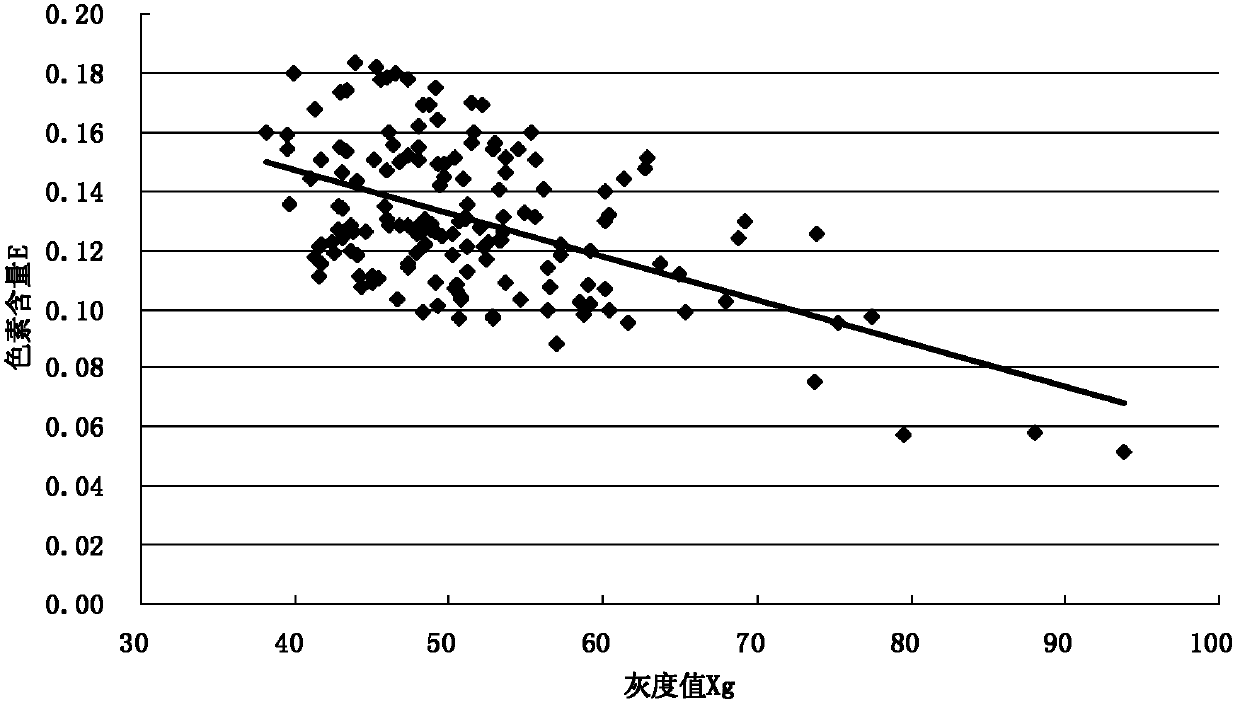
The invention relates to a nondestructive testing method for the pigment content of a color wheat grain. In the nondestructive testing method, a computer is used to determine the gray value of color wheat on the premise of not destroying the grain, thus the pigment content of the color wheat grain can be directly acquired, and a mathematical model of the gray value and the pigment content of the color wheat grain can be simultaneously constructed; the gray value of the wheat grain can be used for directly reflecting the depth of the color of the wheat grain; and the depth of the color wheat grain is related to the pigment content of the color wheat grain, so that the pigment content of the wheat grain can be reflected by determining the gray value of the color wheat grain, thus the integrity of the color wheat grain is ensured, so as to carry out next study and application on the color wheat. The mathematical model which is provided by the invention and can be used for showing the pigment content of the color wheat grain by utilizing the gray value can be used for conveniently and rapidly calculating the pigment content of the color wheat grain.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
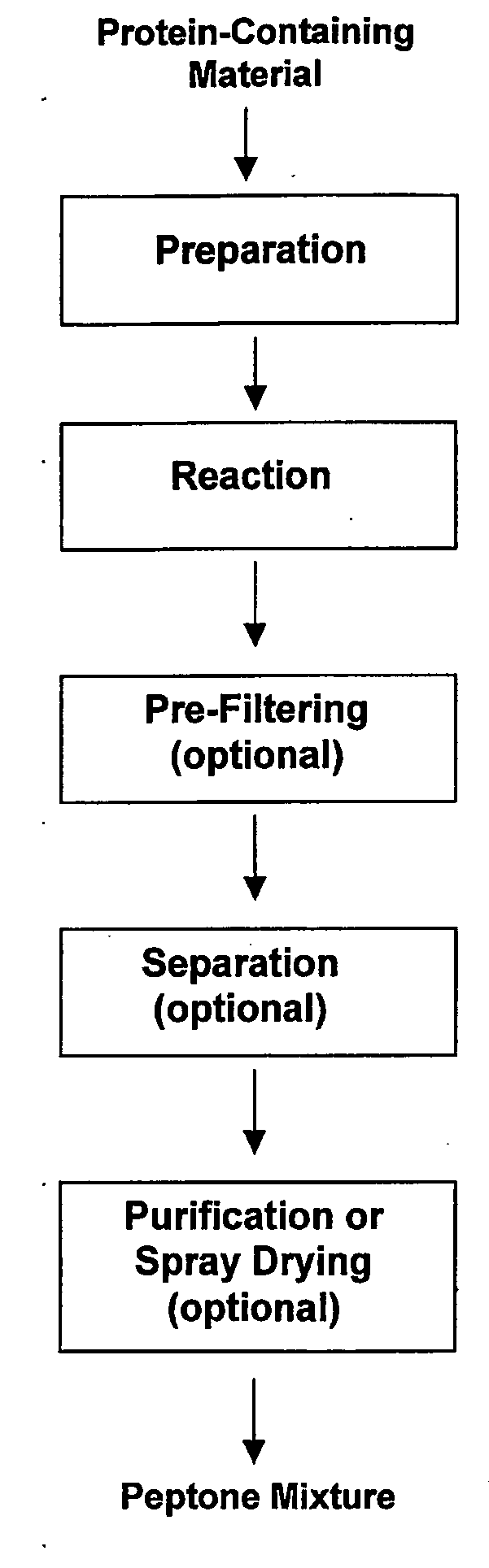
Recovery of peptones
The present invention relates to an effective process for converting animal-derived protein-containing material into a peptone mixture. The process comprises a step involving alkaline hydrolysis of the protein-containing material. The hydrolysis step can be rapid and typically requires only a low concentration of alkaline material. The overall conversion process can produce a high yield of small peptones and other peptones. The resulting peptones may be further separated, purified or otherwise processed to provide desired properties such as molecular weight distribution, water solubility, dry color and dry flowability.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Nanomaterial and method of production of a nanomaterial for medical applications, such as MRI or sers
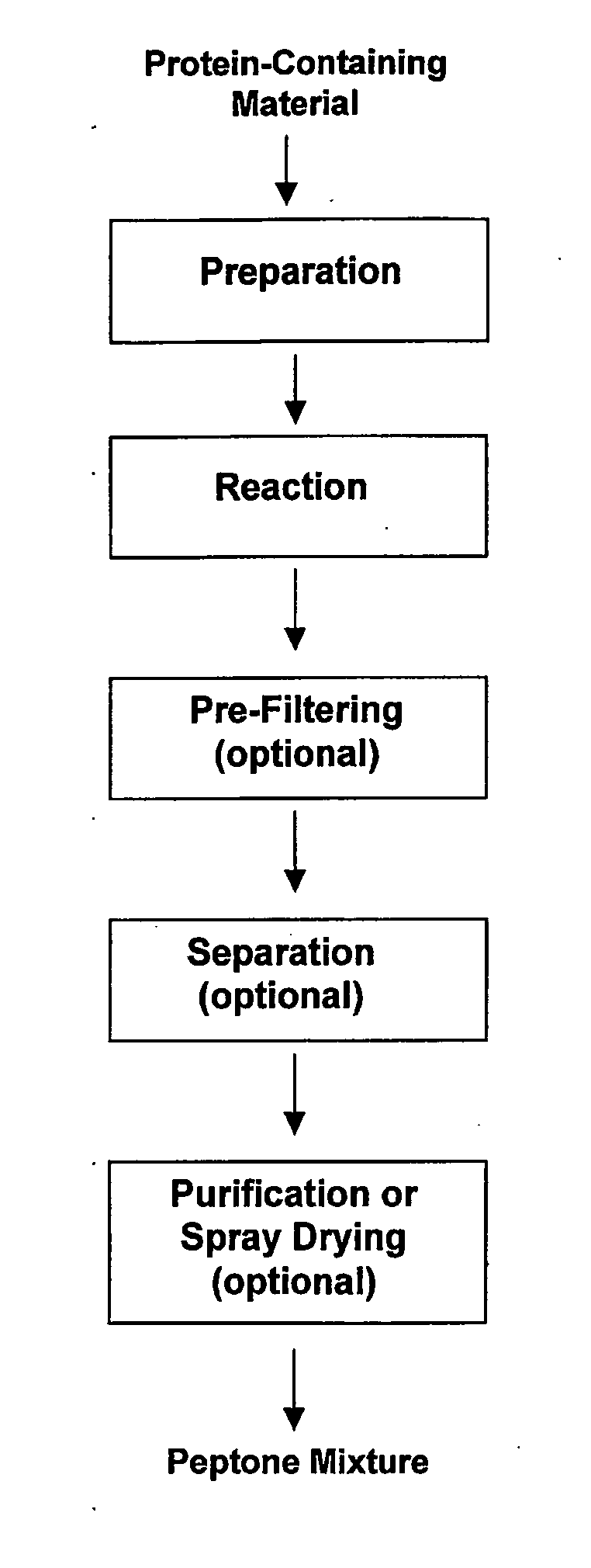
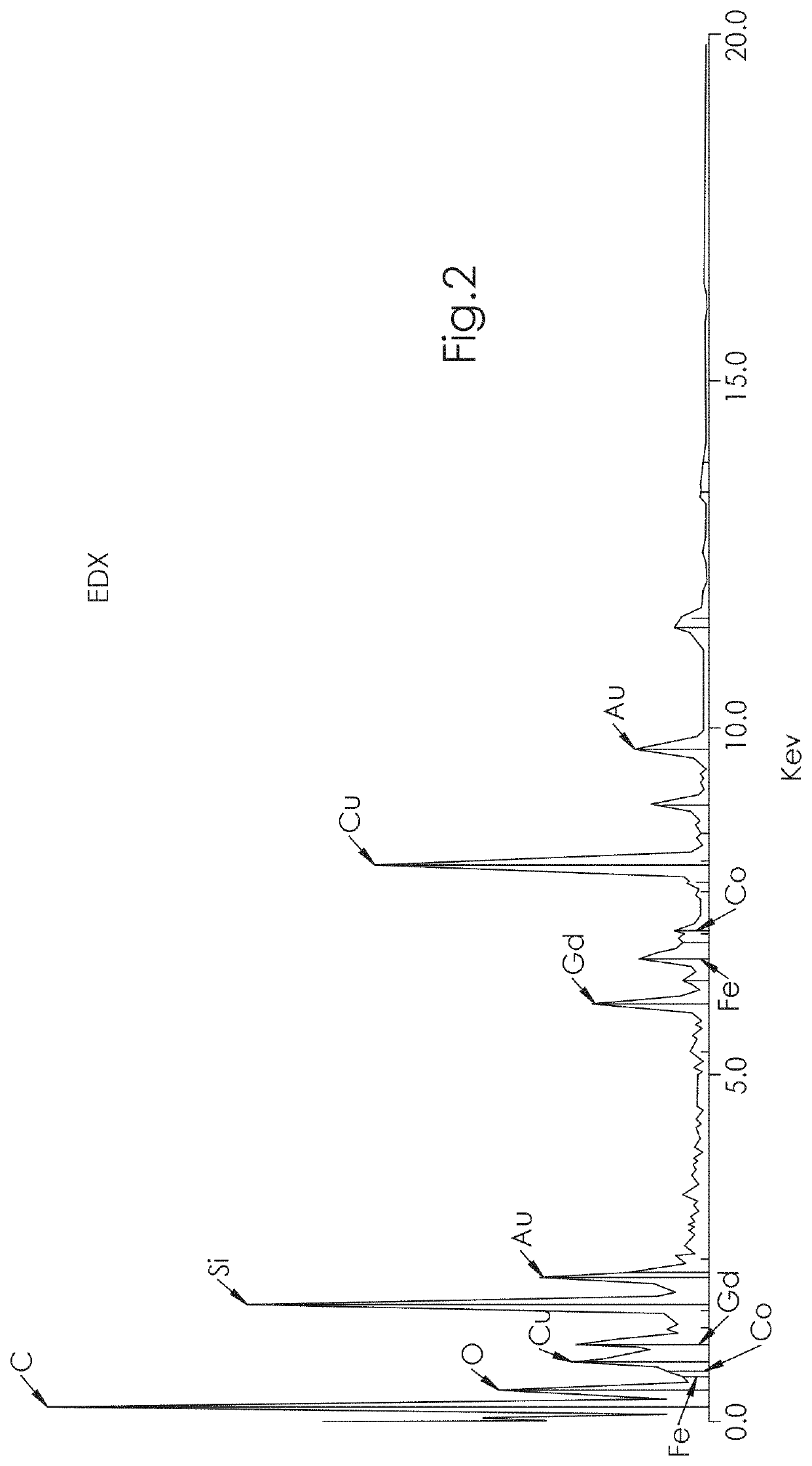
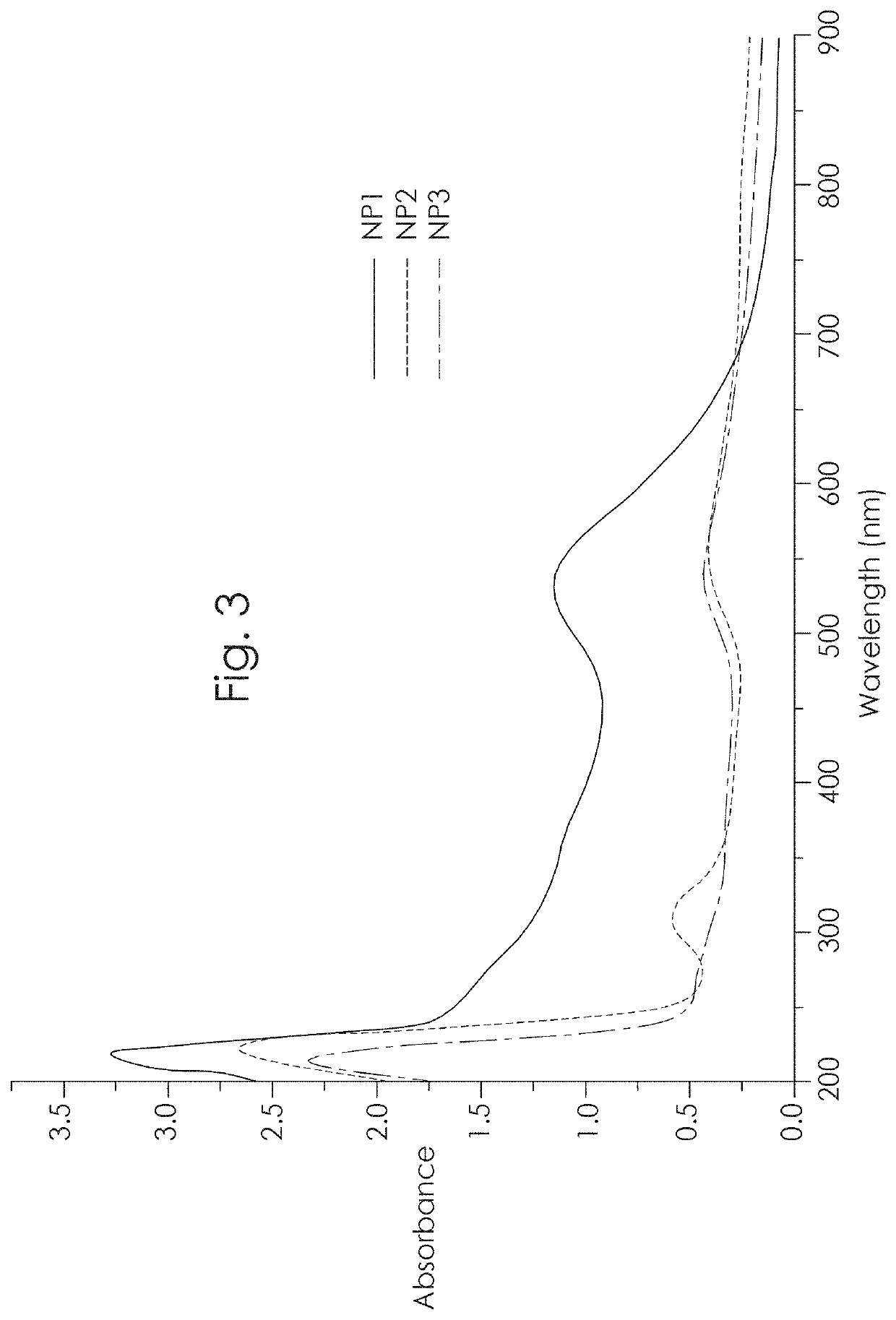
InactiveUS20190336620A1Selectivity of reactionSmall sizePhotodynamic therapyTransportation and packagingNanoparticleBiopolymer
A method for producing nanomaterial product which comprises at least one hybrid nanoparticle Gold-metal-Polymer, the polymer comprising at least one biopolymer, the atoms of metal being linked with the atom of Gold, the metal being chosen among: Gd, Co, Eu, Tb, Ce, Mn, Fe, Zn, Cu, the method being realized in an aqueous solvent, without reactive or stabilizer agent, and presenting a step of reducing: tetrachloroauric acid (HAuCl4) and metal ions, in the presence of the biopolymer, the biopolymer being used as a stabilizer agent.
Owner:PARIS 13 UNIVERSITY +1
Method for magnetic component extraction in soil and strong/weak magnetic component separation in extract
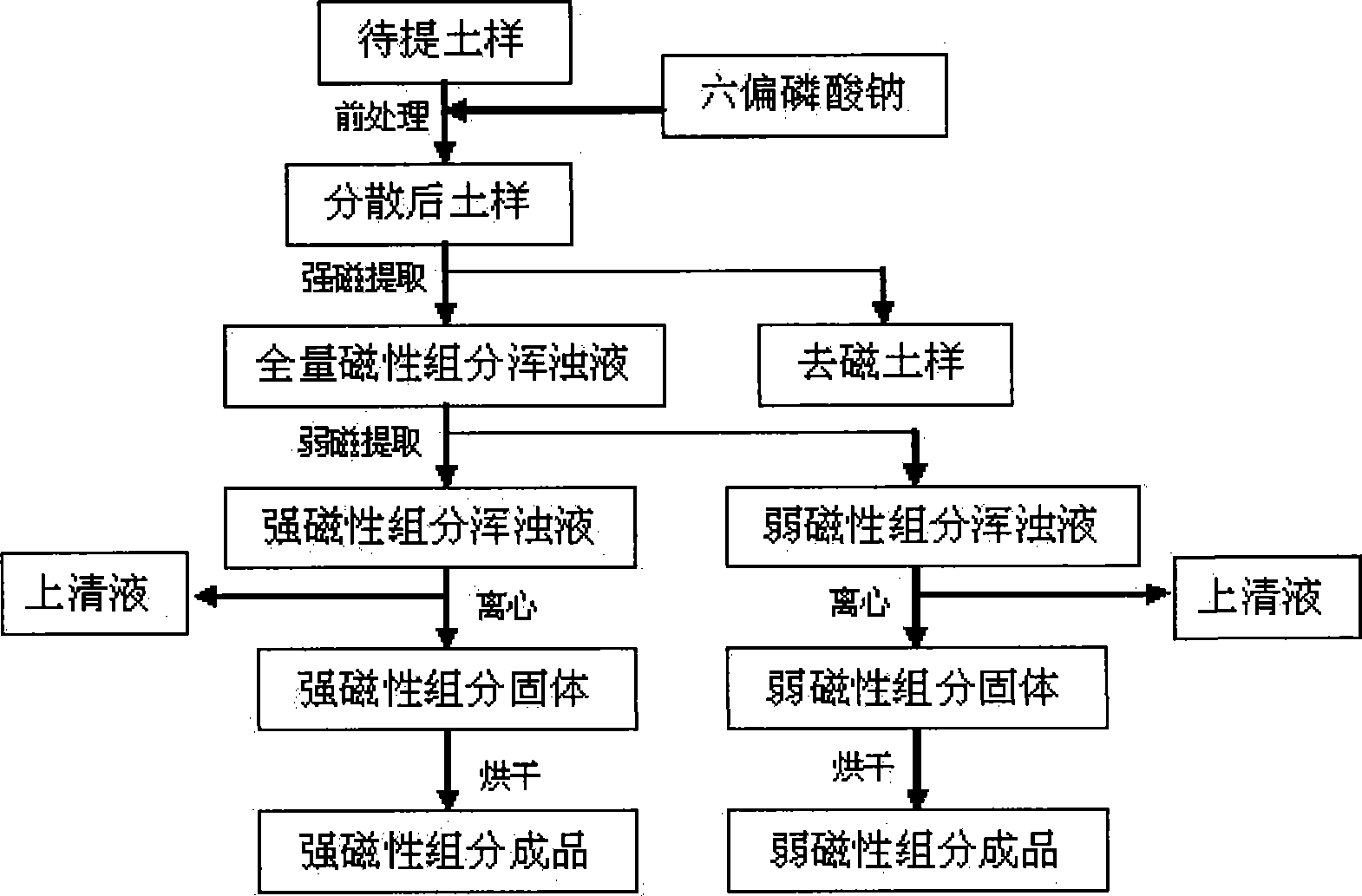
ActiveCN101430260AEasy to operateSimple stepsPreparing sample for investigationDistilled waterOperability
The invention provides a method for picking up magnetic component in soil and separating strong magnetic component form weak magnetic component and belongs to the technical field of soil pollution monitoring. In the method, soil sample is air-dried, ground and filtered for removing sundries firstly; then certain quantity of the soil sample is added with distilled water and dispersant for preliminary treatment; after the preliminary treatment, total magnetic component is picked up from the soil sample by strong magnet; then the weak magnetic component is separated by weak magnet; and the strong magnetic component and the weak magnetic component are centrifugated and dried respectively. The invention has high purity of the picked-up and separated magnetic component, simple and fast steps, strong operability and no damage to sample form.
Owner:JIANGSU YINONG FERTILIZER GROUP
Event processing apparatus and methods
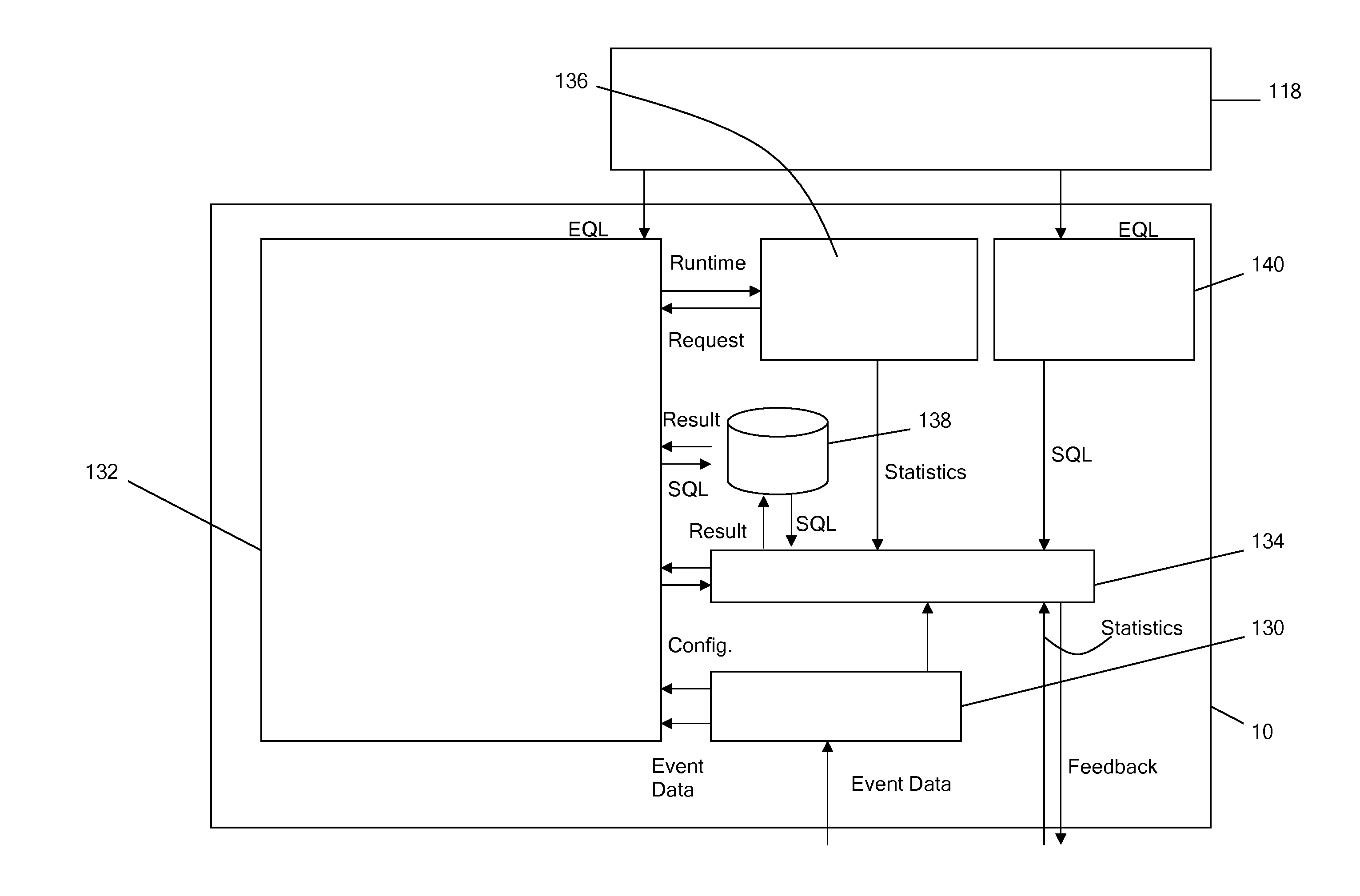
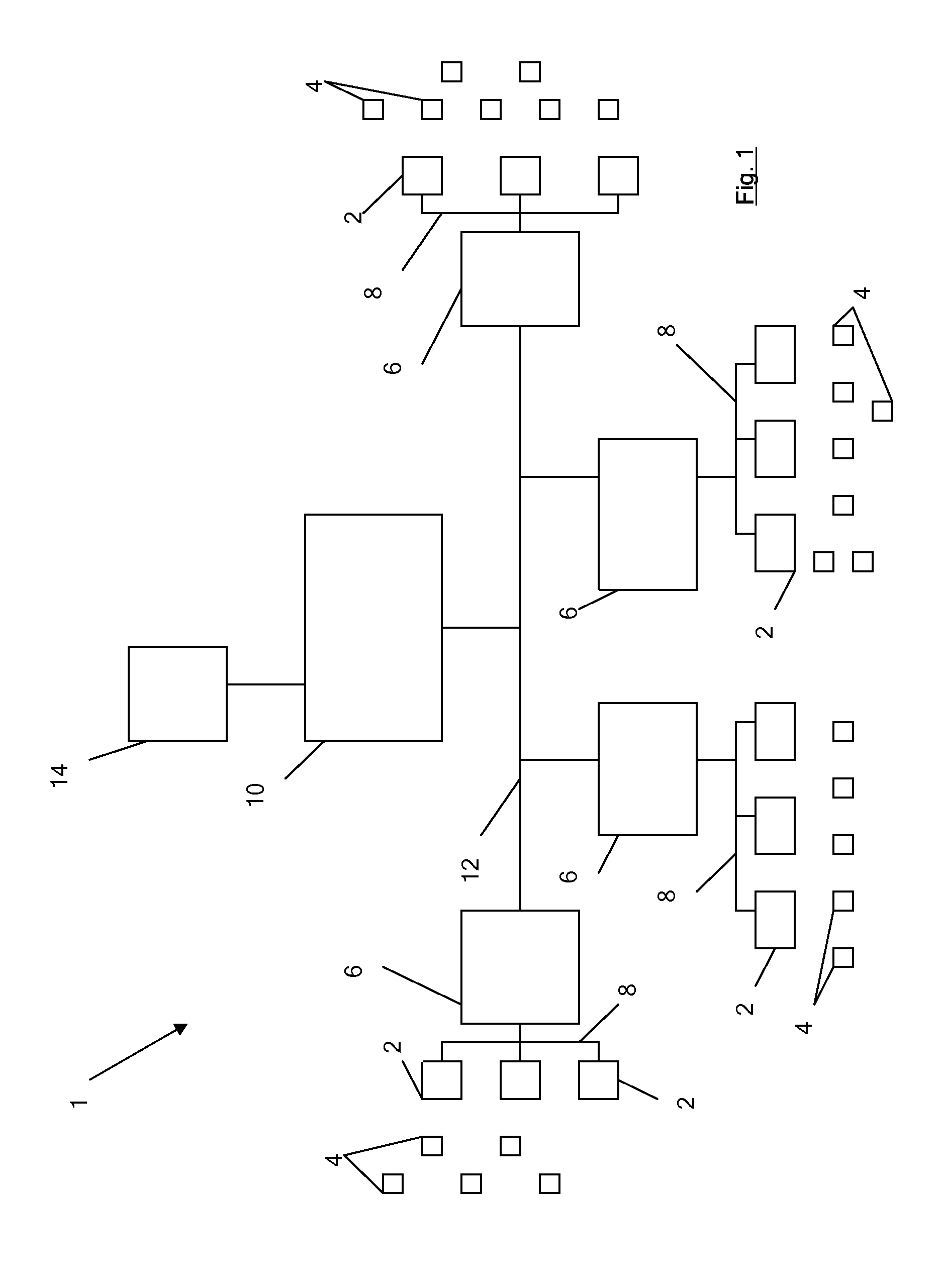
InactiveUS20120025955A1Easy to controlImprove performanceSubscribers indirect connectionInstrumentsControl signalElectronic tagging
Event processing apparatus for processing electronic tag reading events comprising a first event processing module and one or more second event processing modules. The or each second event processing module is operable to receive event data records concerning electronic tag reading events from electronic tag readers, and to transmit to the first event processing module processed event data records concerning selected electronic tag reading events. A filter control module transmits filter definitions to the second event processing modules and subsequently transmits filter control signals indicating that filters should be activated or deactivated in order to avoid overloading of the first event processing module. Statistics concerning the selectivity of filters, including filters which are currently inactive, are used to determine which filters should be activated or deactivated.
Owner:TRAAK SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com