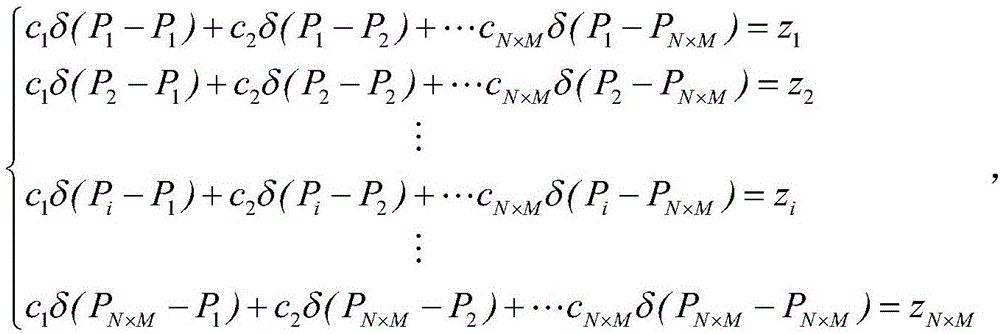Patents
Literature
57 results about "Electrohydrodynamics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
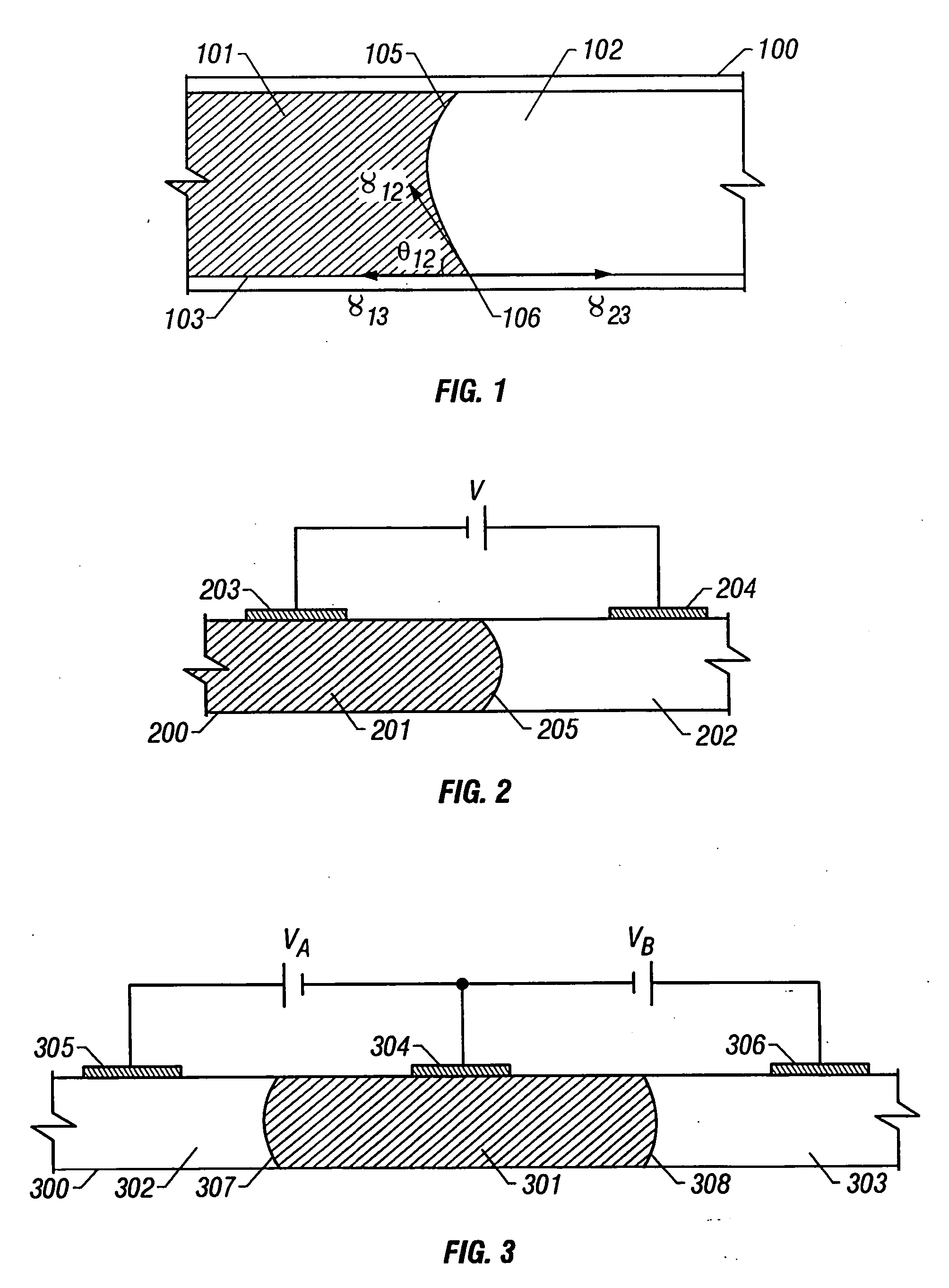
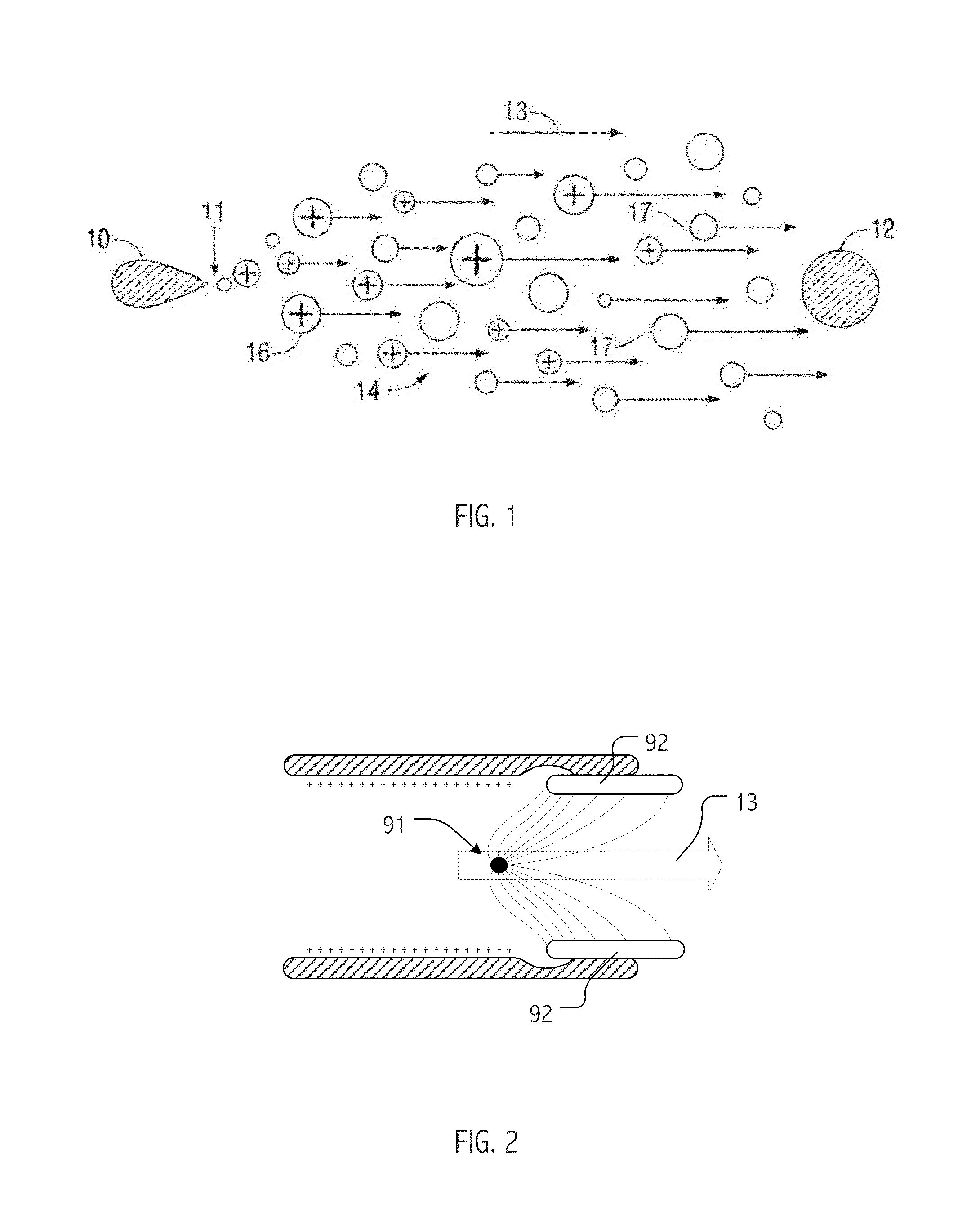
Electrohydrodynamics (EHD), also known as electro-fluid-dynamics (EFD) or electrokinetics, is the study of the dynamics of electrically charged fluids. It is the study of the motions of ionized particles or molecules and their interactions with electric fields and the surrounding fluid. The term may be considered to be synonymous with the rather elaborate electrostrictive hydrodynamics. ESHD covers the following types of particle and fluid transport mechanisms: electrophoresis, electrokinesis, dielectrophoresis, electro-osmosis, and electrorotation. In general, the phenomena relate to the direct conversion of electrical energy into kinetic energy, and vice versa.
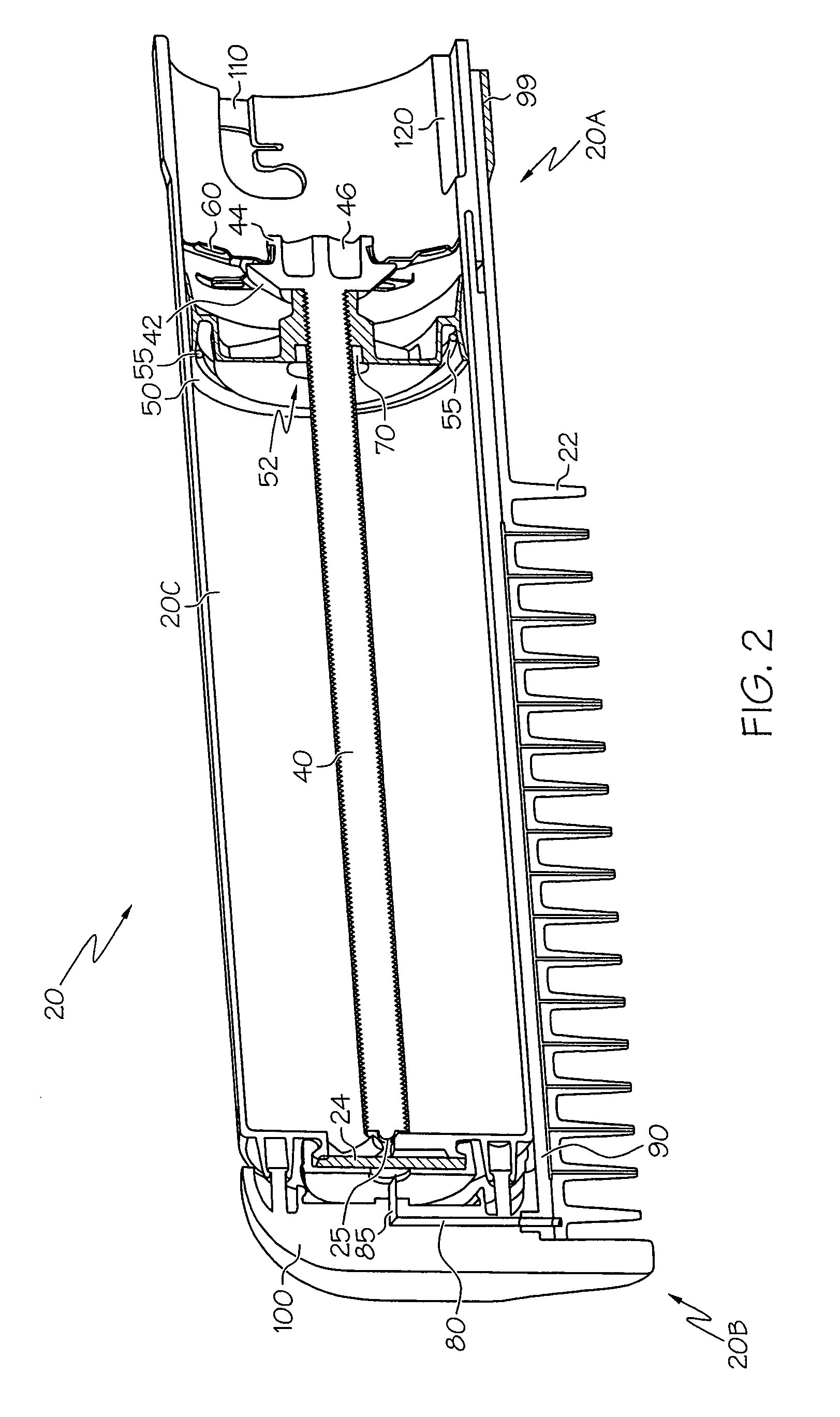
Microfluidic control for waveguide optical switches, variable attenuators, and other optical devices
InactiveUS7016560B2Reduce power consumptionGood workmanshipTransportation and packagingMixersDifferential pressureThermal expansion
Devices utilize elements carried by a fluid in a microchannel toswitch, attenuate, shutter, filter, or phase shift optical signals. In certain embodiments, a microchannel carries a gaseous or liquid slug that interacts with at least a portion of the optical power of an optical signal traveling through a waveguide. The microchannel may form part of the cladding of the waveguide, part of the core and the cladding, or part of the core only. The microchannel may also have ends or may be configured as a loop or continuous channel. The fluid devices may be self-latching or may be semi-latching. The fluid in the microchannel is moved using e.g., e.g., electrocapillarity, differential-pressure electrocapillarity, electrowetting, continuous electrowetting, electrophoresis, electroosmosis, dielectrophoresis, electro-hydrodynamic electrohydrodynamic pumping, magneto-hydrodynamic magnetohydrodynamic pumping, thermocapillarity, thermal expansion, dielectric pumping, and / or variable dielectric pumping.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
Microfluidic control for waveguide optical switches, variable attenuators, and other optical devices
InactiveUS20060083473A1Improve efficiencyIncrease functional densityTransportation and packagingMixersDifferential pressureEngineering
Devices utilize elements carried by a fluid in a microchannel to switch, attenuate, shutter, filter, or phase shift optical signals. In certain embodiments, a microchannel carries a gaseous or liquid slug that interacts with at least a portion of the optical power of an optical signal traveling through a waveguide. The microchannel may form part of the cladding of the waveguide, part of the core and the cladding, or part of the core only. The microchannel may also have ends or may be configured as a loop or continuous channel. The fluid devices may be self-latching or may be semi-latching. The fluid in the microchannel is moved using e.g., e.g., electrocapillarity, differential-pressure electrocapillarity, electrowetting, continuous electrowetting, electrophoresis, electroosmosis, dielectrophoresis, electro-hydrodynamic electrohydrodynamic pumping, magneto-hydrodynamic magnetohydrodynamic pumping, thermocapillarity, thermal expansion, dielectric pumping, and / or variable dielectric pumping.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
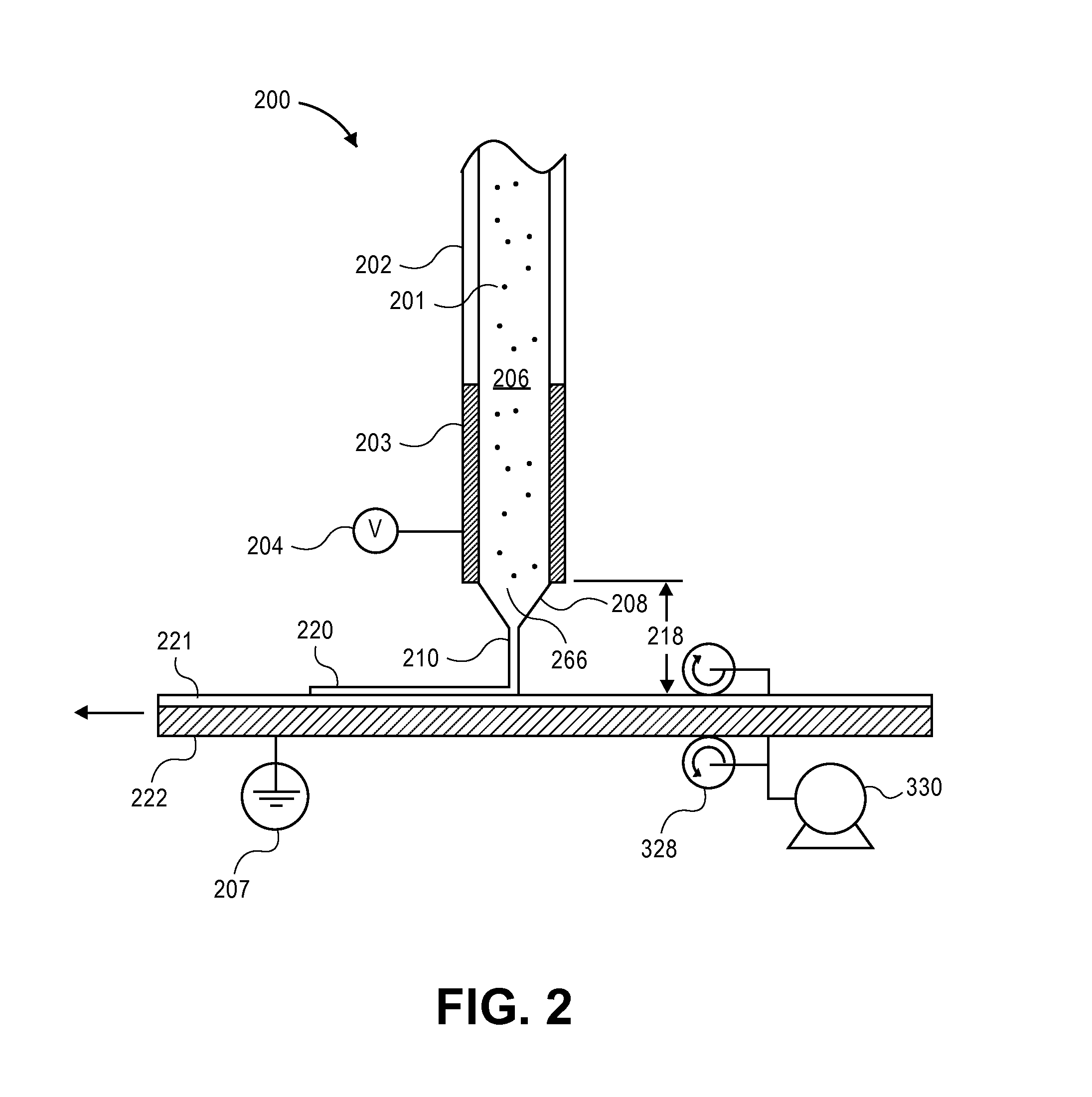
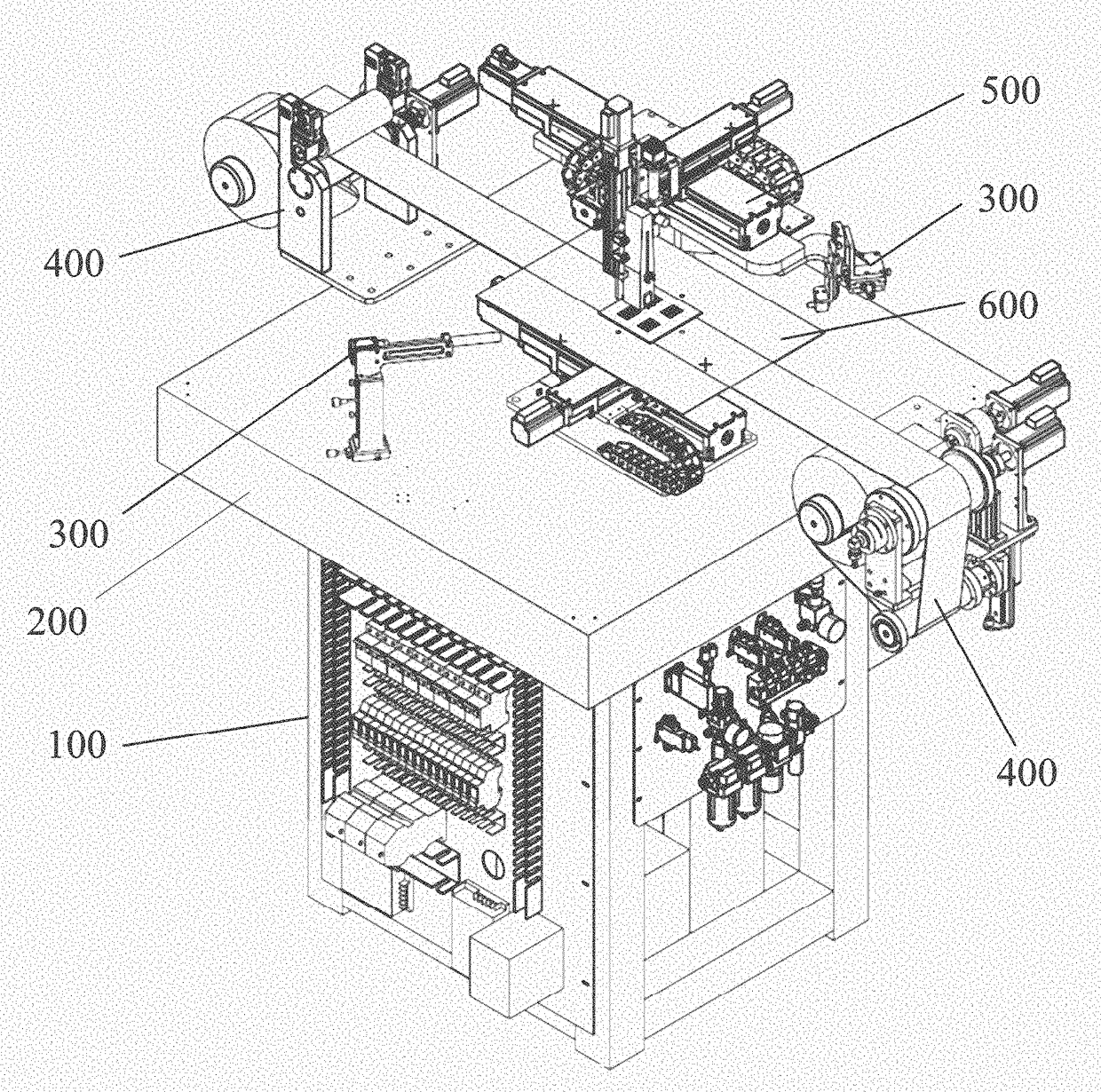
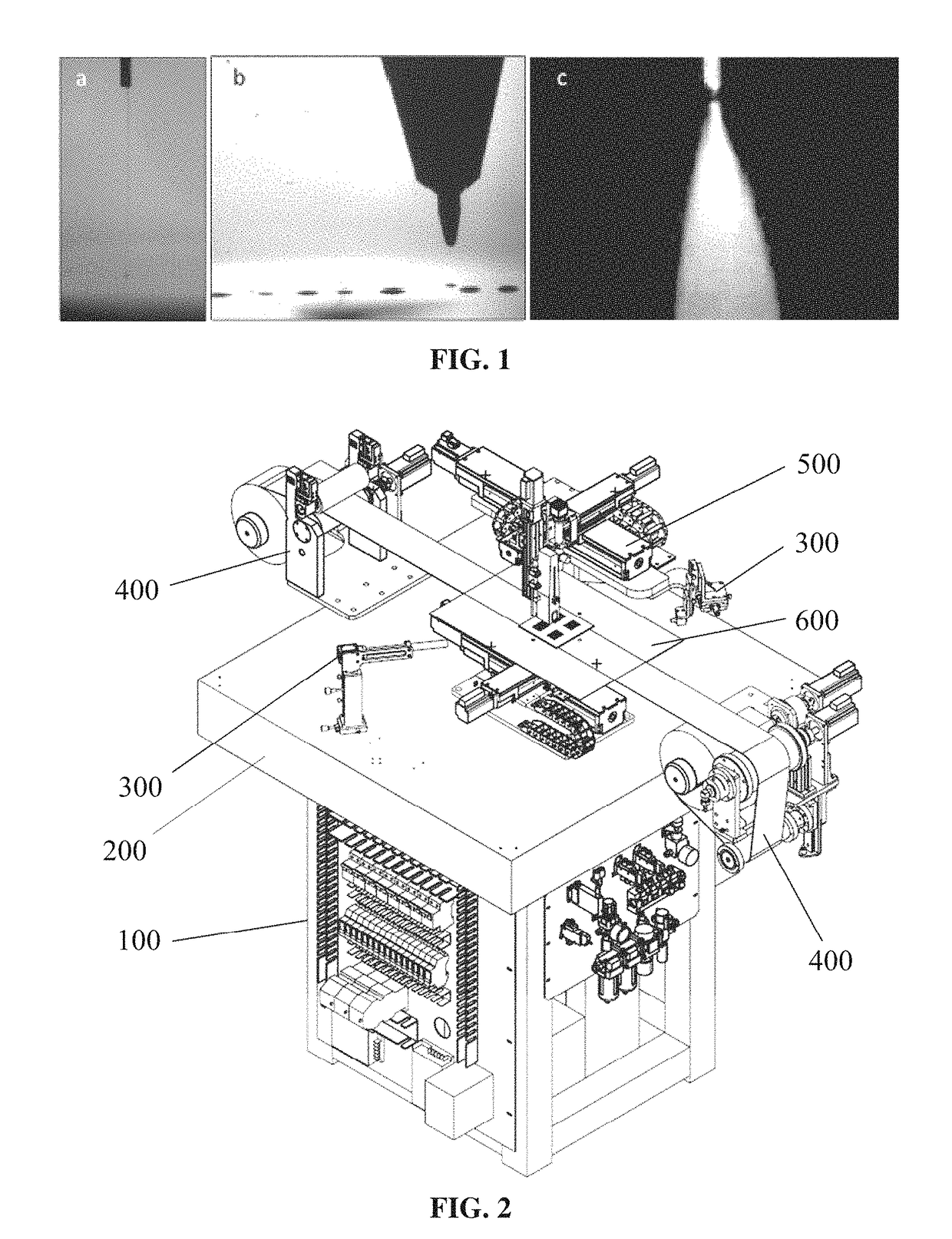
Control device, equipment and method for controlling electrohydrodynamics printing resolution
ActiveCN105772722ALimit diffusionReduce flight angleAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyImage resolutionClosed loop
The invention provides a control device, equipment and method for controlling the electrohydrodynamics printing resolution. The control device for controlling the electrohydrodynamics printing resolution comprises a magnetic field generation device used for generating centripetal Lorentz force and a controller connected with the magnetic field generation device. The controller is connected with two vision detection devices. A closed-loop control circuit is formed by the vision detection devices, the controller and the magnetic field generation device. An annular magnetic field is generated through an annular electromagnetic induction coil in a jetted liquid drop flying area, the movement of electrified liquid drops in the annular magnetic field is subjected to the effect of the centripetal Lorentz force, control parameters of the control device are adjusted in real time according to detection results of the vision detection devices so that the centripetal Lorentz force can be changed, the movement of the electrified liquid drops is effectively restrained, diffusion of the liquid drops to the periphery is restrained, the flying angle of the liquid drops is reduced, and therefore the electrohydrodynamics printing resolution is increased.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
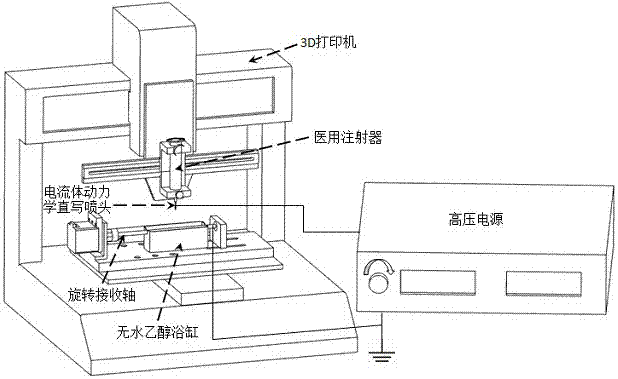
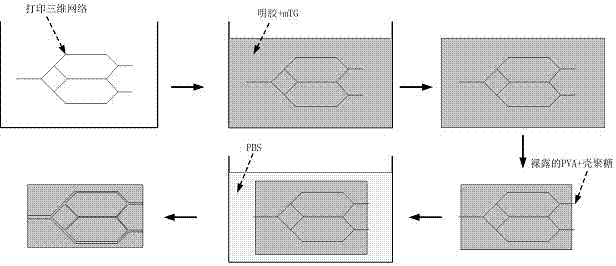
System and method for constructing a three-dimensional multi-scale vascularized stent
ActiveCN109124821AAchieve preparationGood removal effectAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood vesselsManufacturing technologyHazardous substance
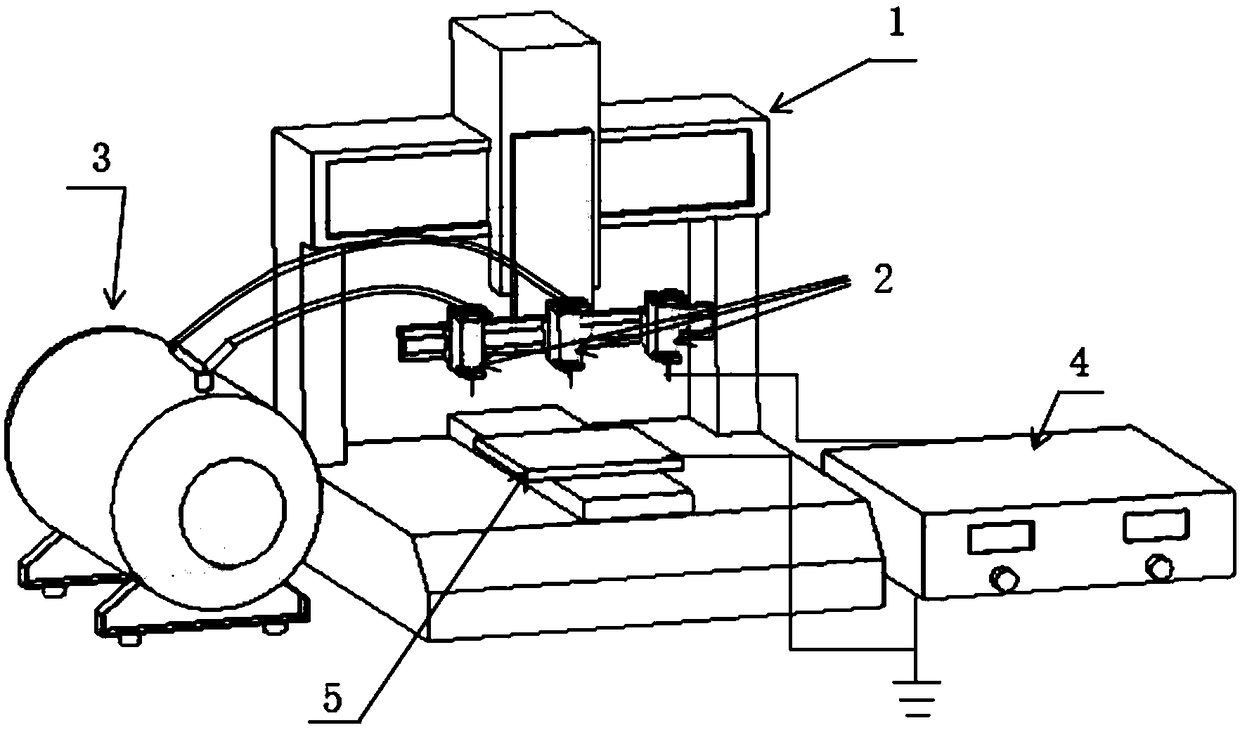
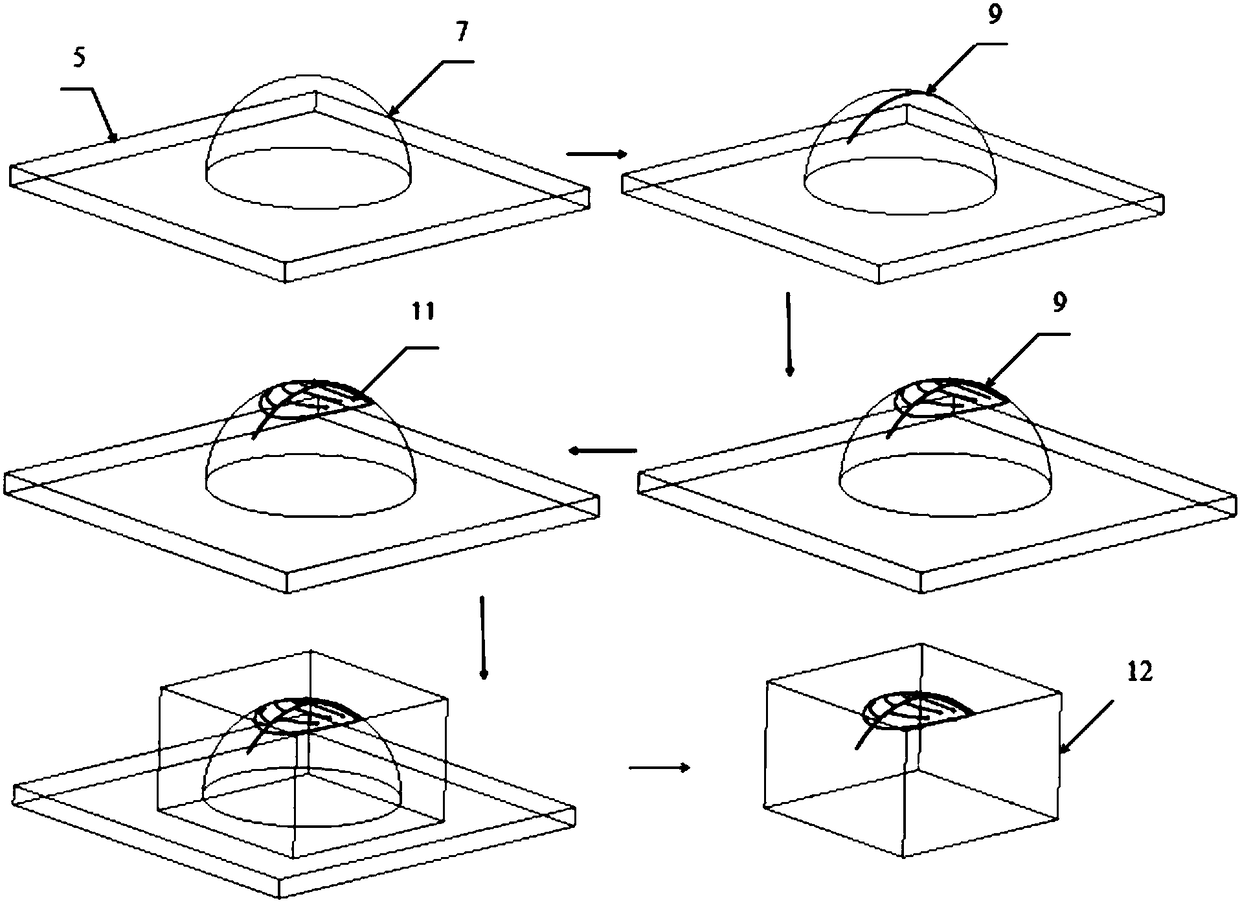
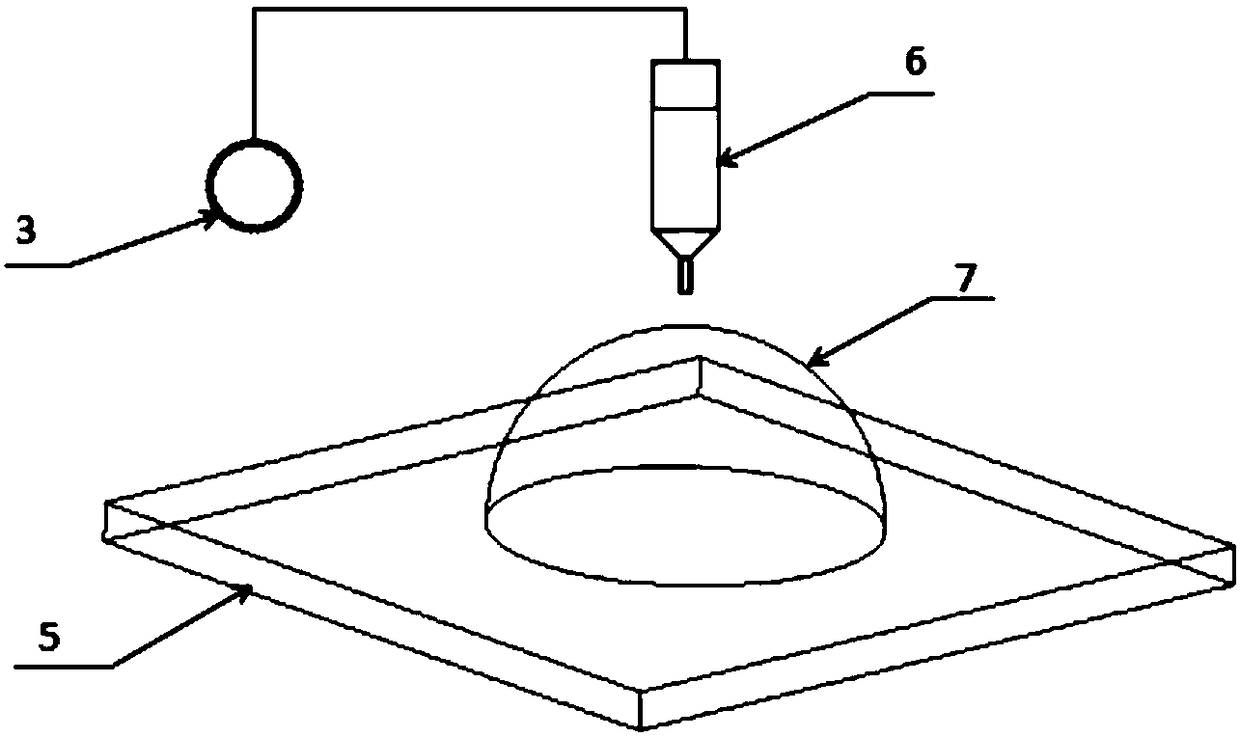
The invention discloses a system and method for constructing a three-dimensional multi-scale vascularized stent. The system comprises a 3D printer, a medical syringe, an air compressor and a high-voltage electric power. The method adopts a biological 3D printing technology combined with electrohydrodynamics direct writing to manufacture a stent containing a three-dimensional multi-scale vascularized network channel by a composite method of increasing and decreasing material manufacturing technology. As that three-dimensional shape of the sacrificial template require by the invention is imparted by the shape of the prin gelatin hemisphere, no harmful substances are generated in the whole process and the material is easy to obtain. By means of the printability of gelatin, Plannick F127 and PCL, three-dimensional and multi-scale vascularized stents can be fabricated, which solves the problem that three-dimensional and multi-scale vascularized stent network can not be obtained by biological 3D printing alone. It is of great significance to solve the vascularization problem of human tissue repair in clinical medicine.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Handheld sprayer with removable cartridge and method of using same
Owner:EFIELD INNOVATIONS
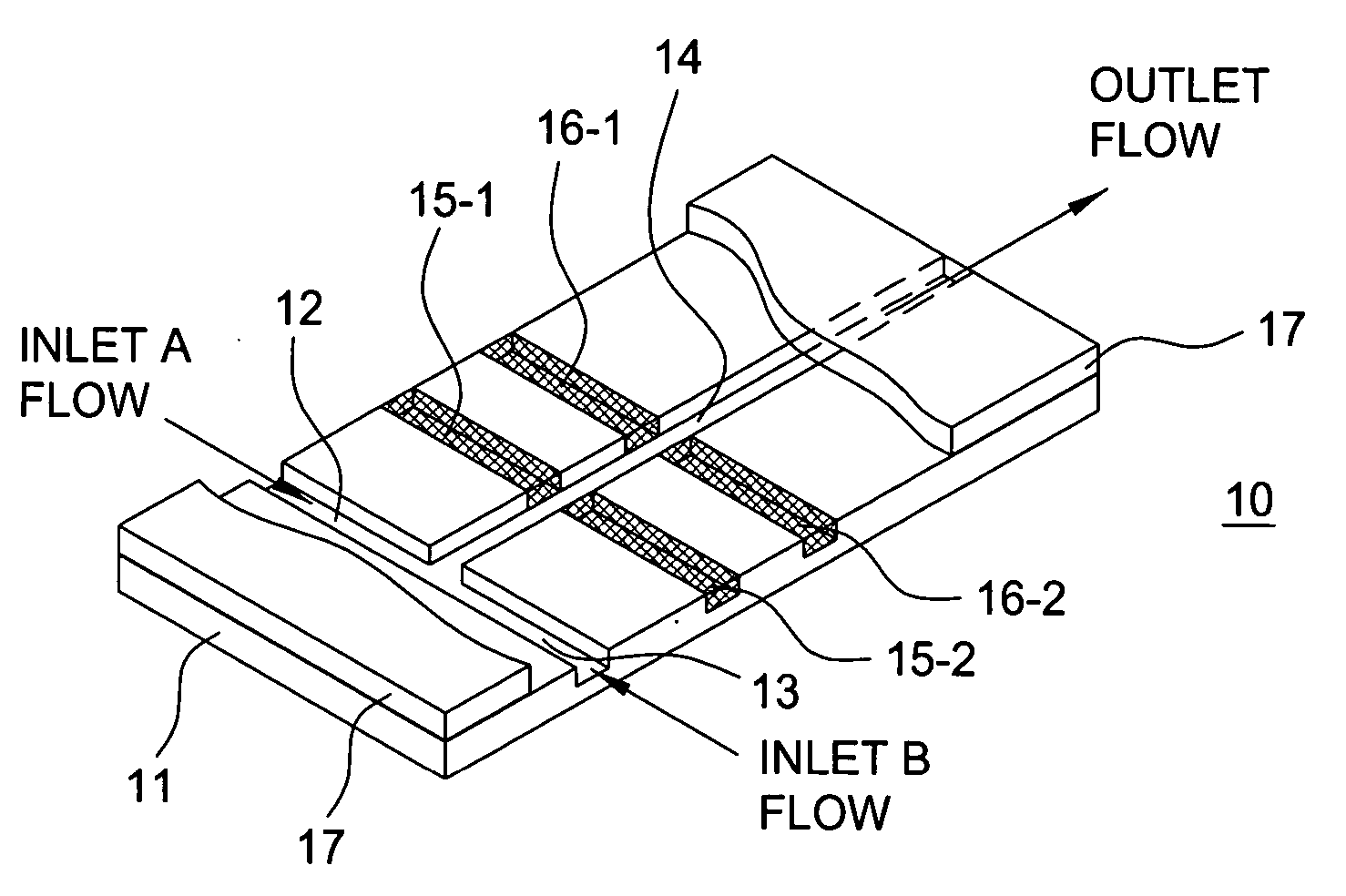
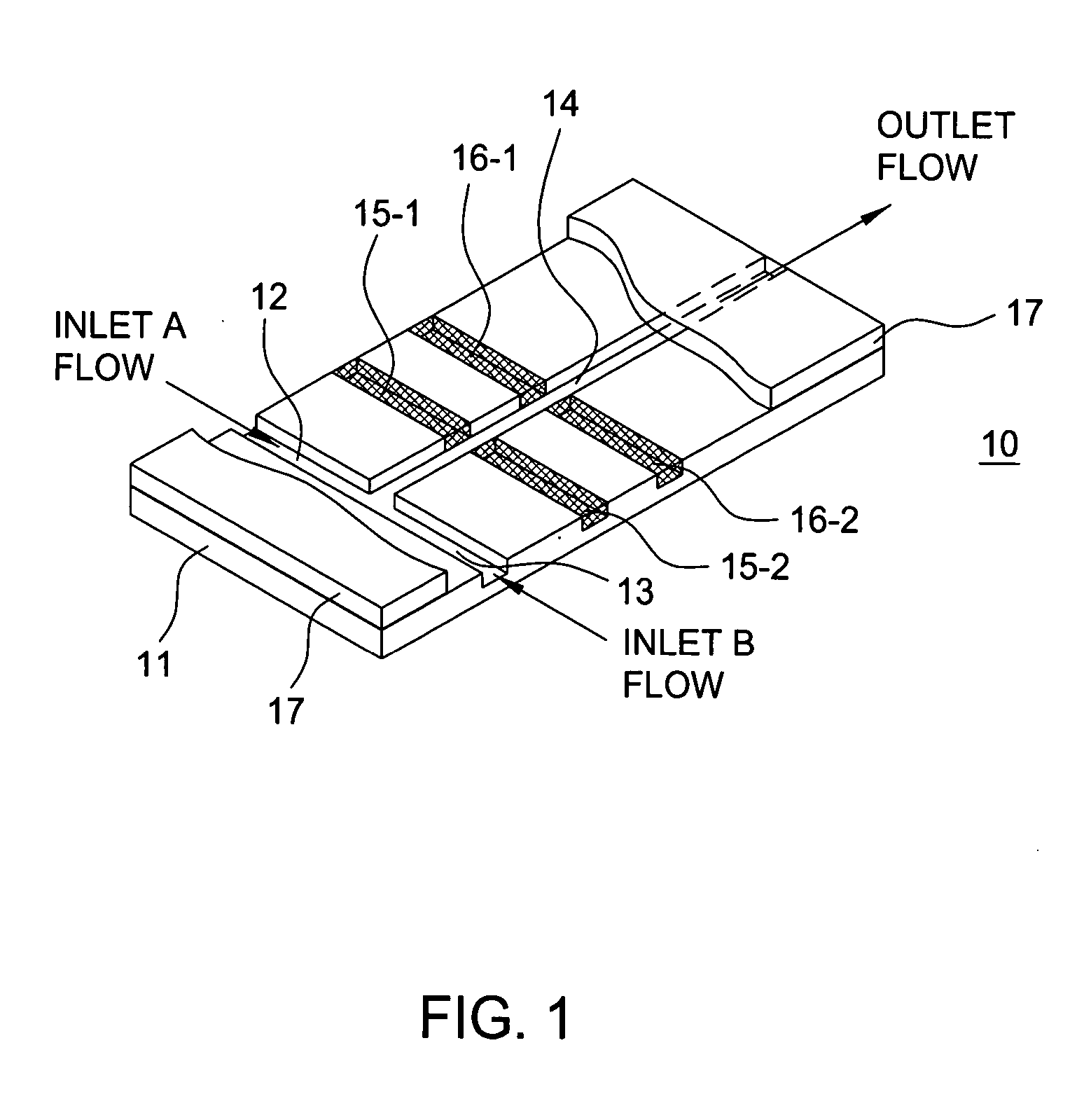
Electrohydrodynamic microfluidic mixer using transverse electric field
Simplicity of design is achieved for an electrohydrodynamic microfluidic mixer by applying an electric field substantially transverse to the flow direction and substantially orthogonal or normal to the interfacial plane between the fluids being mixed in the main channel. The electric field is wide enough to encompass substantially the entire depth of the main channel in the microfluidic mixer. In one exemplary embodiment, the electrohydrodynamic microfluidic mixer comprises a substrate, one main channel disposed on the substrate, first and second inlet channels disposed on the substrate and individually coupled to the main channel, and first and second electrodes disposed on opposite sides of the main channel for applying an electric field across the main channel substantially transverse to the flow direction in the main channel. Field uniformity across the desired cross-section of the main channel is achieved by having the electrode thickness be substantially equal to the main channel depth. Disposition of the electrodes is judiciously controlled to generate the electric field in a direction substantially orthogonal or normal to the interfacial plane between the fluids in the main channel.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
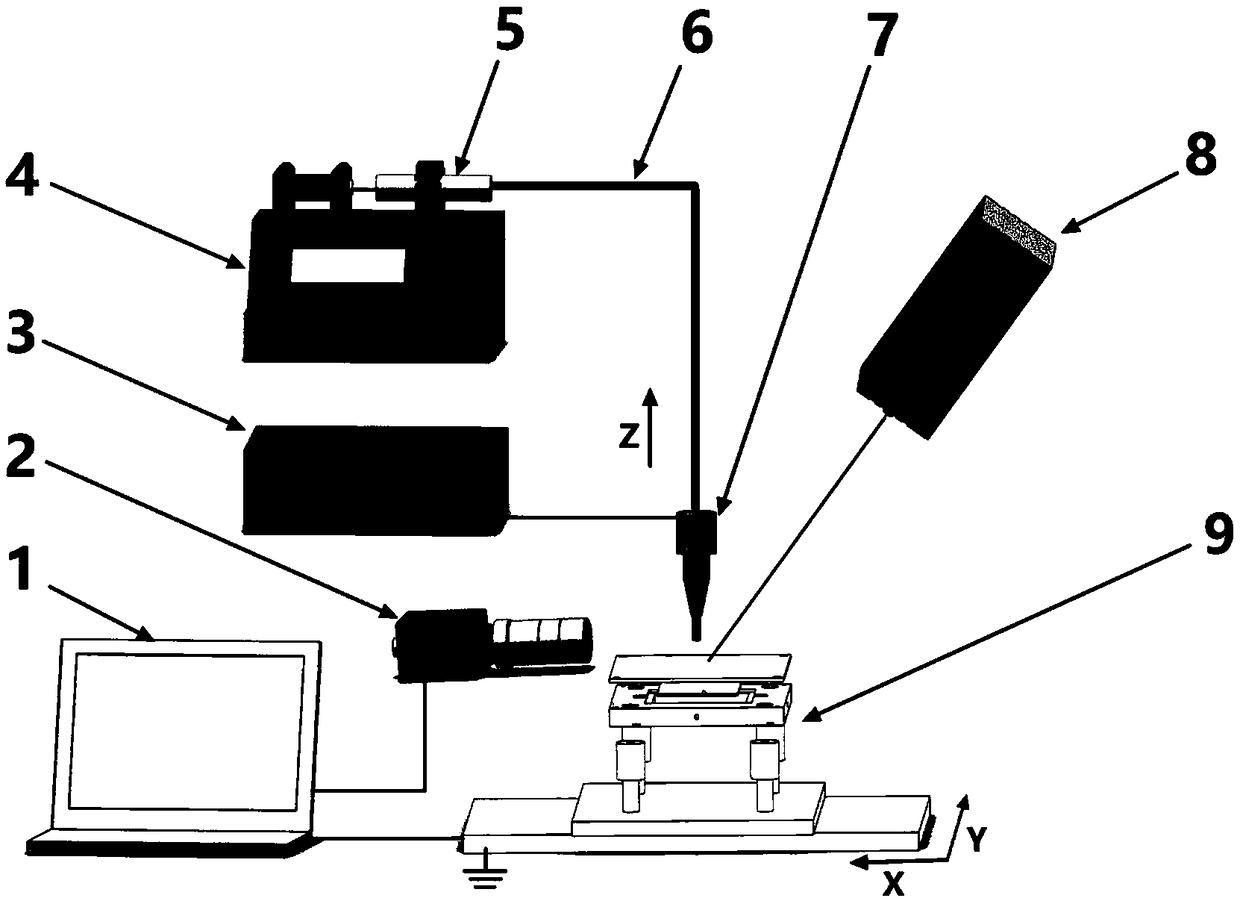
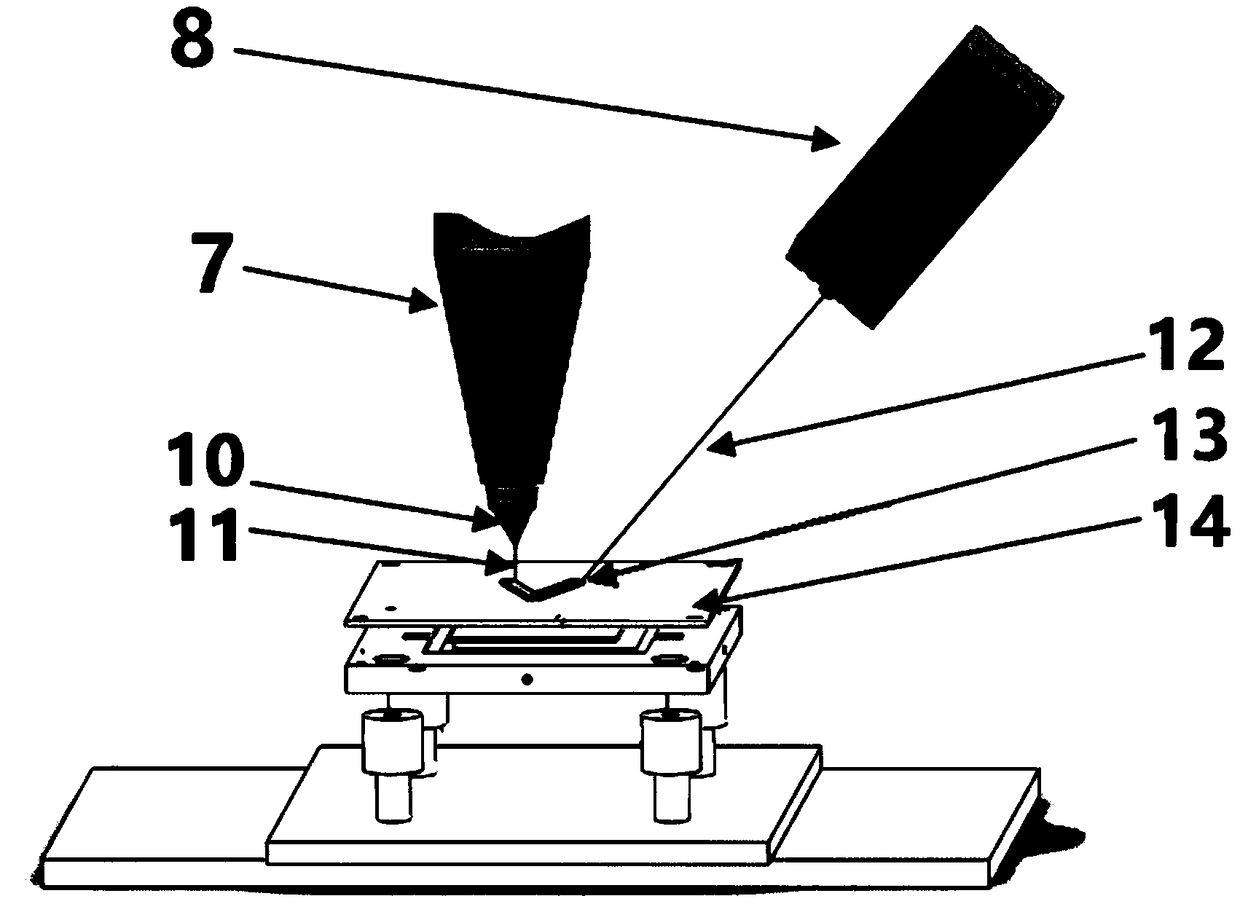
Electrohydrodynamics printing device for cambered substrate and control method of electrohydrodynamics printing device for cambered substrate
ActiveCN106183446ARealize space compound movementTypewritersOther printing apparatusHigh pressureHigh voltage
The invention discloses an electrohydrodynamics printing device for a cambered substrate and a control method of the electrohydrodynamics printing device for the cambered substrate. The electrohydrodynamics printing device comprises a machine frame, a printing module, a printing platform and a high voltage power supply module. The printing module can move horizontally along the X axis and the Z axis correspondingly, and the printing platform is provided with a printing surface and a Y-axis slipping mechanism; and the printing surface is arranged on the Y-axis slipping mechanism to move horizontally in the Y-axis direction, and simultaneously, the printing surface rotates circumferentially along the X axis and the Z axis correspondingly, so that the printing surface rotates around the A axis and the Z axis. According to the control method of the electrohydrodynamics printing device for the cambered substrate, the printing surface is driven to move horizontally along the X axis, the Y axis and the Z axis and rotate around the A axis and C axis correspondingly, so that spatial compound motion of the printing platform is achieved, and the electrohydrodynamics printing device can print electrohydrodynamics patterns on the cambered substrate.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
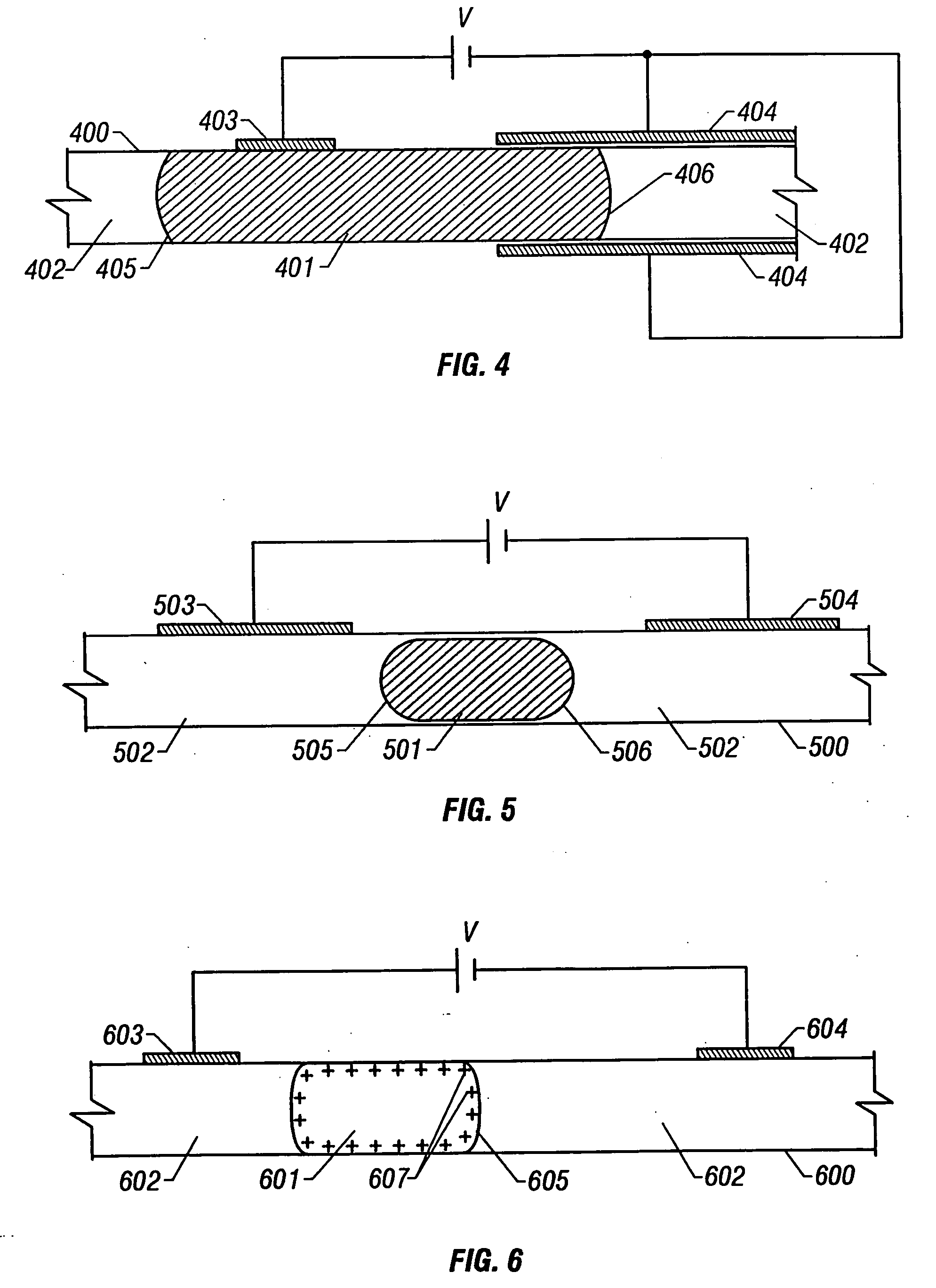
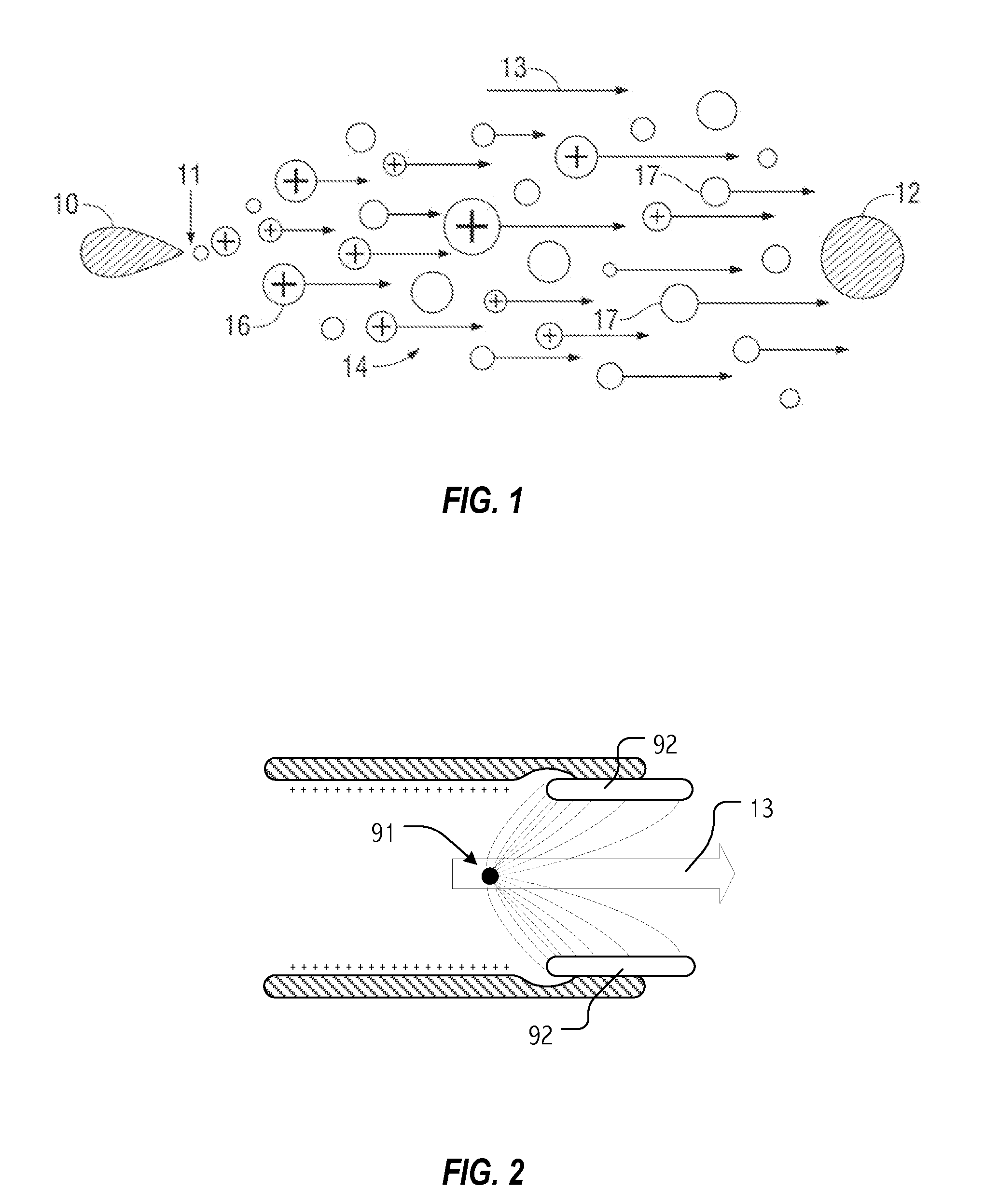
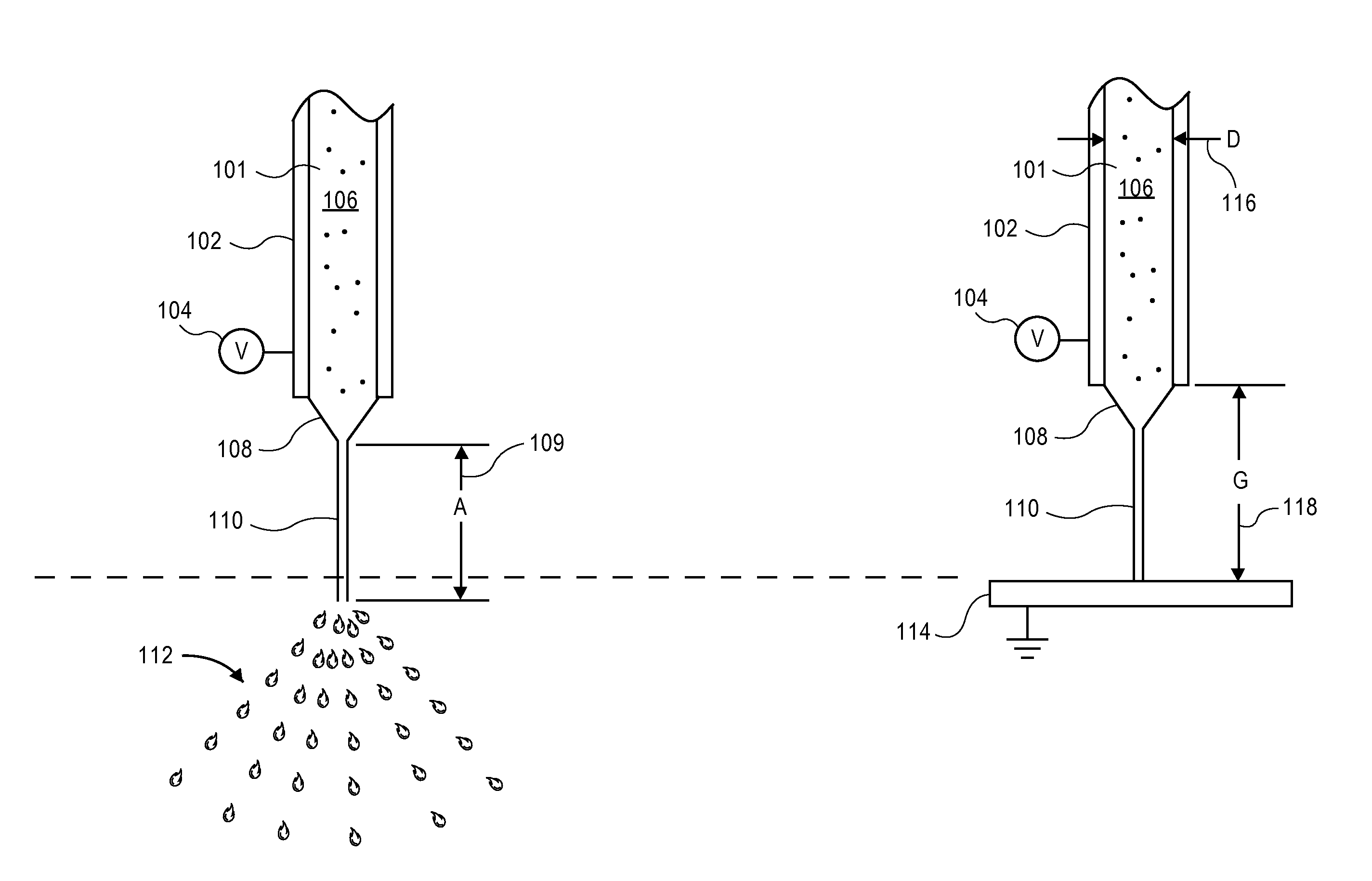
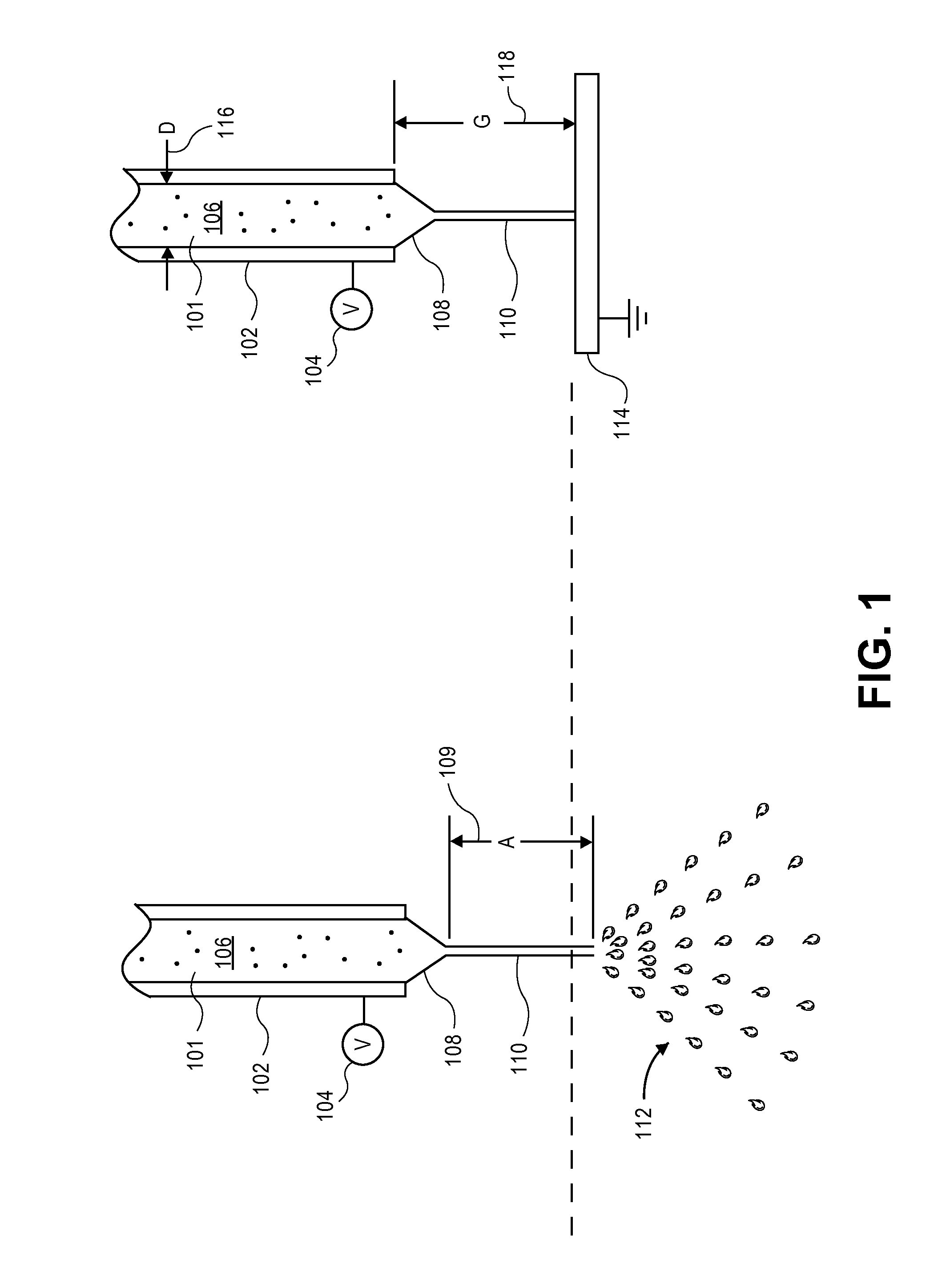
Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) fluid mover with field shaping feature at leading edge of collector electrodes
InactiveUS8508908B2Minimizing ion migrationSpeed up the flowWave amplification devicesDigital data processing detailsLeading edgeElectricity
Small form-factor ion flow fluid movers that provide electrostatically operative surfaces in a flow channel adjacent to an emitter electrode, but upstream of a collector electrode or electrodes, can shape operative electric fields and influence ion flows in ways that accentuate downstream flow while minimizing upstream ion migration. In some cases, dielectric surfaces (or even electrically isolated conductive surfaces) along a flow channel adjacent to an emitter electrode can be configured to collect and retain an initial population of generated ions and thereafter electrostatically repel further ions. Depending on the configuration of such dielectric or electrically isolated conductive surfaces, these repelling electrostatic forces may dissuade ion migration or flow from sensitive but closely proximate components and / or may shape fields to enhance ion flows in a desired downstream direction.
Owner:TESSERA INC
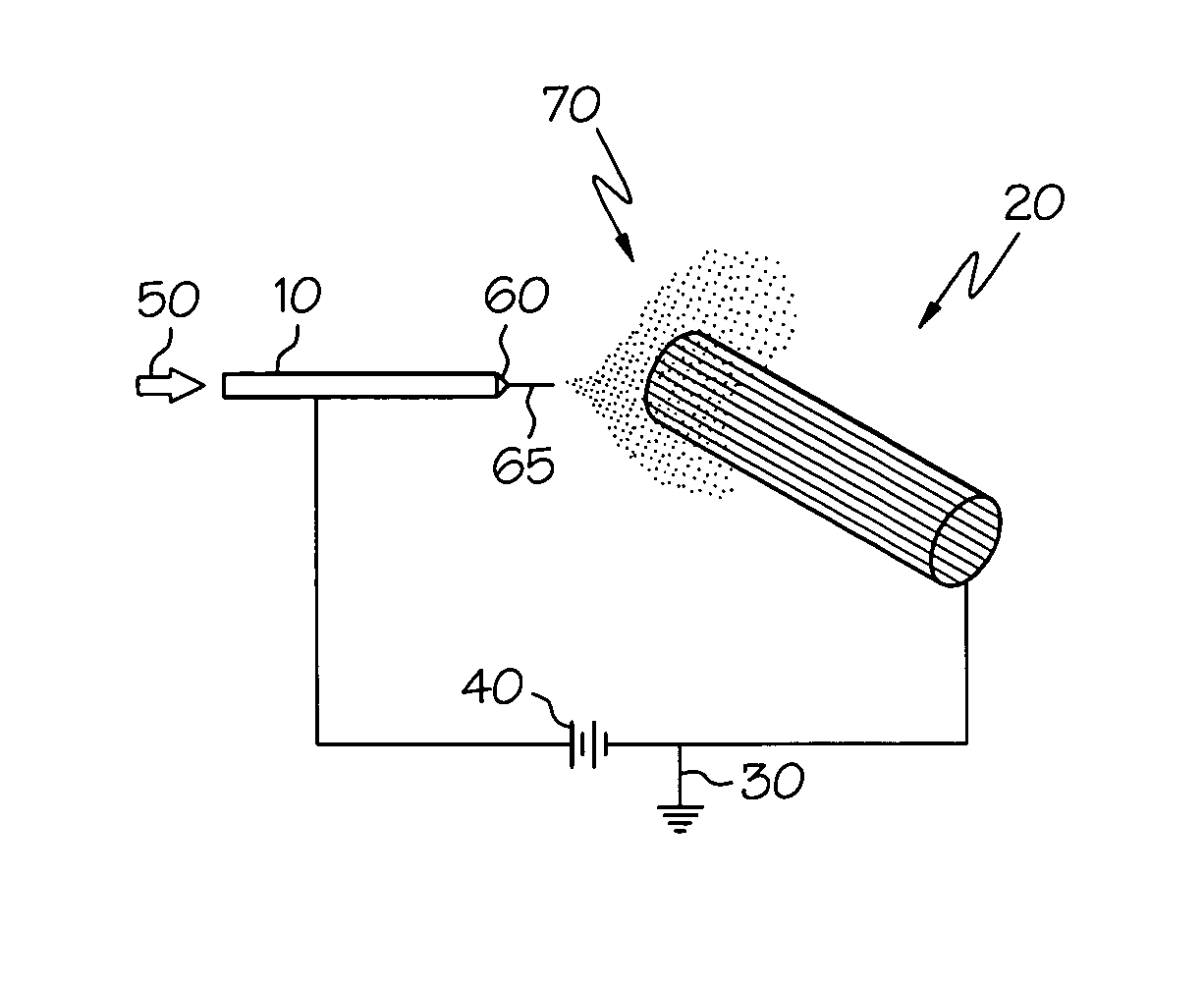
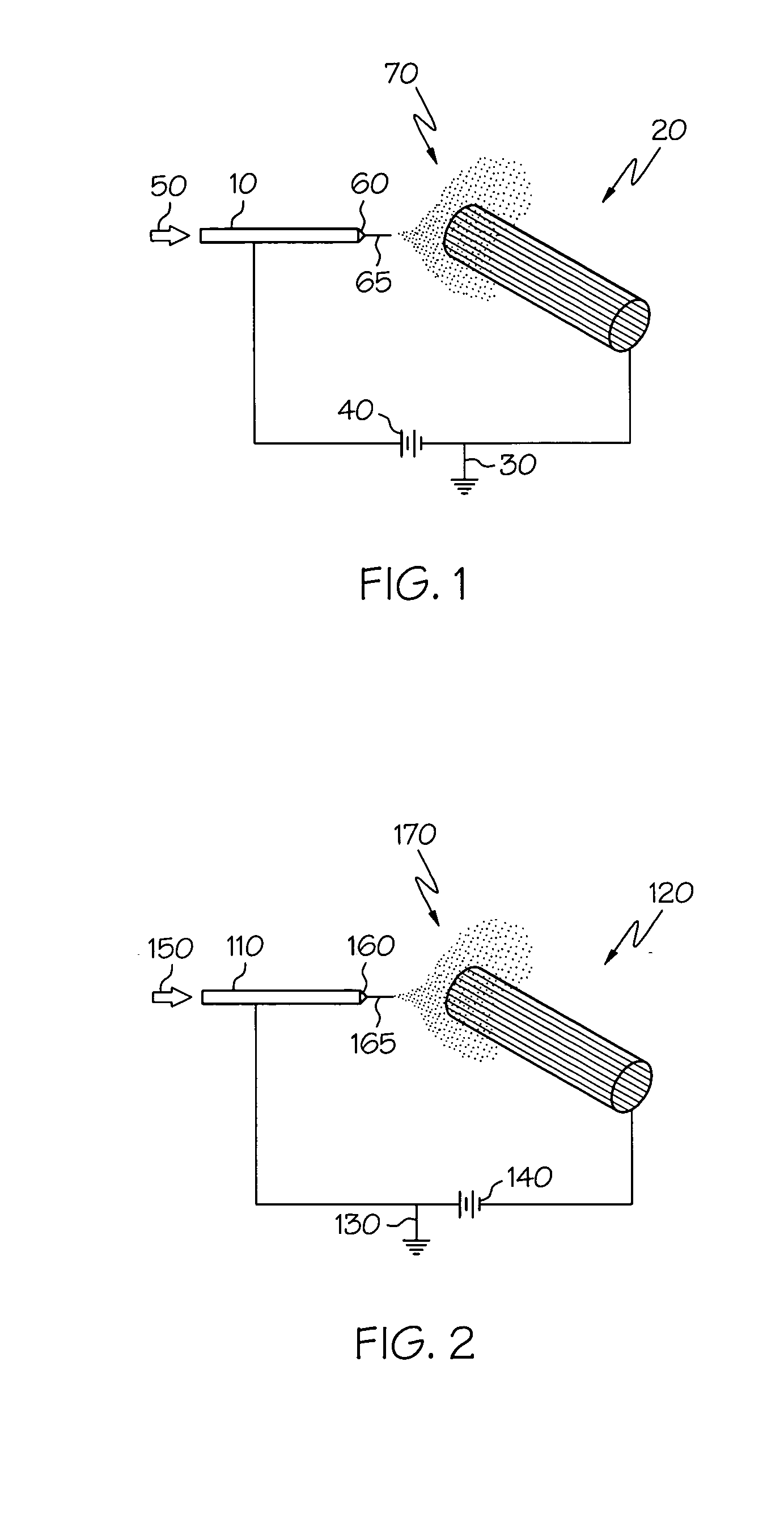
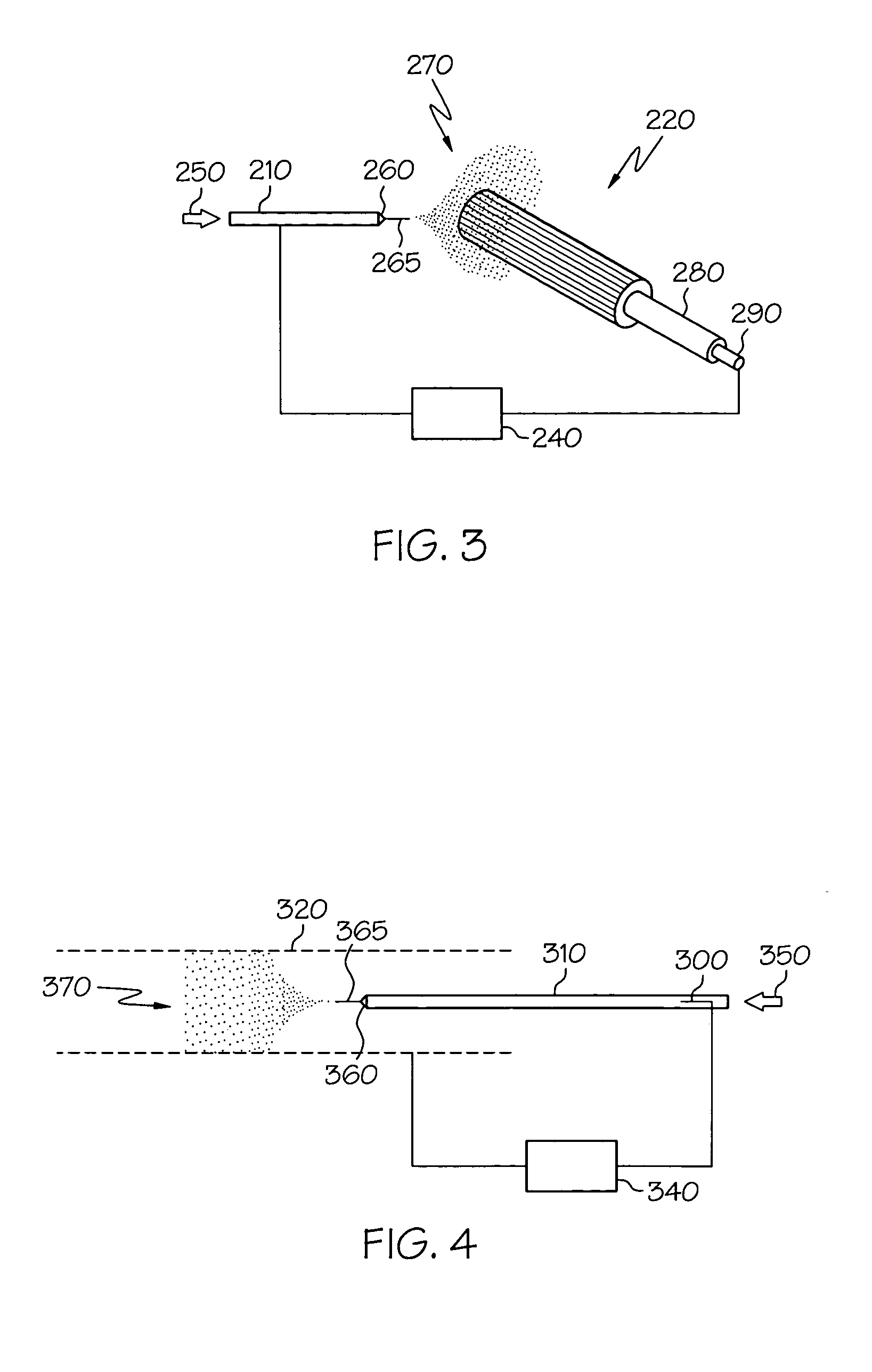
Electric field spraying of surgically implantable components
This invention relates to a method for depositing a coating onto an implantable medical component using electrohydrodynamics (“EHD”). The method utilizes EHD to comminute a suitable liquid which then form fibers or particles. The thus-formed fibers or particles are electrically attracted to the medical component and coat at least one surface of the medical component. A wide-variety of liquid formulations can be utilized to deliver a wide-variety of, for example, therapeutic substances, either alone of in combination. Fiber-based and particle-based coatings may be applied as well as combinations thereof. Also disclosed are medical components comprising such coatings, particularly stents.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
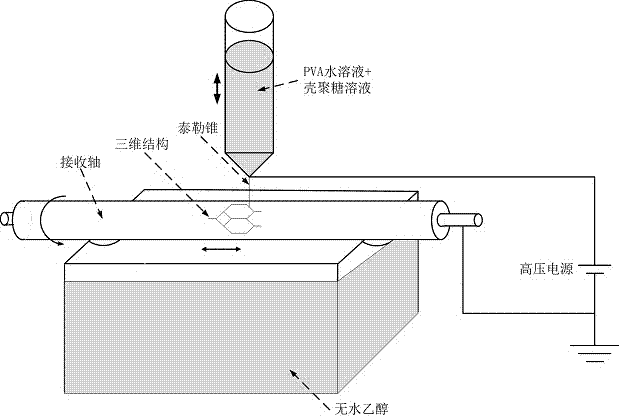
Construction system and method of 3D (three-dimensional) micro/nano-scale prefabricated vessel network of bone tissues
ActiveCN107296983AAchieve preparationEasy to getAdditive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanism3d shapesManufacturing technology
The invention discloses a construction system and method of a 3D (three-dimensional) micro / nano-scale prefabricated vessel network of bone tissues, which are used for the field of bio-manufacturing and used for manufacturing a micro / nano-scale prefabricated vessel access structure by combining an electrohydrodynamics direct-writing process and a subtractive manufacturing technology. A 3D shape of a required sacrificial material is prepared by promoting the sacrificial material to form sacrificial material solution with anhydrous ethanol, no harmful substance is generated in the whole process, and the material is easily available. The micro / nano-scale vessel structure is formed by virtue of printability of PVA (Polyvinyl Acetate), PGA (propylene glycol alginate) and chitosan, and the problem that the 3D micro / nano-scale vessel network cannot be obtained through biological 3D printing is solved, therefore, the system and the method have significance for solving the problem of the scale of a vessel in repair of human tissues in clinical medicine.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
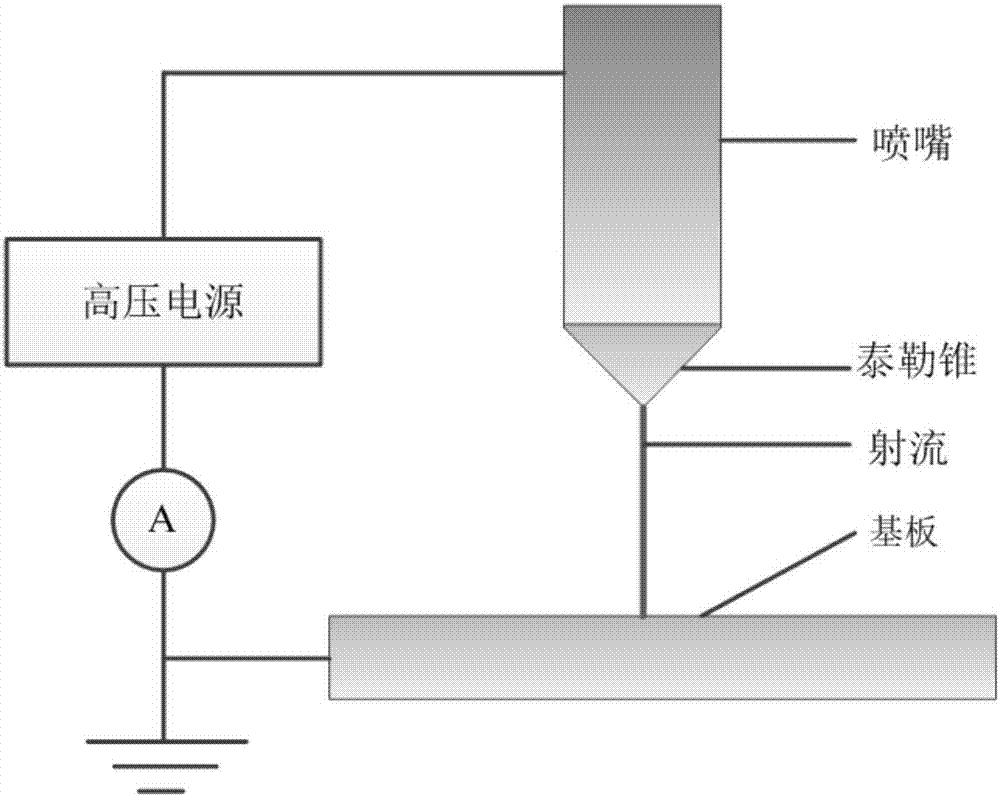
Analyte separator with electrohydrodynamic taylor cone jet blotter
Devices, systems, and methods are disclosed that analyze a biological or other fluid sample using an electrophoresis or other separation method and then emit the fluid sample with separated constituents using an electrohydrodynamic spray to form a Taylor cone and jet, without dispersion into droplets, onto a substrate that moves with respect to the emitter. Electrodes can be shared between the electrophoresis and electrospray elements, and an adjunct fluid can help draw the separated sample into the Taylor cone. A micro-machined capillary channel on a chip can supply multiple lines to a substrate.
Owner:LI COR
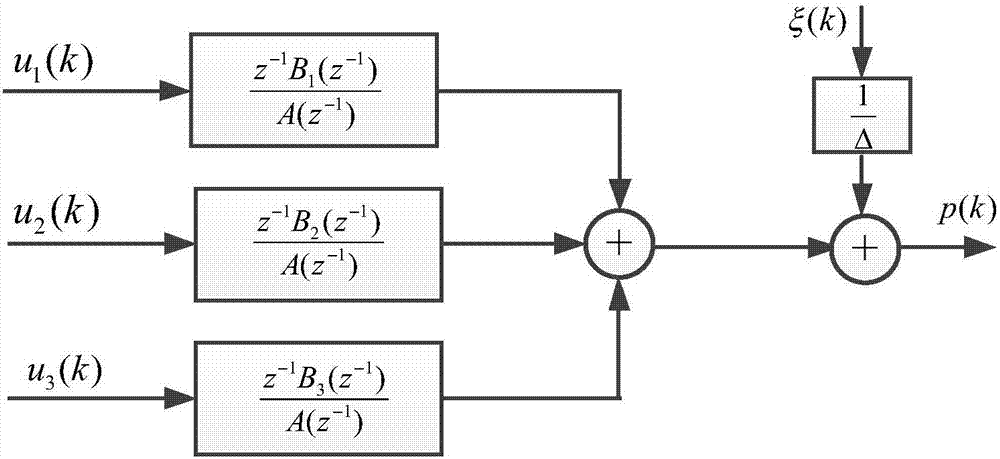
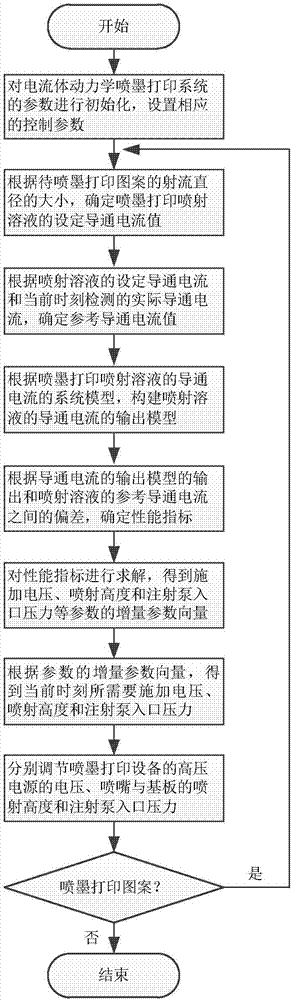
Electrohydrodynamics high-resolution ink jet printing control method
The invention discloses an electrohydrodynamics high-resolution ink jet printing control method. The control method comprises multi-physical field parameter coupling model modeling of electrohydrodynamics ink jet printing and real-time high-resolution ink jet printing; the multi-physical field parameter coupling model modeling of the electrohydrodynamics ink jet printing comprises two aspects of conduction current multi-physical field parameter coupling model modeling of electrohydrodynamics spraying solution and building of a mapping relation between an electrohydrodynamics jet diameter and conduction current of the spraying solution; through real-time detection of magnitude of the conduction current, the jet diameter is effectively monitored in real time; through real-time detection of a conduction current value of the electrohydrodynamics spraying solution, such parameter values as voltage applied by the electrohydrodynamics ink jet printing, a spraying distance and the inlet pressure of an injection pump are adjusted in real time; and the jet diameter of the electrohydrodynamics ink jet printing is controlled to effectively improve the resolution of electrohydrodynamics ink jet printing patterns.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
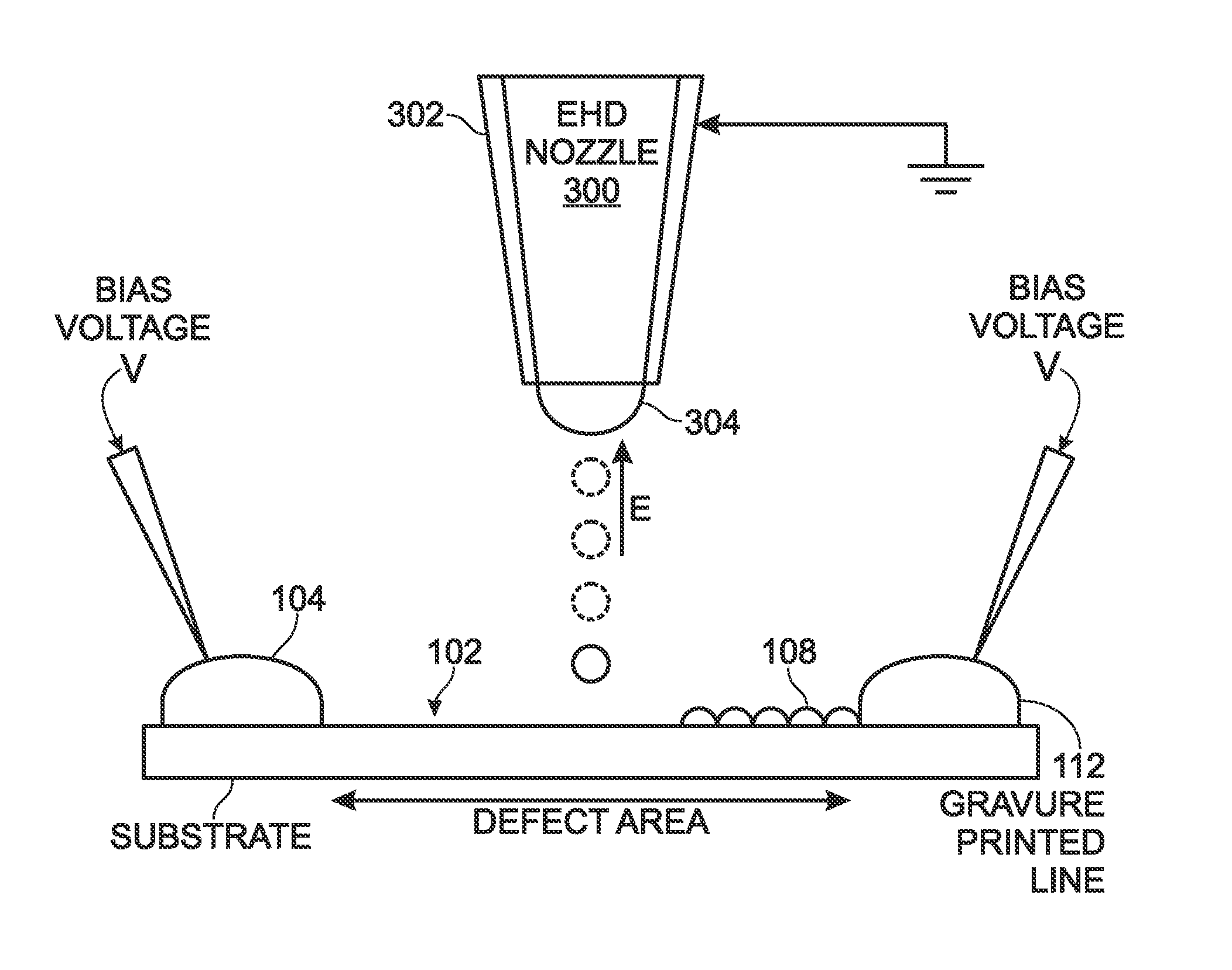
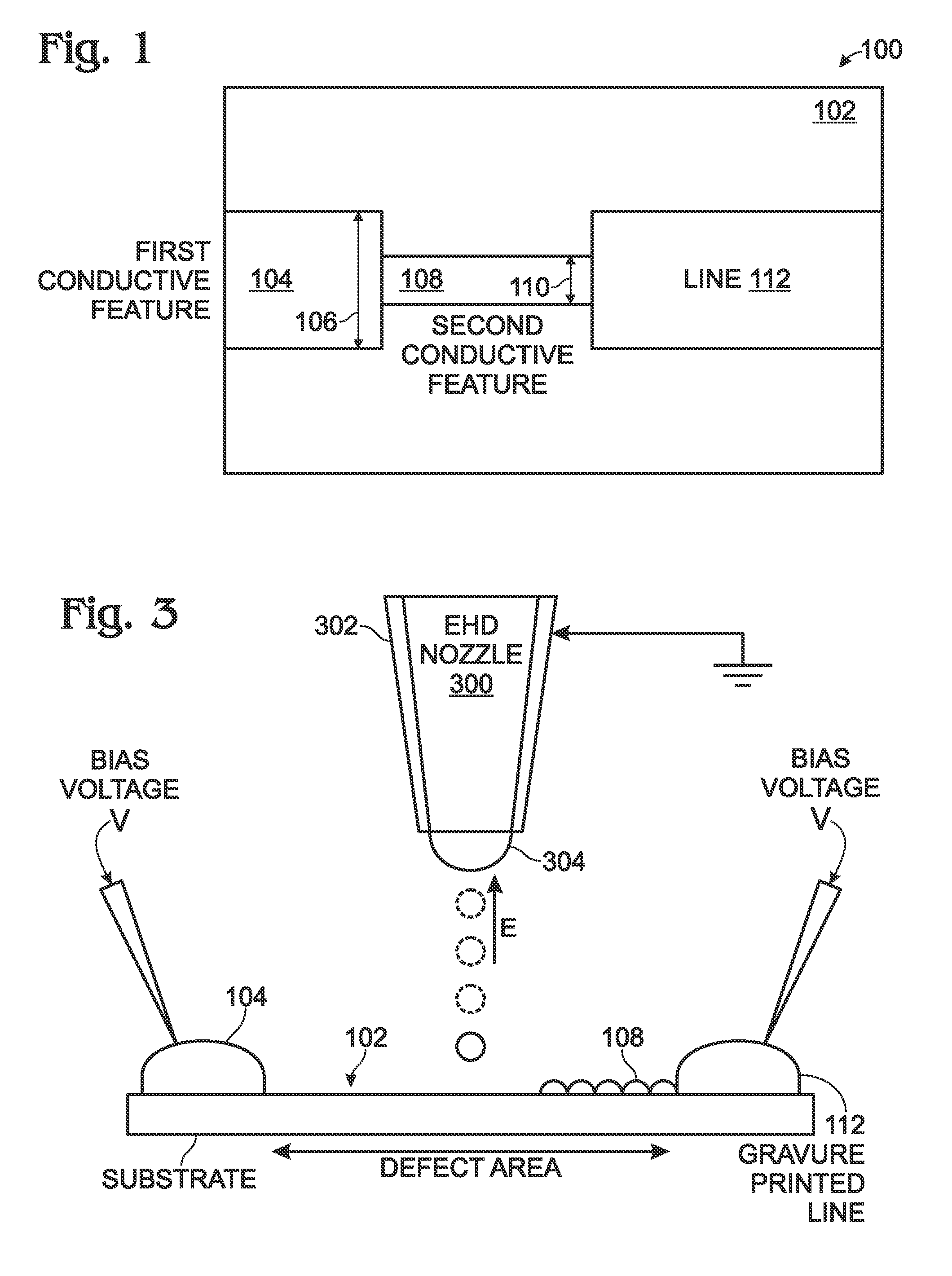
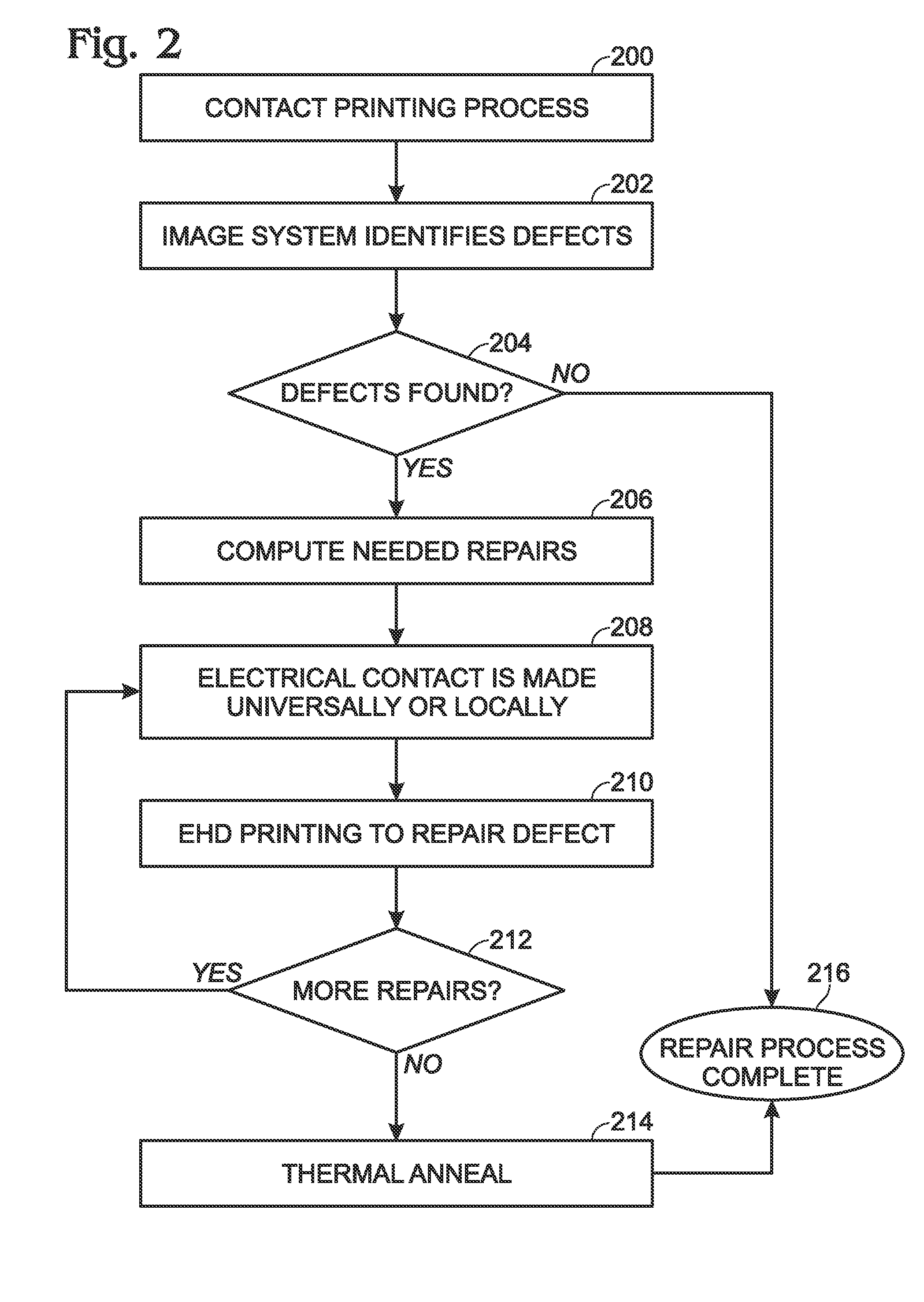
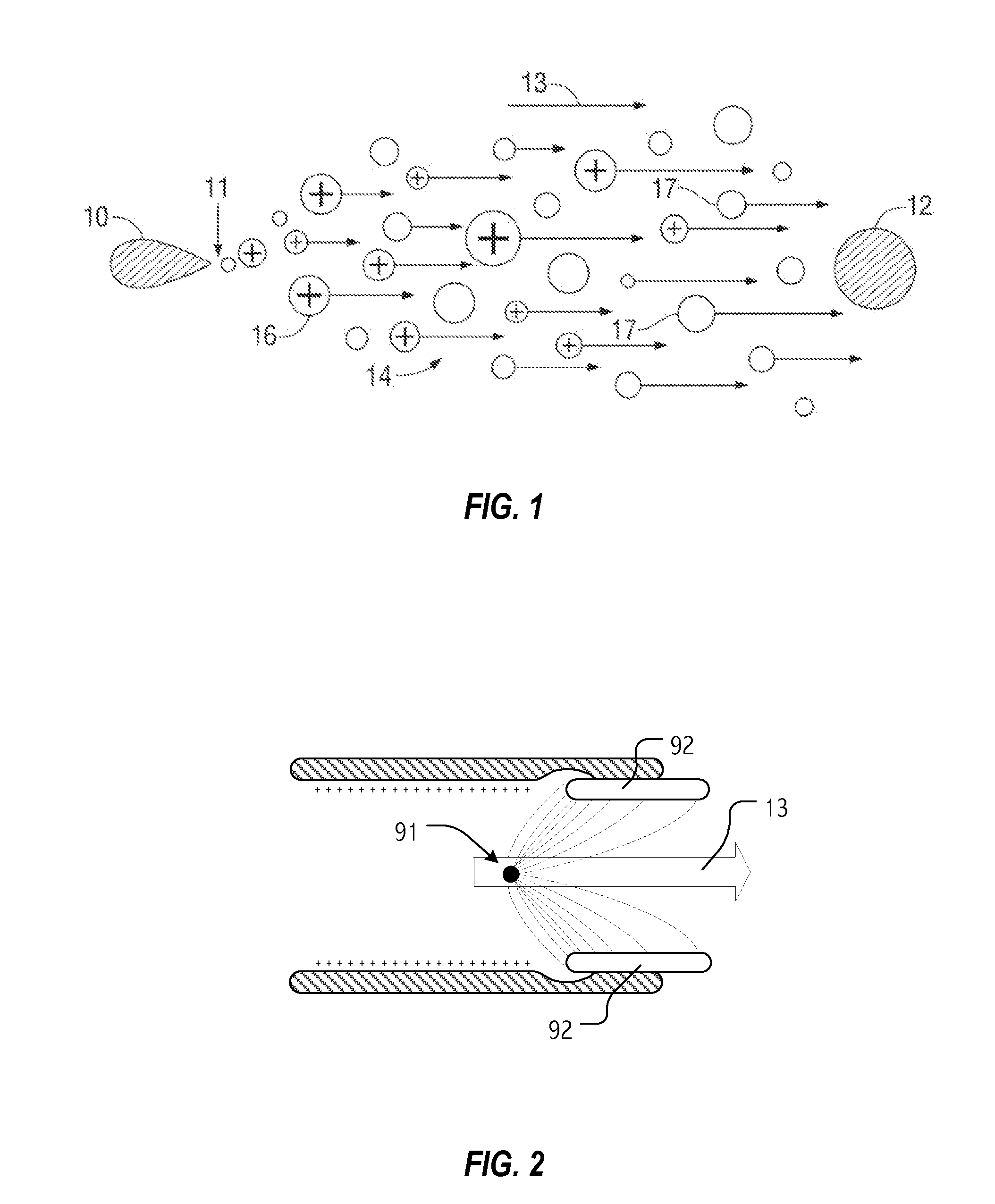
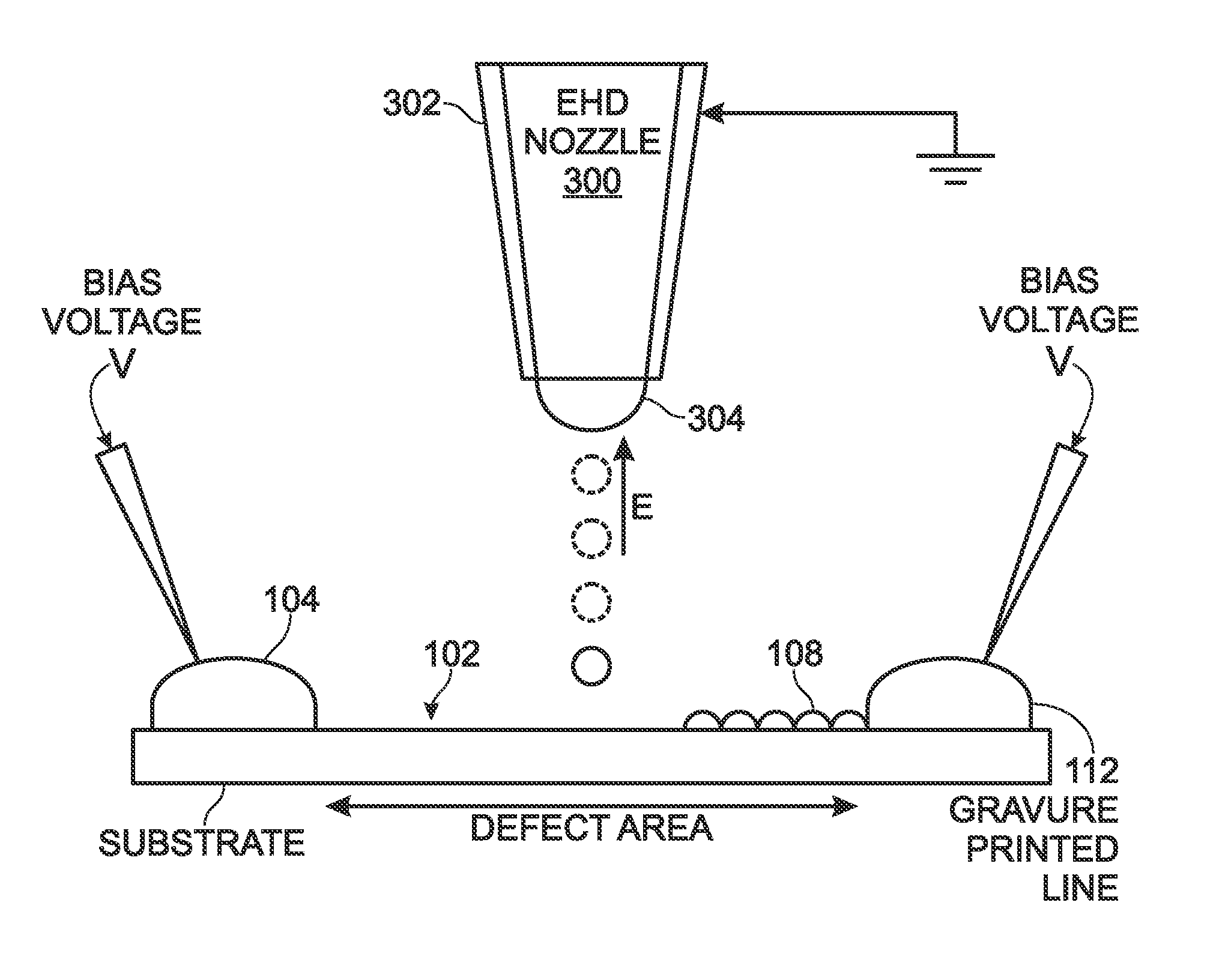
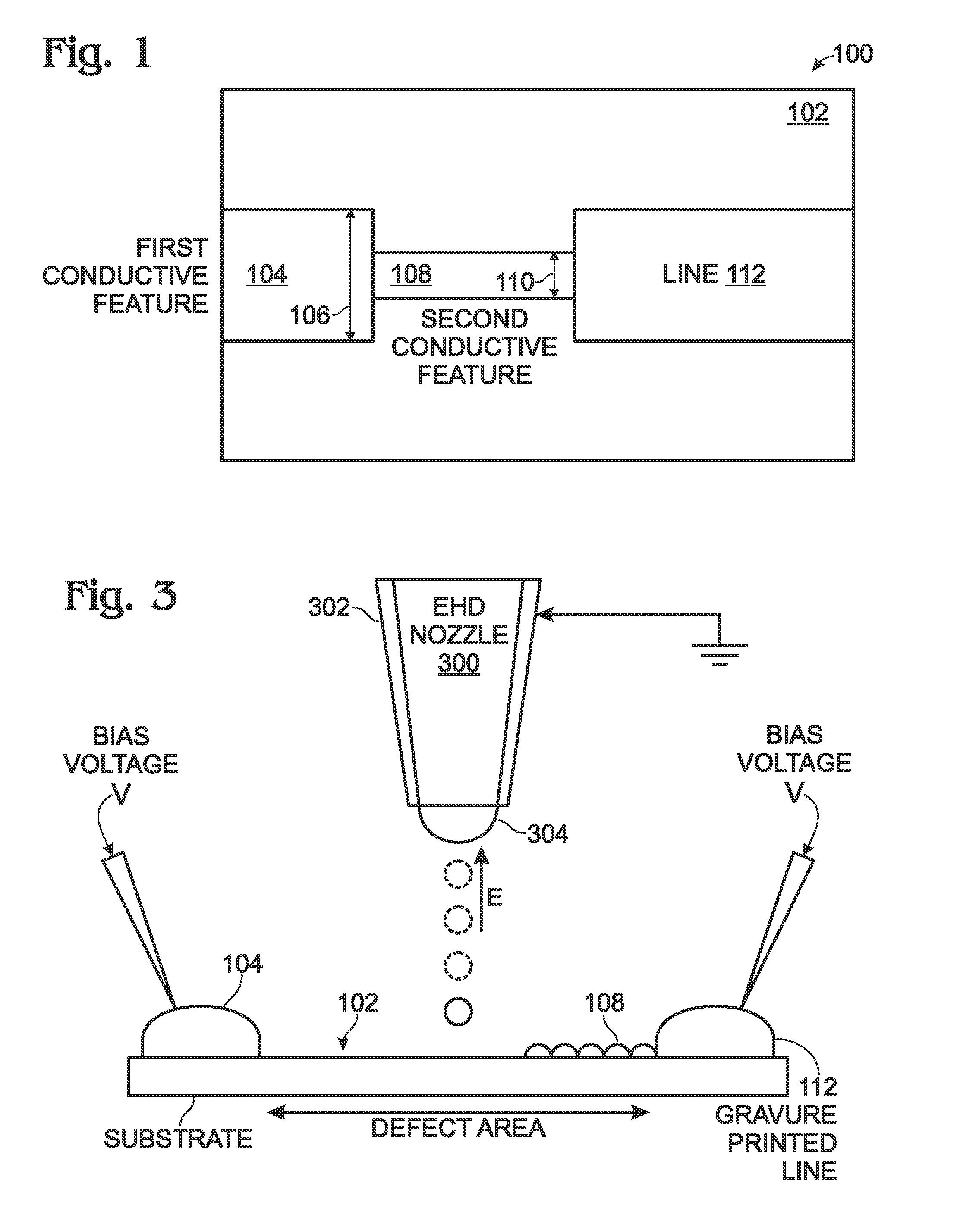
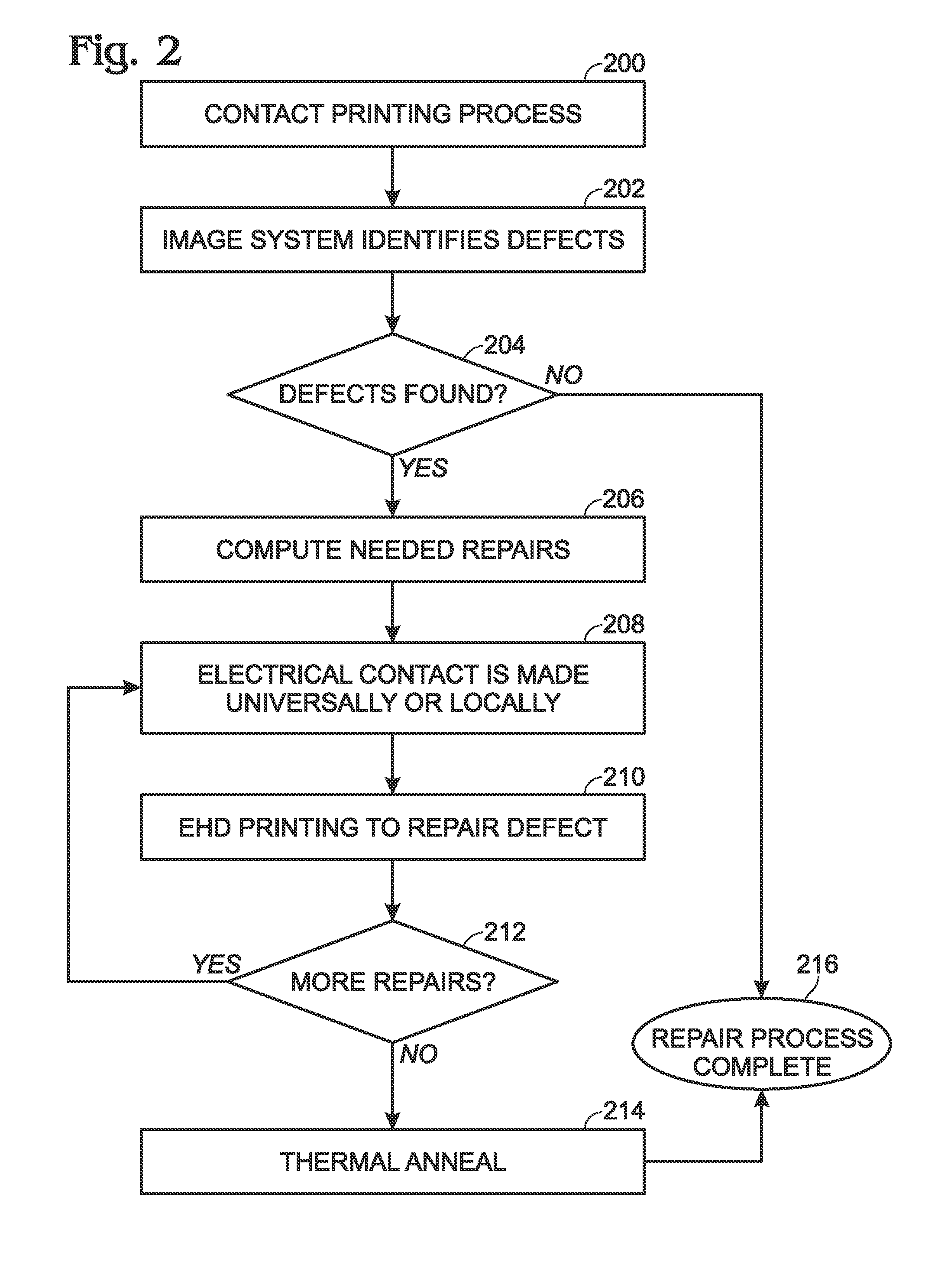
Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) printing for the defect repair of contact printed circuits
ActiveUS9198299B2Reduce discontinuityConductive pattern formationPrinted circuits repair/correctingEngineeringContact print
A method is provided for repairing defects in a contact printed circuit. The method provides a substrate with a contact printed circuit formed on a substrate top surface. After detecting a discontinuity in a printed circuit feature, a bias voltage is applied to at least one of a first region of the printed circuit feature or a second region of the printed circuit feature. The bias voltage may also be applied to both the first and second regions. An electric field is formed between the bias voltage and an ink delivery nozzle having a voltage potential less than the bias voltage. Conductive ink is attracted into the electric field from the ink delivery nozzle. Conductive ink is printed on the discontinuity, forming a conductive printed bridge. Typically, the ink delivery nozzle is an electrohydrodynamic (EHD) printing nozzle.
Owner:SHARP KK
Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) fluid mover with field shaping feature at leading edge of collector electrodes
InactiveUS20120268857A1Increase flow of ionMinimizing ion migrationLine/current collector detailsWave amplification devicesLeading edgeSmall form factor
Small form-factor ion flow fluid movers that provide electrostatically operative surfaces in a flow channel adjacent to an emitter electrode, but upstream of a collector electrode or electrodes, can shape operative electric fields and influence ion flows in ways that accentuate downstream flow while minimizing upstream ion migration. In some cases, dielectric surfaces (or even electrically isolated conductive surfaces) along a flow channel adjacent to an emitter electrode can be configured to collect and retain an initial population of generated ions and thereafter electrostatically repel further ions. Depending on the configuration of such dielectric or electrically isolated conductive surfaces, these repelling electrostatic forces may dissuade ion migration or flow from sensitive but closely proximate components and / or may shape fields to enhance ion flows in a desired downstream direction.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) Printing for the Defect Repair of Contact Printed Circuits
ActiveUS20140158399A1Fix bugsReduce discontinuityElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementPrinting inkContact print
A method is provided for repairing defects in a contact printed circuit. The method provides a substrate with a contact printed circuit formed on a substrate top surface. After detecting a discontinuity in a printed circuit feature, a bias voltage is applying to at least one of a first region of the printed circuit feature or a second region of the printed circuit feature. The bias voltage may also be applied to both the first and second regions. An electric field is formed between the bias voltage and an ink delivery nozzle having a voltage potential less than the bias voltage. Conductive ink is attracted into the electric field from the ink delivery nozzle. Conductive is printed ink on the discontinuity, forming a conductive printed bridge. Typically, the ink delivery nozzle is an electrohydrodynamic (EHD) printing nozzle.
Owner:SHARP KK
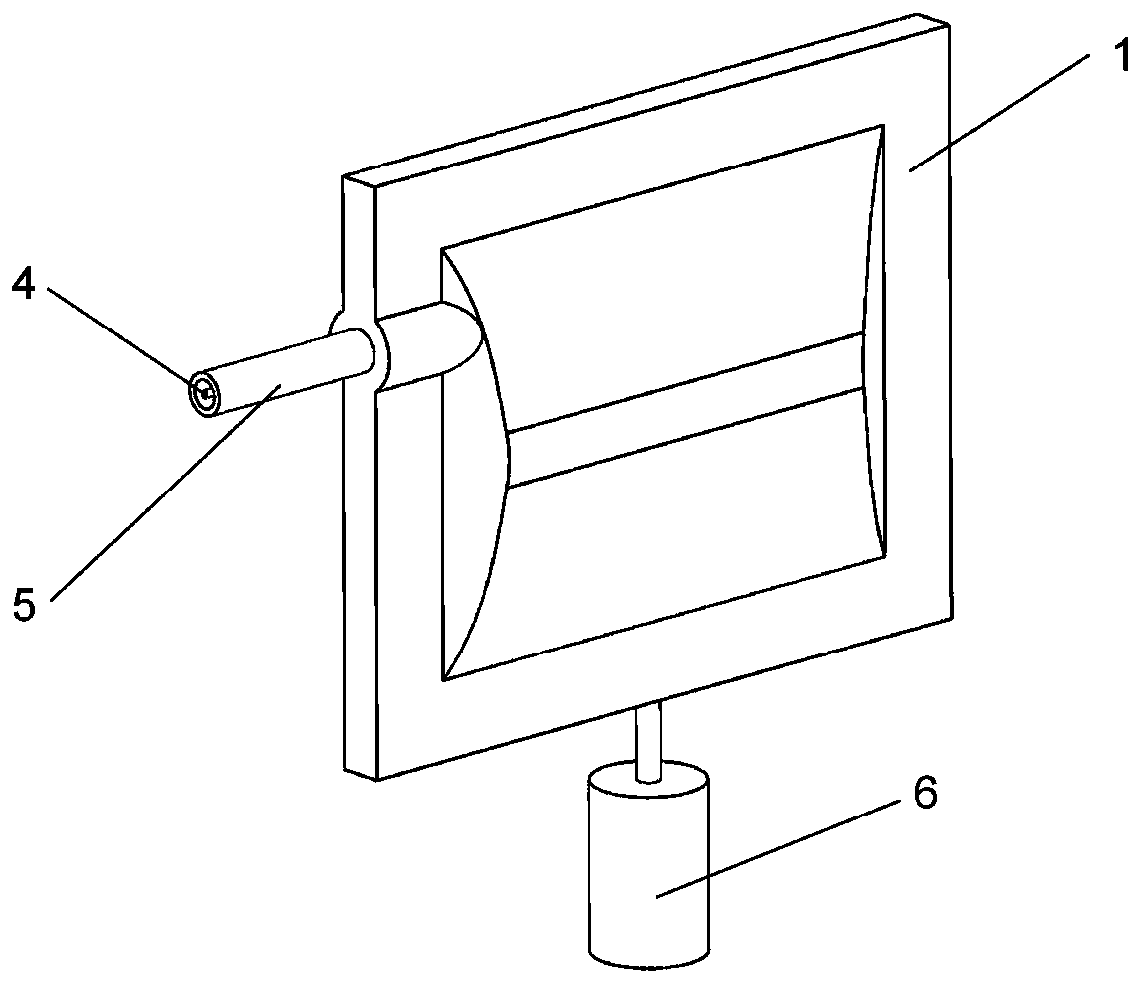
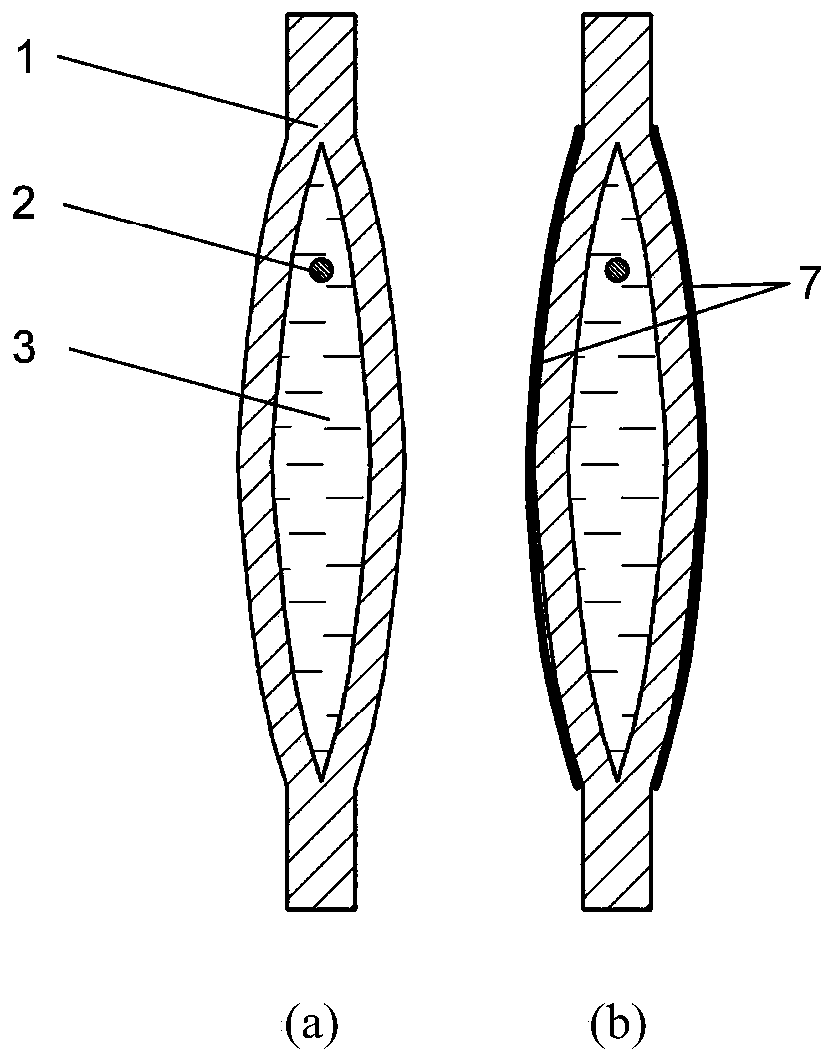
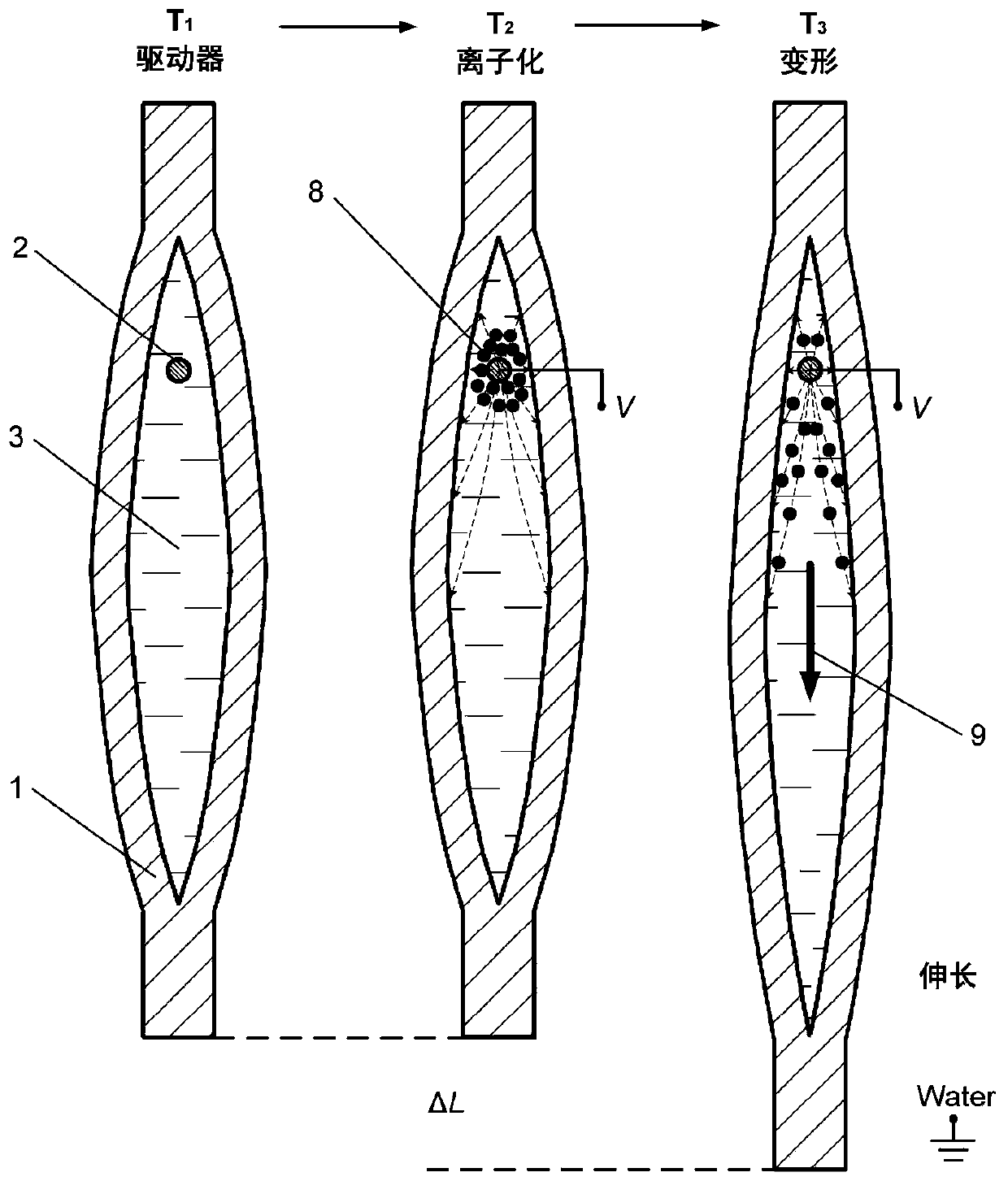
Flexible electrohydrodynamics driver
ActiveCN111152210ASolve the main problemSolve efficiency problemsProgramme-controlled manipulatorFlexible member pumpsDielectricElectrical connection
The invention discloses a flexible electrohydrodynamics driver. A drive unit comprises a flexible bag, a columnar electrode, dielectric fluid, a varnished wire, a hose and a plane flexible electrode.An inner cavity of the flexible bag is provided with the columnar electrode and fully filled with the dielectric fluid. The side portion of the flexible bag is in sealed connection with the hose, thevarnished wire is sleeved with the hose in a sealed manner, after penetrating through the hose, one end of the varnished wire stretches into the inner cavity of the flexible bag and is electrically connected with the end portion of the columnar electrode, and the other end of the varnished wire is connected with a high-voltage positive electrode. The outer surface of the flexible bag is coated with a layer of conductive flexible material to serve as the plane flexible electrode, or the flexible bag is arranged in water, and the water environment around the flexible bag serves as the plane flexible electrode. The flexible electrohydrodynamics driver is a novel drive based on the drive and deformation principle, the advantages of electrohydrodynamics flowing is brought into play, the main problems in the prior art are solved, and great application prospects are achieved in the field of soft body robots.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Multifunctional electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing device and printing method using the same
An electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing device, including: a support part; a jet printing module; a substrate bearing and moving module; and a roll-to-roll thin film conveying module. The jet printing module is disposed on the support part and includes a nozzle for ejecting printing fluid onto a substrate for pattern printing. The substrate bearing and moving module is disposed on the support part, and fixedly bears a rigid substrate as the substrate for pattern printing, and drives the rigid substrate to move with respect to the jet printing module. The roll-to-roll thin film conveying module is disposed on the support part, and transfers a flexible thin film as the substrate for pattern printing, and drives the flexible film to move with respect to the jet printing module.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
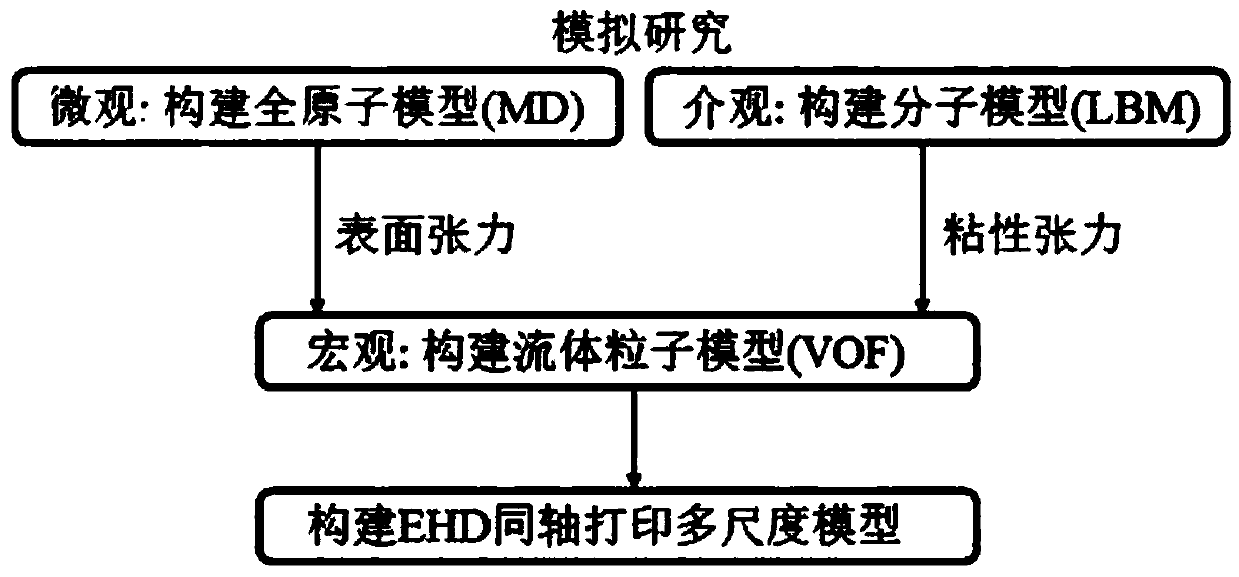
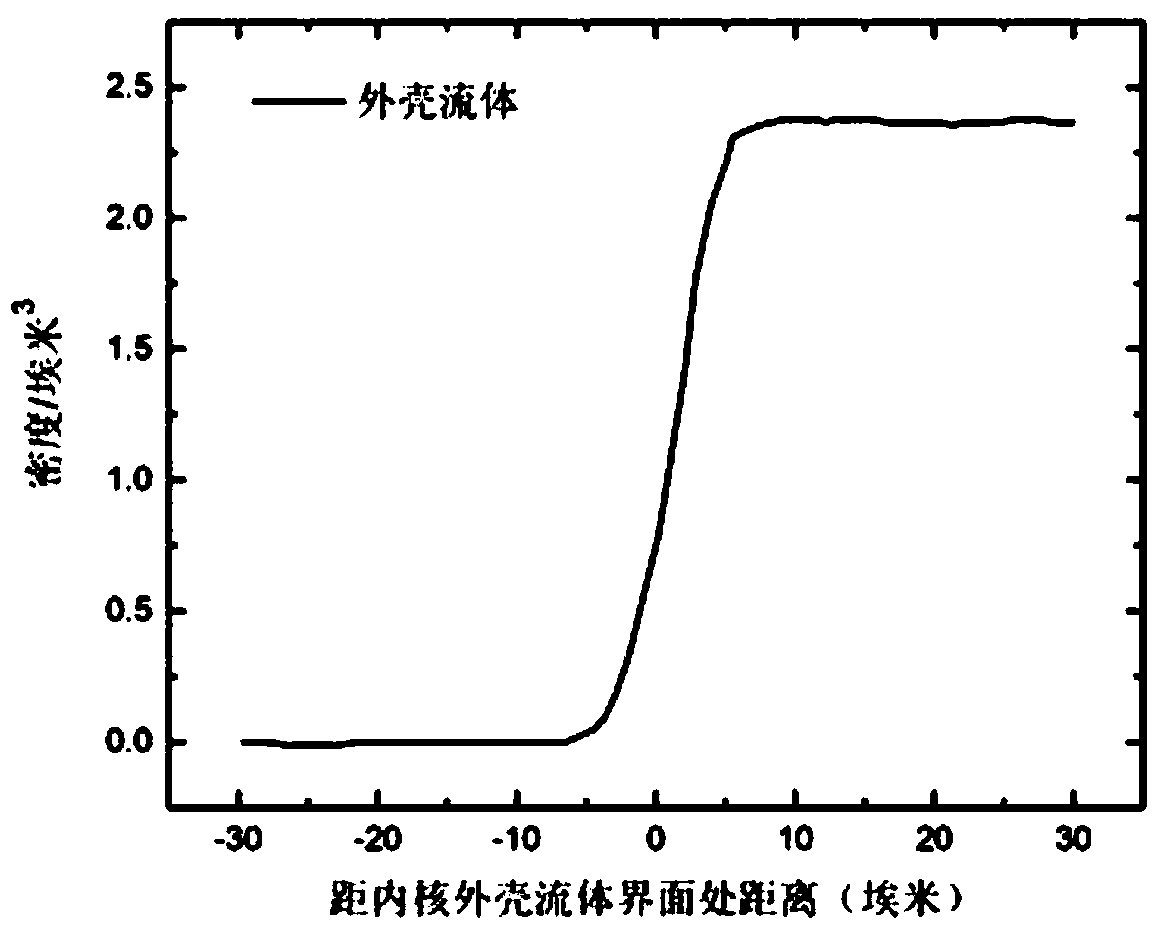
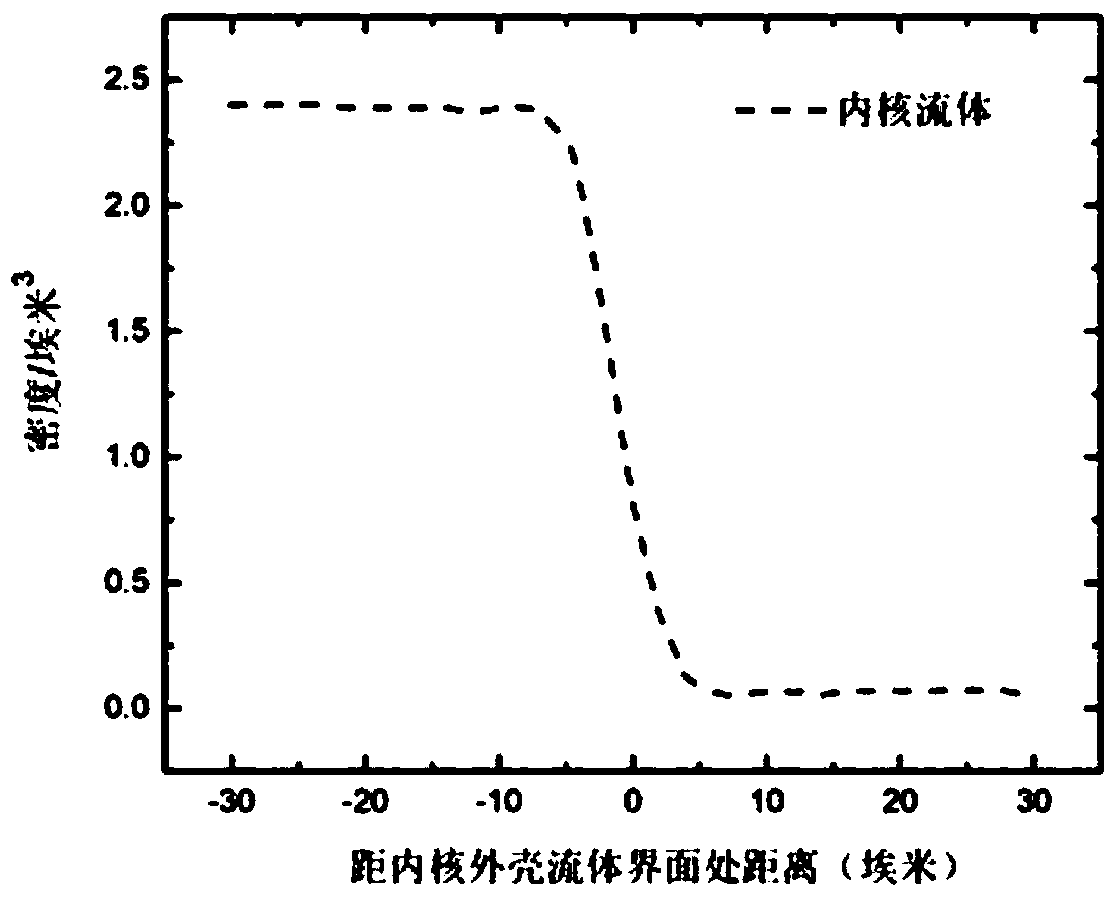
Multi-scale simulation method for multiphase electrohydrodynamics of core-shell structure
ActiveCN108829919AThe calculation result is accurateDetailed modeling considerationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic methodFluid interface
The invention discloses a multi-scale simulation method for multiphase electrohydrodynamics of core-shell structure. According to the method, three-phase fluids are considered and include core and shell printing fluids and surrounding wrapping air; tensions at different fluid interfaces are calculated by adopting a micro-scale all-atomic molecular dynamics method; a viscosity pressure tensor is calculated by adopting a meso-scale lattice Boltzmann method; information obtained by micro-scale and meso-scale calculation is substituted into a macro-scale; a multi-scale calculation model is built;and an injection characteristic is obtained. The multi-scale calculation model can improve the calculation efficiency, save the calculation resources and take the calculation precision into account, and has important theoretical significance for perfecting a multiphase electrohydrodynamics theory of the core-shell structure.
Owner:嘉兴南湖学院
Multifunctional electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing device and printing method using the same
ActiveUS20160001550A1Simple processSimple structureTypewritersPower drive mechanismsEngineeringElectrohydrodynamics
An electrohydrodynamic inkjet printing device, including: a support part; a jet printing module; a substrate bearing and moving module; and a roll-to-roll thin film conveying module. The jet printing module is disposed on the support part and includes a nozzle for ejecting printing fluid onto a substrate for pattern printing. The substrate bearing and moving module is disposed on the support part, and fixedly bears a rigid substrate as the substrate for pattern printing, and drives the rigid substrate to move with respect to the jet printing module. The roll-to-roll thin film conveying module is disposed on the support part, and transfers a flexible thin film as the substrate for pattern printing, and drives the flexible film to move with respect to the jet printing module.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
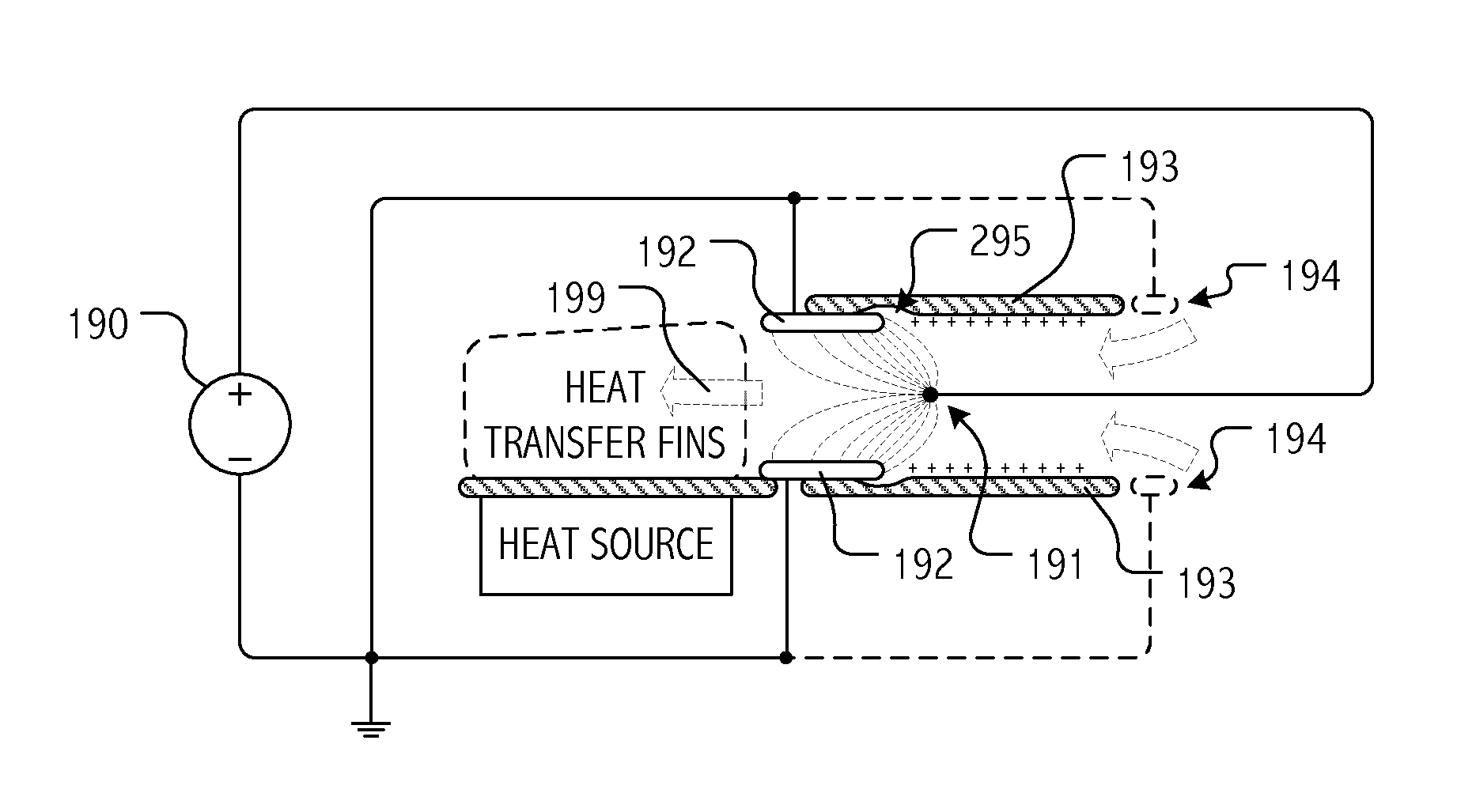
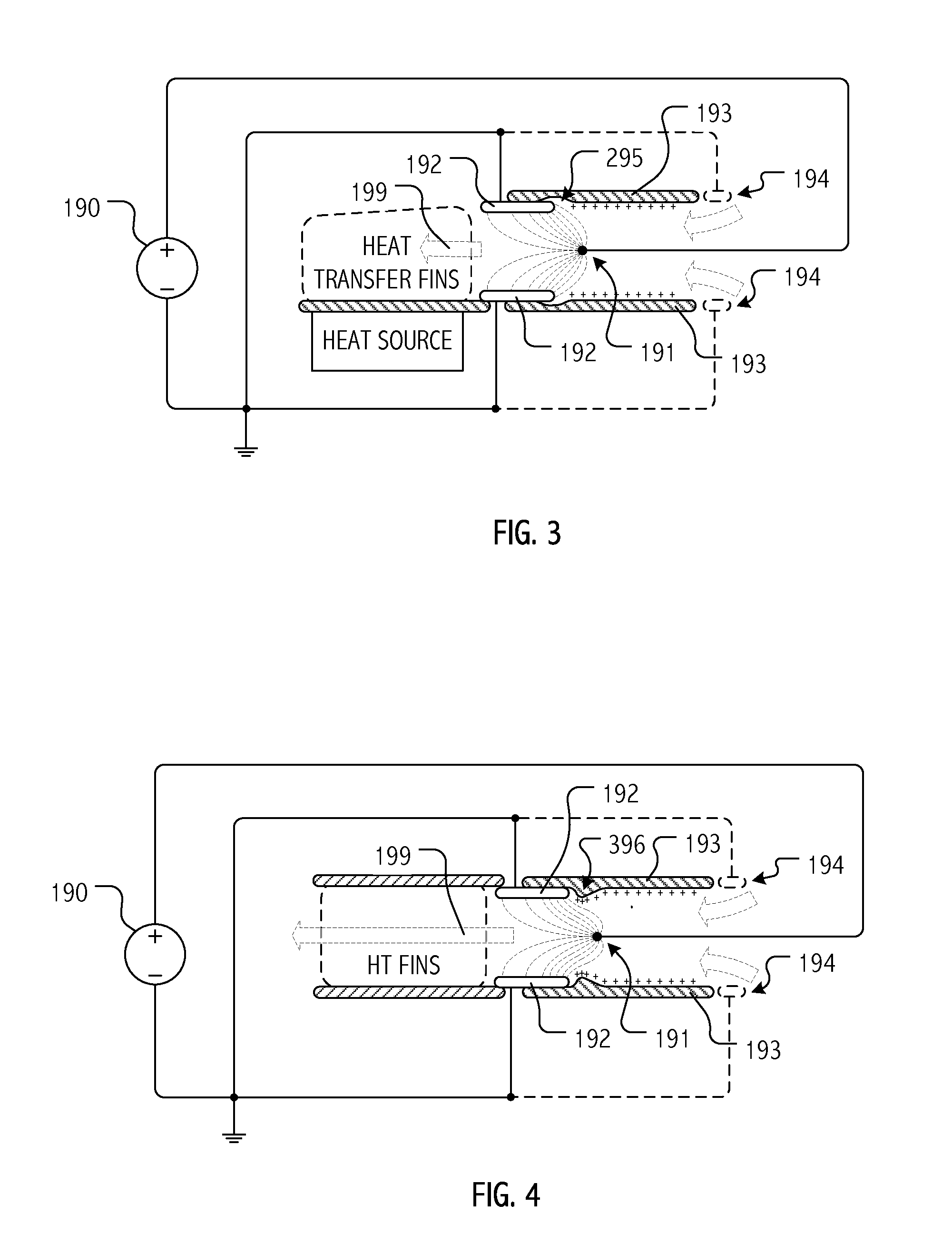
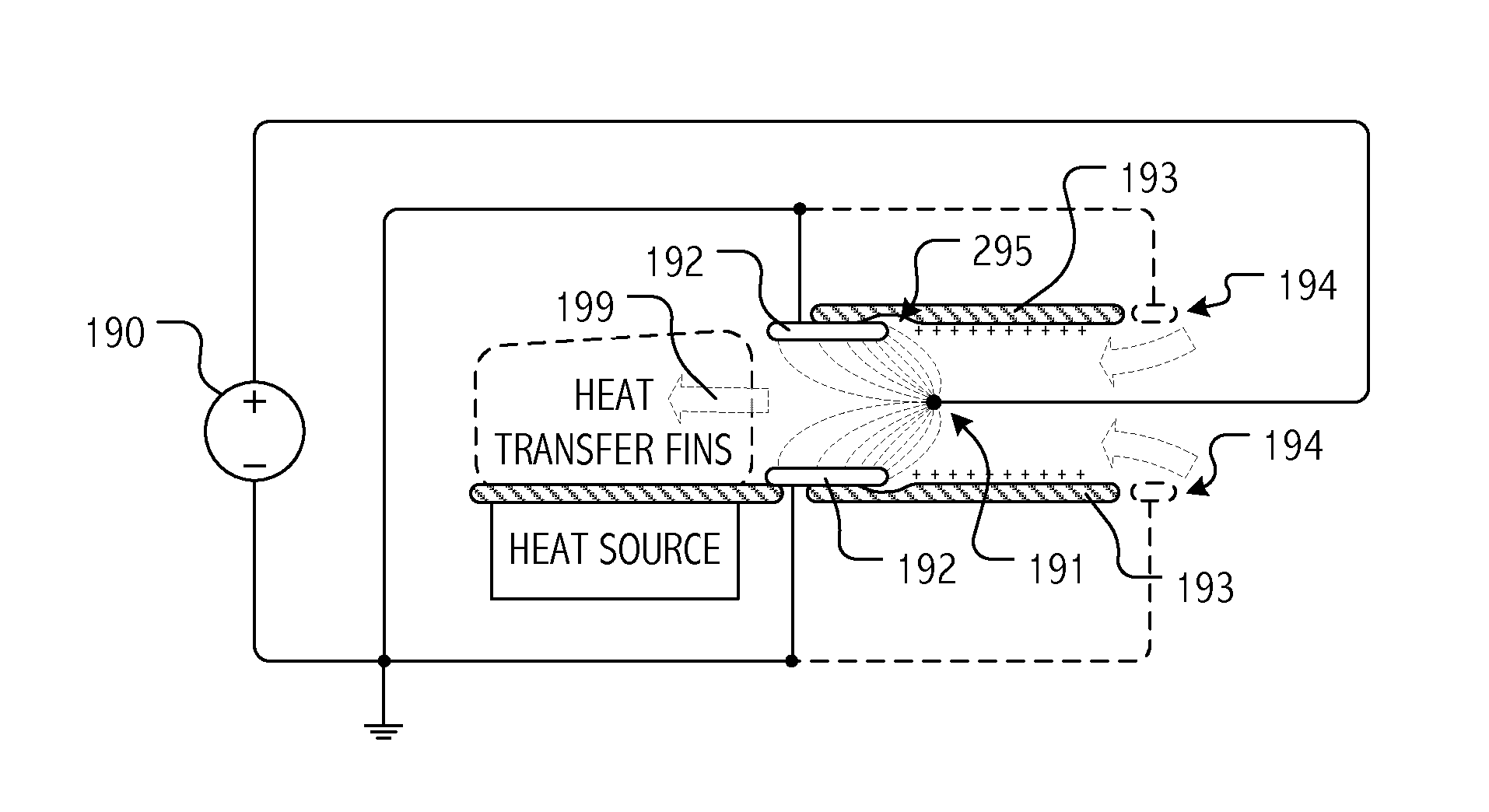
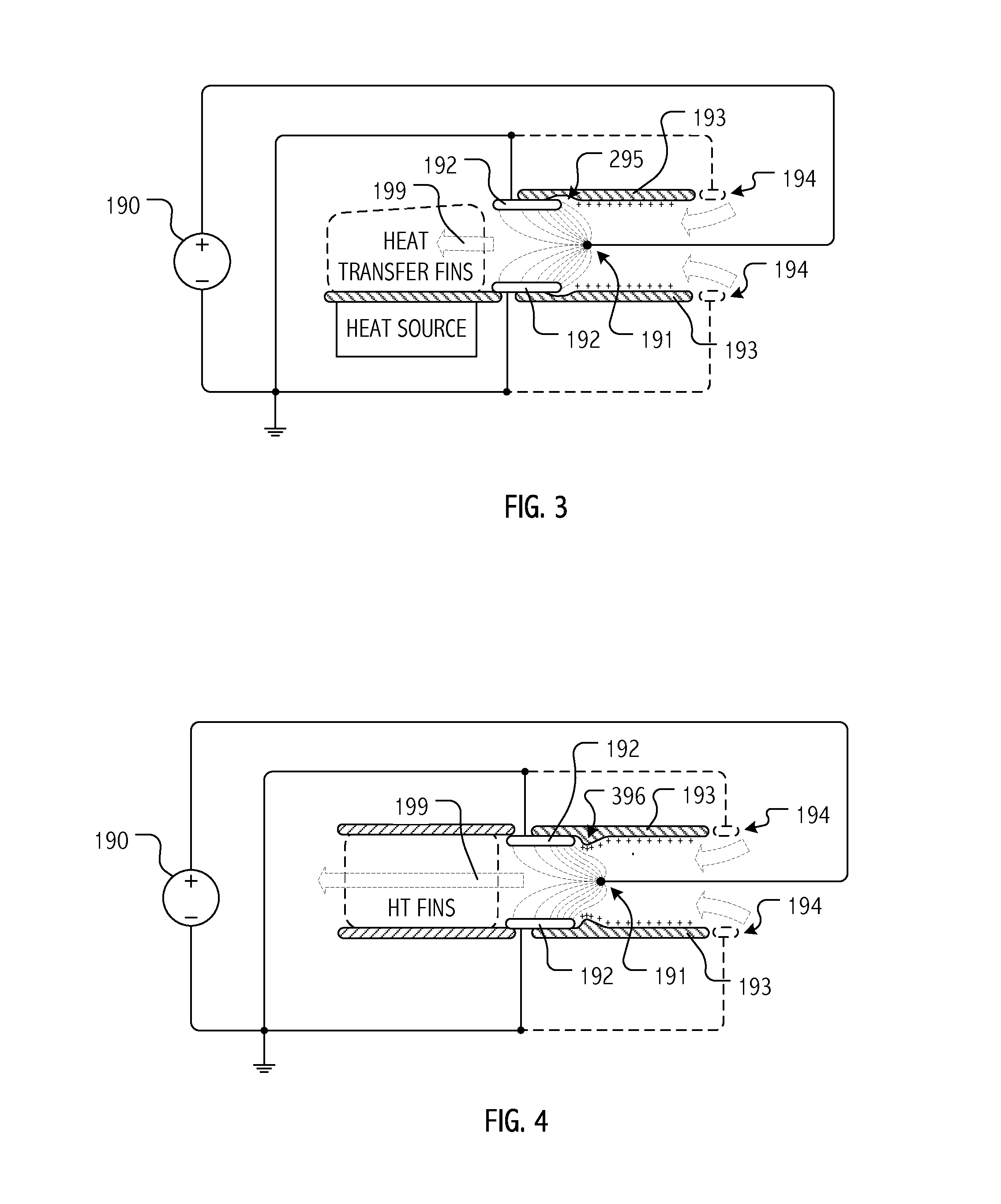
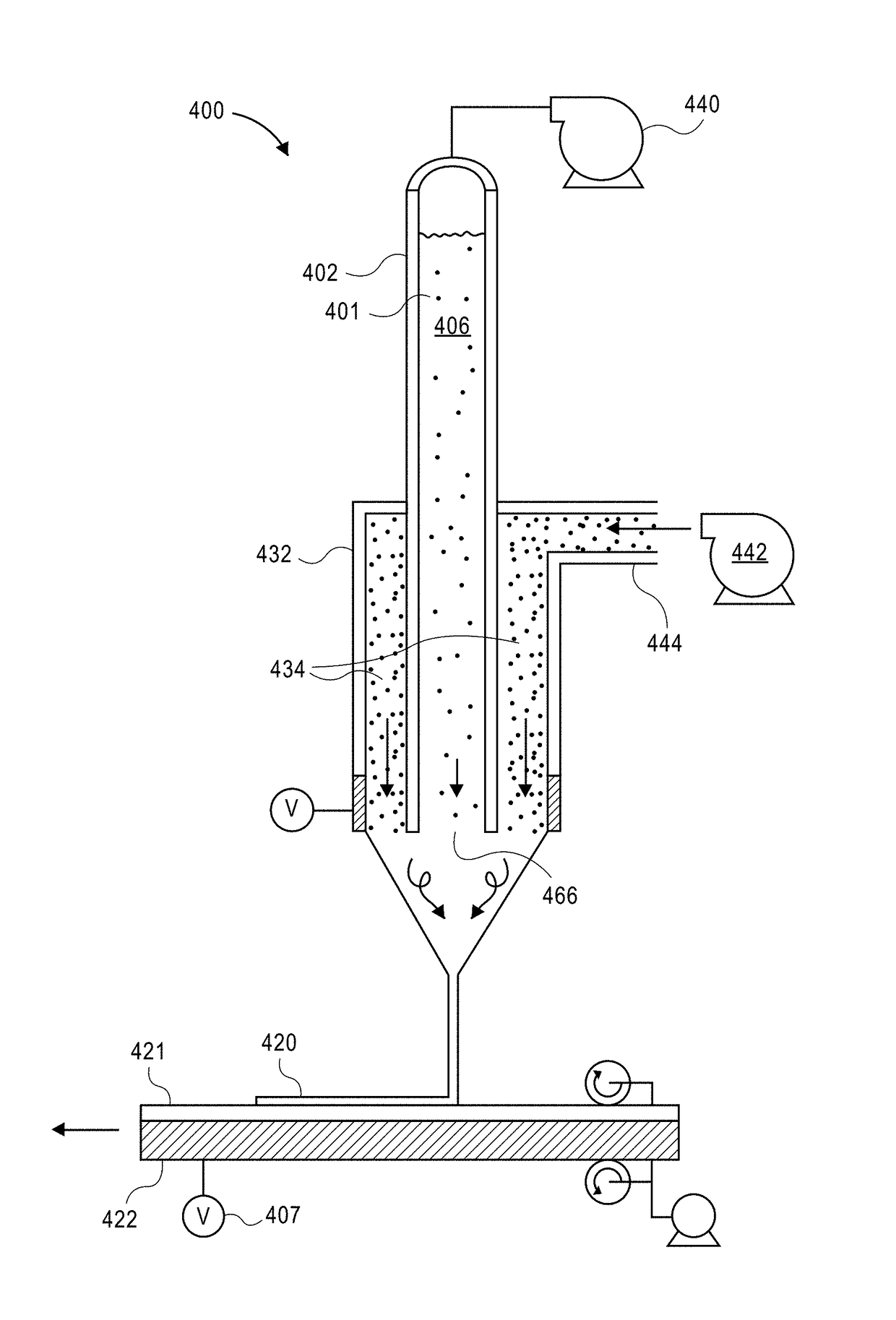
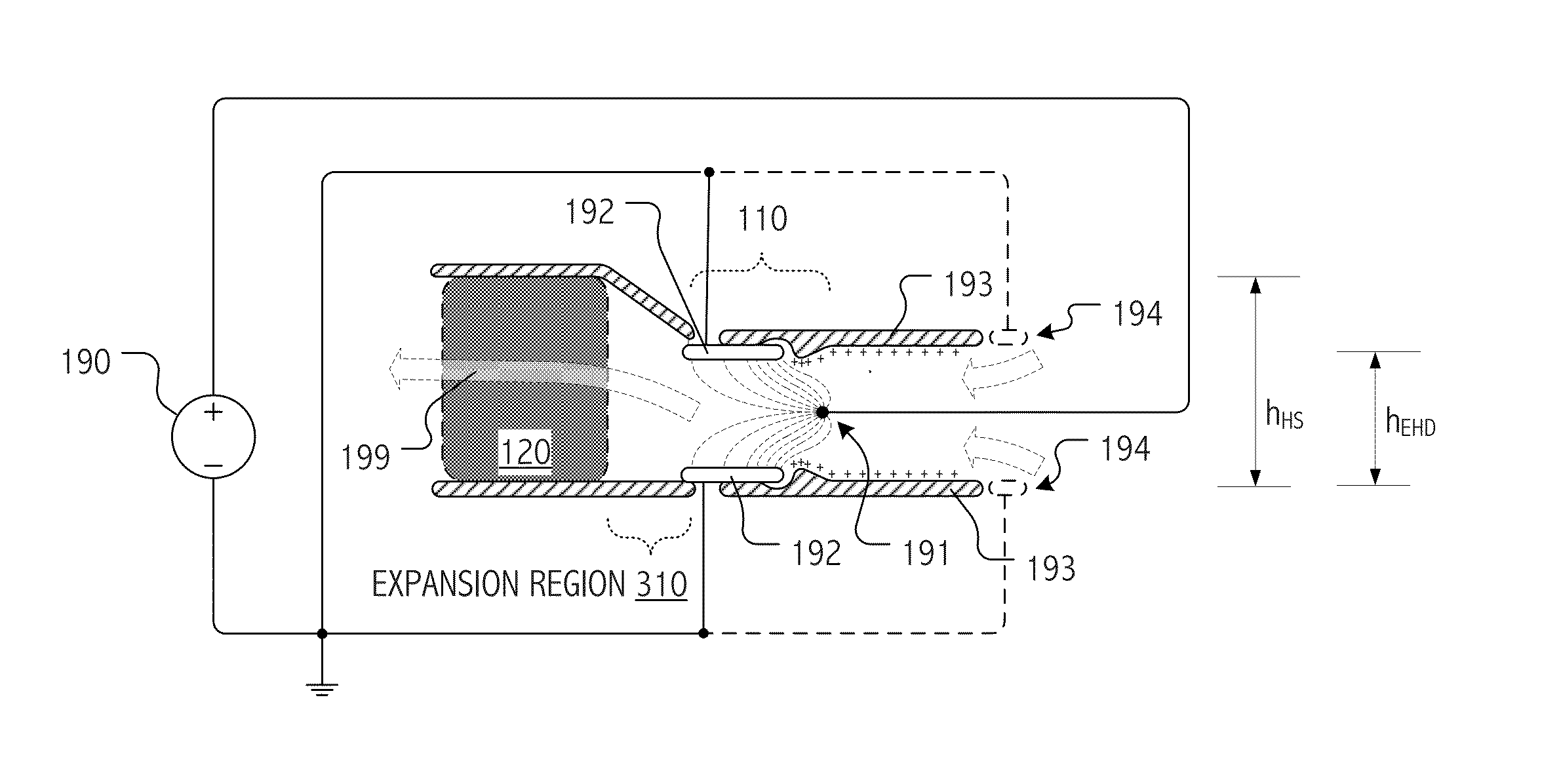
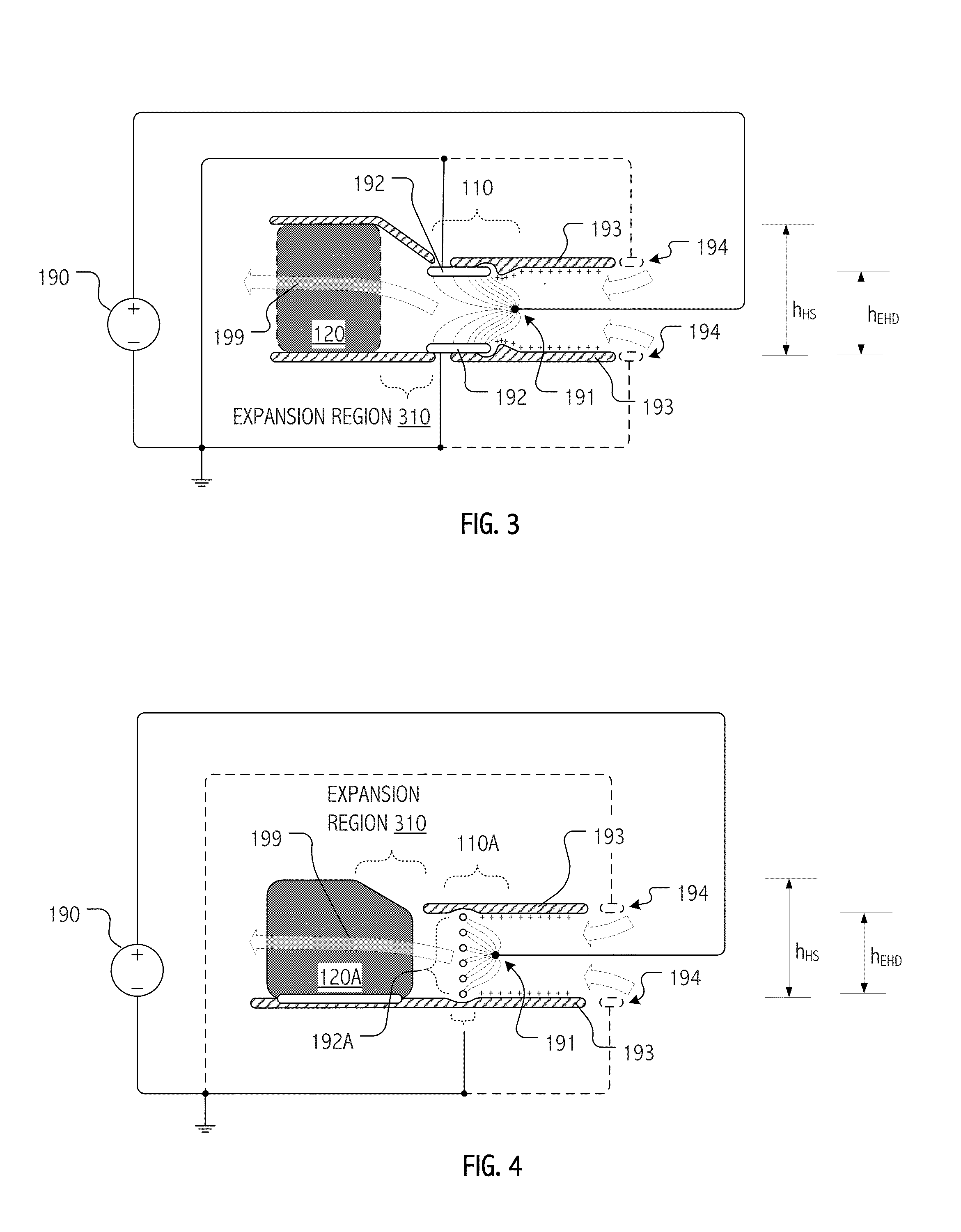
Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) air mover configuration with flow path expansion and/or spreading for improved ozone catalysis
Provision of an expansion region (e.g., a flow path with increasing cross-section downstream of the EHD air mover) can provide operational benefits in EHD air mover-based thermal management systems. In contrast, such a design would generally be disfavored for conventional mechanical air mover-based systems. In some cases, an expansion chamber or volume may be provided between the EHD air mover and heat transfer surfaces. In some cases, expansion of the flow cross-section may be provided (at least in part) within the heat transfer surface volume itself. In some cases, leading surfaces of heat transfer surface (e.g., heat sink fins) may be shaped, disposed or otherwise presented to EHD motivated flow to reduce “laminarity” of the impinging air flow so as to reduce thermal transfer boundary layer effects and / or to divert flow outward in the flow channel so as to more evenly distribute ozone molecules over catalytic sites.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
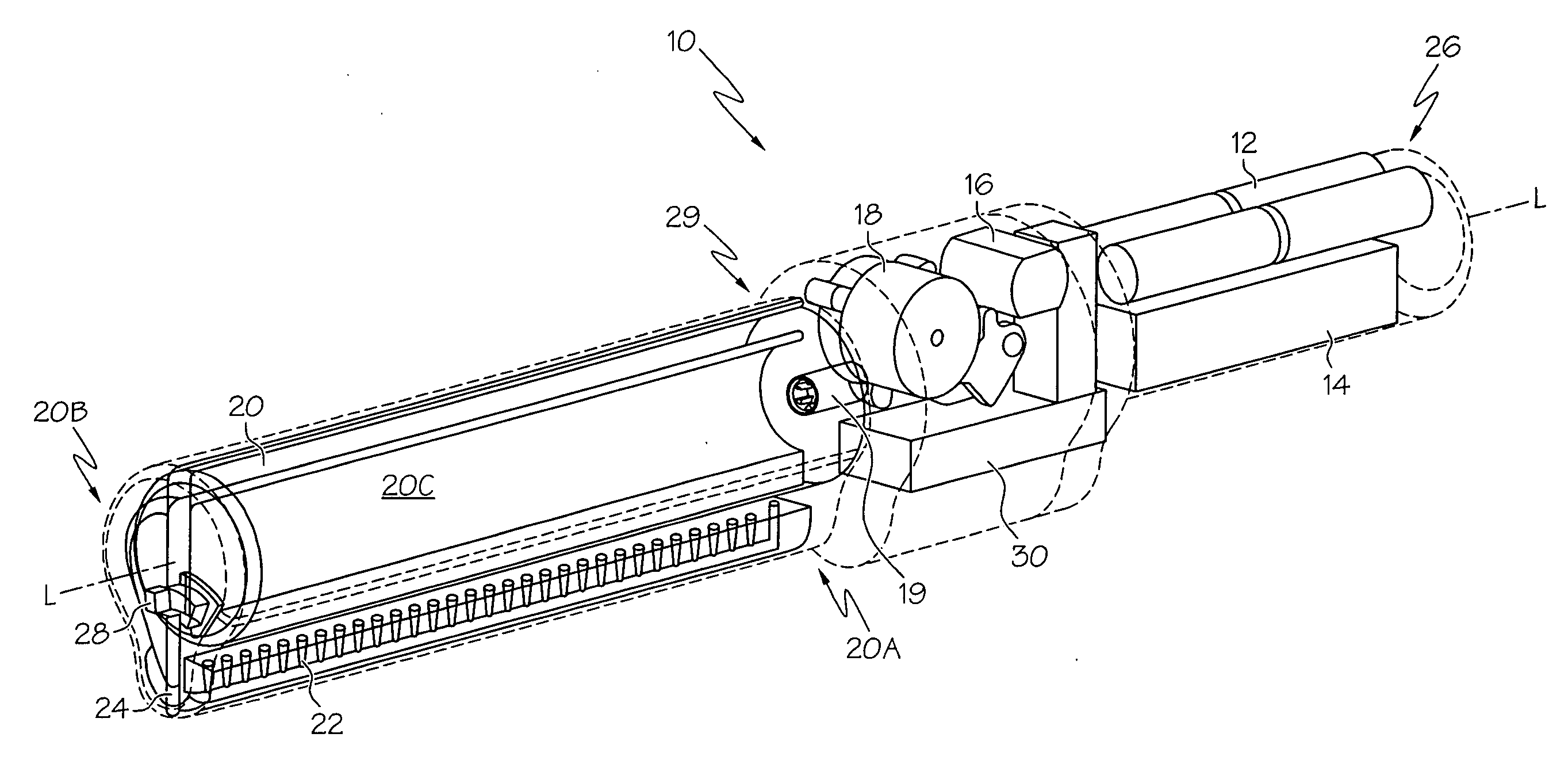
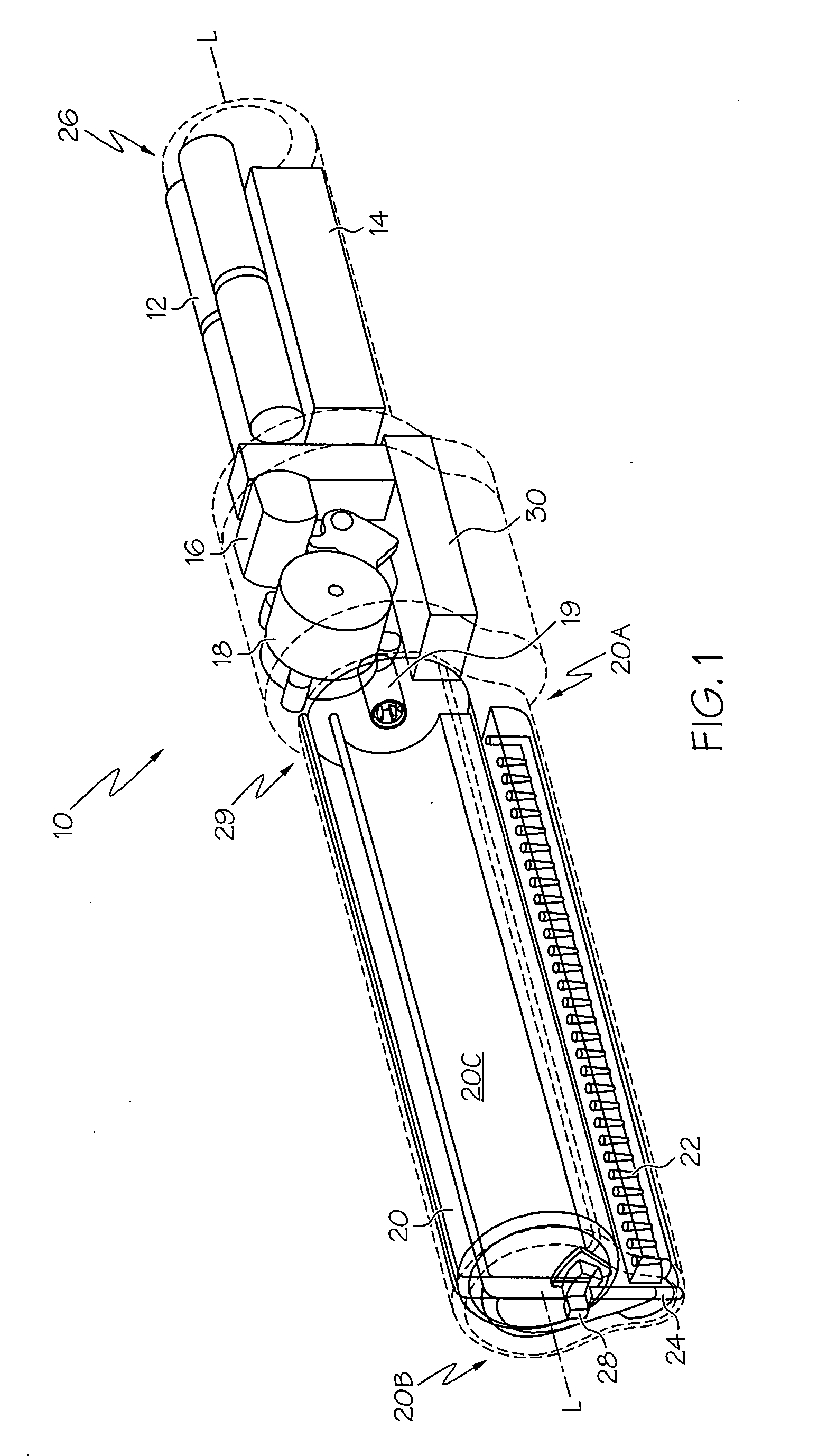
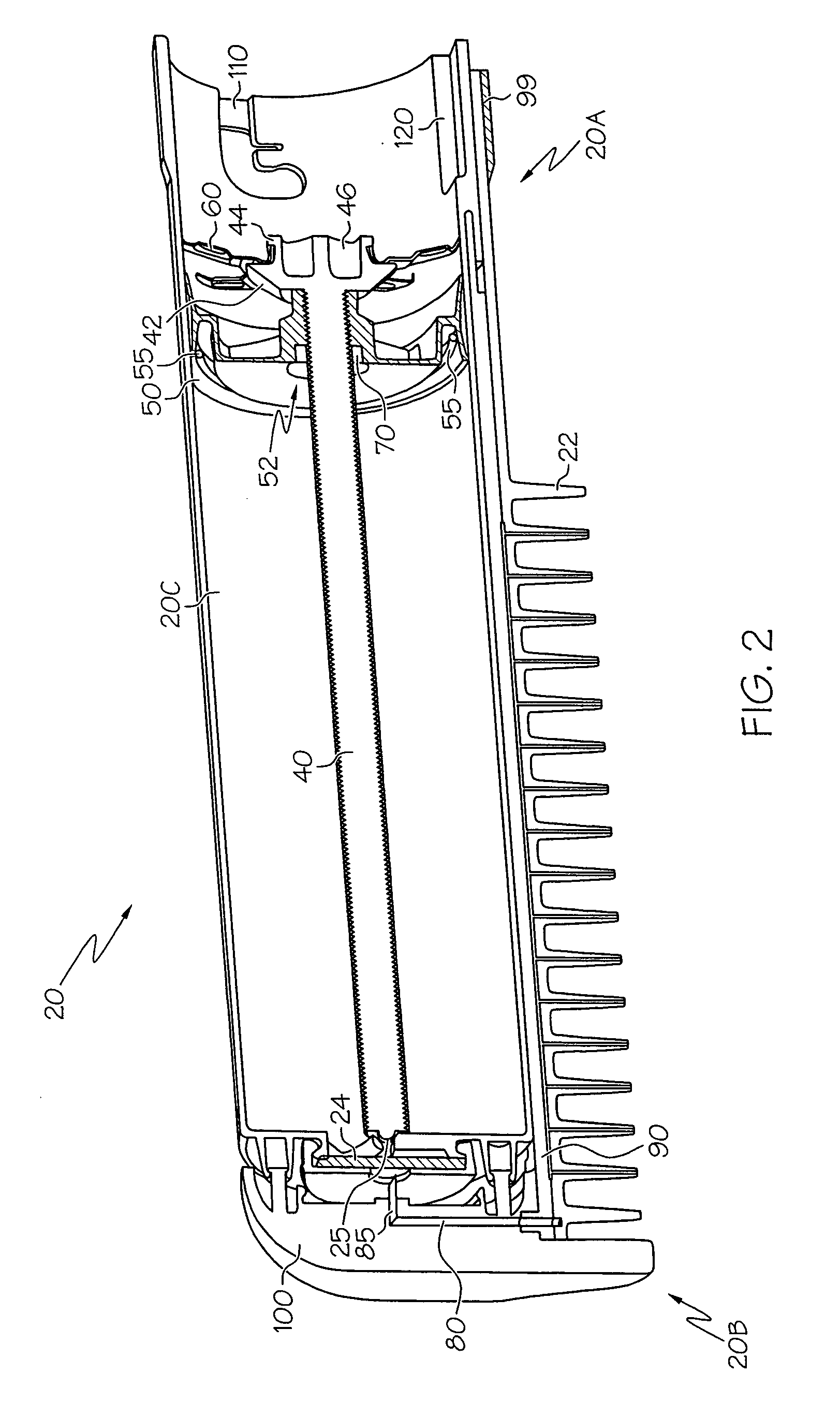
Handheld sprayer with removable cartridge and method of using same
A cartridge for a handheld electrohydrodynamic (EHD) spraying device and a spraying device incorporating the cartridge. The cartridge is disposable, and can contain therapeutic products. The device includes a wetted lead screw with a compliant seal, where the placement of the seal relative to the screw inhibits leakage during both cartridge use and storage. A frame disposed within the cartridge acts as a load-transferring mechanism for the weight of the cartridge to a handle of the spraying device.
Owner:EFIELD INNOVATIONS
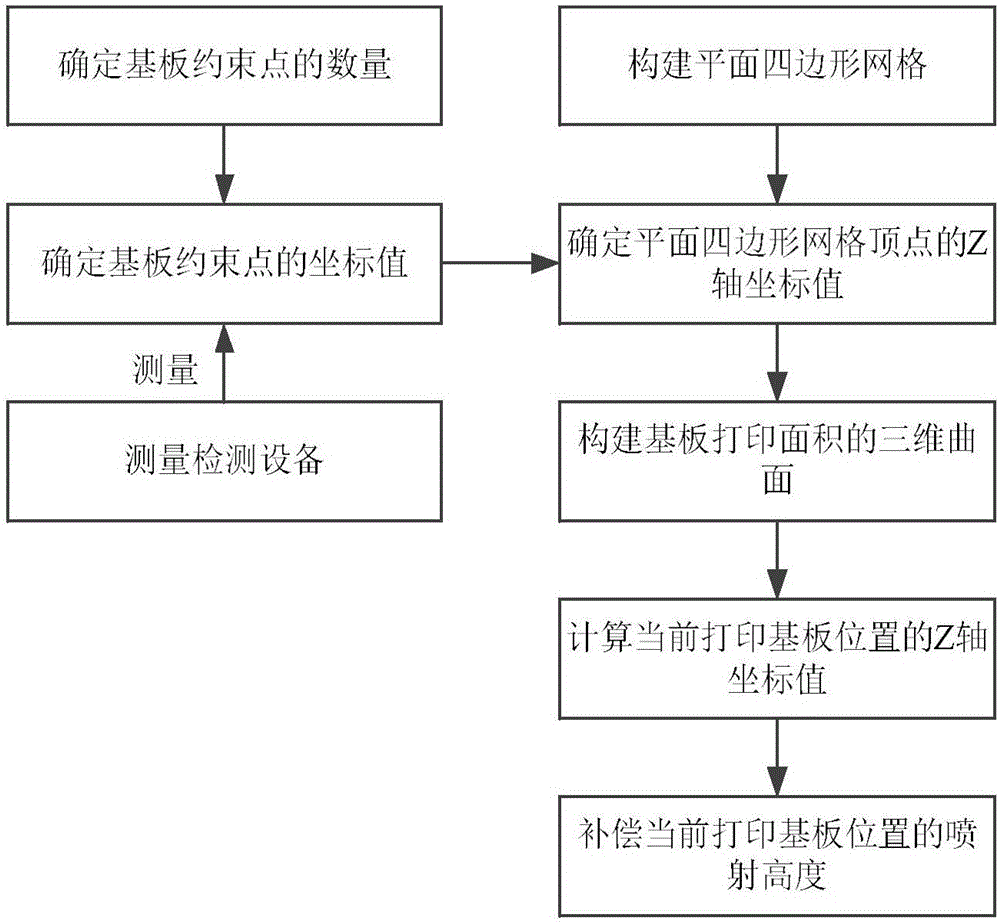
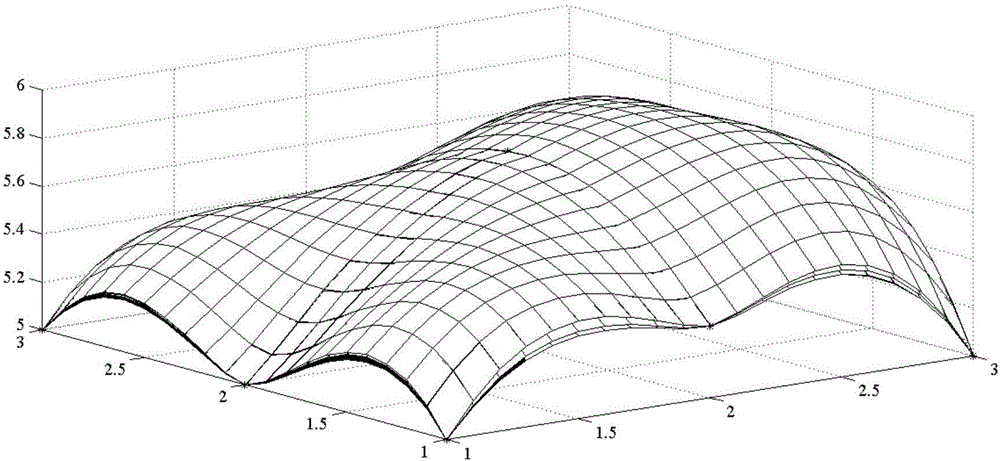
Jetting height error compensation method for large-area micro-nano structure electrohydrodynamics printing
The invention discloses a jetting height error compensation method for large-area micro-nano structure electrohydrodynamics printing. The jetting height error compensation method comprises the following steps that (1) the number of constrained points of a base plate is determined; (2) the coordinate value z of the Z axis of the constrained points of the base plate is obtained; (3) a quadrilateral mesh of an XY plane is built; (4) the coordinate value z<j> of the Z axis of the vertex of the quadrilateral mesh of the XY plane is determined; (5) a three-dimensional curved surface of the printing area of the base plate is built; (6) the coordinate value z<c> of the Z axis of the current position of the printing base plate is obtained; and (7) the jetting height of electrohydrodynamics printing is compensated. According to the jetting height error compensation method for large-area micro-nano structure electrohydrodynamics printing, limitation of the existing electrohydrodynamics printing technology to precise forming of a device of a large-area micro-nano structure is broken through, and ink-jet printing of a micro-nano device of a large-area structure and preparation of a device of a micro-nano structure are achieved.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Laser auxiliary electric jetting in-situ printing manufacturing method
ActiveCN109366980AHigh dimensional accuracyHigh bonding strength3D object support structuresManufacturing data aquisition/processingUnit structureEnergy device
The invention belongs to the technical field of advanced manufacturing, and provides a laser auxiliary electric jetting in-situ printing manufacturing method. A functional material ink flows out froma spraying needle port under the action of pressure, and due to the action of the electrohydrodynamics effect, a stable Taylor cone is formed to jet out stable fine jet flow to a base body to form a printing layer. Meanwhile, a laser energy device is used for carrying out composite processing on the printing layer, emitting laser beams and irradiating the printing layer according to printing tracks, and high-temperature curing, crystallization and other functional processing on a printing structure can be synchronously realized in situ. According to the method, functional structures and devices are directly realized on the base body in situ, the problem of secondary positioning errors of transferring, gluing, splicing and the like in a traditional method is eliminated, the problems that binding force is weak, and sensitivity is low due to a gluing process are avoided, and the feature size of a functional unit can be reduced by means of the high-resolution printing advantage of electricjetting; and the size precision and the bonding strength of a printing unit structure are improved, so that the sensitivity and the stability of the devices are improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
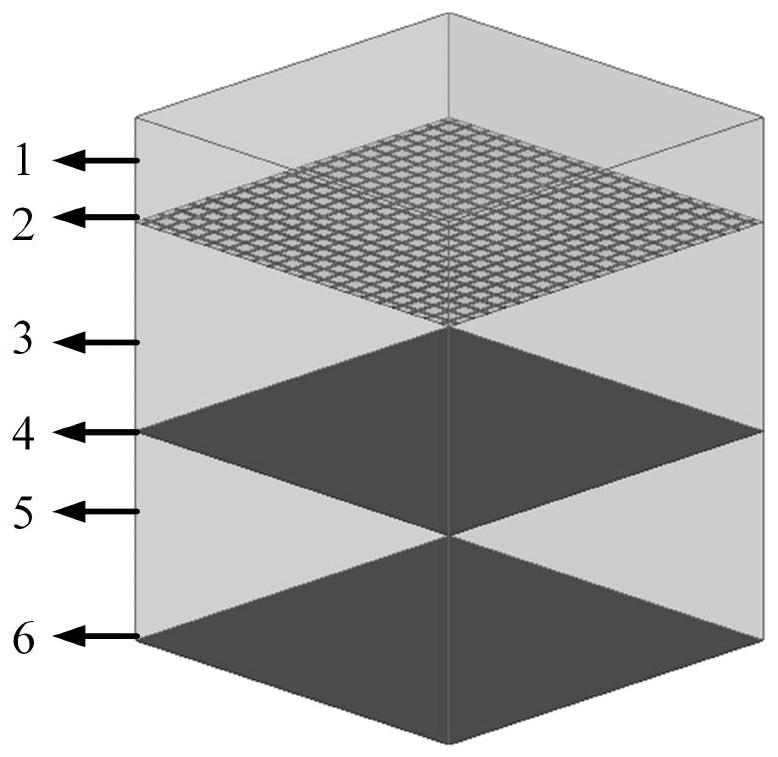
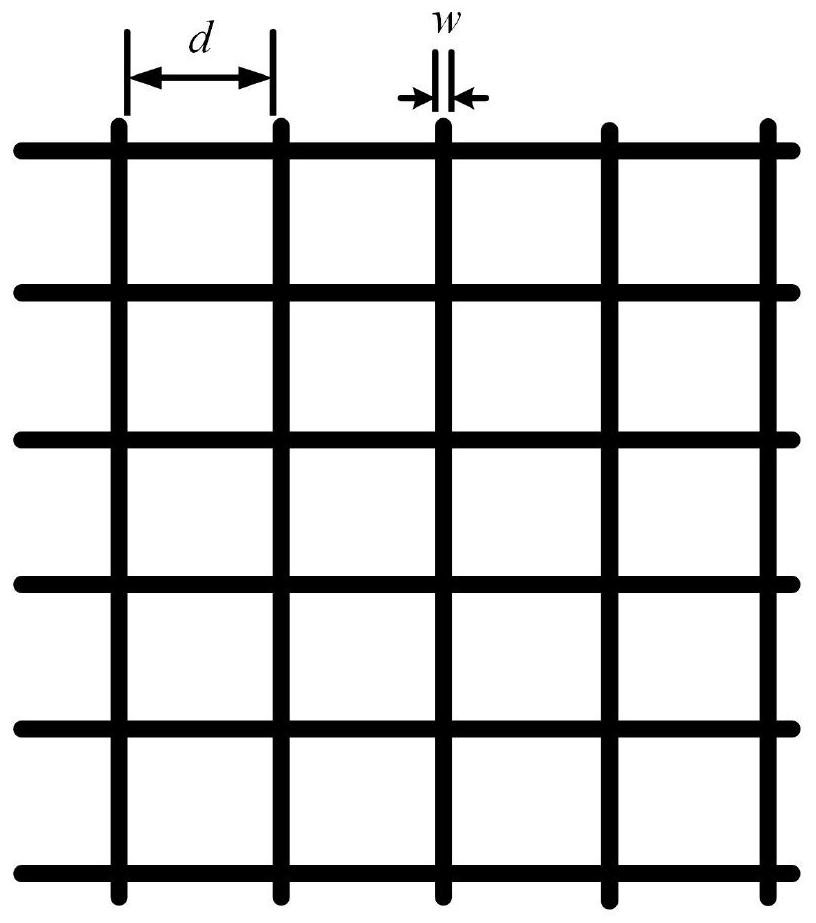
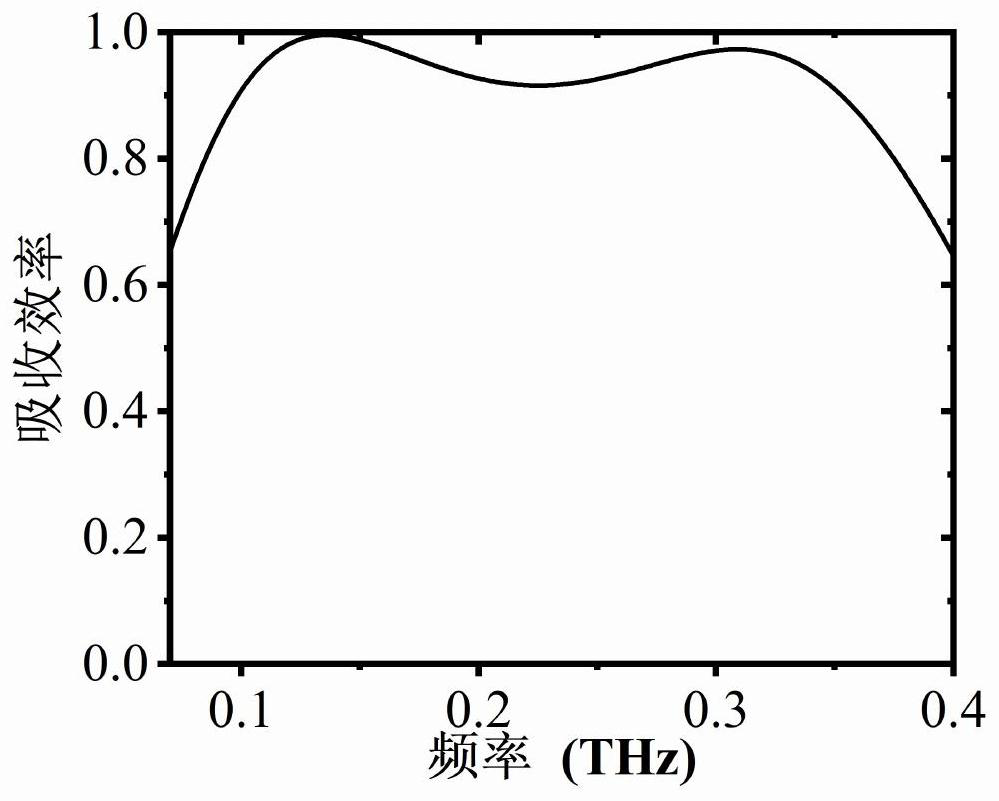
Broadband terahertz wave absorber with high tolerance
The invention discloses a high-tolerance broadband terahertz wave absorber which comprises a metasurface protection layer, a metasurface, an upper dielectric layer, a loss layer, a lower dielectric layer and a bottom plate from top to bottom, and is characterized in that the metasurface is printed on the lower surface of the metasurface protection layer through conductive ink. The metasurface structure is selected as an inductance grid structure, and is prepared by adopting a hyperfine electrostatic ink-jet printing technology based on an electrohydrodynamics principle. Through optimization design, the wave absorber has the advantage of high tolerance, is insensitive to the line width and the surface resistance of the metasurface, and meanwhile, keeps an ultra-wideband wave absorbing effect within a 45-degree incident range. The method has a wide application prospect in the aspects of imaging, sensing and electromagnetic stealth.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
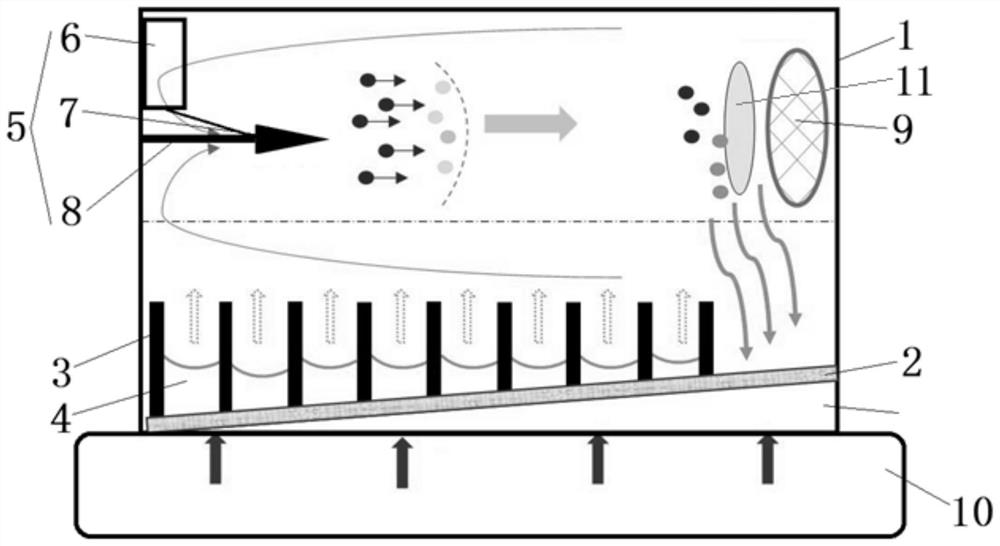
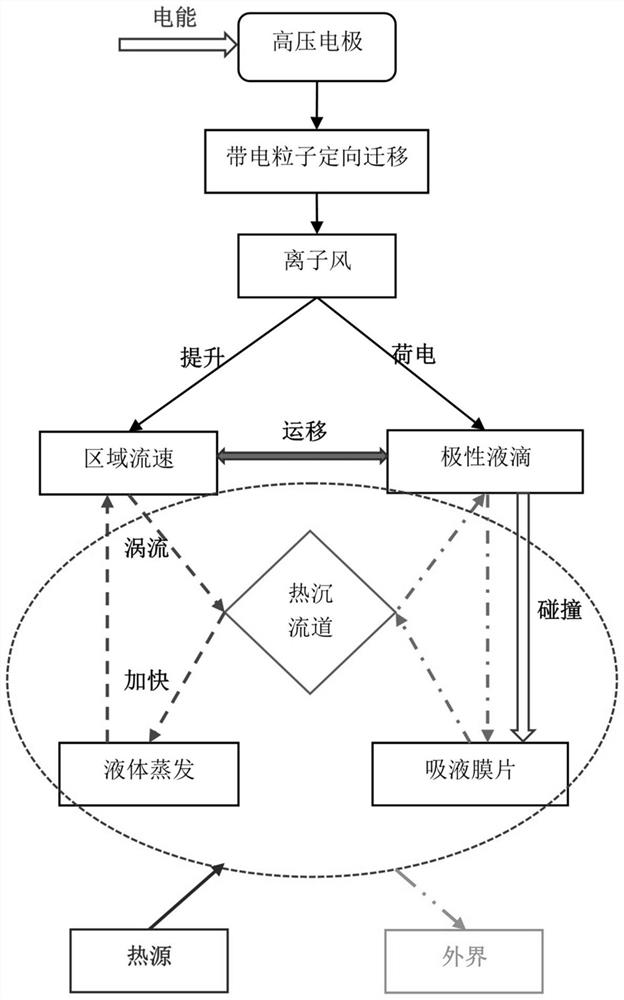
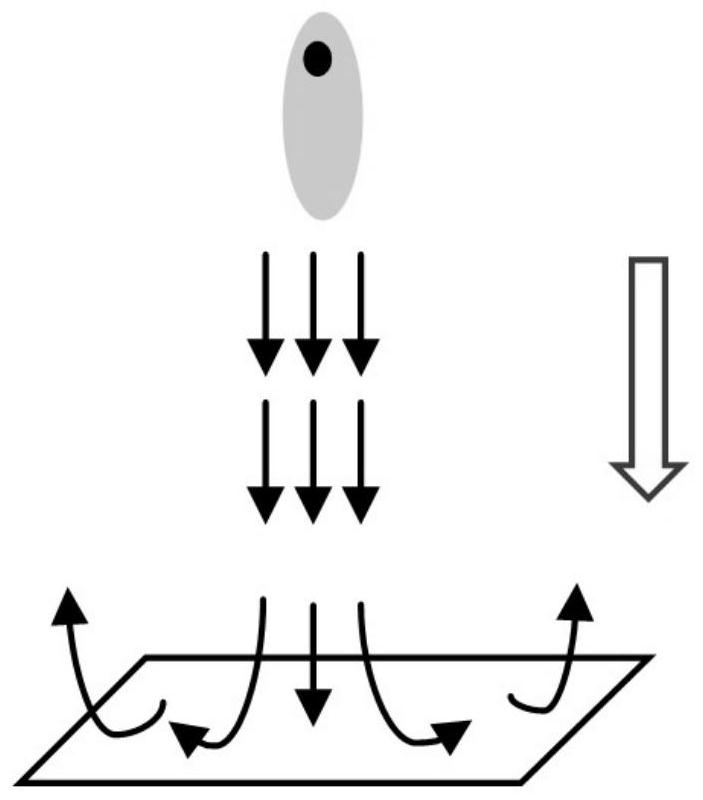
Novel coupling cooling device based on ionic wind, cooling method and application thereof
ActiveCN113163678APhase change heat increasesStrengthen cycle frequencyModifications using liquid coolingIon windStainless steel wire
The invention discloses a novel coupling cooling device based on ionic wind, a cooling method and application thereof. The bottom of a shell is provided with a uniform temperature plate substrate in contact with a heat source, the uniform temperature plate substrate is vertically provided with a plurality of metal radiating fins at intervals, and a flow channel is formed between every two adjacent metal radiating fins; the bottom side of the interior of the shell is filled with cooling liquid, and the cooling liquid is evenly distributed in the flow channel; an ionic wind generator is arranged at the front part of the shell and comprises a high-voltage power supply, a plurality of electrodes and an electrode support; the plurality of electrodes are fixed on the electrode support at equal intervals, and the plurality of electrodes are electrically connected to the high-voltage power supply; and a receiving electrode made of a stainless steel wire mesh material is arranged at the rear part of the shell and is attached to the side wall of the rear part of the shell. The invention creatively provides a novel heat exchanger combining electrohydrodynamics and phase-change heat exchange, and organic coupling of two heat exchange modes of increasing convective heat exchange in the metal radiating fins and phase-change heat exchange at the roots of the metal radiating fins 3 is realized.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Nozzle of electrohydrodynamics coaxial-printed polymer metal composite metamaterial
The invention discloses a nozzle of an electrohydrodynamics coaxial-printed polymer metal composite metamaterial. The nozzle is characterized in that an inner core is arranged in an outer shell; an insulation cavity is formed between the inner core and the outer shell; the outer shell is provided with an insulation liquid inlet and an insulation liquid outlet communicating with the insulation cavity; a spraying mouth is arranged in the bottom center of the outer shell, and is connected with a high-voltage electrode; a metal melt inlet channel, a polymer inlet channel and a metal melt outlet runner and a polymer outlet channel respectively pointed to the spraying mouth are formed on the inner core; the metal melt inlet channel communicates with the metal melt outlet runner; and the polymer inlet channel communicates with the polymer outlet channel. The nozzle has the following advantages: insulation liquid is filled in the insulation cavity to satisfy high-temperature condition in the printing process to prevent curing of molten-state material; and meanwhile, a metal melt and a polymer melt are directly filled in the spraying mouth for spraying under the effect of a high-voltage electric field of the high-voltage electrode without needing solvent auxiliary, so that the jet process is controlled more easily.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Micro-fluidic chip based on electrohydrodynamics and micro sample application device and method
ActiveCN113522378AReduce operating costsSkilledRaman scatteringBurettes/pipettesCapillary TubingMechanical engineering
The invention provides a micro-fluidic chip based on electrohydrodynamics, a micro sample application device and a micro sample application method. The chip comprises: at least one capillary tube having an inlet end and an outlet end; a chip body, which comprises at least one sample inlet, and a micro-channel connected with the sample inlet and a capillary tube embedding channel connected with the micro-channel, wherein the capillary tube embedding channel is provided with an outlet end, the capillary tube is arranged in the capillary tube embedding channel and connected with the micro-channel, and the length of the capillary tube is larger than that of the capillary tube embedding channel; an upper electrode which is positioned on the chip body and is close to the capillary tube; and a lower electrode which is provided with an insulating support body, and the lower electrode is positioned below the outlet of the capillary tube. According to the chip, the capillary tube is embedded into the micro-fluidic chip, so that an accurate fixing effect is achieved, the structure is simplified, and full-automatic loading of a sample can be realized.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
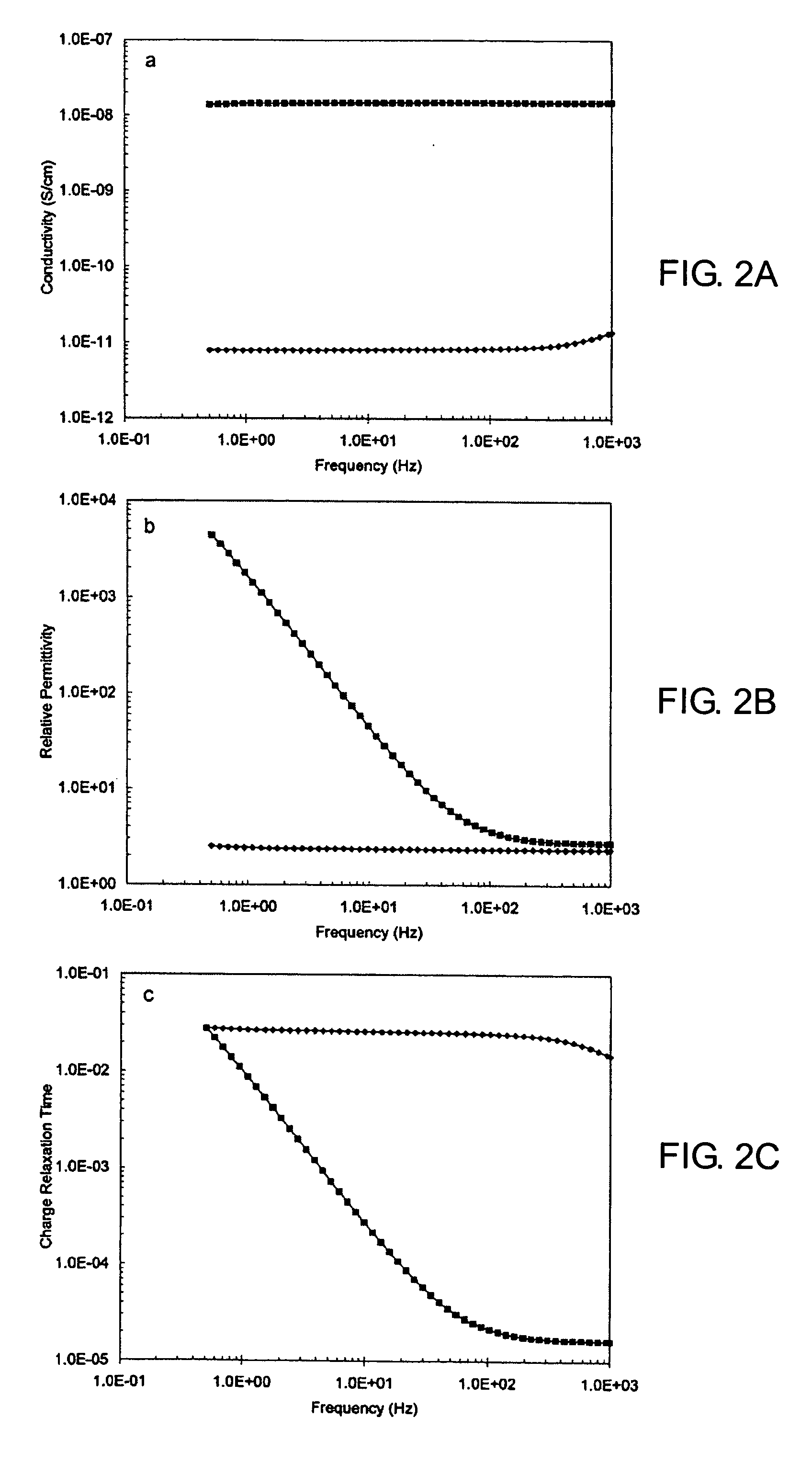
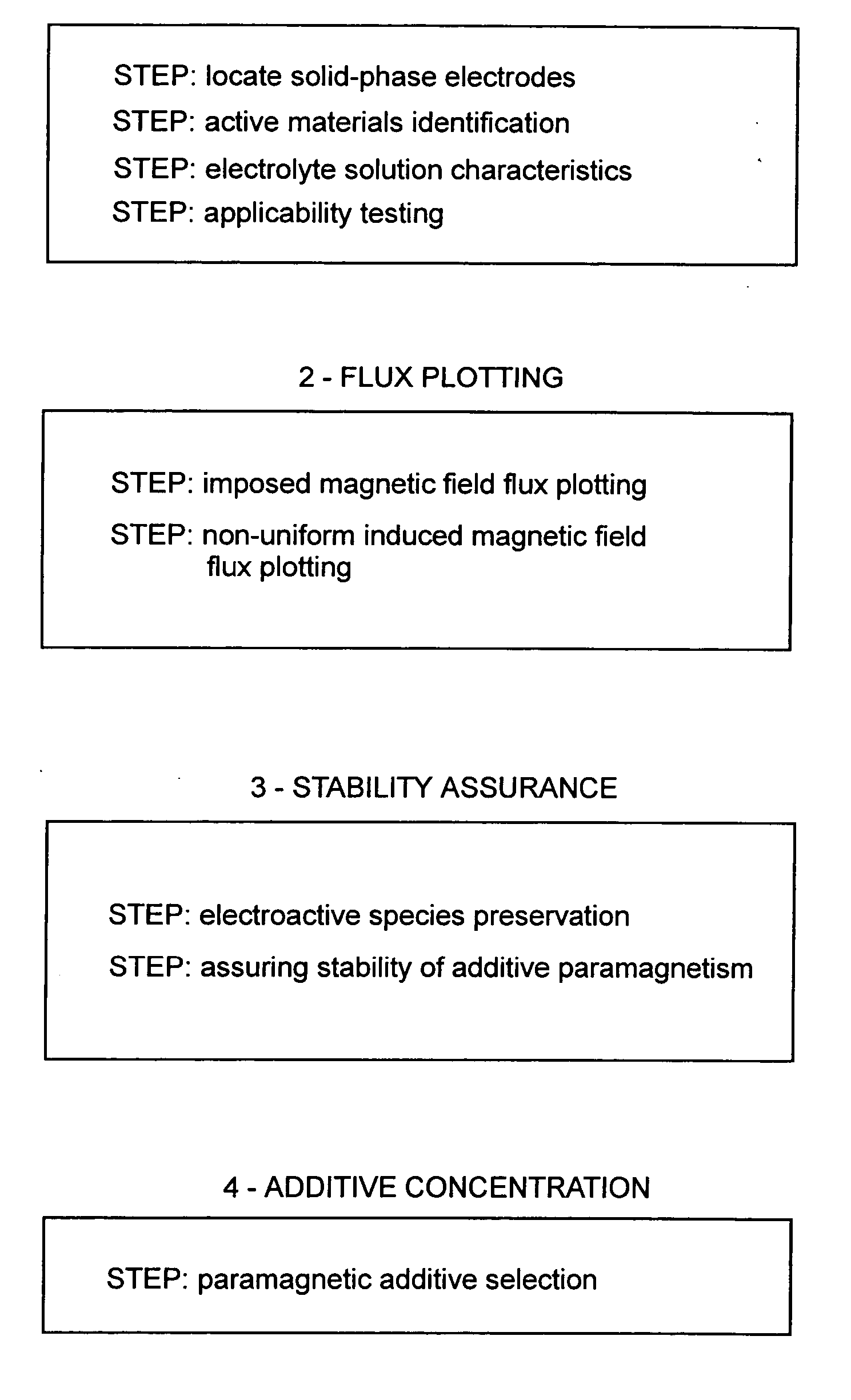
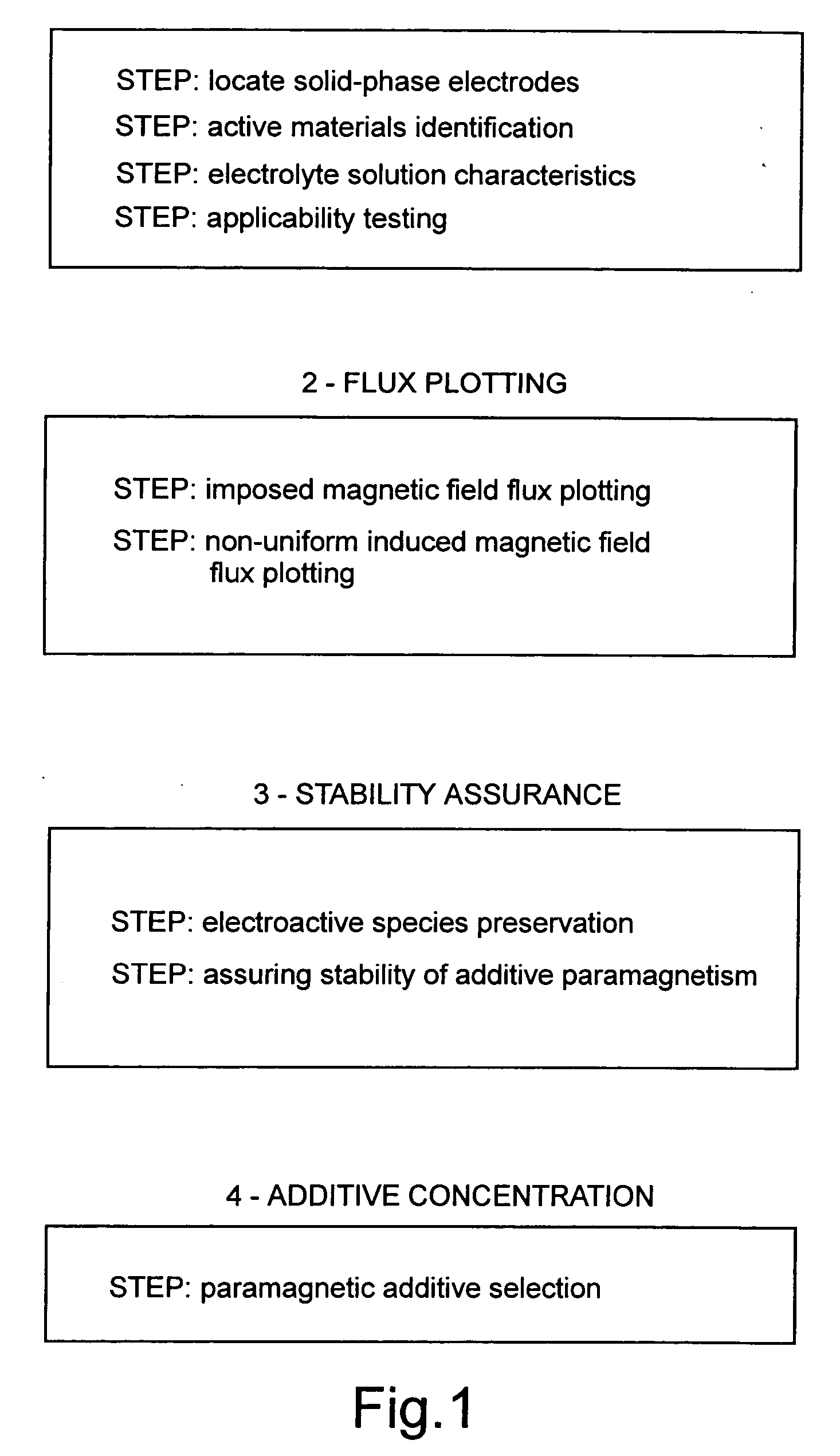
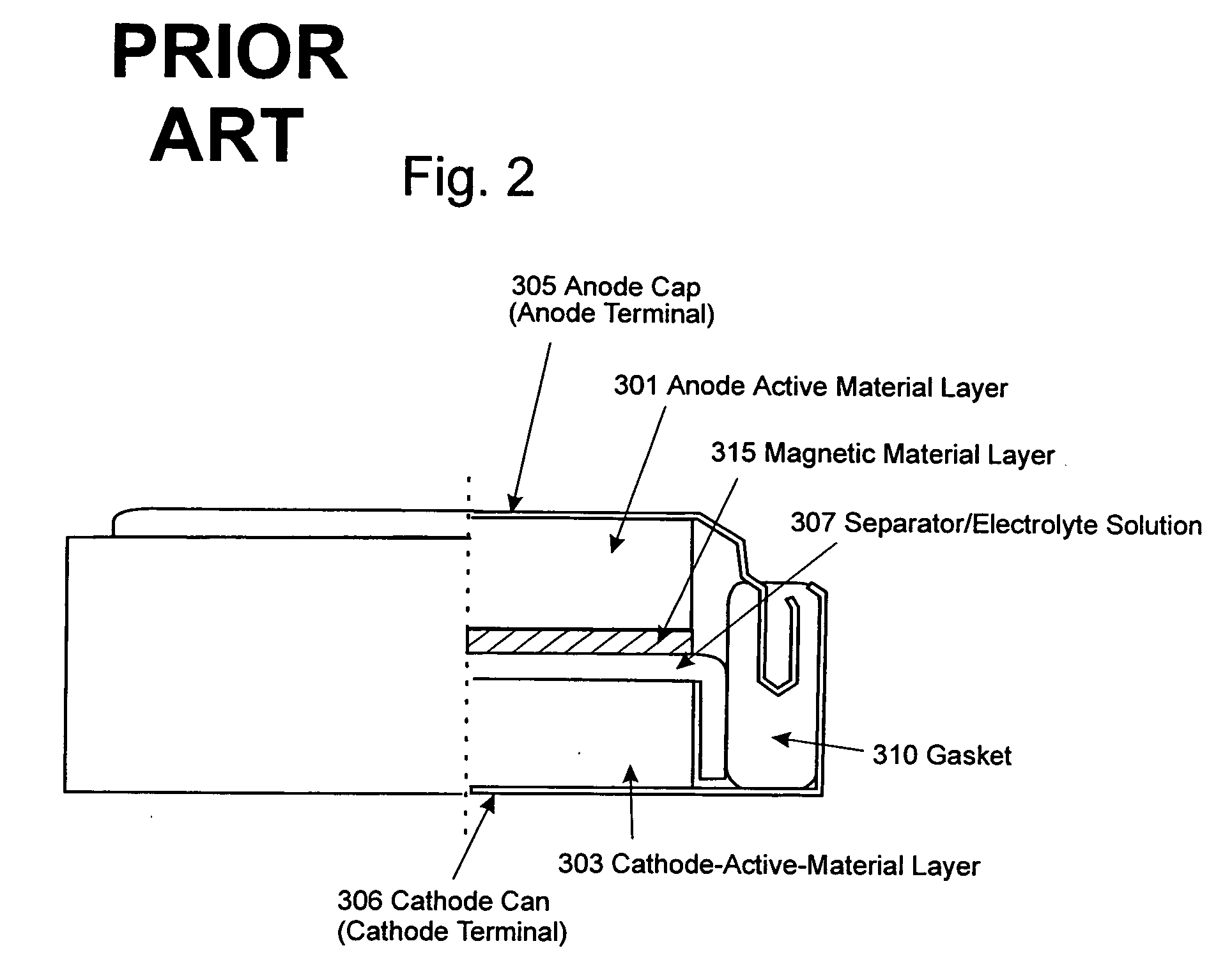
Paramagnetic additive method of optimizing cell electrohydrodynamics
InactiveUS20060180471A1Improve acceleration performanceLow densityAlkaline accumulatorsElectrolysis componentsLanthanideAqueous electrolyte
Magnetoelectrolysis cells known to operate successfully without utilizing a non-electrogenerated paramagnetic additive added to an aqueous electrolyte solution of such a cell may in some instances be further enhanced by utilizing such an additive. However, excessive amounts of additive are impracticable and formerly proposed transition metal salts used as paramagnetic additives were never demonstrated as effective except when used in large amounts. Now it is disclosed that small amounts of a salt of a paramagnetic lanthanide solve the problem, if methodically applied to enhancing the magnetoelectrolysis cell in accordance with the specified steps of the invention.
Owner:OBRIEN ROBERT NEVILLE
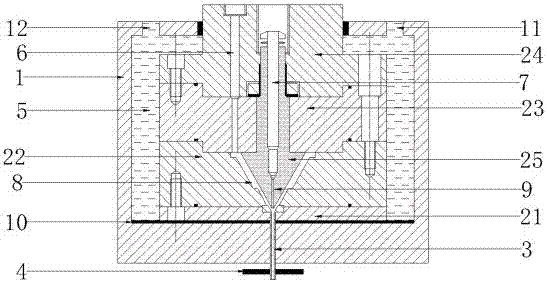
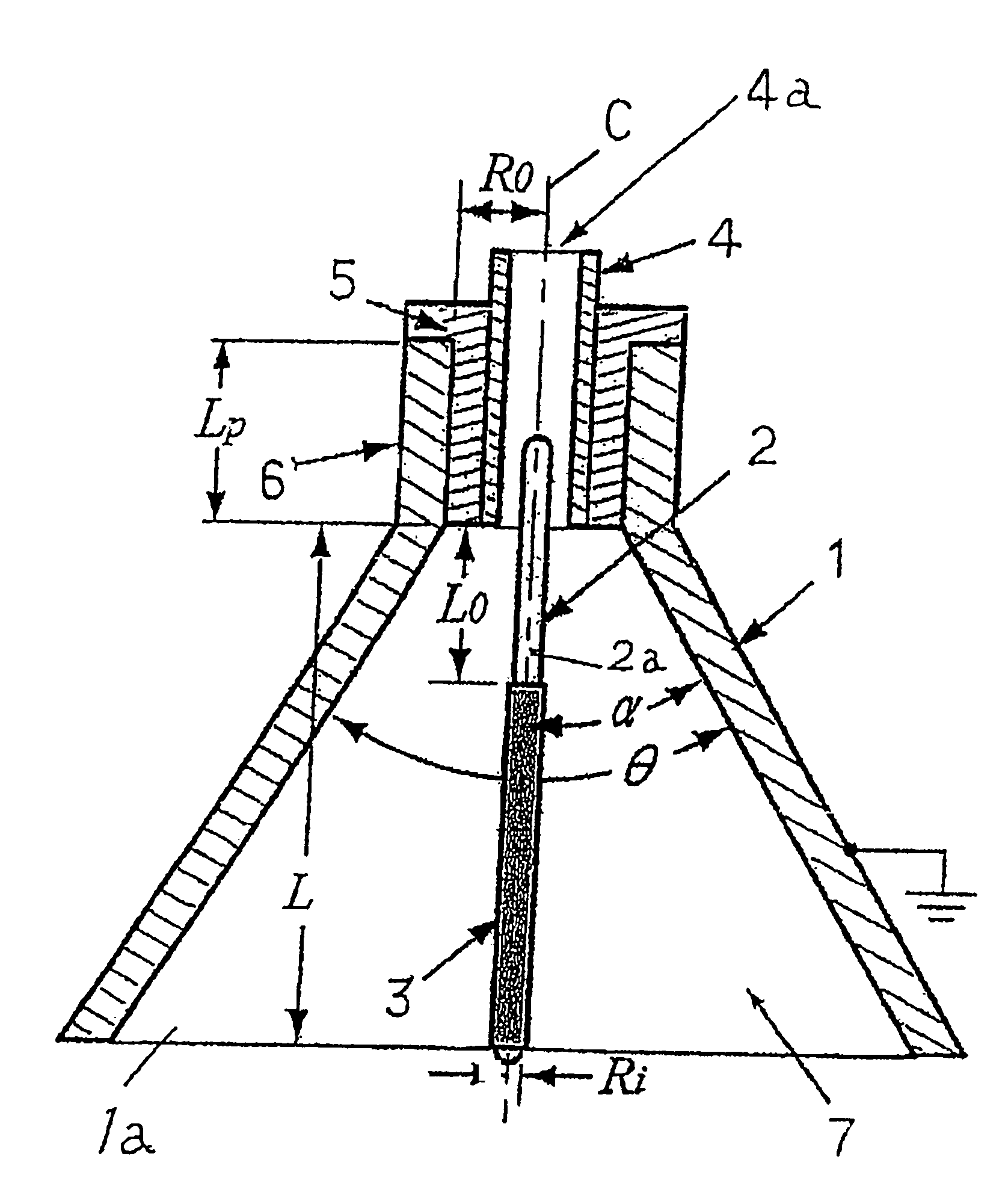
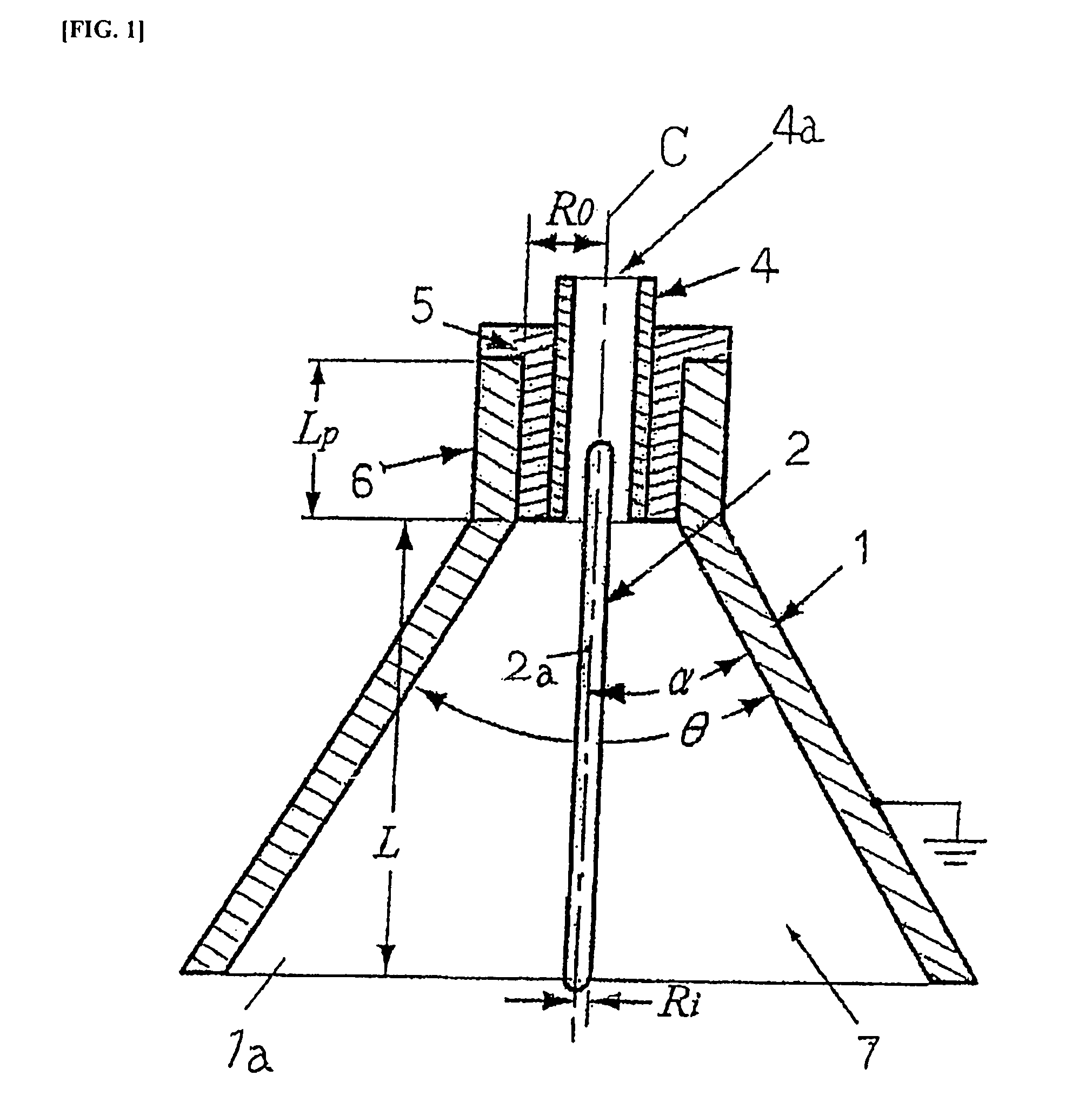
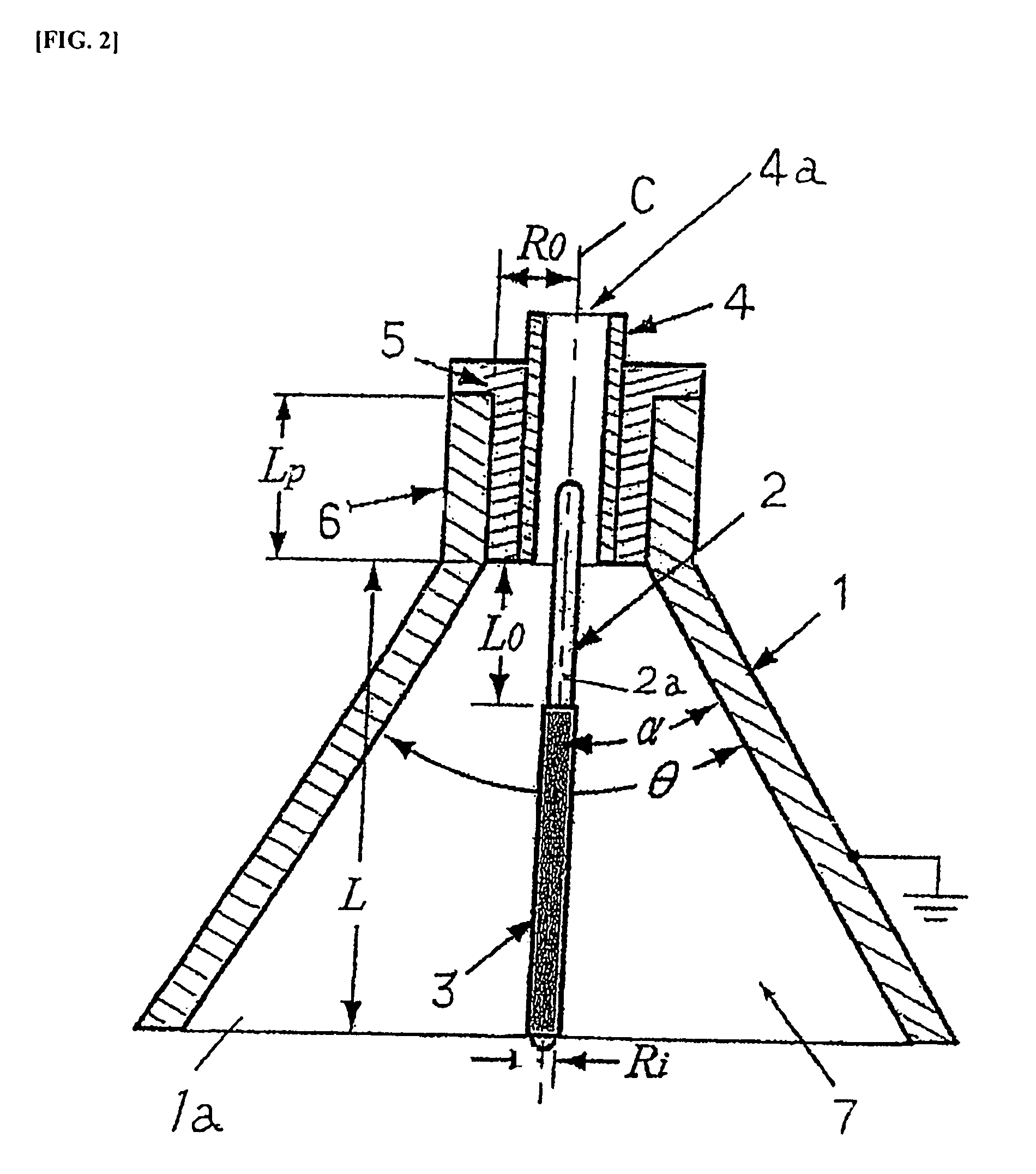
Electrohydrodynamic pump (EHD pump) with electrode arrangement
InactiveUS7914262B2Improve configurationHigh pumping pressureBurnersPump componentsForming faceHigh-voltage direct current
To improve the configuration of electrodes disposed in the fluid channel of EHD pumps, and to reduce of the fluid channel of EHD pumps, as well as to reduce the cost of producing EHD pumps, and to increase the pumping pressure of EHD pumps. A hollow conical metal electrode open at the top end and the bottom end is used facing a rod-shaped metal electrode, and an electrically insulated fluid outflow channel is formed facing the hollow conical metal electrode, with the hollow conical metal electrode and rod-shaped metal electrode sharing a central axis, so that the two electrodes are disposed coaxially, and the rod-shaped metal electrode is disposed from the inner portion of the hollow conical metal electrode to the inner portion of the fluid outflow channel, and a portion of the rod-shaped metal electrode, positioned at the interface of at least the inner portion of the hollow conical metal electrode and the fluid outflow channel, serves as an exposed metal part, with this exposed metal part being caused to face the inner surface of the hollow conical metal electrode, and when an electric field is applied across the hollow conical metal electrode and the rod-shaped metal electrode, there is introduced a fluid wherein are formed dissociated ions, and high voltage direct current is applied across the hollow conical metal electrode and the rod-shaped metal electrode.
Owner:KANAZAWA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com