Patents
Literature
143 results about "Soyauxia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Soyauxia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Peridiscaceae. They are small trees or erect shrubs from wet forests of tropical West Africa. Eight specific names have been published in Soyauxia. Additional species have been discovered, but their names and descriptions will not be published until 2009 or 2010. The type species for the genus is Soyauxia gabonensis.
Herbicidal compositions for tolerant or resistant soybean crops
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Methods for evaluating insect resistance in a plant
Methods are provided for evaluating the insect resistance of a plant of interest. Specifically, methods are provided for high-throughput screening of soybean plants for resistance to kudzu bugs and stink bugs, including the brown marmorated stink bug and the southern green stink bug. In some embodiments, infesting emergent soybean seedlings with second instar stink bug nymphs and maintaining the nymphs in a closed environment with the seedling for only about 7 days allows evaluation of the stink bug resistance of a soybean variety of interest. Also provided are insect resistant plants, particularly plants resistant to kudzu bugs and stink bugs, as well as seeds produced by the resistant plants. Plants disclosed herein can be used to transfer the resistant trait into plant lines of interest.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
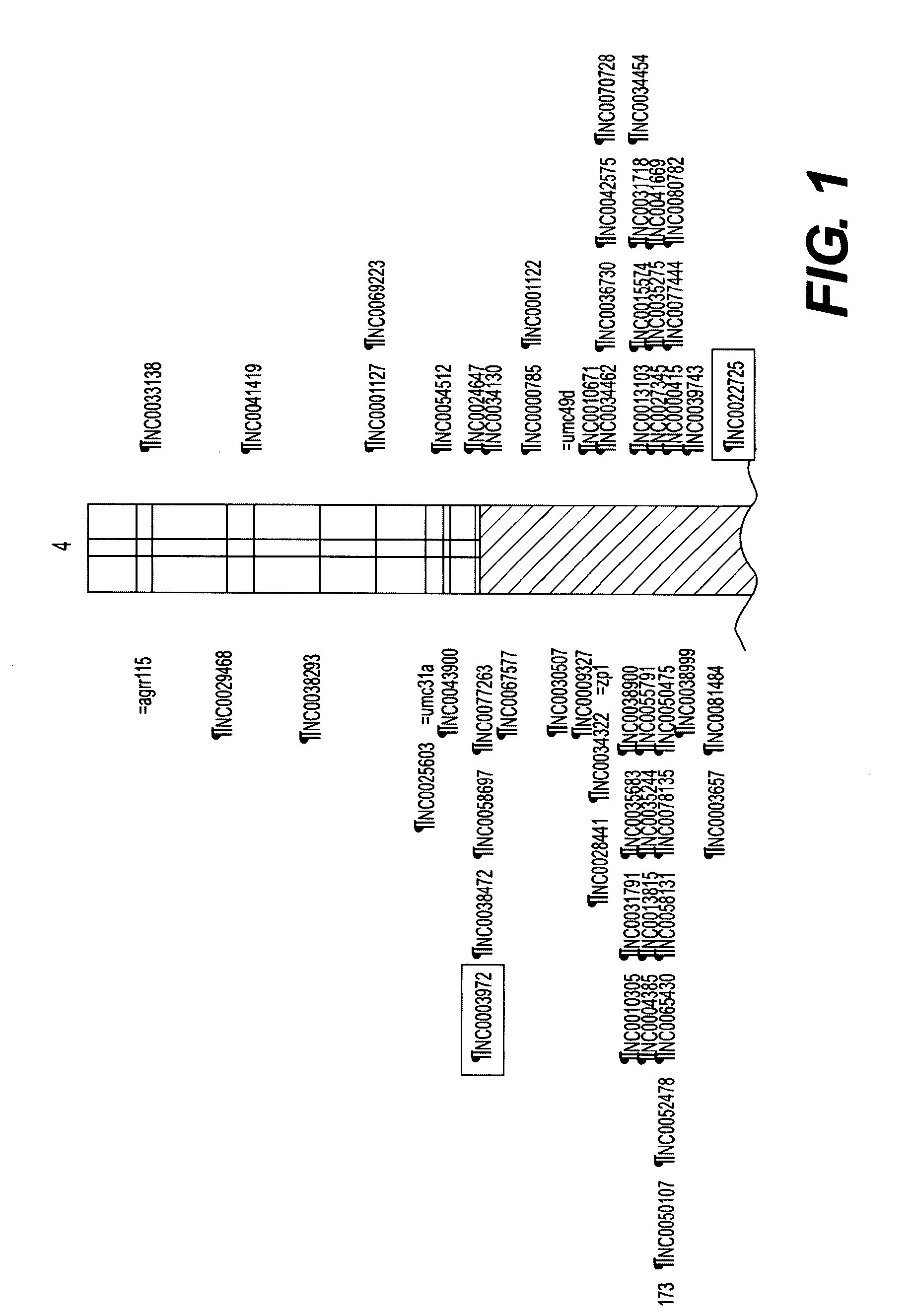
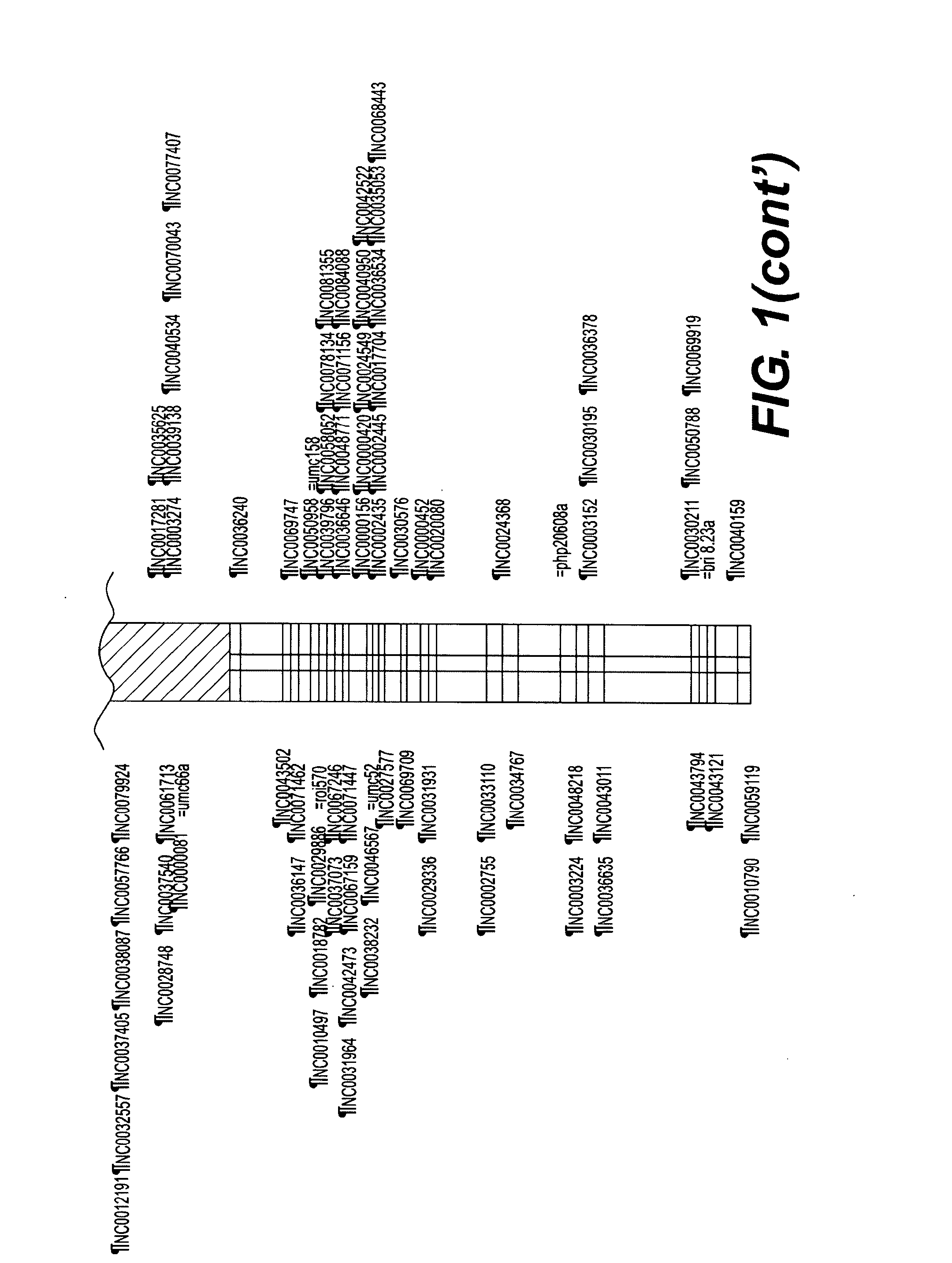
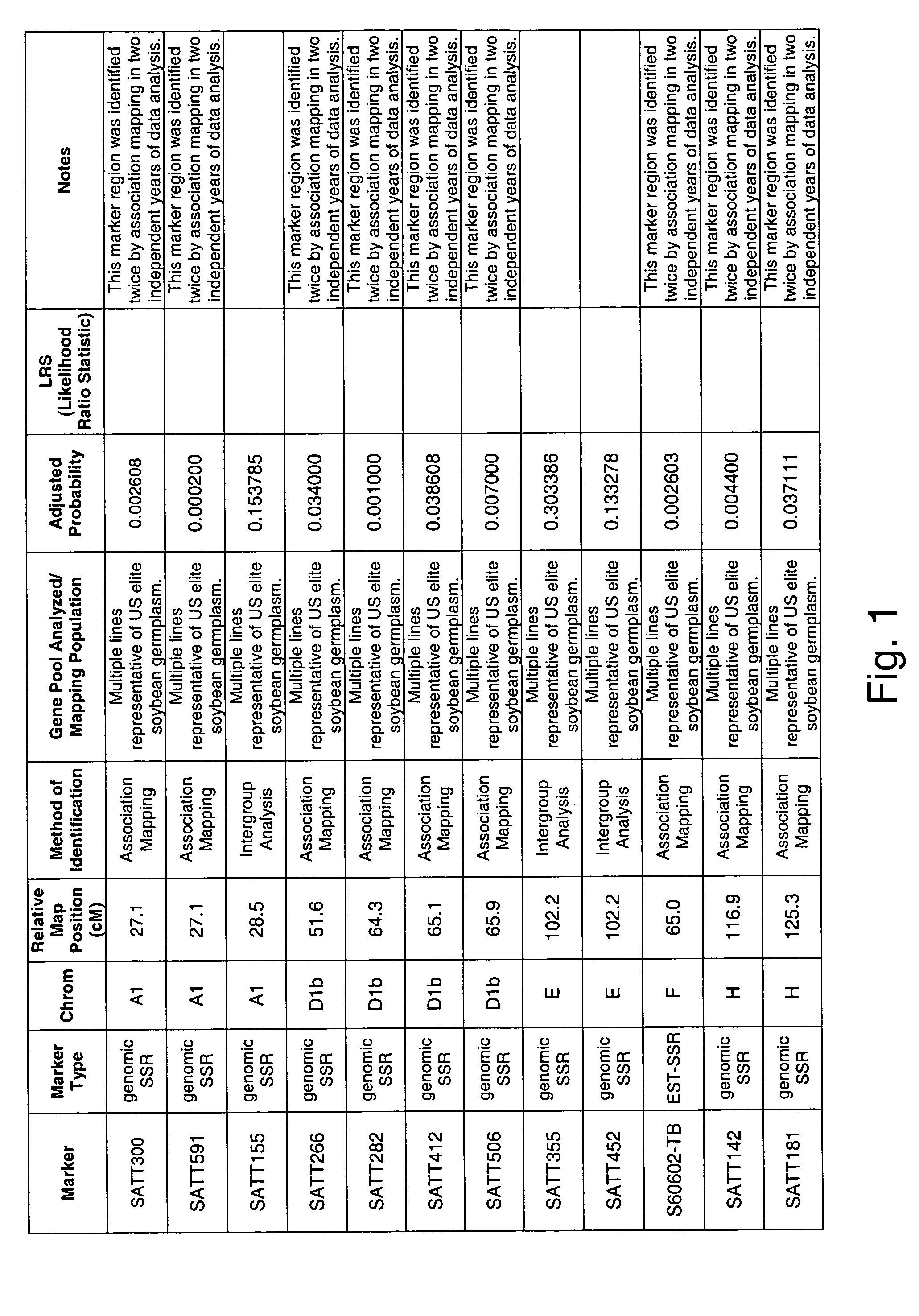
Method to identify disease resistant quantitative trait loci in soybean and compositions thereof
ActiveUS20080166699A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycineQuantitative trait locus
The present invention is in the field of plant breeding and genetics, particularly as it pertains to the genus, Glycine. More specifically, the invention relates to a method for screening soybean plants containing one or more quantitative trait loci for disease resistance, species of Glycine having such loci and methods for breeding for and screening of Glycine with such loci. The invention further relates to the use of exotic germplasm in a breeding program.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from soybean are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:BUEHLER ROBERT E +3
Compositions and Methods of Plant Breeding Using High Density Marker Information
InactiveUS20100293673A1Microbiological testing/measurementKnowledge representationGlycineHigh density
The present invention relates to breeding methods to enhance the germplasm of a plant. The methods describe the identification and accumulation of preferred haplotype genomic regions in the germplasm of breeding populations of maize (Zea mays) and soybean (Glycine max). The invention also relates to maize and soybean plants comprising preferred haplotypes.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
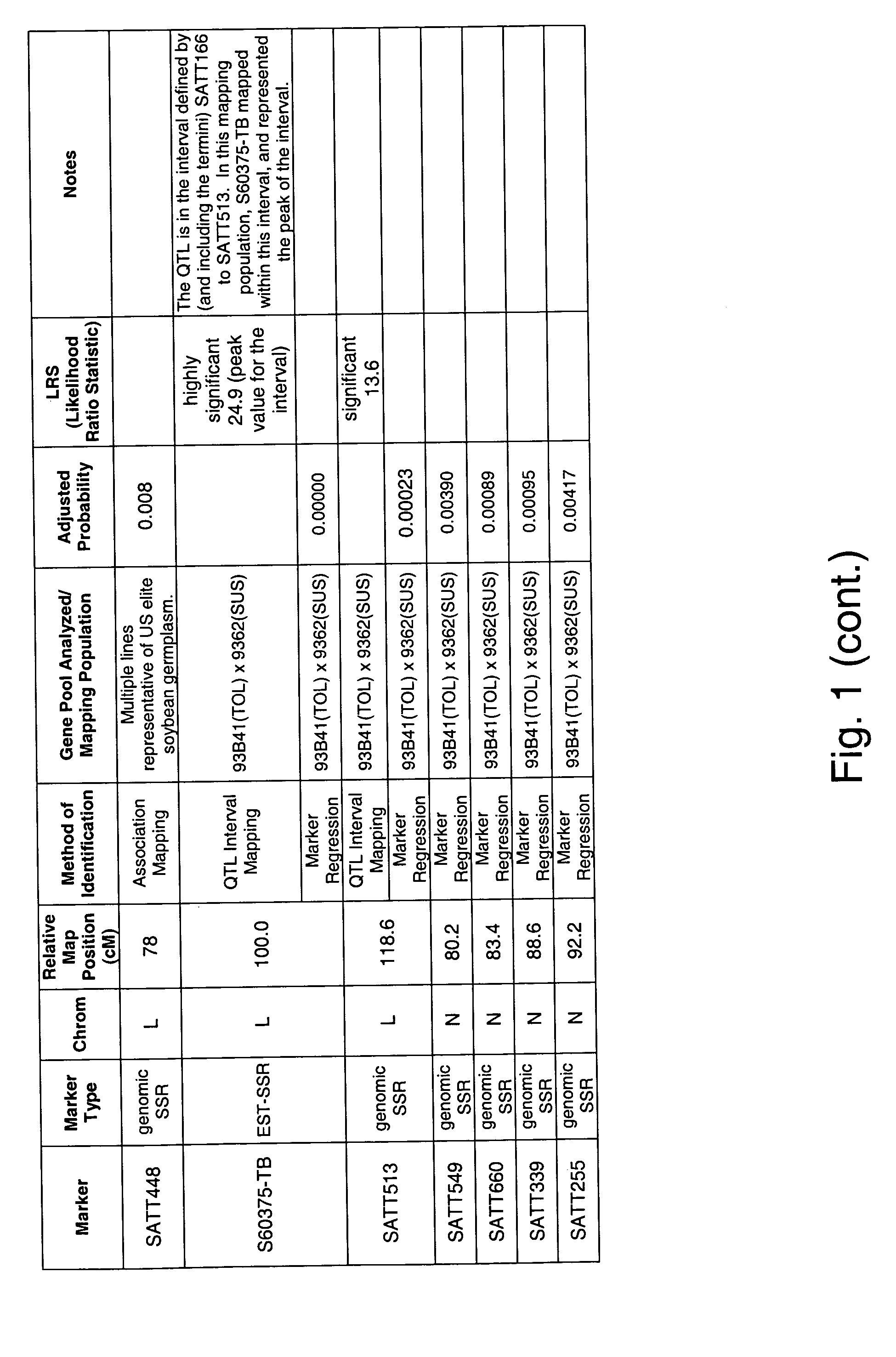
Genetic loci associated with Fusarium solani tolerance in soybean
ActiveUS7767882B2Rapid lossLosses in viabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyFUSARIUM INFECTIONS
The invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying soybean plants that are tolerant, have improved tolerance or are susceptible to Fusarium solani infection (the causative agent of sudden death syndrome or SDS). The methods use molecular genetic markers to identify, select and / or construct disease-tolerant plants or identify and counterselect disease-susceptible plants. Soybean plants that display tolerance or improved tolerance to Fusarium solani infection that are generated by the methods of the invention are also a feature of the invention.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20070283459A1Desirable effectIncrease profitImmunoglobulinsFermentationNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from soybean are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH +2
Method for identifying resistance against heterodera glycines
The invention relates to a method for identifying resistance against heterodera glycines. The method comprises the following steps: scissoring the tissue of young part of the soybean vegetative part of the susceptible control variety and the variety to be identified to perform inductive rooting culture; after the transplanted seedling survives, inoculating the seedling with heterodera glycines suspension containing 400 eggs and / or second-stage larvae / mL; continuing culture at 20-30 DEG C; when white cyst appears at the seedling root, separating counting the number of root cyst of the susceptible control variety and the variety to be identified; and defining the disease resistance of the material according to the resistance grading standard. The method provided by the invention has the positive and beneficial effects that: as the genotype is not changed when the vegetative body roots, the resistance of the vegetative body can represent the resistance of the parent material; one part of the vegetative body of the material to be identified replaces the entire plant for identification, and the resistive material can be completely stored; and for the population of segregative generation (for example, F2), 3-5 branches on one individual plant can be fetched for identification so as to realize repeated identification of the segregation population.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Protein related to flowering time of plant, and coding gene and application thereof
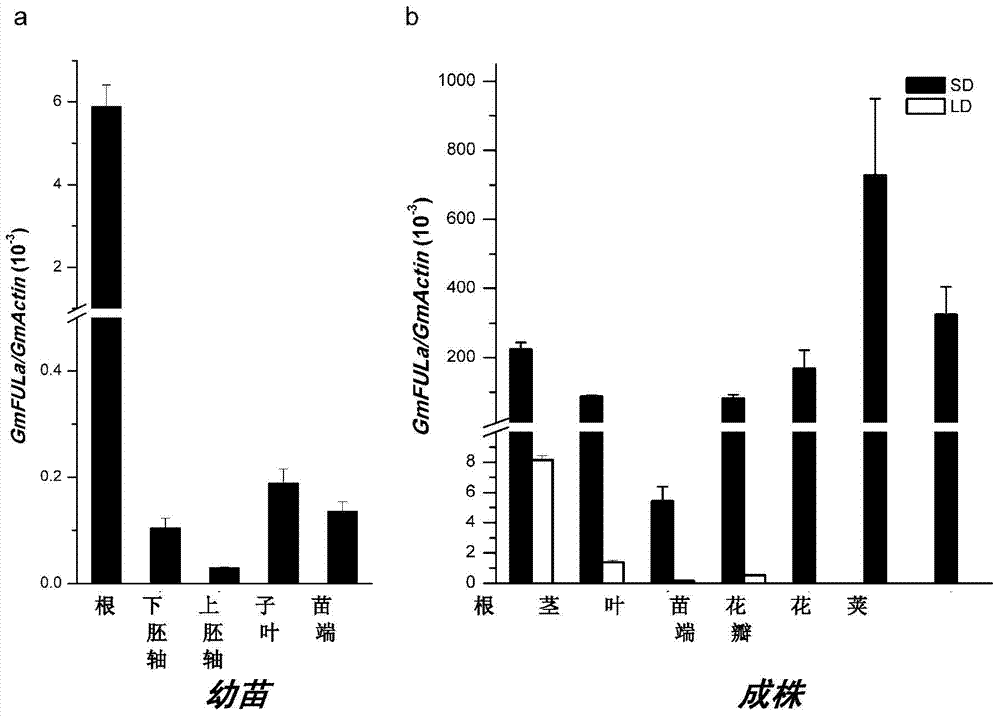
The invention discloses a protein related to flowering time of a plant, and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is protein 1) or 2), wherein 1) is a protein composed of an amino acid sequence as shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table, and 2) is a protein related to the flowering time of the plants and derived from the sequence 2 through substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table. Experimental results of the invention prove that a gene GmFULa is found in soybean and overexpressed in arabidopsis so as to obtain a, and the flowering time of the transgenic plant is earlier than the flowering time of a non-transgenic wild plant; thus, it is observed that the gene or the protein expressed by the gene plays a role in promoting earlier flowering of plants.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for identifying soybean cytoplasmic male sterile line seed purity through molecular marker
InactiveCN103160599ANovel extraction methodQuick extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenomic DNA
The invention provides a method for identifying soybean RN type cytoplasmic male sterile line seed purity through a molecular marker. The method comprises the steps of: extracting genomic DNA of an RN type cytoplasmic male sterile line seed; carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by taking the genomic DNA as a template and utilizing a primer InDel-cms1, and carrying out gel electrophoresis analysis on an amplification product, wherein the length of a sterile line fragment after amplification is 200bp, and the length of a maintainer line fragment after amplification is 212bp; and accurately distinguishing the sterile line and the maintainer line through the length difference of the fragments, wherein the seed with the amplified fragment different from the amplified sterile line fragment is a false sterile line seed, and the percentage of the number of sterile line fragments with specific length obtained by detection accounting for all the detected seeds is the purity of RN type cytoplasmic male sterile line seeds. The method can be used for rapidly, accurately and reliably identifying the maintainer line mixed in the RN type soybean cytoplasmic male sterile line by a molecular biology experiment means so as to ensure the purity of sterile line seeds.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Herbicide compound containing flumioxazin and acetochlor
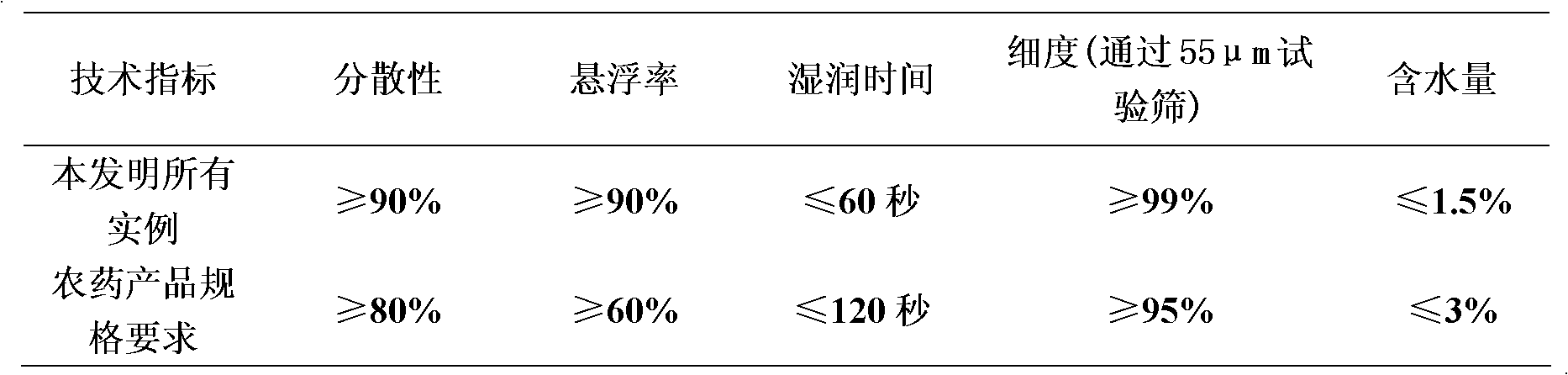
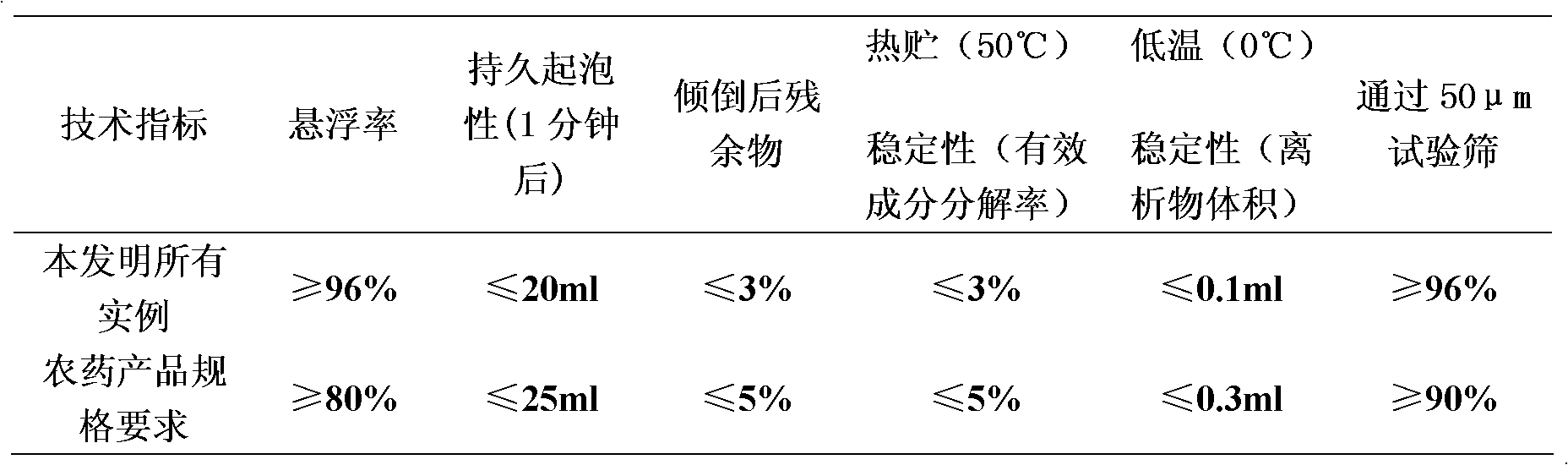
InactiveCN102428936AIncrease productionExpand the spectrum of weed controlBiocideAnimal repellantsAdjuvantWater dispersible
The invention relates to a herbicide compound containing flumioxazin and acetochlor. The herbicide compound is mainly characterized in that the herbicide compound contains 0.1 to 60 percent of flumioxazin, 0.1 to 80 percent of acetochlor and the balance of adjuvant, and is prepared into wettable powder, water-dispersible granules, oil-based suspoemulsion, suspoemulsion, emulsion in water and microemulsion. The herbicide compound is used for controlling weeds in soybean and peanut fields, and is characterized in that: the dosage of the pesticide is reduced, the residue of the pesticide is decreased, and the herbicide compound is highly compatible with the environment, and is safe for the human being and livestock.
Owner:SHAANXI MEIBANG PHARMA GRP CO LTD
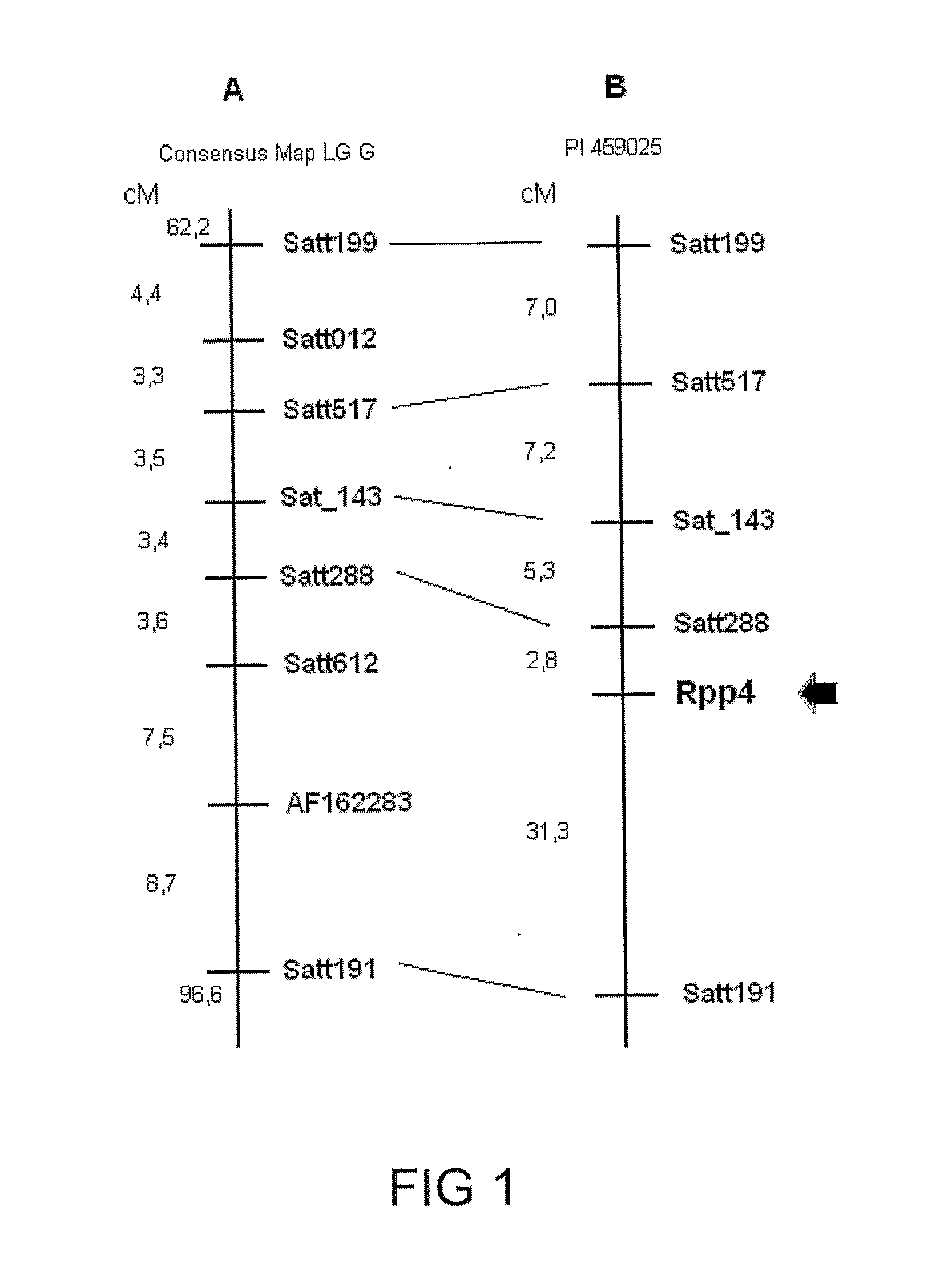
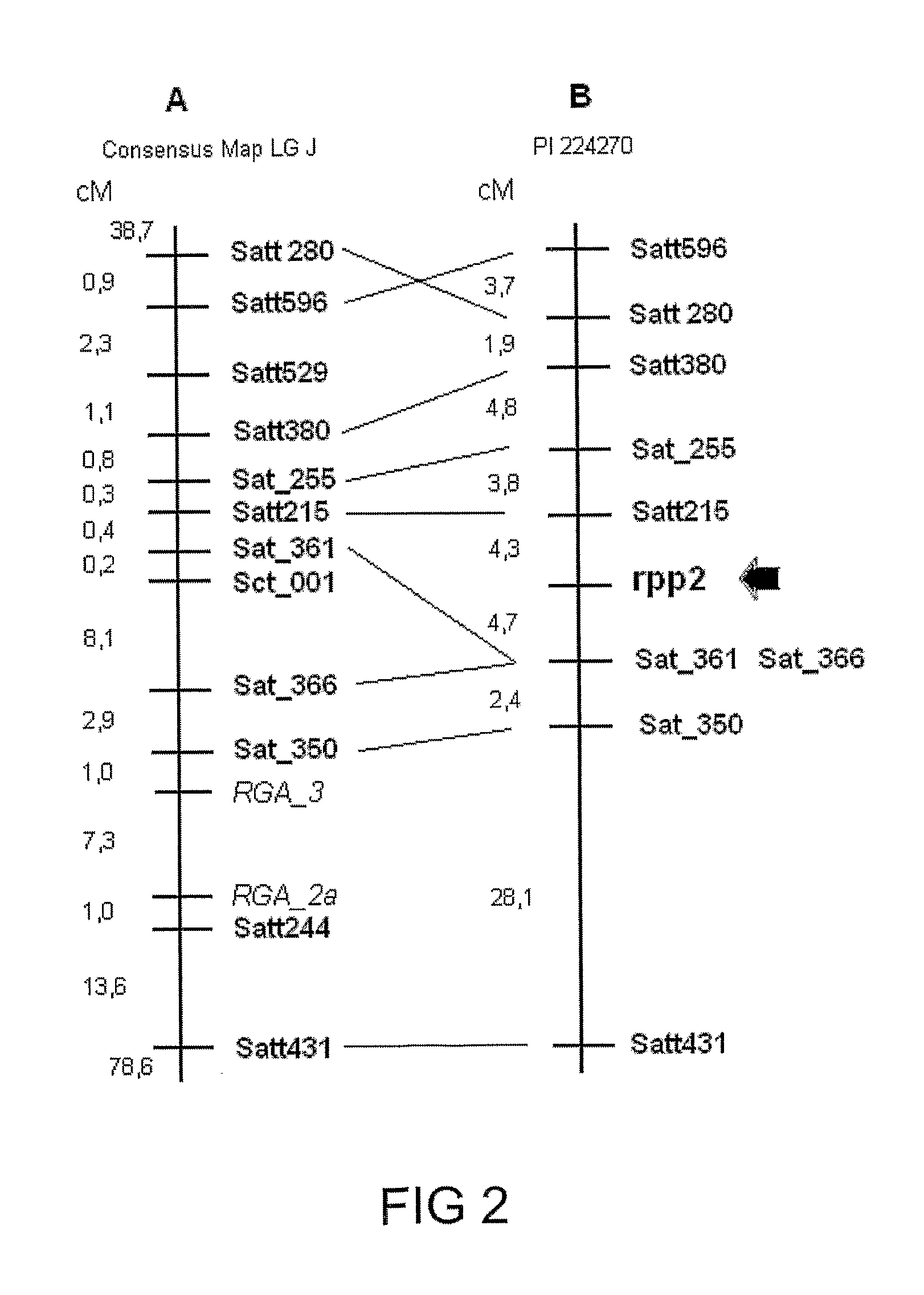
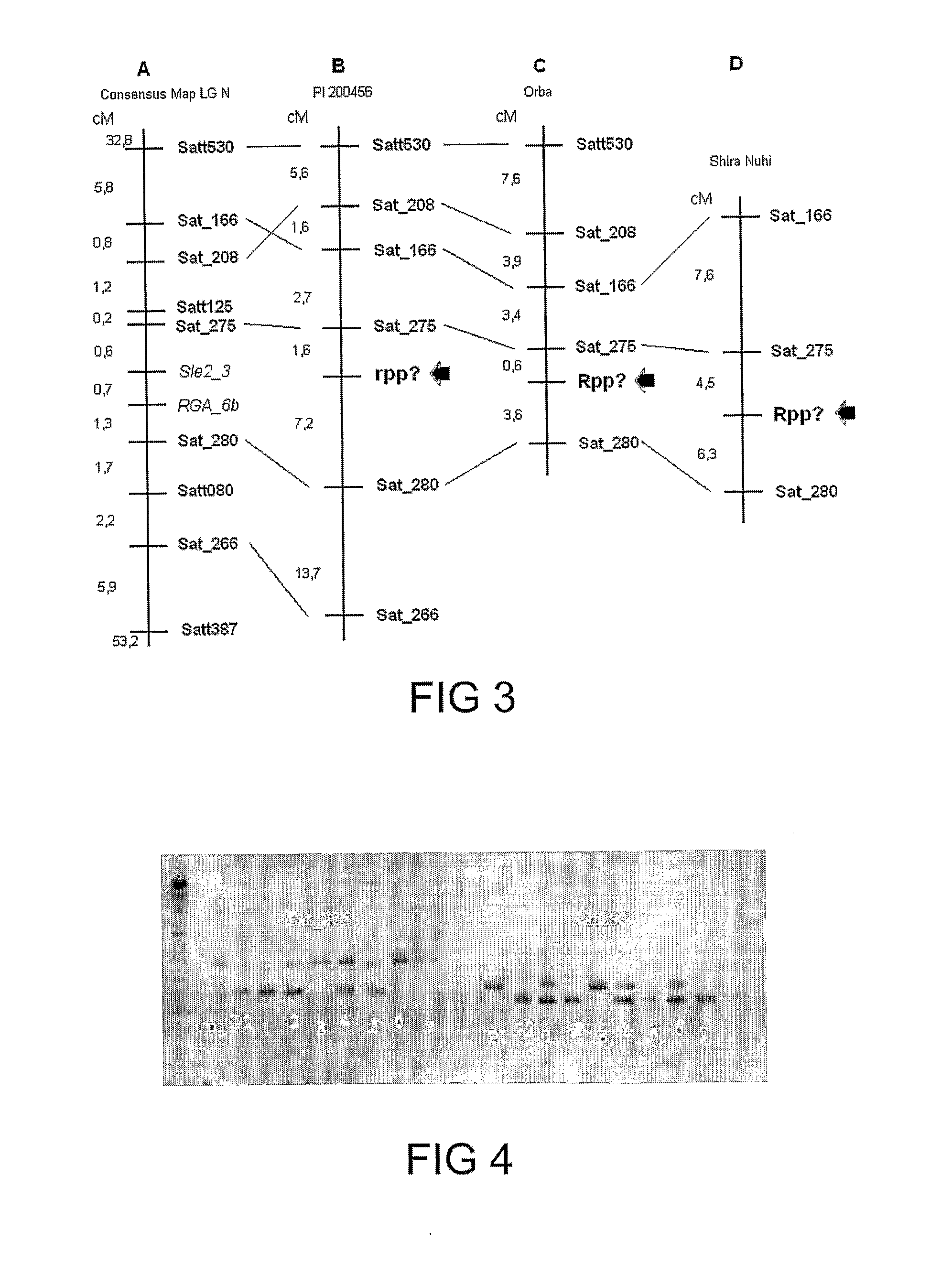
Genotypes, alleles and molecular markers associated with asian soybean rust, as well as methods, processes and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110191893A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyPlant population
The present invention relates to screening methods for rust resistance or tolerance, in particular, Asian soybean rust (ASR—Phakopsora pachyrhizi). In addition, the present invention relates to the use of molecular markers for the Glycine genus, in particular, for the Glycine max species. The present invention further relates to a method for identifying loci with quantitative and / or qualitative traits associated with rust resistance or tolerance in plants by means of molecular markers. Said markers can be used for assisted screening in improvement programs directed to selecting disease-resistant or -tolerant plants. The present invention also relates to gene pyramiding related to rust resistance. The markers of the present invention are also useful for the positional cloning of rust-resistant or -tolerant genes. Also disclosed are a method for obtaining disease-resistant or—tolerant cultivars, process for obtaining a plant population and a method for controlling diseases in a plant population. Another object of the present invention is the use of species from the Glycine genus as a source of resistance for obtaining ASR-resistant or tolerant cultivars.
Owner:TMG TROPICAL MELHORAMENTO E GENETICA LTDA
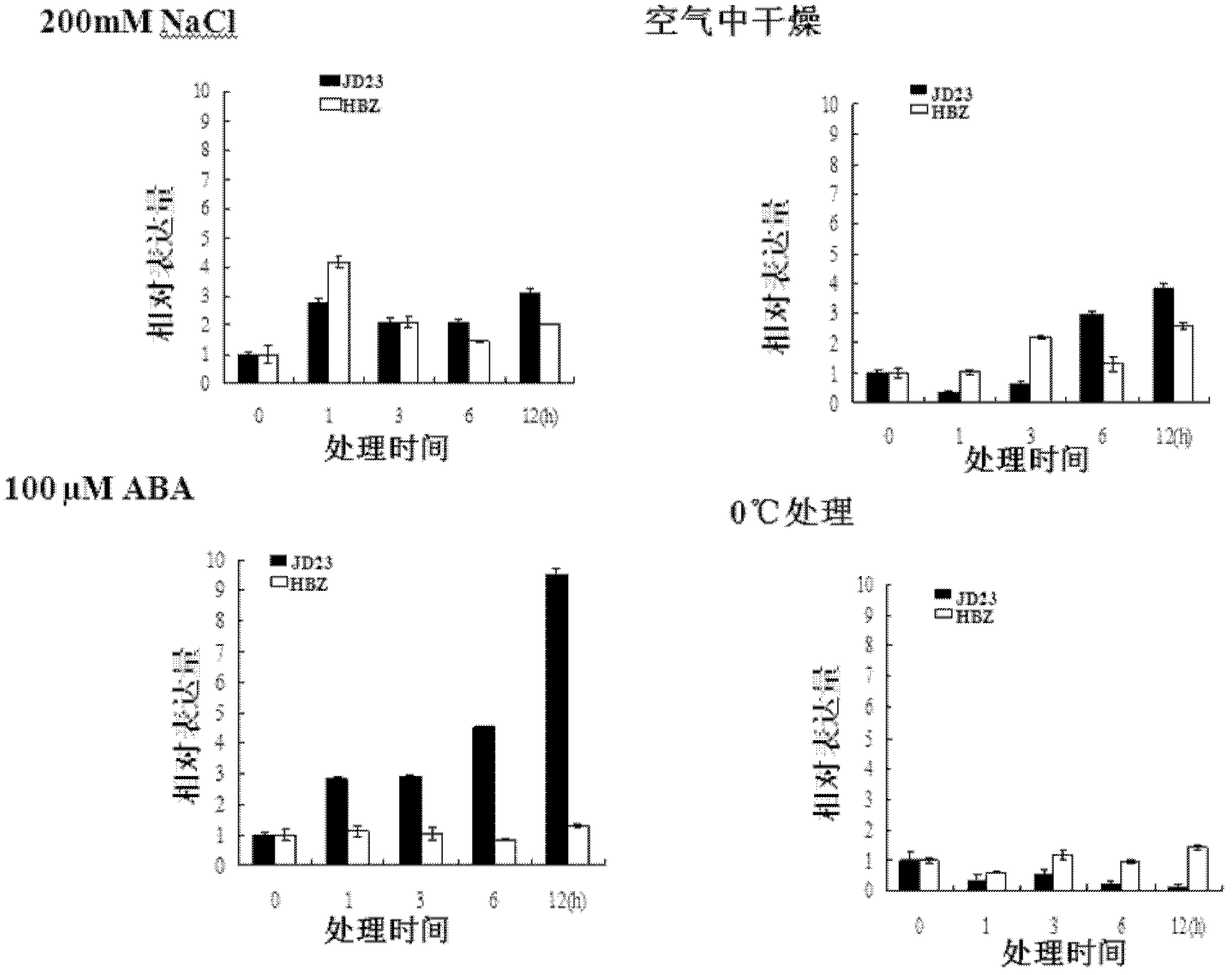
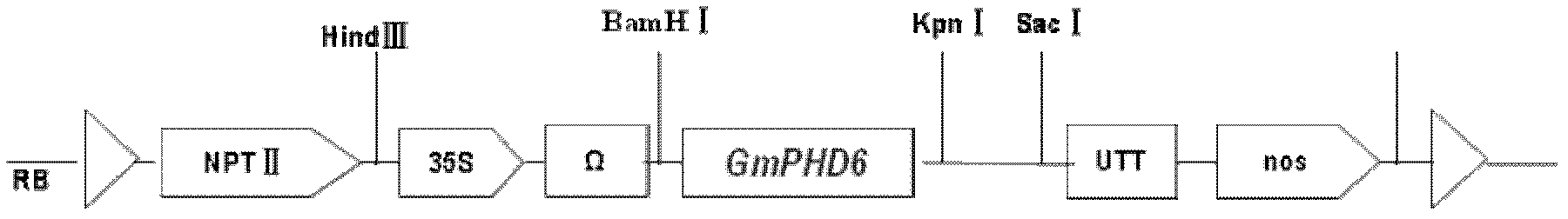
Soybean transcription active protein GmPHD6, and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a soybean transcription active protein GmPHD6, and a coding gene and application thereof. The soybean PHD transcription factor is: (a) a protein composed of an amino acid sequence shown as Sequence 2 in a sequence table; or (b) a protein which is derived from the Sequence 2, is formed by the amino acid sequence shown as the Sequence 2 in the sequence table through the substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or some amino acid residues and is related to stress tolerance of plants. Experiments of the invention prove that the soybean PHD transcription factor GmPHD6 and the coding gene thereof can be used for the cultivation of stress-tolerant plant species, especially stress-tolerant soybean species such as salt-tolerant and drought-tolerant soybeans.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
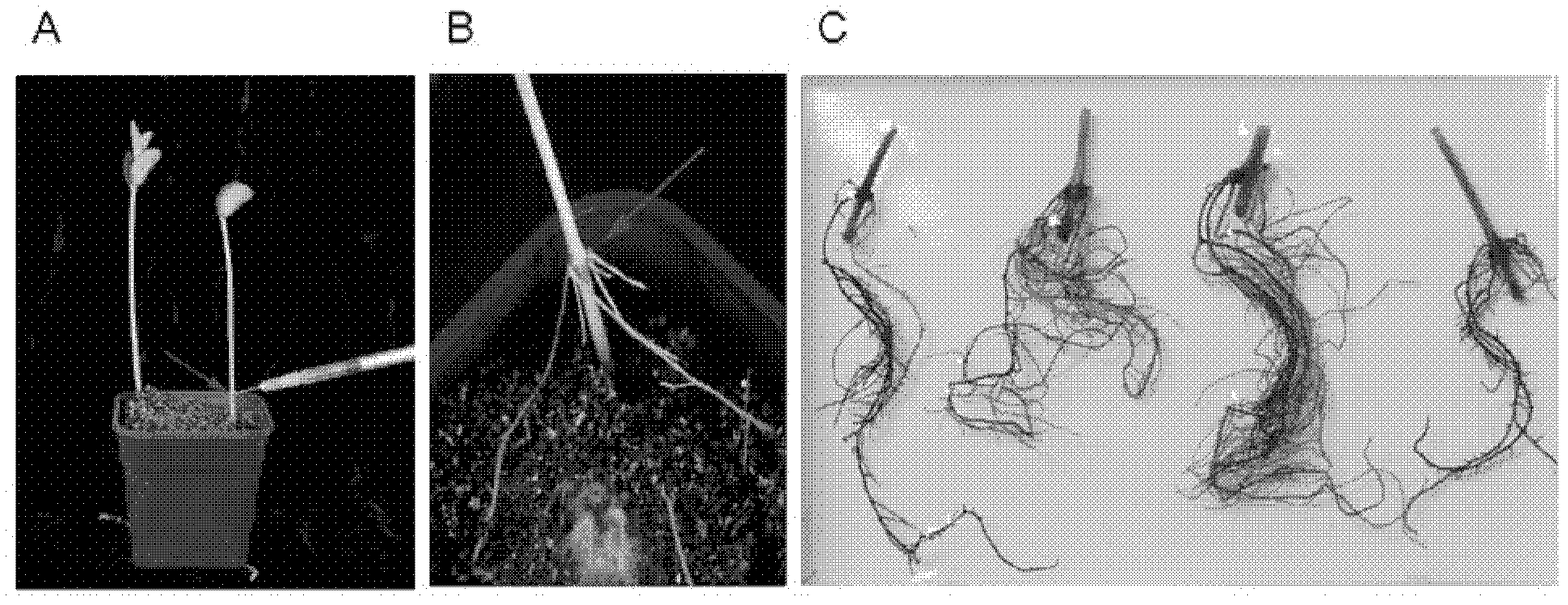
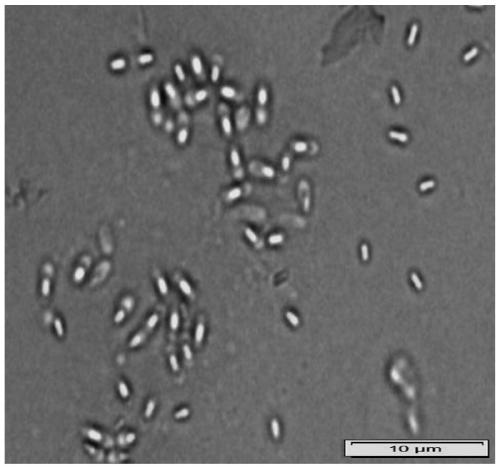
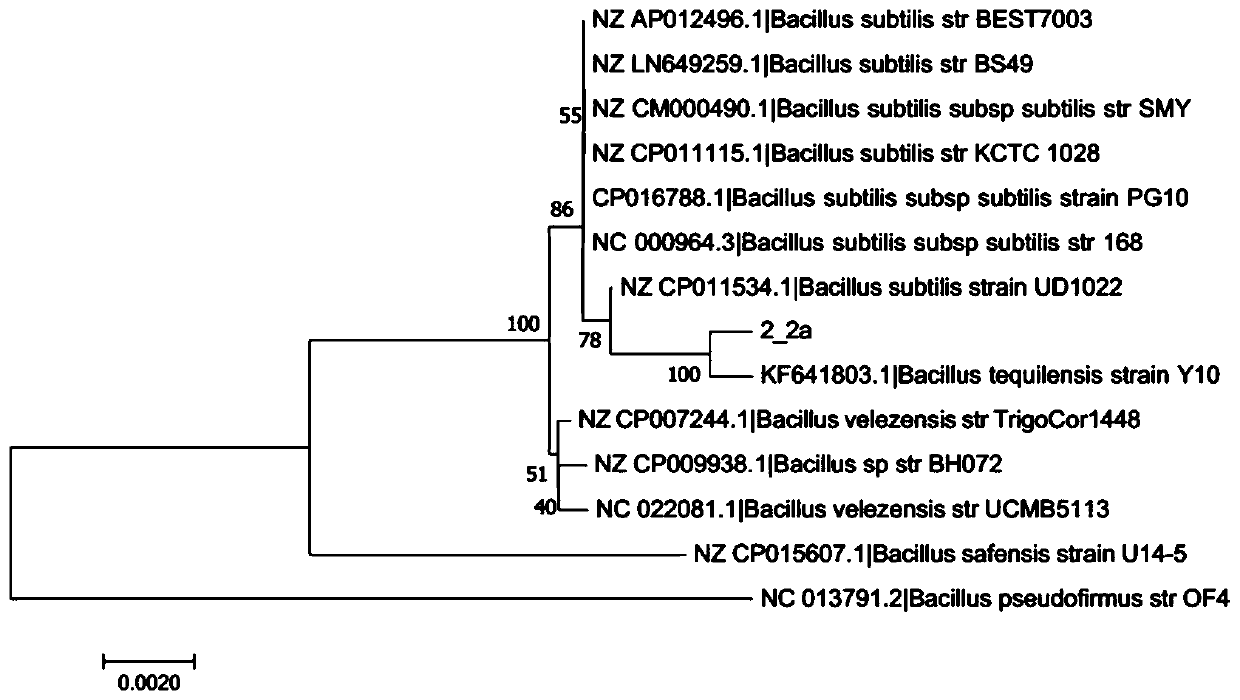
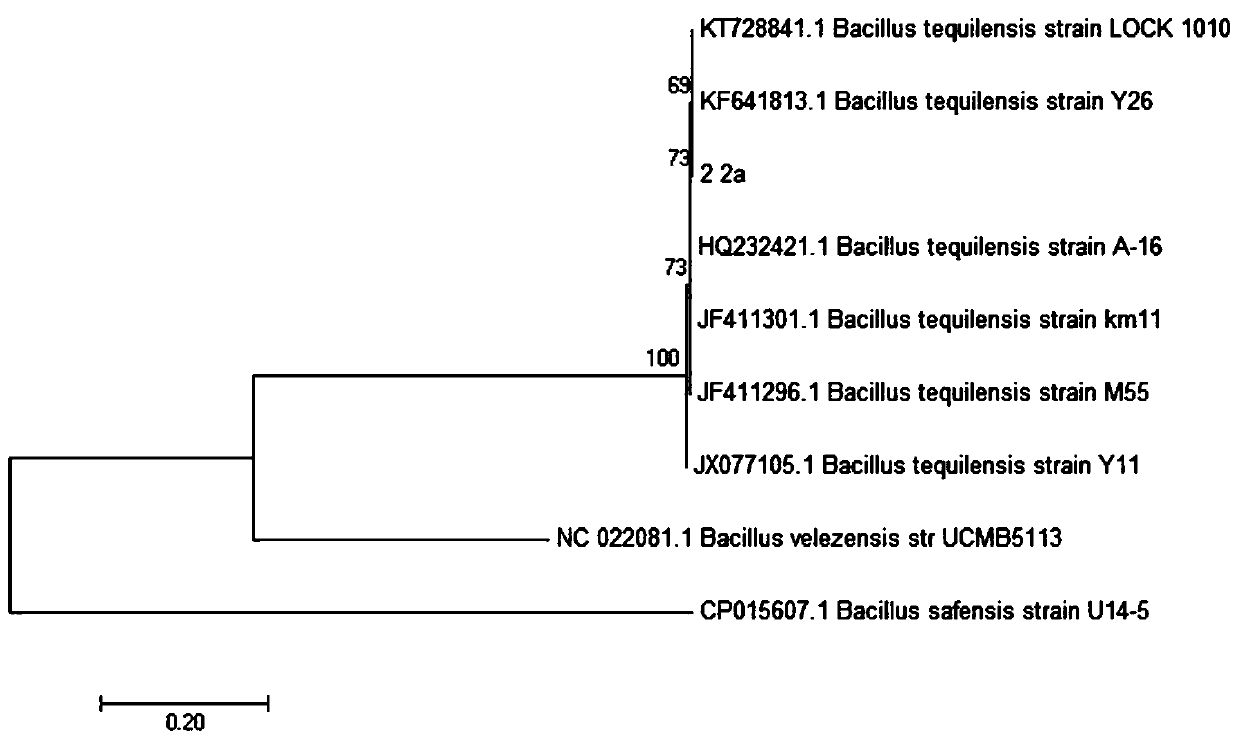
Bacillus tequilensis and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to bacillus tequilensis and application thereof. The bacillus tequilensis 2_2a provided by the invention is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 19446. The bacillus tequilensis 2_2a is capable of being quickly and stably colonized in soybean plants, high in propagation speed and strong in multiplication capacity, has a high-efficiency and broad-spectrum plant pathogen resistance, and has a combined treatment effect on plant diseases of overground parts such as anthracnose, leaf spot disease, black spot disease, gray spot disease, etc. and underground soil-borne diseases such as root rot disease, wilt disease, stem rot disease, blight disease, etc., with a high prevention effect and a good application prospect in prevention and control of plant diseases, thus laying a foundation for developing high-efficiency and broad-spectrumbiocontrol agents.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
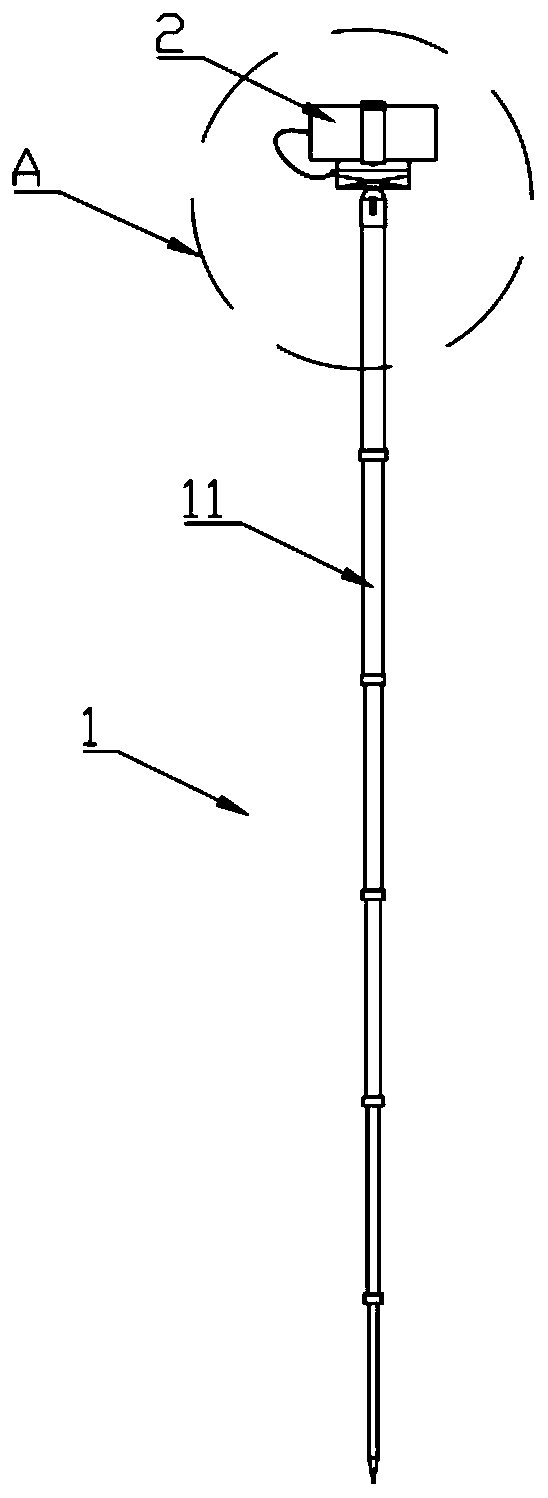
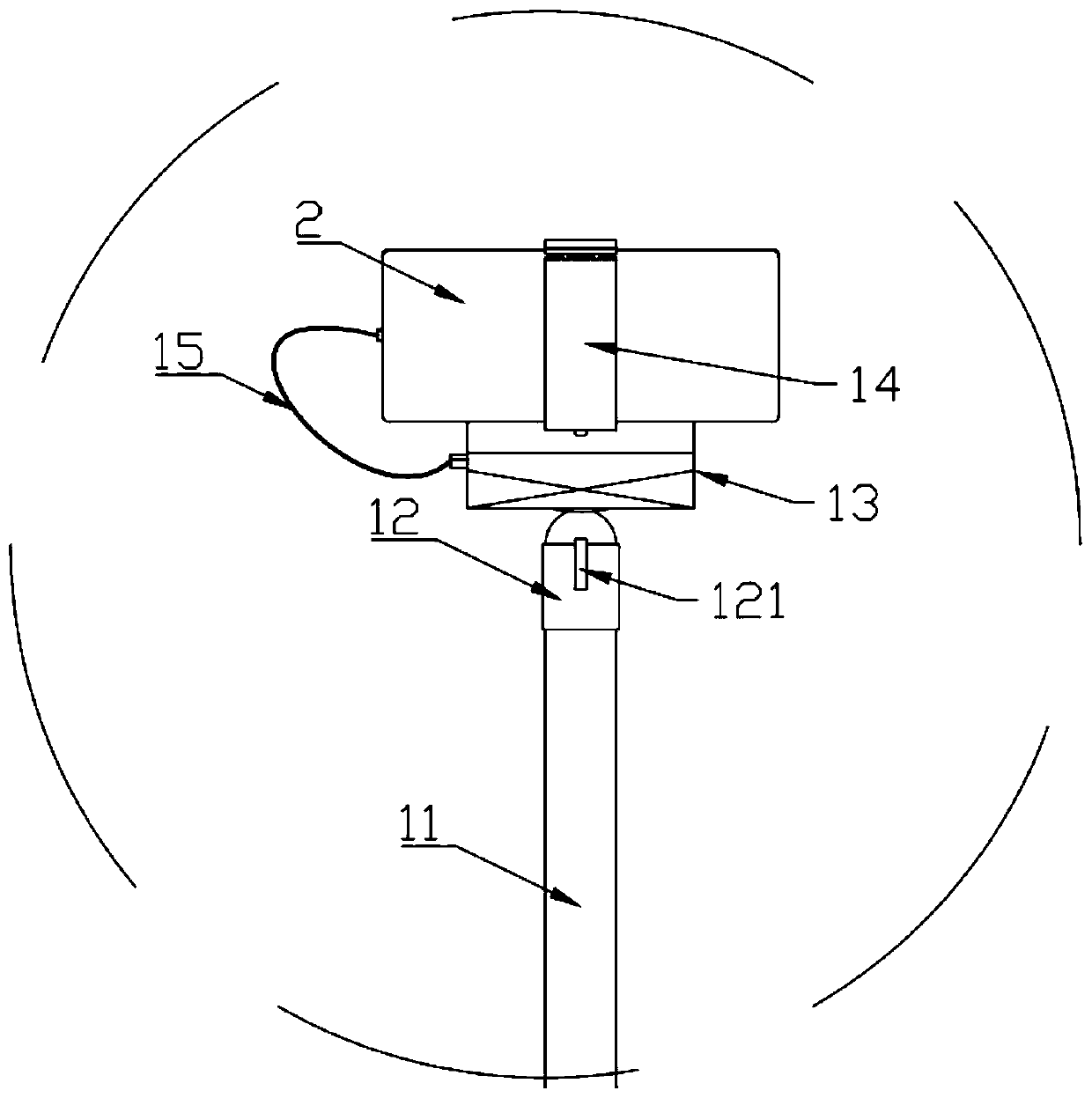
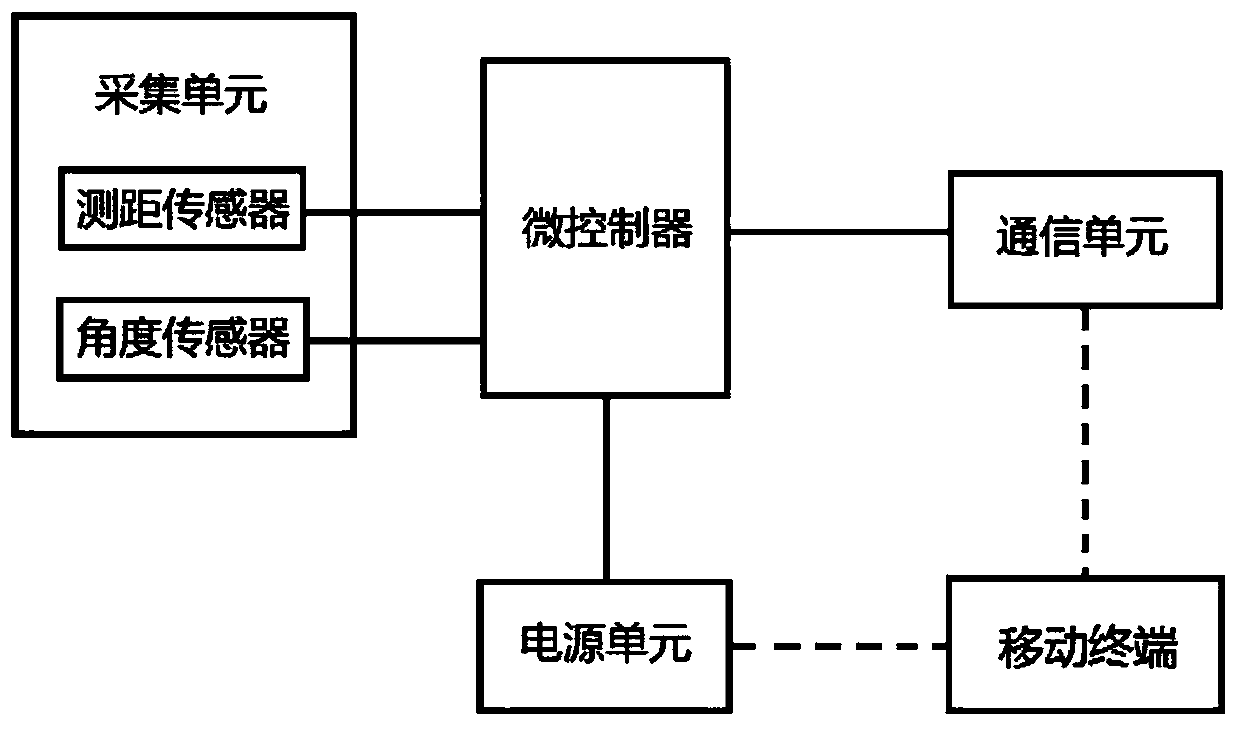
Portable long-distance plant size measuring instrument and measuring method thereof
PendingCN110749286AEasy to measureReduce workloadUsing optical meansAgricultural engineeringPlantlet
The present invention provides a portable long-distance plant size measuring instrument and the measuring method thereof which are used for acquiring phenotypic data of soybean plants in a field at any time and can also be used for acquiring phenotypic data of other outdoor plant images. The measuring instrument provided by the invention is a portable long-distance plant size measuring instrument,and comprises a measuring device and a mobile terminal. The mobile terminal is fixedly connected to the measuring device, and can be used for shooting plants. The mobile terminal receives measuring data sent by the measuring device, wherein the measuring data comprises parameters including the height from the mobile terminal to the ground during photographing of the mobile terminal, the distancebetween the mobile terminal and the highest point of the plants, an inclination angle during photographing of the mobile terminal and the like, various data and corresponding plant photos are bound, and the bound data is transmitted in a cloud server, the pictures are processed according to the data by adopting an artificial intelligence algorithm to obtain plant phenotypic data, namely the actualheight of a plant, and finally, the plant phenotypic data is stored into a plant phenotypic database.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S +1
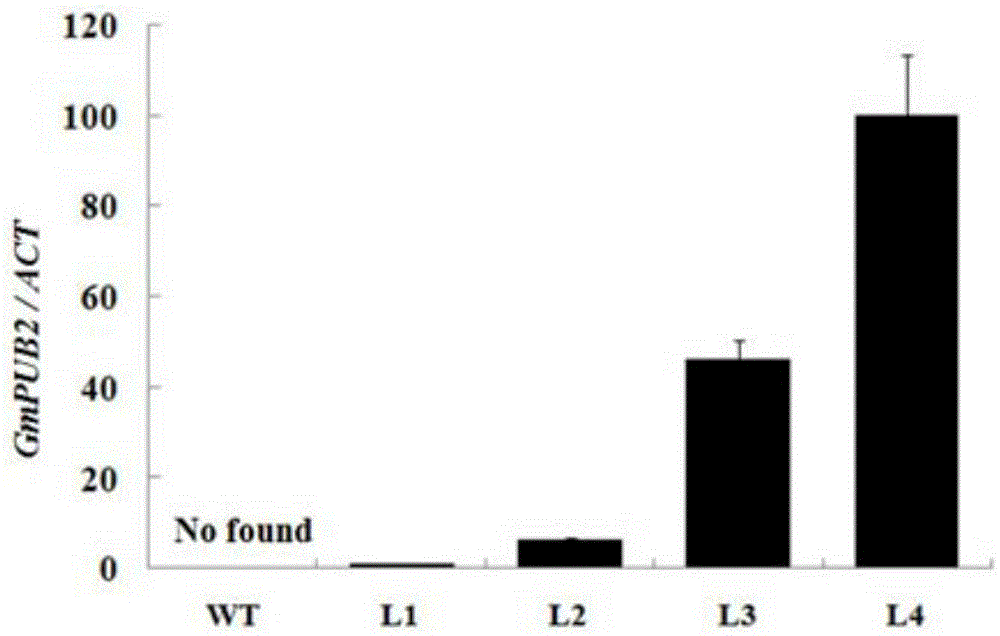
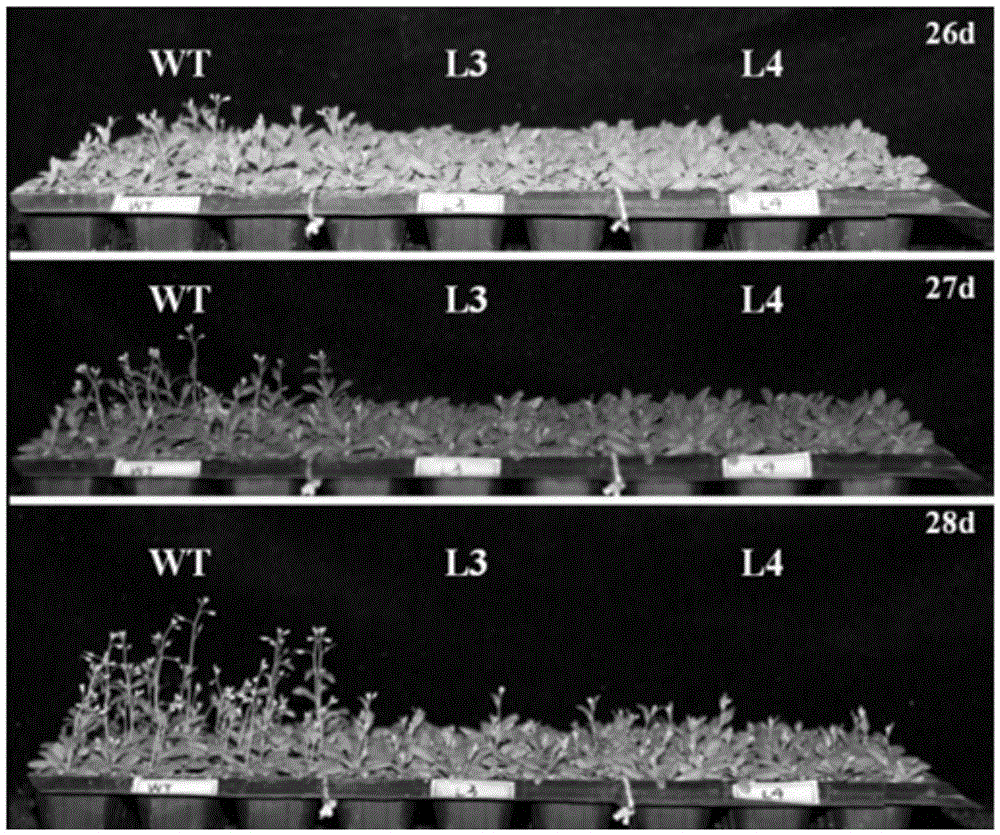
Application of soybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 capable of regulating flowering of plants
ActiveCN105400800ADelayed floweringLate floweringEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin ligaseWild type
The invention discloses an application of soybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 capable of regulating flowering of plants, namely, the application of the oybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 in regulating flowering of plants. A late-flowering plant is obtained after the GmPUB2 gene is transplanted into a target plant through a plant expression vector; an early-flowering plant is obtained after the GmPUB2 gene is transplanted into a target plant through a gene silencing carrier; after the target gene GmPUB2 is transplanted into arabidopsis thaliana, compared with the wild arabidopsis thaliana, the results show that the bolting time and the flowering time of the transgenic plant are obviously later than those of the wild plant, namely, the GmPUB2 gene has the function of delaying the flowering of the plants. With the established GmPUB2 gene silencing carrier to silence the transgenic arabidopsis thaliana with over-expressed target gene GmPUB2, the results show that the flowering time of the plant after silencing is obviously earlier than that of a control plant.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistant gene GmGST1 and the construction and application of a GmGST1 transgenic plant
ActiveCN110904130ABoosts Soluble Pigment LevelsIncrease resistanceTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention discloses a sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistant gene GmGST1 and the construction and application of a GmGST1 transgenic plant, which belong to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The invention aims to solve the problem of few available gene resources in the aspect of soybean sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistance at present. The invention provides the sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistant gene GmGST1, wherein the sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 1. According to the invention, the transgenic soybean plant is obtained by overexpression of the disease-resistant gene GmGST1; later representative identification determines that GmGST1 can participate in a soybean sclerotinia sclerotiorum resisting reaction; the soluble pigment level in stems of receptor soybean germplasm and the resistance of GmGST1 to sclerotinia sclerotiorum can be remarkably improved; and effective molecular markers and gene resources are provided for soybean sclerotinia sclerotiorum resisting molecular design and breeding.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for cultivating transgenic plants with blooming ahead of time
InactiveCN105420273AEarly floweringEarly flowering promotionVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGMO PlantsExpression vector
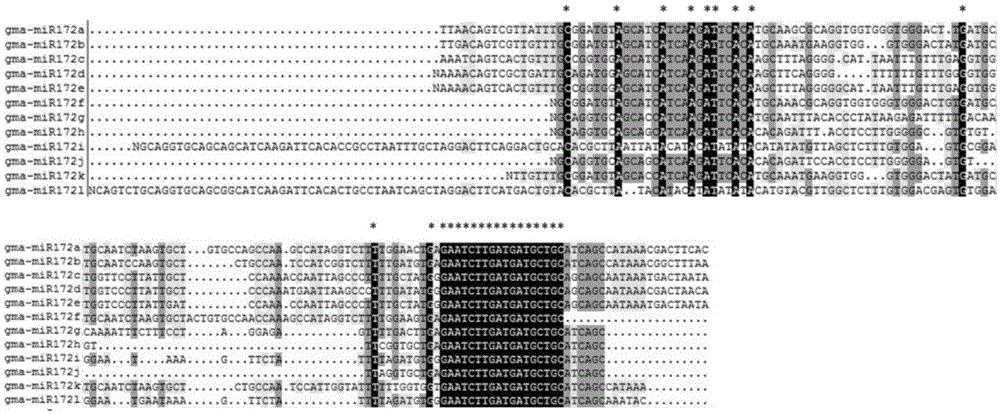
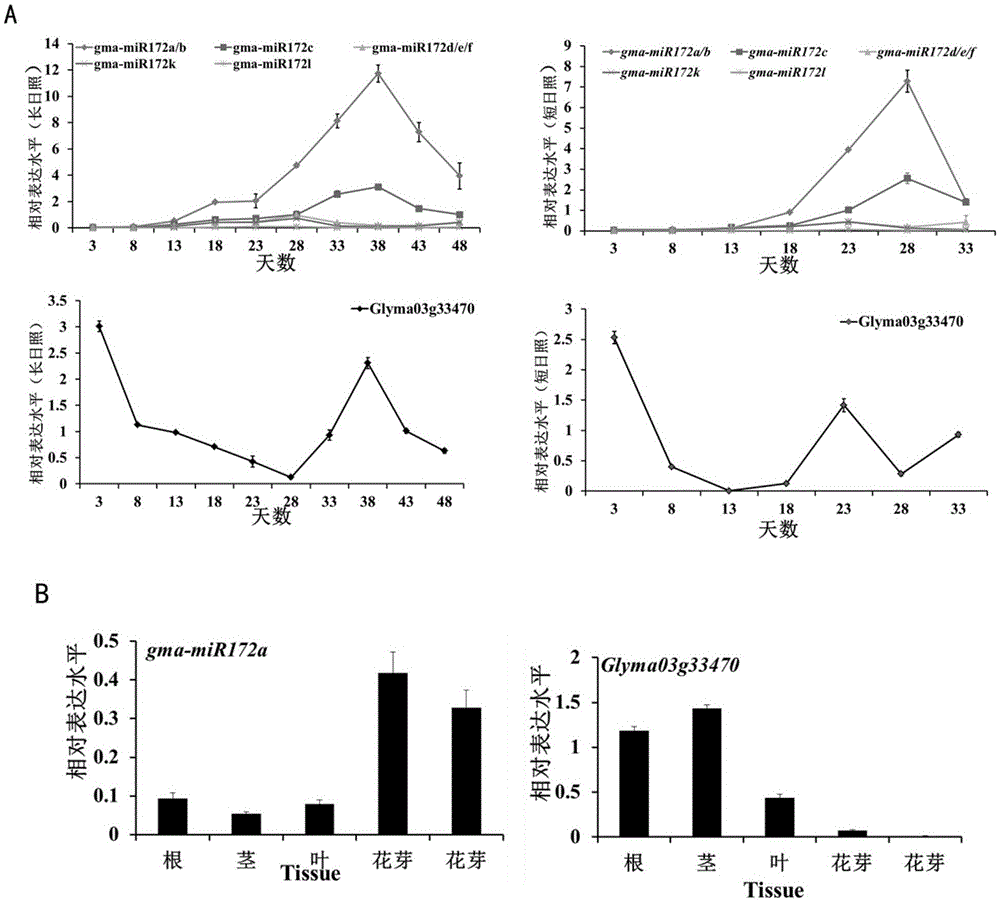
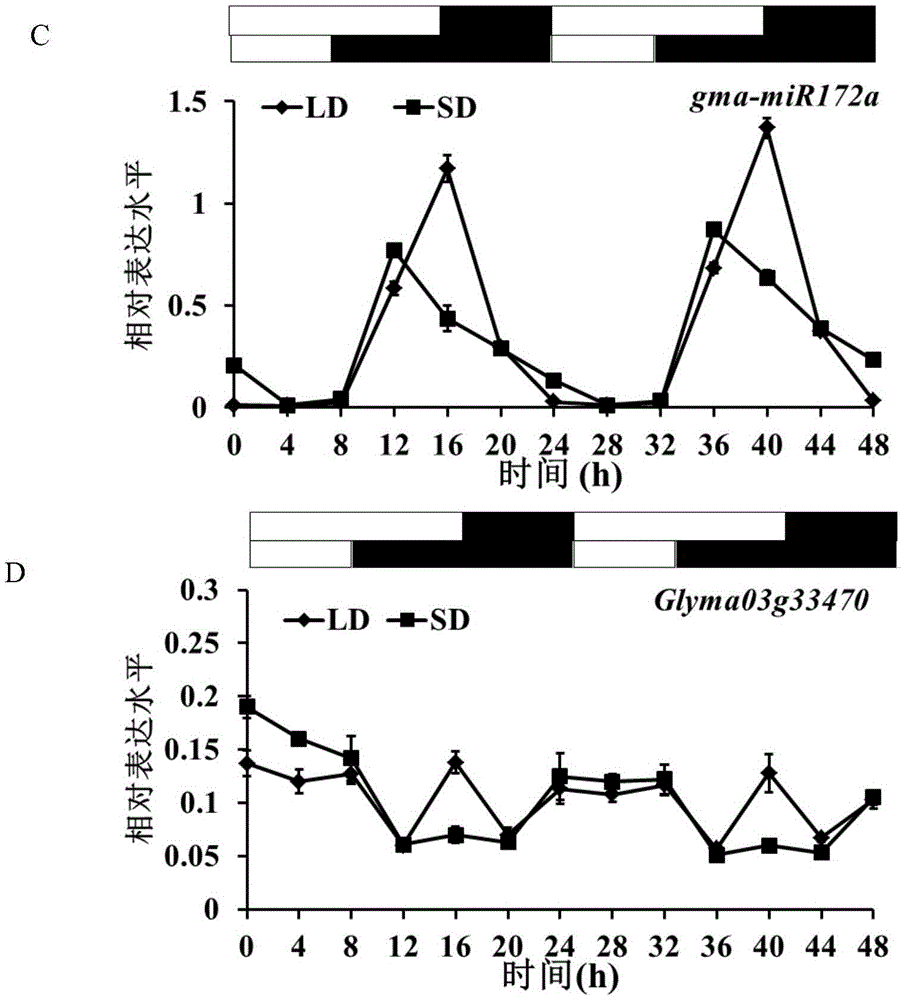
The invention discloses a method for cultivating transgenic plants with blooming ahead of time and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. According to the method, miRNA172a of soybean is transferred into agrobacteria through an expression vector and then infects a host plant through the agrobacteria, and a transgenic positive single plant is obtained through verification, screening and identification of a target gene degrading loca. According to the method, a miRNA172a gene is cloned from a soybean whole genome, the gene is transferred into arabidopsis by building the expression vector to successfully obtain a transgenic purified plant and a corresponding phenotype, and the blooming arabidopsis can be ahead of time effectively.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
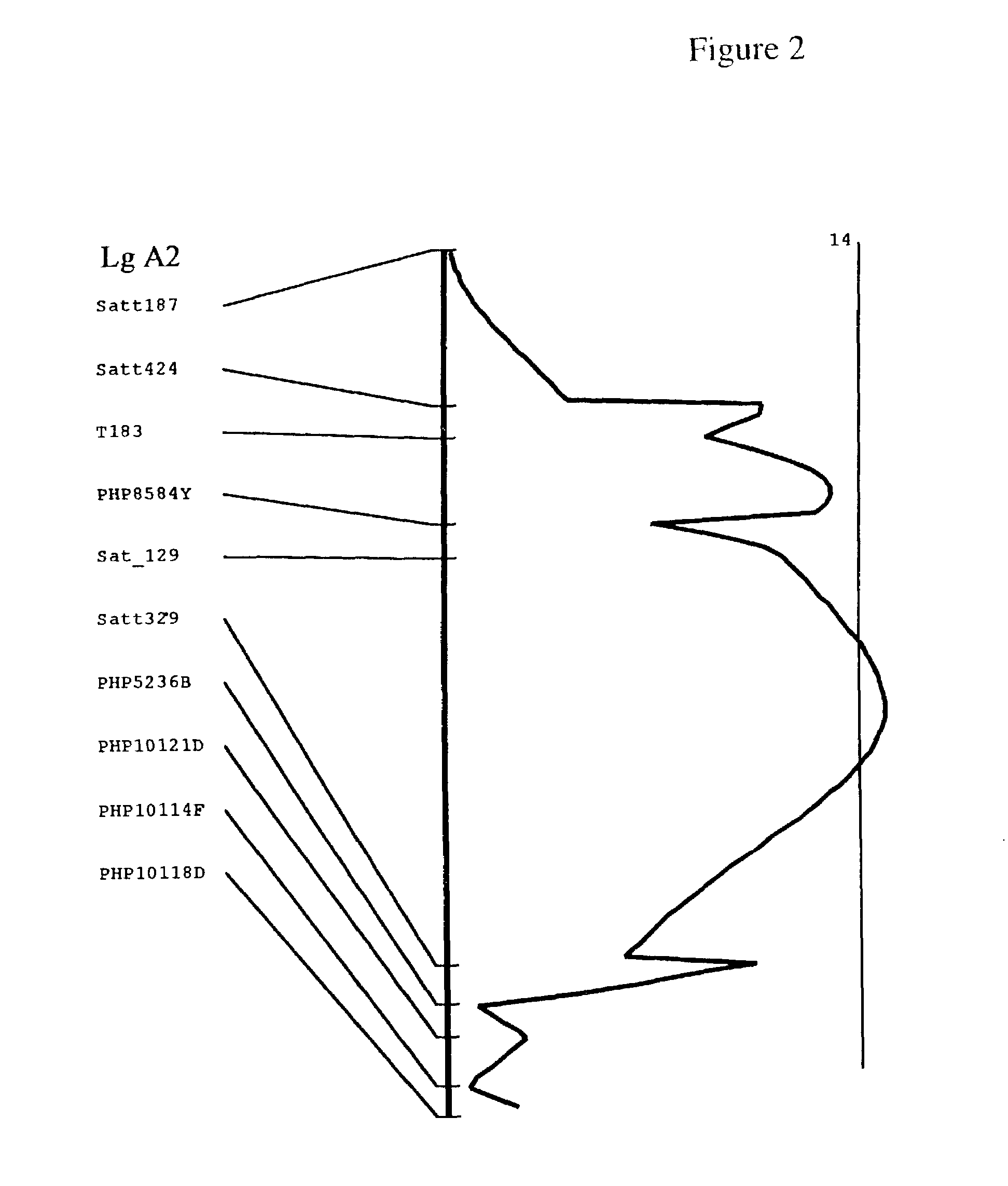
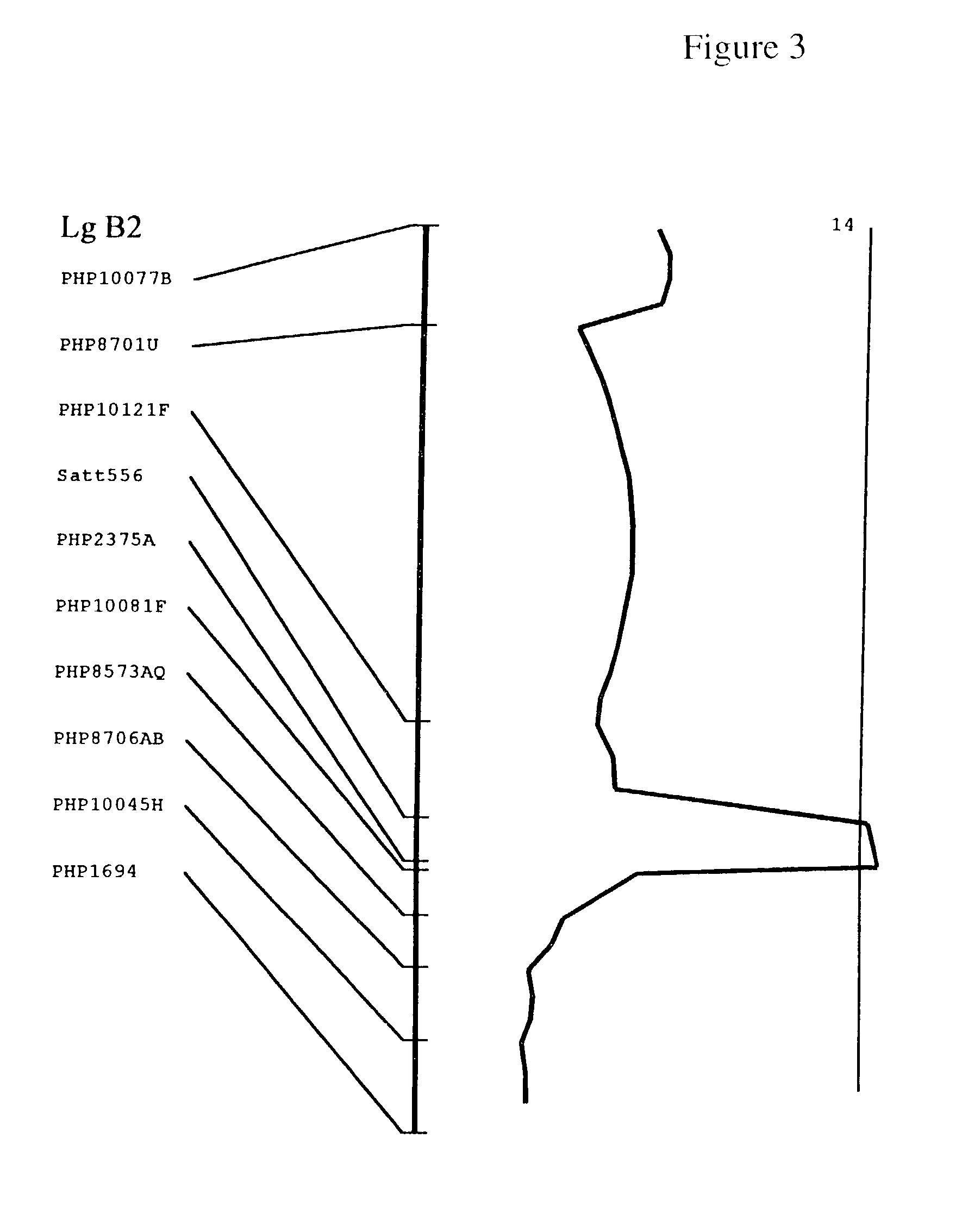
QTL controlling sclerotinia stem rot resistance in soybean
InactiveUS7250552B2Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesSclerotiniaStem rot
Markers associated with Sclerotinia stem rot resistance are provided. Methods of identifying resistant, and susceptible plants, using the markers are provided. Methods for identifying and isolating QTL are a feature of the invention, as are QTL associated with Sclerotinia stem rot resistance.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
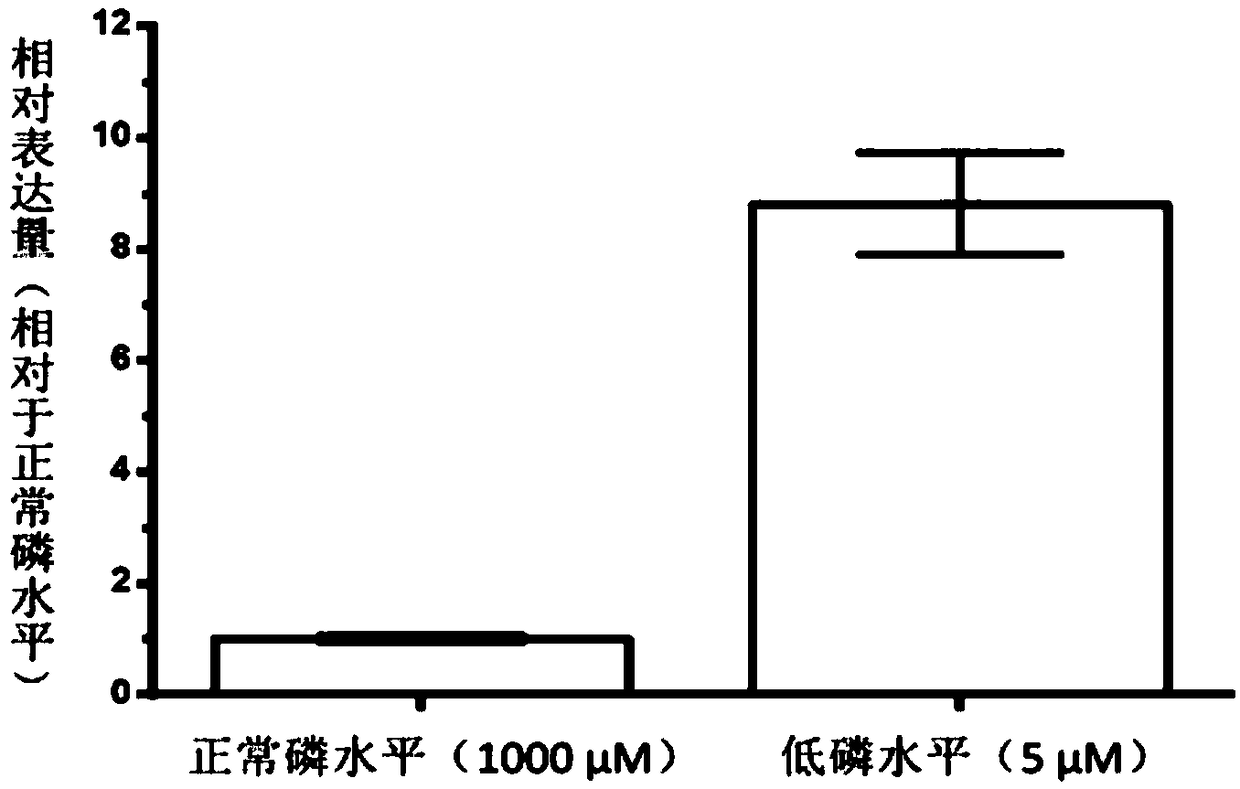
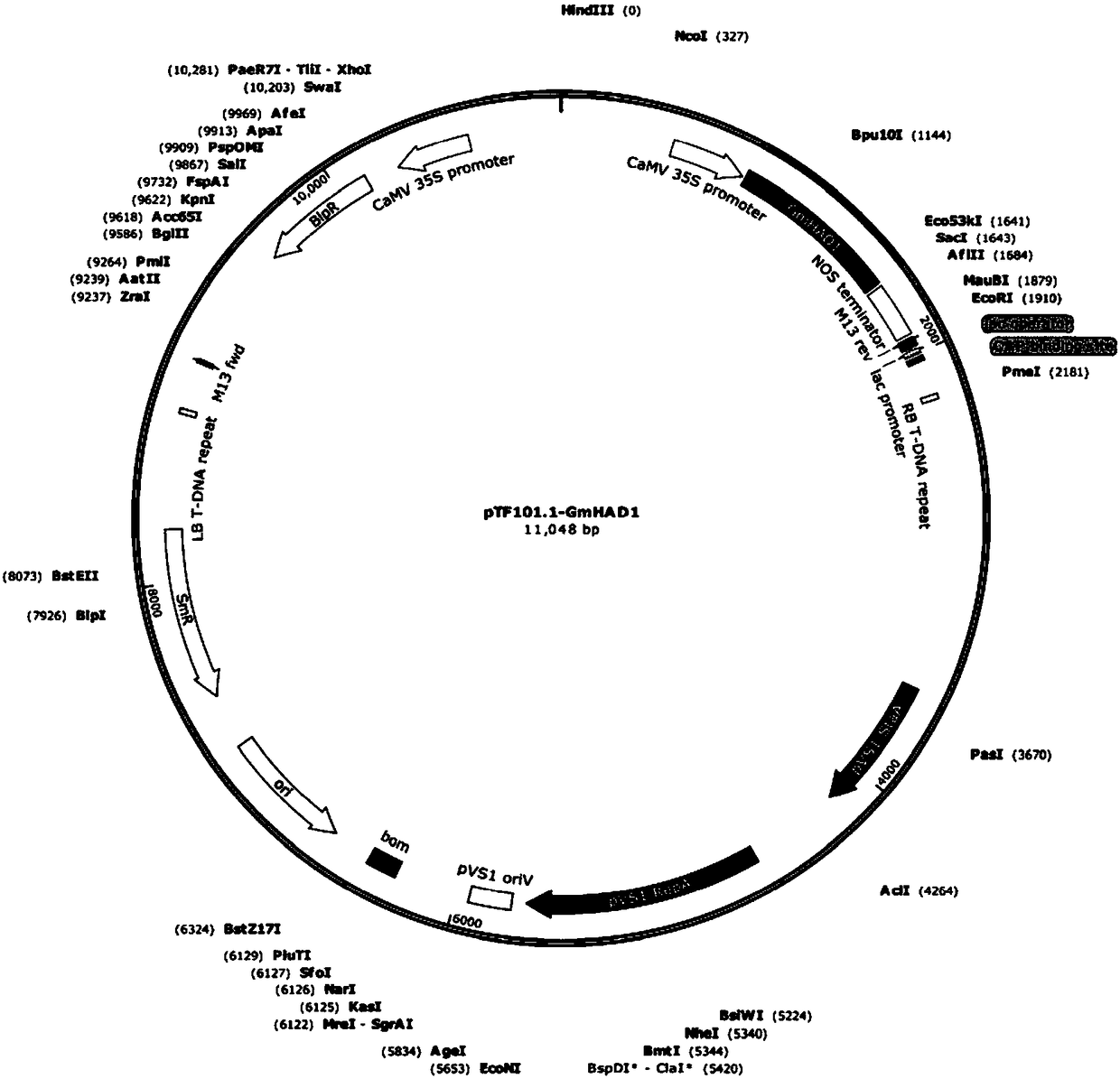
Protein GmHAD1 related to plant stress tolerance and encoding gene and application thereof
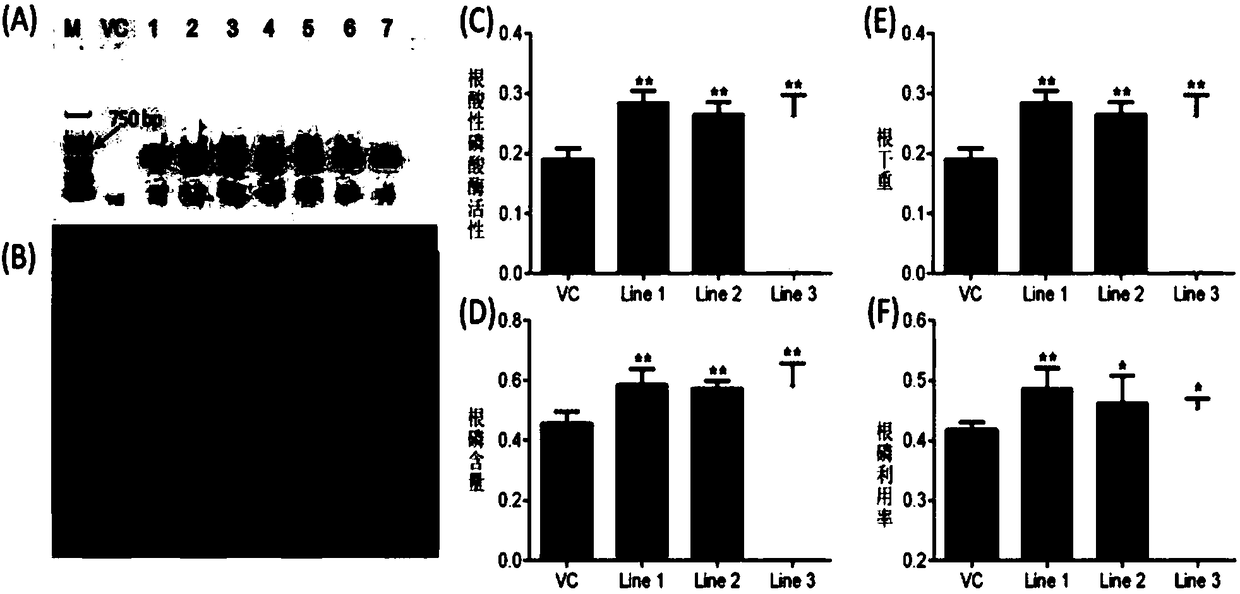
The invention discloses a protein GmHAD1 related to plant stress tolerance and an encoding gene and application thereof. An amino acid sequence of the protein GmHAD1 related to plant stress toleranceis shown in a second sequence, and an encoding gene sequence of the protein GmHAD1 related to plant stress tolerance is shown in a first sequence. It is proved through experiments that the GmHAD1 geneis overexpressed in soybean hairy roots and arabidopsis thaliana, and the low-phosphorus tolerance of transgenic plants can be improved. The gene can be introduced into plants as a target gene to improve the low-phosphorus tolerance of the plants, have important significance to the cultivation of low-phosphorus-tolerant soybean varieties, and lay a foundation for the research on the cultivation of the transgenic plants with high low-phosphorus tolerance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for identifying hybrid soybeans seeds by molecular markers
ActiveCN102329869AClear bandGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyHybrid seed
The invention discloses a method for identifying the purity of hybrid soybeans seeds by molecular markers, comprising the following steps of: using identified hybrid soybean varieties improved by RN cytoplasmic male sterility triple system and parental gene groups DNA thereof as a template, by SSR (simple sequence repeat) analysis, establishing SSR specificity fingerprint of the hybrid soybean and respective parents, successfully obtaining codominant an SSR marker which can distinguish the parents and the hybrid seeds definitely, and carrying out seed purity detection of the identified hybridsoybean variety improved by the RN cytoplasmic male sterility triple system according to the specificity markers. The result and the field identification are consistent by random group identificationof the hybrid soybean varieties. The method is simple and convenient to operate, the seed purity of the hybrid soybean varieties improved by the RN cytoplasmic male sterility triple system can be fast, accurately and reliably identified by experiment means through the screened specific molecular markers, so that the risk causing possible production reduction due to insufficient purity of the seeds in the sales process of the hybrid soybean seeds can be reduced.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Soybean leaf wrinkling disease field identification method
ActiveCN111121629AEasy to breedAccurate grasp of reliabilityFabaceae cultivationUsing optical meansBiotechnologyEvaluation result
The invention relates to the technical field of plant disease identification, in particular to a soybean leaf wrinkling disease field identification method which comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a control material; (2) field planting test; (3) counting the number of soybean plants with different leaf wrinkling symptom levels; (4) calculating the disease index of the soybean leaf wrinkling disease; and (5) determining the leaf wrinkle resistance grade of the identified material. According to the method, the field occurrence situation of the soybean leaf wrinkling is investigated andstudied, the control variety with high leaf wrinkling degree and stable performance is tracked, and the control variety is used as a control group to divide the leaf wrinkling symptom level. According to the method, more than three experimental groups are arranged, the morbidity conditions of soybeans in the V6 stage, the R2 stage and the R5 stage are counted respectively, the disease index is calculated, and the leaf wrinkling disease resistance grade of the soybeans can be evaluated objectively by averaging the disease indexes. The evaluation result is accurate and visual. The identification method is used for identifying the leaf wrinkle resistance of different soybean germplasms, so that resistant varieties can be effectively screened out, and further research on the soybean wrinklingdisease is facilitated.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Gene GmCTRL2 used for improving osmotic stress resistance of alfalfa, preparation and protein coded by gene GmCTRL2
The invention belongs to preparation of new genes, and particularly provides a gene GmCTRL2 used for improving osmotic stress resistance of alfalfa, preparation and a protein coded by the gene GmCTRL2. The gene GmCTRL2 is prepared by a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification method with 5'-ATAGG TACCGAGCTCTCAGATCCAAATAAATCATG-3'serving as a forward primer S1, 5'-CTGGGATCCCTC GAGCCTCAGCTATATATCCATTG3' serving as a reverse primer A1, and cDNA (complementary Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) serving as a template, wherein the cDNA is synthesized by the reverse transcription of RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) in root, stem and leaf organization of soybean subjected to salt stress treatment. The gene GmCTRL2 solves the problems in the prior art that plants are lack of resistance genes, and the resistant spectrum, adaptive ecological zones and resistance mechanisms and the like of most of the genes are unclear, and has the advantage that the salt tolerance and drought resistance of a transgenic callus are improved obviously by comparing with a wild type callus.
Owner:LANGFANG NORMAL UNIV
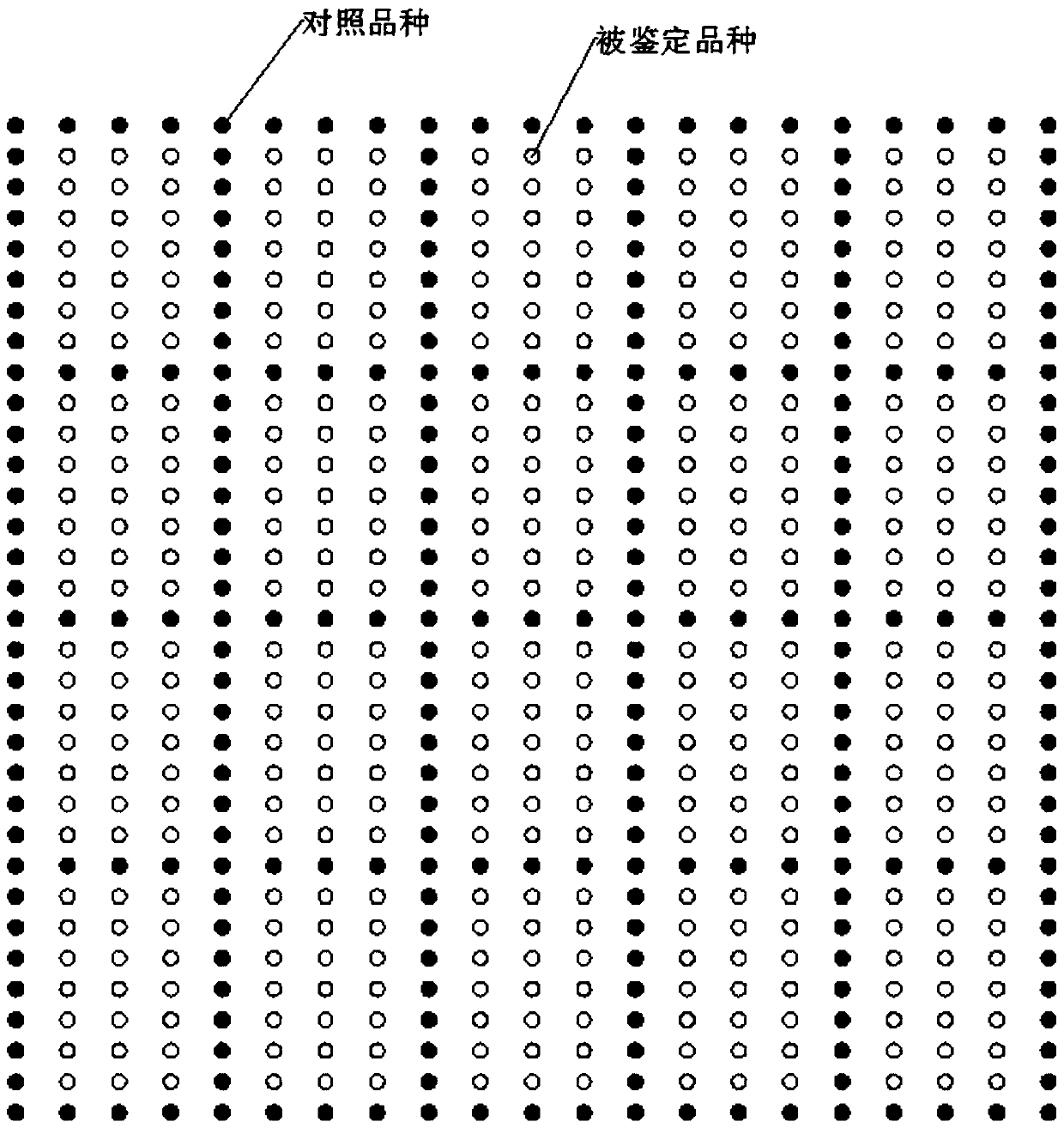
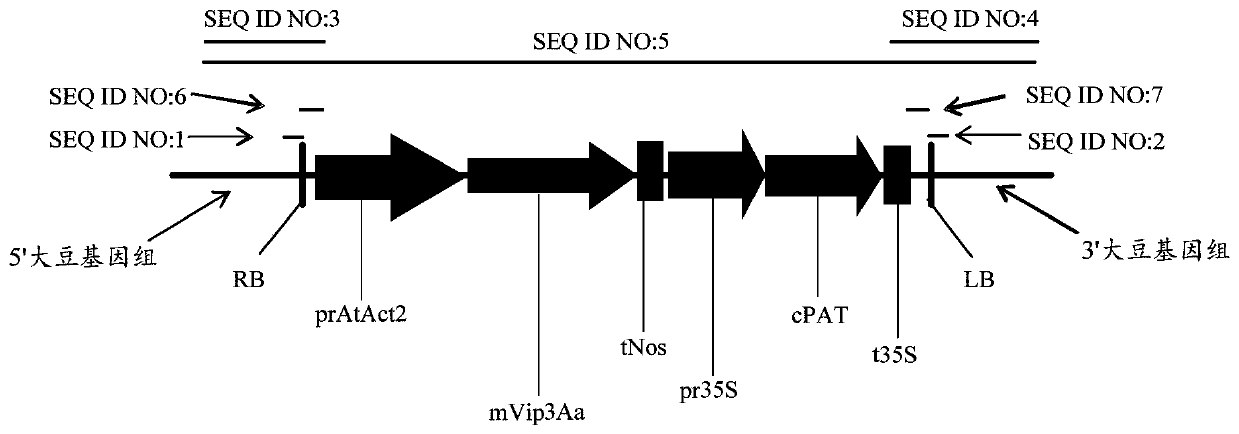
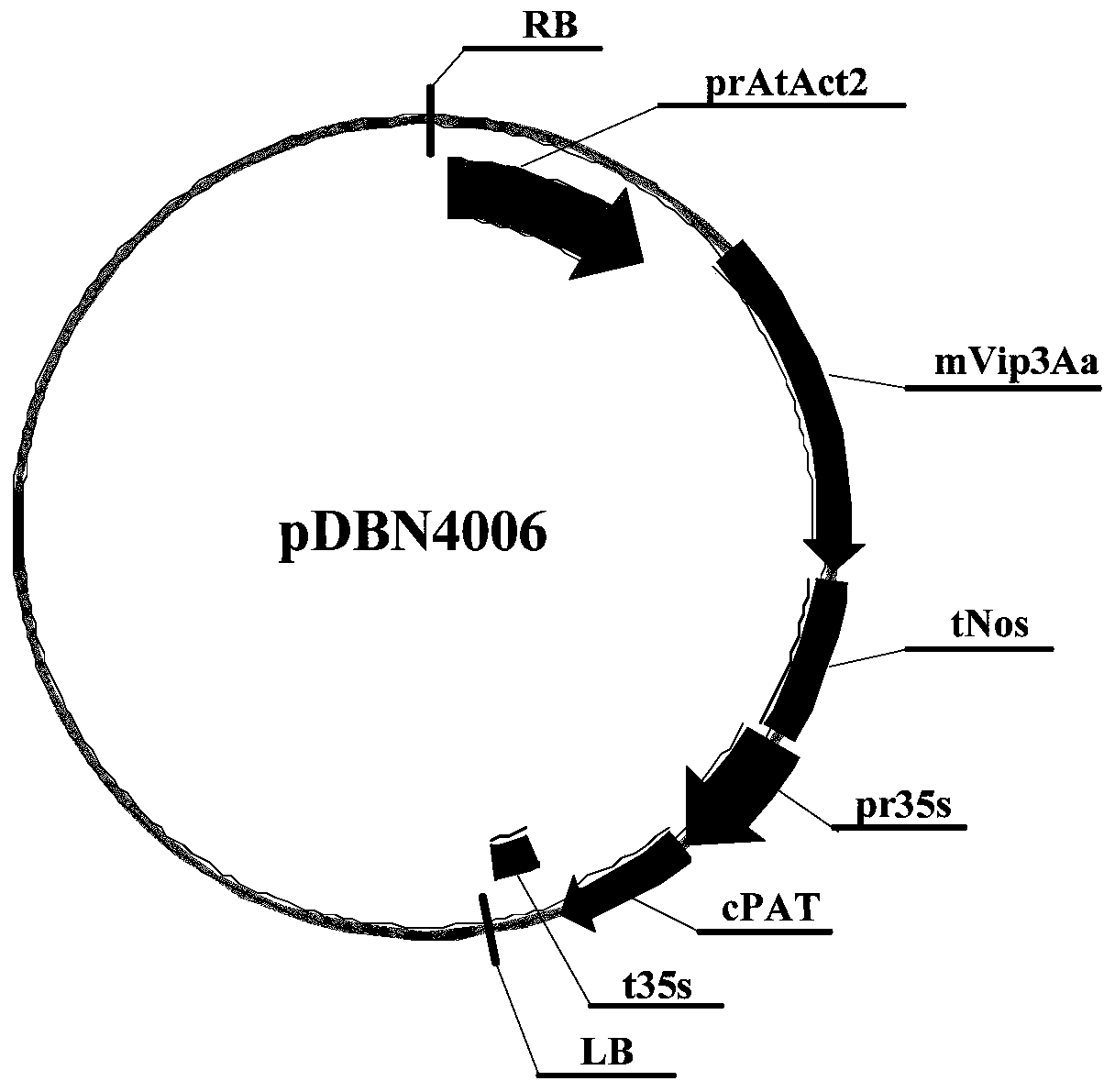
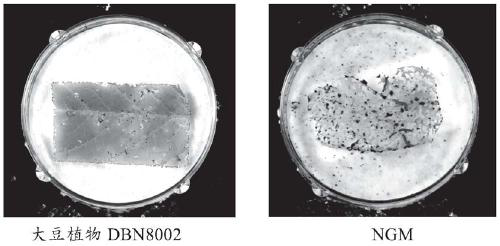
Nucleic acid sequence for detecting soybean plant DBN8002 and detection method thereof
ActiveCN111406117AMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyGlufosinate-ammonium
The invention relates to a nucleic acid sequence for detecting soybean plant DBN8002 and a detection method thereof. The nucleic acid sequence comprises SEQ ID NO: 1 or a complementary sequence thereof, and / or SEQ ID NO: 2 or a complementary sequence thereof. The soybean plant DBN8002 has better resistance to lepidoptera insects, has better tolerance to glufosinate-ammonium herbicides, and has noinfluence on the yield, and the detection method can accurately and rapidly identify whether a biological sample contains the DNA molecule of the transgenic soybean event DBN8002.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Soybean bHLH transcription factor and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN105753955AImprove toleranceReduce accumulationMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid vectorAgricultural scienceBHLH Transcription Factors
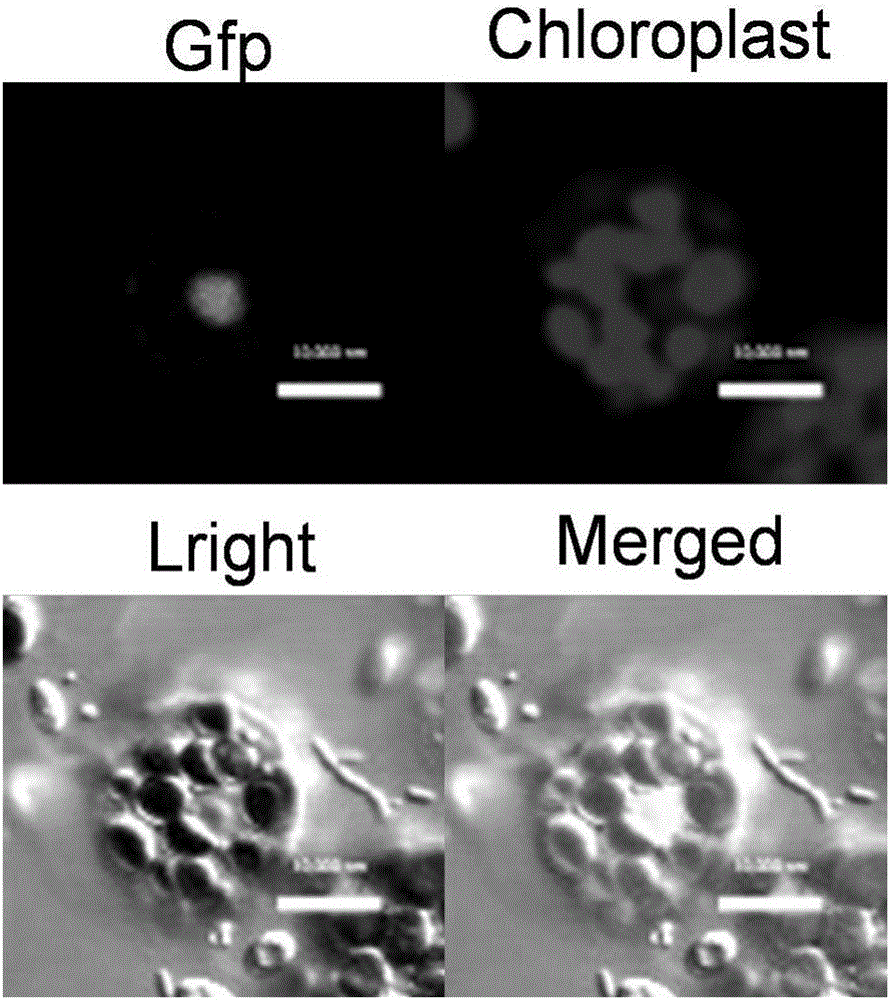
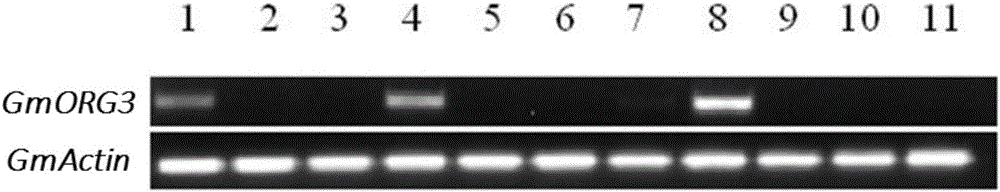
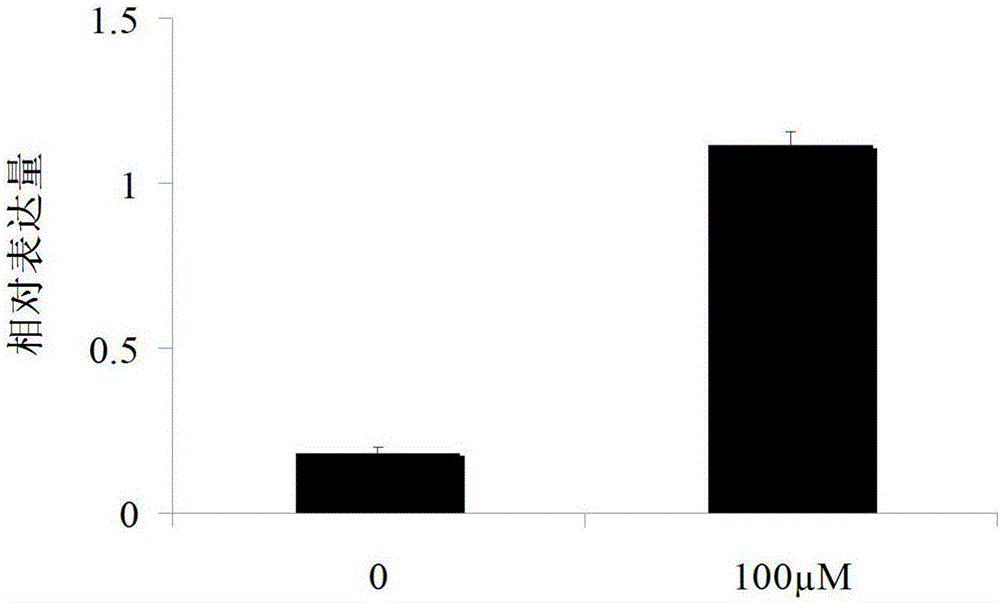
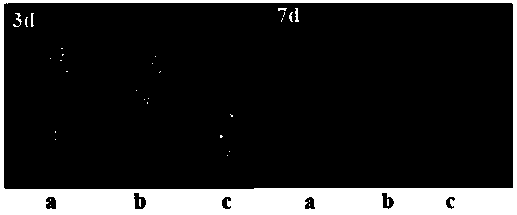
The invention discloses a bHLH transcription factor and an encoding gene and application thereof. The protein has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2 or the amino acid sequence which is formed by replacing, missing or adding one or more amino acids in the sequence and has the same function. The encoding gene GmORG3 of the bHLH transcription factor shows resistance on Cd stress when in over-expression, so that the GmORG3 gene in the soybean is separated and cloned; the anti-Cd mechanism of the soybean is disclosed; and the anti-Cd molecular breeding of plants can be carried out through gene operation means to improve the Cd resistance of the plants.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Construction and application of anti-sclerotinia sclerotiorum gene GmPR5 and GmPR5 transgenic plant
ActiveCN110862995AEffective resourcesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention discloses construction and application of an anti-sclerotinia sclerotiorum gene GmPR5 and a GmPR5 transgenic plant, and belongs to the technical field of genetic breeding. In order to research the sclerotinia sclerotiorum resisting mechanism of soybeans and accelerate the sclerotinia sclerotiorum resisting breeding process of the soybeans, the invention provides the anti-sclerotiniasclerotiorum gene GmPR5, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the anti-sclerotinia sclerotiorum gene GmPR5 is shown as SEQ ID No. 1; and a recombinant vector and a recombinant bacterium containing the gene. According to the invention, a transgenic soybean plant is obtained by overexpression of the disease-resistant gene GmPR5. Through post-phenotypic identification, the GmPR5 is determined to participate in the sclerotinia sclerotiorum resisting reaction, a new thought is provided for obtaining a soybean variety which is completely resistant to sclerotinia sclerotiorum, a basis is provided for further researching the function and the disease resisting mechanism of the gene, and effective molecular markers and gene resources are provided for molecular design and breeding of sclerotinia sclerotiorum resisting of soybeans.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
microRNA for promoting plant nodulation and nitrogen fixation and application thereof
InactiveCN103695432AImprove the ability of nodulation to fix nitrogenIncrease productionVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsNucleotideMicroRNA
The invention discloses microRNA for promoting plant nodulation and nitrogen fixation and an application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the microRNA is shown as SEQ ID NO:1; a precursor sequence of the microRNA is shown as SEQ ID NO:3; coding genes of the precursor sequence of the microRNA are shown as SEQ ID NO:4. The application method comprises the following steps: constructing an overexpression recombinant vector containing the genes shown as SEQ ID NO:3, constructing a transformant by utilizing the recombinant expression vector, infecting a target plant by utilizing the transformant, and screening to obtain a transgenic plant which has higher nitrogen fixation capacity compared with a normal plant. The microRNA has high significance for improving the soybean yield, and novel gene resources are provided for cultivating novel soybean types with high nitrogen fixation capacity.
Owner:中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所农业资源研究中心
Soybean photoreceptor GmPLP1 and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102453084AIncrease the number of branchesEarly floweringFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyPlant traits
The invention discloses a soybean photoreceptor GmPLP1 and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is named as GmPLP1 and is a protein as described in the following (1) or (2): (1) protein with an amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 2 in a sequence table; and (2) protein which is derived from (1) by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence of the sequence 2, and is associated with plant traits. The plant traits comprise at least one of the following (1)-(10): (1) branch number; (2) time of flowering; (3) plant height; (4) blade area; (5) distance between nodes; (6) root length; (7) photosynthetic rate; (8) stress tolerance; (9) stem diameter; and (10) node number. The photoreceptor gene GmPLP1 disclosed by the invention can be used for changing the plant morphology, increasing the plant branches and changing the time of flowering and ripening of the plant, and has great importance for plant breeding and research on the function and action mechanism of the photoreceptor gene.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
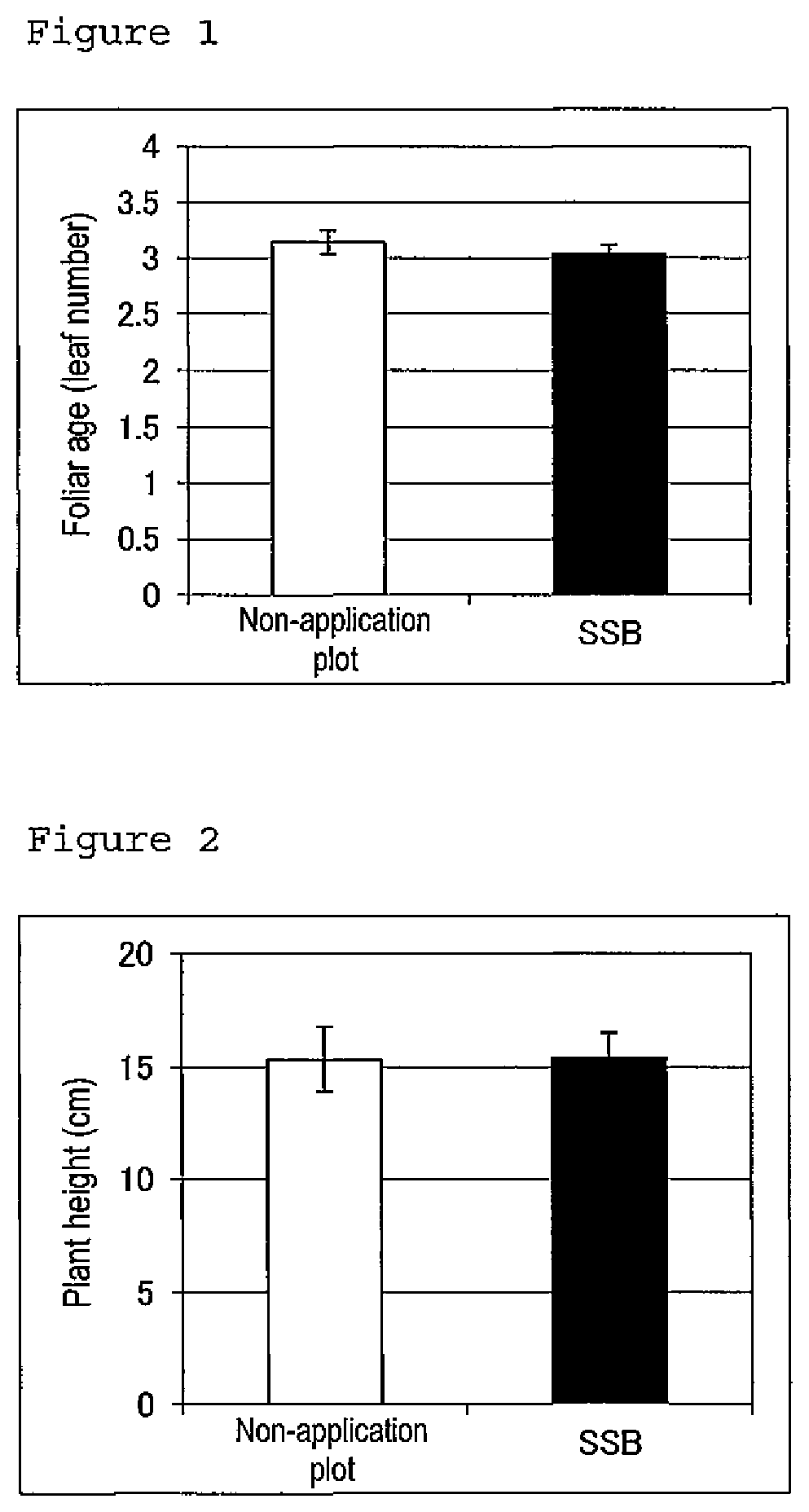
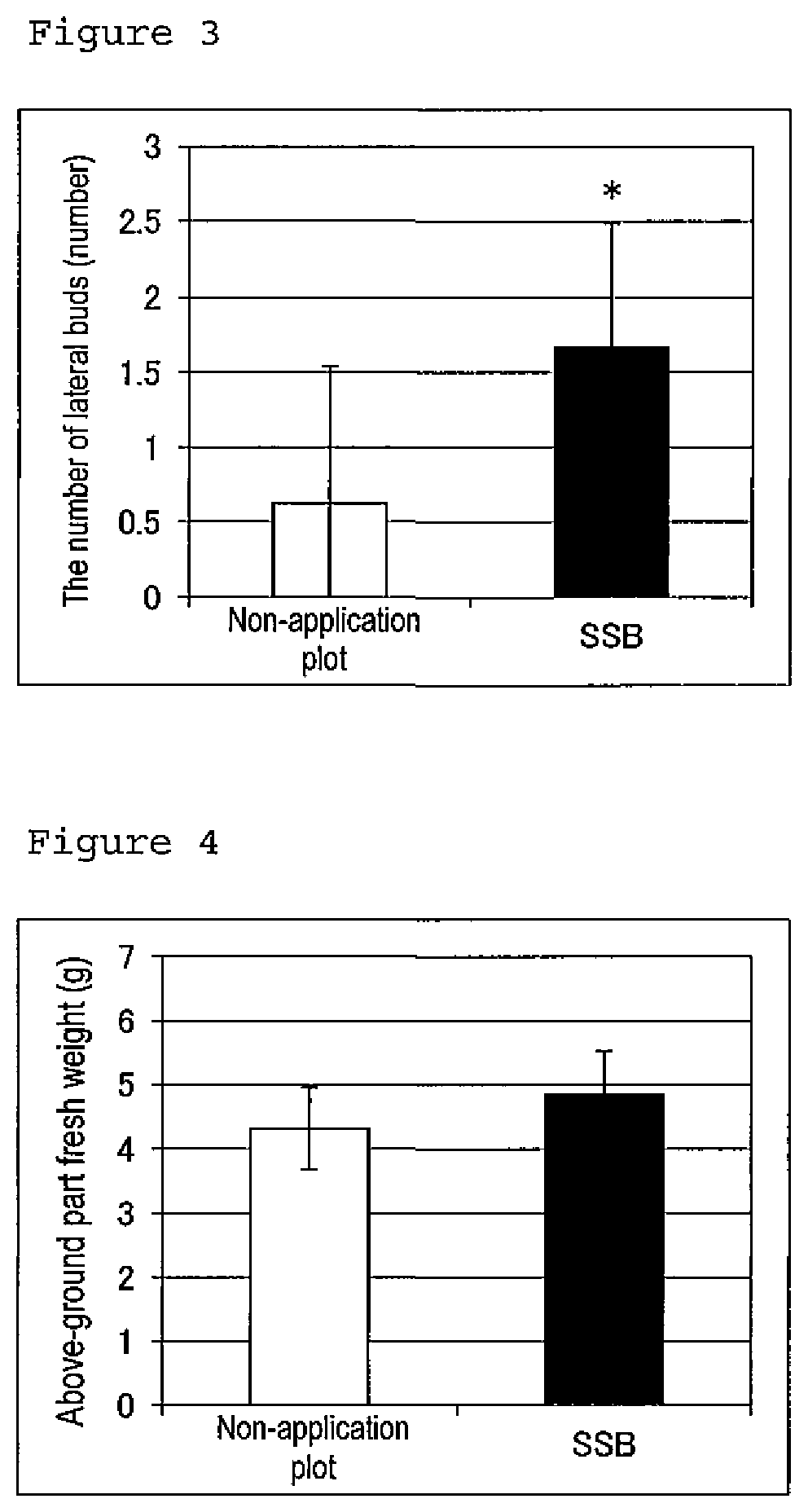
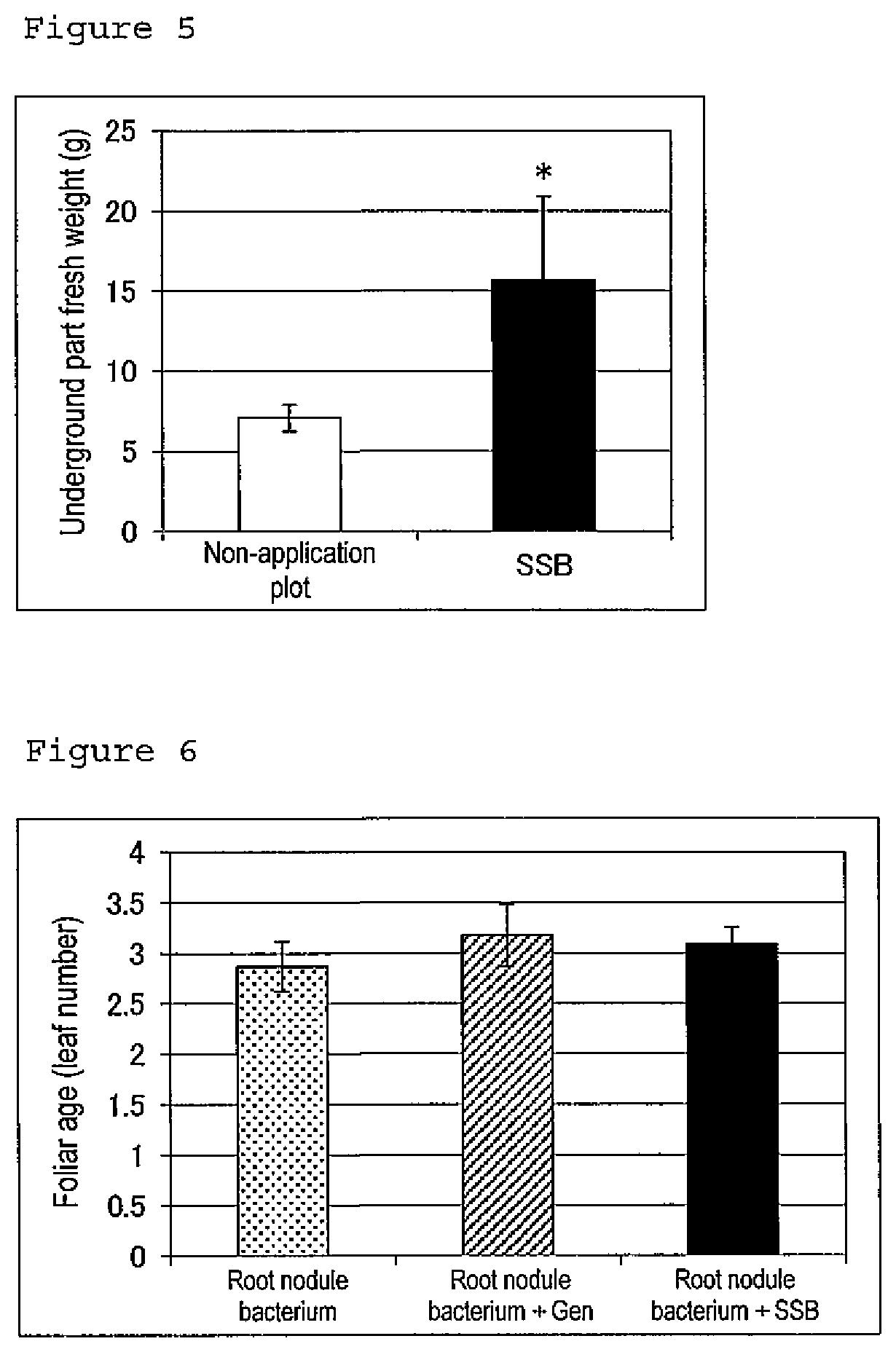
Promoter for leguminous plant growth
It is intended to provide a component promoting the growth of leguminous plants. The present invention provides a promoter for leguminous plant growth comprising a glycoside of soyasapogenol B as an active ingredient, and a method for promoting the growth of a leguminous plant using a glycoside of soyasapogenol B as an active ingredient. The glycoside of soyasapogenol B is a glycoside having a hydroxy group at position C-22 of the soyasapogenol B and having a saccharide bonded to a hydroxy group at position C-3 of the soyasapogenol B.
Owner:KAO CORP
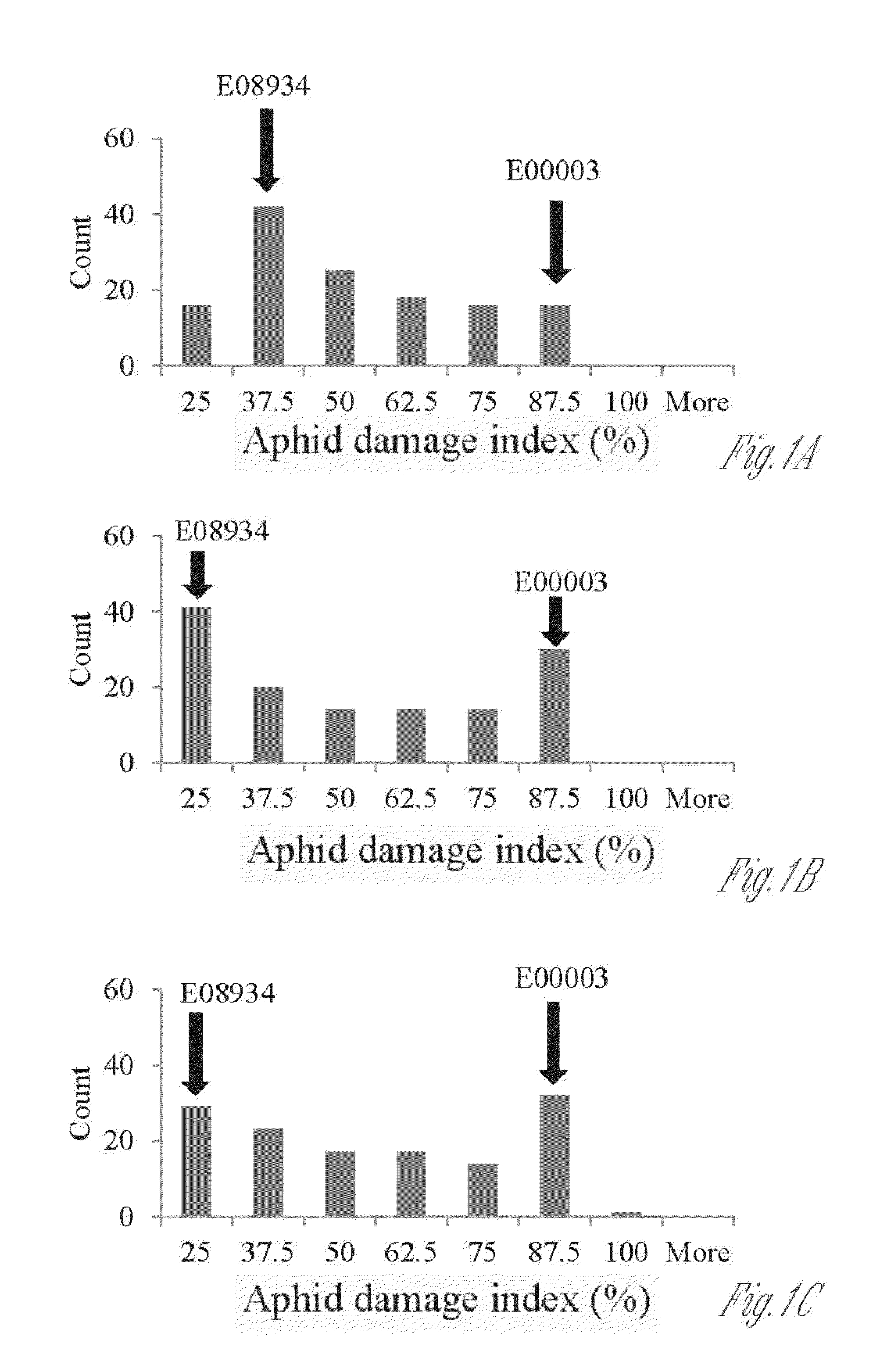
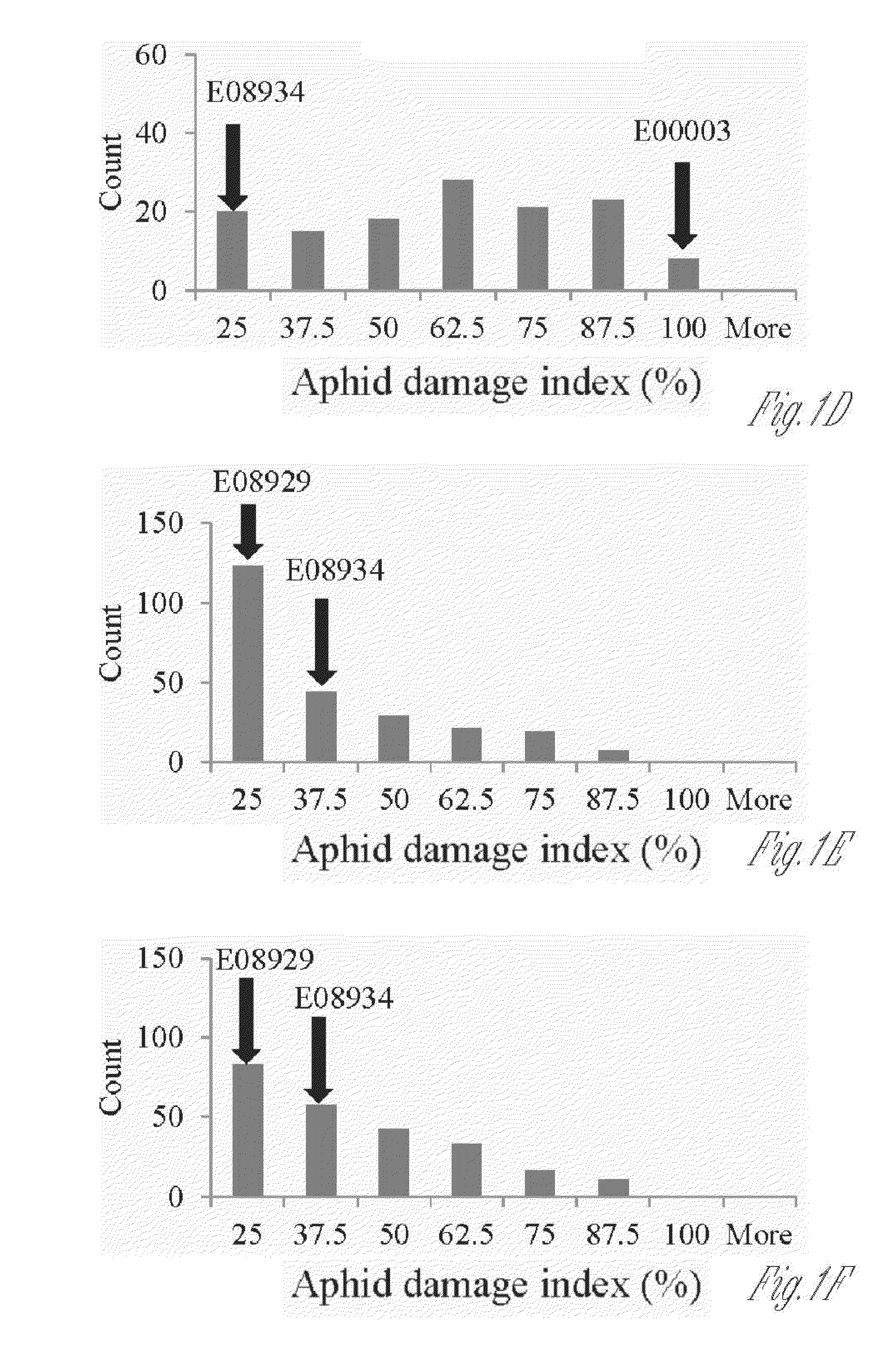
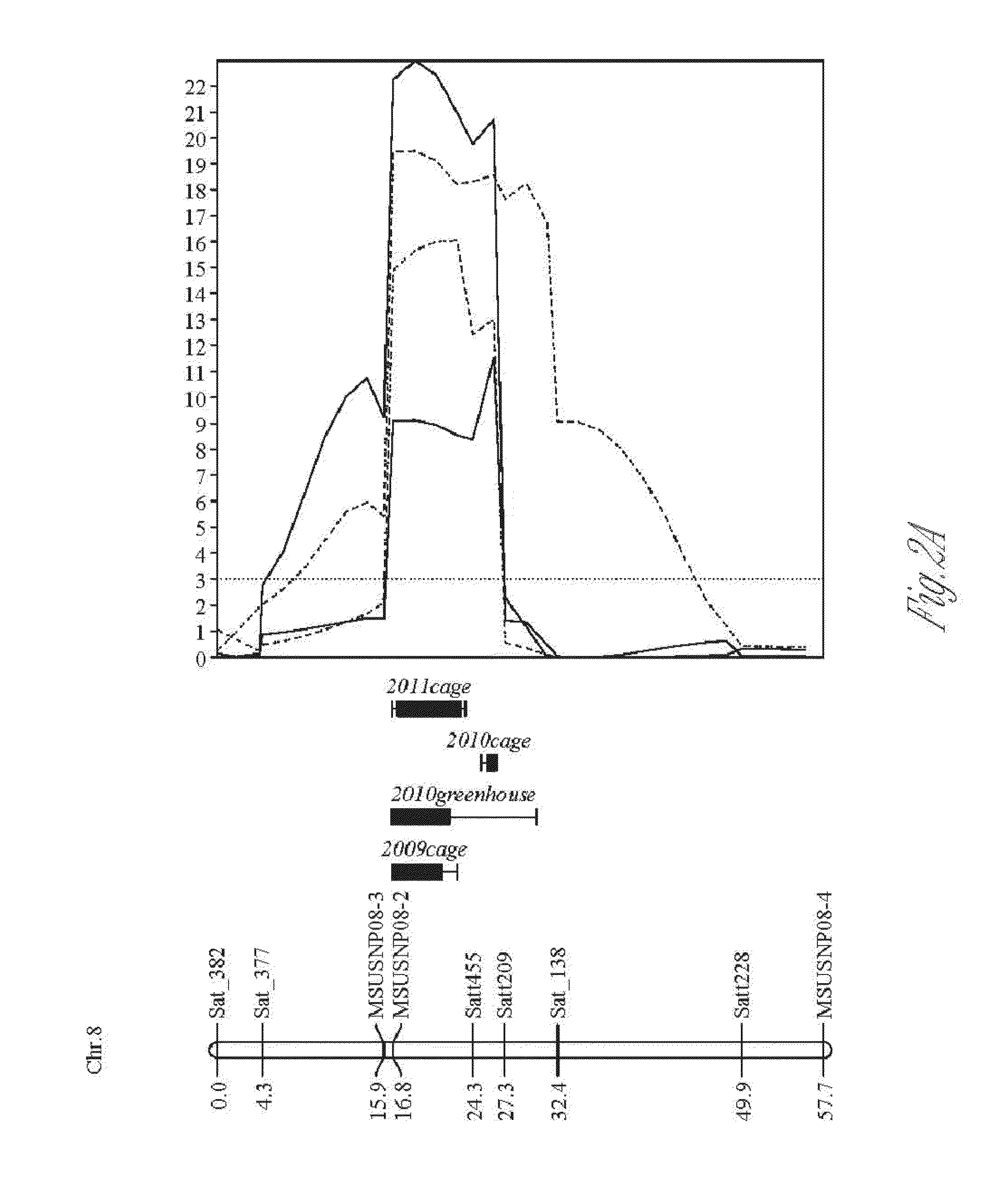
New sources of aphid resistance in soybean plants
InactiveUS20140196167A1Increase resistanceReduce harmMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGenetics
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for identifying and using new germplasm providing aphid resistant in soybean plants, particularly for use in breeding soybean plant lines and cultivars representing specific set(s) of germplasm. In particular, aphid resistant soybean plants comprising new sources of germplasm and stacked germplasm / genes conferring enhanced aphid resistance are provided. These enhanced aphid resistant plants find use in breeding soybean plant lines (cultivars) including lines having superior aphid resistance. Further, the inventions relate to providing new aphid resistant germplasm identified by markers associated with plants having decreased damage from aphid feeding, as well as plants having enhanced tolerance to aphid infestation. Even further, the invention relates to compositions and methods for using genetic markers in breeding methods for producing plants and plant cultivars having increased resistance to aphid damage and increased tolerance to aphids, while retaining and acquiring desired agronomic traits.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com