Patents
Literature
170results about How to "Eliminate leakage current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
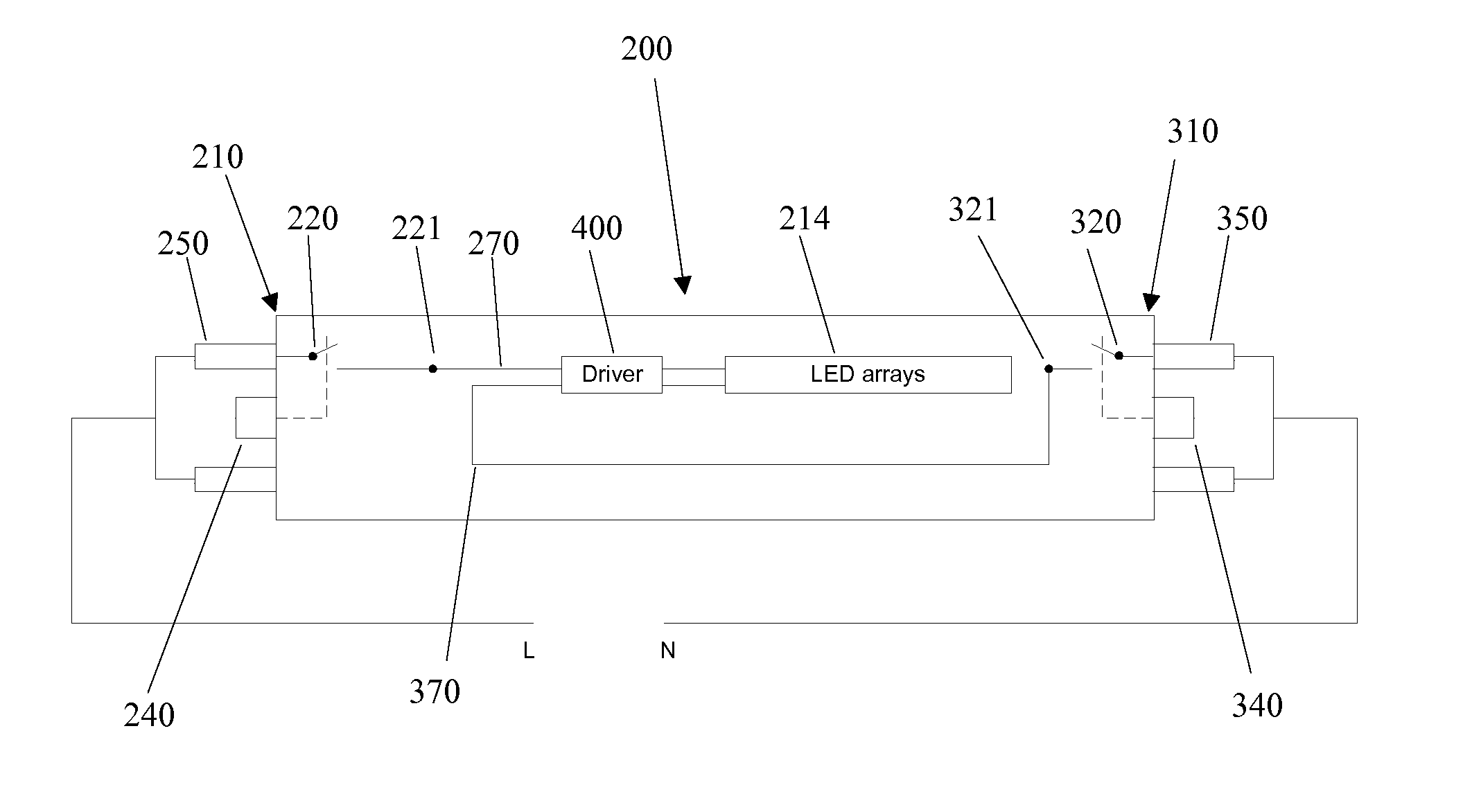
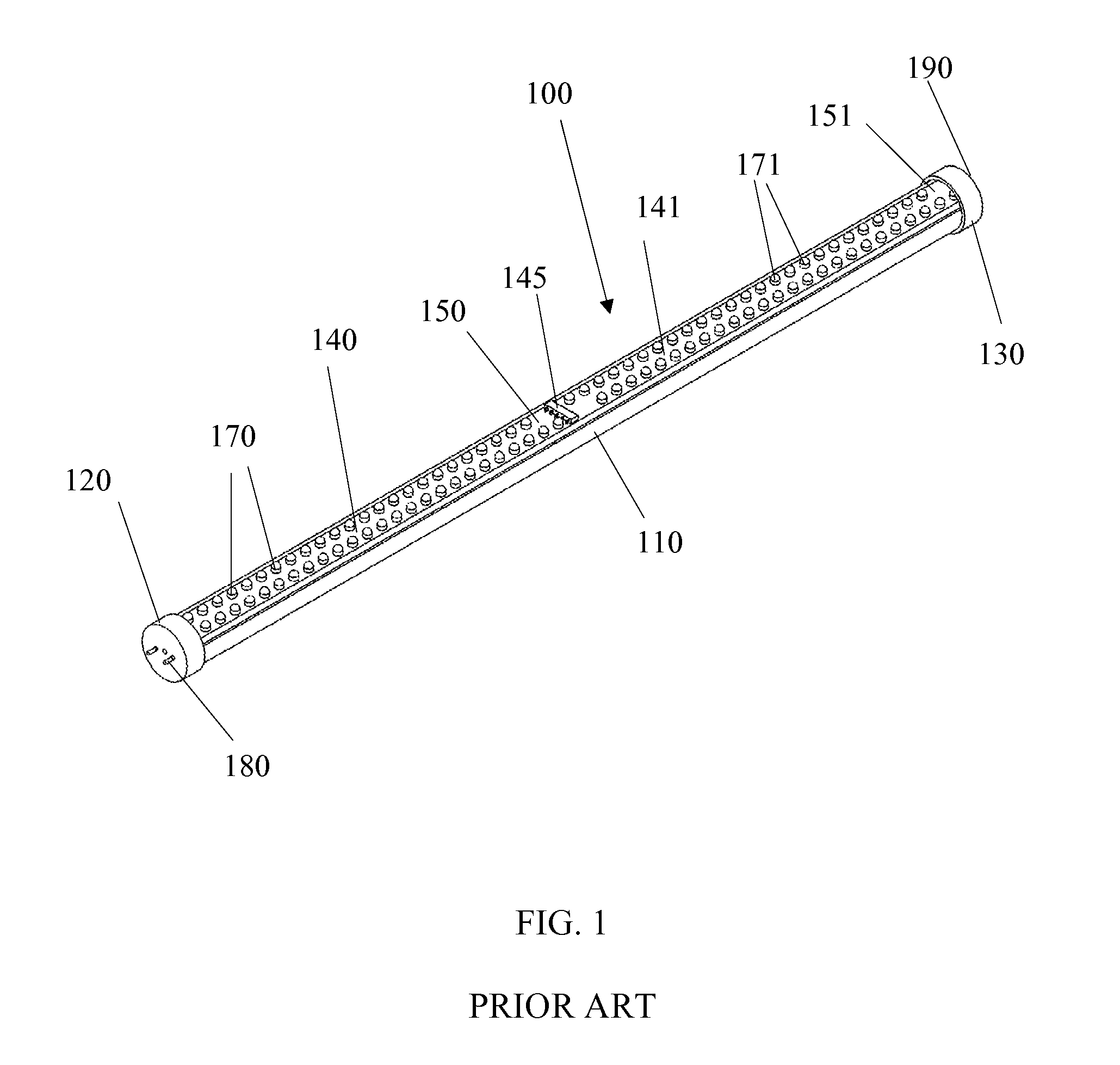
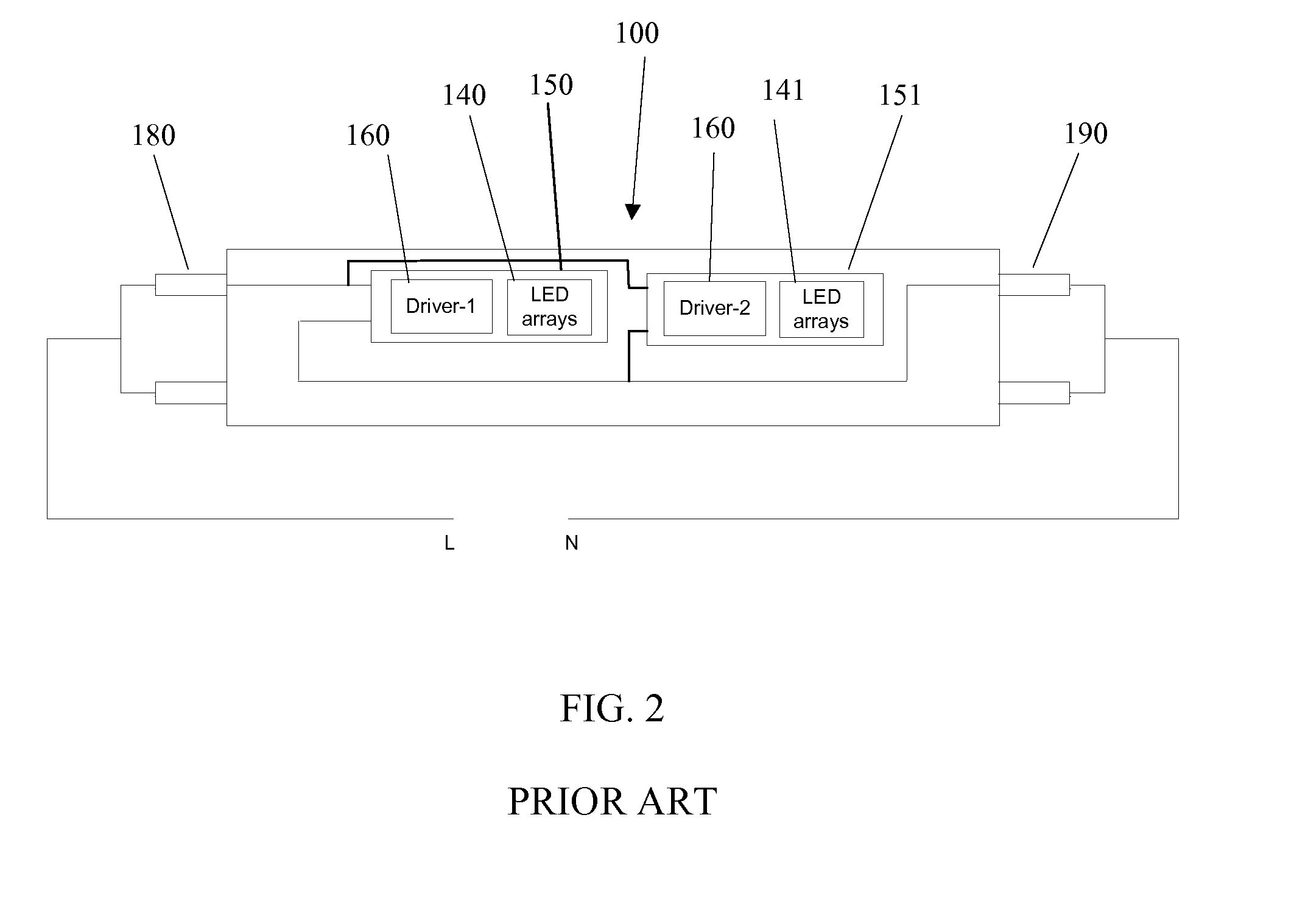
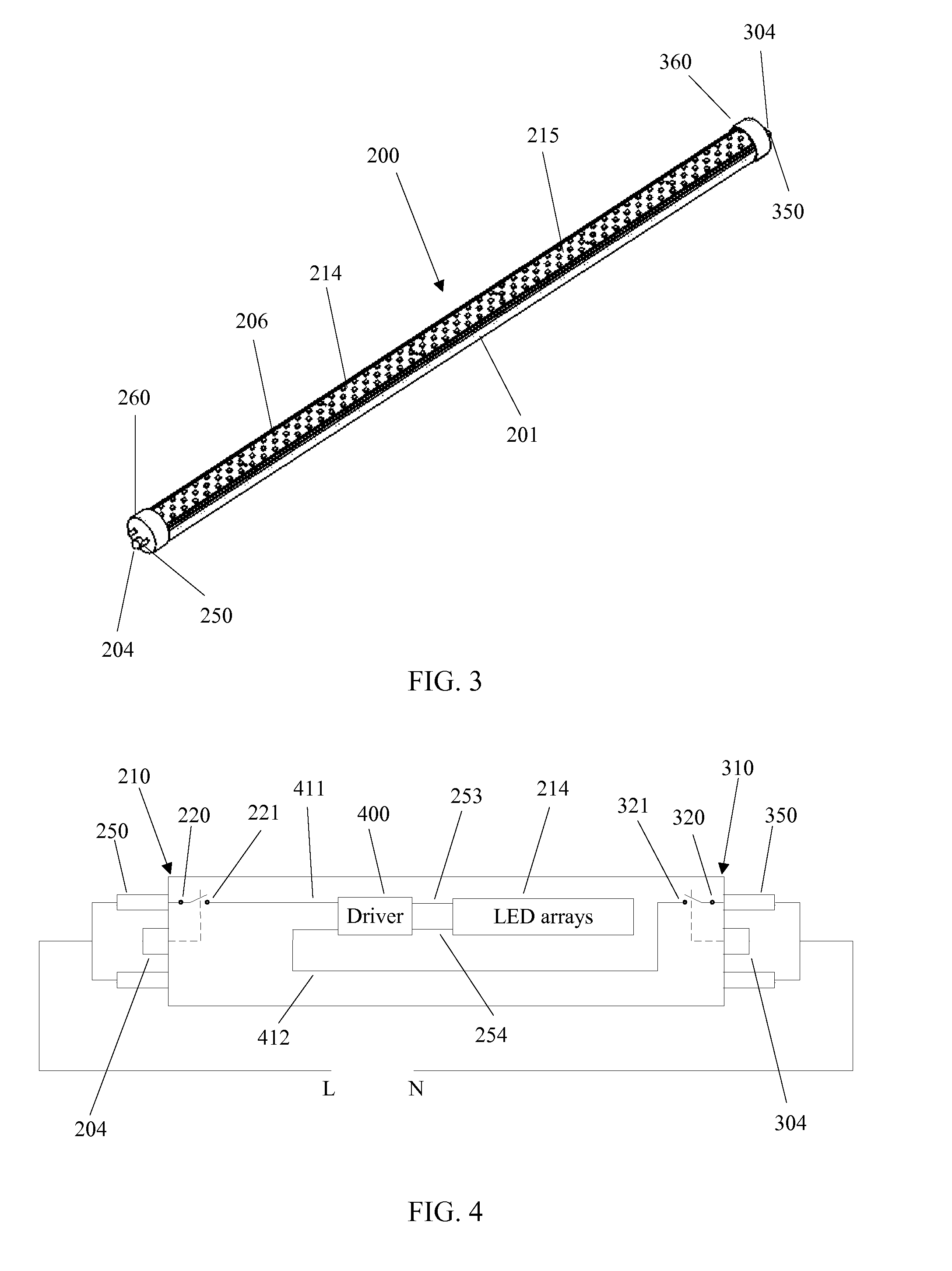
Linear solid-state lighting with shock protection switches
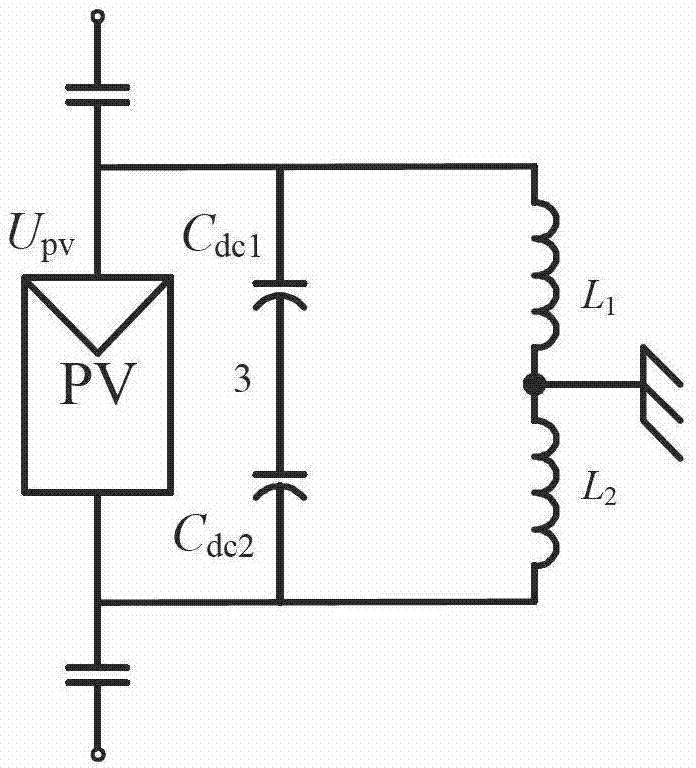
ActiveUS20110149563A1Leakage currentEliminate leakage currentPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesSmart lightingEngineering
A linear light-emitting diode (LED)-based solid-state device comprising at least two shock protection switches, at least one each at the two ends of the device, fully protects a person from possible electric shock during re-lamping with LED lamps.
Owner:ALEDDRA INC
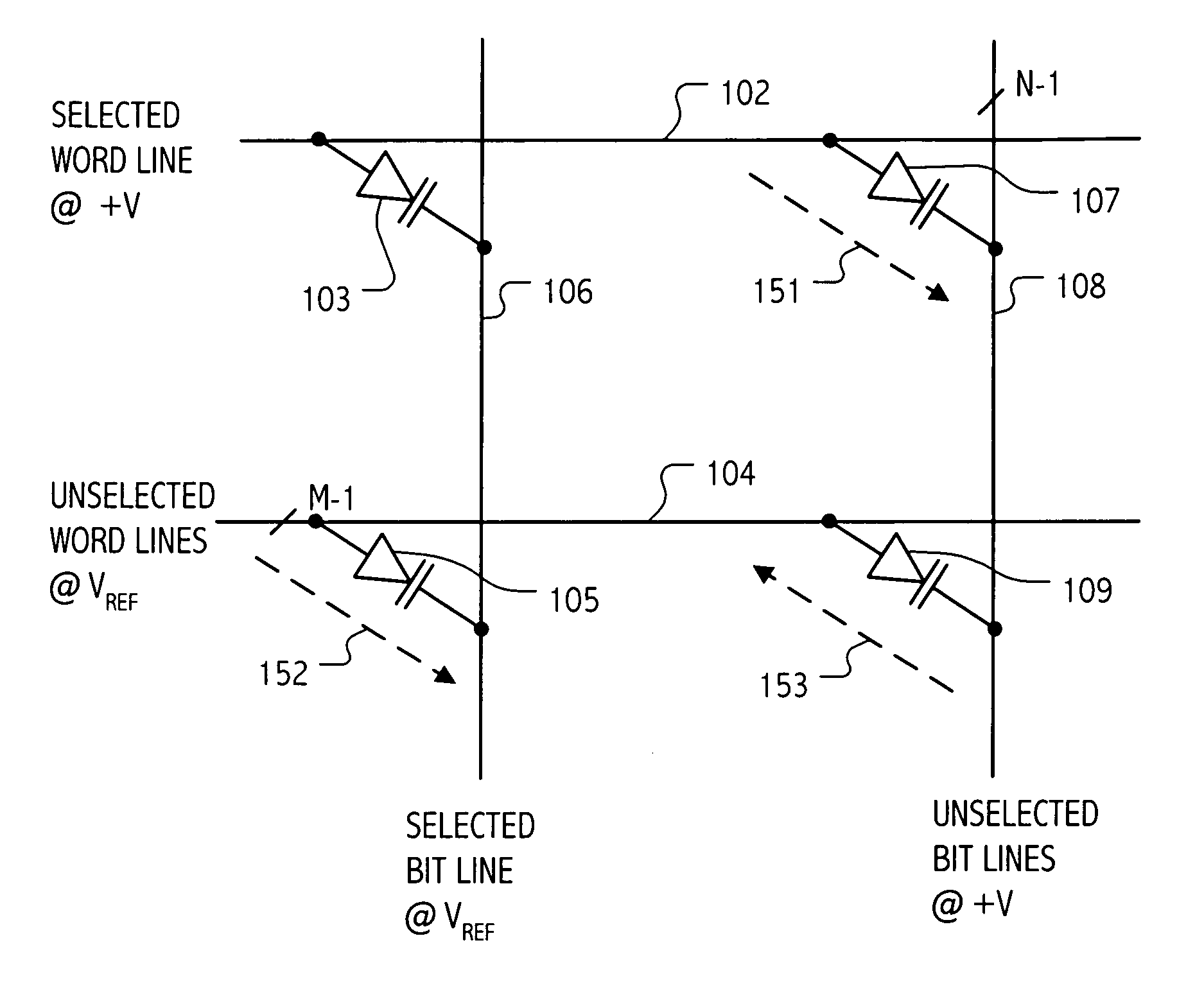
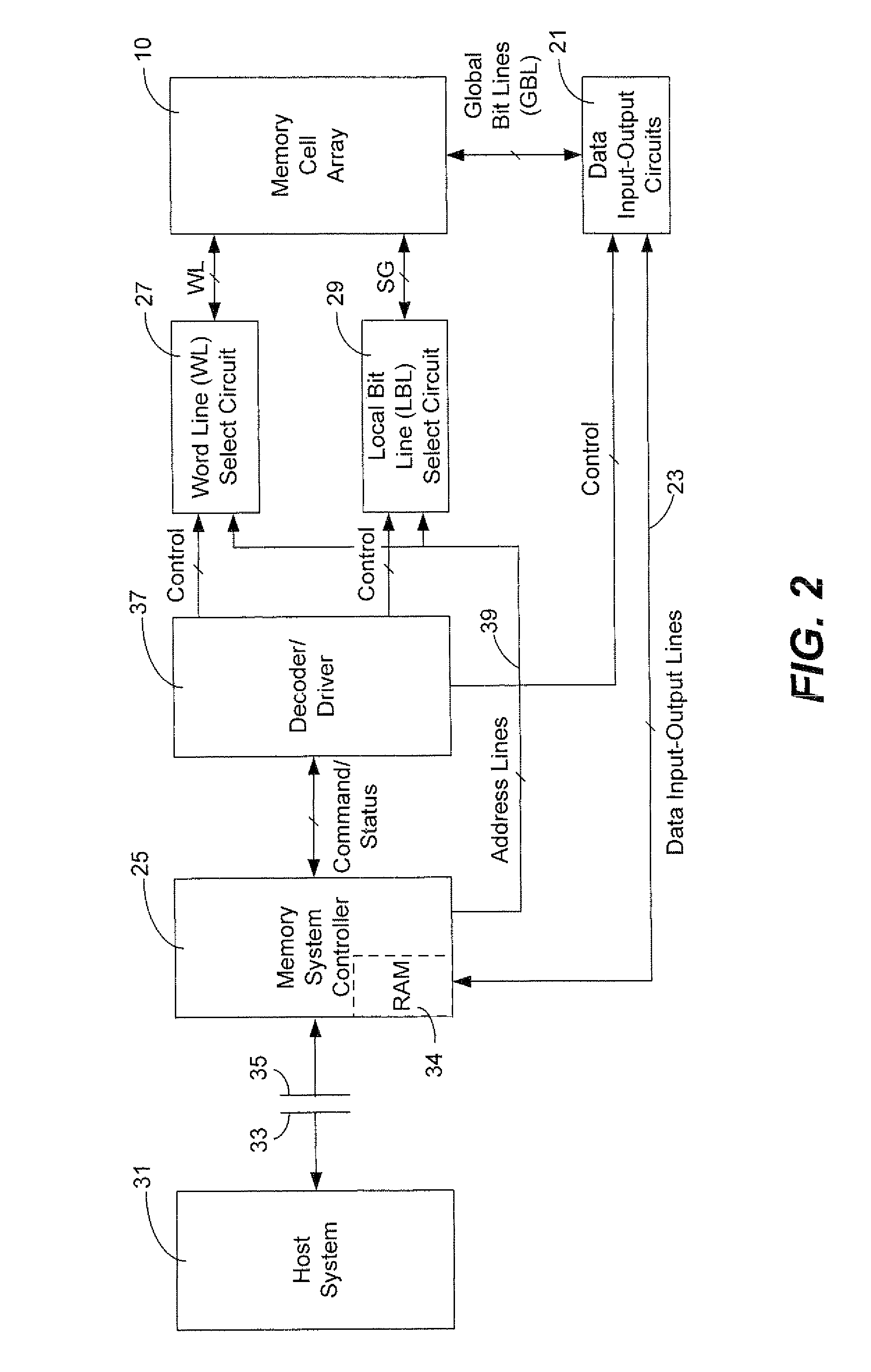
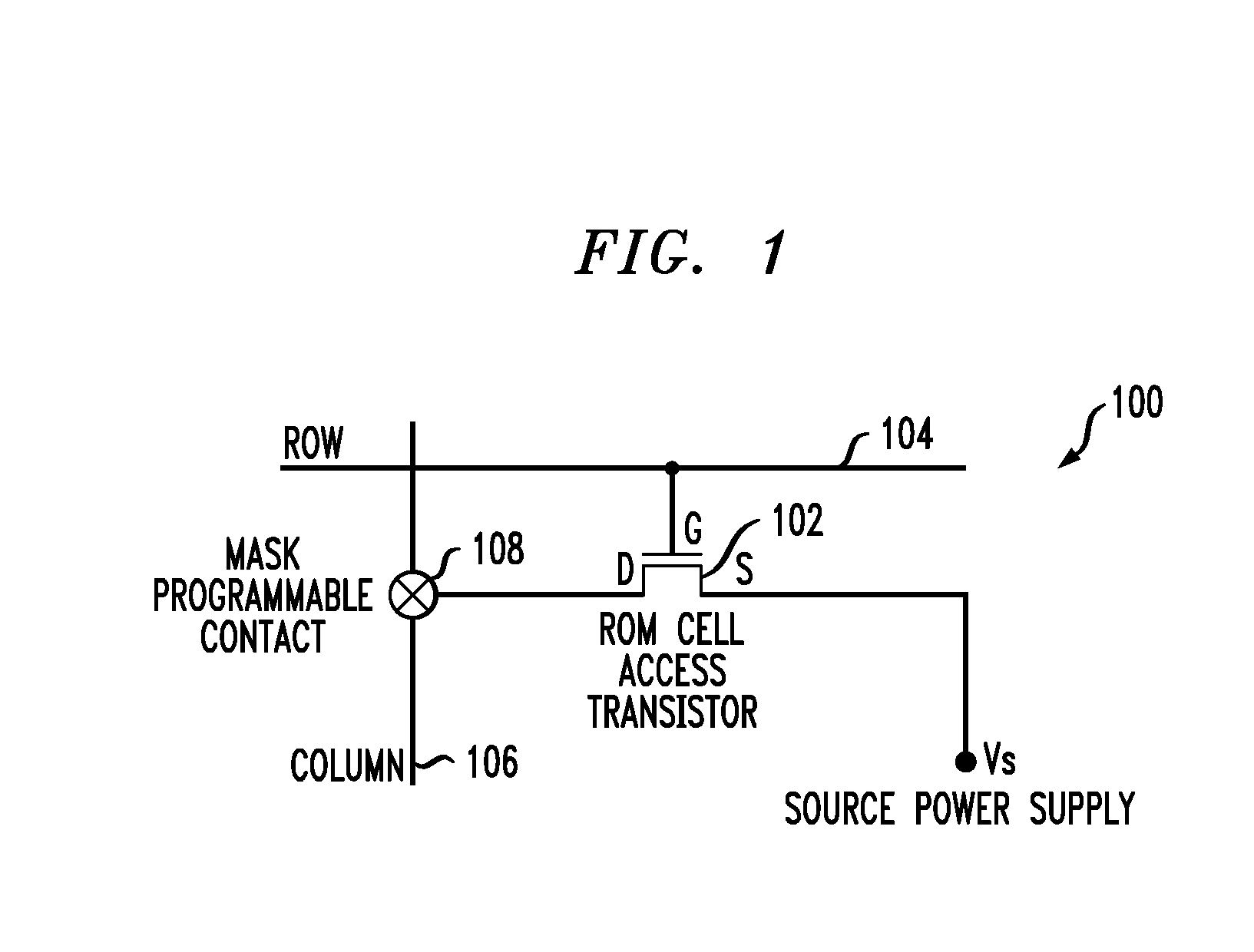
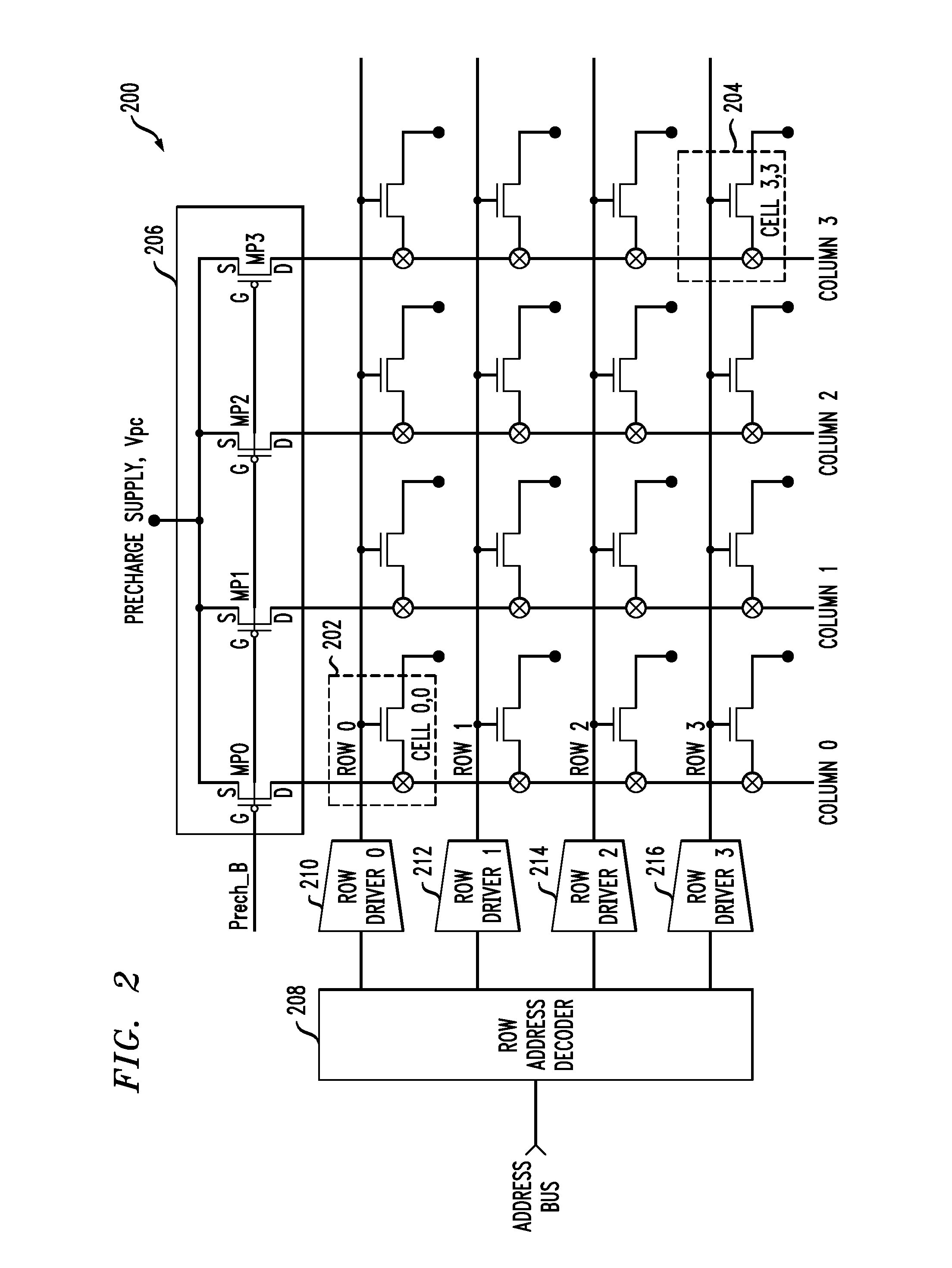
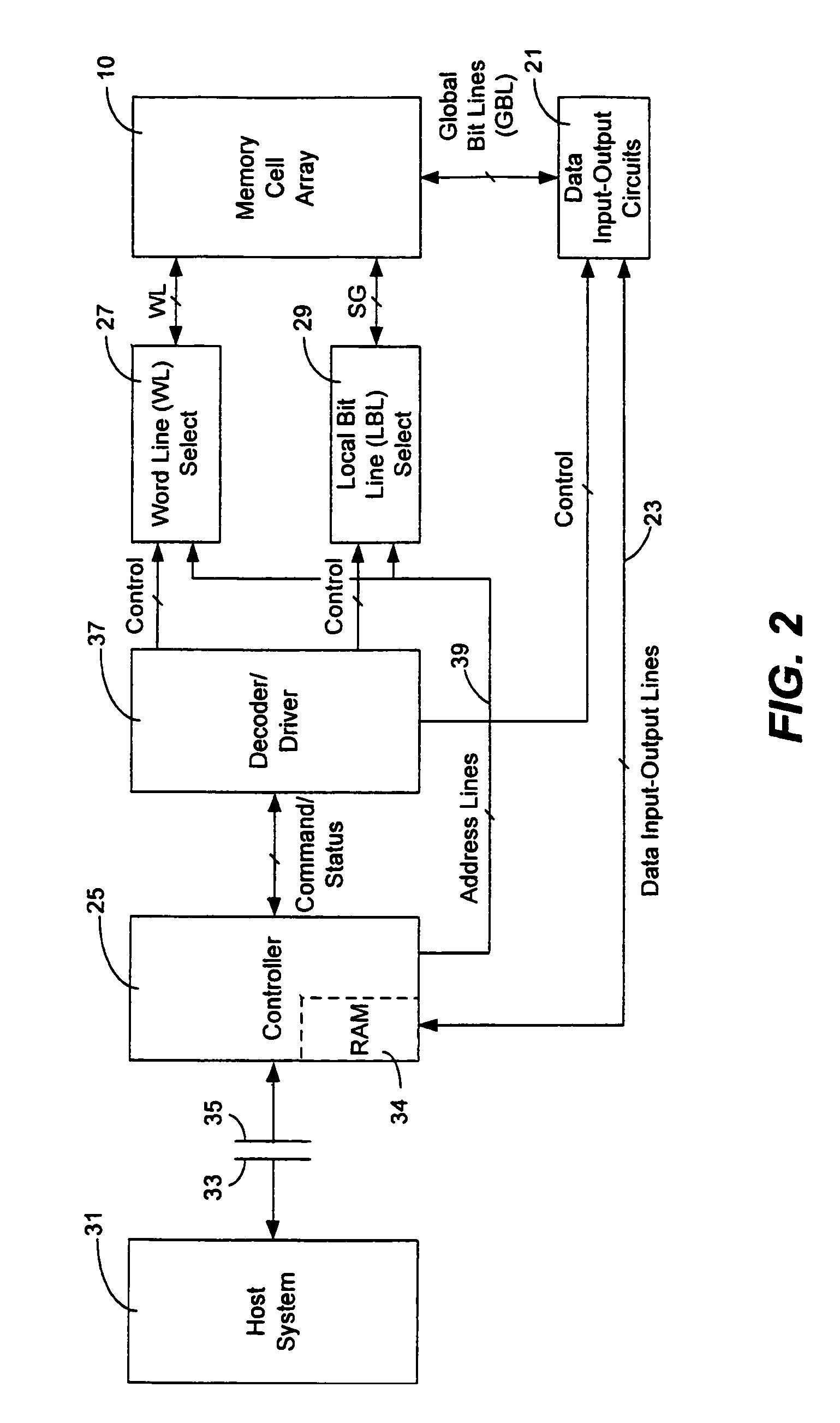
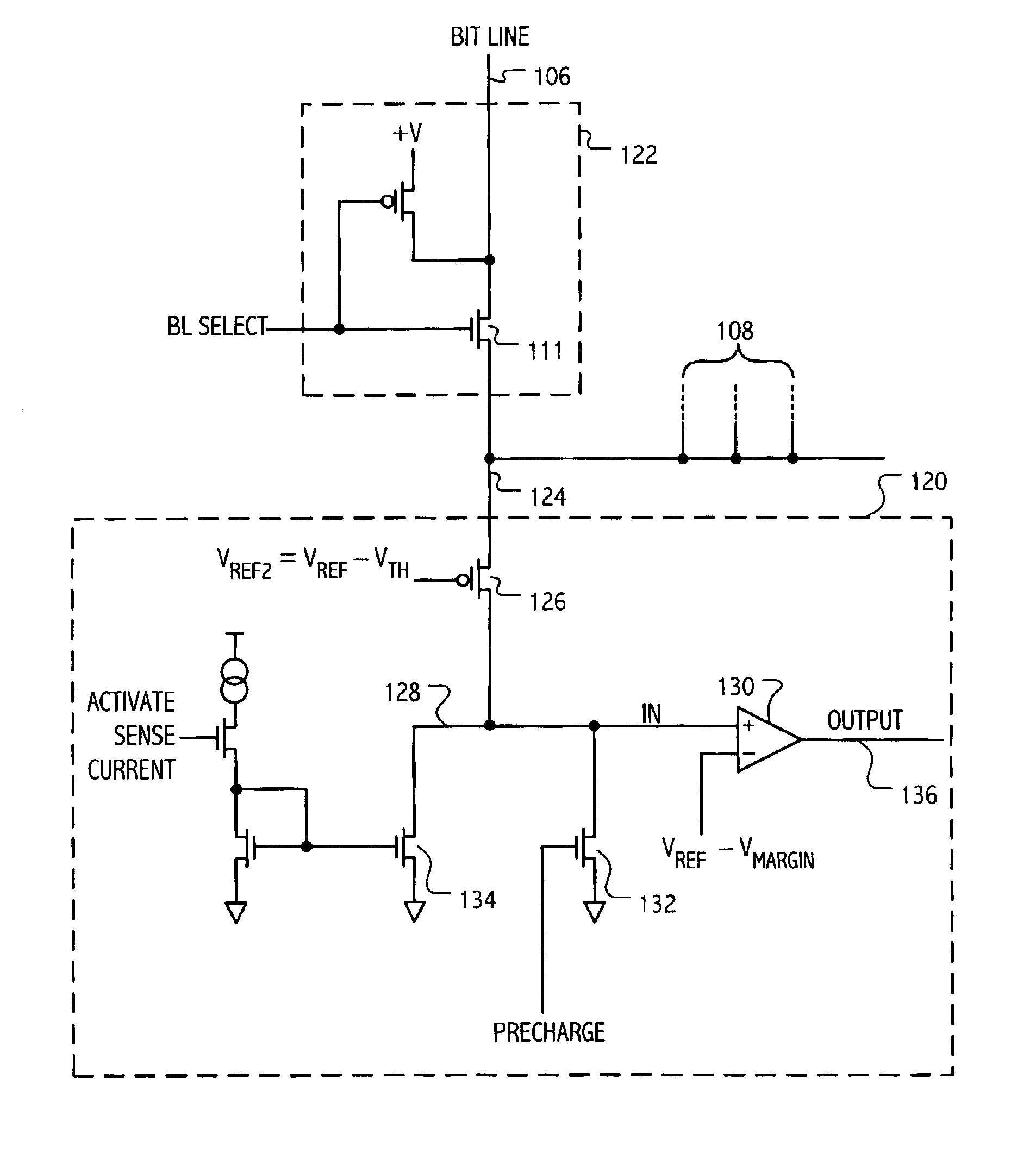
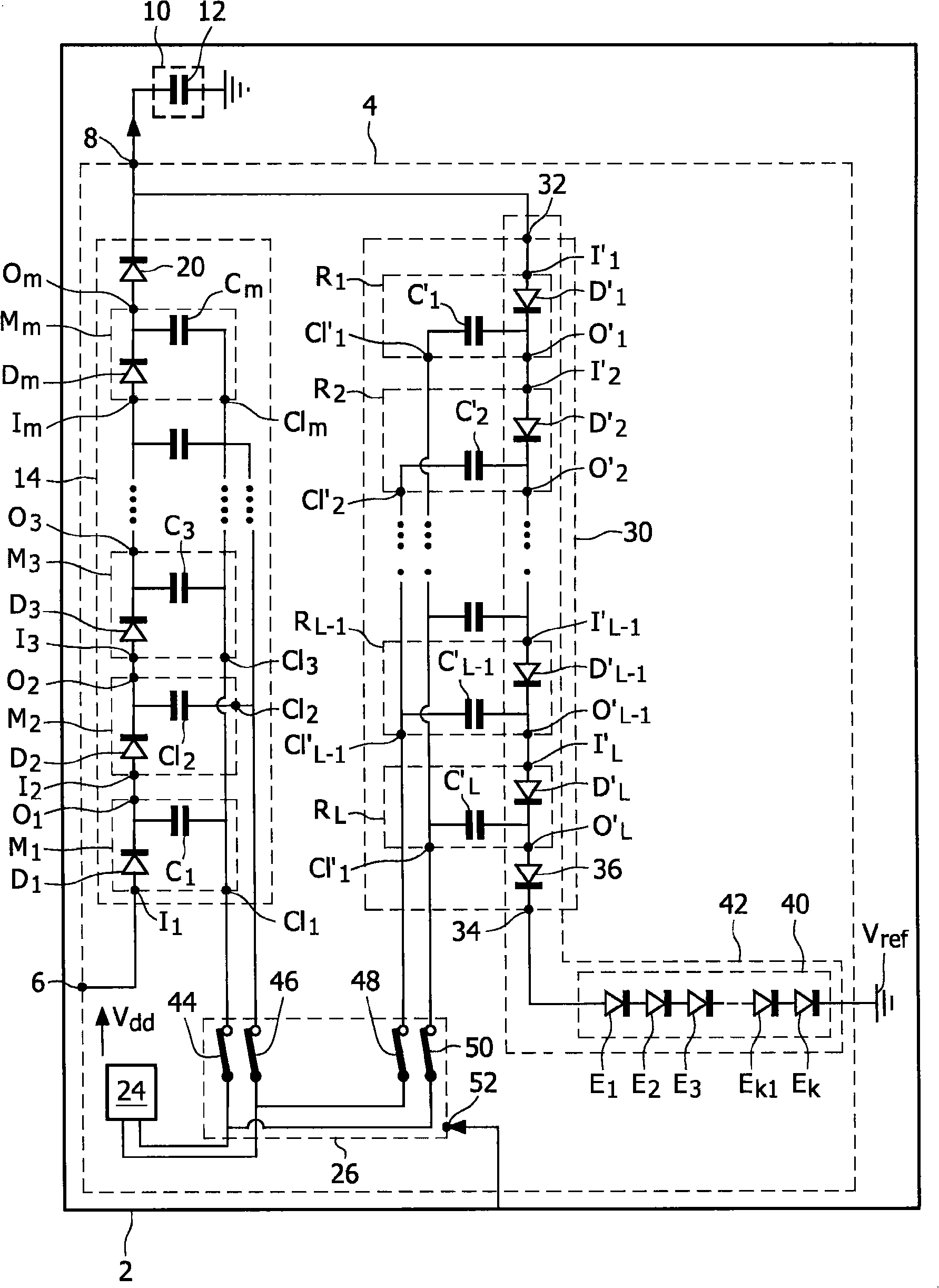
Current sensing method and apparatus particularly useful for a memory array of cells having diode-like characteristics
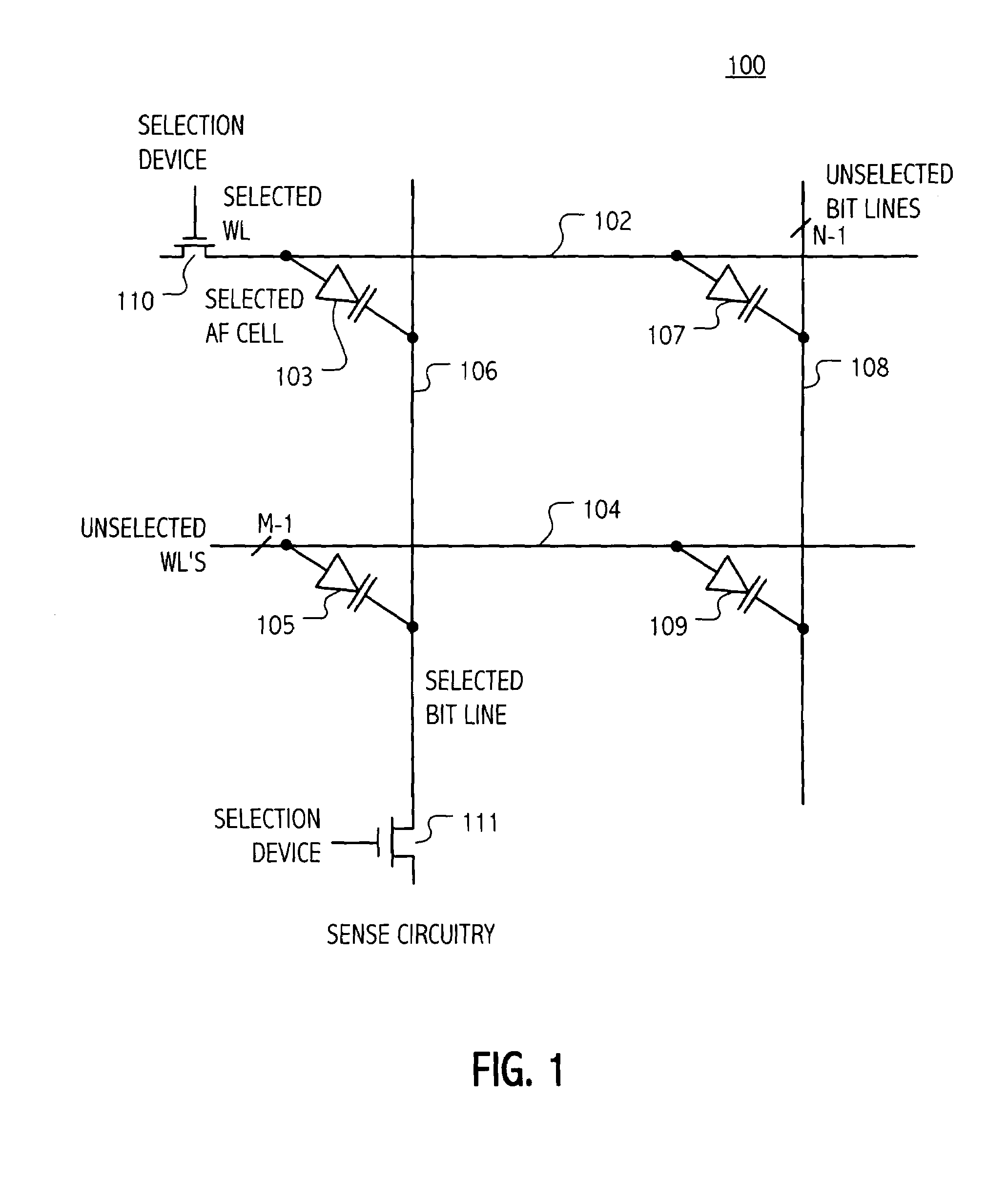
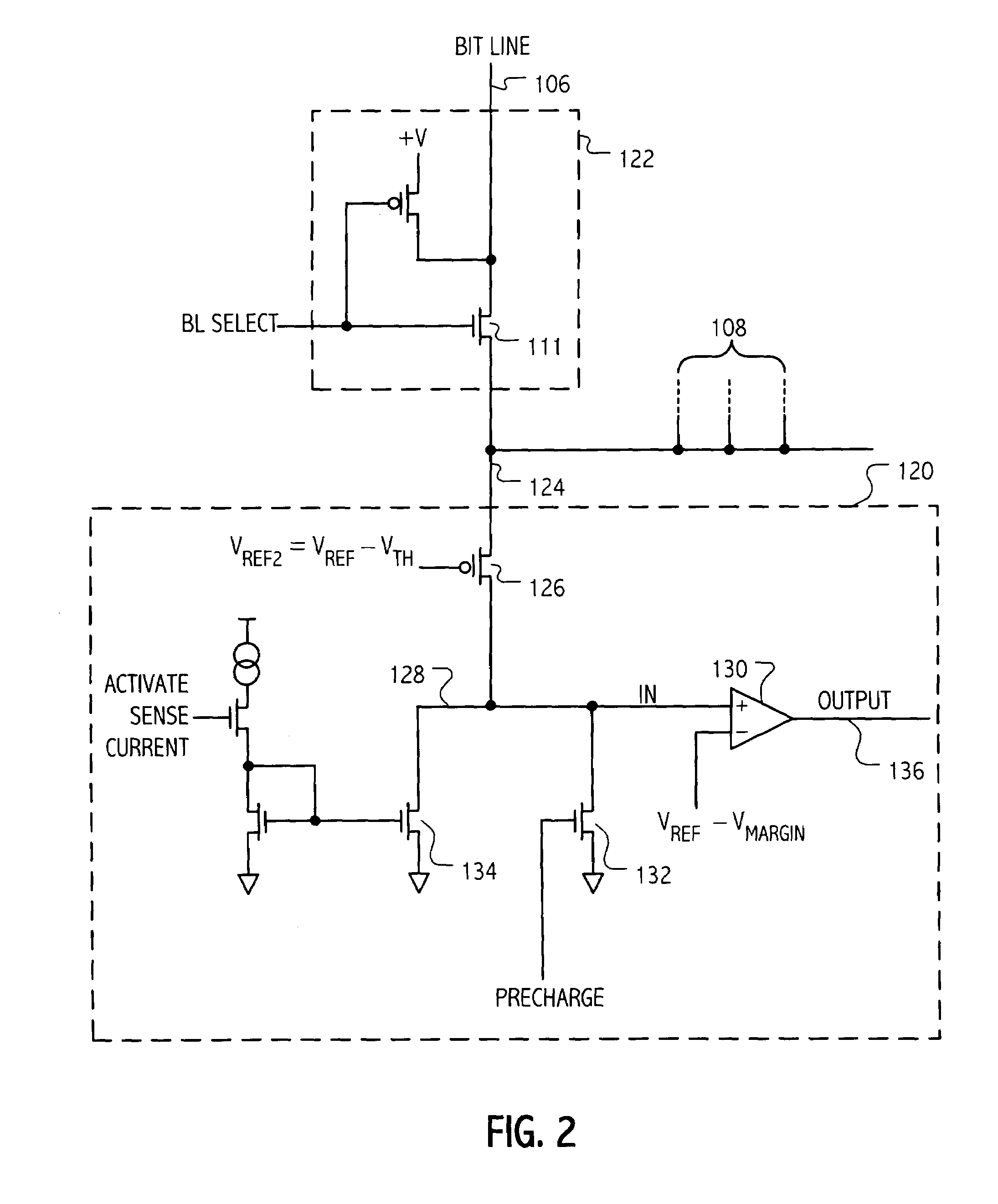
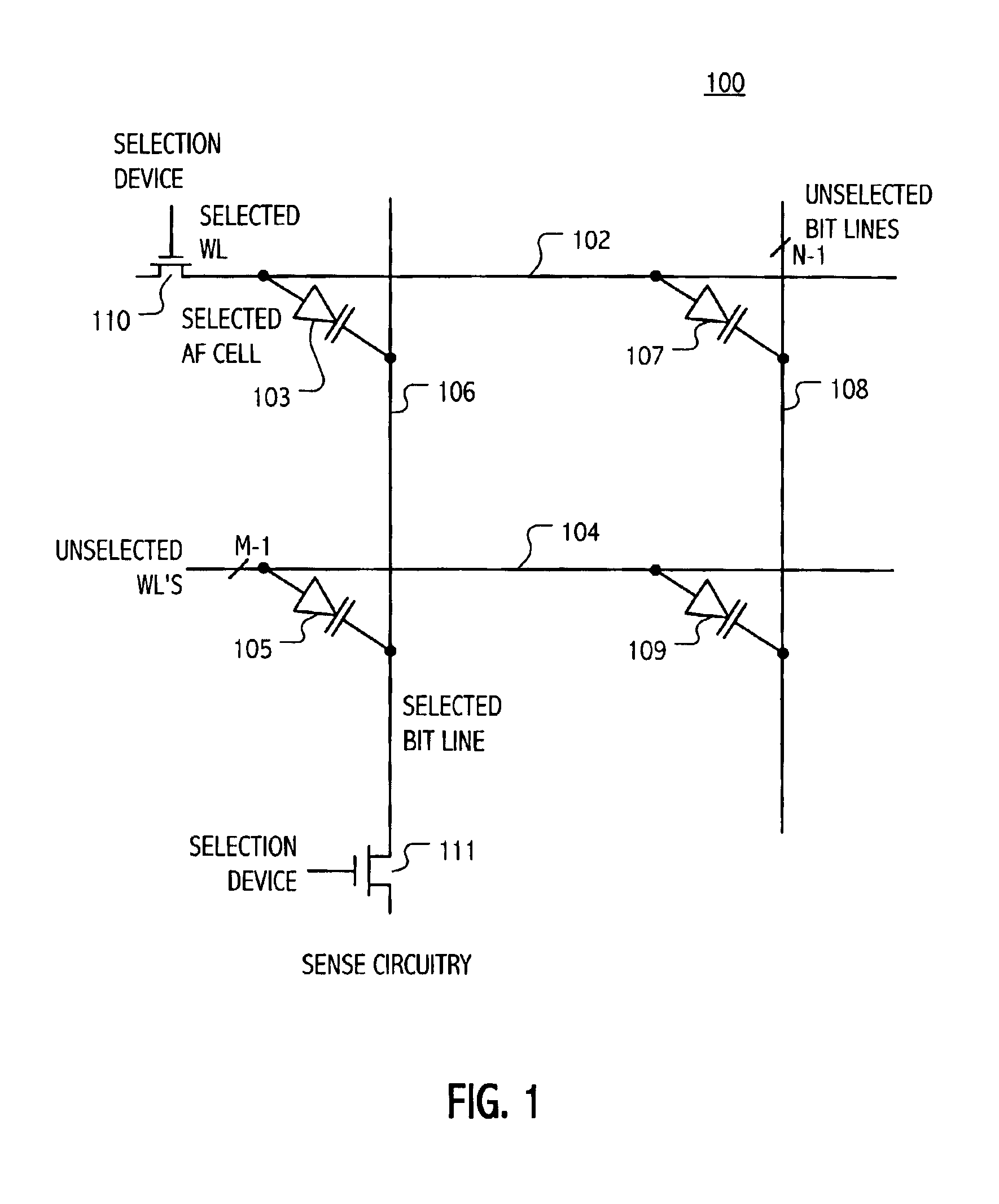
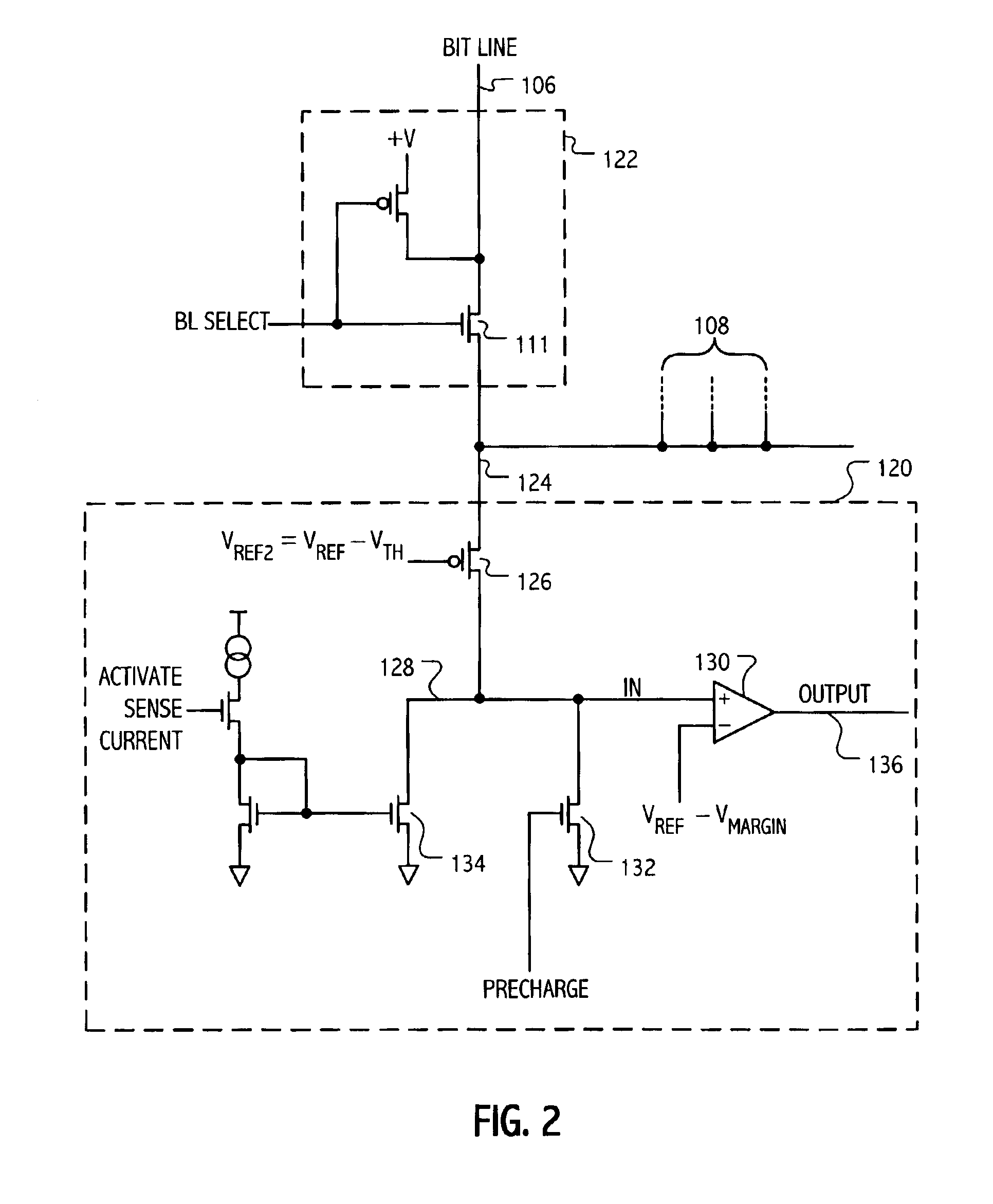
InactiveUS7177181B1Reduce impactEliminate leakage currentRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineNoise detection
A memory array includes a sensing circuit for sensing bit line current while keeping the voltage of the selected bit line substantially unchanged. The word lines and bit lines are biased so that essentially no bias voltage is impressed across half-selected memory cells, which substantially eliminates leakage current through half-selected memory cells. The bit line current which is sensed arises largely from only the current through the selected memory cell. A noise detection line in the memory array reduces the effect of coupling from unselected word lines to the selected bit line. In a preferred embodiment, a three-dimensional memory array having a plurality of rail-stacks forming bit lines on more than one layer, includes at least one noise detection line associated with each layer of bit lines. A sensing circuit is connected to a selected bit line and to its associated noise detection line.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Linear solid-state lighting with a double safety mechanism free of shock hazard
ActiveUS20110149564A1Eliminate leakage currentPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesSolid-stateEngineering
A linear light-emitting diode (LED)-based solid-state lamp having a double safety mechanism that comprises at least three shock protection switches, fully protects a person from possible electric shock during re-lamping or maintenance. One protection switch provided at each end of the lamp is able to cut off power when the associated end of the lamp is not inserted into the lamp socket. A third protection switch can be used to turn off the power from the AC main for additional shock protection.
Owner:ALEDDRA INC
Semiconductor device and method
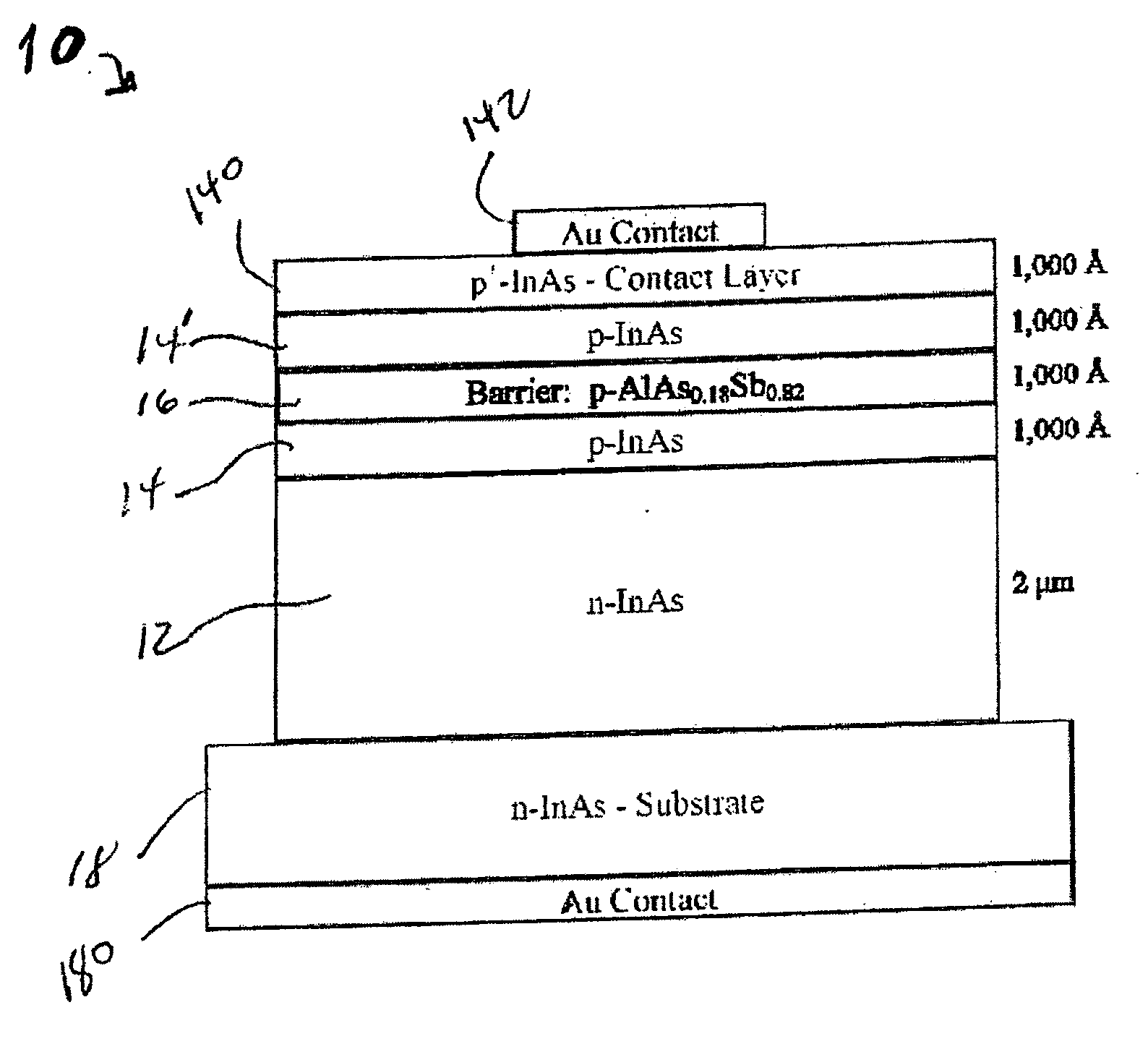
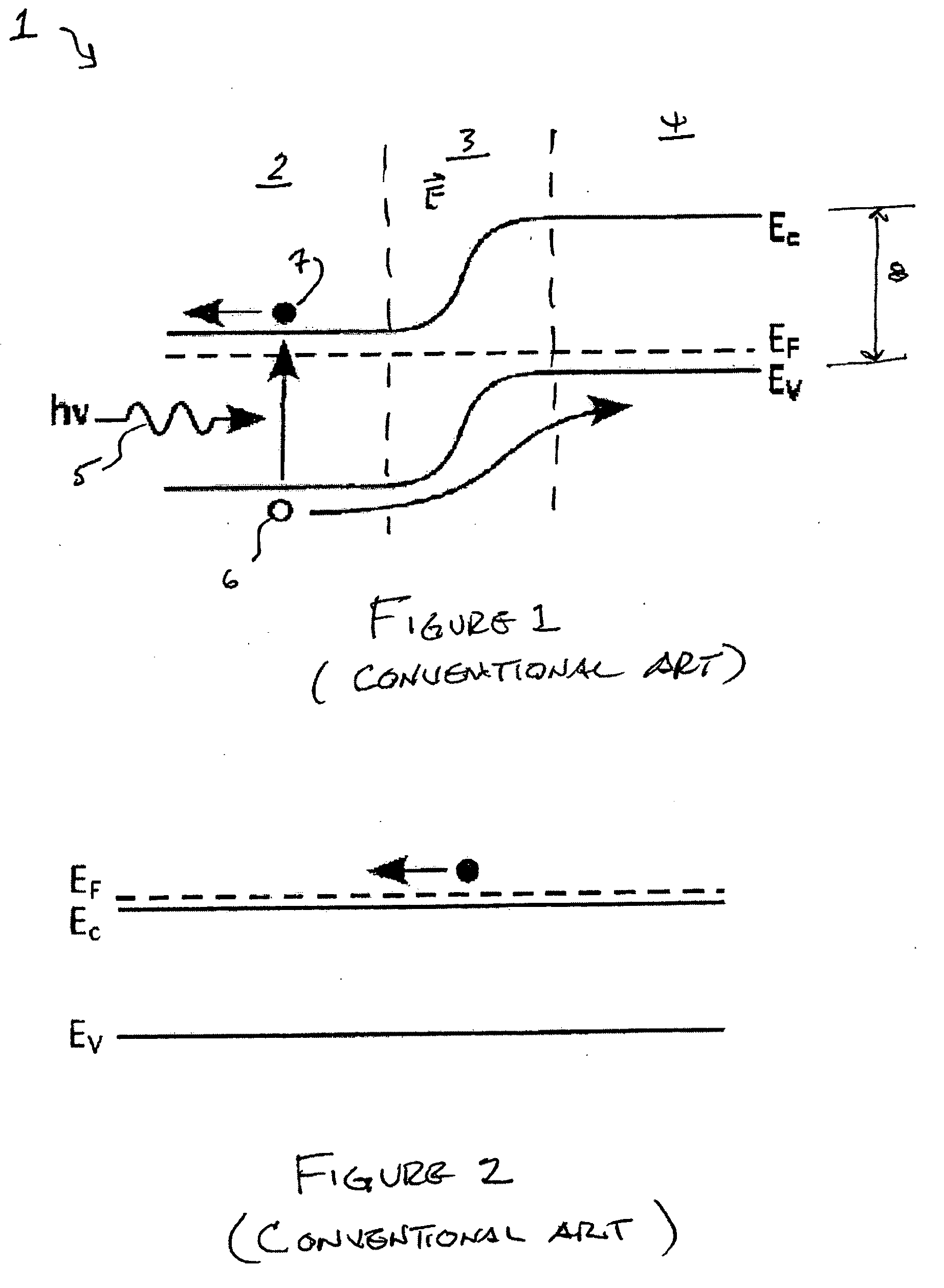
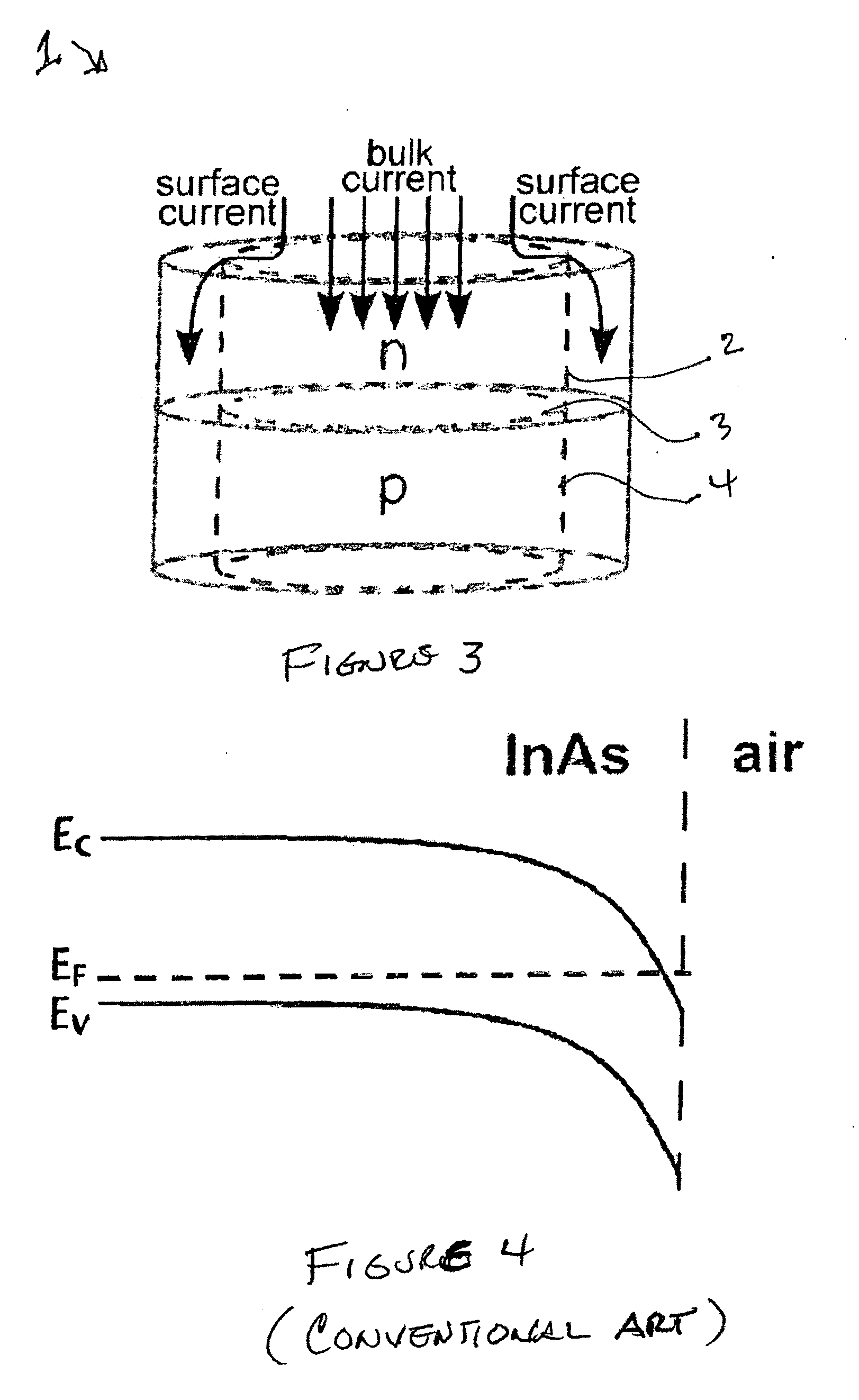
ActiveUS20100230720A1Eliminate surface leakage currentReduce surface currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsValence bandConduction band
The present invention is directed to a semiconductor device that includes at least one p-n junction including a p-type material, an n-type material, and a depletion region. The at least one p-n junction is configured to generate bulk photocurrent in response to incident light. The at least one p-n junction is characterized by a conduction band energy level, a valence band energy level and a surface Fermi energy level. The surface Fermi energy level is pinned either near or above the conduction band energy level or near or below the valence band energy level. A unipolar barrier structure is disposed in a predetermined region within the at least one p-n junction. The unipolar barrier is configured to raise the conduction band energy level if the surface Fermi energy level is pinned near or above the conduction band energy level or lower the valence band energy level if the surface Fermi energy level is pinned near or below the valence band energy level such that the unipolar barrier is configured to propagate the bulk photocurrent and substantially block surface leakage current. The at least one p-n junction and the unipolar barrier are integrally formed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
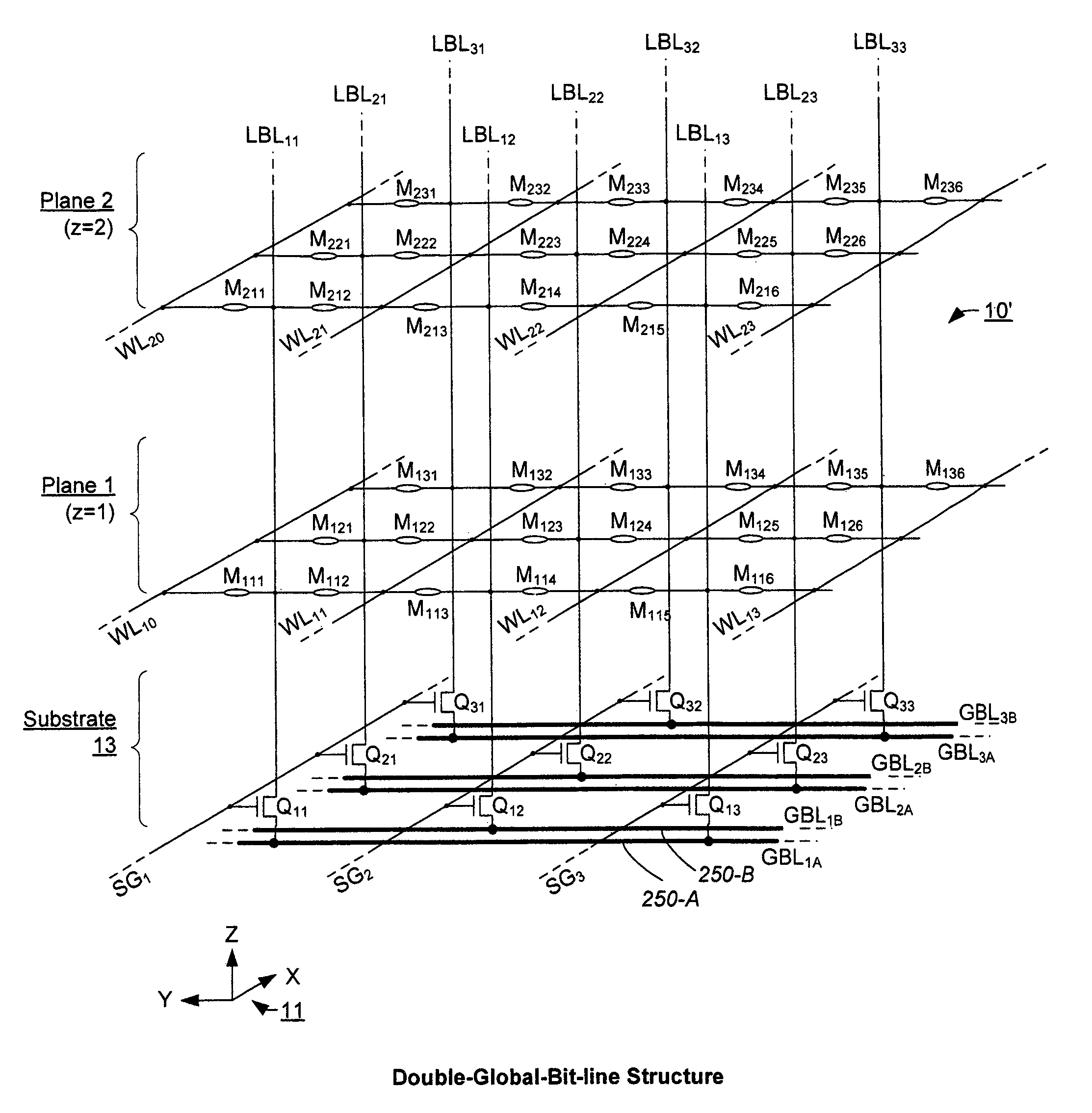
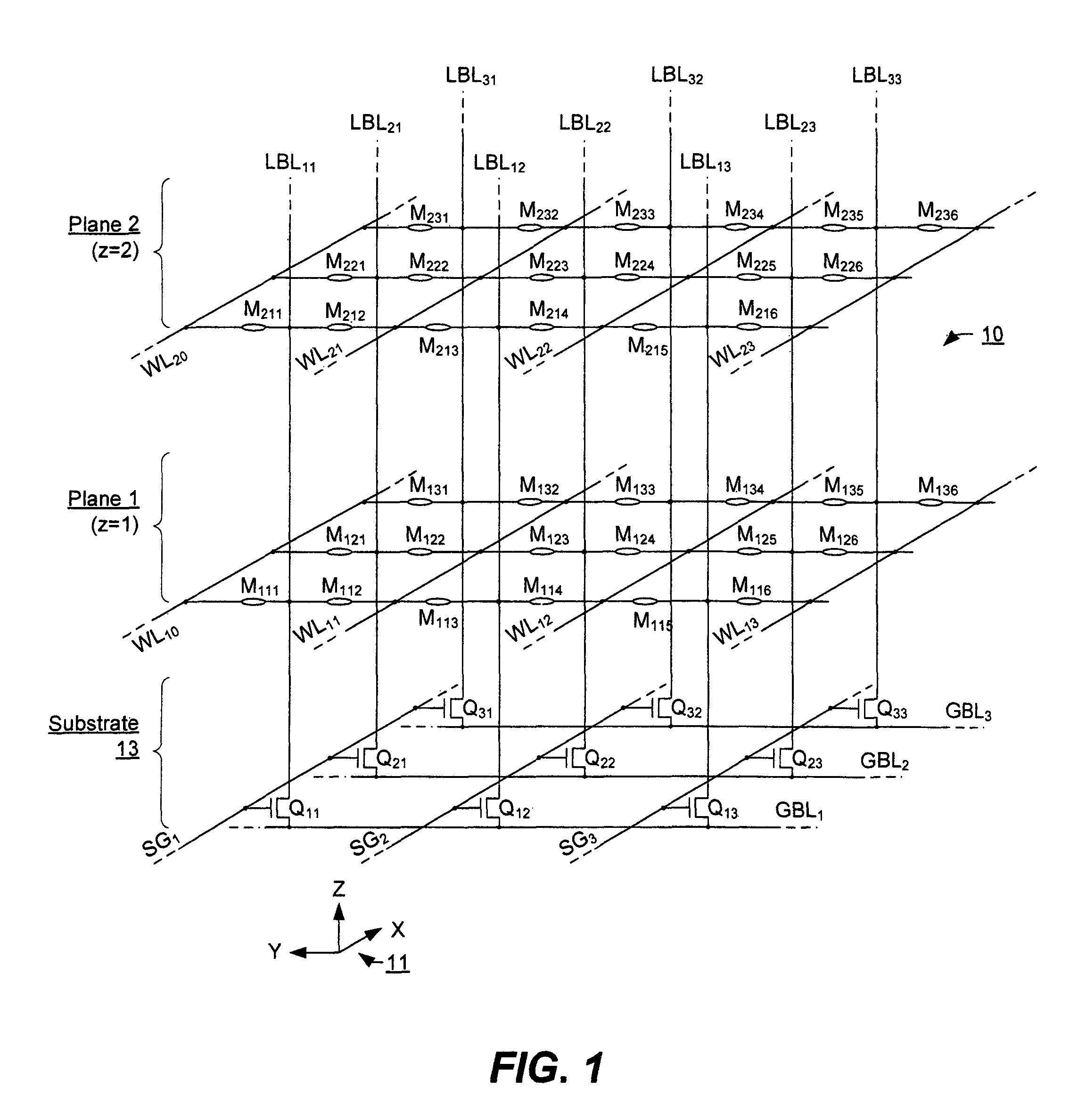
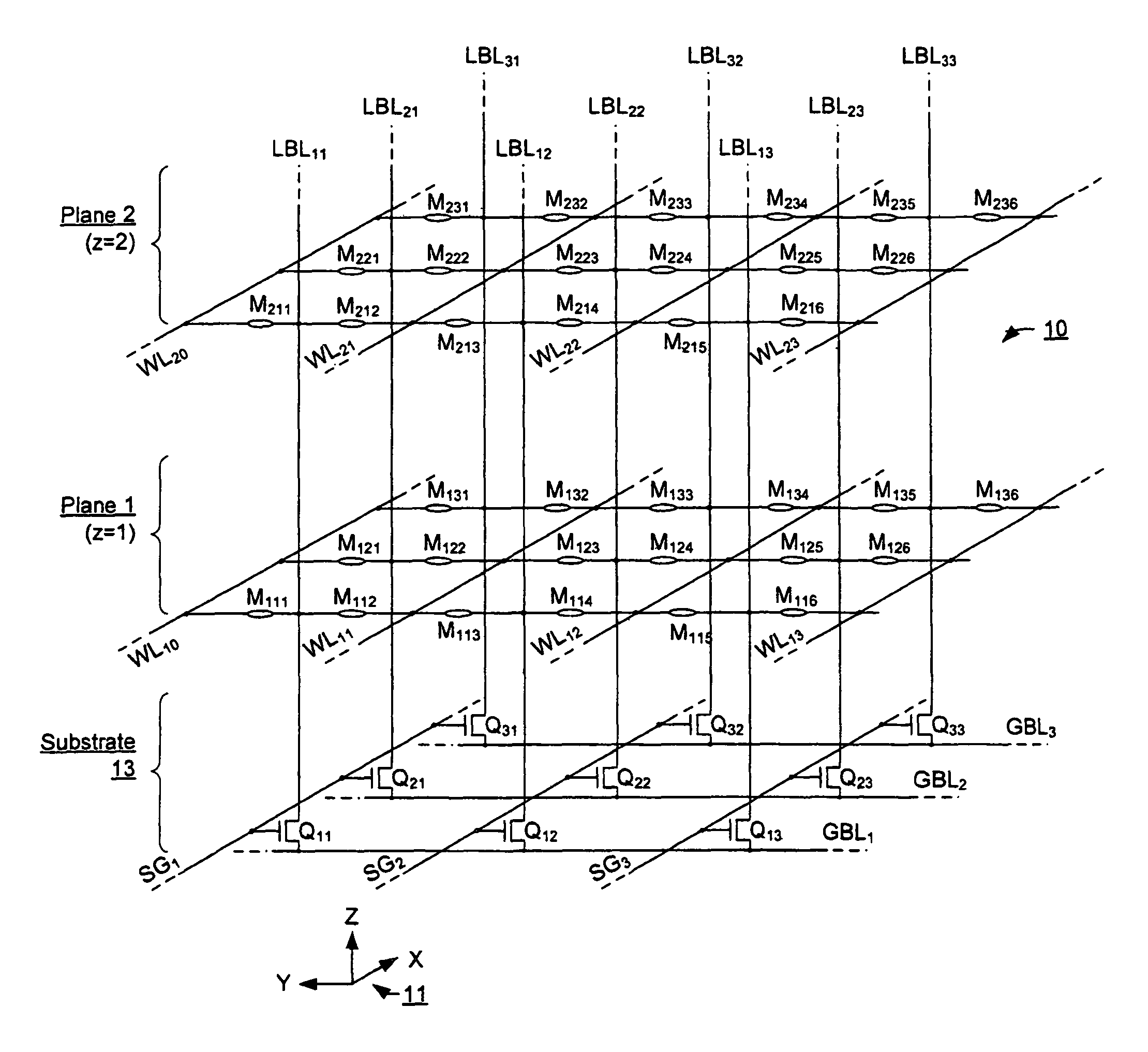
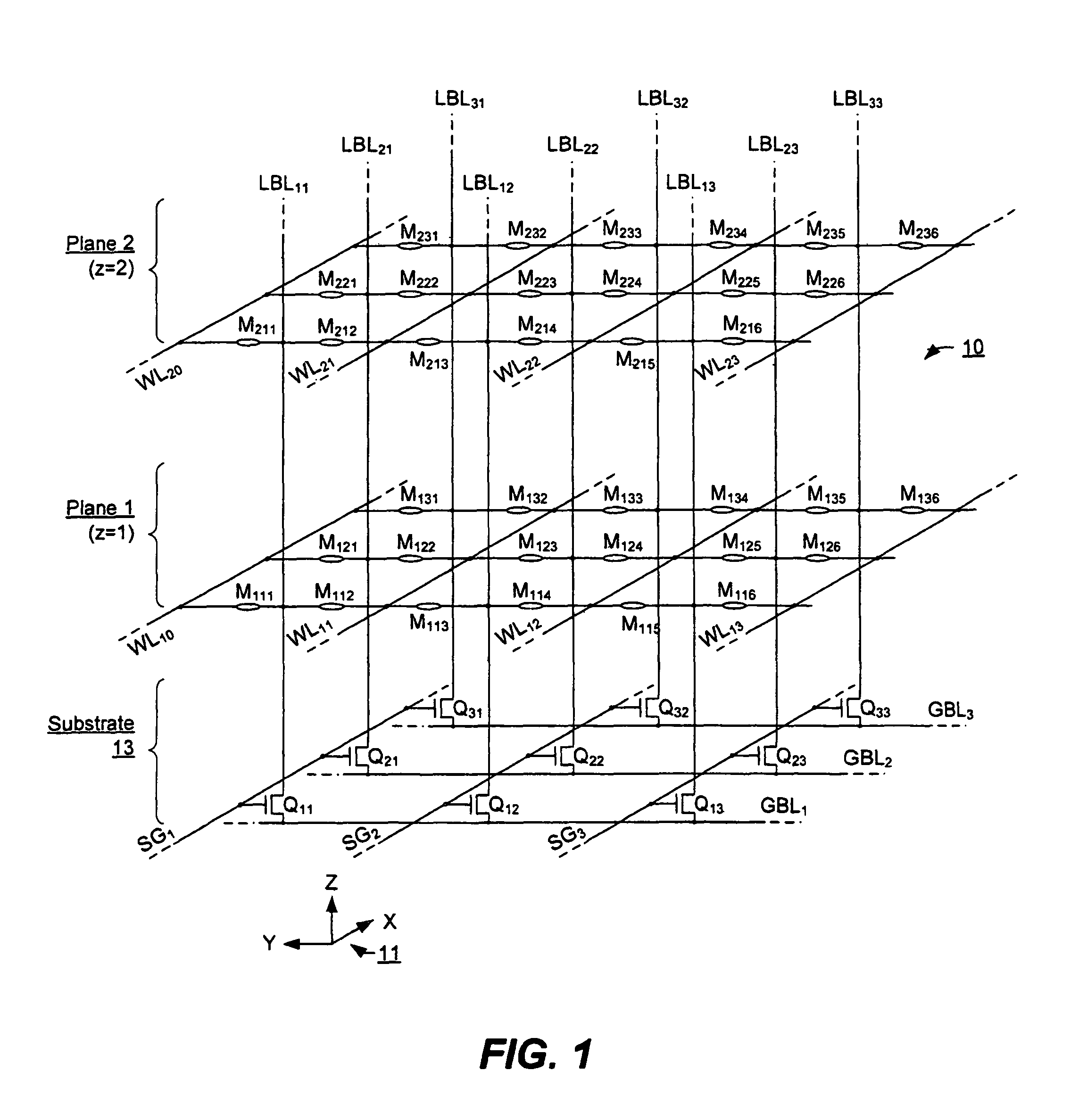
Three-dimensional array of re-programmable non-volatile memory elements having vertical bit lines and a double-global-bit-line architecture
ActiveUS8199576B2Reduce leakage levelGuaranteed true stateNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesBit lineEngineering
A three-dimensional array especially adapted for memory elements that reversibly change a level of electrical conductance in response to a voltage difference being applied across them. Memory elements are formed across a plurality of planes positioned different distances above a semiconductor substrate. A two-dimensional array of bit lines to which the memory elements of all planes are connected is oriented vertically from the substrate and through the plurality of planes. A double-global-bit-line architecture provides a pair of global bit lines for each bit lines for accessing a row of memory elements in parallel. A first one of each pair allows the local bit lines of the row to be sensed while a second one of each pair allows local bit lines in an adjacent row to be set to a definite voltage so as to eliminate leakage currents between adjacent rows of local bit lines.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
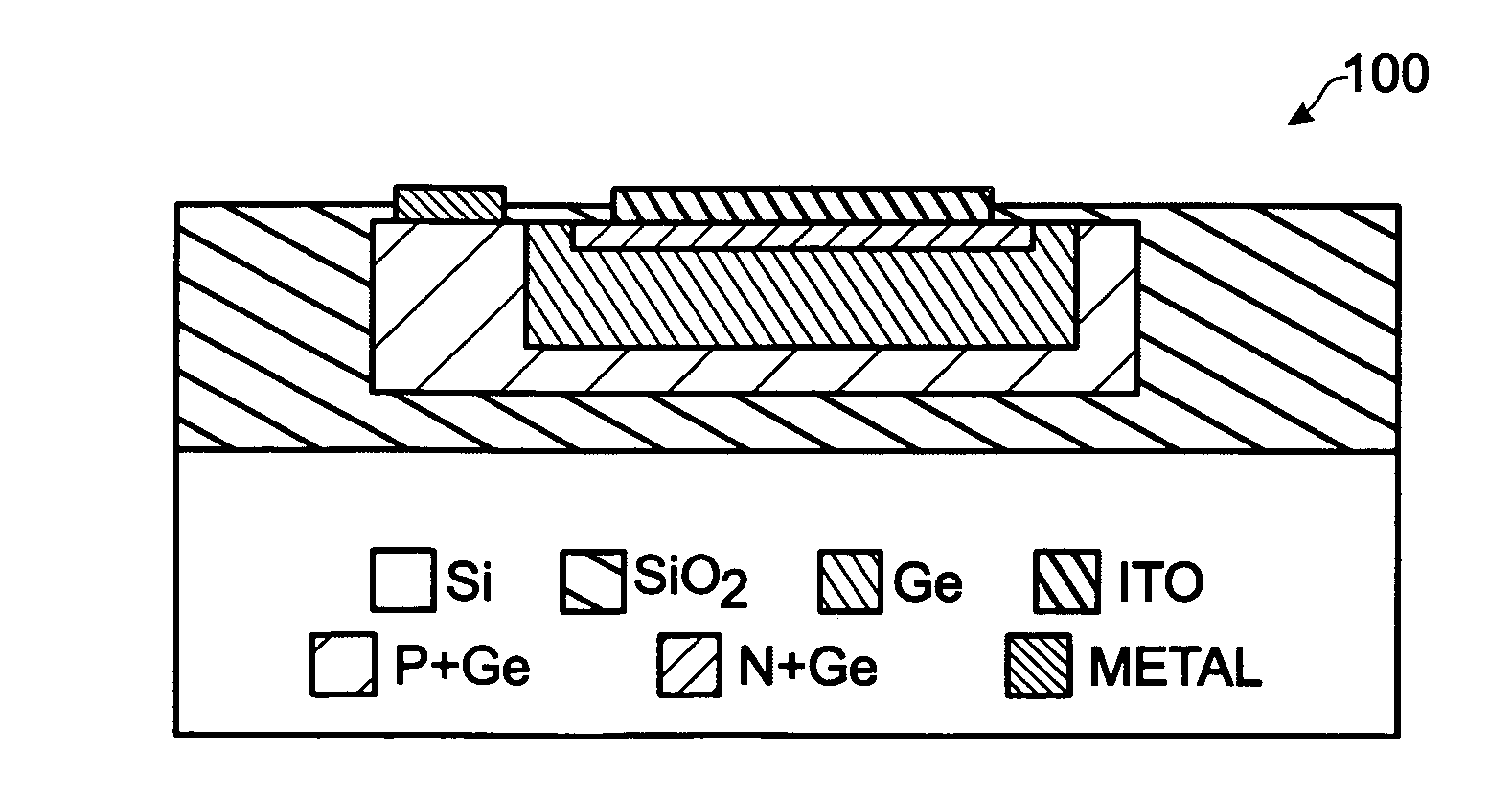
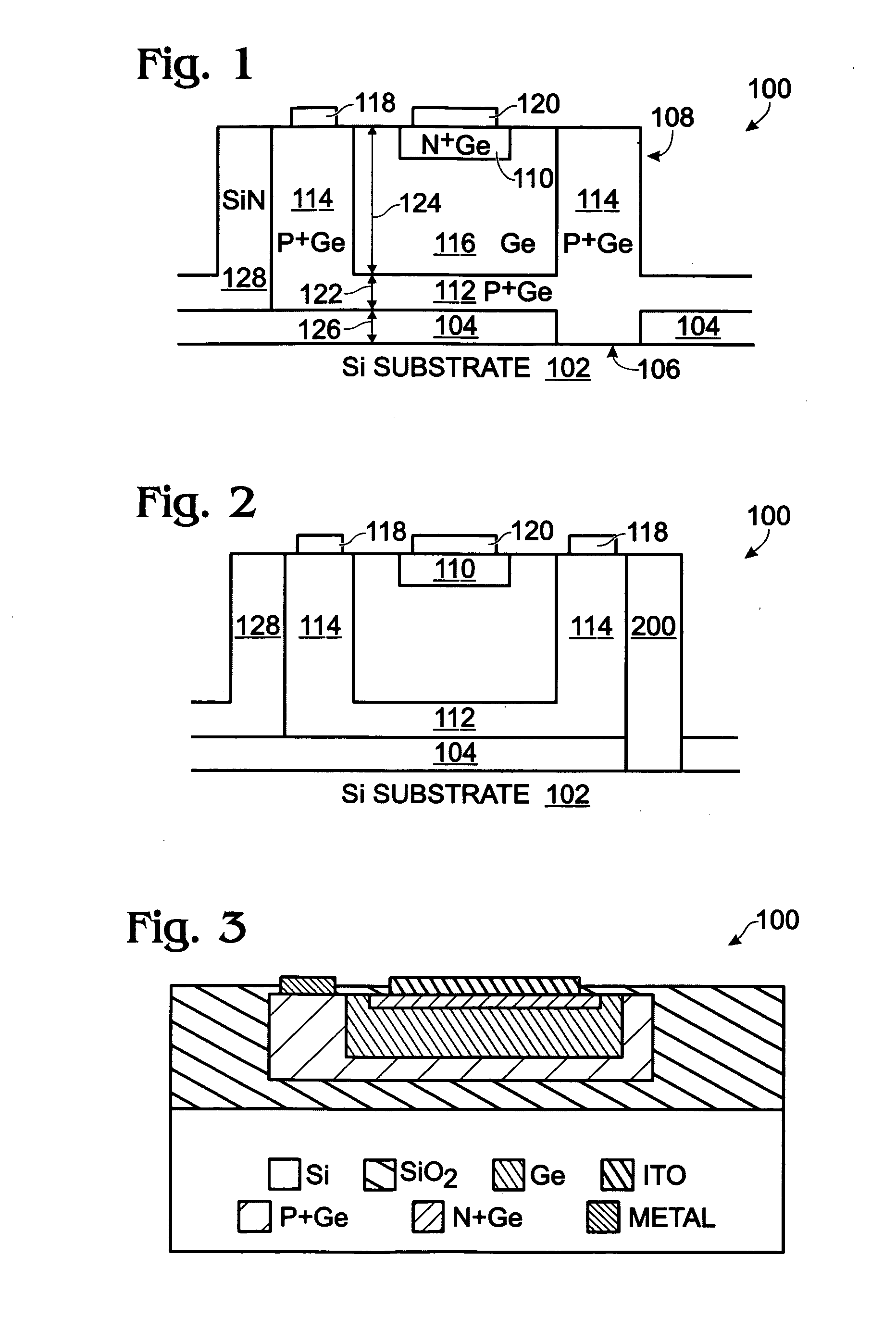
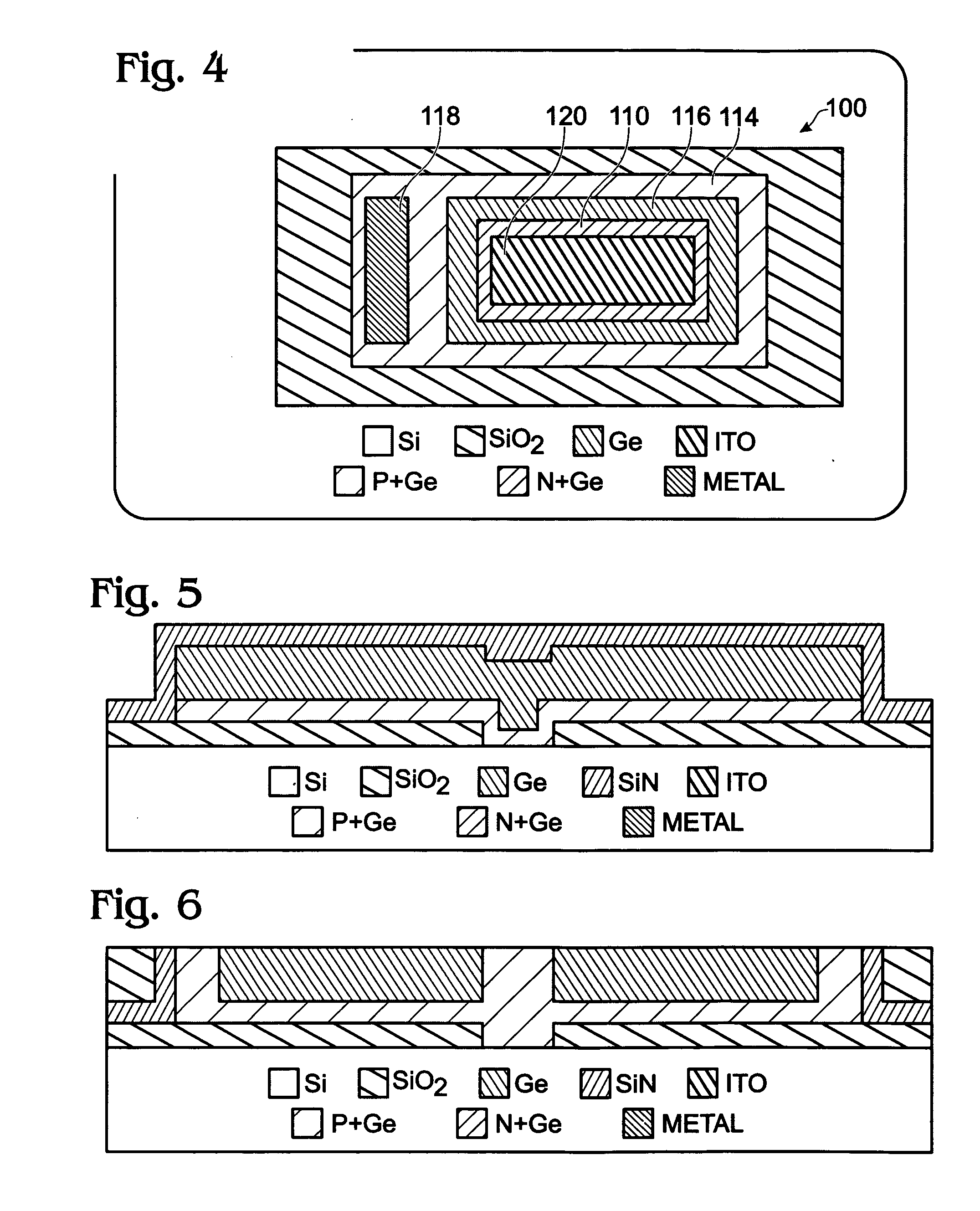
Liquid phase epitaxial GOI photodiode with buried high resistivity germanium layer
InactiveUS20070170536A1Significant problemEliminate leakage currentPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHigh resistivityAdemetionine
A device and associated method are provided for fabricating a liquid phase epitaxial (LPE) Germanium-on-Insulator (GOI) photodiode with buried high resistivity Germanium (Ge) layer. The method provides a silicon (Si) substrate, and forms a bottom insulator overlying the Si substrate with a Si seed access area. Then, a Ge P-I-N diode is formed with an n +-doped (n+) mesa, a p+-doped (p+) Ge bottom insulator interface and mesa lateral interface, and a high resistivity Ge layer interposed between the p+ Ge and n+ Ge. A metal electrode is formed overlying a region of the p+ Ge lateral interface, and a transparent electrode is formed overlying the n+ Ge mesa. In one aspect, the method deposits a silicon nitride layer temporary cap overlying the high resistivity Ge layer, and an annealing is performed to epitaxially crystallize the Ge bottom interface and high resistivity Ge layer.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
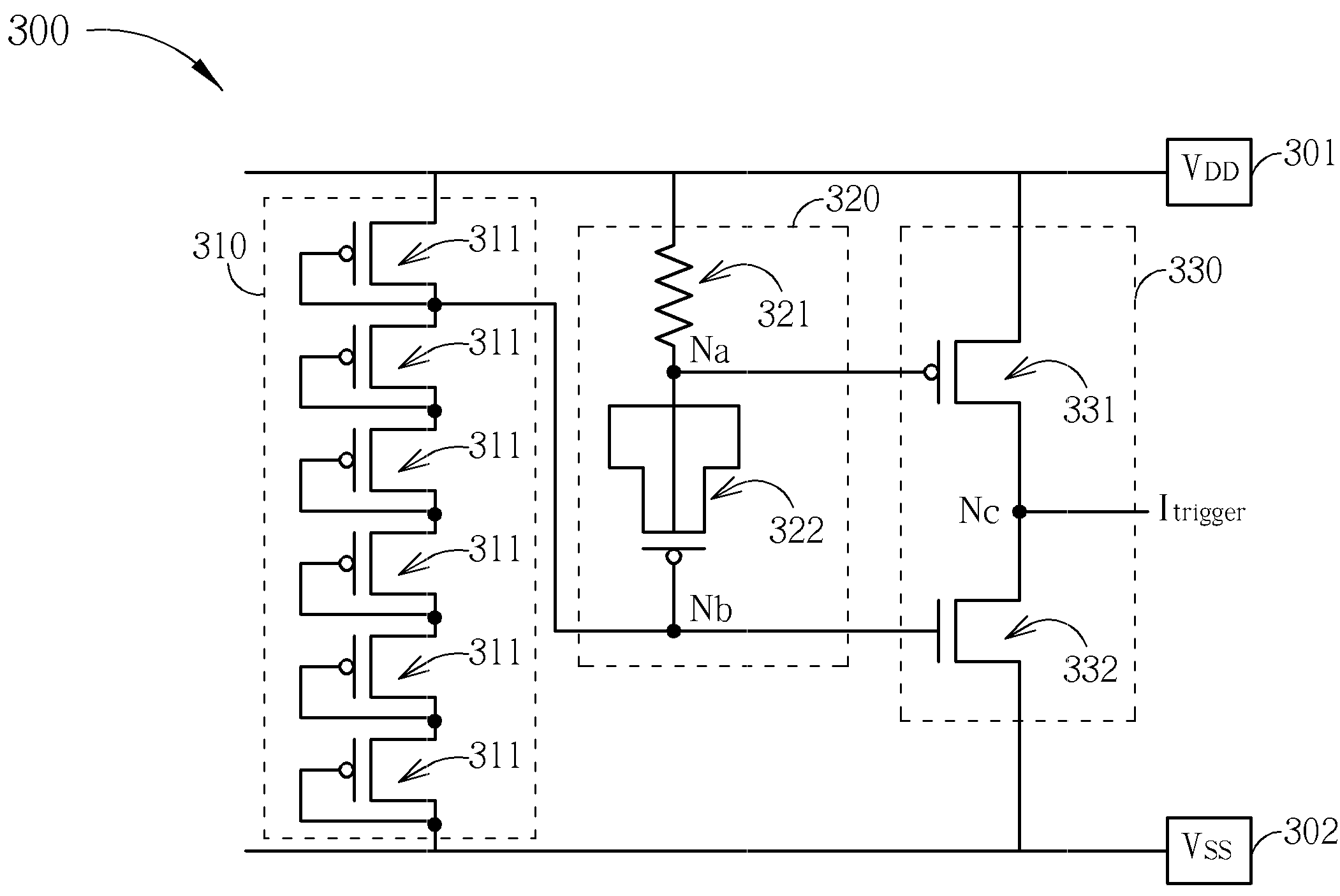
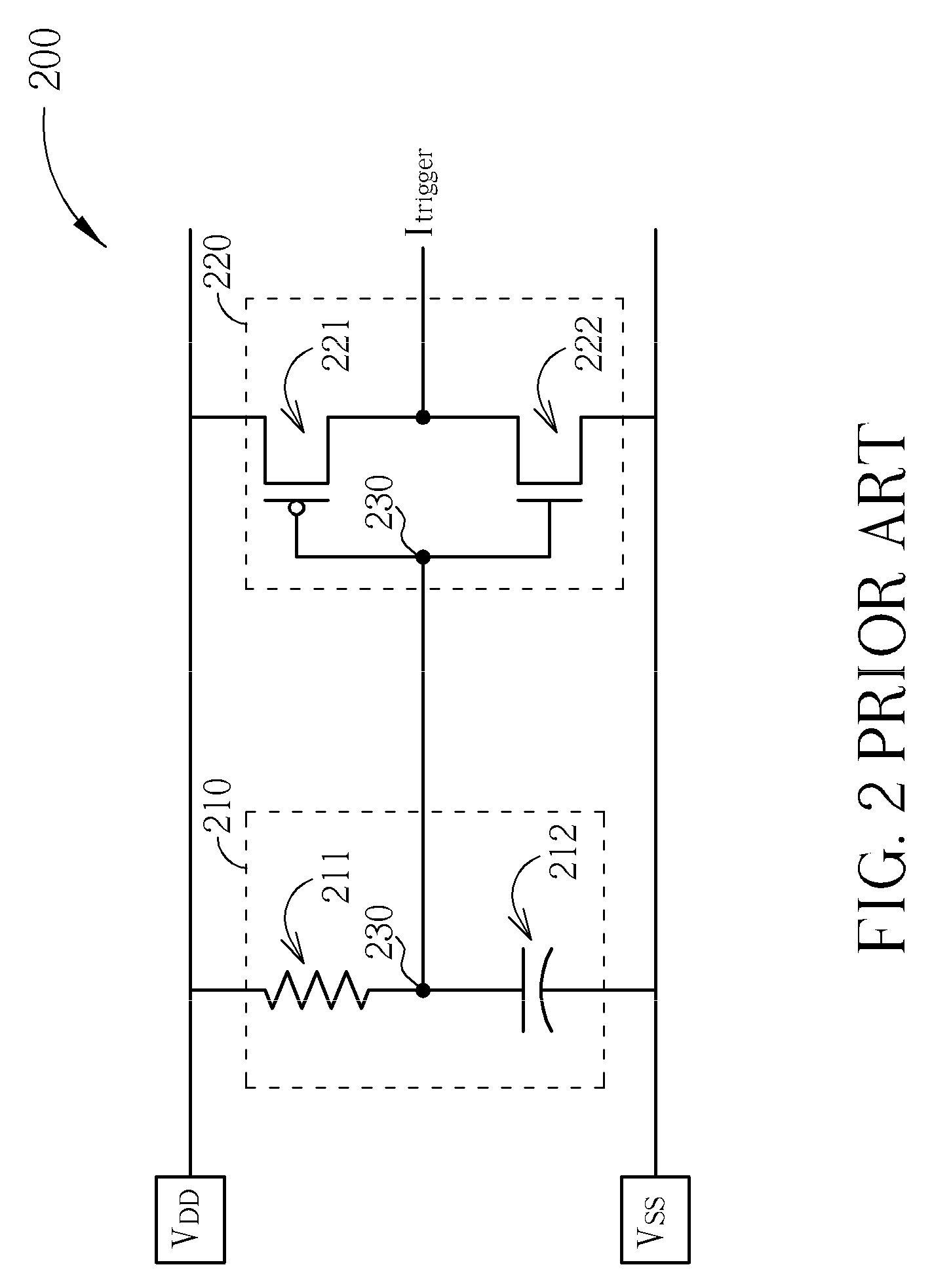
ESD detection circuit and related method thereof
ActiveUS20100148797A1Eliminate unwanted leakage currentEliminates the excessive unwanted leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
An electro-static discharge (ESD) detection circuit is provided. The ESD detection circuit includes: a first power pad for receiving a first supply voltage; a second power pad for receiving a second supply voltage; an RC circuit having an impedance component coupled between the first power pad and a first terminal and having an capacitive component coupled between the first terminal and a second terminal, wherein the second terminal is not directly connected to the second supply voltage; a trigger circuit couples to the first power pad, the second power pad, and the RC circuit, for generating an ESD trigger signal according to a voltage level at the first terminal and a voltage level at the second terminal, and a bias circuit coupled between the first power pad and the second power pad for providing a bias voltage to the second terminal.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
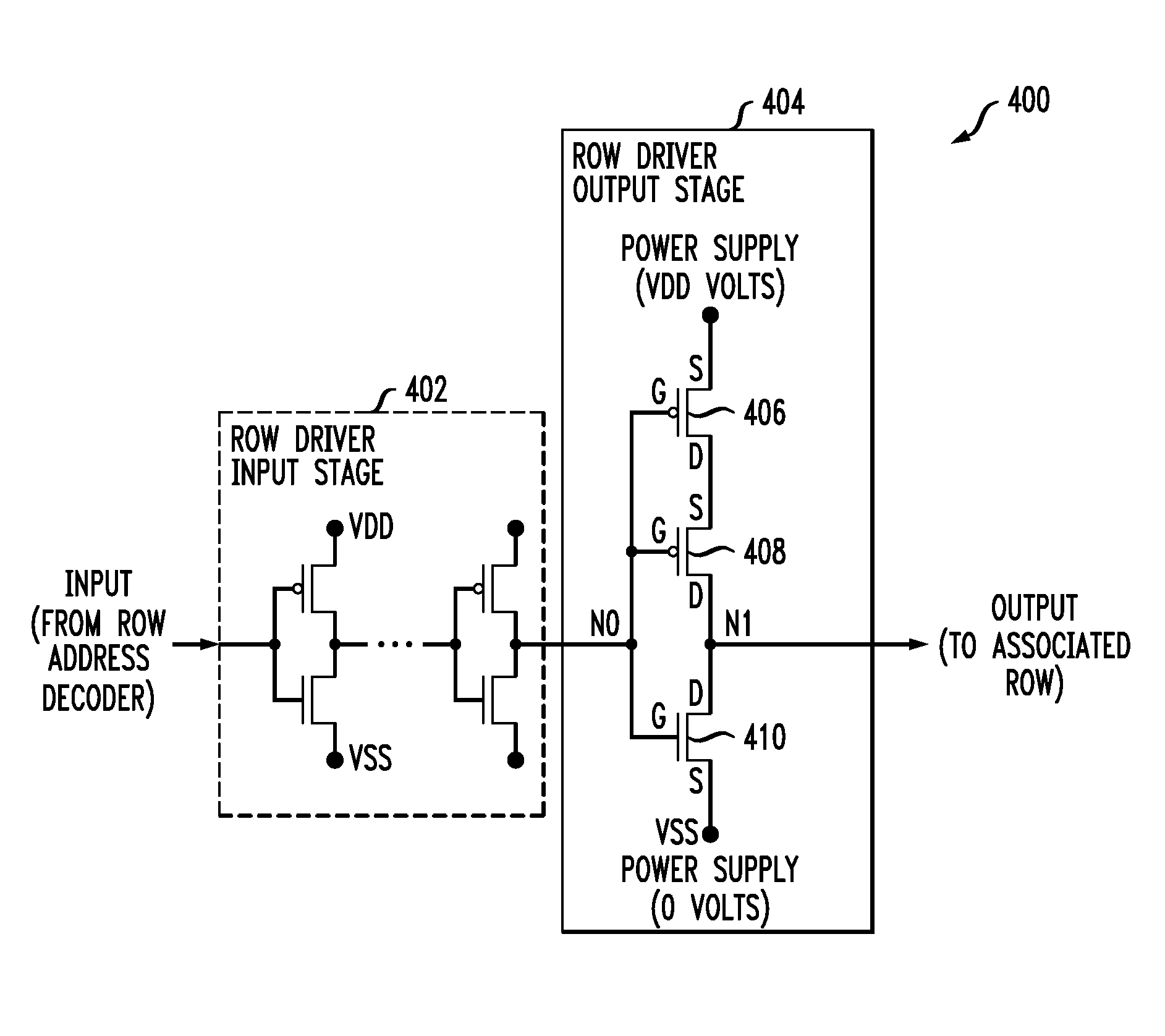
Reduced Leakage Driver Circuit and Memory Device Employing Same
ActiveUS20090141580A1Reduce leakage currentIncreasing performance of circuitDigital storageDriver circuitControl signal
A row line driver circuit for use in a memory array including multiple memory cells and multiple row lines coupled to the memory cells for selectively accessing the memory cells includes an output stage adapted for connection to a corresponding one of the row lines and a control circuit connected to the output stage. The output stage is operative during an active phase of a given memory cycle to drive the corresponding row line to a potential as a function of at least one address signal received by the driver circuit. The control circuit is operative to generate at least one control signal for disabling the output stage at least during an inactive phase of the memory cycle to thereby substantially eliminate a leakage current path in the driver circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Three-dimensional array of re-programmable non-volatile memory elements having vertical bit lines and a single-sided word line architecture
ActiveUS8351236B2Reduce leakage levelGuaranteed true stateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsBit lineEngineering
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Current sensing method and apparatus particularly useful for a memory array of cells having diode-like characteristics
InactiveUS6937495B2Eliminate leakage currentReduce impactRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineElectrical battery
A memory array includes a sensing circuit for sensing bit line current while keeping the voltage of the selected bit line substantially unchanged. The word lines and bit lines are biased so that essentially no bias voltage is impressed across half-selected memory cells, which substantially eliminates leakage current through half-selected memory cells. The bit line current which is sensed arises largely from only the current through the selected memory cell. A noise detection line in the memory array reduces the effect of coupling from unselected word lines to the selected bit line. In a preferred embodiment, a three-dimensional memory array having a plurality of rail-stacks forming bit lines on more than one layer, includes at least one noise detection line associated with each layer of bit lines. A sensing circuit is connected to a selected bit line and to its associated noise detection line.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Vertical solid state devices
ActiveUS20170186907A1Eliminate leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMetal insulatorCurrent mode
A vertical current mode solid state device comprising a connection pad and side walls comprising a metal-insulator-semiconductor (MIS) structure, wherein leakage current effect of the vertical device is limited through the side walls by biasing the MIS structure.
Owner:VUEREAL INC
Liquid crystal display with a heat shield between the inverter and the backlight assembly
InactiveUS6933990B2Increase display areaAvoid a lotTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayComputer module
There is disclosed a liquid crystal display (LCD) device that prevents degeneration of a displaying performance due to heat generated in the LCD. A heat shielding thin film of an aluminum-contained material, which is disposed in a receiving container, shields the heat additionally generated during a converting process of power for driving a lamp in an inverter module, thereby minimizing the heat to be transferred to a reflector panel. Therefore, the heat generated during a process of producing light is efficiently blocked and discharged, thereby minimizing the degeneration of displaying characteristic.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Capacitor device
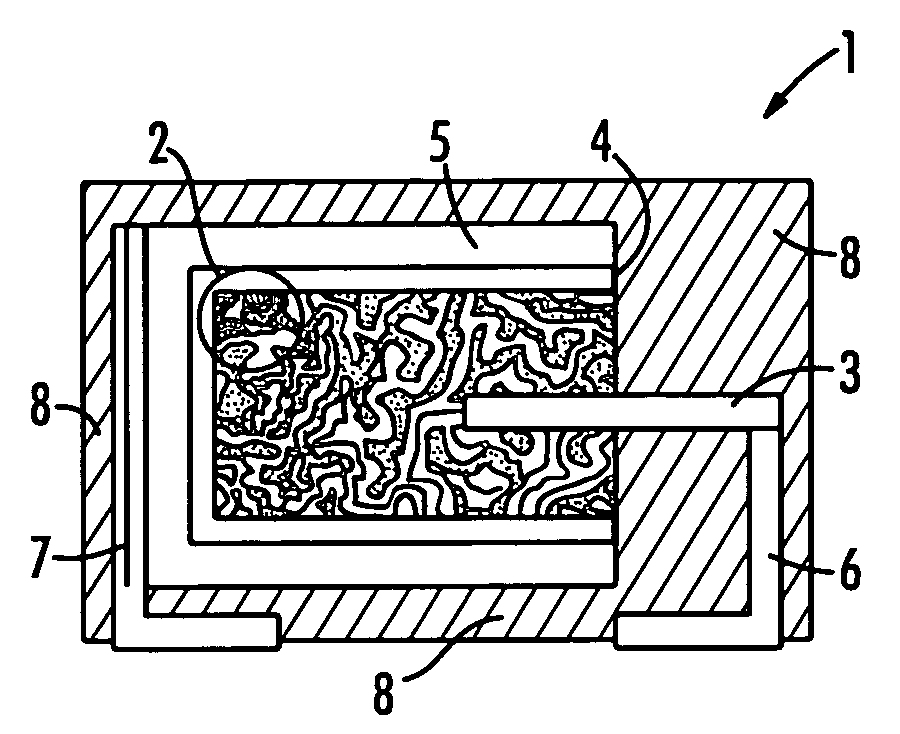
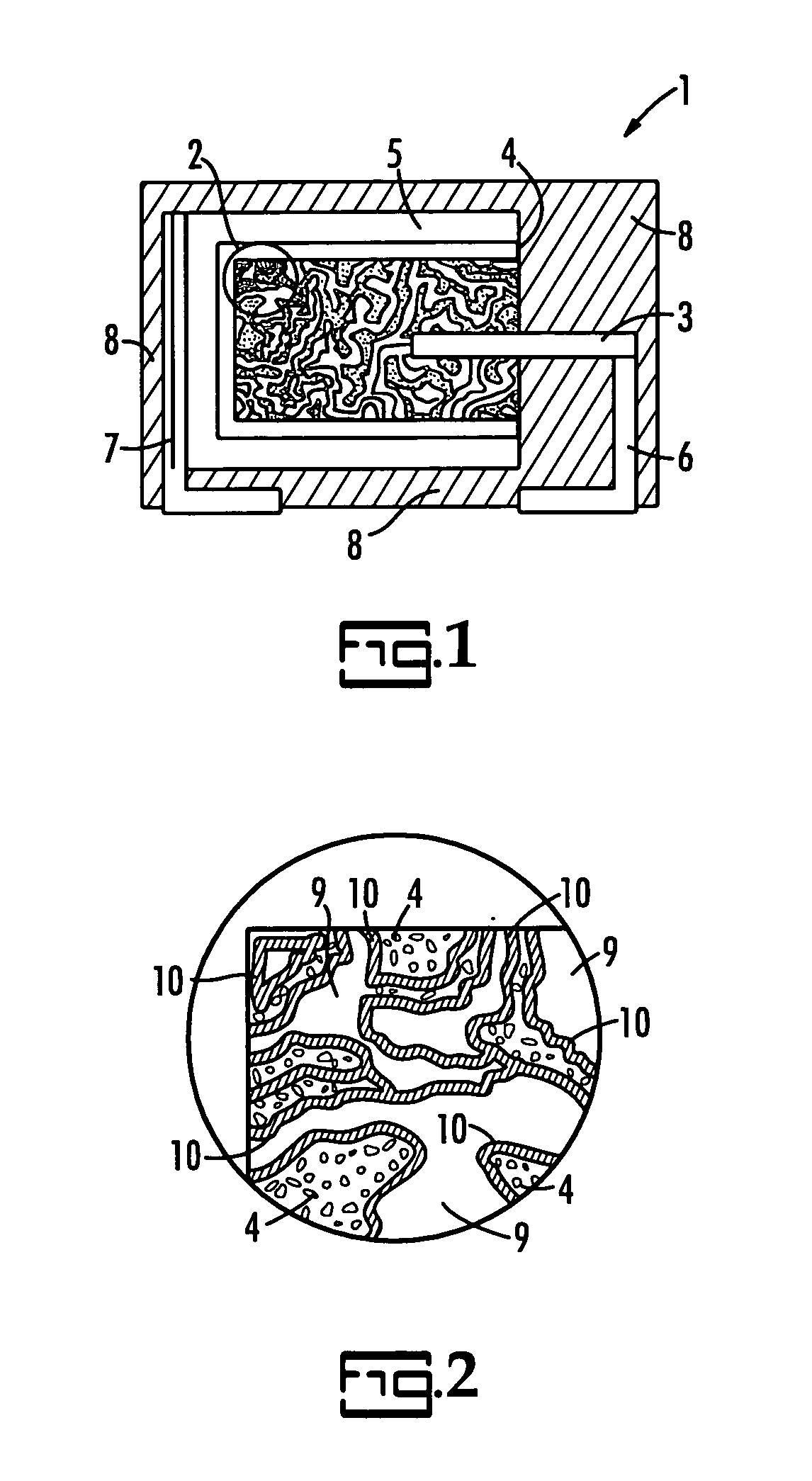
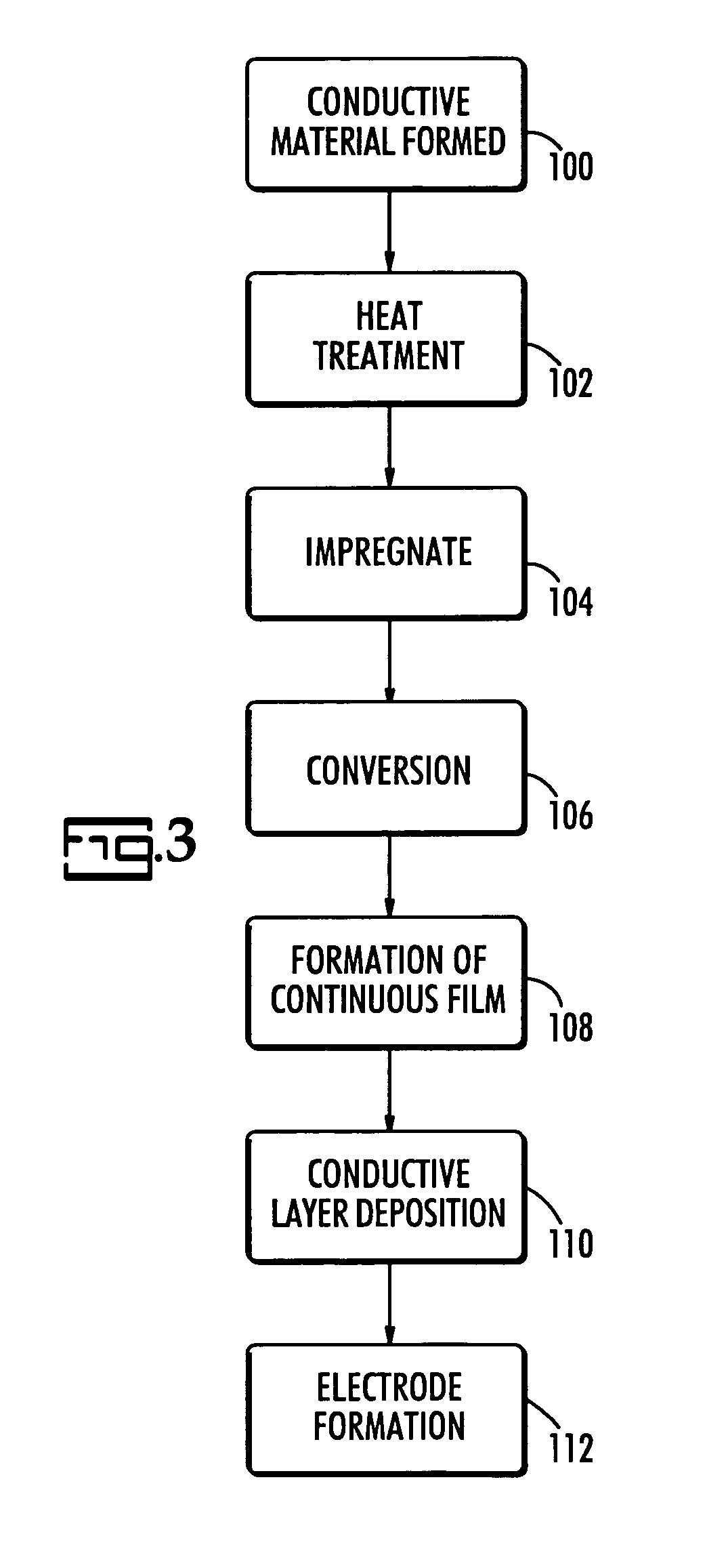
InactiveUS20080123251A1Eliminate electrical shortEliminate leakage currentSolid electrolytic capacitorsFixed capacitor dielectricCapacitanceDielectric layer
A process for forming a capacitive couple. The process includes forming a highly porous body of a conducting material with interior struts and voids in electrical contact. A dielectric layer is formed in the voids on the struts with a material having a dielectric constant above 100. An insulating layer is formed on the struts not covered by the dielectric layer. A conductive layer is formed on the dielectric layer and on the insulating layer.
Owner:KEMET ELECTRONICS CORP
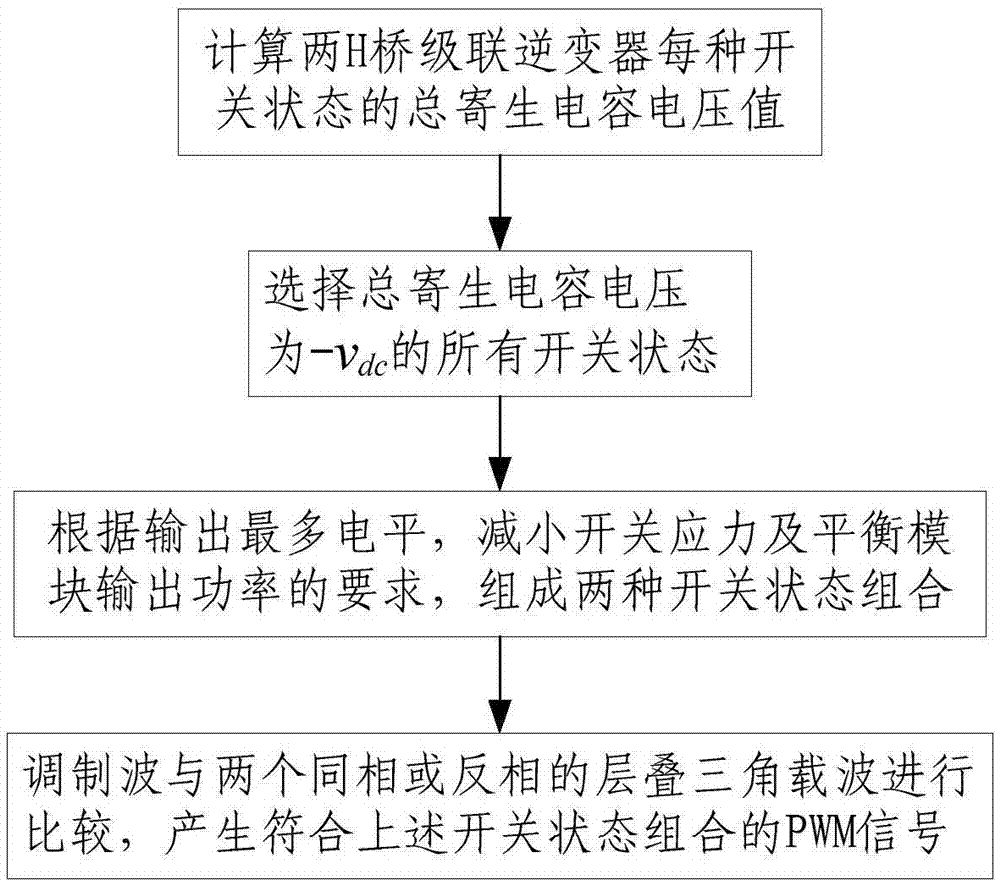
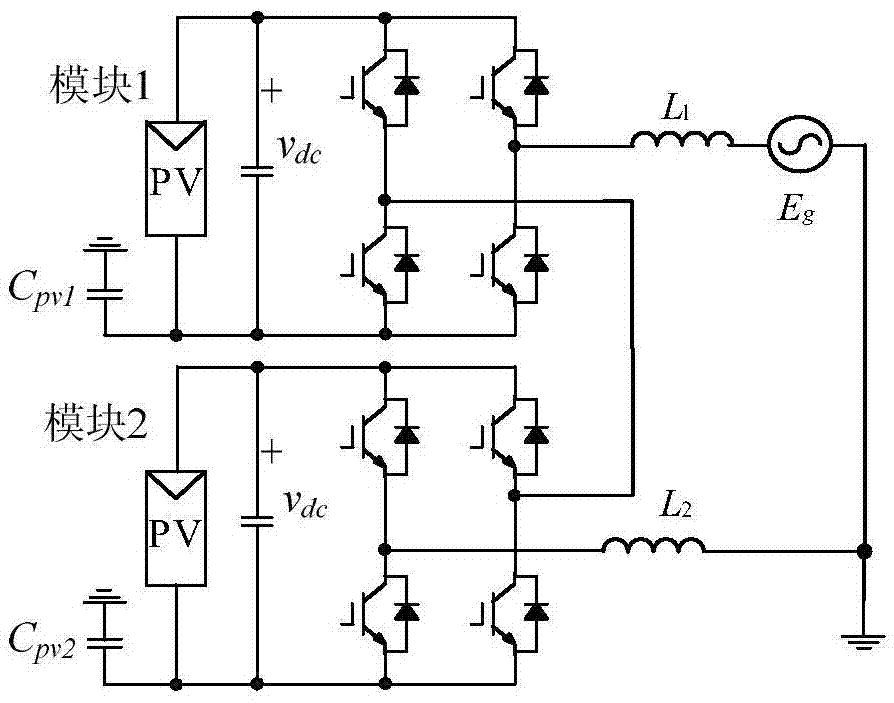
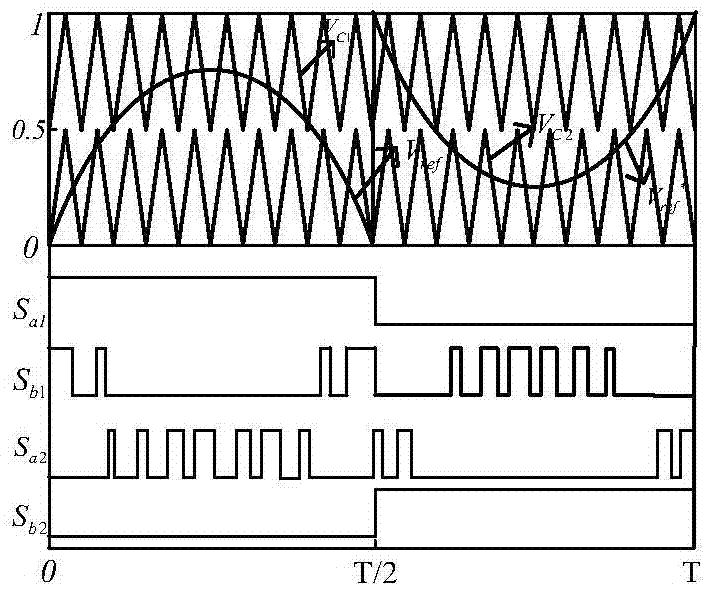
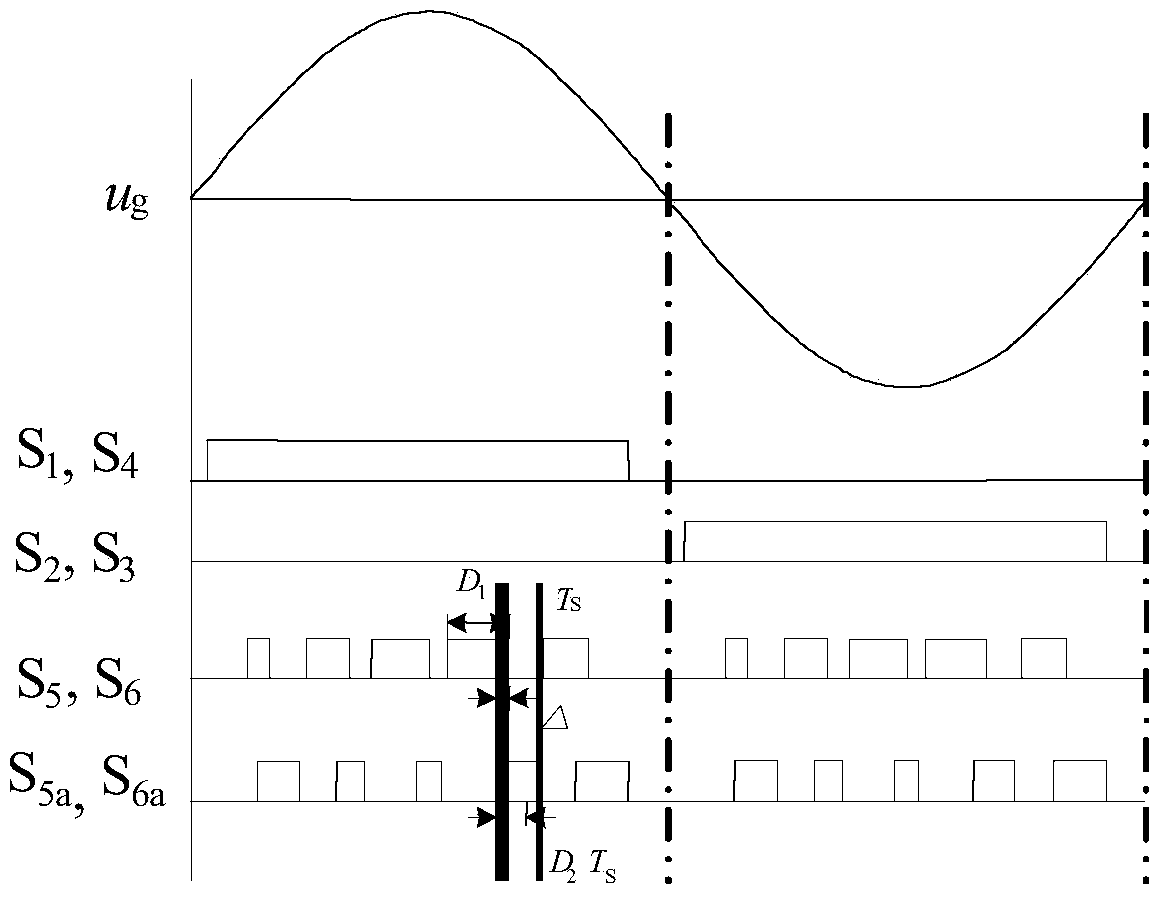
Modulation method for suppressing leakage current of two-H-bridge cascaded inverter
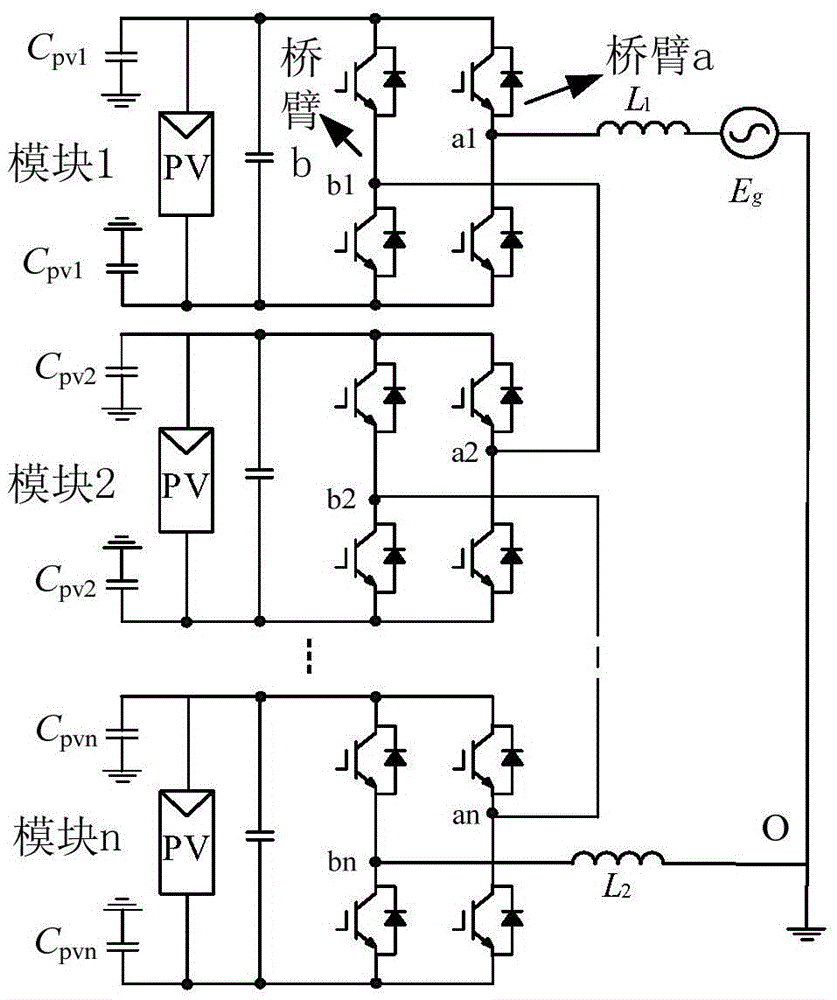
ActiveCN105450059AOverall small sizeLow costSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationMaximum levelCarrier signal
The invention discloses a modulation method for suppressing leakage current of a two-H-bridge cascaded inverter. The method comprises the following steps of calculating total parasitic capacitor voltage v<Nto> value of the two-H-bridge cascaded inverter at each switch-on state; selecting all switch-on states when the total parasitic capacitor voltage v<Nto) is -v<dc>; forming a combination of two switch-on states according to requirements of maximum level output, switch stress reduction and output power balance of a module; and comparing a modulation wave with a triangle carrier wave which is laminated by two same or opposite phases, and generating pulse width modulation (PWM) signals conforming to the above switch-on state combination, and allocating the PWM signals to corresponding pins. By the scheme, extra hardware cost is not needed, leakage current flowing into a power grid can be eliminated, and meanwhile, the leakage current of a single module is suppressed; and the method only requires two carrier waves to compare, the computation of a processor is reduced, and the implementation mode is simple.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
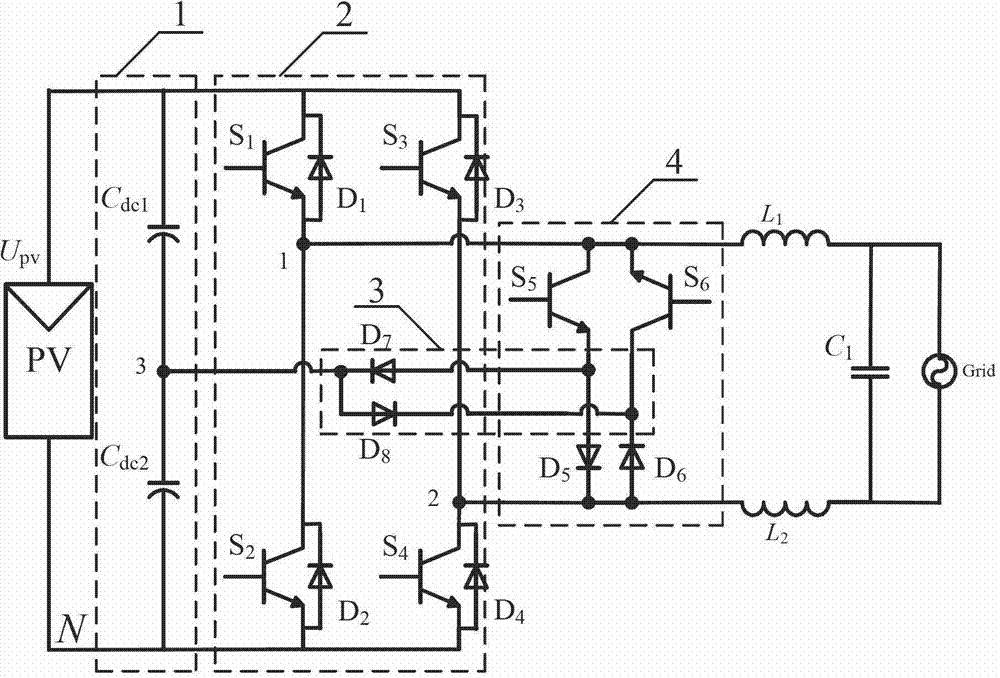
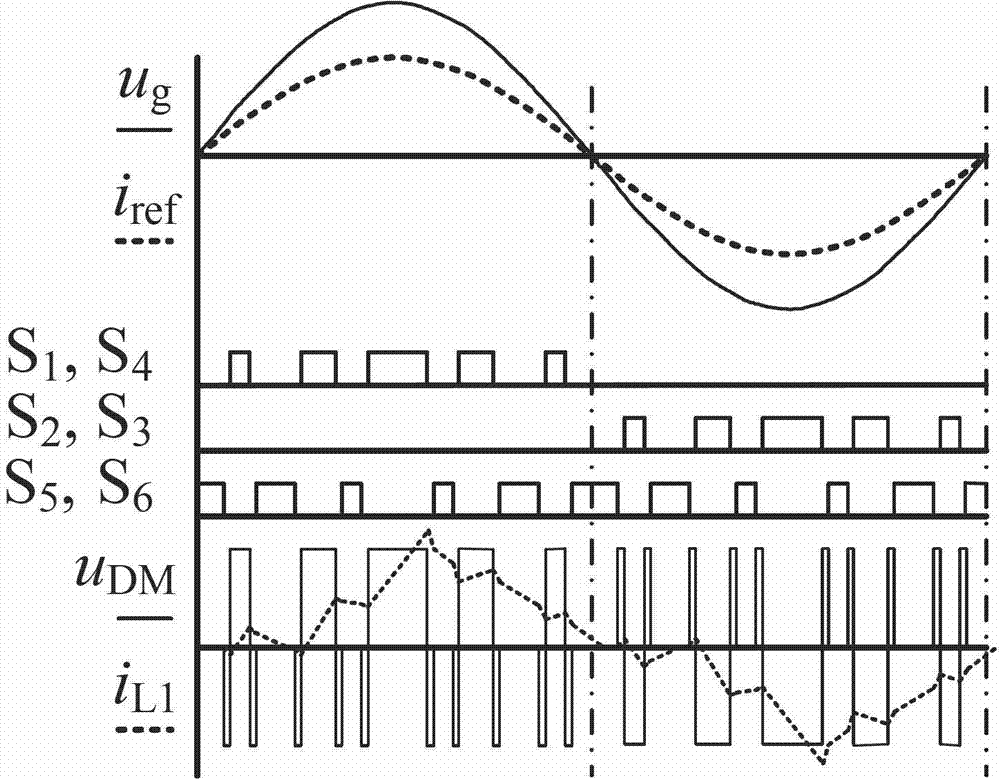
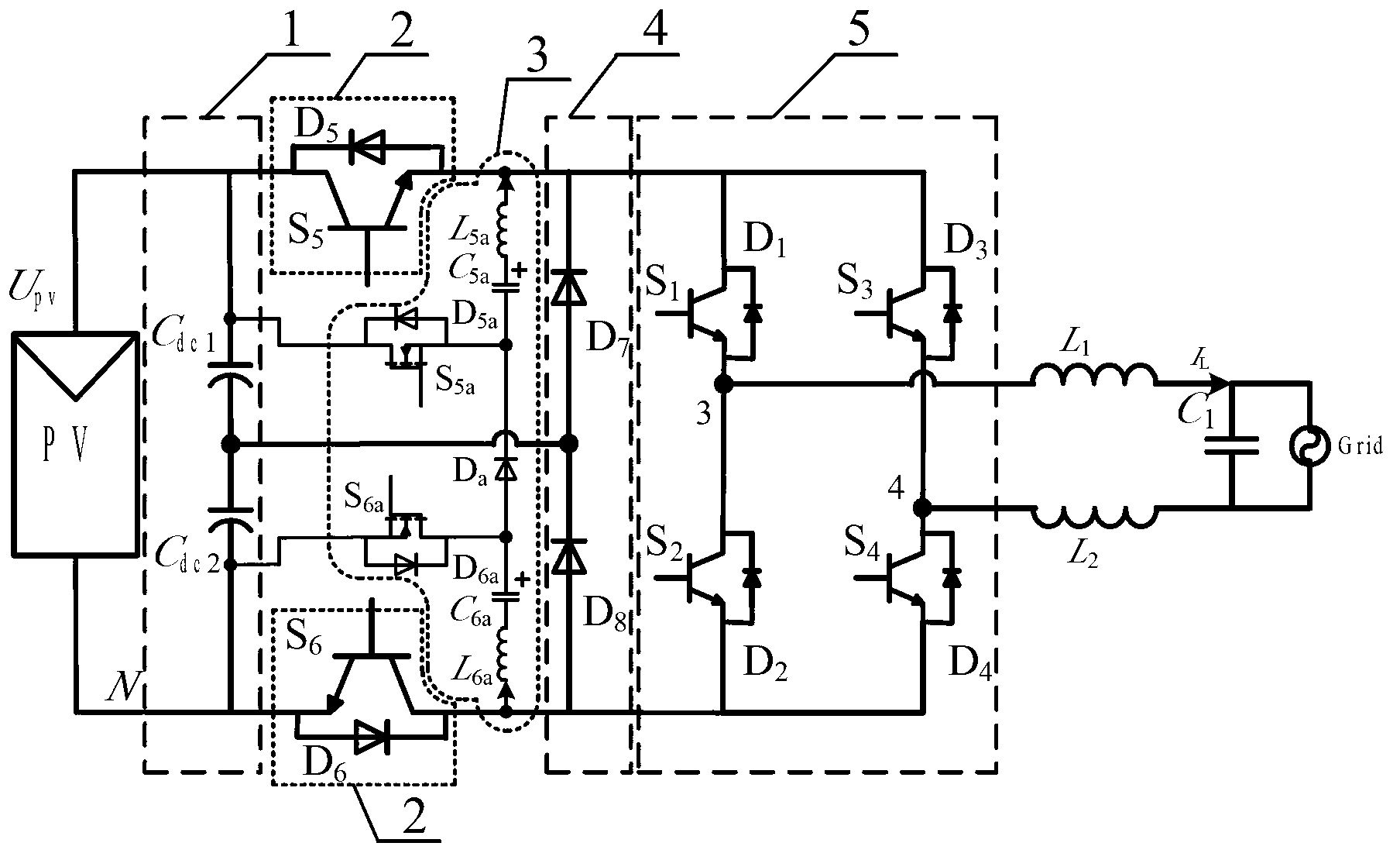
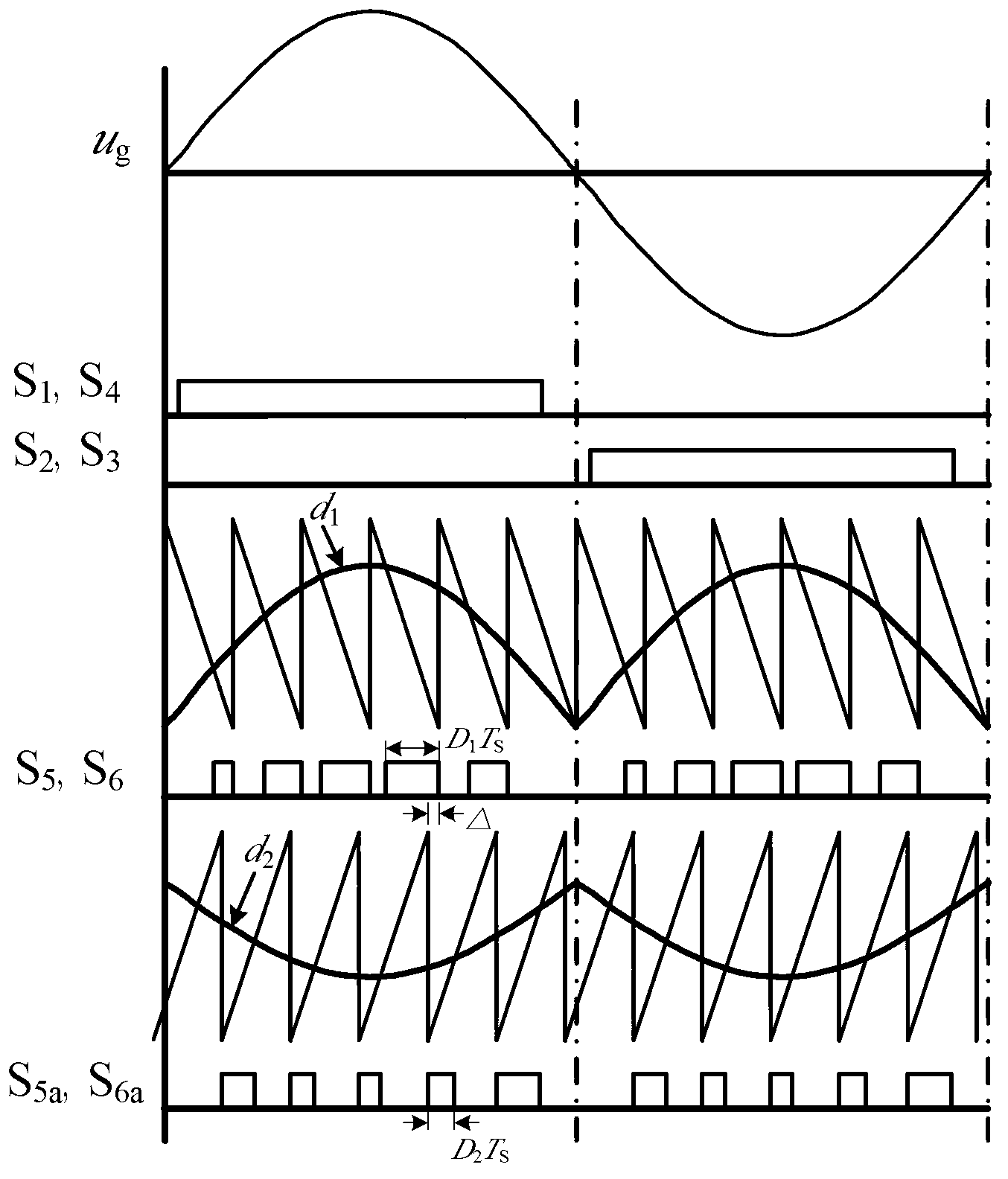
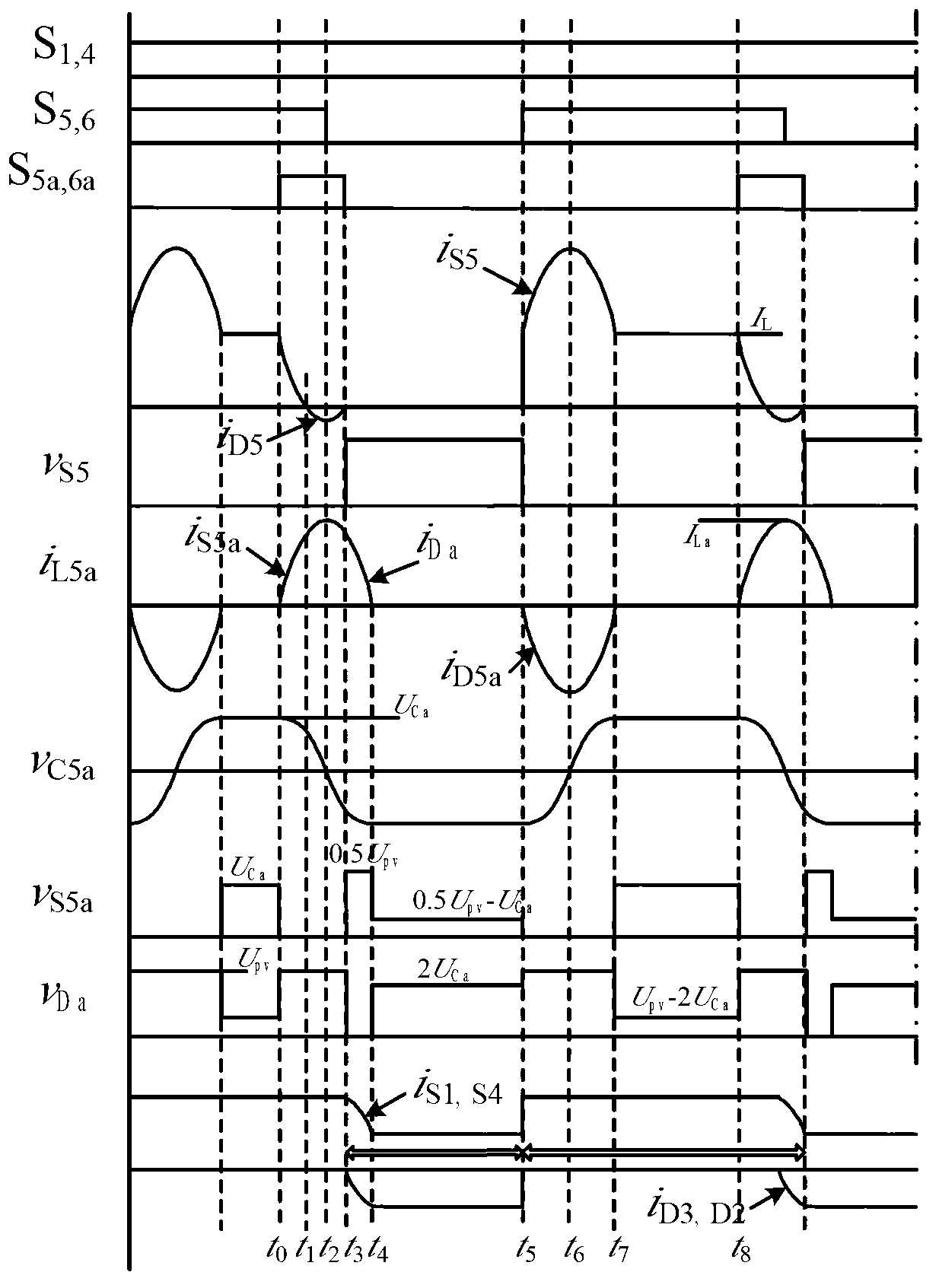
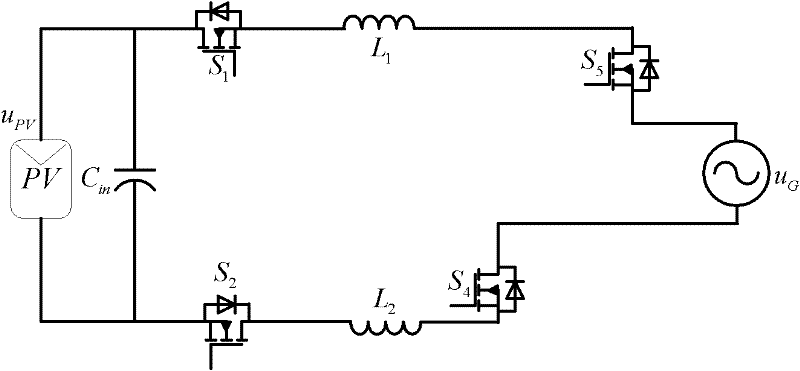
Non-isolated single-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and on-off control timing sequence thereof
ActiveCN103051233AEliminate leakage currentReduce conduction lossAc-dc conversionPhotovoltaic energy generationSingle phaseCapacitance
The invention provides a non-isolated single-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter which is low in conduction loss and leakage current, and an on-off control timing sequence of the non-isolated single-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter. The photovoltaic grid-connected inverter comprises a voltage-dividing capacitor branch (1), a full-bridge basic unit (2), a clamping branch (3) and a follow current branch, which are connected with each other. According to the non-isolated single-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and the on-off control timing sequence thereof disclosed by the invention, two controllable switch tubes and two diodes are additionally arranged on the basis of the single-phase full-bridge inverter circuit respectively to form a zero-level flow current branch; two diodes and a voltage-dividing capacitor are additionally arranged in the zero-level flow current branch to form a dual-direction clamping branch; the dual-direction clamping branch is matched with the on-off timing sequence to realize that common-mode voltage is the same constant voltage value at a power transmission stage, a dead zone stage and a flow current stage, so that leakage current of the non-isolated grid-connected inverter is removed. Moreover, the output current is enabled to only flow through two power tubes at the power transmission stage and the flow current stage, so that the conduction loss is the lowest.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and device for inhibiting and eliminating leakage current of photovoltaic grid connection system without transformer
ActiveCN102136736ASuppresses and eliminates leakage currentEliminate leakage currentSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationLarge applicationsDrain current
The invention relates to a method and a device for inhibiting and eliminating leakage current of a photovoltaic grid connection system without a transformer. The device is composed of a leakage current detector, a central controller and a waveform generator, wherein, the central controller is provided with a waveform analyzing circuit, a command current computing circuit and a current tracking control circuit; the waveform generator is provided with a drive circuit and a power module; the leakage current detector is arranged on the direct-current side of an inverter and is connected with the central controller; the central controller is used for analyzing and processing the leakage current waveform and generating compensatory current control signals; and the waveform generator is arrangedin a photovoltaic array and is connected with the output end of the current tracking control circuit of the central controller, and is used for injecting the corresponding compensatory current generated according to the command of the central controller into a photovoltaic system. In the invention, the compensating current the size of which is the same as that of the leakage current, and the phase position of which is opposite to that of the leakage current is generated through detecting, analyzing and processing the leakage current waveform. The compensating current is overlaid and offset with the leakage current after being injected with circuit, thus achieving the purpose of inhibiting and eliminating the leakage current; and the method and device provided by the invention has the characteristics of real-time monitoring, tracking, less dynamic compensation power consumption and smaller environment influence, can effectively inhibit and eliminate the leakage current, and has large application prospects and economic effect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Zero current switching full-bridge type non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
ActiveCN103199727AAchieve high frequencyMiniaturizationEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitanceFull bridge
The invention provides a non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and switch control timing sequence thereof, wherein the non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter enables high-frequency soft switching work to be achievable and is low in leakage current. The non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter comprises a voltage division capacitance branch (1), a high-frequency master switch unit (2), a resonance network (3), a clamping branch (4) and a low-frequency change-over switch unit (5). According to the non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and the switch control timing sequence thereof, two controllable switching tubes, a diode and two groups of inductor and capacitor series branches are added to a one-phase six-switch full bridge inversion circuit (also know as 'H6' topology) to form the resonance network to provide the zero current switching work condition for the master switch unit, and therefore the soft switching work of high-frequency switching is achieved, and switching loss can be reduced greatly; common-mode voltage values at a power transmission stage, at a resonance stage and at a follow current stage are enabled to be identical and constant by matching with the switch control timing sequence, and therefore the leakage current of the non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter is eliminated; and high frequency of the non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter is achieved, and size, weight and cost of a grid-connected inverter can be reduced greatly.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
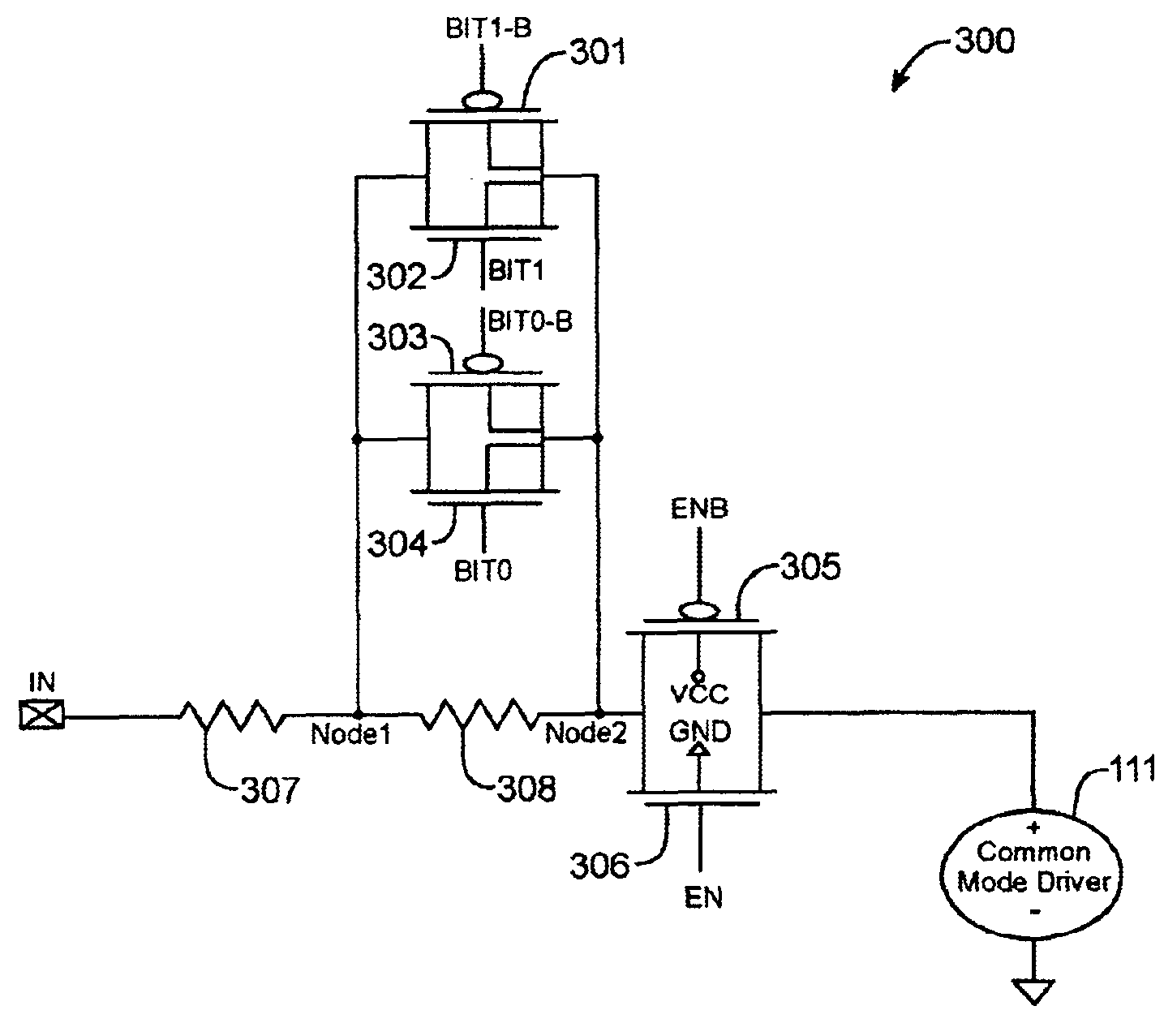
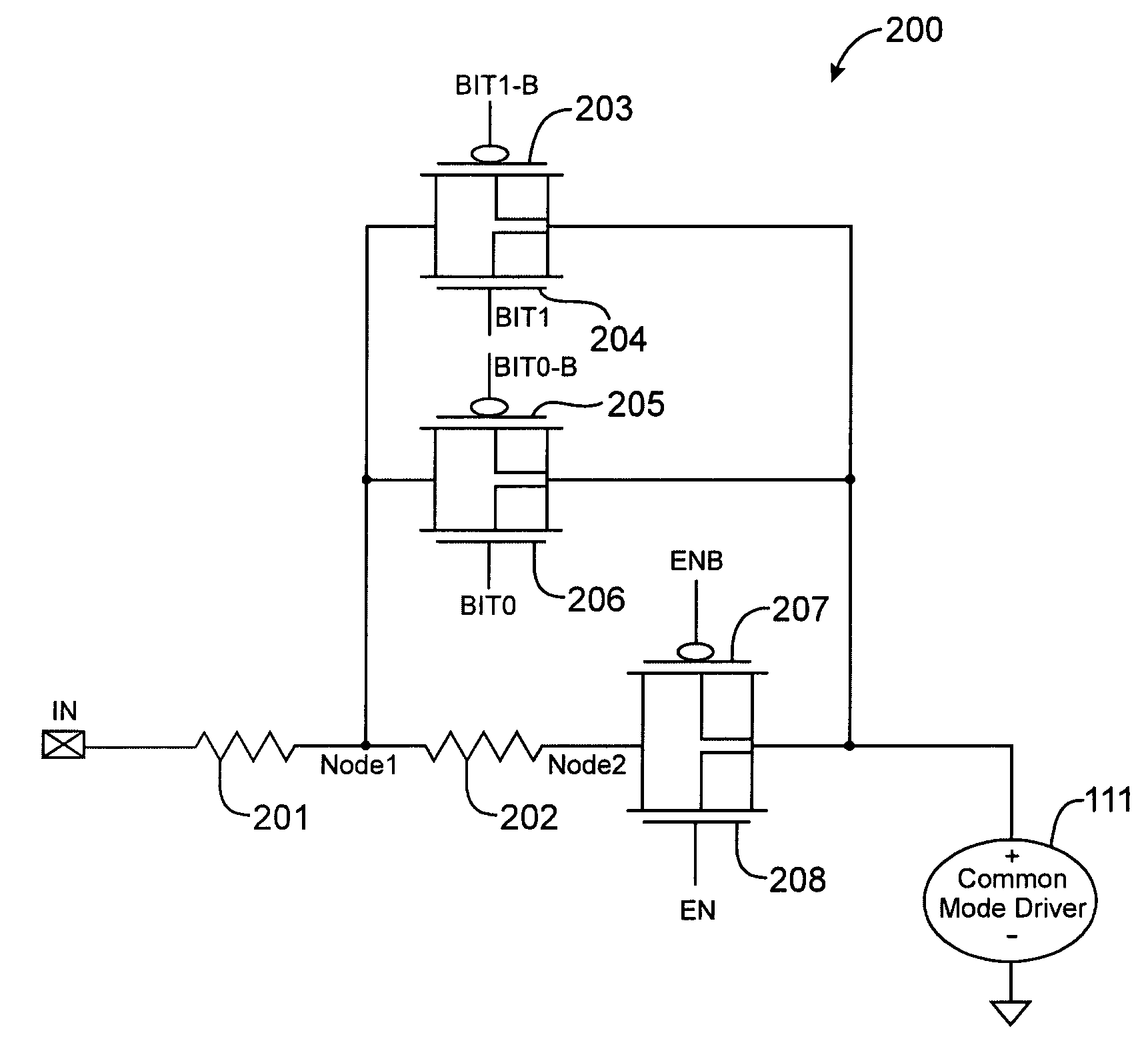
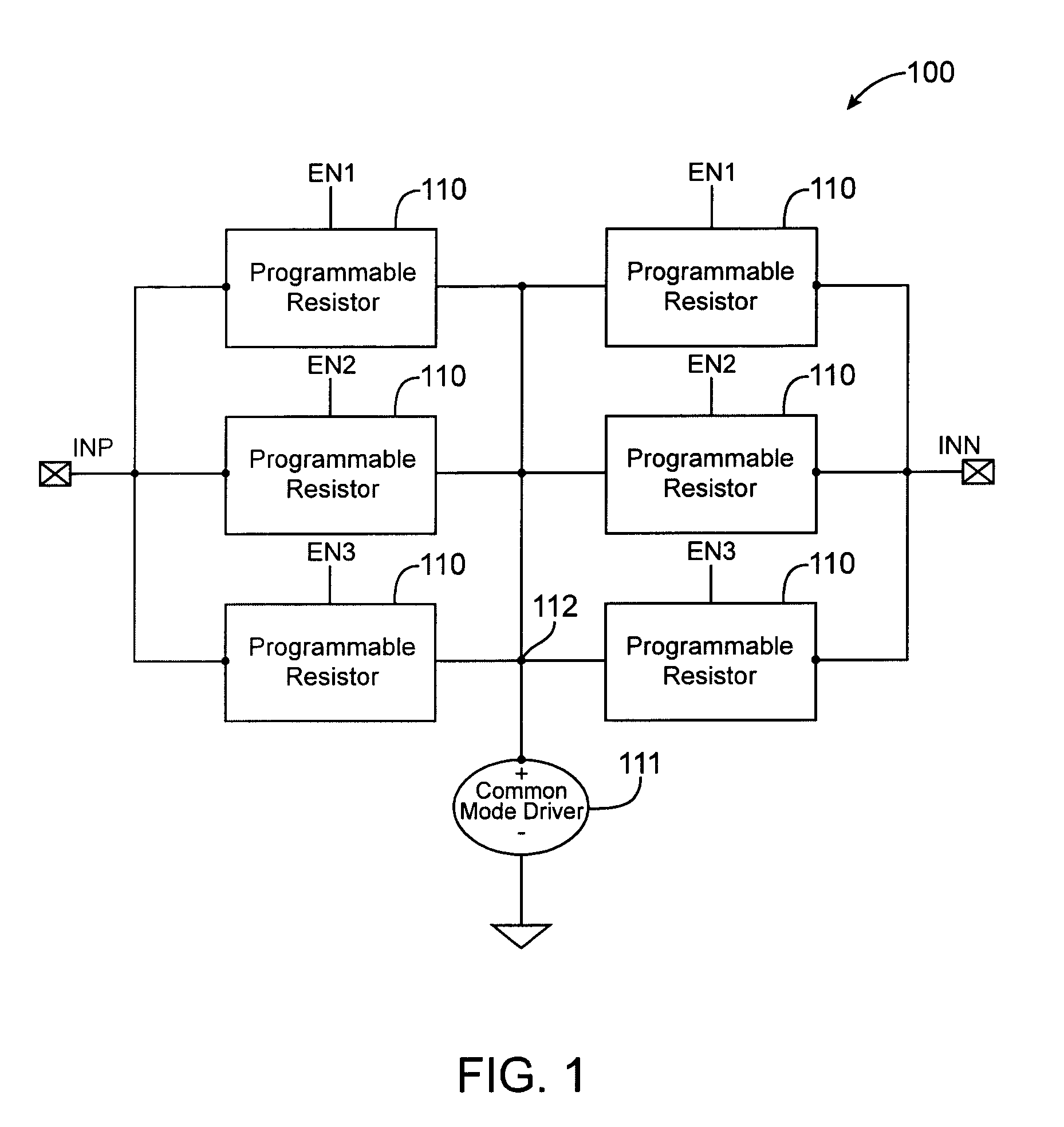
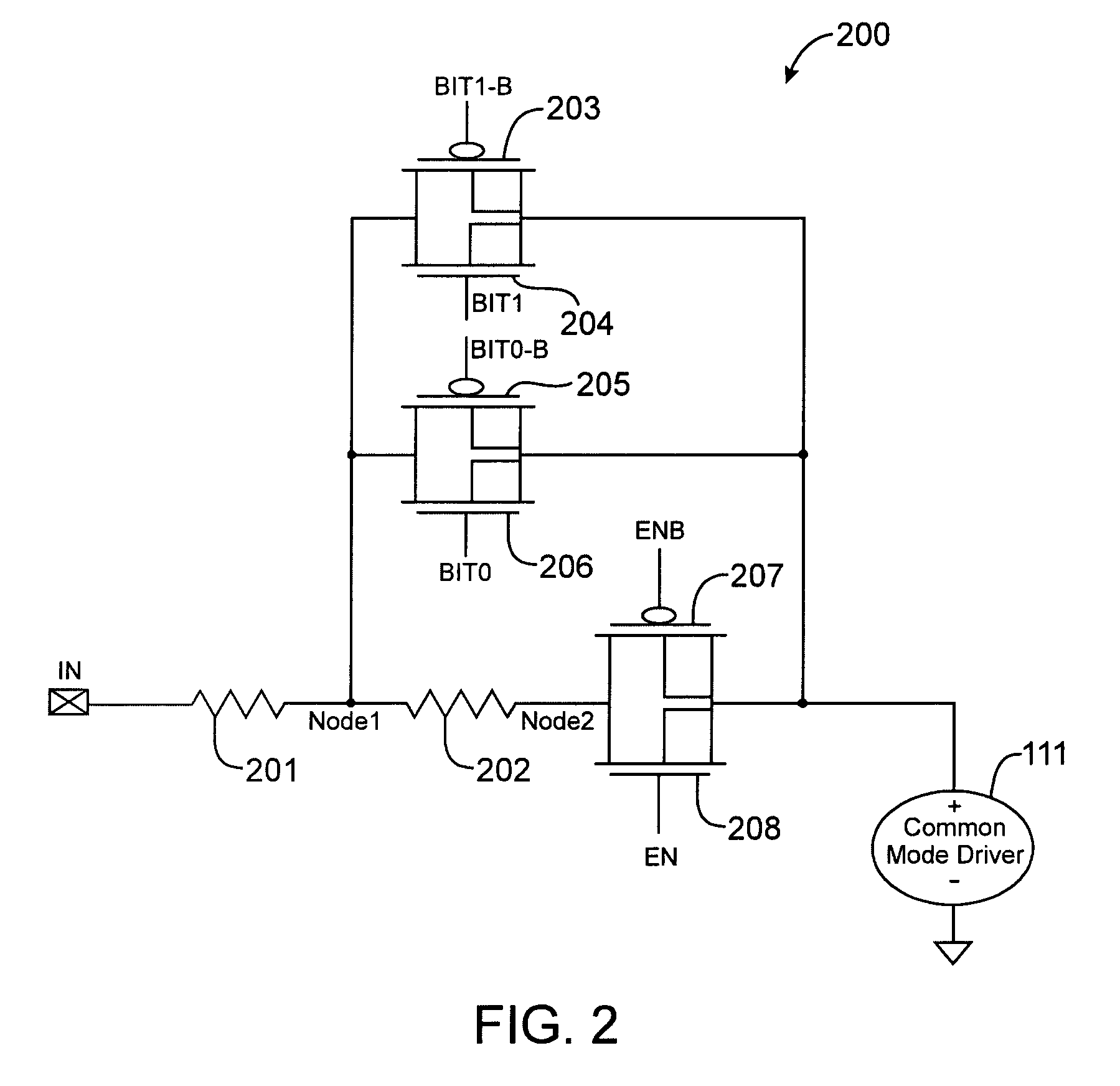
Techniques for reducing leakage current in on-chip impedance termination circuits
InactiveUS6859064B1Prevent unwanted leakage currentEliminate leakage currentReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDrain currentIntegrated circuit
Techniques for reducing the leakage currents through on-chip impedance termination circuits are provided. An on-chip impedance termination circuit includes a network of resistors and transistors formed on an integrated circuit. The termination circuit is coupled to one or more IO pins. The transistors can be turned ON and OFF to couple or decouple subsets of the resistors from the IO pins. The bodies of transistors 305-306 are coupled to a supply voltage to cut off leakage current. By pulling the body of these transistors to a supply voltage, the transistor's drain / source-to-body diodes turn OFF preventing unwanted leakage current. Also, by moving the source / drain / body node of transistors 301-304 to Node 2, leakage currents through transistors 301-304 are eliminated.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Switching-loss-free full-bridge non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and on-off control timing sequence
ActiveCN104242719AAchieve high frequencyMiniaturizationAc-dc conversionPhotovoltaic energy generationCapacitanceFull bridge
The invention discloses a switching-loss-free full-bridge non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and an on-off control timing sequence. The inverter comprises a voltage division capacitance branch, a high-frequency main switching unit, a resonant network and a low-frequency change-over switch unit. Two sets of zero-current switching branches composed of the resonant network composed of full control switches, resonant capacitors and resonant inductors and auxiliary follow current clamping diodes are added, the on-off control timing sequence is matched, the zero-current turning-on and zero-current turning-off conditions of a fifth power switch tube S5 and a sixth power switch tube S6 can be achieved, the zero-current turning-on and zero-current turning-off conditions of a fifth auxiliary power switch tube Sa5 and a sixth auxiliary power switch tube Sa6 can be achieved, the reverse restoration of low-frequency change-over switch unit diodes D1-D4 can be eliminated, it is guaranteed that the common-mode voltage of the inverter is constantly one second of a battery voltage in the power transmission process, the resonance period and the follow current stage to eliminate leak currents, and therefore high frequency and minimization of the non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Techniques for reducing leakage current in on-chip impedance termination circuits
InactiveUS7064576B1Avoid leakage currentEliminate leakage currentReliability increasing modificationsBaseband system detailsEngineeringDrain current
Owner:ALTERA CORP
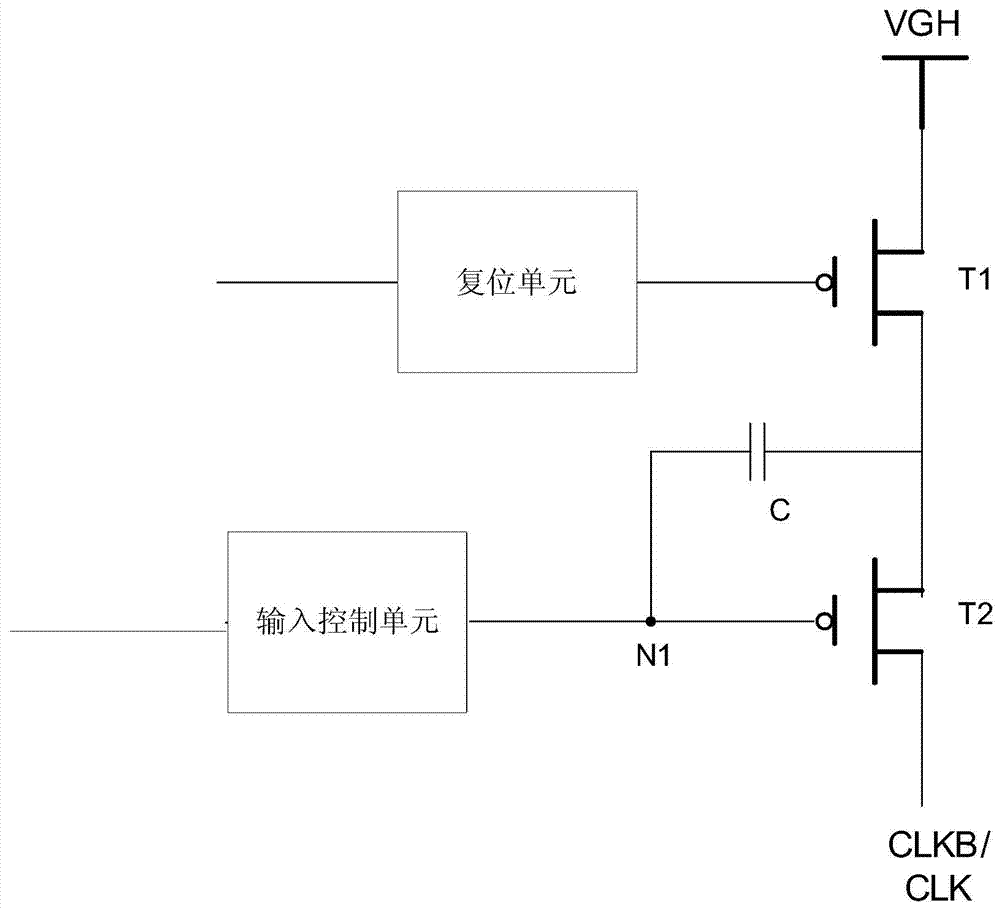
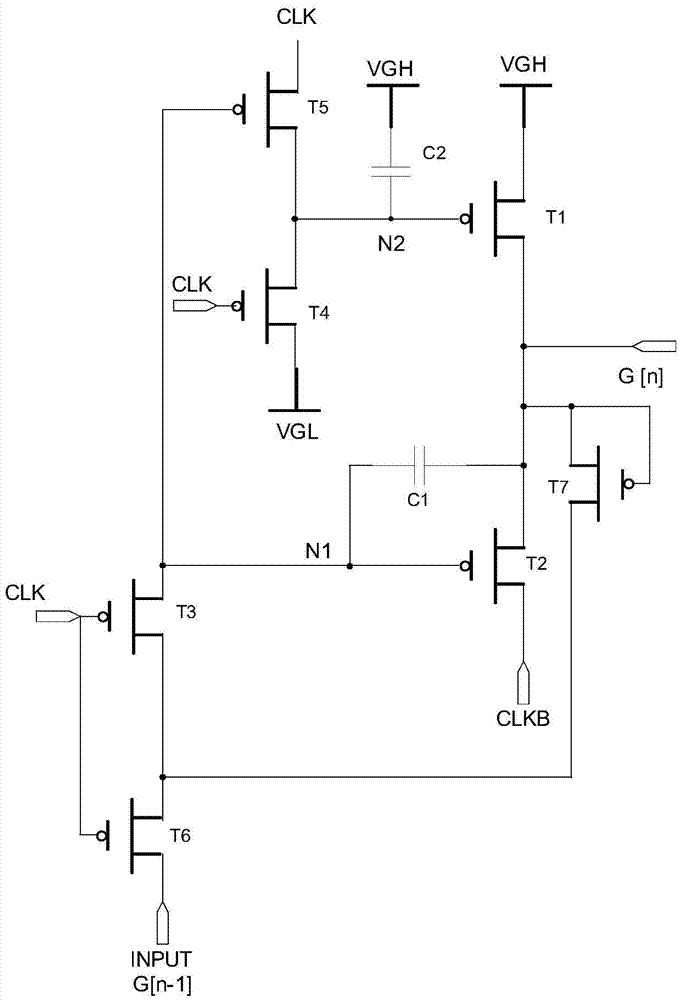
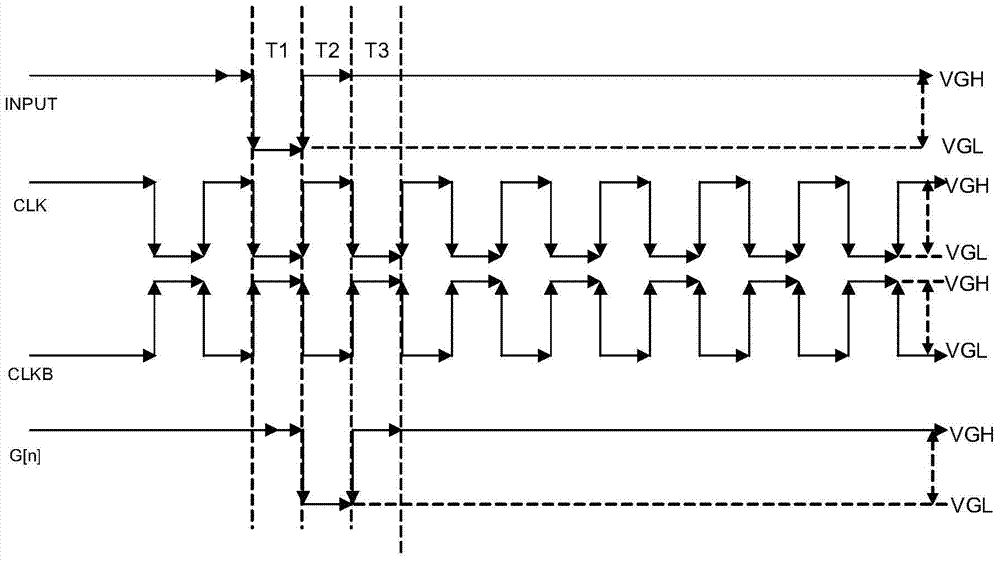
Shifting register unit, shifting register, array substrate and display device
InactiveCN103489423AGuaranteed voltageEliminate leakage currentStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerControl signal
The invention provides a shifting register unit, a shifting register, an array substrate and a display device. The shifting register unit is characterized by comprises a sampling unit, an output unit and a reset unit, wherein the sampling unit is connected with the sampling signal input end and the first clock signal input end, the output unit is connected with the output end, a first power supply, a third power supply and the second clock signal input end, the reset unit is connected with the first clock signal input end and a second power supply, the sampling unit is used for sampling input signals of the sampling signal input end under the control of the first clock signal input end and transmitting the obtain sampling signals to the output unit, the output unit is used for outputting the sampling signals to the output end of the sampling unit under the control of the second clock signal input end, and the reset unit is used for sending reset control signals to the output unit to reset under the control of the first clock signal input end.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
High temperature pressure sensor and process method thereof
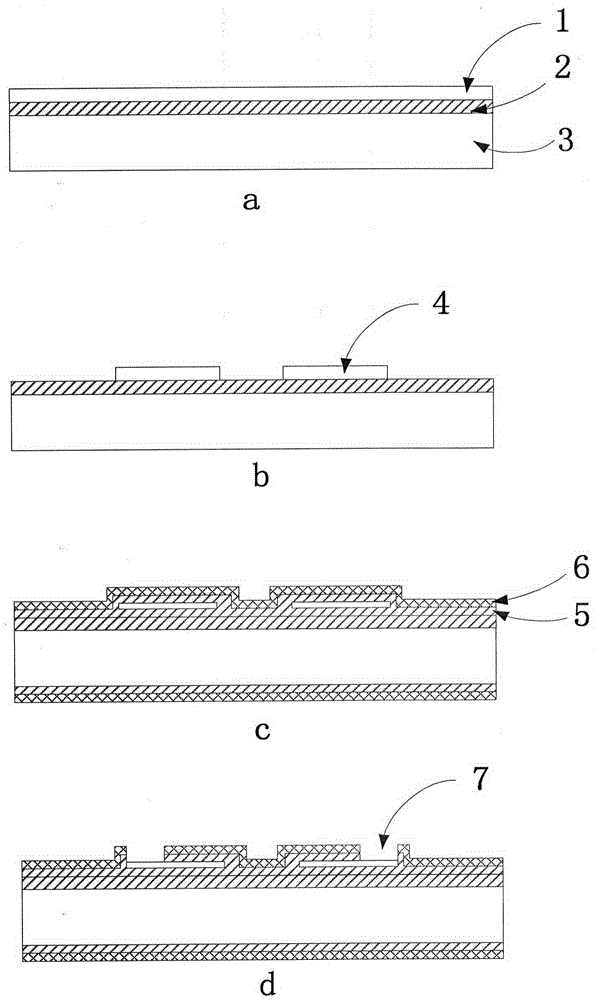
ActiveCN104535253AEliminate leakage currentGood thermal stabilityFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationDiaphragm structureAnodic bonding
The invention discloses a high temperature pressure sensor and a process method thereof, the pressure sensor comprises a silicon-sensitive diaphragm, a pedestal and a TO tube case, wherein a SOI monocrystalline silicon wafer is used as a substrate of the silicon-sensitive diaphragm. A wheatstone bridge is formed by resistance processing and leading wire interconnection in a device layer, and a diaphragm structure which is sensitive to pressure is formed by conducting anisotropy corrosion at a substrate layer. Anodic bonding or silicon-silicon direct bonding or silicon-silicon medium bonding is conducted by the pedestal and the silicon-sensitive diaphragm, wherein the glass sheet or the monocrystalline silicon wafer is used as a substrate of the pedestal. Chip scale package is achieved by using the TO metal tube case for a shell. The high temperature pressure sensor and the process method thereof use a buried oxide layer of the SOI monocrystalline silicon wafer and an illuvial silicon dioxide / silicon nitride passivation layer to wrap and isolate a silicon resistor, and leakage current at high temperature is eliminated. A high temperature ohmic contact electrode structure of multiple layers of silicon dioxide / titanium / silicon dioxide / platinum / gold is grown in a spurting mode. Through high temperature resistance bonding and TO packaging technology, the working stability at high temperature is improved. The problem that long term working is difficult to conduct in a high temperature environment by a traditional silicon substrate sensor is solved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method apparatus comprising integrated circuit and method of powering down such circuit
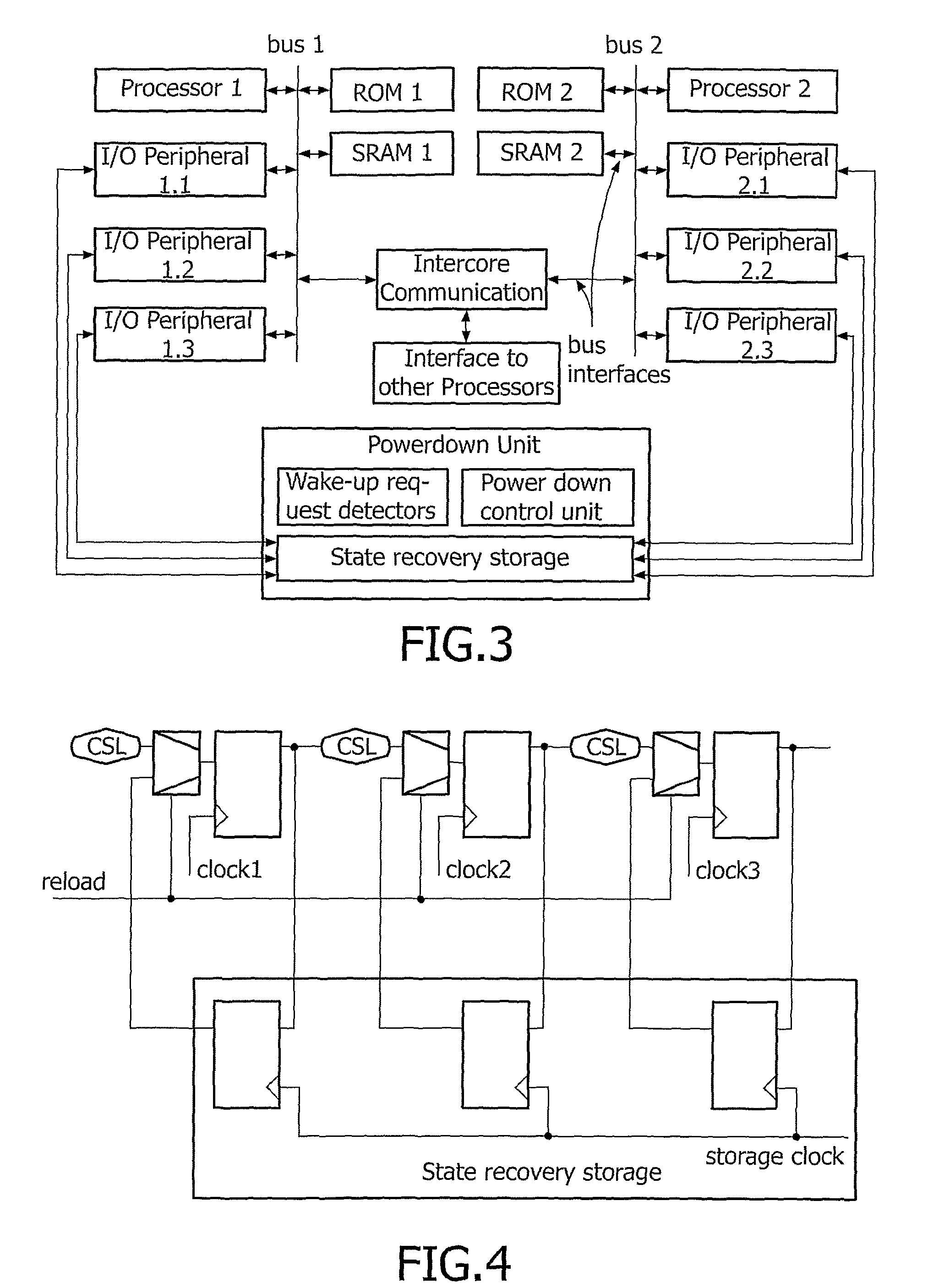
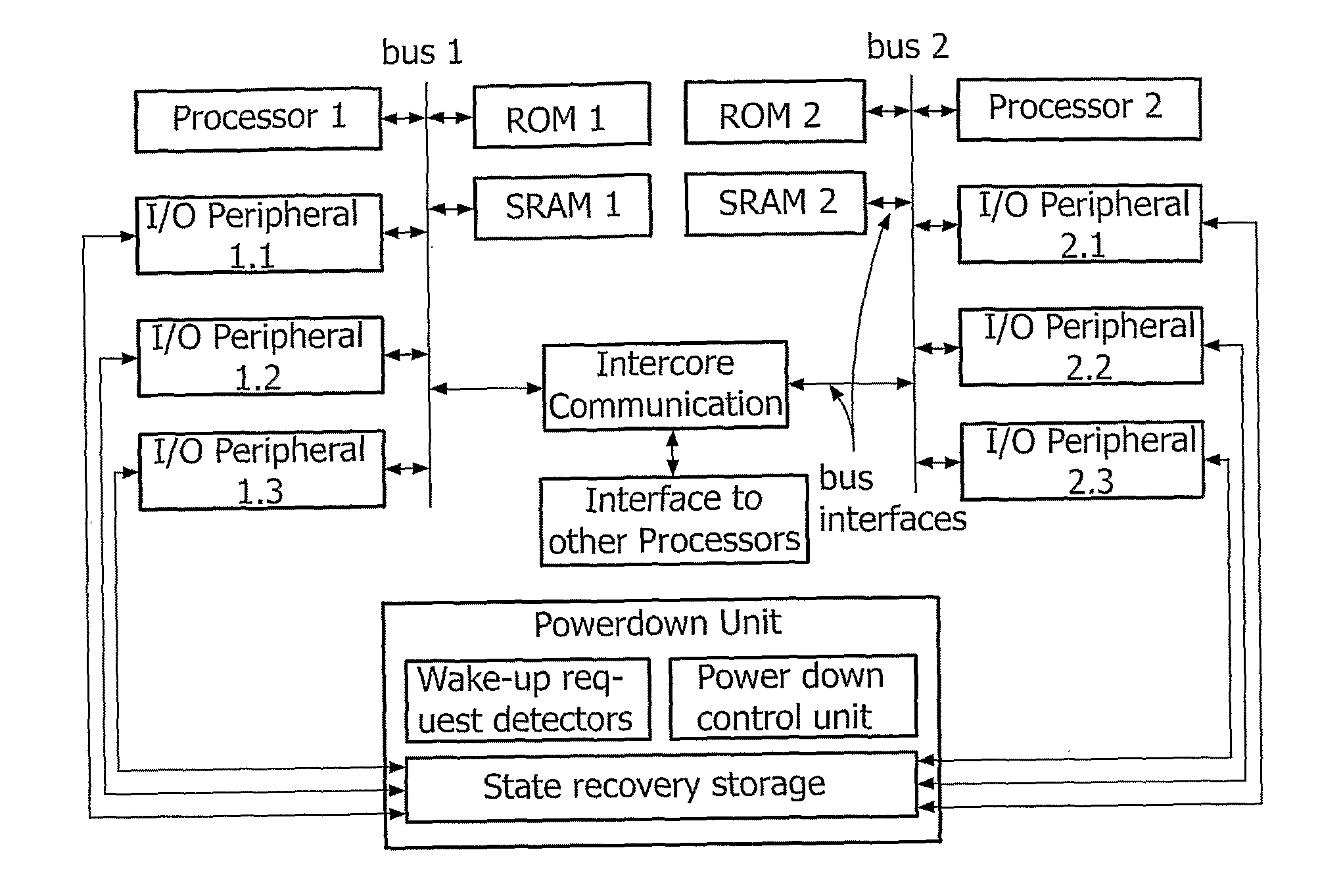
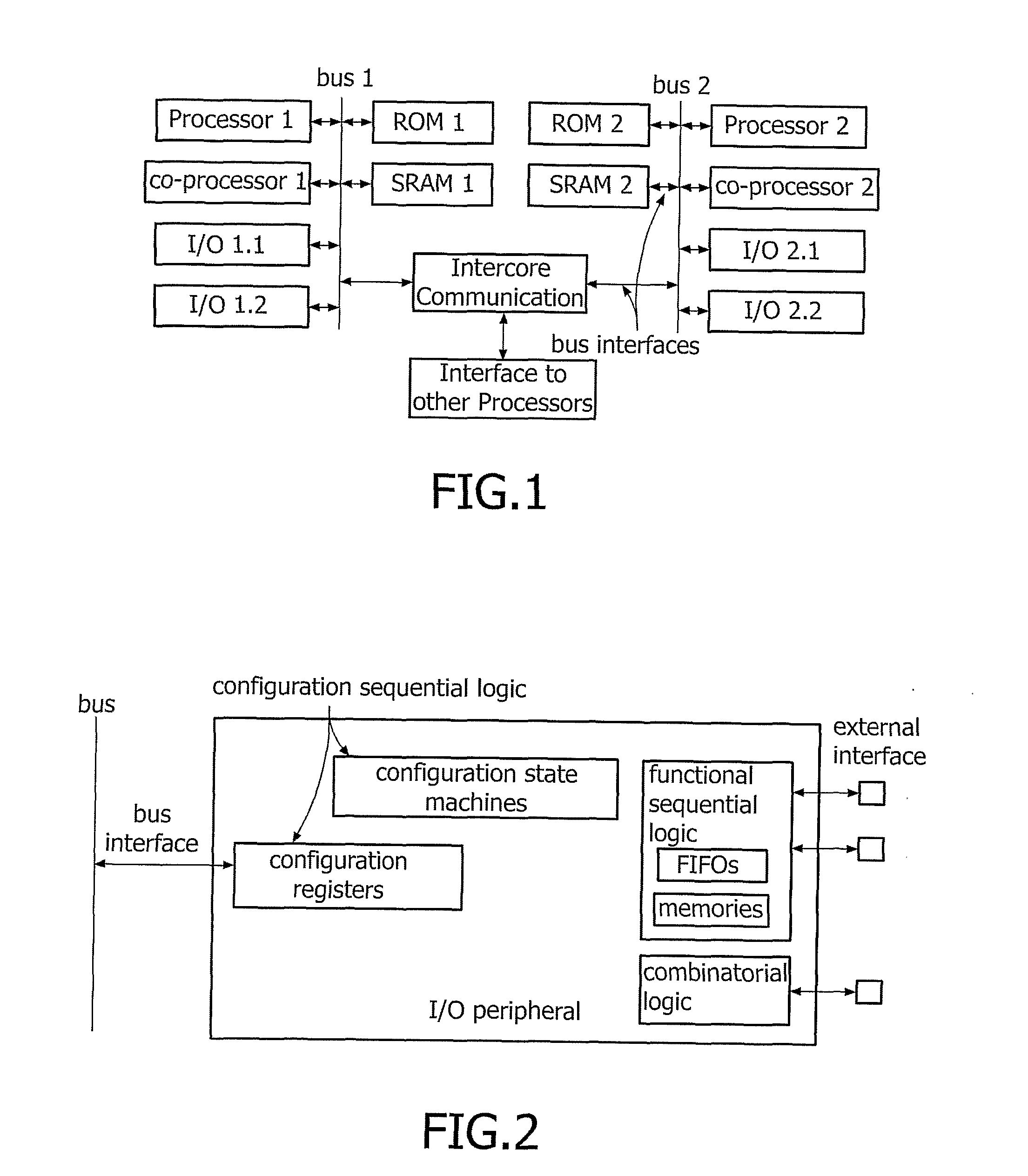
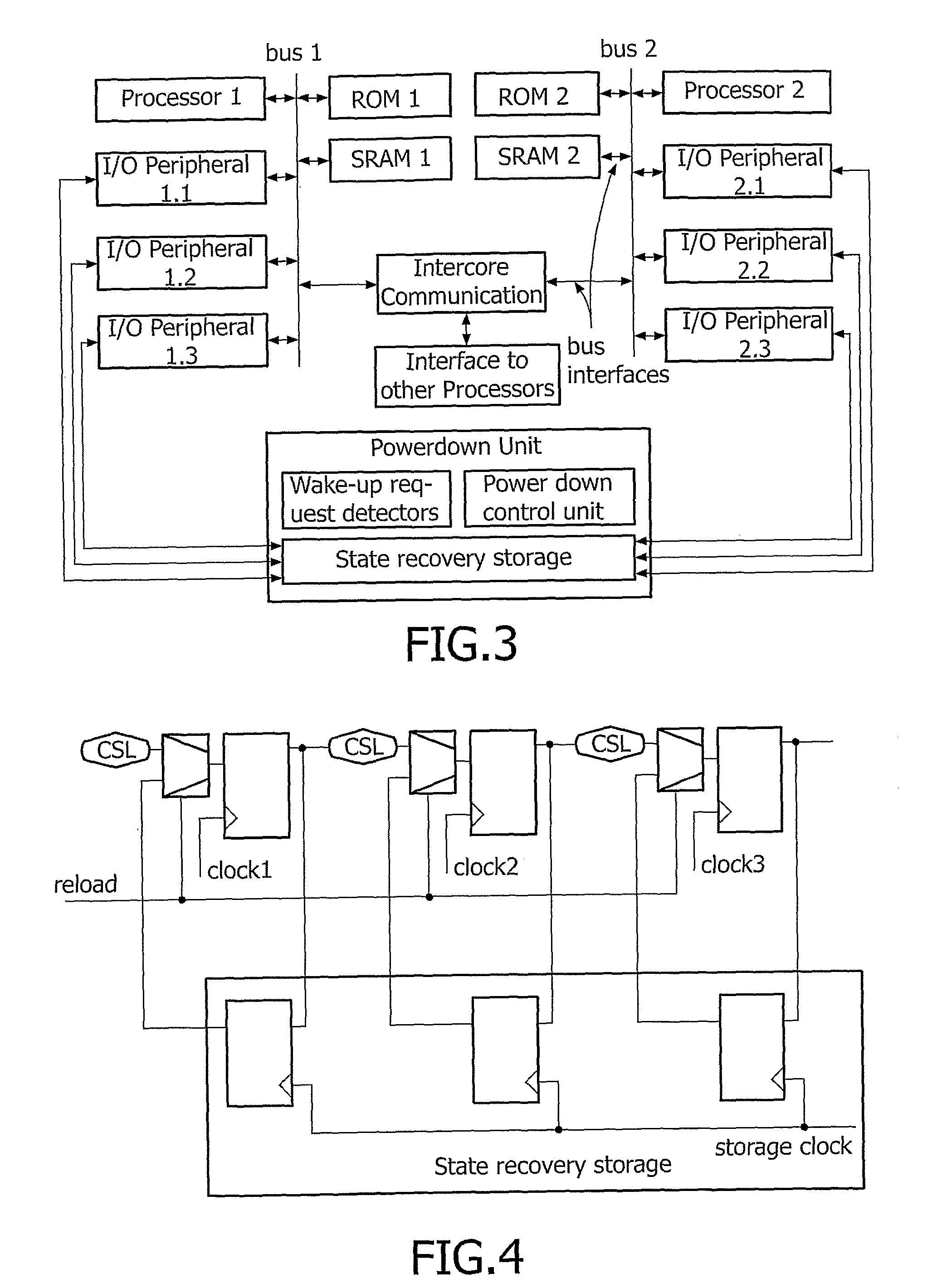
ActiveUS7848718B2Total current dropMinimizing leakage currentAnalogue computers for vehiclesResonant long antennasLow leakageEngineering
The present invention relates to a mobile apparatus comprising an integrated circuit to operate predefined functions, which integrated circuit is susceptible to be set in a standby operating mode wherein which said circuit can resume operation within a predefined delay. The circuit comprises configuration sequential logic having defined states that need to be stored before the circuit enters in standby mode. The mobile apparatus further comprises a power down unit for storing the states of the configuration sequential logic into a low leakage storage area during standby mode that reduces standby current considerably.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Zero-voltage transition full-bridge non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
ActiveCN103178739AThe opening time is the sameEliminate leakage currentEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitanceSoft switching
The invention provides a non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter capable of performing high-frequency soft switching operation, with low leakage current, and a switching control time sequence thereof. The non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter comprises voltage-dividing capacitance branch (1), a high-frequency main switch unit (2), a resonance network (3), a clamping branch (4) and a low-frequency reversing switching unit (5). The non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter has the advantages that two controllable switching tubes, a diode and two inductance-capacitance branches are respectively added on the basis of a single-phase six-switch full-bridge inverter circuit (known as 'H6' topology) to form the resonance network to provide zero-voltage switching operating conditions for the main switch unit, the soft switching operation of a high-frequency switch is realized, and the switch loss can be greatly reduced; common mode voltage can also be ensured to be a constant voltage value at a power transmission stage, a resonance stage and a continuous current stage through the switching time sequence, so that the leakage current of the non-isolated grid-connected inverter is eliminated; and the non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter can realize high frequency, and is beneficial to greatly reducing the volume, the weight and the cost.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
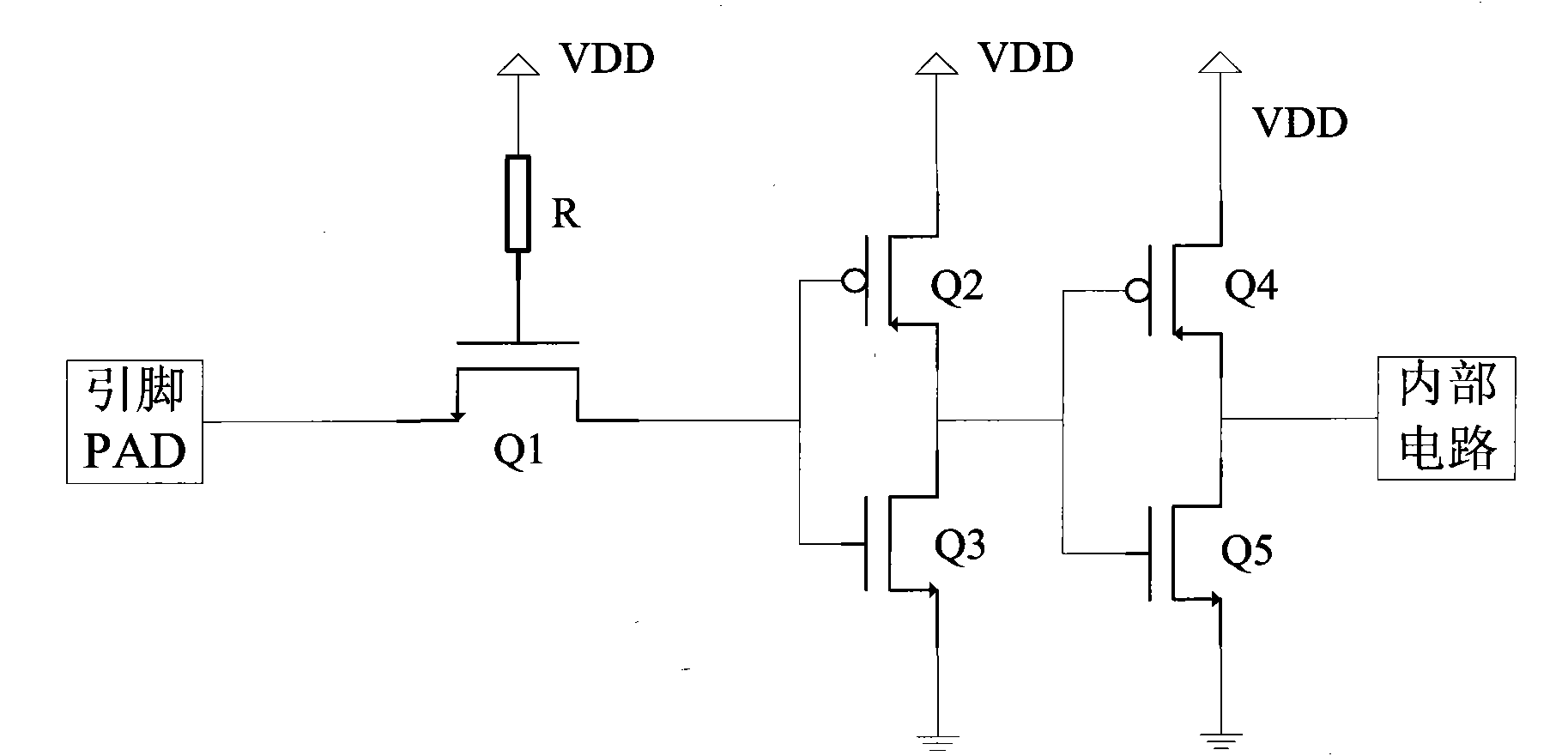
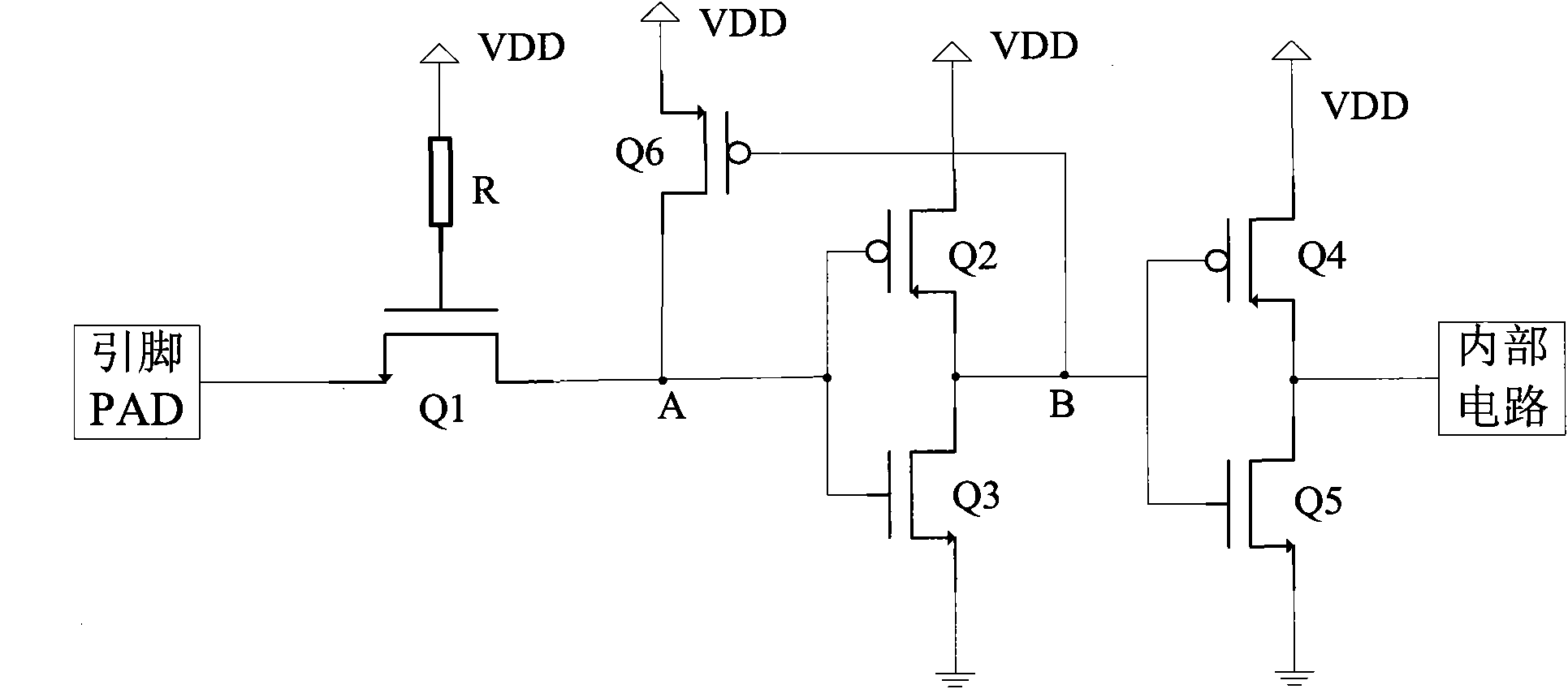
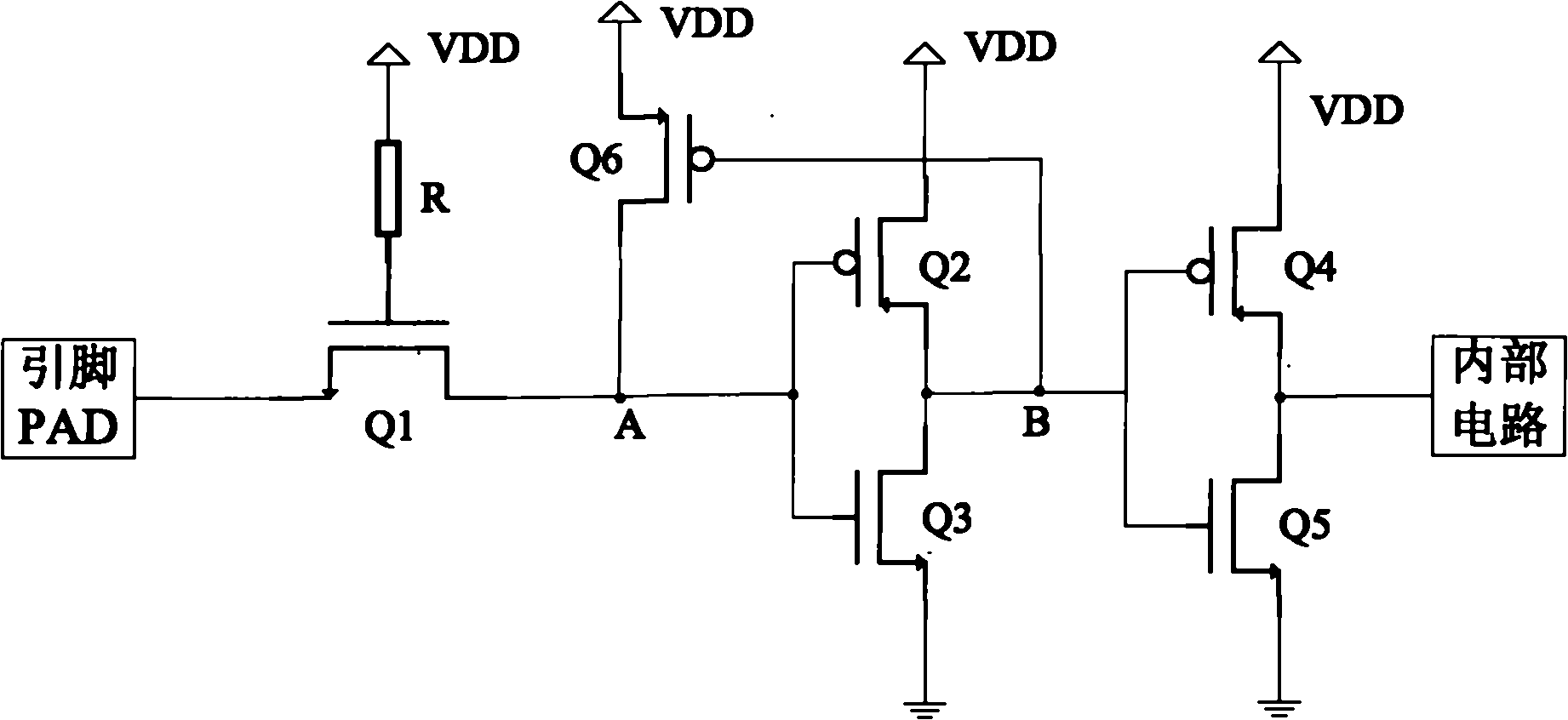
Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) input/output interface circuit
The invention discloses a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) input / output interface circuit. The CMOS input / output interface circuit comprises a first N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) transistor, a second P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) transistor, a third NMOS transistor, a fourth PMOS transistor, a fifth NMOS transistor, a resistor and a sixth PMOS transistor, wherein the grid electrode of the first NMOS transistor is connected with a power supply through the resistor; the source electrode of the first NMOS transistor is connected with a pin; the drain electrode of the first NMOS transistor is connected with the grid electrode of the second PMOS transistor and the grid electrode of the third NMOS transistor; the drain electrode of the second PMOS transistor is connected with the power supply; the source electrode of the third NMOS transistor is grounded; the source electrode of the second PMOS transistor and the drain electrode of the third NMOS transistor are connected with the grid electrode of the fourth PMOS transistor and the grid electrode of the fifth NMOS transistor; the drain electrode of the fourth PMOS transistor is connected with the power supply; the source electrode of the fifth NMOS transistor is grounded; the source electrode of the fourth PMOS transistor and the drain electrode of the fifth NMOS transistor are connected with an internal circuit; the grid electrode of the sixth PMOS transistor is connected with the source electrode of the second PMOS transistor and the drain electrode of the third NMOS transistor; the drain electrode of the sixth PMOS transistor is connected with the grid electrode of the second PMOS transistor and the grid electrode of the third NMOS transistor; and the source electrode of the sixth PMOS transistor is connected with the power supply. The CMOS input / output interface circuit can effectively avoid the generation of leakage current.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUA HONG NEC ELECTRONICS
Thin film transistor in liquid crystal display and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101592829AReduce areaMaintain propertiesTransistorSolid-state devicesLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The invention discloses a thin film transistor in a liquid crystal display and a manufacturing method thereof. The liquid crystal display comprises a plurality of display units. Each display unit comprises a scanning wire, a data wire, a pixel electrode and a thin film transistor. Each thin film transistor comprises a grid electrode connected with the scanning wire, a drain electrode connected with the data wire and a source electrode connected with the pixel electrode; and the areas of the source electrode and the drain electrode extending out of the grid electrode are reduced. In each thin film transistor, the areas of the source electrode and the drain electrode extending out of the grid electrode are reduced, thereby basically eliminating the leakage current caused by a photon-generated carrier and ensuring the characteristics of each display unit in a liquid crystal panel in a hold mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI SVA LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY
Non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and control method thereof
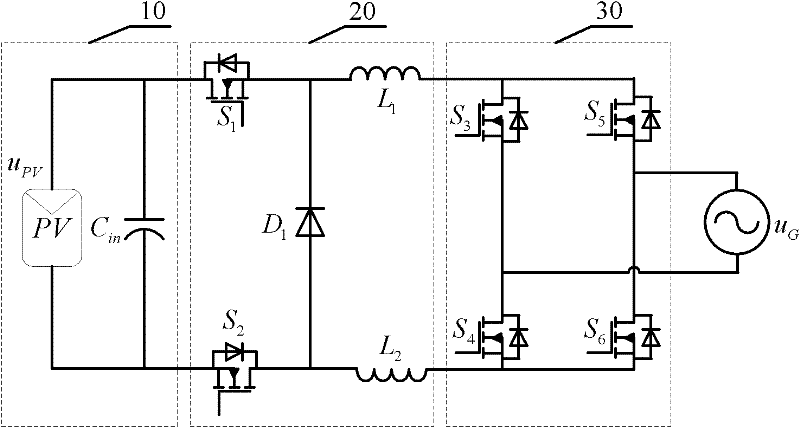
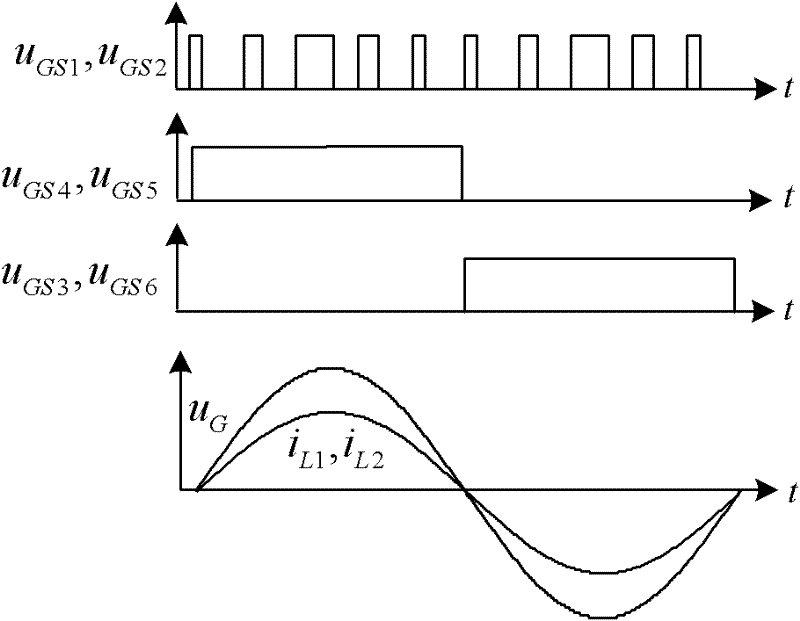
InactiveCN102684522AEliminate leakage currentImprove waveform qualityDc-dc conversionPhotovoltaic energy generationCapacitanceGrid-tie inverter
The invention discloses a non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and a control method thereof and belongs to the technical field of power electronics converters. The inverter comprises a power supply circuit (10), a high-frequency chopper circuit (20) and a low frequency inverter circuit (30), wherein the power supply circuit (10) is formed by a photovoltaic array and an input filter capacitor, the high-frequency chopper circuit (20) is formed by a first to a second power switch tube, a first diode and a first to a second filter inductor, the low frequency inverter circuit comprises a third, a fourth, a fifth and a sixth power switch tube, the first power switch tube and the second power switch tube are high frequency switches, and the third power switch tube, the fourth power switch tube, the fifth power switch tube and the sixth power switch tube are low frequency switches. The non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and the control method thereof have the advantages that leakage current of the grid-connected inverter can be eliminated, grid-connected current waveforms qualities are improved, simultaneously the efficiency is high, the controlling is simple, the reliability is high and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI CONVERTERGY ENERGY TECH
Charge pump circuit and integrated circuit
InactiveCN101317320AThe forward bias voltage decreasesEliminate leakage currentApparatus without intermediate ac conversionEngineeringHigh voltage
A charge pump circuit for increasing a circuit voltage, comprising: a DC-DC up-converter (14) having an array of capacitors arranged to charge-pump to a higher voltage than the circuit voltage, the DC-DC up-converter having an output lead (8) arranged to output the higher voltage, a DC-DC down-converter (30) connected to the output lead, the DC-DC down-converter having an array of capacitors and diodes arranged to down-pump the higher voltage, and an ESP (Electrostatic Discharge Protection) circuit comprising a series (42) of N series-connected diodes arranged to sink current from the output lead, wherein N is an integer larger than two, each diode having its anode permanently connected to the output lead and its cathode permanently connected to a reference potential, wherein the series includes the diodes of the DC-DC down-converter.
Owner:NXP BV
Method Apparatus Comprising Integrated Circuit and Method of Powering Down Such Circuit
ActiveUS20080045166A1Eliminate leakage currentSafe storageAnalogue computers for vehiclesResonant long antennasEngineeringOperation mode
The present invention relates to a mobile apparatus comprising an integrated circuit to operate predefined functions, which integrated circuit is susceptible to be set in a standby operating mode wherein which said circuit can resume operation within a predefined delay. The circuit comprises configuration sequential logic having defined states that need to be stored before the circuit enters in standby mode. The mobile apparatus further comprises a power down unit for storing the states of the configuration sequential logic into a low leakage storage area during standby mode that reduces standby current considerably.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Modulation method for inhibiting leakage current of H-bridge cascade inverters
ActiveCN105610343AOverall small sizeWon't add weightEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCarrier signalParasitic capacitance
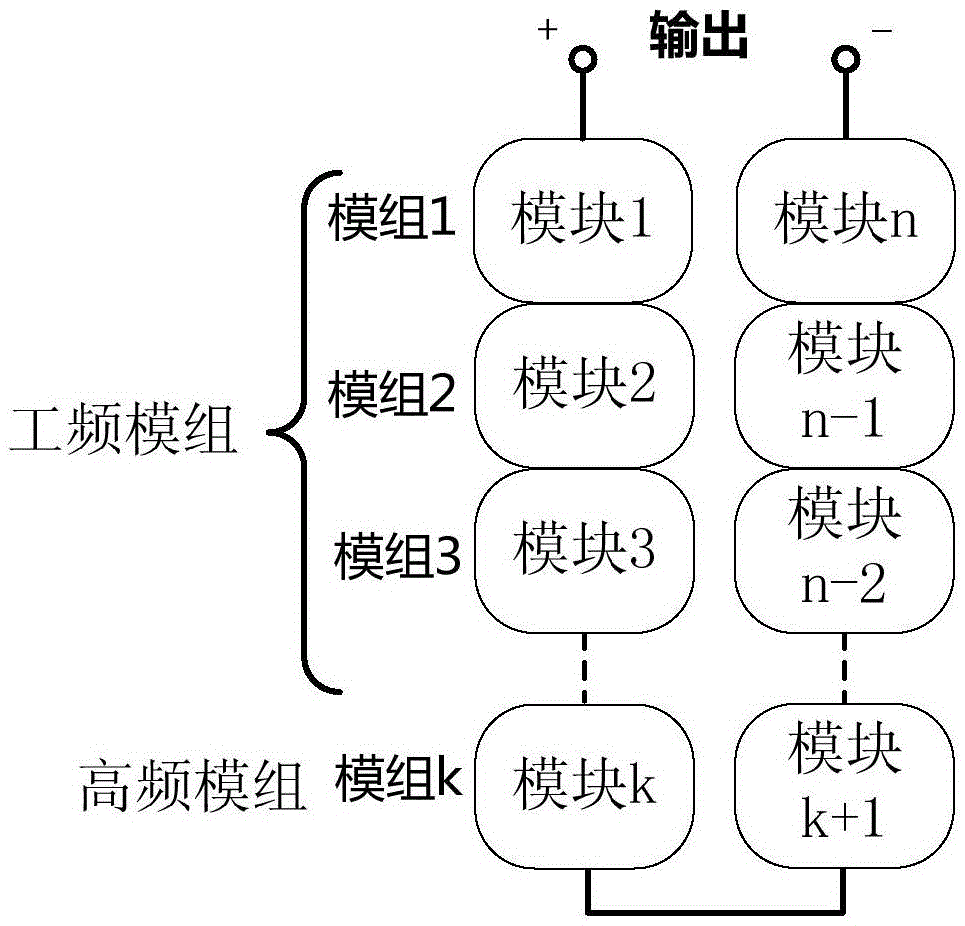
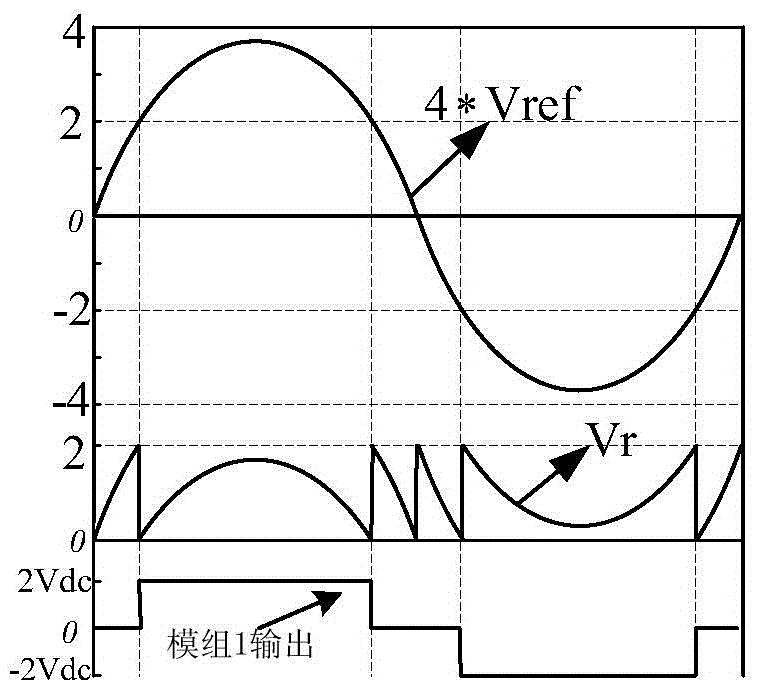
The invention discloses a modulation method for inhibiting leakage current of H-bridge cascade inverters. The modulation method can maintain the sum of parasitic capacitance voltages of all modules to be constant, and thus the leakage current is eliminated. The method comprises the following steps: dividing all modules into module groups in pairs according to rules, and dividing into a power frequency module group and a high frequency module group; obtaining the on-off state of the power frequency module group through comparison of modulating waves and fixed values; obtaining the on-off state of the high frequency module group through comparison of corrected modulating waves and two stacked triangle carriers; and generating corresponding PWM signals through the combination of the on-off states, and distributing to corresponding pins. The scheme can be used for multiple H-bridge cascade inverters, and extra hardware cost does not need to be added, so that the leakage current flowing into a power grid can be eliminated, meanwhile the switching loss is relatively low, and the implementation manner is simple.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com