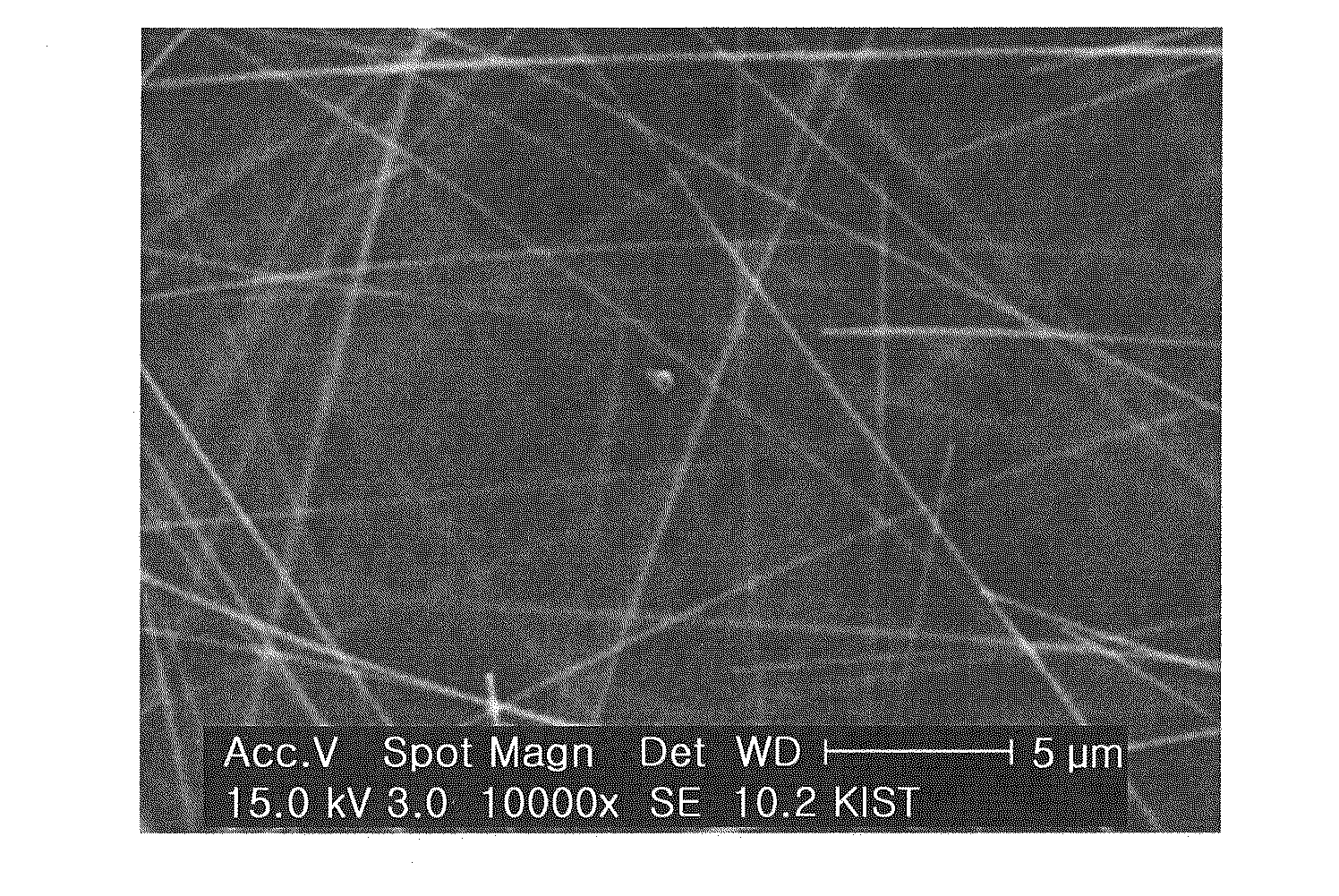Patents
Literature
79results about How to "Improve sheet resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
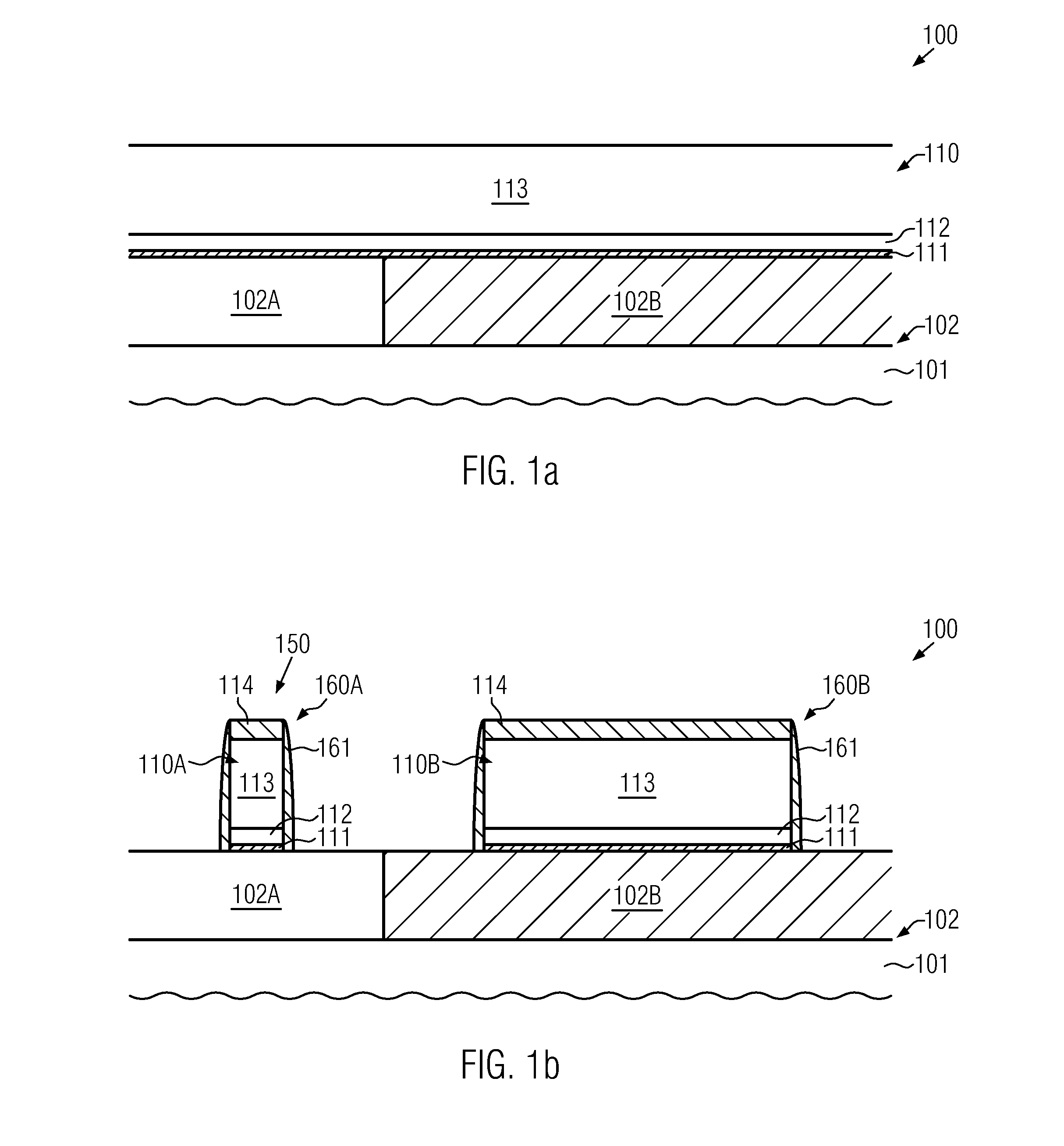
Metal nanowires with high linearity, method for producing the metal nanowires and transparent conductive film including the metal nanowires
ActiveUS20130087363A1Improve linearityExcellent thermalMaterial nanotechnologySingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsConductive polymerCarbon nanotube
Metal nanowires with high linearity can be produced using metal salts at a relatively low temperature. A transparent conductive film can be formed using the metal nanowires. Particularly, the transparent conductive film has high transmittance, low sheet resistance, and good thermal, chemical and mechanical stability. The transparent conductive film has a high electrical conductivity due to the high linearity of the metal nanowires. The metal nanowires take up 5% or less of the volume of the transparent conductive film, ensuring high transmittance of the transparent conductive film. Furthermore, the metal nanowires are useful as replacements for existing conductive materials, such as ITO, conductive polymers, carbon nanotubes and graphene. The metal nanowires can be applied to flexible substrates and other various substrates due to their good adhesion and high applicability to the substrates. Moreover, the metal nanowires can find application in various fields, such as displays and solar cell devices.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
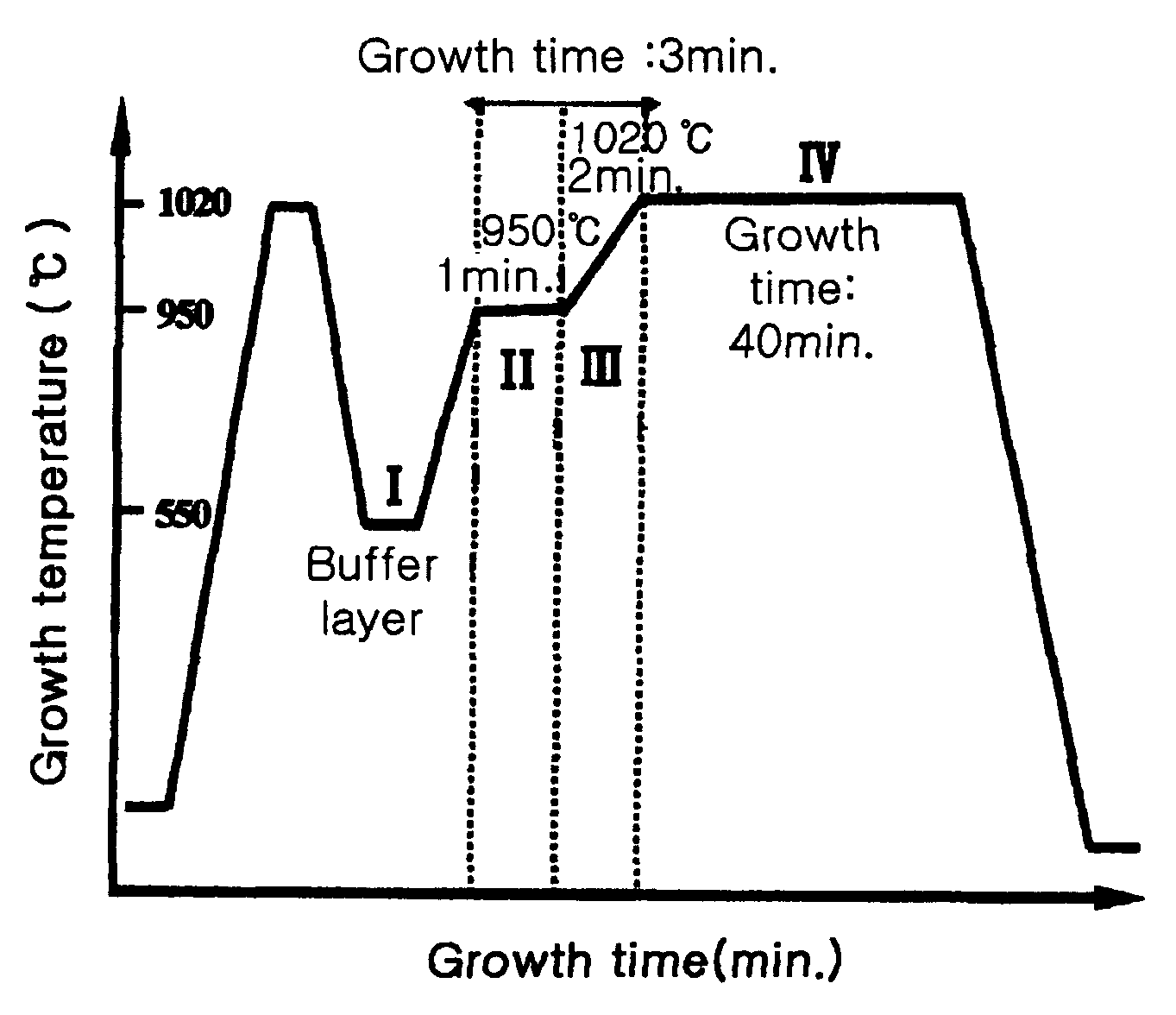
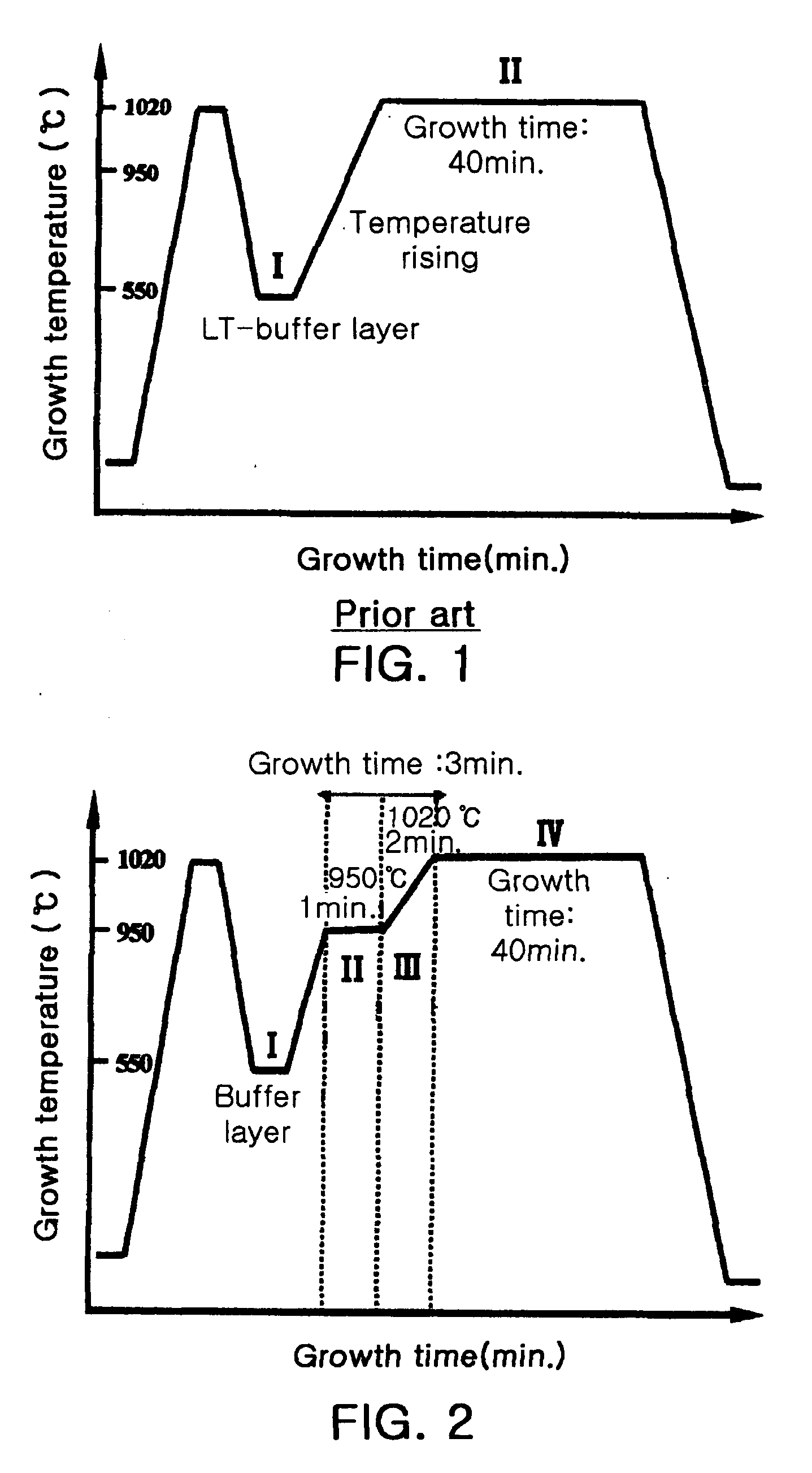
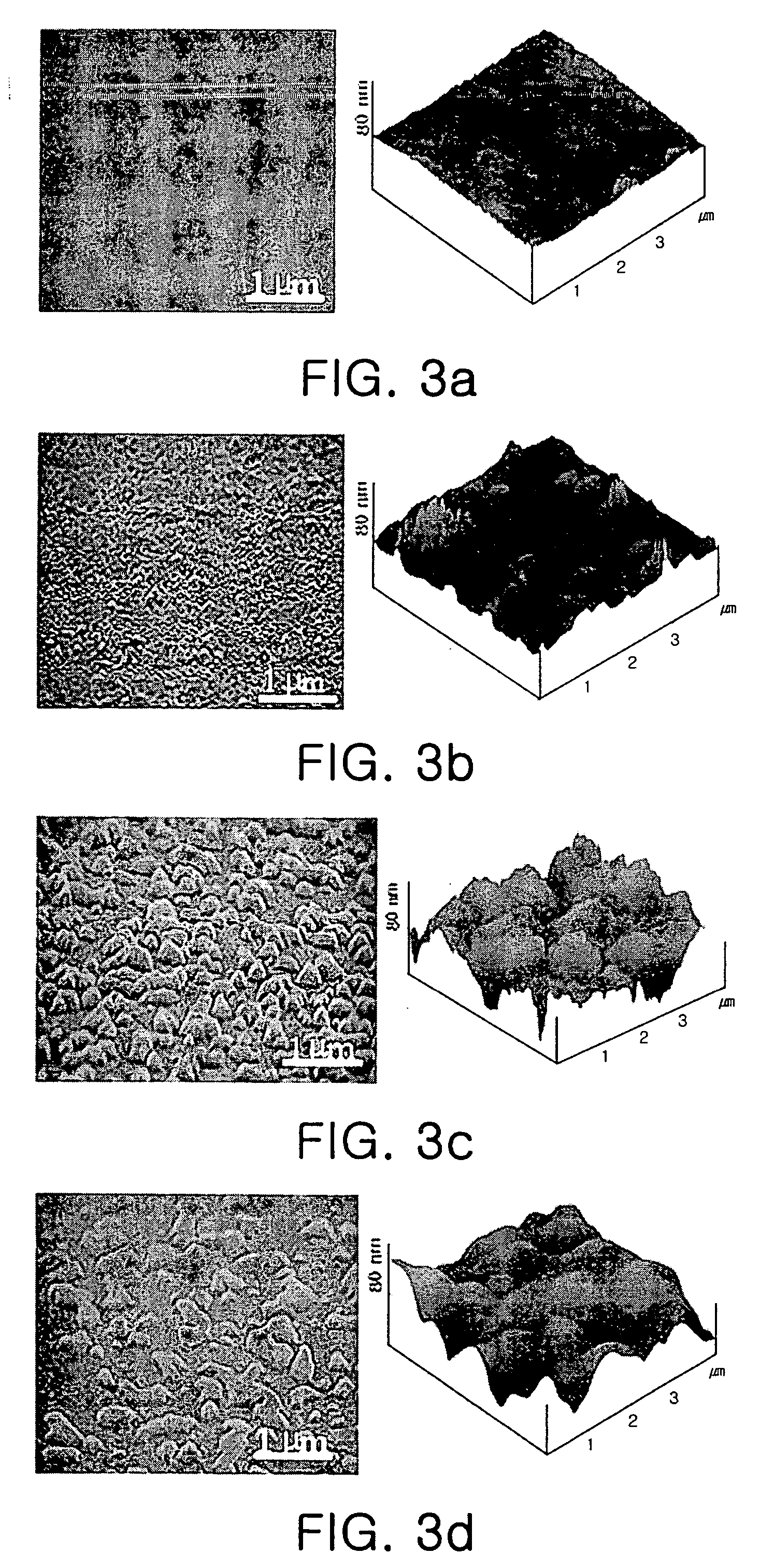
Method of growing semi-insulating GaN layer
InactiveUS20060003556A1Improve sheet resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantBiology
Disclosed herein is a method for growing a semi-insulating GaN layer with high sheet resistance by controlling the size of grains through changes in growth temperature at the initial growth stage of the layer, without doping of dopants. The method comprises the steps of growing a buffer layer on a substrate at a first growth temperature, growing a GaN layer on the buffer layer at a second growth temperature higher than the first growth temperature for a first growth time (a first growth step), growing the GaN layer at increasing temperatures from the second growth temperature to a third growth temperature higher than the second growth temperature for a second growth time (a second growth step), and growing the GaN layer at the third growth temperature for a third growth time (a third growth step).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
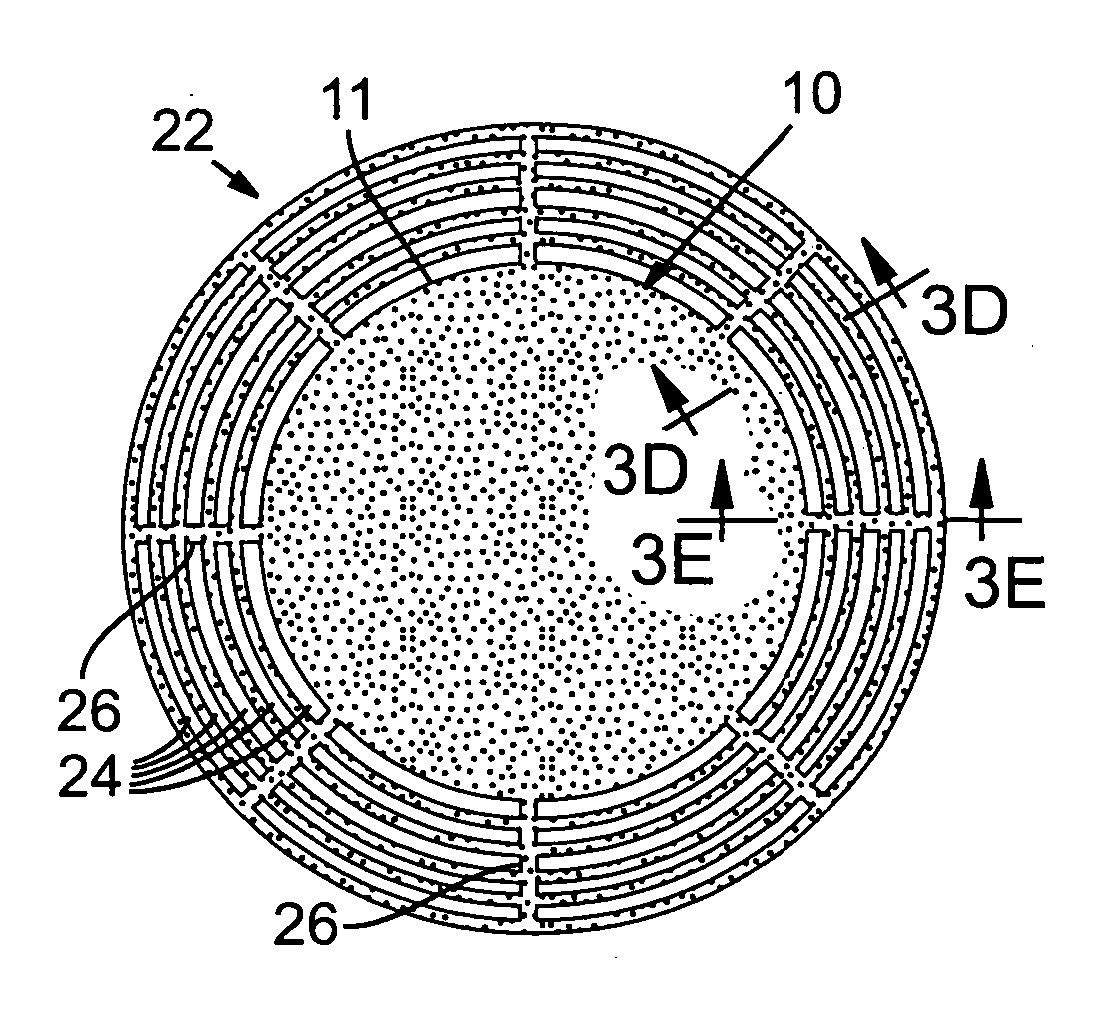
Junction termination structures for wide-bandgap power devices
InactiveUS20060118900A1High blocking voltageSimple and controllable processTransistorRadial gradientElectrical resistivity and conductivity
Disclosed are a variety of junction termination structures for high voltage semiconductor power devices. The structures are specifically aimed at providing a high breakdown voltage while being constructed with a minimal number of process steps. The combination of an RIE etch and / or implantation and anneal process with a finely patterned mesh provides the desired radial gradient for maximum breakdown voltage. The structures provide control of both the conductivity and charge density within the region. These structures can beneficially be applied to all high voltage semiconductor device structures, but are of particular interest for wide bandgap devices as they tend to have very high breakdown fields and scaled dimensions of the depletion layer width.
Owner:MICROSEMI
Semiconductor device incorporating elements formed of refractory metal-silicon-nitrogen and method for fabrication
InactiveUS20020130367A1Improve sheet resistanceIncrease resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor structureNitrogen
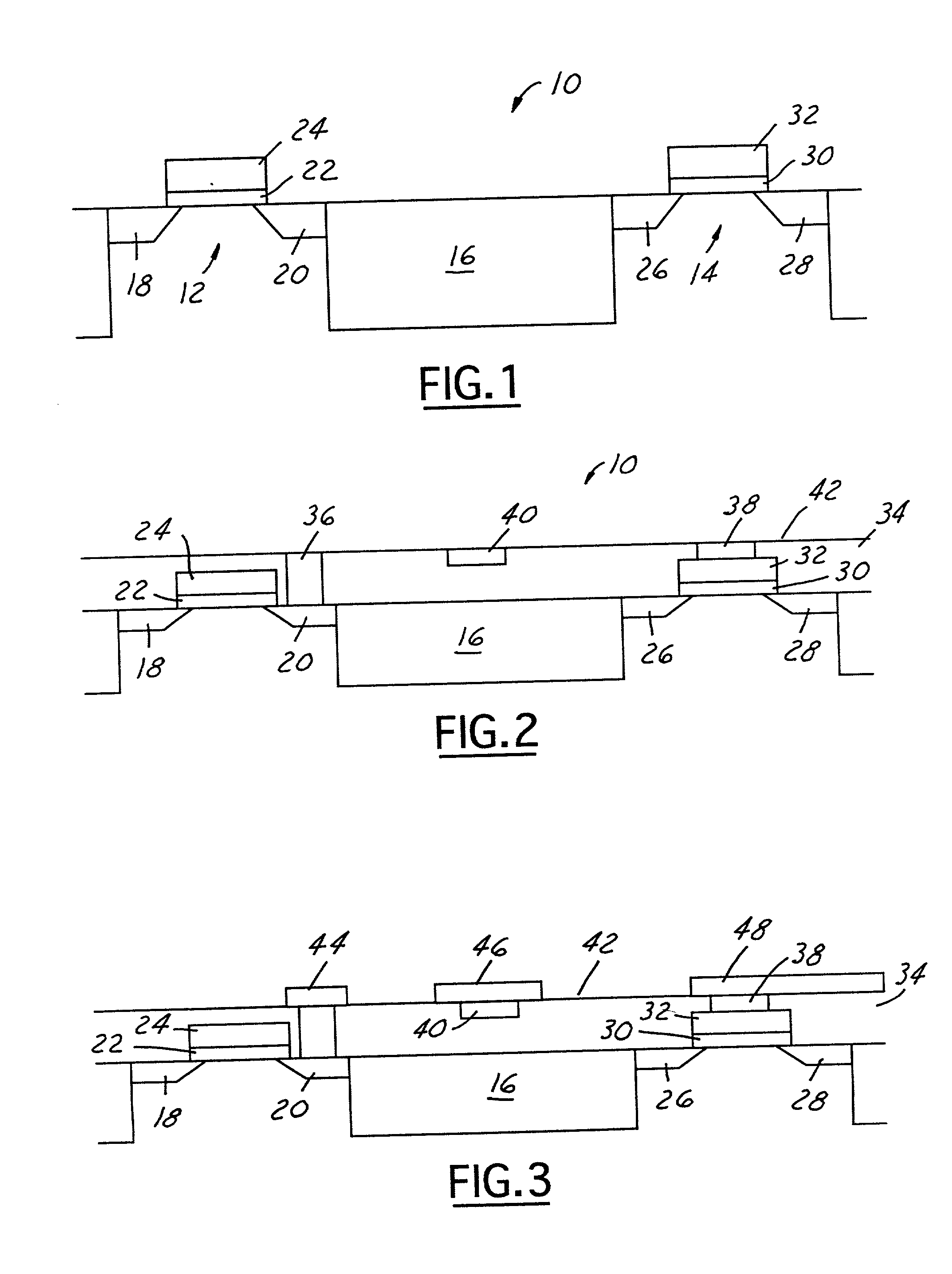
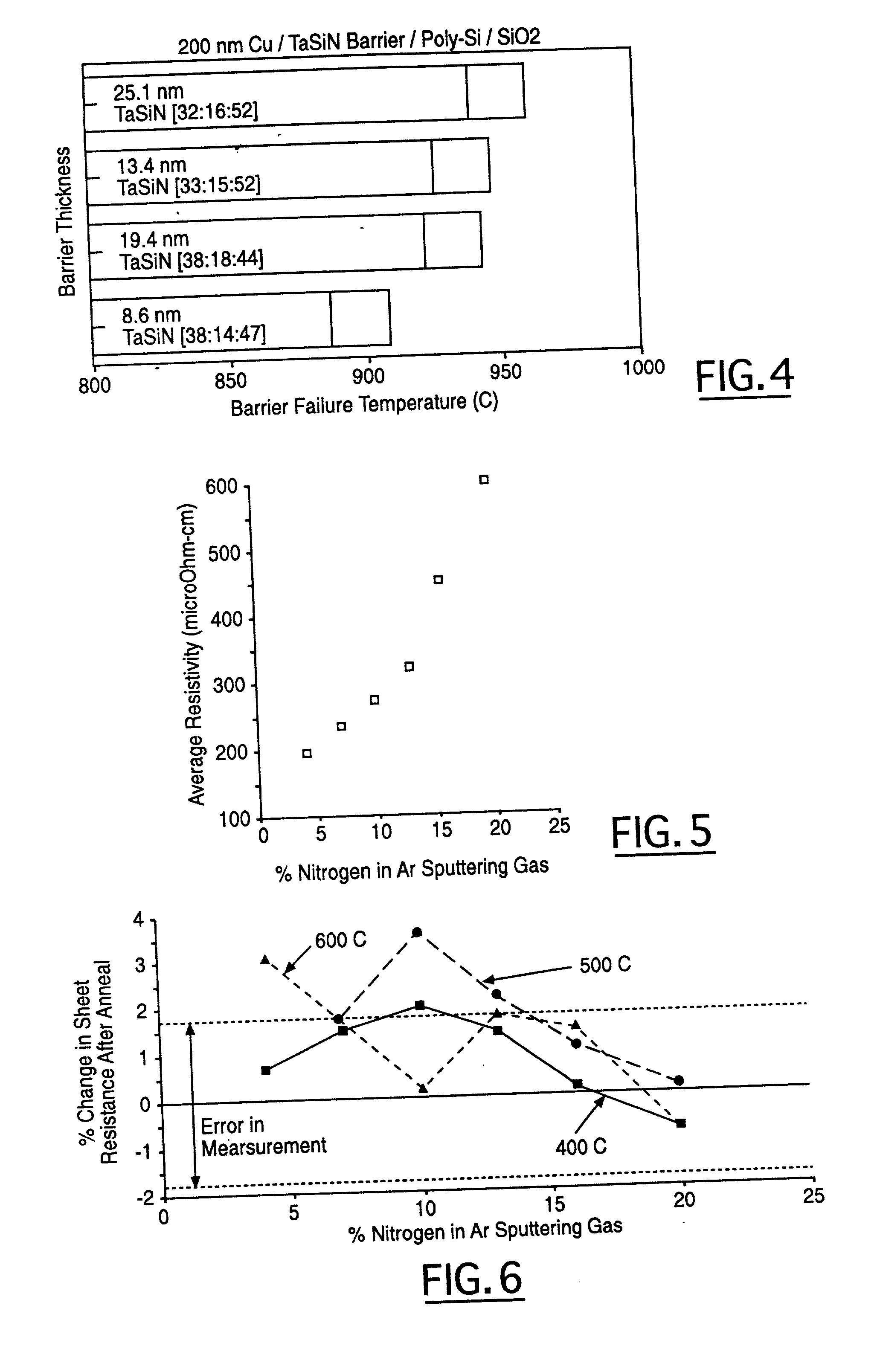
A semiconductor structure that includes at least one circuit element of a fuse, a diffusion barrier or a capacitor that is formed by refractory metal-silicon-nitrogen is disclosed. A method for fabricating such semiconductor structure that includes a fuse element, a diffusion barrier, a resistor or a capacitor by a refractory metal-silicon-nitrogen material is further disclosed. A suitable refractory metal-silicon-nitrogen material to be used is TaSiN which provides a wide range of resistivity by changing the ratio of Ta:Si:N. The invention provides the benefit that the various components of diffusion barriers, fuses, capacitors and resistors may be formed by a single deposition process of a TaSiN layer, the various components are then selectively masked and treated by either heat-treating or ion-implantation to vary their resistivity selectively while keeping the other shielded elements at the same resistivity.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor device with resistor pattern and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20060246654A1Improve sheet resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialLine width
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
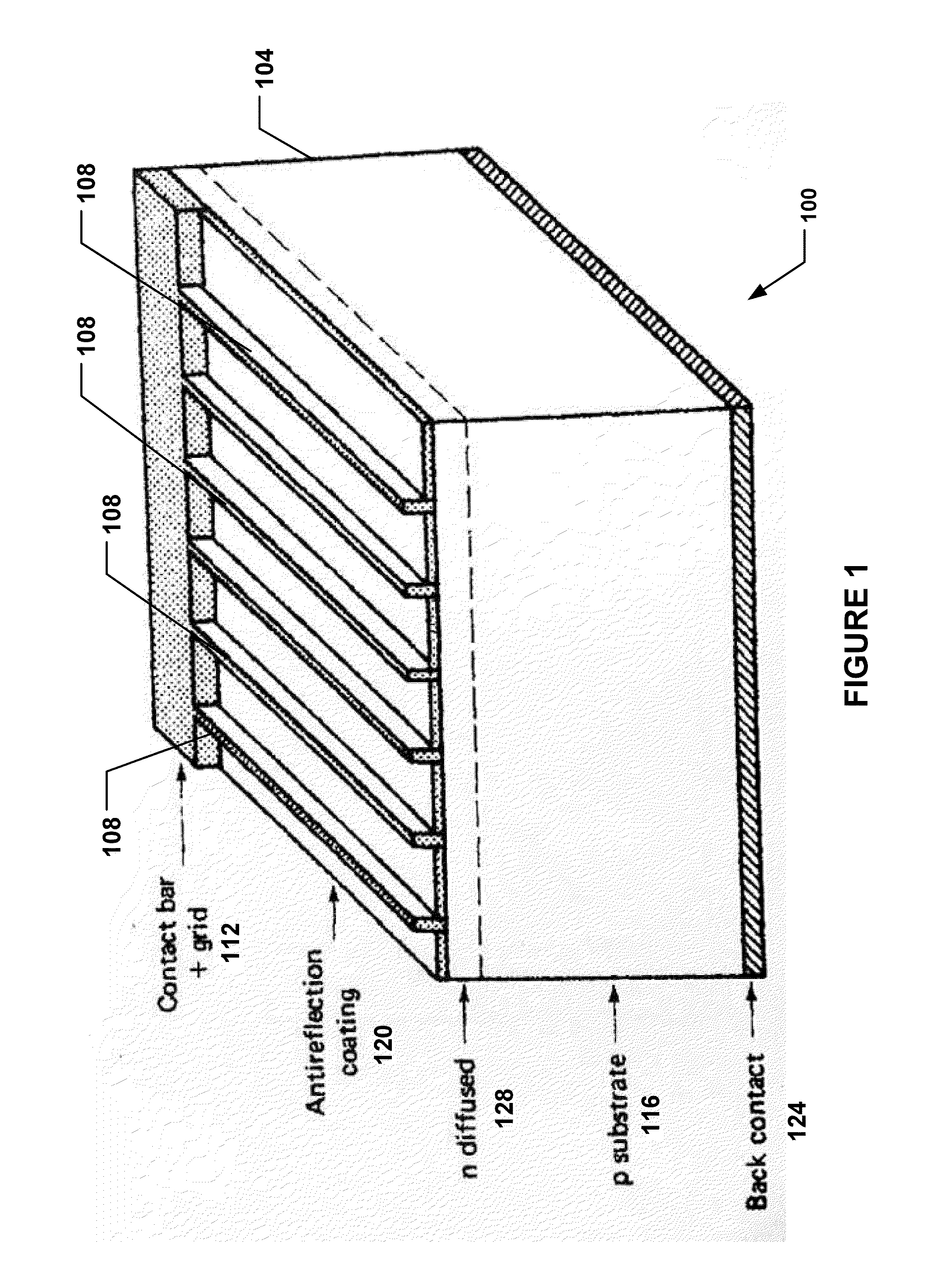
Method for manufacturing silicon solar cell
InactiveCN101783374ALow sheet resistanceLower ohmic contactFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesMetallic electrodeOhmic contact
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a silicon solar cell. In the process of manufacturing a PN junction on a silicon wafer, a selective diffusion technology method is adopted, i,e. laser is utilized to heat a position, on which a positive electrode intends to be manufactured, on the surface of the silicon wafer; and under the action of heating, phosphorus in a phosphorus source uniformly adhered on the surface diffuses towards the inner of the silicon wafer, thus a heavy doping zone with smaller sheet resistance is formed at the position on which the positive electrode intends to be manufactured to effectively reduce the sheet resistance of the silicon solar cell, thereby not only being beneficial for increasing the open-circuit voltage of the silicon solar cell; the increase of the open-circuit voltage effectively improves the conversion efficiency of the silicon solar cell, reduces ohmic contact of a metal electrode and the silicon solar cell, thereby reducing the series resistance of the silicon solar cell, and being capable of meeting the purpose of industrialized production better.
Owner:SUN EARTH SOLAR POWER
Method of improving copper pad adhesion
InactiveUS7026721B2Increasing area occupiedReduce contact resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTantalum nitrideLead bonding
This invention relates to a new improved method and structure in the fabricating of aluminum metal pads. The formation special aluminum bond pad metal structures are described which improve adhesion between the tantalum nitride pad barrier layer and the underlying copper pad metallurgy by a special interlocking bond pad structure. It is the object of the present invention to provide a process wherein a special grid of interlocking via structures is placed in between the underlying copper pad metal and the top tantalum nitride pad barrier layer providing improved adhesion to the aluminum pad metal stack structure. This unique contact bond pad structure provides for thermal stress relief, improved wire bond adhesion to the aluminum pad, and prevents peeling during wire bond adhesion tests.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
CMOS transistors and methods of forming same
InactiveUS20050059260A1Easy to operateEasy to optimizeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSDriving current
The present invention teaches the formation of CMOS transistors using interfacial nitrogen at the interface between the lightly doped extension regions and an overlying insulating layer in combination with a capping layer of silicon nitride, both prior to the final source / drain anneal. Doses and energies may be increased for the P-channel lightly-doped drain, source and drain regions. The resulting transistors exhibit desirably high drive current and low off-state leakage current and overlap capacitance.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Formation of high sheet resistance resistors and high capacitance capacitors by a single polysilicon process
ActiveUS20070281418A1Improve sheet resistanceIncrease capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a transistor, a capacitor and a resistor wherein the capacitor includes a doped polysilicon layer to function as a bottom conductive layer with a salicide block (SAB) layer as a dielectric layer covered by a Ti / TiN layer as a top conductive layer thus constituting a single polysilicon layer metal-insulator-polysilicon (MIP) structure. While the high sheet rho resistor is also formed on the same single polysilicon layer with differential doping of the polysilicon layer.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Semiconductor device, method of manufacturing the same, and electronic device
InactiveUS7602273B2Improve operating characteristicsImprove sheet resistanceCurrent responsive resistorsSolid-state devicesNegative temperatureEngineering
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for producing a layer system on a substrate and layer system
InactiveUS20110220382A1Improve sheet resistanceAvoid yield lossVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingElectrical resistance and conductanceDielectric substrate
In the method for producing a layer system on a dielectric substrate in which a metal layer is applied onto the substrate by a coating step (110) and a further layer with a predetermined layer thickness is subsequently applied by a further coating step (140), the metal layer having a sheet resistance >10 Mohm and an average reflectance >50%, the further layer would have a sheet resistance <1 Mohm if it had been applied onto the substrate with the same layer thickness by the further coating step (140), and the layer system consisting of the metal layer and the further layer has a sheet resistance >10 Mohm, where the invention furthermore relates to a layer system on a dielectric substrate in which a metal layer is applied onto the substrate by a coating step (110) and a further layer with a predetermined layer thickness is subsequently applied by a further coating step (140), the metal layer having a sheet resistance >10 Mohm and an average reflectance >50%, where the further layer, if it had been applied onto the substrate with the same layer thickness by the further coating step (140), would have a sheet resistance <1 Mohm, and the layer system consisting of the metal layer and the further layer has a sheet resistance >10 Mohm, the invention further providing a housing including a layer system.
Owner:LEYBOLD OPTICS
Semiconductor device with spacer layer between carrier traveling layer and carrier supplying layer
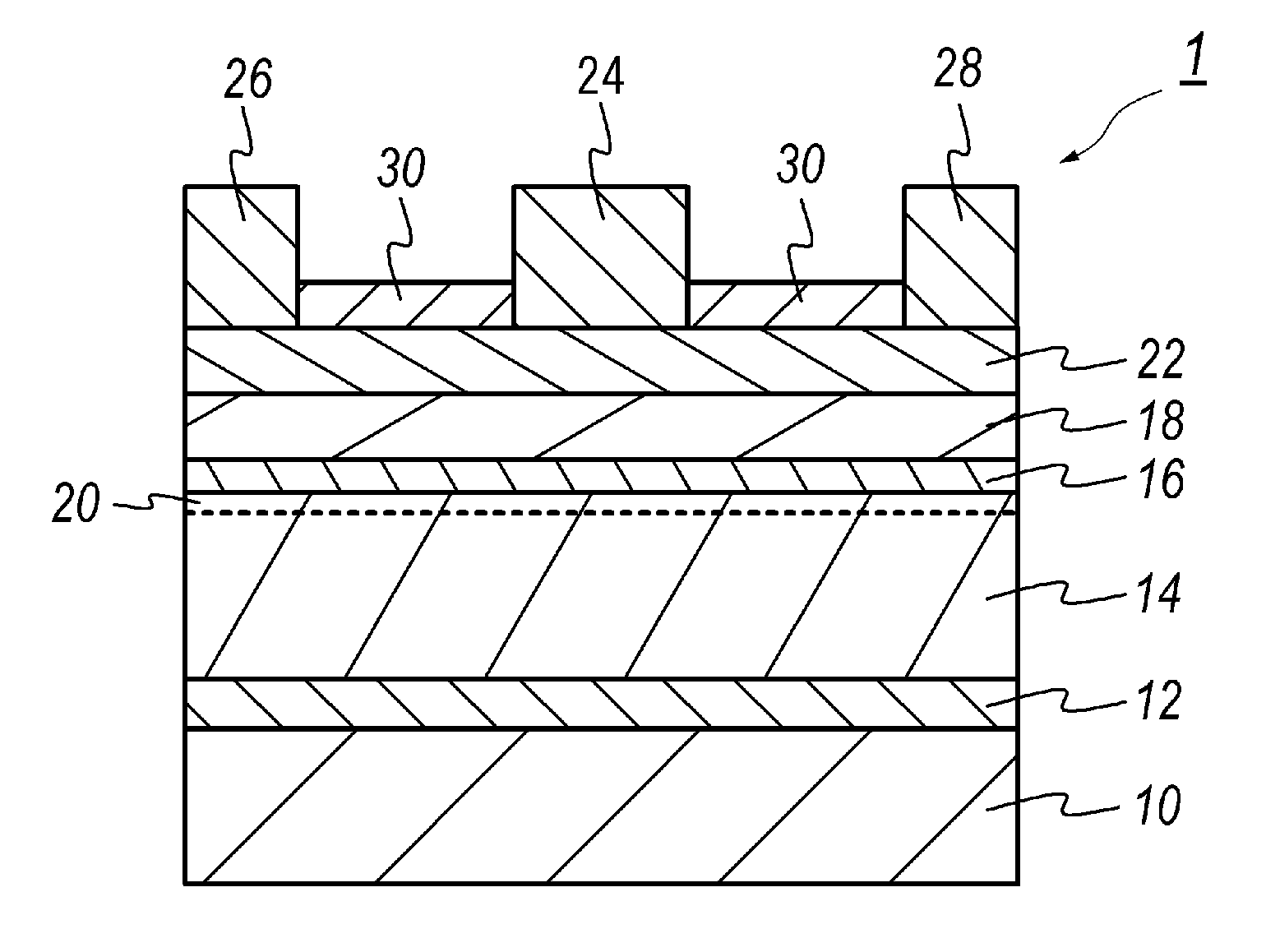
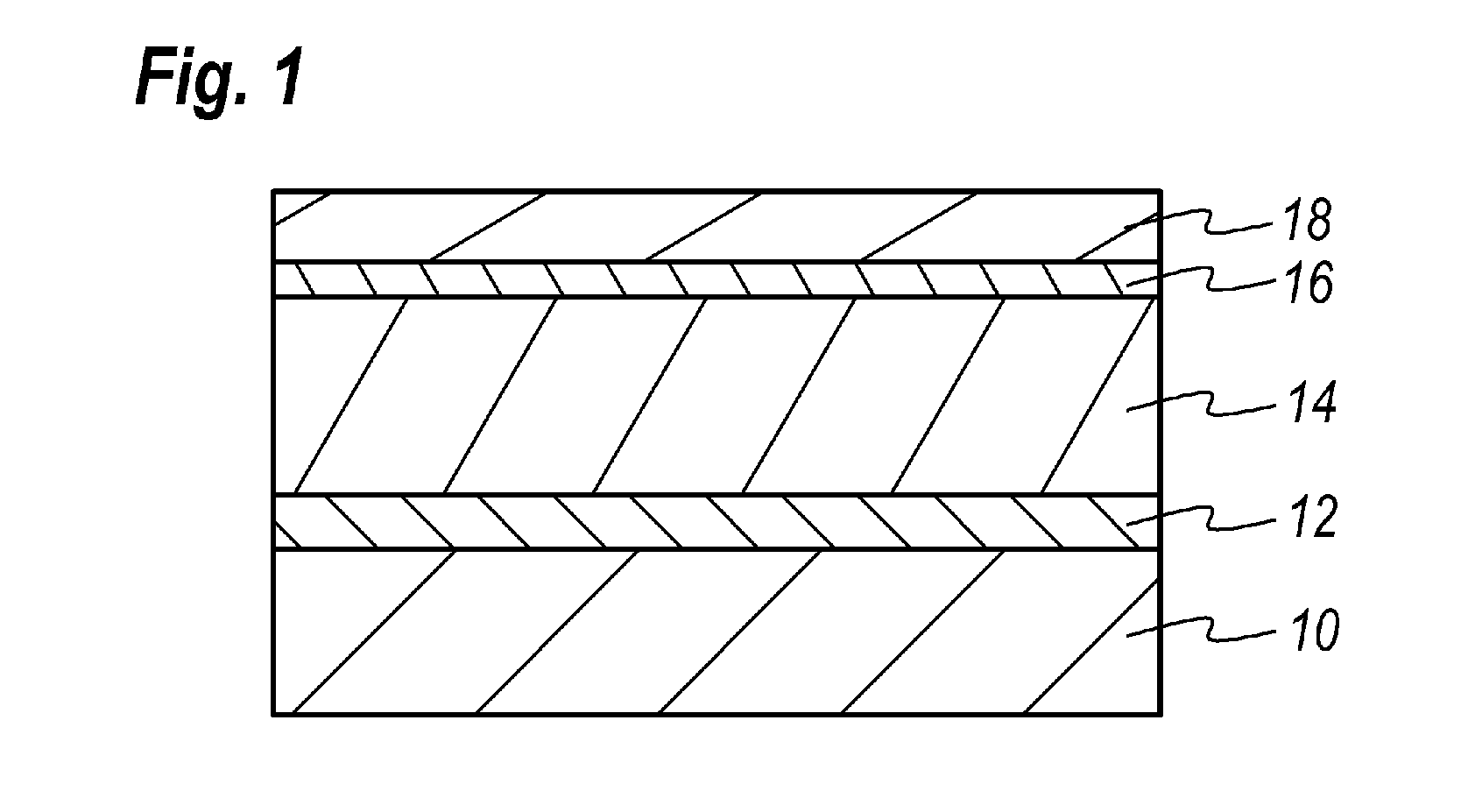
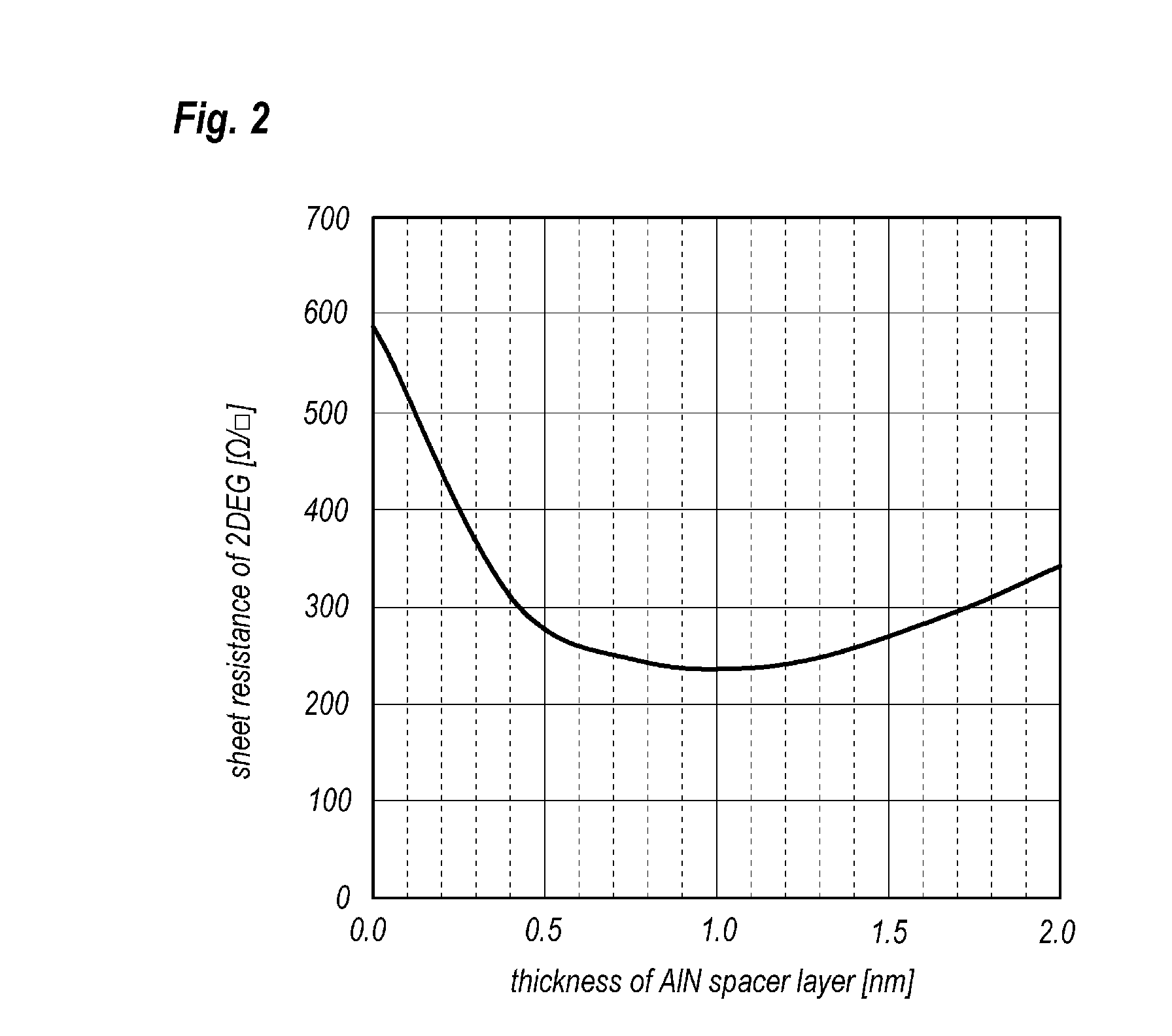
ActiveUS20120313145A1Improve sheet resistanceGood surface smoothnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge carrierNitride semiconductors
A nitride semiconductor device is disclosed. The device includes a stack of semiconductor layers including the channel layer, the spacer layer, and the doped layer. The spacer layer is made of AlN while the doped layer is InAlN. A feature of the embodiment is that the spacer layer has a thickness of 0.5 to 1.25 nm.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Polysilicon Resistors Formed in a Semiconductor Device Comprising High-K Metal Gate Electrode Structures
InactiveUS20120049291A1Adjustable resistanceImprove sheet resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricMaterials science
In sophisticated semiconductor devices, resistors may be provided together with high-k metal gate electrode structures by using a polycrystalline silicon material without requiring a deterioration of the crystalline nature and thus conductivity of a conductive metal-containing cap material that is used in combination with the high-k dielectric gate material. In this manner, superior uniformity of the resistance values may be obtained, while at the same time reducing the overall process complexity.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
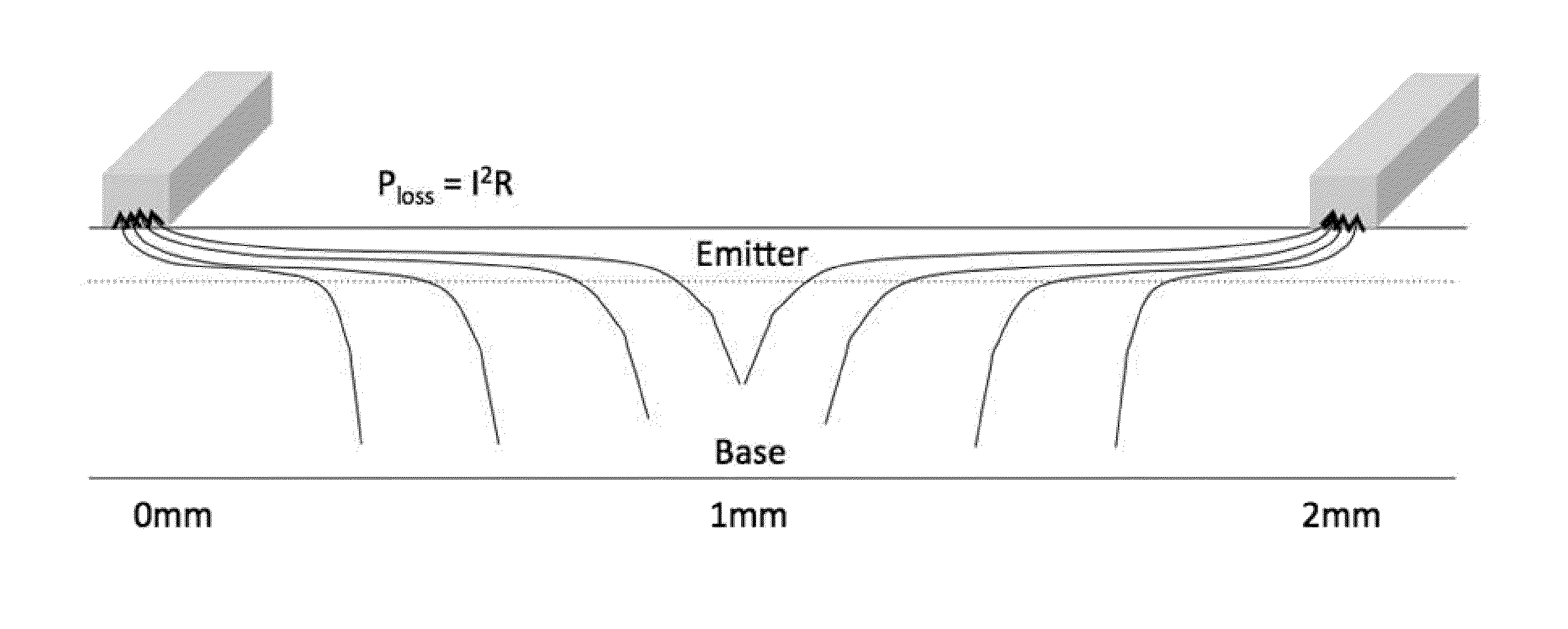
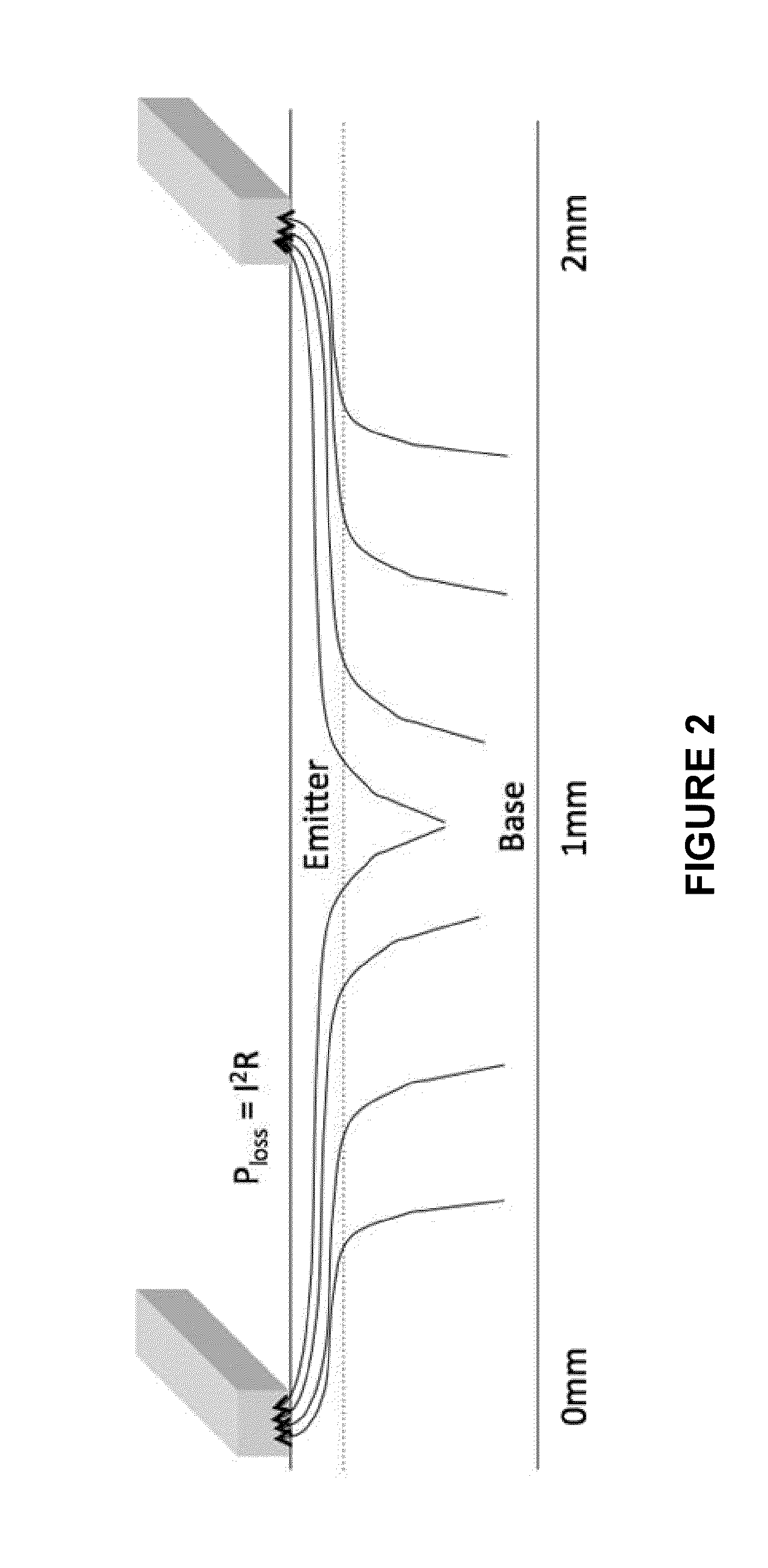
Solar cells having graded doped regions and methods of making solar cells having graded doped regions
InactiveUS20140166087A1Reduce sheet resistanceImprove sheet resistanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsSheet resistance
A photovoltaic cell having a graded doped region such as a graded emitter and methods of making photovoltaic cells having graded doped regions such as a graded emitter are disclosed. Doping is adjusted across a surface to minimize resistive (I2R) power losses. The graded emitters provide a gradual change in sheet resistance over the entire distance between the lines. The graded emitter profile may have a lower sheet resistance near the metal lines and a higher sheet resistance farther from the metal line edges. The sheet resistance is graded such that the sheet resistance is lower where I2R power losses are highest due to current crowding. One advantage of graded emitters over selective emitters is improved efficiency. An additional advantage of graded emitters over selective emitters is improved ease of aligning metallization to the low sheet resistance regions.
Owner:INTEVAC
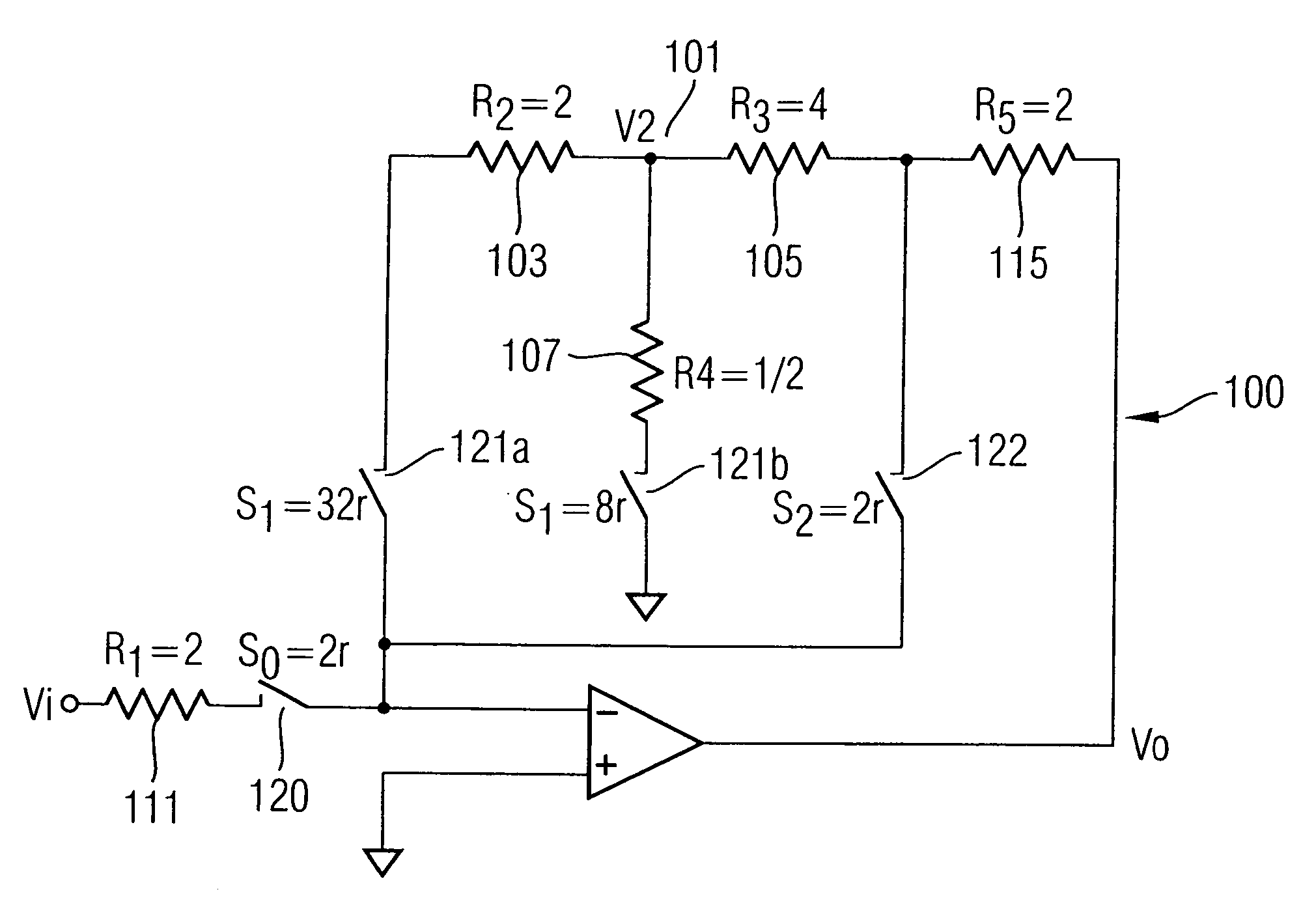
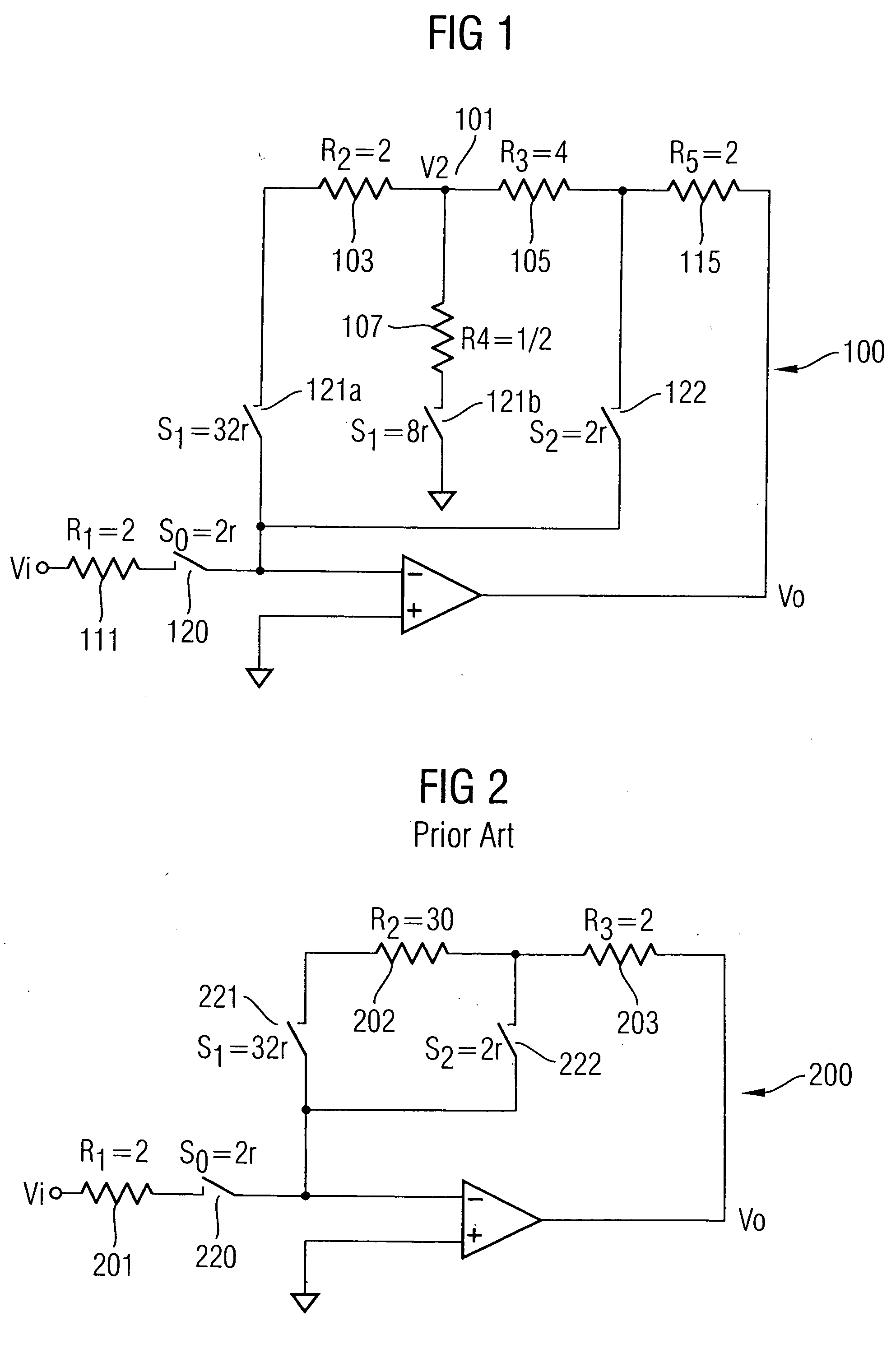
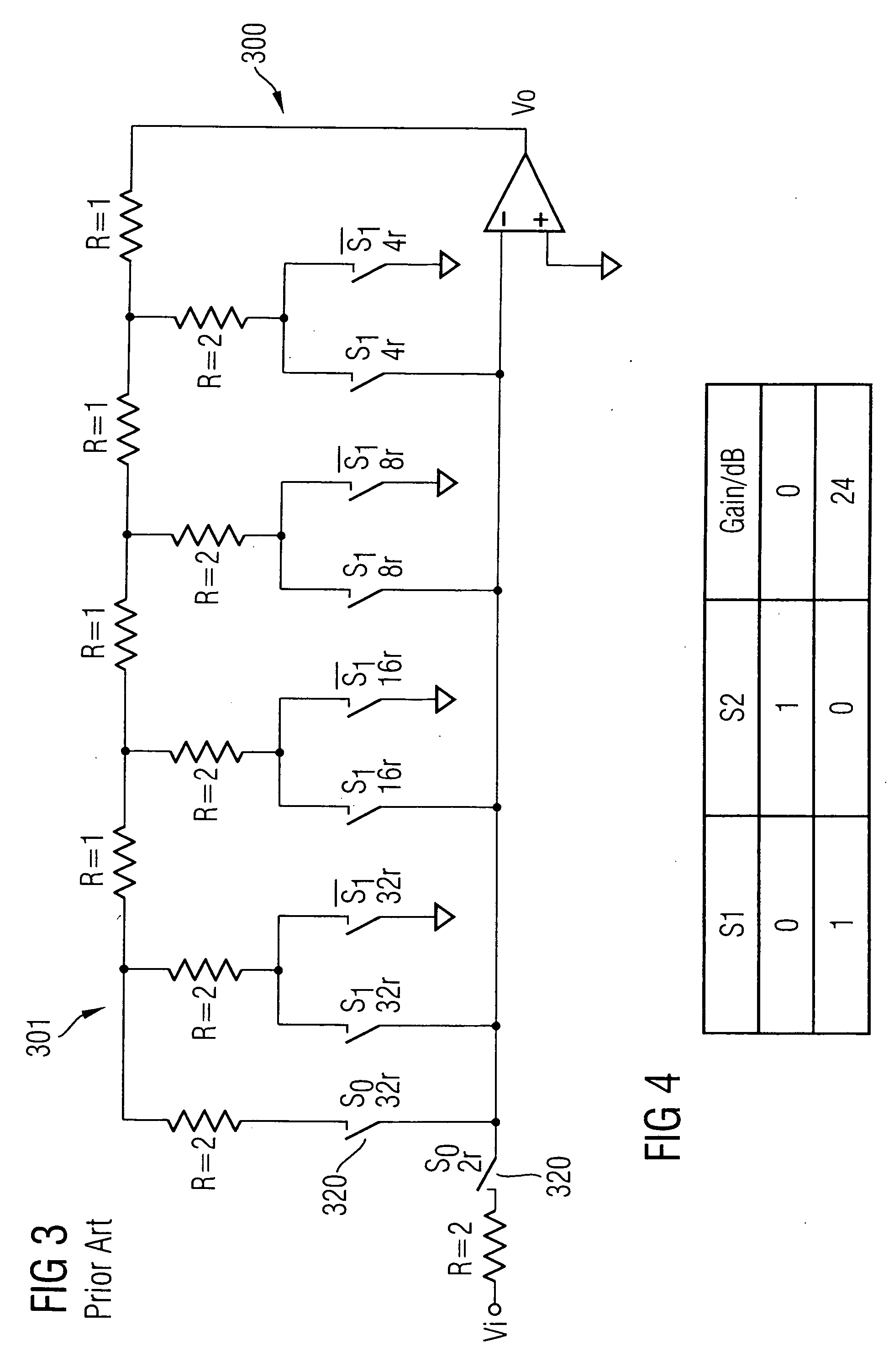
Resistor and switch-minimized variable analog gain circuit
InactiveUS20050264360A1Improves gain accuracyHigh sheet resistanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlDifferential amplifierJunction point
A DSM variable high-gain circuit includes a differential amplifier and a negative feedback loop comprising low resistance poly resistors and switches configured in a T-structure having a junction point as part of the negative feedback loop. A third resistor branch of the T-structure includes a switch that connects the junction point through the third resistor branch to ground when in a closed state and that turns the third resistor branch into an open circuit when in an open state The switch of the third resistor branch, when in the closed state, produces a gain at the output of the variable high-gain circuit.
Owner:LANTIQ BET GMBH & CO KG
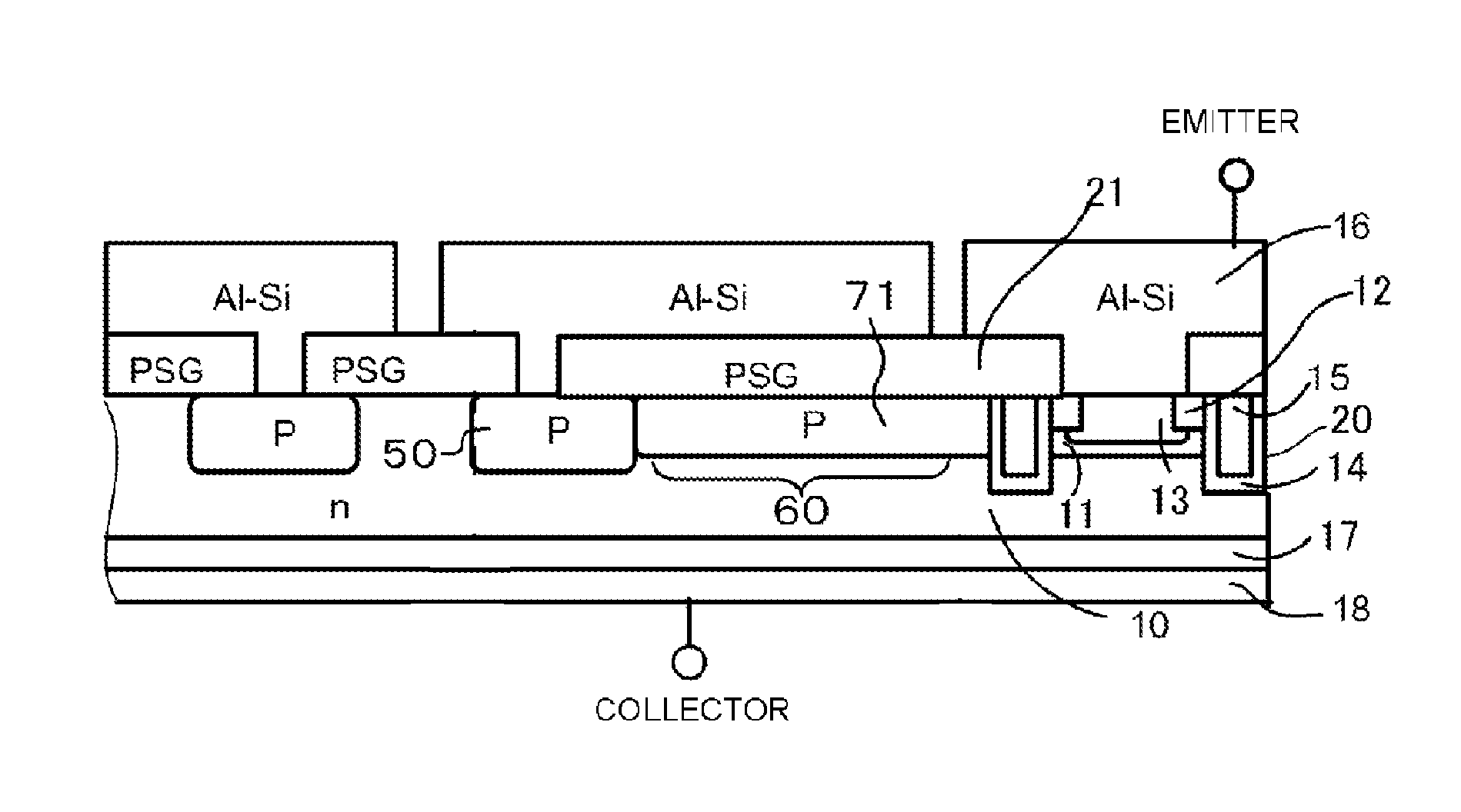
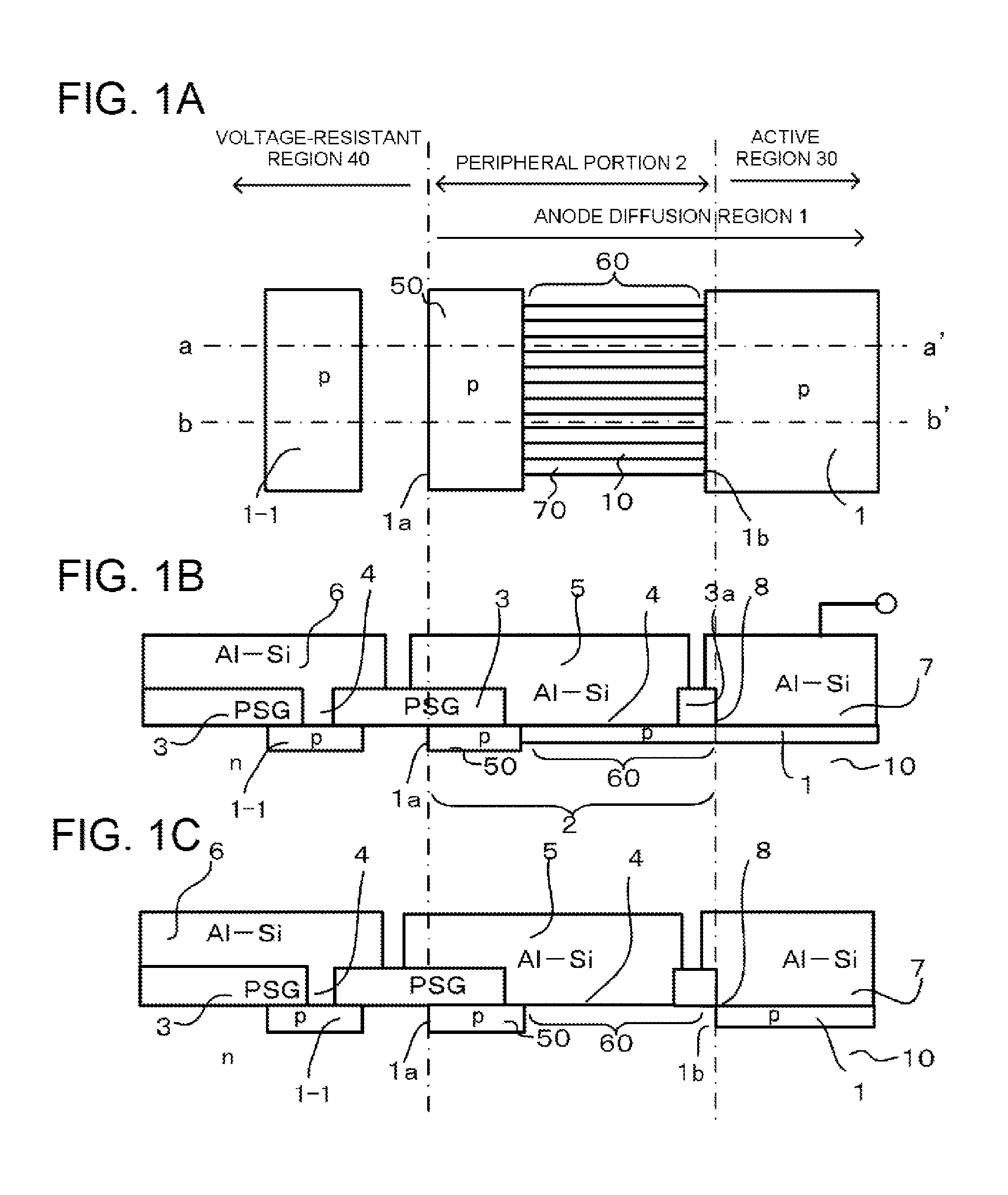
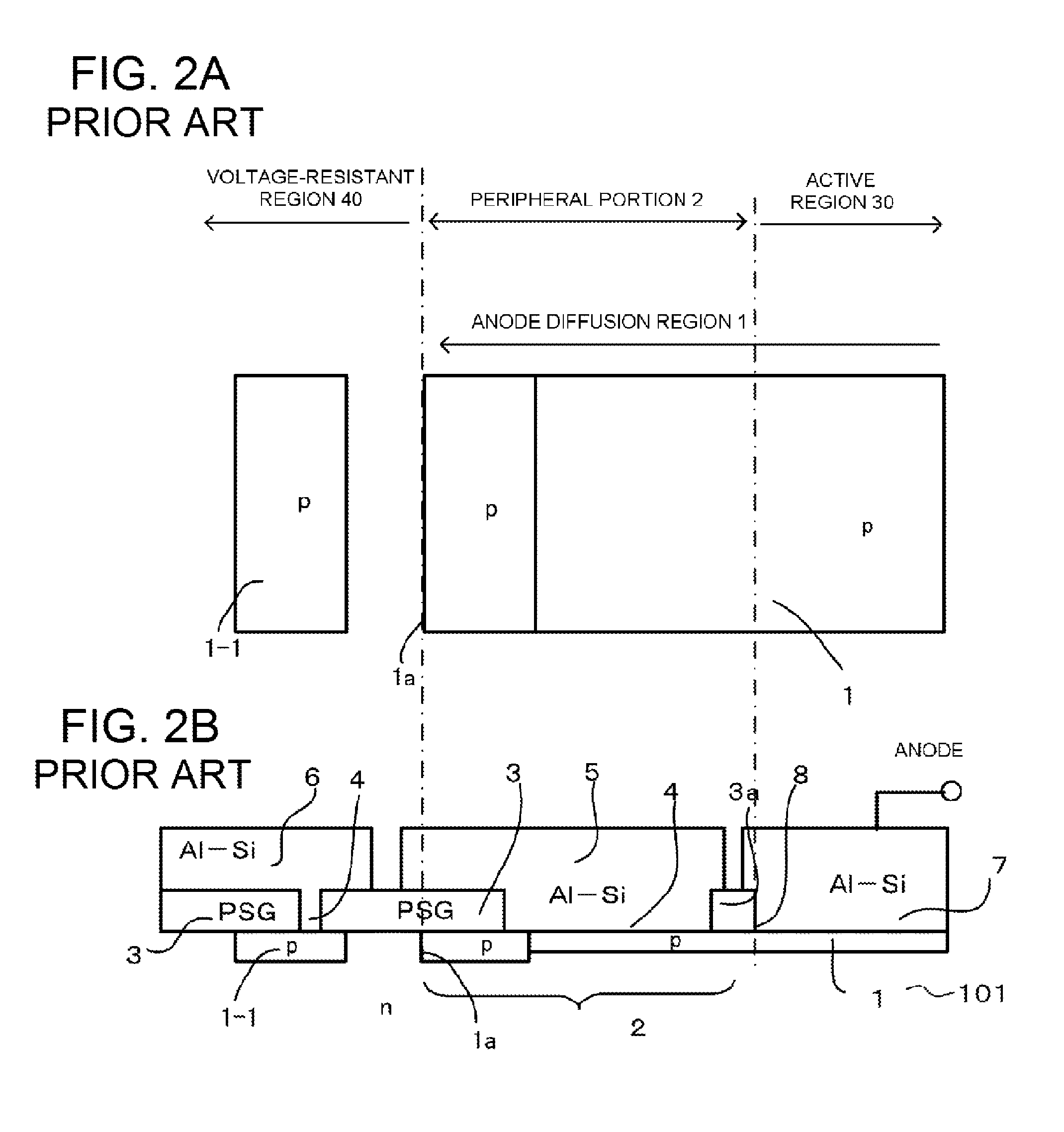
Semiconductor device having a diffusion region
ActiveUS9236460B2Reduce the amount of solutionIncrease resistanceTransistorElectrical resistance and conductanceSurface layer
A semiconductor device is disclosed. The semiconductor device is capable of obtaining a high reverse recovery resistant amount by allowing sheet resistance of a peripheral portion in a p type diffusion region that is in contact with a metal electrode through an insulating film on a surface to be as high as possible and reducing an increase in cost if possible. The semiconductor device includes: a p type diffusion region that is disposed in a surface layer of the one main surface of an n type semiconductor substrate; and a voltage-resistant region that surrounds the p type diffusion region.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
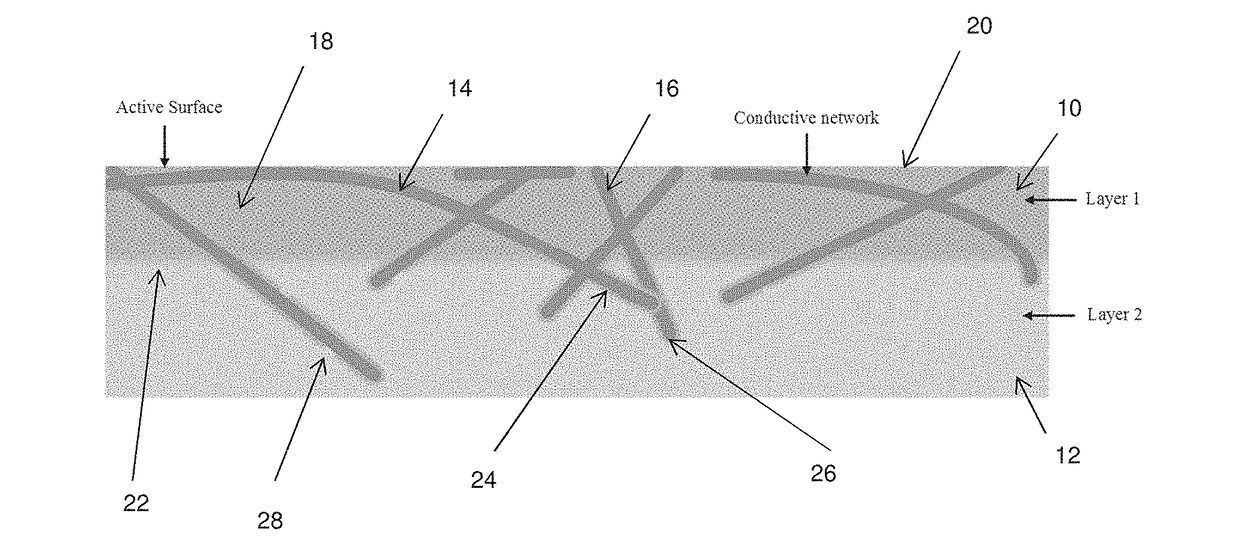
Transparent electrode materials and methods for forming same
InactiveUS20170229668A1Good curative effectImprove sheet resistanceConductive layers on insulating-supportsConductive materialNanowireConductive materials
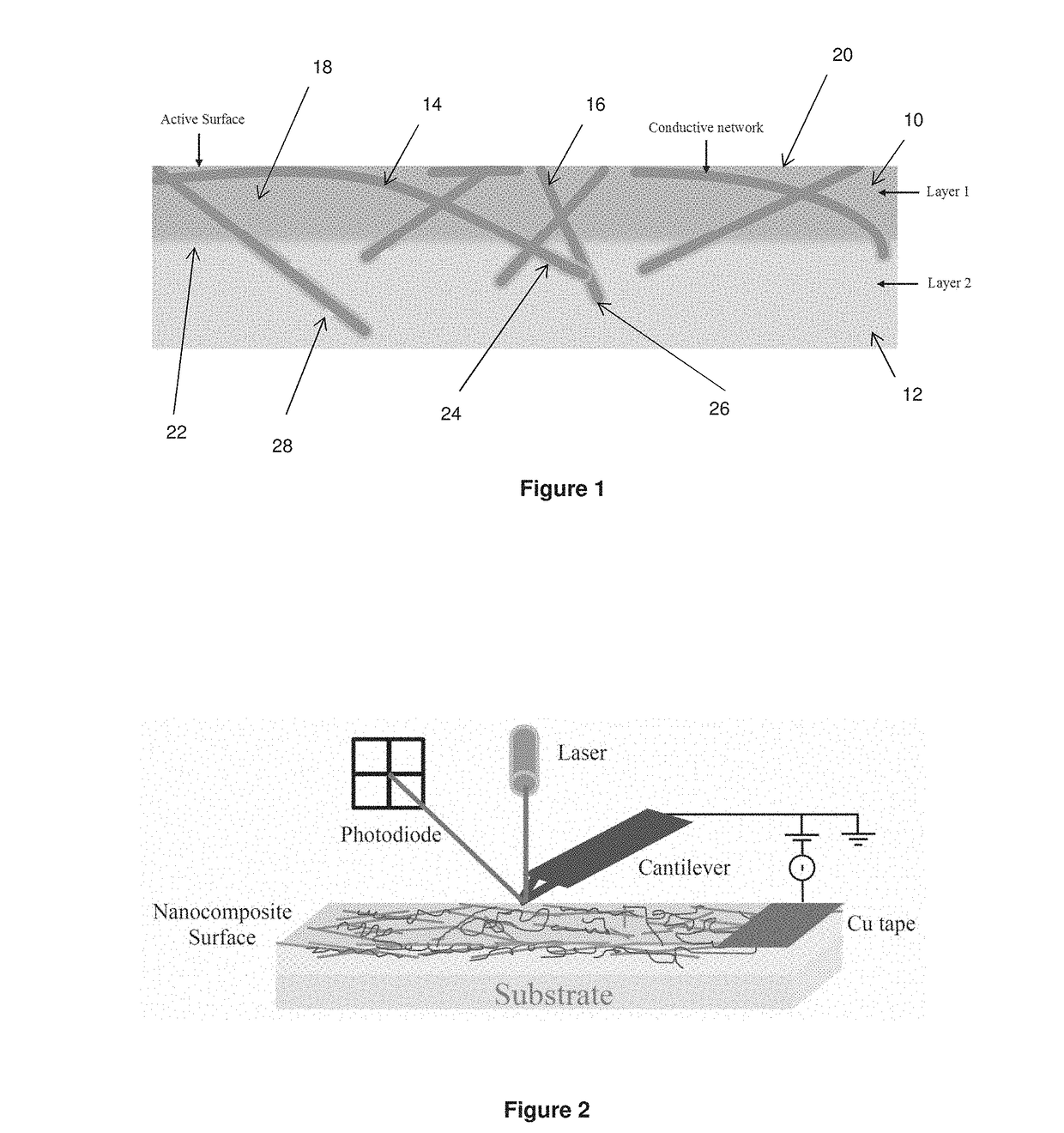
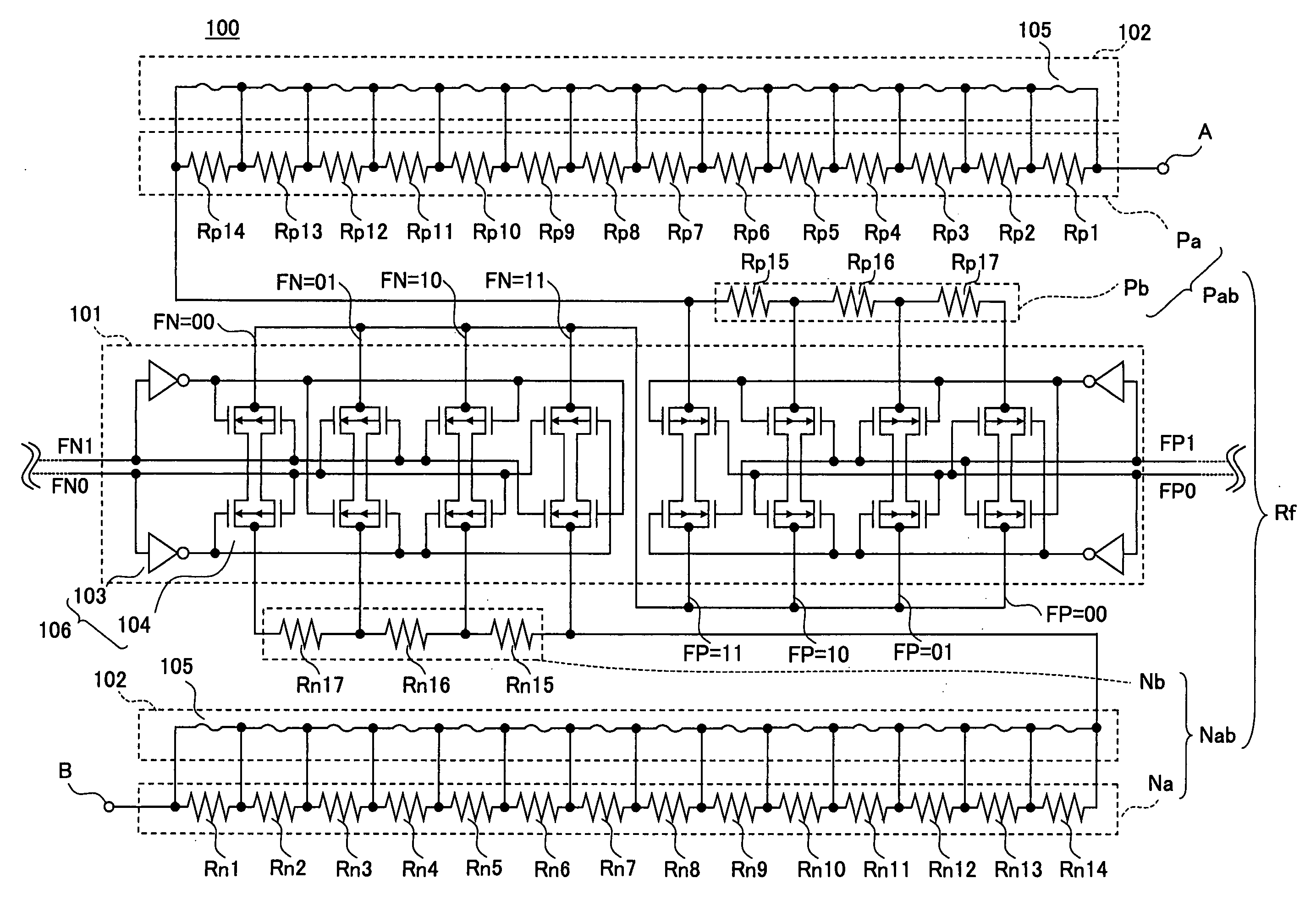
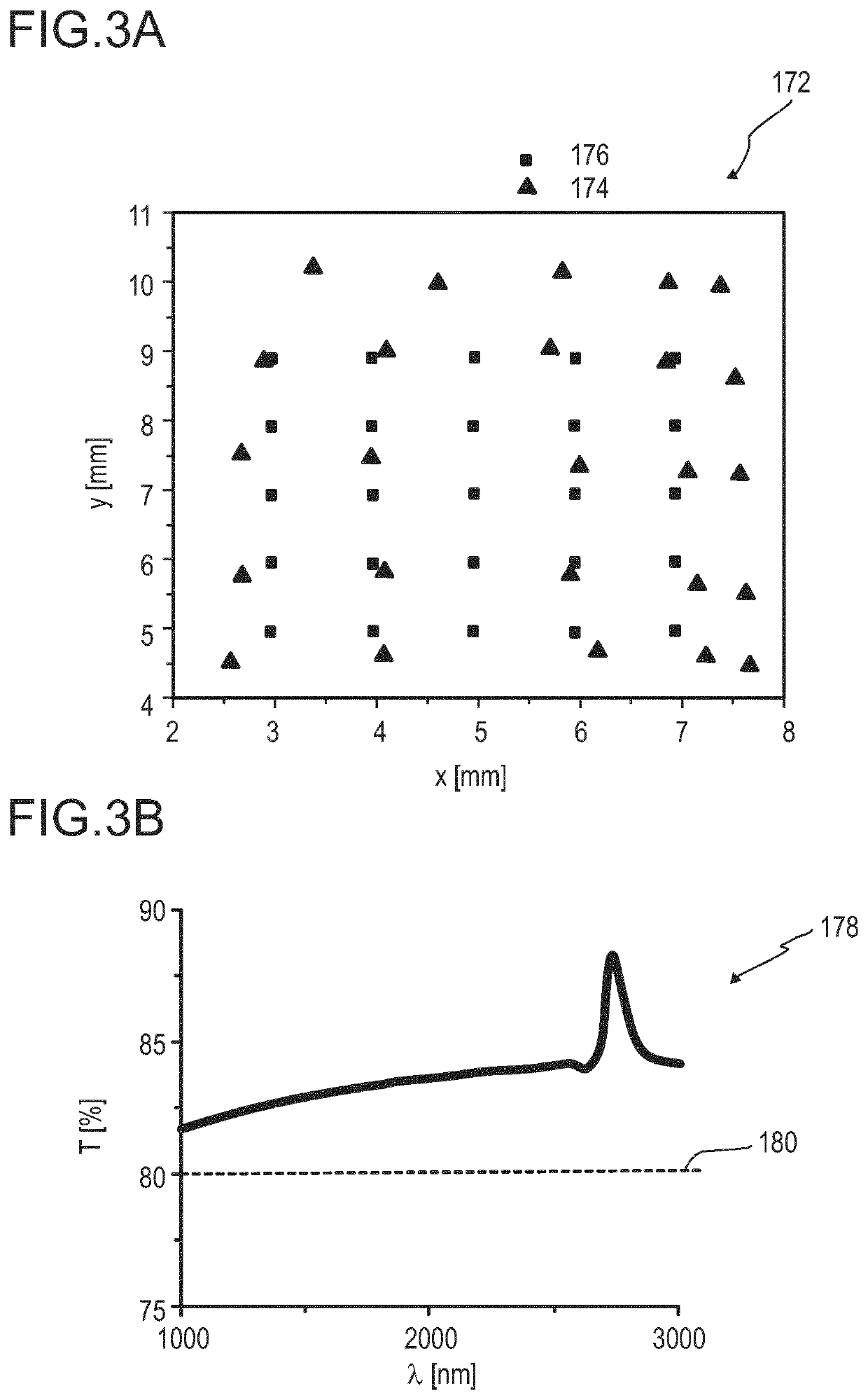
A transparent electrode material including a conductive layer having an active surface and a second surface, and an adjacent base layer, wherein: ∘ the conductive layer includes a conductive network formed by metallic nanowires and carbon nanotubes encapsulated in a conductive material; ∘ the second surface of the conductive layer has encapsulated nanowires and / or nanotubes projecting therefrom; and ∘ the encapsulated nanowires and / or nanotubes projecting from the second surface of the conductive layer are embedded in the adjacent base layer; whereby the active surface of the conductive layer is smooth and electrically active, and the transparent electrode material has a sheet resistance less than 50 Ω / sq and a transparency greater than 70%.
Owner:FLINDERS PARTNERS
Semiconductor device, method of manufacturing the same, and electronic device
InactiveUS20050219034A1Improve accuracyImprove sheet resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNegative temperatureDevice material
A semiconductor device is disclosed that includes a resistive element including a first resistor having a positive temperature coefficient and a second resistor having a negative temperature coefficient. The first resistor includes a metal film.
Owner:RICOH KK
Ring oscillator
InactiveUS20100327983A1Control delay timeSuppressing signal reflectionTransistorSingle output arrangementsRing oscillatorElectrical and Electronics engineering
Multiple multi-stage delay circuits each have n (n is an integer) output terminals. The multi-stage delay circuits each apply delay times to a corresponding input signal, and output, via n output terminals, n delayed signals to which different delay times have been applied. Multiple inverters invert the respective input signals. The multiple multi-stage delay circuits and multiple inverters are alternately connected in the form of a ring.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Formation of high sheet resistance resistors and high capacitance capacitors by a single polysilicon process
ActiveUS7855422B2Improve sheet resistanceIncrease capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceSalicide
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
High-performance double-silver-layer low-radiation glass and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103879088AImprove insulation performanceDoes not affect light transmittanceGlass/slag layered productsMetal layered productsElectrical resistance and conductanceTransmittance
The invention relates to a high-performance double-silver-layer low-radiation glass and a preparation method thereof. The high-performance double-ilver-layer low-radiation glass comprises a glass substrate and a first low surface resistance transparent conductive layer, a first silver layer, a first protective layer, a second low surface resistance transparent conductive layer, a second silver layer, a second protective layer, a third low surface resistance transparent conductive layer and a top protective layer which are successively form on the glass substrate. The high-performance double-silver-layer low-radiation glass, on the premise of better transmittance, also has increased heat insulation performance.
Owner:CSG HOLDING
Conductive paste composition for solar cell
InactiveUS20130099181A1Improve sheet resistanceEasy to controlNon-metal conductorsConductive materialConductive pasteSolar cell
A conductive paste composition for a solar cell includes a conductive powder, a glass frit, and a vehicle, the glass frit consisting of glass containing 0.6 to 18.0 (mol %) Li2O, at least one of 0.1 to 6.0 (mol %) P2O5 and 0.1 to 4.0 (mol %) Sb2O5, 20 to 62 (mol %) PbO, 1 to 18 (mol %) B2O3, 18 to 65 (mol %) SiO2, 0 to 6 (mol %) Al2O3, 0 to 6 (mol %) TiO2, and 0 to 30 (mol %) ZnO in oxide conversion, the glass having a ratio of Pb / Si (mol ratio) within a range of 0.5 to 1.7.
Owner:NORITAKE CO LTD
Junction termination structures for wide-bandgap power devices
InactiveUS7498651B2High blocking voltageThe process is simple and controllableTransistorEngineeringHigh pressure
Disclosed are a variety of junction termination structures for high voltage semiconductor power devices. The structures are specifically aimed at providing a high breakdown voltage while being constructed with a minimal number of process steps. The combination of an RIE etch and / or implantation and anneal process with a finely patterned mesh provides the desired radial gradient for maximum breakdown voltage. The structures provide control of both the conductivity and charge density within the region. These structures can beneficially be applied to all high voltage semiconductor device structures, but are of particular interest for wide bandgap devices as they tend to have very high breakdown fields and scaled dimensions of the depletion layer width.
Owner:MICROSEMI CORP
Method of fabricating novel seed layers for fabricating spin valve heads
ActiveUS7234228B2Improving output of sensorReduce thicknessManufacture head surfaceElectrical transducersSpin valveAtomic physics
A method for forming a bottom spin valve sensor element with a novel seed layer and synthetic antiferromagnetic pinned layer. The novel seed layer comprises an approximately 30 angstrom thick layer of NiCr whose atomic percent of Cr is 31%. On this seed layer there can be formed either a single bottom spin valve read sensor or a symmetric dual spin valve read sensor having synthetic antiferromagnetic pinned layers. An extremely thin (approximately 80 angstroms) MnPt pinning layer can be formed directly on the seed layer and extremely thin pinned and free layers can then subsequently be formed so that the sensors can be used to read recorded media with densities exceeding 60 Gb / in2. Moreover, the high pinning field and optimum magnetostriction produces an extremely robust sensor.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Detector for an optical detection of at least one object
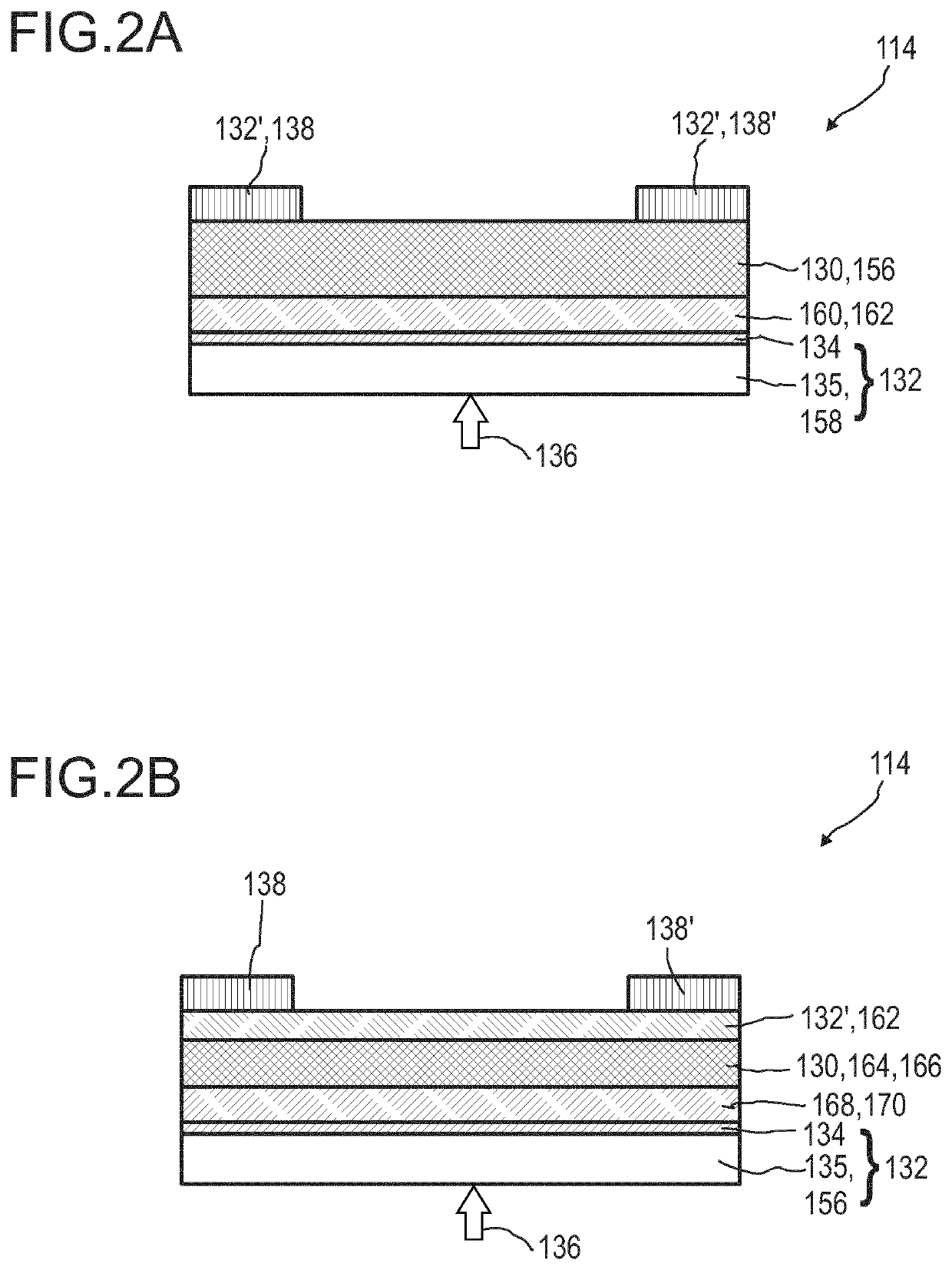
InactiveUS20190386064A1High strengthSufficient signal-to-noise ratioFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesLight beamGraphene
Disclosed herein is a detector including (i) a transversal optical sensor adapted to determine a transversal position of a light beam traveling from the object to the detector, wherein the transversal optical sensor has a photosensitive layer embedded between at least two conductive layers such that at least one of the conductive layers contains an at least partially transparent graphene layer on an at least partially transparent substrate, and wherein the transversal optical sensor generates a transversal sensor signal indicative of the transversal position of the light beam in the photosensitive layer, and (ii) an evaluation device designed to generate at least one item of information on a transversal position of the object by evaluating the at least one transversal sensor signal.
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
Decorative laminated sheet, structure including the decorative laminated sheet, and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150321452A1Improve resistance of filmImprove sheet resistanceDecorative surface effectsSynthetic resin layered productsVacuum pressurePolyolefin
A decorative laminated sheet with excellent scratch resistance that is capable of adhering to a polyolefin-based resin substrate, and that is a hardly adhesive material, through an extrusion method, a vacuum-pressure molding method, a mold integrated injection molding method, and the like. The decorative laminated sheet includes a surface layer, a design layer, and an adhesive layer containing a polymer having a propylene unit of 85 mass % or more, in that order.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Apparatus for treating a substrate
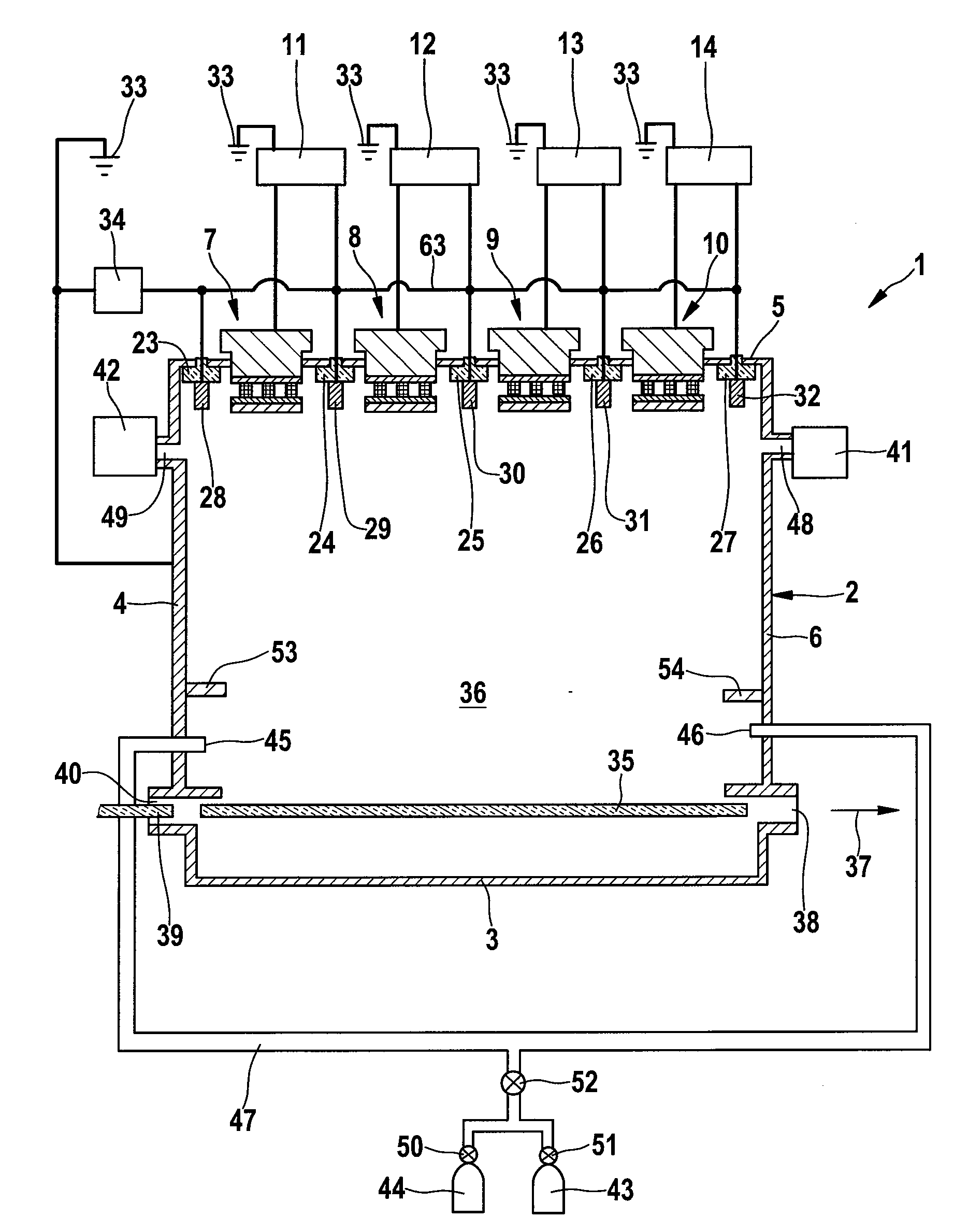
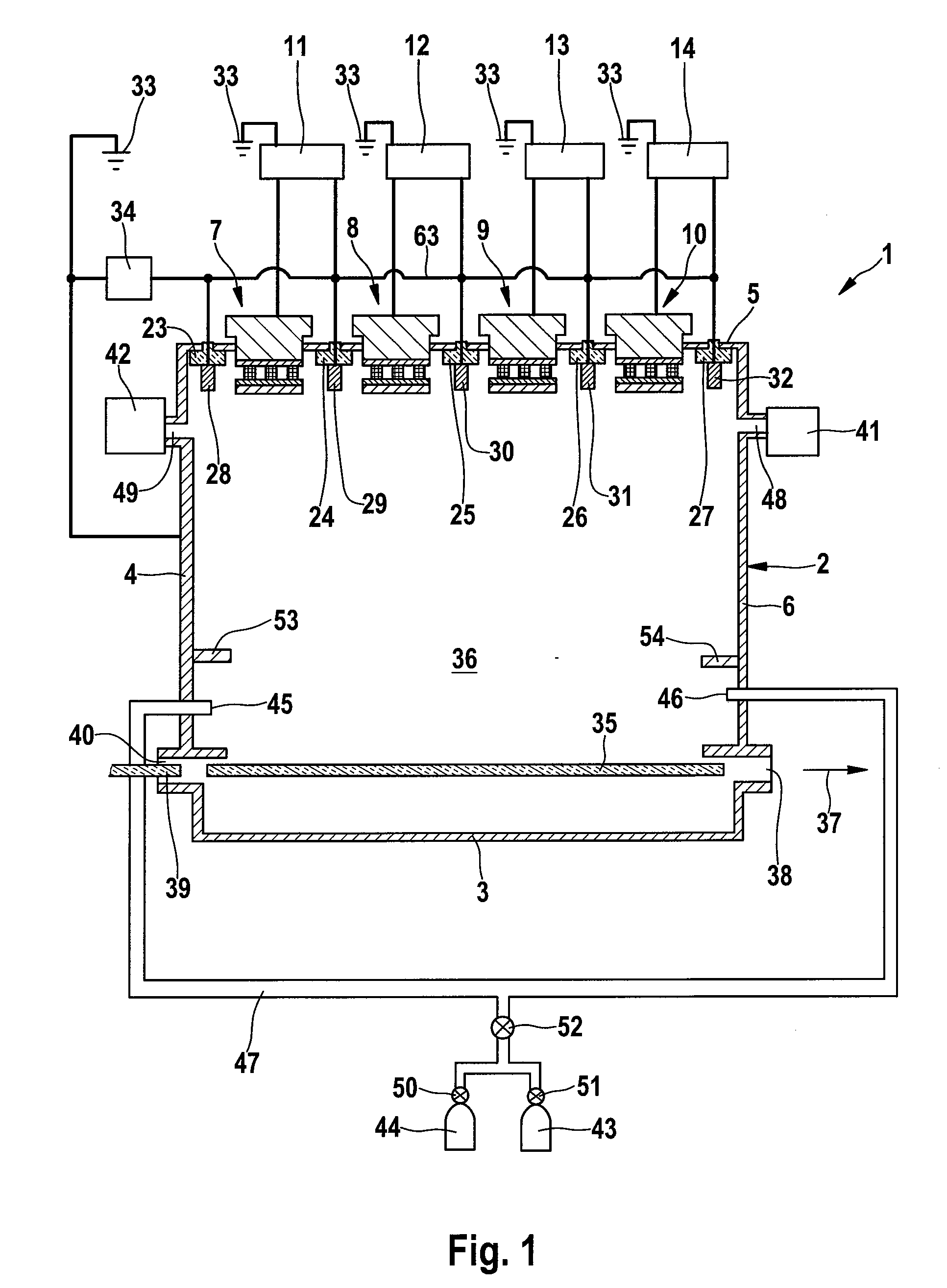
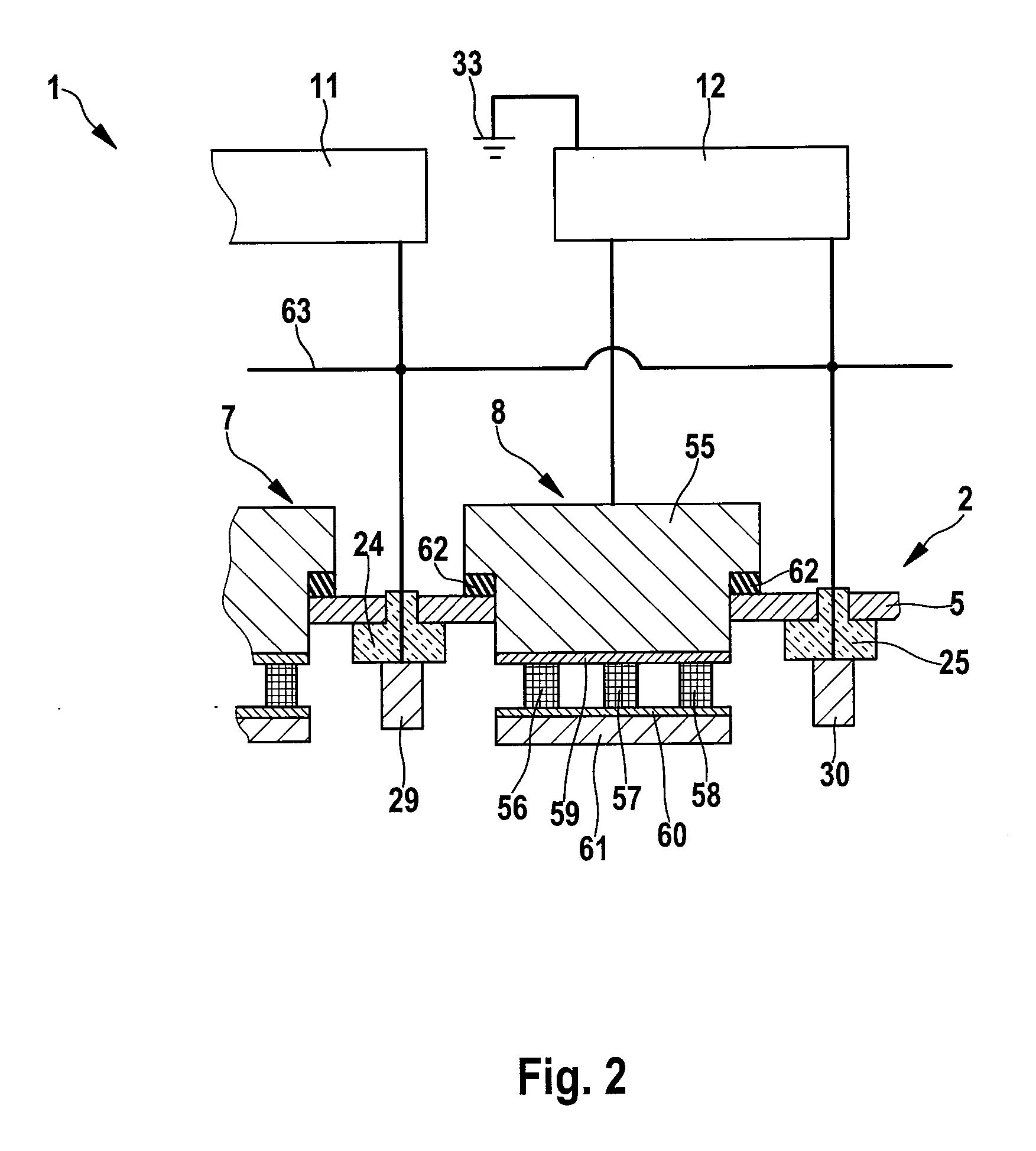
ActiveUS20090205954A1Improve stabilityImprove sheet resistanceCellsElectric discharge tubesVacuum chamberResistor
This invention relates to an apparatus (1) for treating, e.g. coating, a substrate (35, 39) in a vacuum chamber (2). In this vacuum chamber (2) there are arranged n cathodes (7-10) and n+1 anodes (28-32), each of said anodes adjacent to a cathode (7-10). Each of the n cathodes (7-10) and n of the assigned anodes (29-32) are connected to a power supply (11-14). One of the anodes (28) not being assigned to a cathode (7-10) is connected to an electrical line (63) which is connecting each of the anodes (28-32). A pull-down resistor (34) is connected to said line (63) at its one end and to ground (33) at its other end.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Paste composition for solar battery electrode
ActiveUS20120168691A1Reduce line widthGood ohmic contactConductive materialOxide conductorsSolar batteryElectrically conductive
It is provided a paste composition for a solar battery electrode, that includes electrically conductive powder, glass frit, and a vehicle, wherein the glass frit is made of glass that comprises, as amounts converted into those of oxides as ratios, Li2O within a range from 0.6 to 18 [mol %], PbO within a range from 20 to 65 [mol %], B2O3 within a range from 1 to 18 [mol %], and SiO2 within a range from 20 to 65 [mol %].
Owner:HERAEUS PRECIOUS METALS NORTH AMERICA CONSHOHOCKEN
Methods of forming silicide layer of semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050142727A1Improve sheet resistanceIncrease resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialNitride
Methods of forming silicide layers of a semiconductor device are disclosed. A disclosed method comprises depositing a polysilicon layer, a buffer oxide layer, and a buffer nitride layer on a semiconductor substrate; forming a gate on the semiconductor substrate by removing some portion of the polysilicon layer, the buffer oxide layer, and the buffer nitride layer; forming sidewall spacers on the sidewalls of the gate; forming source and drain regions in the semiconductor substrate by performing an ion implantation process; forming a first silicide layer on the source and drain regions; depositing a first ILD layer over the semiconductor substrate including the gate and the first silicide layer; removing some portion of the first ILD layer to expose the top surface of the gate; and forming a second silicide layer on the gate.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ring oscillator
InactiveUS8378754B2Improve accuracyDelay time can be adjustedTransistorPulse generation by logic circuitsRing oscillatorElectrical and Electronics engineering
Multiple multi-stage delay circuits each have n (n is an integer) output terminals. The multi-stage delay circuits each apply delay times to a corresponding input signal, and output, via n output terminals, n delayed signals to which different delay times have been applied. Multiple inverters invert the respective input signals. The multiple multi-stage delay circuits and multiple inverters are alternately connected in the form of a ring.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com