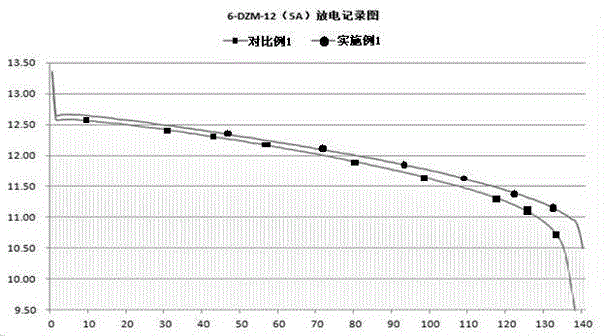
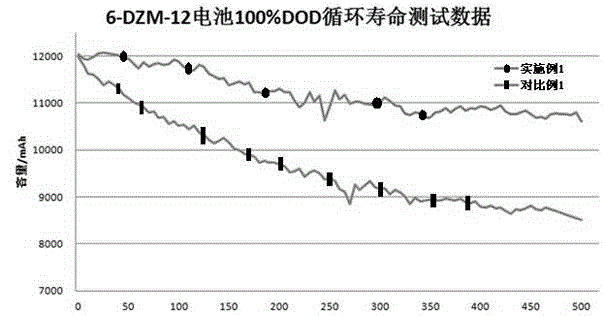
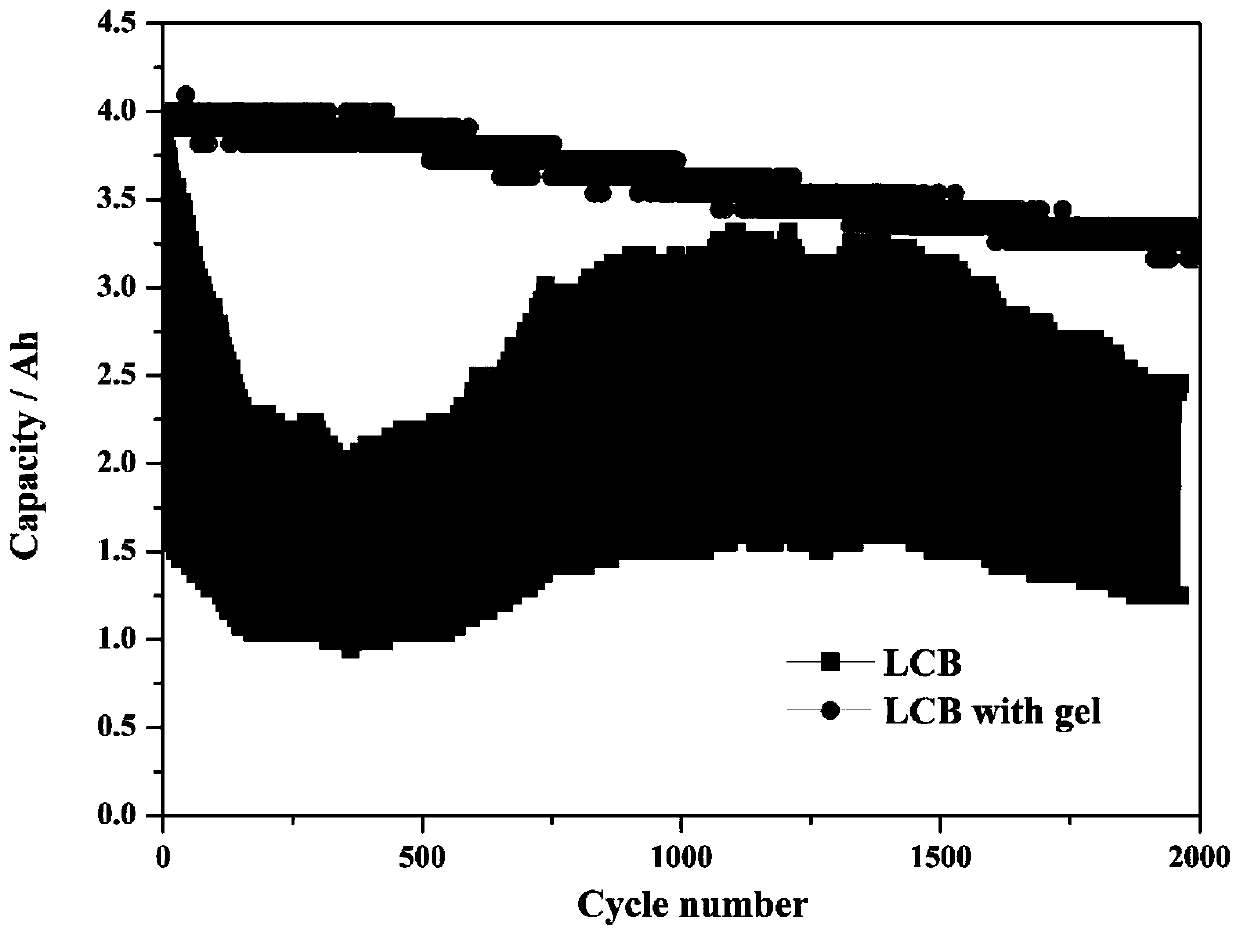
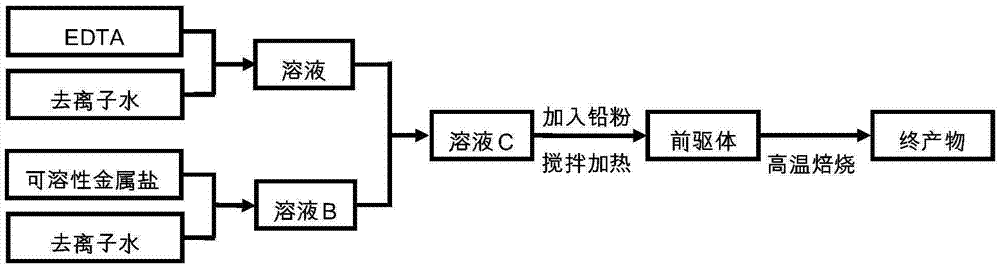
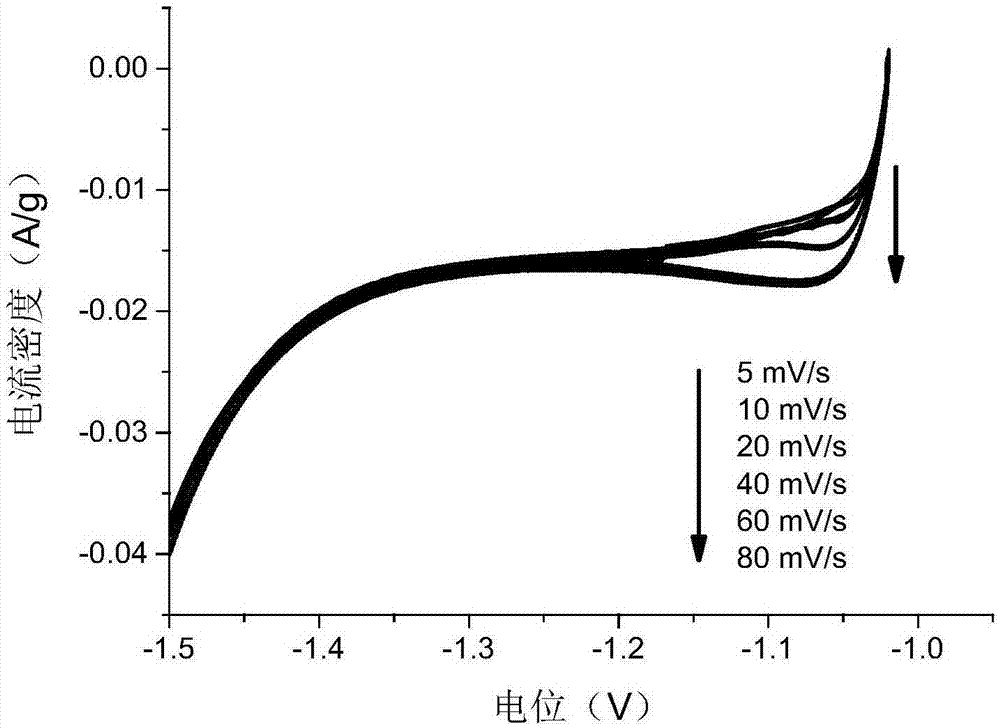
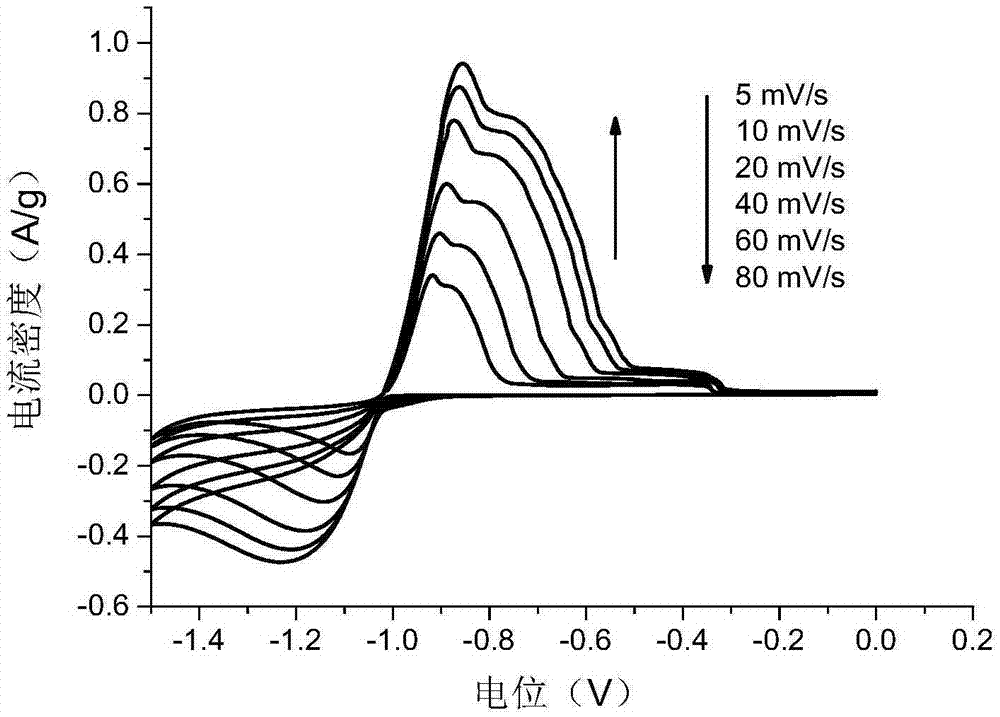
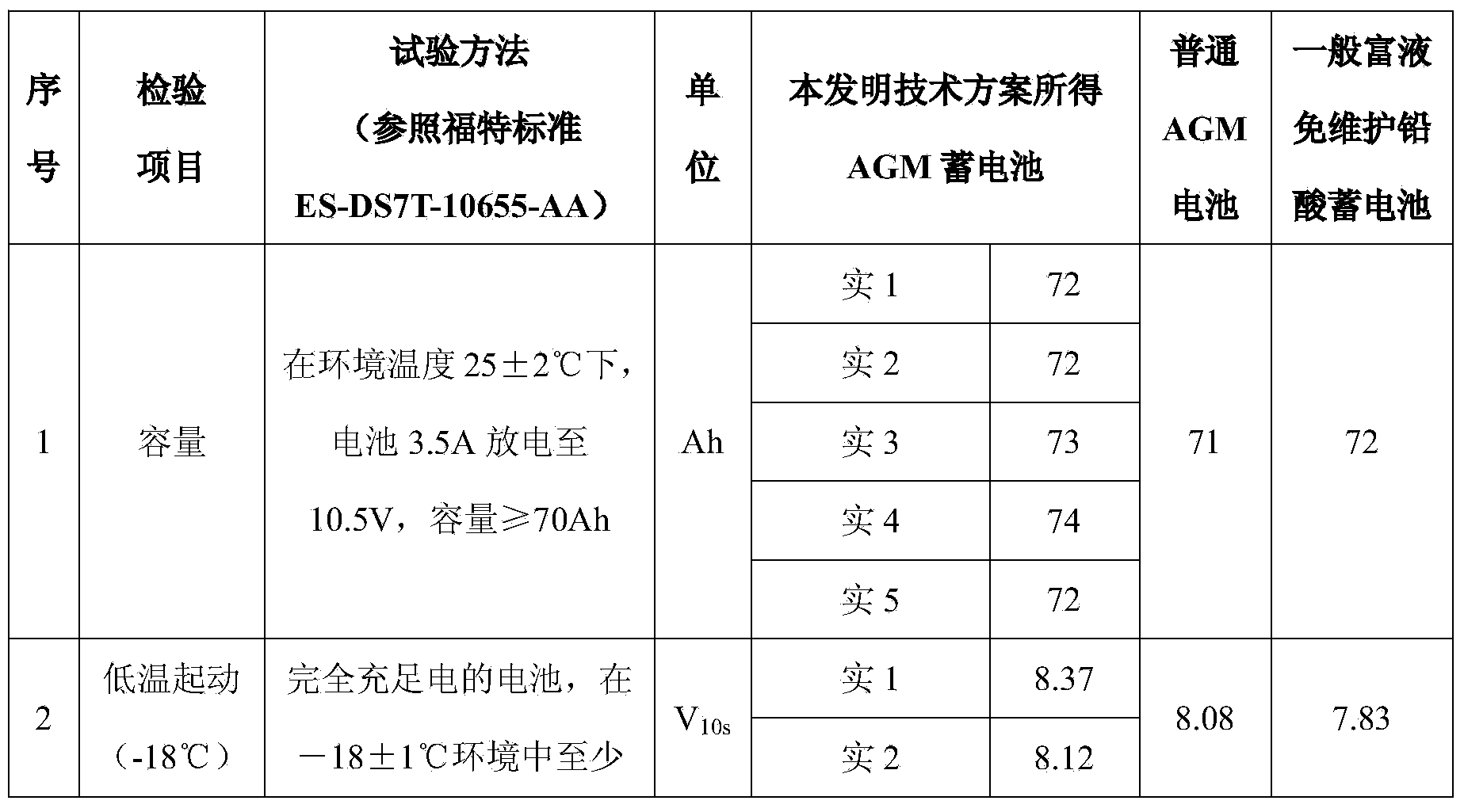
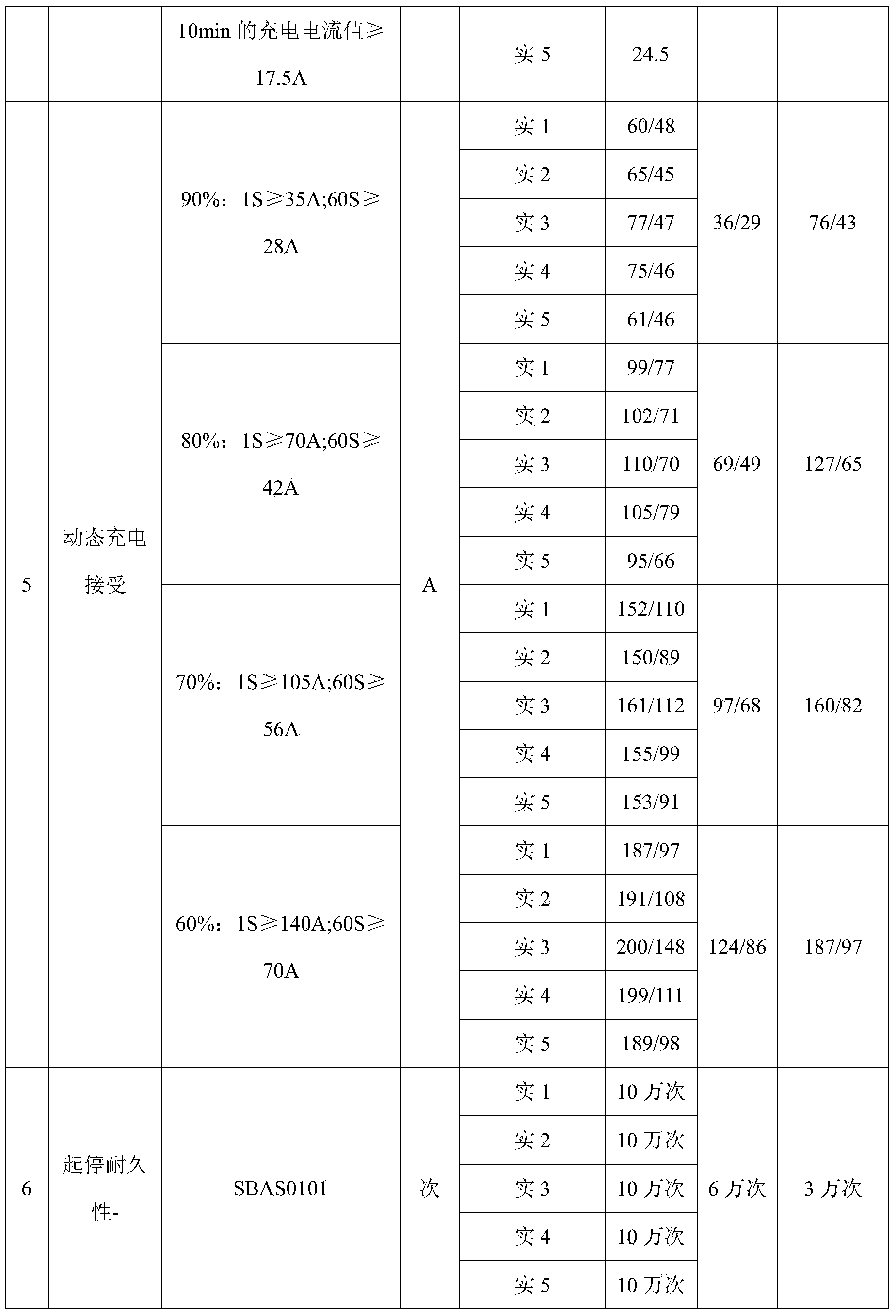
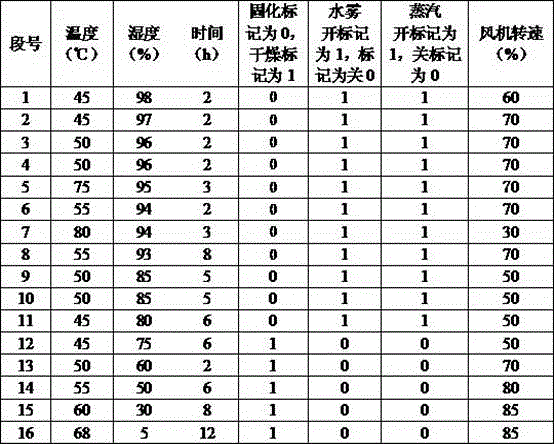
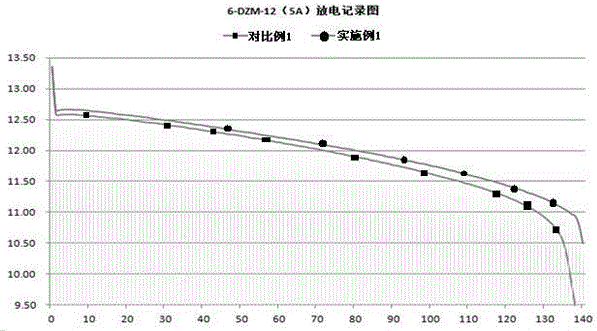
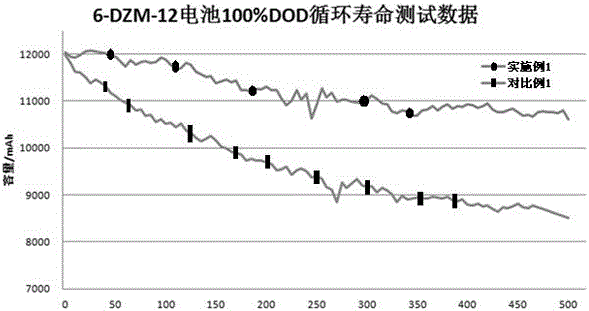
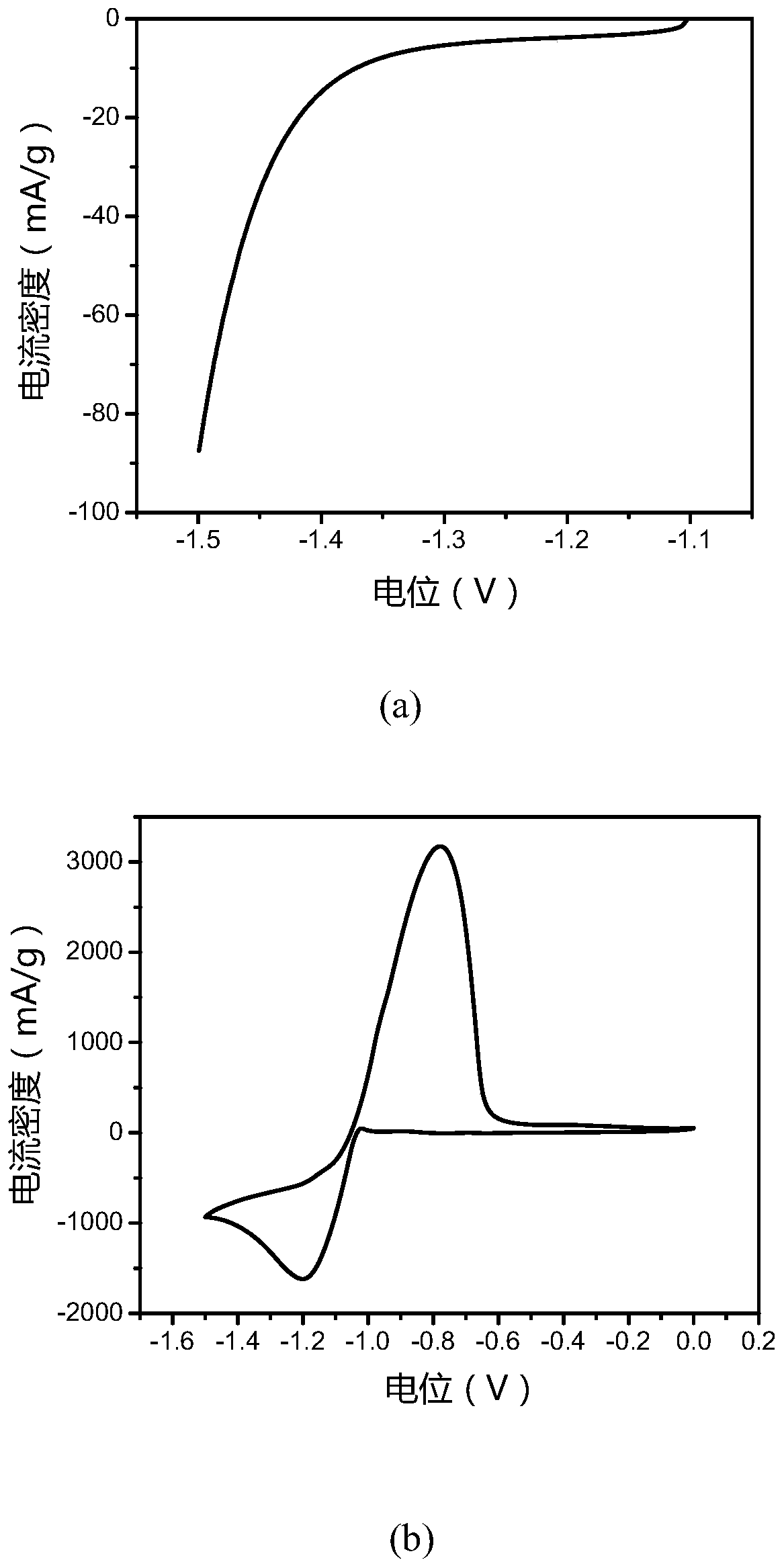
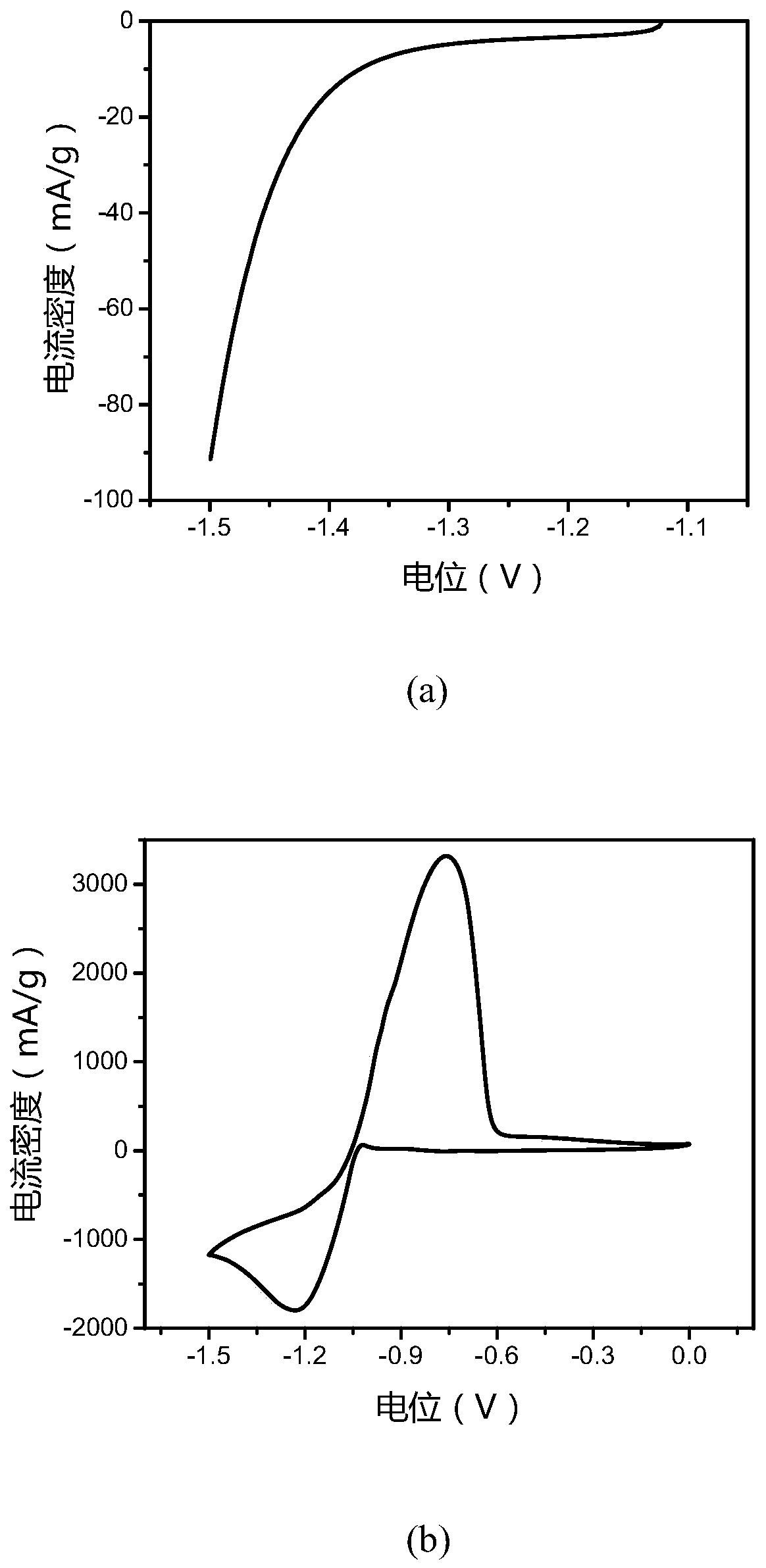
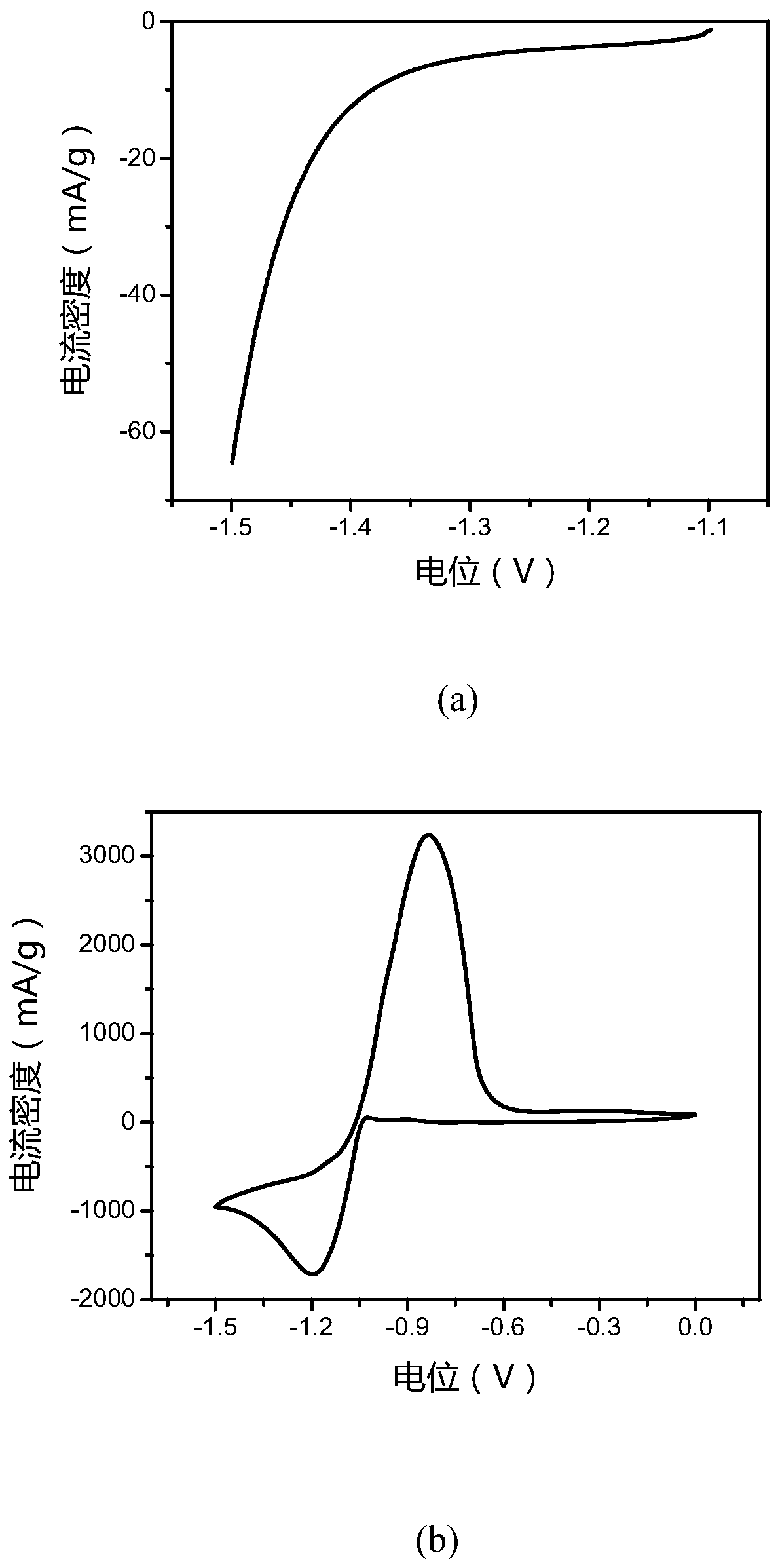
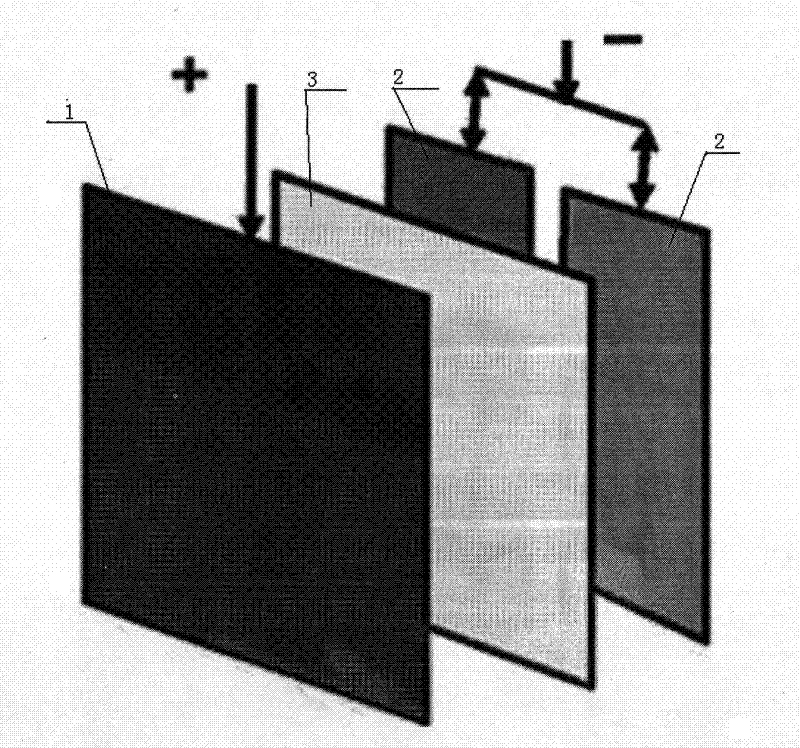
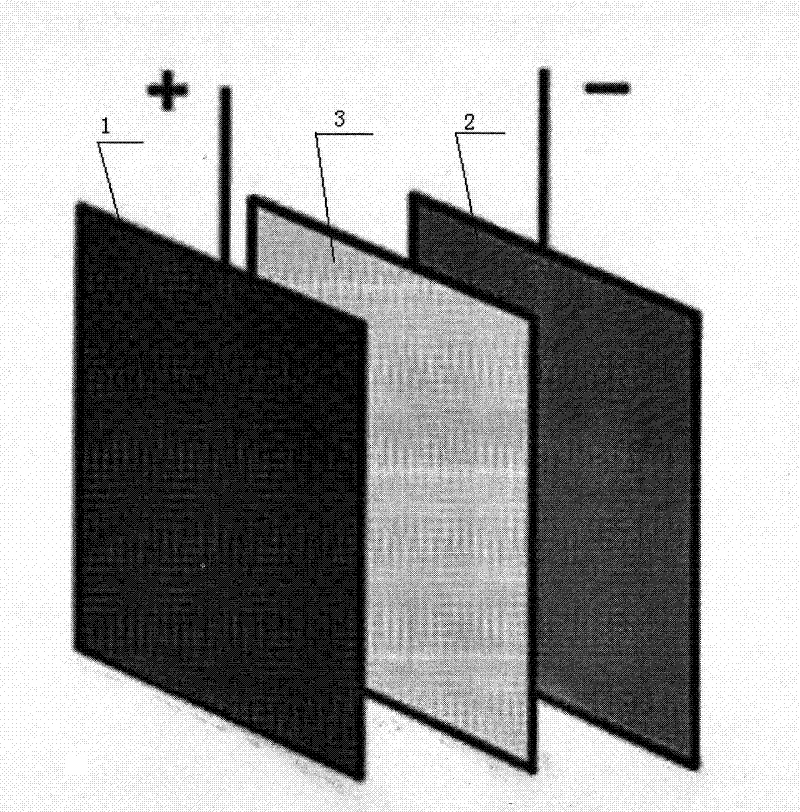
Patents
Literature
40results about How to "Reduce Sulfation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lead carbon battery cathode diachylon as well as preparation method thereof, lead carbon battery cathode plate as well as lead carbon battery
InactiveCN103811752AReduce SulfationExtended service lifeLead-acid accumulatorsLead-acid accumulator electrodesFiberPseudocapacitance
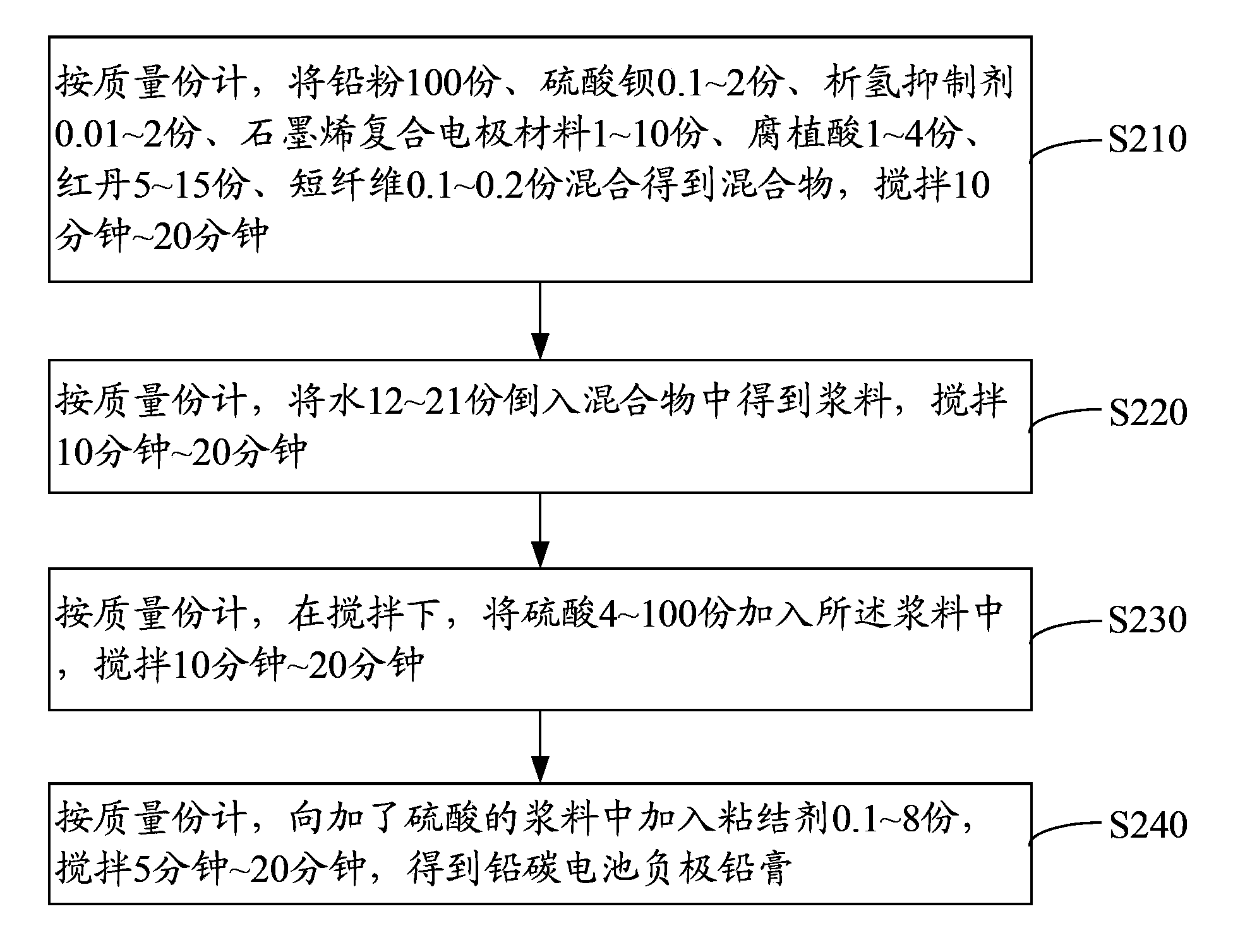
The invention discloses lead carbon battery cathode diachylon. The lead carbon battery cathode diachylon is prepared from raw materials of 100 parts of lead powder, 4-100 parts of sulfuric acid, 0.1-8 parts of bonding agents, 0.1-2 parts of barium sulfate, 0.01-2 parts of hydrogen evolution inhibitors, 50-100 parts of graphene oxide, 0.05-1 part of acetylene black, 1-4 parts of humic acid, 5-15 parts of red lead, 12-21 parts of water and 0.1-0.2 part of short fibers. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the cathode diachylon as well as a lead carbon battery cathode comprising the diachylon as well as a preparation method of the lead carbon battery cathode and a lead carbon battery. According to the invention, graphene oxide is added into the cathode diachylon; graphene oxide contains a plurality of oxygen-containing functional groups, and a plurality of faradaic pseudocapacitance can be generated in sulfuric acid, so that the using quantity of lead powder in the cathode material can be reduced; meanwhile, electricity of the lead cathode can be shared under the condition of high-current charge and discharge; sulfation of a storage battery is relieved greatly; the service life of a storage battery is prolonged.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
Lead-carbon battery anode, preparation method thereof and applications thereof
InactiveCN103794796AExtended service lifeReduce SulfationLead-acid accumulator electrodesPhysical chemistryGraphite
The invention relates to a lead-carbon battery anode. The lead-carbon battery anode is prepared from following raw materials parts by weight: 100 parts of lead powder, 4-100 parts of sulfuric acid, 0.1-8 parts of a binder, 0.1-2 parts of barium sulfate, 0.01-2 parts of a hydrogen evolution inhibitor, 1-10 parts of graphene, 1-4 parts of humic acid, 5-15 parts of red lead, 12-21 parts of water and 0.1-0.2 part of short fiber. The invention also relates to a preparation method and applications of the lead-carbon battery anode. According to the lead-carbon battery anode, the graphene is introduced into the anode material and replaces active carbon and a conductive agent in lead-carbon batteries at present, and therefore the graphene can effectively take a share in a part of current in the lead anode under large-current charge-discharge conditions. The specific power of a battery prepared by the lead-carbon battery anode is 50% higher that of a common lead-acid battery. In large-current pulse charge-discharge cycles, the service lifetime of the battery prepared by the lead-carbon battery anode is prolonged by 10 times of that of the common lead-acid battery. Sulfation of a storage battery is largely delayed. The service lifetime of the storage battery in partial charge state working conditions is prolonged.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
Storage battery electrolyte and storage battery
ActiveCN104779414AImprove high temperature resistanceImprove cycle performanceLead-acid accumulatorsAcid electrolytesPolyvinyl alcoholCarbonate
The invention discloses a storage battery electrolyte and a storage battery. The storage battery electrolyte comprises sulfuric acid, potassium sulfate, ammonium sulfate, magnesium sulfate, 4,5-diethylvinylene carbonate, 4-methyl-5-propylvinylene carbonate, propylene sulfite, methyl tert-butyl ether, polyvinyl alcohol, sodium ethylene diamine tetracetate, sulfone additives, trisodium 2,4,6-trithio-s-triazine solution and deionized water. The storage battery electrolyte is used for overcoming the shortages of the prior art, and capable of remarkably increasing the cycle time of the storage battery and prolonging the service life of the storage battery; meanwhile, the storage battery is good in stability and easy to popularize and use.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PINGHU HUALONG IND CO LTD
Flat-plate type sulfur-resistant low-temperature SCR denitration catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105289644AStrong mechanical propertiesExtended service lifeDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSulfurActive component
The invention specifically relates to a flat-plate type sulfur-resistant low-temperature SCR denitration catalyst and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the fields of environmental protection and environmental catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: with nanometer composite oxide Ce-ZrO2 as a carrier, manganese oxide as an active component and iron oxide and molybdenum oxide as cocatalysts, carrying out equivalent-volume impregnation, drying, roasting and crushing so as to prepare a powdery catalyst; and subjecting the prepared powdery catalyst to acidification by sulfuric acid and then carrying out mixing, rolling coating, fold pressing, shearing, drying and roasting so as to obtain the flat-plate type sulfur-resistant low-temperature SCR denitration catalyst. The prepared catalyst has denitration activity of 85 to 98% in a temperature range of 80 to 150 DEG C and has excellent resistance to sulfur dioxide poisoning.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
High-temperature heavy-load negative lead paste for start-stop battery and preparation method of negative lead paste
ActiveCN105702953AHigh mechanical strengthImprove bindingLead-acid accumulatorsCell electrodesPolyesterFiber
The invention relates to a high-temperature heavy-load negative lead paste for a start-stop battery and a preparation method of the negative lead paste, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemistry. The high-temperature heavy-load negative lead paste for the start-stop battery is prepared from the following components: dilute sulfuric acid with the density rho of 1.38g / mL, deionized water, a high-performance organic additive Expander 1, a high-performance organic additive Expander 2, a conductive polyester staple fiber, barium sulfate, a carbon material additive Carbon A and lead powder. The invention provides the high-temperature heavy-load negative lead paste for the start-stop battery with long service lifetime and deep discharge cycle performance under the partial state of charge and a preparation method of the negative lead paste. The negative electrode produced by the formula can significantly improve sulfation of the negative electrode under the partial state of charge, reduces the electrochemical polarization phenomenon of the battery in the high-temperature deep circulating charge and discharge processes, and improves the conductivity and the electrochemical property of the negative electrode and the thermodynamic structure stability, so that the high-temperature deep discharge cycle lifetime of the negative electrode under the partial state of charge is prolonged.
Owner:骆驼集团蓄电池研究院有限公司
Graphene composite electrode material and preparation method thereof, lead-carbon battery negative electrode lead plaster and preparation method thereof as well as lead-carbon battery
InactiveCN103682357AIncrease layer spacingReduces electrochemical polarizationLead-acid accumulatorsCell electrodesComposite electrodeNitrogen
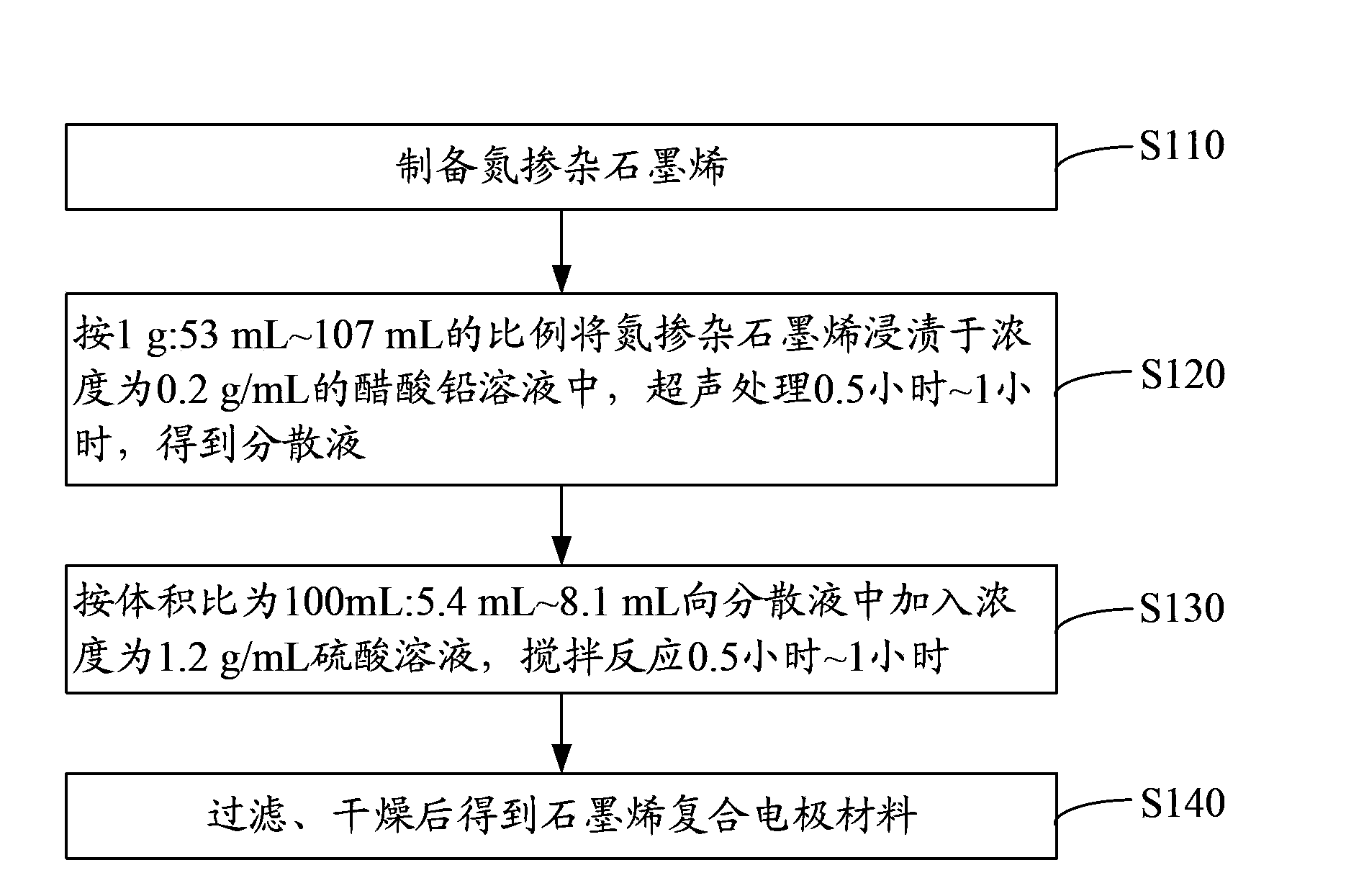
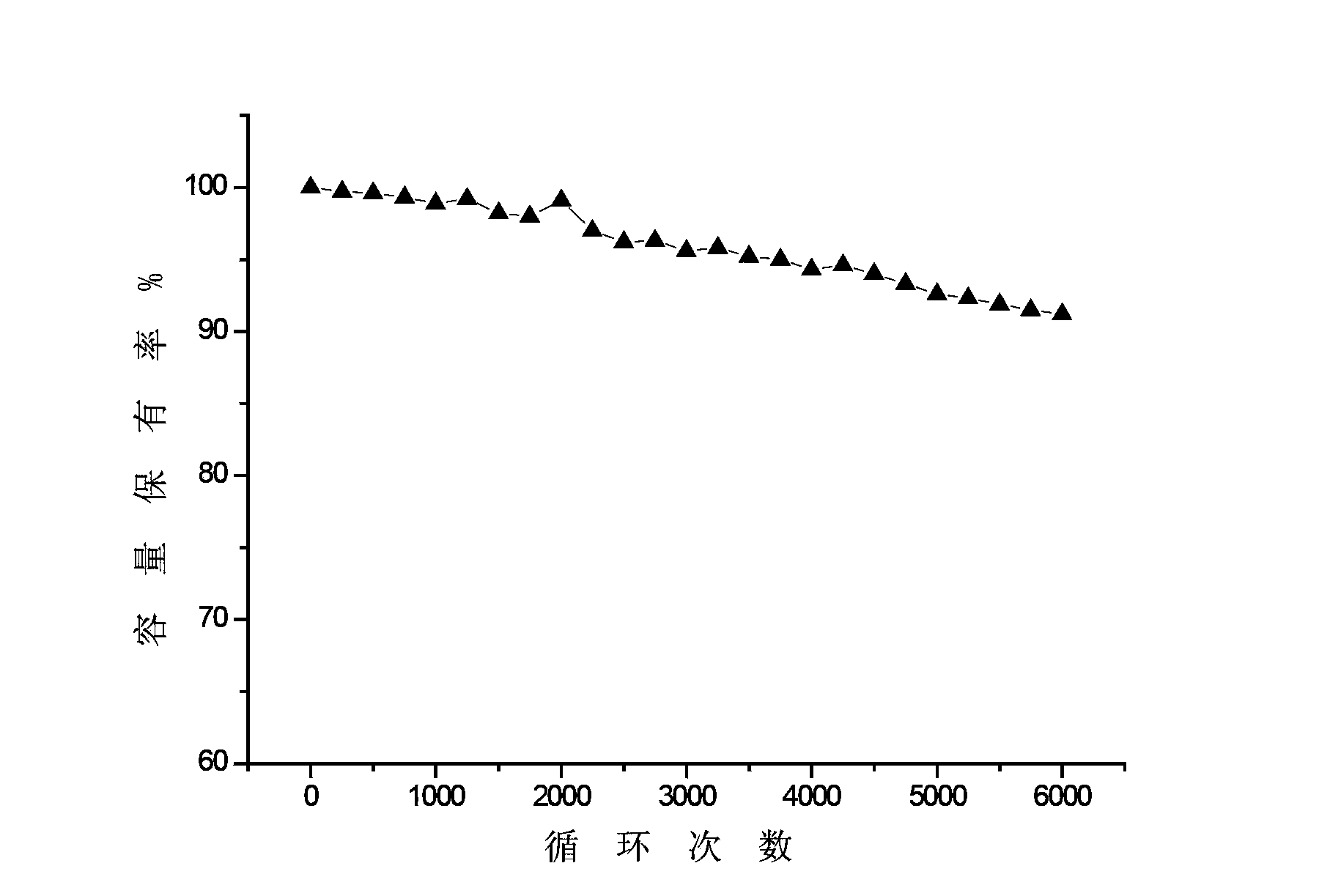
The invention provides a graphene composite electrode material. The graphene composite electrode material comprises nitrogen-doped graphene and lead sulfate adsorbed between nitrogen-doped graphene sheet layers; the mass ratio of the nitrogen-doped graphene to the lead sulfate is 1:(10-20). When the graphene composite electrode material is applied to a negative electrode of a lead-carbon battery, the nitrogen-doped graphene is a non-polarity material and can be well compatible with electrolyte-sulfuric acid of the lead-carbon battery, so that reduction of the electrochemical polarization of the negative electrode is facilitated. The interlayer spacing of the nitrogen-doped graphene is large so that the specific surface area is large and the nitrogen-doped graphene is suitable for being used as a growing point of a lead sulfate crystalline grain under a large-power condition; the sulfation of the negative electrode under the large-power condition is reduced so that the cycle life of the negative electrode is prolonged and the cycle performance of the lead-carbon battery is improved. The invention further provides a preparation method of the graphene composite electrode material, lead-carbon battery negative electrode lead plaster and a preparation method thereof, and the lead-carbon battery.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
Negative electrode diachylon used for high-performance AGM battery and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN103456930AImprove dynamic reception characteristicsImprove overall performanceCell electrodesEngineeringPartial charge
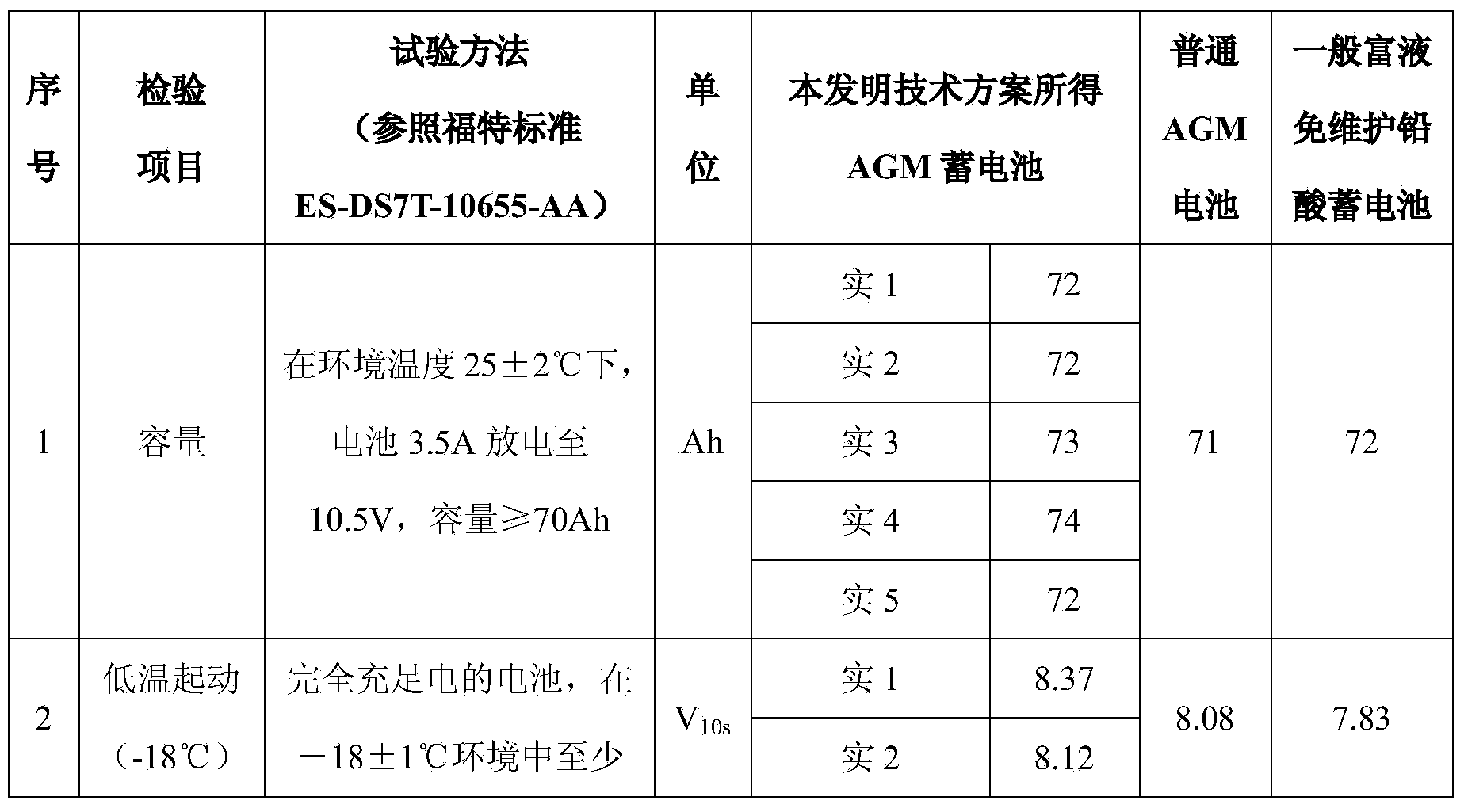
The invention belongs to the technical field of lead storage batteries and relates to a negative electrode diachylon which is capable of improving dynamic charging acceptance performance of an AGM battery and a preparing method thereof. The negative electrode diachylon is capable of improving the dynamic charging acceptance performance of the AGM battery under the condition that the AGM battery has the advantages of being long in service life and strong in starting capacity, the probability of sulfation of a negative plate when the negative plate is in a partial charge state for a long time is reduced, and then starting and shut-down requirements are met.
Owner:骆驼集团蓄电池研究院有限公司
Colloidal electrolyte and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101877419AImprove effective utilizationGood physical and chemical propertiesLead-acid accumulatorsSodium sulphideStannous sulfate
The invention relates to an electrolyte for a lead-acid accumulator, in particular to a colloidal electrolyte and a preparation method thereof. The invention adopts the following technical scheme that the colloidal electrolyte is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 0.3 to 1.0 percent of silicon dioxide, 0.05 to 0.25 percent of cobaltous sulphate, 0.5 to 1.0 percent of sodium sulphide, 0.05 to 0.5 percent of stannous sulfate, 92 to 95 percent of dilute sulphuric acid of which the density is 1.330 to 1.400g / cm<3> and the balance of water of which the pH value is 7 to 9.
Owner:长兴诺力电源有限公司
Lead-carbon battery composite negative electrode additive, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN108123136ASimple preparation processEnergy savingLead-acid accumulator electrodesGraphite oxideHigh activity
The invention relates to a lead-carbon battery composite negative electrode additive and a preparation method thereof, wherein the lead-carbon battery composite negative electrode additive is formed by coating the surface of a reduced graphene oxide lamella with a metal element modified porous carbon material, and contains 0.1-50 wt% of reduced graphene oxide, 40-90 wt% of porous carbon, and 0.1-10 wt% of a metal element. According to the present invention, the lead-carbon battery composite negative electrode additive has high specific surface area and high electronic conductivity; and by doping the lead-carbon battery composite negative electrode additive into a lead-acid battery negative electrode, the lead-carbon battery negative electrode with characteristics of high activity, high charge-discharge reversibility and low hydrogen evolution can be obtained.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Lead Carbon Batteries for Electric Vehicles
InactiveCN102299304ALarge capacitySolution to short lifeLead-acid accumulator electrodesActivated carbonElectric-vehicle battery
The invention provides a new type of lead-carbon battery for electric vehicles. The positive pole is a PbO2 positive pole, and the negative pole is coated with a porous activated carbon material on the lead current collector. The composition and proportion (weight) of the porous activated carbon material are: activated carbon 55 ~95%, conductive agent 5~30%, binder 0.1~15%, the positive electrode is wrapped with a separator, and the negative electrode is immersed in the H2SO4 electrolyte with a concentration of 1.0~2.0mol / L. The lead-carbon battery of the present invention has the advantages of large capacity, long life and low price, especially its high-current and low-temperature performance, good charge acceptance, reduced lead consumption, and environmental friendliness, and is suitable for the use of electric vehicles that are increasingly developed Require.
Owner:NANJING SHUANGDENG SCI TECH DEV RES INST
Lead-acid storage battery electrolyte additive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104064817AReduce SulfationImprove electrochemical performanceLead-acid accumulatorsAcid electrolytesEthylenediamineElectrochemistry
The invention relates to a lead-acid storage battery electrolyte additive which contains s-triazine, sulfate, stannous mono-sulphate and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium, wherein each liter of lead-acid storage battery electrolyte contains 1,500-2,000mg / L of s-triazine, 1,000-1,200mg / L of sulfate, 1,500-2,000mg / L of stannous mono-sulphate, 3,000-6,000mg / L of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium and the balance of a sulfuric acid solution. The s-triazine and sulfuric acid are mixed according to a certain ratio to form a sulfuric acid electrolyte additive; due to the ligand mixing working mechanism of the s-triazine, the sulfation of a lead-acid storage battery polar plate is reduced, the electrochemical performance of a battery is improved, and the cycle service life of the battery is prolonged.
Owner:ANHUI YONGHENG STORAGE BATTERY
Preparation method of high-power external application type lead-carbon battery negative electrode
ActiveCN111081986AImprove effective utilizationImprove power densityNegative electrodesLead-acid accumulator electrodesElectrode potentialElectrolytic agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-power external application type lead-carbon battery negative electrode. The negative electrode consists of three parts, namely, lead plaster, a carbon plate and gel. The structure that the carbon plate is attached to the surface of the lead plaster can improve electrode potential distribution, inhibit surface sulfation and improve the effective utilization rate of active substances. When lead ions in an electrolyte contact with the carbon plate of the negative electrode, lead and lead sulfate oxidation-reduction circulation occurs on the surface of the carbon plate under the electrochemical action, sulfation is generated, and the power density and the cycling stability of the electrode are reduced. The gel can inhibit lead ions from contacting the surface of the carbon material, avoid reduction of the lead ions, inhibit sulfation of the surface of the carbon material, ensure normal exertion of beneficial effects of the carbon material, improve the charge-discharge efficiency of the electrode and prolong the cycle service life of the electrode. The external application type lead-carbon battery composed of the negative electrodehas higher large-current bearing capacity and cycling stability, and is suitable for the fields of start-stop automobiles, solar energy, wind energy storage and the like.
Owner:吉林省凯禹电化学储能技术发展有限公司
Storage battery electrolyte and storage battery
InactiveCN105449292AImprove high temperature resistanceImprove cycle performanceLead-acid accumulatorsAcid electrolytesElectrolytic agentMeth-
The invention discloses a storage battery electrolyte and a storage battery, comprising sulfuric acid, stannous sulfate, ammonium sulfate, sodium sulfate, 4,5-diethyl vinylene carbonate, 4-methyl-5- propyl vinylene carbonate, cyclohexyl-benzene, anisole, modified polyacrylamide, EDTA disodium, 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol, 1(H)-2-p-chlorobenzyl benzimidazole, sulfones additive, 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-trithiol trisodium salt solution, nanoscale silicon dioxide and deionized water. The invention can solve the deficiency of the prior art and can remarkably improve the using times and service life of the storage battery; simultaneously the storage battery is good in stability and easy in popularization and use.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BOSSE POWER
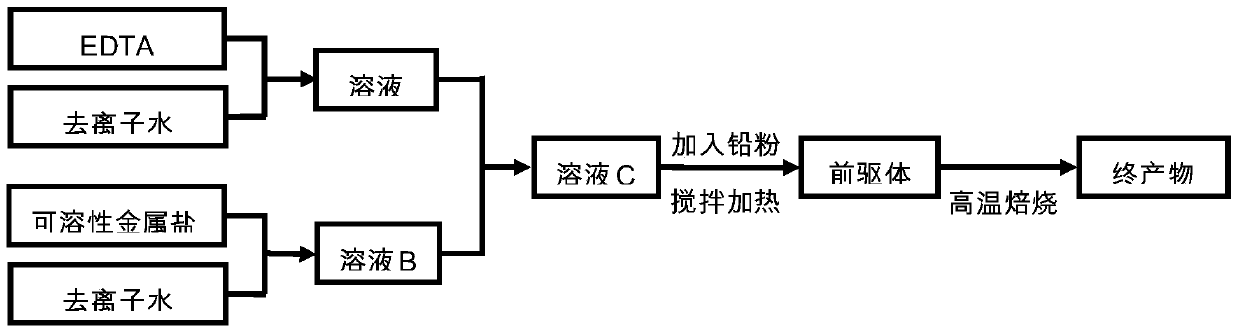
Metal element-doped and carbon-coated lead powder and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106876711AImprove electrochemical performanceHigh charge and discharge reversibilityLead-acid accumulator electrodesCarbon coatingCarbonization
Disclosed is metal element-doped and carbon-coated lead powder used as a negative electrode material of a lead-carbon battery. The lead powder is characterized in that the surfaces of lead oxide granules which constitute the lead power are coated with metal element-containing carbon; the preparation method for the lead powder comprises the steps of adding a metal element soluble salt solution which is used as a hydrogen evolution inhibitor into a complexing agent solution firstly, and mixing uniformly; after metal ions and the complexing agent are fully reacted to form a metal ion complex solution, adding lead powder into the complex solution to be fully stirred, and performing heating to remove water content to enable the surfaces of the lead powder granules to be coated with the complex; and finally, performing carbonization treatment on the product in inert gas to obtain the metal element-doped and carbon-coated lead powder. The method is characterized in that carbon coating on the lead powder and hydrogen evolution inhibition modification of the coated carbon are realized through in-situ composite in one time; and the negative electrode material, which is compounded by the metal element-doped and carbon-coated lead powder, of the lead-carbon battery has high electrochemical performance.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Negative electrode diachylon used for high-performance AGM battery and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN103456930BImprove dynamic reception characteristicsImprove performanceCell electrodesEngineeringDynamic charging
The invention belongs to the technical field of lead storage batteries and relates to a negative electrode diachylon which is capable of improving dynamic charging acceptance performance of an AGM battery and a preparing method thereof. The negative electrode diachylon is capable of improving the dynamic charging acceptance performance of the AGM battery under the condition that the AGM battery has the advantages of being long in service life and strong in starting capacity, the probability of sulfation of a negative plate when the negative plate is in a partial charge state for a long time is reduced, and then starting and shut-down requirements are met.
Owner:骆驼集团蓄电池研究院有限公司
Battery plate with multiple tabs and mixed pore diameters
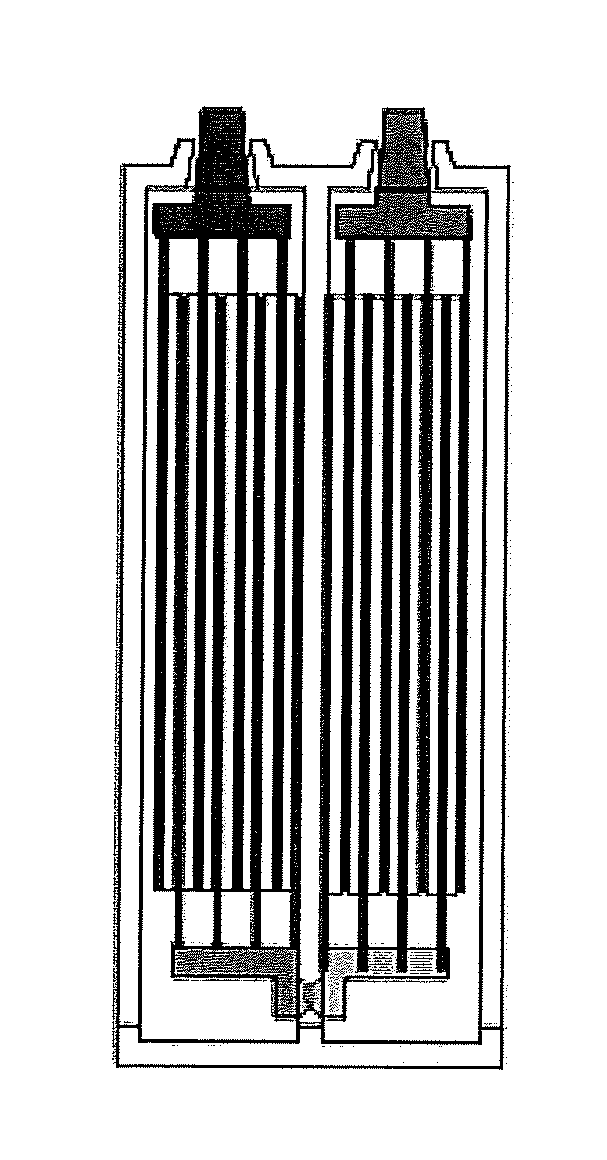
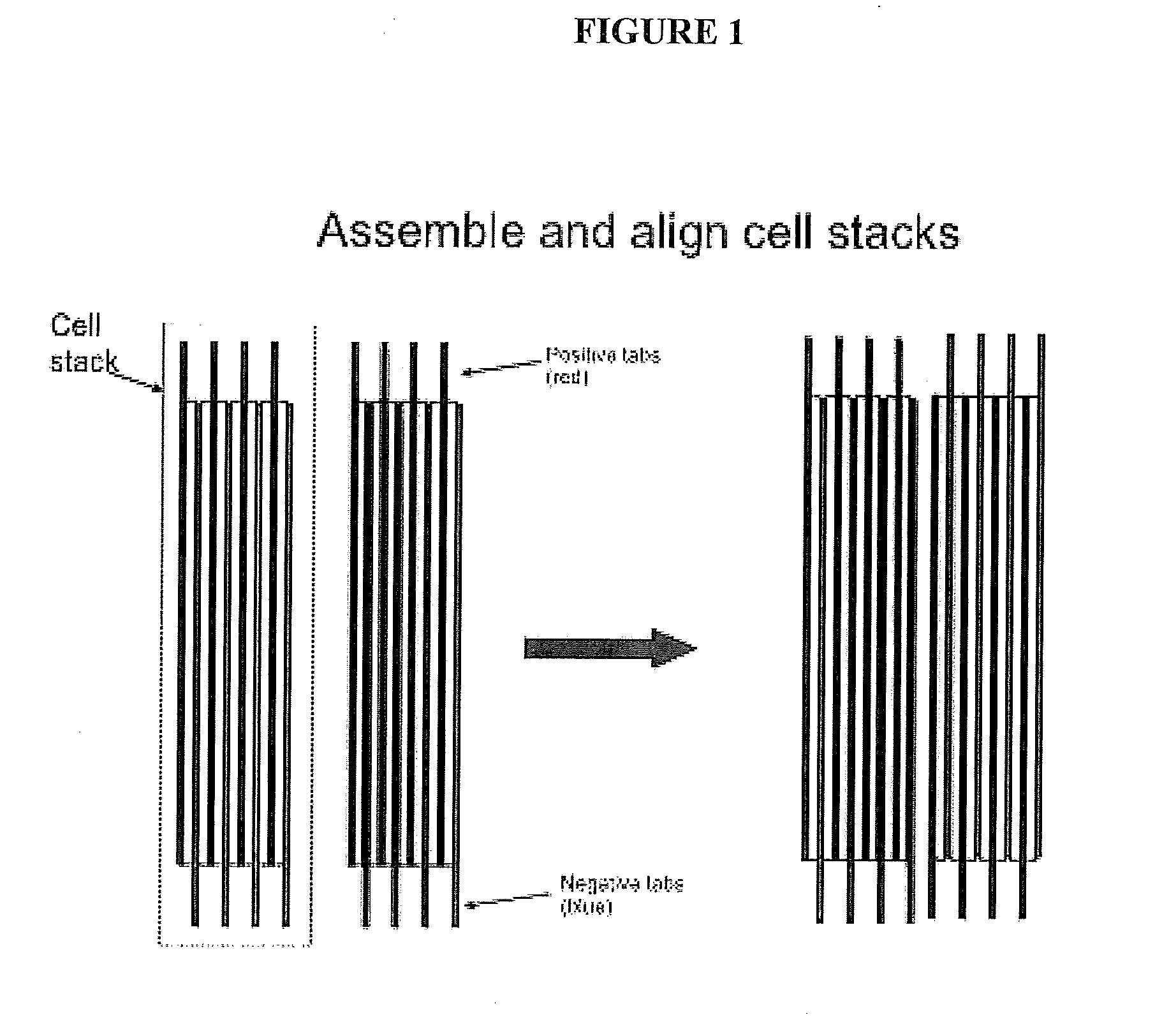
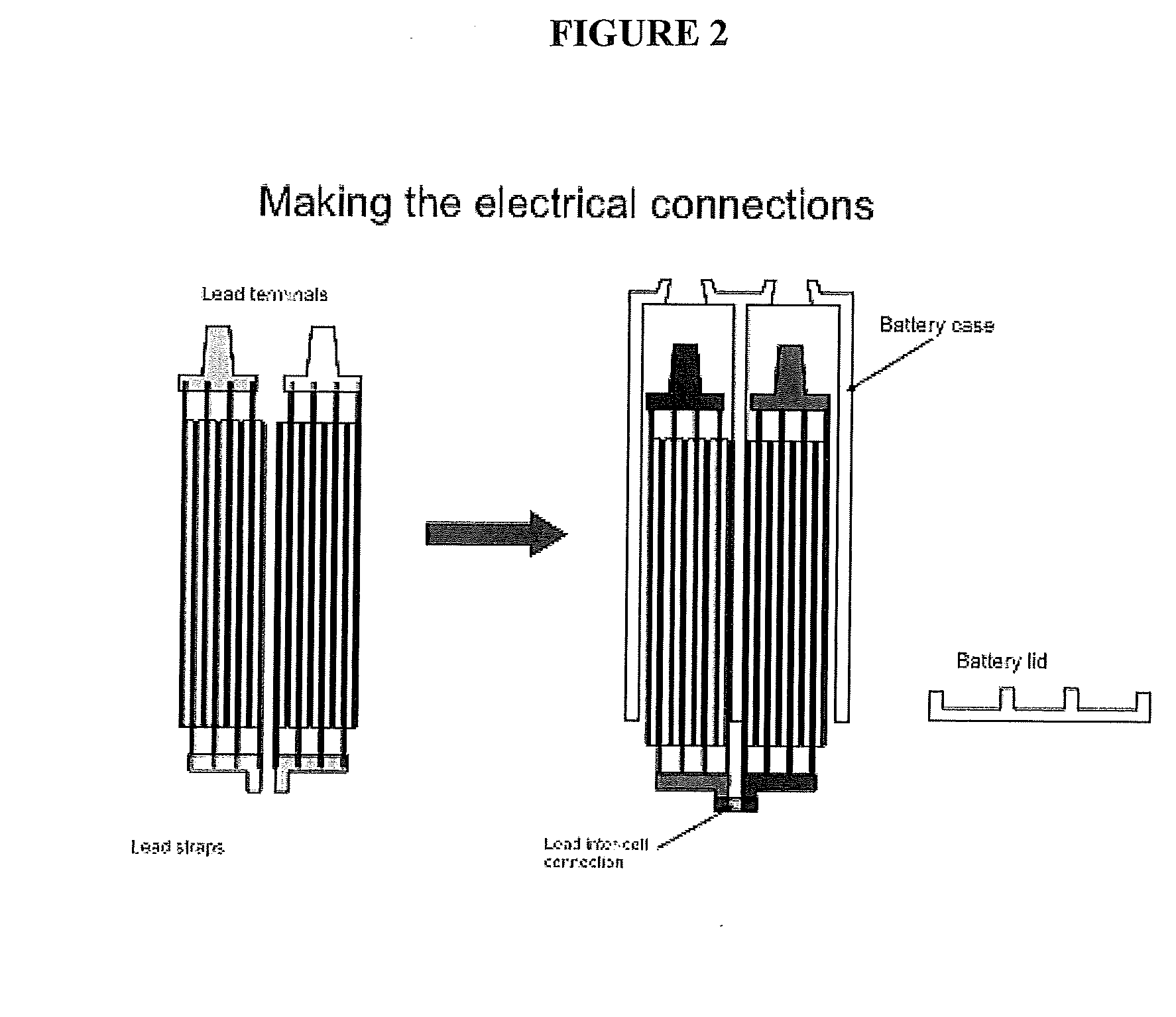
InactiveUS20140087238A1Reduce functionReduce diameter of porePrimary cell to battery groupingLarge-sized flat cells/batteriesBiomedical engineeringPore diameter
A battery electrode assembly comprises a porous electrode plate having a plurality of large and small pores, a pore insert within a plurality of pores, the pore insert maintaining an electrolyte in the pores substantially throughout a discharge / charge cycle. The pore insert may be a gelled electrolyte. The pore insert may be a particulate material. The electrodes may be used in a battery having cells with opposing positive and negative tabs connected in series by an intercell connector.
Owner:FIREFLY ENERGY INC
Super battery plate
ActiveCN101556997BIncrease specific energyHigh specific powerElectrolytic capacitorsHybrid capacitor electrodesFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a super battery plate which comprises a positive plate and a negative plate; the raw materials of the positive plate consist of lead powder, carbon fibers, carbon materials, short fibers and sulfuric acid solution; the raw materials of the negative plate consist of lead powder, PTFE, barium sulphate, humic acid, lignin sodium sulplate, carbon fibers, carbon materials, shortfibers and dilute sulfuric acid; the super battery prepared by the super battery plate has the advantages of high specific power and specific energy as well as long charge and discharge service lifeof a large pulse current. Moreover, the discharge of a low-temperature large current is batter than that of a common battery.
Owner:CHISEN POWER JIANGSU CO LTD
A metal element-doped carbon-coated lead powder and its preparation and application
ActiveCN106876711BHigh charge and discharge reversibilityLow hydrogen evolution currentLead-acid accumulator electrodesCarbon coatingCarbonization
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low temperature-resistant high-rate AGM start-stop battery anode lead plaster and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109301175AAchieve high magnificationRealize the start and stop functionLead-acid accumulatorsCell electrodesFiberHigh rate
Low temperature-resistant high-rate AGM start-stop battery anode lead plaster and a preparation method thereof. The lead plaster includes: 83-85% of lead powder, 7-7.5% of a sulfuric acid solution, 6-8.5% of water, 0.04-0.08% of short fibers, 0.17-0.34% of a carbon material, 0.6-0.85% of BaSO4, and 0.15-0.65% of a composite additive. The anode lead plaster can improve dynamic receiving feature andcycle performance of an AGM start-stop battery on the basis of the advantages of long service life and durable cycle performance of the AGM battery assembled with the lead plaster, thereby greatly improving the comprehensive performance of the battery. The lead plaster can satisfy high-rate, long-life and charge / discharge performances of an automobile under partial charge status during start andstop, especially a brake energy recovery function for the automobile, thus reducing sulfation of interior of the battery and improving charge receiving capacity. The lead plaster greatly improves low-temperature start capability of the AGM storage battery and increasing cold-start power and improving the charge receiving capacity of the battery.
Owner:CAMEL GRP XIANGYANG BATTERY
Superbattery negative plate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103413919BIncrease profitIncrease contact areaLead-acid accumulator electrodesFiberCarbon layer
The invention relates to a superbattery negative plate and a manufacturing method thereof. A front surface coating adopting lead powder as a main component is coated on the front surface of a substrate, and a carbon material coating is coated on the back surface of the substrate. The front surface coating comprises the following components by weight percent relative to the content of the lead powder: 0.2 to 2.0(wt)% of acetylene black, 1.0 to 2.0 (wt)% of barium sulfate, 0.2 to 0.5 (wt)% of lignin, 0.3 to 0.5 (wt)% of humic acid, 0.1 to 0.8 (wt)% of short fibers and 1 to 5.0(wt)% of adhesives. The carbon material coating 3 comprises the following components by weight percent: 65 to 90(wt)% of carbon material, 5 to 25(wt)% of acetylene black and 1 to 10(wt)% of adhesives. The carbon layer having a double-electric-layer structure is introduced onto the traditional storage battery negative plate, so that the superbattery has high specific power and can be charged and discharged at a large current, the sulfation of the lead paste on the front surface of a cathode at the HRPSOC (high-rate partial state of charge) state can be reduced, and the HEV (hybrid electrical vehicle) application can be met.
Owner:CAMEL GRP XIANGYANG BATTERY
Preparation process of battery pole plate of lead-acid battery with high cycle performance
PendingCN114335445AGood conductivity and dispersionReduce SulfationLead-acid accumulator electrodesBattery cellAlloy
The invention relates to a preparation process of a battery pole plate of a lead-acid battery with high cycle performance, the battery pole plate of the lead-acid battery comprises a positive pole plate and a negative pole plate, the preparation process of the positive pole plate comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing raw materials of the positive pole plate, including 0.07-0.10 part of calcium, 0.004-0.025 part of lanthanum, 1.4-1.5 parts of tin, 0.015-0.025 part of aluminum, 0.002-0.0025 part of silver and the balance of lead powder; 2, preparing a lanthanum-tin master alloy, wherein the lanthanum-tin master alloy comprises 20% by weight of lanthanum and 80% by weight of tin; step 3, preparing a calcium-aluminum master alloy; step 4, preparing a positive plate, adding lead powder into a smelting furnace, heating to melt, then sequentially adding the calcium-aluminum master alloy, the lanthanum-tin master alloy and the residual tin, and uniformly stirring to obtain a positive plate alloy; and preparing the positive plate alloy into the positive plate. The positive plate battery plate prepared by the invention has good corrosion resistance and high mechanical strength.
Owner:ZHANGZHOU HUAWEI POWER SUPPLY TECH
A kind of lead-acid battery electrolyte delamination alleviating agent
ActiveCN106571491BRealize the manufacturing processEnough exerciseLead-acid accumulatorsAcid corrosionMolecular materials
The invention provides a lead-acid storage battery electrolyte delamination mitigation agent, which is one or more of PP, PE, PVC, PU and polyvinyl fluoride polymer materials. The present invention utilizes the inertial effect when the vehicle starts, stops, accelerates, decelerates and other non-uniform motions or bumps, or the density change of the electrolyte itself when the battery is charged and discharged, to mix the electrolyte and slow down the stratification of the electrolyte. It is mainly a fine particle composed of a series of properties such as acid corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, and non-conductivity. It is added into the electrolyte after the battery is formed, and has the advantages of simple manufacture, convenient addition, low cost, and obvious effect.
Owner:CAMEL GRP XIANGYANG BATTERY
A high-temperature heavy-duty start-stop battery negative lead paste and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105702953BHigh mechanical strengthImprove bindingLead-acid accumulatorsCell electrodesFiberPolyester
Owner:湖北弘本能源有限公司
A kind of lead carbon electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104600254BIndustry technology upgradeTechnology upgradeLead-acid accumulator electrodesMaterials scienceRaw material
The invention discloses a lead carbon electrode and a preparation method thereof. The lead carbon electrode contains mixed carbon, a carrier, an expansive agent, an intermiscibility additive, nanocarbon coated lead, and lead powder. Among the components, the lead powder is the basic component; the mass ratio of mixed carbon to lead powder is 1%-3%, the mass ratio of the carrier to the lead powder is 1%-2%, the mass ratio of the expansive agent to the lead powder is 1.4%-1.7%, the mass ratio of the intermiscibility additive to the lead powder is 0.1%-0.3%, and the mass ratio of the nanocarbon coated lead to the lead powder is 1%-2%. The invention adopts a six-step process to obtain the lead carbon electrode, and the technological steps include raw material preparation, raw material mixing, paste mixing process, coating process, curing process, and polar plate formation. The purpose of the invention is to acquire a lead carbon electrode by formulation technique and a preparation method thereof.
Owner:HUNAN ANSHENG BATTERY
A kind of lead-acid storage battery electrolyte additive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104064817BReduce SulfationImprove electrochemical performanceLead-acid accumulatorsAcid electrolytesEthylenediamineSulfation
The invention relates to a lead-acid storage battery electrolyte additive which contains s-triazine, sulfate, stannous mono-sulphate and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium, wherein each liter of lead-acid storage battery electrolyte contains 1,500-2,000mg / L of s-triazine, 1,000-1,200mg / L of sulfate, 1,500-2,000mg / L of stannous mono-sulphate, 3,000-6,000mg / L of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium and the balance of a sulfuric acid solution. The s-triazine and sulfuric acid are mixed according to a certain ratio to form a sulfuric acid electrolyte additive; due to the ligand mixing working mechanism of the s-triazine, the sulfation of a lead-acid storage battery polar plate is reduced, the electrochemical performance of a battery is improved, and the cycle service life of the battery is prolonged.
Owner:ANHUI YONGHENG STORAGE BATTERY
A kind of lead-carbon battery negative lead paste for energy storage and preparation method thereof
Owner:CHAOWEI POWER CO LTD
A kind of tubular battery cathode lead paste and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109148846BIncrease capacityExtended service lifeFinal product manufactureCell electrodesElectrical batteryInternal resistance
Owner:湖南超威新材料有限公司
Partially graphitized activated carbon-based composite additive and preparation, negative electrode and application
ActiveCN108123137BLarge specific surface areaLimit growthLead-acid accumulatorsLead-acid accumulator electrodesElectrical batteryCarbon particle
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Lead-acid ultra-battery
InactiveCN101764264BFaraday pseudocapacitive properties have bothExcellent high magnification performanceLead-acid accumulatorsElectrode carriers/collectorsCapacitanceHigh rate
The invention discloses a lead-acid ultra-battery which comprises a negative plate and is characterized in that the negative plate comprises a negative grid, and the paste coating the negative grid contains conducting polymer provided with Faraday pseudo-capacitor energy storage. Compared with the prior art, the lead-acid ultra-battery of the invention has the following advantages: 1, by introducing the conducting polymer having the characteristics of the Faraday pseudo-capacitor, the lead-acid ultra-battery also has the characteristics of the Faraday pseudo-capacitor; and 2, the lead-acid ultra-battery of the invention has good high-rate performance, particularly, the lead-acid ultra-battery is capable of keeping more than 85% of the initial capacity (1C) when charging or discharging at 10C; and 3, thanks to the capacitor energy storage, the invention reduces the current on the lead negative plate of the lead-acid ultra-battery, and meanwhile, the invention correspondingly reduces the depth of discharge of the lead-acid ultra-battery, greatly reduces the sulfation on the surface of the lead negative plate, greatly prolongs the service of the lead-acid batteries and solves the problem that the service life of the lead-acid batteries is short.
Owner:李庆余
A kind of flat type anti-sulfur low-temperature SCR denitrification catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105289644BImprove oxygen storage capacityImprove redox abilityDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSulfurActive component
The invention specifically relates to a flat-plate type sulfur-resistant low-temperature SCR denitration catalyst and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the fields of environmental protection and environmental catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: with nanometer composite oxide Ce-ZrO2 as a carrier, manganese oxide as an active component and iron oxide and molybdenum oxide as cocatalysts, carrying out equivalent-volume impregnation, drying, roasting and crushing so as to prepare a powdery catalyst; and subjecting the prepared powdery catalyst to acidification by sulfuric acid and then carrying out mixing, rolling coating, fold pressing, shearing, drying and roasting so as to obtain the flat-plate type sulfur-resistant low-temperature SCR denitration catalyst. The prepared catalyst has denitration activity of 85 to 98% in a temperature range of 80 to 150 DEG C and has excellent resistance to sulfur dioxide poisoning.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com