Patents
Literature
48results about How to "Stable breakdown voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
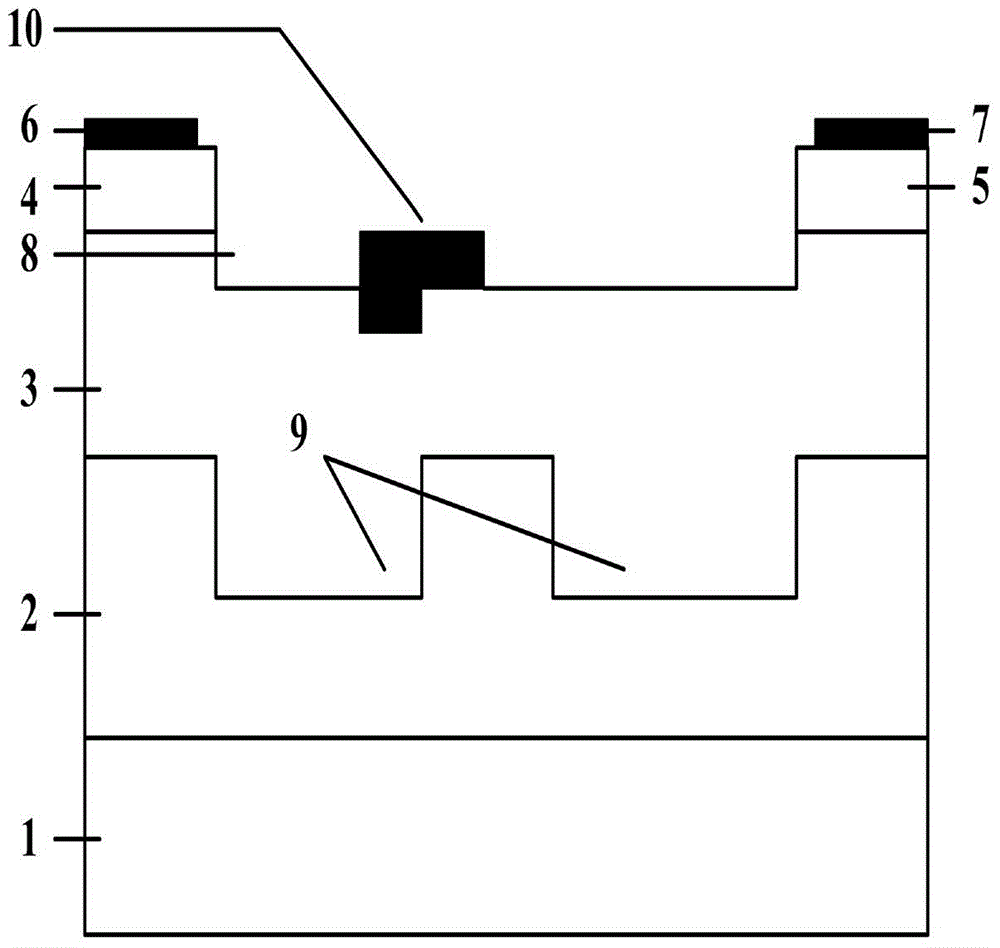
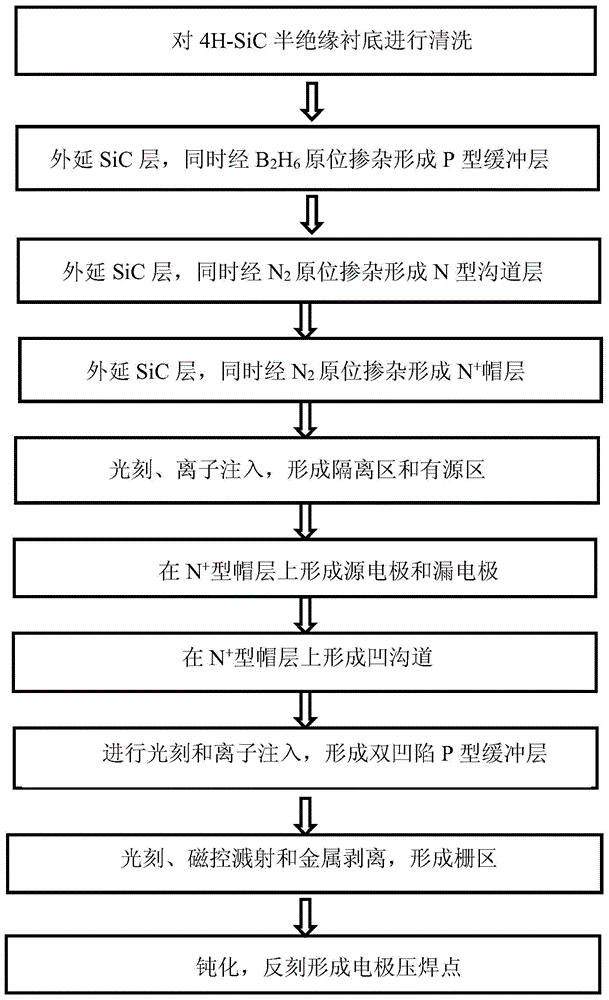
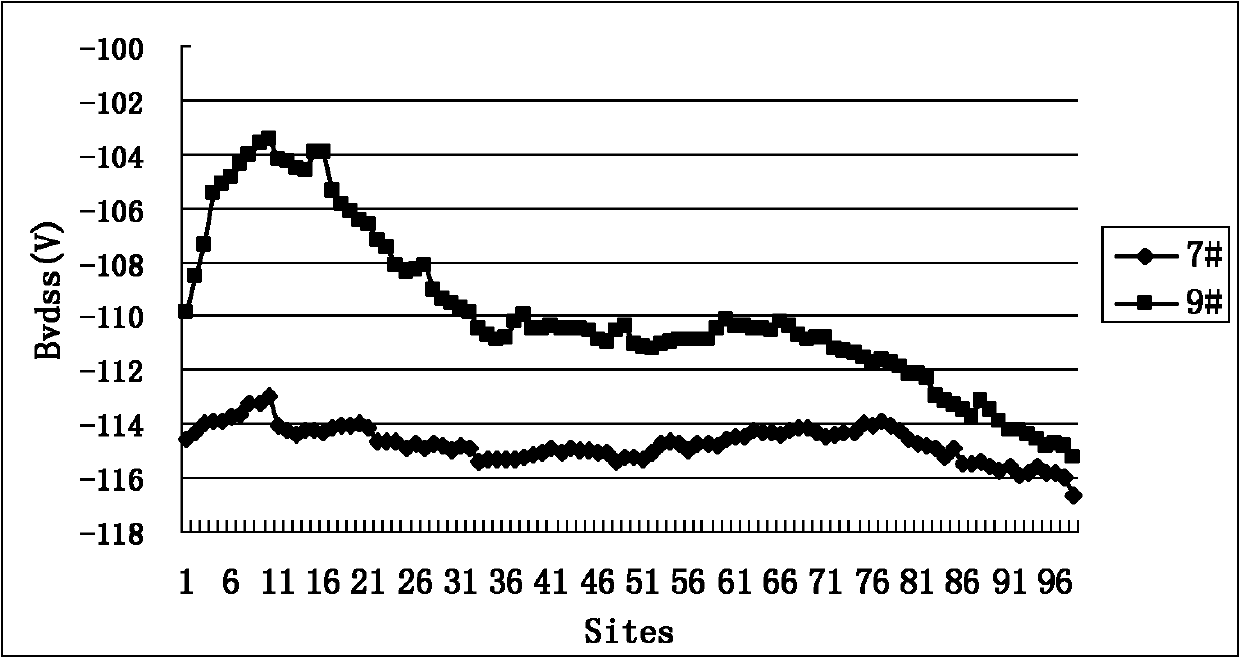
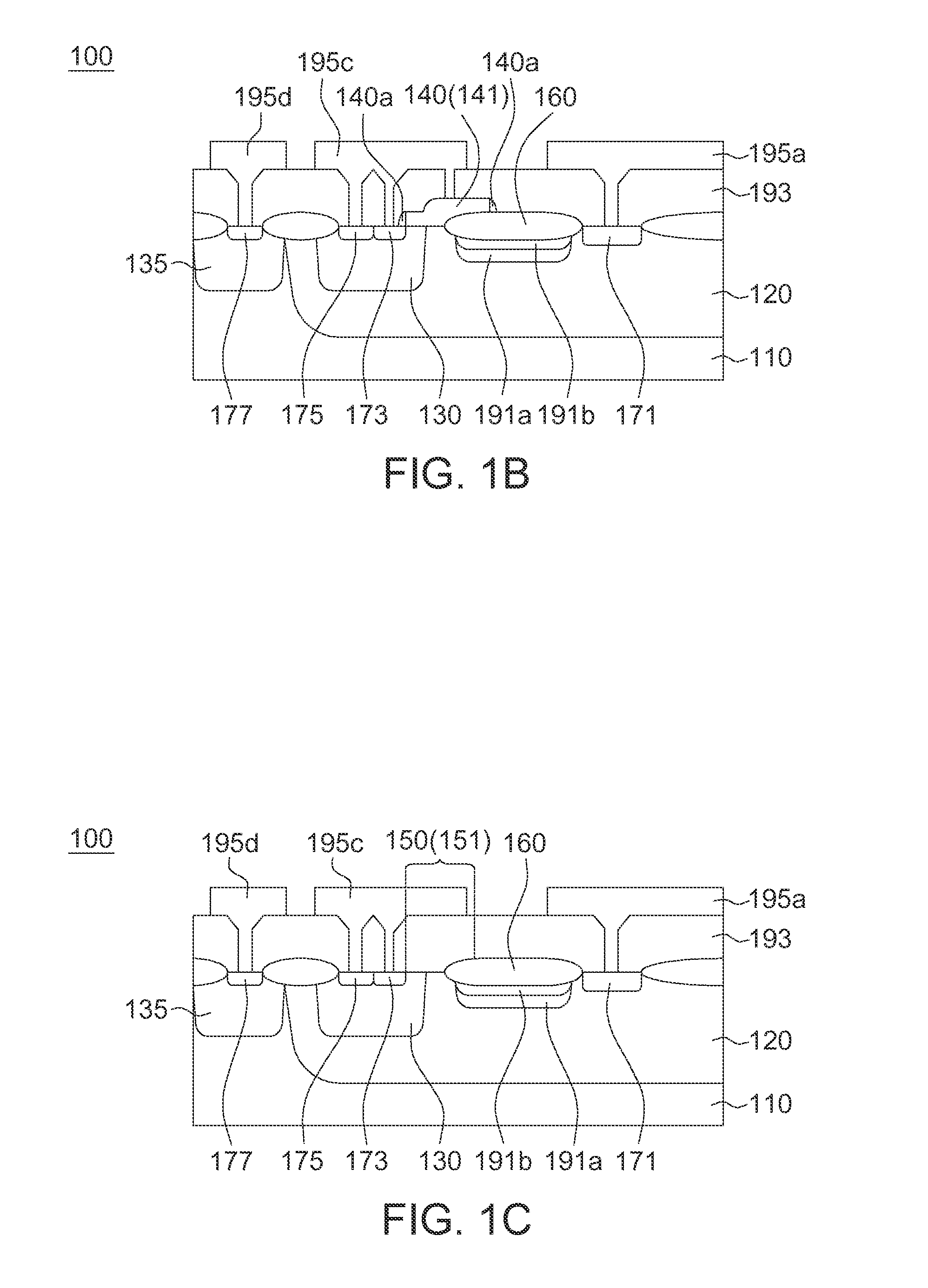
4H-SiC metal-semiconductor field effect transistor with double-sunken buffer layer
ActiveCN104681618ADrain current increasesLarge channel thicknessSemiconductor devicesPower flowSemi insulating
The invention discloses a 4H-SiC metal-semiconductor field effect transistor with a double-sunken buffer layer. The 4H-SiC metal-semiconductor field effect transistor comprises a 4H-SiC semi-insulating substrate, a P type buffer layer and an N type channel layer from bottom to top, wherein a source electrode cap layer and a drain electrode cap layer are respectively arranged on two sides of the N type channel layer; a source electrode and a drain electrode are respectively arranged on the surfaces of the source electrode cap layer and the drain electrode cap layer; a gate electrode is formed on one side, close to the source electrode cap layer, above a channel; grooves are arranged on the upper end face of the P type buffer layer and under a gate source and a gate leakage. The 4H-SiC metal-semiconductor field effect transistor has the advantages that the output drain electrode current is obviously improved, and the breakdown voltage is stable.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Semiconductor device
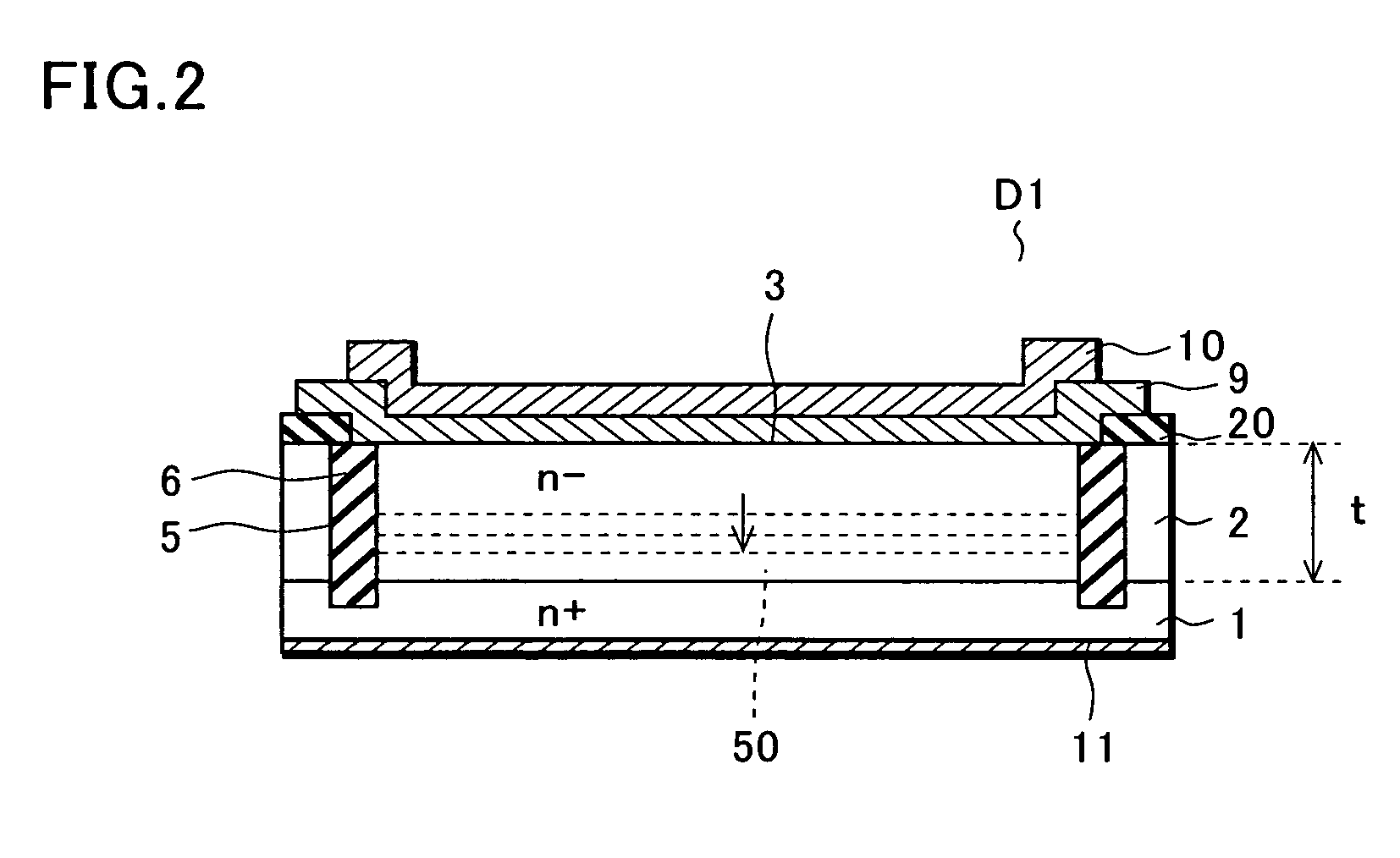
InactiveUS20050184355A1Stable breakdown voltageReduce capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceSchottky barrier
Conventionally, a guard ring for securing a breakdown voltage is provided around a Schottky barrier diode. Since the guard ring is a p+ type region, a depletion layer expands around the guard ring when a reverse voltage is applied to prevent a reduction in capacitance. In addition, there is a problem in that, when a forward voltage is applied, holes are injected from the guard ring if the applied voltage exceeds a predetermined voltage and high-speed operation cannot be realized. To solve the problems, a trench is provided in a guard ring region of the conventional technique and an insulating film is provided inside the trench. The trench is provided to reach an n+ type semiconductor substrate. Consequently, since the depletion layer expands only in a depth direction until the depletion layer reaches the n+ type semiconductor substrate, it is possible to realize a reduction in capacitance. In addition, since the p+ type region is made unnecessary, a reverse recovery time (Trr) does not occur. Therefore, it is possible to improve switching operation speed.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
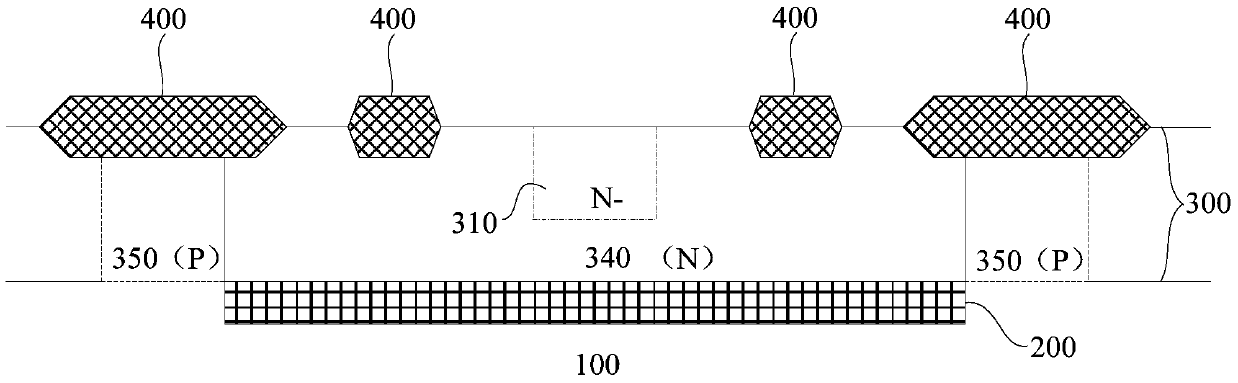
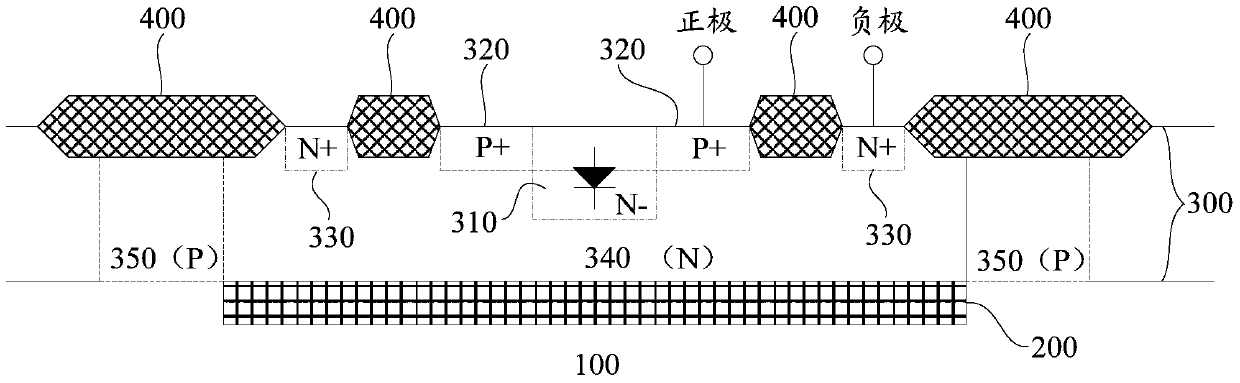
Zener diode and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111710729AStable breakdown voltageEliminate the problem of inconsistent breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPhysicsZener diode
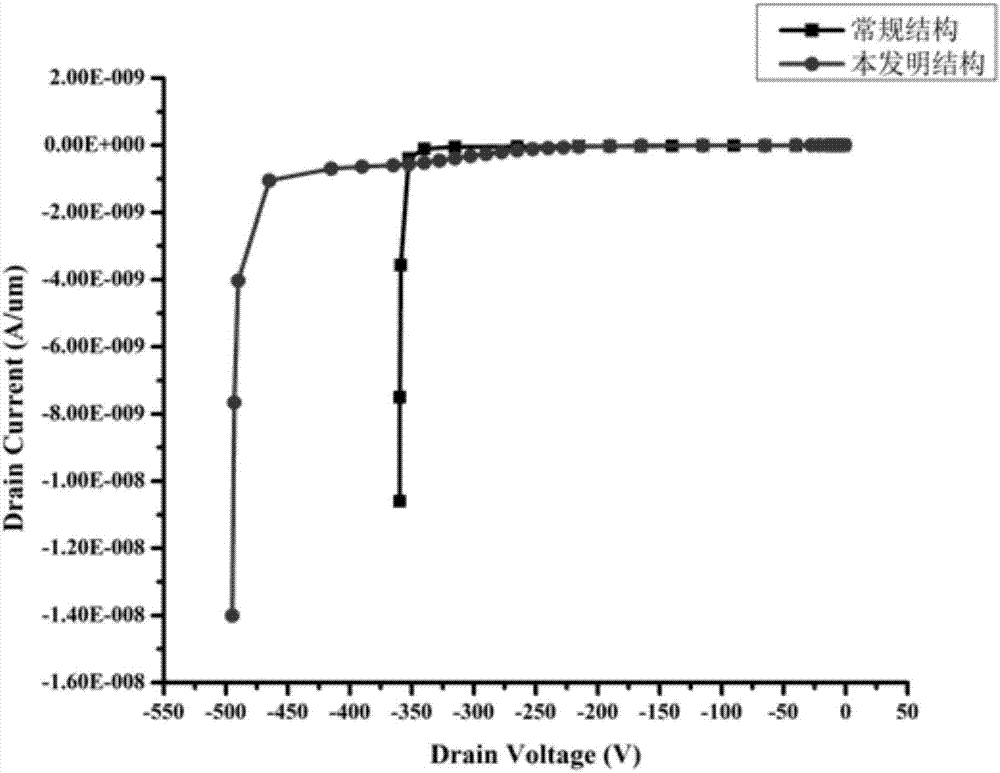
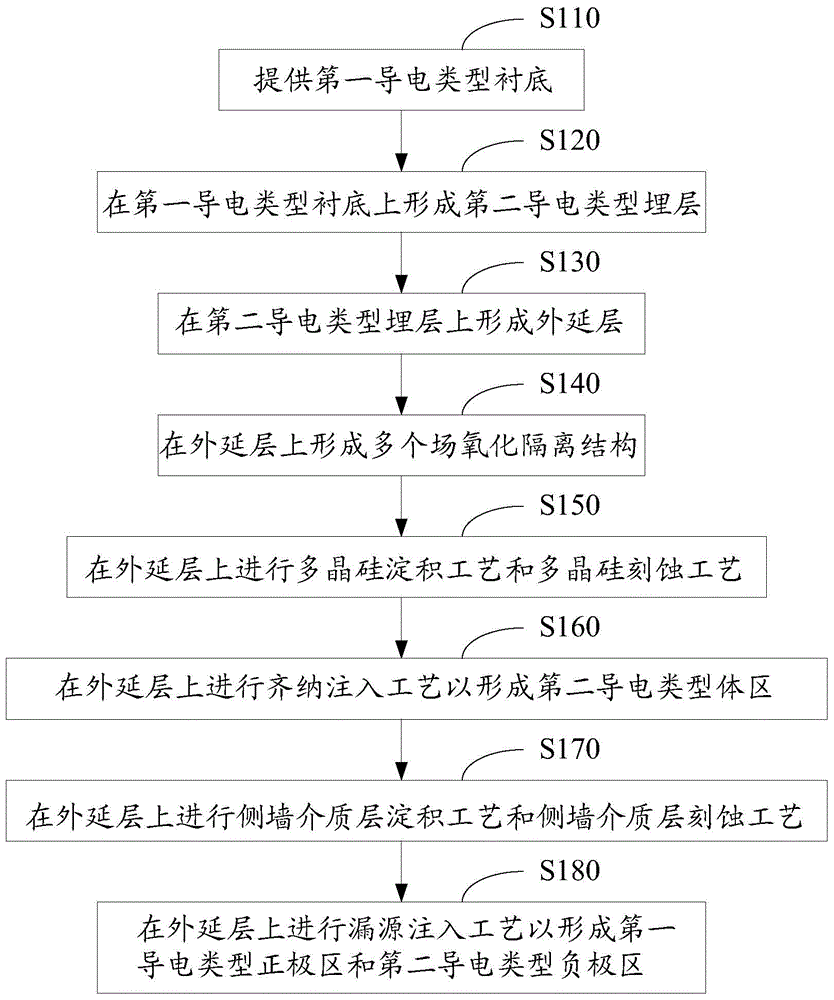
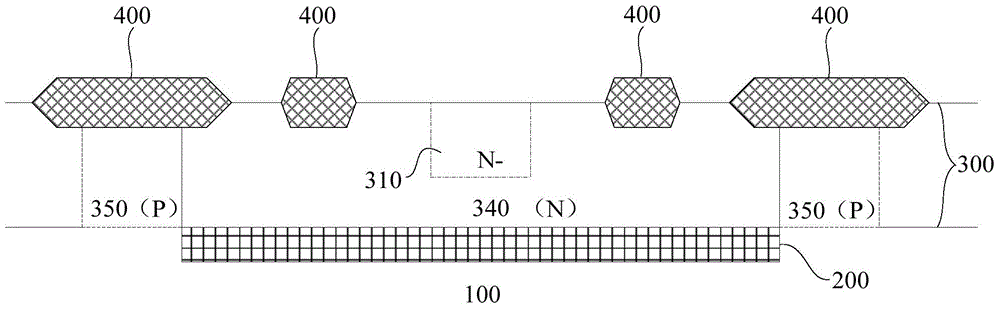
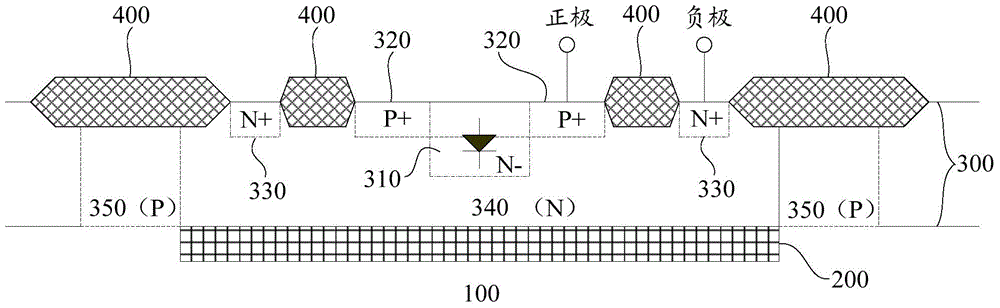
The invention relates to the technical field of semiconductors, and provides a Zener diode and a manufacturing method thereof. The formed Zener diode comprises: a well region located on a substrate; afirst doped region located on the substrate and second doped regions ocated on the two sides of the first doped region respectively; field oxygen regions respectively positioned on one sides, far away from the first doped region, of the second doped regions, wherein the beak regions, close to one sides of the second doped regions, of the field oxygen regions are adjacent to the second doped regions; a polycrystalline silicon layer positioned above the field oxide regions and transversely extending to cover the second doped regions; and a first electrode in ohmic contact with the first doped region and the polycrystalline silicon layer, and a second electrode in ohmic contact with the substrate. According to the invention, the equipotential of the PN junction formed by the second doped region, the first doped region and the well region on the side surface of the second doped region is adjusted through the polycrystalline silicon layer positioned above the field oxide region and transversely extending to cover the upper surface of the second doped region, so that the breakdown voltage of the PN junction at each position is stabilized.
Owner:JOULWATT TECH INC LTD
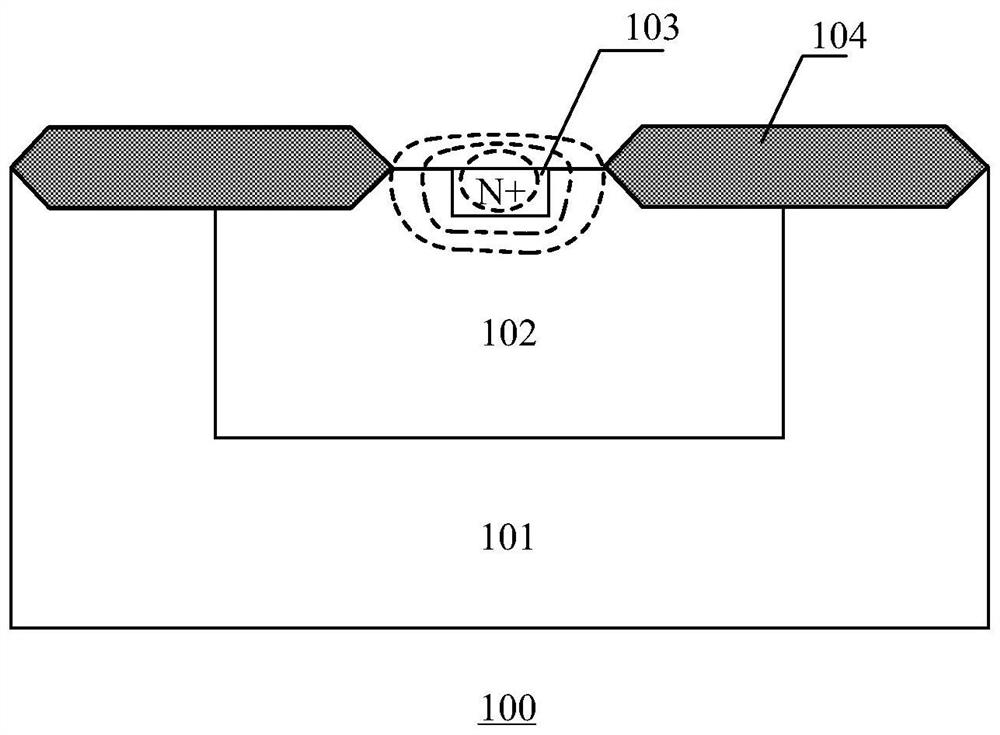
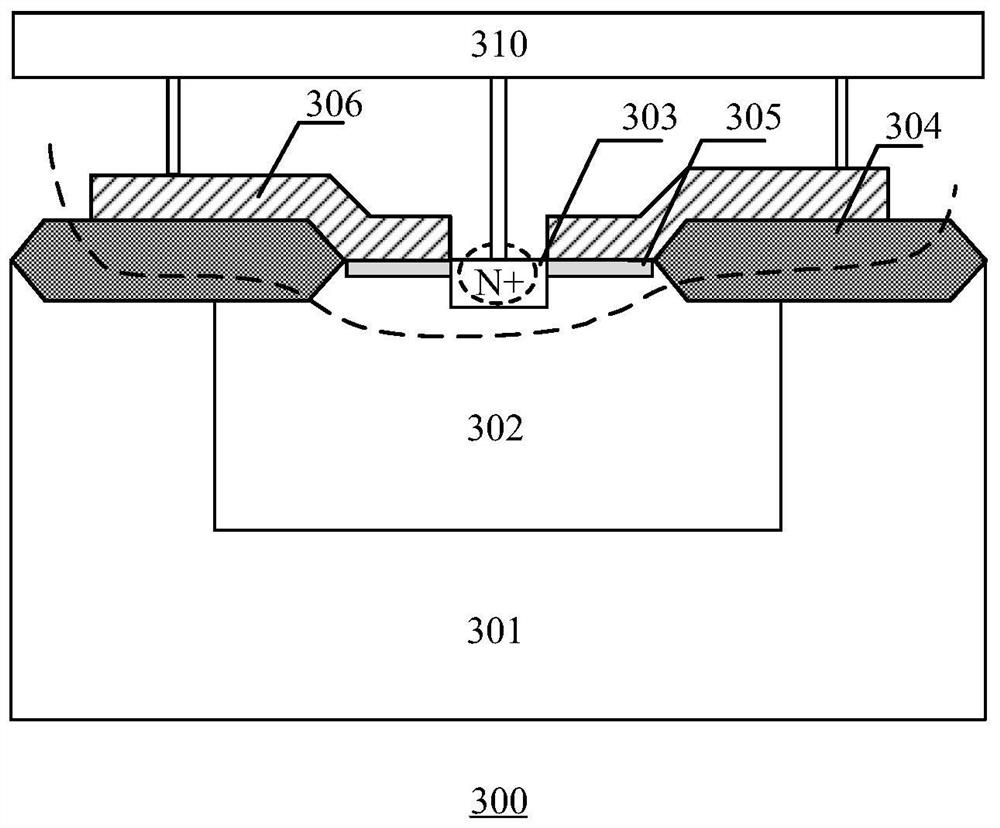
Graphene high-sensitivity photoelectric detector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112701173AHigh sensitivityQuick responseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsComposite substrate
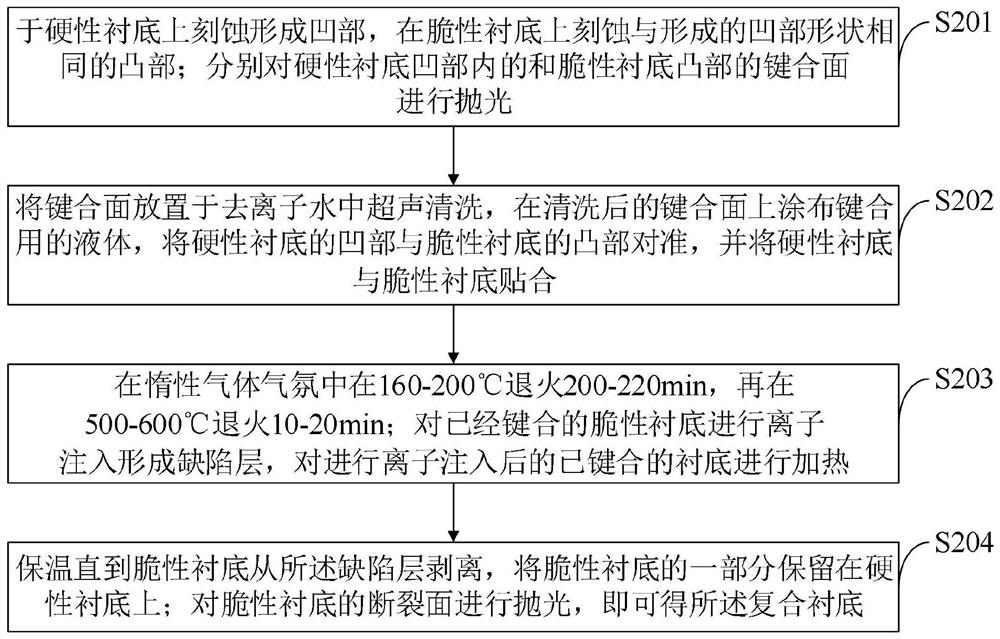
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectric devices, and discloses a graphene high-sensitivity photoelectric detector and a preparation method thereof. The graphene high-sensitivity photoelectric detector comprises a composite substrate, an isolation layer, a graphene contact electrode, carbon quantum dots, a graphene film and an anti-reflection layer; the isolation layer is located on the composite substrate; the electrode is positioned on the isolation layer; the carbon quantum dots are positioned on the electrode; the graphene film is positioned on the electrode; the surface of the graphene film is covered with an anti-reflection layer; the composite substrate is formed by bonding a hard substrate and a brittle substrate; the hard substrate is made of silicon dioxide, and the brittle substrate is made of InP or Ge; and the anti-reflection layer is a transparent film composed of silicon dioxide. The prepared photoelectric detector is ultrathin, easy to integrate in a large area and high in sensitivity, the response speed of the photoelectric detector can be increased, and the photoelectric detector has wide application prospects in the fields of ray measurement and detection, industrial automatic control, photometers and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Insulating paint for enameled wire and application method of insulating paint
The invention discloses an insulating paint for an enameled wire and an application method of the insulating paint. The insulating paint disclosed by the invention is 225 polyesterimide insulating paint and 1766 polyesterimide insulating paint of which the temperatures are both 200 DEG C. By virtue of the insulating paint, the relatively high adhesive strength as well as relatively high temperature resistant index of the product are ensured. By mixing the insulating paint with a matched solvent, a suitable viscosity is reached; after the enameled wire is coated with the insulating paint, the experiment shows that the enameled wire has good adherence; after the enameled wire is elongated by 20% (with respect to the national standard, by 15%), the thickness of the insulating layer losing the adherence is not more than 1b. The breakdown voltage of the enameled wire is stable and can be stabilized at 4000-5500V.
Owner:济南宝世达实业发展有限公司
P-type doubled diffusion metal-oxide-semiconductor (DMOS) device and making method thereof
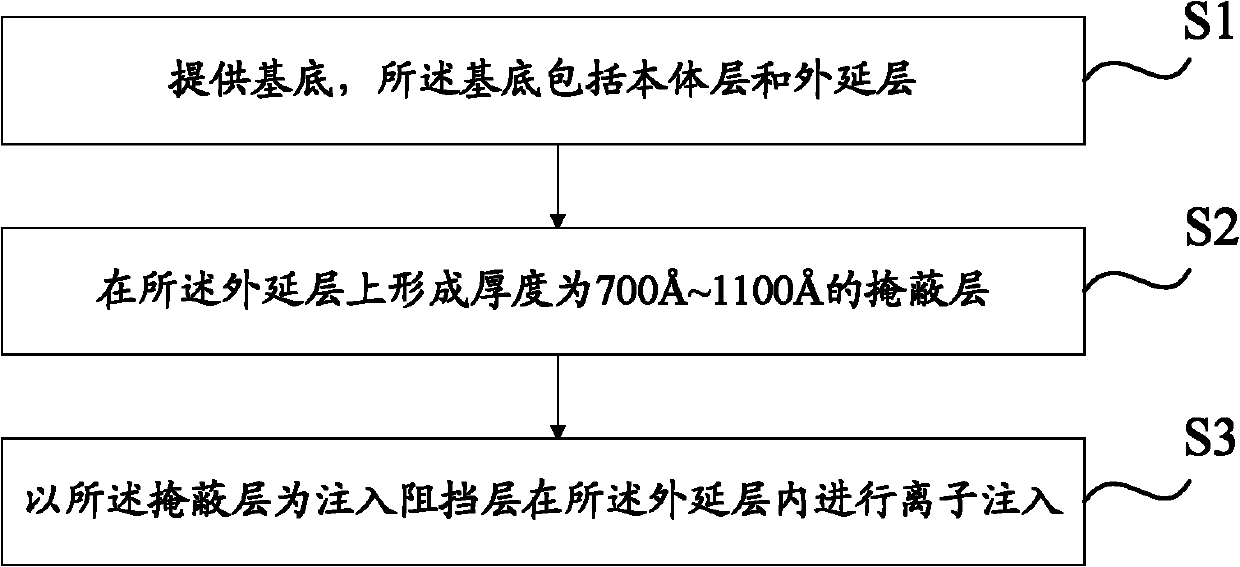
InactiveCN102468177AInhibited DiffusionPrevent self-dopingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDouble diffusionOptoelectronics
The embodiment of the invention discloses a P-type doubled diffusion metal-oxide-semiconductor (DMOS) device and a making method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: providing a substrate, wherein the substrate comprises a body layer and an epitaxial layer; forming a masking layer with thickness of 700 to 1,100A on the epitaxial layer; and performing ion implantation in the epitaxial layer by taking the masking layer as an injection barrier layer. The P-type DMOS device comprises the substrate, wherein the substrate comprises the body layer and the epitaxial layer, the epitaxial layer comprises the masking layer and an ion implantation layer, the masking layer is positioned on the epitaxial layer and has the thickness of 700 to 1,100A, and the ion implantation layer is formed by blocking an ion implantation process. With the adoption of the making method of the P-type DMOS device, which is provided by the invention, the problem of auto-doping on the back side of the substrate can be solved under the condition of using the low-resistivity substrate; therefore, the product area can be reduced, the product cost is reduced, and the competitiveness is increased.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB1 +1
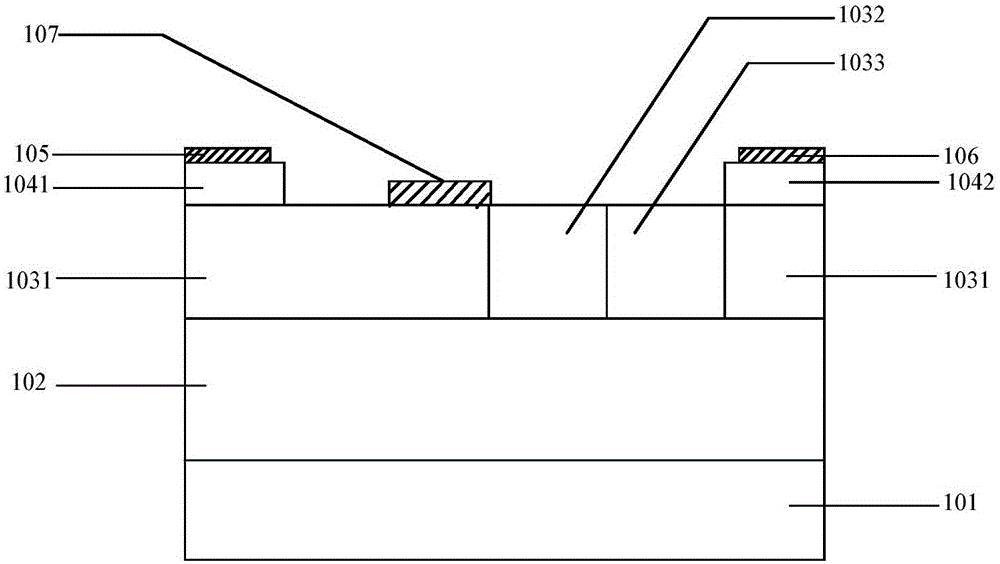
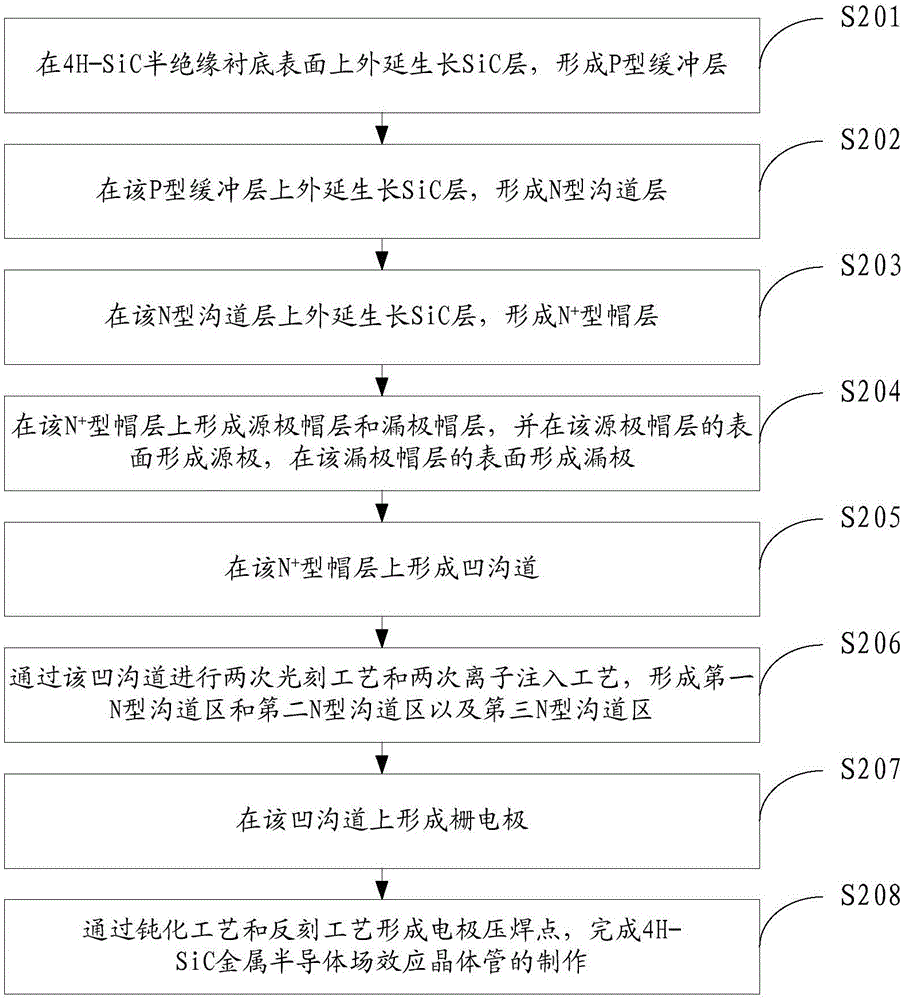
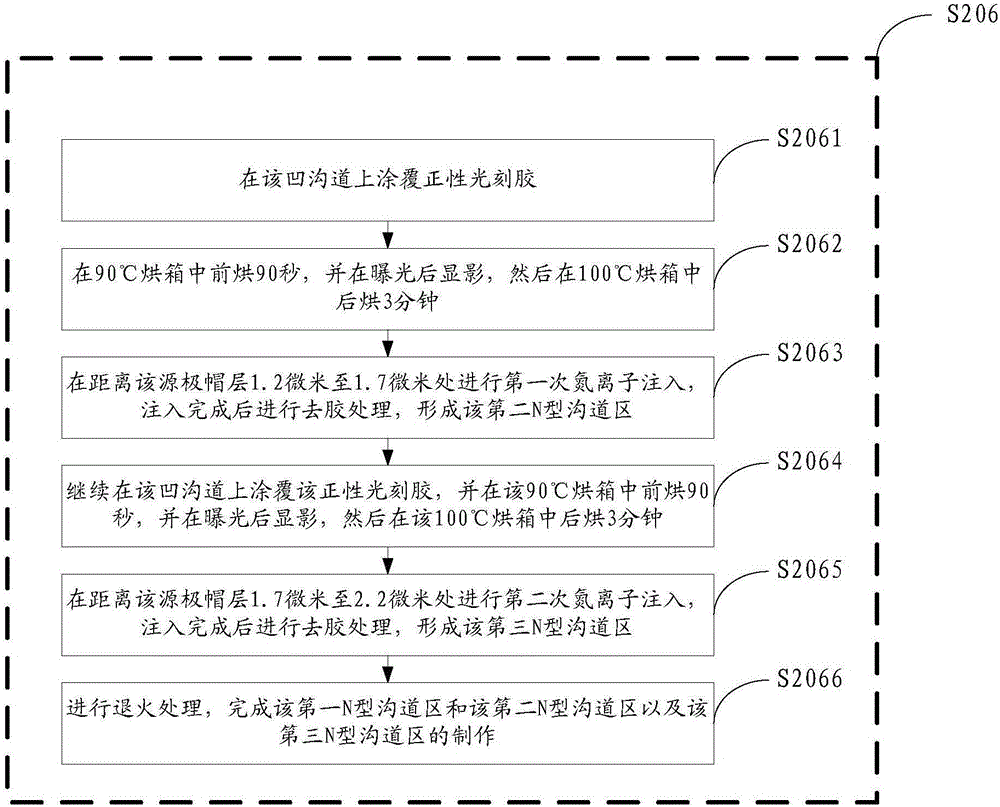
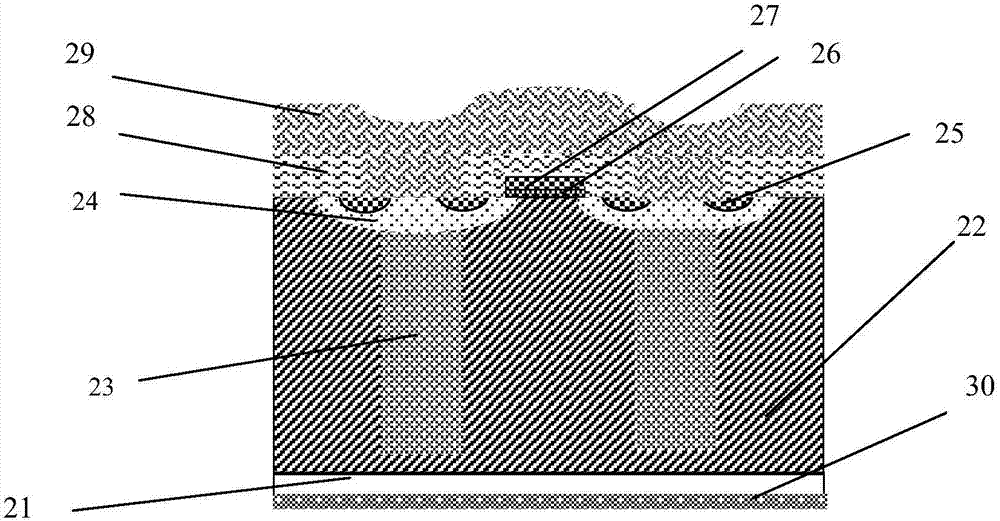
4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105161531AImprove power densityImprove DC characteristicsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower flowBreakdown voltage
The invention discloses a 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor and a manufacturing method thereof. The field effect transistor comprises a 4H-silicon carbide SiC semi-insulating substrate, a P-type buffer layer and an N-type channel layer, wherein the P-type buffer layer covers the 4H-silicon carbide SiC semi-insulating substrate; the N-type channel layer covers the P-type buffer layer and comprises a first N-type channel region, a second N-type channel region and a third N-type channel region; the second N-type channel region is formed between the first N-type channel region and the second N-type channel region; a source cap layer and a drain cap layer are formed on two sides of the surface of the N-type channel layer; a source is formed on the surface of the source cap layer; a drain is formed on the surface of the drain cap layer; and a gate electrode is formed on the N-type channel layer and close to the source cap layer. According to the 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor, the technical problems that the existing 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor is unstable in current and low in breakdown voltage are solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Super junction structure and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111341829AReduce processing difficultyIncrease widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical field strength
The invention discloses a super junction structure, and the structure is formed by superposing two layers of super junction substructures, wherein the two layers of P-type subcolumns are both composedof P-type sub epitaxial layers filled in corresponding sub grooves, the width of the P-type column at the top of each subcolumn is larger than that of the N-type column, and the doping concentrationof the P-type columns can be reduced while the doping concentration of the N-type columns is improved. Charge balance between the P-type column and the N-type column is set according to the fact thatonly one longitudinal position in the whole super-junction unit structure has the maximum electric field intensity when the device is reversely biased. The invention further discloses a manufacturingmethod of the super junction structure. According to the invention, the consistency of device performances such as breakdown voltage and avalanche tolerance can be improved; meanwhile, the on resistance of the device is kept or reduced, and high-temperature application of the device is facilitated.
Owner:SHENZHEN SANRISE TECH CO LTD
Groove type power device and manufacturing method thereof
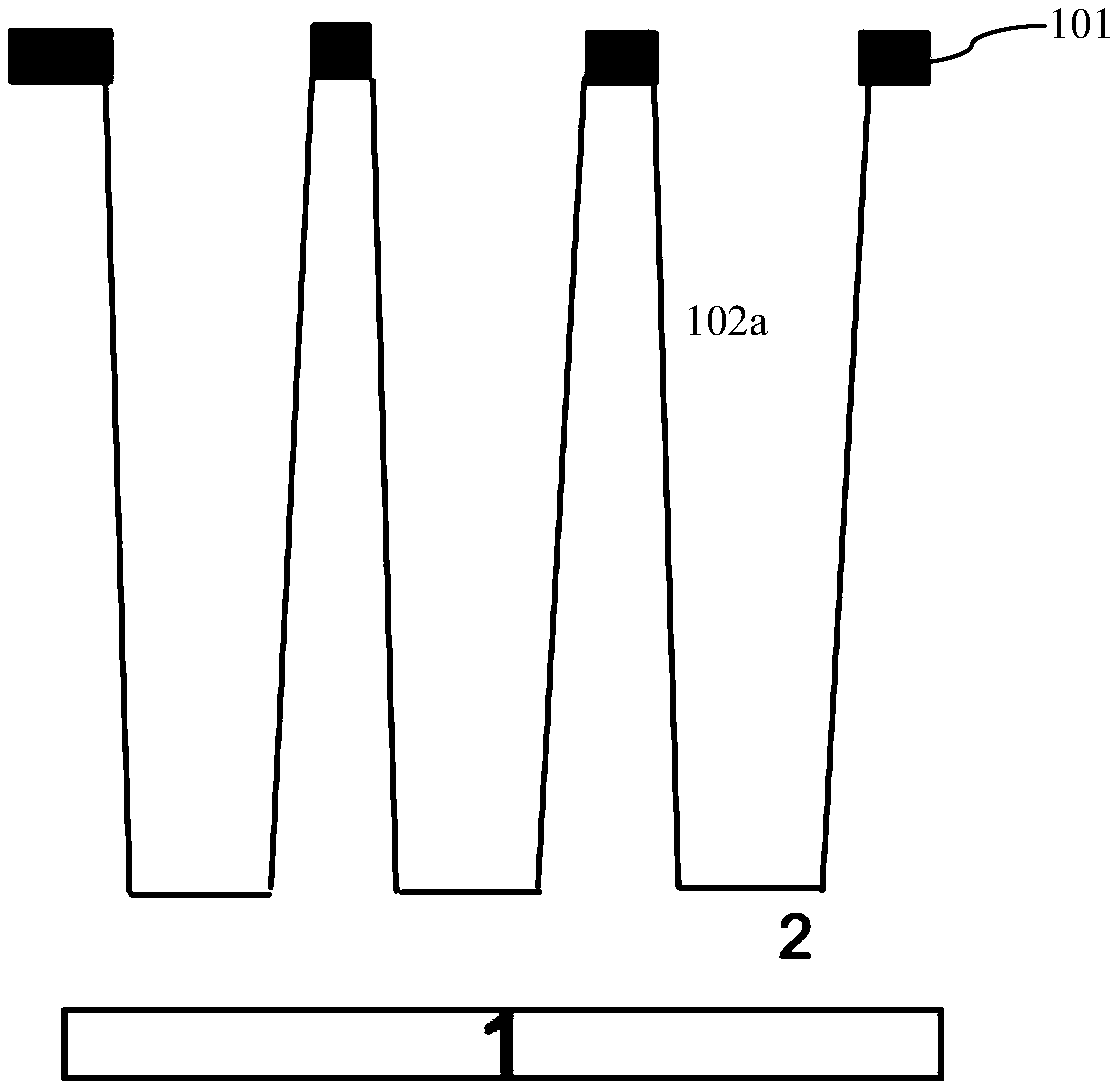
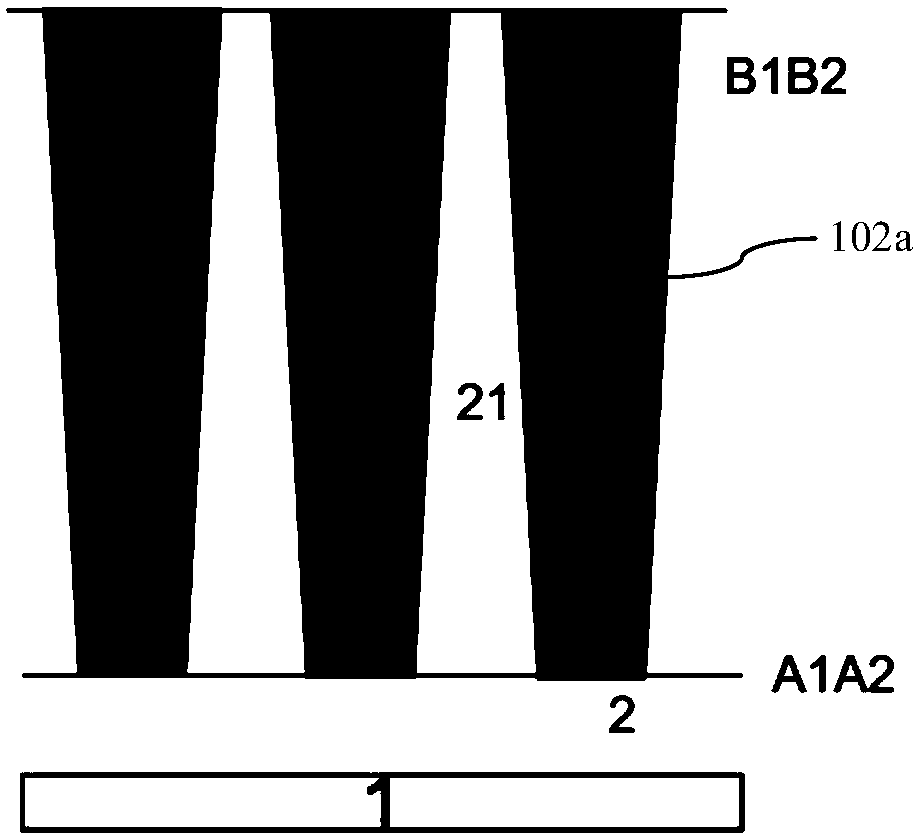
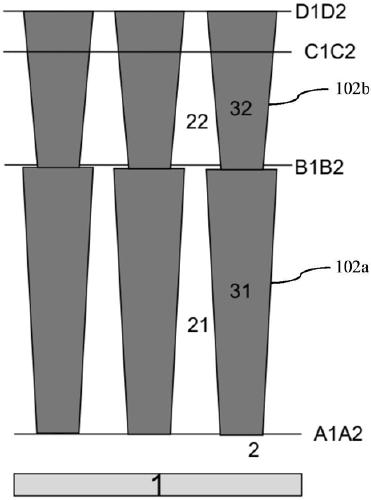
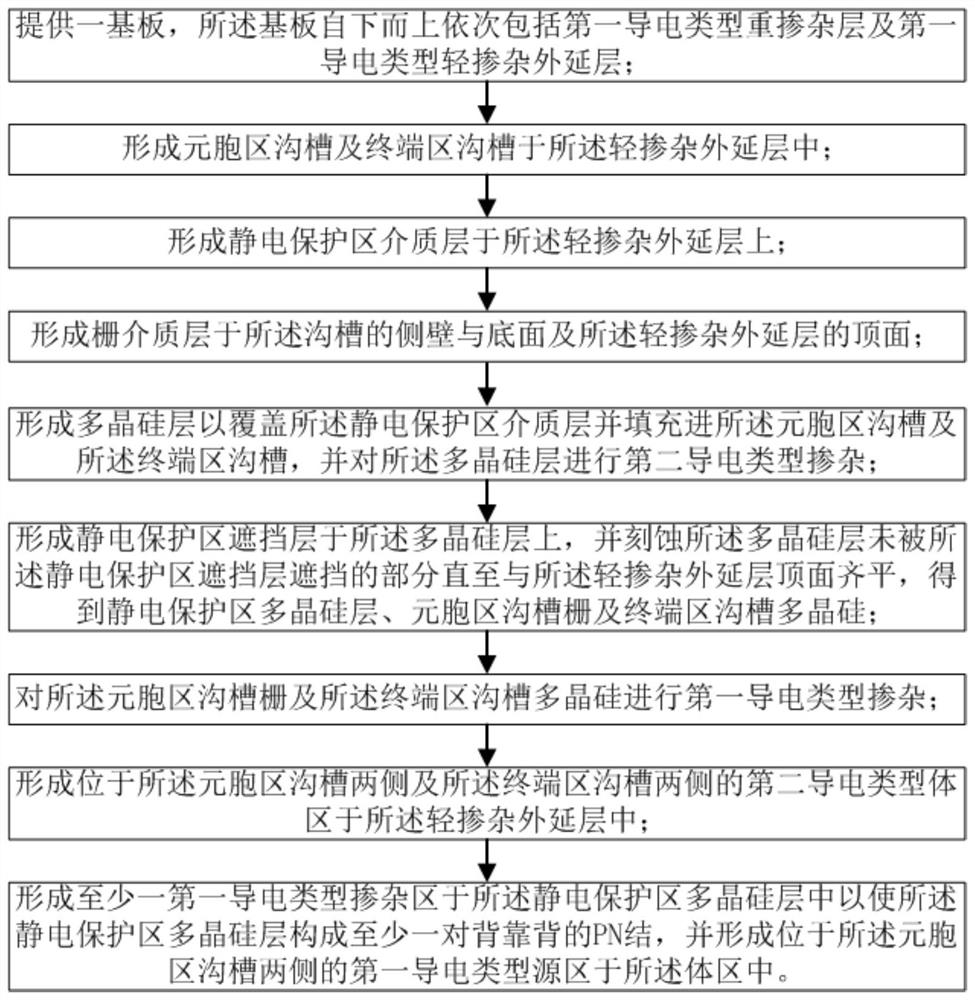
PendingCN113035714AStable Threshold Voltage and Breakdown VoltageThreshold Voltage StabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBody regionElectrically conductive
The invention provides a groove type power device and a manufacturing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: providing a substrate sequentially comprising a first conductive type heavily doped layer and a first conductive type lightly doped epitaxial layer from bottom to top; forming a cellular region groove and a terminal region groove in the lightly doped epitaxial layer; forming a gate dielectric layer on the side wall and the bottom surface of the groove and the top surface of the lightly doped epitaxial layer; forming a polycrystalline silicon layer so as to fill the cellular region groove and the terminal region groove, and carrying out second conduction type doping on the polycrystalline silicon layer; etching the polycrystalline silicon layer until the polycrystalline silicon layer is flush with the top surface of the lightly doped epitaxial layer to obtain a cellular region groove gate and terminal region groove polycrystalline silicon; performing first conduction type doping on the cellular region groove gate and the terminal region groove polycrystalline silicon; forming a body region in the lightly doped epitaxial layer; and forming a source region in the body region. According to the invention, the groove type terminal is adopted, and body region injection can be carried out by adopting relatively high energy, so that the device has more stable threshold voltage and breakdown voltage.
Owner:CHINA RESOURCES MICROELECTRONICS (CHONGQING) CO LTD
A production process for improving bipolar transistor bvcbo
ActiveCN103346085BReasonable depthStable breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTwo step
The invention discloses a technology for improving bipolar transistor BVcbo production. The groove field oxide isolation process technology is combined with the junction terminal process technology, firstly, after a groove is formed through a dry etching process technology and before field oxidation of the groove is carried out, P-type element boron ions are pre-doped into groove field silicon through an ion implantation technology, then a field oxidation process of the groove is divided into two steps, and junction terminal boron ion implantation is arranged to be carried out between the two steps of field oxidation. According to a NPN silicon bipolar microwave power transistor device manufactured by using the process technology, not only is BVcbo breakdown voltage improved by more than 50%, but also high output power can be provided, stray capacitance of a collector junction is reduced, and high-frequency performance of the device is guaranteed.
Owner:江苏博普电子科技有限责任公司
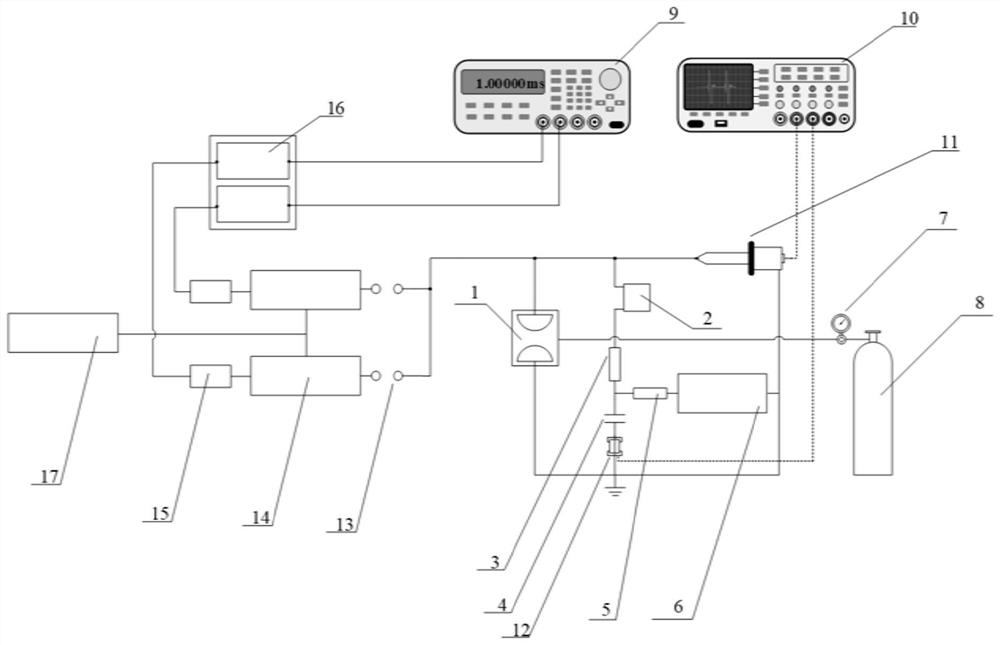
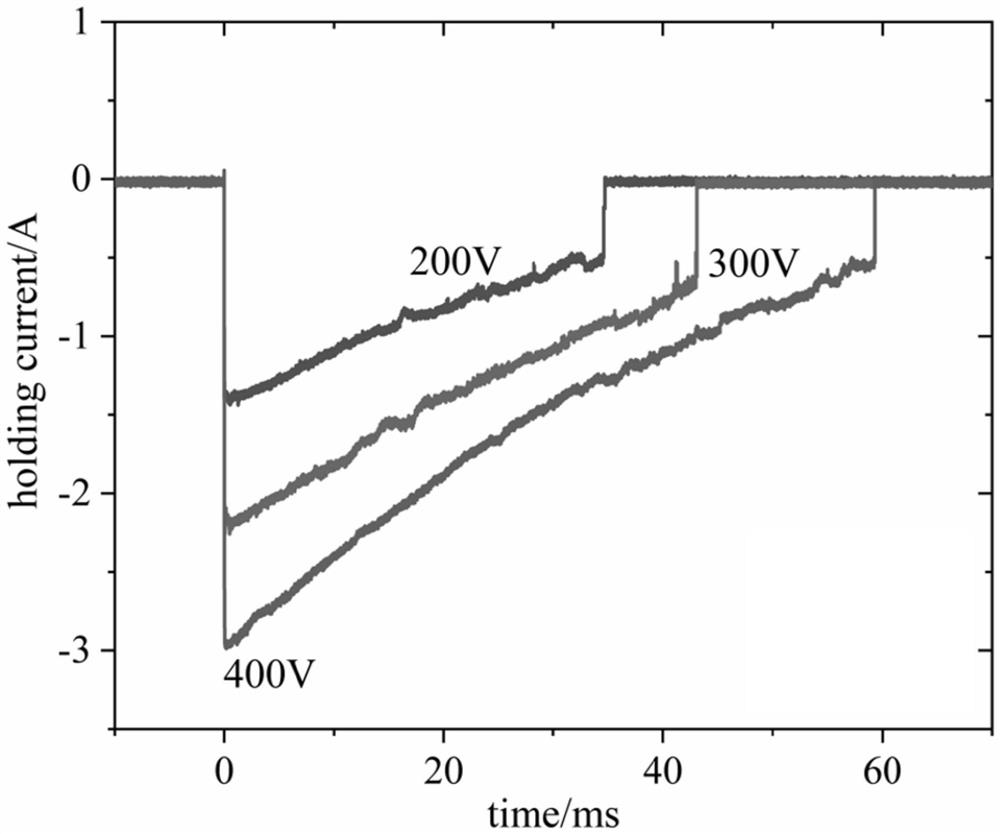
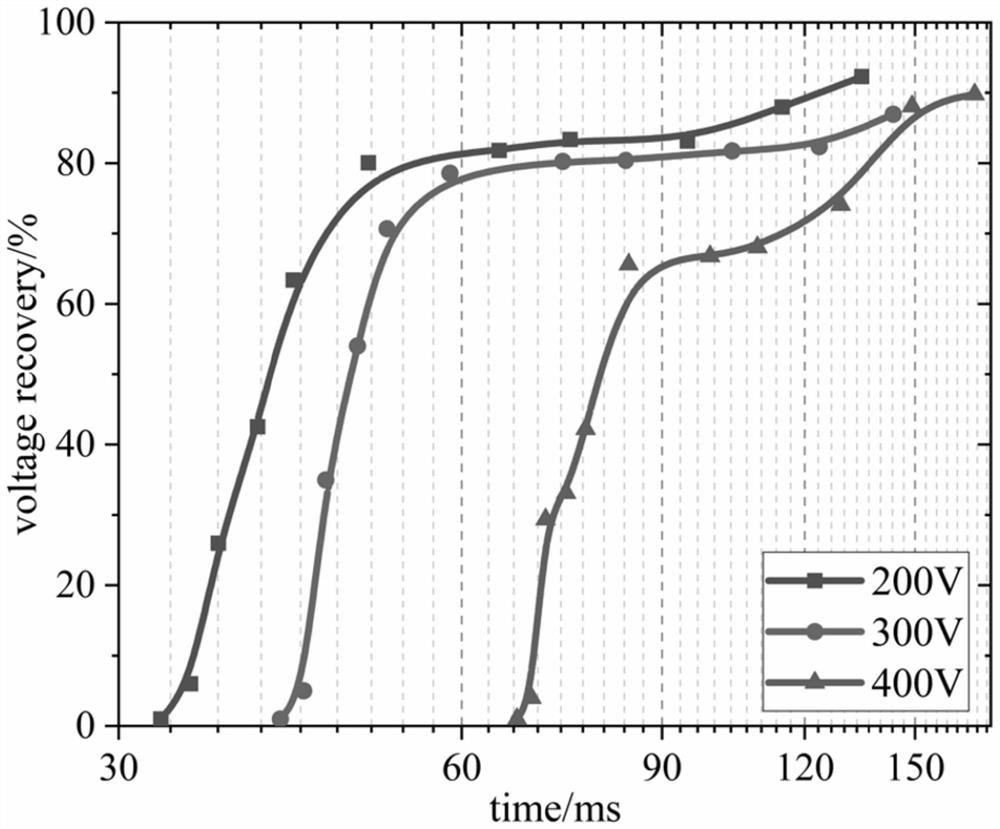
Experimental device for testing insulation recovery characteristic of gas switch
PendingCN114545221AReduce inductanceAdjustable resistanceCircuit interrupters testingCapacitanceVoltage pulse
The invention discloses a gas switch insulation recovery characteristic test experimental device, which is characterized in that an energy storage capacitor, an isolation resistor and an isolation magnetic core coil are connected in series at one end of a two-electrode gas gap, and the other electrode of the two-electrode gas gap is grounded to form a discharge follow current loop. And the signal generator and the low-voltage pulse generation circuit are used for controlling the time sequence of outputting the double nanosecond pulses. The two pulse output ends are connected to the high-voltage end of the gas gap of the two electrodes through the gap of the two isolation balls. The first nanosecond pulse enables the gas gap to be broken down, the breakdown voltage is Ub1, and electric energy in the energy storage capacitor is released through a follow current loop; the time interval of the second nanosecond pulse acting on the gas gap can be adjusted through the signal generator, the breakdown voltage of the second nanosecond pulse acting on the gas gap is Ub2, and Ub2 / Ub1 reflects the recovery degree of insulation after breakdown of the gas gap in the presence of follow current. And the gas gap insulation recovery condition under different follow current working conditions can be explored by changing the charging voltage of the isolation resistor and the energy storage capacitor.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
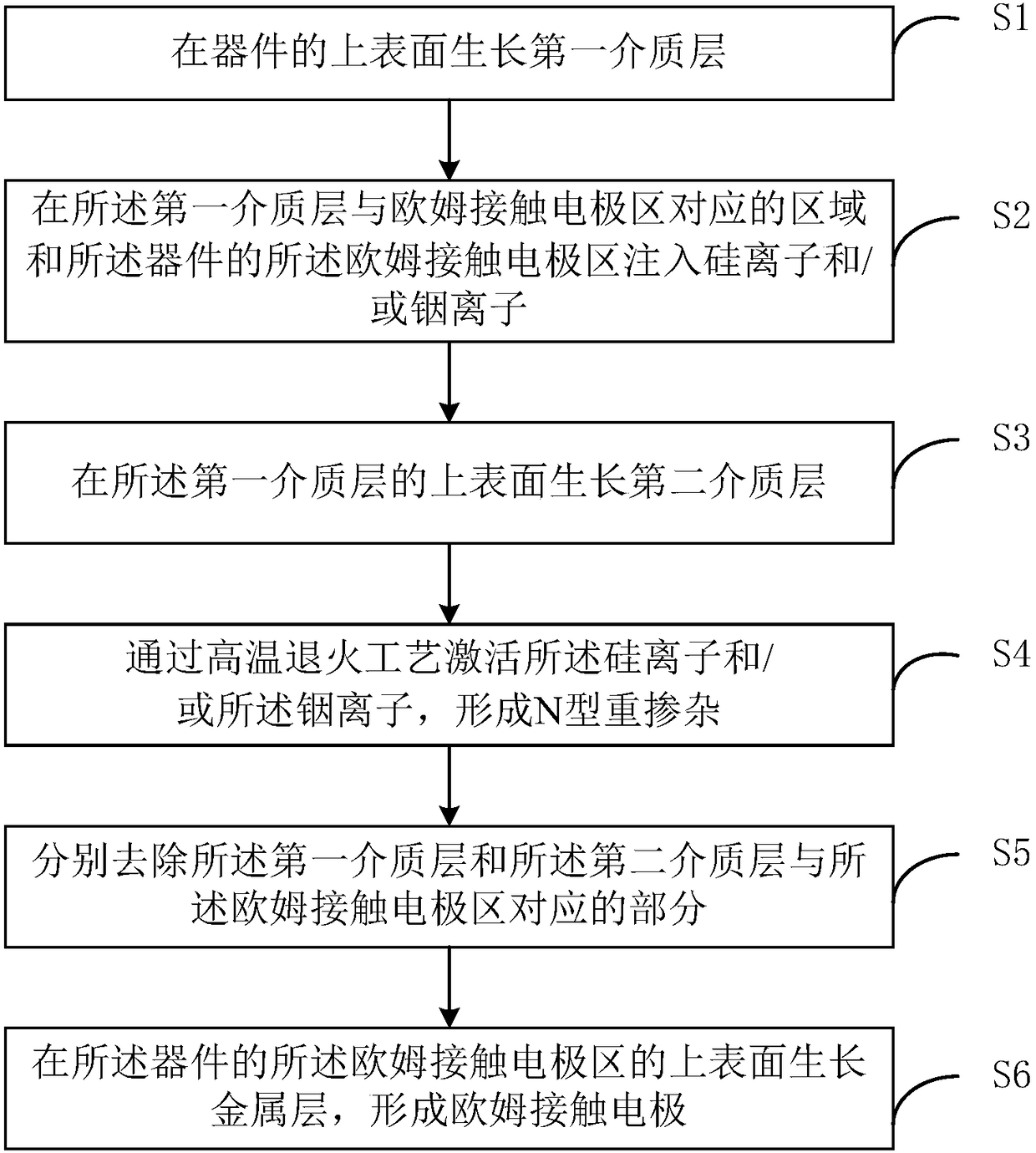
Method for preparing ohmic contact electrode of GaN-base device
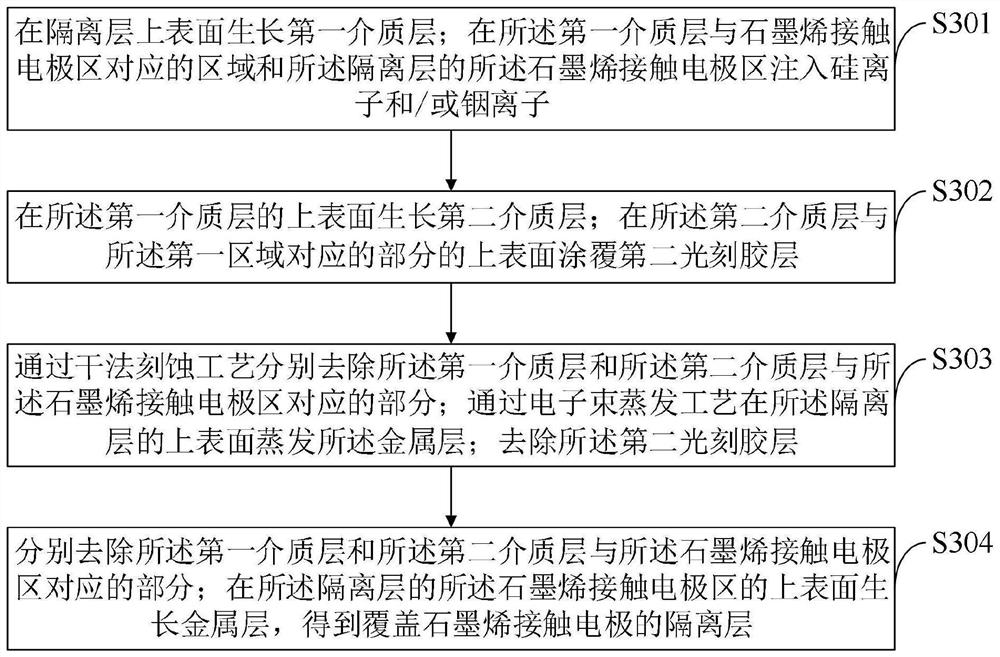
ActiveCN108597997AStable breakdown voltageQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIndiumOhmic contact
The invention is suitable for the field of semiconductors, and provides a method for preparing an ohmic contact electrode of a GaN-base device. The method comprises the following steps: growing a first dielectric layer on the upper surface of a device; injecting silicon ions and / or indium ions in a region, corresponding to an ohmic contact electrode region, of the first dielectric layer and the ohmic contact electrode region of the device; growing a second dielectric layer on the upper surface of the first dielectric layer; activating the silicon ions and / or the indium ions by a high-temperature annealing process, and forming N-type heavy doping; respectively removing the parts, corresponding to the ohmic contact electrode region, of the first dielectric layer and the second dielectric layer; growing a metal layer on the upper surface of the ohmic contact electrode region of the device, and forming the ohmic contact electrode. The prepared ohmic contact electrode can guarantee the flatsurface of the metal layer and the smooth and aligned edges, is stable in breakdown voltage of the device, is high in reliability, and is long in service life.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
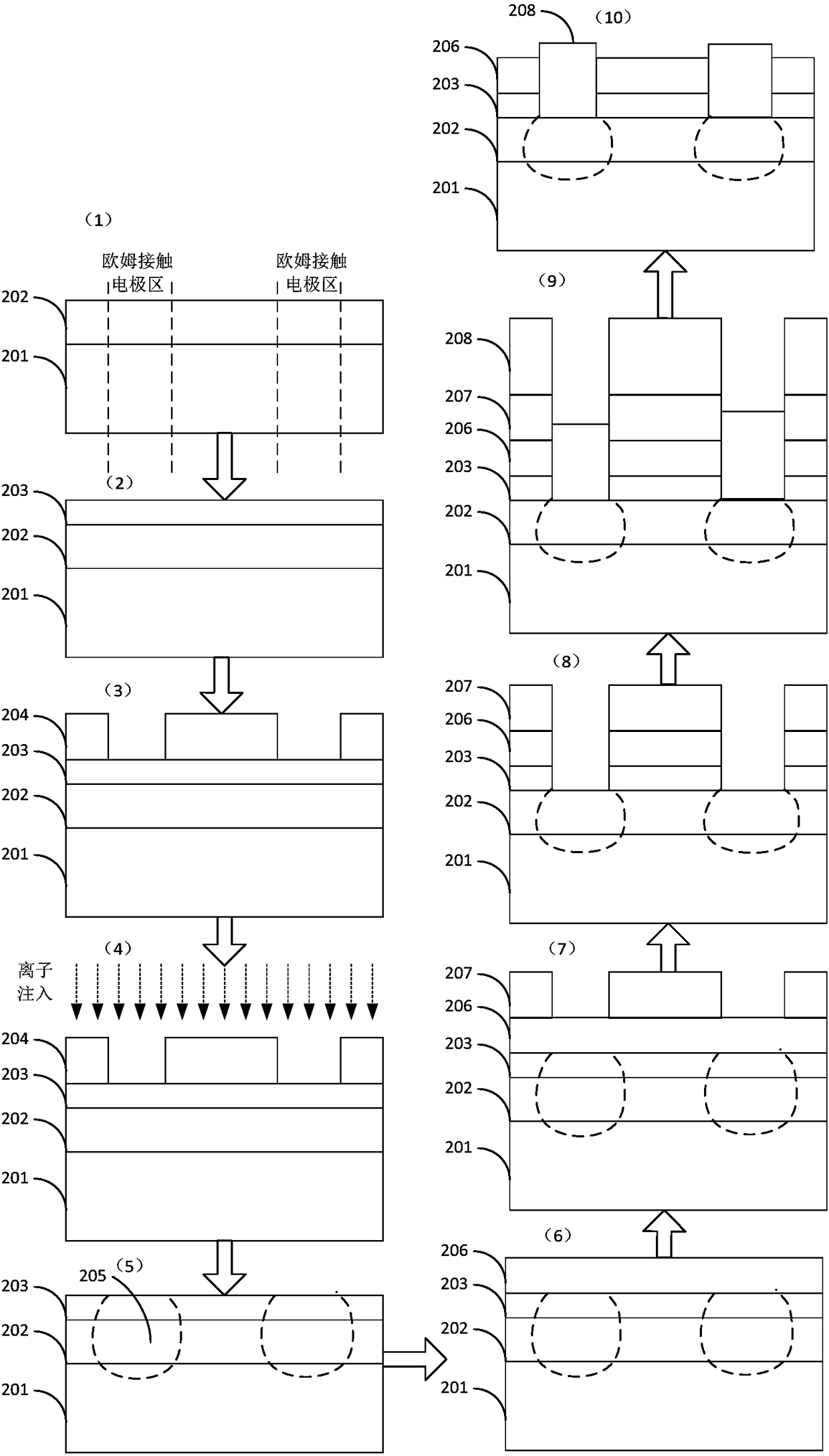
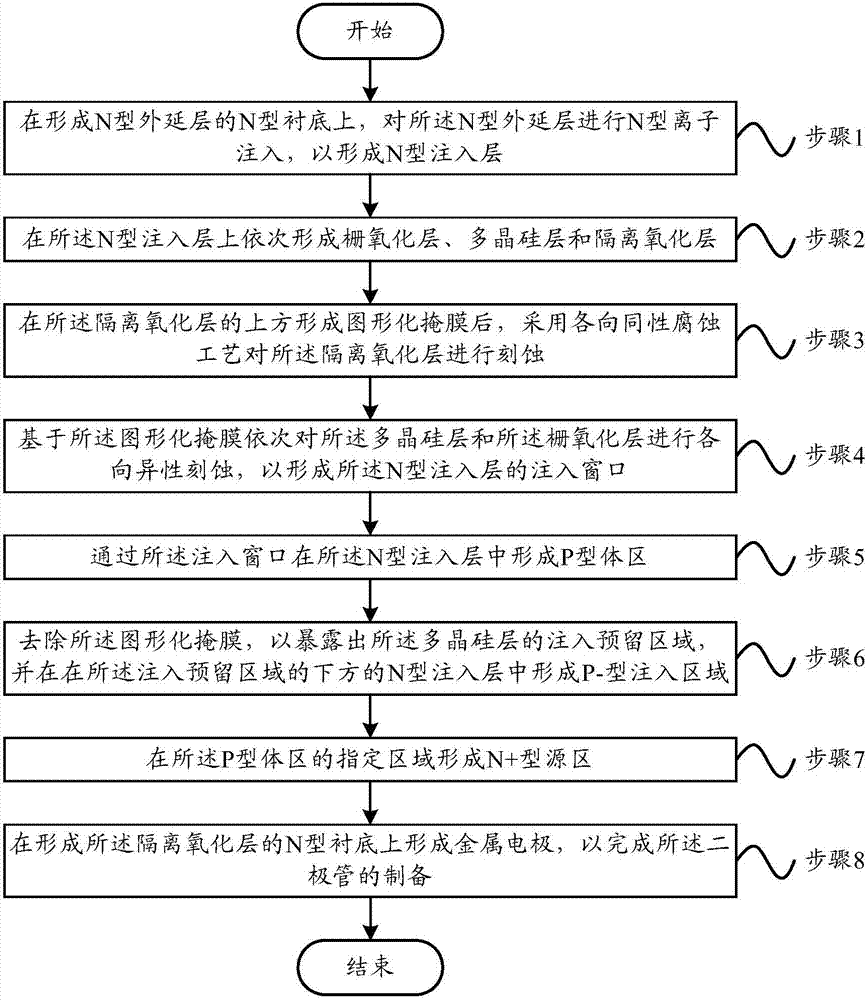
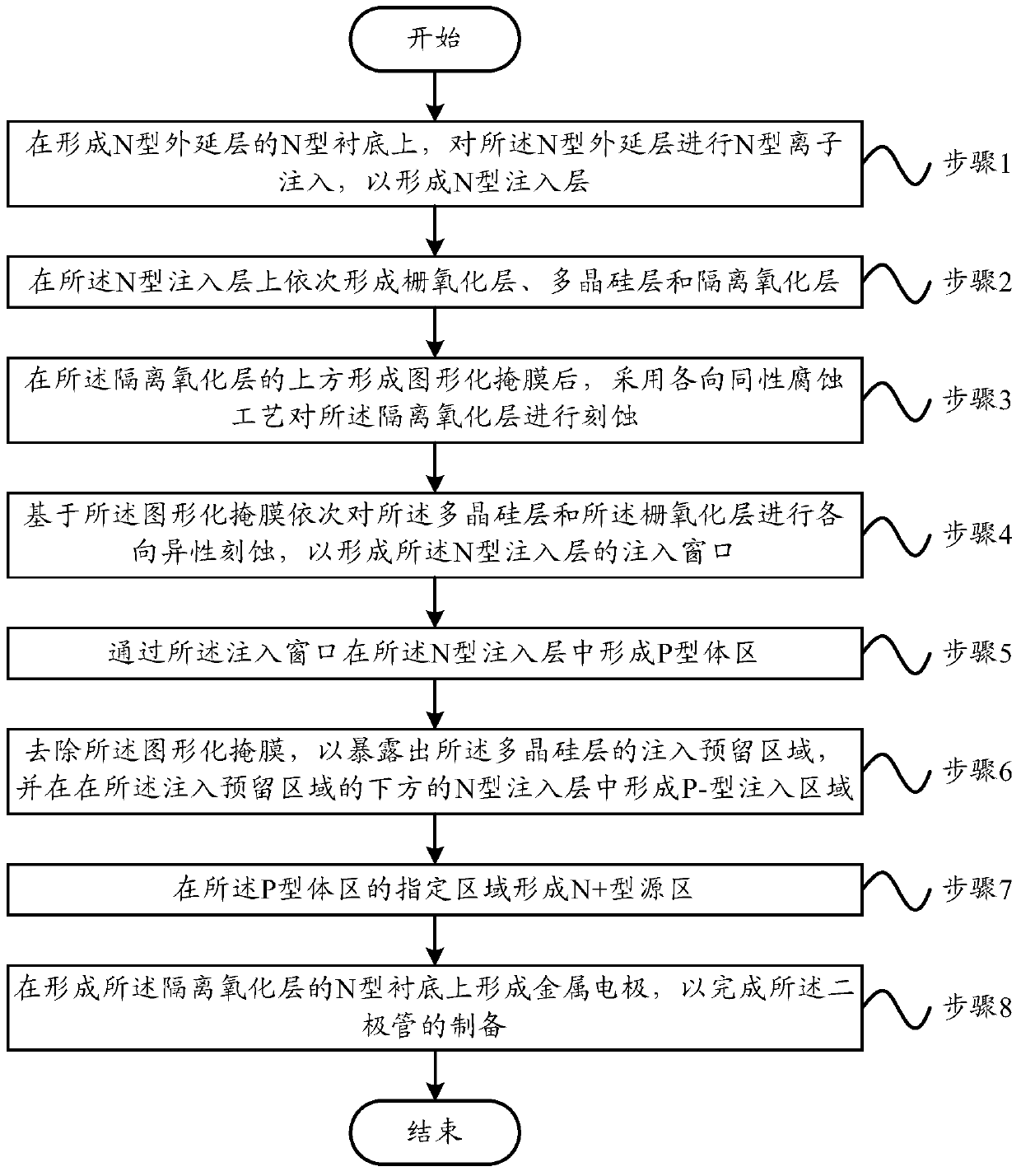
Preparation method of diode and diode
ActiveCN107346734AReduce conduction voltage dropImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower flowReverse recovery
The present invention provides a preparation method of a diode and a diode. The preparation method of the diode comprises the following steps that: N type ion implantation is performed on an N type epitaxial layer; a gate oxide layer, a polysilicon layer and an isolation oxide layer are sequentially formed on the N type implant layer; an isotropic etching process is adopted to etch the isolation oxide layer; anisotropic etching is performed on the polysilicon layer and the gate oxide layer based on a patterned mask; P type body regions are formed in the N type implantation layer through injection windows; the patterned mask is removed, so that implantation reserved regions of the polysilicon layer can be exposed, P- type implantation regions are formed in the N type implantation layer below the implantation reserved regions; N+ type source regions are formed in designated regions of the P type body regions; and a metal electrode is formed on the N type substrate of the isolation oxide layer. A diode prepared by using the preparation method of the invention has the advantages of large reverse voltage, short reverse recovery time, small reverse recovery peak current and the like.
Owner:FOUNDER MICROELECTRONICS INT
Power device with fixed interface charge field limitation ring
ActiveCN106876441AIncrease current densityImprove power densitySemiconductor devicesImpurity diffusionOxygen
The invention discloses a power device with a fixed interface charge field limitation ring. The power device comprises a field oxide layer and an active layer, wherein the field oxide layer is arranged on the active layer, at least one fixed interface charge region is arranged in the field oxide layer, and the fixed interface charge region is arranged at a lower part of the field oxide layer and is in contact with a lower surface of the field oxide layer, namely an interface surface of the field oxide layer and the active layer. By the power device, the problems of breakdown voltage drop and device failure caused by impurity diffusion in an FLR region of an existing power device can be solved, the breakdown voltage of the device is effectively improved, the electric field distribution of a surface of the active layer is improved, and the electric field distribution is more uniform.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH +1
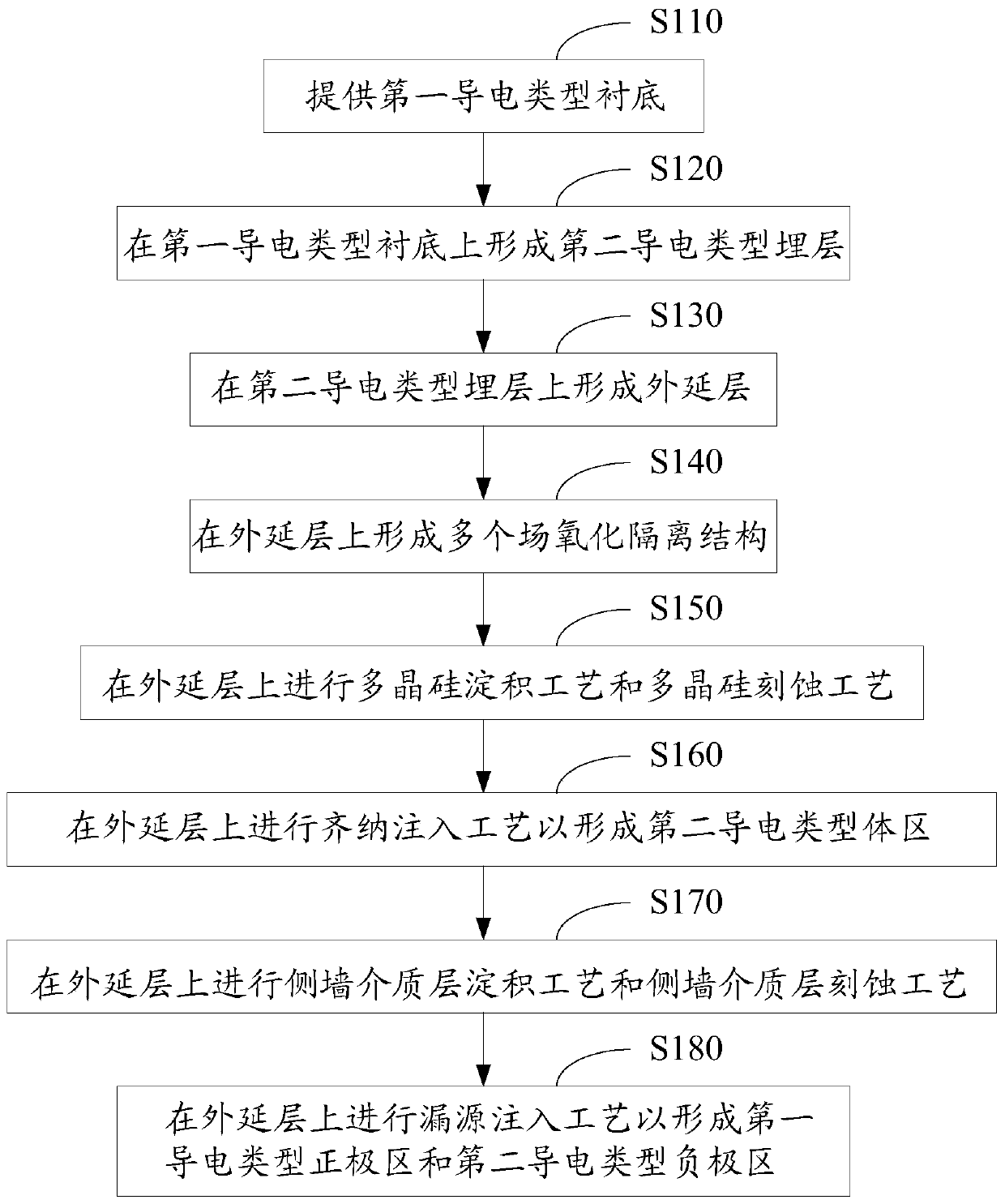
Zener diode manufacturing method based on CMOS manufacturing process
ActiveCN106033722AStable breakdown voltageAvoid uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSZener diode
The invention provides a Zener diode manufacturing method based on a CMOS manufacturing process. A polysilicon deposition process, a Zener implanting process, a sidewall dielectric layer deposition process, a sidewall dielectric layer etching process and a source / drain implanting process are successively performed. The traditional Zener implanting process is performed before the sidewall dielectric layer deposition process, the sidewall dielectric layer etching process and the source / drain implanting process, thereby preventing substrate damage by the sidewall dielectric layer etching process and substrate damage in formation of amorphous structures which may caused by the source / drain implanting process, so that concentration distribution uniformity of impurities which are implanted into the Zener diode is improved, thereby obtaining a stable breakdown voltage in breakdown of the Zener diode, preventing defects of large leakage current and low uniformity of the leakage current before breakdown of the Zener diode, and improving market competitiveness of the product.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
CMOS-based planar type silicon avalanche photo diode using silicon epitaxial layer and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7994553B2Good effectReduce harmSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSP–n junction
A complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS)-based planar type avalanche photo diode (APD) using a silicon epitaxial layer and a method of manufacturing the APD, the photo diode including: a substrate; a well layer of a first conductivity type formed in the substrate; an avalanche embedded junction formed in the well layer of the first conductivity type by low energy ion implantation; the silicon epitaxial layer formed in the avalanche embedded junction; a doping area of a second conductivity type opposite to the first conductive type, formed from a portion of a surface of the well layer of the first conductivity type in the avalanche embedded junction and forming a p-n junction; positive and negative electrodes formed on the doping area of the second conductivity type and the well layer of the first conductivity type separated from the doping area of the second conductivity type, respectively; and an oxide layer formed on an overall surface excluding a window where the positive and negative electrodes are formed.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Voltage-resistant terminal ring structure and power device
ActiveCN106847878AImprove reliabilityWeaken the effect of reverse breakdown voltageSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsComputer terminal
The invention provides a voltage-resistant terminal ring structure and a power device. The voltage-resistant terminal ring structure comprises a substrate, multiple field rings, multiple field plates, dielectric films and at least one additional ion injection area; the field rings are arranged on the portion, close to a second surface, in the substrate at intervals, the conduction type of the field rings is opposite to that of the substrate, the field rings comprise at least one voltage-resistant ring and two equipotential rings, and the two equipotential rings are sequentially arranged in the direction far away from the voltage-resistant rings; the field plates and the field rings are arranged in a one-to-one corresponding mode, parallel segments corresponding to the voltage-resistant rings extend in the direction close to a third surface, and parallel segments corresponding to the equipotential rings extend in the direction far away from the third surface; the dielectric films are arranged on a second part surface and part of a first part surface; the additional ion injection areas are arranged on the portions, between the adjacent voltage-resistant rings and equipotential rings, of the substrate, and the conduction type of the additional ion injection areas is opposite to that of the substrate. The reverse breakdown voltage of the power device with the structure is stable.
Owner:LEADING ENERGY BEIJING ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Semiconductor structure and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140175560A1Stable breakdown voltageHigh gate voltage stressTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureCondensed matter physics
A semiconductor structure and a method for manufacturing the same are provided. The semiconductor structure comprises a first doped region, a second doped region, and a gate structure. The first doped region has a first type conductivity. The second doped region is formed in the first doped region and has a second type conductivity opposite to the first type conductivity. The gate structure is formed on the first doped region and the second doped region. The gate structure comprises a first gate portion and a second gate portion, which are separated from each other by a gap.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
4h-sic metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor with stepped buffer layer structure
ActiveCN104393047BDrain current increasesIncrease currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTwo stepSemi insulating
The invention discloses a 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor with a step buffer layer structure. The 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor comprises a 4H-SiC semi-insulating substrate, a P-type buffer layer and an N-type channel layer from the bottom to the top. The two sides of the N-type channel layer are respectively provided with a source electrode cap layer and a drain electrode cap layer. The surface of the source electrode cap layer and the drain electrode cap layer is respectively provided with a source electrode and a drain electrode. A gate electrode is formed on one side which is arranged above the N-type channel layer and close to the source electrode cap layer. A concave gate source drift region is formed between the gate electrode and the source electrode cap layer. A concave gate drain drift region is formed between the gate electrode and the drain electrode cap layer. The position, which is arranged on the upper end surface of the P-type buffer layer and close to the source electrode cap layer, is provided with a groove. One side, which is arranged in the groove and close to the drain electrode cap layer, is provided with two steps. The 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor with the step buffer layer structure has advantages of being stable in breakdown voltage and high in output drain electrode current.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A method of forming a semiconductor device
ActiveCN104681438BStable breakdown voltageStable on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceMetal electrodes
The invention discloses a forming method of a semiconductor device. The method comprises the following steps of 1) etching a deep groove in one side of a semiconductor silicon substrate; 2) performing injection and drive-in on the bottom of the groove; 3) filling the inner part of the groove with a silicon epitaxial layer and leveling the silicon epitaxial layer; and forming a base region, a source region, a grid, a dielectric layer and a front metal electrode; 4) thinning the other side of the semiconductor silicon substrate, and performing ion injection, laser annealing and back metal electrode formation on the other side. By the forming method disclosed by the invention, the breakdown voltage and the on-resistance of the semiconductor device are stabilized through adjusting the silicon epitaxial doping concentration, the groove depth and wafer thickness. By the method disclosed by the invention, the manufacturing cost of superjunction devices can be reduced, the production efficiency can be improved, and the on-resistance of the devices can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
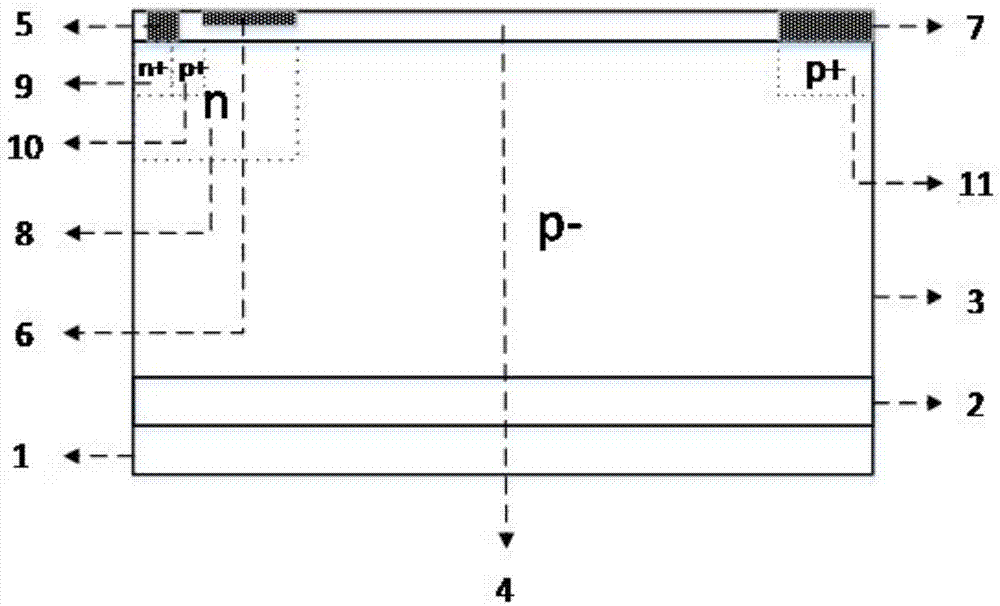
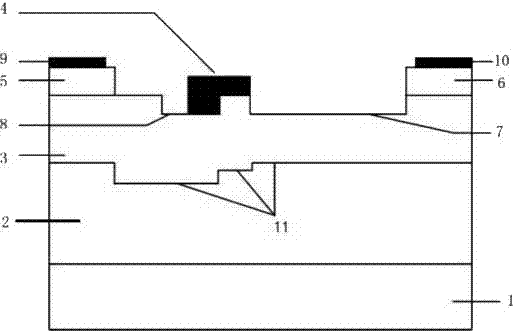
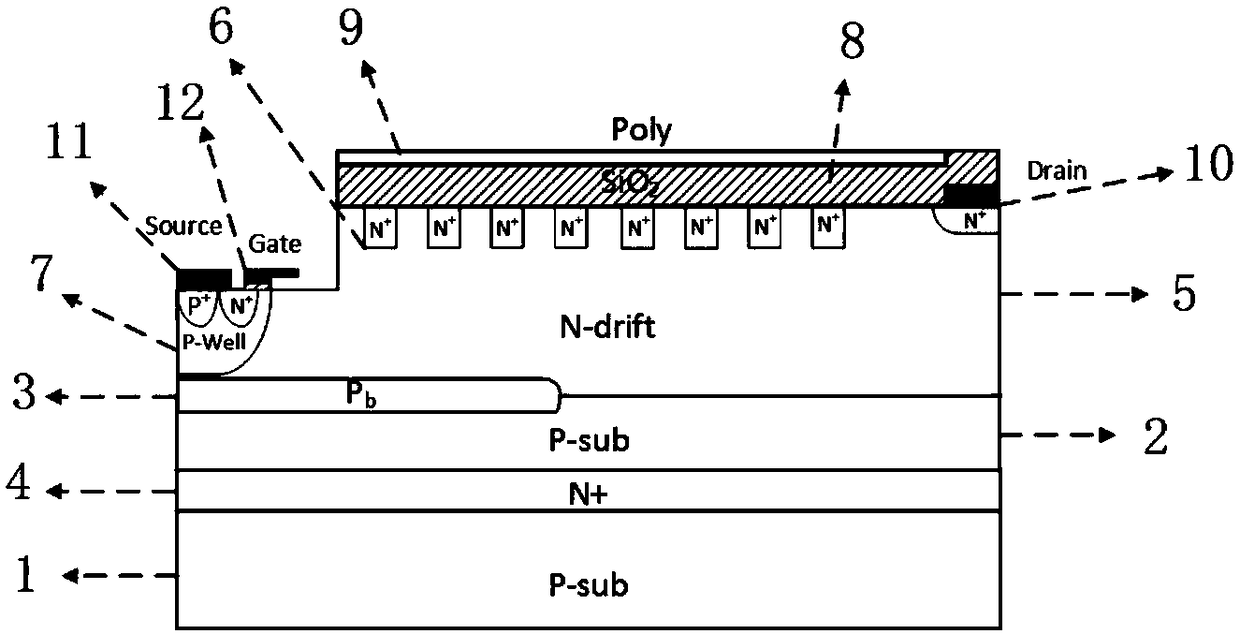
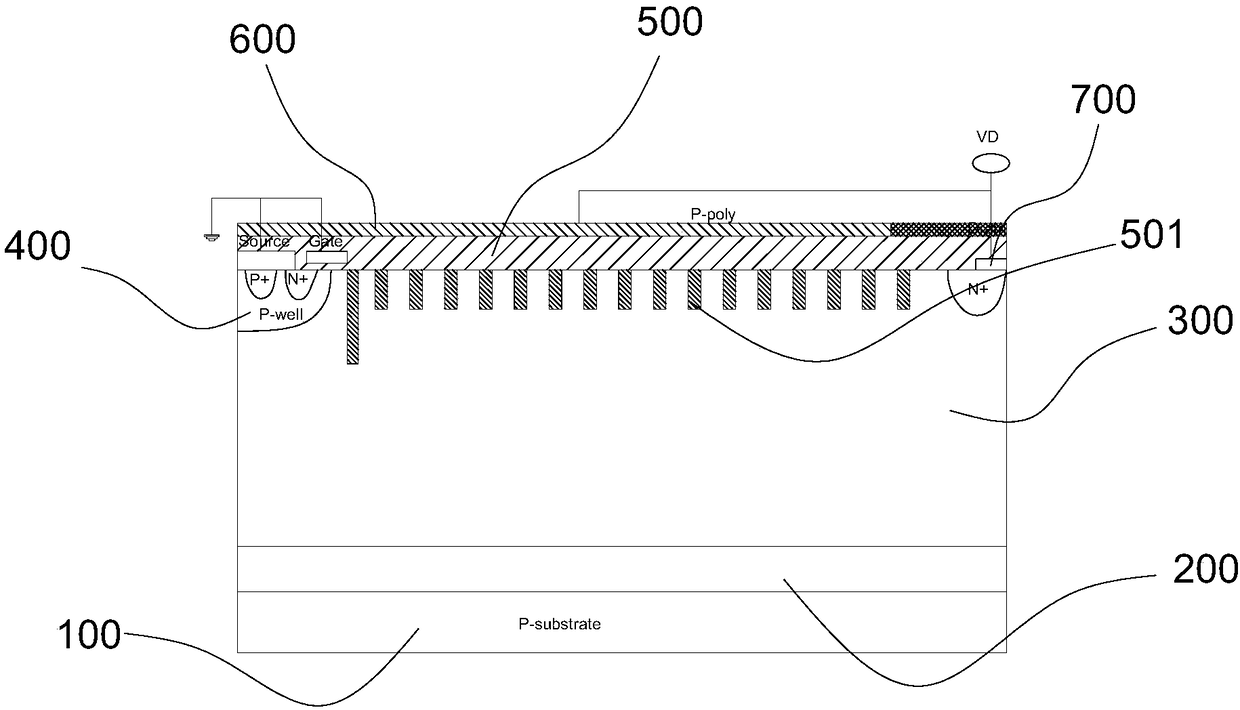
Power device with surface charge region structure
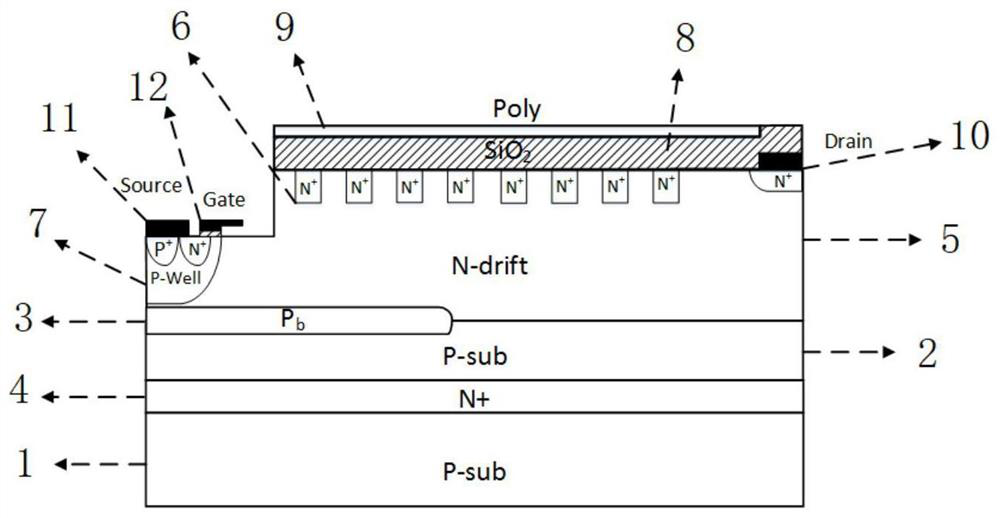
The invention provides a power device with a surface charge region structure, and the power device comprises a P substrate I (1), a floating equipotential layer (4), a P substrate II (2) and a drift region (5), wherein the P substrate I (1), the floating equipotential layer (4), the P substrate II (2) and the drift region (5) are arranged in order from the bottom to the top. The drift region (5) is provided with an N+ drain region, a drain electrode (10), a gate electrode (12), a source electrode (11), an N+ contact region, a P well (7), and a P+ source region. A series of laterally and equidistantly distributed N+ charge regions (6) are disposed at the top of the drift region (5) and within the drift region to form the surface charge region. Because the surface of the drift region is provided with a surface charge region structure of a series of equidistantly distributed N+ charge regions, the surface charge region generates interface charges, and the electric field in the charge region is improved, and the lateral withstand voltage of the device is improved. The interface charge improves the longitudinal electric field and longitudinal withstand voltage of a buried layer at the same time, reduces the electric field nearby the drain electrode and prevents the surface of the device from being broken down too early. Because the power device employs the surface charge region structure of equidistantly distributed N+ charge regions, the power device is simple and feasible in technology, is better in technological tolerance, and is compatible with the conventional CMOS technology.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
A flat terminal passivation method and semiconductor power device
ActiveCN107768260BImprove sealingImprove mechanical propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesImpurity ionsDielectric layer
The invention provides a planar terminal passivation method and a semiconductor power device. The method includes sequentially depositing a dielectric layer, a glass passivation layer and a polyimide protective layer on the semiconductor power device to form a multilayer composite passivation layer; the semiconductor power device is manufactured by the above-mentioned method. Compared with the prior art, the present invention provides a planar terminal passivation method and semiconductor power device, which can improve the sealing performance of the semiconductor power device by adopting a multi-layer composite passivation layer, prevent harmful impurity ions from diffusing to the substrate surface, and at the same time The use of a glass passivation layer can reduce the requirements on the thickness and expansion coefficient of the polyimide protective layer, so that the semiconductor power device has high mechanical properties and is not easy to fall off when it works in a high temperature environment.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY INTERCONNECTION RES INST CO LTD +2
Manufacturing method of zener tube based on cmos manufacturing process
ActiveCN106033722BStable breakdown voltageAvoid uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSZener diode
The invention provides a Zener diode manufacturing method based on a CMOS manufacturing process. A polysilicon deposition process, a Zener implanting process, a sidewall dielectric layer deposition process, a sidewall dielectric layer etching process and a source / drain implanting process are successively performed. The traditional Zener implanting process is performed before the sidewall dielectric layer deposition process, the sidewall dielectric layer etching process and the source / drain implanting process, thereby preventing substrate damage by the sidewall dielectric layer etching process and substrate damage in formation of amorphous structures which may caused by the source / drain implanting process, so that concentration distribution uniformity of impurities which are implanted into the Zener diode is improved, thereby obtaining a stable breakdown voltage in breakdown of the Zener diode, preventing defects of large leakage current and low uniformity of the leakage current before breakdown of the Zener diode, and improving market competitiveness of the product.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
Diode preparation method and diode
ActiveCN107346734BReduce conduction voltage dropImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPeak currentPeak value
Owner:FOUNDER MICROELECTRONICS INT
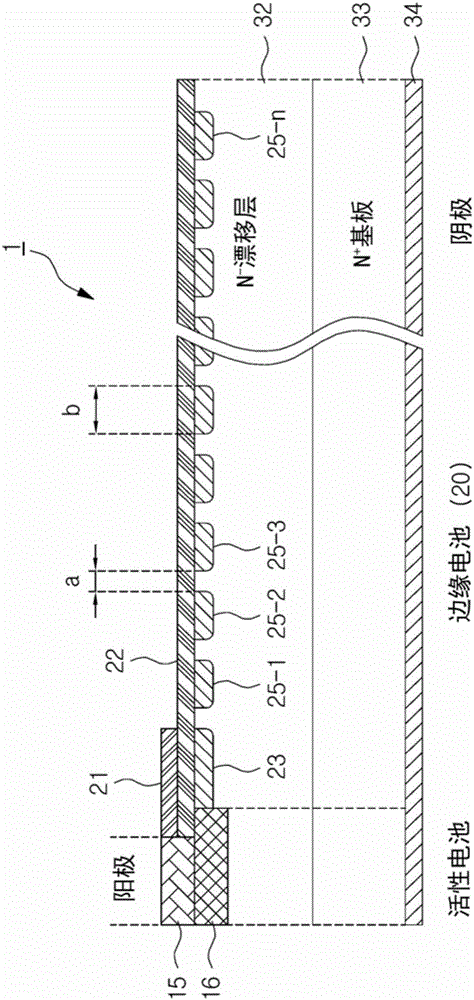
Semiconductor device having edge cell of internal pressure stabilization structure
InactiveCN106449735AStable withstand voltageStable breakdown voltageSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceInternal pressure
According to an embodiment of the present invention, in a power semiconductor device comprising an active battery and an edge cell formed adjacent to the active battery for stabilizing the electric field,the active battery comprising: an N + substrate formed on an upper side of the second electrode; an N-drift layer formed on the upper side of the N + substrate; a P-base region formed on an upper portion of the N-drift layer; and a first electrode formed on an upper side of the P-base region for receiving a signal; the edge battery comprising: a field plate extending from the first electrode as a conductor; a buffer ring formed underneath the field plate by injecting the first impurity ions above the N-Drift layer extending from the active battery; a plurality of field loops having a predetermined horizontal gap and width from the buffer ring formed by injecting the first impurity ions over the N-drift layer; and a field effect oxide film formed between the field plate and the buffer ring and covering a plurality of field loops.
Owner:美普森半导体公司(股)
Semiconductor device
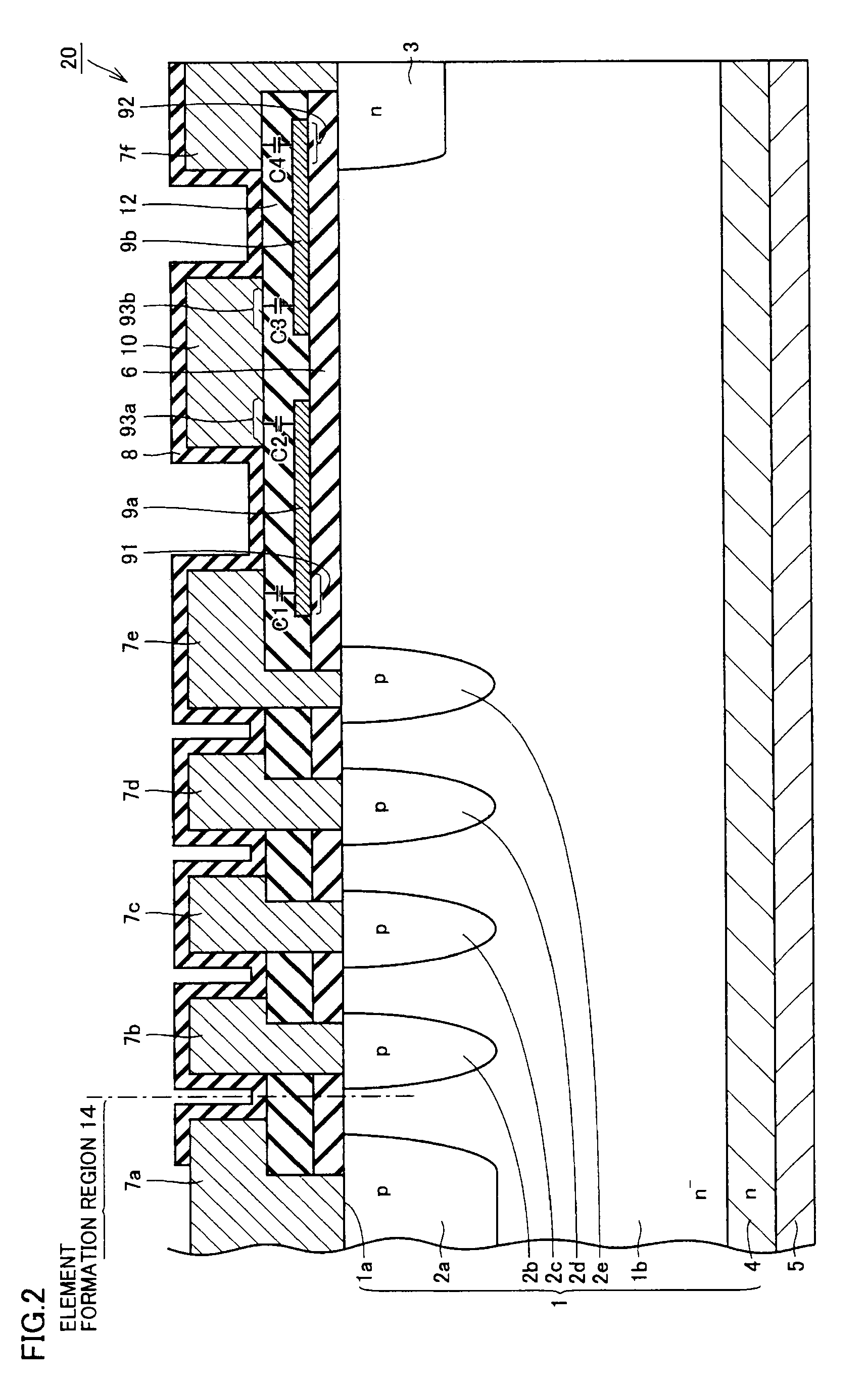
ActiveUS9236436B2Stable breakdown voltageAvoid concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceChannel-stopper
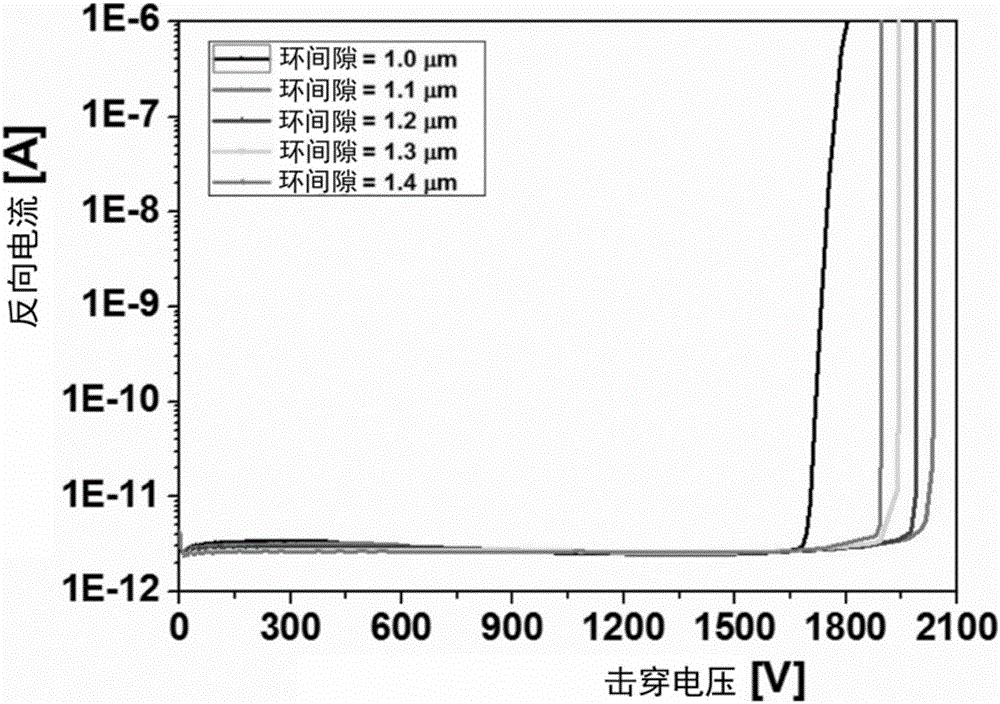
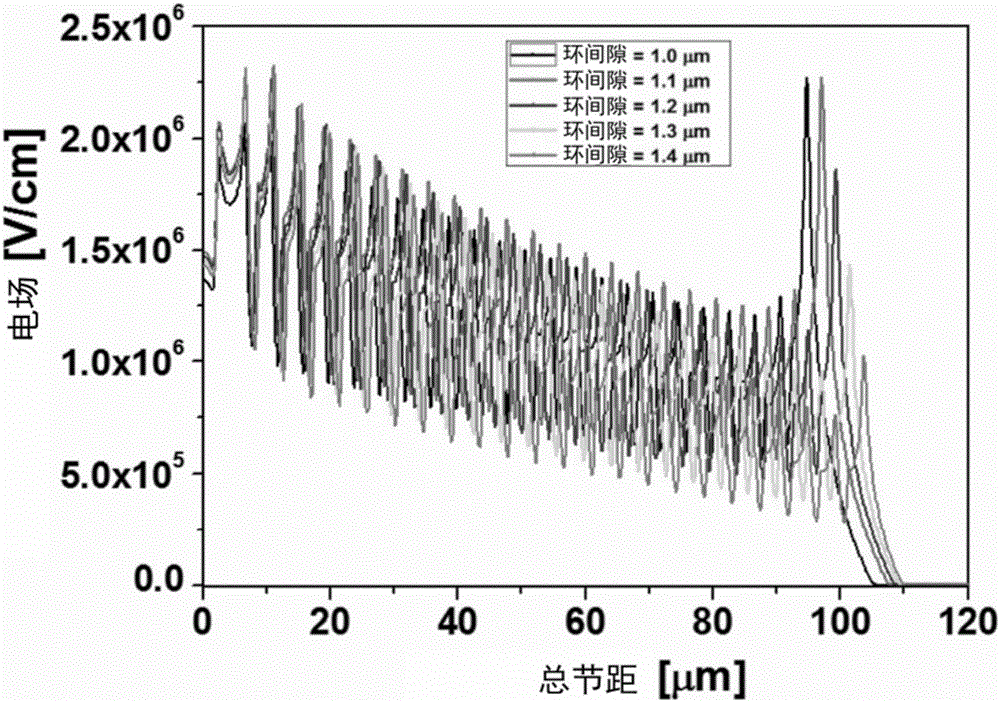
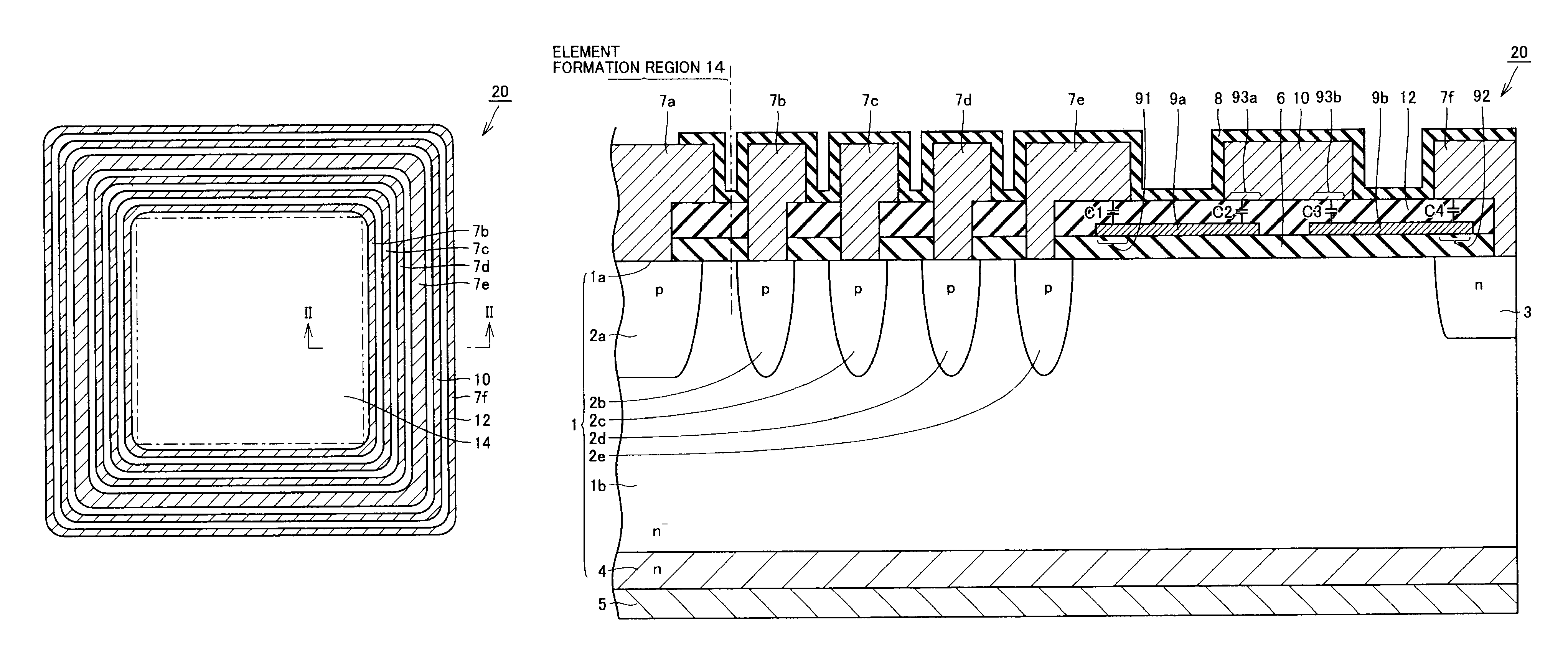
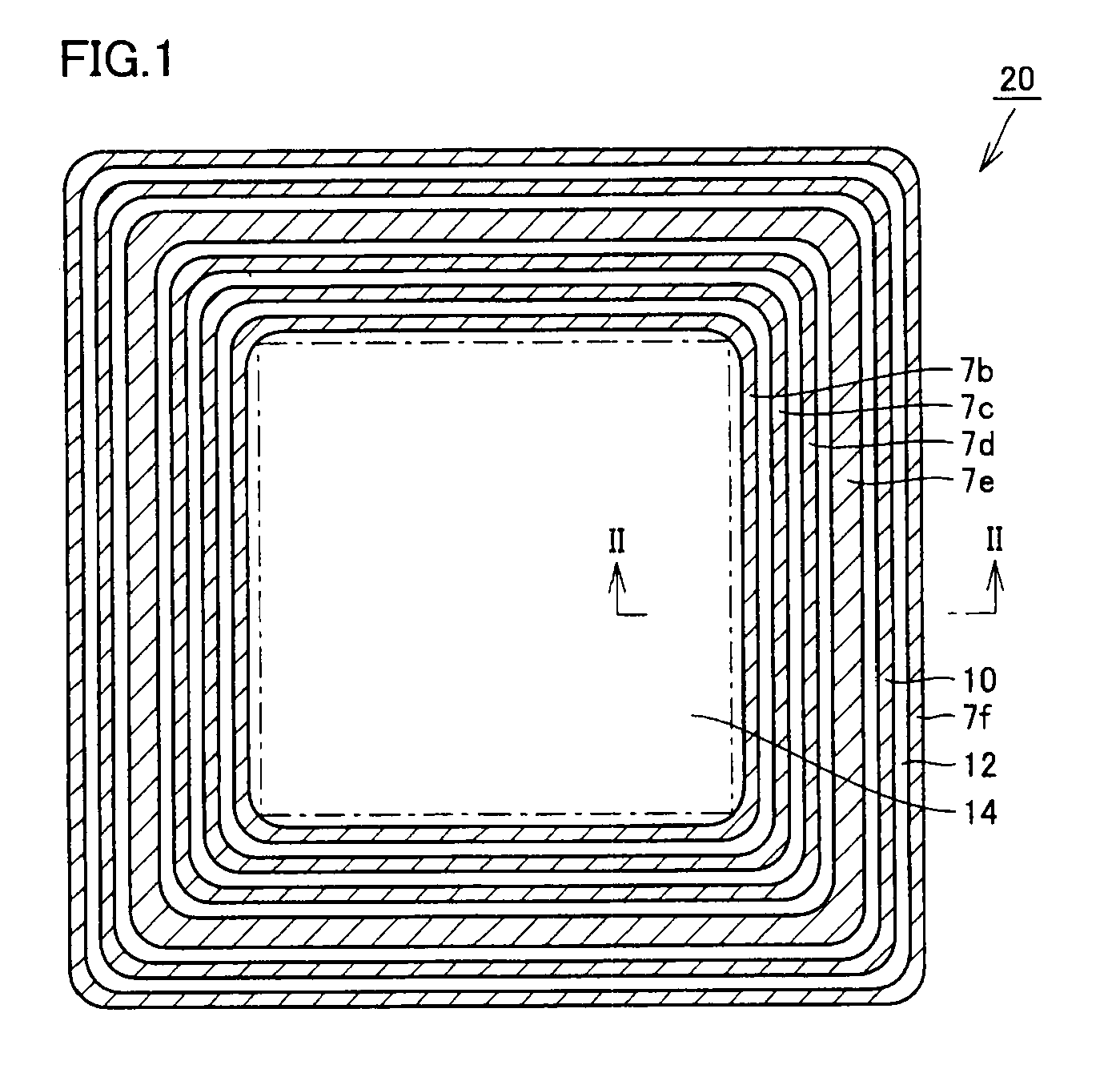
A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor substrate having a main surface having an element formation region, a guard ring, a guard ring electrode, a channel stopper region, a channel stopper electrode, and a field plate disposed over and insulated from the semiconductor substrate. The field plate includes a first portion located between the main surface of the semiconductor substrate and the guard ring electrode, and a second portion located between the main surface of the semiconductor substrate and the channel stopper electrode. The first portion has a portion overlapping with the guard ring electrode when viewed in a plan view. The second portion has a portion overlapping with the channel stopper electrode when viewed in the plan view. In this way, a semiconductor device allowing for stabilized breakdown voltage can be obtained.
Owner:ARIGNA TECH LTD
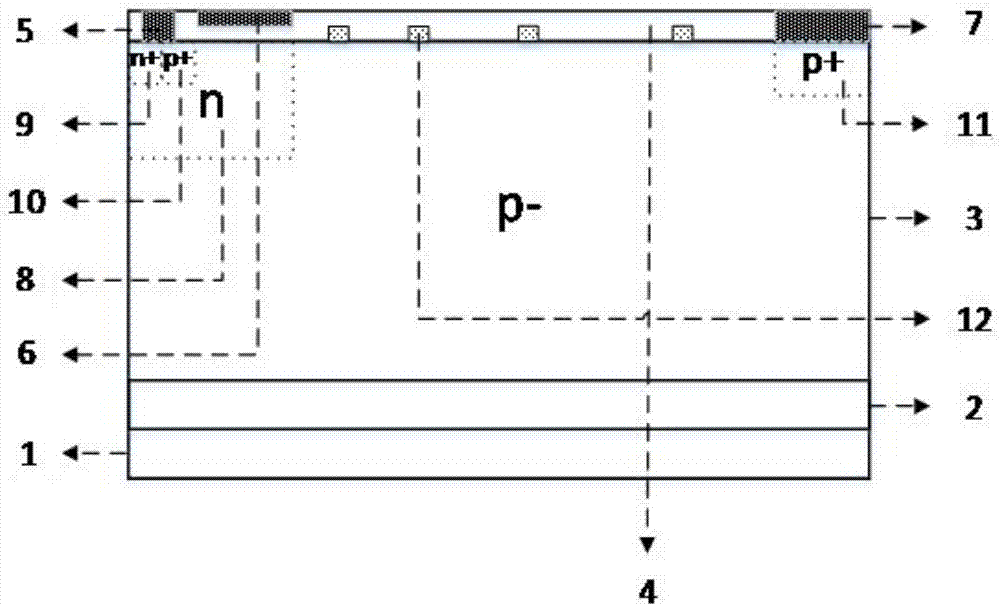
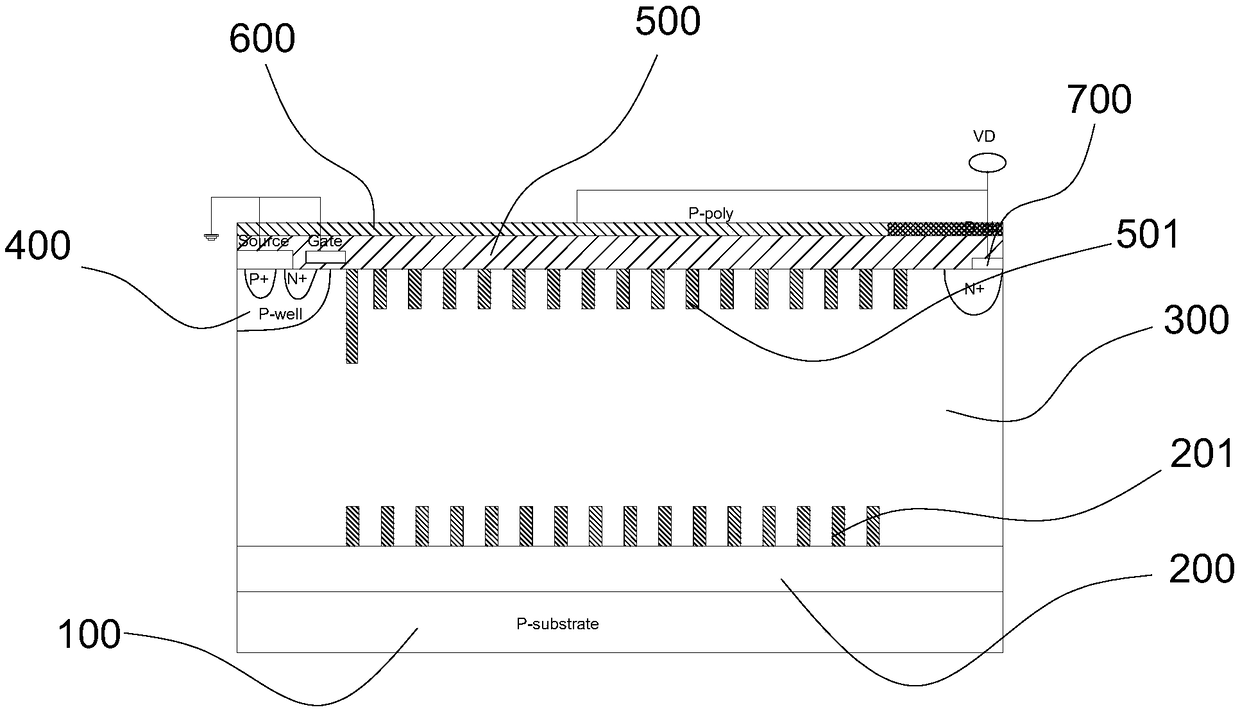
A power device with a surface charge region structure
ActiveCN108550628BImprove breakdown voltageStable breakdown voltageTransistorEngineeringElectrode Contact
The invention provides a power device with a surface charge region structure, comprising a P substrate I (1), a floating equipotential layer (4), a P substrate II (2) and a drift region (5) arranged in sequence from bottom to top ); the drift region (5) is provided with an N+ drain region, a drain electrode (10), a gate electrode (12), a source electrode (11), an N+ contact region, a P well (7) and a P+ source region; the A series of N+ charge regions (6) distributed laterally and equidistantly on the top of the drift region (5) and located in the drift region form a surface charge region. The present invention sets a series of equidistant N on the surface of the drift region + The surface charge region structure of the charge region, the surface charge region generates interface charges, which enhances the electric field in the charge region and improves the lateral withstand voltage of the device; the interface charge simultaneously enhances the vertical electric field and vertical withstand voltage of the buried layer, reduces the electric field near the drain, and prevents the device from The surface breaks down prematurely; due to the use of the surface charge region structure with equal spacing N+, the process is simple and feasible, the process tolerance is good, and it is compatible with the conventional CMOS process.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
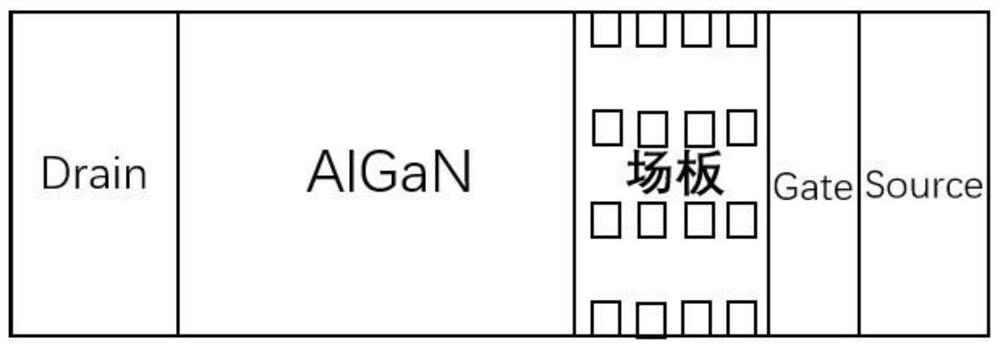
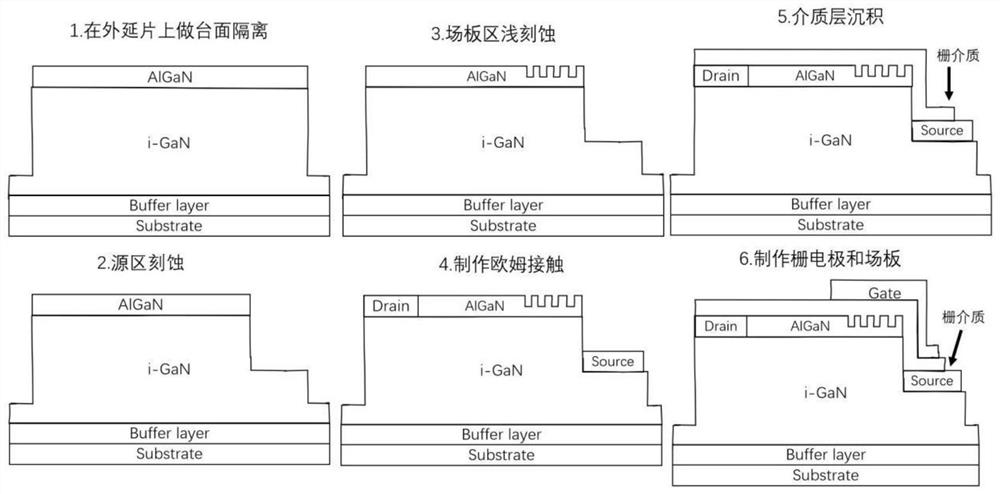
A normally-off hemt device with a honeycomb groove barrier layer structure under a field plate and its preparation method
ActiveCN111081763BImprove pressure resistanceLow on-state on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricDevice material
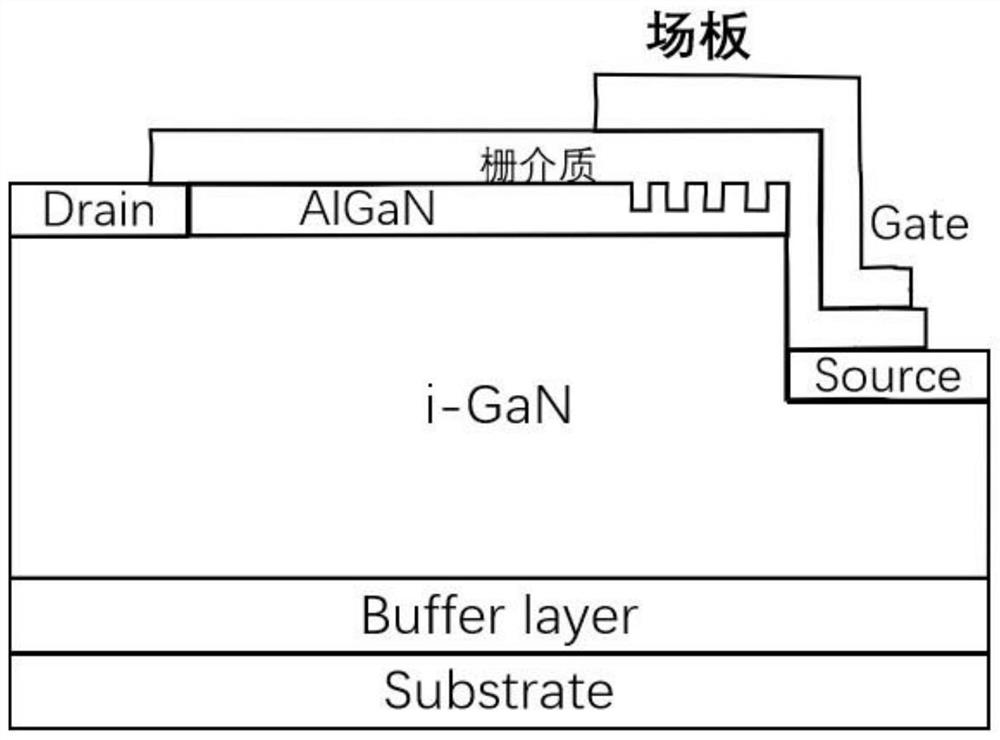
A normally-off HEMT device with a honeycomb groove barrier layer structure under a field plate and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of semiconductor devices. Technical solution: sequentially grow a buffer layer, an i-GaN layer, an insertion layer, a barrier layer, and a gate dielectric layer on a semiconductor substrate, where a number of honeycomb grooves are etched in a local area of the barrier layer, and the i-GaN layer One side is etched into a step layer, a source electrode is set on the step layer, a drain electrode is set on the other side of the i-GaN layer, a gate dielectric layer is set above the barrier layer, and one end of the gate dielectric layer is connected to the The drain electrode is contacted and connected, the other end covers and grows into the honeycomb groove, and extends to the source electrode, and a gate electrode is arranged on the gate dielectric layer and in the corresponding area of the honeycomb groove, and the gate electrode extending toward the source electrode. Beneficial effects: the invention can realize stable, large threshold voltage and normally-off operation with low on-resistance of the HEMT device, while effectively reducing the off-state leakage of the device and improving the breakdown voltage of the device.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Insulating paint for enameled wire and using method thereof
The invention discloses an insulating varnish for an enameled wire and a using method thereof. The insulating varnish used in the present invention is 225 polyesterimide insulating varnish and 1766 polyamideimide insulating varnish, both of which have a temperature resistance of 200°C. It not only ensures that the product has a higher bonding strength but also ensures a higher temperature resistance index of the product. After mixing with a matching solvent to achieve a suitable viscosity, after coating, the enameled wire produced has been tested and has good adhesion. After stretching 20% (national standard 15%), the insulating layer loses adhesion by no more than 1b. The breakdown voltage is stable, and the breakdown voltage can be stabilized at 4000-5500V.
Owner:济南宝世达实业发展有限公司
Power device having interface charge trench high-voltage interconnection structure
ActiveCN108231870AStable breakdown voltageImprove pressure resistanceSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceInterconnection
The present invention discloses a power device having an interface charge trench high-voltage interconnection structure capable of generating interface charges, enhancing a surface transverse electricfield and improving a surface horizontal withstand voltage. The power device comprises a drift region, a buried layer 1 and a substrate which are arranged from top to bottom in order; a buried layer2 is arranged above the drift region, and a surface structure is arranged above the buried layer 2; and the buried layer 2 is provided with medium grooves 2 extending into the drift region, and the medium grooves 2 are uniformly distributed in a transverse direction. The breakdown voltage of the power device provided by the invention can reach 427V, a traditional groove-gate structure breakdown voltage is 258V, and the breakdown voltage is increased by 65.5%. The power device is uniform in equipotential line distribution, a charge shielding effect allows the surface high voltage to reduce theeffect on the drift region, and therefore, the concentration of the drift region is greatly improved, the resistance is reduced, and the breakdown voltage is increased.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com