Patents
Literature
270results about How to "Suppress scatter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
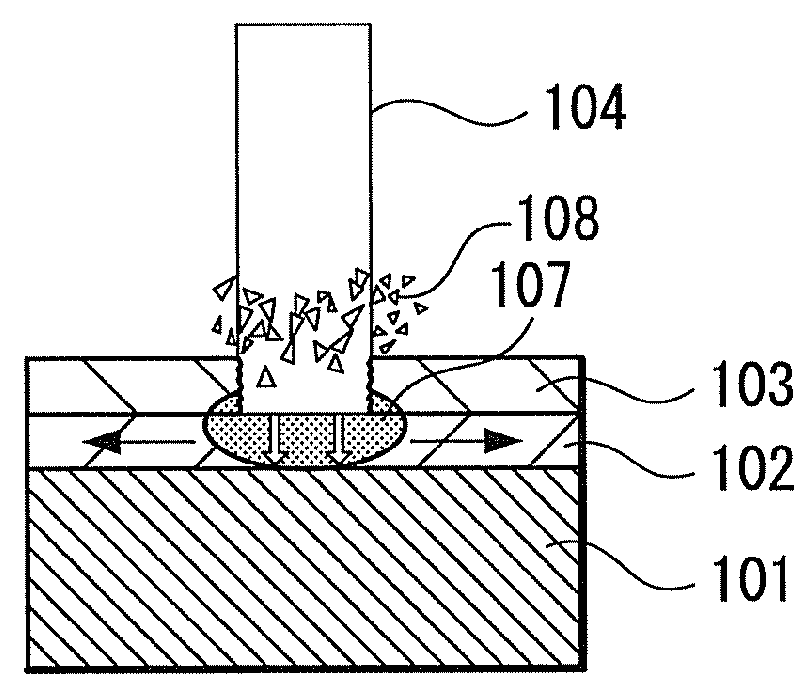
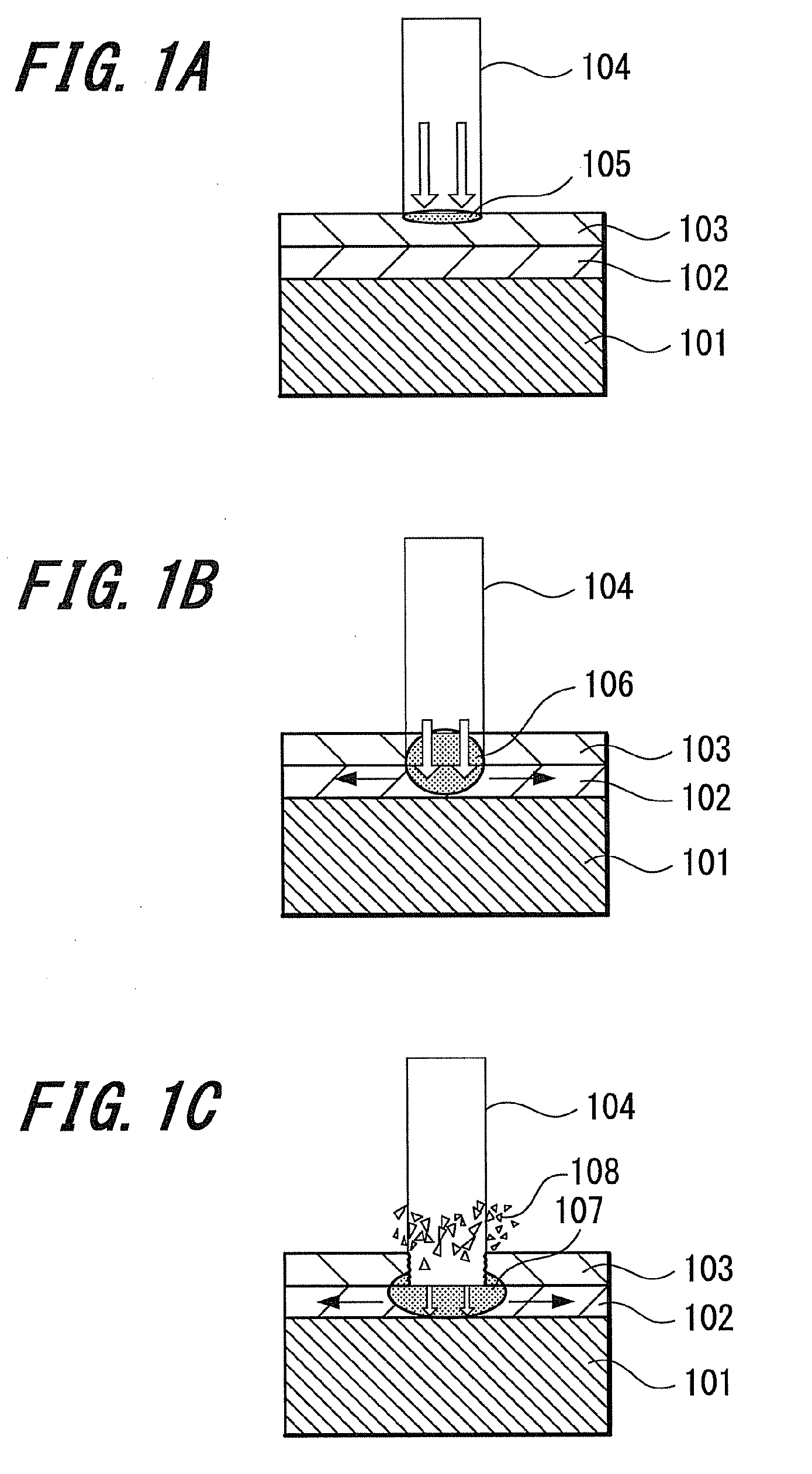
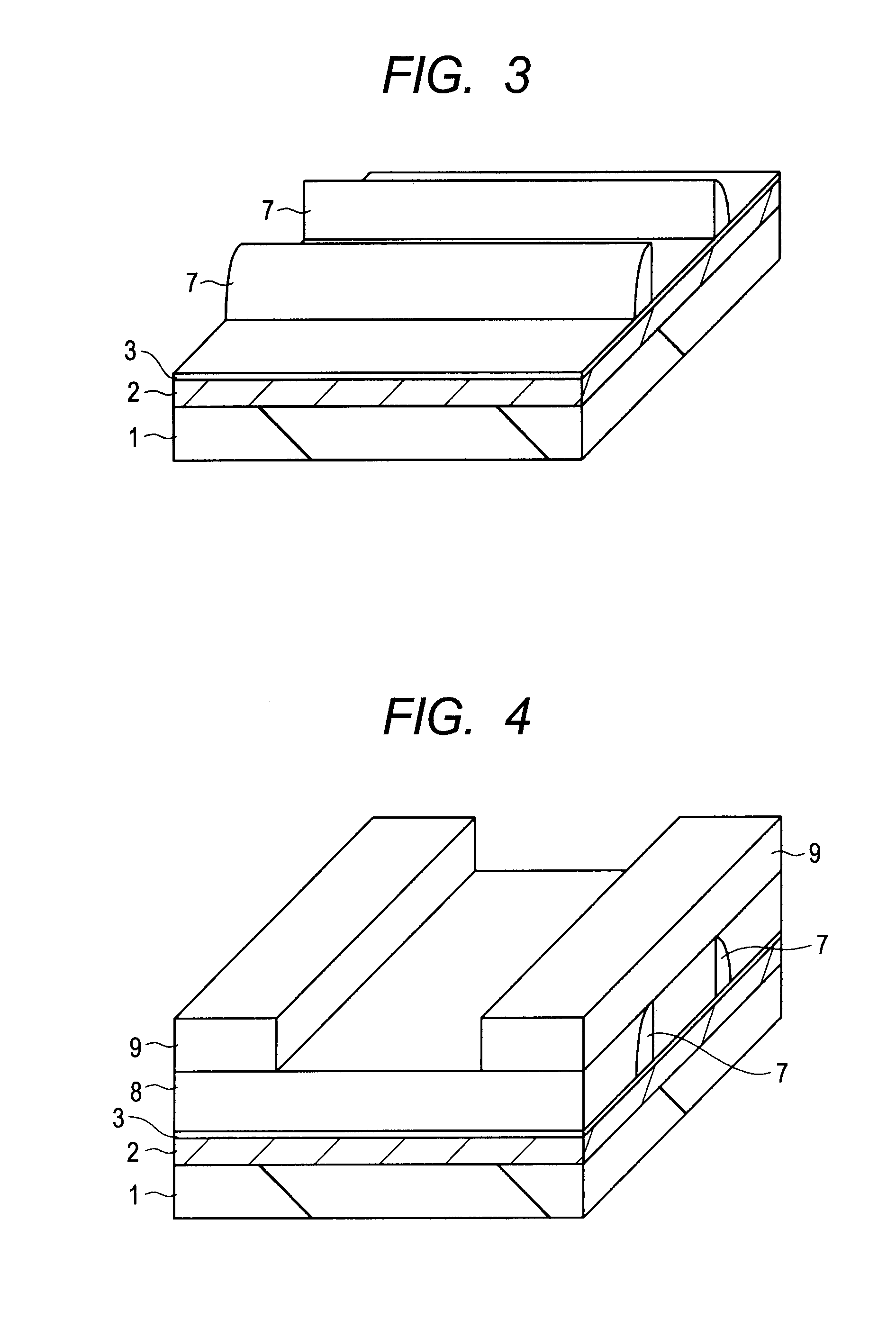
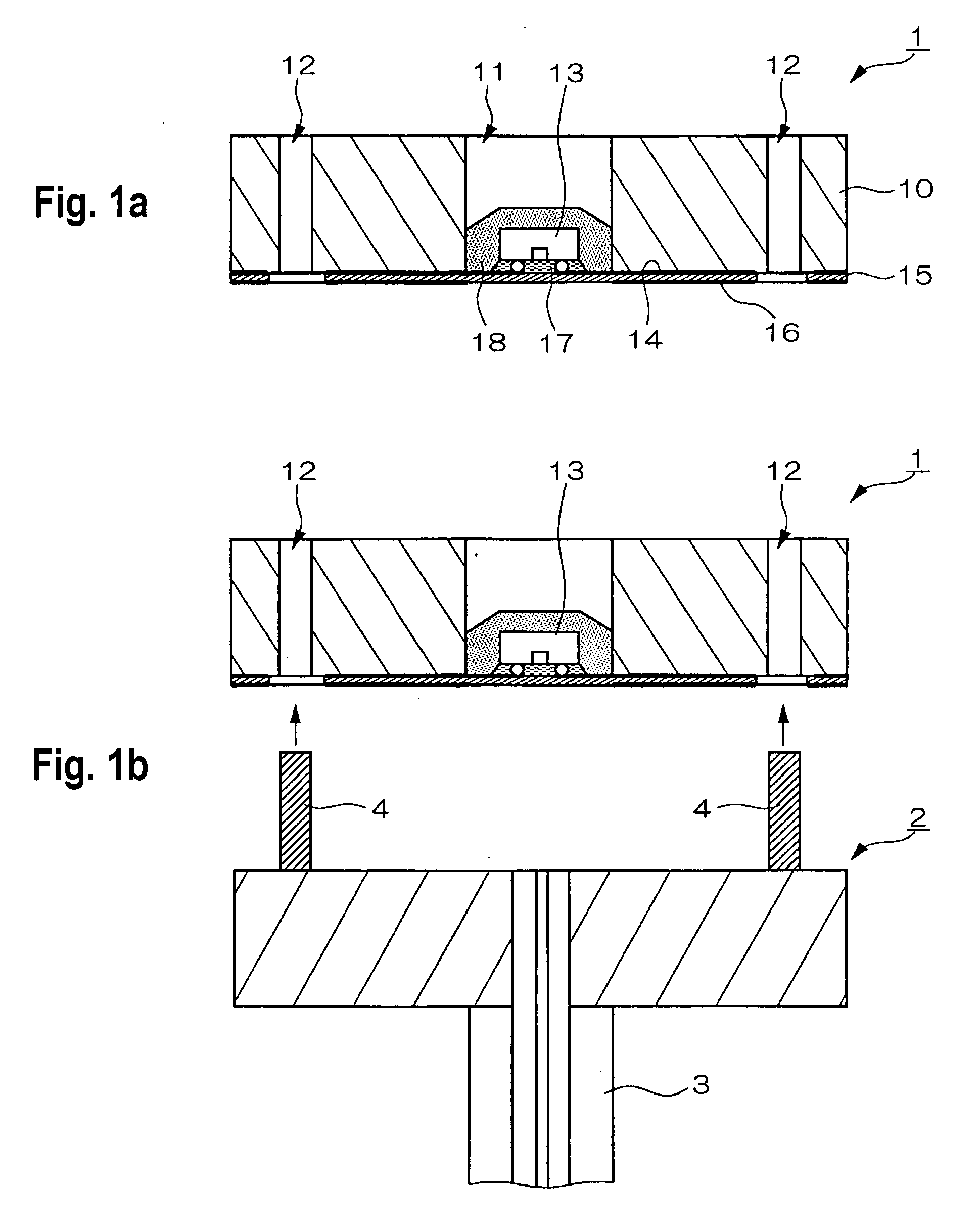
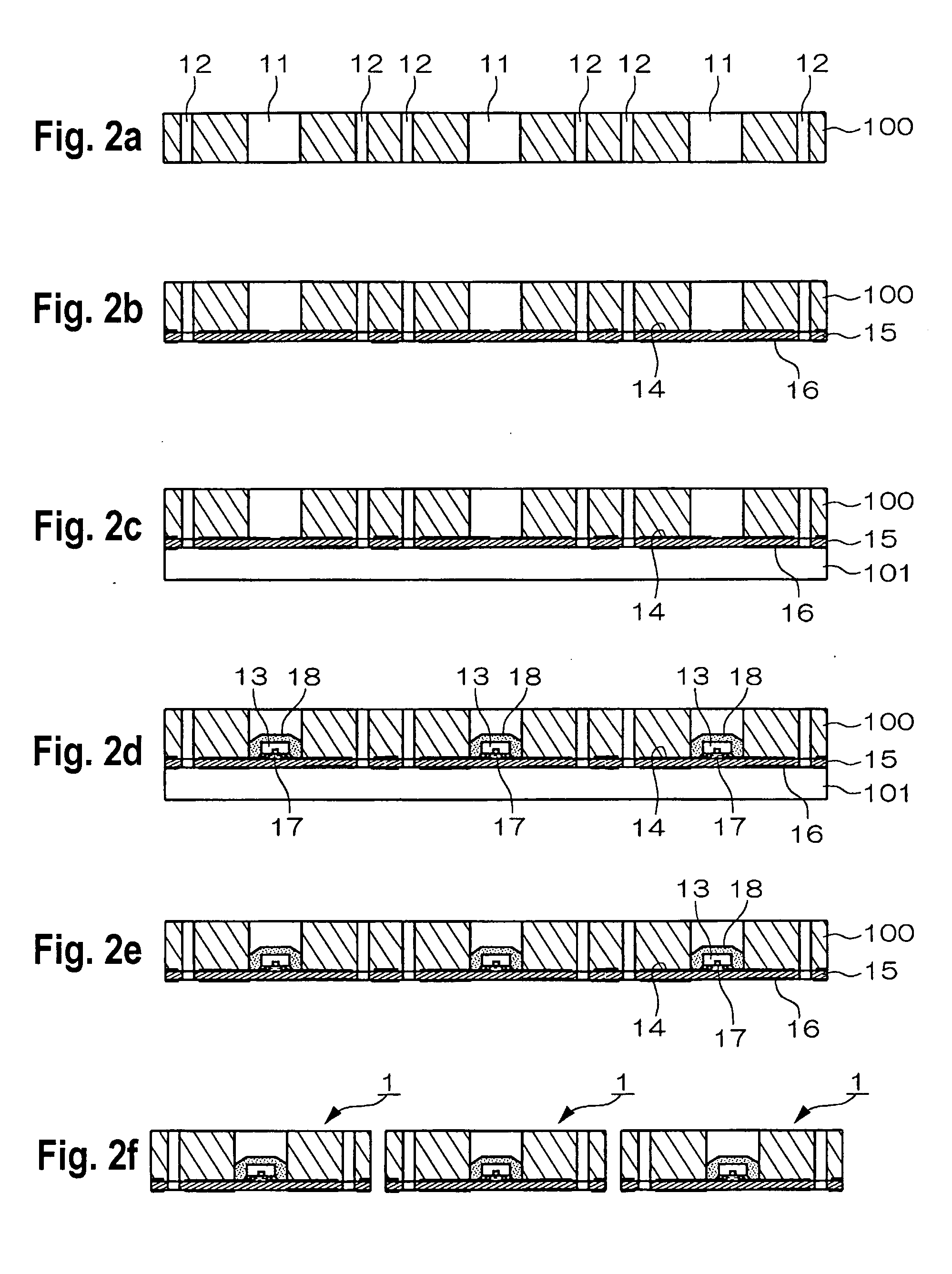
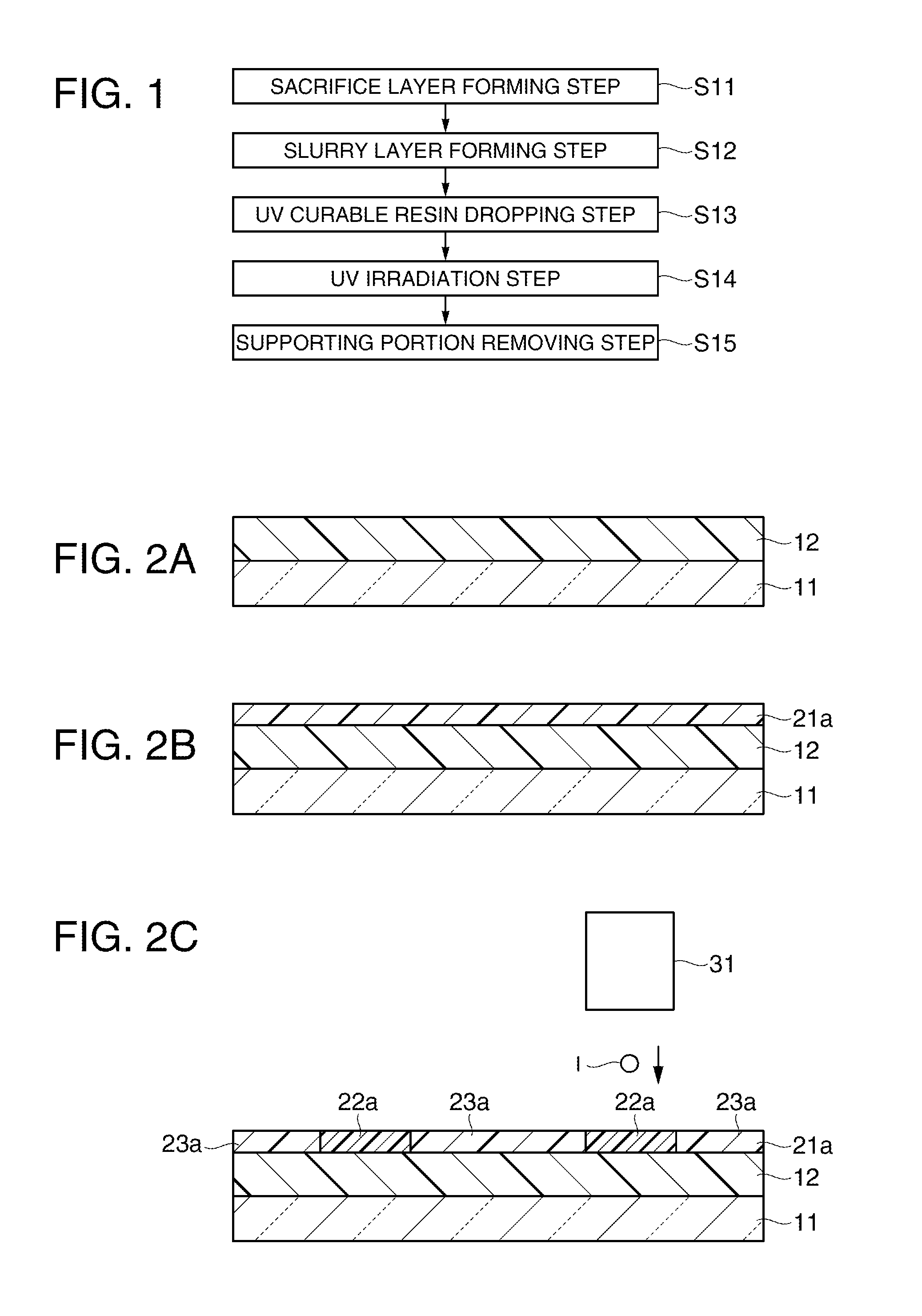
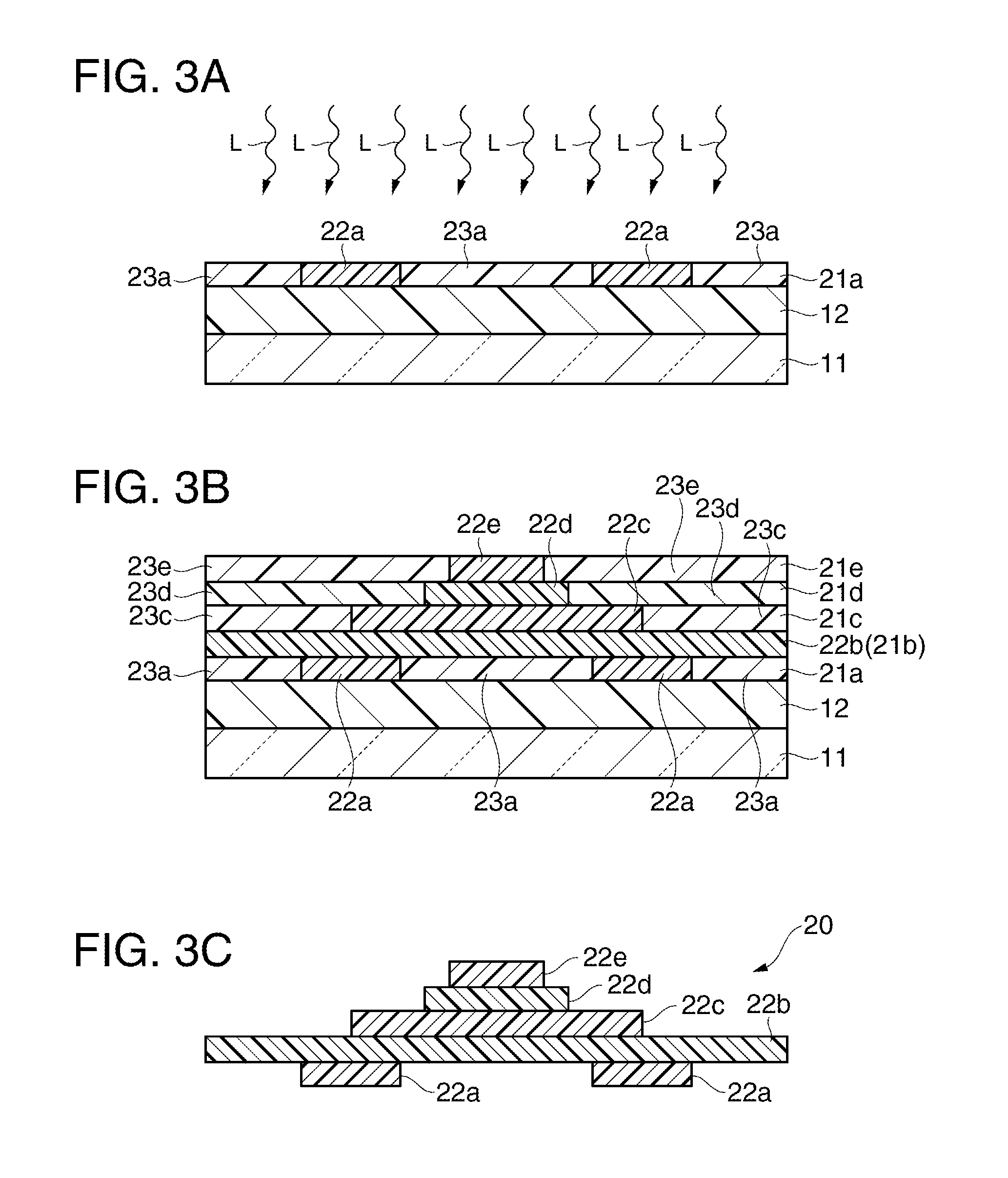
Substrate processing apparatus, method of manufacturing semiconductor device and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120119337A1Avoid processing qualitySuppress scatterLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsForeign matterThermodynamics
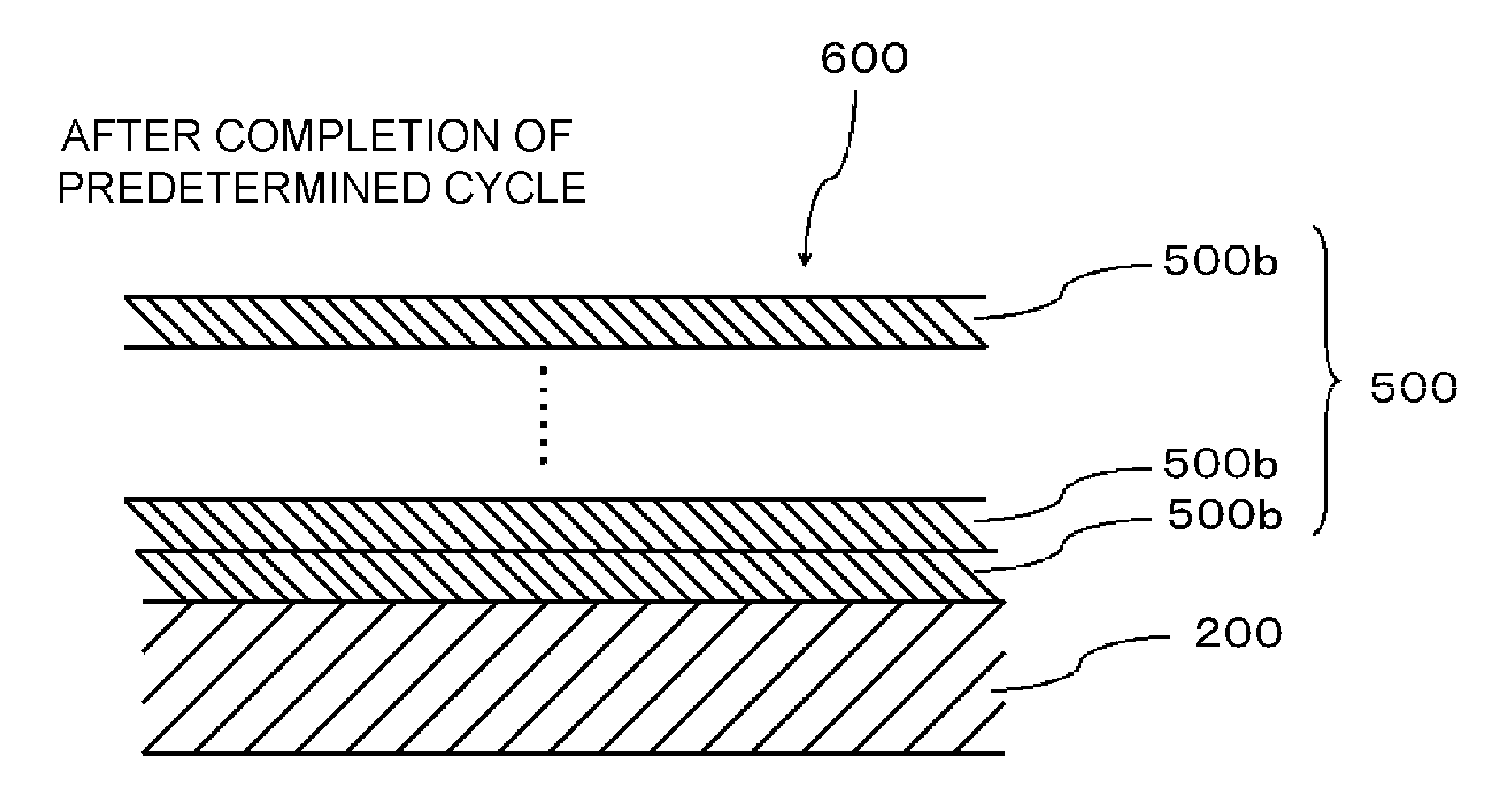
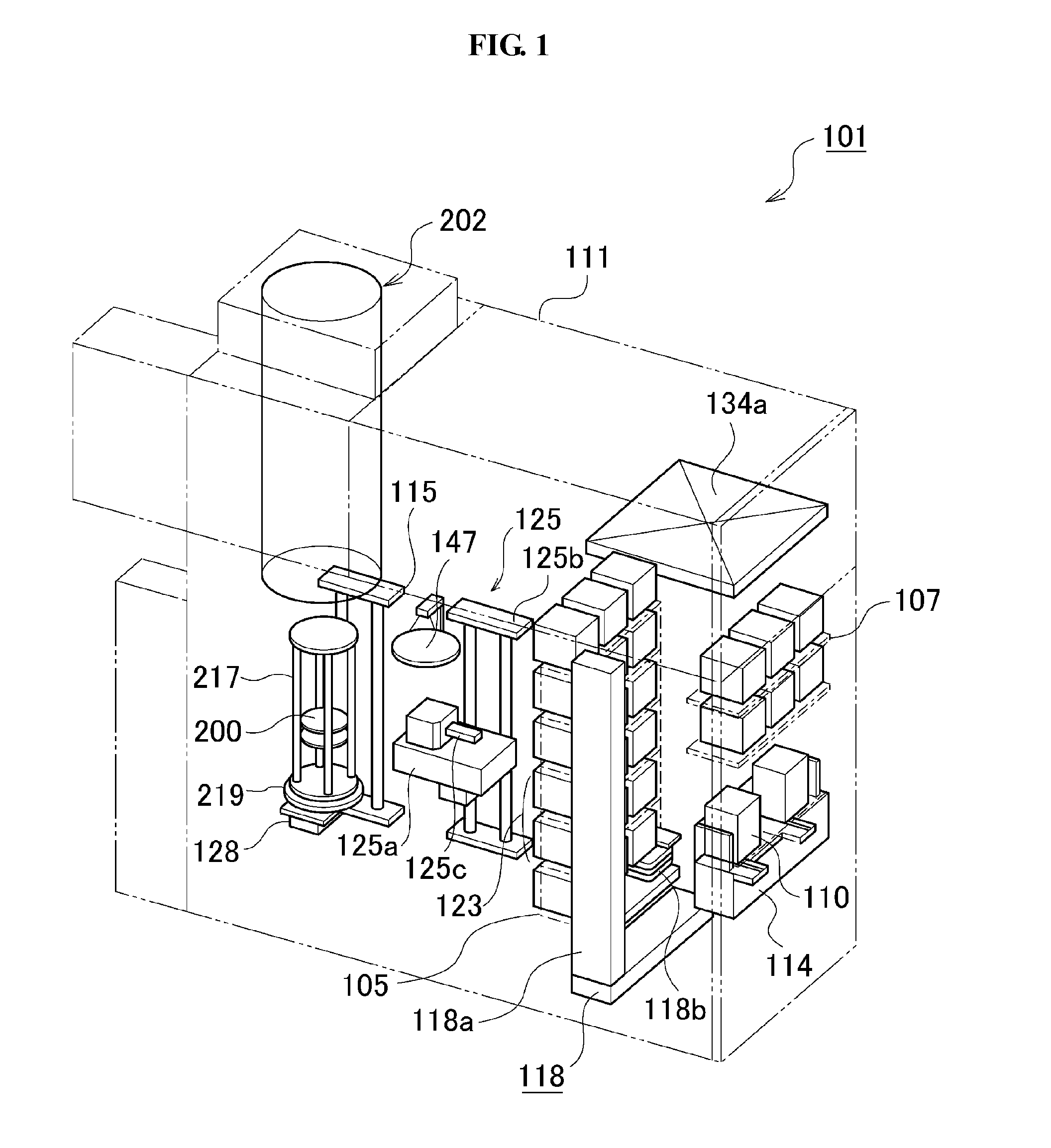
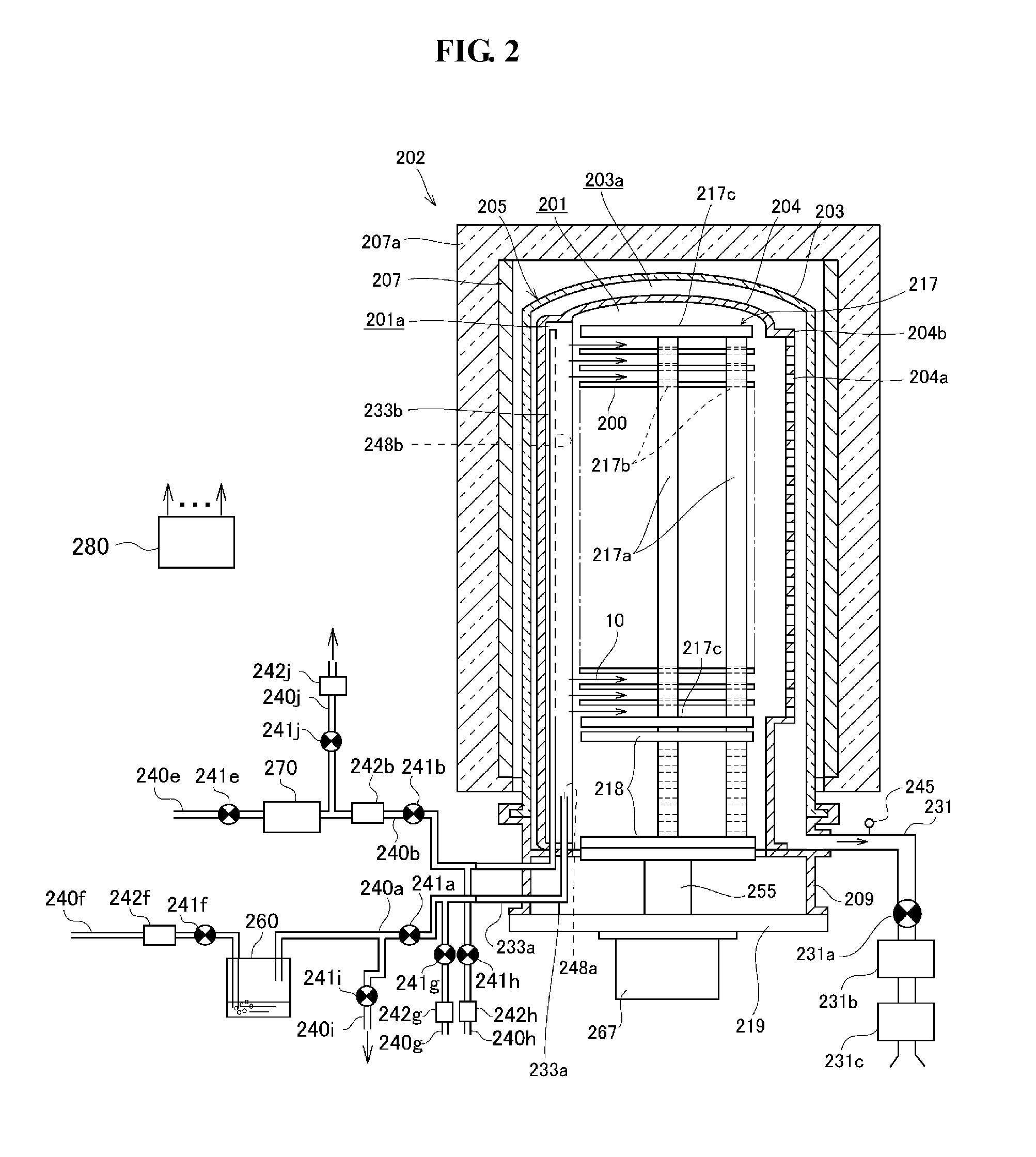
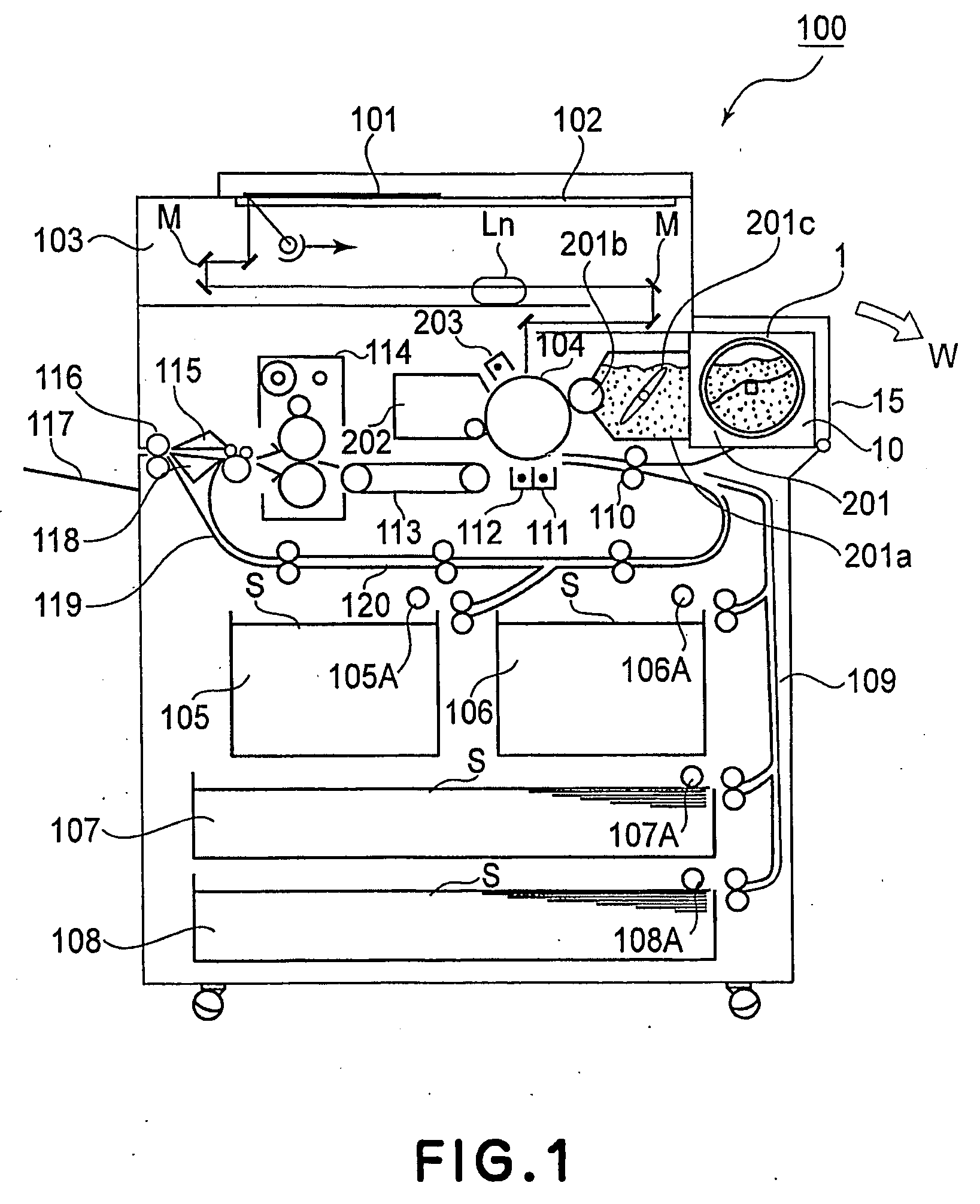
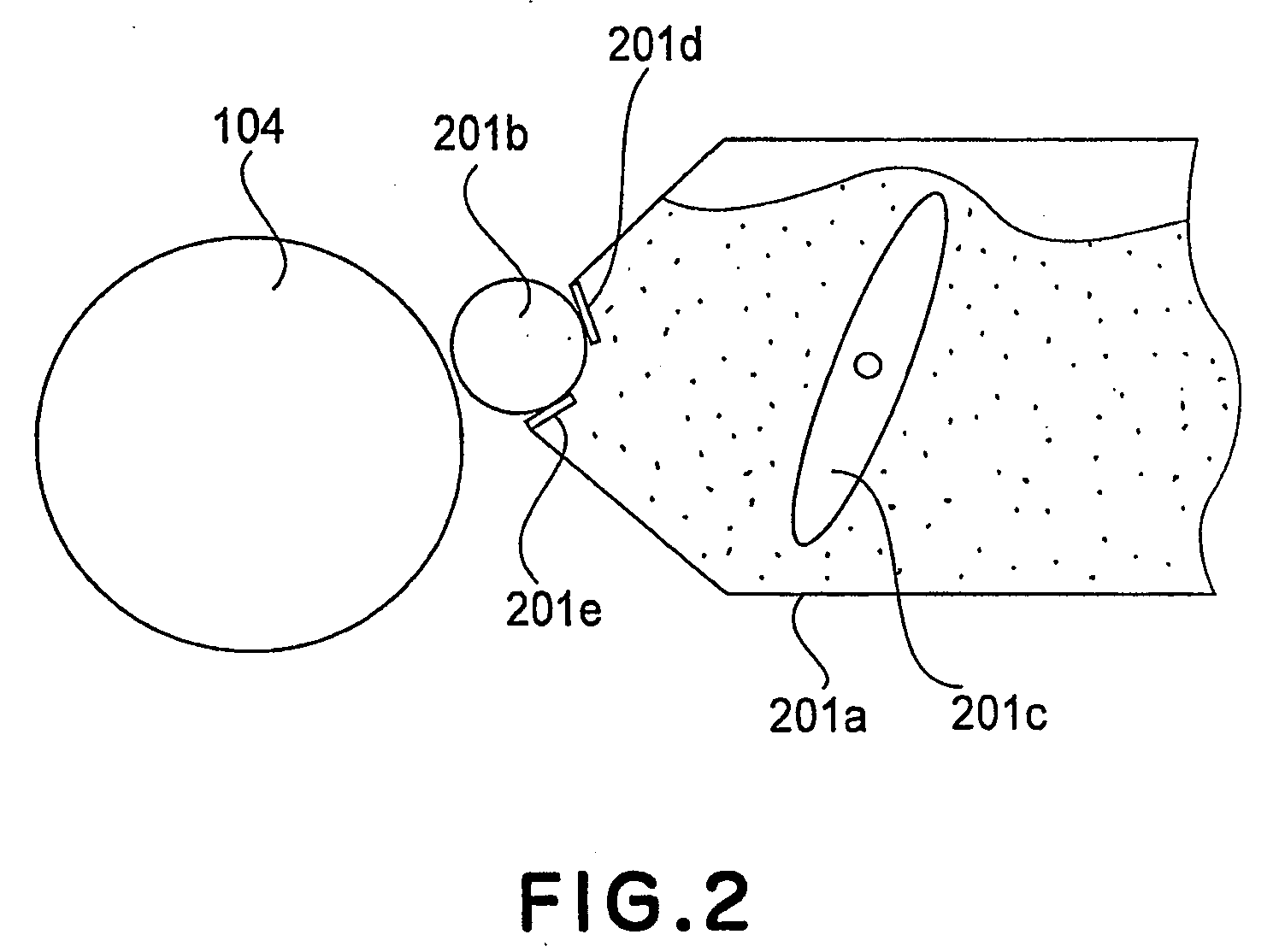
Provided is a substrate processing apparatus capable of suppressing accumulation of reaction products or decomposed matters on an inner wall of a nozzle and suppressing scattering of foreign substances in a process chamber. The substrate processing apparatus includes a process chamber, a heating unit, a source gas supply unit, a source gas nozzle, an exhaust unit, and a control unit configured to control at least the heating unit, the source gas supply unit and the exhaust unit. The source gas nozzle is disposed at a region in the process chamber, in which a first process gas is not decomposed even under a temperature in the process chamber higher than a pyrolysis temperature of the first process gas, and the control unit supplies the first process gas into the process chamber two or more times at different flow velocities to prevent the first process gas from being mixed.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
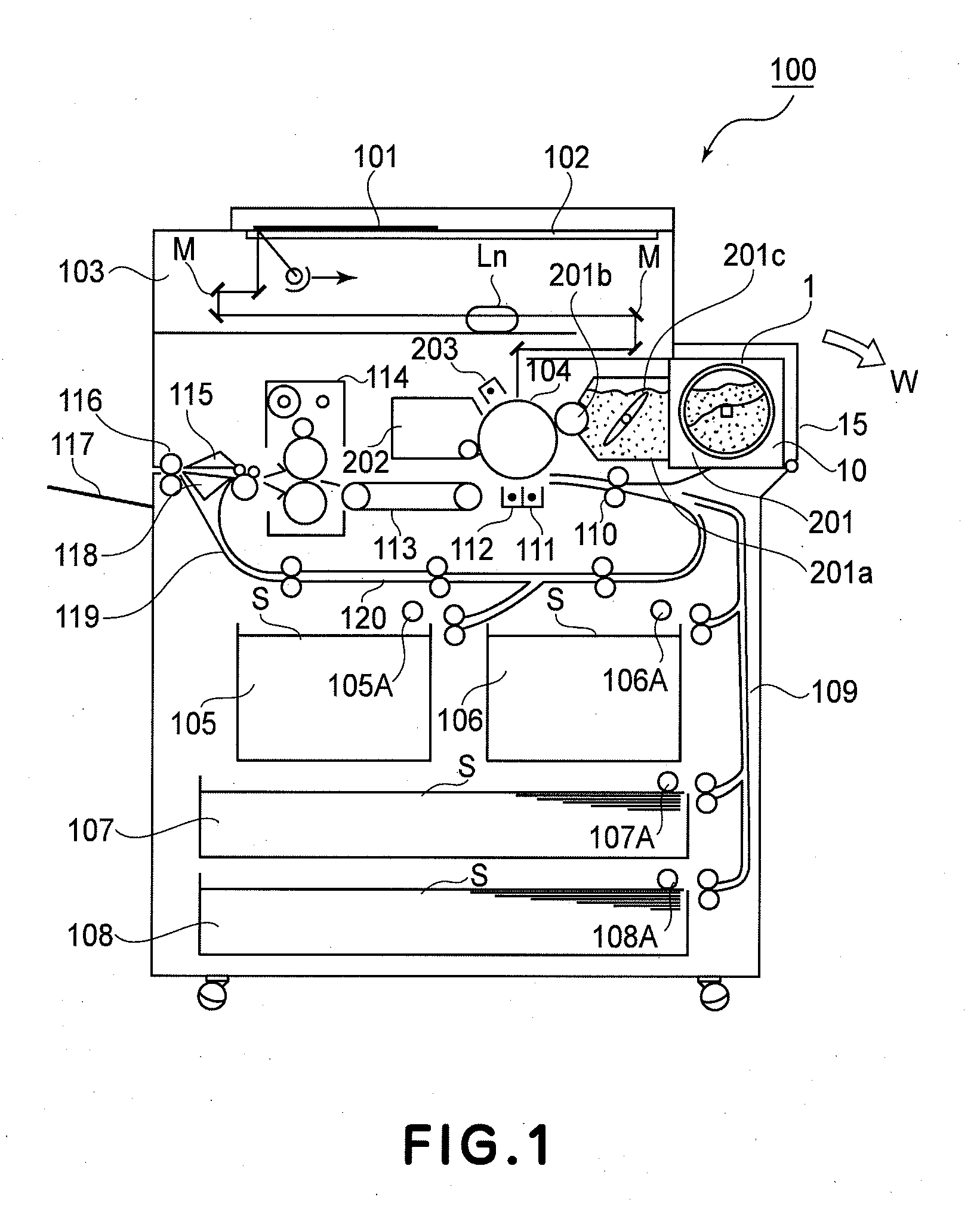
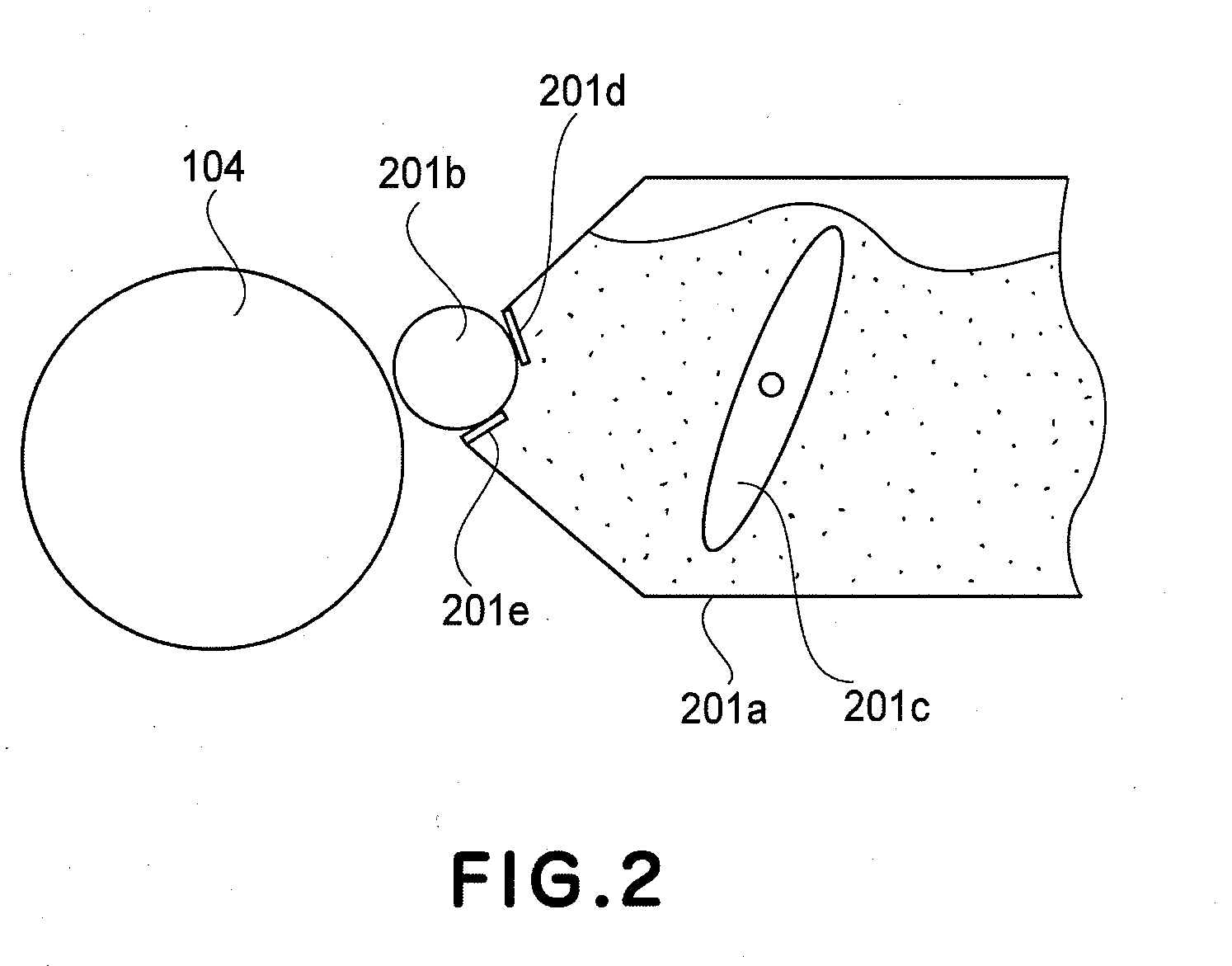
Developer supply container and developer supplying system
ActiveUS20090129813A1Discharging property is highSuppress scatterElectrographic process apparatusMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:CANON KK
Light emitting device
ActiveUS20110147778A1Light efficiency of lightUnevenness light of lightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLength waveLight emitting device
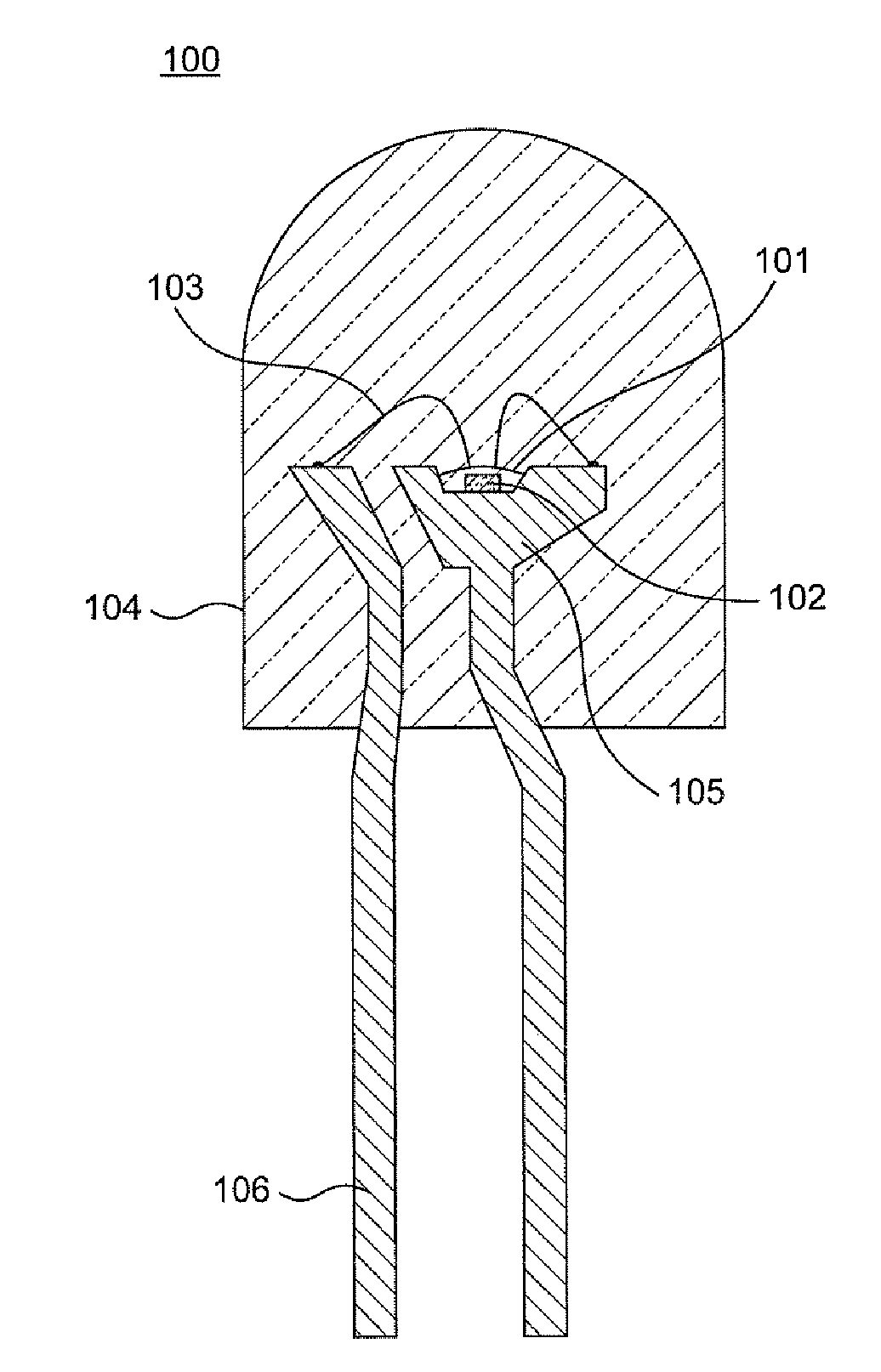
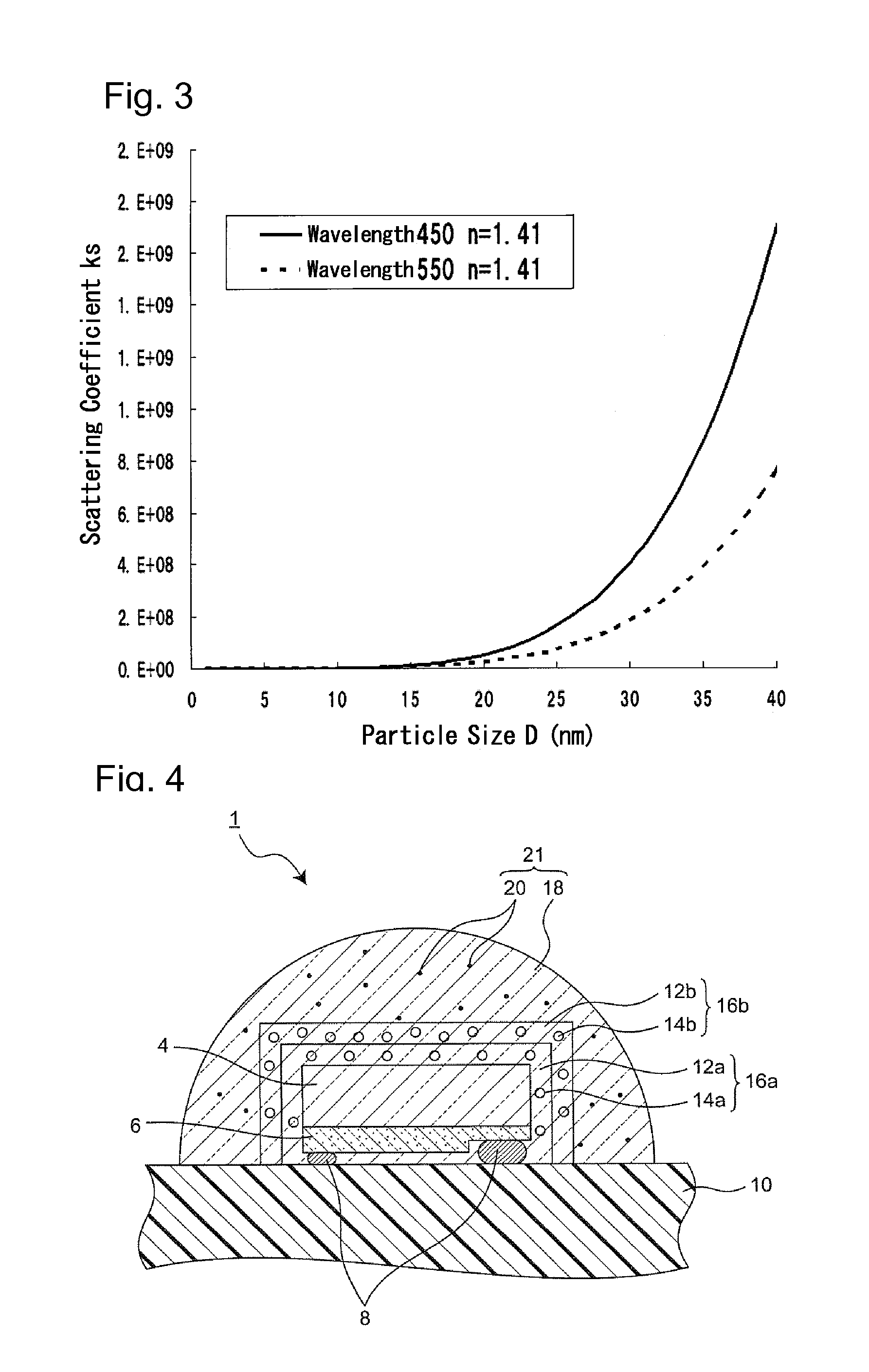
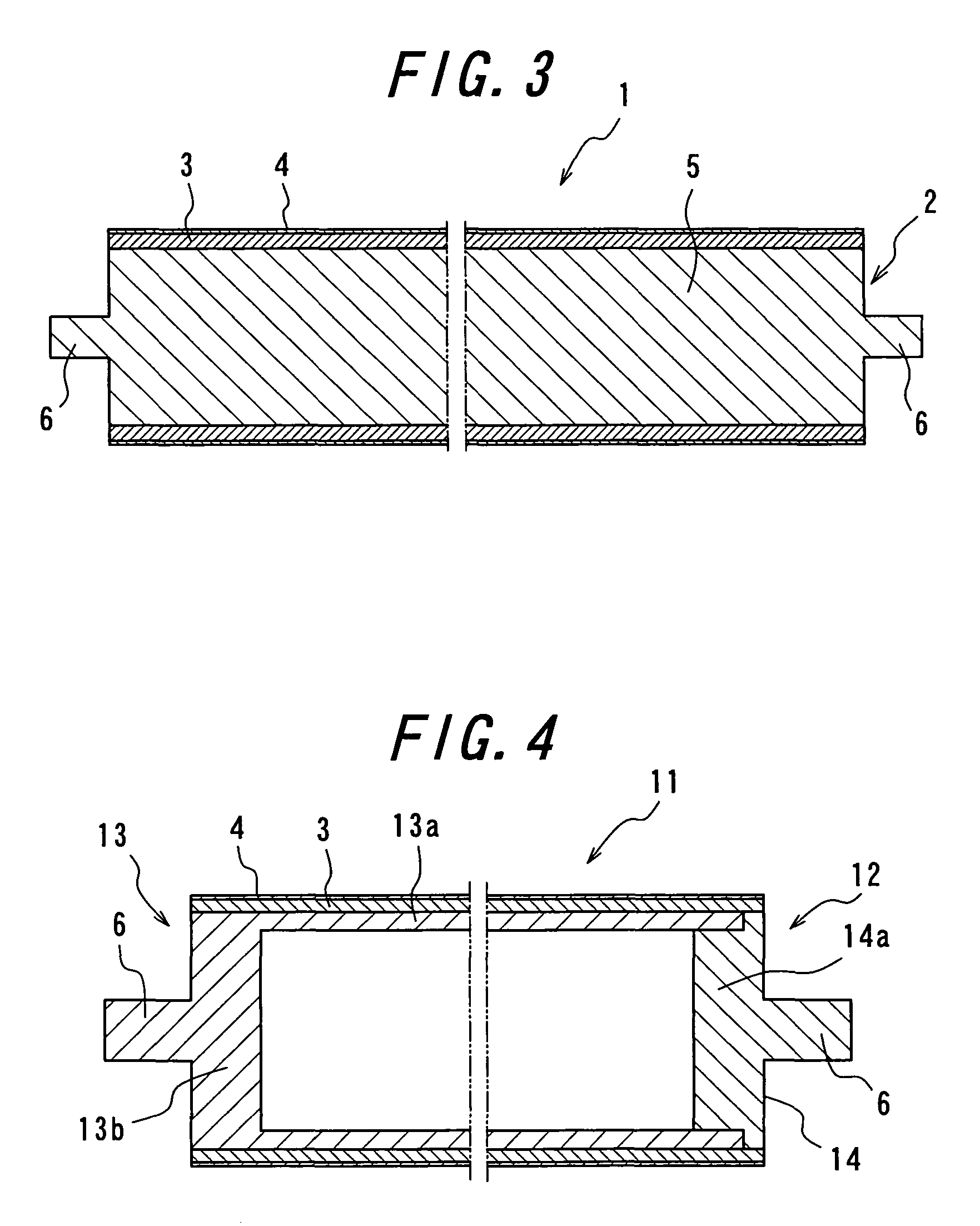
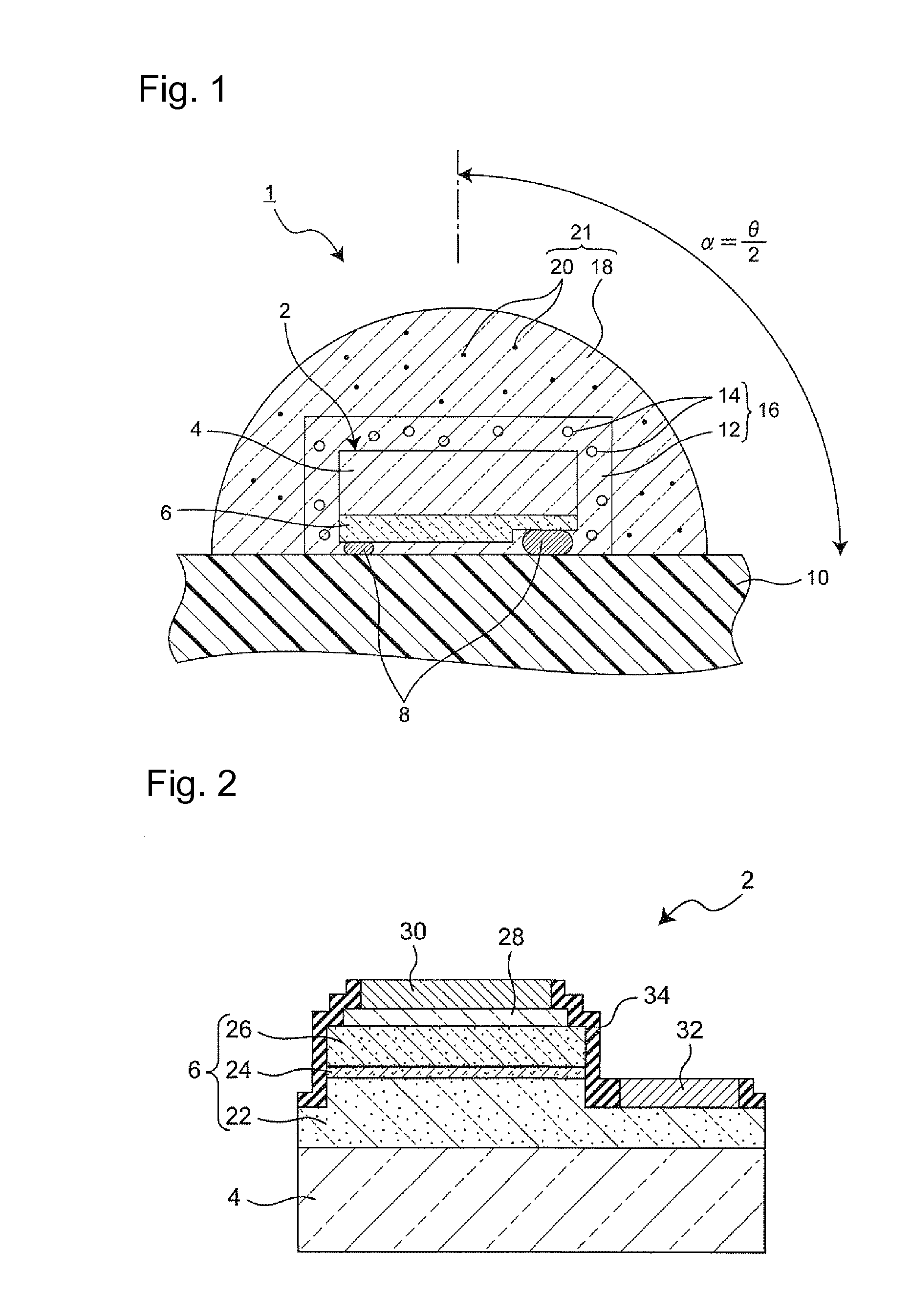
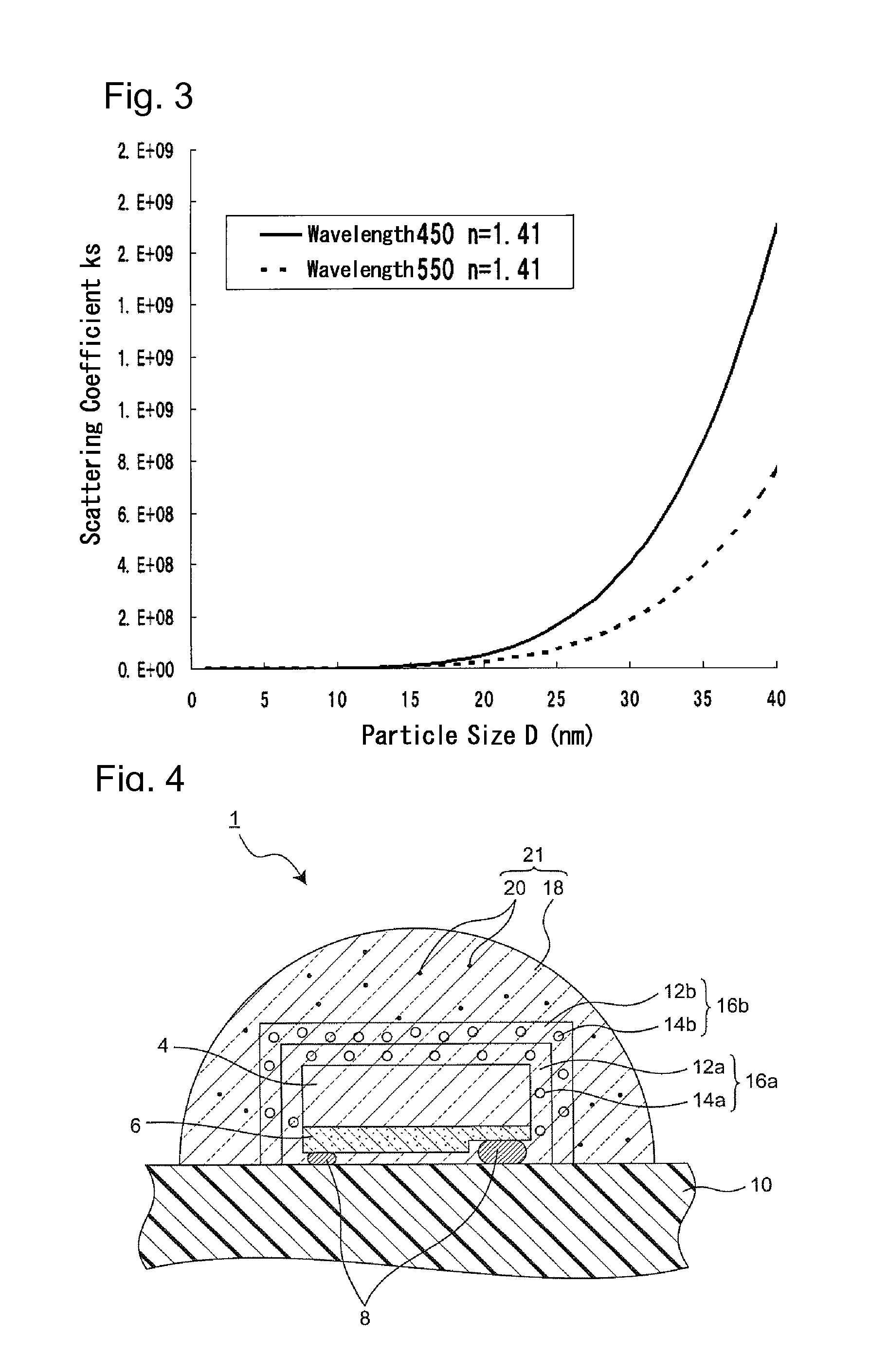
To provide a light emitting device capable of improving both color unevenness and an emission output power.The light emitting device includes a semiconductor light emitting element including a semiconductor layer that emits primary light; and a fluorescent material layer disposed on the light emitting side of the semiconductor light emitting element, that absorbs a part of the primary light and emits secondary light having a wavelength longer than that of the primary light; and emits light of blended color of the primary light and the secondary light of the light emitting element, and further includes a scattering layer in which particles having a mean particle size D that satisfies the inequality: 20 nm<D≦0.4×λ / π are dispersed in a transparent medium.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Method for manufacturing plugged honeycomb structure
ActiveUS8277880B2Suppress scatterIncrease production costCatalyst carriersPretreated surfacesHoneycomb structureMaterials science
A method for manufacturing a plugged honeycomb structure including a step of mixing ceramic particles with a gas on one end face side of the plugged honeycomb structure, and a step of sucking the gas containing the ceramic particles from the other end face side of the plugged honeycomb structure to send the ceramic particles mixed in the gas into cells of the plugged honeycomb structure to allow the ceramic particles to adhere to surfaces in the cells of the plugged honeycomb structure.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
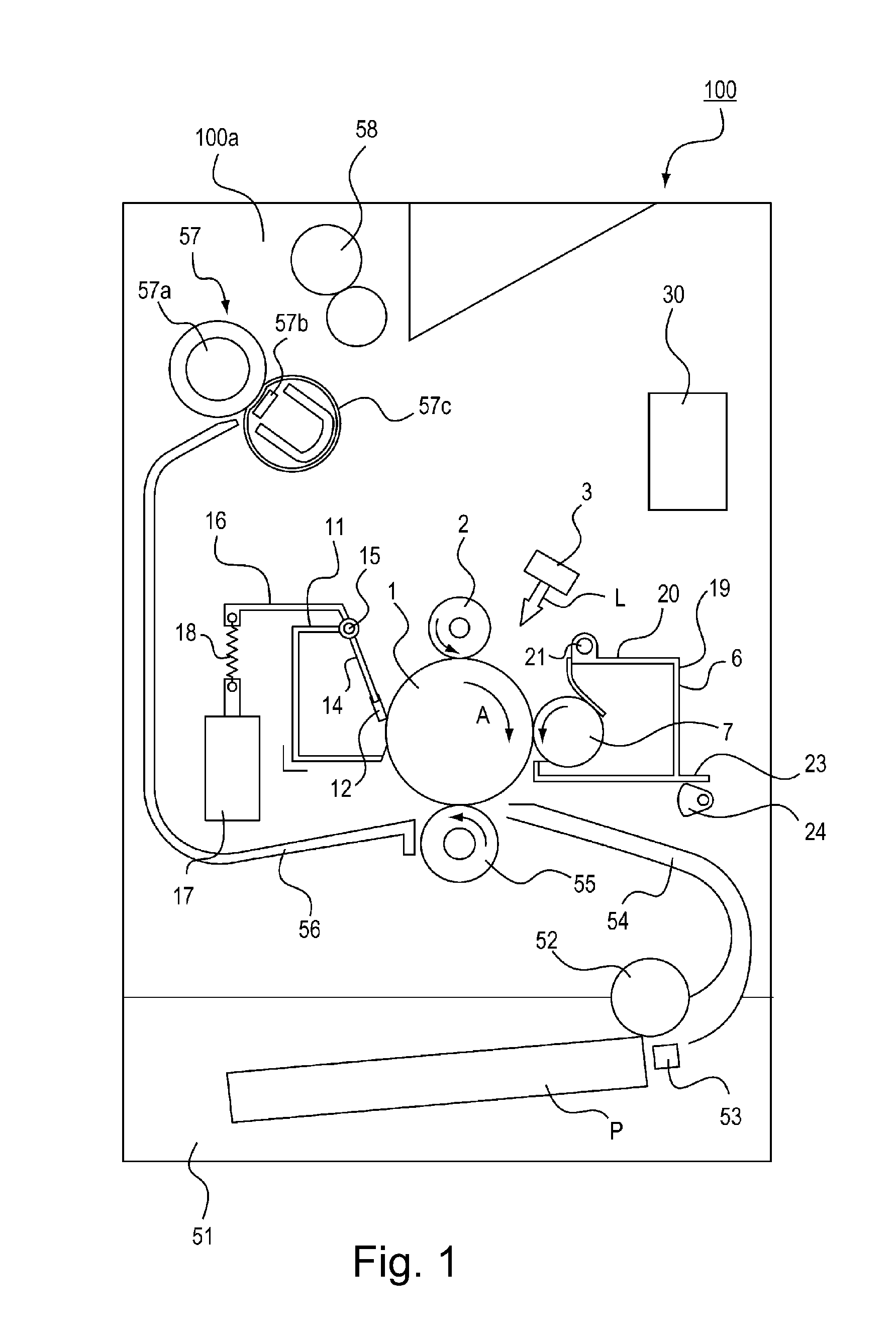
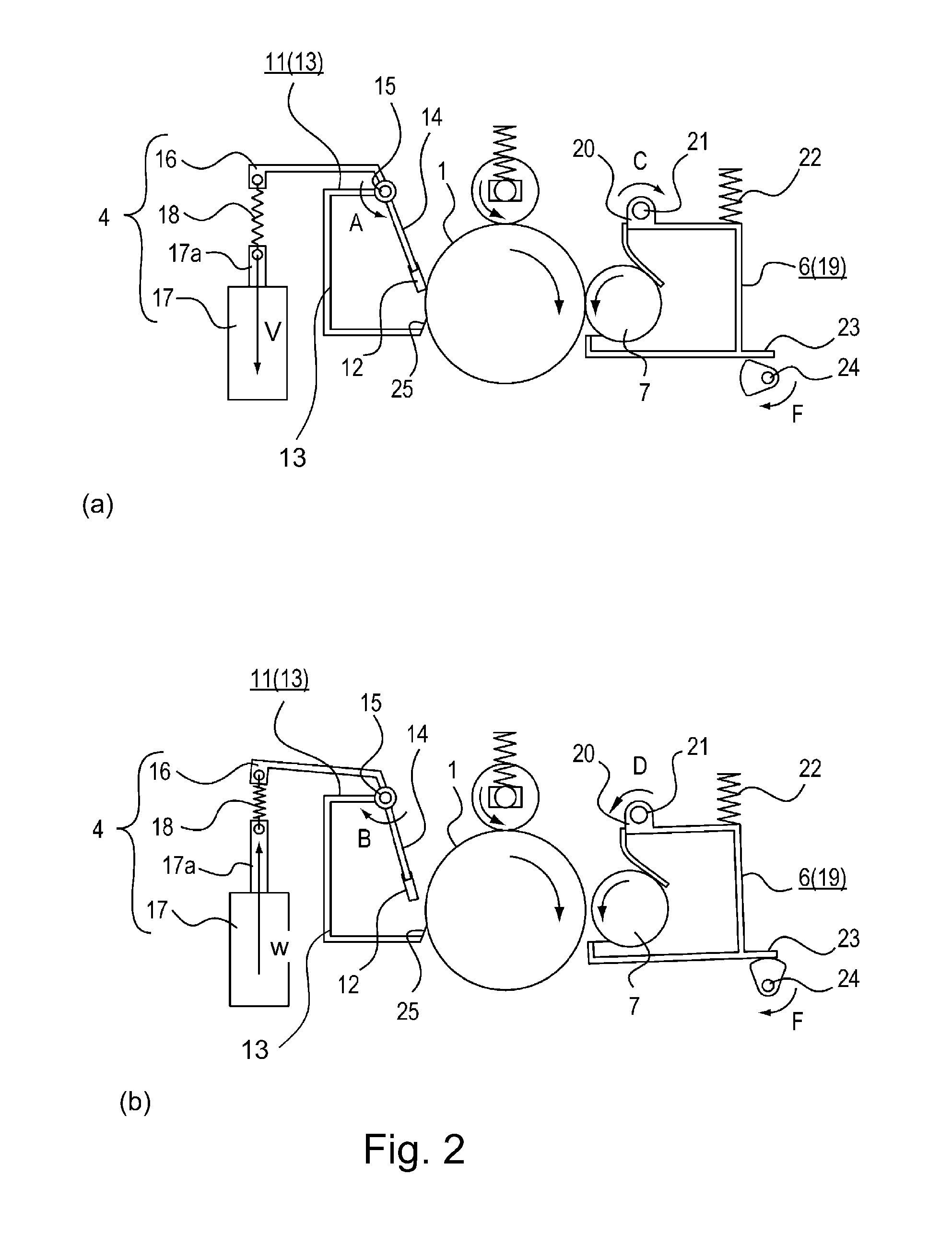
Substrate processing apparatus and substrate processing method
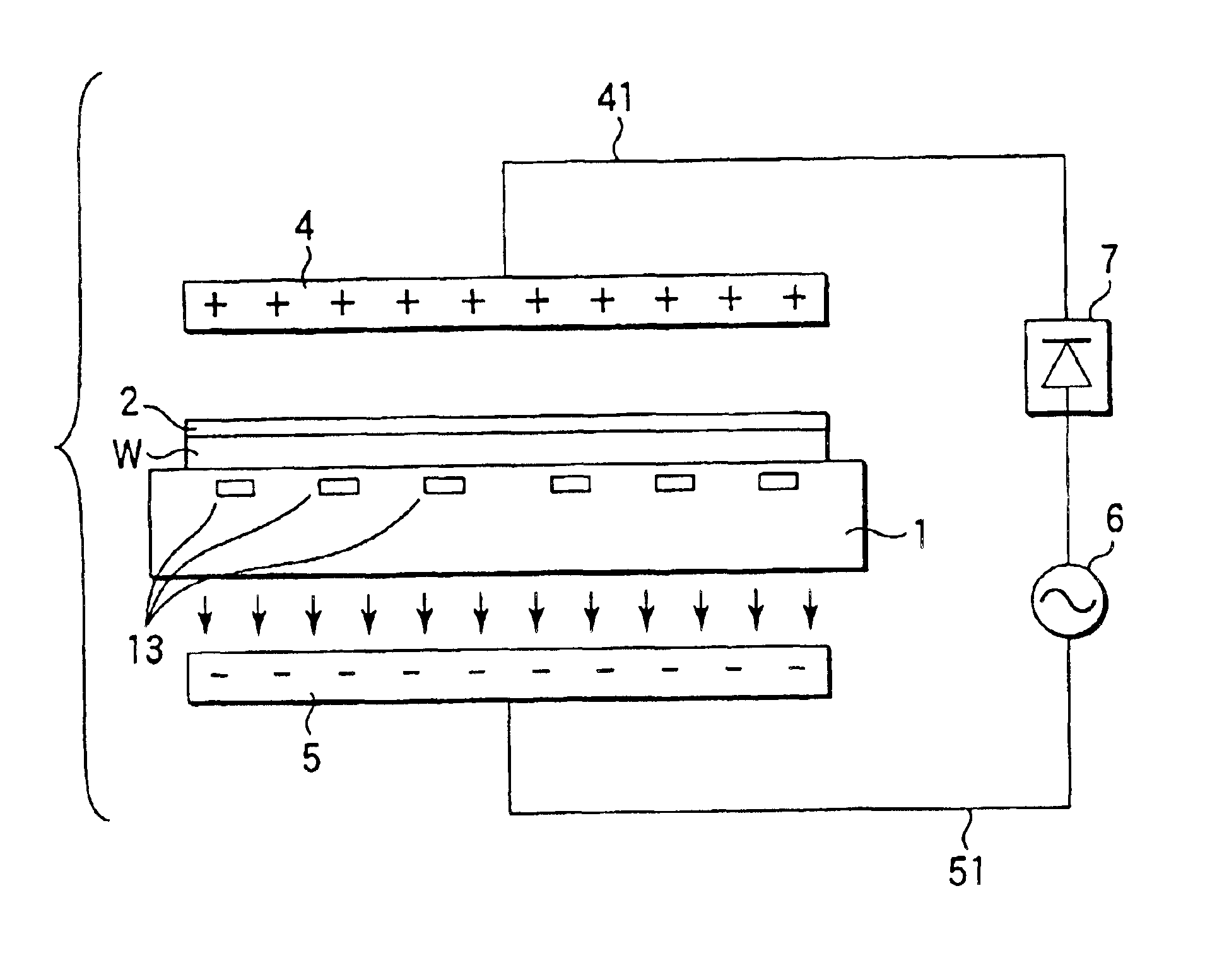
InactiveUS6841342B2Suppress scatterEvenly distributedLiquid surface applicatorsDrying solid materials with heatResistLight exposure
A substrate processing apparatus for processing a substrate coated with a chemical amplification type resist and subjected to a light-exposure treatment comprises a substrate table on which is disposed a substrate, a heater for heating the substrate disposed on the substrate table, and an electric field forming mechanism for forming an electric field exerting force, which is directed toward the substrate, on the protons generated in the resist formed on the substrate disposed on the substrate table.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Developer supply container and developer supplying system
InactiveUS20100278564A1Discharging property is highDeveloper scattering is suppressedElectrographic process apparatusMechanical engineering
Owner:CANON KK
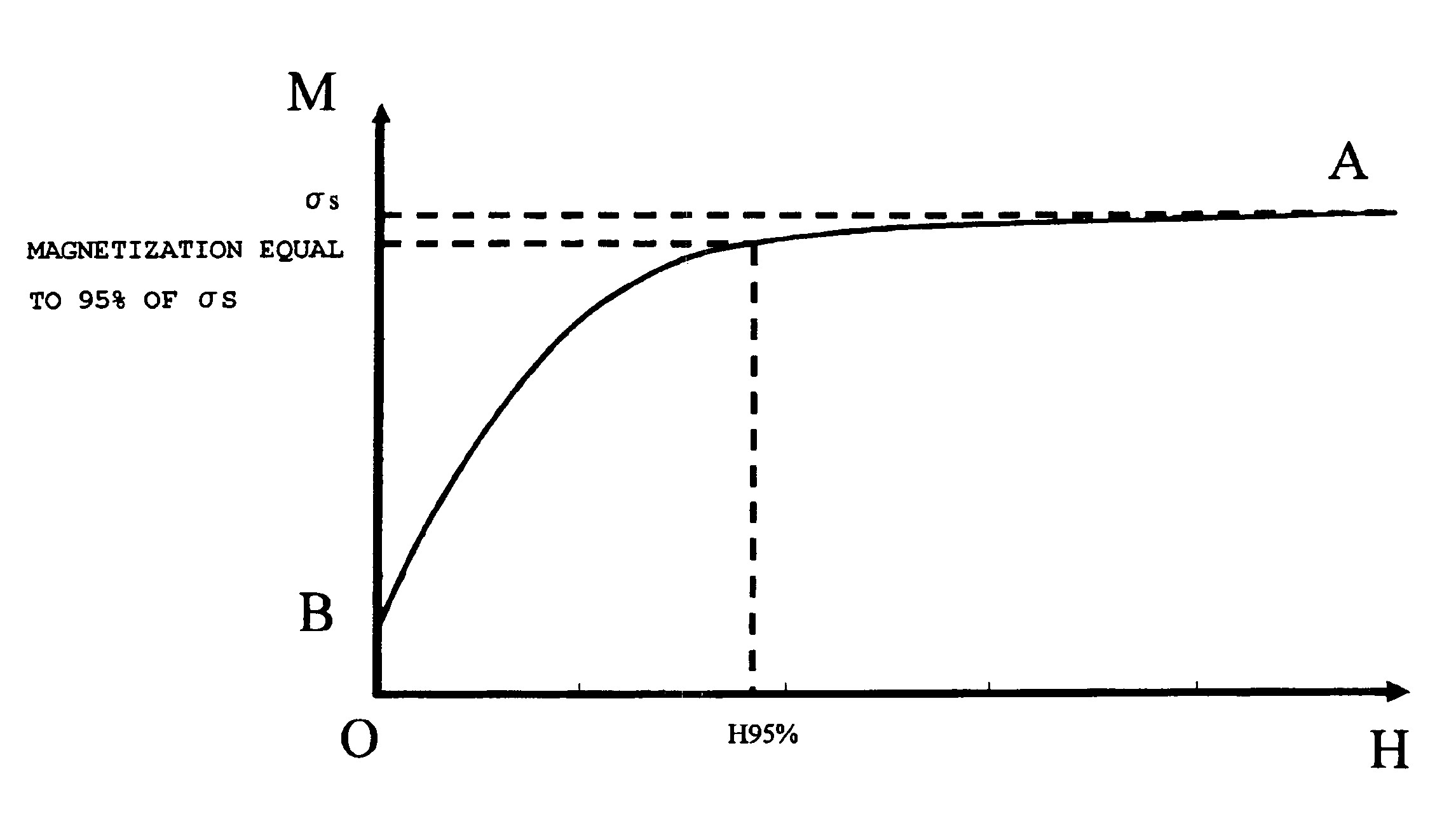
Magnetic toner
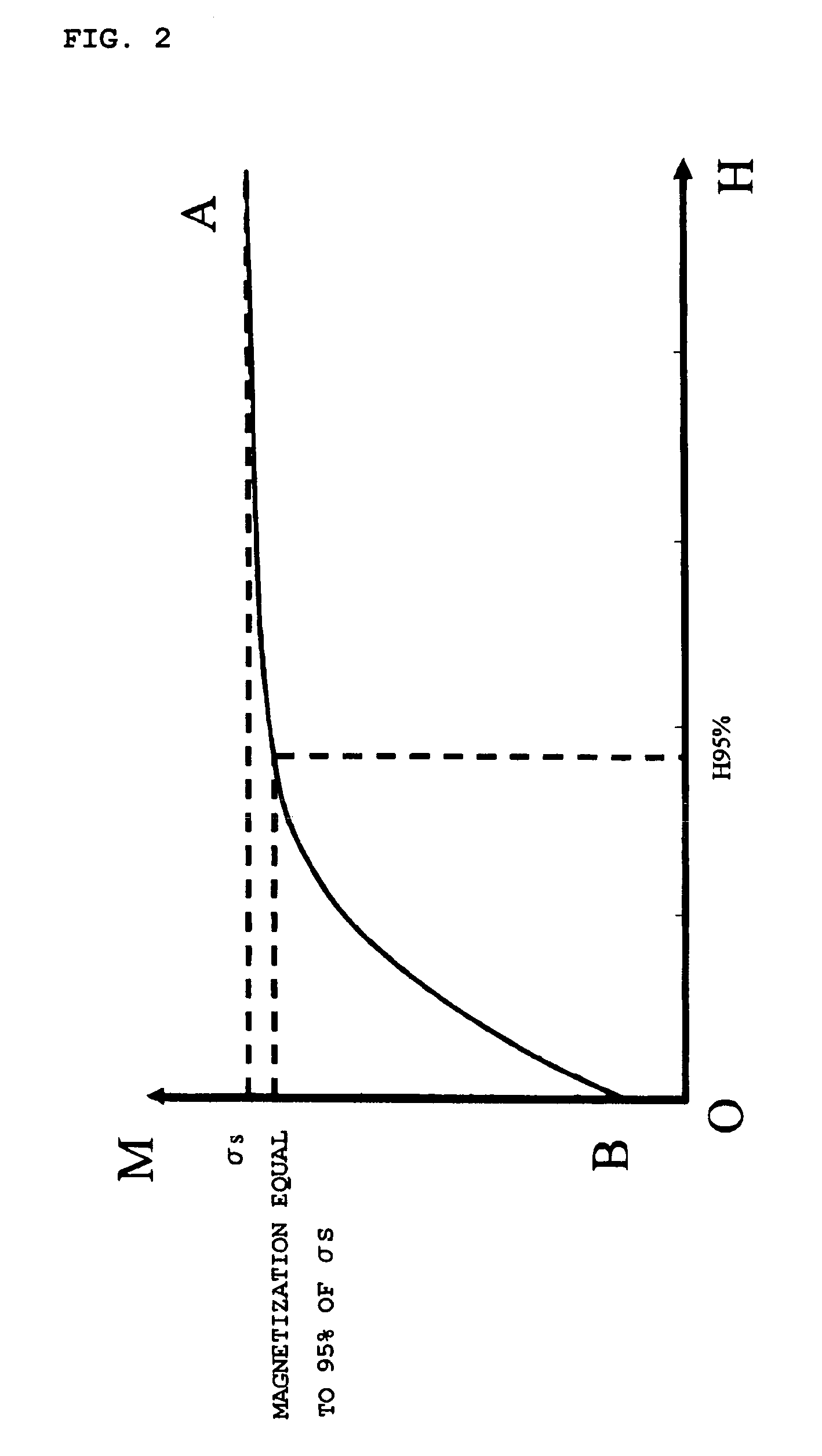
A magnetic toner including at least: a binder resin; and a magnetic body, in which, when magnetization at a magnetic field strength of 397.9 kA / m and a coercive force of the magnetic toner are denoted by σs (Am2 / kg) and Hc (kA / m), respectively, a magnetic field strength at which the magnetic toner shows a magnetization value equal to 95% of σs is denoted by H95% (kA / m), and a number average particle size of the magnetic body is denoted by d (μm), H95%, Hc, and d satisfy the following expressions.151<H95%<200 (1)7.1<Hc<12 (2)40<Hc / d<150 (3)
Owner:CANON KK
Solid-state imaging device, method of manufacturing solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20110241079A1Suppress scatterQuality improvementTransistorTelevision system detailsCharge retentionPhotoelectric conversion
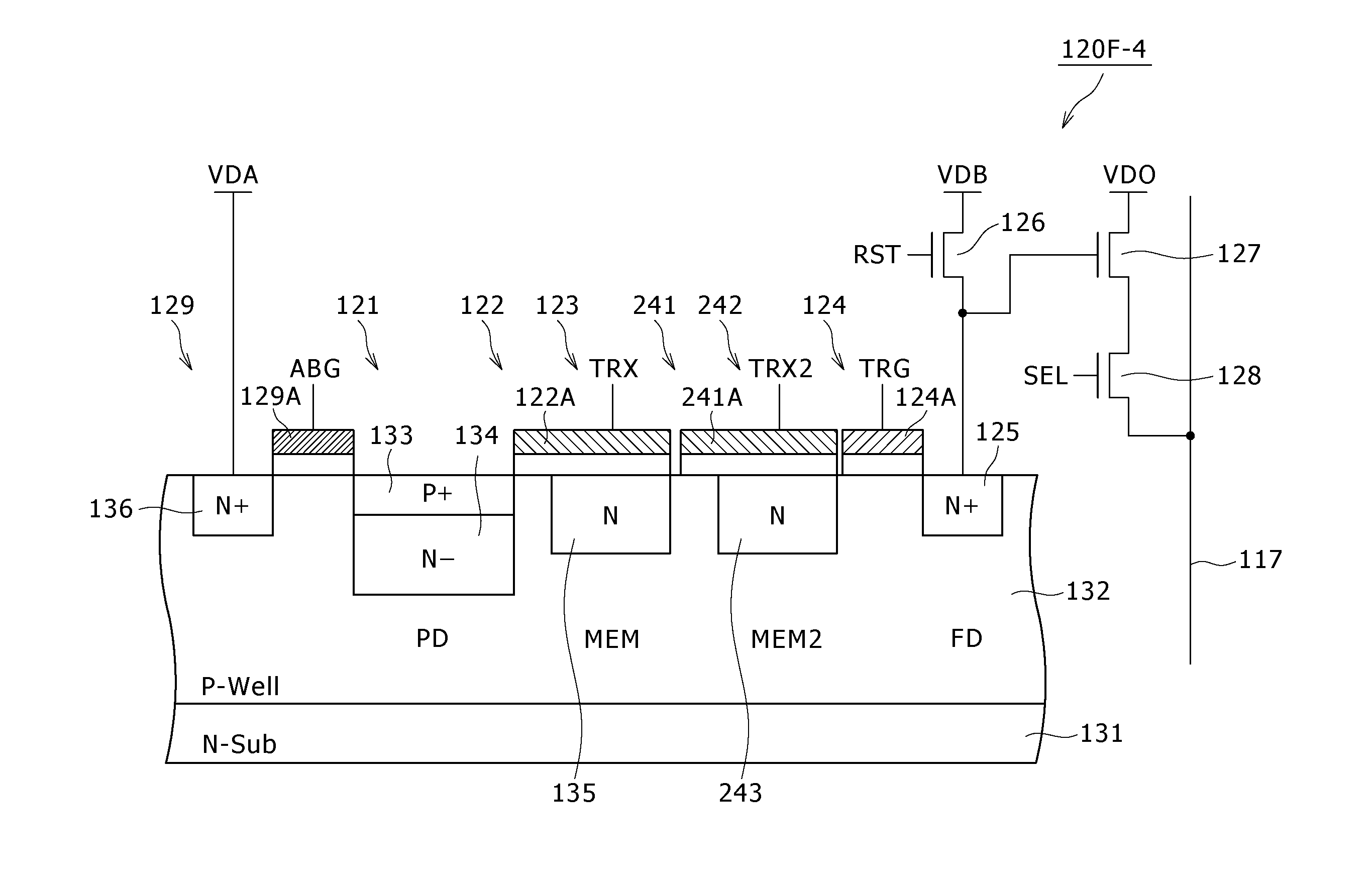
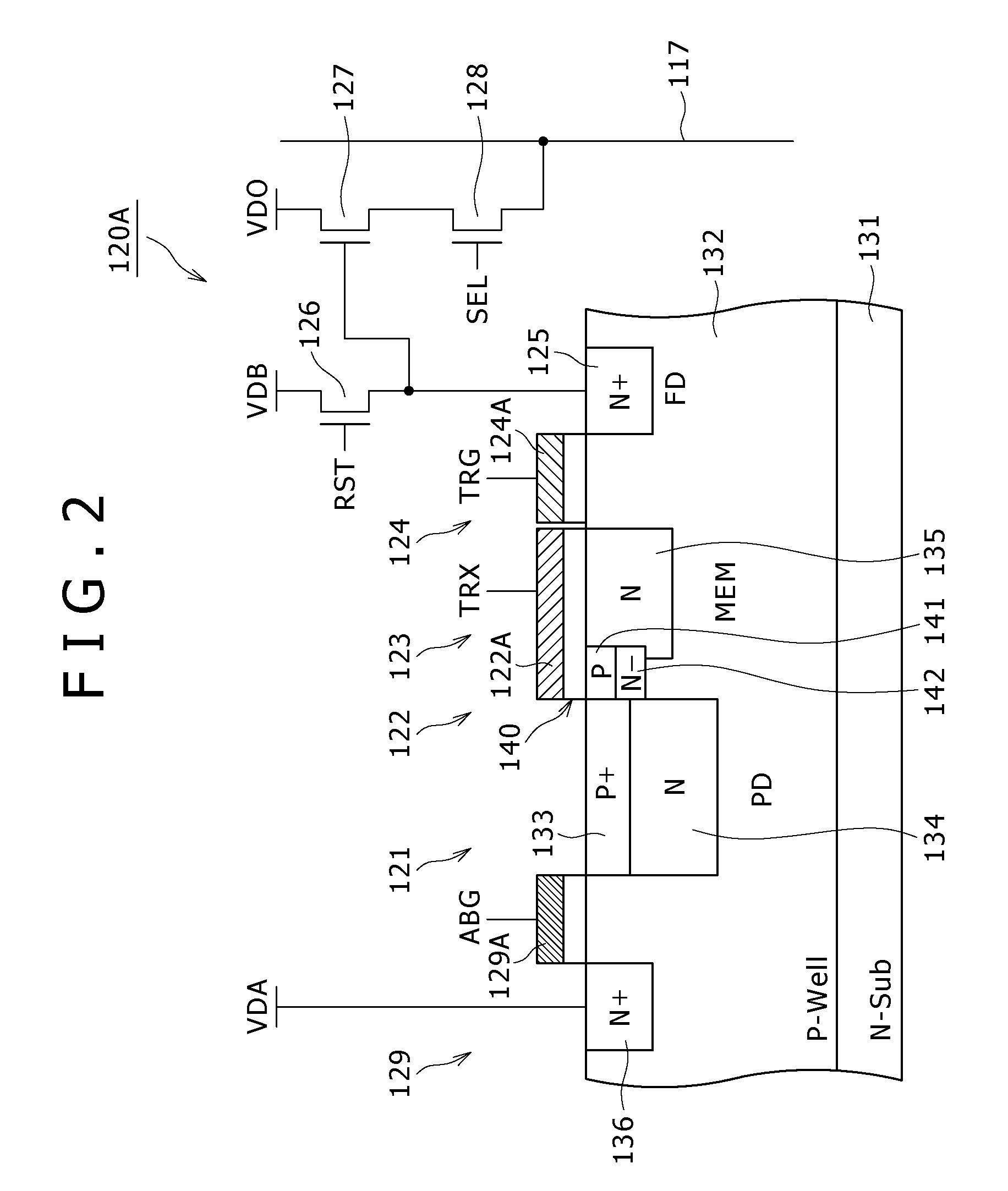
Disclosed herein is a solid-state imaging device including a photoelectric conversion element operable to generate electric charge according to the amount of incident light and to accumulate the electric charge in the inside thereof, an electric-charge holding region in which the electric charge generated through photoelectric conversion by the photoelectric conversion element is held until read out, and a transfer gate having a complete transfer path through which the electric charge accumulated in the photoelectric conversion element is completely transferred into the electric-charge holding region, and an intermediate transfer path through which the electric charge generated by the photoelectric conversion element during an exposure period and being in excess of a predetermined charge amount is transferred into the electric-charge holding region. The complete transfer path and the intermediate transfer path are formed in different regions.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Developer supply container and developer supplying system
ActiveUS7848685B2Discharging property is highDeveloper scattering is suppressedElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CANON KK
Light Reflecting Film, And Light Controlling Film, Optical Film, Functional Glass And Head-Up Display Including The Light Reflecting Film
ActiveUS20170235030A1Improve visibilityImprove reflectivityMirrorsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsHead-up displayLength wave
A light controlling film comprises a light reflecting film and a light controlling layer that are laminated. The light reflecting film comprises at least two laminated light reflecting layers including at least one of light reflecting layers PRL-1 to PRL-3 that a central reflection wavelength of 400 nm-500 nm, 500 nm-600 nm, and 600 nm-700 nm, respectively, and a reflectance to ordinary light at the central reflection wavelength of 5%-25%. The at least two light reflecting layers have central reflection wavelengths that are different from each other. All of the at least two laminated light reflecting layers have a property of reflecting polarized light having the same orientation. The light controlling layer comprises two quarter wave plates, and the light reflecting film is laminated so as to be interposed between the two quarter wave plates.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Remelting of rare earth magnet scrap and/or sludge, magnet-forming alloy, and sintered rare earth magnet
InactiveUS6960240B2Improve efficiencyIncrease productionPermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismMischmetalAlkaline earth metal
Rare earth magnet scrap and / or sludge is remelted for reuse. Once a rare earth-free magnet-constituent metal feed is loaded in a melting furnace and heated into a melt, a rare earth-containing metal feed and the rare earth magnet scrap and / or sludge are added to the melt, a particulate flux of an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal or rare earth metal halide and having an average particle size of 1-50 μm, preferably wrapped in a metal foil, is added to the melt, and the resulting mixture is melted, from which an alloy ingot is obtained. The valuable elements in the scrap and / or sludge can be recycled. Better separation between the slag and the molten metal ensures that the ingot is obtained from the melt in a high yield.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
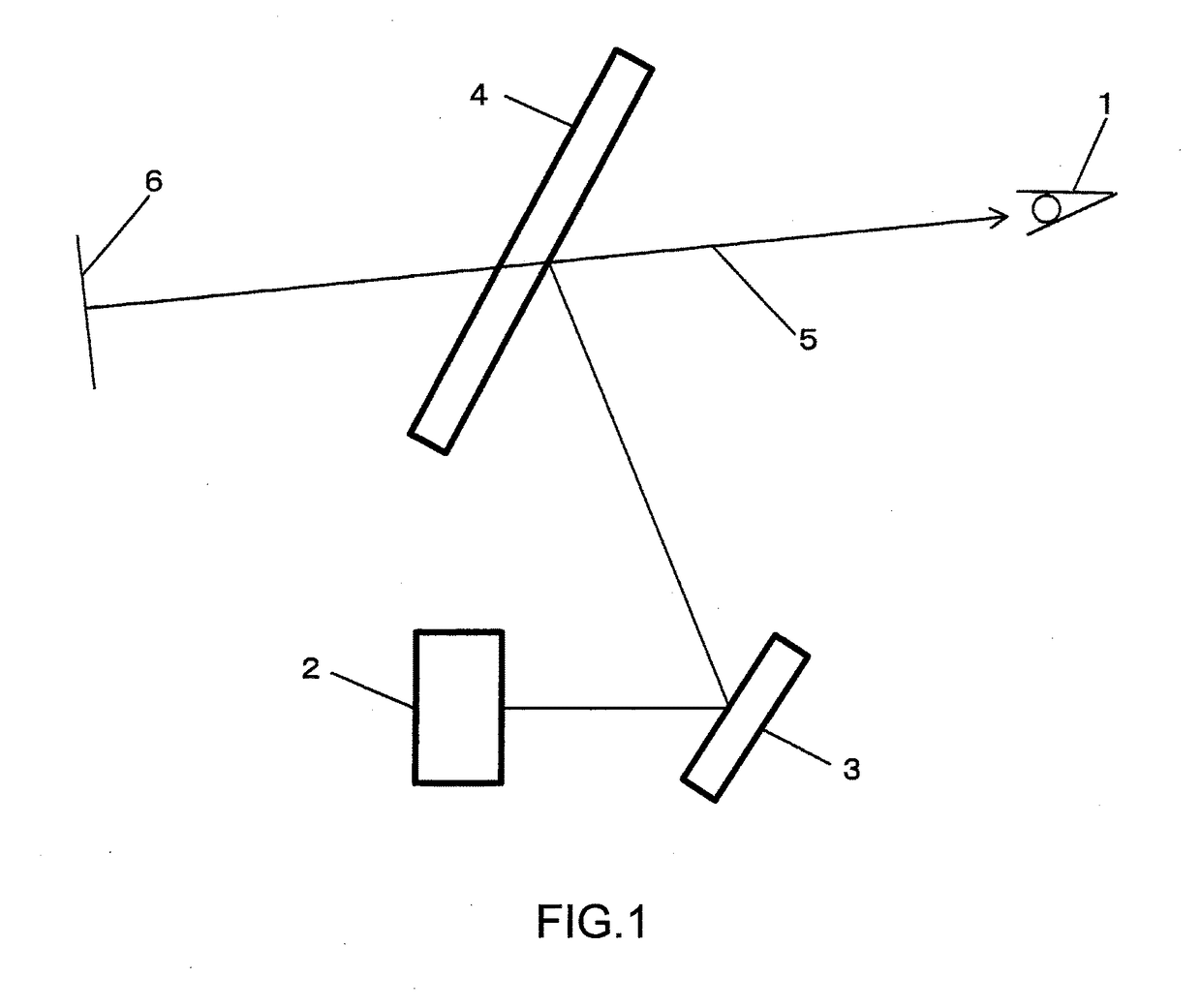
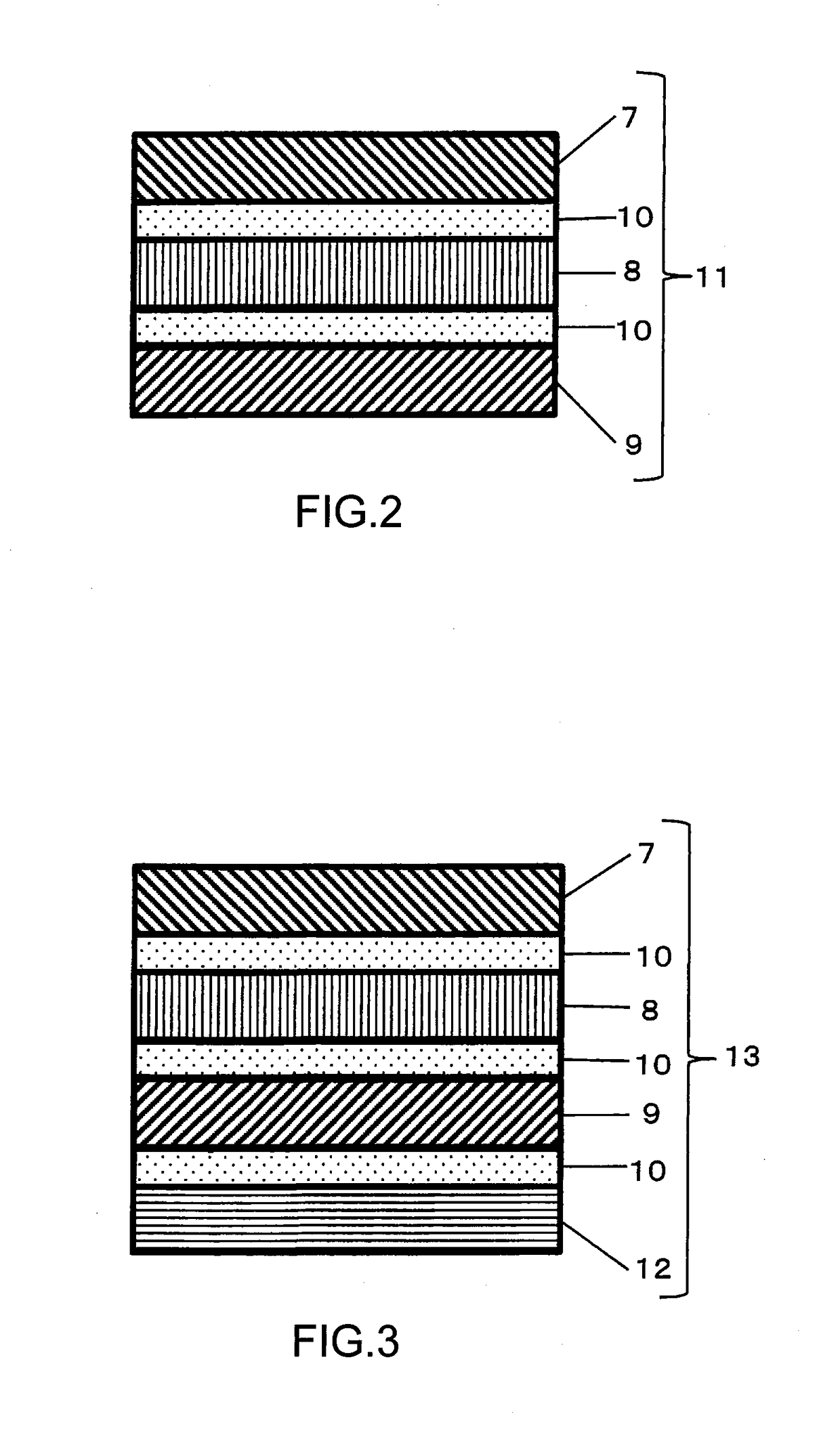
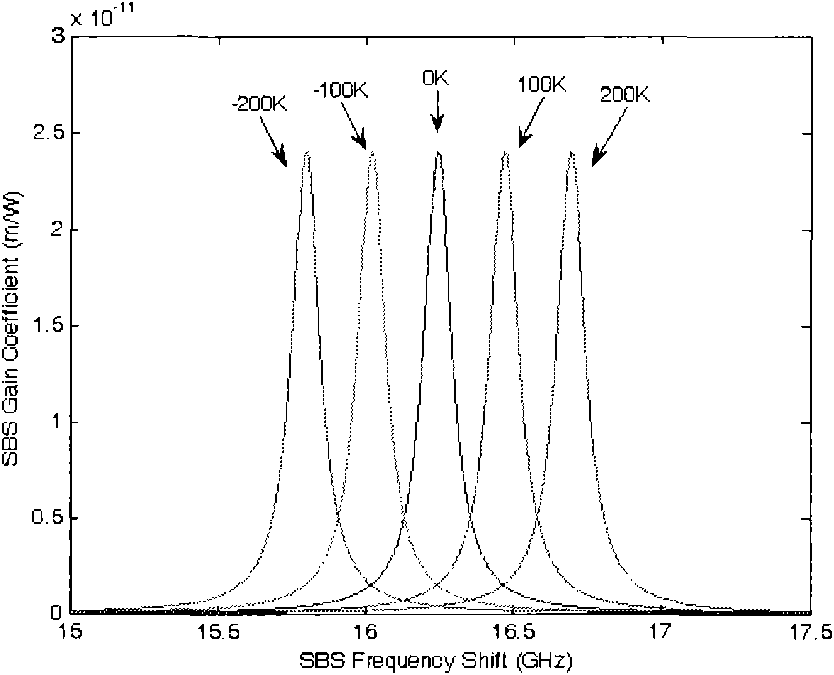
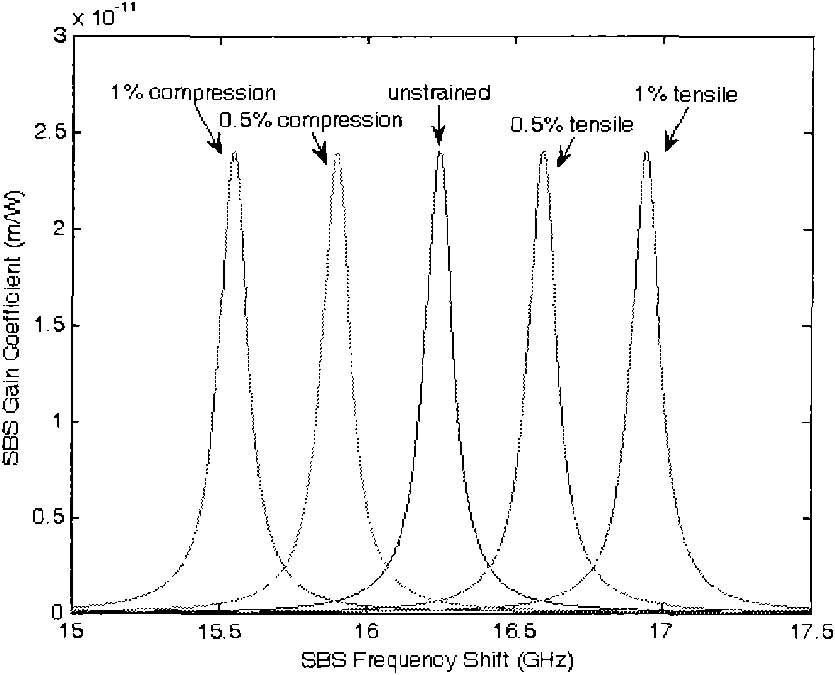
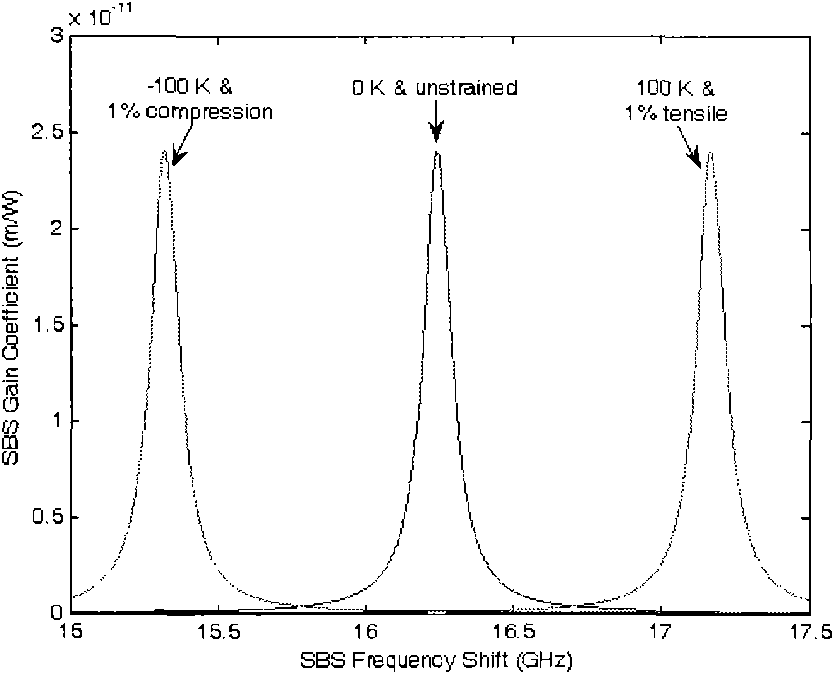
Stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) suppression method for narrow band fiber Raman amplifier
InactiveCN101800396ASuppress scatterIncrease powerLaser using scattering effectsNegative temperaturePositive temperature
The invention relates to a stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) suppression method for a narrow band fiber Raman amplifier (FRA). By exerting negative temperature gradient and longitudinal pressure at the same time or exerting positive temperature gradient and longitudinal pressure at the same time, the method can effectively suppress stimulated Brillouin scattering in a high-power narrow band FRA, and the method has no high requirement to the equipment and is easy to realize.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Laser processing apparatus and laser processing method, debris collection mechanism and debris collection method, and method for producing display panel
InactiveUS20090068598A1Reduce amountEfficiently collectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive material electric discharge removalLaser lightAirflow
A laser processing apparatus is provided for patterning with laser light a resin film or a metal film formed on a substrate. The apparatus includes a laser light source; and a debris collection device having a transmission window through which the laser light is transmitted, a vortex generation mechanism generating a vortex gas flow by allowing gas to flow into a region near a laser light-irradiated area of the resin film or the metal film, and a screening device having an opening through which the incident laser light passes and screening a flow of debris. The mechanism is placed close to the resin film or the metal film on the substrate. Debris generated by laser light irradiation and before and after being stacked on the object film is entrained in the vortex gas flow generated by the vortex generation mechanism and is exhausted to outside through the screening device.
Owner:SONY CORP
Color toner
ActiveUS7112395B2Sufficient fixable rangeGreat can be contaminationMobile jacksDevelopersPolyesterEngineering
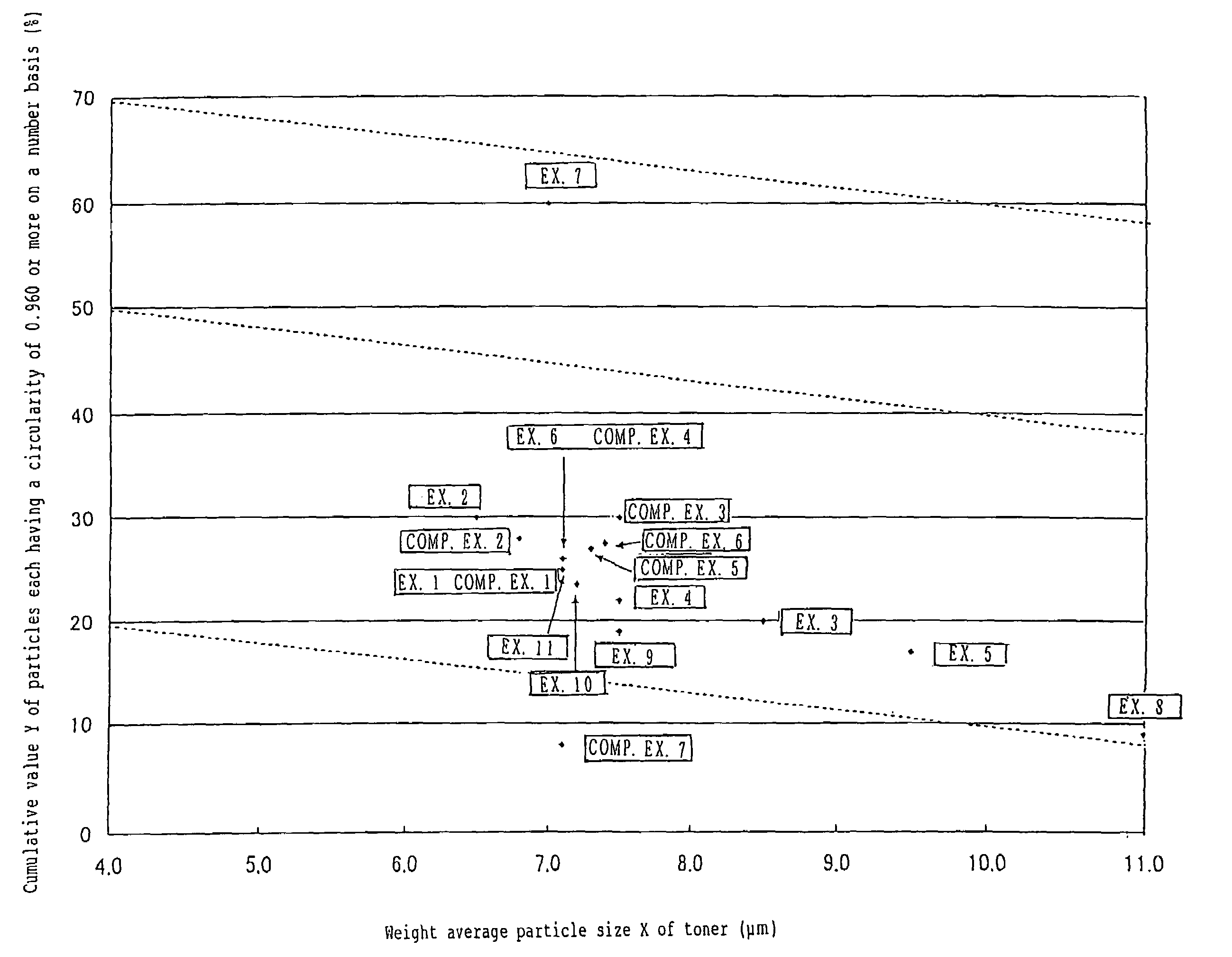
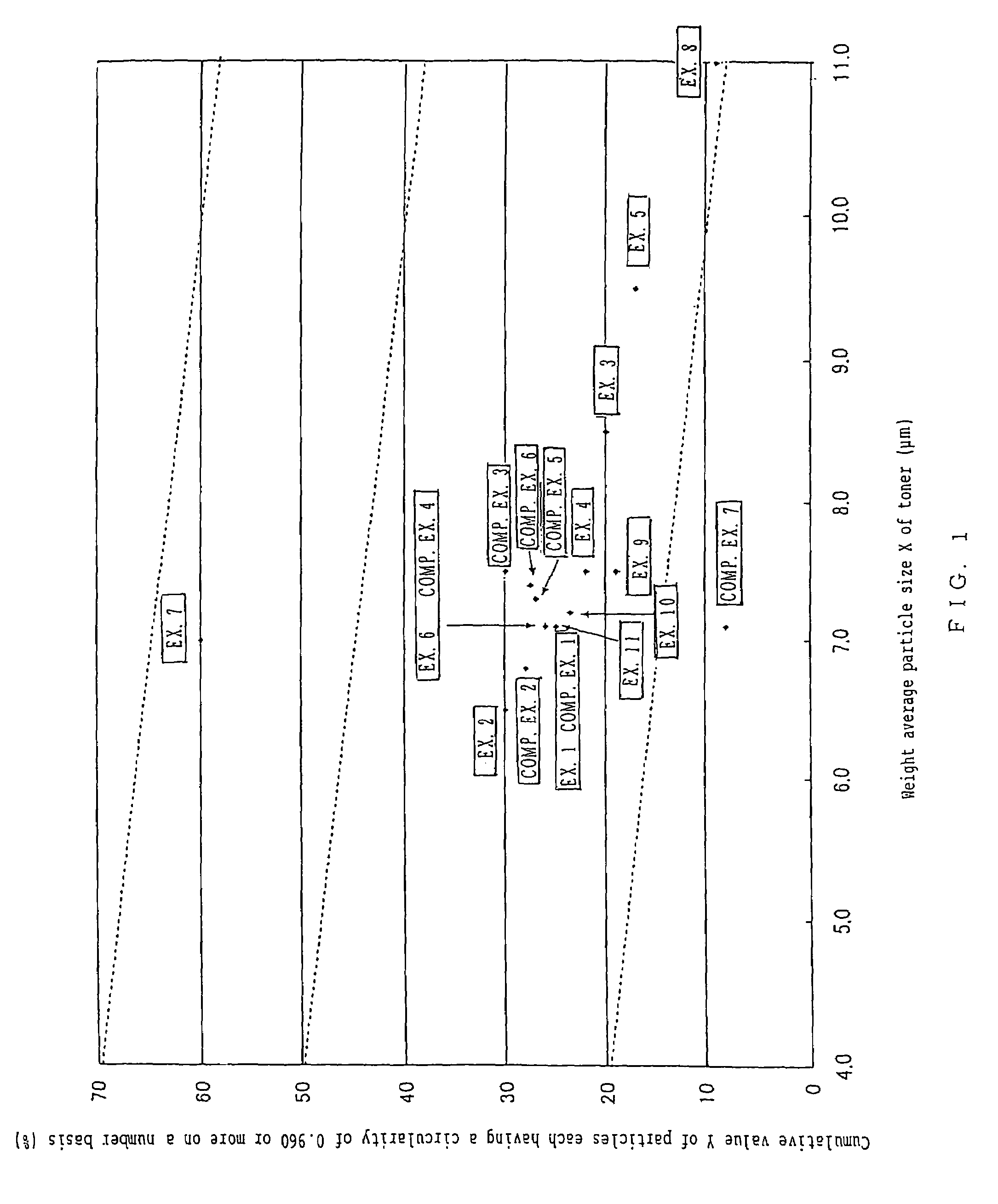
To provide a color toner which is effective in mitigating contamination of a charging member, which is good at low temperature fixing in high-speed copying, and which is excellent in blocking resistance and electrification stability in continuous copying. Provided is a color toner containing at least a binder resin, a colorant, and a releasing agent, in which: (i) the binder resin contains at least a polyester unit; (ii) a weight average particle diameter of the color toner is greater than 6.5 μm and equal to or less than 11 μm; (iii) an average circularity A of particles in the color toner each having a circle-equivalent diameter of 3 μm or more satisfies the relationship of 0.915≦A≦0.960; (iv) a permeability B (%) of the color toner in a 45 vol % aqueous solution of methanol satisfies the relationship of 10≦B≦70; and (v) an endothermic curve obtained through differential thermal analysis (DSC) measurement of the color toner has one or multiple endothermic peaks in the temperature range of 30 to 200° C., and a temperature Tsc of the highest endothermic peak of the one or multiple endothermic peaks satisfies the relationship of 65° C.<Tsc<105° C.
Owner:CANON KK
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20120008974A1Suppress position deviationImproper transferElectrographic process apparatusLatent imageImage formation
An image forming apparatus includes a rotatable image bearing member; a cleaning blade for removing toner in contact with the image bearing member; a load adjusting device for adjusting a contact load between the cleaning blade and the image bearing member; a developing roller for developing an electrostatic latent image on the image bearing member; a developing roller moving device for moving the developing roller between a developing position in which the electrostatic latent image is to be developed and a non-developing position retracted from the developing position; and a control device for effecting control such that the developing roller is moved from the developing position to the non-developing position by the developing roller moving device during rotation of the image bearing member and after an area on the image bearing member opposed to the developing roller at the time when the developing roller is started to be moved from the developing position to the non-developing position passes through a contact area between the cleaning blade and the image bearing member, the contact load is made smaller than that during development by the load adjusting device and then the rotation of the image bearing member is stopped.
Owner:CANON KK
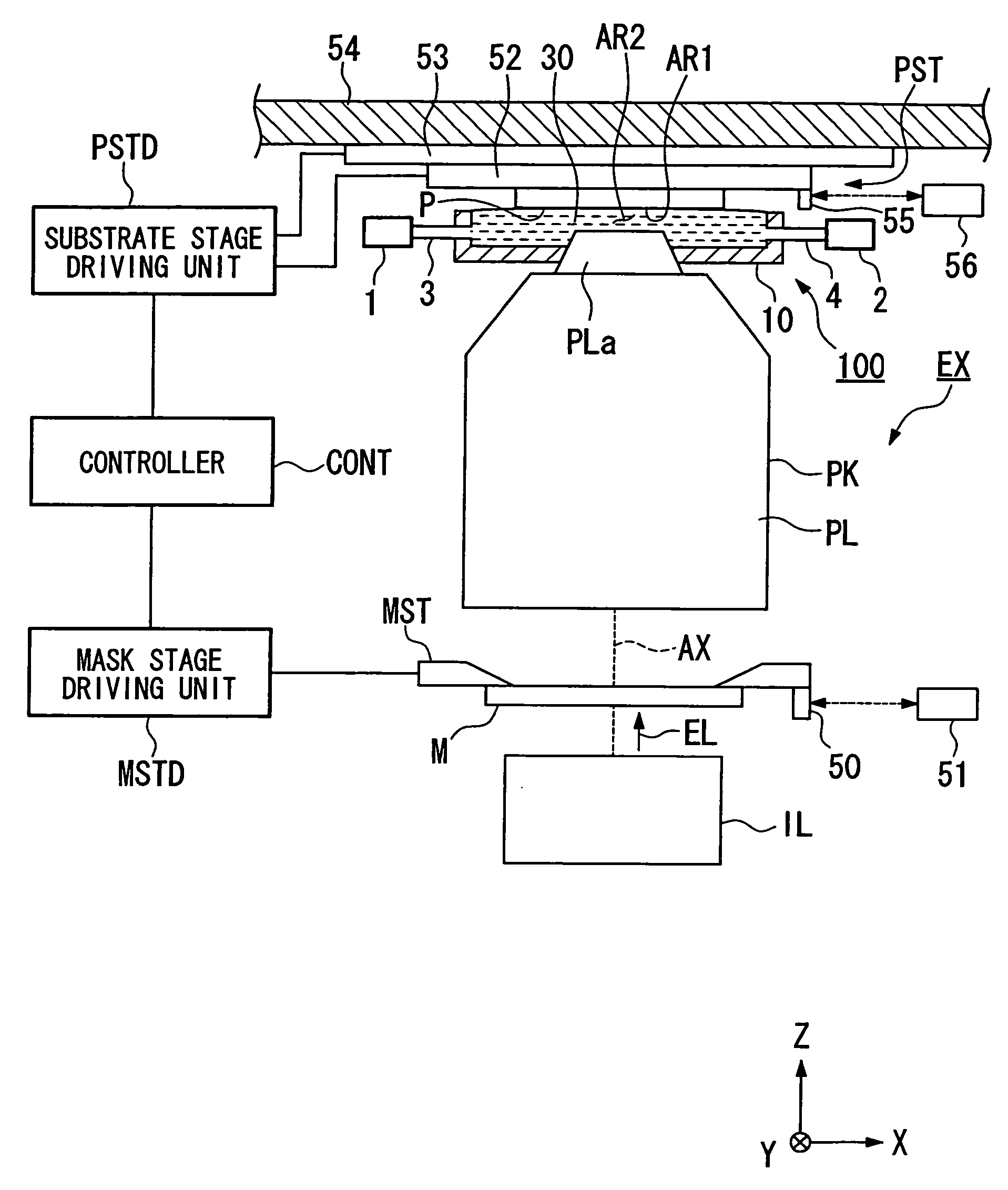
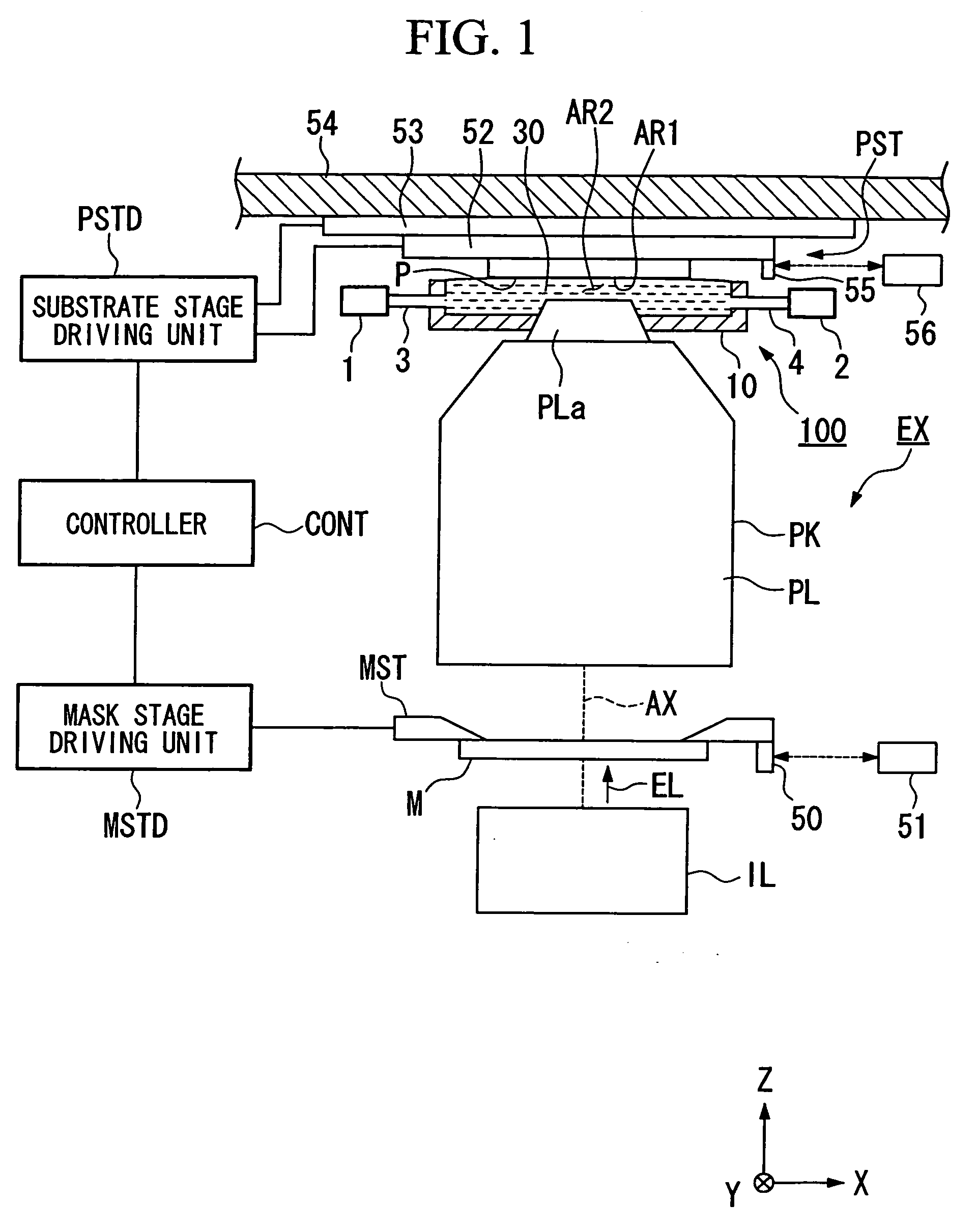
Exposure apparatus and method for manufacturing device
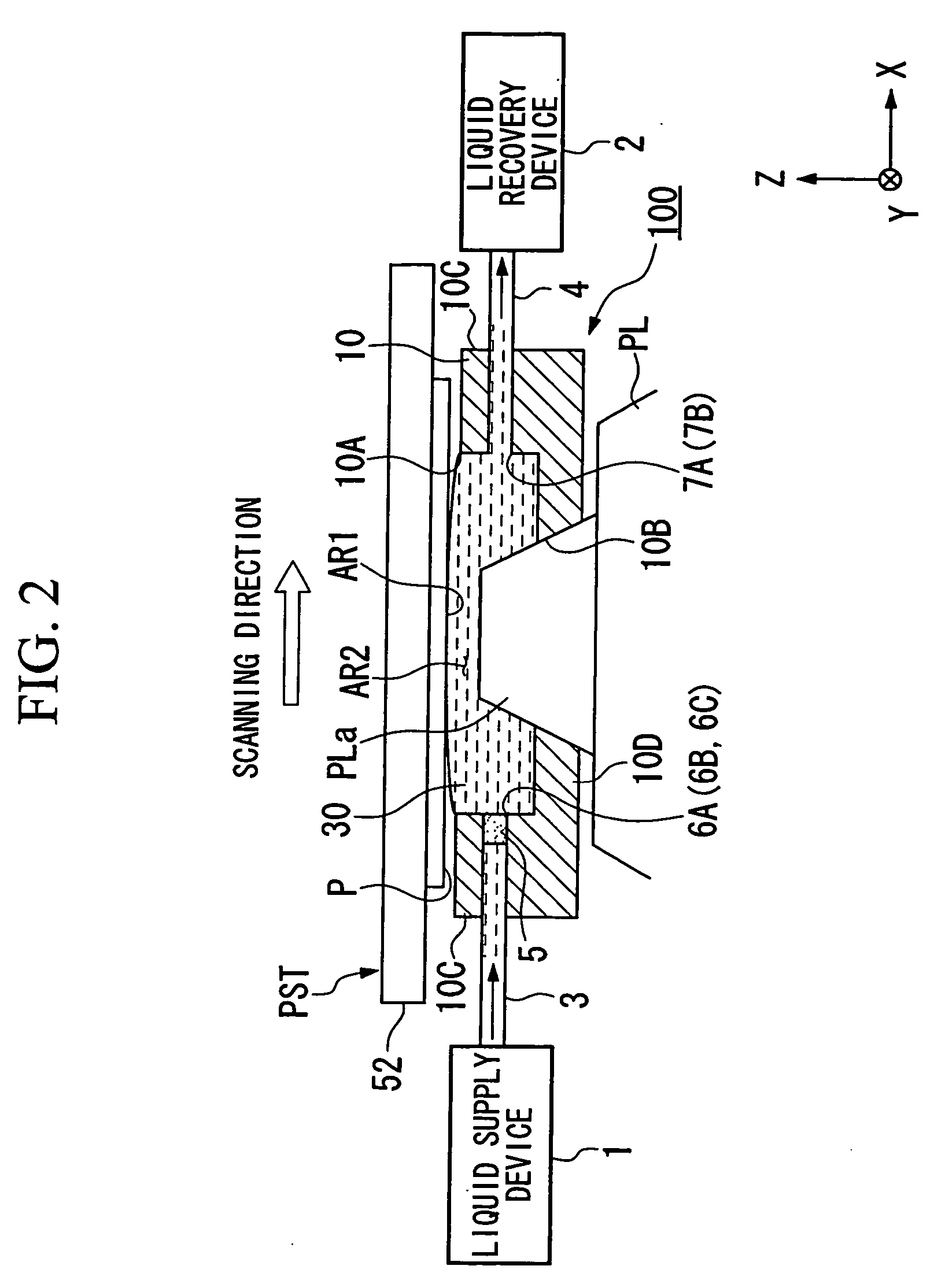
InactiveUS20060033901A1Suppress scatterReduced movement accuracy requirementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptics
An exposure apparatus wherein an image of a pattern is projected onto a substrate via a projection optical system to expose the substrate, includes: a substrate moving device that is movable while holding the substrate above the projection optical system; and a liquid immersion unit that fills at least a portion of the space between the projection optical system and the substrate with a liquid, wherein the image of the pattern is projected onto the substrate via the projection optical system and the liquid.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Heat radiation device for memory module
InactiveUS7257002B2Effective coolingImprove adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal radiationMemory module
There is disclosed a heat radiation device for memory modules intended for radiating heat that is generated from a memory module group wherein a plurality of memory modules equipped with memory elements on both the front and rear face sides of a substrate are placed in parallel. The device comprises heat radiation plates in pairs composed of front face side heat radiation plates in contact with memory elements that are installed on the front face side of the substrate for each of the memory modules, and of rear face side heat radiation plates in contact with memory elements that are installed on the rear face side of the substrate; and connecting members for heat radiation plates in pairs which connect the heat radiation plates in pairs so that heat is conducted among a plurality of the heat radiation plates in pairs.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Heat radiation device for memory module
InactiveUS20080013284A1Effective coolingTemperature homogenizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal radiationEuhedral and anhedral
There is disclosed a heat radiation device for memory modules intended for radiating heat that is generated from a memory module group wherein a plurality of memory modules equipped with memory elements on both the front and rear face sides of a substrate are placed in parallel. The device comprises heat radiation plates in pairs composed of front face side heat radiation plates in contact with memory elements that are installed on the front face side of the substrate for each of the memory modules, and of rear face side heat radiation plates in contact with memory elements that are installed on the rear face side of the substrate; and connecting members for heat radiation plates in pairs which connect the heat radiation plates in pairs so that heat is conducted among a plurality of the heat radiation plates in pairs.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
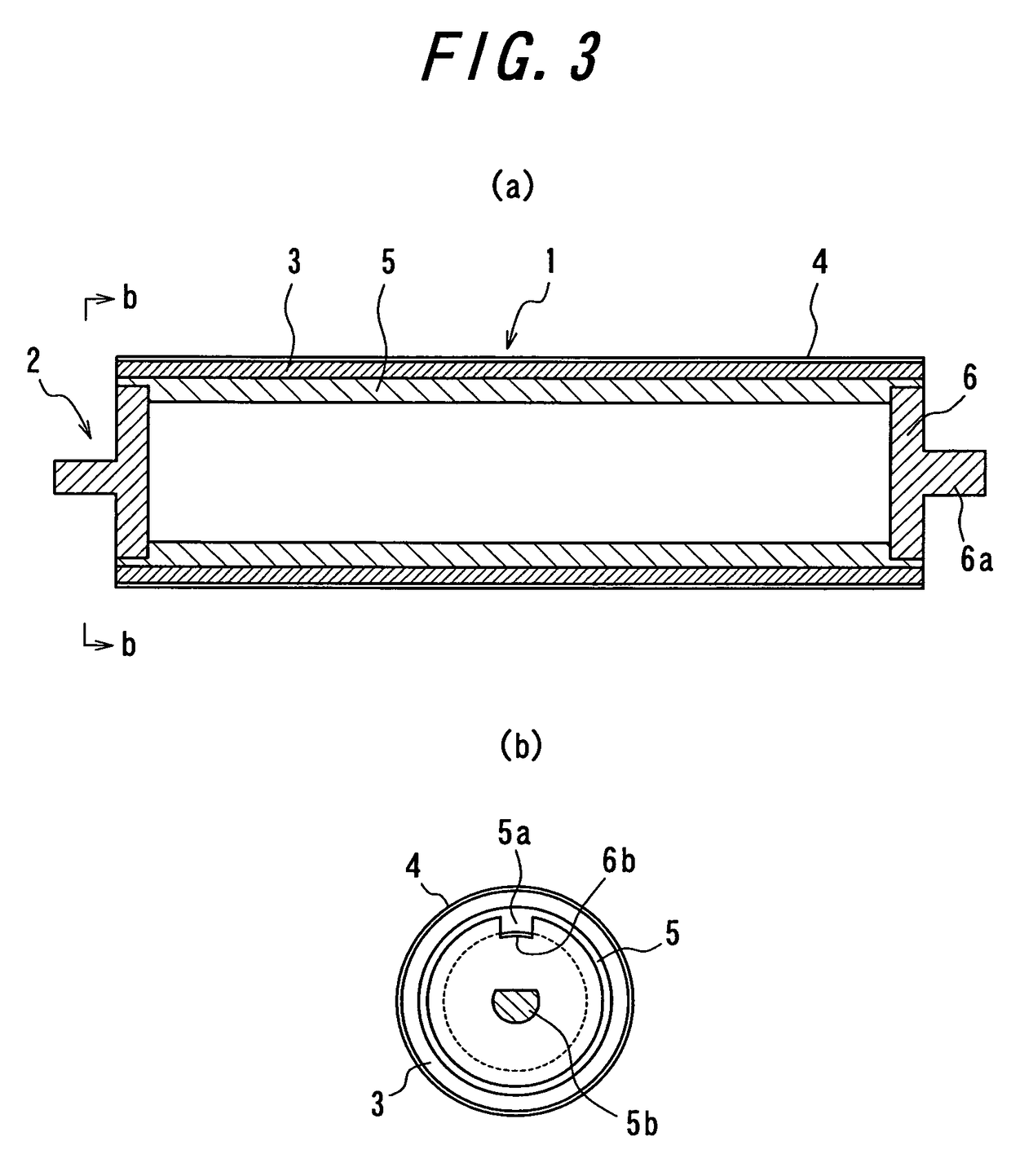
Developing roller and imaging apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7907878B2Easy curingReduce the amount requiredElectrographic process apparatusUV curingUltraviolet
A developing roller includes an ultraviolet-curing type resin layer and using a carbon-based electrically conducting agent for giving an electrical conductivity to the resin layer, as well as an imaging apparatus using the same. The developing roller 1 includes a shaft member 2 of a metal pipe and a resin layer 4. The resin layer 4 is a resin having fine particles dispersed therein, wherein the ratio a / b of average particle size of fine particles a to total thickness of resin layers b is greater than 2.0 and less than or equal to 5.0.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS8252651B2Scattering of characteristics of the FIN type transistor can be suppressedImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
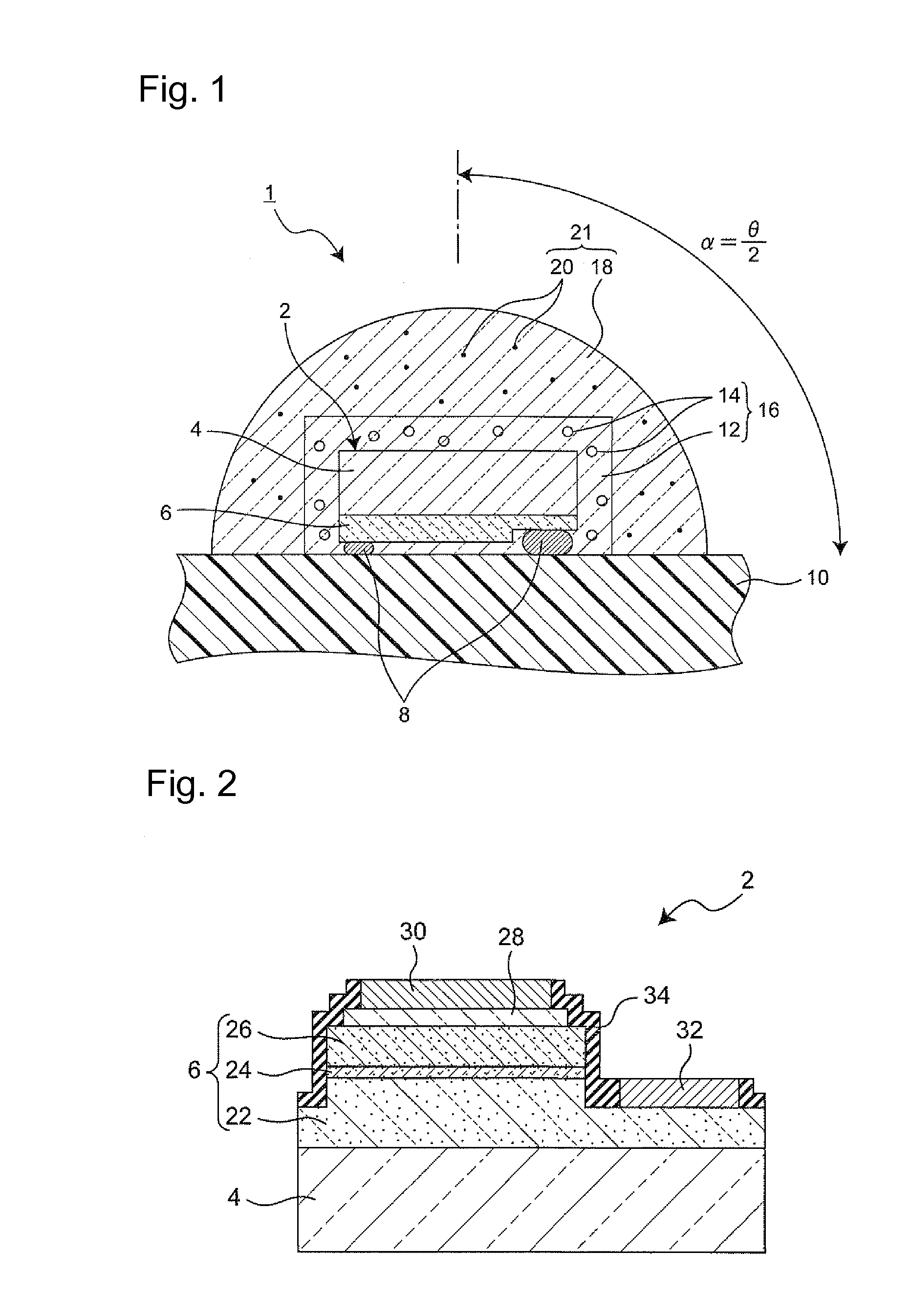
A semiconductor device having a FIN type transistor including a FIN-shape semiconductor portion improved for reliability by suppressing scattering of the characteristics of the FIN-shape transistor by decreasing a difference between impurity concentration at an upper surface and impurity concentration on a lateral side of the FIN-shape semiconductor portion, in which a pad insulating film at a thickness of about 2 to 5 nm is formed to the upper surface of the FIN-shape semiconductor portion, cluster ions are implanted to one lateral side of the FIN-shape semiconductor portion from an oblique direction at a first implantation angle θ1 and then cluster ions are implanted to another lateral side of the FIN-shape semiconductor portion from an oblique direction at a second implantation angle θ2 in symmetrical with the first implantation angle θ1 and, subsequently, the cluster ions implanted to the FIN-shape semiconductor portion 10 are activated to form a diffusion region that forms a portion of a source region and a drain region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
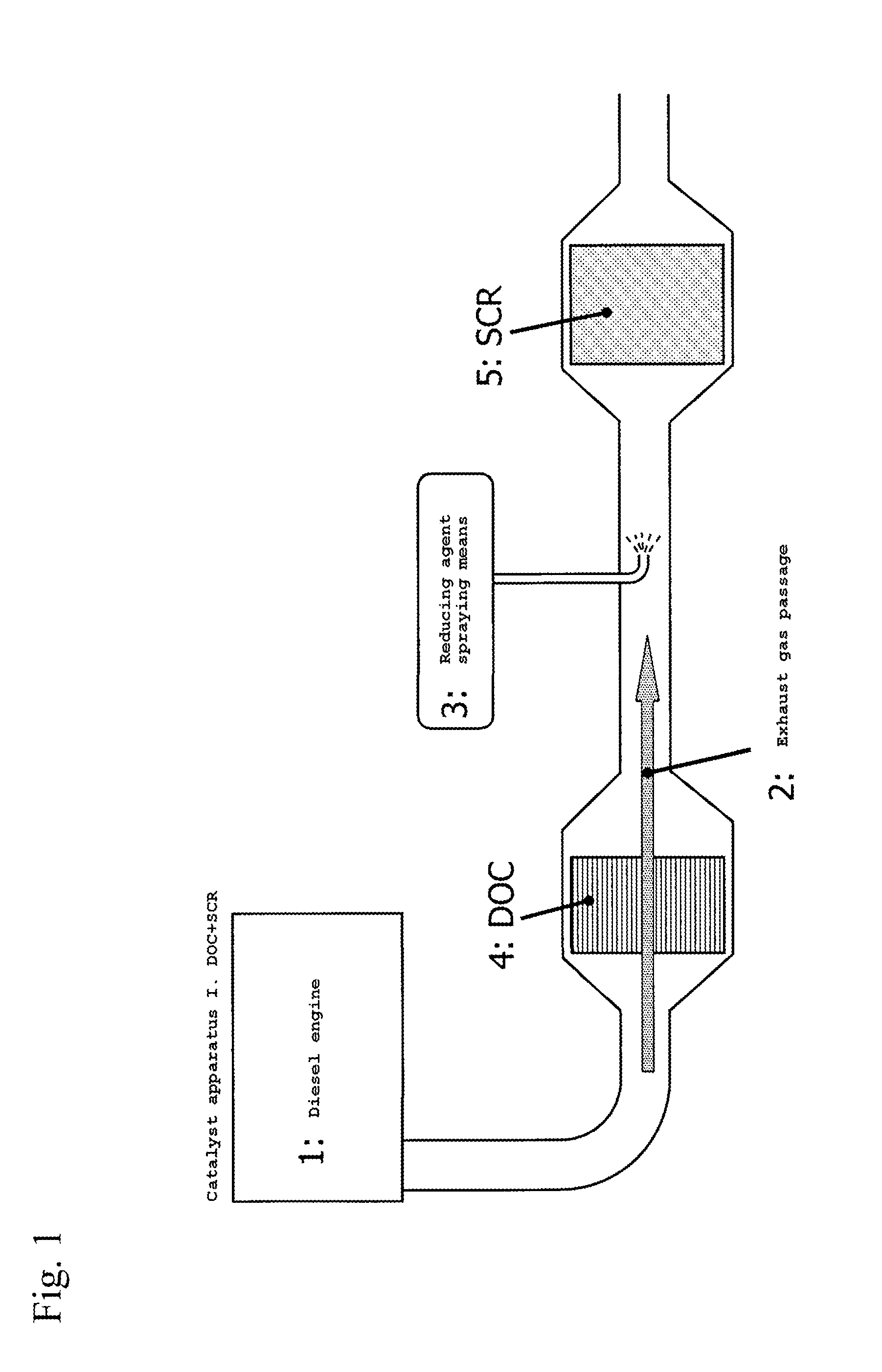
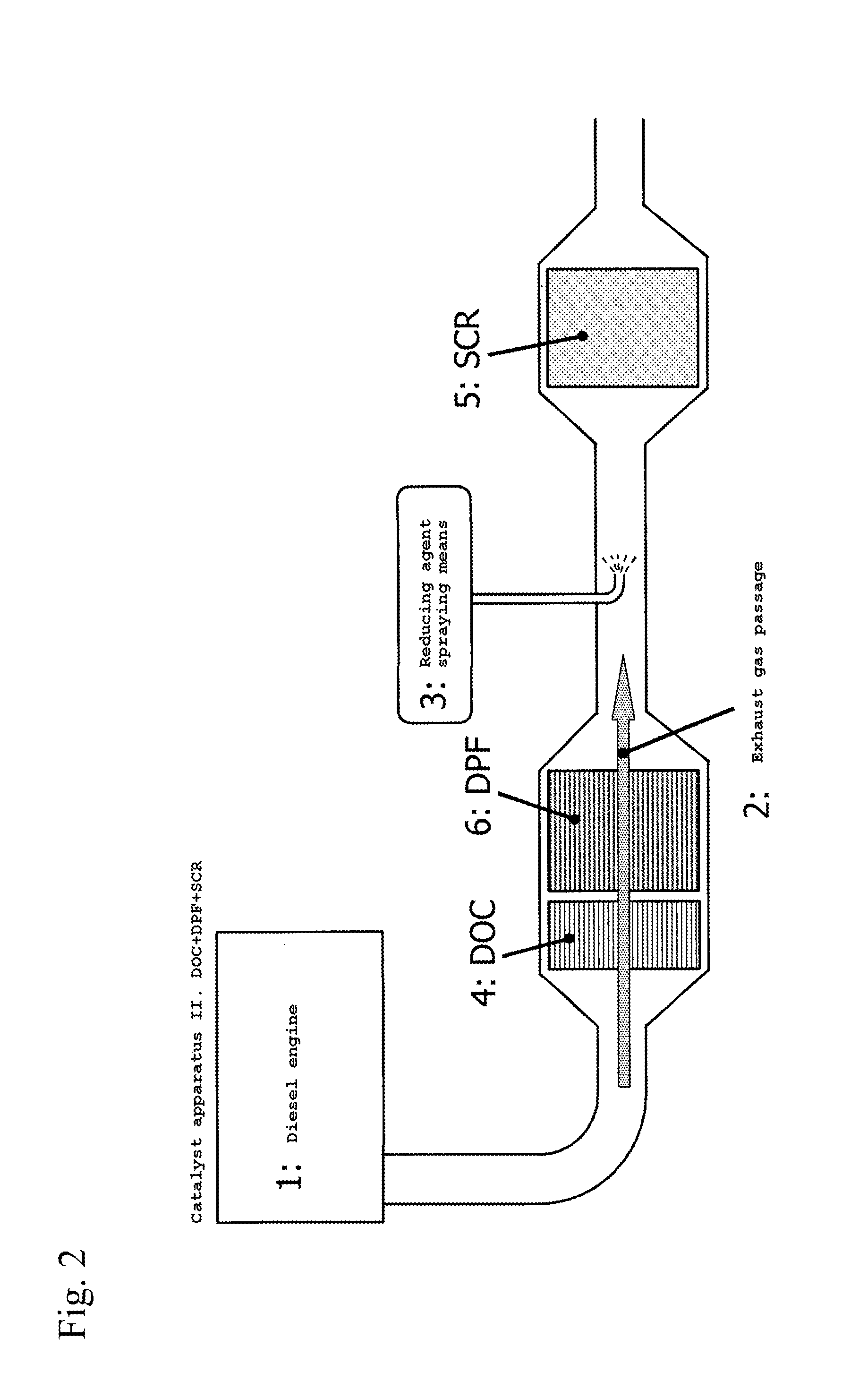
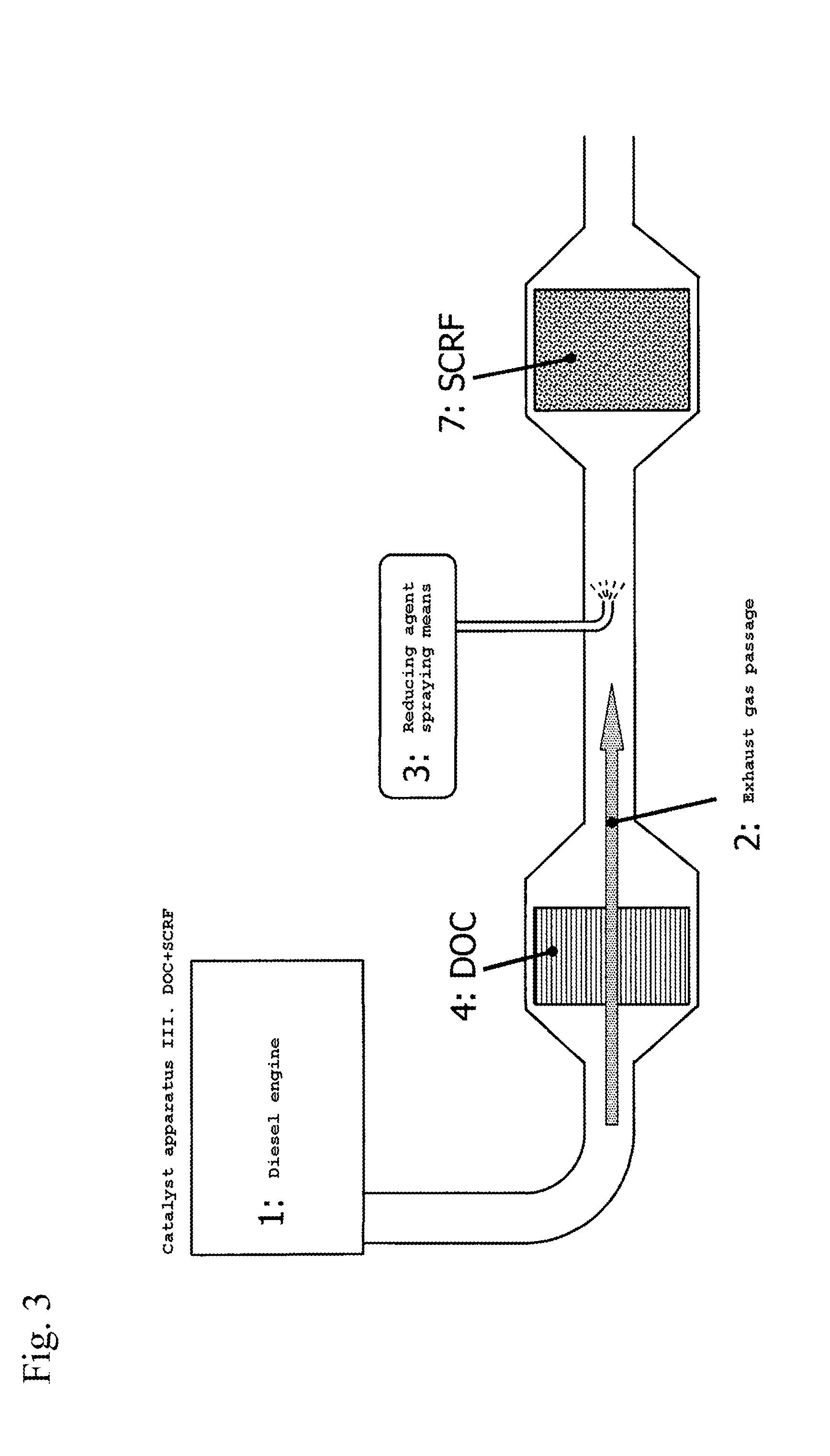
Off gas purification device
ActiveUS20140050627A1Suppress scatterEfficient use ofCombination devicesGas treatmentPlatinumAmmonia
An exhaust gas purification catalyst apparatus. The apparatus has a noble metal component for oxidizing NOx in an exhaust gas discharged from a diesel engine, a reducing agent spraying means for supplying the reducing agent selected from a urea component or an ammonia component, and a selective reduction catalyst (SCR) not comprising a noble metal for removing by reduction NOx by contacting with the reducing agent, in this order from the upstream side of an exhaust gas passage. Activity of the selective reduction catalyst (SCR) is maintained by setting that the noble metal component of the oxidation catalyst (DOC) comprises platinum and palladium, and ratio of platinum particles existing alone is 20% or less, or average particle diameter of the noble metal is 4 nm or larger, and by suppressing volatilization of platinum from the oxidation catalyst (DOC), even when catalyst bed temperature increases up to 900° C.
Owner:N E CHEMCAT
Surge Absorber
ActiveUS20080049370A1Good chemical stabilityExtend your lifeEmergency protective arrangement detailsOvervoltage protection resistorsConductive coatingBarrel Shaped
There is provided a surge absorber which has excellent chemical stability in a high-temperature region upon a sealing process and main discharge and has a long life span, by applying an oxide layer having excellent adhesion to a main discharge surface. A columnar ceramics in which conductive coating films are separately formed via a discharge gap, a pair of main discharge electrode members which face each other and are in contact with the conductive coating films and a barrel-shaped ceramics in which the columnar ceramics is enclosed together with sealing gas are included, and a glass member is enclosed in the barrel-shaped ceramics.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Optical module and manufacturing method of the same, optical-communication apparatus, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20050025435A1Simple structureSimple manufacturing processPrinted circuit detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical ModuleComputer module
The invention provides an optical module that enables to increase the optical coupling efficiency without being dependent on the thickness of a substrate. The optical module, detachably coupled to a connector provided at one end side of an optical fiber, can include a substrate having a first hole, a translucent layer arranged so as to cover, at least, the first hole on one surface side of the substrate, and an optical element that is arranged inside the first hole and on the translucent layer and carries out transmission or reception of light signal to / from the optical fiber through the translucent layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Developing roller and imaging apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7912411B2Easy curingReduce the amount requiredElectrographic process apparatusUV curingUltraviolet
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Light emitting device
ActiveUS8552448B2Light efficiency of lightUnevenness light of lightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWavelengthLight emitting device
A light emitting device capable of improving both color unevenness and emission output power is provided. The light emitting device includes a semiconductor light emitting element including a semiconductor layer that emits primary light; and a fluorescent material layer disposed on the light emitting side of the semiconductor light emitting element, that absorbs a part of the primary light and emits secondary light having a wavelength longer than that of the primary light; and emits light of blended color of the primary light and the secondary light of the light emitting element, and further includes a scattering layer in which particles having a mean particle size D that satisfies the inequality: 20 nm<D≦0.4×λ / π are dispersed in a transparent medium.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070018255A1Quality improvementLower resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
The method for fabricating a semiconductor device according to the present invention comprises the step of forming a Ni film 66 on source / drain diffused layers 64, the step of performing a first thermal processing to react a lower part of the Ni film 66 and an upper part of the source / drain diffused layers 64 with each other to form Ni2Si films 70b on the source / drain diffused layers 64, the step of etching off selectively a part of the Ni film 66, which has not reacted, and the step of performing a second thermal processing to further react the Ni2Si film 70b and an upper part of the source / drain diffused layers 64 with each other.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Shaping slurry and shaping method
ActiveUS8425816B2Suppress scatterNon-fibrous pulp additionAdditive manufacturing apparatusWater basedPolymer science
Owner:COLUMBIA PEAK VENTURES LLC
Particle beam treatment apparatus and irradiation nozzle apparatus
InactiveUS20110182411A1Increase costLimited imaging rangeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyParticle beamLight beam
A particle beam treatment apparatus and an irradiation nozzle apparatus achieve a beam with a small diameter by a beam scanning irradiation method, and ensure a space for installation of a beam transport chamber in the irradiation nozzle apparatus. An X-ray tube is located outside the scanning type irradiation nozzle apparatus that includes scanning magnets, while an X-ray tube is located in an irradiation nozzle apparatus in a conventional structure. An X-ray detector is located inside the irradiation nozzle apparatus. The thickness of the X-ray detector in the direction of a beam axis is smaller and the structure thereof is simpler than that of the X-ray tube. This makes it possible to ensure the space for installation of the beam transport chamber in the irradiation nozzle apparatus and to increase the length of the beam transport chamber that is included in the irradiation nozzle apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
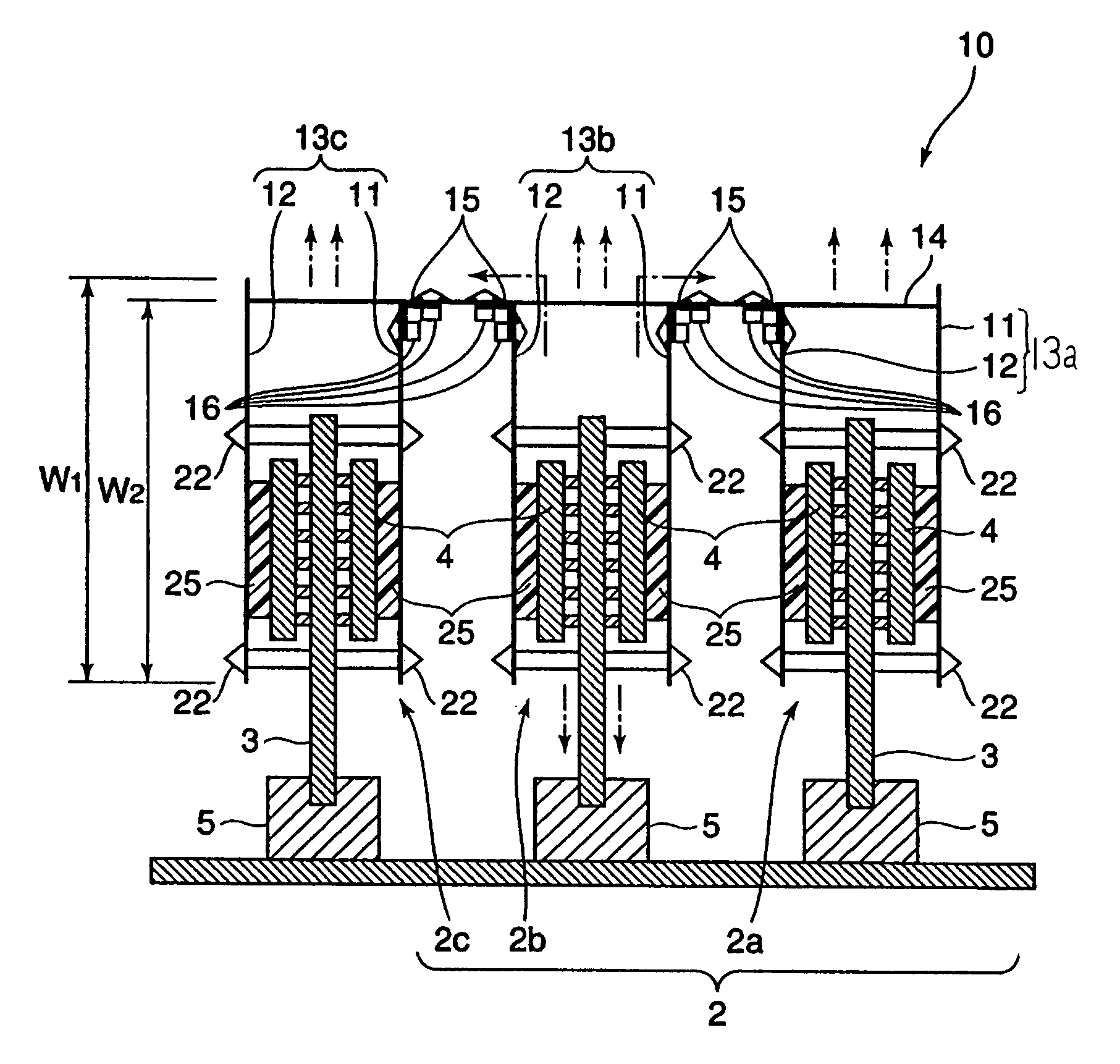
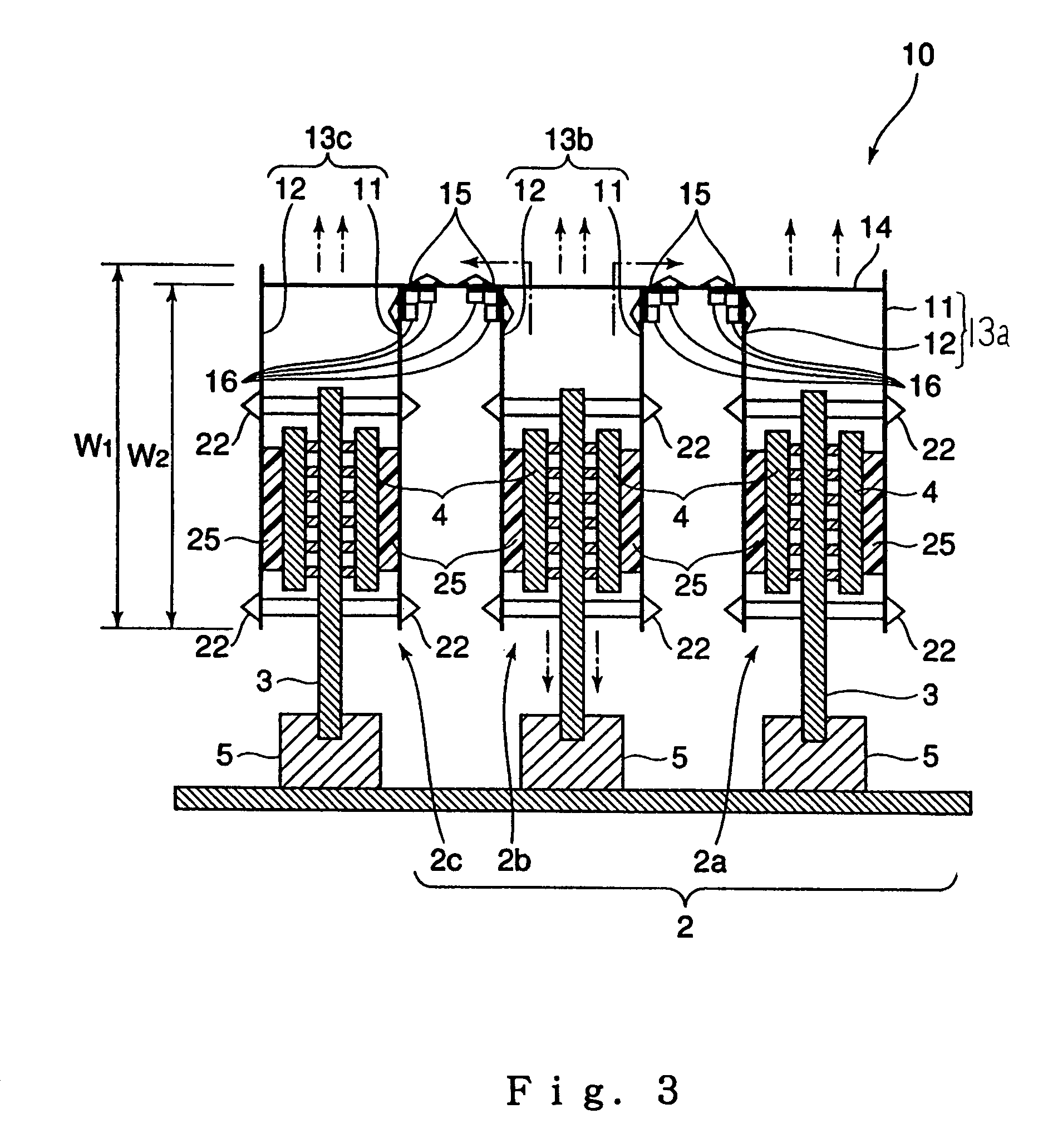
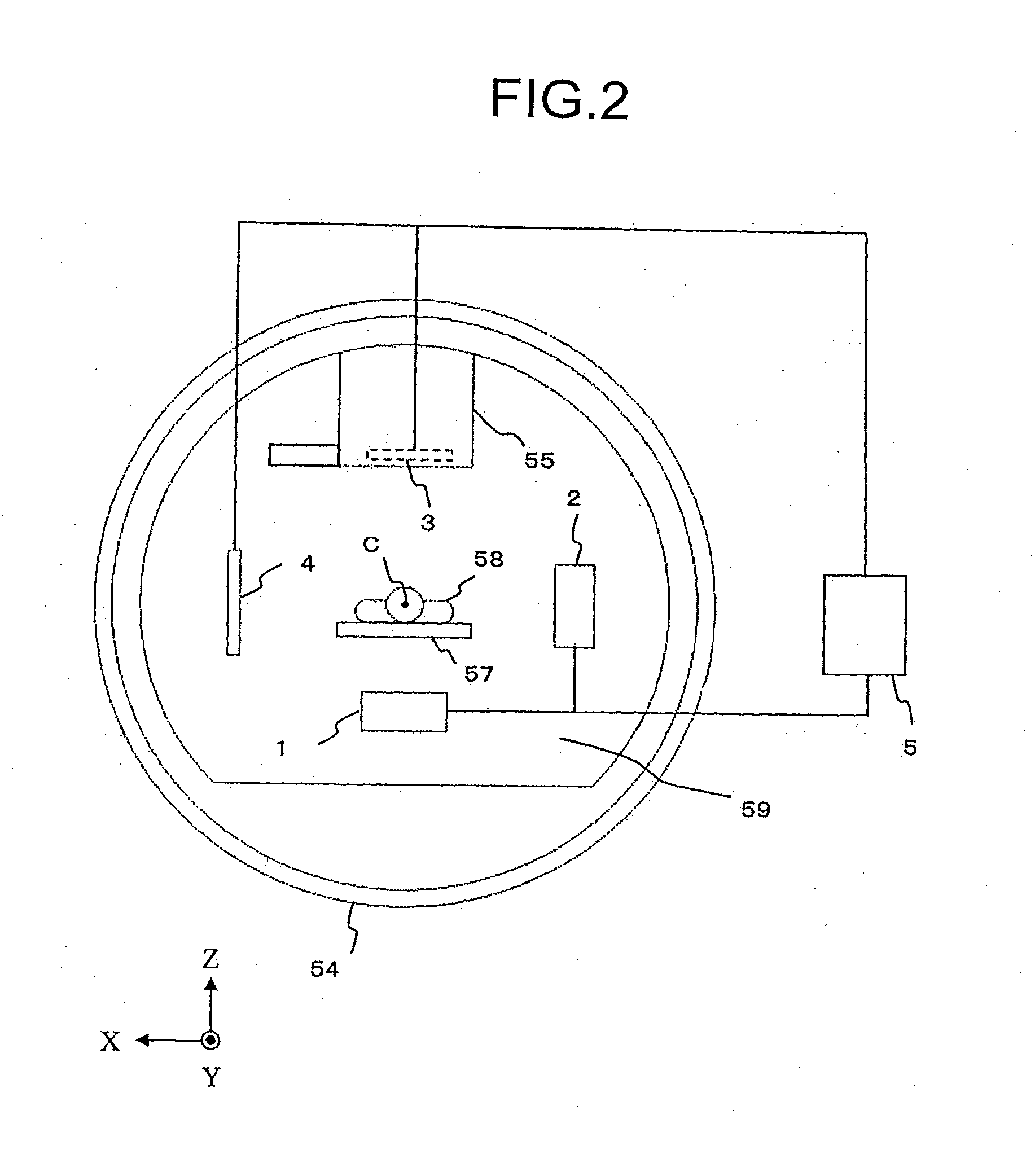
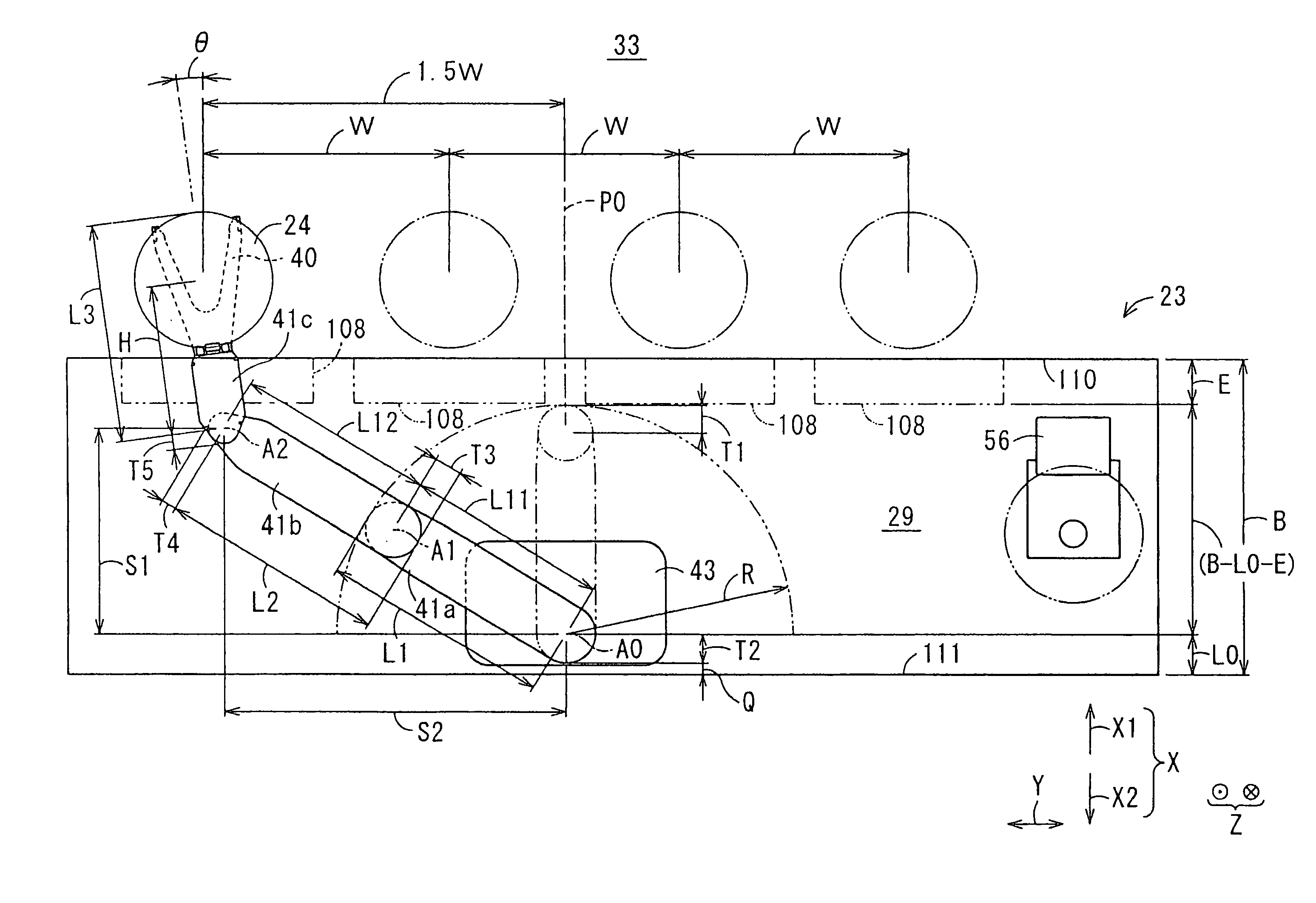
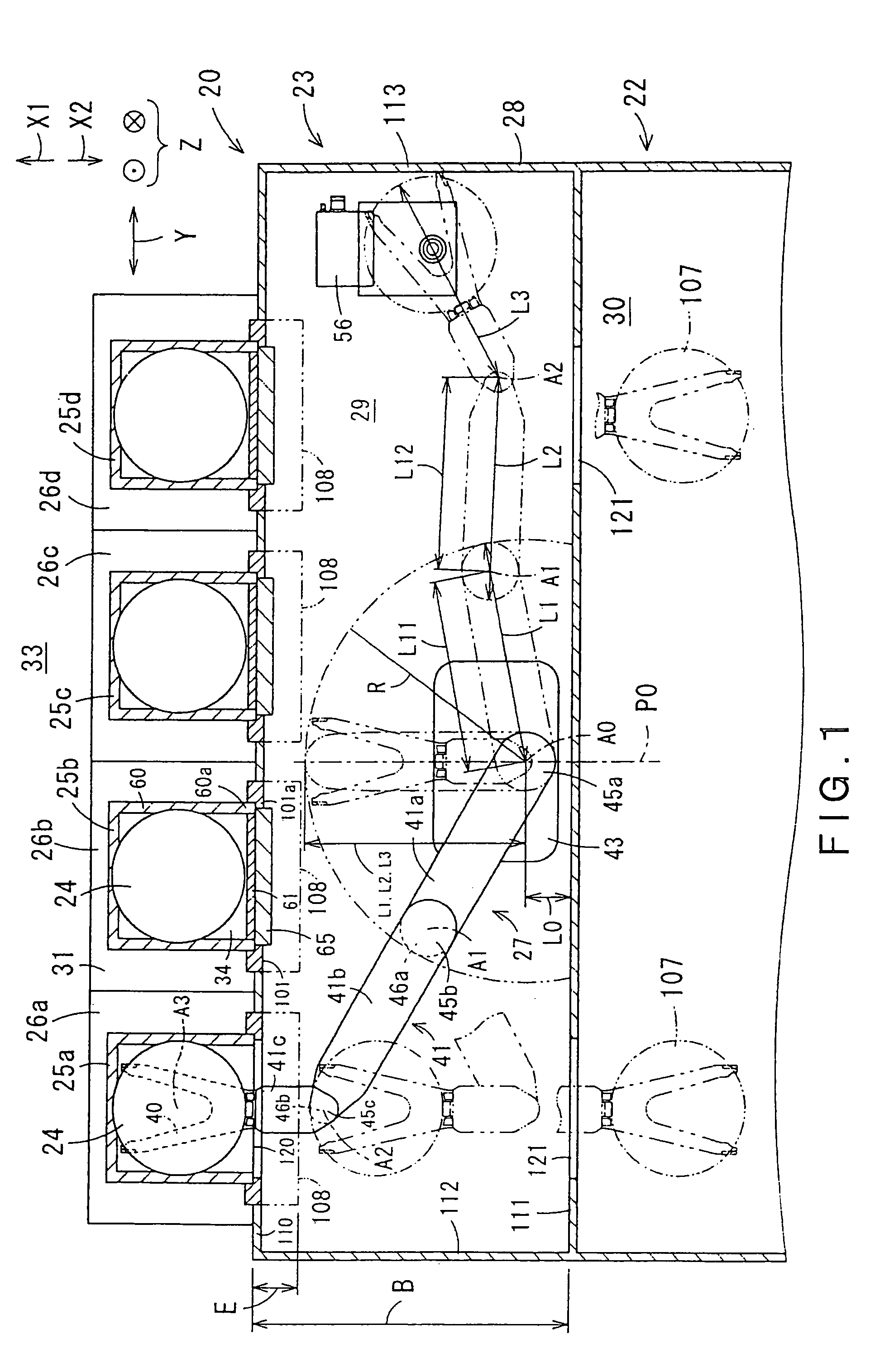
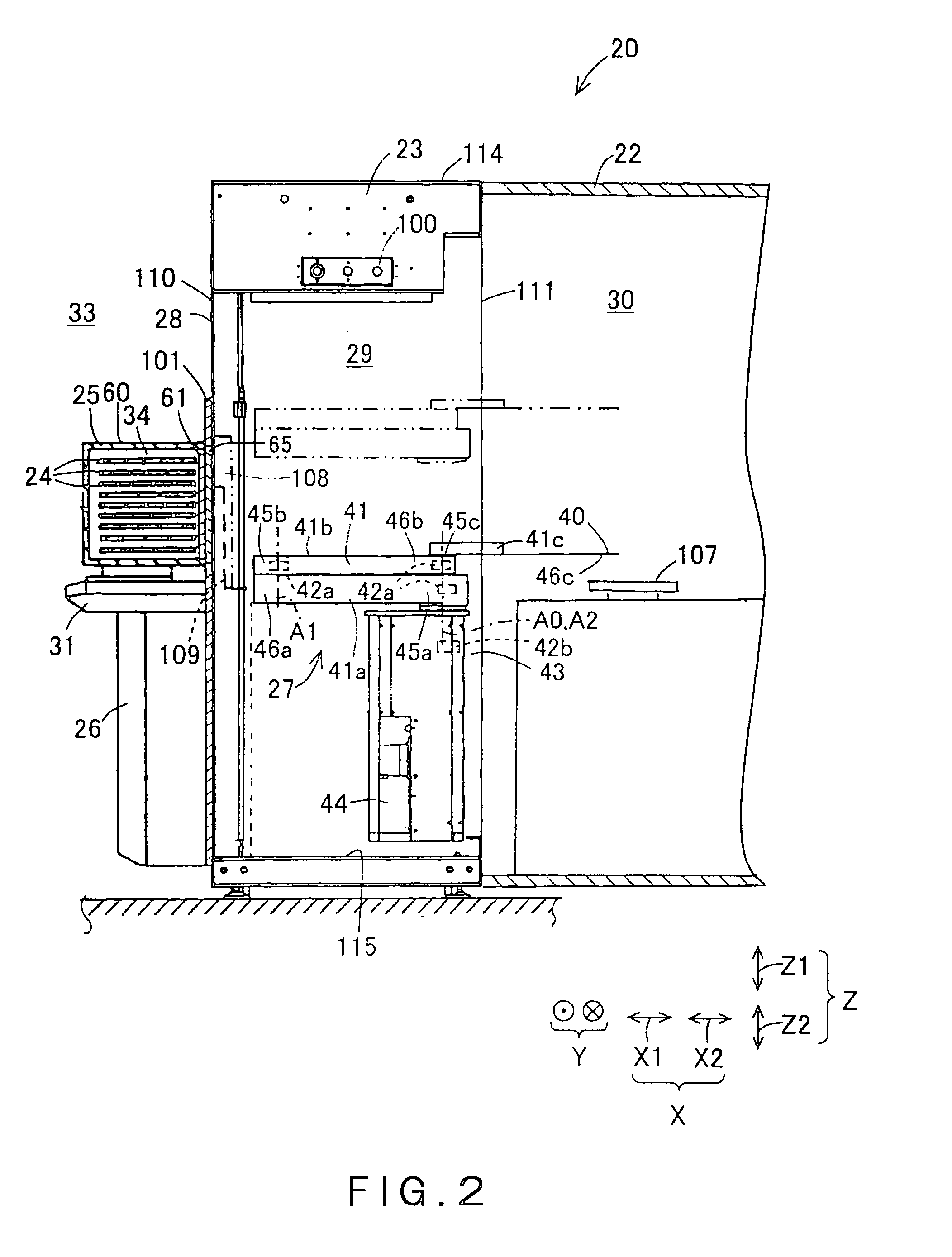
Wafer transfer apparatus and substrate transfer apparatus
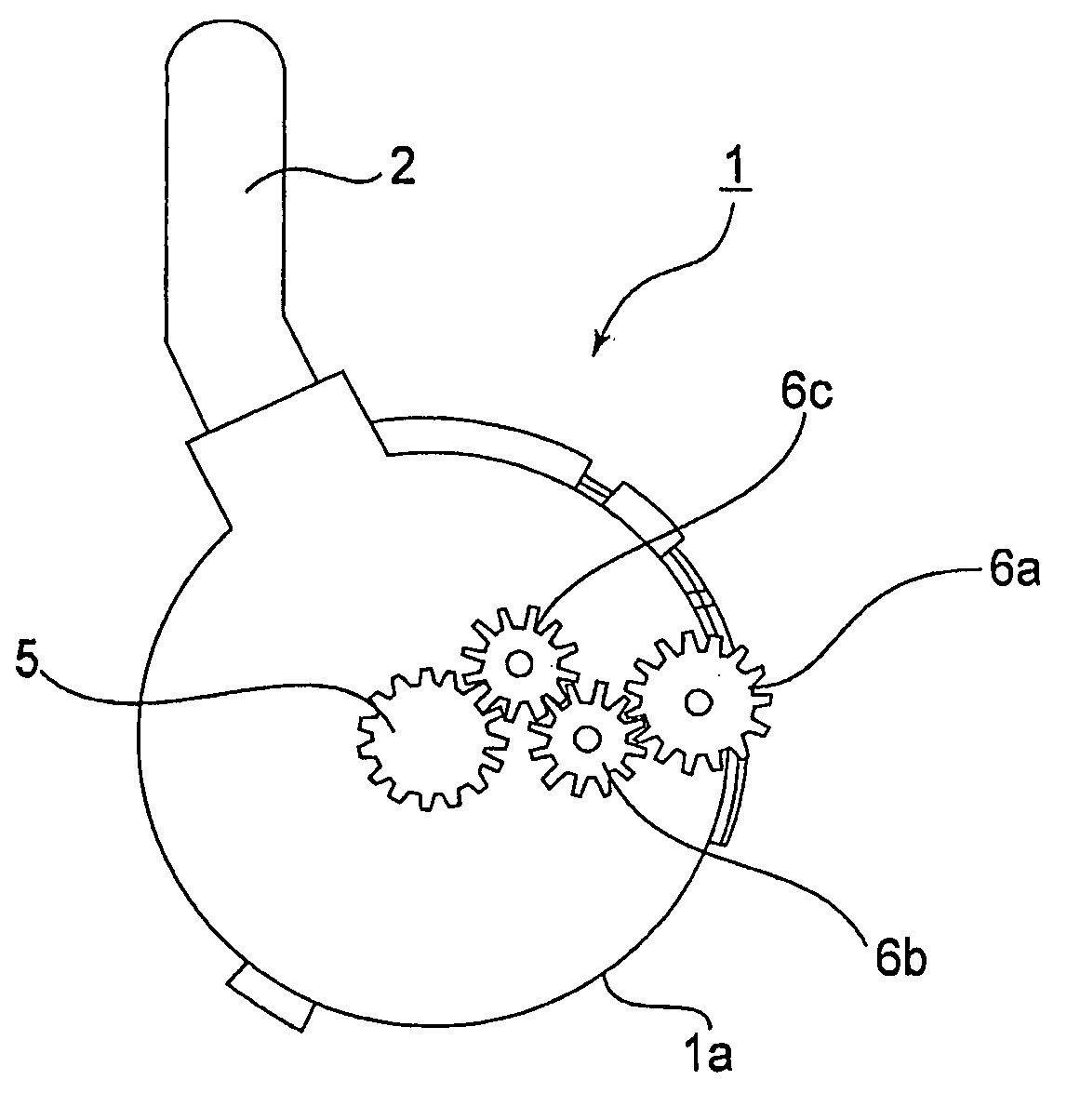
ActiveUS7874782B2Suppress scatterAvoid it happening againProgramme controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A wafer transfer apparatus is provided. In a minimum transformed state where a robot arm is transformed such that a distance defined from a pivot axis to an arm portion, which is farthest in a radial direction relative to the pivot axis, is minimum, a minimum rotation radius R, is set to exceed ½ of a length B in the forward and backward directions of an interface space, the length B corresponding to a length between the front wall and the rear wall of the interface space forming portion, and is further set to be equal to or less than a subtracted value obtained by subtracting a distance L0 in the forward and backward directions from the rear wall of the interface space forming portion to the pivot axis, from the length B in the forward and backward directions of the interface space (i.e., B / 2<R≦B−L0).
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
Octagonal flat-type array antenna
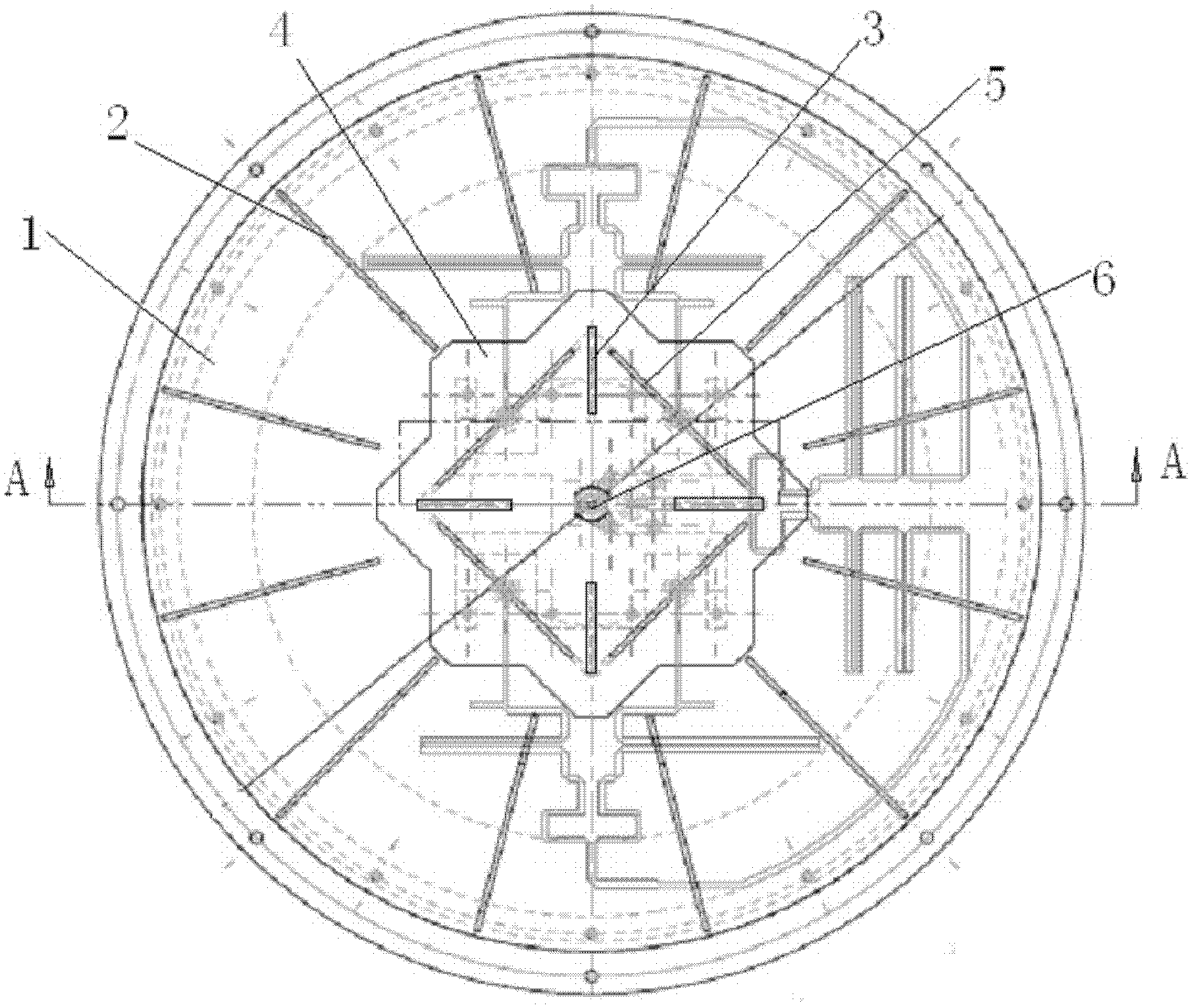
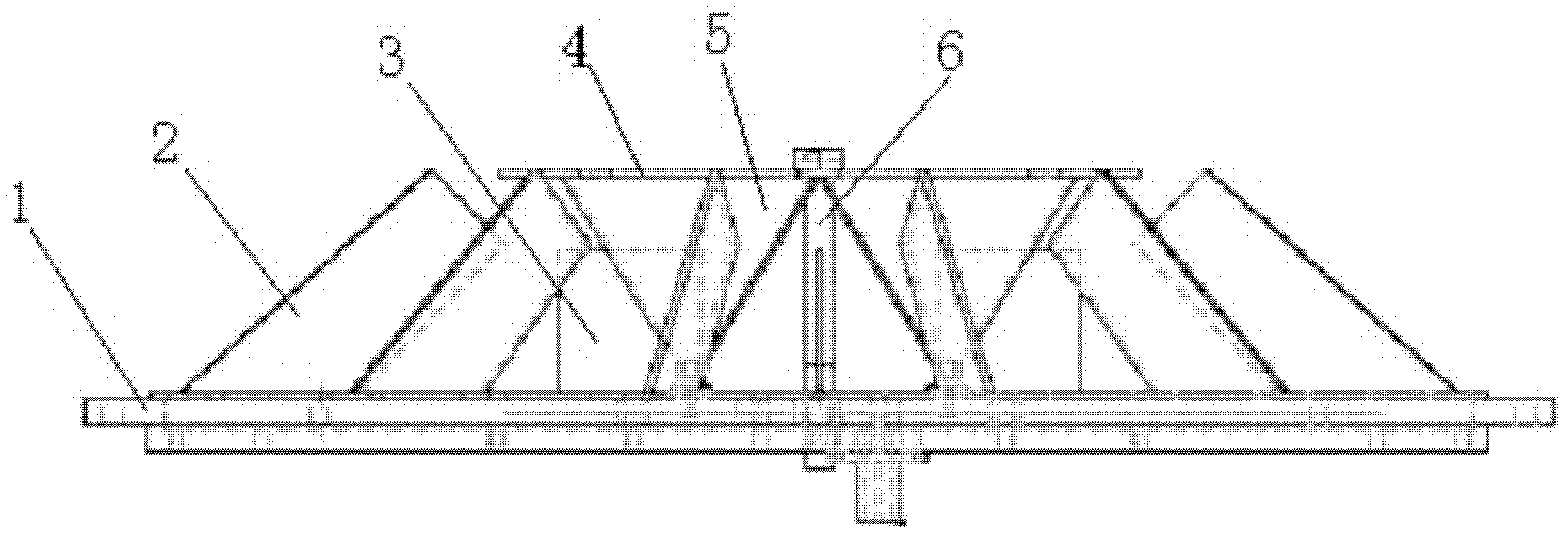
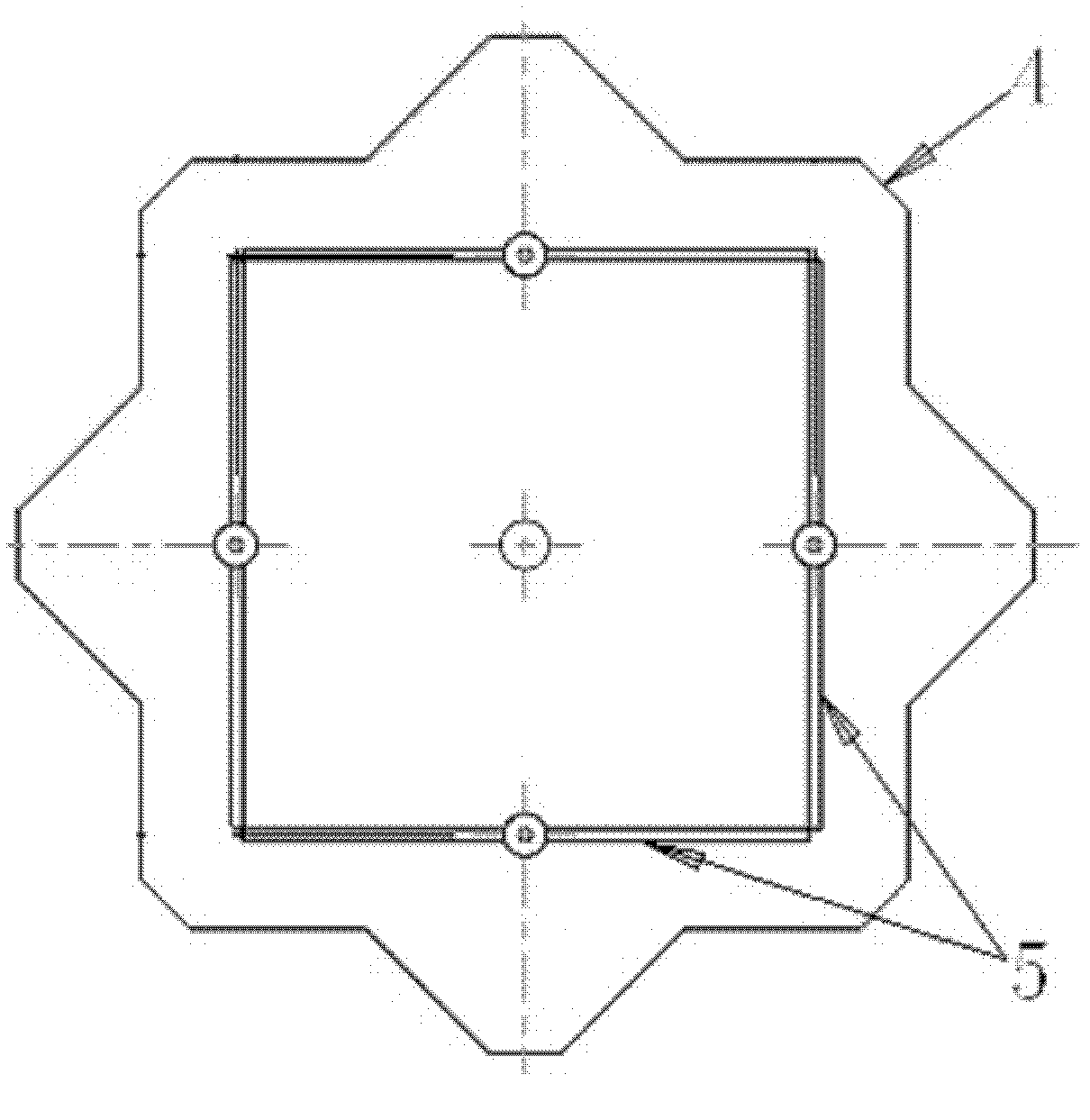
ActiveCN102437408AGood central symmetryRadiation phase center stableAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsPhysicsBroadband
The invention discloses an octagonal flat-type array antenna comprising an earth plate and a circularly-polarized four-point feeding network, wherein the earth plate is provided with a central radiating element assembly and two groups of coupling plates arranged by equal distance along the radial direction. The octagonal flat-type array antenna can receive signals transmitted by a plurality of navigation and positioning satellite constellations and meet the requirement for high-precision carrier phase measurement. A high-precision receiver antenna for GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) carrier phase measurement can be provided for users of ocean, land, air and space, and the octagonal flat-type array antenna can also be popularized and applied to a radio transmitting and receiving system with a stable radiating phase center and a circular polarization and hemisphere beam coverage requirement. The octagonal flat-type array antenna has the characteristics of stable radiating phase center, circular symmetry of radiation pattern, high roll-off, high front-to-back ratio and favorable wide angle circular polarization, has favorable anti-multipath and broadband operation capacity and is a novel GNSS high-precision carrier phase measurement type user compatible receiver antenna.
Owner:北京华力创通科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com