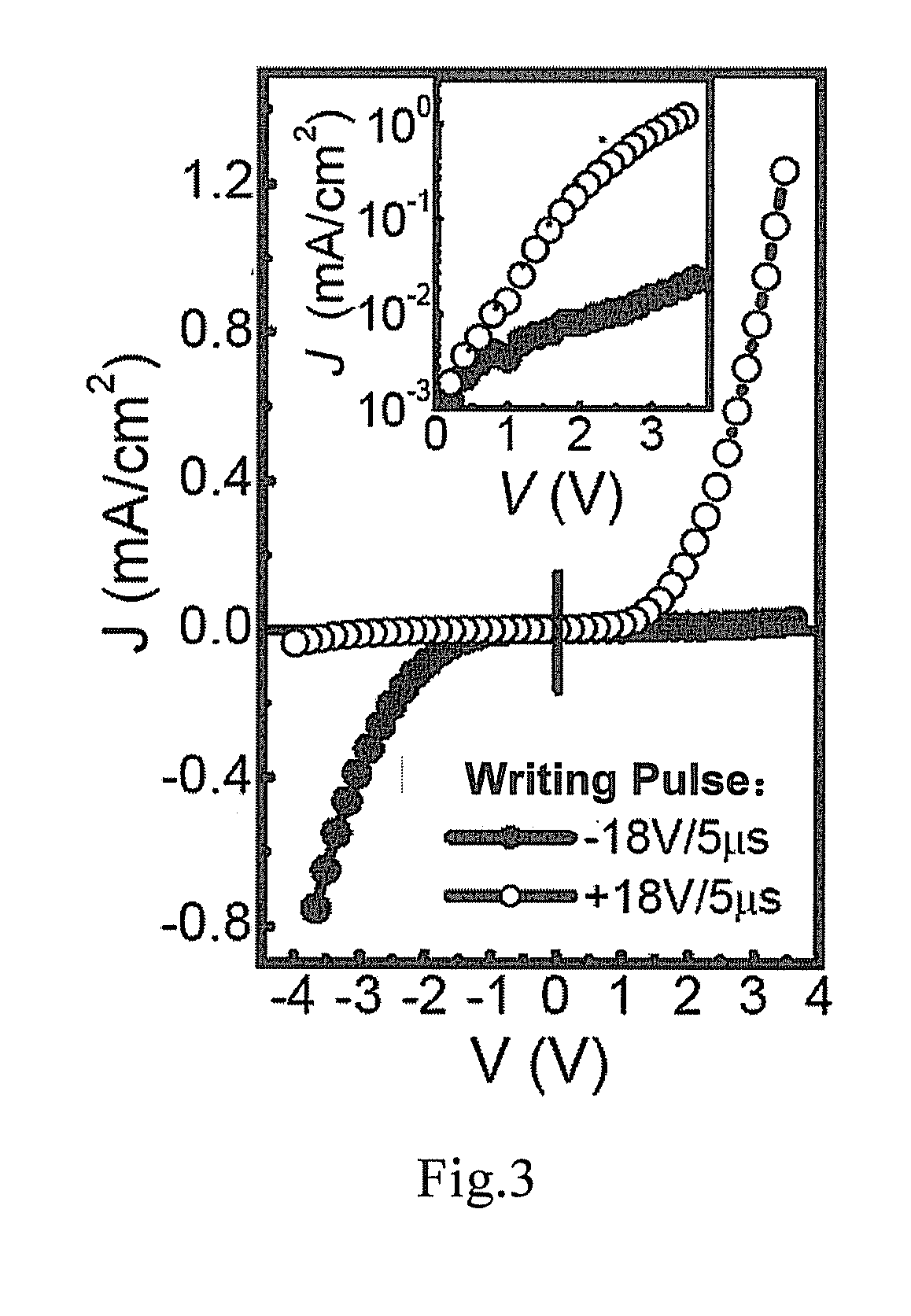
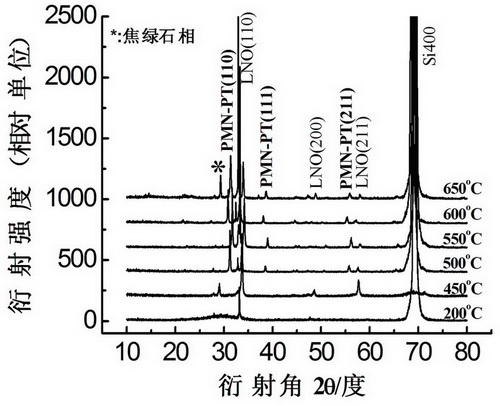
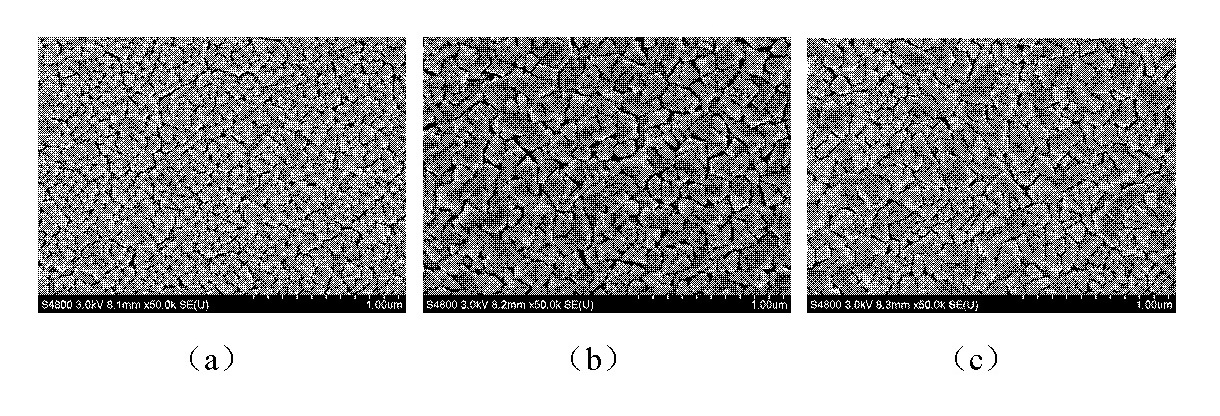
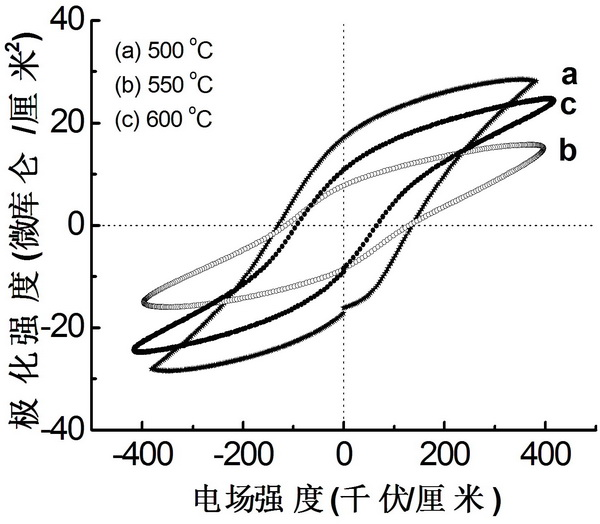
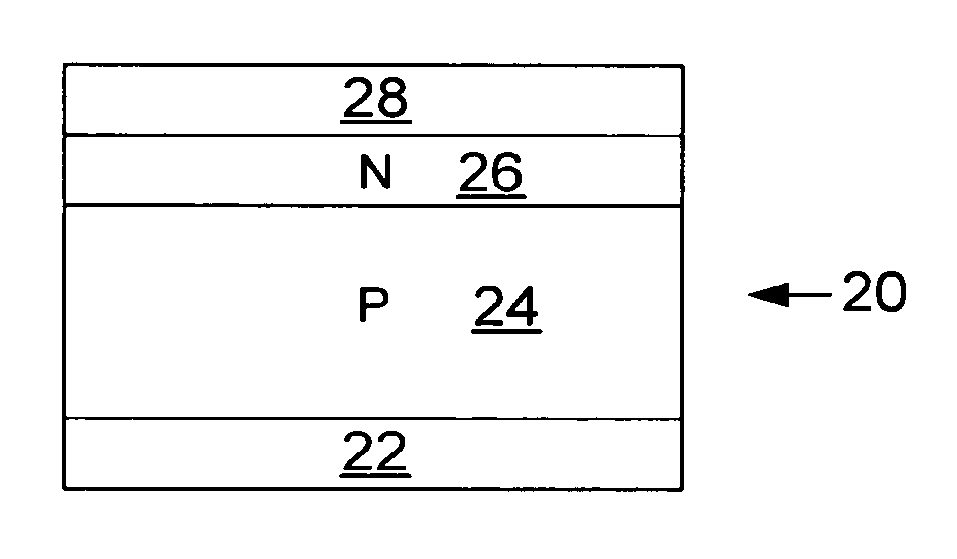
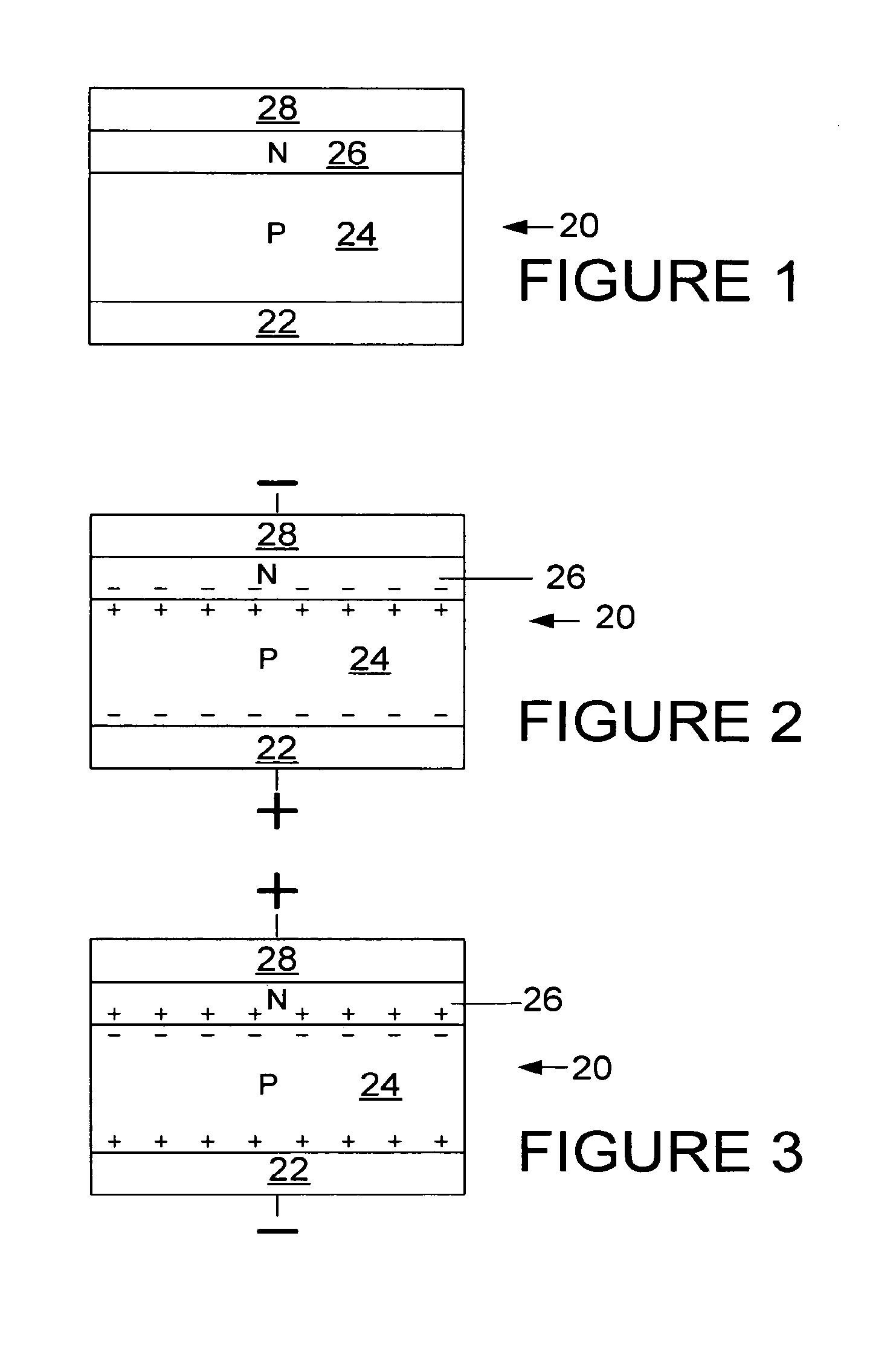
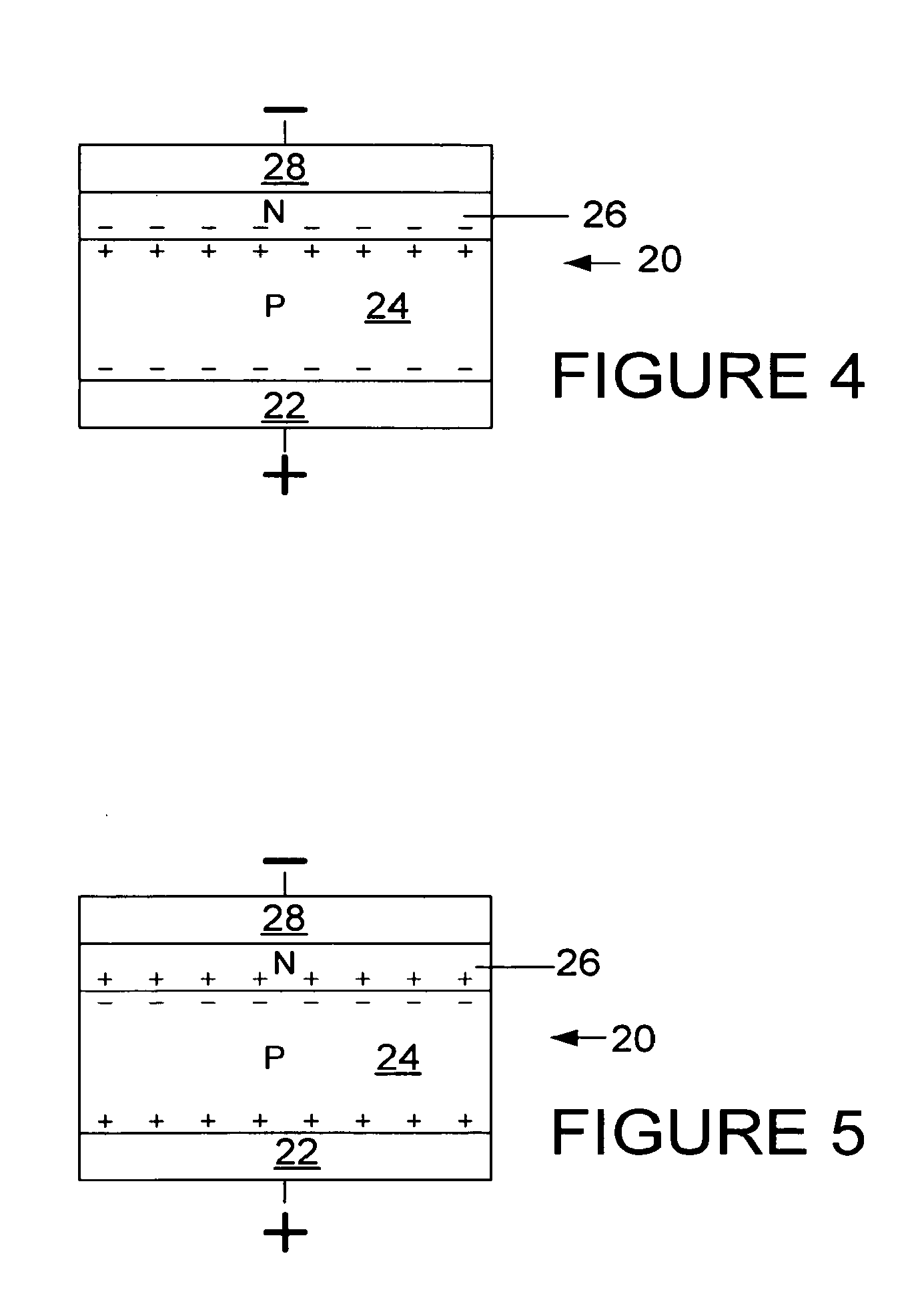
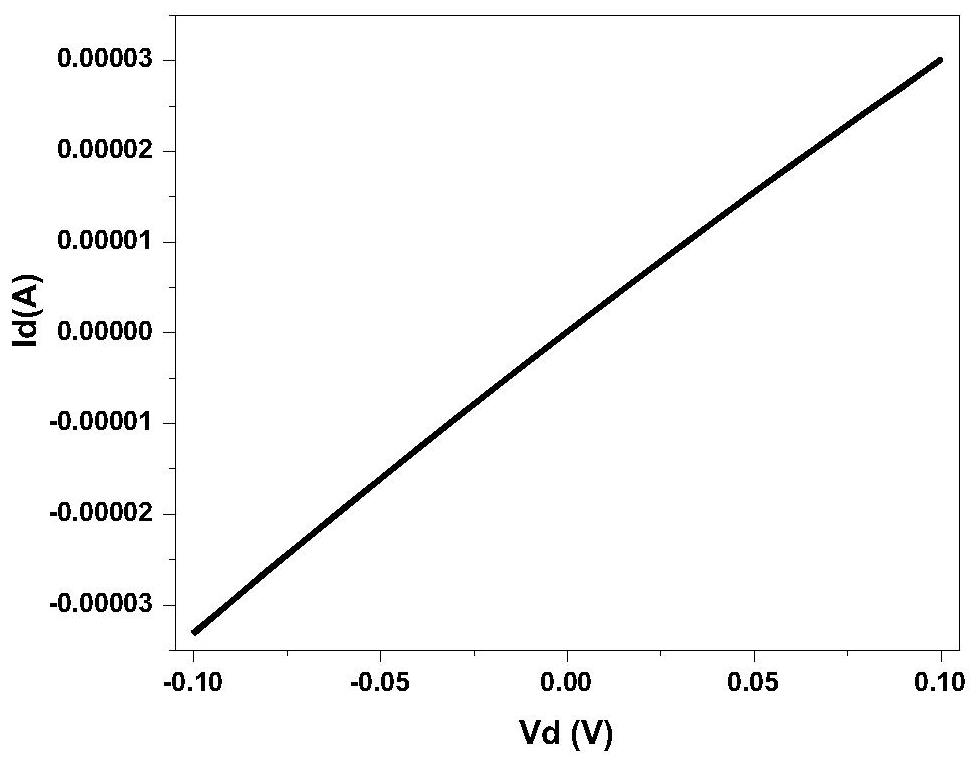
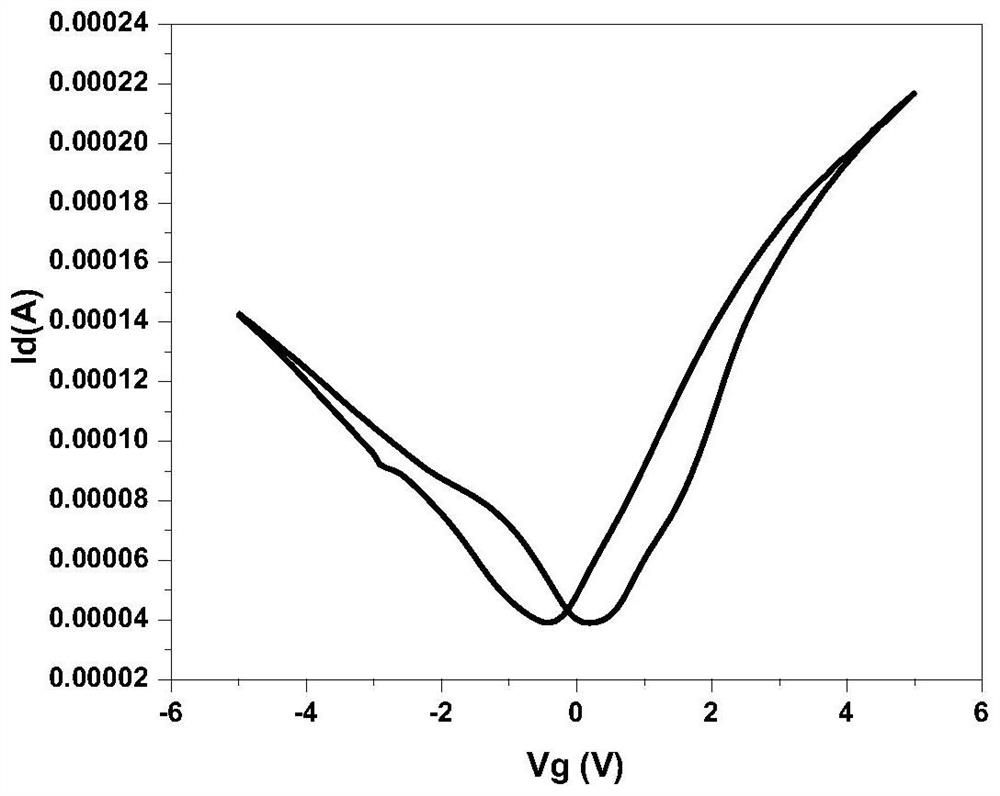
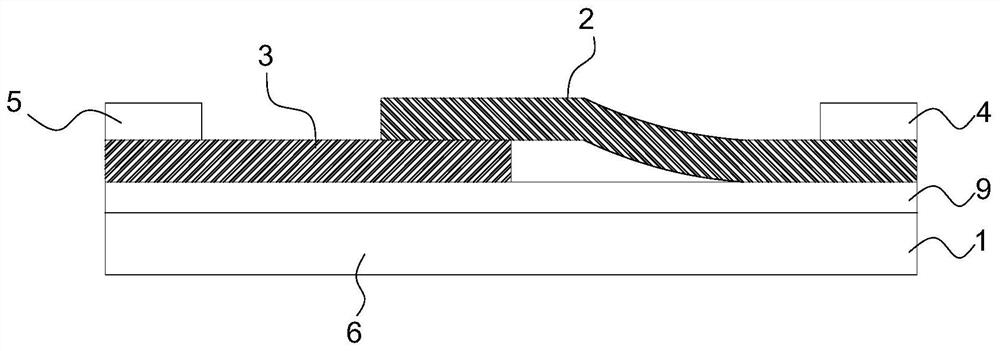
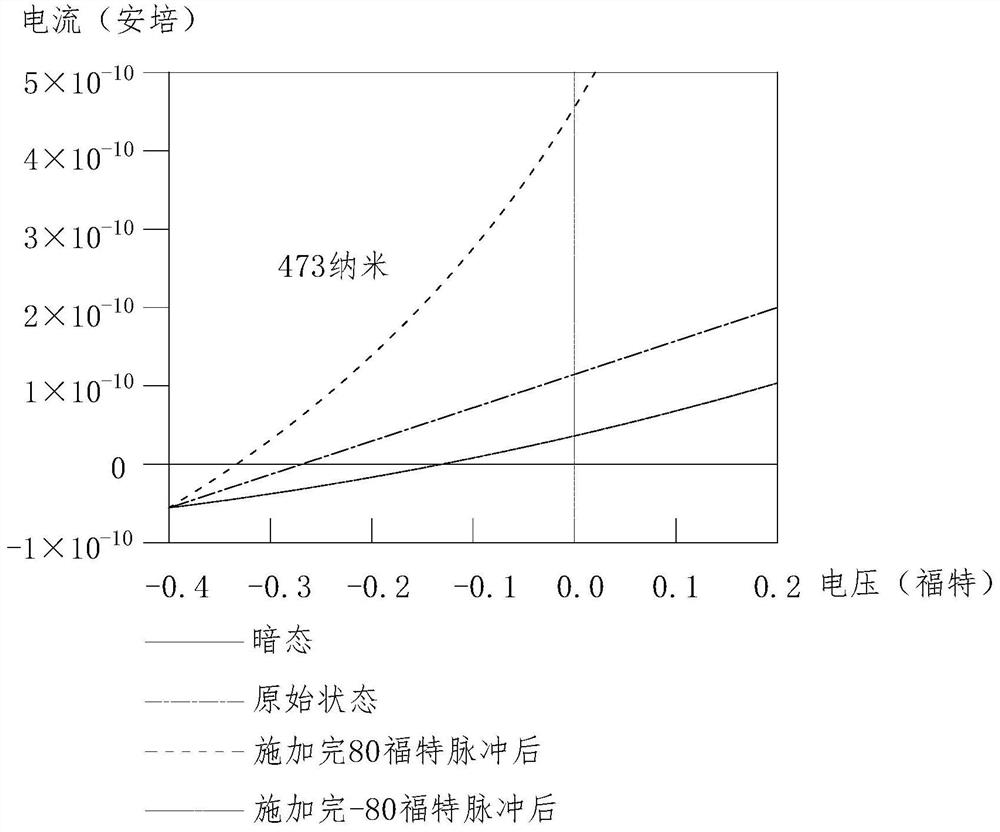
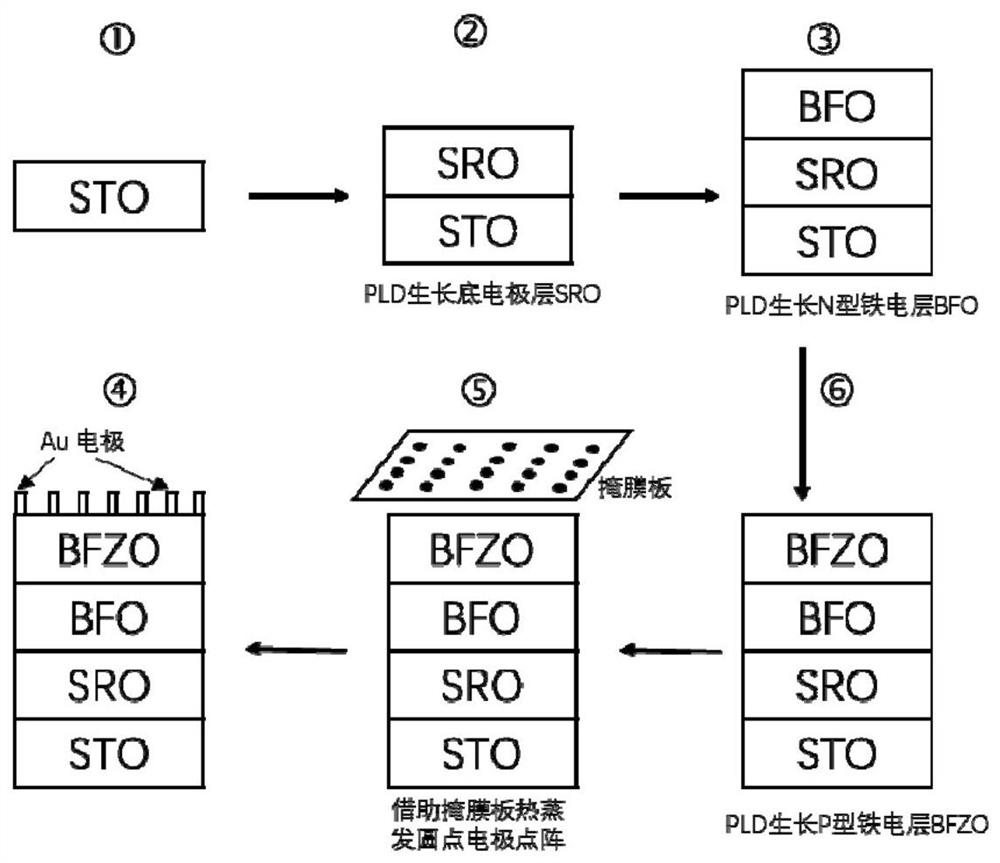
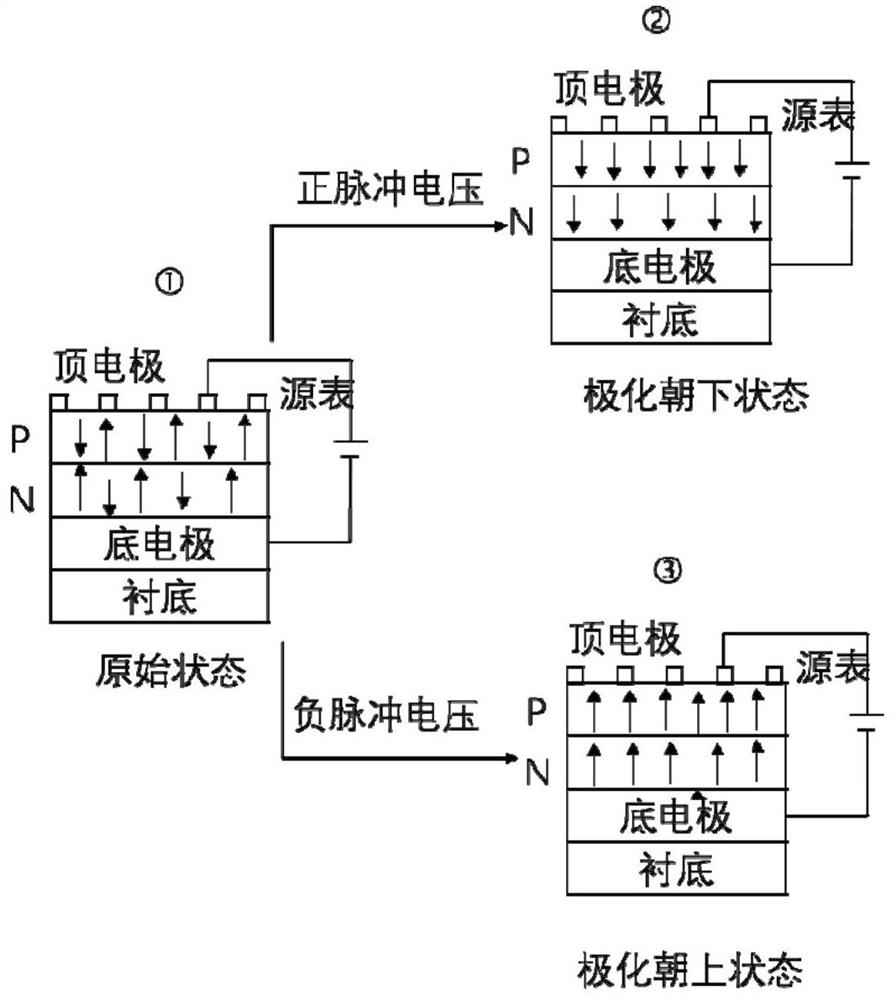
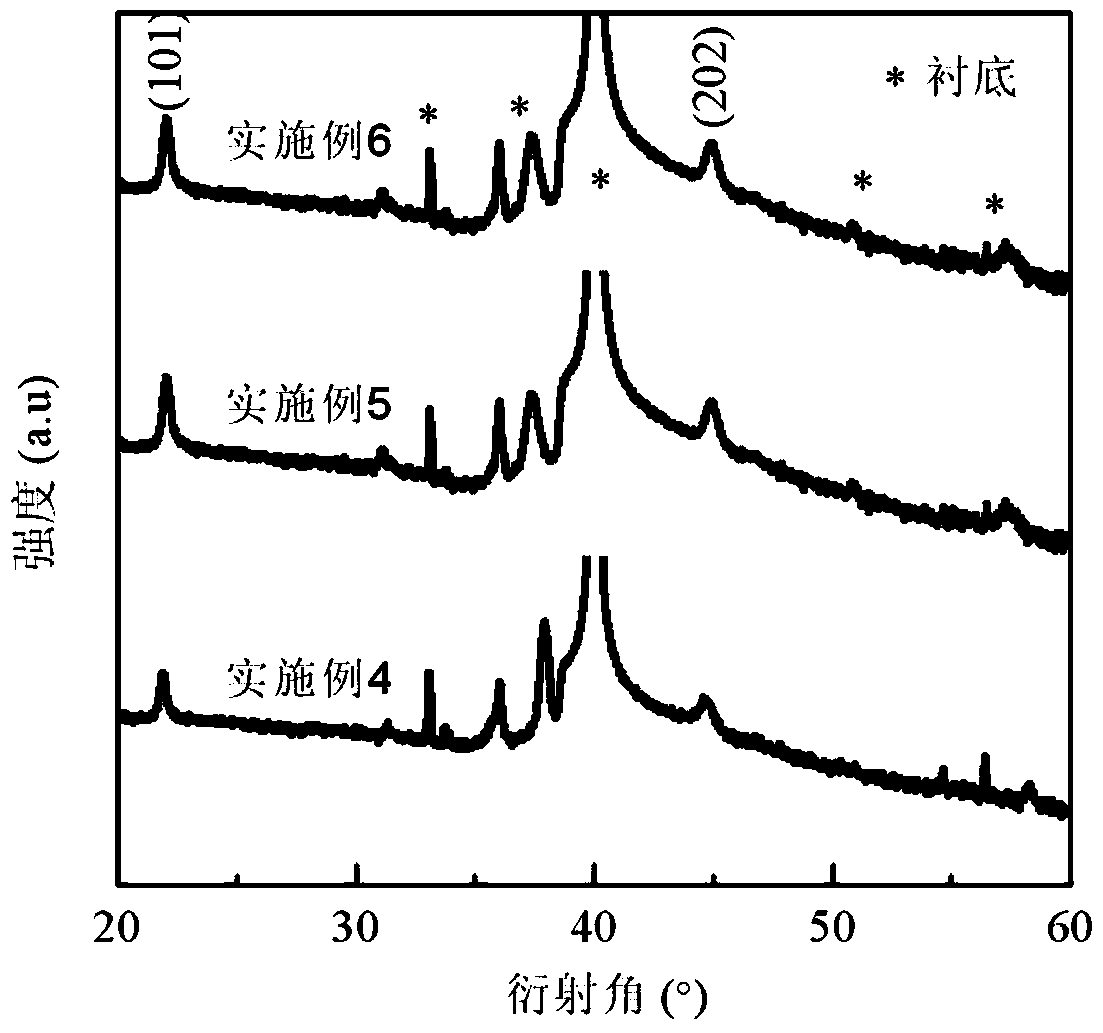
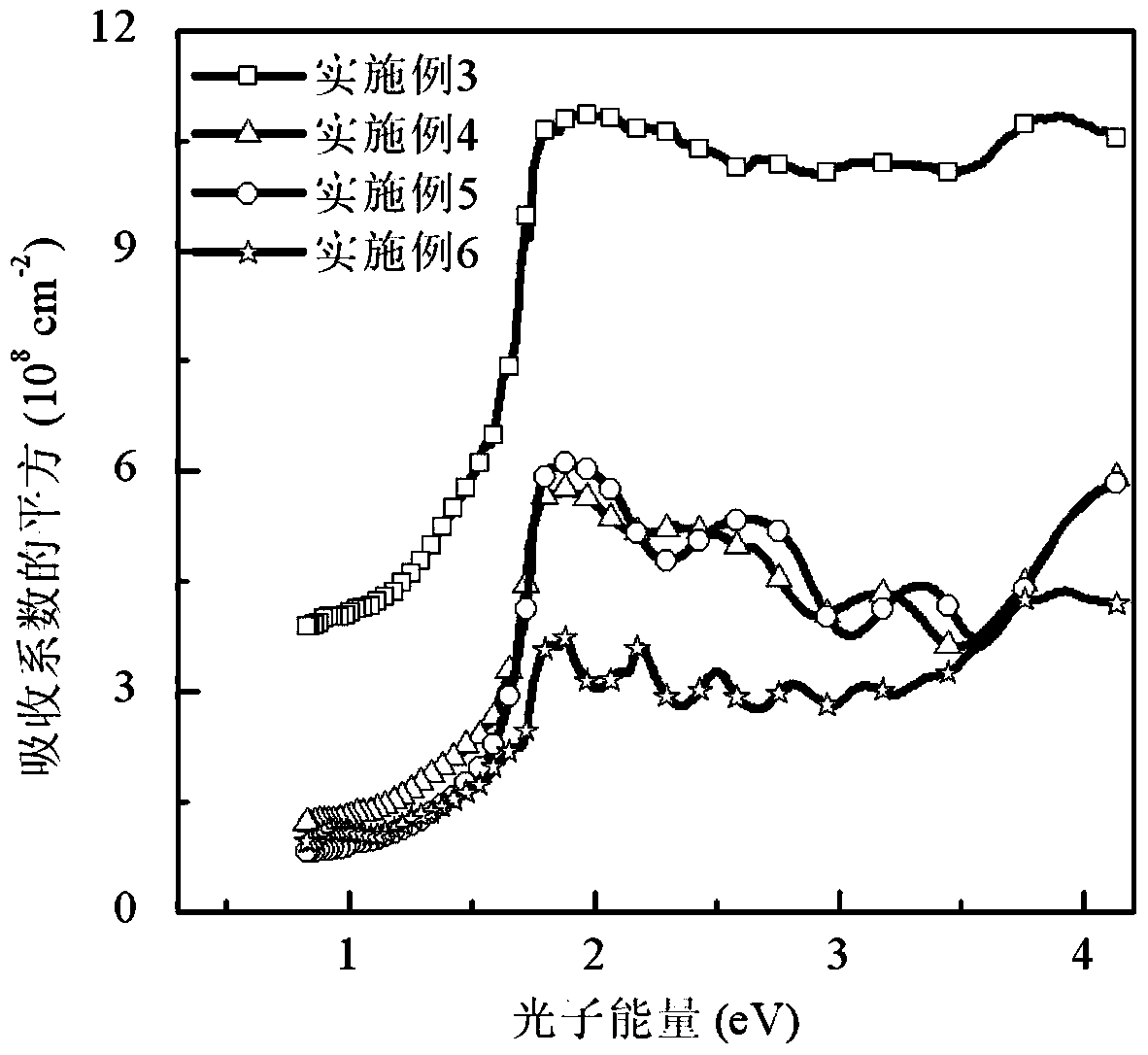
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Ferroelectric semiconductors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
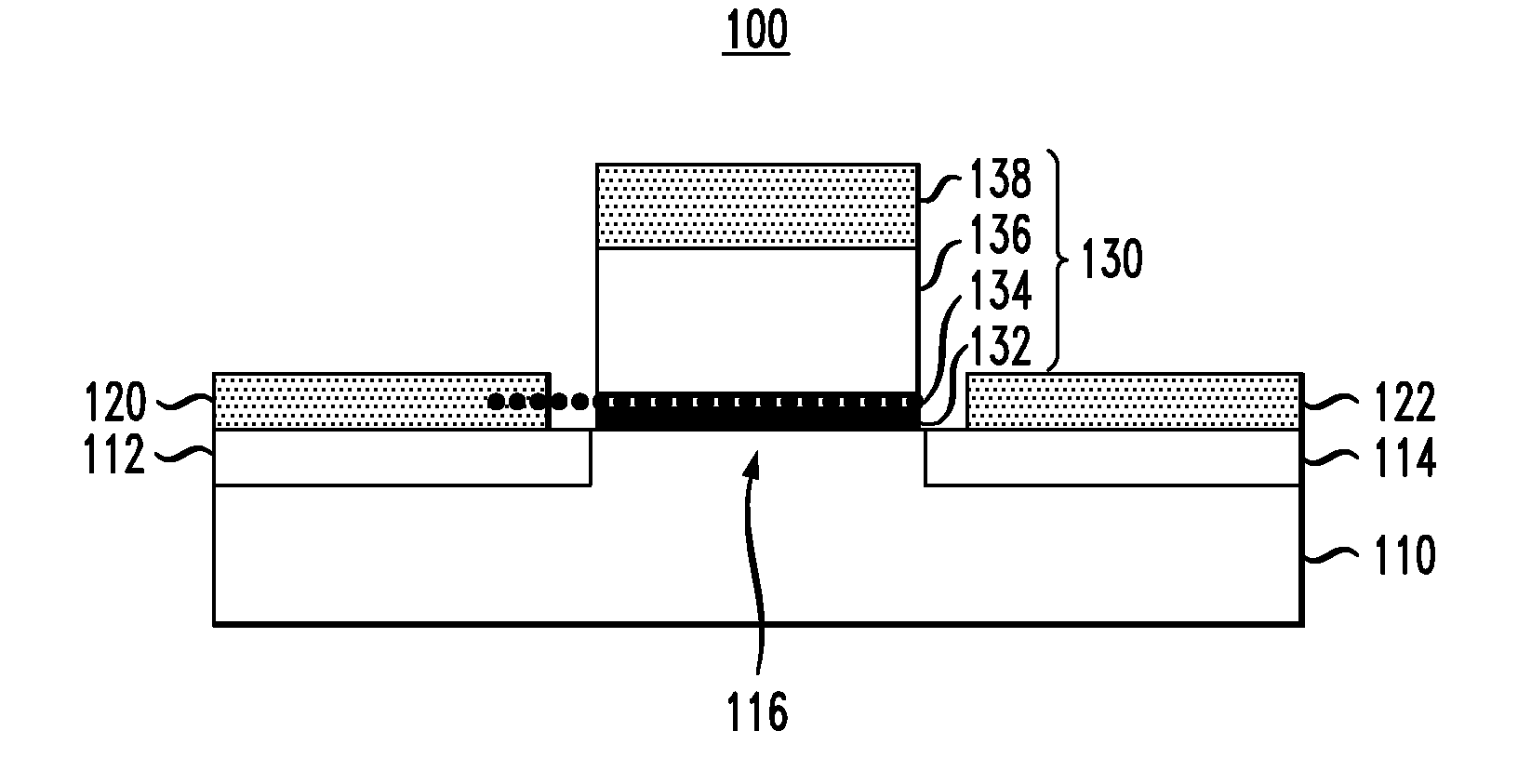
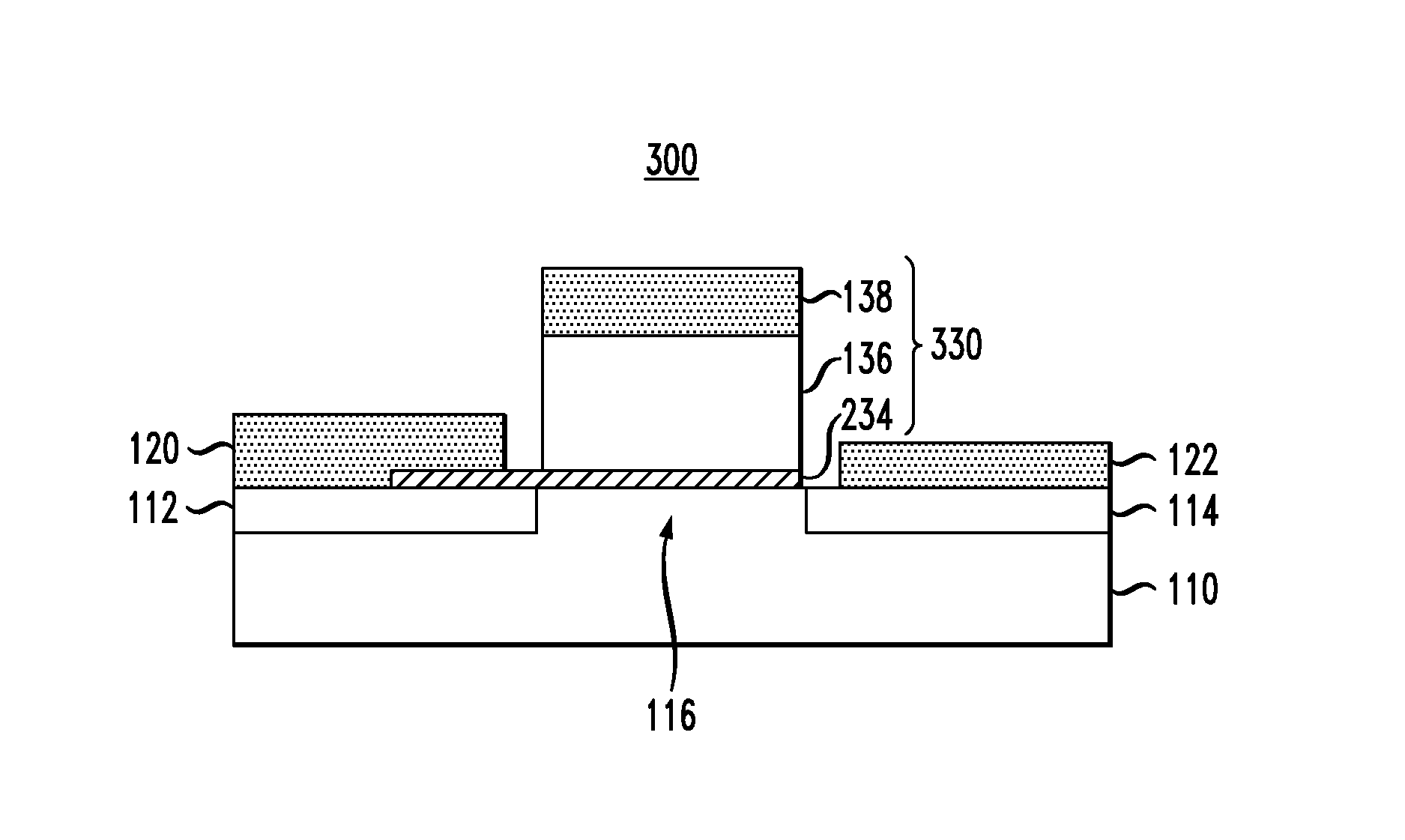
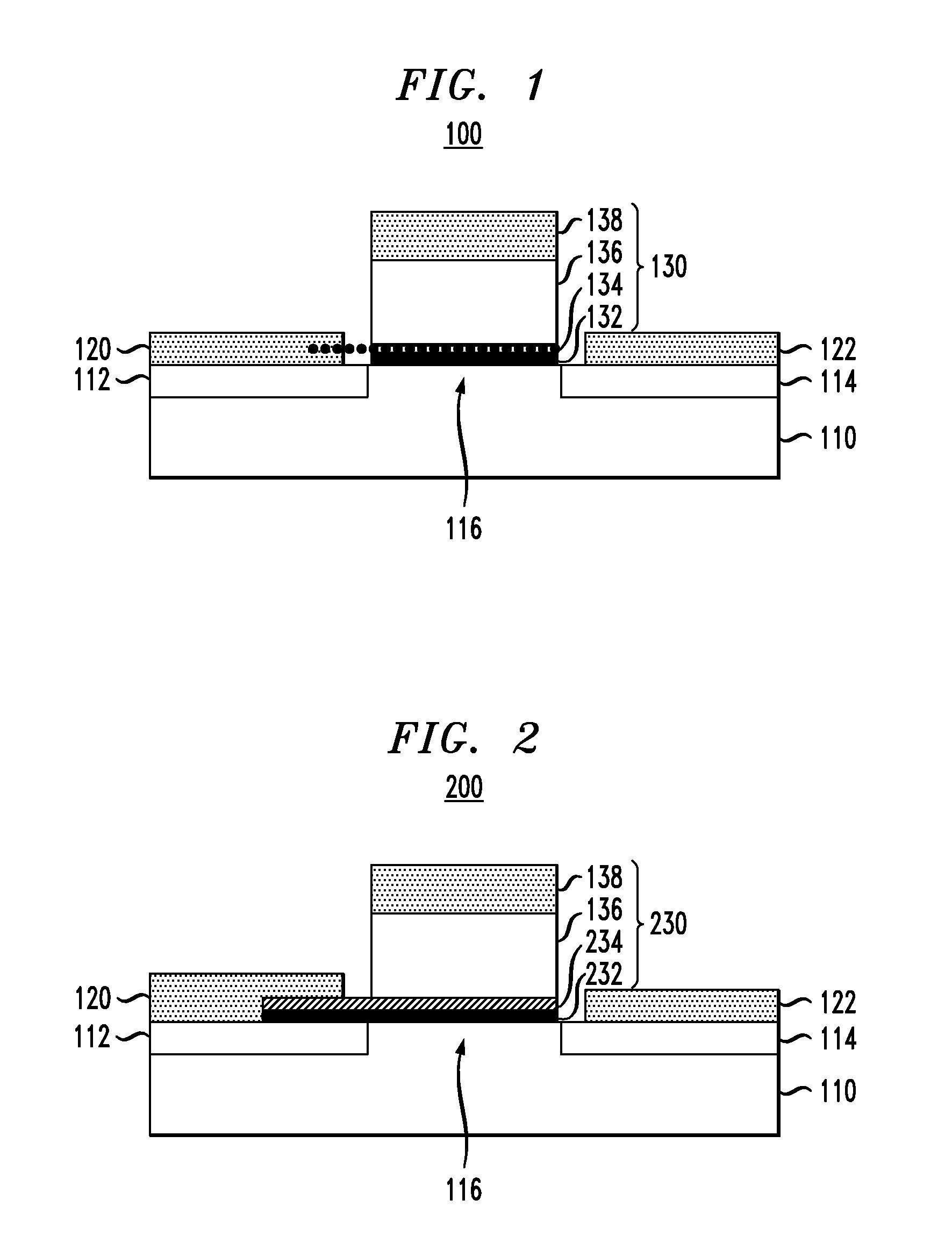
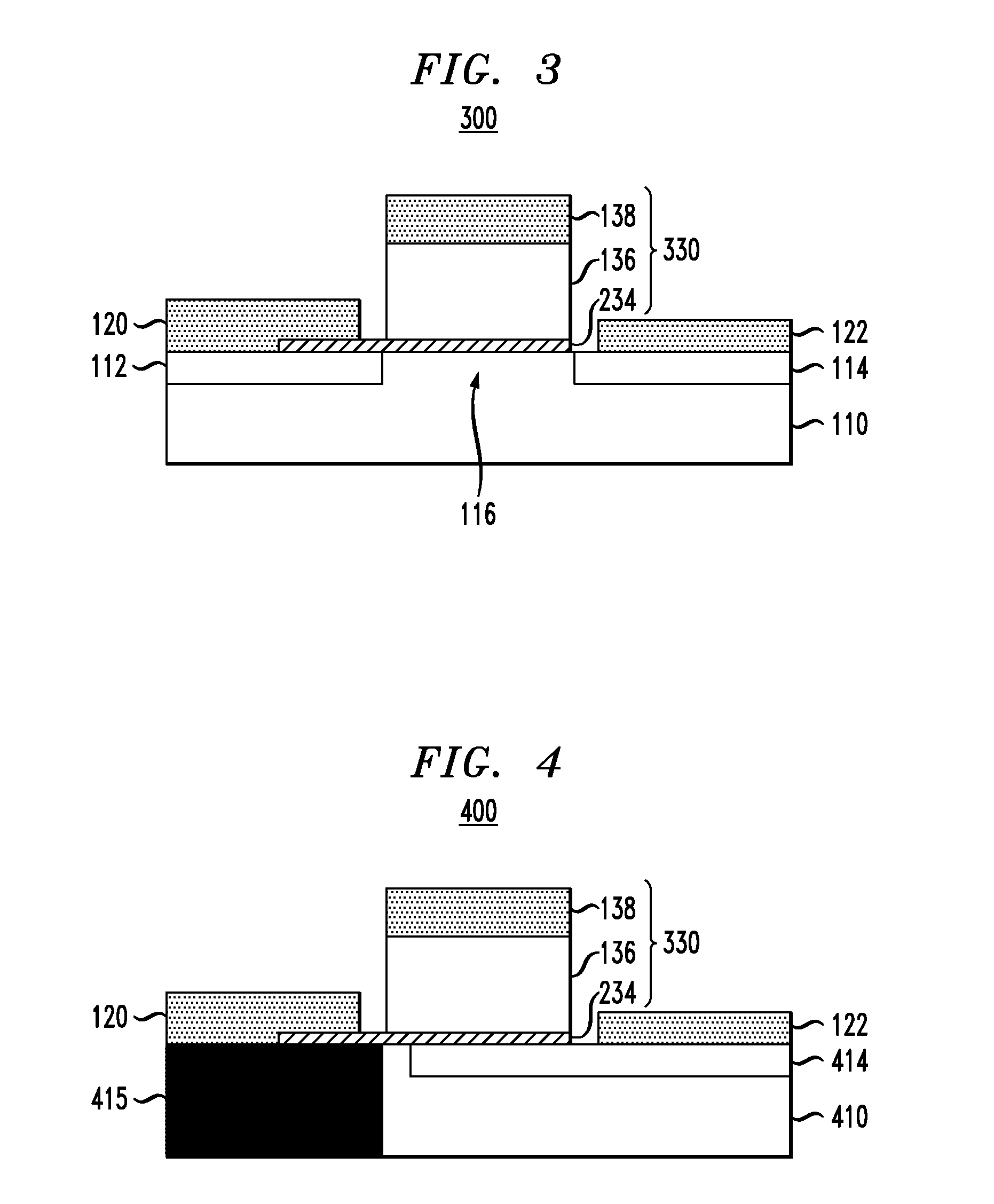
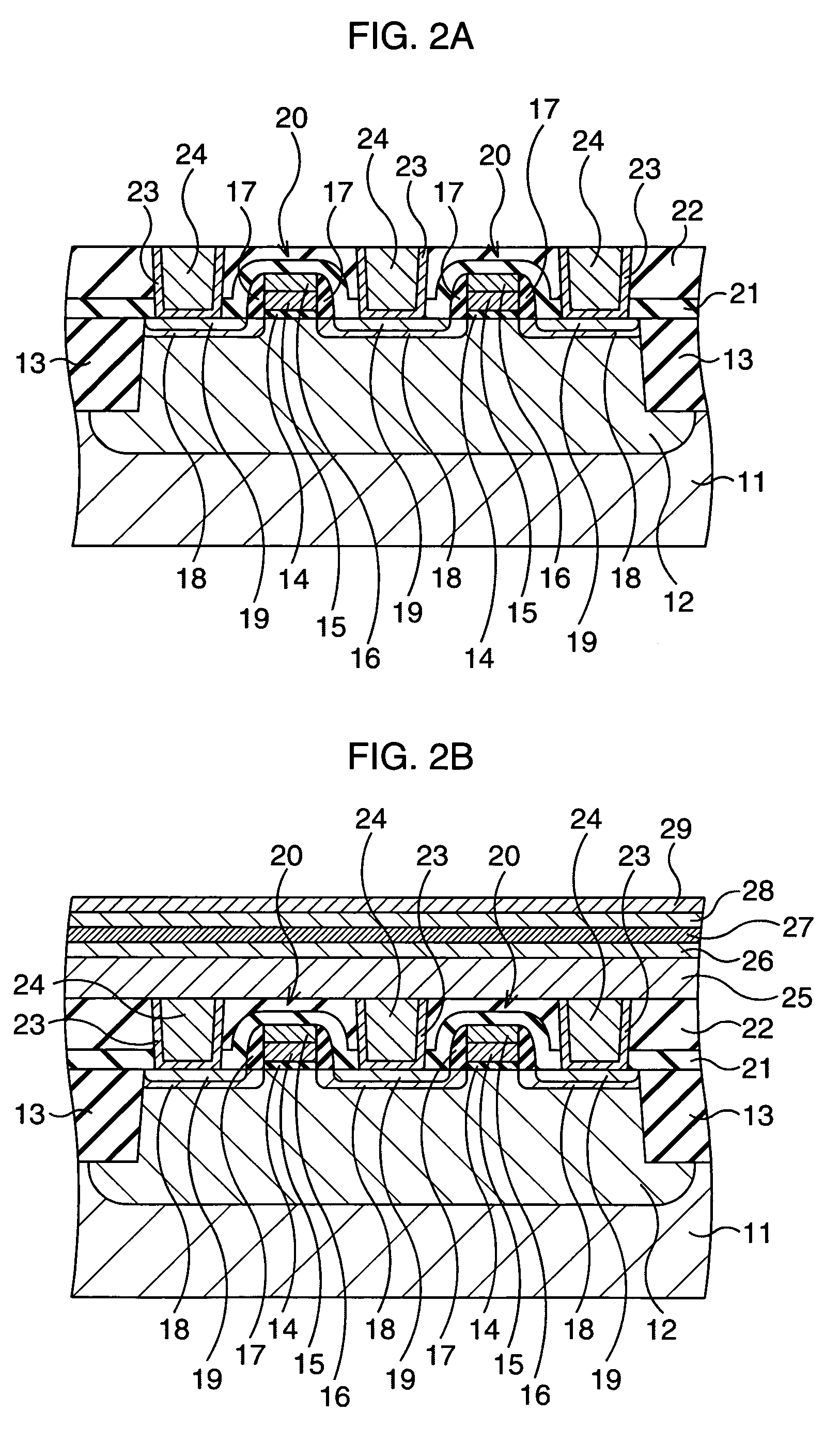
Ferroelectric semiconductor transistor devices having gate modulated conductive layer
ActiveUS20120292677A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSub thresholdWork function
Ferroelectric semiconductor switching devices are provided, including field effect transistor (FET) devices having gate stack structures formed with a ferroelectric layer disposed between a gate contact and a thin conductive layer (“quantum conductive layer”) . The gate contact and ferroelectric layer serve to modulate an effective work function of the thin conductive layer. The thin conductive layer with the modulated work function is coupled to a semiconductor channel layer to modulate current flow through the semiconductor and achieve a steep sub-threshold slope.
Owner:IBM CORP
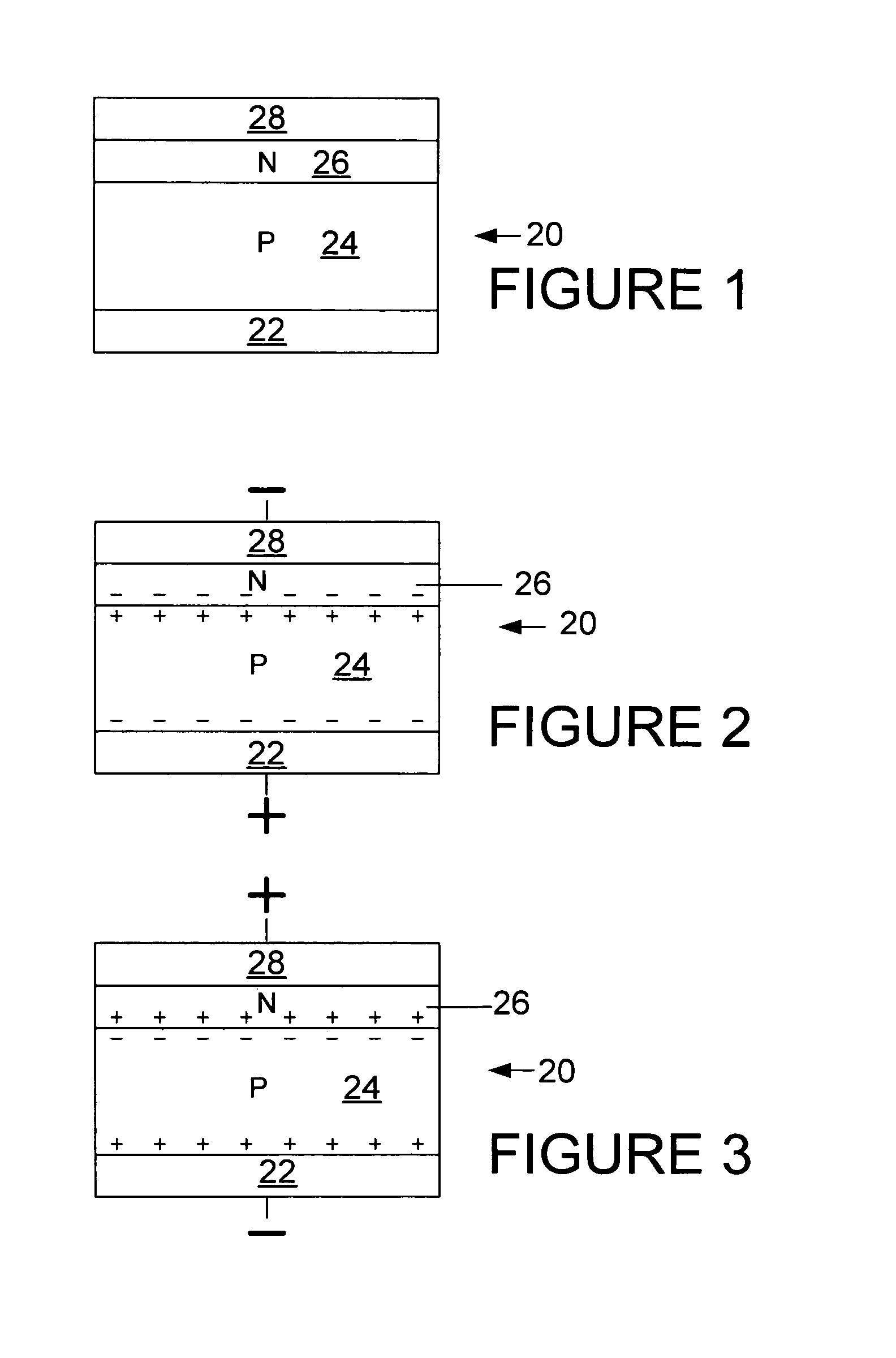
Ferroelectric memory device and fabrication process thereof, and methods for operation thereof
InactiveUS20160172365A1Significant probabilityDifference in resistanceSolid-state devicesDigital storageSchottky barrierLithium niobate
A new form of a solid-state non-volatile memory cell is presented. The solid-state memory cell comprises a series of different layers of ferroelectric materials, semiconductors, ferroelectric semiconductors, metals, and ceramics, and oxides. The memory device stores information in the direction and magnitude of polarization of the ferroelectric layers. Additionally, a method is presented for storing multiple bits of information in a single memory cell by allowing partial polarization of a single ferroelectric layer and stacking of multiple ferroelectric functional units on top of each other. Additionally, a technique for reading and writing said memory cell is presented. Additionally, the memory cell design allows for the formation of Schottky barriers which act to improve functionality and increase resistance. Additionally, a method is presented for depositing textured lithium niobate thin films.
Owner:MCKINNON THOMAS J +1
Ferro-Resistive Random Access Memory (FERRO-RRAM), Operation Method and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20120281451A1Simple in fabricationSimple structureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceNon destructive
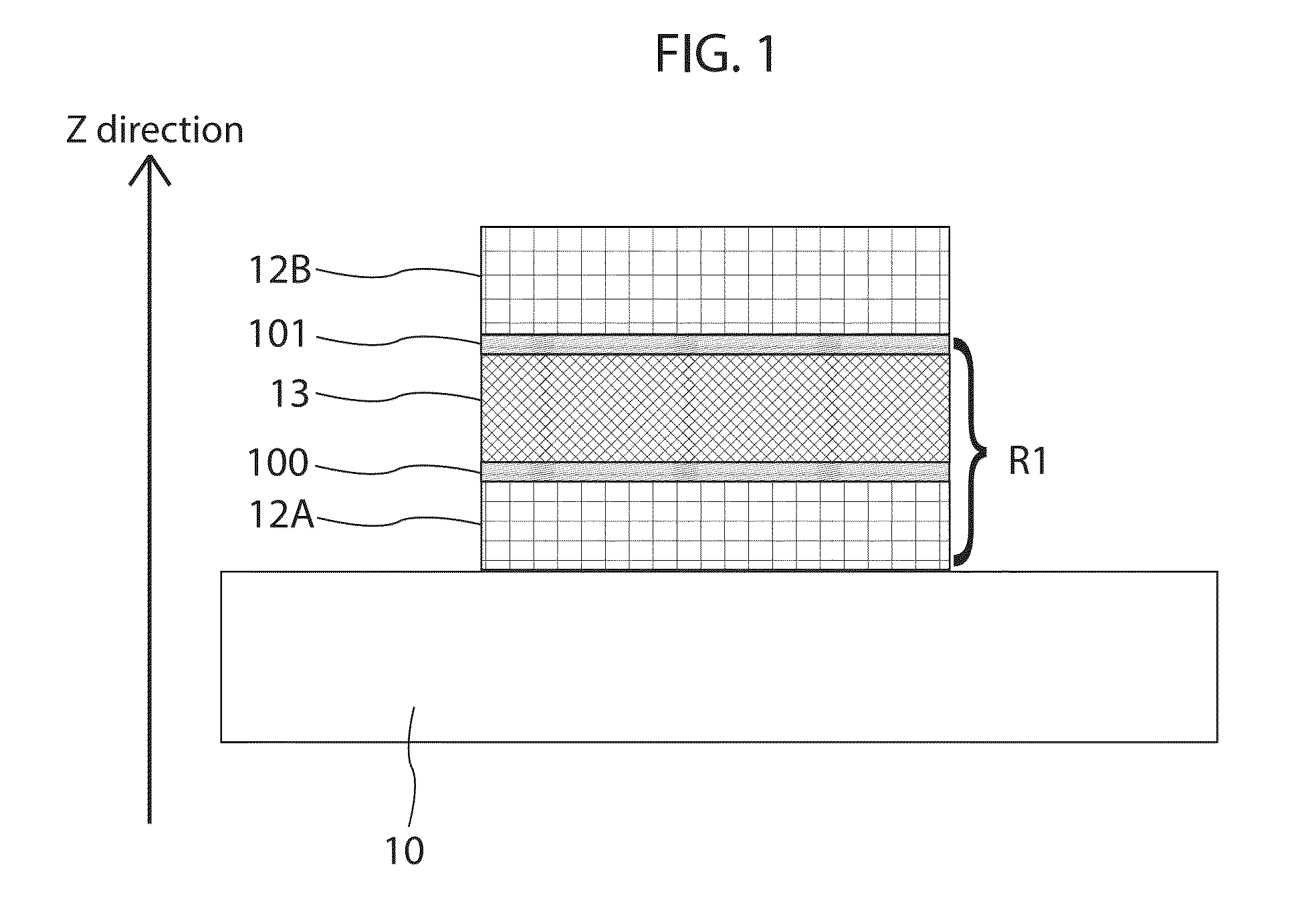
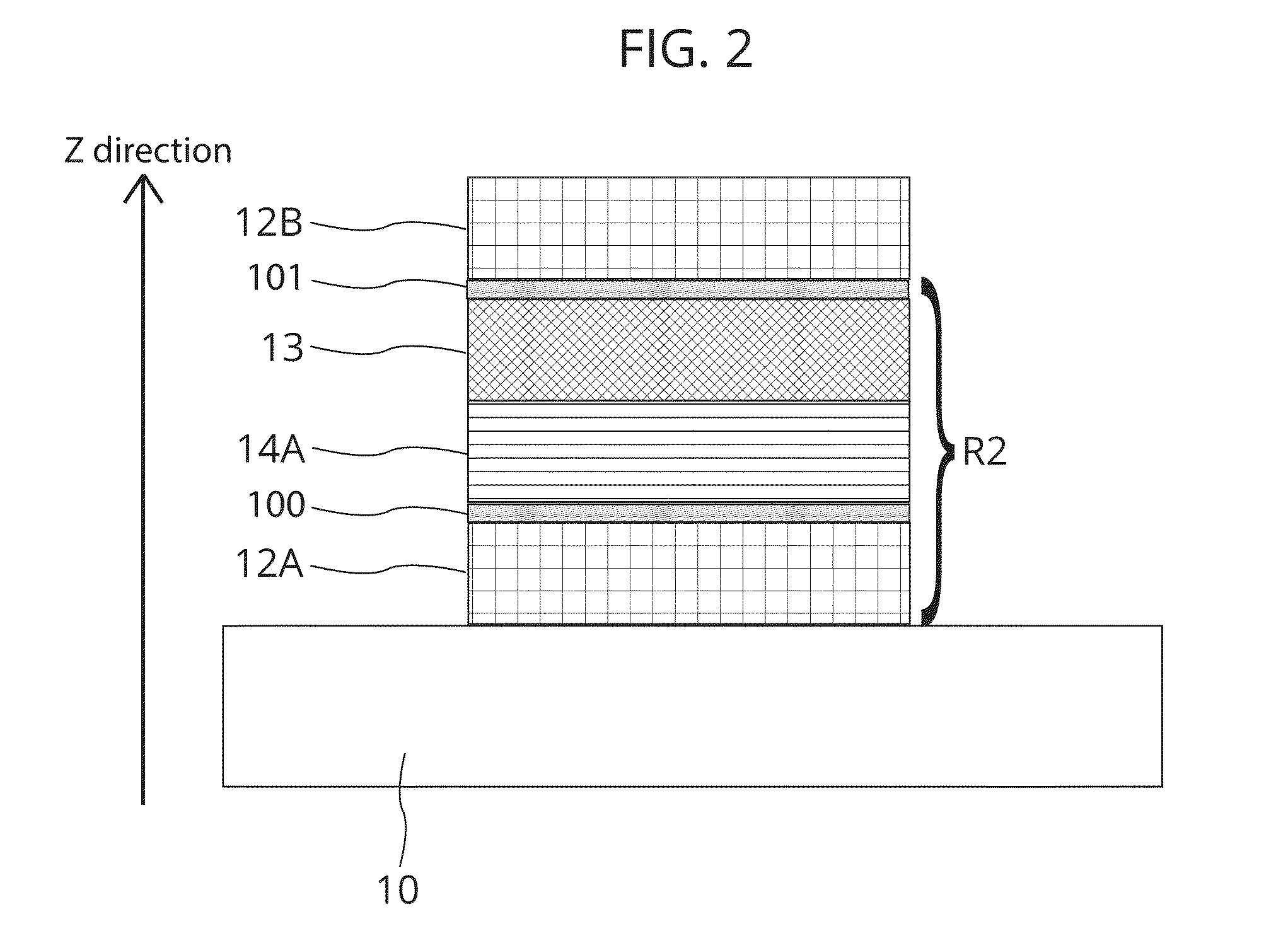
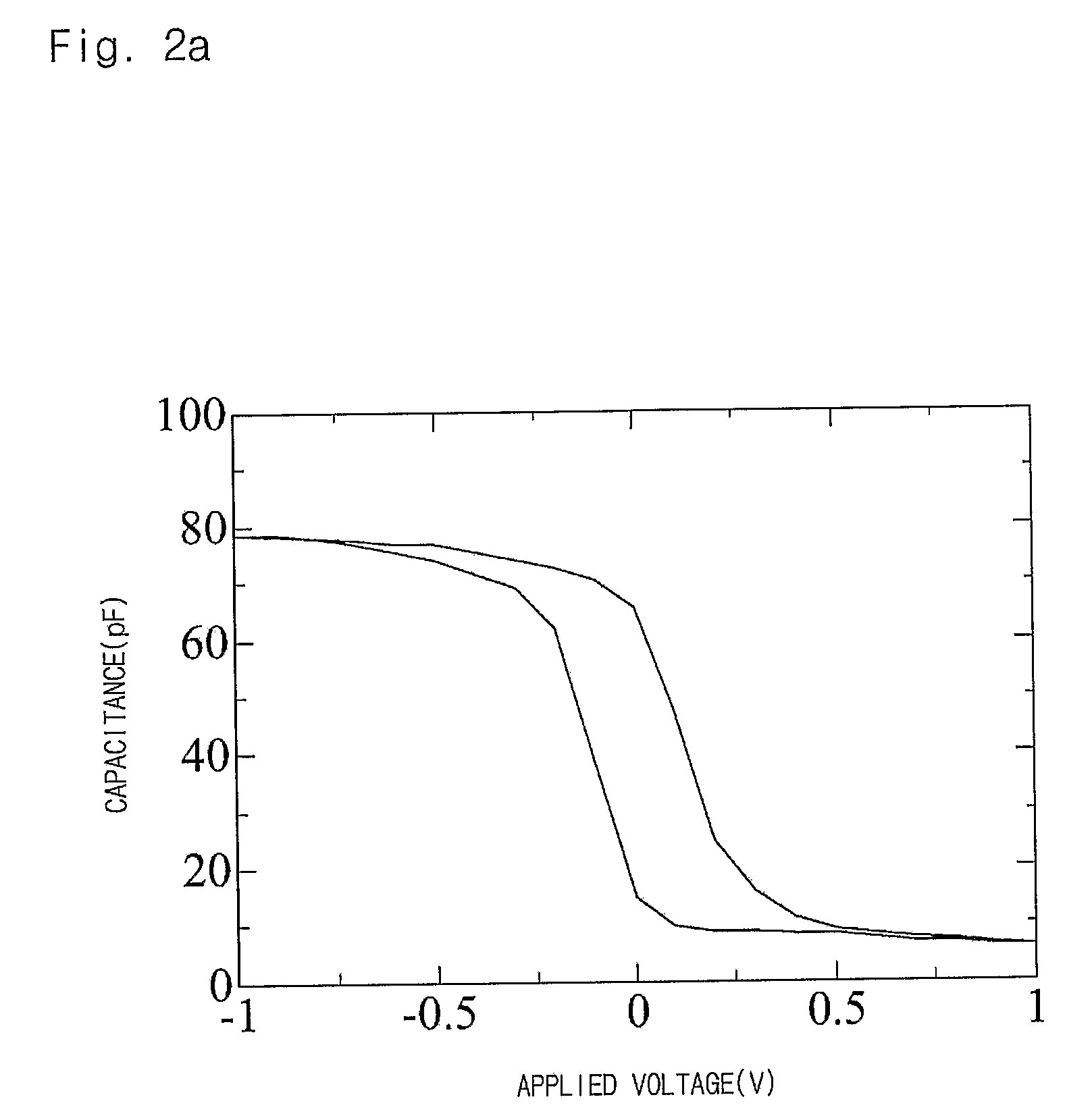
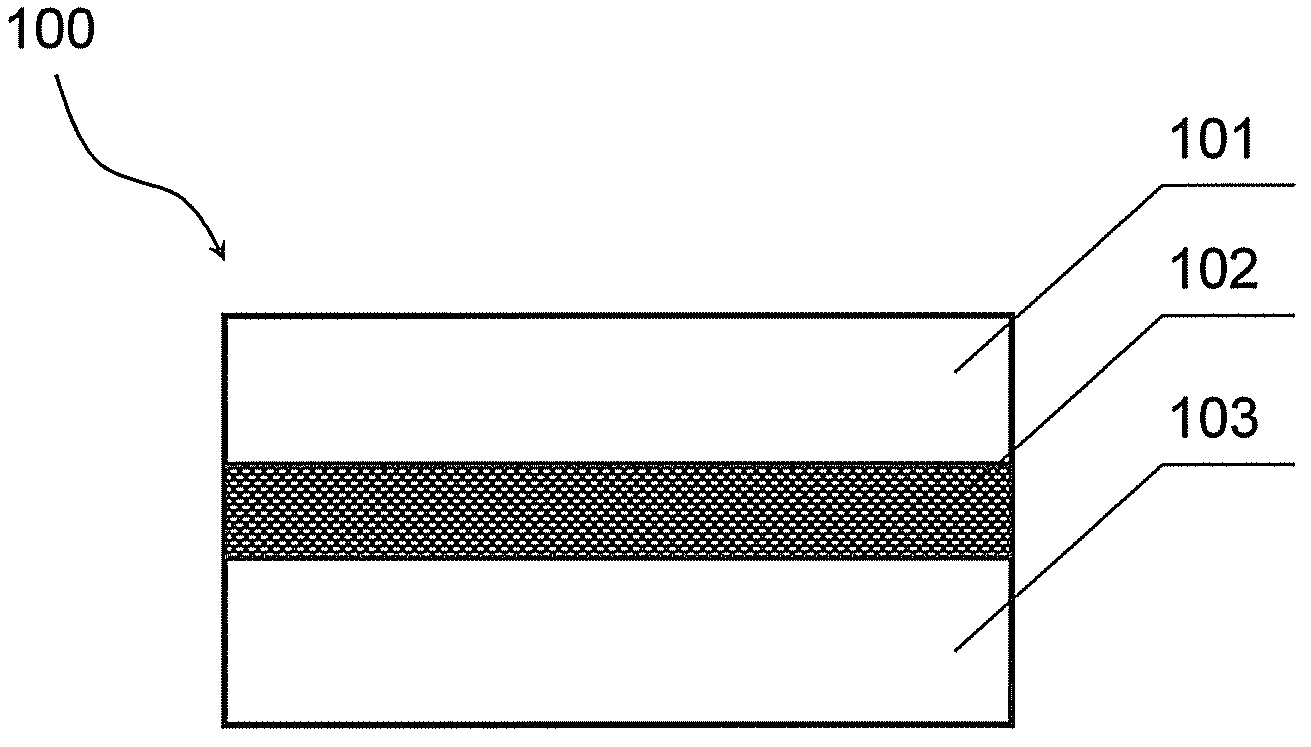
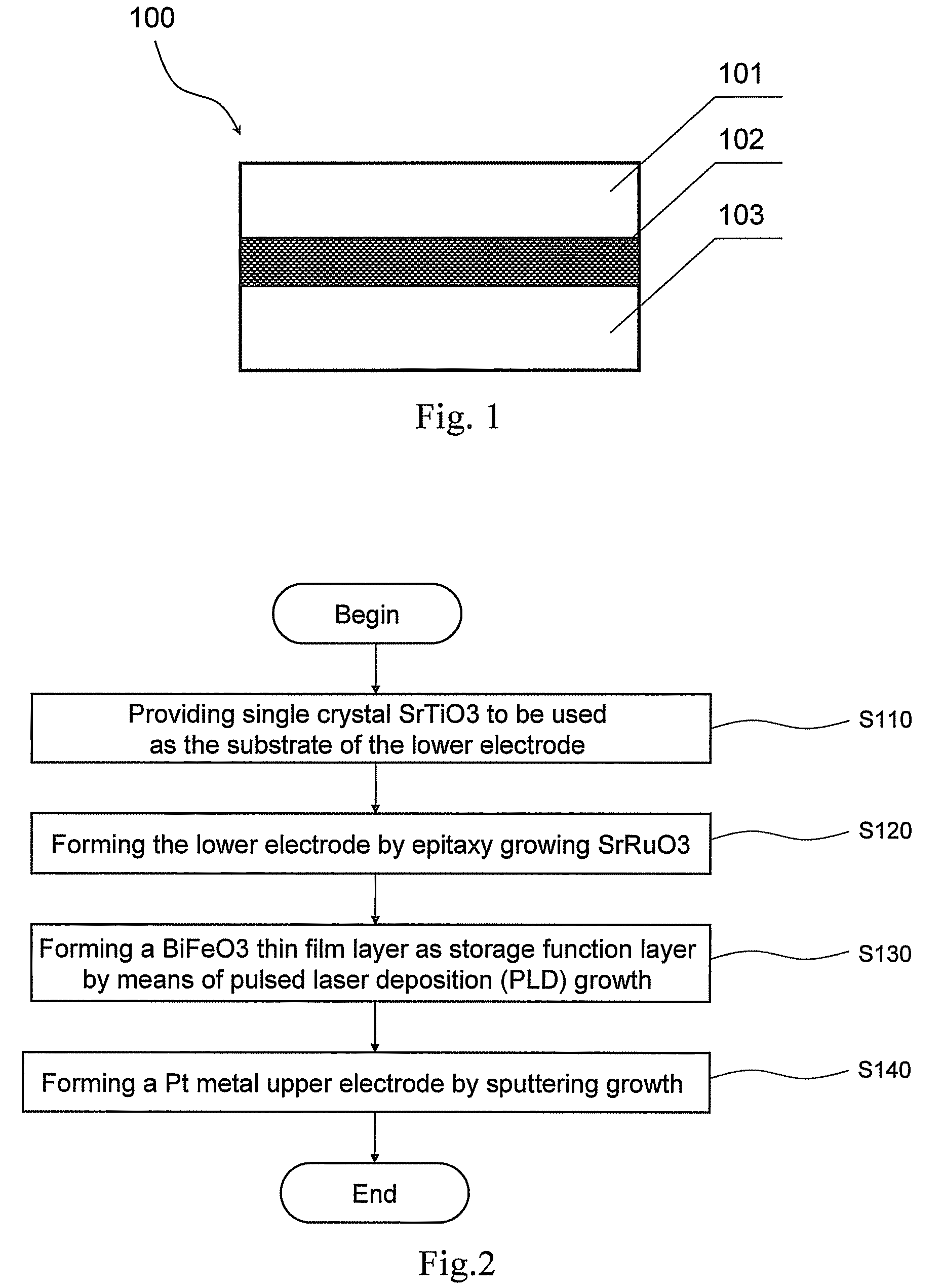
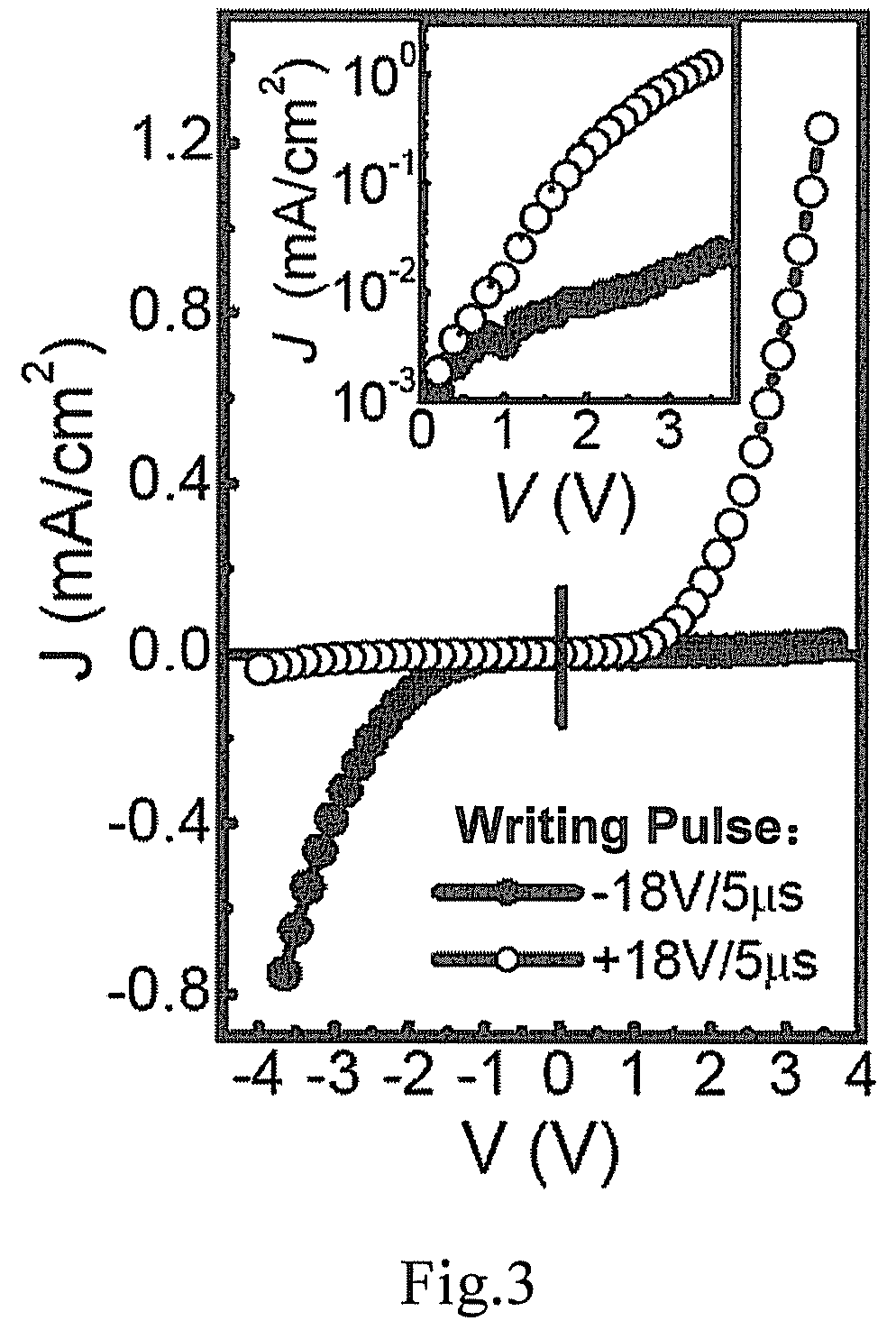
The invention provides a Ferro-RRAM, a method of operating the Ferro-RRAM, and a method of fabricating the Ferro-RRAM, and pertains to the technical field of memory. The Ferro-RRAM comprises an upper electrode, a lower electrode, and a ferroelectric semiconducting thin-film layer provided between the upper electrode and the lower electrode and serving as a storage function layer; wherein the ferroelectric semiconducting thin-film layer is operable to generate a diode conduction characteristic by ferroelectric domain reorientation, and is operable to modulate the diode conduction characteristic by variation of the ferroelectric domain orientation; the Ferro-RRAM stores information according to variation of modulation of the diode conduction characteristic. The Ferro-RRAM has such characteristics of being simple in structure and fabrication, non-destructive readout and nonvolatile storage.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for preparing plumbum magnesium niobate-plumbum titanate ferroelectric film
InactiveCN101956166ASimple preparation processGood repeatabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingFerroelectric thin filmsPerovskite (structure)
The invention belongs to the field of ferroelectric film materials and relates to a method for preparing a plumbum magnesium niobate-plumbum titanate (PMN-PT) ferroelectric film. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a PMN-PT ceramic target; secondly, cleaning a silicon (Si) substrate; thirdly, preparing a LaNiO3 conductive buffer layer; and finally, preparing the PMN-PT ferroelectric film. The method for preparing the PMN-PT ferroelectric film has the advantages of simple process, high repeatability, capacity of preparing the large-area PMN-PT film with pure perovskite structure preferred orientation on a cheap silicon substrate with an actual application value, compatibility with a Si integrated process, low preparation cost and contribution to mass production of devices. The prepared film has the advantages of high ferroelectric properties and suitability for ferroelectric-semiconductor integrated devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Ferroelectric semiconductor transistor devices having gate modulated conductive layer
ActiveUS8785995B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSub thresholdWork function
Ferroelectric semiconductor switching devices are provided, including field effect transistor (FET) devices having gate stack structures formed with a ferroelectric layer disposed between a gate contact and a thin conductive layer (“quantum conductive layer”). The gate contact and ferroelectric layer serve to modulate an effective work function of the thin conductive layer. The thin conductive layer with the modulated work function is coupled to a semiconductor channel layer to modulate current flow through the semiconductor and achieve a steep sub-threshold slope.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
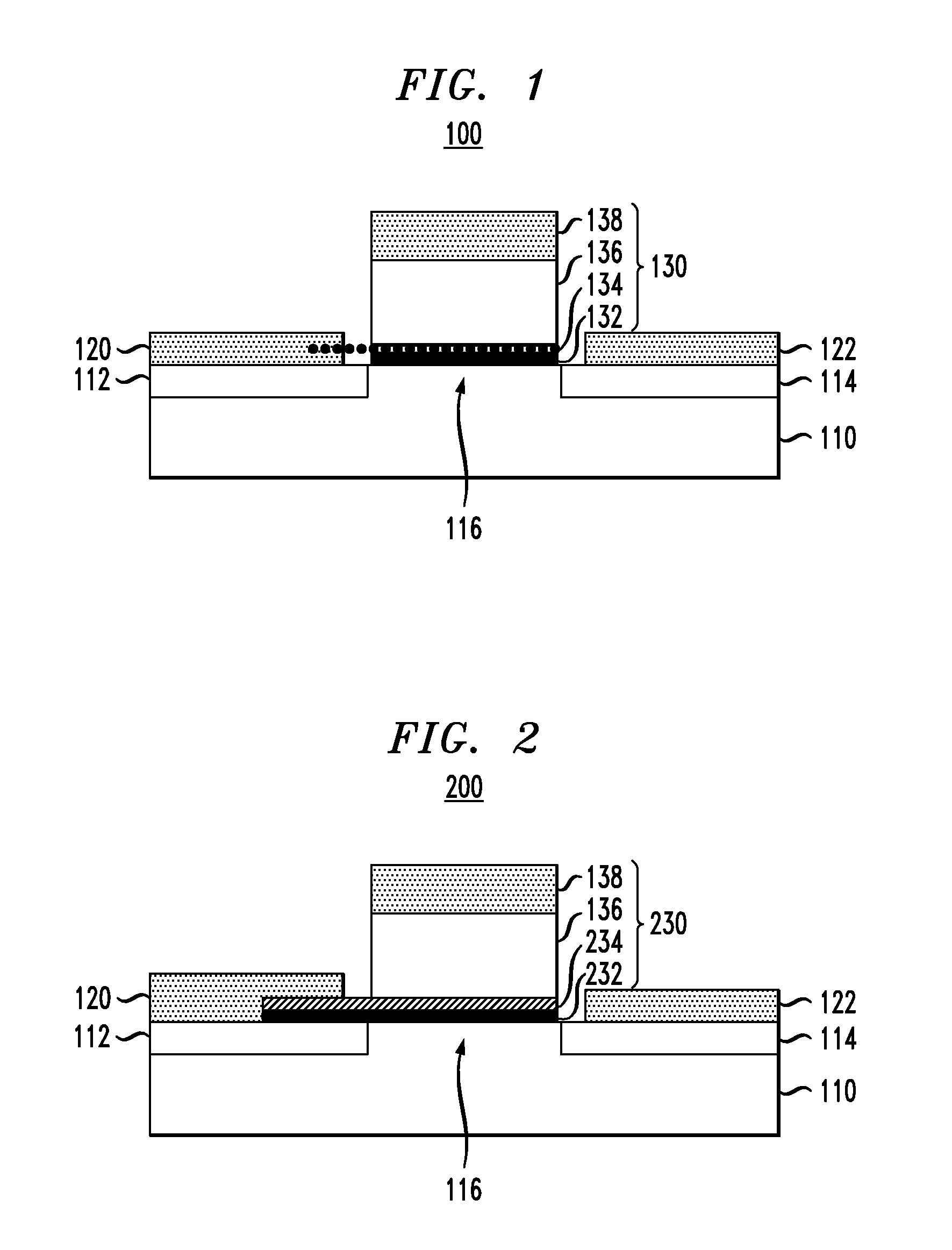
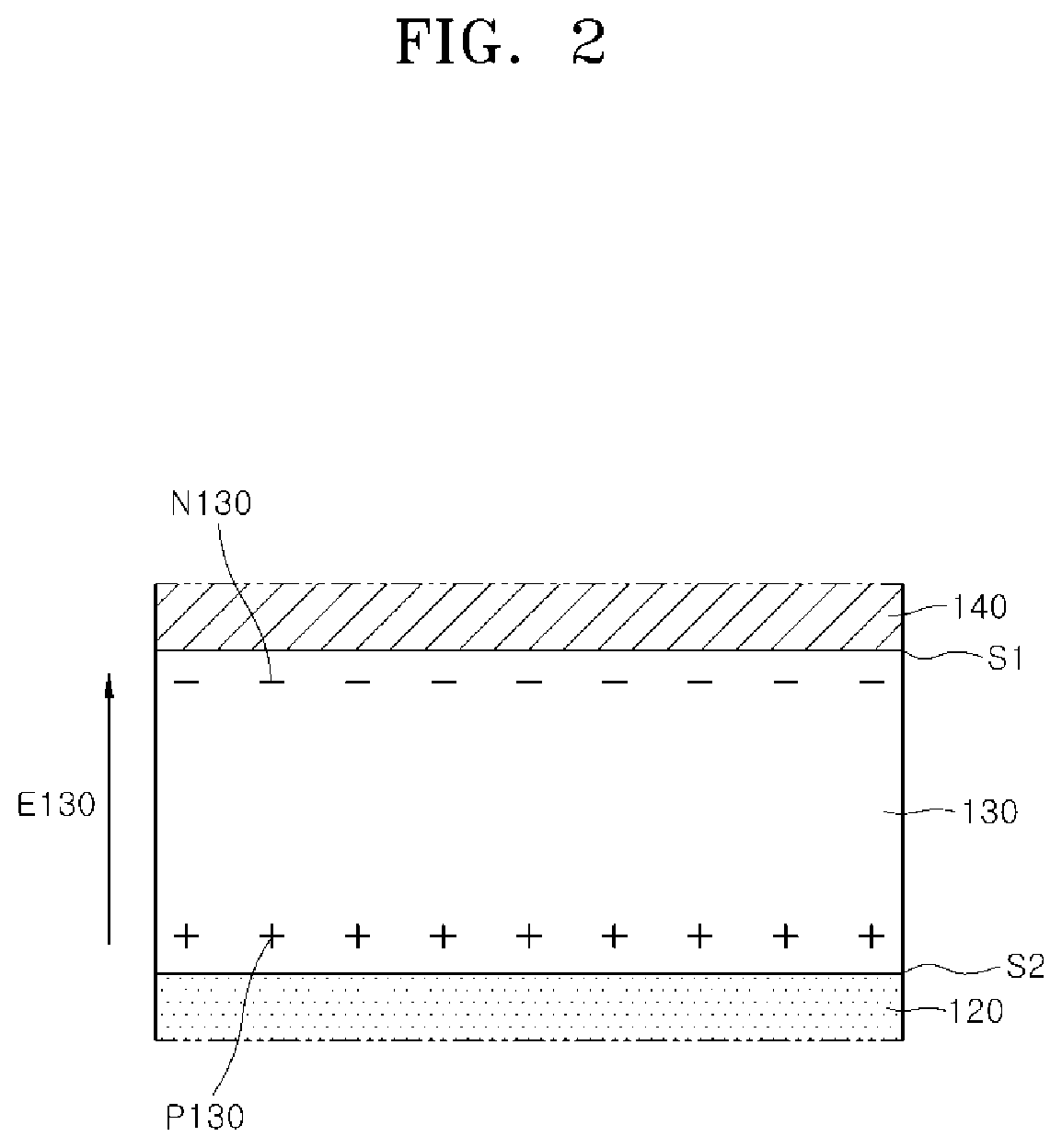
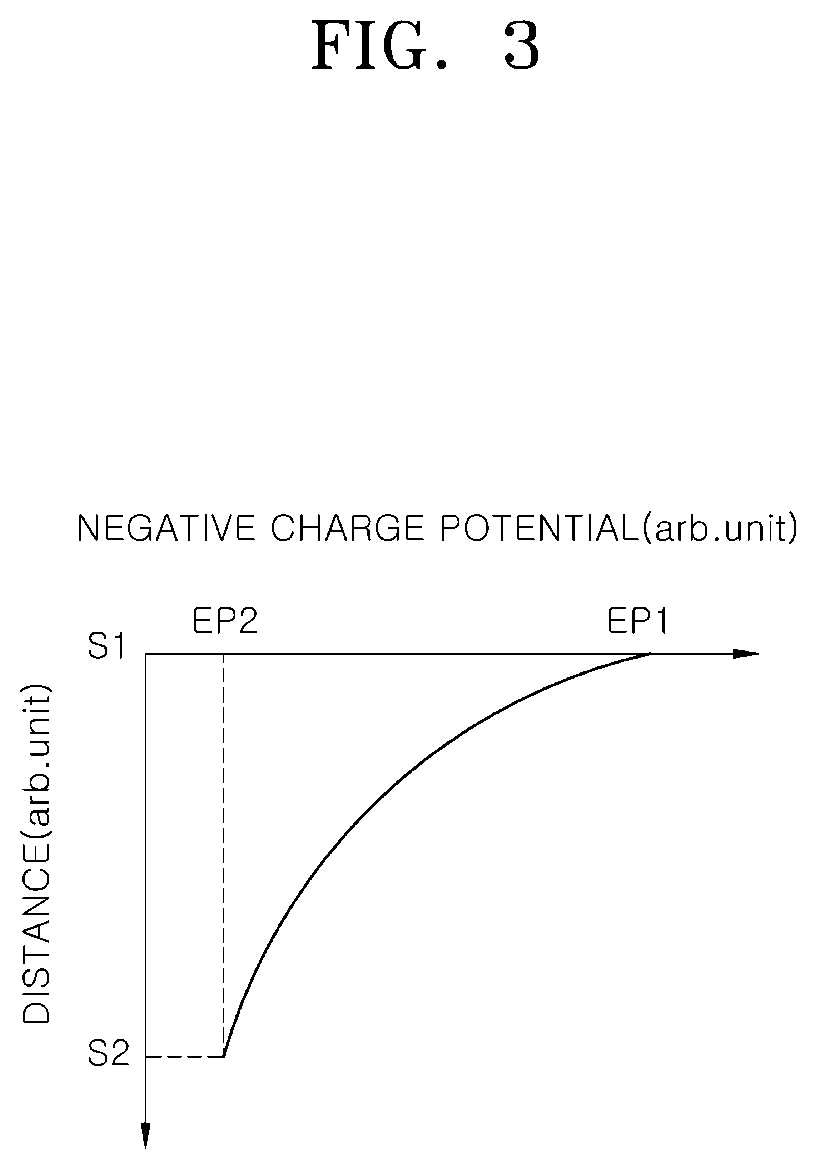
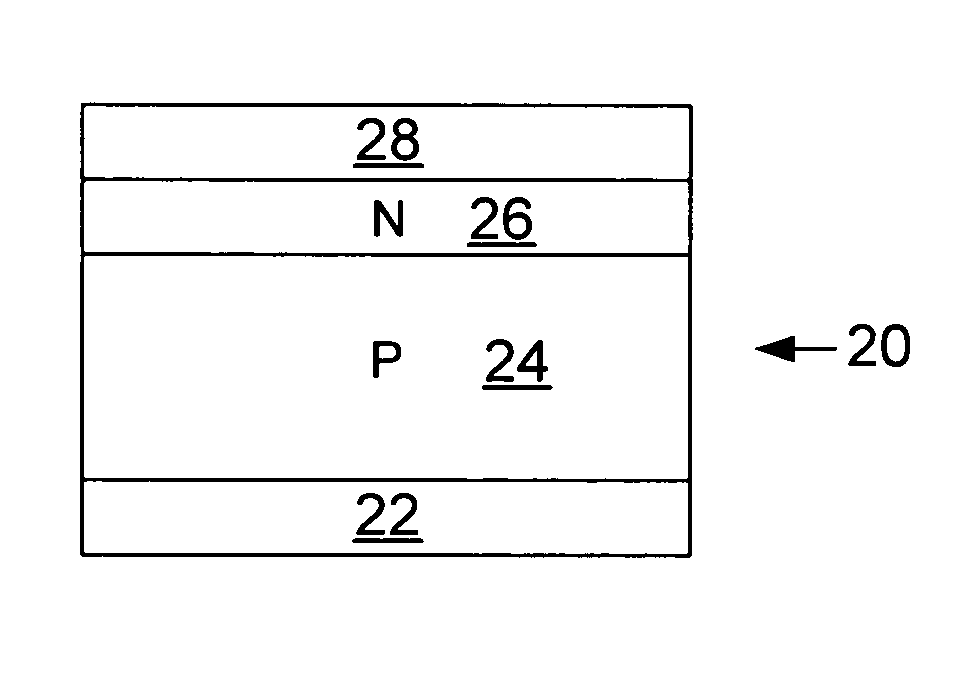
Ferroelectric semiconductor device
ActiveUS20190393355A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl layerFerroelectric semiconductors
A ferroelectric semiconductor device of the present disclosure includes a substrate, a ferroelectric layer disposed on the substrate, an electric field control layer that is disposed on the ferroelectric layer and has a predetermined internal electric field formed without the application of an external electric power to alter the magnitude of a coercive electric field of the ferroelectric layer, and a gate electrode layer disposed on the electric field control layer.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method of manufacturing ferroelectric semiconductor device
ActiveUS7368298B2Suppress DiffuseSuppressing removalSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryThin membrane
An Ir film, an IrOx film, a Pt film, a PtO film and a Pt film are formed, and thereafter a PLZT film is formed. Then, heat treatment at 600° C. or lower is performed by the RTA method in an atmosphere containing Ar and O2 to thereby crystallize the PLZT film. Subsequently, an IrOx film and an IrO2 film are formed. Then, these films are patterned at once. Thereafter, an alumina film is formed as a protective film. Subsequently, heat treatment at 650° C. for 60 minutes in an oxygen atmosphere is performed as recovery annealing. Note that no heat treatment is performed from the crystallization of the PLZT film to the recovery annealing.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Polarized tuning ferroelectric film diode memory
ActiveCN101859779ASufficient identificationImprove storage densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsFerroelectric thin films
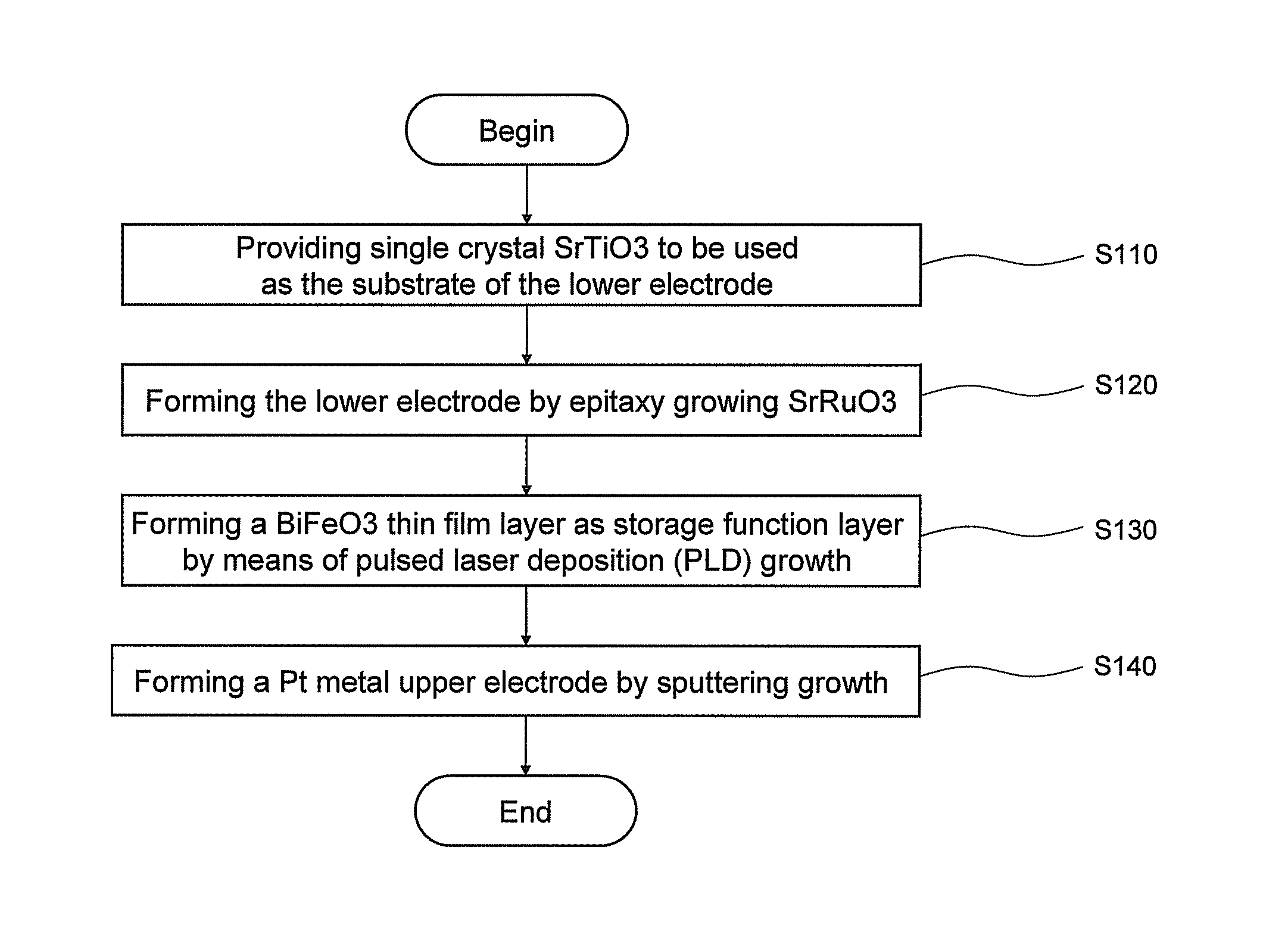
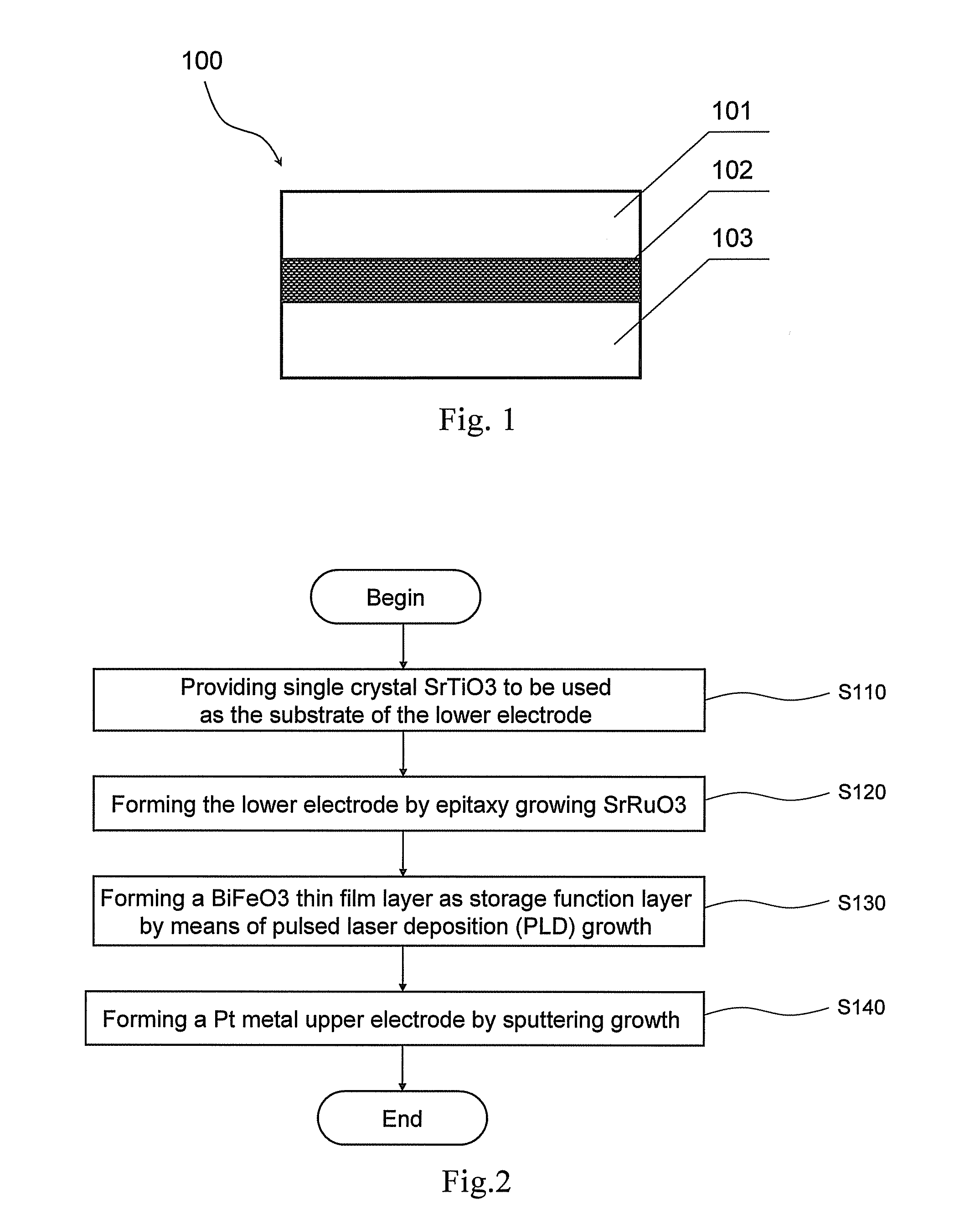
The invention belongs to the technical field of information storage, and particularly relates to a polarized tuning ferroelectric film diode memory, which comprises a substrate, a film bottom electrode prepared through electron beam evaporation or magnetron sputtering, a bismuth ferrite film prepared through pulse laser deposition or magnetron sputtering and a top electrode in sequence. Due to the polar modulation diode current density of 5.4A / cm2, the novel bismuth ferrite film made of semiconductor material in the invention is very suitable for high-density information storage and application, and the stored information simultaneously has the advantages of non-volatile performance, fatigue resistance, radiation resistance and non-destructive reading function of the variable resistance memory. Therefore, the invention improves the programming / erasing speed (the picosecond level) of the non-volatile memory cell, and has broad development space and market potential.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
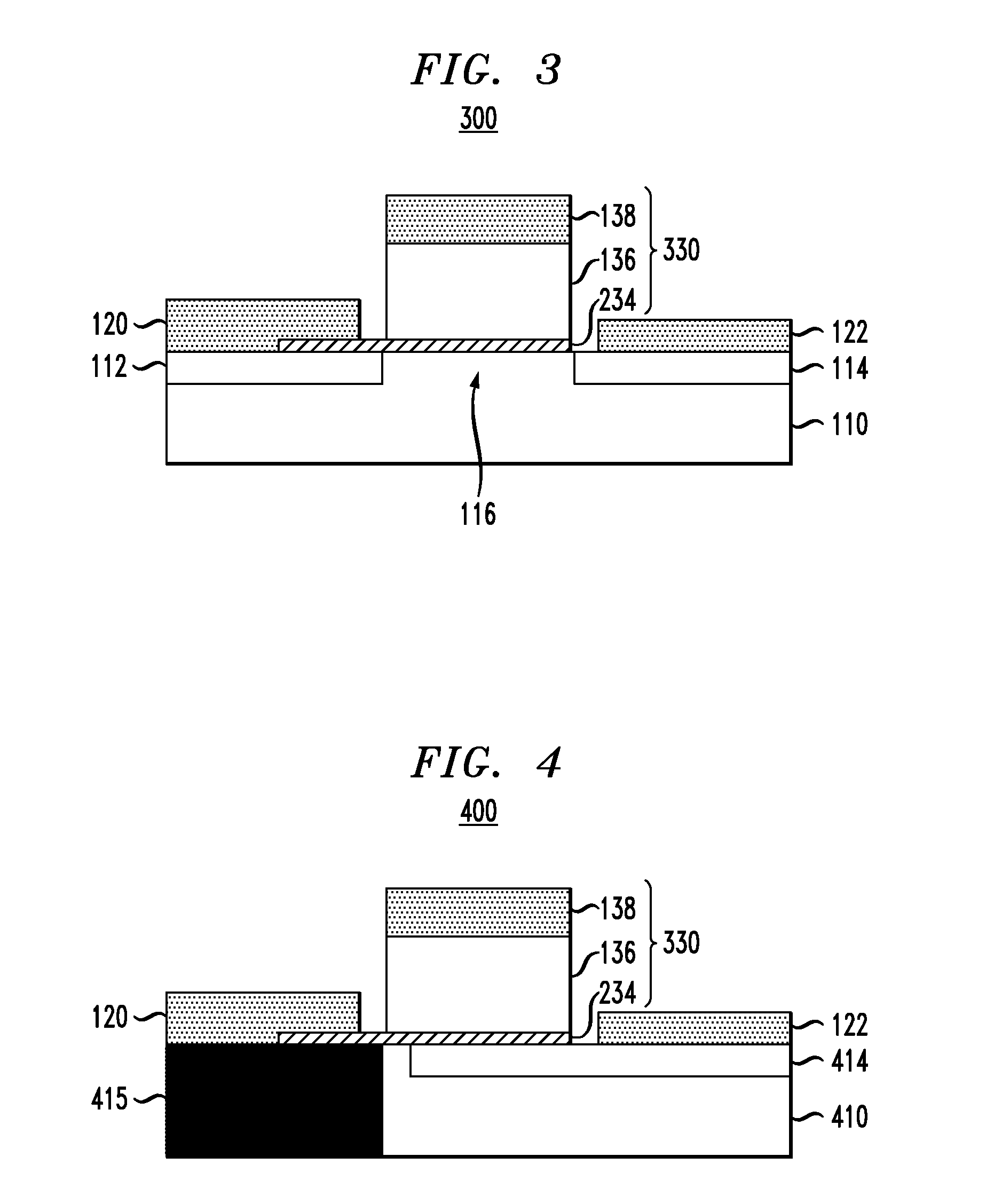
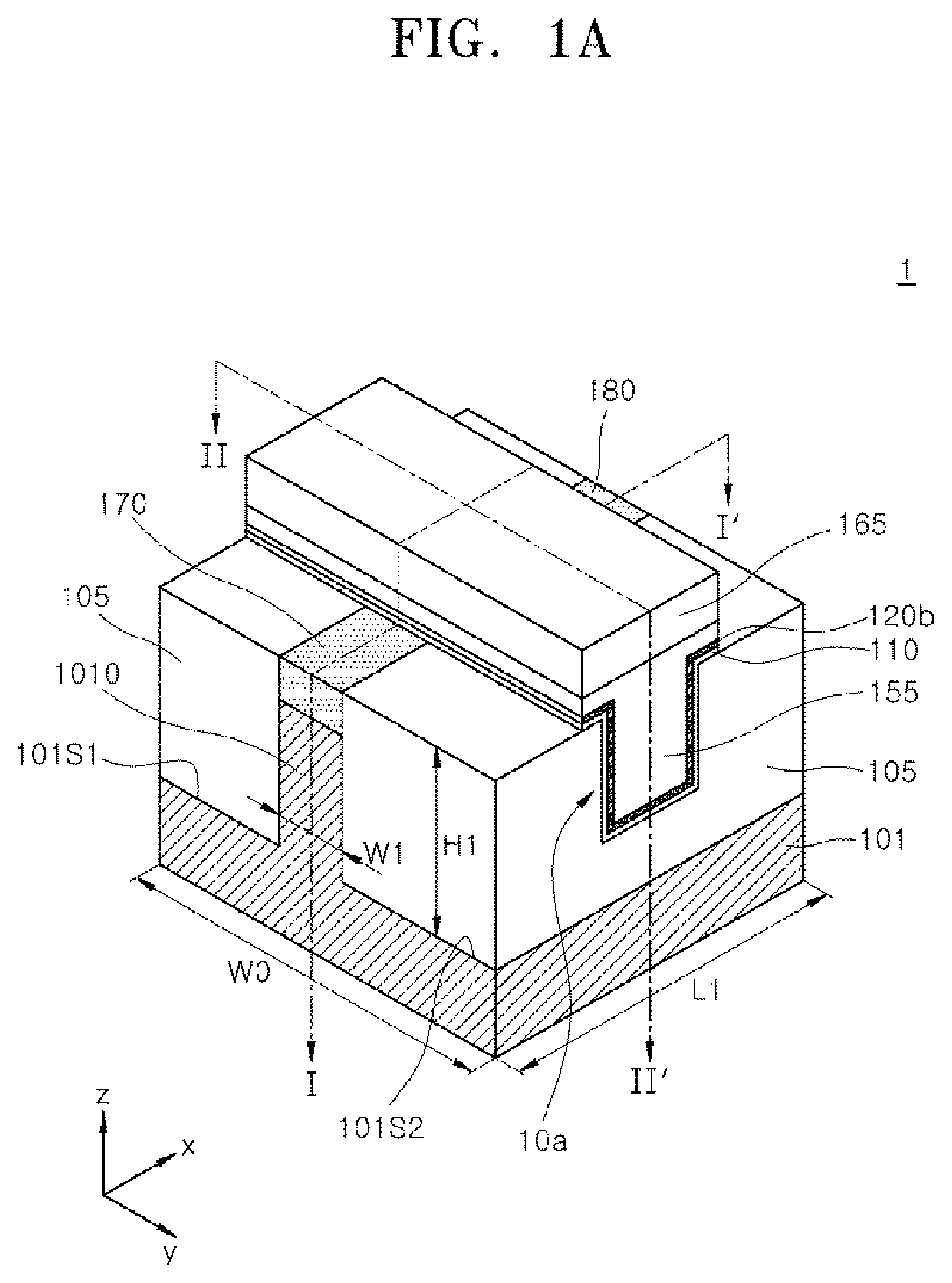
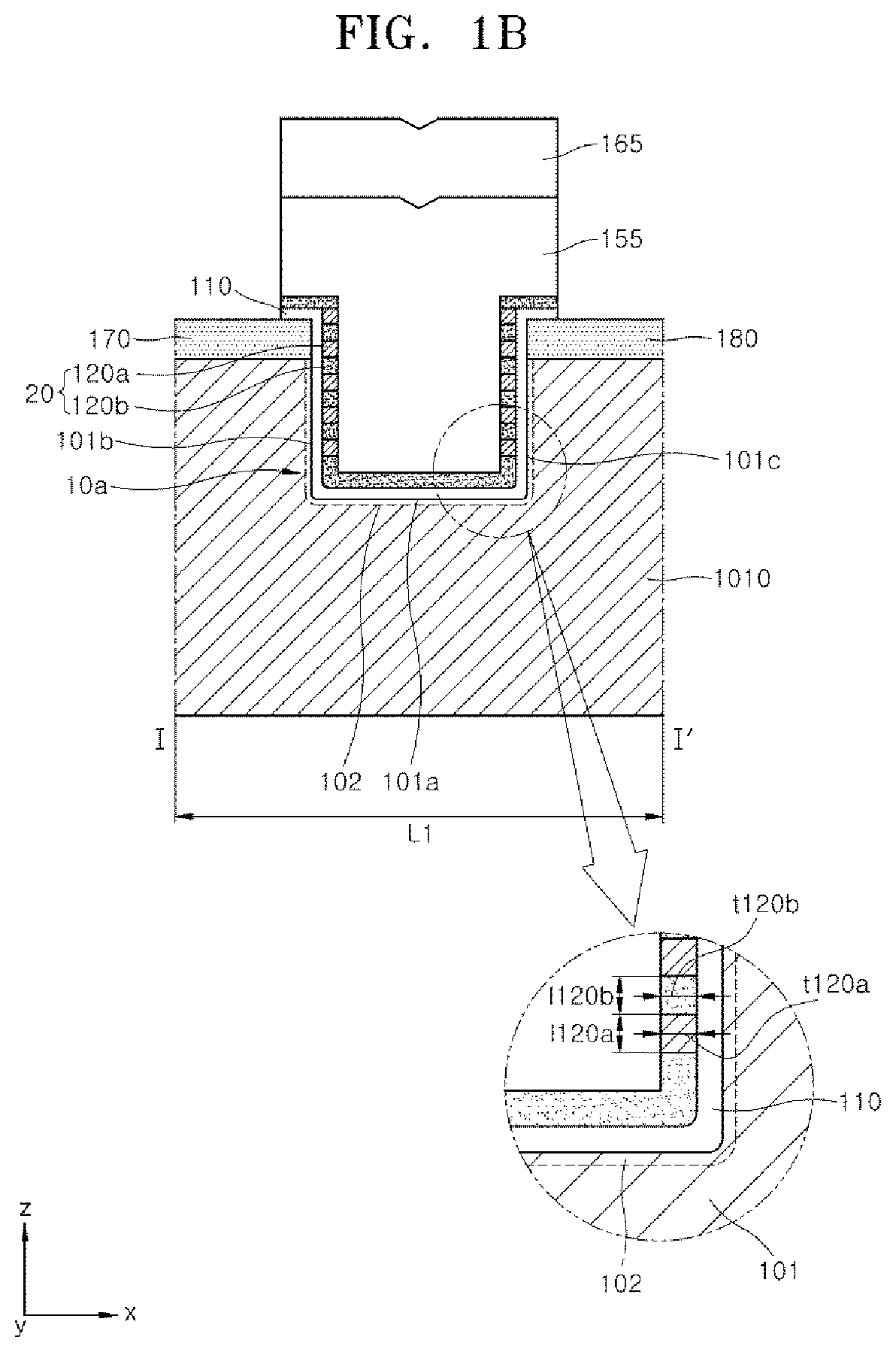
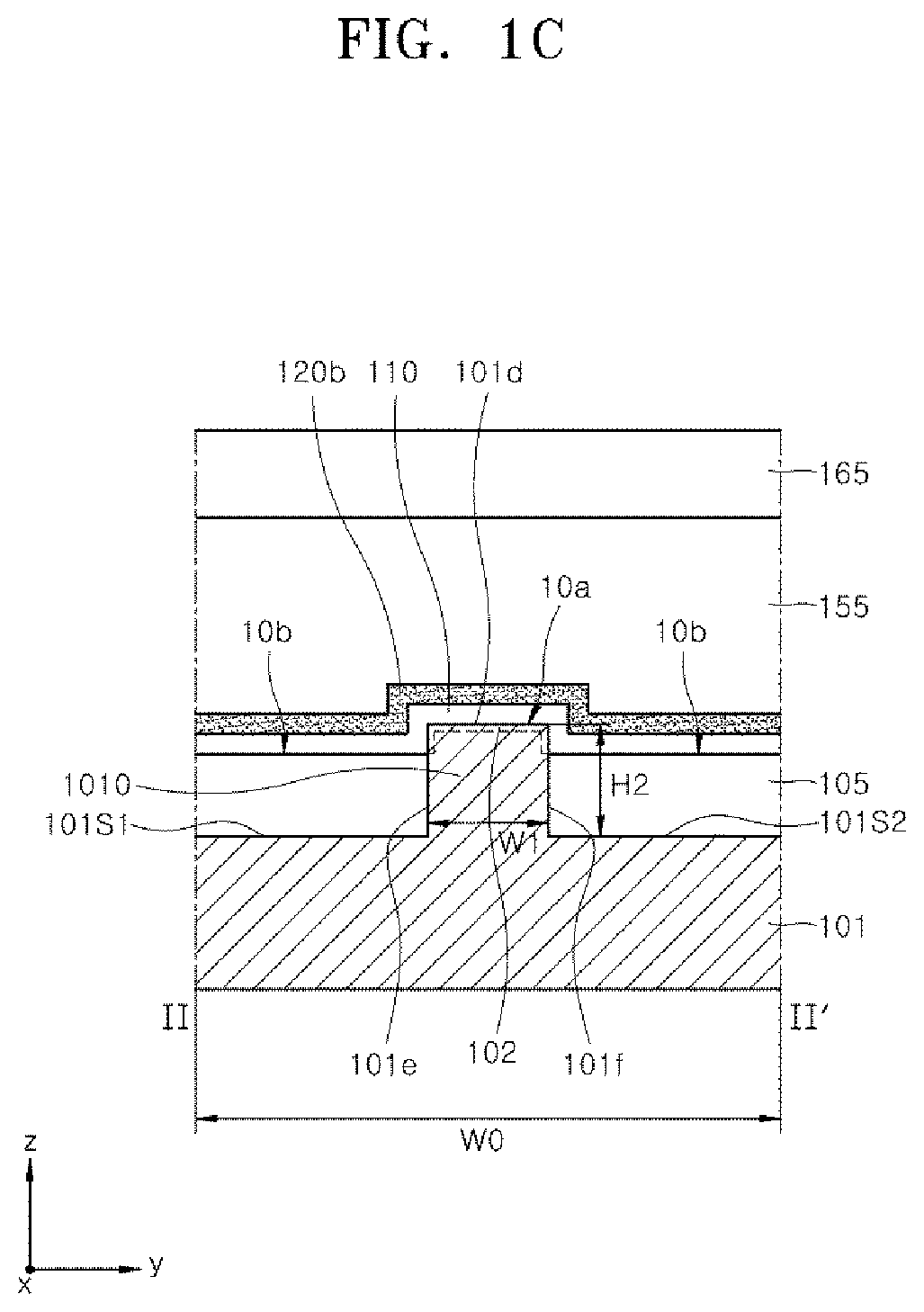
Ferroelectric semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20190348539A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDielectric layer
A ferroelectric semiconductor device of the present disclosure includes a substrate having a channel structure, a trench pattern having a bottom surface and a sidewall surface in the channel structure, a dielectric layer disposed on the bottom surface and the sidewall surface of the trench pattern, and a gate electrode layer disposed on the dielectric layer. The dielectric layer includes a ferroelectric layer pattern and a non-ferroelectric layer pattern that are disposed along the sidewall surface of the trench pattern.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
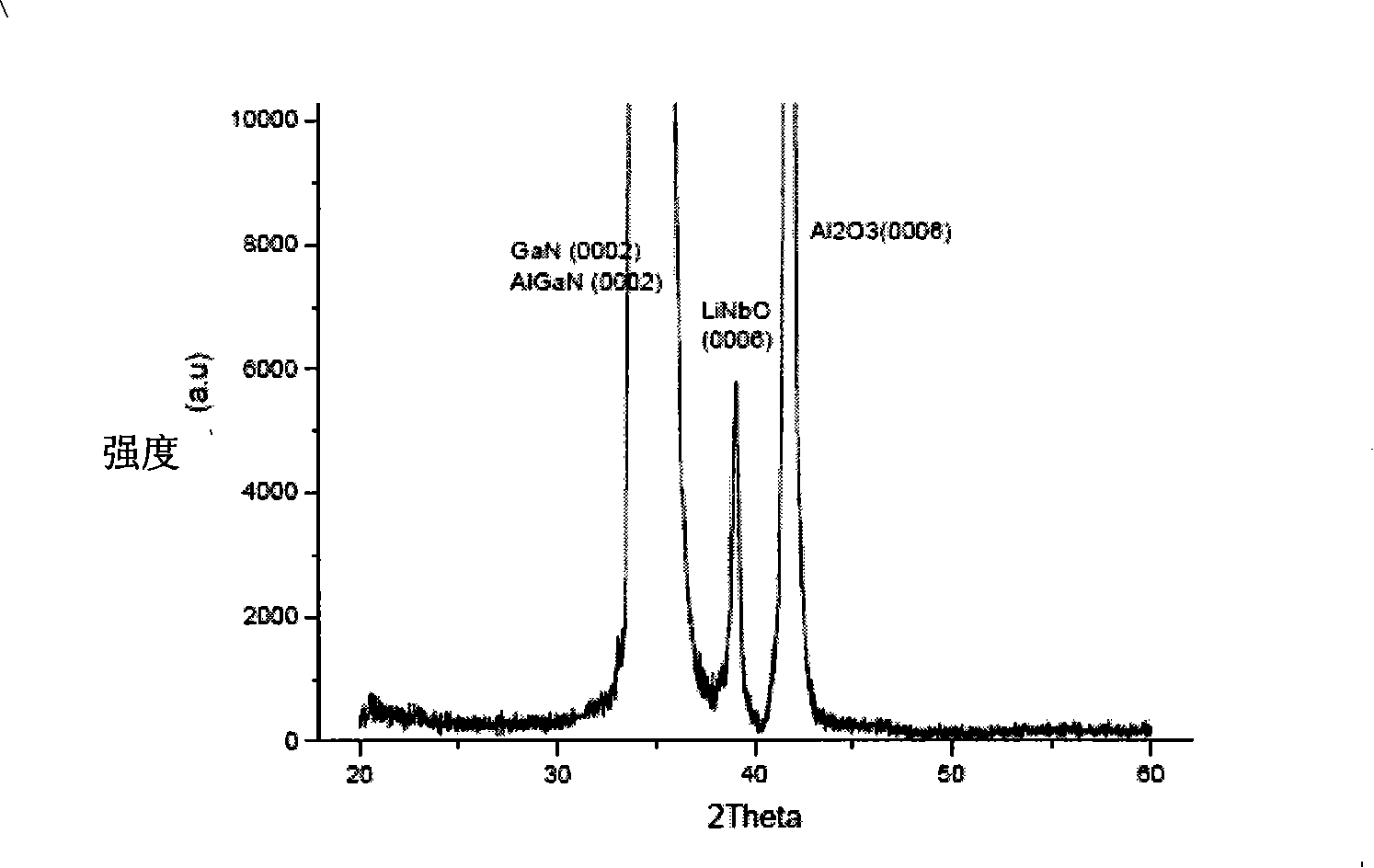
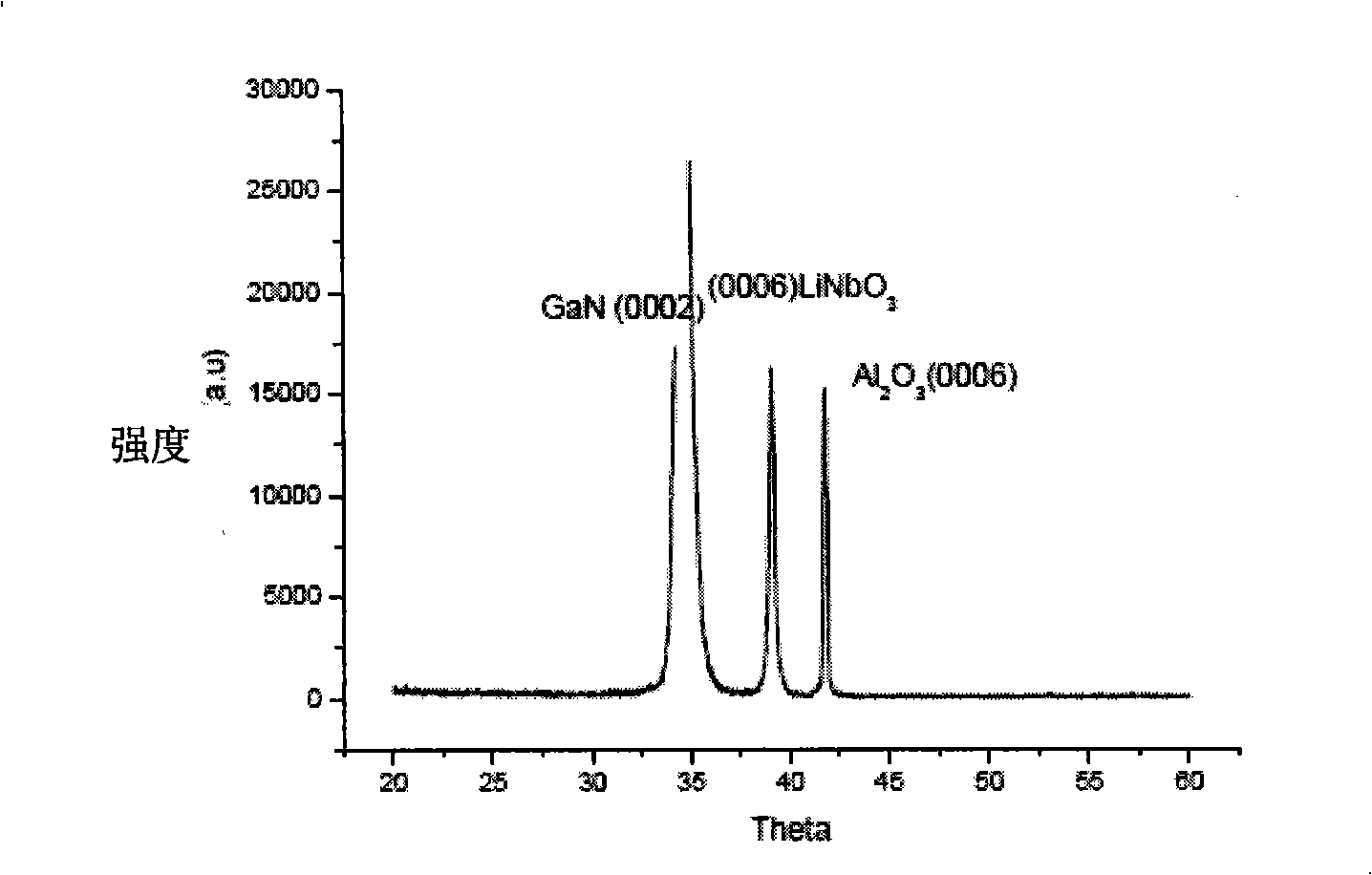
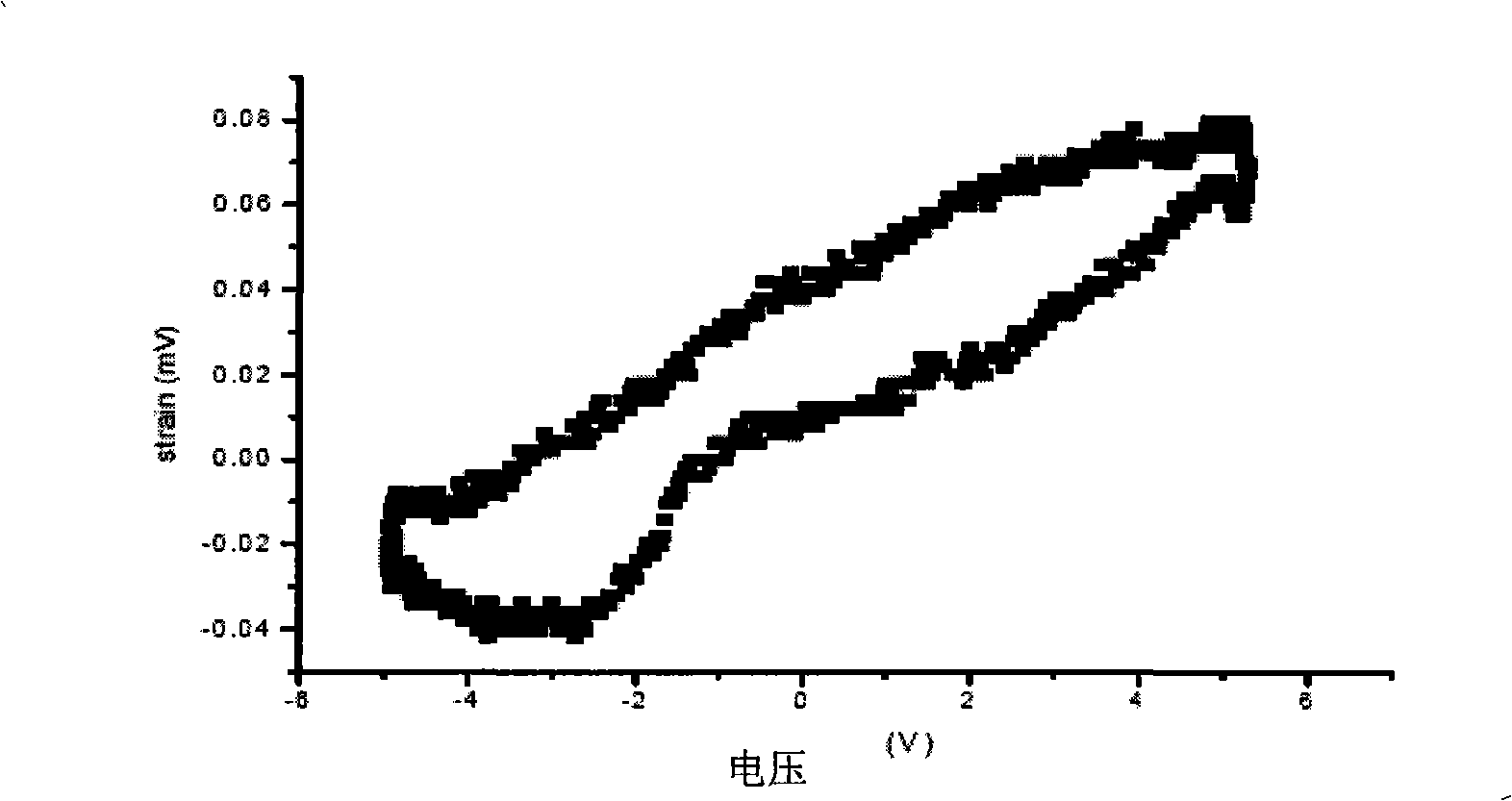
Production method and application of lithium niobate/III family nitride heterojunction ferroelectric semiconductor film
ActiveCN101315881AReduce power consumptionExtended use timeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHeterojunctionGas phase
The invention relates to a preparation method of a LiNbO3 / III nitride heterostructure ferroelectric semiconductor thin film, the metal organic chemical vapor deposition method is firstly adopted to grow AlN / AlGaN and other heterostructure materials on a (0001)-plane sapphire substrate as a buffer layer or a compound substrate; then the buffer layer adopts a high-purify 5N ferroelectric material as a target material, the pulsed laser deposition method is used to obtain a high-quality ferroelectric material thin film on the heterostructure buffer layer or the compound substrate; the vacuum of a growth cavity is controlled to be more than 10 Torr; the temperature of the substrate is increased to 300 to 900 DEG C, then high-purity oxygen is introduced into the cavity, the oxygen pressure is controlled at 5 to 90 Pa; the frequency of a laser is adjusted to be 5HZ, the energy is 300mJ, the target material is carried out the laser pre-sputtering in advance for 3 to 5 minutes, and the surface pollution of the substrate is cleaned; finally, the pulsed laser is focused on the target material, and a target source is opened to grow the LiNbO3 / III nitride heterostructure ferroelectric semiconductor thin film on the heterostructure compound substrate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
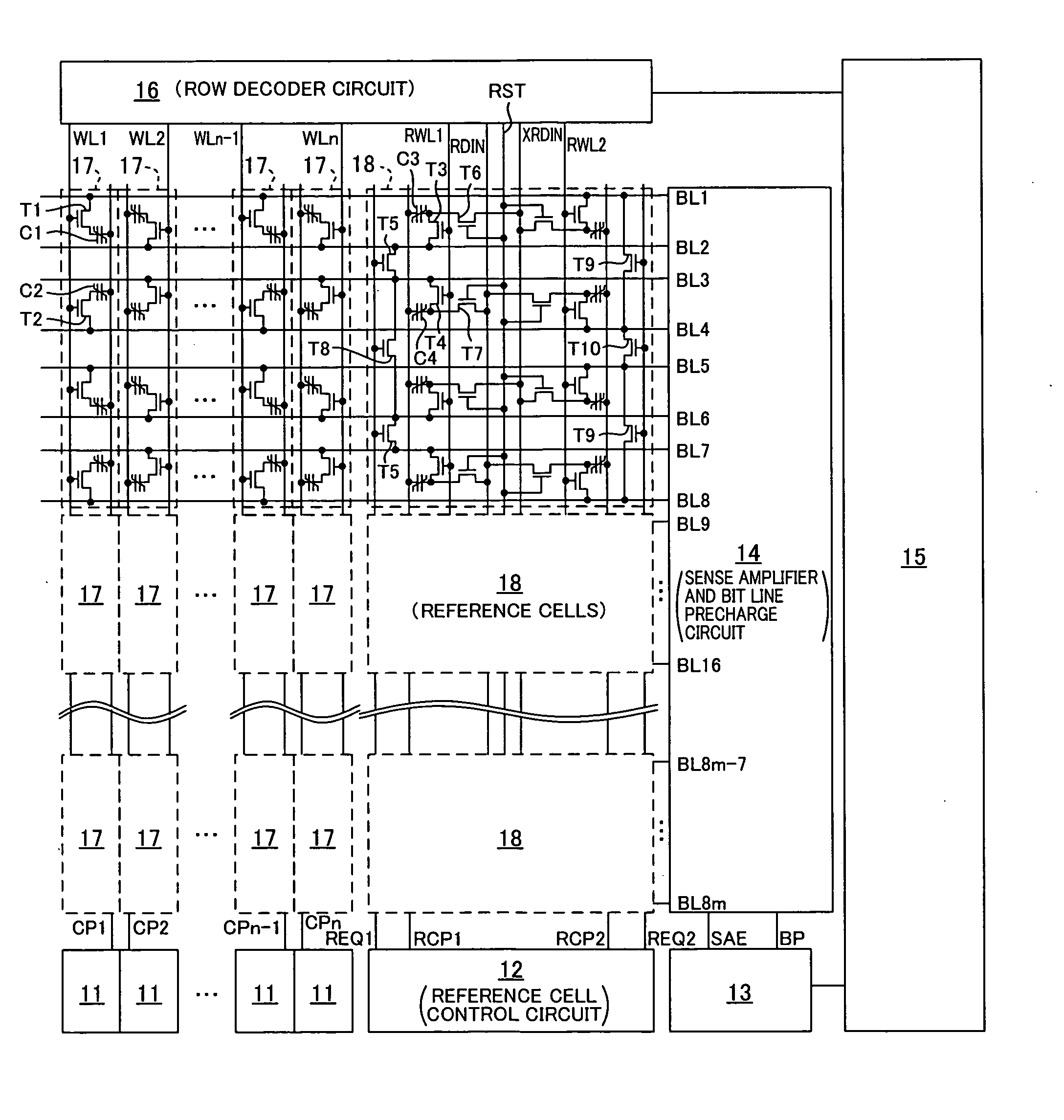
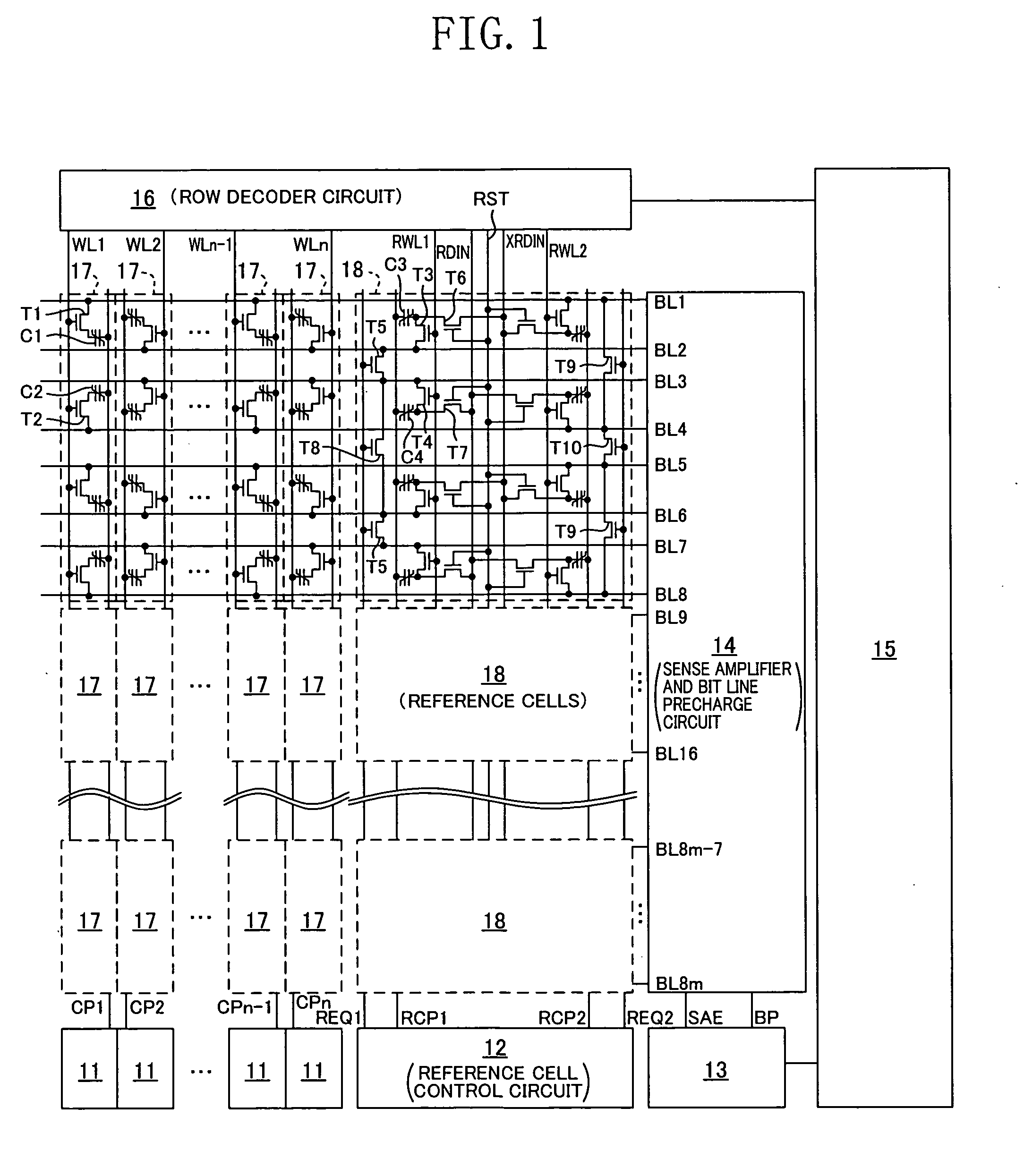
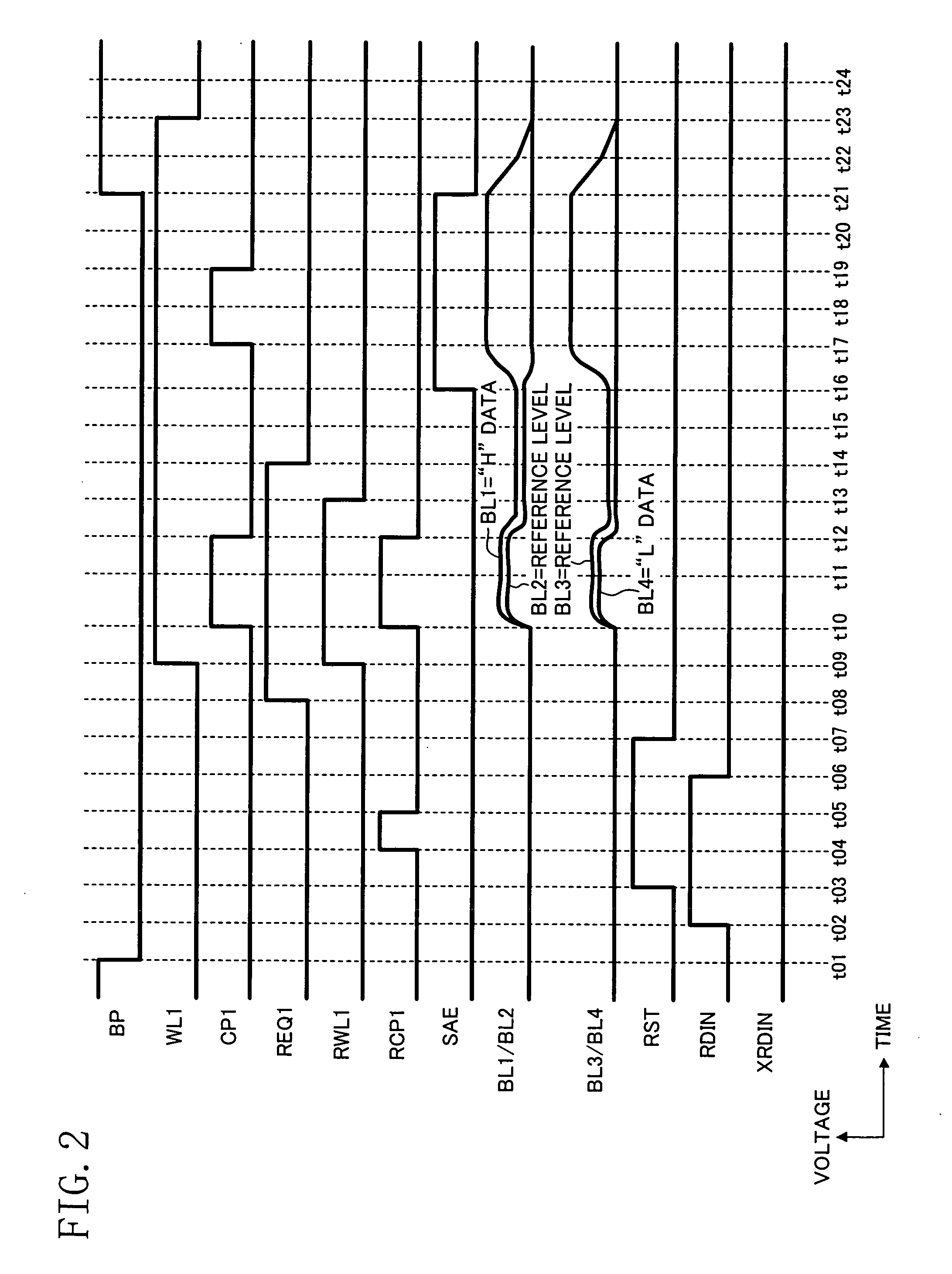
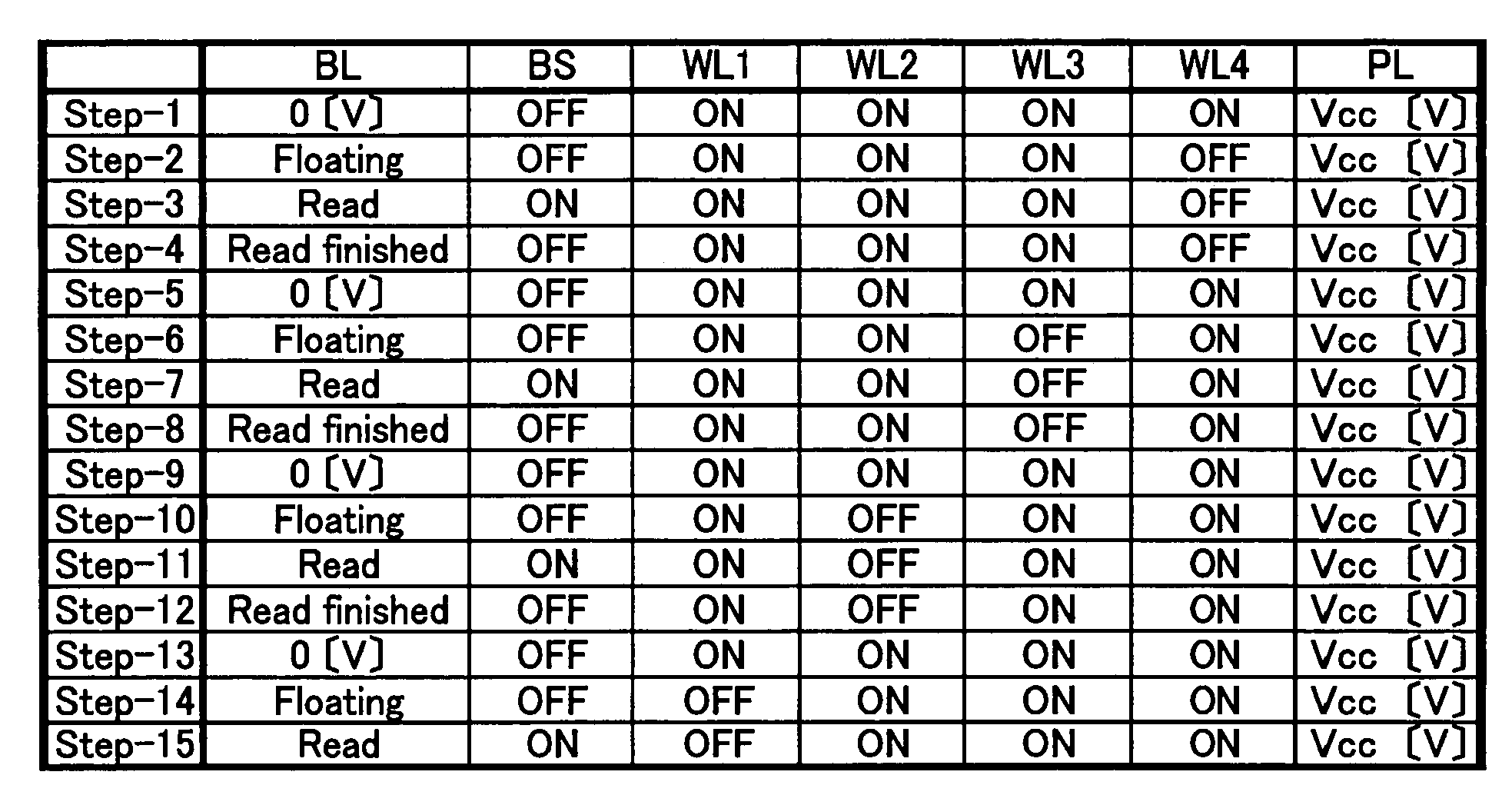
Ferroelectric semiconductor memory device
The present invention provides a ferroelectric semiconductor memory device in which the potential of data read out from a normal cell is compared with the reference level of a reference cell so as to determine whether the readout data is the “H” data or the “L” data, wherein since the reference cell is in the relaxed state when reading out data from the normal cell for the first time, the reference cell is reset before reading out data from the normal cell. Then, data is read out from the normal cell, and then the reference cell is reset. In second and subsequent data read operations of reading out data from a normal cell of another address, the reference cell is in the reset state, whereby the reference level is the same between the first data read operation and the second or subsequent data read operation. Thus, the reference level is always kept at a predetermined constant level when data is read out from normal cells.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor channel ferroelectric dielectric layer field effect transistor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112968055AProlong remanent polarizationHigh dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesField-effect transistorDielectric layer
The invention discloses a two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor channel ferroelectric dielectric layer field effect transistor and a preparation method thereof. The two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor channel ferroelectric dielectric layer field effect transistor comprises an insulating substrate, a graphene grid electrode is arranged on the insulating substrate, and a two-dimensional ferroelectric dielectric layer and a metal grid electrode are arranged on the graphene grid electrode; and the two-dimensional ferroelectric dielectric layer is provided with a two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor channel, and the two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor channel is provided with a metal source electrode and a metal drain electrode which are separated from each other. The invention also comprises the preparation method of the two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor channel ferroelectric dielectric layer field effect transistor. According to the invention, the two ferroelectric bodies are combined with each other, and the bound charges of the two ferroelectric bodies at the interface can perform charge shielding on a depolarization field, so that the residual polarization of the ferroelectric bodies can be prolonged, and the problems that stable nonvolatile storage is difficult to realize and a silicon-based semiconductor process cannot be compatible in the prior art are effectively solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
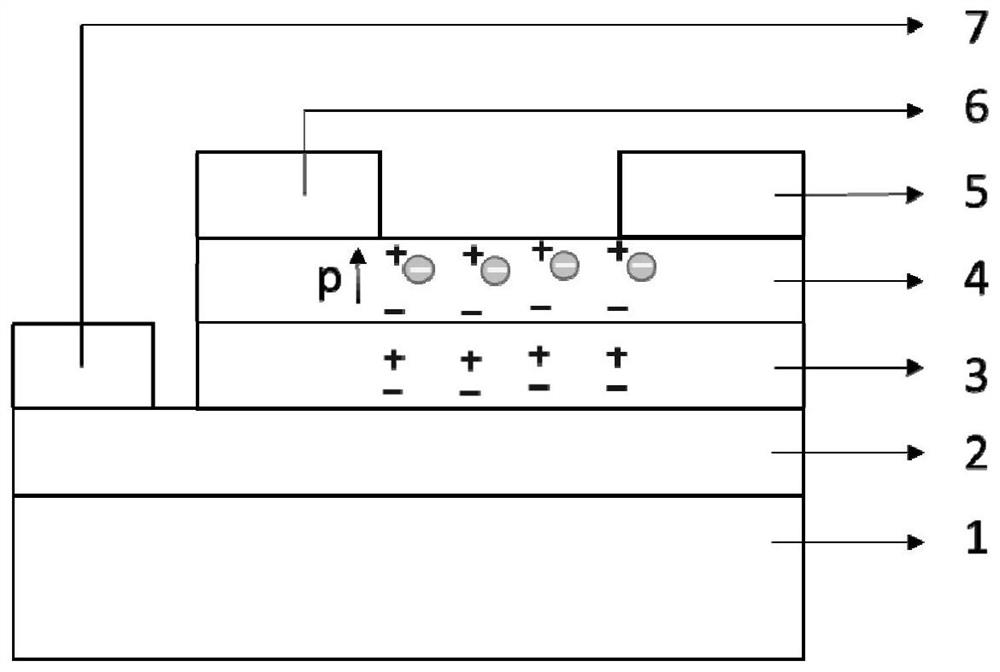
Switchable memory diodes based on ferroelectric/conjugated polymer heterostructures and/or their composites
ActiveUS8089110B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFerroelectric semiconductorsCondensed matter physics
An embodiment of the present memory cell includes a first layer of a chosen conductivity type, and a second layer which includes ferroelectric semiconductor material of the opposite conductivity type, the layers forming a pn junction. The first layer may be a conjugated semiconductor polymer, or may also be of ferroelectric semiconductor material. The layers are provided between first and second electrodes. In another embodiment, a single layer of a composite of conjugated semiconductor polymer and ferroelectric semiconductor material is provided between first and second electrodes. The various embodiments may be part of a memory array.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
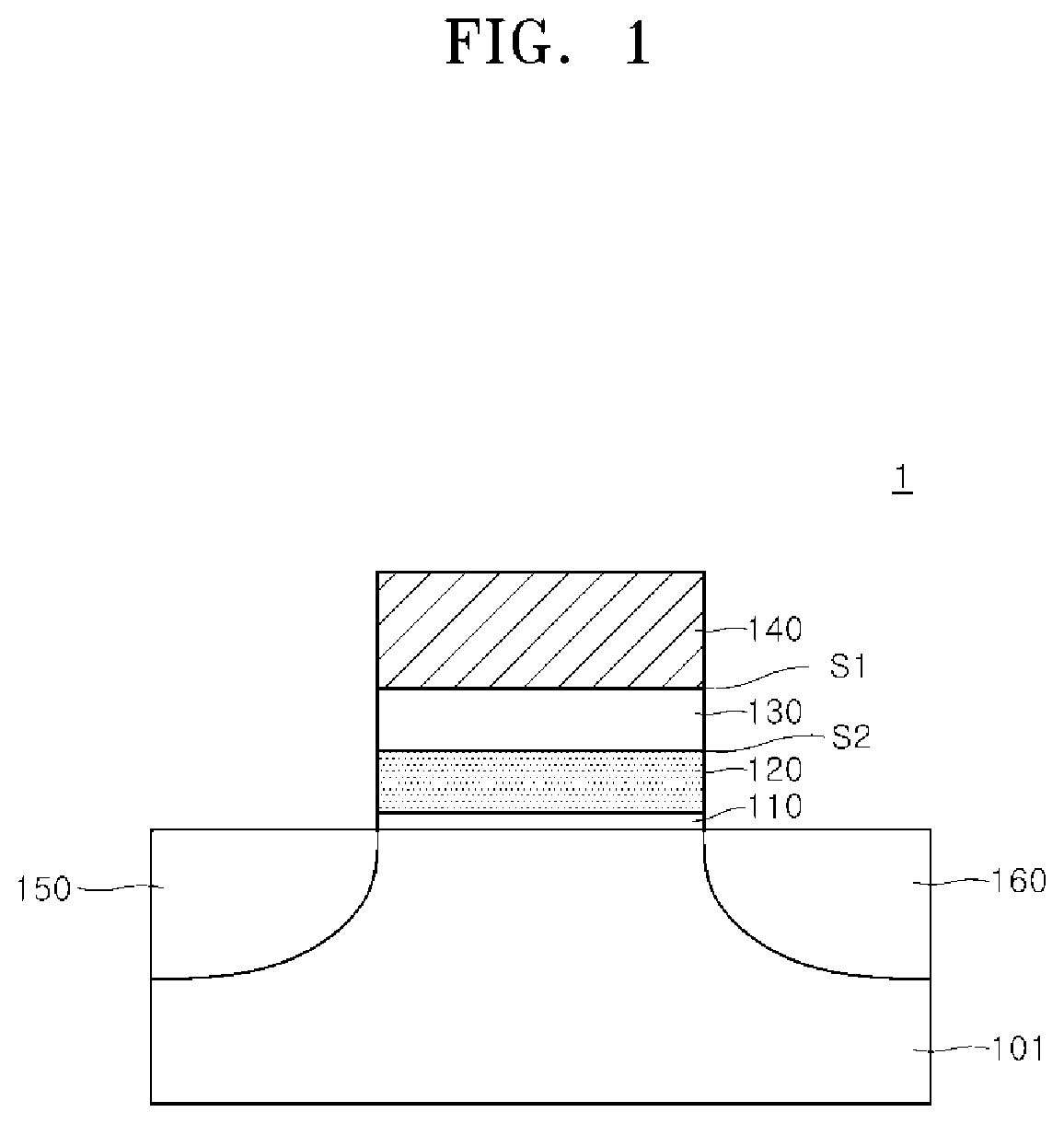
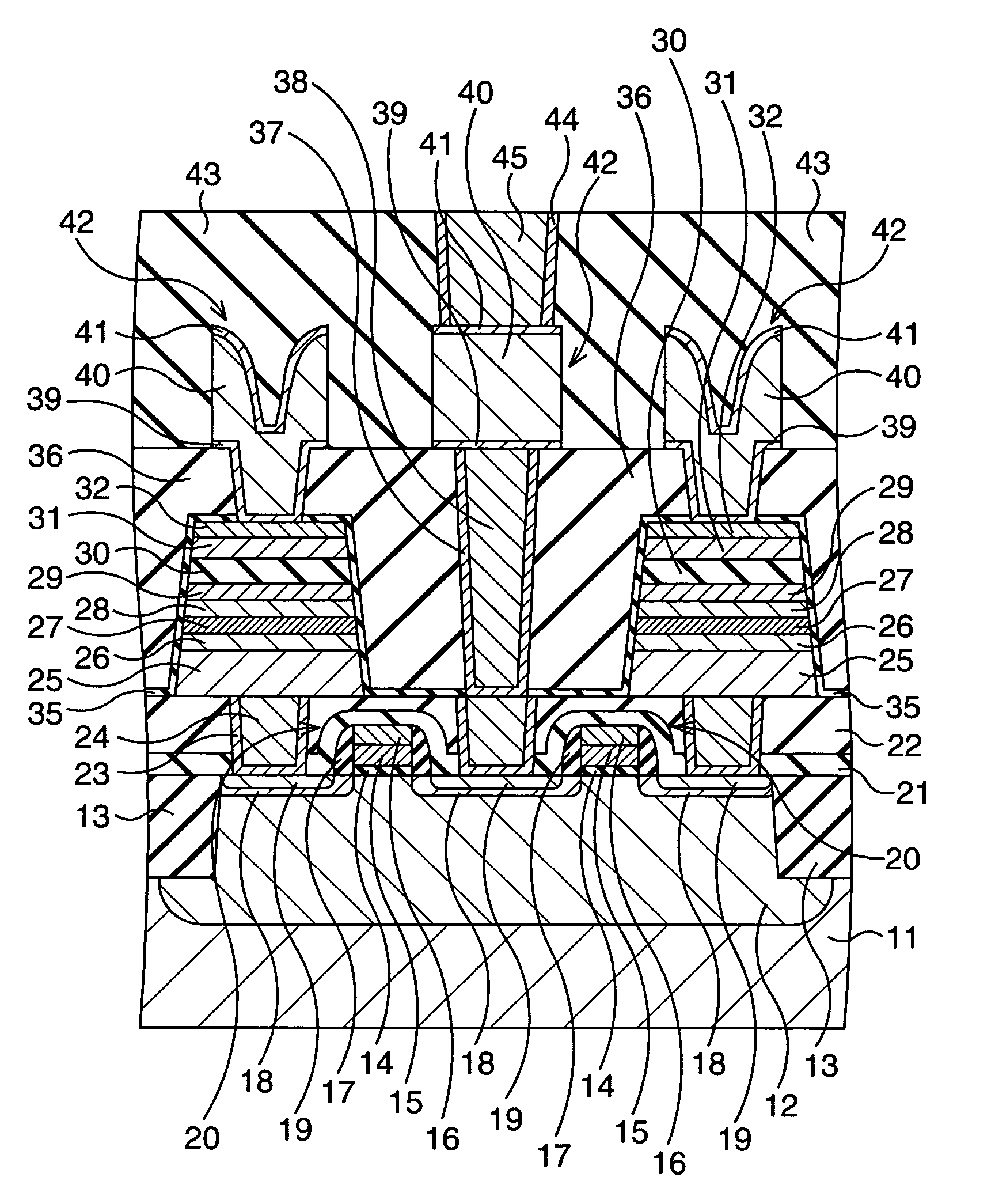
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device including ferroelectric semiconductor pattern and methods for writing data in and reading data from the same
Provided are a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device including ferroelectric semiconductor patterns in respective memory cells and methods of writing and reading data. The device includes a substrate; a plurality of first conductive lines disposed in or on the substrate; a plurality of second conductive lines disposed in or on the substrate and having a different height from the first conductive lines, wherein the second conductive lines intersect the first conductive lines, respectively, to define a plurality of intersection regions; and a plurality of memory cells disposed on the substrate. Herein, the memory cells include ferroelectric semiconductor patterns, respectively, which are disposed between the first conductive lines and the second conductive lines that define the intersection regions.
Owner:DONGGUK UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing low-band gap ferroelectric photovoltaic film through pulsed laser deposition
InactiveCN104388894AStable oxygen pressureSave raw materialsFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingSolar cellVacuum chamber
The invention provides a method for preparing a low-band gap ferroelectric photovoltaic film through pulsed laser deposition. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: taking Pt / Ti / SiO2 / Si(100) as a substrate; cleaning for 10 minutes through an ultrasonic cleaner by sequentially using acetone, absolute ethyl alcohol and deionized water, wherein the working frequency of ultrasonic waves is 40 kHz; then blow-drying by using nitrogen, then immediately loading into a vacuum cavity, and determining the temperature of the substrate at 600-800 DEG C, the oxygen pressure of a vacuum chamber at 0-5 Pa, the energy of a laser pulse at 100-500 mJ and the frequency of the laser pulse at 1-20 Hz; ablating a ceramic target material to obtain a low-band gap film product. The method provided by the invention is a physical vapor deposition method, has the advantages of fewer selected raw materials, economy, no pollution, simple preparation process, convenience for operation and easiness for production, and opens up a fire-new way for developing a solar cell based on a ferroelectric semiconductor.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Ferroelectric semiconductor device and method for producing a memory cell
ActiveUS20210151445A1Reduce coercive fieldSafe storageSolid-state devicesDigital storageMemory cellDevice material
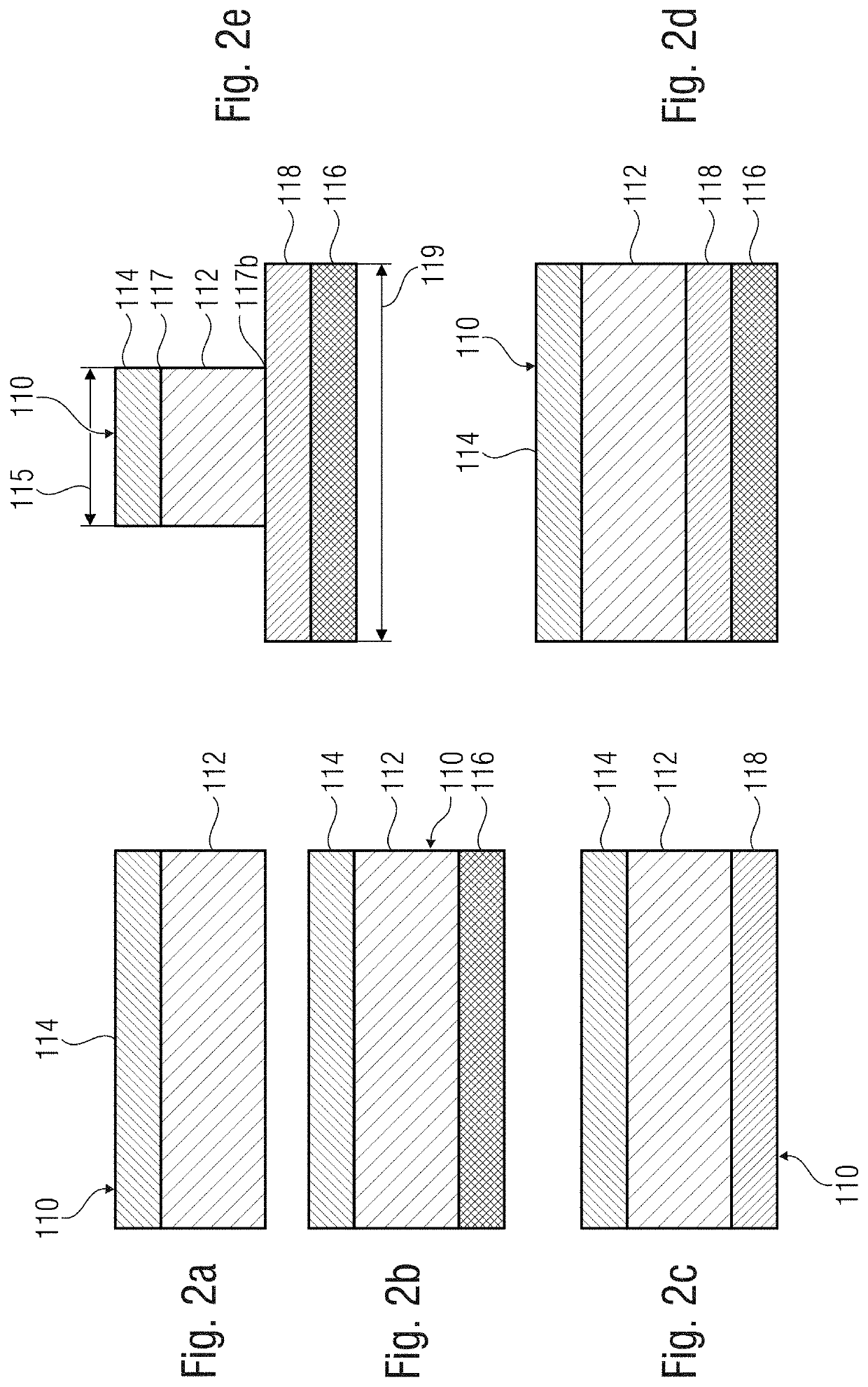
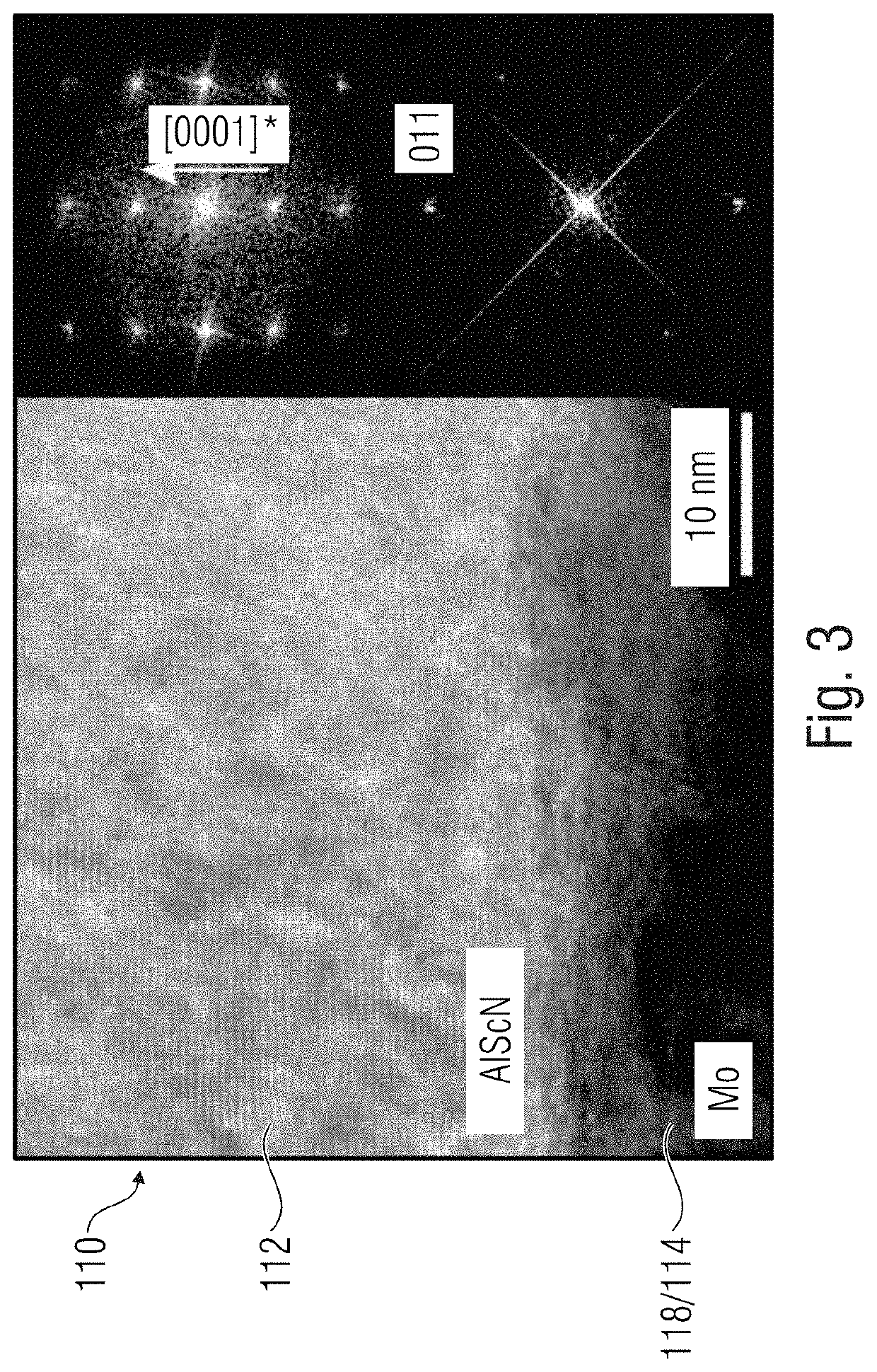
Ferroelectric semiconductor device with a memory cell, with a ferroelectric memory layer and a first conductive layer disposed on the ferroelectric memory layer; and a semiconductor device connected to the memory cell. The ferroelectric memory layer of the memory cell can include a mixed crystal with a group III nitride and a non-group III element.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Heterosynaptic electronic device based on two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor and preparation method of heterosynaptic electronic device
PendingCN113497063ARealize dual-input regulationMaintain ferroelectricitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a heterosynapse electronic device based on a two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor and a preparation method of the heterosynapse electronic device. The heterosynapse electronic device comprises a supporting substrate, a back gate electrode, a dielectric layer, a source-drain electrode and a packaging layer which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top, the source and drain electrode comprises a source electrode and a drain electrode, a conducting channel is arranged between the source electrode and the drain electrode, and the conducting channel is made of a III2-VI3 type two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor material; the source electrode and the drain electrode are respectively connected with two ends of the conducting channel and form Schottky contact with a Van der Waals interface; and the preparation method comprises the steps of preparing the packaging layer h-BN and the graphene electrode, preparing a PVA dry-method transfer film, performing dry-method transfer on the graphene electrode, preparing the graphene source and drain electrode and preparing the metal extraction electrode. The invention provides a memristive transistor which takes a III2-VI3 two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor material as a conducting channel, and realizes a heterosynaptic electronic device for regulating and controlling synaptic weight by inputting from two ends of a source electrode, a drain electrode and a grid electrode.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
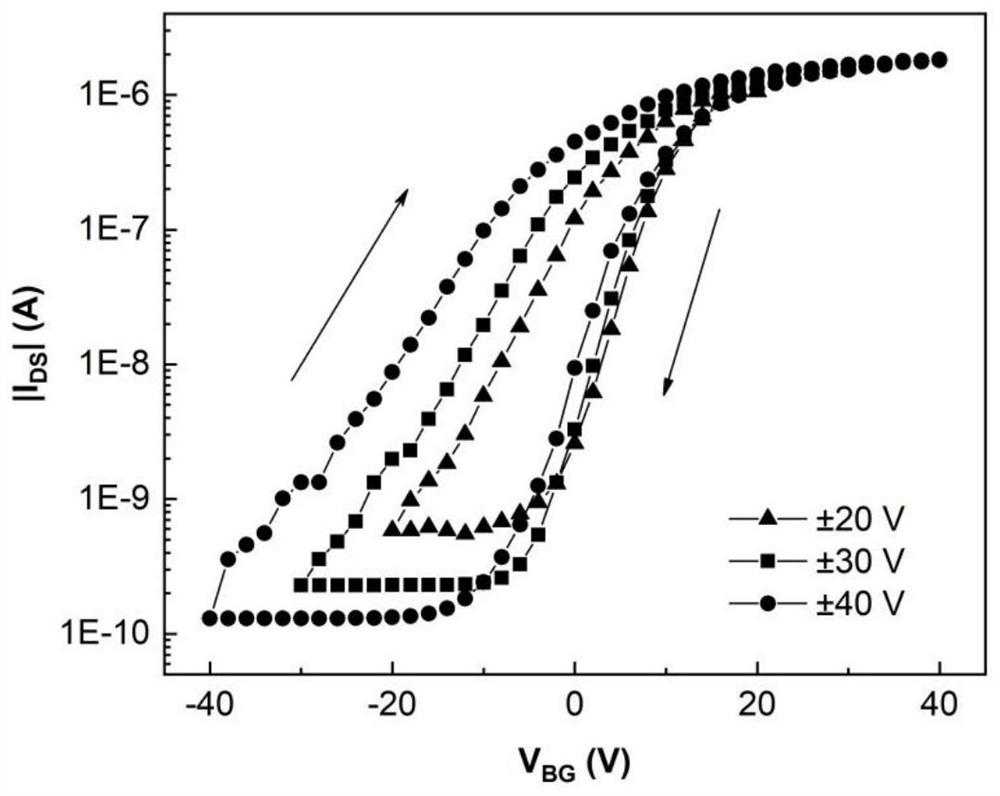
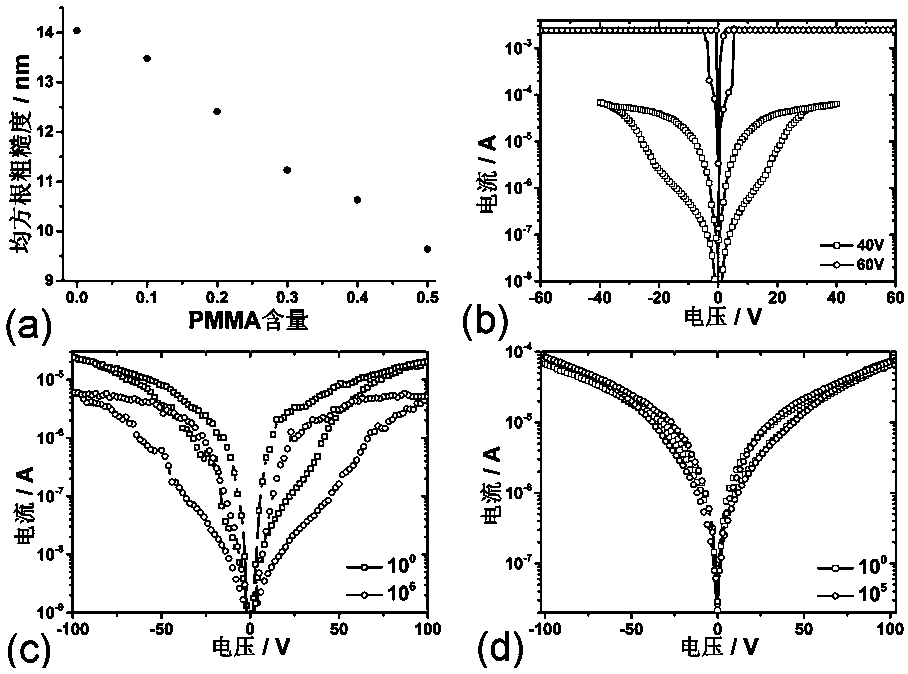
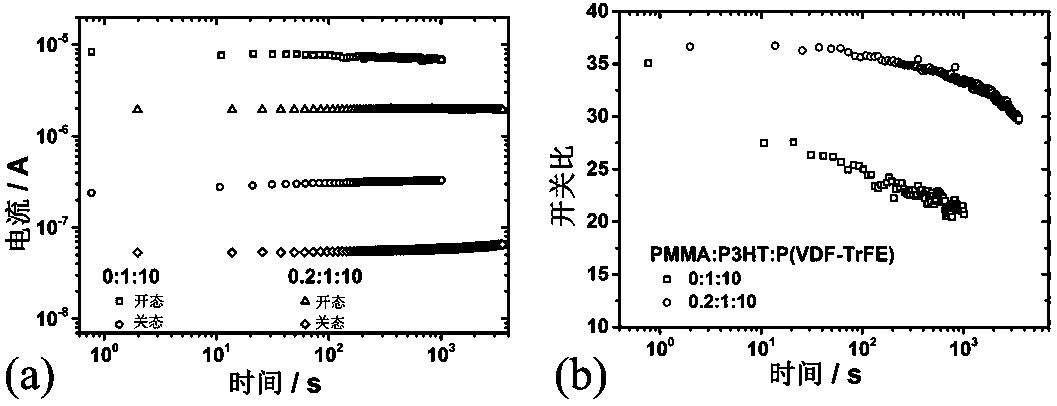
Ferroelectric/semiconductor/PMMA ternary composite resistive film with high electrical stability and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105514273AImprove breakdown resistanceImprove featuresSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFerroelectric polymersElectric breakdown
The invention belongs to the technical field of resistive random access memories, and specifically relates to a ferroelectric / semiconductor / PMMA ternary composite resistive film with high electrical stability and a preparation method thereof. The ternary composite resistive film is obtained by doping polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) in a ferroelectric / semiconductor composite film, and the mass ratio of the doped PMMA to ferroelectric polymer is 0.1:10 to 0.3:10. The surface roughness, anti-electric fatigue property and resistance state maintaining performance of the ternary composite film are improved obviously. As the mutual solubility of PMMA and ferroelectric polymer P(VDF-TrFE) is good, the leakage characteristic of ferroelectric phase can be reduced effectively. PMMA and an organic semiconductor, such as P3HT, form a lamellar phase separation structure, which can inhibit the leakage of semiconductor phase effectively, and reduce the risk of semiconductor phase electric breakdown.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
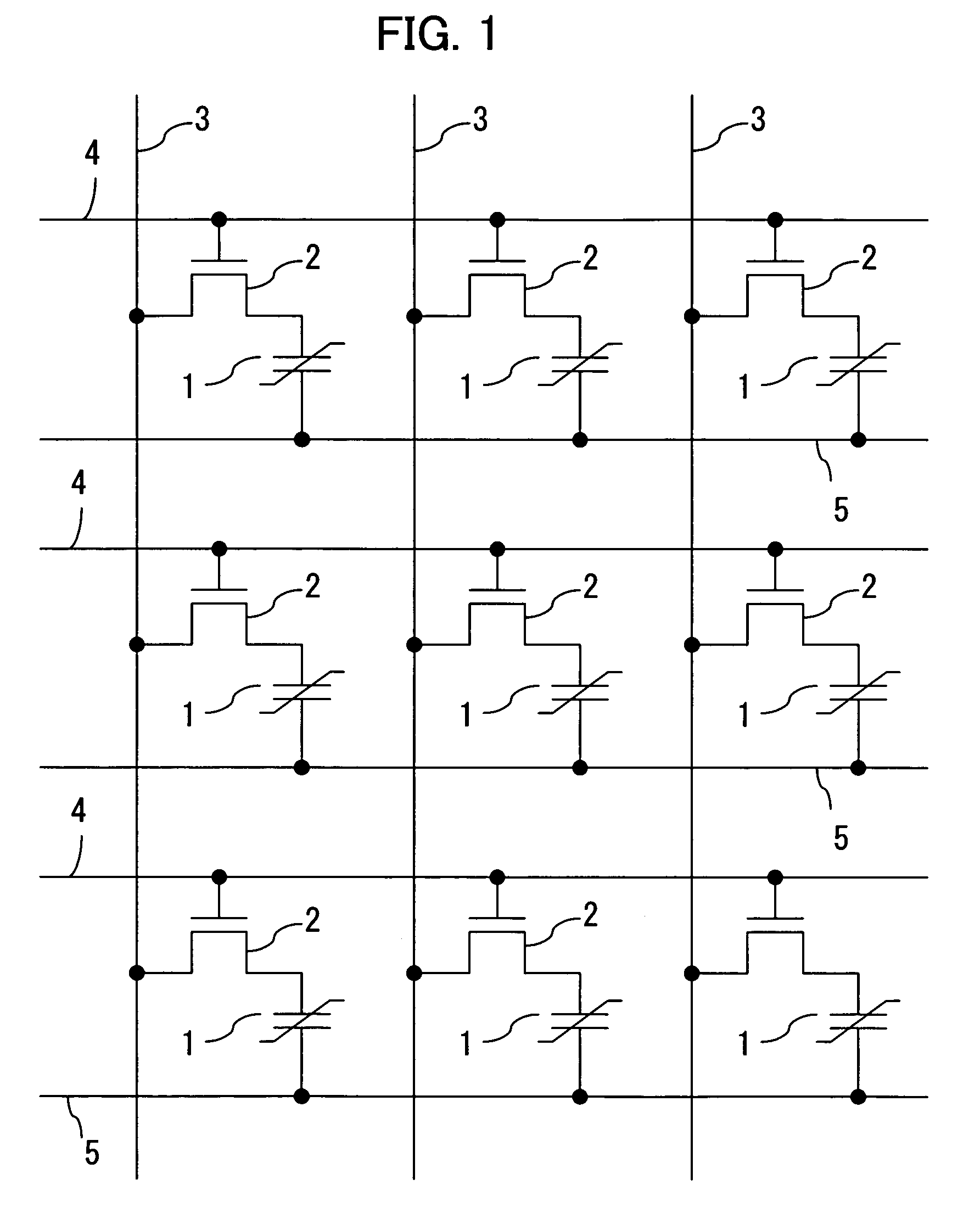
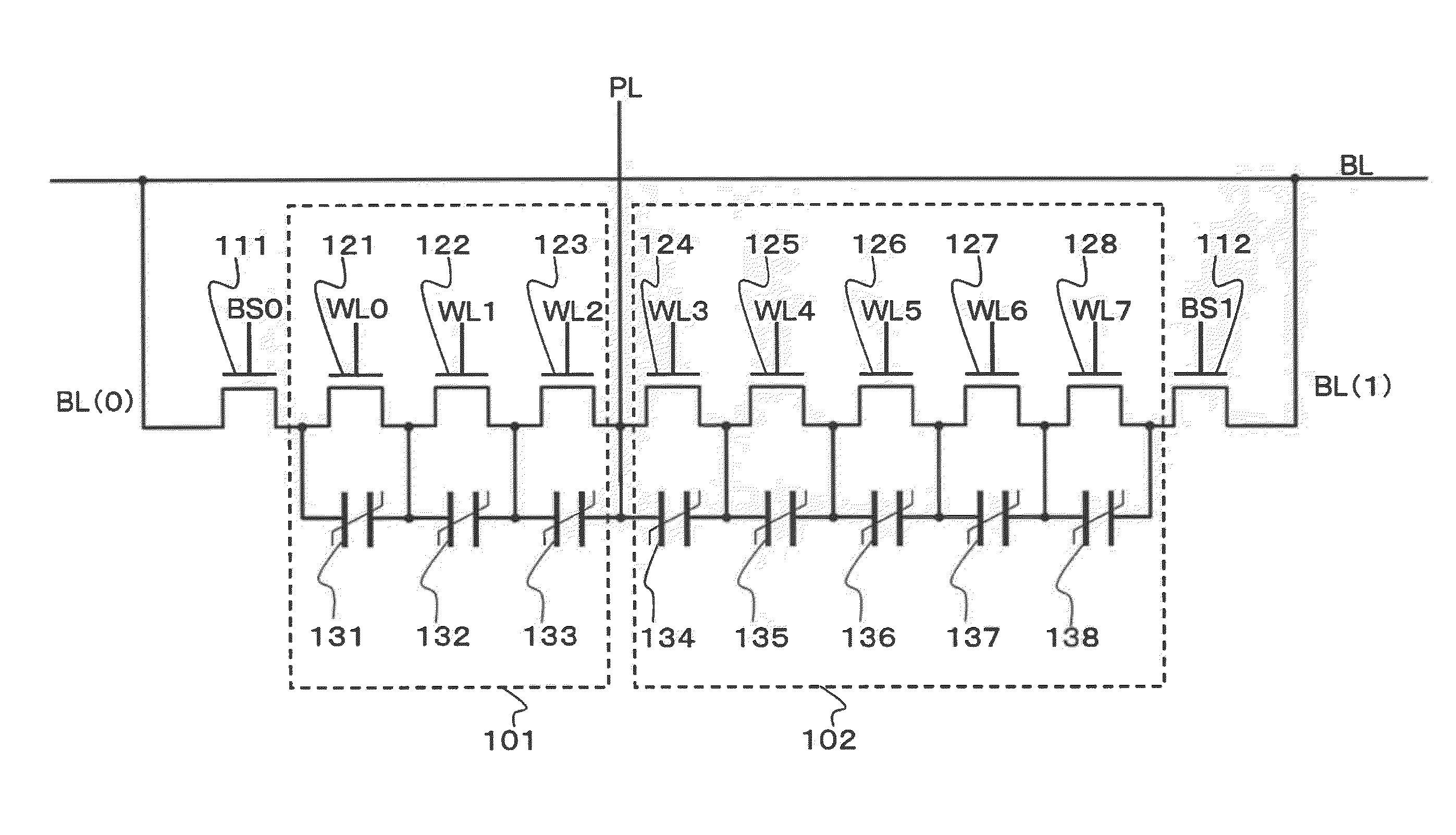
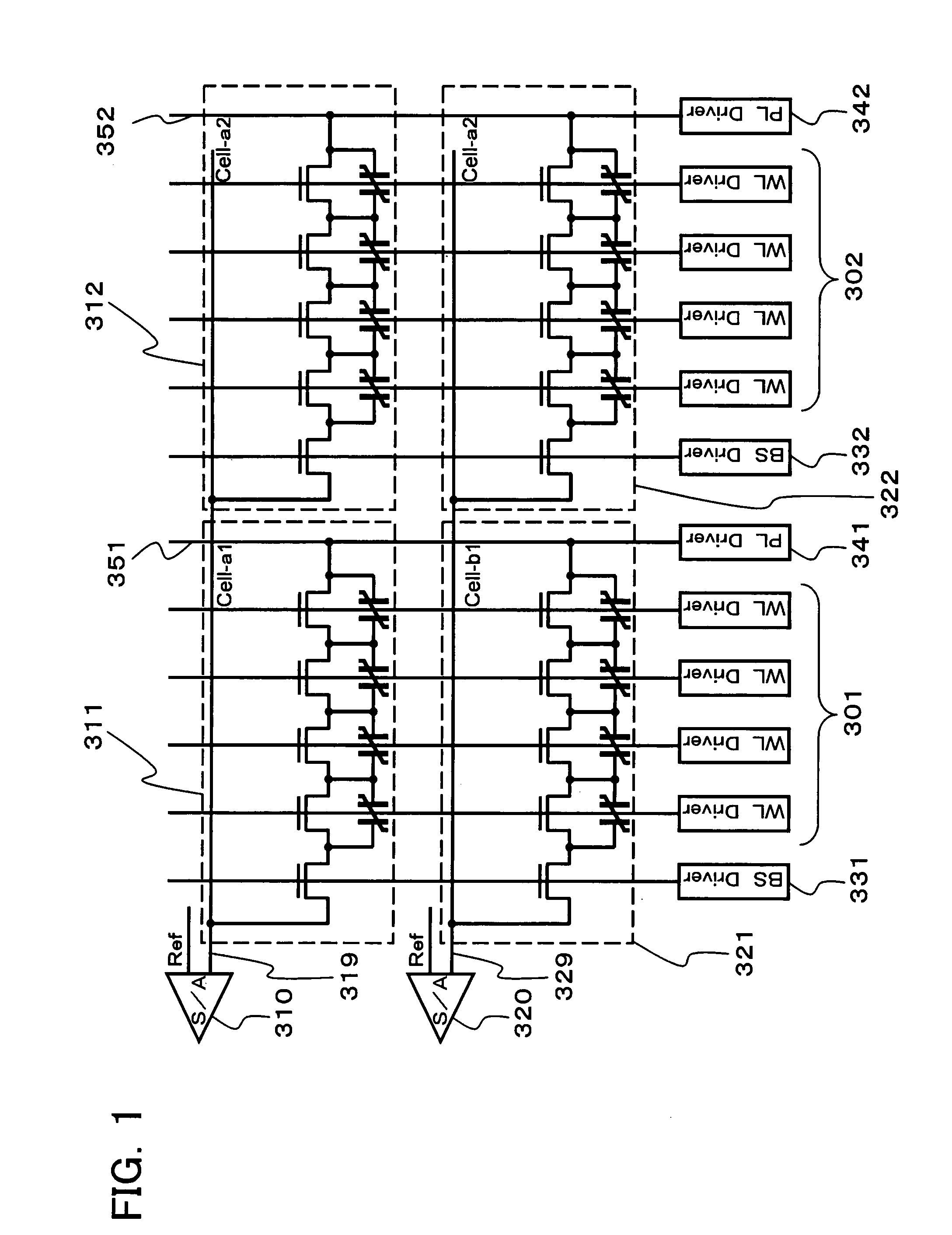
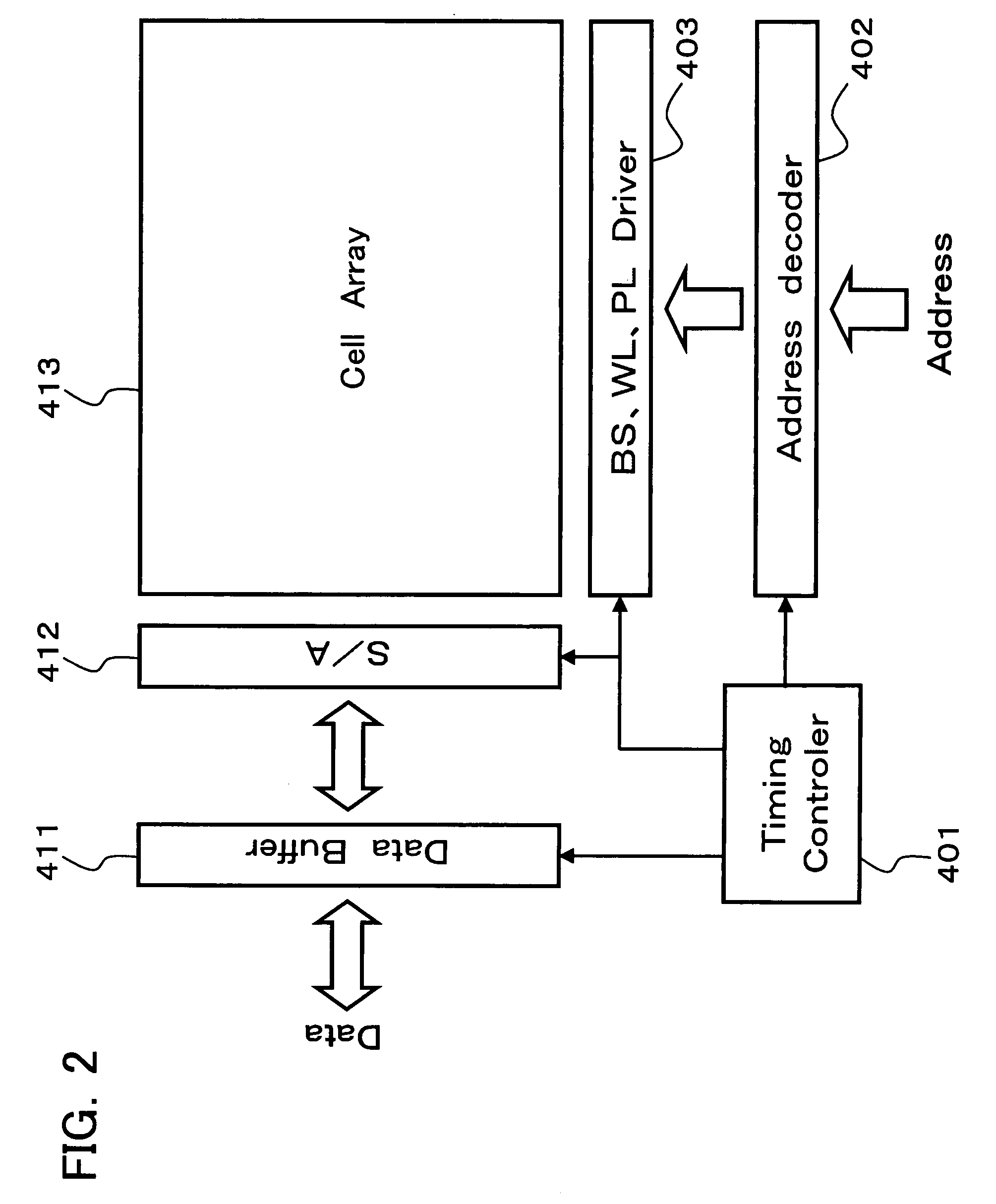
Ferroelectric semiconductor storage device
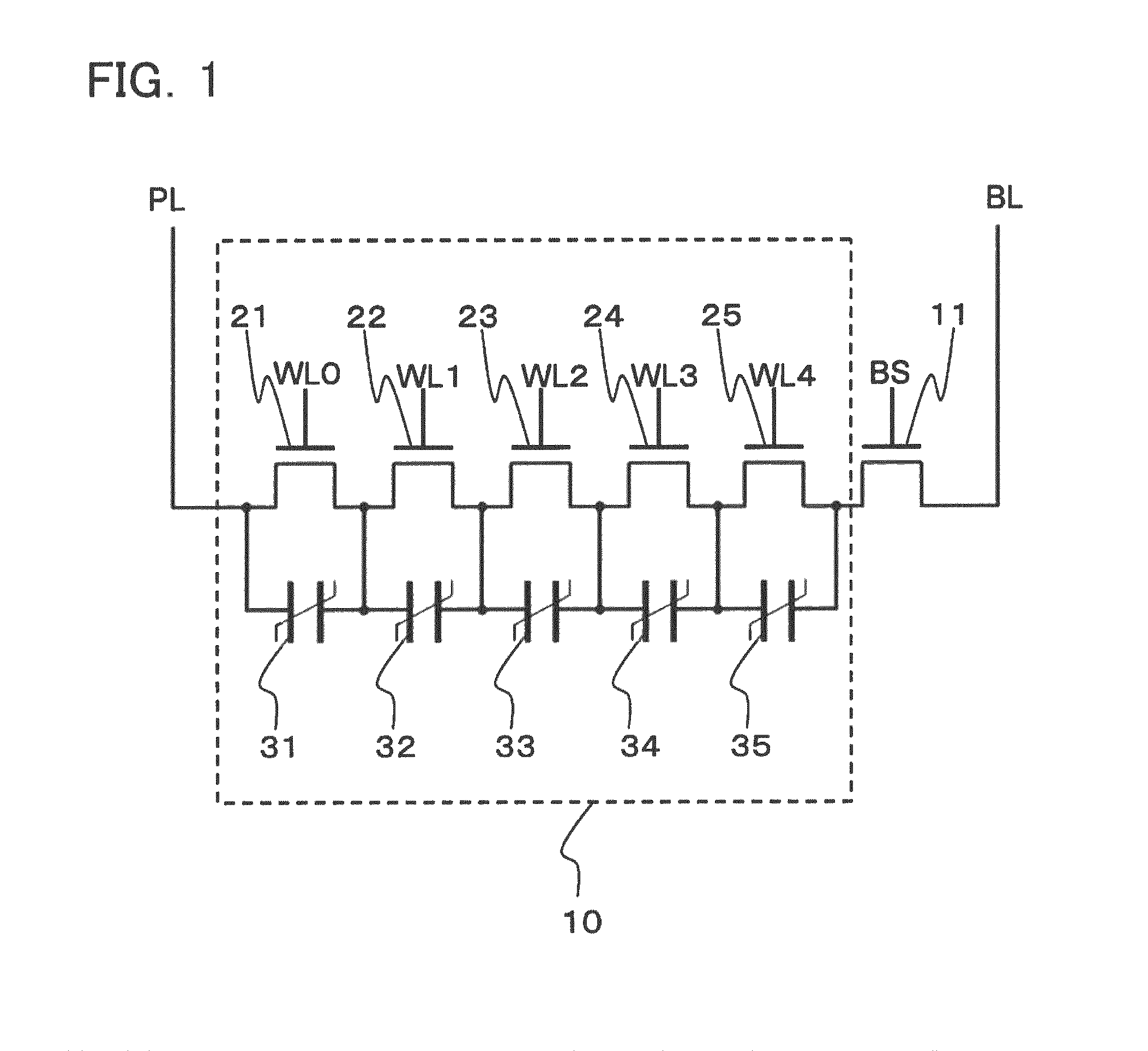
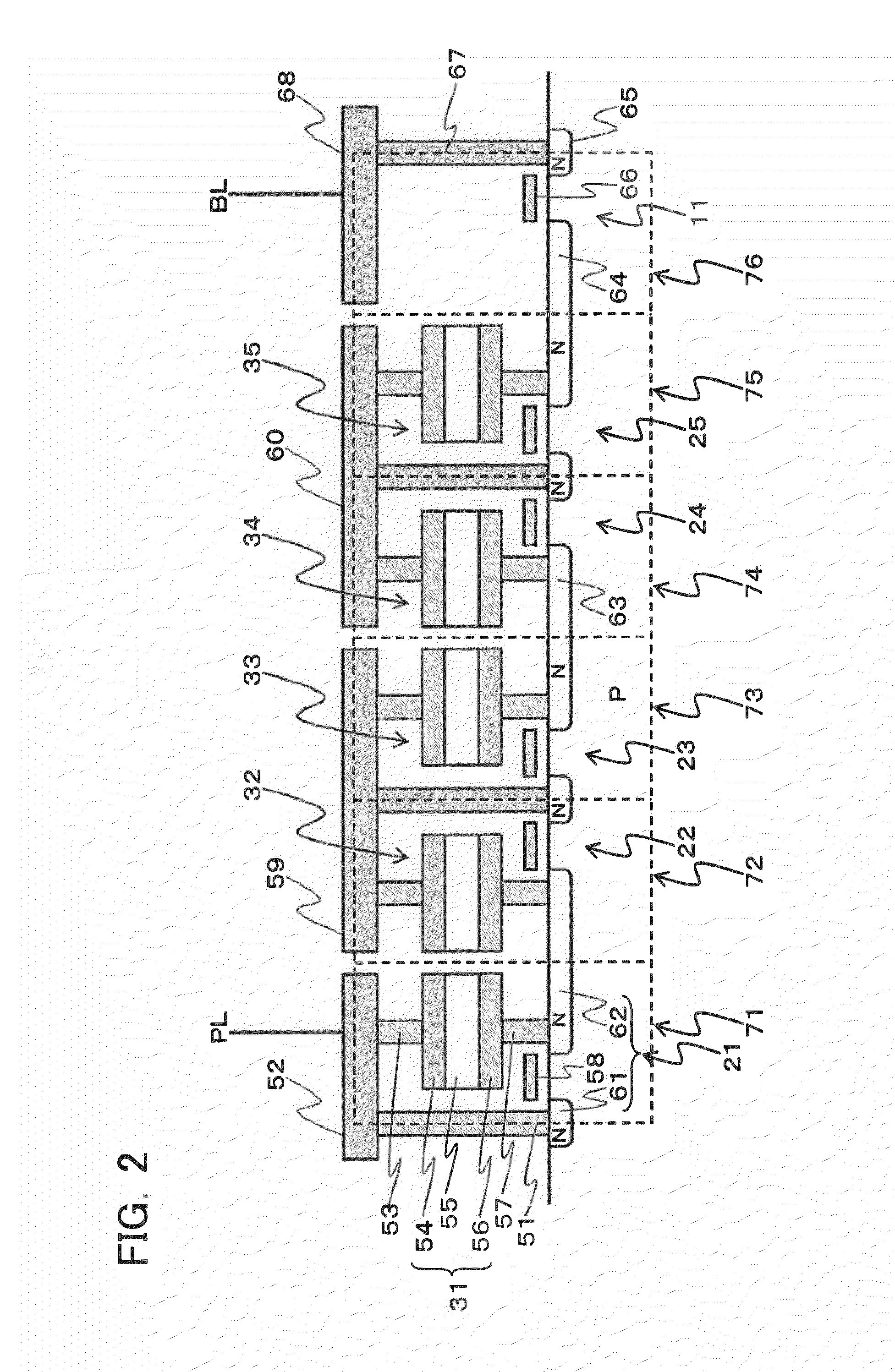
A ferroelectric semiconductor storage device includes: a block having a plurality of ferroelectric memory cells connected in series, each of the plurality of ferroelectric memory cells including a ferroelectric capacitor and a transistor connected in parallel to both ends of the ferroelectric capacitor; a word line connected to each of the transistors; a selection transistor connected to one end of the block; a bit line connected to the selection transistor; and a plate line connected to the other end of the block. The number of ferroelectric memory cells connected in each block in the ferroelectric semiconductor storage device is odd.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Organic Material For Ferroelectric Semiconductor Device
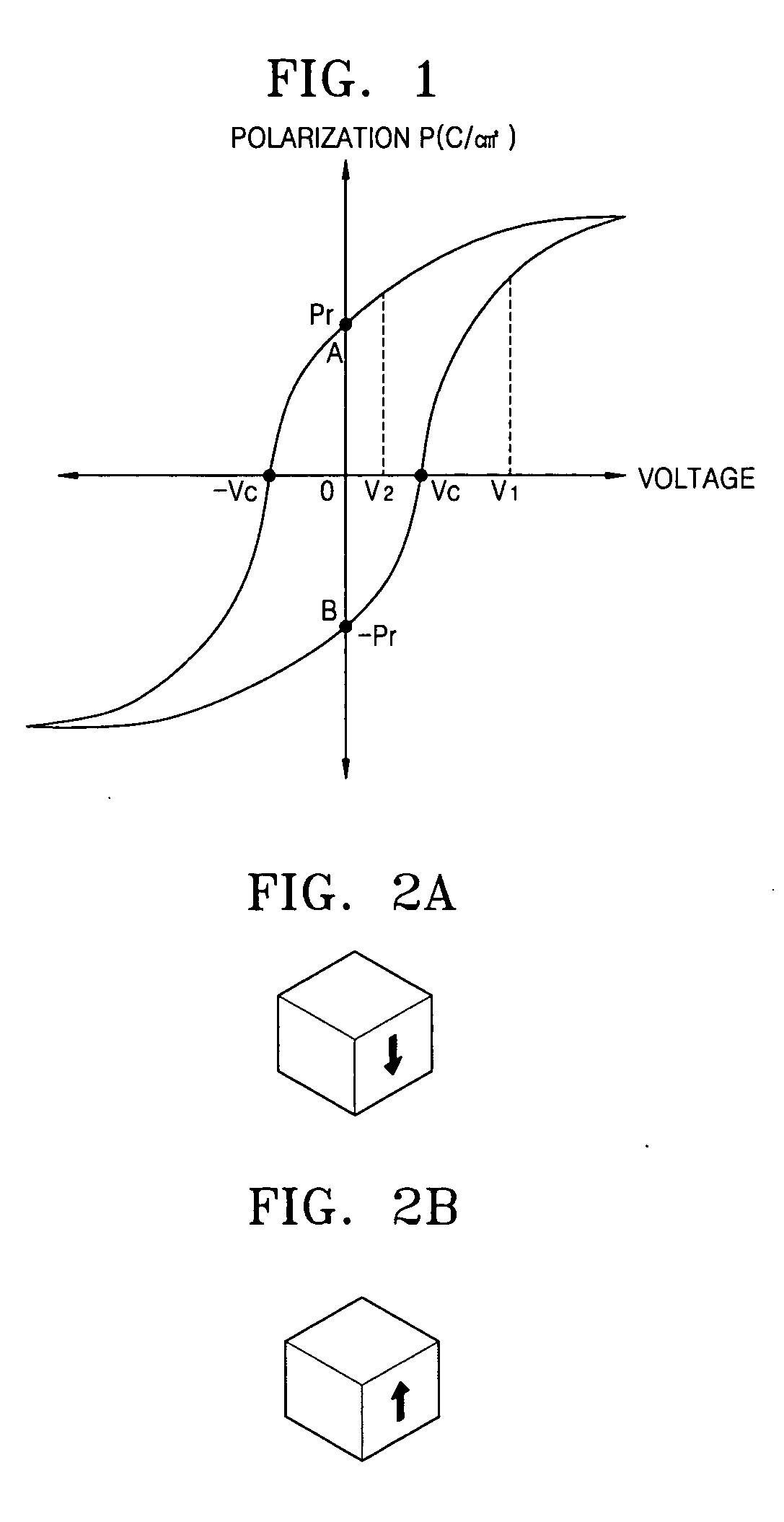
InactiveUS20080027196A1Improve featuresLow costFerroelectric carrier recordingDigital storageCapacitanceHysteresis
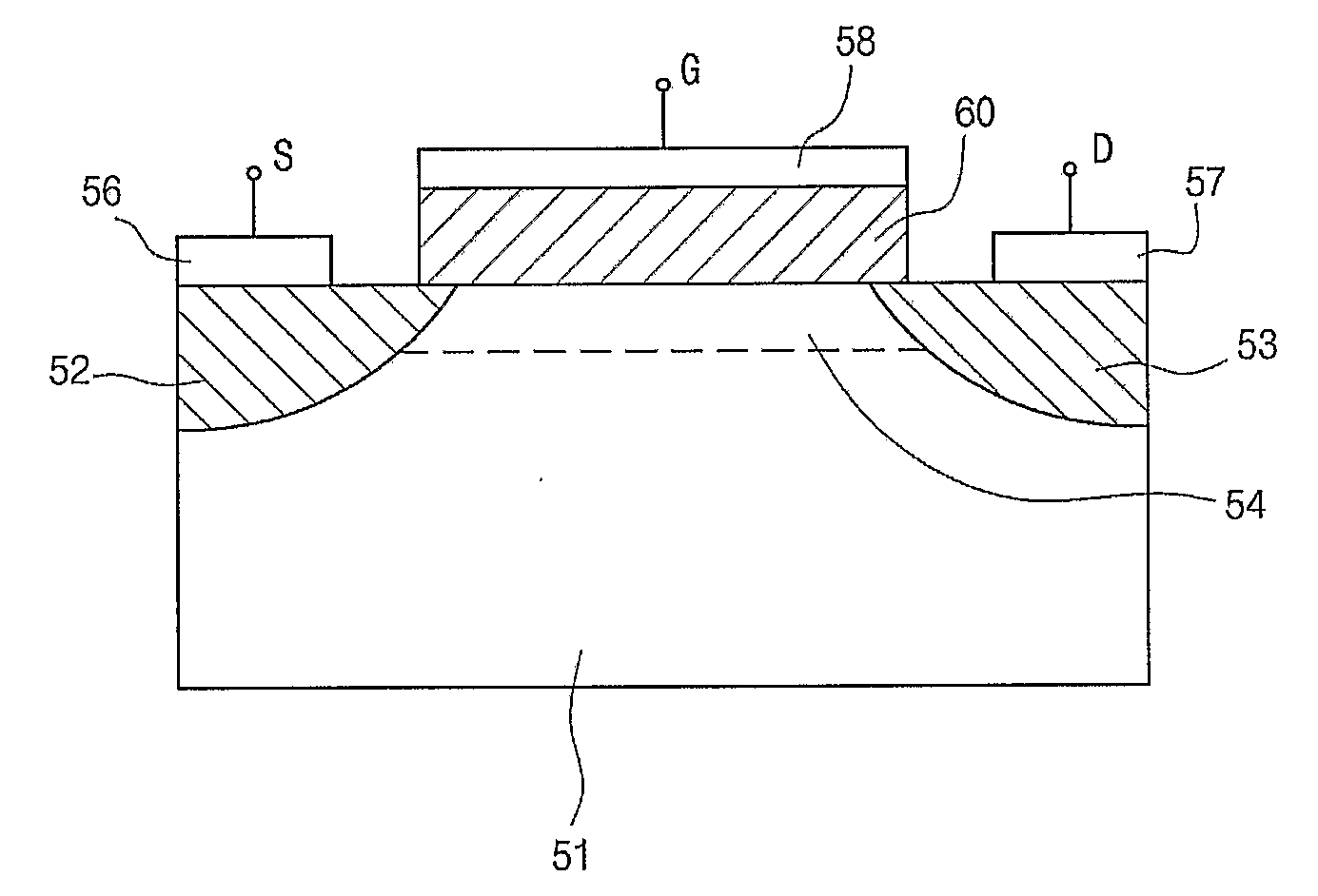
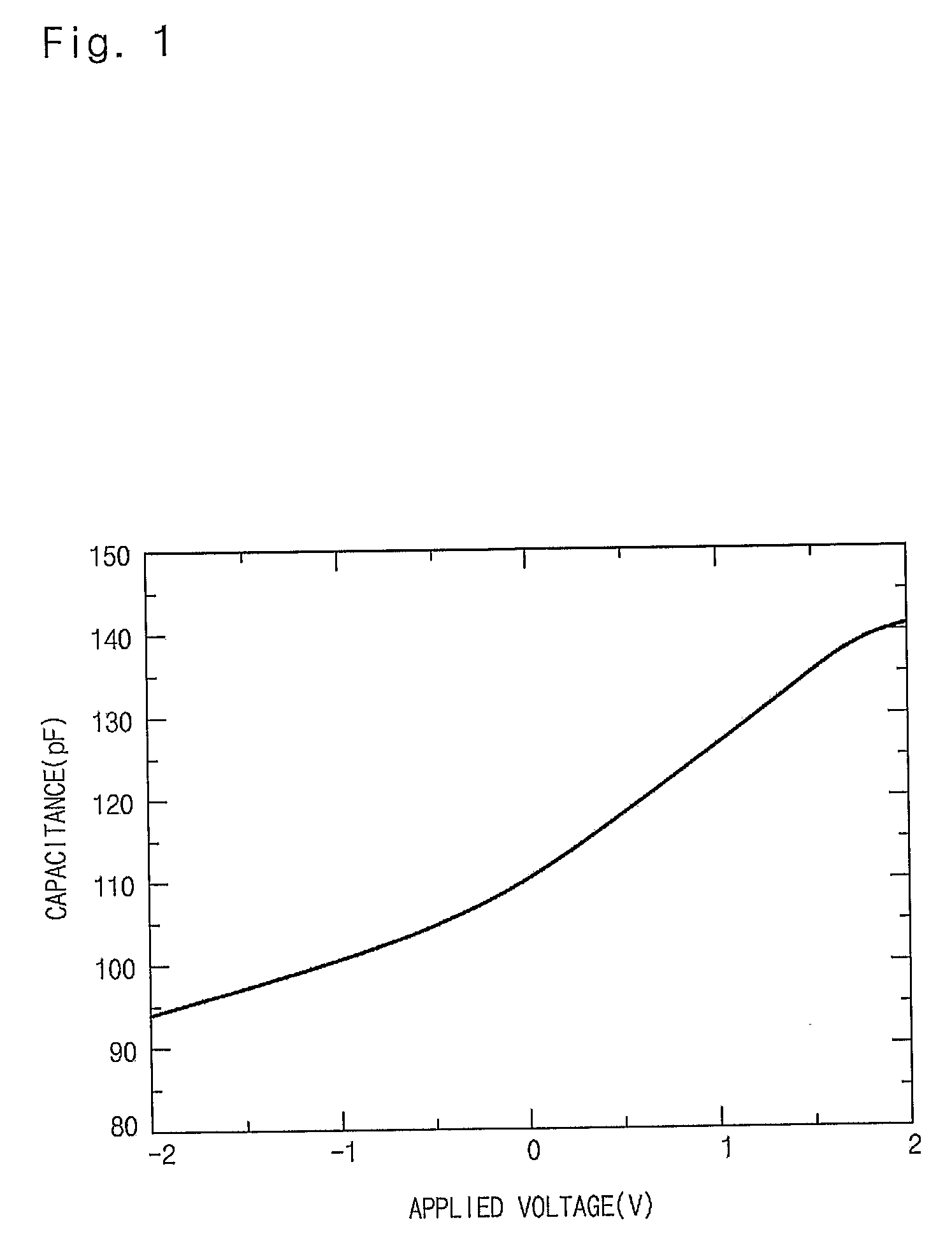
Disclosed relates to an organic material for a ferroelectric semiconductor device, which can be effectively used as a dielectric material of the ferroelectric semiconductor device, such as PVDF, etc. The PVDF having four crystal structures of α, β, γ, and δ shows a good hysteresis characteristic in the crystal structure of β-phase. A PVDF thin film having a crystal structure of β-phase has excellent hysteresis characteristics that show a capacitance value is decreased with the increase of an applied voltage in about 0 to 1V and increased with the decrease of an applied voltage in about 0 to −1V. A ferroelectric organic material having a crystal structure of β-phase is used on a channel region (54) between source and drain regions (52 and 53) of a silicon substrate (51). As ferroelectric organic materials, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), PVDF polymer, PVDF copolymer or PVDF terpolymer and, further, odd-numbered nylon, cyano-polymer and their polymer or copolymer, etc. may be used.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL FOUND OF IND - ACADEMIC
Ferro-resistive random access memory (Ferro-RRAM), operation method and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS8687401B2Simple in fabricationSimple structureRead-only memoriesDigital storageNon destructiveStatic random-access memory
The invention provides a Ferro-RRAM, a method of operating the Ferro-RRAM, and a method of fabricating the Ferro-RRAM, and pertains to the technical field of memory. The Ferro-RRAM comprises an upper electrode, a lower electrode, and a ferroelectric semiconducting thin-film layer provided between the upper electrode and the lower electrode and serving as a storage function layer; wherein the ferroelectric semiconducting thin-film layer is operable to generate a diode conduction characteristic by ferroelectric domain reorientation, and is operable to modulate the diode conduction characteristic by variation of the ferroelectric domain orientation; the Ferro-RRAM stores information according to variation of modulation of the diode conduction characteristic. The Ferro-RRAM has such characteristics of being simple in structure and fabrication, non-destructive readout and nonvolatile storage.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Switchable memory diodes based on ferroelectric/conjugated polymer heterostructures and/or their composites
ActiveUS20120080773A1Solid-state devicesDigital storageFerroelectric semiconductorsCondensed matter physics
An embodiment of the present memory cell a first layer of a chosen conductivity type, and a second layer which includes ferroelectric semiconductor material of the opposite conductivity type, the layers forming a pn junction. The first layer may be a conjugated semiconductor polymer, or may also be of ferroelectric semiconductor material. The layers are provided between first and electrodes. In another embodiment, a single layer of a composite of conjugated semiconductor polymer and ferroelectric semiconductor material is provided between first and second electrodes. The various embodiments may be part of a memory array.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
Field effect transistor device based on two-dimensional interlayer slippage ferroelectric semiconductor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114709257ASmall sizeHighly integratedFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField effectField-effect transistor
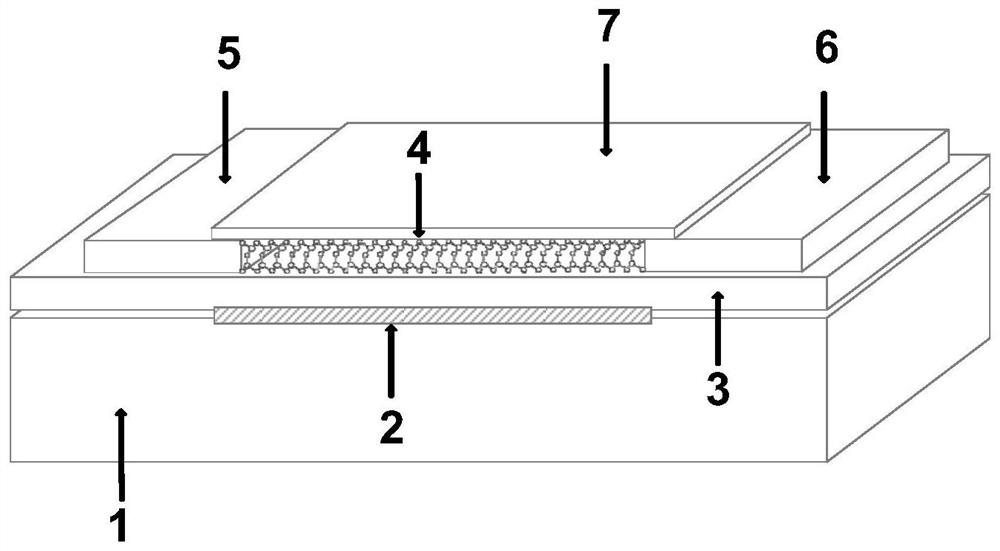
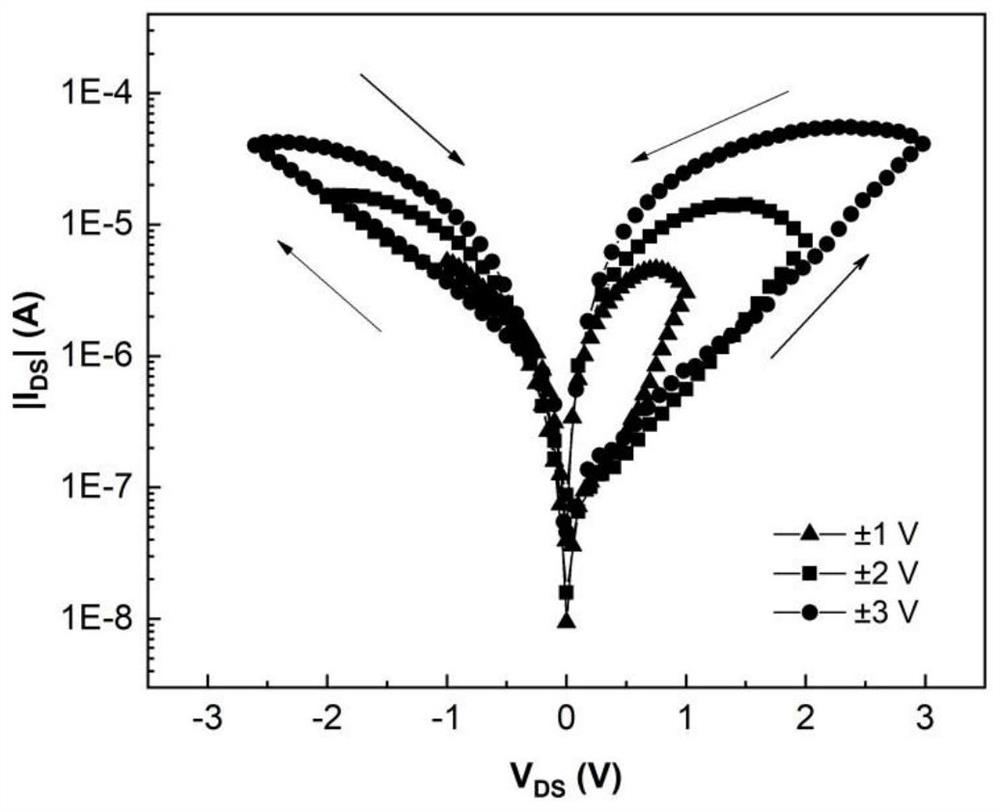
According to the III-VI group material (GaSe)-based interlayer slippage ferroelectric field effect transistor device, the characteristic that interlayer slippage is controlled by an electric field in the material to achieve polarization overturning is utilized, regulation and control over the Fermi level and the conductivity of a channel can be achieved, and compared with a traditional ferroelectric field effect transistor, the device has the advantages that the device is simple in structure and convenient to implement. According to the two-dimensional ultrathin ferroelectric, the size of the device can be remarkably reduced, an effective gate electric field is increased, and the voltage required by overturning or polarization can be further reduced, so that low-power-consumption storage can be realized. The novel ferroelectric field effect transistor device for regulating and controlling interlayer slippage by the external electric field provides a new platform for realizing high-performance ferroelectric storage and a high-integration-level storage chip.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Photoelectric device based on ferroelectric PN junction, and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113793882AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySemiconductor devicesElectrical connectionFerroelectric semiconductors
The invention relates to a photoelectric device based on ferroelectric PN junction, and a preparation method thereof. The photoelectric device comprises: a substrate; a ferroelectric semiconductor material layer and a photosensitive material layer which are located on the substrate to form the PN junction, wherein the ferroelectric semiconductor material layer and the photosensitive material layer are partially overlapped in the vertical direction, and the PN junction is formed on the contact face of the ferroelectric semiconductor material layer and the photosensitive material layer; and a first electrode and a second electrode which are electrically connected with the ferroelectric semiconductor material layer and the photosensitive material layer respectively. The built-in potential can be formed after the ferroelectric semiconductor material and the photosensitive material in the PN junction are in contact, and after the grid voltage pulse is applied, the built-in potential can be regulated and controlled in a non-volatile manner, so that the short-circuit current of the device under illumination is regulated and controlled in a non-volatile manner, and the efficiency of the photoelectric device is further improved.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Alpha-indium selenide two-dimensional photoelectric detector based on transparent electrode
PendingCN112071940ASmall sizeIncrease the photoelectric response rangeSemiconductor devicesIndiumPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses an alpha-indium selenide two-dimensional photoelectric detector based on a transparent electrode, which comprises an alpha indium selenide two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor layer, a hafnium oxide dielectric layer and a doped silicon substrate which are sequentially distributed from top to bottom, the alpha-indium selenide two-dimensional ferroelectric semiconductor layer is provided with the transparent electrode, and the detector is small in size and low in cost. Photoelectric responsivity is high.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
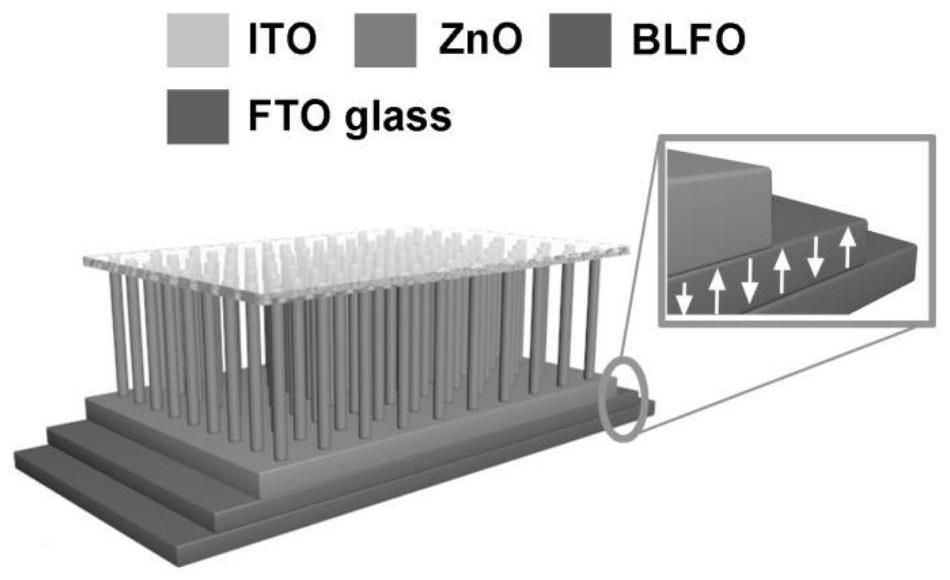
Method for improving photoelectric property of BLFO/ZnO heterojunction by utilizing ferroelectricity and piezoelectric optoelectronics effects
PendingCN111725337AQuick responseImprove mechanical stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureHeterojunctionElectric properties
The invention discloses a method for improving the photoelectric property of a BLFO / ZnO heterojunction by utilizing ferroelectricity and piezoelectric optoelectronics effects and relates to the fieldof ferroelectric semiconductor heterojunction devices. A pulse bias voltage is applied to a BLFO / ZnO heterojunction device, ferroelectricity of the BLFO is called, the BLFO / ZnO heterojunction device calls the ferroelectricity of the BLFO, compressive strain is applied to the BLFO / ZnO heterojunction device to introduce a piezoelectric photoelectronic effect, a purpose of simultaneously calling ferroelectricity and piezoelectric photoelectronic effects is achieved, and the total driving force of current carriers is enhanced. The preparation method is advantaged in that the BLFO / ZnO heterojunction device is prepared by adopting a sol-gel method and a hydrothermal method, influence of the piezoelectric photoelectronic effect and the ferroelectric effect on the photovoltaic characteristics is researched, carrier transport operation is modulated by using a piezoelectric photoelectronic effect, an open-circuit voltage and a short-circuit current of the BLFO / ZnO heterojunction device are remarkably improved, external electric field polarization is introduced on the basis of compressive strain, the piezoelectric photoelectronic effect and ferroelectricity are called, the total driving forceof a heterojunction energy band structure and carriers is modulated, and therefore photoelectric performance of the heterojunction is improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
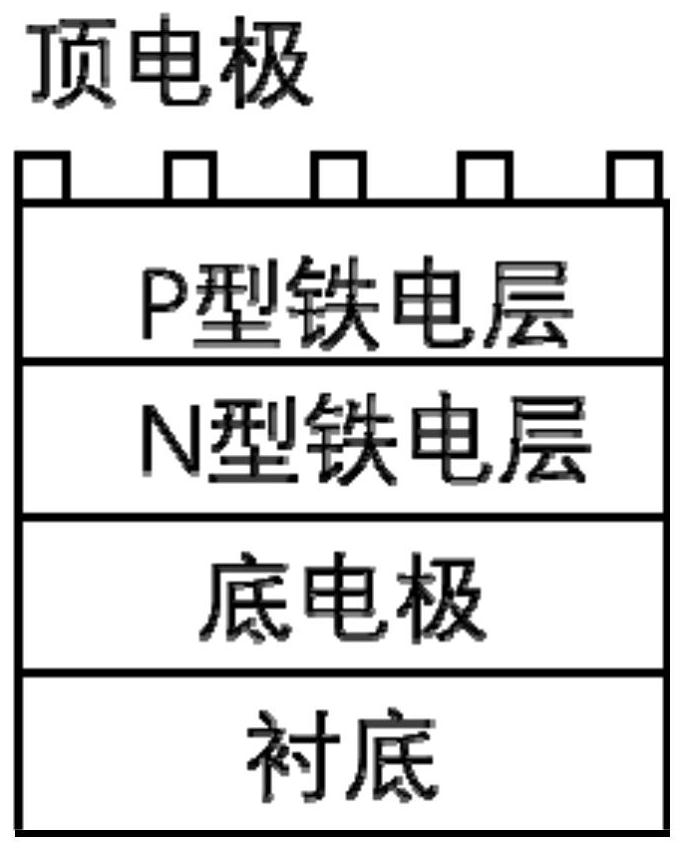
All-ferroelectric semiconductor PN junction thin film device and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113990974ABuilt-in electric field effect modulationEnables non-destructive readFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringCondensed matter physics
An all-ferroelectric semiconductor PN junction thin film device comprises a substrate, a bottom electrode, an N-type ferroelectric layer, a P-type ferroelectric layer and a top electrode in sequence from bottom to top, or comprises the substrate, the bottom electrode, the P-type ferroelectric layer, the N-type ferroelectric layer and the top electrode. Wherein the N-type ferroelectric layer is made of an N-type ferroelectric material, and the P-type ferroelectric layer is made of a P-type ferroelectric material. The invention further provides a preparation method of the all-ferroelectric semiconductor PN junction thin film device. The all-ferroelectric semiconductor PN junction thin film device can be used for solving the problem of destructive reading of data in an existing ferroelectric memory, and meanwhile more excellent non-destructive reading of electricity and light on the ferroelectric polarization state is achieved.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing low-bandgap ferroelectric photovoltaic thin films by pulsed laser deposition
InactiveCN104388894BSave raw materialsNo pollution in the processFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingSolar cellVacuum chamber
The invention provides a method for preparing a low-band gap ferroelectric photovoltaic film through pulsed laser deposition. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: taking Pt / Ti / SiO2 / Si(100) as a substrate; cleaning for 10 minutes through an ultrasonic cleaner by sequentially using acetone, absolute ethyl alcohol and deionized water, wherein the working frequency of ultrasonic waves is 40 kHz; then blow-drying by using nitrogen, then immediately loading into a vacuum cavity, and determining the temperature of the substrate at 600-800 DEG C, the oxygen pressure of a vacuum chamber at 0-5 Pa, the energy of a laser pulse at 100-500 mJ and the frequency of the laser pulse at 1-20 Hz; ablating a ceramic target material to obtain a low-band gap film product. The method provided by the invention is a physical vapor deposition method, has the advantages of fewer selected raw materials, economy, no pollution, simple preparation process, convenience for operation and easiness for production, and opens up a fire-new way for developing a solar cell based on a ferroelectric semiconductor.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Ferroelectric semiconductor memory device
A memory cell includes a ferroelectric capacitor for holding a charge and a transistor connected in parallel with the ferroelectric capacitor. A plurality of the ferroelectric memory cells are connected in series to form a memory cell block. A selection transistor connects, to one end of the block. A bit line connects to the selection transistor. A plate line connects to the other end of the block. A control circuit changes potentials of the word line and the bit line. With the potential of the plate line being held constant, the potential of the word line is changed, thereby erasing information or writing information to the ferroelectric memory cells.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
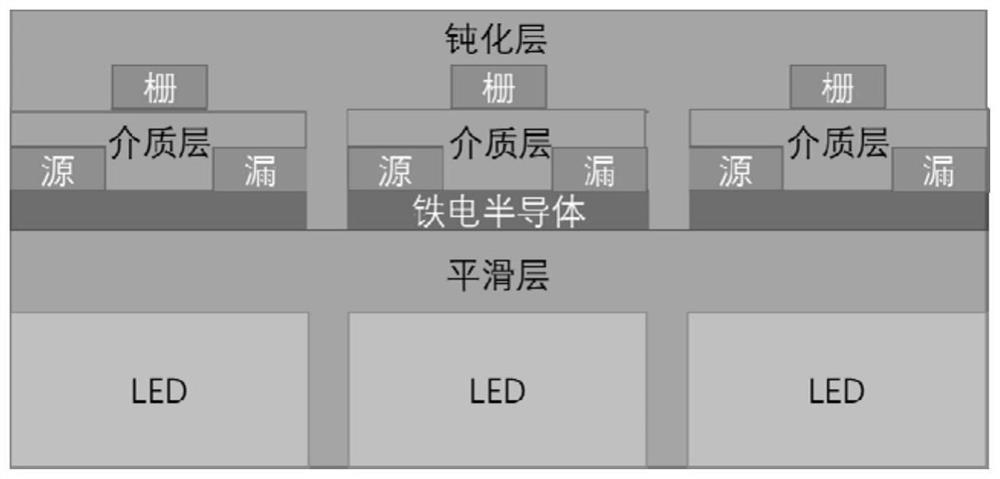
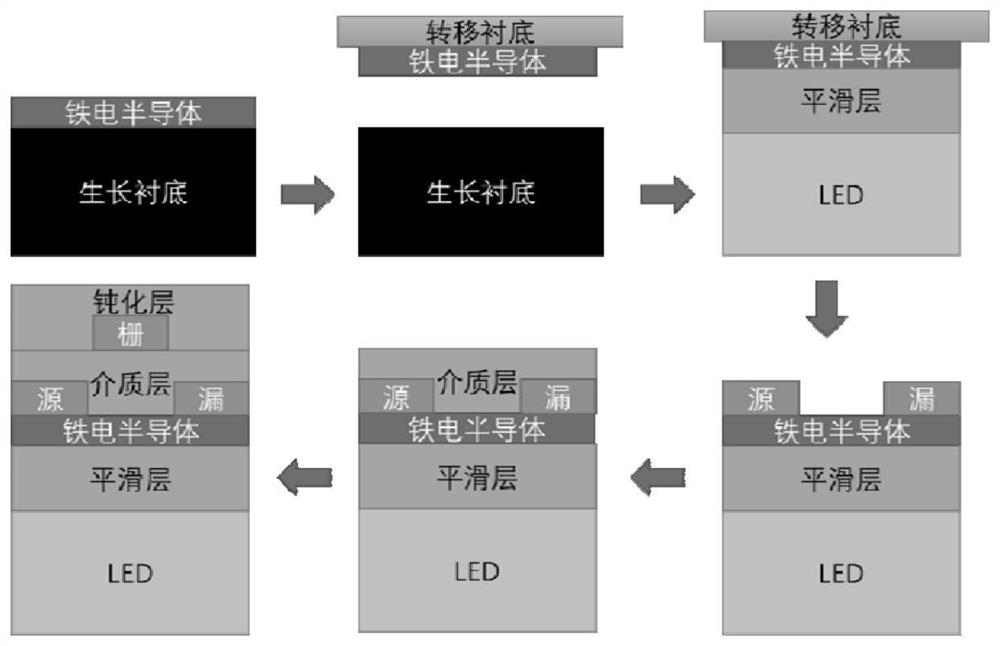
Micro-LED optical information sensing and storage unit, photonic integrated chip, array and preparation method
ActiveCN113745261AImplement storageSimple structureFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsDielectric layer
The invention discloses a Micro-LED optical information sensing and storage unit, a photonic integrated chip, an array and a preparation method. The information sensing and storage unit of the photonic integrated chip comprises a Micro-LED, a smooth layer, a ferroelectric semiconductor, a dielectric layer and a passivation layer which are sequentially aligned with one another and superposed from bottom to top; and the information sensing and storage unit also comprises a source electrode, a drain electrode and a grid electrode, wherein the source electrode and the drain electrode are respectively embedded into two sides of the bottom of the dielectric layer and are in contact with the ferroelectric semiconductor, and the grid electrode is embedded into the bottom of the passivation layer and is located at the middle position above the dielectric layer. According to the micro-LED optical information sensing and storage unit, the photonic integrated chip, the array and the preparation method of the invention, synchronous sensing and storage of optical information can be realized, the signal processing efficiency is improved, and the circuit structure is simplified. The micro-LED optical information sensing and storage unit has important application prospects in the fields of photon chips and image recognition in the future.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com