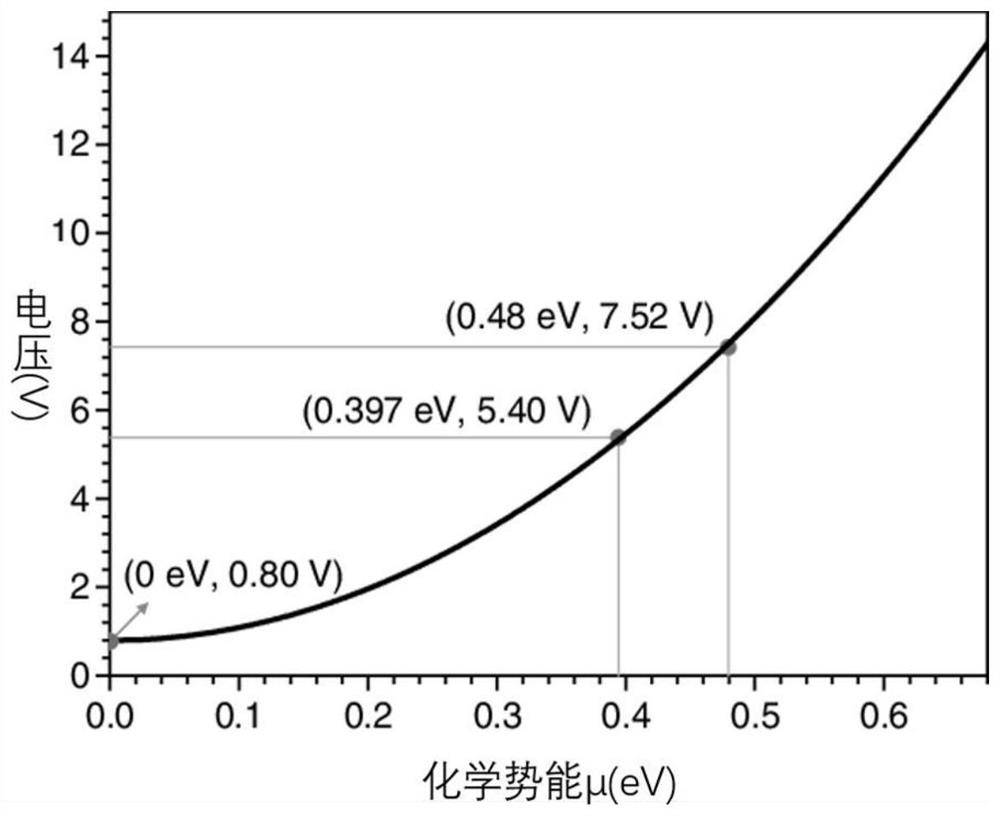
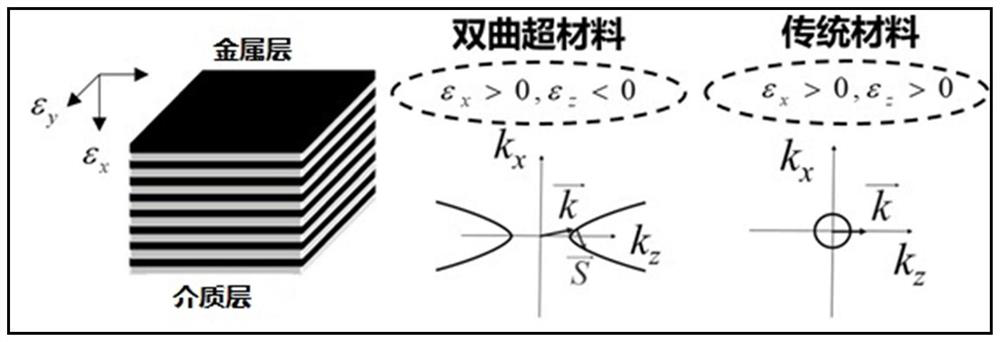
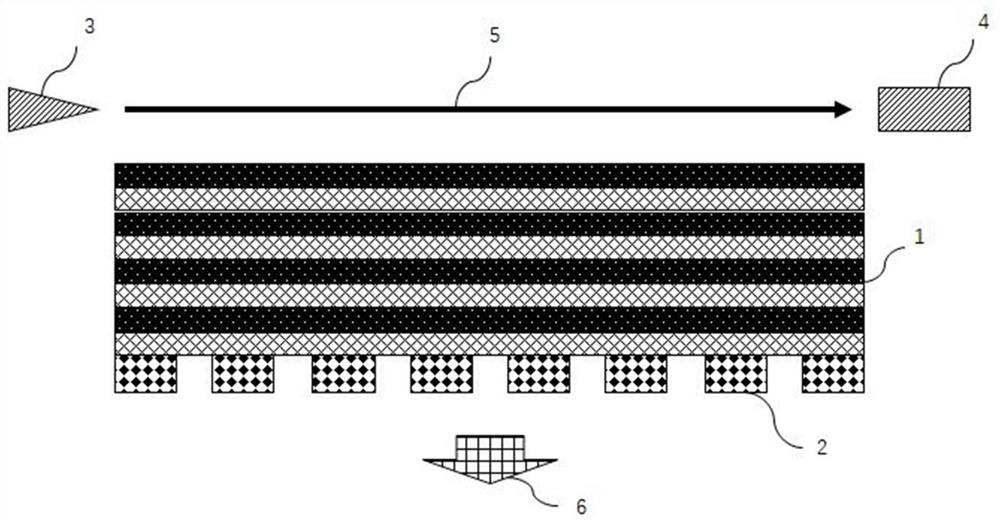
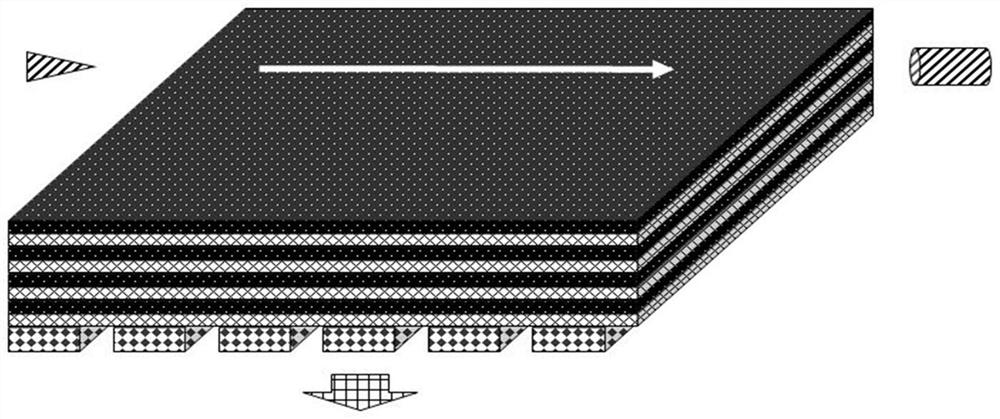
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Hyperbolic metamaterials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
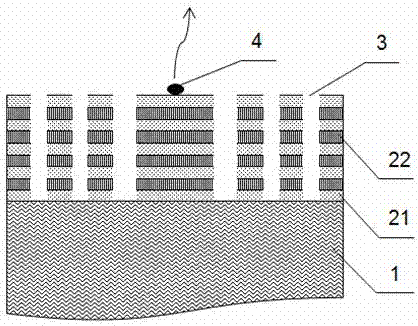
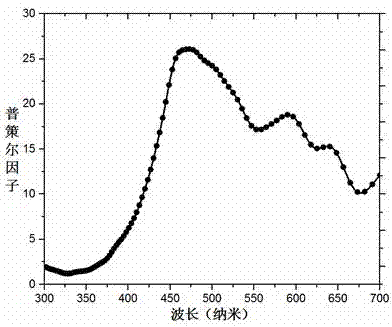
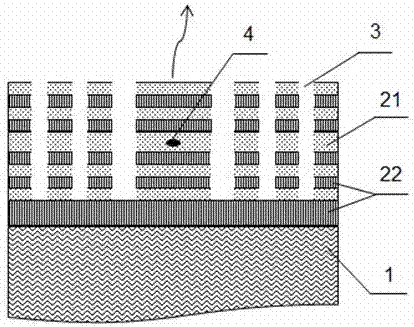
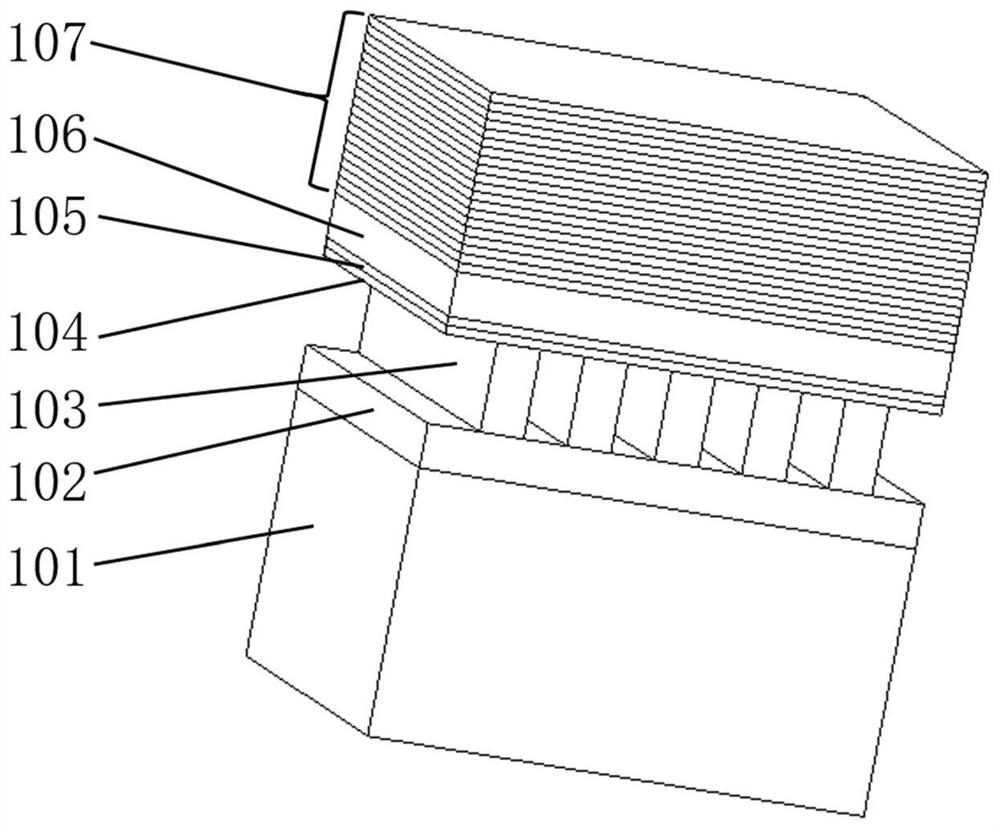
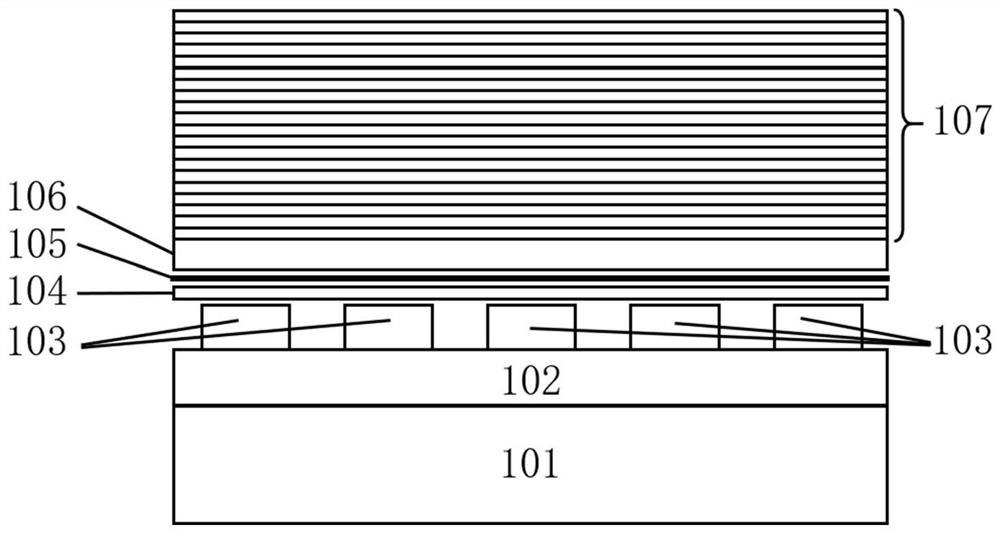
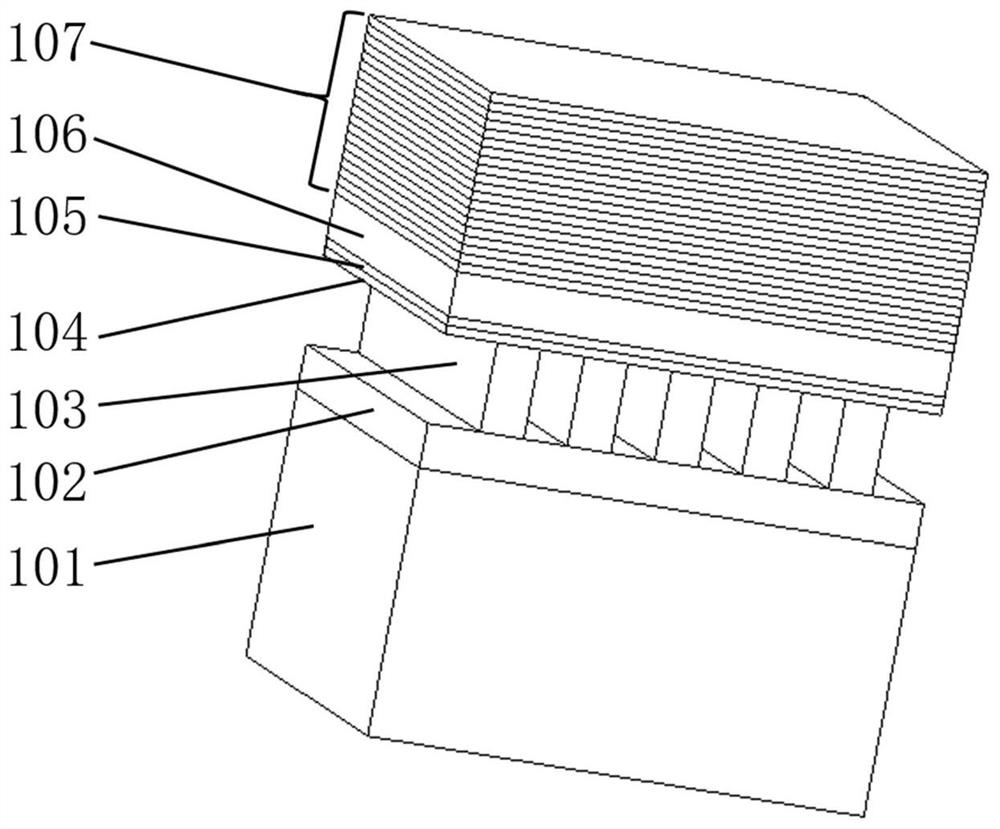
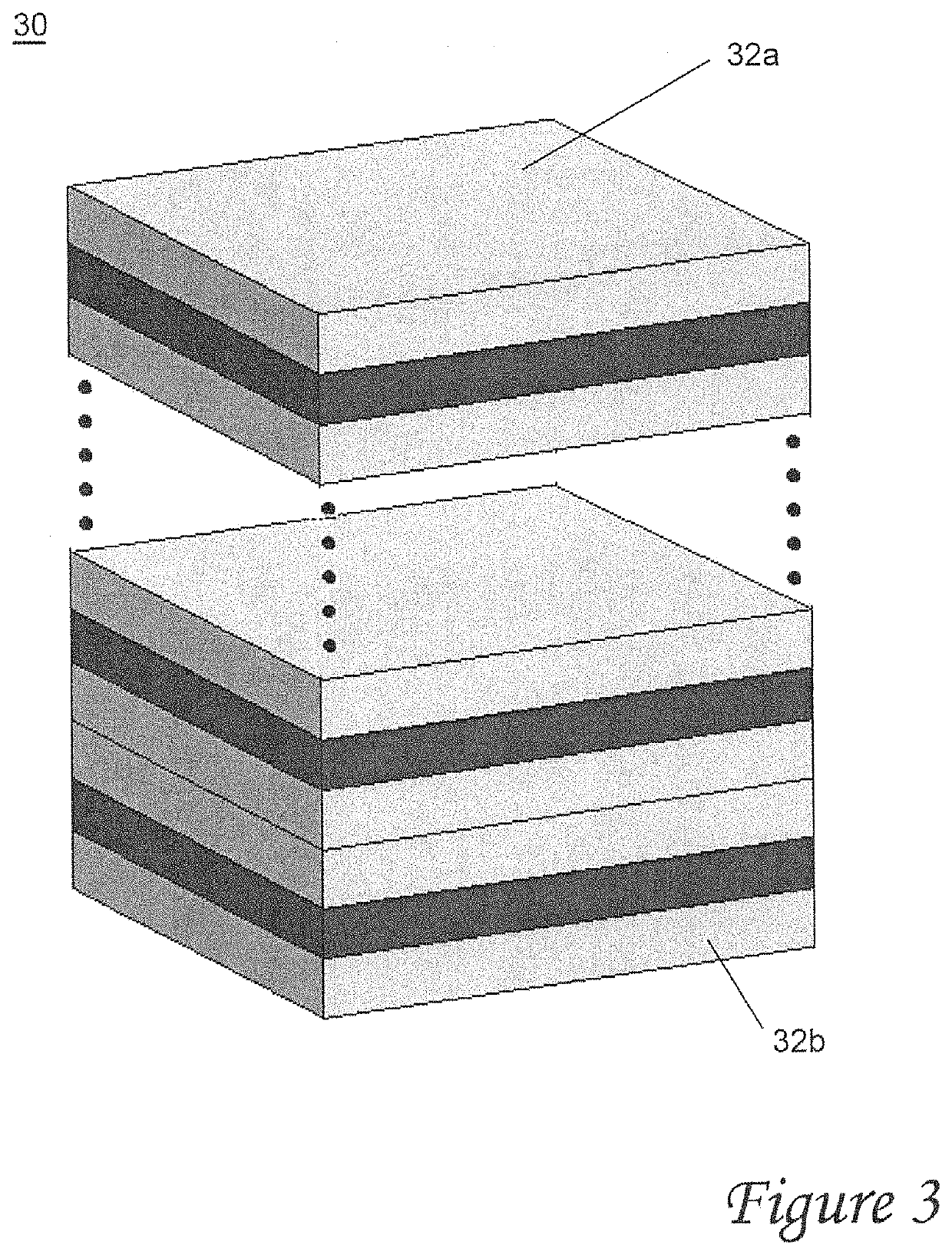
Hyperbolic metamaterial composite grating-enhanced high-frequency quantum-dot single photon source
ActiveCN107452844AIncrease spawn rateImprove production efficiencySemiconductor devicesGratingParticle physics
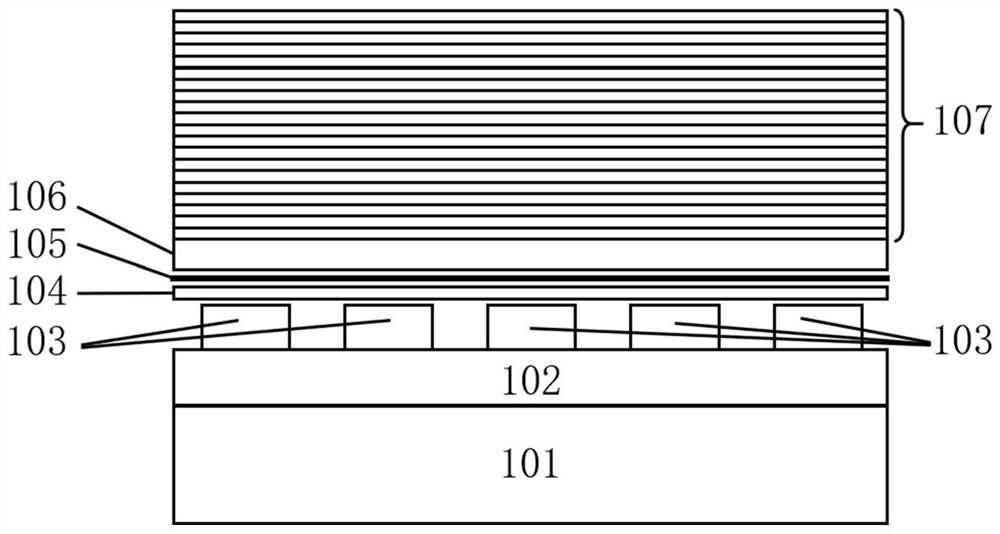
The invention discloses a hyperbolic metamaterial composite grating-enhanced high-frequency quantum-dot single photon source. The hyperbolic metamaterial composite grating-enhanced high-frequency quantum-dot single photon source comprises a substrate, a hyperbolic metamaterial and quantum dots, wherein a grating microstructure is arranged on a surface of the hyperbolic metamaterial or in the hyperbolic metamaterial, the hyperbolic metamaterial is of a one-dimensional periodic structure formed by alternatively arranging dielectric thin films and metal thin films or the dielectric thin films and metal-like thin films, and the quantum dots are arranged in the one-dimensional periodic structure or a near field of the hyperbolic metamaterial. Spontaneous radiation enhancement of wideband of the quantum dots is achieved by the hyperbolic metamaterial, the light emergent efficiency is improved by simultaneously combining directional coupling output characteristic of the grating, the photon generation ratio and the collection and utilization ratio of the quantum-dot single photon source are greatly improved, and the high-frequency, high-brightness and directional-emission quantum-dot single photon source of GHz or above can be achieved; and meanwhile, two excitation modes of optical pumping and electric pumping are compatible, and the quantum-dot single photon source is suitable for various wave bands to an infrared band from an ultraviolet band and can be widely applied to related fields of quantum information, quantum computation, quantum imaging, quantum authentication and quantum precision measurement.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
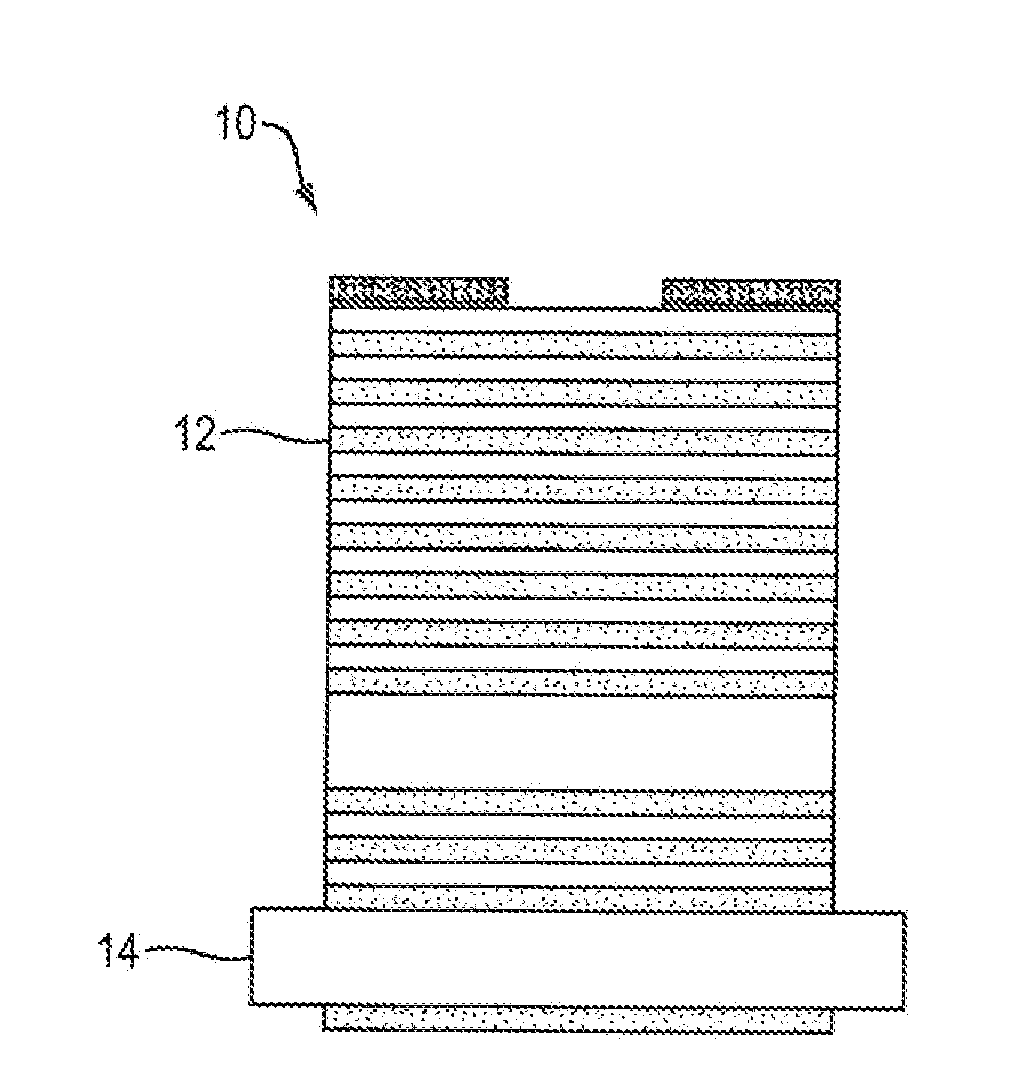
Hyperbolic metamaterials as distributed bragg mirrors for high power vcsel devices
InactiveUS20140059830A1Improved thermal managementImprove thermal conductivityNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserDistributed Bragg reflector
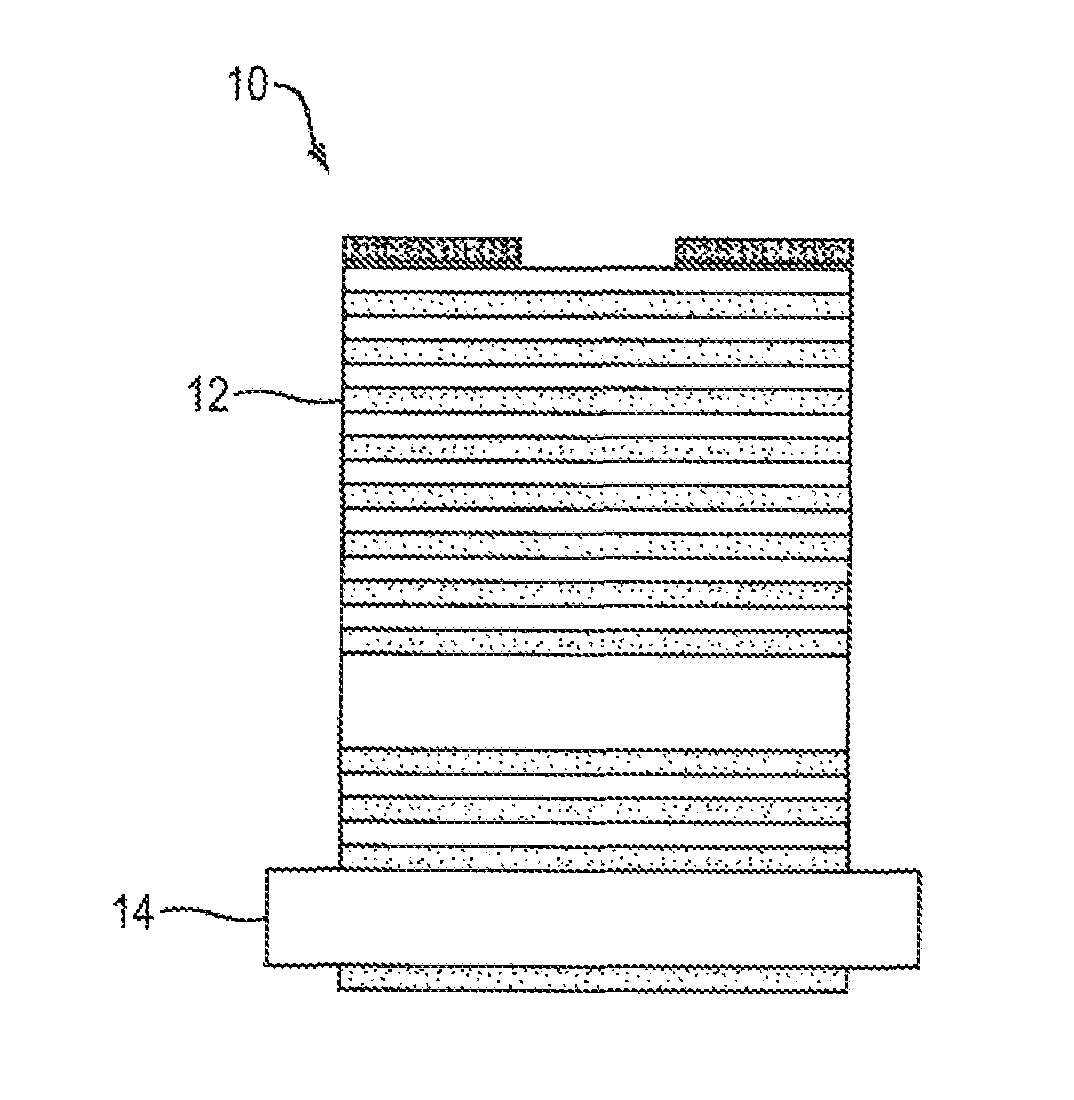
Implementing a layered hyperbolic metamaterial in a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) to improve thermal conductivity and thermal dissipation thereby stabilizing optical performance. Improvement in the thermal management and power is expected by replacing the distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) mirrors in the VCSEL. The layered metamaterial structure performs the dual function of the DBR and the heat spreader at the same time.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method for realizing selective wave absorption through using hyperbolic metamaterial grating and wave absorption device
ActiveCN109270609AExcellent choice of absorbing performanceExcellent selective absorption propertiesOptical elementsGratingOpto electronic
The invention discloses a method for realizing selective wave absorption through using a hyperbolic metamaterial grating. According to the method, on the basis of the hyperbolic dispersion characteristic of a metal-dielectric periodic film stack, with a sub-wavelength grating structure used in combination, the electromagnetic field enhancement effect of the hyperbolic metamaterial grating is utilized to realize the selective absorption enhancement of light absorptivity for TM polarized incident light; on the basis of determining metal and dielectric material parameters, grating ridge width, metal film layer thickness, dielectric film layer thickness and a film stack number are optimized, the selective absorption enhancement of the light absorptivity under different wave bands can be realized; and the grating ridge width can be adjusted, so that the selection of an absorption peak position can be achieved; and the selective absorption characteristic of the structure is insensitive to the metal-dielectric film stack number, and therefore, the method has high experimental tolerance. Therefore, the method of the present invention has a bright application prospect in fields such as enhanced nano imaging, stealth materials, optoelectronic detection and biosensing. A film stack number can be flexibly selected as needed during practical application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
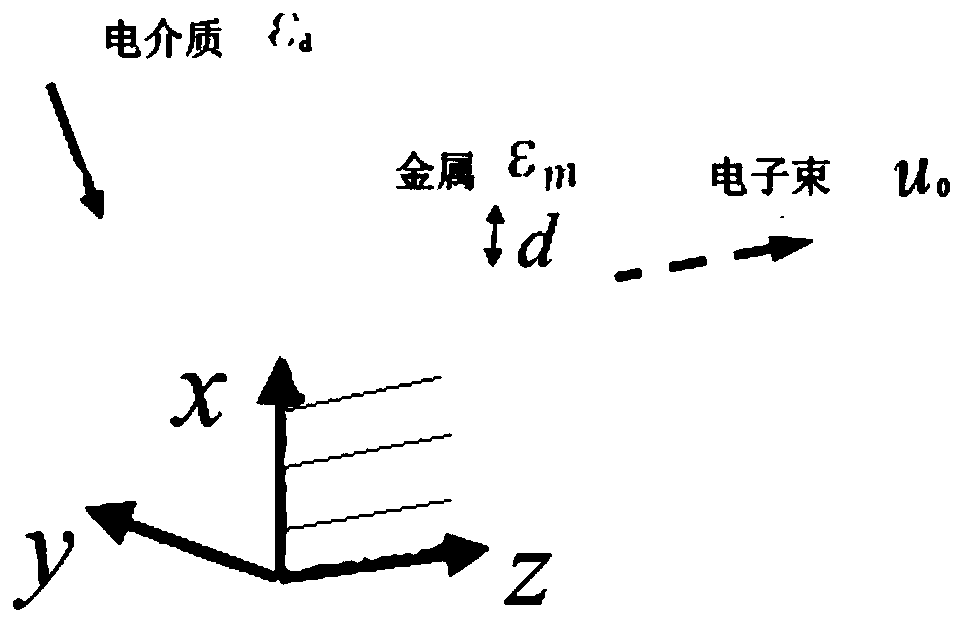
Cerenkov radiation device and manufacturing method thereof, and radiation extraction method
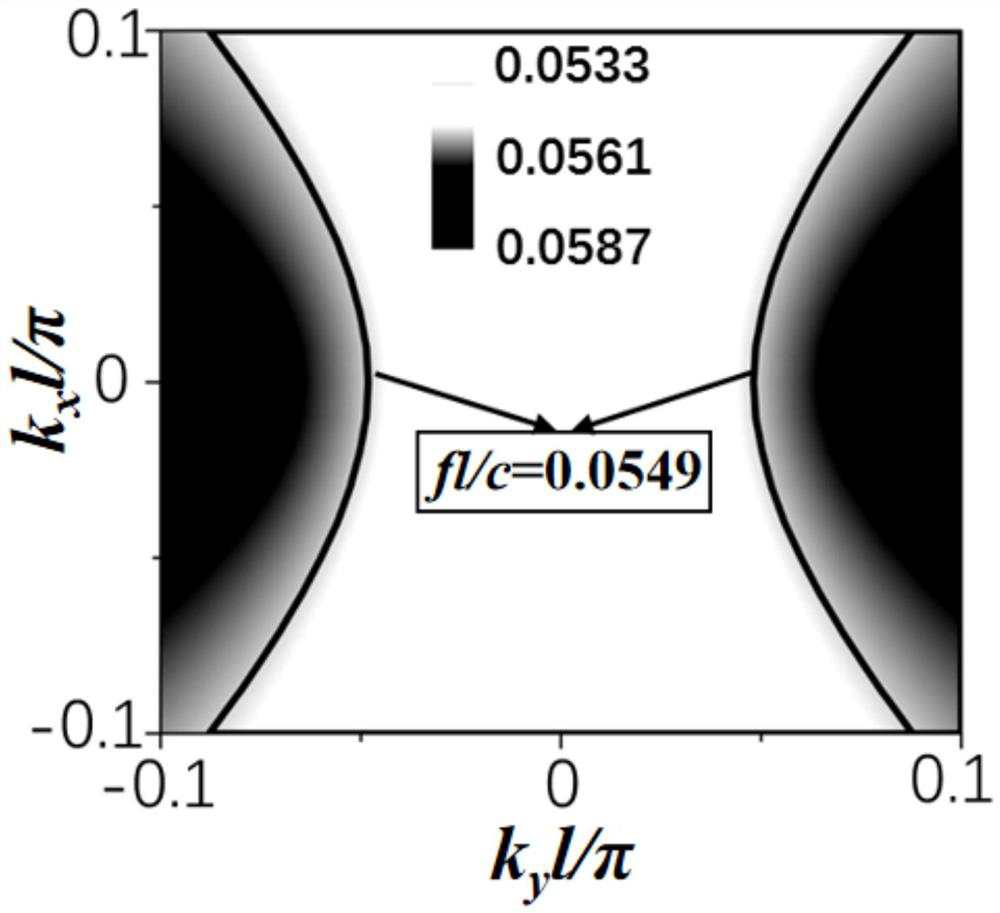
ActiveCN106569248ASlow flightReduce manufacturing costRadiation intensity measurementHyperbolic metamaterialsOrder of magnitude
The invention discloses a Cerenkov radiation device and a manufacturing method thereof, and a radiation extraction method. The Cerenkov radiation device comprises a metal cycle nanometer slit structure, a hyperbolic metamaterial structure and an electron-emitting source, wherein the hyperbolic metamaterial structure is arranged on an upper surface of the metal cycle nanometer slit structure; the electron-emitting source is arranged on an upper surface of the hyperbolic metamaterial structure; and the electron-emitting source includes an anode, a cathode and a grid electrode. The Cerenkov radiation device does not need a high voltage. A characteristic that a phase velocity of light in the hyperbolic metamaterial structure can be reduced by several orders of magnitudes compared to a velocity in a traditional material is used so that a required electronic flight speed generated by Cerenkov radiation can be greatly reduced; and then production cost generated by the Cerenkov radiation device is decreased and safety performance is increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Radiative cooling of optoelectronic devices using hyperbolic metamaterials
InactiveUS20130340990A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStefan–Boltzmann lawLaws of thermodynamics
A method of radiative cooling of optoelectronic devices using a hyperbolic metamaterial TIM layer below the heat generating optoelectronics is disclosed. Optoelectronic devices are optimized for high radiative heat conductance due to broad hyperbolic frequency band in the Long-Wavelength Infrared (LWIR) range with an efficient electromagnetic black hole thermal interface between the metamaterial TIM layer and a metallic heat sink. A modified Stefan-Boltzmann law in the hyperbolic metamaterial layer enables domination of the radiative heat transfer in the TIM layer. The broadband divergence of the photonic density of states in hyperbolic metamaterials leads to an increase in radiative heat transfer, beyond the limit set by the Stefan-Boltzmann law. The resulting radiative thermal hyper-conductivity approach or even exceed heat conductivity via electrons and phonons in regular solids.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC +1
Thermal emitter comprising near-zero permittivity materials
A novel thermal source comprising a semiconductor hyperbolic metamaterial provides control of the emission spectrum and the angular emission pattern. These properties arise because of epsilon-near-zero conditions in the semiconductor hyperbolic metamaterial. In particular, the thermal emission is dominated by the epsilon-near-zero effect in the doped quantum wells composing the semiconductor hyperbolic metamaterial. Furthermore, different properties are observed for s and p polarizations, following the characteristics of the strong anisotropy of hyperbolic metamaterials.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Devices with Semiconductor Hyperbolic Metamaterials
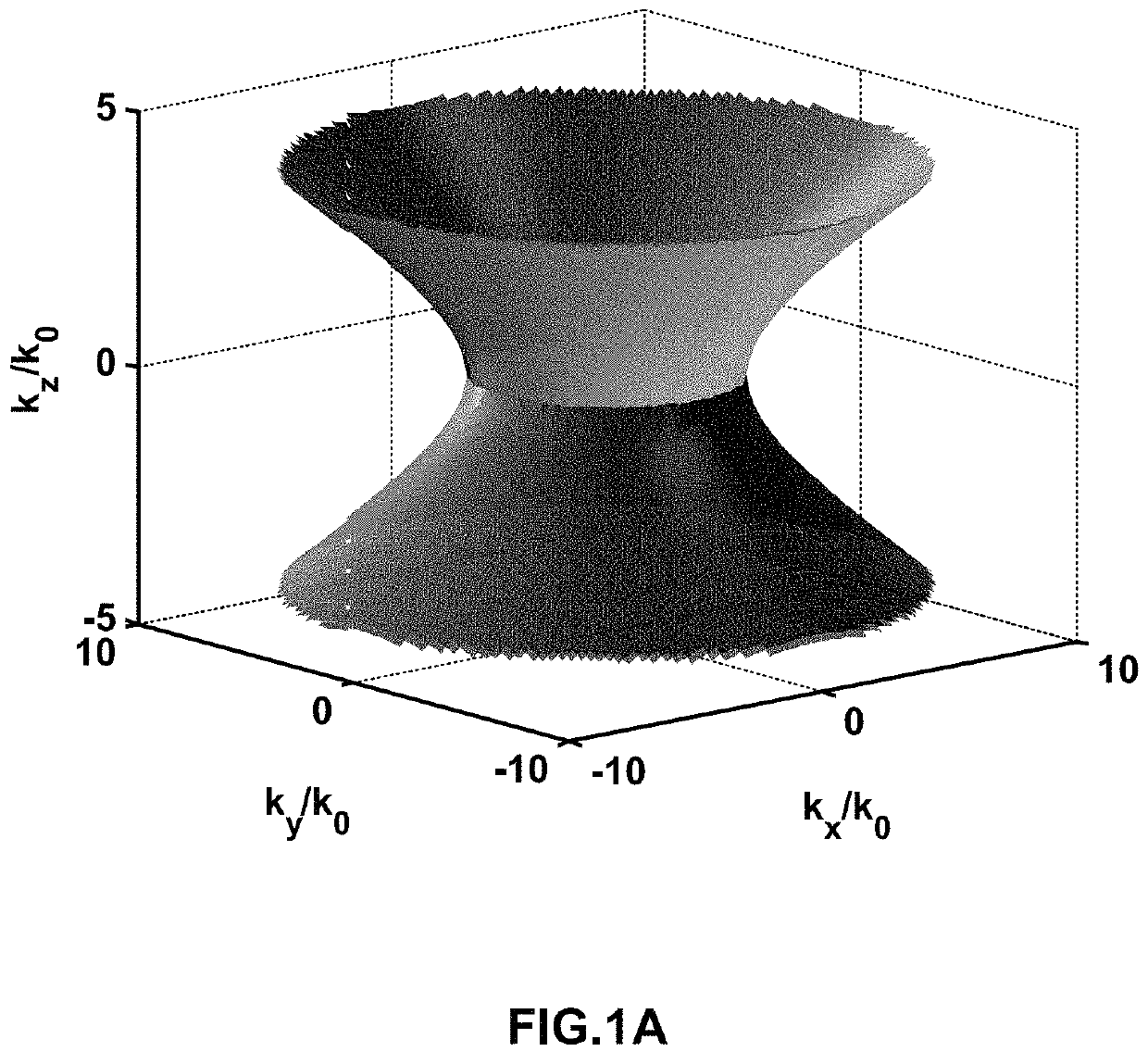
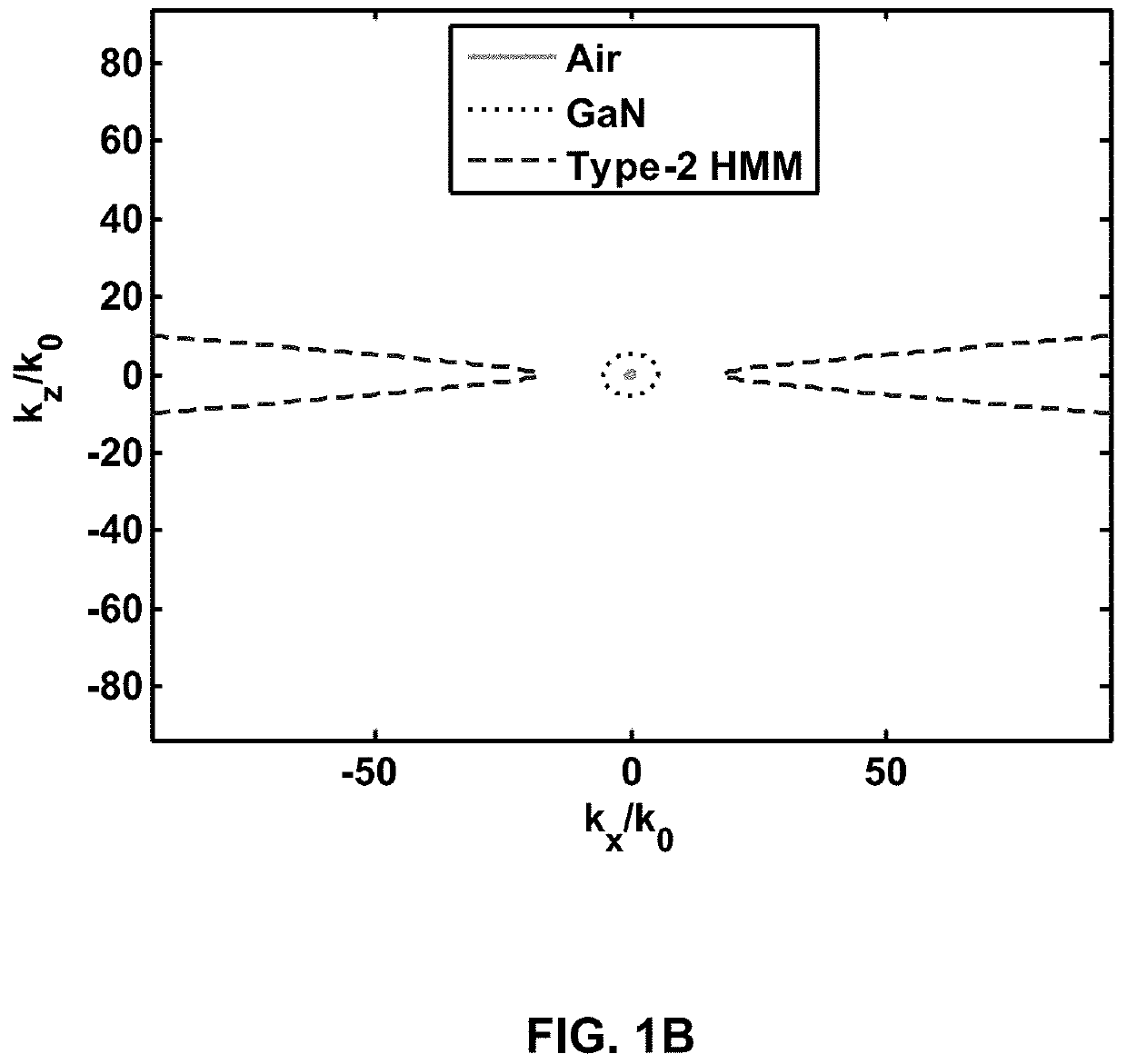
ActiveUS20160274301A1Improve cooling effectImprove responseCoupling light guidesSemiconductor lasersIn planePermittivity
A hyperbolic metamaterial assembly comprising alternating one or more first layers and one or more second layers forming a hyperbolic metamaterial, the one or more first layers comprising an intrinsic or non-degenerate extrinsic semiconductor and the one or more second layers comprising a two-dimensional electron or hole gas, wherein one of in-plane or out-of-plane permittivity of the hyperbolic metamaterial assembly is negative and the other is positive.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Hyperbolic metamaterials as distributed bragg mirrors for high power VCSEL devices
InactiveUS8831058B2Improved thermal managementImprove thermal conductivityNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserDistributed Bragg reflector
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
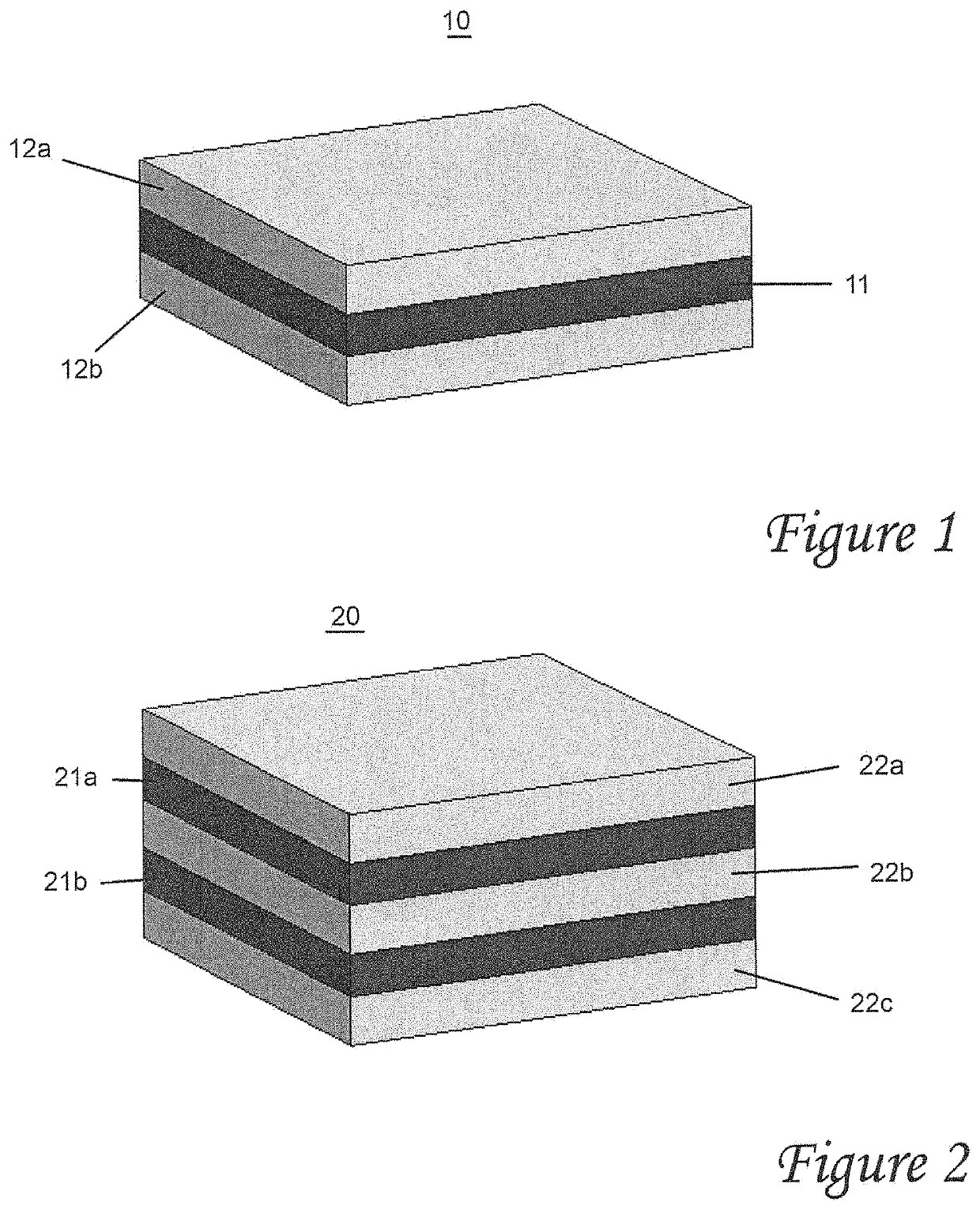
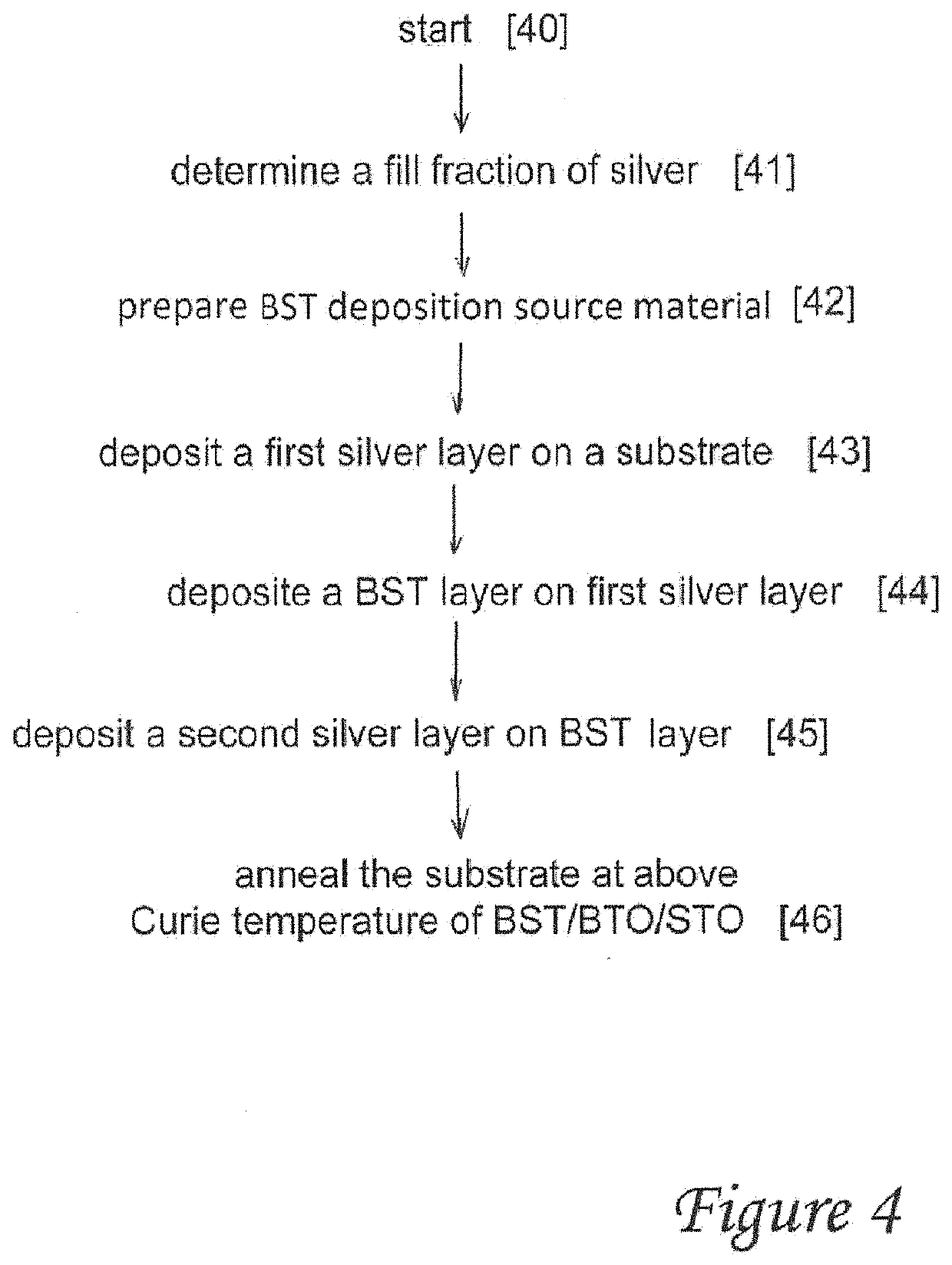
Cone-shaped hyperbolic metamaterial photonic structure and preparation method thereof
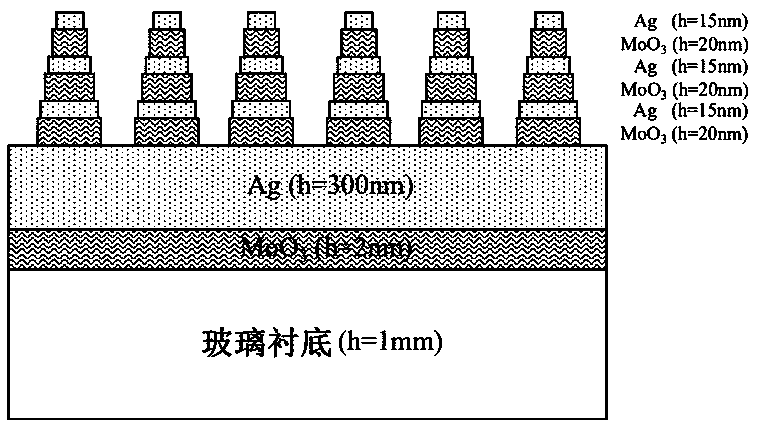
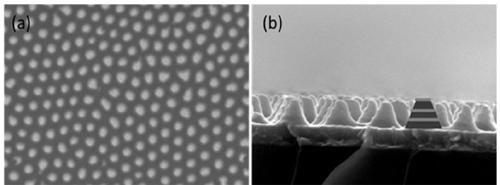
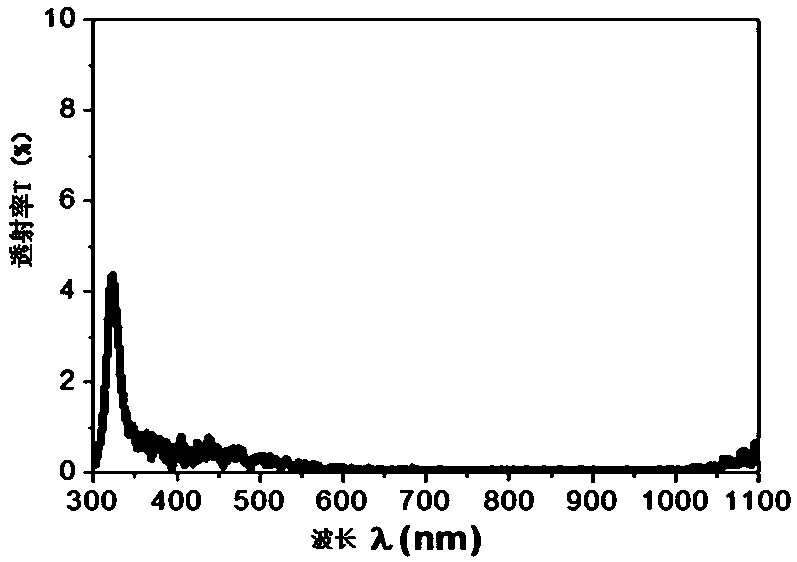
InactiveCN110320579AGuaranteed high growthImprove anti-reflection effectVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhotonicsHyperbolic metamaterials
The invention belongs to the technical field of metamaterial photonic devices, in particular to a cone-shaped hyperbolic metamaterial photonic structure and a preparation method thereof. The cone-shaped hyperbolic metamaterial photonic structure comprises, from top to bottom in turn, a cone-shaped MoO3 / Ag composite layer, an Ag film, a MoO3 dielectric layer and a glass substrate, wherein the MoO3dielectric layer has a thickness of 2nm, the Ag film has a thickness of 300nm, the cone-shaped MoO3 / Ag composite layer is composed of 2 to 3 layers of MoO3 / Ag, wherein each layer of MoO3 / Ag has a MoO3thickness of 20nm and an Ag thickness of 15nm. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the cone-shaped hyperbolic metamaterial photonic structure. The cone-shaped hyperbolic metamaterial photonic structure provided by the invention has good anti-reverse performance in a wide spectrum range of 300-1100nm.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Adjustable and controllable heat exchange device construction method and system based on near-field radiation
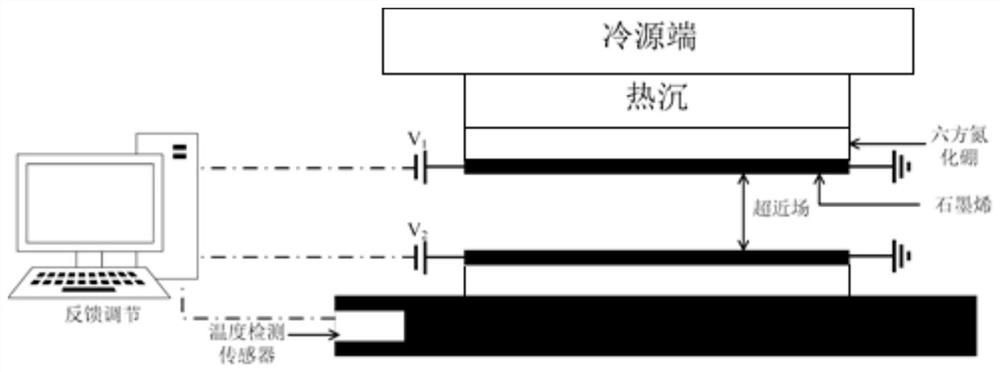
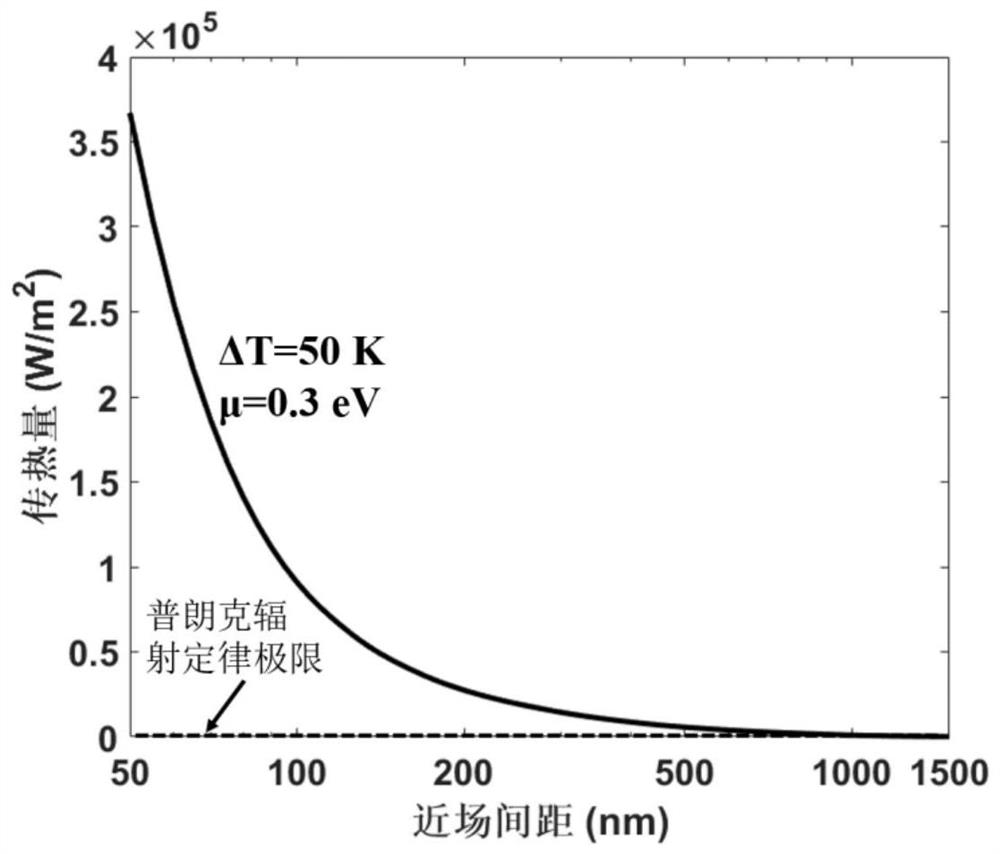
InactiveCN111609750AOvercoming the interface thermal resistance problemFast transmissionHeat transfer modificationHexagonal boron nitrideEngineering
The invention provides an adjustable and controllable heat exchange device construction method and system based on near-field radiation. The adjustable and controllable heat exchange device construction method comprises the steps that S1, a heat exchange device main body part is built, and a temperature monitoring sensor and a voltage regulator are used as test regulation and control sensors; S2,the feedback heat exchange of a heat exchange device is regulated and controlled by regulating and controlling the voltage applied to graphene; S3, the graphene and hyperbolic metamaterial hexagonal boron nitride are selected to build the adjustable and controllable heat exchange device; S4, the adjustable and controllable heat exchange device is built by adopting a near-field heat radiation heatdissipation mechanism; and S5, the near-field distance is controlled, and the adjustable and controllable heat exchange device based on near-field radiation is obtained. According to the adjustable and controllable heat exchange device construction method and system, the graphene voltage is applied for regulation and control, so that selective regulation and control of a near-field wave spectrum can be realized, an electronic component is ensured to work in an optimal temperature range, and the corresponding regulation and control temperature difference can reach 50 DEG C.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
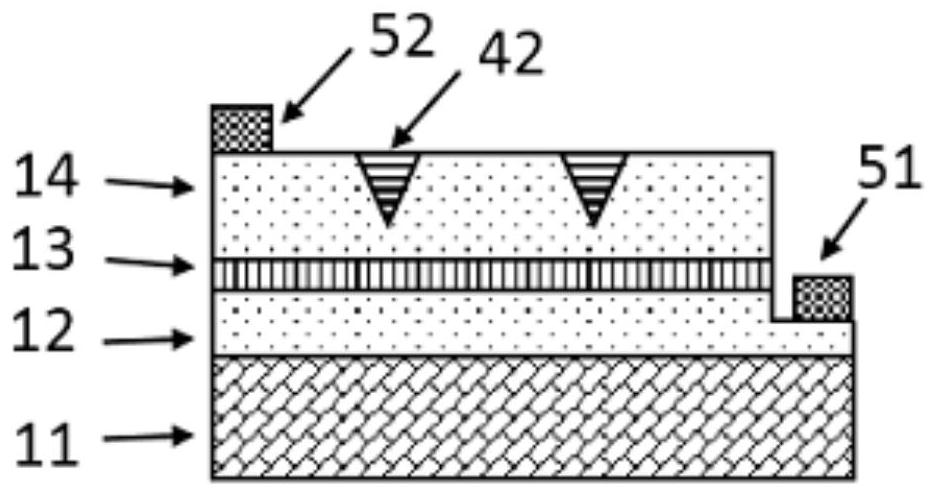
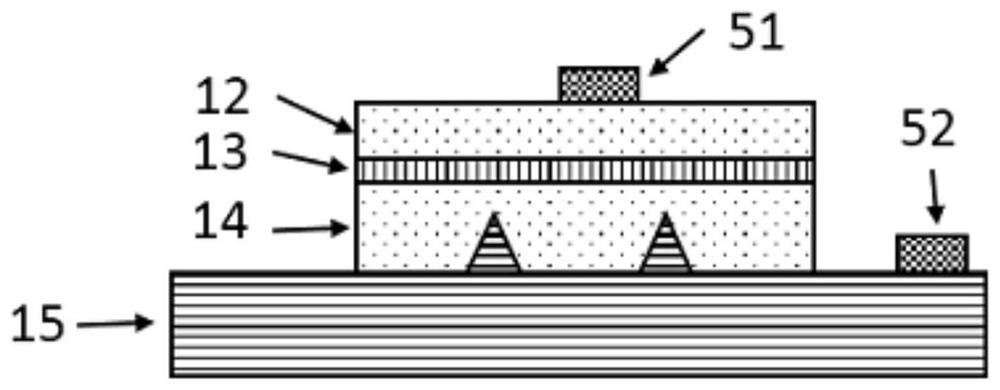
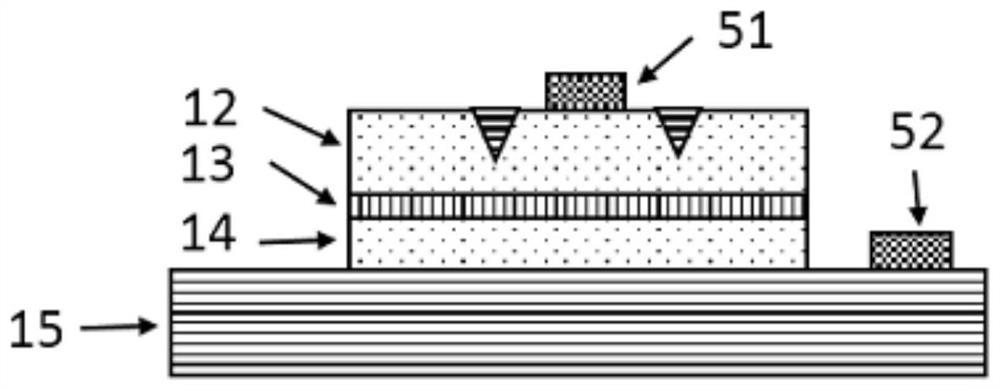
On-chip terahertz source based on hyperbolic metamaterial and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112563863AWide Terahertz Radiation SpectrumContinuous and stable outputSolid masersGratingTerahertz radiation
The invention provides an on-chip terahertz source based on a hyperbolic metamaterial and a preparation method of the on-chip terahertz source; the hyperbolic metamaterial structure layer is formed bythe material of which the terahertz waveband is covered by the plasma frequency and the material which is dielectric in the terahertz waveband, and a slit grating is arranged on the first surface ofthe hyperbolic metamaterial structure layer; and an electron beam is arranged on the second surface of the hyperbolic metamaterial structure layer, so that the hyperbolic metamaterial structure layercan generate terahertz radiation, and the terahertz radiation in the free space is extracted through the slit grating. Terahertz radiation is generated by using the hyperbolic metamaterial structure layer, so that relatively wide terahertz radiation frequency spectrum, miniaturization of a terahertz source and on-chip integration can be realized; terahertz radiation is generated by the action between the hyperbolic metamaterial structure layer and an electromagnetic field formed by electrons in an electron beam, and continuous and stable output of the terahertz radiation can be realized underthe condition that the kinetic energy of the electrons in the electron beam is stable.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
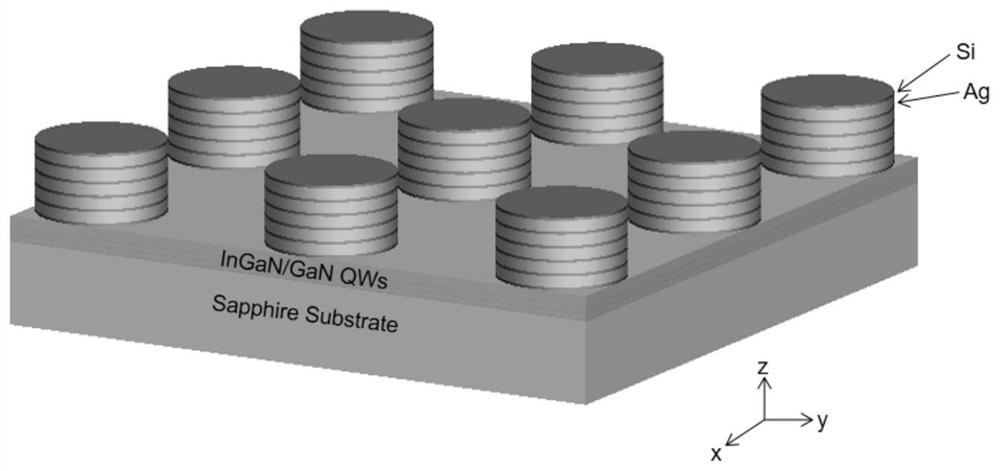
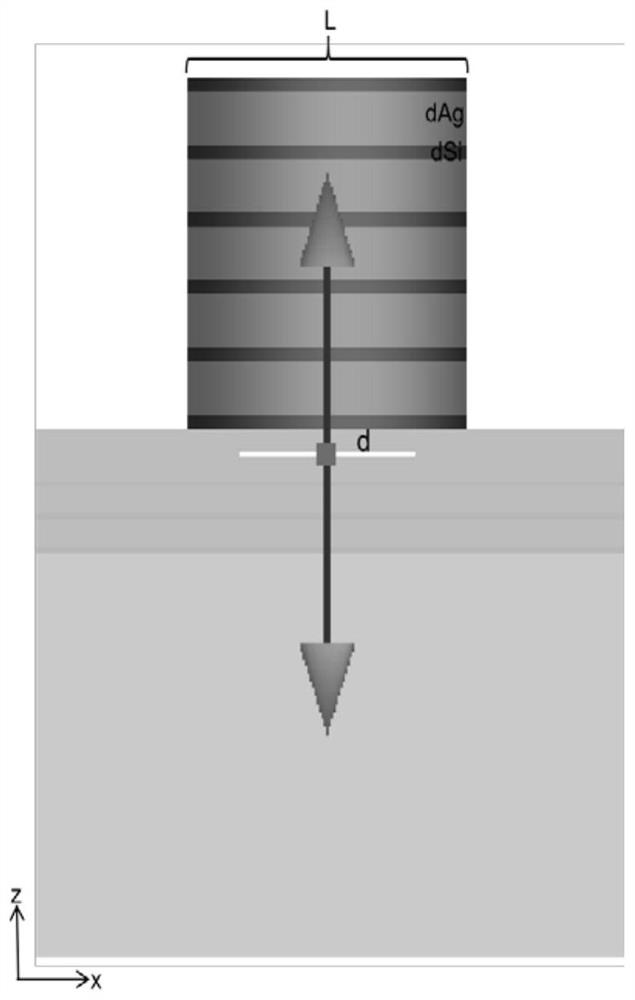
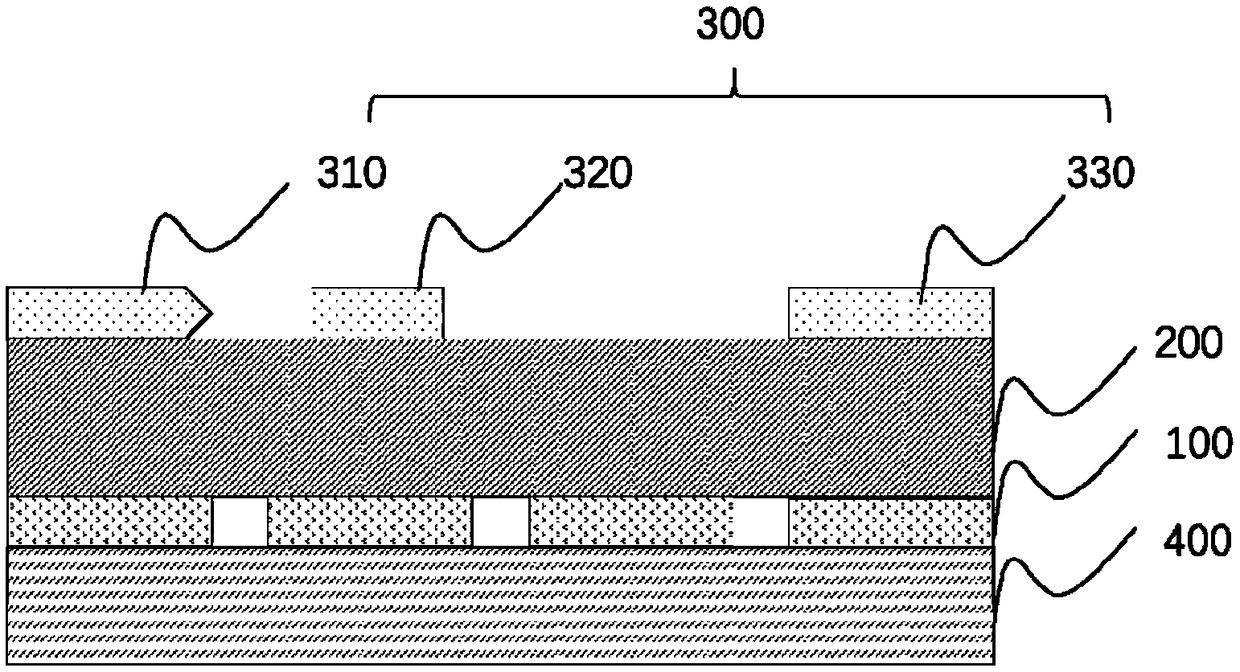
LED based on patterned substrate and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an LED based on a patterned substrate and a preparation method thereof. The LED based on the patterned substrate structurally and sequentially comprises a sapphire substrate with two polished sides, three pairs of InGaN / GaN layer quantum wells, a barrier layer made of GaN, five pairs of Ag / Si layer hyperbolic metamaterials and a surface protection layer Si layer from bottomto top. On the basis of a traditional LED, a plurality of layers of hyperbolic metamaterials are added, so that the LED luminous efficiency of the patterned substrate reaches 180 times and is far higher than that of the traditional LED, and the LED is simple in technological process, low in cost, stable in processing technology and easy to produce in batches. Therefore, the LED and the preparation method a great application prospect in LED research.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Cherenkov infrared radiation source and free electron light source based on natural hyperbolic material
The invention provides a natural hyperbolic material-based Cherenkov infrared radiation source and free electron light source, which comprises a natural hyperbolic material layer and an on-chip free electron emission source, and the on-chip free electron emission source comprises an on-chip electron source cathode and an on-chip electron source anode. In this way, the on-chip free electron emission source generates a stable electron beam to excite infrared Cherenkov radiation in the natural hyperbolic material. As the natural hyperbolic material is low in cost, easy to obtain and simple in preparation process, the natural hyperbolic material has remarkable advantages compared with an artificial hyperbolic metamaterial. Meanwhile, the natural hyperbolic material is easy to grow, good in stability and few in defect, and the influence of the material processing technology precision on the device performance can be avoided. And on the basis of a natural dielectric material, the intrinsic loss is lower, so that the corresponding device is higher in radiation power, higher in efficiency and smaller in heat emission. In addition, based on a natural crystal material, layout and arraying are easy to realize, and a possible scheme is provided for a high-power array integrated free electron light source.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
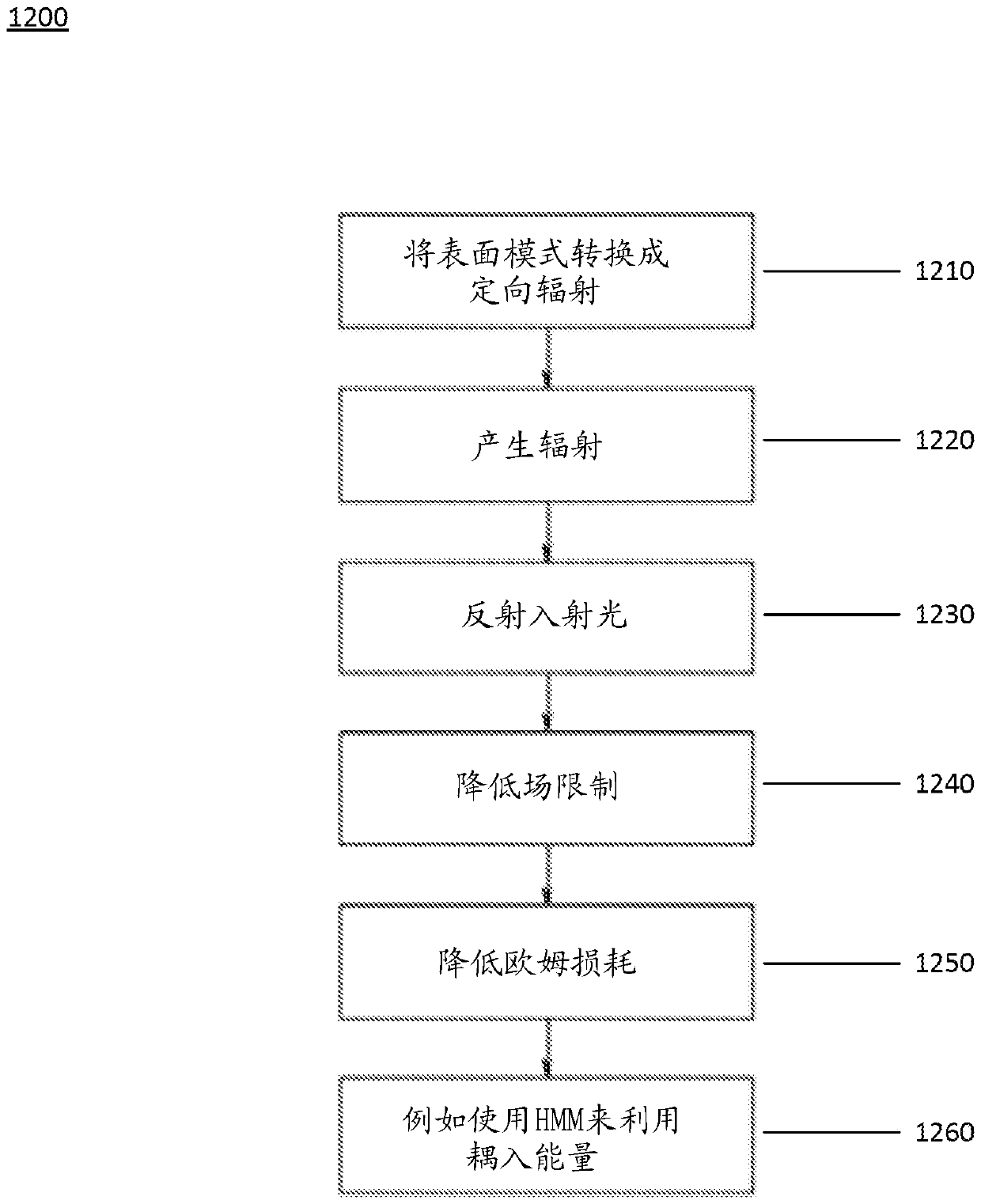
LED emitters with integrated nano-photonic structures to enhance eqe
PendingCN111466034AIncrease kinetic energyReduce Field LimitsSemiconductor devicesOptical elementsQuantum efficiencyRefractive index
A device, system and method for producing enhanced external quantum efficiency (EQE) LED emission are disclosed. The device, system and method include a patterned layer configured to transform surfacemodes into directional radiation, a semiconductor layer formed as a III / V direct band gap semiconductor to produce radiation, and a metal back reflector layer configured to reflect incident radiation. The patterned layer may be one-dimensional, two-dimensional or three-dimensional. The patterned layer may be submerged within the semiconductor layer or within the dielectric layer. The semiconductor layer is p-type gallium nitride (GaN). The patterned layer may be a hyperbolic meta-materials (HMM) layer and may include Photonic Hyper-crystal (PhHc), or may be a low or high refractive index material or may be a metal.
Owner:LUMILEDS
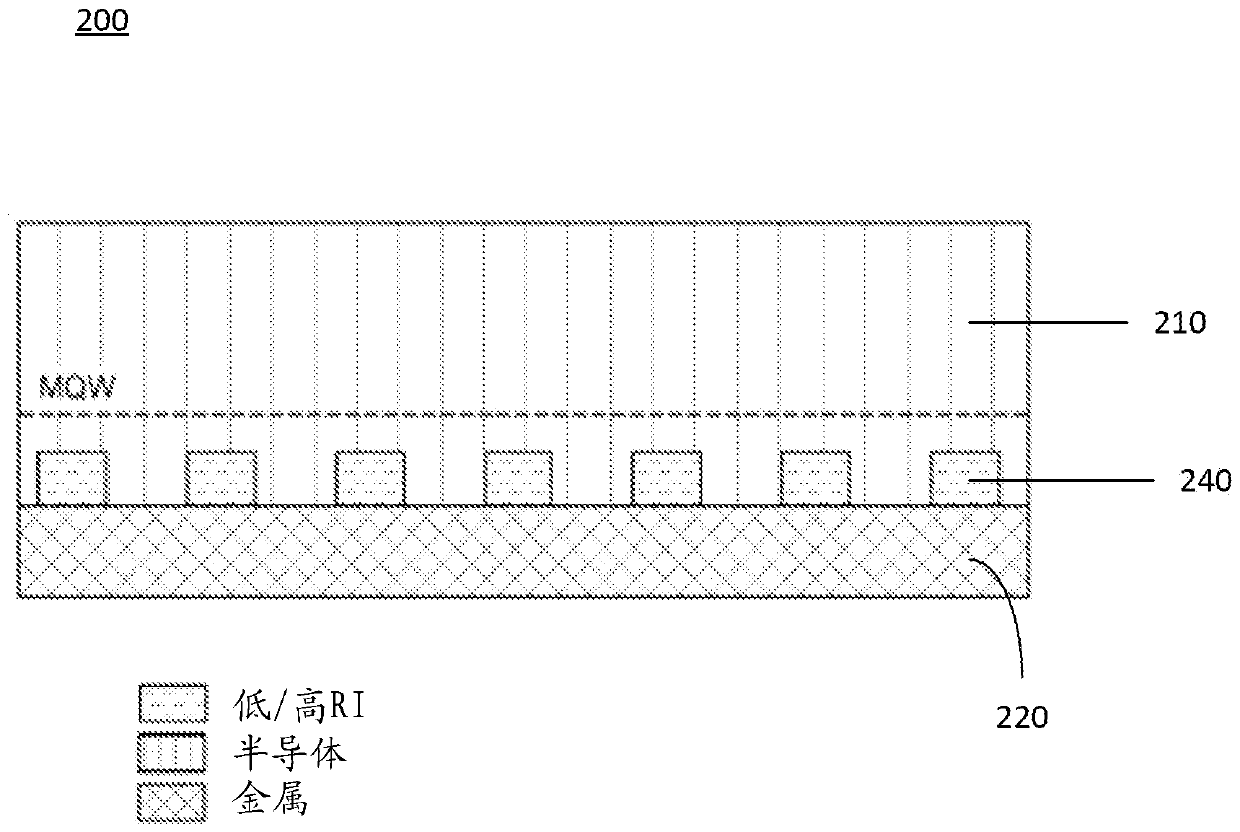
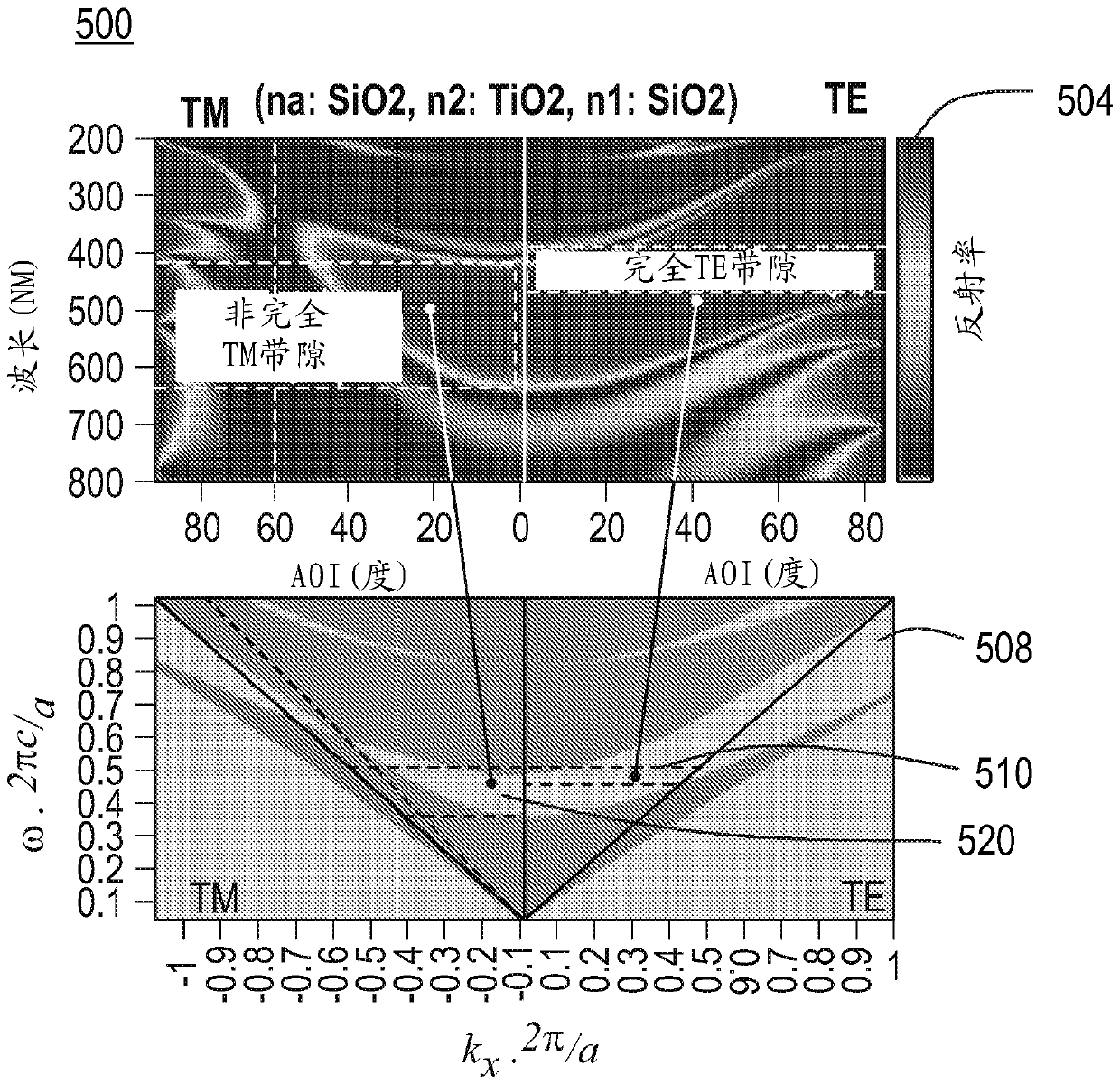
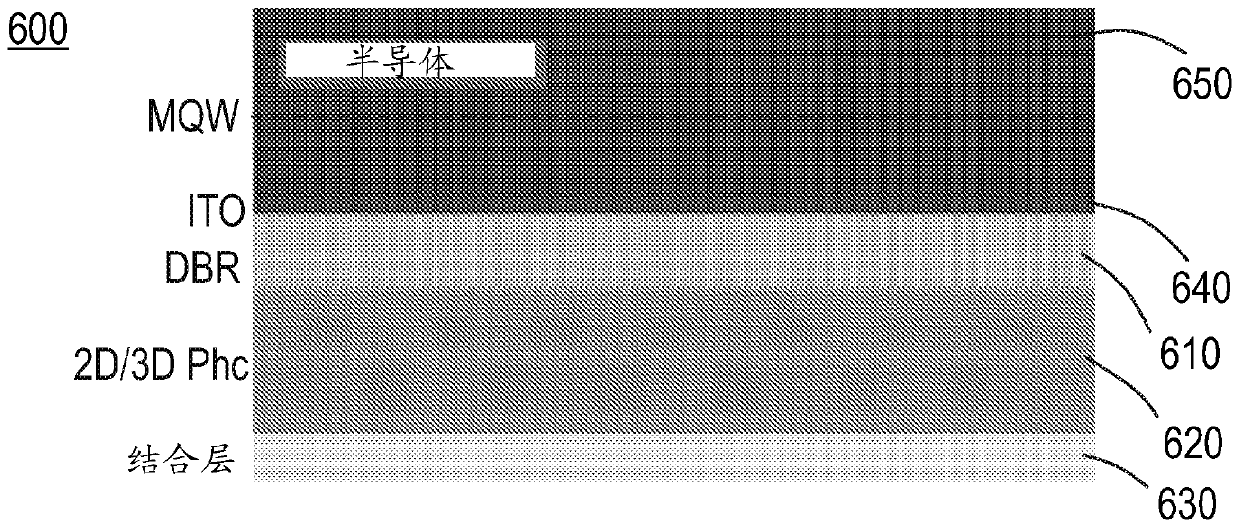
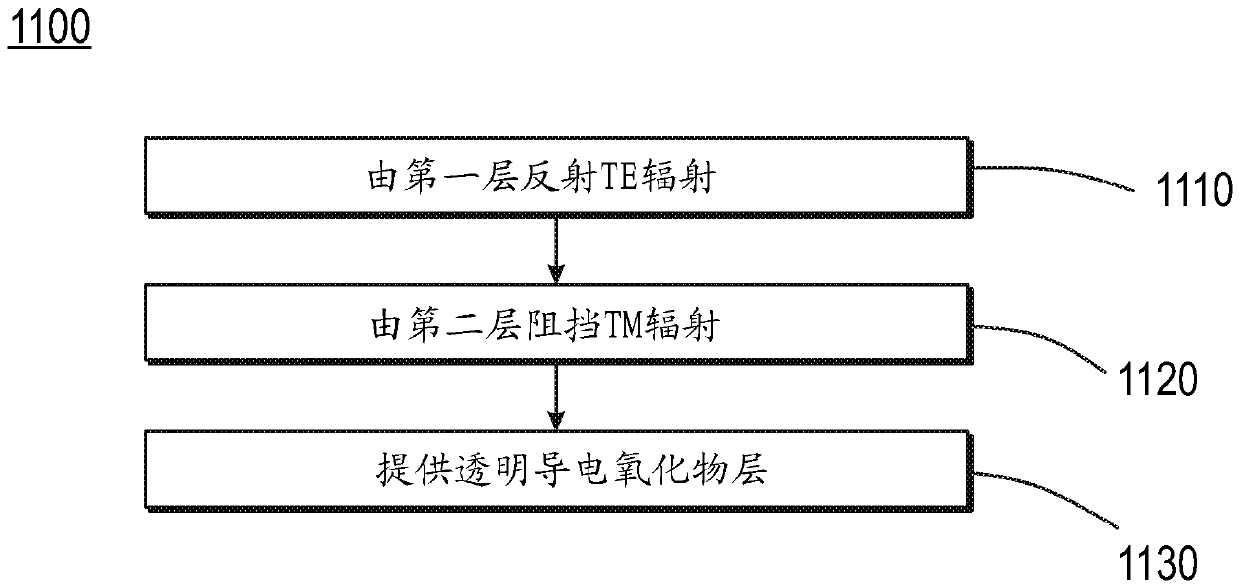
Nano-photonics reflector for LED emitters
A system, method and device for use as a reflector for a light emitting diode (LED) are disclosed. The system, method and device include a first layer designed to reflect transverse-electric (TE) radiation emitted by the LED, a second layer designed to block transverse-magnetic (TM) radiation emitted from the LED, and a plurality of ITO layers designed to operate as a transparent conducting oxidelayer. The first layer may be a one-dimension (1D) distributed Bragg reflective (DBR) layer. The second layer may be a two-dimension (2D) photonic crystal (PhC), a three-dimension (3D) PhC, and / or a hyperbolic metamaterial (HMM). The 2D PhC may include horizontal cylinder bars, vertical cylinder bars, or both. The system, method and device may include a bottom metal reflector that may be Ag free and may act as a bonding layer.
Owner:LUMILEDS
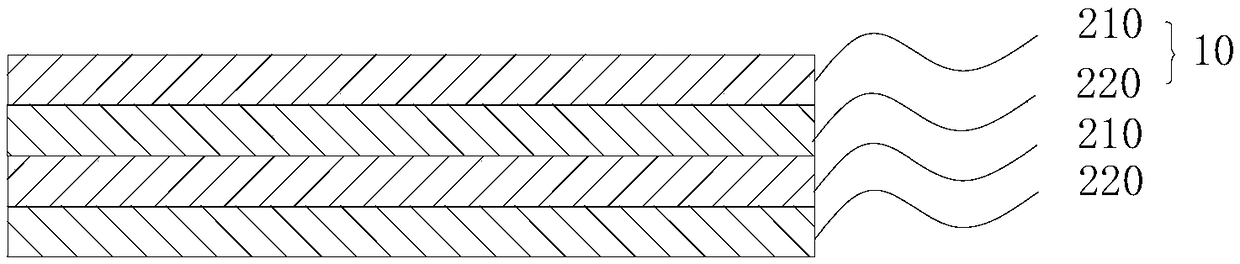
Planar waveguide type hyperbolic metamaterial and ultra-small resonant cavity
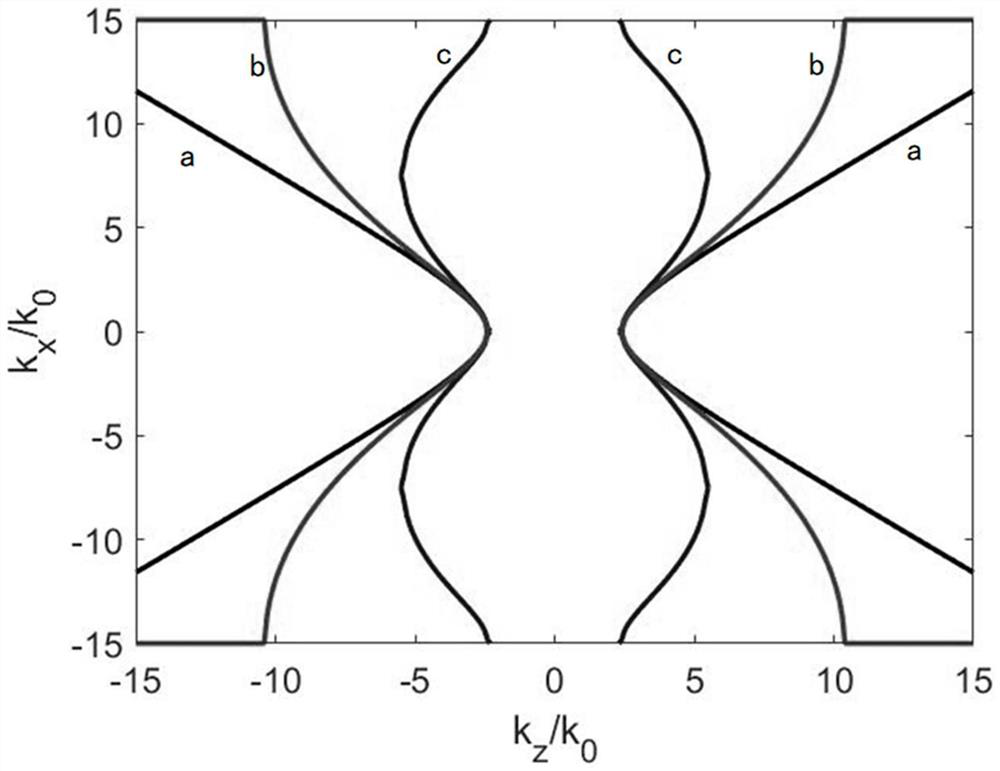
The invention discloses a planar waveguide type hyperbolic metamaterial and an ultra-small resonant cavity. A planar waveguide is formed by two metal plates in the height direction, two kinds of dielectric sheets are alternately and periodically arranged in the planar waveguide, the dielectric sheets are uniform sheets with sub-wavelength thicknesses, the height of the dielectric sheets is the same with that of the planar waveguide, and a metal wire array is arranged on interfaces of the adjacent dielectric sheets and used for restraining mode coupling. The planar waveguide works in a TE modeand can be homogenized into a waveguide type metamaterial, an equal-frequency curve is a hyperbolic curve, and a large wave vector which is more than ten times that of a free space wave vector is supported; the shape of the equal-frequency curve can be adjusted through matching of geometrical parameters and dielectric constants of dielectric materials, and different opening directions are achieved; and the metalmaterial is suitable for all frequency bands from terahertz to microwaves to radio frequency and optical frequency bands. The metamaterial is low in loss, supports large wave vectors,is flexible and adjustable in equal-frequency curve, and is convenient to integrate in a waveguide loop. The ultra-small resonant cavity is realized by adopting the waveguide type hyperbolic metamaterial.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Design method of plasma sensor and sensor prepared by design method
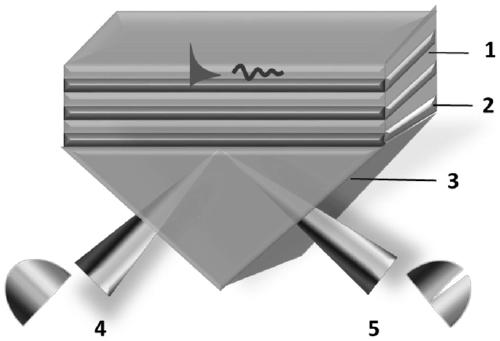
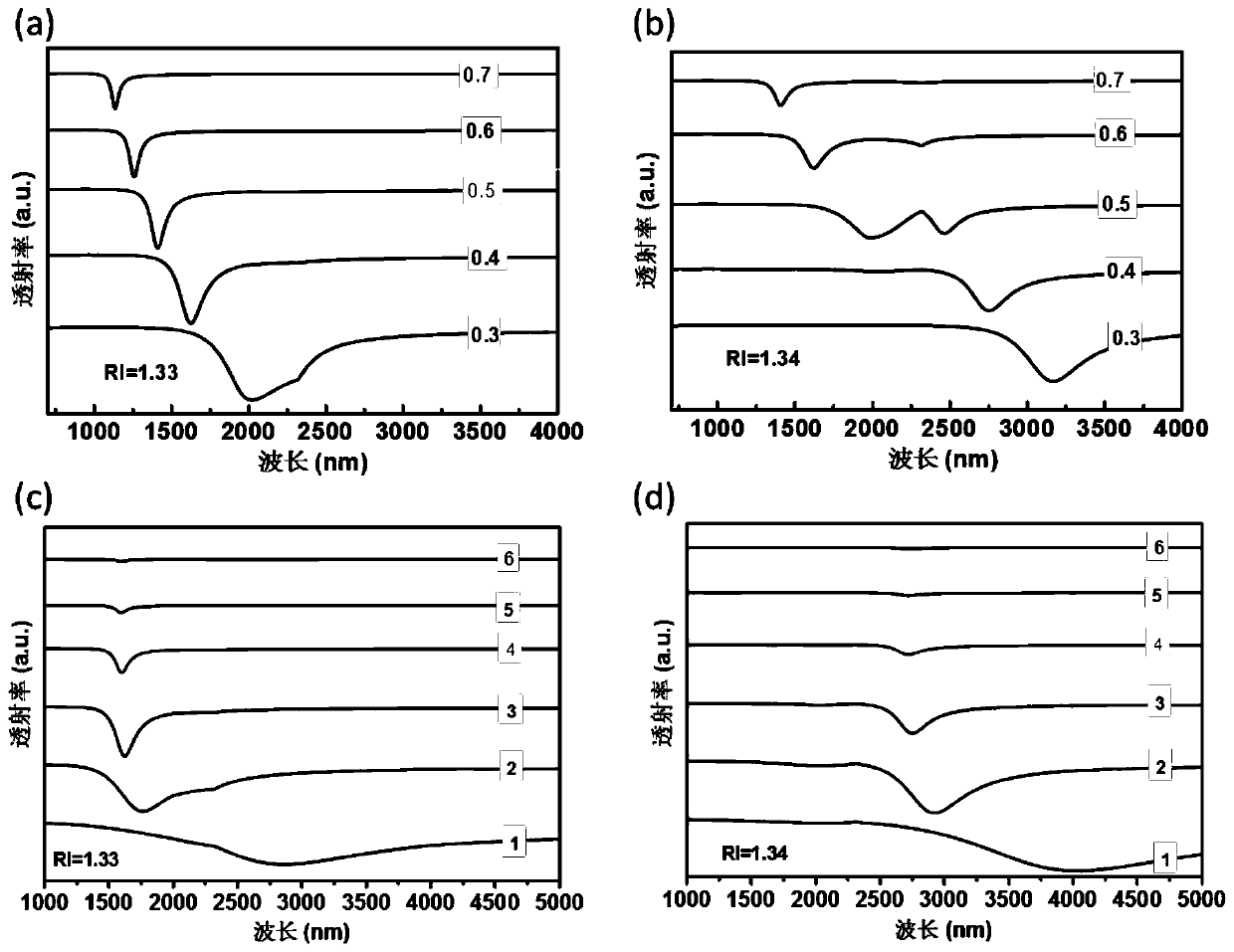
PendingCN111175234AHigh sensitivityReduce FWHMMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanosensorsComputational physicsHyperbolic metamaterials
The invention discloses a design method of a plasma sensor and a sensor prepared by the design method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, utilizing software simulation calculation to obtain optimal combination parameters of a metal filling ratio rho of a hyperbolic metamaterial and a logarithm Nbi of a metal-dielectric layer; and then combining the hyperbolic metamaterial with a polishing surface of a Kretschmann structure or a side polishing optical fiber by a multilayer film structure with the optimal combination parameters to manufacture a corresponding plasma sensor. Compared with the prior art, the design method provided by the invention has the advantages that the performance parameters of the sensor can be controlled by regulating and controlling the metal filling ratio (rho) of the hyperbolic metamaterial and the logarithm (Nbi) of the metal-dielectric layer, so that the controllability of the performance parameters is realized; the plasma sensor prepared by themethod has the advantages of adjustable wavelength, high sensitivity, high quality factor (FOM), simple manufacturing and the like, and is far better than an existing plasma sensor.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Cerenkov radiation device, preparation method and method for extracting radiation
ActiveCN106569248BSlow flightReduce manufacturing costRadiation intensity measurementElectronHigh voltage
The invention discloses a Cerenkov radiation device and a manufacturing method thereof, and a radiation extraction method. The Cerenkov radiation device comprises a metal cycle nanometer slit structure, a hyperbolic metamaterial structure and an electron-emitting source, wherein the hyperbolic metamaterial structure is arranged on an upper surface of the metal cycle nanometer slit structure; the electron-emitting source is arranged on an upper surface of the hyperbolic metamaterial structure; and the electron-emitting source includes an anode, a cathode and a grid electrode. The Cerenkov radiation device does not need a high voltage. A characteristic that a phase velocity of light in the hyperbolic metamaterial structure can be reduced by several orders of magnitudes compared to a velocity in a traditional material is used so that a required electronic flight speed generated by Cerenkov radiation can be greatly reduced; and then production cost generated by the Cerenkov radiation device is decreased and safety performance is increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for fabricating a hyperbolic metamaterial having a near-zero refractive index in the optical regime
A method for fabricating a hyperbolic metamaterial coating having a near-zero refractive index is disclosed. The direction of propagating light changes by means of generating subwavelength structures that alter the coatings permittivity and permeability. The coating can be deposited on lenses or incorporated into optical devices. This type of metamaterial can be utilized to direct light towards sensors or to collect light efficiently.
Owner:THE BOARD OF REGENTS OFTHE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Perfect matching layer method of hyperbolic metamaterial based on time domain finite difference
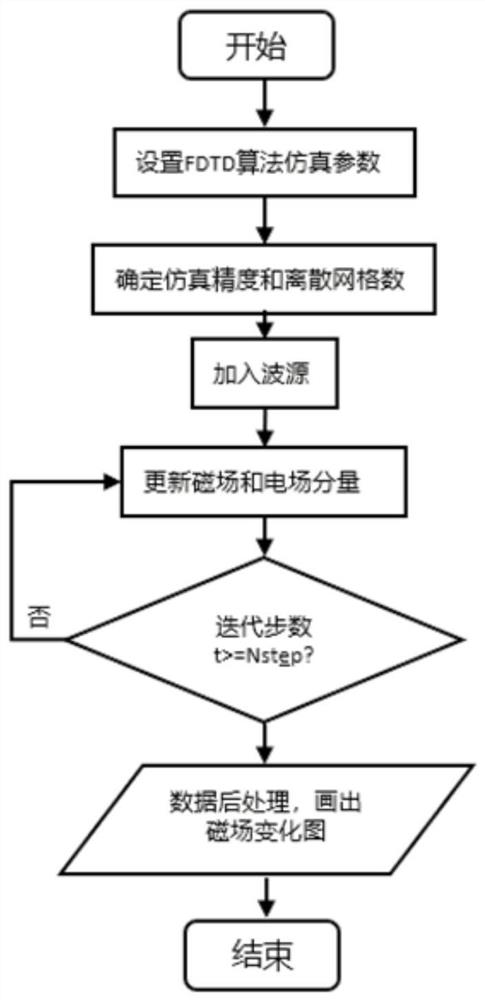
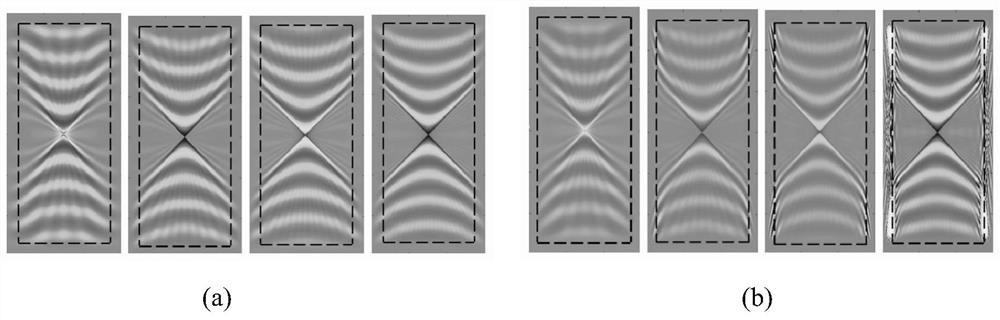
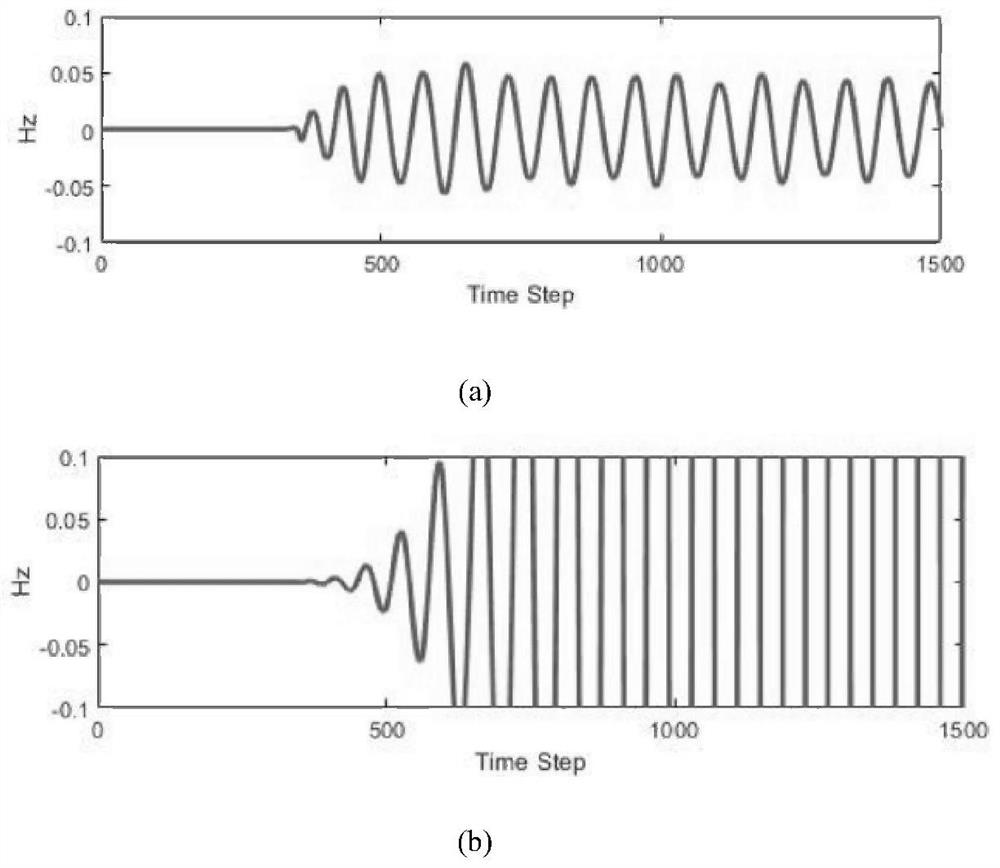
PendingCN114417667AVerify validitySolve the problem of not being able to absorb electromagnetic waves in hyperbolic materialsDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingParticle physicsFdtd algorithm
The invention discloses a hyperbolic metamaterial perfect matching layer method based on time domain finite difference, and belongs to the field of computational electromagnetic simulation. Comprising the following steps: 1) setting simulation parameters of an FDTD algorithm; 2) determining simulation precision and the number of discrete grids; 3) adding a sine wave source into the hyperbolic medium; 4) updating electric field and magnetic field components; 5) drawing magnetic field distribution, and analyzing stability; and 6) data post-processing: if the result of the field quantity of the magnetic field obtained in the step 5) is not convergent or the error is large, the PML is unstable, and the PML needs to be corrected. The problem that electromagnetic waves propagated in a hyperbolic material have numerical divergence in frequency domain PML simulation of traditional PML and COMSOL is solved, the problem that the frequency domain PML in the time domain traditional PML and COMSOL cannot absorb the electromagnetic waves in the hyperbolic material is solved, high stability is shown, and a numerical result further verifies the effectiveness of a PML improvement technology.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
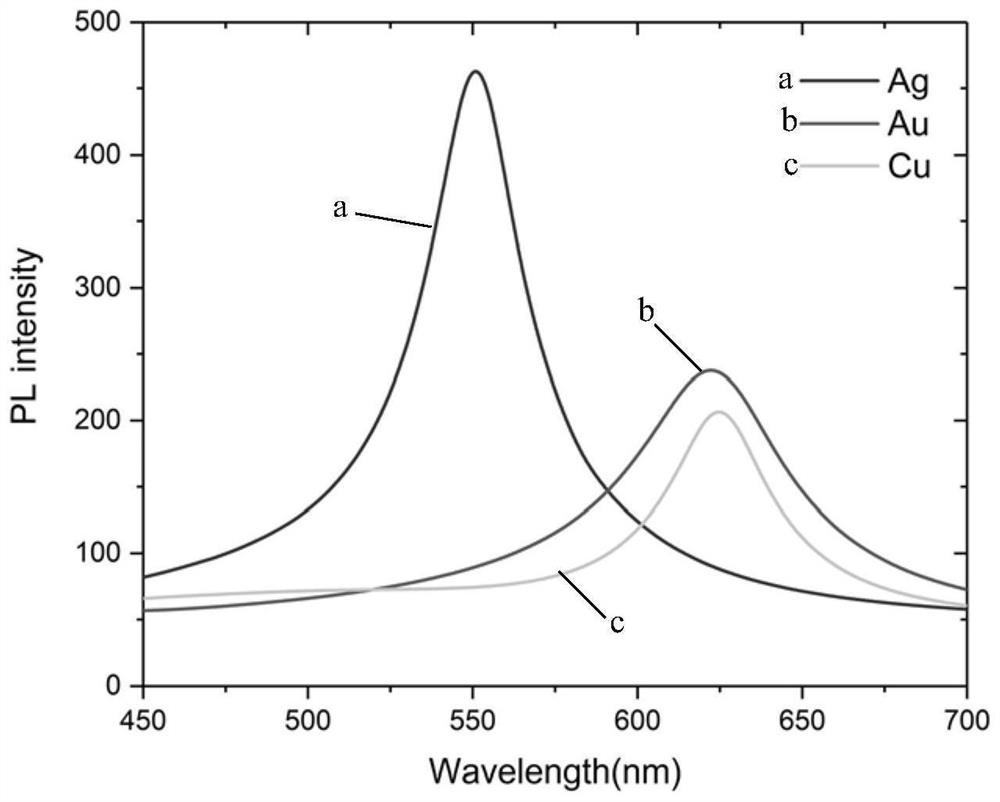
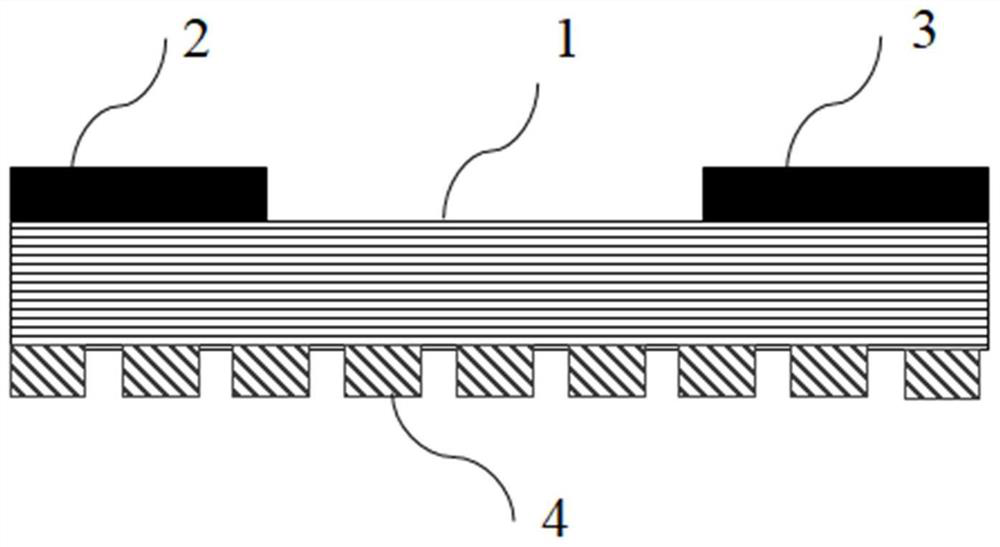
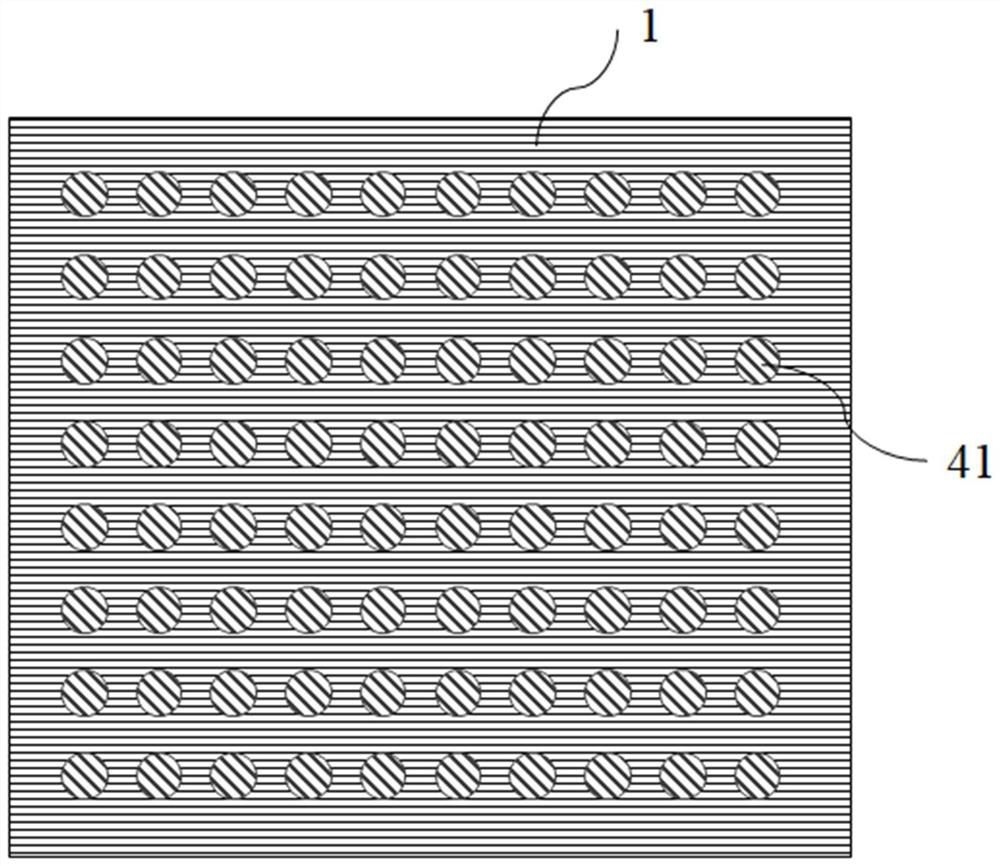
Blue light emitting diode with luminous efficiency enhanced by metamaterial and preparation method of blue light emitting diode
ActiveCN113066909AStrong coupling effectImprove internal quantum efficiencySemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyHyperbolic metamaterials
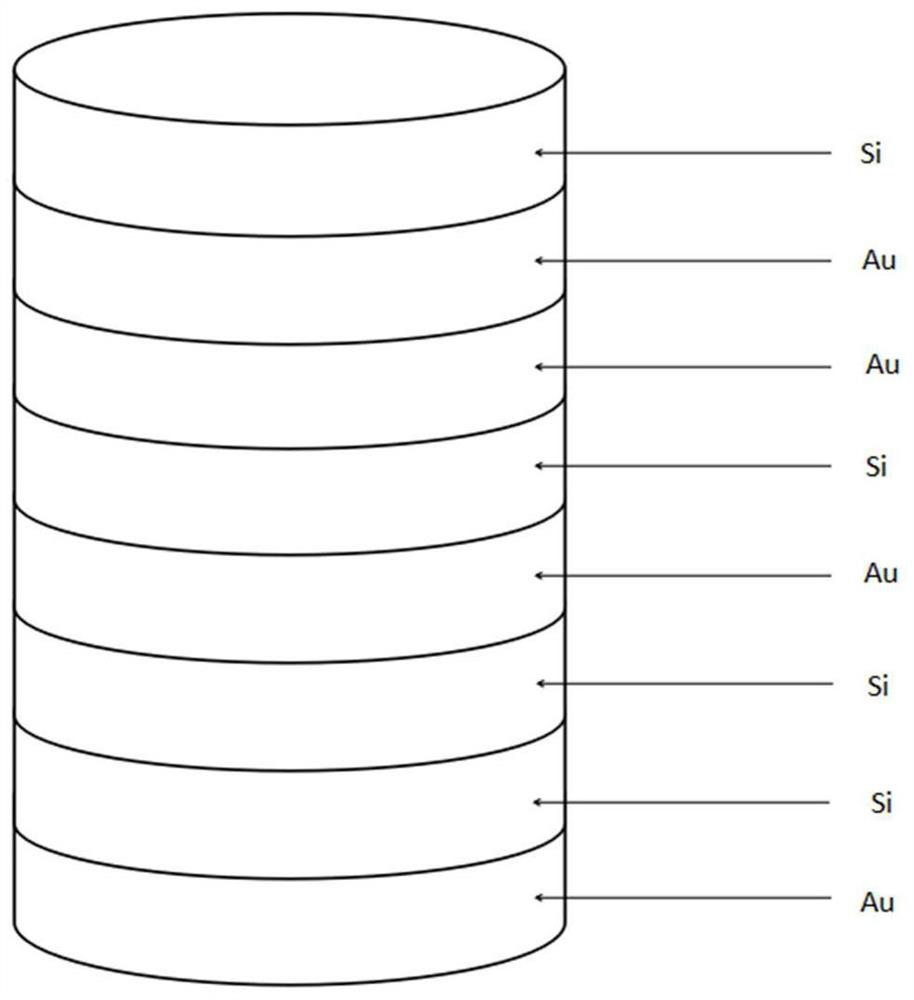
The invention relates to a blue light emitting diode with luminous efficiency enhanced by the metamaterial. The blue light emitting diode comprises a buffer layer, an n-type GaN layer, a multi-quantum well layer, a metamaterial layer and a p-type layer which are sequentially stacked on a substrate, the metamaterial layer is composed of a hyperbolic metamaterial unit structure array and a GaN covering layer, the GaN covering layer is in contact with the multi-quantum well layer, and the hyperbolic metamaterial unit structure array is formed by arranging hyperbolic metamaterial unit structures formed by stacking Au and Si. The unique structure of the quasi-periodic hyperbolic metamaterial is formed by alternately stacking Au and Si according to the Thue-Morse sequence, and the distance between the quasi-periodic hyperbolic metamaterial structure and the quantum well is relatively short, so that the coupling effect between the surface plasmon polaritons and the multiple quantum wells is relatively strong, and the internal quantum efficiency of the blue light LED is further improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
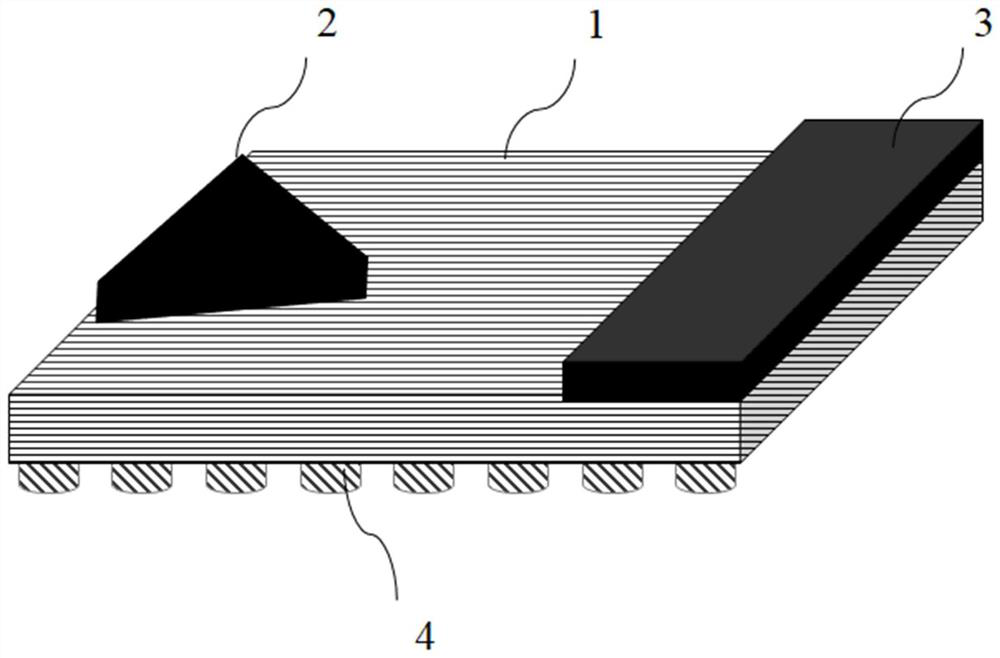
A hyperbolic metamaterial planar antenna
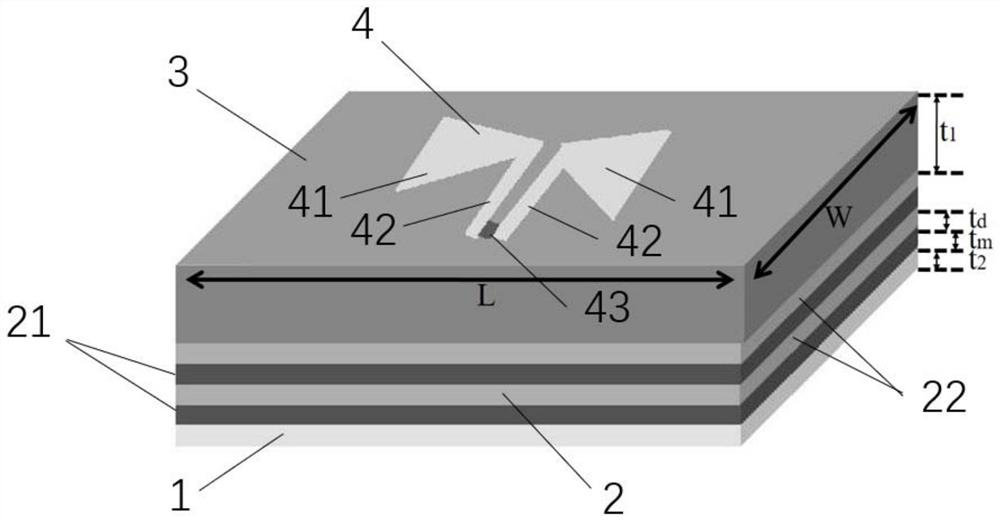
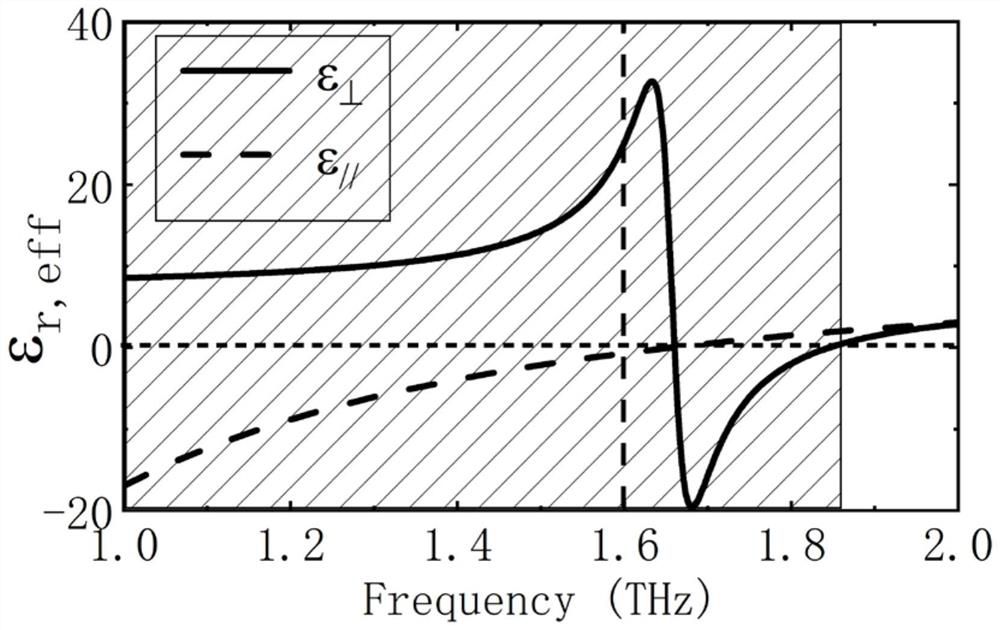
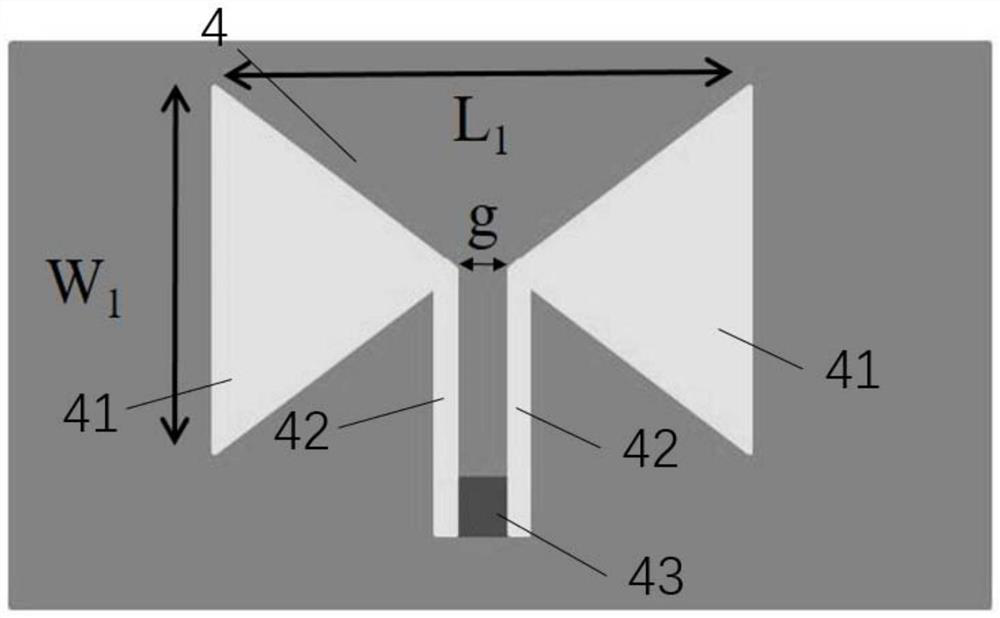
ActiveCN110707422BRealize a planar structureEasy to integrate with each otherRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsInterference resistancePlanar antennas
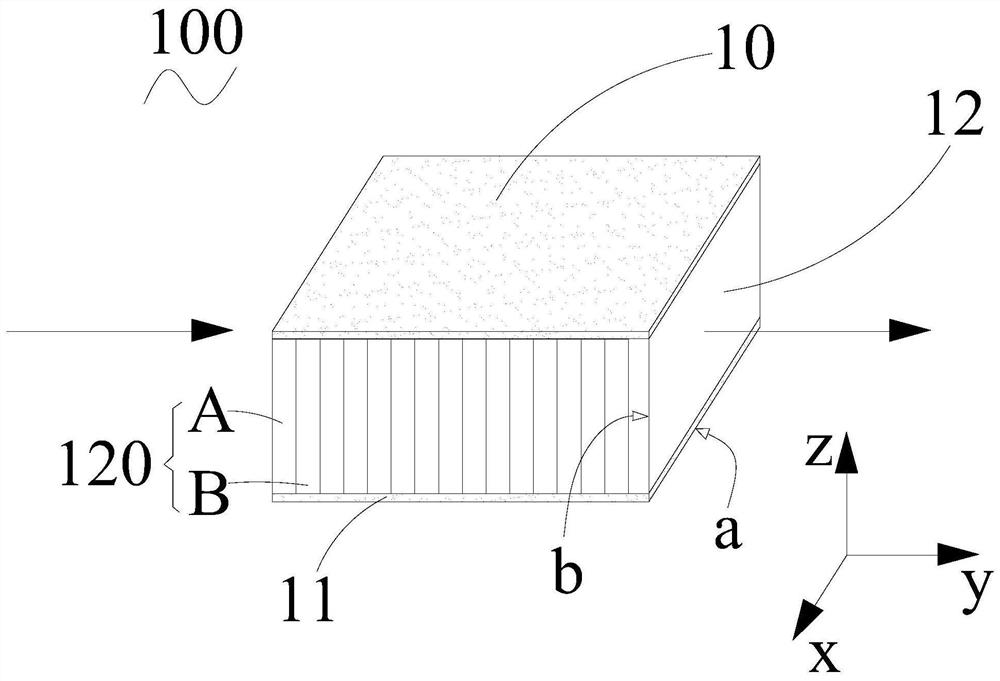
A hyperbolic metamaterial planar antenna, comprising a ground plane, a hyperbolic metamaterial structure layer, a substrate, and a radiation antenna; the hyperbolic metamaterial structure layer is formed by alternately stacking semiconductor layers and dielectric layers, formed on the ground plane The substrate is formed on the hyperbolic metamaterial layer; the radiation antenna is formed on the substrate. The hyperbolic metamaterial planar antenna structure is easy to produce and manufacture, can effectively improve the gain and anti-interference ability of the planar antenna, is easy to integrate with other devices, and is not easily damaged.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
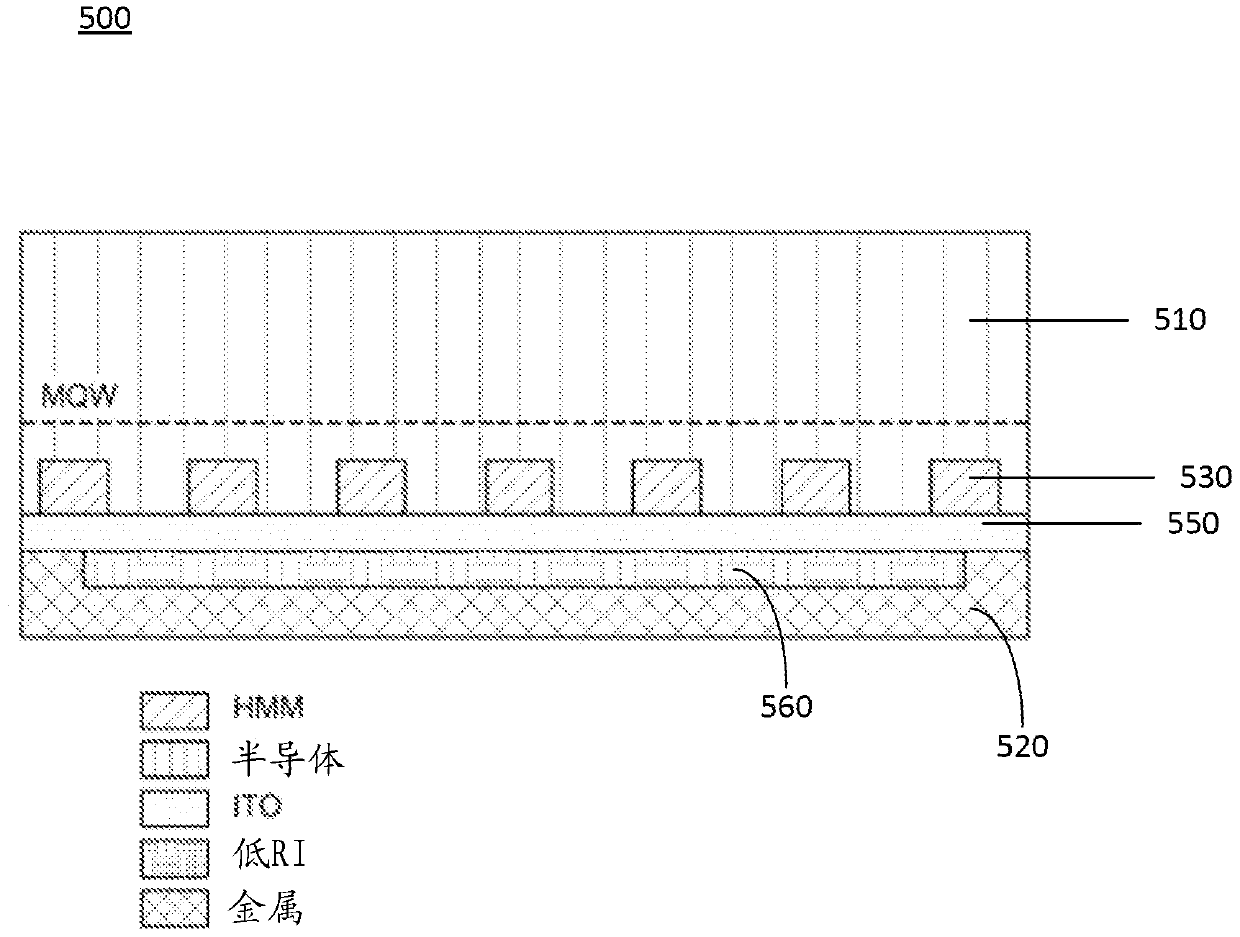
On-chip light source, preparation method of on-chip light source, and optoelectronic device
ActiveCN113097356BHigh luminous intensityGood integration process compatibilitySemiconductor devicesLuminous intensityLuminescence
The invention provides an on-chip light source, a preparation method of an on-chip light source and an optoelectronic device. An insulating layer is formed on a substrate, an optical array layer is formed on the insulating layer, an isolation layer is formed on the optical array layer, and a two-dimensional optical array layer is formed on the isolation layer. The material layer forms a medium layer on the two-dimensional material layer, and forms a hyperbolic metamaterial layer on the medium layer. Wherein, when the resonance peak of the photon mode of the optical array layer is equal to the wavelength of the exciton peak of the two-dimensional material layer, the luminous intensity of the two-dimensional material layer will be enhanced. In addition, the surface plasmons of the hyperbolic metamaterial layer will have a strong coupling with the two-dimensional material layer, further enhancing the Purcell effect. The present invention utilizes hyperbolic metamaterials to enhance the Purcell effect of two-dimensional materials, which can not only significantly improve the luminous intensity of the on-chip light source, but also achieve high luminous efficiency and fast response speed, small size, compact structure, and easy high-density integration And have good CMOS integration process compatibility.
Owner:NAT INNOVATION INST OF DEFENSE TECH PLA ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
On-chip light source, preparation method of on-chip light source and optoelectronic device
ActiveCN113097356AHigh luminous intensityGood integration process compatibilitySemiconductor devicesLuminous intensityEngineering
The invention provides an on-chip light source, a preparation method of the on-chip light source and a photoelectronic device. An insulating layer is formed on a substrate, an optical array layer is formed on the insulating layer, an isolating layer is formed on the optical array layer, a two-dimensional material layer is formed on the isolating layer, a dielectric layer is formed on the two-dimensional material layer, and a hyperbolic metamaterial layer is formed on the dielectric layer. When the wavelength of the resonance peak of the photon mode of the optical array layer is equal to the wavelength of the exciton peak of the two-dimensional material layer, the luminous intensity of the two-dimensional material layer is enhanced. In addition, the surface plasmon polaritons of the hyperbolic metamaterial layer can generate a strong coupling effect with the two-dimensional material layer, and the Purcell effect is further enhanced. According to the invention, the hyperbolic metamaterial is utilized to enhance the Purcell effect of the two-dimensional material, so that not only can the luminous intensity of the on-chip light source be remarkably improved, but also high luminous efficiency and high response speed can be realized, the size is small, the structure is compact, high-density integration is easy, and good CMOS integration process compatibility is realized.
Owner:NAT INNOVATION INST OF DEFENSE TECH PLA ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
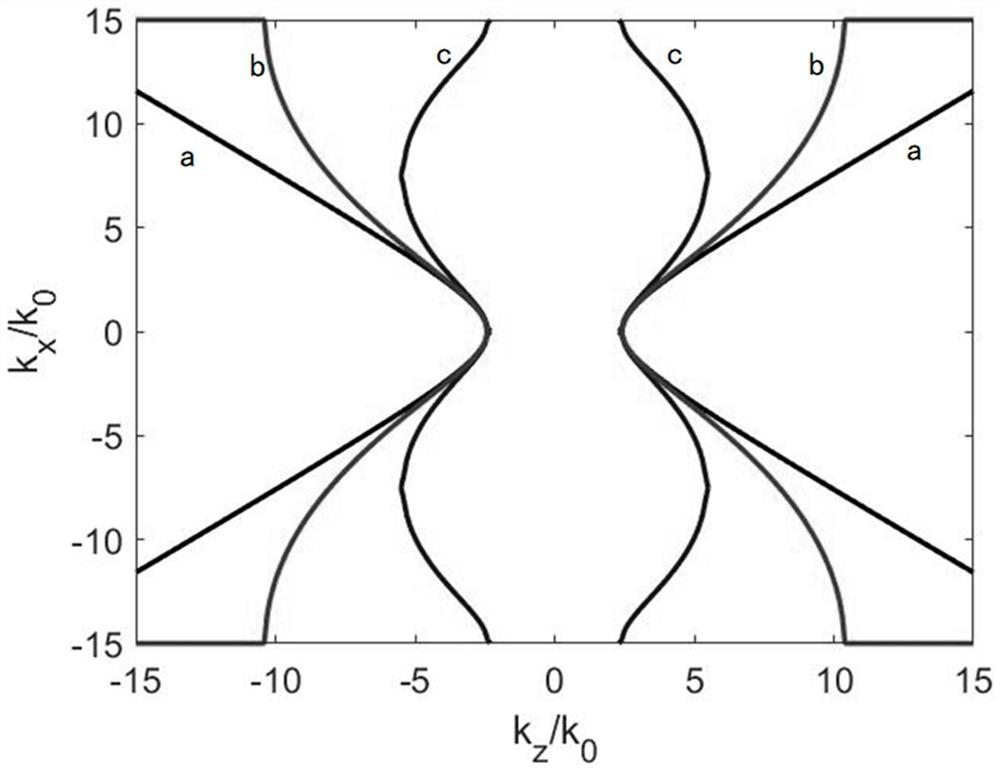
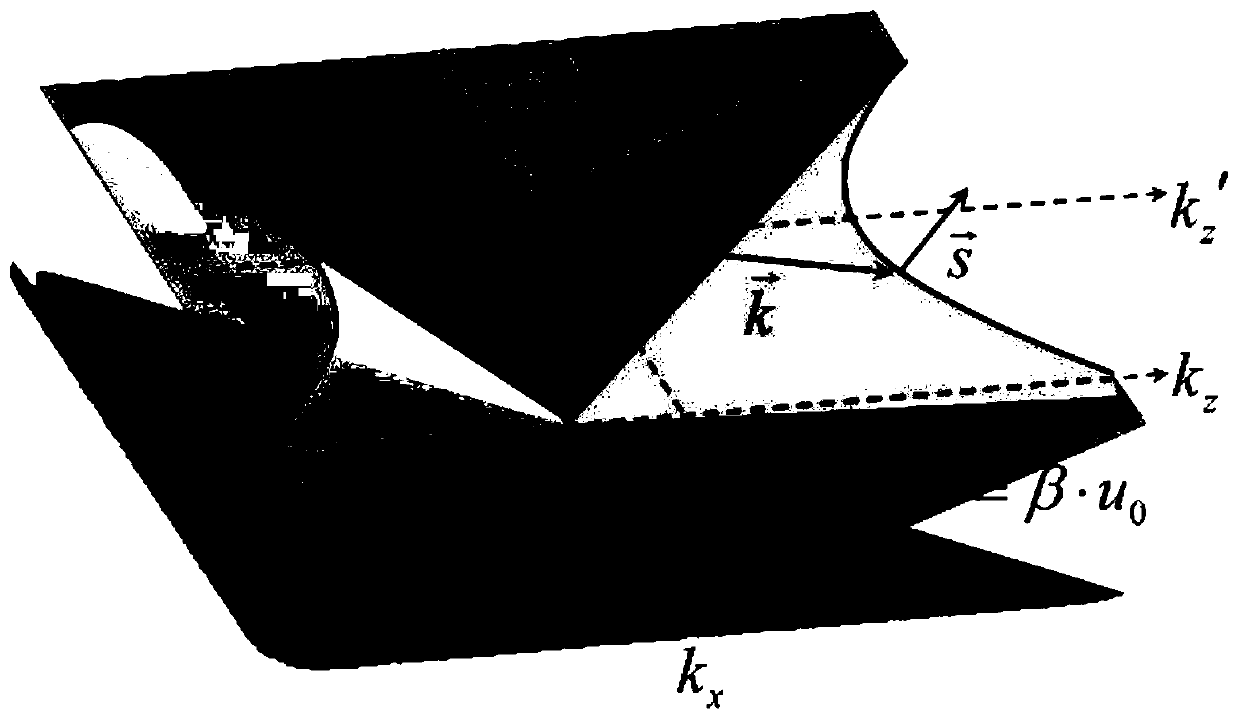
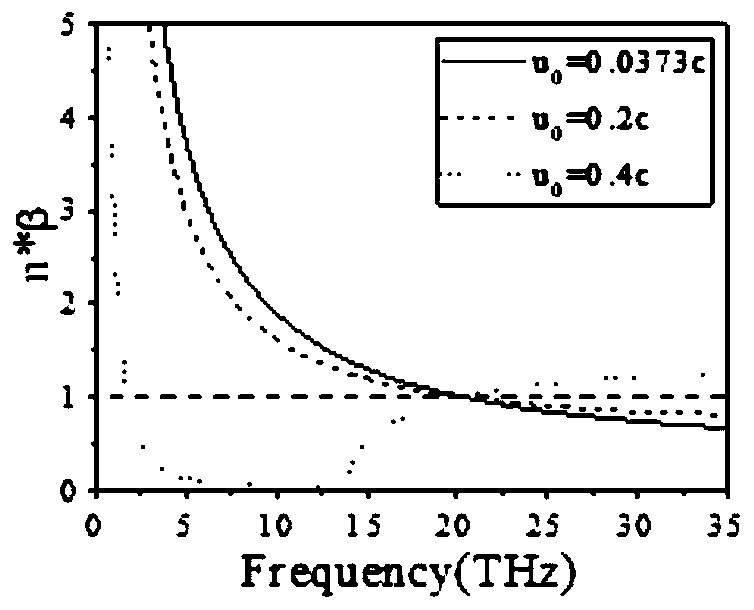
Free electron source design method based on threshold-free Cherenkov radiation
InactiveCN110783011AAchieve couplingRealize disseminationSolid masersCharged particle radiation pressure manipulationElectron sourceParticle physics
The invention discloses a free electron source design method based on threshold-free Cherenkov radiation. A hyperbolic metamaterial can convert an evanescent field around electrons into a propagationfield due to its hyperbolic dispersion curve; and the speed limit of CR electrons generation is broken through in virtue of the hyperbolic metamaterial, so realization of a terahertz free electron source is made possible. Directed at the characteristics of CR generation, transmission and coupling of a low-energy electron beam in the hyperbolic metamaterial, the rules of wave vector compression andenergy flow density of CR in the hyperbolic metamaterial are explored; the method realizes the design of a terahertz free electron light source; and the terahertz free electron light source can be widely applied to the fields of biomedicine, imaging and communication.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
Devices with semiconductor hyperbolic metamaterials
ActiveUS11448824B2Improve propertiesLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionElectron holeEngineering
A hyperbolic metamaterial assembly comprising alternating one or more first layers and one or more second layers forming a hyperbolic metamaterial, the one or more first layers comprising an intrinsic or non-degenerate extrinsic semiconductor and the one or more second layers comprising a two-dimensional electron or hole gas, wherein one of in-plane or out-of-plane permittivity of the hyperbolic metamaterial assembly is negative and the other is positive.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Silicon based mid-ir super absorber using hyperbolic metamaterial
InactiveUS20190212471A1Wide absorption bandBroaden applicationOptical elementsGratingHyperbolic metamaterials
An absorber for energy harvesting is provided comprising a structure of a multilayered N-doped Si / Si hyperbolic metamaterial (HMM) integrated with a sub-hole Si grating, wherein the structure has a tunable absorption peak tunable from 4.5 μm to 11 μm through changing the grating parameters.
Owner:AMERICAN UNIVERSITY IN CAIRO
Method for fabricating a hyperbolic metamaterial having a near-zero refractive index in the optical regime
A method for fabricating a hyperbolic metamaterial coating having a near-zero refractive index is disclosed. The direction of propagating light changes by means of generating subwavelength structures that alter the coatings permittivity and permeability. The coating can be deposited on lenses or incorporated into optical devices. This type of metamaterial can be utilized to direct light towards sensors or to collect light efficiently.
Owner:THE BOARD OF REGENTS OFTHE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com