Patents
Literature
205 results about "Insoluble fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Soluble fiber is found in oat bran, barley, nuts, seeds, beans, lentils, peas, and some fruits and vegetables. It is also found in psyllium, a common fiber supplement. Some types of soluble fiber may help lower risk of heart disease. Insoluble fiber is found in foods such as wheat bran, vegetables, and whole grains.
Method of producing effective bacterial cellulose-containing formulations
A new method to produce formulations of bacterial cellulose that exhibit improved viscosity-modifying properties particularly with low energy applied to effectuate viscosity changes therewith is provided. Such a method includes the novel co-precipitation with a water soluble co-agent that permits precipitation in the presence of excess alcohol to form an insoluble fiber that can than be utilized as a thickener or suspension aid without the need to introduce high energy mixing. Such bacterial cellulose properties have been available in the past but only through highly labor and energy intensive processes. Such an inventive method as now proposed thus provides a bacterial cellulose-containing formulation that exhibits not only properties that are as effective as those for previous bacterial celluloses, but, in some ways, improvements to such previous types. Certain end-use compositions and applications including these novel bacterial cellulose-containing formulations are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Continuously fragrance-emitting dry or wet wipe fabric article and method for preparing same
Described is a permanently and continuously fragrance-emitting dry or wet wipe laminar fabric article comprising a non-woven fabric lamina having woven therethrough and substantially throughout at least a major portion of the lamina surface at least one continuous fragrance-containing thermoplastic, substantially water-insoluble fiber, which controllably and continuously releases fragrance at least for the time period during which the fabric article is in use. Such fragrance may also have antimicrobial properties. Optionally, one or more antimicrobial substances may also be releasably contained in the fiber containing the fragrance or in a fiber apart therefrom. The fabric article optionally contains additional fragrance and / or antimicrobial agent absorbed in or adsorbed on the non-woven fabric lamina. Also described is a process for preparing the permanently fragrance-emitting dry or wet wipe laminar fabric article by means of (a) creation of a non-woven fabric lamina optionally containing fragrance which may also have antimicrobial properties and / or at least one antimicrobial agent; (b) creation of a fragrance-containing polymeric fiber which, optionally, also contains at least one antimicrobial agent; and (c) weaving the fragrance-containing fiber through the non-woven fabric lamina substantially across at least a major portion of the surface area of the non-woven fabric lamina.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Bacterial cellulose-containing formulations
ActiveUS20070197779A1Need for networkReserved functionNatural cellulose pulp/paperStarch adhesivesAlcoholHigh energy
A new method to produce formulations of bacterial cellulose that exhibit improved viscosity-modifying properties particularly with low energy applied to effectuate viscosity changes therewith is provided. Such a method includes the novel co-precipitation with a water soluble co-agent that permits precipitation in the presence of excess alcohol to form an insoluble fiber that can than be utilized as a thickener or suspension aid without the need to introduce high energy mixing. Such bacterial cellulose properties have been available in the past but only through highly labor and energy intensive processes. Such an inventive method as now proposed thus provides a bacterial cellulose-containing formulation that exhibits not only properties that are as effective as those for previous bacterial celluloses, but, in some ways, improvements to such previous types. Certain end-use compositions and applications including these novel bacterial cellulose-containing formulations are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Chia seed composition
InactiveUS20090181127A1Enhancing gastrointestinal regularityEnhancing heart healthMilk preparationDough treatmentVitamin antagonistGlycoside formation
A composition of matter is disclosed and formed from a stable, defatted whole grain flour derived from Salvia hispanica L. whole ground seed using a suitable solvent that is free of cyanogenic glycosides, vitamin antagonists, and gluten. The composition includes minerals, about 30% wt / wt protein, about 30-40% insoluble fiber and about 2-3% of fructo-oligosaccarides.
Owner:US NUTRACEUTICALS LLC
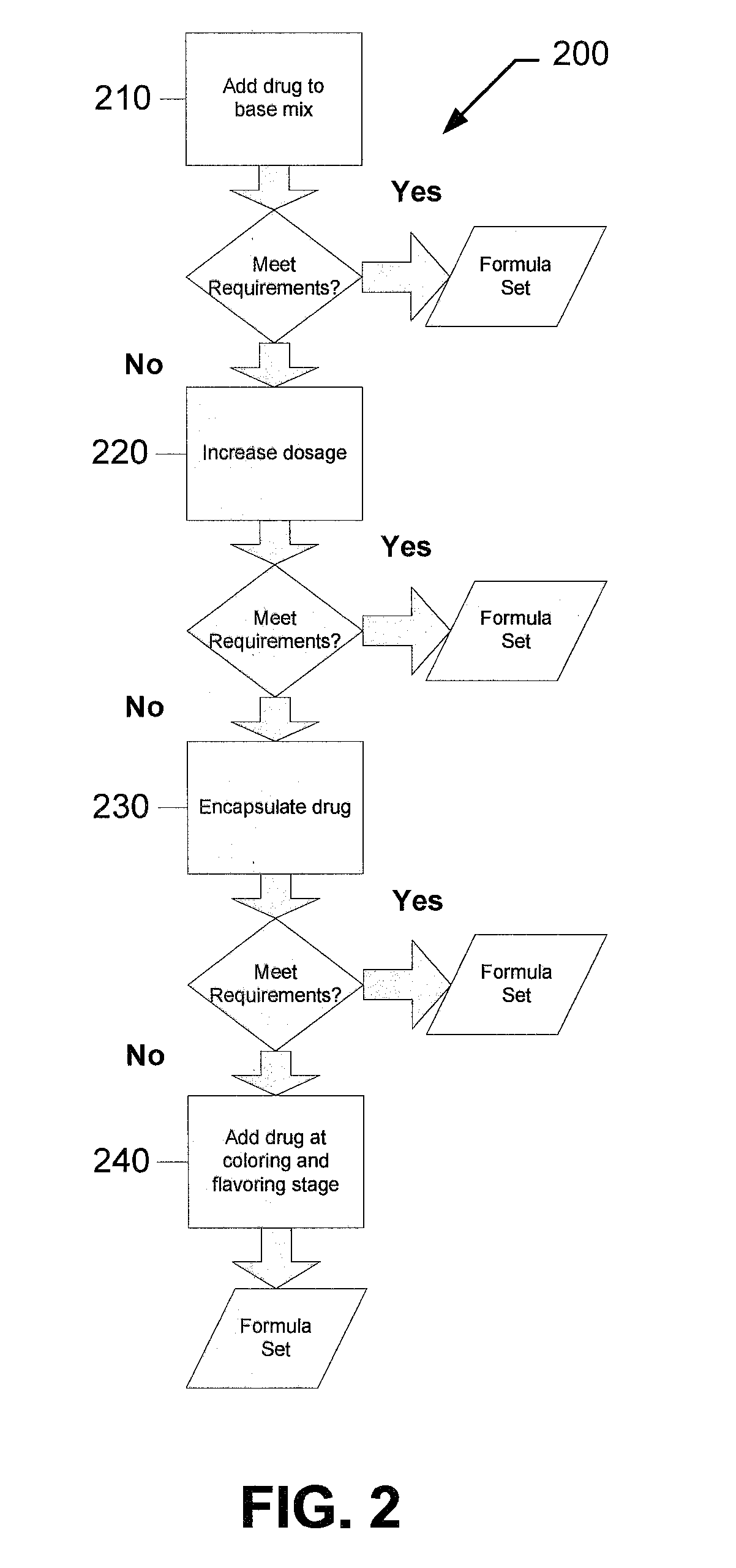
Controlled extended drug release technology
ActiveUS20060003007A1Longer resident timeEasy to controlCapsule deliveryCoatingsActive agentWater insoluble
A controlled extended drug release technology for the controlled extended release of hydrophobic or hydrophilic drugs or therapeutically active agents consisting of a homogeneous blend of one or more therapeutic agents, gas generators and surrounded by one or more layers of coat made of thermoplastic water insoluble cellulose derivatives, acrylic polymers, superdisintegrants and optionally an oil, antioxidants and electrolytes. The technology platform is capable of releasing therapeutic agents via zero, first or pseudo first order release.
Owner:INTELLIPHARMACEUTICS
High fiber high protein ready-to-eat cereal
Disclosed are cooked dried farinaceous food products such as cooked cereal doughs, ready-to-eat cereals and grain based snacks fabricated from such cooked cereal doughs containing high levels of both insoluble and soluble fiber as well as high levels of protein. The cereals contain about 5 to 15% (dry weight) insoluble fiber; 5% to 15% soluble fiber in an excess of insoluble fiber; 15% to 30% (dry weight) plant protein and the balance cereal ingredients especially rice and wheat flour. The soluble fiber is preferably provided at least in part by inulin ingredient that can be incorporated into the dough and / or topically applied.
Owner:CREIGHTON DEAN W +4
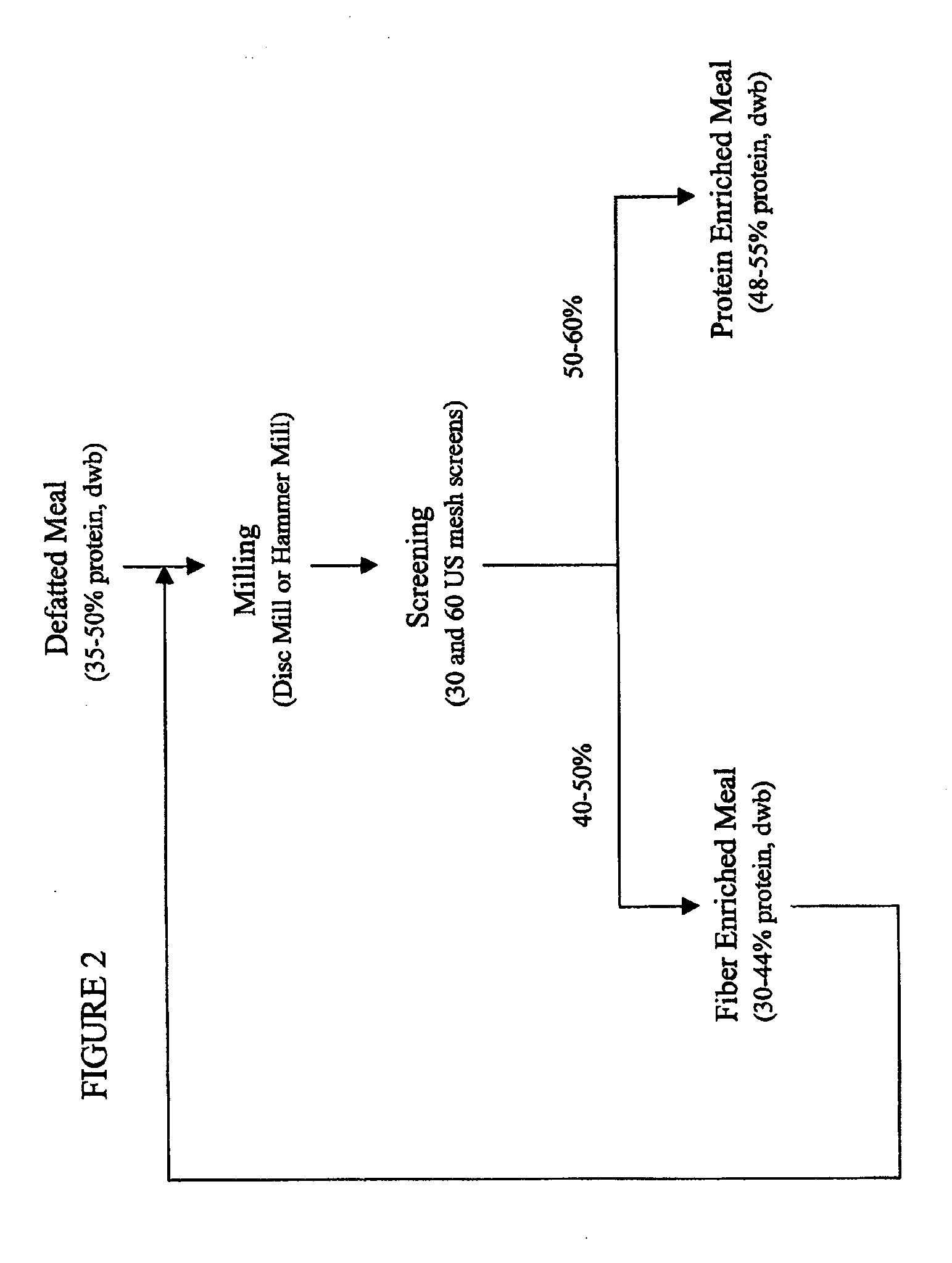
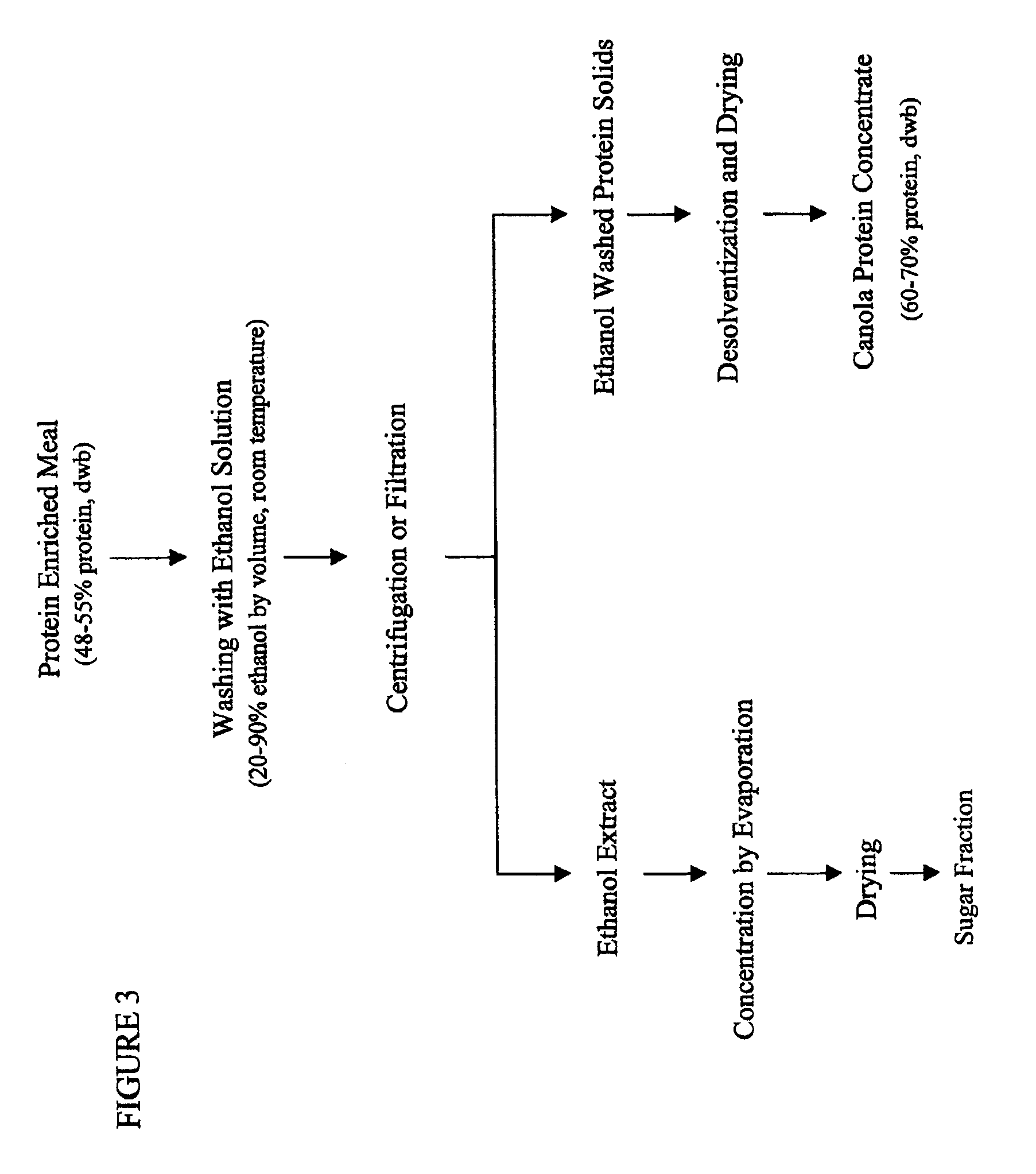
Protein concentrates and isolates, and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS20090286961A1Protein composition from vegetable seedsDepsipeptidesInsoluble proteinProtein isolate
Protein concentrates and protein isolates, in addition to processes for the production of protein concentrates and protein isolates, are disclosed. In particular, the disclosure relates to a process for removing fiber from an oilseed meal, comprising:i) mixing an oilseed meal with a blending solvent, optionally water, saline solution, polysaccharide solution or protein containing solution, to form a mixture;ii) optionally adjusting the pH of the protein slurry to a pH of about 2 to about 10; andiii) separating the mixture to form a protein slurry comprising soluble and insoluble proteins and an insoluble fiber fraction.
Owner:SIEBTE PMI VERW
Methods and related systems and formulations to normalize and improve human body chemistry and healing ability
InactiveUS20080260708A1Improve the situationImprove abilitiesBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSodium BentoniteOlive leaf
Methods, systems and formulations for normalizing and improving human body chemistry and the body's natural ability to heal itself. In one embodiment a system including effective amounts of a digestive enzyme, soluble and insoluble fiber, laxative, probiotics, vitamin C, potassium, protease enzymes, lipase, lysine, taurine, proline, choline, inositol, inositol hexaphosphate, policosanol, charcoal, bentonite clay, thyme, ascorbic acid, magnesium citrate, calcium citrate, methylsulfonyl methane, cayenne pepper, magnesium, potassium, ester-c, ginger and niacin, lysine calcium, stevia leaf, citric acid, a tincture of bayberry bark, juniper berries, yam root, cramp bark, golden seal root, fennel seed, uva ursi leaves, ginger root, lobelia herb, catnip herb, and peppermint leaf, golden seal root, Echinacea angustifolia root, ginger root, and licorice root, a tincture of black walnut hulls, venus fly trap, chaparral, wormwood, licorice root, slippery elm, cloves and comfrey root, burdock root, sheep sorrel, rhubarb root, slippery elm, olive leaf and yarrow flower is provided.
Owner:HALL MICKEY A
Method for providing nutrition to elderly patients
InactiveUSRE37020E1Improve tolerancePromote absorptionBiocideVitamin food ingredientsLarge CalorieVitamin
The present invention provides a method for providing nutrition to elderly patients. Pursuant to the present invention, the enteral composition includes a protein source, a lipid source, and a carbohydrate source. Preferably, the protein source includes at least 18% of the total calories. In an embodiment, the carbohydrate source includes a source of dietary fiber including a balance of soluble to insoluble fiber ratio of approximately 1:3. Still further, the composition of the present invention also includes increased levels of certain vitamins and minerals.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Chia seed composition
InactiveUS8652544B2Good for healthImprove regularityBiocideDough treatmentVitamin antagonistAdditive ingredient
Owner:US NUTRACEUTICALS LLC
Dental care pet food
InactiveUS6841178B2Reduce brittlenessReduce buildDigestive systemAnimal feeding stuffInsoluble fiberBrittleness
A dried pet food which is able to mechanically clean the teeth of pets when chewed. The dried pet food is based on a matrix of a denatured protein source and a gelatinized carbohydrate source. Insoluble fiber is bound within the matrix. Further, a humectant is included within the gelatinized matrix is an amount sufficient for reducing the brittleness of the dried pet food.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Preparation method for soluble dietary fiber with apple pomace as raw material
The invention discloses a preparation method for a soluble dietary fiber with apple pomace as a raw material. According to the method, an expanding method and an enzymatic hydrolysis method are combined. By the application of an expansion process, the structures of cellulose molecules become loose, and partial glycosidic bonds are broken, so that partial insoluble dietary fibers are transformed into soluble ones. After separation of the insoluble dietary fibers and the soluble dietary fibers, the expanded insoluble dietary fibers, which have the loose molecular structures, are hydrolyzed by utilizing a cellulase; and then the insoluble dietary fibers are further transformed into soluble dietary fibers. According to the invention, the modification of the insoluble dietary fibers in the apple pomace enables the insoluble dietary fibers to become high-quality soluble dietary fibers, so that an achievement rate of the soluble dietary fibers can substantially be enhanced as well as water binding capacity and expansibility of dietary fibers can also be improved. According to the test, the achieve rate of the soluble dietary fibers can reach 21.2%; the water binding capacity and expansibility can be enhanced by 110.3% and 7.0% respectively.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV
Dietary fiber food
An edible-fiber food for decreasing blood fat and cholesterol, regulating blood sugar, moistening intestine, and preventing constipation, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, diabetes, intestinal cancer and breast cancer is prepared from water-insoluble fibers (19-80 Wt%) and water-soluble fibers (20-79%).
Owner:袁维理
Food product for hairball treatment
A pet food product for hairball treatment that includes a shell component completely surrounding an inner component to form one dual textured pet food product, wherein the shell component is harder than the inner component. The shell component can include a mixture of soluble and insoluble fiber and can include at least one ingredient comprising a carbohydrate, fat, protein or combination thereof. The inner component comprises a mixture of ingredients, wherein the ingredients include a lubricant.
Owner:MARS INC
Organic chewable supplement
An organic chewable composition for delivering dietary supplements and pharmaceutical compounds. The chewable composition includes an organic delivery vehicle and an active ingredient. The delivery vehicle may include an organic gummy candy. The active ingredient may include an over-the-counter drug or a prescription drug to provide a desired effect on the user. The active ingredient may also include any combination of nutraceuticals, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, soluble and insoluble fiber, herbs, plants, amino acids, and digestive enzymes.
Owner:HERO NUTRITIONALS
Low carbohydrate fiber containing emulsion
ActiveUS20050089620A1Great tasteEdible oils/fats ingredientsEdible oils/fats with reduced calorie/fat contentEmulsionViscosity
An edible emulsion with insoluble fiber is described. The edible emulsion is suitable for use as a base for making reduced oil food products. The reduced oil food products made with the edible emulsion having insoluble fiber have consumer acceptable viscosities and texture and sensorial properties consistent with full fat food products.
Owner:UNILEVER BESTFOODS NORTH AMERICA DIV OF CONOPCO
Process for preparing feruoylated oligosaccharide by enzymolysis of wheat bran
InactiveCN1840673APromote growthProtection from oxidative stressMicroorganism based processesFermentationFood additiveTriticeae
The invention relates to a method for enzymolyzing wheat bran to prepare asafetida oligosaccharide, wherein it uses wheat bran as raw material; uses enzymatical to remove amidon, remove protein to prepare wheat bran insoluble fiber; then uses bacillus subtilis xylanase to hydrolyze wheat bran insoluble fiber to prepare the asafetida oligosaccharide. And the density of asafetida oligosaccharide will reach 1.497mmol / L. the invention can effectively utilize wheat bran, while prepared asafetida oligosaccharide has significant biological activity, to accelerate the generation of bifidobacteria, and restrain the erythrocyte oxidisability damage indused by free group, with better social and economic benefits.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Novel enzyme and preparation and use thereof
The invention provides a novel enzyme, and preparation and use thereof. In terms of 217 kcal of calories, the total content of every 100g of the novel enzyme comprises 0.6g of fat, 1.31g of protein, 0.5g of minerals, 911mg of sodium, 31.2g of oligosaccharide, 2166u of superoxide dismutase, 856mg of vitamin B, 1276mg of vitamin C, 24g of soluble fibers, and 6.7g of insoluble fibers. After the novel enzyme is absorbed by a human body, the cells can be activated rapidly, and the red blood cells can be increased rapidly; meanwhile, the novel enzyme resists bad bacteria and viruses, has the anti-aging effect and can prevent functional aging.
Owner:吴文煌
Method for preparing a fibre containing emulsion
InactiveUS20100233342A1High viscosityMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingButter manufactureEmulsionLiquid state
The present invention provides a method for preparing a fiber-in-water slurry containing insoluble fibres, wherein said method comprises the steps of (a1) preparing a fiber-in-water slurry containing the insoluble fibres, (a2) freezing said slurry and (a3) grinding said frozen slurry.The present invention also provides a method for preparing an edible emulsion comprising oil, water and insoluble fibers, said method comprising the steps of (a) raising the temperature of the fiber-in-water slurry obtained in above step (a3) until said slurry is in the liquid state; (b) adding any further ingredients of the edible emulsion; and (c) homogenizing the thus-obtained mixture.It was found that by applying this method a low-oil edible emulsion can be prepared which emulsion has reduced insoluble fiber content but favorable texture and sensorial properties.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
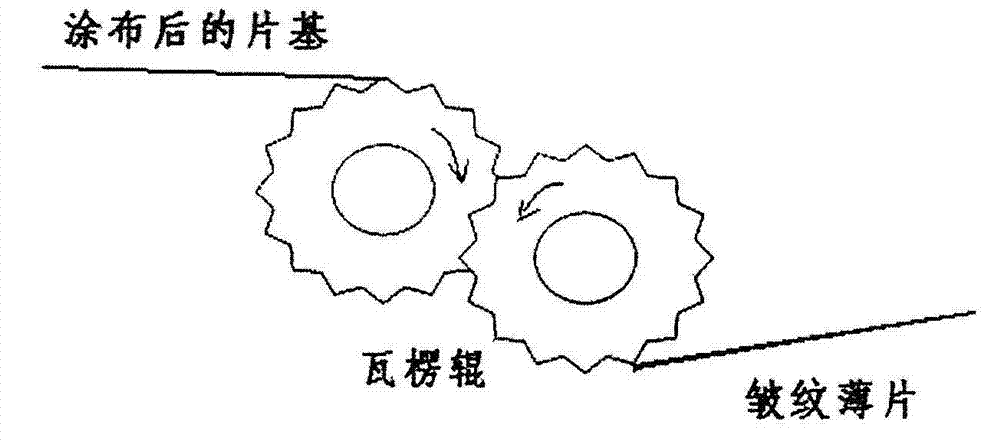
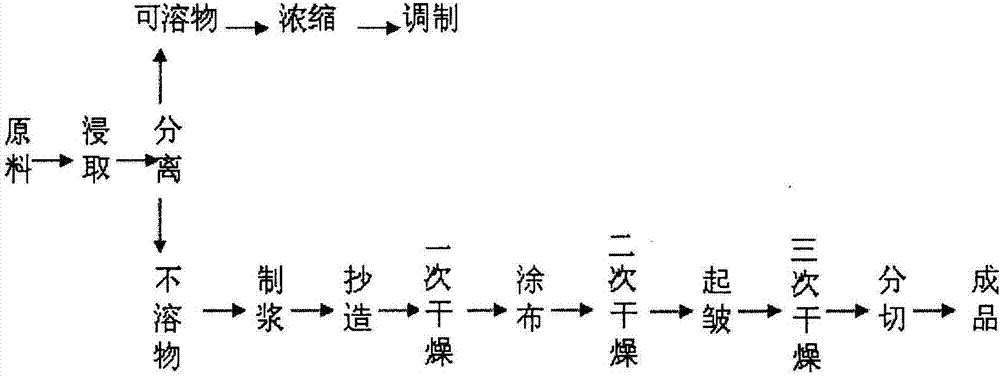
Manufacturing technique of tobacco remaking with fold paper-making method
InactiveCN103082396AEasy to fillGood size controllabilityTobacco preparationCombustionInsoluble fiber
The invention provides a manufacturing technique of tobacco remaking with a fold paper-making method. The manufacturing technique of tobacco remaking with the fold paper-making method comprises the following steps: raw materials of tobacco are soaked and extracted through extraction agent, insolubility fiber materials are separated from soluble substances, film base is made of insoluble substances through pulping, coating liquid is made of the soluble substances by concentration in a modulation mode, and the coating liquid is dip-coated or spray-coated on a slice film base, and enters a drying machine to dry. The manufacturing technique of tobacco remaking with the fold paper-making method is characterized in that slice film base after being dried is made to be diamond-shaped through a pair of corrugated rollers reversely rotating, and is made into a fold tobacco slice after being dried and cut. The manufacturing technique of tobacco remaking with the fold paper-making method is not limited by drying modes, is simple in manufacturing technique, and capable of being widely applied to the production of tobacco remaking with the fold paper-making method, and facilitates improving padding performance of remade tobacco, and reducing consumption of raw materials and production cost. According to measurement and calculation, compared with the prior ordinary tobacco remaking, the manufacturing technique of tobacco remaking with the fold paper-making method can save the consumption of the raw materials by 1.0% or so, improve combustion performance of cigarettes, reduce suction resistance and improve suction quality of the cigarettes.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Low carbohydrate fiber containing emulsion
InactiveUS20070172572A1Great tasteEdible oils/fats ingredientsEdible oils/fats with reduced calorie/fat contentInsoluble fiberEmulsion
An edible emulsion with insoluble fiber is described. The edible emulsion is suitable for use as a base for making reduced oil food products. The reduced oil food products made with the edible emulsion having insoluble fiber and diary ingredients have consumer acceptable viscosities and texture and sensorial properties consistent with full fat food products.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Preparation method of plant-enzyme-containing drink capable of improving respiratory system
The invention relates to a preparation method of a plant-enzyme-containing drink capable of improving a respiratory system. The preparation method comprises the steps of adding water to soak and boil out malt, folium mori, fig, buckwheat, platycodon grandiflorum, rhizoma phragmitis, liqorice, dried tangerine peel, poria cocos, lily, almond and purple perilla, carrying out low-temperature vacuum decompression concentration on decoction, blending black sugar and peptone with the decoction, and disinfecting and filtering the mixture to obtain filtrate, namely a nutrition solution; and inoculating probiotics to the nutrition solution at 30 DEG C in a fermentation tank, mixing and fermenting by four stages, and performing quality detection to obtain the drink. By taking various plants as a nutrition solution culture medium and various composite probiotics as a conversion tool and adopting multistage deep liquefied fermentation, toxic and harmful substances in the raw materials can be degraded to form new active ingredients, nutrient elements in the materials can be released, effective ingredients, such as saccharifying enzyme and protease, can be produced in a fermentation process, original active ingredients can be retained, phytic acid is changed into functional lactic acid and acetic acid, and insoluble fiber is changed into soluble dietary fiber, so that the self immunocompetence of a human body can be effectively improved, and the diseases of the respiratory system can be relieved and prevented.
Owner:湖北源馥泰生物科技有限公司
Bacterial cellulose-containing formulations
ActiveUS8053216B2Promote activationImprove efficiencyNatural cellulose pulp/paperStarch adhesivesAlcoholHigh energy
A new method to produce formulations of bacterial cellulose that exhibit improved viscosity-modifying properties particularly with low energy applied to effectuate viscosity changes therewith is provided. Such a method includes the novel co-precipitation with a water soluble co-agent that permits precipitation in the presence of excess alcohol to form an insoluble fiber that can than be utilized as a thickener or suspension aid without the need to introduce high energy mixing. Such bacterial cellulose properties have been available in the past but only through highly labor and energy intensive processes. Such an inventive method as now proposed thus provides a bacterial cellulose-containing formulation that exhibits not only properties that are as effective as those for previous bacterial celluloses, but, in some ways, improvements to such previous types. Certain end-use compositions and applications including these novel bacterial cellulose-containing formulations are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Methods and compositions for improving gastrointetinal health
ActiveUS20110034411A1Improve Gut HealthImprove stool qualityBiocideDigestive systemFecesSoluble fiber
Methods for maintaining or improving the gastrointestinal health of animals susceptible to or suffering from poor gastrointestinal health by administering to the animal a gastrointestinal health maintaining or improving amount of a food composition comprising from about 1 to about 20% carbohydrate; from about 3 to about 10% total dietary fiber, wherein the total dietary fiber contains from about 10 to about 40% soluble fiber and from about 90 to about 60% insoluble fiber; and from about 0.1 to about 10% omega-3 fatty acids; wherein the composition has a digestibility coefficient of at least 80. Generally, the compositions are administered to the animal to prevent or treat diarrhea or to improve stool quality. Further, the compositions may be administered in conjunction with one or more probiotics, prebiotics, anti-gastritis drugs, anti-enteritis drugs, or anti-diarrhea drugs, microbial exopolysaccharides, or combinations thereof to maintain or improve gastrointestinal health.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Grain product with increased soluble fiber content and associated methods
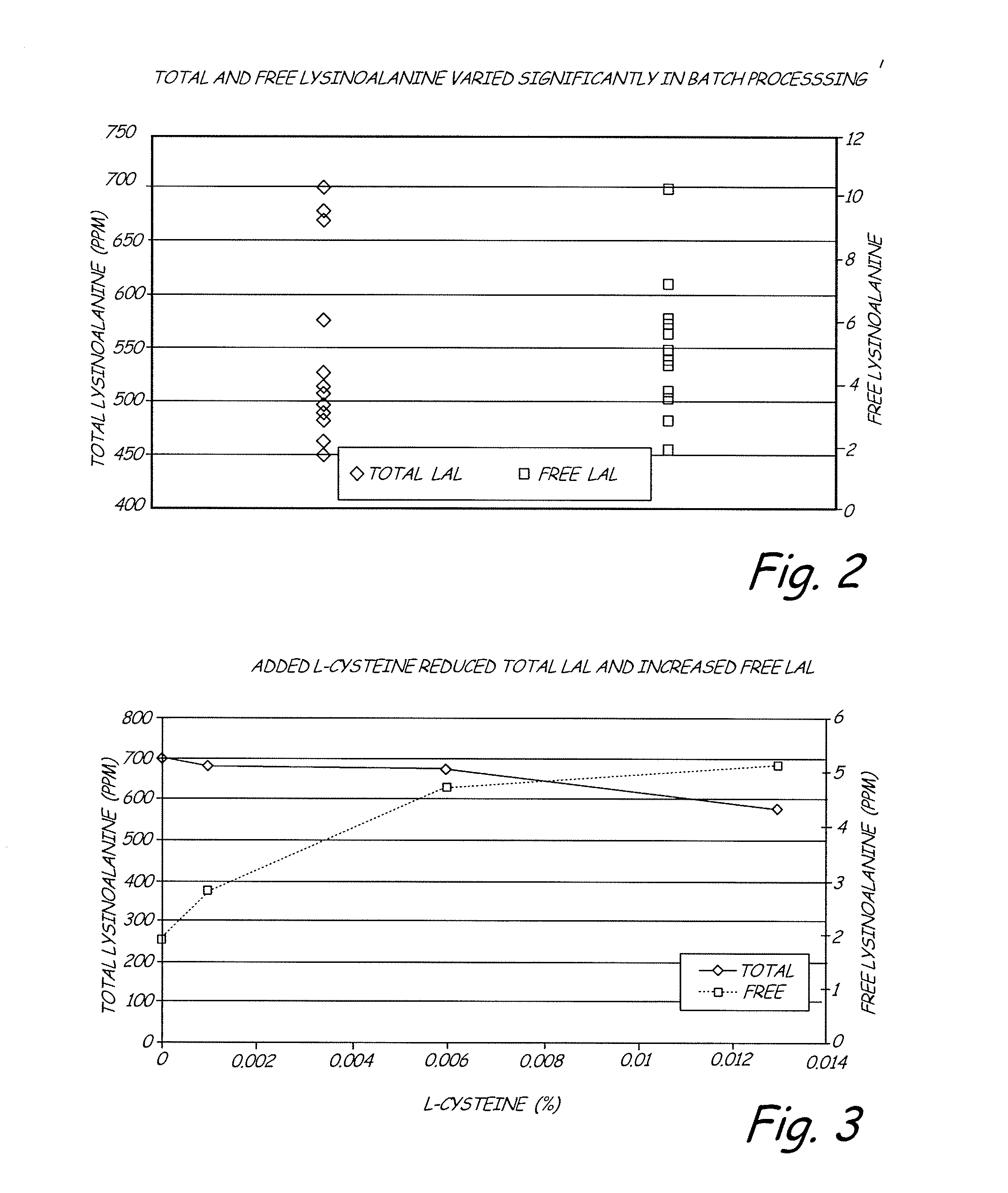
An improved method for hydrolysis of a grain product results in an increase soluble fiber content without producing undesirable levels of by-products associated protein hydrolysis. The method comprises mixing at high shear a mixture with a grain product having dietary fiber, a base and water at a pH from about 10 to about 13. A homogenous mixture is formed that hydrolyzes following heating with respect to the insoluble fiber. As described herein, a grain product can comprise at least about 30% dietary fiber comprising polysaccharides with arabinoxylan linkages, having at least about 8% soluble fiber, a ratio of soluble fiber to insoluble fiber of at least about 0.1 and no more than about 500 ppm total lysinoalanine. Similarly, some food compositions can comprise at least about 15% soluble fiber with polysaccharides having arabinoxylan linkages, from about 35% to about 65% water, a pH from about 10 to about 13.
Owner:GEN MILLS IP HLDG II
Process for creating a thermo-irreversible konjac gel food
InactiveUS20070065558A1Improves konjac gel food textureImprove textureFood preparationSoluble fiberNetwork structure
The present invention is a process for creating a konjac glucomannan based food product. More specifically, the method for transforming konjac glucomannan solutions into heat-stable gels requires the use of heat and a high pH to deacetylate the konjac glucomannan molecule. A minimum concentration of 1.5-2% konjac glucomannan is necessary to adjust the system to a pH of approximately 9.0. When the solution is heated to 85° C. with a mild alkali condition (pH 9-10) it forms a gel which is unaffected by heat. Thus, the gel remains stable when additional heat is applied and remains unchanged under repeated heating at 100° C. or even at 200° C. Alternatively, the addition of an alkali, like Ca(OH)2 in a konjac glucomannan solution removes its acetyl group forming a stable network structure to form the gel structure. By mixing the konjac glucomannan soluble fiber, with any kind of insoluble fibers and alkalis together, a pure fiber konjac gel food can be made by simply pouring the complex powder into water applying heat. The traditional konjac gel foods texture is hard, chewy and rubbery, the new gel foods in which the insoluble fiber is added improves the texture of the gel foods.
Owner:DING YAPING
Dual-textured snack with fiber blend
InactiveUS20160286826A1Increase moisture contentDough treatmentBakery productsSoluble fiberRelative humidity
A dual-textured foodstuff comprising a total fiber content of about 2.5 g to about 5.0 g of fiber; a baked dough-based component including a dough-based component fiber blend with soluble fiber and insoluble fiber in a ratio of about 9:1 to about 0.43:1; about 40 wt % to about 60 wt % of the total fiber content; and a crispy texture throughout the shelf life of the foodstuff; along with a baked filling component present in an amount of about 35 wt % to about 60 wt % of the foodstuff, the baked filling component being in direct contact with the baked dough-based component, and having a soft texture throughout the shelf life of the foodstuff; a relative humidity of about 0.6 to about 0.8.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS LLC
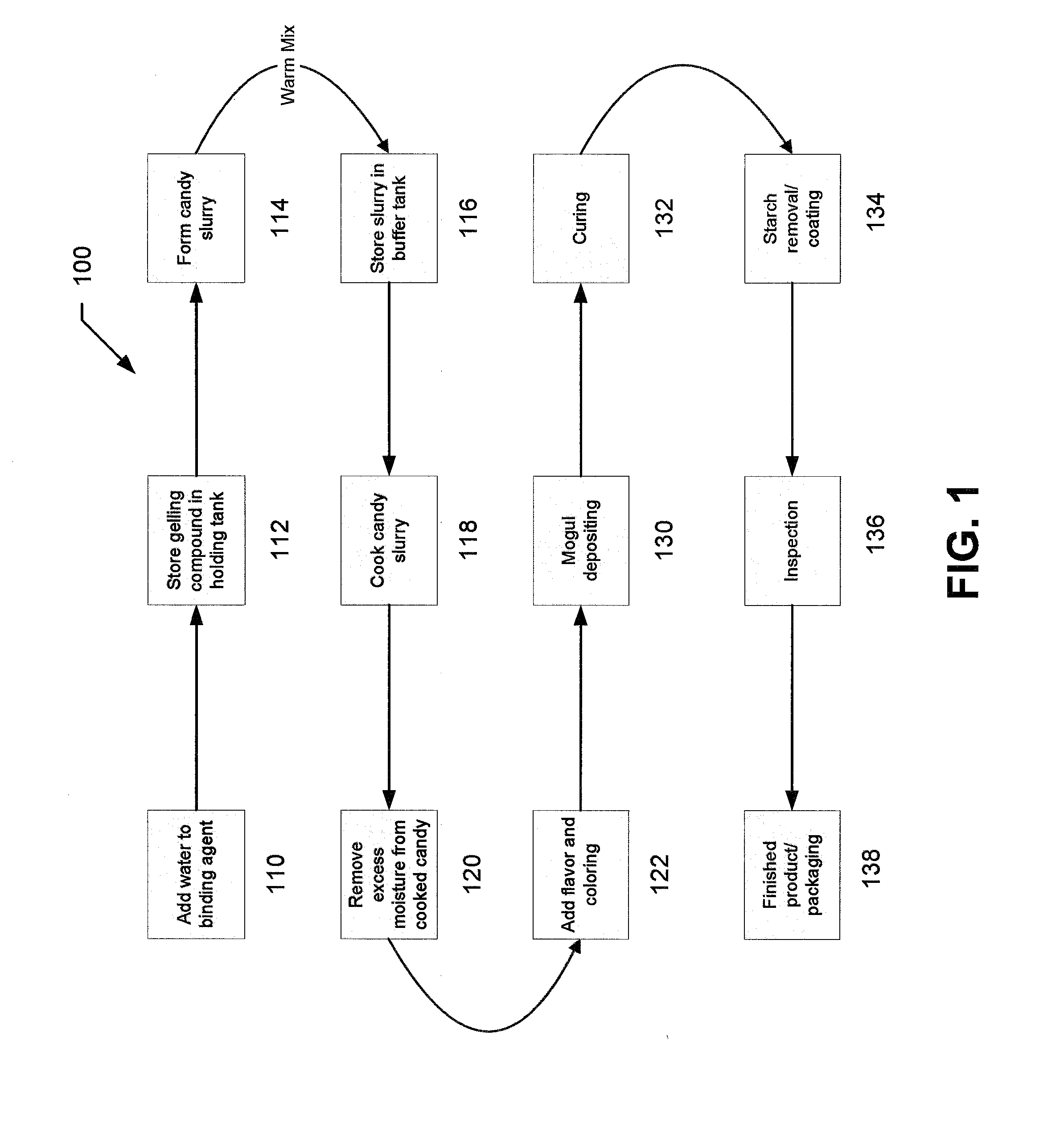
Chewable supplement with live microorganisms
A chewable composition for the oral delivery of live microorganisms is provided. The chewable composition includes a delivery vehicle and an active ingredient incorporated therein. The delivery vehicle may include an organic or non-organic gummy candy including a binding agent, sweetener, flavoring, and / or coloring. The active ingredient may include a predetermined amount of at least one probiotic. The delivery vehicle may also include a predetermined amount of at least one prebiotic. The delivery vehicle may also include any combination of nutraceuticals, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, soluble and insoluble fiber, herbs, plants, probiotics, prebiotics, antioxidants, amino acids, fatty acids, digestive enzymes, dietary supplements, or any other health promoting ingredient.
Owner:HERO NUTRITIONALS
Liquid-filled chewable supplement
A liquid-filled chewable composition for the oral delivery of nutritional supplements and / or pharmaceuticals is provided. The chewable composition includes a delivery vehicle and an active ingredient incorporated therein. The delivery vehicle may include an organic or non-organic gummy candy including a binding agent, sweetener, flavoring, and / or coloring. The active ingredient may include a predetermined amount of any combination of pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, soluble and insoluble fiber, herbs, plants, probiotics, prebiotics, antioxidants, amino acids, fatty acids, digestive enzymes, dietary supplements, or any other health promoting ingredient. The delivery vehicle may also include a predetermined amount of at least one nutritional supplement and / or pharmaceutical compound.
Owner:HERO NUTRITIONALS
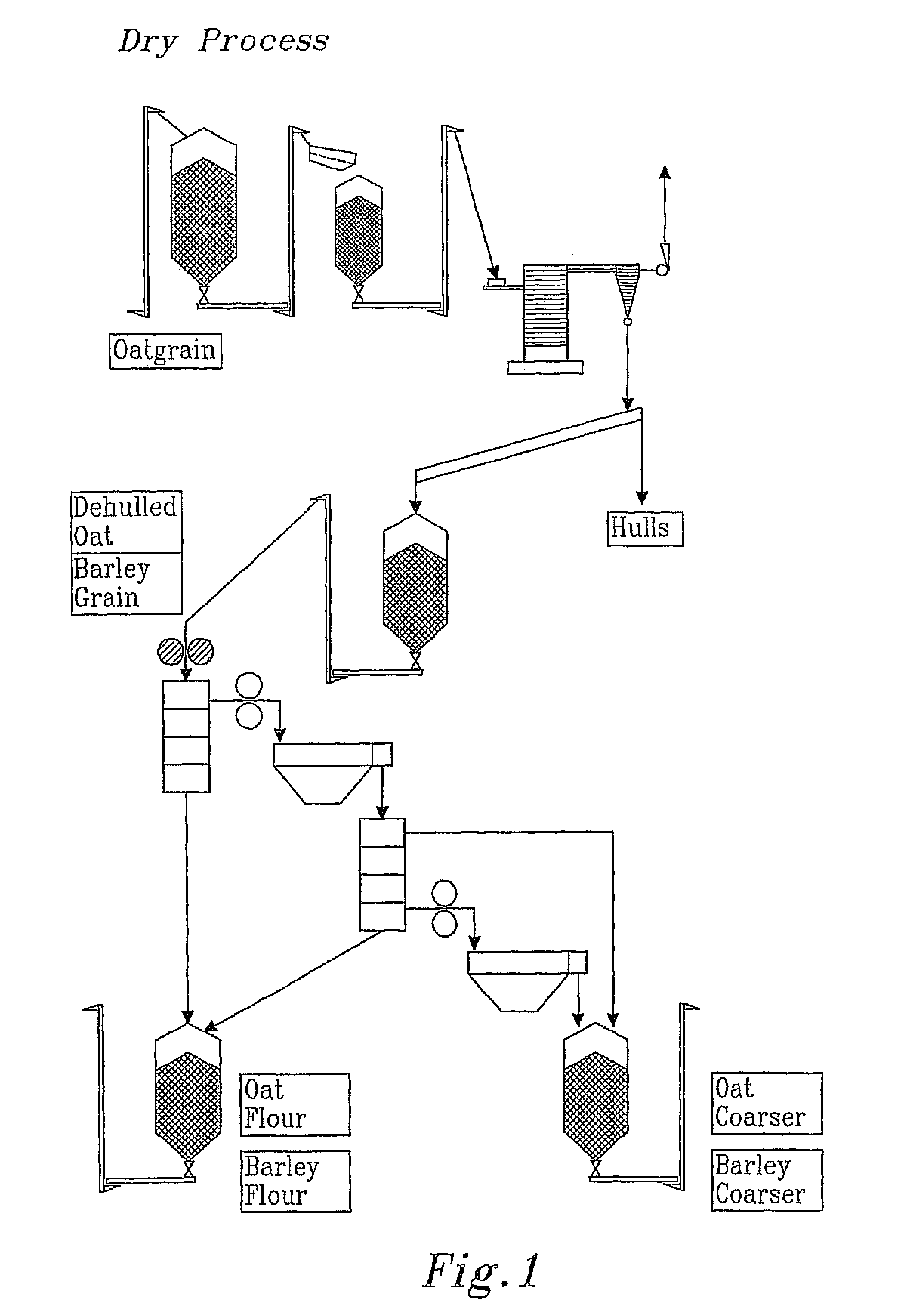
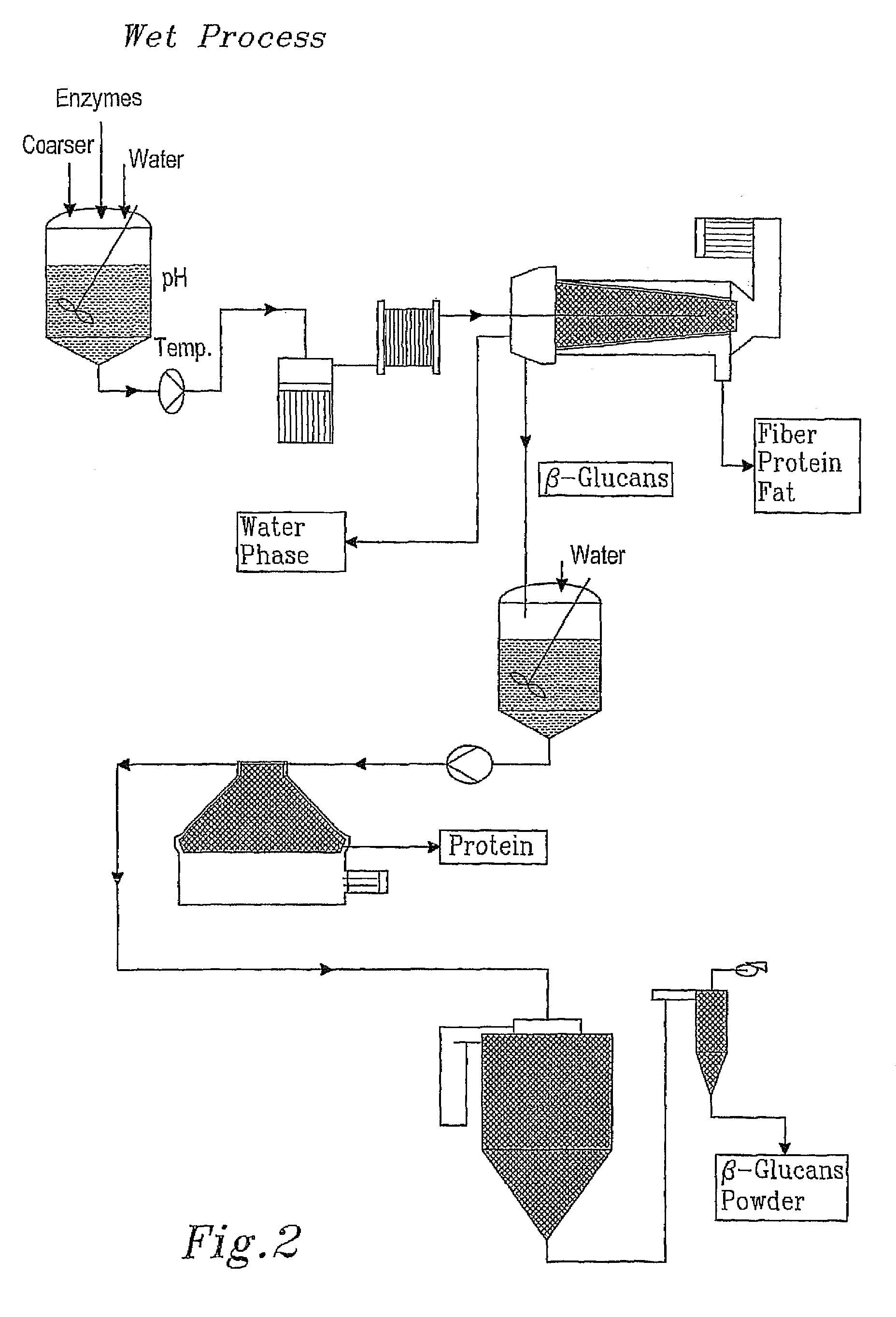
Soluble dietary fibre from oat and barley grains, method for producing a fraction rich in B-glucan and use of the fraction in foods, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics
InactiveUS7910143B2Industrial processSmall molecular weightCosmetic preparationsDough treatmentHydrolysateHordeum vulgare
The present invention relates to a process for the extraction of soluble dietary fiber from oat and barley grains using enzymatic hydrolysis treatment, wherein the grain is milled and any endosperm depleted fractions thereof being rich in B-glucans are recombined, without further heat treatment, dispersed in water and then subjected to sequential enzymatic treatment with starch degrading enzymes, followed by an optional step of enzyme inactivation by wet heat treatment, and a subsequent step wherein the hydrolysate mixture is spontaneously or centrifugally separated into at least 3 distinct fractions: a first fraction, which comprises the soluble dietary fiber complex, containing more than 20% B-glucan on a dry matter basis, a second aqueous fraction, and a third fraction comprising most of the protein and oil together with the insoluble fibrous material from the milled grain.
Owner:LANTMANNEN OATS AB +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com