Patents
Literature
72 results about "Propionine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
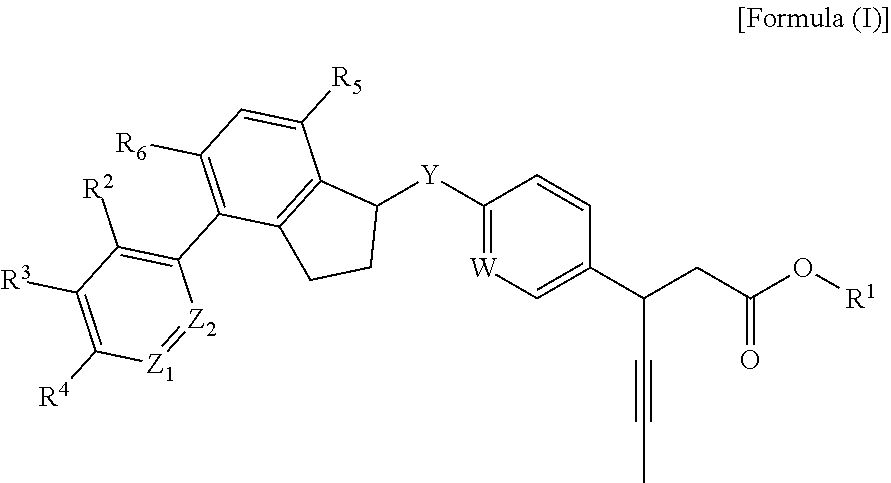
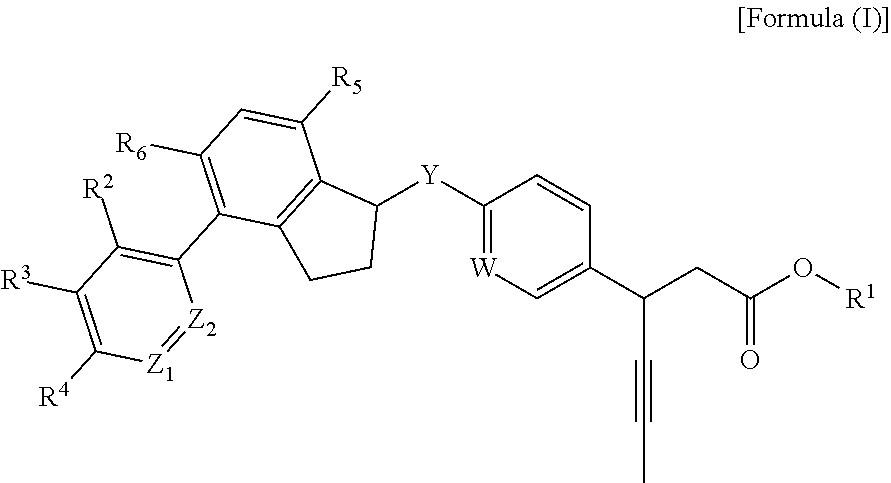
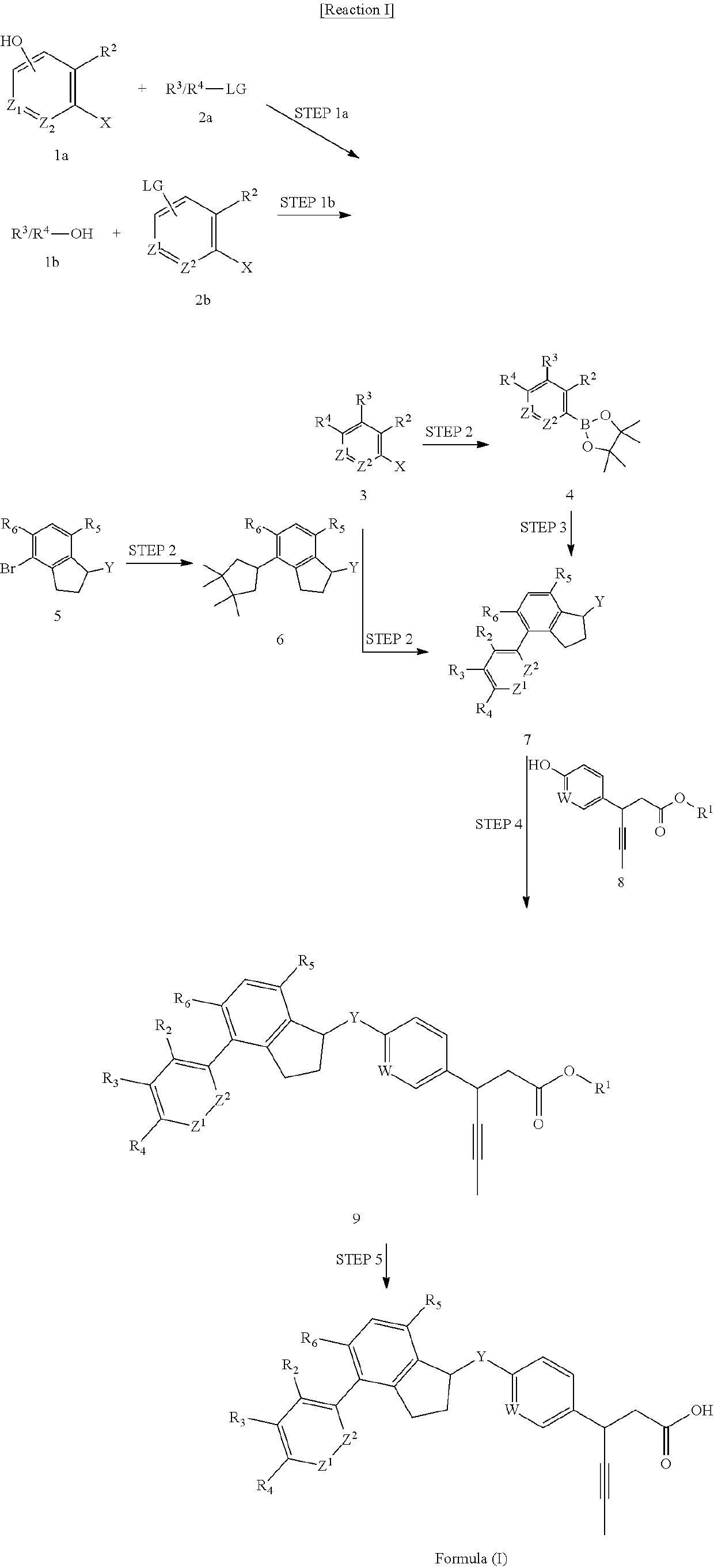
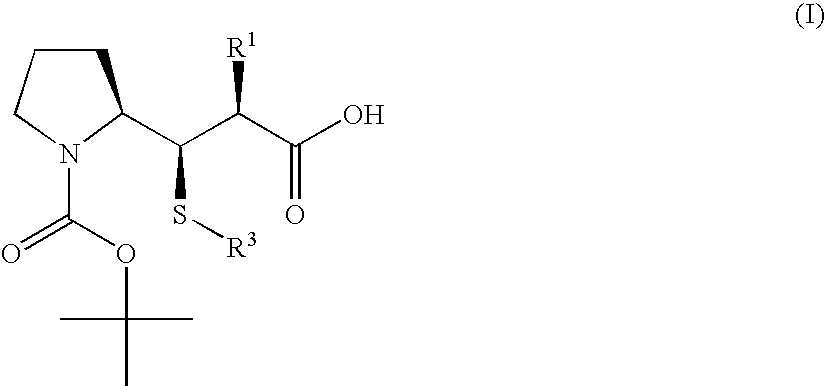
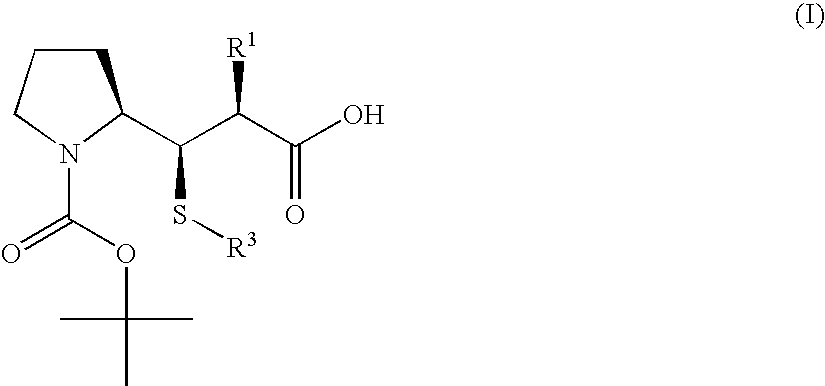
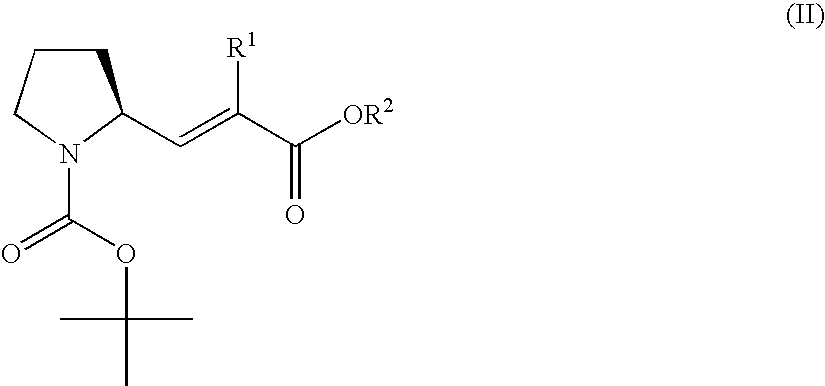
3-Pyrrolidin-2-yl-propionic acid derivatives
The present invention relates to the manufacture of the compounds of formula (I) said compounds of formula (I) being valuable intermediates in the manufacture of Dolastatin 10 analogues, which are useful in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
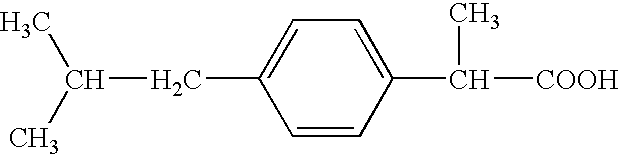
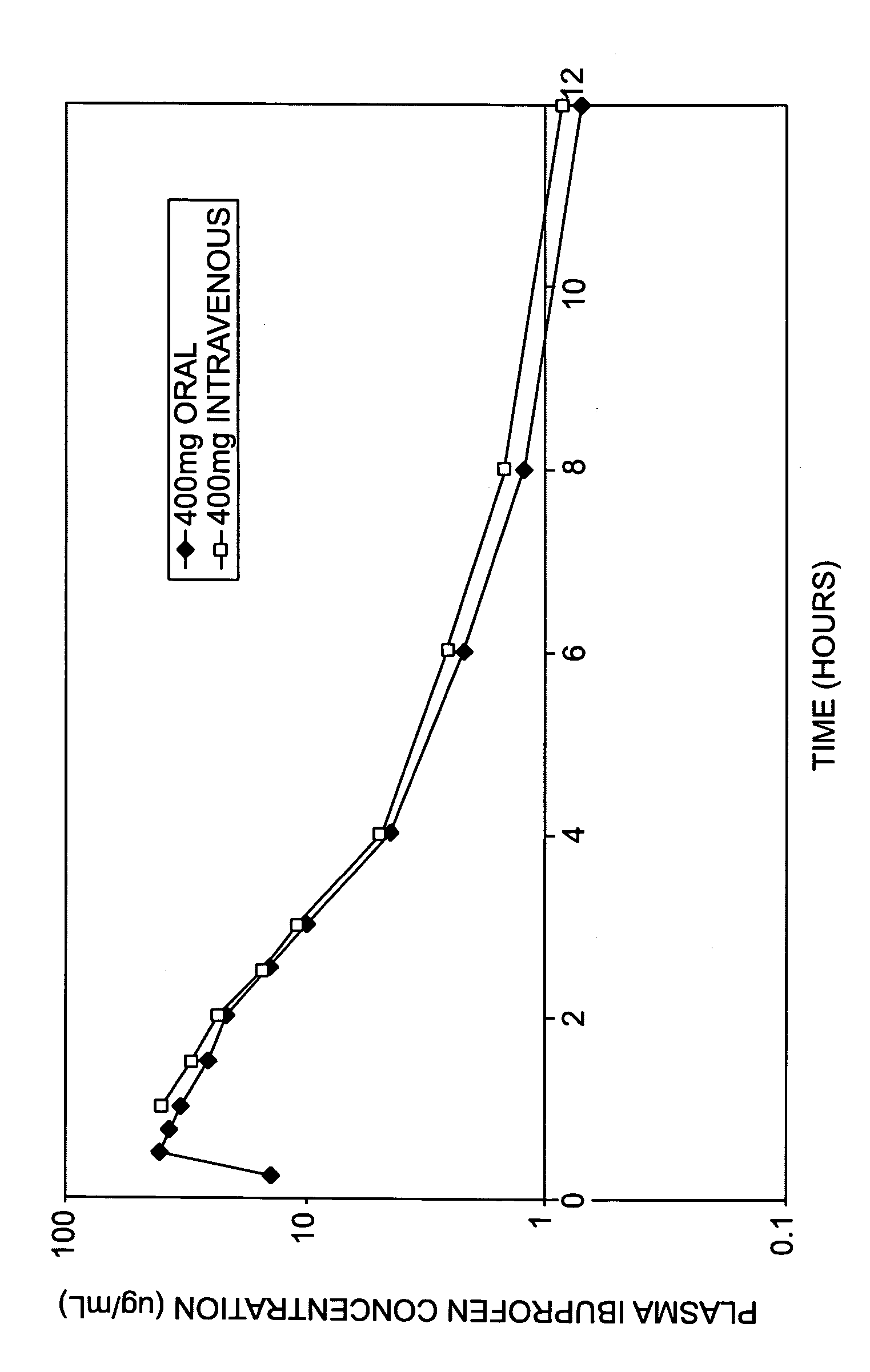
Pharmaceutical composition of 2-(4-isobutylphenyl) propionic acid
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising an aqueous solution of arginine and ibuprofen, wherein the molar ratio of arginine to ibuprofen is less than 1:1, as well as a method of making the same. The present invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising an aqueous solution of arginine and ibuprofen, wherein the solution has a pH of less than about 7.8, as well as a method of making the same. The present invention also provides a method of treating a condition chosen from pain, inflammation, fever, and / or other conditions alleviated by ibuprofen comprising administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising an aqueous solution of arginine and ibuprofen, wherein the molar ratio of arginine to ibuprofen is less than 1:1, and wherein the molar ratio of arginine to ibuprofen is selected to achieve a pH of less than about 7.8.
Owner:CUMBERLAND PHARM INC
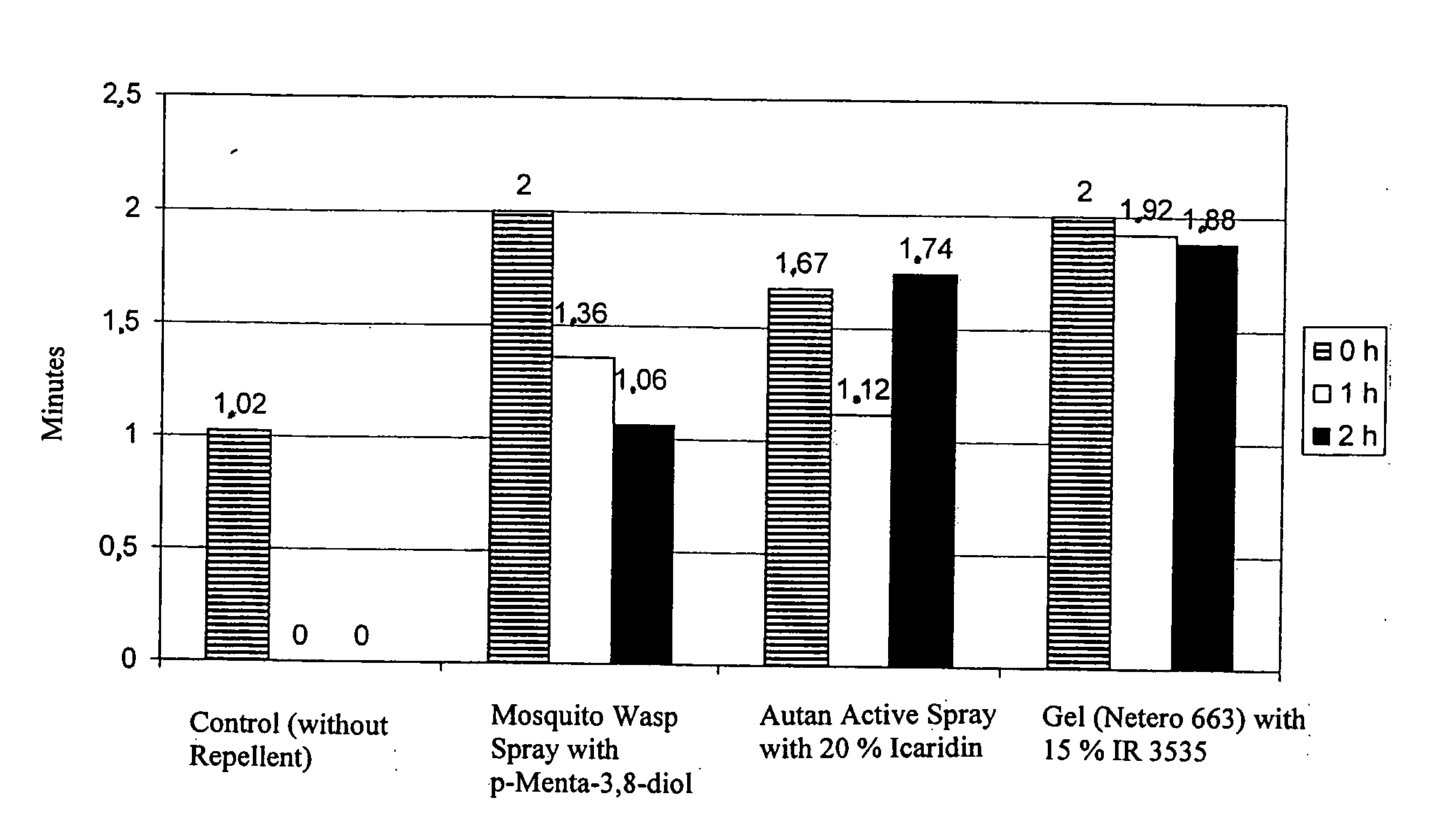
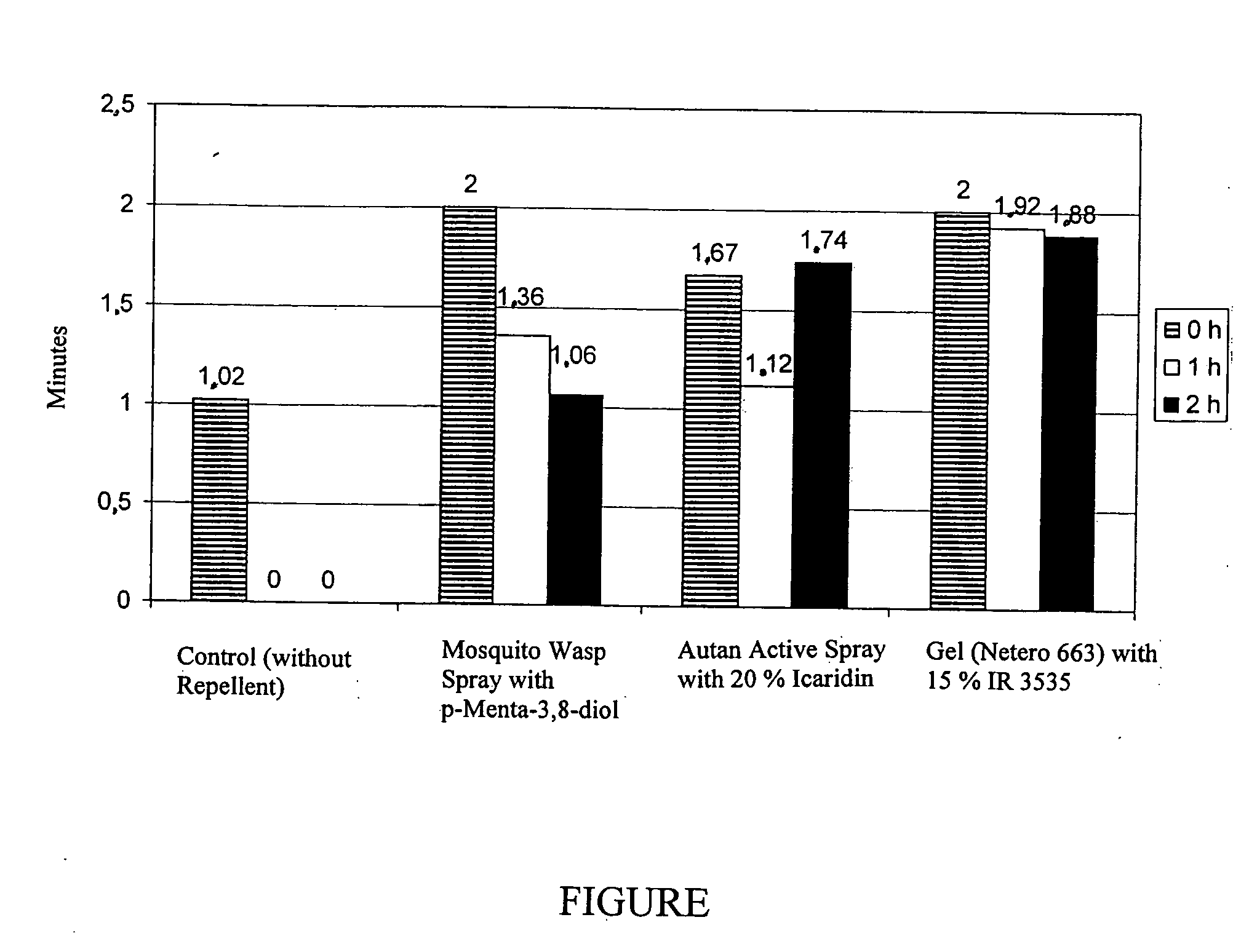
Wasp repellents
A method of repelling wasps, which method comprises using a preparation comprising (a) one or more of ethyl 3-(N-n-butyl-N-acetylamino)propionate, dihydronepetalactone, and extract of catmint, and (b) at least one compound selected from certain perfume ingredients. This abstract is neither intended to define the invention disclosed in this specification nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:BEIERSDORF AG
Novel 2-(2-fluorine-4biphenyl)-propionic acid pharmaceutical composition
ActiveCN103301101AReduce gastrointestinal adverse reactionsIndustrial applicabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderArgininePropionine
The invention provides a novel 2-(2-fluorine-4biphenyl)-propionic acid pharmaceutical composition. Flurbiprofen and basic amino acid arginine or lysine form a pharmaceutical composition solution. The composition can be administrated in an injection or oral administration manner and can also be further administrated in a freeze-drying manner. Compared with a flurbiprofen axetil injection, a flurbiprofen composition not only does not influence the antipyretic, anti-inflammation and analgestic effects of the flurbiprofen, but also has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, high quality, stable long shelf life and convenience in quality control, storage and transportation; moreover, compared with a conventional oral preparation, the flurbiprofen composition has the same low gastrointestinal tract adverse reaction as the flurbiprofen axetil injection.
Owner:南京星福星医药科技有限公司
Method for Diagnosing Propionibacterium Bacterial Infections
InactiveUS20130123132A1Efficient detectionPeptide librariesLibrary screeningMicrobiologyPropionibacterium acnes
The invention concerns an in vitro method for determining if an individual is infected by a bacterium of the Propionibacterium genus comprising: (i) detecting antibodies directed against at least one protein of sequence SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO: 6 or SEQ ID NO: 8, in a biological sample of the individual, and (ii) deducing therefrom that the individual is infected by a bacterium of the Propionibacterium genus. The invention further concerns the kit for diagnosing of such an infection.
Owner:DIAXONHIT
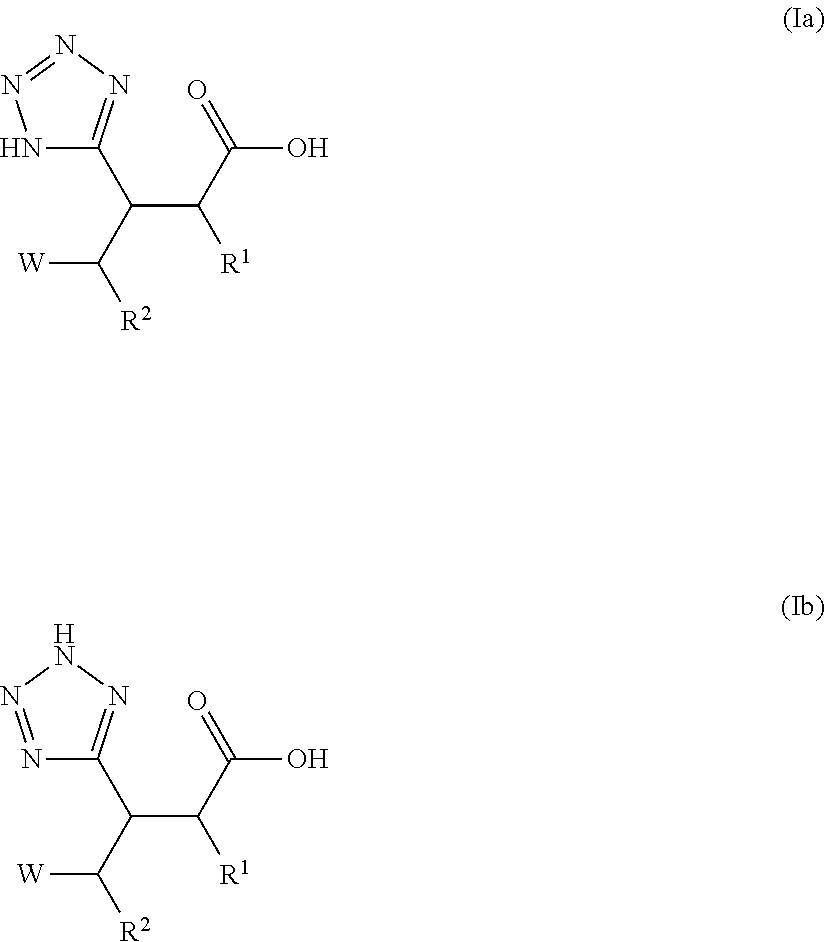
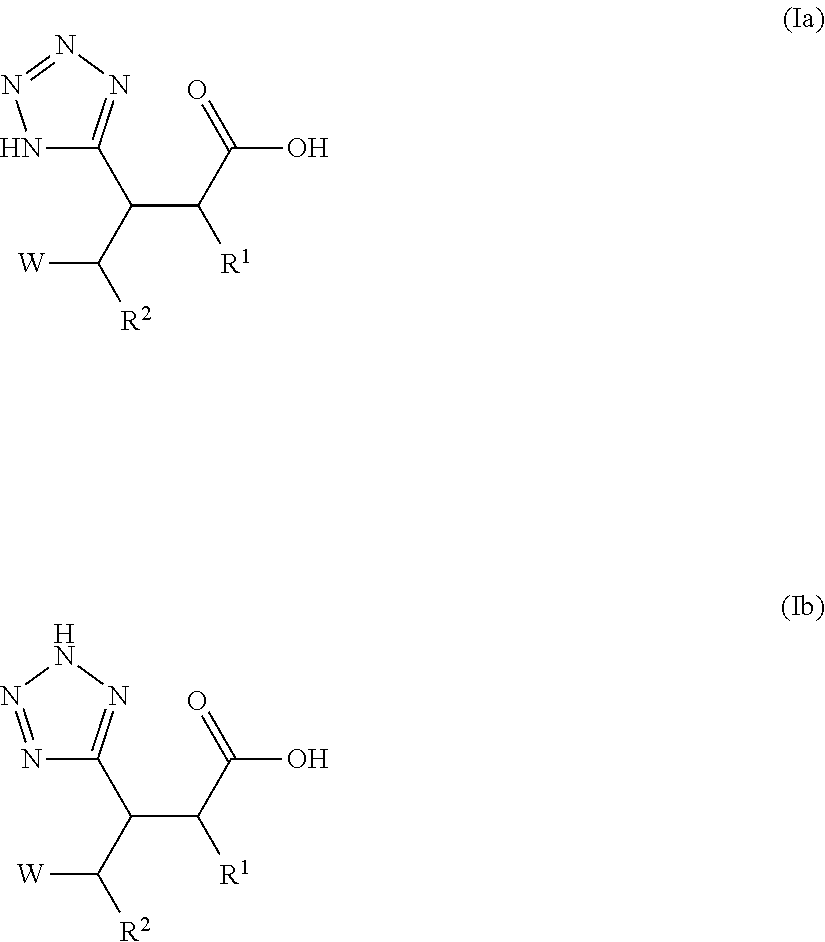
Beta-tetrazolyl-propionic acids as metallo-beta-lactamase inhibitors
ActiveUS20170173035A1Synergize antibacterial effectPrevent bacterial growthOrganic chemistryIn-vivo testing preparationsTetrazoleBiochemistry
The present invention relates to compounds of formula I that are metallo-β-lactamase inhibitors, the synthesis of such compounds, and the use of such compounds for use with β-lactam antibiotics for overcoming resistance.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
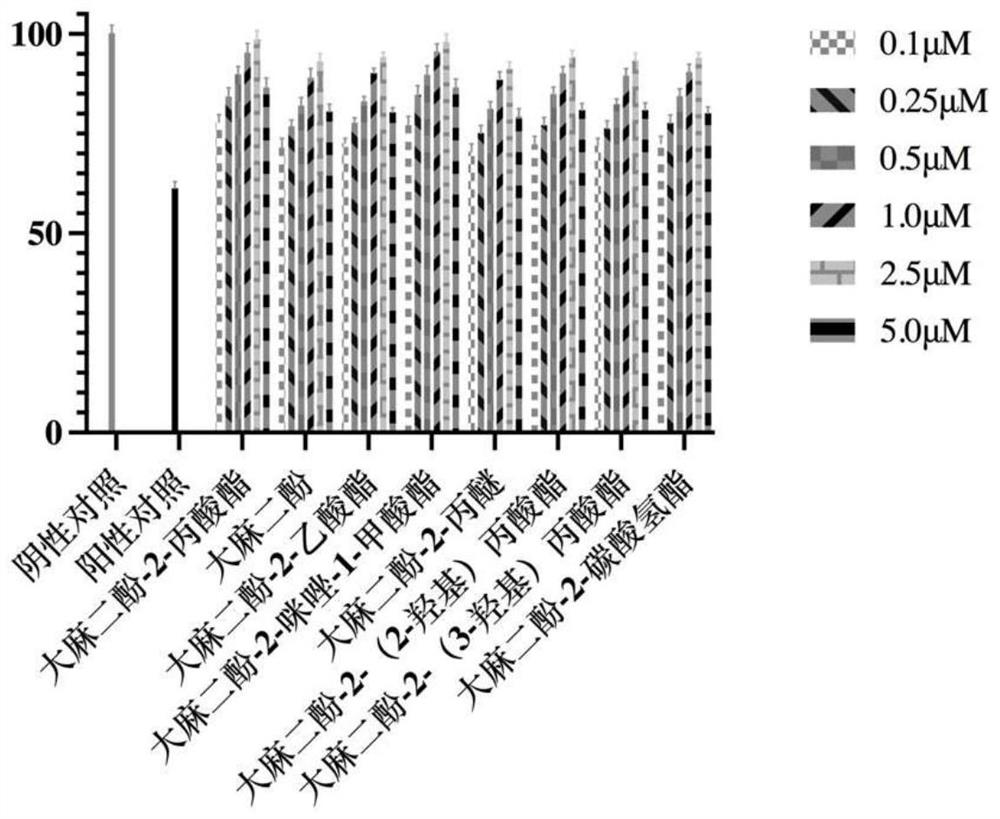
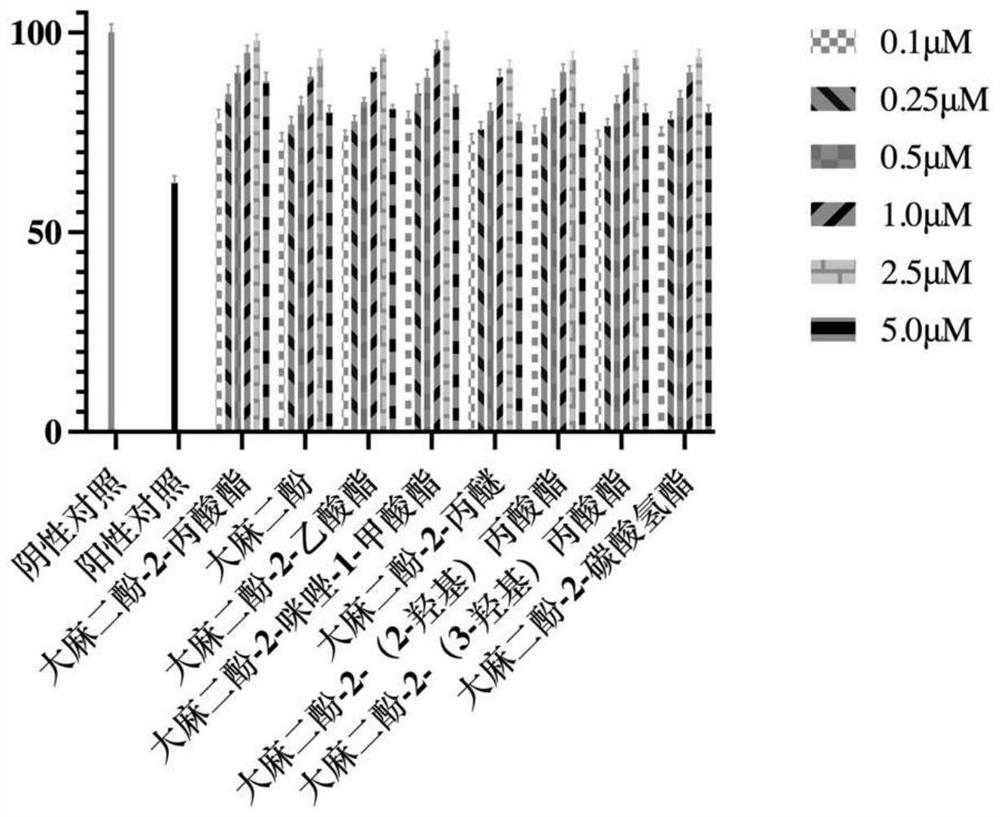
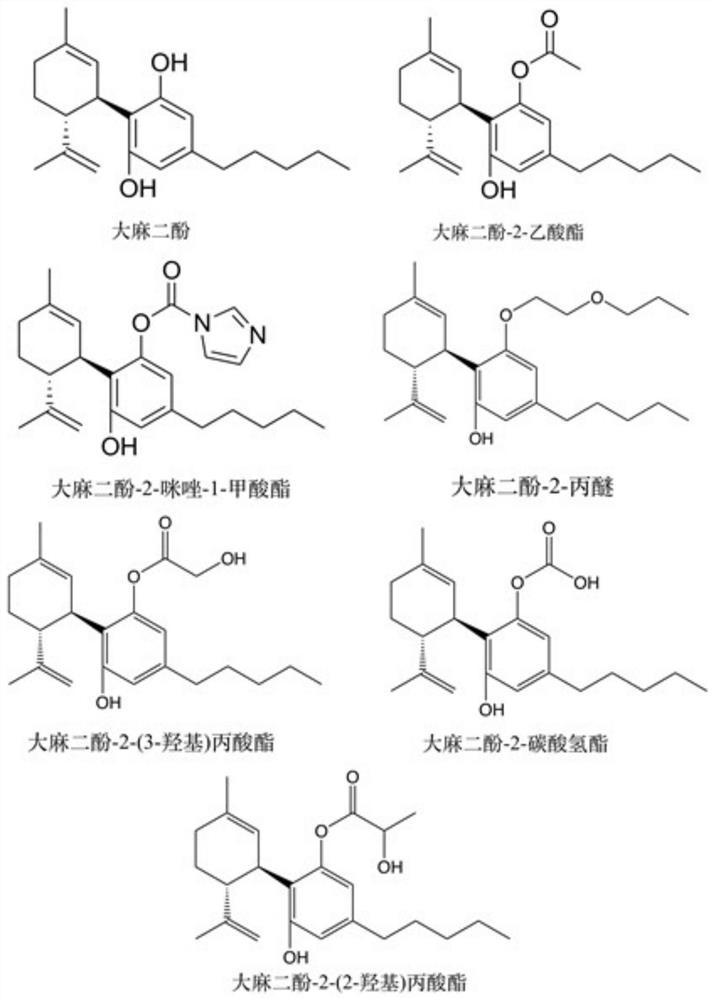
Cannabidiol 2-propionate and application thereof
ActiveCN113666824AInduce apoptosisProtectiveOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsPropionatePharmaceutical medicine
The invention discloses cannabidiol 2-propionate and application thereof, and particularly relates to a compound shown in the formula I and a stereoisomer or pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the compound. The cannabidiol 2-propionate has a protection effect on nerve cell injury and skin cell injury, can induce apoptosis of human breast cancer cells, and has practical application value in medicine and cosmetic production.
Owner:黑龙江丰佑麻类种植有限公司
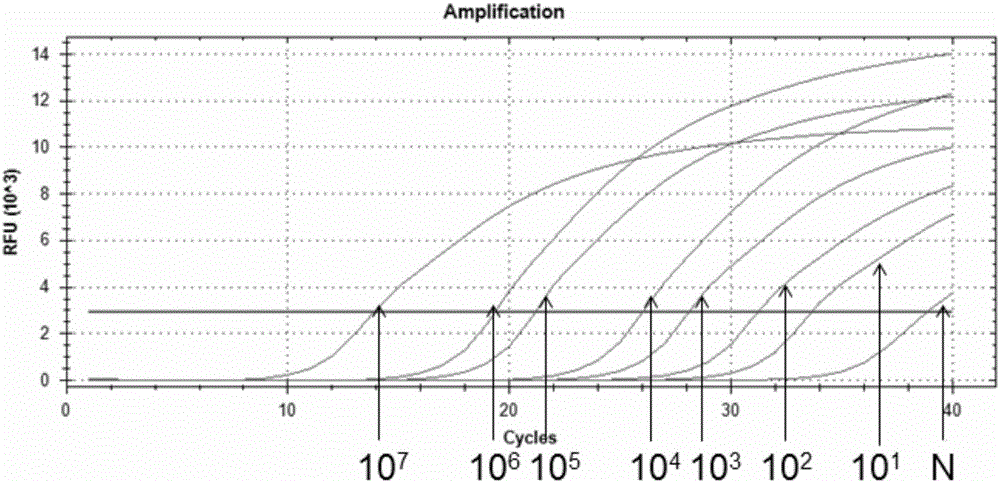
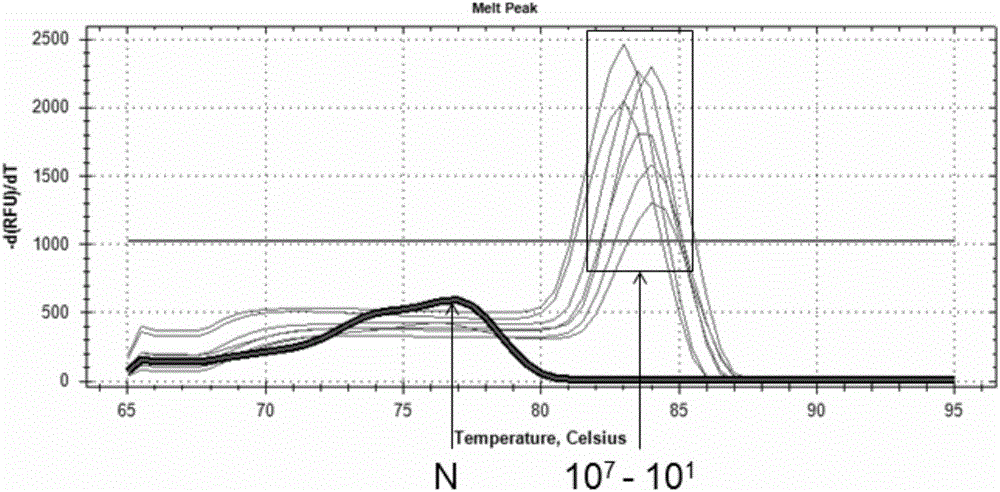
Special primers for identification or assisted identification of Propionibacterium acnes, and applications thereof
InactiveCN106167820AThe spectrum is clearAccelerateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSpecies identificationBiology
The present invention relates to the field of biotechnology, particularly to special primers for identification or assisted identification of Propionibacterium acnes, and applications thereof, wherein the primers are a primer pair formed by combining any two sequences selected from sequences represented in SEQ ID NO:1-6. According to the present invention, the special primers provide great significance for the species identification of the Propionibacterium acnes and the prevention and control of facial diseases caused by the Propionibacterium acnes infection.
Owner:沈阳中科赛尔生物科技有限公司
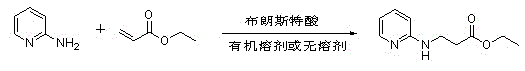
Preparation method of 3-(2-pyridine amino) ethyl propionate
The invention discloses a preparation method of 3-(2-pyridine amino) ethyl propionate. The preparation method comprises that 2-aminopyridine and ethyl acrylate serve as raw materials, in inorganic solvent or organic solvent, Bronsted acid serves as a catalyst, the temperature is controlled between 80 DEG C and 120 DEG C through oil bath heating so that a catalytic reaction is conducted, vacuum concentration is conducted to the obtained reaction liquid under the temperature between 40 DEG C and 45 DEG C and the pressure is between 0.09MPa and 0.1MPa, chromatography is conducted to concentrated solution by silicagel columns or sesquioxide uranium aluminum posts so as to obtain the 3-(2-pyridine amino) ethyl propionate. The preparation method of the 3-(2-pyridine amino) ethyl propionate has the advantages of being simple in preparation method, convenient to operate, low in production cost and short in reaction time, the product yield of the obtained 3-(2-pyridine amino) ethyl propionate reaches between 50% and 76%.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Beta-tetrazolyl-propionic acids as metallo-beta-lactamase inhibitors
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Method for purifying propionibacterium strain plasmid
ActiveCN102321617AHigh purityIncrease concentrationDNA preparationTerra firmaPropionibacterium acnes
The invention discloses a method for purifying propionibacterium strain plasmid. By performing pretreatment and subsequent treatment on thallus, high-purity plasmid can be obtained from a propionibacterium strain. Compared with the conventional method, the method has the advantages of greatly improving the concentration and the purity of the plasmid. The method lays a solid foundation for research in the aspect of molecular operation of propionibacterium and possibly has universal application significance to other gram-positive bacteria (such as lactic acid bacteria).
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
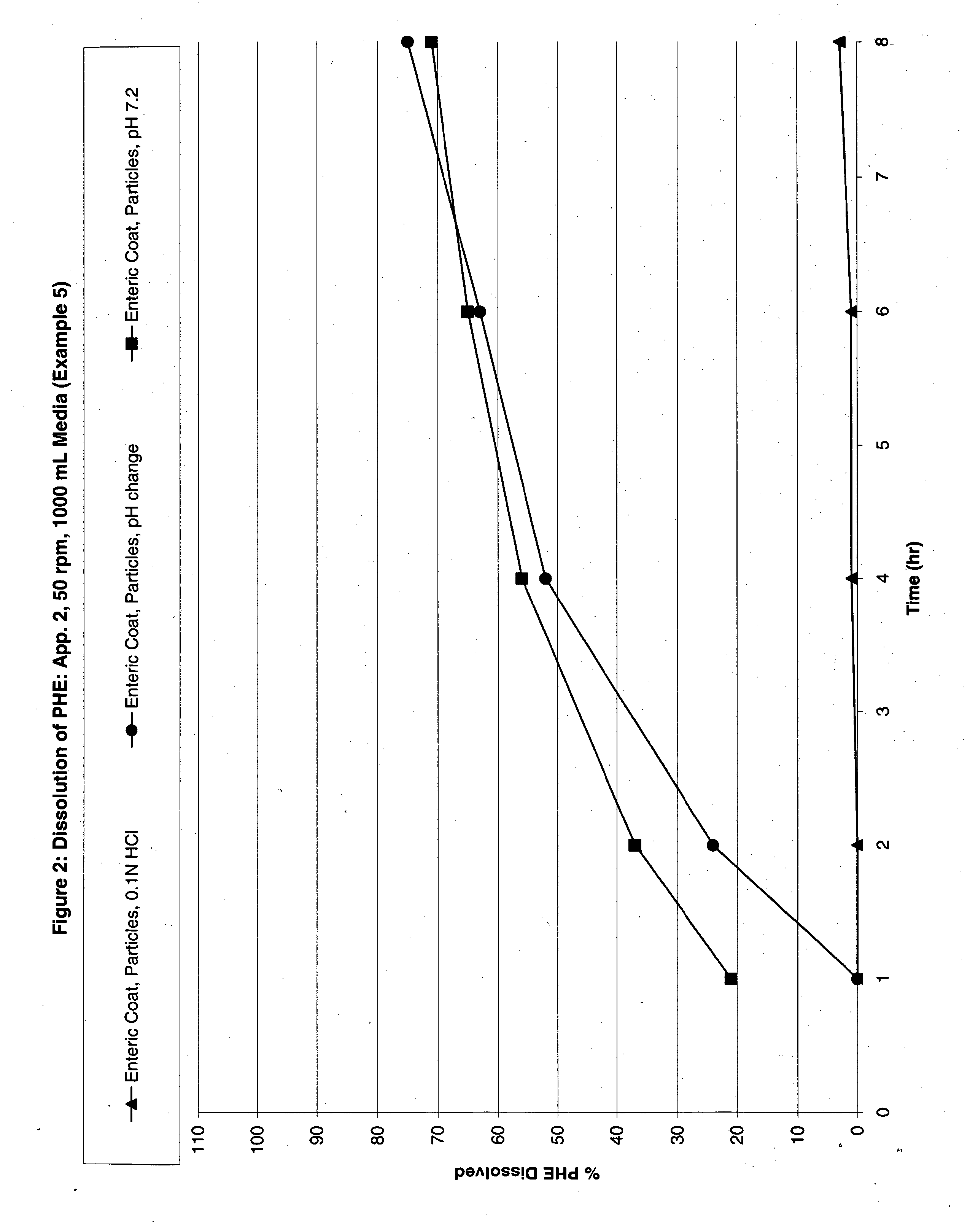
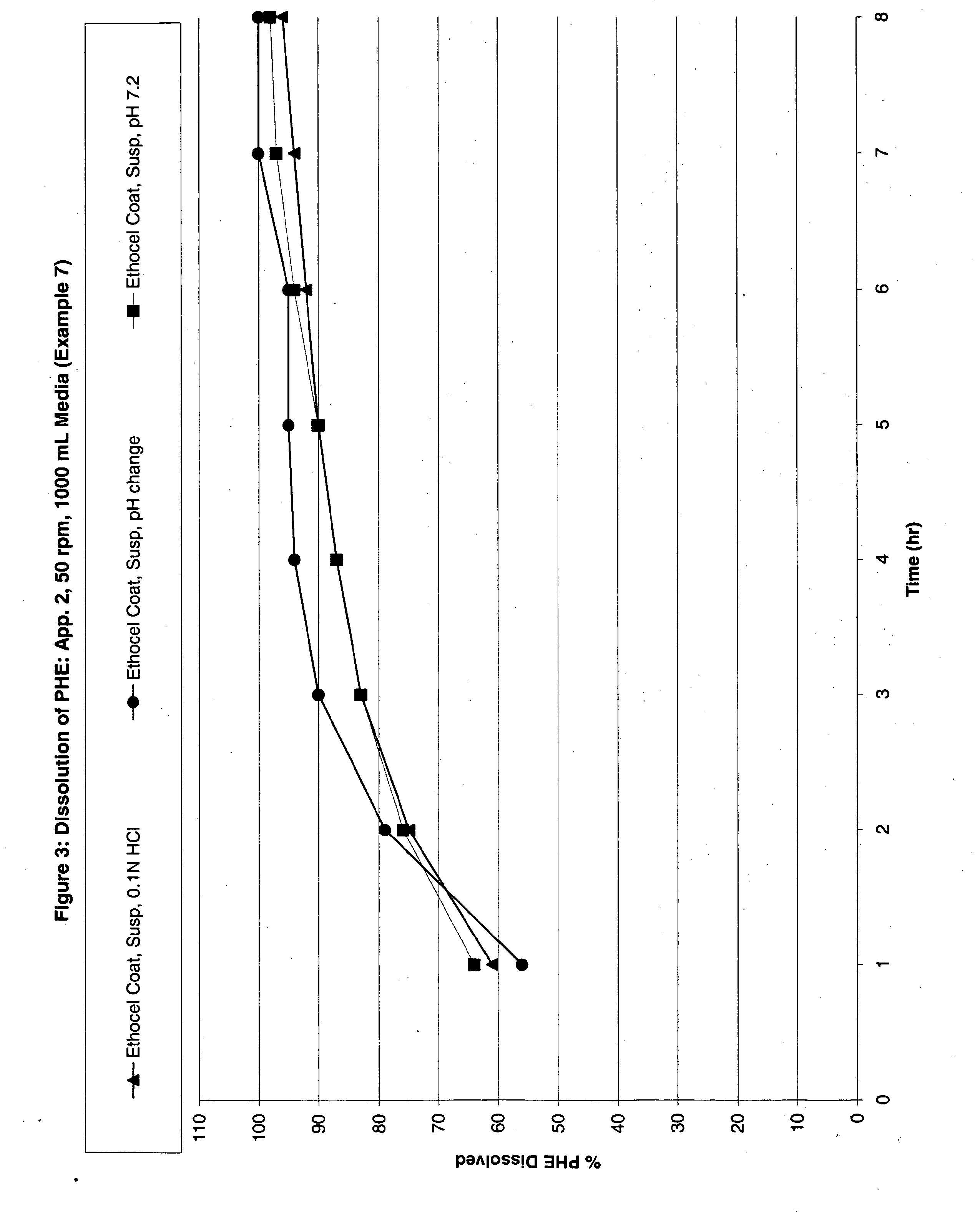
Modified Release Analgesic Suspensions
ActiveUS20130142846A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderNon steroid anti inflammatory drugAntiinflammatory drug
A pharmaceutical dosage form comprising non-steroidal-anti-inflammatory drugs, in particular propionic acid derivatives such as ibuprofen, along with a second active ingredient having a shorter therapeutically effective plasma concentration duration, such as phenylephrine, and methods of administering the same are provided. This method provides improved therapeutic effect, in particular pain relief along with decongestant relief, over extended time periods.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
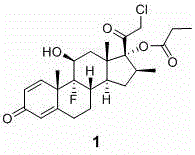
One-pot preparation method of clobetasol propionate intermediate
The invention discloses an improved production technology of a clobetasol propionate intermediate (betamethasone-17-propionate). Two steps namely cyclo-esterification and hydrolysis in the conventional technology are merged into one step. By merging the steps, the procedure and production period are shortened, the product purity and yield are increased, the energy consumption is reduced, the raw materials and auxiliary materials are saved; the environment pollution is reduced, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG TAIHUA BIO & TECH
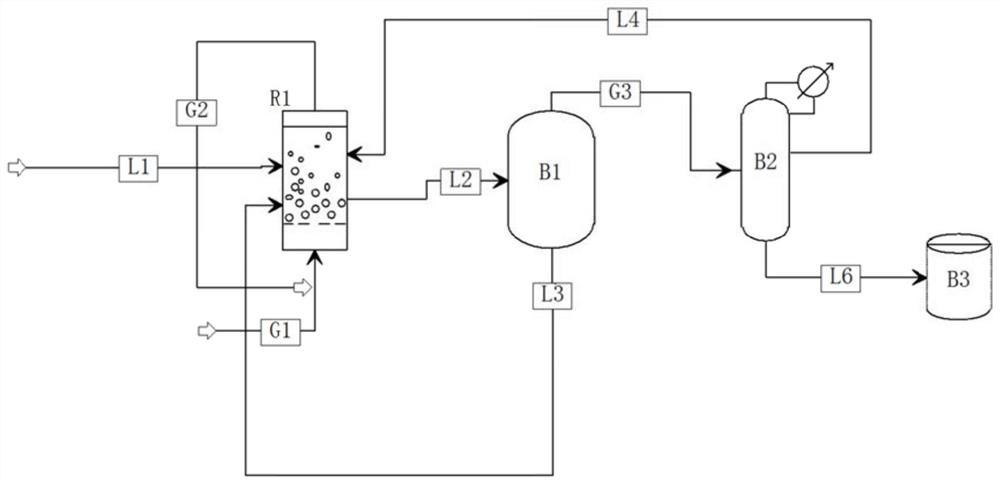
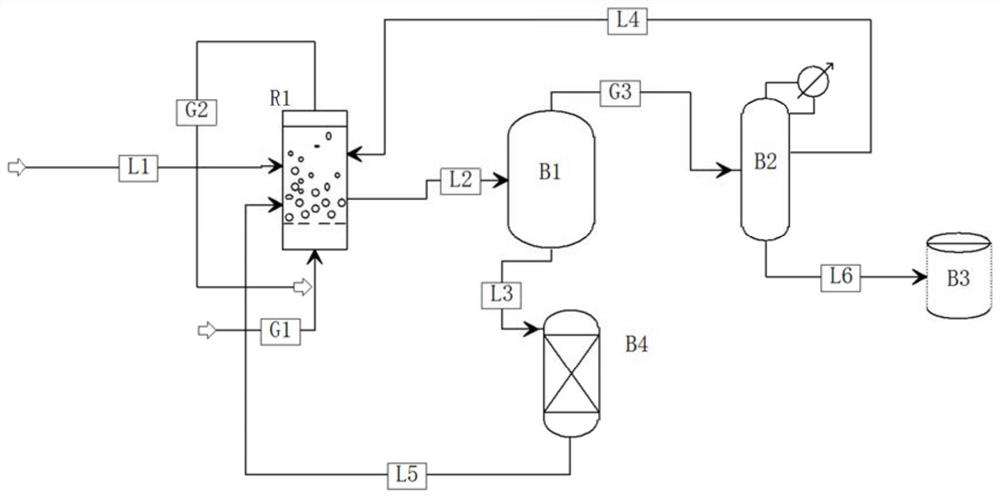
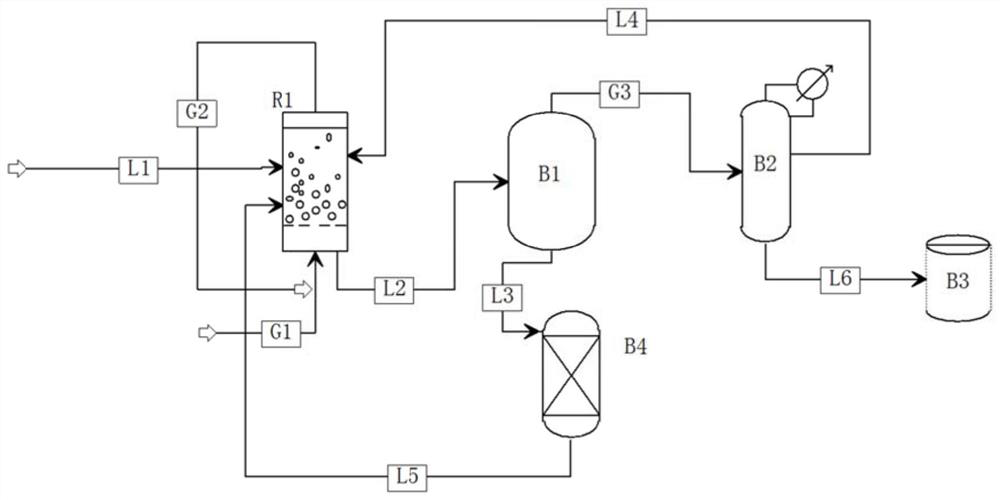
System for preparing propionate through ethylene carbonylation
PendingCN114409541AFully contactedIncrease reaction rateLiquid-gas reaction as foam/aerosol/bubblesOrganic compound preparationPropionatePtru catalyst
The invention relates to a system for preparing propionate through ethylene carbonylation. The system comprises a separating and refining unit and a bubbling reactor (R1) coupled with the separating and refining unit, a gas-phase reaction raw material (G1) and a liquid-phase reaction raw material (L1) for preparing the propionate product (L6) are subjected to a carbonylation reaction in a bubbling reactor (R1), and a generated propionate-containing material (L2) is separated and purified by a separating and refining unit to prepare the propionate product (L6). Compared with the prior art, through the bubbling reactor, gas-liquid two-phase contact is more sufficient, the gas-liquid two-phase reaction rate is increased, and the raw material conversion rate is increased; the content of the deactivated catalyst in the material returned to the reactor is reduced through the membrane-based solid-liquid separator, the enrichment and regeneration of the deactivated catalyst can be realized, and the utilization rate of the catalyst is also improved.
Owner:PUJING CHEM IND SHA
Synthetic method of beta, beta-disubstituted propionate derivative
ActiveCN110746253AFew synthetic stepsHigh reaction yieldCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationPropionateAlcohol
The invention discloses a synthetic method of beta, beta-disubstituted propionate derivative, and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. An aldehyde compound, an iodide and an alcohol are adoptedto synthesize the beta, beta-disubstituted propionate derivative through a one-pot method, and the synthetic method is used for realizing beta-bit arylation and esterification of carbonyl groups of alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehyde to synthesize beta, beta-disubstituted methyl propionate. The synthesis steps of a traditional method are reduced, the reaction yield is increased, and according to thesynthetic method, raw materials are cheap, the operation steps are simple, the reaction condition is mild, and applicability of reaction substrates is greatly enriched.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
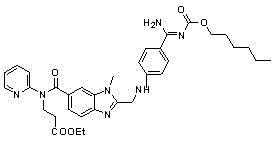
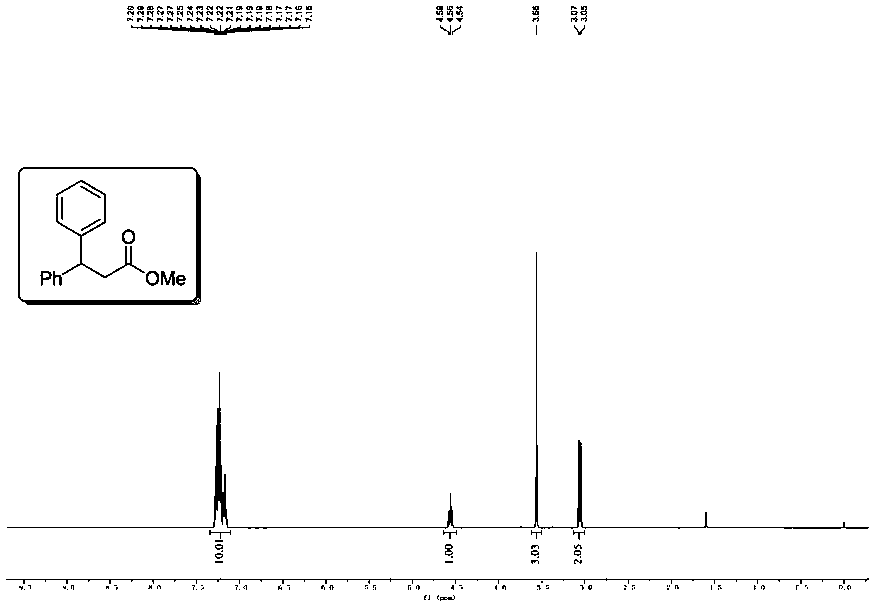
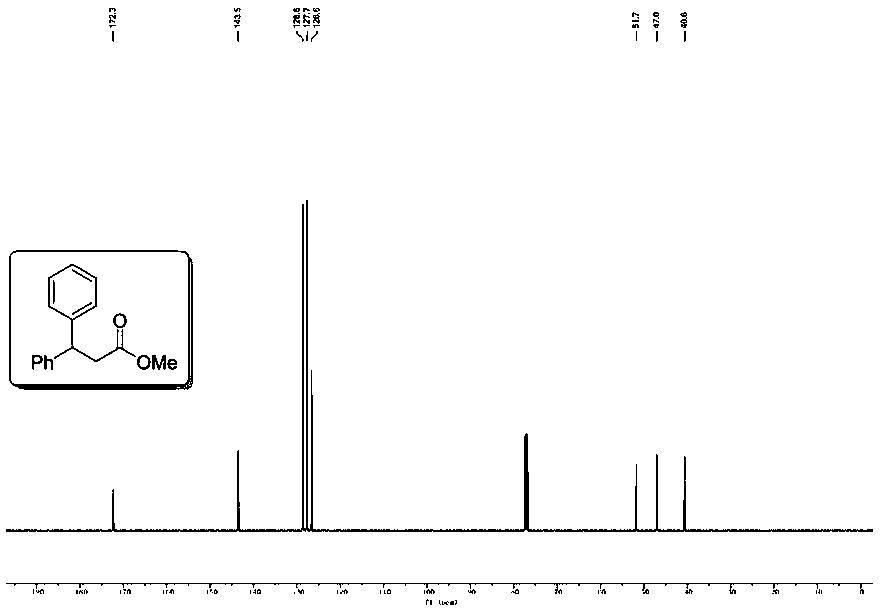
Preparation methods of 3-[N-(2-pyridyl)-3-amino-4-methylamino benzamido]-ethyl propionate
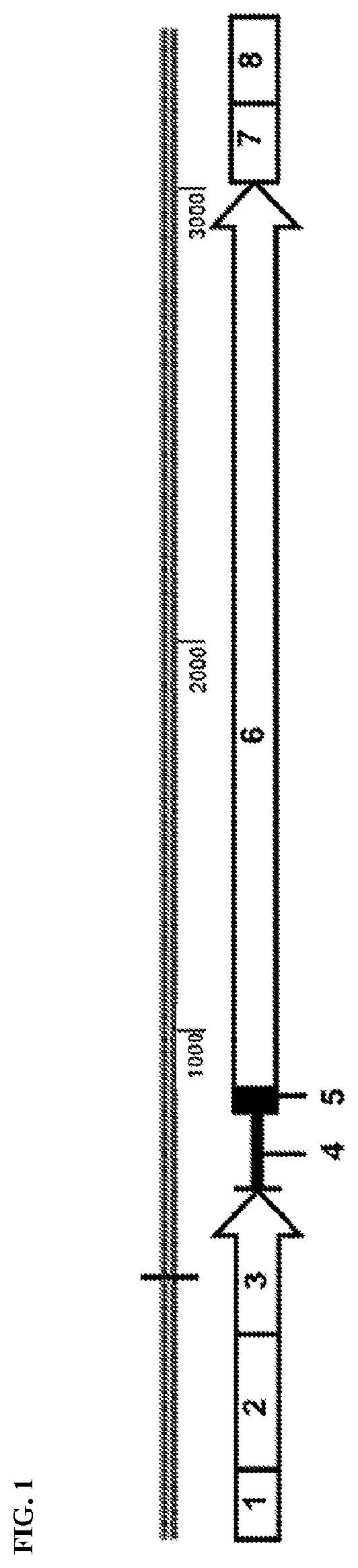
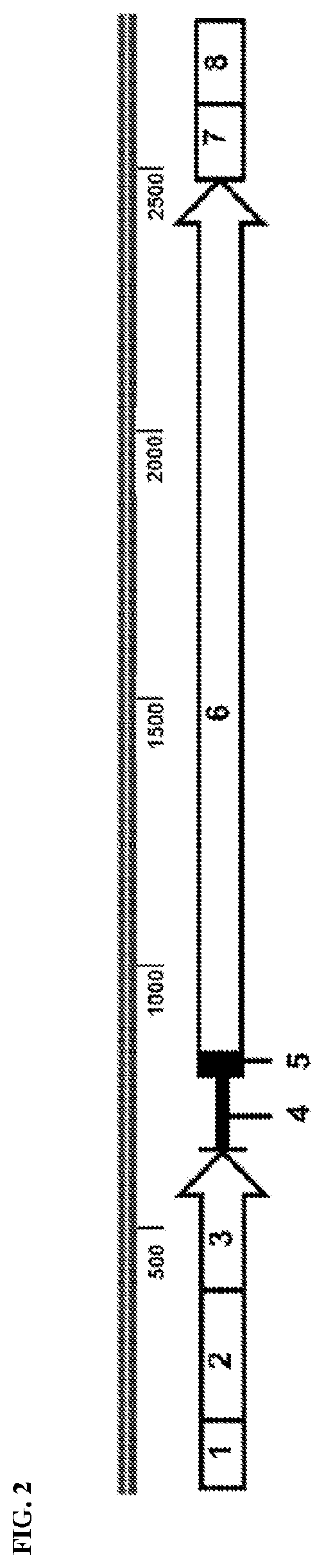
InactiveCN103539730AReduce processing operationsReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistryEthyl propionateEthyl ester
The invention discloses two methods of preparing a dabigatran etexilate intermediate 3-[N-(2-pyridyl)-3-amino-4-methylamino benzamido]-ethyl propionate (I).
Owner:SHANGHAI AOBO PHARMTECH INC LTD
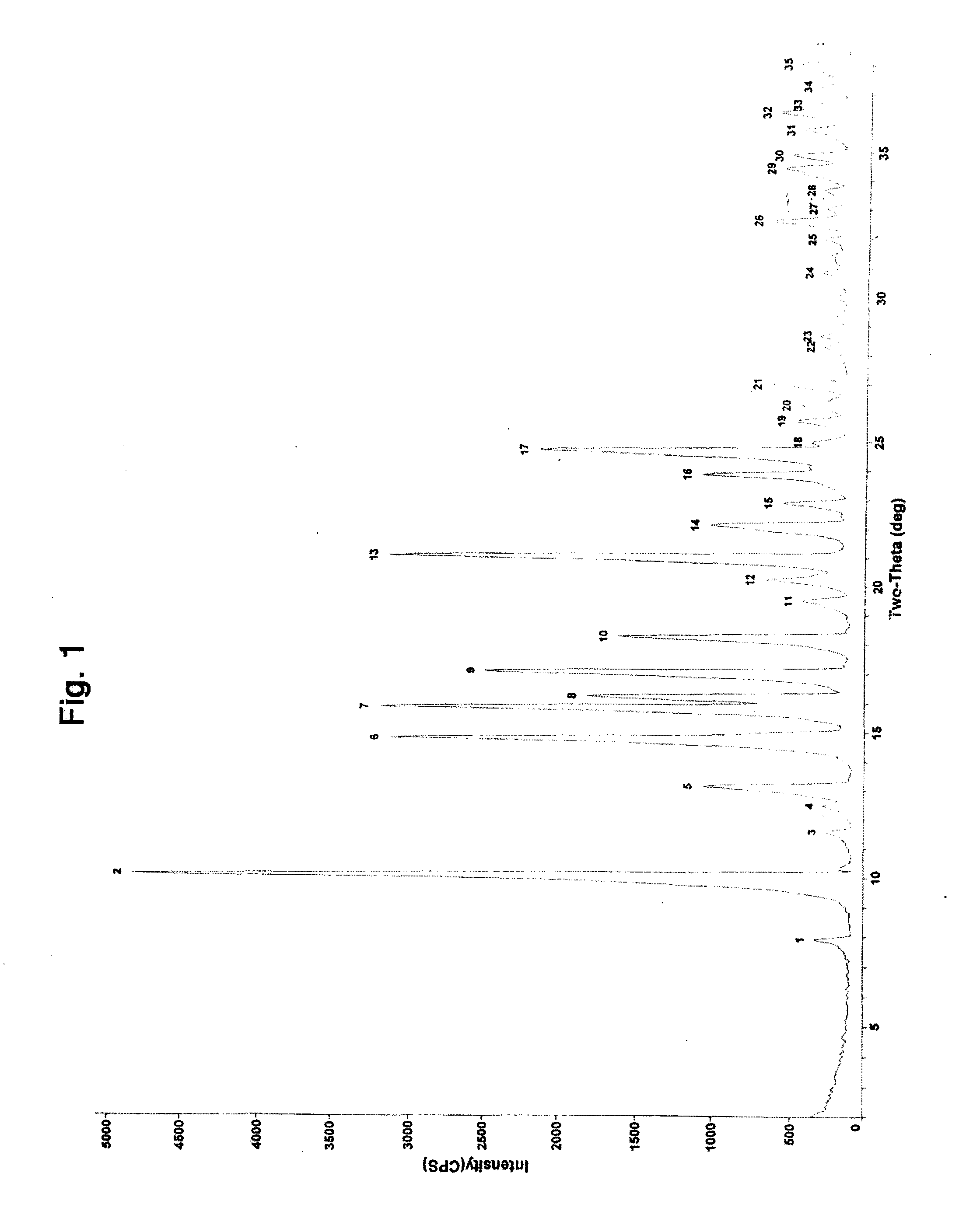
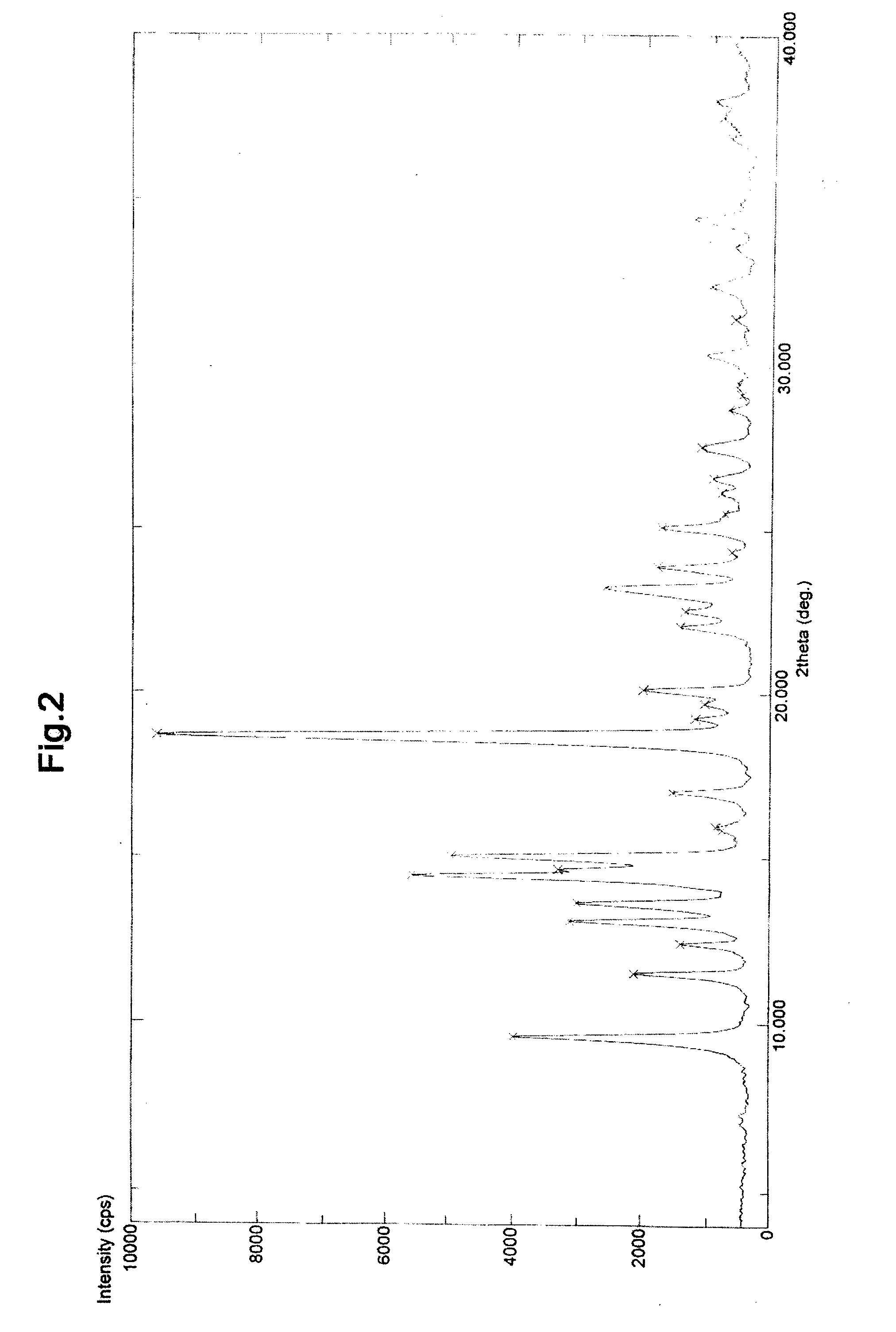
Process for preparing fluticasone propionate/furoate
InactiveUS20140148593A1Improve product qualityReduce the possibilitySteroidsFluticasone propionatePerylene derivatives
The present invention relates to an improved process for the preparation of substituted Fluticasone derivatives. The invention also reveals the processes for the purification of Fluticasones and related intermediates to provide the highly pure product.
Owner:CADILA HEALTHCARE LTD
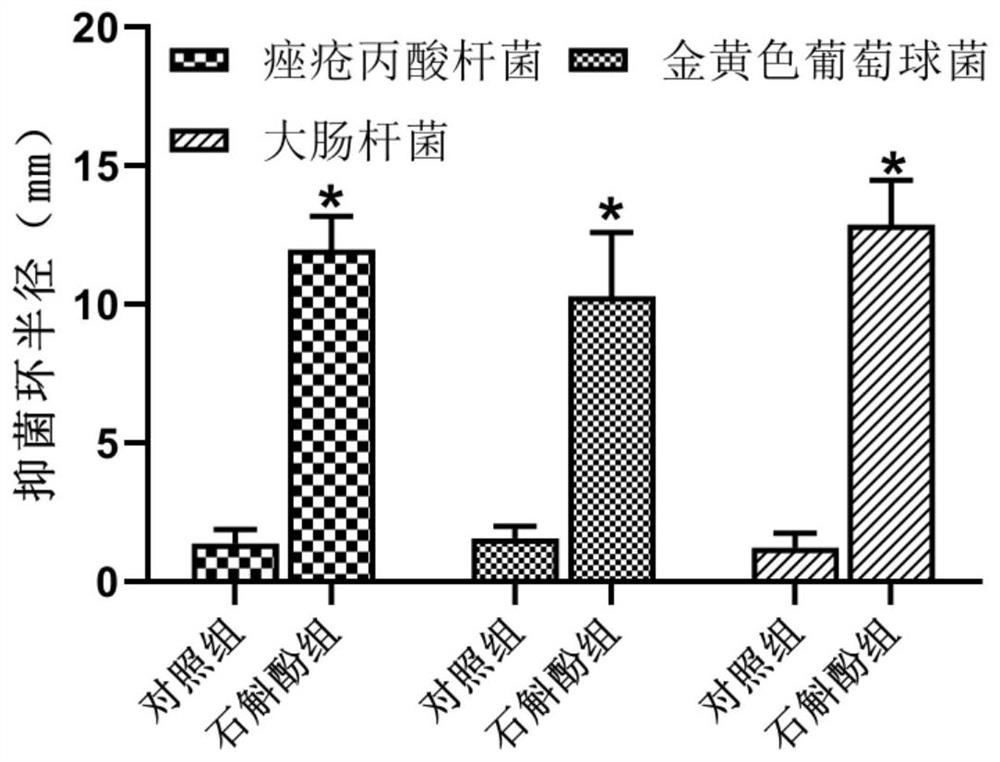
Medical application of gigantol and drug for resisting propionibacterium acnes
The invention discloses medical application of gigantol and a drug for resisting propionibacterium acnes. The gigantol is applied to preparation of the drug for resisting the propionibacterium acnes,has no toxic and side effects to human bodies, can be used as the drug for resisting the propionibacterium acnes to replace conventional antibiotic drugs which cause relapse and infections easily andis prone to produce drug resistance in some aspects and becomes the first choice clinically, and has great application prospects.
Owner:HEFEI NORMAL UNIV
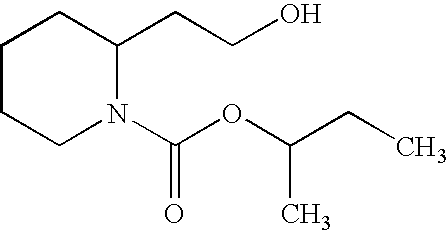
4-substituted-4-(N-propionyl) aniline piperidine compound and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a 4-substituted-4-(N-propionyl) aniline piperidine compound and a preparation method and application thereof. The structure of the compound is shown in Formula (I) or hydrochloride thereof, wherein R1 is a substituent with a mother nucleus structure of propofol, and R2 is 3-methyl propionate group or a benzyl group. The compound can be dissolved in water, and can achieve analgesic and sedative effects simultaneously. Thus, the compound is applicable to analgesia and sedation of patients needing postoperative care, and is particularly conducive to operation of the automatic dosing system by patients, and the operations by anesthesia doctors can be reduced. According to the basic preparation method, the compound is prepared via condensation of propofol (III) and a 4-formyl-4-(N-phenyl propoxy amide)-N-substituted piperidine compound (II).
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
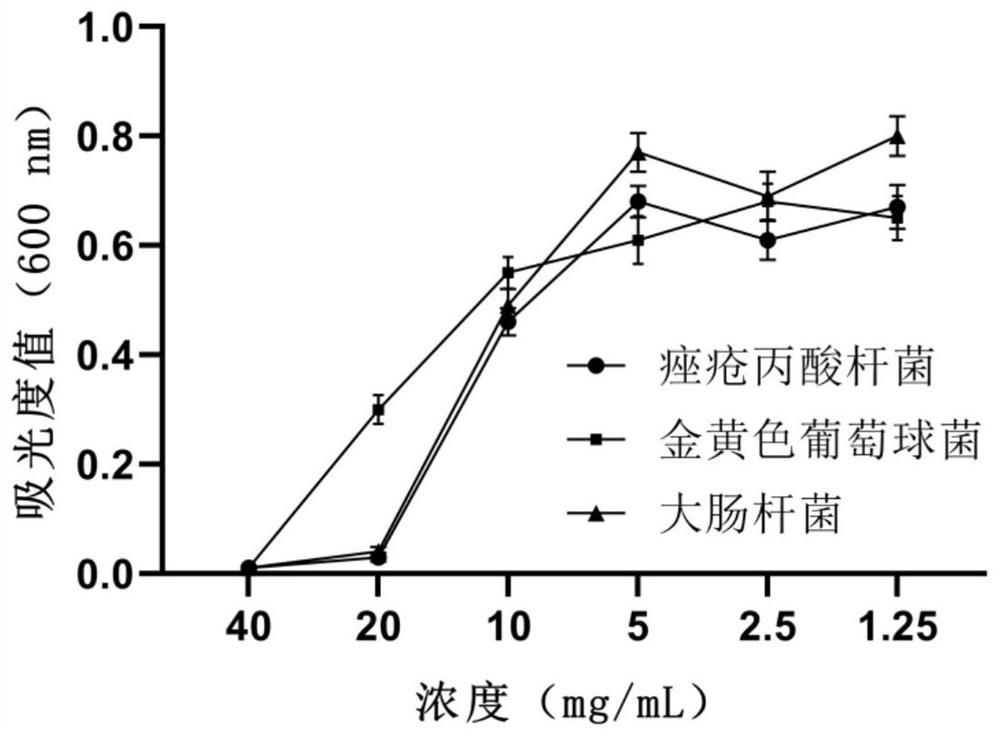
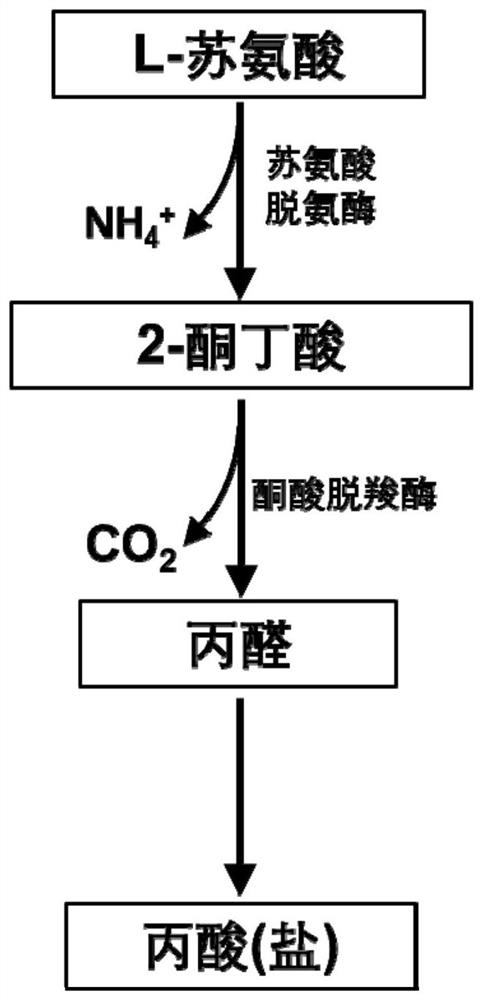
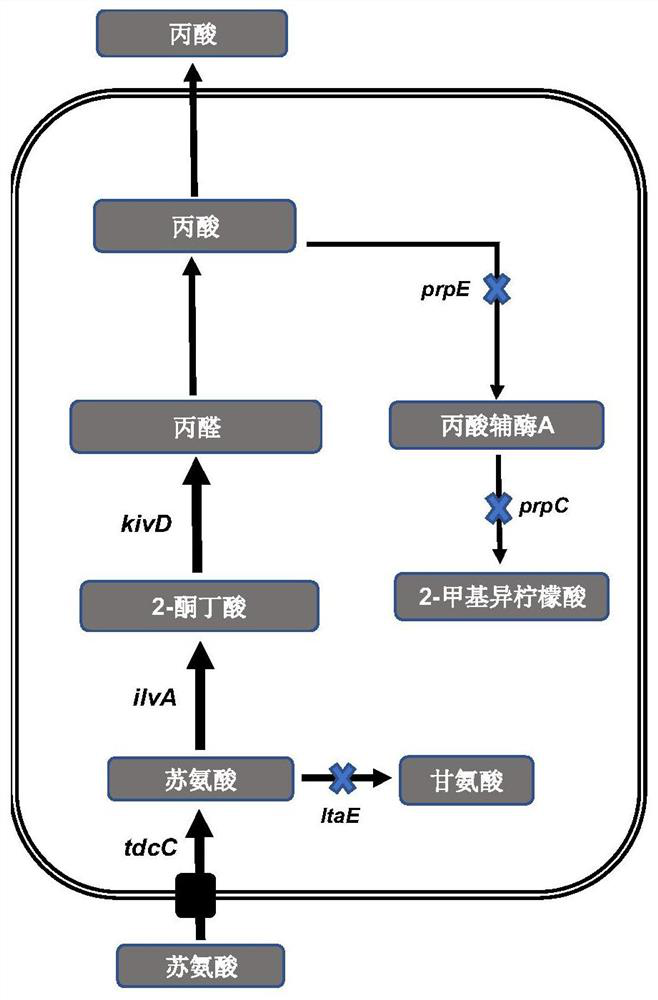
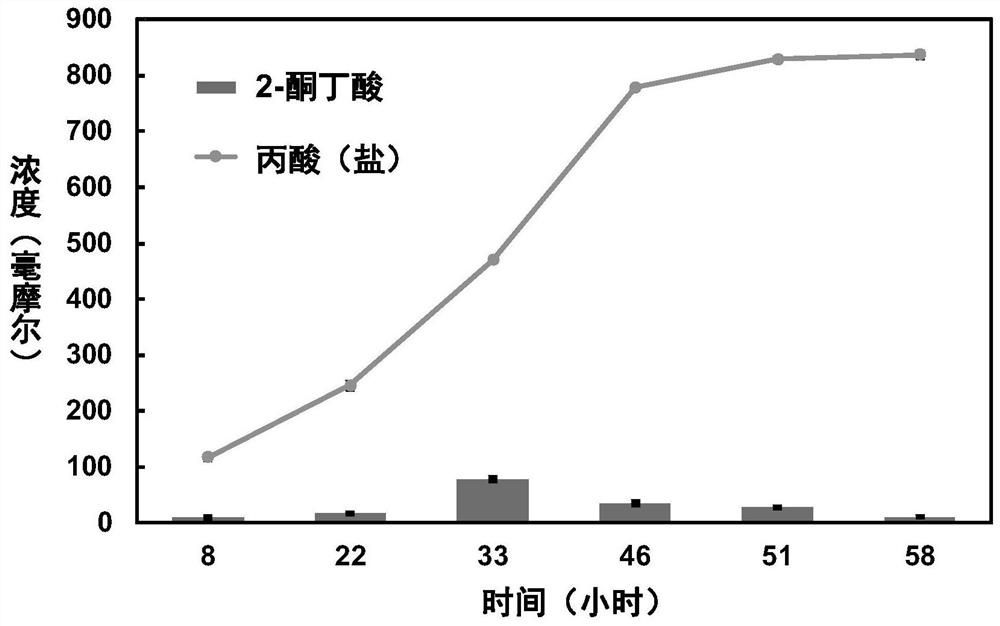
Method for synthesizing propionic acid by using threonine and recombinant bacterium used in method
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium. The recombinant bacterium is used for expressing 2-ketoisovalerate deacidification enzyme (also called ketoacid decarboxylase). The recombinant bacterium is obtained by modifying a genome of a recipient bacterium, wherein the modification comprises the step of enabling the recipient bacterium to express the 2-ketoisovalerate deacidification enzyme, and the recipient bacterium is pseudomonas or escherichia coli. The method for synthesizing the propionic acid by using the recombinant bacterium is characterized in that the propionic acid is synthesized from 2-ketobutyric acid under the catalysis of 2-ketoisovalerate deacidilase. A novel metabolic pathway for synthesis of propionic acid is provided. The transformation rate of propionic acid is 96.67% when the recombinant pseudomonas PS32 obtained after transformation in the invention is used for catalyzing threonine synthesis for 24 hours; and after material supplementation, the conversion rate of the propionic acid can be 98.47% during catalysis of threonine synthesis by the PS32. The recombinant escherichia coli obtained after transformation in the invention can be used for transforming L-threonine with a concentration of 400 mM into propionate with a concentration of 393 mM within 24 hours, and a conversion rate is 98.25%.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phenyl propionic acid derivatives and uses thereof
ActiveUS11225472B2Improve the level ofDelayOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryEfficacyHypoglycemia
Owner:IL DONG PHARMA CO LTD
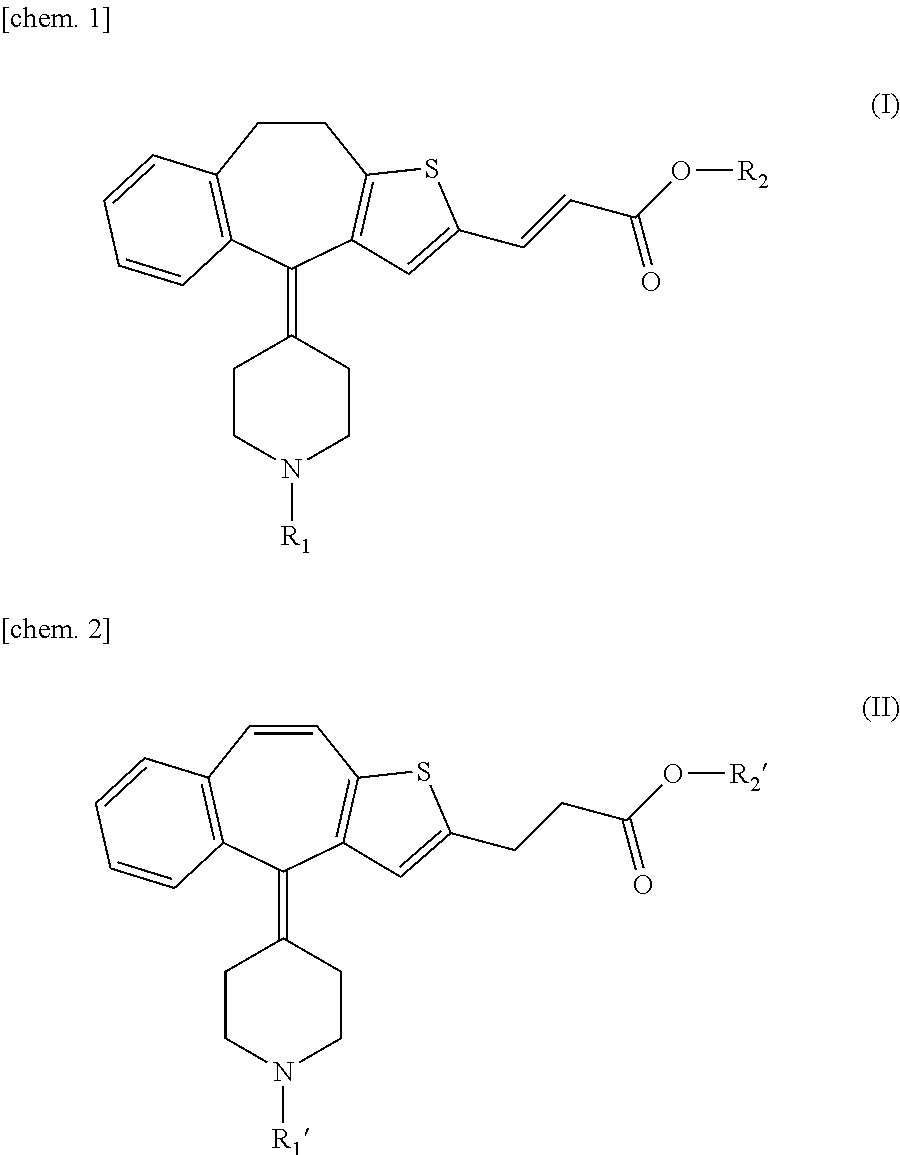
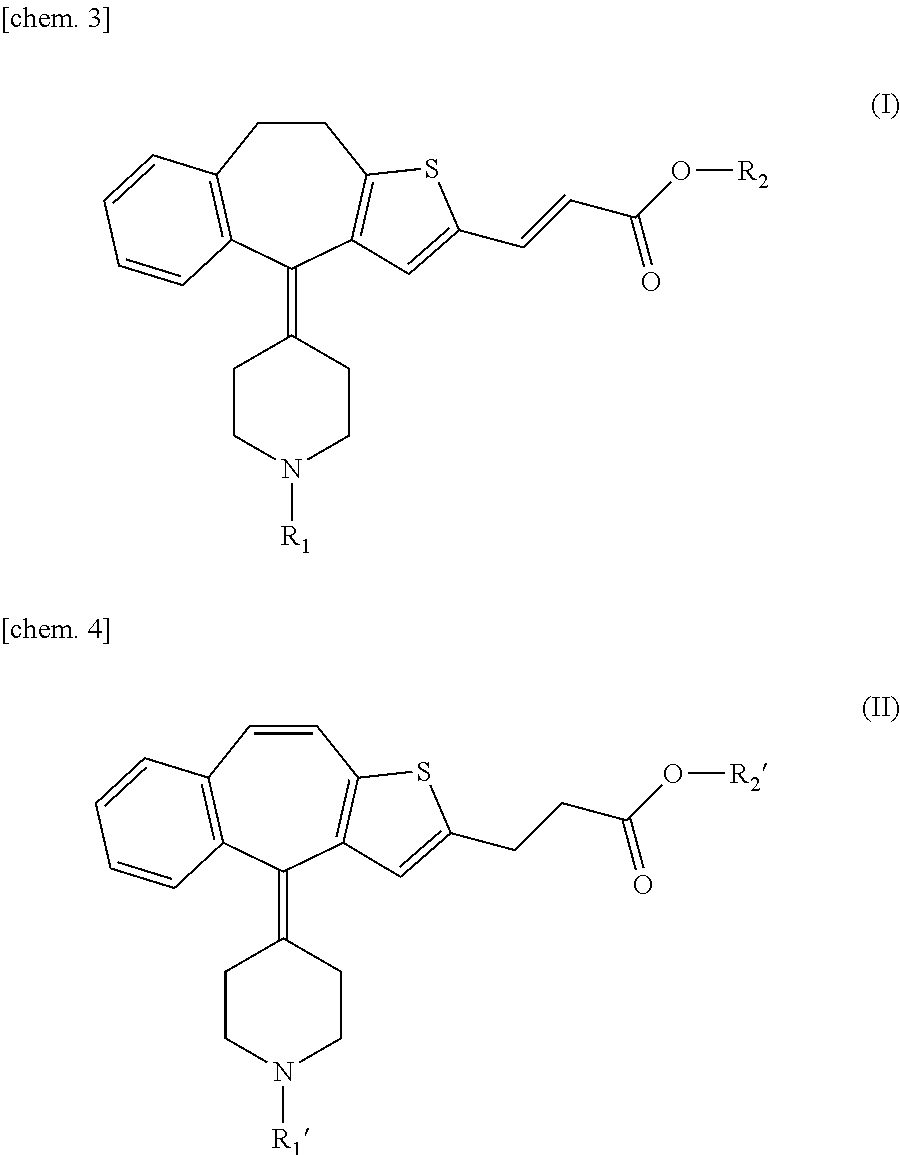
Process for producing thiabenzoazulene-propionic acid derivative
InactiveUS20120123127A1Increase resistanceLow intracerebral transmigrationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPropanoic acidH1 histamine receptors
Disclosed is a process for producing a thiabenzoazulene-propionic acid derivative which is useful as an active ingredient of an antihistaminic agent or the like. According to the producing process of the present invention, it is possible to produce a thiabenzoazulene-propionic acid derivative where the 2-position of the thiabenzoazulene skeleton is substituted with propionic acid. The thiabenzoazulene propionic-acid derivative thus synthesized has excellent antagonistic action to histamine H1 receptor and low intracerebral transmigration and, therefore, is useful as an active ingredient of the pharmaceutical composition such as an antihistaminic agent.
Owner:NIPPON ZOKI PHARM CO LTD
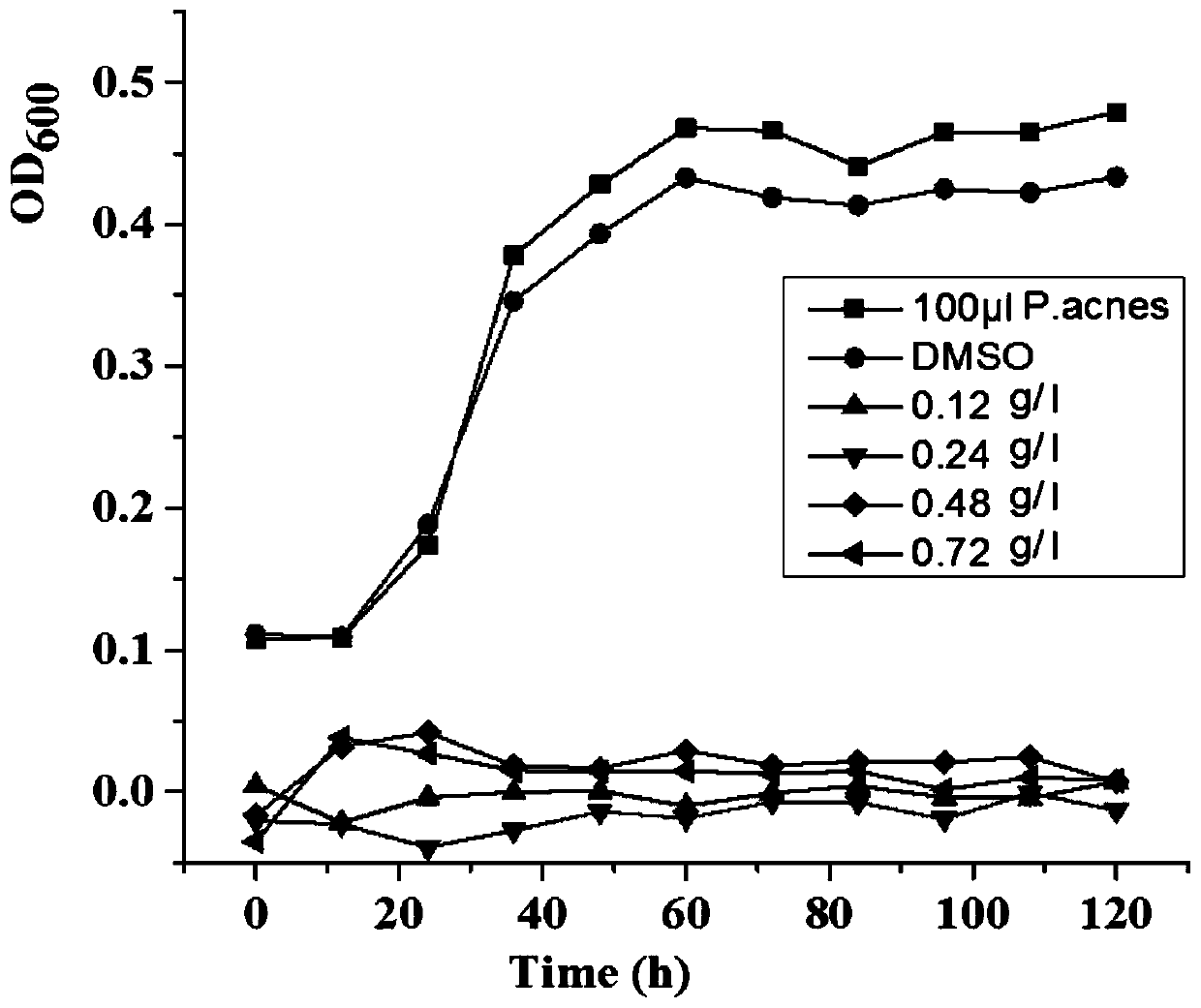
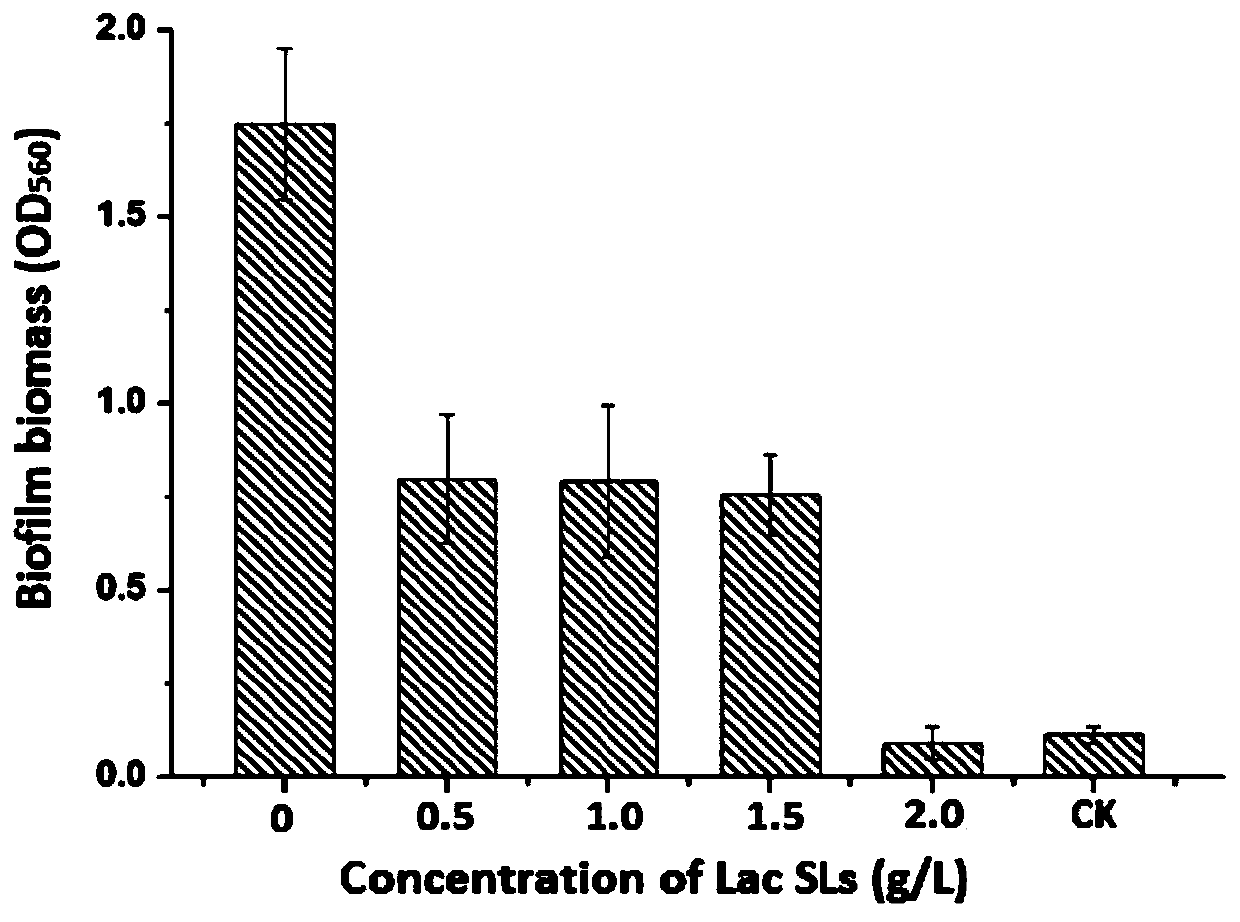
Application of sophorolipid in preparation of medicine for preventing against propionibacterium acnes and biofilm thereof
InactiveCN111202739ASimple processing methodLow costAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologySide effect
The present invention discloses an application of sophorolipid in preparation of a medicine for preventing against propionibacterium acnes and a biofilm thereof. The sophorolipid is prepared from Wickerhamiella domercqiae var. sophorollipid CGMCC No.1576 through a fermentation method; a concentration of the sophorolipid in effectively inhibiting propionibacterium acnes is 0.12-1.5 g / L and a concentration of the sophorolipid in effectively inhibiting propionibacterium acnes biofilm is 2.0-2.5 g / L. Experiments confirm that the sophorolipid has a significant bacteriostatic effect, does not have any toxic and side effects on human body, can be used to replace a conventional antibiotic medicine that is prone to enable people to relapse and infect and have drug resistance after therapy in certain aspects, and has great application prospects.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
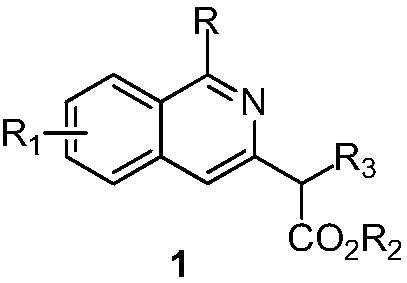
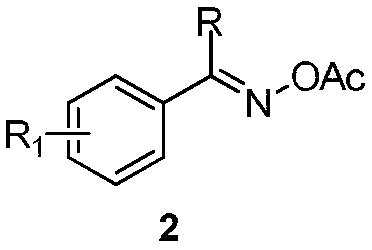
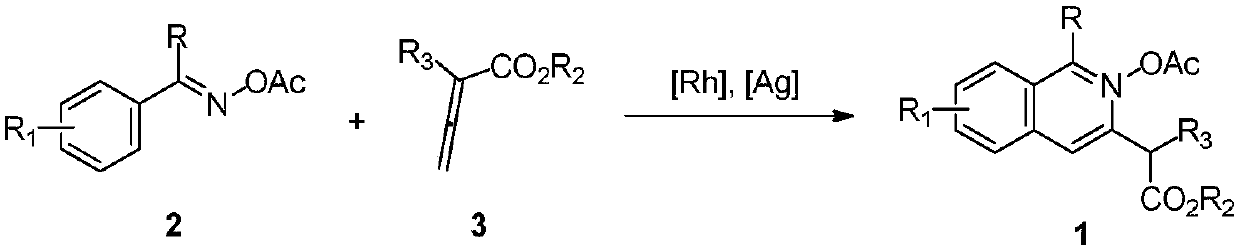
2-(3-isoquinolinyl)-ethyl propionate derivative and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN111018779AEasy to manufactureWith structural diversityOrganic chemistryIsoquinolineQuinoline
The invention discloses a 2-(3-isoquinolinyl)-ethyl propionate derivative and a synthesis method thereof. According to the invention, O-acetyloxime with characteristics of easy preparation, structuraldiversity and multiple reaction centers is used as a raw material, the ortho-position C-H bond of the aromatic ring in the O-acetyloxime is activated under the action of a rhodium salt, a coupling reaction with allenoate is carried out, a series of 2-(3-isoquinolinyl)-ethyl propionate derivatives with different structures are synthesized, and the product can be further converted into a functionalproduct.; and the method has the advantages of easily available raw materials, simple operation, mild reaction conditions, diverse functional groups, and no need of pre-functionalization.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
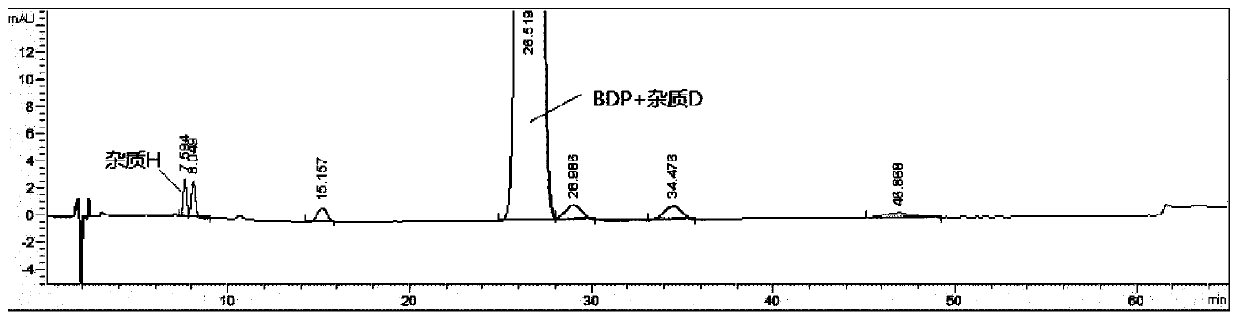
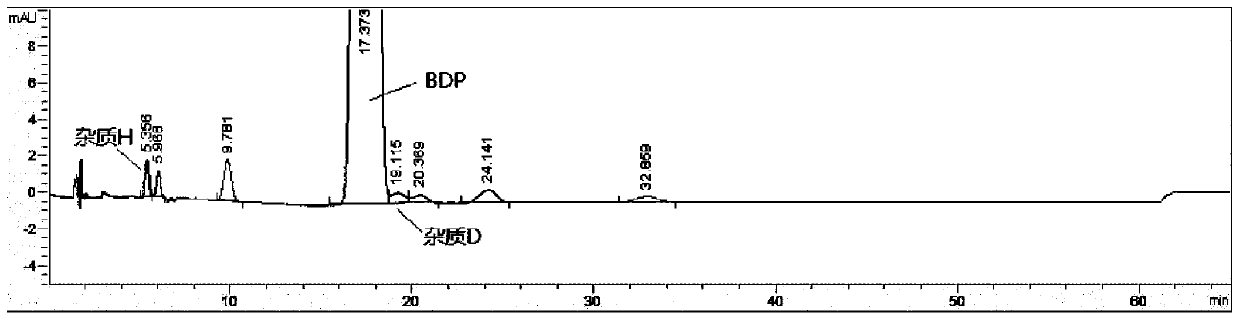
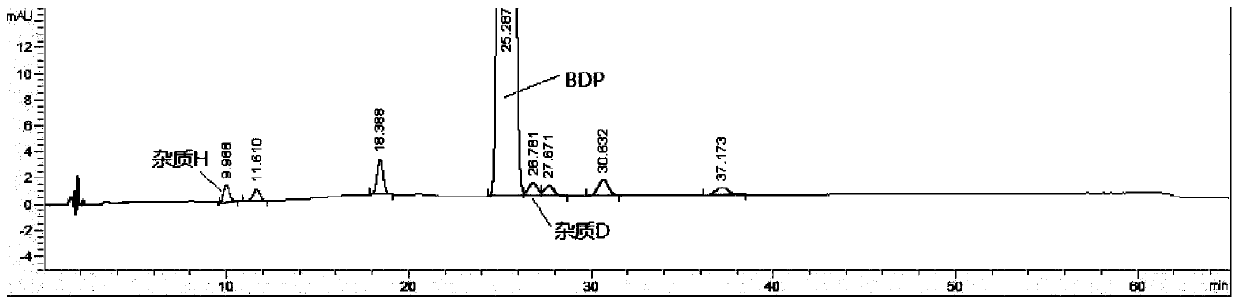
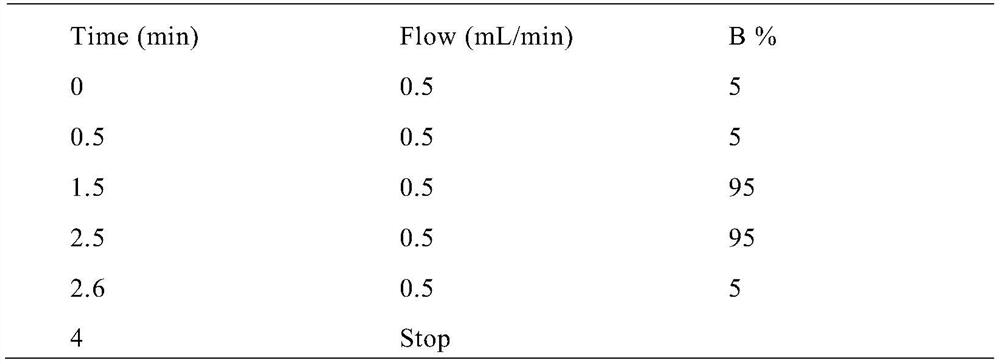
Method for detecting beclomethasone propionate related substances
The invention provides a method for detecting beclomethasone propionate related substances. The method optimizes the separation degree of an impurity D and a main peak of beclomethasone propionate through liquid chromatography, and detects the main metabolite (impurity H), and is beneficial to the quality control of beclomethasone propionate and the improvement of dosing accuracy.
Owner:SICHUAN PURITY PHARM CO LTD
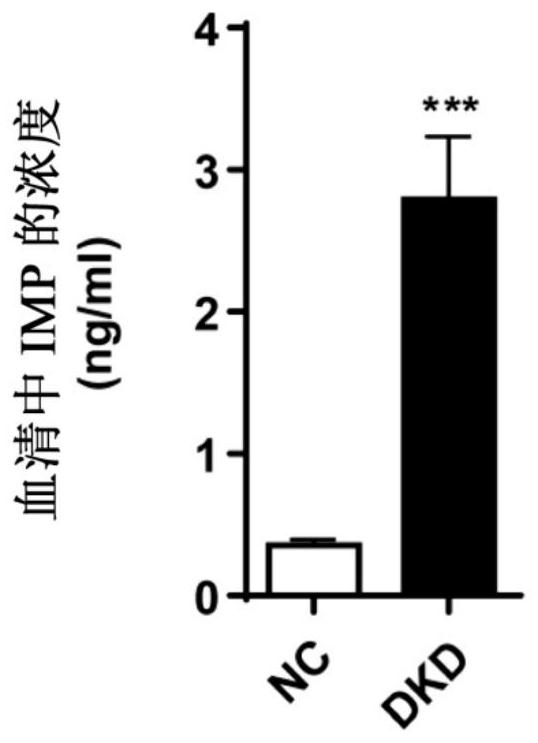
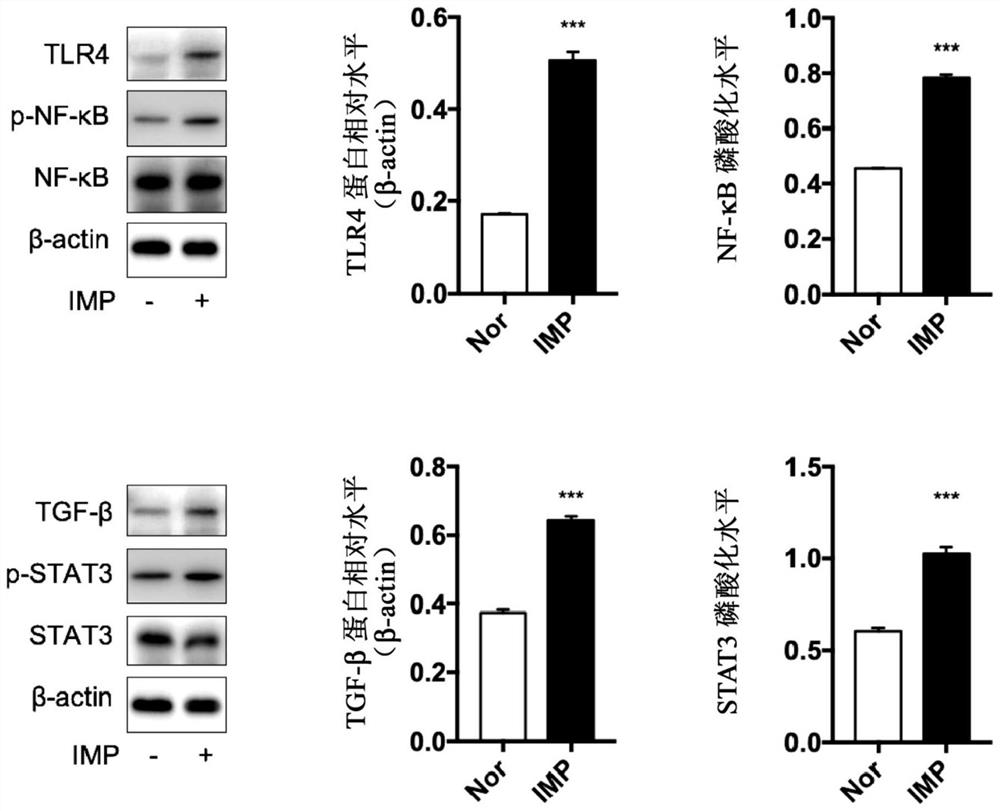
Application of imidazole propionic acid as biomarker for predicting diabetic nephropathy and detection kit
The invention provides application of imidazole propionic acid as a biomarker in preparation of a kit for predicting diabetic nephropathy and a related detection kit. The biomarker can be effectively used as an early diagnosis marker for predicting diabetic nephropathy, and has the advantages of accuracy, early stage and high precision.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
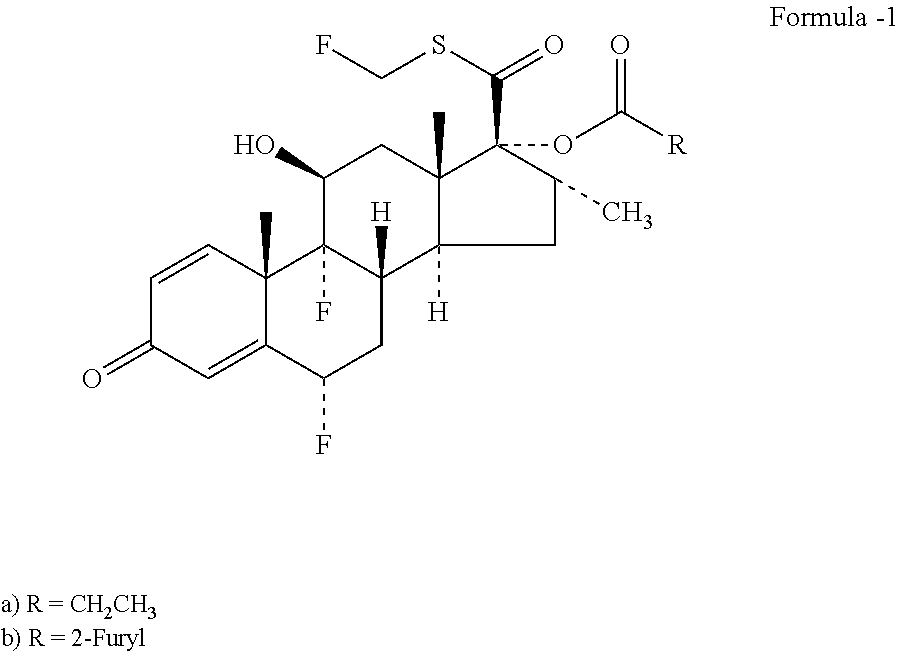
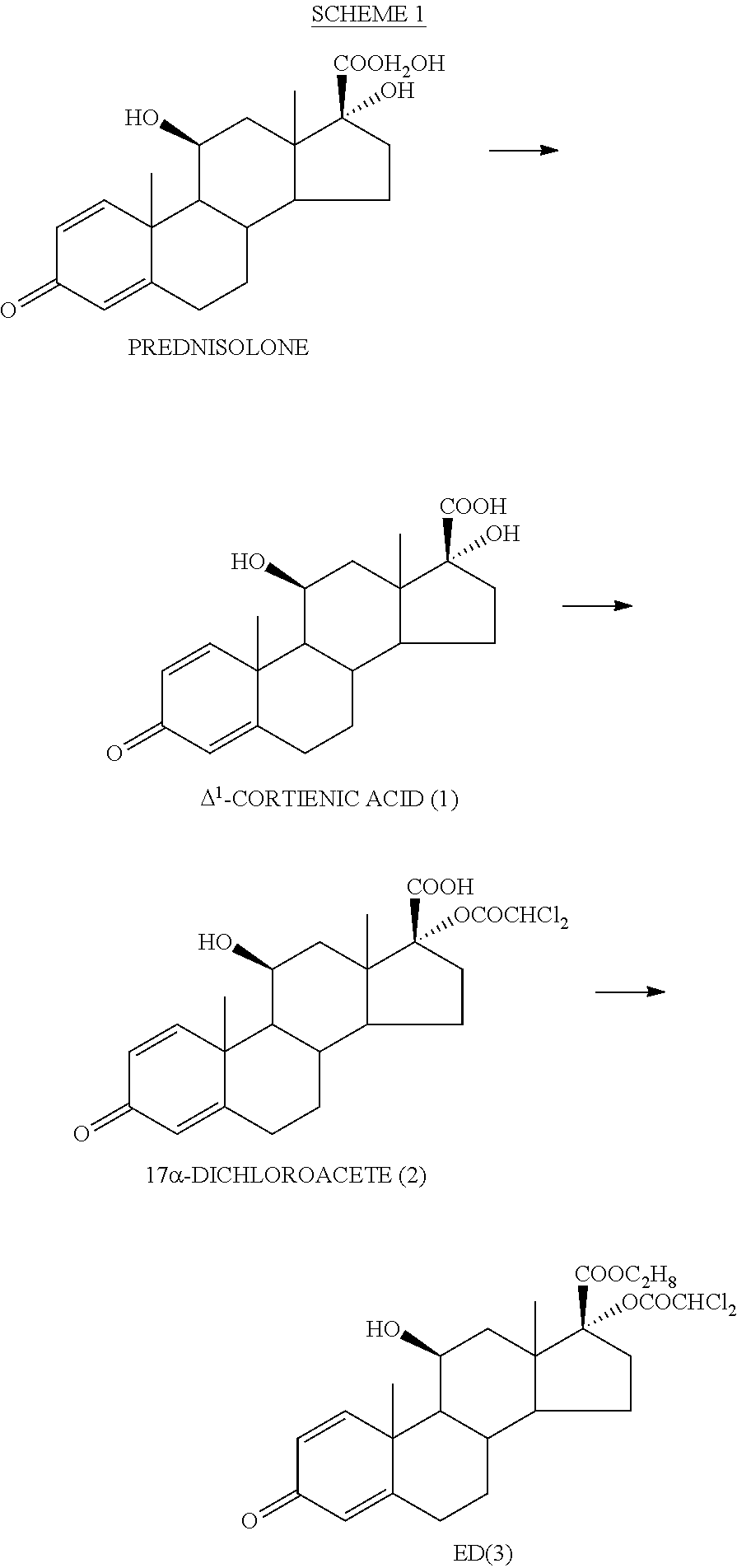
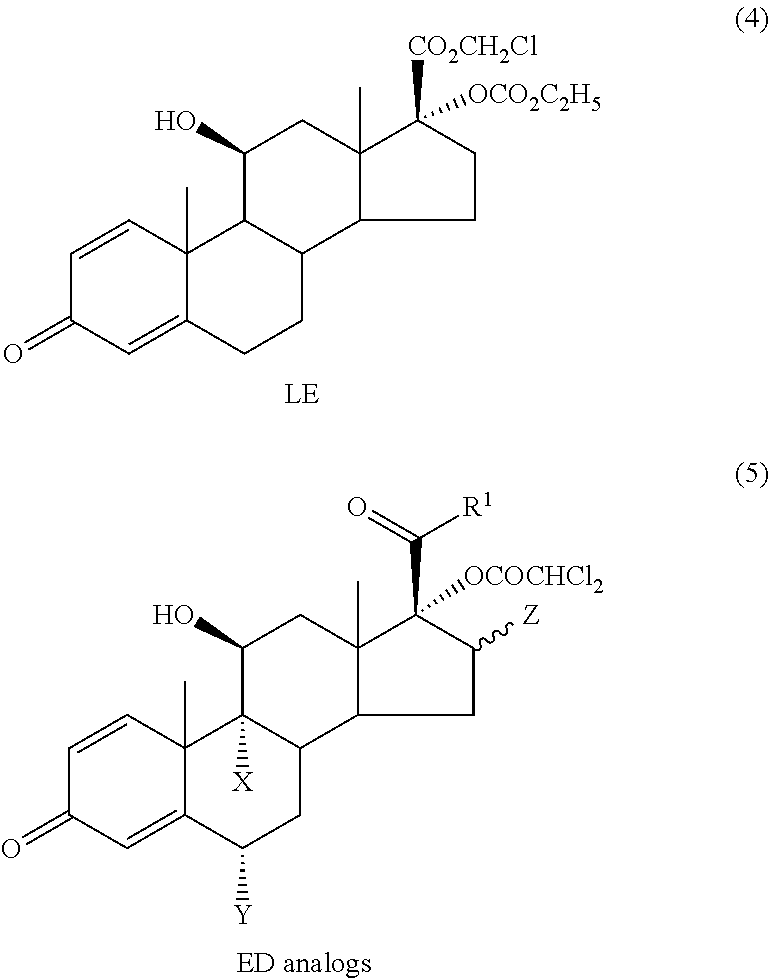
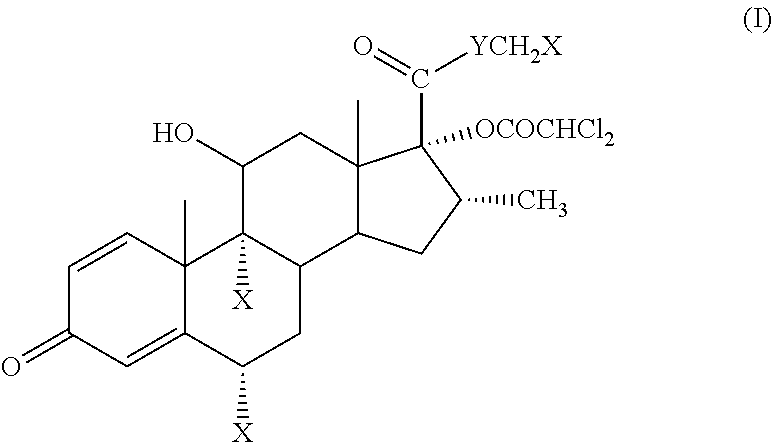
Potent soft anti-inflammatory corticosteroid compounds and uses thereof
ActiveUS11447522B2High local and topical anti-inflammatory activityImproved therapeutic indexSenses disorderAntipyreticFluticasone propionateCarboxylic acid
Potent soft corticosteroid pharmaceutical compositions comprising them and method for use as anti-inflammatory agents. Also, a method for softening fluticasone propionate and similar corticosteroids to arrive at potent but safer alternatives. The compound 5-fluoromethyl 17α-dichloroacetoxy-6α,9α-difluoro-11β-hydroxy-16a-methyl-3-oxoandrosta-1,4-diene-17β-carbothioate, which is equally potent to but safer than fluticasone, is among those provided. Another compound of particular interest is 2-hydroxyethyl 17α-dichloroacetoxy-6α,9α-difluoro-11β-hydroxy-16β-methyl-3-oxoandrosta-1,4-diene-17β-carboxylate.
Owner:BODOR LAB
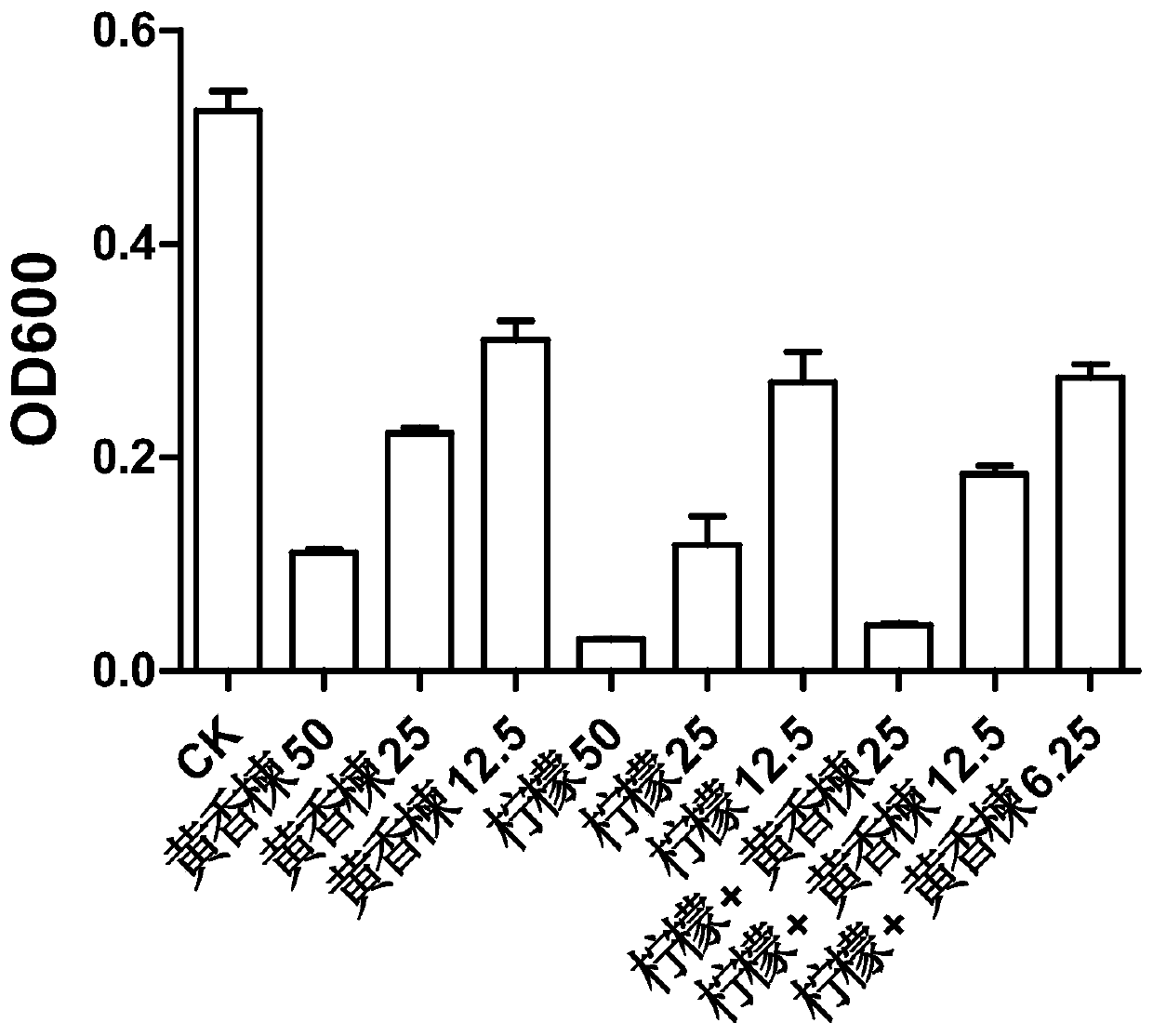
Neem-lemon extract and its application for preventing and treating Propionibacterium acnes
ActiveCN108125850BAvoid damageNo side effectsAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBacillus acnesMicrobiology
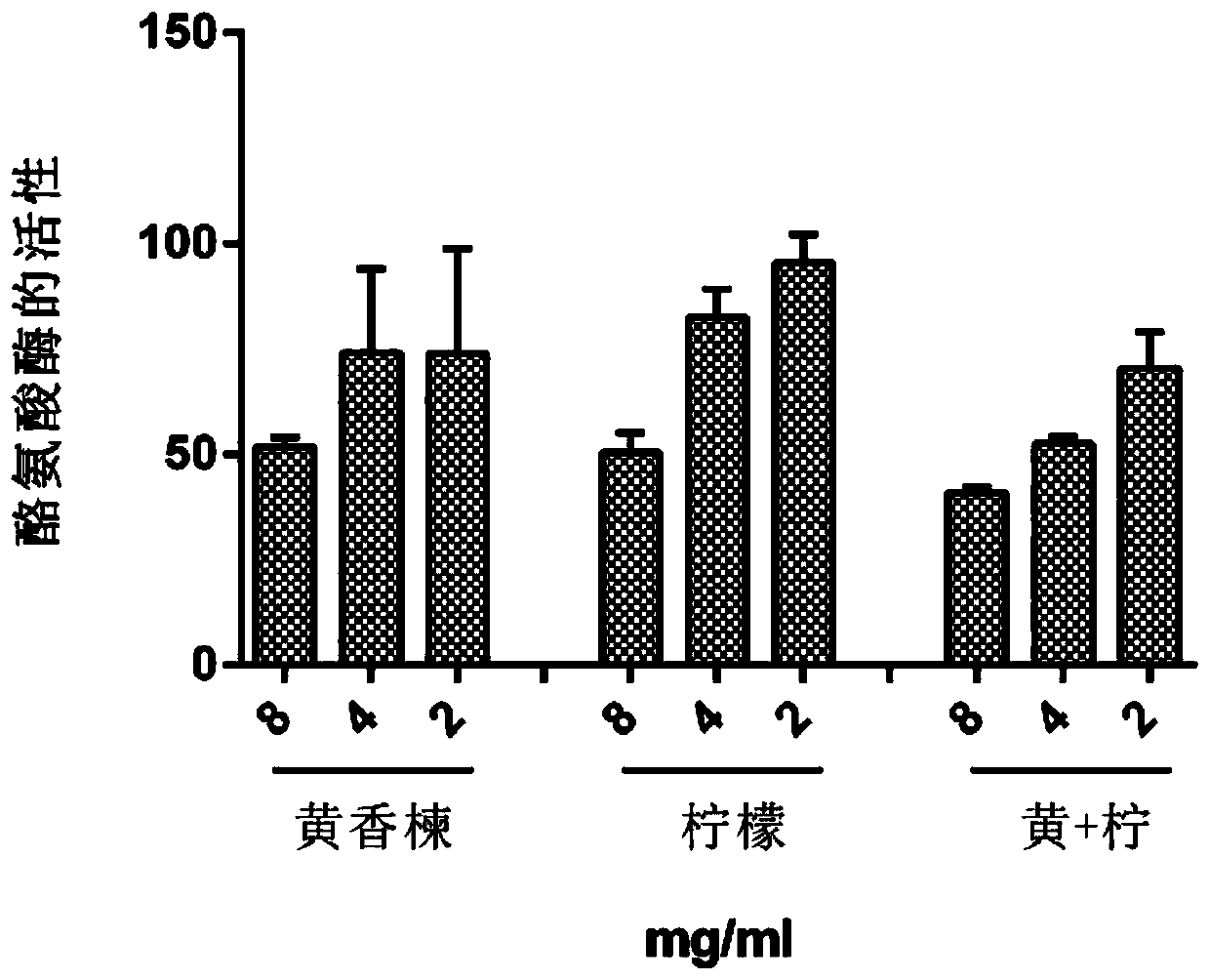
The invention discloses Hesperethusa crenulata-lemon extract for preventing and controlling propionibacterium acnes and an application thereof. The extract is a compound prepared from Hesperethusa crenulata extract and lemon extract through mixing according to a certain ratio. The extract has effects of resisting propionibacterium acnes, diminishing inflammation, resisting ultraviolet and oxidation, removing free radicals and reducing skin damage. The Hesperethusa crenulata extract and lemon extract can produce a synergistic effect of resisting bacteria.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
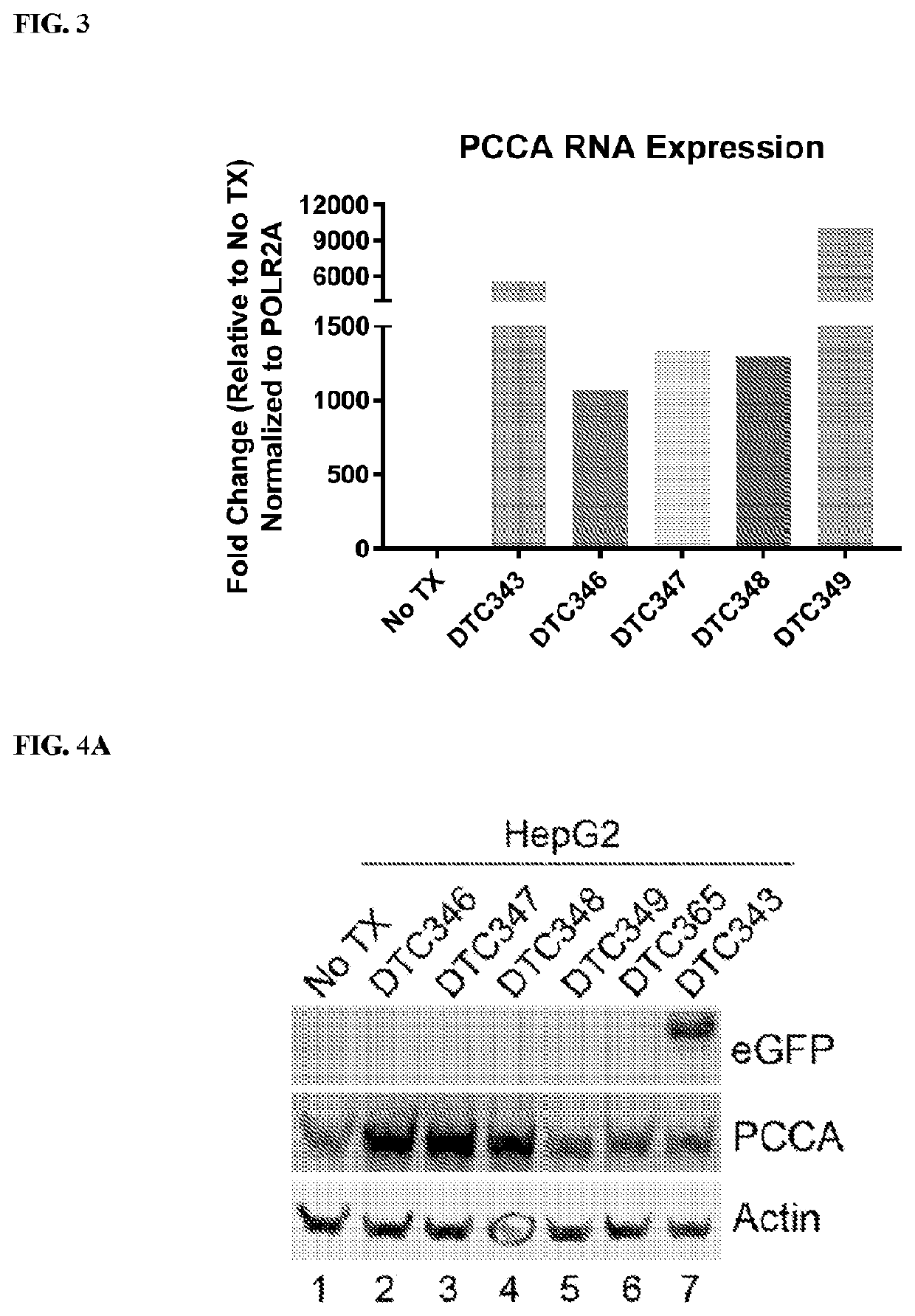
Gene therapy for treating propionic acidemia
PendingUS20210283272A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic therapy composition manufacturePharmaceutical drugViral vector
This present disclosure provides adeno-associated viral vectors, recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV), and methods of their use in gene therapy for treating propionic acidemia (PA). Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions comprising a recombinant adeno-associated virus of the invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient. These pharmaceutical (compositions may be useful in gene therapy for the treatment of PA caused by mutations in propionyl-CoA carboxylase α-subunit (PCCA) or mutations in propionyl-CoA carboxylase β-subunit (PCCB).
Owner:ULTRAGENYX PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
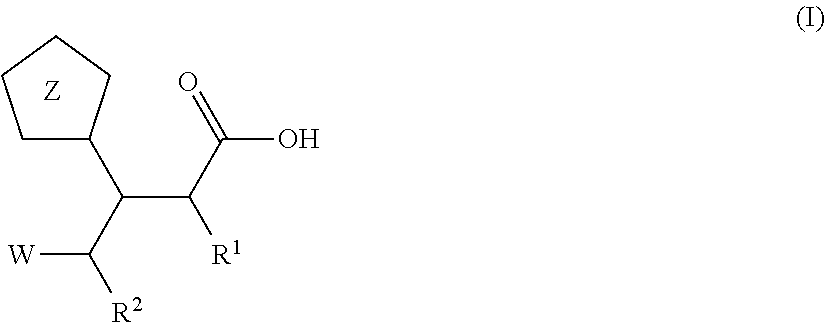

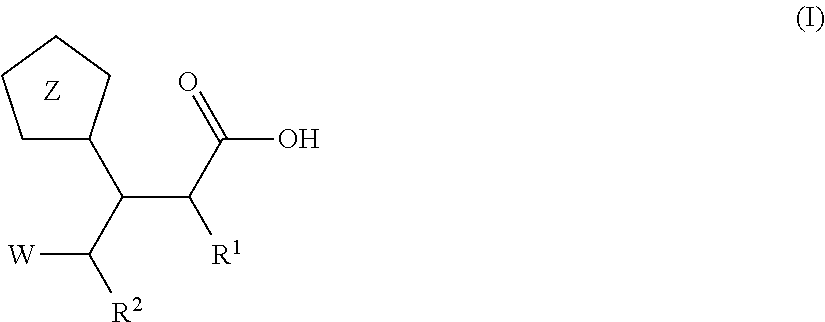
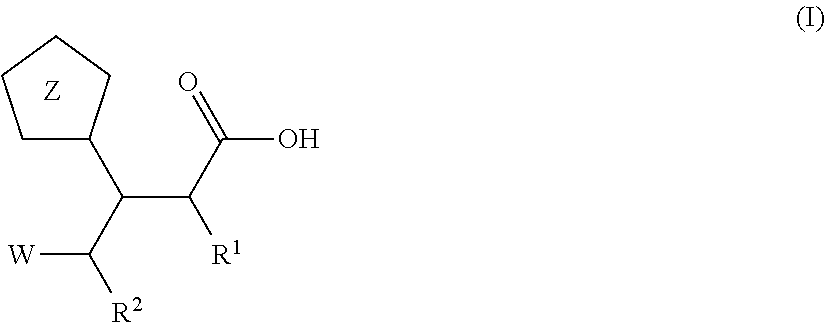
![Preparation methods of 3-[N-(2-pyridyl)-3-amino-4-methylamino benzamido]-ethyl propionate Preparation methods of 3-[N-(2-pyridyl)-3-amino-4-methylamino benzamido]-ethyl propionate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/90b29b4e-c1af-4d5d-b5ea-a6293cb5ddc1/BSA00000748925600011.PNG)
![Preparation methods of 3-[N-(2-pyridyl)-3-amino-4-methylamino benzamido]-ethyl propionate Preparation methods of 3-[N-(2-pyridyl)-3-amino-4-methylamino benzamido]-ethyl propionate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/90b29b4e-c1af-4d5d-b5ea-a6293cb5ddc1/BSA00000748925600012.PNG)
![Preparation methods of 3-[N-(2-pyridyl)-3-amino-4-methylamino benzamido]-ethyl propionate Preparation methods of 3-[N-(2-pyridyl)-3-amino-4-methylamino benzamido]-ethyl propionate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/90b29b4e-c1af-4d5d-b5ea-a6293cb5ddc1/BSA00000748925600021.PNG)