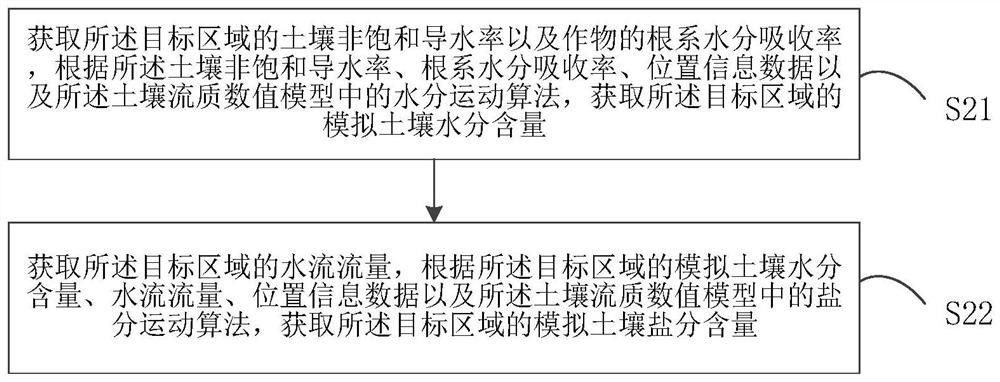
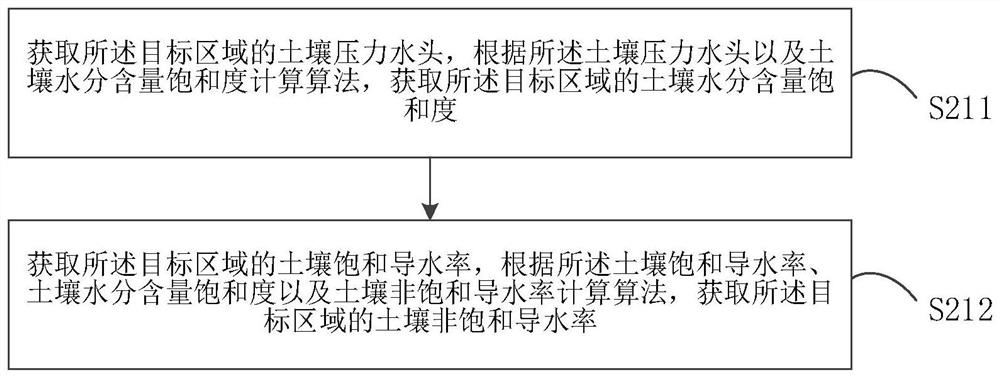
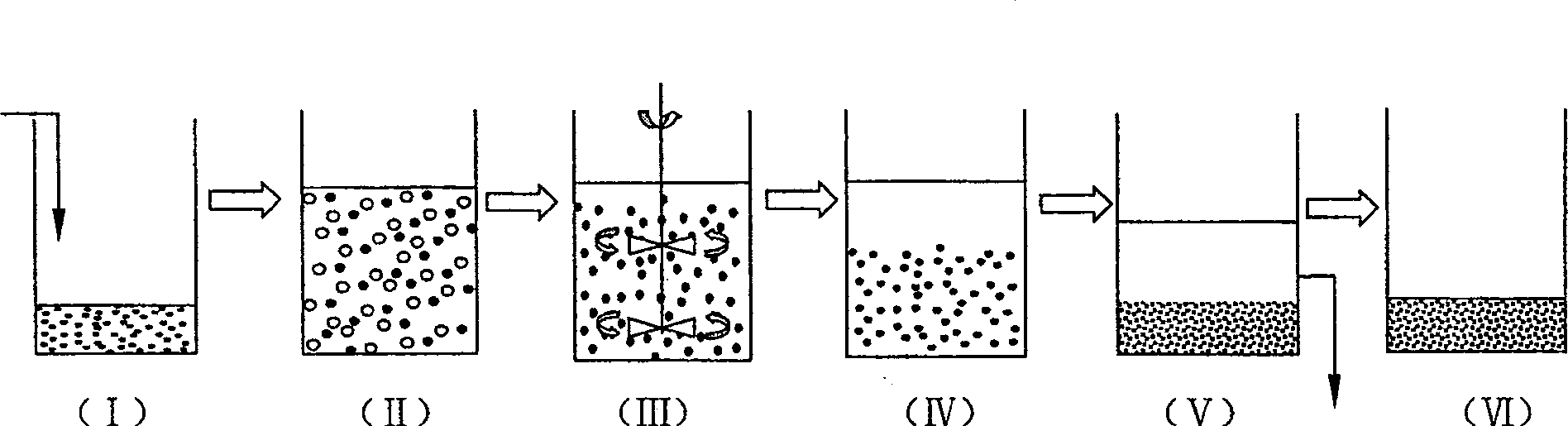
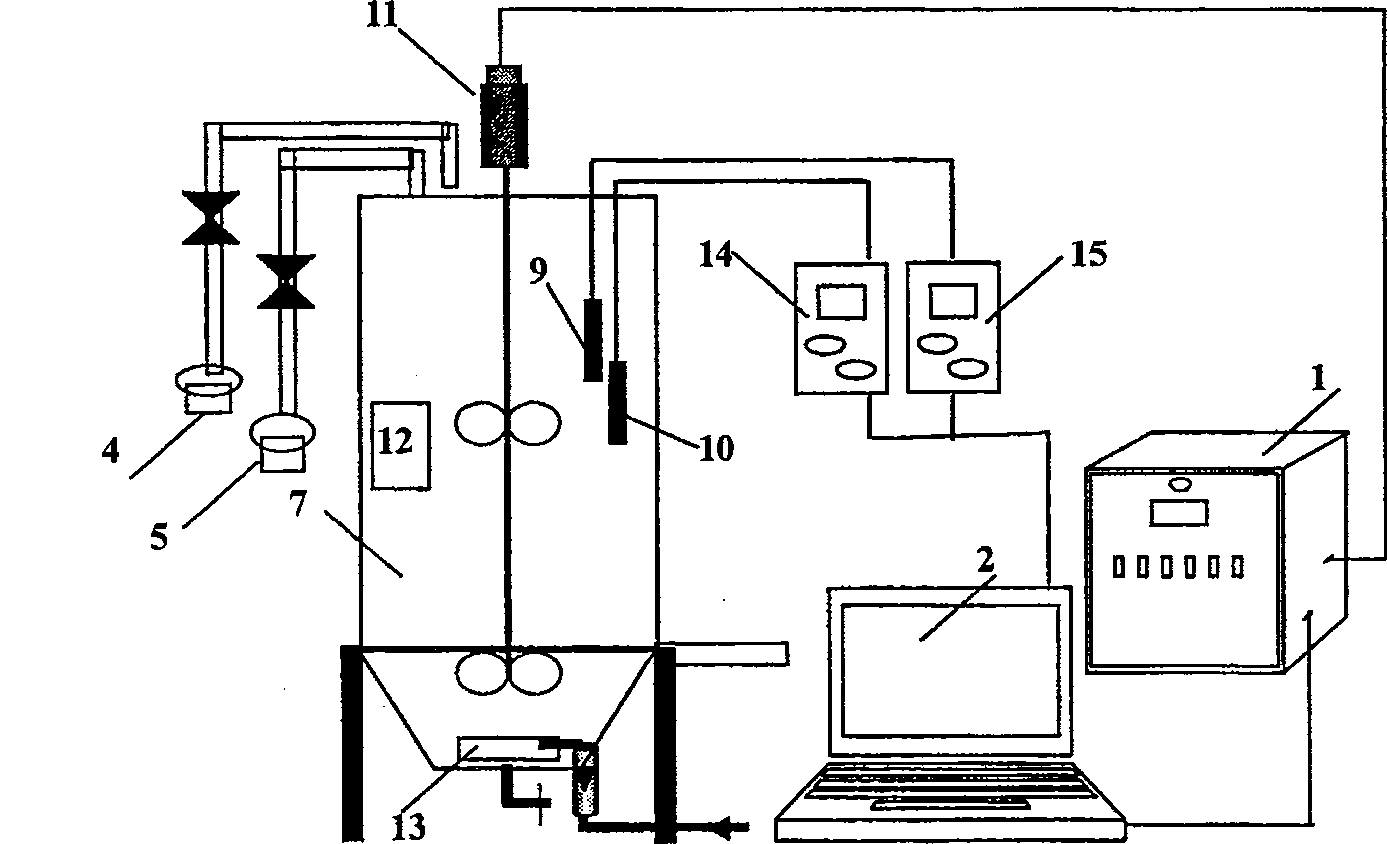
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Salinity stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Salinity stress involves changes in various physiological and metabolic processes, depending on severity and duration of the stress, and ultimately inhibits crop production [4–7]. Initially soil salinity is known to represses plant growth in the form of osmotic stress which is then followed by ion toxicity [4, 5].
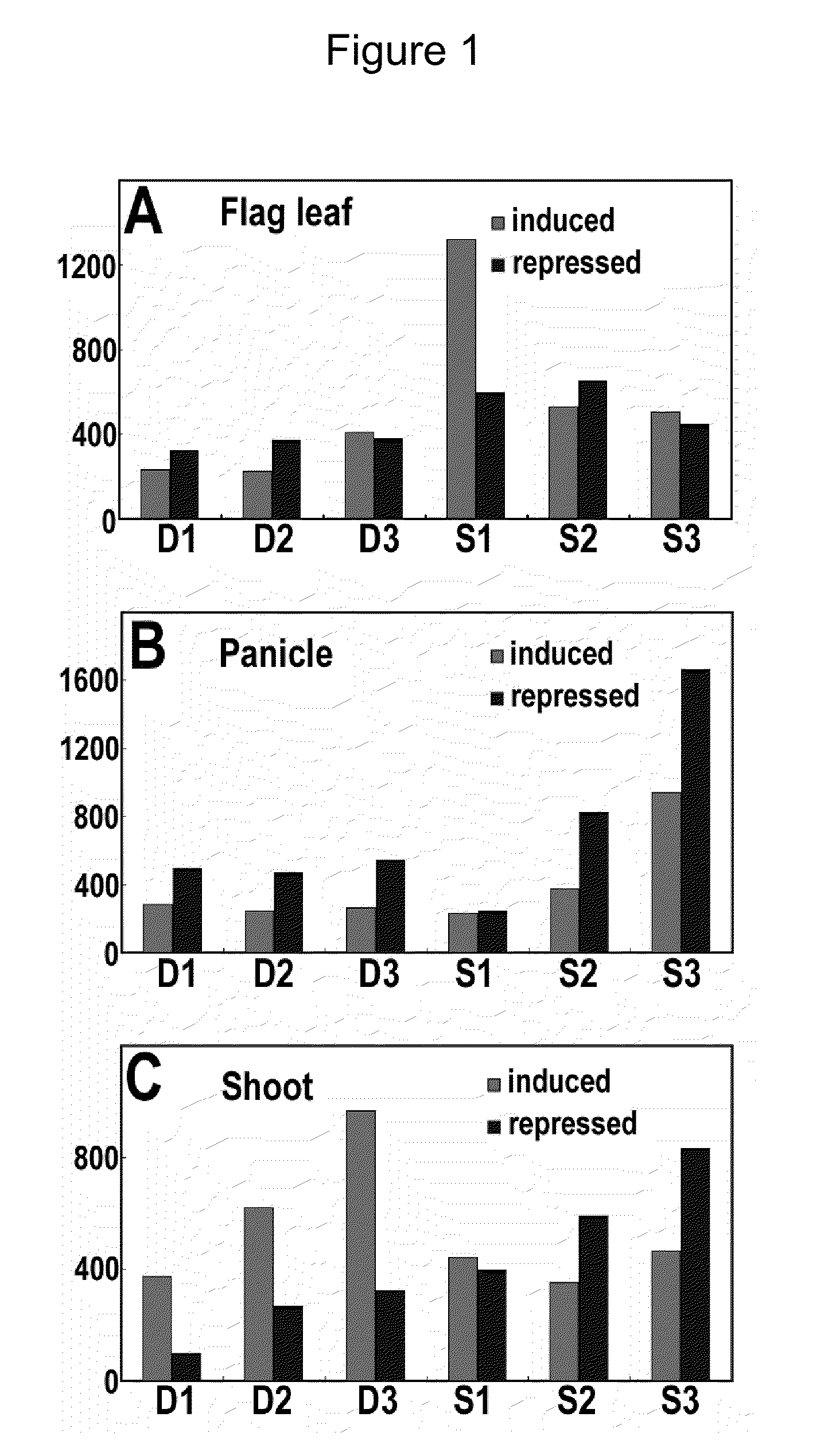
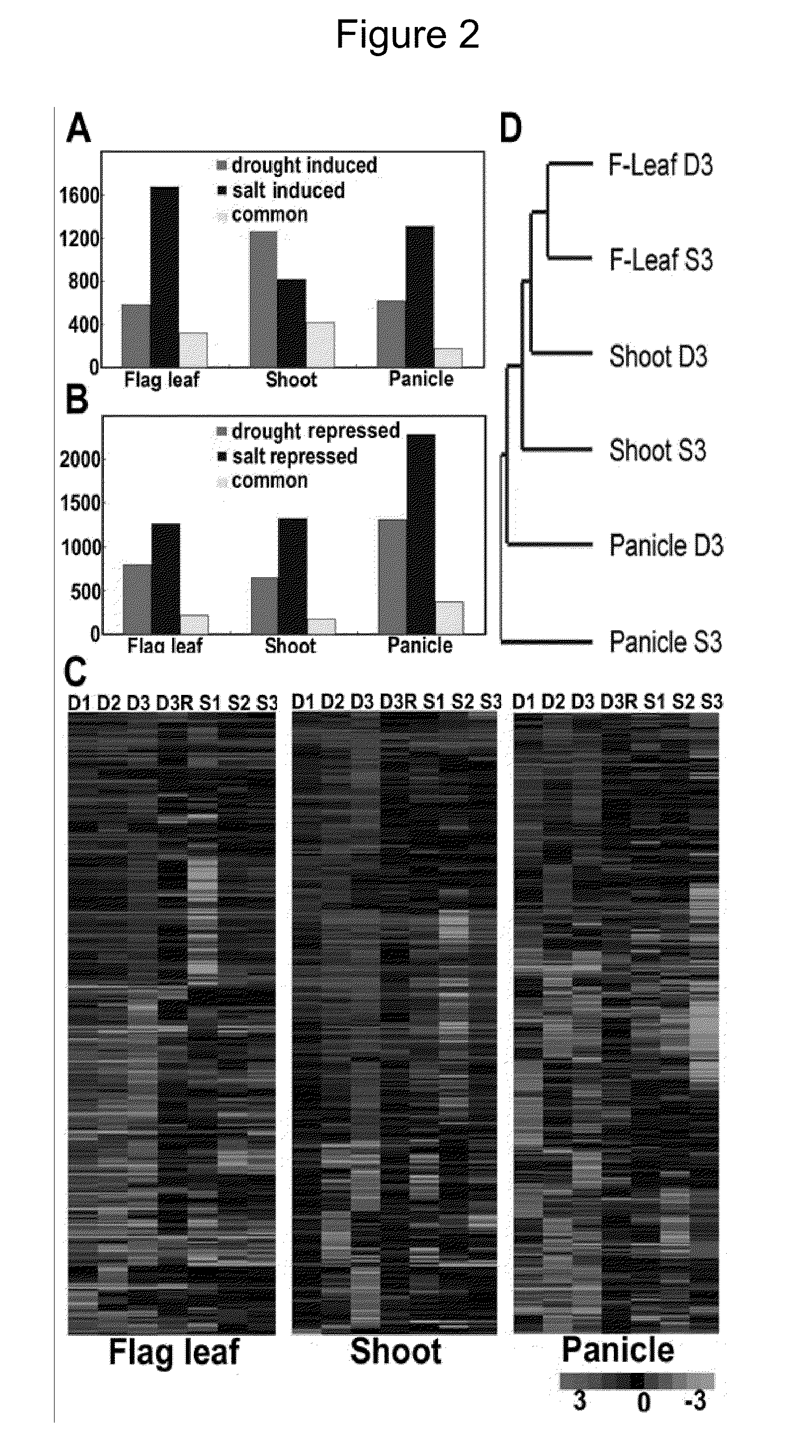
Drought and High Salinity Stress Induced Rice Promoters
InactiveUS20090229014A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesRice plantsGene
Rice promoters described herein promote the expression of drought and high-salinity stress responsive genes of rice so as to enable young and adult rice plants to withstand drought and high salinity stresses.
Owner:BEIJLING KAITUO DNA BIOTECH RES CENT CO LTD
Special insect-derived health-care feed for shrimp fry
PendingCN110432381ADevelopmentExpand applicationFood processingClimate change adaptationAnti stressPrawn
The invention belongs to the technical field of shrimp feed, and particularly relates to a special insect-derived health-care feed for shrimp fry. The health-care feed comprises the following components in parts by weight: 15-20% of black soldier fly dry powder, 5-10% of fish meal, 15-25% of peanut meal, 10-28% of flour, 2-5% of mixed oil, 5-15% of soybean powder and 10-25% of corn flour. The special health-care feed for shrimp fry can enhance the anti-stress capability of shrimp fry, improve the growth speed and improve the survival rate. The growth experiment of penaeus vannamei fry shows that the health-care feed not only can promote the growth of shrimp fry, but also can improve the survival rate of the shrimp fry. The salinity stress experiment, the temperature stress experiment and the desalination standard thickening experiment of the penaeus vannamei fry show that the health-care feed can improve the stress capacity of the penaeus vannamei fry on salinity and temperature change, thereby improving the survival rate of the fry in the desalination standard thickening stage and improving the economic benefit of shrimp fry culture.
Owner:清远海贝生物技术有限公司
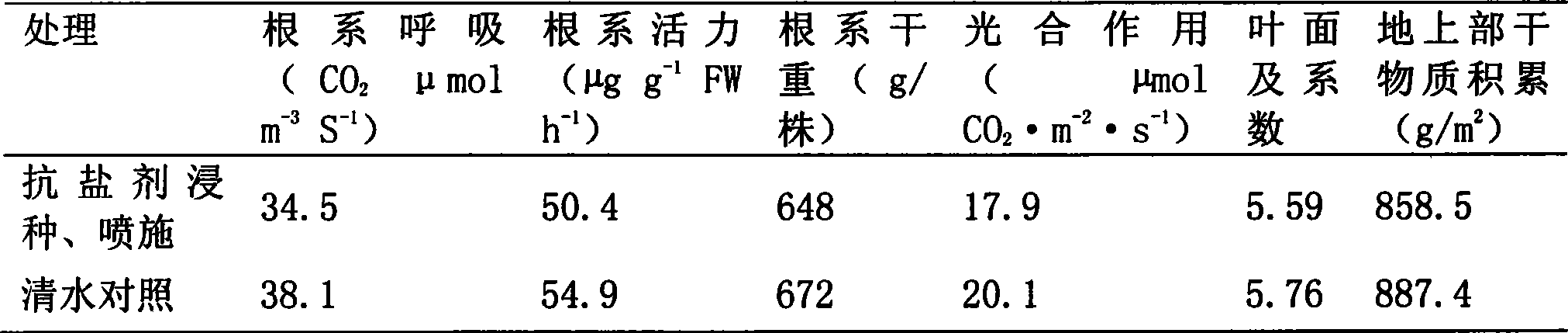
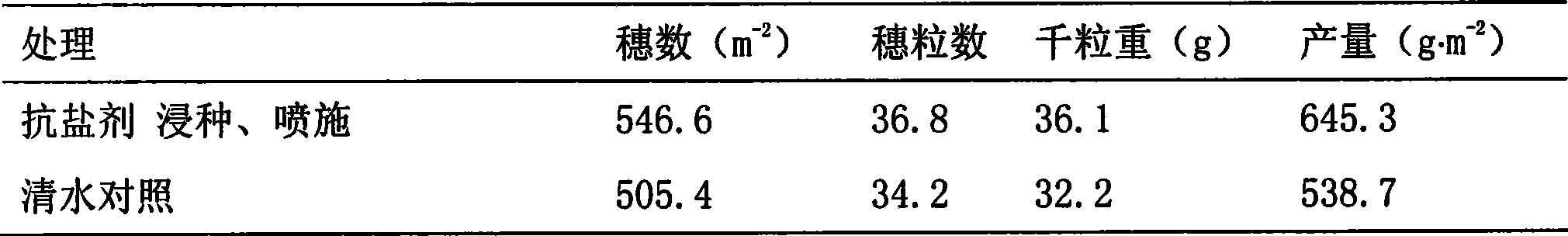
Salt-resistance formulation for improving salt resistance of wheat and method of use thereof
InactiveCN101375688AImprove salt resistanceImprove toleranceBiocideAnimal repellantsSalt resistanceAgricultural science
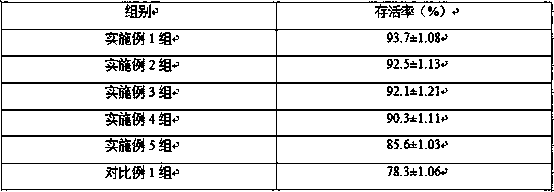
A salt-resistant preparation for improving the salt resistance of the wheat and an application method thereof belong to the technical field of improving the salt resistance of the wheat to increase the wheat production. The method comprises the following steps: 1) soaking in the salt resistance preparation, wherein, with the overall weight being 1kg , the final composite ingredients are 3-4g of Ca (NO3)2, 1.2-1.5g of KH2PO4, 1.5-2g of KI, 0.35g of MnSO4, 10mg of Na2SeO3, 40-60mg of cytokinin, and water in balancing amount; 2) spraying the salt resistant preparation on the surfaces of leaves, wherein, with the overall weight being 1kg, the final composite ingredients are 1-1.2g of Ca (NO3)2, 0.25-0.3g of KH2PO4, 0.35g of KI, 0.1g of MnSO4, 2mg of Na2SeO3, 2-10mg of cytokinin, and water in balancing amount. Wheat seeds are soaked in the salt resistant preparation for one time before being planted, and the salt resistant preparation is sprayed on the surfaces of the leaves after the fifteen days of wheat seedlings turn green in the spring of the next year. The invention has the advantages of significantly improving the ratio of emergence of wheat seeds under high salinity, promoting the growing development of wheat plants, increasing the production of the wheat by 15-20 percent, and being suitable for the soil with salt contents being 0.3 percent.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
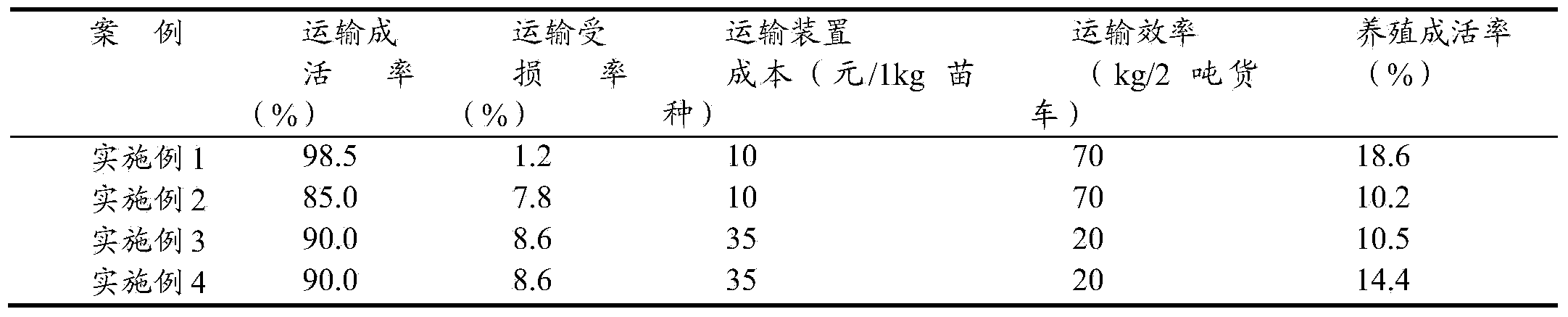
High-efficiency portunus trituberculatus seedling conveying method
ActiveCN103478030AQuality improvementTransport highClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTransport timeBubble chamber
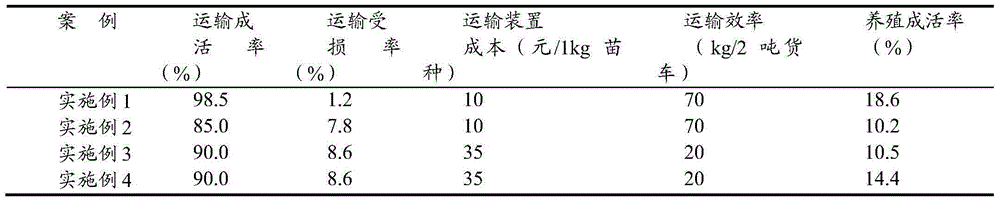
The invention provides a high-efficiency portunus trituberculatus seedling conveying method, and belongs to the technical field of cultivation of portunus trituberculatus. The high-efficiency portunus trituberculatus seedling conveying method comprises the following steps of (1) seedling selection: randomly selecting a first stage of juvenile portunus trituberculatus from a nursery pond by using 72-hour low-salt medial lethal concentration 10.79 of the first stage of the juvenile portunus trituberculatus as dosage, performing a salinity stress experiment, calculating the survival rate after 72 hours, and selecting a second stage of juvenile portunus trituberculatus in a nursery pond with the survival rate higher than 50% as conveying seedlings; and (2) a conveying method: uniformly mixing wheat shells which are soaked and then are drained off and the second stage of the juvenile portunus trituberculatus according to the weight ratio of 1:1 at first, placing the mixture in a seedling bag, inflating oxygen in the seedling bag, binding the opening of the bag by using a rubber band, placing the seedling bag in a bubble chamber, finally, placing biological ice bags in the bubble chamber, and sealing the bubble chamber by using adhesive tapes. By the high-efficiency portunus trituberculatus seedling conveying method, the seedling conveying time can be 10-12 hours, the conveying yield reaches 98.5%, the damage rate of the juvenile portunus trituberculatus reaches 1.2%, and the seedling cultivation survival rate is guaranteed.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Bacillus cereus and application thereof in relieving plant salt stress
ActiveCN113373096ADamage reliefPromote growth and developmentPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyHalophyte
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly discloses bacillus cereus and application thereof in relieving plant salt stress. According to the invention, a growth promoting rhizobacteria is screened from rhizosphere soil of a halophyte suaeda salsa on a coastal mud flat; the strain is identified as bacillus cereus through physiological and biochemical characteristics and 16SrDNA sequence analysis; the strain is named as SSR-7; and the strain has growth promoting characteristics of producing IAA and siderophore at the same time. Culture medium components and fermentation conditions of the SSR-7 are optimized; and the strain is inoculated to rhizosphere of potted tomatoes, so that the growth state of the tomatoes can be remarkably improved under salt stress.
Owner:YANCHENG TEACHERS UNIV
Preparation method of compound feed specially used for aquacultural breeding of prawns
InactiveCN106852416AStrong disease resistanceImprove survival rateFood processingClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention belongs to the field of feeds and relates to a preparation method of a compound feed specially used for aquacultural breeding of prawns. The invention provides a preparation method of a feed especially for high-salinity breeding of penaeus vannamei. The feed can satisfy demand on nutrition for the penaeus vannamei under high salinity (higher than 3%), is good in stability in water, has strong anti-stress capability, is high in survival rate and accelerates growth, is low in feed coefficient, and is economical and practical, thereby solving the problems of slow growth, high diseases incidence and low survival rate of the penaeus vannamei under high salinity stress breeding. The feed can promote healthy development of the aquacultural breeding of prawns.
Owner:容家杨
Abiotic stress tolerance conferred by J-domain-containing proteins
InactiveCN101553569AReduce water consumptionPlant growth regulatorsPlant peptidesNucleotide sequencingAbiotic stress
The invention provides methods and constructs for enhancing the expression of nucleotide sequences encoding proteins that comprise at least a DnaJ-type J-domain to provide tolerance to plants or plantcells against abiotic stress, especially dehydration and salinity stress.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Immersed dunaliella salina liquid ultrafiltration system and dunaliella salina liquid concentration method
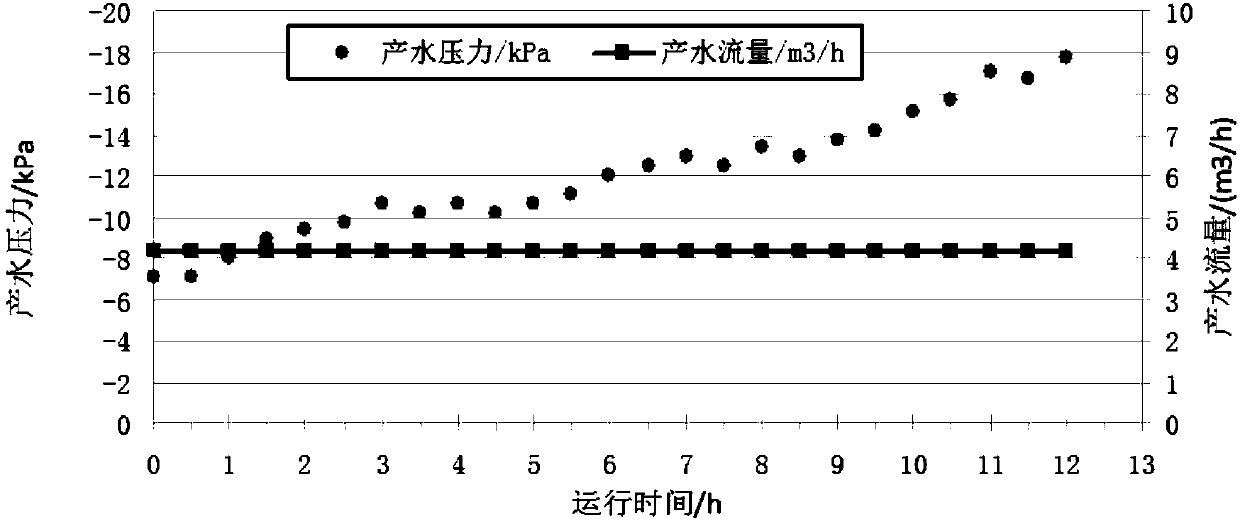
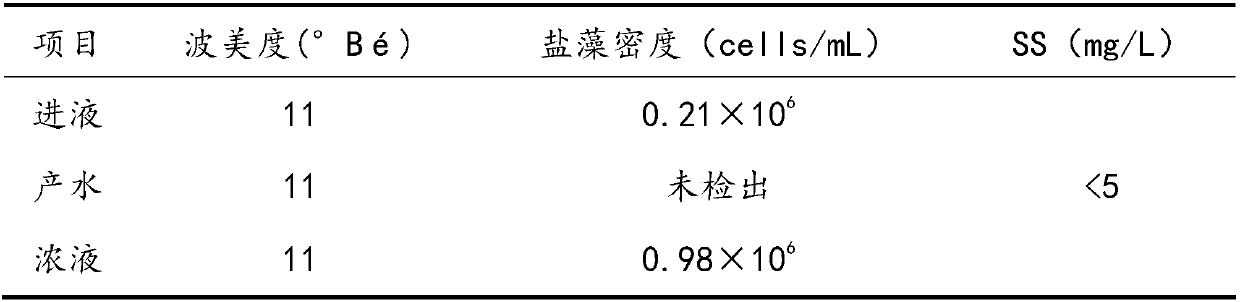
The invention provides an immersed dunaliella salina liquid ultrafiltration system. The system comprises a track tank, an immersed ultrafiltration assembly, a concentration tank, a water producing system, an aeration system and a backwashing system. By means of a dunaliella salina liquid concentration method of the ultrafiltration system, dunaliella salina heavily proliferated under the approximate optimum growth salinity condition is effectively concentrated, the size of low-salinity dunaliella salina liquids is greatly reduced while the biomass is kept, high brine amount added to realize thehigh-salinity stress growth condition later is reduced, the death rate of dunaliella salina in the concentration process can be reduced to the greatest extent through precise control on ultrafiltration work pressure, and more effective biomass can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN MOTIMO MEMBRANE TECH
Low-fish-meal compound feed for litopenaeus vannamei suitable for low-salinity culture conditions
ActiveCN112293570AImprove resistance to salinity stressGuarantee the breeding effectFood processingClimate change adaptationEssential amino acidMultivitamin
The invention discloses a low-fish-meal compound feed for litopenaeus vannamei suitable for low-salinity culture conditions. The feed is prepared from, by weight, 60-75 parts of protein-sourced raw material, 3-6 parts of fat-sourced raw material, 22-28 parts of sugar-sourced raw material, 0.3-1 part of anti-salinity stress substance, 0.05-0.3 part of immunopotentiator, 0.2-1 part of essential amino acid, 0.5-2 parts of compound vitamin, 0.25-0.45 part of monovitamin, 0.5-2 parts of compound mineral salt, 0.01-0.05 part of an enzyme preparation, 1-2 parts of a phosphorus raw material and 0.9-1.1 parts of a feed adhesive. According to the feed, the content of fish meal is reduced to 14-16 wt% by balancing the composition of amino acids, and the salinity-resistant stress substance and immunopotentiator are added to improve the culture effect under low salinity. The litopenaeus vannamei fed with the low-fish-meal compound feed is high in growth speed, can utilize the feed well, has high survival rate, good oxidation resistance and high salinity stress resistance under the low-salinity culture condition, and the culture effect basically the same as that of common high-fish-meal feed canbe achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY +1
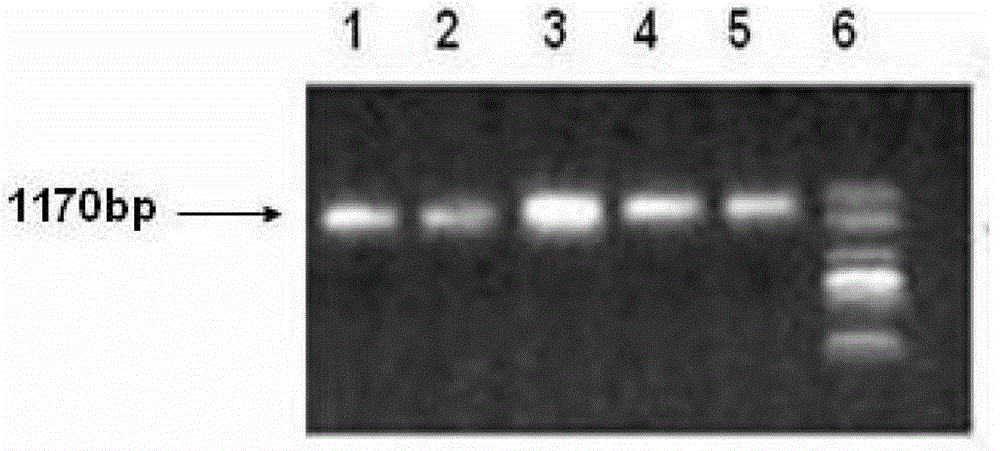
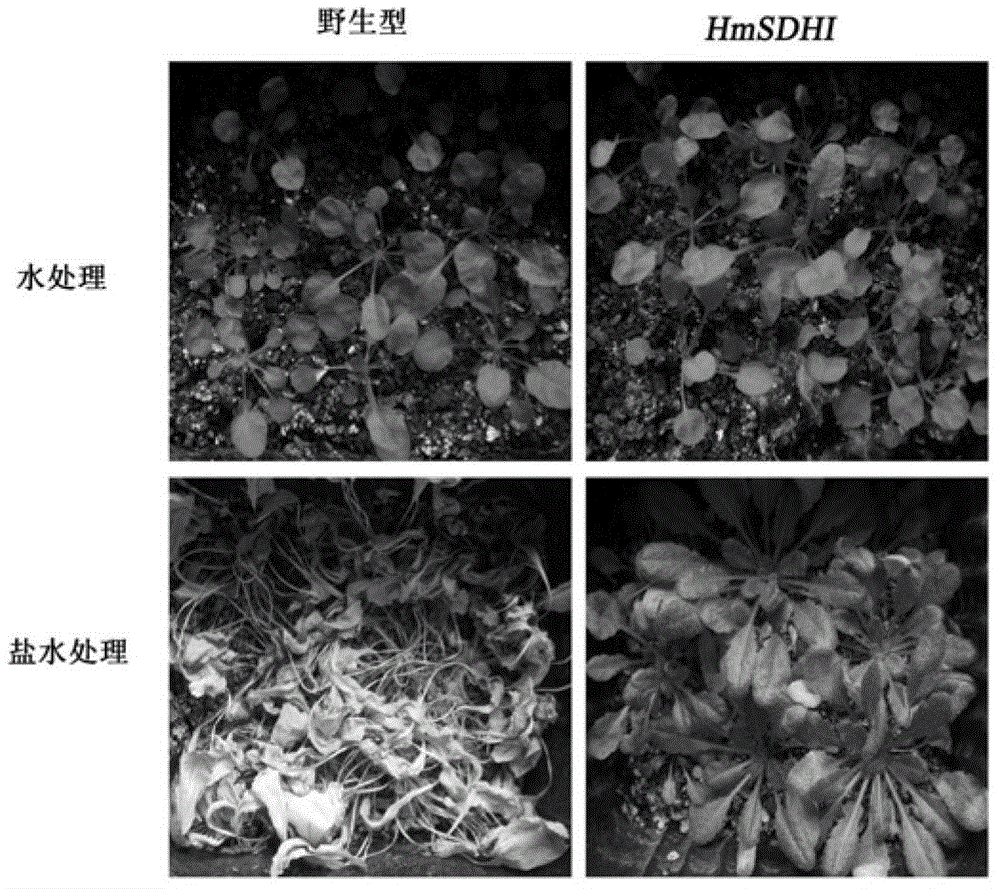
Sorbitol dehydrogenase gene derived from haloarcula marismortui and applications thereof
The invention relates to a sorbitol dehydrogenase gene derived from haloarcula marismortui and applications thereof. The sorbitol dehydrogenase gene is synthesized by a manual method. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO 1. The coded amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO2. Results of arabidopsis thaliana transformation by utilization of the sorbitol dehydrogenase gene by adopting an agrobacterium floral-dip method show that: the sorbitol dehydrogenase gene can successfully improve the salt tolerance performance of transgenic arabidopsis thaliana, so that the sorbitol dehydrogenase gene can be widely applied in plants under high-salinity stress.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
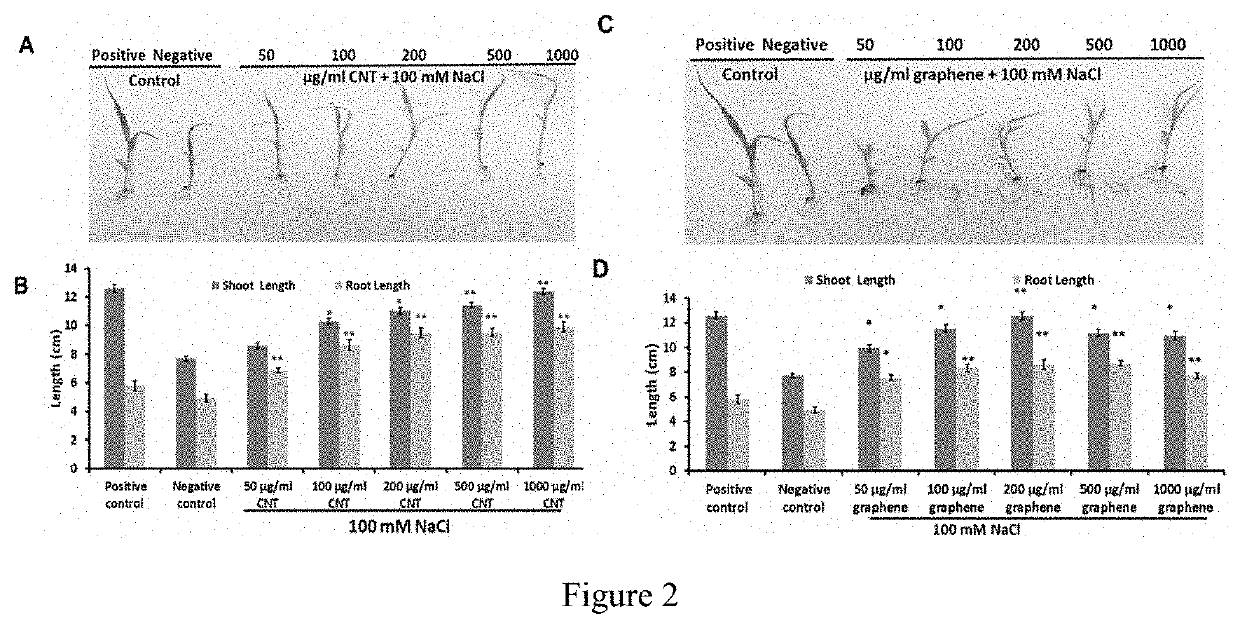
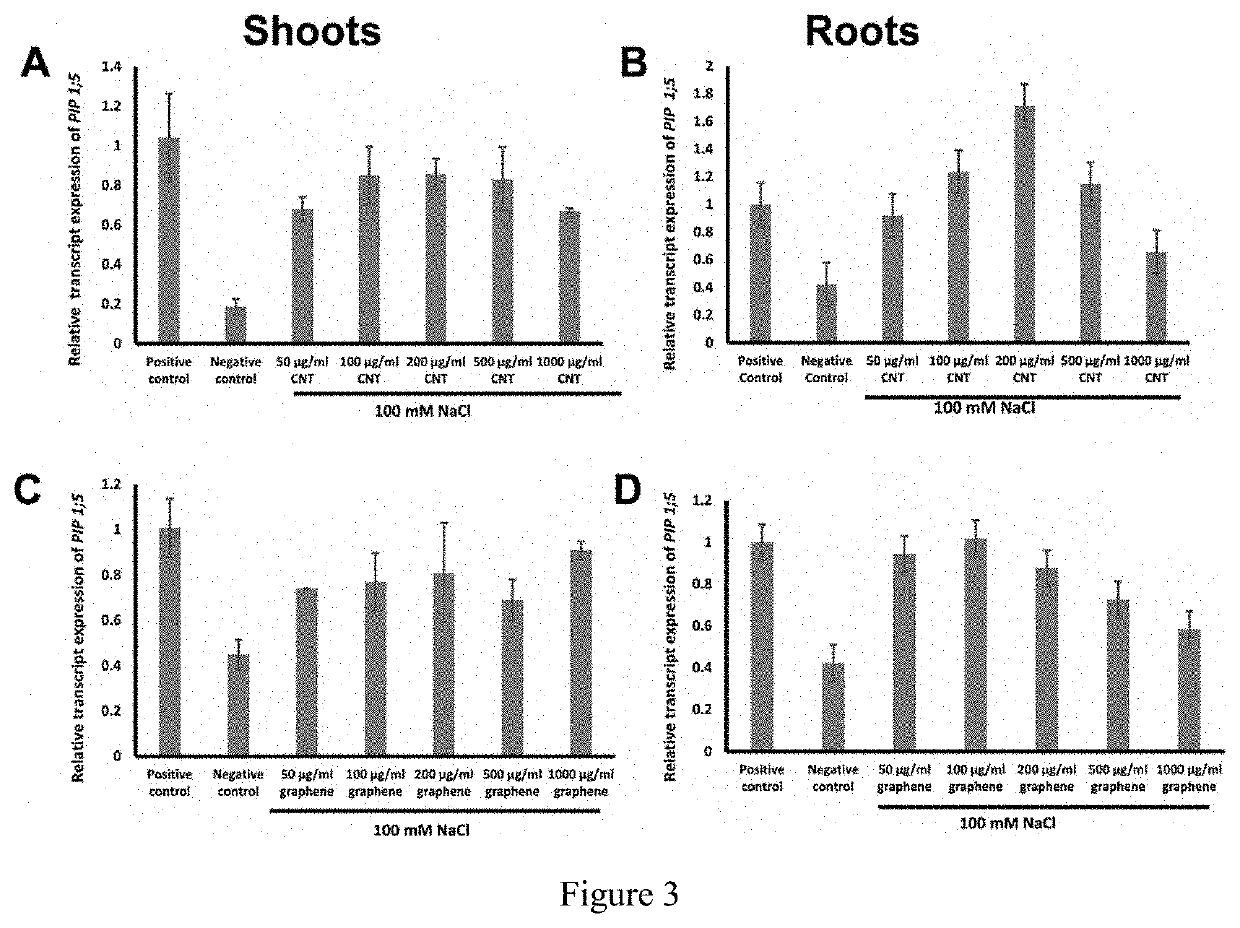
Method for reduction of salt stress symptoms during plant cultivation in saline conditions by application of carbon-based nanomaterials (CBN) to growth medium and applications of same
PendingUS20210068336A1Reduced germination rateShorten the lengthMaterial nanotechnologySeed and root treatmentCarbon based nanomaterialsPlant cultivation
A method for reducing salinity stress symptoms in a seed plant, comprising the step of adding carbon-based nanomaterials into a salinity growth medium in which the seed plant is cultivated, the salinity growth medium is in a salinity condition which causes the seed plant cultivated in the growth medium demonstrates the salinity stress symptom.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
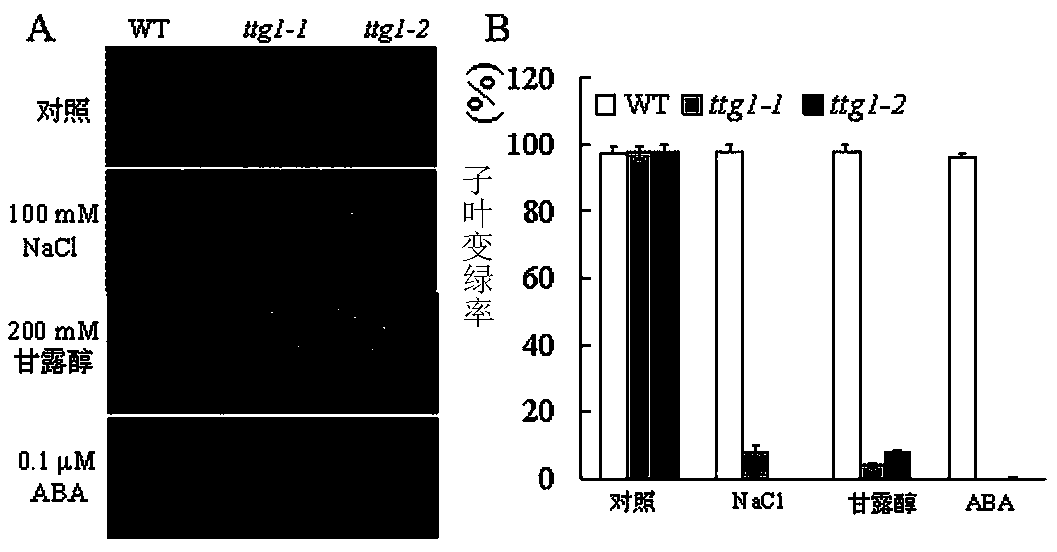
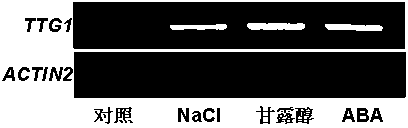
Novel application of arabidopsis TTG1 genes to plant salinity-resisting and drought-resisting aspects
InactiveCN104263735ASalt and drought resistanceExcellent salt and drought tolerant plant varietiesClimate change adaptationFermentationEngineered geneticGMO Plants
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering application, and particularly relates to application of arabidopsis TTG1 genes to cultivation of new salinity-resisting and drought-resisting plant varieties. A code of arabidopsis genomes is At5g24520. By means of the genes, arabidopsis can tolerate the salinity stress or drought stress growing environment; plants with the genes transformed can tolerate the salinity stress or drought stress growing environment. According to a series of experimental studies, it is found that regulation plants with the gene specificity show salinity-resisting and drought-resisting characteristics on osmotic stress reactions caused by salinity and drought; the huge potential application function of the genes on the plant salinity-resisting and drought-resisting aspects is proved; new transgenic plant varieties related to the salinity stress resistance and the drought stress resistance can be obtained; the salinity-resisting and drought-resisting functions of the plants are achieved accordingly. Theoretical and production practice foundations are laid for cultivating the new salinity-resisting and drought-resisting transgenic crop varieties.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Additive and feed for improving anti-stress capability of penaeus vannamei boone and application of additive and feed
PendingCN113712136AReduce stressImprove antioxidant capacityFood processingClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention discloses an additive for improving the anti-stress capability of penaeus vannamei boone. The additive is prepared from the following components: vitamin C and myo-inositol in a mass ratio of (200-300) to (200-300). The invention further discloses a feed for improving the anti-stress ability of the penaeus vannamei boone. The feed is prepared from a basal feed, vitamin C and myo-inositol, and in each kilogram of the feed, the content of the vitamin C is 200-300mg, and the content of the myo-inositol is 200-300mg. The invention further discloses application of the additive and the feed. The additive and the feed can improve the salinity stress resistance, hypoxia stress resistance, ammonia nitrogen stress resistance and high copper stress resistance of the penaeus vannamei boone, especially improve the environmental stress resistance of the penaeus vannamei boone and relieve oxidative stress caused by high copper.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for screening sinonovacula constricta with strong salt tolerance by utilizing osmotic pressure
PendingCN111838035ALower requirementEasy to operateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBiotechnologySalt resistance
The invention discloses a method for screening sinonovacula constricta with strong salt tolerance by utilizing osmotic pressure. The method comprises the following steps: culturing sinonovacula constricta in a same culture environment, performing grouping salinity stress treatment, determining osmotic pressure and carrying out final screening. By screening the sinonovacula constricta through the method, the sinonovacula constricta with good salt resistance can be effectively screened out, and the method is simple, free of complex equipment, high in screening efficiency and high in commercial value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Western balsam poplar PtrZFP103 gene as well as coding protein and application thereof
InactiveCN106399327AIncrease resistanceReduce damagePlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideMolecular breeding
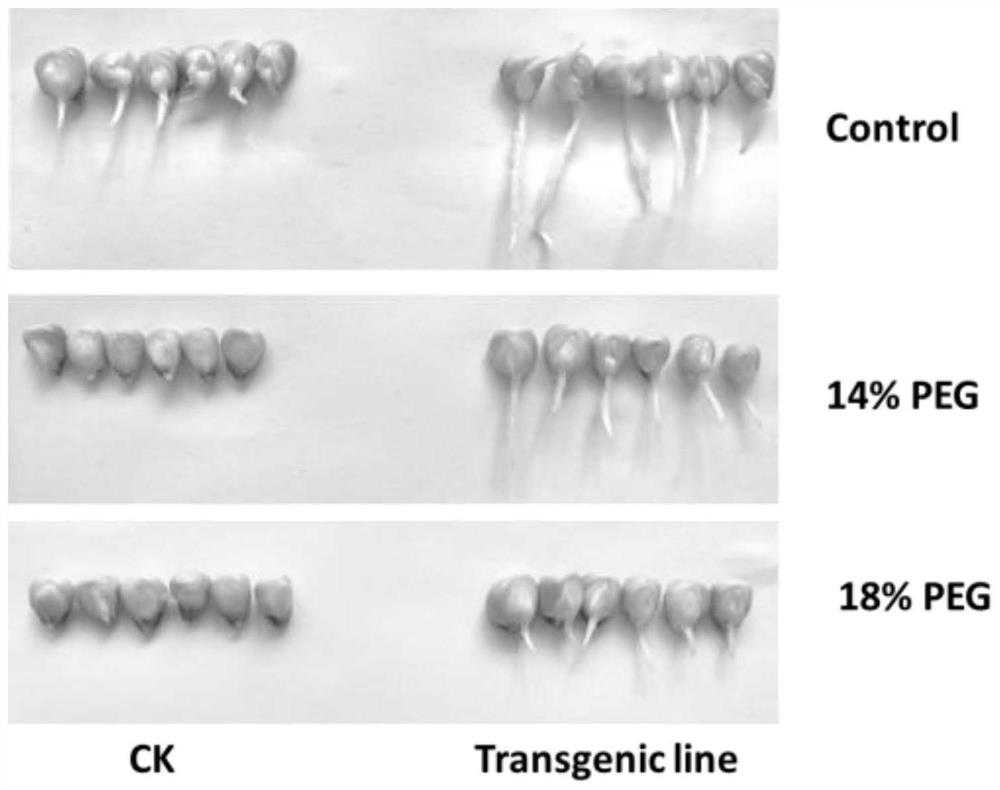
The invention discloses a western balsam poplar PtrZFP103 gene as well as a coding protein and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. A nucleotide sequence of the western balsam poplar PtrZFP103 gene is shown as SEQ ID No: 1. An amino acid sequence of the coding protein of the western balsam poplar PtrZFP103 gene is shown as SEQ ID No: 2. The application is to improve the anti-adversity ability of a plant under high salinity stress. A full-length sequence of a coding region of the western balsam poplar PtrZFP103 gene is 507bp, and 168 amino acids are coded. The damage extent of transgenic line cells is discovered to be obviously lower than that of WT under the high salinity stress, and physiological index results also verify that the anti-adversity ability of an overexpression line of the PtrZFP103 gene is obviously higher than that of the WT. As the PtrZFP103 is discovered to specifically improves the resistance of the plant under the high salinity stress, a high salinity-resistant new variety of a PtrZFP103 transgene can be cultivated, and important significance is supplied for forest tree molecular breeding on the aspect of cultivating the new variety.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
A kind of sorbitol dehydrogenase gene derived from Halobacterium dead sea and its application
The invention relates to a sorbitol dehydrogenase gene derived from haloarcula marismortui and applications thereof. The sorbitol dehydrogenase gene is synthesized by a manual method. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO 1. The coded amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO2. Results of arabidopsis thaliana transformation by utilization of the sorbitol dehydrogenase gene by adopting an agrobacterium floral-dip method show that: the sorbitol dehydrogenase gene can successfully improve the salt tolerance performance of transgenic arabidopsis thaliana, so that the sorbitol dehydrogenase gene can be widely applied in plants under high-salinity stress.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
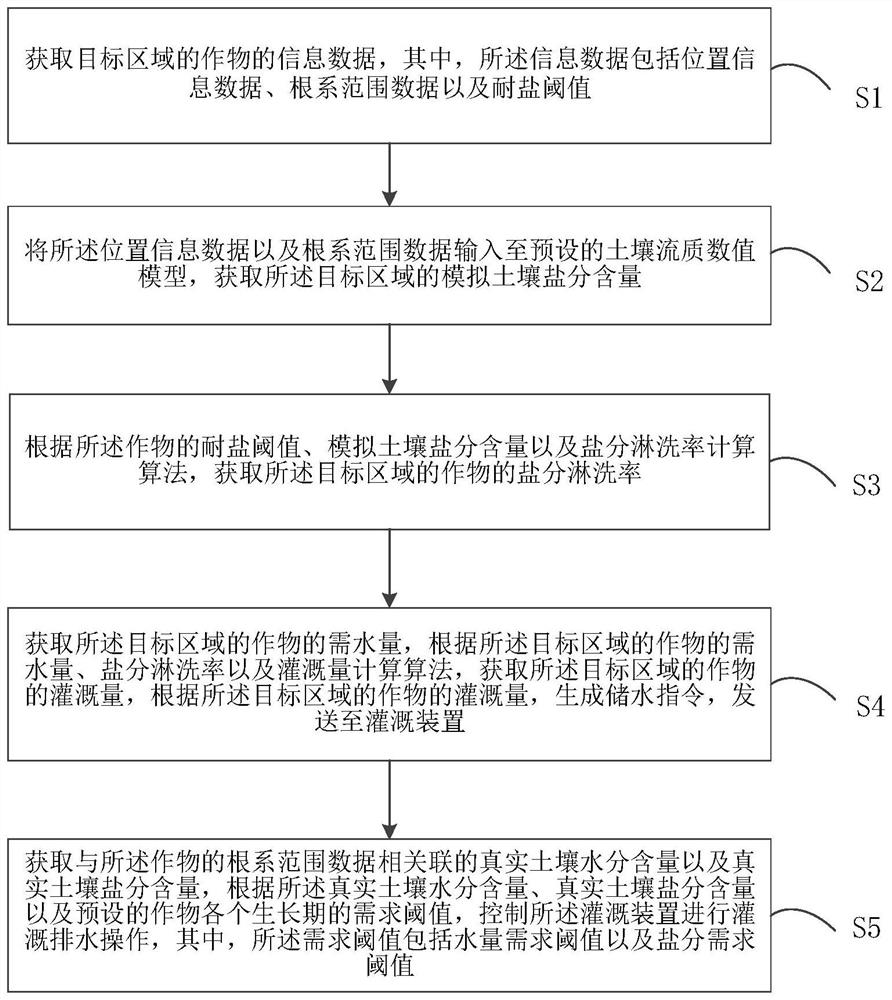
Crop irrigation method, device and equipment based on salinity elution rate and storage medium
ActiveCN114651708AReduce stressGuaranteed outputClimate change adaptationWatering devicesSoil scienceSoil depth
The invention relates to the technical field of irrigation, in particular to a crop irrigation method based on salinity elution rate, which is characterized in that the salinity elution rate of crops is calculated by combining the influence of salinity stress, water quality and the like on the irrigation amount of the crops, and the salinity elution rate of the crops is calculated by monitoring the moisture and salinity of the soil depth corresponding to the root systems of the crops. The irrigation device is controlled to conduct irrigation and drainage operation, redundant salt of crop roots is removed, the stress effect of the salt on crop growth is reduced, the crop yield is guaranteed, efficient utilization of existing water resources is achieved, and meanwhile waste of the water resources is reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOGRAPHY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for quickly realizing short range biological denitrification by salinity suppressing combined with fuzzy control
ActiveCN100498832CAchieve normal startupShorten the timeTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentStart timeSludge
A device for fast realization of shortcut biological denitrification through salinity inhibition combined with fuzzy control and methods thereof pertain to the technical field of sewage biological denitrification of SBR method and are suitable for sewage disposal in nitrogen-containing industry and advanced treatment of town sewage. The invention adjusts the mass concentration of crude salt of inlet water in 5-7.5 g / L (Cond value is 8.92-12.95 mc / cm) to quick realize the accumulation of nitrite in normal temperature above 90 percent by adding crude salt of a certain concentration (the crude salt is obtained directly by basking seawater without any processing) and combining with controlling the time of nitrification and denitrification in real time, the method is designed to solve the problems of long starting time of the existing shortcut biological denitrification technology and difficulty to maintain. The method can not only fast realize the accumulation of nitrite in high proportion stably in reaction system to enable the nitrating types to be fast and long-time stabilized on shortcut nitrification, but also has the advantages of low cost, flexibility in operation and management and seldom causing sludge bulge, etc.
Owner:CHONGQING KANGDA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION IND GRP
Method and device for detecting degree of plant saline-alkali stress
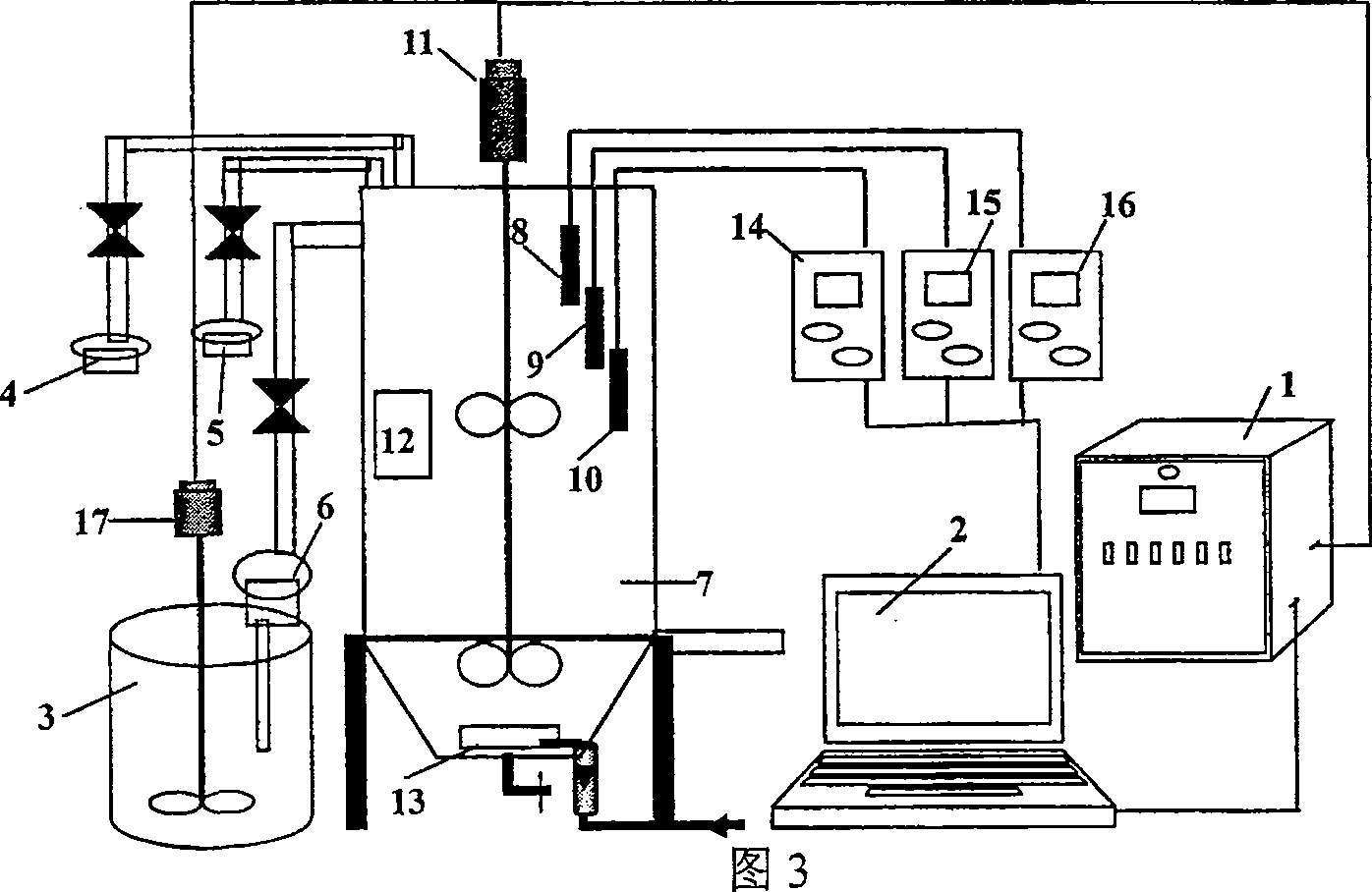
ActiveCN110907393BSo as not to damageHigh-precision detectionClimate change adaptationMaterial analysis by optical meansFeature extractionEngineering
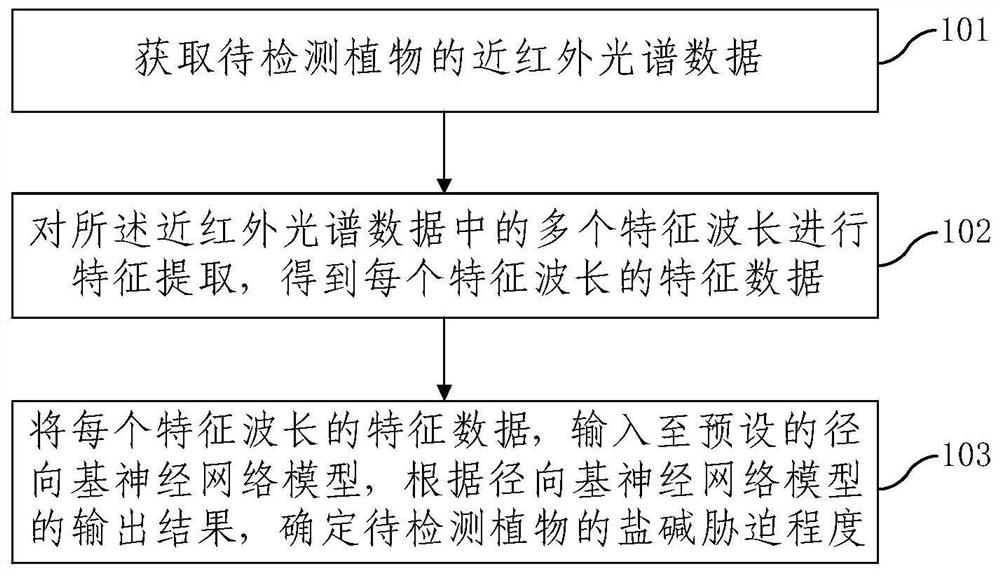
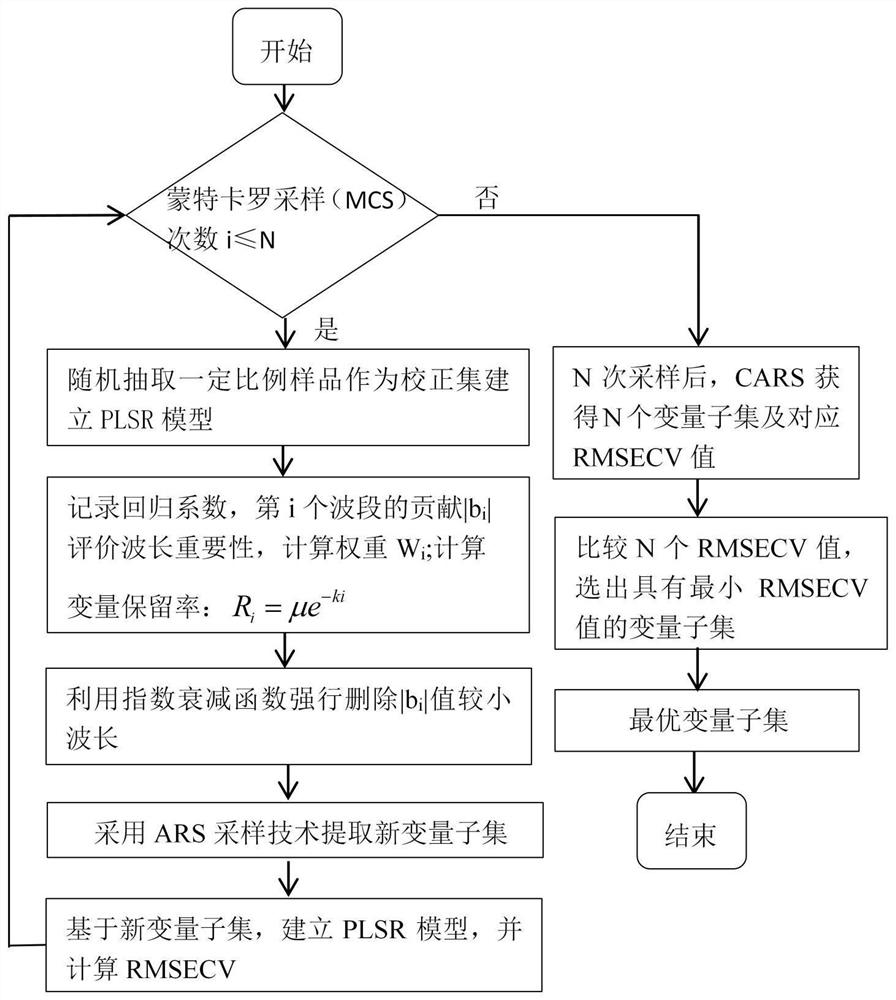
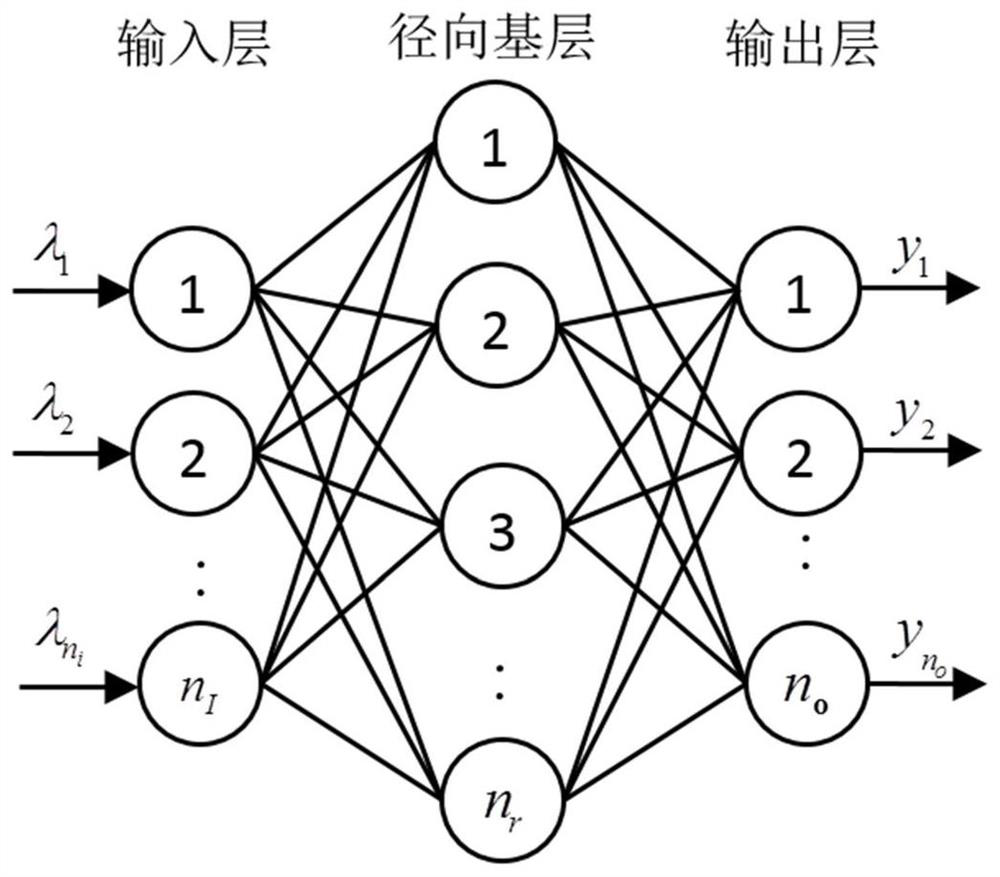
The embodiments of the present invention provide a method and device for detecting the degree of saline-alkali stress in plants. The method includes: acquiring near-infrared spectrum data of the plant to be detected; performing feature extraction on multiple characteristic wavelengths in the near-infrared spectrum data to obtain each characteristic data of each characteristic wavelength; input the characteristic data of each characteristic wavelength into a preset radial basis neural network model, and determine the degree of saline-alkali stress of the plant to be detected according to the output result of the radial basis neural network model ; Wherein, the radial basis neural network model is obtained after training based on the near-infrared spectrum data samples labeled as the known degree of saline-alkali stress. Compared with the current method, this method does not require excessive measuring equipment, and only needs to obtain near-infrared spectral data, so that the canopy leaves will not be damaged. At the same time, through the trained neural network, the degree of saline-alkali stress can be detected simply, efficiently and accurately.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for selecting plant symbiotic microbes, and microbial mixture
ActiveUS11363820B2Improve stress conditionImprove toleranceBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
A kind of high-efficiency portunus trituberculatus seed transportation method
ActiveCN103478030BQuality improvementImprove the survival rate of breedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAdhesive beltHusk
A high-efficiency transport method for portunus trituberculatus seedlings belongs to the technical field of portunus trituberculatus cultivation, and comprises the following steps: (1) seedling selection: taking the dose of 10.79 of the low-salt semi-lethal concentration of young crabs in the I stage for 72 hours, randomly selecting I For juvenile crabs in the salinity stress experiment, the survival rate was counted after 72 hours, and the juvenile crabs in the second stage in the nursery pond with a survival rate of more than 50% were selected as the seedlings for transportation; (2) transportation method: first soak and drain wheat husks with II Crab juveniles are evenly mixed according to the weight ratio of 1:1, the mixture is put into the seed bag, then oxygen is filled into the seed bag, the bag mouth is tied tightly with a rubber band, and the seed bag is put into the foam box, and finally Put the biological ice bag into the foam box, and seal the foam box with adhesive tape; the present invention enables the seedlings to be transported continuously for 10-12 hours, the transportation survival rate is 98.5%, and the damage rate of young crabs is 1.2%, which ensures the survival of seedling breeding Rate.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for Heterologous Synthesis of γ-polyglutamic Acid in Plants to Improve Plant Stress Resistance and Yield
ActiveCN113512562BImprove stress resistanceIncrease productionOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyHeterologous
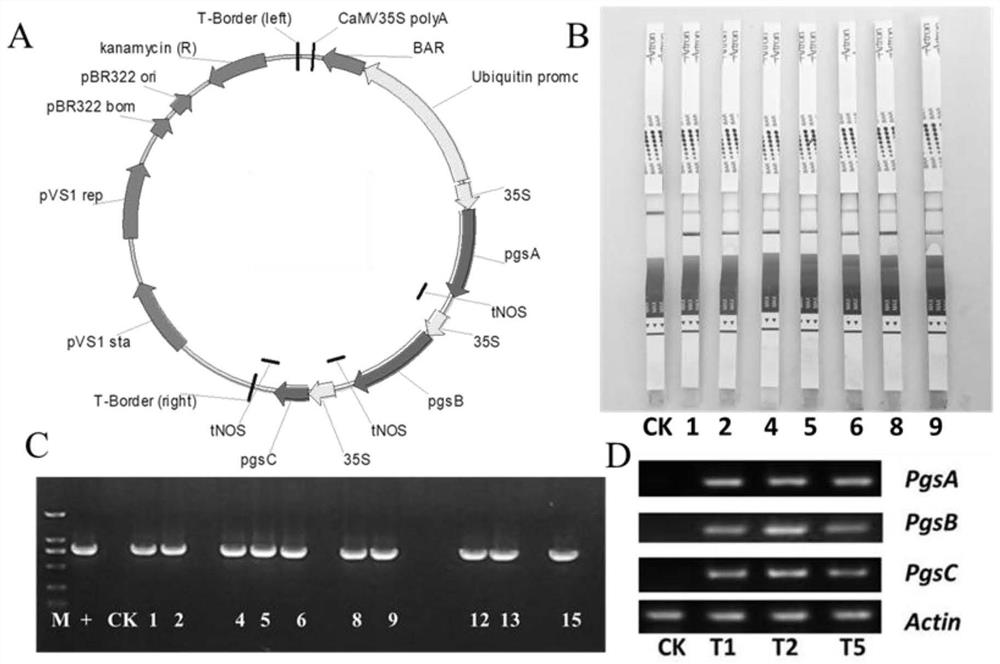
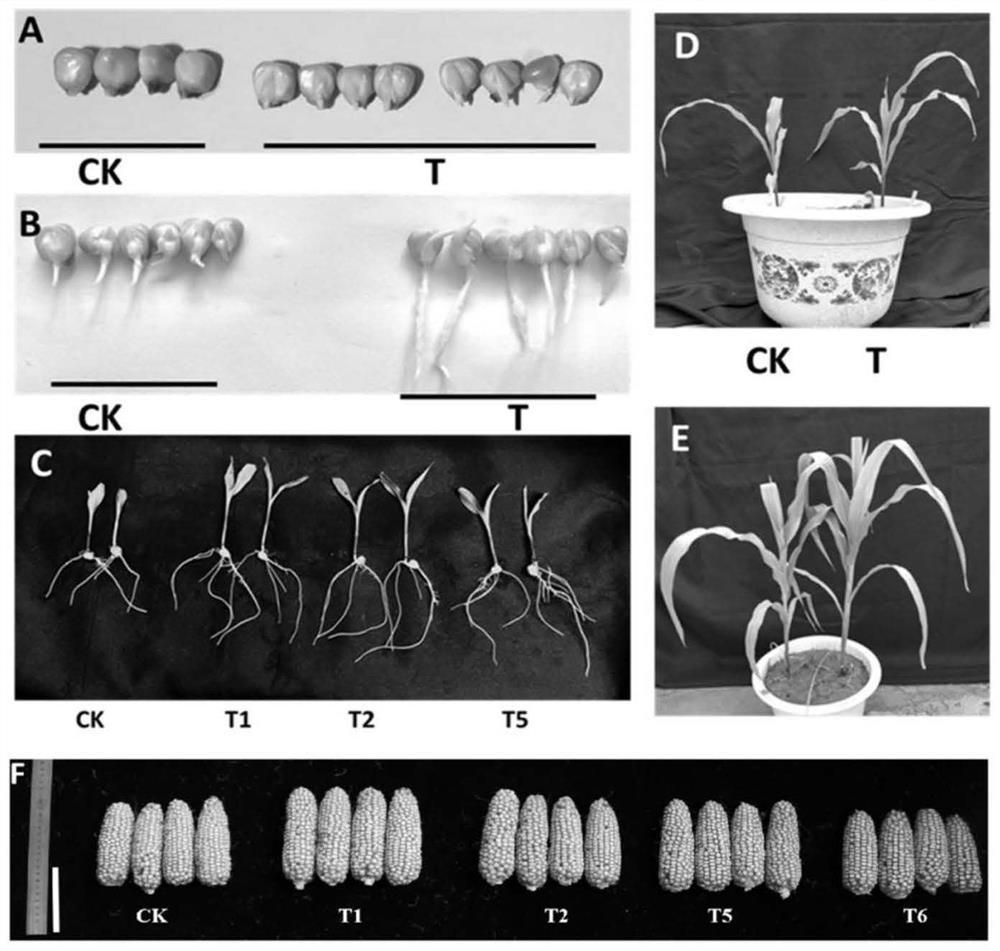
The invention discloses a method for heterologously synthesizing gamma-polyglutamic acid in plants to improve plant stress resistance and yield, which is to clone three key enzyme genes PgsA and PgsA for synthesizing gamma-PGA from a strain producing gamma-PGA PgsB, PgsC, and re-synthesize the codon-optimized gene sequences of PgsA, PgsB, and PgsC according to the codon preference in plants, and connect them into the vector pU130‑bar to obtain the plant expression vector PGA001, which was transferred into the In plants, a new line of transgenic plants producing γ-polyglutamic acid is obtained. Experiments have proved that the new line of transgenic maize obtained by the method of the present invention can not only improve drought resistance but also salt resistance, and can also significantly increase the biomass of maize under drought stress conditions and normal growth conditions. The above results indicate that the method of the present invention is a green, efficient and sustainable solution to the stable or reduced yield of crops under drought, water shortage, and saline-alkali stress. It can be widely used in drought-resistant, salt-tolerant molecular breeding and new Breeding.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Modified biochar as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114702351AWell-developed microporous structureImprove convenienceAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersEdaphicPlant soil
The invention discloses modified biochar and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medicinal plant planting, the preparation method of the modified biochar provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) diluting a hydrogen peroxide solution with a solution containing phosphorus and potassium compounds to obtain a modified solution; (2) uniformly mixing and stirring biochar and the modified solution, standing, filtering and drying to obtain modified biochar; according to the application, on one hand, soil and modified biochar are mixed according to the mass ratio of 100: (1-5), and sowing is conducted after incubation is conducted for 0.5-2 months. By utilizing the characteristics of increased specific surface area, oxygen-containing functional groups, phosphorus elements, reduced chloride ions and the like of the modified biochar, the modified biochar is applied to planting soil, so that the defects that nutrients of the biochar are imbalanced, salt stress is easily caused by excessive addition and the like are overcome; the physicochemical property, the water holding capacity, the nutrient level and the beneficial microorganism abundance of the soil are comprehensively improved, so that the yield and the quality of medicinal plants are improved.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Judgment method for viability of juvenile eriocheir sinensis
ActiveCN113412804AImprove qualityImprove reliabilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileAnimal science
The invention discloses a judgment method for viability of juvenile eriocheir sinensis, and relates to the field of river crab culture in the modern agricultural industry. According to the judgment method for the viability of the juvenile eriocheir sinensis, the viability of the juvenile eriocheir sinensis is judged by analyzing the stress expression and osmotic pressure regulation condition of the eriocheir sinensis under salinity stress. The judgment method for the viability of the juvenile eriocheir sinensis established by the invention has extremely good reliability, the breeding resources from the juvenile crab to the adult crab stage are saved, and meanwhile, the survival of the superior and the inferior is carried out according to the judgment result of the viability, so that the product quality of the adult crab after the eriocheir sinensis is fattened can be effectively improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
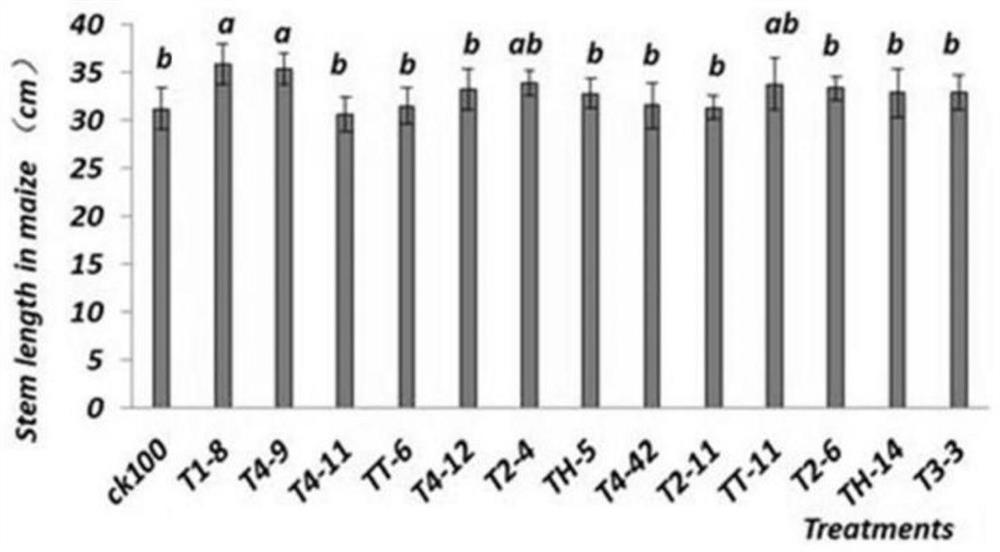
A rhizosphere growth-promoting bacterium that enhances crop salt tolerance and its microbial fertilizer and application
ActiveCN110117560BIncrease productionImprove physical and chemical propertiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
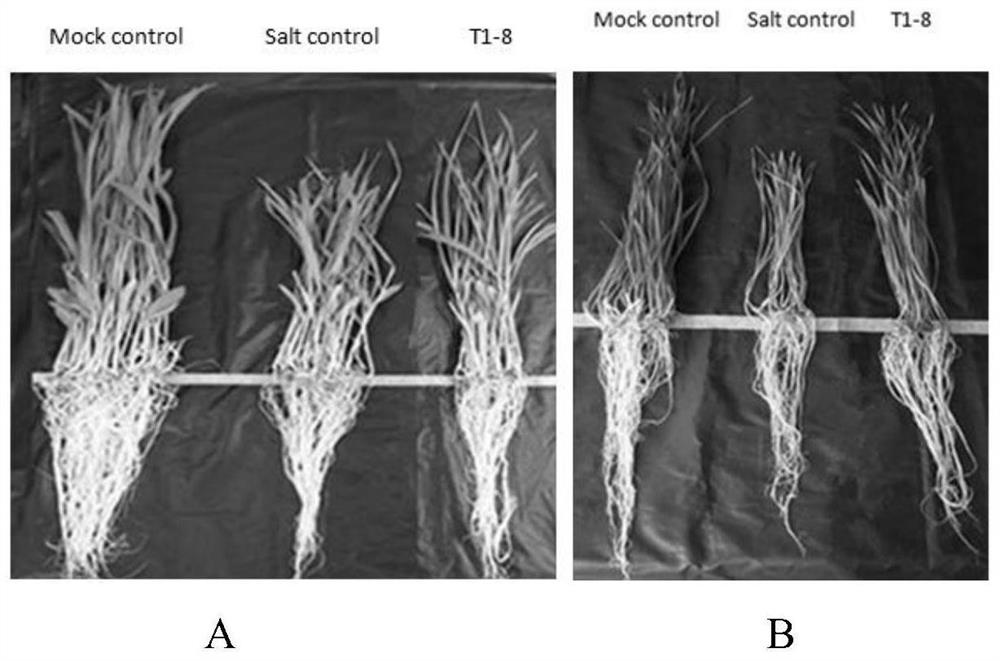
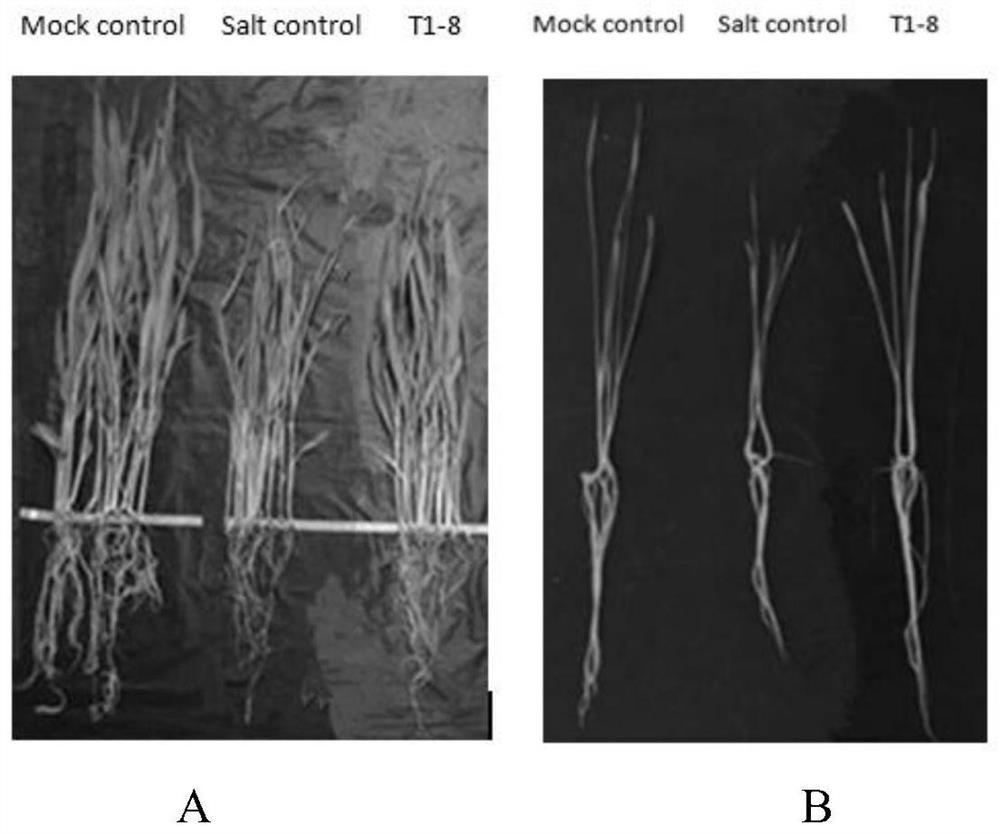
The invention discloses a rhizosphere growth-promoting bacterium for enhancing the salt-tolerant ability of crops, microbial fertilizer and application thereof. The Bacillus paralicheniformis T1-8 provided by the present invention has a preservation number of CGMCC No.17335. The bacterial strain is inoculated in potted corn and wheat rhizosphere, and can improve the growth indexes of corn and wheat under salt stress. The fermented bacterial liquid is uniformly mixed with common cow dung, pig manure, straw, and composted, and then secondarily fermented to produce a microbial organic fertilizer. The microbial organic fertilizer can increase corn yields in saline-alkali land and improve soil physical and chemical properties to a certain extent. The invention has great significance for the development of functional microbial organic fertilizers (enhancing crops tolerance to salt stress, improving crop yield in saline-alkali land).
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
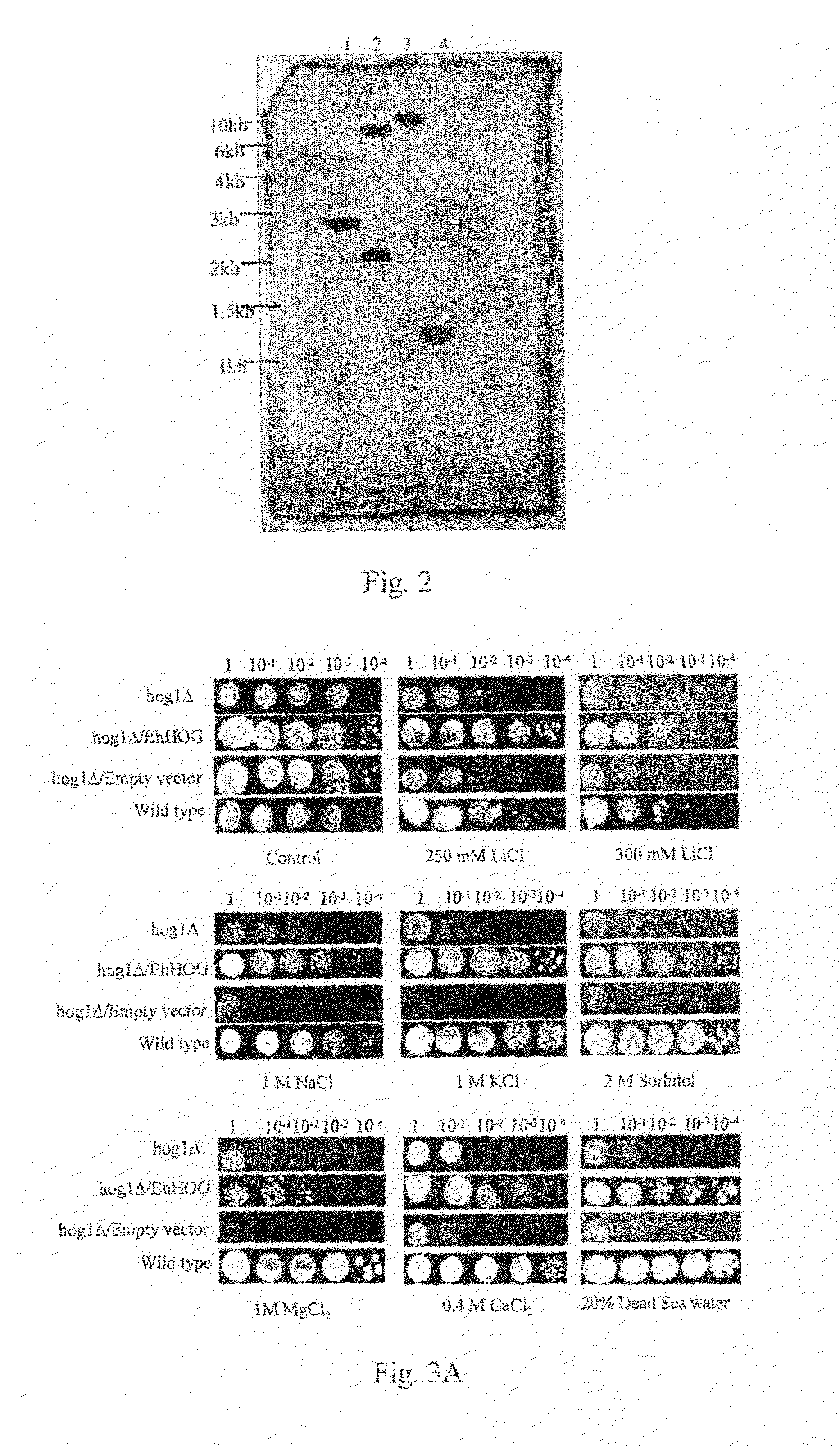
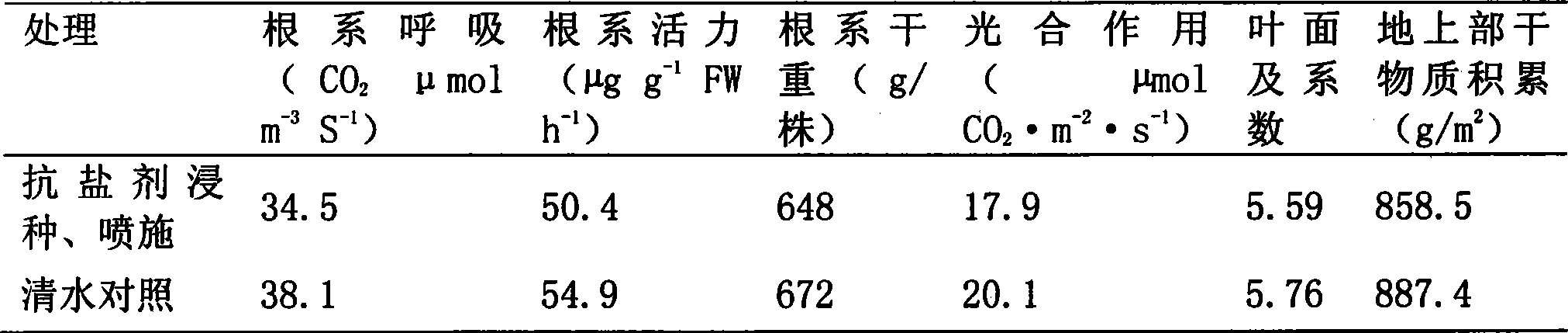
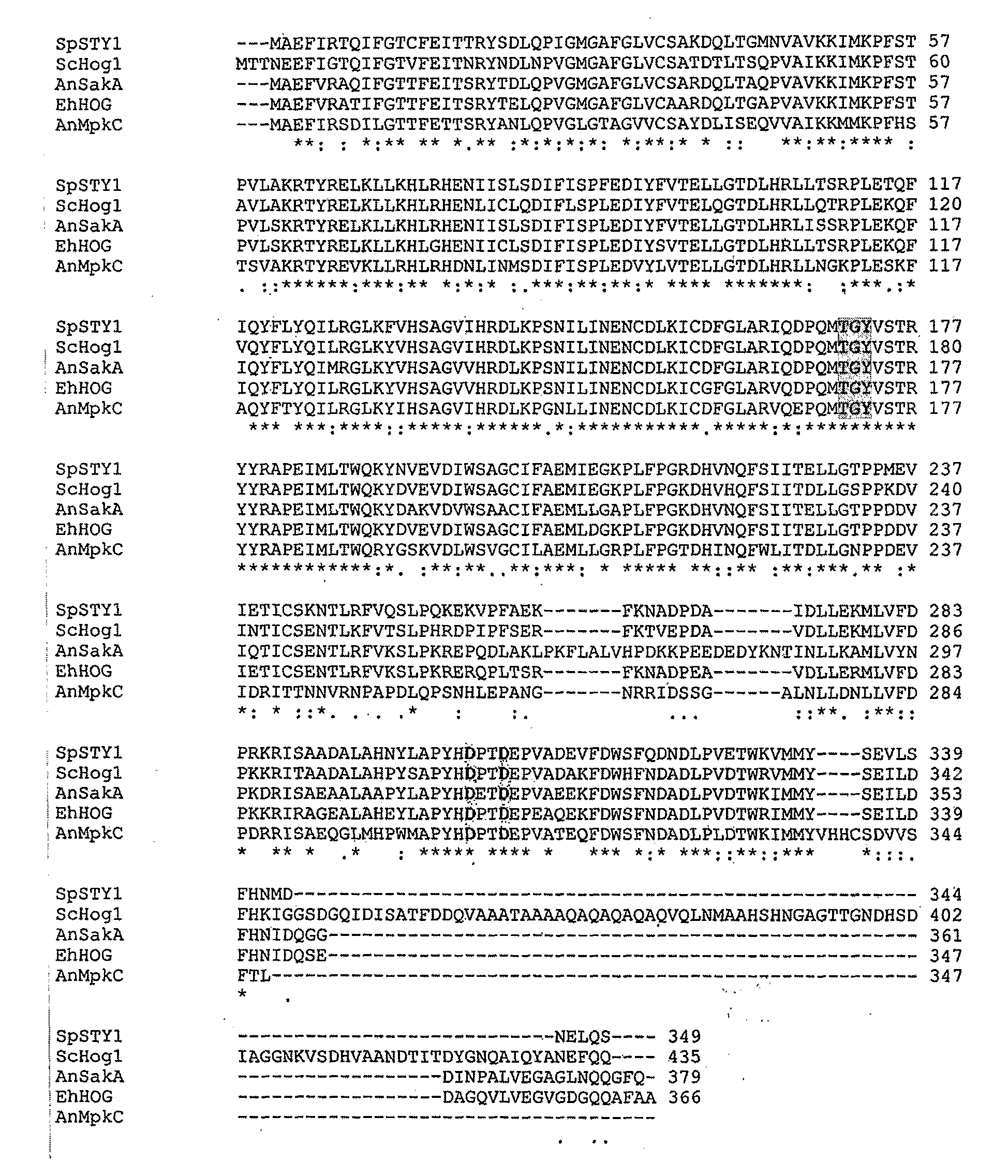
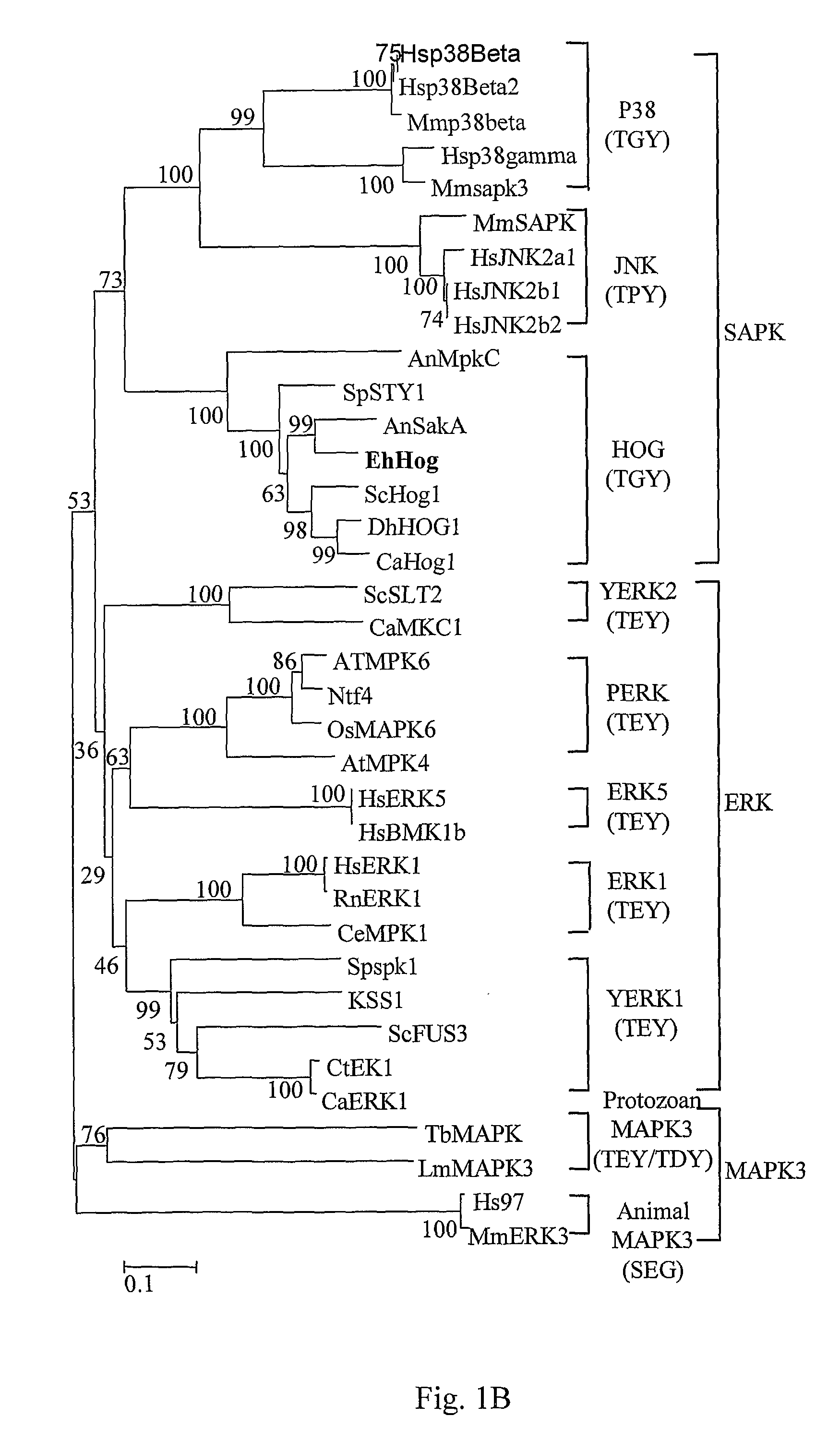
Stress tolerant organisms expressing a map kinase homologue
The present invention provides a MAP kinase homologue gene, designated EhHOG, isolated from Eurotium herbariorum, a common fungal species from the extreme hypersaline environment of the Dead Sea, capable of improving tolerance of plants and other organisms to abiotic stresses such as osmotic, heat, dehydration, freezing-thawing, oxidative and salinity stress.
Owner:SUD CHEM INC
Salt-resistance formulation for improving salt resistance of wheat and method of use thereof
InactiveCN101375688BImprove salt resistanceImprove toleranceBiocideAnimal repellantsSalt resistanceAnimal science
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Stress Tolerant Organisms Expressing a Map Kinase Homologue
The present invention provides a MAP kinase homologue gene, designated EhHOG, isolated from Eurotium herbariorum, a common fungal species from the extreme hypersaline environment of the Dead Sea, capable of improving tolerance of plants and other organisms to abiotic stresses such as osmotic, heat, dehydration, freezing-thawing, oxidative and salinity stress.
Owner:SUD CHEM INC
Application of rice osdrap1 gene in enhancing plant drought resistance
ActiveCN103468740BImprove resistance to drought stressImprove stress resistanceFermentationGenetic engineeringAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention discloses application of OsDRAP1 genes of rice in enhancing plant drought resistance and provides application of proteins shown in the second sequence of a sequence list in enhancing the plant drought resistance and application of encoding genes of the proteins shown in the second sequence of the sequence list in enhancing the plant drought resistance. Experimental results show that the expression quantity of the OsDRAP1 genes increases rapidly under high salinity stress and drought stress, but has a small increase under low-temperature stress. OsDRAP1 transcription factors can be combined with a GCC box and a DRE in a downstream gene promoter area to regulate and control expression of downstream genes and participate in plant stress response reaction. The over-expression OsDRAP1 genes of the rice can improve the ability of drought-stress resisting of the rice. The application of the OsDRAP1 genes of the rice in enhancing the plant drought resistance has important theoretical and practical significance in improving and enhancing the stress resistance of the rice and accelerating the process of stress-resisting molecular breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
New application of Arabidopsis at4g09820 gene in plant salt tolerance
ActiveCN103540607BVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyGenetic engineering
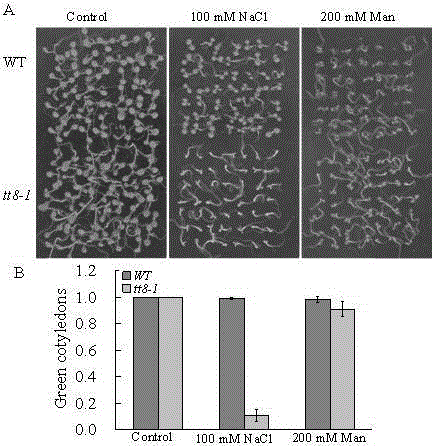
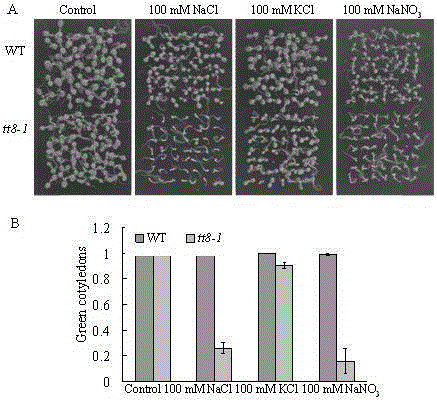
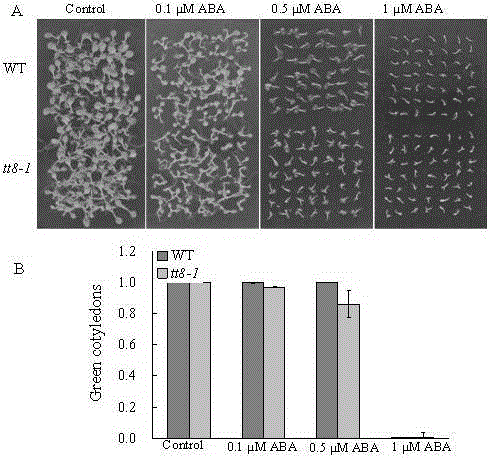
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering application, and in particular relates to the application of Arabidopsis thaliana At4g09820 gene in cultivating new varieties of salt-tolerant plants. Arabidopsis At4g09820 gene, also known as TT8 The gene, whose CDS length is 1557bp, encodes a protein of 518 amino acids, belongs to the bHLH (basic? helix-loop-helix) type transcription factor, and regulates the biosynthesis of proanthocyanidins and anthocyanins in the flavonoid synthesis pathway. Through the research of the At4g09820 gene in high-salinity stress, the inventor found that the gene specifically regulates the ion poisoning response caused by NaCl , It shows good salt-resistance characteristics, so it has a relatively important application in plant salt-resistance. Through further research and transformation of the gene, excellent salt-tolerant plant varieties can be bred.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com