Patents
Literature
1668results about How to "Improve stress condition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
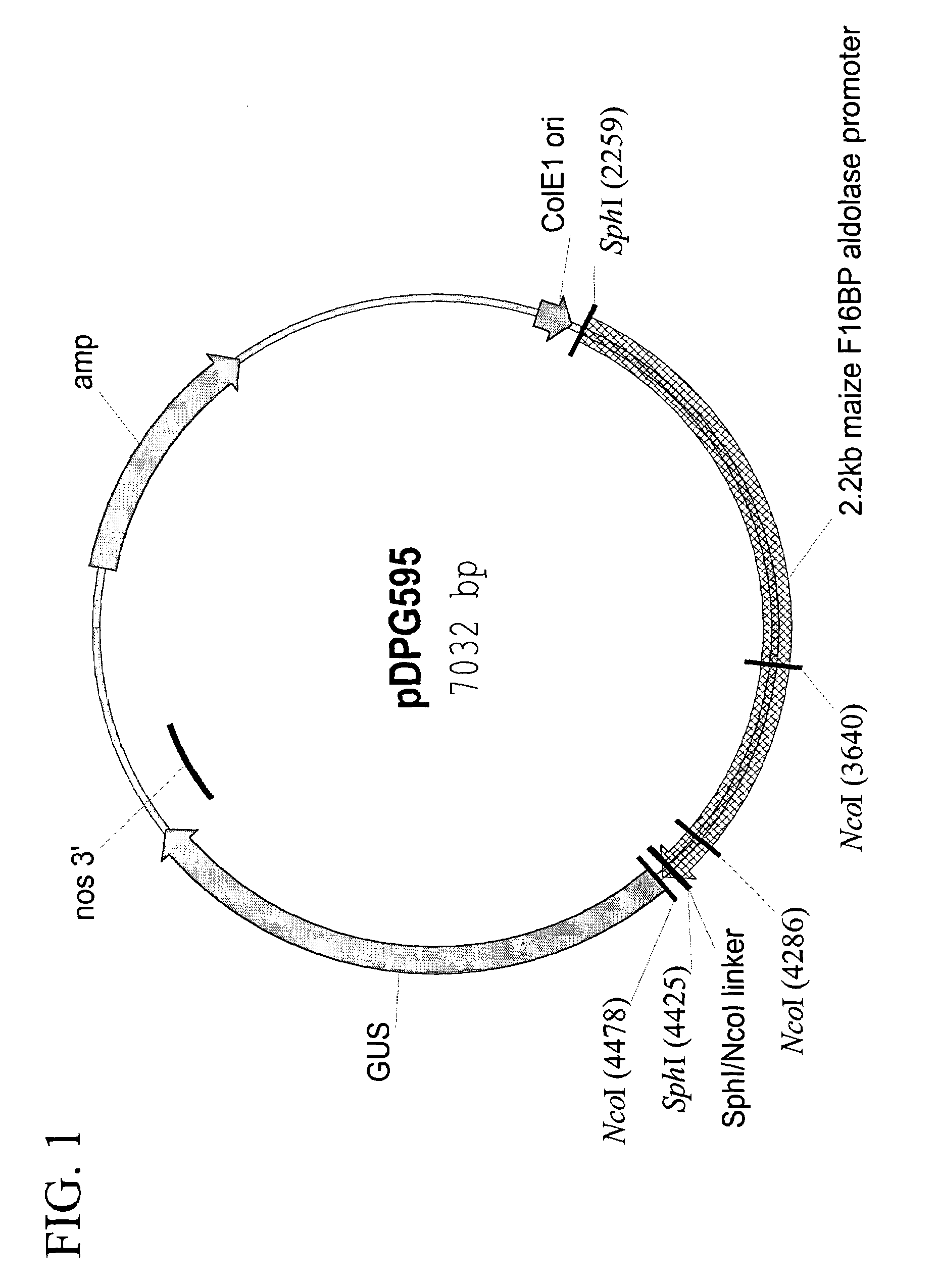
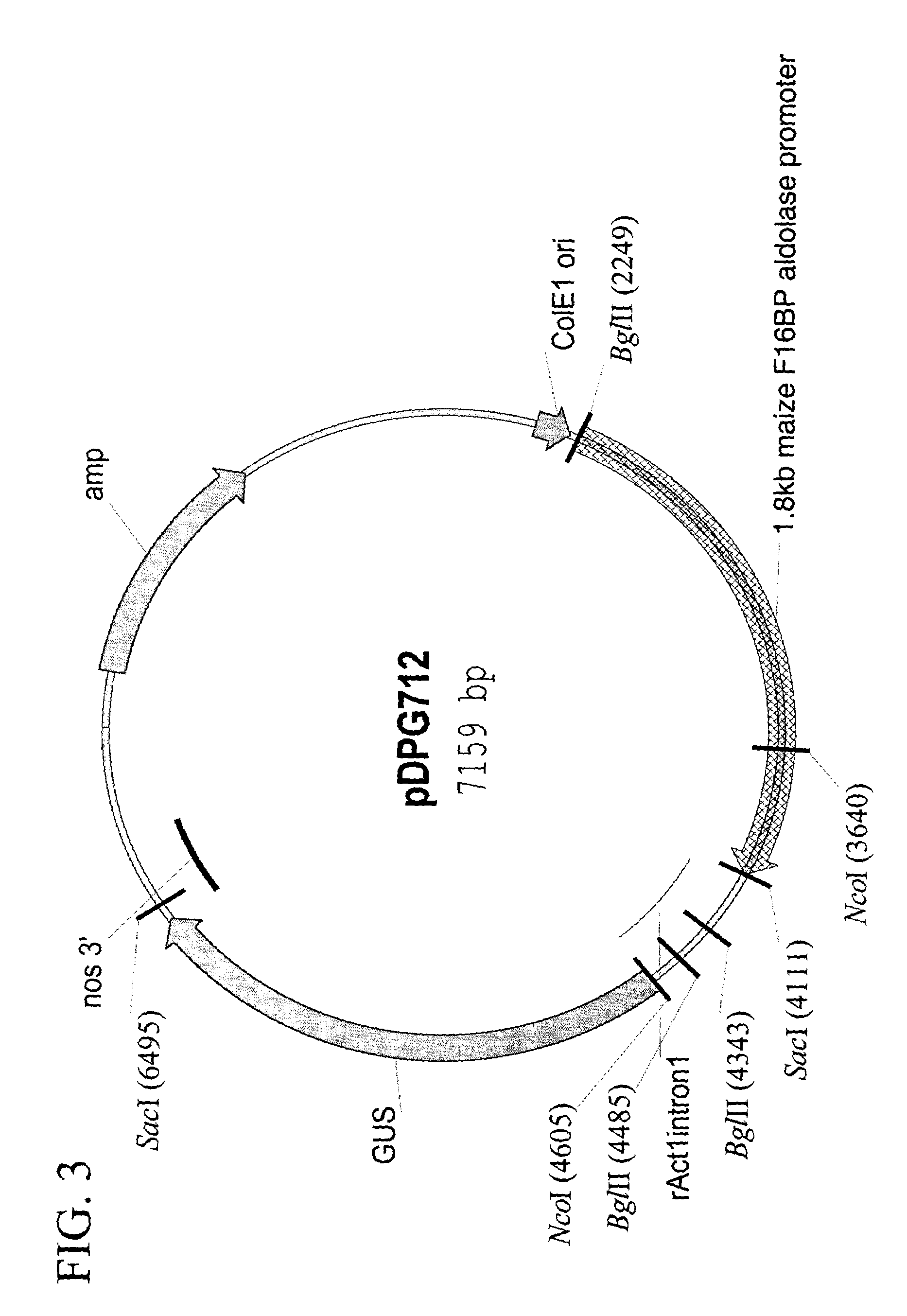
Maize chloroplast aldolase promoter compositions and methods for use thereof
ActiveUS7151204B2Simple compositionQuality improvementSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesFructoseTransgene
The current invention provides the promoter of the Zea mays nuclear gene encoding chloroplast-localized fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F16BP) aldolase. Compositions comprising this sequence are described, as are plants transformed with such compositions. Further provided are methods for the expression of transgenes in plants comprising the use of these sequences. The methods of the invention include the direct creation of transgenic plants with the chloroplastic F16BP aldolase promoter by genetic transformation, as well as by plant breeding methods. The sequences of the invention represent a valuable new tool for the creation of transgenic plants, preferably having one or more added beneficial characteristics.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
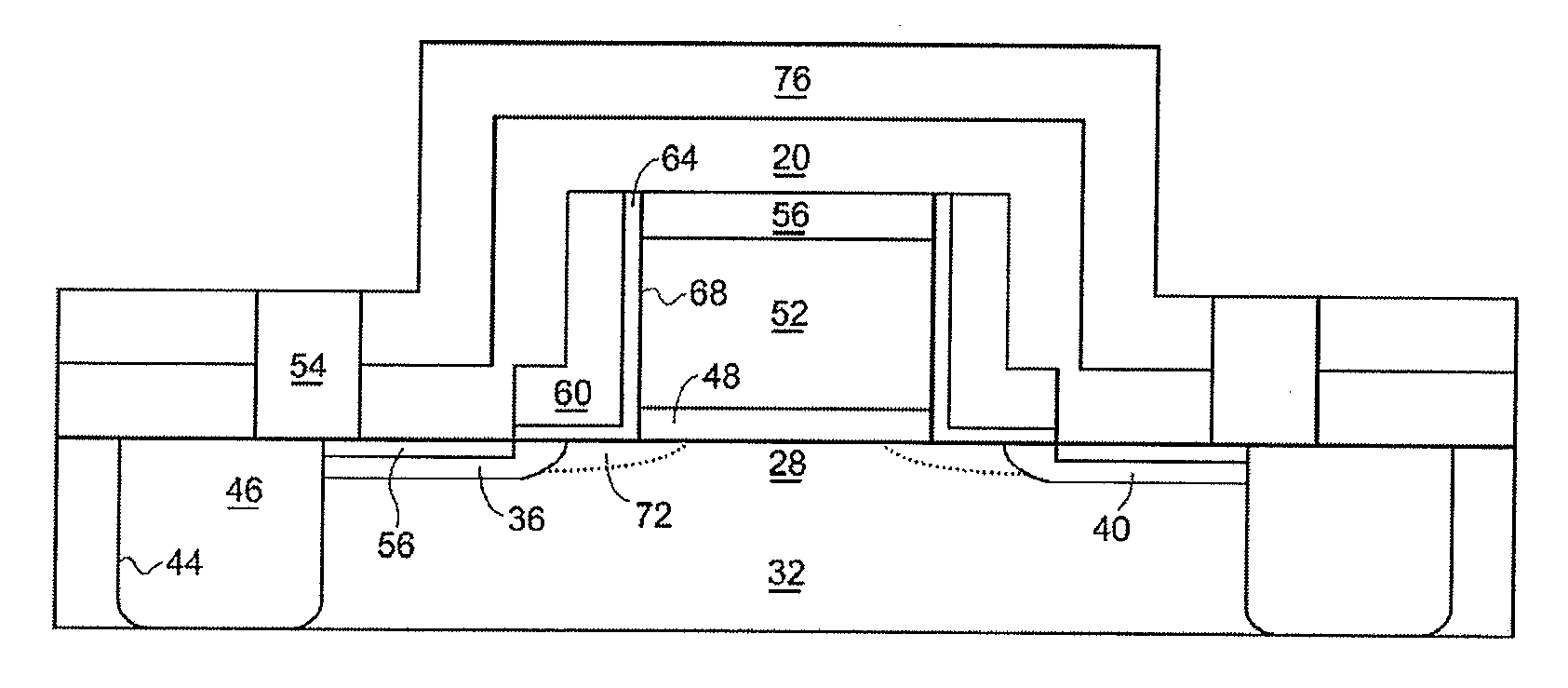
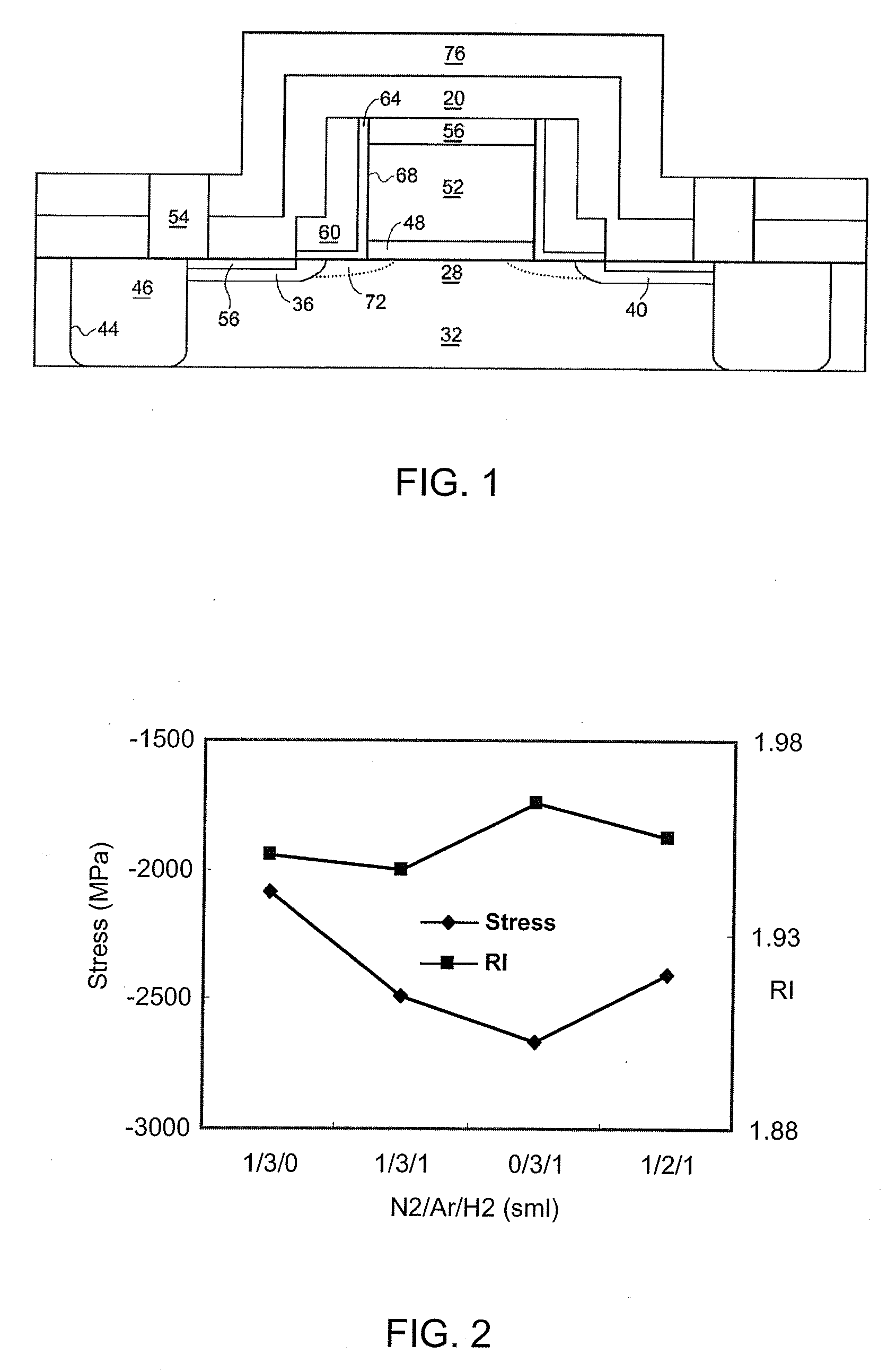
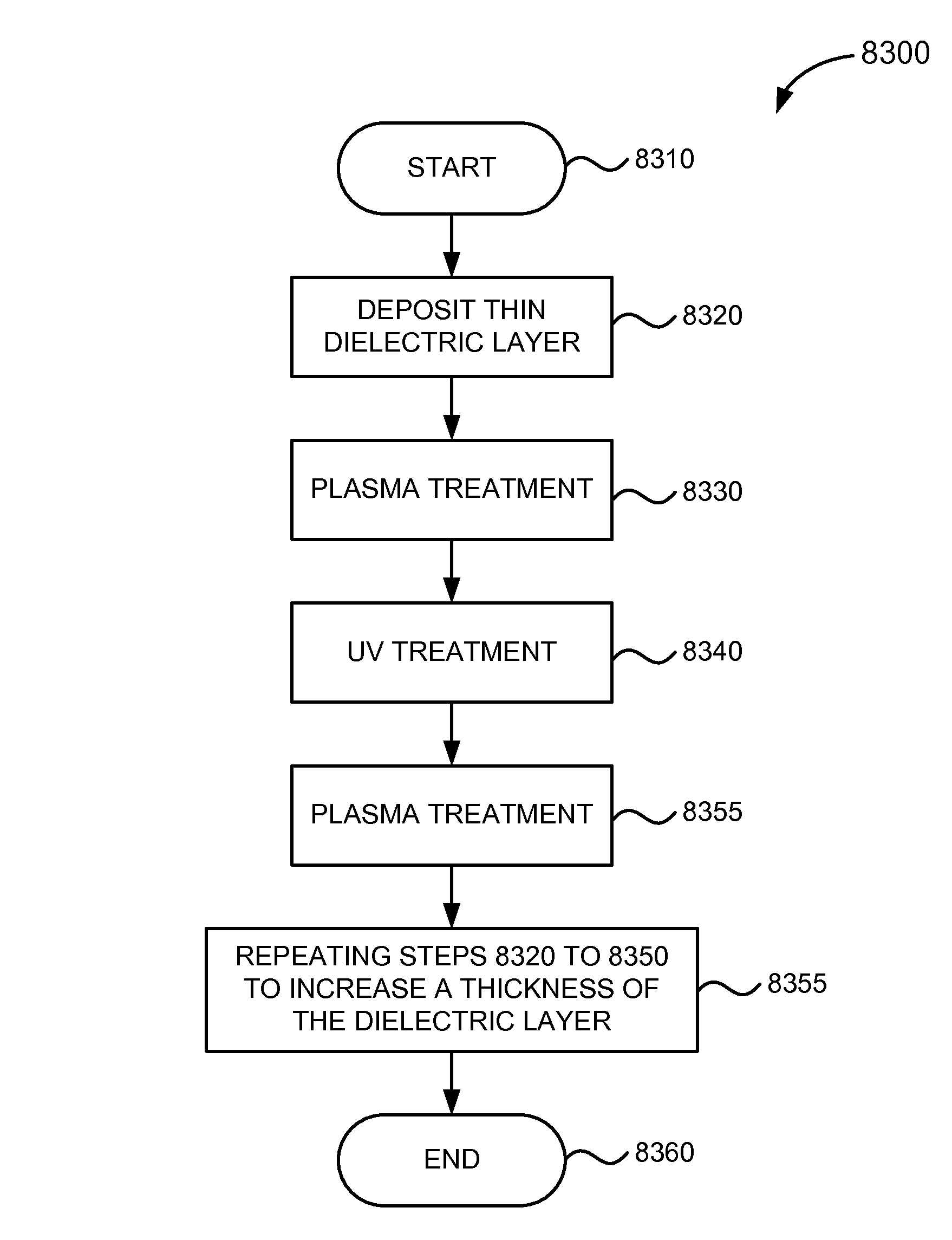
Method to increase silicon nitride tensile stress using nitrogen plasma in-situ treatment and ex-situ UV cure
ActiveUS20080020591A1Improve performanceFilm stress is increasedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogen plasmaUV curing
Stress of a silicon nitride layer may be enhanced by deposition at higher temperatures. Employing an apparatus that allows heating of a substrate to substantially greater than 400° C. (for example a heater made from ceramic rather than aluminum), the silicon nitride film as-deposited may exhibit enhanced stress allowing for improved performance of the underlying MOS transistor device. In accordance with alternative embodiments, a deposited silicon nitride film is exposed to curing with ultraviolet (UV) radiation at an elevated temperature, thereby helping remove hydrogen from the film and increasing film stress. In accordance with still other embodiments, a silicon nitride film is formed utilizing an integrated process employing a number of deposition / curing cycles to preserve integrity of the film at the sharp corner of the underlying raised feature. Adhesion between successive layers may be promoted by inclusion of a post-UV cure plasma treatment in each cycle.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method to increase silicon nitride tensile stress using nitrogen plasma in-situ treatment and ex-situ UV cure
InactiveUS20120196450A1Increase pressureImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogen plasmaHydrogen
Stress of a silicon nitride layer may be enhanced by deposition at higher temperatures. Employing an apparatus that allows heating of a substrate to substantially greater than 400° C. (for example a heater made from ceramic rather than aluminum), the silicon nitride film as-deposited may exhibit enhanced stress allowing for improved performance of the underlying MOS transistor device. In accordance with some embodiments, a deposited silicon nitride film is exposed to curing with plasma and ultraviolet (UV) radiation, thereby helping remove hydrogen from the film and increasing film stress. In accordance with other embodiments, a silicon nitride film is formed utilizing an integrated process employing a number of deposition / curing cycles to preserve integrity of the film at the sharp corner of the underlying raised feature. Adhesion between successive layers may be promoted by inclusion of a post-UV cure plasma treatment in each cycle.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
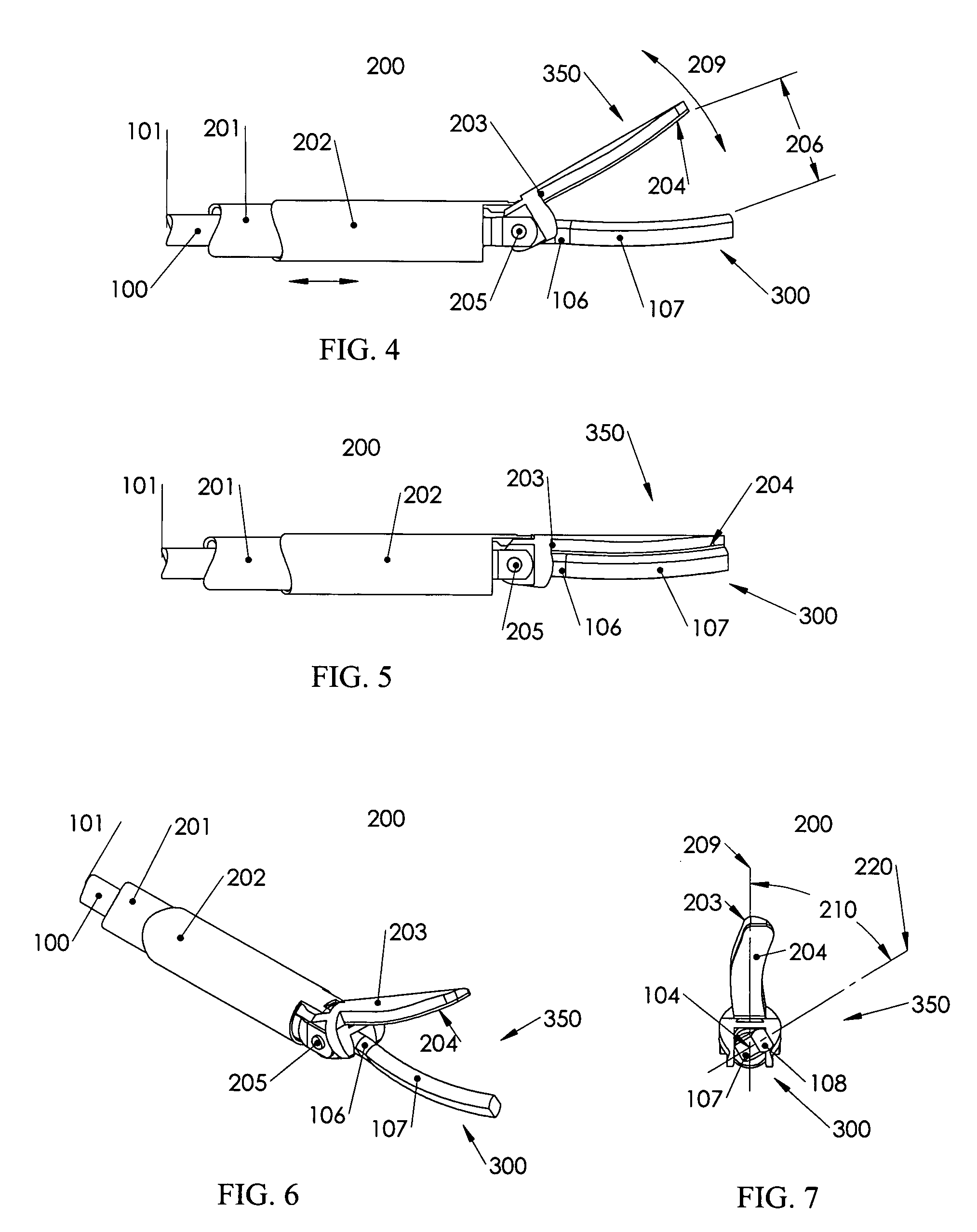
Balanced ultrasonic curved blade
InactiveUS20070016236A1Reduce lateral movementAdd additional massSurgeryEngineeringUltrasound energy
Methods and devices that provide reduced transverse motion in a curved ultrasonic blade and / or ultrasonic surgical instrument with functional asymmetries. An ultrasonic blade in accordance with embodiments of the present invention includes a curved functional portion of an ultrasonic blade, wherein the center of mass of the curved functional portion lies on the mid-line of a waveguide delivering ultrasonic energy to the blade. Balancing in accordance with embodiments of the present invention, using placement of the center of mass of the curved portion of the blade appropriately, provides blade balance in a proximal portion of the blade, without reduction of mass and inherent stress increase proximal to the end-effector.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Optical image-based position tracking for magnetic resonance imaging applications
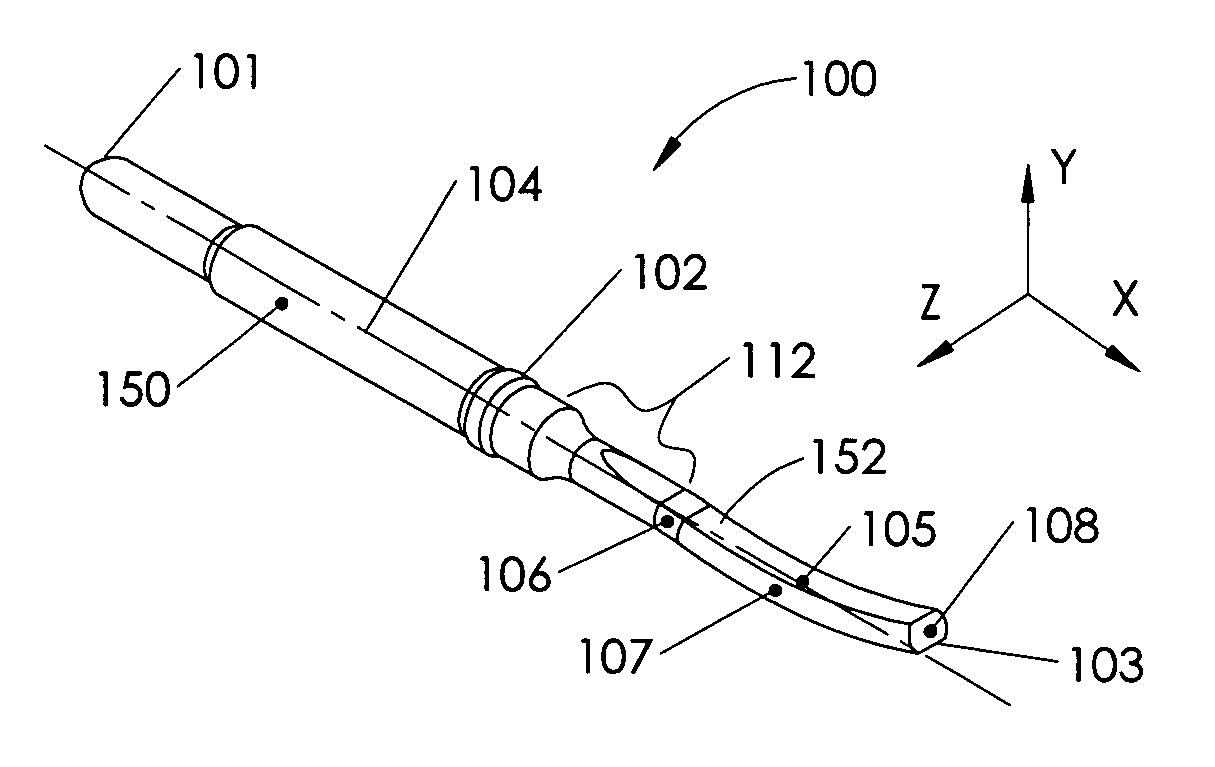
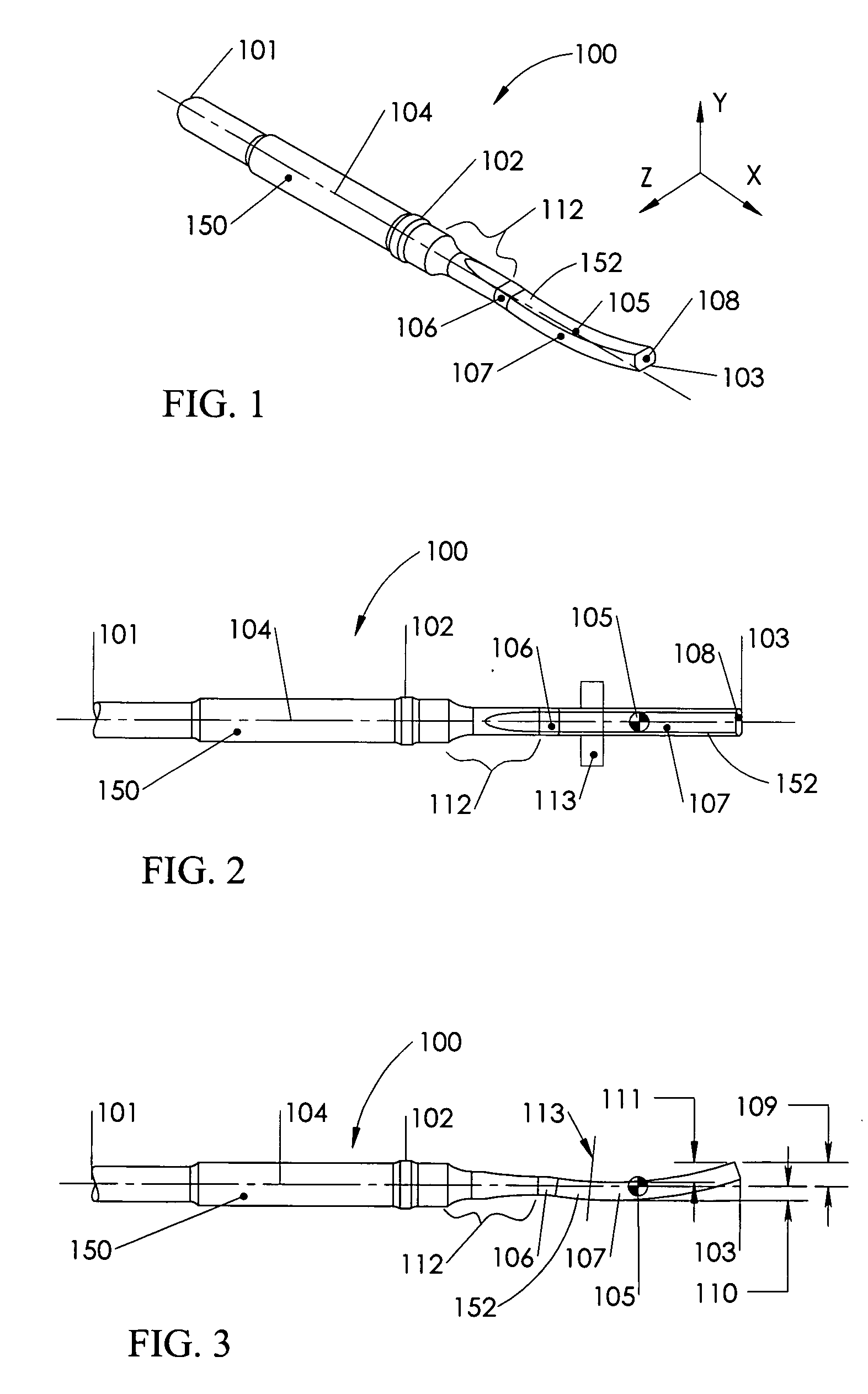
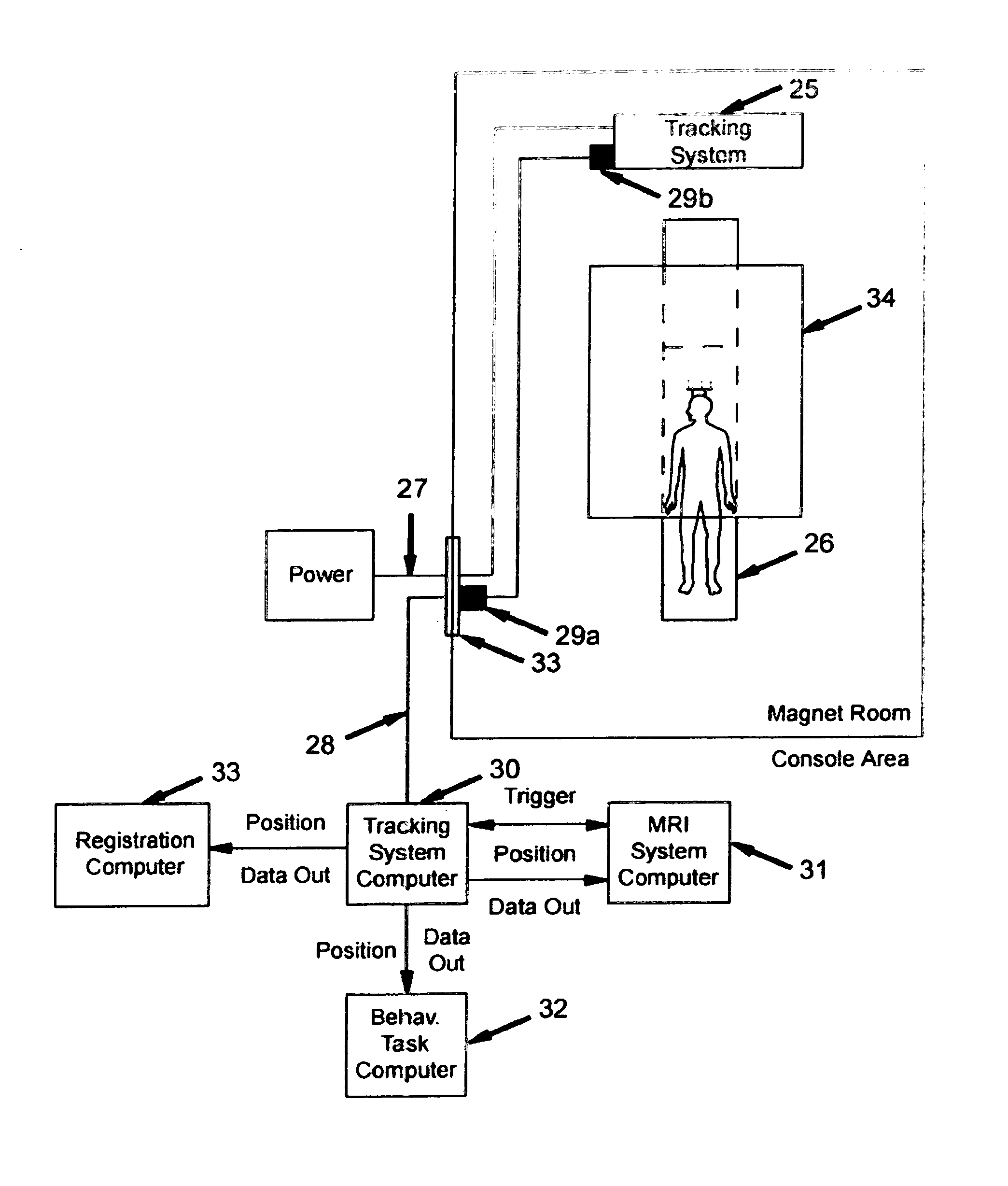
InactiveUS20050054910A1Improve data qualityImprove stress conditionImage analysisMagnetic measurementsThermal energyIonizing radiation
An optical image-based tracking system determines the position and orientation of objects such as biological materials or medical devices within or on the surface of a human body undergoing Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Three-dimensional coordinates of the object to be tracked are obtained initially using a plurality of MR-compatible cameras. A calibration procedure converts the motion information obtained with the optical tracking system coordinates into coordinates of an MR system. A motion information file is acquired for each MRI scan, and each file is then converted into coordinates of the MRI system using a registration transformation. Each converted motion information file can be used to realign, correct, or otherwise augment its corresponding single MR image or a time series of such MR images. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides real-time computer control to track the position of an interventional treatment system, including surgical tools and tissue manipulators, devices for in vivo delivery of drugs, angioplasty devices, biopsy and sampling devices, devices for delivery of RF, thermal energy, microwaves, laser energy or ionizing radiation, and internal illumination and imaging devices, such as catheters, endoscopes, laparoscopes, and like instruments. In other embodiments, the invention is also useful for conventional clinical MRI events, functional MRI studies, and registration of image data acquired using multiple modalities.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK & WOMENS COLLEGE HEALTH SCI CENT
Method to increase silicon nitride tensile stress using nitrogen plasma in-situ treatment and ex-situ UV cure
ActiveUS8138104B2Increase pressureImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogen plasmaHydrogen
Stress of a silicon nitride layer may be enhanced by deposition at higher temperatures. Employing an apparatus that allows heating of a substrate to substantially greater than 400° C. (for example a heater made from ceramic rather than aluminum), the silicon nitride film as-deposited may exhibit enhanced stress allowing for improved performance of the underlying MOS transistor device. In accordance with alternative embodiments, a deposited silicon nitride film is exposed to curing with ultraviolet (UV) radiation at an elevated temperature, thereby helping remove hydrogen from the film and increasing film stress. In accordance with still other embodiments, a silicon nitride film is formed utilizing an integrated process employing a number of deposition / curing cycles to preserve integrity of the film at the sharp corner of the underlying raised feature. Adhesion between successive layers may be promoted by inclusion of a post-UV cure plasma treatment in each cycle.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Hydroxyl bond removal and film densification method for oxide films using microwave post treatment
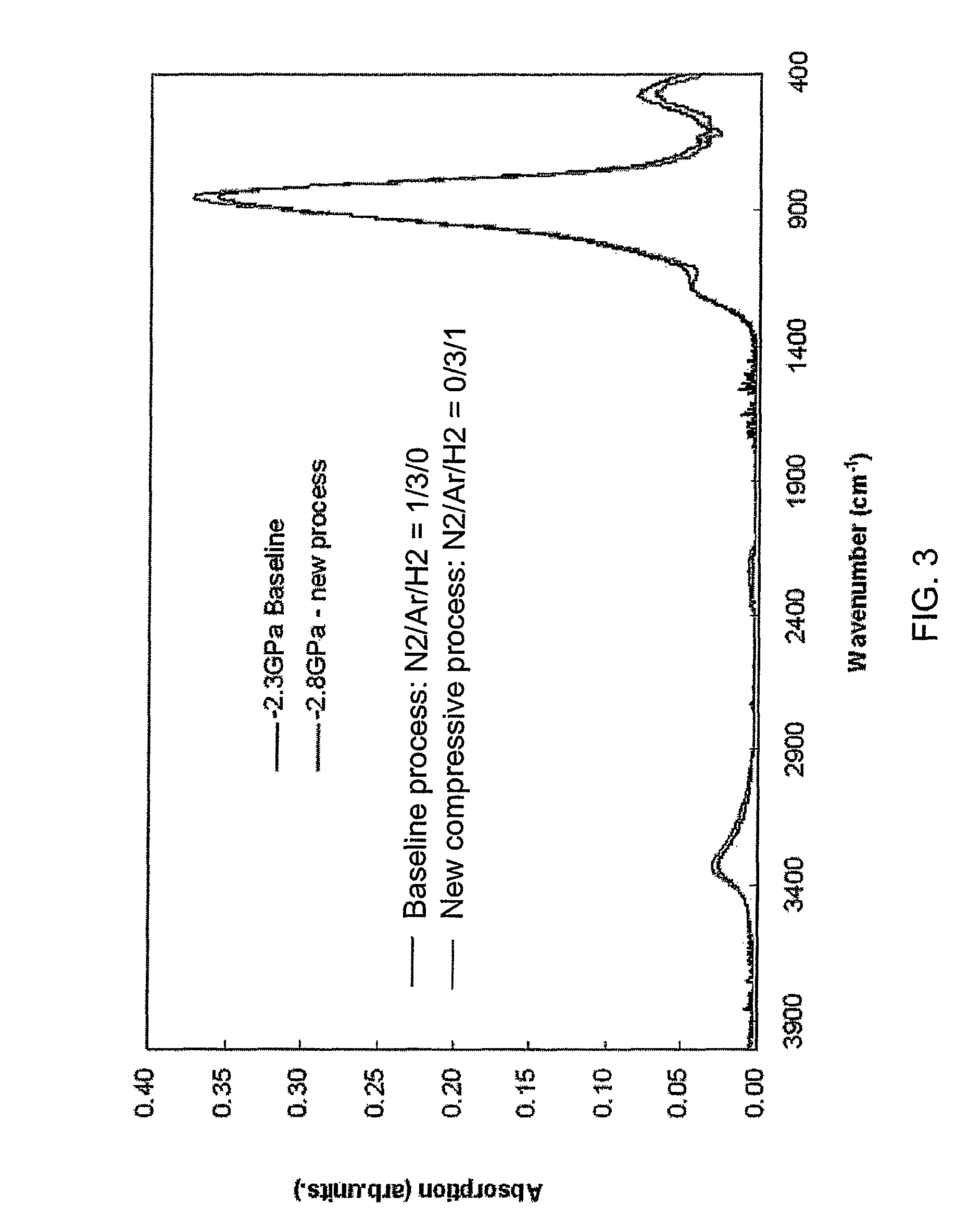
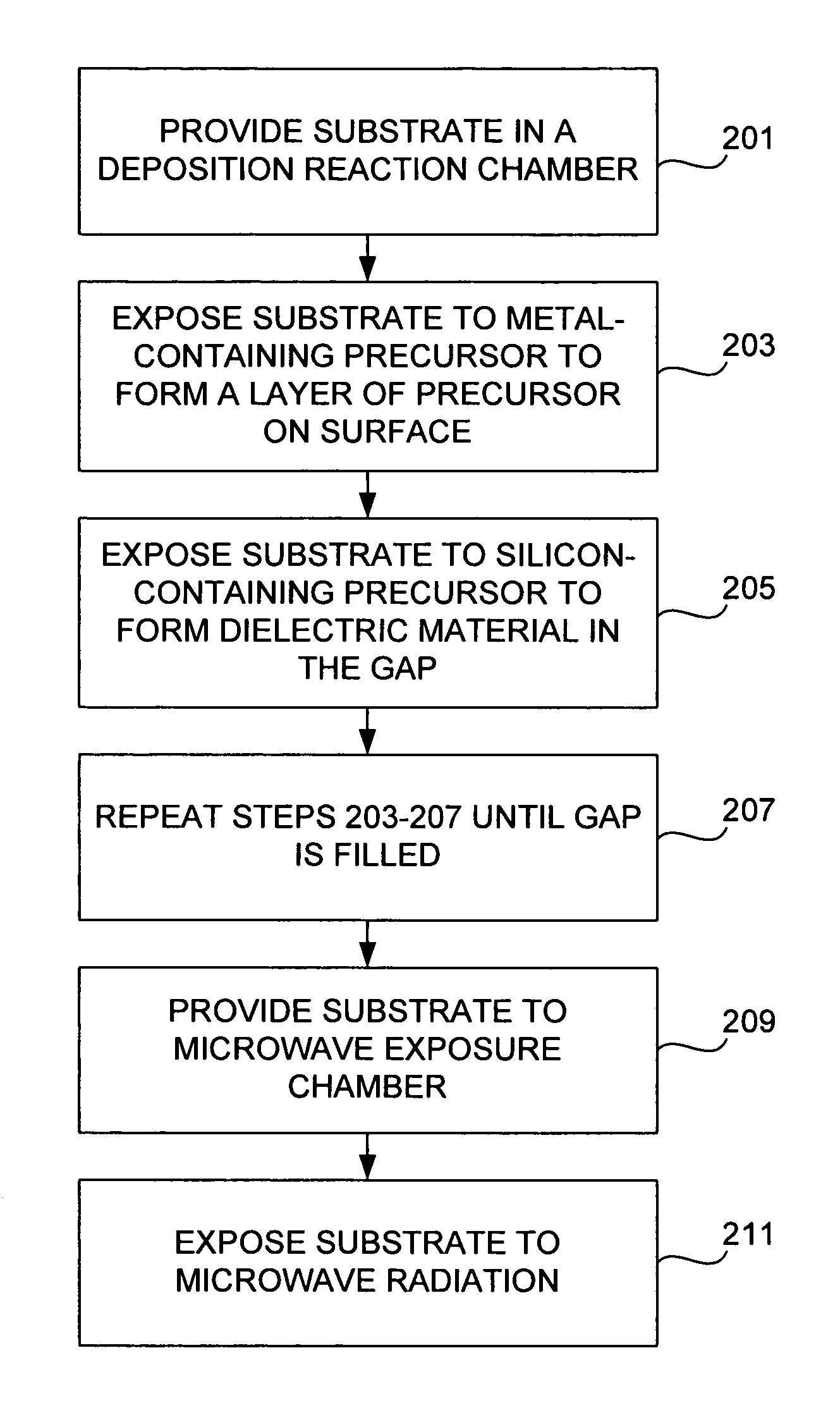
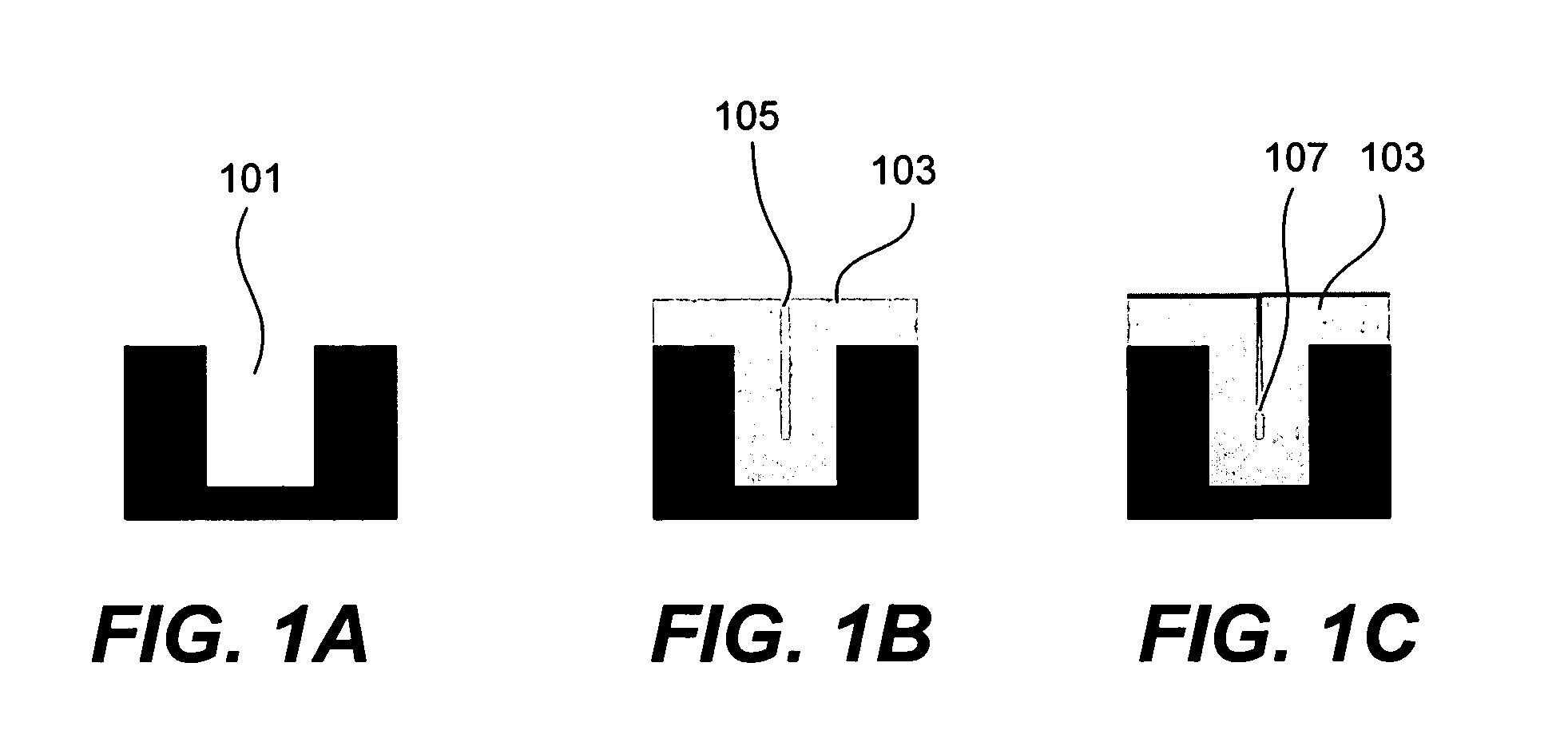
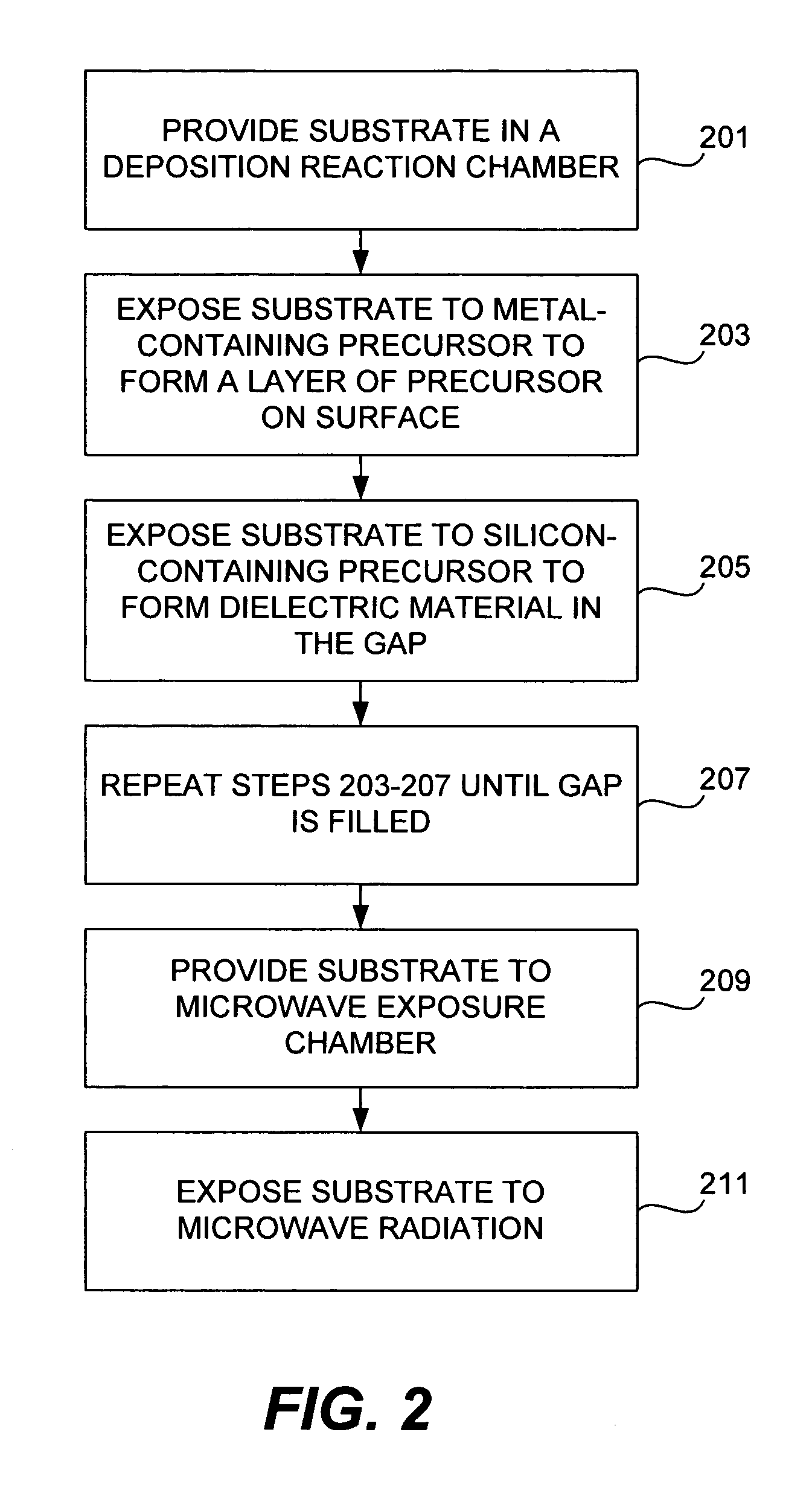
ActiveUS7589028B1High densityImprove film propertiesRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricMicrowave
Methods of forming dielectric films with increased density and improved film properties are provided. The methods involve exposing dielectric films to microwave radiation. According to various embodiments, the methods may be used to remove hydroxyl bonds, increase film density, reduce or eliminate seams and voids, and optimize film properties such as dielectric constant, refractive index and stress for particular applications. In certain embodiments, the methods are used to form conformal films deposited by a technique such as PDL. The methods may be used in applications requiring low thermal budgets.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Golf club having an improved face plate
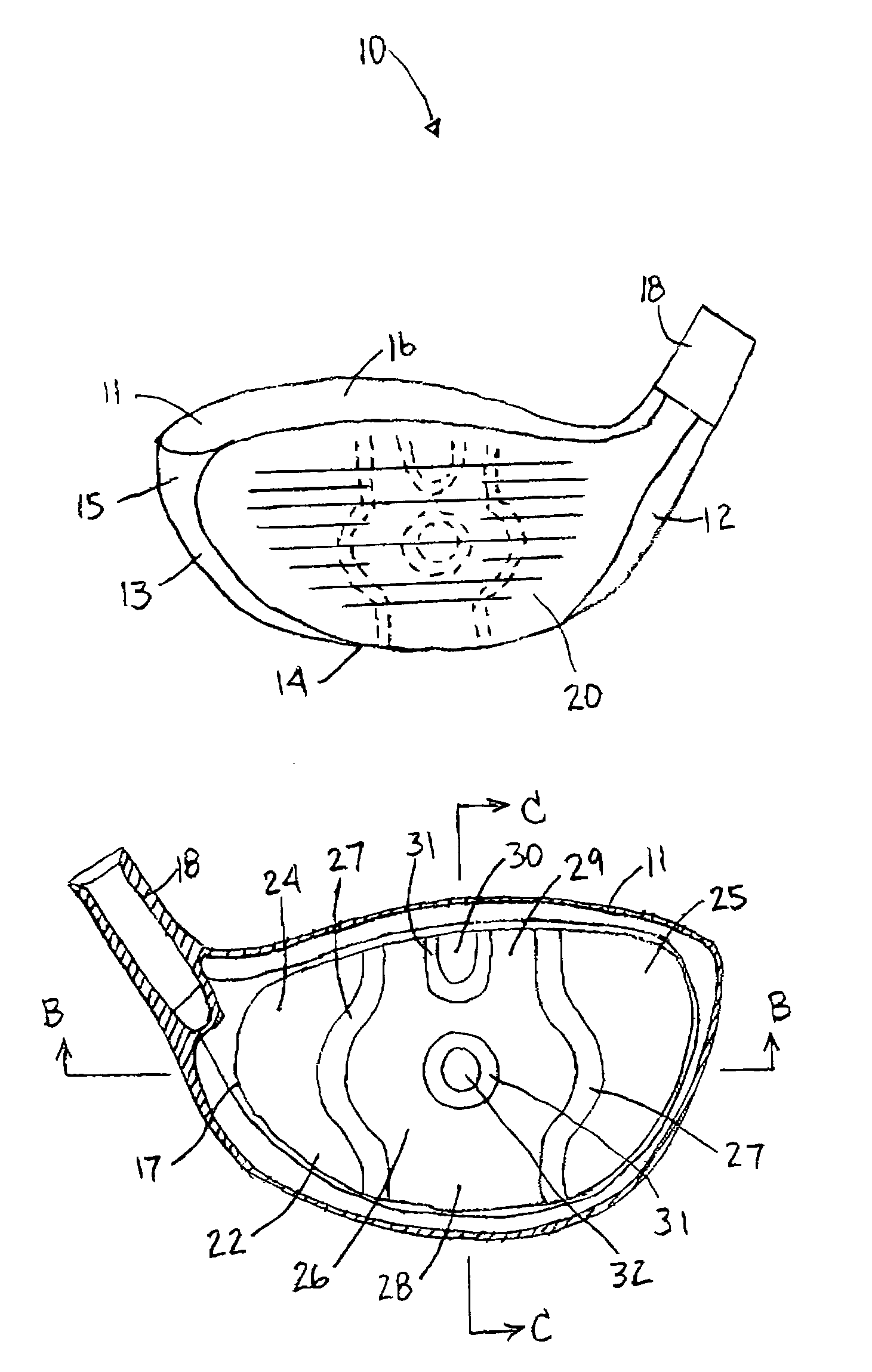
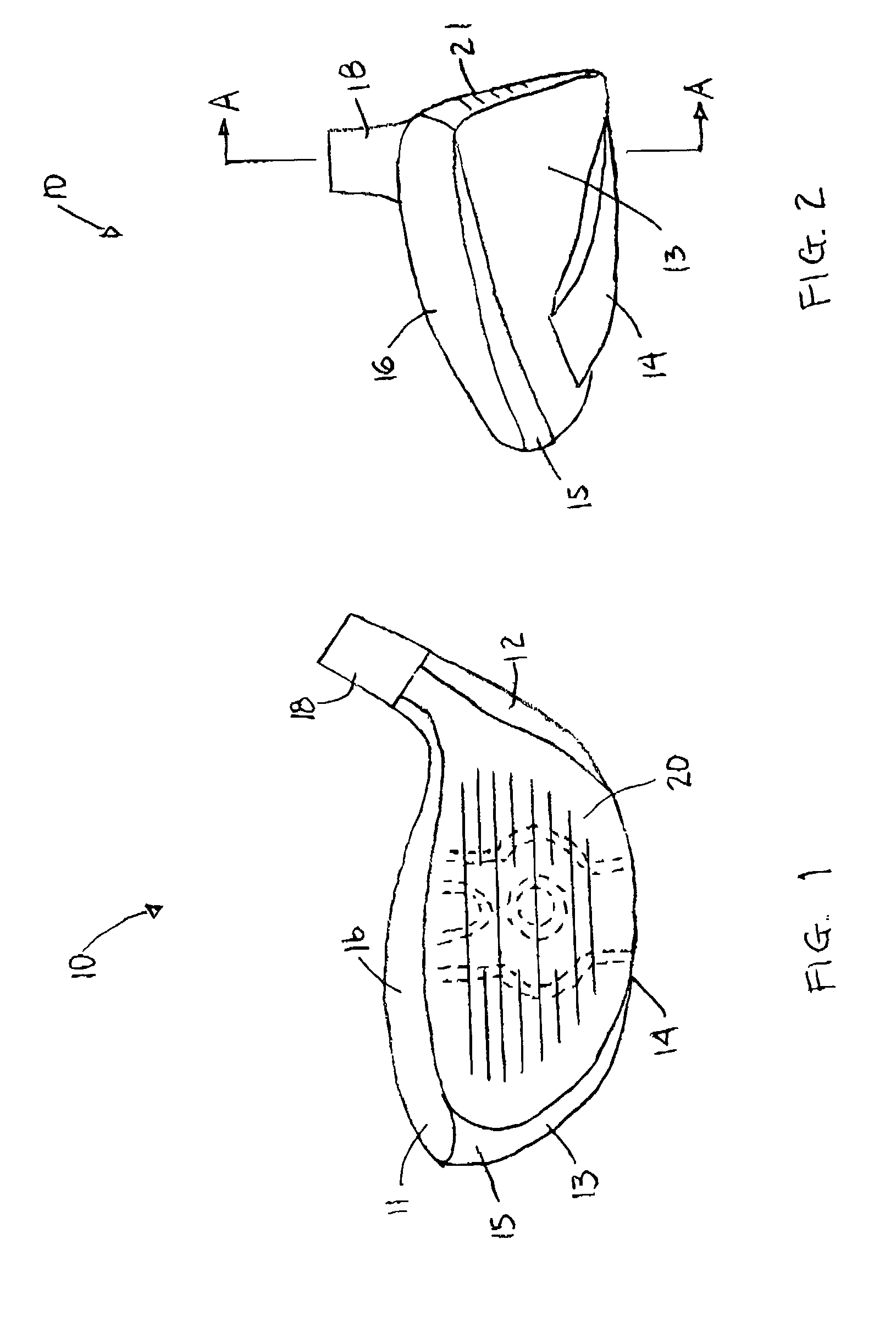
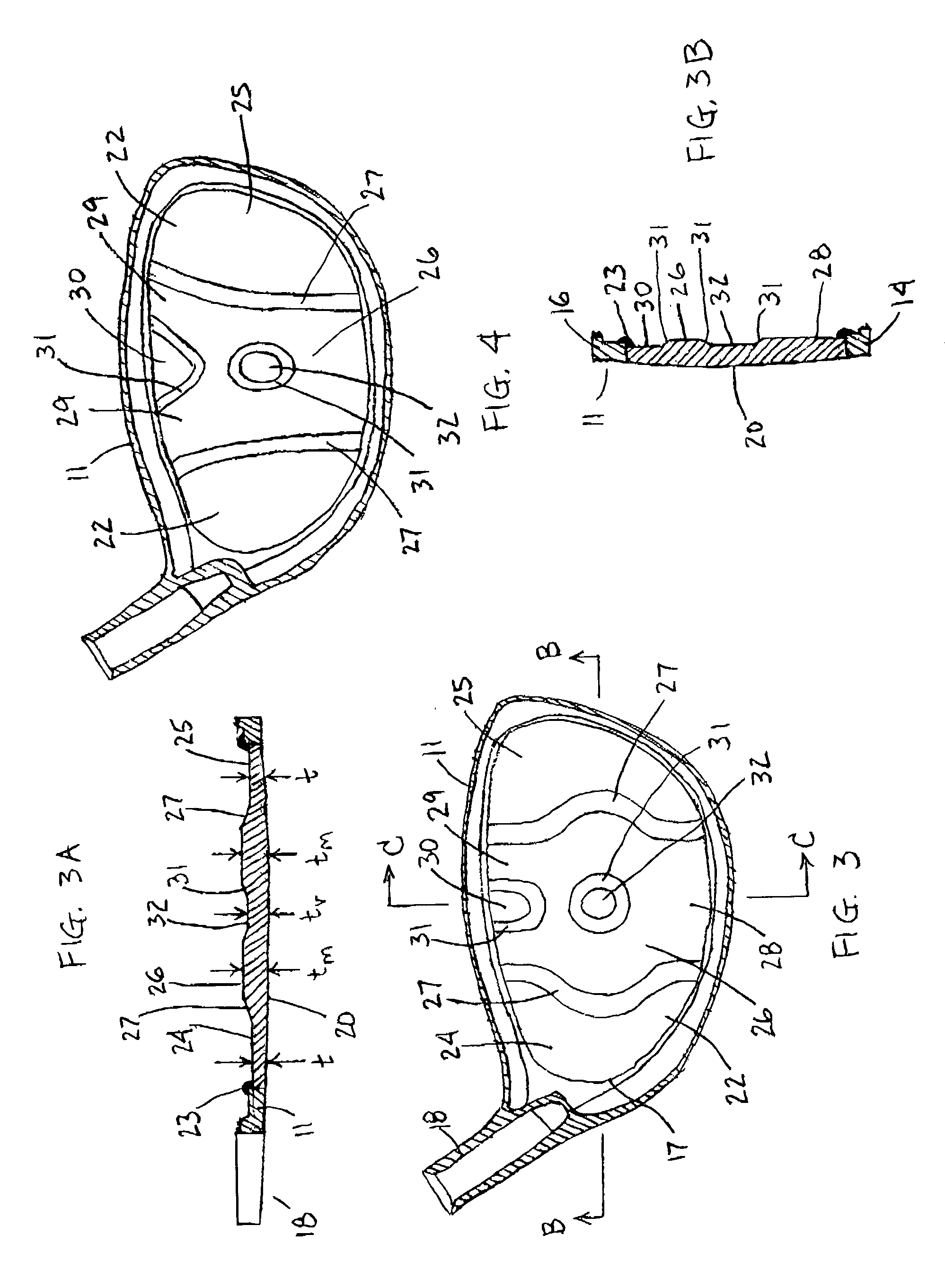
InactiveUS6997820B2Increasing the thicknessReduce thicknessGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringMetallic materials
A golf club head is provided having an increased sweet spot across its club face. A preferred construction includes a face plate having vertical zone of increased thickness and a central region having a reduced thickness. An upward extension of the vertical zone comprises divergent segments separated by an upper region of reduced thickness. The face plate material is preferably metallic, but in alternative embodiments may be formed of a composite or non-metal material. Methods for manufacturing a golf club head having a face plate with the thicknesses of the present invention include forging and machining techniques. The club head may be a wood-type or iron.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Structure of an optical interference display unit
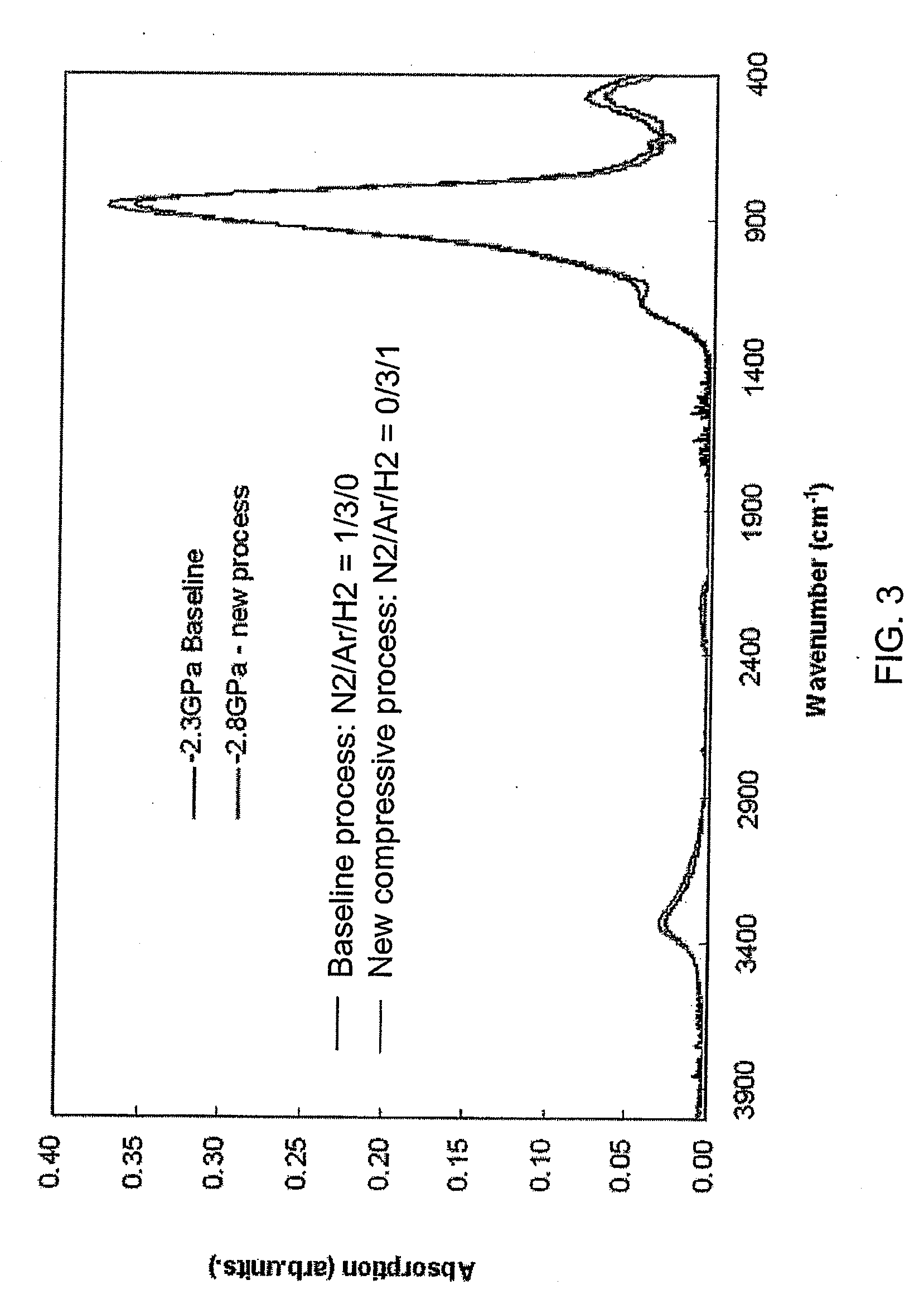
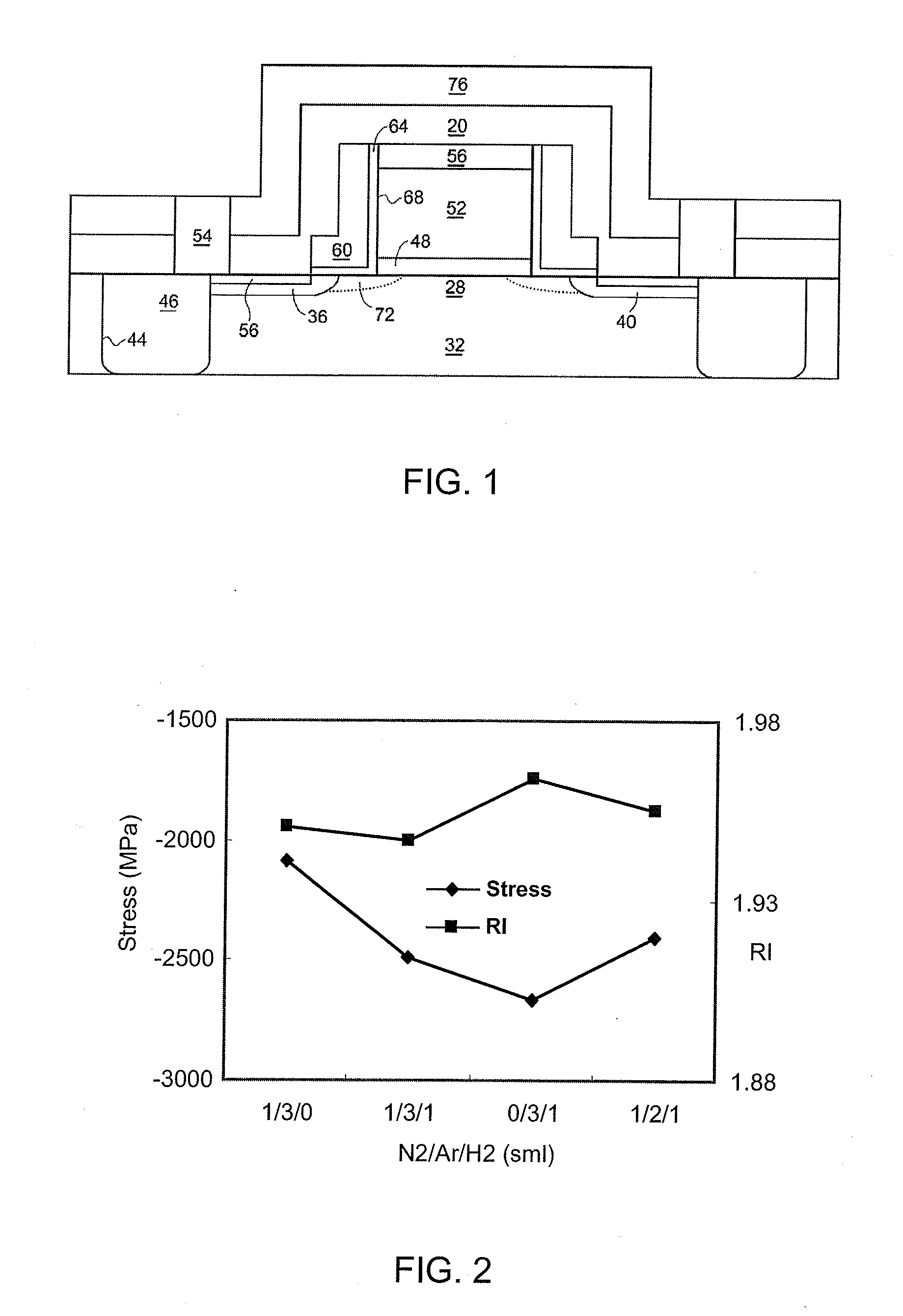
InactiveUS6958847B2Avoid pollutionIncreased process complexityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight reflectionReflective layer
Owner:SNAPTRACK
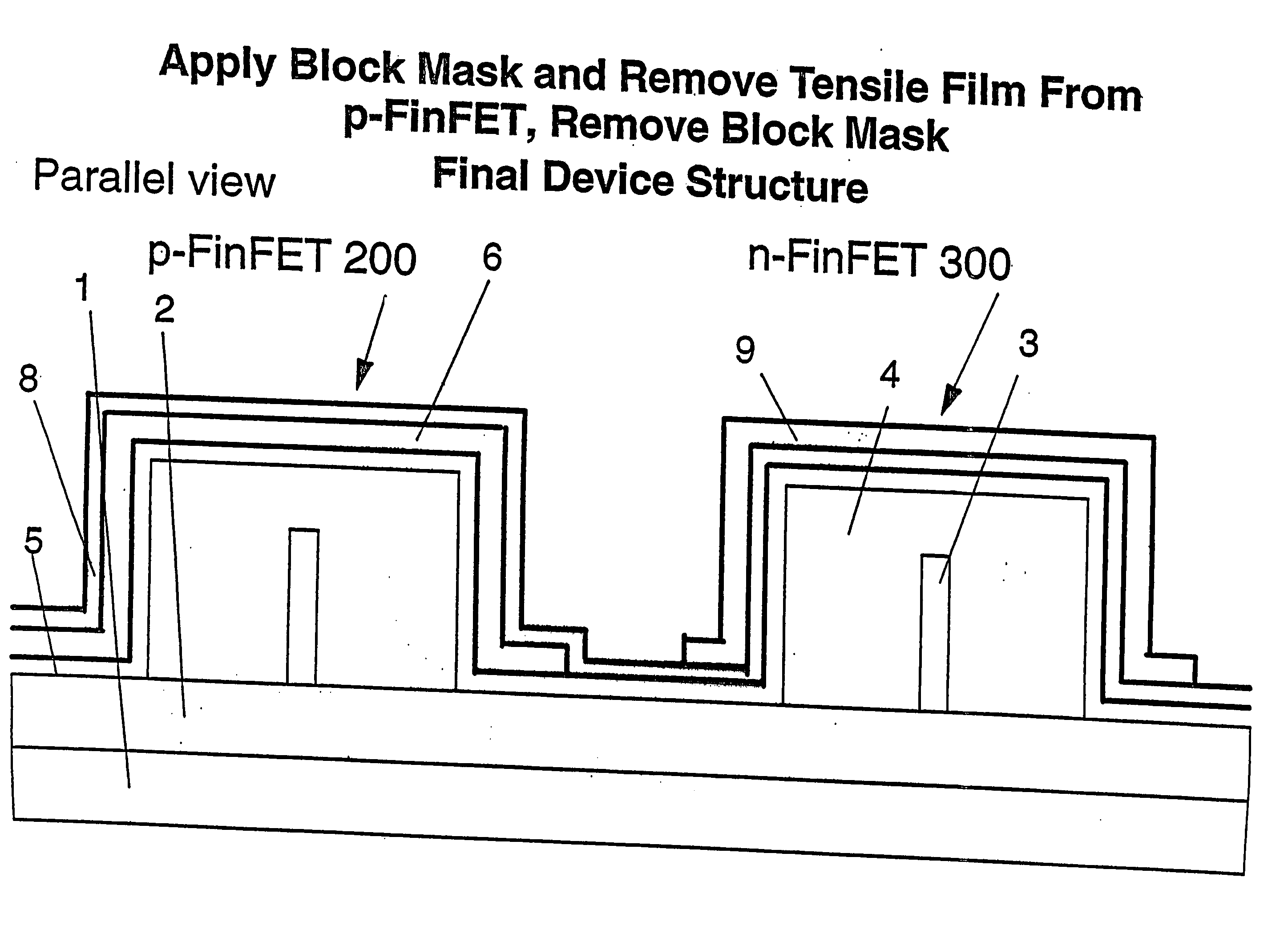
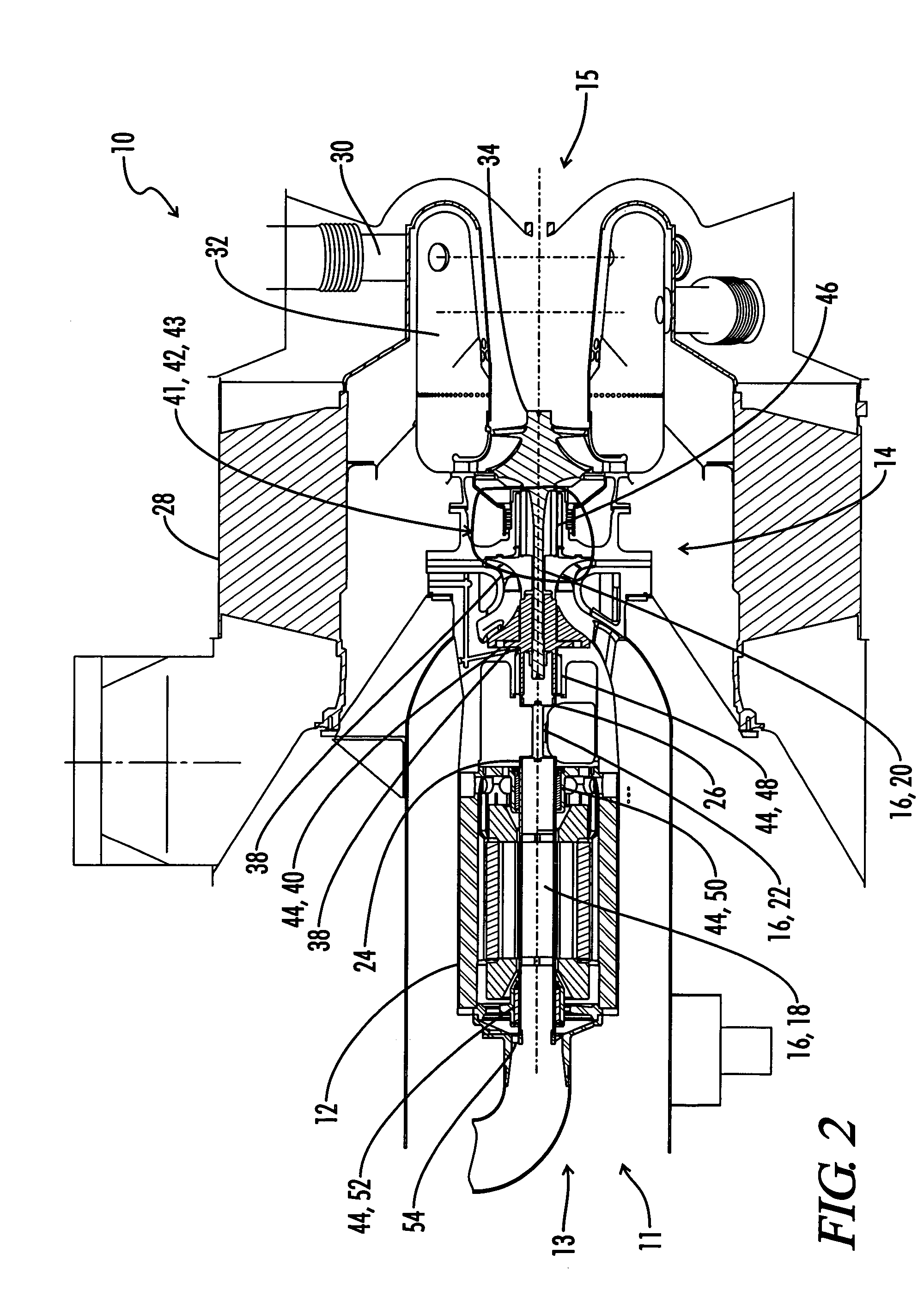
Strained finfet cmos device structures
InactiveUS20060057787A1Improve mobilityImprove device performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSEngineering
A semiconductor device structure, includes a PMOS device 200 and an NMOS device 300 disposed on a substrate 1,2, the PMOS device including a compressive layer 6 stressing an active region of the PMOS device, the NMOS device including a tensile layer 9 stressing an active region of the NMOS device, wherein the compressive layer includes a first dielectric material, the tensile layer includes a second dielectric material, and the PMOS and NMOS devices are FinFET devices 200, 300.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Dual-SiGe epitaxy for MOS devices
ActiveUS20080128746A1Increase pressureReduce impurity diffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate stackStressor
A semiconductor includes a semiconductor substrate, a gate stack on the semiconductor substrate, and a stressor having at least a portion in the semiconductor substrate and adjacent to the gate stack. The stressor includes a first stressor region and a second stressor region on the first stressor region, wherein the second stressor region extends laterally closer to a channel region underlying the gate stack than the first stressor region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
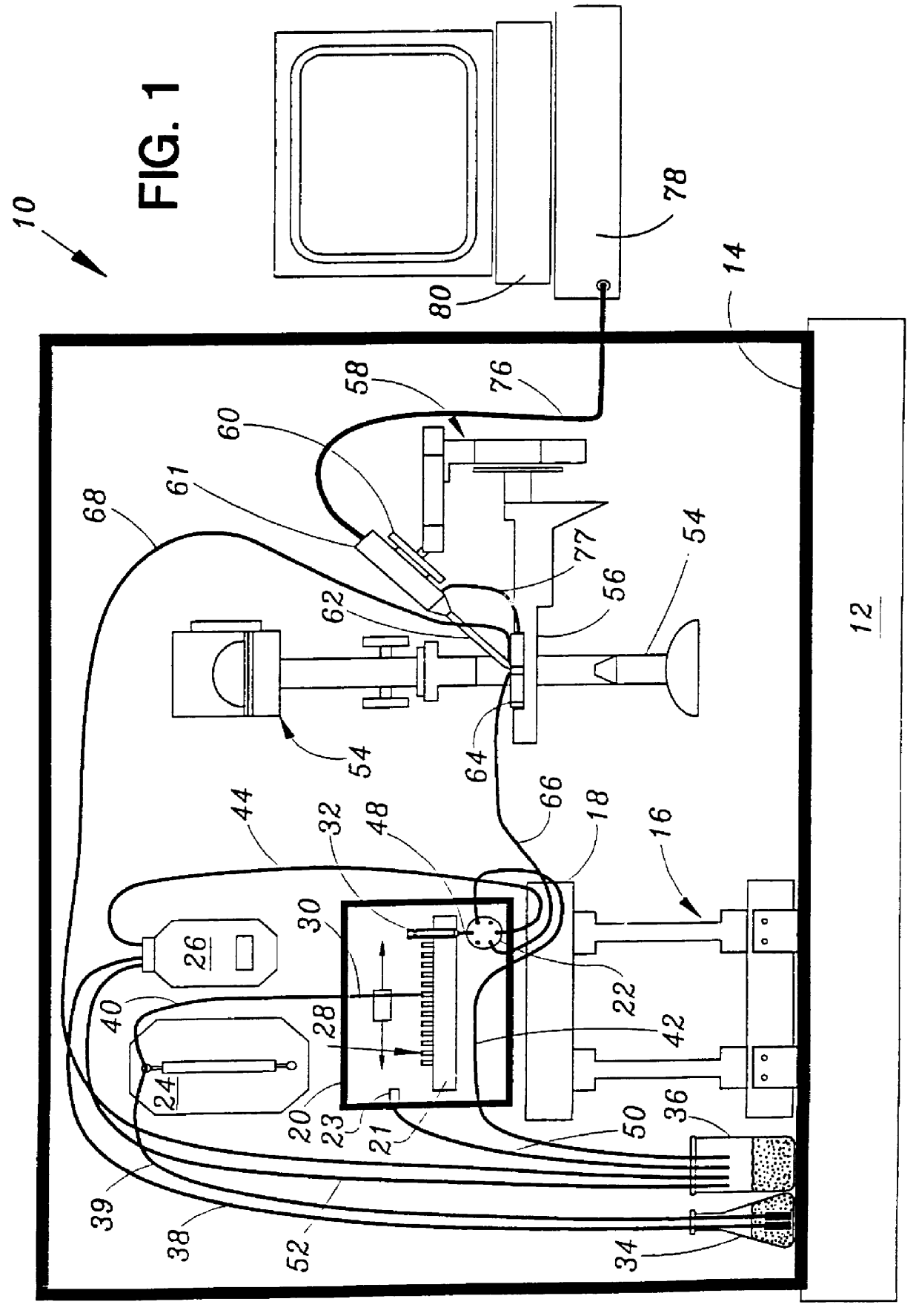
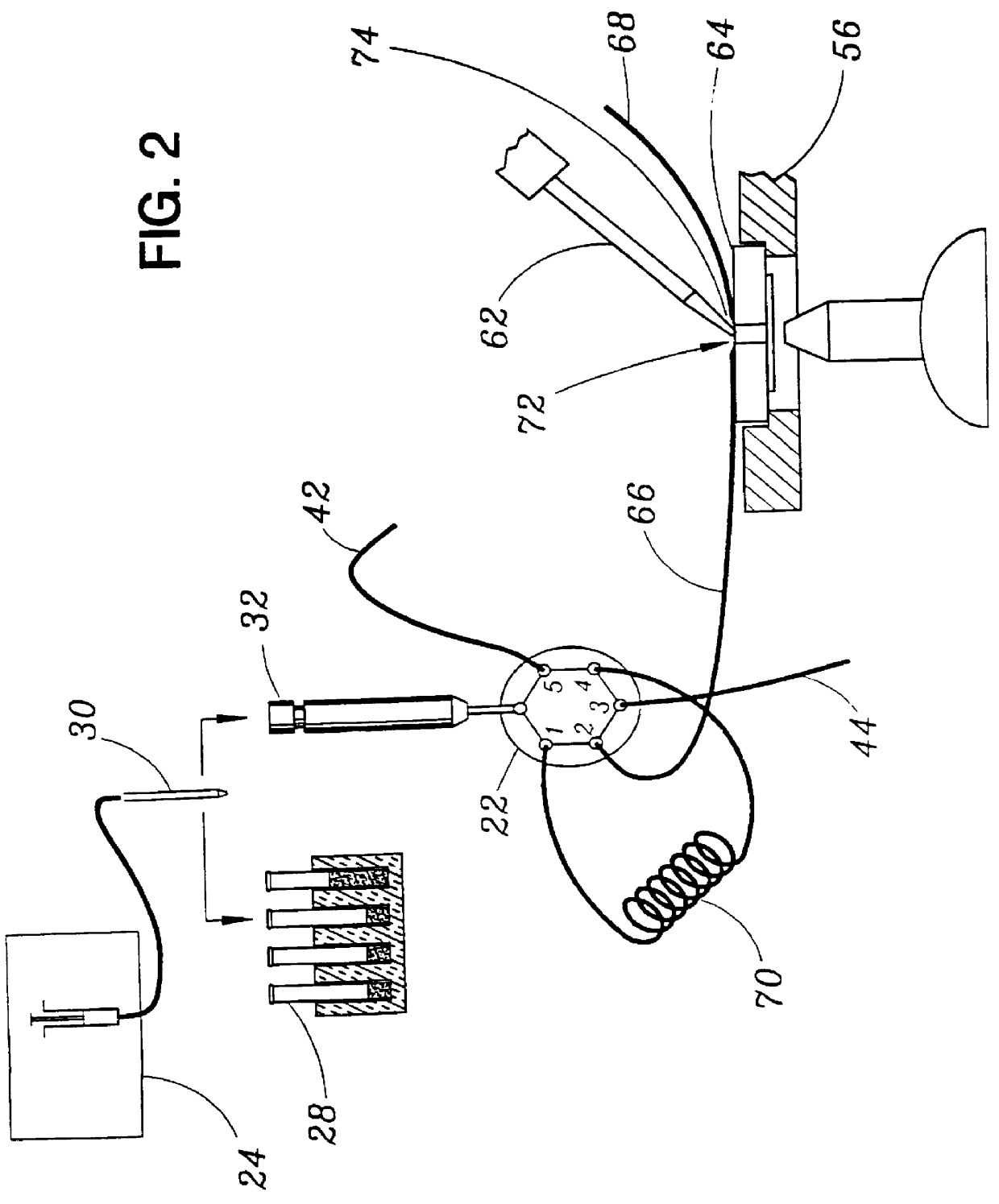
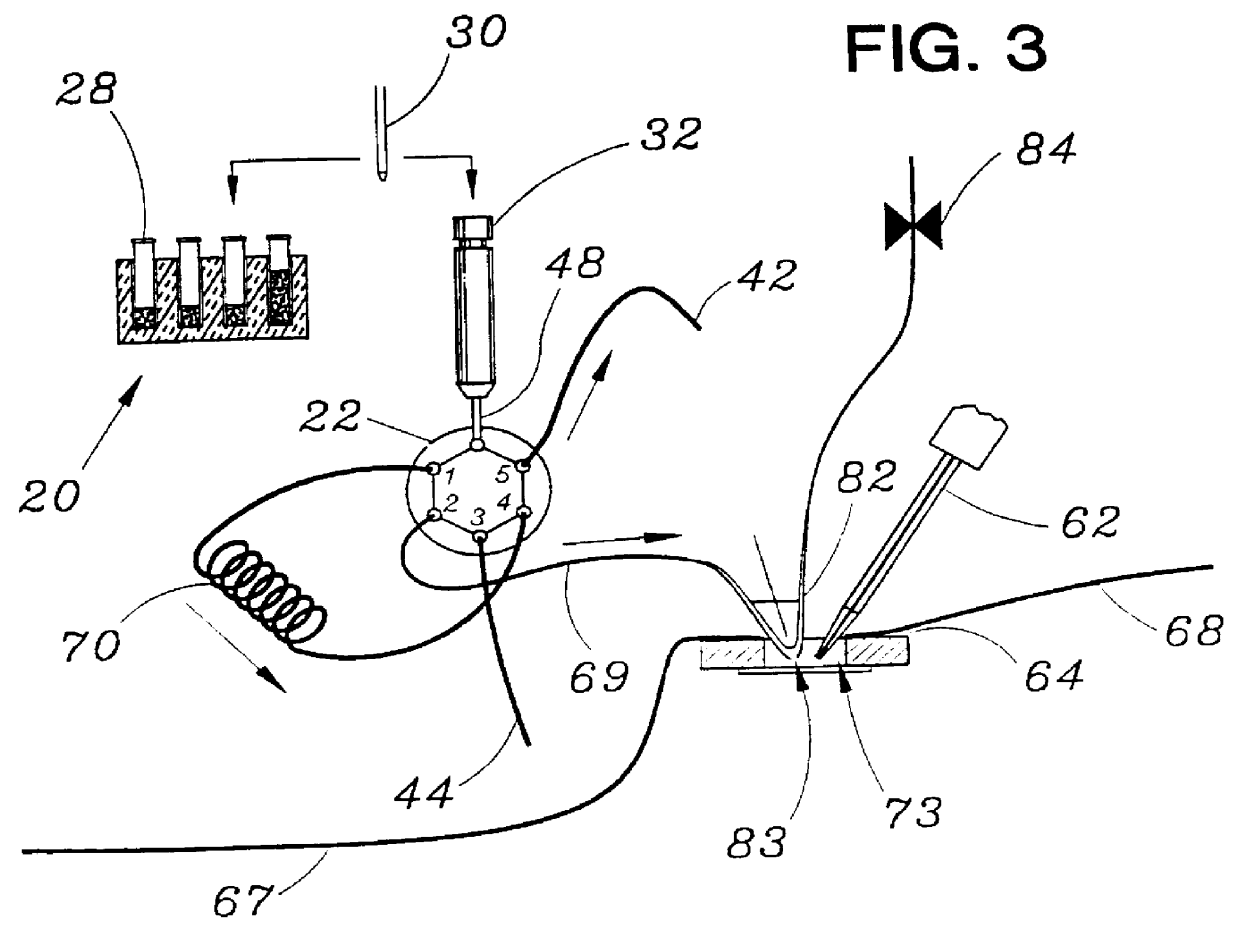
Patch clamp apparatus and technique having high throughput and low fluid volume requirements
InactiveUS6063260ALow sample volume requirementLower the volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAutosamplerIon transfer
PCT No. PCT / EP95 / 02204 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 25, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 25, 1997 PCT Filed Jun. 7, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 13721 PCT Pub. Date May 9, 1996Apparatus for carrying out patch clamp technique utilized in studying the effect of certain materials on ion transfer channels in biological tissue, and more particularly patch clamp apparatus utilizing an autosampler, such as those utilized with HPLC apparatus, to provide high throughput, is disclosed. The invention additionally includes novel microperfusion chamber assemblies capable of utilizing only small amounts of material to be tested and only small amounts of liquid carrier, thereby enabling many tests to be completed in a short period of time. The invention more broadly relates to a novel electrophysiology drug handling and application set up for screening of chemical substances while providing high throughput and requiring only low volume of solutions and samples to be tested. The invention also comprises several novel procedures for utilizing the apparatus of the invention.
Owner:SOPHION BIOSCI
Hybrid Process for Forming Metal Gates of MOS Devices
ActiveUS20090230479A1Increase of stress appliedLower threshold voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricSemiconductor structure
A semiconductor structure includes a first MOS device including a first gate, and a second MOS device including a second gate. The first gate includes a first high-k dielectric over a semiconductor substrate; a second high-k dielectric over the first high-k dielectric; a first metal layer over the second high-k dielectric, wherein the first metal layer dominates a work-function of the first MOS device; and a second metal layer over the first metal layer. The second gate includes a third high-k dielectric over the semiconductor substrate, wherein the first and the third high-k dielectrics are formed of same materials, and have substantially a same thickness; a third metal layer over the third high-k dielectric, wherein the third metal layer and the second metal layer are formed of same materials, and have substantially a same thickness; and a fourth metal layer over the third metal layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
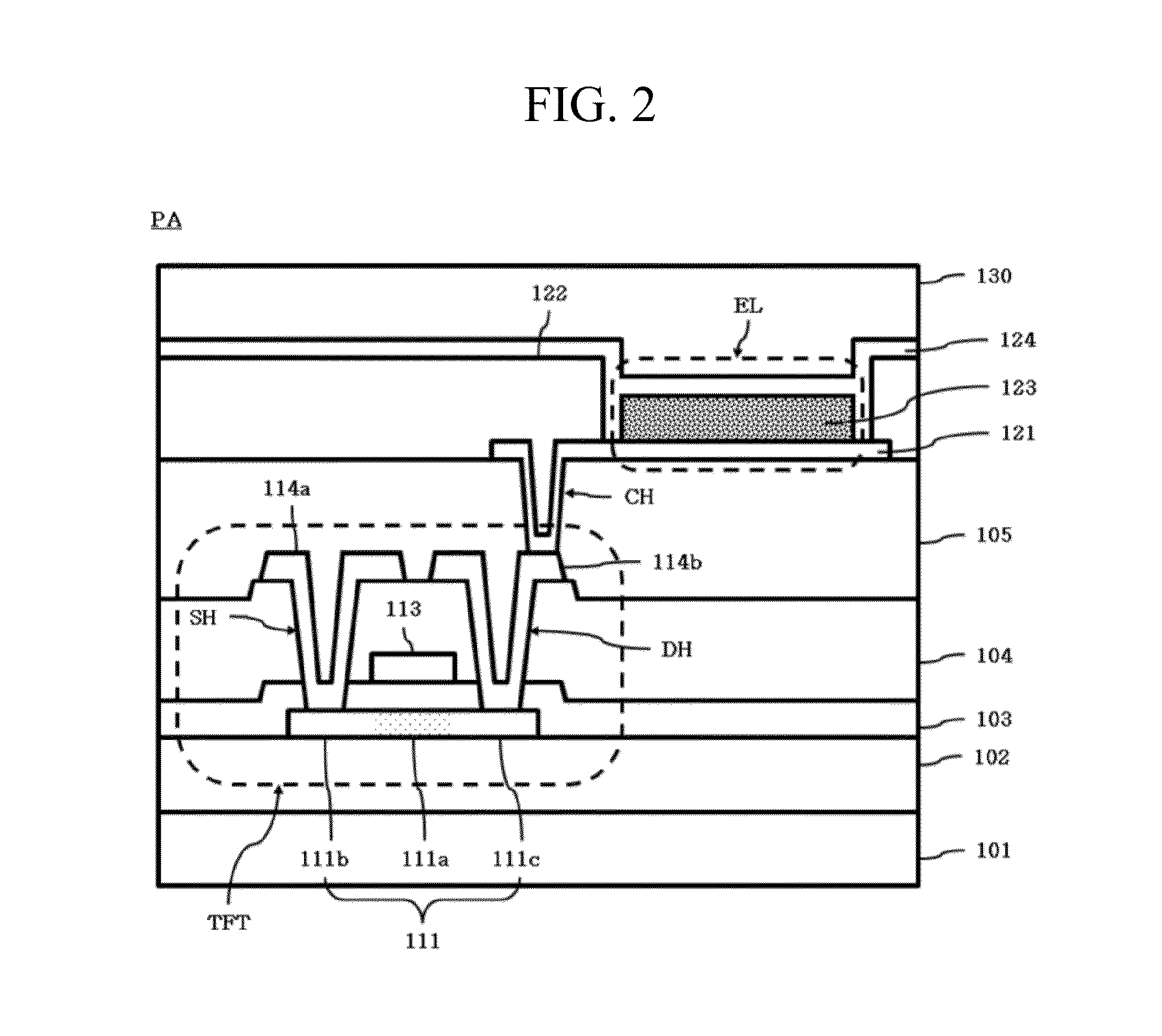
Flexible display device and method for manufacturing the same
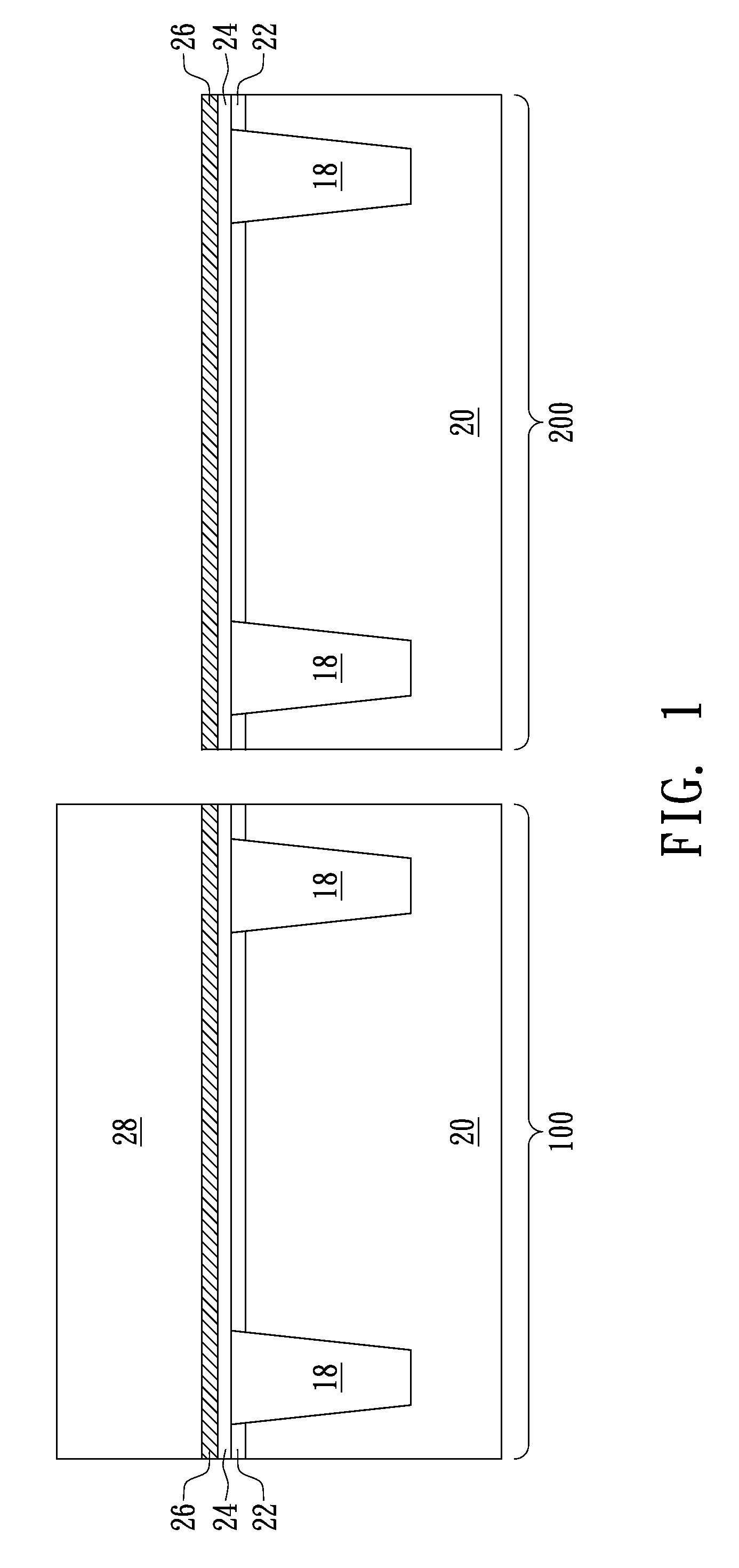
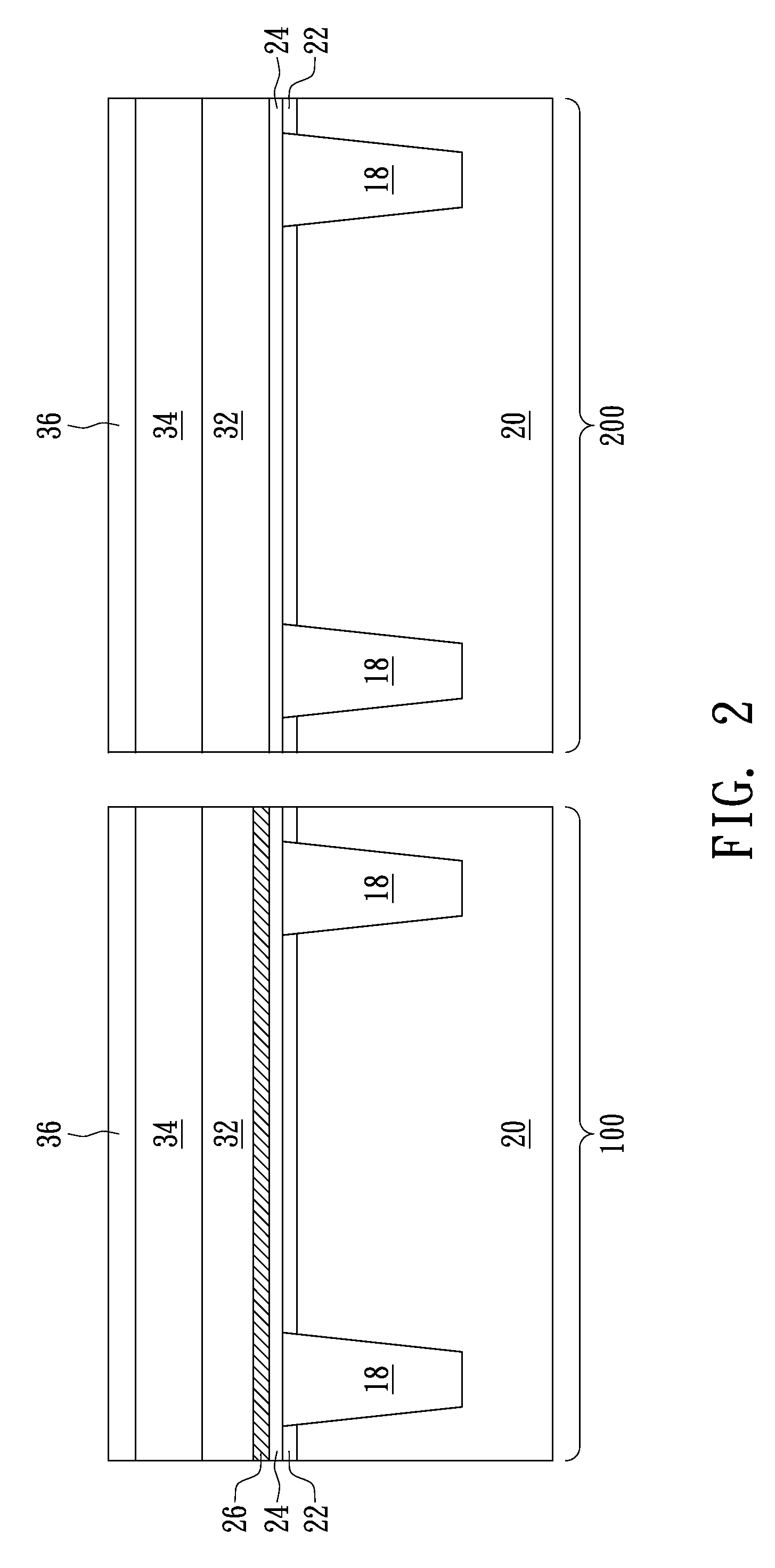
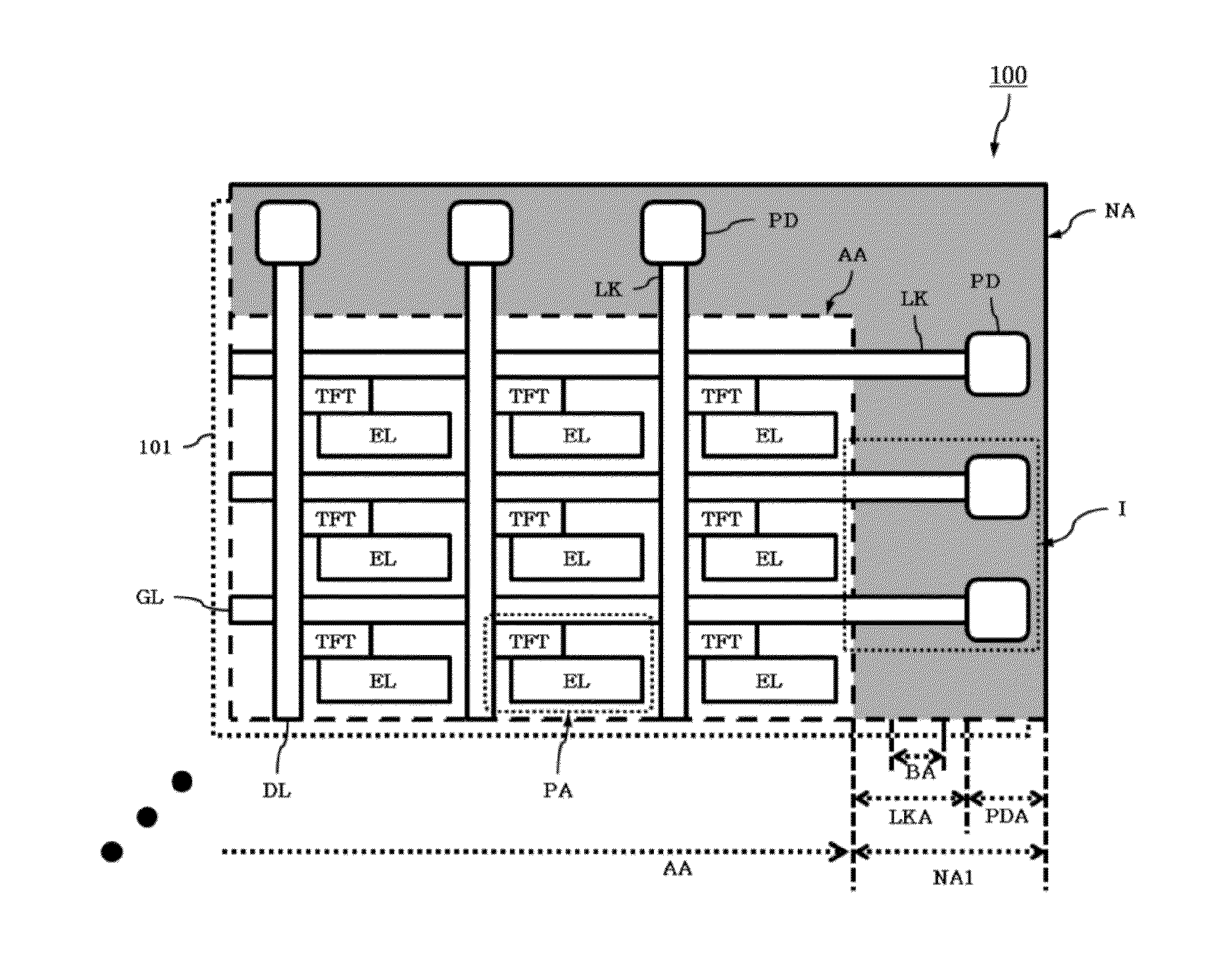
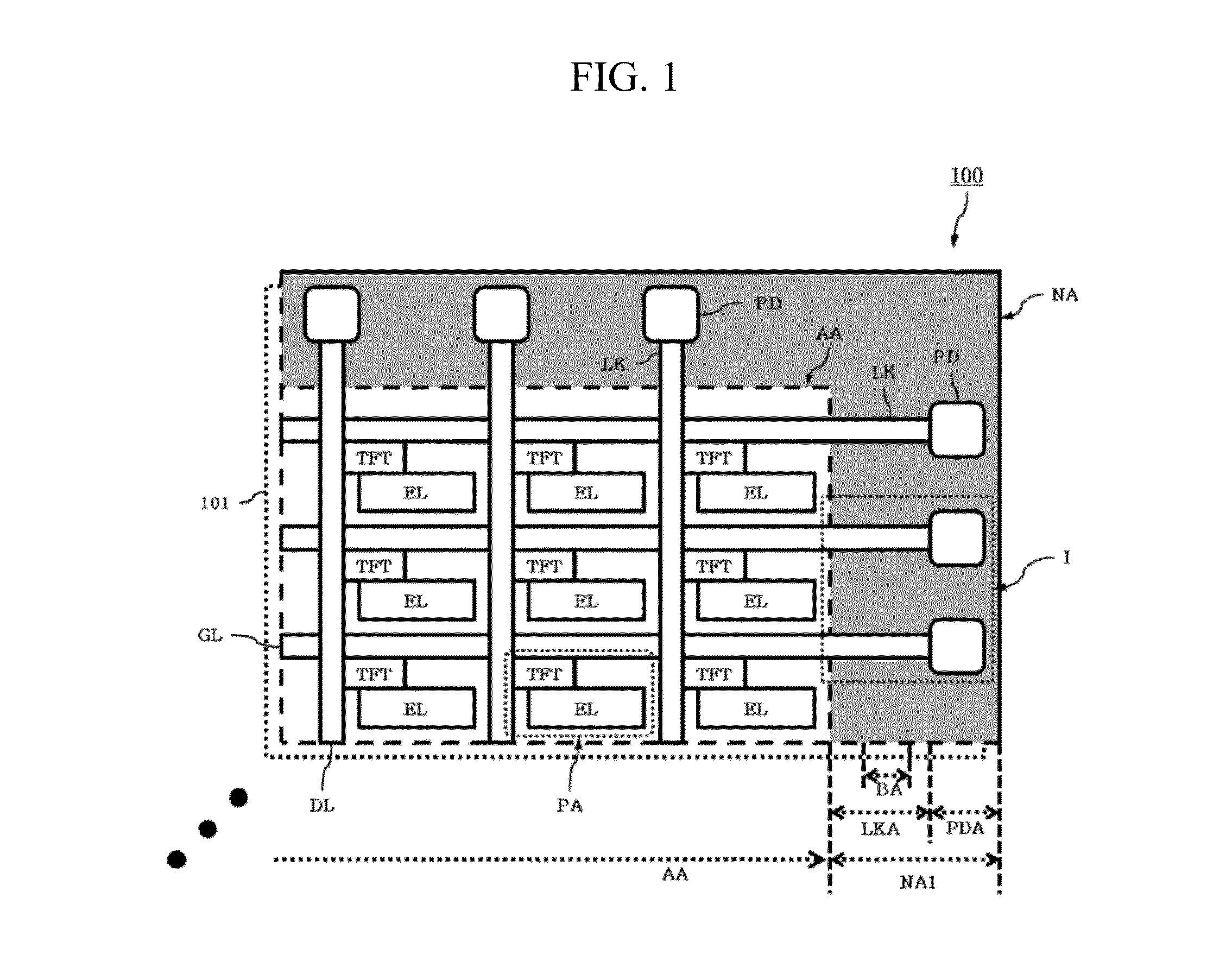
ActiveUS20140353670A1Reduce widthImprove product valueFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesEngineeringFlexible display
Discussed is a flexible display device to reduce a width of a bezel. The flexible display device includes a substrate being formed of a flexible material, a plurality of gate lines and a plurality of data lines crossing each other, a plurality of pads formed in a pad area of a non-display area, a plurality of links formed in a link area of the non-display area, a plurality of insulation films formed over the entire surface of the substrate, and a first bending hole formed in a bending area of the non-display area, the first bending hole passing through at least one of the insulation films disposed under the link, wherein the bending area is bent such that the pads are disposed on the lower surface of the substrate.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
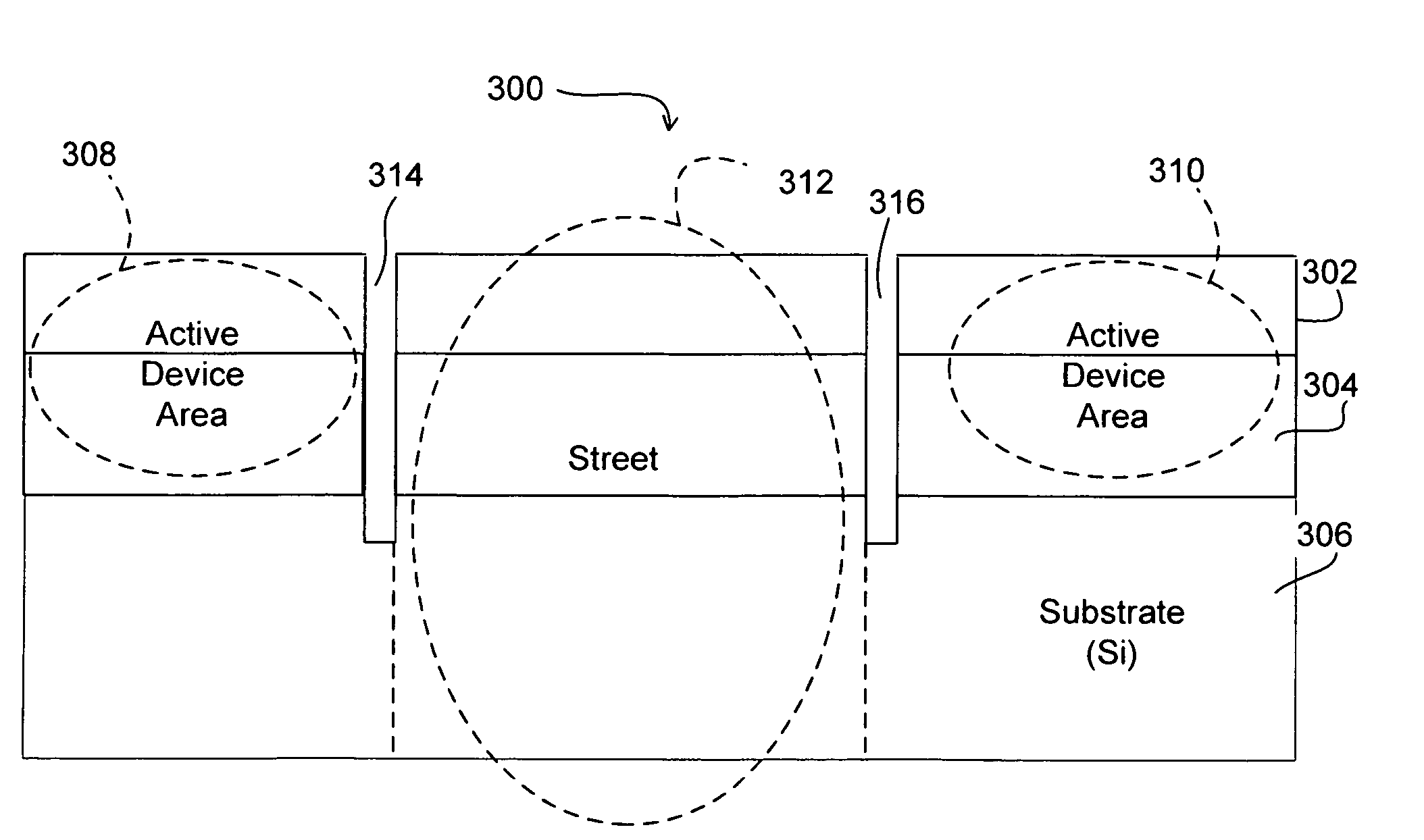
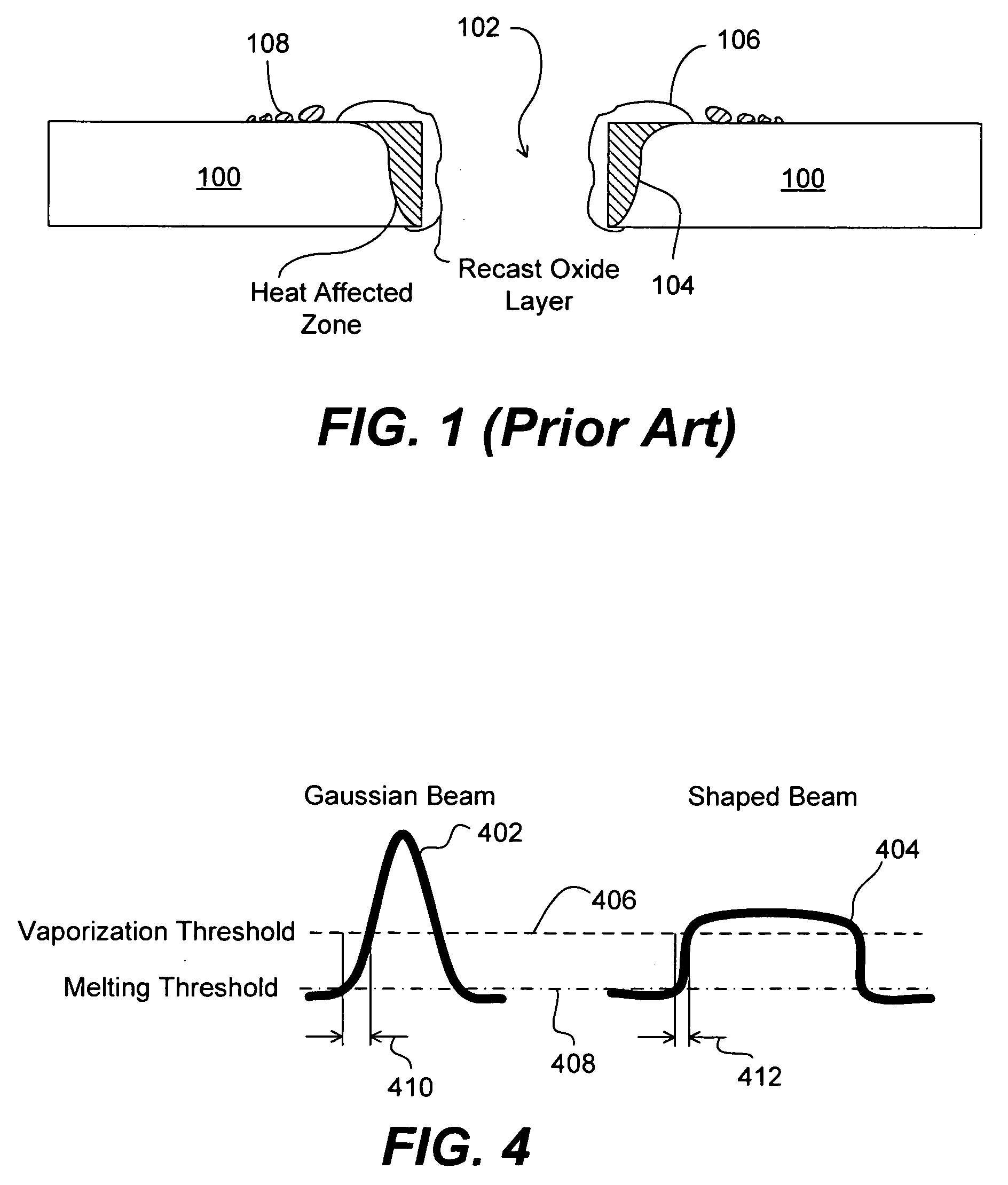
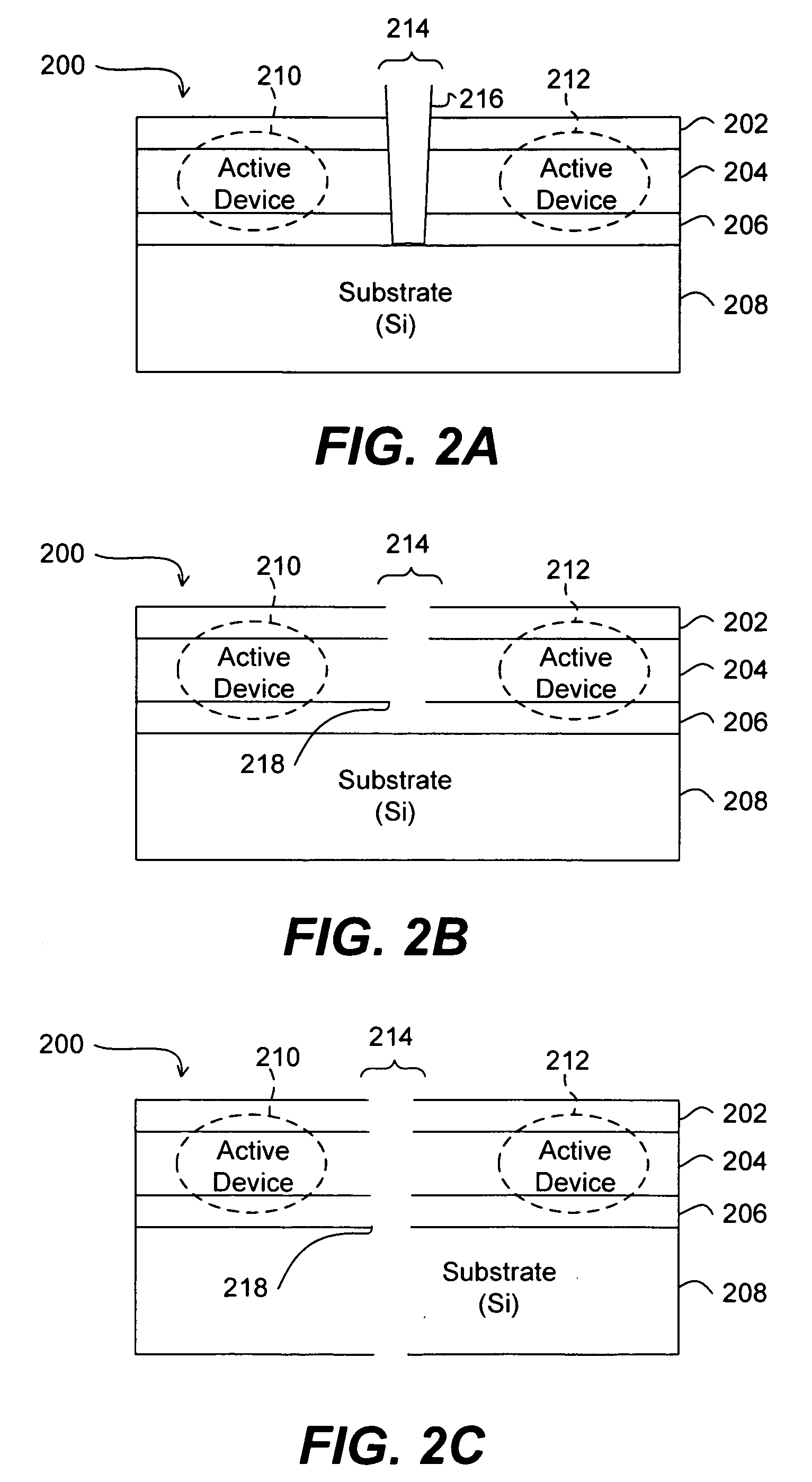
Ultrashort laser pulse wafer scribing
InactiveUS20070272668A1Improve mechanical stressImprove thermal stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLight beamOptoelectronics
Systems and methods are provided for scribing wafers with short laser pulses so as to reduce the ablation threshold of target material. In a stack of material layers, a minimum laser ablation threshold based on laser pulse width is determined for each of the layers. The highest of the minimum laser ablation thresholds is selected and a beam of one or more laser pulses is generated having a fluence in a range between the selected laser ablation threshold and approximately ten times the selected laser ablation threshold. In one embodiment, a laser pulse width in a range of approximately 0.1 picosecond to approximately 1000 picoseconds is used. In addition, or in other embodiments, a high pulse repetition frequency is selected to increase the scribing speed. In one embodiment, the pulse repetition frequency is in a range between approximately 100 kHz and approximately 100 MHz.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Multi-piece putter head having an insert
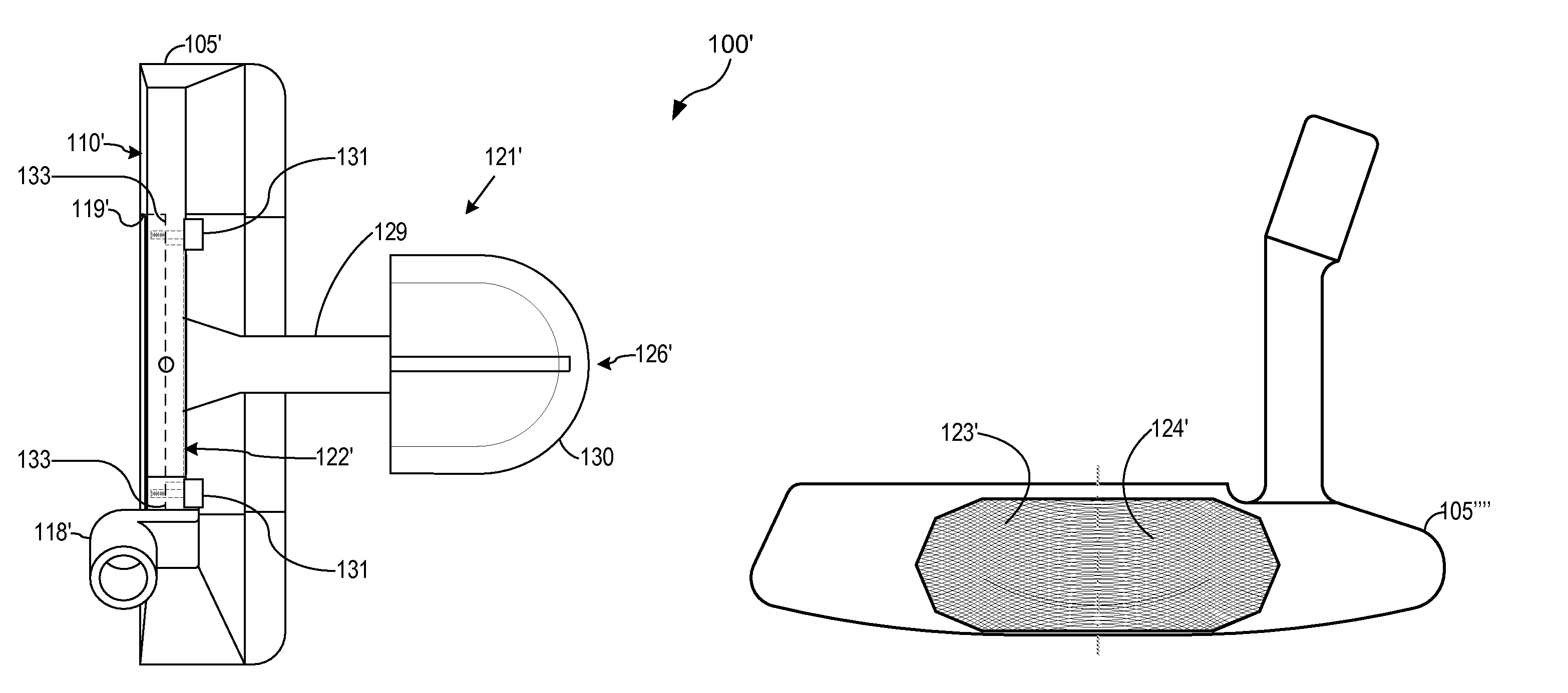
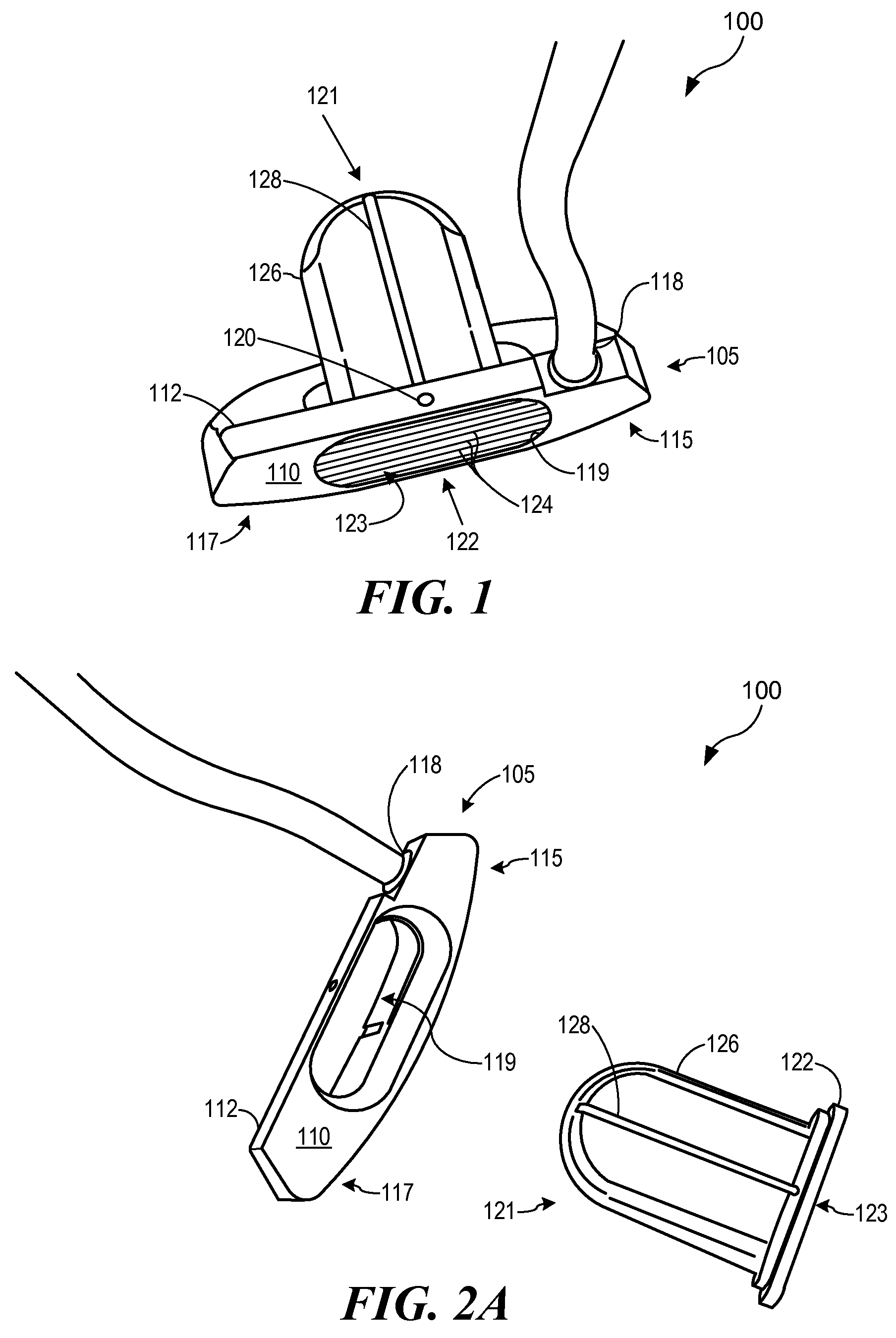
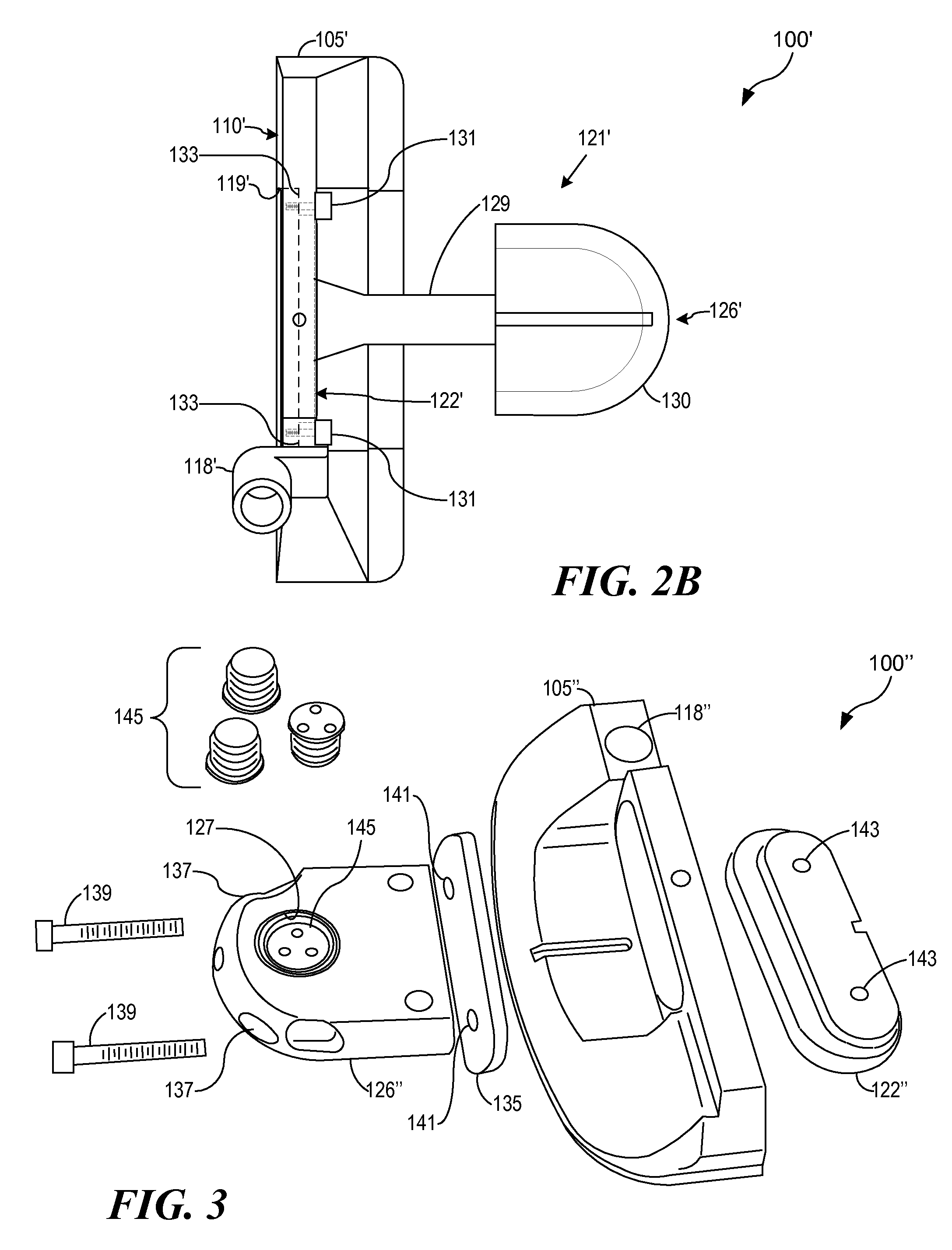
InactiveUS7566276B2Improved ergonomic stroke mechanicsConfidenceGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringCenter of percussion
A golf putter head with a front portion comprising traditional shape and appearance, with an integral face insert extending through the head to an alignment and weighting portion extending beyond the main body of the putter, adding improved alignment, increased MOI and adjustable weighting and adjustable balance and optimizable Center of Percussion. The putter head comprises a central face insert portion extending through the body and above the traditional weight flange, with mass relieved portions below the top of the alignment piece in order to receive one or more optional weights, and the upper side of the rearwardly extending portion being engraved or marked with various alignment indicia, and the whole through-head insert face portion and rearwardly extending portion being affixed to the base portion of the head at least in part with threaded fasteners.
Owner:DOGLEG RIGHT CORP
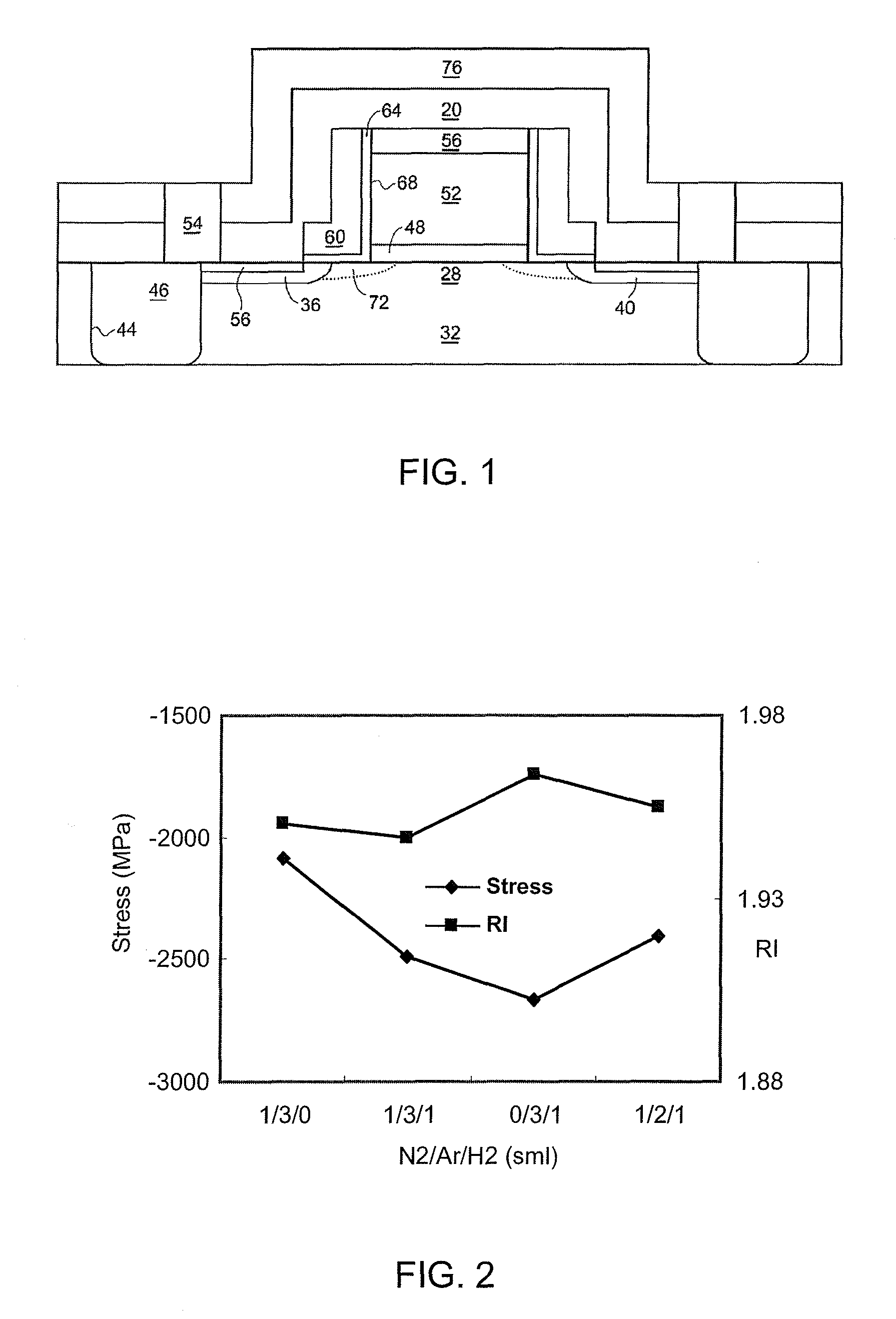
Method of producing highly strained pecvd silicon nitride thin films at low temperature
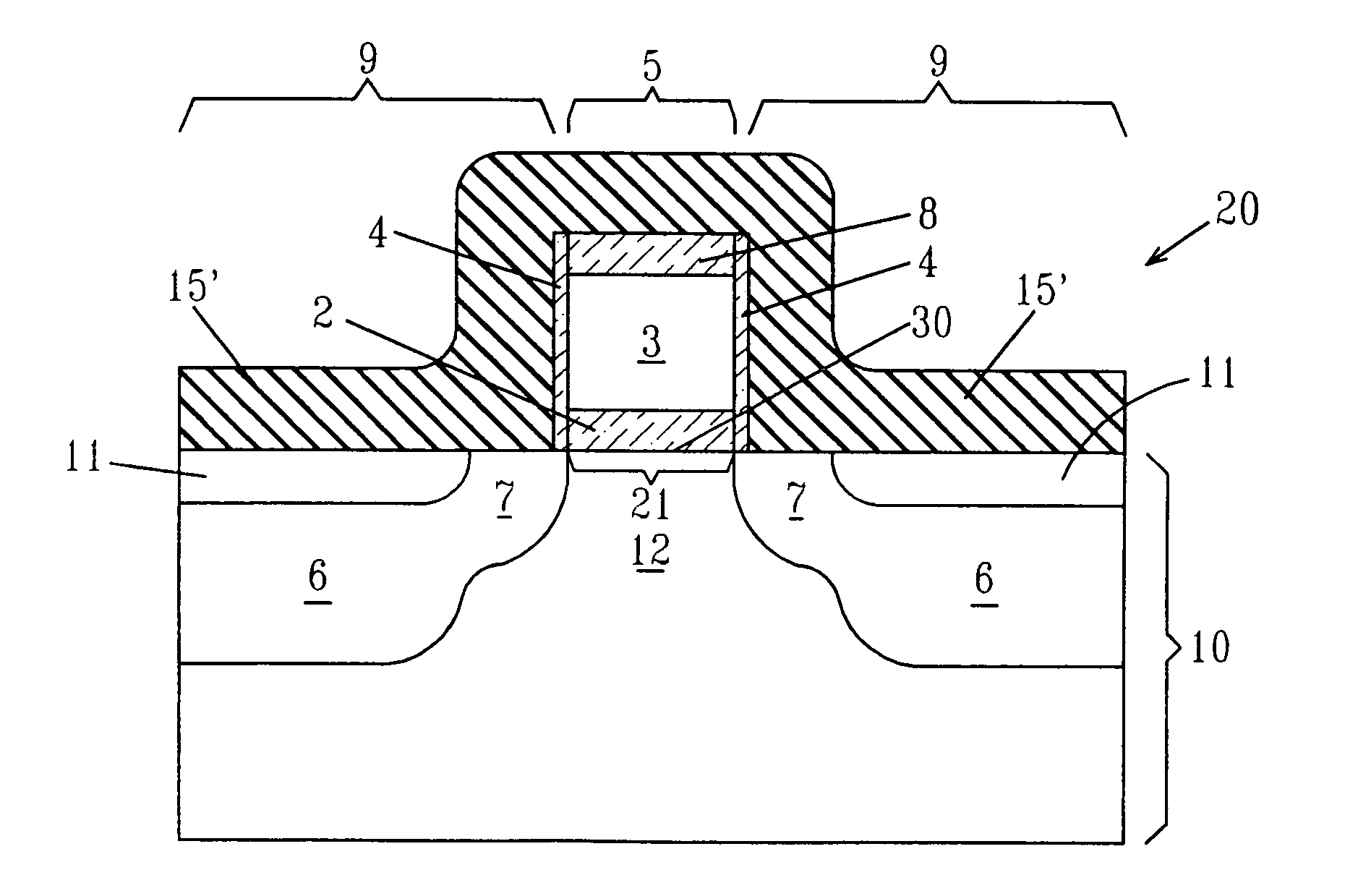
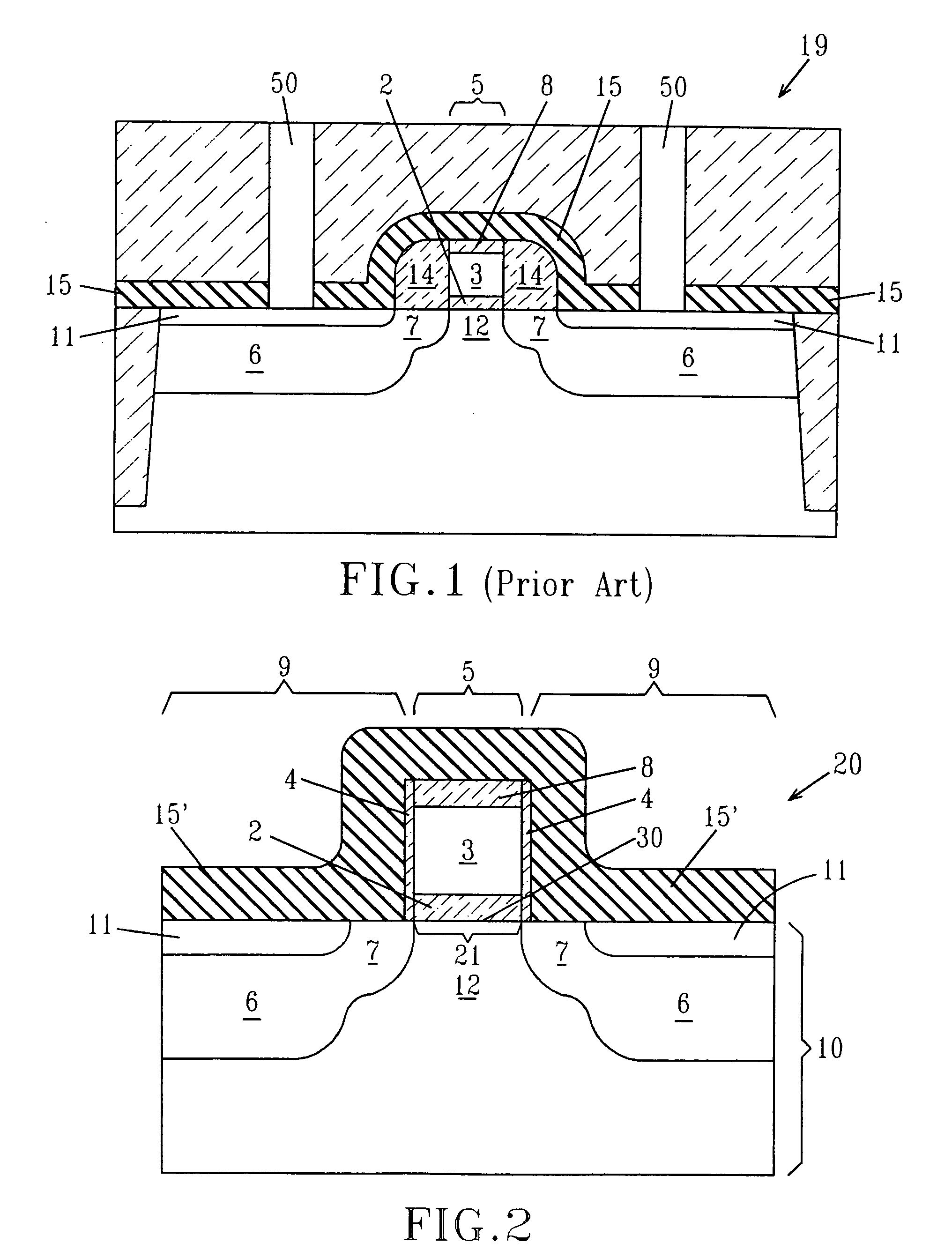
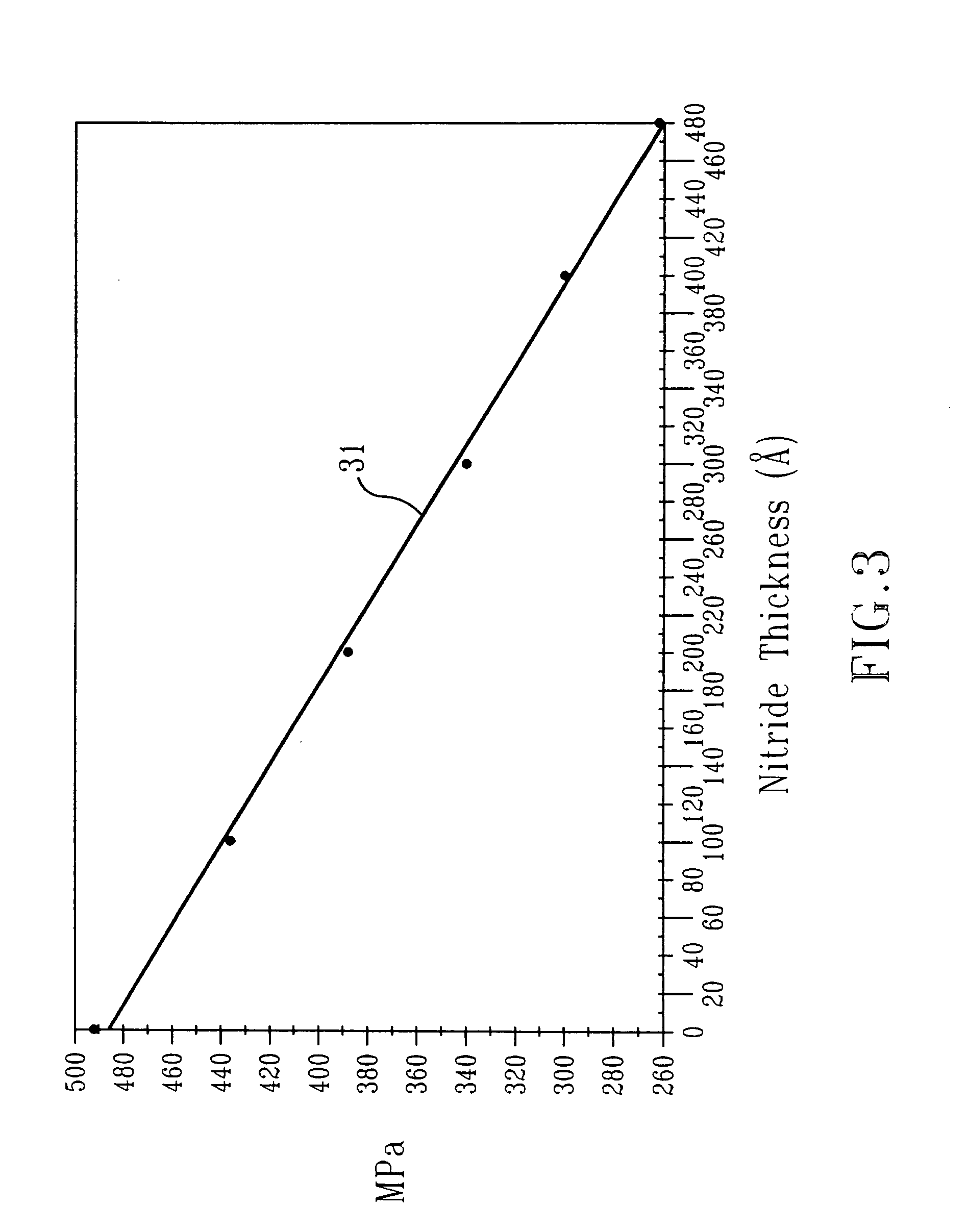
InactiveUS20060223290A1Increase pressureImprove stress conditionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingStressorMaterials science
A method for increasing the level of stress for amorphous thin film stressors by means of modifying the internal structure of such stressors is provided. The method includes first forming a first portion of an amorphous film stressor material on at least a surface of a substrate, said first portion having a first state of mechanical strain defining a first stress value. After the forming step, the first portion of the amorphous film stressor material is densified such that the first state of mechanical strain is not substantially altered, while increasing the first stress value. In some embodiments, the steps of forming and densifying are repeated any number of times to obtain a preselected and desired thickness for the stressor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Joining structure
InactiveUS6857808B1Reduce stiffnessReduce stress concentrationMachine supportsFoundation engineeringStress concentrationPrincipal stress
The present invention provides a joining structure capable of greatly improving the proof stress and the fatigue property by alleviating the stress concentration and residual stress caused by welding heat at one or both ends of a tabular member.In the present invention, one or both ends 4 of a tabular member 3 such as a reinforcing rib, fixed to the surface of a structural member 1 in the direction of the principal stress of the structural member 1 so as to protrude in the shape of T, is / are bent in a direction deviating from the direction of the principal stress and, by this, the rigidity at the end(s) 4 of the tabular member 3 decreases and the stress concentration is alleviated. It is preferable to bend one or both ends of a tabular member 3 in the shape of an gradual curve and to the extent that each bent end is formed at a right angle to the direction of the principal stress. The tabular member may have the shape of a flat plate, or it may be bent so that it has the shape of U or V as a whole. Further, the tabular member may be welded to a structural member or formed as an integral part of a structural member.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +2
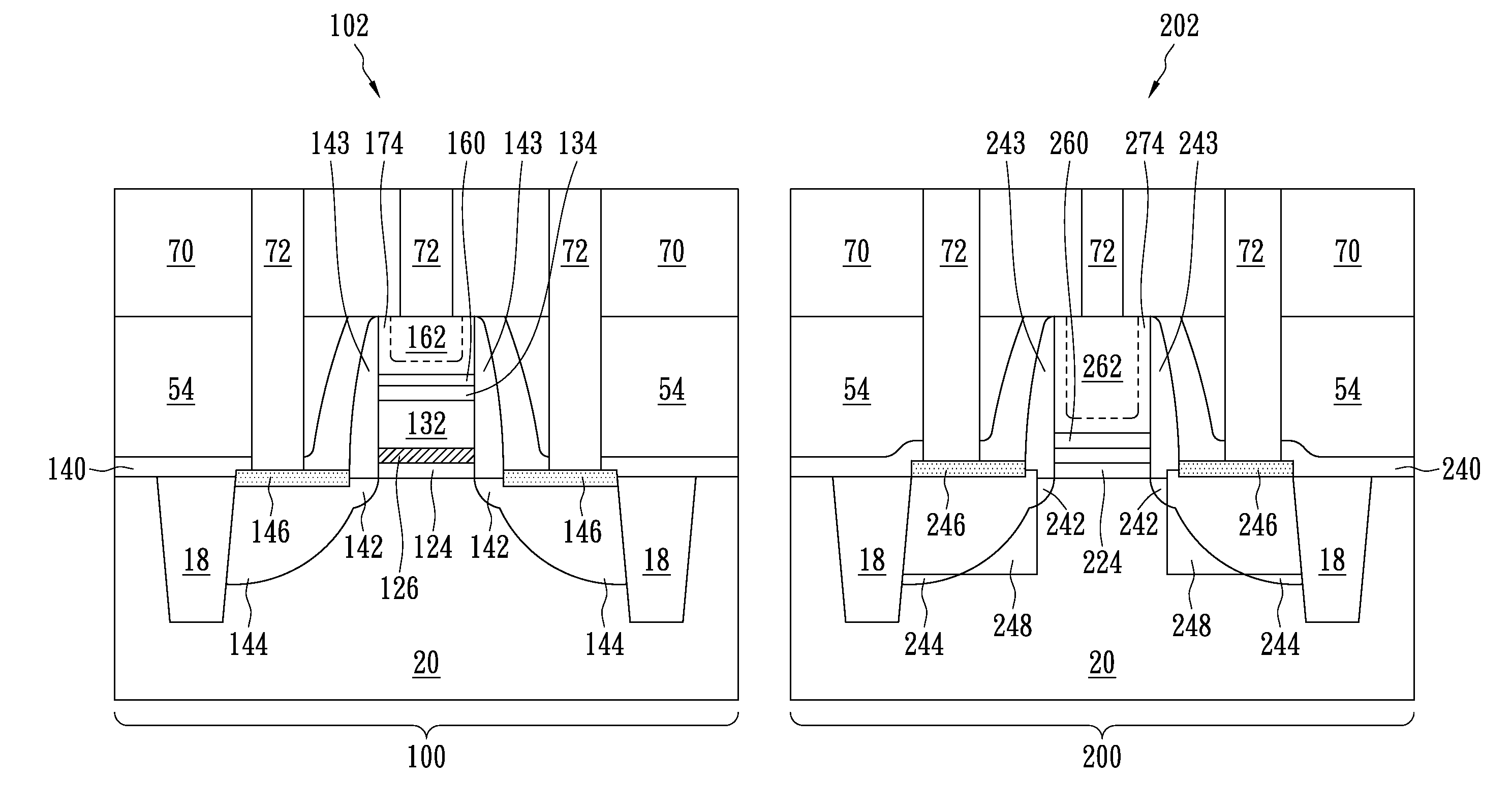
Semiconductor device having stress and its manufacture method
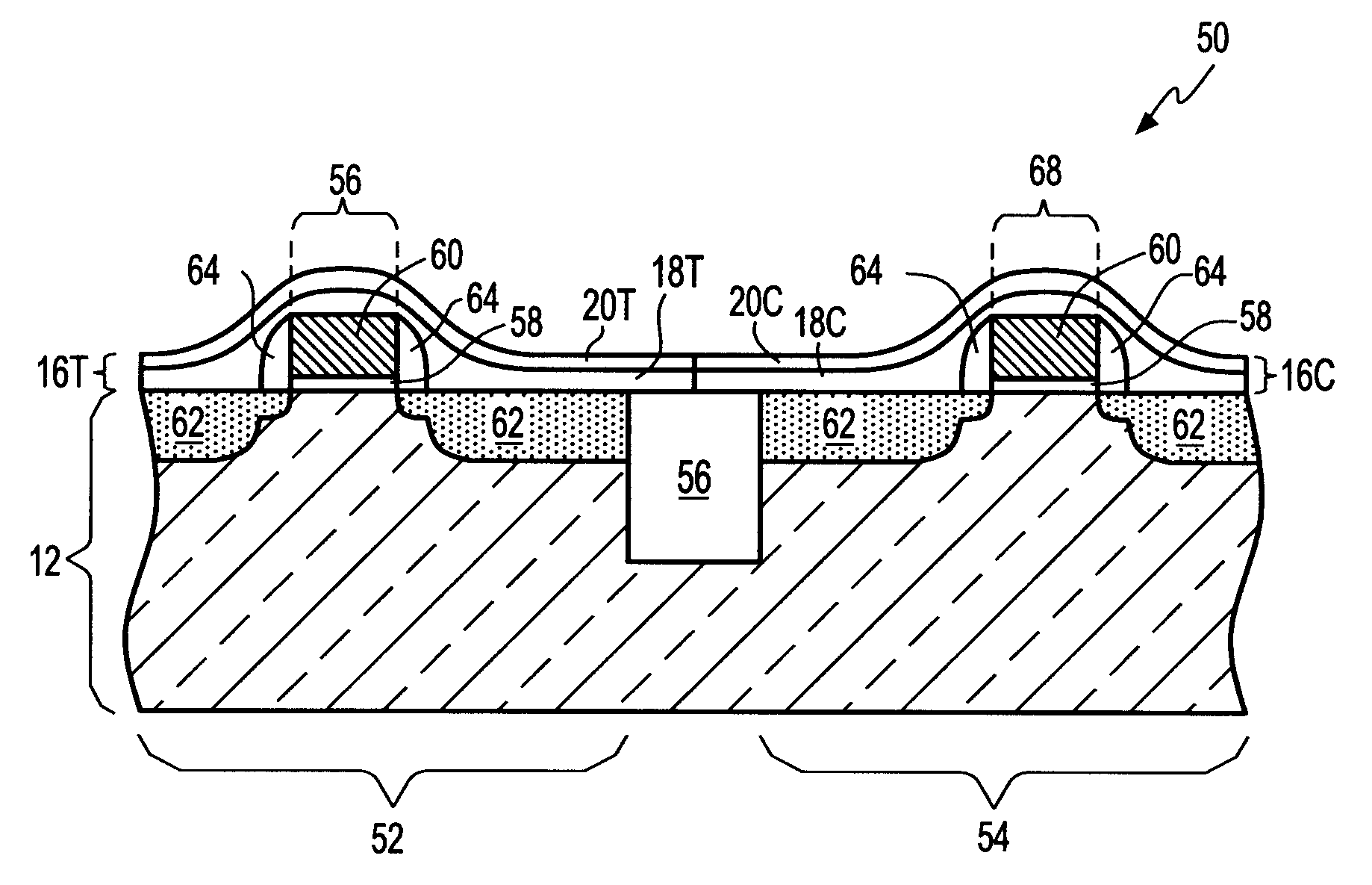
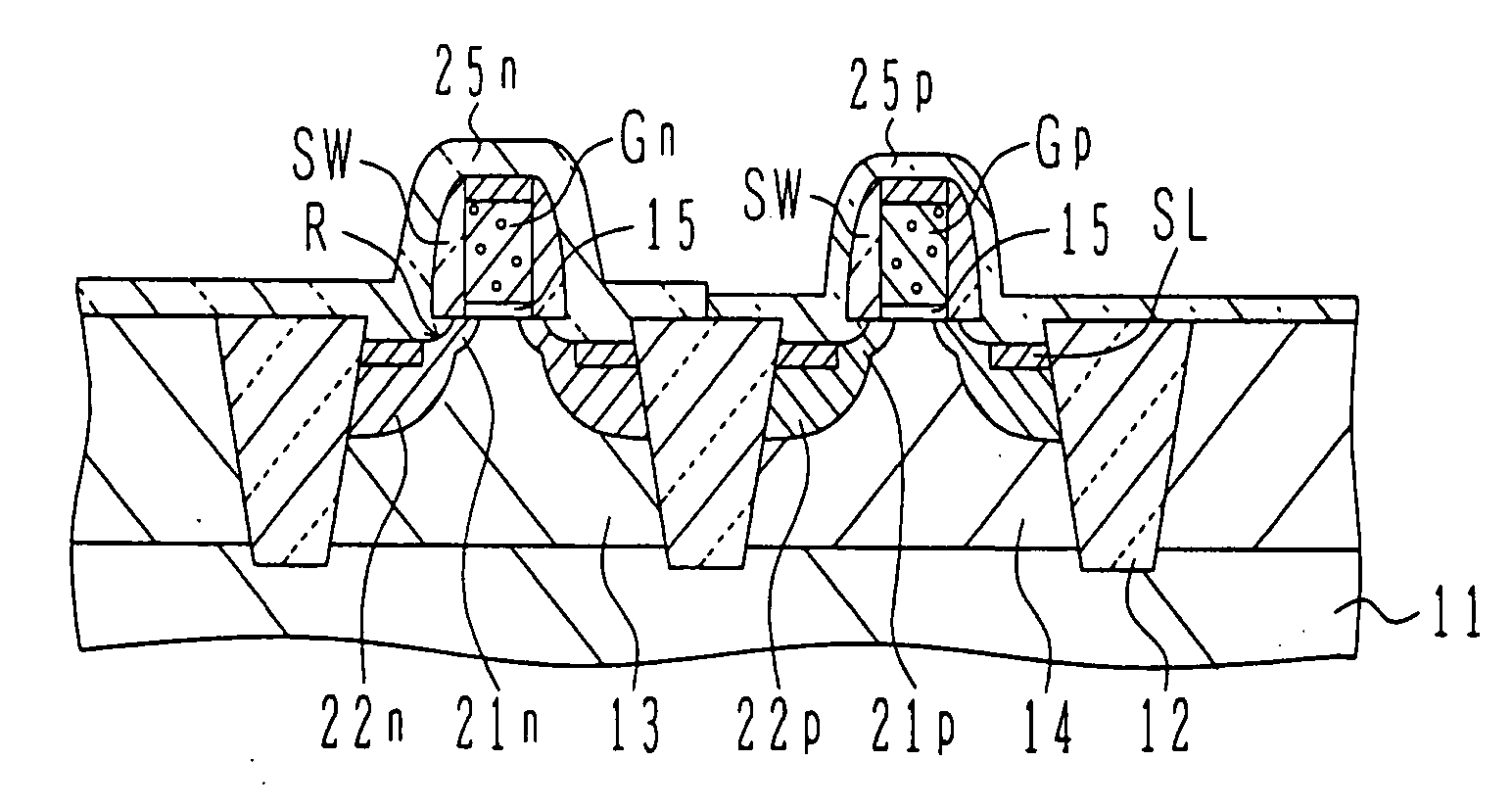
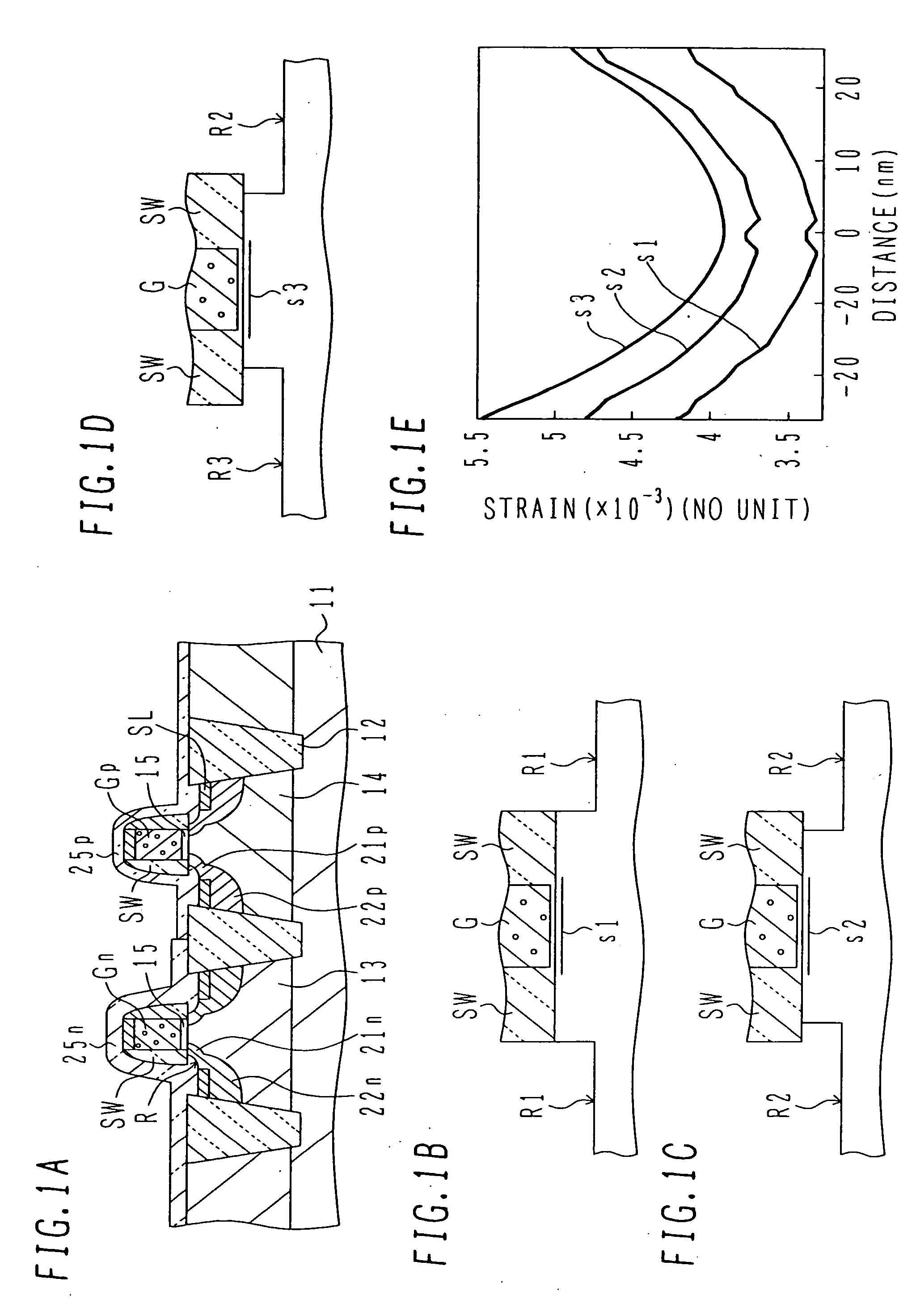
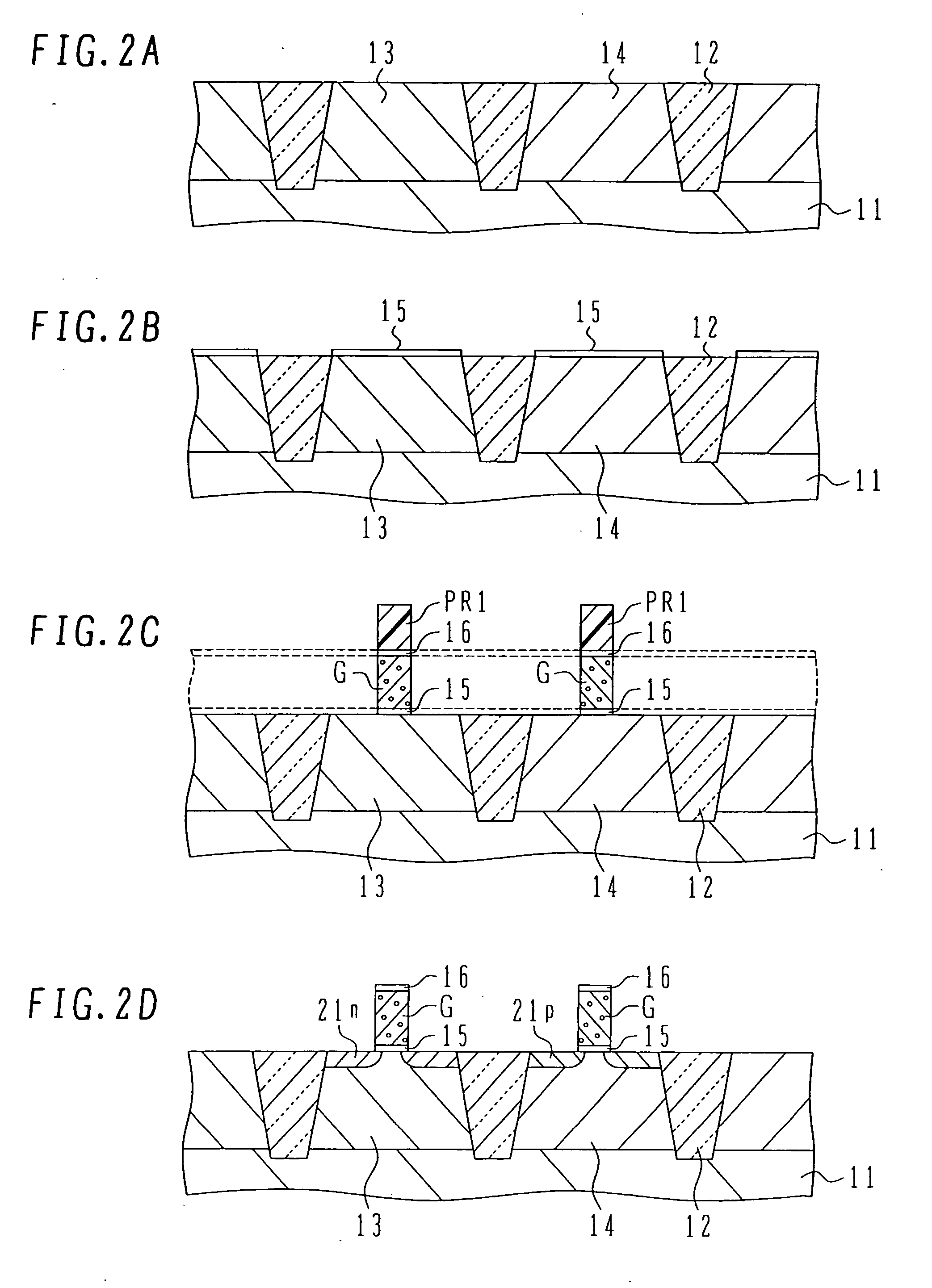
ActiveUS20050269650A1Improve stress conditionIncrease pressureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialNitride
A semiconductor device has: active regions including a p-type active region; an insulated gate electrode structure formed on each of the active regions, and having a gate insulating film and a gate electrode formed thereon; side wall spacers formed on side walls of the insulated gate electrode structures; source / drain regions having extension regions having the opposite conductivity type to that of the active region and formed on both sides of the insulated gate electrode structures and source / drain diffusion layers having the opposite conductivity type and formed in the active regions outside of the side wall spacers; first recess regions formed by digging down the n-type source / drain regions in the p-type active region from surfaces of the n-type source / drain regions; and a first nitride film having tensile stress formed covering the p-type active region and burying the first recess regions.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Piezoactive actuator with dampened amplified movement
ActiveUS6927528B2Reduce vibrationIncrease capacityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesElastomerAudio power amplifier
The piezoactive actuator with amplified movement comprises a first sub-assembly formed by a mechanical movement amplifier and a second sub-assembly equipped with piezoactive elements. An interface with a load and an interface with a base, respectively placed at the peaks of a small axis of the shell and designed for actuating the load with respect to the base, define an actuating axis. A longitudinal deformation of the large axis enables a deformation of the small axis to be induced, designed to generate a movement at the interface with the load, the component of which movement along the small axis is amplified. At least one zone made of elastomer material is arranged at least substantially along the actuating axis to dampen deformations and increase the capacity of the actuator to resist external stresses. The actuator comprises at least one free space adjacent to the elastomer material zones in a direction orthogonal to the actuating axis.
Owner:CEDRAT TECH
Impact-modified polycarbonate blends
ActiveUS7067567B2High impact strengthEasy to processCoatingsPhosphorus organic compoundsPhosphoric Acid EstersPolyolefin
A thermoplastic molding composition having improved flammability rating and mechanical properties is disclosed. The composition contains aromatic polycarbonate having a weight-average molecular weight Mw≧25,000 g / mol., polyalkylene terephthalate, graft (co)polymer characterized in that its grafted phase includes structural units derived from acrylate monomers, an oligomeric organic phosphoric acid ester, and an optional fluorinated polyolefin. In a preferred embodiment the graft (co)polymer is characterized in its core-shell morphology.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Apparatus for assisting with the physiological recovery from fatigue, stress or injury
InactiveUS20150297909A1Improve recoveryIncrease metabolic stress and adaptationElectrotherapyPneumatic massageTherapeutic AreaViscosity
The disclosure relates to the process of enhanced recovery from injury or body fatigue due to strenuous activity or strenuous conditions using a contemplated apparatus. Generally the apparatuses disclosed utilize two or more physiological properties and / or body interfaces selected from 1) thermoregulation enhancer via cooling or heating sources; 2) blood flow viscosity enhancer via electromagnetic forces; 3) a circulatory pull by creating a negative pressure or vacuum environment which draws more blood to the treatment area; 4) muscle release apparatus via pressure point applicators and / or electric stimulation devices, which enhance the bodies natural abilities to recover from stress, fatigue or injury; and 5) a fatigue stimulator may be utilized to accelerate the amount of inflammation, stress, and / or fatigue applied to an area of the body via a restrictive cuff which prevent the body from constantly experiencing enhanced recovery techniques and depriving the body of natural adaptation.
Owner:PEASHOCK THOMAS J
MOSFET structure with high mechanical stress in the channel
ActiveUS7002209B2Increase pressureImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETStress induced
The present invention provides a semiconducting device including at least one gate region including a gate conductor located on a surface of a substrate, the substrate having an exposed surface adjacent the gate region; a silicide contact located adjacent the exposed surface; and a stress inducing liner located on the silicide contact, the exposed surface of the substrate adjacent to the gate region and the at least one gate region, wherein the stress inducing liner provides a stress to a device channel portion of the substrate underlying the gate region. The stress produced on the device channel is a longitudinal stress on the order of about 200 MPa to about 2000 MPa. The present invention also provides a method for forming the above-described semiconducting device.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
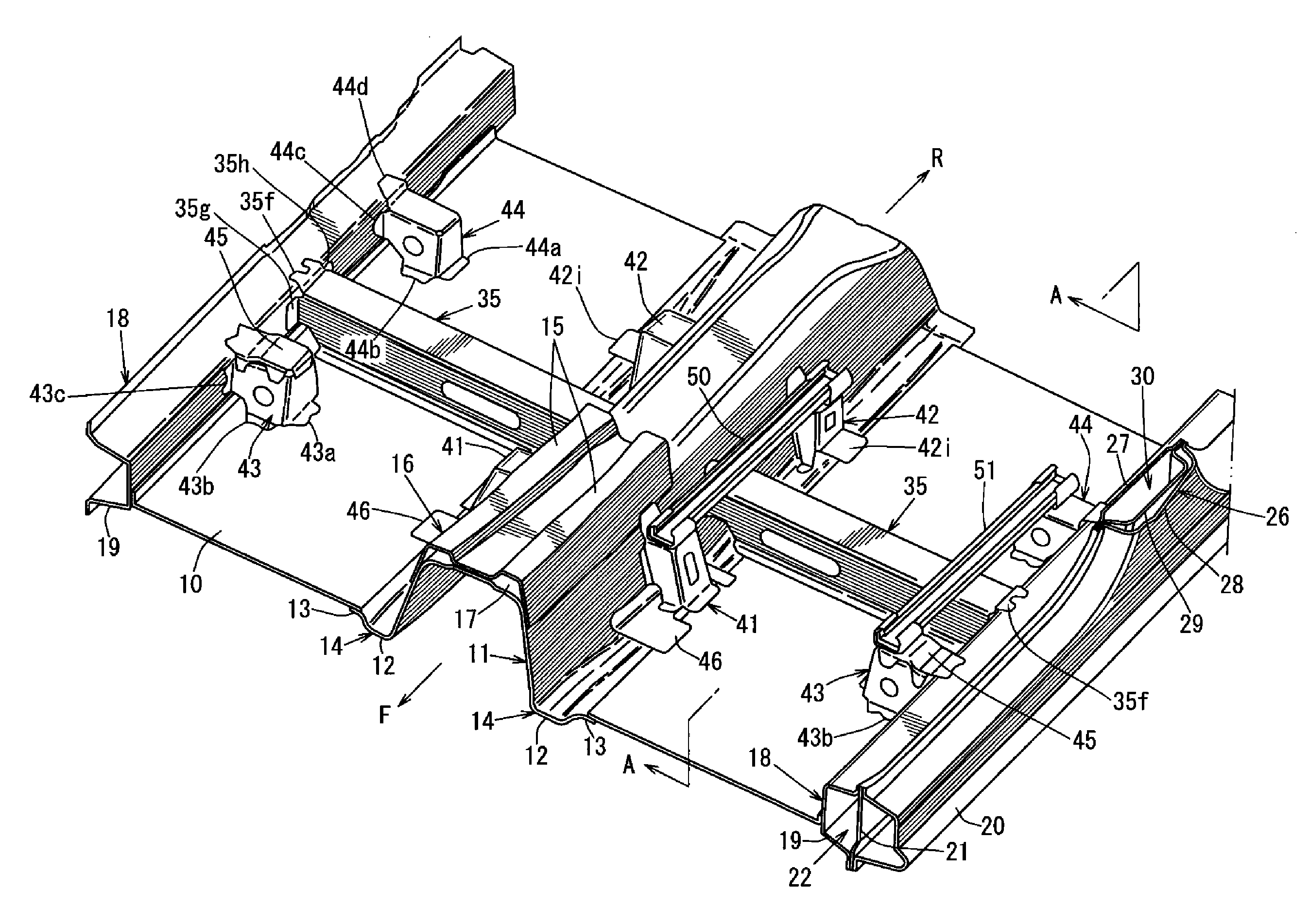
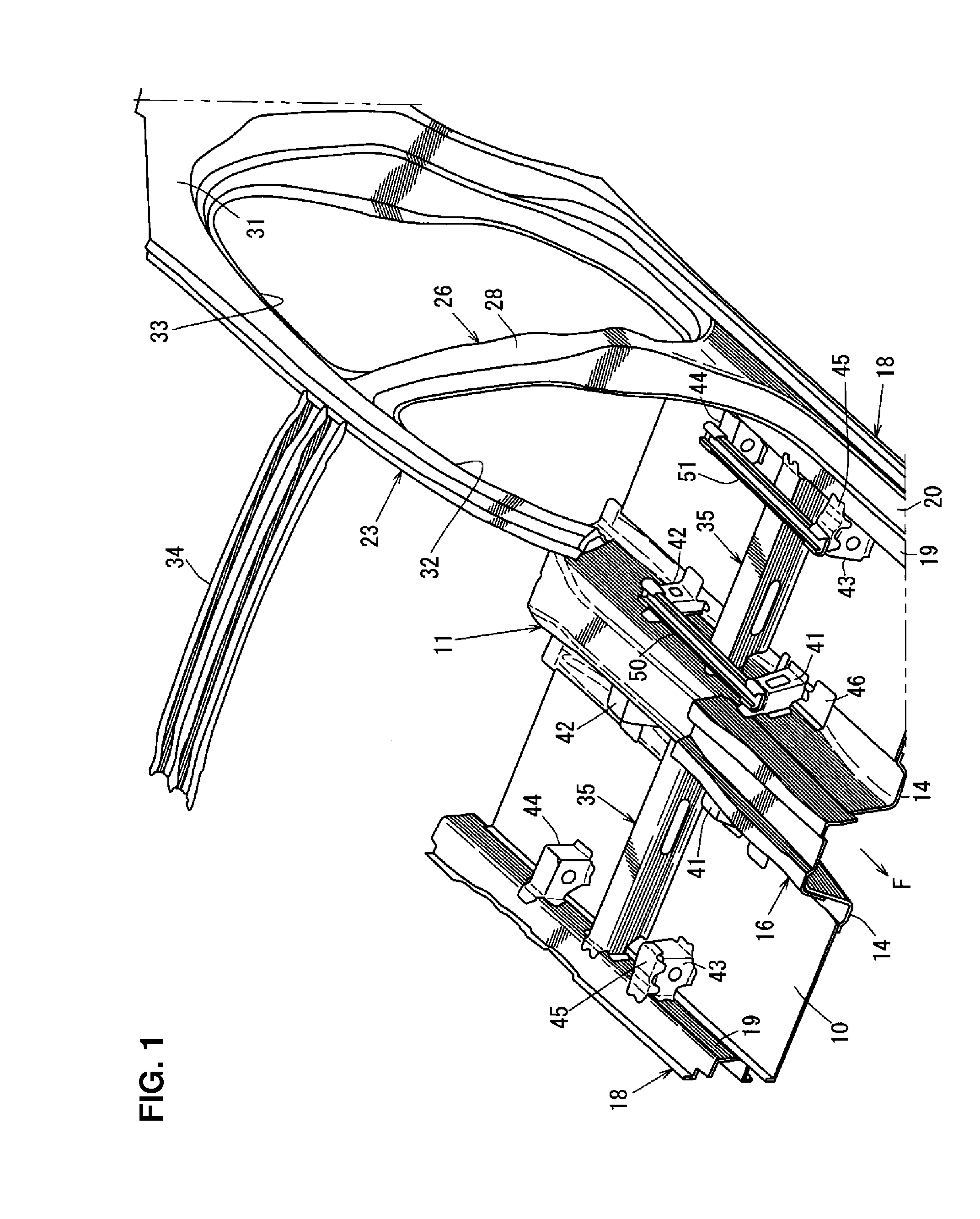
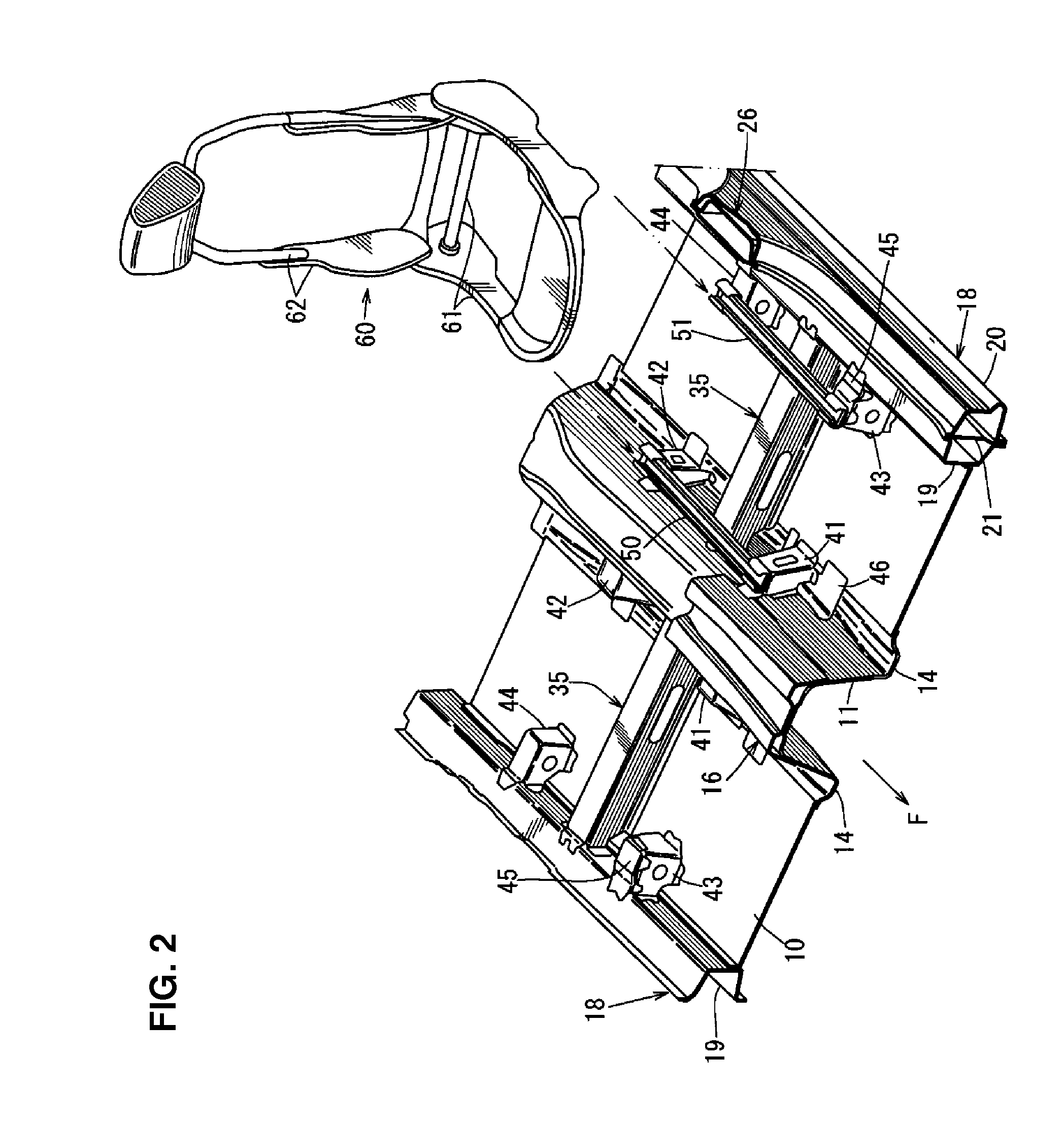
Lower vehicle-body structure of automotive vehicle
ActiveUS20160159402A1Improve rigiditySimple structureVehicle seatsUnderstructuresEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Electroacoustic converter film, flexible display, vocal cord microphone, and musical instrument sensor
ActiveUS20140210309A1Increase flexibilityExcellent acoustic characteristicsElectrophonic musical instrumentsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThin film electrodeDisplay device
Provided is an electroacoustic converter film including: a polymeric composite piezoelectric body having piezoelectric particles dispersed in a viscoelastic matrix which is formed of a polymer material exhibiting viscoelasticity at ordinary temperatures; thin film electrodes formed on both sides of the polymeric composite piezoelectric body; and protective layers formed on surfaces of the thin film electrodes. The electroacoustic converter film serves as a speaker capable of being integrated with a flexible display without impairing lightweightness or flexibility, and has considerable frequency dispersion in the storage modulus and also has a local maximum of the loss tangent around ordinary temperatures. A flexible display, a vocal cord microphone and a musical instrument sensor, in each of which the electroacoustic converter film is used, are also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Rotor and bearing system for a turbomachine
ActiveUS7112036B2Reduce wear and temperatureHeavy loadPump componentsPiston pumpsImpellerDrive shaft
A rotor and bearing system for a turbomachine. The turbomachine includes a drive shaft, an impeller positioned on the drive shaft, and a turbine positioned on the drive shaft proximate to the impeller. The bearing system comprises one gas journal bearing supporting the drive shaft between the impeller and the turbine. The area between the impeller and the turbine is an area of increased heat along the drive shaft in comparison to other locations along the drive shaft. The section of the drive shaft positioned between impeller and the turbine is also a section of the drive shaft that experiences increased stressed and load in the turbomachine. The inventive bearing machine system positions only one radial bearing in this area of increased stress and load.
Owner:CAPSTONE GREEN ENERGY CORP
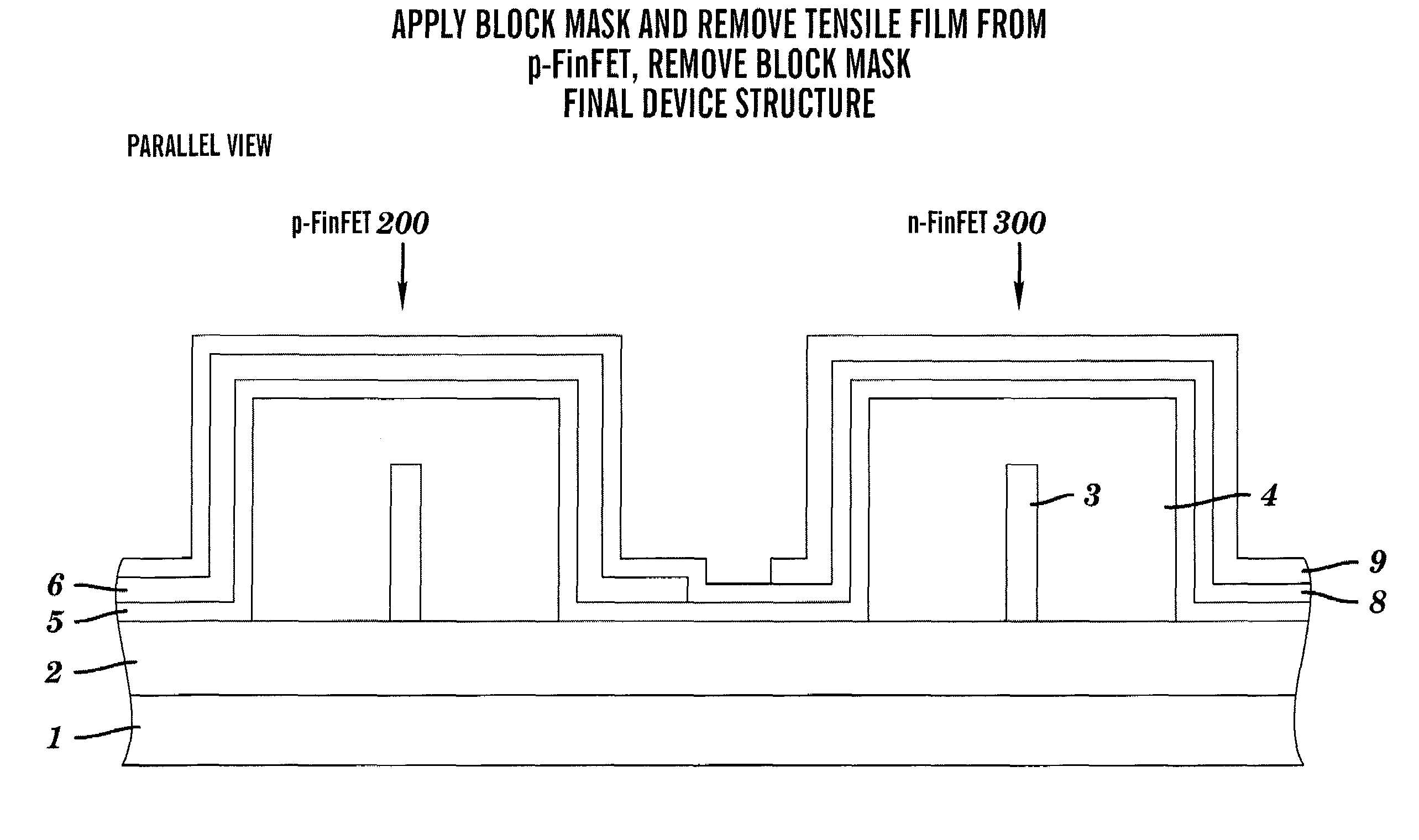
Strained finFET CMOS device structures
InactiveUS7388259B2Improve mobilityImprove device performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSEngineering
A semiconductor device structure, includes a PMOS device 200 and an NMOS device 300 disposed on a substrate 1,2, the PMOS device including a compressive layer 6 stressing an active region of the PMOS device, the NMOS device including a tensile layer 9 stressing an active region of the NMOS device, wherein the compressive layer includes a first dielectric material, the tensile layer includes a second dielectric material, and the PMOS and NMOS devices are FinFET devices 200, 300.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
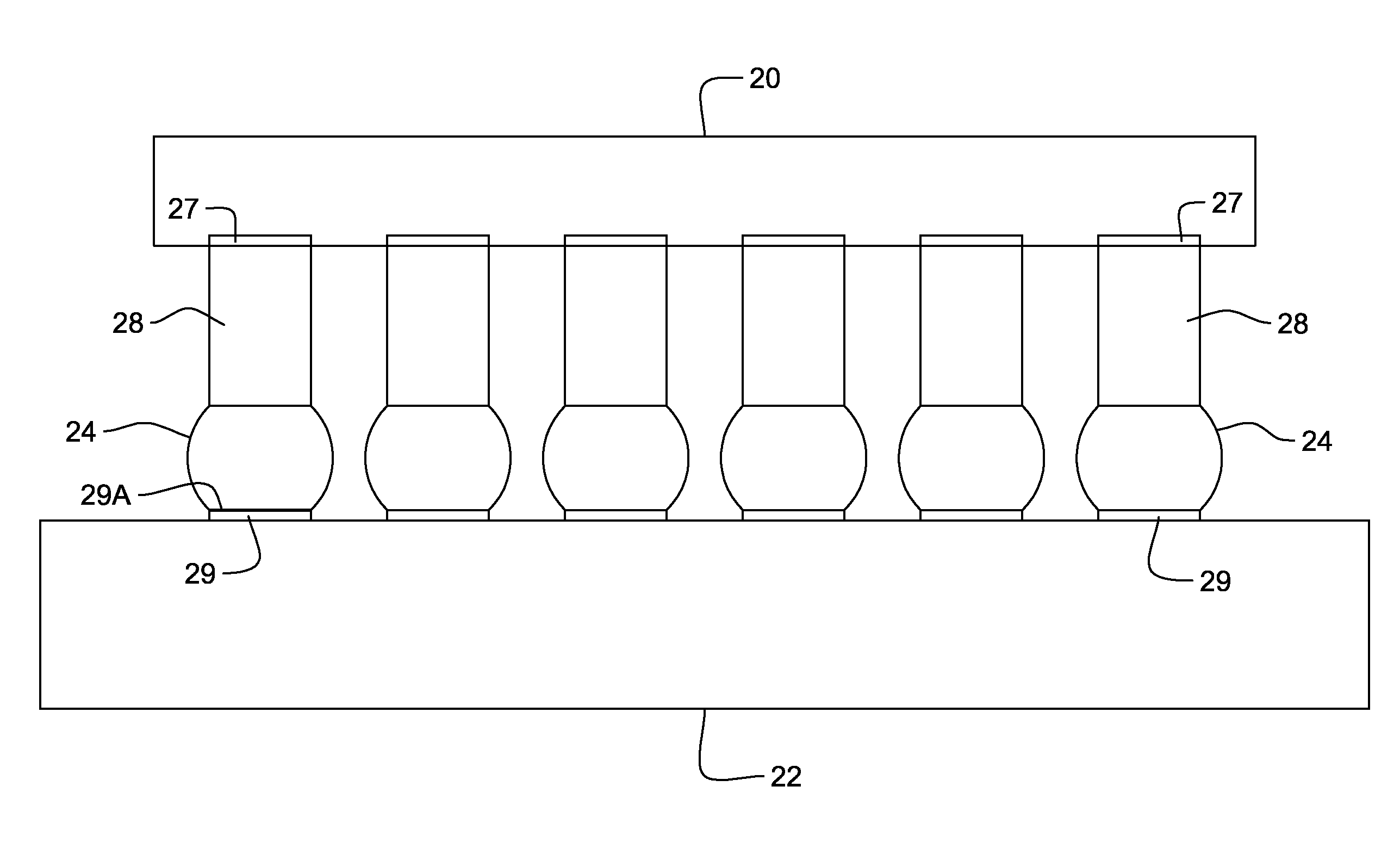
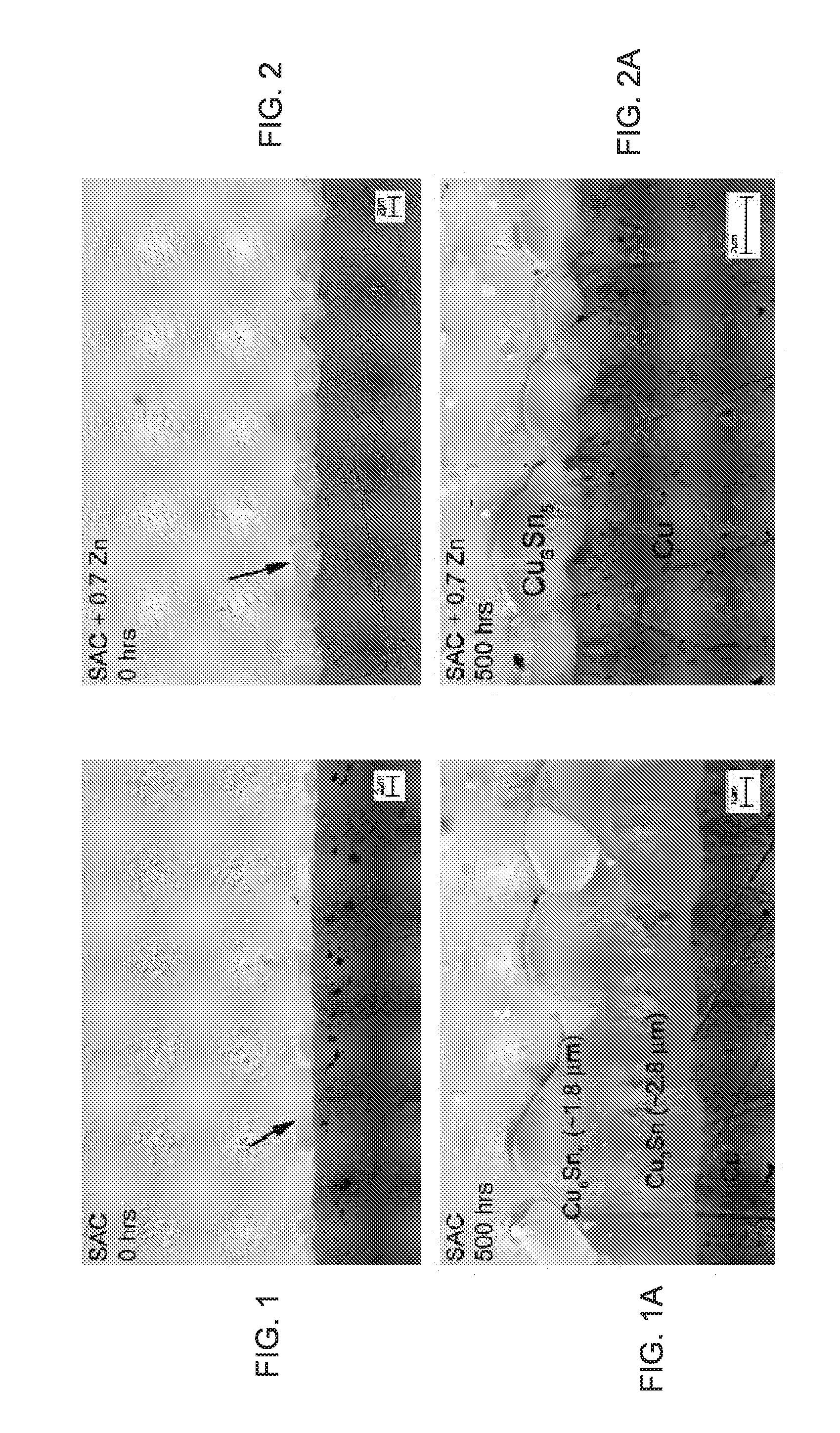
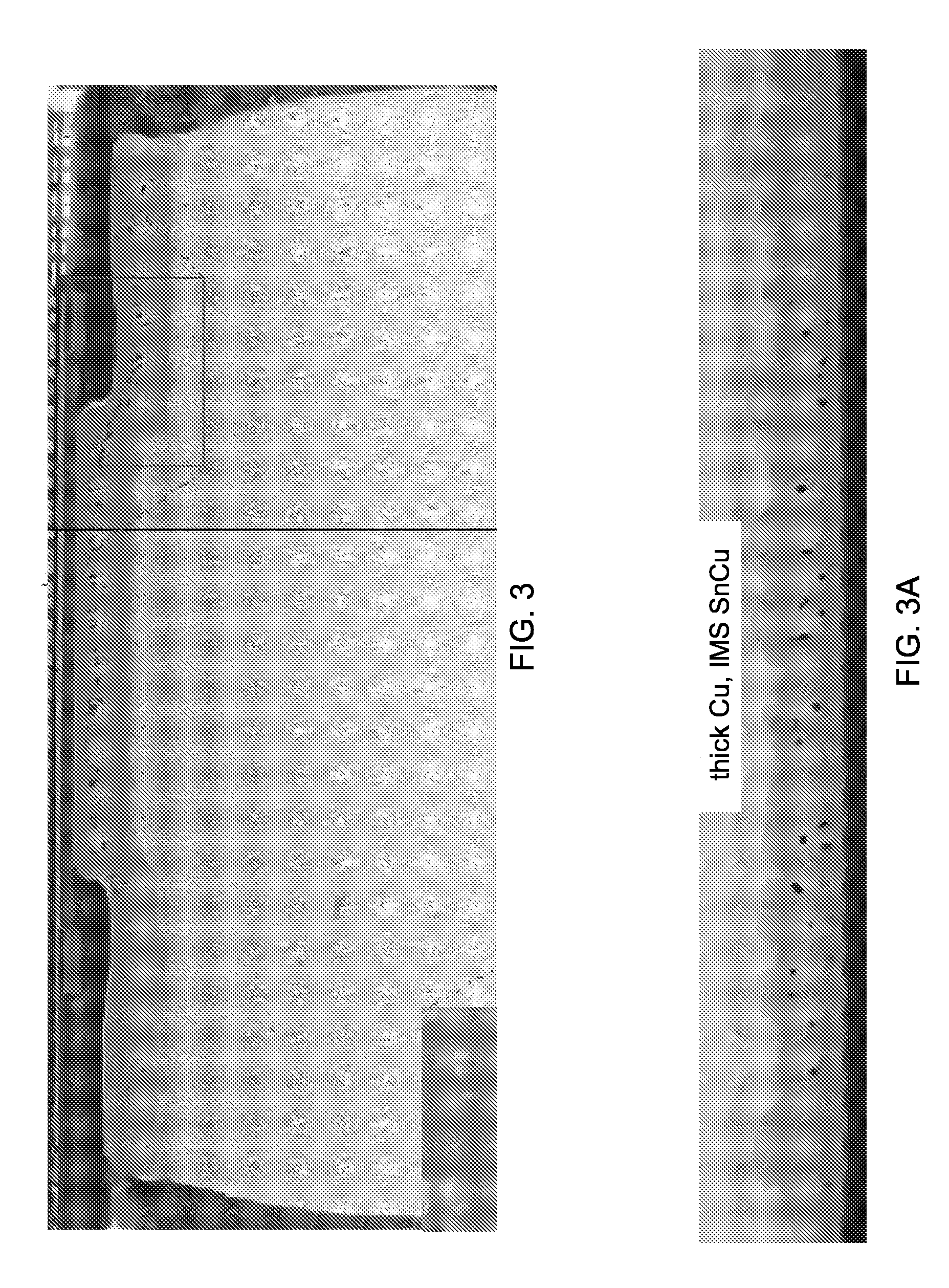
Modification of pb-free solder alloy compositions to improve interlayer dielectric delamination in silicon devices and electromigration resistance in solder joints
InactiveUS20090197114A1Good mechanical integrityImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesPrinted circuit manufactureDielectricSilicon
A solder joint comprising a solder capture pad on a substrate having a circuit; and a lead free solder selected from the group comprising Sn—Ag—Cu solder and Sn—Ag solder adhered to the solder capture pad; the solder selected from the group comprising between 0.1 to 2.0% by weight Sb or Bi, and 0.5 to 3.0% Ag. Formation of voids at an interface between the solder and the solder capture pad is suppressed, by including Zn. Interlayer dielectric delamination is suppressed, and electromigration characteristics are greatly improved. Methods for forming solder joints using the solders.
Owner:SHIH YUAN +5
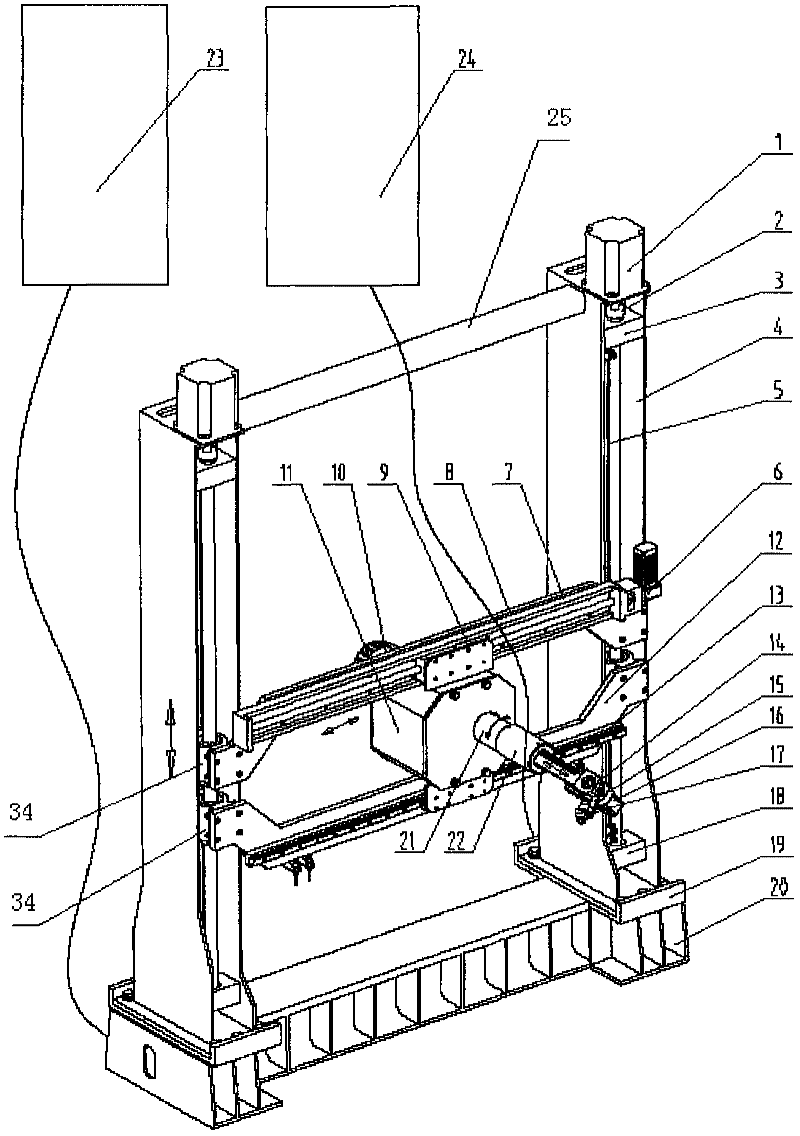
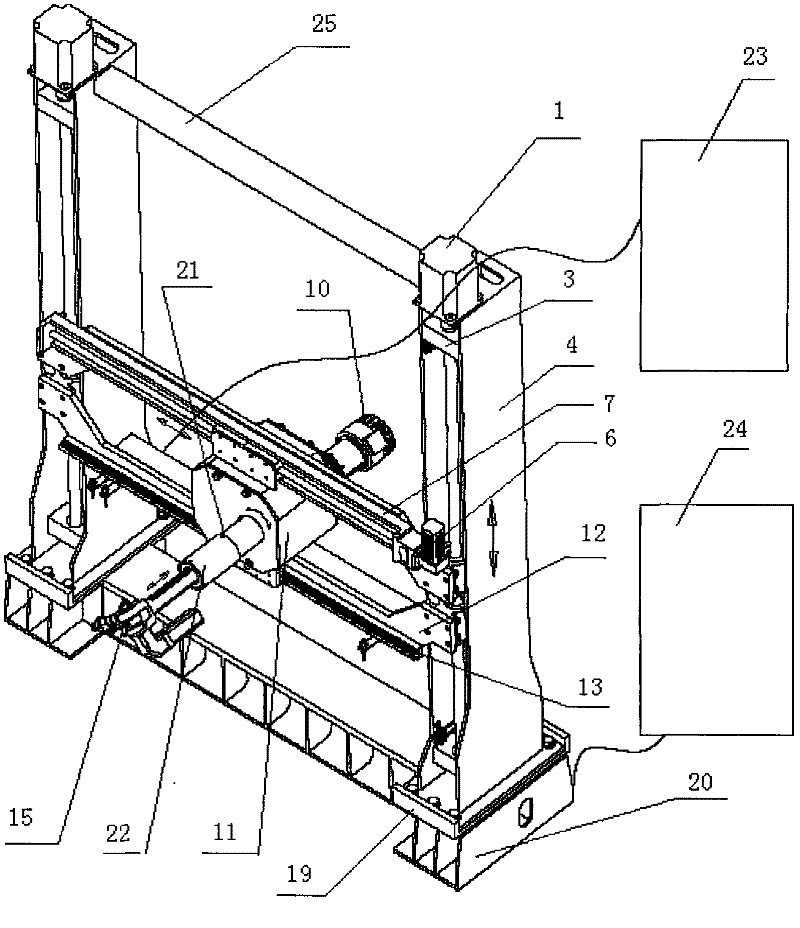
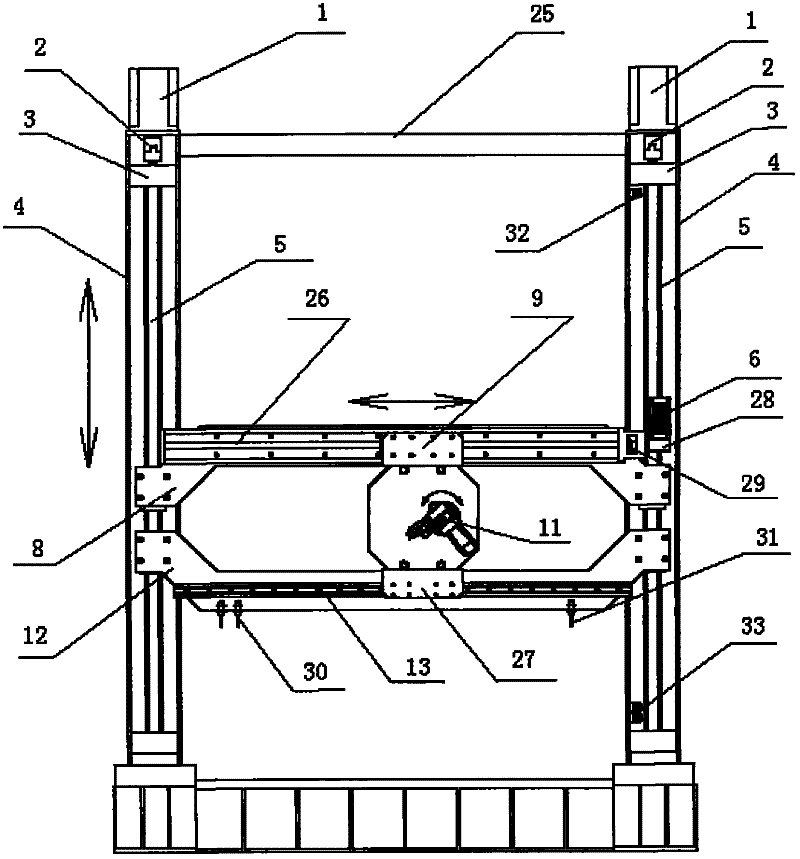
Spraying robot driving device
The invention relates to a robot driving device, comprising a planar intraframe driving device and a mechanical arm driving device, wherein the planar intraframe driving device comprises an up-down lifting driving device and a left-right horizontal driving device. The left-right horizontal driving device drives a spraying robot to horizontally move right and left with a linear module sliding block by virtue of a servo motor, the up-down lifting driving device drives the left-right horizontal driving device to do lifting motion up and down with a ball screw by virtue of the servo motor; the mechanical arm driving device comprises an intermediate rotating driving mechanism, a telescopic driving mechanism and a swinging driving mechanism at the front end, the intermediate rotating driving mechanism drives a mechanical arm to rotate by virtue of the servo motor; the telescopic driving mechanism drives the mechanical arm to do telescopic motion by virtue of the servo motor; and the swinging driving mechanism at the front end drives a spray gun to swing and rotate around by virtue of the servo motor and a reducer.
Owner:JIANGSU CHANGHONG INTELLIGENT EQUIP CO LTD
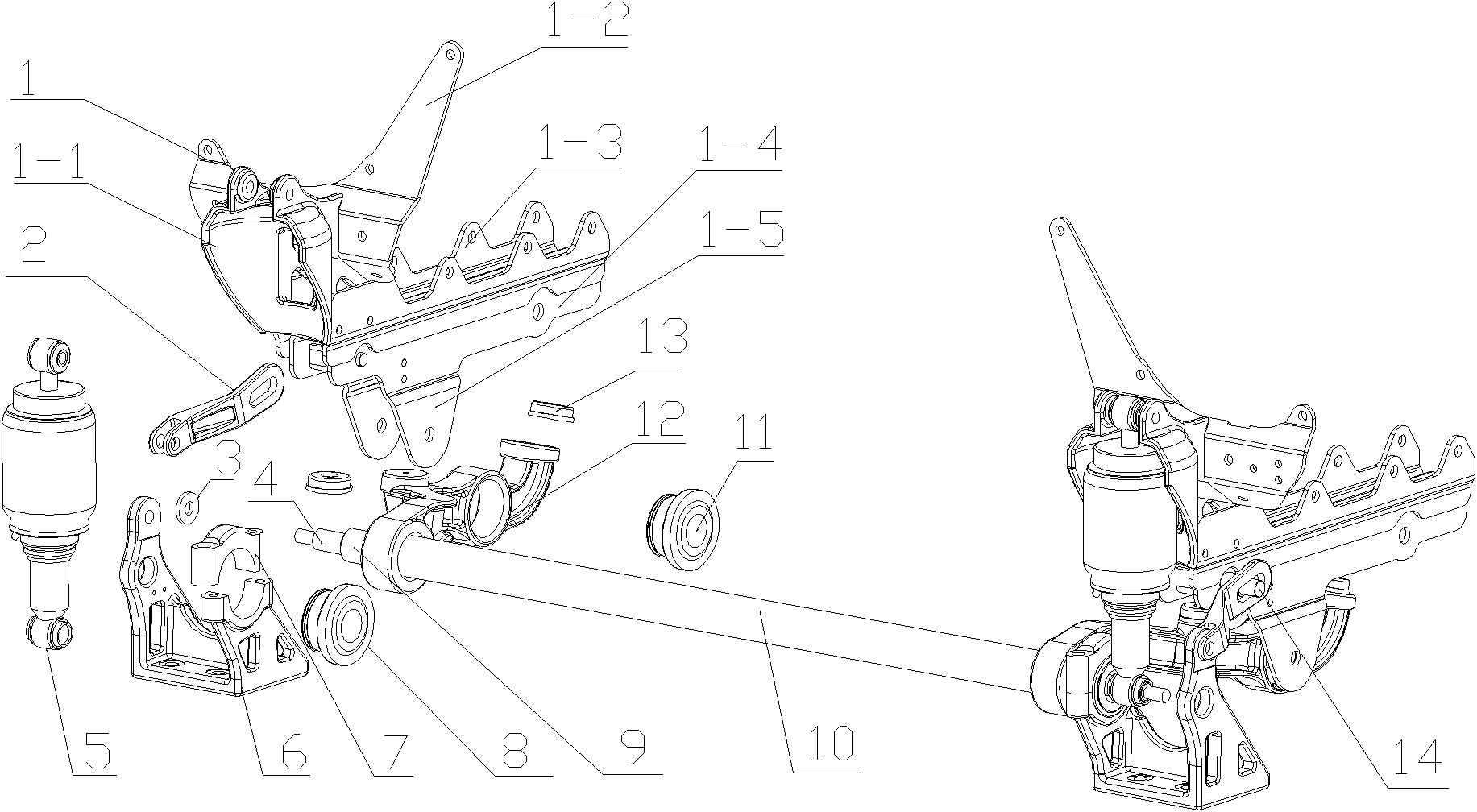
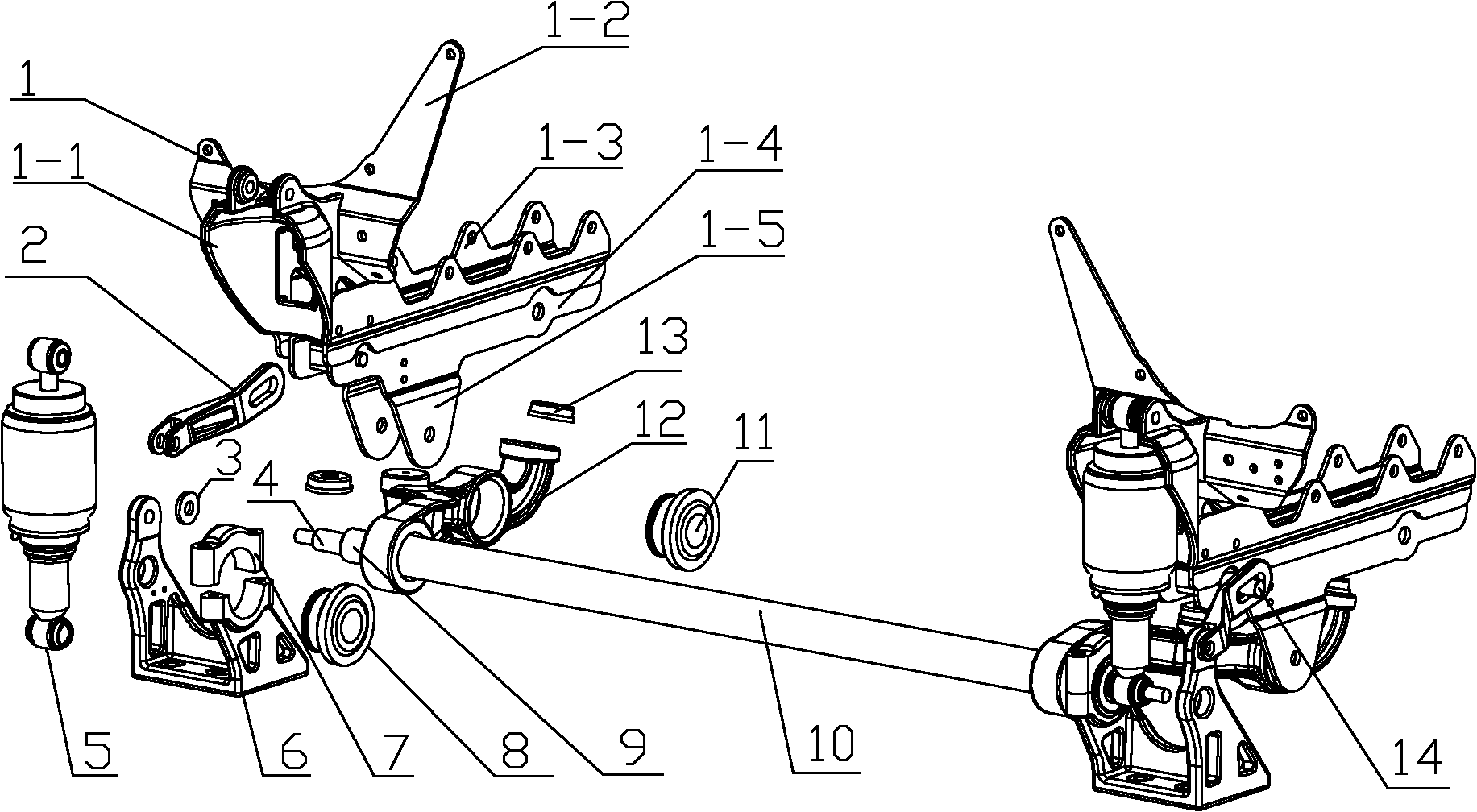
Suspension device in front of vehicle driving cab and heavy vehicle
InactiveCN102320337AImprove roll resistanceImprove stabilityLoading-carrying vehicle superstructuresCar drivingVehicle driving
The invention discloses a suspension device in front of a vehicle driving cab, relating to the technical field of vehicle shock absorption. The suspension device comprises a transverse stabilizer bar (10) and a first suspension device, wherein the first suspension device is arranged at the end part of the transverse stabilizer bar (10) and comprises an upper bracket (1), a shock absorber (5), an overturning arm (12) and an overturning seat (6). The suspension device in front of the vehicle driving cab is characterized in that the overturning arm (12) is located at one side of the transverse stabilizer bar (10), and the other end of the overturning arm (12) is fixedly connected with one end of the transverse stabilizer bar (10); the upper end of the shock absorber (5) is connected with the upper bracket (1), and the lower end of the shock absorber (5) is connected with the transverse stabilizer bar (10); the bottom of the upper bracket (1) is connected with the overturning arm (12); and the end part of the transverse stabilizer bar (10) is supported by the overturning seat (6). The invention also discloses a heavy vehicle with the suspension device in front of the vehicle driving cab.
Owner:SANY AUTOMOBILE MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com