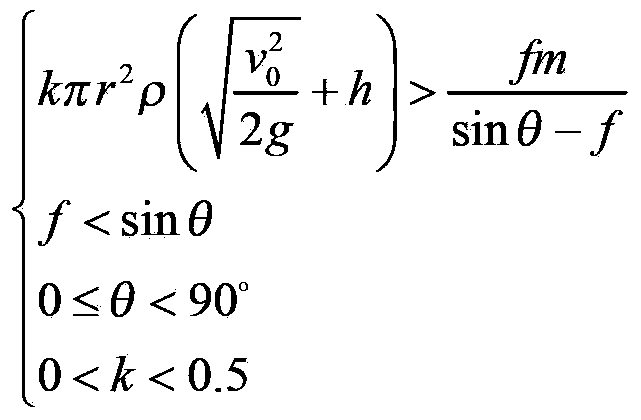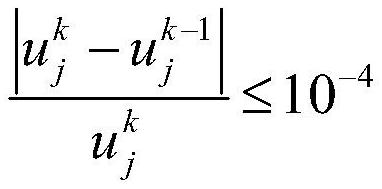Patents
Literature
49 results about "Thermomechanical coupling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Austenitizing determination method in metal material heat treatment process
ActiveCN109858085AAchieve heat treatment process optimizationAccurately calculate temperatureSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelMulti field
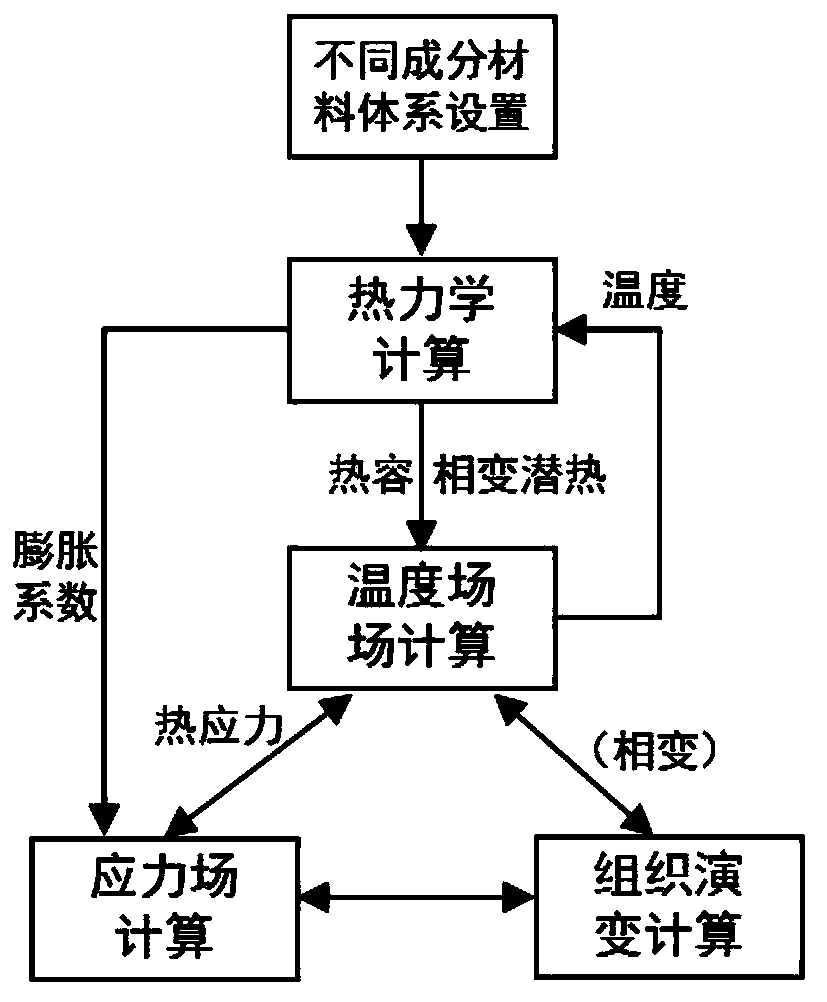
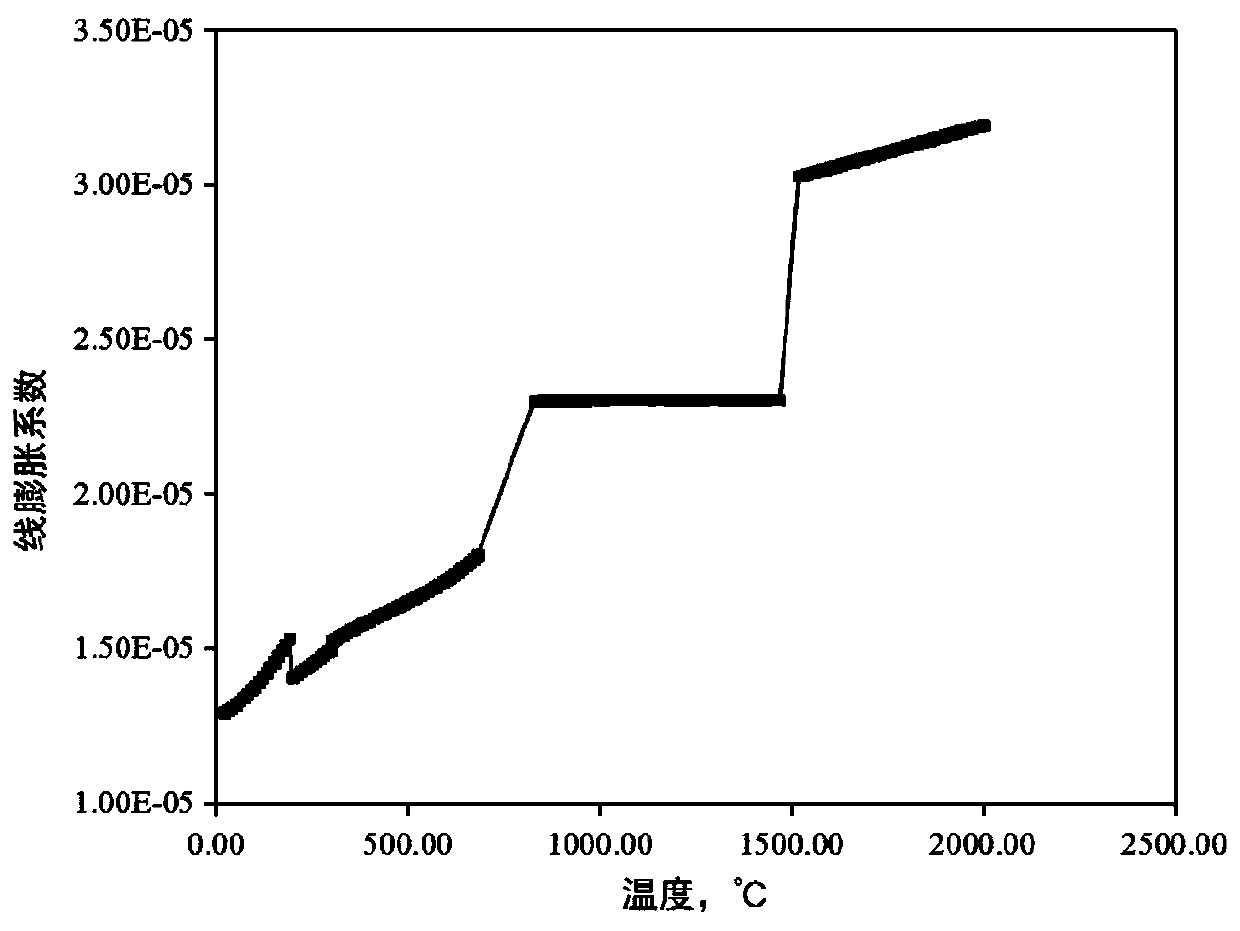
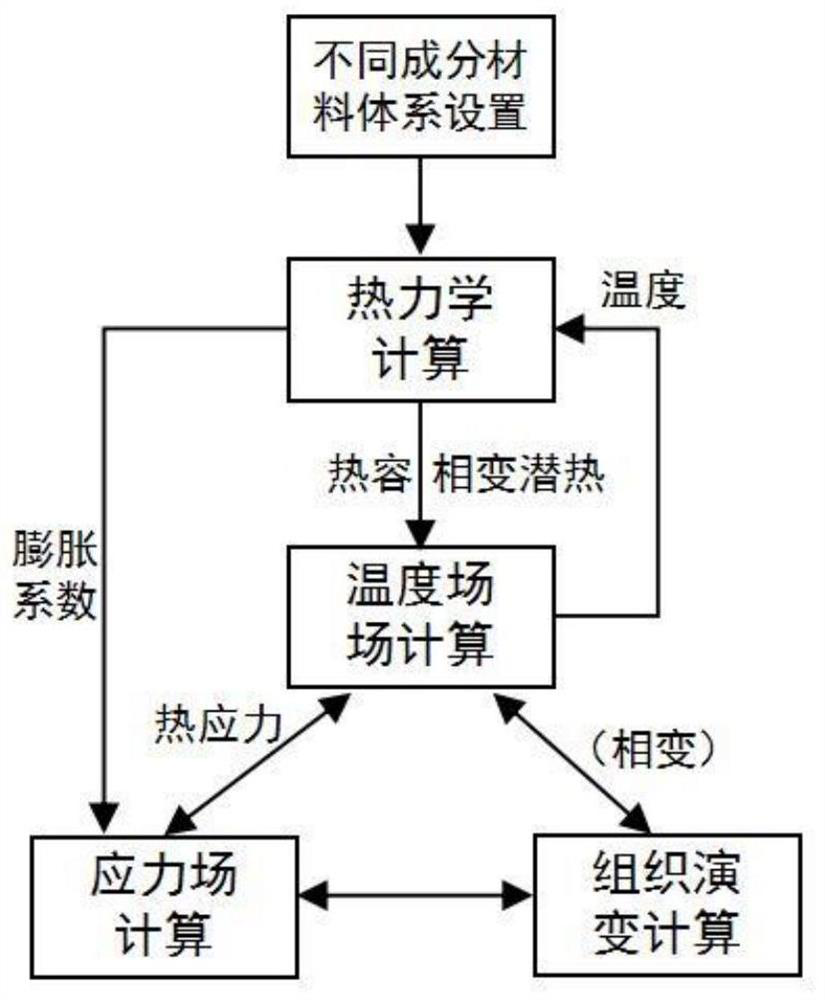
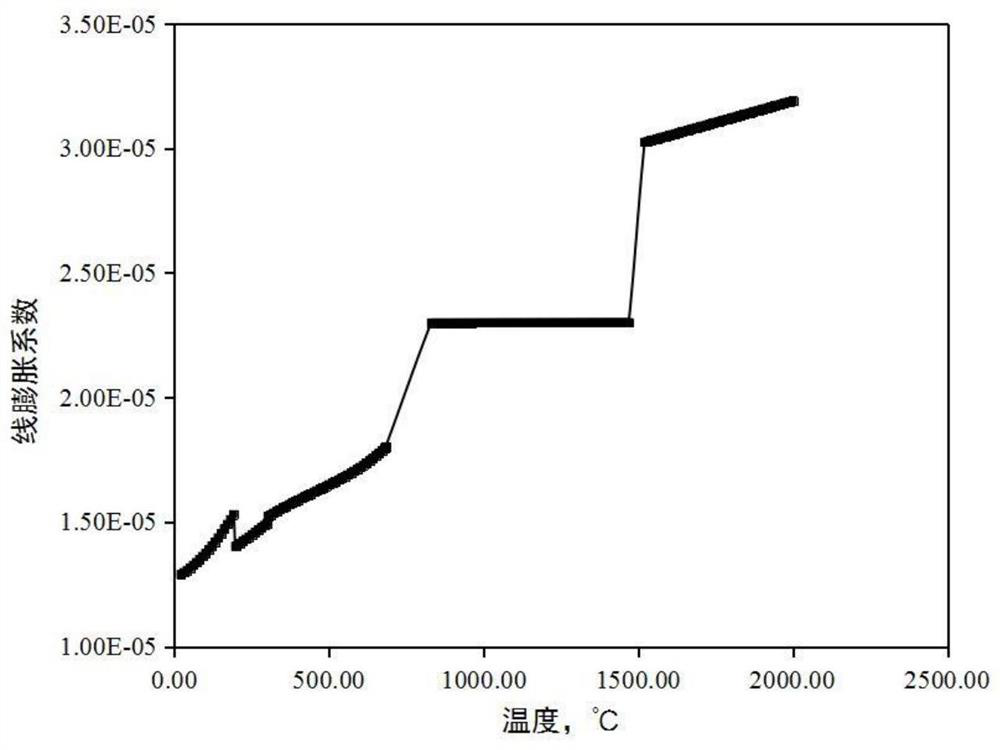
The invention relates to an austenitizing determination method in a metal material heat treatment process, and belongs to the technical field of multi-field coupling numerical simulation, and is usedfor solving the technical problems that existing numerical simulation cannot obtain thermophysical property experimental data of a material in a high-temperature stage and the influence of phase change and thermophysical property parameter difference on a multi-field coupling calculation result is not considered when material components are changed. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a method for acquiring phase change and thermophysical parameters of a material according to components and temperature of a metal material; S2, establishing a finite element model of a thermal coupling calculation or heat transfer calculation of a temperature field-stress field; S3, calculating the temperature field or thermal stress of the metal material; S4, acquiring the distribution condition of the temperature field and the thermal stress of the metal material along with the time change; and S5, obtaining an austenitizing determination result in the heat treatment process of the metal material. According to the method, the influence of components on thermophysical parameters and phase change stress is considered, the influence of phase change on a temperature field and residual stress can be accurately calculated, and the method is used for optimizing the heat treatment process of different materials.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST +1
Material high-temperature mechanical performance test device in aerodynamic heat-force coupling environment
PendingCN107727487AAdjustable lengthAdjustment diameterStrength propertiesElectro hydraulicEngineering
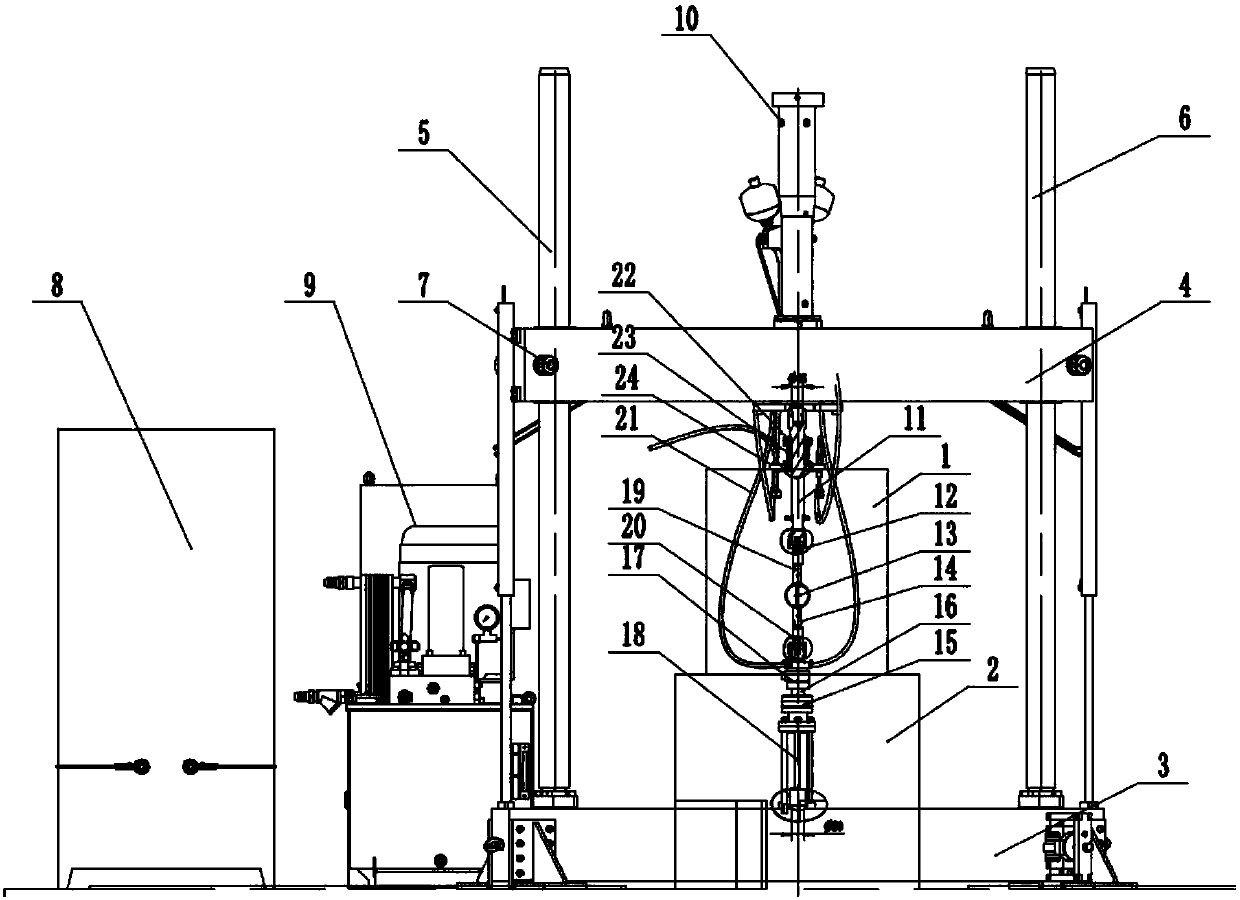
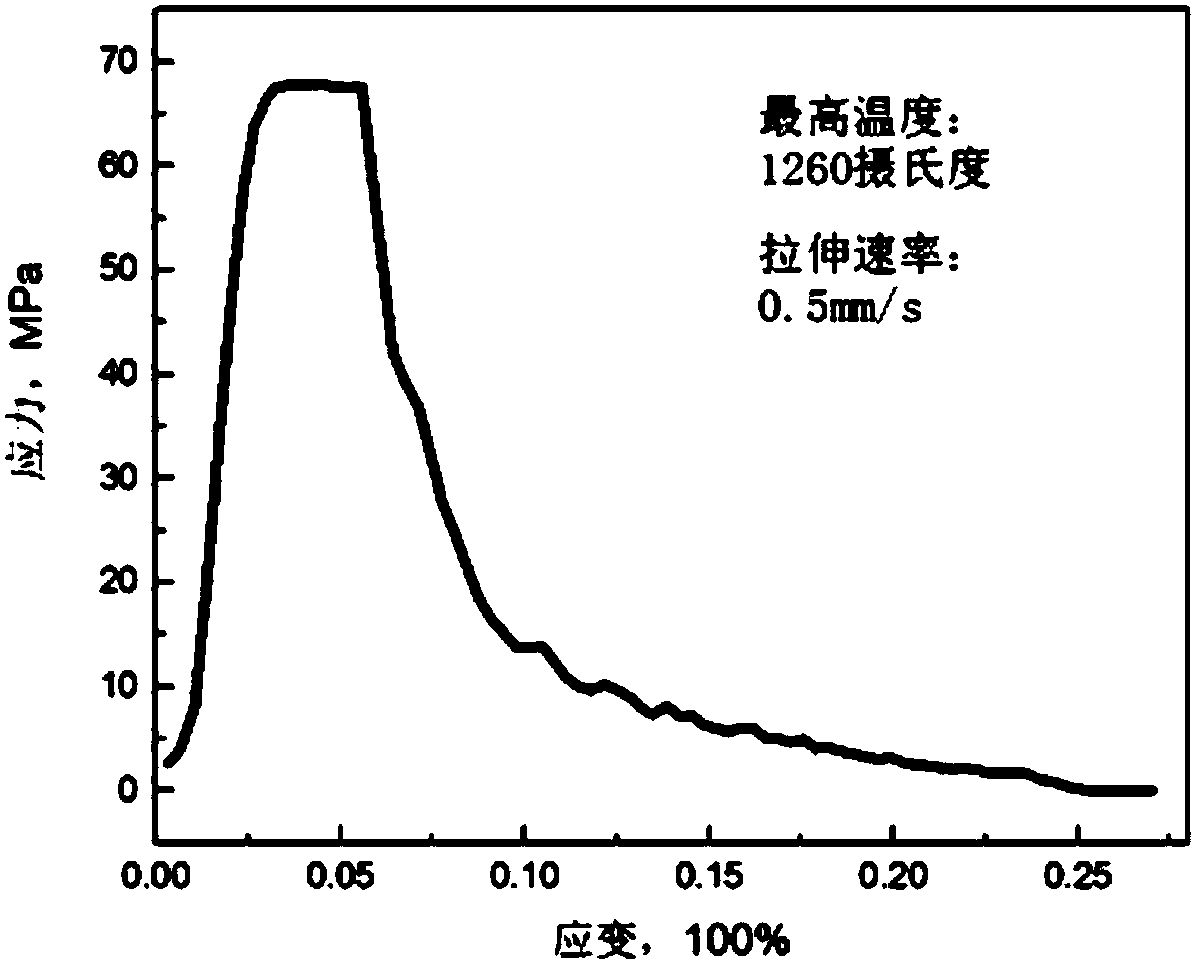
The invention provides a material high-temperature mechanical performance test device in an aerodynamic heat-force coupling environment, which belongs to the technical field of the test of material high-temperature mechanical performance. The material high-temperature mechanical performance test device comprises a main machine framework, a mechanical loading system and a clamp water cooling system, wherein the main machine framework adopts a double-stand-column design, the lower end of an oil cylinder mechanism of the mechanical loading system penetrates through an upper crossbeam of the mainmachine framework and is fixed with the upper crossbeam in a thread manner, an upper drawing bar, an upper clamp and the like of the mechanical loading system are connected to the lower end of the oilcylinder mechanism, and other parts of the mechanical loading system are successively connected with a lower crossbeam. The clamp water cooling system is used for cooling a sample clamping mechanismin the mechanical loading system. The material high-temperature mechanical performance test device designs the main machine which can be matched with a coherent jet aerodynamic-heat coupling environment simulation test cabin, has a unique structure design, integrates multiple advanced test technologies, and can well implement the ultrahigh-temperature mechanical performance test of a ceramic material in the coherent jet aerodynamic-heat coupling environment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Gas permeation testing method in low-permeability rock time-dependent deformation under action of thermal-gas-mecha-nical coupling
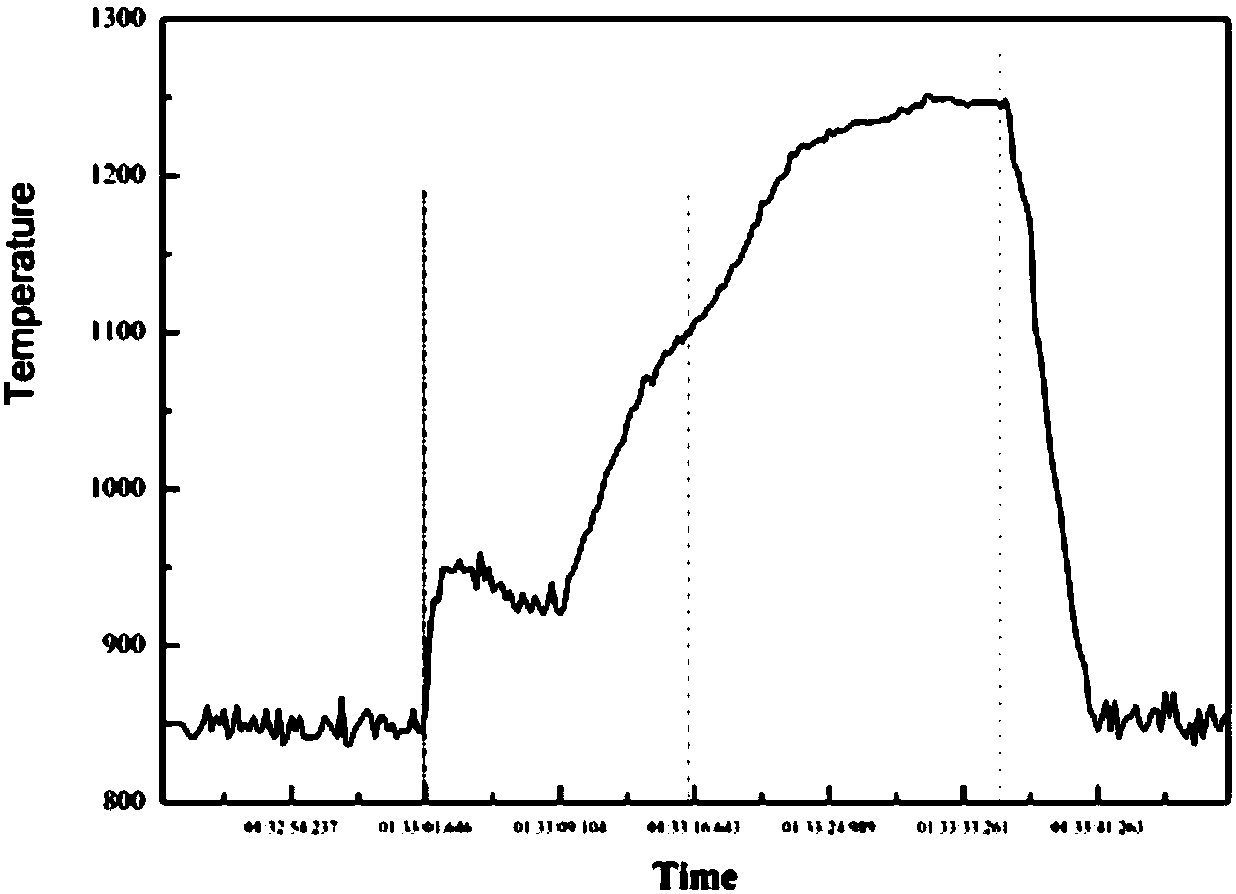
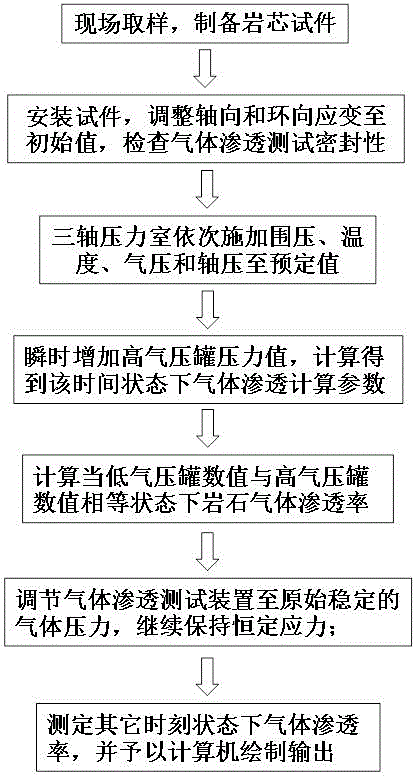
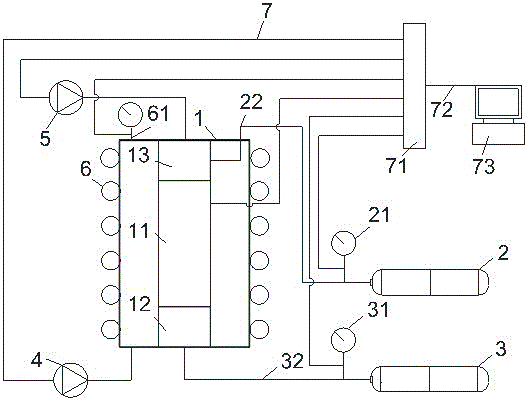
InactiveCN105004650AHigh degree of automationAvoid experimental errorPermeability/surface area analysisAxial pressureMulti field
The invention belongs to the field of deep high-temperature and high-pressure oil and gas exploitation rock mechanical testing, and particularly relates to a gas permeation testing method in low-permeability rock time-dependent deformation under the action of thermal-gas-mecha-nical coupling. The method includes the following steps that a rock core test piece is installed into a clamp holder, and the leakproofness of gas permeation testing is checked; the confining pressure, the temperature, the air pressure and the axial pressure are sequentially applied to a triaxial cell to predetermined values; the pressure of a high air pressure tank is increased instantaneously, the gas permeation parameters in the time state are calculated, and accordingly the rock gas permeation rate existing when the numerical value of a low air pressure tank is equal to the numerical value of the high air pressure tank is calculated; the gas pressure is adjusted to an initial value, the gas permeation rates at other moments are determined, and the gas permeation rates are given to a computer for drawing output. By the adoption of the method, the gas permeability of low-permeability rock under different time-dependent scales can be determined, the relation among the permeability parameter, the temperature parameter, the time parameter, the stress parameter and the strain parameter can be drawn automatically through a computer program, data result errors caused by not taking multi-field coupling and time-dependent factors into account in an existing device are avoided, and measurement accuracy is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Cutting device
ActiveCN103418847AGuarantee quality and efficiencyGuaranteed work efficiencyDriving apparatusMaintainance and safety accessoriesParticulatesEngineering
A cutting device is characterized in that the cutting device comprises a particulate knife, a cutting worktable, a micro-jet spray head and a hydraulic device, relative linear movement is achieved between the cutting worktable and the micro-jet spray head, the particulate knife comprises a cutter body and a cutter bit, the cutter bit is arranged on the outer surface of the cutter body in an outward-protruding mode, the geometric dimension of the cutter bit is 10nm-1mm, a balancing weight is arranged in the cutter body, a spray cavity is formed in the micro-jet spray head, a spray mouth is formed in the bottom of the spray cavity, the spray mouth can generate an annular flow, the particulate knife is captured by the annular flow, and the outer diameter of the particulate knife is matched with the inner diameter of the annular flow. The cutting device has the advantages that the particulate knife is driven by water-caused rotation (namely the rotation of micro-jets) or is fixedly clamped to achieve micro-cutting, the micro-flow takes away heat generated during cutting in time, the inhomogeneous deformation field caused by thermomechanical coupling is greatly reduced, quality and working efficiency of micro-cutting are guaranteed, and a novel micro-cutting method is obtained.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
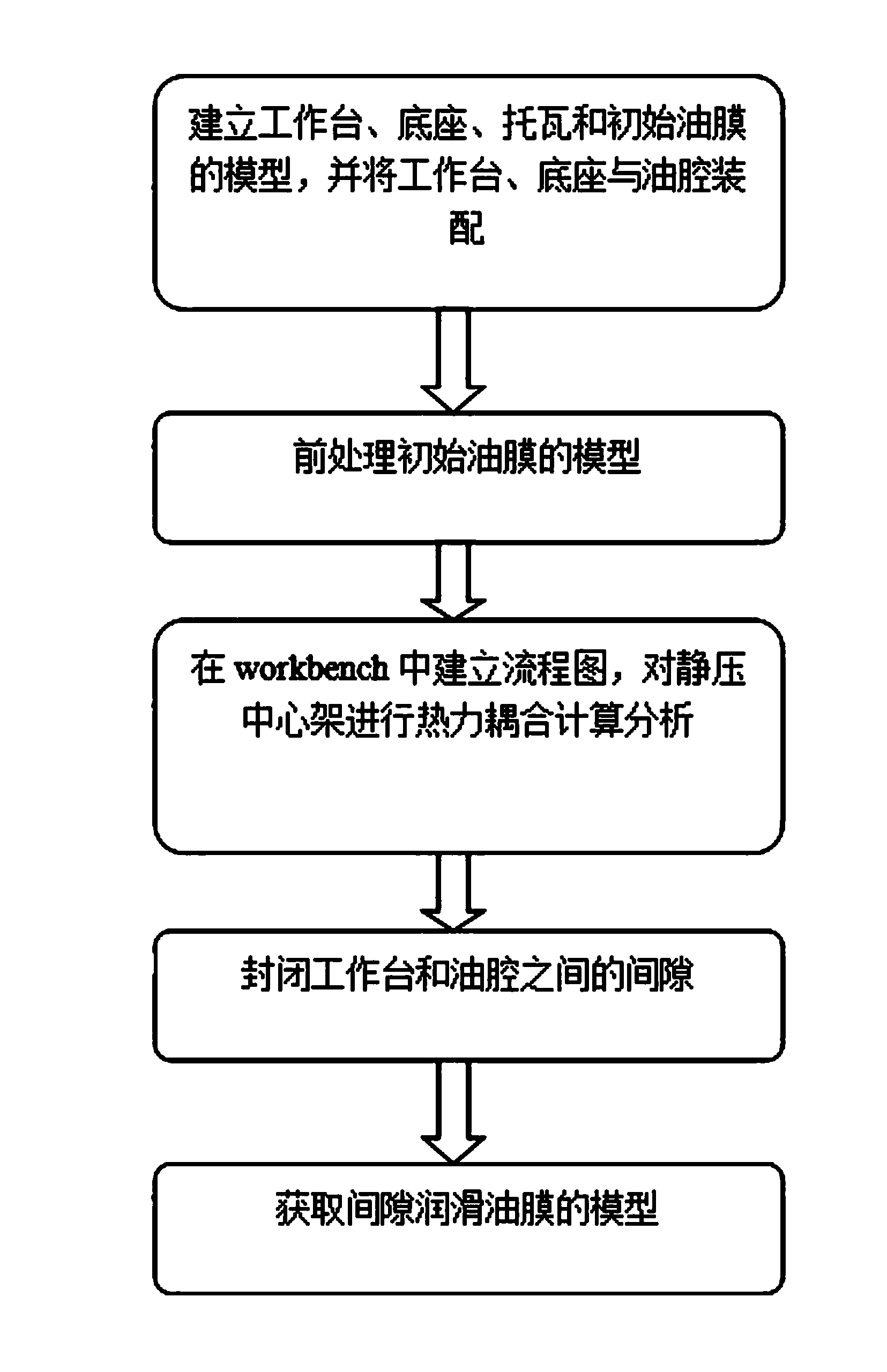
Method for building lubricating oil film model after thermal coupling deformation of static pressure center frame
InactiveCN103593537AAvoid lubrication failureImprove work efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsThermodynamicsEngineering
The invention relates to a method for building a lubricating oil film model, in particular to a method for building a lubricating oil film model after thermal coupling deformation of a static pressure center frame. The method aims to solve the problem that an existing method for building an oil film model has errors in workpiece efficiency and precision. The method comprises the steps that 1, a workbench, a base, supporting tiles on the two sides, a flat bottom deep oil chamber middle supporting tile and the model of an initial oil film are built, and the workbench, the base and the supporting tiles are assembled; 2, the model of the initial oil film is pretreated; 3, a flow diagram is built in the workbench, and thermal coupling computational analysis is carried out on the static pressure center frame; 4, the clearance between the workbench and an oil chamber is sealed; 5, the model of a clearance lubricating oil film is acquired. In actual application, the method is used for verifying the reasonable control over the flow of the lubricating oil of a large-size machine tool by the large-size machine tool so that it can be guaranteed that the large-size machine tool operates normally and safely, and the situations of dry friction, boundary lubrication and other lubrication failures are avoided.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
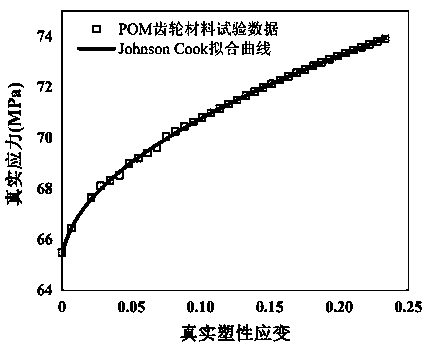
Plastic gear contact fatigue life evaluation method considering temperature influence
PendingCN111144044AReduce accidentsReduce economyDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelGear wheel
The invention discloses a plastic gear contact fatigue life evaluation method considering temperature influence. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, testing plastic temperature-related mechanical behaviors according to standards; 2, fitting a plastic thermoelastic-plastic constitutive equation according to the test data, and writing a subprogram UMAT of ABAQUS; 3, determining the temperature of the plastic gear in the operation process by calculation or test; 4, establishing a two-dimensional gear complete thermal coupling contact finite element model on the ABAQUS platform; 5, fitting a limit tensile stress equation changing along with temperature according to the material test parameters, and obtaining plastic fatigue parameters according to the conversion relation betweenthe tensile yield limit and the fatigue parameters; and step 6, calculating the fatigue life of the plastic gear by using a Brown-Miller multi-axis fatigue criterion. The method has the technical effect that the problem of contact fatigue failure of the plastic gear under the influence of the operating temperature is solved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
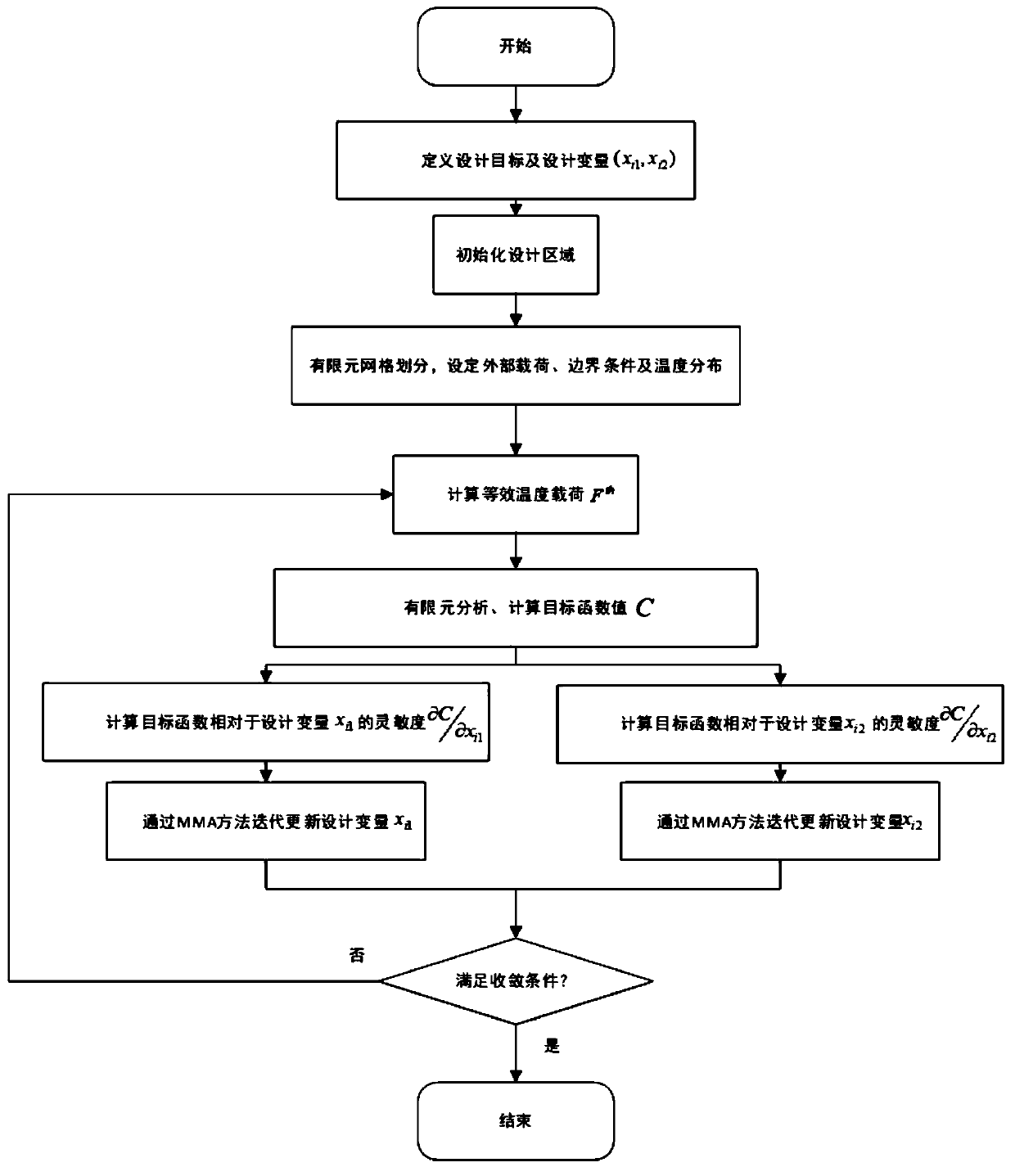
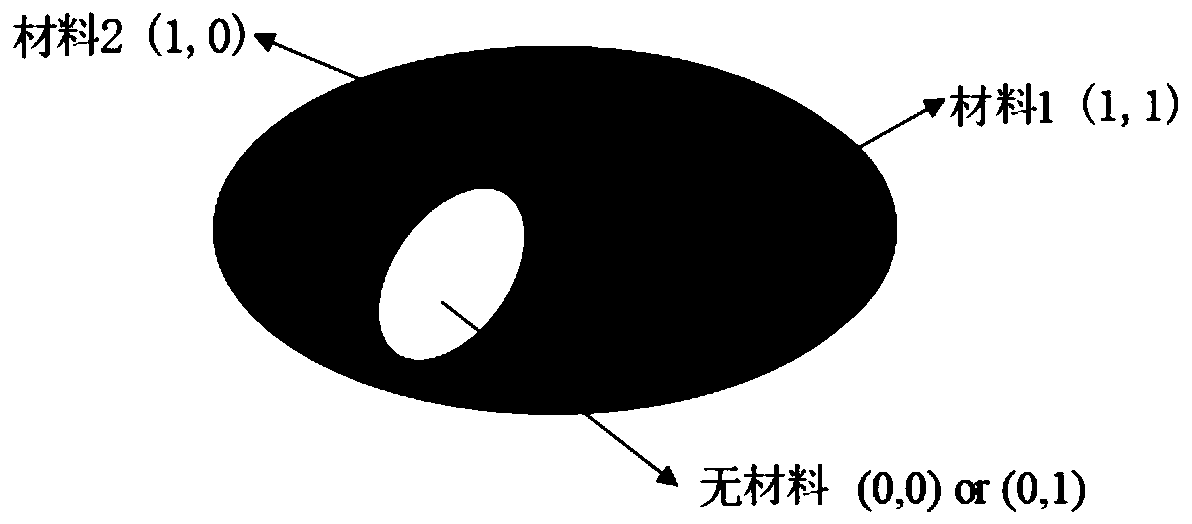
Additive manufacturing-oriented multiphase material thermal coupling topological optimization design method
InactiveCN111008499AImprove manufacturabilityContinuityAdditive manufacturing apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationMacroscopic scaleYoung's modulus
The invention belongs to the field of material structure optimization design, and particularly discloses an additive manufacturing-oriented multiphase material thermal coupling topological optimization design method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, dispersing a multiphase material structure into a plurality of macroscopic units; according to the material type of each macroscopic unitand determination of whether material filling exists or not, carrying out interpolation on the Young modulus and the thermodynamic coefficient of the multiphase material structure, and establishing amultiphase material topological optimization model which takes the minimization of the flexibility of the multiphase material structure as an objective function and takes the upper limit of the use amount of each solid material forming the multiphase material structure as a design constraint; performing sensitivity analysis on the design variables of the topological optimization model, and iteratively updating the design variables in the macroscale and the microscale, so that an optimal result with a clear boundary is obtained. According to the method, clear boundaries exist between differentmaterials, a supporting structure is omitted in the additive manufacturing process, and the manufacturability of the optimized structure and the adaptability to the thermal working condition are improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Simulation analysis method for reducing welding deformation and welding process obtained through simulation analysis method
InactiveCN112775578APreferred welding processWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesStructural engineeringThermomechanical coupling
The invention discloses a simulation analysis method for reducing welding deformation and a welding process obtained through the simulation analysis method in the technical field of ships. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a thin plate model is established; 2, thin plate splicing models of different welding schemes are established; 3, computer thermal-mechanical coupling finite element analogue simulation is carried out; and 4, post-welding deformation distribution conditions of the thin plate splicing model of different welding schemes are analyzed and compared. The welding process obtained through the method comprises the following steps that 1, a thin plate A and a thin plate B are welded, and the welding direction is from top to bottom; 2, a second thin plate and a third thin plate are welded, and the welding direction is from the middle to the two sides; 3, the third thin plate and a fourth thin plate are welded, and the welding direction is from the middle to the two sides; and 4, a first thin plate and the second thin plate are welded, and the welding direction is from the middle to the two sides. The simulation analysis method for reducing welding deformation and the welding process have the advantage that the welding process with high welding quality is obtained by analyzing and comparing different welding sequences and different welding directions.
Owner:AVIC DINGHENG SHIPBUILDING
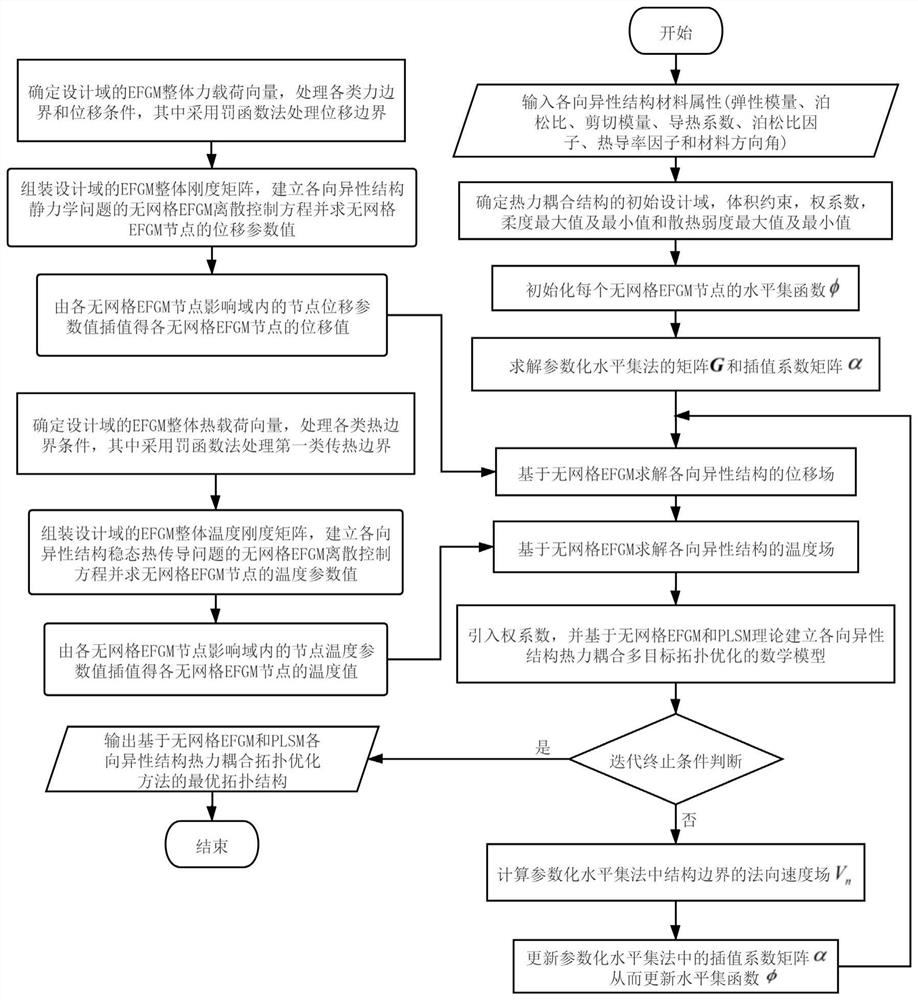
Anisotropic structure thermal-mechanical coupling topological optimization method based on meshless EFGM and PLSM
ActiveCN113821887AEliminate prone to aliasingEliminate checkerboardGeometric CADSustainable transportationMathematical modelEngineering
The invention discloses an anisotropic structure thermal-mechanical coupling multi-objective topological optimization method based on a meshless EFGM and a parameterized level set method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting a Poisson's ratio factor, a thermal conductivity factor, a material direction angle and other material attributes of an anisotropic structure, and carrying out the discrete design of a domain through meshless nodes; (2) initializing a level set function of the meshless nodes; (3) interpolating a level set function by adopting a radial basis function in combination with the parameterized level set method; (4) solving a displacement field and a temperature field of the anisotropic structure based on meshless EFGM; (5) based on meshless EFGM and PLSM theories, establishing a mathematical model for thermal coupling multi-target topological optimization of the anisotropic structure; (6) inputting a termination condition, and judging whether an optimization loop is converged or not; (7) calculating a normal velocity field of a structure boundary; (8) programming, solving and optimizing the model, and updating the level set function. According to the method, thermal-mechanical coupling multi-target topological optimization of the anisotropic structure is carried out based on the meshless EFGM and PLSM, the calculation efficiency is high, the boundary of the topological structure is clear and smooth, and the method is simple and practical.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
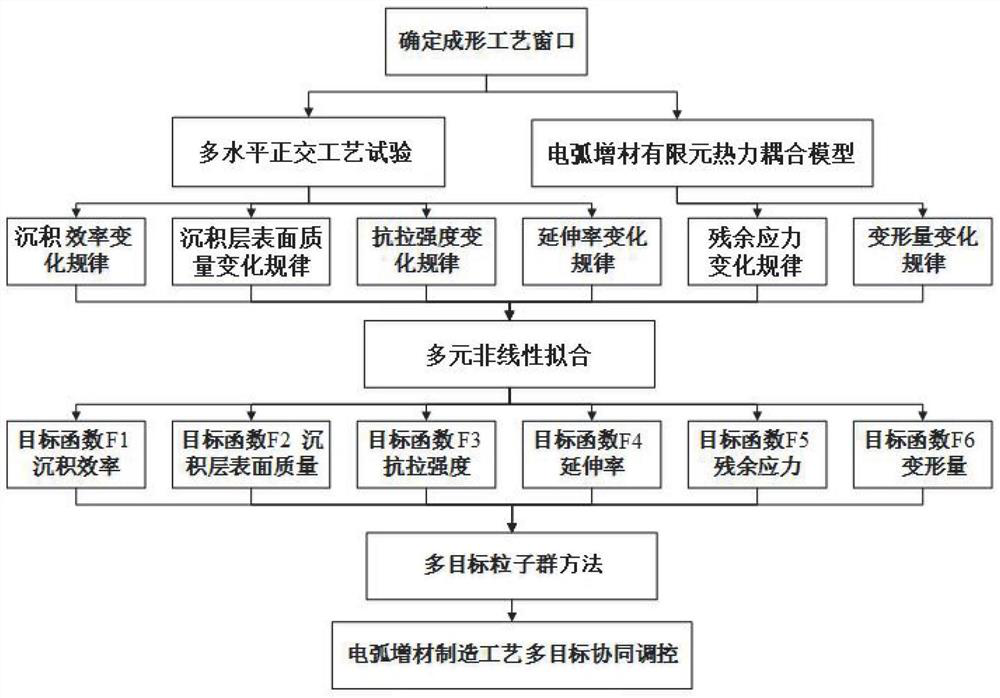
Multi-target cooperative regulation and control method for electric arc additive manufacturing
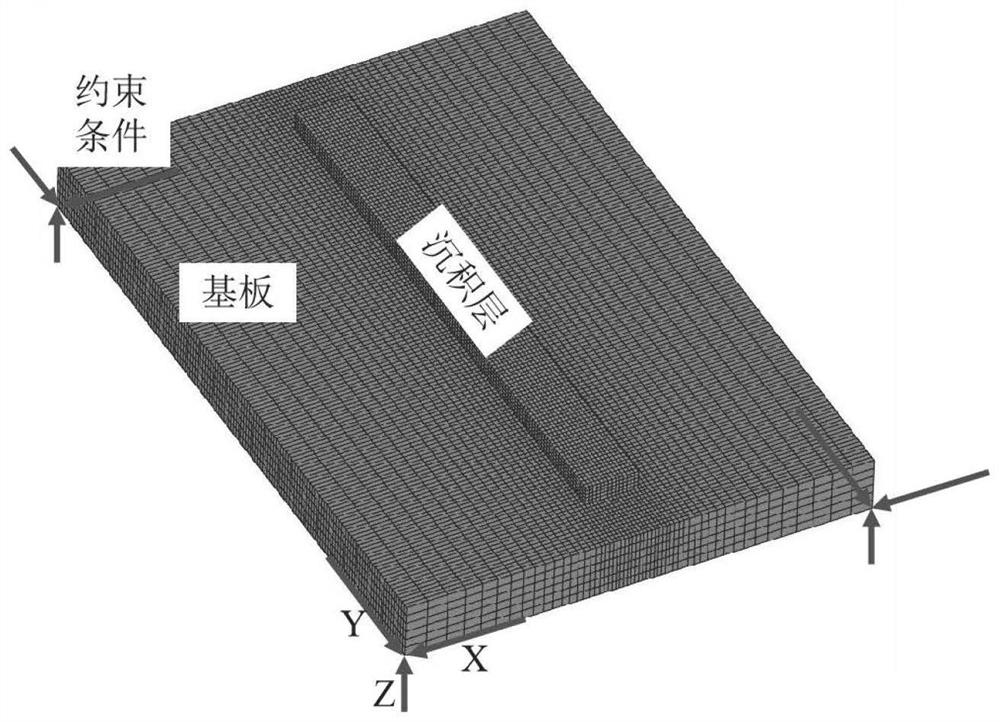
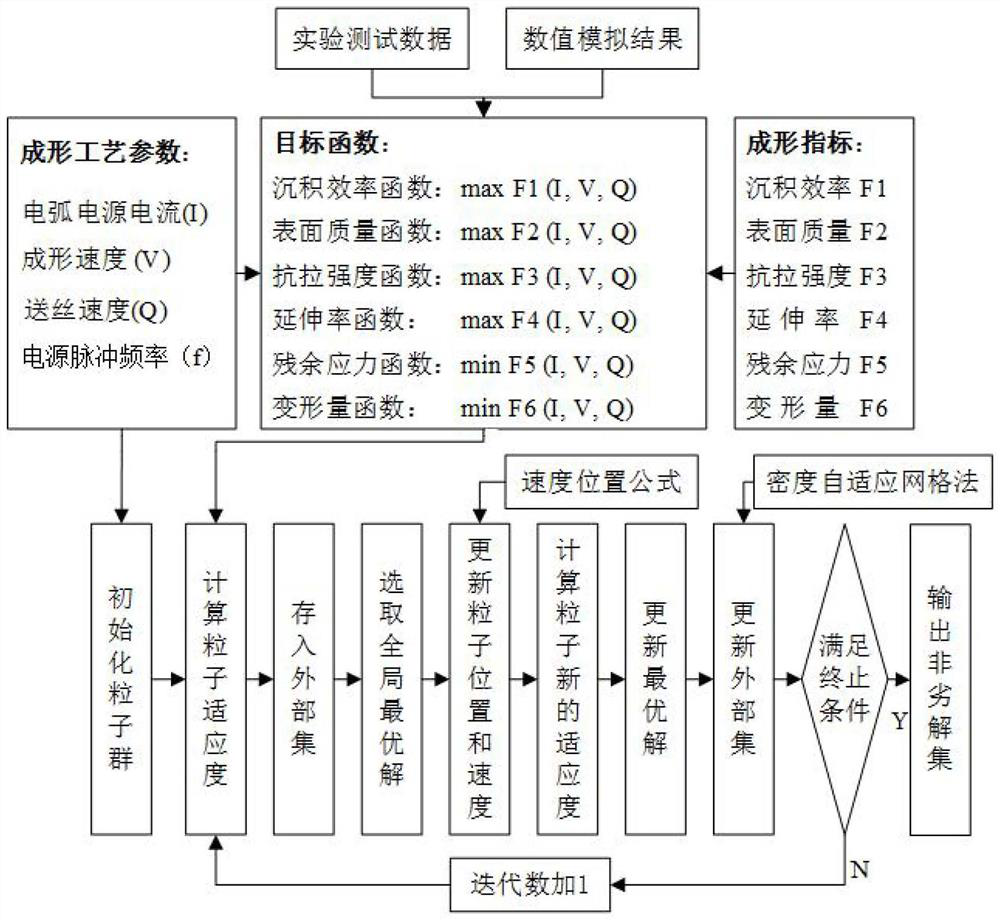
PendingCN114818435ASolve the problem that performance indicators are difficult to balanceImprove deposition efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationMulti-objective optimisationThermomechanical couplingMechanical property
The invention discloses an electric arc additive manufacturing multi-target cooperative regulation and control method which comprises the following steps: determining an electric arc additive forming process window, and carrying out a single-factor electric arc additive process test and a component mechanical property test on the basis of the electric arc additive forming process window, establishing a multivariate nonlinear objective function of the process parameters on deposition efficiency, deposition layer surface quality and mechanical properties; establishing a finite element thermal coupling model to calculate residual stress and deformation of the component, and obtaining an objective function of the residual stress and the deformation according to experimental test and numerical simulation results; and a multi-target particle swarm method is adopted to realize cooperative regulation and control among the indexes, and an optimal process parameter combination is obtained. According to the method, forming of the electric arc additive component with high efficiency, high surface quality, high mechanical property and low residual stress and deformation can be achieved at the same time, so that multi-target collaborative regulation and control in the electric arc additive manufacturing process are achieved, and the method has important reference significance for collaborative optimization of other additive manufacturing processes.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Design method of engine cylinder gasket
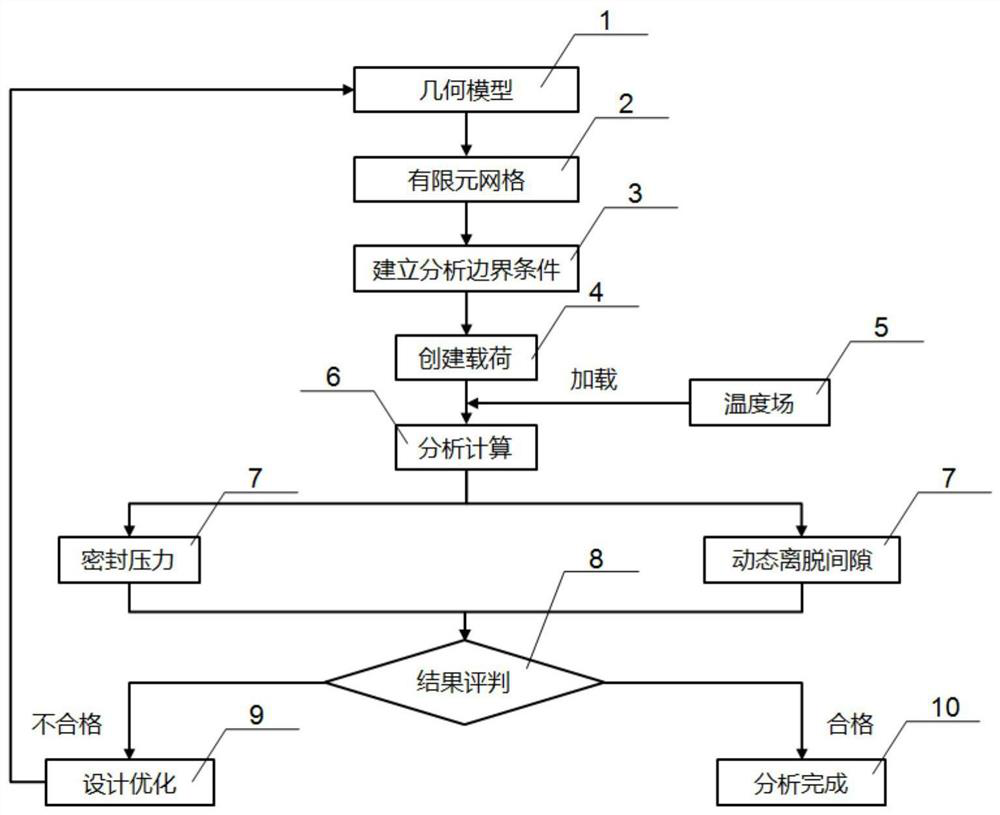
ActiveCN112733294AImprove robustnessGuide design developmentGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCombustion chamberElement analysis
The invention relates to a design method of an engine cylinder gasket. The design method comprises the steps that geometric models of a cylinder cover, a cylinder body, the cylinder gasket and bolts are established; dividing grids; boundary condition processing: applying bolt pre-tightening force, applying assembly interference magnitude between a valve retainer and a cylinder cover of a cylinder body, applying assembly interference magnitude between a valve guide pipe and the cylinder cover of the cylinder body, and performing CFD temperature field result mapping corresponding to three reliability bench tests of the engine respectively; applying gas explosion pressure in the combustion chamber of the cylinder body, and enabling the applied gas explosion pressure and the temperature field to form sequential thermal force coupling; performing finite element analysis calculation; obtaining respective sealing pressure and dynamic disengagement gap of the cylinder gasket under a gas explosion pressure working condition and a temperature field working condition; judging whether each sealing pressure is within a preset standard sealing pressure range and each dynamic separation gap is within a preset standard dynamic separation gap range or not; and if yes, determining that the cylinder gasket meets design requirements.
Owner:CHONGQING CHANGAN AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Numerical simulation calculation method for multi-layer and multi-pass welding process of header tube socket
PendingCN113158380AComprehensive forecastFull controlGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationWeld seamTube socket
The invention discloses a numerical simulation calculation method for a multi-layer and multi-pass welding process of a header tube socket. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a three-dimensional thermal coupling calculation model of a tube socket, a header and a welding seam, and performing finite element mesh generation on a solid model of the header tube socket weldment to form a plurality of mesh units of the solid model; S2, setting initial conditions and boundary conditions of the welding model; S3, determining a heat source equation and welding parameters used by the saddle-shaped welding seam of the header pipe base; and 4, submitting and solving the task, and carrying out post-processing and analysis. According to the structural features of the saddle-shaped welding seam of the tube socket header, the entity model is established in a targeted mode, grids are divided in a regional mode, welding heat source parameters are corrected, the change rule of a post-welding temperature field and a stress-strain field can be predicted, and the actual saddle-shaped welding seam welding process is guided.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
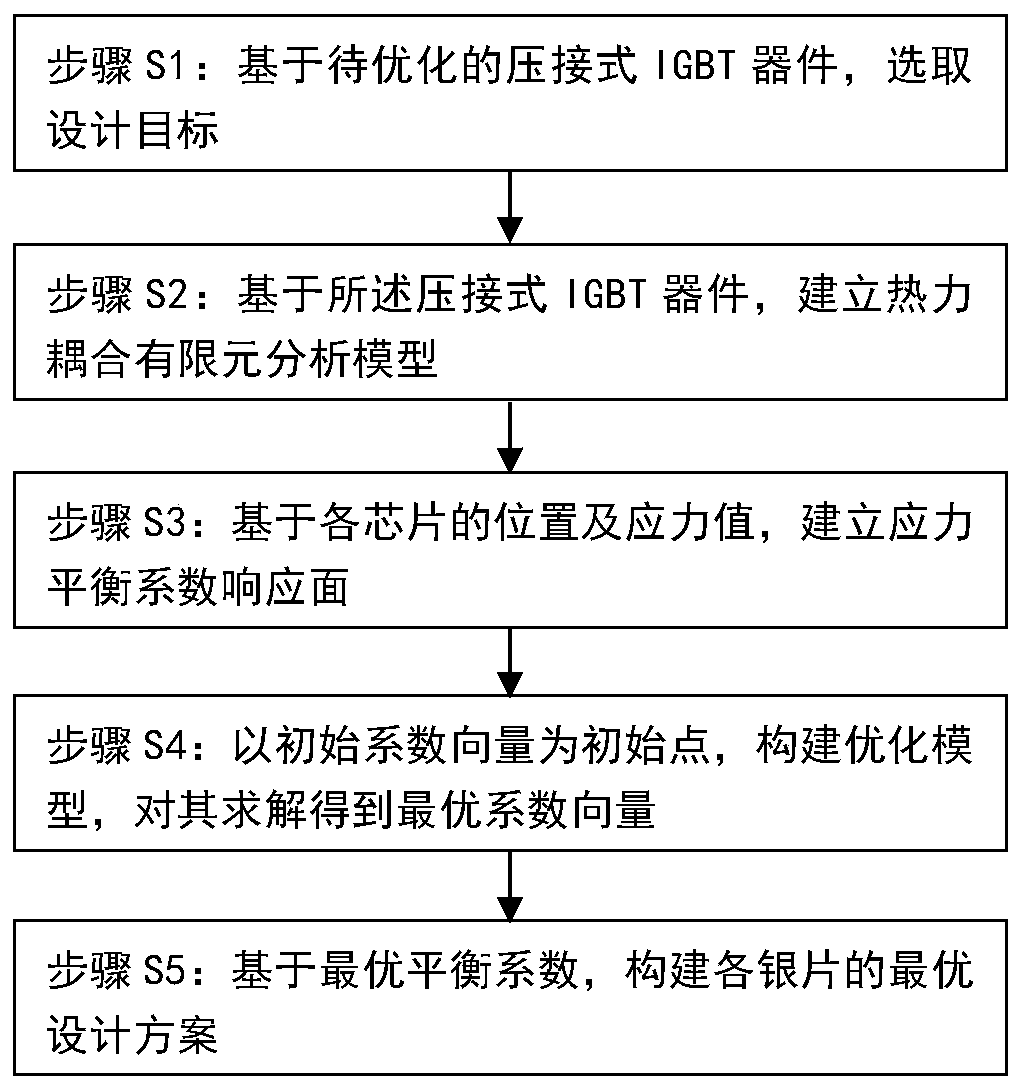
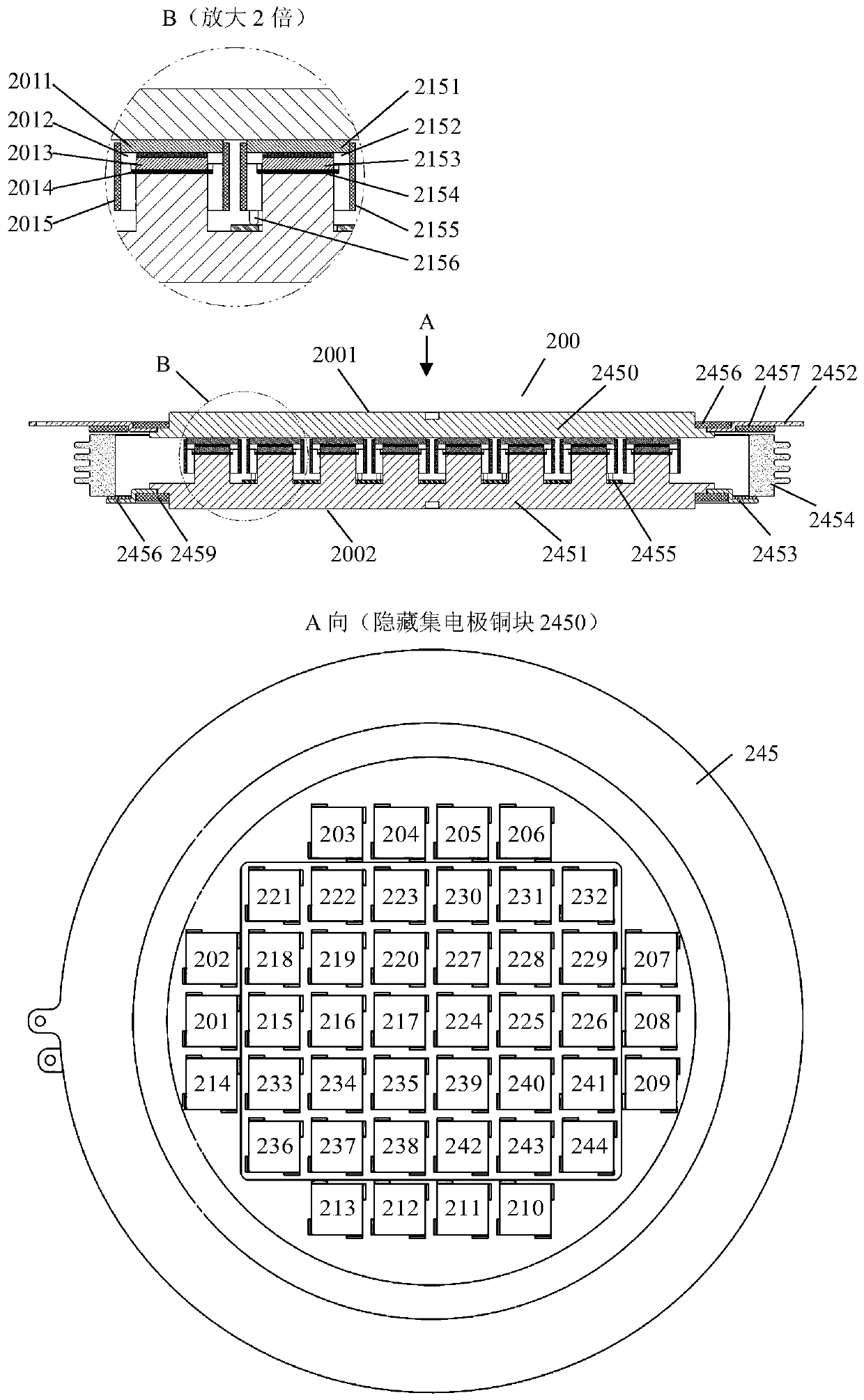
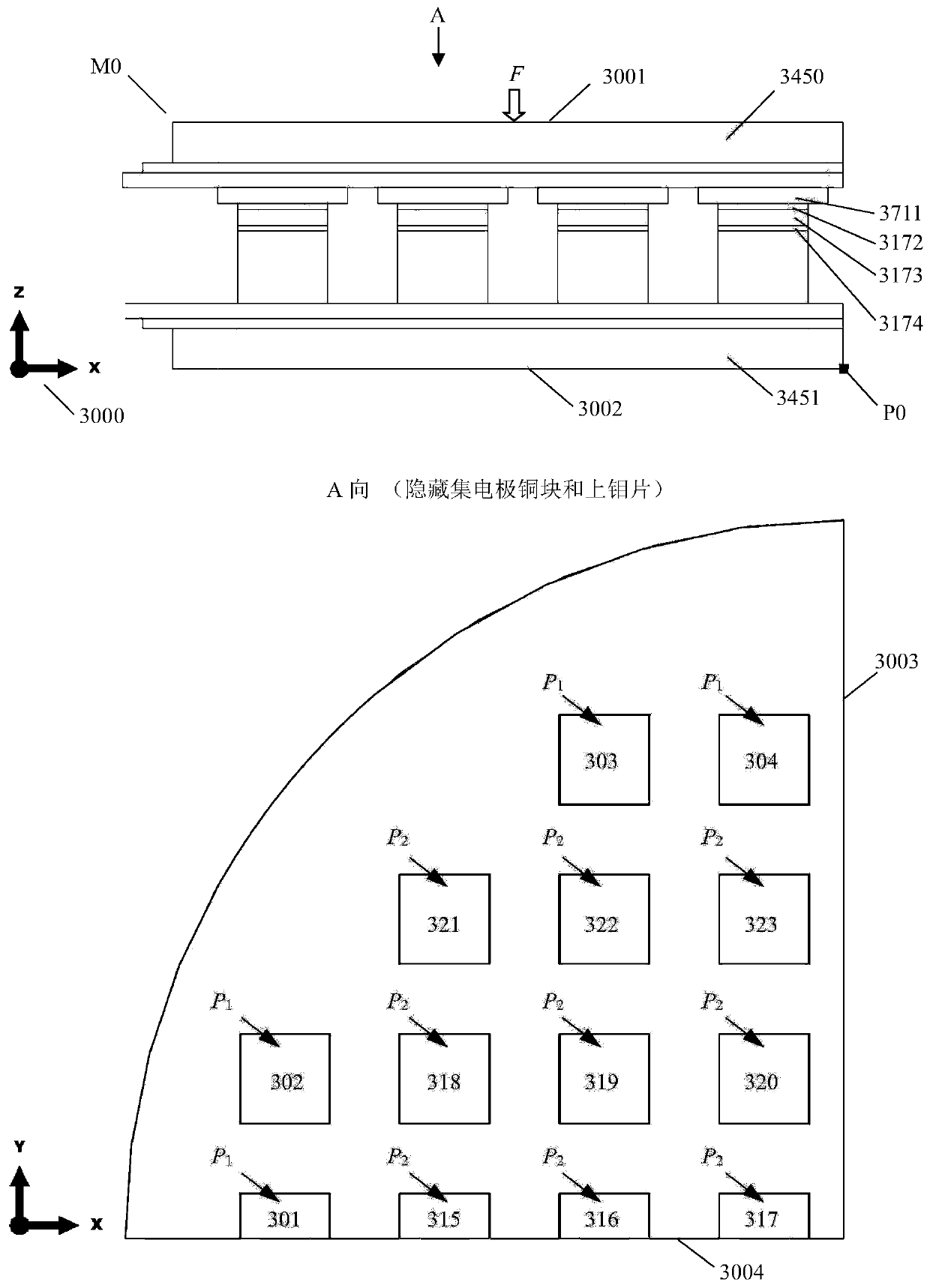
Crimping type IGBT device structure optimization design method
ActiveCN110991100AReduce in quantityImprove engineering ease of useDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of high-power semiconductor device structure design. The invention discloses a crimping type IGBT device structure optimization design method, which comprises the following processing steps of selecting a design target based on a crimping type IGBT device to be optimized; based on the crimping type IGBT device, establishing a thermal coupling finite element analysis model M0, and further selecting a coupling temperature-displacement steady-state solver to solve the finite element analysis model M0; based on the position and the stress value of eachchip, establishing a stress balance coefficient response surface; forming an initial coefficient vector a (0) as an initial point, constructing an optimization model, and solving the optimization model to obtain an optimal coefficient vector a *; and constructing a silver sheet design scheme based on the optimal balance coefficient. Compared with the prior art, the structure optimization model established by the method can be solved on the basis of existing finite element analysis commercial software and a classical optimization algorithm, so that a tedious and complex programming process is avoided, and the method has good engineering usability.
Owner:HUNAN CITY UNIV
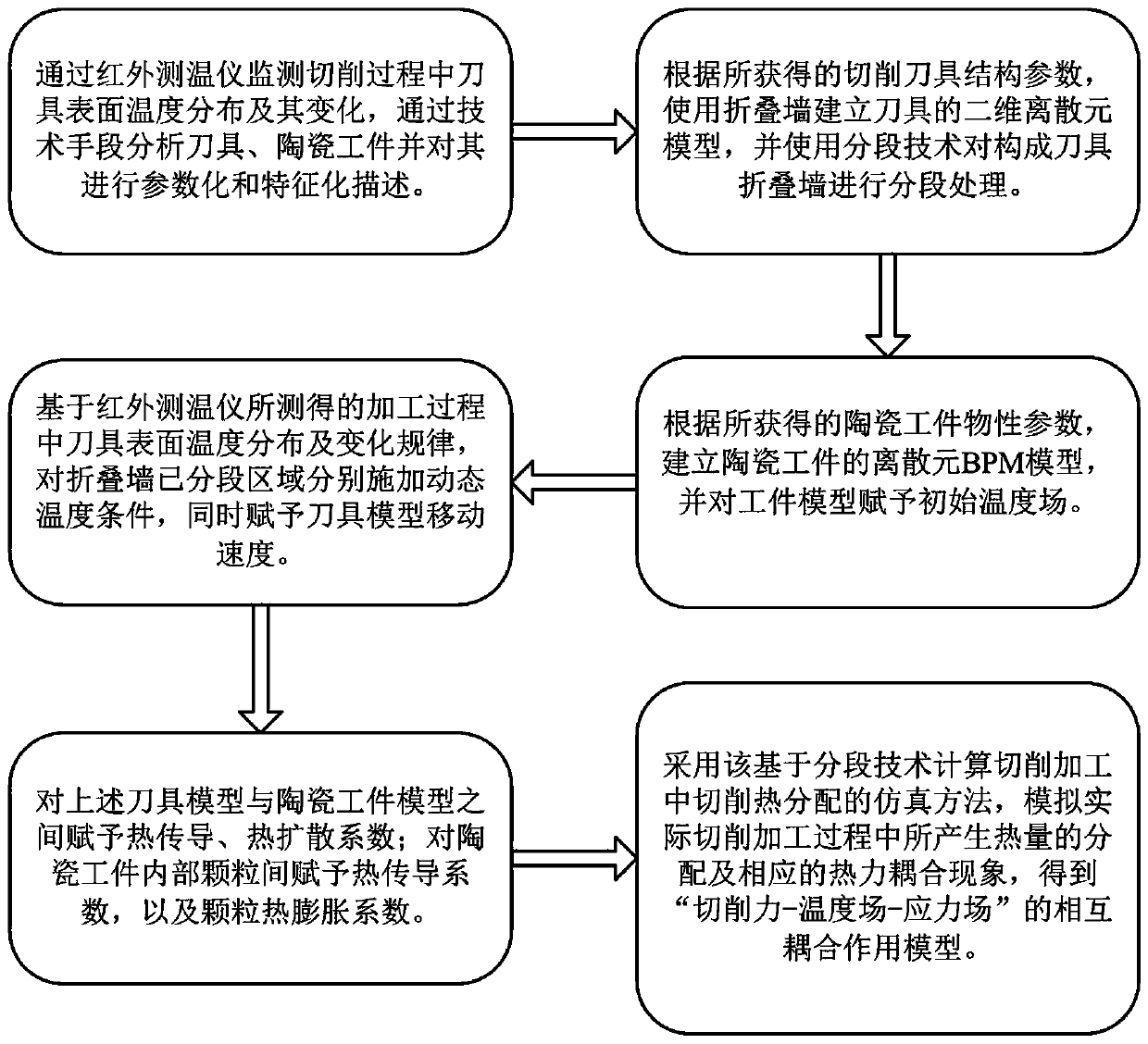
Method for cutting thermal simulation calculation in brittle material cutting machining
The invention discloses a method for cutting thermal simulation calculation in brittle material cutting machining. The method comprises the following steps that structural parameters of a cutter and material characteristics of a ceramic workpiece are obtained; according to the obtained cutter structure parameters and the material characteristics of the ceramic workpiece, cutter and ceramic workpiece discrete element models conforming to the reality are established in discrete element software; then discrete element simulation of cutting machining of the ceramic workpiece is established by adding conditions such as a heat exchange contact model, the rotating speed of a cutter, the cutting depth and the feeding speed; through discrete element simulation, the mutual coupling effect rule of acutting force-temperature field-stress field during cutting machining of the ceramic workpiece is researched. According to the method, the discrete element simulation technology is used for researching the thermal-mechanical coupling action rule of the ceramic workpiece under the cutting machining condition, and response behaviors such as crack propagation and surface damage occurring under the condition that thermal-mechanical coupling is considered during material cutting machining can be further researched.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Device for simulating cracking of hot dry rock to form fracture morphology and method
PendingCN111595694AEasy to operatePrevent splashMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesRock coreClassical mechanics
The invention provides a device for simulating cracking of a hot dry rock to form fracture morphology and a method, relates to the technical field of rock mass mechanics experiments, and provides a novel simulation device and a method for simulating expansion fracture net morphology under a hot dry rock thermal-mechanical coupling effect. The device comprises a frame body, a rock core limiting structure and a heating device, wherein the rock core limiting structure is arranged on the frame body, an accommodating cavity used for accommodating a rock core is formed in the rock core limiting structure, and the rock core limiting structure is used for simulating a surrounding crustal stress effect borne by the rock core when the rock core in the accommodating cavity expands and cracks; and theheating device is connected with the rock core limiting structure and used for heating the rock core in the accommodating cavity so as to simulate the geothermal temperature. The device and the method are used for simulating the expansion fracture net morphology under the hot dry rock thermo-mechanical coupling effect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Cutting device
ActiveCN103418847BGuarantee quality and efficiencyGuaranteed work efficiencyDriving apparatusMaintainance and safety accessoriesParticulatesEngineering
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
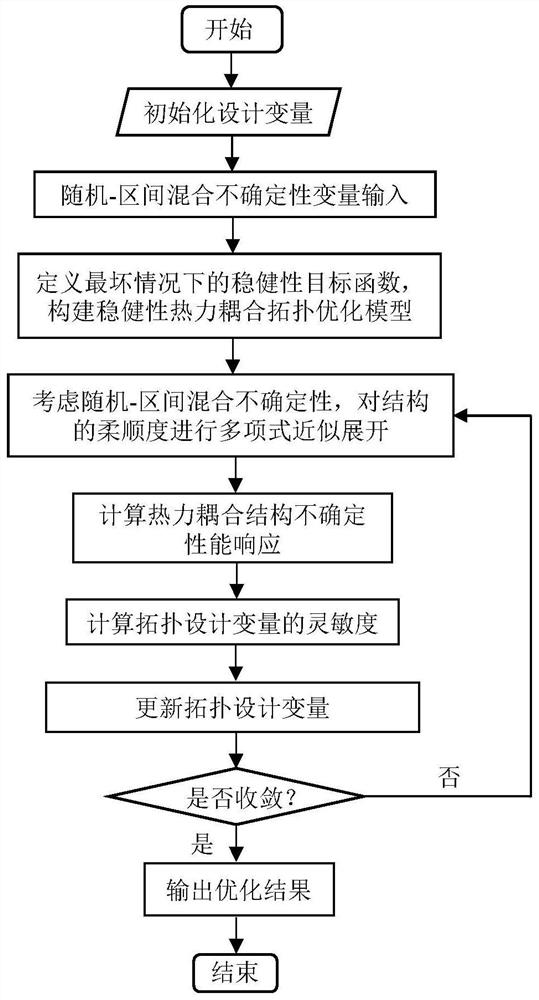
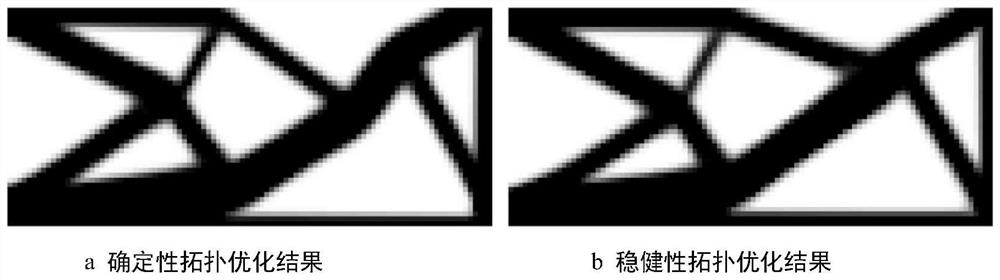
A Robust Thermomechanical Coupled Topology Optimization Method Considering Stochastic-Interval Mixture
ActiveCN113378326BSimple designAvoid the problem of a sharp increase in the amount of calculationGeometric CADMulti-objective optimisationAlgorithmDimensionality reduction
The invention relates to a robust thermal-mechanical coupled topology optimization method considering random-interval mixing. First, based on the mean and variance intervals of structural compliance, the worst-case robust objective function is defined and a robust thermal-mechanical coupled topology optimization model is constructed; then, the univariate dimensionality reduction method and the chaos-Chebyshev polynomial expansion method are combined , developed an efficient mixed uncertainty analysis method to calculate the uncertain performance response of thermally coupled structures; finally, based on the proposed mixed uncertainty analysis method, the sensitivity of structural topology design variables was derived, and a gradient-based The optimization algorithm is used to solve the problem, and finally the robust topological configuration of the thermal-mechanical coupling structure is obtained. By constructing a polynomial expansion model based on a dimension reduction integral strategy, the present invention effectively improves the efficiency of solving the uncertain performance response of the thermal-mechanical coupling structure, and realizes the efficient and robust topology optimization design of the structure under the thermal-mechanical coupling working condition.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for controlling vibration based on bifurcation and chaotic analysis
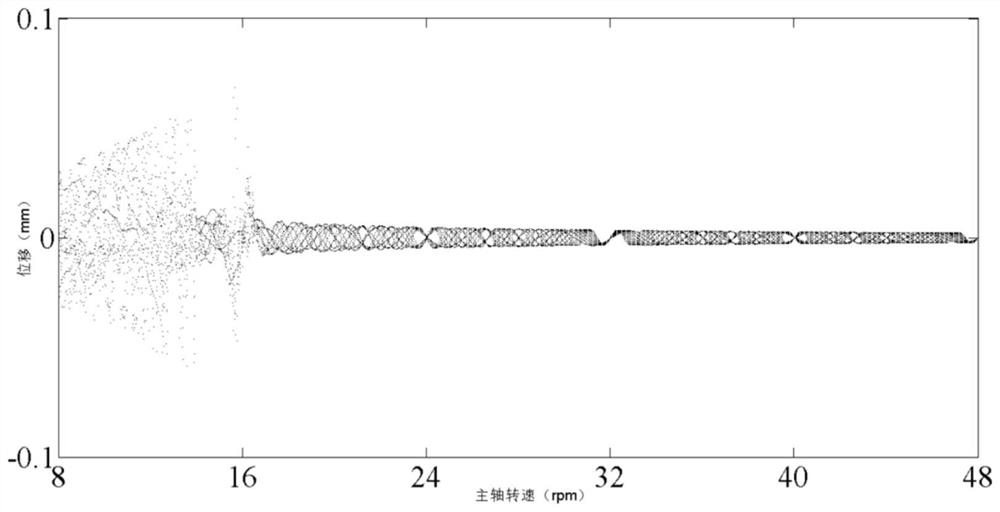
ActiveCN113221260AOptimization parametersGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsVibration controlThermomechanical coupling
The invention relates to a method for controlling a workpiece vibration system in the milling process of a thin-walled workpiece through bifurcation and chaotic analysis. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a nonlinear kinetic equation of a rectangular thin-walled workpiece under the thermal coupling effect in the milling process is established; then, the condition that a nonlinear vibration system generates Smale horseshoe chaos is revealed through a Melnikov function; meanwhile, according to the bifurcation and chaotic analysis method, the influence rule of the change of the load, the temperature, the technological parameters and the like on the nonlinear dynamic behavior of the system in the thin-wall workpiece machining process is analyzed, and the thin-wall workpiece vibration control method optimized through the machining parameters is finally established. According to the method, by using the bifurcation and chaotic analysis method, the influence rule of the change of the load, the temperature, the technological parameters and the like on a workpiece vibration system in a milling process is analyzed based on an established kinetic equation of the workpiece vibration system in the machining process. Processing parameters can be scientifically selected by using a chaos and bifurcation analysis vibration control method, so that the processing quality can be effectively improved.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of determination method of austenitization during heat treatment of metal materials
ActiveCN109858085BAchieve heat treatment process optimizationAccurate calculation of residual stress effectsDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelMetallic materials
The invention relates to a method for measuring austenitization in the heat treatment process of metal materials, which belongs to the technical field of multi-field coupling numerical simulation, and is used to solve the problem that the existing numerical simulation cannot obtain the experimental data of the thermal physical properties of the material at the high temperature stage and does not consider changing the material composition The technical problem of the influence of phase change and thermal physical parameter difference on the calculation results of multi-field coupling. The method comprises the following steps: S1. Establishing a method for obtaining the phase transition and thermophysical parameters of the material for the composition and temperature of the metal material; S2. Establishing a finite element model for thermomechanical coupling calculation or heat transfer calculation of the temperature field-stress field; S3 . Calculating the temperature field or thermal stress of the metal material; S4. Obtaining the distribution of the temperature field and thermal stress of the metal material over time; S5. Obtaining the austenitization measurement results during the heat treatment of the metal material. This method takes into account the influence of composition on thermophysical parameters and phase transformation stress, and can accurately calculate the influence of phase transformation on temperature field and residual stress, which can be used to optimize the heat treatment process of different materials.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST +1
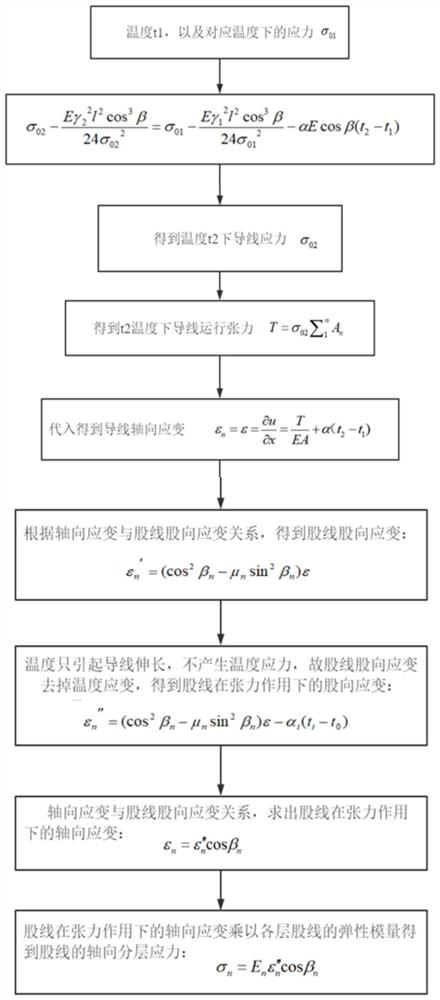
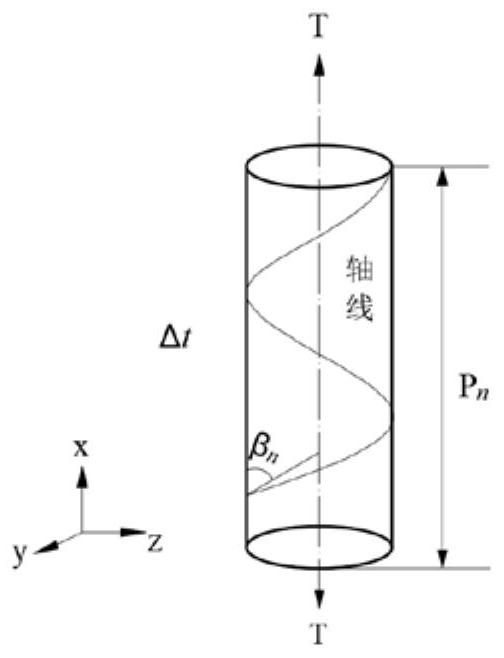
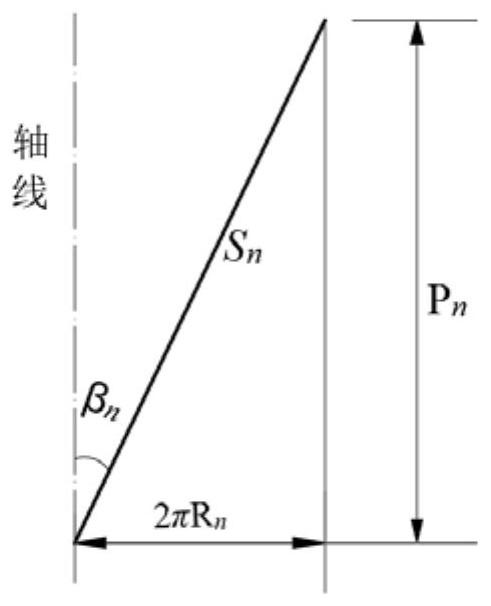
Layered stress calculation method of steel-cored aluminum stranded wire under thermo-mechanical coupling effect
PendingCN113901687ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsExtreme weatherEngineering
The invention relates to a layered stress calculation method of a steel-cored aluminum stranded wire under a thermo-mechanical coupling effect. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating to obtain the average running tension of a conductor at a solved temperature; substituting the average operation tension of the conductor at the temperature into an axial total strain calculation expression to obtain the axial total strain of the conductor and the strand direction strain of stranded wires; removing the temperature strain from the strand direction strain of the stranded wires to obtain the strand direction strain of the stranded wires under the action of tension; solving the axial strain of the stranded wires under the action of tension; acquiring the axial stratification stress of the stranded wires by multiplying the axial strain of the stranded wires under the action of tension by the elastic modulus of each layer of stranded wires; and calculating the layered stress of the wire steel core and the aluminum stranded wires under the extreme weather condition, and judging whether the conductor meets the safety design and the anti-fatigue performance under the extreme weather condition. According to the layered stress calculation method, layered stress calculation expressions of stranded wires of different materials are obtained through theoretical derivation, layered stress values of all layers can be obtained through programming calculation, and important reference is provided for safety design and selection of overhead lines and anti-fatigue performance research.
Owner:ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST CEEC
Numerical Simulation Research Method of Irregular Particles Based on Microwave Induced Damage in Particle Flow
ActiveCN105844032BDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingParticle flowDiscrete element method
Owner:贵州省洋霖科技服务有限公司
Finite element solution optimization method for structural thermal response induced by re-entry aerodynamic environment
ActiveCN112364544BHigh simulationGeometric CADSustainable transportationPartial differential equationEngineering
The invention discloses a finite element solution optimization method for structural thermal response caused by re-entry aerodynamic environment, which includes: discretizing the coupled control equation based on heat conduction and material thermoelastic dynamics through the finite element method and providing a corresponding algorithm flow; wherein, In the algorithm process, for time-dependent partial differential equations, the finite element method discretizes the spatial region first, and obtains the grid division of the solution region, and then differentially discretizes the time item. According to the iterative coupling relaxation calculation principle, step by step Advance to capture the vibration of structural materials in space and the nonlinear behavior of thermal response deformation of large spacecraft after de-orbiting and re-entry into a strong aerodynamic thermal environment. The present invention provides an optimization method based on the finite element method for solving thermal-mechanical coupling response, which is beneficial for analyzing and researching the thermal-mechanical coupling response of material structures under strong aerodynamic / thermal environments, and is conducive to carrying out the performance prediction of aircraft and spacecraft structures with simulation.
Owner:中国空气动力研究与发展中心超高速空气动力研究所 +2
Numerical simulation method for multi-particle characteristic of dispersion type fuel
ActiveCN114861424AOvercome limitationsNo change to the solution processNuclear energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationThermodynamicsThermal force
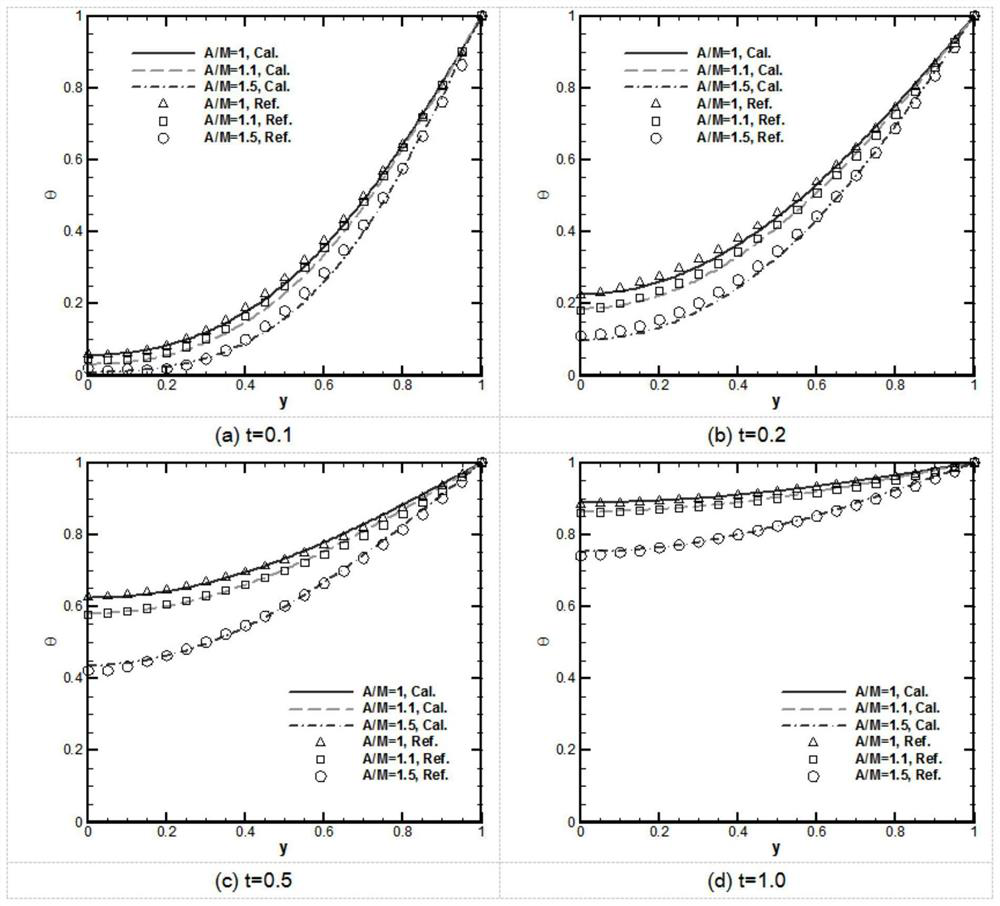
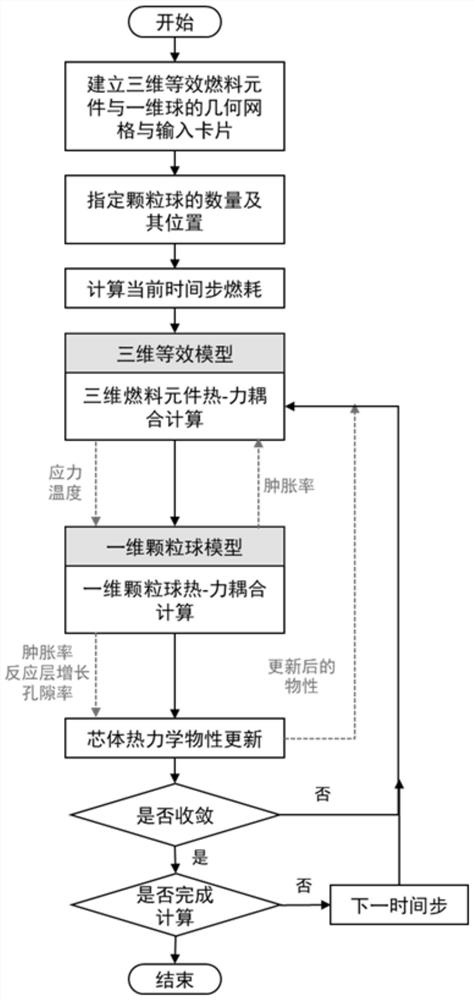
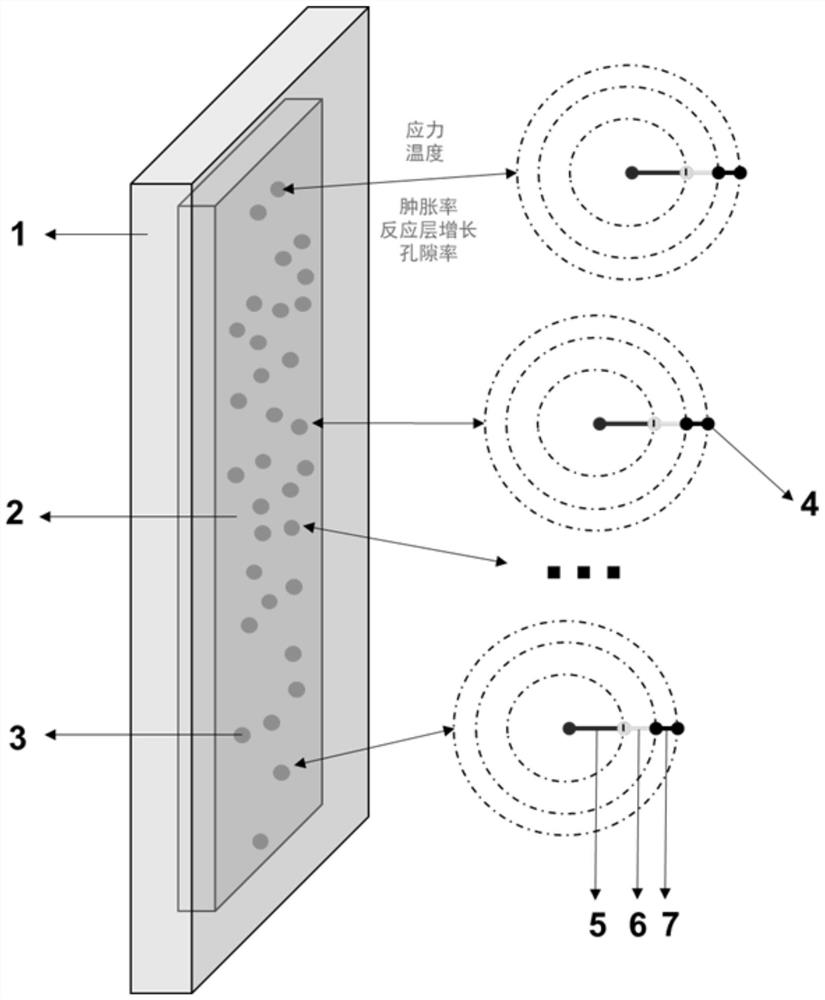
The invention discloses a numerical simulation method aiming at the multi-particle characteristic of dispersion type fuel. The method is suitable for the overall simulation of a dispersion type fuel element, considers the behaviors and influences of local particles, and comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a geometric model of a three-dimensional equivalent fuel element and a one-dimensional particle ball; 2, assigning the number and positions of one-dimensional particle balls; 3, calculating the burnup of the current time step; 4, the equivalent physical property of the three-dimensional fuel element is calculated, and heat-force coupling calculation is carried out; 5, acquiring the stress and the temperature calculated in the step 4, and taking the stress and the temperature as boundary conditions of a one-dimensional ball model to carry out heat-force coupling calculation; 6, feeding back the particle swelling rate calculated in the step 5 to the three-dimensional fuel element; 7, updating the physical property of the three-dimensional equivalent fuel element material according to the calculation result of the step 5; 8, repeating the steps 4, 5, 6 and 7 at the current time step until the convergence requirement is met; and 9, entering the next time step, and repeating the steps 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 until all-time calculation is completed.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
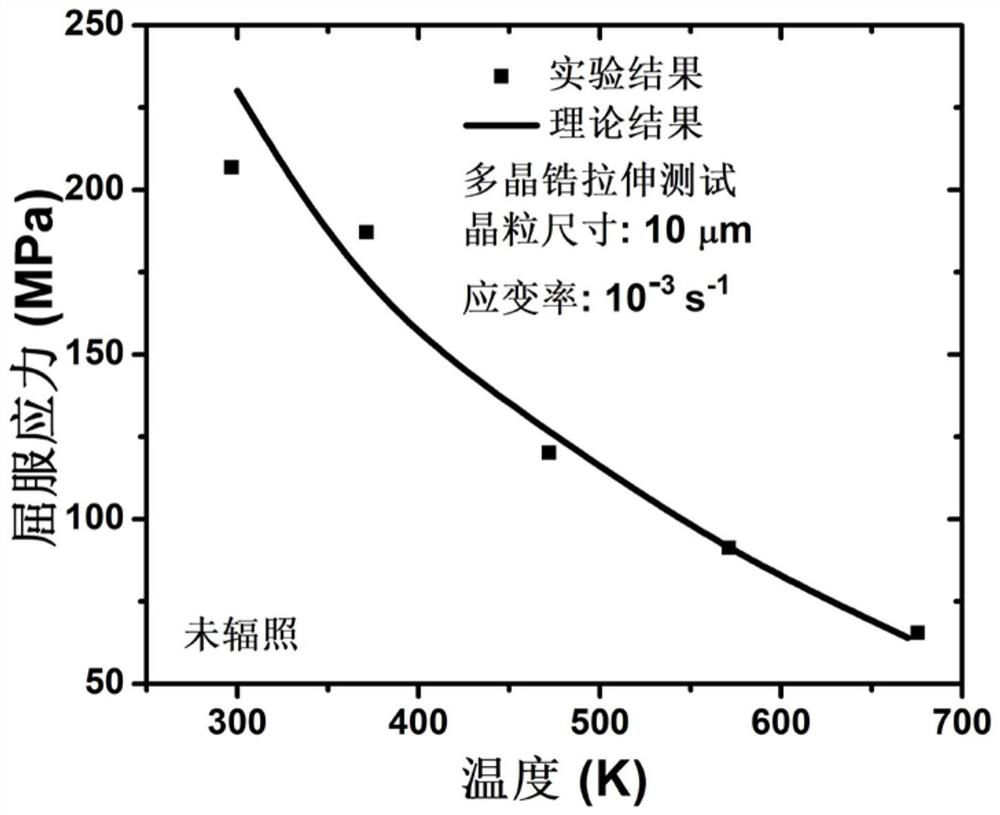
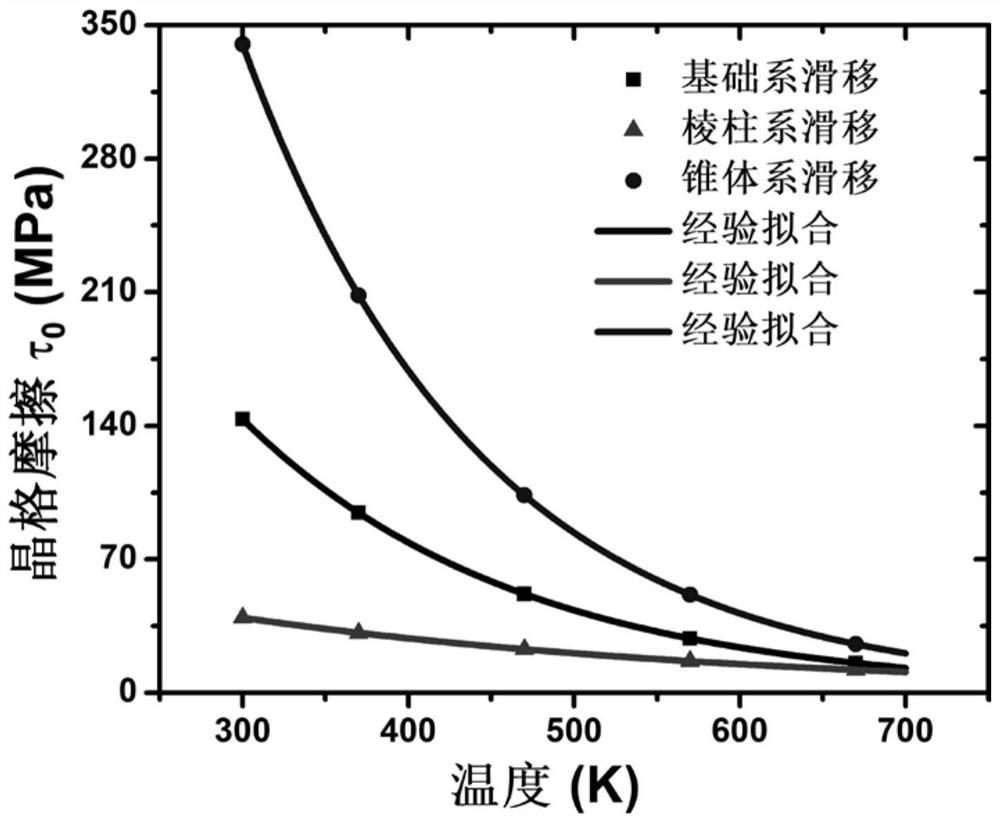
A Construction Method of Thermal-Mechanical Coupling Constitutive Relationship of Zirconium Alloy Under Neutron Irradiation
ActiveCN110543744BEasy CalibrationFast and accurate calibrationDesign optimisation/simulationNeutron irradiationSingle crystal
The invention discloses a method for constructing the thermal-mechanical coupling constitutive relationship of zirconium alloys under neutron irradiation conditions. The method of the invention combines the elasto-viscoplastic self-consistent theory to establish a cross-scale theoretical system from single crystal to polycrystal. The Matlab calculation program can easily, quickly and accurately calibrate the model parameters, and the numerical results of the model can be in good agreement with the experimental data under different external load conditions. The theoretical model framework has wide applicability and scalability, and can provide a reliable theoretical basis for the study of the macroscopic mechanical behavior of nuclear materials.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
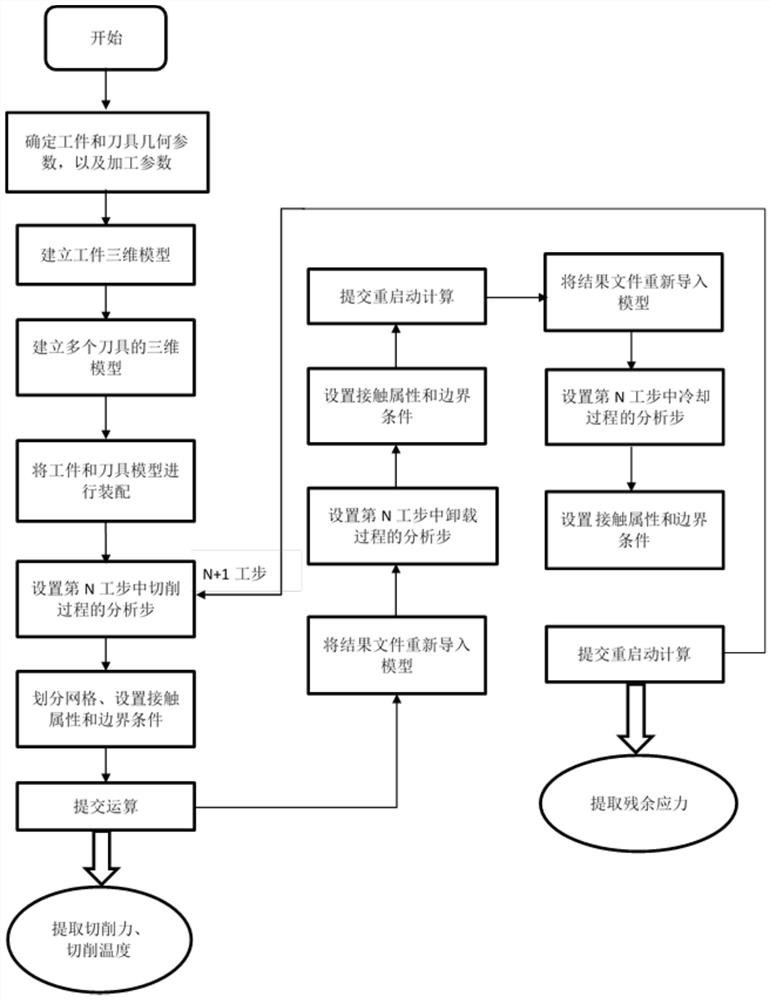
Three-dimensional finite element simulation method of metal cutting process based on multi-step
ActiveCN109783968BGuaranteed accuracyReduce computing timeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringCutting force
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Optimization design method for structural parameters of solid rocket engine jet pipe
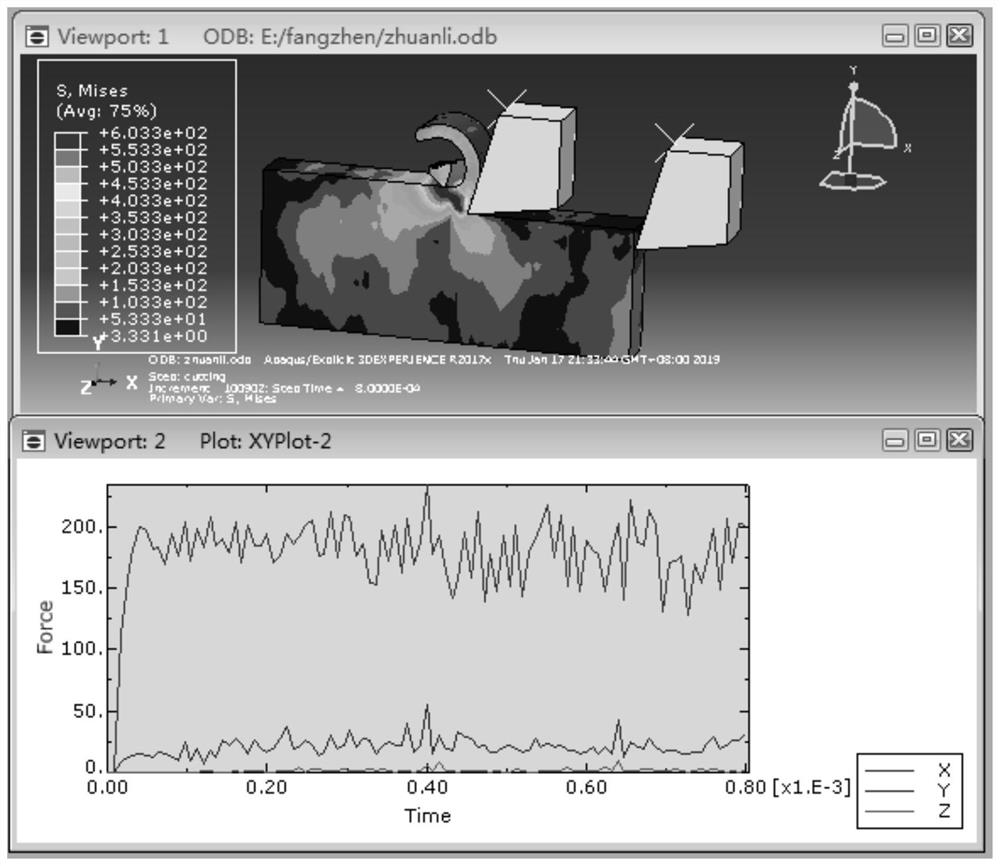
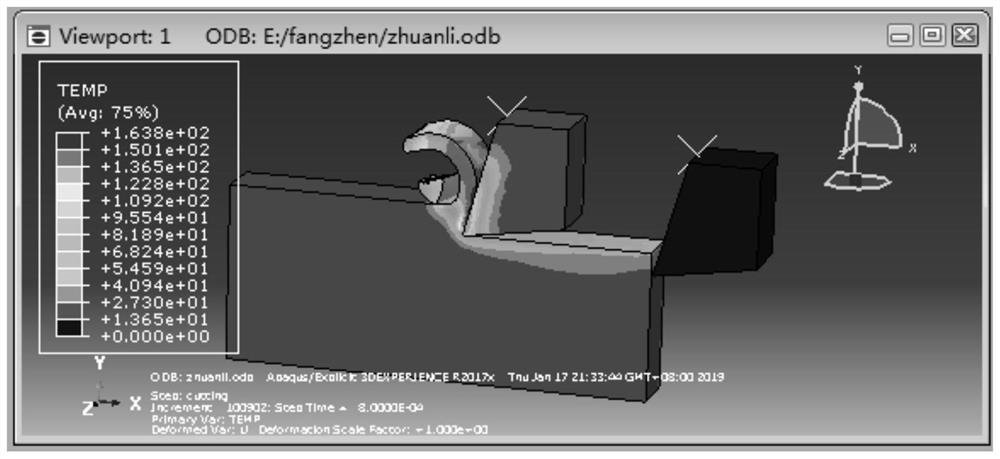
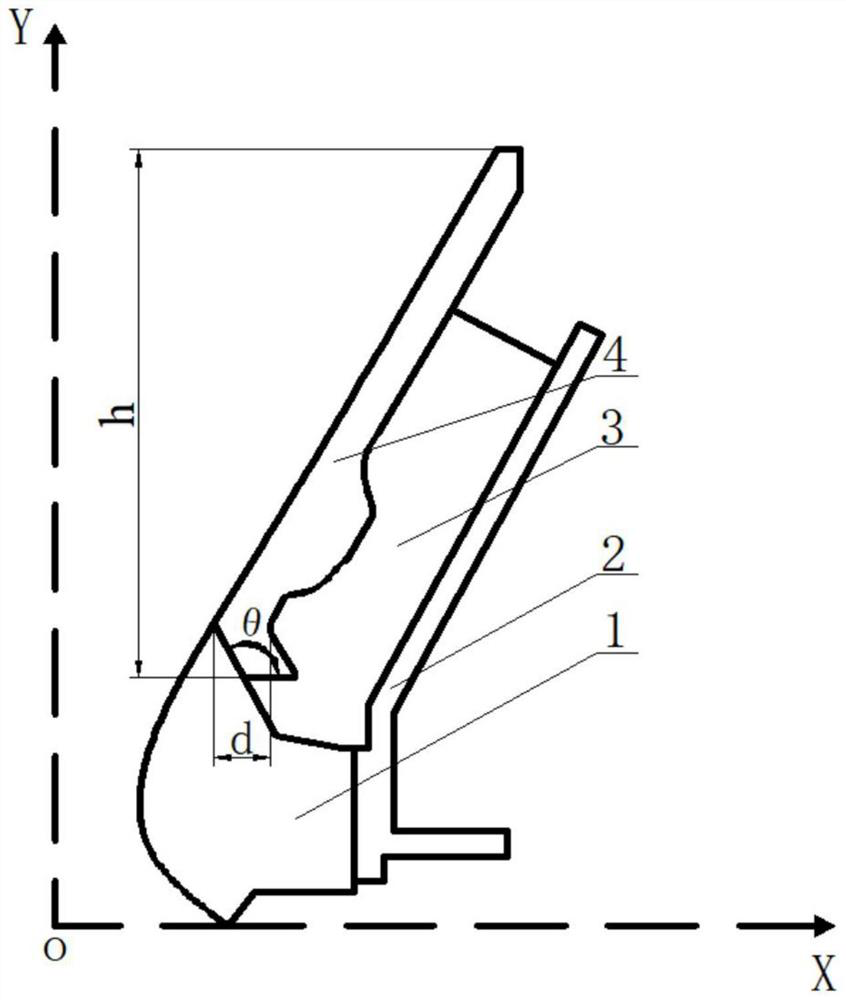
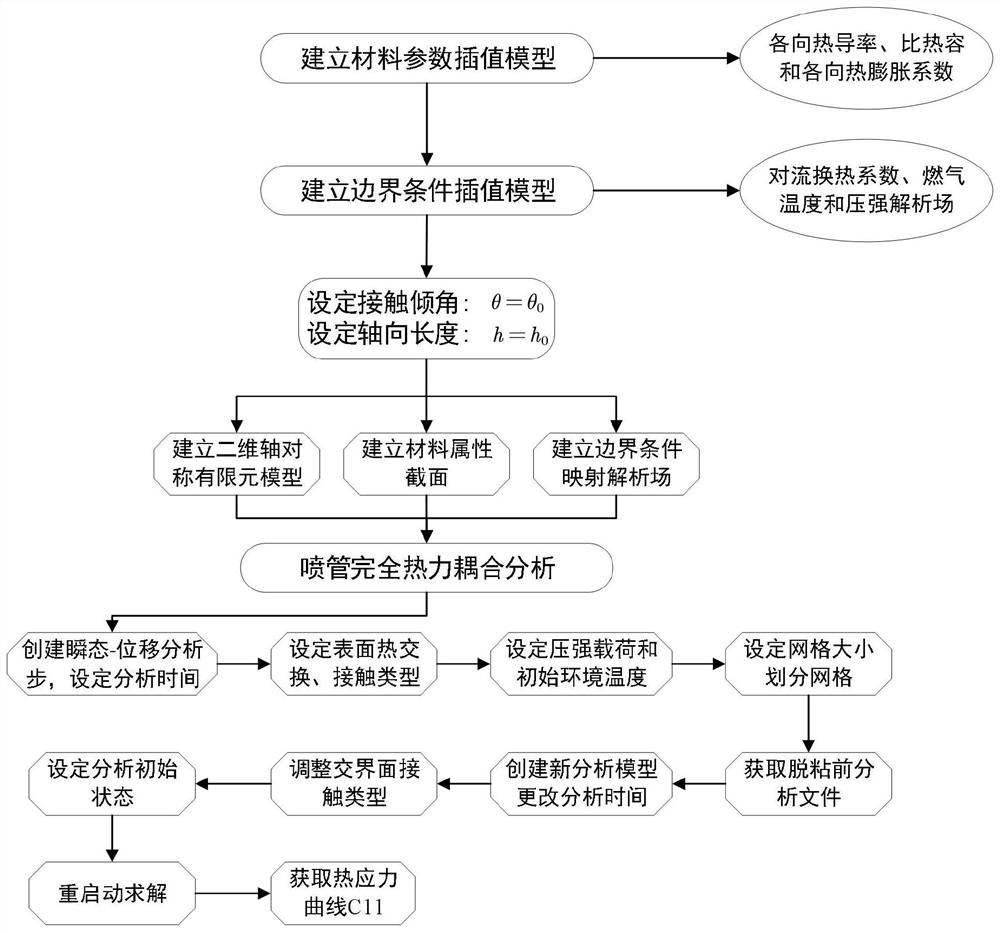
ActiveCN114528736ASolve the value rangeAvoid uncertaintyGeometric CADSustainable transportationThermal forceThermomechanical coupling
The invention discloses an optimization design method for structural parameters of a solid rocket engine jet pipe. The optimization design method comprises the following steps: 1, constructing a material thermophysical parameter model of each component of the jet pipe through a segmented cubic Hermite interpolation method; 2, constructing a thermal boundary condition model of the inner wall of the spray pipe through a Lagrange interpolation method; 3, analyzing and considering the temperature distribution and the thermal failure stress of the nozzle in the complex environment of interface debonding through a complete thermal coupling finite element method or a sequential thermal coupling finite element method; and 4, calculating peak values of thermal stress curves of the nozzle in working time under different axial lengths of the expansion section and different inclination angles of the contact surface of the expansion section and the throat liner, and obtaining the relationship between the maximum thermal stress value of the nozzle and the axial height of the expansion section and the inclination angles of the contact surface of the expansion section and the throat liner for structural optimization of the solid rocket engine nozzle. According to the method, the parameter selection and design of the nozzle structure can be optimized while the thermal stress extreme value of the nozzle is effectively reduced.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
A multi-objective optimization method for load-bearing and thermal protection structures of micro-truss structures
InactiveCN108009336BSimple designStable internal working environmentGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMaterial DesignEngineering
The invention discloses a micro-truss structure carrying and thermal protection structure multi-objective optimization method, and belongs to the field of spacecraft instrumentation overall design andmultifunctional structure material design. A flow channel is introduced into a micro-truss sandwich structure, multi-objective optimization of temperature and stress is realized by thermal transfer and force transfer coupling calculation, and final design meets a design process and the lightest front edge structure of a design boundary. The problem of thermal mechanical coupling under practical working conditions is taken into full consideration, the influence of the temperature on strength is introduced, processing technology boundary conditions are considered, and optimum structural designis realized by an optimization algorithm. The method is simple and effective, optimum design can be realized by small calculated amount, and time and cost consumed by trial and errors are greatly reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +2
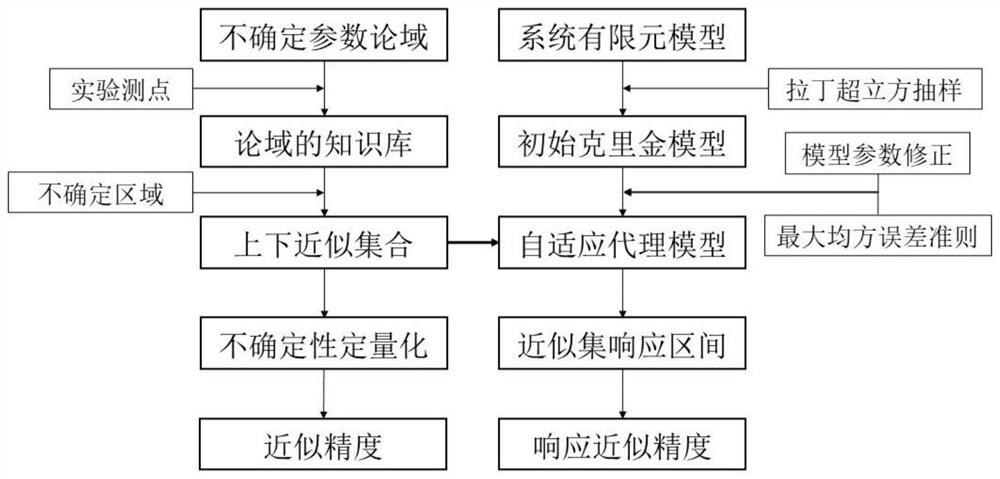
Method for analyzing uncertainty of thermal coupling system based on rough set theory
PendingCN114169192AHigh precisionEasy to calculateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLower approximationModel parameters
The invention discloses a rough set theory-based uncertainty analysis method for a thermal coupling system, relates to the field of mechanical engineering, and is used for solving the problems that the uncertainty analysis of the thermal coupling system depends on priori knowledge and is low in efficiency. The method comprises the following steps: determining a discourse domain of uncertain parameters of the coupling system, and constructing a knowledge base of the discourse domain according to experimental measuring points; for any uncertain region in the discourse domain, constructing an upper and lower approximation set and calculating approximation precision; an initial Kriging model is established through Latin hypercube sampling and system finite element calculation, and Kriging model parameter correction is realized by using a maximum likelihood estimation and pattern search method; and based on a maximum mean square error point adding criterion, establishing an adaptive Kriging model, and further calculating response upper and lower bounds of the upper and lower approximation sets to obtain response approximation precision. By applying the rough set theory, when uncertainty analysis is carried out on the thermal coupling system, dependence on priori knowledge is not needed, and efficiency is high.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A Calculation Method of Bloom Rolling Temperature Field Considering Non-uniform Deformation Heat
ActiveCN110852007BReduce complexityReduce the amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationWire rodIndirect coupling
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
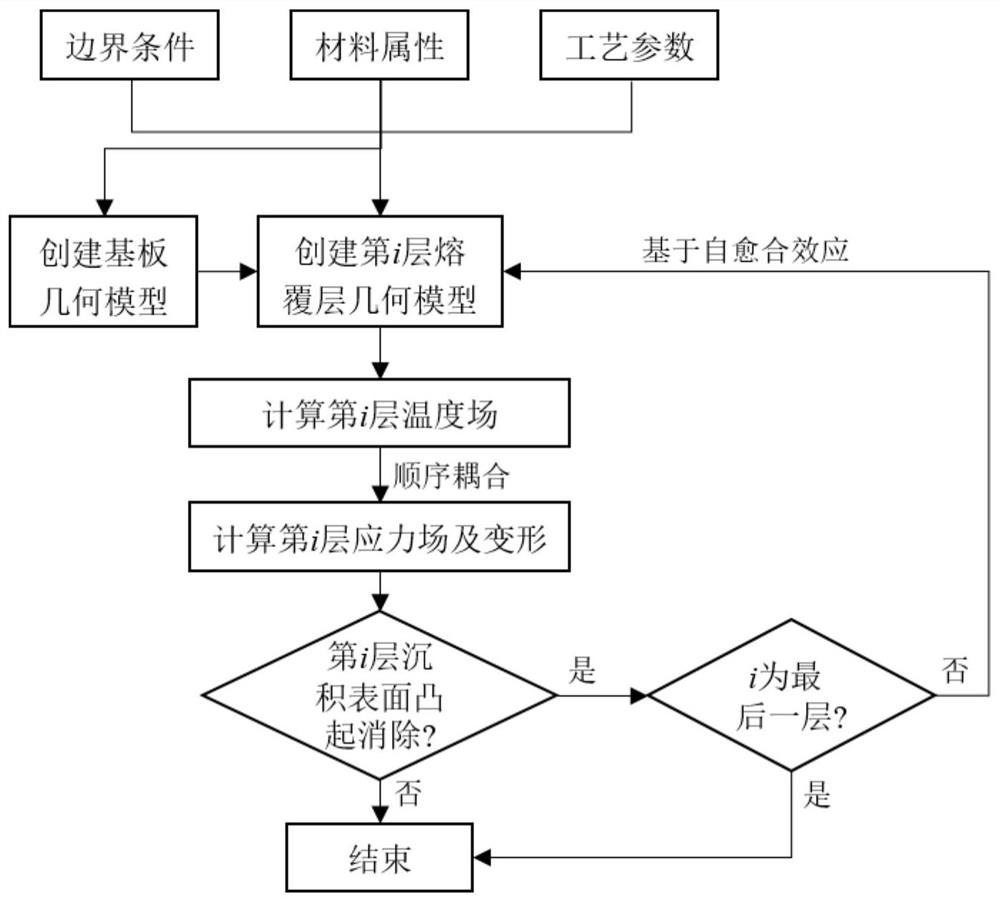
Finite element modeling method of macroscopic thermal stress field based on self-healing effect of laser stereoforming
ActiveCN108763704BReduce stressImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scaleEngineering
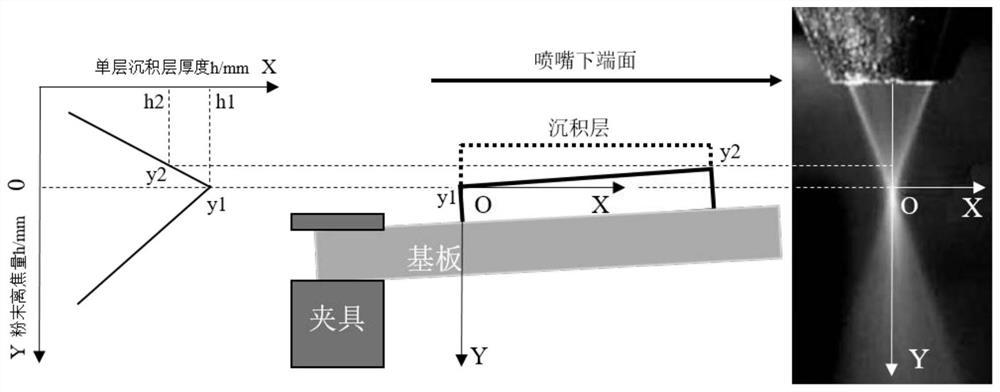
A finite element modeling method of macroscopic thermal stress field based on the self-healing effect of laser stereoforming in the present invention comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a thermomechanical coupling model for unilateral clamping of a laser stereoforming substrate; step 2, establishing a laser stereoforming Thermal-mechanical coupling model of the i-th cladding layer of the formed component; Step 3, calculate the temperature field of the i-th cladding layer of the laser three-dimensional forming component; Step 4, calculate the stress field and deformation of the i-th cladding layer of the laser three-dimensional forming component ; Step 5, judging whether the bulge on the deposition surface of the i-th cladding layer of the component can be eliminated; Step 6, judging whether the i-th cladding layer is the last layer; In the case that the process is eliminated, if the i-th cladding layer is the last layer, the simulation processing ends, otherwise, enter step 2, and repeat this cycle until the macroscopic thermal stress field simulation calculation of the entire laser stereoforming is completed.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com