Patents
Literature
70results about "Secondary emission electrodes manufacture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
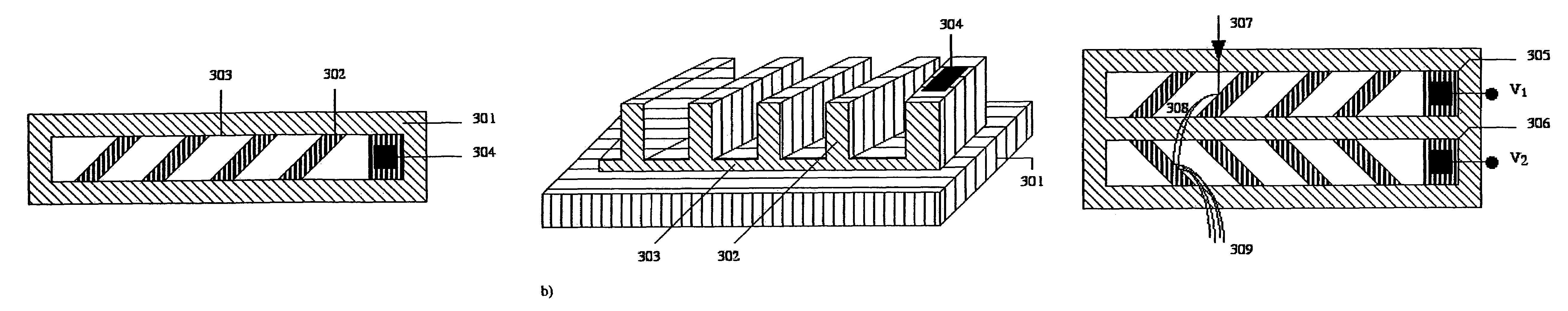
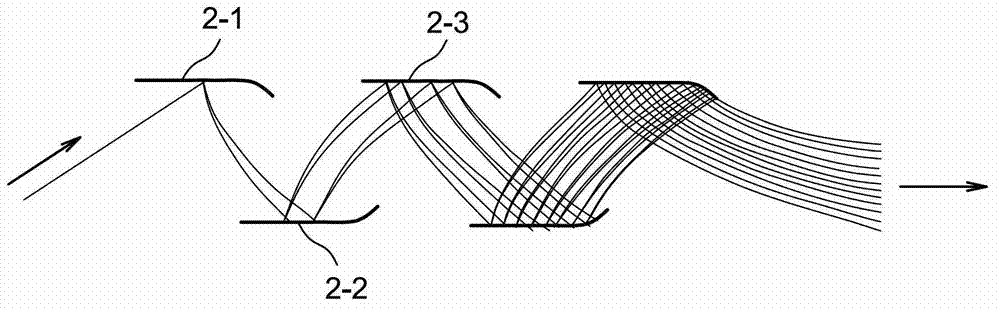
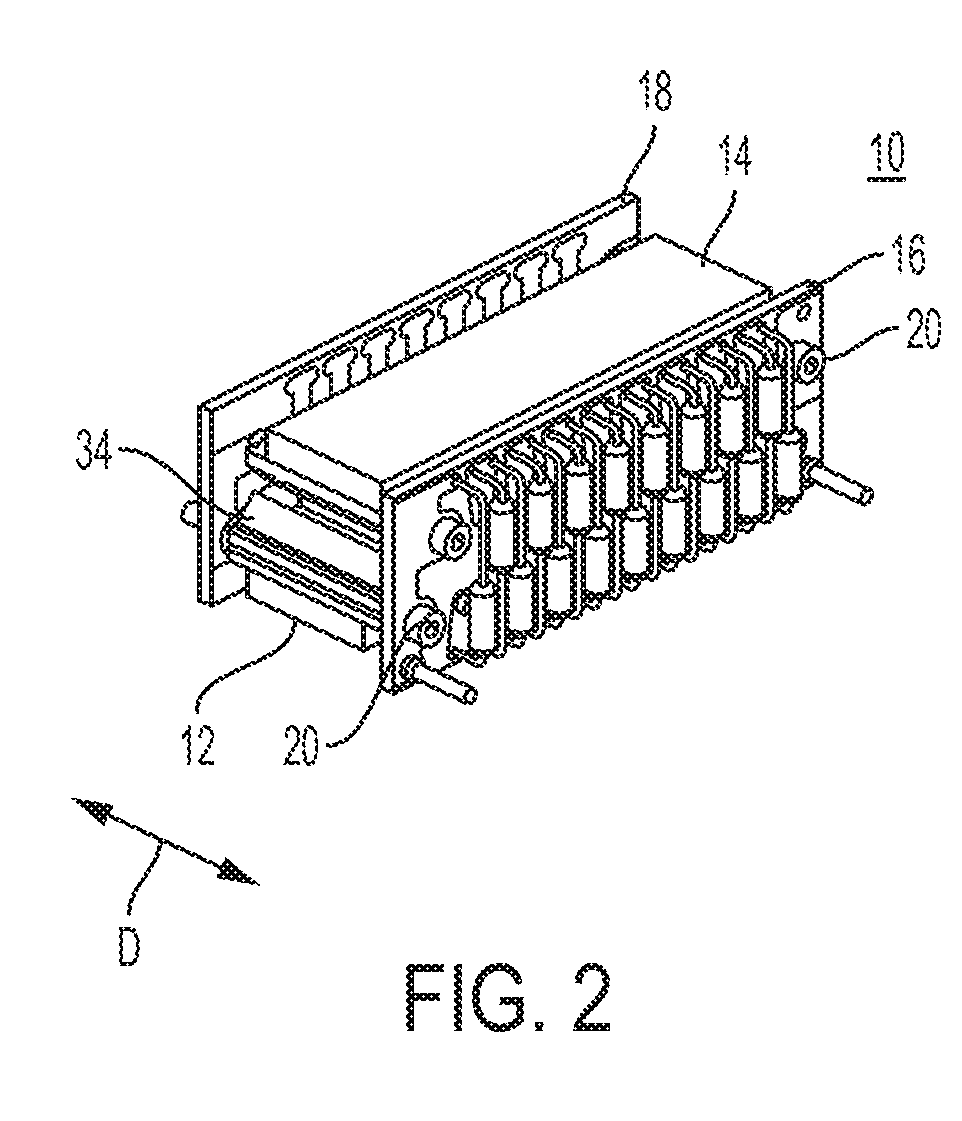
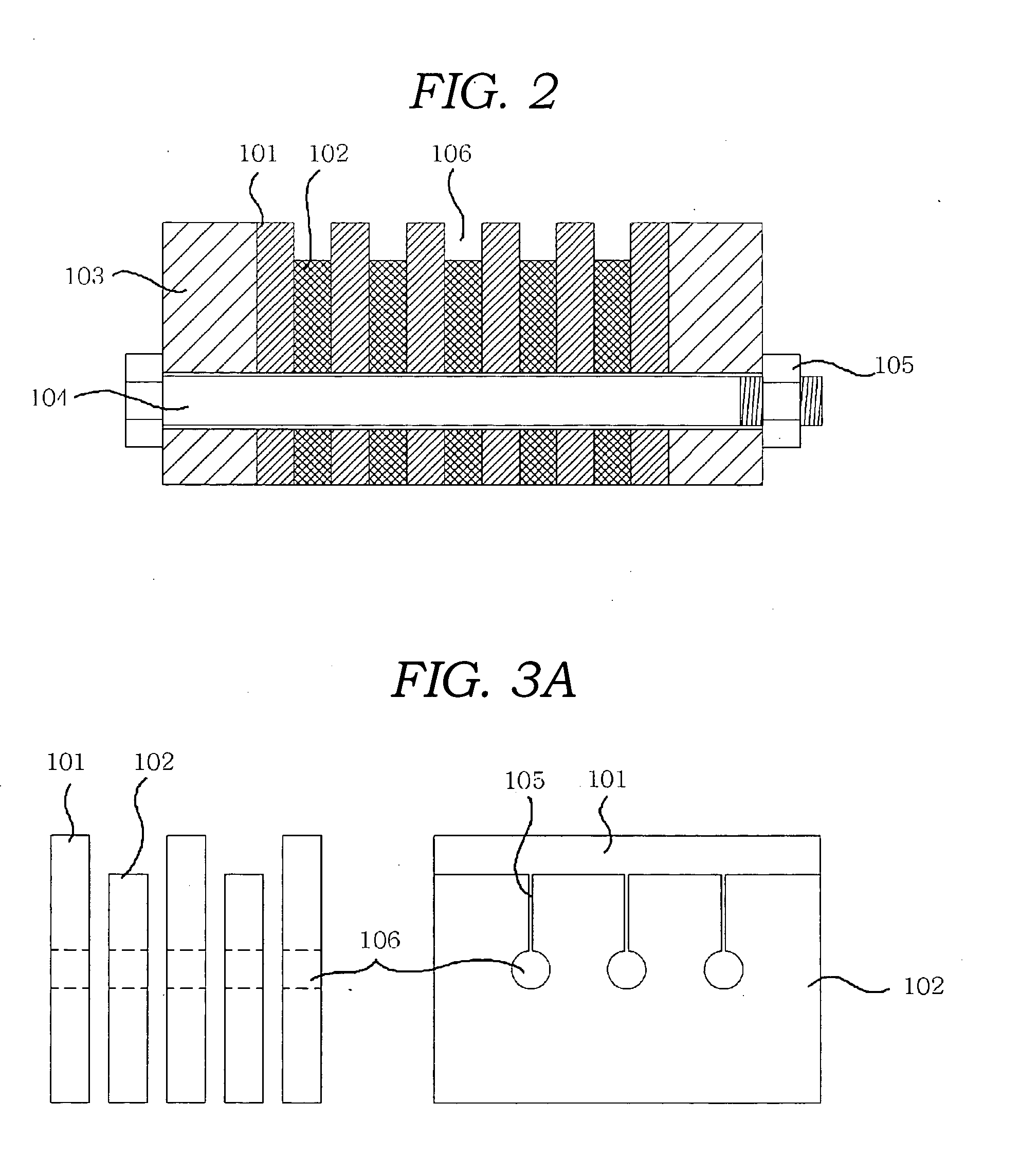
Micro-engineered electron multipliers
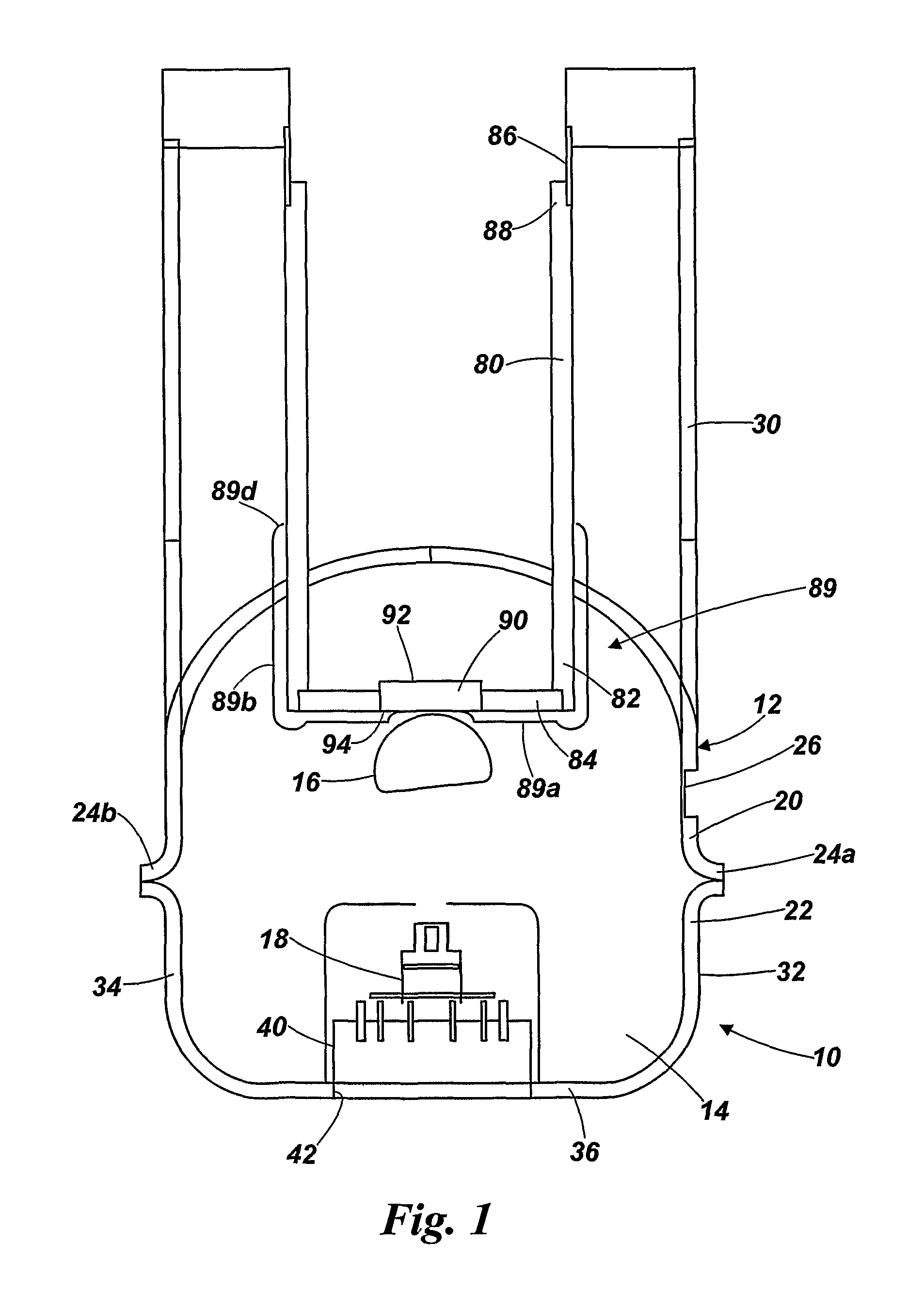
ActiveUS7294954B2Accelerate emissionsEasy to manufactureMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesIn planeStandard plane
This invention provides for a simple method of fabricating miniature electron multipliers, in an in-plane configuration suitable for use with miniature analytic instruments such as mass filters. The materials involved are predominantly silicon and compatible oxides, allowing the possibility of integration with a mass filter formed in a similar materials system. The materials are selected simultaneously to withstand high voltages and to enhance secondary electron emission. Fabrication is based on standard planar processing methods. These methods also allow the construction of an integrated set of bias resistors in a multi-electrode device, so that the device may be operated from a single high-voltage source.
Owner:MICROSAIC SYST
X-ray tubes
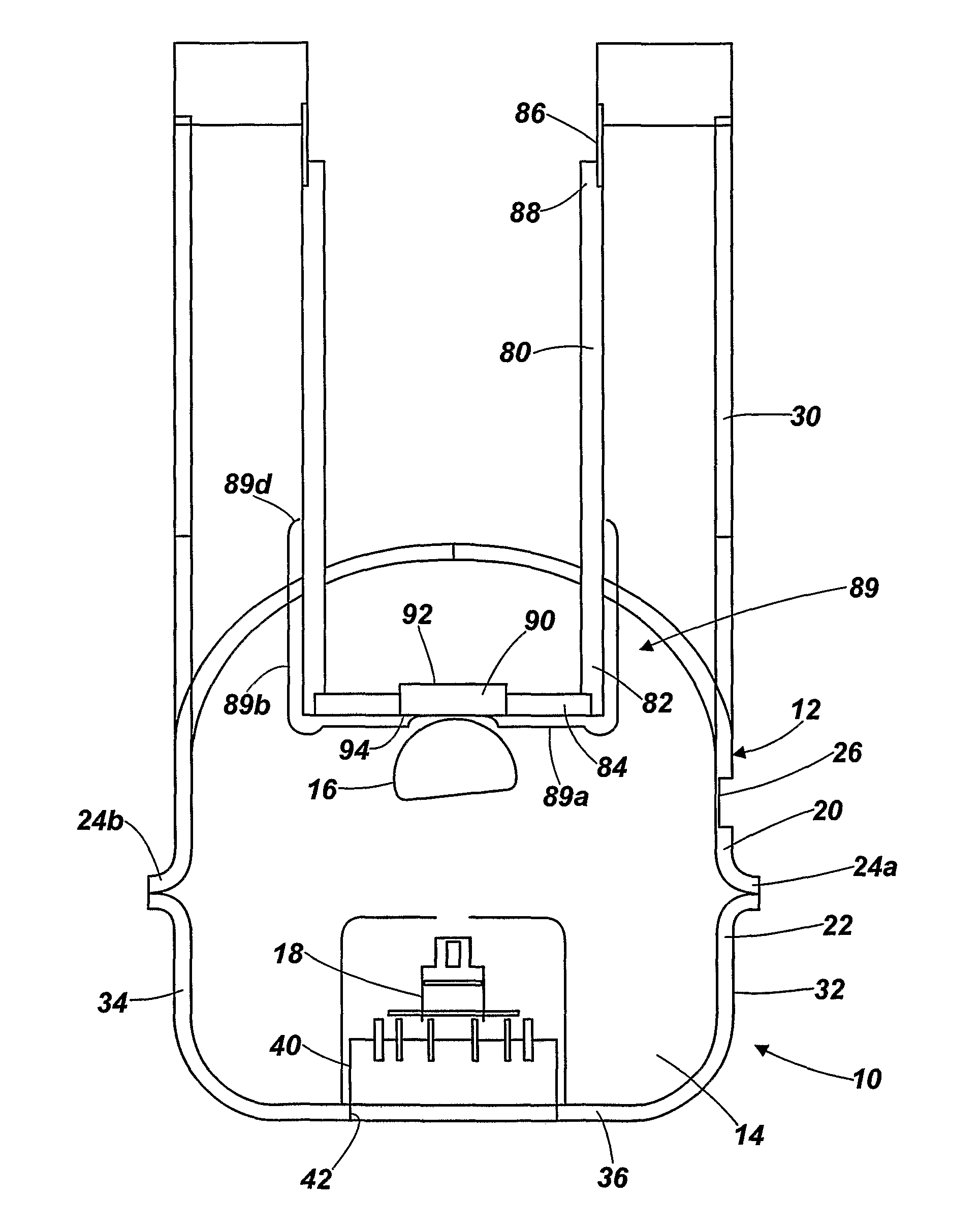
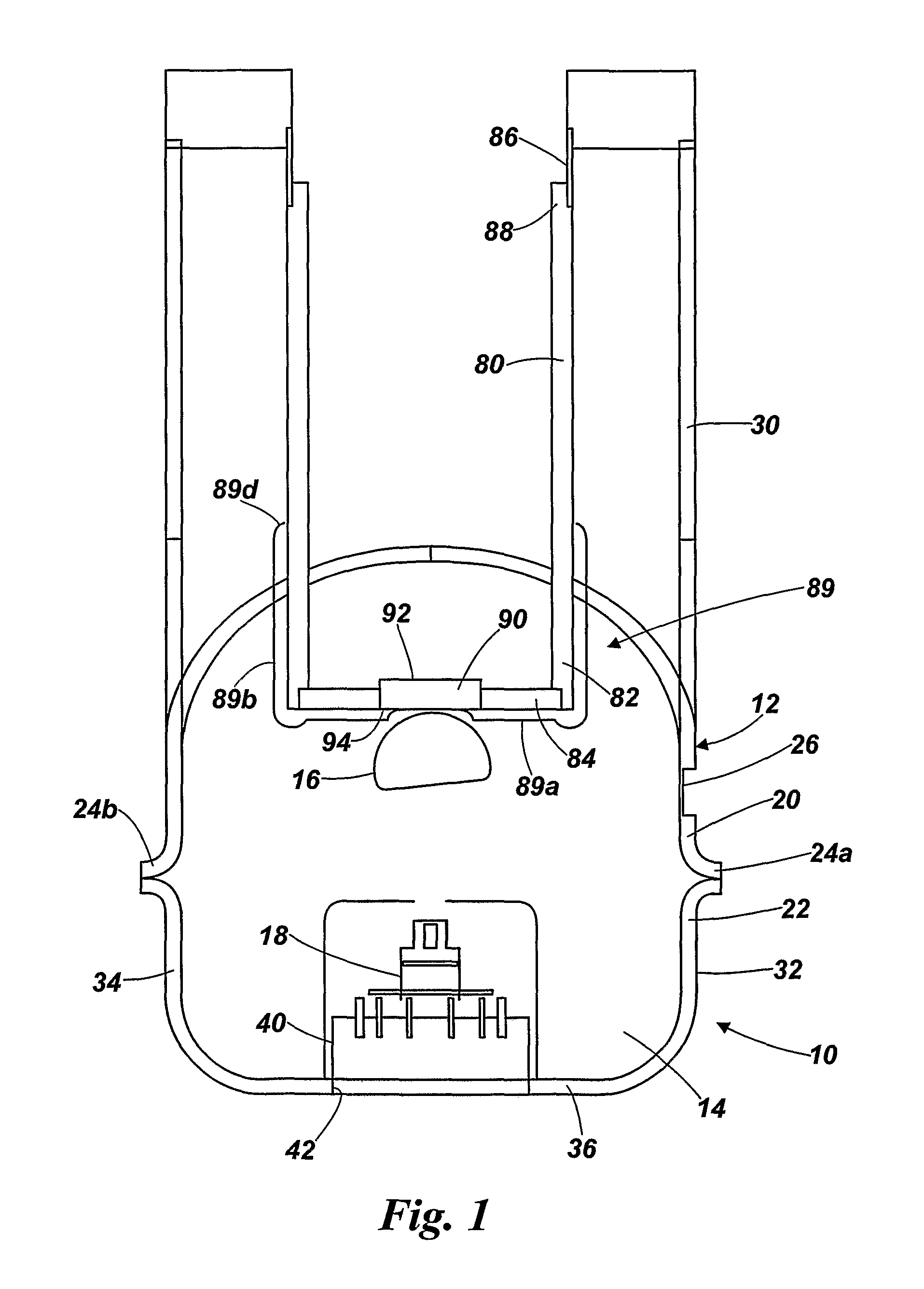
ActiveUS8824637B2Quick and efficientWave amplification devicesDischarge tube assemblyElectron sourceX-ray
An X-ray tube is produced by forming a first housing section 20 from sheet metal; forming a second housing section 22 from sheet metal, mounting an electron source 18 in one of the housing sections; mounting an anode 16 in one of the housing sections; and joining the housing sections 20, 22 together to form a housing defining a chamber with the electron source 18 and the anode 16 therein.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Electron multiplier device having a nanodiamond layer
ActiveUS20130240907A1High global gainIncrease the multiplier device's number of steps of multiplicationMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSecondary electronsElectron multiplier
An electron multiplier for a system for detecting electromagnetic radiation or an ion flow is disclosed. The multiplier includes at least one active structure intended to receive a flow of incident electrons, and to emit in response a flow of electrons called secondary electrons. The active structure includes a substrate on which is positioned a thin nanodiamond layer formed from diamond particles the average size of which is less than or equal to about 100 nm.
Owner:PHOTONIS FRANCE
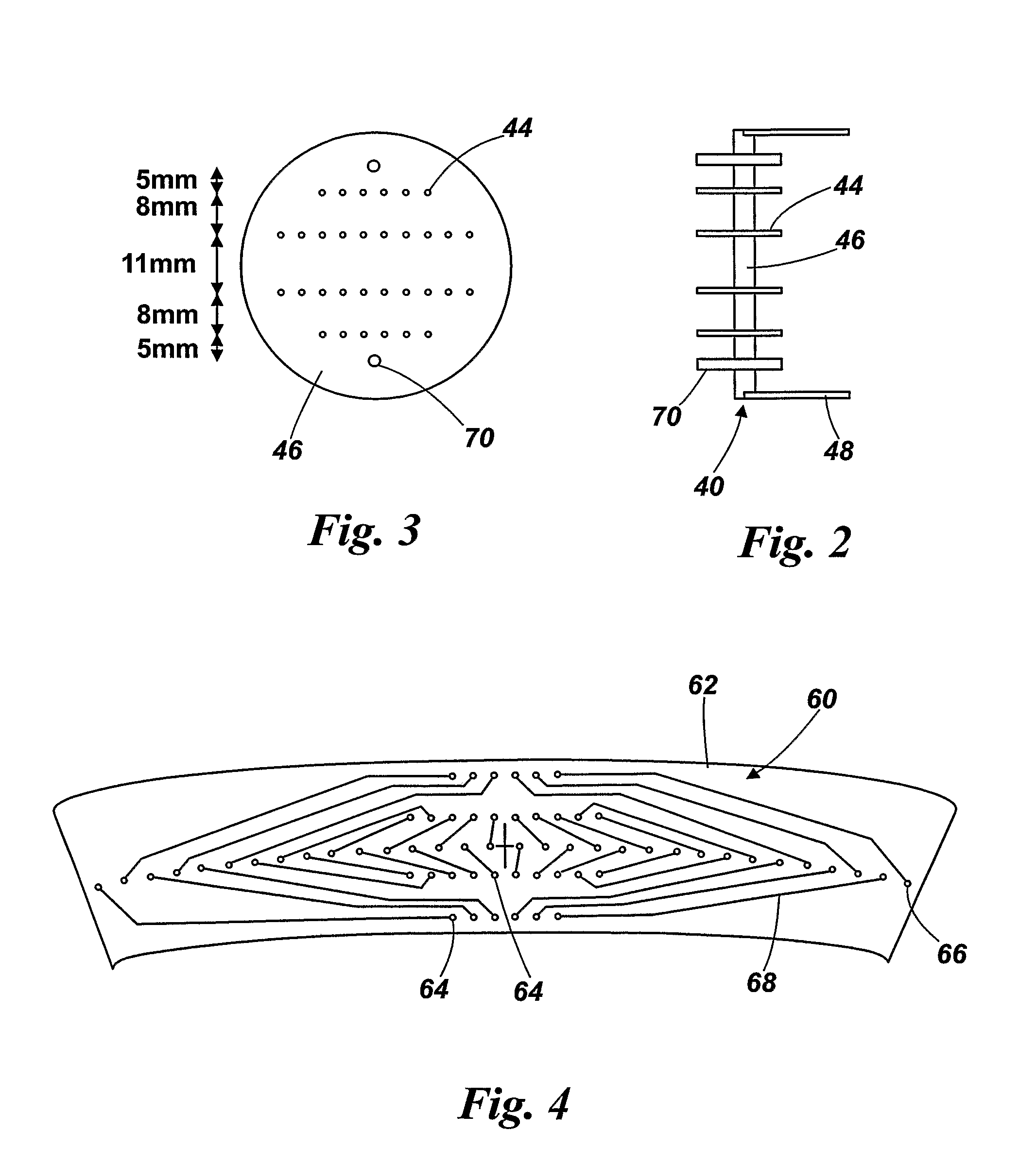
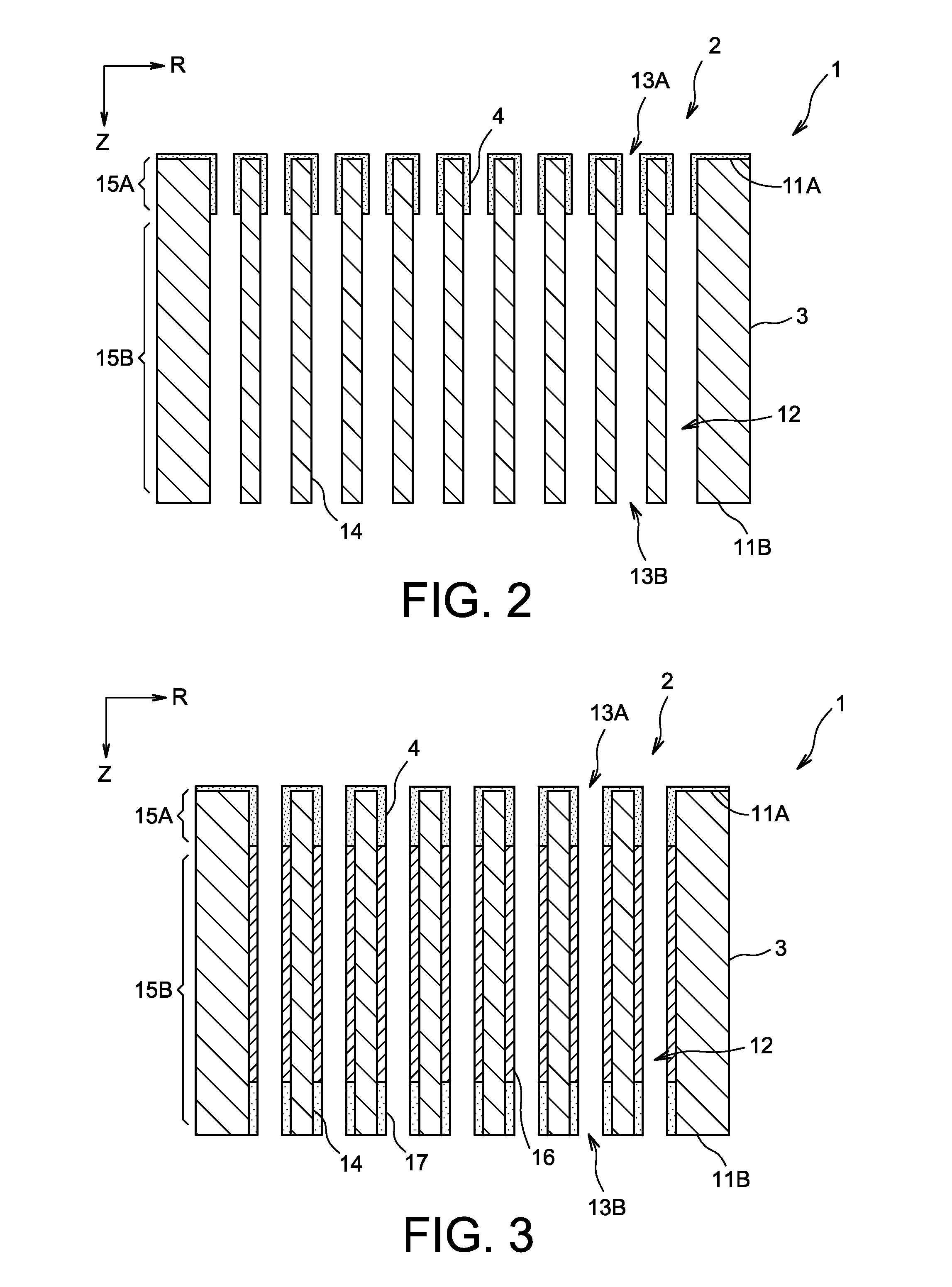
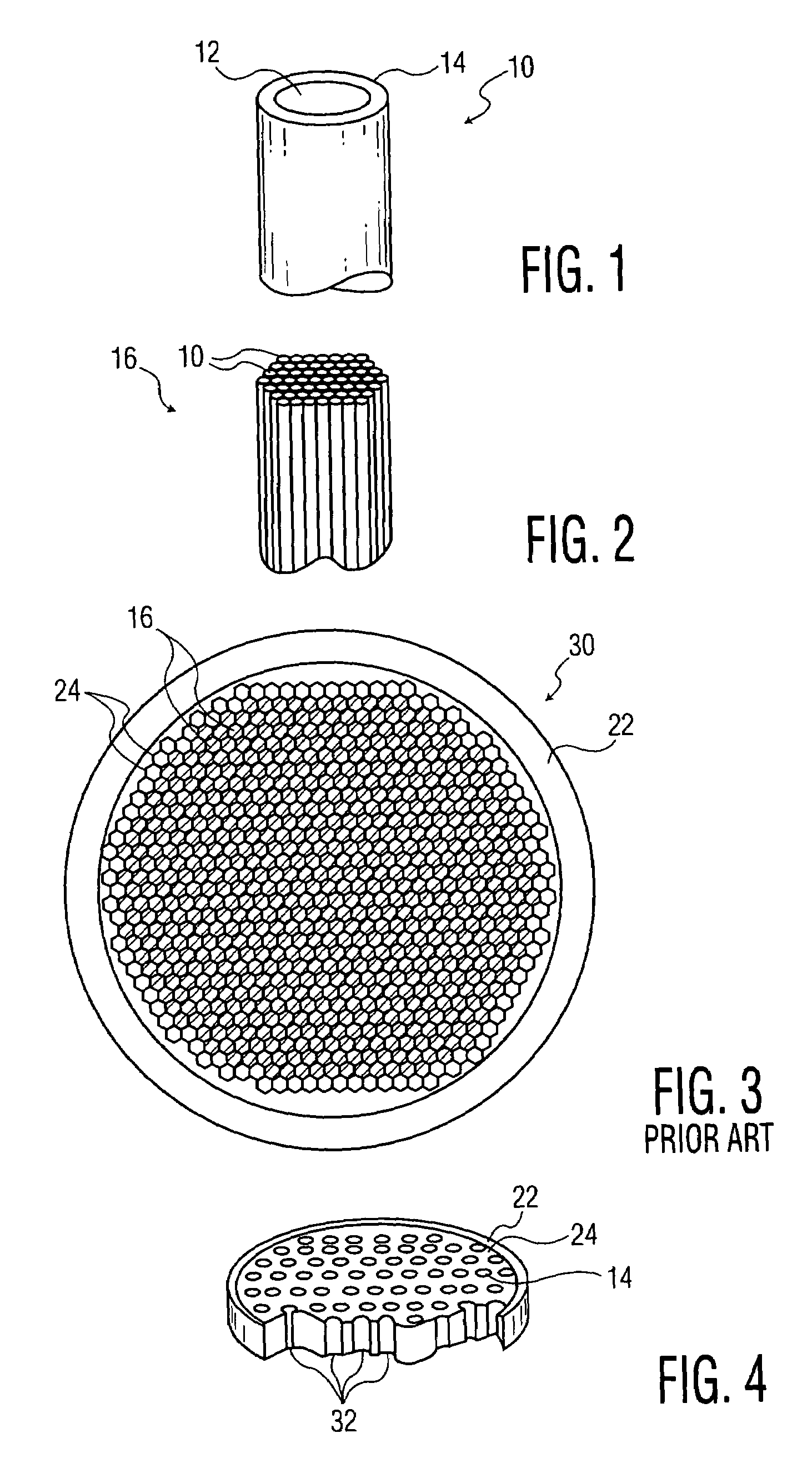
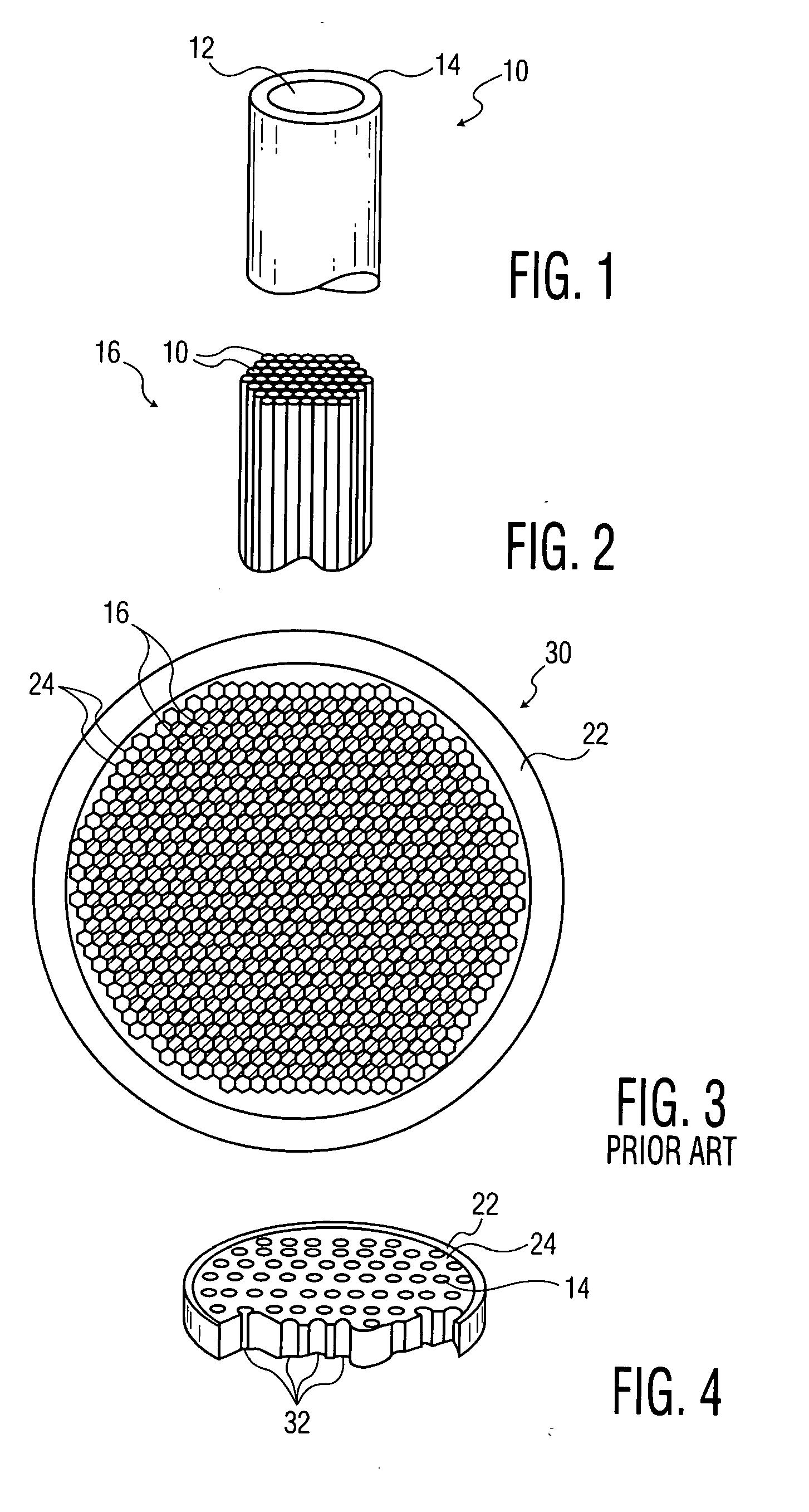
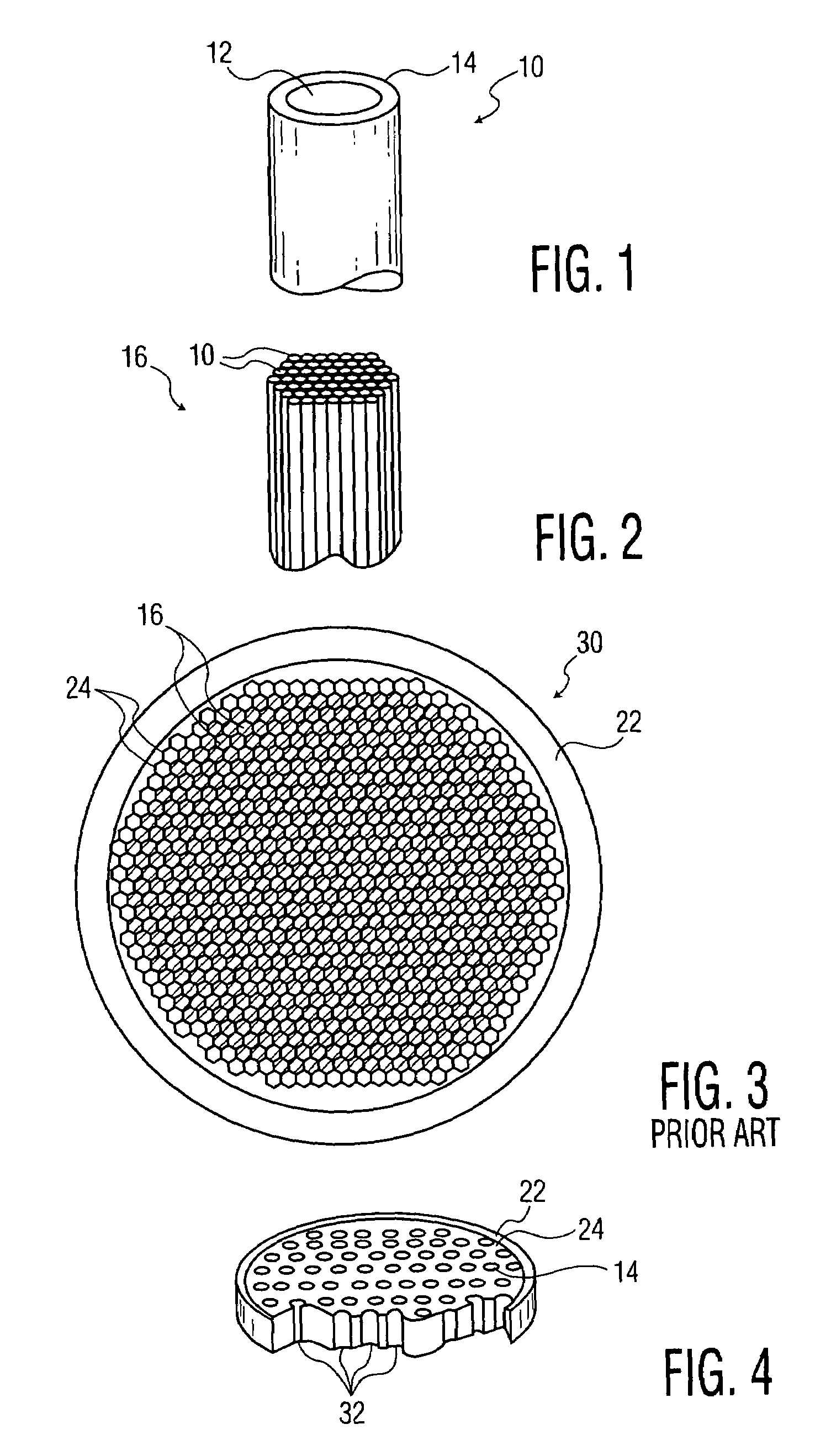
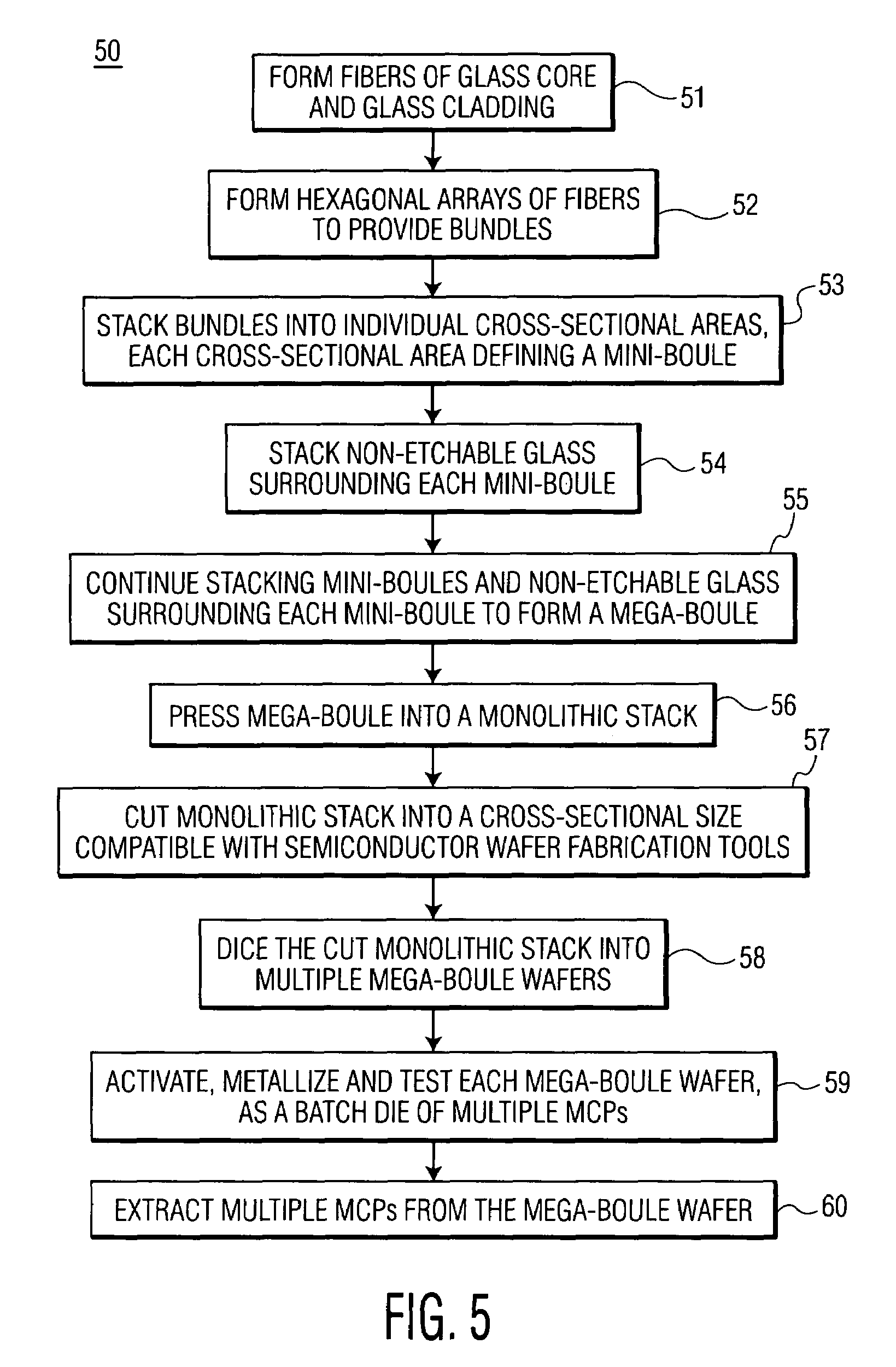
Perforated mega-boule wafer for fabrication of microchannel plates (MCPs)
InactiveUS7126263B2Sufficient cross-sectional widthLayered productsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringMaterial Perforation
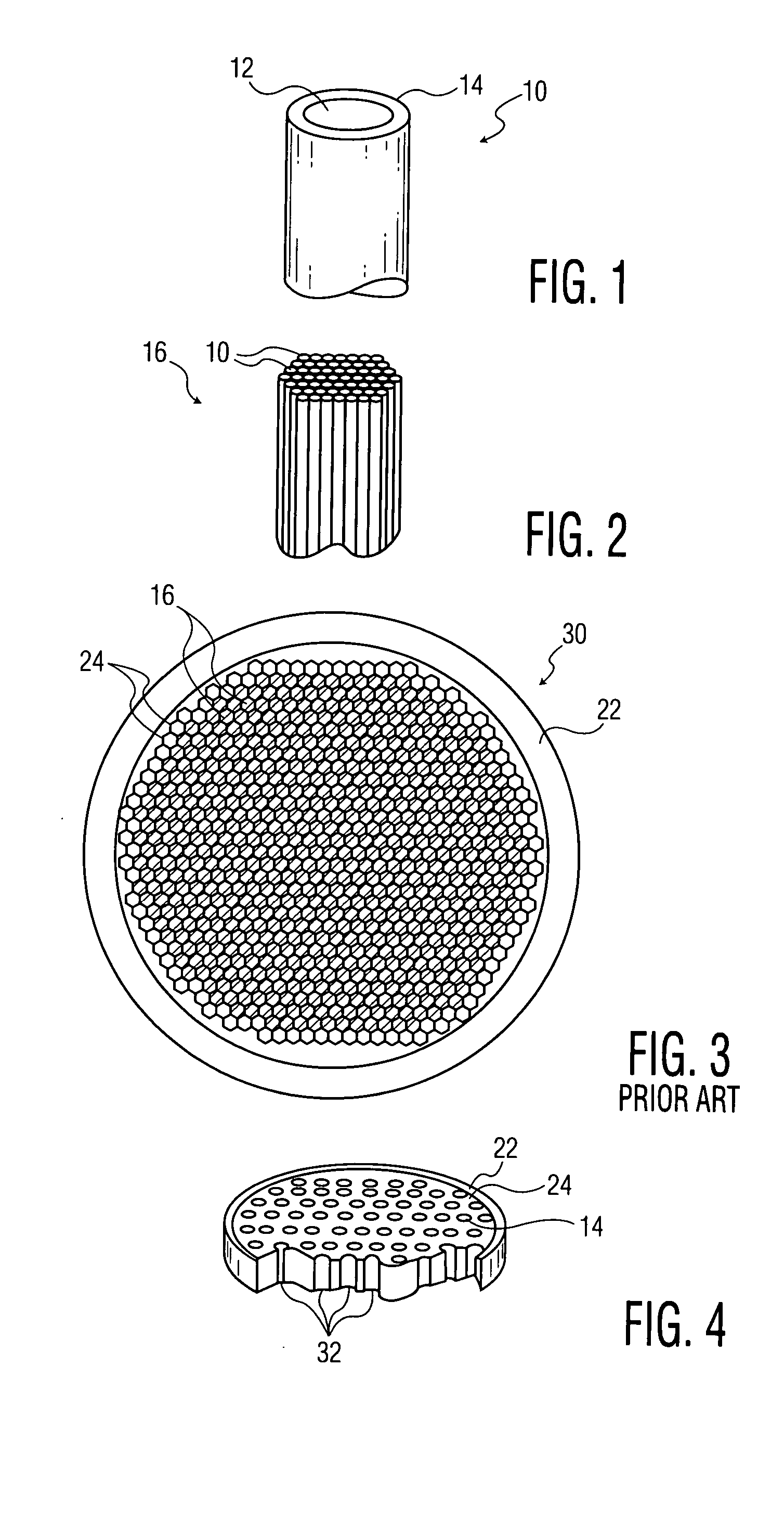
A mega-boule is used in fabricating microchannel plates (MCPs). The mega-boule has a cross-sectional surface including an island section, an inner perimeter section and an outer perimeter section, each section occupying a distinct portion of the cross-sectional surface. The island section is formed of a first plurality of optical fibers, transversely oriented to the cross-sectional surface, each optical fiber including a cladding formed of non-etchable material and a core formed of etchable material. The inner perimeter section is formed of non-etchable material and is disposed to surround the island section. The outer perimeter section is formed of a second plurality of optical fibers, transversely oriented to the cross-sectional surface, each optical fiber including a cladding formed of non-etchable material and a core formed of etchable material, and the outer perimeter section is disposed to surround the island section and the inner perimeter section. The first plurality of optical fibers of the island section form transverse microchannels for an MCP, when the island section is etched, and the second plurality of optical fibers of the outer perimeter section form perforated cleave planes, when the outer perimeter section is etched.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
High-collecting-efficiency micro-channel plate, micro-channel plate type photomultiplier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106298427AImprove reflectivityFlat reflective surfaceMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureGlass ballElectron multiplication
The invention discloses a high-collecting-efficiency micro-channel plate, a micro-channel plate type photomultiplier and a preparation method thereof. The photomultiplier has a structure which can realize high gain, high collecting efficiency, good single photoelectron spectrum, and collecting efficiency uniformity. The photomultiplier disclosed by the invention comprises a glass ball shell, an electronic focusing barrel, a photocathode and a micro-channel plate electron multiplication system. A metal electrode surface of a first micro-channel plate in an electron incident direction of an electron multiplier of the micro-channel plate type photomultiplier disclosed by the invention and the inner wall surface of a channel are both covered with a thin film with a high secondary electron emission coefficient, so that effective multiplication of electrons can be realized and the high collecting efficiency and the collecting efficiency uniformity of the photomultiplier can be improved.
Owner:NORTH NIGHT VISION TECH
Electron multiplier device having a nanodiamond layer
ActiveCN103168339AHigh global gainMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsSecondary electronsElectron multiplier
The invention relates to an electron multiplier (1) for a system for detecting electromagnetic radiation or an ion flow. The multiplier (1) comprises at least one active structure (2) for receiving a flow of incident electrons and for emitting a flow of so-called secondary electrons in response. Said active structure (2) comprises a substrate (3) on which a thin nanodiamond layer (4) is arranged, wherein said layer consists of diamond particles, the average size of which is no greater than 100 nm.
Owner:FOTONIS FRANS SAS
Method for improving gain of microchannel plate
ActiveCN106847649AHigh gainImprove yield rateMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureSilicon dioxideMetal
The invention discloses a method for improving gain of a microchannnel plate. A dielectric film layer is evaporated on the input end of the microchannel plate by means of a vacuum evaporating method, thereby covering a metal input electrode. The dielectric film layer covers an input electrode at a chananel inlet of the microchannel plate and furthermore covers an input electrode on the input-end surface of the microchannel plate. The dielectric film layer is made of silicon dioxide (SiO2), titanium dioxide (TiO2) and aluminum oxide (Al203). After the method of the invention is utilized, the gain of the microchannel plate is improved by more than one time without characteristic change of the original microchannel plate, such as parameters of plate resistance, dark current, resolution, etc. The method settles a problem of image intensifier discard caused by incapability of satisfying the requirement by partial MCPs in the manufacture process of the image intensifier, and furthermore improves yield rate of super-second-generation image intensifiers in manufacture.
Owner:NORTH NIGHT VISION TECH
X-Ray Tubes
ActiveUS20110222665A1Quick and efficientWave amplification devicesX-ray tube electrodesElectron sourceX-ray
An X-ray tube is produced by forming a first housing section 20 from sheet metal; forming a second housing section 22 from sheet metal, mounting an electron source 18 in one of the housing sections; mounting an anode 16 in one of the housing sections; and joining the housing sections 20, 22 together to form a housing defining a chamber with the electron source 18 and the anode 16 therein.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
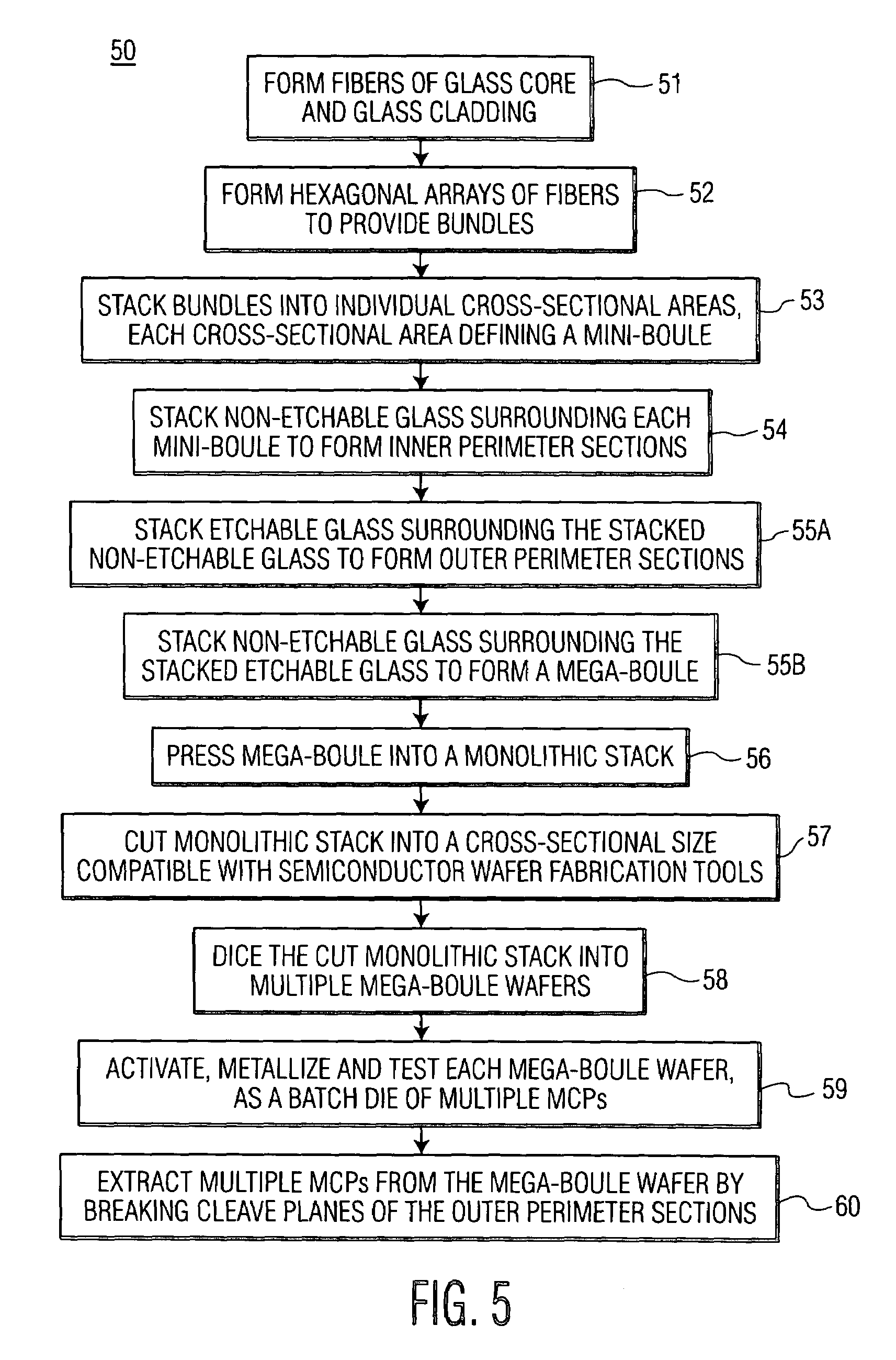
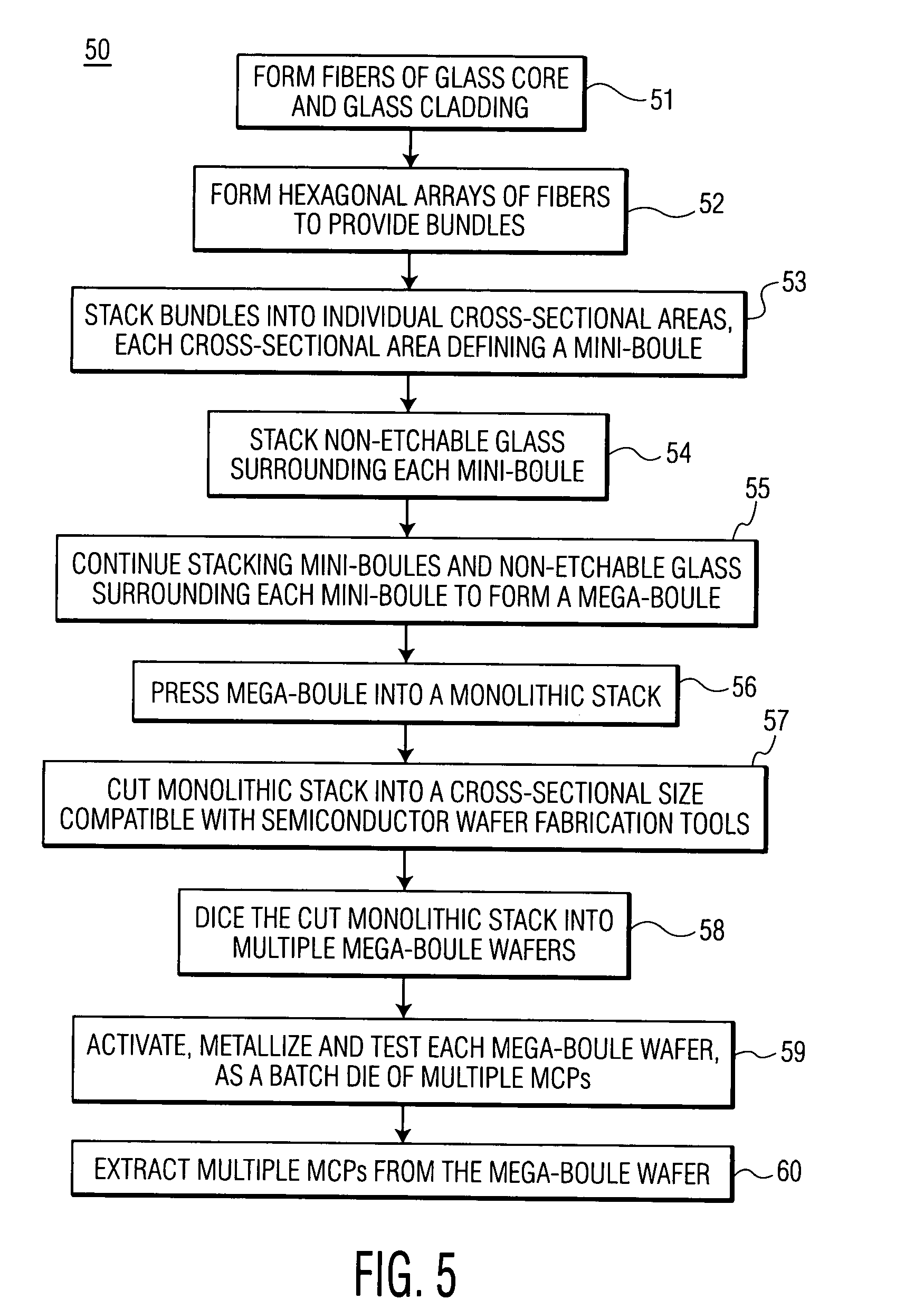
Device and method for fabrication of microchannel plates using a mega-boule wafer
InactiveUS20050122022A1Specialized toolMutiple dynode arrangementsBundled fibre light guideEngineeringMicrochannel plate detector
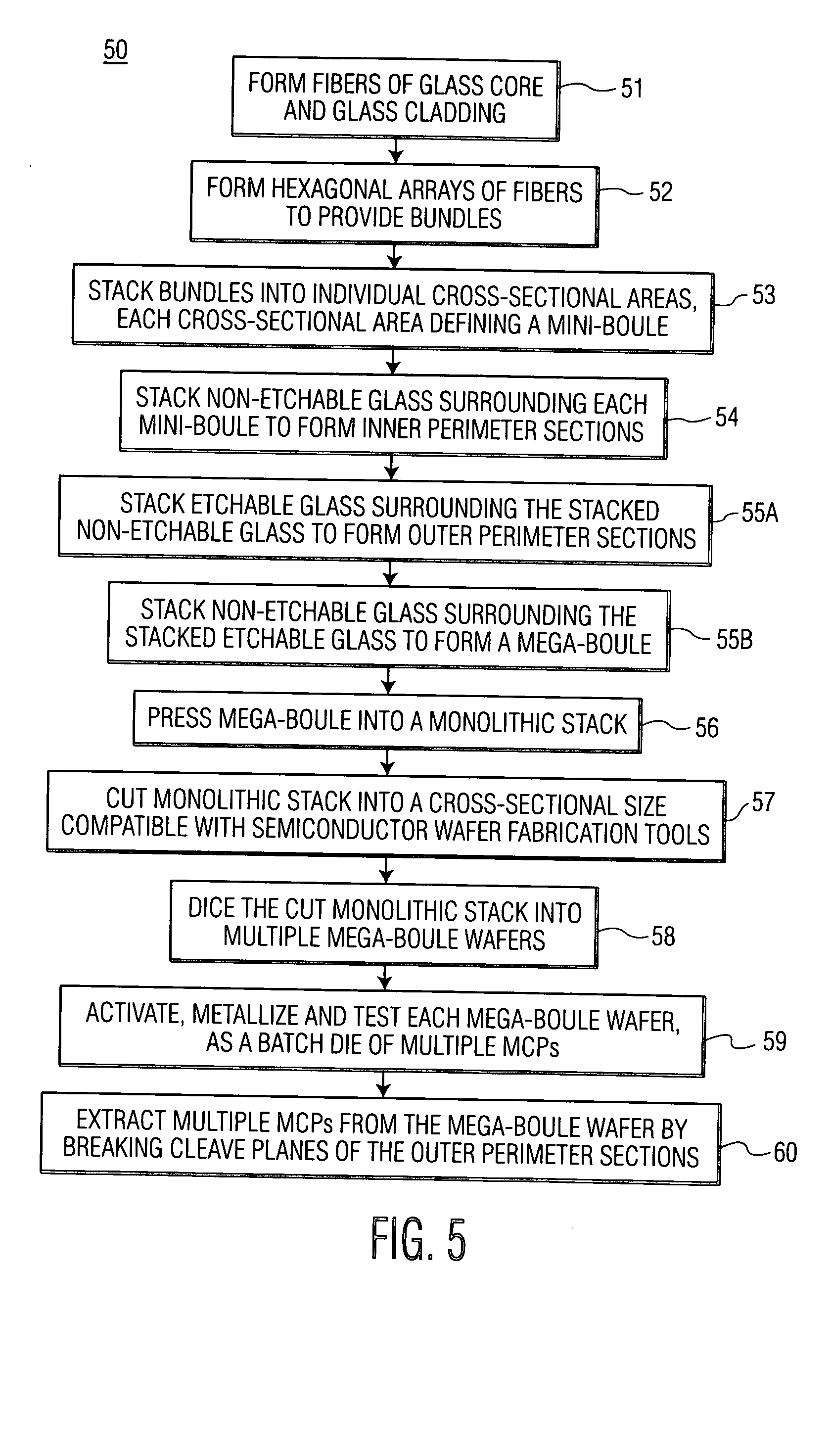
The present invention provides a mega-boule for use in fabricating microchannel plates (MCPs). The mega-boule includes a cross-sectional surface having at least first, second and third areas, each area occupying a distinct portion of the cross-sectional surface. The first and second areas include a plurality of optical fibers, transversely oriented to the cross-sectional surface, each optical fiber having a cladding formed of non-etchable material and a core formed of etchable material. The third area is disposed interstitially between and surrounding the first and second areas, and includes non-etchable material.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
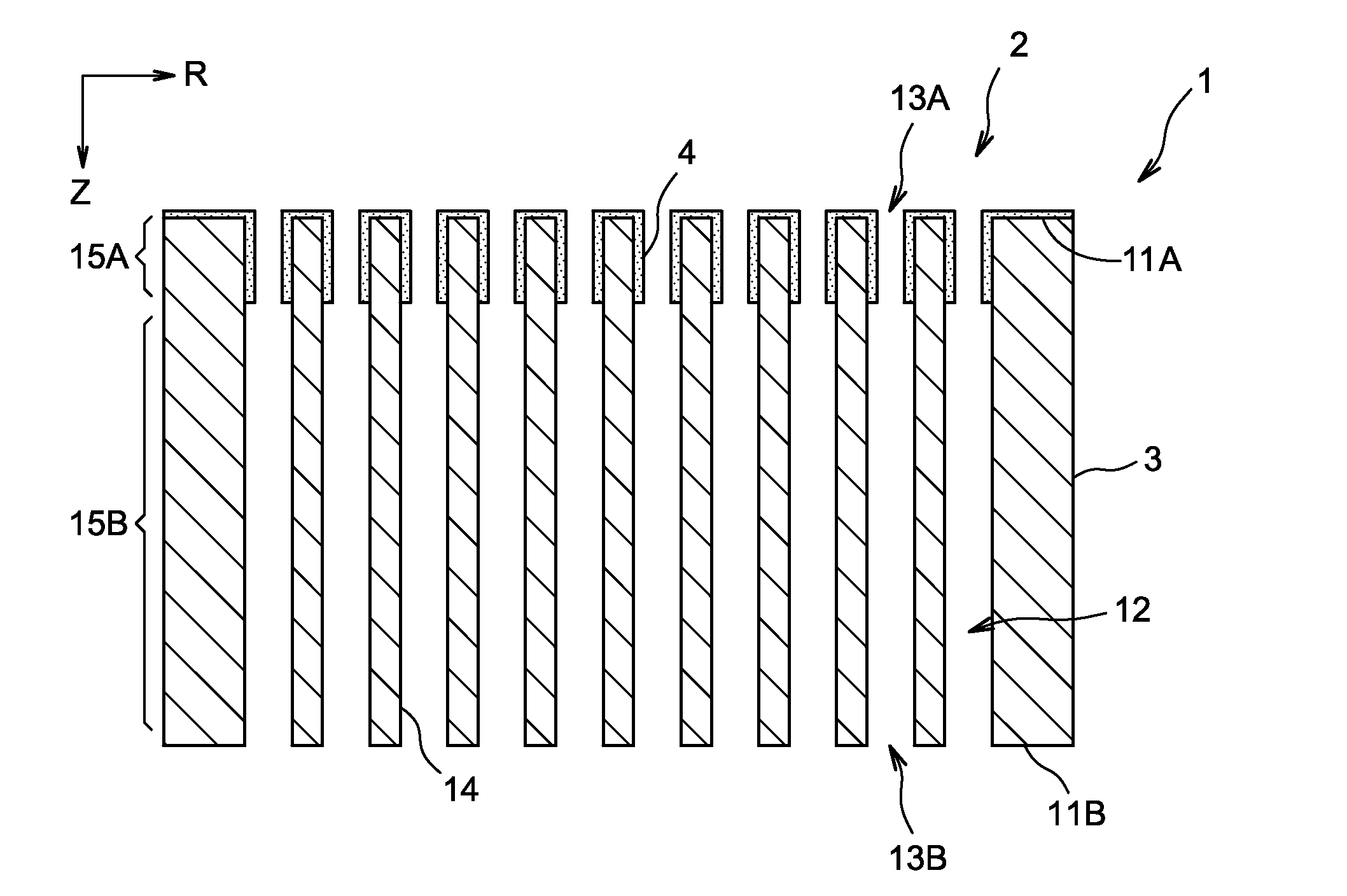
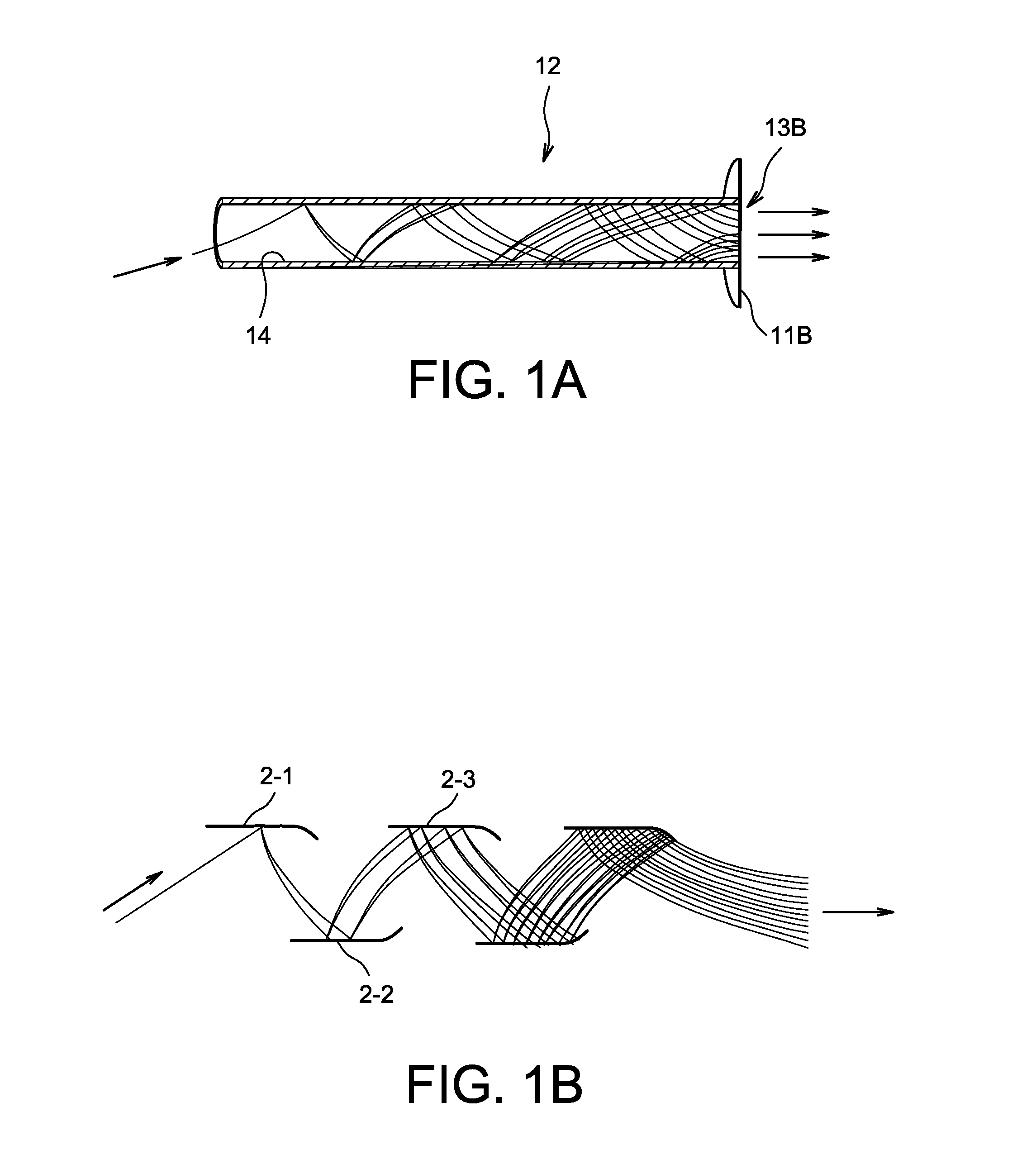
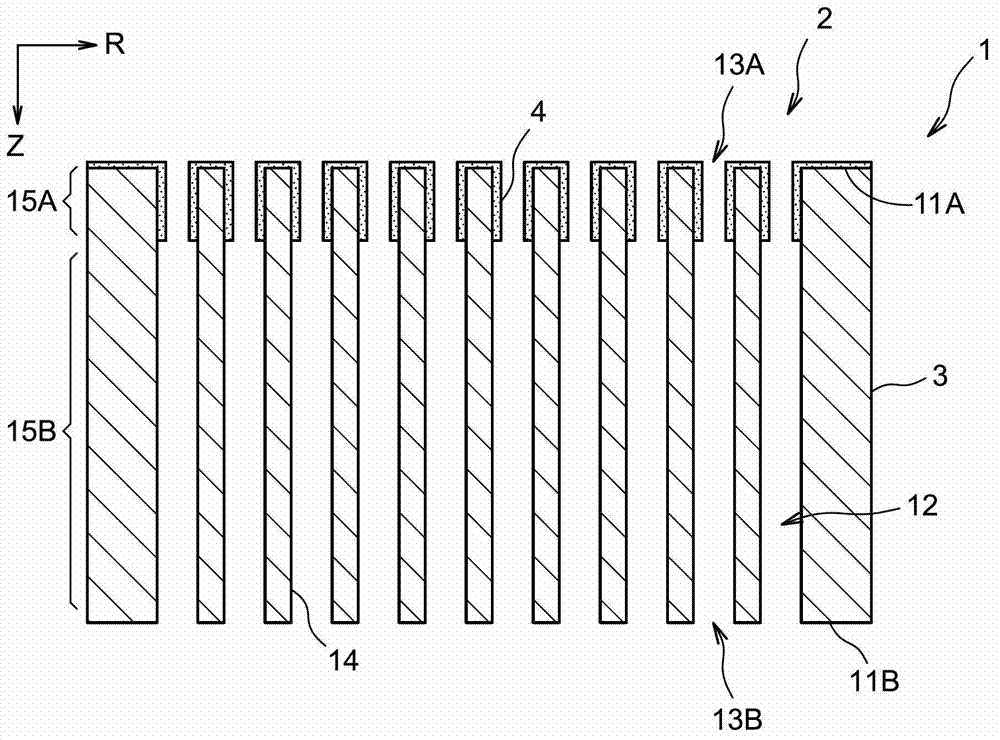
Discrete dynode electron multiplier fabrication method
ActiveUS20170352515A1Mutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureElectrical conductorElectron multiplication
A process of fabricating a discrete-dynode electron multiplier (DDEM) including the steps of mounting an insulator block to a conductor block, and forming a series of ion-optics geometrical structures in the conductor block, each ion-optics geometrical structure having a smallest dimension of less than 1 millimeter. The forming step may be performed by electrical discharge machining (EDM), laser cutting, and / or water jet cutting.
Owner:ADAPTAS SOLUTIONS LLC
Micro-engineered electron multipliers
ActiveUS20050151054A1Enhance secondary electron emissionEasy to manufactureMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesIn planeElectron multiplier
This invention provides for a simple method of fabricating miniature electron multipliers, in an in-plane configuration suitable for use with miniature analytic instruments such as mass filters. The materials involved are predominantly silicon and compatible oxides, allowing the possibility of integration with a mass filter formed in a similar materials system. The materials are selected simultaneously to withstand high voltages and to. enhance secondary electron emission. Fabrication is based on standard planar processing methods. These methods also allow the construction of an integrated set of bias resistors in a multi-electrode device, so that the device may be operated from a single high-voltage source.
Owner:MICROSAIC SYST
Microchannel plate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107818902AExtended service lifeHigh gainMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureRubidiumIon exchange
The invention relates to a microchannel plate and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of 1) performing bar-tube combination, wiredrawing, plate layout, melting, pressing, mechanical processing and acid cleaning on a core glass bar and a skin glass tube to obtain a microchannel plate blank; 2) performing ion exchange, cleaning, high-temperature reduction and film coating on the microchannel plate blank in molten salt to obtain a microchannel plate, wherein the molten salt comprises rubidium salt and / or cesium salt. According to the invention, ion exchange isperformed on the microchannel plate blank, so that rubidium ions and cesium ions with high atomic weight and large atomic radius replace potassium ions and sodium ions in a reflecting layer, the electron flushing resistant performance of the reflecting layer is improved by the aid of increase in atomic weight of alkali metal ions and a volume congestion effect, so that the service life and the gain performance of the microchannel plate are improved, and the service life and the gain of the microchannel plate are improved by more than 30% and 20% respectively.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Micro-channel plate with high detection efficiency and low noise and fabrication method of micro-channel plate
ActiveCN108281344AImprove detection efficiencyReduced detection efficiencyMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureLow noiseEngineering
The invention relates to a micro-channel plate with high detection efficiency and low noise and a fabrication method of the micro-channel plate. The micro-channel plate comprises a quartz glass micropore array, an input electrode, an output electrode and an ion feedback prevention film, wherein a conductive layer and an emission layer are sequentially deposited on a hole wall of the quartz glass micropore array, and the ion feedback prevention film is arranged at one side of the input electrode and is a graphene film. A graphene film layer is used as the ion feedback prevention film and can beangstrom level, the ion feedback phenomenon can be prevented, meanwhile, the detection efficiency of the micro-channel plate is improved, and the gain performance of the micro-channel plate is improved.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Preparation method of aluminum oxide anti-ion feedback film of micro-channel plate
ActiveCN111613500AAvoid pollutionReduce manufacturing costNanotechnologyMutiple dynode arrangementsAl powderMetallurgy
The invention discloses a preparation method of an aluminum oxide anti-ion feedback film of a micro-channel plate. According to the technical scheme, a room-temperature gallium-based liquid alloy is used as a solvent; high-purity aluminum powder is added into the room-temperature gallium-based liquid alloy to form a room-temperature aluminum-containing gallium-based liquid alloy; the room-temperature aluminum-containing gallium-based liquid alloy is exposed in an air environment to form a sub-nano aluminum oxide film on a liquid alloy-air interface, the input surface of the micro-channel plateis in contact with the aluminum oxide film, and the high-quality sub-nano aluminum oxide anti-ion feedback film is prepared on the micro-channel plate. Ion feedback of the micro-channel plate can beprevented, the service life of a photoelectric imaging device is prolonged, and the imaging background is improved. The method has the advantages of being simple, low in cost, free of thin film deposition equipment and the like.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Perforated mega-boule wafer for fabrication of microchannel plates (MCPs)
InactiveUS20050122020A1Sufficient cross-sectional widthLayered productsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringMaterial Perforation
A mega-boule is used in fabricating microchannel plates (MCPs). The mega-boule has a cross-sectional surface including an island section, an inner perimeter section and an outer perimeter section, each section occupying a distinct portion of the cross-sectional surface. The island section is formed of a first plurality of optical fibers, transversely oriented to the cross-sectional surface, each optical fiber including a cladding formed of non-etchable material and a core formed of etchable material. The inner perimeter section is formed of non-etchable material and is disposed to surround the island section. The outer perimeter section is formed of a second plurality of optical fibers, transversely oriented to the cross-sectional surface, each optical fiber including a cladding formed of non-etchable material and a core formed of etchable material, and the outer perimeter section is disposed to surround the island section and the inner perimeter section. The first plurality of optical fibers of the island section form transverse microchannels for an MCP, when the island section is etched, and the second plurality of optical fibers of the outer perimeter section form perforated cleave planes, when the outer perimeter section is etched.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
Method and apparatus for producing microchannel plate using corrugated mold
InactiveUS20050136178A1Low costPretreated surfacesDischarge tube cold cathodesSecondary emissionEngineering
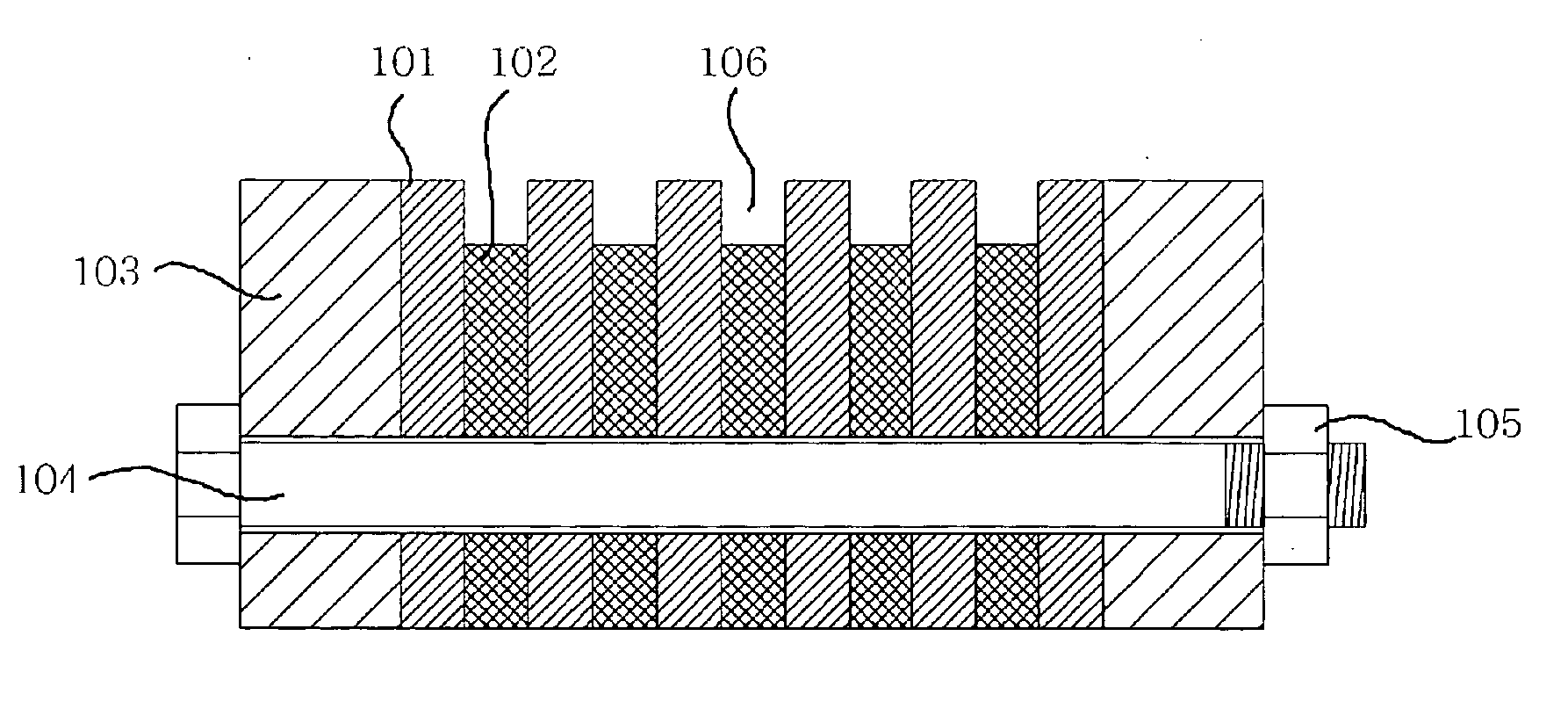
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for producing a microchannel plate (MCP) using a corrugated mold, characterized in that each of corrugated substrates formed by the corrugated mold is coated with a secondary emitter and then layered, thereby easily producing a large area of the MCP and decreasing production costs of the MCP. The MCP producing method includes placing a first flat substrate on the corrugated mold, vacuum forming the first flat substrate so that both surfaces thereof are corrugated, coating a secondary emitter onto both surfaces of each of the first corrugated substrate and a second flat substrate, and alternately layering a plurality of the first corrugated substrates and a plurality of the second substrates each coated with the secondary emitter, to form microchannels.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
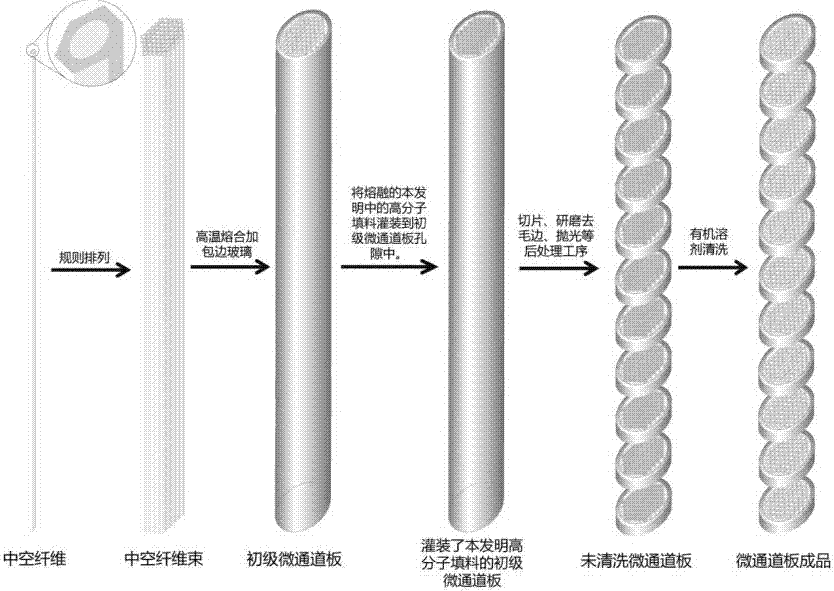
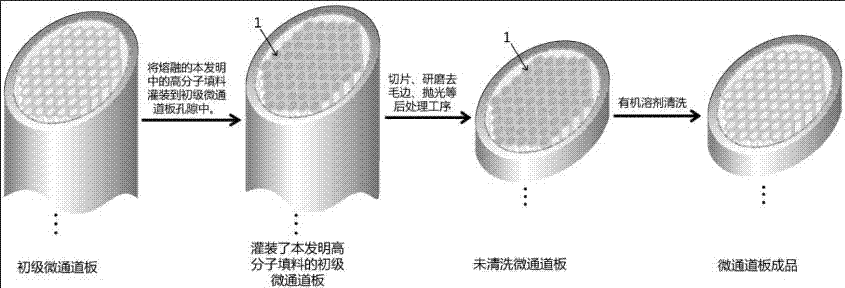
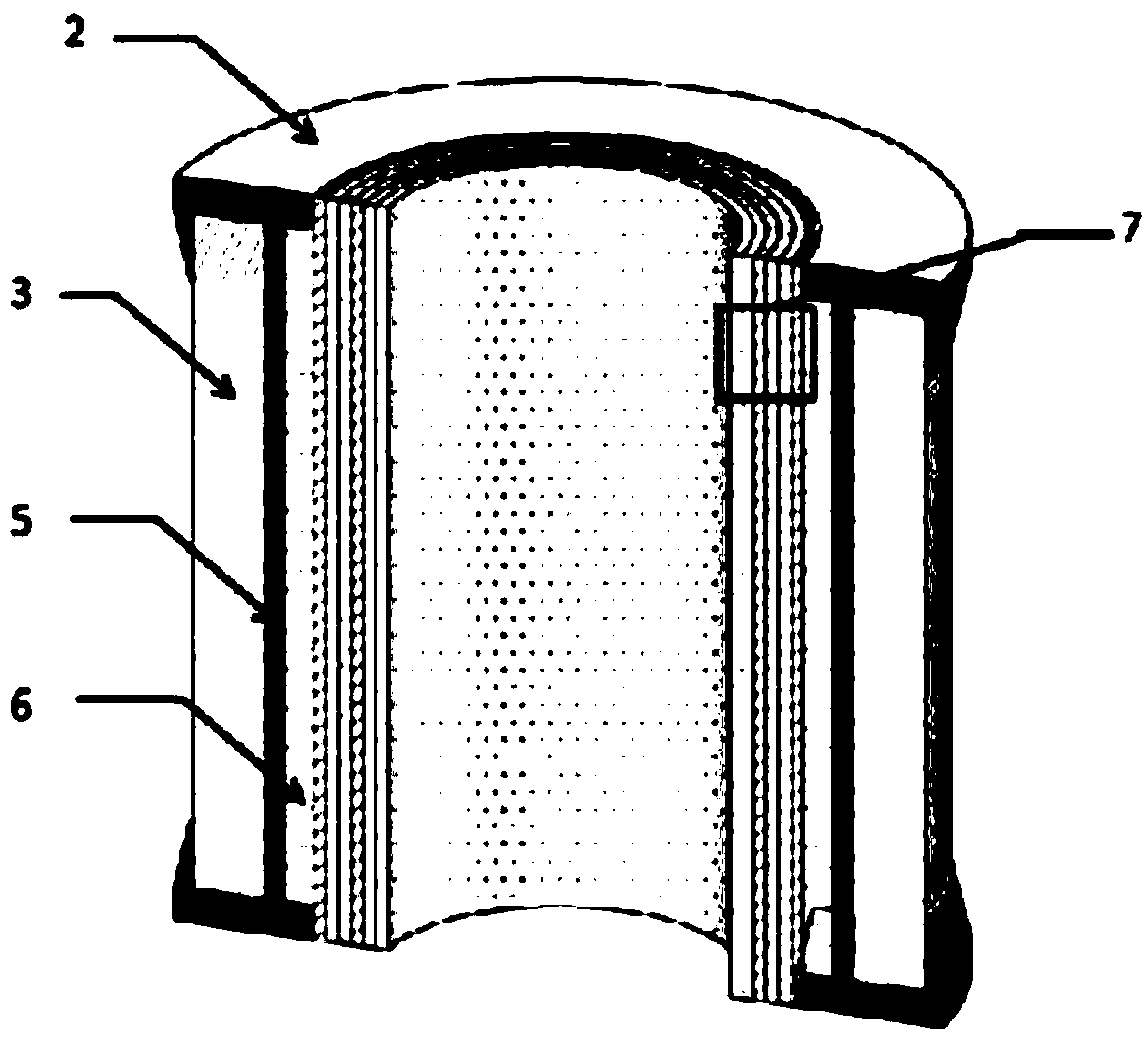
Method for preparing microchannel plate from high polymer filler
InactiveCN107293462AGuaranteed mechanical strengthIntegrity guaranteedPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureSecondary emission electrodes manufacturePolymer scienceOrganic solvent
The invention provides a method for preparing a microchannel plate from a high polymer filler, and relates to the technical field of manufacturing of micro-optical elements. The method comprises the following steps: melting the high polymer filler into liquid, and filling pores of a primary microchannel plate prepared by a hollow core method; curing the liquid and performing a posttreatment procedure; and lastly, removing the liquid with an organic solvent to obtain a finished microchannel plate. Through filling of the high polymer filler, the problems of cracking and deformation of the microchannel plate prepared by the hollow core method in the posttreatment procedure are solved effectively.
Owner:SHANXI CHEM RES INST
Microchannel plate with ultralow-temperature stable resistance-temperature characteristic and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN108493083AEasy to adjustImprove the stability of temperature resistance coefficientMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureBulk resistanceEngineering
The invention relate to a microchannel plate with ultralow-temperature stable resistance-temperature characteristic and a fabrication method thereof. The fabrication method comprises the steps of fabricating a conductive layer on an inner wall of a microchannel plate substrate; fabricating a secondary electron emission layer on the conductive layer; and fabricating a resistance-temperature characteristic modification layer on the secondary electron emission layer to obtain the microchannel plate with ultralow-temperature stable resistance-temperature characteristic. The resistance-temperaturecharacteristic modification layer which still has favorable positive resistant-temperature characteristic under an ultralow-temperature condition is deposited on a surface of the inner wall of a micropore passage of the microchannel plate by an atomic layer deposition technology, so that the trend that the resistance of the microchannel plate is abruptly increased with a temperature under the ultralow-temperature condition is reduced, the high-stable temperature-resistance characteristic of the microchannel plate under the ultralow-temperature condition is achieved, the ultralow-temperature bulk resistance of the microchannel plate is reduced, and the ultrafast signal reading capability and the response capability of the microchannel plate under the ultralow-temperature condition are improved.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Device and method for fabrication of microchannel plates using a mega-boule wafer
InactiveUS7109644B2Specialized toolMaterial analysis by optical meansMultiplier circuit arrangementsEngineeringMicrochannel plate detector
The present invention provides a mega-boule for use in fabricating microchannel plates (MCPs). The mega-boule includes a cross-sectional surface having at least first, second and third areas, each area occupying a distinct portion of the cross-sectional surface. The first and second areas include a plurality of optical fibers, transversely oriented to the cross-sectional surface, each optical fiber having a cladding formed of non-etchable material and a core formed of etchable material. The third area is disposed interstitially between and surrounding the first and second areas, and includes non-etchable material.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
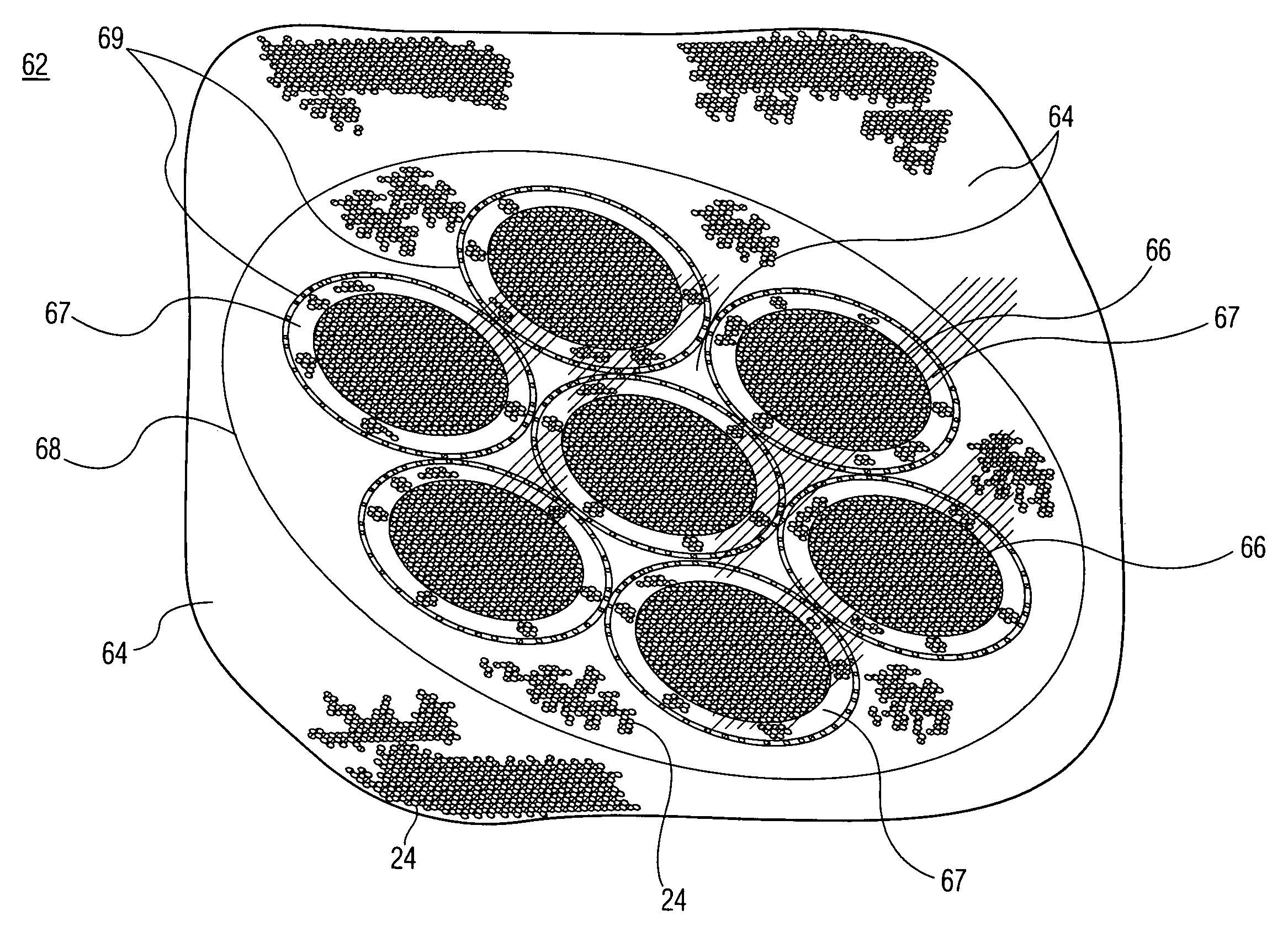
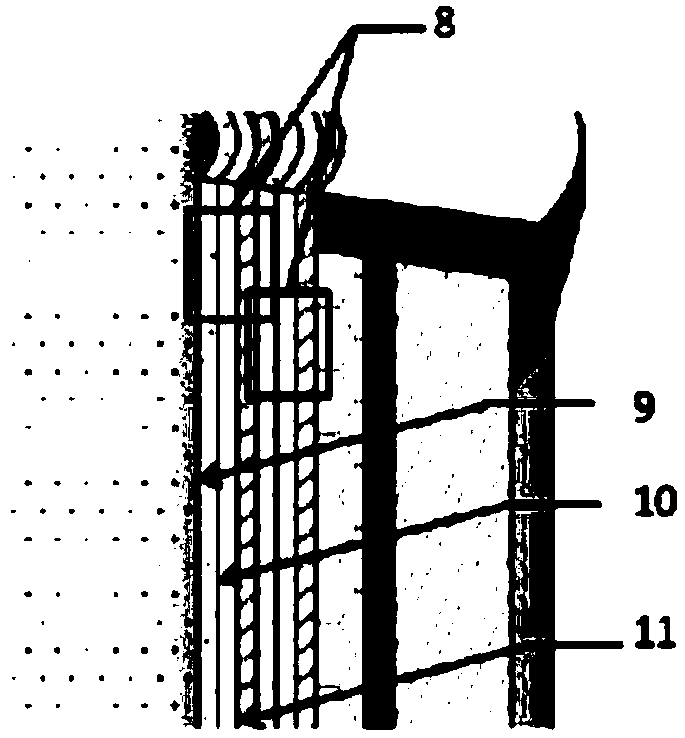
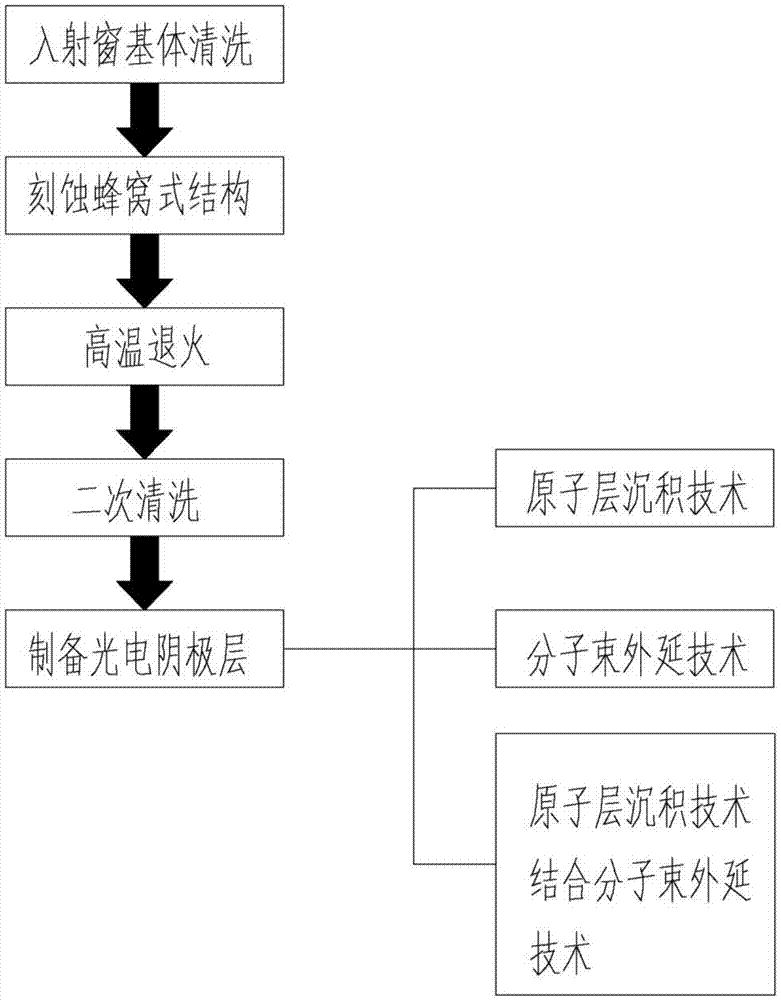
Micro-channel type incident window and production method thereof
ActiveCN105448638AHigh electronic gainHigh gainElectron multiplier detailsFinal product manufactureQuantum efficiencyPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectric detection, and in particular relates to a micro-channel type incident window and a production method thereof. The micro-channel type incident window comprises an incident window substrate, wherein the incident window substrate is of the honeycomb structure including a plurality of through hole, the through holes are formed by common photoetching and ion beam etching or acid corrosion technology; and photoelectric cathode layers are deposited on the surface of the incident window substrate and in the plurality of through holes. The specific implementing method comprises the steps of cleaning the incident window substrate, etching the incident window substrate to form the honeycomb structure, cleaning the incident window substrate etched with the honeycomb structure for the second time, and at last preparing the photoelectric cathode layers on the surface of the incident window substrate and the honeycomb structure. The incident window has the advantages that the traditional photoelectric cathode layer preparation technology is combined with the micro-channel plate electron multiplication technology, photovoltaic conversion and electron multiplication functions are achieved directly through the micro-channel type photoelectric cathode technology, and the photoelectric detector is simplified in structure, reduced in cost, and meanwhile greatly improved in photoelectric cathode quantum efficiency.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cold cathode supporting use of magnetron and production method for cold cathode head
InactiveCN107068517AStrong ability to emit electronsOvercome the shortcomings of long warm-up time, slow start, short service life, etc.Transit-tube cathodesPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureFrequency spectrumCarbon nanotube
The invention provides a cold cathode supporting use of a magnetron and a production method for the cold cathode head. The cold cathode includes an upper shielding cap and a lower shielding cap, and a power connection rod and the integral post tooth-shaped cold cathode head. The method includes preparing material, ball grinding and mixing, blank pressing and molding. According to the invention, since grapheme or / and carbon nanometer tubes, zinc oxide nanometer wires are adopted to mix with metal power for blank pressing, sintering and processing so as to prepare the integral post tooth-shaped cold cathode head, after primary electrons are emitted by the cold cathode head under the effect of high voltage, back bombardment of the primary electrons excites gear teeth to emit secondary electrons, and stable electron emission is formed in the repeat process and stable output can be achieved within only 40 nanoseconds. Therefore, compared with a thermionic cathode, advantages such as electron emitting capability of the thermionic cathode, high electron bombardment resistance and the like are kept and shortcomings of long pre-heating time, low starting rate and short service lifetime and the like are overcome. Compared with a cold cathode in background art, the cold cathode provided by the invention has characteristics of simple structure, high electron emitting capability, high electron bombardment resistance, pure frequency spectrum output, high and stable emitting speed and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Novel silver-magnesium alloy dynode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110400737AIncreased secondary emission coefficientExempt from high temperature sensitization processPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureSecondary emission electrodes manufactureSecondary emissionSurface layer
The invention relates to a novel silver-magnesium alloy dynode and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of photomultipliers and photoelectric device dynodes. The surface layer of the dynode is a magnesium nitride film layer, and the core layer is a magnesium oxide film layer. The secondary emission coefficient is 5 to 6 (150V), which is more than 20% higher than that of the existing magnesium oxide type silver-magnesium alloy dynode. The sensitivity and the gains of the tube can be significantly improved, the service life is prolonged and the yield of products is increased, and miniaturization and portability of the tube and the assembly are also facilitated. The core magnesium oxide film is formed by oxidation of the silver-magnesium alloy base layer, the surface magnesium nitride film is formed by nitridation of the silver-magnesium alloy, an extra-tube high-temperature activation process of the conventional magnesium oxide type silver-magnesium alloy dynode is saved in the process, the production cost is reduced, and the influences on the dynode by exposed air are completely eliminated. The novel silver-magnesium alloy dynode can be used in a photomultiplier tube electron multiplier and used as a multiplier in a optoelectronic device.
Owner:陈新云 +1
Pumping speed limiting method and device in fabrication of negative electrode of photomultiplier
InactiveCN106298400ALimit churnReduce pollutionMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureVacuum pumpingPhotomultiplier
The invention relates to a pumping speed limiting method and device in fabrication of a negative electrode of a photomultiplier. The pumping speed limiting device comprises a photomultiplier and a vacuum pumping tube, wherein the photomultiplier is connected with one end of the vacuum pumping tube by a connection tube, the other end of the vacuum pumping tube is connected with a vacuum pumping device, a horizontal glass tube is arranged between the connection tube and the vacuum pumping tube and is perpendicular to the axis of the vacuum pumping tube, a sliding block is arranged in the horizontal glass tube and is used for sealing an air inlet of the vacuum pumping tube. By the pumping speed limiting device in fabrication of the negative electrode of the photomultiplier, alkali metal loss is effectively limited, the vacuum degree during the fabrication process and the vacuum degree in a finished tube cannot be affected, and the pumping speed limiting device is low in cost and is convenient to operate and simple to maintain.
Owner:山东东仪光电仪器有限公司
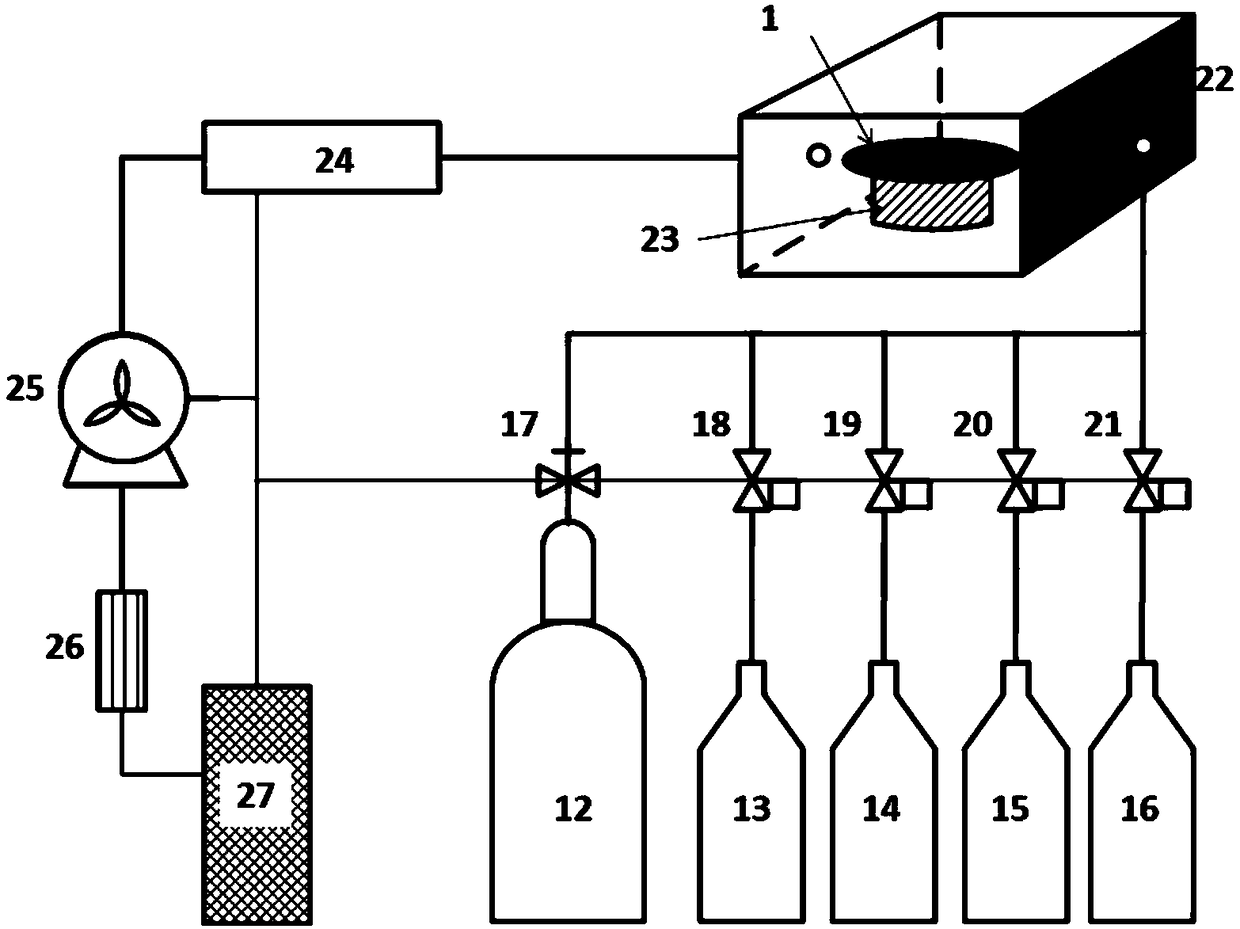
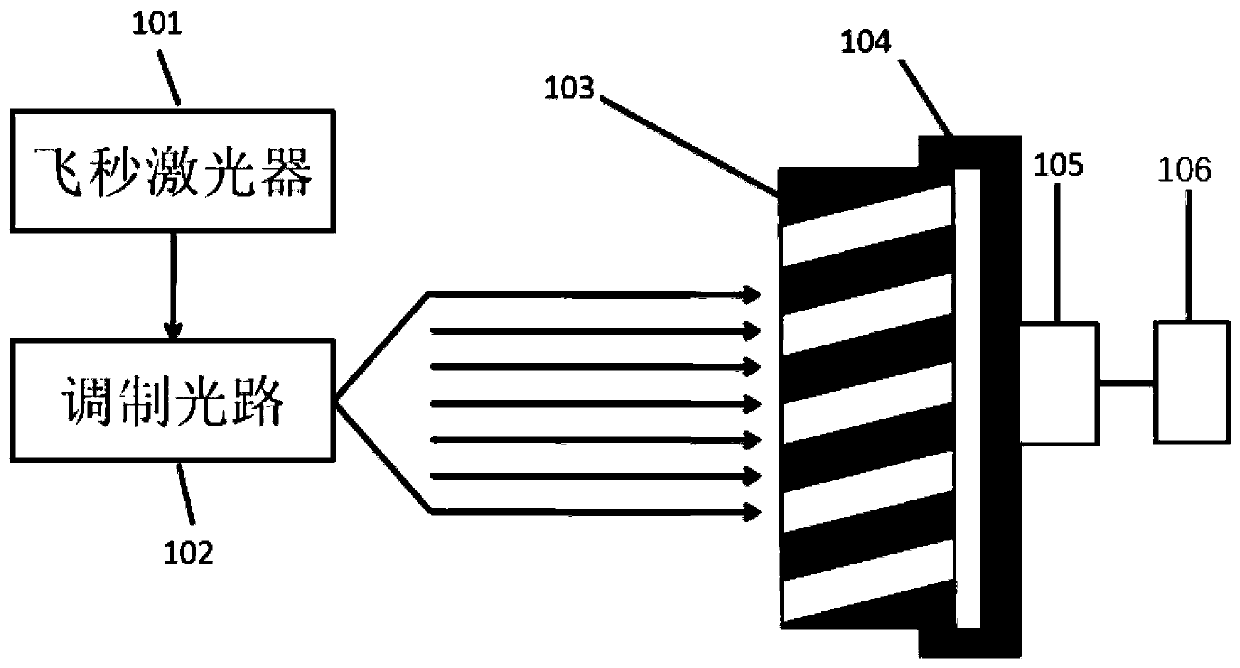
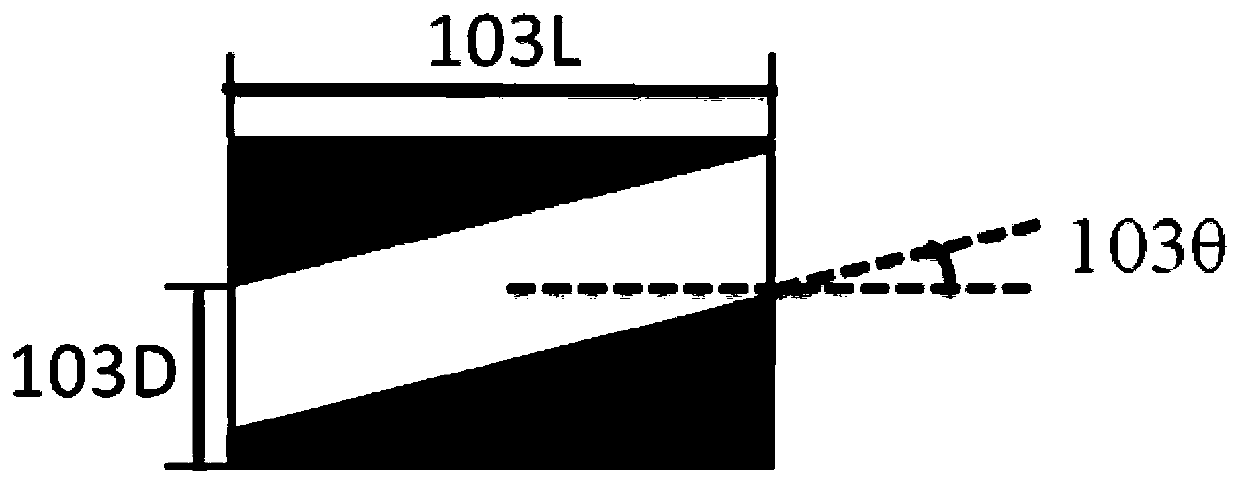
System and method for reducing inner surface roughness of microchannel plate channel
ActiveCN110560906AReduce inner surface roughnessLow densityMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureFixed frameSurface roughness
The invention provides a system and method for reducing inner surface roughness of a microchannel plate channel. The system comprises a femtosecond laser, a modulation optical component, a microchannel plate fixing frame, an attitude adjustment assembly, a first motor; the femtosecond laser is used for generating and outputting pulse optical signals; the modulation optical component is arranged on the light emitting side of the femtosecond laser and is used for converting a pulse optical signal generated by the femtosecond laser into a parallel pulse light beam; the microchannel plate fixingframe arranged to fix a microchannel plate to be processed, the microchannel plate is an optical element with a microporous structure, and each microporous structure forms a channel; the attitude adjustment assembly fixed to the microchannel plate fixing frame; the first motor is connected to the posture adjusting mechanism through the driving mechanism and transmits the rotating torque to the posture adjusting mechanism, so that the posture adjusting mechanism drives the posture adjustment of the microchannel plate fixing frame, thus adjusting the angle and position of the parallel pulse beamentering the microchannel plate channel for purging. Through the uniform laser pulse purging, the inner surface roughness and dark current density of the microchannel plate can be obviously reduced.
Owner:NORTH NIGHT VISION TECH
Organic material microchannel plate and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN107993917AImprove detection efficiencyImprove usabilityMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureEngineeringMicrochannel plate detector
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
A method for increasing the gain of microchannel plate
ActiveCN106847649BHigh gainImprove yield rateMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureSilicon dioxideMetal
The invention discloses a method for improving gain of a microchannnel plate. A dielectric film layer is evaporated on the input end of the microchannel plate by means of a vacuum evaporating method, thereby covering a metal input electrode. The dielectric film layer covers an input electrode at a chananel inlet of the microchannel plate and furthermore covers an input electrode on the input-end surface of the microchannel plate. The dielectric film layer is made of silicon dioxide (SiO2), titanium dioxide (TiO2) and aluminum oxide (Al203). After the method of the invention is utilized, the gain of the microchannel plate is improved by more than one time without characteristic change of the original microchannel plate, such as parameters of plate resistance, dark current, resolution, etc. The method settles a problem of image intensifier discard caused by incapability of satisfying the requirement by partial MCPs in the manufacture process of the image intensifier, and furthermore improves yield rate of super-second-generation image intensifiers in manufacture.
Owner:NORTH NIGHT VISION TECH
3D printed micro channel plate, method of making and using 3D printed micro channel plate
ActiveUS20190096623A1Shorten the timeEasy to operateAdditive manufacturing apparatusSecondary electron emitting electrodesBiomedical engineeringPolymer
The invention provides a gain device having a plurality of channels having a polygonal shape with four or more sides. The invention also provides a method for producing microchannel plates (MCPs) having the steps of providing a pre-polymer; and directing a laser over the pre-polymer into a pre-determined pattern. Also provided is method for efficiently 3D printing an object.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Detection-level micro-channel plate with large size and small opening area ratio and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111128641AReduce noiseLess total adsorptionMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureEngineeringSecondary electrons
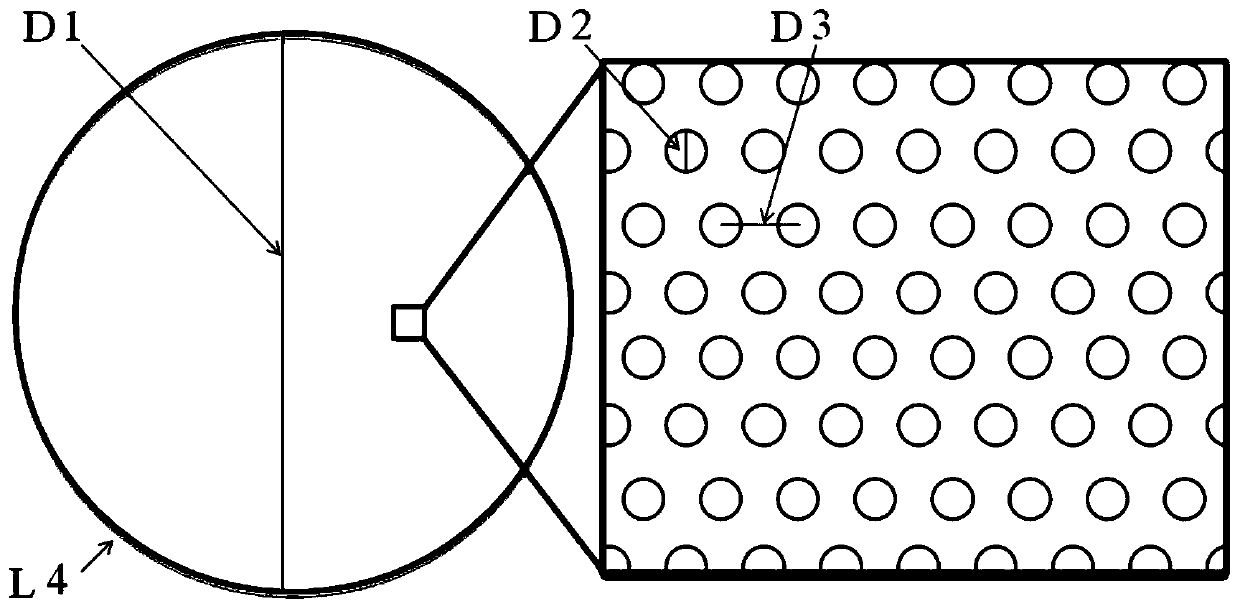
The invention provides a detection-level micro-channel plate with a large size and a small opening area ratio and a preparation method of the detection-level micro-channel plate. The appearance diameter size (D1) of the micro-channel plate ranges from 50mm to 200mm, and the effective detection diameter ranges from 45mm to 190mm; the ratio of the hole spacing (D3) of the micro-channel plate to thehole diameter (D2) of the channel ranges from 1.5 to 5, and the opening area ratio of the micro-channel plate under the condition ranges from 3.6% to 40%; and the non-channel position of the input surface of the micro-channel plate has secondary electron emission capability, so that the micro-channel plate generates secondary electrons when colliding with the non-channel position during signal detection, and the secondary electrons enter the channel of the micro-channel plate again under the action of an electric field to form effective signals. When the micro-channel plate provided by the invention is applied to the field of detection, the mechanical strength of the micro-channel plate can be improved while meeting the requirement of a large detection area; and under the same detection area, the total surface area is smaller, the total gas adsorption amount is smaller, and the noise of the micro-channel plate is lower.
Owner:NORTH NIGHT VISION TECH
Micro-channel plate and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113838726AConsistent structureUniform gainGlass making apparatusMutiple dynode arrangementsSilicate glassLead silicate
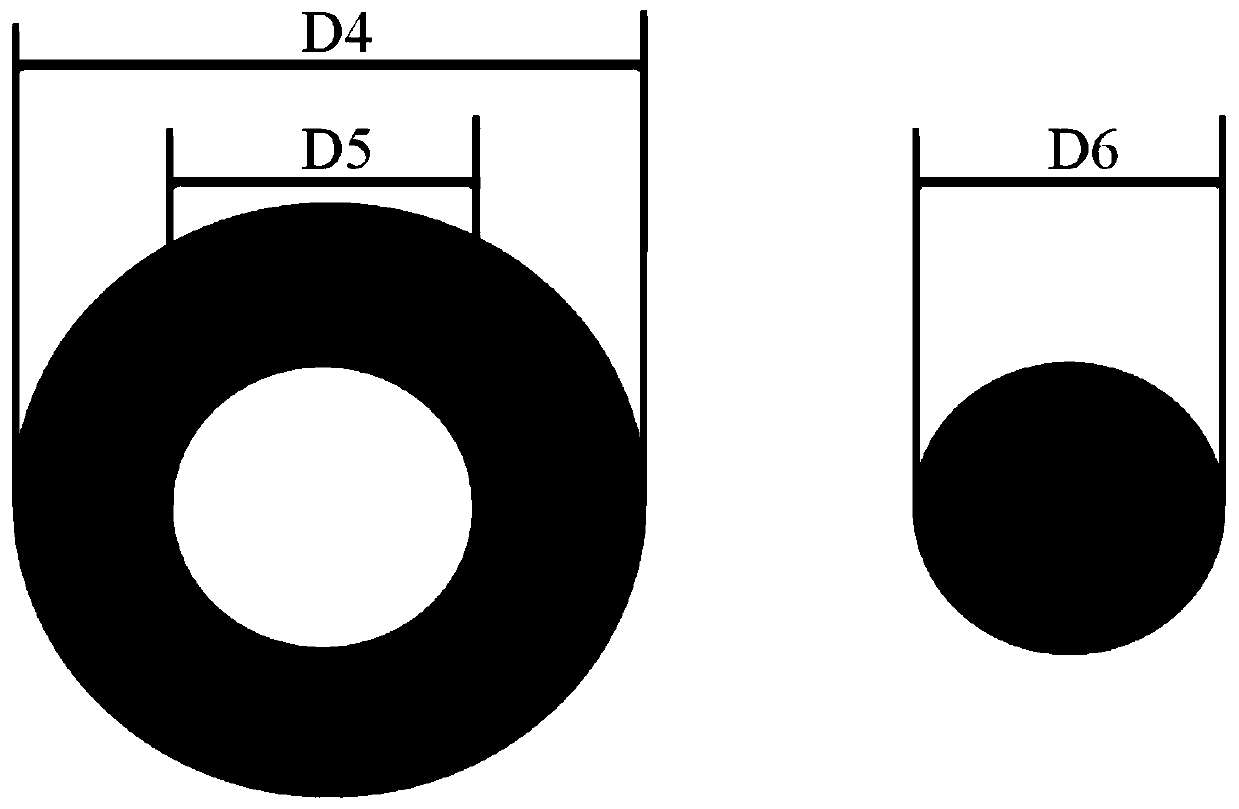
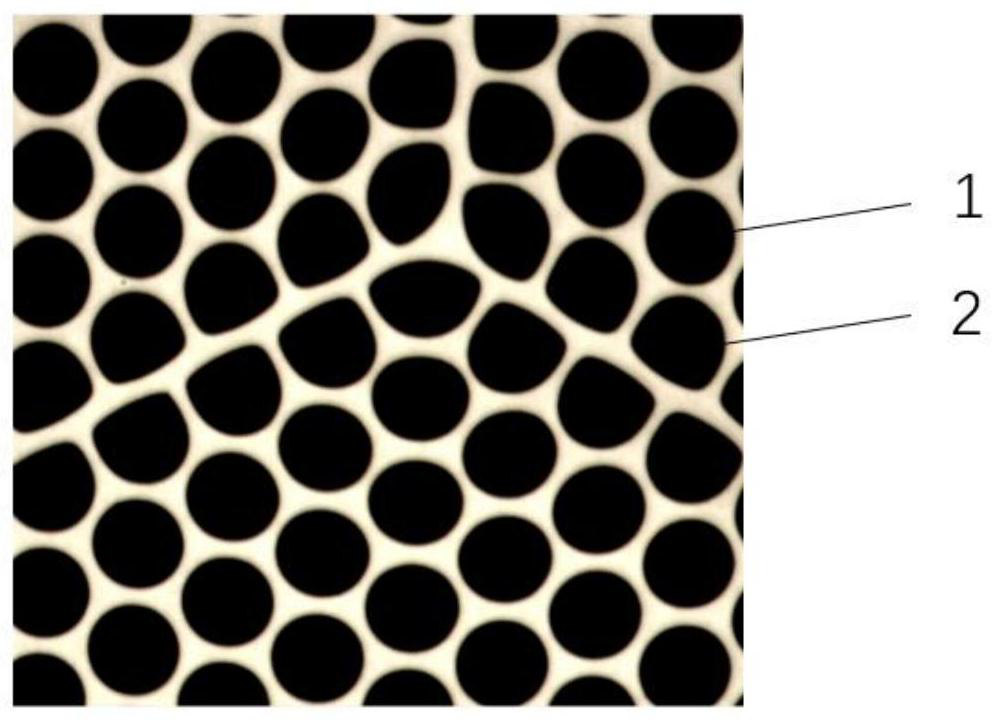
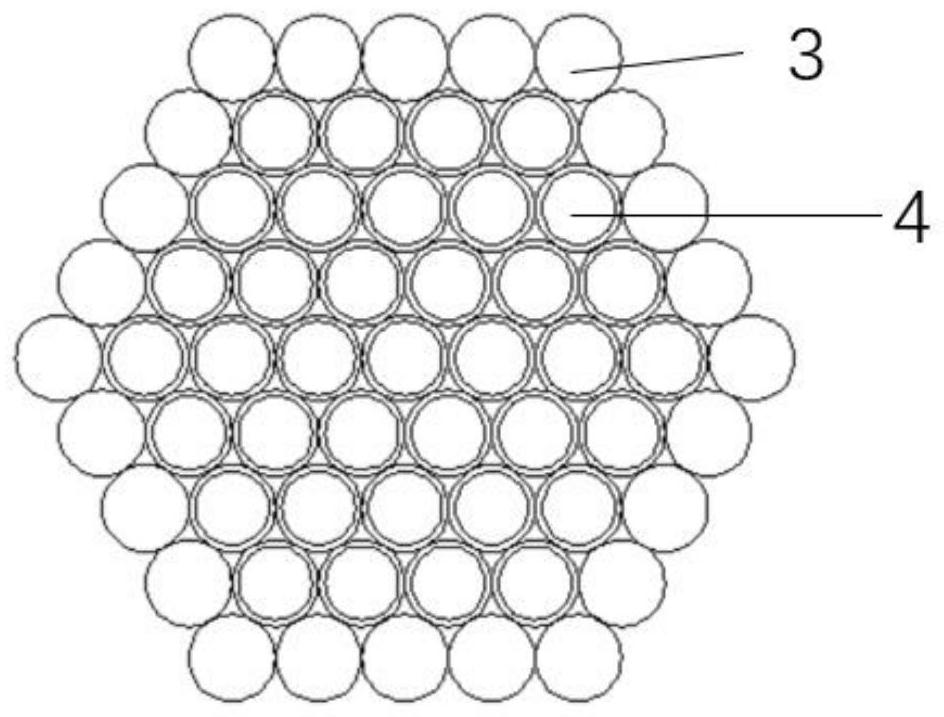
The invention relates to a micro-channel plate and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: nesting a borosilicate glass prefabricated rod and a lead silicate glass prefabricated tube, and drawing to obtain multifilament internal monofilaments; drawing the borosilicate glass preform to obtain monofilaments on the outermost layer of the multifilament; arranging and binding the obtained internal monofilament of the multifilament and the outermost monofilament of the multifilament to obtain a multifilament rod; drawing the multifilament rod to obtain multifilaments; immersing the multifilament into a dilute acid solution to dissolve the monofilament on the outermost layer; cleaning the multifilament by using a NaOH solution, deionized water and isopropanol; cutting off the corroded parts at the two ends of the multifilament; cutting off the residual multifilaments at a fixed length, and arranging the multifilaments into a blank plate; and melting and pressing the blank plate, slicing and polishing, dissolving out a channel with acid, reducing and plating an electrode to prepare the micro-channel plate. The micro-channel plate provided by the invention has no fixed pattern noise under working voltage.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Method for making field emission device
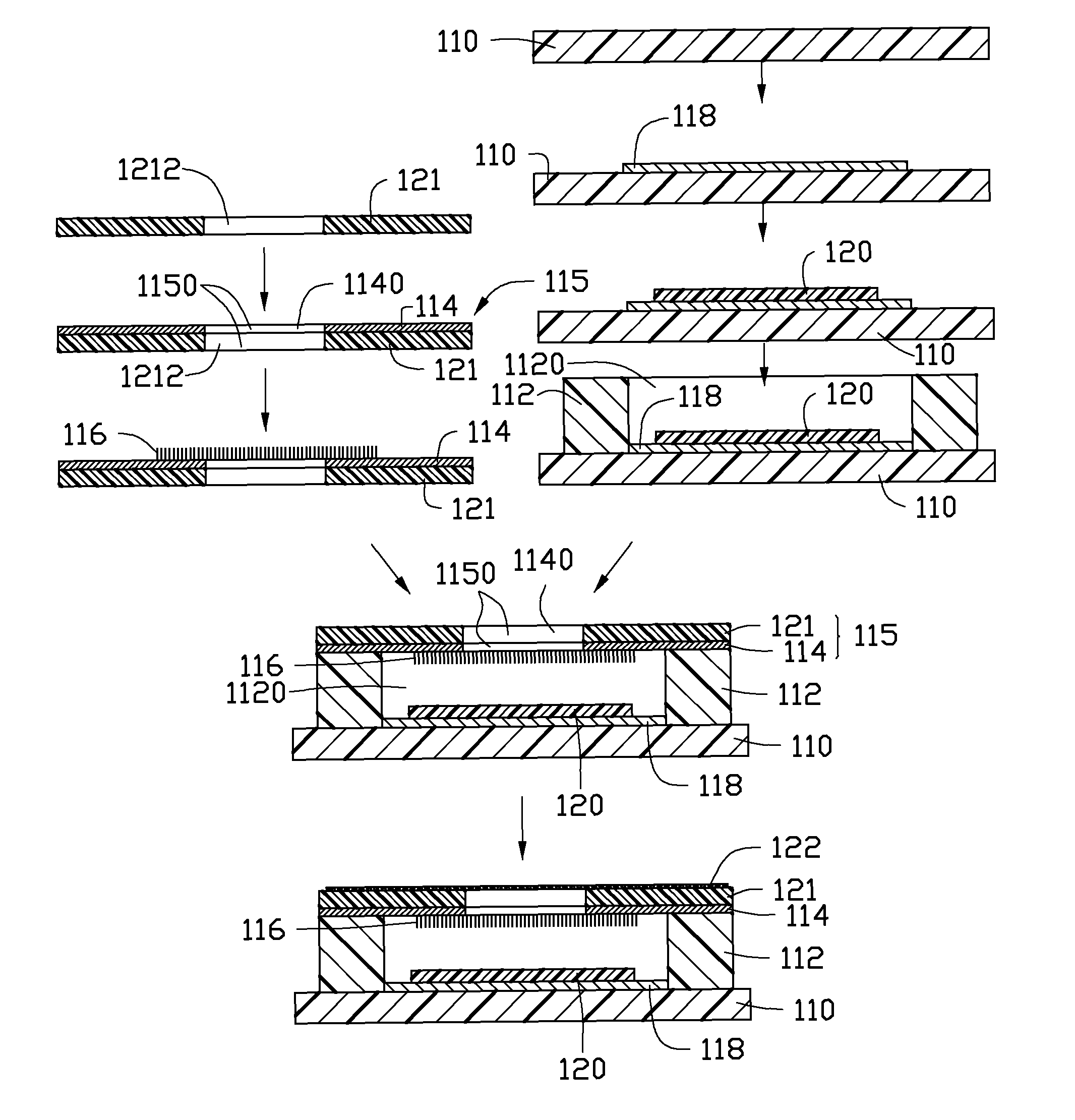
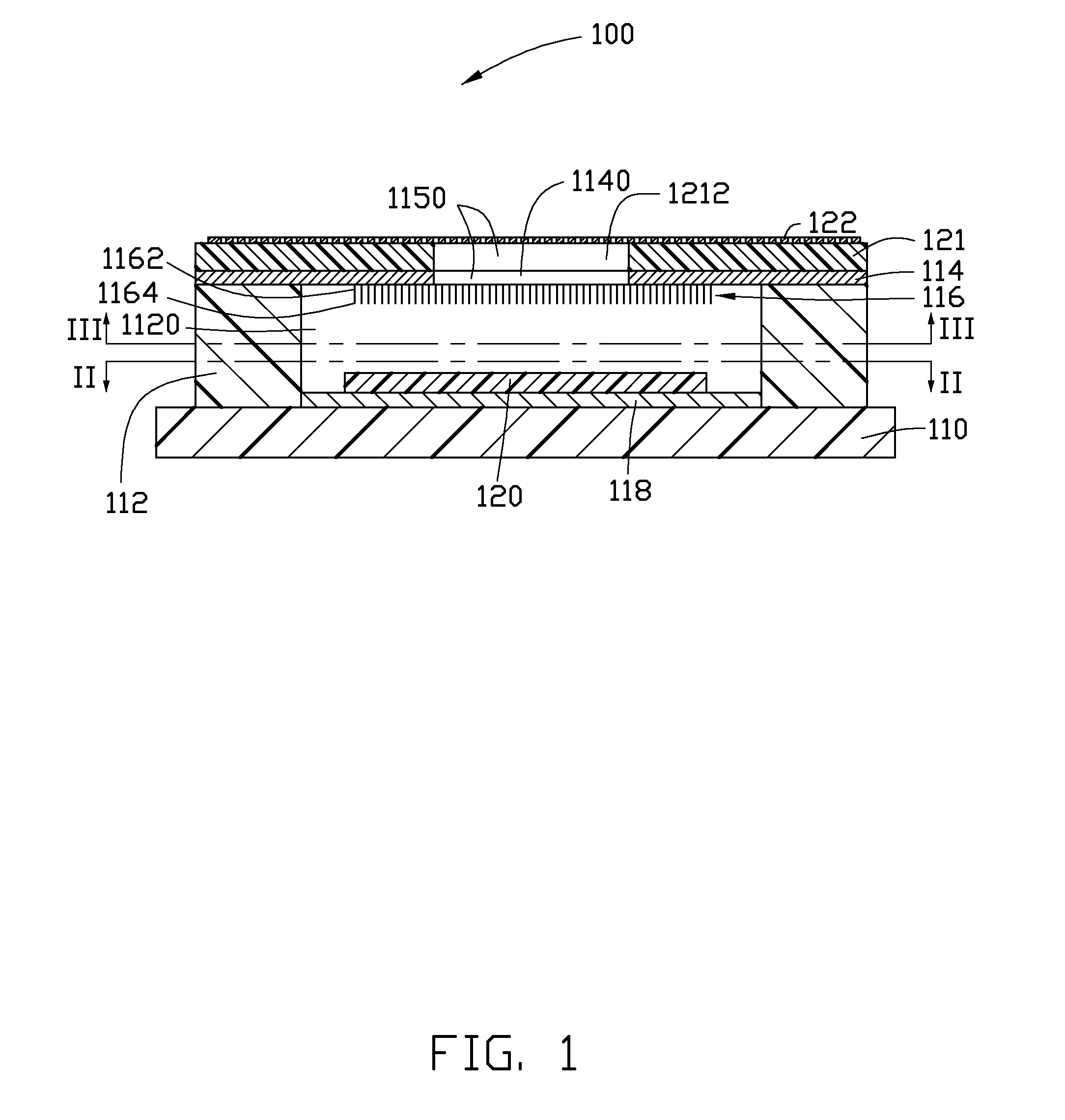
ActiveUS8246413B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsField emission deviceSecondary electrons
A method for making a field emission device includes the following steps. An insulative substrate is provided. An electron pulling electrode is formed on the insulative substrate. A secondary electron emission layer is formed on the electron pulling electrode. A first dielectric layer is fabricated. The first dielectric layer has a second opening to expose the secondary electron emission layer. A cathode plate having an electron output portion is provided. An electron emission layer is formed on part surface of the cathode plate. The cathode plate is placed on the first dielectric layer. The electron output portion and the second opening have at least one part overlapped, and at least one part of the electron emission layer is oriented to the secondary electron emission layer via the second opening.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com