Patents
Literature
58results about How to "Reduced DC voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
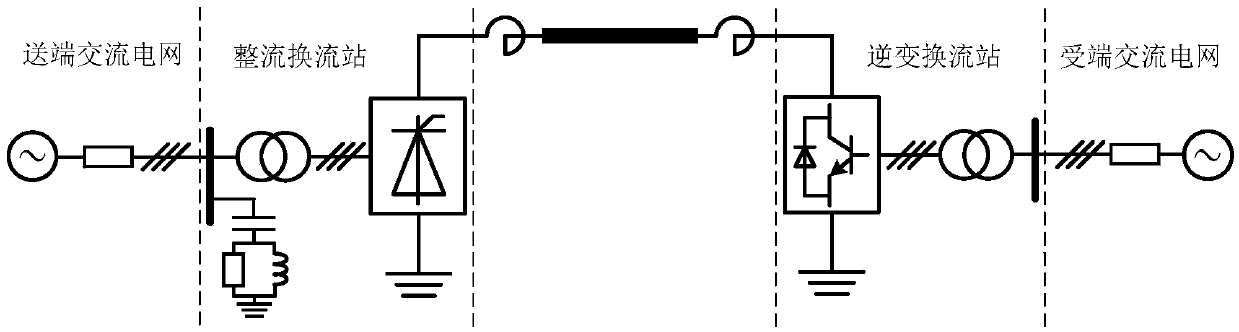
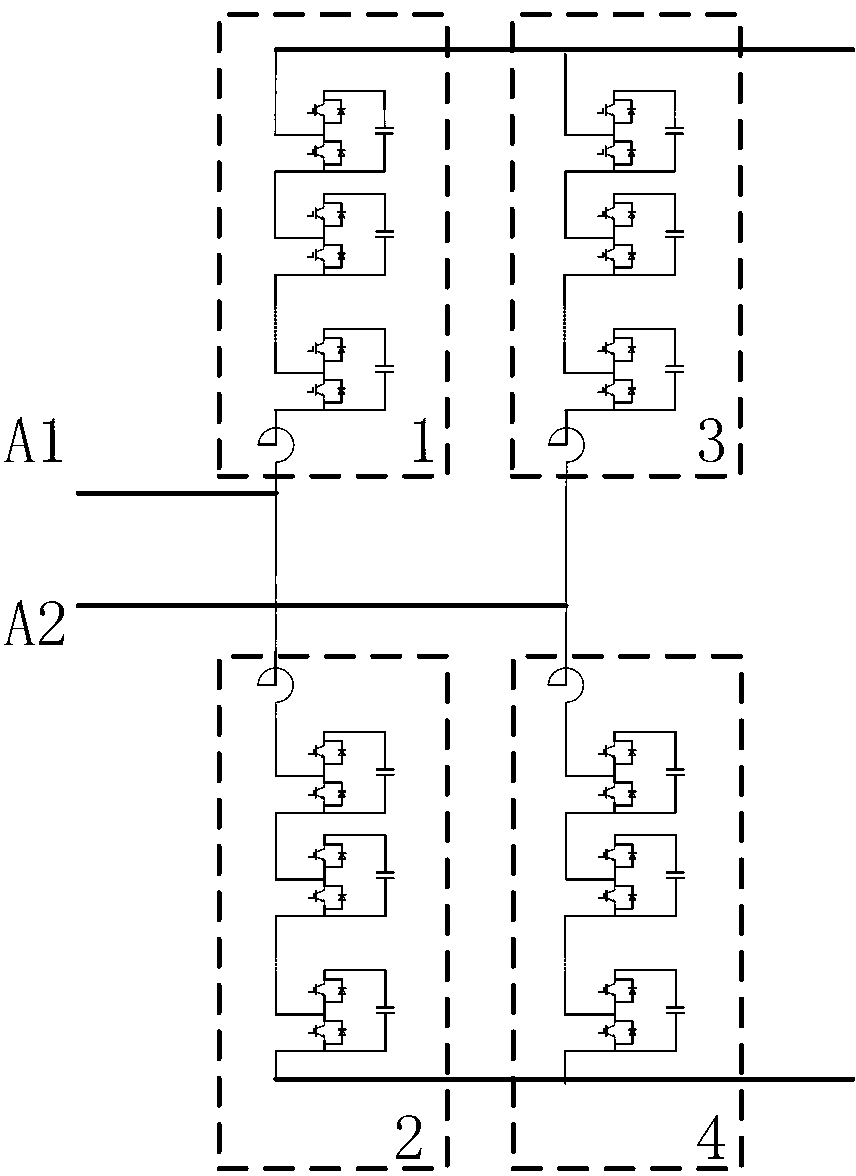
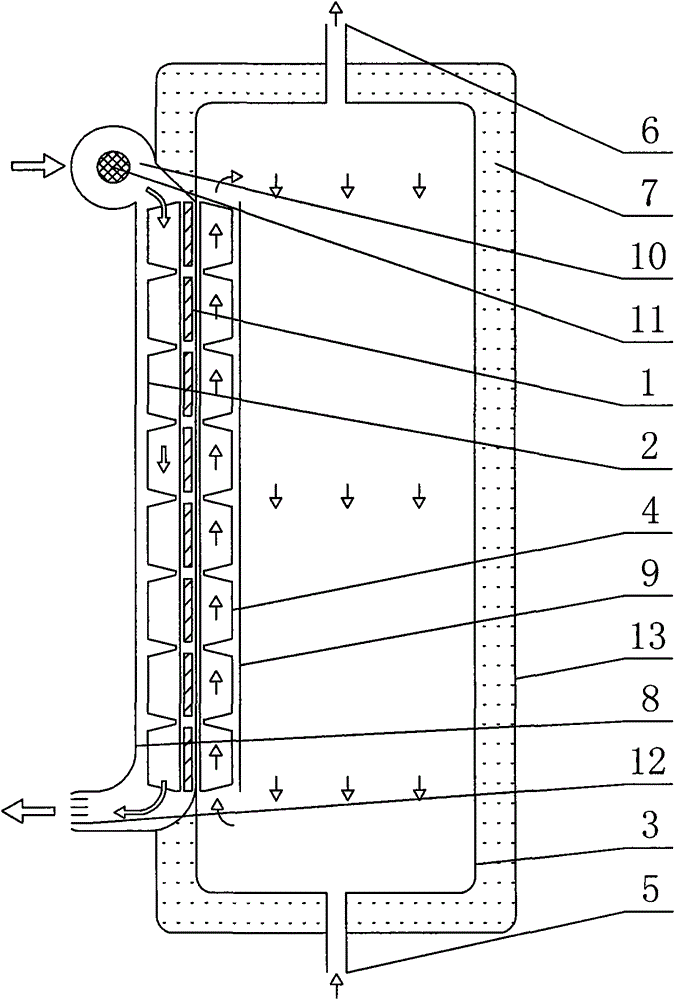
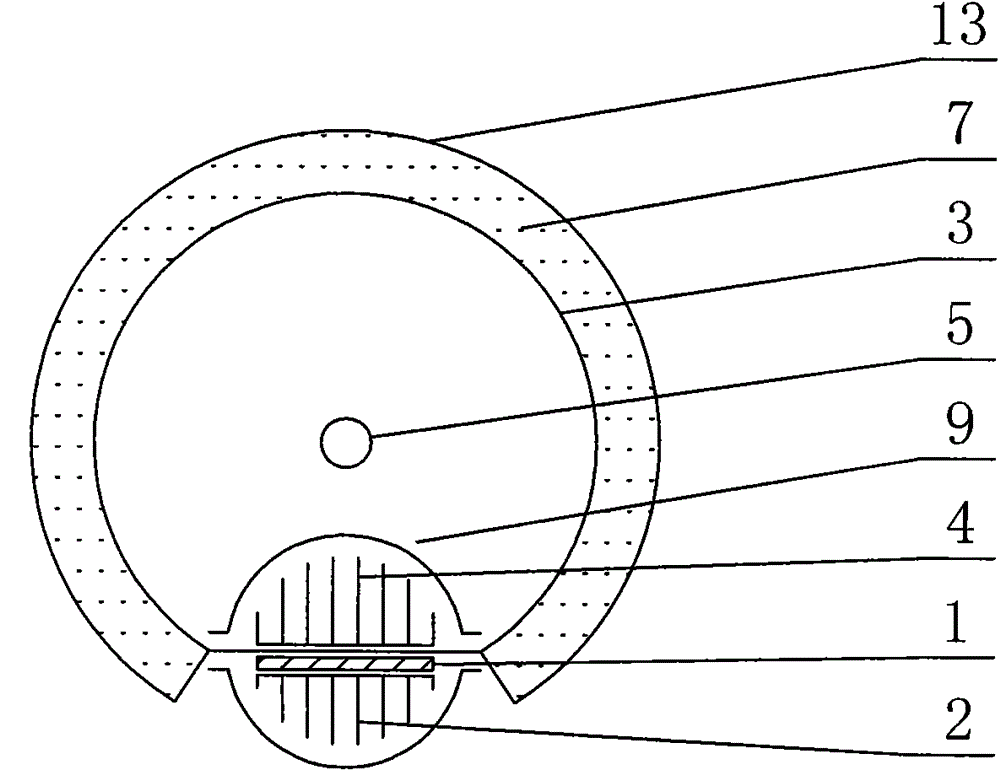
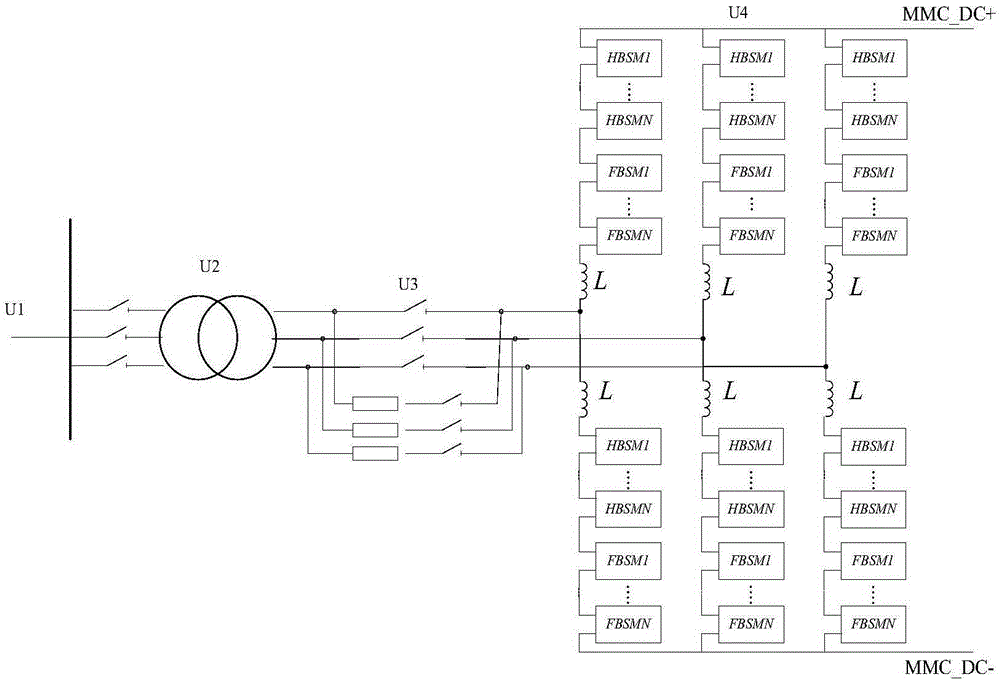
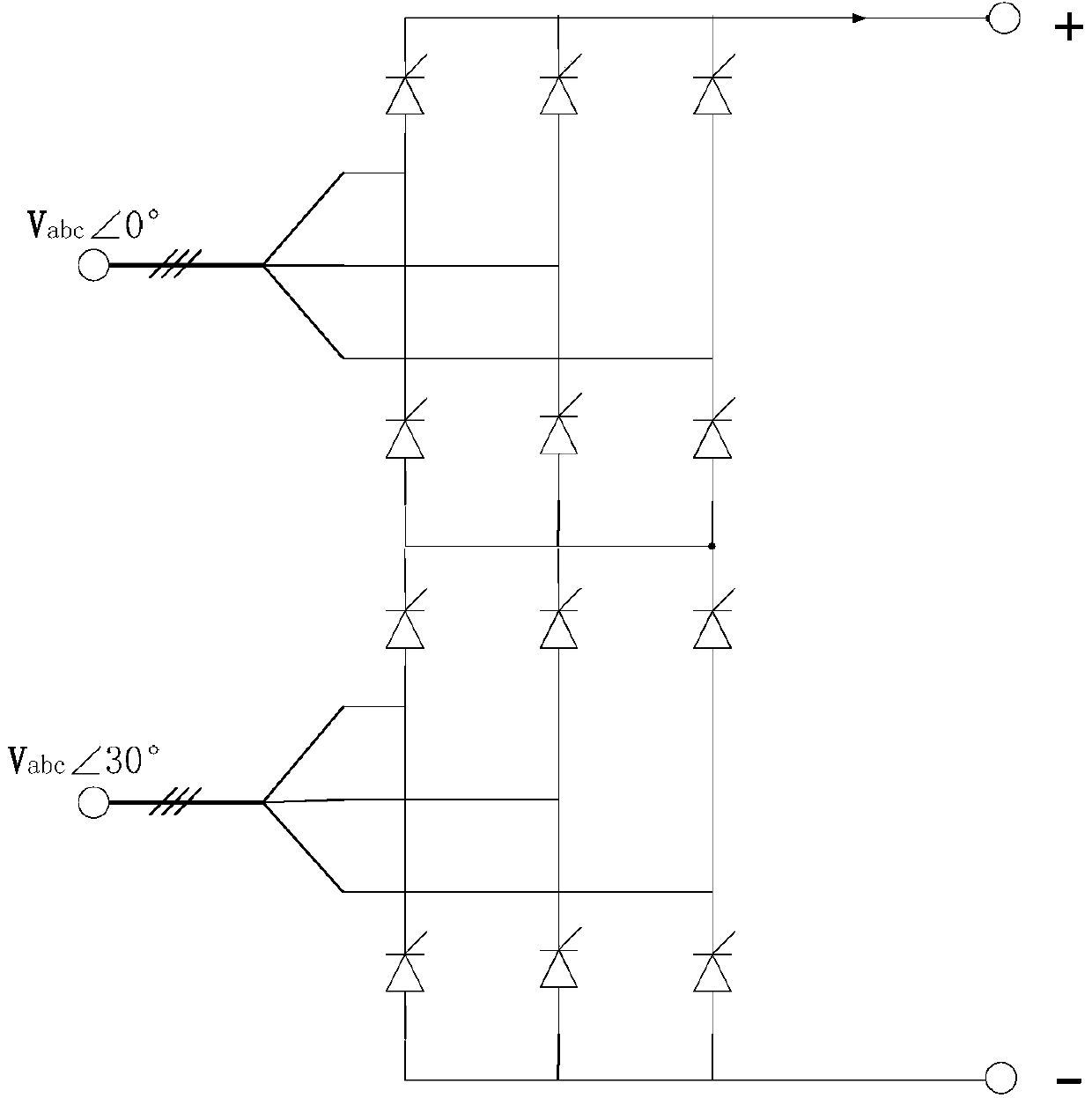
Mixed MMC-based mixed direct current power transmission system
InactiveCN103701145ANo risk of commutation failureWith DC fault self-clearing capabilityAc-dc conversionElectric power transfer ac networkHybrid typeFull bridge
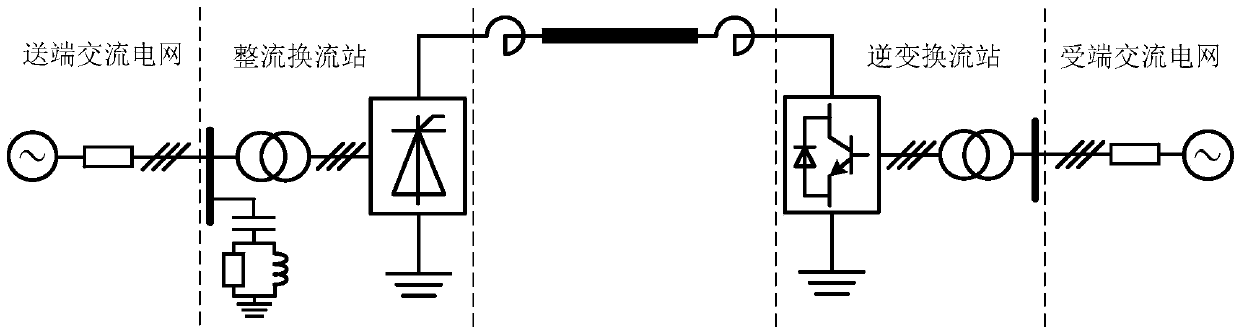
The invention discloses a mixed MMC-based mixed direct current power transmission system, comprising a rectifying converter station and an inversion converter station, wherein the inversion converter station adopts a mixed MMC. The direct current power transmission system has the active and reactive decoupling control capacity, can transmit power to a reactive network without the phase change failure risk and has direct current fault self-cleaning capacity; under the condition that a feeding end alternating current system has a fault; the mixed MMC has the capacity of outputting a negative level by using a full-bridge submodule, the direct current voltage output by the system can be reduced under the premise of ensuring the controllability and stability of the system, the direct current voltage can be matched with the direct current voltage of a rectifying station, and the direct current power is maintained to be continuously transmitted; due to the optimization on the number of two types of submodules in the mixed MMC, the use number of power electronic components is greatly reduced and the investment cost is reduced under the condition that the mixed modularized multi-level converter meets the stable and transient operation demands of the direct current system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
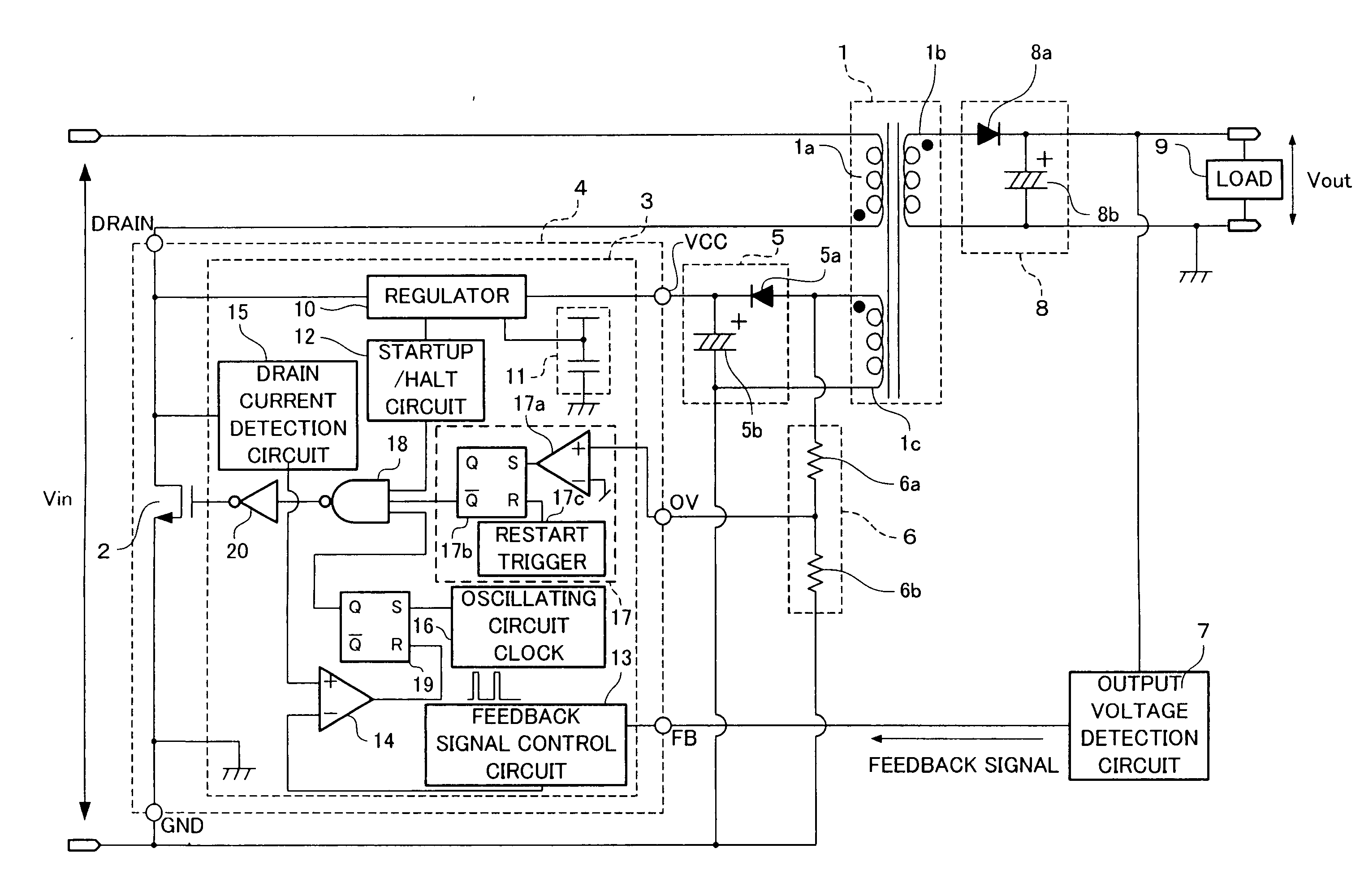
Switching power supply apparatus and semiconductor device used in the switching power supply apparatus
InactiveUS20090180302A1Highly accurate overvoltage protectionIncrease in costDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPeak valuePower semiconductor device
A switching power supply apparatus having a highly accurate overvoltage protection function which is free of erroneous operation is provided. A regulating circuit connected to an auxiliary winding generates an AC voltage proportional to a voltage component in which the ringing component has been removed from the AC voltage induced in the auxiliary winding by the switching operation of a switching element. If the peak value of the AC voltage generated by the regulating circuit is equal to or greater than a prescribed value, an overvoltage detection circuit controls the switching operation of the switching element so as to reduce the output DC voltage.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Apparatus for driving electric car by inverter-controlled motor through gear mechanism
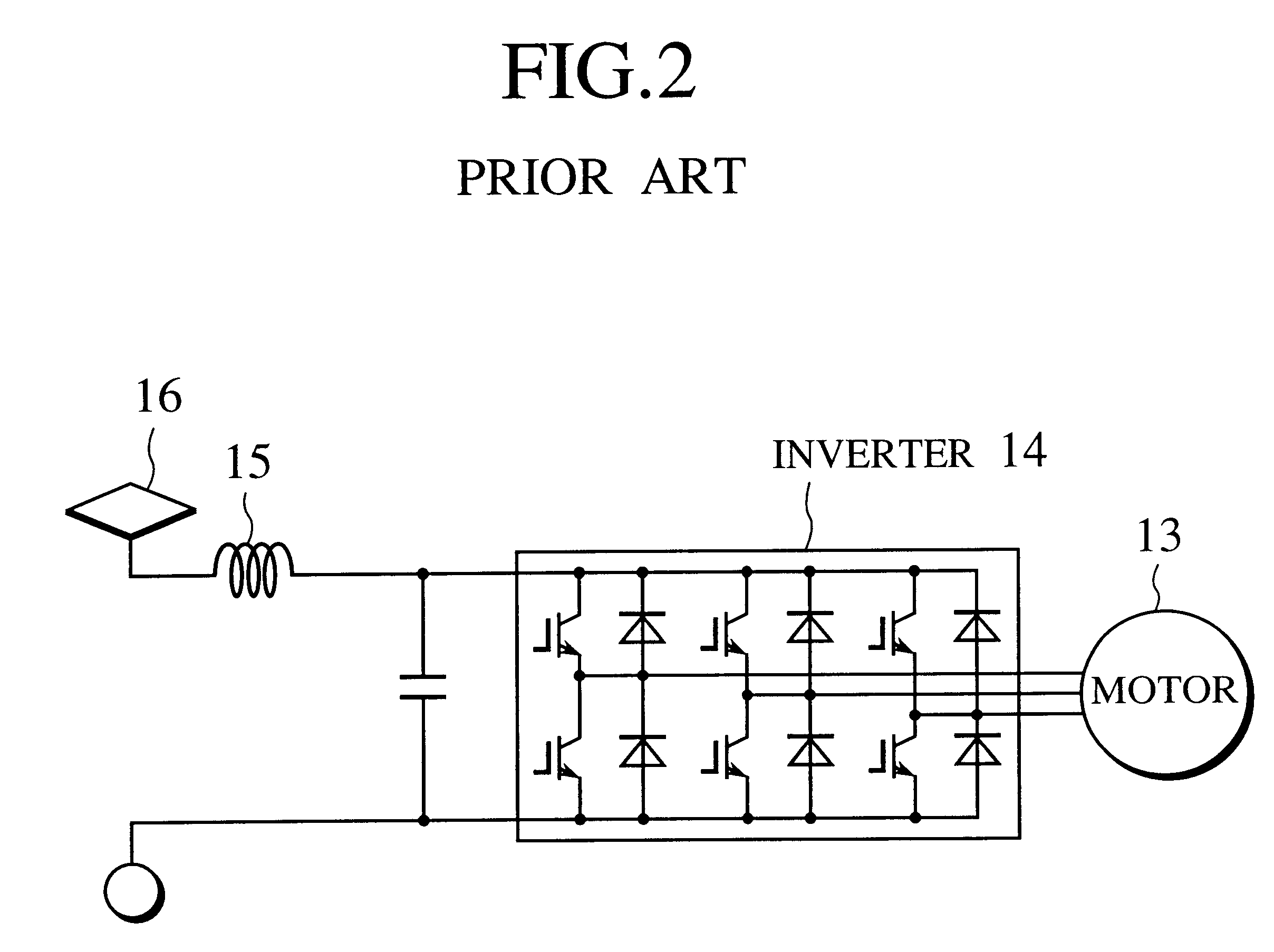
InactiveUS6431297B1Reduced DC voltageMinimizes problemSpeed controllerElectric devicesFrequency changerHigh-voltage direct current
An apparatus for driving and controlling a car has a large gear directly connected to a wheel shaft of the car, small gears meshing with the large gear, AC motors connected to the small gears, respectively, and inverters whose AC output sides are connected to the AC motors, respectively, and whose DC input sides are connected in series in multiple stages to a high-voltage DC power source. Torque for driving the large gear connected to the wheel shaft is divided and borne by the small gears, so that each small gear receives small torque. This enables each tooth of each gear to have small mechanical strength. As a result, the cross-sectional area of each tooth of each small gear can be reduced to increase the number of teeth of the large gear that meshes with the small gears, to increase a gear ratio defined by the large and small gears. The DC input terminals of the inverters are connected in series to the high-voltage DC power source, and a DC input voltage for each inverter is reduced to a standard inverter level. Consequently, the inverters of the apparatus may be mass-produced standard inverters.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
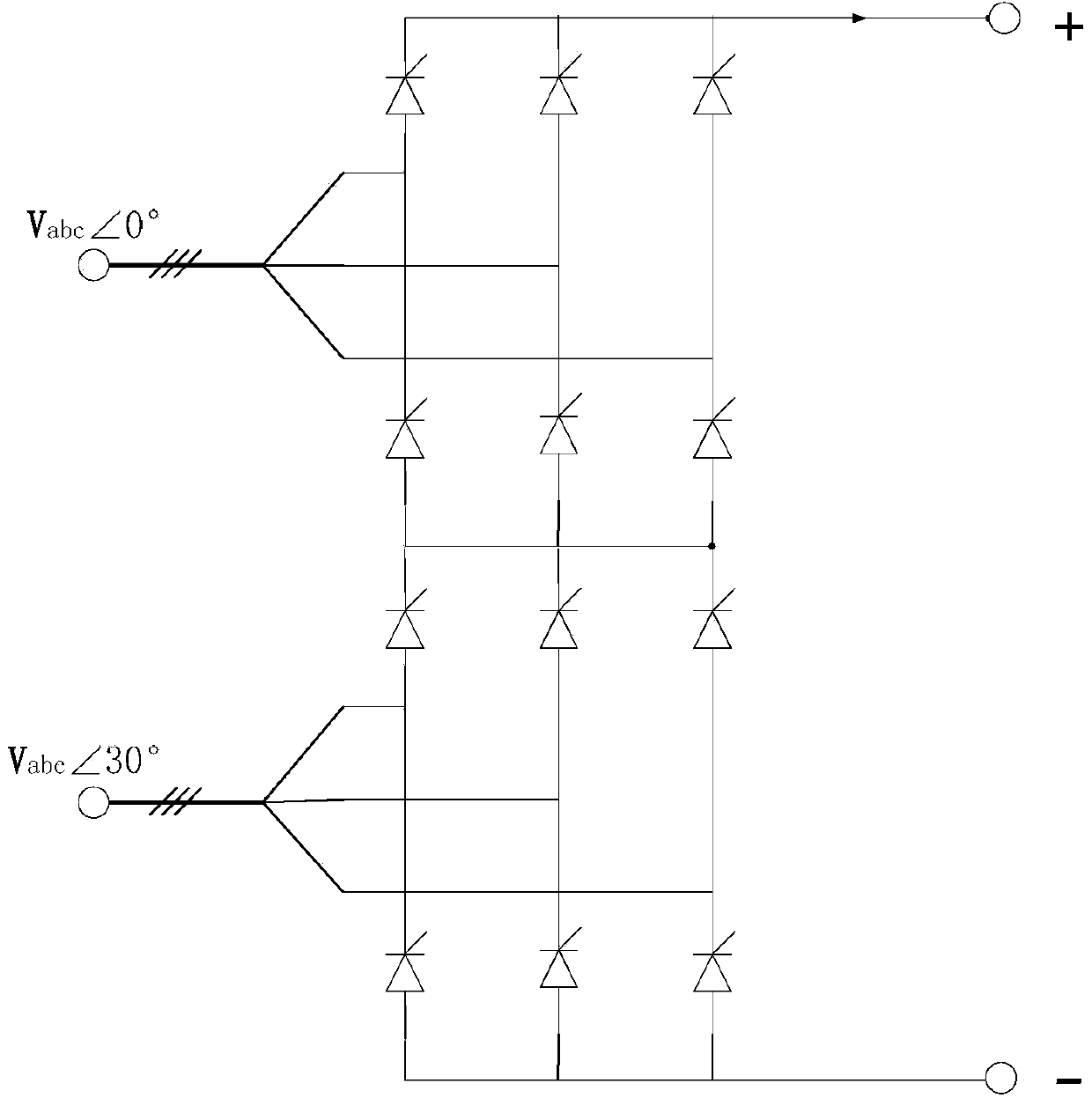
Three-phase rectifier
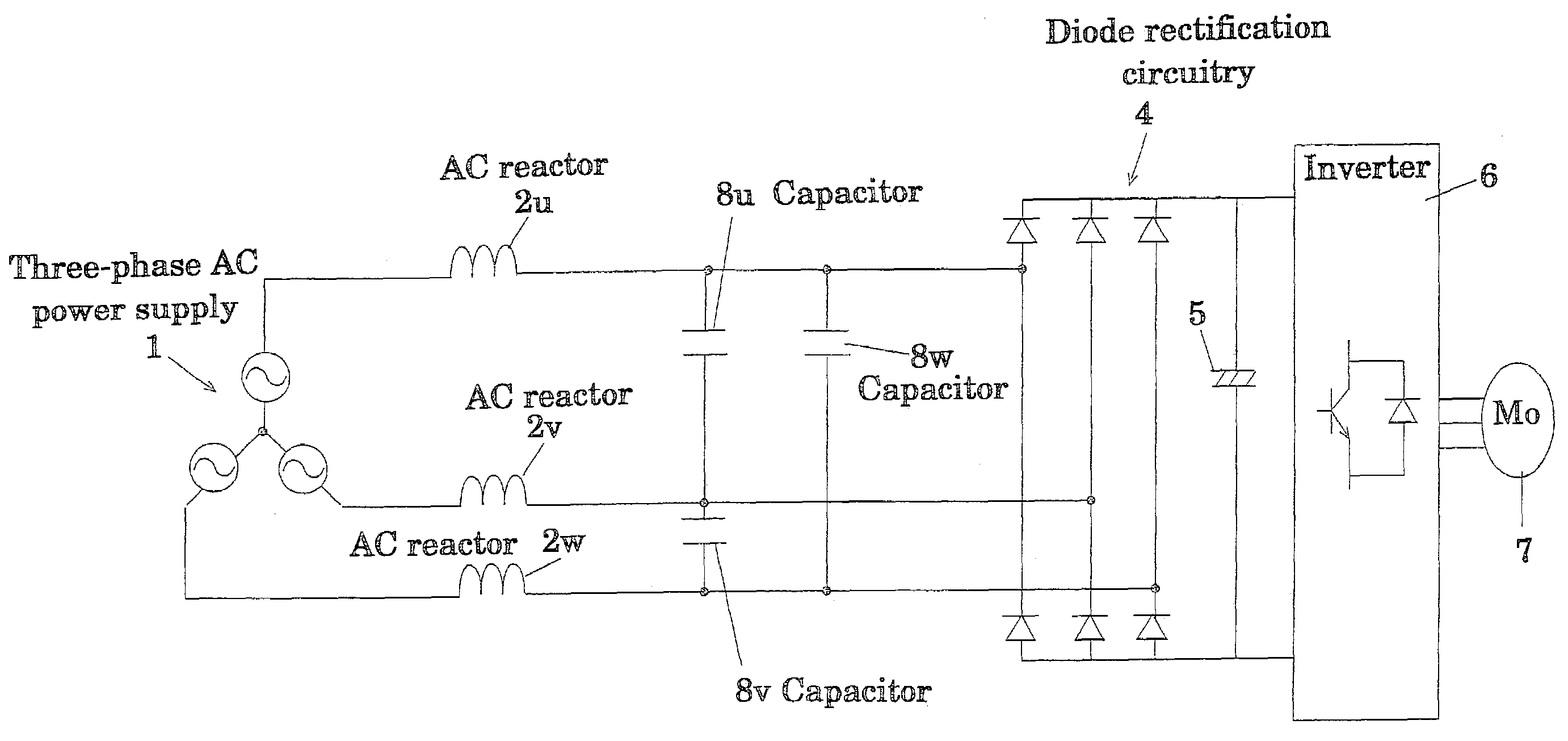
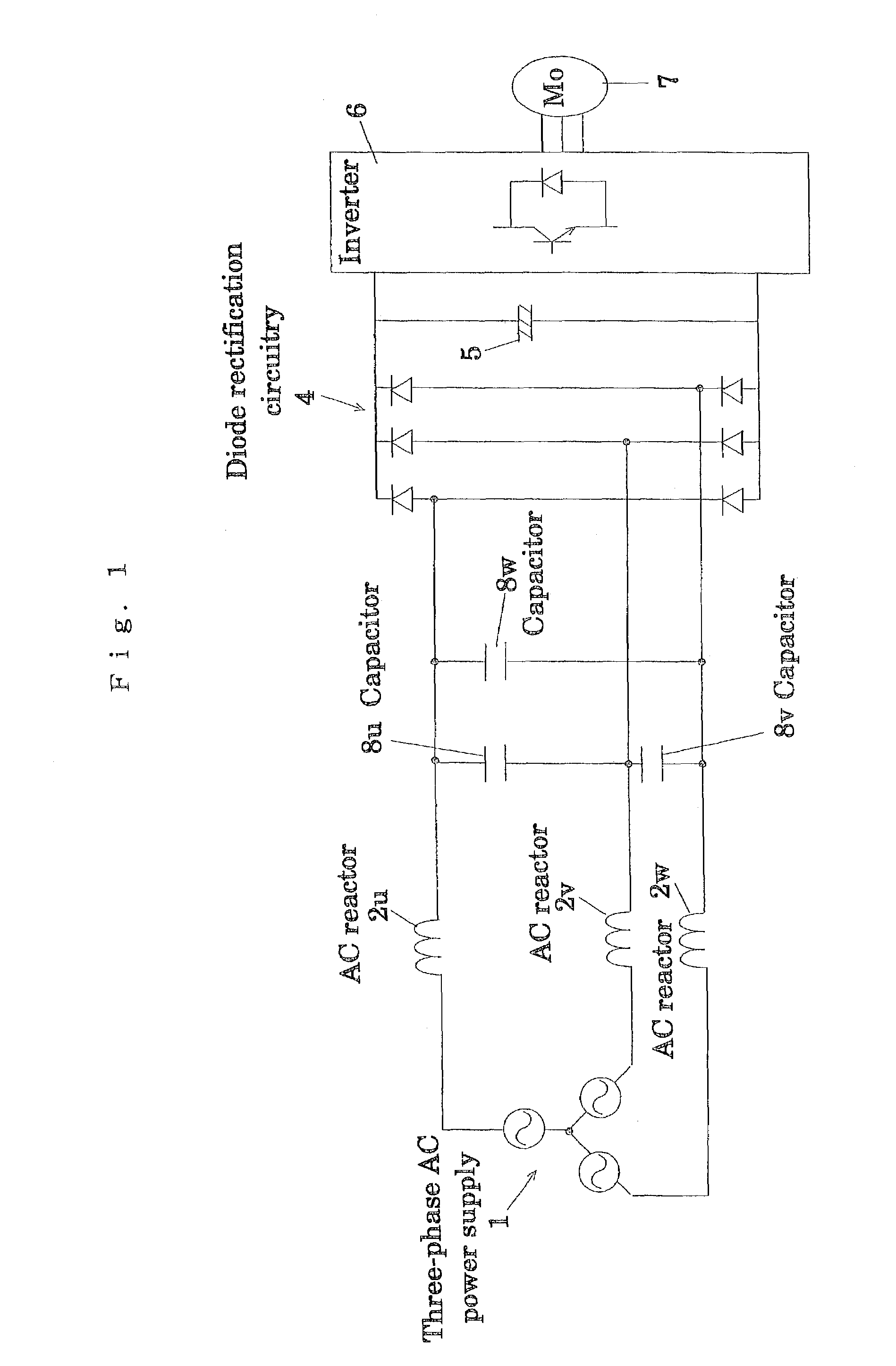
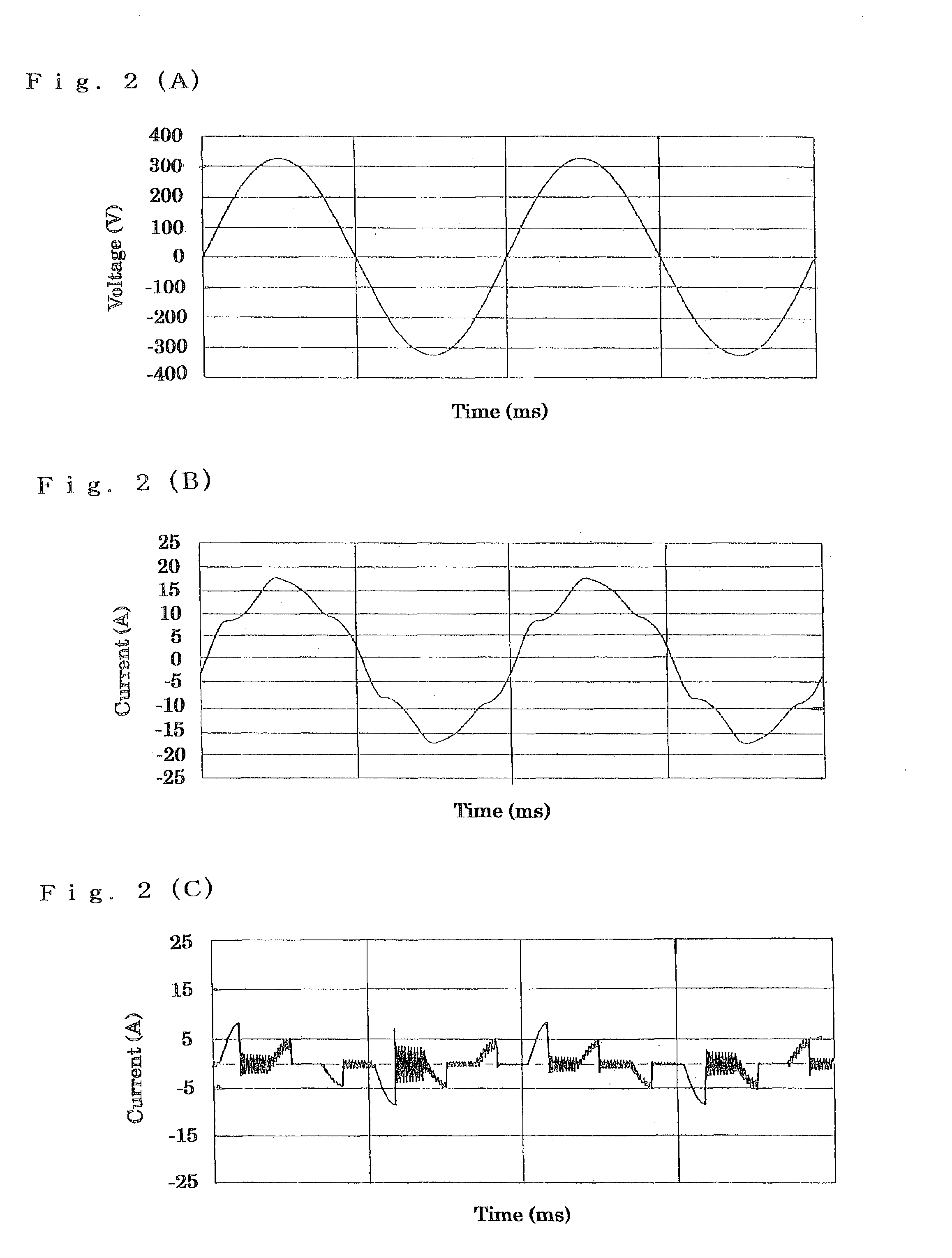
InactiveUS7187566B2Reduce input powerLowering in DC voltage is preventedAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionCapacitanceEngineering
A capacitor-input type three-phase rectification circuit comprises a three-phase AC power supply (1), a diode rectifier circuit (4), and a low-frequency filter connected between the three-phase AC power supply (1) and the diode rectification circuitry (4), the low frequency filter consisting of AC reactors (2u)(2v)(2w) and Δ-connection or Y-connection capacitors (8u)(8v)(8w), so that higher harmonic currents are reduced to be equal to or less than standard values, and that lowering in input power factor and lowering in DC voltage are prevented from occurrence.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Manufacturing method of carbon nanotube gas sensor based on corona discharge
InactiveCN101893599AEasy to controlEasy to measureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGas detectorCarbon nanotube
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a carbon nanotube gas sensor based on corona discharge and is characterized by providing a novel carbon nanotube ion type gas sensor by using the unique physical structure of the carbon nanotube and the tip emission effect based on the gas corona discharge principle. The sensor is formed by aligned carbon nanotube arrays grown on an anodic aluminium oxide template. The carbon nanotubes and the electrodes are integrated, thus simplifying the structure of the device and the process and ensuring convenient control and measurement. Compared with the prior art, the gas sensor has the advantages of simple structure, lower cost, high sensitivity, good detection repeatability, low energy consumption, small occupied space and convenient use. The gas sensor requires lower direct current voltage, thus reducing the danger level of operation and being expected to realize the portable gas monitoring device.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Unified power flow controller in modular structure
ActiveCN103236710AReduced DC voltageReduce voltage stressClimate change adaptationElectric power transfer ac networkHarmonicModularity
The invention relates to the technical field of power electronics and discloses a unified power flow controller in the modular structure. A structurally modified modular multilevel converter is organically combined with a unified power flow controller so that direct-current voltage of the unified power flow controller is halved and the unified power flow controller is imparted with individual phase control capacity; a power electronic bypass switch on the serial side of the unified power flow controller provides higher safety, and the requirement on converter switching devices is lower. In addition, the unified power flow controller has the advantages of compact structure of the modular multilevel converter, flexibility in voltage and power level change, low switch frequency, low loss, low content of output waveform harmonic and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
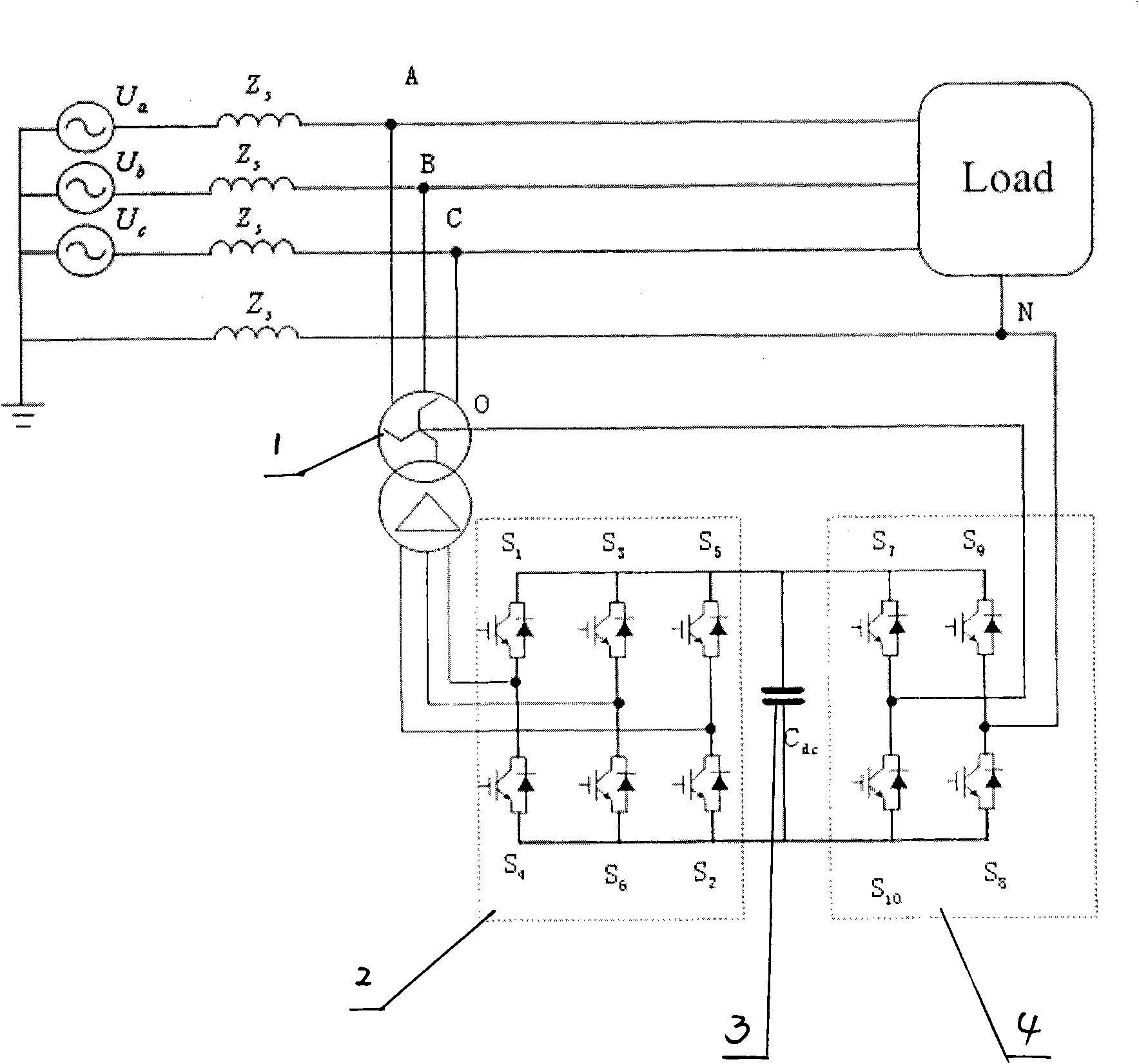
Novel zero-sequence current compensator
InactiveCN101860036AAchieving two-way flowImprove voltage qualityPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionPolyphase network asymmetry reductionCurrent channelCompensation effect
The invention provides a novel zero-sequence current compensator. An inverter bridge is connected between a neutral point and a neutral line of a zigzag transformer; and a current output by the inverter bridge is injected into a system through a low-impedance zero-sequence current channel which is provided by the zigzag transformer so as to compensate for a neutral current. A controllable rectifier module is connected with the secondary side of the zigzag transformer to supply a direct-current power supply to the inverter bridge, and thus, the two-way flow of energy is realized and the problem of direct-current voltage rise caused when the compensator absorbs active power is solved. The novel zero-sequence current compensator has a series of advantages of good compensation effect, low direct-current voltage, small switching stress, few influences of system parameters, flexible control, few influences on system operation and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO LIANYUNGANG POWER SUPPLY CO +1
Electronic and optical devices and methods of forming these devices
InactiveUS7145412B2Reduce lossesAlign dielectric changeOne-port networksCapacitor with electrode distance variationBarium strontium titanatePhotonics
Electronic and optical (or photonic) devices with variable or switchable properties and methods used to form these devices, are disclosed. More specifically, the present invention involves forming layers of conductive material and dielectric material or materials with varying conductivity and indexes of refraction to form various electronic and optical devices. One such layer of adjustable material is formed by depositing epitaxial or reduced grain boundary barium strontium titanate on the C-plane of sapphire.
Owner:NGIMAT CO
Method of manufacturing the thin film
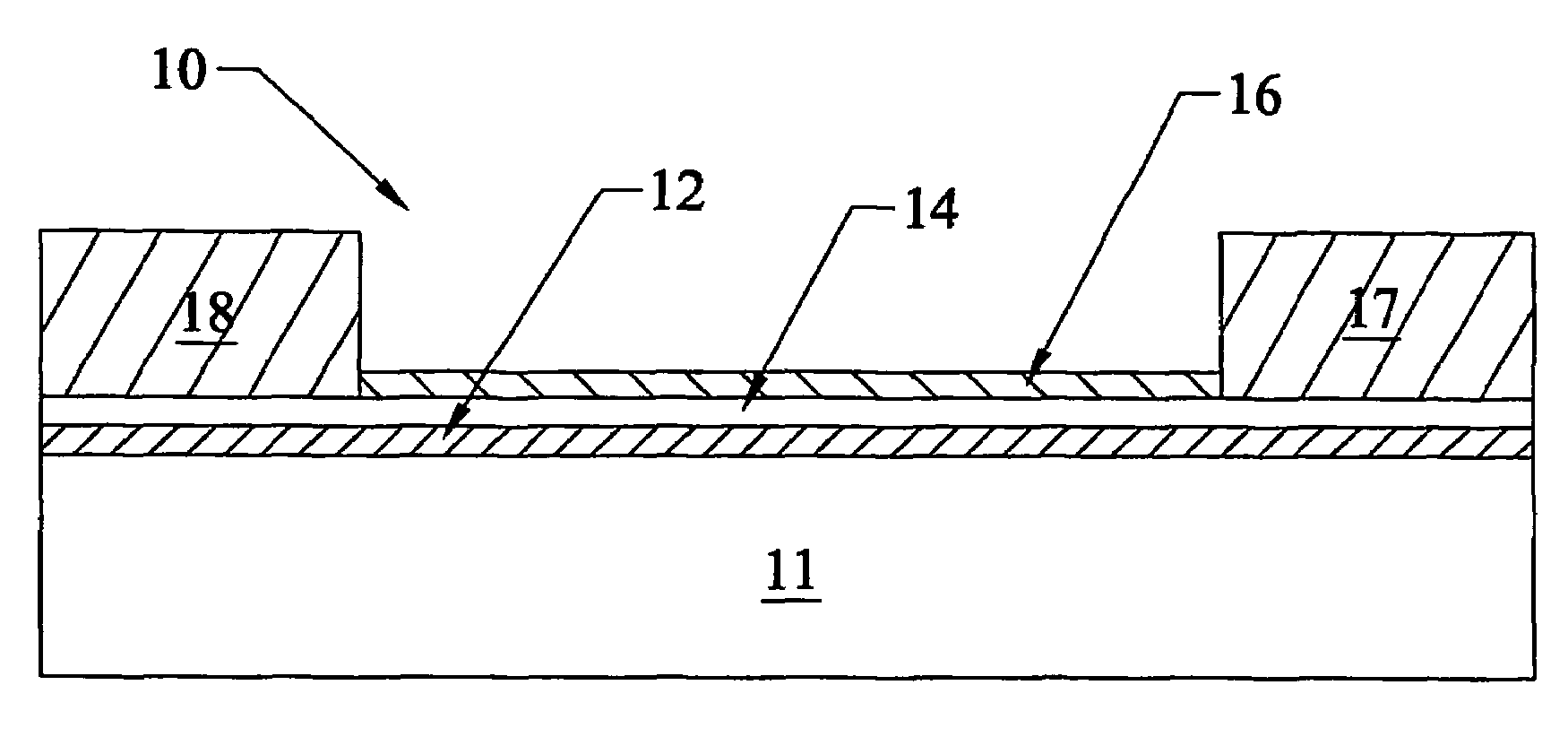
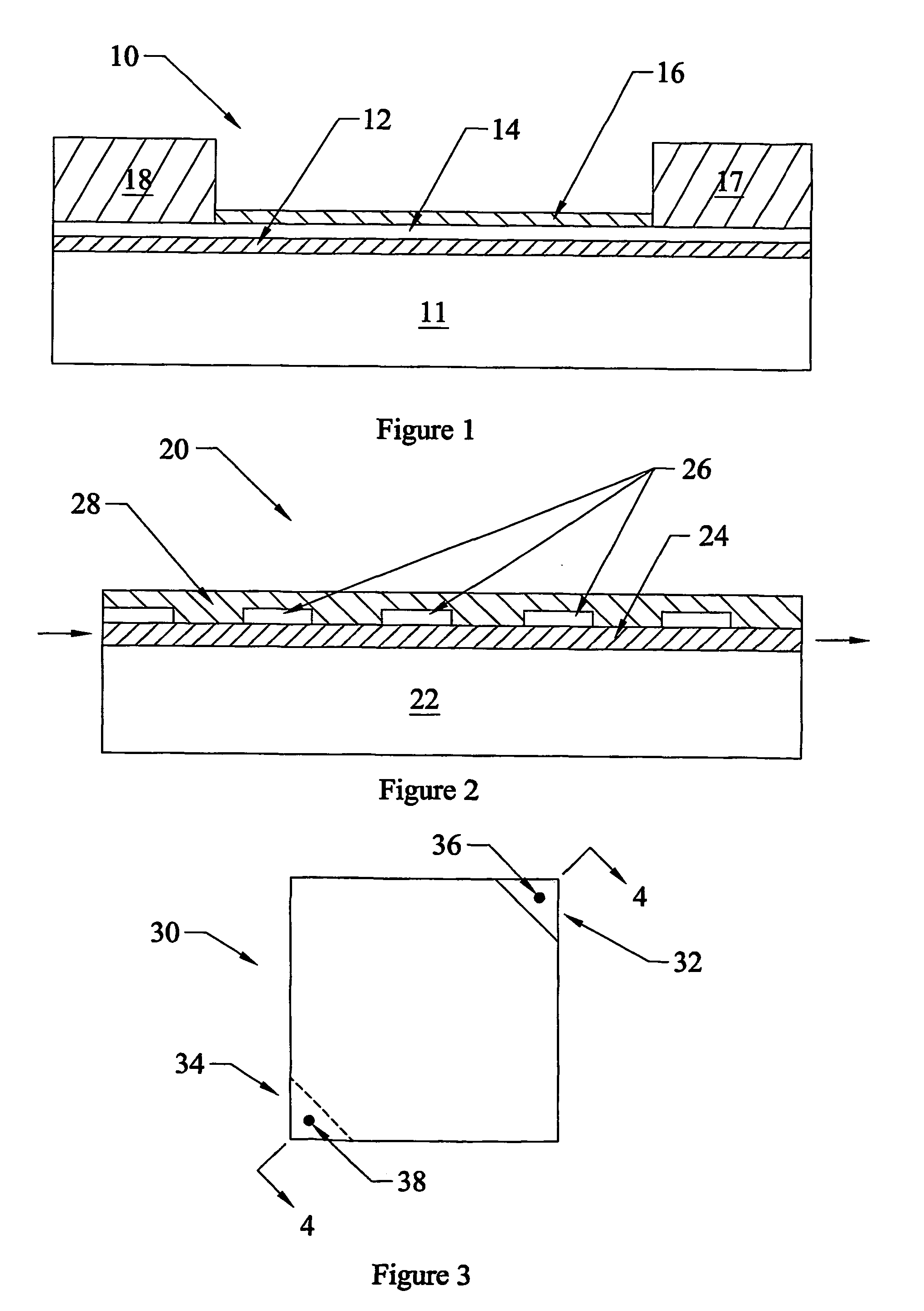
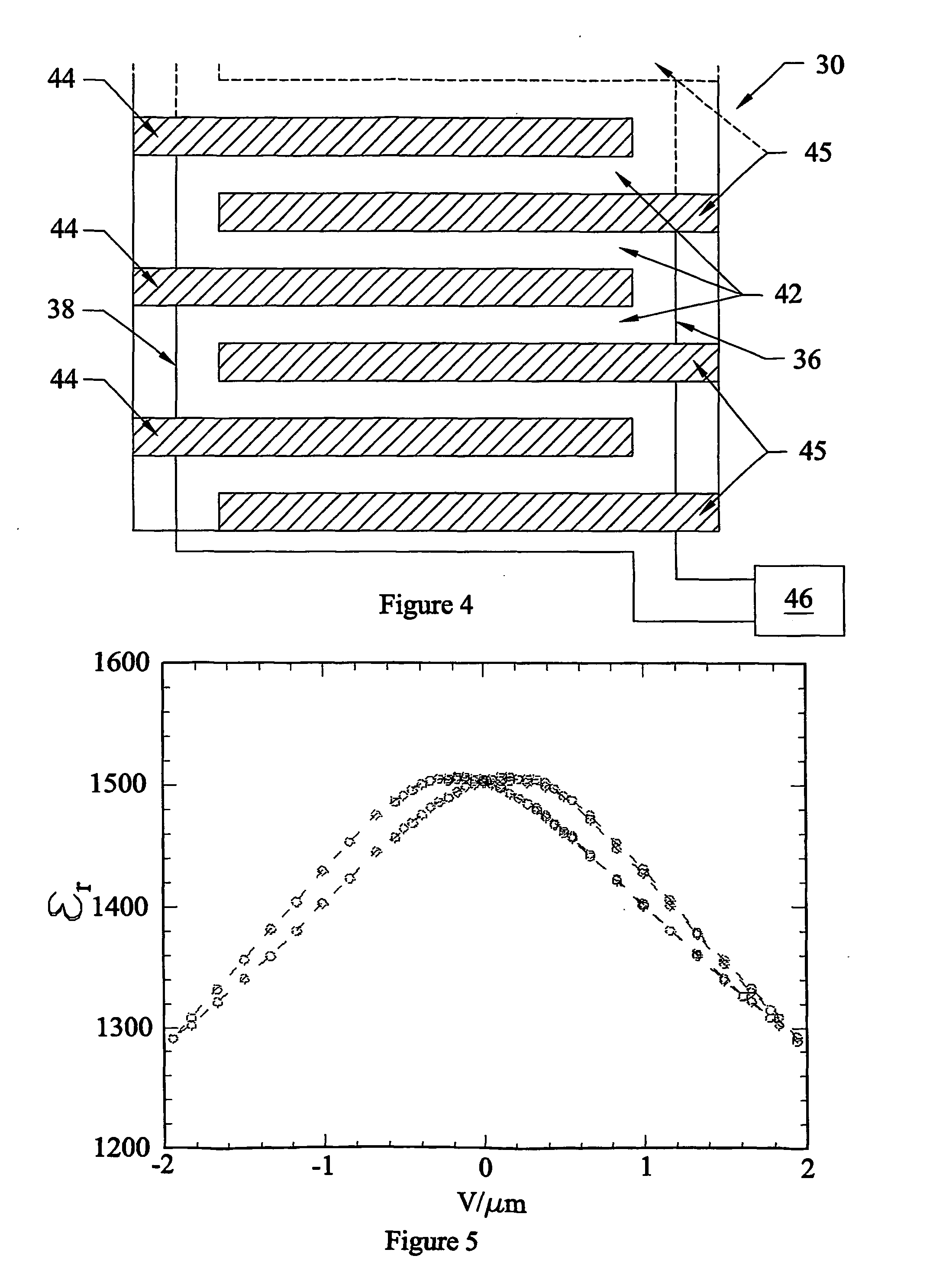
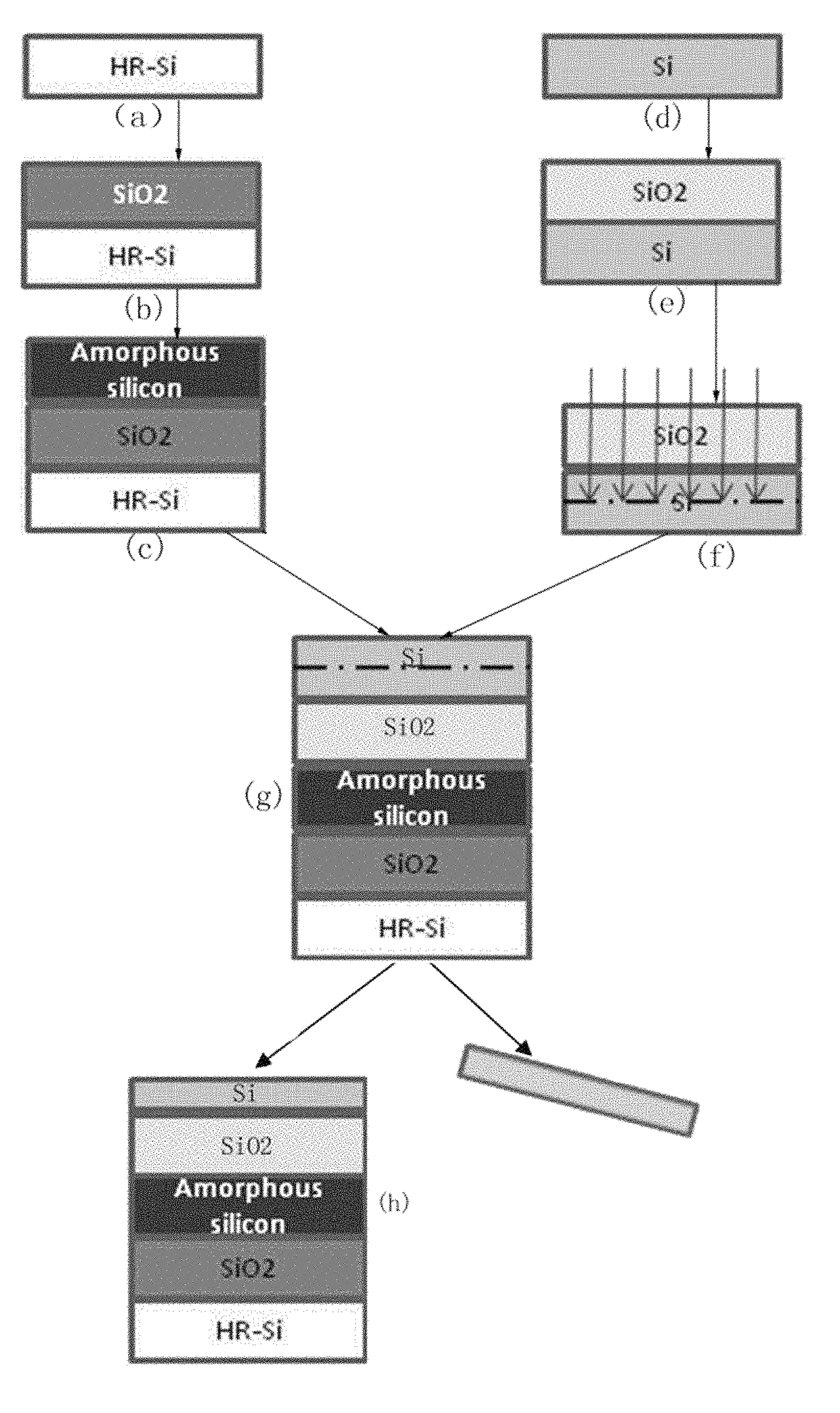
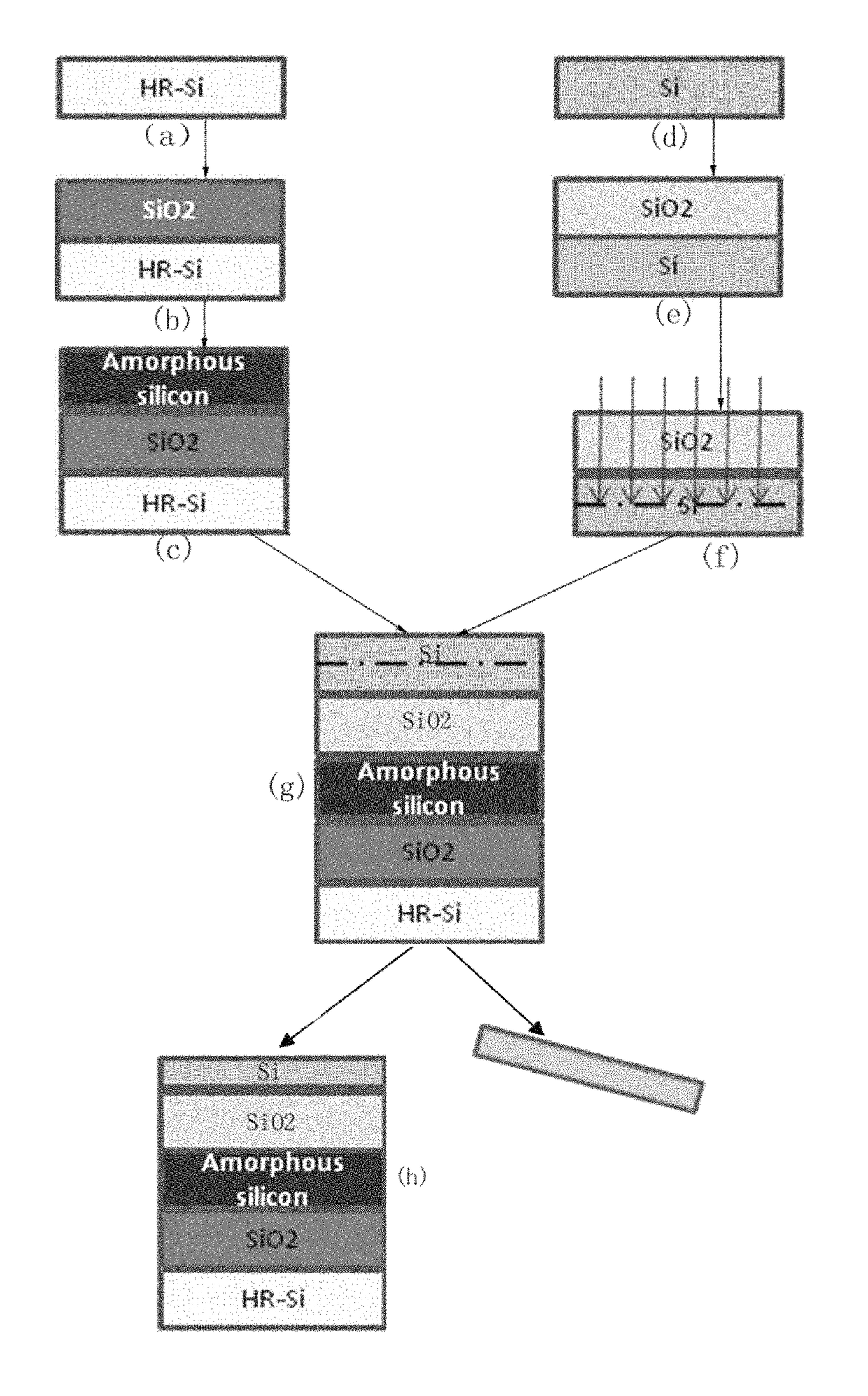
ActiveUS9824891B1Improve thermal stabilityControl changesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconHigh resistivity silicon
The invention disclosed a method of manufacturing the thin film, which belongs to the technological field of SOI wafer manufacture. By growing a layer of dielectric material (silicon oxide) on the provided high-resistivity silicon wafer, then to grow a layer of amorphous silicon on the dielectric material, to transfer a layer of silicon oxide to the amorphous silicon, to make the mono crystalline silicon exist on the oxidation layer, so that a SOI wafer with a layer of amorphous silicon is manufactured. The process above is completed in specific process conditions. The manufactured thin film, e.g. SOI wafer with amorphous silicon layer, is used main for RF apparatus.
Owner:SHENYANG SILICON TECH
Bidirectional unisolated dc-dc converter based on cascaded cells
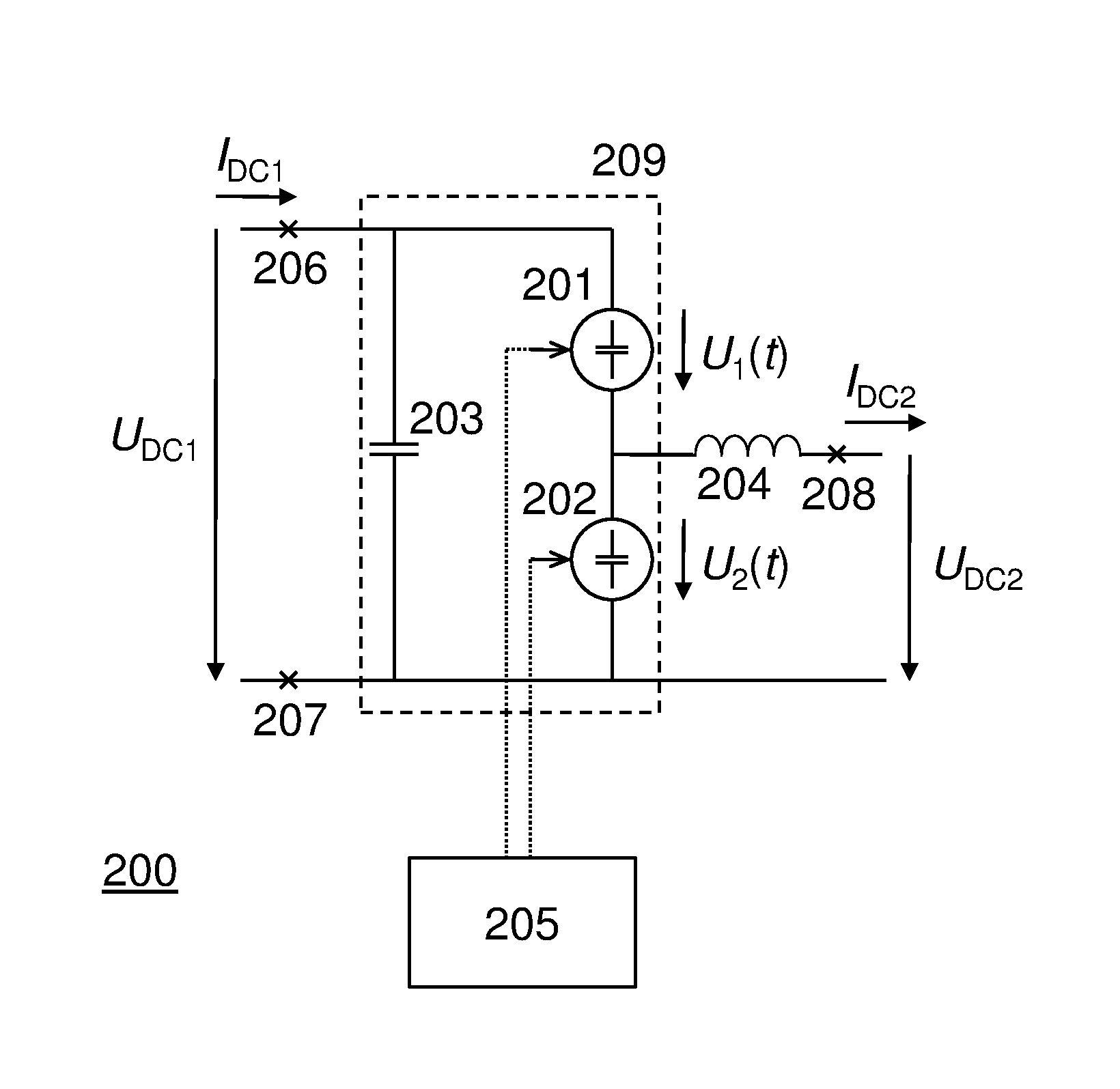
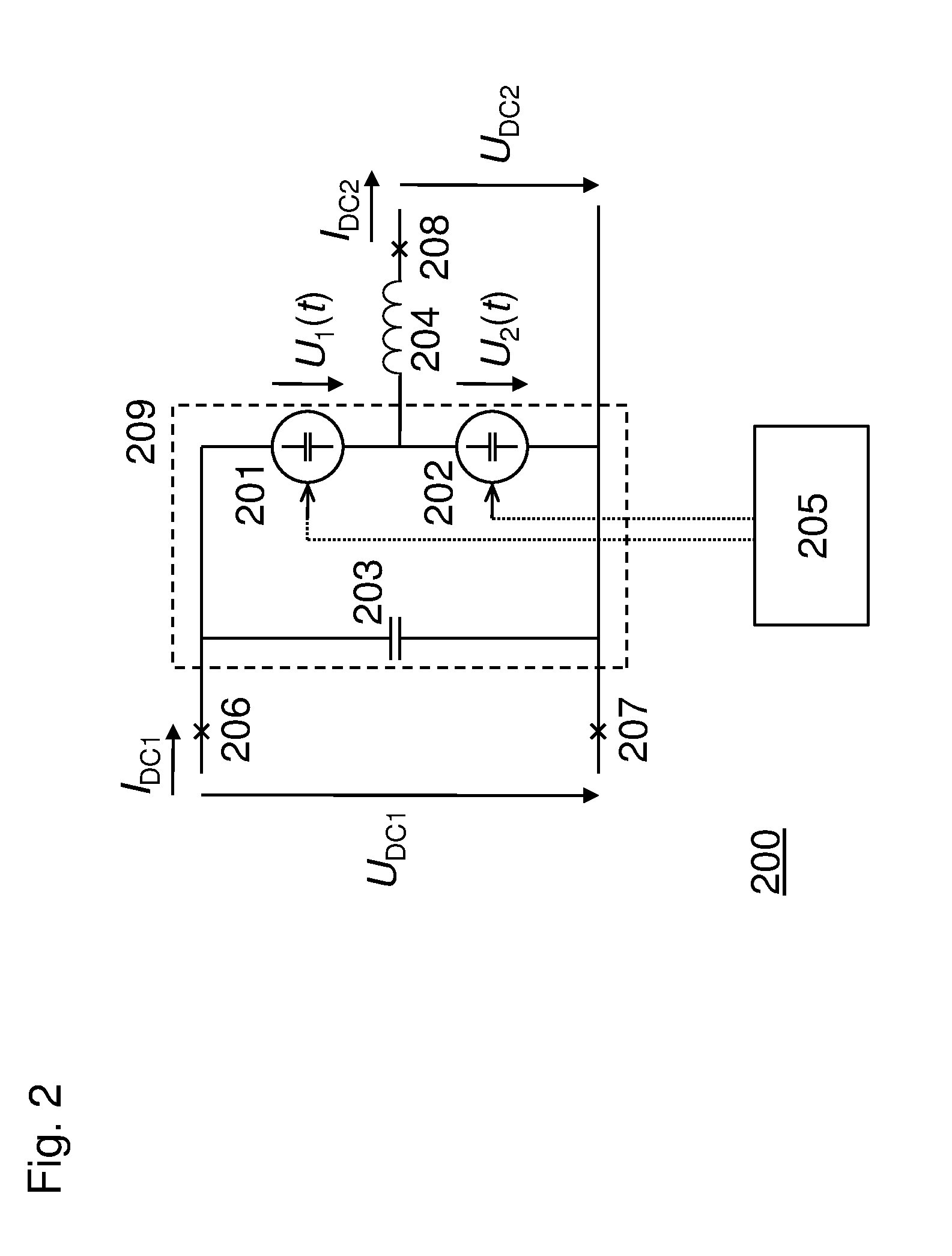
ActiveUS20140160812A1Reduced DC voltageIncrease rated powerAc-dc conversionElectric power transfer ac networkDc dc converterPhase difference
A DC-DC converter (200) comprising a first (201) and a second (202) variable voltage source, a capacitor (203), an alternating current filter (204), and controlling means (205), is provided. A first DC voltage (UDC1) is provided over a series-connection of the first and the second voltage source, and a second DC voltage (UDC2), being lower in magnitude than (UDC1), is provided over the second voltage source. The conversion between (UDC1) and (UDC2) is effected by circulating an alternating current within a circuit comprising the two voltage sources and the capacitor, thereby exchanging power between the two voltage sources. The alternating current is driven by AC voltage components provided by the first and the second voltage source. The controlling means is arranged for controlling the first and the second voltage source so as to maintain a phase difference between the AC components to be close to π.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
High voltage safety system and method for electrical cabinetry
ActiveUS20190228635A1Reduced DC voltageSimple designElectroluminescent light sourcesEnclosed substationsElectricityProgrammable logic controller
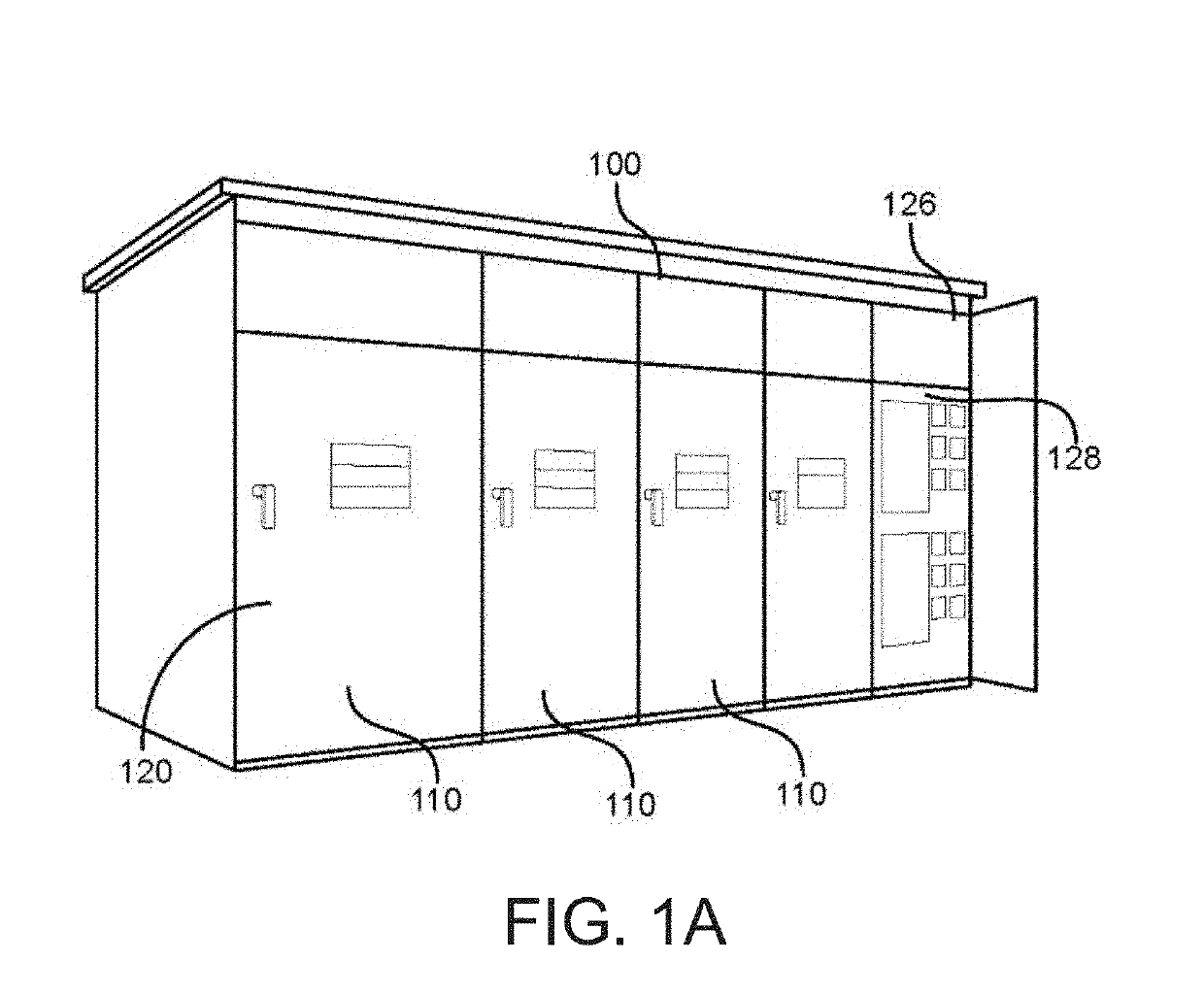
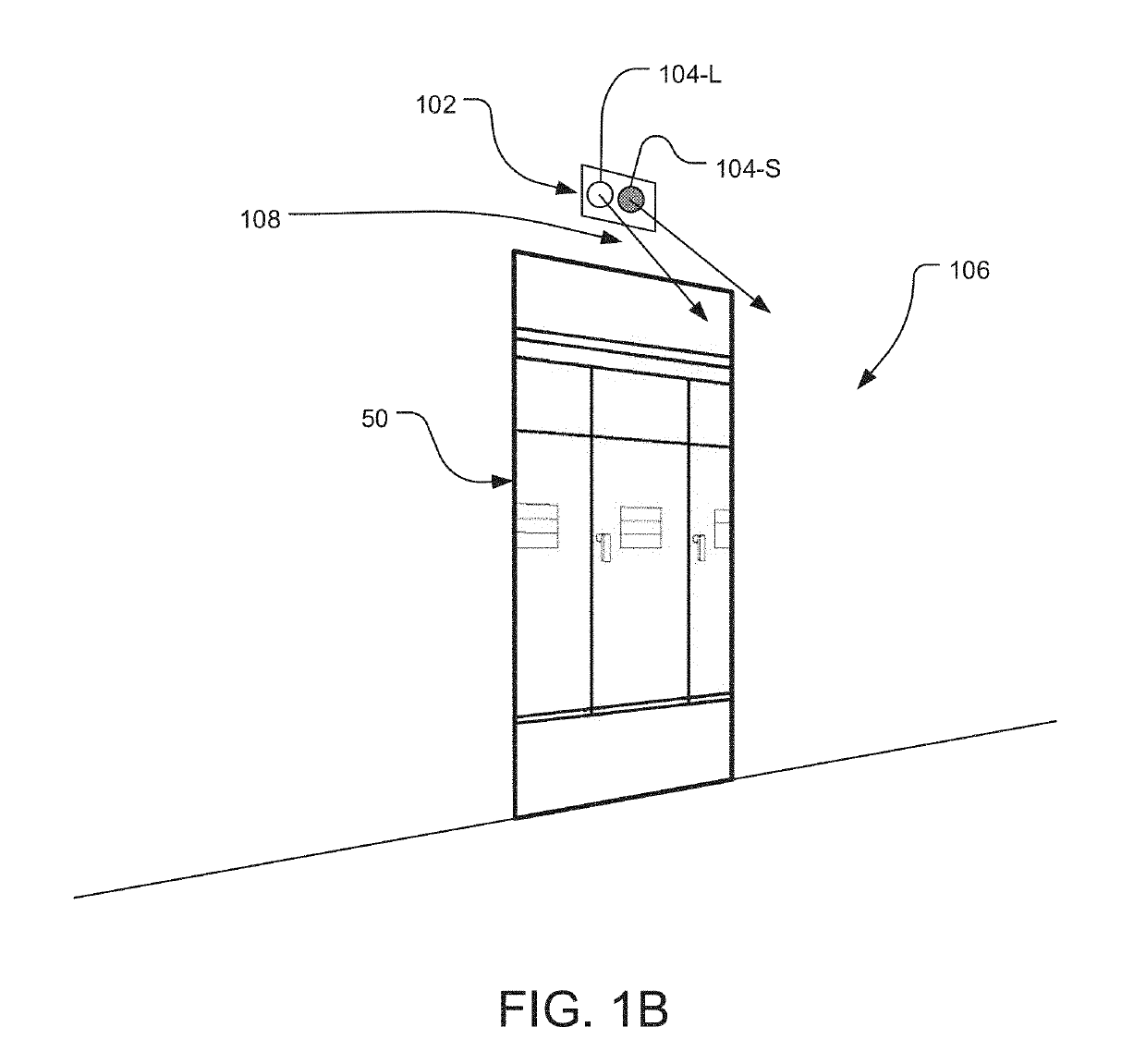
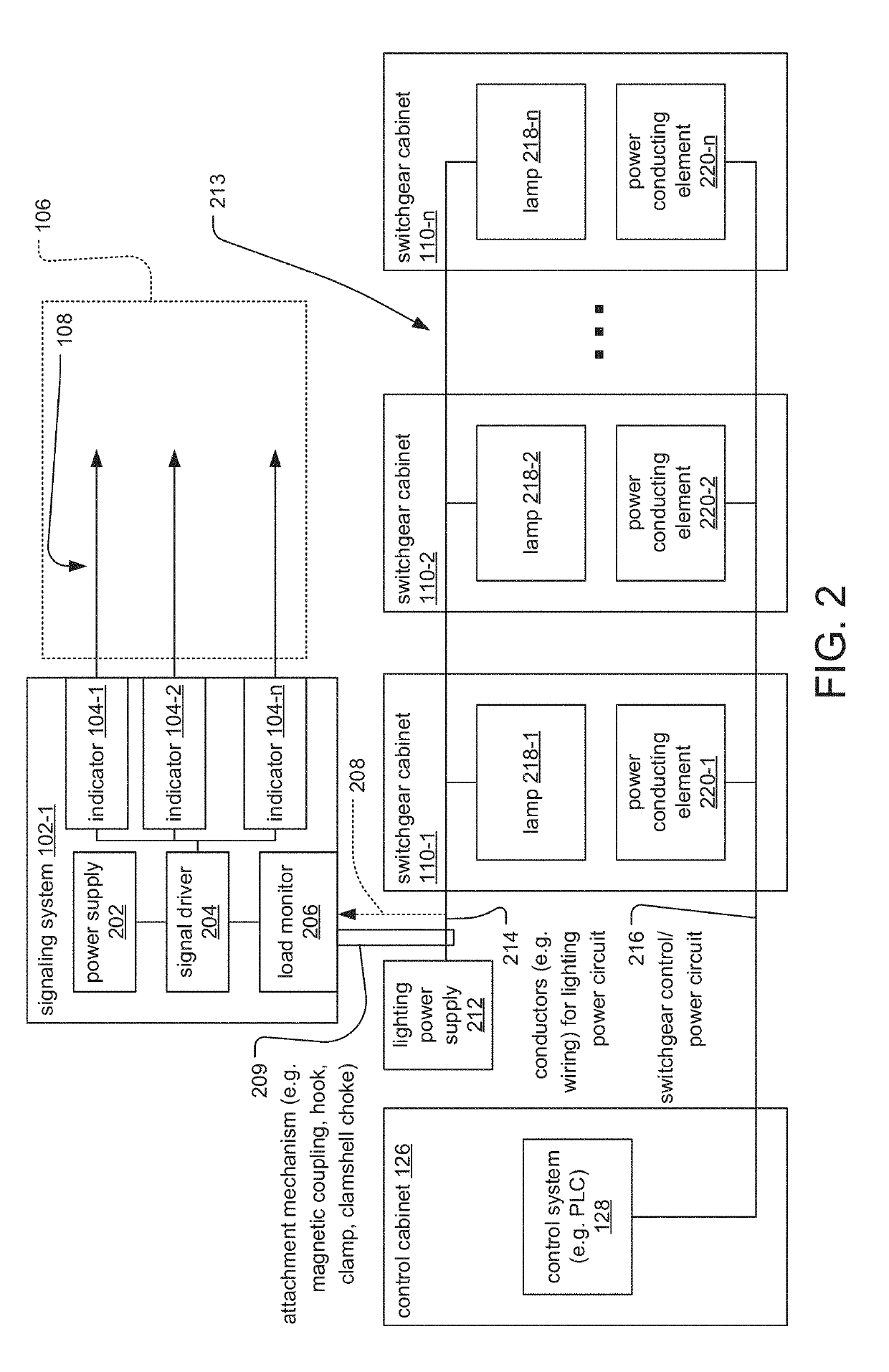
A safety system for high-voltage electrical cabinetry provides active visual and / or audible warnings during maintenance. Load monitors evaluate electrical loads of dedicated power circuits used by an existing automatic lighting system. Light and sound indicators present status information (e.g. indicating maintenance status or normal operating status) to persons in signaling areas based on whether the evaluated electrical loads indicate that at least one lamp is turned on. A common power supply can be used to power the lighting circuit and the indicators. Bridge modules can also be used to monitor the electrical load for different group lighting circuits and report discrete group status information to a programmable logic controller while also sharing the group status information with the other bridge modules. In this case, the indicators present combined status information, for example, indicating a maintenance status if any lamps from any group is turned on.
Owner:ADVANCETREX SENSOR TECH CORP
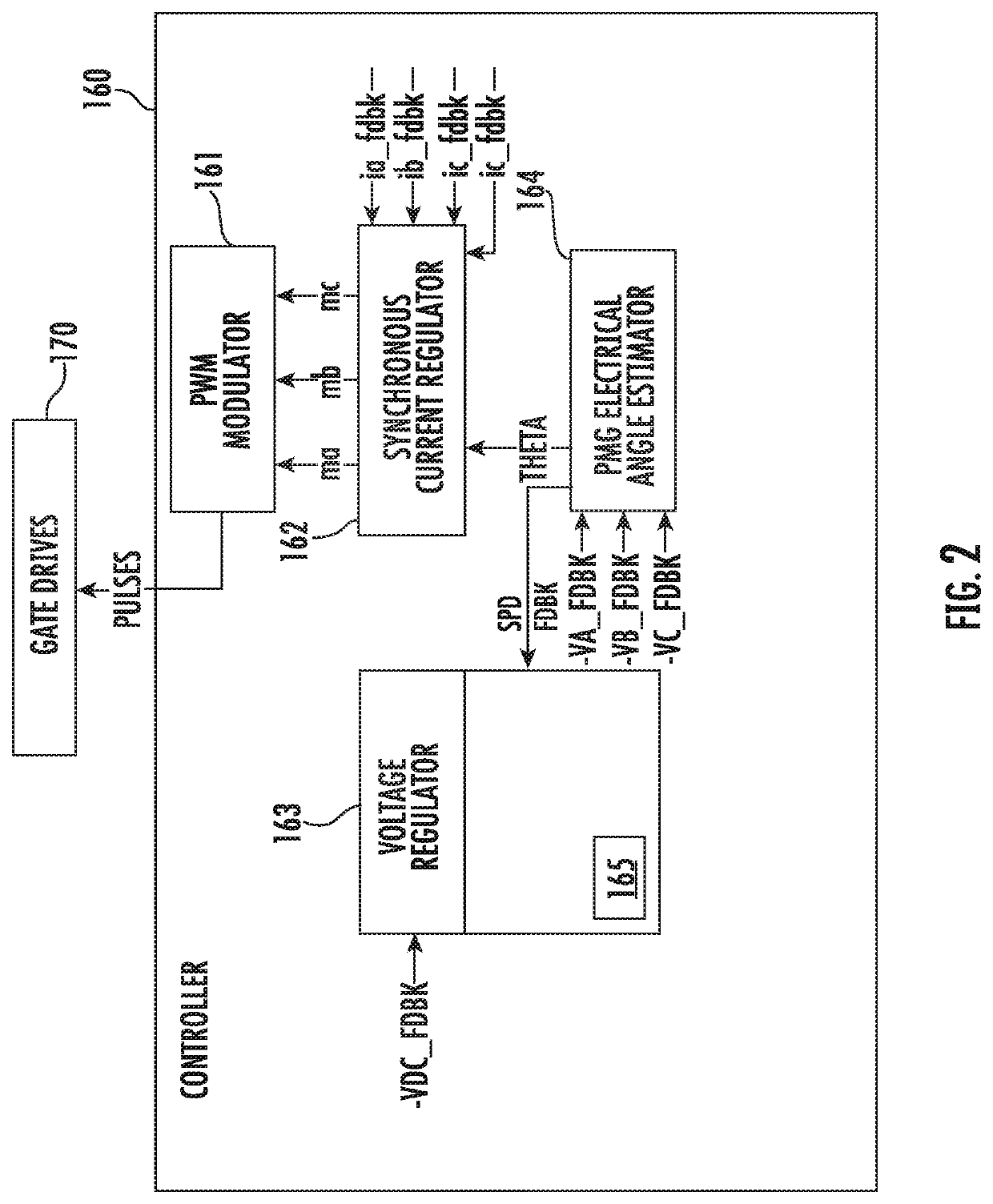
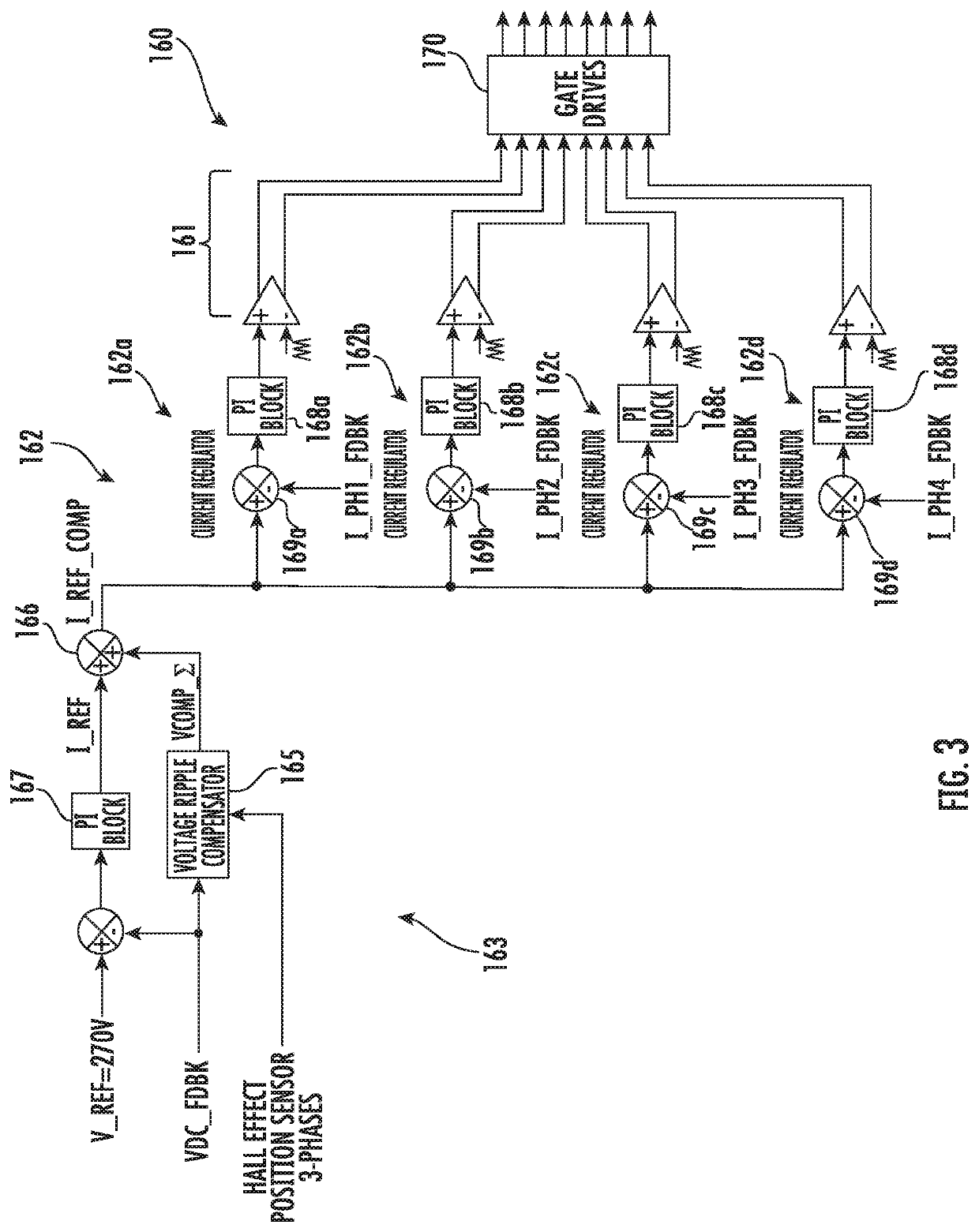
DC power generating system with voltage ripple compensation
ActiveUS10541598B1Reduce voltageReduced DC voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalDc-dc conversionConvertersClassical mechanics
A method and system for providing voltage ripple compensation in a DC power generation system. The system includes a permanent magnet generator (PMG) and a passive rectifier in operable communication with the PMG. The system also includes a boost converter in operable communication with the passive rectifier and a controller in electrical communication with the boost converter. The controller is configured to cause the boost converter to supply a DC bus and to control the boost converter based on a voltage compensation signal to the boost converter to reduce voltage ripple on the voltage of the DC bus.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
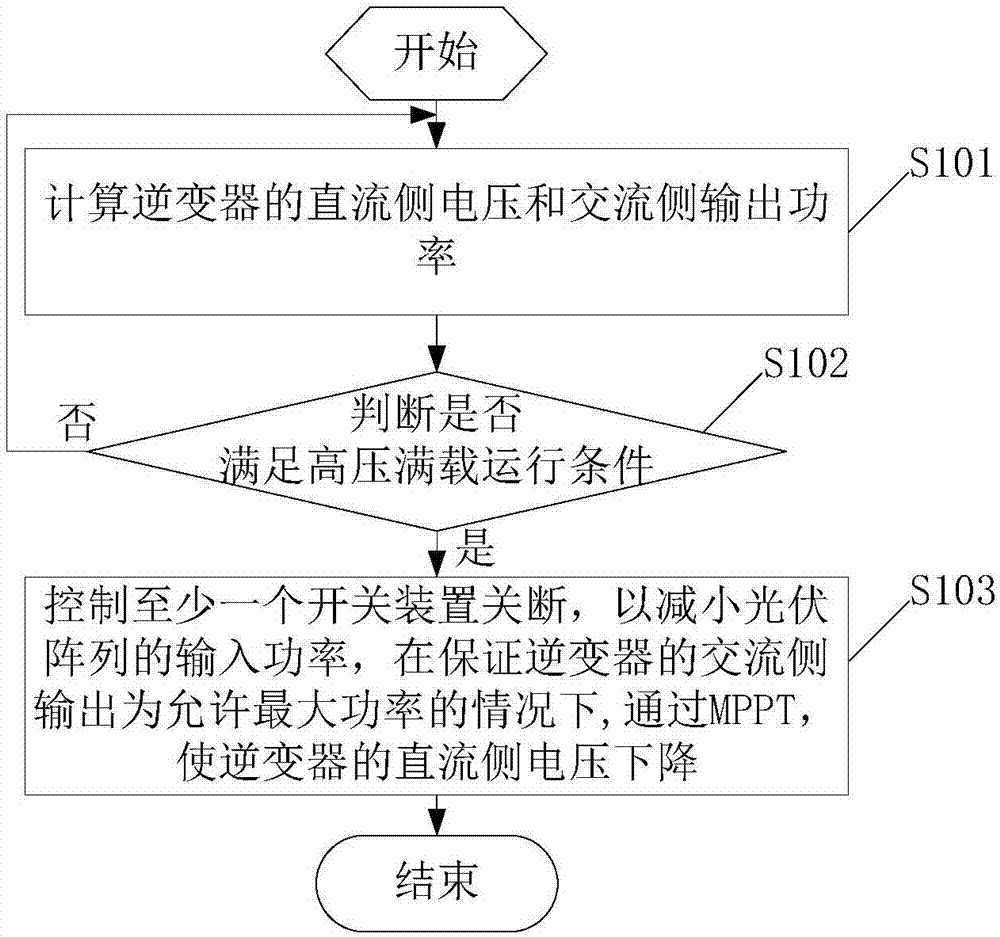
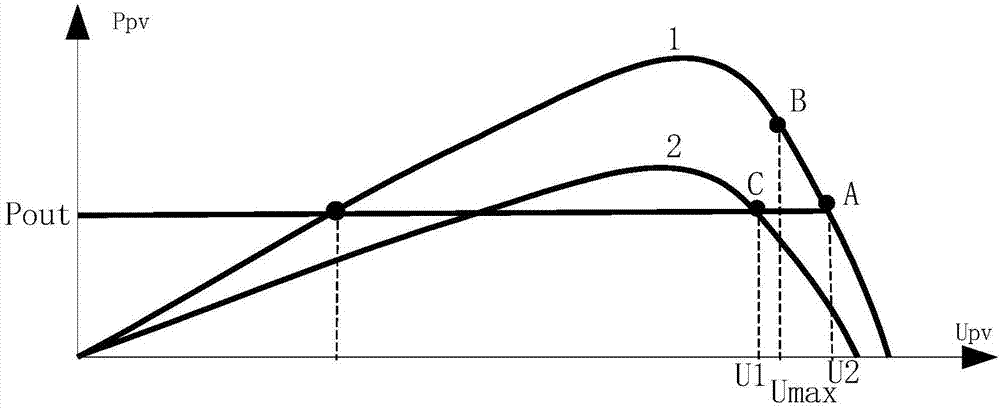
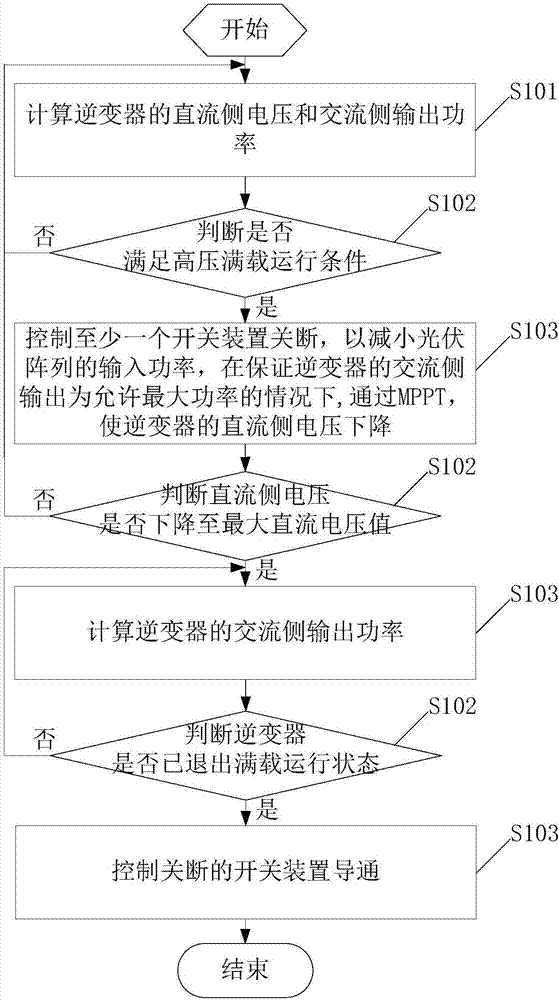
Inverter system and inverter over-capacity-distribution control method
ActiveCN107017665AAffect lifeReduce input powerSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationPower inverterDistribution control
The invention provides an inverter system and an inverter over-capacity-distribution control method. The inverter over-capacity-distribution control method includes the following steps that: the direct current-side voltage and alternating current-side output power of an inverter are calculated, whether the direct current-side voltage and the alternating current-side output power satisfy a high-voltage full-load operating condition is judged; the direct current-side voltage and alternating current-side output power of the inverter satisfy the high-voltage full-load operating condition, at last one switching device at a direct current side is controlled to be turned off, so that the input power of a photovoltaic array can be decreased, the direct current-side voltage of the inverter is made to be decreased through maximum power point tracking control under a condition that the alternating current-side output of the inverter is allowed maximum power; and operation is performed continuously until the direct current-side voltage of the inverter drops to a preset threshold value. With the inverter over-capacity-distribution control method adopted, the maximum power output of the inverter can be ensured, and the working point direct-current voltage of the inverter is decreased. According to the prior art, when the output power of the photovoltaic array is larger than maximum power which can be outputted by the inverter, the working point direct-current voltage will be too high, and as a result, the service life of the inverter will be affected, the operating reliability of a system will be decreased, and the generated power amount of the system will be decreased, while, with the method of the invention adopted, the problems in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
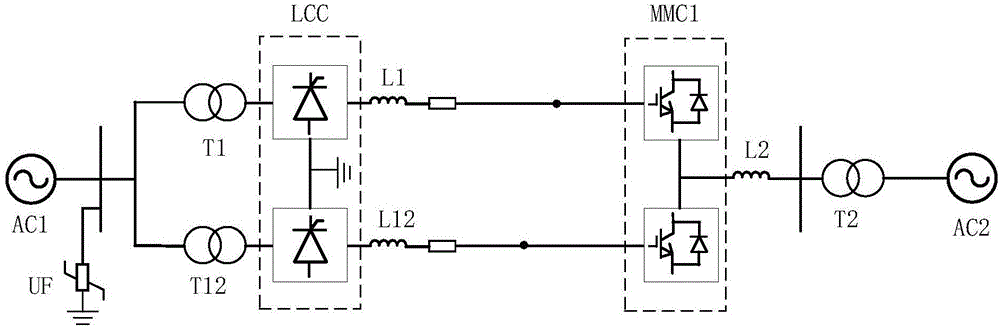
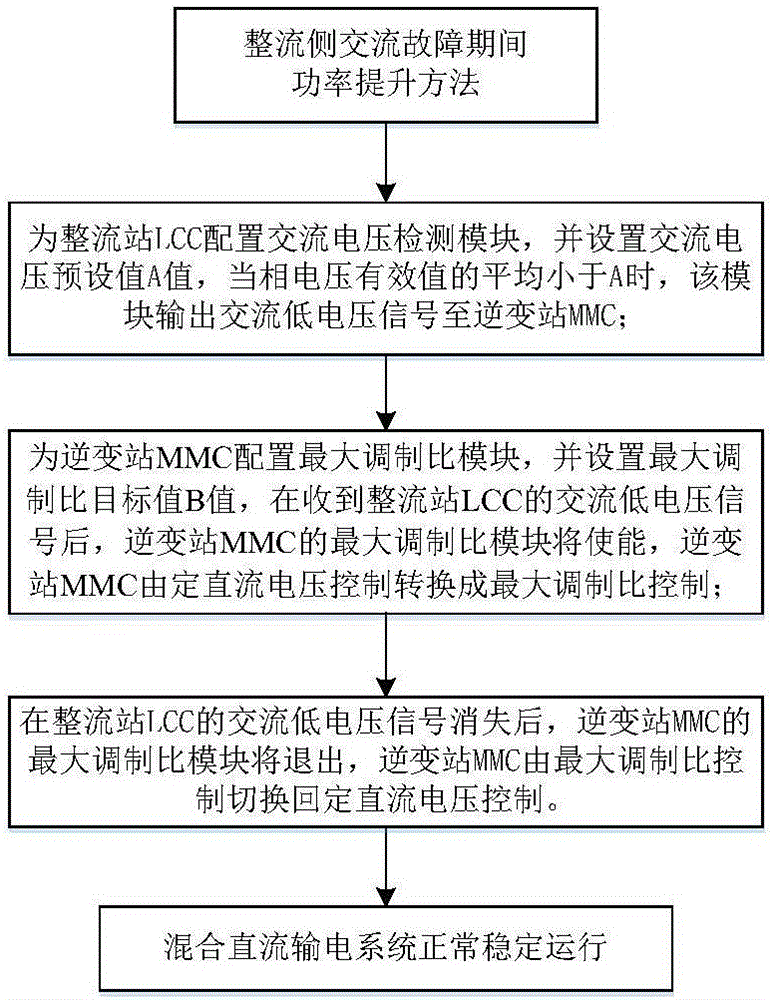
Method for increasing hybrid direct-current rectifier side power in alternating-current fault period
ActiveCN106329560AReduced DC voltageModulation Ratio IncreasedElectric power transfer ac networkDc currentEngineering
The invention discloses a method for increasing hybrid direct-current (DC) rectifier side power in an alternating-current fault period. LCC (line commutation converter) in a rectifier station is controlled by constant DC current and MMC (modular multilevel voltage source converter) in an inversion station is controlled by constant DC voltage; an alternating-current (AC) voltage detection module is configured to the LCC in the rectifier station and a maximum modulation ratio module is configured to the MMC in the inversion station. When AC voltage detected by the alternating-current voltage detection module is lower than a set value, the maximum modulation ratio module of the MMC is enabled and the control mode of the MMC is controlled from the constant DC voltage to the maximum modulation ratio. The method has the beneficial effects that the MMC is controlled by the maximum modulation ratio when the hybrid direct-current power transmission system presents the AC fault on the rectifier side, and DC transmission power can be effectively increased.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION +1
Amplifier common-mode control method
ActiveUS9231542B1Reduce sensitivityImprove common-mode control loop bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthAudio power amplifierMode control
A fully differential amplifier performs common-mode voltage control while having reduced sensitivity to random offsets and mismatches and improved common-mode control loop bandwidth. The amplifier disclosed comprises an additional common-mode control sub-amplifier, which senses common-mode voltage of the fully differential main amplifier at nodes within the continuous-time signal path feedback network, compares the common-mode voltage sensed with a reference voltage, and regulates depending on the result of the comparison the output common-mode voltage via the existing continuous signal path feedback network. Furthermore the internal common-mode control can be implemented in such a manner as to provide a feed-forward transconductance function in addition to common-mode control if desired. Moreover it is possible to use feedback from other amplifier stages in an amplifier chain to implement common-mode feedback.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICON UK
Semiconductor thermoelectric air-conditioning and water-heating device
InactiveCN104534582AAvoid atmospheric greenhouse effectImprove equipment reliabilityMachines using electric/magnetic effectsSustainable buildingsConservation of energyWater tanks
The working principle of a semiconductor thermoelectric air-conditioning and water-heating device is that when one portion of electric energy is input, 1.5 portions of cold energy is generated on a refrigerating end face of a semiconductor thermoelectric element, and indoor return air, which is driven by a draft fan to flow downwardly and passes through vertical air side fins, is cooled by the cold energy through the vertical air side fins, so that an air-conditioning function is achieved; according to the energy conservation law, 2.5 portions of heat is generated on a heating end face of the semiconductor thermoelectric element, and water, which is driven by the siphon effect to flow upwardly and passes through the side wall of a hot water tank and vertical hot water side fins, is heated by the heat energy through the side wall of the hot water tank and the vertical hot water side fins, and the heated water is insulated by a thermal insulation material at the outer side of the hot water tank; while the device is in use, cold water enters the hot water tank from a water inlet, and after the cold water is heated, hot water flows out of the hot water tank from a water outlet, so that a water-heating function is achieved. The energy efficiency ratio of air conditioning to water heating reaches up to 4.
Owner:侴乔力 +1
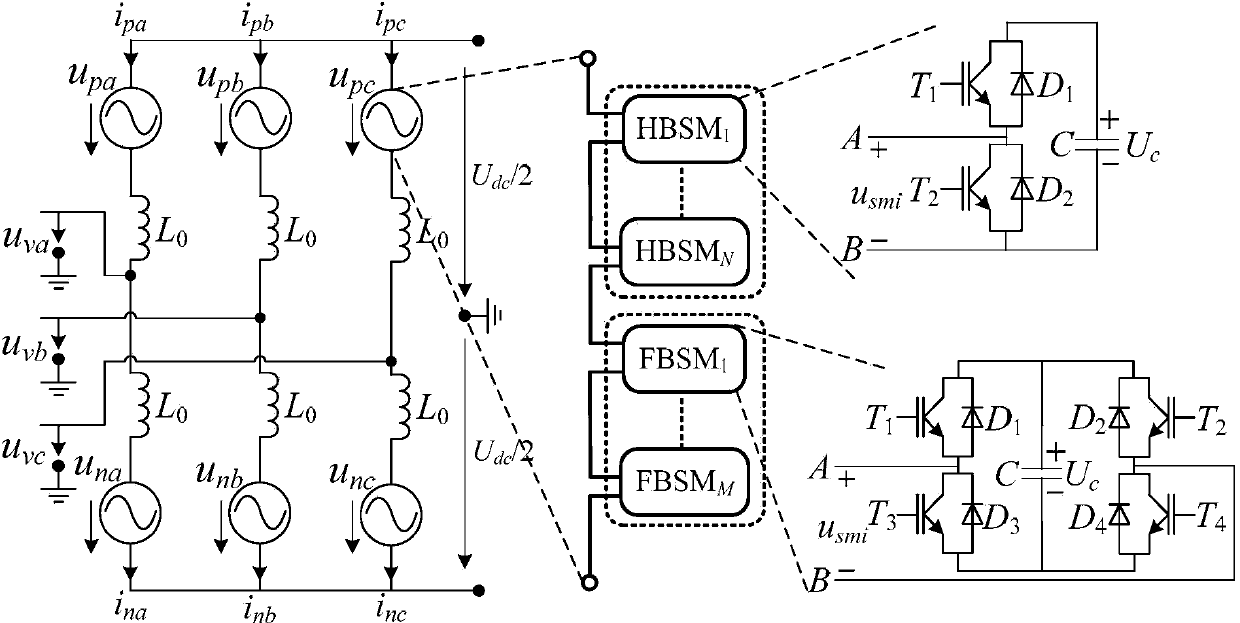
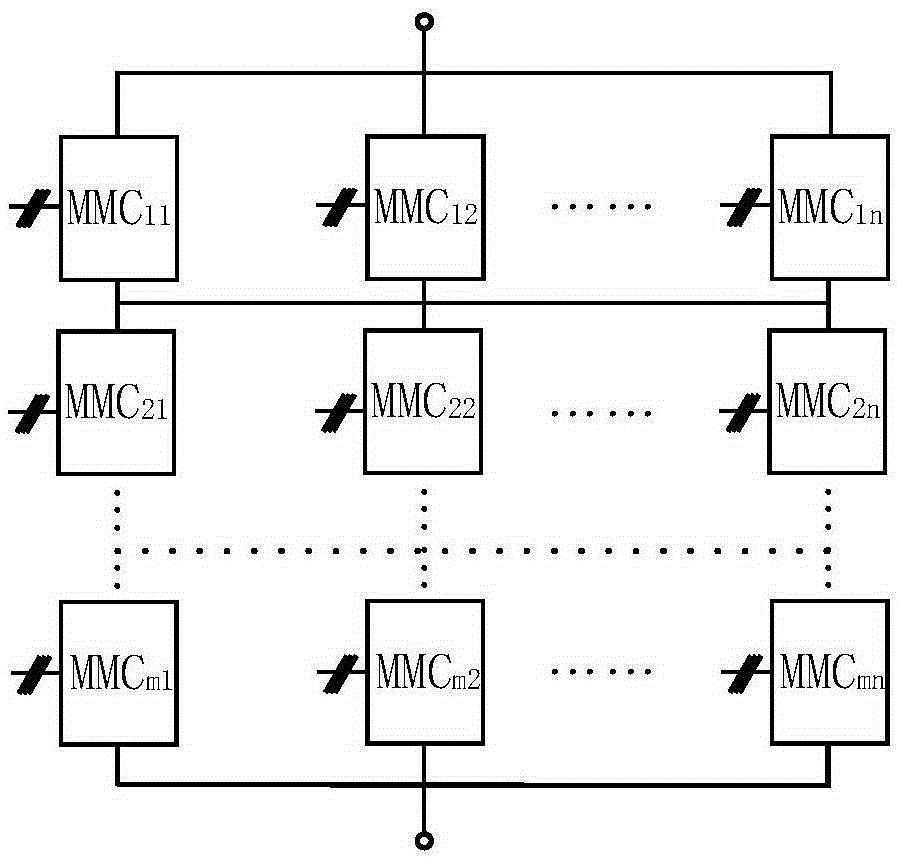
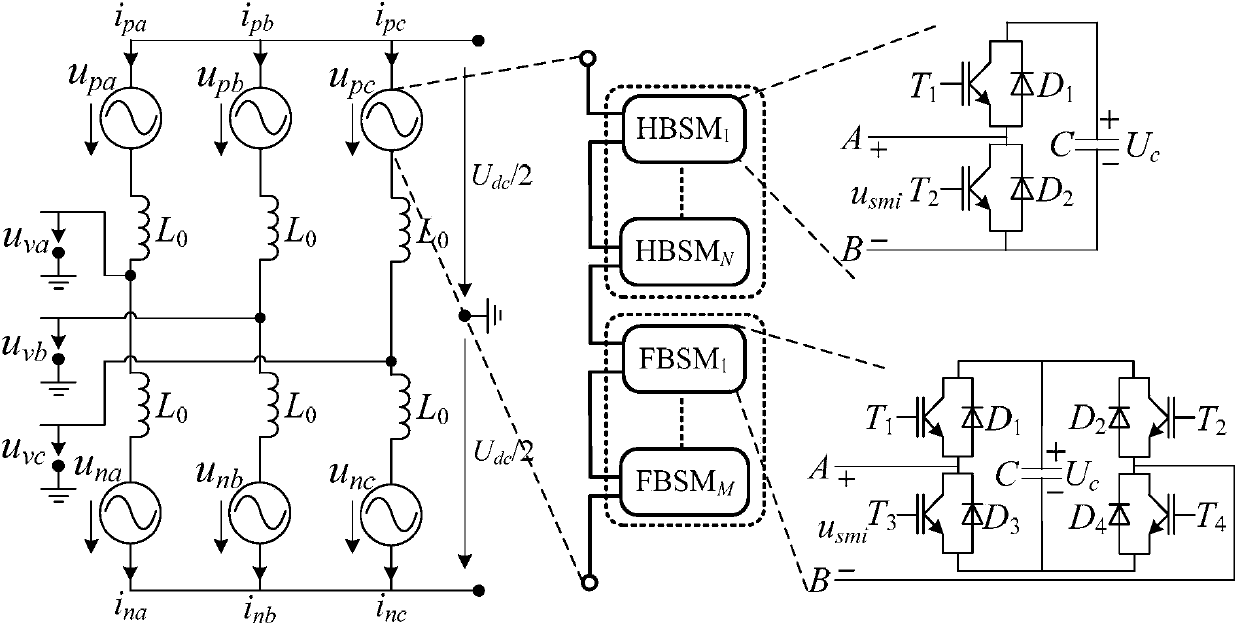
DC power transmission system based on modularized multi-level converter unit
InactiveCN105281314AControl balance and stabilityReduced DC voltageDc network circuit arrangementsElectric power transfer ac networkModularityLevel converter
The invention relates to a DC power transmission system based on a modularized multi-level converter unit. The system is formed by M by N MMCs and (M+1) buses, wherein every N MMCs form a unit layer, and M unit layers are formed in total. The N MMCs in each unit layer are connected in parallel between a positive bus and a negative bus. The M unit layers are connected in series successively, and each MMC in every unit layer is connected to the positive bus which is the negative bus connected with the MMCs in the previous unit layer. The intersecting redundant structure of the system solves the problem of poor fault-tolerant capability of the system.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +4
Internal and external fault recognition method utilizing transient energy
InactiveCN110231538AReliable electrode selectionSimple logical structureFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemTransient stateEnergy products
The invention relates to an internal and external fault recognition method utilizing transient energy and belongs to the technical field of high-voltage direct current transmission line fault recognition of modular multilevel converters. Firstly, voltage and current of a measurement end of a positive pole line acquired by a measurement end high-speed acquisition device are read; secondly, voltageand current fault components in a 5 ms time window are obtained according to the acquired voltage and current and the voltage and the current in a steady state; the obtained fault components are multiplied and integrated so as to obtain the transient energy, afterwards, the positive and negative of the transient energy product of the lines on the two sides are judged, if the transient energy product is positive, the fault is an internal fault, and if the transient energy product is negative, the fault is an external fault. According to the method in the invention, the transient energy in the short-time window after the fault is calculated, the difference between the line fault and the external fault is obvious, and reliable pole selection is facilitated. The algorithm of obtaining the transient energy is simple, and the integral logic structure is simple.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
CMOS single variable frequency circuit
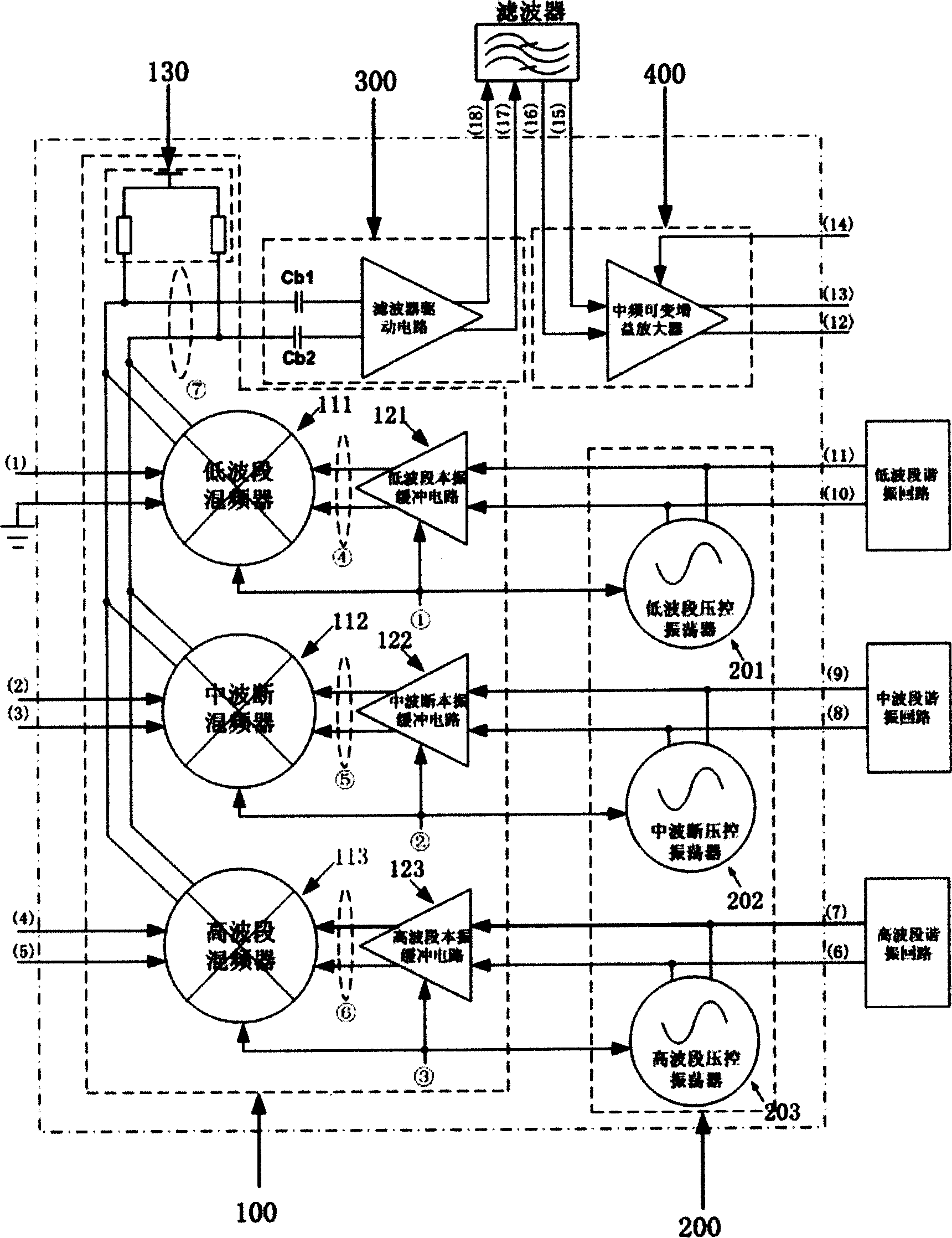
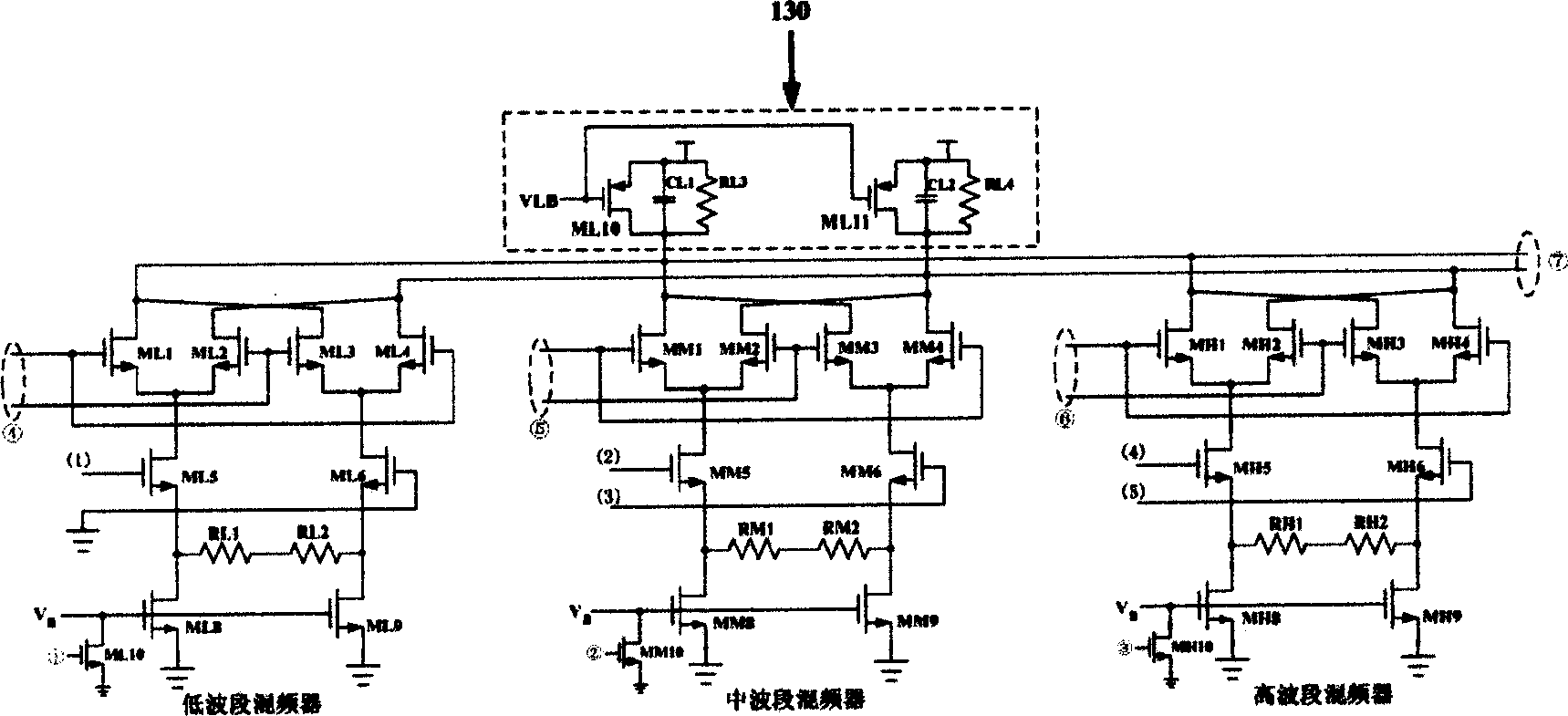
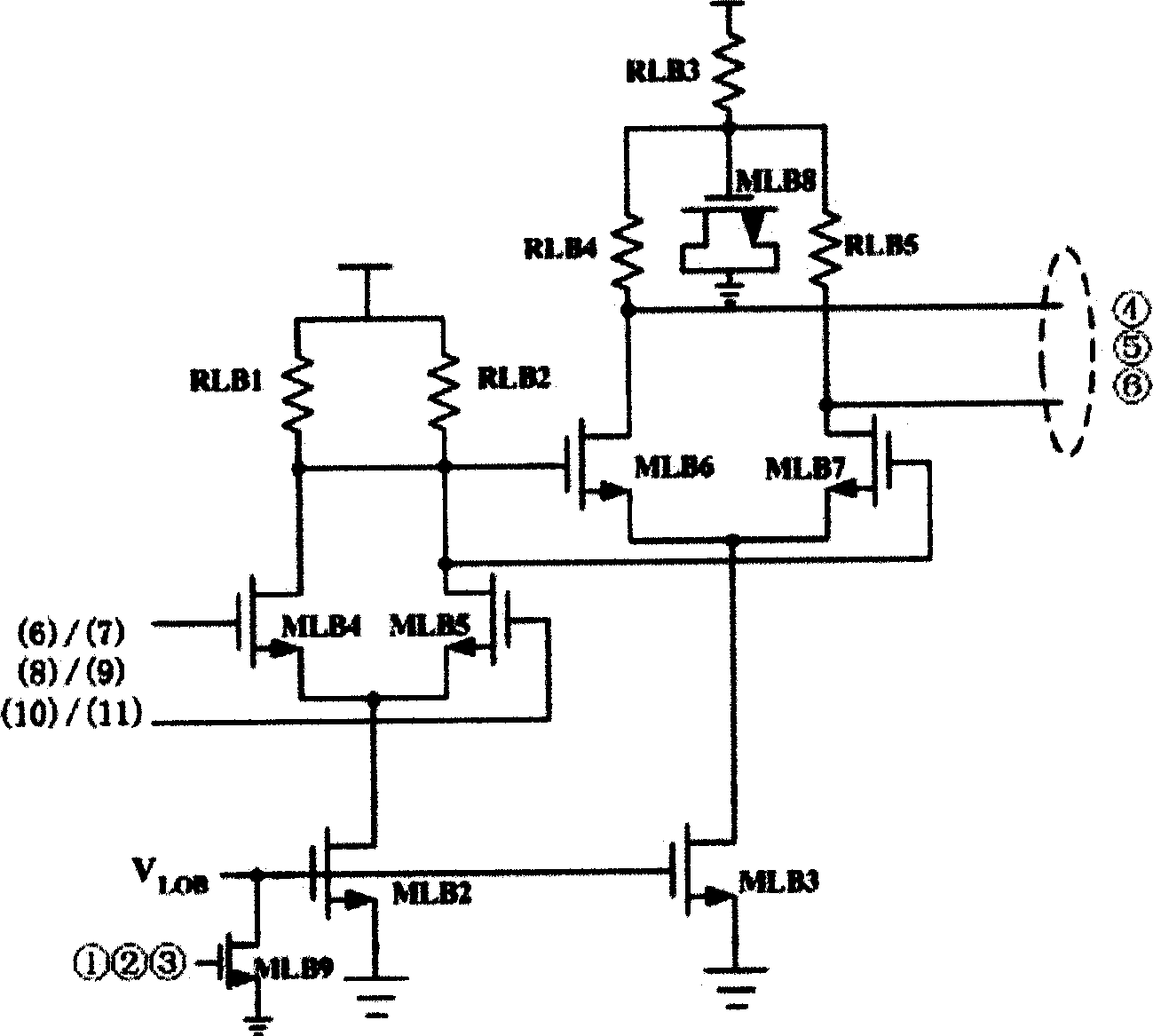
InactiveCN1589001AReduce system costReduced DC voltageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsWave bandCMOS
This invention discloses a CMOS mono-conversion circuit specially used in digital TV tuner chip composed of a three-band frequency-mixer, a three-band voltage-controlled oscillator, a filter drive circuit and an IF variable gain amplifier characterizing that oscillators of low, middle and high bands all apply the voltage-controlled oscillation basic circuits in the same circuit structure which is composed of a voltage-controlled oscillator, an amplitude detection circuit and a first comparator, two output ends of the oscillator are connected with two inputs of the amplitude detection circuit, the out put of which is linked with the negative input end of the first comparator which positive input is linked to vrefh, a second comparator and a charge pump are set between the detection circuit and the oscillator, the negative input of second is linked to output of the detection circuit, its positive is linked to the vreth.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
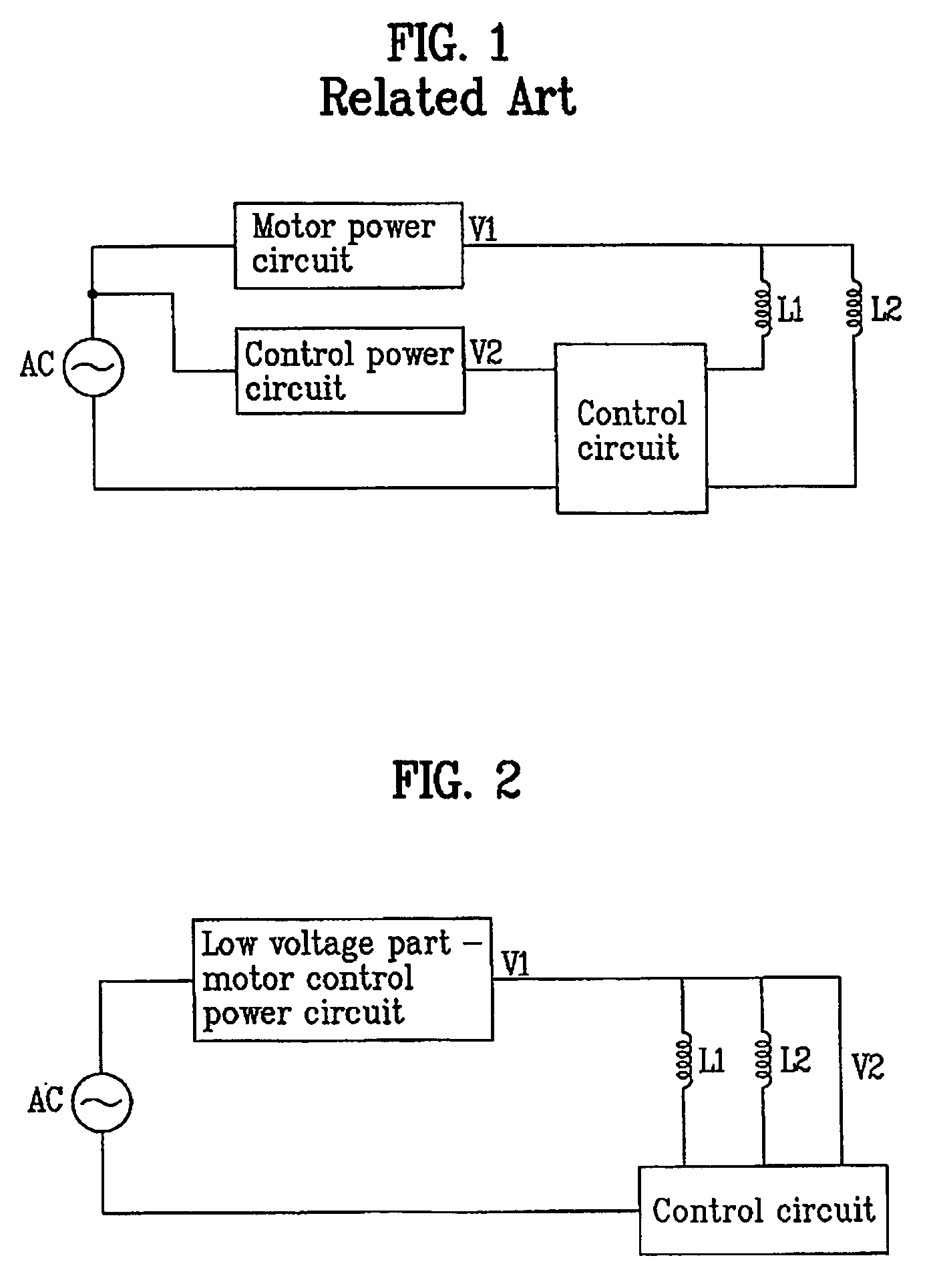
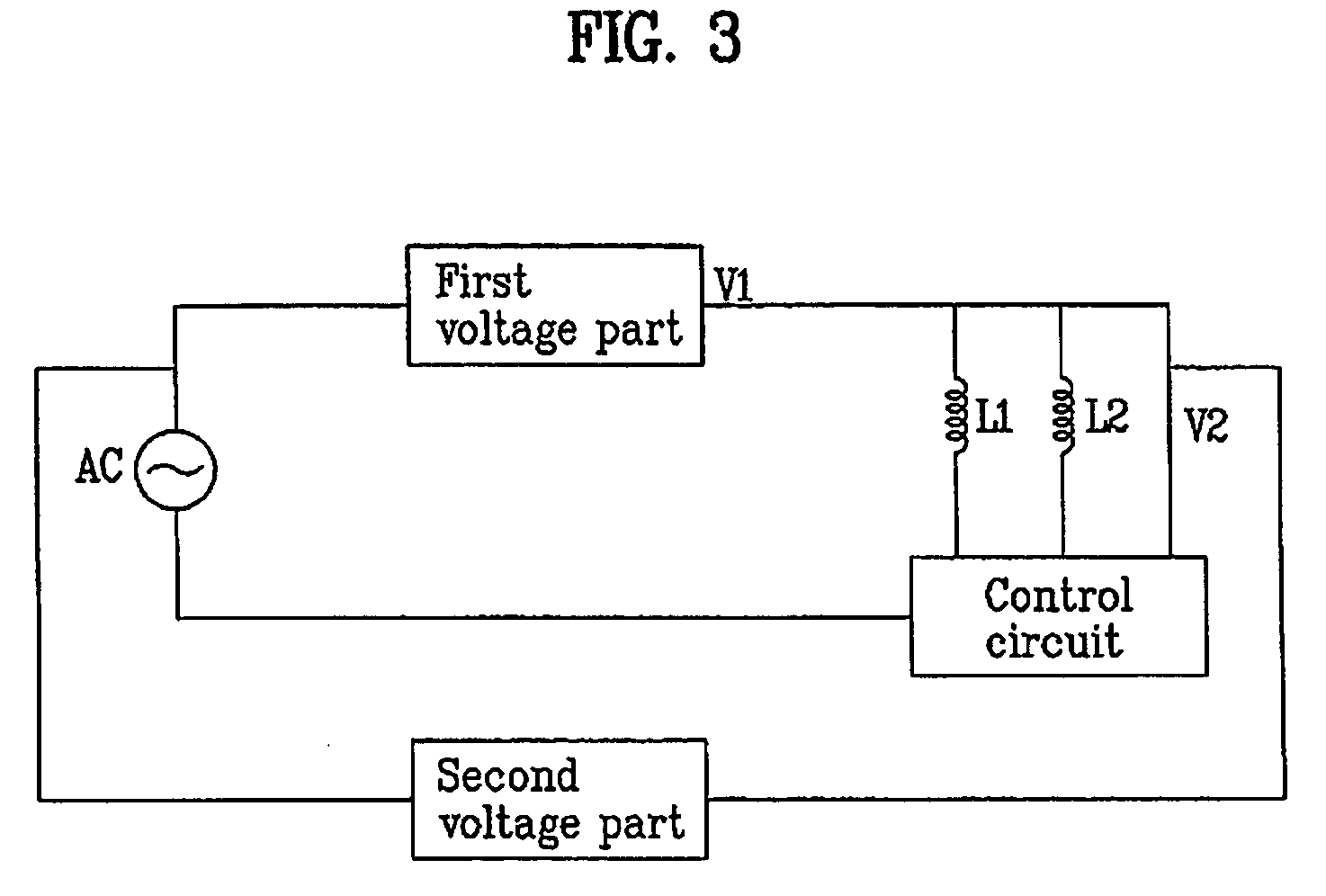
Motor power device and motor including the same
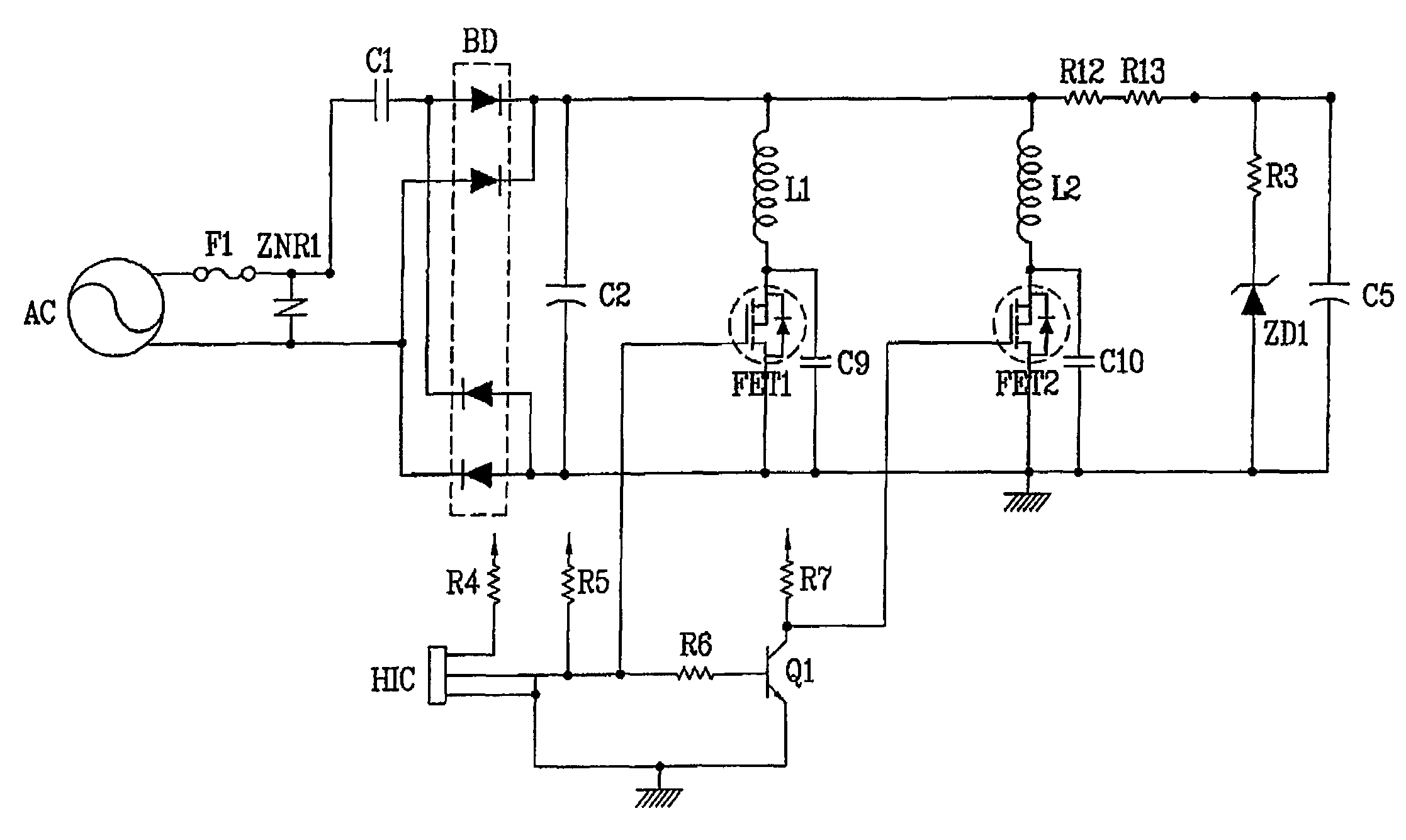
InactiveUS20080137239A1Reduced DC voltageLow costSingle-phase induction motor startersEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionMotor driveLow voltage
A motor power device includes a power circuit having a low voltage part that receives and converts AC power and outputs DC voltage, wherein a first power for a motor drive coil and a second power for a control circuit controlling the motor drive coil are supplied by using the DC voltage outputted from the power circuit, and a motor may include the motor power device. In one aspect, a motor power device is provided that may supply a DC voltage by using an AC power regardless of the magnitude of the AC power. In another aspect, a power circuit may output suitable DC voltage with less cost even though the magnitude of the AC power has changed. In yet another aspect, a motor power device is provided that may supply power for driving a motor drive coil and a power for a control circuit controlling the motor drive coil using one power circuit.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Liquid crystal display with touch keys
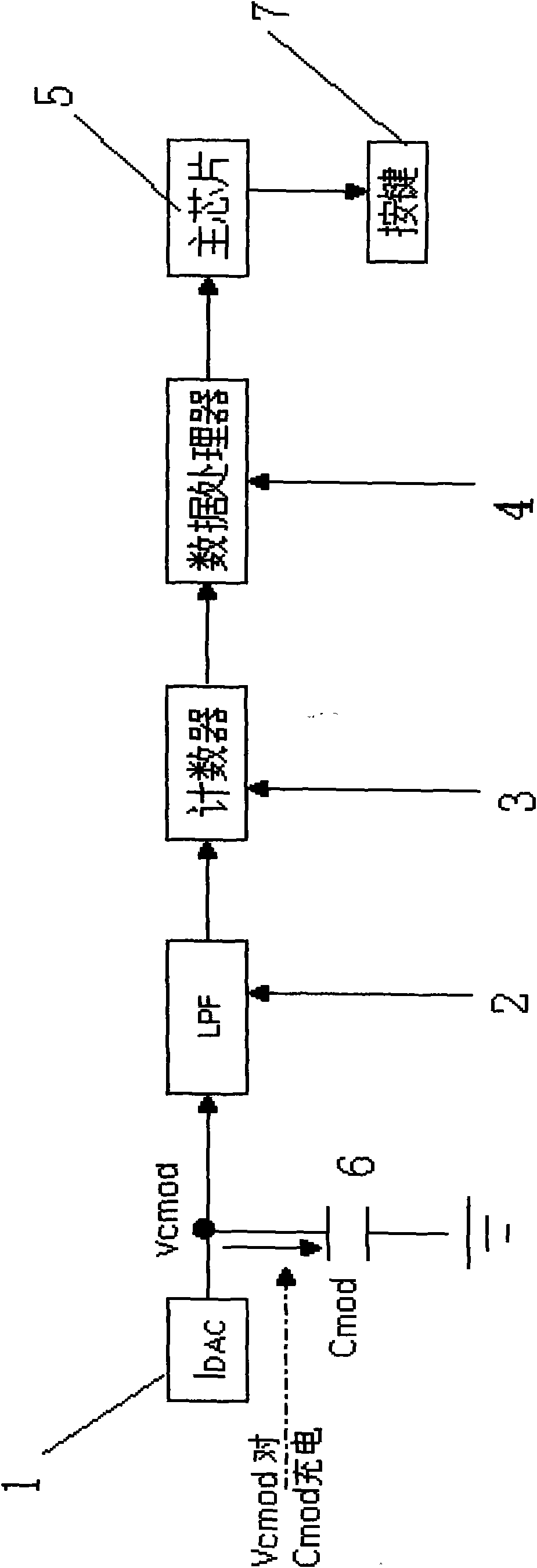
InactiveCN101576671ANovel and fashionable structureTo satisfy the market's needsStatic indicating devicesElectronic switchingControl functionCapacitance
The invention discloses a liquid crystal display with touch keys, which comprises a control panel metal disc, a low pass filter, a counter, a data processor, a main chip and a capacitor; the input end of the low pass filter is connected with the control panel metal disc; the output end of the low pass filter is connected with the counter; the input end of the data processor is connected with the output end of the counter, while the output end is connected with the main chip; the capacitor is arranged between the output end of the control panel metal disc and the input end of the low pass filter; current generated by the control panel metal disc charges the capacitor, and stable voltage signals are transmitted to the counter through the low pass filter to obtain the charging time; and the data processor determines the range of voltage values according to the charging time and sends continuous signals to the main chip, and the main chip processes the continuous signals to obtain a working state. The liquid crystal display utilizes static induction touch keys, can have control function in the condition of not contacting, has fashionable and novel structure, and can meet the market requirement.
Owner:NANJING LG TONGCHUANG COLOR DISPLAYS SYST CO LTD
Single-phase photovoltaic power generation converter topology
InactiveCN106026727AReduced DC voltageAc-ac conversionPhotovoltaic energy generationPower gridGrid connection
The invention discloses a single-phase photovoltaic power generation converter topology, belongs to the technical field of power electronic conversion, and mainly aims at solving the problems that output voltage of a household low-power photovoltaic power generation system cannot meet the grid connection requirements and the requirements of a local load on voltage in general. The single-phase photovoltaic power generation converter topology is mainly characterized by comprising a single-phase inverter and an AC-AC converter, wherein an output end of the single-phase inverter is connected with an input end of the AC-AC converter. DC power generated by photovoltaic modules is converted into AC power by the single-phase inverter; and the obtained AC power is boosted by the AC-AC converter and then is connected to a power grid or used by the local load. The single-phase photovoltaic power generation converter topology has the uniqueness that AC boosting is carried out after inversion, and the single-phase photovoltaic power generation converter topology is suitable for the application of relatively low DC voltage (relatively few photovoltaic modules are connected in series) generated by the photovoltaic modules.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
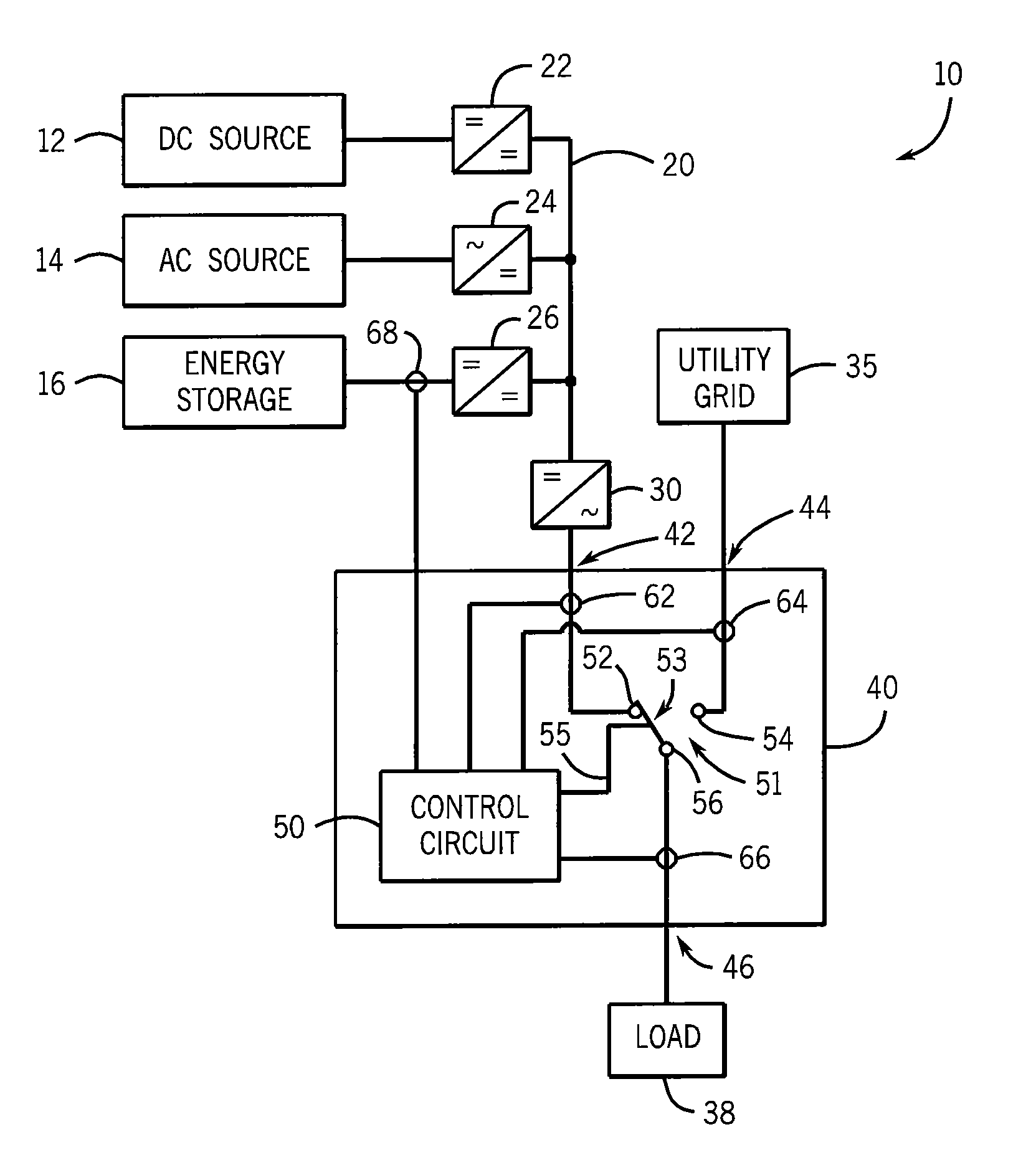
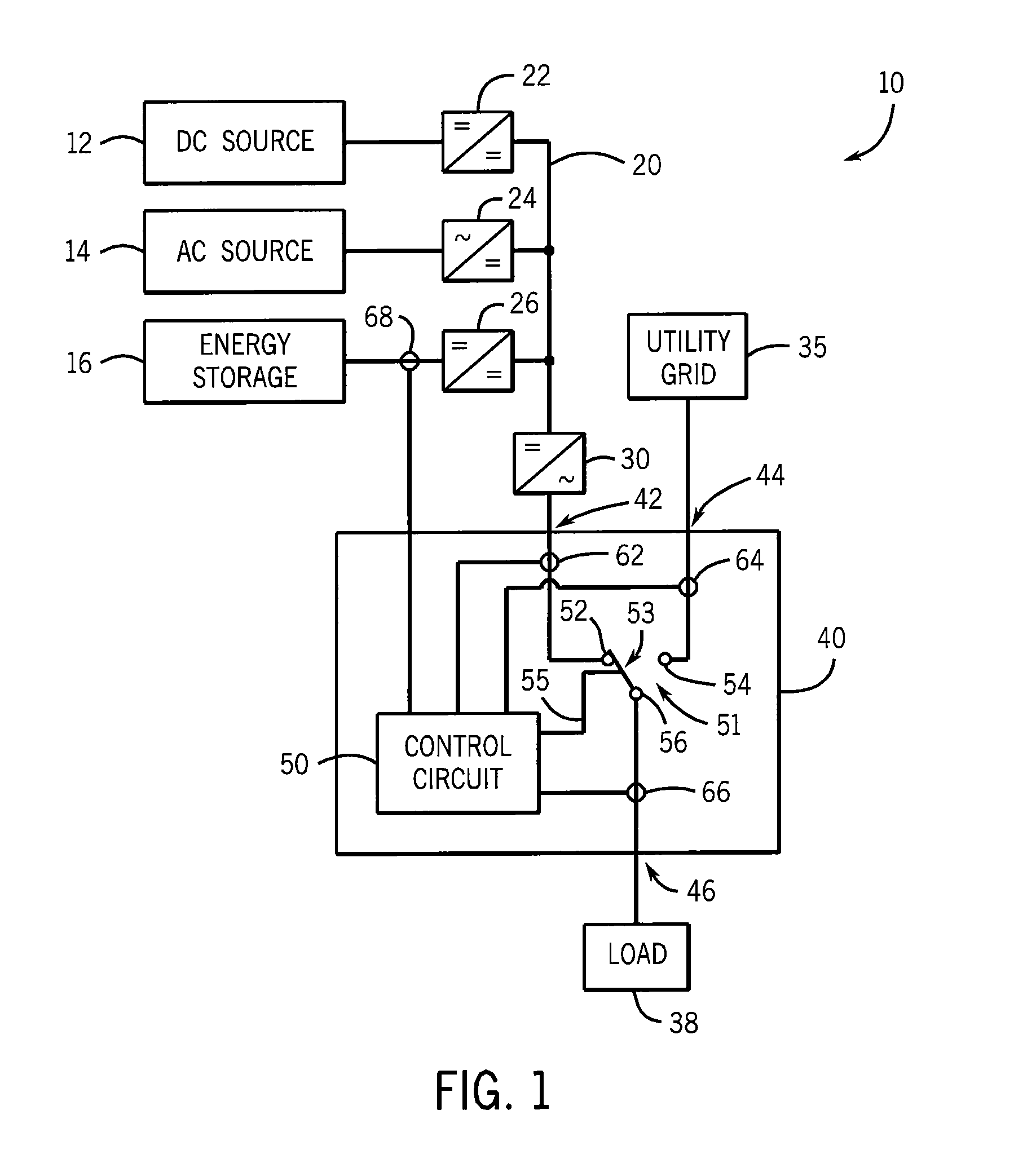
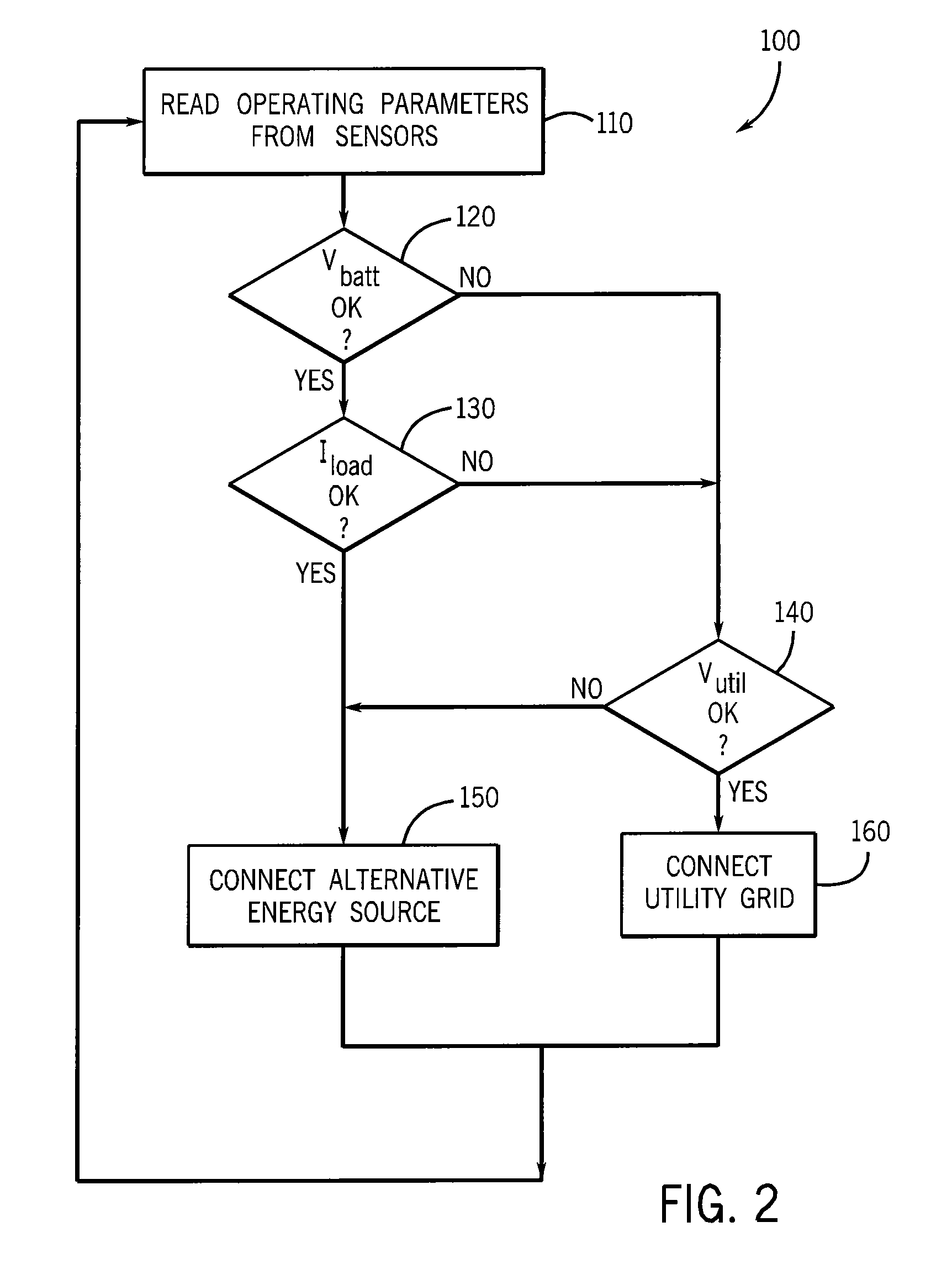
Transfer switch for automatically switching between alternative energy source and utility grid
ActiveUS9583942B2Weaken energyReduced DC voltageElectric signal transmission systemsPower network operation systems integrationElectricityFrequency changer
An automatic transfer switch configured for connection to a non-traditional, full-time or intermittent power source, such as a wind turbine or solar panel, selectively connects the non-traditional power source as a primary power source and a utility-derived power source as a secondary power source. The intermittent power source includes an energy storage device, such as a bank of DC batteries, to supplement power delivery during periods of low energy production. The power is provided to an AC load via a DC-to-AC inverter. The transfer switch includes an input to monitor the voltage level on the energy storage device and will switch from the primary power source to the utility power source when the voltage level on the energy storage device drops below a preset level. Thus, a loading condition that exceeds the rating of the inverter will not fault the inverter or limit the power available to the loads.
Owner:RELIANCE CONTROLS
Light-emitting device and control method of the same
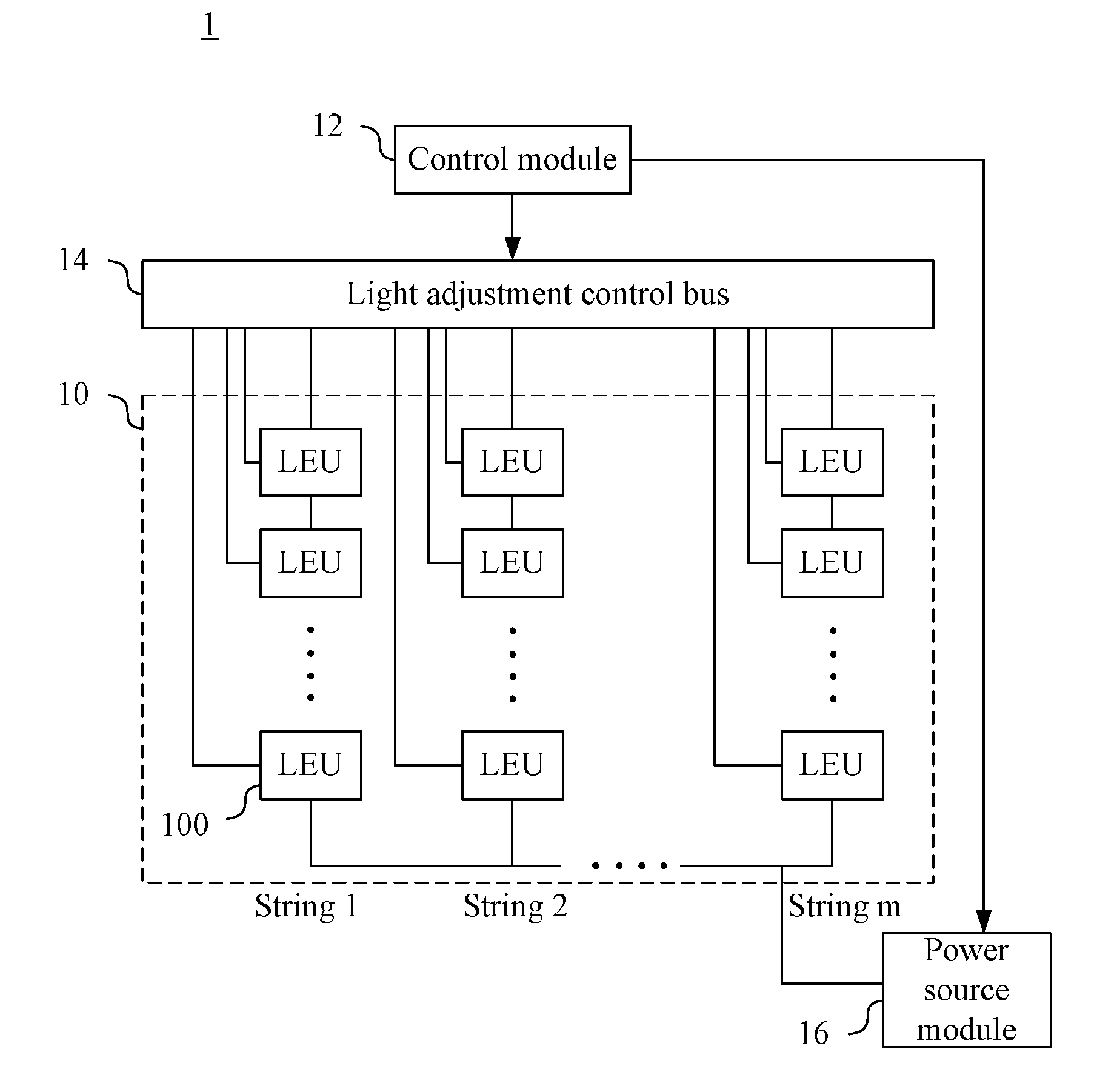
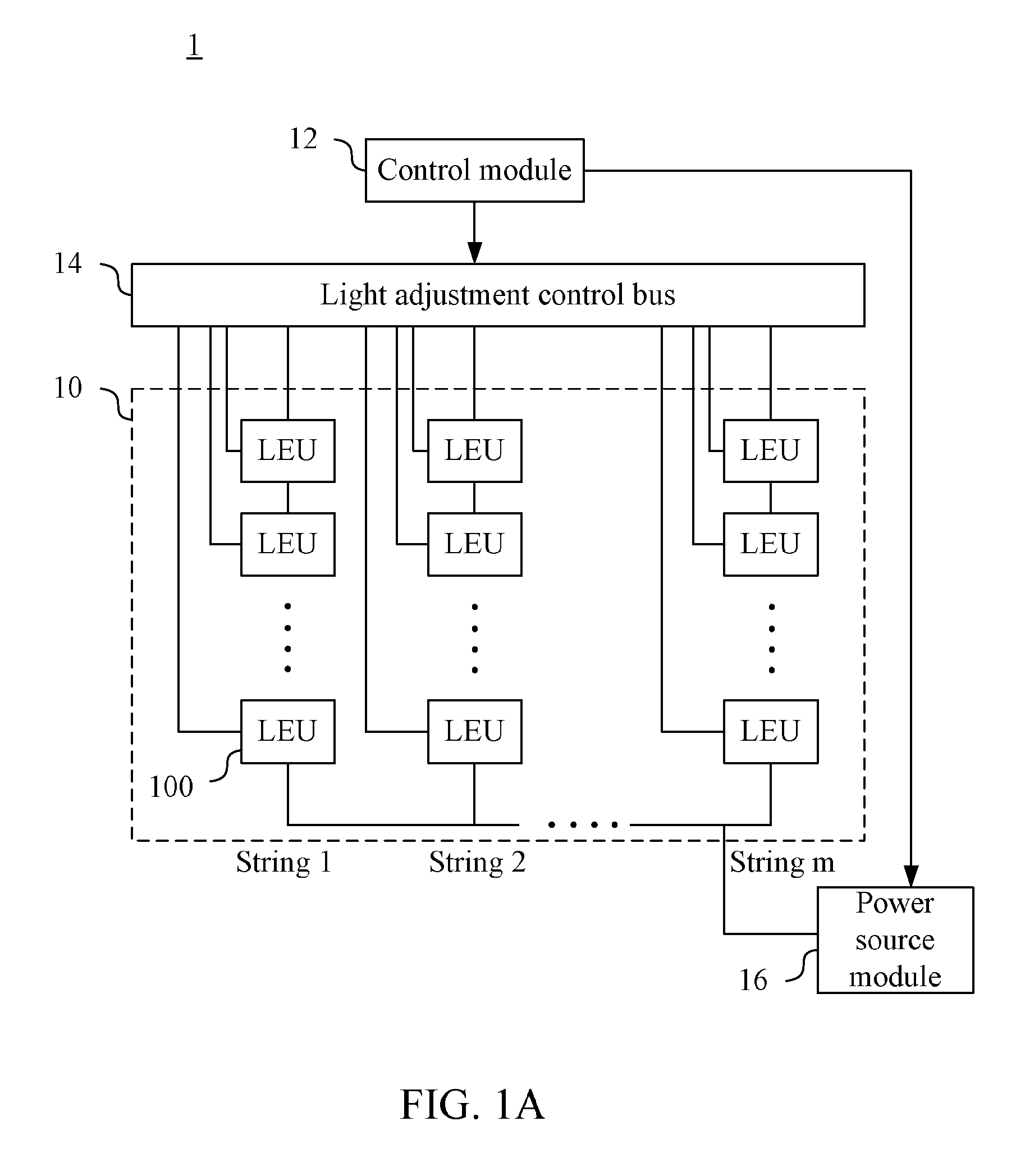
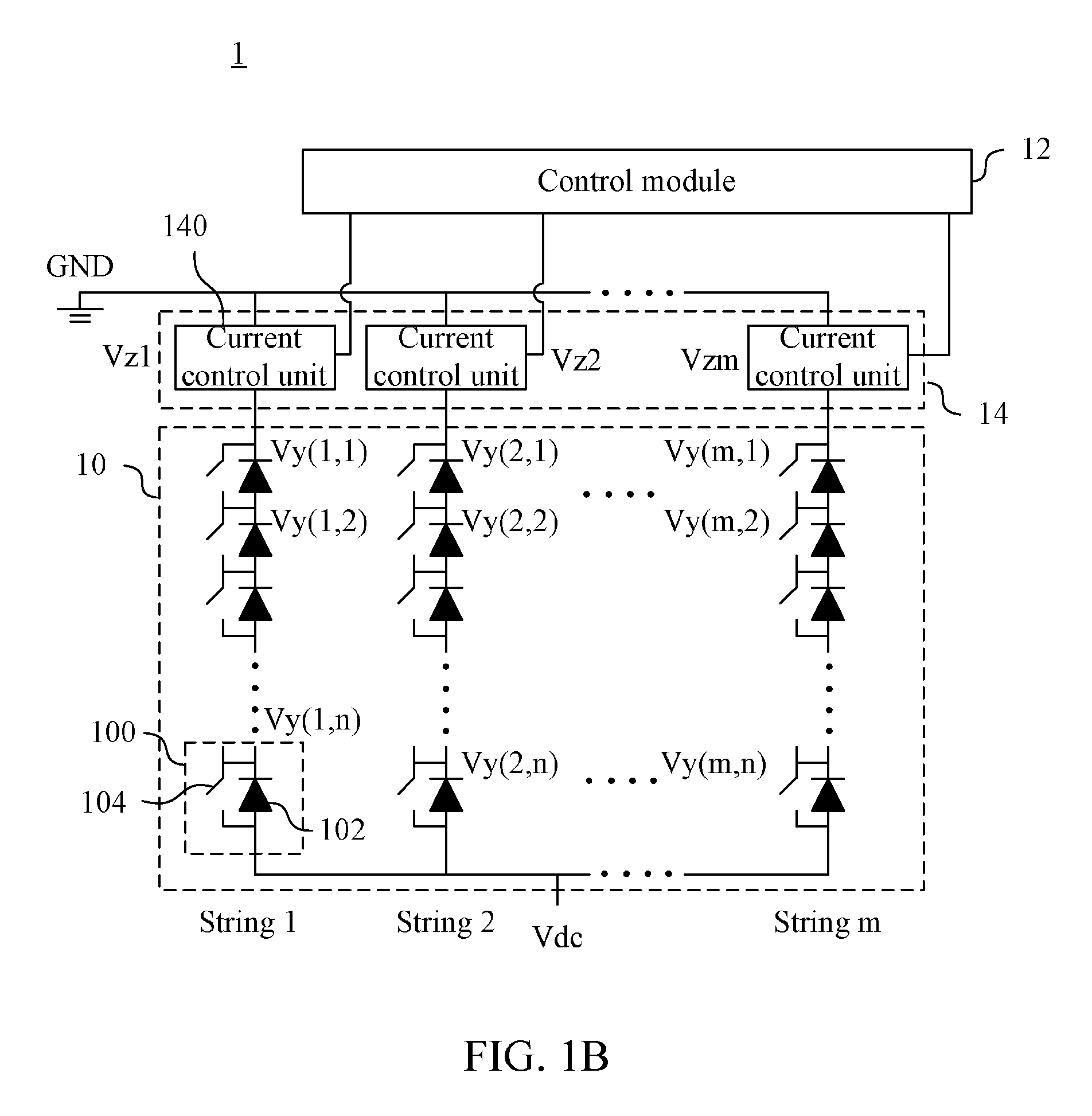
ActiveUS20140210349A1Reduced DC voltageReduce power consumptionElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesVoltage dropLight emitting device
A light-emitting device control method is provided. The light-emitting device control method comprises the steps outlined below. A light-emitting module of a light-emitting device having light-emitting unit string each having light-emitting units connected in series is operated. One end of each light-emitting unit strings receives a same DC voltage. A voltage drop value across each current control units connected in series to at least one of the light-emitting unit strings is retrieved to further determine whether the light-emitting unit of each of the light-emitting unit strings malfunctions. When x light-emitting units of a specific string malfunction and x is larger than or equal to a malfunction threshold value p, the x malfunctioned light-emitting units are shorted and (x−p+1) light-emitting units in each of the light-emitting unit strings other than the specific string are shorted. The DC voltage received by each of the light-emitting units is decreased.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Mixed MMC-based mixed direct current power transmission system
InactiveCN103701145BNo risk of commutation failureWith DC fault self-clearing capabilityElectric power transfer ac networkAc-dc conversionHybrid typeFull bridge
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator designed for use in a magnetic resonance imaging environment
InactiveUS20130046354A1Consume energyReduced DC voltageHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical batteryCommunication interface
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator includes a communication interface operable to receive a communication signal from an external programmer. The communication signal includes a command to switch the ICD from a first mode to a second mode. A processor is in electrical communication with the communication interface and configured to switch the ICD between the first and second modes. A battery is configured to supply low DC voltage. A converter is configured to convert the low DC voltage to a high DC voltage. An energy storage capacitor is electrically coupled to the converter and configured to store a therapeutic energy or high DC voltage including at least 15 joules. The second mode includes activating the converter to convert the low DC voltage to the high DC voltage and storing the therapeutic energy or at least 15 joules within the energy storage capacitor during a period of time of the second mode.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
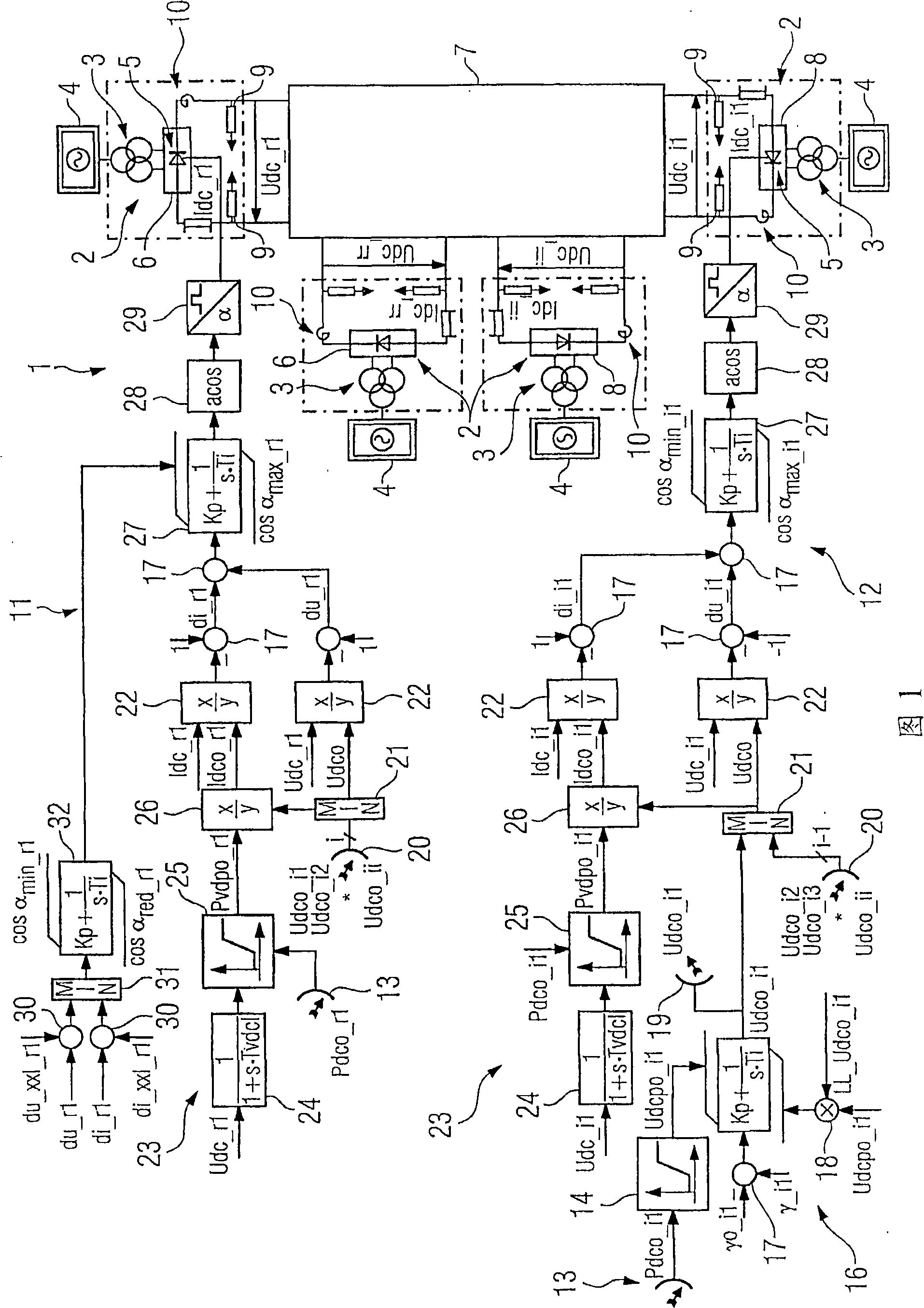
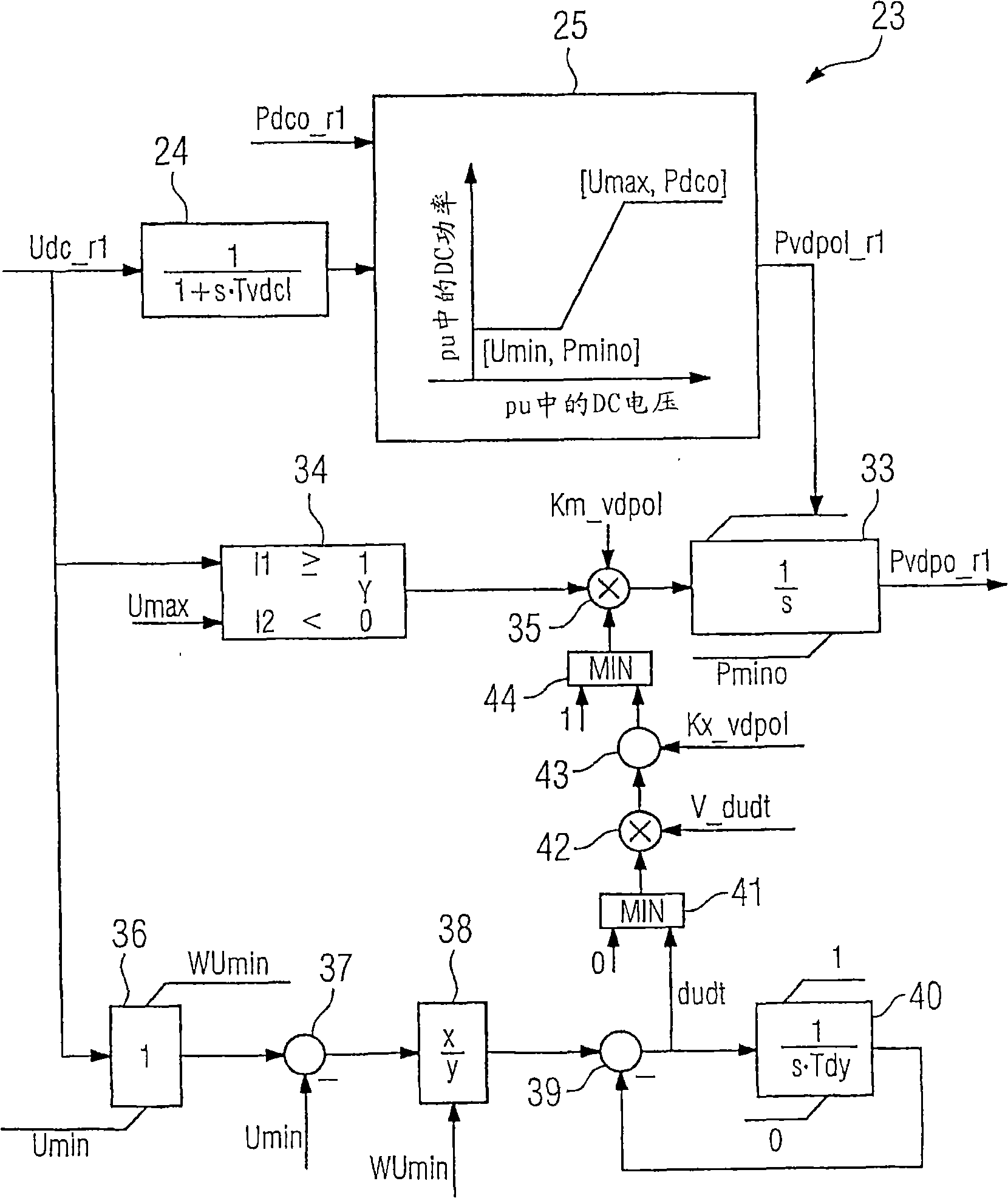
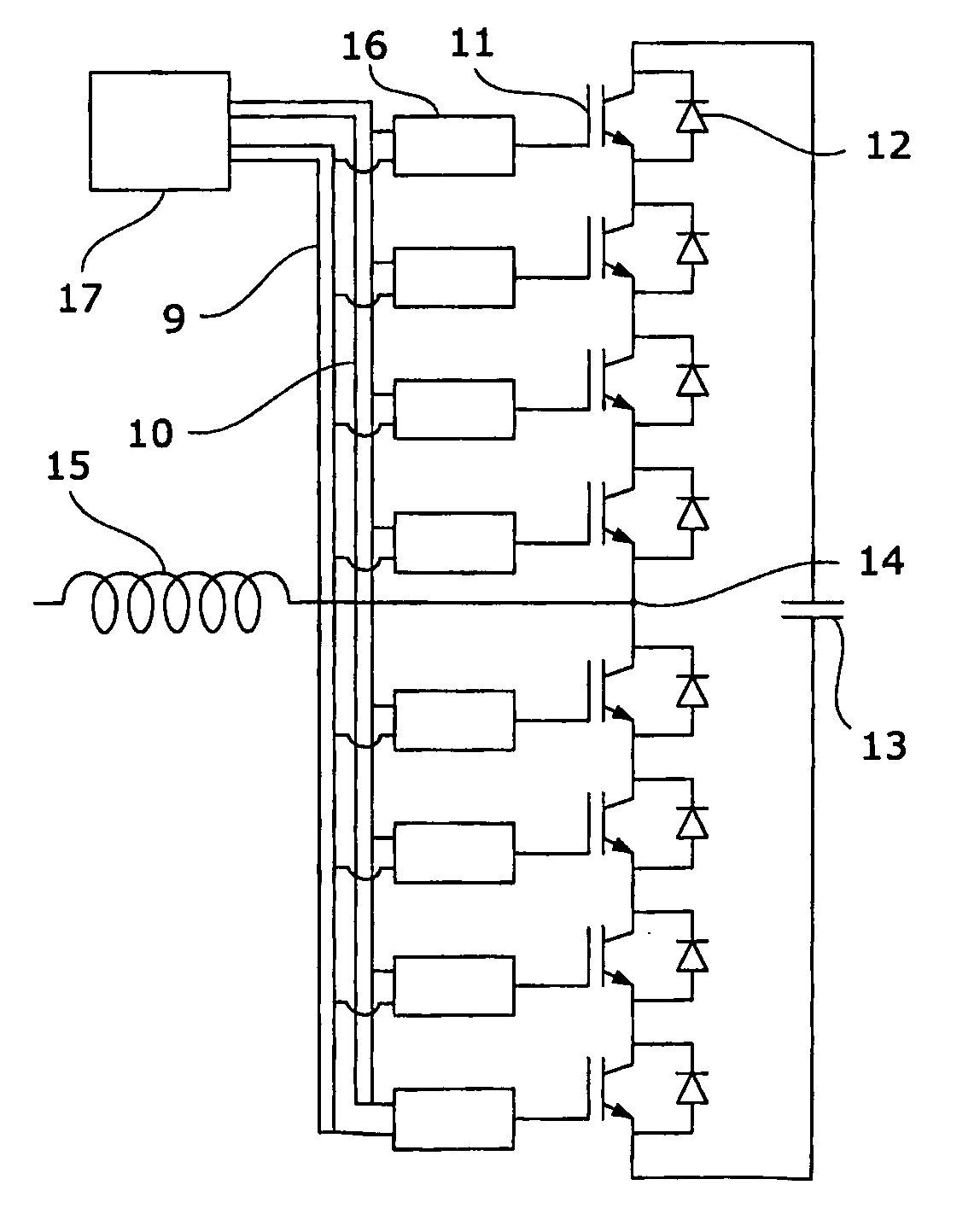
Direct-current transmission regulating method with multiple current transformers
InactiveCN101273518AAvoid HierarchyAvoid Regulatory SeparationElectric power transfer ac networkAc-dc conversionDc currentPower grid
The invention relates to a method for controlling at least three power converters (2), which can be controlled by a rectifier (6) or an inverter (8) and are connected together by a direct current network (7), in the region of power distribution and power transmission. The aim of the invention is to provide a method which has a simple structure and also works in a reliable manner. As a result, a measuring direct current voltage (Udc_l, ... Udc_rr; Udc_il ... Udc_ii) and a measuring direct current (Idc__rl, ... Idc_rr; Idc__il, ... Idc_ii) are measured on each power converter and respectively, transmitted to the respective rectifier control (11) and / or inverter control (12), and a rectifier desired direct power and / or inverter desired direct power (Pdco_rl, ... Pdco-rr,- Pdco_il, ... Pdco_ii) is determined for each power converter. The total of all desired direct powers (Pdco_rl, ...; Pdco_rr; Pdco-il, ... Pdco_ii) is equal to zero, and a desired direct voltage (¿˜dco_rl, ... Udco_rr; Udco__il, ... Udco_ii) is determined from each desired direct power, the smallest inverter desired direct voltage (Udco_il, ... Udco_ii) of all connected inverters (8) is fixed as minimal direct voltage (Udco) by means of a minimal direct voltage and the desired direct voltage, a desired direct current (Idco_rl; ... Idco_rr; Idco_il, ... Idco_ii) is formed from the minimal voltage (Udco) and the measuring direct voltage, a differential direct voltage (du_rl, ... du_rr, du_il, ... du_ii) is formed from the minimal voltage (Udco) and the differential direct current (di_rl; ... di_rr; di_il, ... di_ii) is formed from the desired direct current and the measuring direct current.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Electric Power Converter
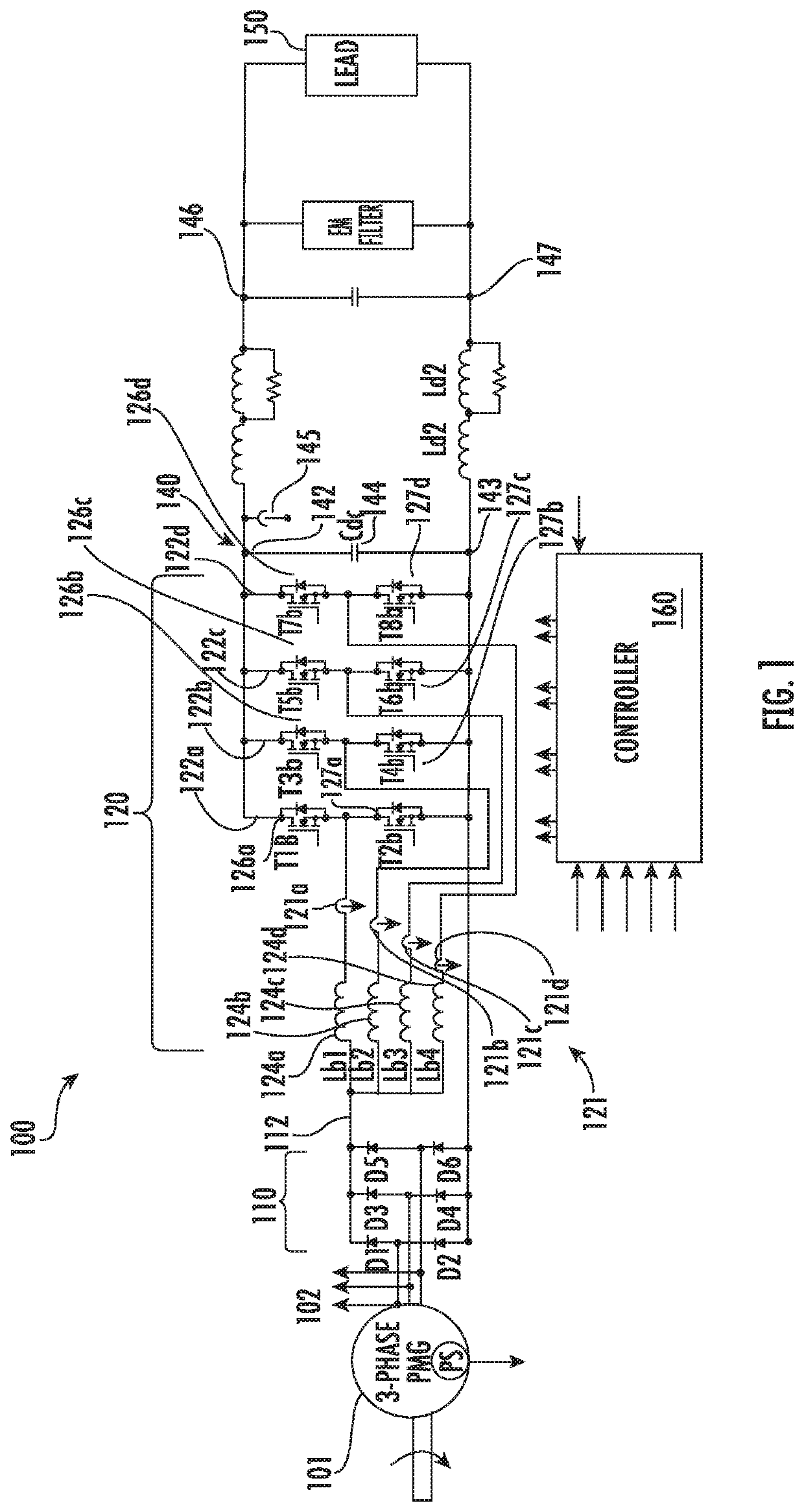
InactiveUS20090284876A1Improve usabilityReduction of converter voltage ratingAc-dc conversionSolid-state devicesEngineeringVoltage source
A voltage source converter including a string of series connected active semiconducting elements. The converter includes in case of an active semiconducting element failure a calculation element configured to calculate an operation dc voltage including a sum of dc ratings of each remaining active semiconducting element in the string, and a regulator configured to regulate the converter to assume the operation dc voltage over the converter.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Apparatus for neuromuscular stimulation
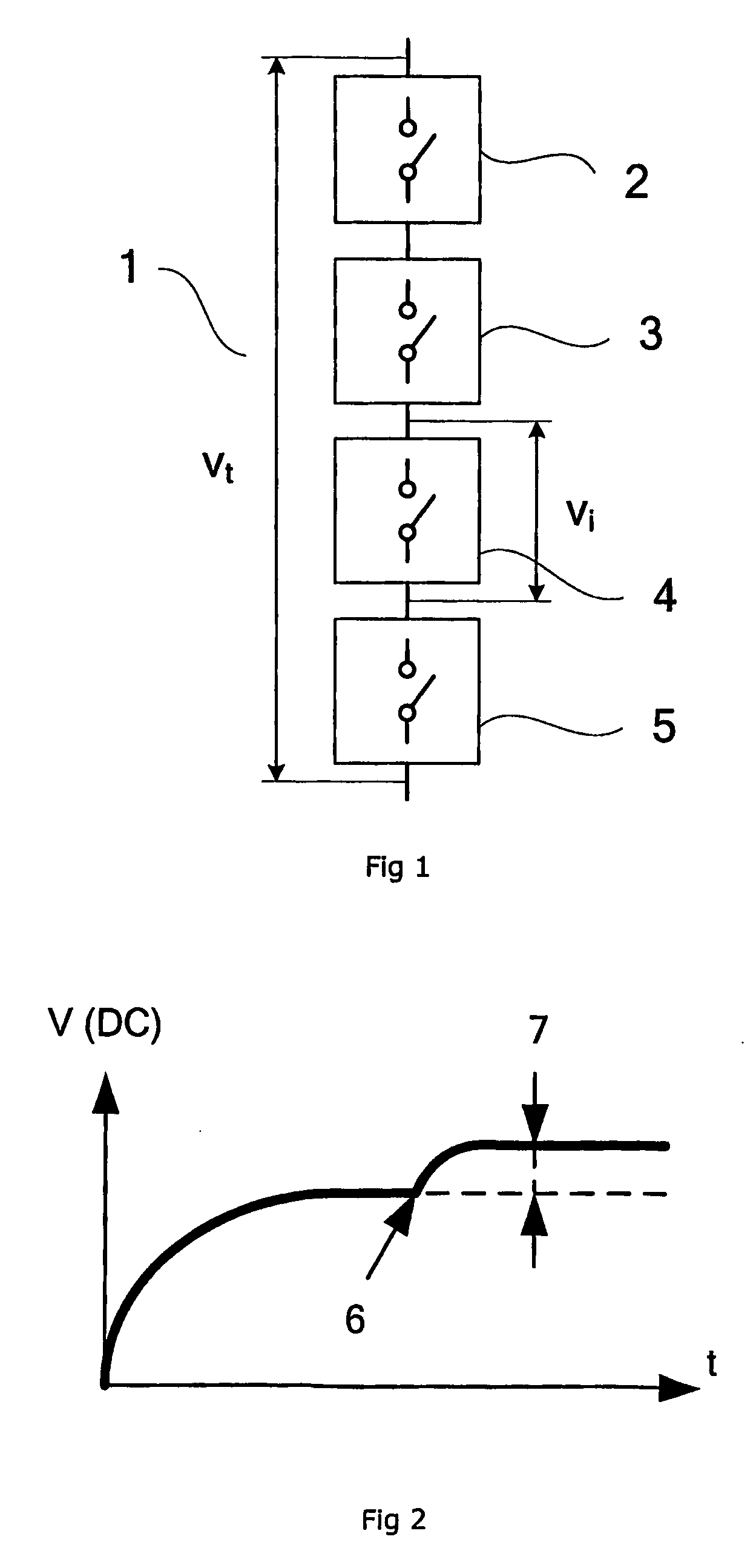
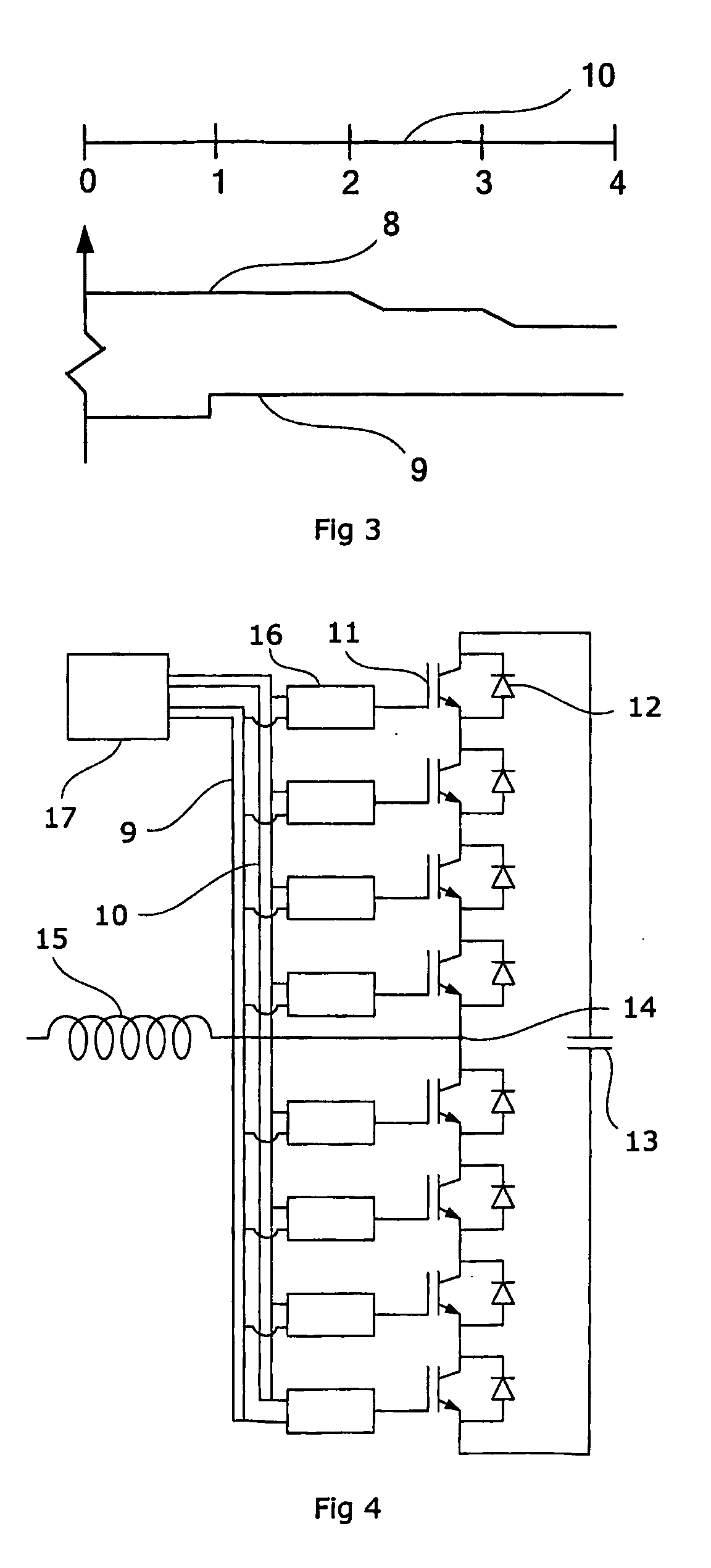
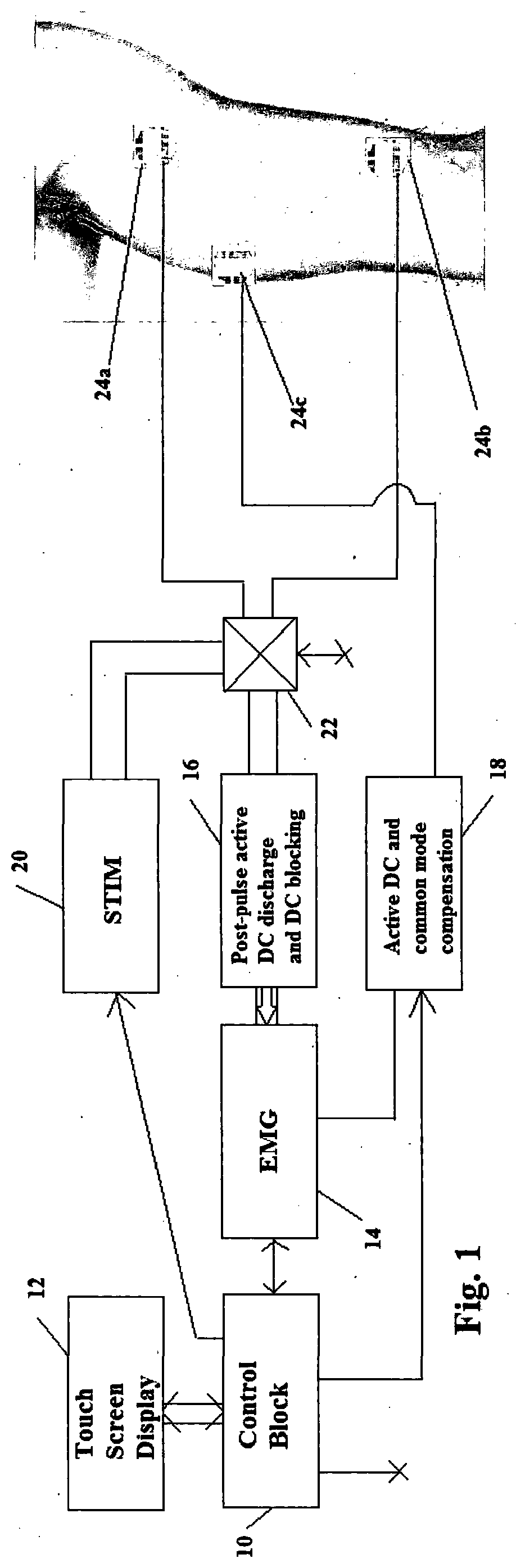
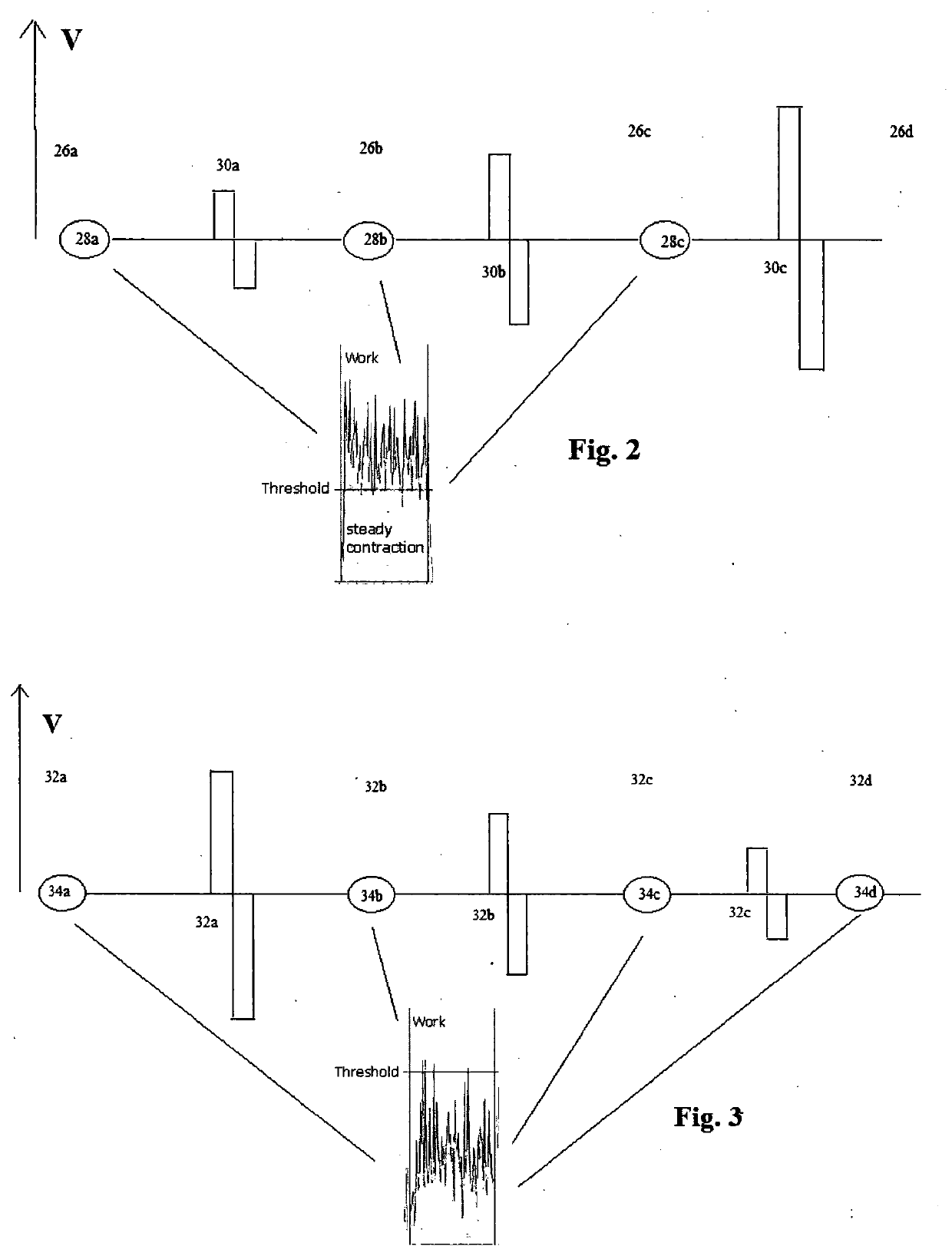
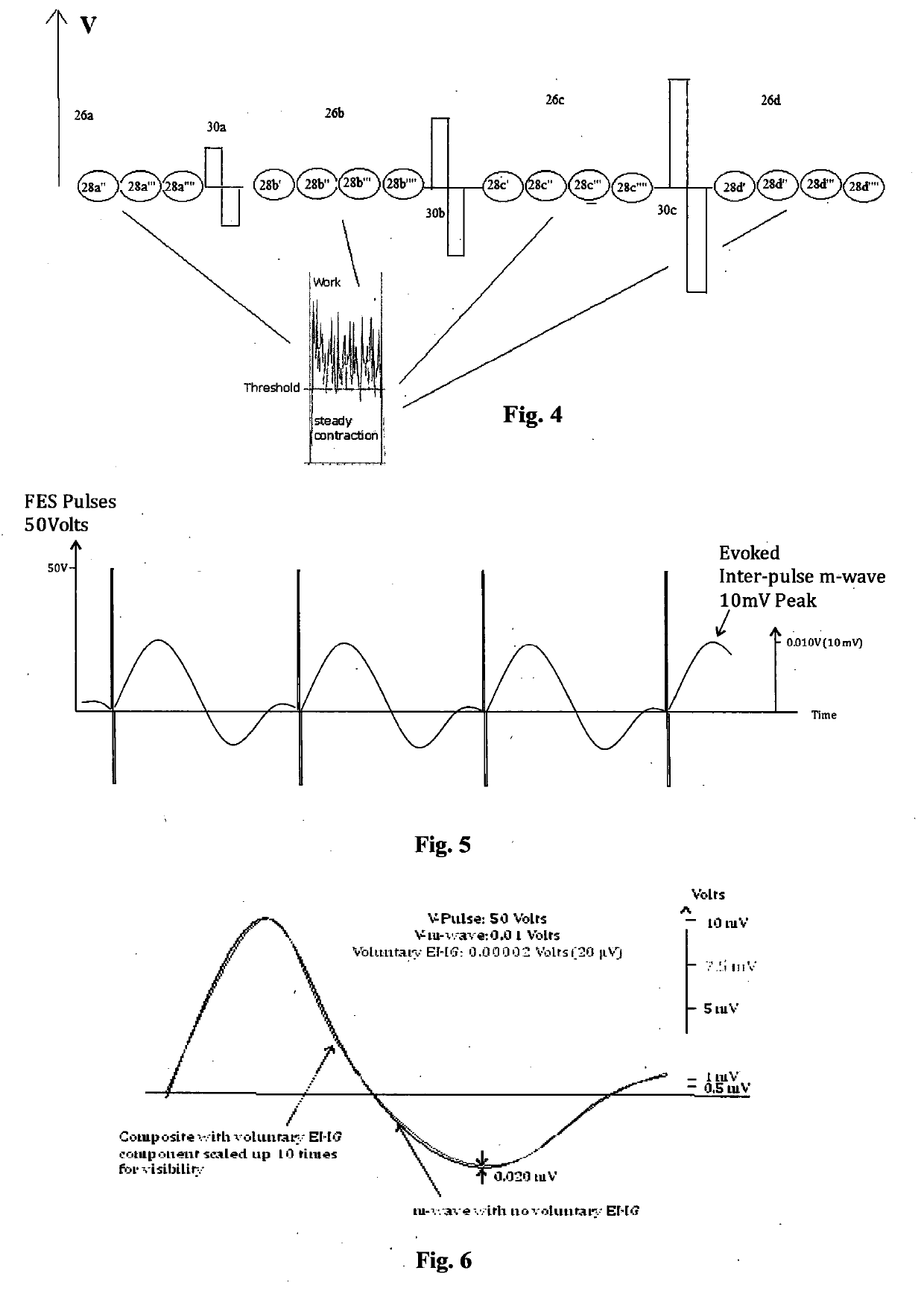
ActiveUS20200139115A1Good stabilityPrecise controlExternal electrodesArtificial respirationNeuromuscular controlNeuromuscular stimulation
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for neuromuscular stimulation which is useful for stimulation of weak muscles in general, in sports clinical mode for muscle growth and endurance and in clinical mode for muscular rehabilitation. EMG signals are received from the subject adjacent a muscle whose contraction is to be stimulated. A succession of stimulation (STIM) pulses are supplied to the muscle to be stimulated. The EMG-receiving module is operated during quiescent periods between successive pulses, and the amplitude of stimulation pulses supplied to the subject in the succession is modulated proportionately depending on the a detected voluntary component of the received EMG signals. Modulation is in real time during supply of stimulation pulses whereby the subject is given a sensation of natural muscle control and / or the possibility for greater precision of neuromuscular control.
Owner:VERITY NIGEL CHARLES
Positive feedback latch amplitude limiting control circuit and method of passive radio frequency identification tag
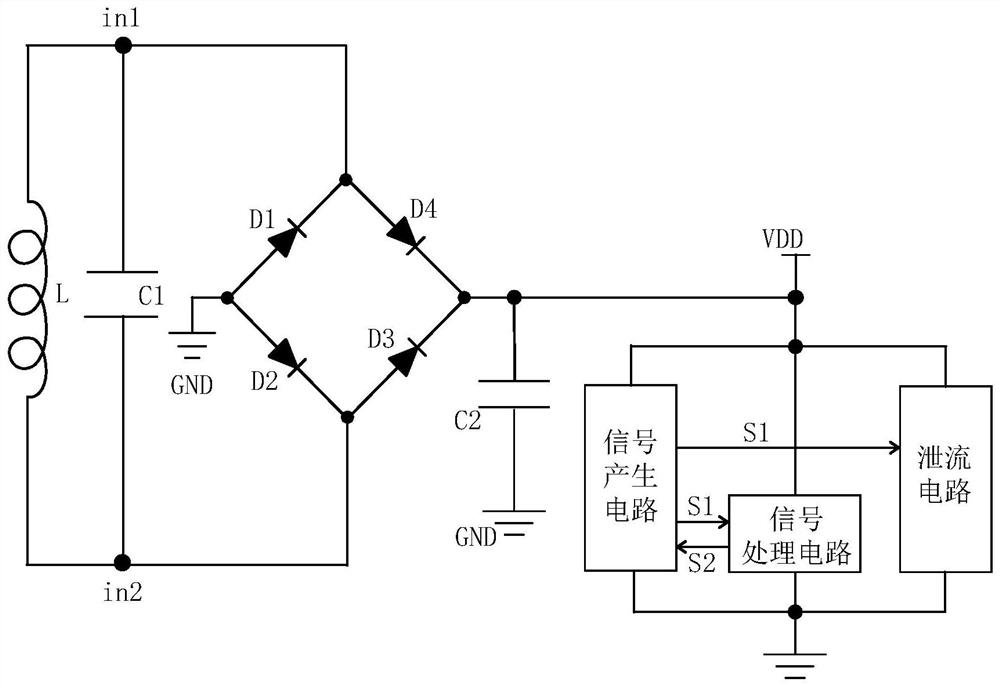
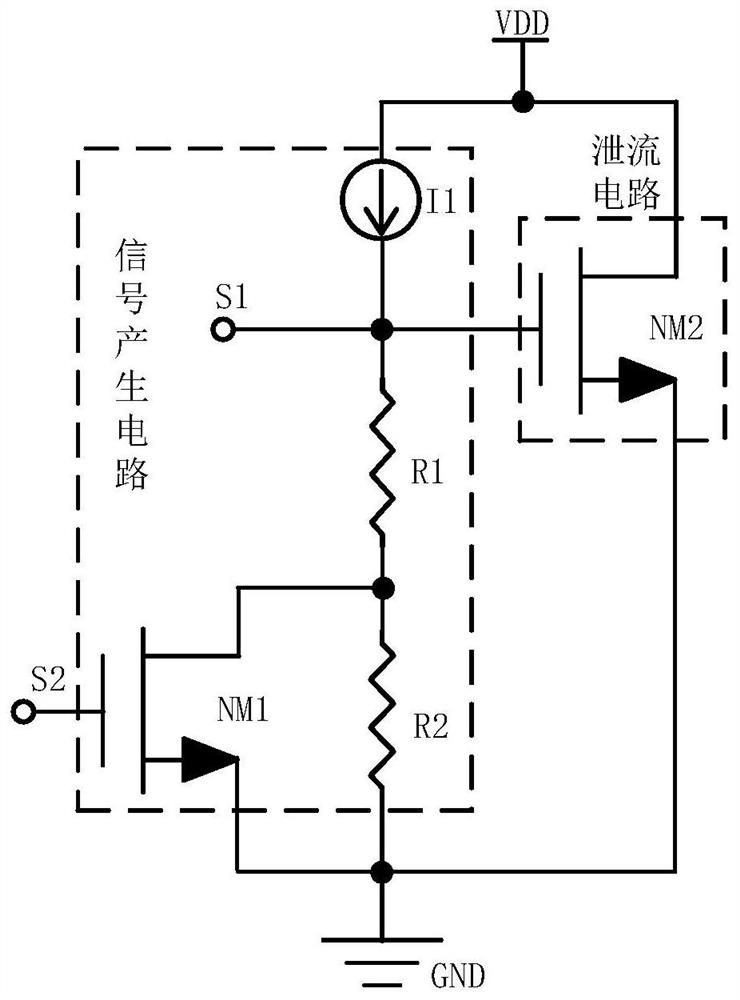
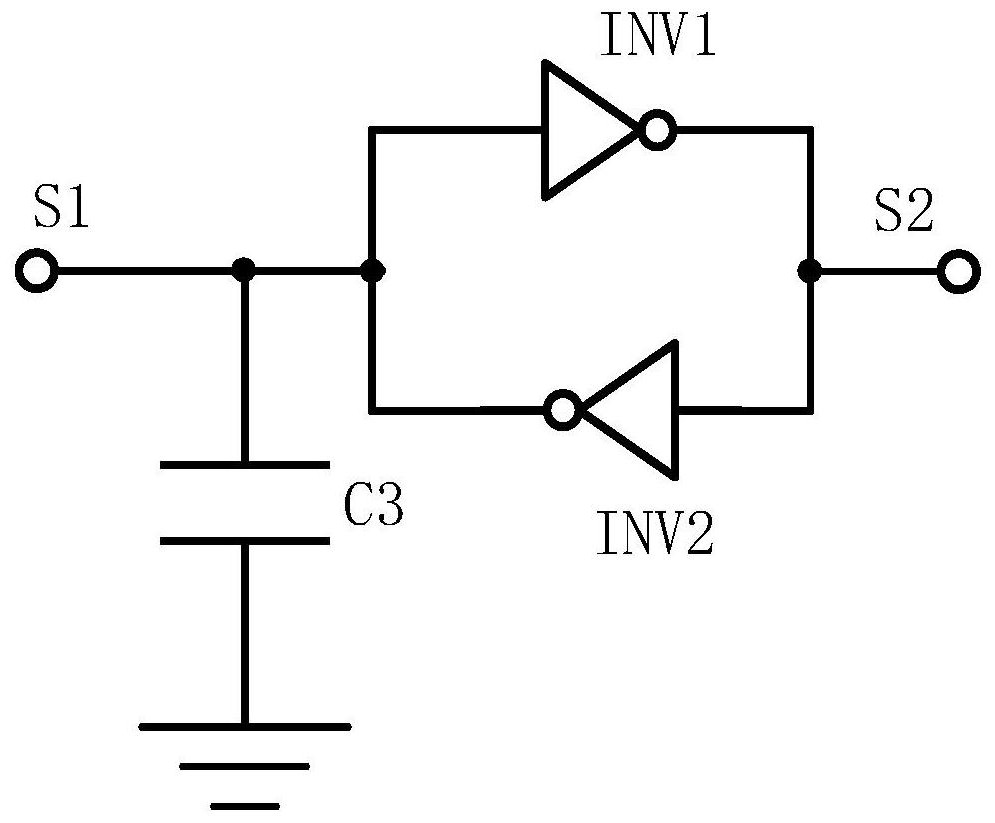
PendingCN112288068ASimple structureEasy to implementCircuit arrangementsRecord carriers used with machinesLoad circuitControl signal
According to the positive feedback latch amplitude limiting control circuit and method of the passive radio frequency identification tag, dynamic rectification control can be carried out on the voltage between the first antenna end and the second antenna end, and when the voltage of the antenna end is too high, the signal generation circuit conducts the bleeder circuit, so that charges at the antenna end are output to the ground, and rectified direct-current voltage is reduced; when the voltage of the antenna terminal is within a limited voltage, the signal generation circuit enables the bleeder circuit to be in a cut-off state, and the rectification circuit rectifies all charges of the antenna terminal into a direct-current power supply for the load circuit to use, so that the current consumption is controlled to a certain extent. Moreover, the bleeder circuit is an MOS transistor of which the gate voltage is controlled by a latch, and a positive feedback latch mechanism in the latchenables a first control signal S1 to have very strong pull-down driving force when being pulled to a low level, so that the control gate of the bleeder circuit is thoroughly turned off, the electric leakage state of a sub-threshold region is avoided, The leakage current in the discharge path is effectively reduced, and the communication performance is improved.
Owner:EXCELIO TECH SHENZHEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com