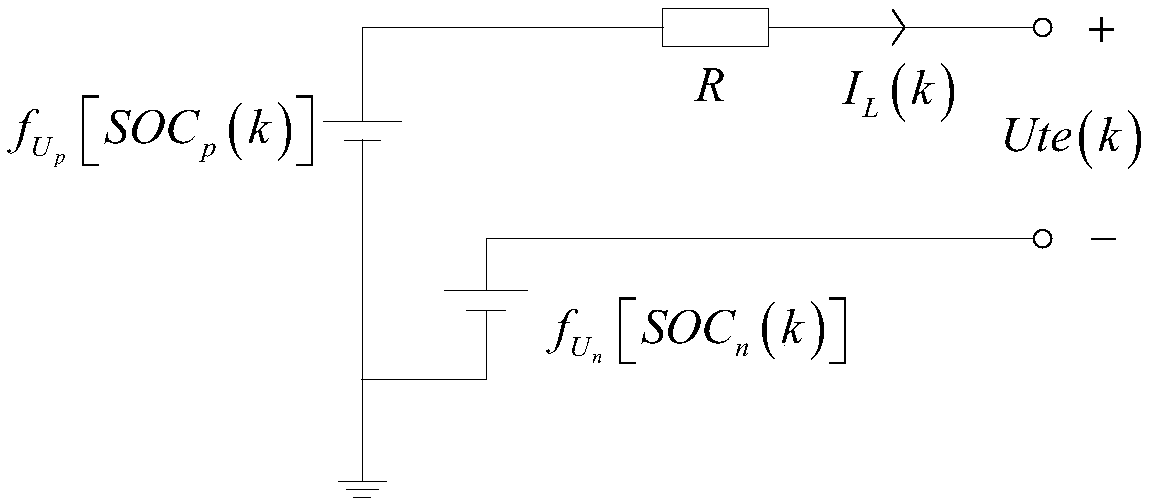Patents
Literature
49 results about "Cell potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cell potential (often called the electromotive force or emf) has a contribution from the anode which is a measure of its ability to lose electrons - it will be called its "oxidation potential". The cathode has a contribution based on its ability to gain electeons, its "reduction potential".
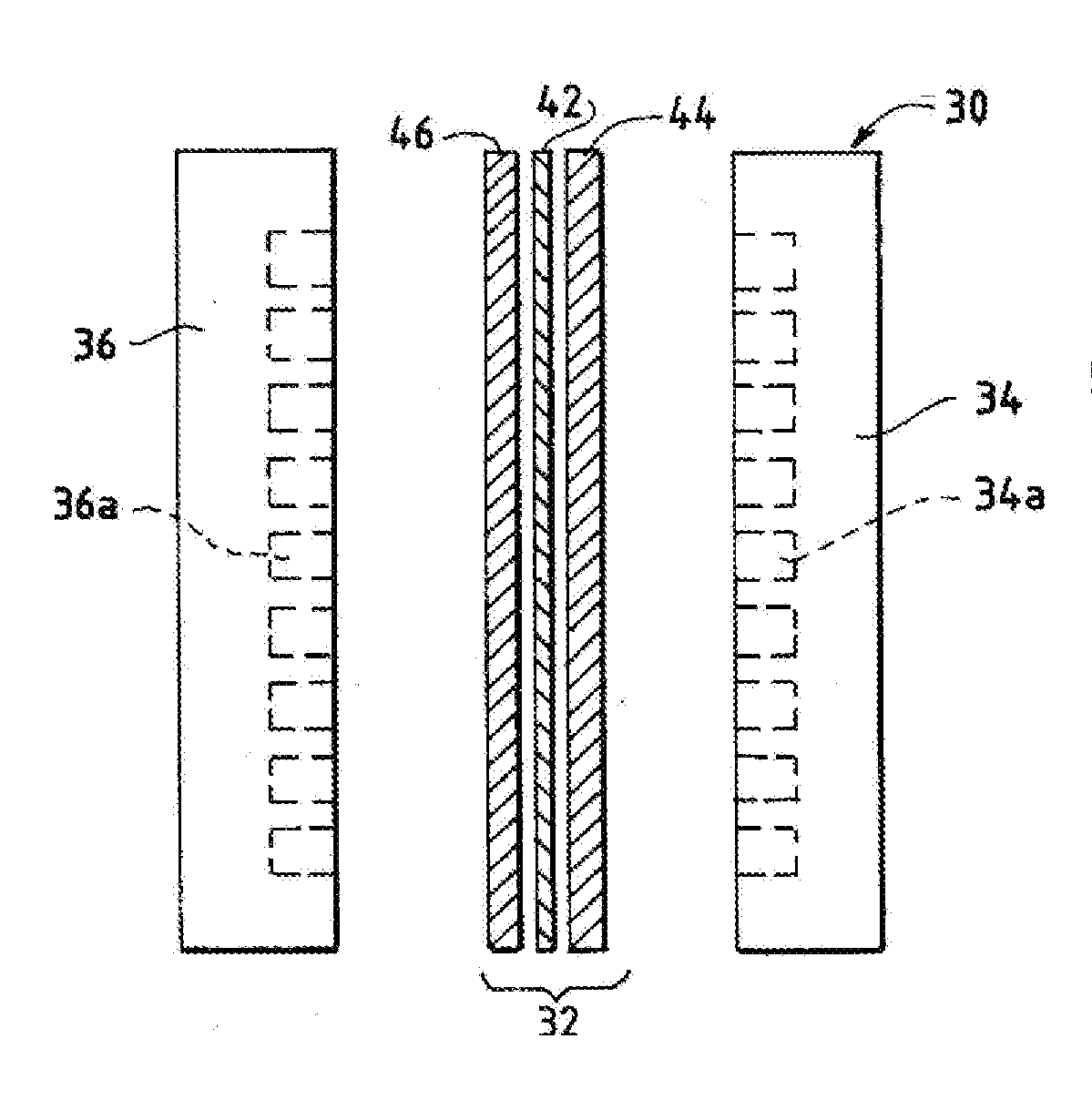
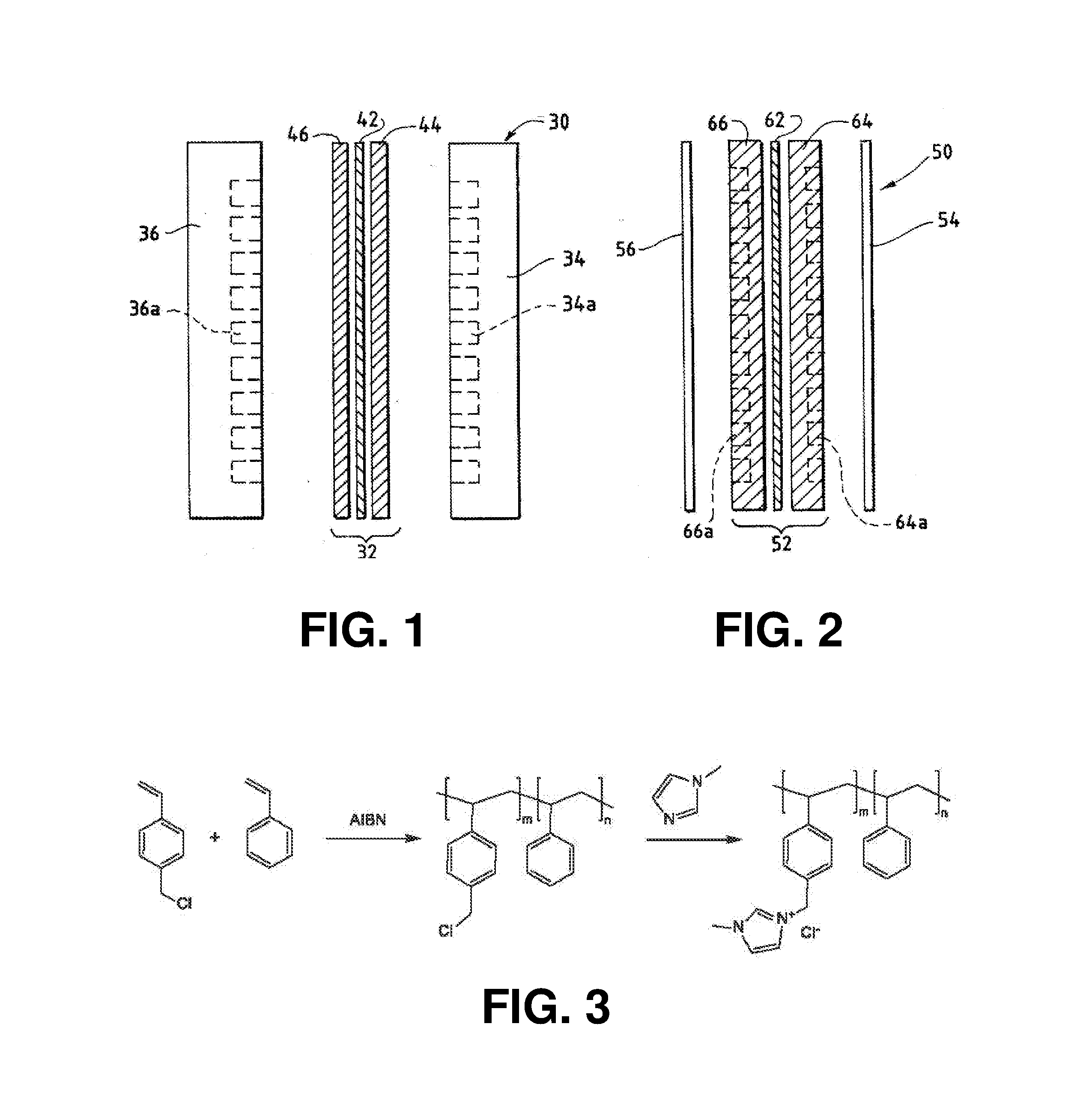
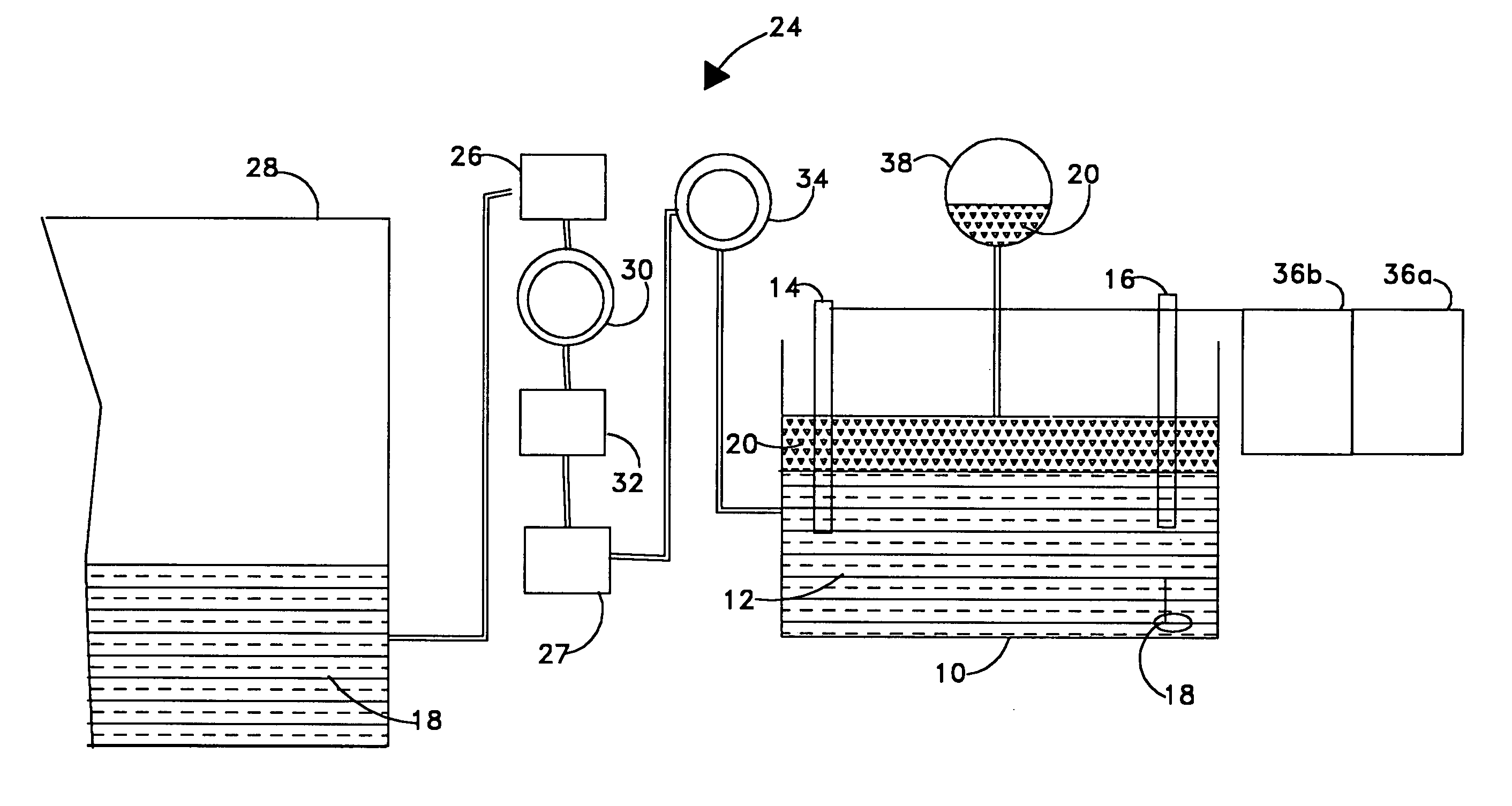
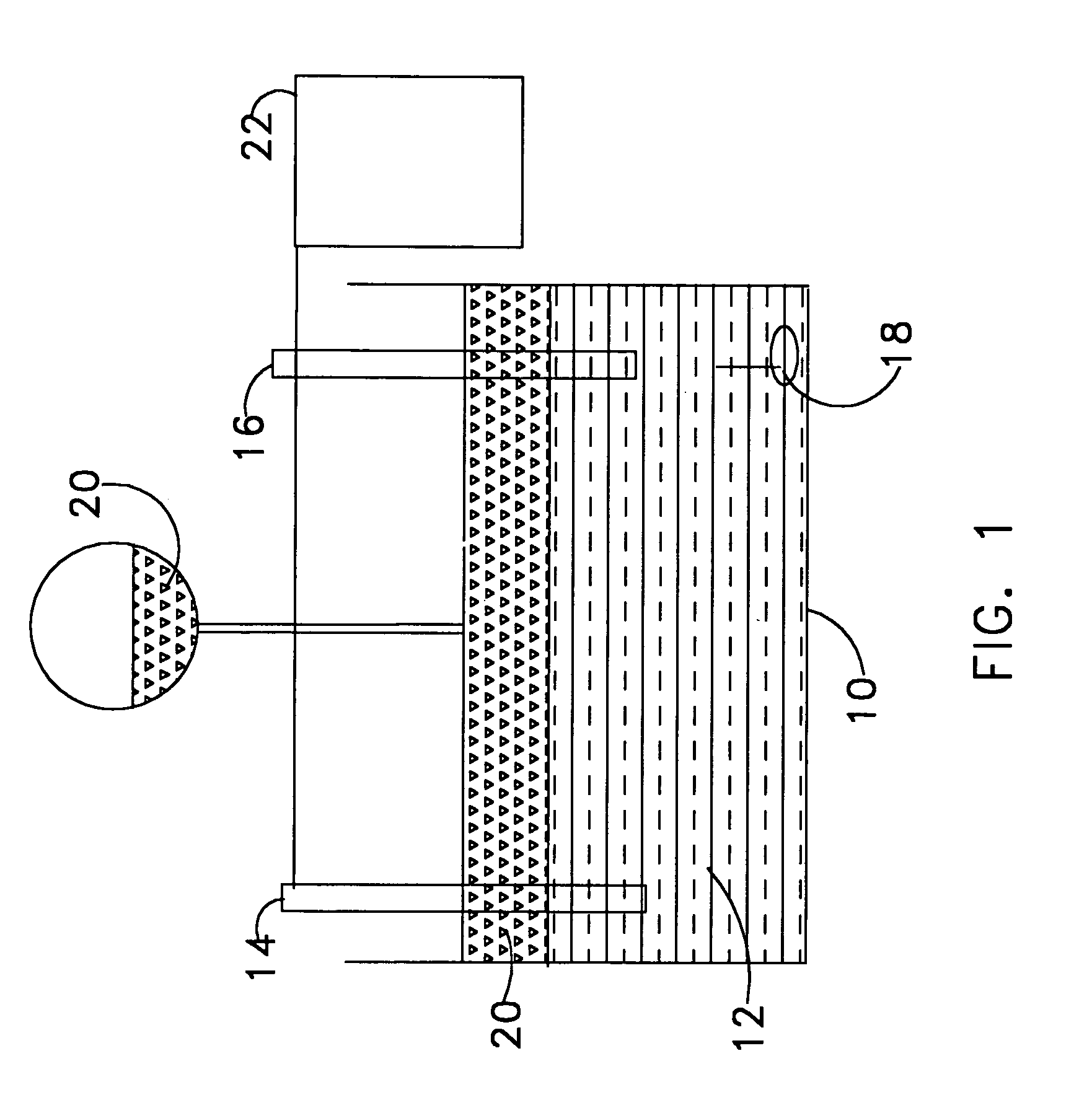
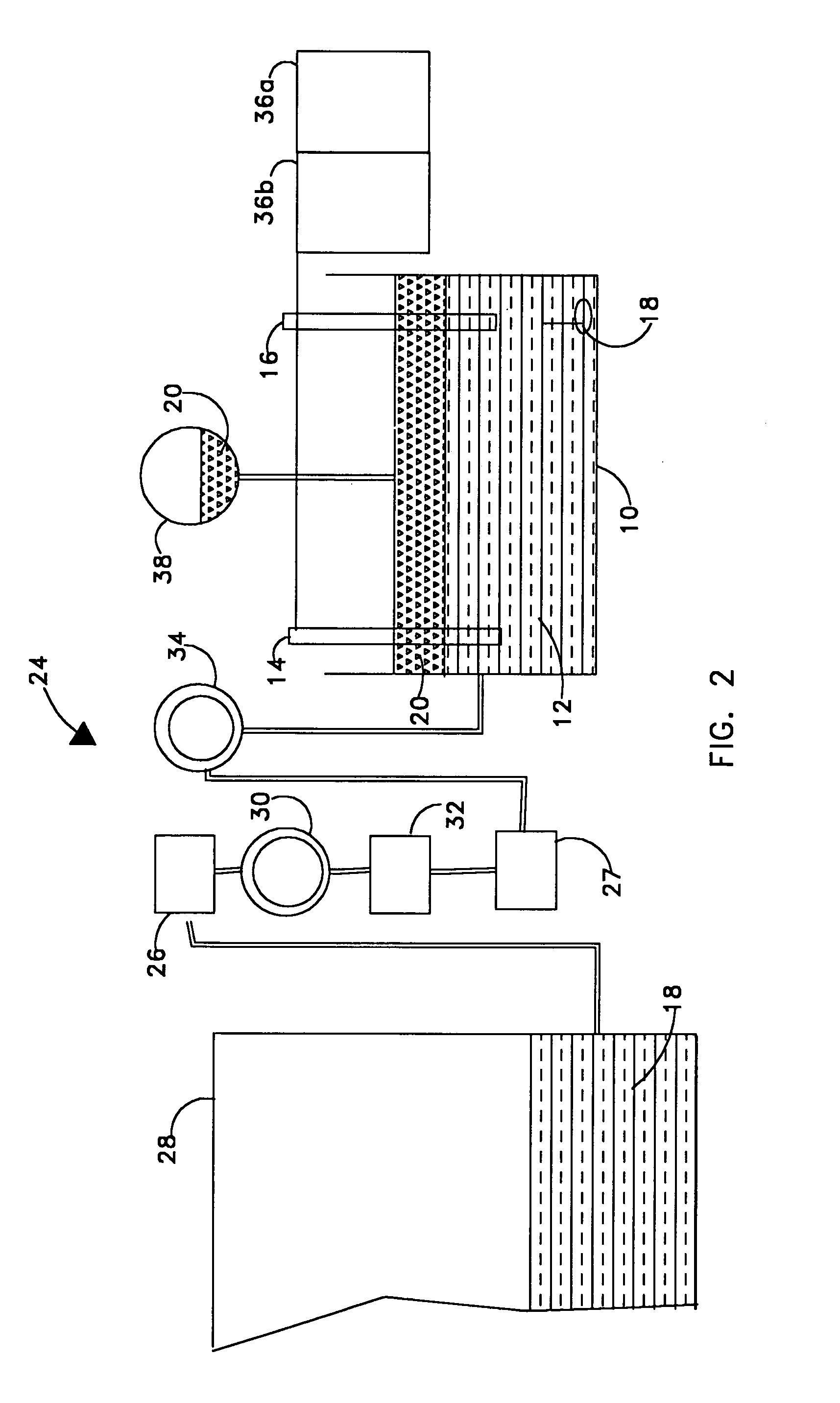
Method And System For Electrochemical Production Of Formic Acid From Carbon Dioxide
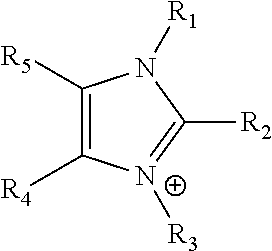
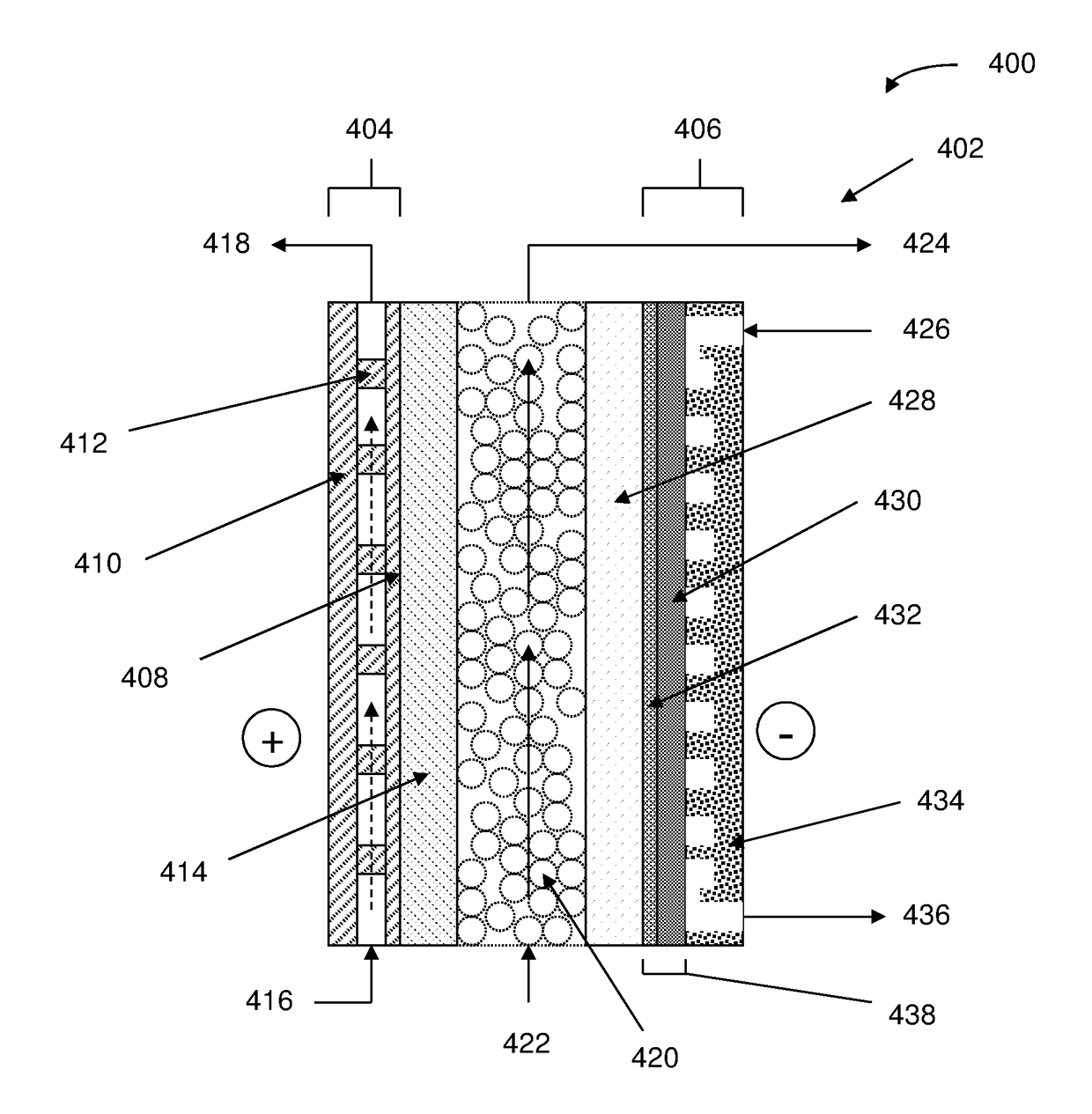
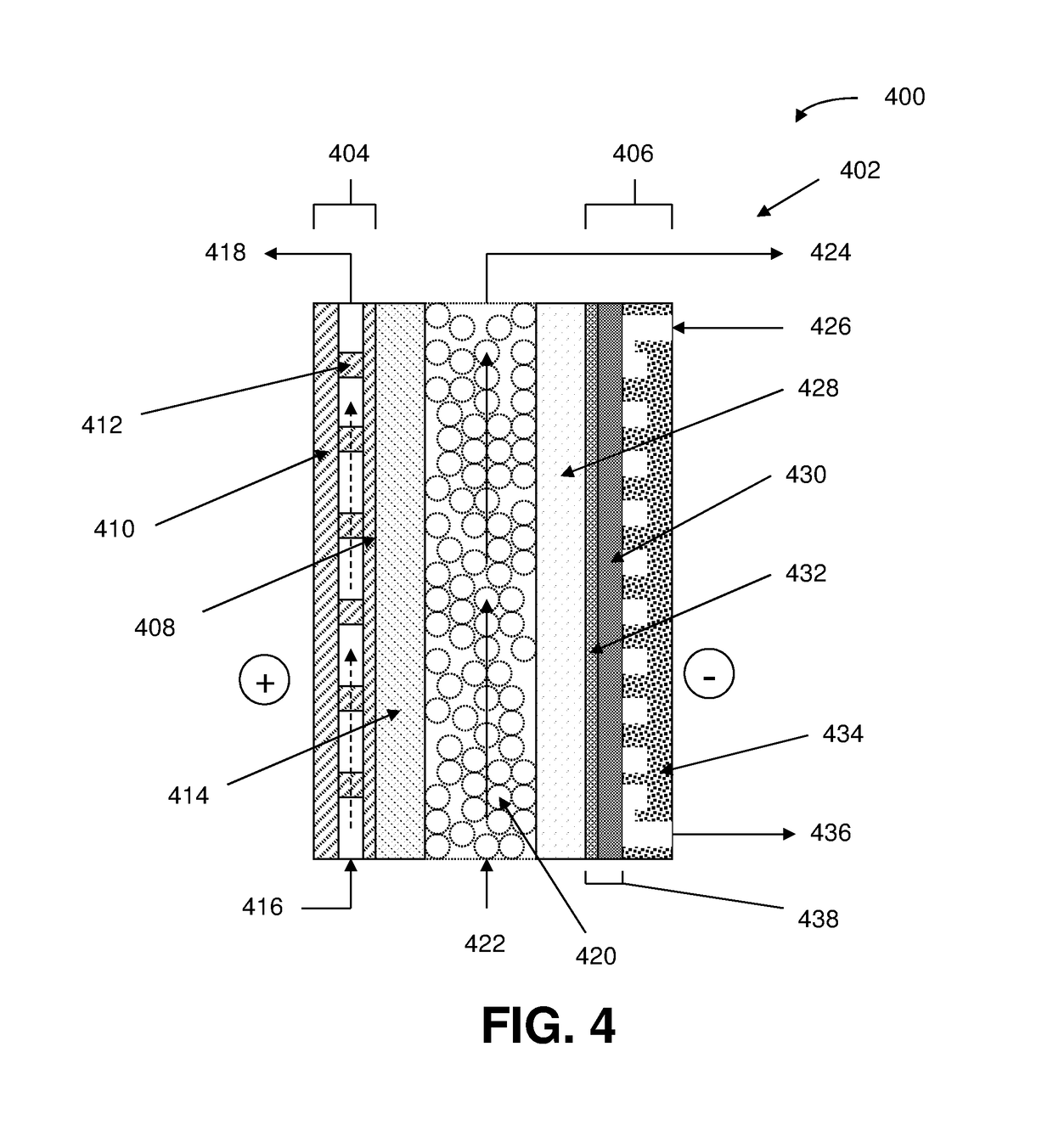
An electrochemical device converts carbon dioxide to a formic acid reaction product. The device includes an anode and a cathode, each comprising a quantity of catalyst. The anode and cathode each have reactant introduced thereto. Two membranes, a cation exchange polymer electrolyte membrane and an anion exchange polymer electrolyte membrane, are interposed between the anode and the cathode, forming a central flow compartment where a carbon dioxide reduction product, such as formic acid, can be recovered. At least a portion of the cathode catalyst is directly exposed to gaseous carbon dioxide during electrolysis. The average current density at the membrane is at least 20 mA / cm2, measured as the area of the cathode gas diffusion layer that is covered by catalyst, and formate ion selectivity is at least 50% at a cell potential difference of 3.0 V. In some embodiments, at least one polymer electrolyte membrane comprises a polymer in which a constituent monomer is (p-vinylbenzyl)-R, where R is selected from the group consisting of imidazoliums, pyridiniums and phosphoniums. In some embodiments, the polymer electrolyte membrane is a Helper Membrane comprising a polymer containing an imidazolium ligand, a pyridinium ligand, or a phosphonium ligand.
Owner:DIOXIDE MATERIALS
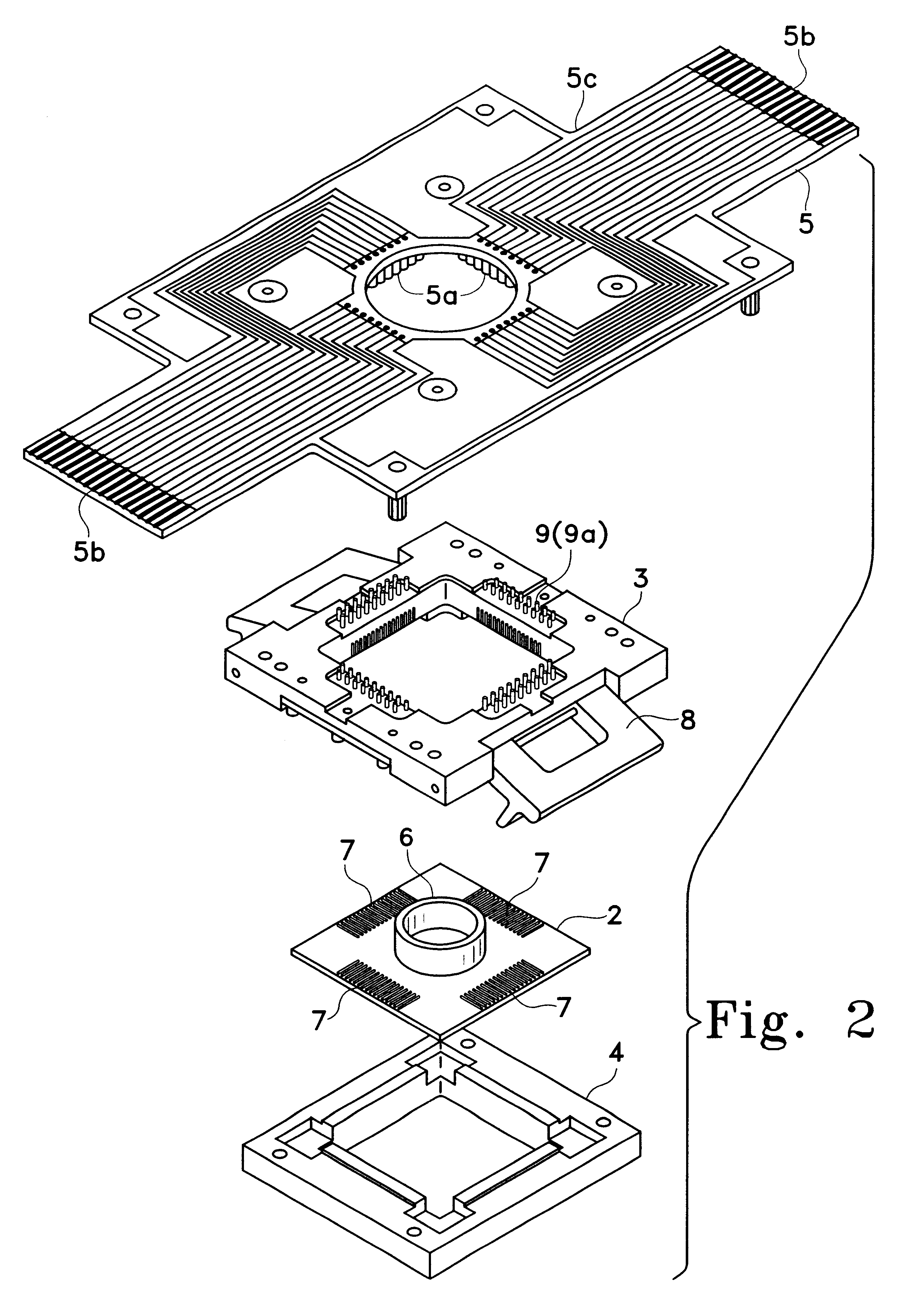
Cell potential measurement apparatus having a plurality of microelectrodes
InactiveUSRE38323E1Precise positioningReduce surface resistanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMeasurement devicePotential change
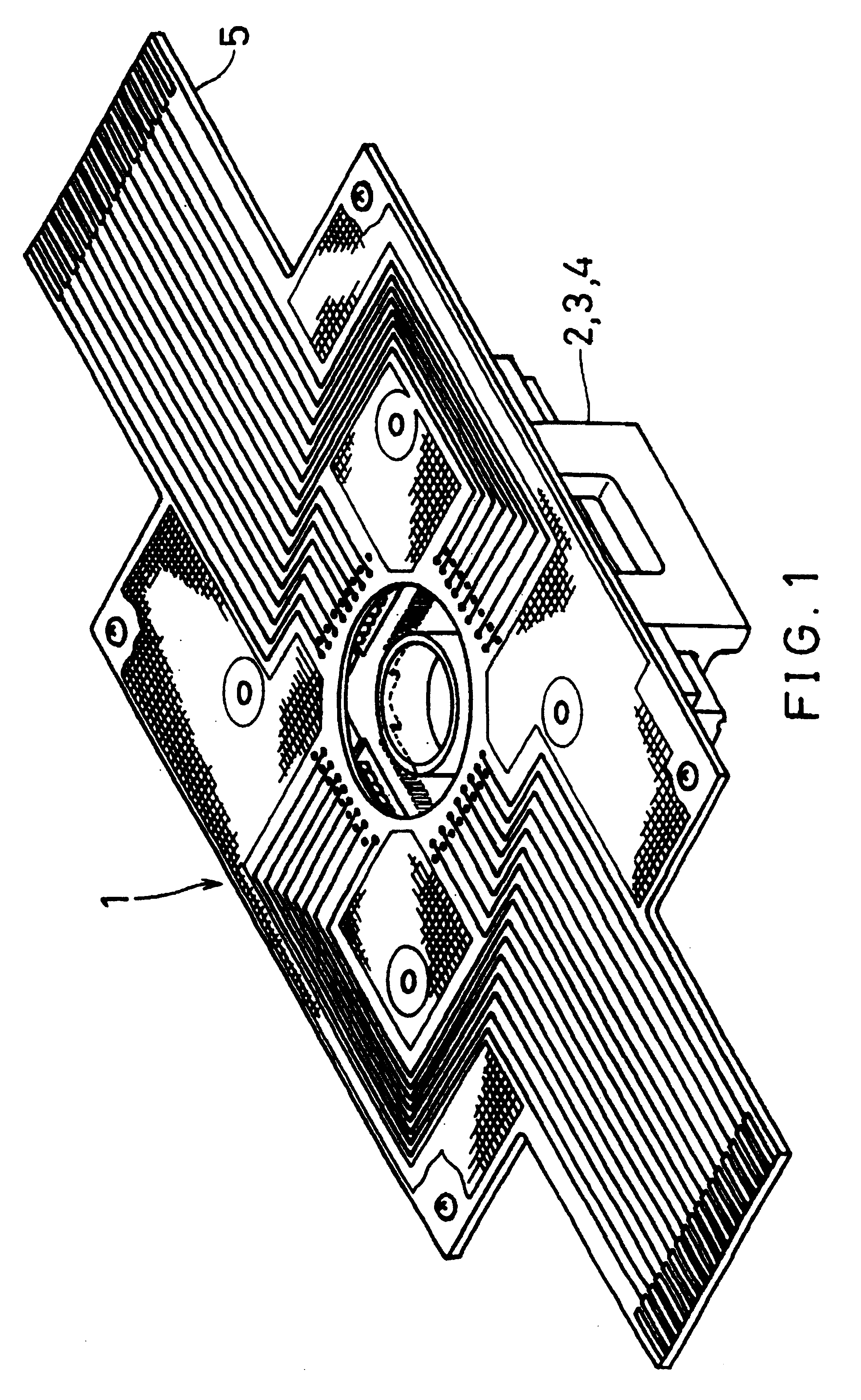
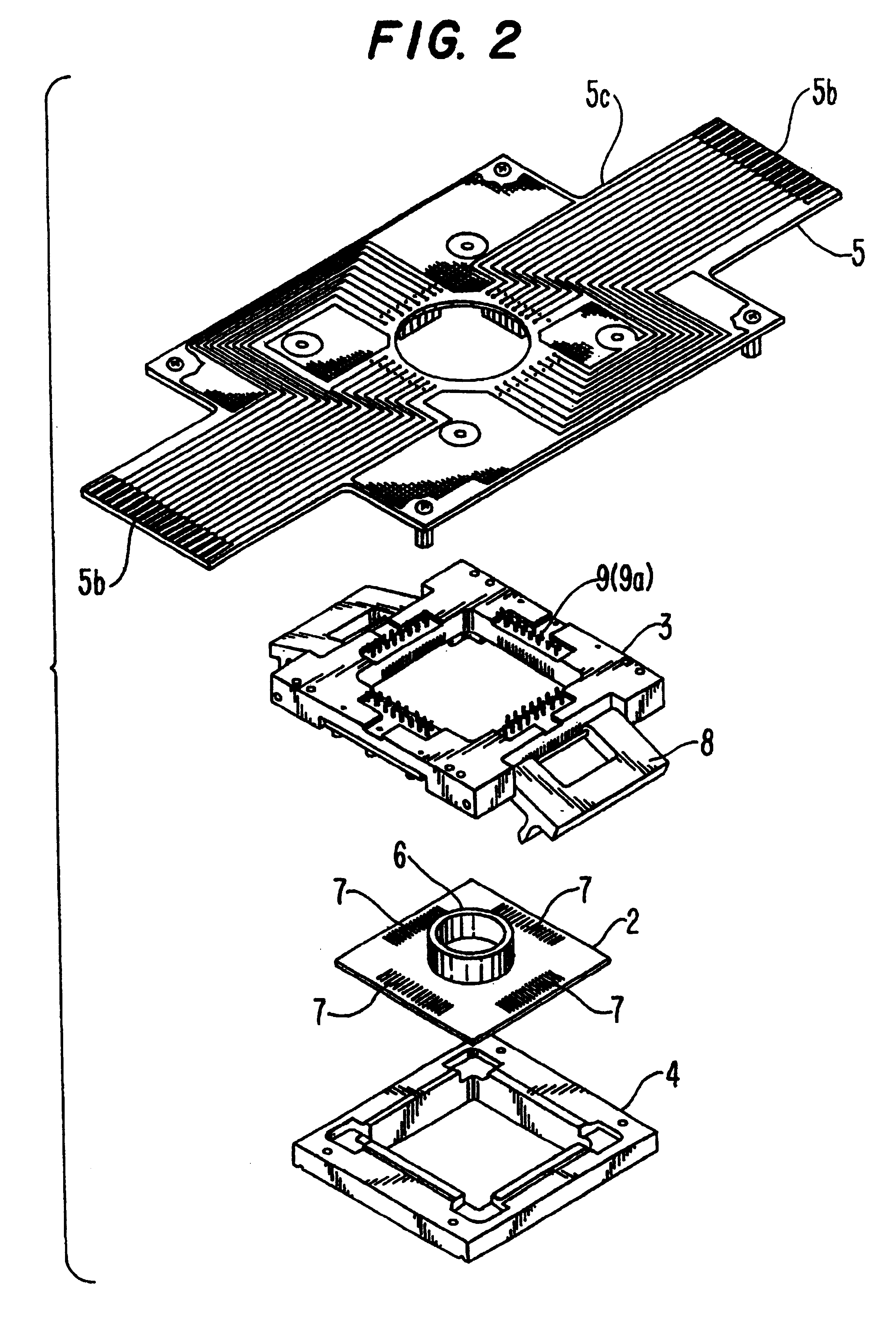
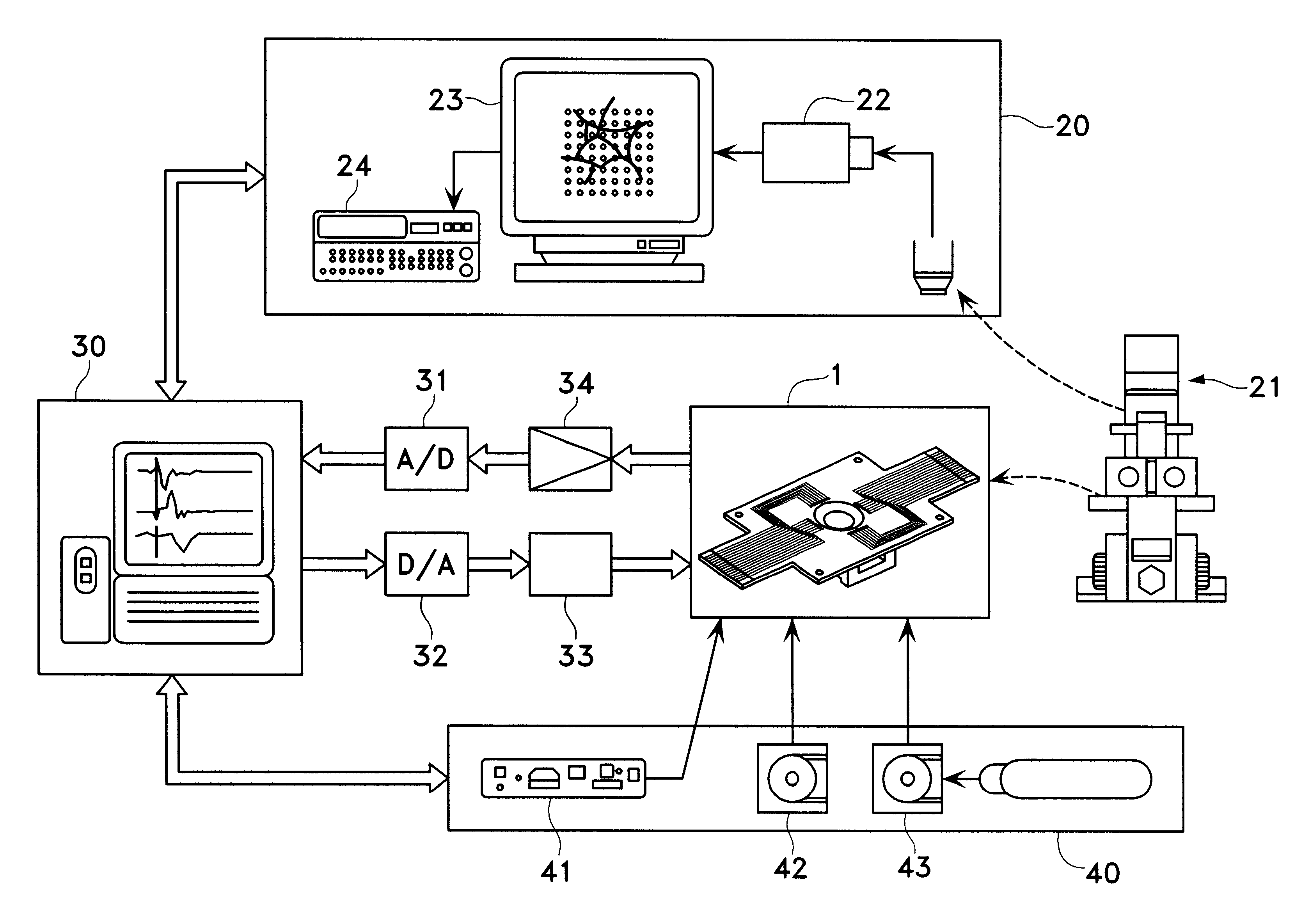
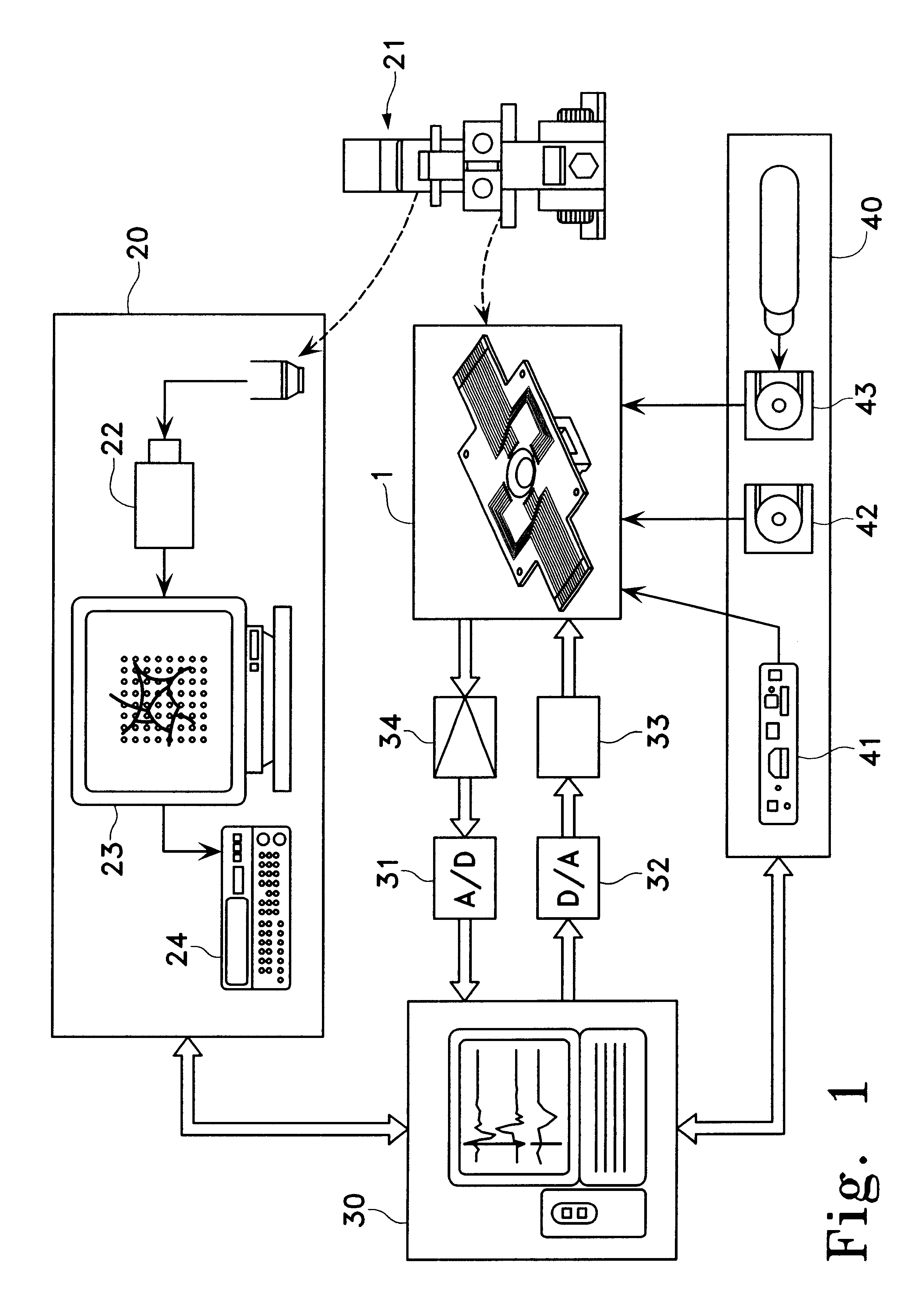
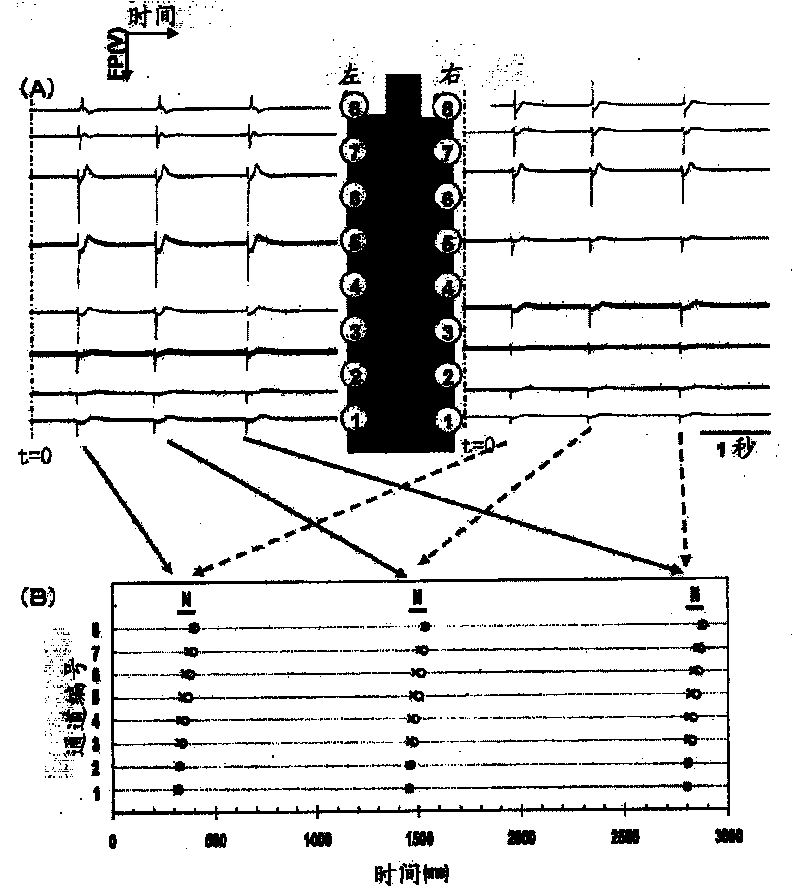
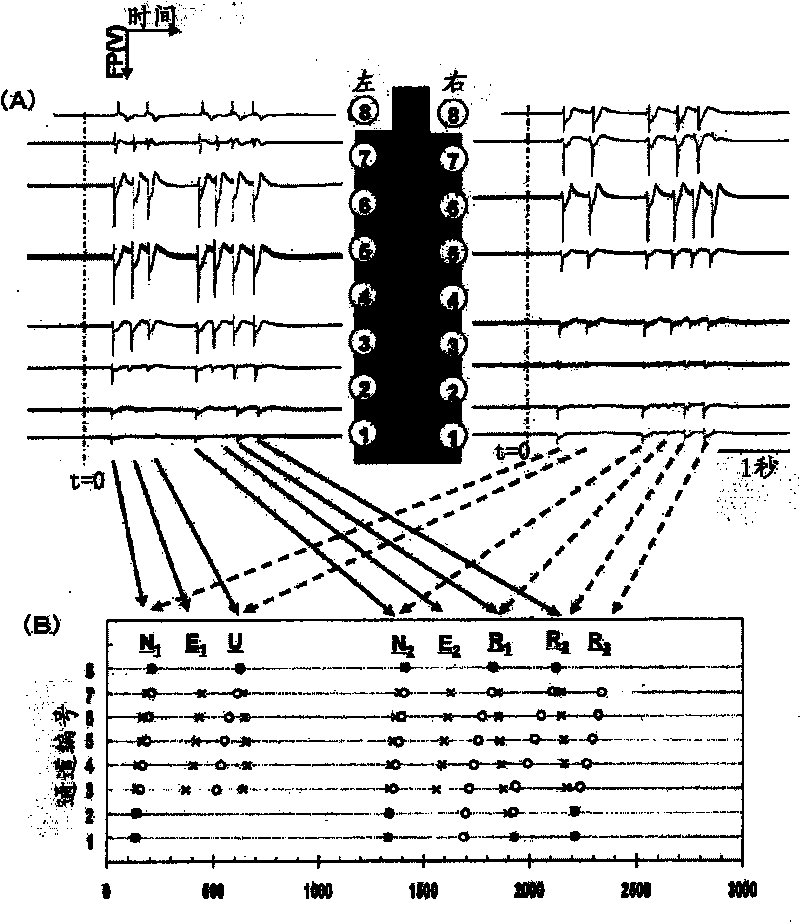
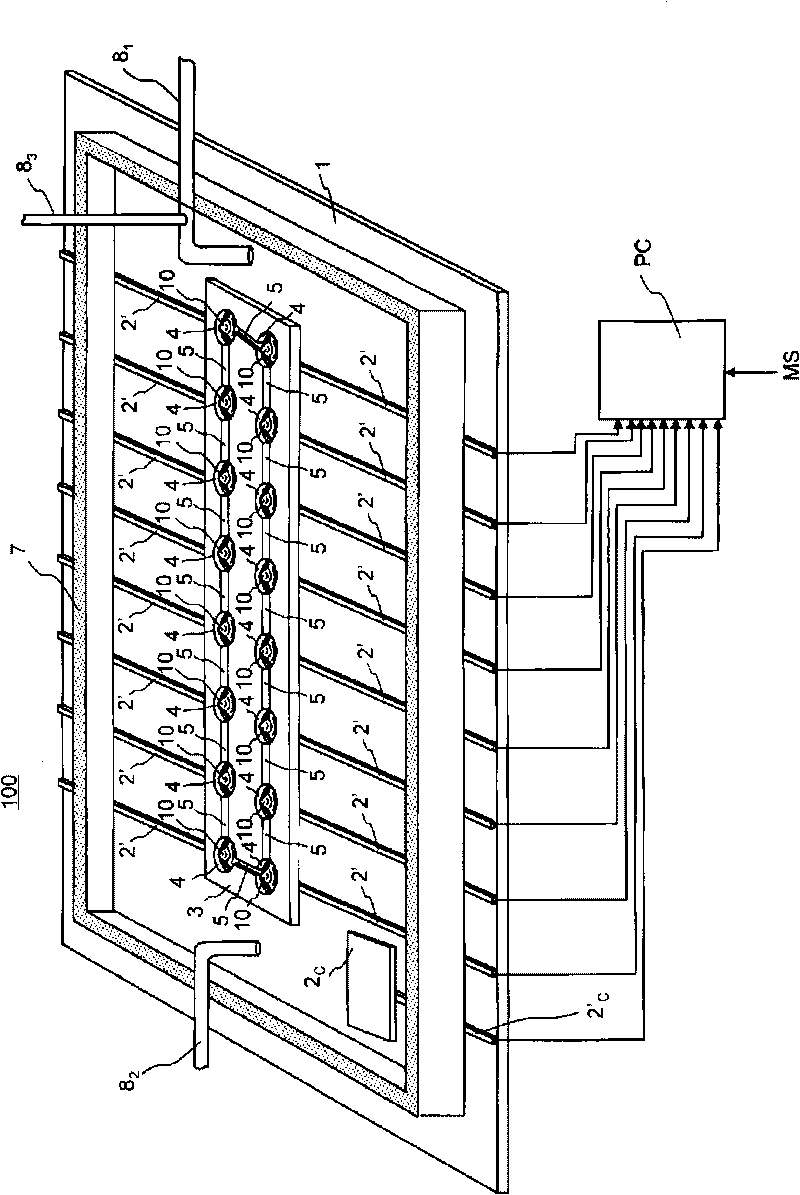
A cell potential measurement apparatus, which uses a planar electrode enabling a multi-point simultaneous measurement of potential change arising from cell activities, is provided which can conduct measurements accurately and efficiently as well as can improve convenience of arranging measurement results. According to the configuration of the cell potential measurement apparatus of this invention, it includes an integrated cell holding instrument 1, which includes a planar electrode provided with a plurality of microelectrodes arranged in a matrix form on the surface of a substrate, a cell holding part for placing cells thereon, drawer patterns from the microelectrodes, and electric contact points for outside connections; an optical observation means 20 for optical observations of cells; a stimulation signal supply means 30 to be connected to the cell holding instrument for providing electric stimulation to the cells; and a signal processing means 30 to be connected to the cell holding instrument for processing an output signal arising from electric physiological activities of the cells. It is preferable that a cell culturing means 40 is also provided for maintaining a culture atmosphere of the cells placed on the integrated cell holding instrument.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Cell potential measuring electrode and measuring apparatus using the same
InactiveUSRE37977E1Simple manufacturing processCost benefitImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMicroelectrodeBattery cell
This invention relates to a low impedance cell potential measuring electrode assembly typically having a number of microelectrodes on an insulating substrate and having a wall enclosing the region including the microelectrodes. The device is capable of measuring electrophysiological activities of a monitored sample using the microelectrodes while cultivating those cells or tissues in the in the region of the microelectrodes. The invention utilizes independent reference electrodes to lower the impedance of the overall system and to therefore lower the noise often inherent in the measured data. Optimally the microelectrodes are enclosed by a physical wall used for controlling the atmosphere around the monitored sample.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
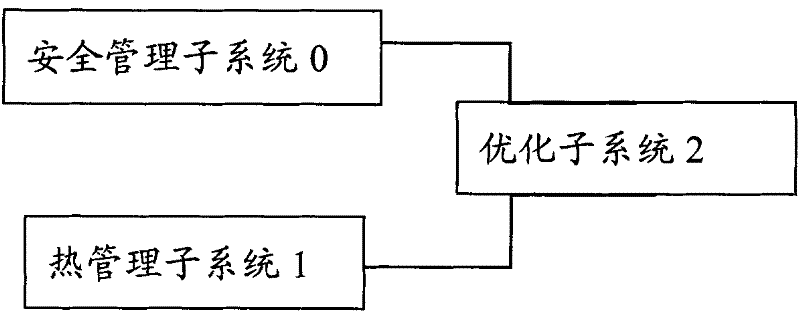
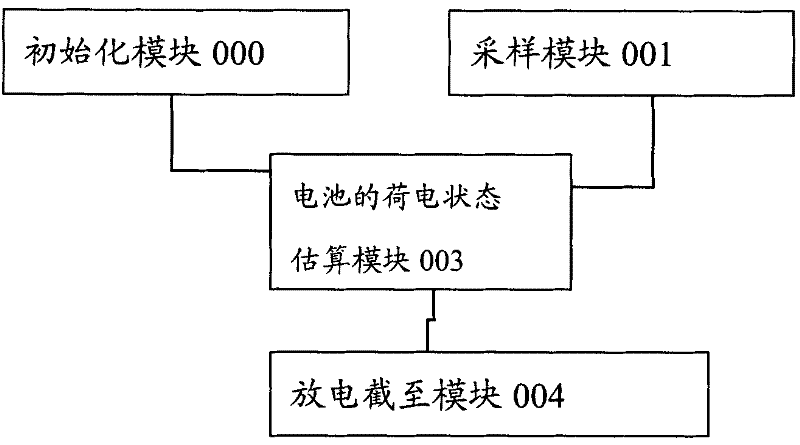
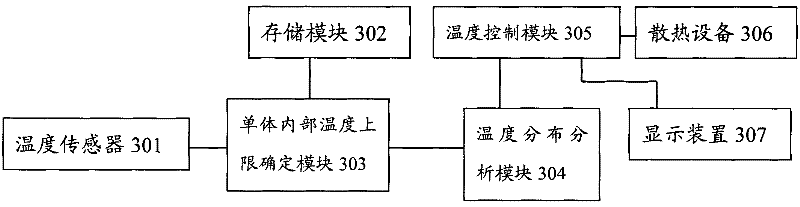
Power battery management system and method thereof
InactiveCN102195101AUnleash your full potentialOptimize quantityCell temperature controlSecondary cells servicing/maintenancePower batteryHeat management
The invention relates to an electrical design field and discloses a power battery management system and a method thereof. Estimation algorithm of cell state of charge (SOC), a heat management technology, a safety management and other new technologies are researched and implemented. The system in the invention comprises a safety management subsystem, a heat management subsystem, an optimization subsystem and the like. The safety management subsystem is used for monitoring charged states of cell monomers; determining whether the cell monomers are in discharge end states according to charged states of cell monomers and terminating cell discharges if the cell monomers are in discharge end states. The heat management subsystem is used for detecting temperatures of cell monomer surfaces; determining upper limits of temperature ranges in cell monomers according to temperature history information of cell monomer surfaces; determining temperature distribution information of a cell box consisting of all cell monomers; controlling an operating temperature of the battery according to temperature distribution information so that the operating temperature is in a range of preset temperatures. The optimization subsystem is respectively connected with the safety management subsystem and the heat management subsystem, and is used for controlling working states of the safety management subsystem and the heat management subsystem. In the invention, the safety management, the heat management and the like are applied in a management field of a power battery, which can improve safety performance, prolong service life, raise usage efficiency, give fully play to cell potential and guarantee the safety of using.
Owner:SHANGHAI FANGYA ENERGY TECH CO LTD
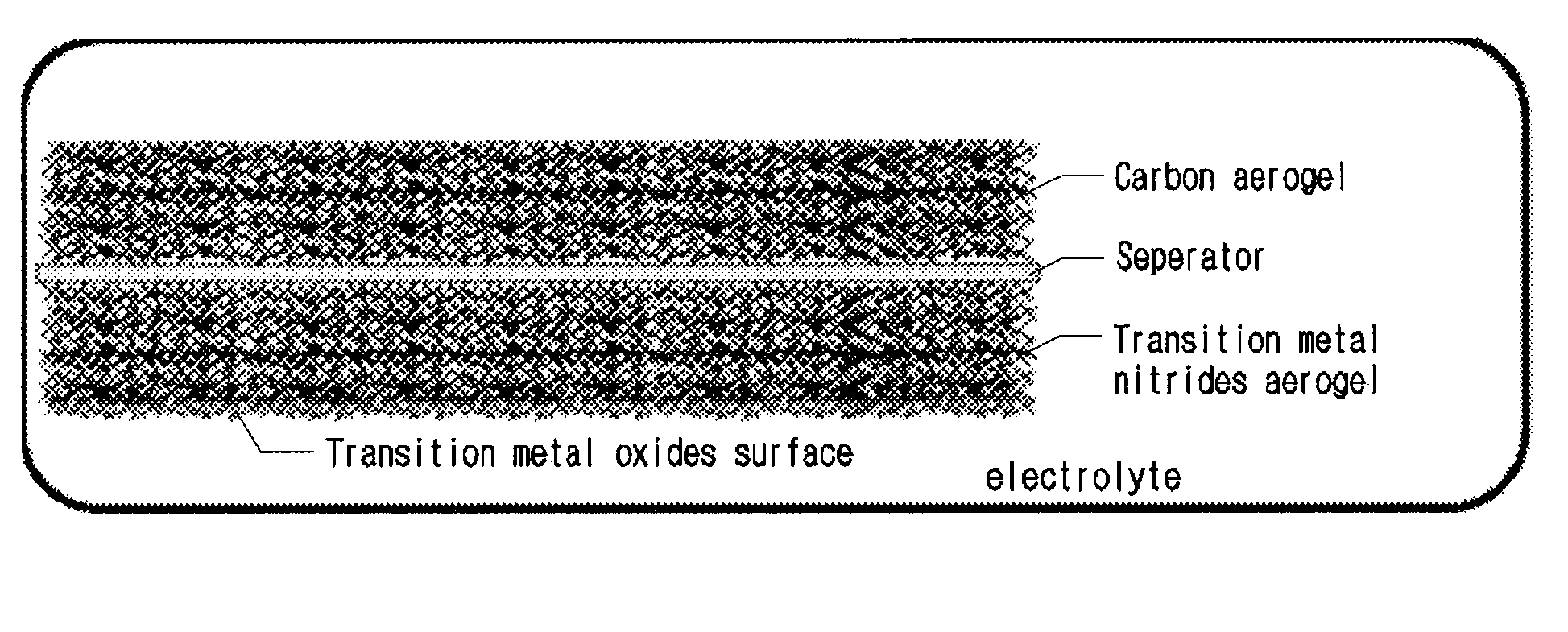
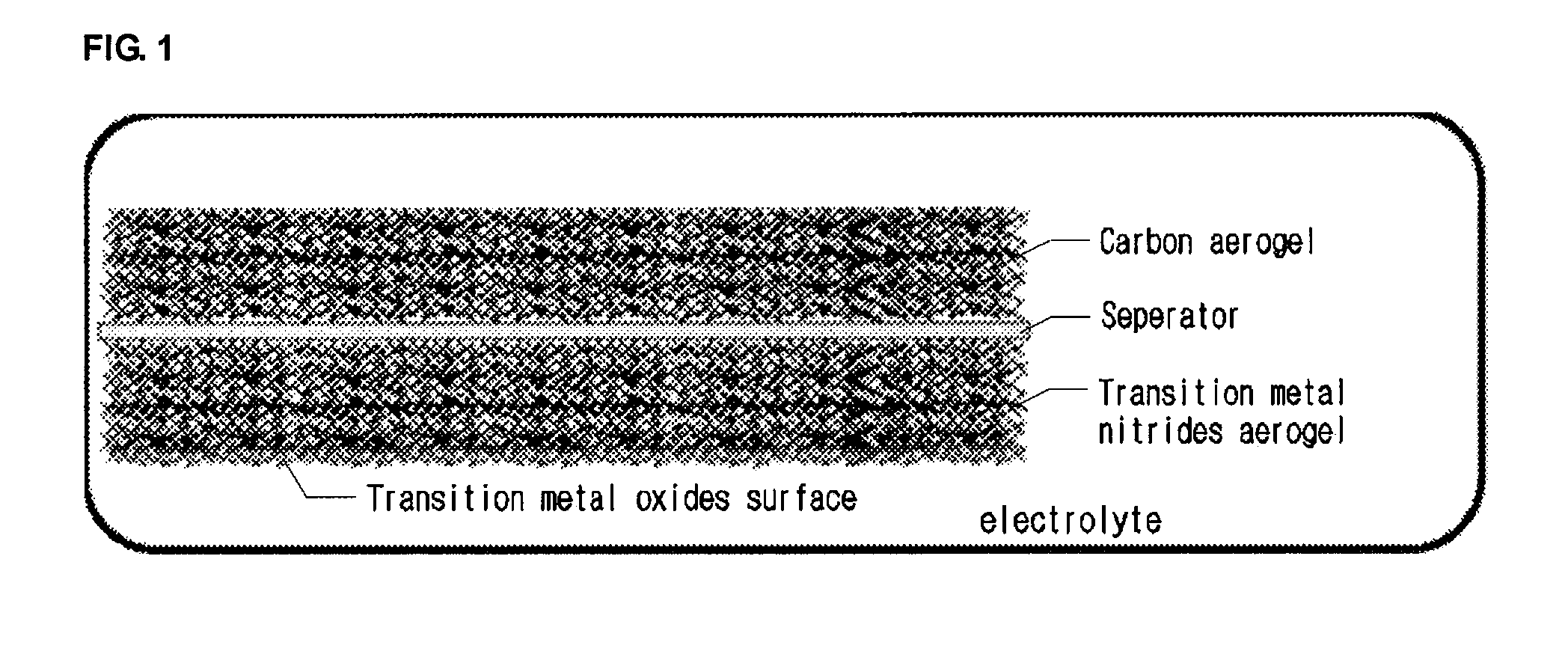
Hybrid supercapacitor using surface-oxidized transition metal nitride aerogel
InactiveUS20100195269A1Increase capacitanceIncrease energy densityHybrid capacitor electrodesDouble layer capacitorsInternal resistanceMaterials science
It discloses a hybrid supercapacitor including a carbon aerogel cathode and a surface-oxidized transition metal nitride aerogel anode which is able to increase energy density and power density with increase of overall cell potential and at the same time lower internal resistance of the electrode and equivalent series resistance by using a monolithic electrode with no use of current collector and binder.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Electrochemical Device For Converting Carbon Dioxide To A Reaction Product
ActiveUS20160108530A1Low faradaic efficiencyLow conversion currentCellsSolid electrolytesElectrolysisPyridinium
An electrochemical device converts carbon dioxide to a reaction product. The device includes an anode and a cathode, each comprising a quantity of catalyst. The anode and cathode each has reactant introduced thereto. A polymer electrolyte membrane is interposed between the anode and the cathode. At least a portion of the cathode catalyst is directly exposed to gaseous carbon dioxide during electrolysis. The average current density at the membrane is at least 20 mA / cm2, measured as the area of the cathode gas diffusion layer that is covered by catalyst, and CO selectivity is at least 50% at a cell potential of 3.0 V. In some embodiments, the polymer electrolyte membrane comprises a polymer in which a constituent monomer is (p-vinylbenzyl)-R, where R is selected from the group consisting of imidazoliums, pyridiniums and phosphoniums. In some embodiments, the polymer electrolyte membrane is a Helper Membrane comprising a polymer containing an imidazolium ligand, a pyridinium ligand, or a phosphonium ligand.
Owner:DIOXIDE MATERIALS
Fluid regulating microvalve assembly for fluid consuming cells
InactiveUS20060257701A1Low costInexpensive and straightforward to produceFuel and primary cellsReactant parameters controlElectrochemical cellBiomedical engineering
A fluid regulating microvalve assembly for use to control fluid flow to a fluid consuming electrode, such as an oxygen reduction electrode, in an electrochemical cell. The microvalve assembly includes a stationary valve body having an aperture and a microactuator movable from a first position where the microvalve body aperture is closed to fluid flow to at least a second position where fluid is able to pass through the microvalve body aperture. The fluid regulating microvalve assembly can utilize cell potential or a separate source to open and close the microvalve. The fluid regulating microvalve assembly can be located outside the cell housing or inside the cell housing, for example between one or more fluid inlet apertures and the fluid consuming electrode. The invention includes a method of making a multilayer microvalve assembly, particularly one for use in a fluid depolarized battery, using a printing process to deposit at least one of the layers.
Owner:SCHUMM BROOKE JR +3
Secondary cell charger and charging method
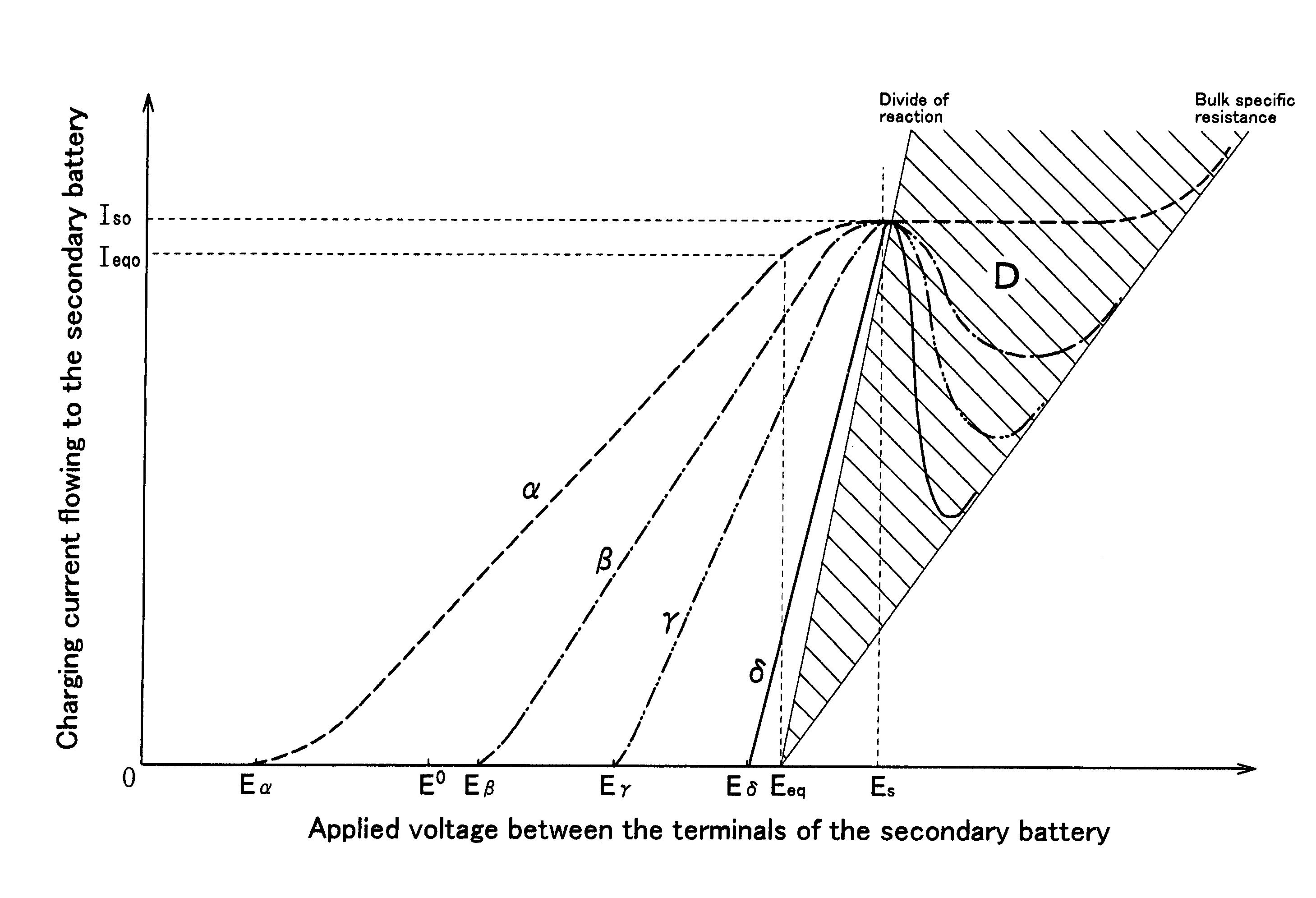
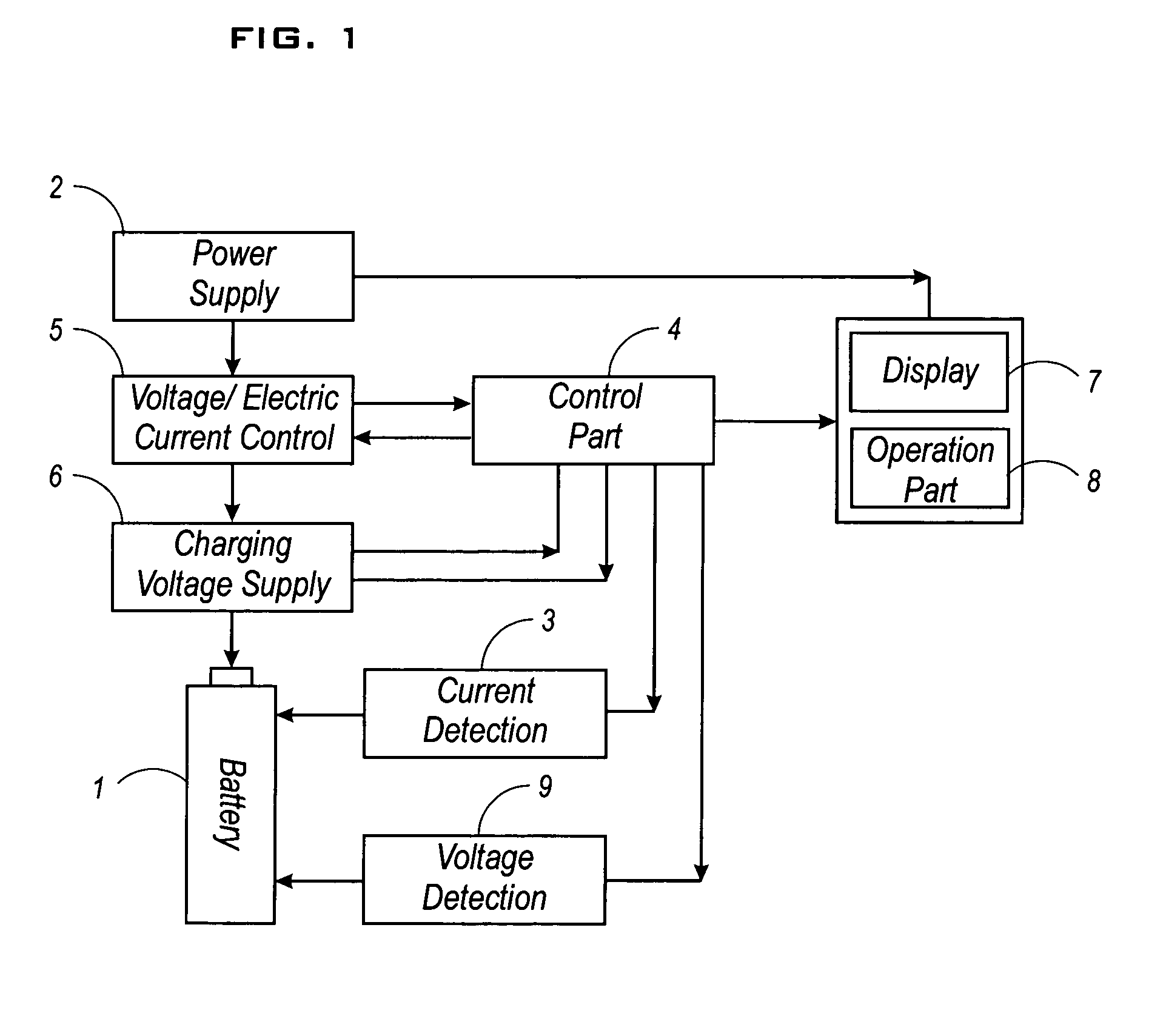
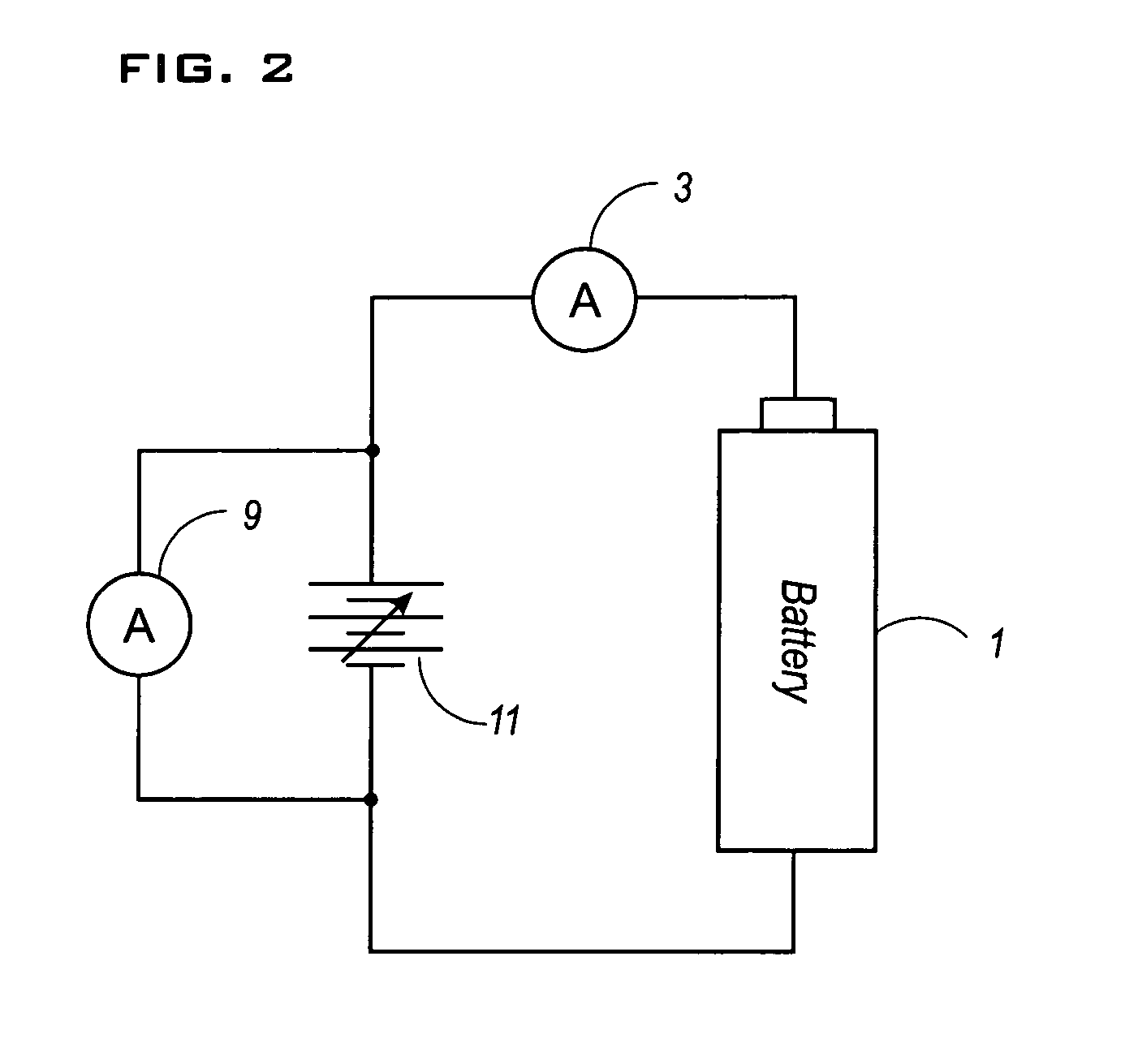
InactiveUS7109684B2Solve insufficient chargingEasy to useElectrical testingSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectrical batteryPhysical chemistry
An equipment and method for charging a secondary battery are provided to quickly and surely charge a secondary battery (secondary batteries) while preventing the secondary battery (batteries) from overcharging or insufficient charging. Special charging voltage Es is applied to a secondary battery for a predetermined time, and then the applied voltage is switched to equilibrium voltage Eeq for establishing equilibrium cell potential of the secondary battery in its fully charged condition, wherein the special charging value Es is larger than the equilibrium value Eeq. Electric current i is detected while application of the equilibrium voltage Eeq. If the detected electric current i is larger than standard electric current J for finishing charging, the above detection and charging are repeated; otherwise, charge of the secondary battery 1 is halted.
Owner:TECHNO CORE INT +1
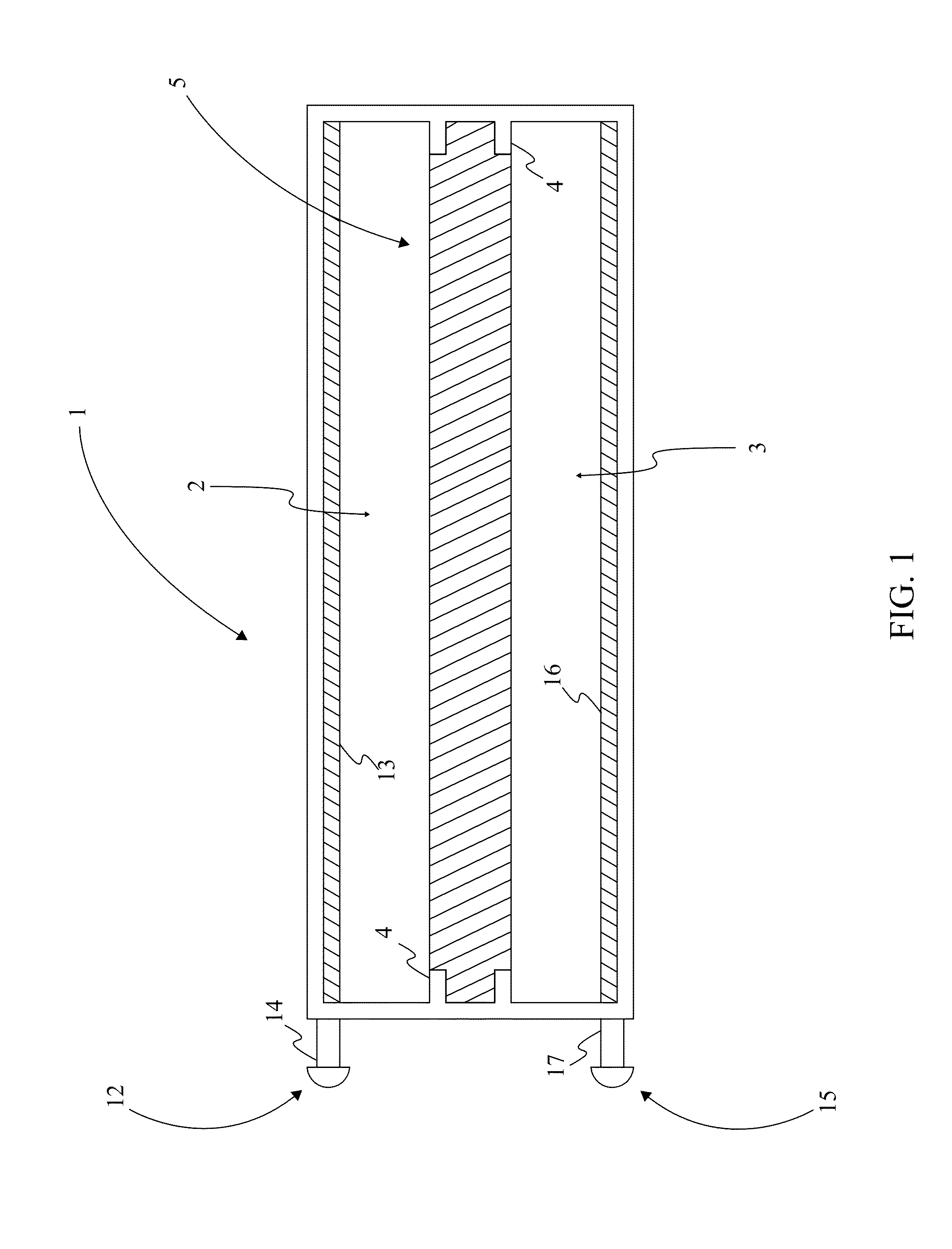
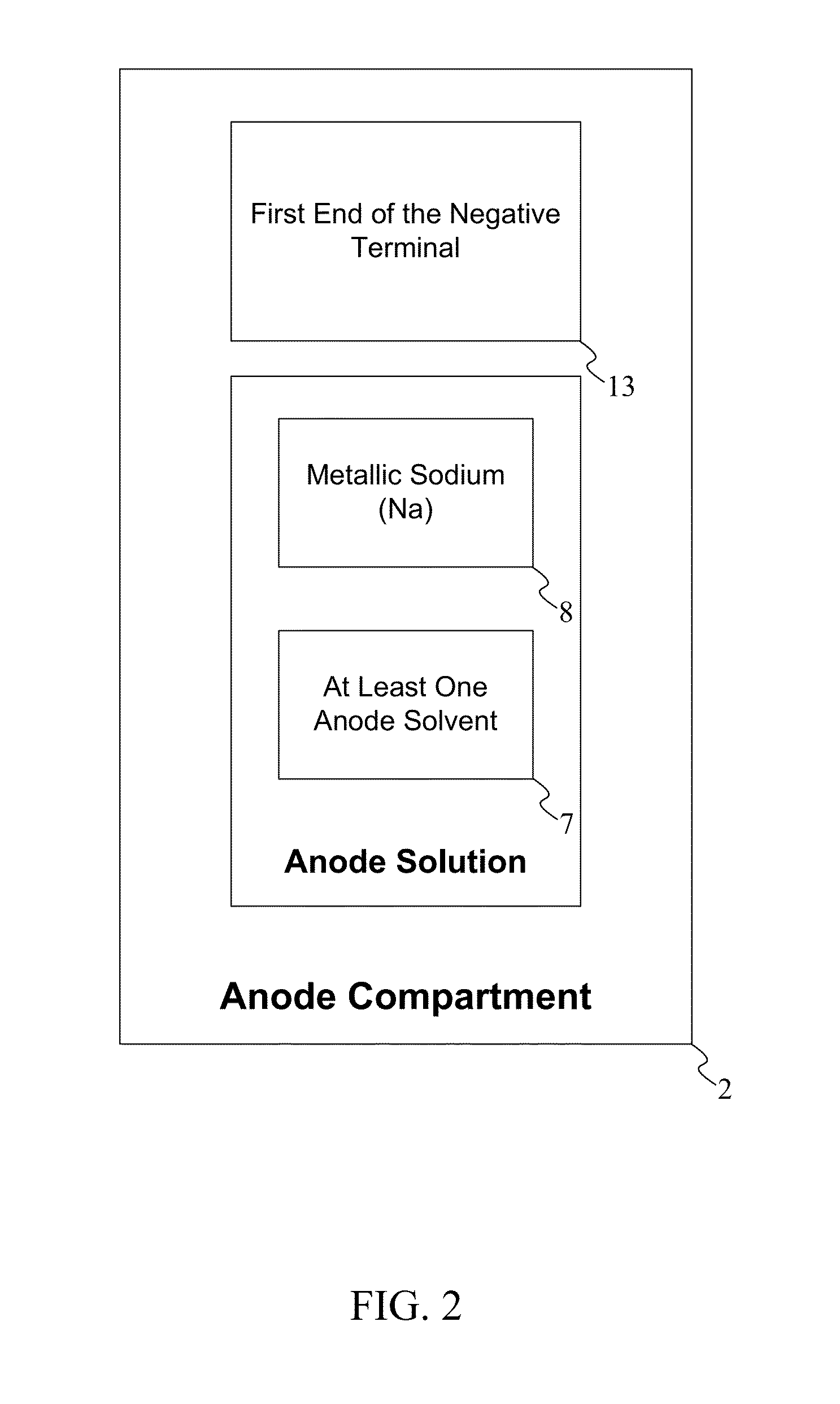
Sodium-Sulfur Battery
InactiveUS20130288153A1High operating cell potentialReduce the temperatureRegenerative fuel cellsSecondary cellsElectrode potentialNanowire
A sodium sulfur secondary battery is a battery that operates at a comparatively lower temperature, while maintaining a high operating cell potential comparable to existing sodium sulfur battery configurations. The apparatus accomplishes this through the arrangement of component materials selected based on experimentation results demonstrating favorable performance in a secondary battery configuration. The sodium sulfur battery comprises a housing, containing an anode solution, a cathode solution, and a sodium ion conductive electrolyte membrane. The anode solution contains metallic sodium and anode solvent. The cathode solution contains elemental sulfur and a cathode solvent. The sodium ion conductive electrolyte membrane is a Sodium Titanate Nano-membrane formed from long TiO2-nanowires. The electrolyte membrane is positioned between the anode solution and the cathode solution. The electrolyte membrane is able to selectively transports of sodium ion between the anode solution and the cathode solution at temperatures below 75° C. generating an electrode potential.
Owner:MORIS TECH CENT
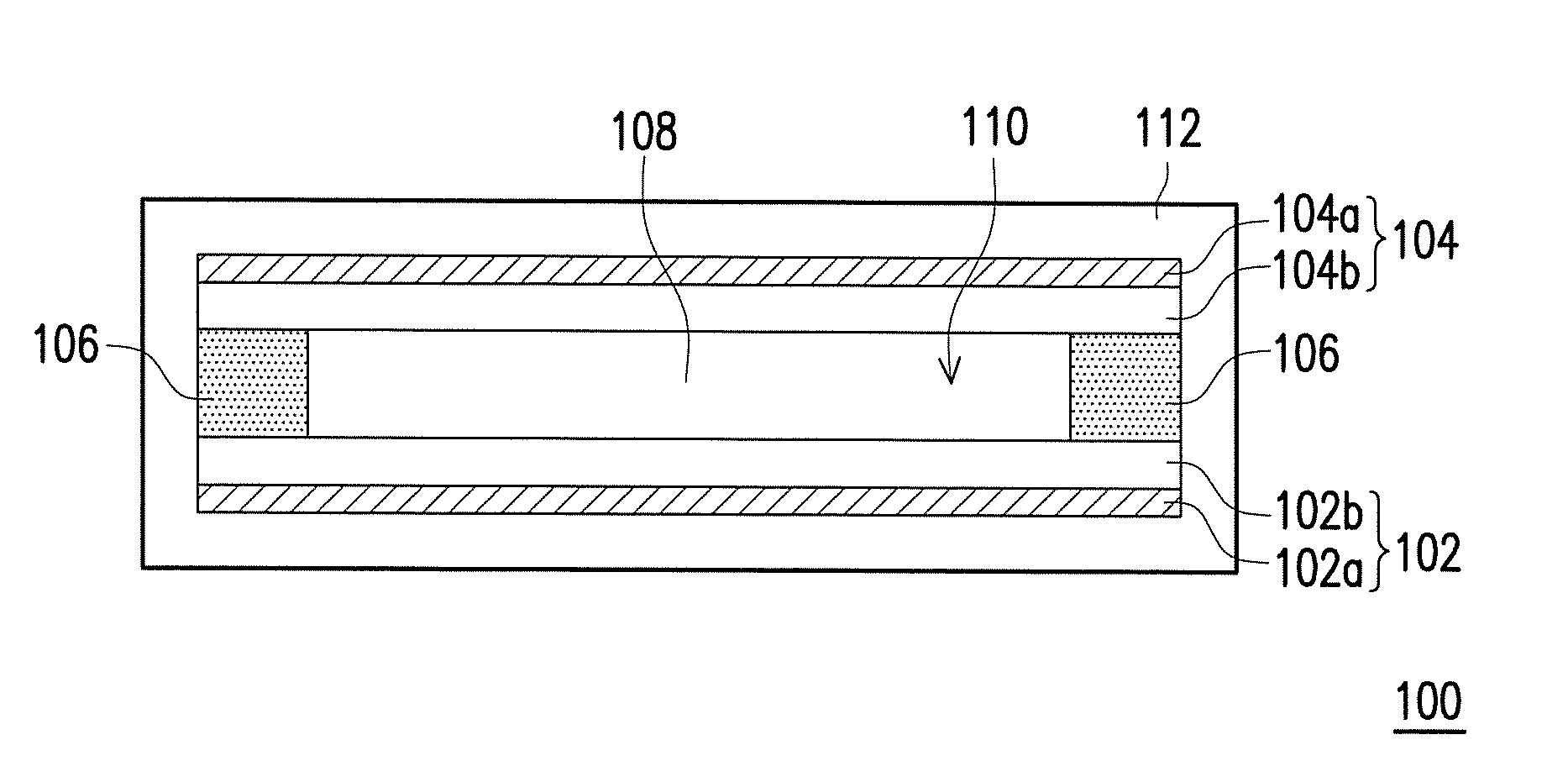
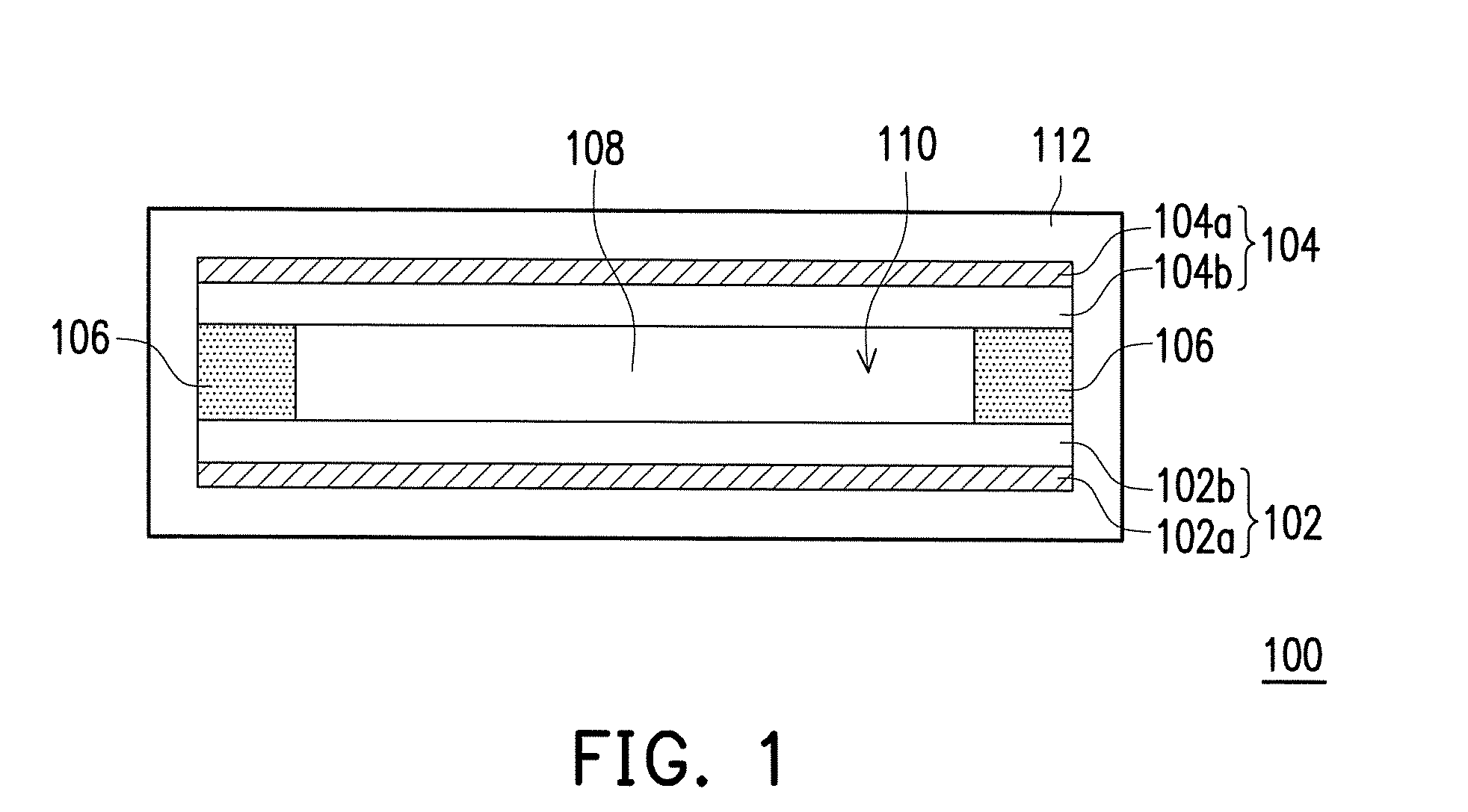
Lithium-ion battery and method for fabricating the same
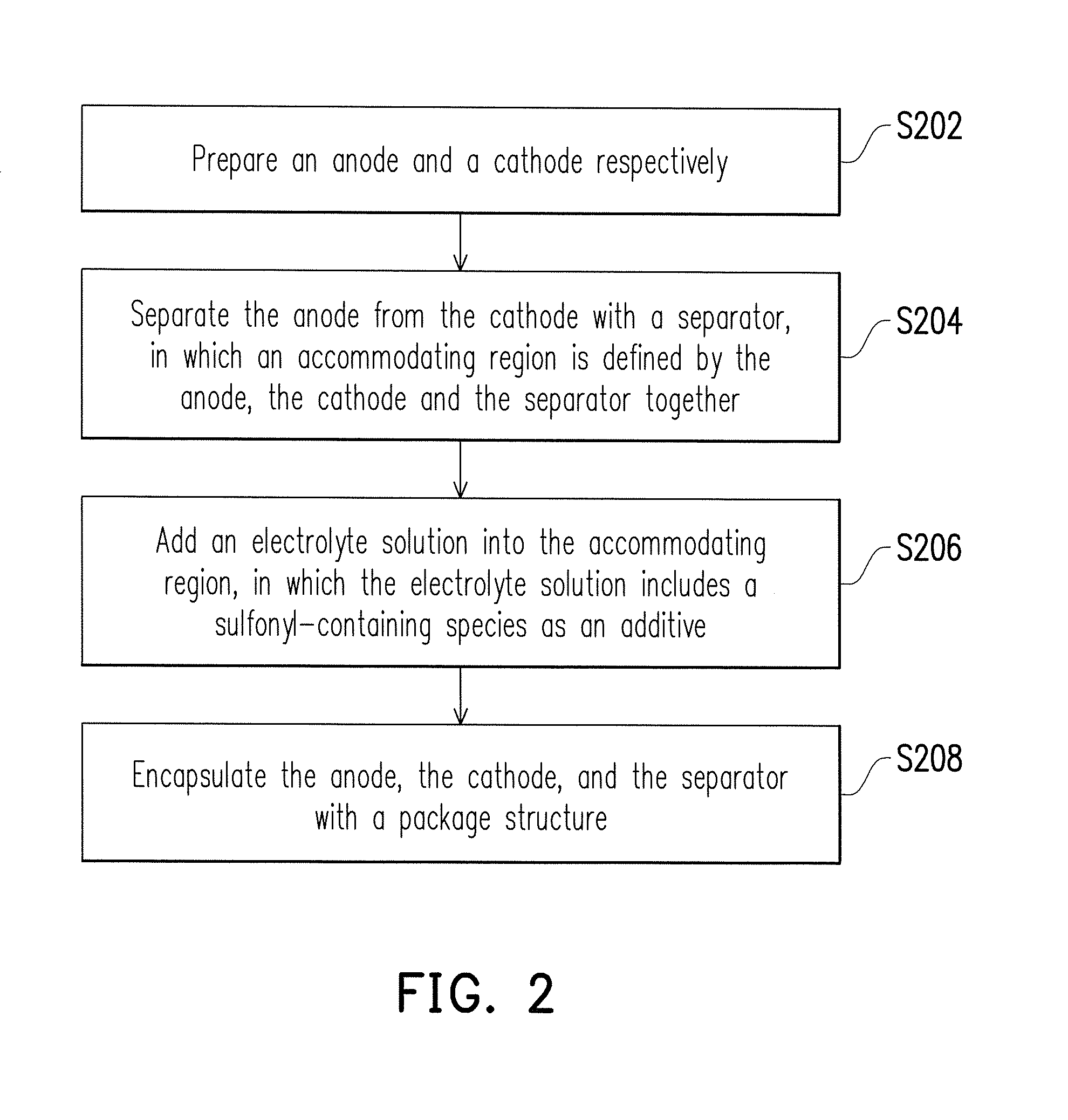
InactiveUS20130122379A1Increase the scope of applicationImprove performanceElectrode carriers/collectorsLi-accumulatorsOrganic solventHigh pressure
A lithium-ion battery and a method for fabricating the same are provided. The lithium-ion battery includes an anode, a cathode, a separator, and an electrolyte solution. The cathode is disposed opposite to the anode. The separator is disposed between the anode and the cathode, where an accommodating region is defined by the anode, the cathode and the separator. The electrolyte solution disposed within the accommodating region includes an organic solvent, a lithium salt and an additive. The additive includes a sulfonyl-containing species, and the content thereof is 0.1 to 5 wt % based on the total weight of the electrolyte solution. The whole-cell potential of the lithium-ion battery is 4.5 V or above. In the lithium-ion battery and the method for fabricating the same of the invention, the sulfonyl-containing species serves as the additive, so that the battery is capable of being operated under a condition of high-voltage charge and discharge.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cell potential measurement apparatus having a plurality of microelectrodes
InactiveUSRE40209E1Easy to displayFacilitates optical observationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPotential changeMeasurement device
A cell potential measurement apparatus, which uses a planar electrode enabling a multi-point simultaneous measurement of potential change arising from cell activities, is provided which can conduct measurements accurately and efficiently as well as can improve convenience of arranging measurement results. According to the configuration of the cell potential measurement apparatus of this invention, it includes an integrated cell holding instrument, which includes a planar electrode provided with a plurality of microelectrodes arranged in a matrix form on the surface of a substrate, a cell holding part for placing cells thereon, drawer patterns from the microelectrodes, and electric contact points for outside connections; an optical observation means for optical observations of cells; a stimulation signal supply means to be connected to the cell holding instrument for providing electric stimulation to the cells; and a signal processing means to be connected to the cell holding instrument for processing an output signal arising from electric physiological activities of the cells. It is preferable that a cell culturing means is also provided for maintaining a culture atmosphere of the cells placed on the integrated cell holding instrument.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and system for electrochemical production of formic acid from carbon dioxide
An electrochemical device converts carbon dioxide to a formic acid reaction product. The device includes an anode and a cathode, each comprising a quantity of catalyst. The anode and cathode each have reactant introduced thereto. Two membranes, a cation exchange polymer electrolyte membrane and an anion exchange polymer electrolyte membrane, are interposed between the anode and the cathode, forming a central flow compartment where a carbon dioxide reduction product, such as formic acid, can be recovered. At least a portion of the cathode catalyst is directly exposed to gaseous carbon dioxide during electrolysis. The average current density at the membrane is at least 20 mA / cm2, measured as the area of the cathode gas diffusion layer that is covered by catalyst, and formate ion selectivity is at least 50% at a cell potential difference of 3.0 V. In some embodiments, at least one polymer electrolyte membrane comprises a polymer in which a constituent monomer is (p-vinylbenzyl)-R, where R is selected from the group consisting of imidazoliums, pyridiniums and phosphoniums. In some embodiments, the polymer electrolyte membrane is a Helper Membrane comprising a polymer containing an imidazolium ligand, a pyridinium ligand, or a phosphonium ligand.
Owner:DIOXIDE MATERIALS
Fluid regulating microvalve assembly for fluid consuming cells with spring-like shape-retaining aperture cover
ActiveUS20120208102A1Inexpensive and straightforward to produceLow costFuel and primary cellsValve arrangementsElectrochemical cellBiomedical engineering
A fluid regulating microvalve assembly for use to control fluid flow to a fluid consuming electrode, such as an oxygen reduction electrode, in an electrochemical cell is proposed. The microvalve assembly includes a stationary valve body having an aperture and microactuators movable from a first closed aperture position to at least a second position where fluid is able to pass through the microvalve body aperture. These microactuators control the movement of spring-like shape-retaining interior aperture covers, which covers can be belleville springs or flat springs. The fluid regulating microvalve assembly can utilize cell potential or a separate source. The latter assembly can be located outside or inside the cell housing, for example between a fluid inlet aperture and the fluid consuming electrode. Using a printing process to deposit at least one of the layers is proposed for making the multilayer microvalve assembly for a fluid depolarized battery.
Owner:SCHUMM JR BROOKE
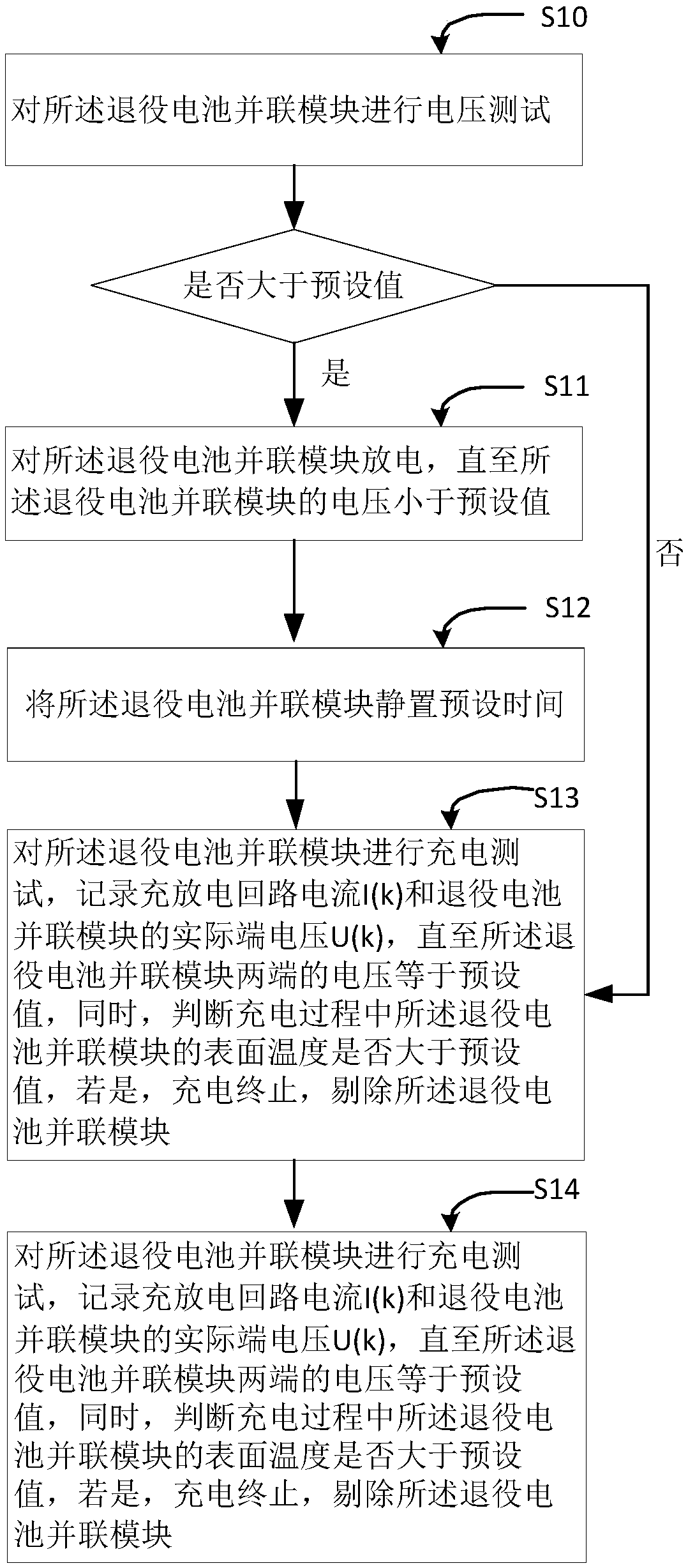
Cascade utilization oriented removal method for decommissioned battery parallel module
The invention discloses a cascade utilization oriented removal method for a decommissioned battery parallel module. The method comprises steps as follows: S1, extracting charge loop current I (k) of kgroups of a charge-discharge process and actual terminal voltage U (k) of the decommissioned battery parallel module; S2, extracting part of data in S1 for cell potential model parameter identification; S3, calculating theoretical voltage Ute (k) corresponding to current I(k) in a cell potential model of the decommissioned battery parallel module; S4, calculating a root-mean-square error of the actual terminal voltage U (k) of the decommissioned battery parallel module and the theoretical voltage Ute (k), and removing the decommissioned battery parallel module if the value of the root-mean-square error is larger than a preset value. According to the method, the decommissioned battery parallel module is not required to be disassembled, whether cell aging phenomenon exists in the decommissioned battery parallel module or not is judged by calculating the root-mean-square error of the actual voltage and the theoretical voltage corresponding to the equivalent model in the decommissioned battery parallel module, the method is simple, a battery is not required to be dismounted, and the method can be widely applied to the field of batteries.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
On-vehicle algorithms to determine if lithium plating has occurred
InactiveUS20190379090A1Efficiency of intercalationRate efficiencyCell electrodesElectrical testingLithium metalHemt circuits
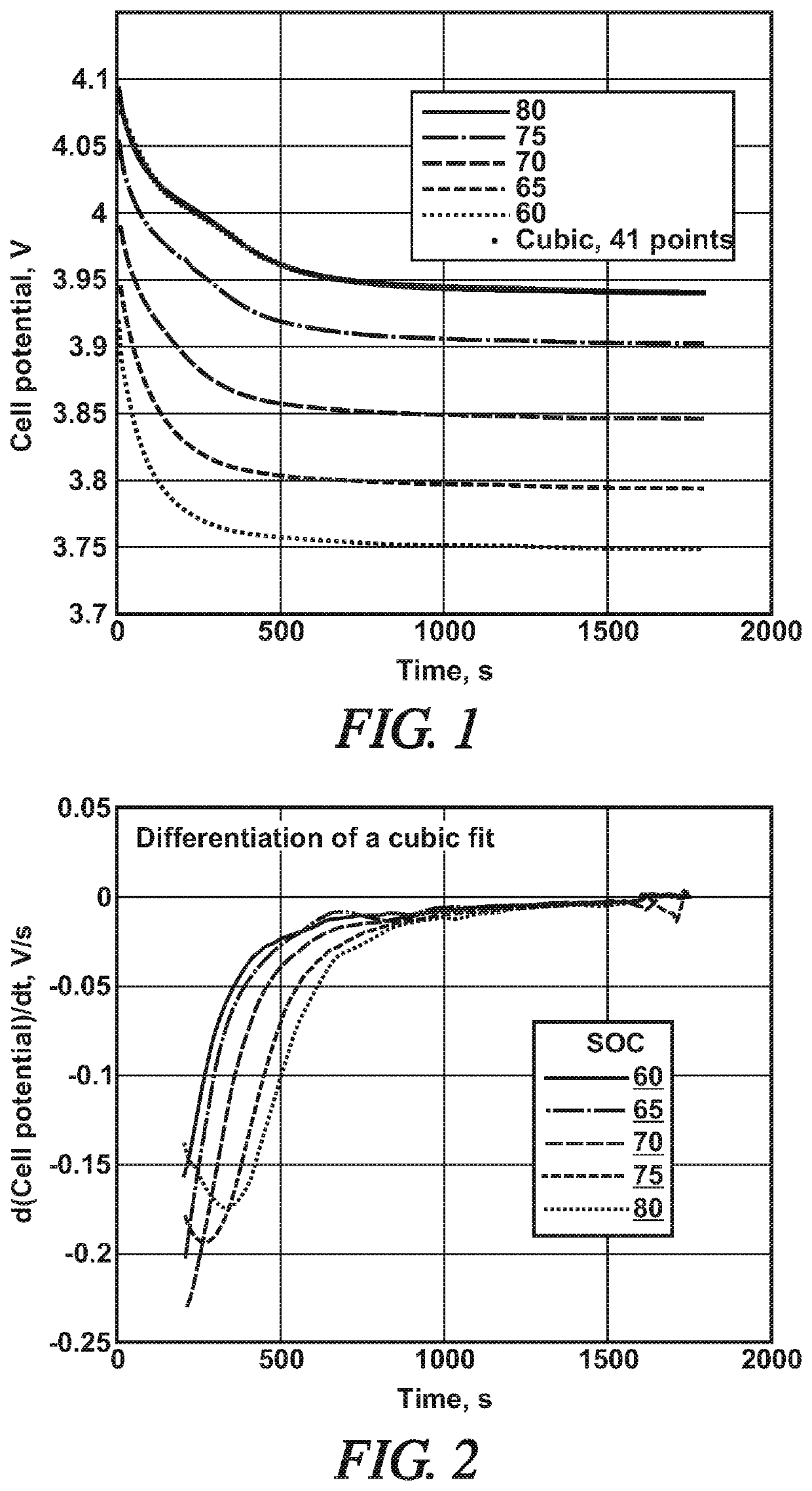
During the charging of lithium-ion batteries, comprising graphite anode particles, the goal is to intercalate lithium into the anode materials as LiC6. But it is possible to conduct the charging process at a rate that lithium is undesirably plated, undetected, as lithium metal on the particles of graphite. During an open-circuit period of battery operation, immediately following such a charging period, the presence of lithium plating can be detected, using a computer-based monitoring system, by continually measuring the cell potential (Vcell) over a brief period of open-circuit time, fitting the open-circuit voltage data to a best cubic polynomial fit, and then determining dVcell / dt (mV / s) from the polynomial fit over a like period of time. It is found that the presence of a maximum or a minimum in the derivative curve (a local minimum) reliably correlates with plated lithium on the graphite particles of the anode.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
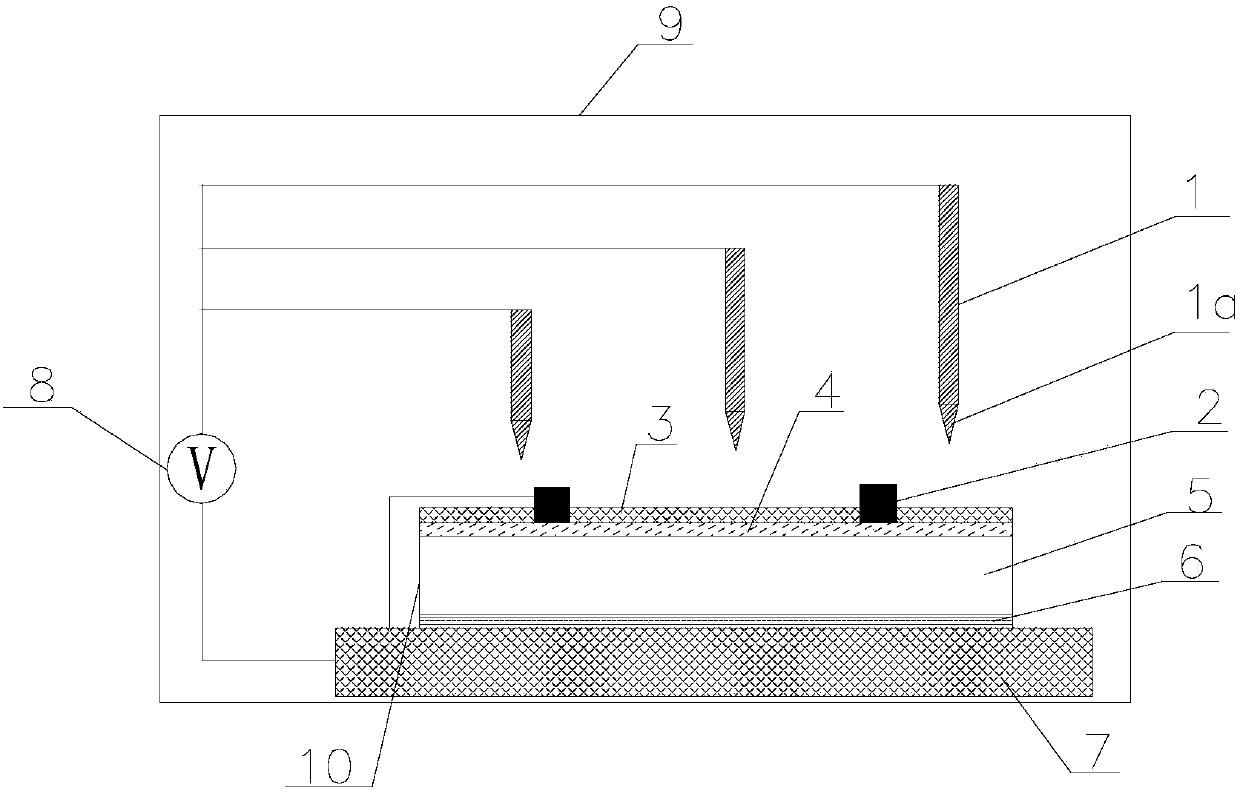
Device and method for rapidly testing potential induced degradation of solar cell
ActiveCN106656041ASpeed up agingImprove usabilityPhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic energy generationPotential induced degradationNon destructive
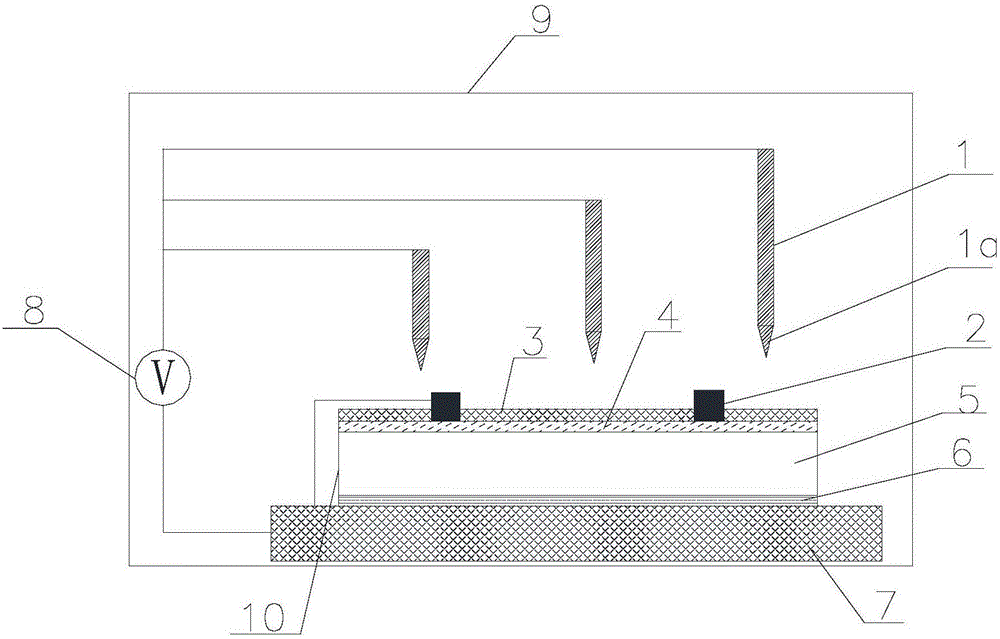
The invention discloses a device for rapidly testing potential induced degradation of a solar cell. The device comprises an environmental box, a metal test bench, an external power supply and a plurality of metal probes, wherein an adjustment device for adjusting temperature and humidity is arranged in the environmental box, the metal test bench is arranged in the environmental box, the temperature of a bench surface of the metal test bench can be adjusted, the external power supply generates a voltage of 200V to 1,000V, and the metal probes are connected with the external power supply by wires and are provided with tip end parts. The invention also discloses a method for rapidly testing the potential induced degradation of the solar cell. The device has the advantages of short test period, reliable test result, high sensitivity and the like; and the method is a battery terminal-based direct method for non-destructive observation on the potential induced degradation of the battery.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD
Device and method for testing food quality
InactiveUS20100237850A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingMeasurement deviceTest food
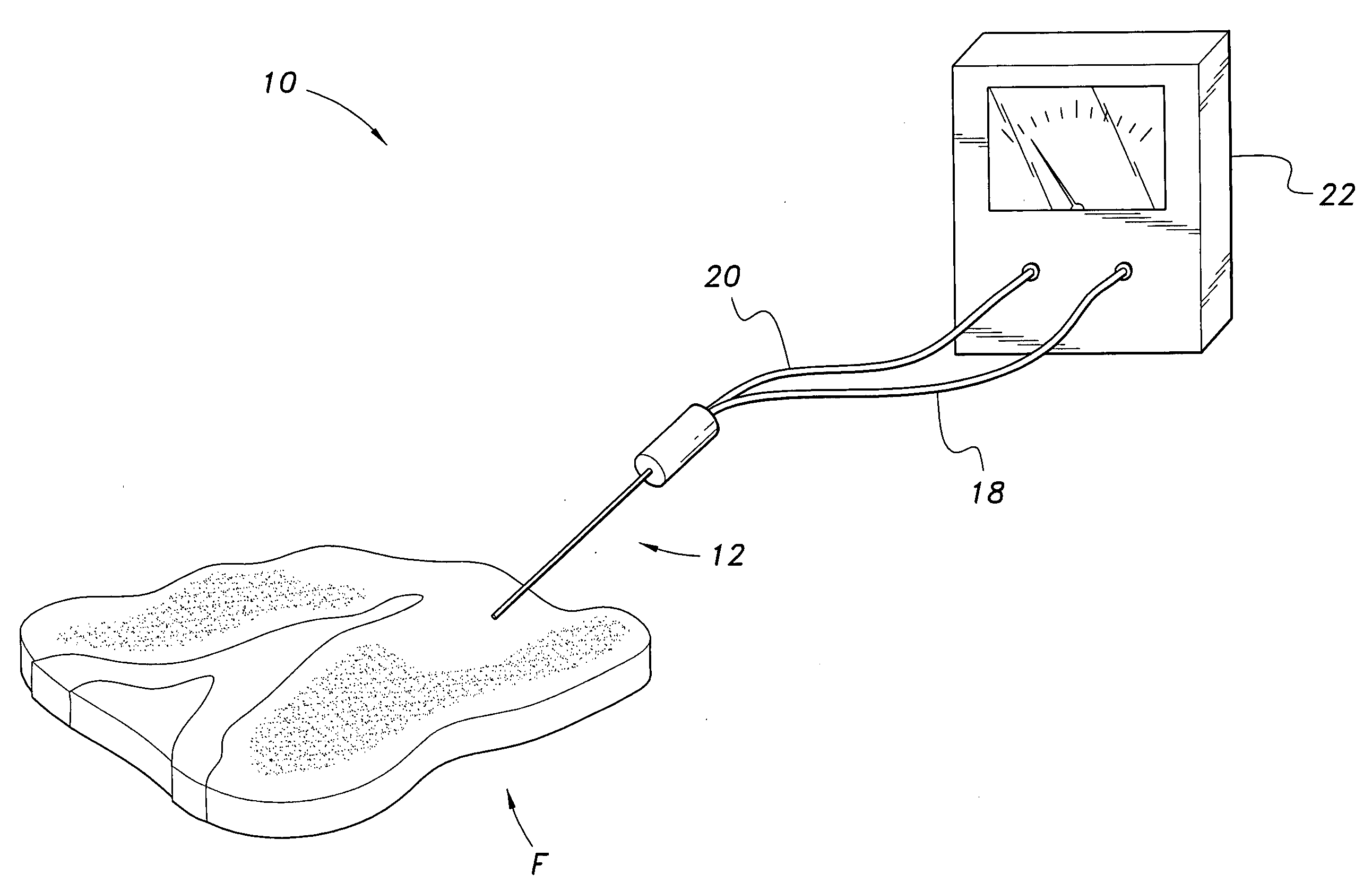
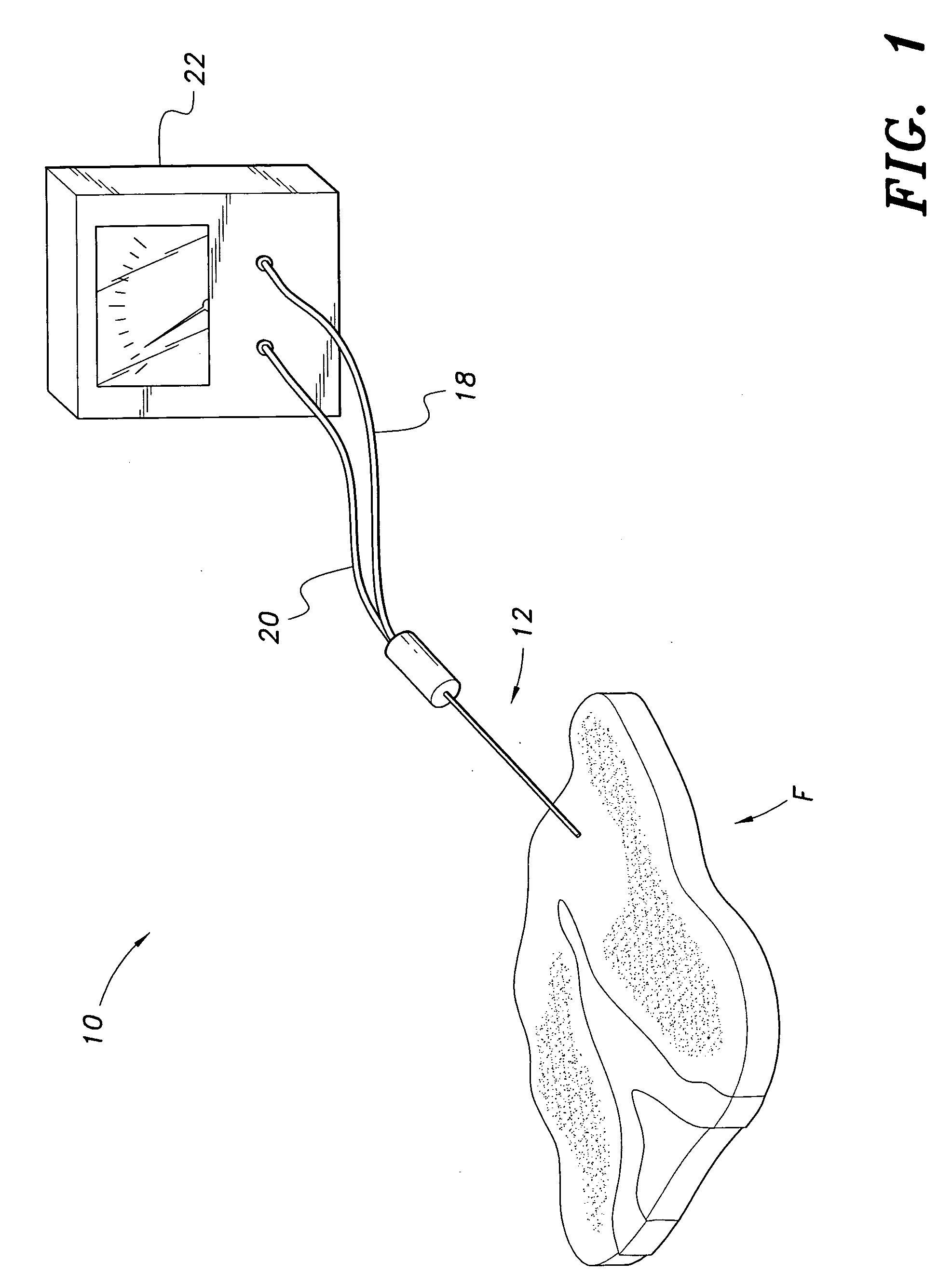
The device for testing food quality is a device for measuring the state of decay of a piece of food based upon measured electrical potential. The device includes a needle probe having an outer cylindrical shell formed from a first metal, such as stainless steel, and a wire mounted coaxially within the outer cylindrical shell. The wire is formed from a second metal, such as copper. A measuring device for electrical potential, such as a voltmeter, is further provided and is in communication with the needle probe. The device forms a galvanic cell when the probe is inserted into the food, the cell potential decreasing as a function of time in a manner corresponding to the state of decay of the piece of the food.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
Cardiac reentry model chip and apparatus and method for evaluating drug using the cardiac reentry model chip
InactiveCN101730736AImprove reliabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberClosed loop
It is intended to develop a chip by which cell potential and cell morphology can be accurately measured on a single cell basis and a heart model comprising a closed loop having myocardial cells and fibroblasts in an appropriately dispersed state can be constructed to evaluate the effect of a drug. An in vitro cardiac reentry model chip is fabricated by constructing a closed loop, wherein myocardial cells and fibroblasts are provided on a transparent electrode formed on a transparent substrate by using a constitution of enclosing a single cell in a specific spatial configuration, and transmitting the pulsating of an arbitrary myocardial cell or a specific myocardial cell in the closed loop to the both sides of the loop so as to electrically detect the pulsating conditions of the cell in the closed loop. The usefulness or toxicity of a drug to myocardial cells is evaluated by loading the drug on this cardiac reentry model chip and measuring the cell potentials of the individual cells.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKYO MEDICAL & DENTAL UNIV
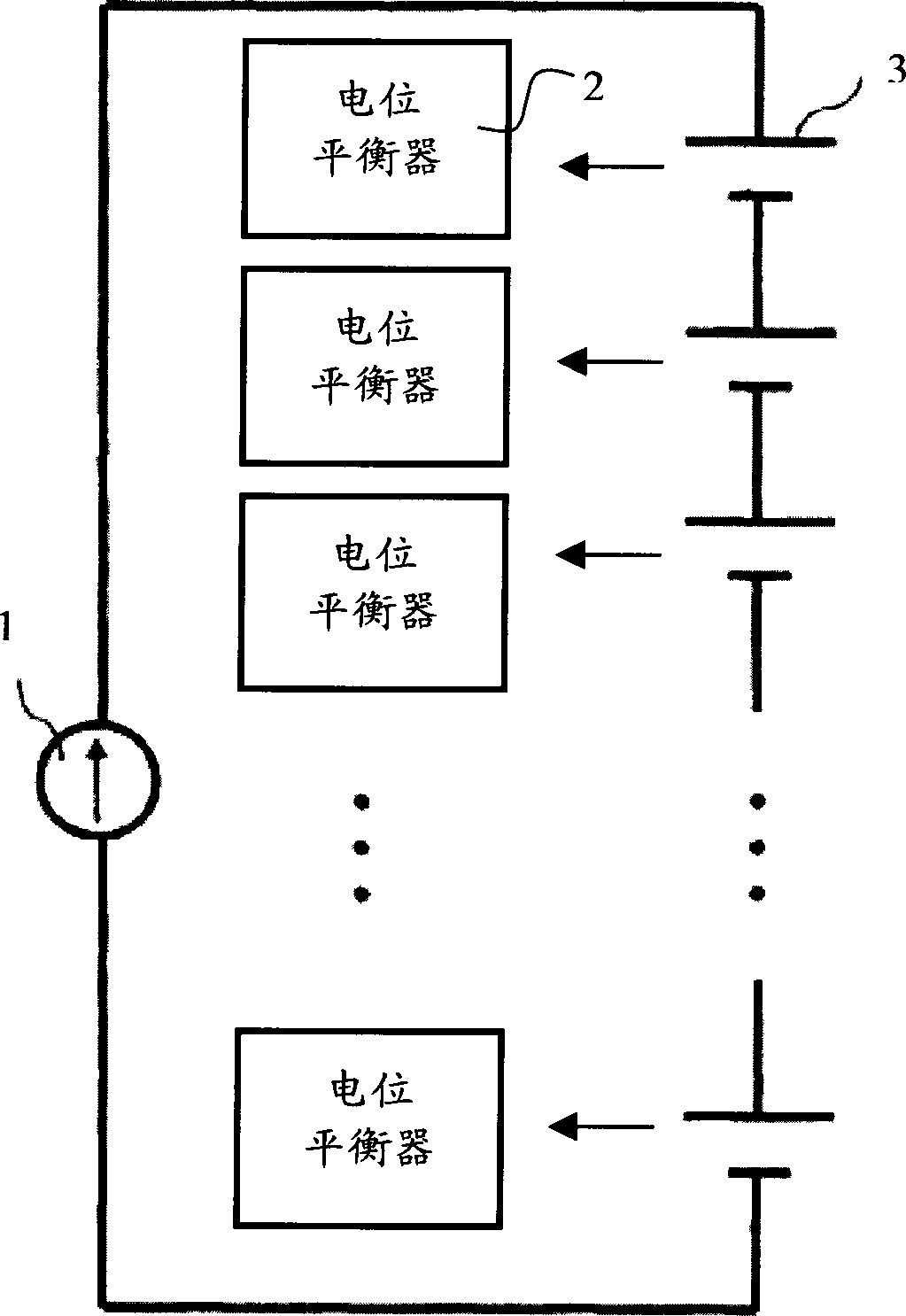
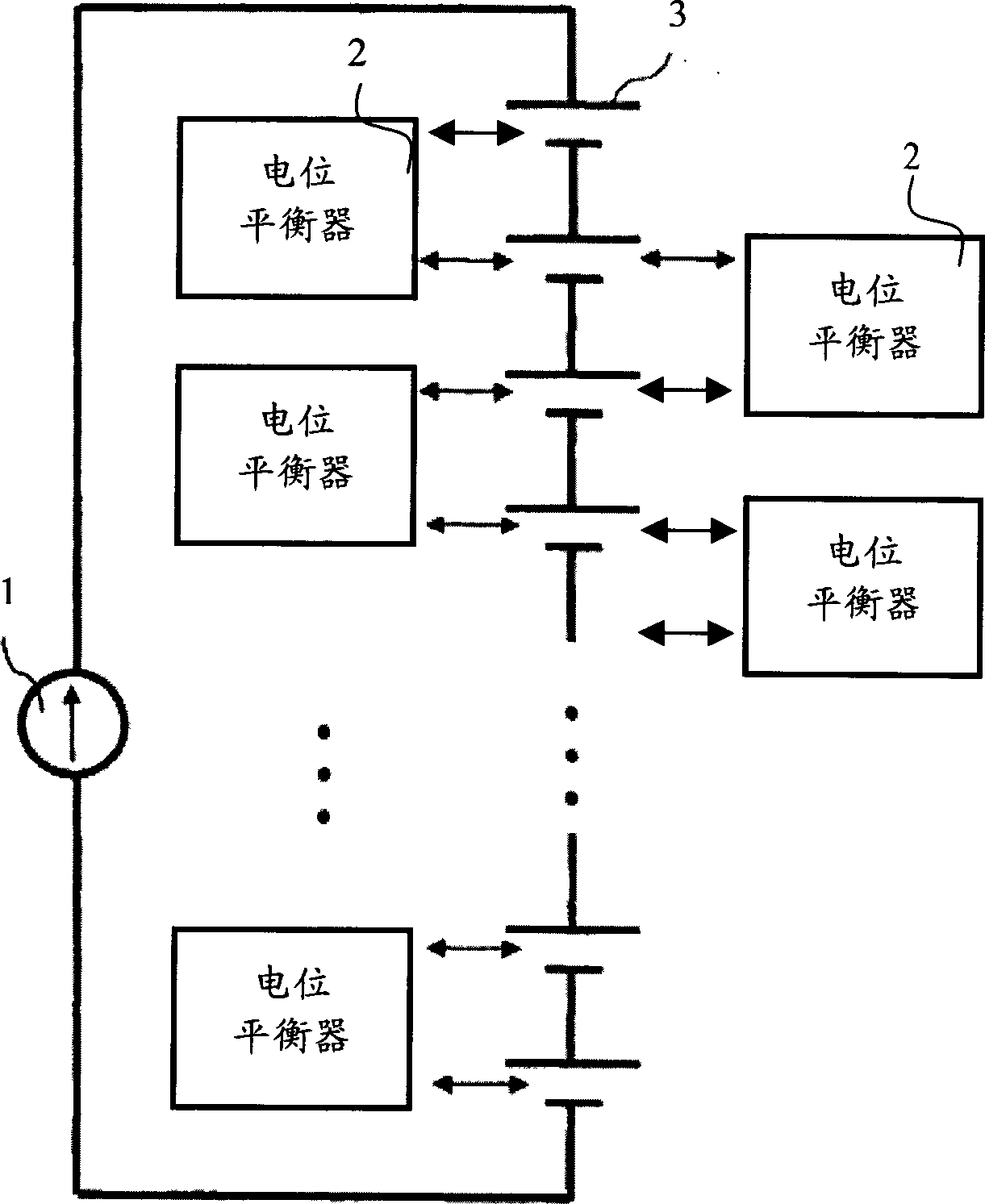
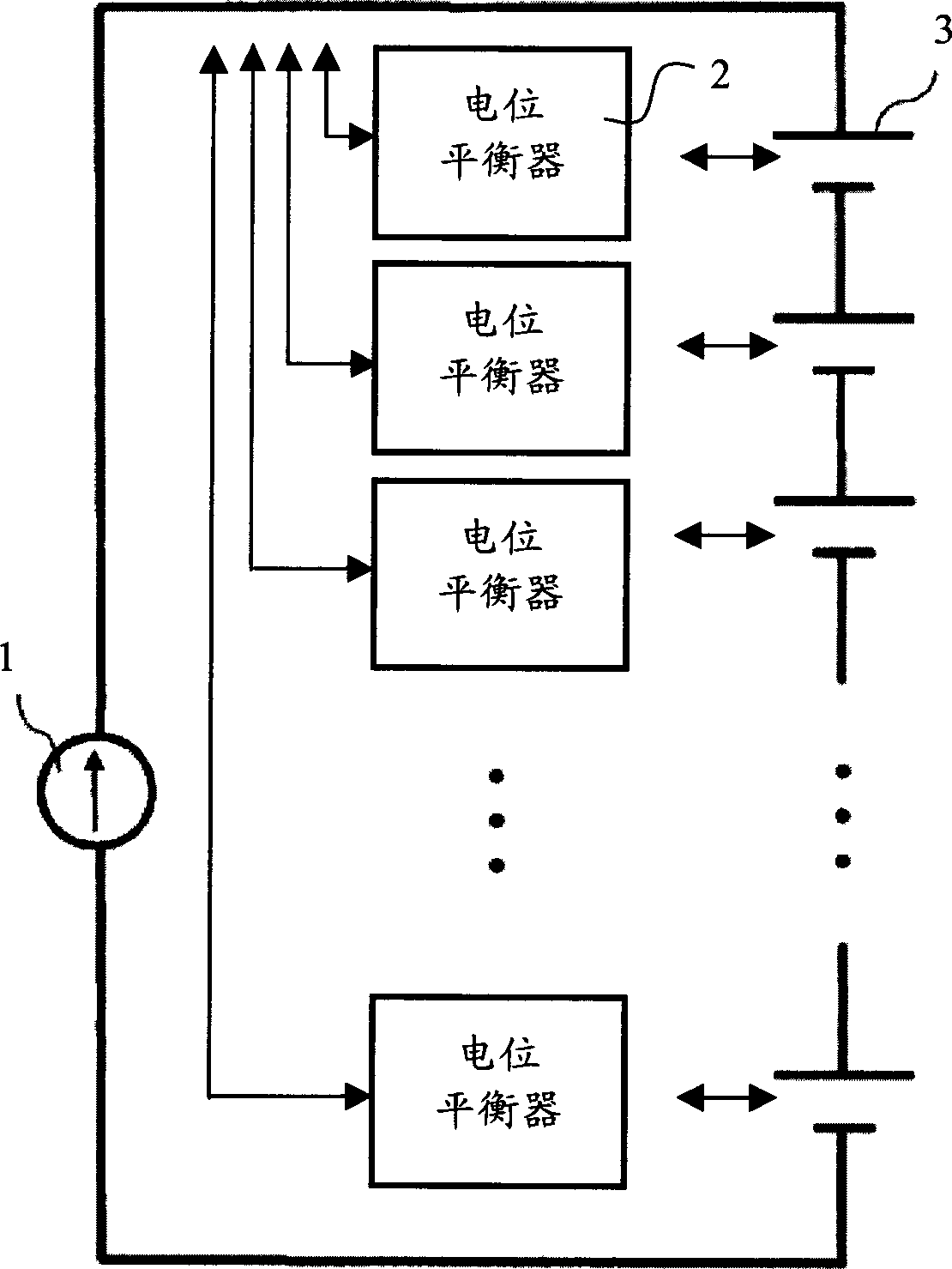
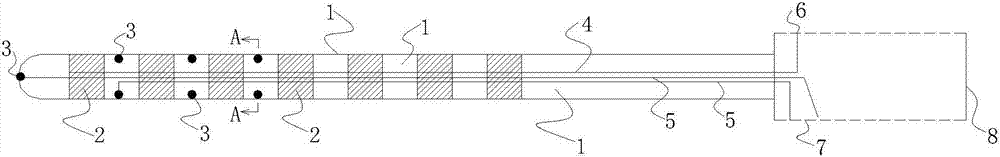
Staged cell potential balancing apparatus
ActiveCN1805193AFast balanceSimple designPrimary cell maintainance/servicingSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceEngineeringCell potential
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Composite electrode for recording deep brain signals
PendingCN107198522AImprove recording effectEasy to collectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityComposite electrode
The invention relates to a composite electrode for recording deep brain signals. The composite electrode comprises at least one large electrode contact capable of recording local field potential and at least one microelectrode contact capable of recording single cells in brain tissue and is characterized in that a large electrode wire and a microelectrode wire are arranged in the composite electrode, the large electrode wire is electrically connected with the large electrode contact, and the microelectrode wire is electrically connected with the microelectrode contact. The composite electrode has the advantages that single cell potential and local field potential in the brain tissue can be recorded at the same time, a good recording effect is achieved, electric signals can be well collected and clearly displayed even when the electric signals are weak, and the composite electrode is of great significance and value to the diagnosis, treatment and researches of various neurologic diseases such as epilepsy.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Potentiometric titration method for quantitative determination of hydrogen peroxide
InactiveUS7534394B1Chemical analysis using titrationWithdrawing sample devicesPlatinumQuantitative determination
An electrochemical potentiometric titration method that entails titration of a known volume of a catholyte containing an unknown amount of hydrogen peroxide in a titration cell having two electrodes, a platinum working electrode and a silver / silver chloride reference electrode. A known concentration of a titrant is added to the catholyte in the titration cell. Simultaneously, as the titrant is added the potential between the working electrode and the reference electrode is monitored. The point at which all of the hydrogen peroxide has been consumed is signaled when the cell potential changes abruptly. Since the concentration of the titrant is already known, the amount of titrant added (concentration multiplied by volume) is directly related to the amount of hydrogen peroxide consumed. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide is calculated from the volume of catholyte and the moles of hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:NAVY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF THE
Method and apparatus for sensing molecular gases
InactiveUS20160169829A1Improve performanceEasy to manufactureWeather/light/corrosion resistanceElectrolytic capacitorsElectrical conductorIon
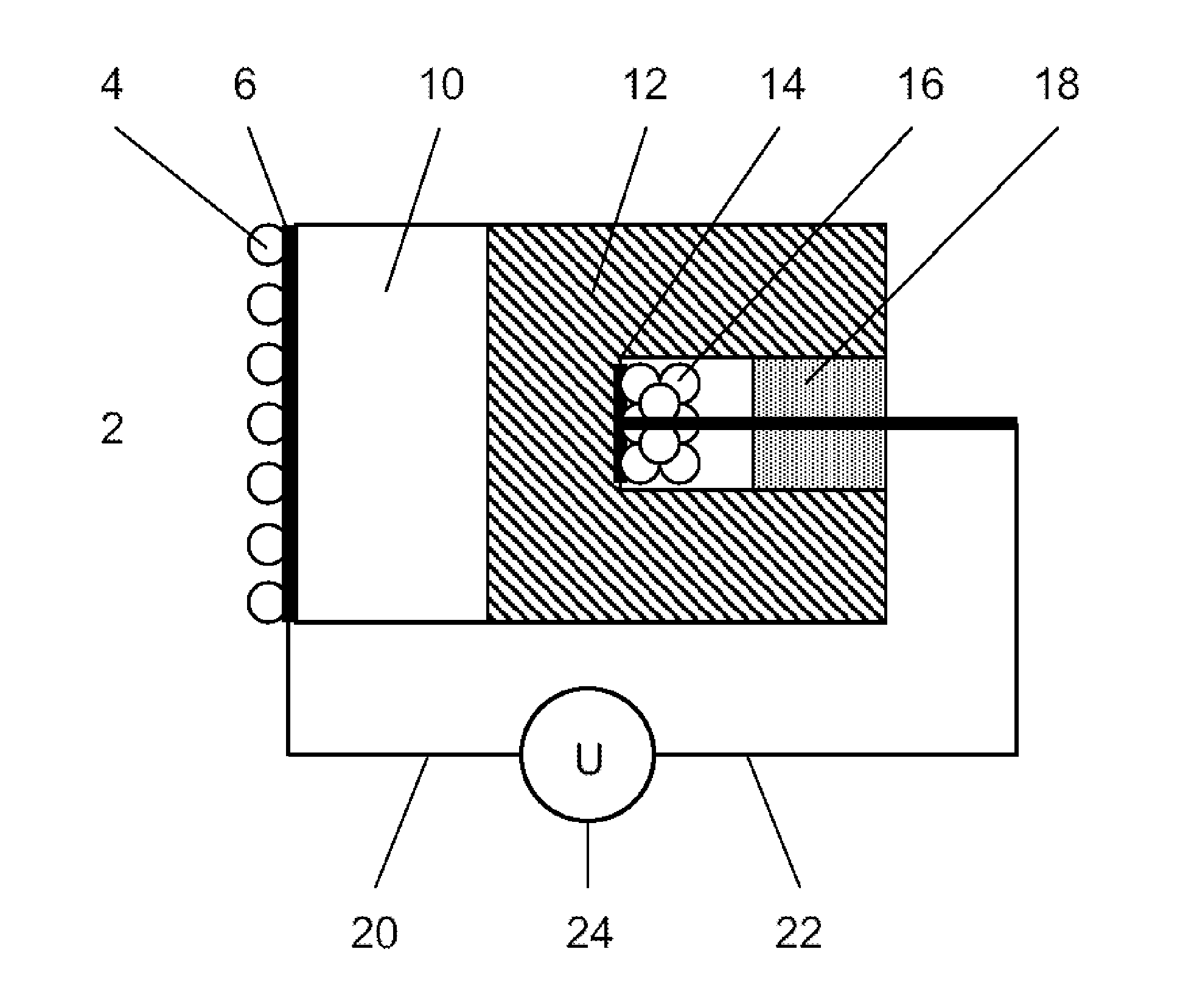
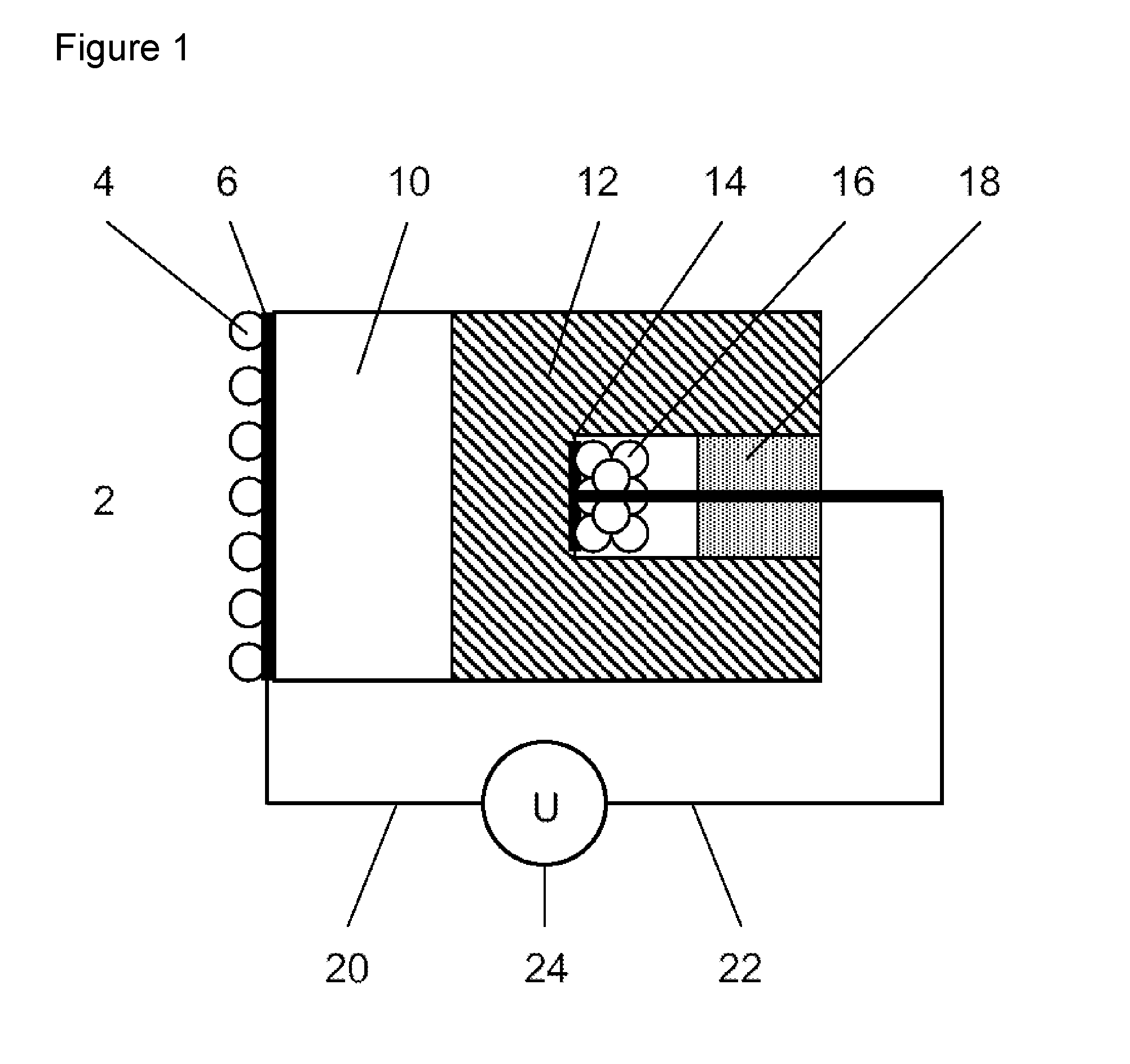
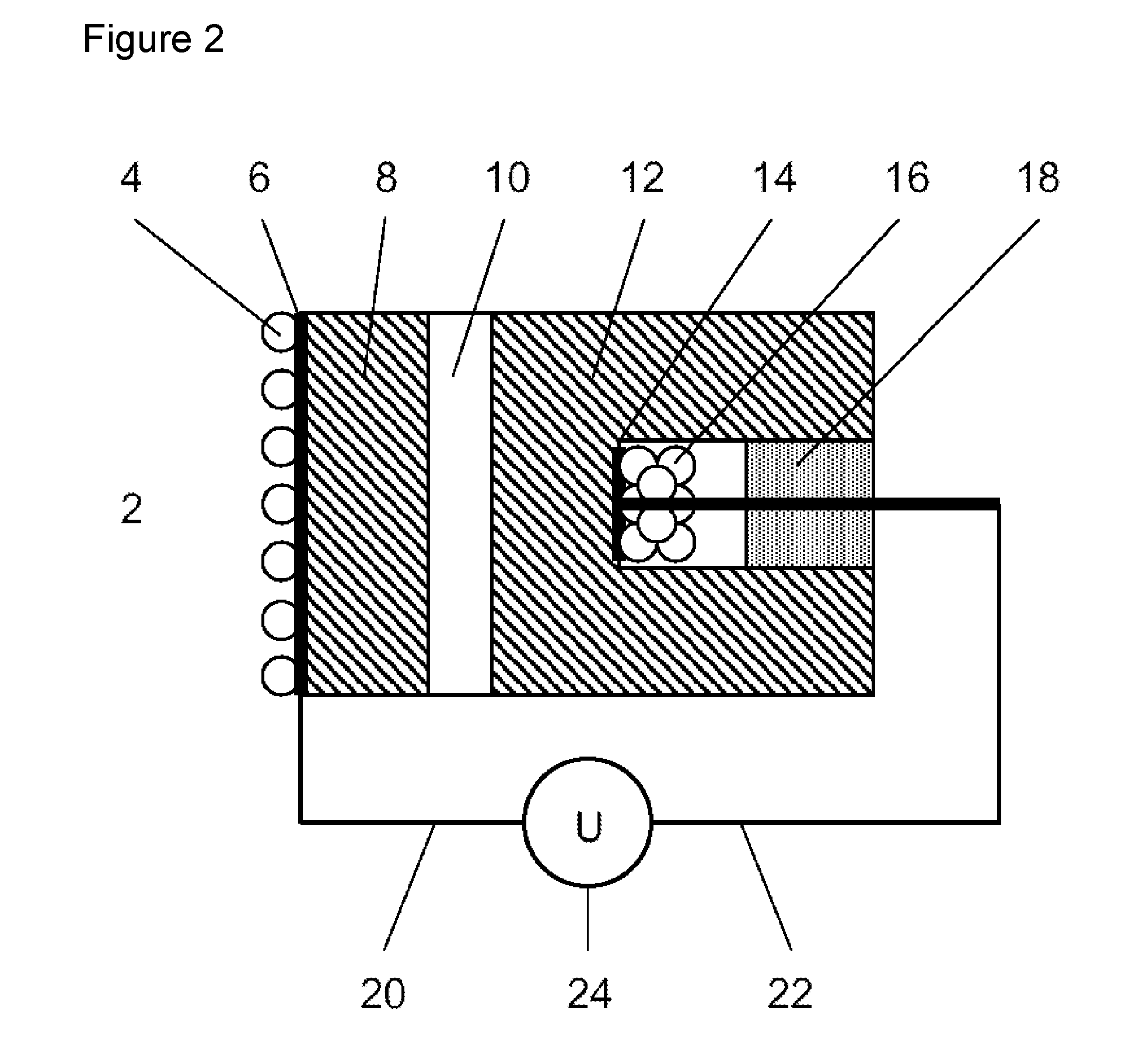
A method and apparatus are provided for the quantitative sensing of molecular gases. The apparatus comprises a gas-sensitive measurement electrode (4,6), a series of solid ion-conductors including at least a salt ion-conductor (10) and a ceramic or glass ion-conductor (12), and a reference electrode (14, 16). The cell potential generated is a direct function of the pressure or concentration of the molecular gas to be sensed.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING & CONTROL +1
An ant colony aggregation cell tracking system based on potential estimation
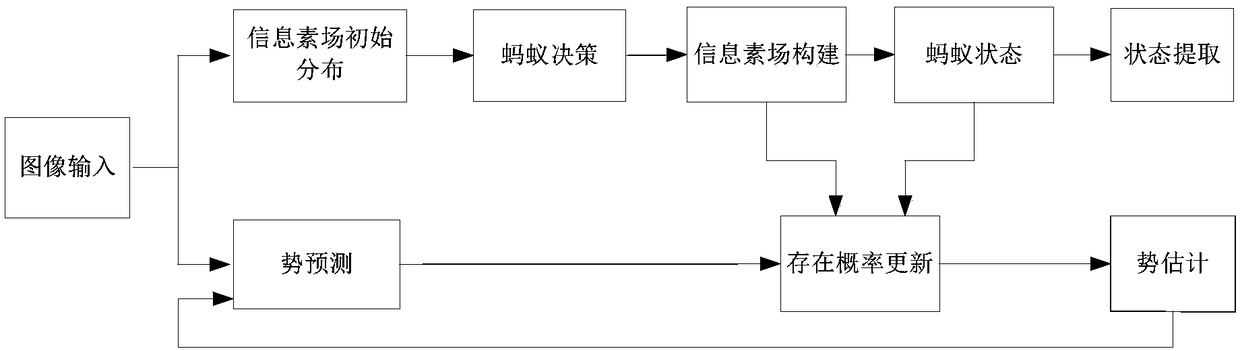
ActiveCN109146881AEasy to trackImprove tracking accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionExponential form
The invention discloses an ant colony aggregation cell tracking system assisted by potential estimation, which realizes the tracking of aggregated cells through the analysis of cell potential prediction and initial distribution module of pheromone field, ant search rule module, pheromone field existence probability update module and cell potential estimation and state extraction module. After theoriginal image is input, the cell potential is predicted by the existence probability of the pheromone field. The pheromone field is constructed by using a pheromone diffusion model based on a conicalcurve in an ant search mode based on pheromone gradient exponential form. On the basis, the existence probability of pheromone field is updated and the cell potential and state are estimated at the same time. Finally, the cell motion trajectory is obtained by using the distance relationship between cells, and the tracking of aggregated cells is realized. The invention can accurately estimate thenumber and the state of the aggregated cells, and has good tracking effect on the multicellular tracking of the cells entering or leaving the view.
Owner:JIANGSU SAIKANG MEDICAL EQUIP
Liquid consuming battery with liquid regulating system
The invention is an electrochemical battery cell with a fluid consuming electrode, such as an oxygen reduction electrode, and a fluid regulating system. The fluid regulating system includes a valve for adjusting the rate of passage of the fluid to the fluid consuming electrode. It is operated by an actuator that responds (e.g., by deforming) to changes in a potential applied across the actuator to open or close the valve. The applied potential can be the cell potential or an adjusted potential. The potential applied across the actuator can vary according to the need for more or less fluid in the fluid consuming electrode. The valve can be contained within the cell housing, for example between the fluid consuming electrode and one or more fluid entry ports in the cell housing, or it can be located outside the cell housing.
Owner:ENERGIZER BRANDS
A device and method for quickly testing solar cell potential-induced decay
ActiveCN106656041BSpeed up agingImprove usabilityPhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic energy generationPotential induced degradationNon destructive
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD
Molten Carboxylate Electrolytes for Electrochemical Decarboxylation Processes
InactiveUS20150083606A1Potential oxidationLow melting pointCellsIsotope separationChemical synthesisCarboxylic salt
Molten salt electrolytes are described for use in electrochemical synthesis of hydrocarbons from carboxylic acids. The molten salt electrolyte can be used to synthesize a wide variety of hydrocarbons with and without functional groups that have a broad range of applications. The molten salt can be used to synthesize saturated hydrocarbons, diols, alkylated aromatic compounds, as well as other types of hydrocarbons. The molten salt electrolyte increases the selectivity, yield, the energy efficiency and Coulombic efficiency of the electrochemical conversion of carboxylic acids to hydrocarbons while reducing the cell potential required to perform the oxidation.
Owner:ENLIGHTEN INNOVATIONS INC
Fluid regulating microvalve assembly for fluid consuming cells
InactiveUS7378168B2Low costInexpensive and straightforward to produceFuel and primary cellsReactant parameters controlElectrochemical cellBiomedical engineering
A fluid regulating microvalve assembly for use to control fluid flow to a fluid consuming electrode, such as an oxygen reduction electrode, in an electrochemical cell. The microvalve assembly includes a stationary valve body having an aperture and a microactuator movable from a first position where the microvalve body aperture is closed to fluid flow to at least a second position where fluid is able to pass through the microvalve body aperture. The fluid regulating microvalve assembly can utilize cell potential or a separate source to open and close the microvalve. The fluid regulating microvalve assembly can be located outside the cell housing or inside the cell housing, for example between one or more fluid inlet apertures and the fluid consuming electrode. The invention includes a method of making a multilayer microvalve assembly, particularly one for use in a fluid depolarized battery, using a printing process to deposit at least one of the layers.
Owner:SCHUMM BROOKE JR +3
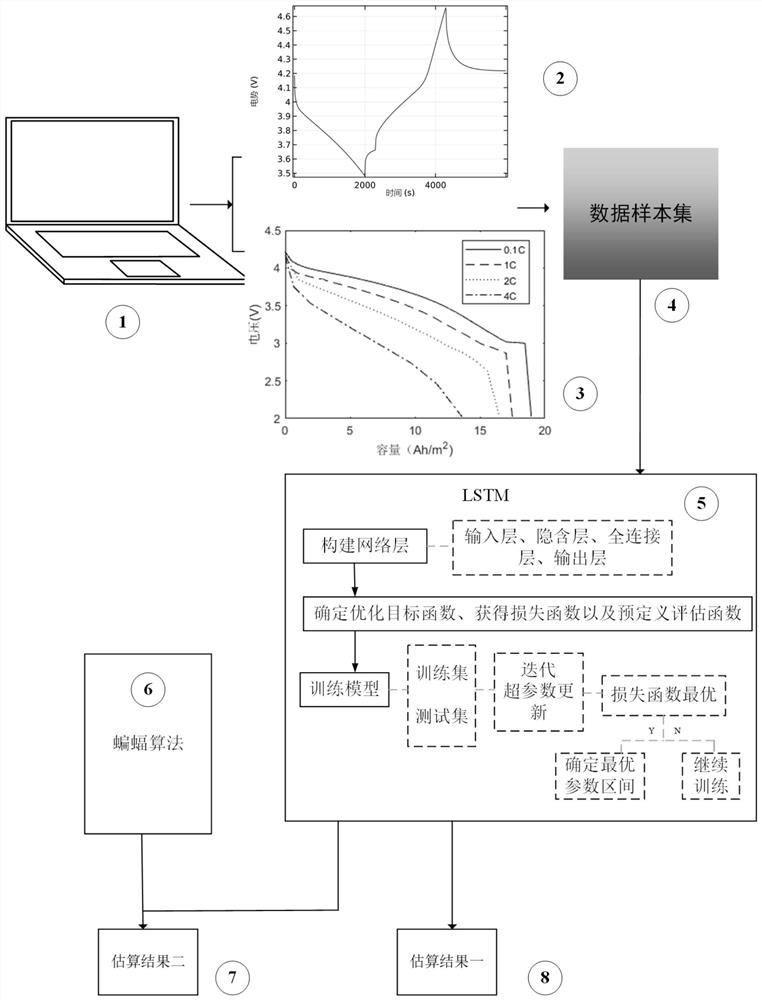
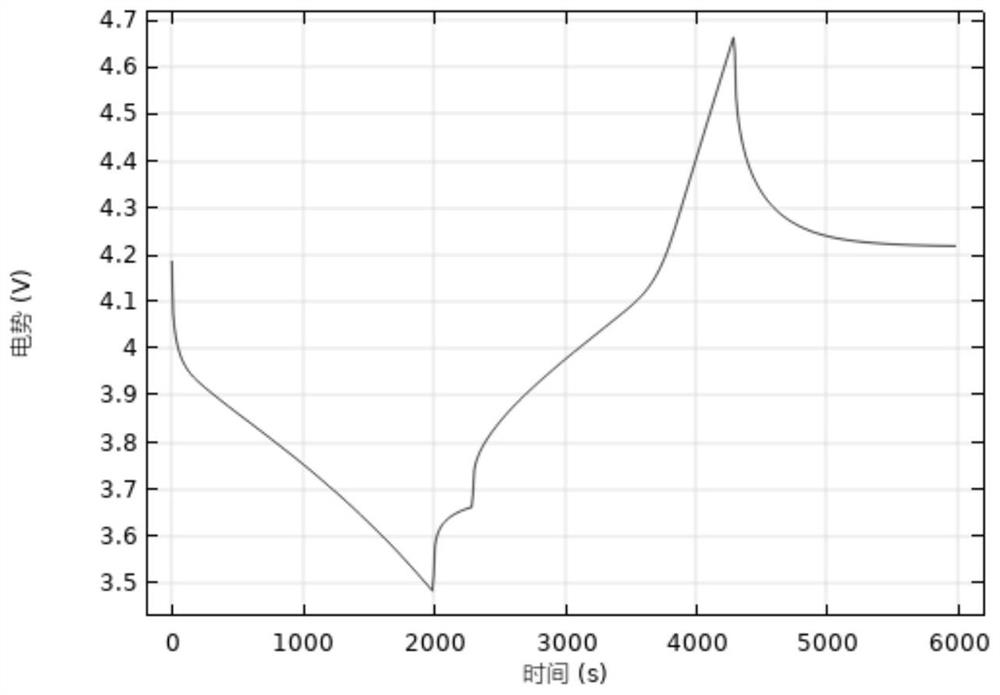
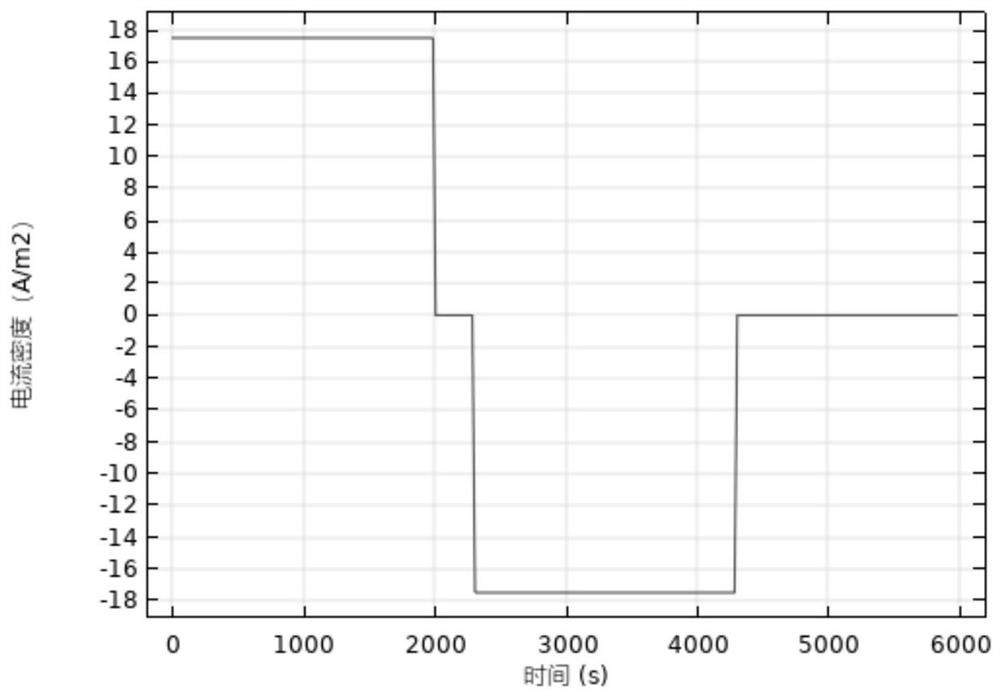
Sample data set generation method and SOC estimation method of power lithium battery
PendingCN114839542AImprove performanceImprove estimation performanceElectrical testingVehicular energy storageBat algorithmBattery cell
The invention discloses a sample data set generation method and an SOC estimation method of a power lithium battery. The generation method comprises the steps of building a lithium battery charging and discharging transient solution model; according to the built lithium battery charging and discharging transient solution model, a lithium battery potential chart, a current density analysis chart and a battery different rate performance analysis chart are obtained; exporting data corresponding to the lithium battery potential chart, the current density analysis chart and the battery different rate performance analysis chart; and preprocessing the exported data to obtain a lithium battery sample data set. According to the SOC estimation method, a bat algorithm is introduced, an iterative optimization process is designed, an optimized hyper-parameter combination is obtained, and updated hyper-parameters are input into a network, so that the SOC of the lithium battery is estimated. The method can be suitable for lithium batteries made of different materials, on one hand, the model calculation amount is reduced, on the other hand, the model prediction performance can be improved to a certain degree, the estimation precision of the SOC of the battery is high, and higher adaptability is achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
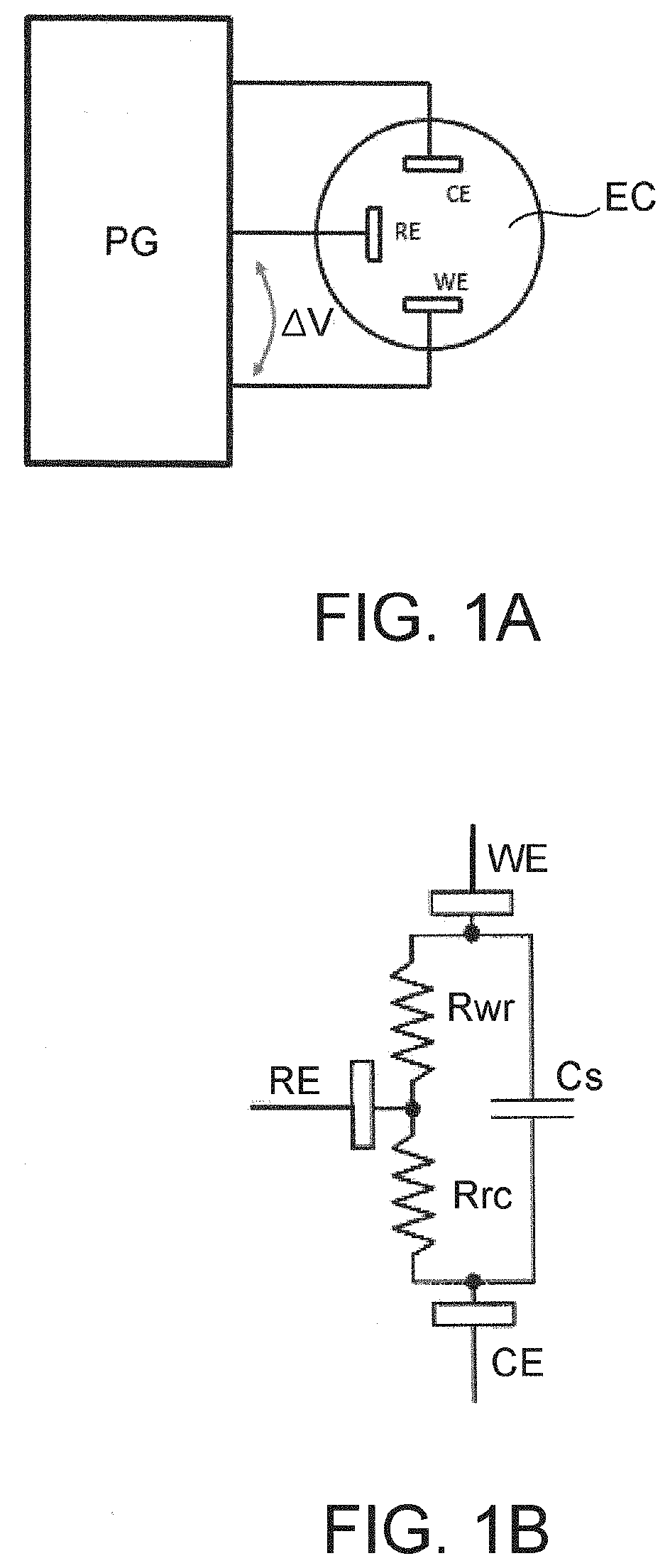
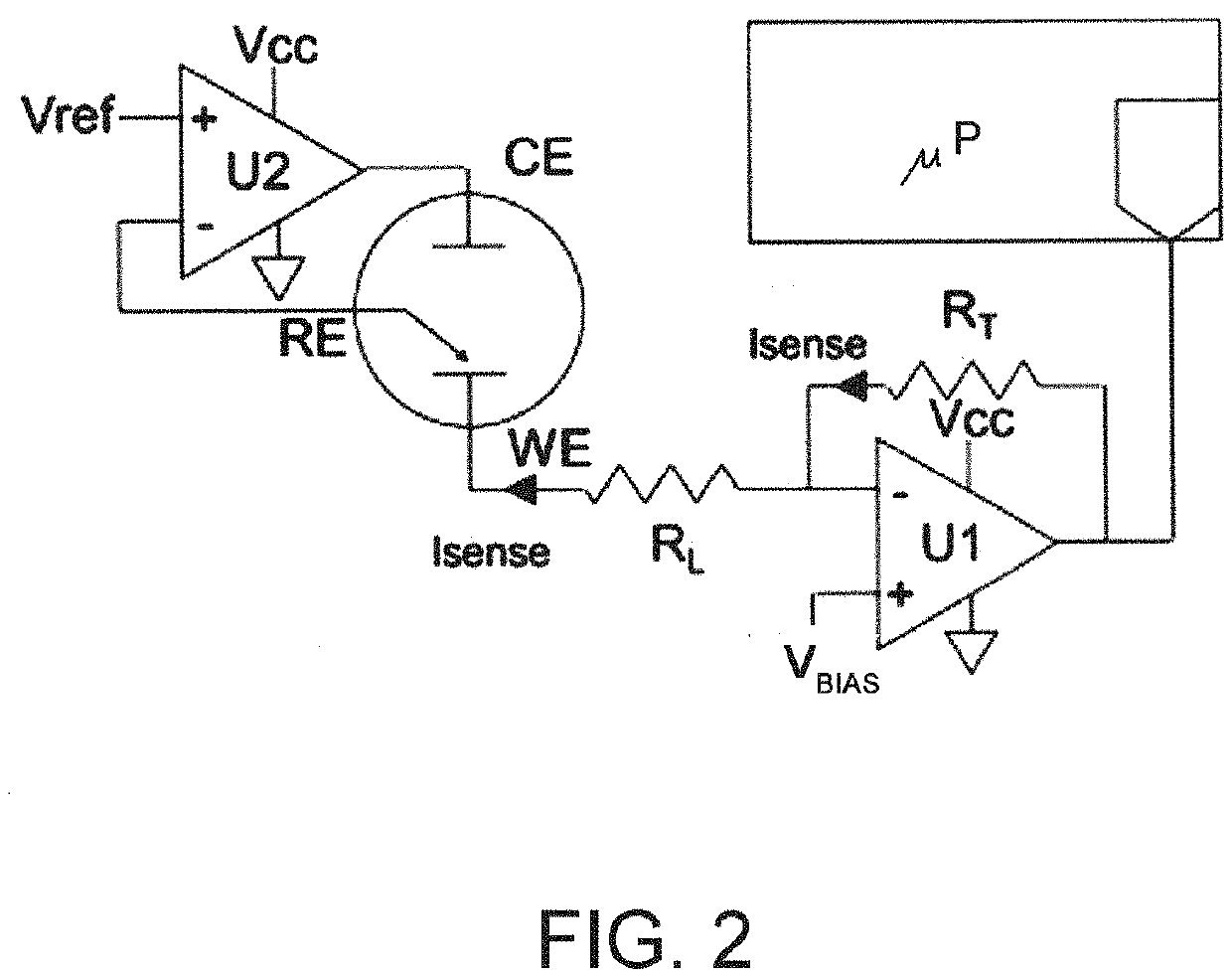
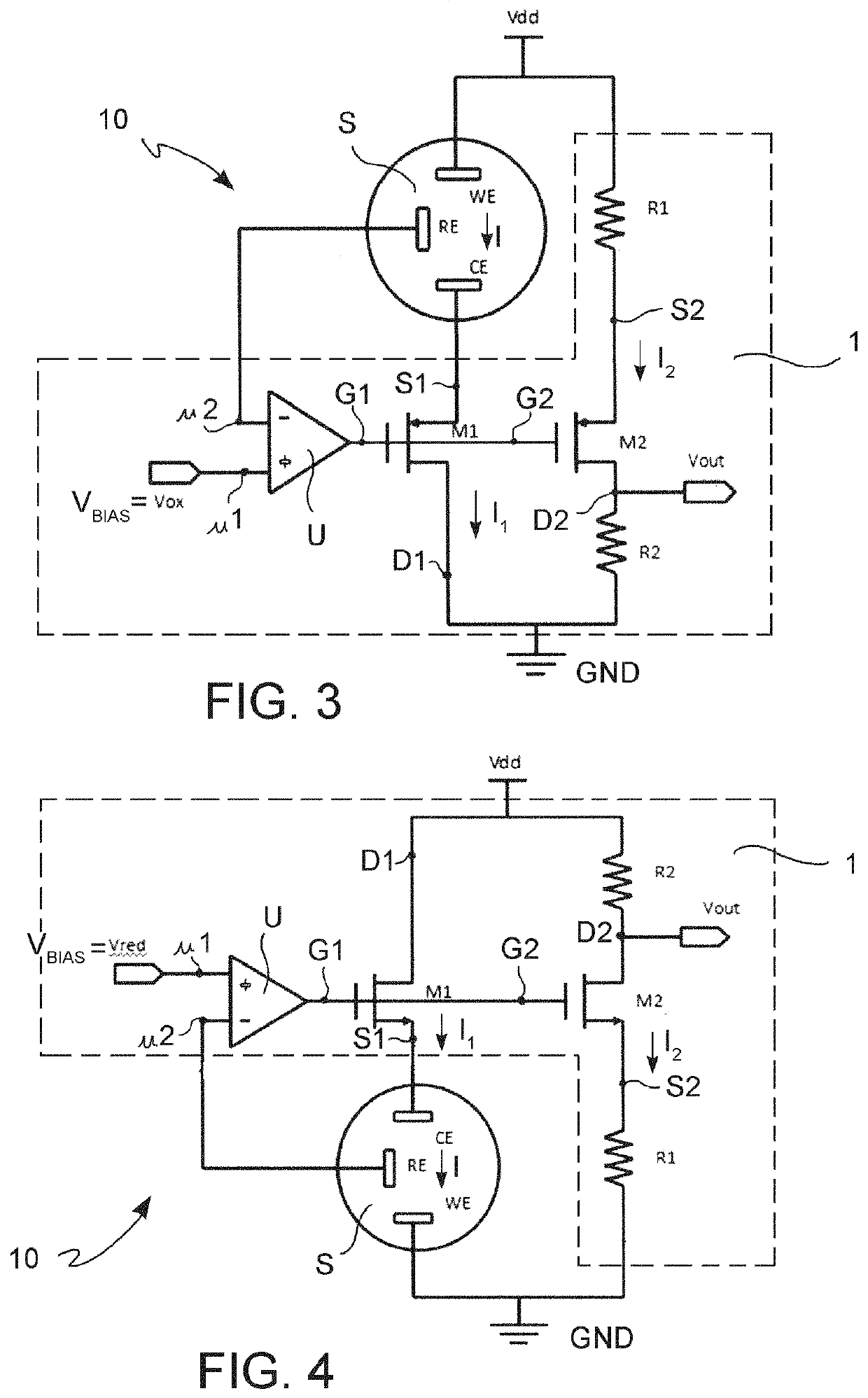
Interface electronic device for reading an output signal and for controlling and conditioning a three-electrodes amperometric sensor
PendingUS20210041391A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical responseControl signal
There is described an electronic interface device (1) for reading an output signal and controlling and conditioning a three-electrode amperometric sensor (S). The device (1) may be used with a sensor having an electro-chemical cell comprising a reference electrode (RE) configured to supply a constant cell electric potential to the electrochemical cell; a working electrode (WE) at which oxidation or reduction reactions occur, connectable to a first reference voltage; and a collector electrode (CE) configured to deliver or receive electric charge carriers. In the electro-chemical cell, a cell impedance (Zcw) is always present between the working electrode (WE) and the collector electrode (CE).The device (1) comprises an operational amplifier (U), having a non-inverting input (u1), adapted to receive a biasing electric potential (VBIAS) depending on the type of electrochemical reaction of the sensor, and an inverting input (u2) connectable to the reference electrode (RE) of the sensor. The operational amplifier is adapted to operate in a feedback configuration to supply the reference electrode (RE) with the aforementioned constant cell electric potential on the basis of the biasing electric potential (VBIAS).The device (1) further comprises a first MOS transistor (M1), having a first MOS gate terminal (G1) connected to the output of the operational amplifier (U), a first MOS drain terminal (D1), connectable to a second reference voltage, and a first MOS source terminal (S1), connectable to the collector electrode CE of the sensor (S) to receive or supply a first MOS transistor channel current (I1) representative of (for example equal to) the cell current (I) which is generated in the amperometric sensor (S).The device (1) further comprises a second MOS transistor (M2) having a second MOS gate terminal (G2) connected to the output of the operational amplifier (U) and to the aforementioned first MOS gate terminal (G1), a second MOS source terminal (S2), connectable to the first reference voltage by means of a first resistor (R1), and a second MOS drain terminal (D2), connectable to the second reference voltage (for example, through a resistor R2 which allows the reading of a voltage proportional to the current).The value of the first resistor (R1) is lower than the cell impedance (Zcw) so that the second MOS transistor channel current (I2) depends on the first MOS transistor channel current (I1), representative of the cell current (I) of the sensor, through a nonlinear gain dependent at least on the value of the first resistor (R1).The second MOS transistor (M2) is of the same type as the first MOS transistor (M1).Also described is a method for reading an output and control signal of a three-electrode amperometric sensor, carried out by the aforementioned device.
Owner:DISTRETTO TECHCO SICILIA MICRO E NANO SISTEMI S C A R L
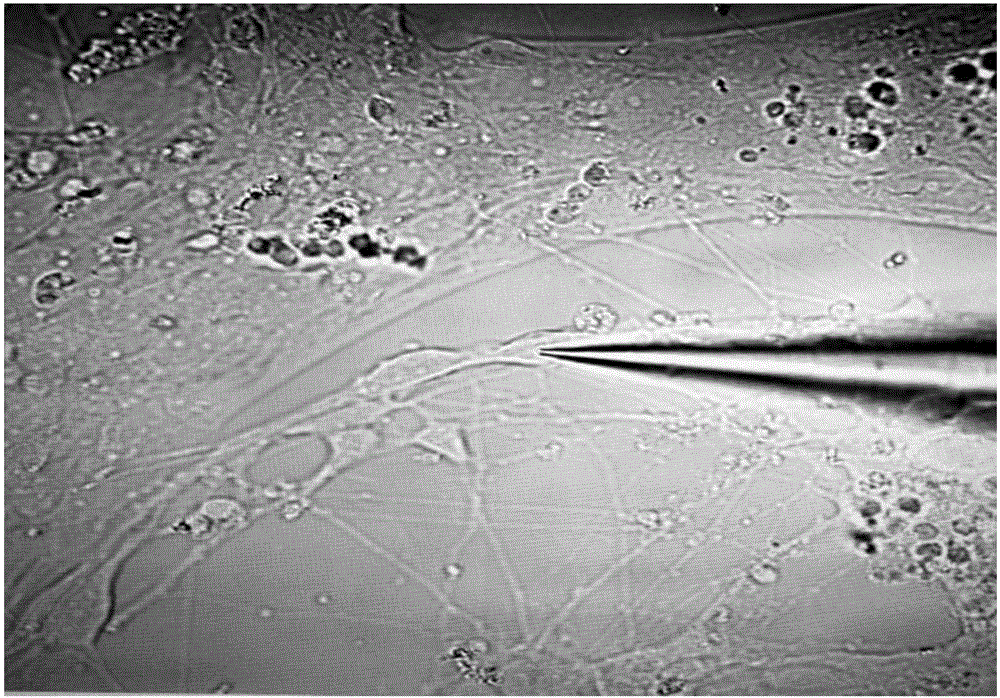
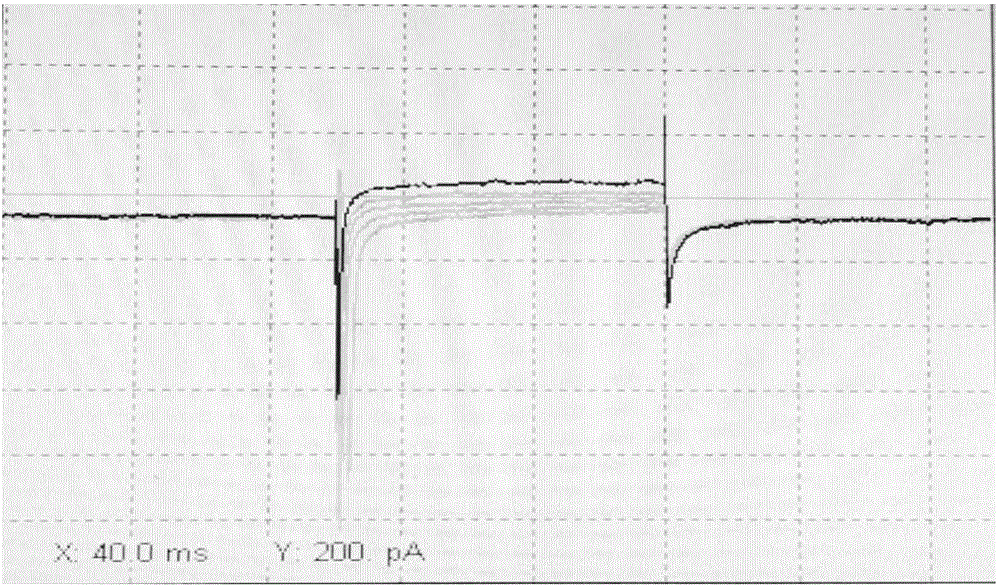
Measuring method for cell potential of bioengineering retina nerve scaffold
The invention discloses a measuring method for cell potential of a bioengineering retina nerve scaffold. The measuring method includes the steps that a nerve fiber layer of human iPSc-derived 3D retina is digested into unicells, the unicells serving as seed cells are resuspended through an induced differentiation medium, then polylactic acid-glycolic acid polymer support coated with matrigel Matrigel is inoculated with the unicells, induced differentiation is conducted in the induced differentiation medium to form the bioengineering retina nerve scaffold, wherein the induced differentiation medium is a medium containing neurotrophic factors and a retina differentiation nutrient solution for maintaining the concentration; ion channel current recording is conducted on nerve-like cells, cultured to a certain stage, on the bioengineering retina nerve scaffold in a whole-cell recording mode, and the neural basis function of the bioengineering retina nerve scaffold is reflected through potential detection of the scaffold cells.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com